Patents
Literature
115 results about "Sum-frequency generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
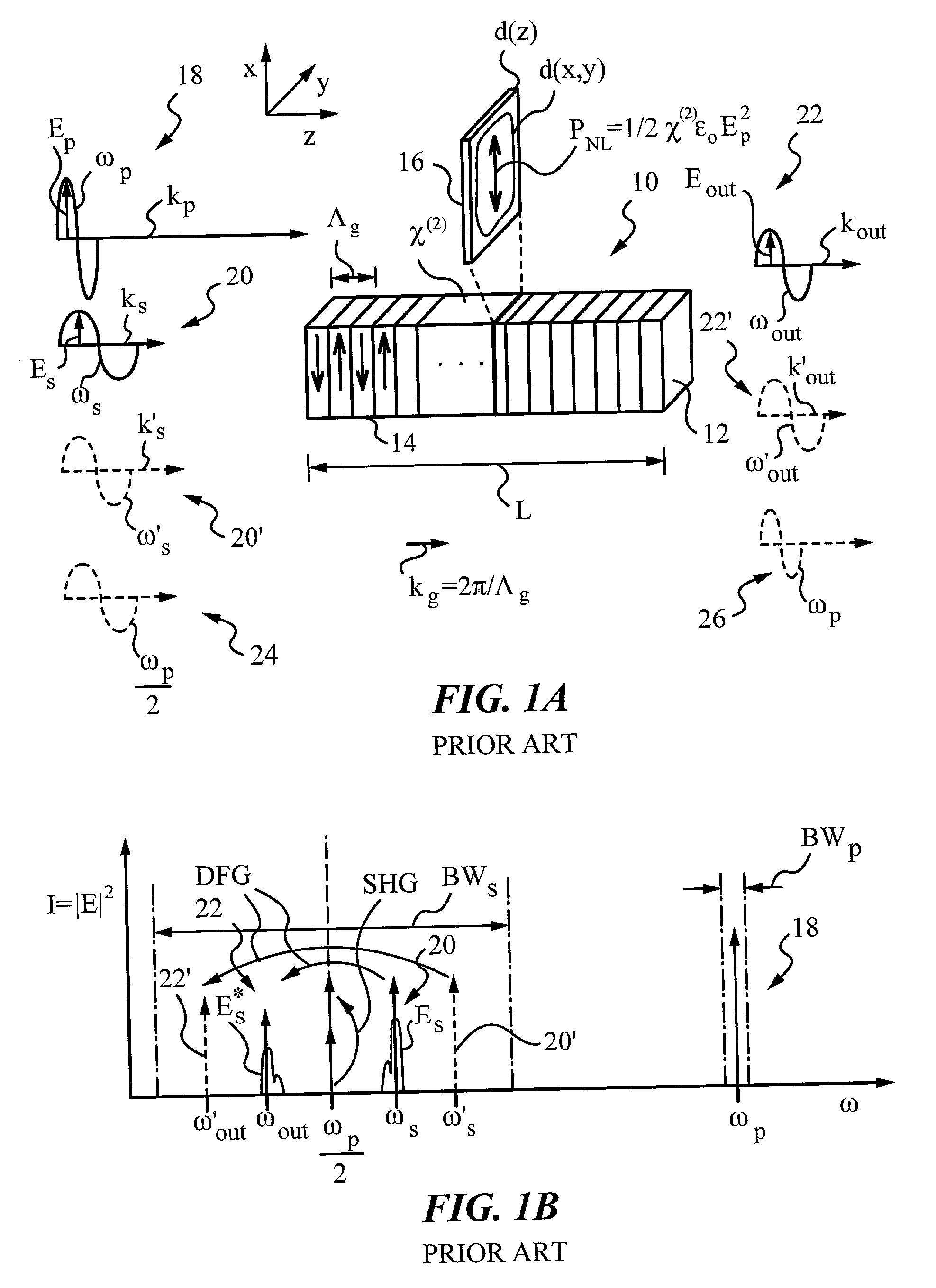
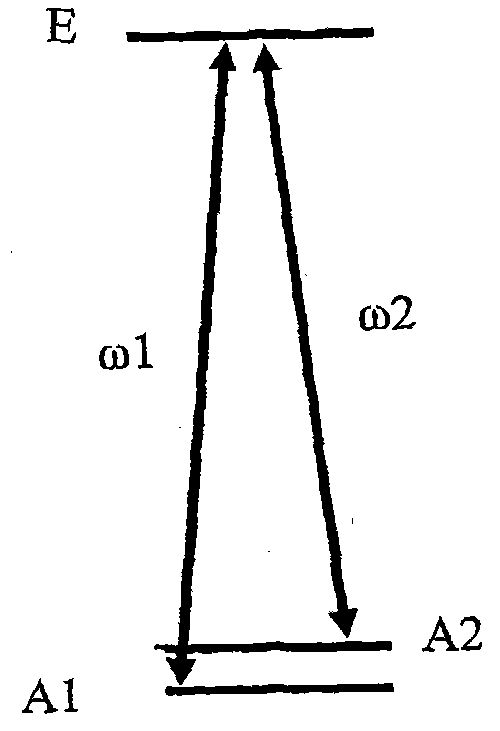
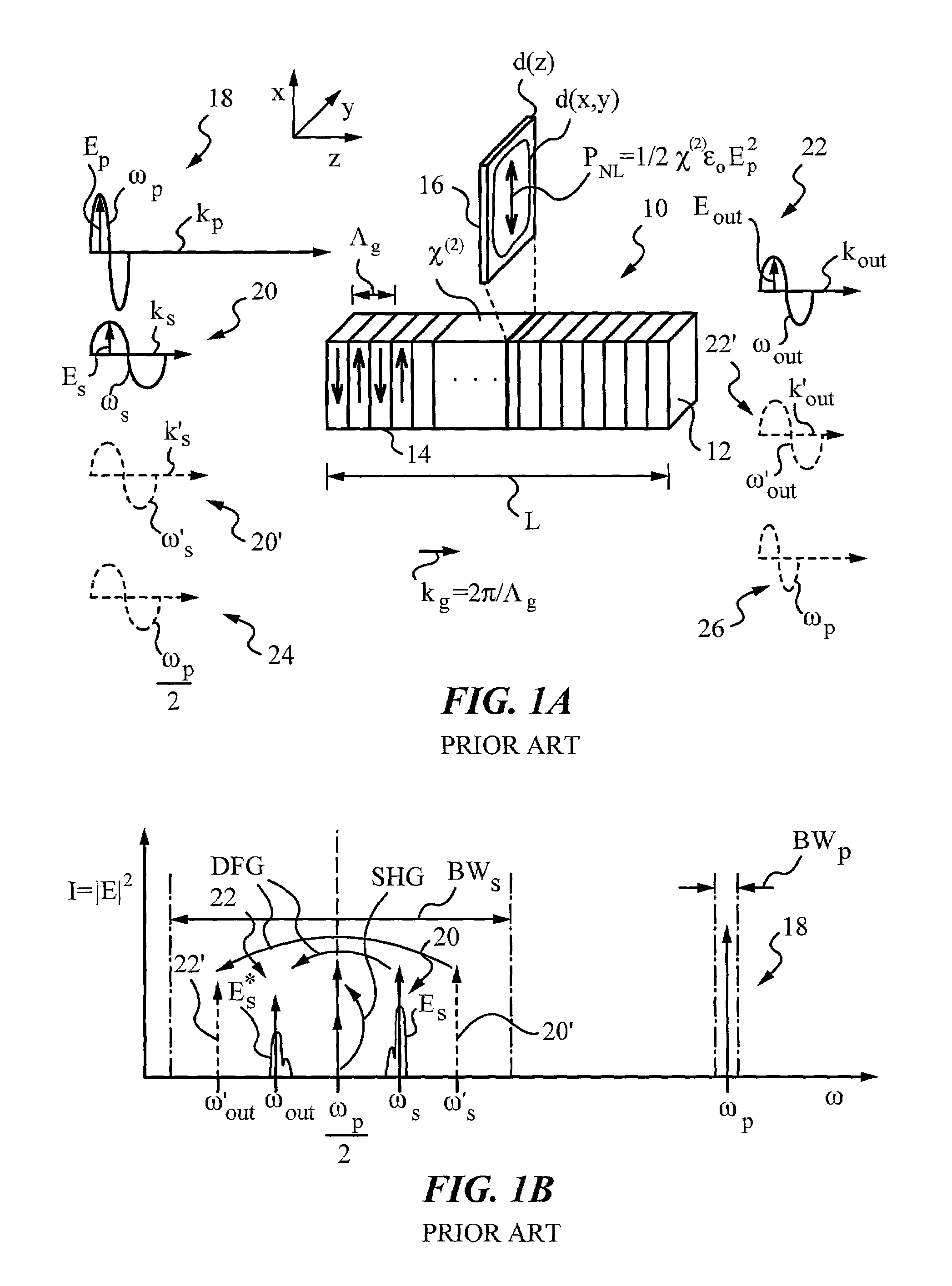
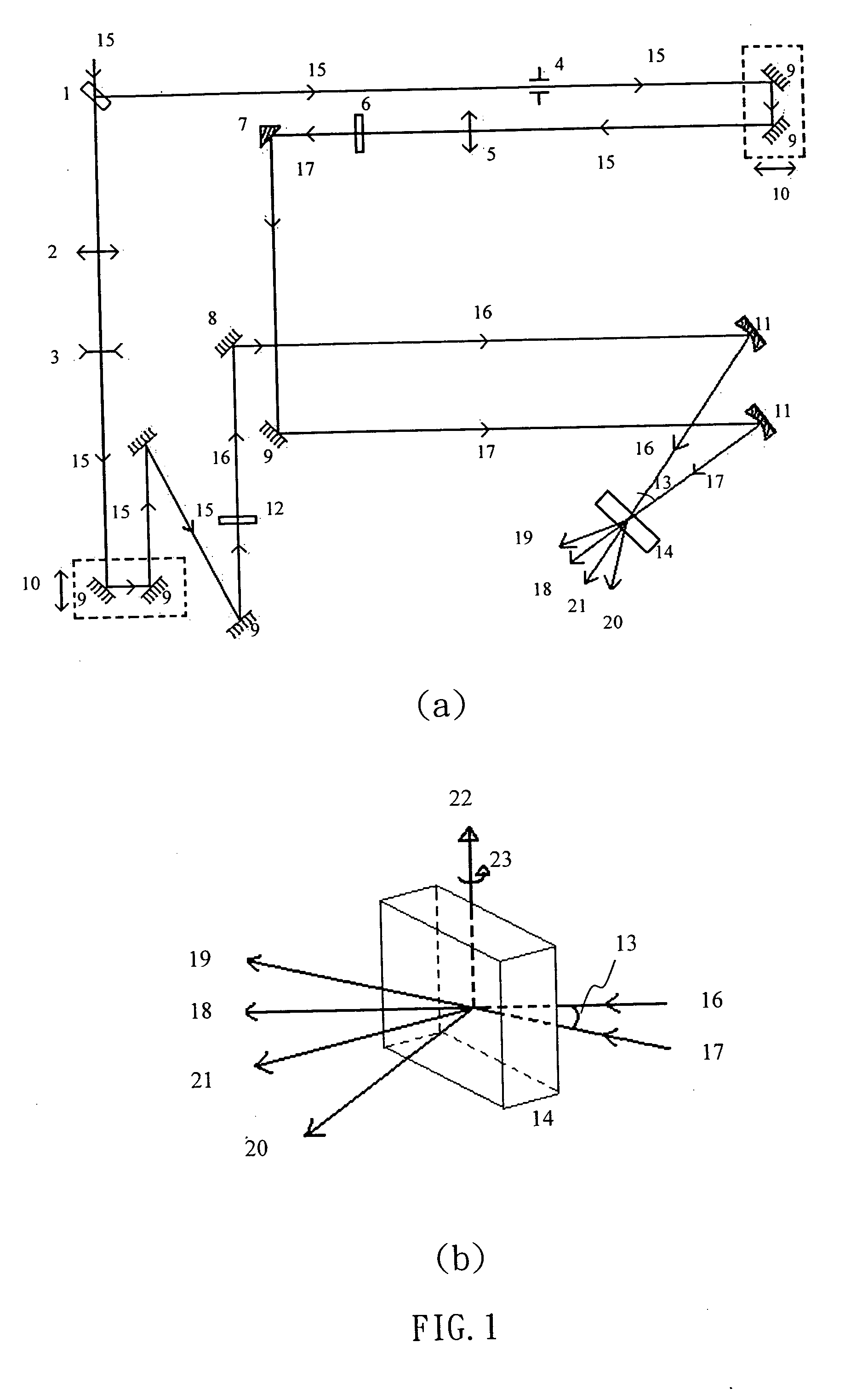
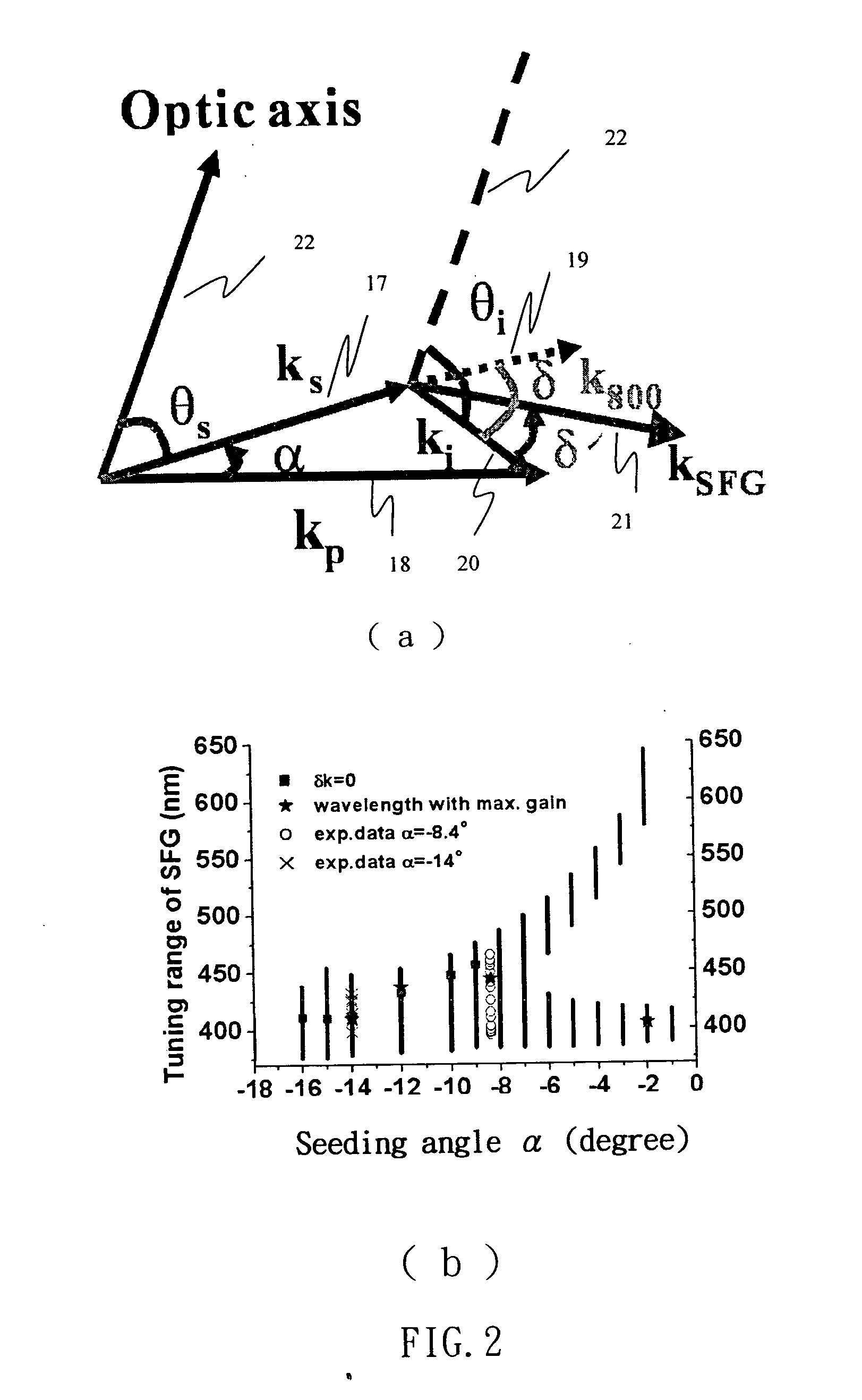
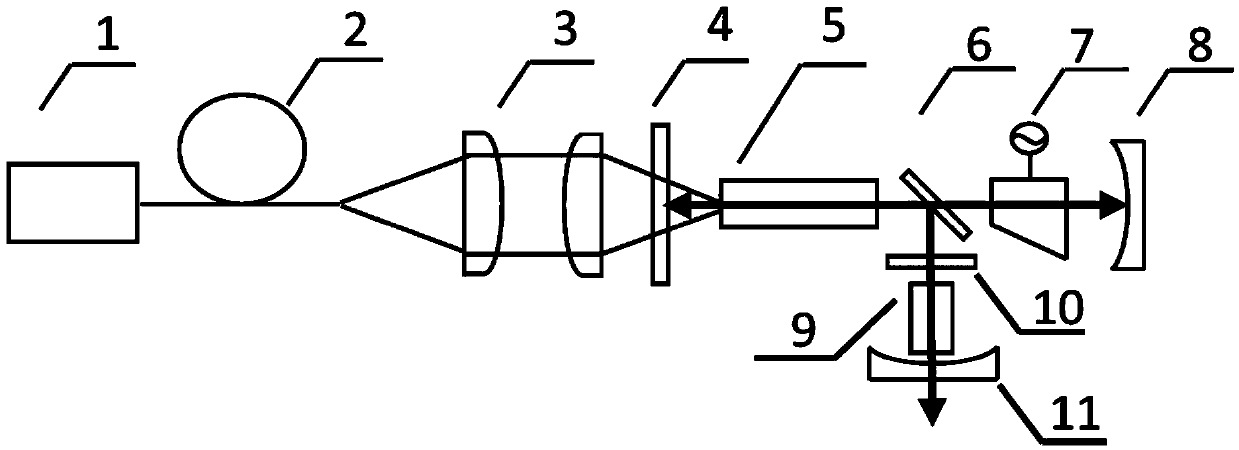
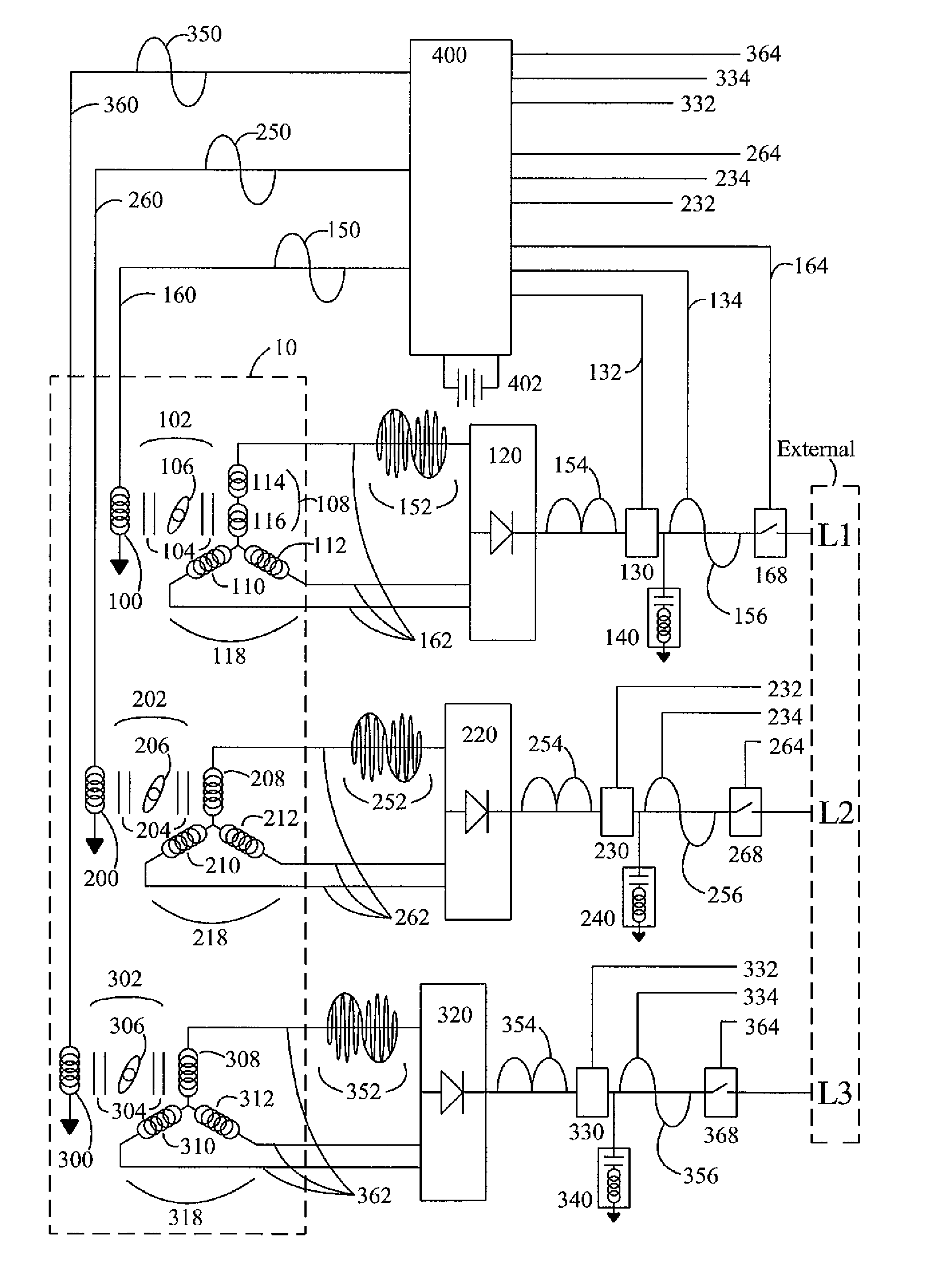
Sum-frequency generation (SFG) is a second order nonlinear optical process based on the annihilation of two input photons at angular frequencies ω₁ and ω₂ while, simultaneously, one photon at frequency ω₃ is generated. As with any second order χ⁽²⁾ phenomenon in nonlinear optics, this can only occur under conditions where: the light is interacting with matter, which is asymmetric (for example, surfaces and interfaces); the light has a very high intensity (typically from a pulsed laser).
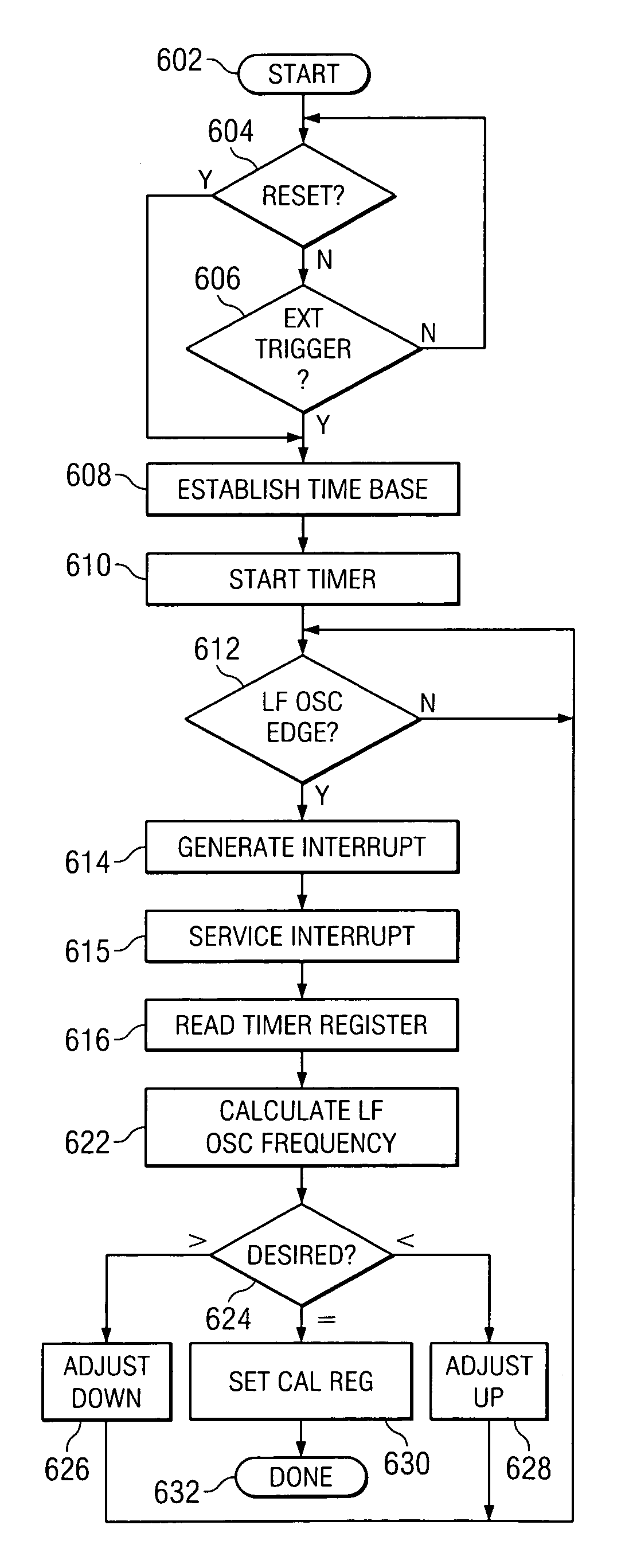
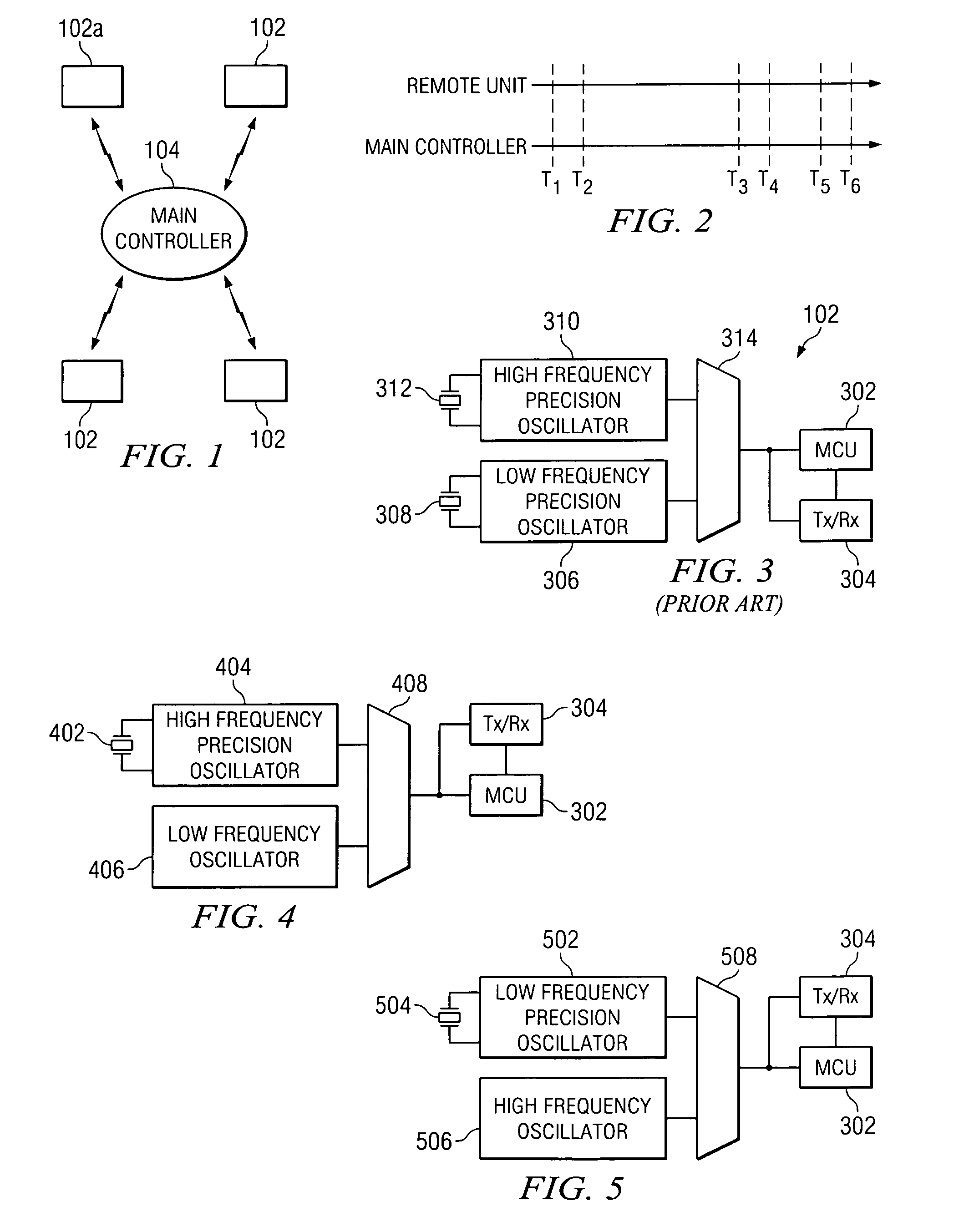
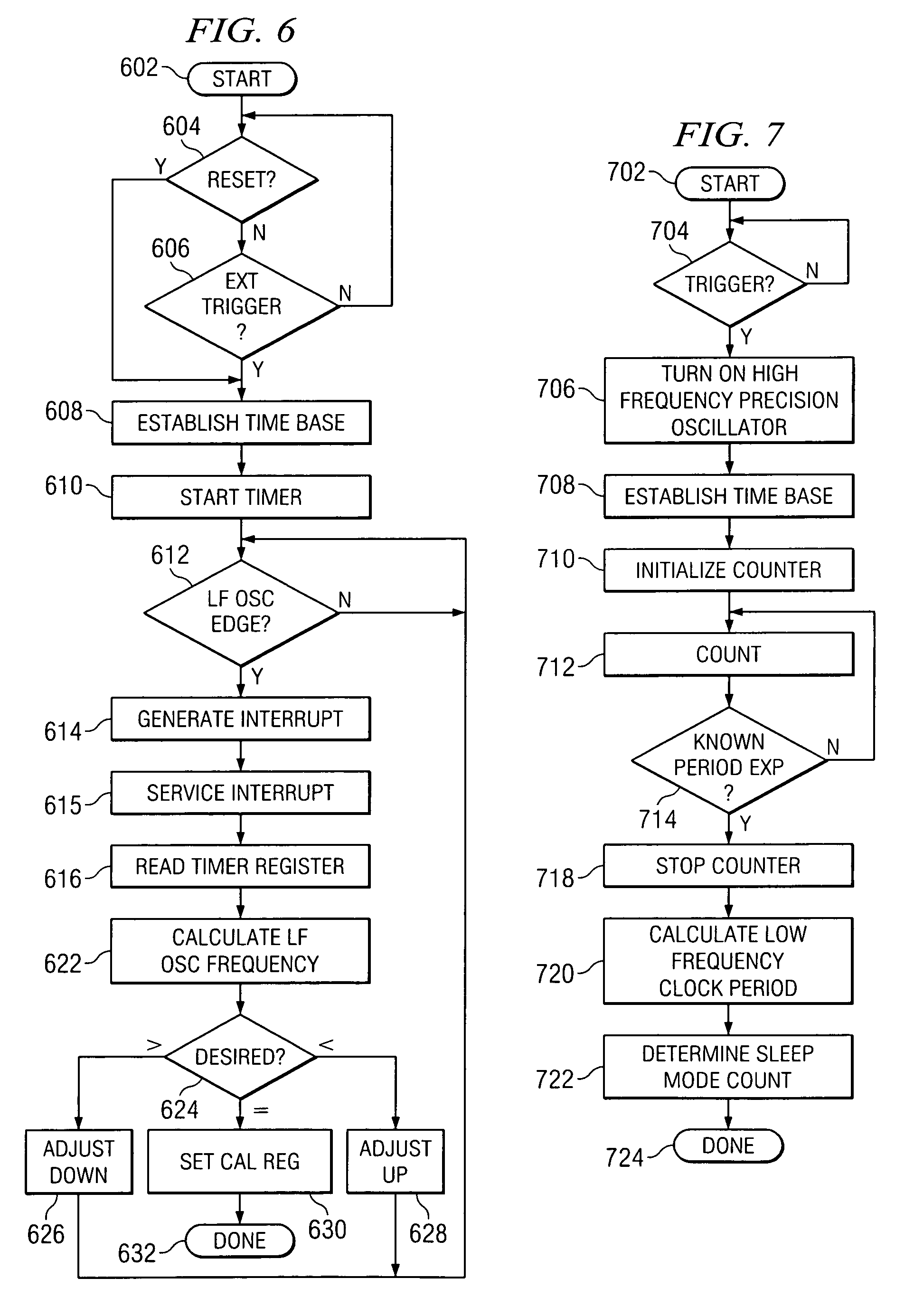
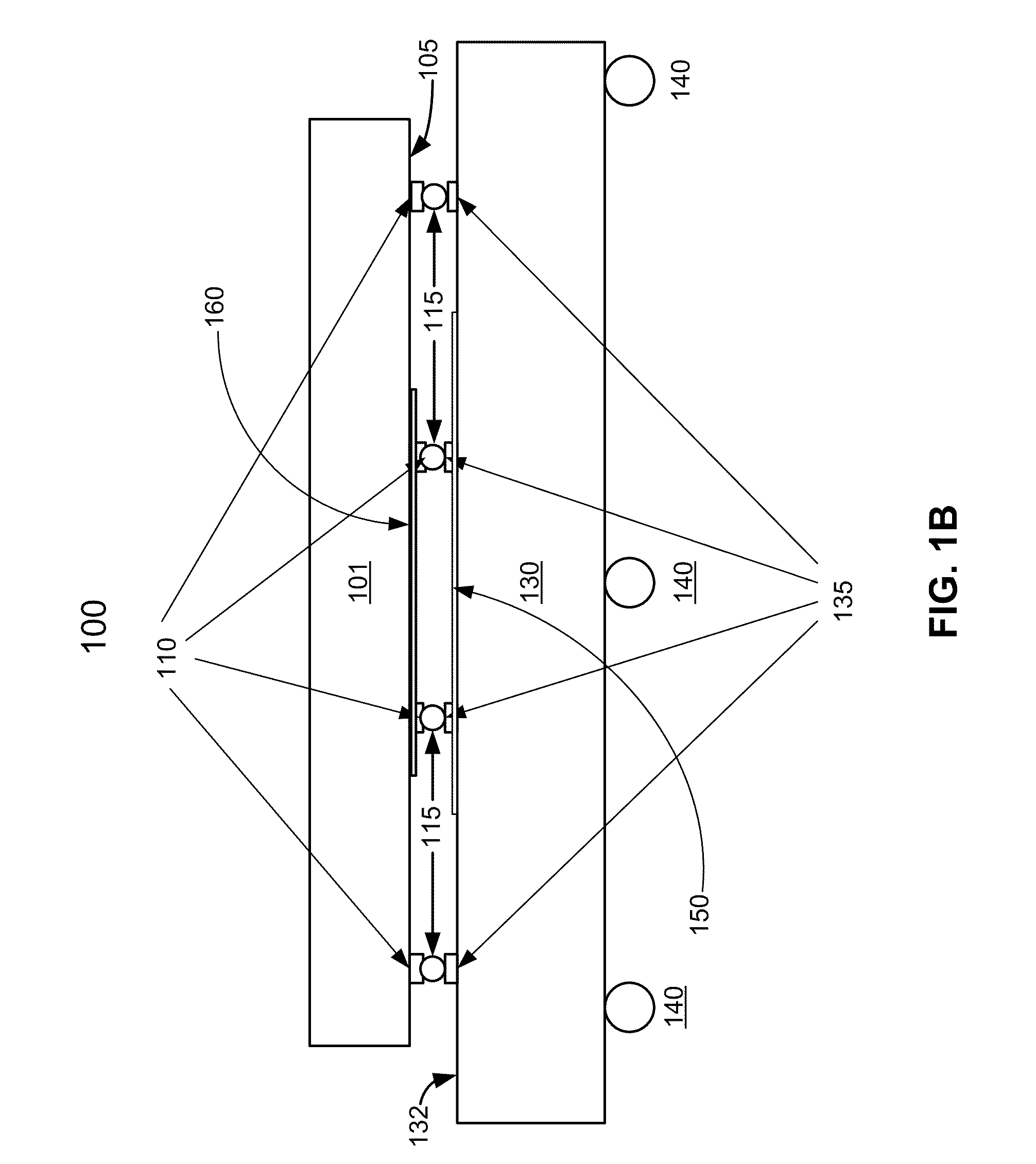
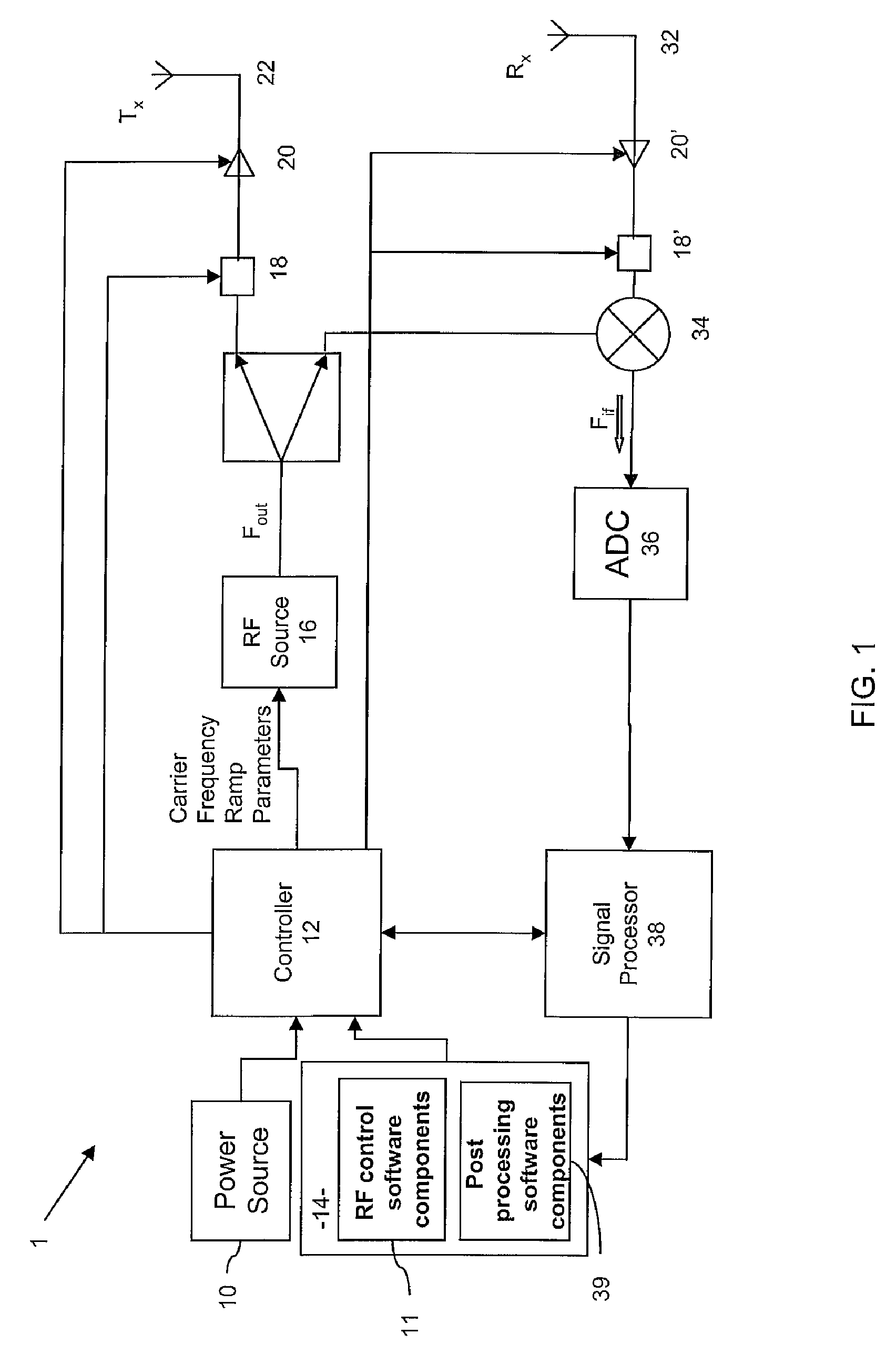
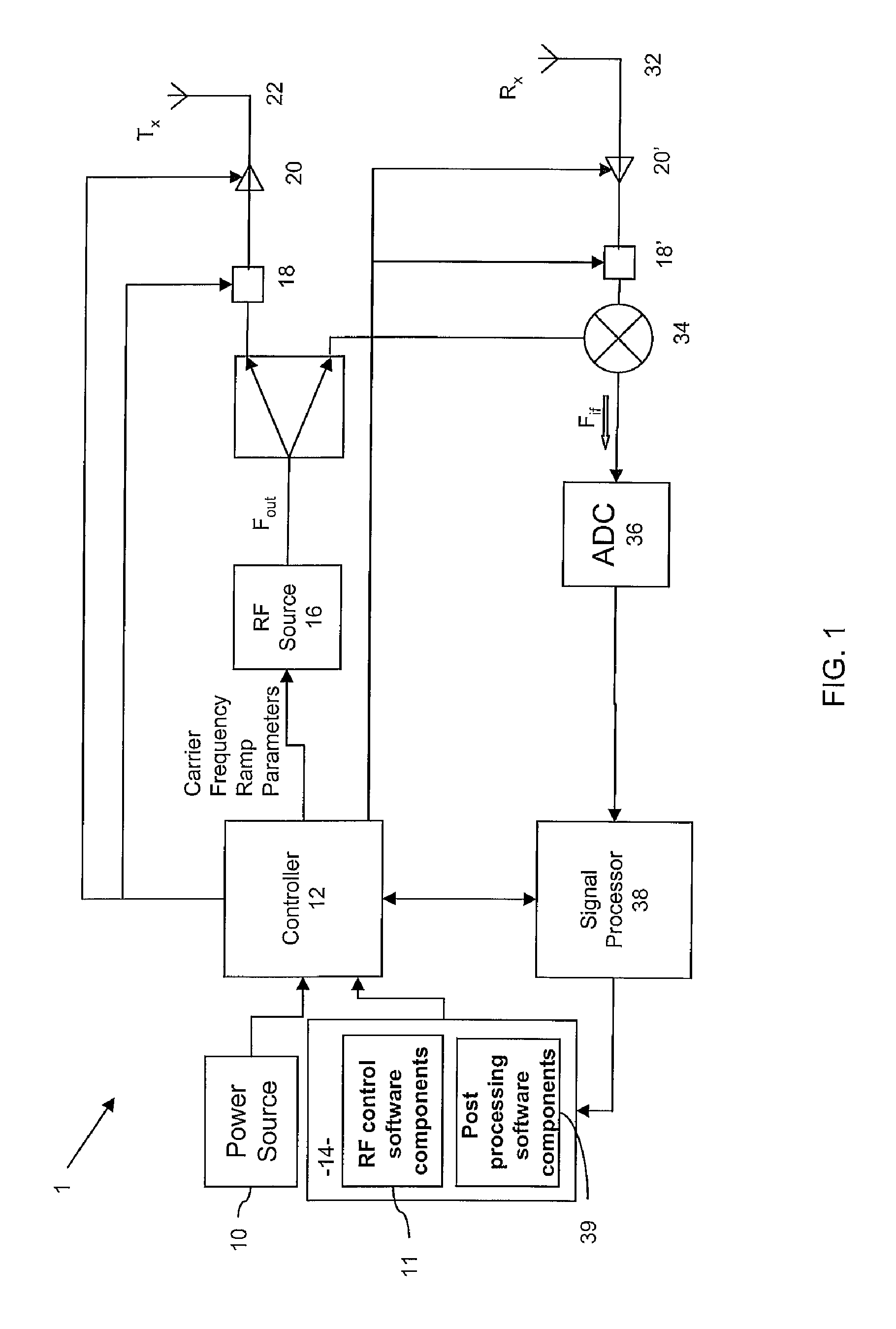
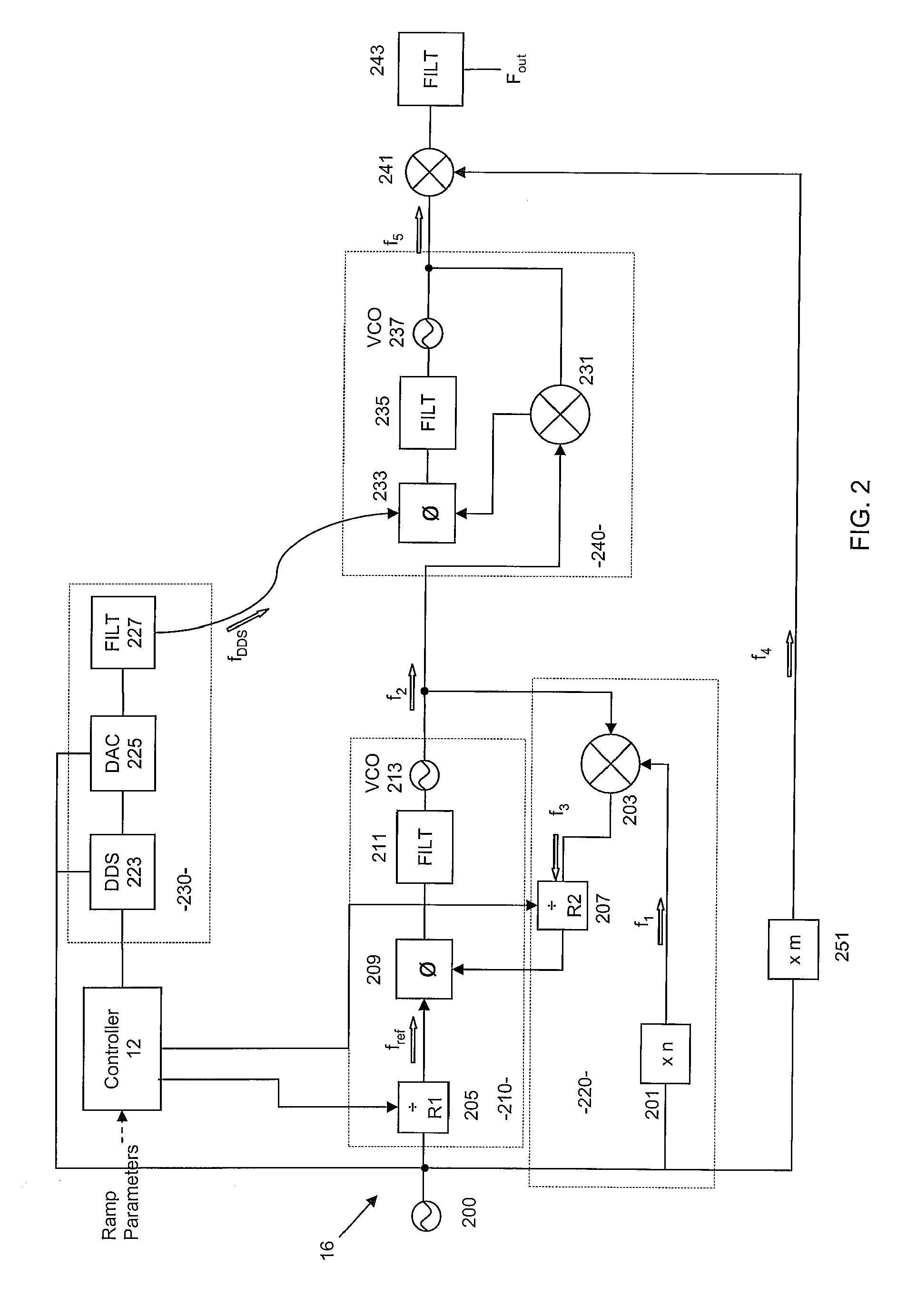
Precise frequency generation for low duty cycle transceivers using a single crystal oscillator
An apparatus and method for calibrating a non-crystal oscillator in a transceiver unit using a crystal-oscillator includes the step of establishing a time base based upon oscillations of the crystal oscillator. A comparison of the number of oscillations for the non-crystal oscillator and the crystal oscillator is made during a known time period is made. An adjustment is determined based upon the established time base and the compared number of oscillations. The transceiving of the transceiver unit is then controlled based upon this adjustment.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
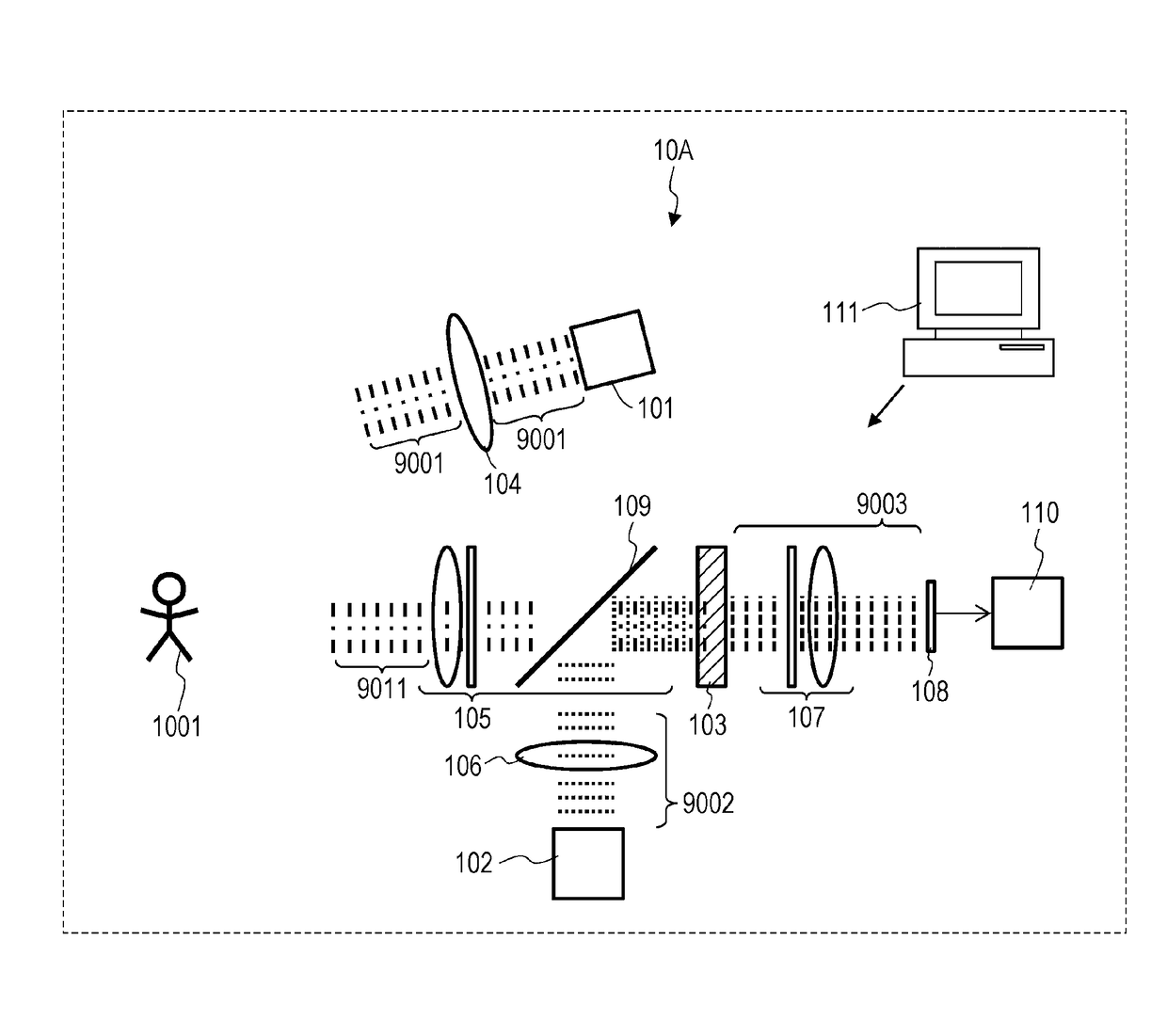
Measurement system
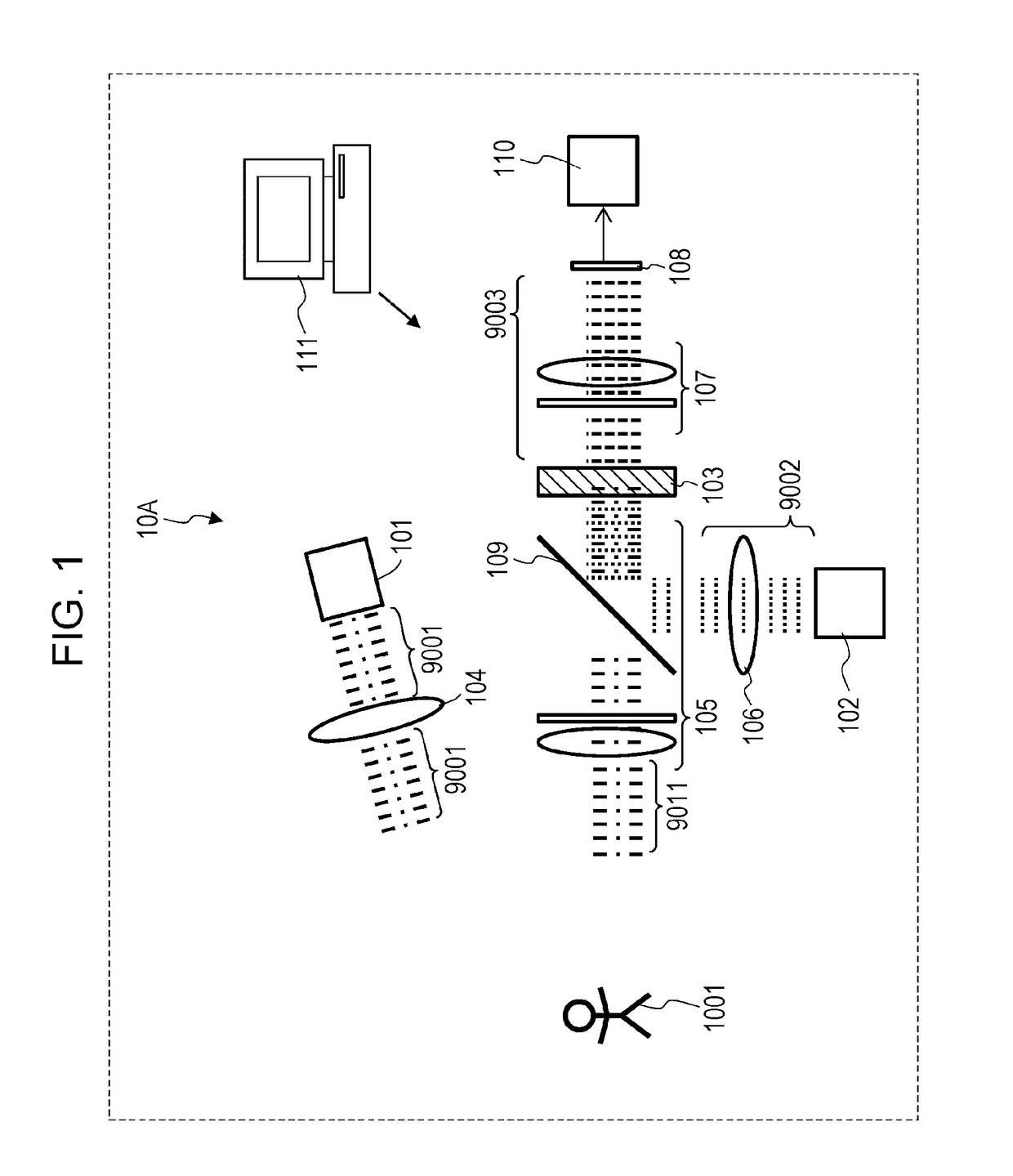
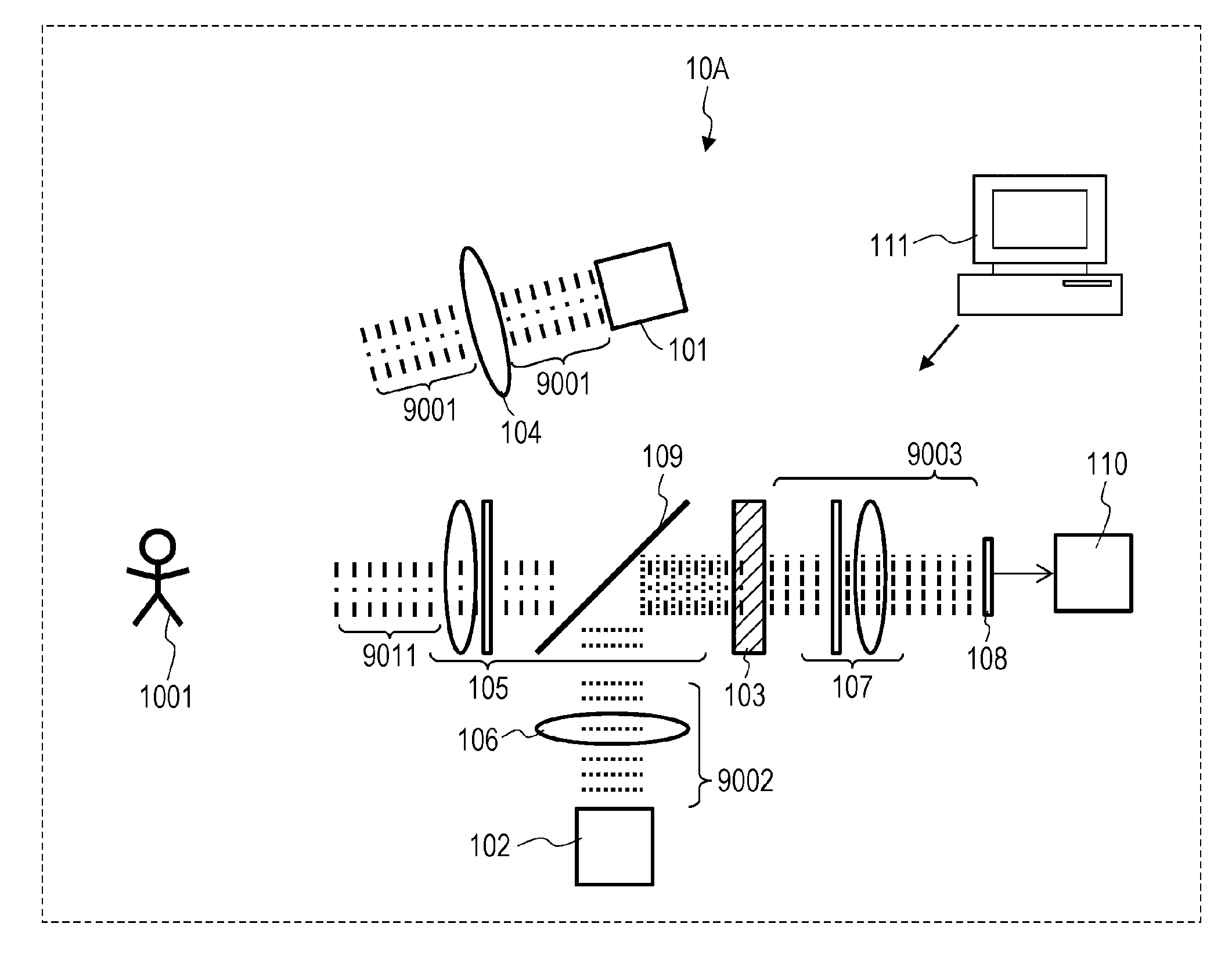
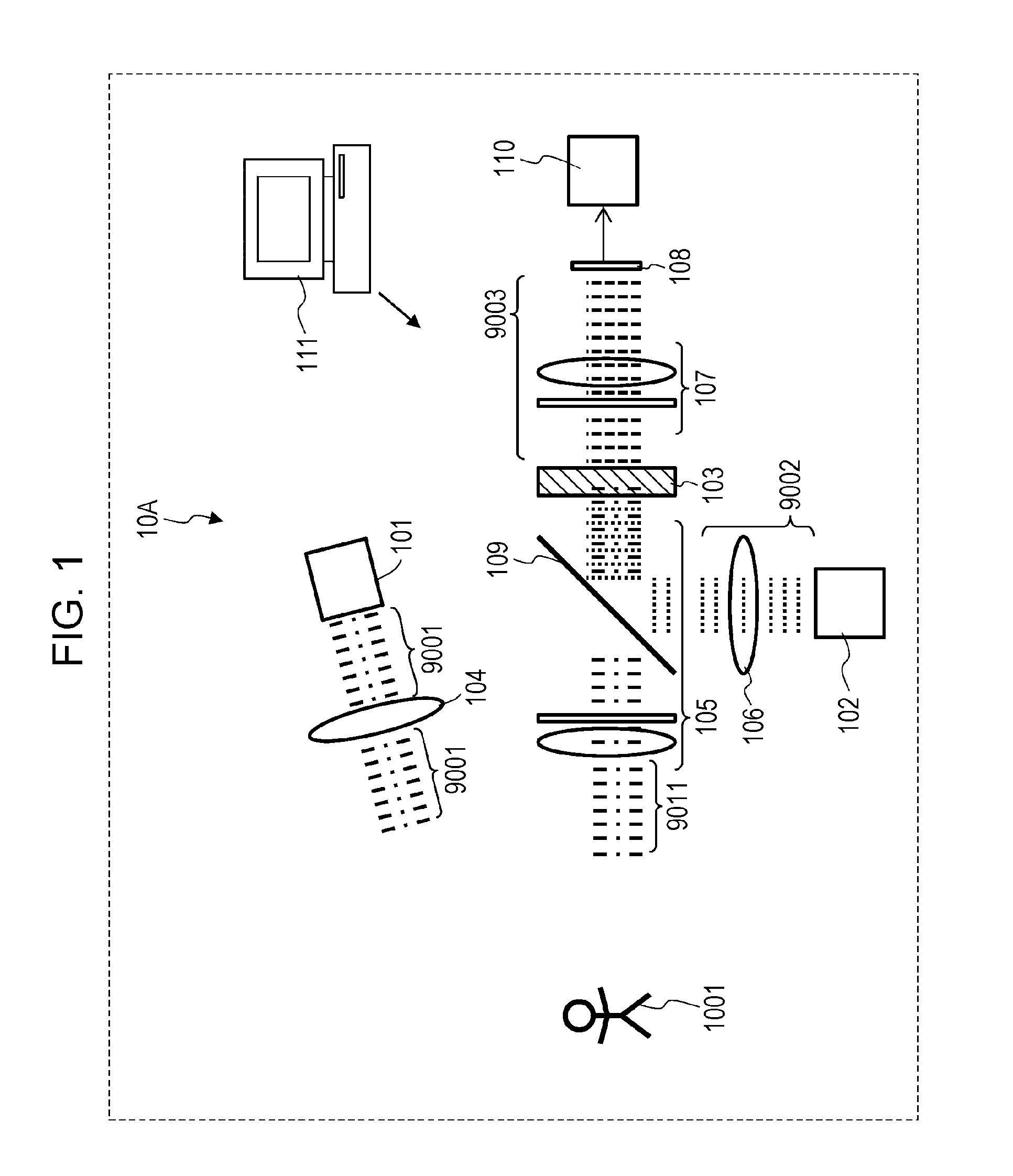
ActiveUS9605998B2Reduce impactAccurate measurementPhotometryElectromagnetic wave reradiationNonlinear optical crystalPhotovoltaic detectors
A measurement system, comprising: a first light source that generates first light and irradiates an object with the first light, at least one of an intensity, a polarization state, and a wavelength being modulated with a first period in the first light; a second light source that generates second light, at least one of an intensity, a polarization state, and a wavelength being modulated with a second period in the second light; a first optical system that mixes light from the object based on the first light with the second light; a nonlinear optical crystal that generates third light from the mixed light by sum-frequency generation phenomenon, the third light having a frequency equivalent to a sum of a frequency of the light from the object based on the first light and a frequency of the second light; and a photodetector that measures an intensity of the third light.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Measurement system
ActiveUS20160061655A1Reduce impactAccurate measurementPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansNonlinear optical crystalObject based
A measurement system, comprising: a first light source that generates first light and irradiates an object with the first light, at least one of an intensity, a polarization state, and a wavelength being modulated with a first period in the first light; a second light source that generates second light, at least one of an intensity, a polarization state, and a wavelength being modulated with a second period in the second light; a first optical system that mixes light from the object based on the first light with the second light; a nonlinear optical crystal that generates third light from the mixed light by sum-frequency generation phenomenon, the third light having a frequency equivalent to a sum of a frequency of the light from the object based on the first light and a frequency of the second light; and a photodetector that measures an intensity of the third light.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
FCSEL that frequency doubles its output emissions using sum-frequency generation
InactiveUS6879615B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionPrismWaveguide
A “Folded Cavity Surface Emitting Laser” (FCSEL) sum frequency generating device capable of generating a second harmonic at room temperatures with high efficiency and output power, while having a small size, low energy consumption, and a low manufacturing cost. A FCSEL sum frequency generating semiconductor diode laser has a multilayered structure that comprises a mode discriminating polyhedral shaped prism waveguide, which is located at one end of two light emitting diodes, a partial photon reflecting mirror, which is located at the opposite end of the two light emitting diodes, and a phase-matching sum-frequency generating superlattice, which is located between the polyhedral shaped prism waveguide and the partial photon reflecting mirror.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
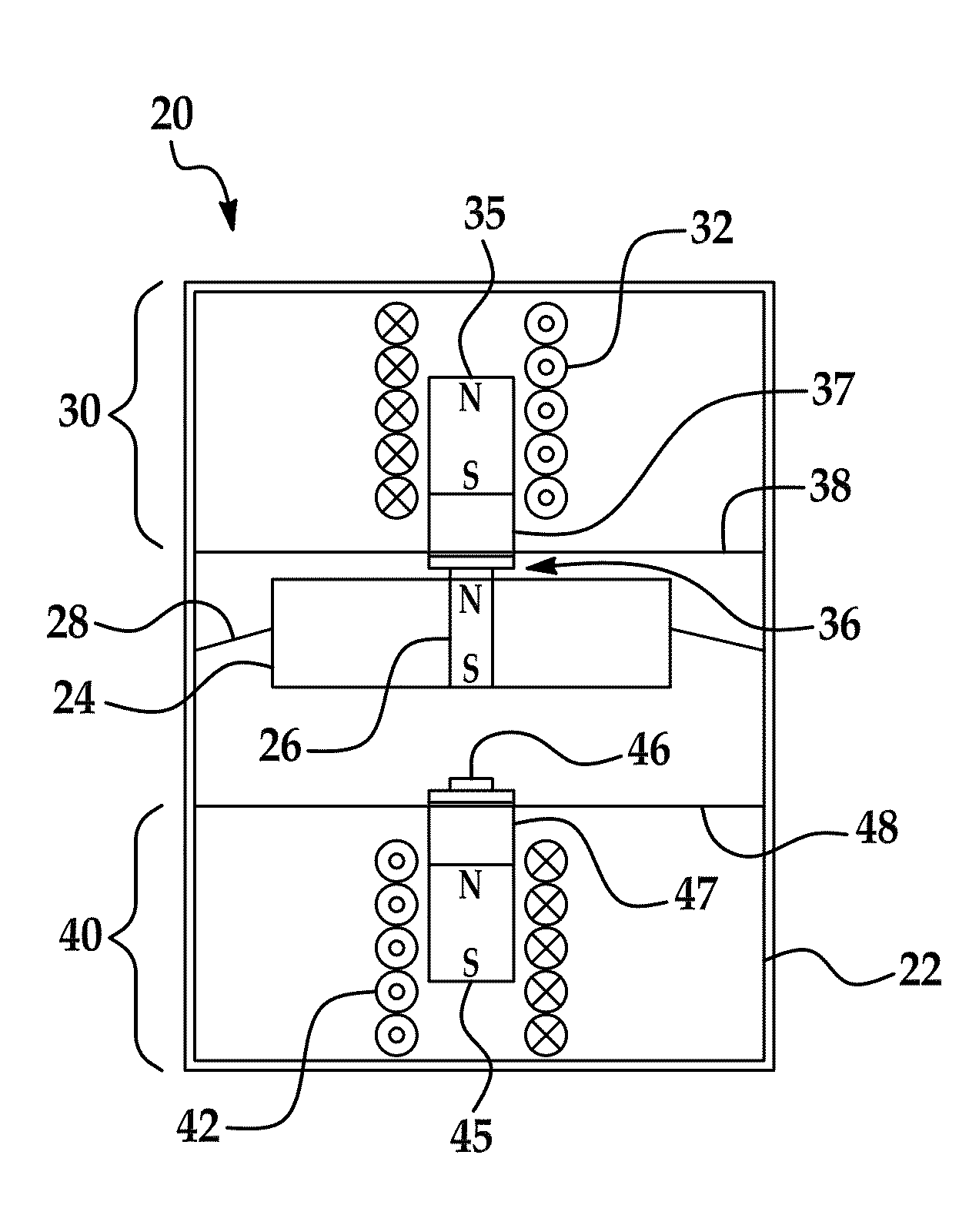
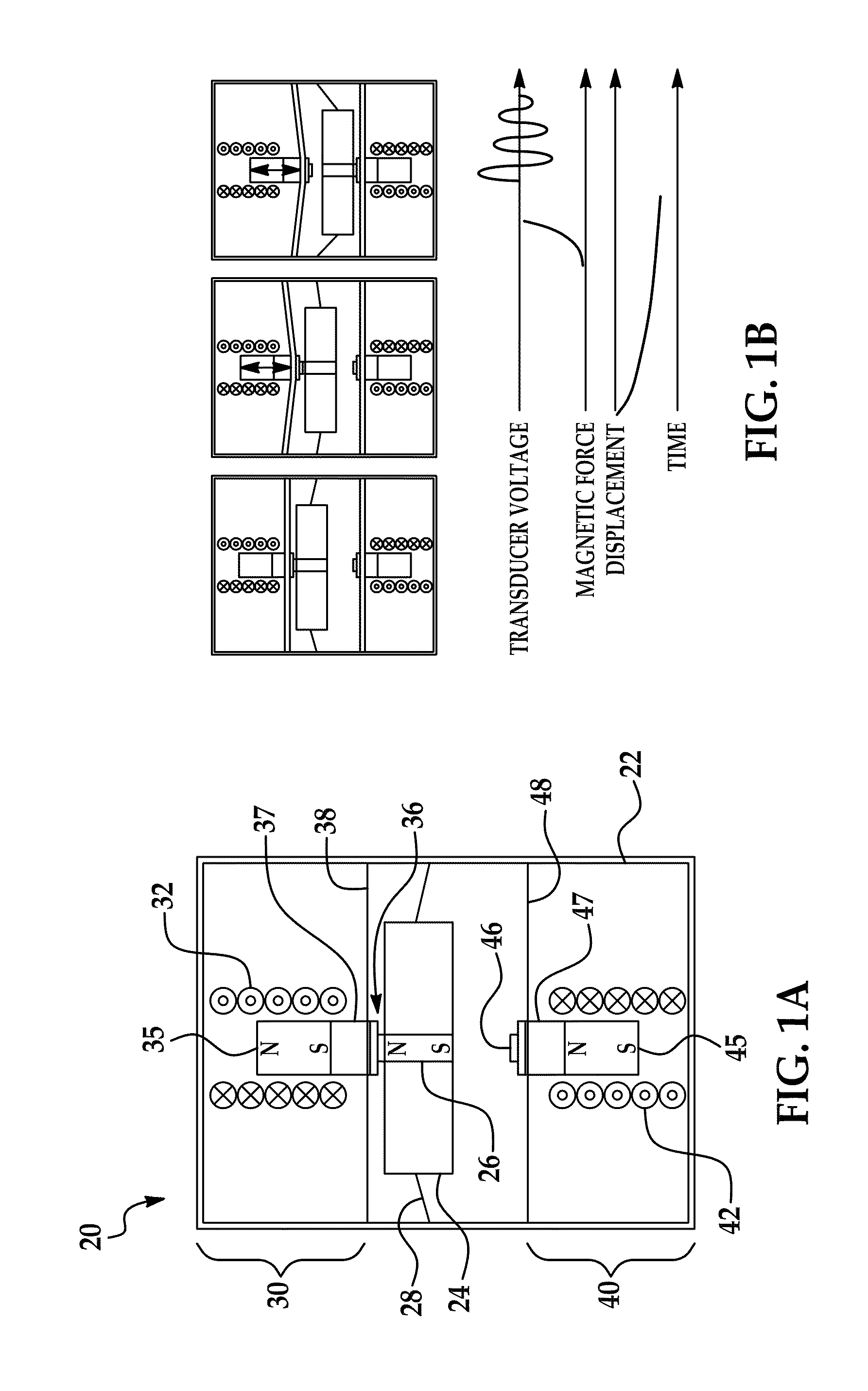
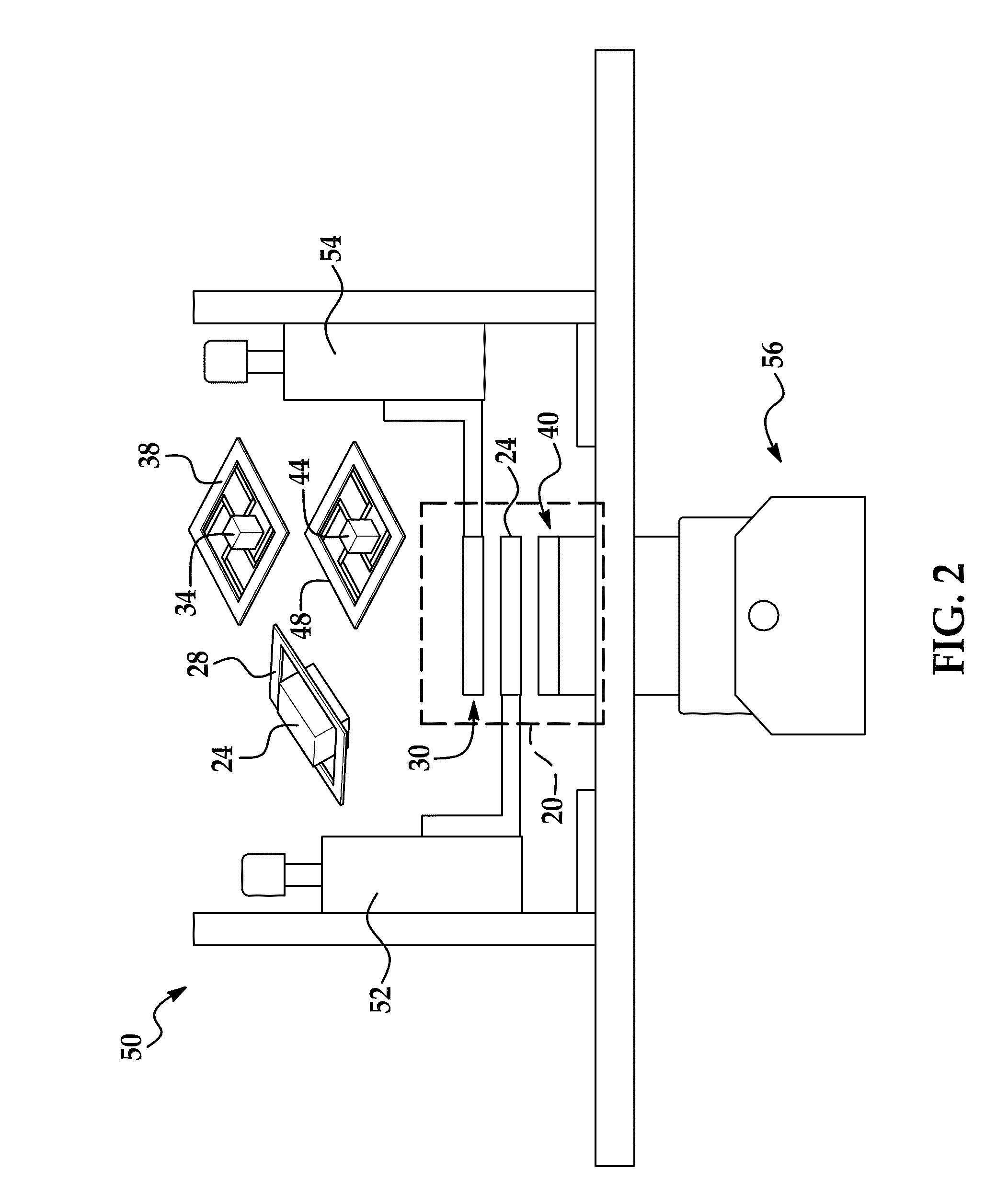
Increased frequency power generation using low-frequency ambient vibrations
ActiveUS20110140577A1Restrict movementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical energy handlingInertial massReciprocating motion
An increased frequency power generator that includes a pair of transducers located on opposite sides of a suspended inertial mass. Magnetic attraction is used to couple the mass to each of the two transducers in alternating fashion in response to vibration and other movement externally imparted on the generator. Each transducer includes a suspended magnetic element that couples and decouples to the inertial mass as it reciprocates in the housing due to the applied external moving force. As the inertial mass decouples from one transducer on its way to magnetically connecting to the other transducer, the decoupled suspended magnetic element oscillates at a frequency greater than the imparting force, thereby generating electrical power.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
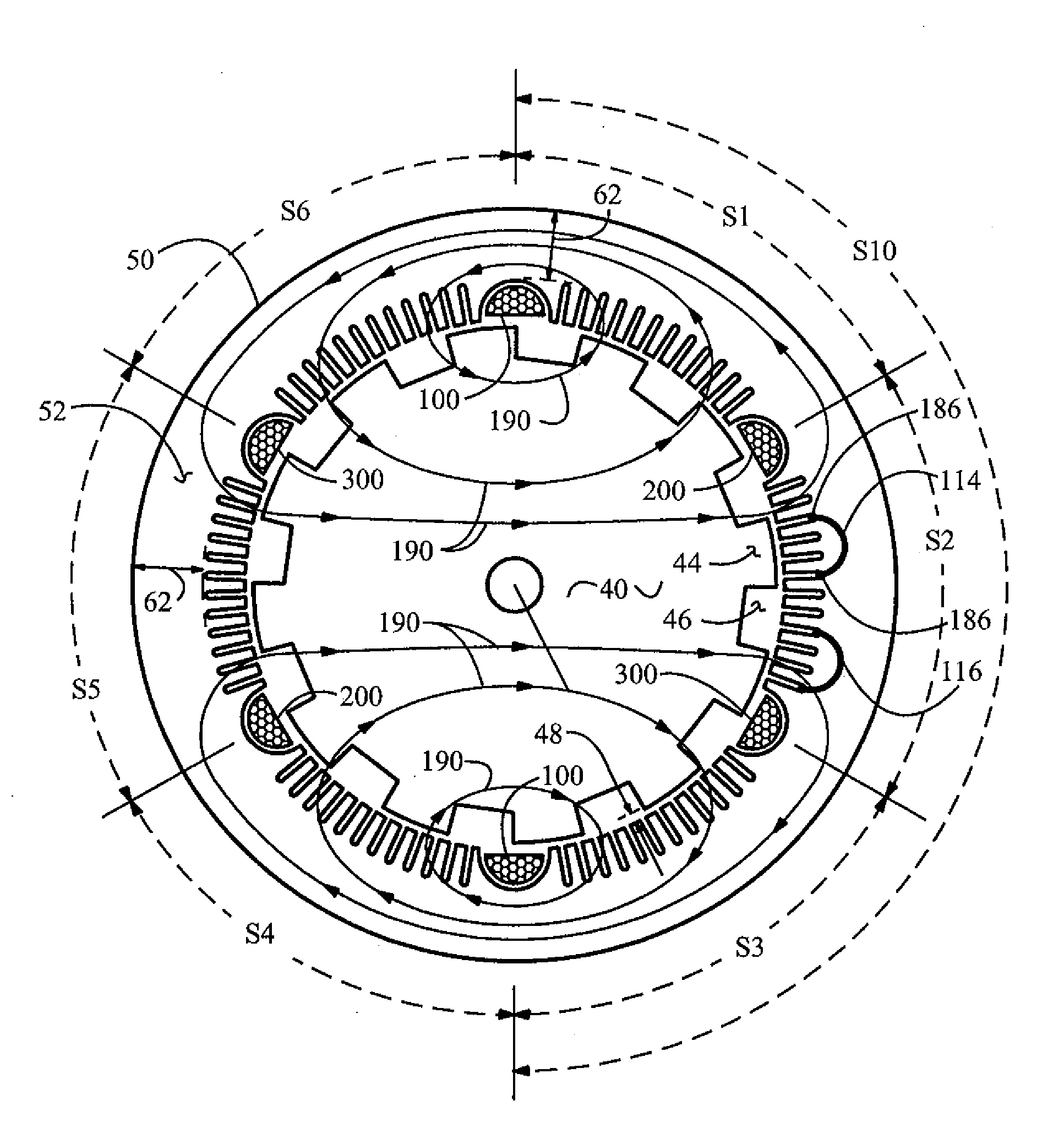
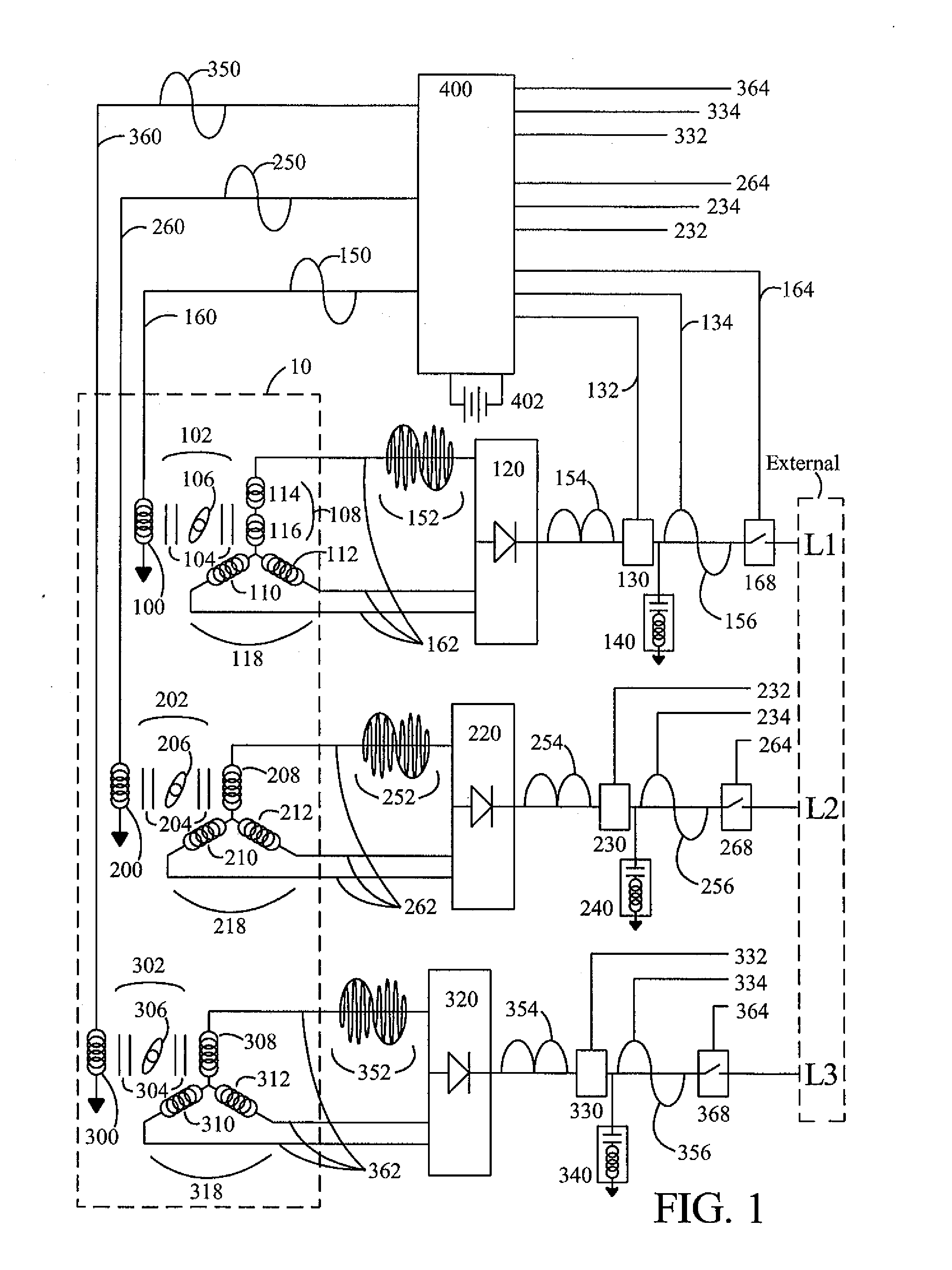
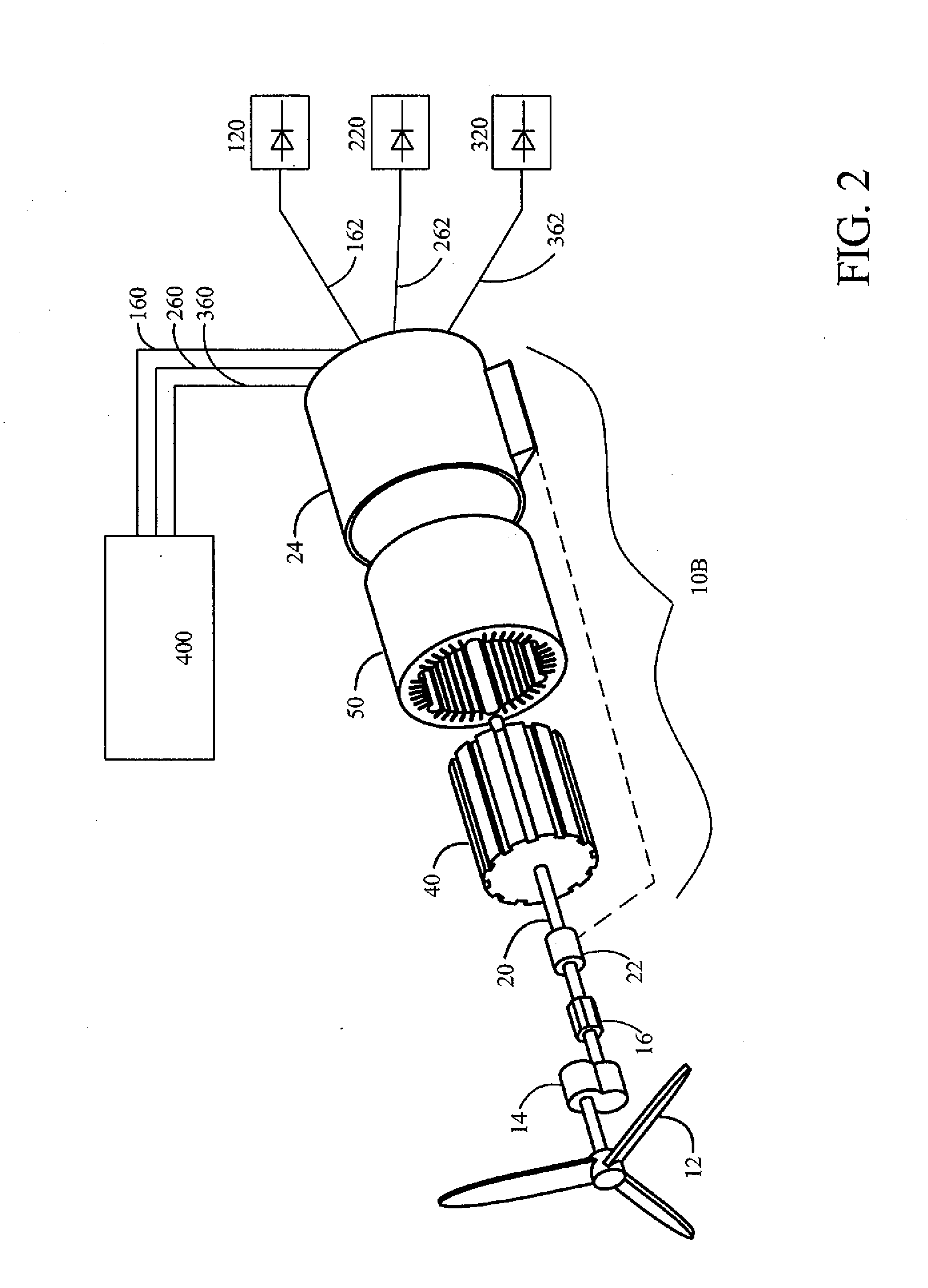
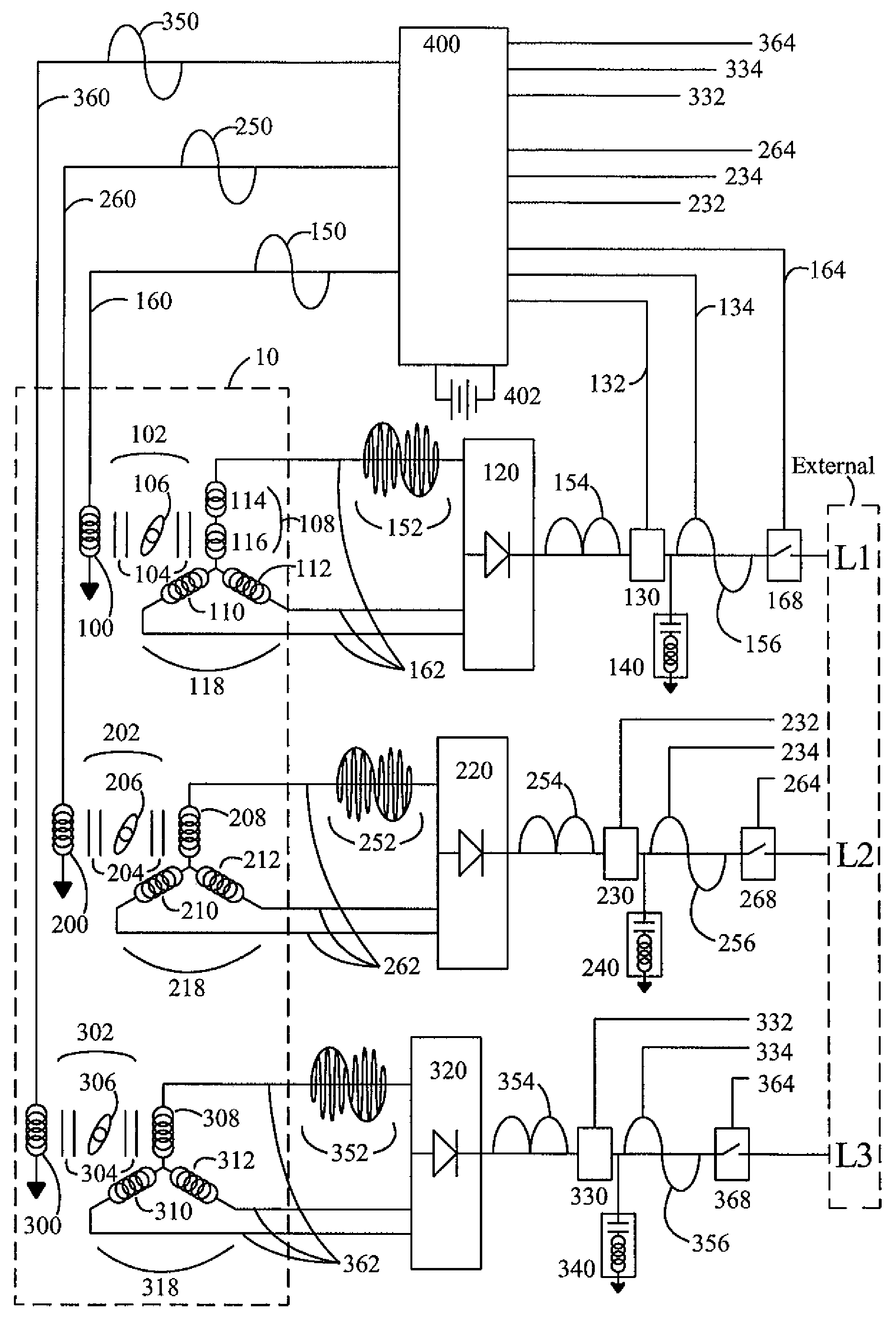
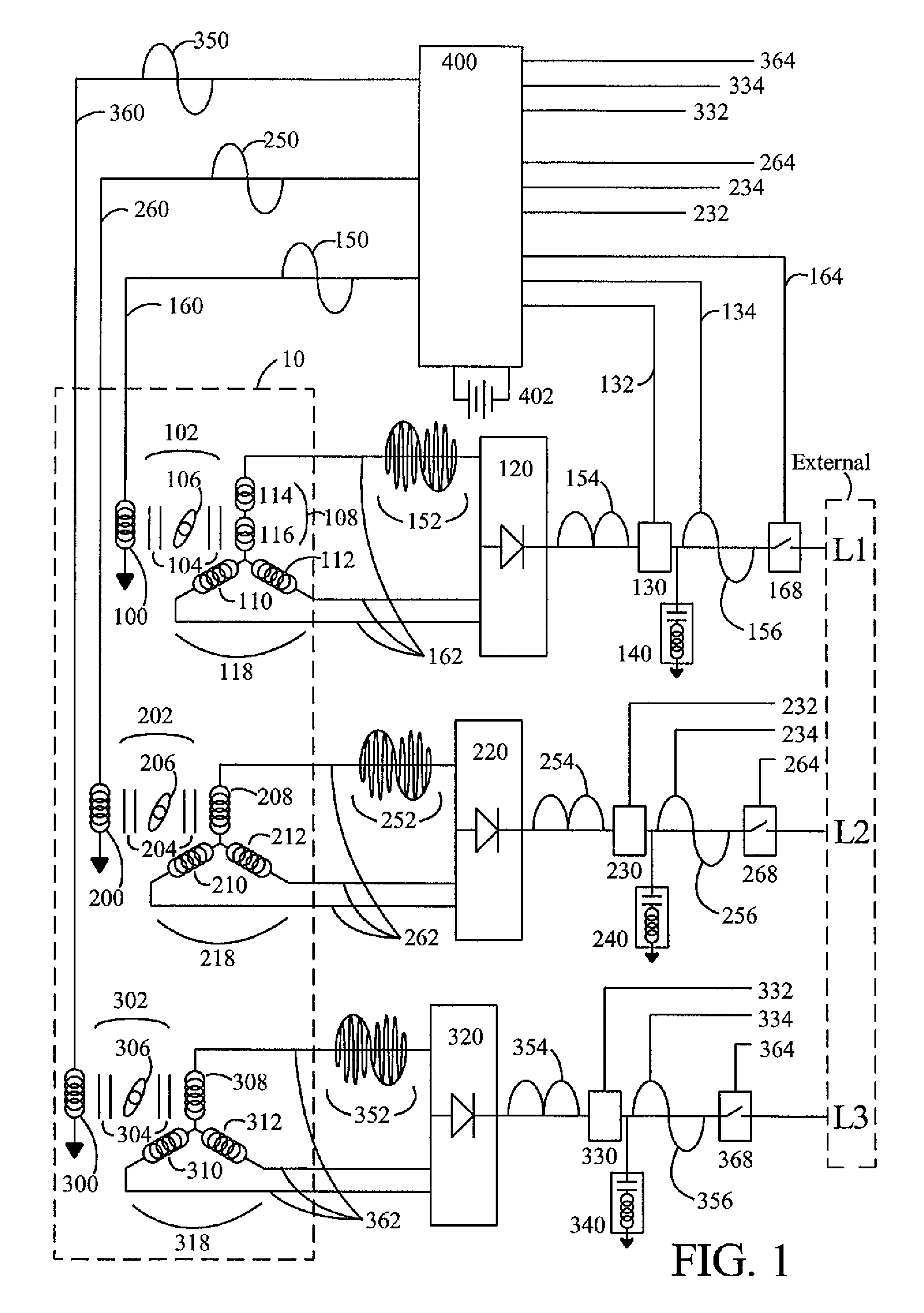
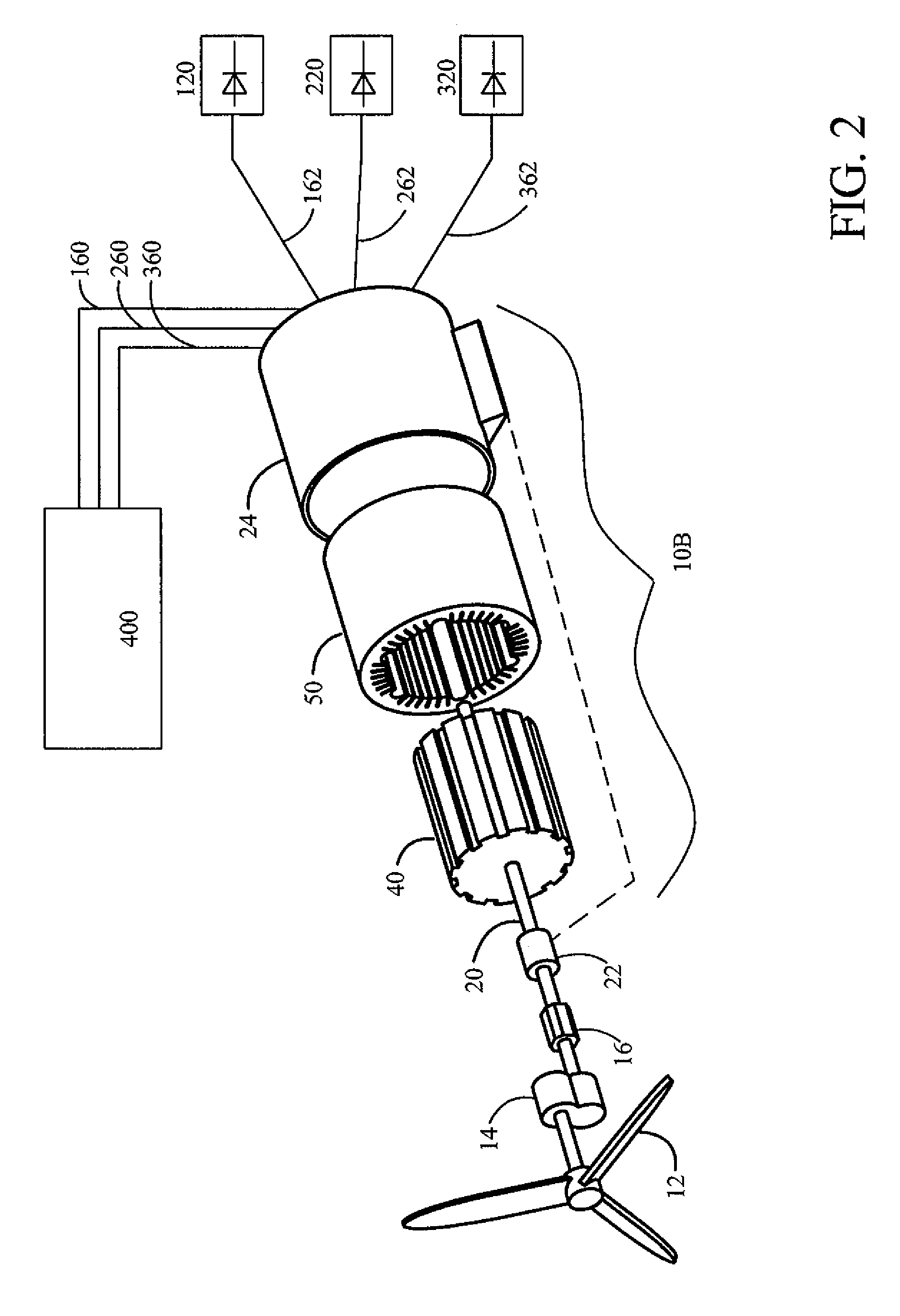
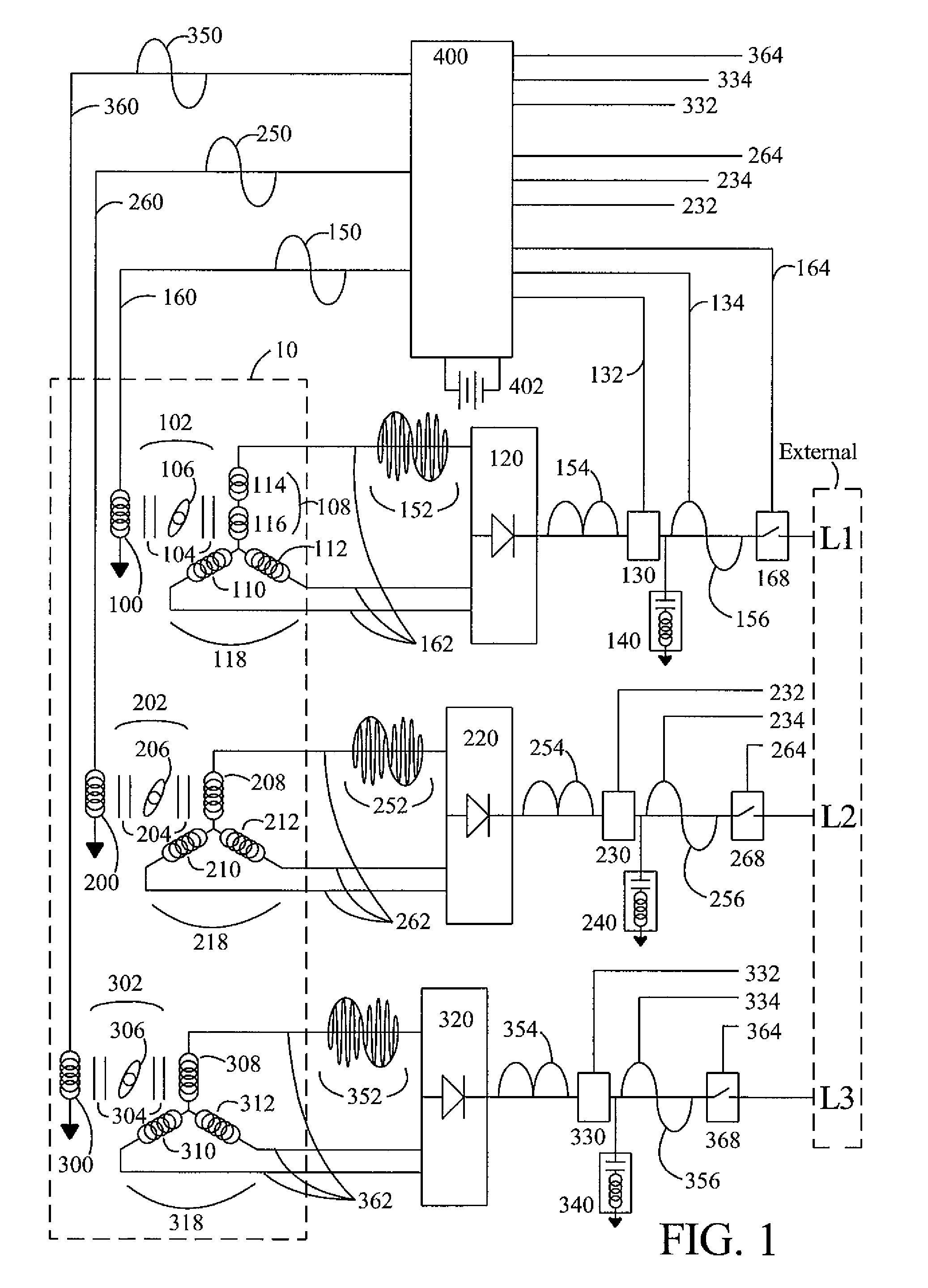
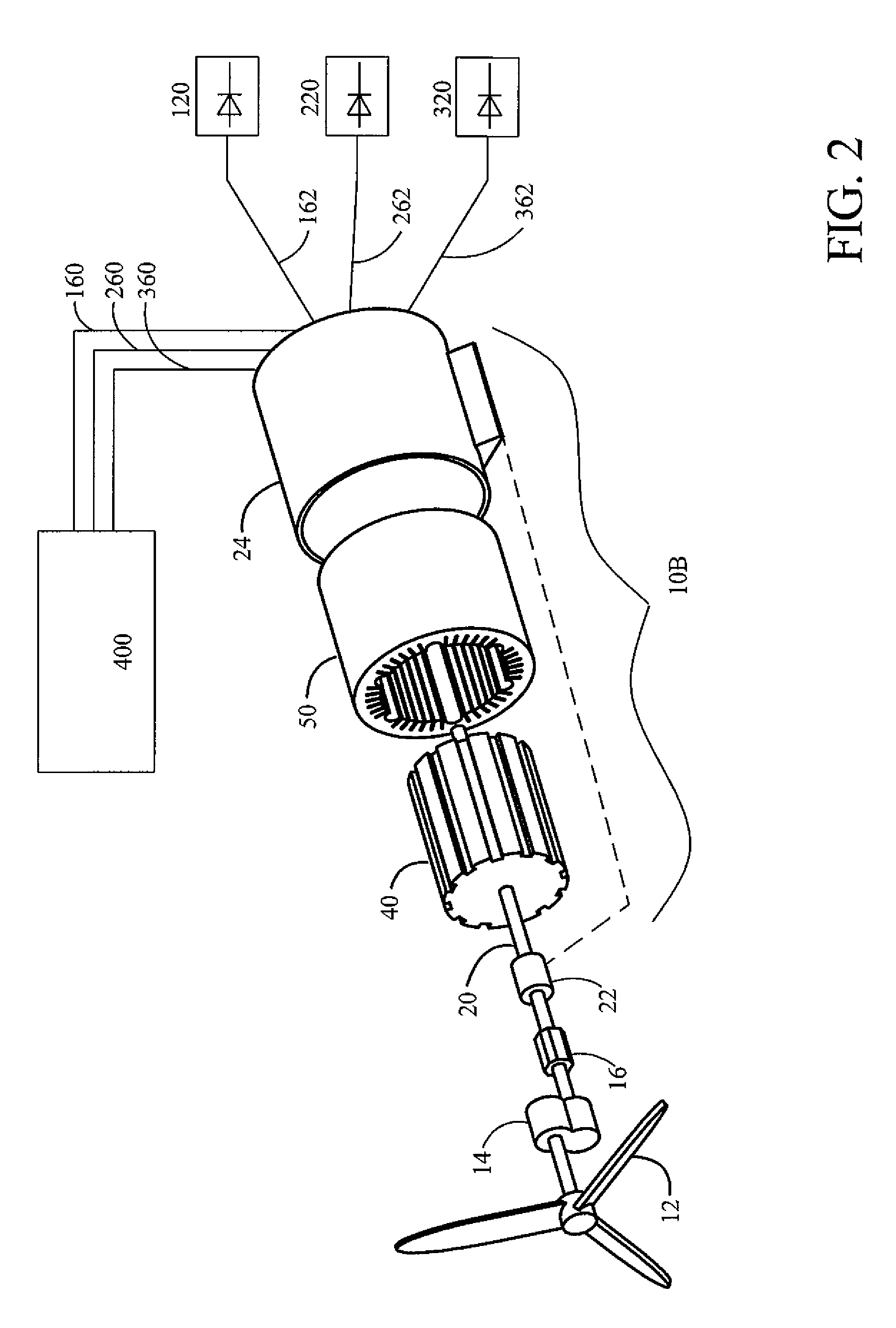
Brushless high-frequency alternator and excitation method for three-phase ac power-frequency generation
InactiveUS20080174195A1Minimise currentSynchronous generatorsWindingsAlternating currentConductor Coil
A method is disclosed for arranging and exciting the stator, rotor and various windings of a multi-stage brushless high frequency alternator so that the resulting multiple high frequency sub-phase armature winding outputs can be rectified and commutated into three phase power frequency alternating current (AC) electrical output. Power frequency currents in field windings control output amplitude, output frequency, and output phase. Devices incorporating this arrangement are suitable of generating fixed frequency electrical power while accommodating variable speed rotation of a generator shaft and offer multiple advantages over existing techniques. The capability to generate speed independent electric power allows natural power sources such as windmills and hydro-power stations to be efficiently coupled to fixed frequency power grids.
Owner:RAVEN ENERGY ALTERNATIVES
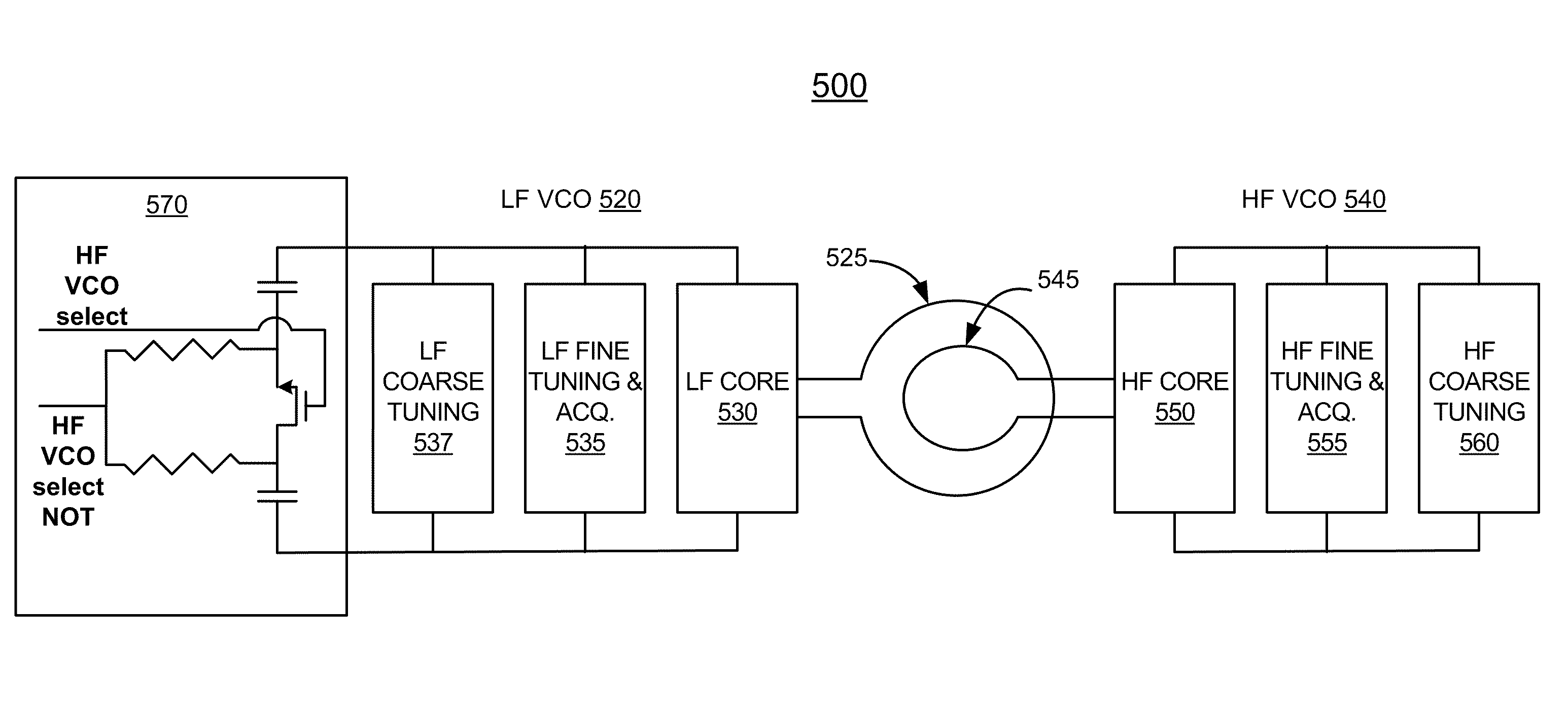
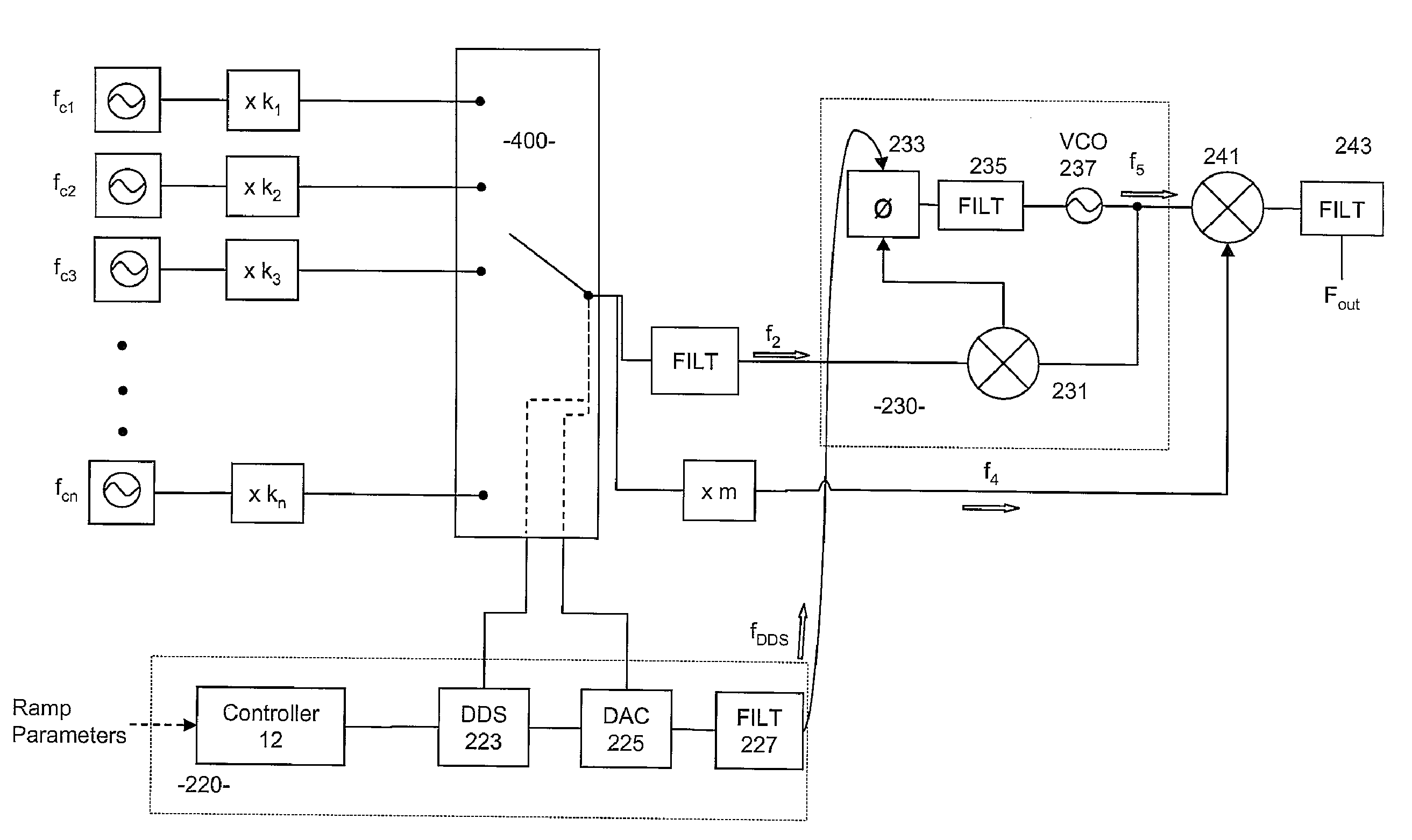
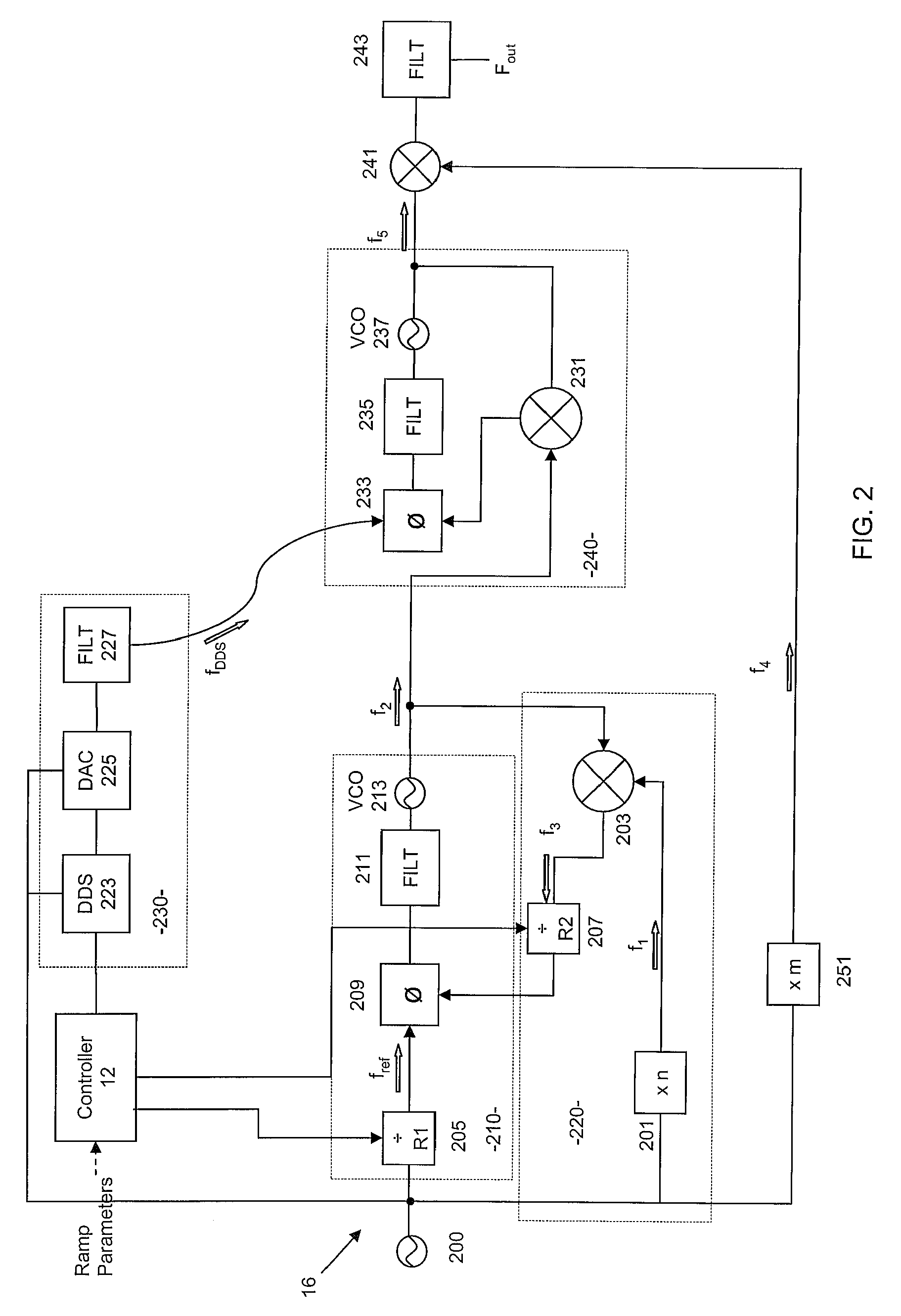
Apparatus and method for frequency generation
ActiveUS8058934B2Expand the adjustment rangeSuppress undesirable oscillation modeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceSum-frequency generation
A wideband frequency generator has two or more oscillators for different frequency bands, disposed on the same die within a flip chip package. Coupling between inductors of the two oscillators is reduced by placing one inductor on the die and the other inductor on the package, separating the inductors by a solder bump diameter. The loosely coupled inductors allow manipulation of the LC tank circuit of one of the oscillators to increase the bandwidth of the other oscillator, and vice versa. Preventing undesirable mode of oscillation in one of the oscillators may be achieved by loading the LC tank circuit of the other oscillator with a large capacitance, such as the entire capacitance of the coarse tuning bank of the other oscillator. Preventing the undesirable mode may also be achieved by decreasing the quality factor of the other oscillator's LC tank and thereby increasing the losses in the tank circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Radar system
ActiveUS7567202B2Easy to controlGenerate accuratelyAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with a radar system, and relates specifically to scanning radar systems that are suitable for detecting and monitoring ground-based targets.In one aspect, the radar system is embodied as a scanning radar system comprising a frequency generator, a frequency scanning antenna, and a receiver arranged to process signals received from a target so as to identify a Doppler frequency associated with the target, wherein the frequency generator is arranged to generate a plurality of sets of signals, each set having a different characteristic frequency, the frequency generator comprising a digital synthesiser arranged to modulate a continuous wave signal of a given characteristic frequency by a sequence of modulation of patterns whereby to generate a said set of signals, and wherein the frequency scanning antenna is arranged to cooperate with the frequency generator so as to transceive radiation over a region having an angular extent dependent on the said generated frequencies.Embodiments of the invention thus combine digital synthesiser techniques, which are capable of precise frequency generation and control, with passive frequency scanning and Doppler processing techniques. This enables accurate control of range and of scan rates, and enables optimisation of range cell size for factors such as slow and fast target detection and Signal to Noise ratio, and thus enables detection of targets located at distances considerably farther away than is possible with known systems having similar power requirements.
Owner:BLIGHTER SURVEILLANCE SYST LTD
Deep ultraviolet laser apparatus
InactiveUS20070064749A1Generate efficientlyIncrease productionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFourth harmonicAudio power amplifier
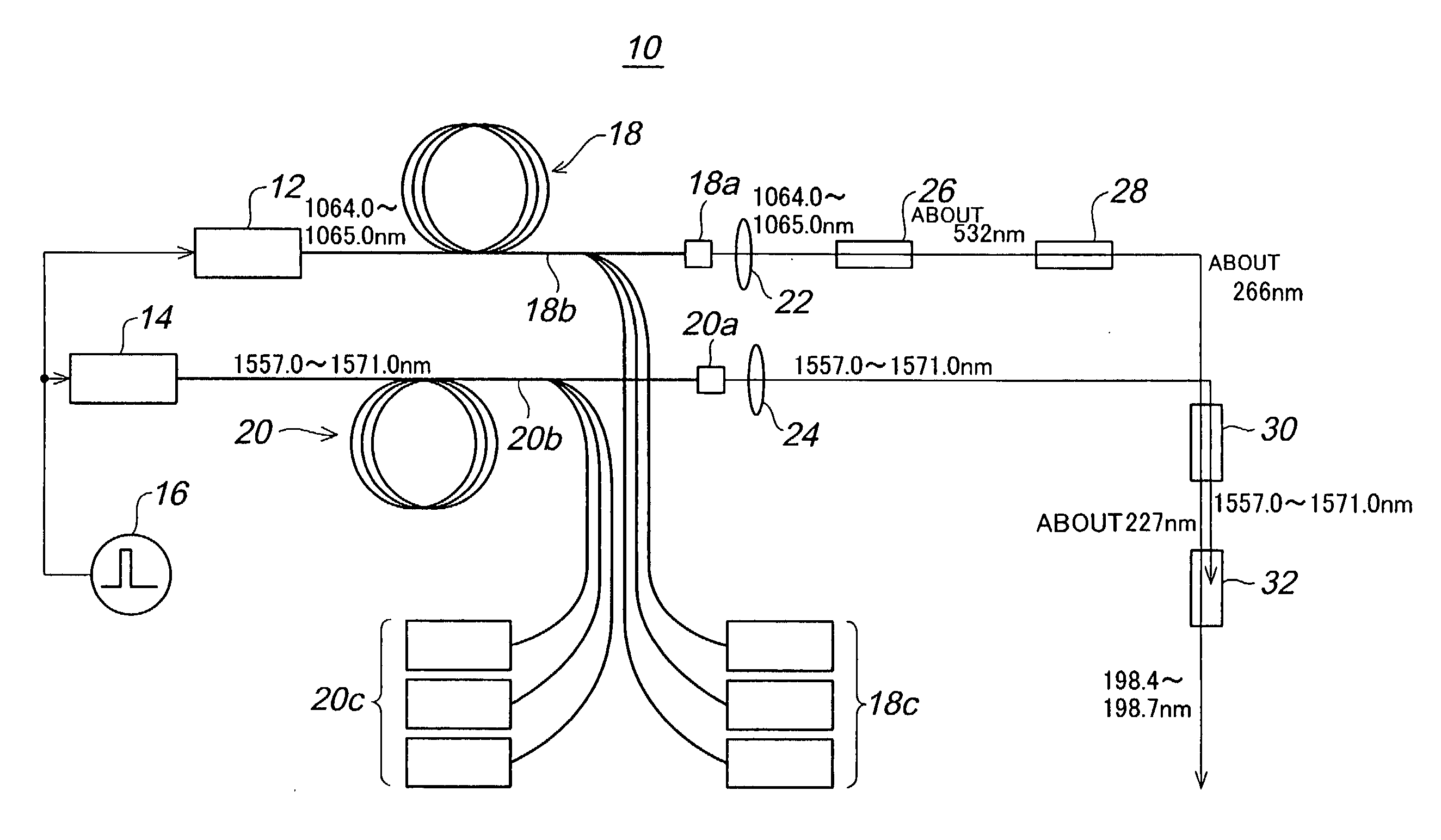
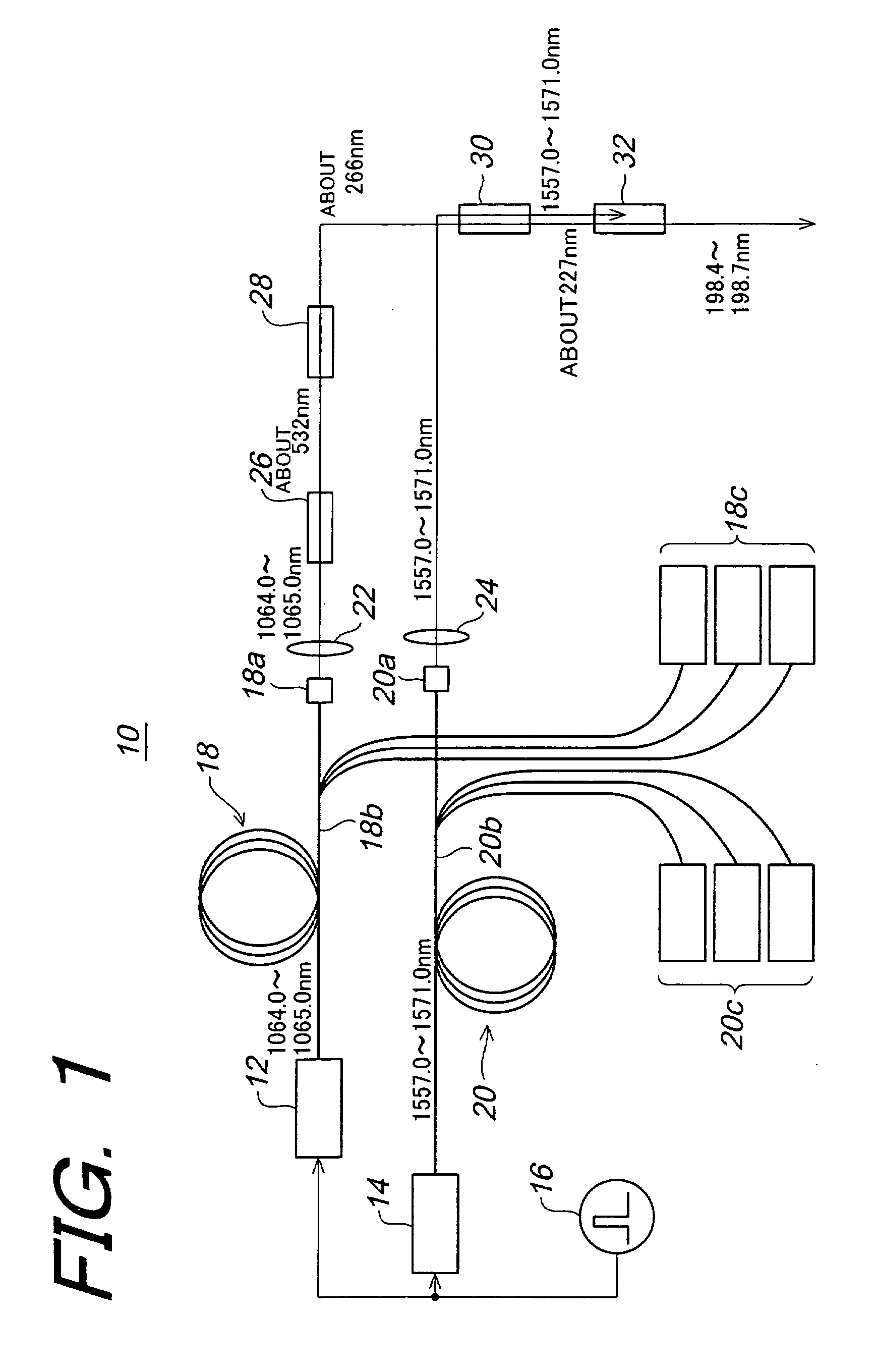
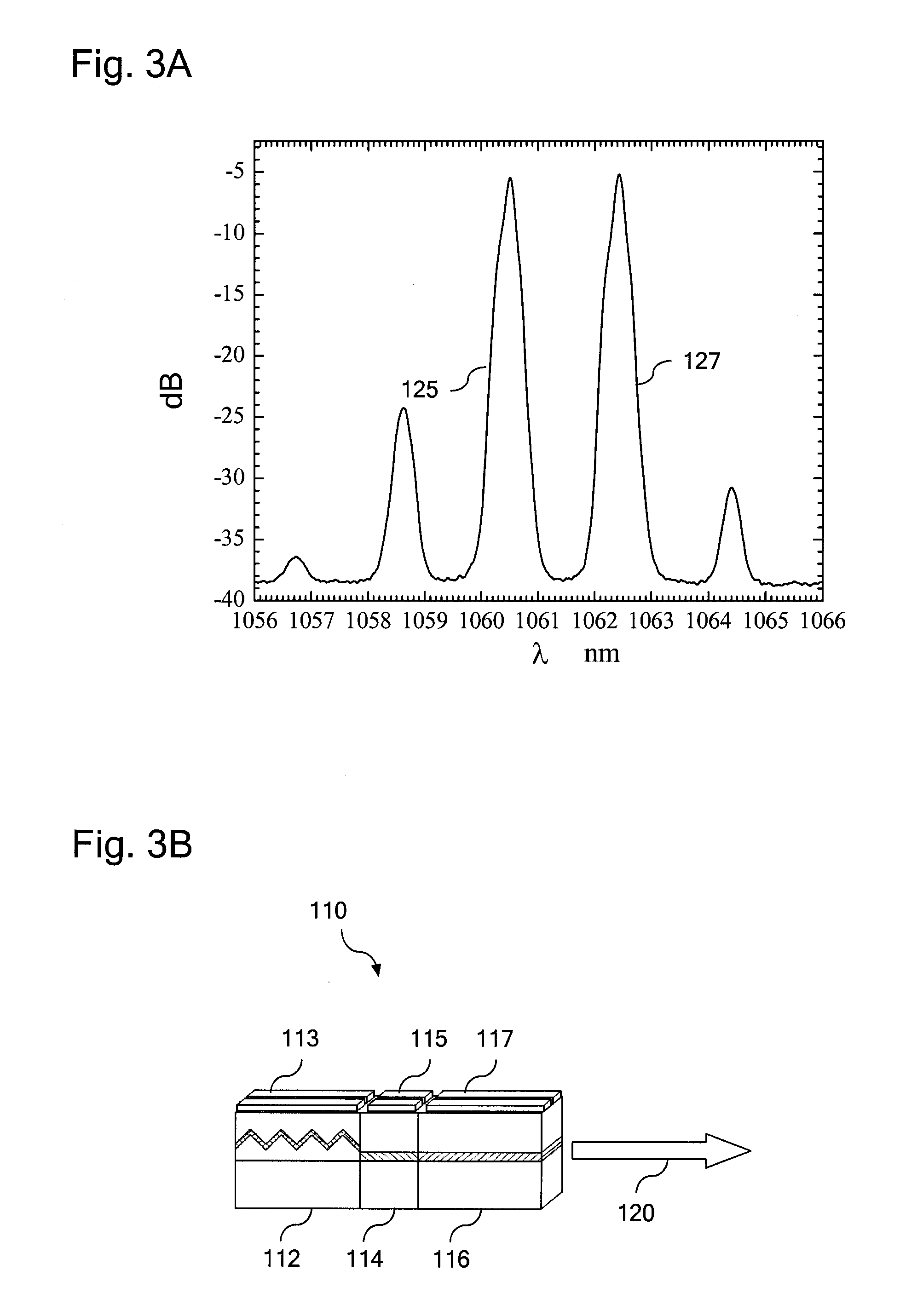
In order to generate efficiently a deep ultraviolet laser beam having a wavelength in a deep ultraviolet region and to make the generated laser beam to be high output, it is arranged in such that a laser beam having about 227 nm wavelength is generated by sum-frequency mixing of fourth harmonic of the laser beams obtained by amplifying semiconductor laser beams having 1064.0 to 1065.0 nm wavelengths by means of an optical fiber amplifier, and the laser beams obtained by amplifying semiconductor laser beams having 1557.0 to 1571.0 nm wavelengths by means of another optical fiber amplifier; and further laser beams having 198.4 to 198.7 nm wavelengths are generated by sum-frequency mixing of the above sum-frequency mixed laser beam and the above-described semiconductor laser beams having 1557.0 to 1571.0 nm wavelengths.
Owner:ADVANCED MASK INSPECTION TECH +1
Multiple Wavelength Optical Systems
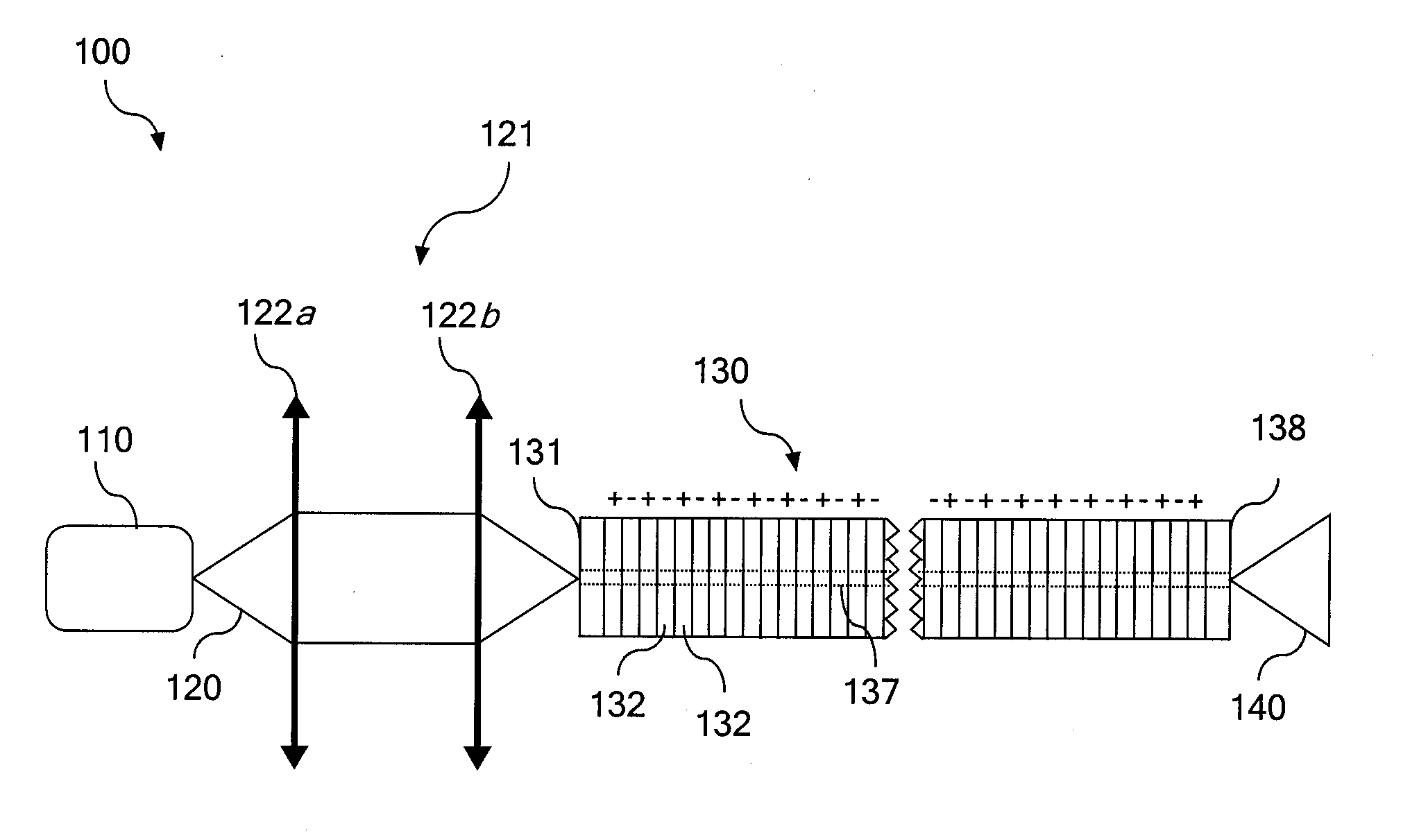
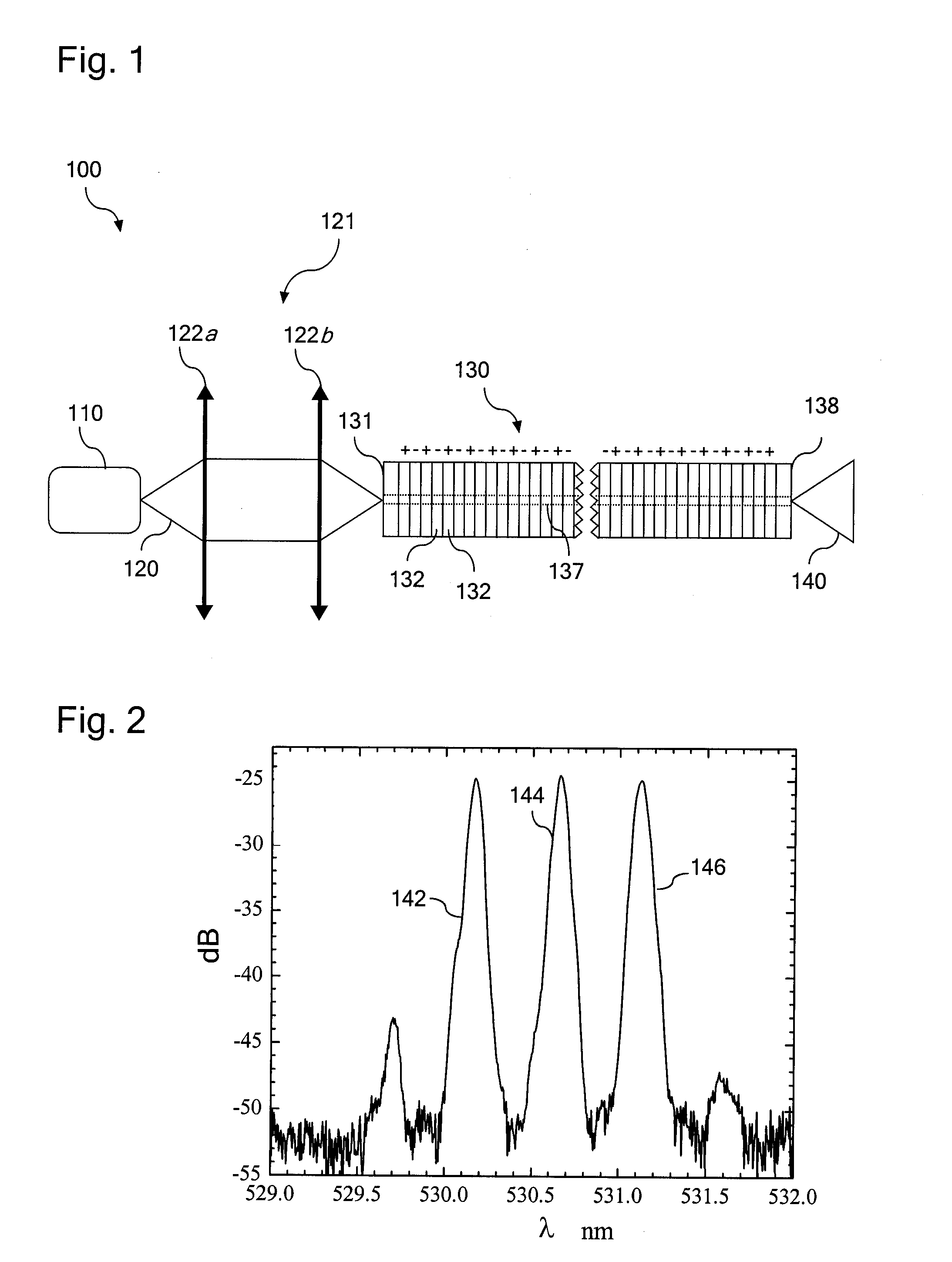
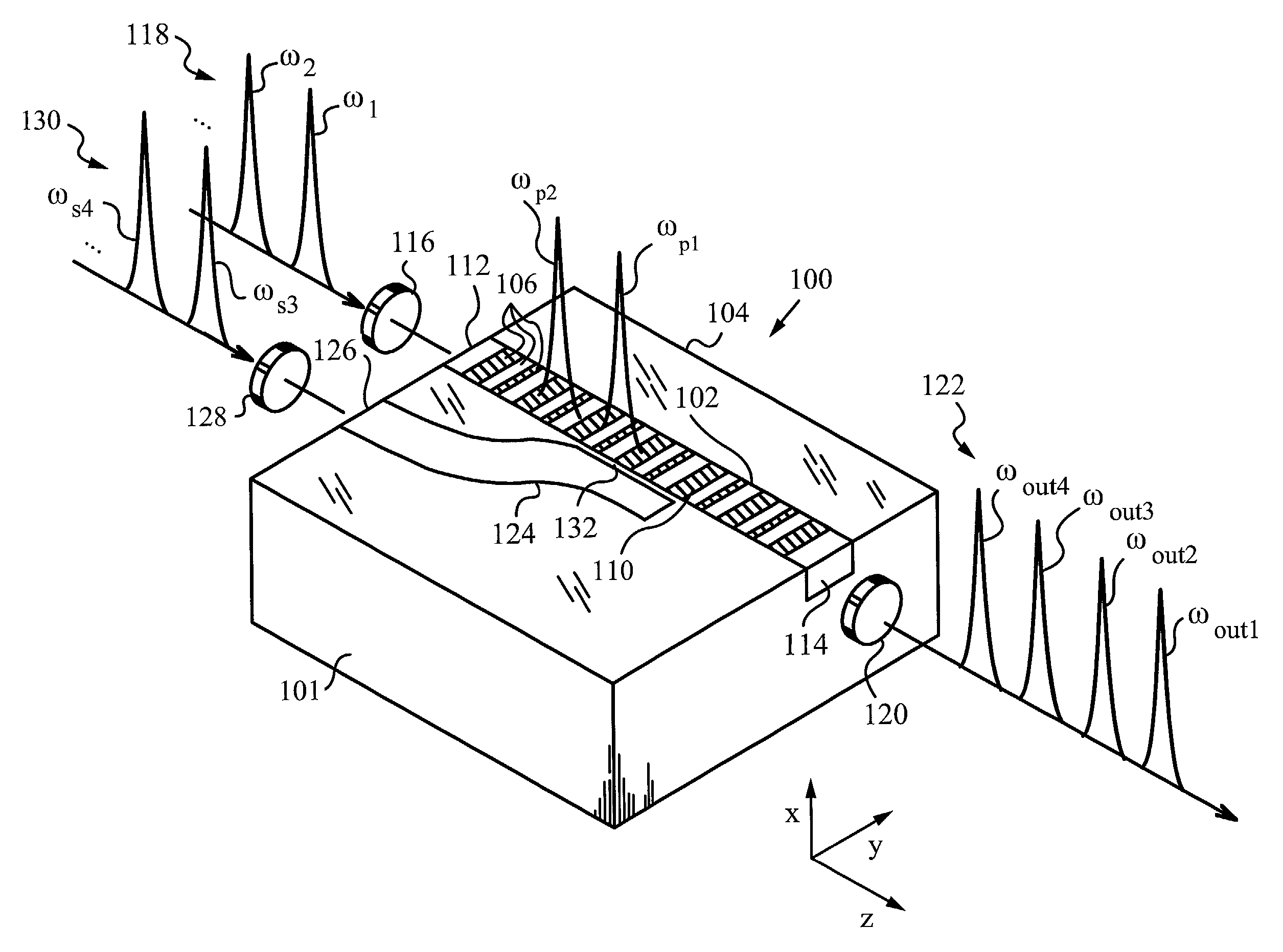
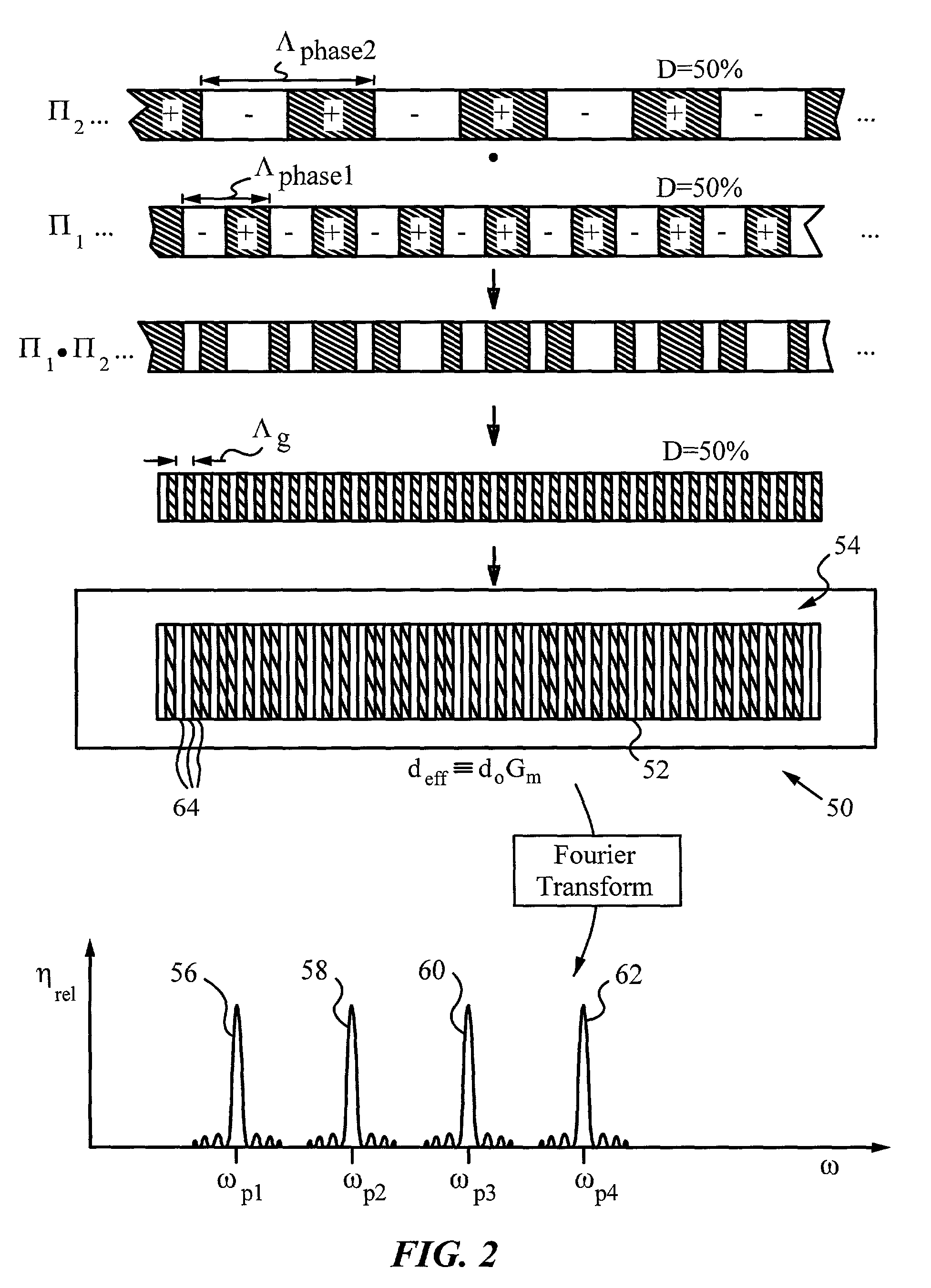
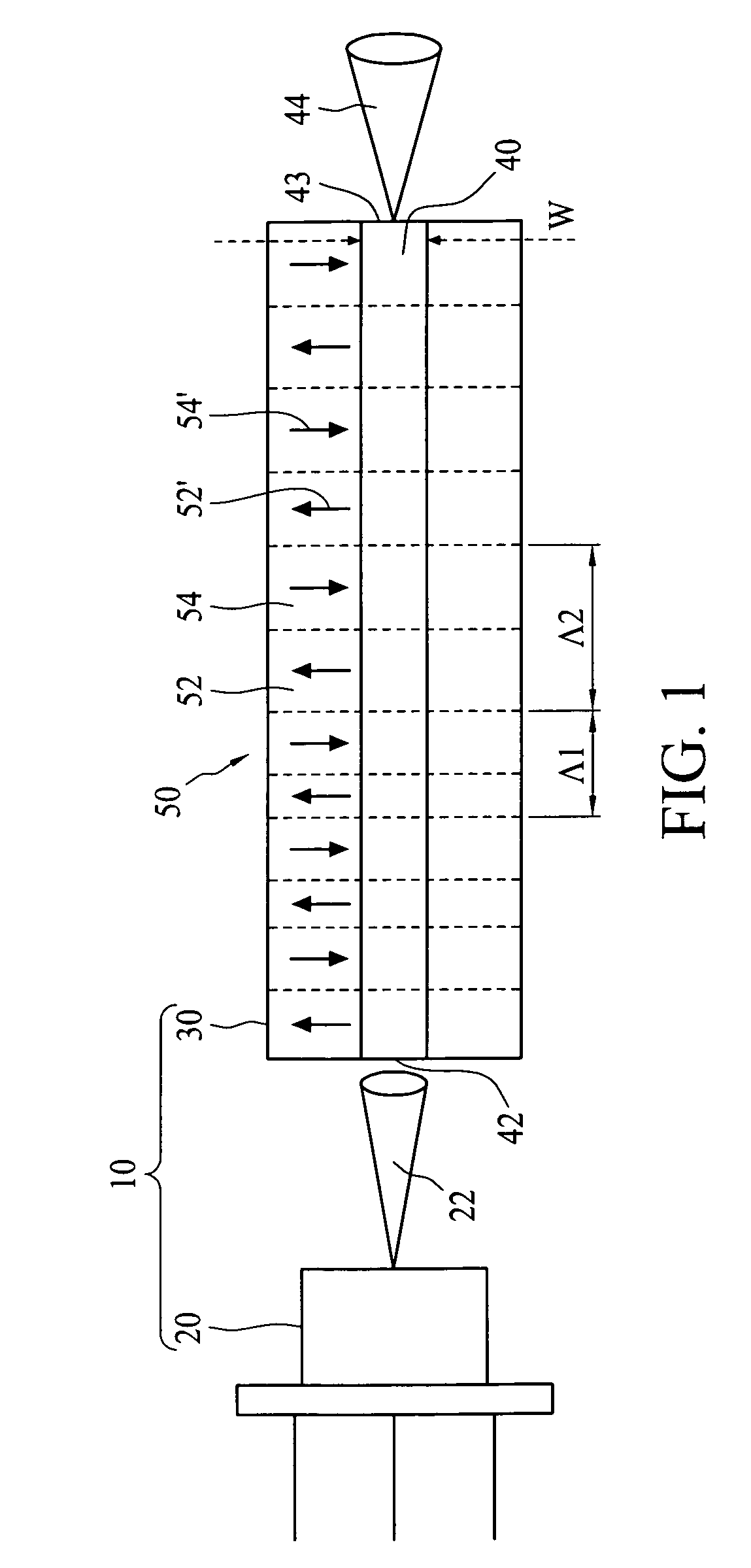
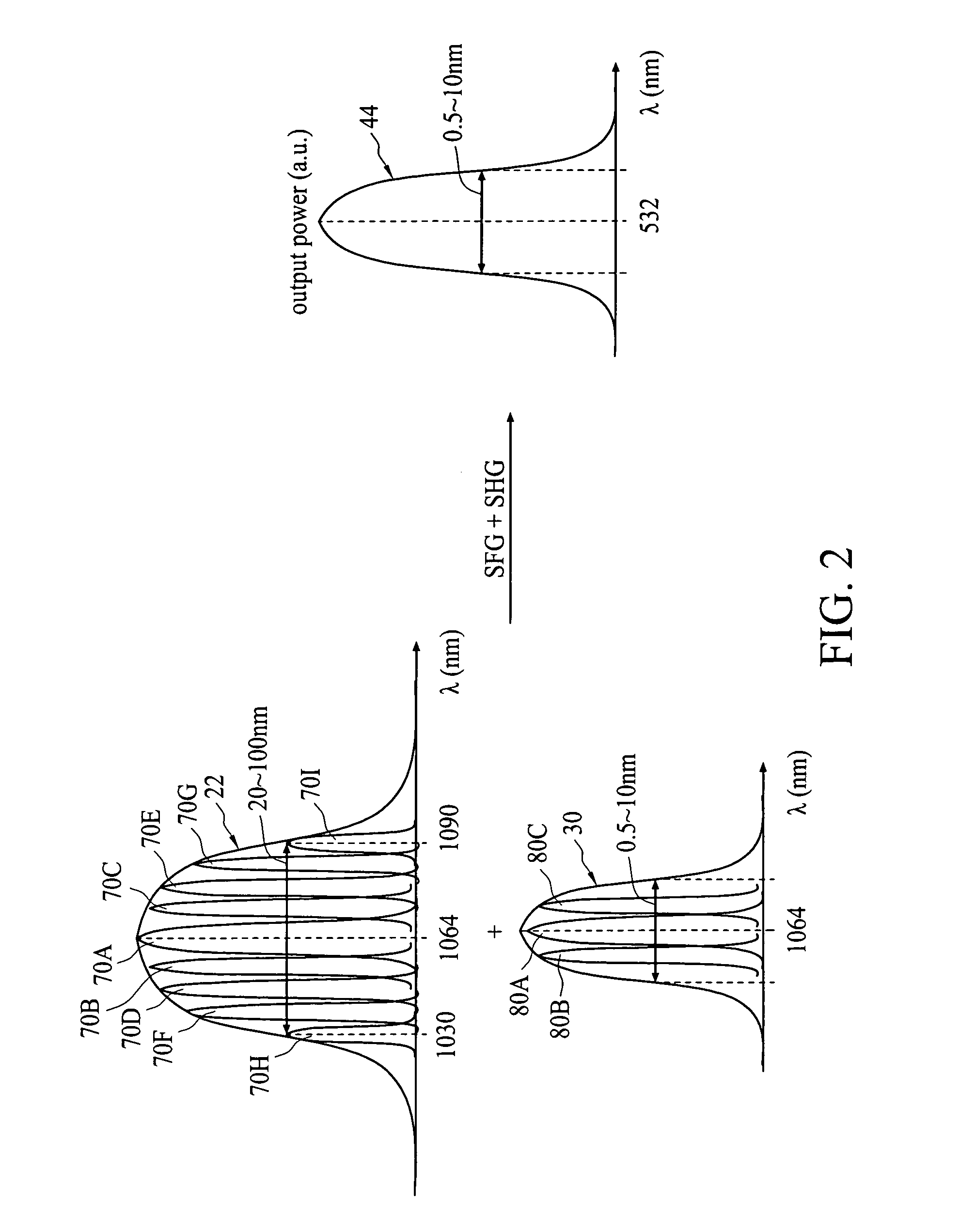
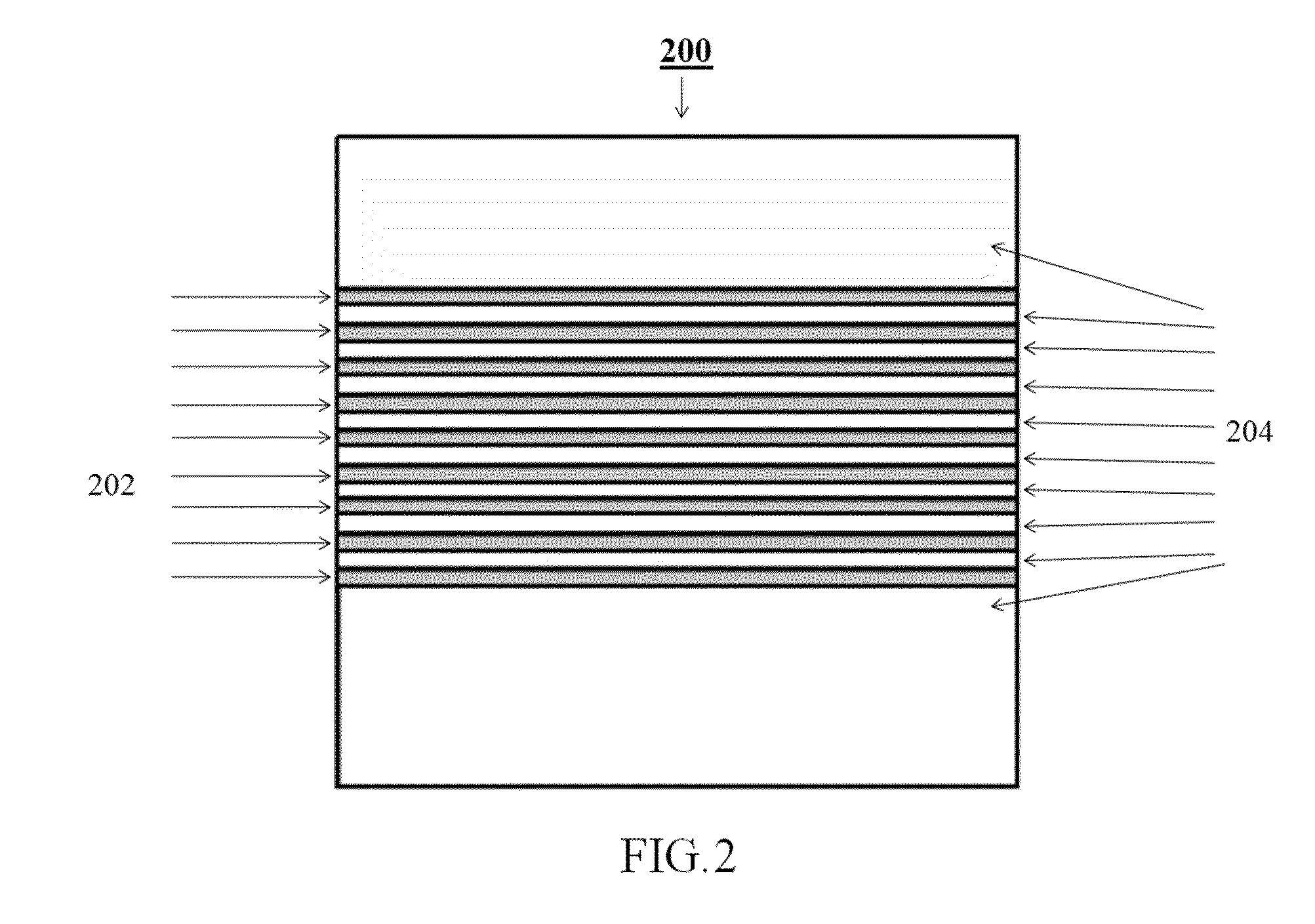
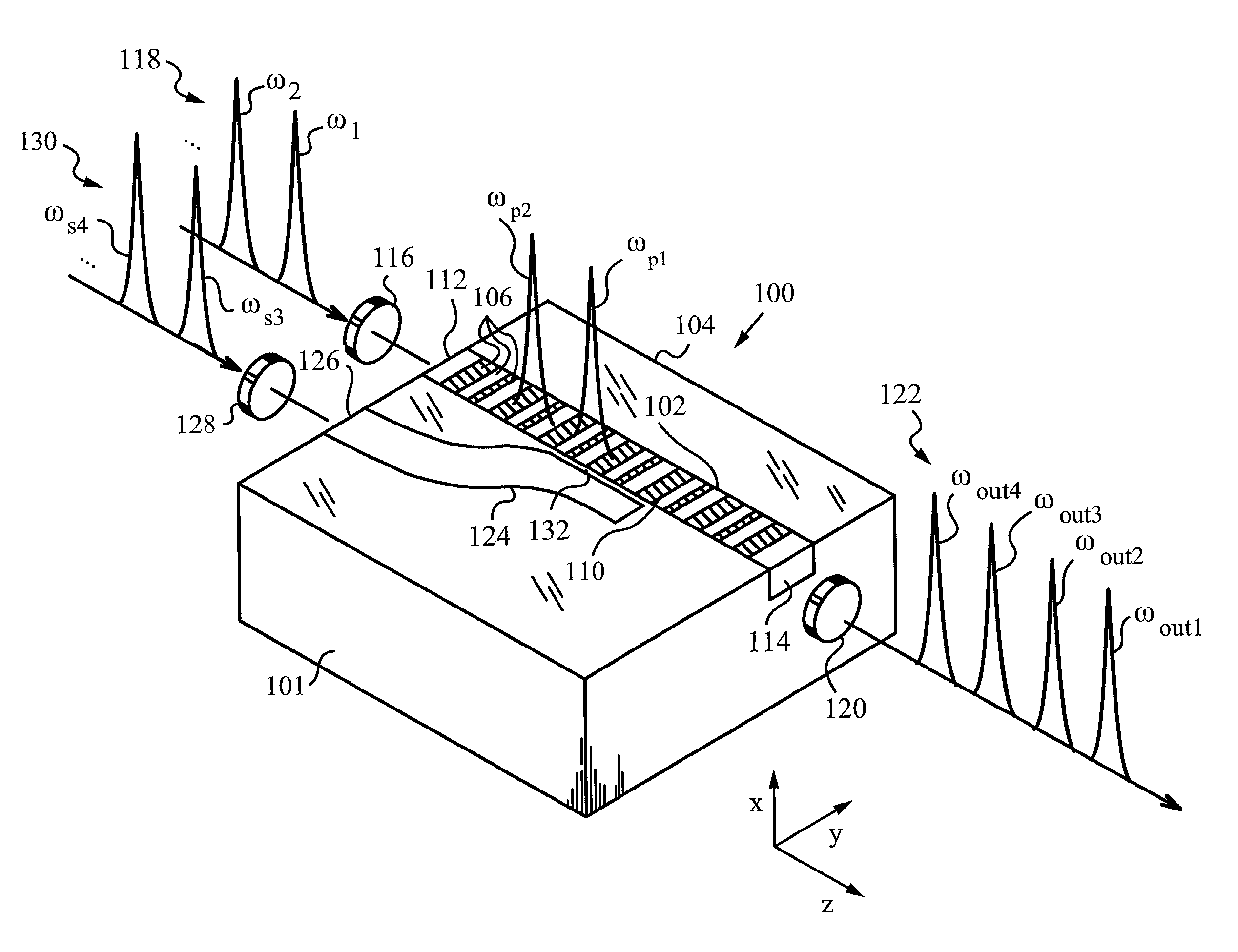
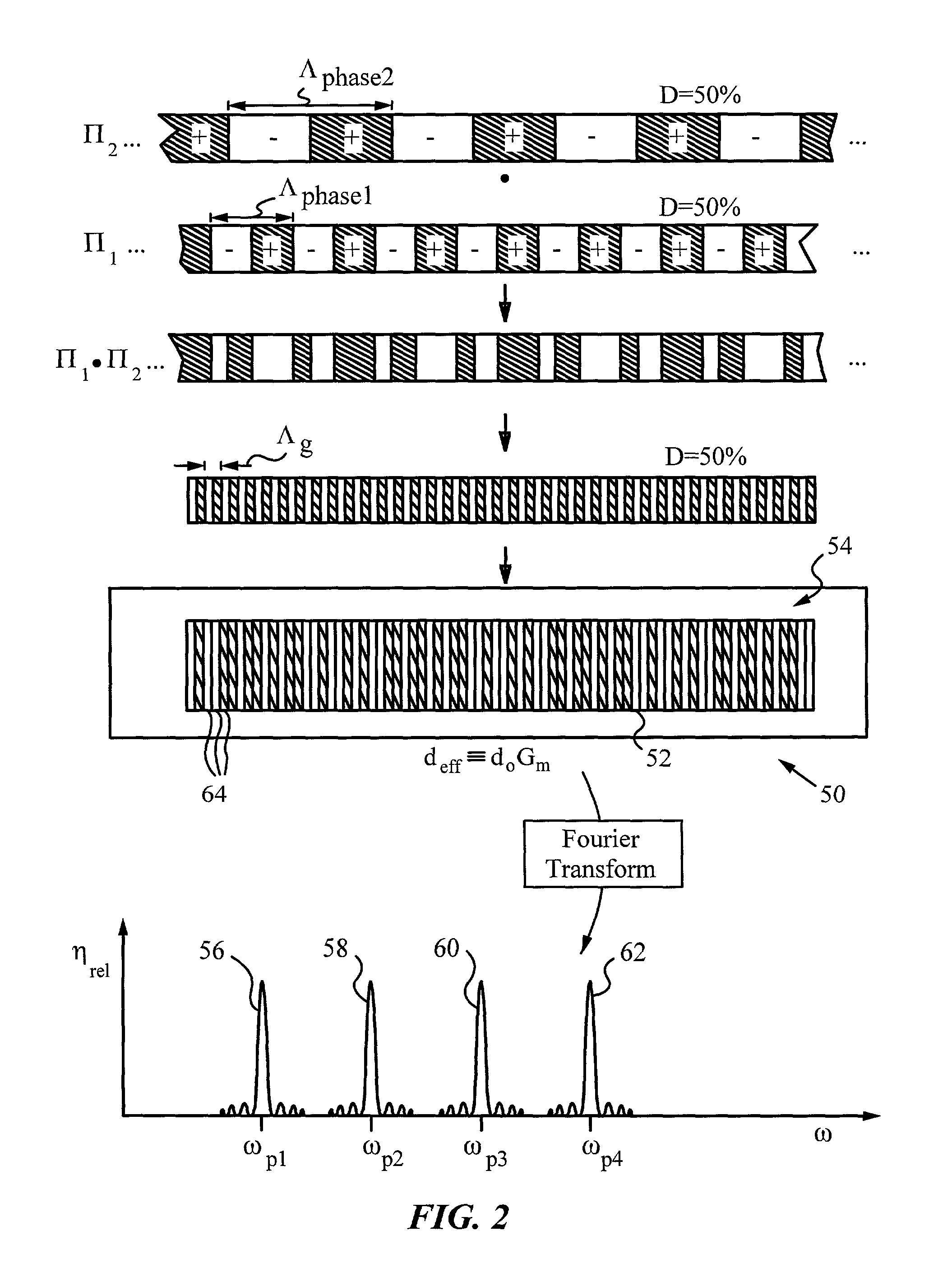
Optical systems operable to emit multiple frequency-converted spectral peaks are provided. In one embodiment, an optical system includes an optical source and a wavelength conversion device. The optical source may include a laser configured to emit a pump beam having at least two fundamental spectral peaks. The wavelength conversion device may include a non-linear optical medium configured to phase match the second harmonic generation of each of the at least two fundamental spectral peaks and sum-frequency generation of the at least two fundamental spectral peaks such that an output beam comprising at least three frequency-converted spectral peaks having approximately equal power is emitted from an output facet of the wavelength conversion device when the pump beam of the optical source is incident on an input facet of the wavelength conversion device.
Owner:CORNING INC
Brushless high-frequency alternator and excitation method for three-phase AC power-frequency generation
A method is disclosed for arranging and exciting the stator, rotor and various windings of a multi-stage brushless high frequency alternator so that the resulting multiple high frequency sub-phase armature winding outputs can be rectified and commutated into three phase power frequency alternating current (AC) electrical output. Power frequency currents in field windings control output amplitude, output frequency, and output phase. Devices incorporating this arrangement are suitable of generating fixed frequency electrical power while accommodating variable speed rotation of a generator shaft and offer multiple advantages over existing techniques. The capability to generate speed independent electric power allows natural power sources such as windmills and hydro-power stations to be efficiently coupled to fixed frequency power grids.
Owner:RAVEN ENERGY ALTERNATIVES
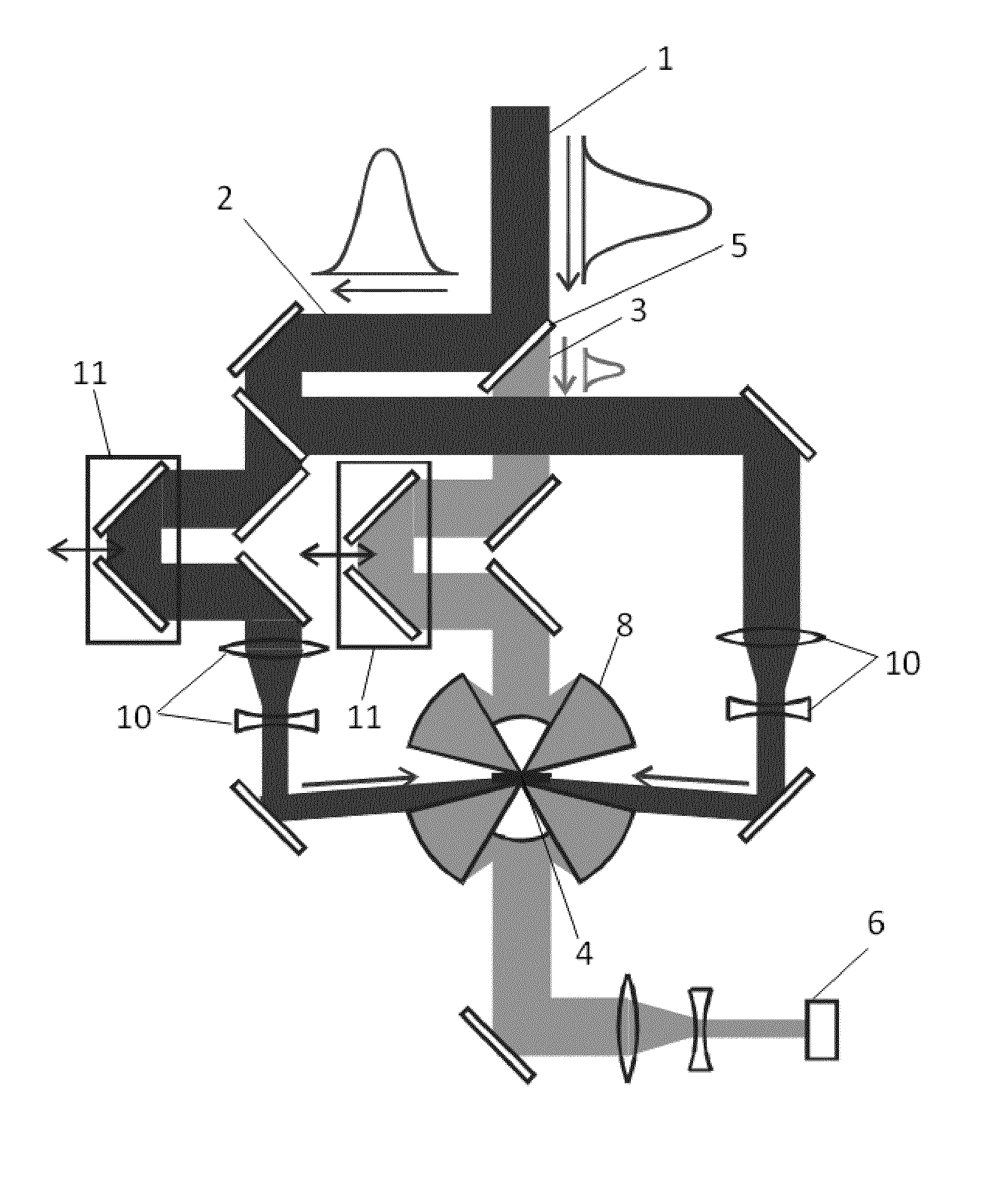
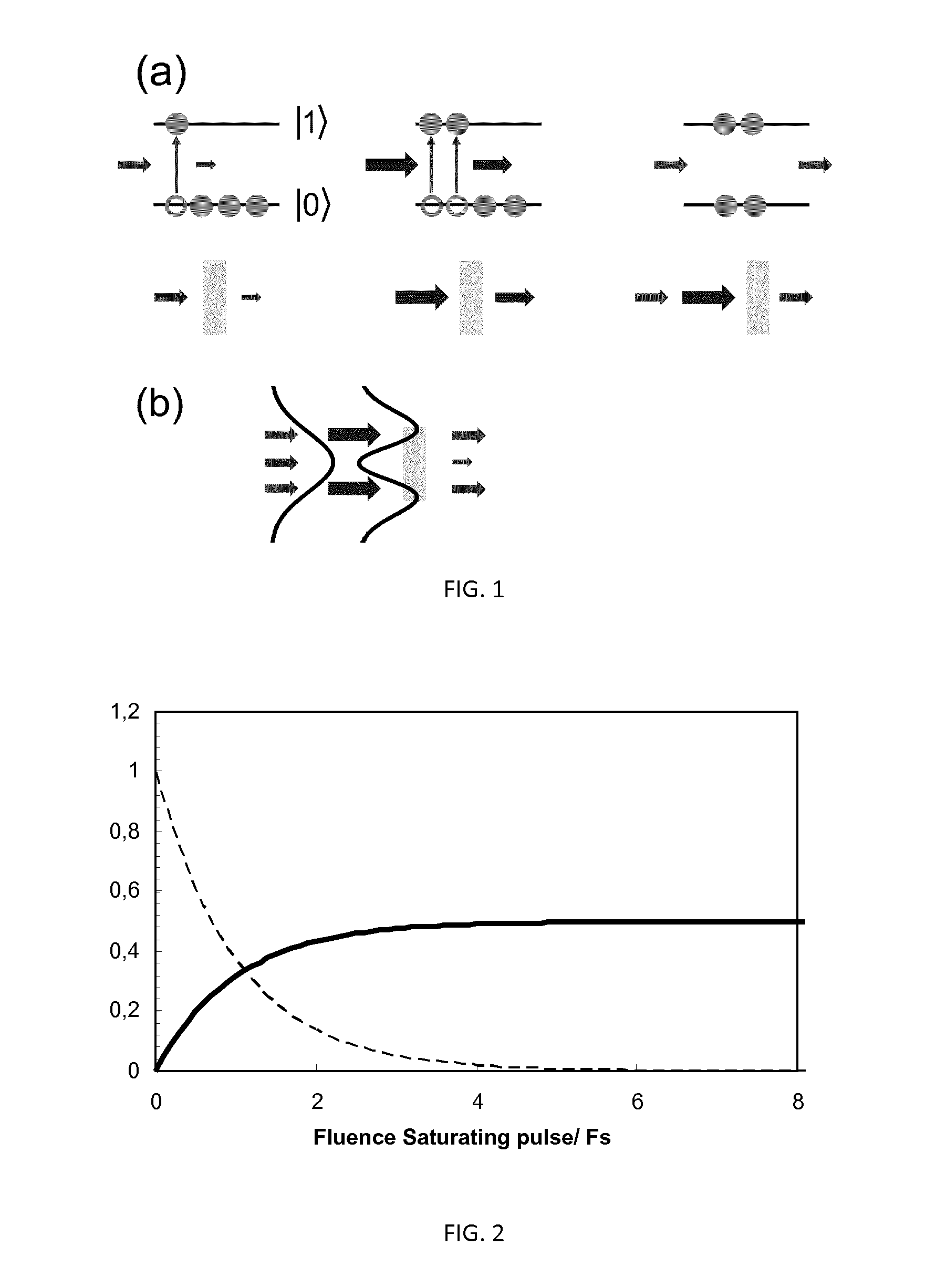
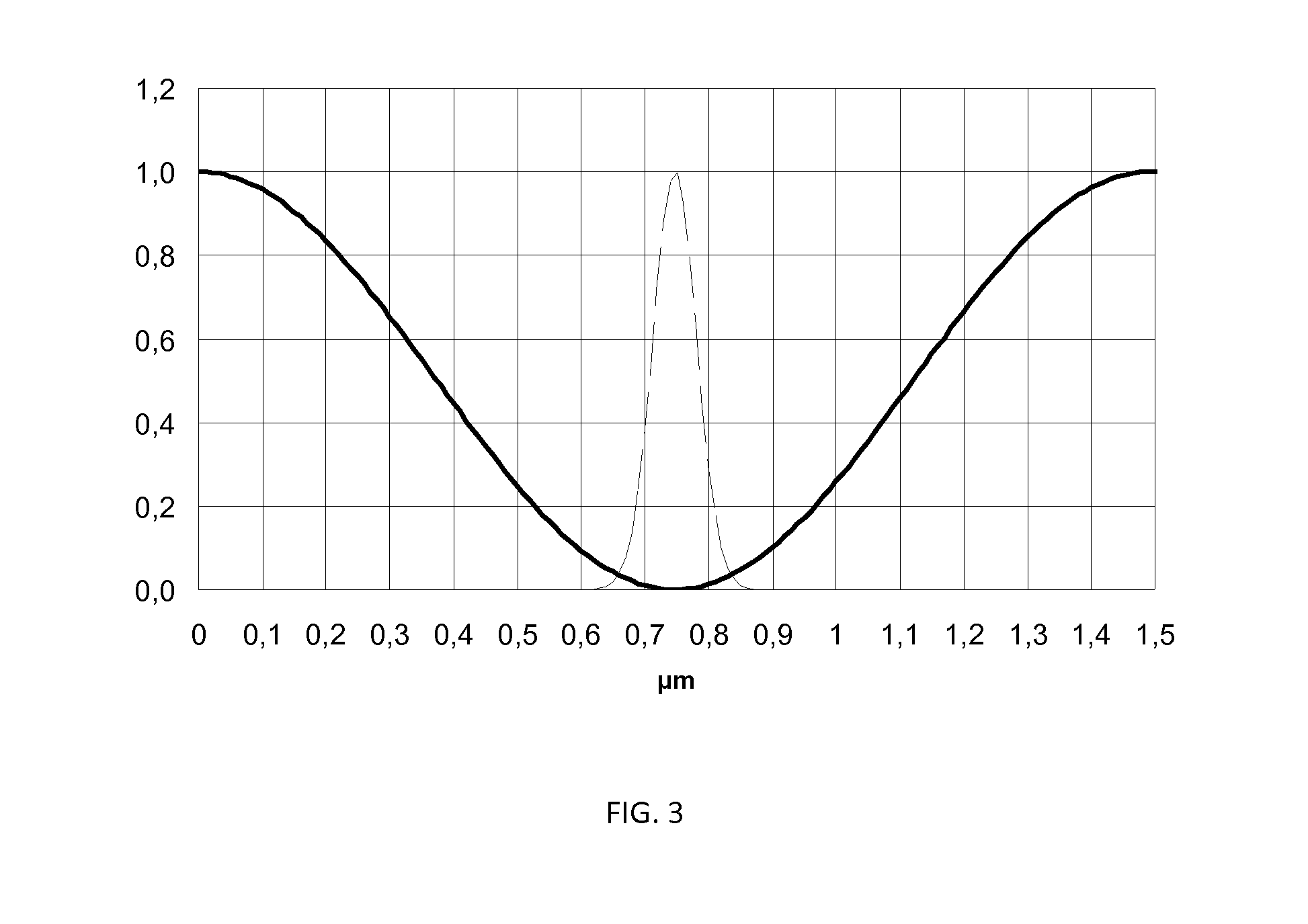
Method for high resolution sum-frequency generation and infrared microscopy
InactiveUS20140307249A1Reduce usageImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesImage resolutionSum-frequency generation
A method for analyzing a sample with a light probe with a spatial resolution smaller than the wavelength of the light probe comprising the steps of: —illuminating the sample by a first light pulse saturating a vibrational and / or electronic transition, said light pulse presenting an intensity spatial distribution on the sample presenting at least one minimum wherein saturation does not occur, —measuring the local absorbance properties and / or the local second order non-linear susceptibility of the sample by using a second light pulse forming the light probe at a wavelength corresponding to said electronic and / or vibrational transition, wherein the second light pulse overlap said first light pulse intensity minimum.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK
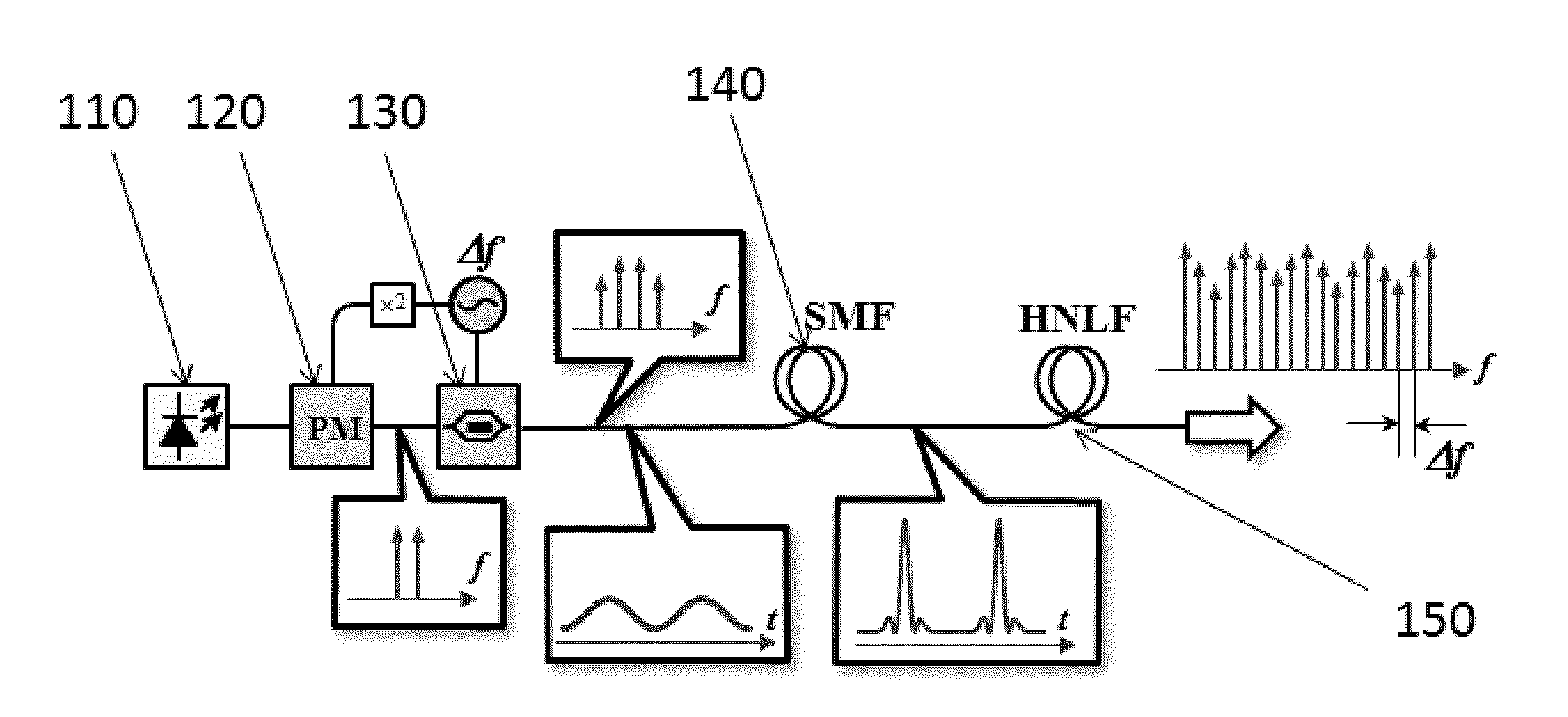
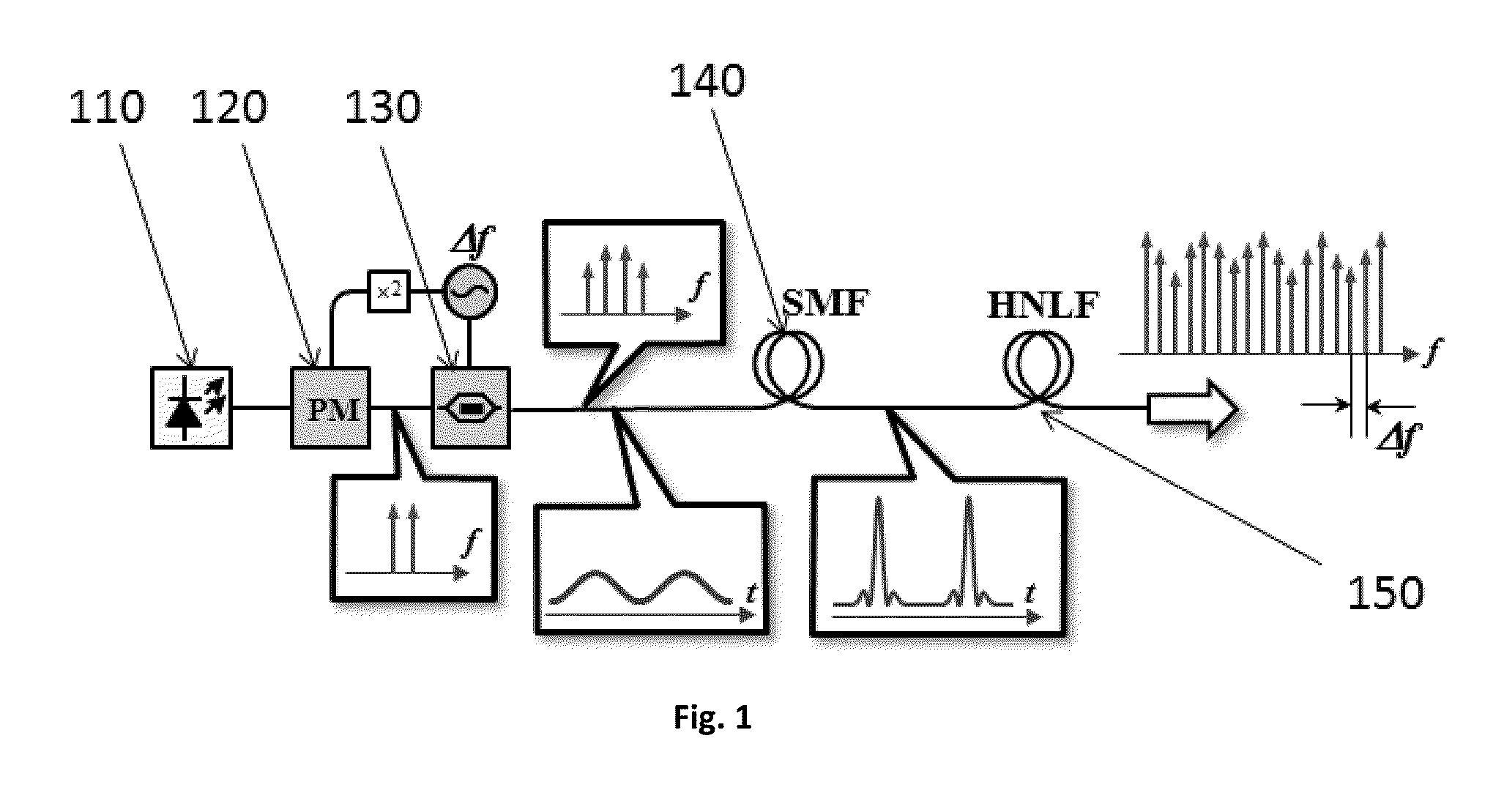
Method for wideband spectrally equalized frequency comb generation
ActiveUS20140254619A1Easy constructionReduce complexityLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
The present invention relates to method for spectrally equalized frequency comb generation. In order to carry this method, the following steps are followed: seed laser or lasers are modulated to acquire frequency chirp necessary to enable temporal compression and an increase in peak optical intensity necessary for an efficient nonlinear optical mixing process to occur; the compressed waveform is reshaped by nonlinear-transfer optical element and subsequently used to generate frequency comb in nonlinear waveguide. Ultimately, at the conclusion of these steps, a frequency comb is generated with substantially flat optical spectrum, while retaining variability with respect to the frequency pitch, high coherency and substantially wide spectral band of coverage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method and apparatus for frequency-converting infrared light
InactiveUS20070018103A1Radiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyLight beam
The invention relates to methods and apparatus for modifying the frequency characteristics of a spatially-dispersed mid-IR spectra for spectroscopy. In a preferred embodiment, sum frequency generation between a frequency-dispersed IR beam and an ultrafast optical pulse generates a spatially-extended optical signal that is collected with a CCD detector.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
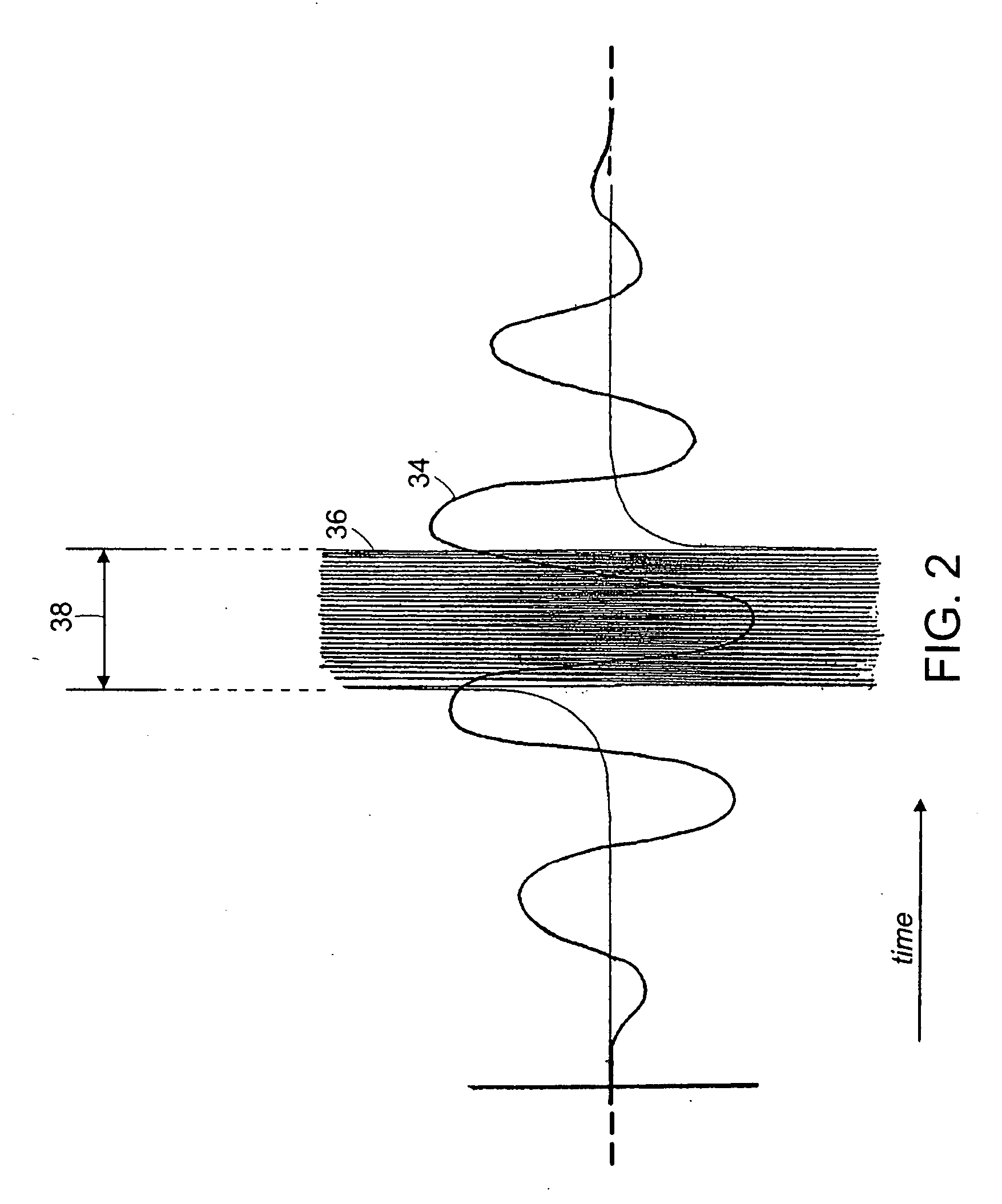
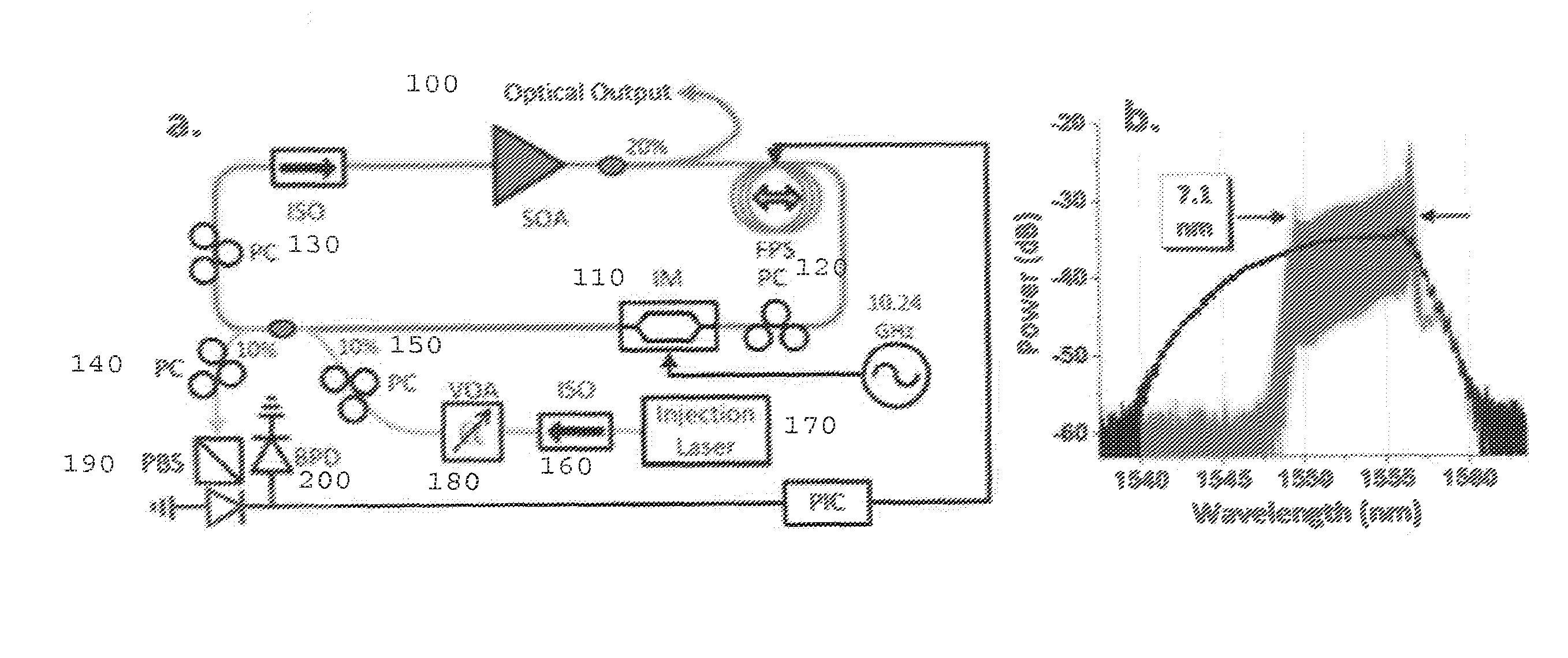
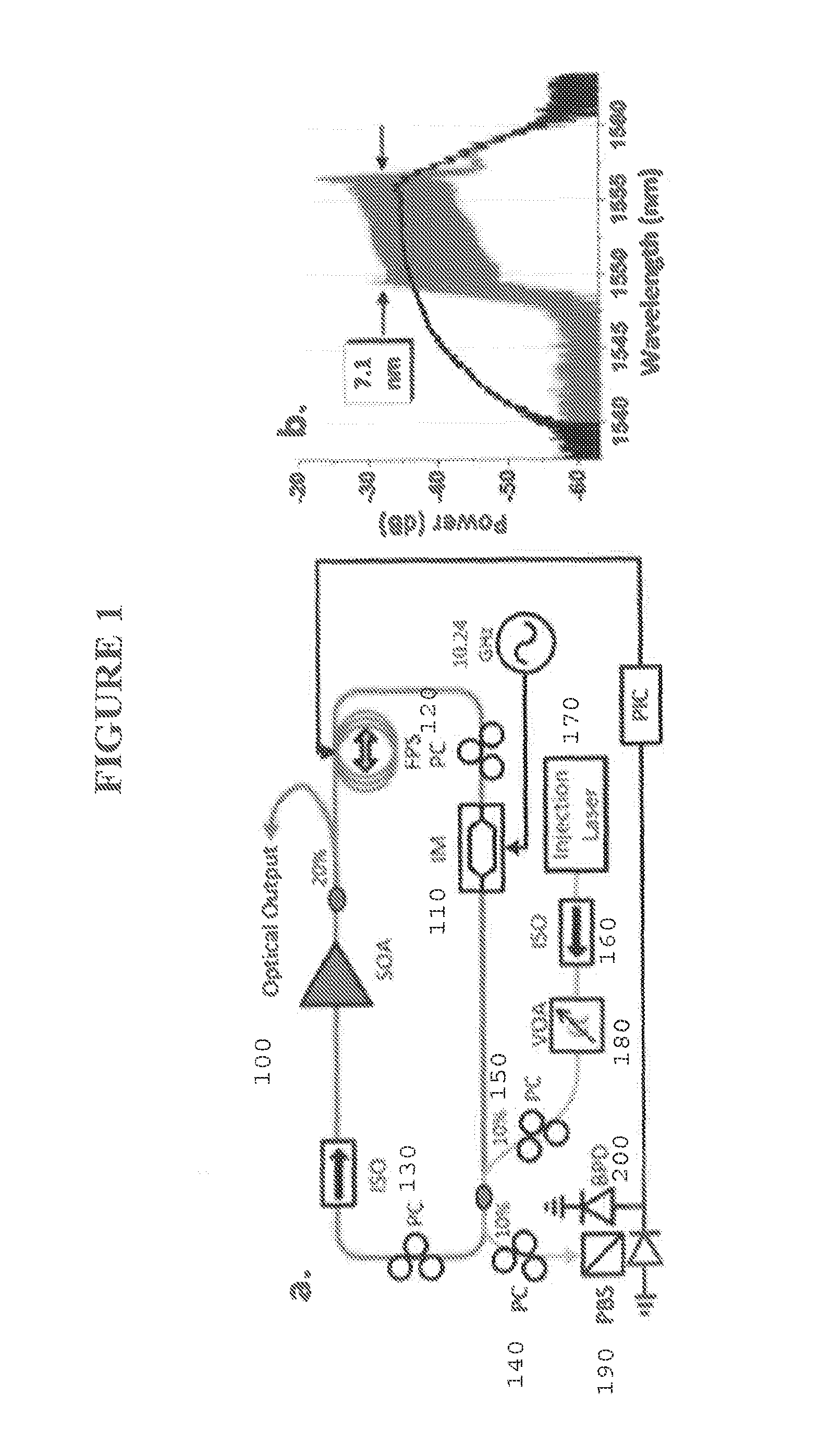
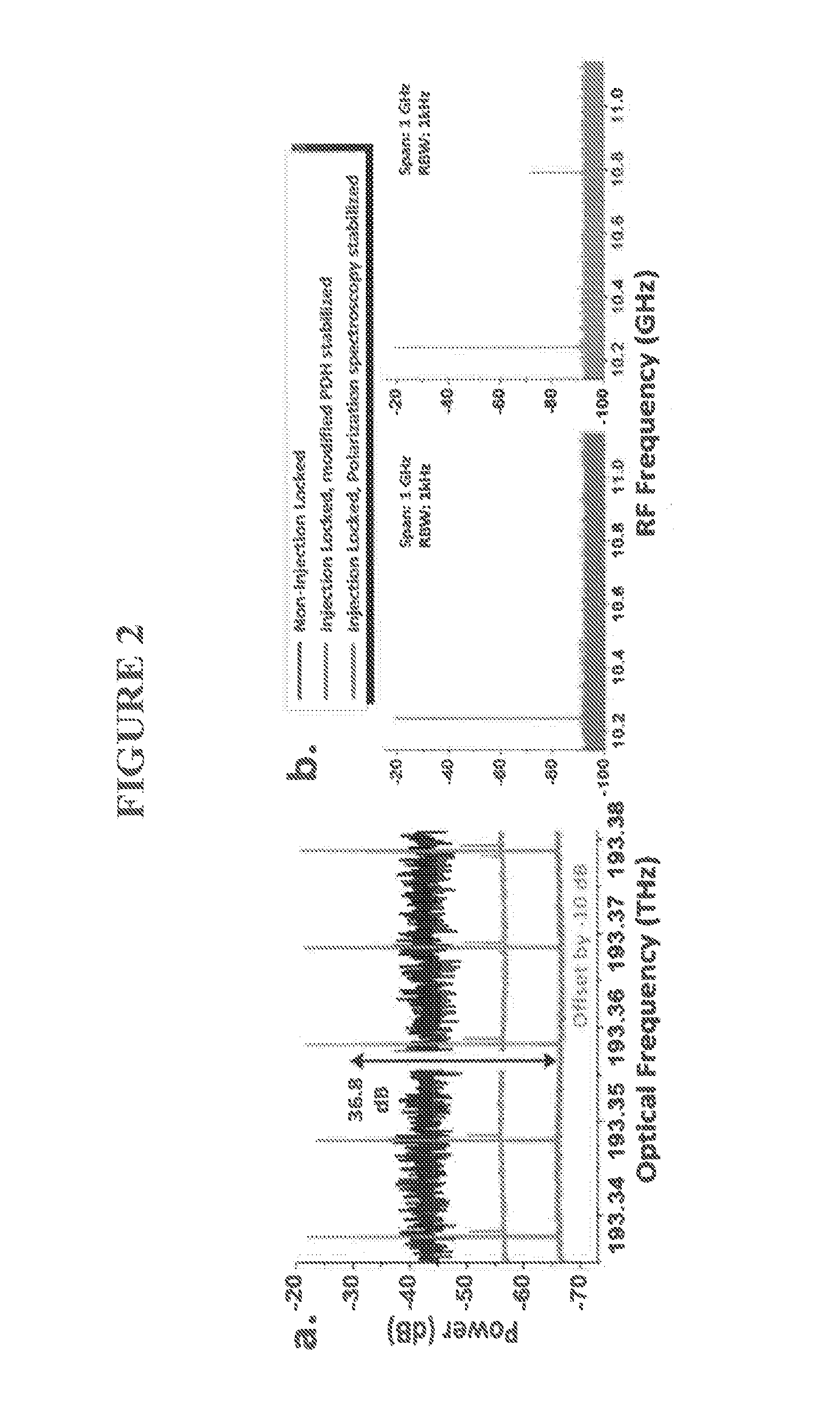
Stabilization of an injection locked harmonically mode-locked laser via polarization spectroscopy for frequency comb generation
ActiveUS20150086151A1Reduce system complexityEliminating unwanted opticalLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionInjection lockedFrequency comb
Stabilization of an injection locked optical frequency comb is achieved through polarization spectroscopy of an active laser cavity, eliminating optical PM sidebands inherent in previous stabilization methods. Optical SNR of 35 dB is achieved. A monolithic AlInGaAs quantum well Fabry-Prot laser injection locked to a passively mode-locked monolithic laser is presented here. The FP laser cavity can be used as a true linear interferometric intensity modulator for pulsed light.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Multiple channel optical frequency mixers for all-optical signal processing
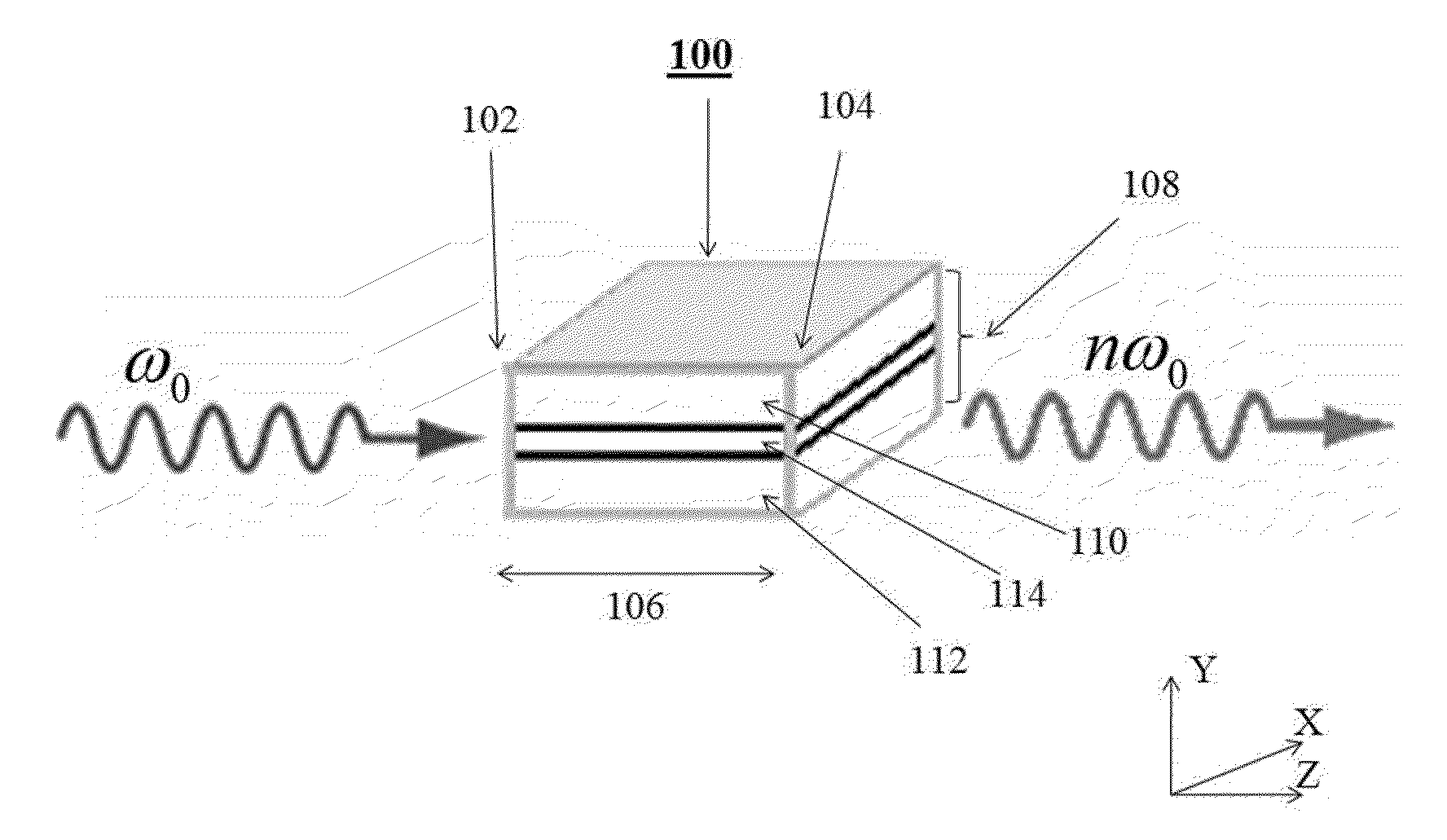
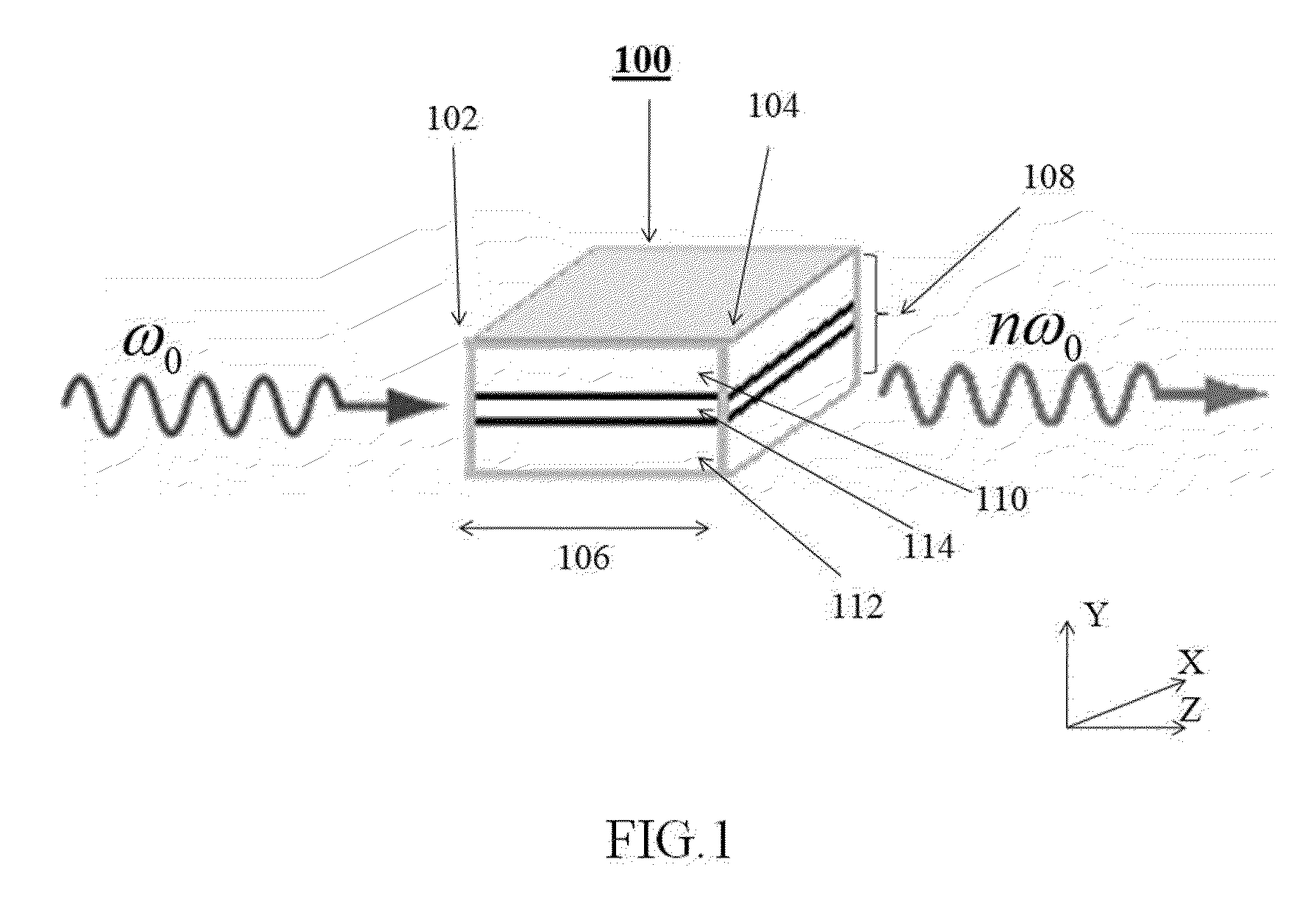
A multi-channel optical frequency mixer for all-optical signal processing and a method for engineering the same. The multi-channel mixer uses a nonlinear optical material exhibiting an effective nonlinearity deff whose spatial distribution is defined by a quasi-phase-matching grating, e.g., a QPM grating. The spatial distribution is defined such that its Fourier transform to the spatial frequency domain defines at least two wavelength channels which are quasi-phase-matched for performing optical frequency mixing. The wavelength channels correspond to dominant Fourier components and the Fourier transform is appropriately adjusted using grating parameters such as grating periods, phase reversal sequences and duty cycles to include an odd or even number of dominant Fourier components. The multi-channel mixer can perform frequency mixing operations such as second harmonic generation (SHG), difference frequency generation (DFG), sum frequency generation (SFG), and parametric amplification.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System integration device and system integration method for test parameters based on unit combination
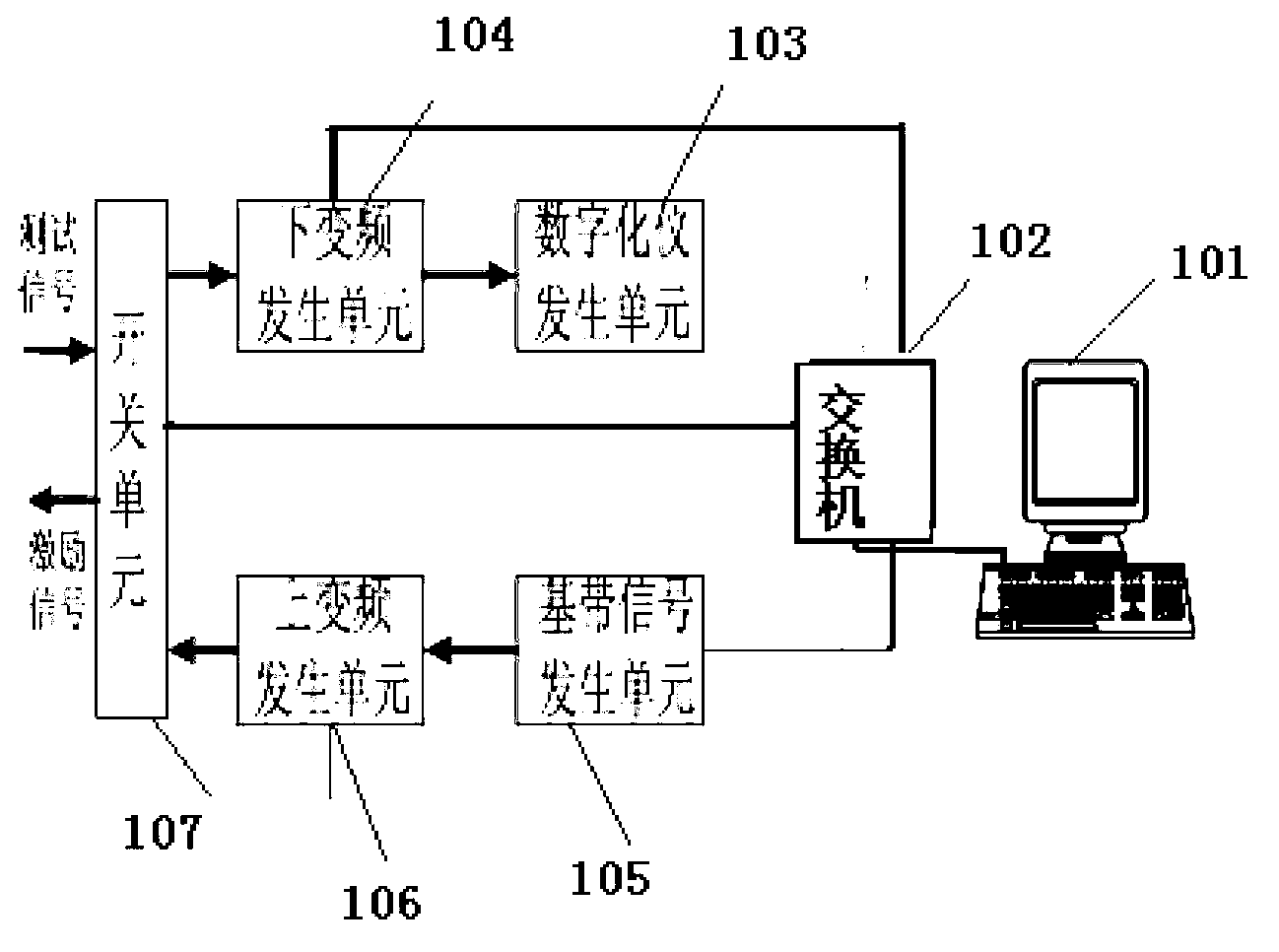
InactiveCN103248444AEasy to buildImprove performancePropogation channels monitoringReal variableInstrument function
The invention relates to a system integration device and a system integration method of test parameters based on the unit combination. The device comprises a main control computer and an exchange board, and also comprises a switch unit, a lower variable-frequency generation unit, a digitalized instrument generation unit, a base band signal generation unit and an upper variable-frequency generation unit, which are connected and communicated with one another; the lower variable-frequency generation unit is matched with the digitalized instrument generation unit and used for receiving and testing a test signal; and the base band signal generation unit is matched with the upper variable-frequency generation unit and used for generating and transmitting an excitation signal. By adopting the scheme, a test system with high performance and low cost is easy to establish, and different instrument functions can be realized by maximally utilizing fewest standard universal units.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
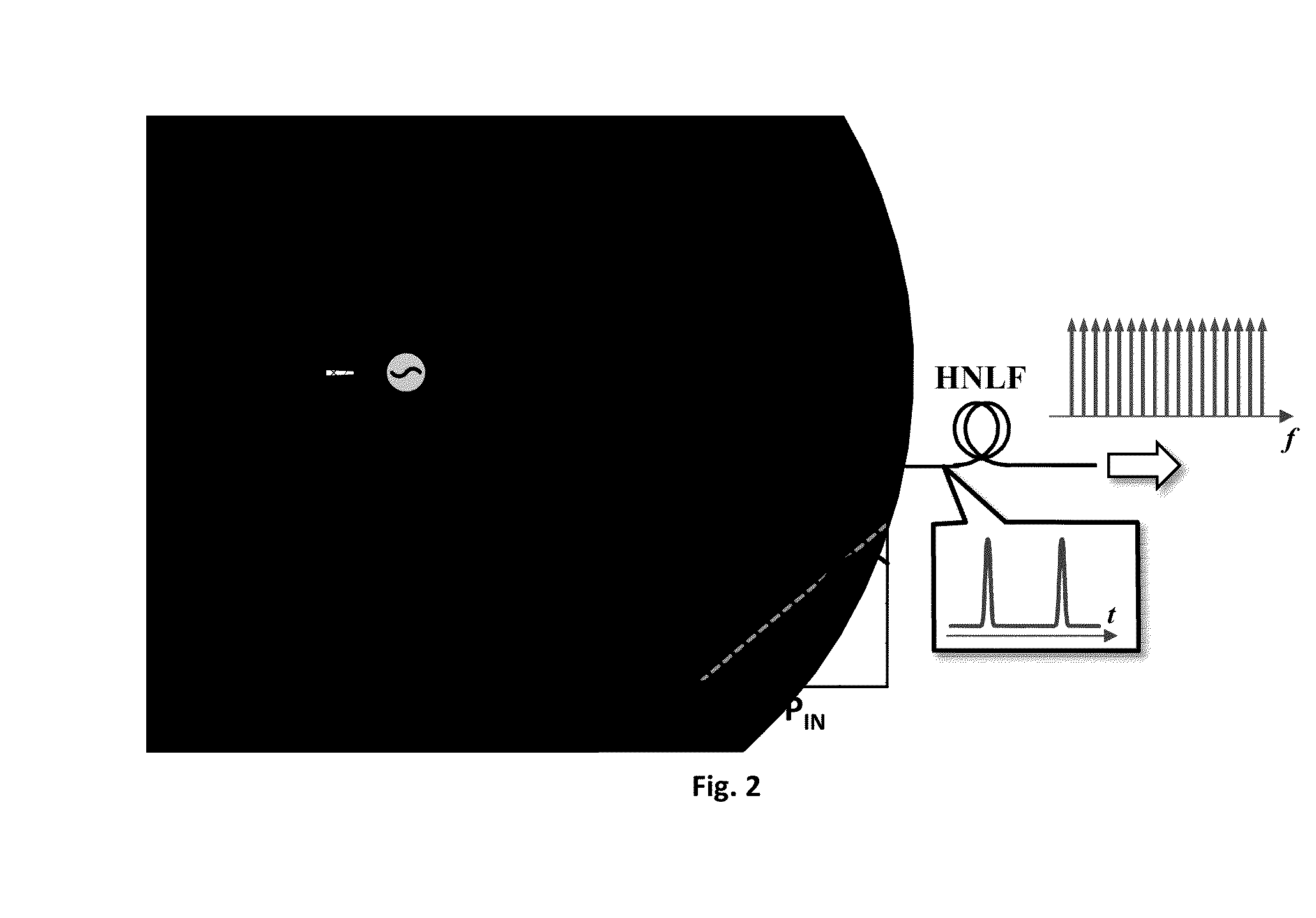
Optical sampling using intermediate second harmonic frequency generation
InactiveUS20030007205A1Improve dynamic rangeHigh speed machiningLaser detailsUsing optical meansBandpass filteringBeam splitter
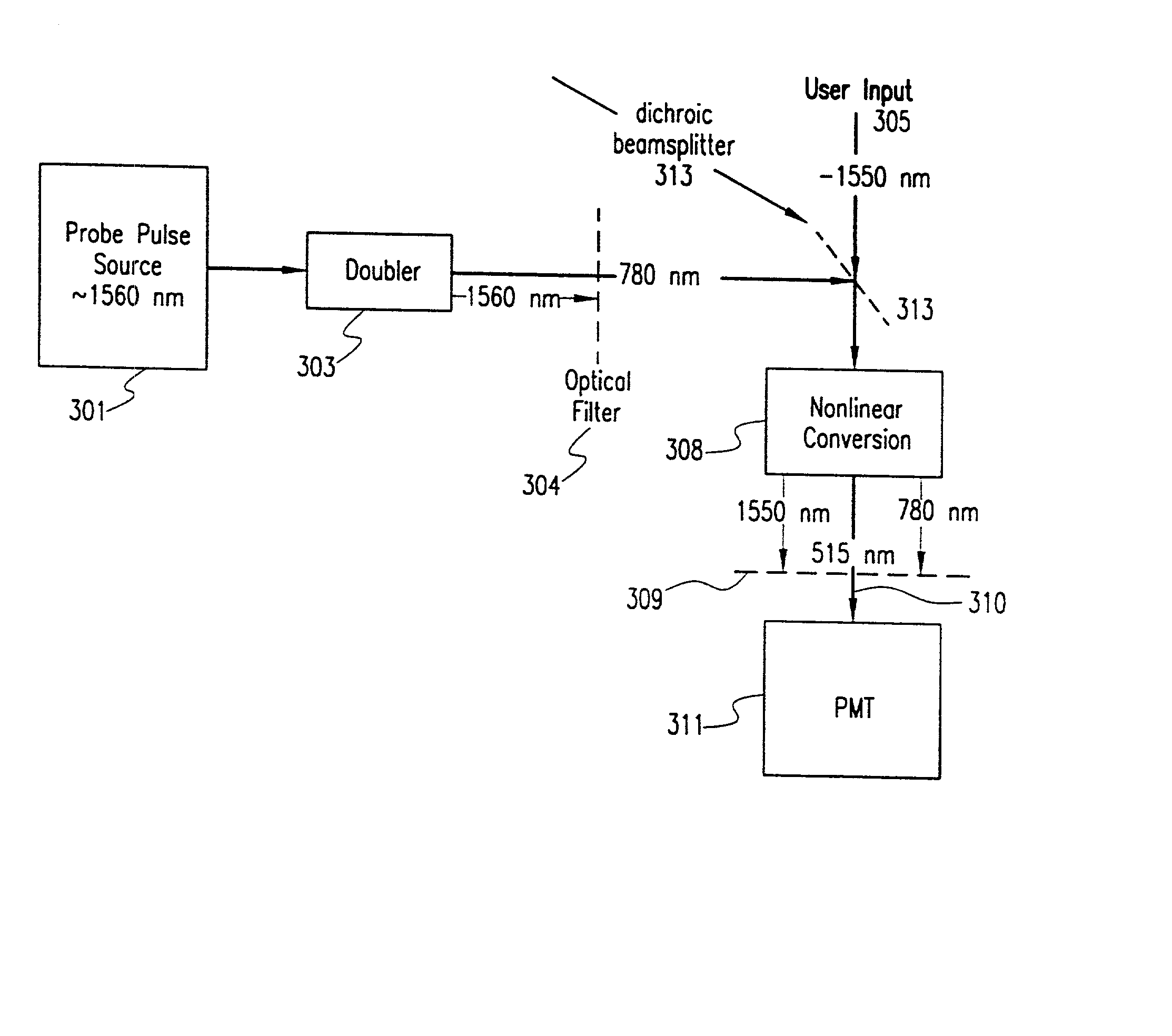
An optical sampling method and apparatus use a probe pulse source of a predetermined optical wavelength range, e.g., 1560 nm, to sample incoming optical pulses in approximately the same wavelength range. The probe pulse source is frequency-doubled e.g., using a frequency doubler such as a nonlinear PPLN crystal, to obtain an intermediate second harmonic which may be filtered with a 780 nm bandpass filter to eliminate at least source frequency noise background. The filtered intermediate second harmonic is then mixed with the user input signal using an optional polarizing beam splitter and a dichroic beam splitter. The mixed signal is sent to a sum frequency generating (SFG) nonlinear crystal, e.g., a PPLN crystal, where the resulting frequency is near the third harmonic. The output from the SFG PPLN crystal may be filtered using a bandpass 515 nm filter to remove unwanted wavelengths and processed to measure / sense the near third harmonic content using a photomultiplier tube (PMT). Beyond the PMT, the output may be sent to a microprocessor for analysis and display on a cathode ray oscilloscope as necessary. 80-85% power conversion efficiency in the frequency doubler, a 60 or 65% photon conversion efficiency in the sampler and handling of 600+ GHz bandwidths, as well as background noise reduction are possible by using the invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Radar system
ActiveUS20080284651A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce frequencyAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with a radar system, and relates specifically to scanning radar systems that are suitable for detecting and monitoring ground-based targets.In one aspect, the radar system is embodied as a scanning radar system comprising a frequency generator, a frequency scanning antenna, and a receiver arranged to process signals received from a target so as to identify a Doppler frequency associated with the target, wherein the frequency generator is arranged to generate a plurality of sets of signals, each set having a different characteristic frequency, the frequency generator comprising a digital synthesiser arranged to modulate a continuous wave signal of a given characteristic frequency by a sequence of modulation of patterns whereby to generate a said set of signals, and wherein the frequency scanning antenna is arranged to cooperate with the frequency generator so as to transceive radiation over a region having an angular extent dependent on the said generated frequencies.Embodiments of the invention thus combine digital synthesiser techniques, which are capable of precise frequency generation and control, with passive frequency scanning and Doppler processing techniques. This enables accurate control of range and of scan rates, and enables optimisation of range cell size for factors such as slow and fast target detection and Signal to Noise ratio, and thus enables detection of targets located at distances considerably farther away than is possible with known systems having similar power requirements.
Owner:BLIGHTER SURVEILLANCE SYST LTD
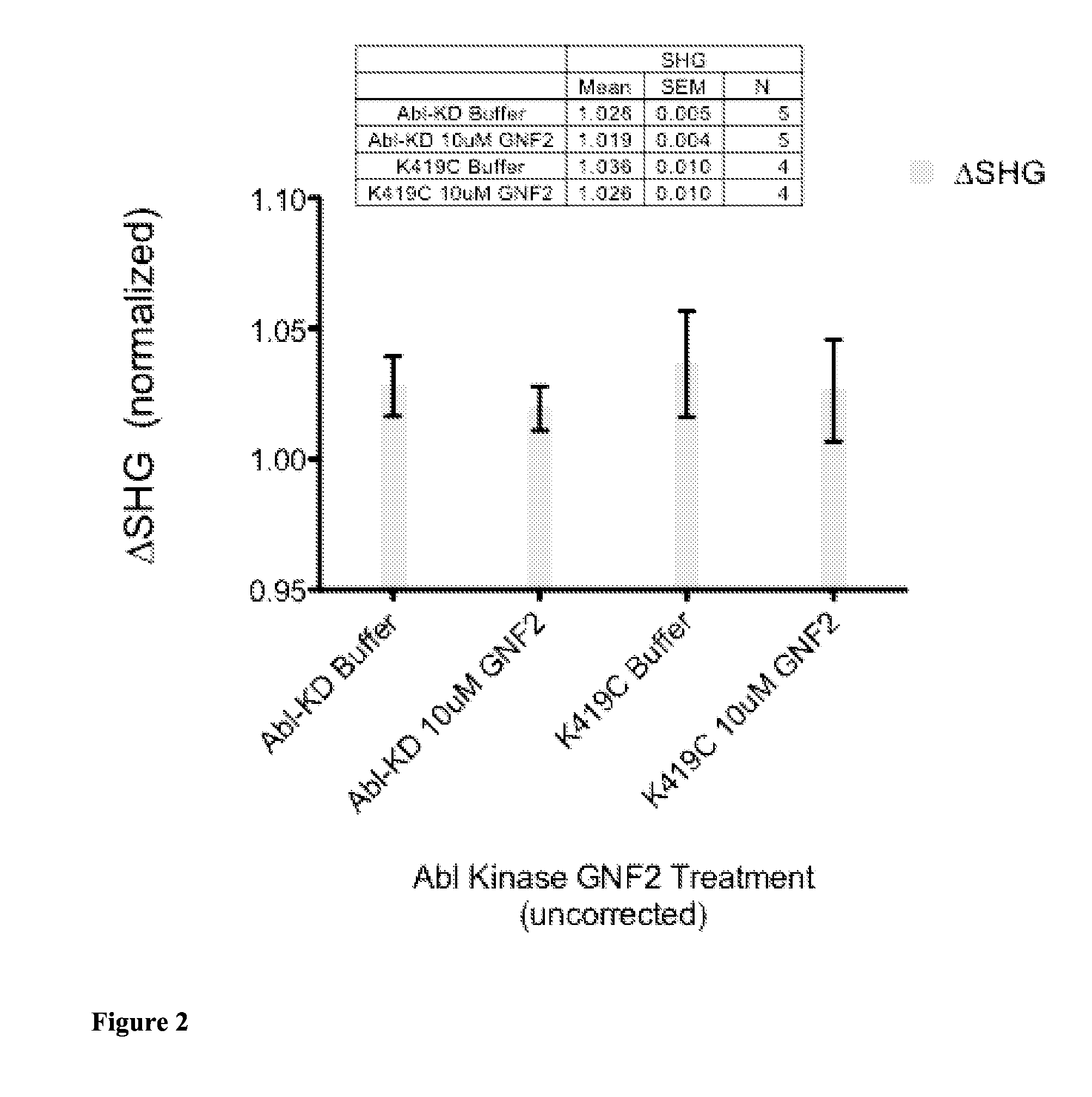
Methods for detecting allosteric modulators of protein
InactiveUS20130288271A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionAllosteric modulatorSum-frequency generation
The present invention discloses, inter alia, methods for labeling a target protein with an SHG-active probe for detection by second harmonic or sum-frequency generation in order to identify agents which bind to an allosteric site on the target protein thereby altering its structural conformation
Owner:QUANTA THERAPEUTICS INC
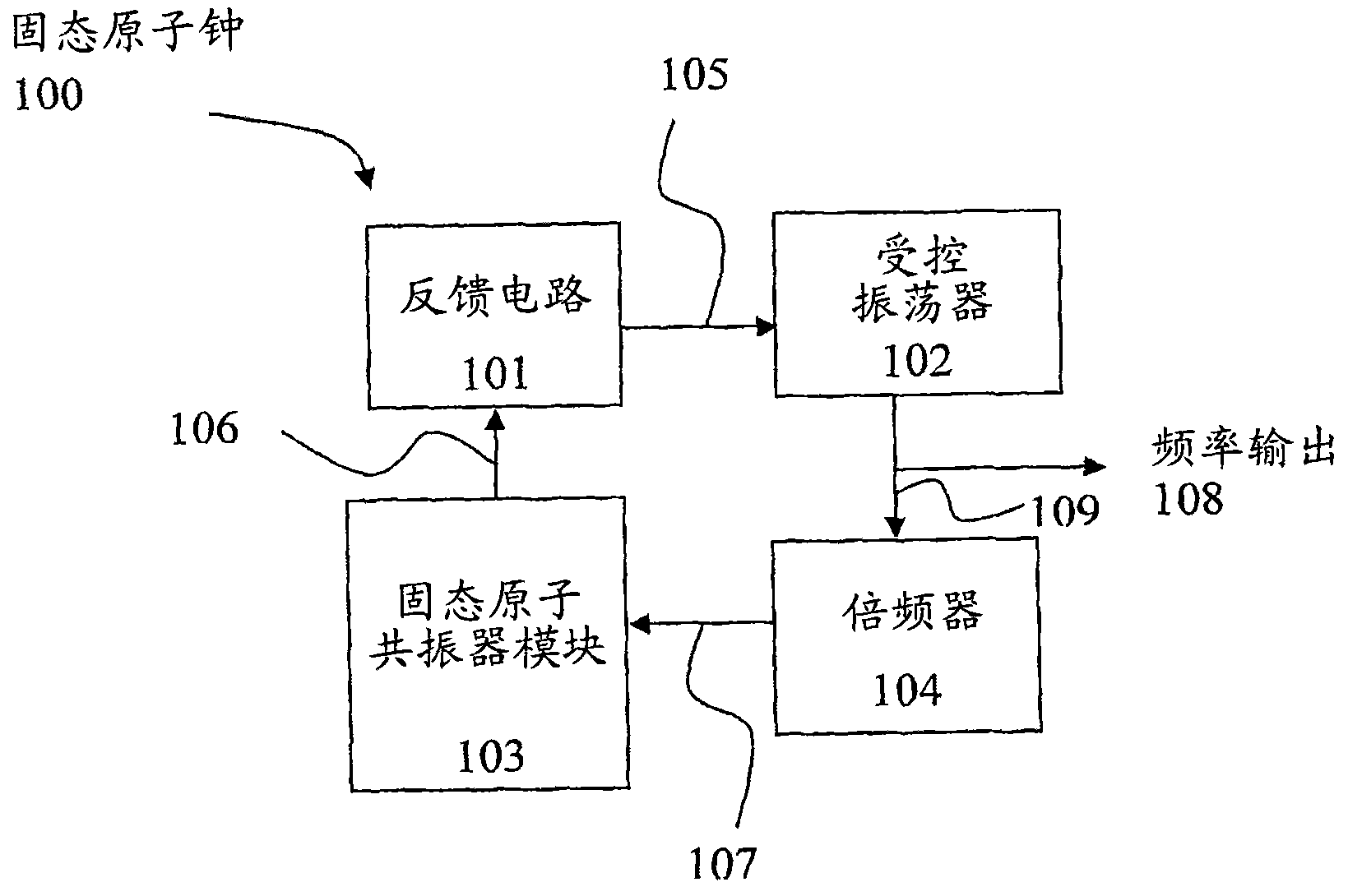
Device, system, and method of frequency generation using an atomic resonator
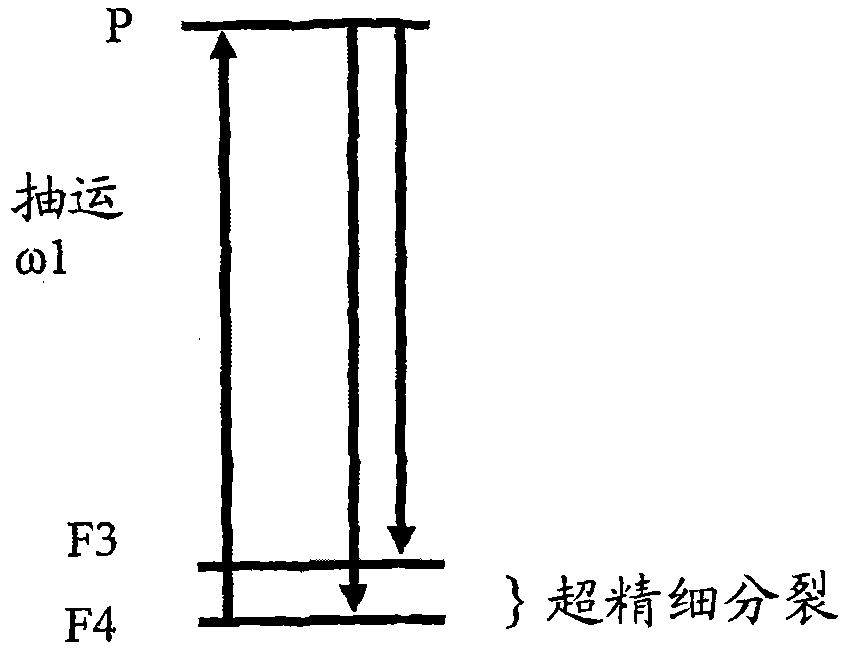
InactiveCN101990742APulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksResonanceFrequency generation
A solid state atomic clock may utilize quantum states capable of exhibiting a hyperfine resonance in order to generate a frequency standard. A device capable of coupling a free running oscillator to the hyperfine resonance frequency in order to generated output signal is described herein. In some aspect of the invention, the atomic clock may be fabricated on a silicon substrate and it may be integrated, in chip scale, as part of an electronic integrated circuit. The principal of operation, the method of making and system which utilized a solid state atomic clock are also disclosed.
Owner:L・甘
Light-generating apparatus with broadband pumping laser and quasi-phase matching waveguide
InactiveUS20090154508A1Avoid low lightAvoid problemsLaser detailsNon-linear opticsSum-frequency generationBroadband
A light-generating apparatus comprises a broadband pumping laser configured to emit a broadband pumping light having a bandwidth larger than 10 nanometers and a broadband wavelength-converting device. The broadband wavelength-converting device includes a domain-inverted structure configured to convert the broadband pumping light into at least one conversion light by using at least a sum frequency generation mechanism and at least one waveguide positioned in the domain-inverted structure, and the waveguide has an input end configured to receive the broadband pumping light and an output end configured to output the conversion light. Since the light-generating apparatus uses the broadband pumping laser and the broadband wavelength-converting device, it is temperature-insensitive and speckle-free.
Owner:HC PHOTONICS
Solid state terahertz radiation frequency multiplier
InactiveUS20100073110A1Improve efficiencyMultiple-port networksNanoopticsTerahertz radiationDistributed structure
A nonlinear solid-state device useful for frequency conversion of electromagnetic radiation and in particular for harmonic generation, comprising a waveguiding electromagnetically distributed structure (WEDS) which includes monolithically a synthetic nonlinear material (SNM). Input radiation coupled into the WEDS is converted into a higher frequency output radiation through a constricted oscillatory motion of charge carriers and phase matched harmonic frequency generation of radiation which builds up coherently over an interaction length many time larger than the radiation wavelengths. In one embodiment, microwave radiation is converted into terahertz radiation. In other embodiments, SNM based WEDS devices are adapted for frequency mixing and parametric oscillation.
Owner:GOVER AVRAHAM +2
Multiple channel optical frequency mixers for all-optical signal processing
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
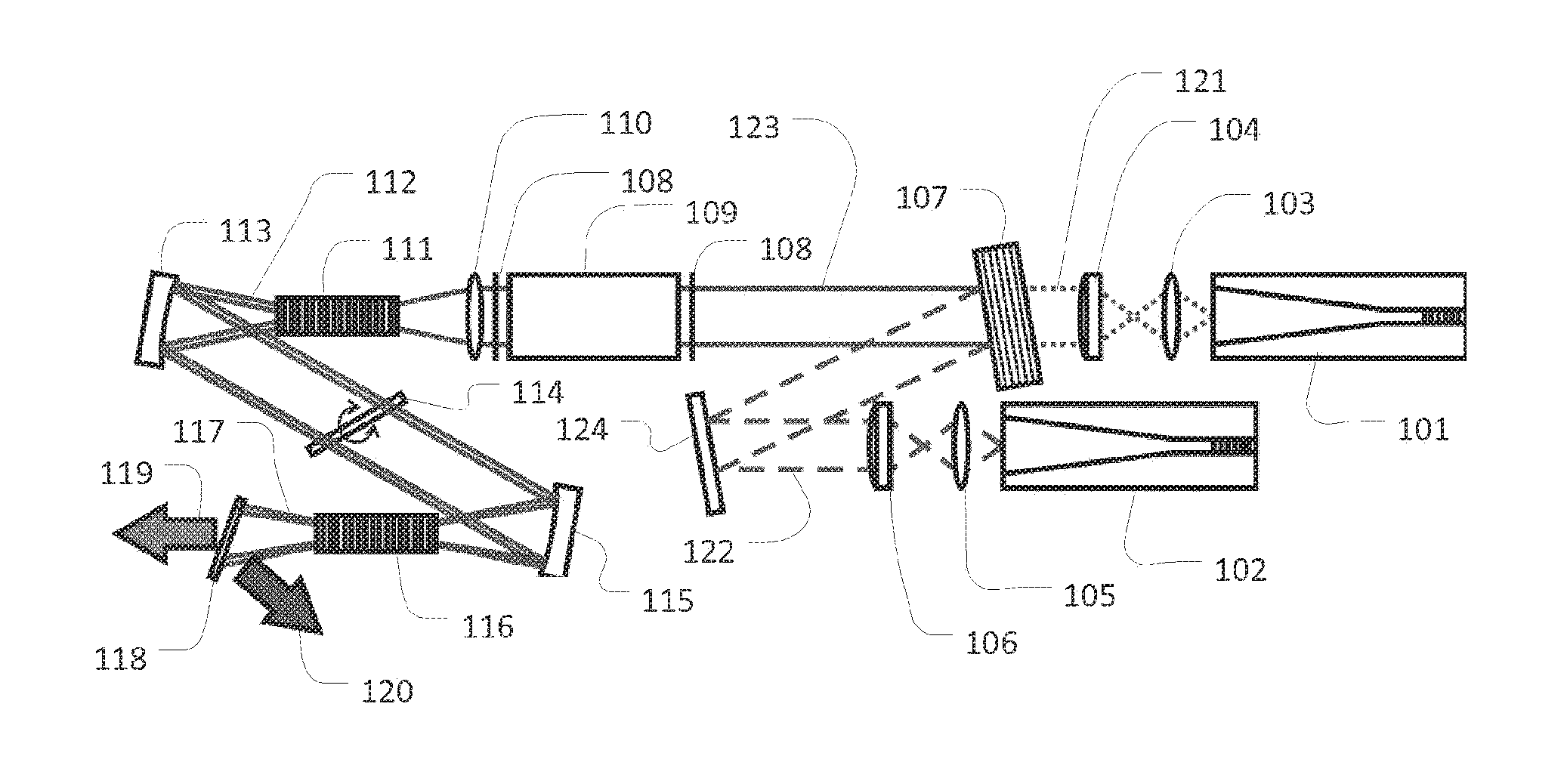
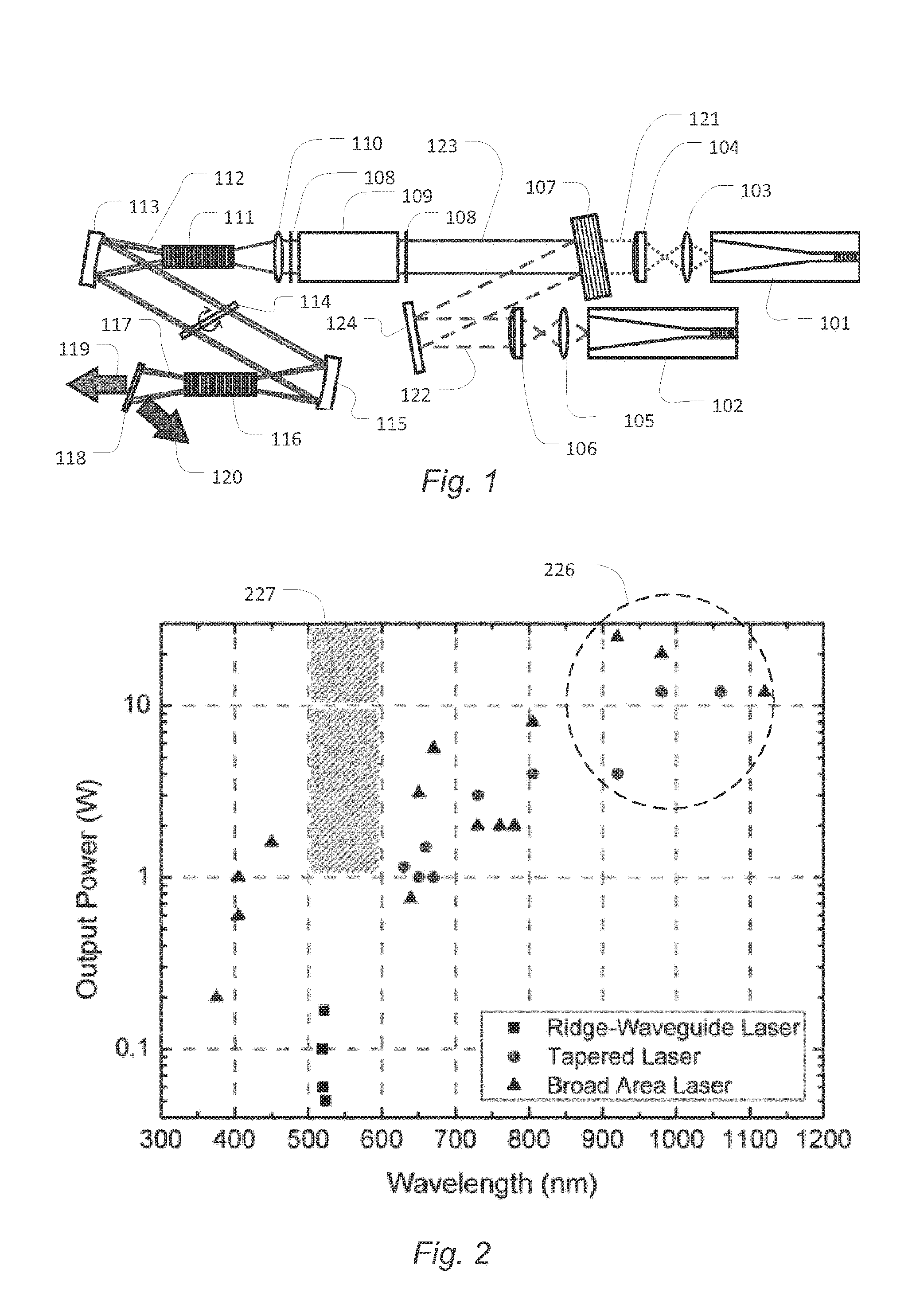
Pulsed, Internal Optical Mixer
InactiveUS20140301417A1Increase powerHigh beam qualityLaser detailsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesOptical parametric amplifierSum-frequency generation
Pulsed, coherent light is generated by optical mixing which takes place inside the resonator of a pulsed laser oscillator. One of the beams to be mixed is generated by the pulsed laser, and the other by a distinct, external laser oscillator. If the light from the external oscillator is modulated, that modulation will be transferred onto the light generated by the optical mixing. This enables modulated light at an expanded range of wavelengths. Using sum frequency generation, light for sodium excitation, such as for a guide star, can be generated with the optimal modulation of spectral and temporal properties. If the type of optical mixing is difference frequency generation, optical parametric amplifiers with improved efficiency and beam quality are enabled.
Owner:FASORTRONICS
Blue-light generating femtosecond wavelength-tunable non-collinear optical parametric amplifier
InactiveUS20060044642A1Low costLight demodulationNon-linear opticsOptical parametric amplifierLight conversion efficiency
The present invention discloses a means of the generation of tunable femtosecond pulses from 380 nm to 465 nm near the degenerate point of a 405-nm pumped type-I BBO non-collinearly phase-matched optical parametric amplifier (NOPA). The tunable UV / blue radiation is obtained from sum frequency generation (SFG) between the OPA output and the residual fundamental beam at 810-nm and cascaded second harmonic generation (SHG) of OPA. With a pumping energy of 75 mJ at 405 nm, the optical conversion efficiency from the pump to the tunable SFG is more than 5% and the efficiency of SHG of the OPA is about 2%.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Self Raman yellow light laser of composite cavity structure
ActiveCN103996968AIncrease output powerShorten the lengthOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberBeam splitter
The invention discloses a self Raman yellow light laser of a composite cavity structure. A laser diode pumping source emits pump light in an absorption belt of a gain medium, the pump light is focused inside the gain medium through a transmitting energy fiber and a coupling lens set, the gain medium absorbs the pump light to form population inversion, and base frequency laser generation is formed under the feedback action of a laser resonant cavity composed of a resonant cavity shared reflector and a laser total reflector; when base frequency laser passes through the gain medium, Raman gains are generated, and after the Raman gains are greater than the cavity loss of a Raman resonant cavity composed of the resonant cavity shared reflector, a beam splitter and a yellow light output mirror, stable Stokes light generation is formed in the Raman resonant cavity; the frequency of Stokes light is doubled in a frequency doubling crystal, and the generated yellow light secondary harmonic wave is output by the yellow light output mirror. The composite cavity structure is adopted, the length of a base frequency laser resonant cavity is largely decreased, and therefore the stable area of the resonant cavity is effectively enlarged, and the effect of improving the output power of the self Raman yellow light laser is achieved by applying higher pumping power.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Brushless high-frequency alternator and excitation method for DC, single-phase and multi-phase AC power-frequency generation
A method is disclosed for arranging and exciting the stator, rotor and various windings of a multi-stage brushless high frequency alternator so that the resulting multiple high frequency sub-phase armature winding outputs can be rectified and commutated into desired phases of power-frequency alternating current (AC) electrical output, including single-phase, split-phase, three-phase and other multiple phase output. Power frequency currents in field windings control output amplitude, output frequency, and output phase. If desired, DC power output can be accommodated as zero power-frequency operation. Devices incorporating this arrangement are suitable of generating fixed frequency electrical power while accommodating variable speed rotation of a generator shaft and offer multiple advantages over existing techniques. The capability to generate speed independent electric power allows natural power sources such as windmills and hydro-power stations to be efficiently coupled to fixed frequency power grids.
Owner:RAVEN ENERGY ALTERNATIVES
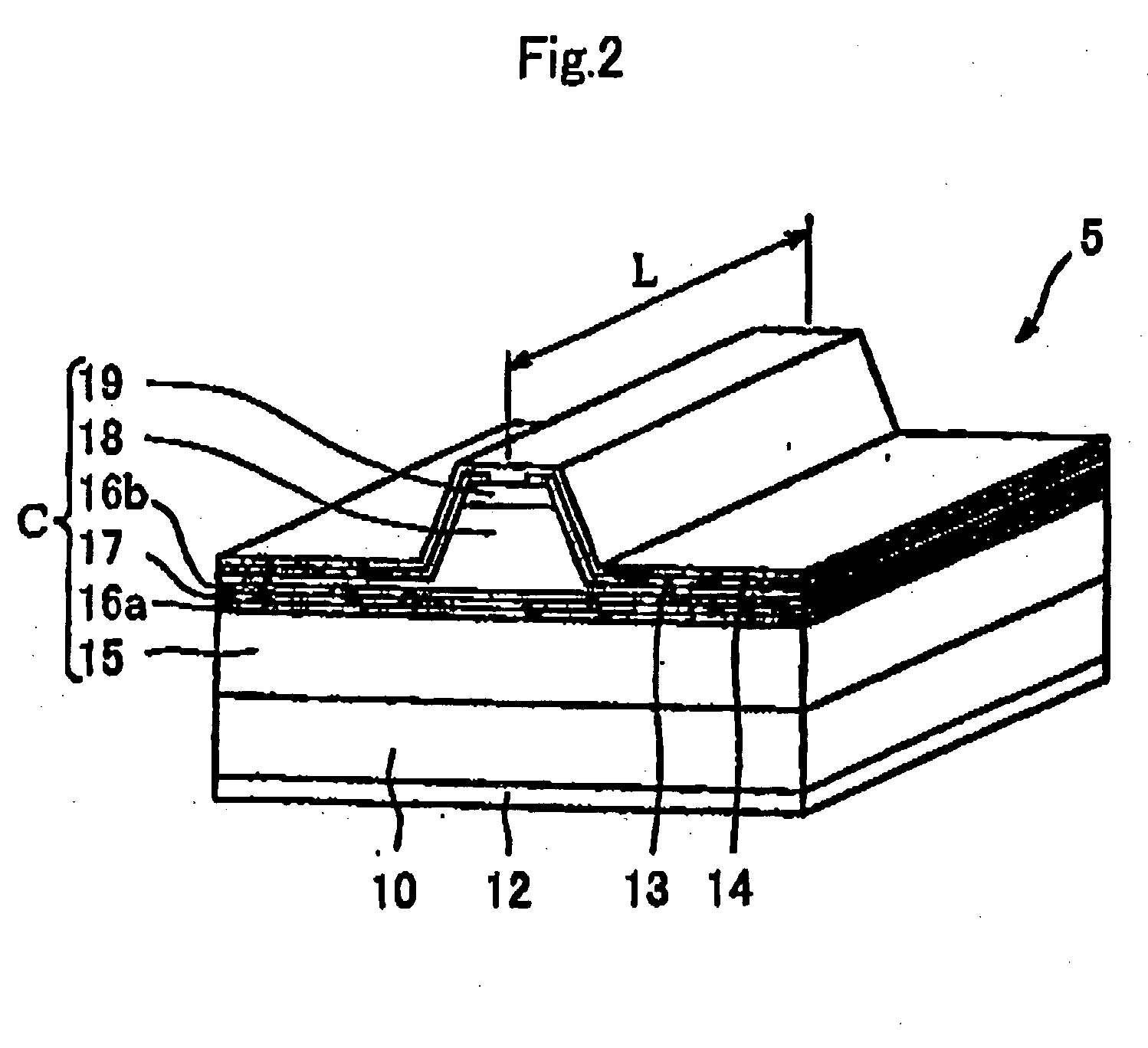
Wavelength conversion module
A wavelength conversion module according to the present invention includes an external resonator, a semiconductor laser module and a wavelength conversion device for converting a wavelength of light output from the semiconductor laser module into a shorter wavelength. This wavelength conversion device includes at least one of a nonlinear crystal for generating SFG (Sum-frequency Generation) light and a nonlinear crystal for generating SHG (Second Harmonic Generation) light. Each of the SFG generating element and the SHG generating element of the wavelength conversion device may have a periodically-poled ridge-waveguide structure or a periodically-poled proton-exchanged-waveguide structure.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Laser apparatus with cascade of nonlinear frequency mixers
ActiveUS20160320686A1Compensation for dispersionAccurate compensationSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsFrequency spectrumFrequency mixer
A laser apparatus generating frequency converted light. Embodiments of the laser apparatus described herein apply a cascade of nonlinear frequency mixers for sum frequency generation (SFG) or difference frequency generation (DFG) between two frequency components of a spectrally combined laser beam with at least two spectral components originating from two respective laser sources, SFG of two frequency components beams offers up to a factor of four amplification of output power over SHG of a single laser beam.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com