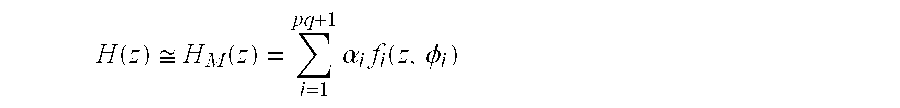Patents
Literature
92 results about "Spatial expansion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
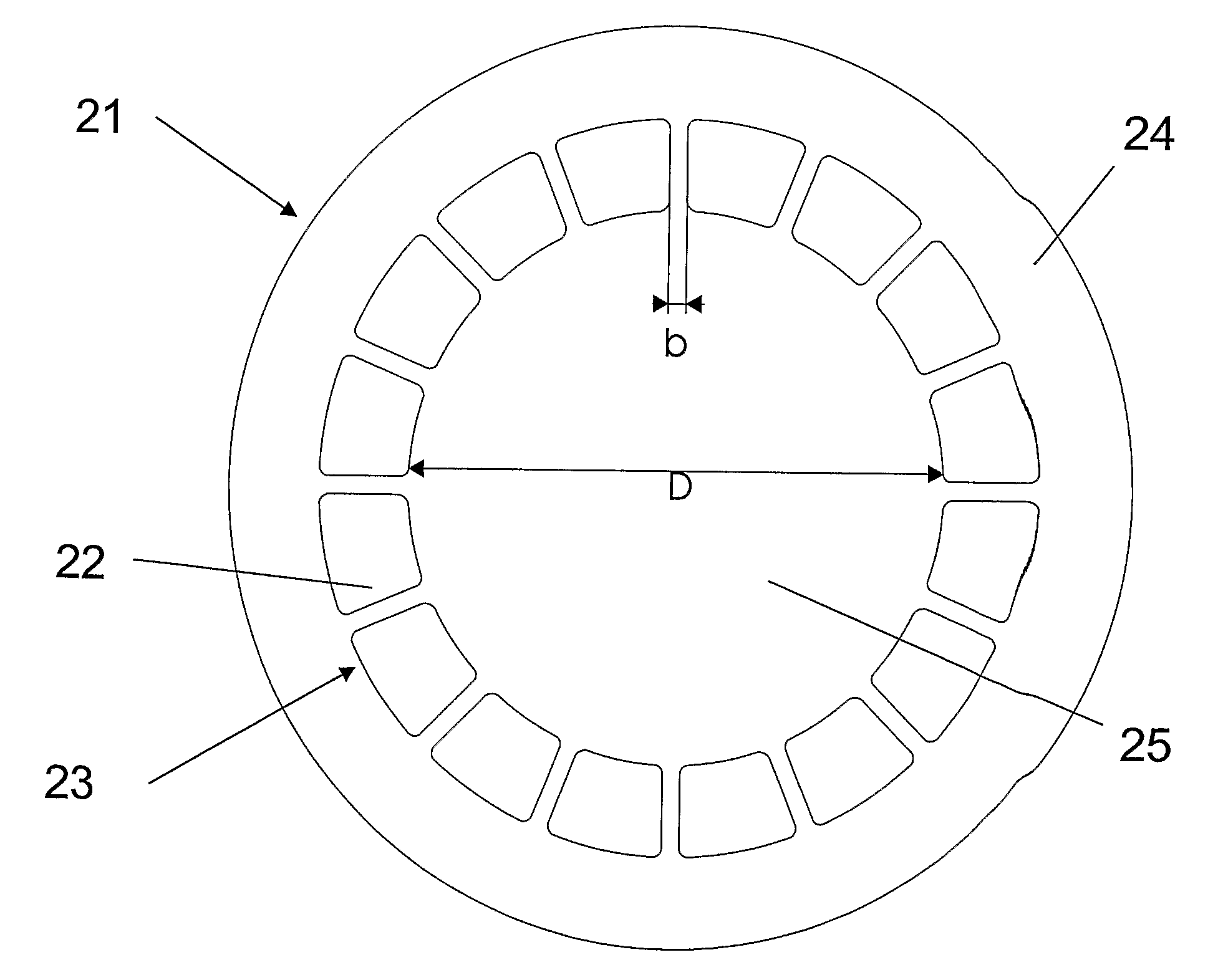
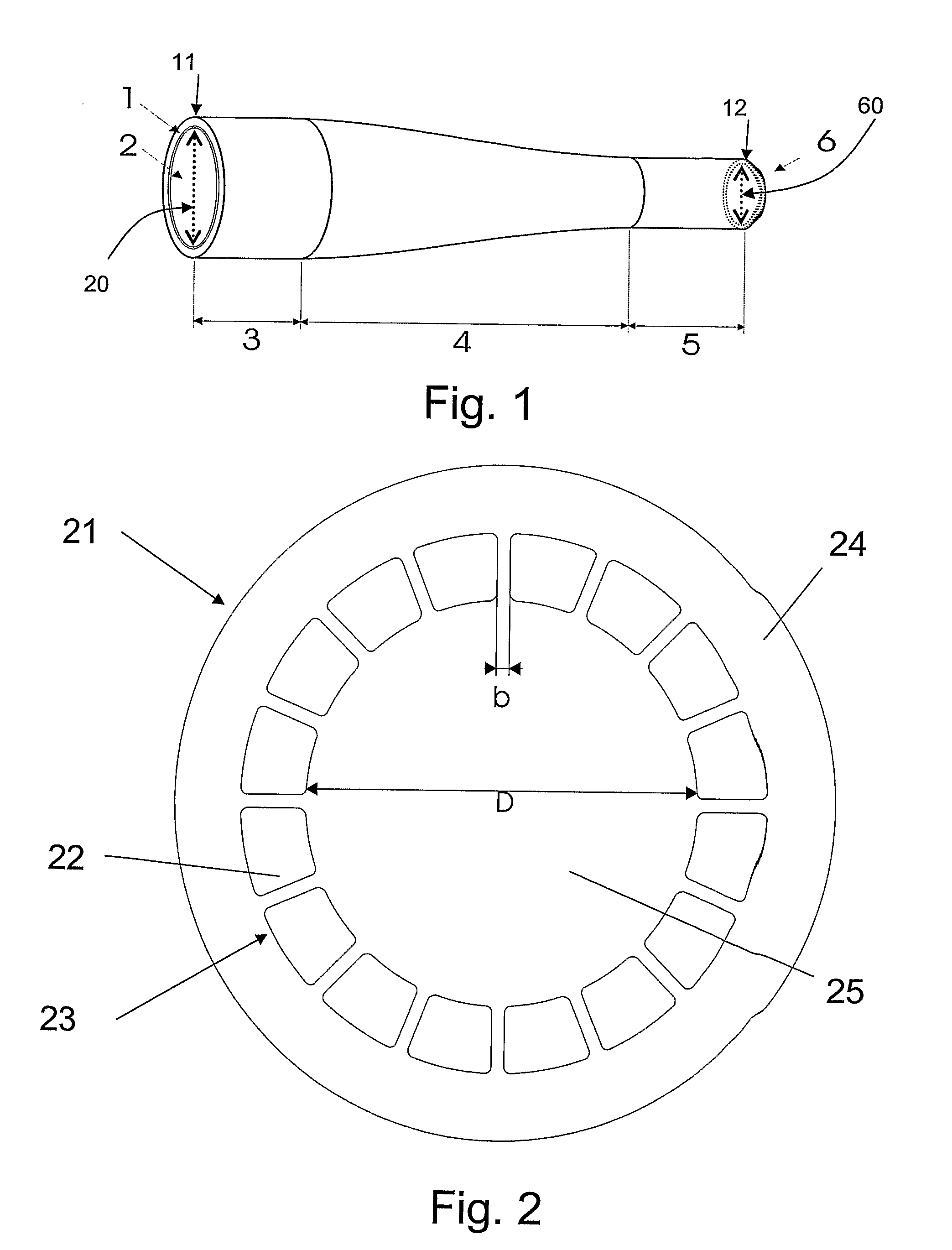
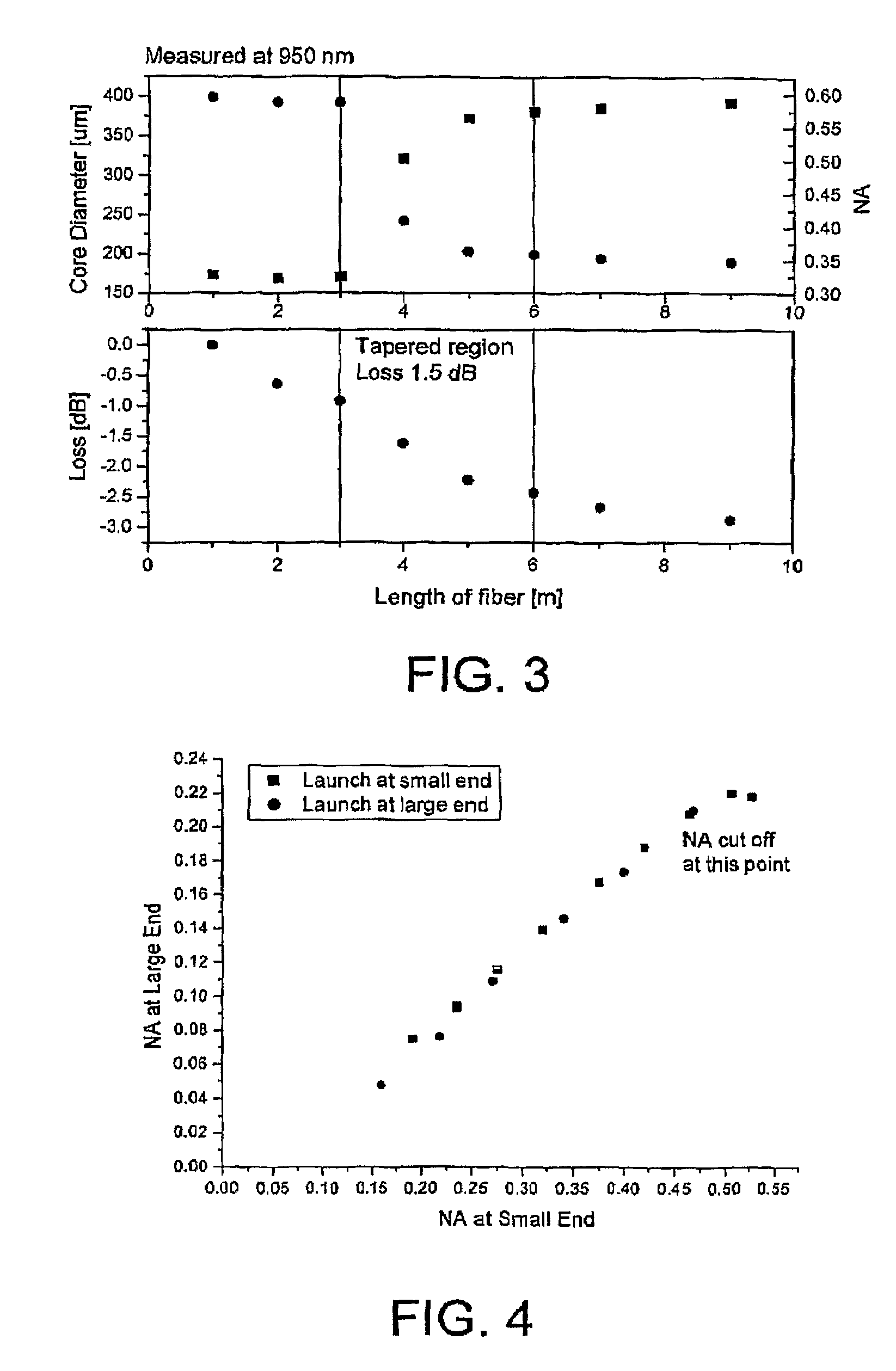
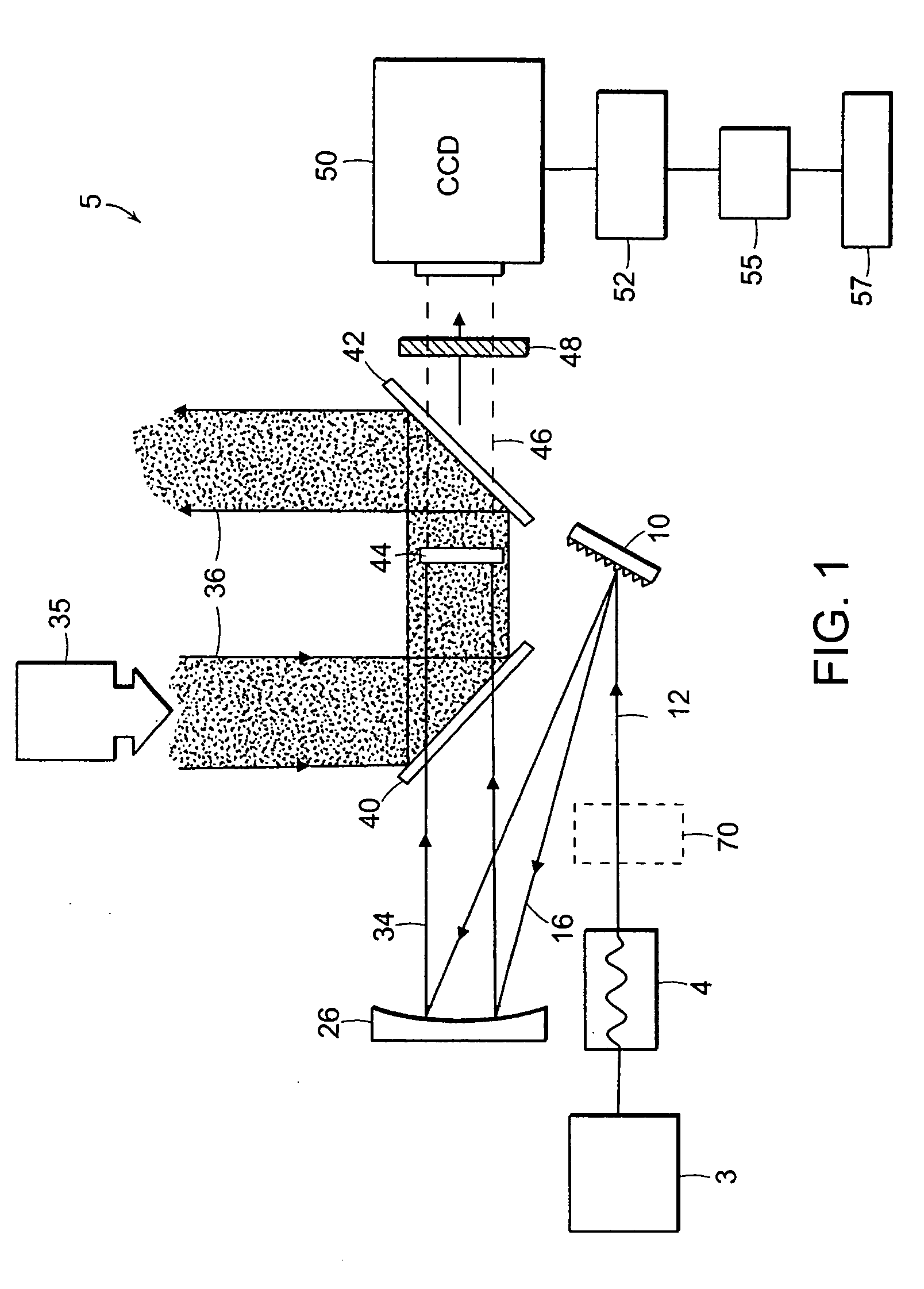
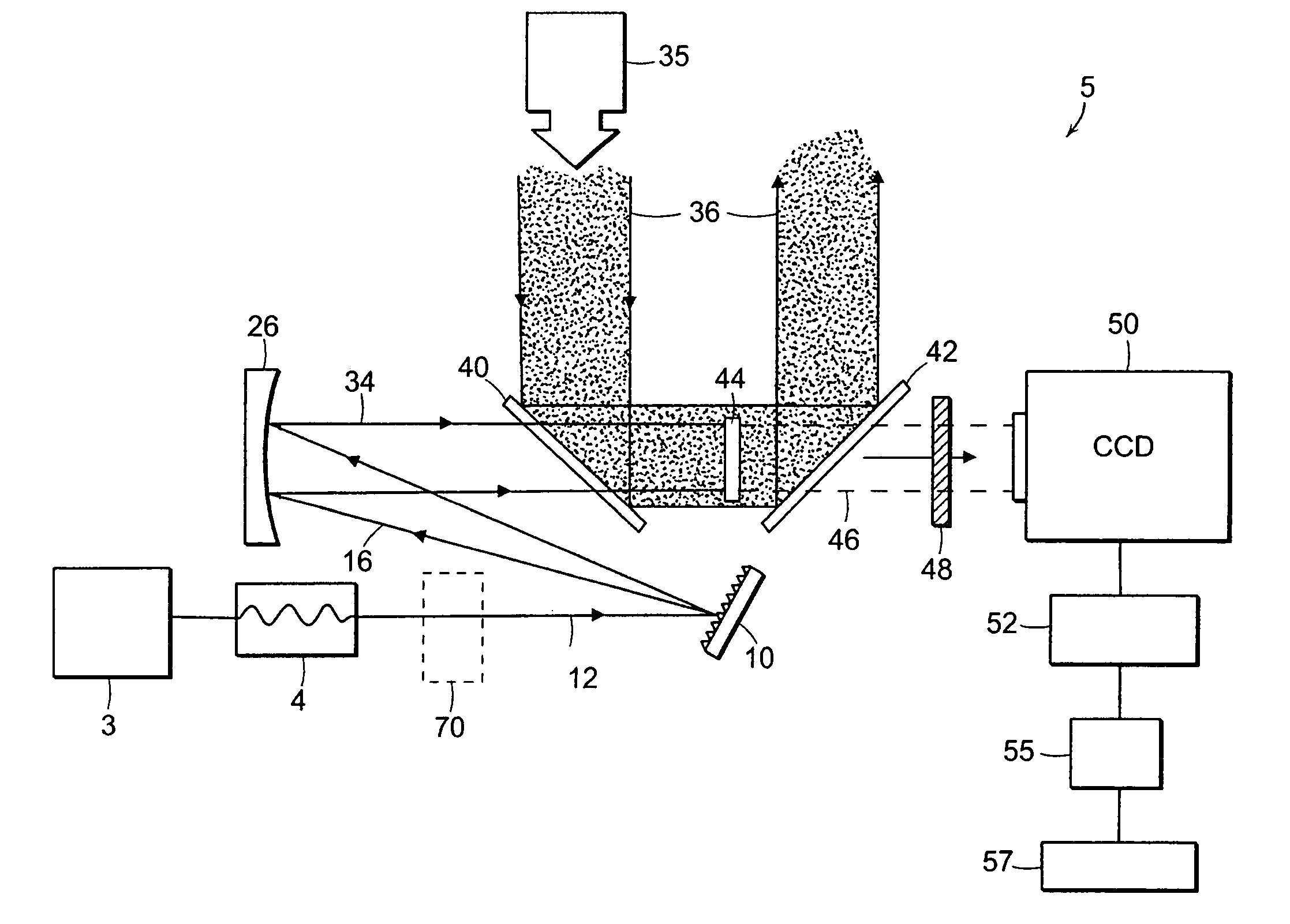
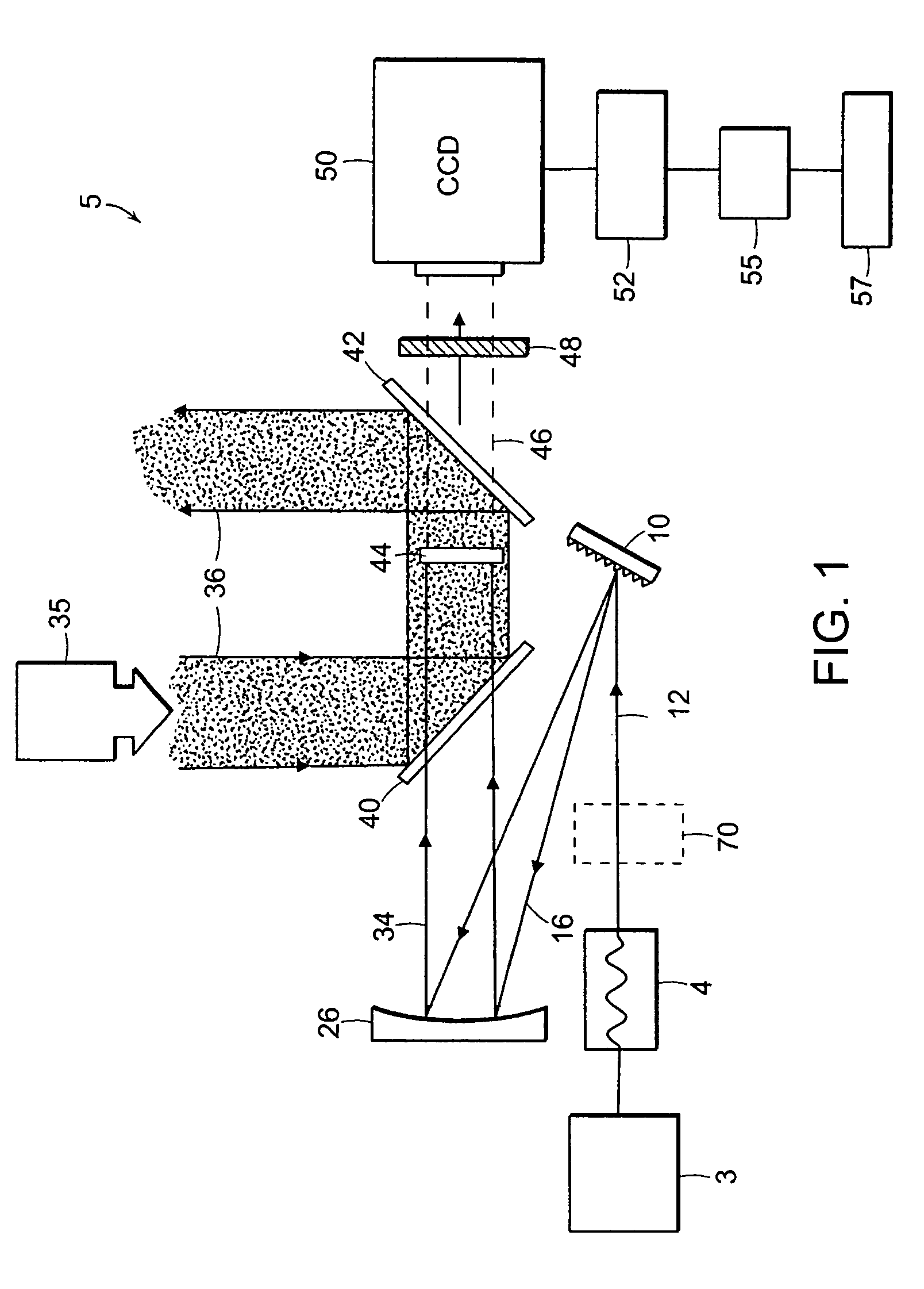
Optical Coupler Devices, Methods of Their Production and Use
InactiveUS20070237453A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberWaveguide
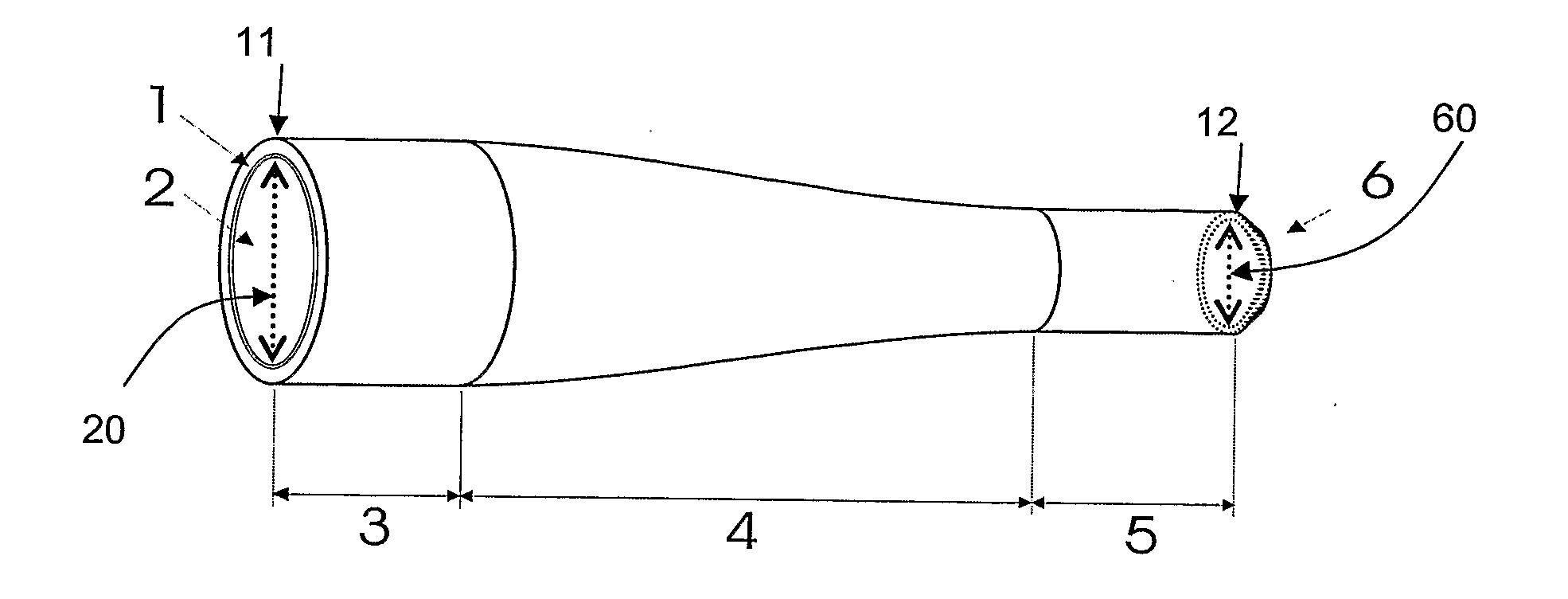
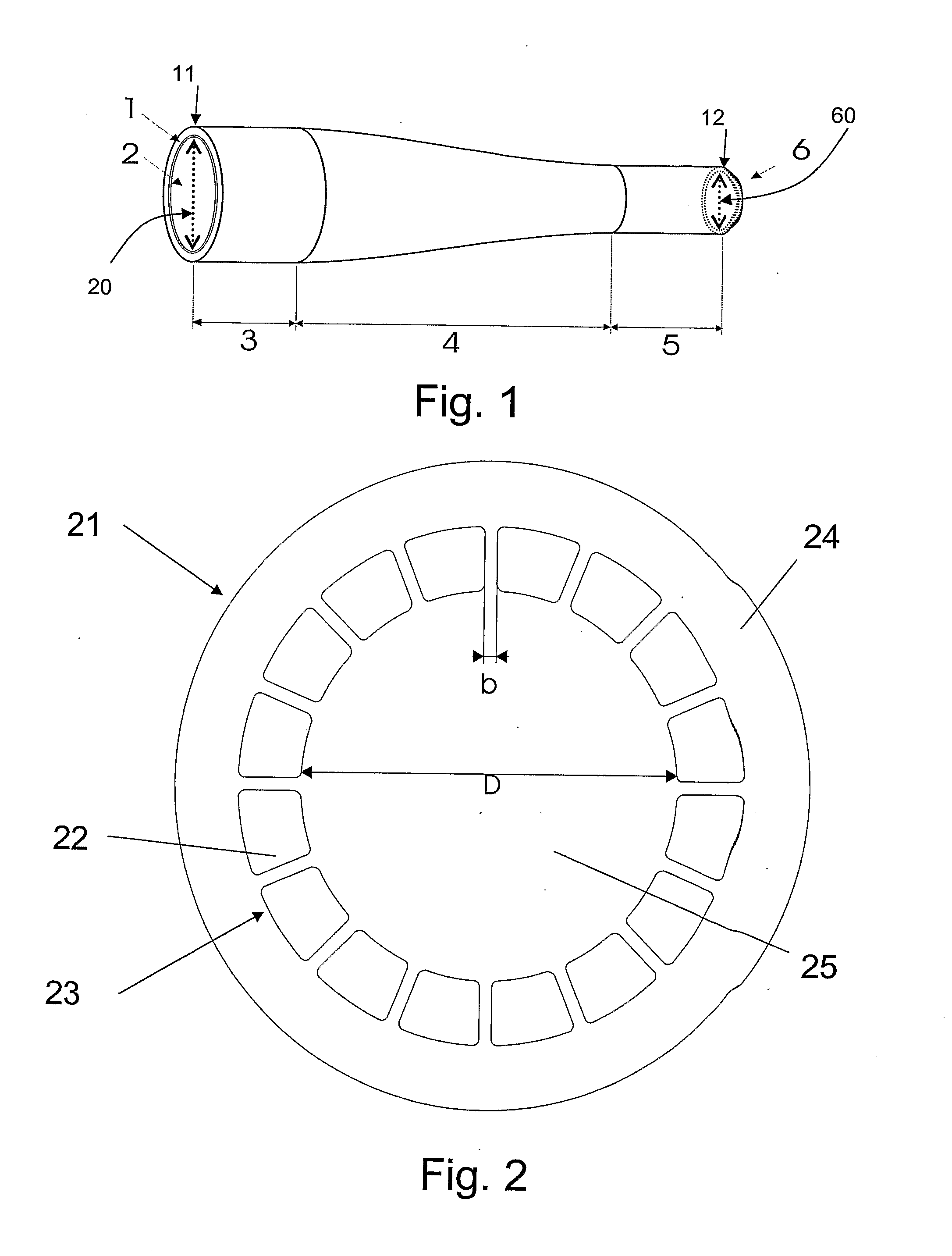
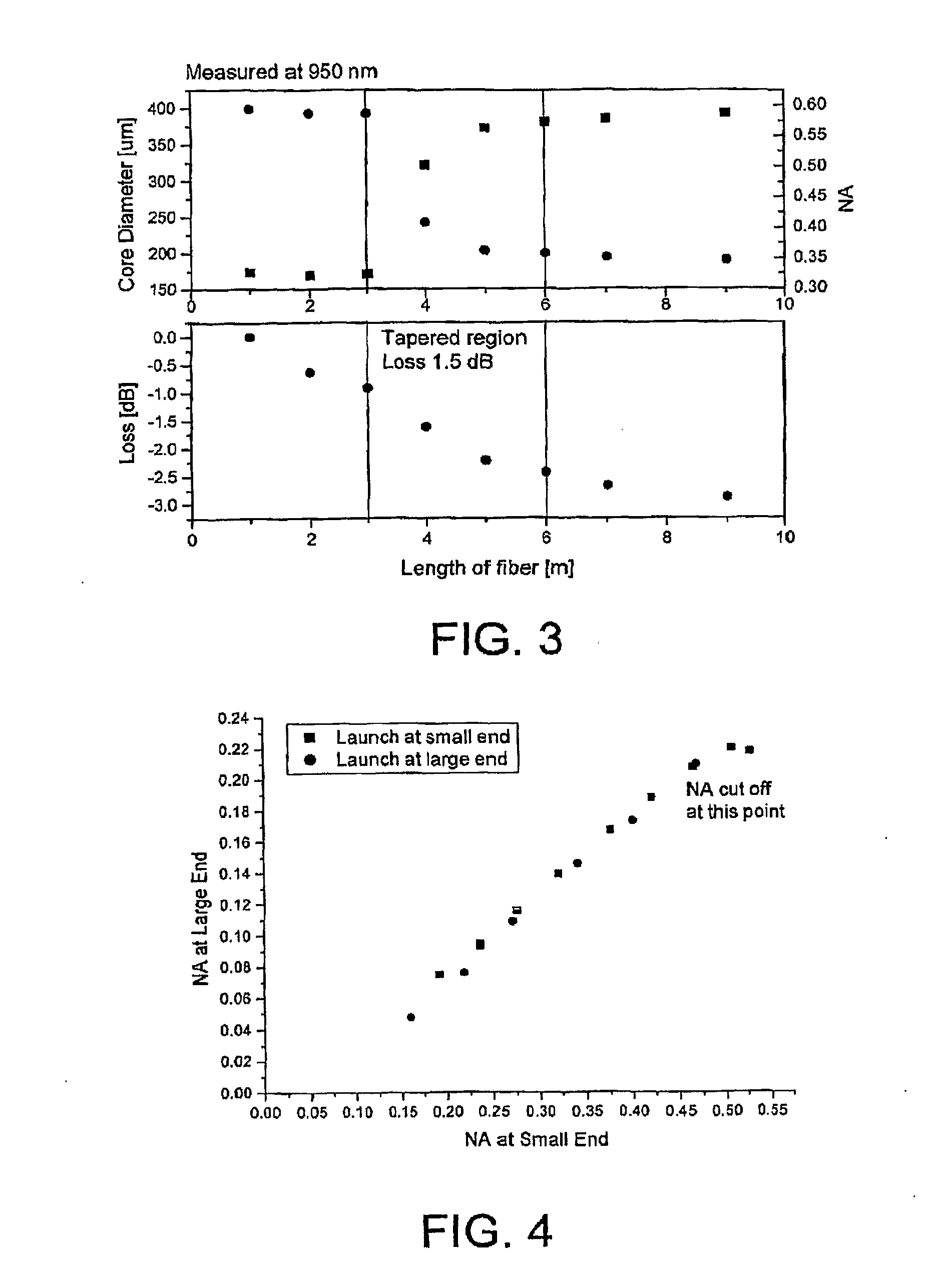
The present invention relates in general to coupling of light from one or more input waveguides to an output waveguide or output section of a waveguide having other physical dimensions and / or optical properties than the input waveguide or waveguides. The invention relates to an optical component in the form of a photonic crystal fibre for coupling light from one component / system with a given numerical aperture to another component / system with another numerical aperture. The invention further relates to methods of producing the optical component, and articles comprising the optical component, and to the use of the optical component. The invention further relates to an optical component comprising a bundle of input fibres that are tapered and fused together to form an input coupler e.g. for coupling light from several light sources into a single waveguide. The invention still further relates to the control of the spatial extension of a guided mode (e.g. a mode-field diameter) of an optical beam in an optical fibre. The invention relates to a tapered longitudinally extending optical waveguide having a relatively larger cross section that over a certain longitudinal distance is tapered down to a relatively smaller cross section wherein the spatial extent of the guided mode is substantially constant or expanding from the relatively larger to the relatively smaller waveguide cross section. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fibre lasers or amplifiers, where light must be coupled efficiently from pump sources to a double clad fibre.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
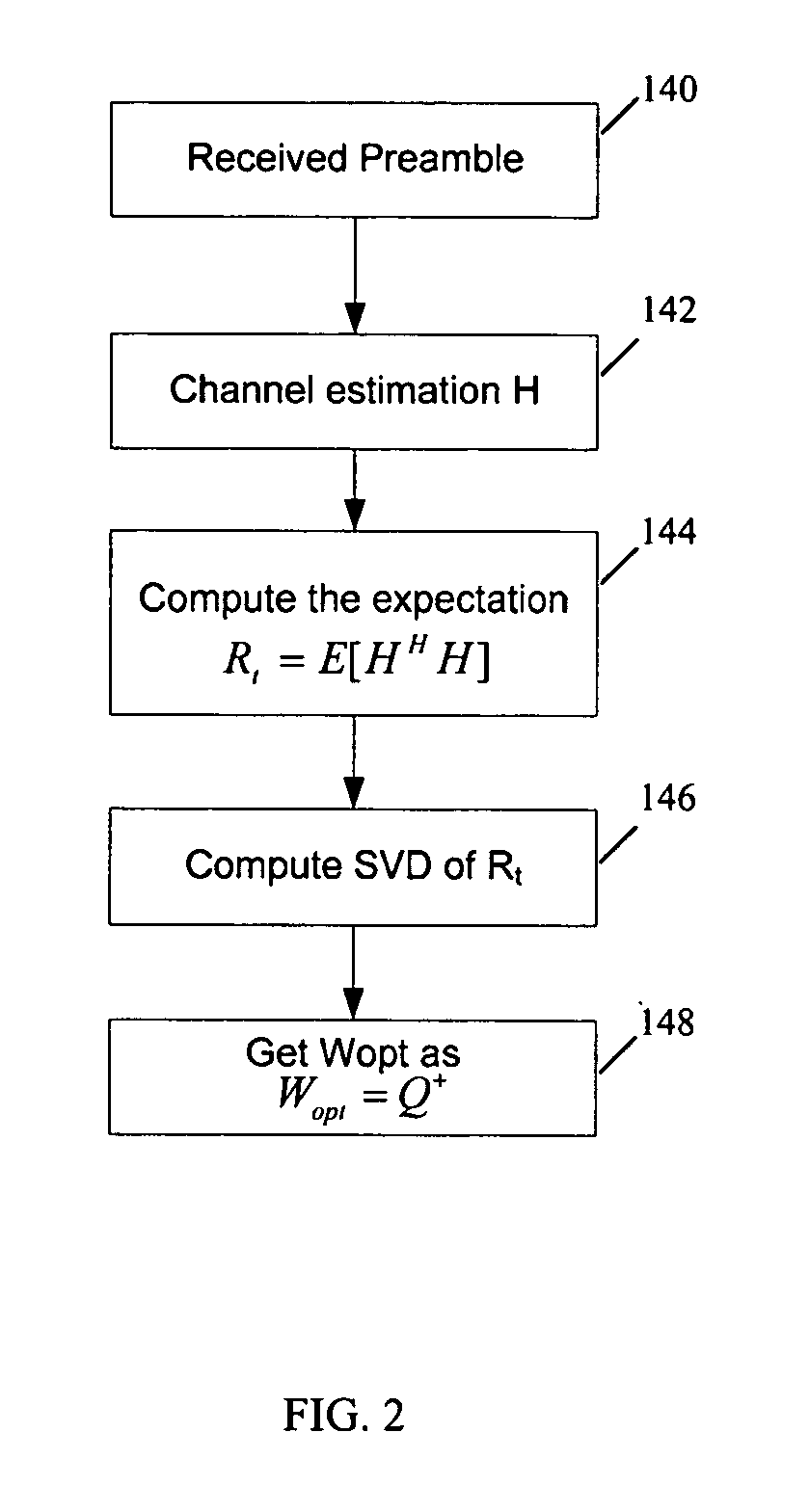
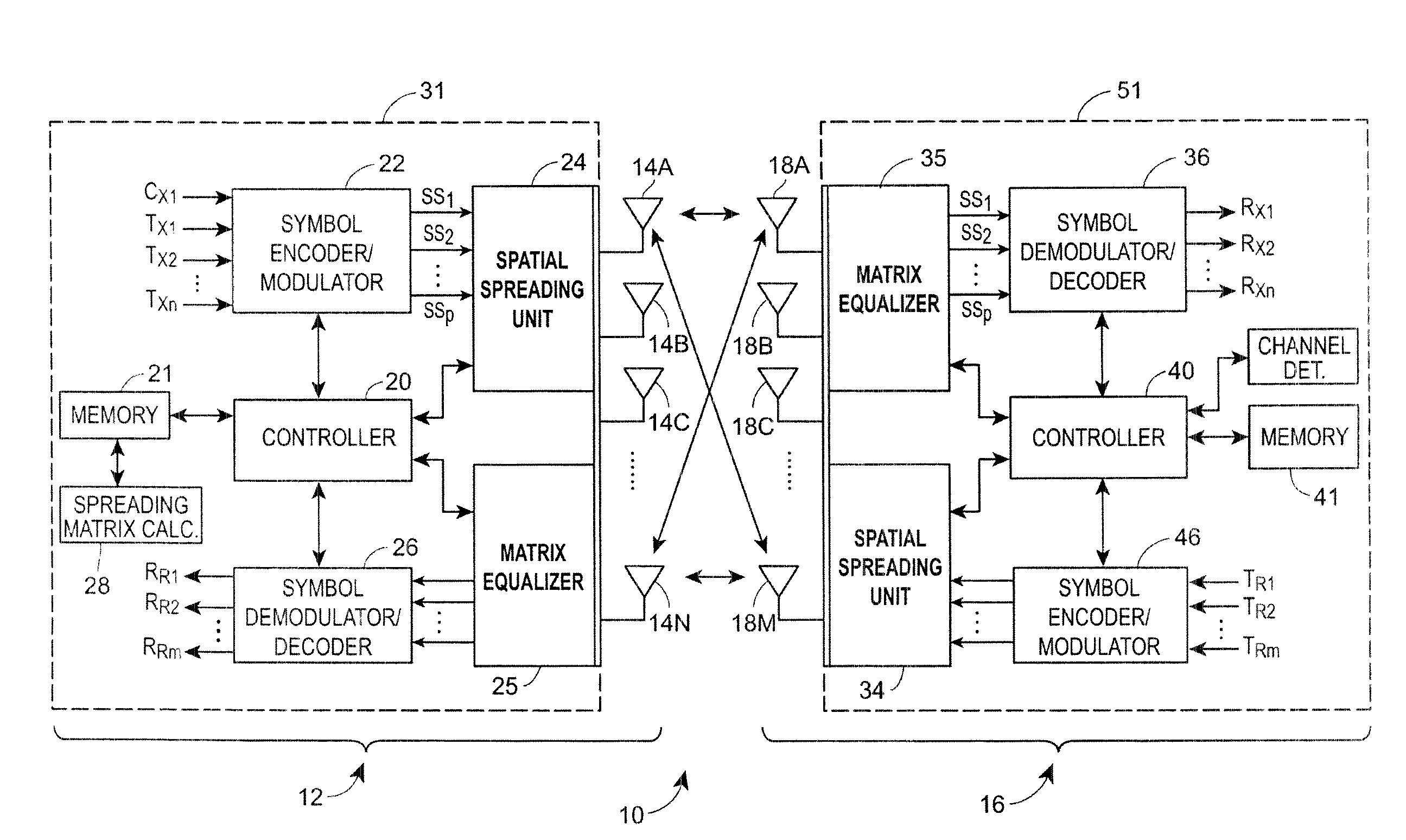
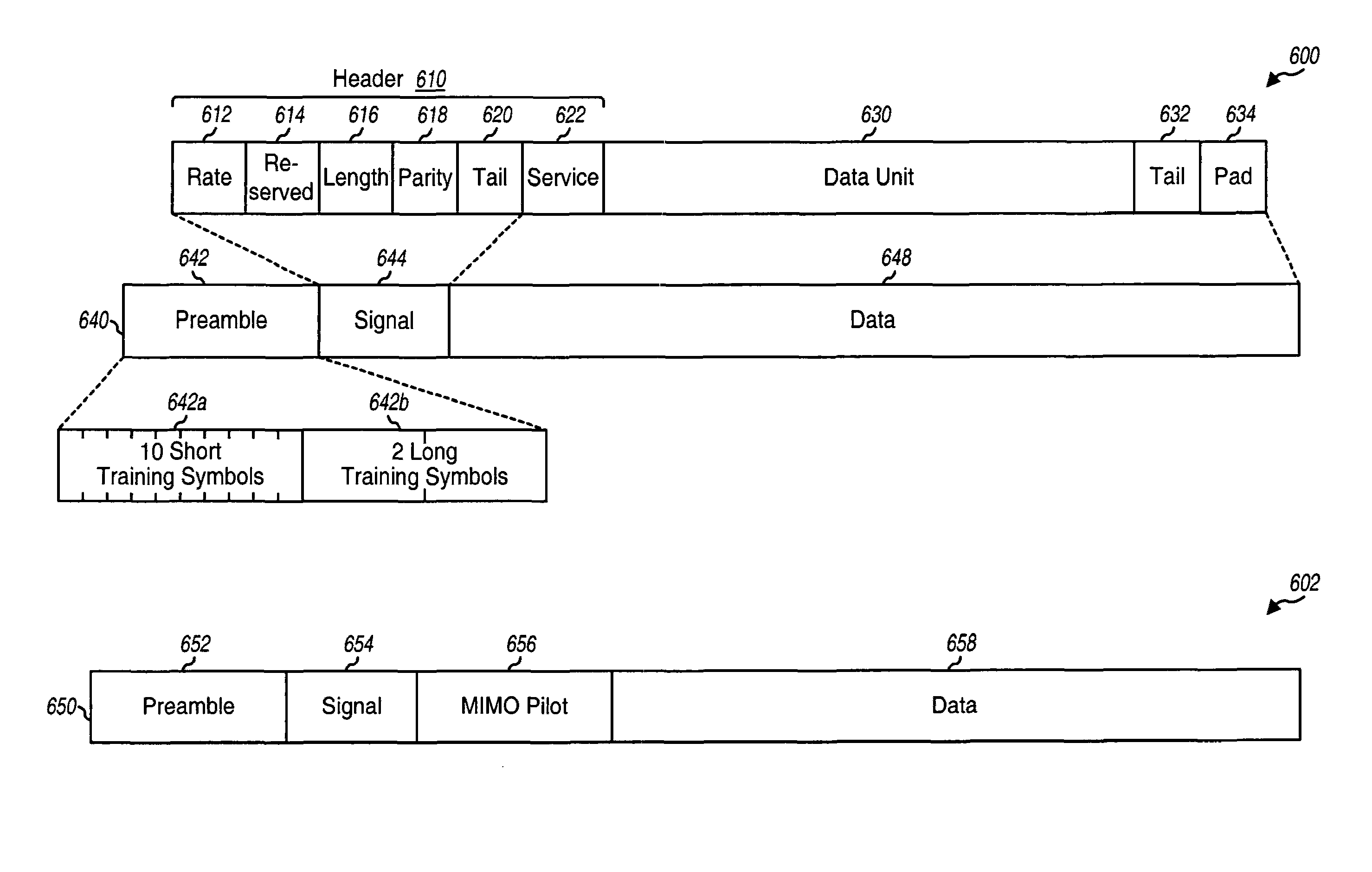
METHOD AND APPARATUS USING SOUNDING PPDUs TO PROVIDE RANGE EXTENSION TO IEEE 802.11n SIGNALS
InactiveUS20100111220A1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSpatial mappingCarrier signal
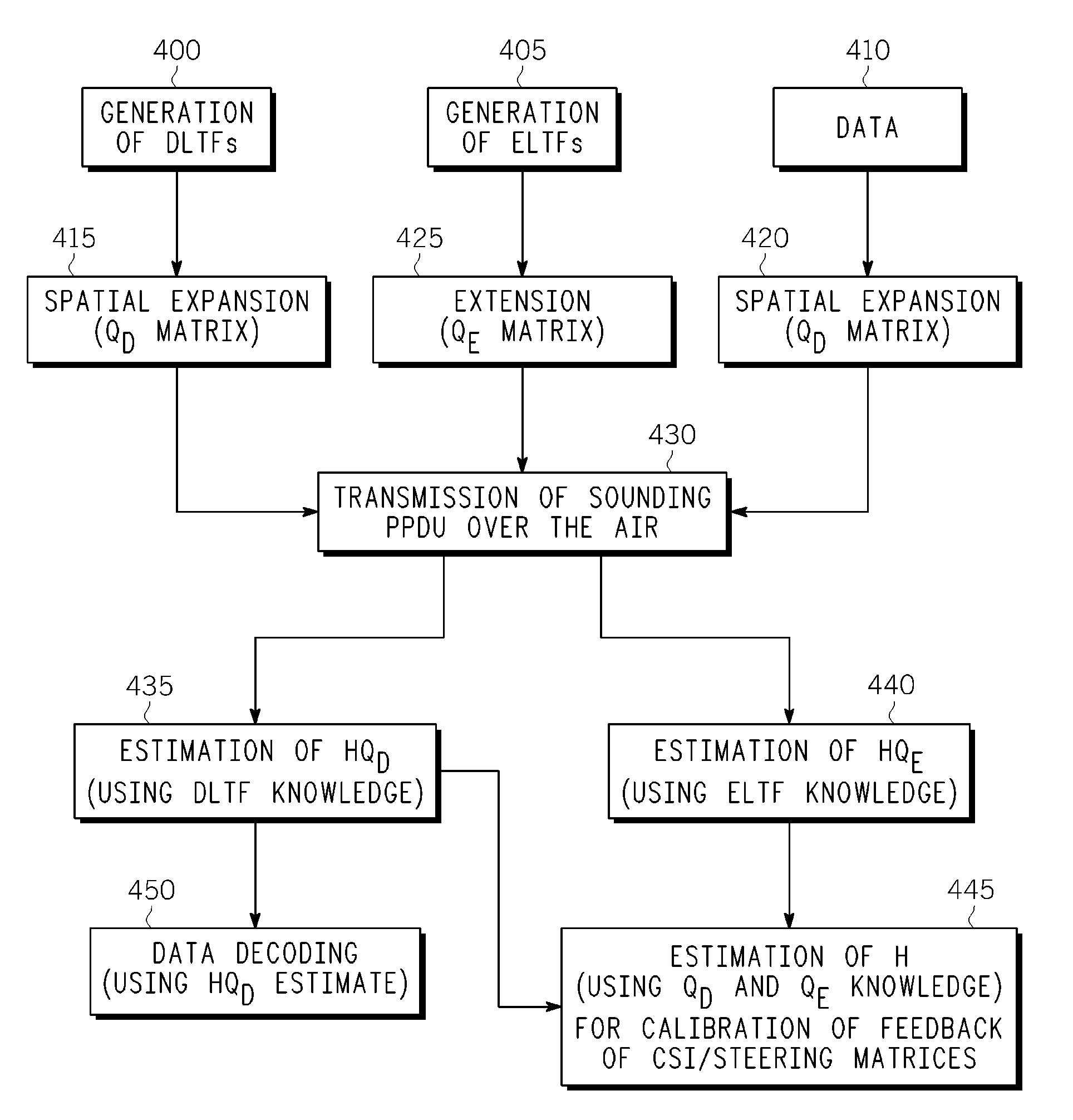
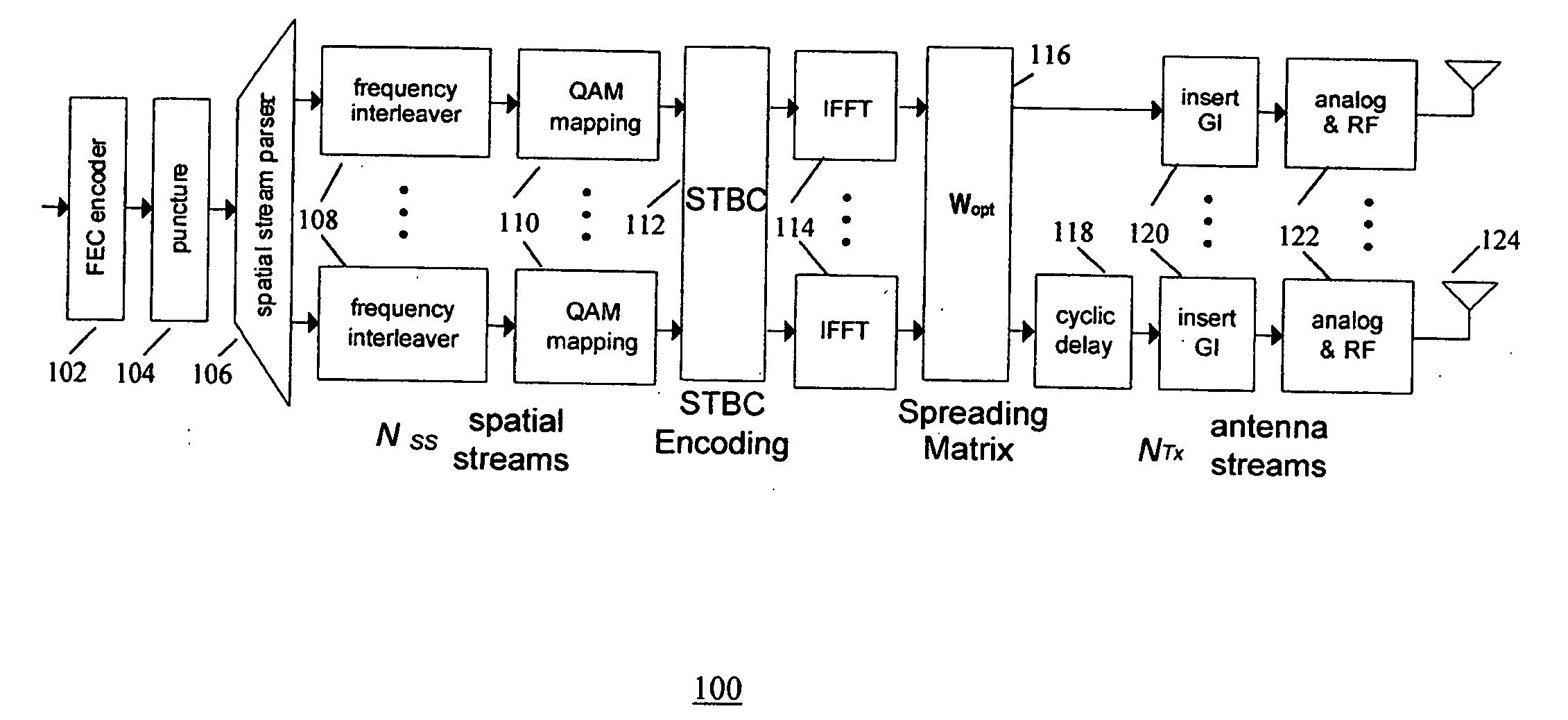
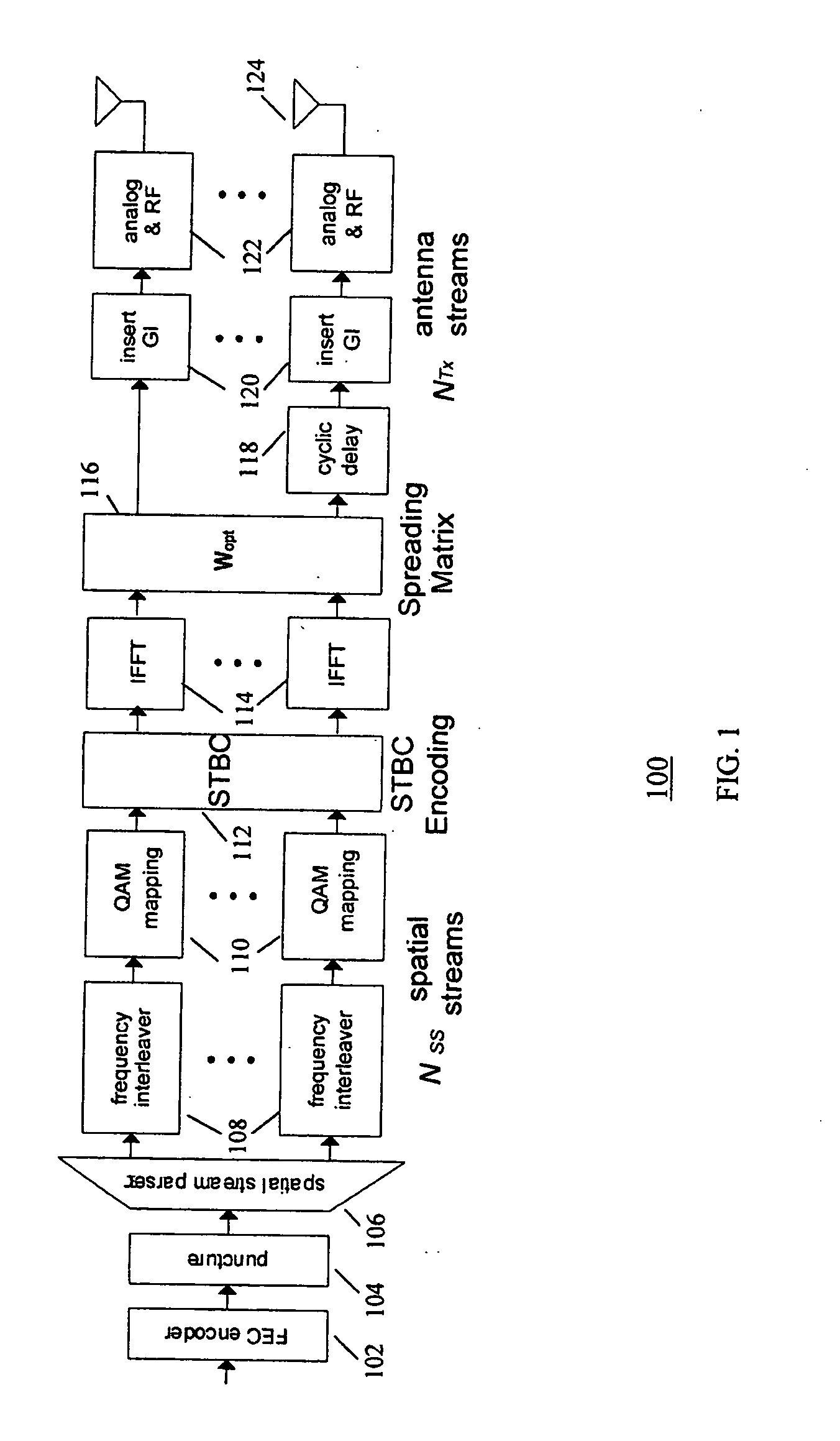
A wireless transmitter includes a stream parser for generating a plurality of spatial streams from a digital signal and a space time block coder (STBC) for mapping each of the spatial streams to a plurality of space-time streams that each include data and a preamble for estimating a channel transfer function. The transmitter also includes a spatial mapper for spatially expanding each of the space-time streams by applying a spatial expansion matrix to data and to first training symbols used in the preamble to probe a channel experienced by the data and by applying an extension matrix to second training symbols used in the preamble to probe at least one additional dimension of the channel to enable use of beamforming to achieve range extension The spatial expansion matrix and the extension matrix form an overall matrix that has at least two orthogonal columns with different norms. The wireless transmitter also includes an analog front end for modulating the spatially expanded space-time streams onto a wireless carrier.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and system for computing a spatial spreading matrix for space-time coding in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20080101493A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionChannel state informationCommunications system
A method and system for wireless communication over a wireless channel combines space-time coding with statistical transmit beamforming. As such, instantaneous channel state information is not required. In one implementation, statistical beamforming is performed by employing an optimal spreading matrix as a function of a transmit correlation matrix, without requiring instantaneous channel state information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical coupler devices, methods of their production and use
InactiveUS7526165B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberWaveguide
The present invention relates in general to coupling of light from one or more input waveguides to an output waveguide or output section of a waveguide having other physical dimensions and / or optical properties than the input waveguide or waveguides. The invention relates to an optical component in the form of a photonic crystal fiber for coupling light from one component / system with a given numerical aperture to another component / system with another numerical aperture. The invention further relates to methods of producing the optical component, and articles comprising the optical component, and to the use of the optical component. The invention further relates to an optical component comprising a bundle of input fibers that are tapered and fused together to form an input coupler e.g. for coupling light from several light sources into a single waveguide. The invention still further relates to the control of the spatial extension of a guided mode (e.g. a mode-field diameter) of an optical beam in an optical fiber. The invention relates to a tapered longitudinally extending optical waveguide having a relatively larger cross section that over a certain longitudinal distance is tapered down to a relatively smaller cross section wherein the spatial extent of the guided mode is substantially constant or expanding from the relatively larger to the relatively smaller waveguide cross section. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fiber lasers or amplifiers, where light must be coupled efficiently from pump sources to a double clad fiber.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Methods Circuits Systems and Associated Computer Executable Code for Performing Beamforming Based Wireless Communication
InactiveUS20150124713A1Spatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringModem deviceSignal processing circuits
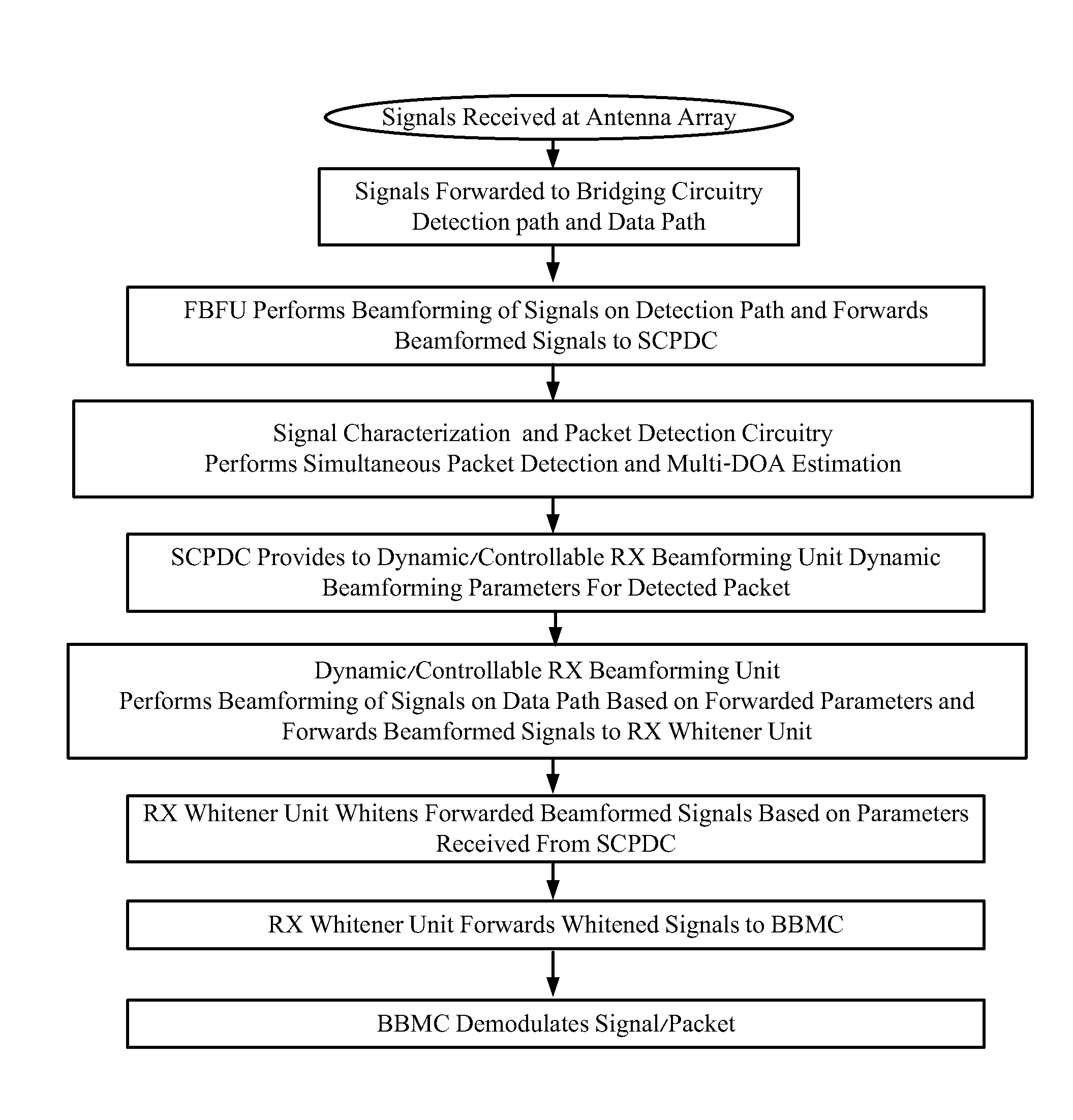
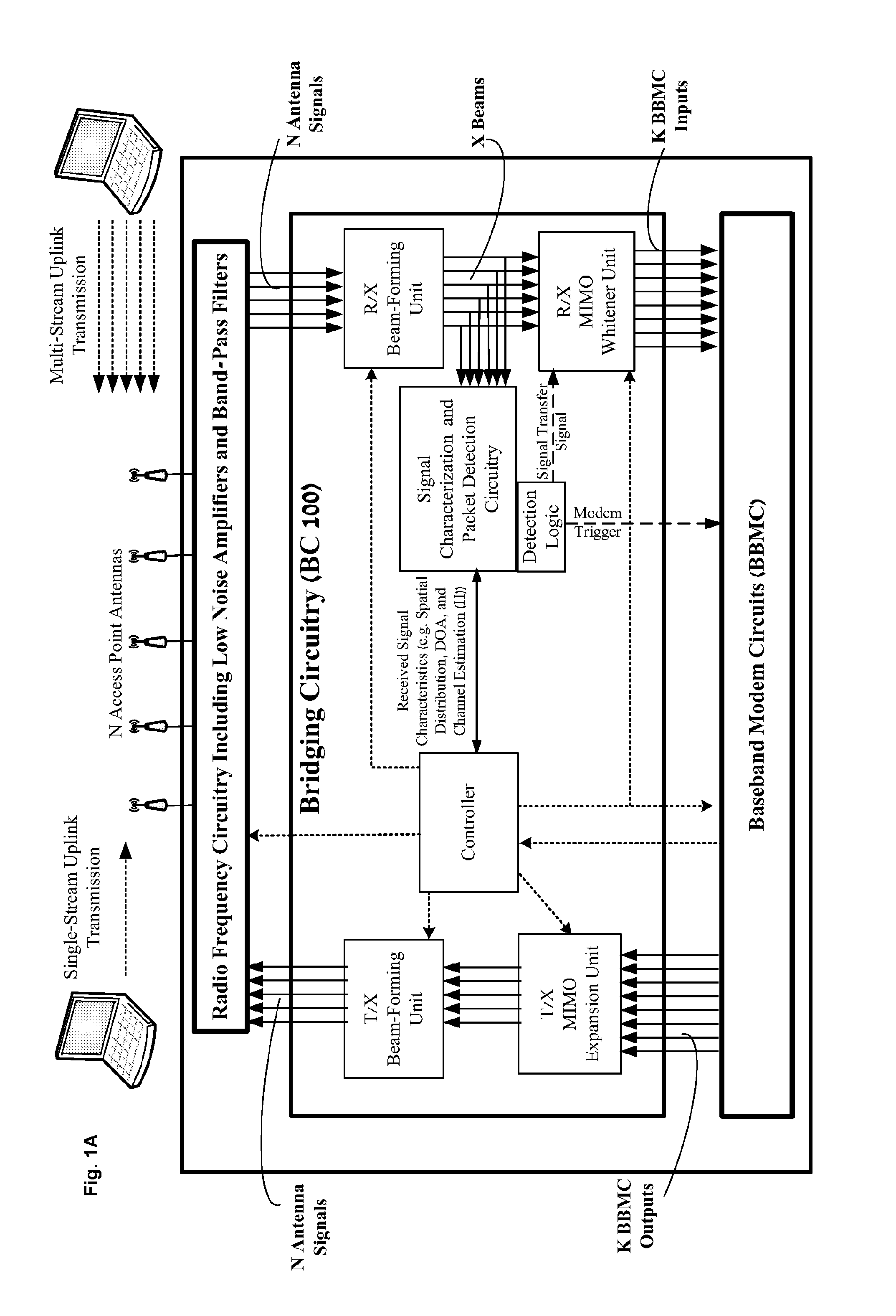
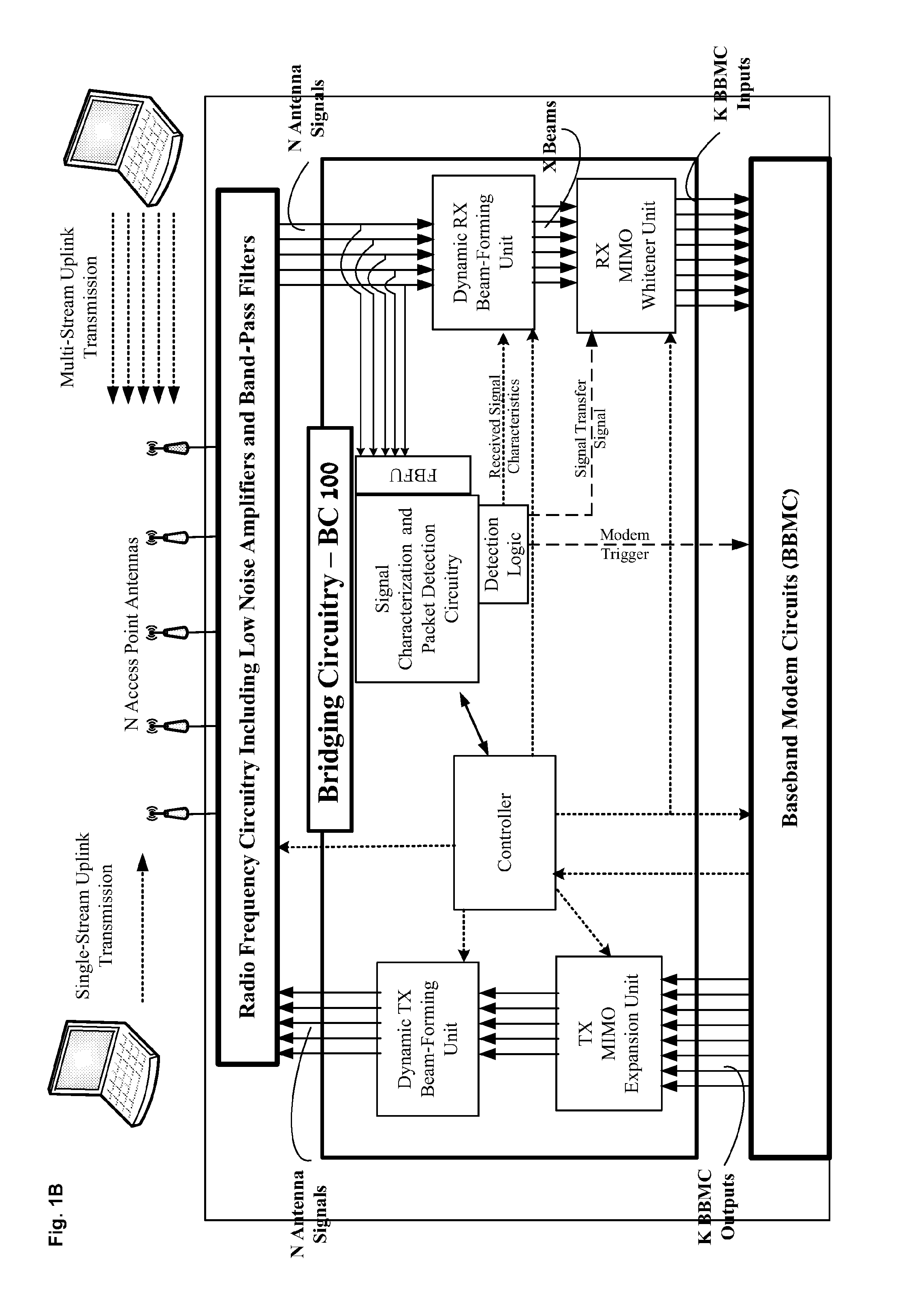
Disclosed are Bridging circuitries (BC100), and access points comprising BC100, which may be adapted to perform signal interfacing, signal conditioning, signal analysis and / or other signal processing to signals passing between RF Chains and Baseband Modem Circuits (BBMC), wherein interfacing, conditioning, analysis and / or processing may include: (1) Tx beam forming, (2) Rx Beam forming, (3) per beam Rx packet detection, (4) signal analysis and characterization and (4) MIMO spatial expansion. BC100 may include signal processing circuitry adapted to perform simultaneous multi-DOA estimation and packet detection upon multiple beams. BC100 may also be adapted to coordinate operation of the RF Chains and BBMC relative to one another. BC100 may also comprise memory for storing signal characteristics which may be utilized to improve its operation
Owner:GO NET SYST
High-resolution remote sensing data atmospheric correction method
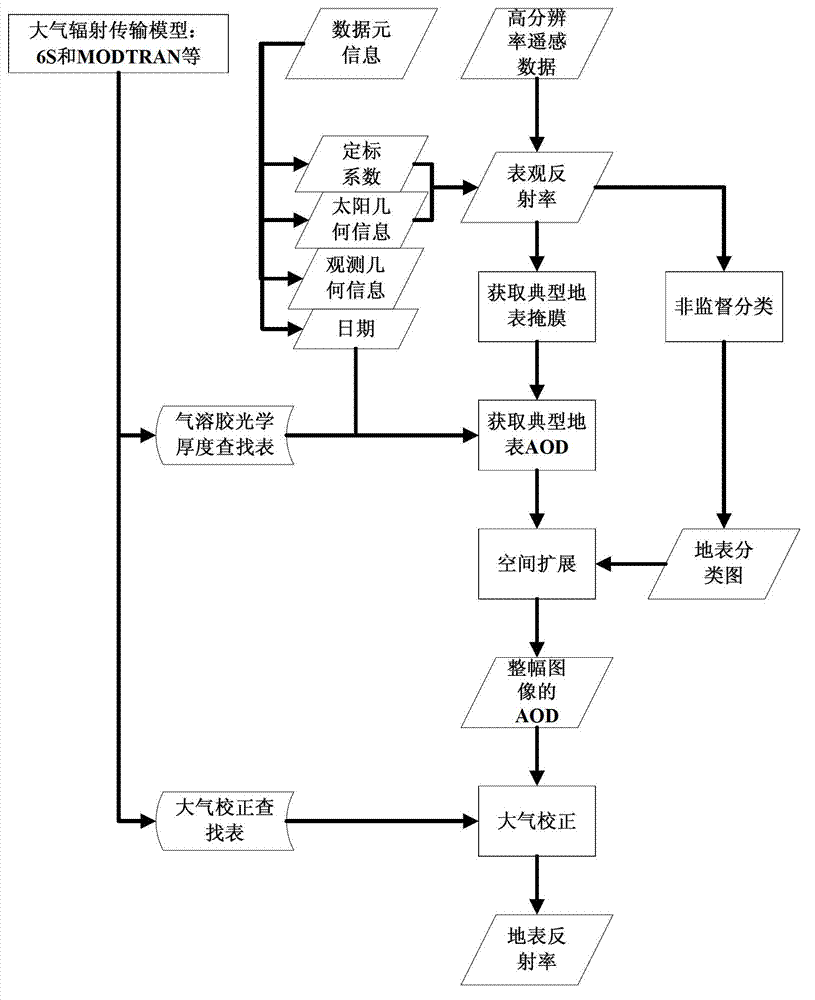
ActiveCN102955154AHigh precisionImprove usabilityWave based measurement systemsSensing dataUsability
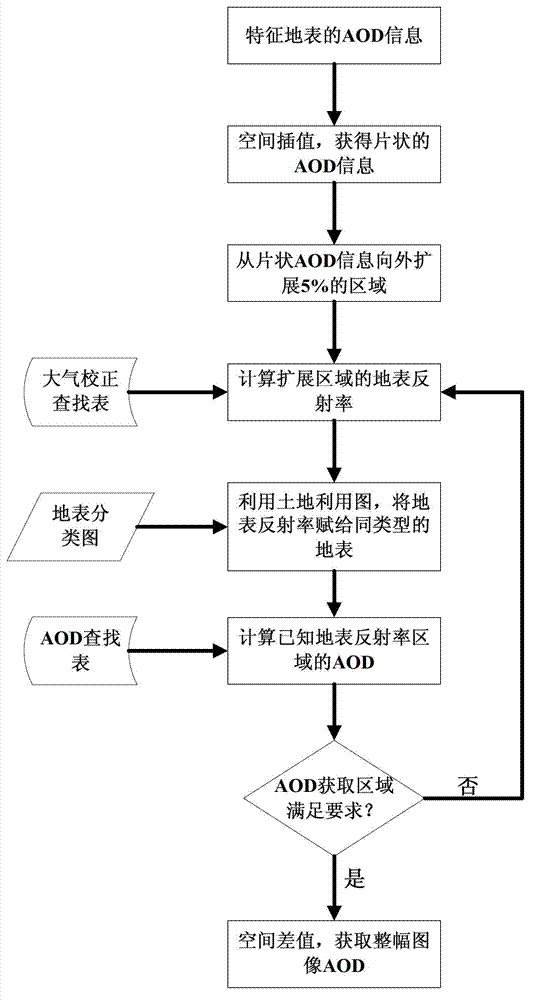
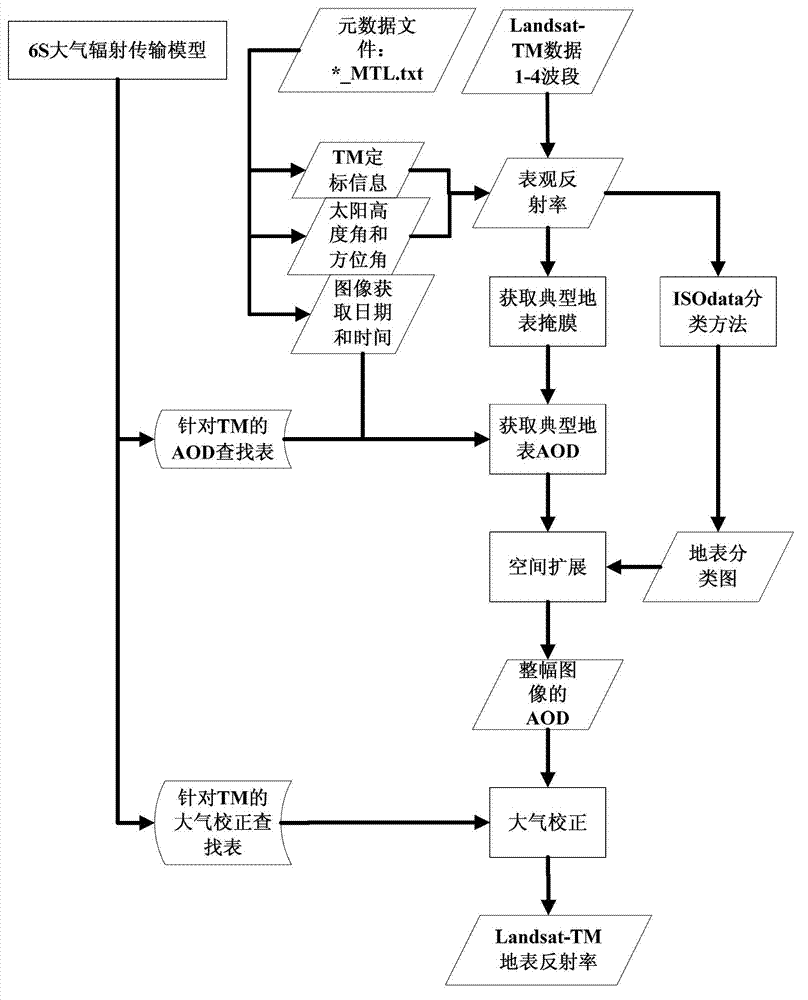
The invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing data atmospheric correction method comprising the following steps of: S1, obtaining related information from data element information; S2, calculating the apparent reflectance of the typical land surface; S3, obtaining a mask of the typical land surface; S4, building an AOD (Aerosol Optical Depth) inversion correction lookup table by utilizing an atmospheric radiation transmission model; S5, calculating the AOD of the typical land surface; S6, obtaining a land surface classification chart; S7, forming the AOD of an whole image through a spatial expansion method; and S8, executing atmospheric correction on the high-resolution remote sensing data according to the AOD of the whole image and the atmospheric correction lookup table to get the land surface reflectance of the high-resolution remote sensing data. In the method, the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data is used for obtaining the AOD of the whole image, the accuracy and usability of the atmospheric correction are improved, and automation of the whole flow from AOD to atmospheric correction is realized.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of image binarization using histogram modeling
InactiveUS6941013B1Simple methodExpanding horizontal and vertical spatial resolutionImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionMethod of images
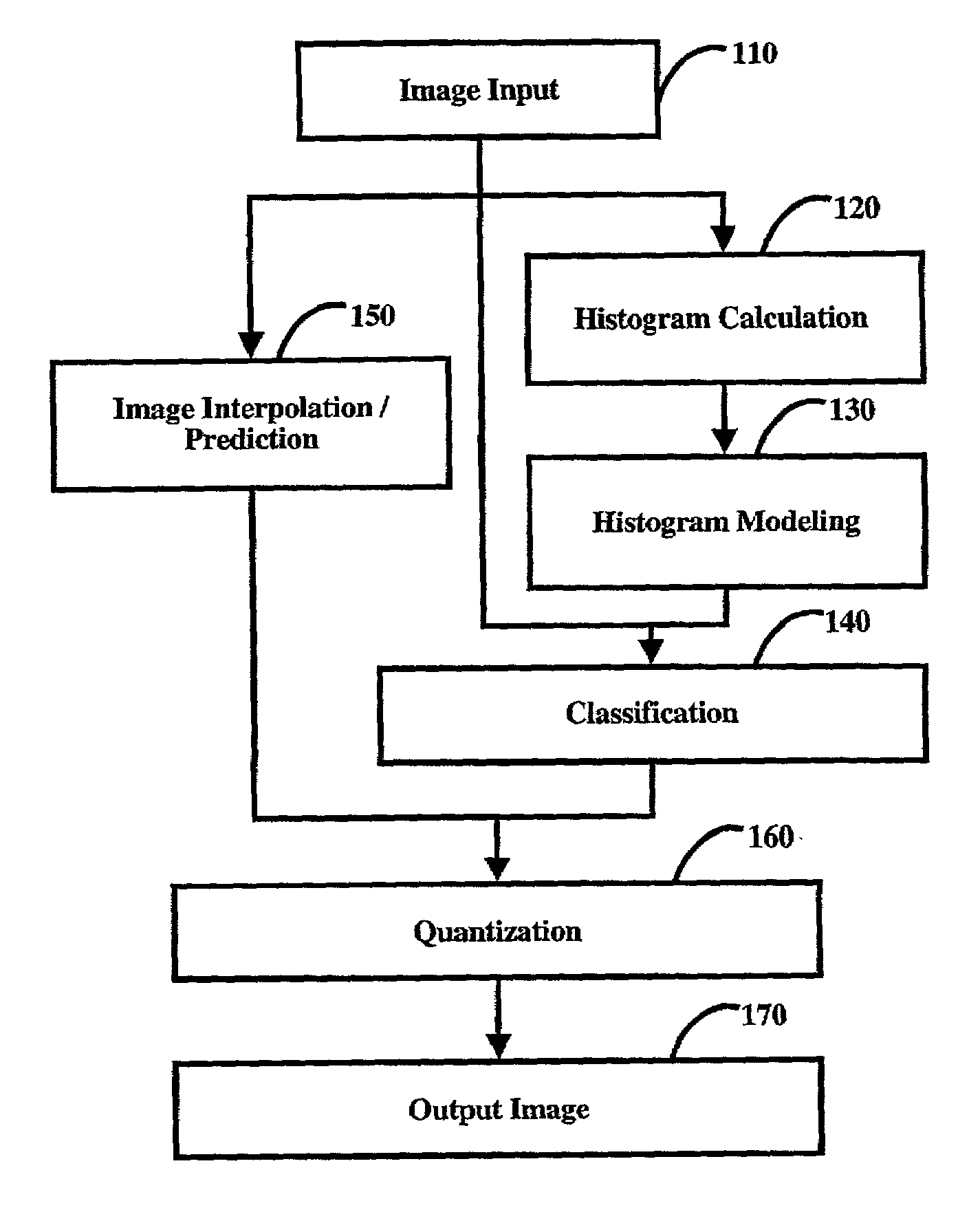
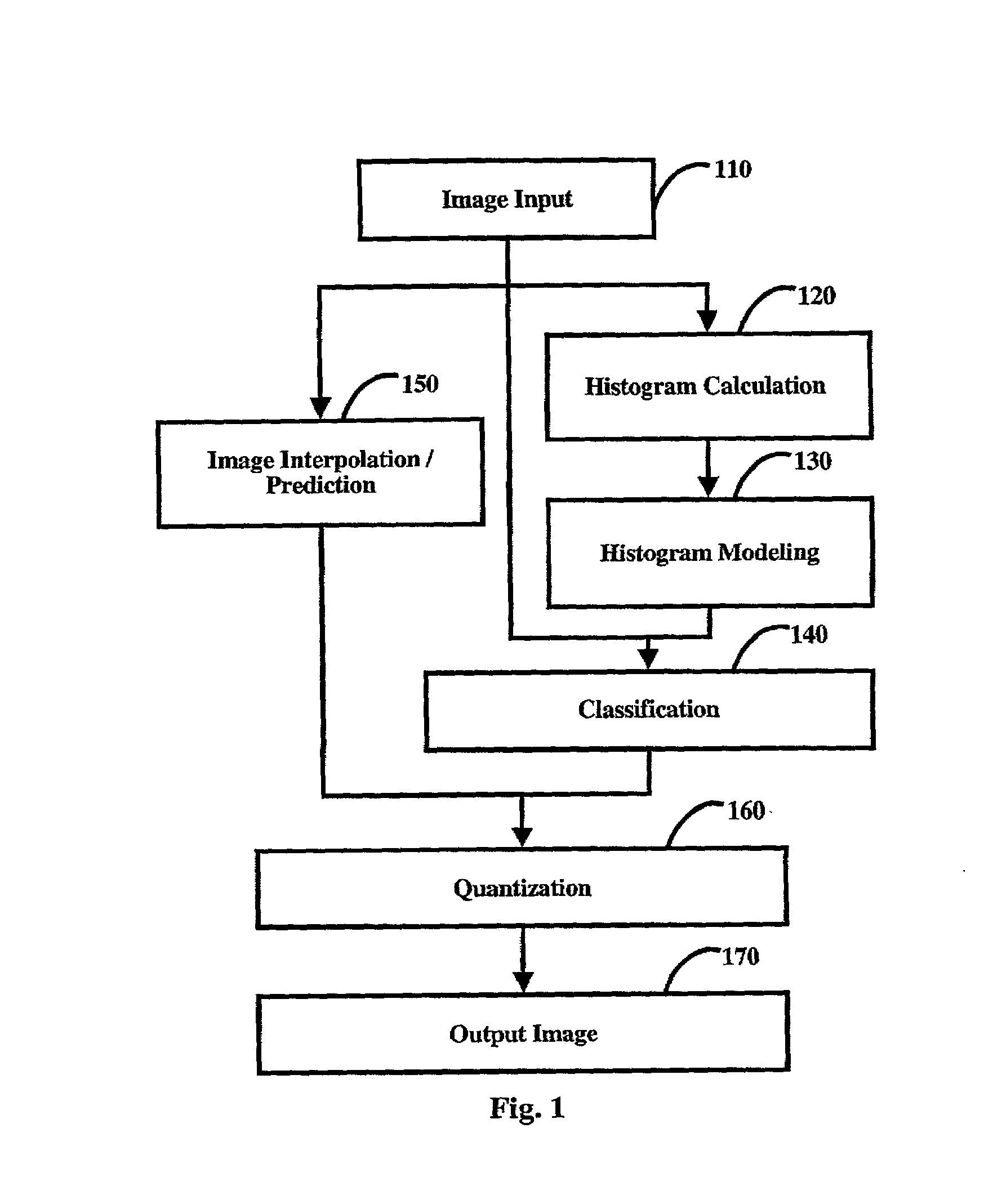
Method of image binarization using histogram modeling, which combines spatial resolution expansion with binarization in a single integrated process using a combination of spatial expansion, histogram modeling, classification, and quantization. Each pixel of the input image is expanded into a higher resolution image, and a count of the number of times each distinct gray scale intensity value occurs in the input image is calculated from pixel values of the input image and then modeled with an approximate histogram that is computed as the sum of weighted modeling functions. The input pixel values are then classified using the modeling functions and the results of the pixel classification are used to quantize the high resolution gray scale image to create a binary output image.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE DIRECTOR NAT SECURITY AGENCY
360-degree three-dimensional display device and method based on splicing of multiple high-speed projectors
ActiveCN104298065AIncrease horizontal spaceIncrease vertical spaceProjectorsStereoscopic photographyImage resolutionDepth of field
The invention discloses a 360-degree three-dimensional display device based on splicing of multiple high-speed projectors. The 360-degree three-dimensional display device comprises an orientation diffuser screen set, a rotating device set, a rotating detection module, a projection splicing integration module, image storage modules and the N high-speed projectors. An algorithm of splicing of the multiple high-speed projectors is used for calculation to obtain a two-dimensional frame image sequence projected by each high-speed projector in real time, and the two-dimensional frame image sequences are sent to all the image storage modules. Under modulation of the rotating detection module, all the high-speed projectors are controlled to be matched with rotation of one set or more sets of orientation diffuser screens, splicing and synthesizing imaging of projection areas of all the high-speed projectors are achieved, and the space resolution ratio of three-dimensional display is improved in a multiplied mode. The algorithm based on splicing of the high-speed projectors is matched with the orientation diffuser screens for imaging, the three-dimensional imaging space is enlarged, the transverse dimension, the longitudinal dimension and the field depth dimension of a three-dimensional image are increased, and spatial expansion of three-dimensional display of the large-dimension space is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
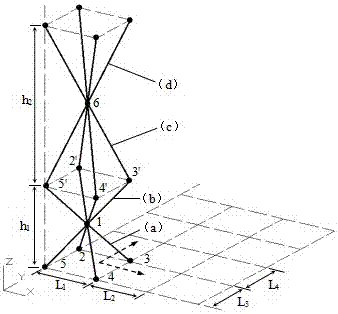
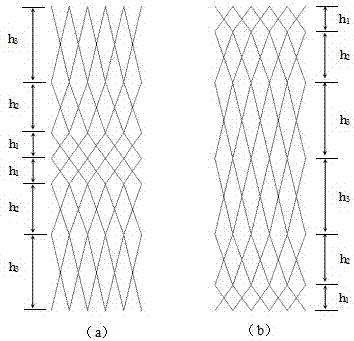
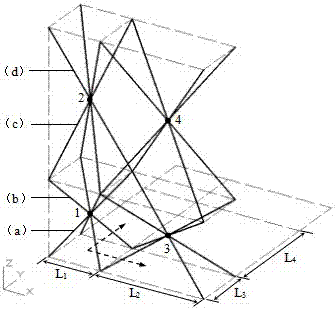
Lattice material with function gradients
The invention discloses a lattice material with function gradients. The lattice material is formed through spatial expansion of a single cell element lattice structure. Single cell elements can be in a pyramid shape or in a tetrahedron shape or in other polyhedron shapes. The height direction of the single cell elements is the Z-axis direction. Dots on the bottom face of the single cell element are located on the X-Y plane. Single chip lattice structures are formed through extended arrangement of the single cell element structures in the X direction and the Y direction. During extended arrangement, the height of the single cell elements on the same layer in the Z direction are kept constant. The distances between upper endpoints of the bottom faces of every two adjacent single cell elements are not equal. The single chip lattice structure with different heights are subjected to mirror symmetry extended arrangement with the X-Y plane where the vertexes of the single cell elements located as the plane of symmetry, so that the multi-layer spatial lattice structure is formed. The physical property parameters of the lattice material represent gradient change along with spatial positions, the lattice material is low in dead load is low, high in designability and excellent in impact resistance, raw materials are easy to obtain, a manufacturing method is simple, and the application prospects are quite considerable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
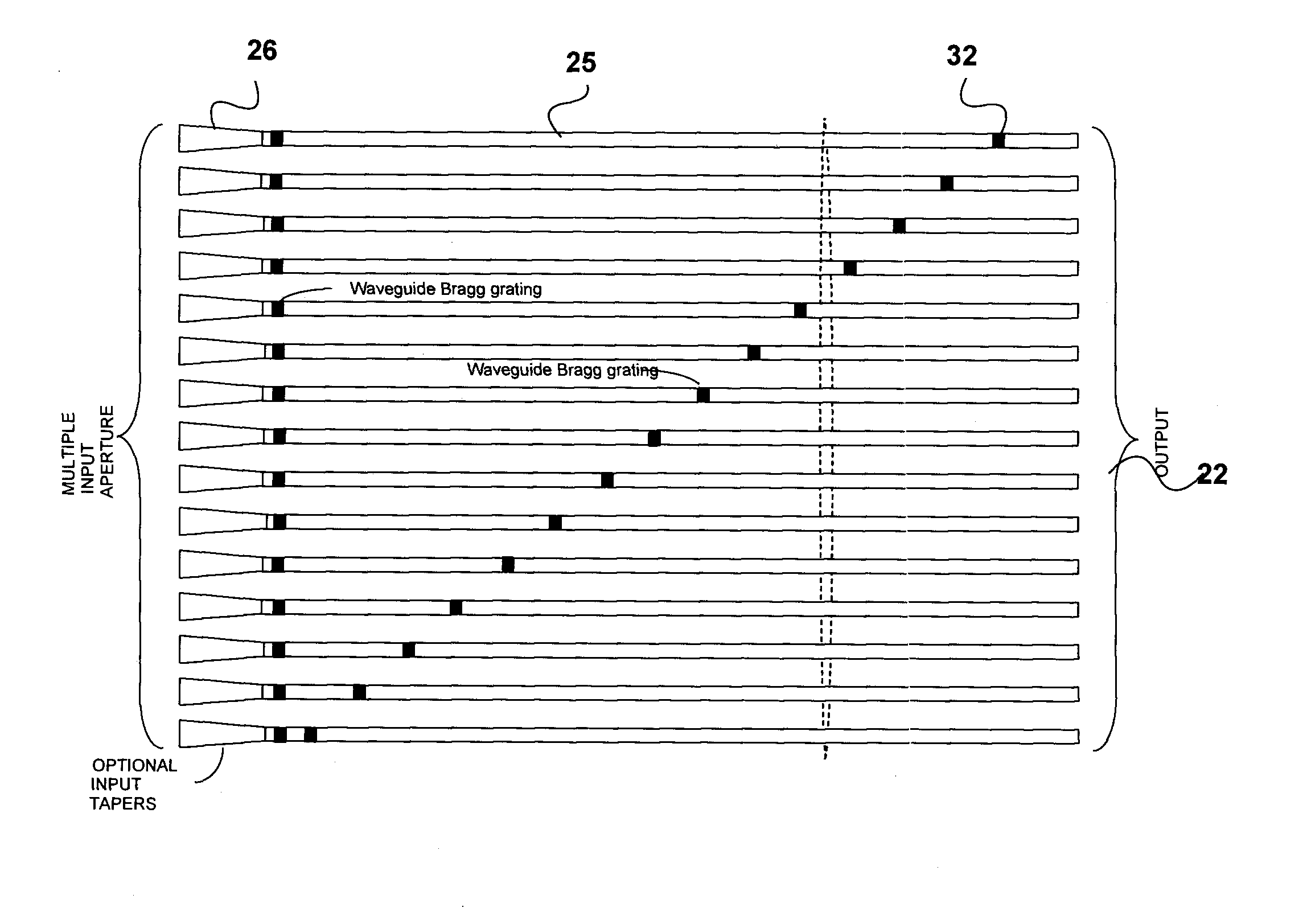
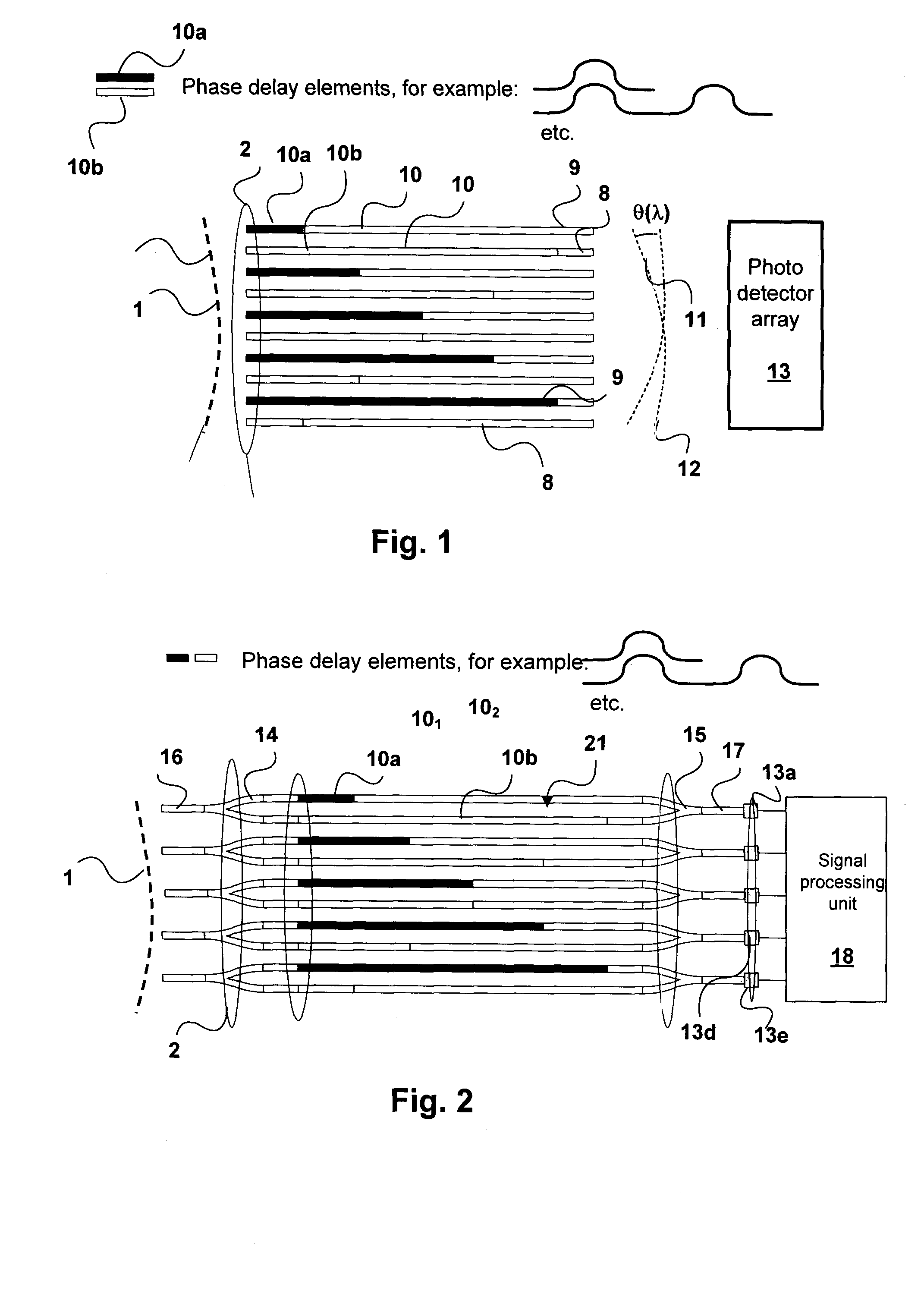
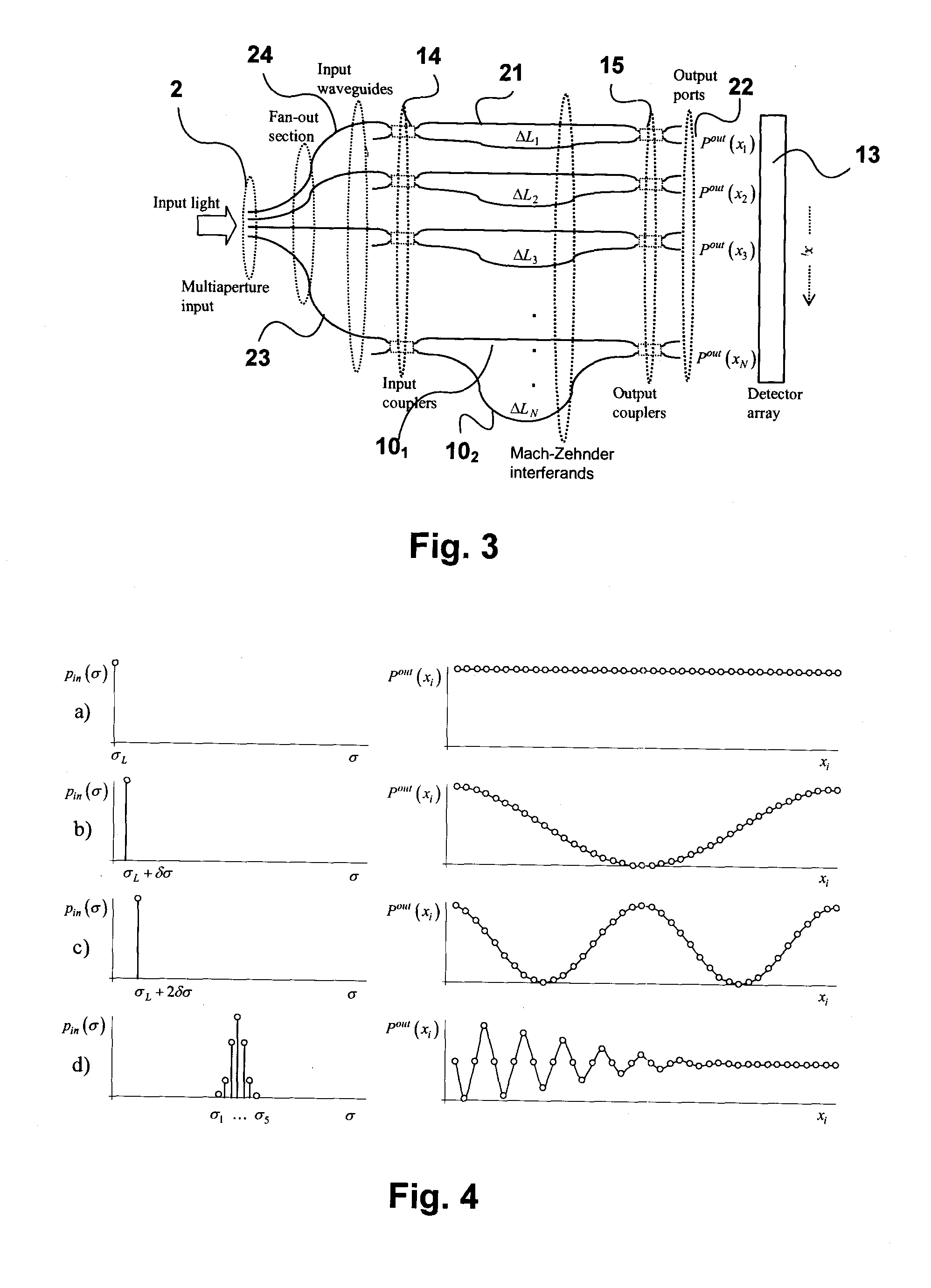
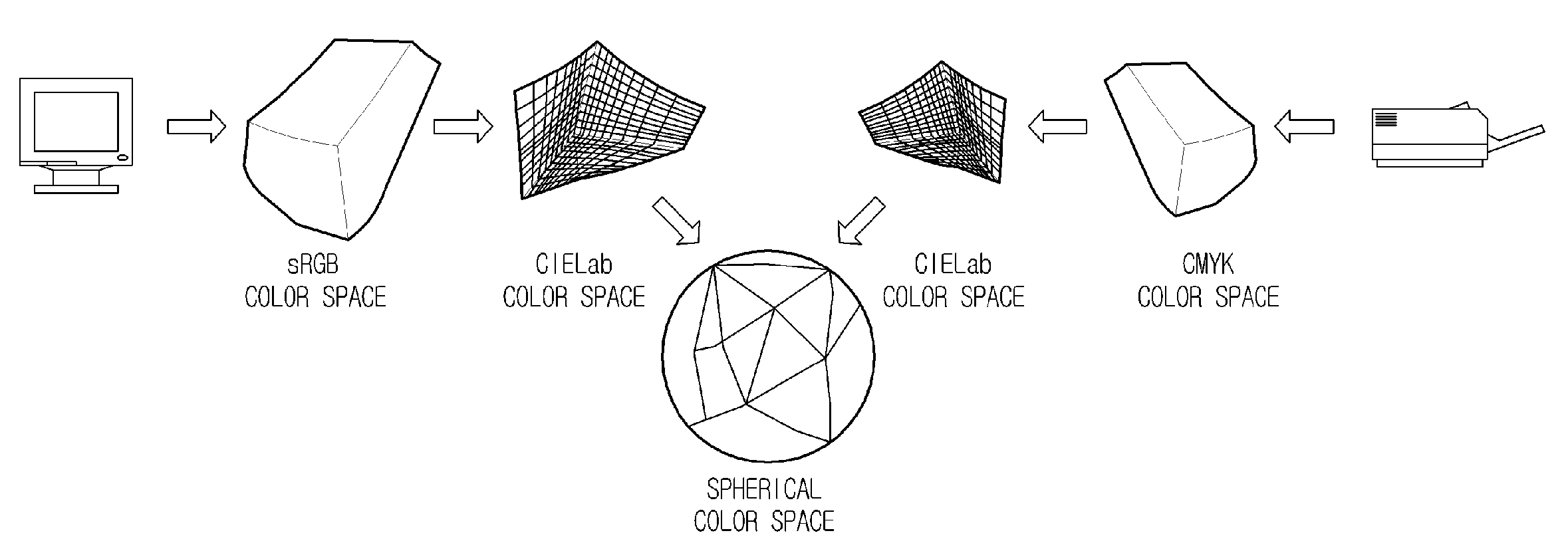
Planar waveguide wavelength dispersive devices with multiple waveguide input aperture
ActiveUS20100110443A1Large optical throughputCompact layoutRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMulti inputWavefront
A spectrometer has a multi-input aperture for admitting an input wavefront and an array of multiple waveguide structures terminating at the multi-input aperture. The input wavefront is incident on each of the waveguide structures, which provide a dispersive function for the input wavefront. Interferometers are formed by elements of the waveguide structures. The interferometers have different optical path length differences (OPDs). The interferometers provide a wavelength responsive output for spatially extended light sources. The output of the interferometers is detected with a detector array. The spectrometer has an improved etendue, and in some embodiments very high resolution.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
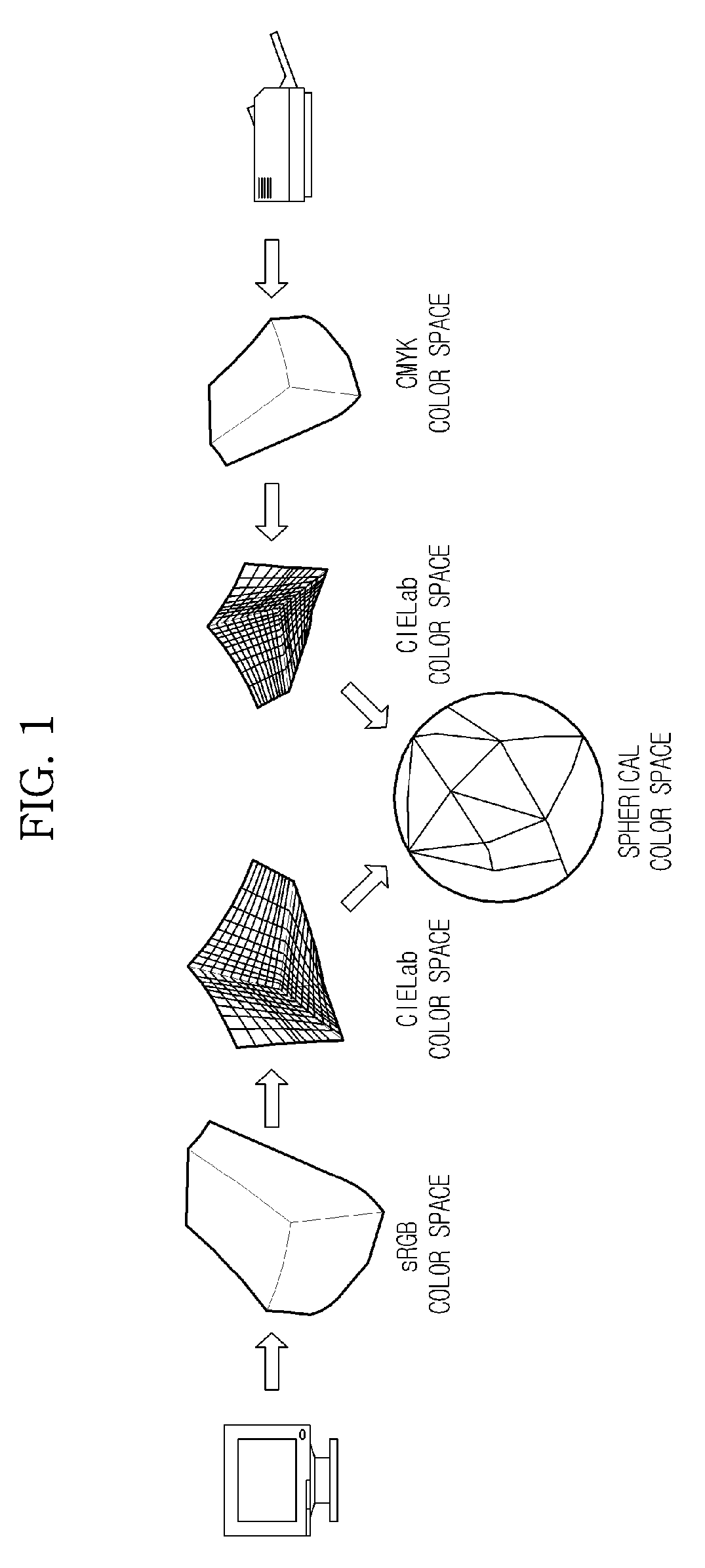
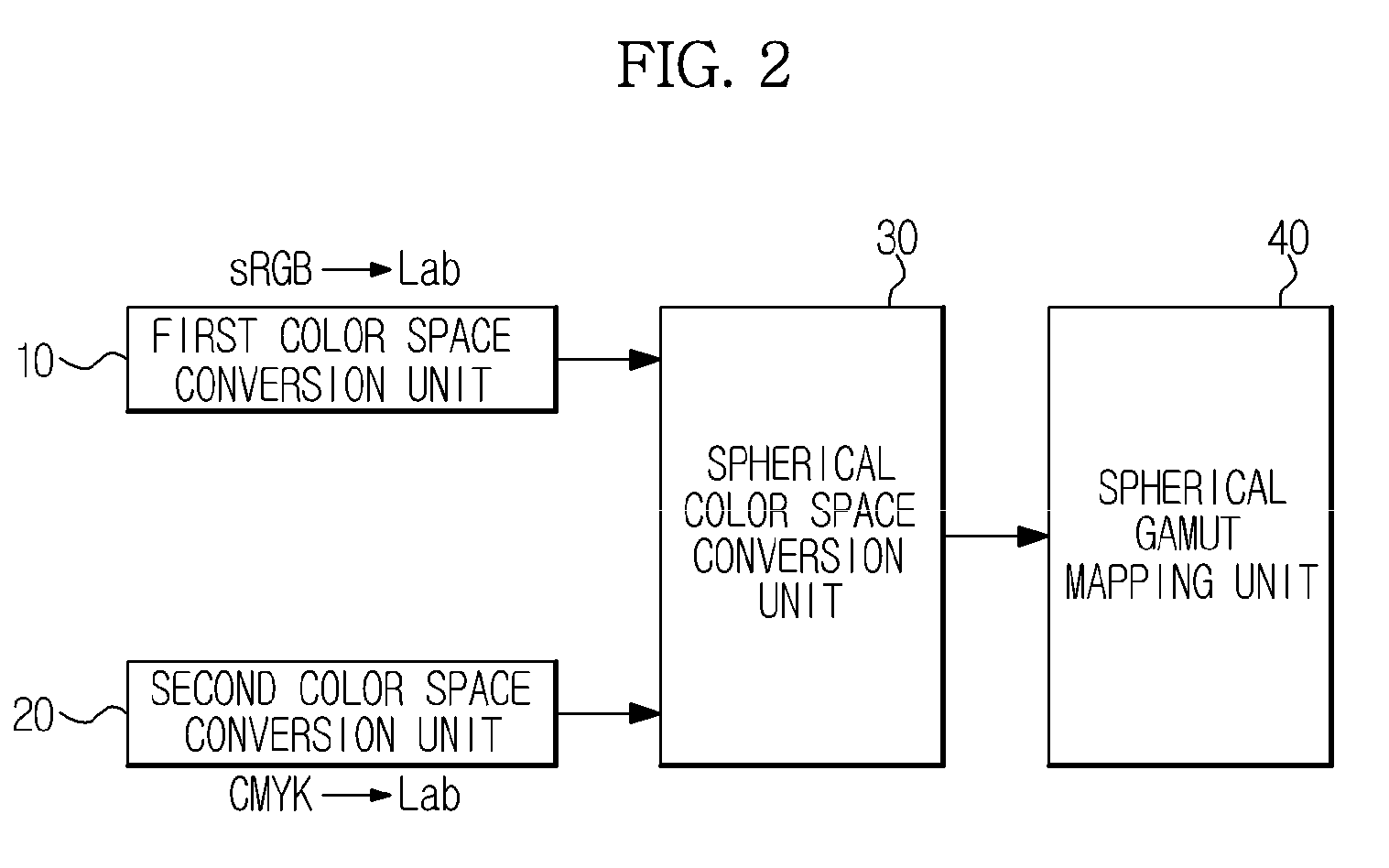
Color space conversion apparatus and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20090059326A1High-quality color reproductionDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsLab color spaceGamut
A color space conversion apparatus and a method of controlling the same, the color space conversion apparatus including: a first color space conversion unit to convert a first color space into a first Lab color space; a second color space conversion unit to convert a second color space into a second Lab color space; a spherical color space conversion unit to expand the first and second Lab color spaces into a spherical color space; and a spherical gamut mapping unit to perform gamut mapping between the first and second color spaces through spherical parametrization, thus avoiding problems in color reproduction caused by the lack of one-to-one correspondence between Lab color space values of the input and output devices.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
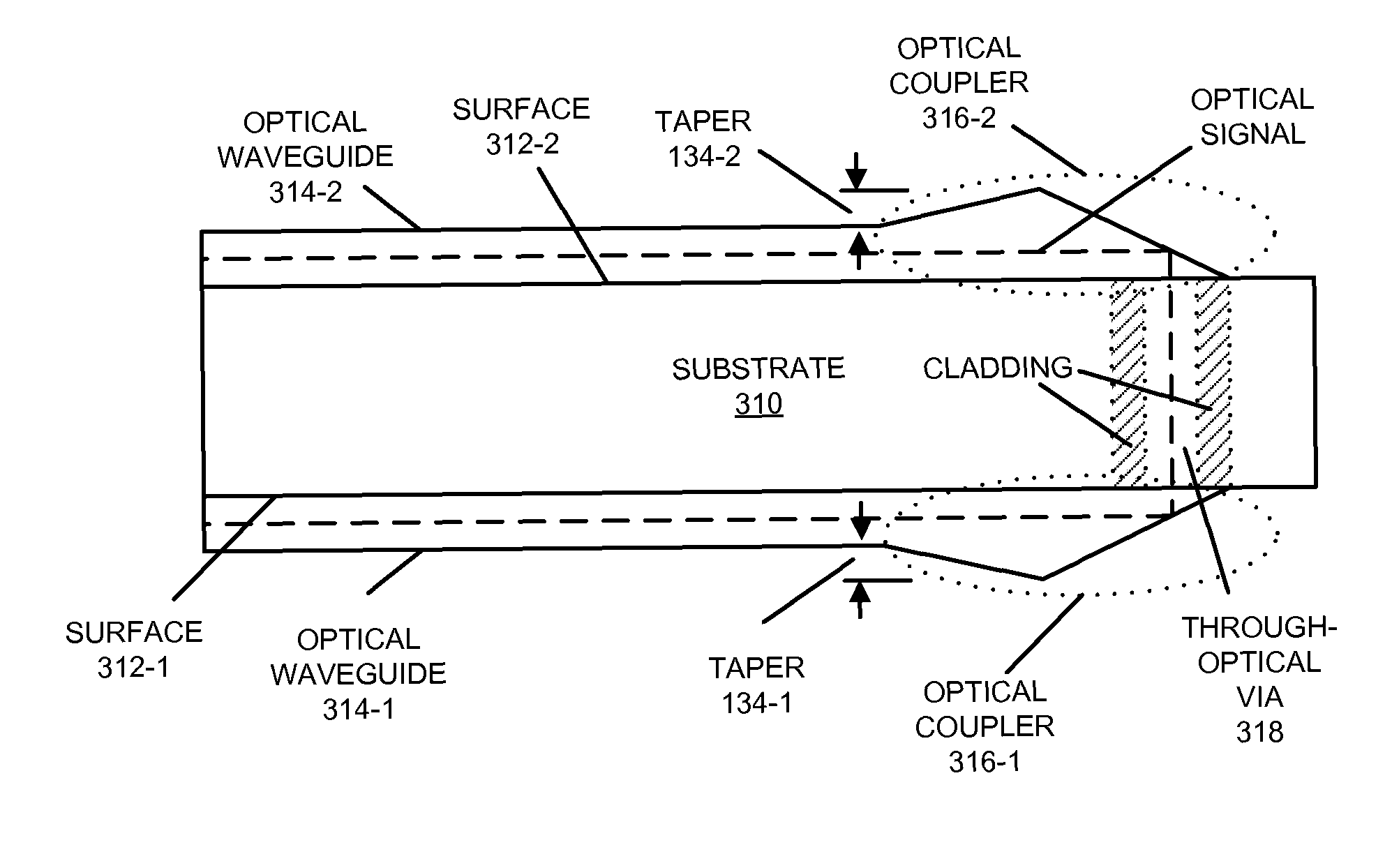
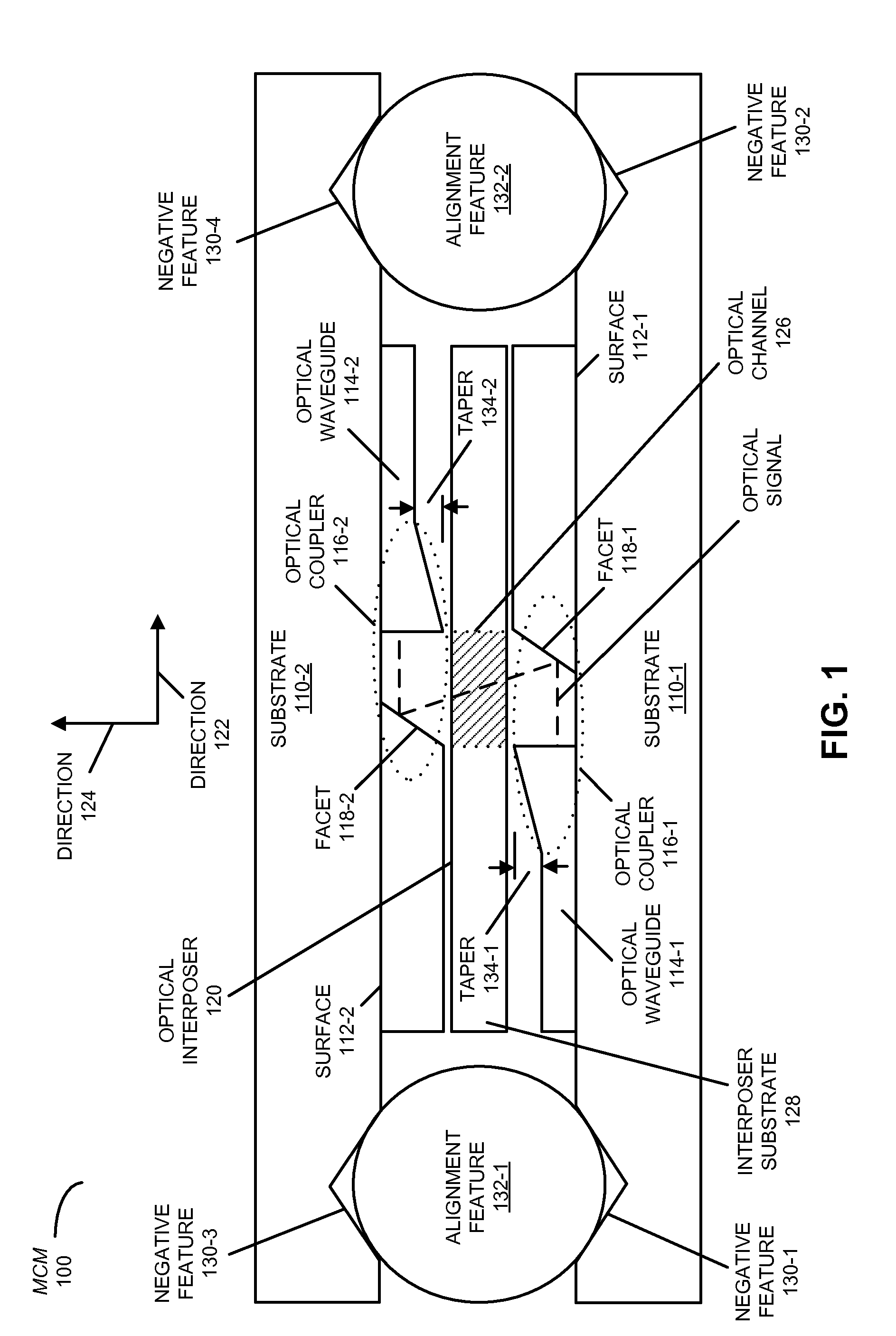
Efficient inter-chip optical coupling
ActiveUS8548288B2Reduce space heightEasy to assembleCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideInterposerWaveguide
In an MCM, an optical signal is conveyed by an optical waveguide disposed on a surface of a first substrate to a first optical coupler. This first optical coupler redirects the optical signal out of the plane of the optical waveguide. Then, an optical interposer guides the optical signal between the first optical coupler and a second optical coupler on a surface of a second substrate, thereby reducing spatial expansion of the optical signal between the optical couplers. Moreover, the second optical coupler redirects the optical signal into a plane of an optical waveguide disposed on a surface of the second substrate, which then conveys the optical signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Equal power output spatial spreading matrix for use in a wireless MIMO communication system
ActiveUS7751495B1Improve powerReduce eliminateDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSignal channelsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
A wireless communication system uses a spatial spreading matrix to simultaneously transmit various different streams of encoded symbol data simultaneously via multiple transmission antennas, wherein the spatial spreading matrix is designed to assure that the different transmission antennas provide equal power output in the presence of both correlated and uncorrelated data within the different encoded symbol streams. The use of this spatial spreading matrix reduces or eliminates the condition in which a particular one of the transmission antennas needs to operate at an output power that is significantly higher than the others of the transmission antennas, which might lead to saturation of, or to the non-linear or abnormal operation of a power amplifier associated with the particular transmission antenna, resulting in improper amplification for that particular transmission antenna.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
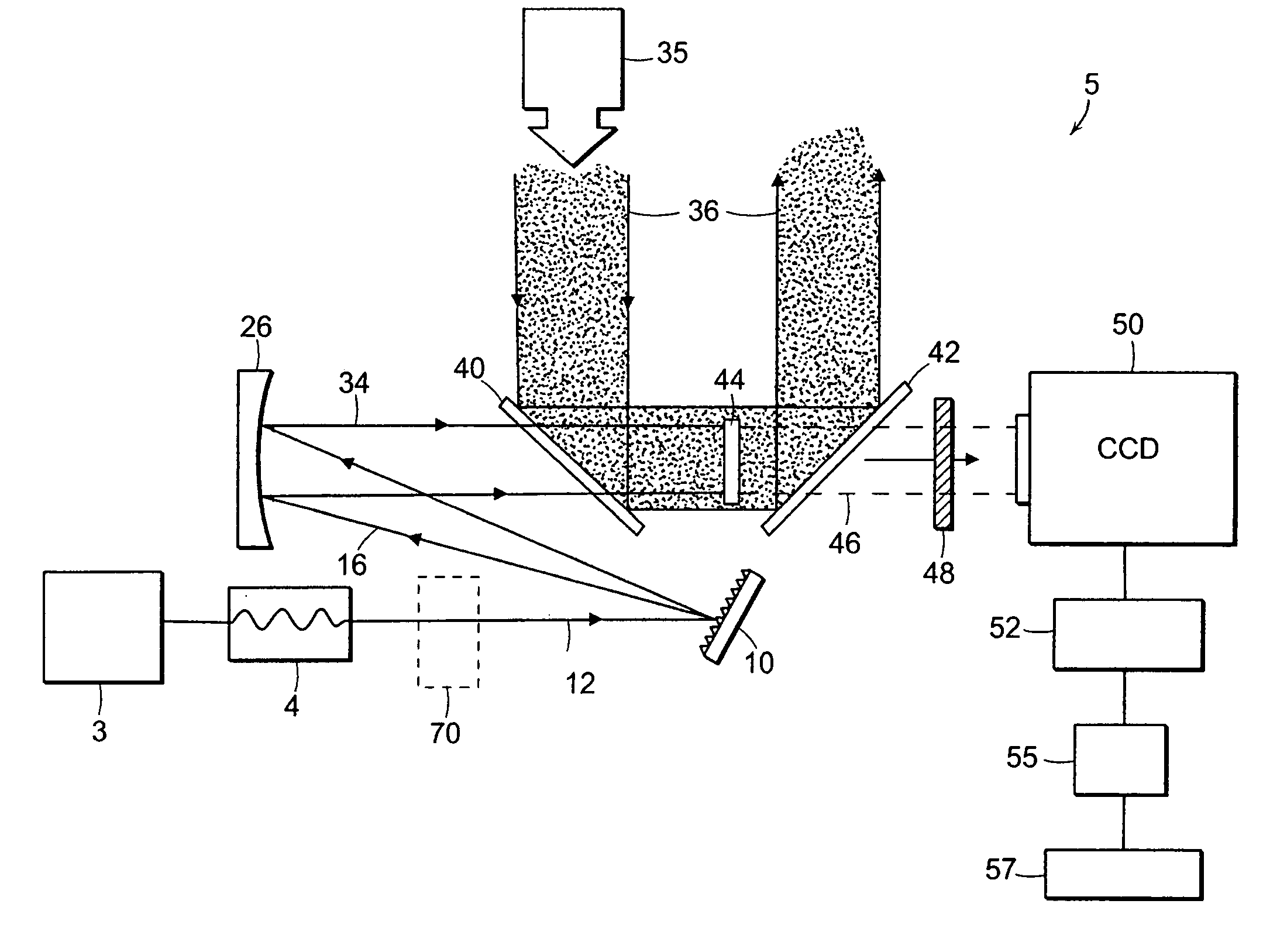
Method and apparatus for frequency-converting infrared light
InactiveUS20070018103A1Radiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyLight beam
The invention relates to methods and apparatus for modifying the frequency characteristics of a spatially-dispersed mid-IR spectra for spectroscopy. In a preferred embodiment, sum frequency generation between a frequency-dispersed IR beam and an ultrafast optical pulse generates a spatially-extended optical signal that is collected with a CCD detector.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
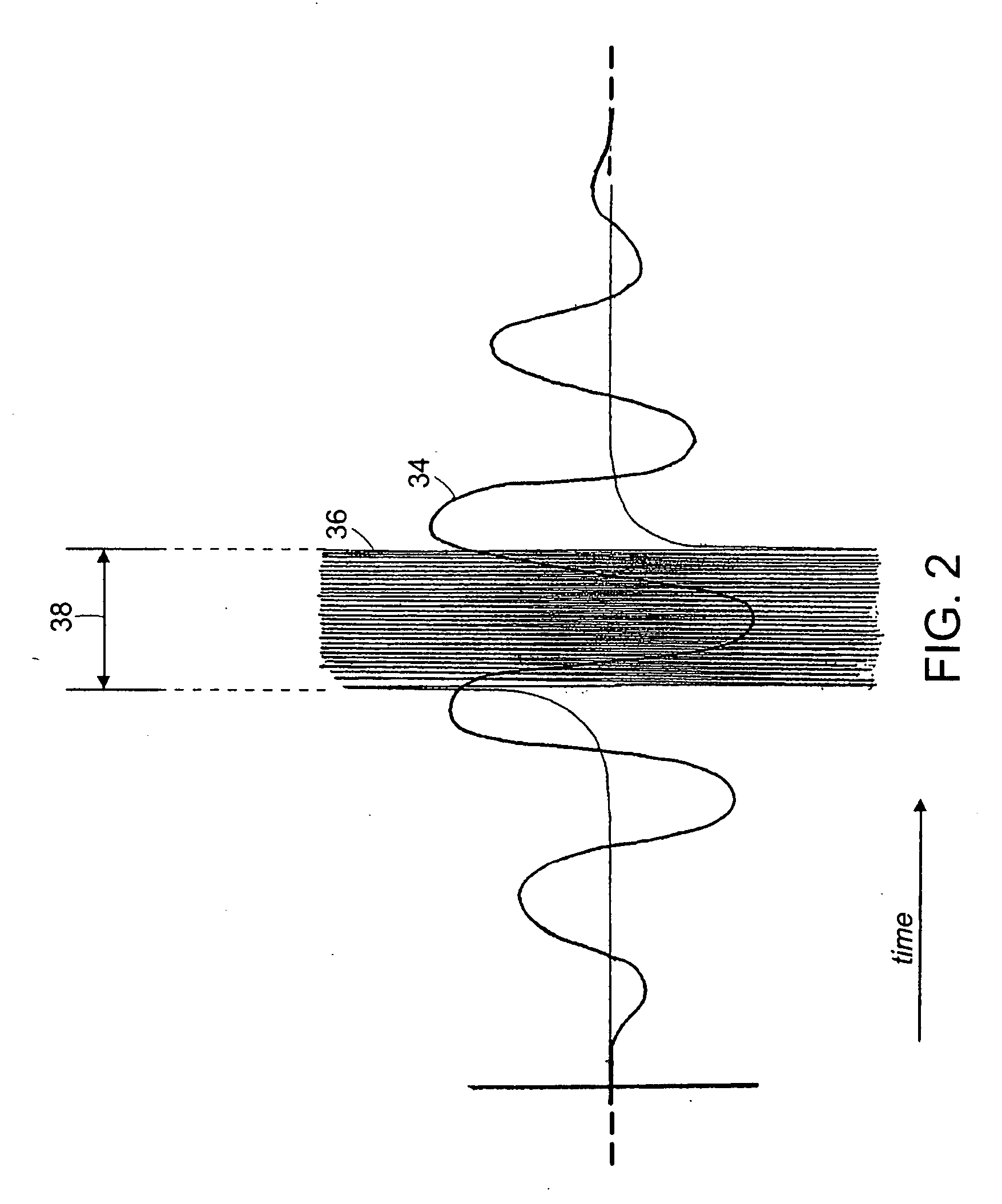
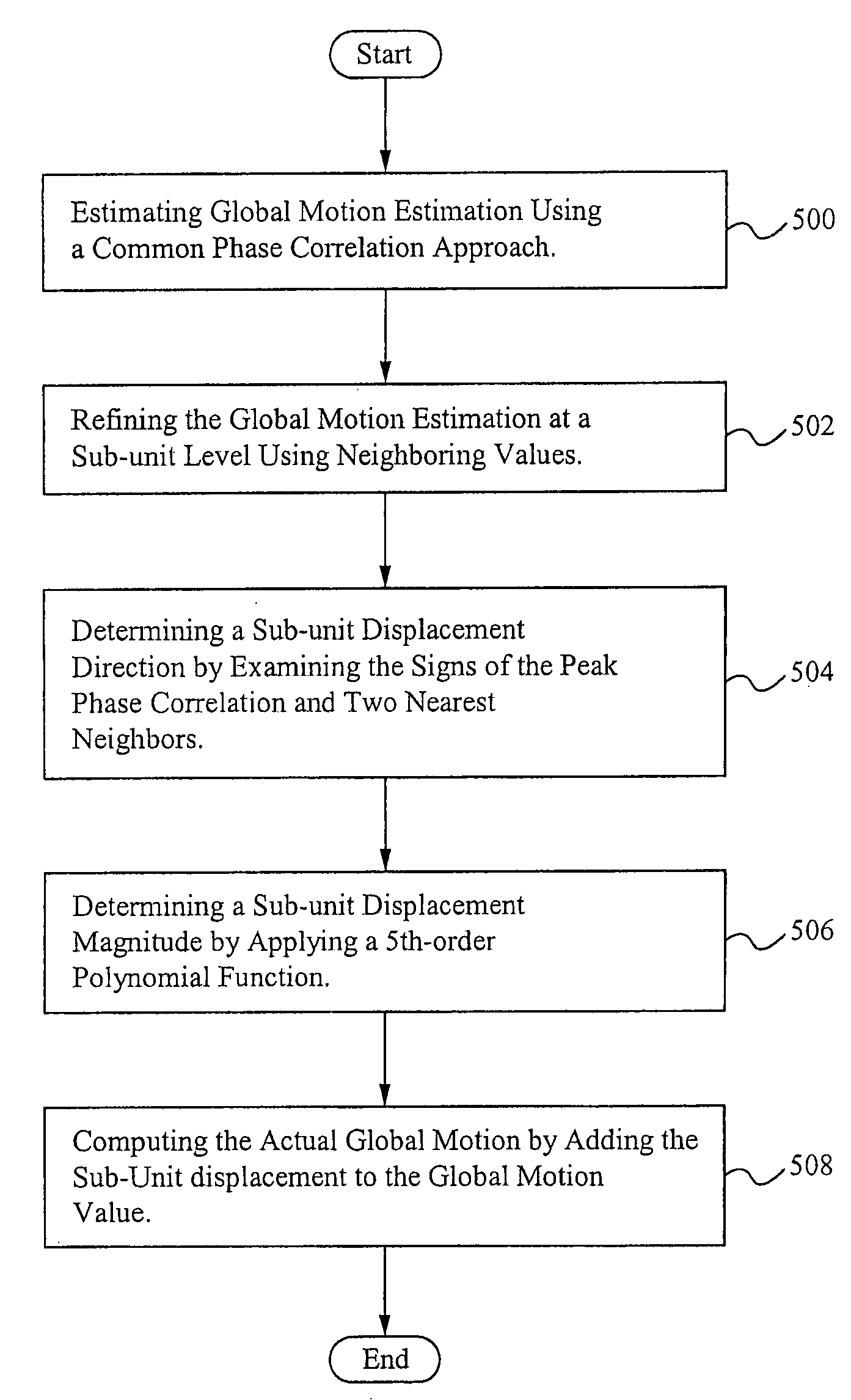
High accurate subspace extension of phase correlation for global motion estimation
InactiveUS20080212687A1High sub-unit accuracyReduce boundary effectsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPhase correlationNear neighbor
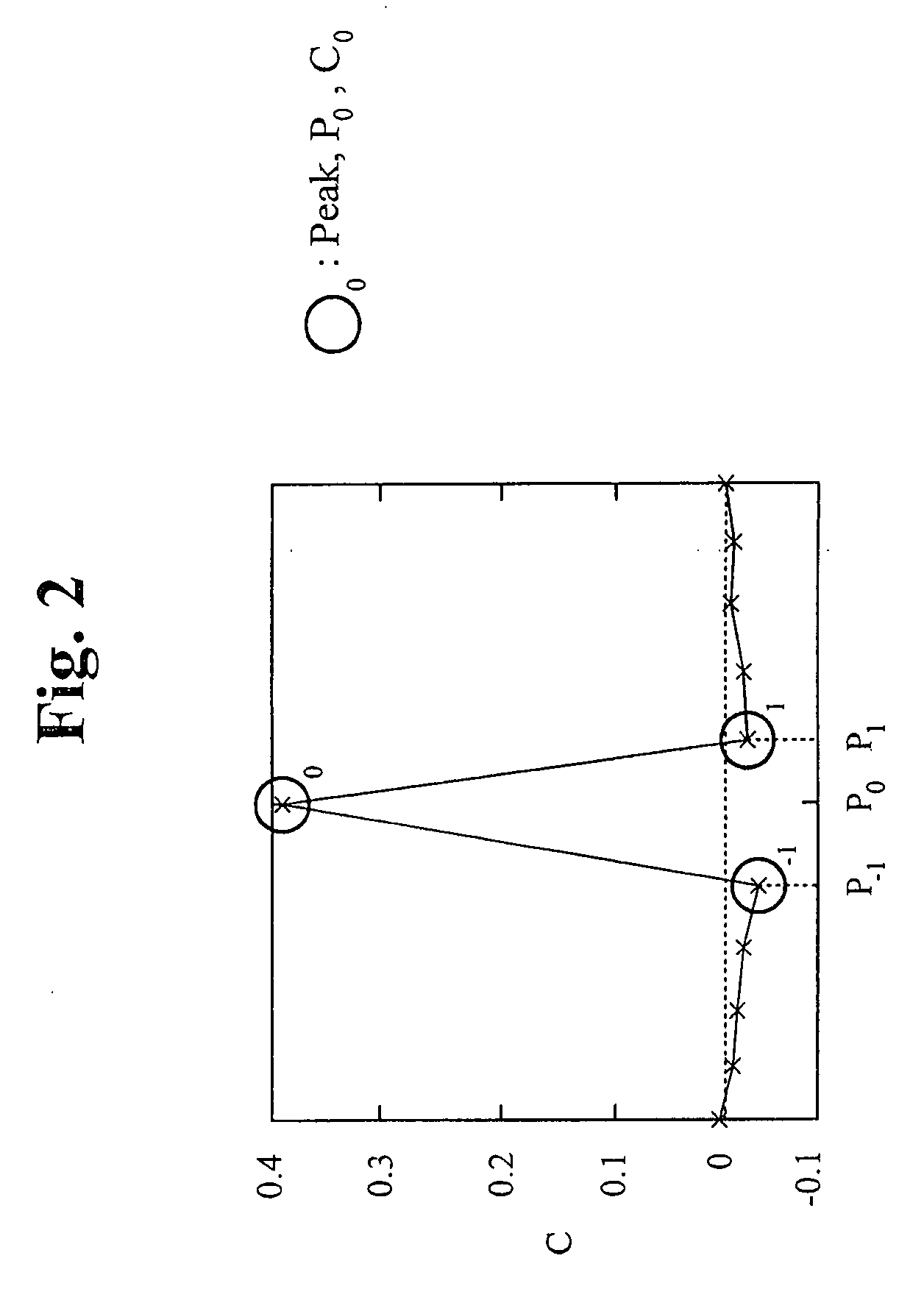
A method for achieving high sub-unit accuracy during global motion estimation of sequential video frame images is described herein. The method estimates the global motion using an existing phase-correlation approach, and further refines it to a sub-unit level using the neighborhood values of the phase correlation surface peak The method determines the sub-unit displacement direction by examining the signs of the peak of phase correlation surface and its two nearest neighbors. The method determines the sub-unit displacement magnitude by applying the ratio of associated phase correlation values to a 5th-order polynomial function. The method then computes the actual motion by adding the sub-unit displacement value to the global motion value as calculated by the phase-correlation approach.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method for extracting and analyzing nidus areas in pneumoconiosis gross imaging
ActiveCN103886318AAccurate extractionReduce mistakesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine classifier
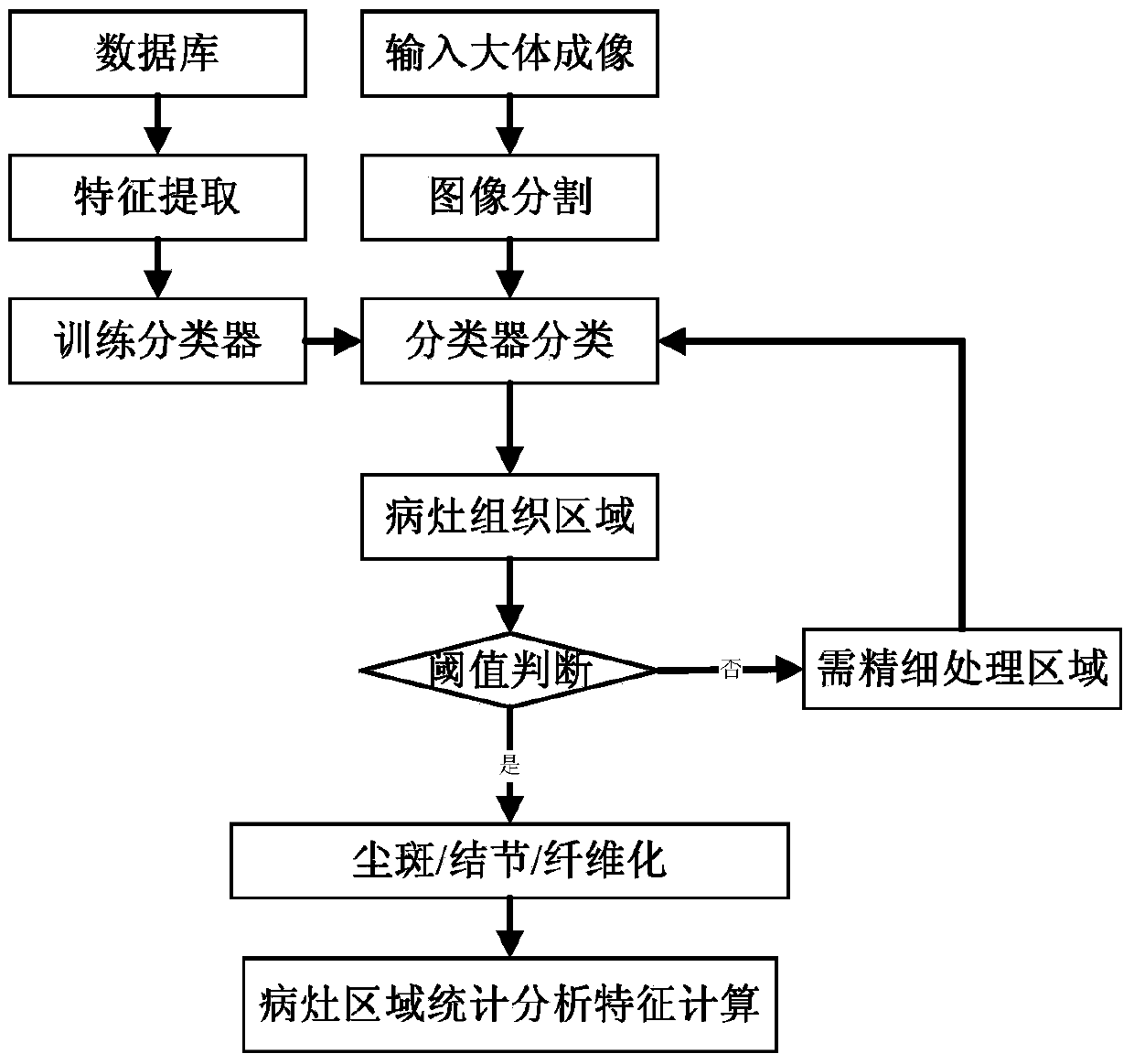
The invention relates to a method for extracting and analyzing nidus areas in pneumoconiosis gross imaging. The method comprises the following steps that the feature vector F1 of a 2k-1 dimension is calculated, pre-training is carried out, a feature vector F2 is calculated, a support vector machine classifier h0 used for judging whether an area is the nidus areas or not is trained, multi-classification support vector machine classifiers h1-hk used for judging an area class are trained, the pneumoconiosis gross imaging is input, the features of the nidus areas are extracted, the nidus areas are classified, and statistical characteristic calculation is carried out on the nidus areas. Spatial expansion is carried out on image pixels to from small surface element areas, the surface element areas are classified by the trained classifiers, the surface element areas with the low classification confidence coefficient are finely processed, and the different nidus areas are extracted accurately. The method is high in efficiency, small in error and free of man-machine interaction.
Owner:WUHAN TIANREN IMAGE TECH CO LTD
Expansion method of logical volume storage space
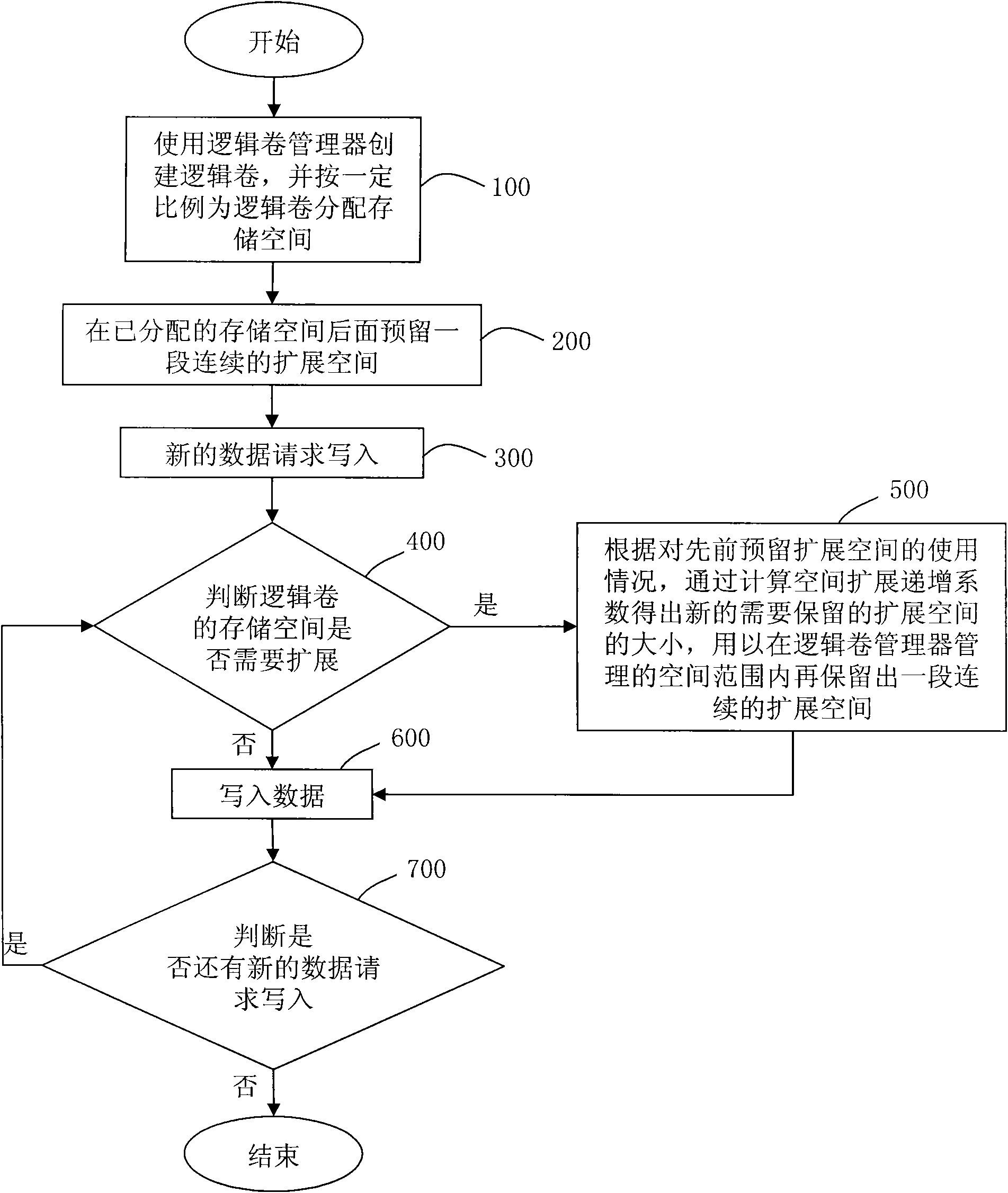
InactiveCN101620569ASolve the problem of discontinuous expansionLow impact on read and write performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer scienceExtension method
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
Method for obtaining spatial data servitization facing geographic information application
InactiveCN103064876AExtensive parsing rule expression scopeEasy to integrateSpecial data processing applicationsExecution planObject Query Language
The invention discloses a method for obtaining spatial data servitization facing geographic information application. The method includes: the spatial data servitization is inquired; a query execution plan is obtained; a spatial processing object query language enables a spatial query function conforming to a structured query language multimedia (SQL / MM) extensions framework rule to be nested in an object query, a query statement is analyzed through a distributed query execution engine, the spatial query function is transferred to a relational database with spatial expansion at the rear end to be executed, the query statement submits query retrieval to the database through data service, and distributed query results are collected to be returned to a data service requester. The method for obtaining the spatial data servitization facing the geographic information application can successfully response to continuously updated heterogeneous mass data resource access queries and enhances query retrieval efficiency of geographic information data through the query statement packaged in object query mode.
Owner:CHINA NAT INST OF STANDARDIZATION
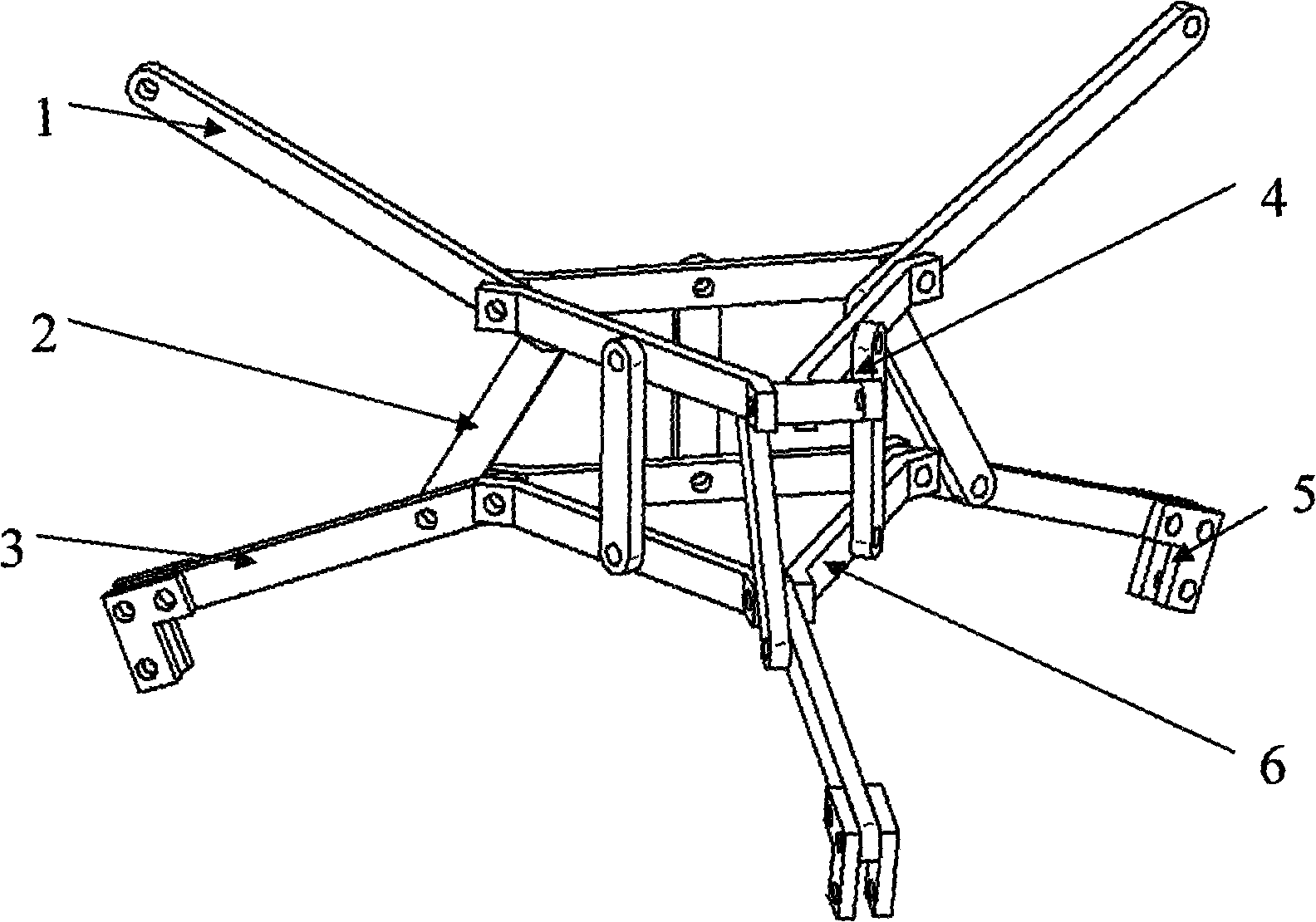
Parallel multi-manipulator mechanism
The invention discloses a parallel multi-manipulator mechanism. The parallel multi-manipulator mechanism comprises an SP-type shaft sleeve set, a machine base, a movable table, four SPS-type driving branches, inner and outer flexible finger mechanisms and three screw drivers. The SP-type shaft sleeve set comprises a core tube, an inner sleeve, a fixed sleeve, an outer sleeve and a ball sleeve. The ball sleeve is connected with a ball pair of the machine base. One end of the fixed sleeve is vertically and fixedly connected with the movable table. The fixed sleeve is further connected with the inner sleeve and the outer sleeve in the radial direction in a sliding mode. The three screw drivers drive the core tube, the inner sleeve and the outer sleeve to be stretched and retracted. The fixed sleeve, the inner sleeve and the outer sleeve form inner and outer manipulator mechanisms which are circumferentially and evenly distributed in a staggered mode through connecting rods and under-actuated branches. One end of the core tube can move along with operation tools like scalpels, hose sight glasses, syringe needles and tooth drilling and polishing utensils to absorb and convey fluid. The long and thin SP-type shaft sleeve set can stretch into a narrow space along with the inner and outer manipulator mechanisms to achieve alternate grabbing and spatial expansion, and the core tube is used for expanding life channels. The parallel multi-manipulator mechanism is simple and compact in structure and suitable for idle station maintenance, deep sea exploration, medical operations and disaster area relief.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
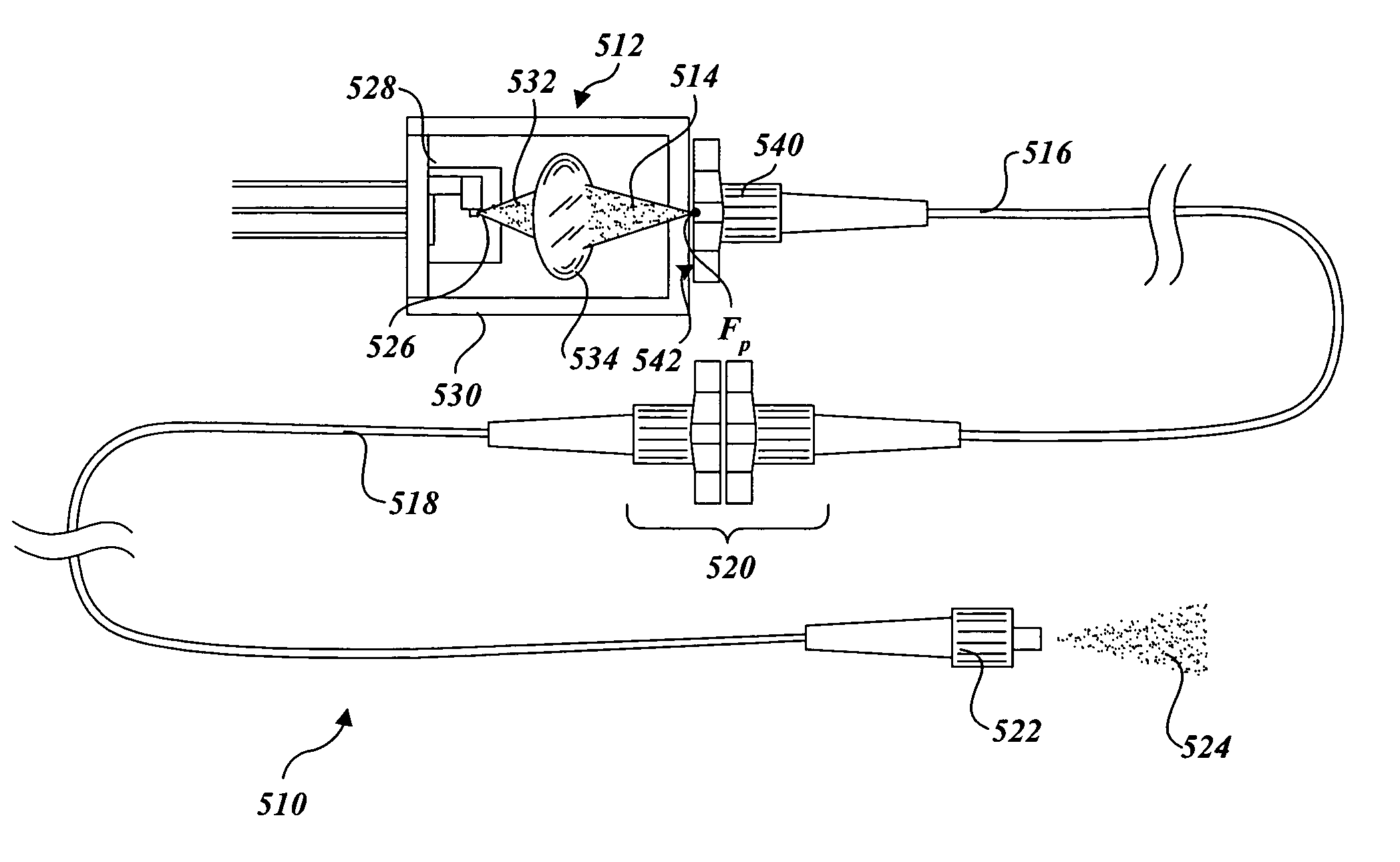
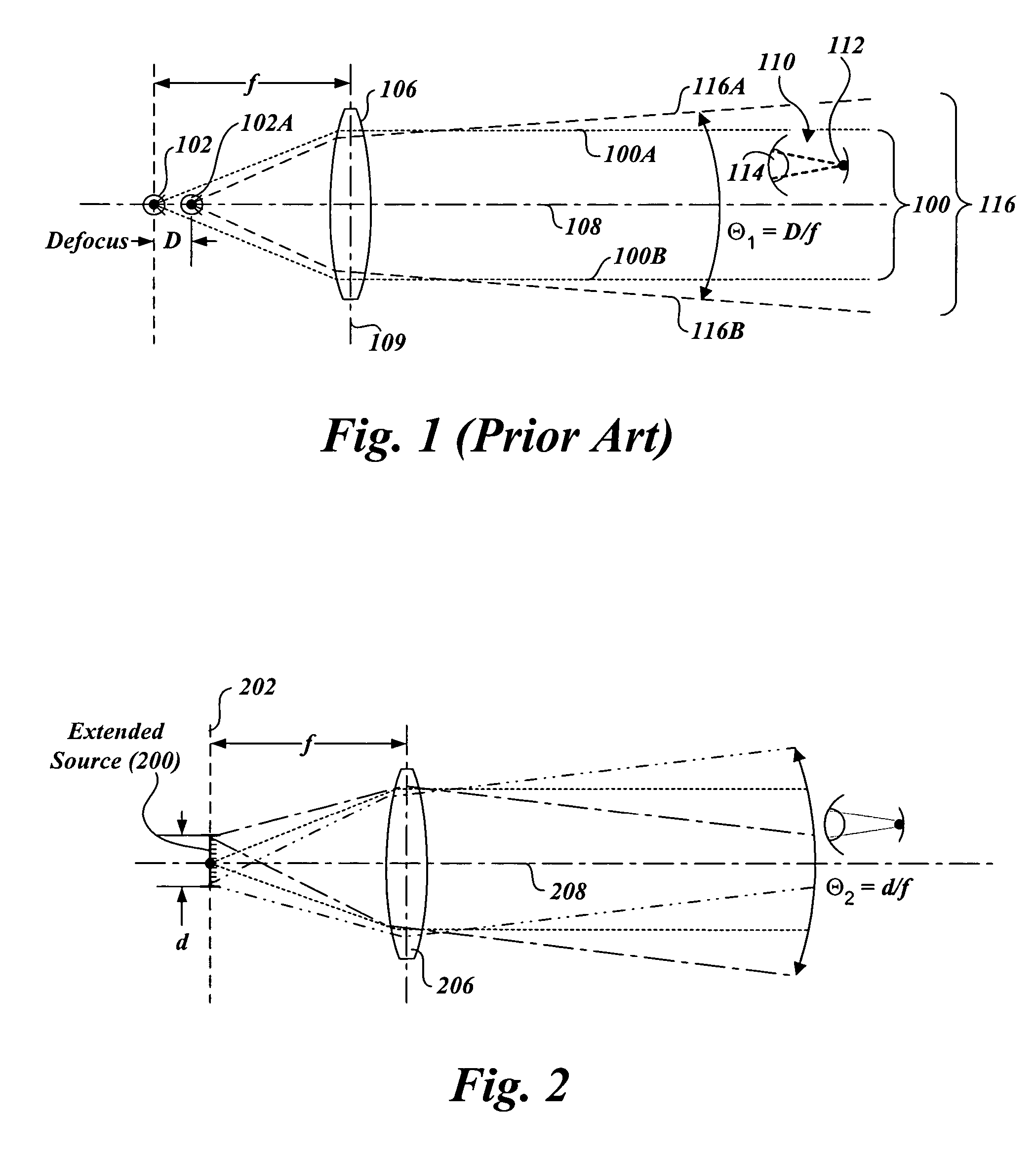
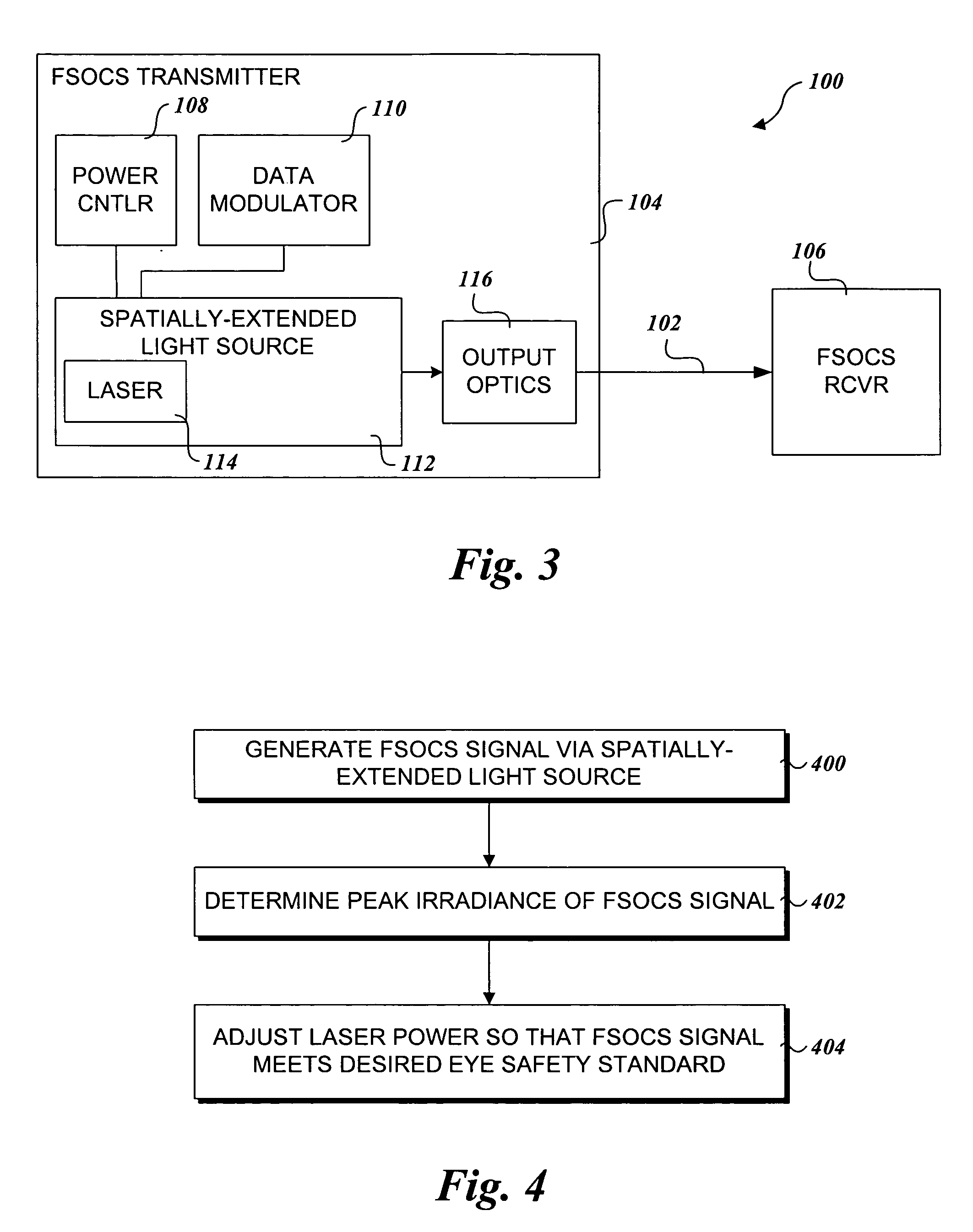
Extended source transmitter for free space optical communication systems
InactiveUS7072543B2Increasing total transmitter powerIncrease powerCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFiberCommunications system
An apparatus for transmission of free space optical communication system signals employing a spatially-extended light source and method of using the same. A laser beam source directs an optical signal into a free end of a segment of multimode fiber. As the optical signal passes through the segment of multimode fiber, the optical signal is converted into a mode-scrambled optical signal. This mode-scrambled signal may then be used as a spatially-extended light source that is directed outward as an optical beam through the use of a collimating lens.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
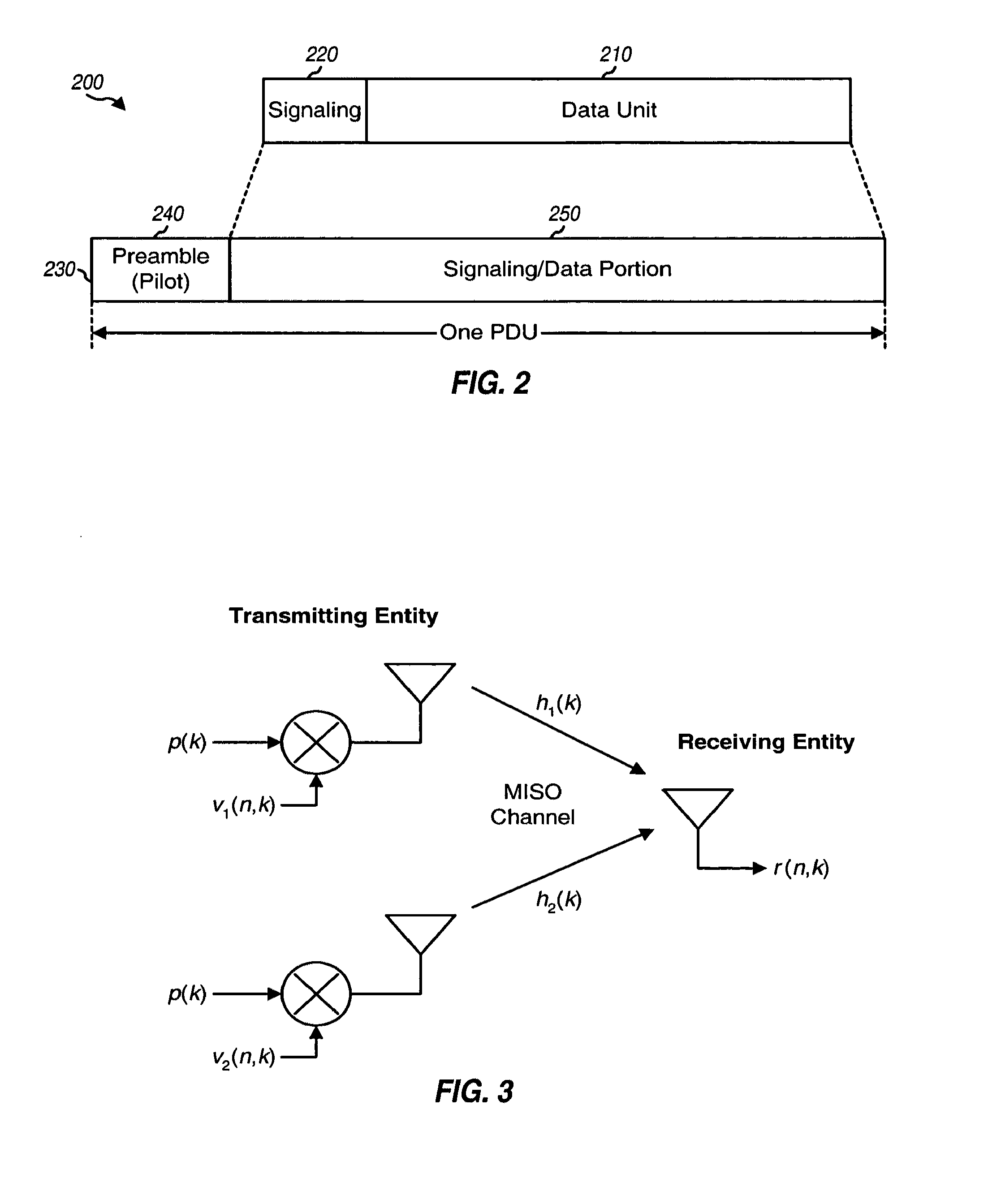
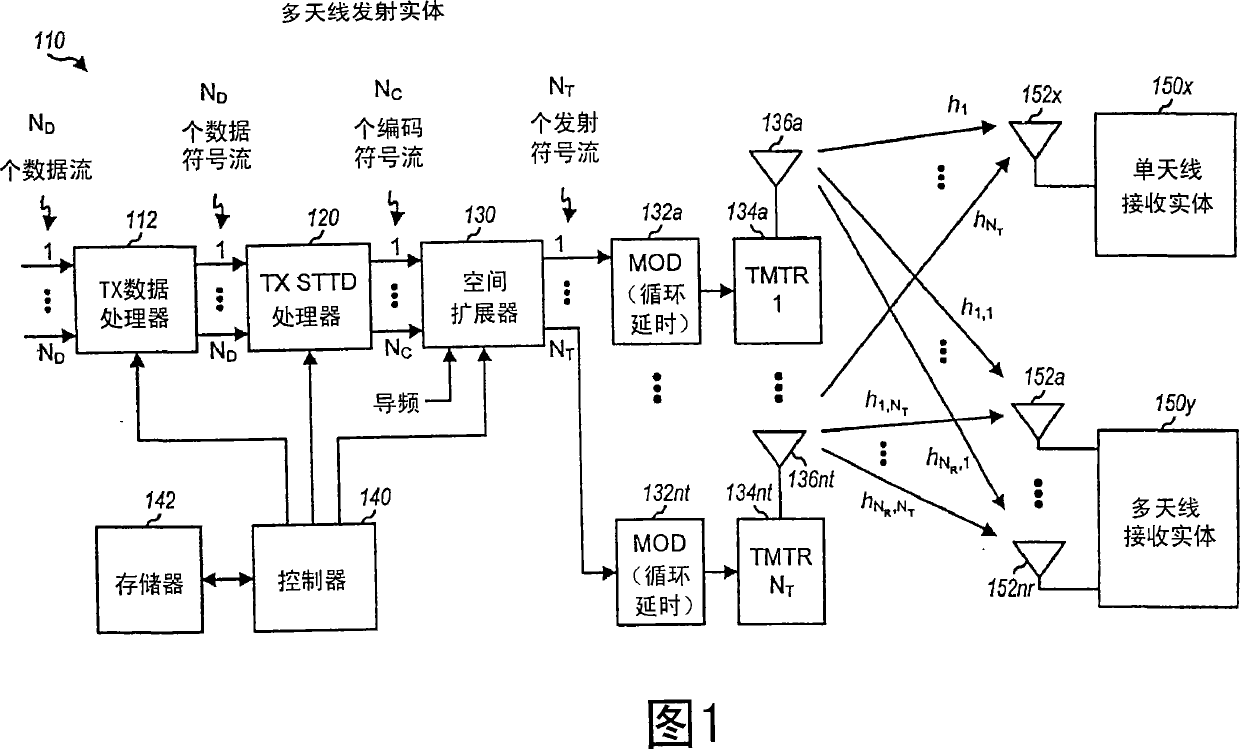
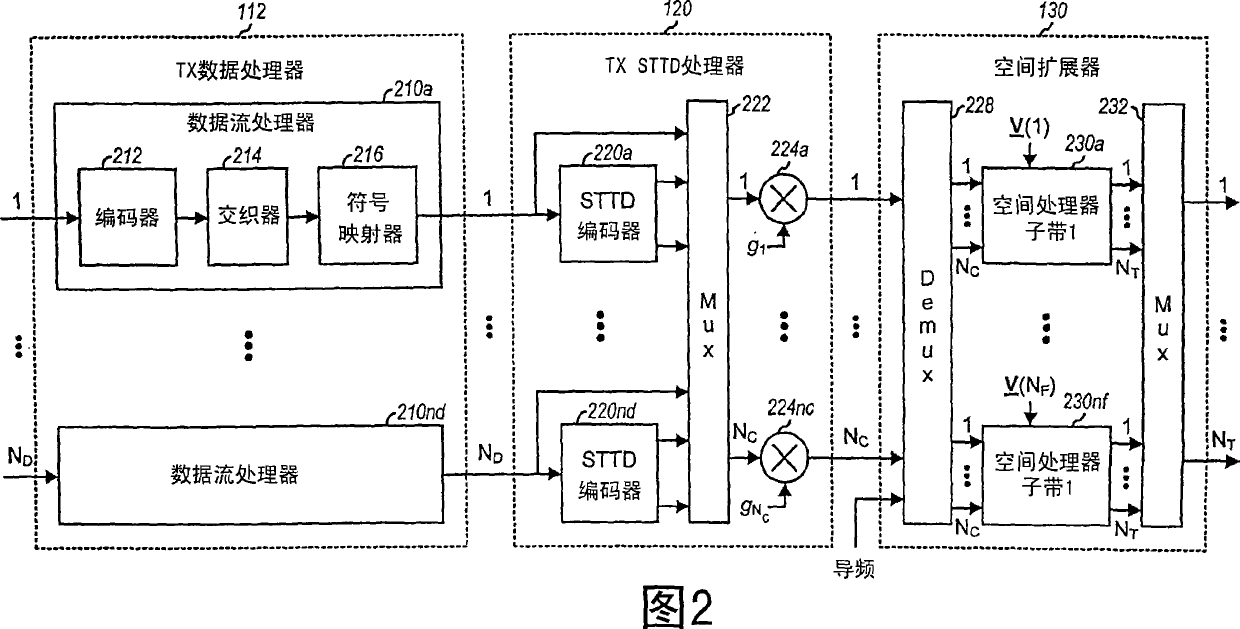
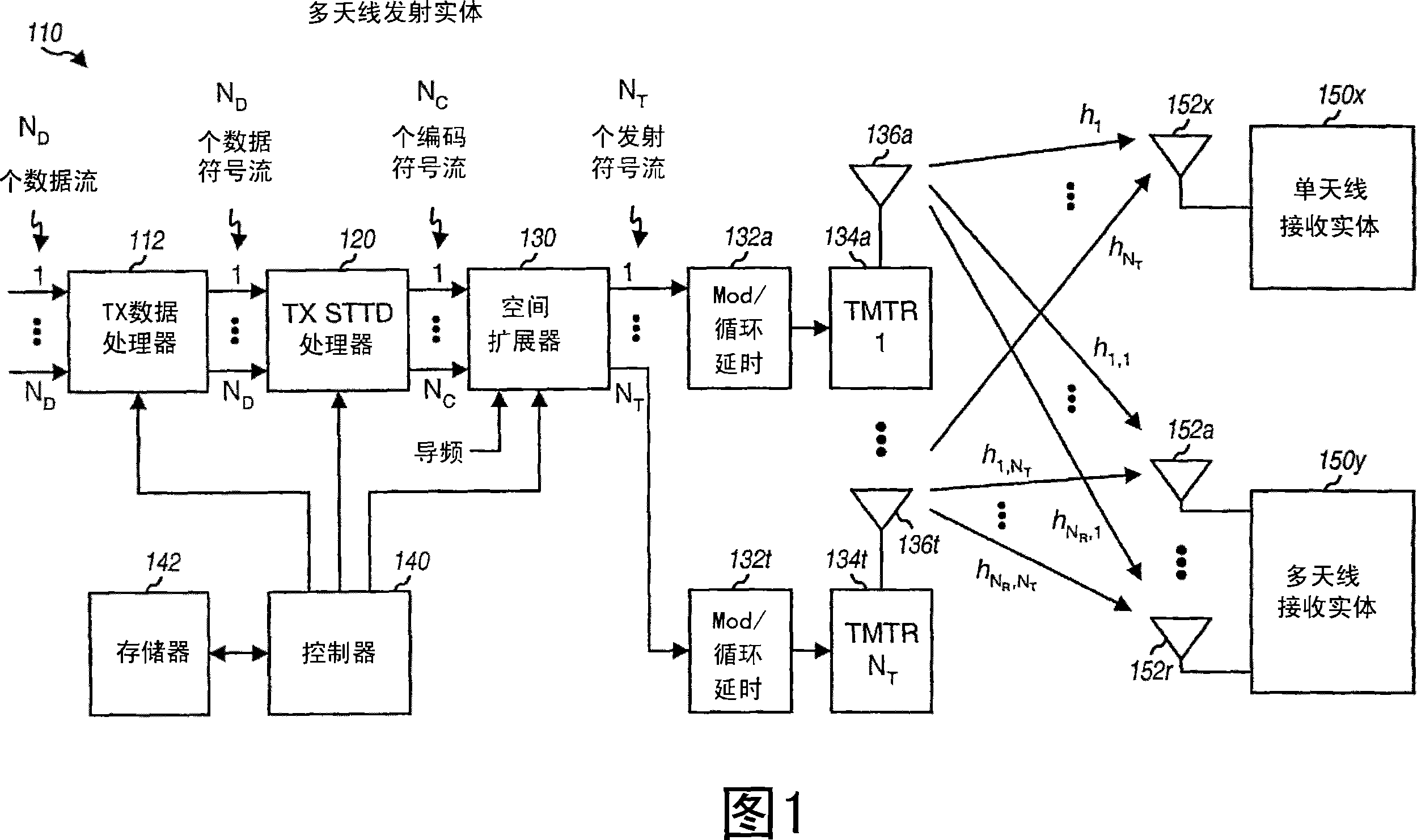
Transmit diversity and spatial spreading for an OFDM-based multi-antenna communication system
InactiveUS8520498B2Spatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A multi-antenna transmitting entity transmits data to a single- or multi-antenna receiving entity using (1) a steered mode to direct the data transmission toward the receiving entity or (2) a pseudo-random transmit steering (PRTS) mode to randomize the effective channels observed by the data transmission across the subbands. For transmit diversity, the transmitting entity uses different pseudo-random steering vectors across the subbands but the same steering vector across a packet for each subband. The receiving entity does not need to have knowledge of the pseudo-random steering vectors or perform any special processing. For spatial spreading, the transmitting entity uses different pseudo-random steering vectors across the subbands and different steering vectors across the packet for each subband. Only the transmitting and receiving entities know the steering vectors used for data transmission. Other aspects, embodiments, and features are also claimed and disclosed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wave aberration detection device for optical system
InactiveCN104181779AIncrease contrastIncrease detection light energyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingPhase shifted
The invention discloses a wave aberration detection device for an optical system. According to the wave aberration detection device, lights emitted by a light source are evenly projected onto an object plane of the optical system by virtue of an illumination module. A pinhole array is positioned on the object plane of the optical system, and has the functions of spatial extension and spatial division. A shearing grating is installed on an image plane of the optical system. The function of phase shift can be realized by means of driving the shearing grating to move horizontally by a fine moving stage. By virtue of a collimating optical lens group, the concentric spherical wave shearing carrying the wave aberration information of the optical system is converted to plane wave shearing. The shearing interferogram light field information in the process of phase shift is recorded by a detector. By virtue of the pinhole array, the luminous energy of the detected system is improved; by virtue of the grating, shearing interference is realized; phase shift is performed by the horizontal movement of the grating; the sphere interference is converted to plane interference by virtue of the collimating optical lens group, so that the error happening when a plane detector receives sphere interference is eliminated and therefore, the wave aberration of the optical system can be detected at high precision.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
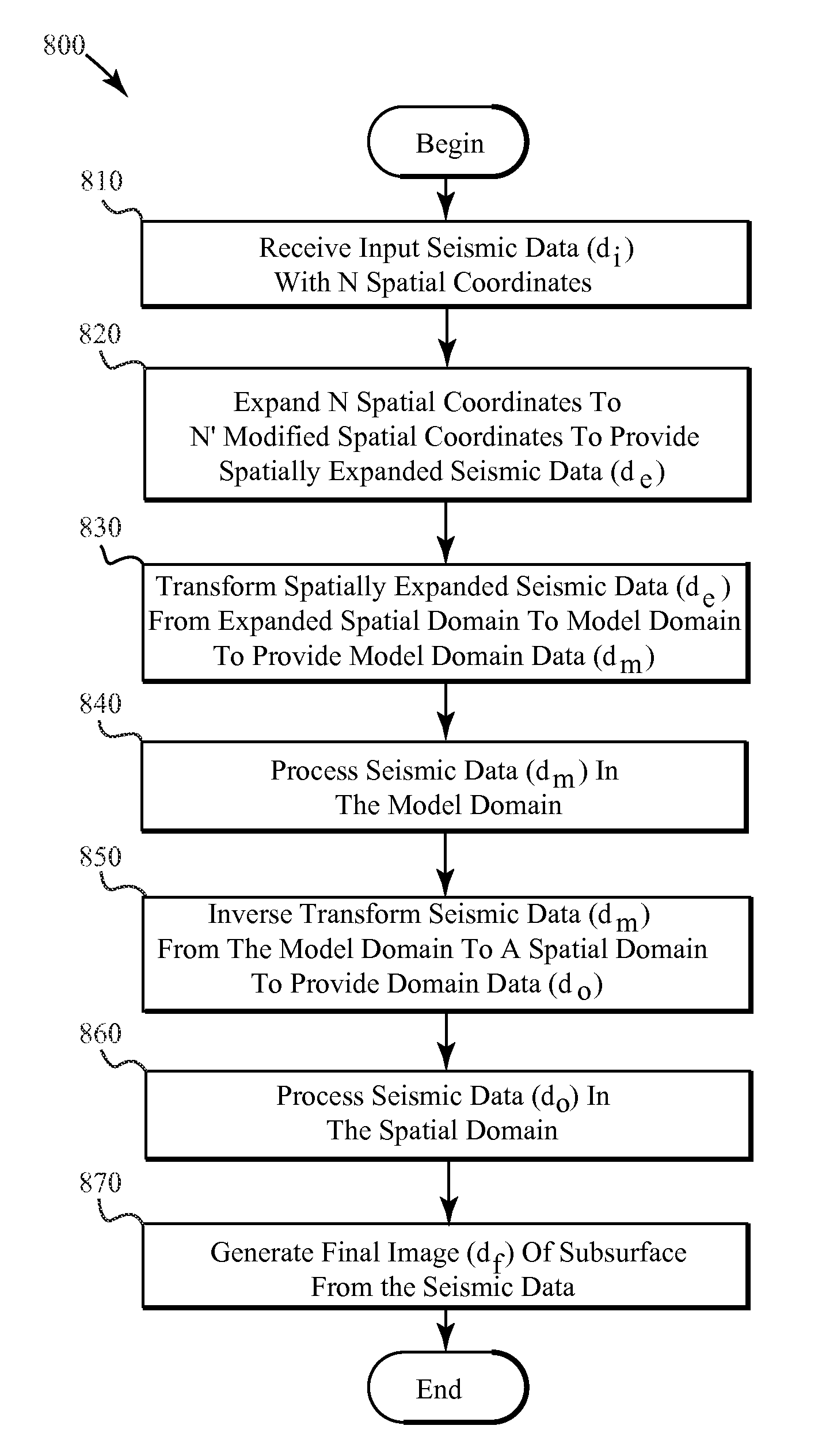
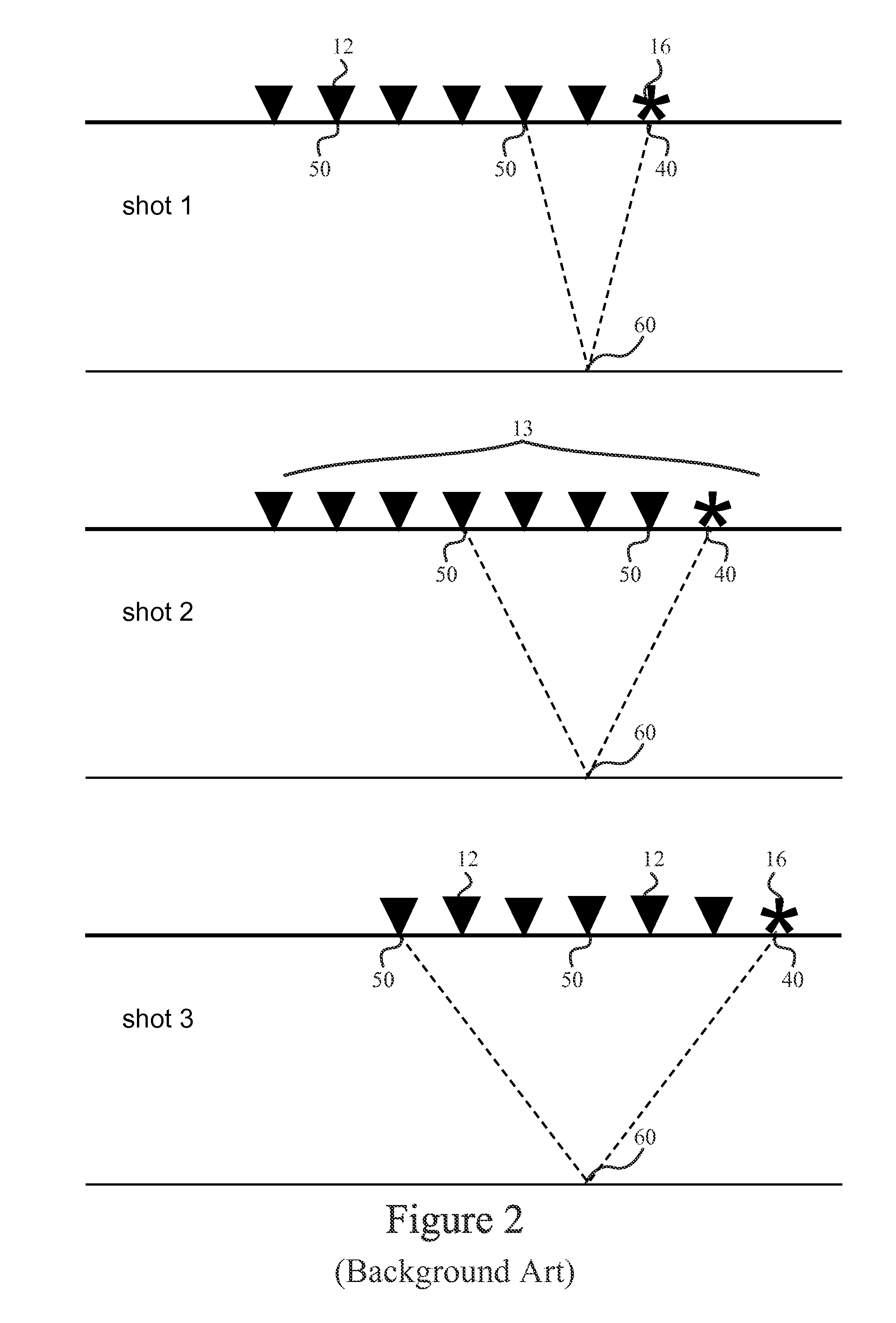
Spatial expansion seismic data processing method and apparatus
A method for processing seismic data may include receiving input seismic data (di) comprising N spatial coordinates, where the input seismic data is in a first spatial domain, expanding the N spatial coordinates of the input seismic data (di) to N′ modified spatial coordinates, where N′ is greater than N, to provide spatially expanded seismic data (de) that is in a second spatial domain, transforming the spatially expanded seismic data (de) to a model domain to provide model domain data (dm), and generating a final image (df) of a subsurface using the model domain data (dm).
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
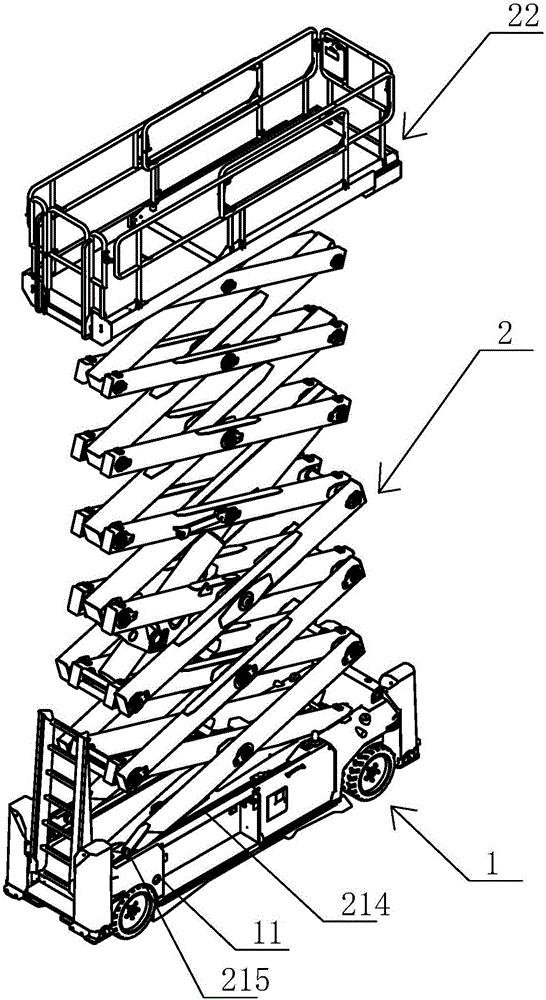
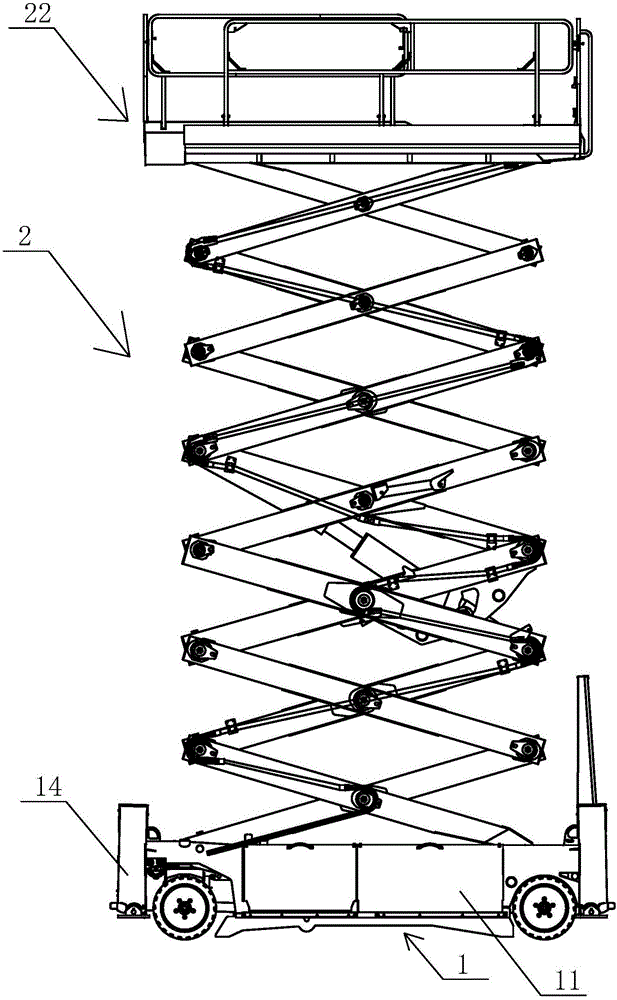
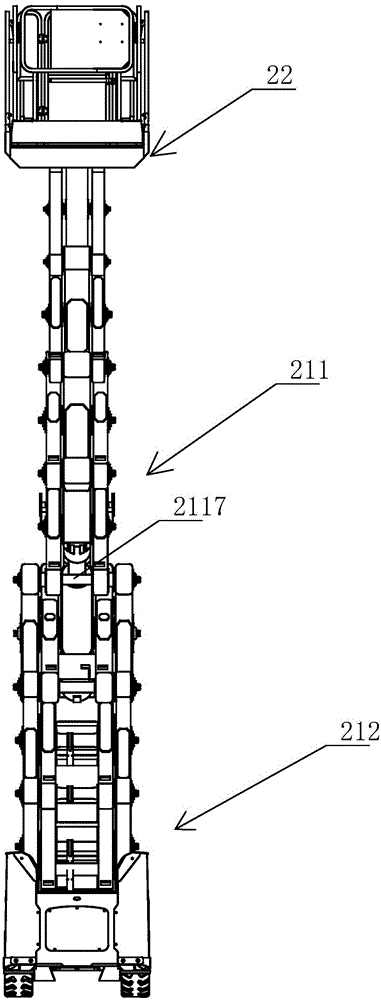
Aerial work platform with easily-operated platform locking structure
InactiveCN105000513AEasy loading and unloadingEasy maintenanceSafety devices for lifting equipmentsMarine engineeringAerial work platform
The invention relates to an aerial work platform with an easily-operated platform locking structure. The aerial work platform comprises a running chassis and a lifting device. The lifting device comprises a scissors lifting structure and a working platform. The working platform comprises a platform fixed bottom plate, railing frames and a railing door. A sliding bottom plate is installed on the platform fixed bottom plate in a sliding mode. The left side and the right side of the platform fixed bottom plate are provided with two platform sliding grooves. The left side and the right side of the sliding bottom plate are each provided with two platform rolling wheels. The platform rolling wheels are arranged in the platform sliding grooves. The railing frames are installed on the platform fixed bottom plate and the sliding bottom plate respectively. The railing frames on the sliding bottom plate are connected with the railing frames on the platform fixed bottom plate through movable platform locks. Each movable platform lock comprises a fixed swing rod, a first platform lock plate and a second platform lock plate. Spatial expansion operation of the working platform is convenient and locking is firm.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DINGLI MACHINERY CO LTD
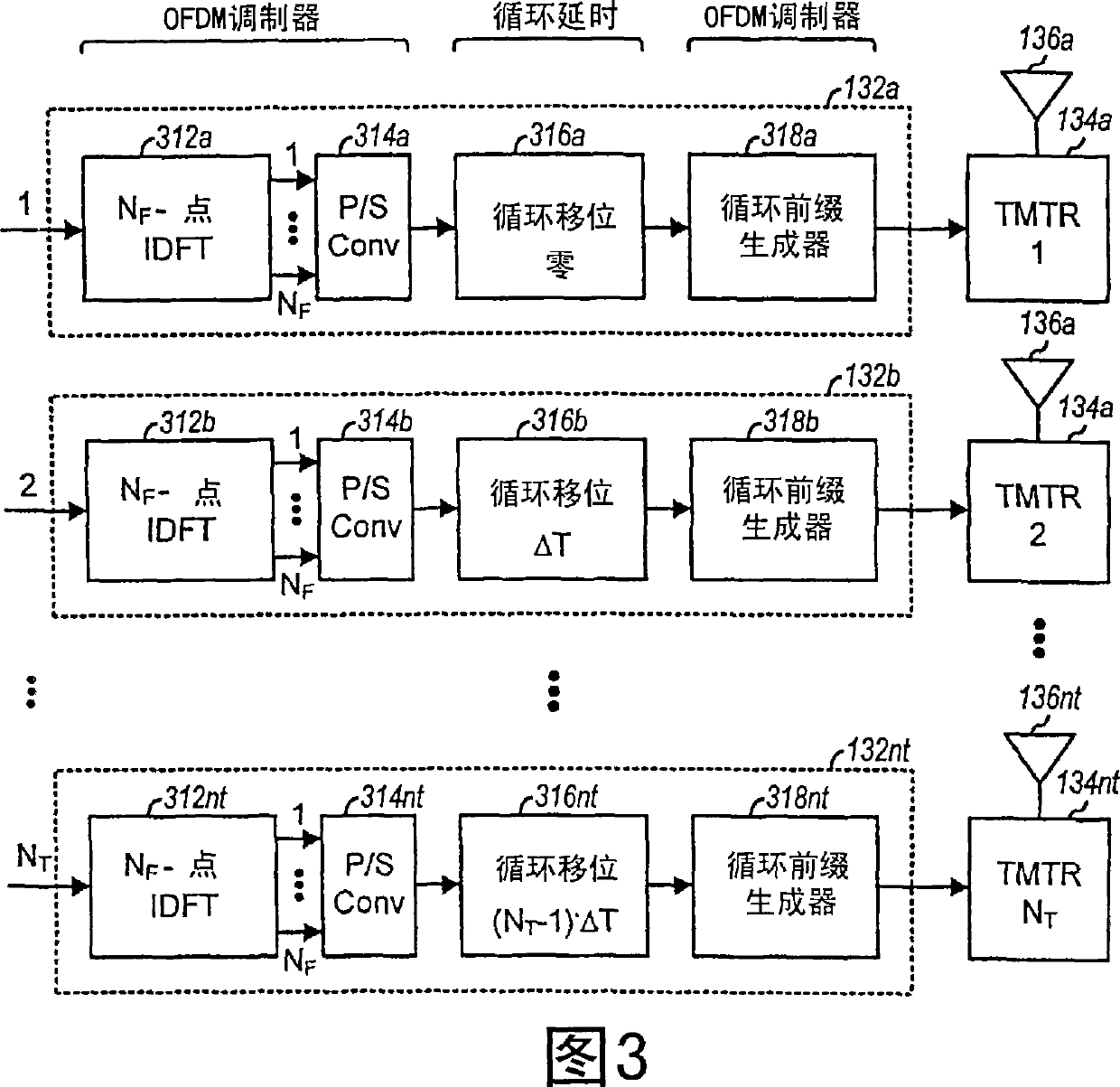
Spatial spreading with space-time and space-frequency transmit diversity schemes for a wireless communication system
ActiveCN101057417ASpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCyclic delay diversitySpace time transmit diversity
Techniques for transmitting data using a combination of transmit diversity schemes are described. These transmit diversity schemes include spatial spreading, continuous beamforming, cyclic delay diversity, space-time transmit diversity (STTD), space-frequency transmit diversity (SFTD), and orthogonal transmit diversity (OTD). A transmitting entity processes one or more (ND) data symbol streams based on a transmit diversity scheme (e.g., STTD, SFTD, or OTD) to generate multiple (NC) coded symbol streams. Each data symbol stream may be sent as a single coded symbol stream or as multiple (e.g., two) coded symbol streams using STTD, SFTD, or OTD. The transmitting entity may perform spatial spreading on the NC coded symbol streams with different matrices to generate multiple (NT) transmit symbol streams for transmission from NT antennas. Additionally or alternatively, the transmitting entity may perform continuous beamforming on the NT transmit symbol streams in either the time domain or the frequency domain.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Spacing telescoping mechanism using inverse parallelogram
InactiveCN101270772ALess materialLarge stretchRod connectionsMechanical engineeringAntiparallelogram
The invention relates to a spatial expansion mechanism utilizing an inverse-parallelogram. The mechanism is composed of a plurality of component units which are superimposed in series. Every component unit is composed of a middle frame, a first bar (1) which is connected at the conjunction of the head and the tail of an upper middle side bar (6) and a third bar (3) which is connected at the conjunction of the head and the tail of the lower middle side bar (6). An upper layer and a lower layer are connected through a middle frame connecting bar (4) and a second bar (2). The component units are connected through a nit connector (5) which is connected with one end of the third bar. The expansion of the mechanism is realized through the rotation of bar parts or the movement of the middle frame. The design is provided with simple structure and reaches the large contraction ratio through a small inverse-parallelogram. Due to the spatial symmetry of the mechanism, the bearing capacities of different directions in the space can be uniformly distributed. The whole mechanism has the characteristics of less used material, large expansion amplitude, good for bearing performance, strong stability, wide application range, simple manufacturing process, etc.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for frequency-converting infrared light
InactiveUS7696479B2Radiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopySum-frequency generation
The invention relates to methods and apparatus for modifying the frequency characteristics of a spatially-dispersed mid-IR spectra for spectroscopy. In a preferred embodiment, sum frequency generation between a frequency-dispersed IR beam and an ultrafast optical pulse generates a spatially-extended optical signal that is collected with a CCD detector.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Transport information management system and method applied to transport company
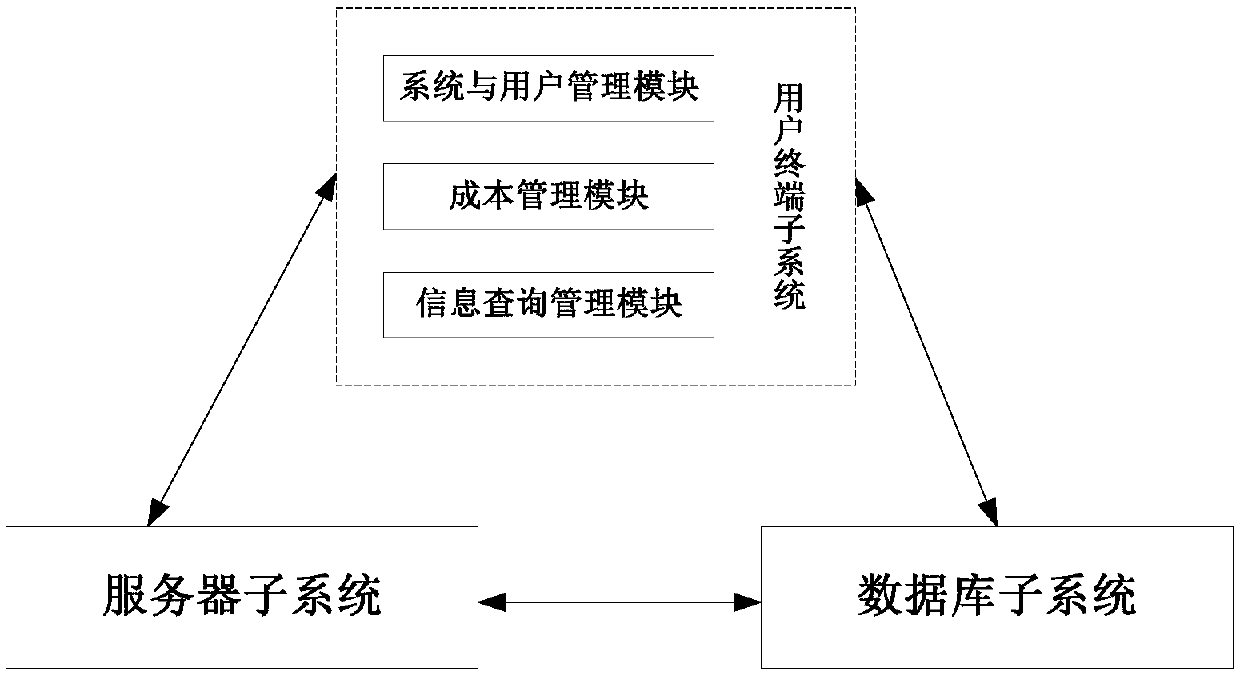
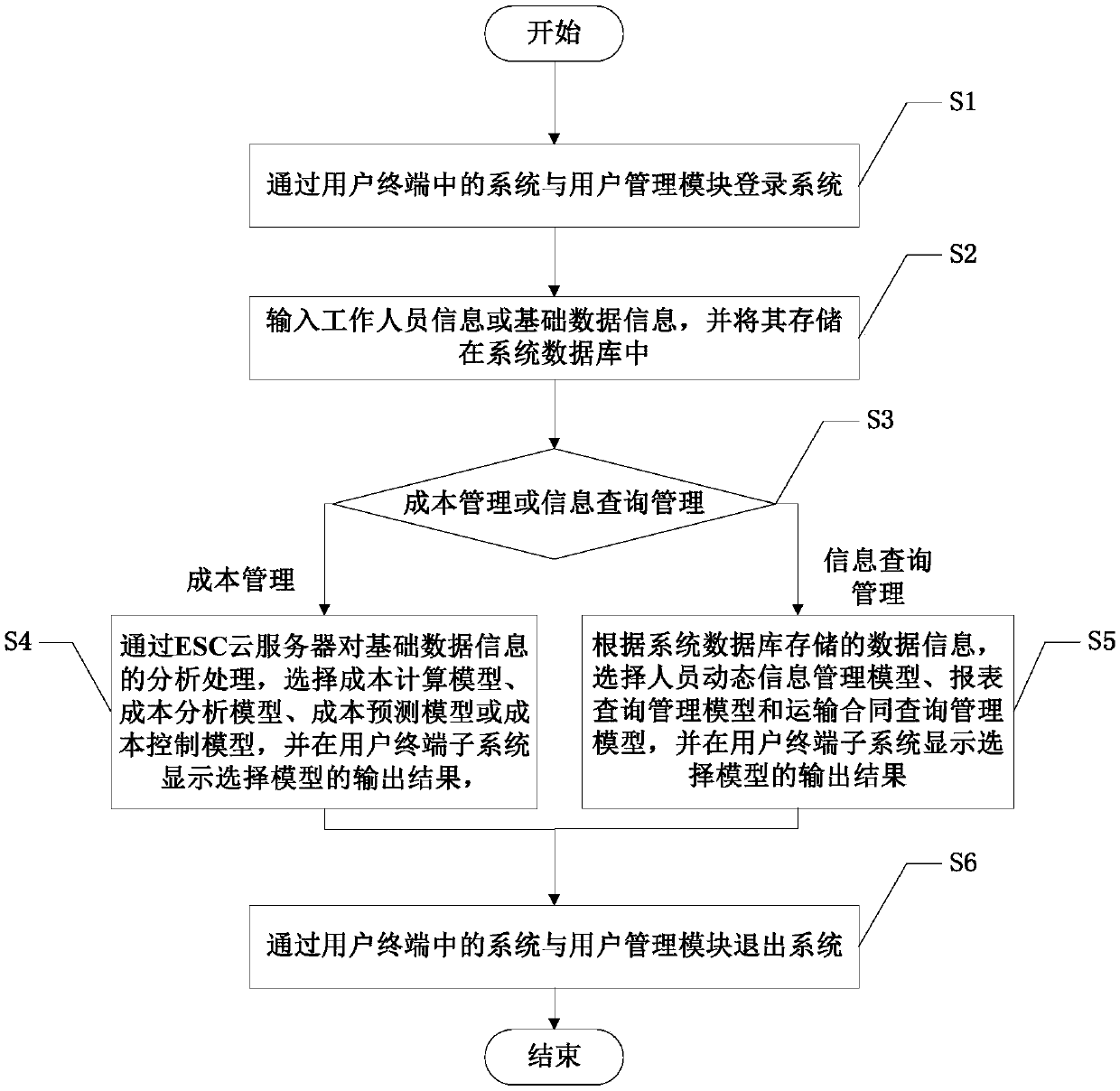
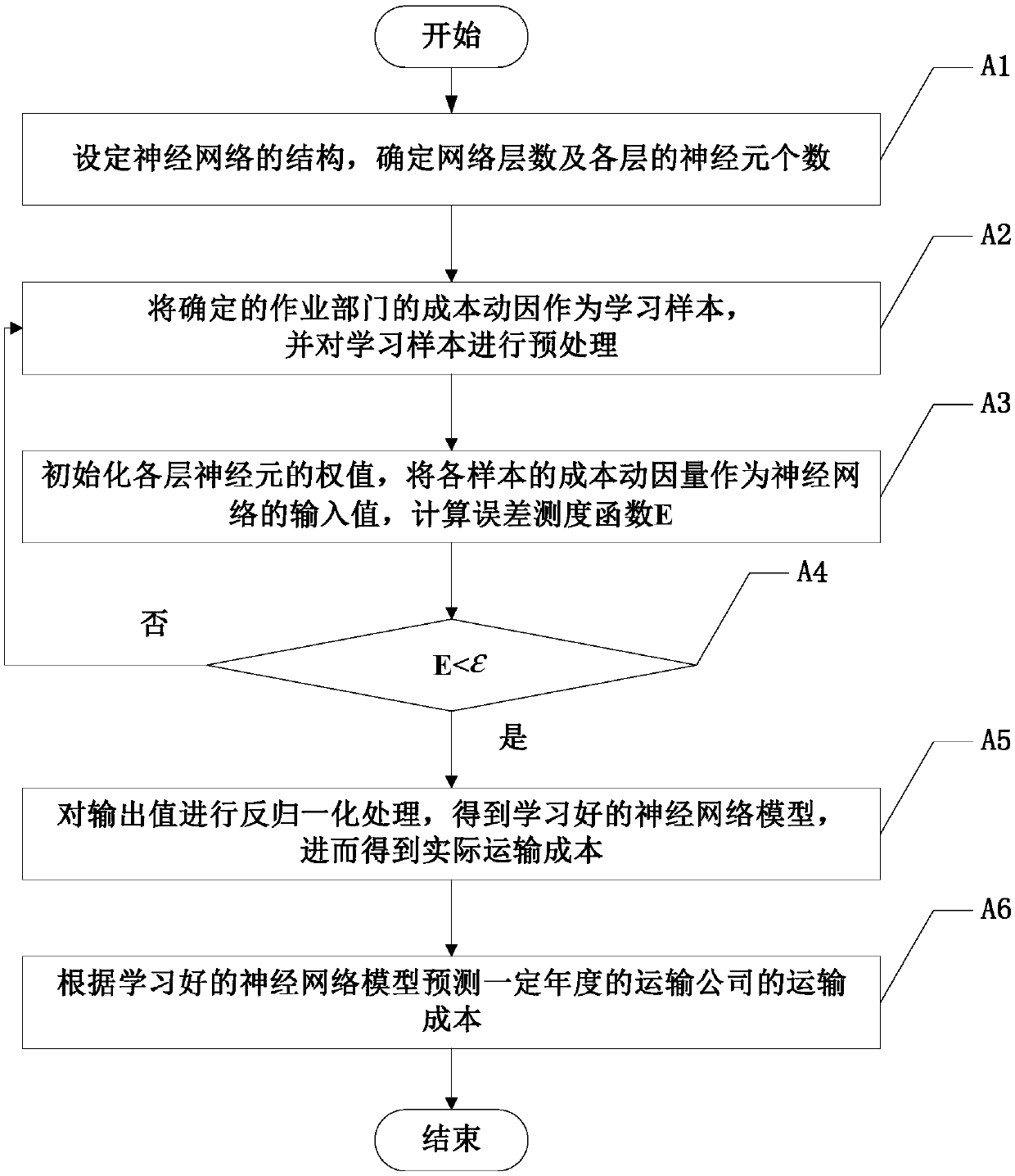
InactiveCN108921422AStrengthening the Effectiveness of Transportation Economic ManagementDelivery lagResourcesLogisticsEconomic managementComputer science
The invention discloses a transport information management system and method applied to a transport company. The transport information management system comprises a user terminal subsystem, a server subsystem and a database subsystem. The user terminal subsystem and the server subsystem are both in communication connection with the database subsystem, and the user terminal subsystem is in communication connection with the server subsystem. According to the transport information management system and method applied to the transport company, the actual effect on transport economic management ofthe transport company and spatial expansion are enhanced, and connection between the systems is strengthened so that the transport company can monitor and analyze the economic operation situation moreconveniently and more rapidly in real time, and lagging of information transfer is avoided; and the influence factor of people is reduced, executive force of a management system is strengthened, andthe working efficiency is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
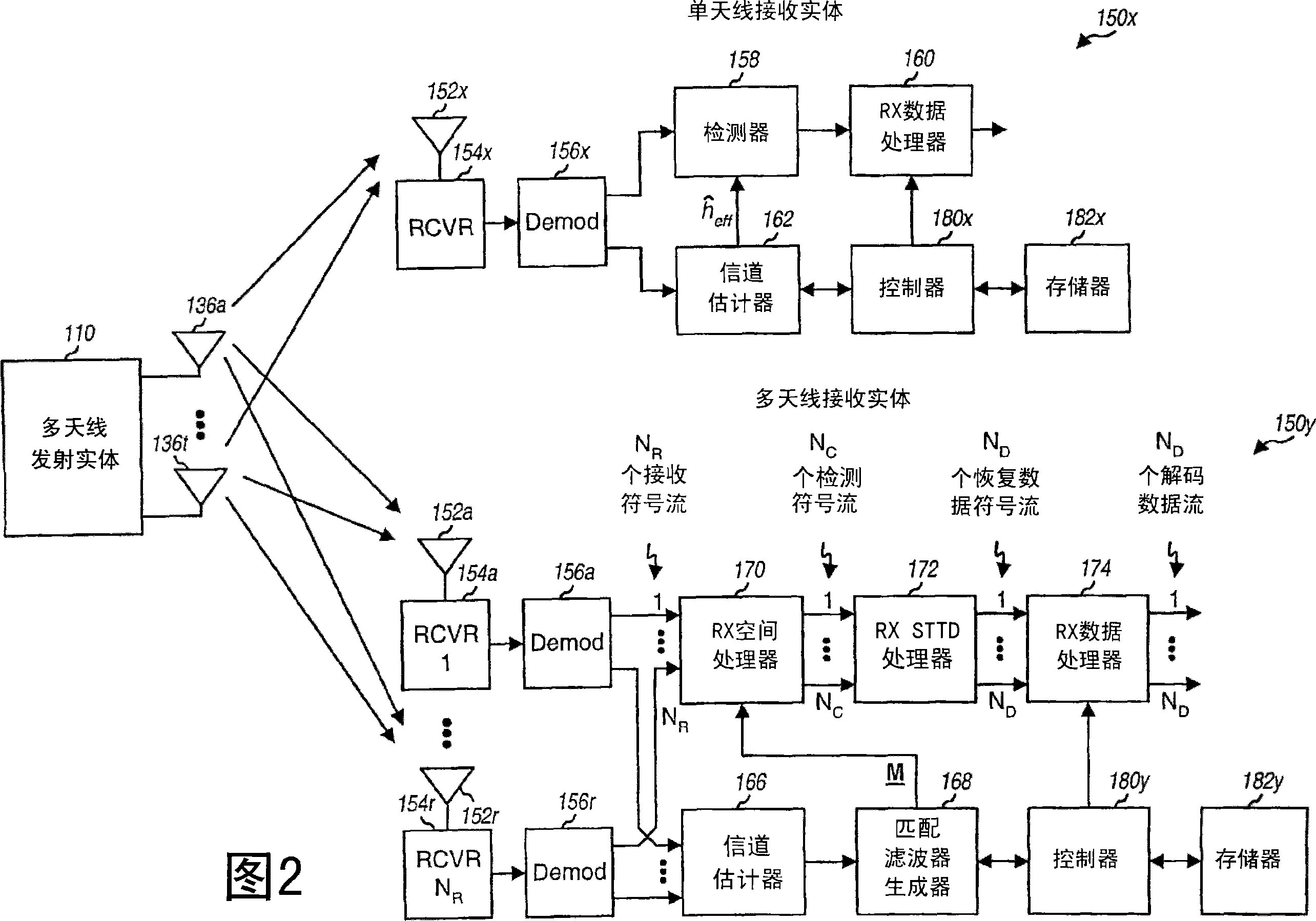
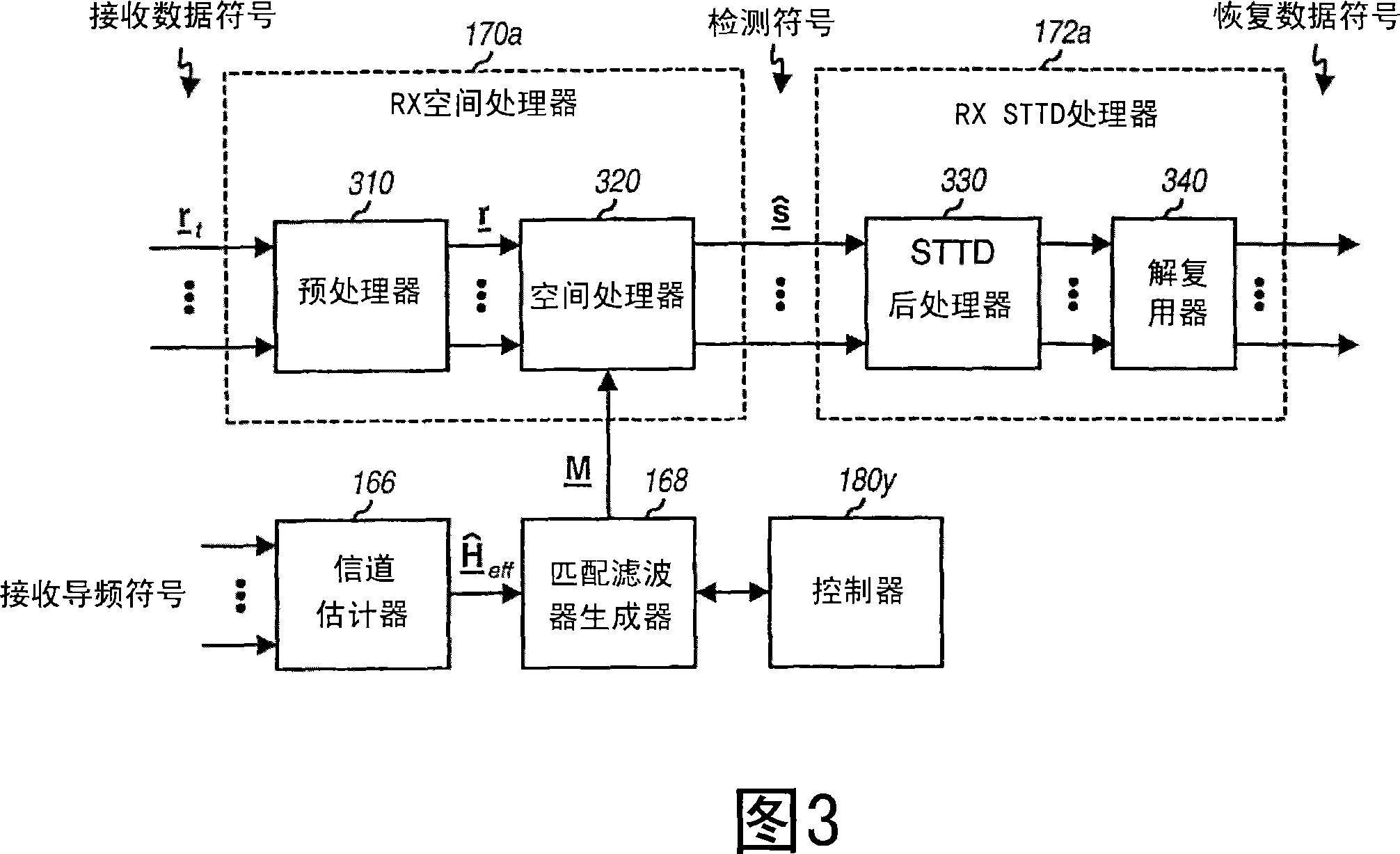
Receiver structures for spatial spreading with space-time or space-frequency transmit diversity
ActiveCN101053174ASpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSpace time transmit diversityDiversity scheme
A receiving entity (150) obtains received symbols for a data transmission having at least one data symbol stream sent with space-time transmit diversity (STTD). The receiving entity derives an overall channel response matrix in accordance with the STTD encoding scheme used for the data transmission, derives a spatial filter matrix based on the overall channel response matrix, and performs spatial matched filtering on a vector of received symbols for each 2-symbol interval to obtain a vector of detected symbols for the 2-symbol interval. The receiving entity may perform post-processing (e.g., conjugation) on the detected symbols if needed. Alternatively, the receiving entity derives a spatial filter matrix based on an effective channel response matrix, performs spatial matched filtering on the received symbols for each symbol period to obtain detected symbols for that symbol period, A receiving entity obtains received symbols for a data transmission having at least one data symbol stream sent with space-time transmit diversity (STTD). The receiving entity derives an overall channel response matrix in accordance with the STTD encoding scheme used for the data transmission, derives spatial filter matrix based on the overall channel response matrix, and performs spatial matched filtering on a vector of received symbols for each 2-symbol interval to obtain a vector of detected symbols for the 2-symbol interval. The receiving entity may perform post-processing (e.g., conjugation) on the detected symbols if needed. Alternatively, the receiving entity derives a spatial filter matrix based on an effective channel response matrix, performs spatial matched filtering on the received symbols for each symbol period to obtain detected symbols for that symbol period, and combines multiple estimates obtained for each data symbol sent with STTD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Simple handheld photoacoustic imaging probe
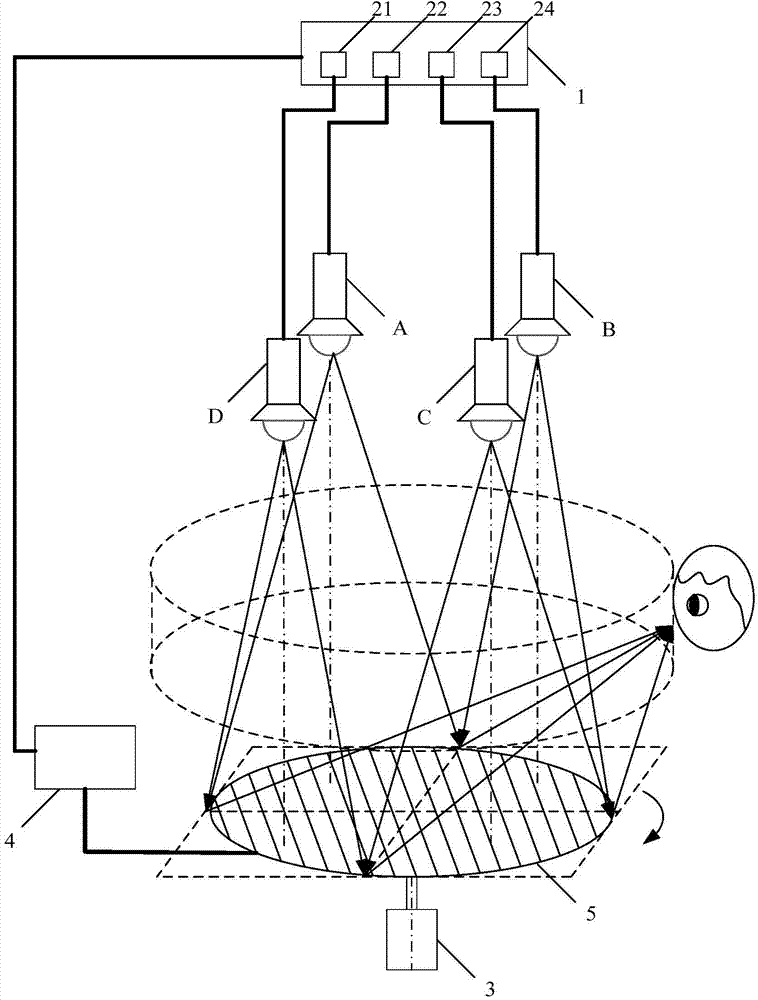
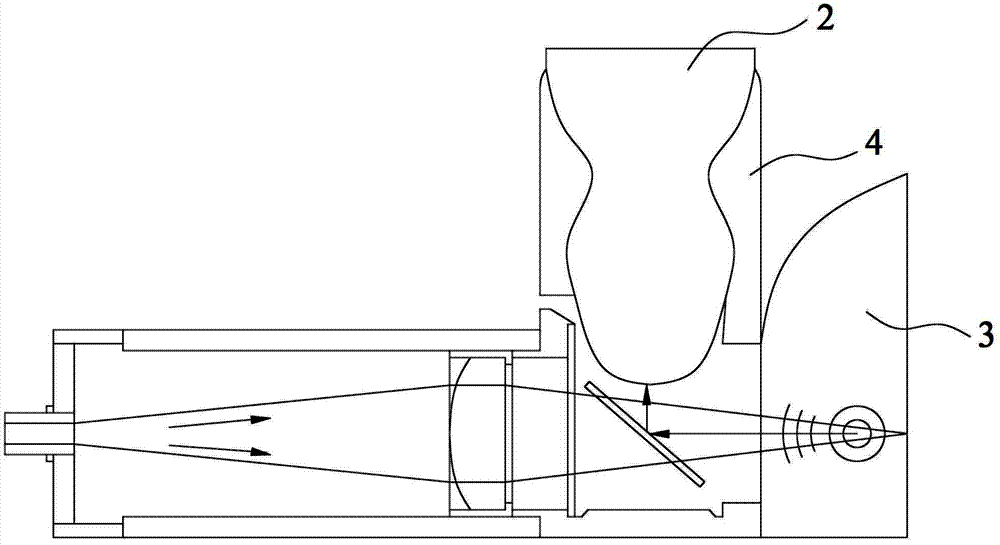
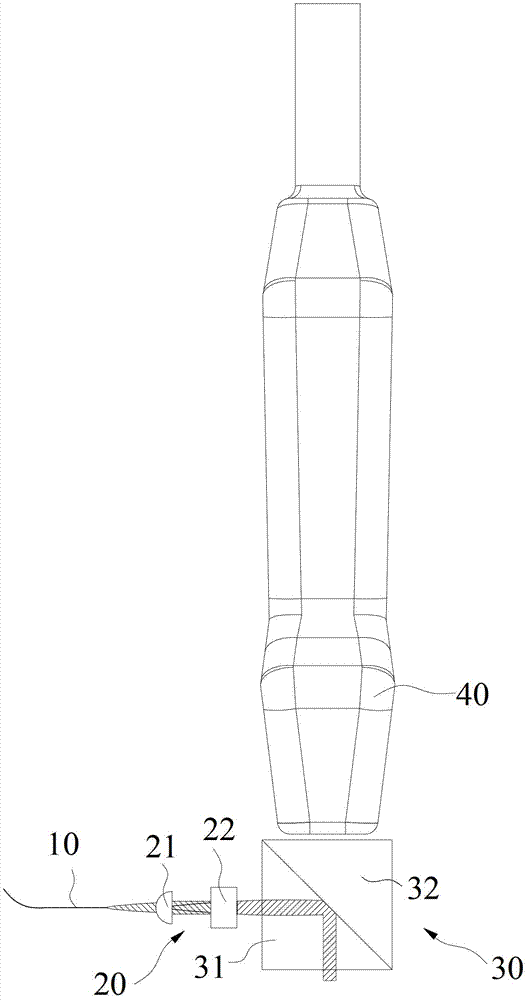
The invention relates to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging and provides a simple handheld photoacoustic imaging probe. Exciting light is coupled into an optical fiber (10); light from the optical fiber (10), in a direction parallel to the surface of an object to be tested, is focused by a spatial expansion and lens group (20) before entering a coupling module (30); the light entering the coupling module (30) is totally reflected by a position, right below an ultrasonic probe (40), corresponding to an ultrasonic probe detection area of the object to be tested and vertically irradiates to the ultrasonic probe detection area of the object to be tested, right below the ultrasonic probe (40), so as to excite a photoacoustic signal; the photoacoustic signal is transmitted into the coupling module (30) through the ultrasonic probe detection area of the object to be tested, and the ultrasonic probe (40) receives the photoacoustic signal. The simple handheld photoacoustic imaging probe has the advantages that the exiting light irradiation area and the ultrasonic probe detection area are allowed to overlap without significantly increasing the size of the ultrasonic probe; the ultrasonic probe is kept traditionally be perpendicular to the object to be tested and is easy for an operator to adapt to.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com