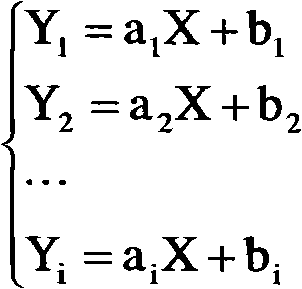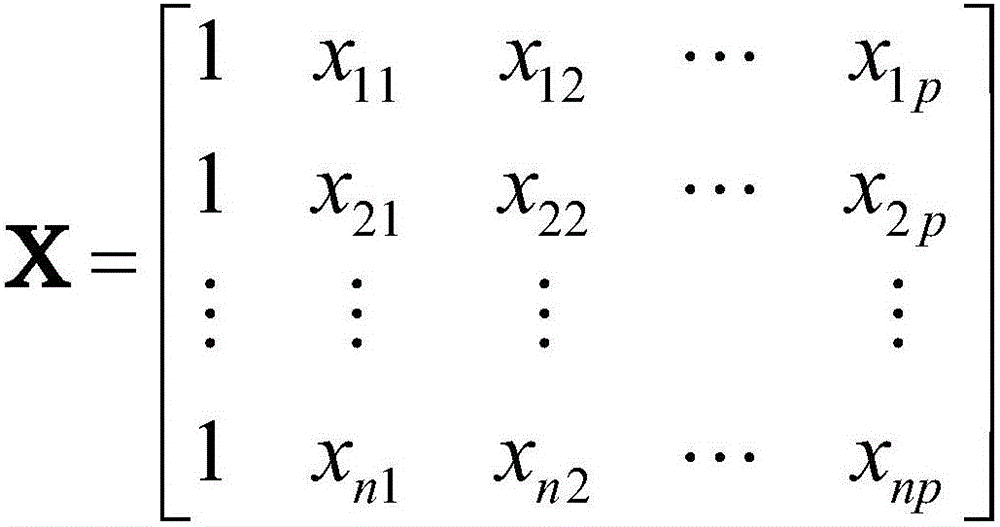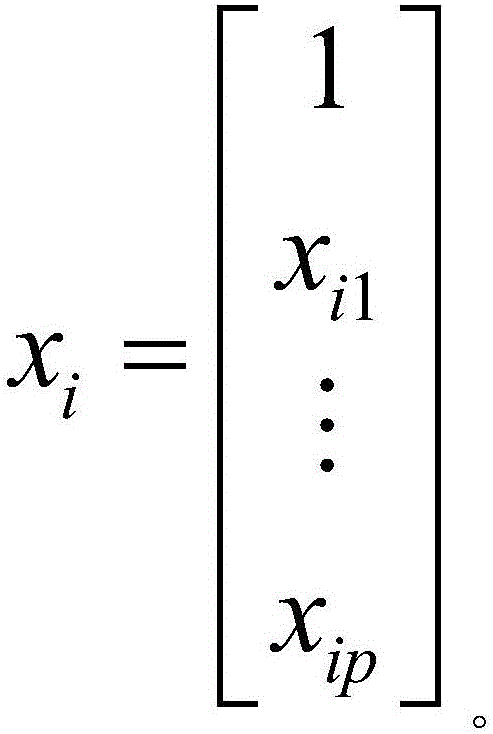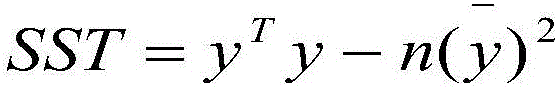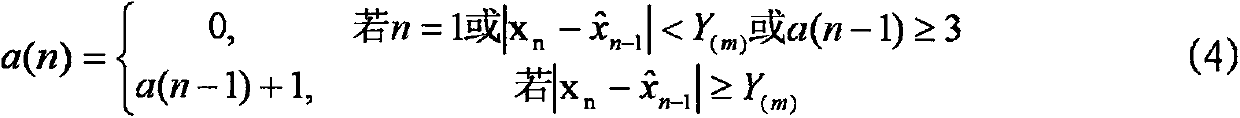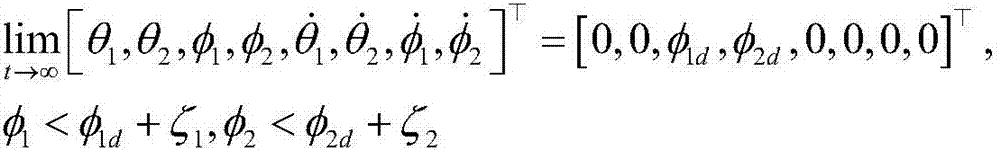Patents
Literature
123 results about "Real variable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of real variable. 1 : a mathematical variable whose values are real. 2 : free variable.
Fault diagnosis method during industrial process
InactiveCN105700518AReduce the "pollution" effectImprove reliabilityElectric testing/monitoringBayes decision rulePollution
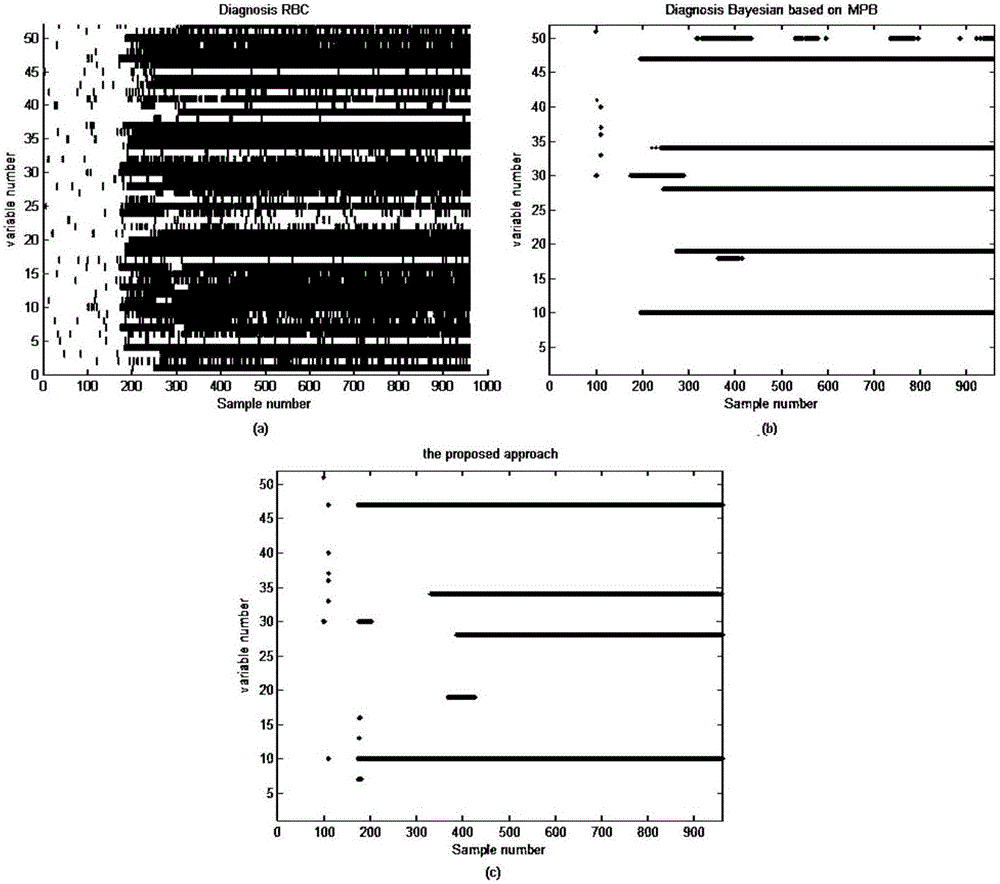
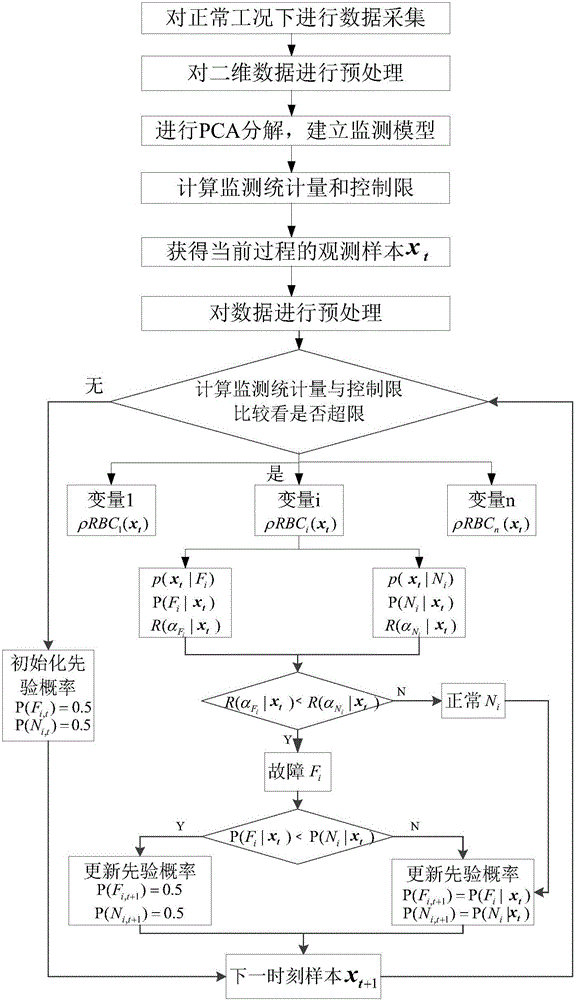
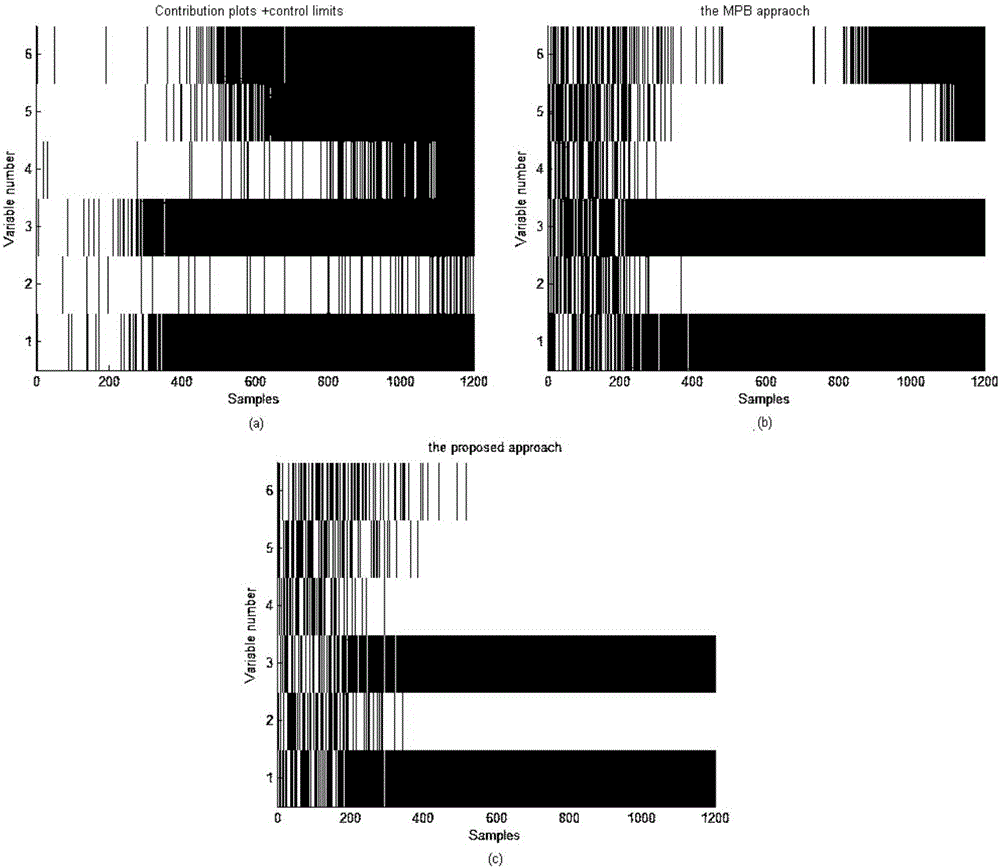
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method during the industrial process. The method comprises the steps of collecting historical normal data during the industrial process; calculating a detection statistics based on the historical normal data during the industrial process; collecting the to-be-detected data of the industrial process; on the condition that the industrial process is detected to be out of order, extracting a statistic feature based on the relative refactoring contribution method; according to the statistic feature, calculating a conditional probability density function in the fault mode and a conditional probability density function in the normal mode; according to the prior probability and the conditional probability density function, calculating a posterior probability; conducting the fault variable recognition on a current time sample based on the minimum risk Bayesian decision theory; according to a diagnosis result, updating the prior probability for the next time sample and conducting the fault diagnosis and recognition again for the next round. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the major failure variable, the secondary process variable and the normal variable of the current sample are distinguished. Meanwhile, the diagnosis result of the process variable of the previous time sample is applied to the diagnosis of the current sample. Therefore, the pollution effect during the fault diagnosis of the industrial process is eliminated.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electro-mechanical mixed stepless speed-changing wind power generation plant
InactiveCN101272084AIncrease working pointImprove utilization efficiencyDynamo-electric gearsWind motor combinationsConstant frequencyEngineering
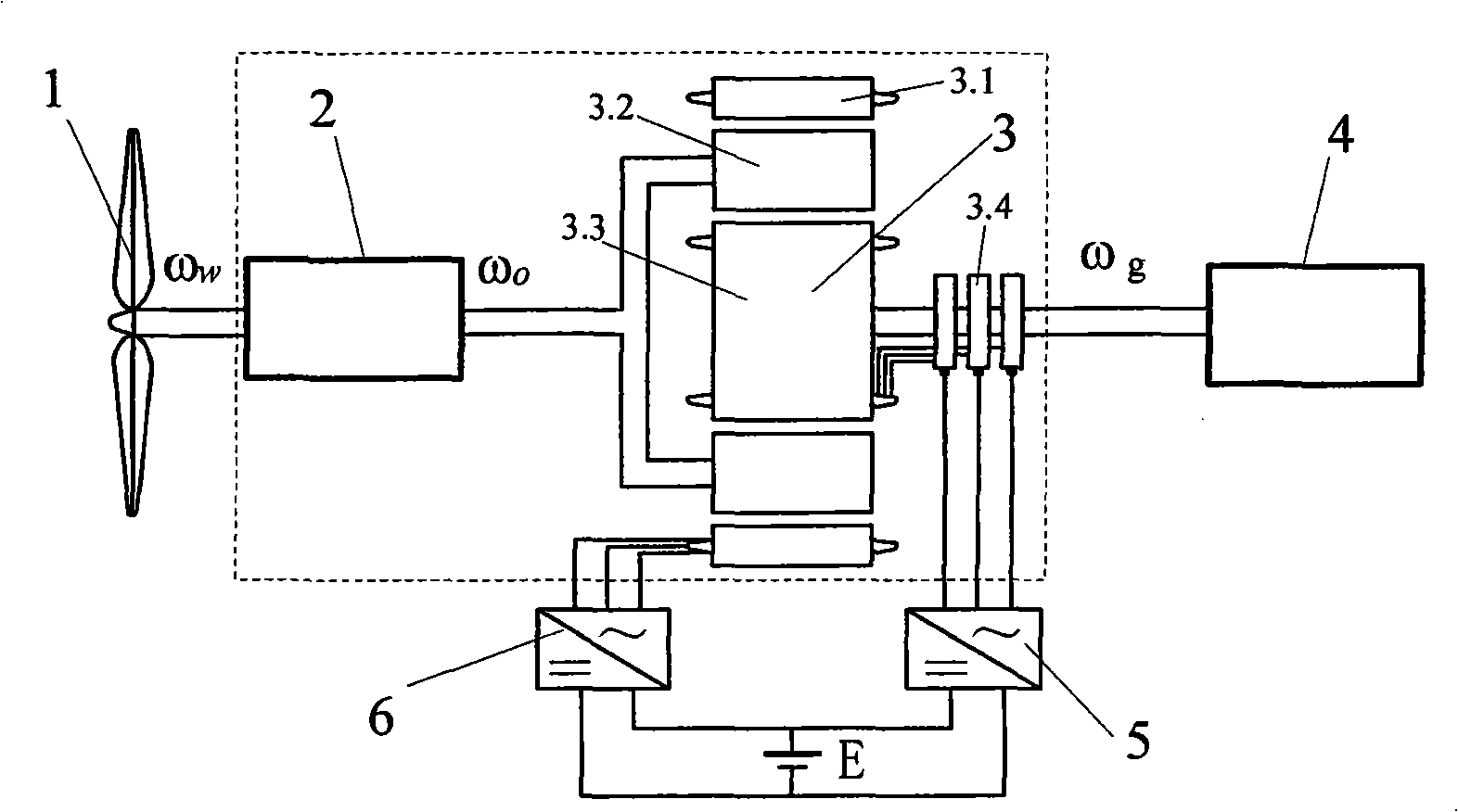
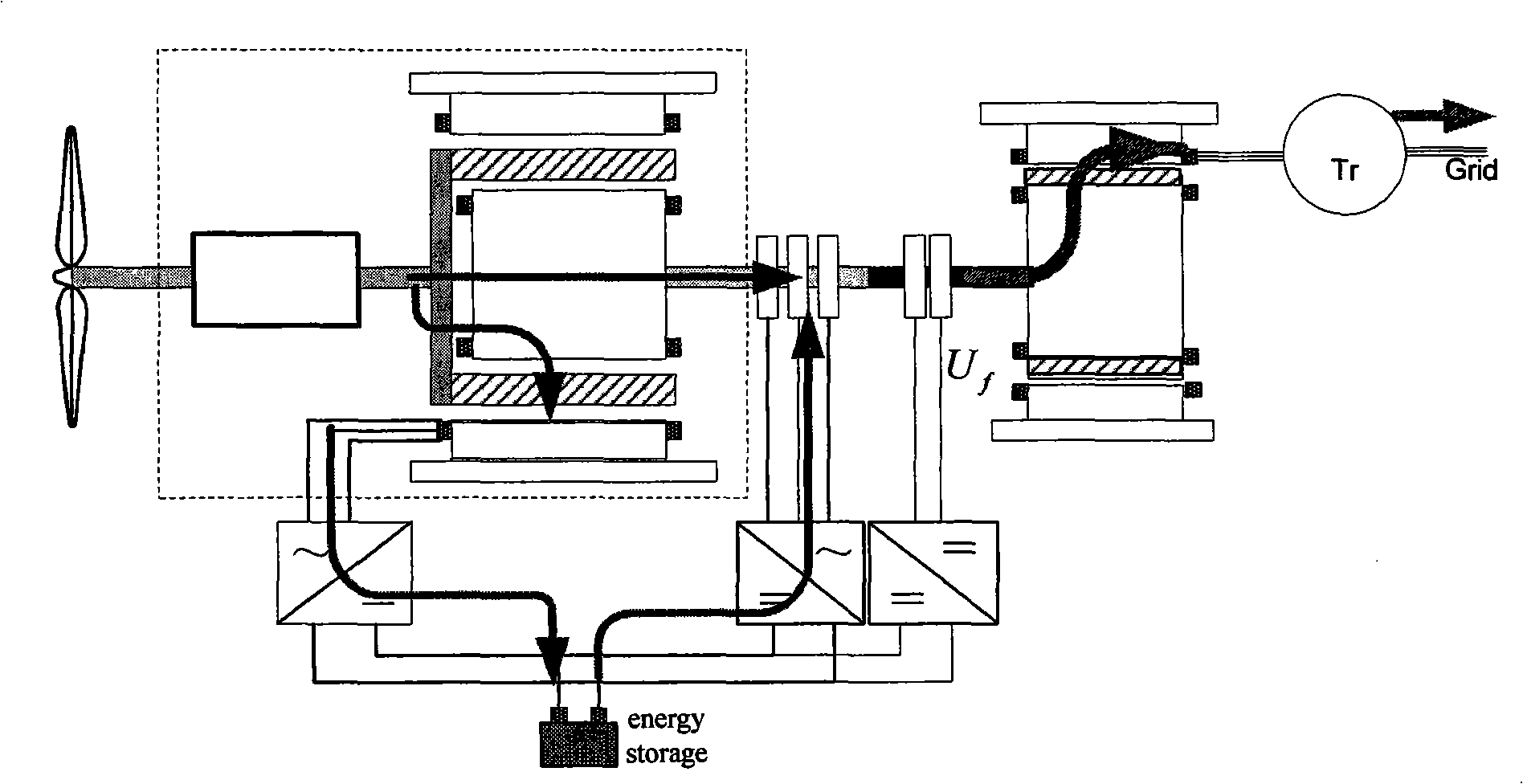
An electromechanical infinite variable speed wind generating device is capable of realizing the real variable speed constant frequency operation, remarkably improving the reliability and the operation efficiency of a system as well as the operating factor of the wind energy, remarkably promoting the working point and the operating efficiency of an electrical variable transmission as well as the efficiency of the whole system. The device includes a wind machine (1), a mechanical speed increaser(2), an electrical transmission (3), a generator (4), a first power inverter (5), a second power inverter (6) and a third power inverter (7). If a DC power consists of an energy storage unit (storage battery, capacitor, etc), partial power can be stored in a form of electricity, or the energy in the energy storage can be released into an output shaft. When the power of the wind machine is larger than that of the generator, the redundant energy can be converted into electricity and stored; on the contrary, when the power of the wind machine is smaller than that of the generator, the energy in the energy storage unit can be released to complement the insufficiency of the inputted power.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
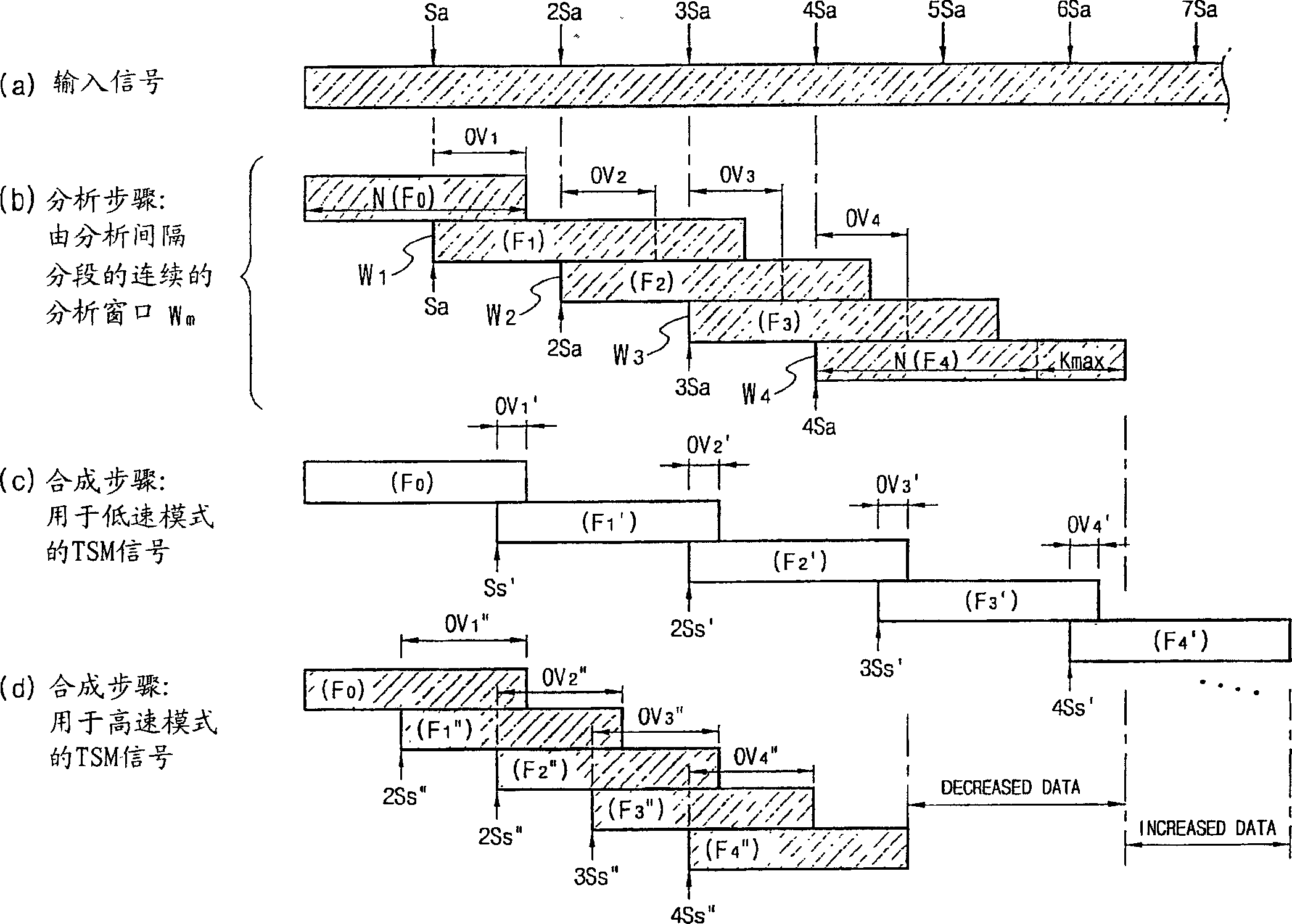
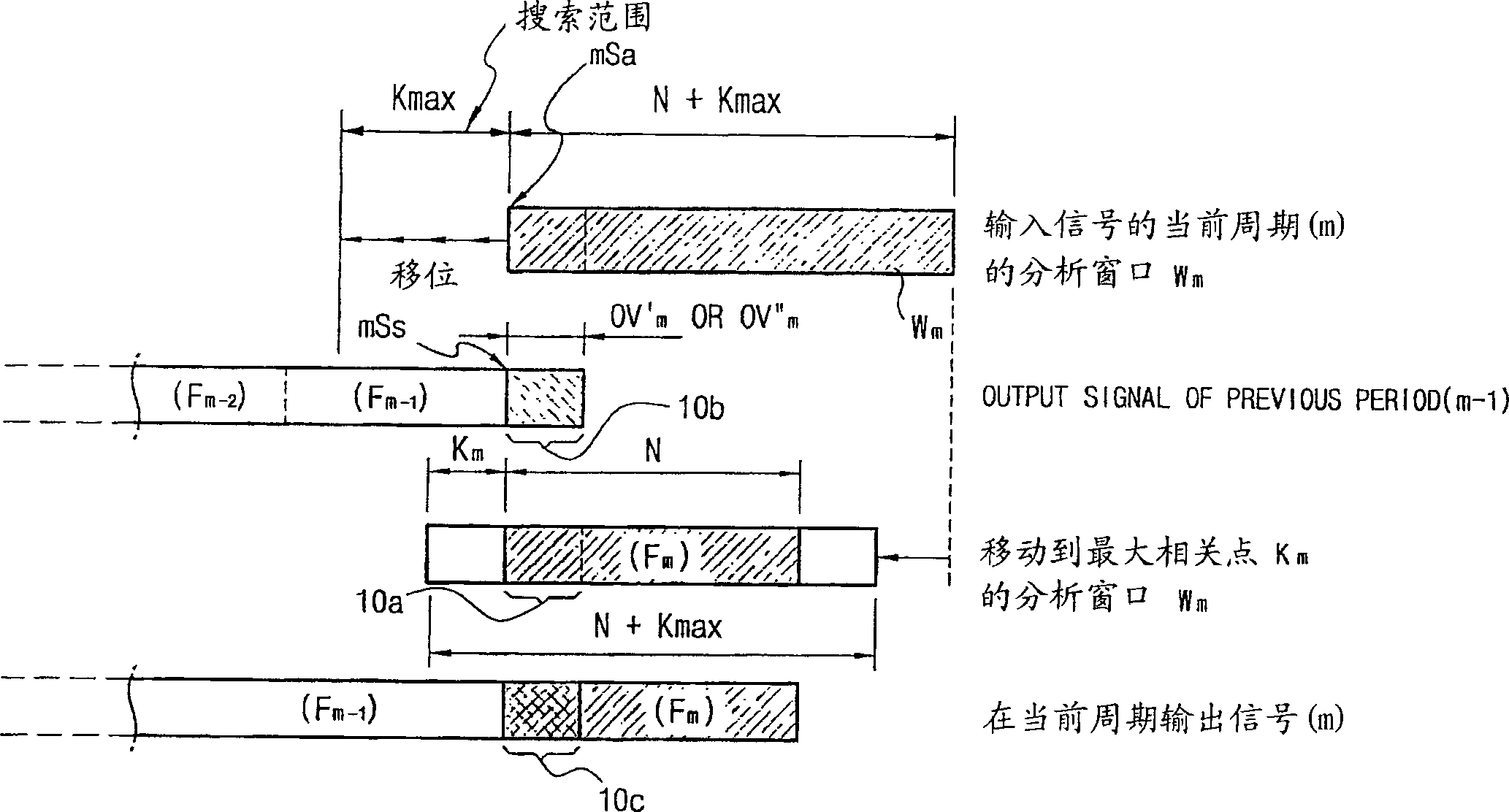
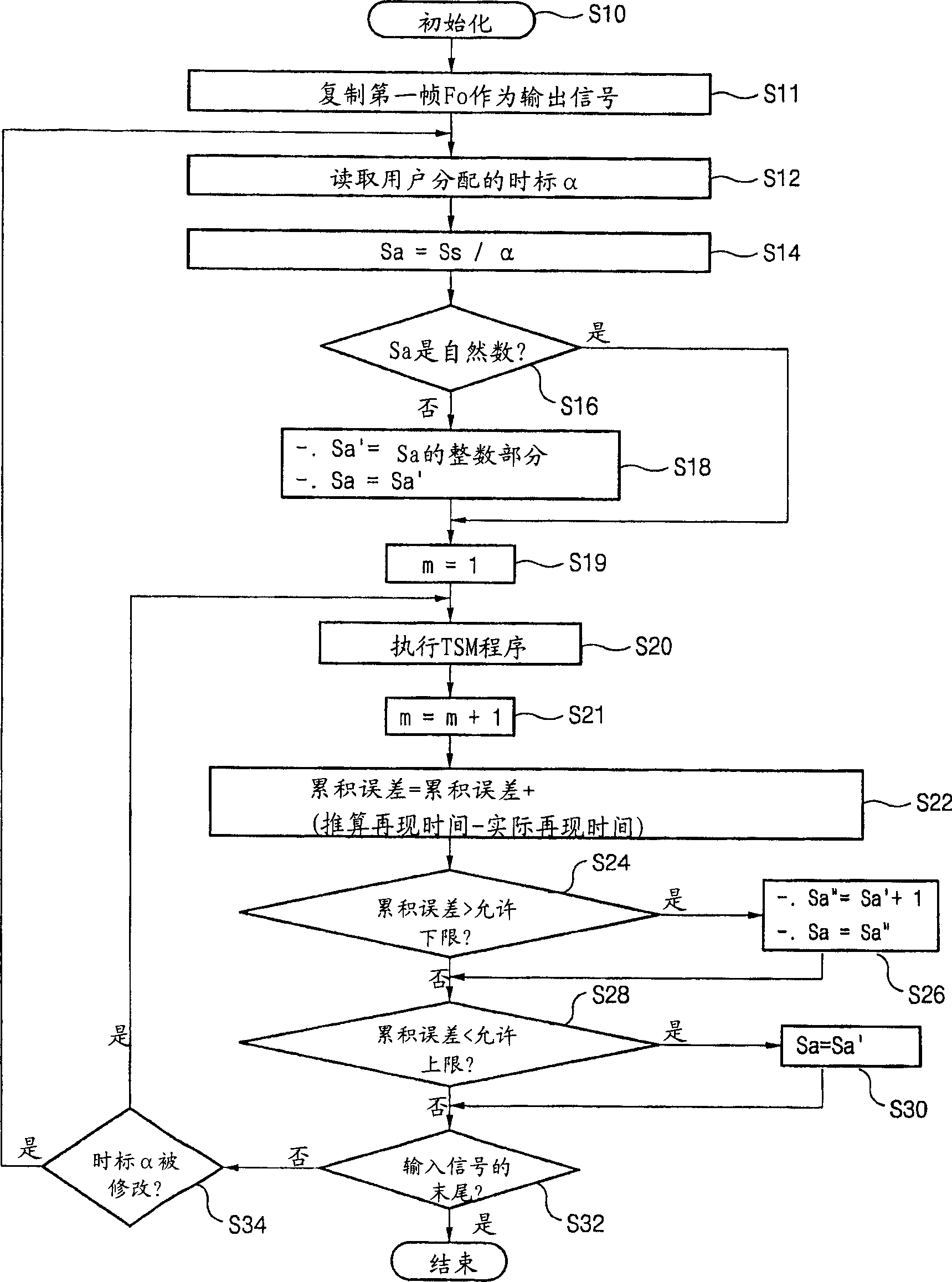
Time-scale modification method for digital audio signal and digital audio/video signal, and variable speed reproducing method of digital television signal by using the same method
InactiveUS20070168188A1Less loadTelevision system detailsSpeech analysisReal variableDigital audio signals
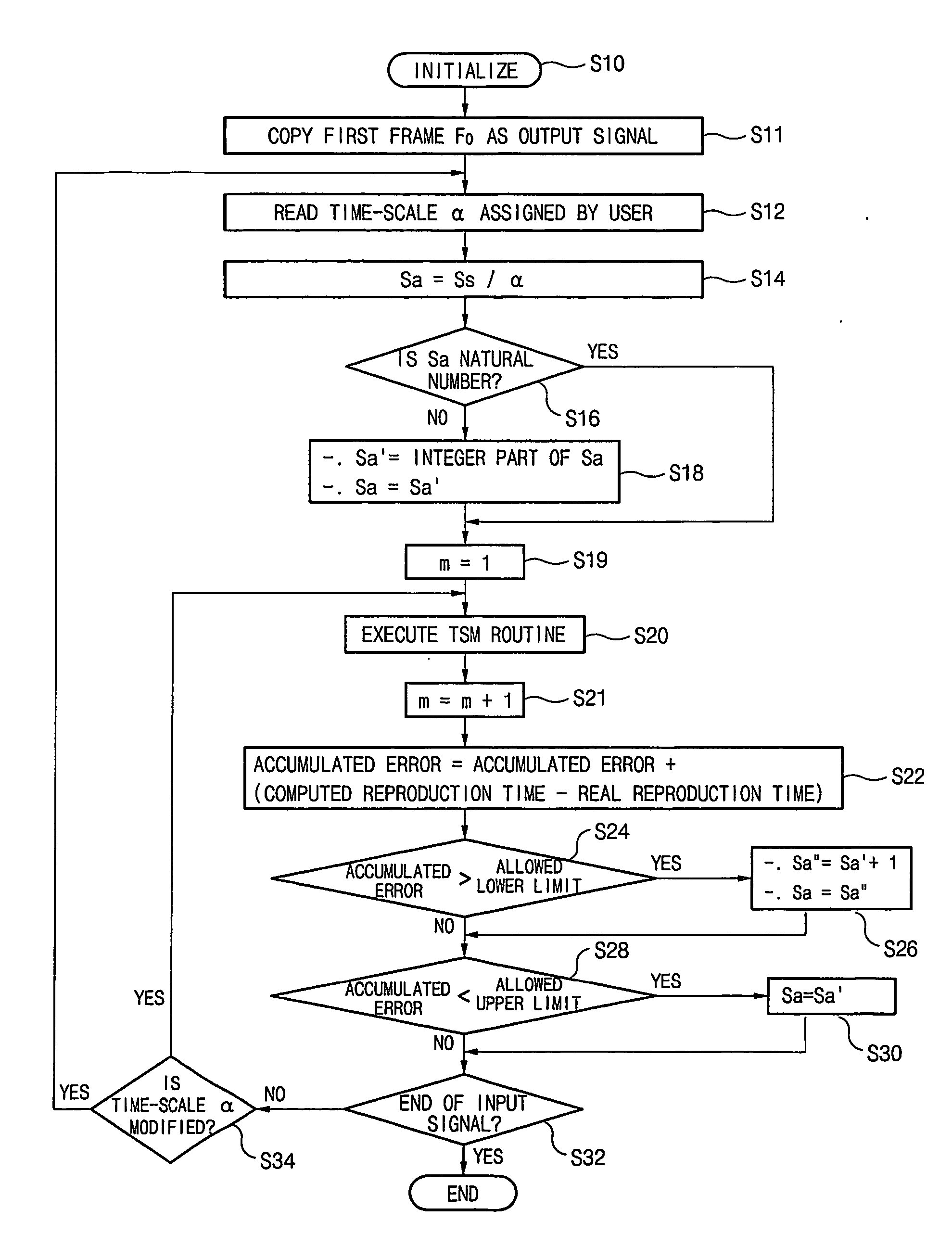
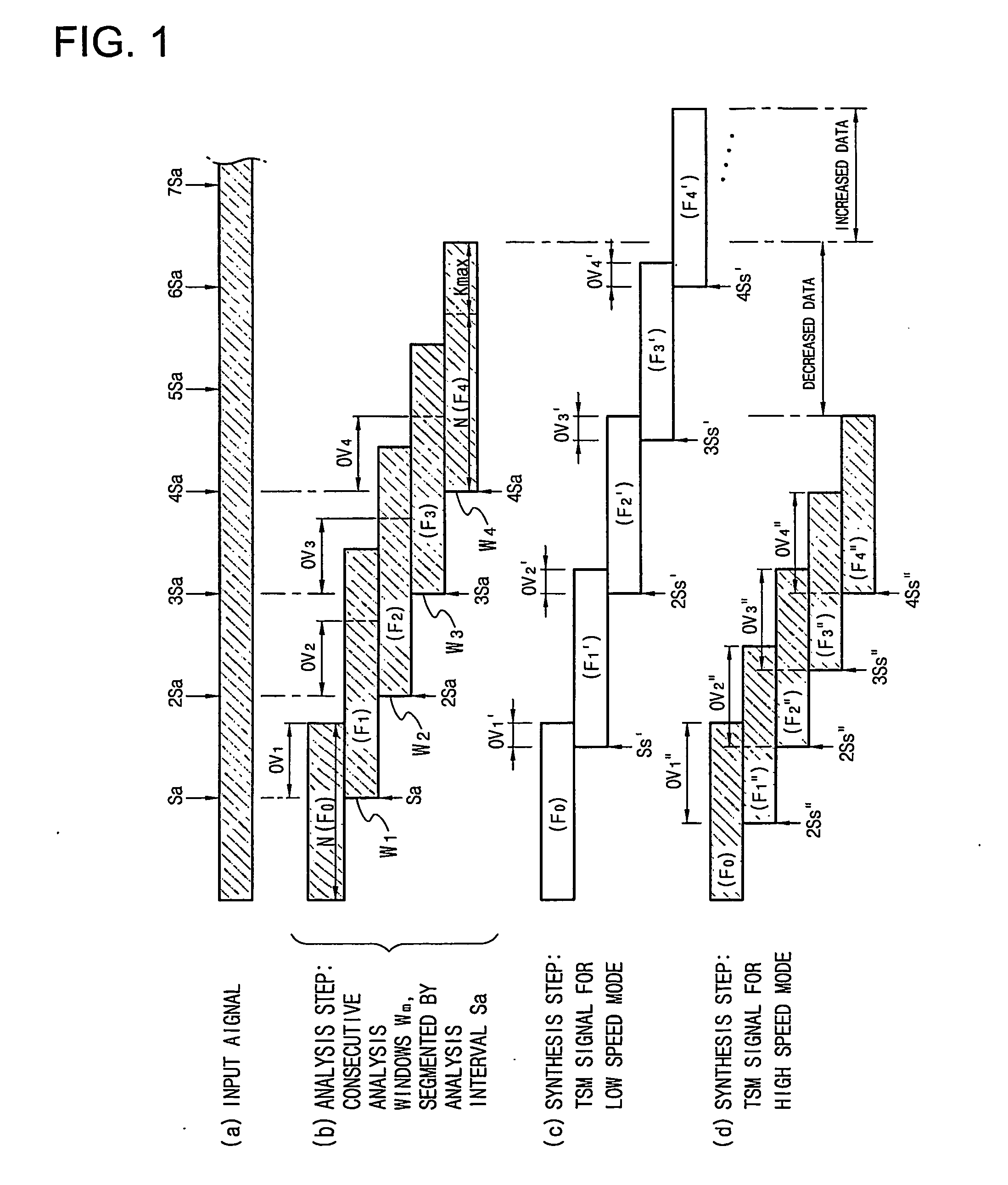
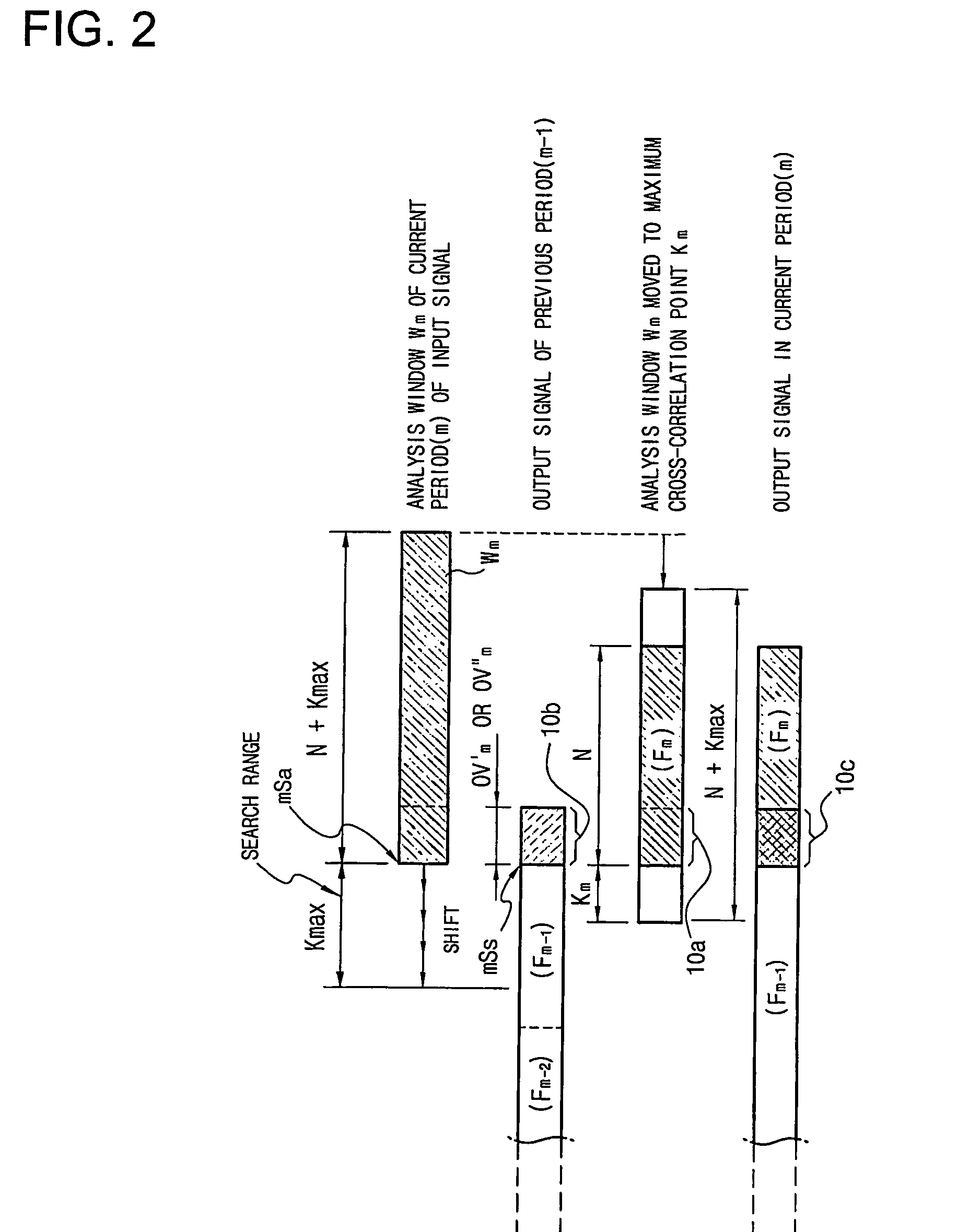
Problem: A method capable of ensuring a synchronization between an audio signal and a video signal both of which are modified in time-scale is needed. Solution: When analysis shift Sa=Ss / α, where Ss is synthesis shift and α is a designated time-scale (variable speed ratio), has a decimal value, two natural numbers which are nearest to the decimal value are selected as a modified analysis shift Sa′ and a compensated analysis shift Sa″, respectively. In time-scale modification of source audio samples to vary playback speed by dividing them into overlapped successive analysis windows, the modified analysis shift Sa′ and the compensated analysis shift Sa″ are alternately applied whenever a predetermined condition is met. The time difference between an estimated playback time and a real playback time of the time-scale modified audio signal is accumulated. The case that the predetermined condition is met is a case than an accumulated time difference goes beyond an upper threshold or a lower threshold of an allowed error range. In a processing of varying the playback speed of an AV signal, if a real variable speed ratio of a playback-speed-varied video signal is given as a target variable speed ratio of an audio signal to vary the playback speed of the audio signal, a synchronization between the video signal and the audio signal can be obtained. By applying this technology to the digital TV or TV phone, consecutive watch of the broadcasting signal for a phone-break time is possible. Catch-up for the currently received broadcasting signal is also possible through a high speed playback mode after a low speed playback mode initiated from a time of the past or the present.
Owner:CHOI WON YONG
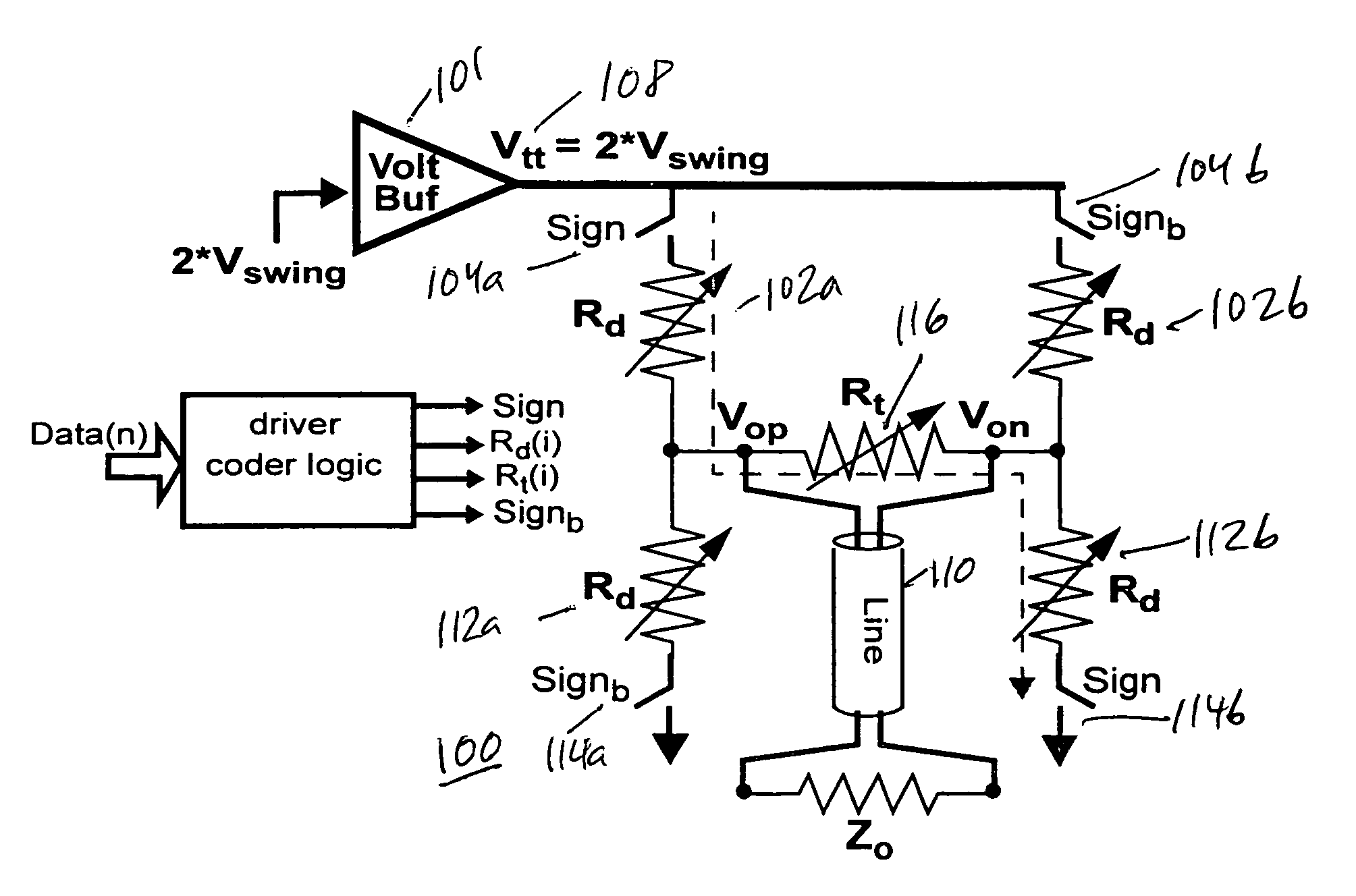
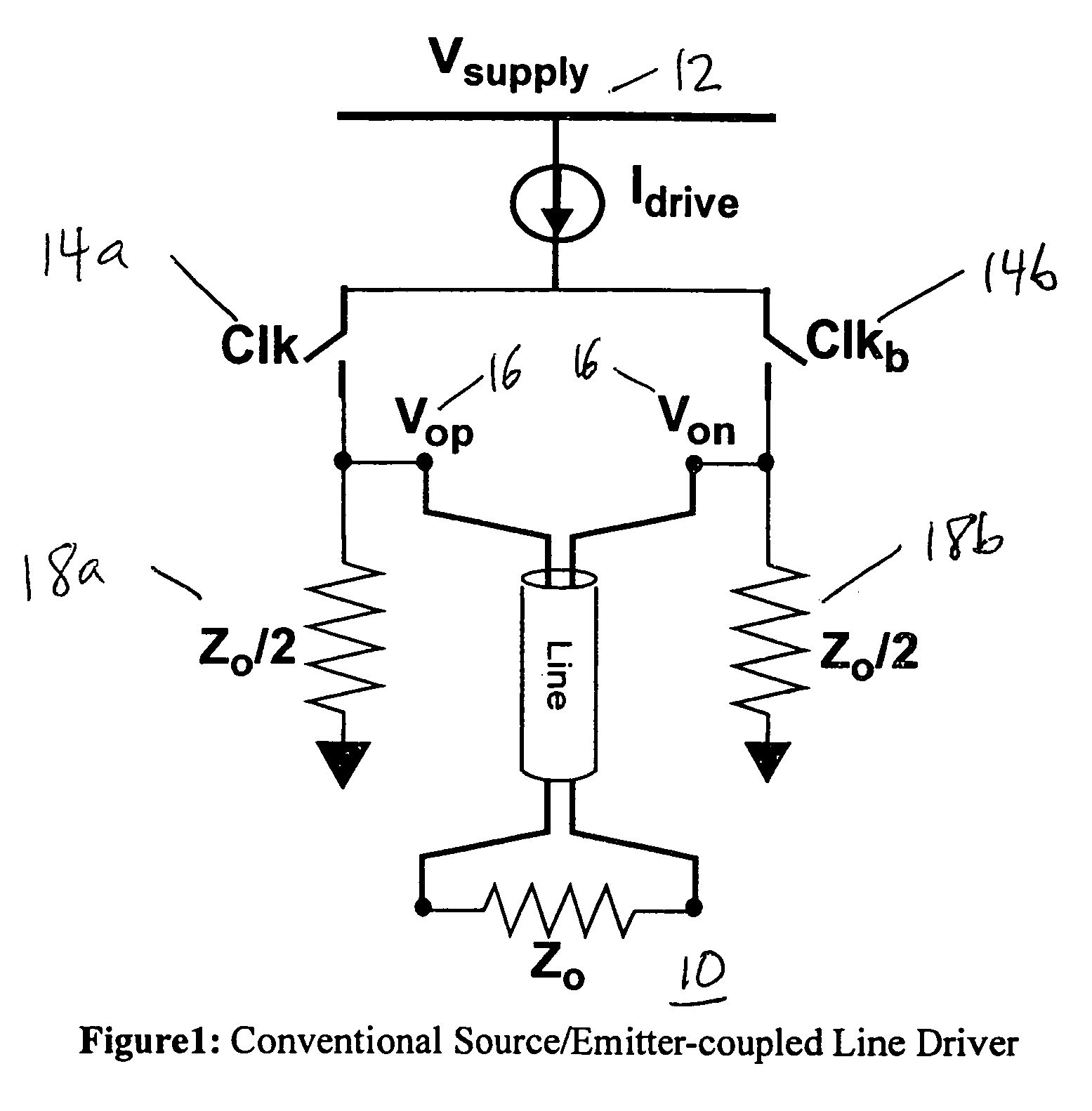
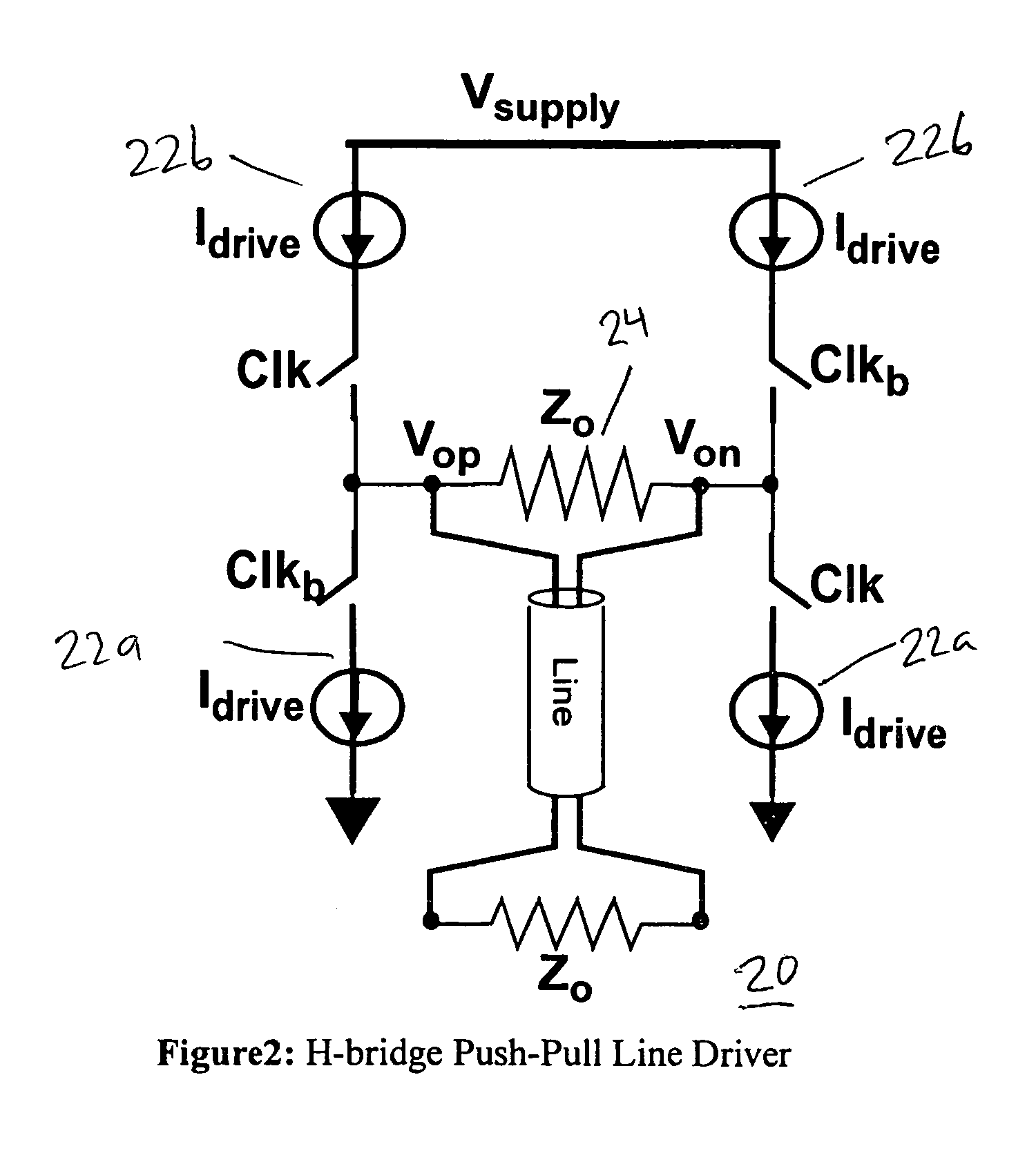
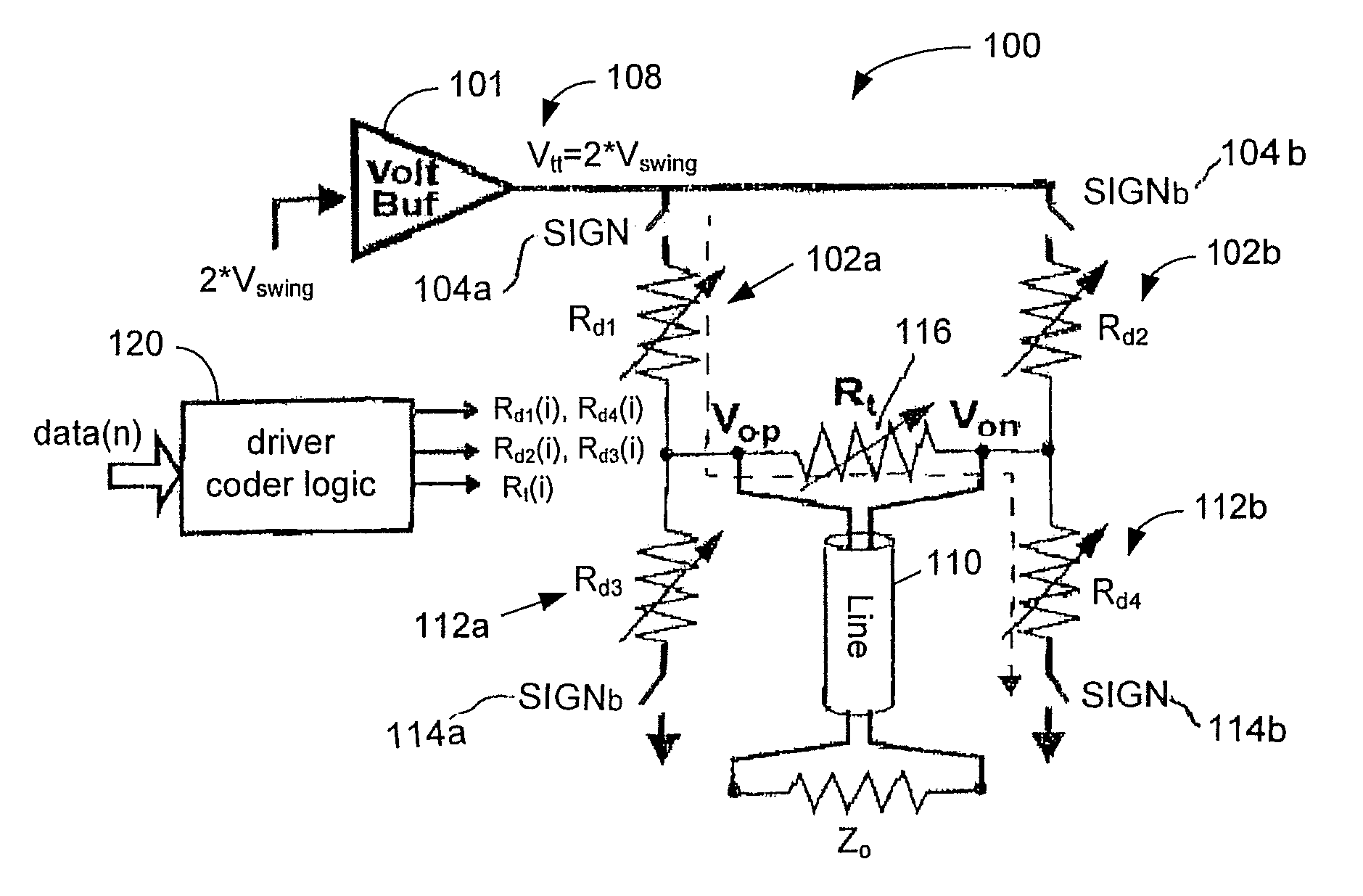
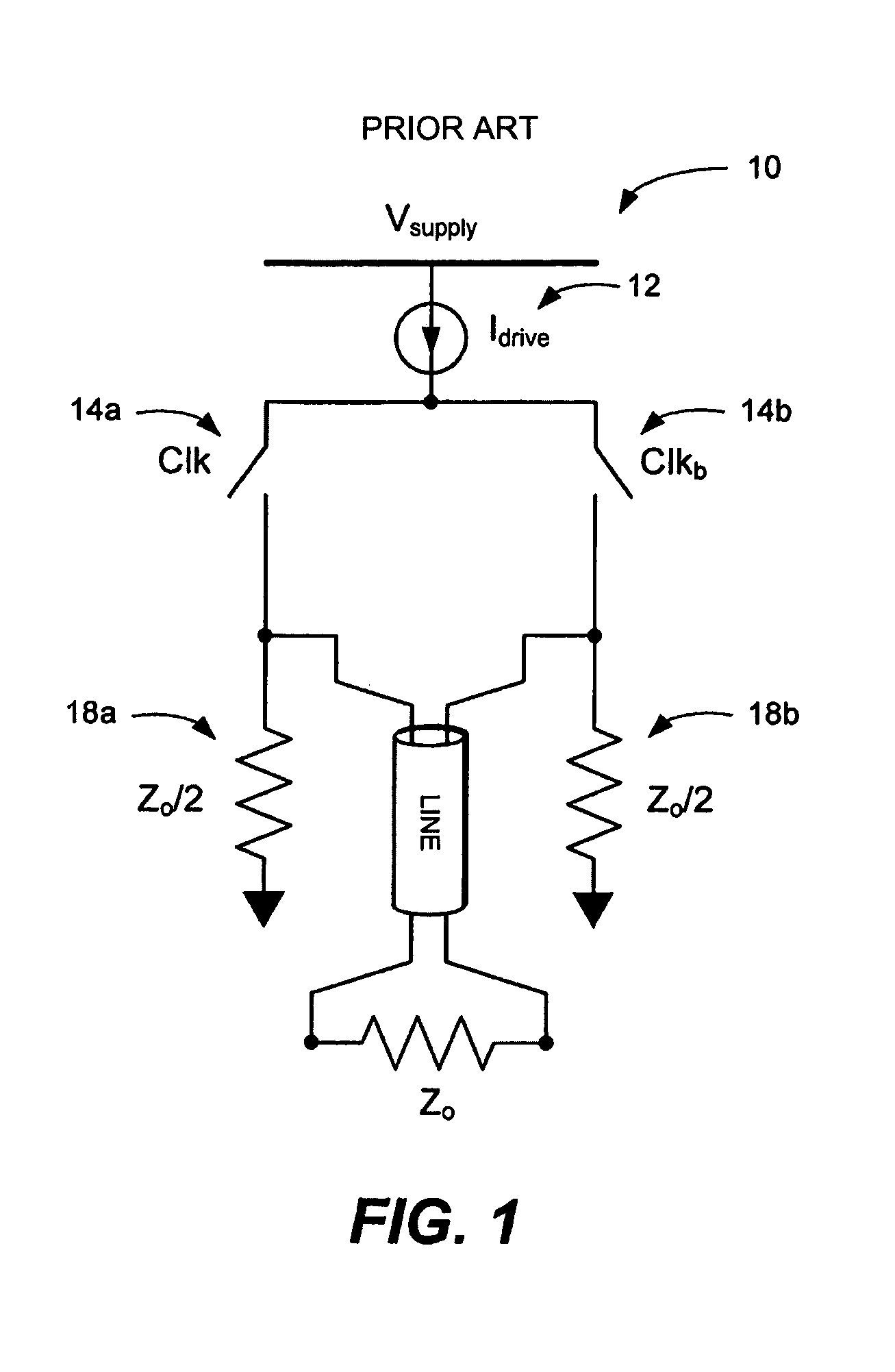
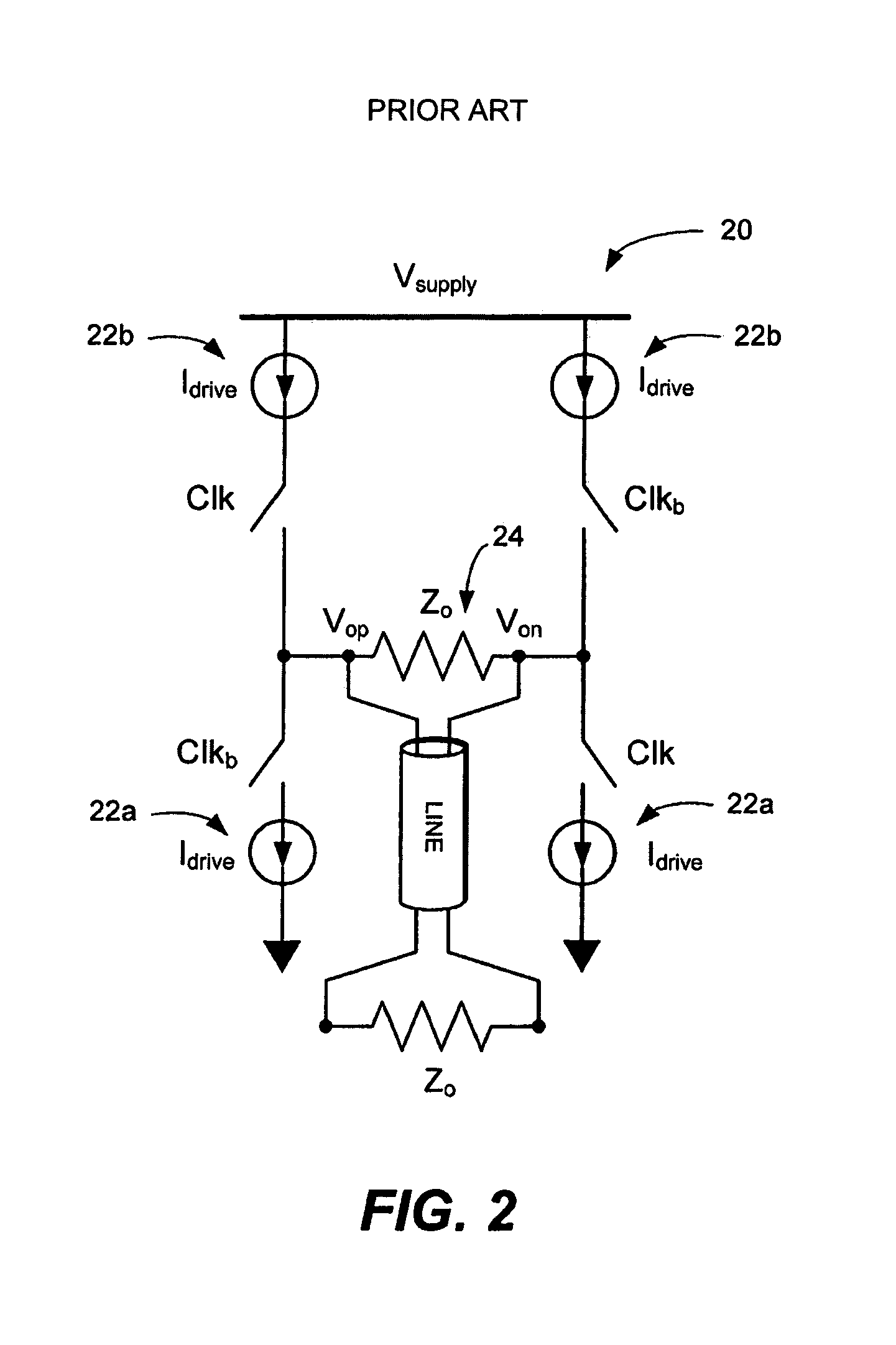
Low-power low-voltage multi-level variable-resistor line driver
InactiveUS7221196B2Improve power efficiencyElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorDigital dataReal variable
A low-power multi-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) line driver using variable resistors is disclosed for transmitting digital data over controlled-impedance transmission lines. This invention discloses the design of a multi-level PAM driver for high-speed wireline communication, with up to four times improvement in power efficiency over conventional drivers. Two key requirements for high-speed line drivers are first generating the target voltage level onto the controlled-impedance line, and second being impedance matched to the line itself to eliminate signal reflections from the transmitter back to the line. The driver in accordance with the present invention satisfies both of these requirements at very high power efficiency.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Design method for end part- and root-reinforced few-leaf variable-section steel plate springs
ActiveCN105673753AImprove transportation efficiencyImprove driving safetyLeaf springsDesign optimisation/simulationReal variableEngineering
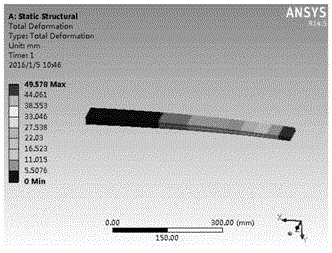
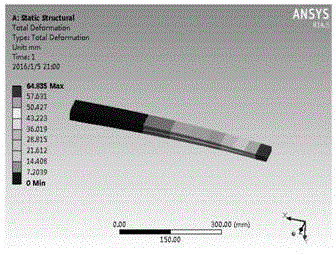
The invention relates to a design method for end part- and root-reinforced few-leaf variable-section steel plate springs, and belongs to the technical field of suspension steel plate springs. The design method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: determining the toot thickness he of an equivalent single leaf according to the structure of each steel plate spring, a design rigidity, the thickness ratio of oblique line segments on the root and the end parts, and the thickness ratio of primarily-selected parabolic segments, and determining the maximum allowable thickness [h2] of the root according to an allowable pressure at first; then designing the number N and the root thickness h2 of the few-leaf variable-section steel plate springs according to he and [h2]; and then designing the thicknesses and the lengths of straight segments on the end parts of each leaf separately according to the end part thickness beta he of the equivalent single leaf. Through ANSYS simulation and verification, the accurate parameter design values of the end part- and root-reinforced few-leaf variable-section steel plate springs can be obtained by virtue of the method, the design level and the performance of products are improved, the weights of the springs are reduced, and the running smoothness of vehicles are improved; and meanwhile, the design and test expenses are reduced, and the development speed of the products is increased.
Owner:山东恒日悬架弹簧股份有限公司
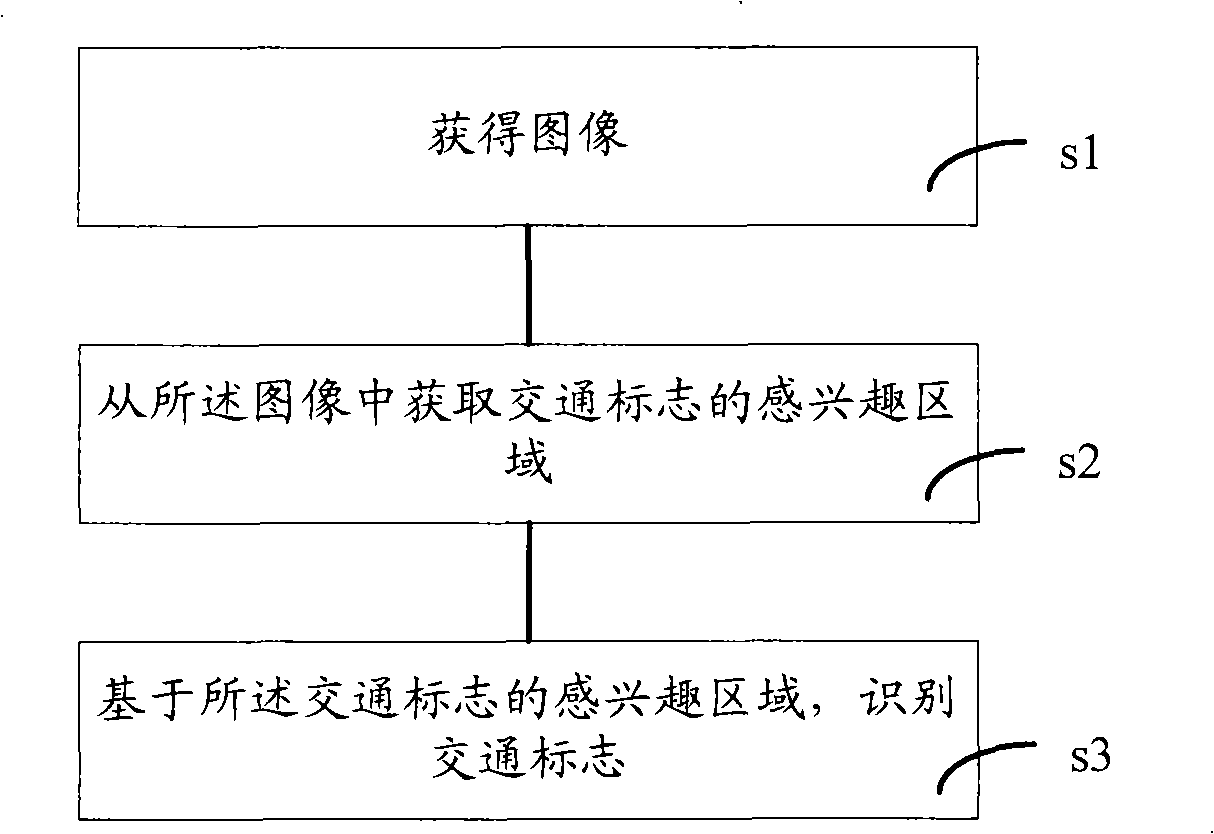
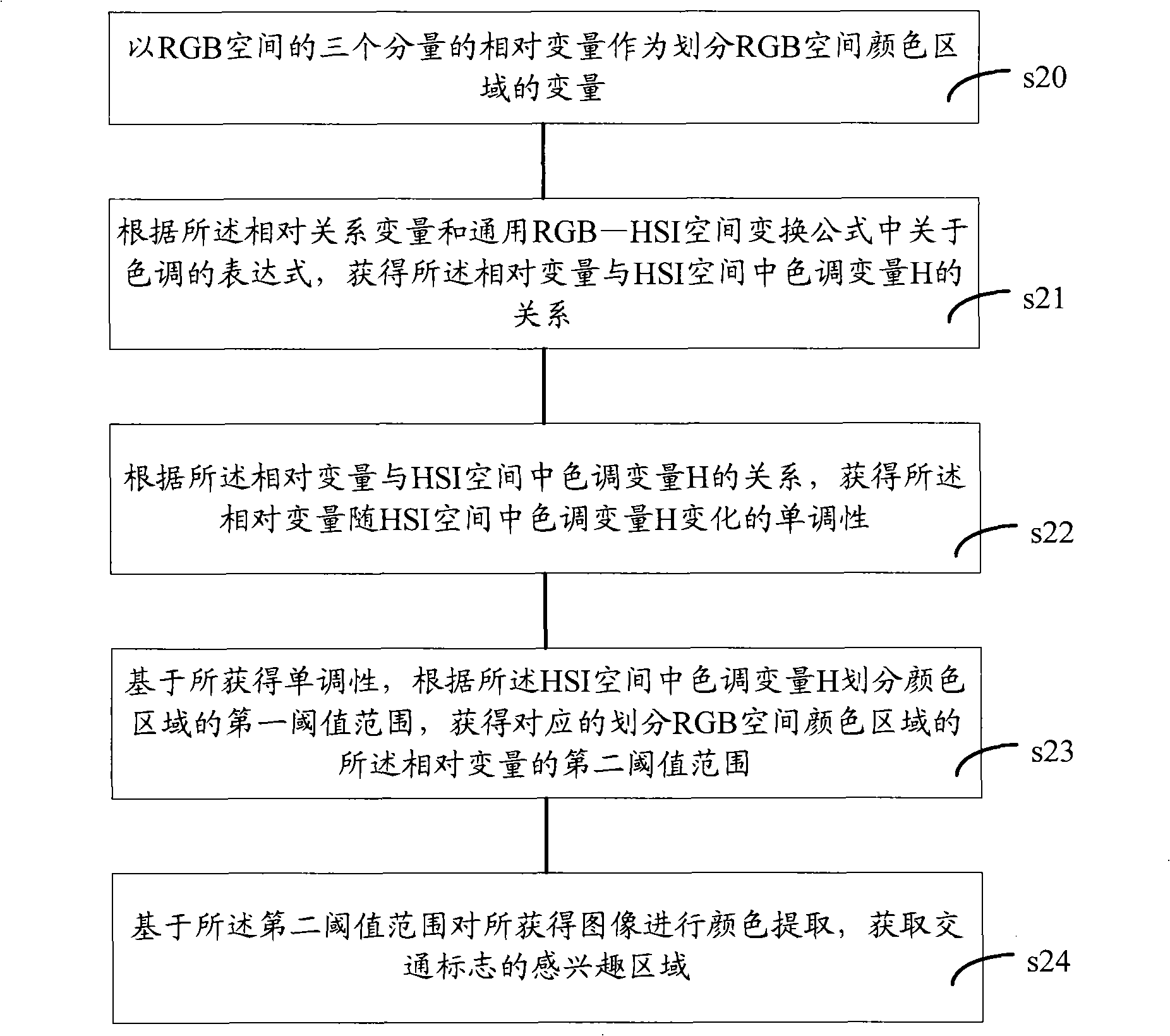
Traffic sign recognition method and device
ActiveCN101404117AImprove recognition efficiencyShorten the timeRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionReal variable
The invention relates to a traffic sign identification method and a device thereof. The traffic sign identification method adopts relative variables of three components in an RGB space as new variables for dividing a color region; the new relation of corresponding variables in the RGB and the HIS spaces is obtained by the variables and the expression of color tone in the transformation formula of the universal RGB-HIS spaces, and a first threshold value scope in the color region is divided according to a color tone variable H in the HSI space; and a second threshold value scope of the relative variables in the corresponding RGB space is obtained, thereby abstracting the color of an image to achieve to obtain the interested region of the traffic sign according to the value of the relative variables obtained from the image. The traffic sign identification method and the device thereof have good real time, as well as higher identification efficient and accuracy.
Owner:NEUSOFT REACH AUTOMOBILE TECH (SHENYANG) CO LTD
Control method of multi-machine-head variable-frequency centrifugal central air conditioning unit
ActiveCN104990211AImprove cooling effectCanon Efficiency StatusMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsReal variableMulti machine
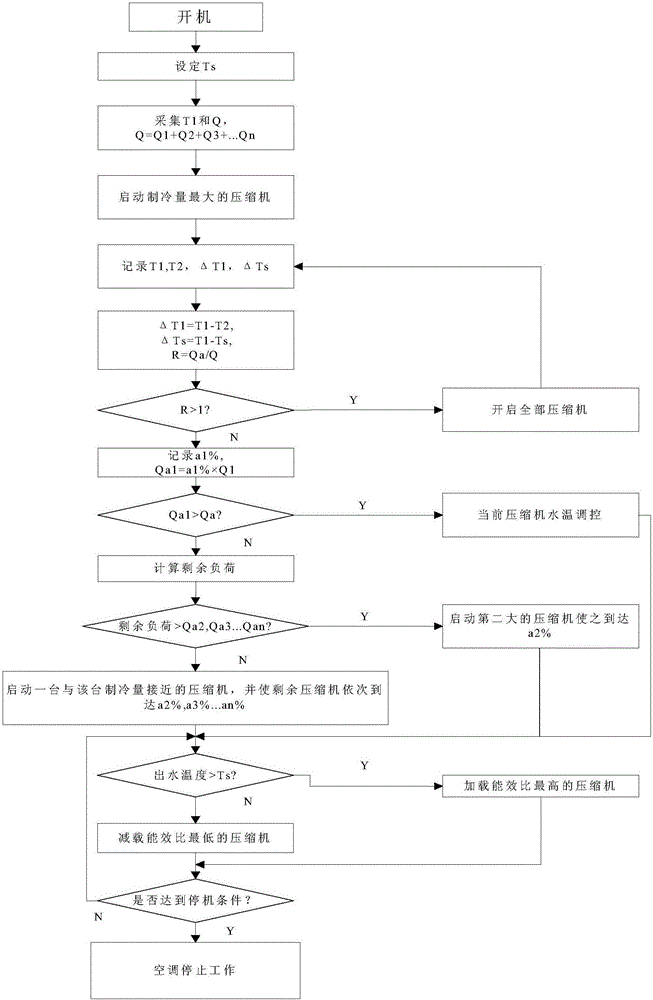
The invention relates to the field of air conditioners, in particular to a control method of a multi-machine-head variable-frequency centrifugal central air conditioning unit. The method includes the following steps that target temperature is set when freezing water flows out; refrigerating total amount is acquired; initial water inflow temperature is acquired; a compressor with the largest refrigerating amount in the central air conditioning unit is started, the difference between the initial water inflow temperature and current water inflow temperature is recorded, the difference between the initial water inflow temperature and the target temperature is recorded, and refrigerating demand amount of a whole system is made; remaining load is calculated, and when the remaining load is larger than the refrigerating amount of a remaining compressor in the optimal energy efficiency state, the second largest compressor is started so that the compressor can run in the optimal energy efficiency; when the remaining load is smaller than the refrigerating amount of the remaining compressor in the optimal energy efficiency state, a compressor with the refrigerating amount close to that of the remaining compressor is started, so that the remaining compressor achieves the optimal energy efficiency state sequentially; water outflow temperature of the freezing water is detected and compared with the target temperature; whether the air conditioner meets the machine stop condition is judged.
Owner:青岛北冰洋冷暖能源科技有限公司
Manufacturing method of thin-wall variable-curvature hollow blade
InactiveCN102029390AUniform wall thicknessMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusReal variableMaterials science
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a thin-wall variable-curvature hollow blade. The method is characterized by being a method for manufacturing the thin-wall variable-curvature hollow blade according to a profile curvature radius and layer number adjusting laser power. The rule of the influence of profile curvature radius change of the blade on a molten pool temperature field is found so as to find a molten pool temperature field distribution rule corresponding to different curvature radiuses. A method for stabilizing the temperature of a molten pool by changing laser power is provided so as to obtain the rule of the change of laser power along with the curvature radius. The change rule is combined with power change along with layer number and laser power on any layer and any curvature are found, so that a thin-wall blade sample with uniform wall thickness can be molded according to the change rule at a stable molten pool temperature.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Multi-scale variable-step autofocusing searching algorithm data transmission device and method
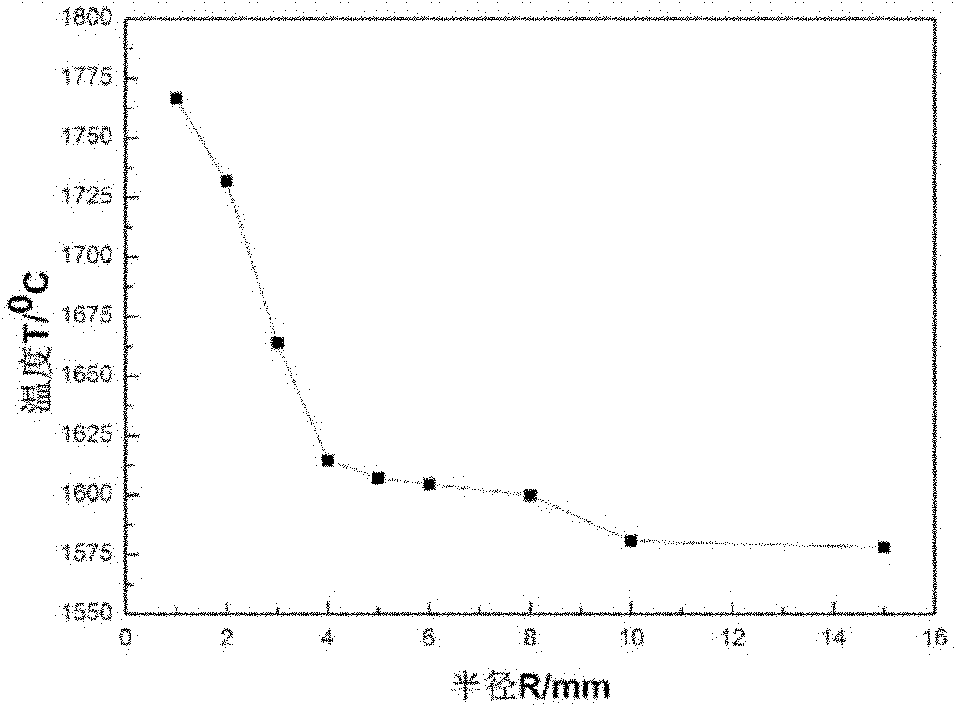
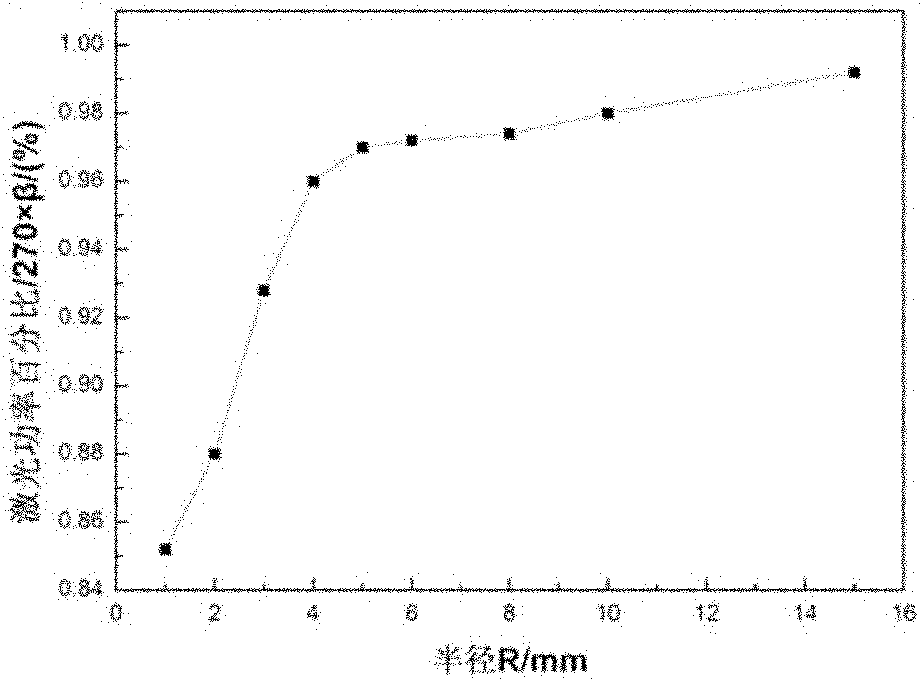
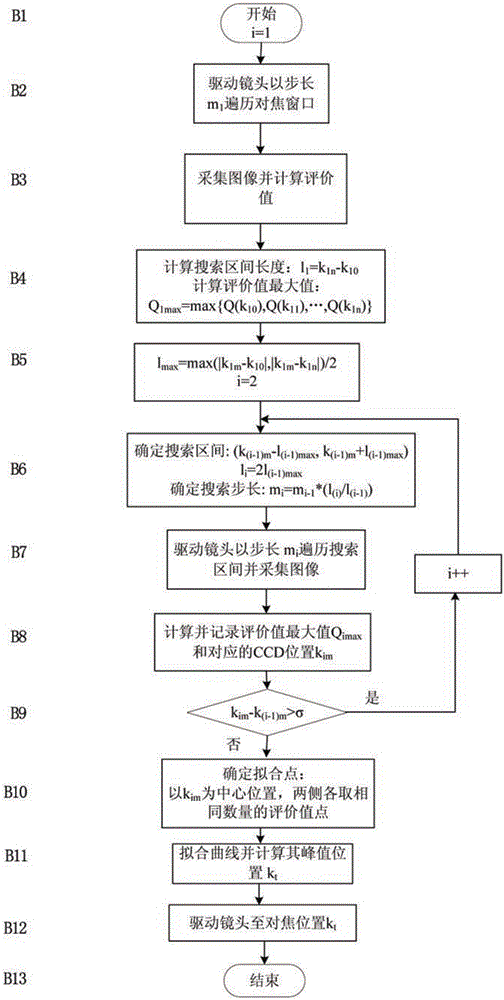
InactiveCN105578029AGet rid of distractionsFocusTelevision system detailsColor television detailsReal variableCurve fitting
The invention discloses a multi-scale variable-step autofocusing searching method. Searching range and searching step length are gradually reduced through multiple times of searching, and the peak of a curve is determined through curve fitting rather than the maximum value of a sharpness evaluation value so that the searched focusing position is enabled to be close to the real focusing point as far as possible; two successive times of searching positions are compared by adopting threshold setting, and completion of searching steps is determined; and the searching position of the maximum value of the evaluation value of each time of searching acts as the center point of the next searching interval to take symmetric intervals for searching in the process of multi-scale searching so that real focusing point is ensured to be included in the interval. According to the method, interference of the local peak value can be effectively eliminated, and optimal searching can be realized, focusing efficiency is high and focusing is accurate.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
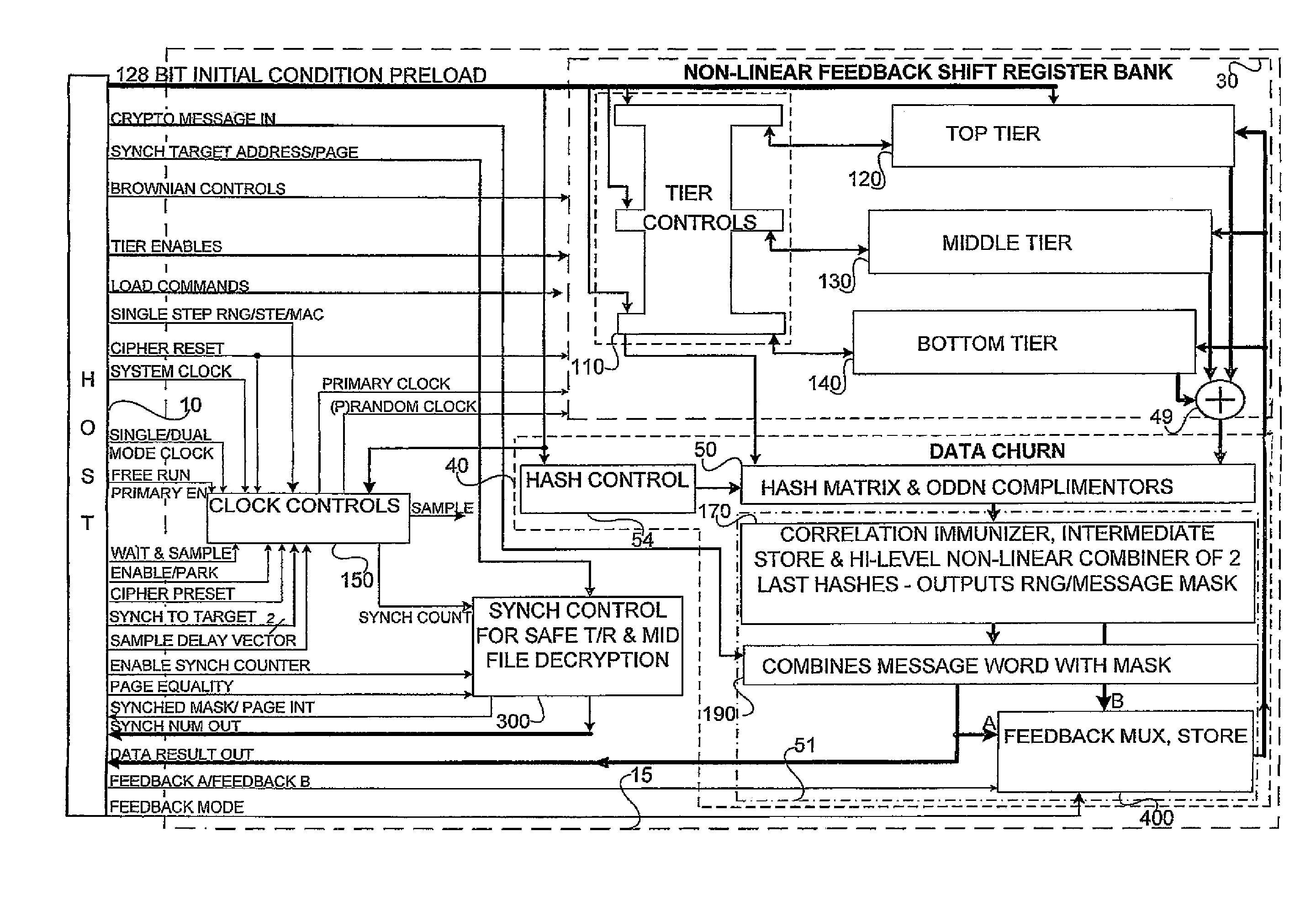
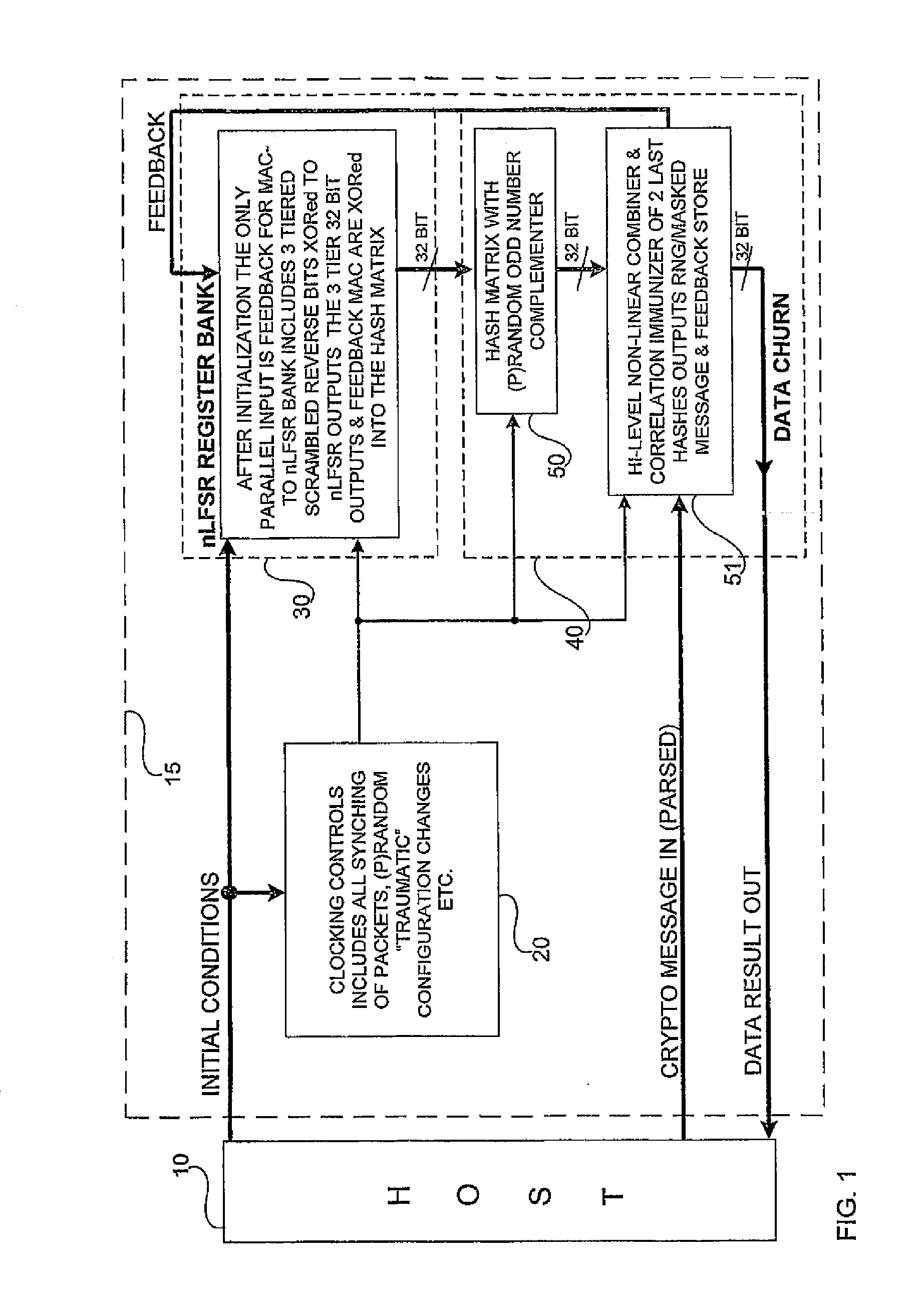
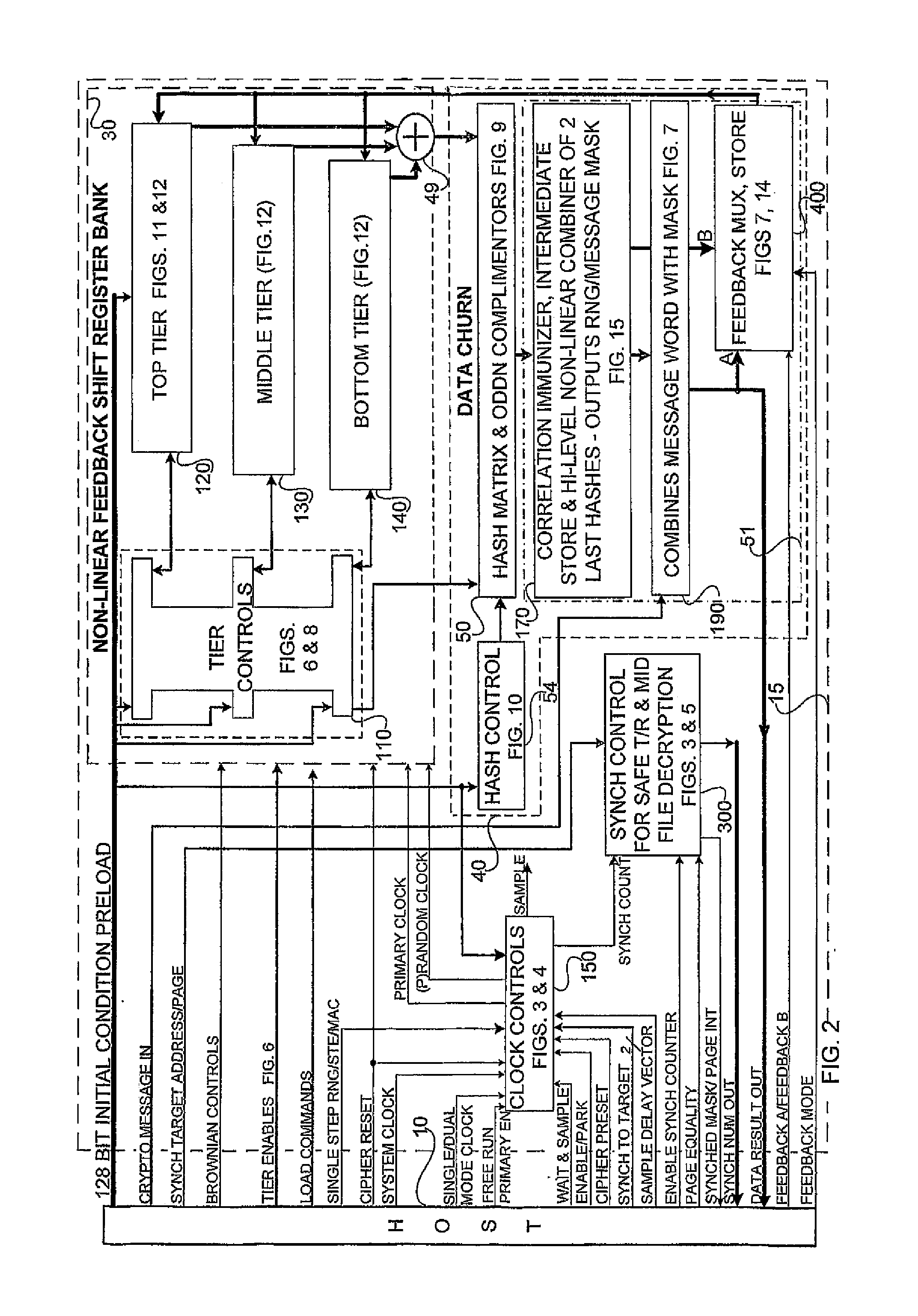
Accelerated throughput synchronized word stream cipher, message authenticator and zero-knowledge output random number generator
ActiveUS7827223B2Small loss of entropyNecessary numberSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesRandom number generatorsComputer hardwareFrame sequence
Systems and methods are disclosed, especially designed for very compact hardware implementations, to generate random number strings with a high level of entropy at maximum speed. For immediate deployment of software implementations, certain permutations have been introduced to maintain the same level of unpredictability which is more amenable to hi-level software programming, with a small time loss on hardware execution; typically when hardware devices communicate with software implementations. Particular attention has been paid to maintain maximum correlation immunity, and to maximize non-linearity of the output sequence. Good stream ciphers are based on random generators which have a large number of secured internal binary variables, which lead to the page synchronized stream ciphering. The method for parsed page synchronization which is presented is especially valuable for Internet applications, where occasionally frame sequences are often mixed. The large number of internal variables with fast diffusion of individual bits wherein the masked message is fed back into the machine variables is potentially ideal for message authentication procedures.
Owner:FORTRESS GB
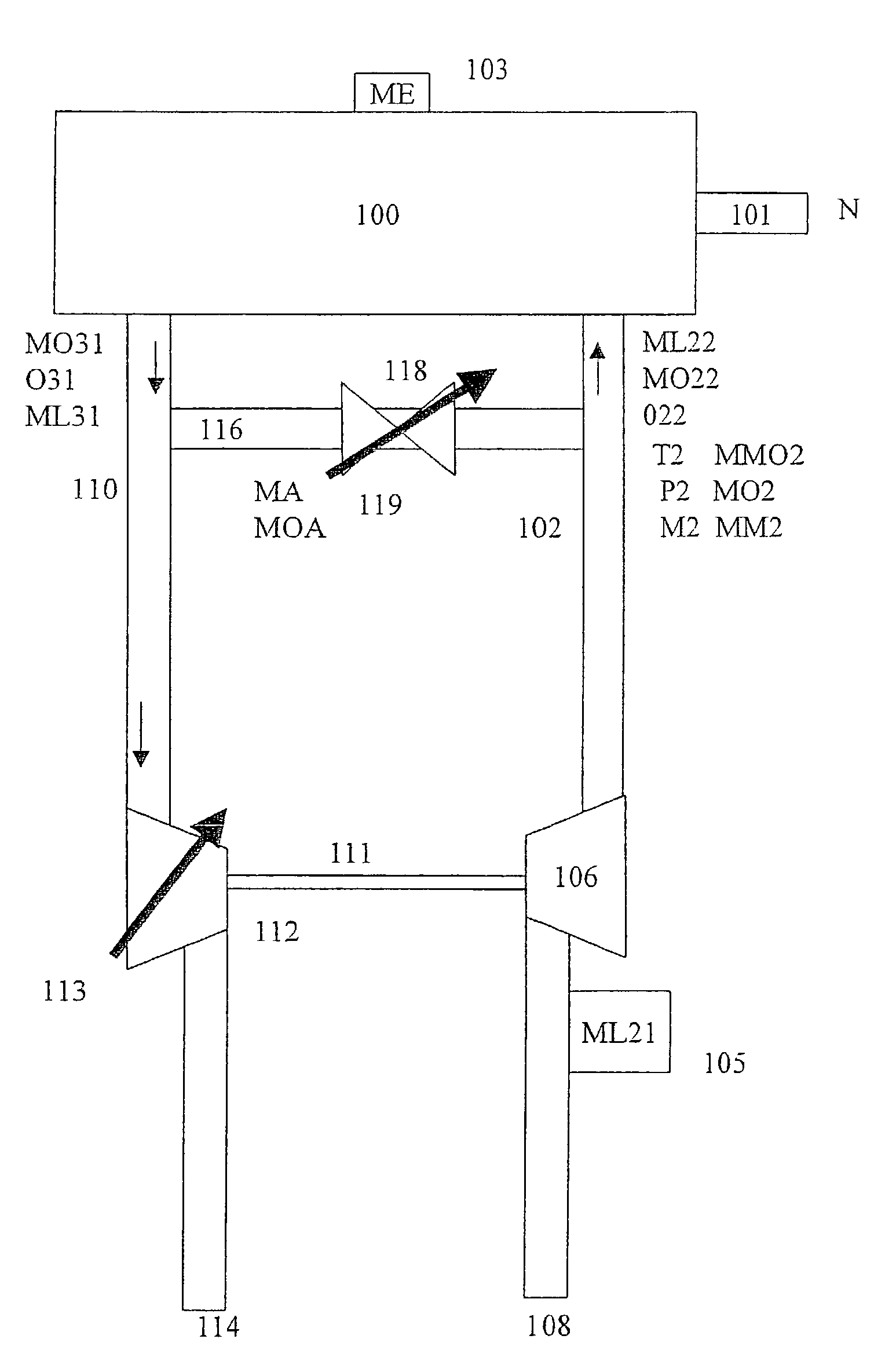
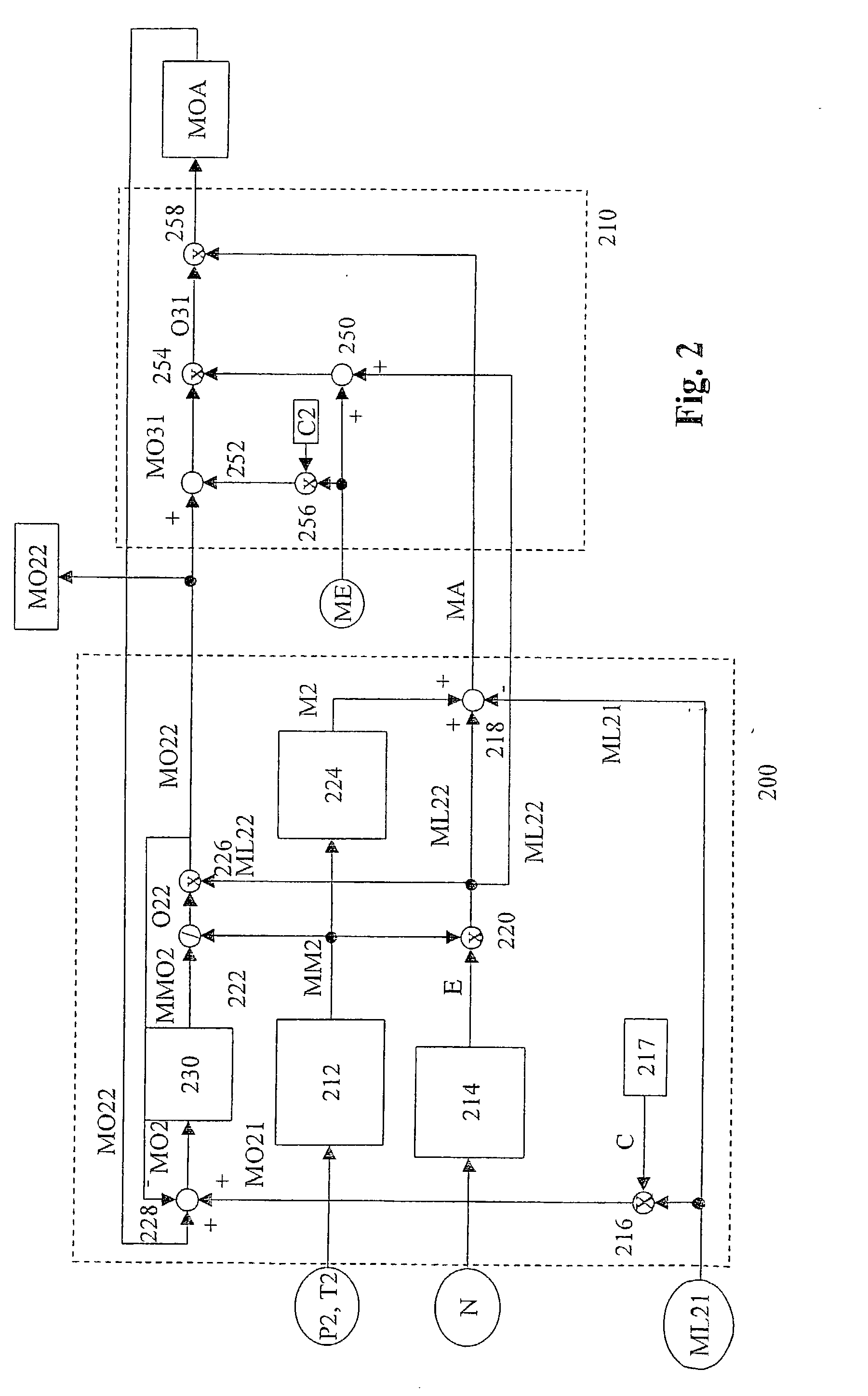
Method and device for controlling an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20020179060A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlReal variableExternal combustion engine
A method and a device are described for controlling an internal combustion engine. Using at least one model, an oxygen quantity (MO22) flowing into the internal combustion engine is determined on the basis of at least one manipulated variable and at least one measured variable which characterizes the condition of the air in an intake manifold. The oxygen quantity (MO22) is determined on the basis of at least one temperature variable (T2), one pressure variable (P2), one speed variable (N), one fuel-quantity variable (ME) and one air variable (ML21).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
System integration device and system integration method for test parameters based on unit combination
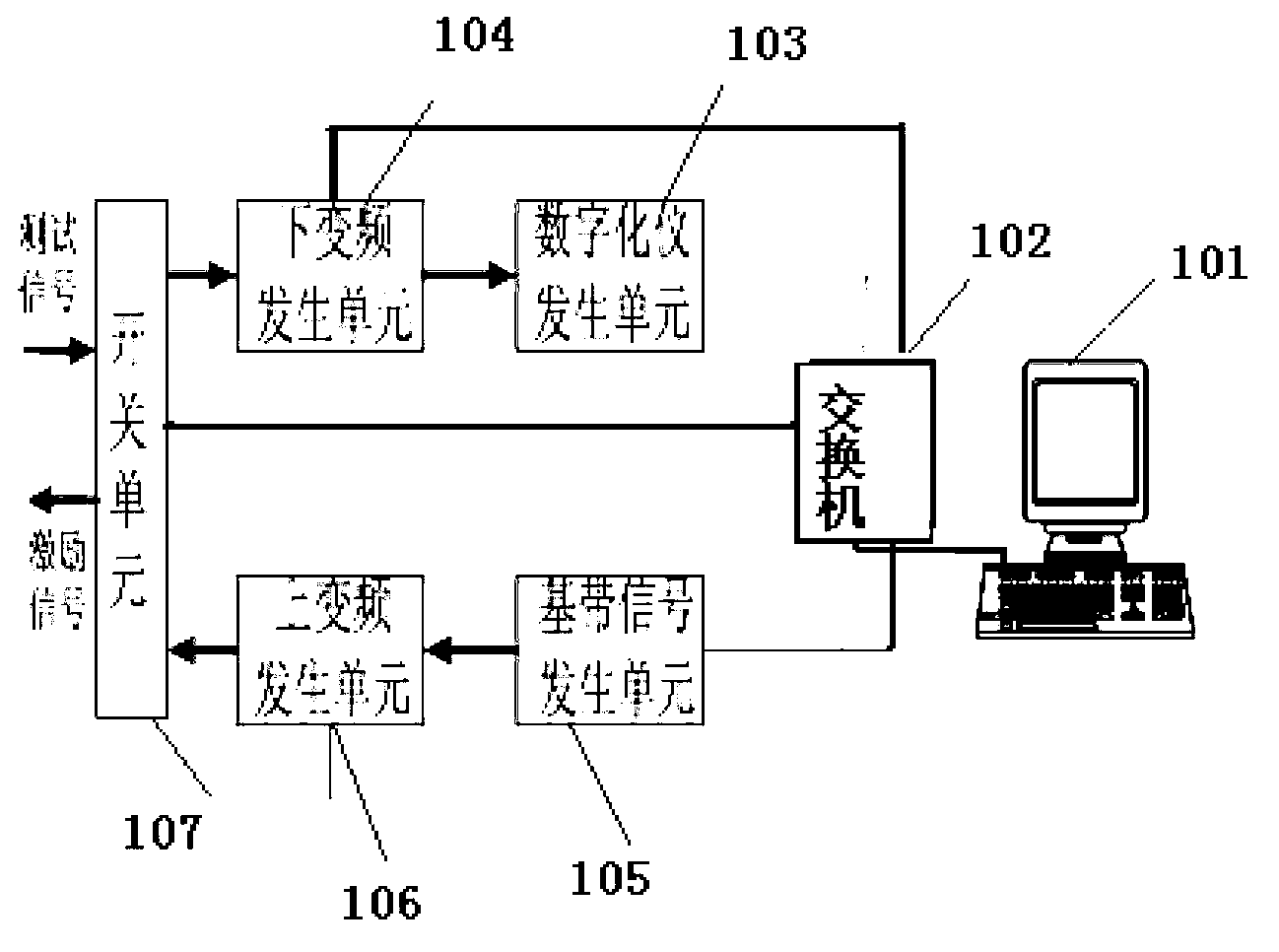
InactiveCN103248444AEasy to buildImprove performancePropogation channels monitoringReal variableInstrument function
The invention relates to a system integration device and a system integration method of test parameters based on the unit combination. The device comprises a main control computer and an exchange board, and also comprises a switch unit, a lower variable-frequency generation unit, a digitalized instrument generation unit, a base band signal generation unit and an upper variable-frequency generation unit, which are connected and communicated with one another; the lower variable-frequency generation unit is matched with the digitalized instrument generation unit and used for receiving and testing a test signal; and the base band signal generation unit is matched with the upper variable-frequency generation unit and used for generating and transmitting an excitation signal. By adopting the scheme, a test system with high performance and low cost is easy to establish, and different instrument functions can be realized by maximally utilizing fewest standard universal units.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
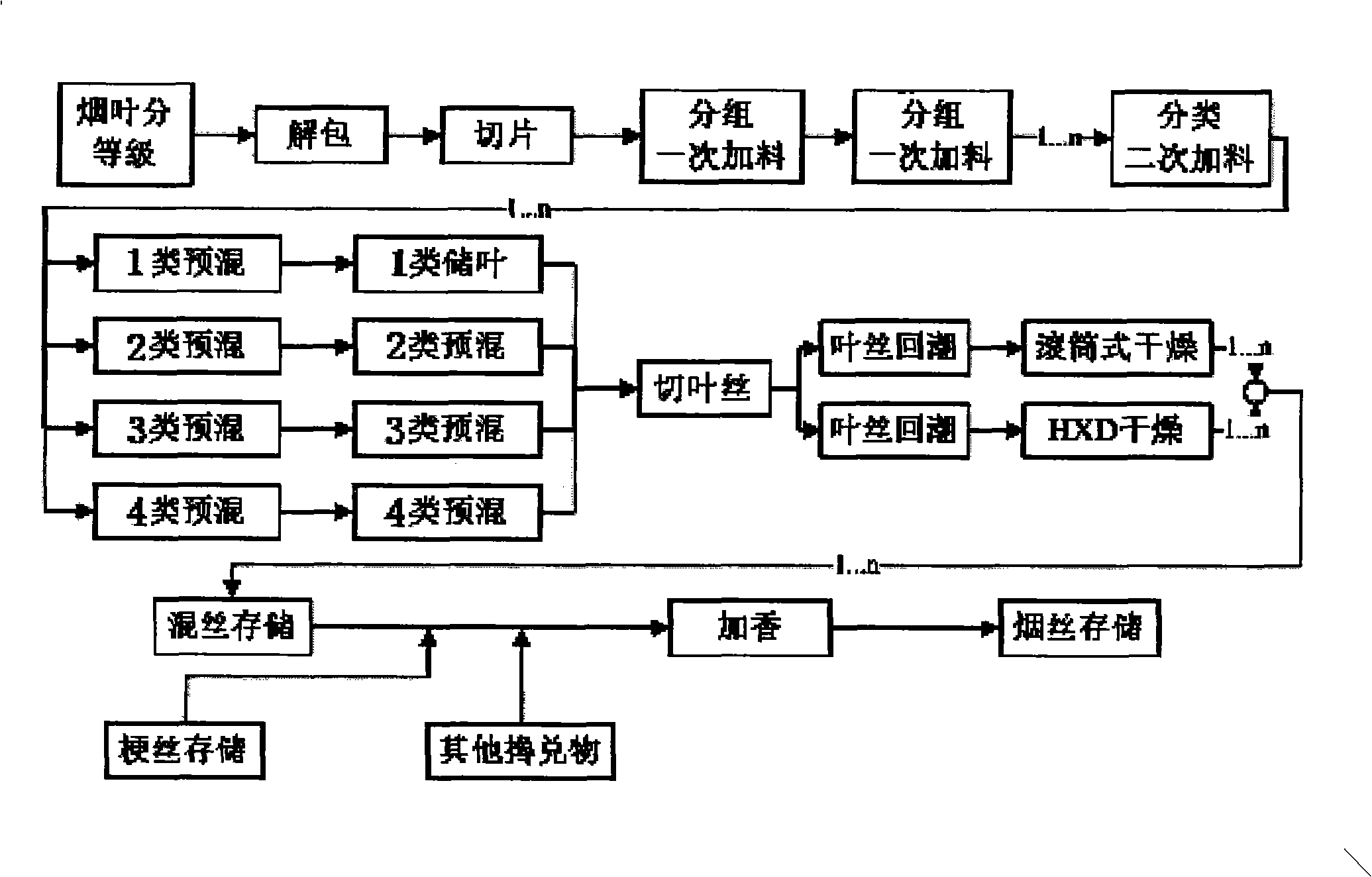
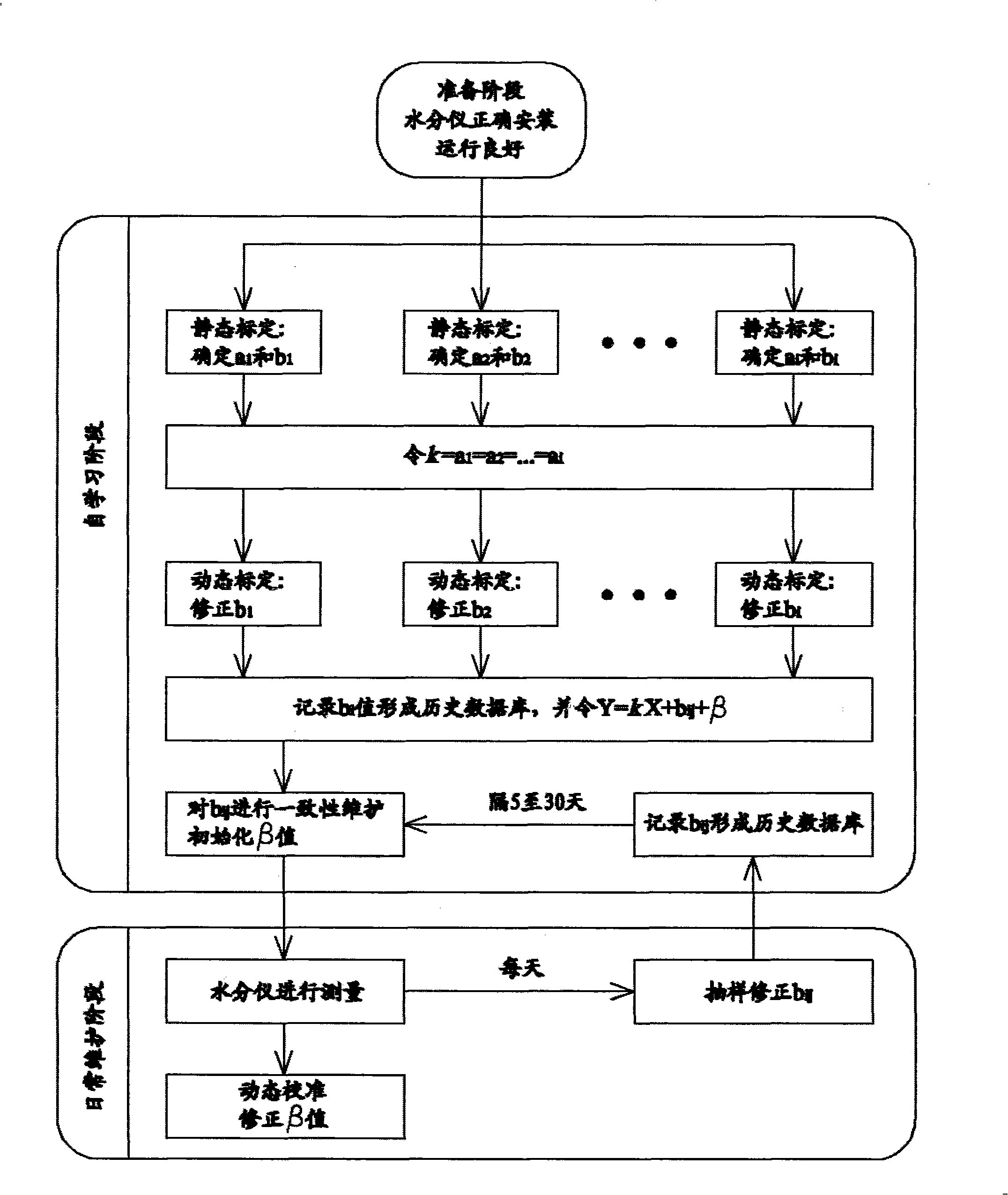
Calibration method for moisture instrument
ActiveCN101344471ARealize real-time calibrationSmall amount of sampleWeighing by removing componentReal variableCalibration curve
The invention relates to the field of calibration methods of measuring equipment, aims at solving the technique problem and overcoming the disadvantage that existing water content calibrating methods are not applicable in the processing technic of cigarette grouping, and provides a method that can quickly and accurately calibrate water content gauges in the working process. The improved calibration method of the invention adds a Beta variable, and consequently builds the connection between mutually independent calibration curves, can finish the revision of all curves in daily dynamic calibration only by adjusting the Beta variable, greatly lowers the sample amount in the sampling, raises calibration efficiency and precision and realizes the real-time calibration of linear water content gauges in the processing technic of grouping.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
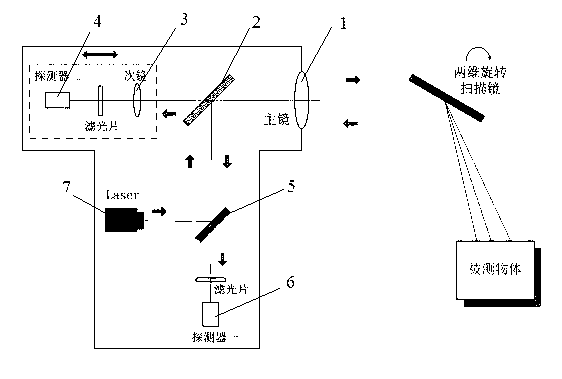
Wide-field-of-view and large-depth-of-field variable-resolution non-scanning streak tube laser imaging system
InactiveCN107422336AIncrease vertical rangeSolve the problem of laser imaging with large depth of fieldElectromagnetic wave reradiationVariable resolutionDistance detection
The invention relates to a wide-field-of-view and large-depth-of-field variable-resolution non-scanning streak tube laser imaging system, and belongs to the technical field of photoelectric imaging. The system mainly comprises a pulse laser, transmitting and receiving optical systems, a reflecting mirror, a micro-lens array, an optical fiber image bundle, streak tubes I / II, CCD cameras I / II and a control and processing system. The basic principle is that the pulse laser emits laser pulses, the laser irradiates to a target object through the transmitting optical system and the reflecting mirror, and the reflected laser is received by the receiving optical system and forms an image on the micro-lens array. The image plane is non-uniformly sampled by the micro-lens array and the optical fiber image bundle and then coupled to the photoelectric cathodes of the two streak tubes, the two CCD cameras acquire the streak image on two fluorescent screens and transmit the streak image to the control and processing system, and finally the intensity image and the distance image of the target can be obtained through the algorithm. The contradiction among the high spatial resolution, long distance detection, wide field of view and large depth of field of the non-scanning streak tube laser imaging radar can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
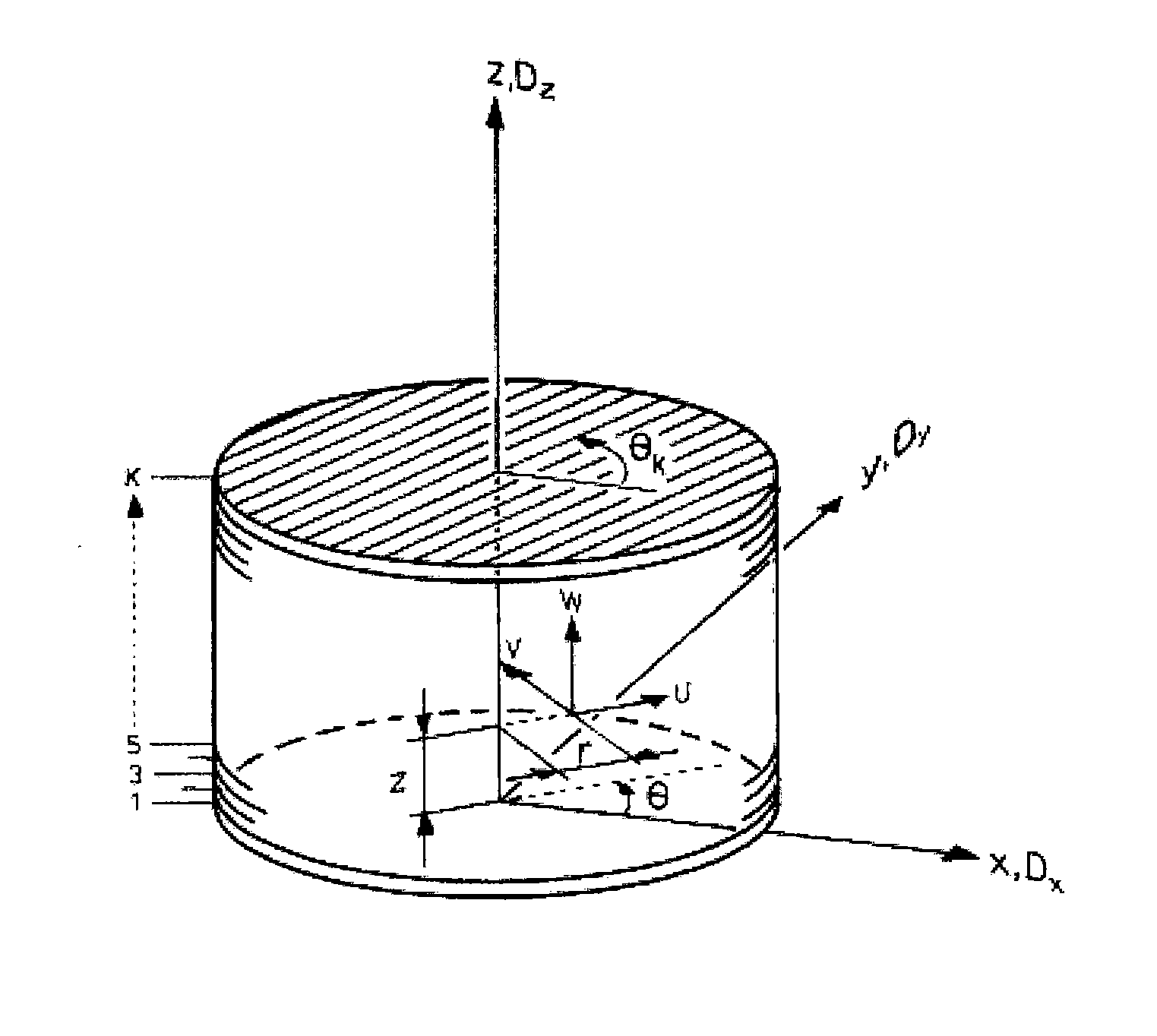
Borehole seismic inversion in anisotropic formation
ActiveUS20100211365A1Improve computing efficiencyEasy to analyzeComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingWave equationComputational model
A method of simulating a borehole acoustic response in an anisotropic formation of the crust of the earth, the method comprising: formulating a geometric model of the formation, the geometric model comprising a plurality of layers definable in a cylindrical coordinate system defined by an axial direction normal to each of the layers, a radial direction relative to the axial direction, and a circumferential direction relative to the axial direction; formulating a computational model of wave propagation in the formation, the computational model comprising one or more field variables and a wave equation describing a behaviour of the one or more field variables, wherein the one or more field variables are represented as respective Fourier series expansions of π-periodic harmonics in the circumferential direction, and numerically solving the computational model.
Owner:TOTAL E&P DANMARK AS
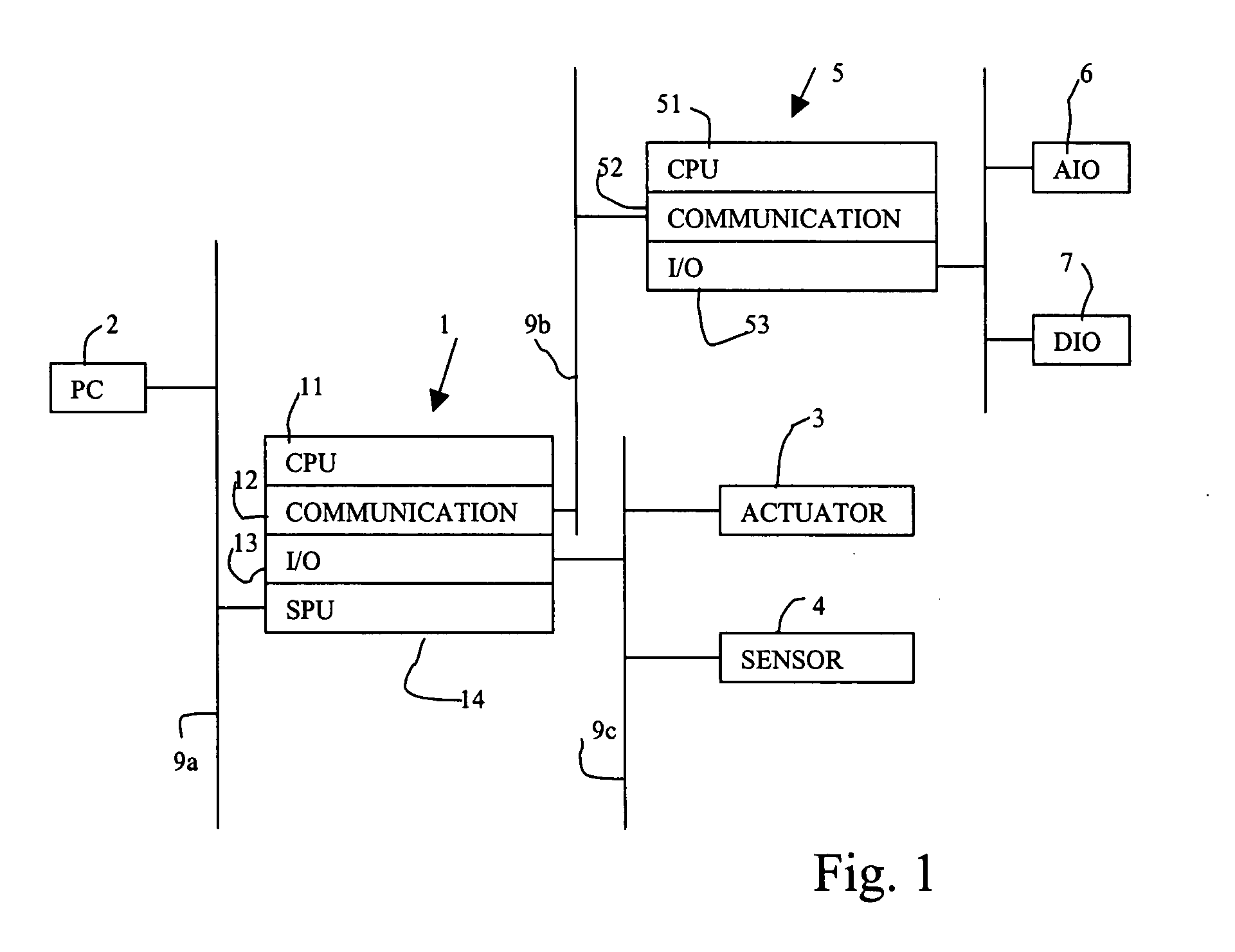
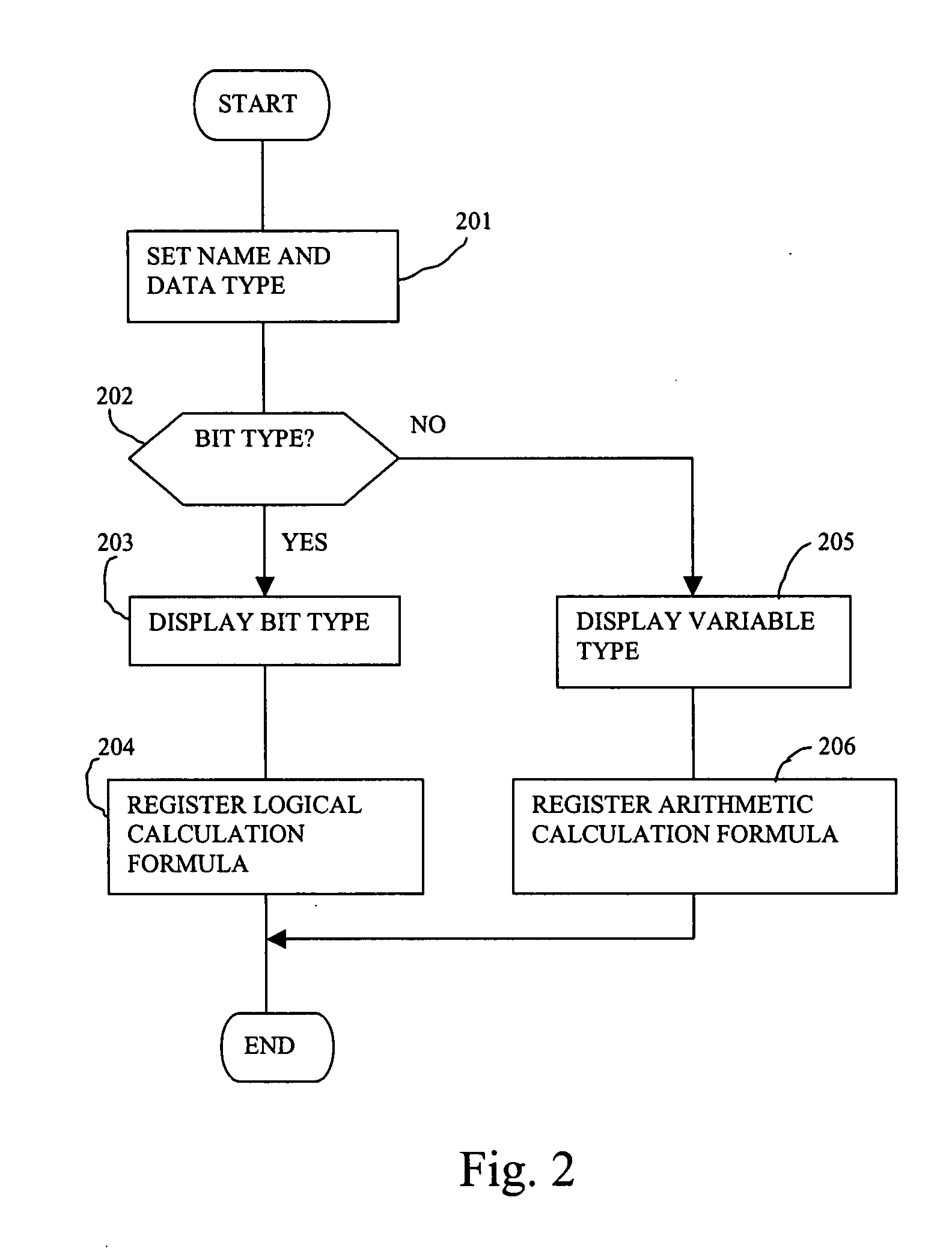
Configuring Variables
ActiveUS20090070736A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsReal variable
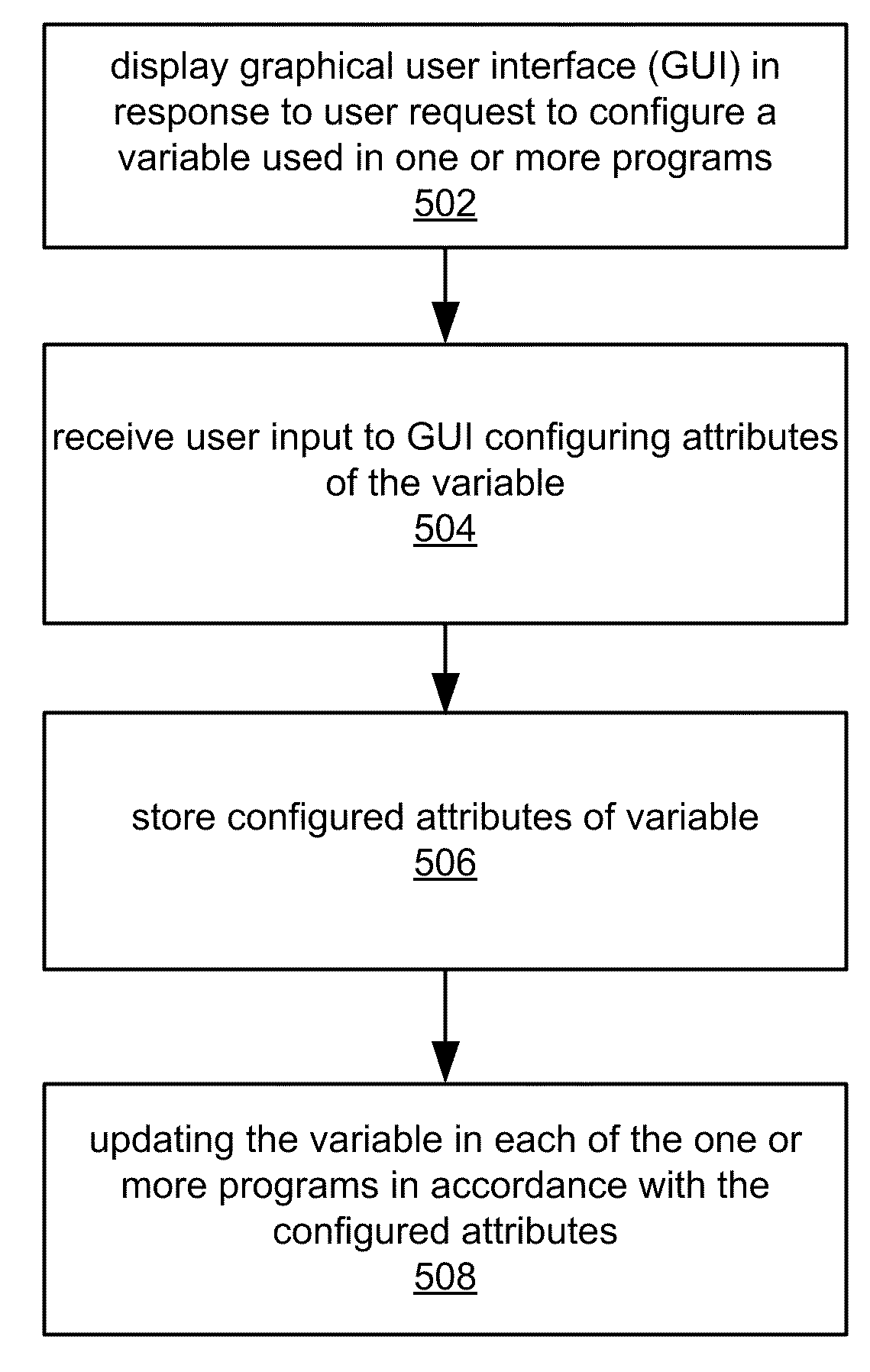
System and method for creating, configuring, representing, and using variables in programs. A graphical user interface (GUI) may be displayed in response to user input requesting creation and / or configuration of a variable for use in or comprised in one or more programs, e.g., on various devices. User input is received to the GUI configuring attributes of the variable, including: name, data type, and / or scope (e.g., local, global, or network). The configured attributes are stored and optionally displayed, e.g., in a resource tree, and the variable in each of the programs updated in accordance with the configured attributes. When at least one of the programs is incompatible with the configured variable, an error condition may be indicated, e.g., by providing information relating to portions of the program that are incompatible with the configured variable. The program may be modified in response to user input for compatibility with the configured variable.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
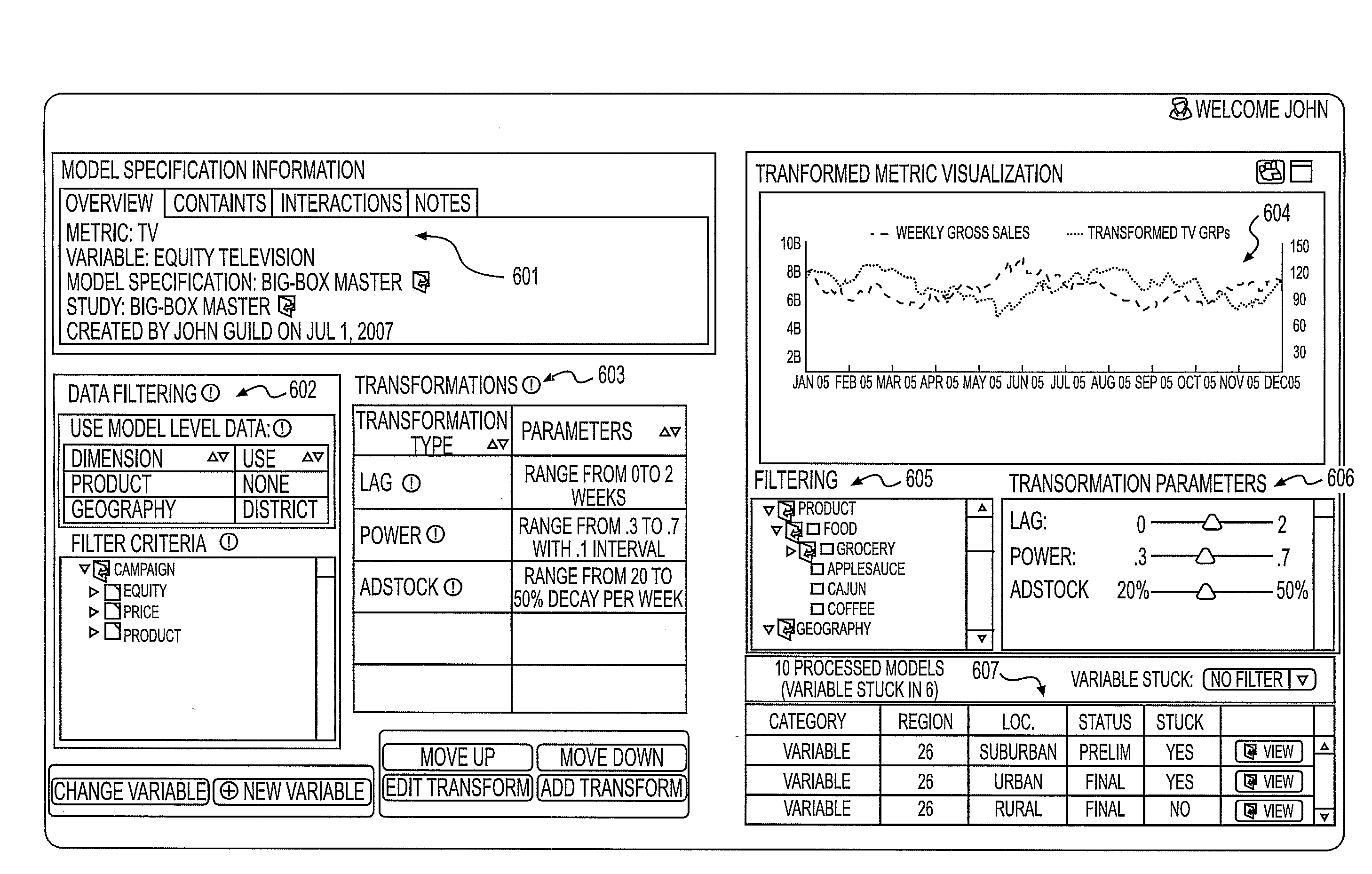
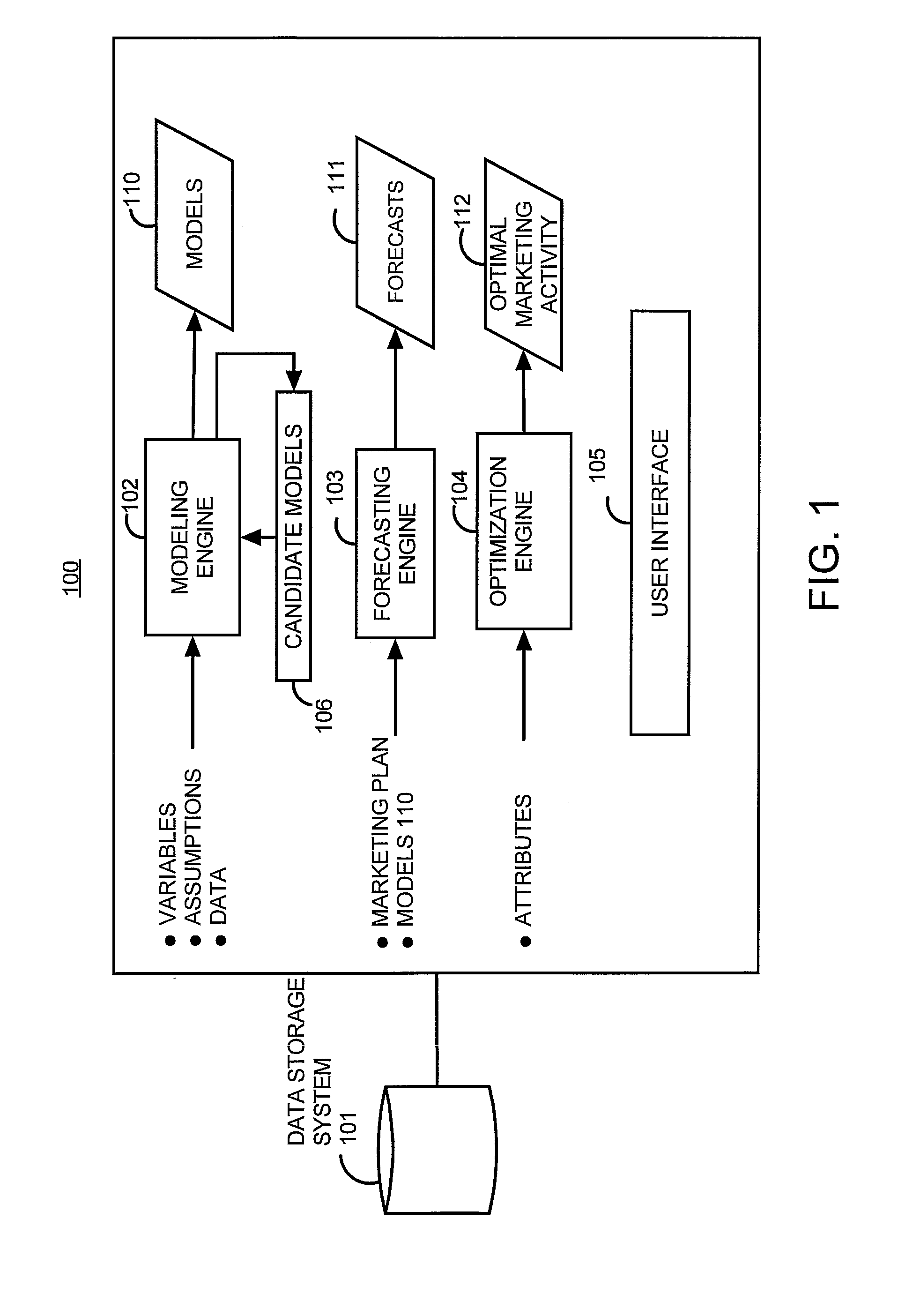
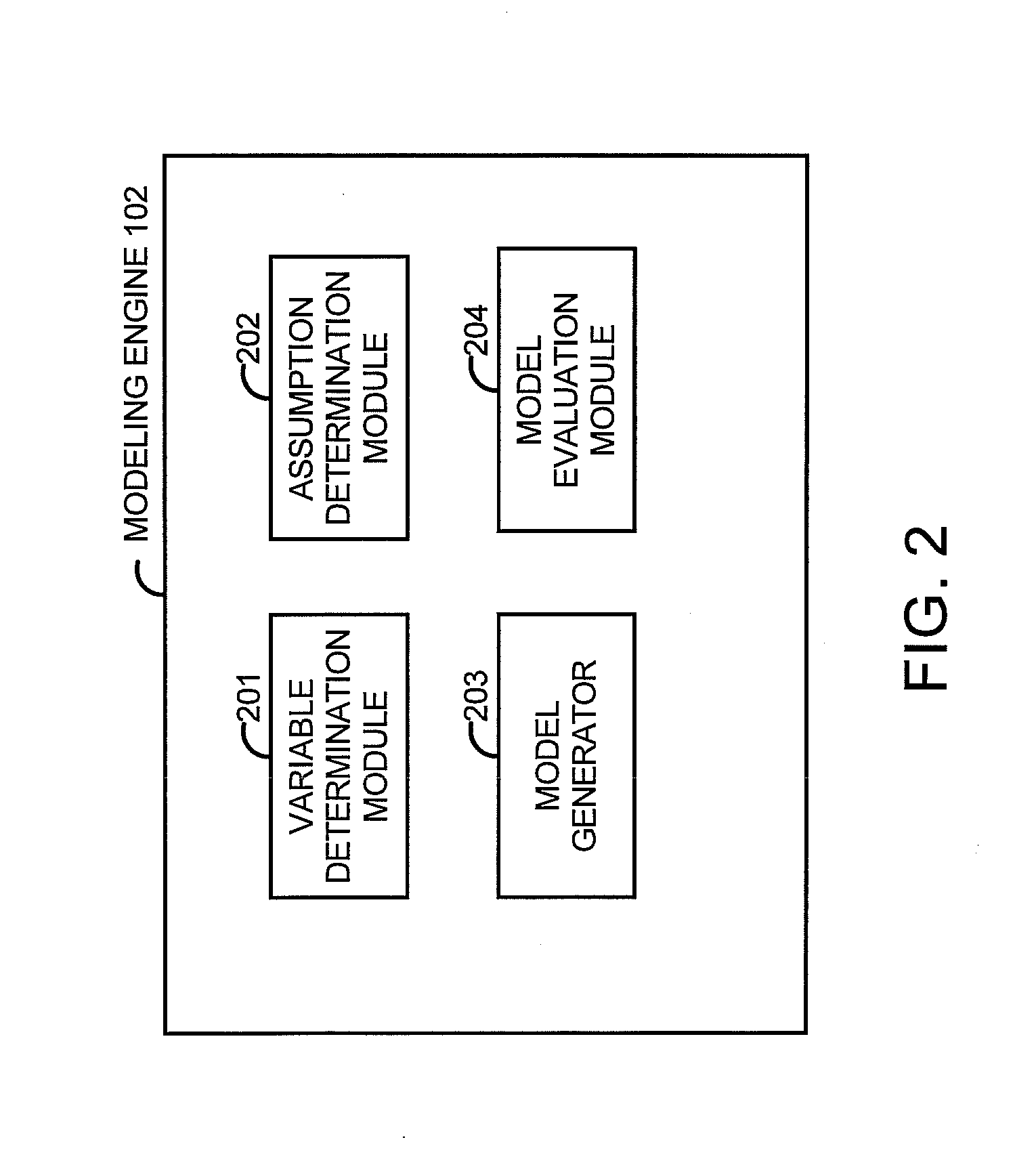
Marketing model determination system
A system includes a variable determination module determining a variable operable to be used for the final model and also determining a modification to the at least one variable. An assumption determination module determines an assumption operable to be used for the final model. The assumption includes a transformation for the variable describing how the variable impacts the marketing objective or how the variable impacts another variable operable to be used in the final model. The assumption module also determines a modification to the assumption. A model generator generates a candidate model using the variable and the assumption, and generates a new candidate model using the modified assumption, the new variable or the modification to the variable. The candidate model or the new candidate model is operable to be selected as the final model based on at least one of a statistical measure and an indication of relevance for the variable in the candidate model and the new candidate model.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Detection and predetermination calculational method for rapid variation light power
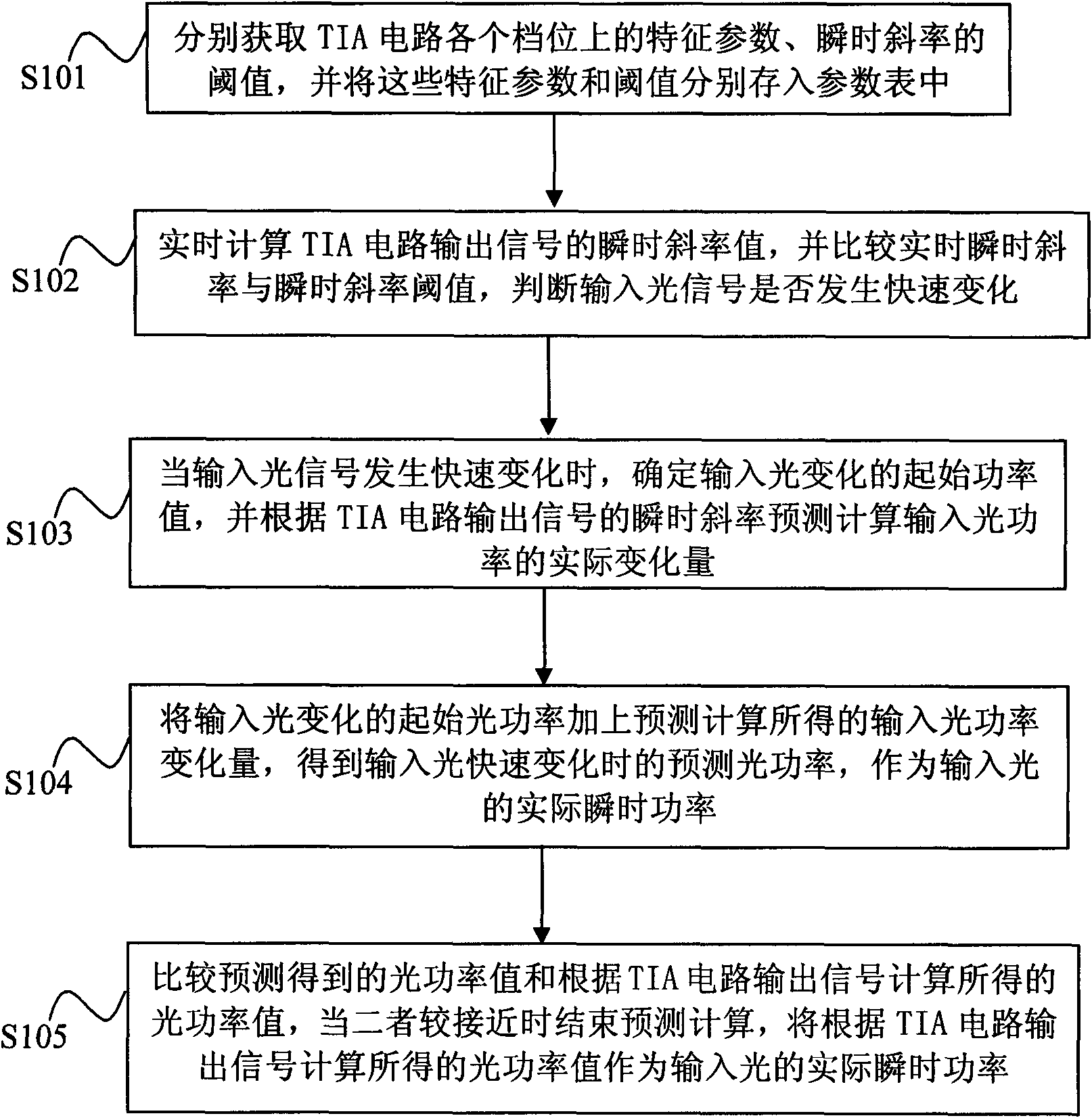
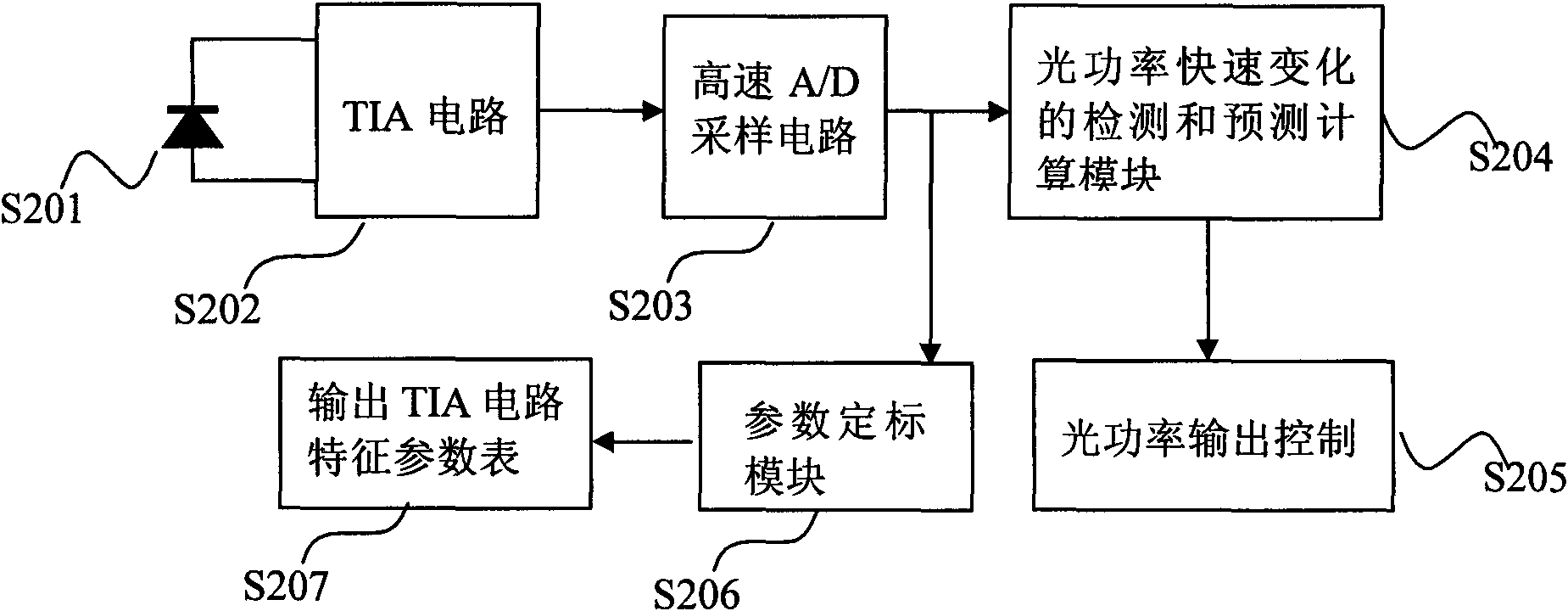
ActiveCN101634590AFast detectionEasy to controlPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsReal variableSlope ratio
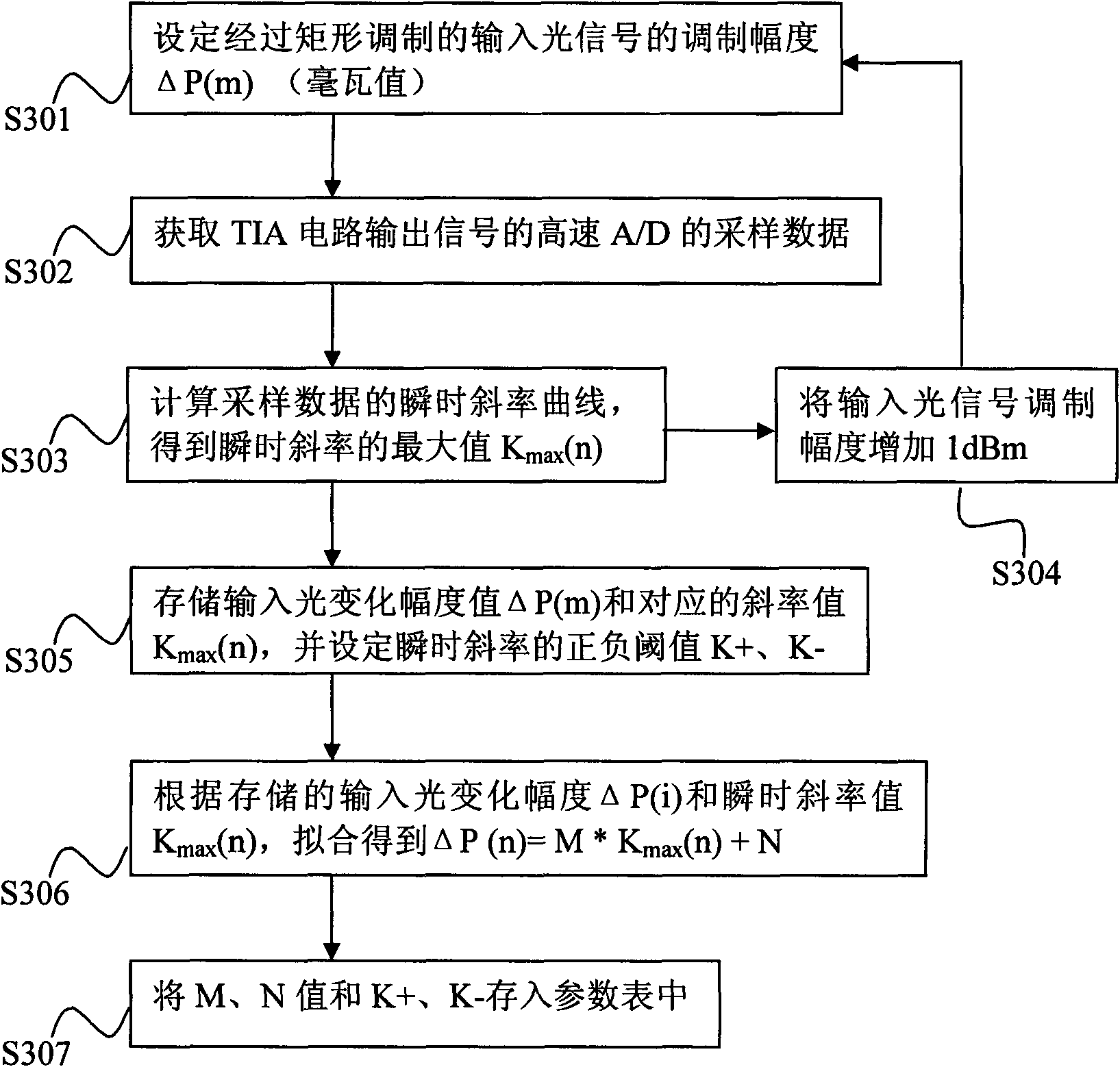
A detection and predetermination calculational method for rapid variation light power comprises steps of: respectively obtaining characteristic parameters and a threshold value of an instant slope ratio of all gears of a TIA circuit which are stored in a parameter table; calculating the instant slope ratio value of output signals of the TIA circuit in real time, and comparing the real time instant slope ratio value and the threshold value of instant slope ratio; when input light signal varies quickly, determining the beginning power value of input light variation, and calculating the real variable quantity of the input light power according to the instant slope ratio of the output signals of the TIA circuit; adding the beginning light power of input light variation and input light power variable quantity obtained by predetermination calculation to obtain determination light power when input light rapid varies to serve as the real instant power of the input light, comparing the light power value obtained by predetermination and the light power value obtained according to the output signals of the TIA circuit, finishing the predetermination calculation when the predetermined light power value and the light power value are closer, using the light power value as the real instant power of the input light. The method greatly speeds up light power detection speed and can accurately display the light power value of fast variation.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Stepwise multivariable regression model for predicting diseased survival time and application thereof
InactiveCN106202988AImproving Survival Prediction AccuracyImprove accuracyMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisDiseaseReal variable
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Double-field variable-focus three-dimensional measurement system
InactiveCN103134444AHigh precision extractionQuickly acquire 3D informationUsing optical meansReal variableMotor drive
The invention relates to a double-field variable-focus three-dimensional measurement system. The system comprises a primary-secondary mirror imaging measuring system, a two-dimensional tracking rotating-mirror device and an adaptive control system. The primary-secondary mirror imaging measuring system is composed of a telephoto subsystem, a short-focus subsystem and a launching light source. The telephoto is composed of a main lens, a first spectroscope, a second spectroscope and a detector. The short-focus system is composed of the main lens, the first spectroscope, the second spectroscope and the detector. The two-dimensional tracking rotating-mirror device is composed of a reflector, a electric rotating motor, a regulating handle, an upper half shaft, a lower half shaft and a horizontal shaft. The adaptive control system is composed of a computer, an input and output (I / O) control circuit, an electromotor and a signal processing and controlling circuit. The system has the advantages of being tight in arrangement, high in measuring efficiency, convenient to measure and is suitable for the three-dimensional measuring of moving and static objects.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
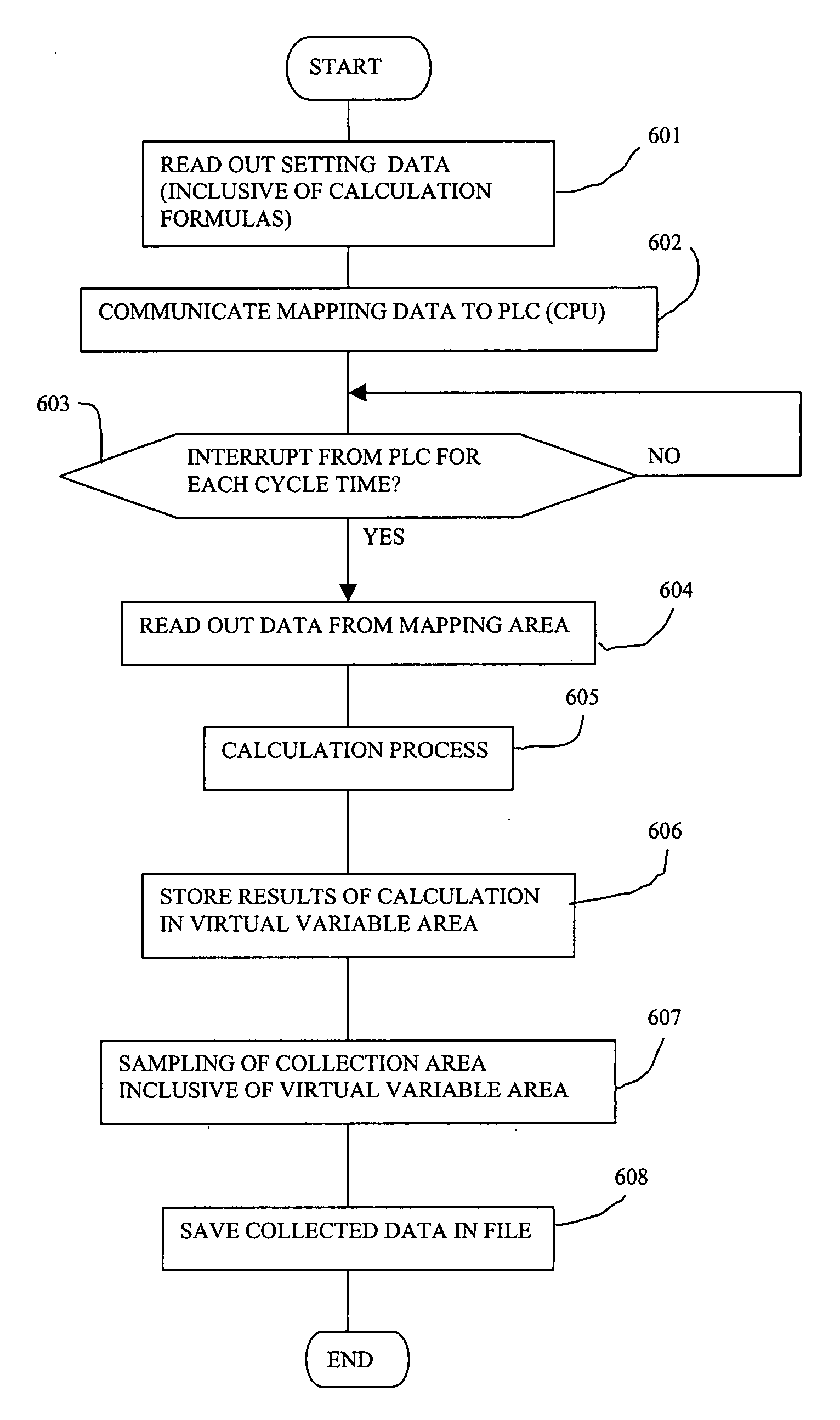
Monitor system, and monitor device and data collecting device therefor
ActiveUS20070203676A1Easy to carryProgramme controlDrawing from basic elementsReal variableMonitoring system
A monitor system is formed with a programmable controller for executing a user program, a data collecting unit connected to the programmable controller for collecting variable data of the programmable controller and a monitor device connected to the data collecting unit through a communication line. The functions of the system include that of storing a preliminarily defined virtual variable apart from the user program of the programmable controller and from the variable data of the programmable controller and a calculation formula using one or more real variables for obtaining the virtual variable, that of collecting real variable data in the stored calculation formula and any other real variables from the programmable controller, that of carrying out a calculation according to the stored calculation formula based on the collected real variable data, and that of displaying correspondence of the collected real variables and the result of the calculation as waveforms on a display device. Some of these functions are carried out by the data collecting unit, the rest being carried out by the monitor device.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Time-scale modification method for digital audio signal and digital audio/video signal, and variable speed reproducing method of digital television signal by using the same method
InactiveCN1902697AReduce the burden onTelevision system detailsSpeech analysisLow speedDigital Audio Tape
A method capable of ensuring a synchronization between an audio signal and a video signal both of which are modified in time-scale is needed. Solution: When analysis shift Sa = Ss / alpha, where Ss is synthesis shift and alpha is a designated time-scale (variable speed ratio), has a decimal value, two natural numbers which are nearest to the decimal value are selected as a modified analysis shift Sa' and a compensated analysis shift Sa'', respectively. In time-scale modification of source audio samples to vary playback speed by dividing them into overlapped successive analysis windows, the modified analysis shift Sa' and the compensated analysis shift Sa'' are alternately applied whenever a predetermined condition is met. The time difference between an estimated playback time and a real playback time of the time-scale modified audio signal is accumulated. The case that the predetermined condition is met is a case than an accumulated time difference goes beyond an upper threshold or a lower threshold of an allowed error range. In a processing of varying the playback speed of an AV signal, if a real variable speed ratio of a playback-speed-varied video signal is given as a target variable speed ratio of an audio signal to vary the playback speed of the audio signal, a synchronization between the video signal and the audio signal can be obtained. By applying this technology to the digital TV or TV phone, consecutive watch of the broadcasting signal for a phone-break time is possible. Catch-up for the currently received broadcasting signal is also possible through a high speed playback mode after a low speed playback mode initiated from a time of the past or the present.
Owner:COSMOTAN
Low-power low-voltage multi-level variable-resistor line driver
ActiveUS7528629B2Improve power efficiencyPulse automatic controlTransmission line coupling arrangementsDigital dataReal variable
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
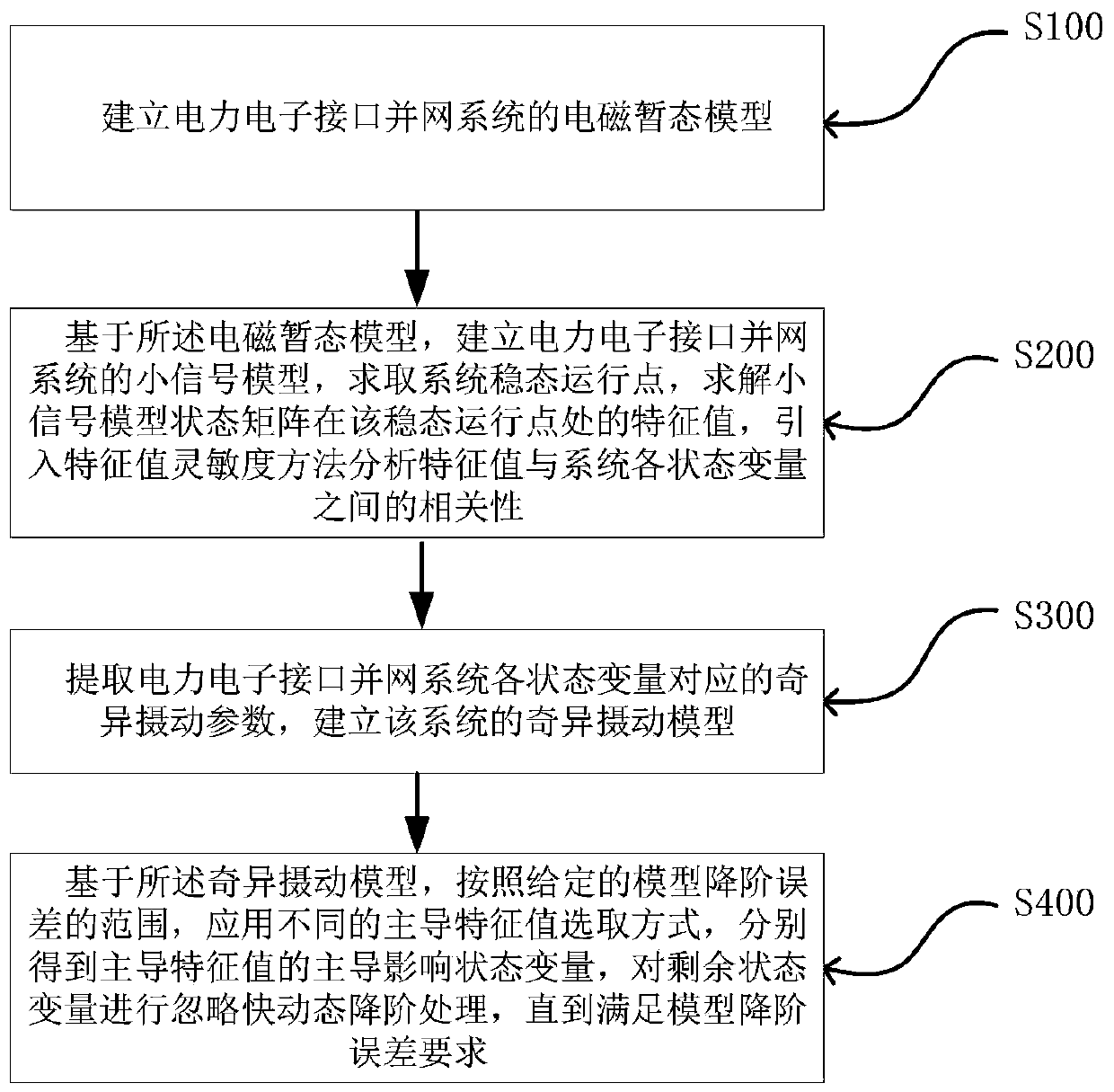
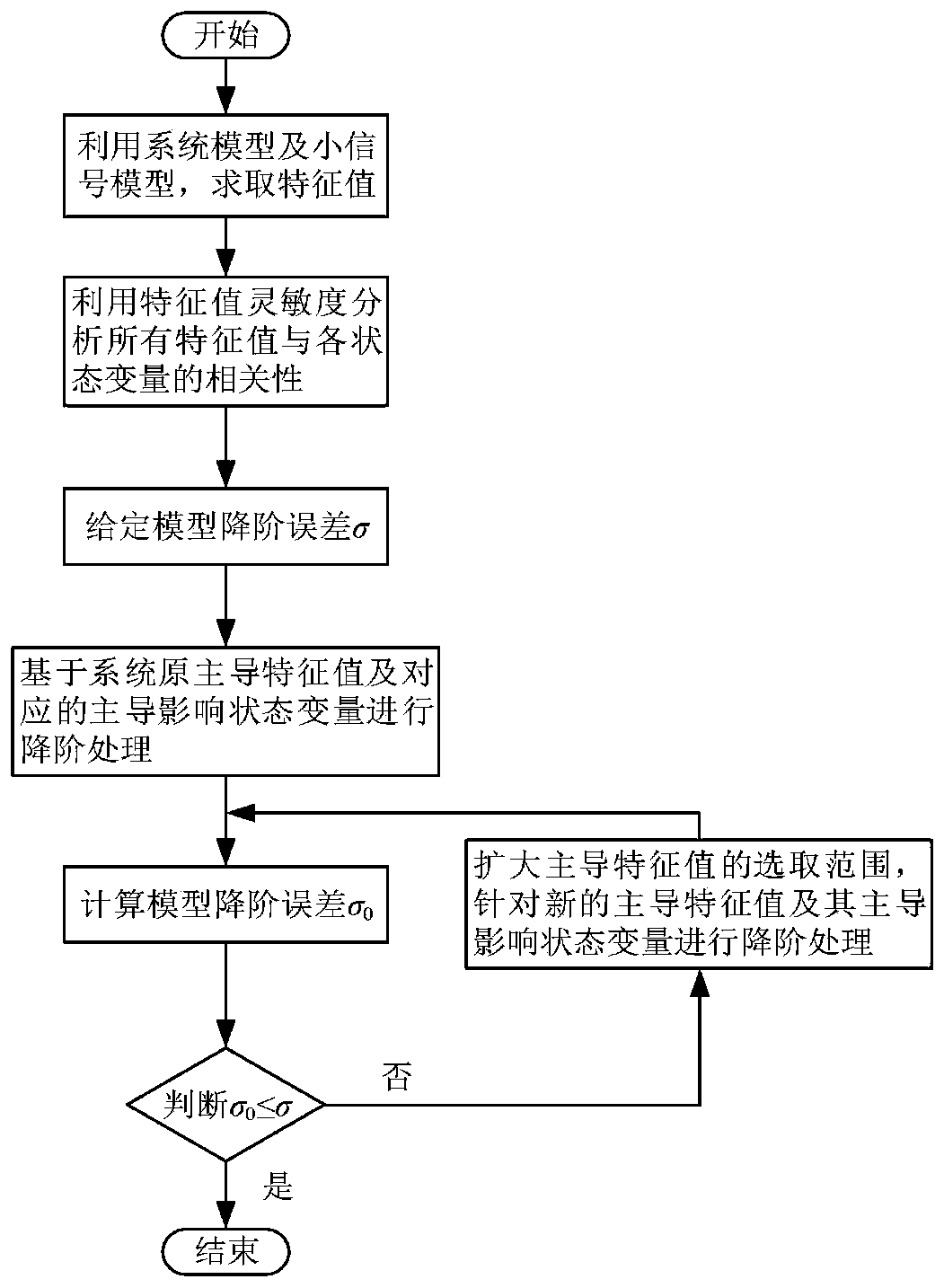
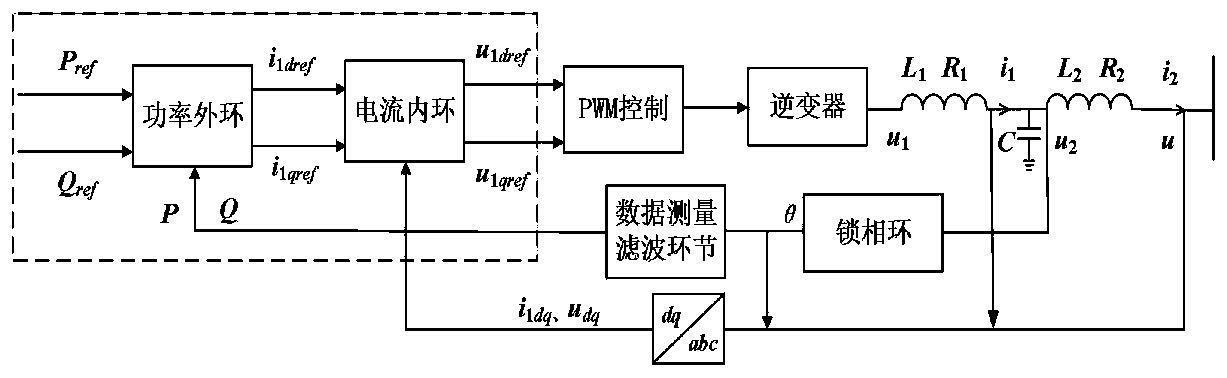
Method for selecting reduced-order variable of power electronic interface grid-connected system model reduced order
ActiveCN110262236AThe order reduction error requirement meets theAdaptive controlEngineeringReduced order
The invention relates to a method for selecting a reduced-order variable of a power electronic interface grid-connected system model reduced order, which can improve the adverse effect that the current application does not consider the reduced-order processing of different state variables aiming at different model reduced order errors. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, establishing an electromagnetic transient model of a power electronic interface grid-connected system; 2, solving a characteristic value of the system at a steady-state operation point, and introducing a characteristic value sensitivity method to analyze the correlation between the characteristic value and each state variable of the system; 3, extracting singular perturbation parameters corresponding to each state variable of the system, and establishing a singular perturbation model of the system; and 4, according to a given model order reduction error range, applying different dominant characteristic value selection modes to obtain the dominant influence state variable of the dominant characteristic value, and the remaining state variables are subjected to order reduction processing. According to the method, different state variables can be selected for order reduction processing according to the requirement of the model order reduction error, and the practicability and the effectiveness of the order reduction variable selection method are fully considered.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
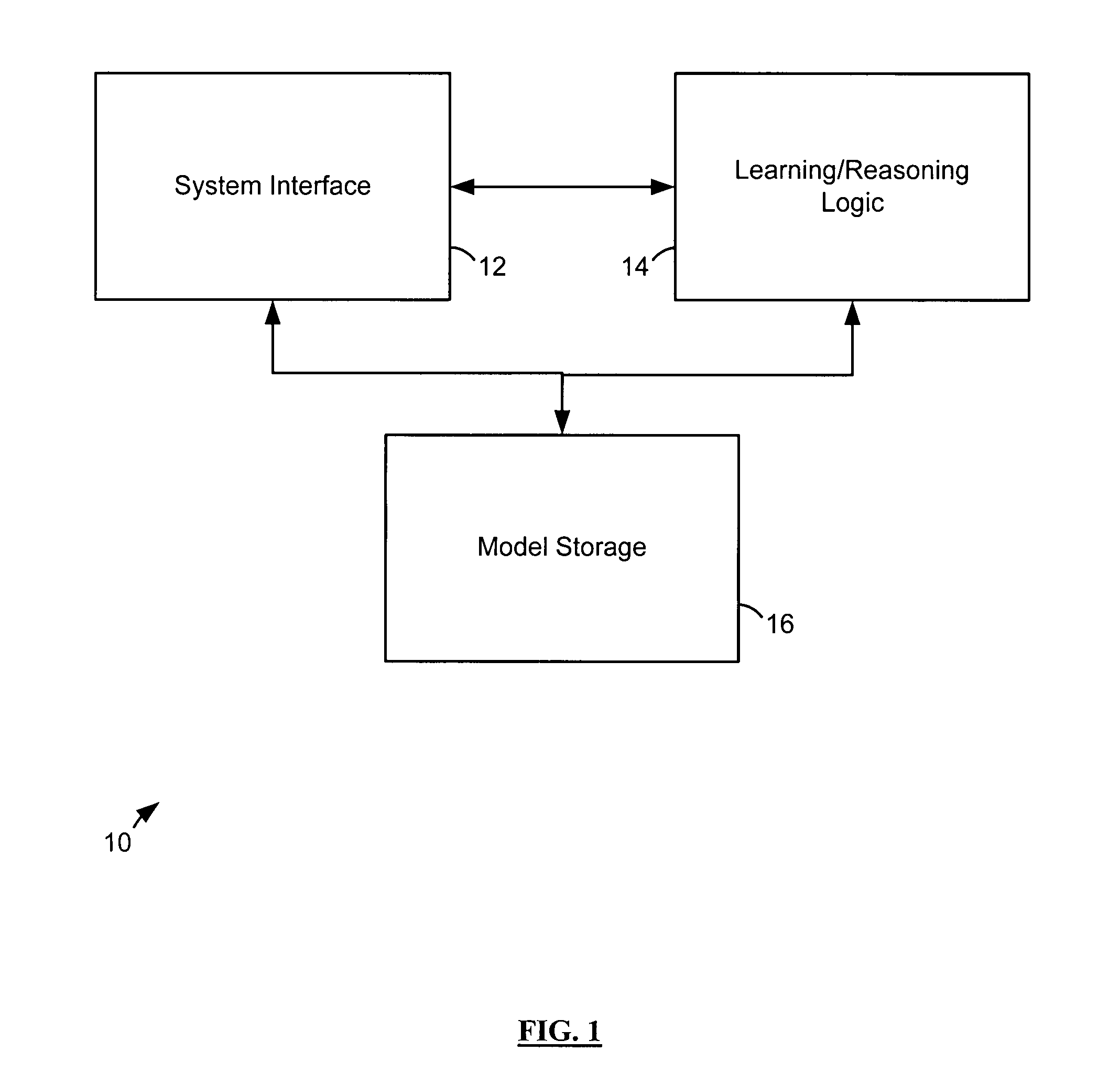
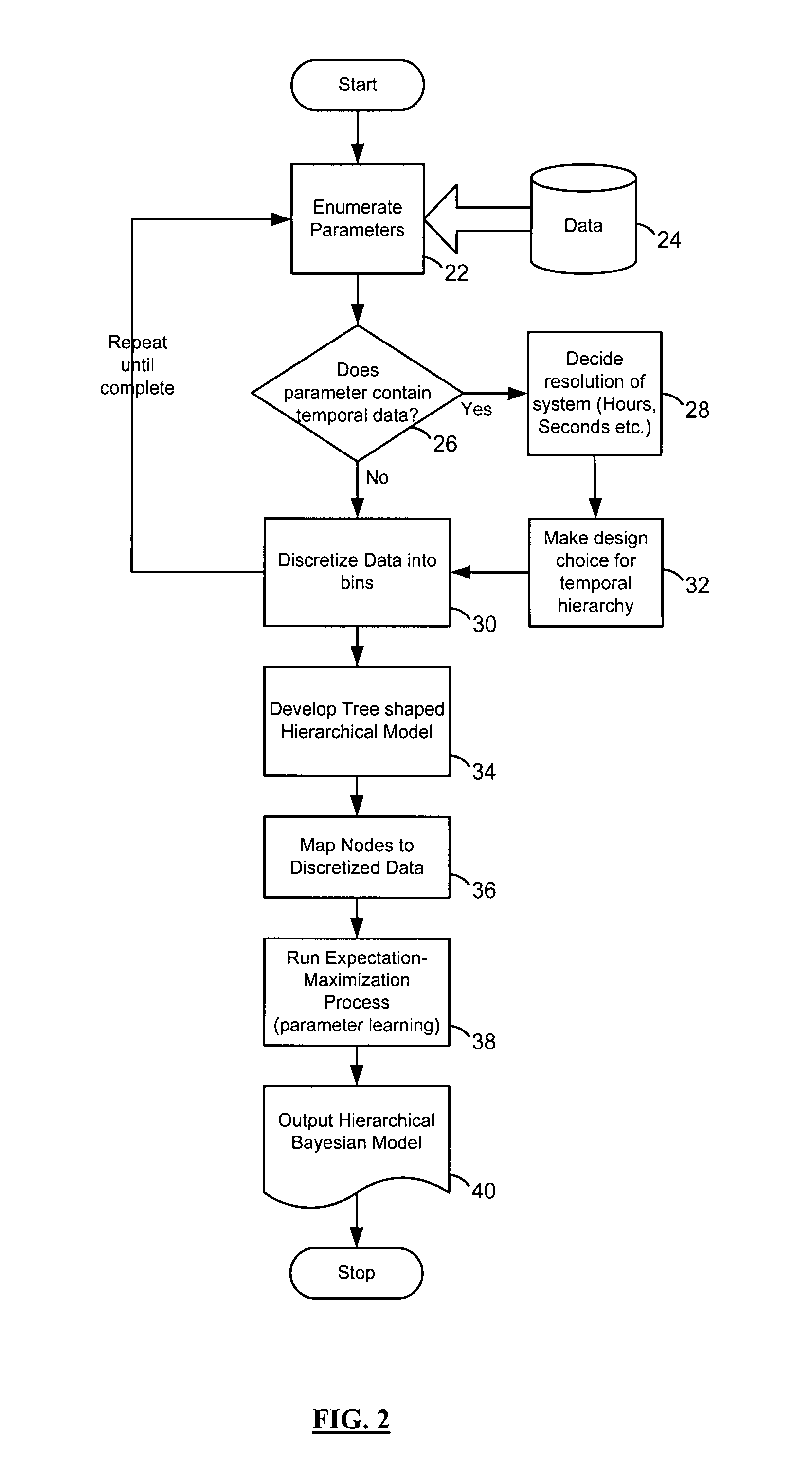
Apparatus and method for learning and reasoning for systems with temporal and non-temporal variables
InactiveUS7792769B2Easy to learnAdd reasonableChaos modelsNon-linear system modelsReal variableGoal system
In one general aspect, a method of deriving information about behavior of a target system is disclosed. The method includes accessing one or more temporal variables for the target system, providing an identifier node at the top of a hierarchy of a tree-structured belief network, and assigning a different sub-tree in the network to each of the accessed temporal variables. The method also involves accessing evidence data, and deriving information about the behavior of the target system for the evidence data based on the tree-structured belief network.
Owner:COGNIKA INTELLIGENCE & DEFENSE SOLUTIONS
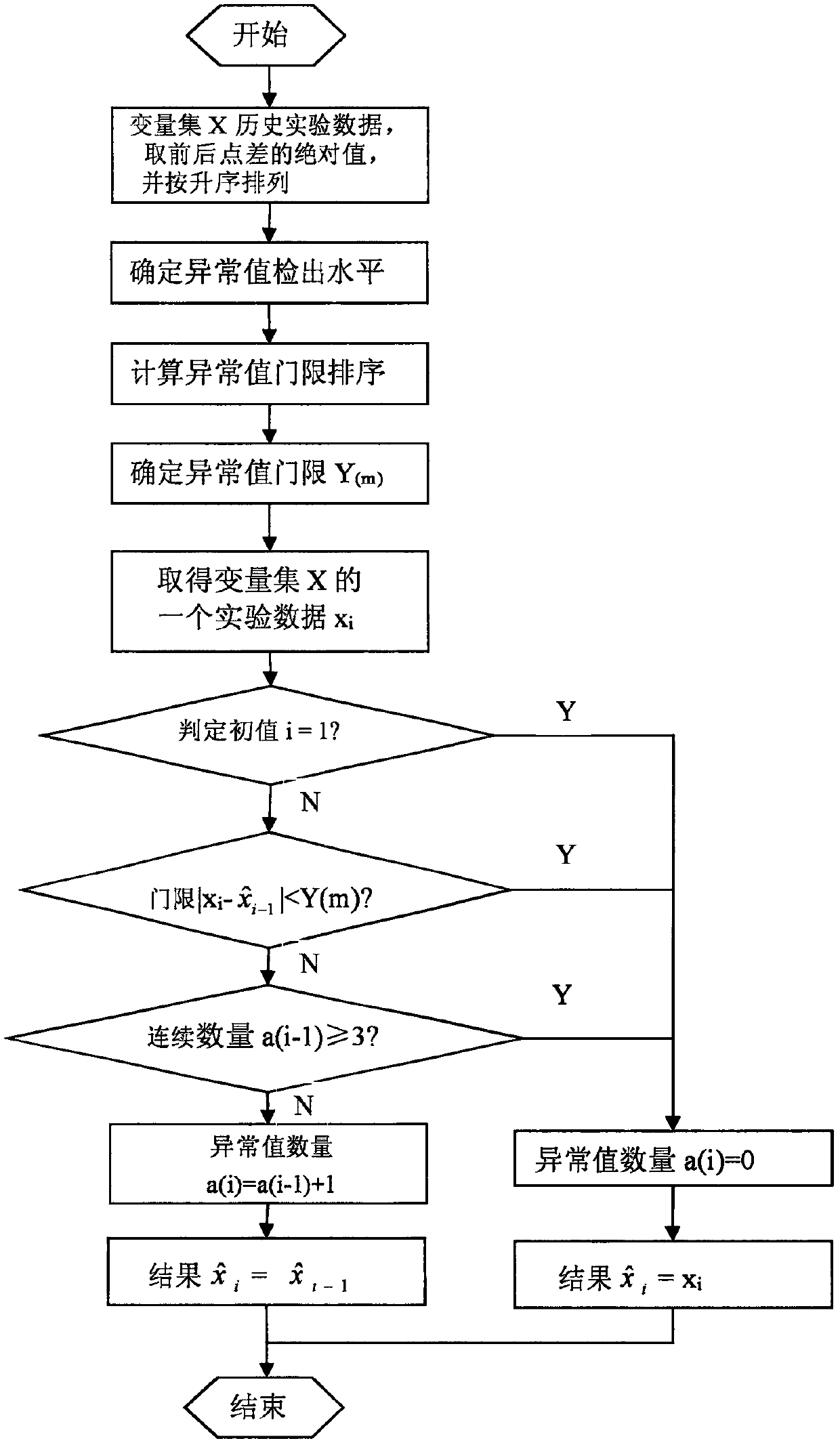
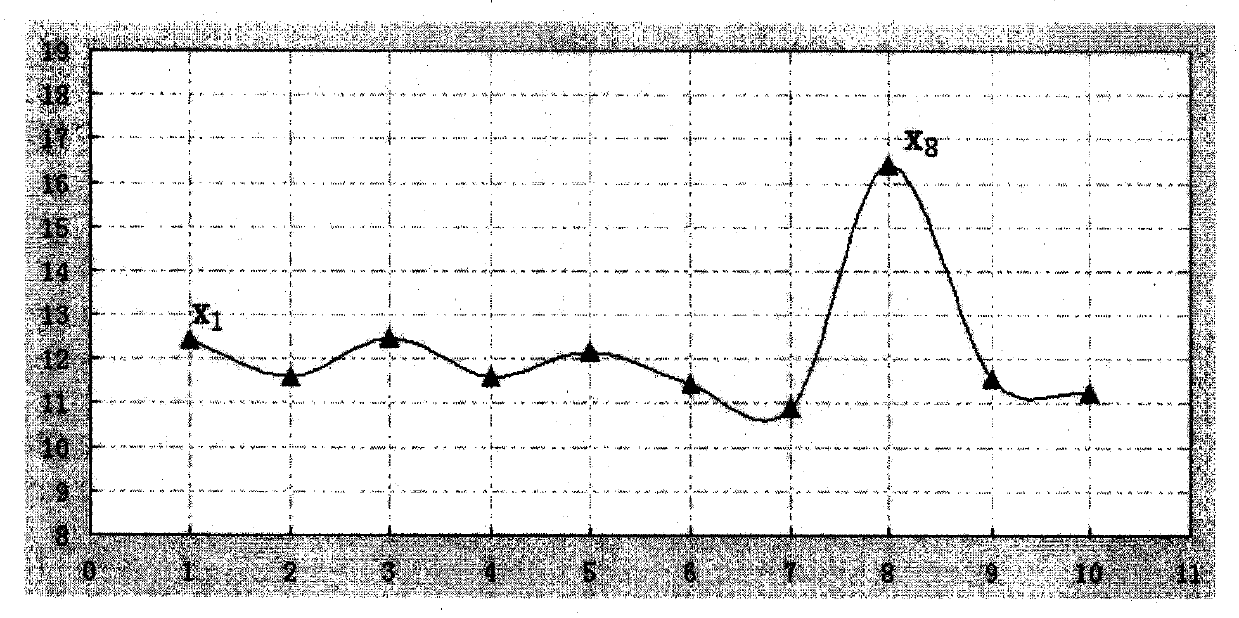
Real-time rejecting method for observed experimental data outliers
ActiveCN108205432ATrue forecastTrue restorationData sortingComplex mathematical operationsReal variableMathematical model
The invention provides a real-time rejecting method for observed experimental data outliers. The method comprises following steps: performing statistics on existing experimental data of a certain variable set X to determine an outlier threshold; performing real-time detection and rejecting on outliers of experimental data according to a given engineering mathematical model according to the outlierthreshold. The invention determines the outlier threshold by counting the historical experimental data of the continuously changing variable to be observed. The dynamic processing mathematical modelis used to dynamically judge the current experimental data observed by the experimental system, and the outliers can be judged and the outliers can be eliminated, which helps to more realistically evaluate, predict or restore the real variable to be observed. The method provided by the invention is not limited by the use conditions and has a wider application range, and provides an effective dynamic processing method for observing outliers in experimental data.
Owner:HIWING TECH ACAD OF CASIC
Large variable-pitch wind turbine control system with trailing edge flaps and control method
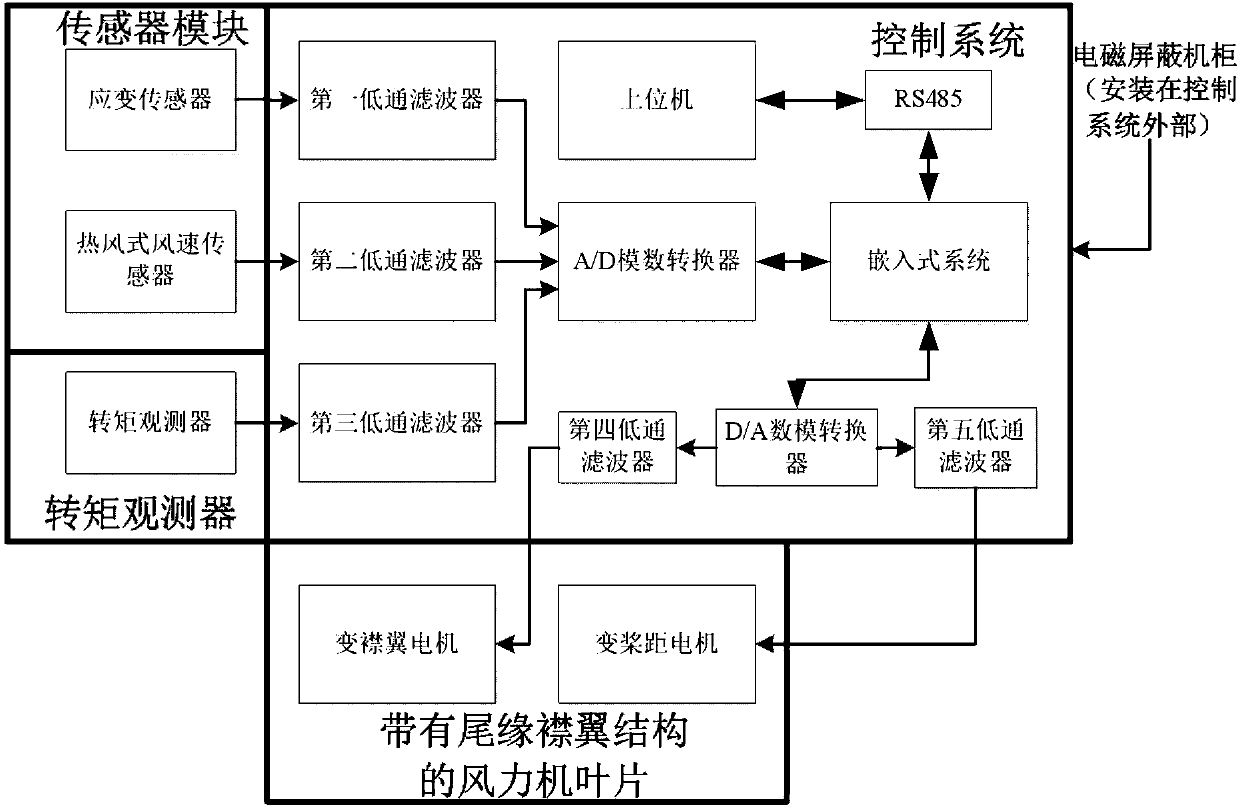
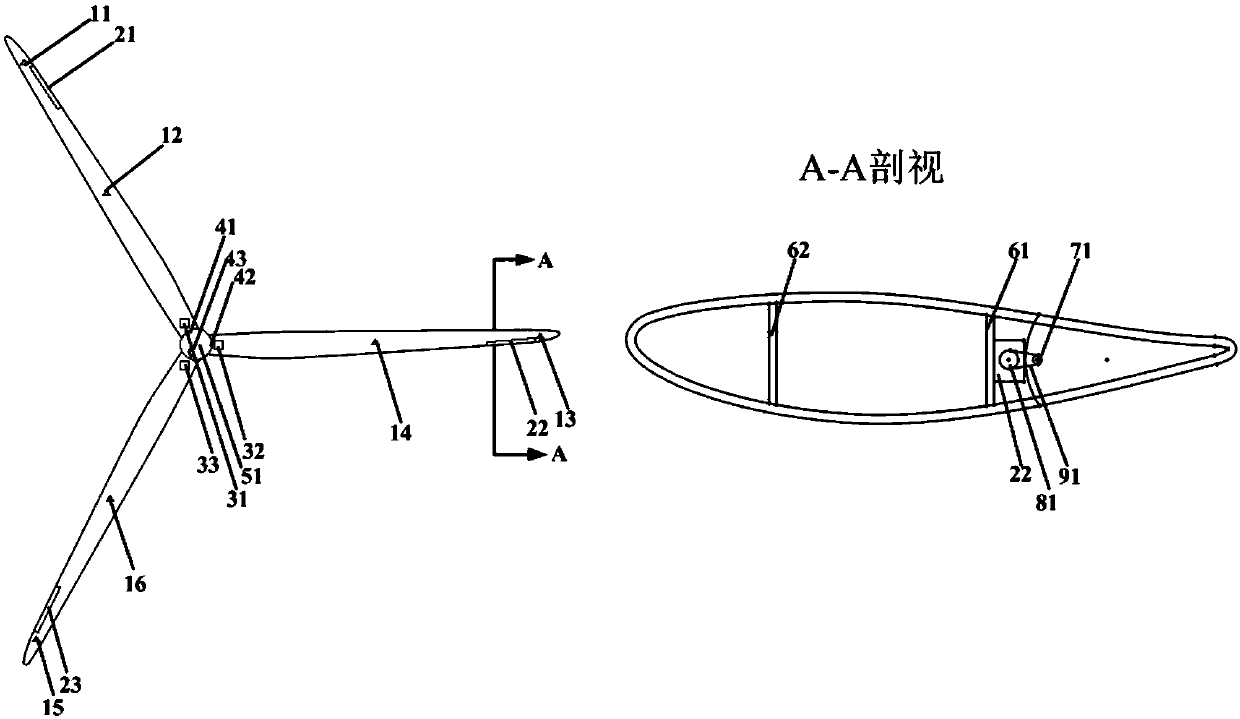
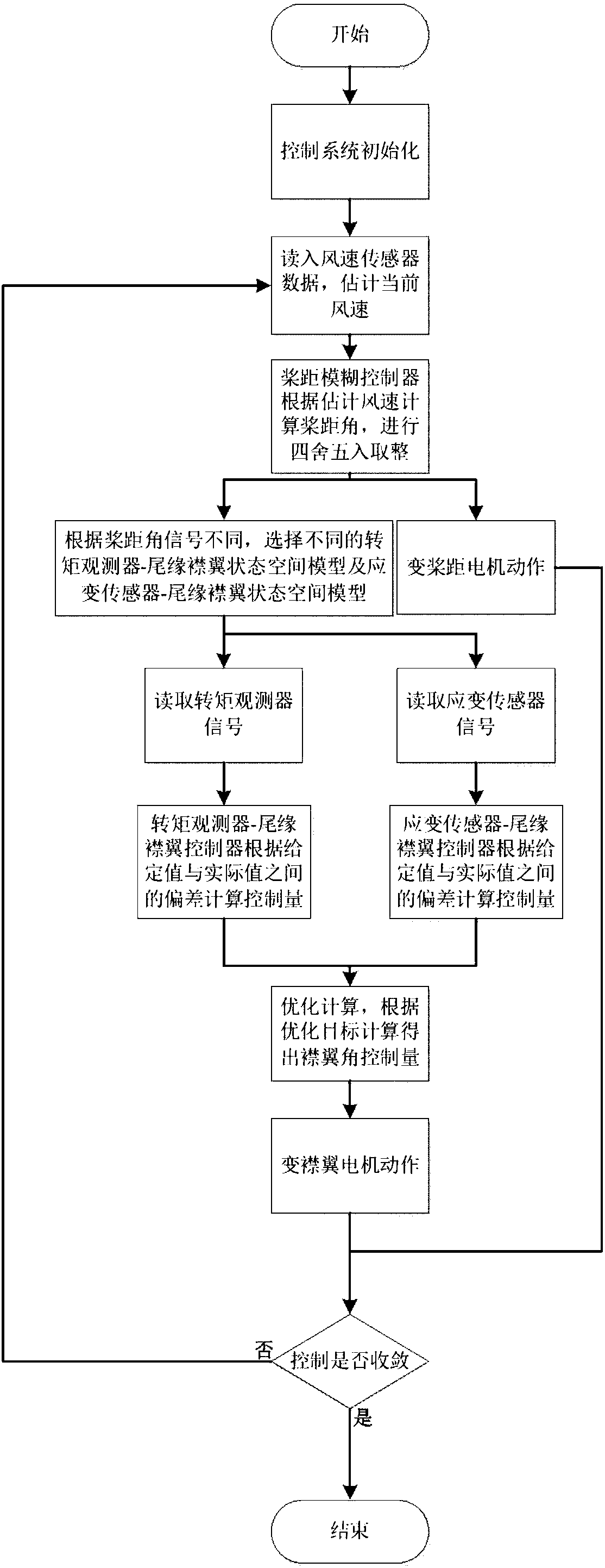
ActiveCN107762730ASuppression of torque rippleSuppress fluctuationsWind motor controlMachines/enginesReal variableTurbine blade
The invention discloses a large variable-pitch wind turbine control system with trailing edge flaps and a control method. The large variable-pitch wind turbine control system with the trailing edge flaps comprises wind turbine blades with the trailing edge flaps, a sensor module, a torque observation device and a control system body. The control method of the large variable-pitch wind turbine control system with the trailing edge flaps comprises the following steps that (1) experimental measurement and system model identification are carried out on the large variable-pitch wind turbine with the trailing edge flaps, and the step size of the large variable-pitch wind turbine is mu; (2) the blade pitch of the wind turbine blades with the trailing edge flap structures is controlled; (3) the flap of the wind turbine blades with the trailing edge flap structures is controlled; (4) the real-time control amounts of the blade wheel torque and the blade root fatigue load can be obtained according to the step (3), and the real-time control amounts include the flap angle input amounts mu1(k), mu21(k), mu22(k) and mu23(k), the controlled amounts include the estimation torque obtained by the torque observation device and corresponding strain sensor signal values of the blade 1, the blade 2 and the blade 3. According to the flap angle input amount mu1(k), mu21(k), mu22(k) and mu23(k) and thecorresponding optimizing indexes, three flap angle control amounts of the blade 1, the blade 2 and the blade 3 can be obtained.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
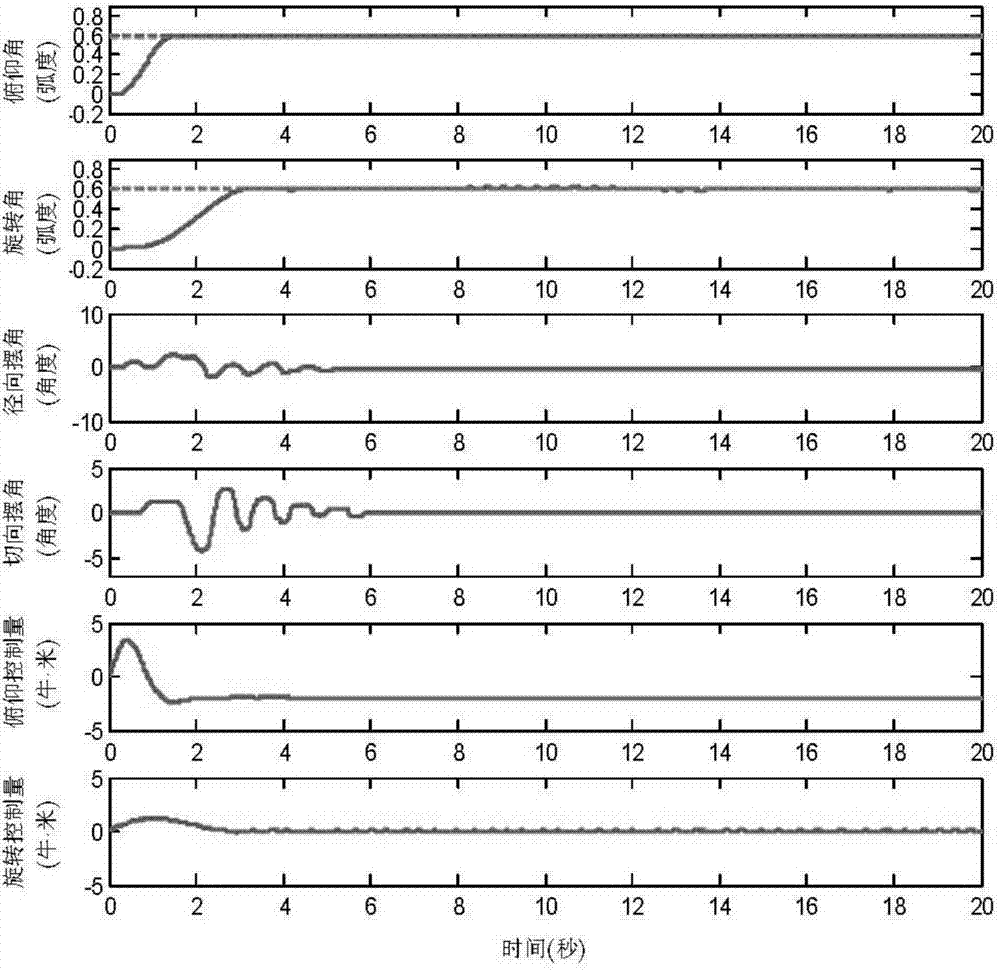
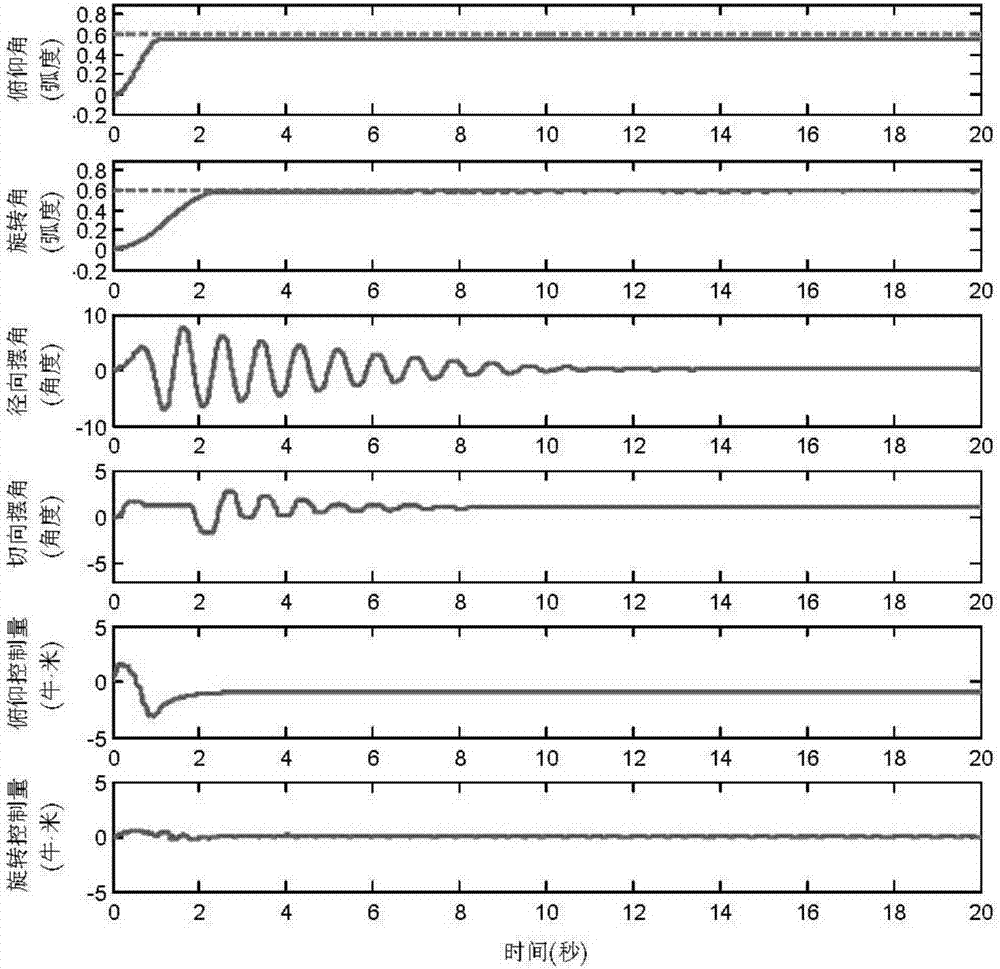
Under-actuated mast crane positioning anti-swing nonlinear control method
The invention relates to an under-actuated mast crane positioning anti-swing nonlinear control method and belongs to the field of electromechanical system control. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing an energy function according to the kinetic model of a crane and constructing a Lyapunov candidate function by fully using a coupling relation between drivable variables (rotation angle and pitch angle of a boom) and un-drivable variables (radial swing angle and tangential swing angle of a load) so as to design a novel nonlinear controller. In addition, in order to limit the overshoot of the rotation of the boom, an amplitude limiting item is added to the controller to prevent the boom from swinging near a target position. The method can achieve accurate positioning control and rapid anti-swing control.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
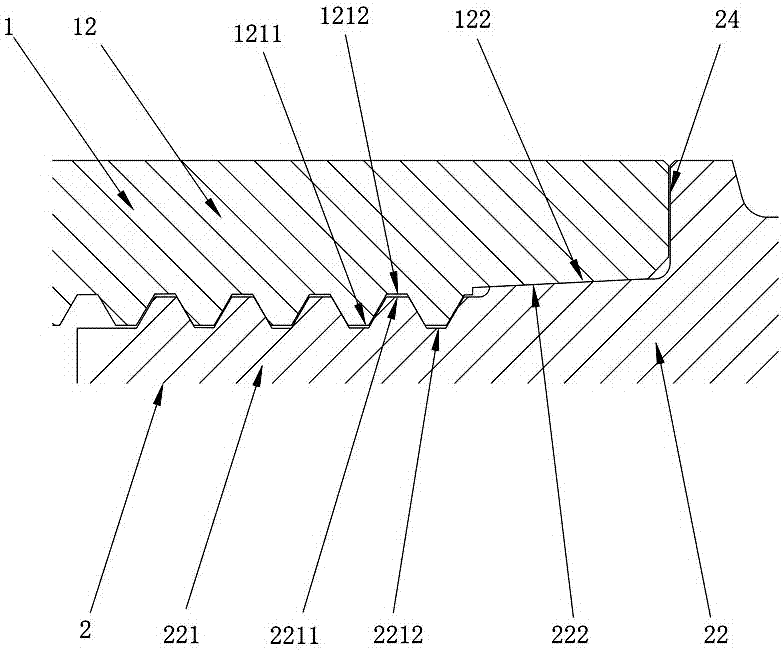
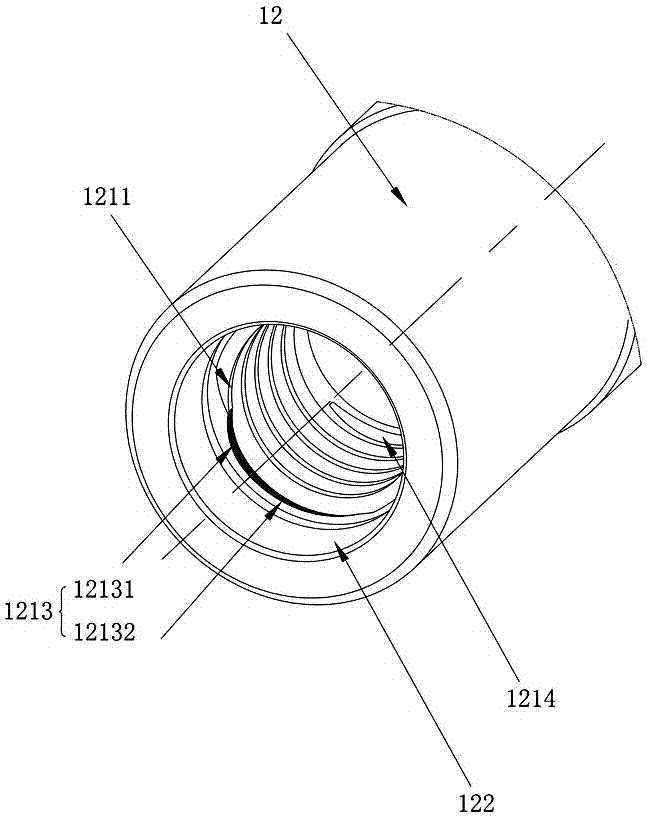
Cutting tool
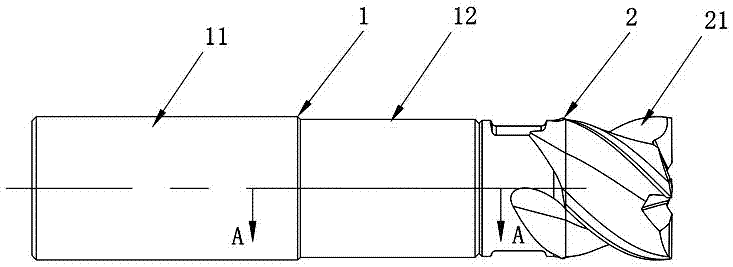
The invention discloses a cutting tool. The cutting tool comprises a clamping component and a cutting component capable of being installed on the clamping component, wherein the clamping component comprises a clamping handle part and a clamping head part; the cutting component comprises a cutting head part and a cutting tail part; a clamping bulge is arranged on the end surface of the cutting tail part; an external thread is formed on the clamping bulge; a clamping recession is formed in the end surface of the clamping head part; an internal thread matched with the external thread on the clamping bulge is formed on the clamping recession; an external transition surface located between the external crest and the external root of the external thread is formed at the beginning part of the external thread; the external transition surface comprises an external variable-diameter surface and an external equal-diameter surface; the external variable-diameter surface is connected with the external equal-diameter surface and the external crest; and the distance between the external equal-diameter surface and the external crest in the radial direction of the external thread is r, the internal crest of the internal thread has a constant diameter d1, and the external crest has a constant diameter d2, and r is not less than 0.02mm and not greater than 0.45(d1-d2). The cutting tool disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being stable in structure, high in anti-impact capacity, long in service life and the like.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CEMENTED CARBIDE CUTTING TOOLS CO LTD
Digital circuit verification monitor
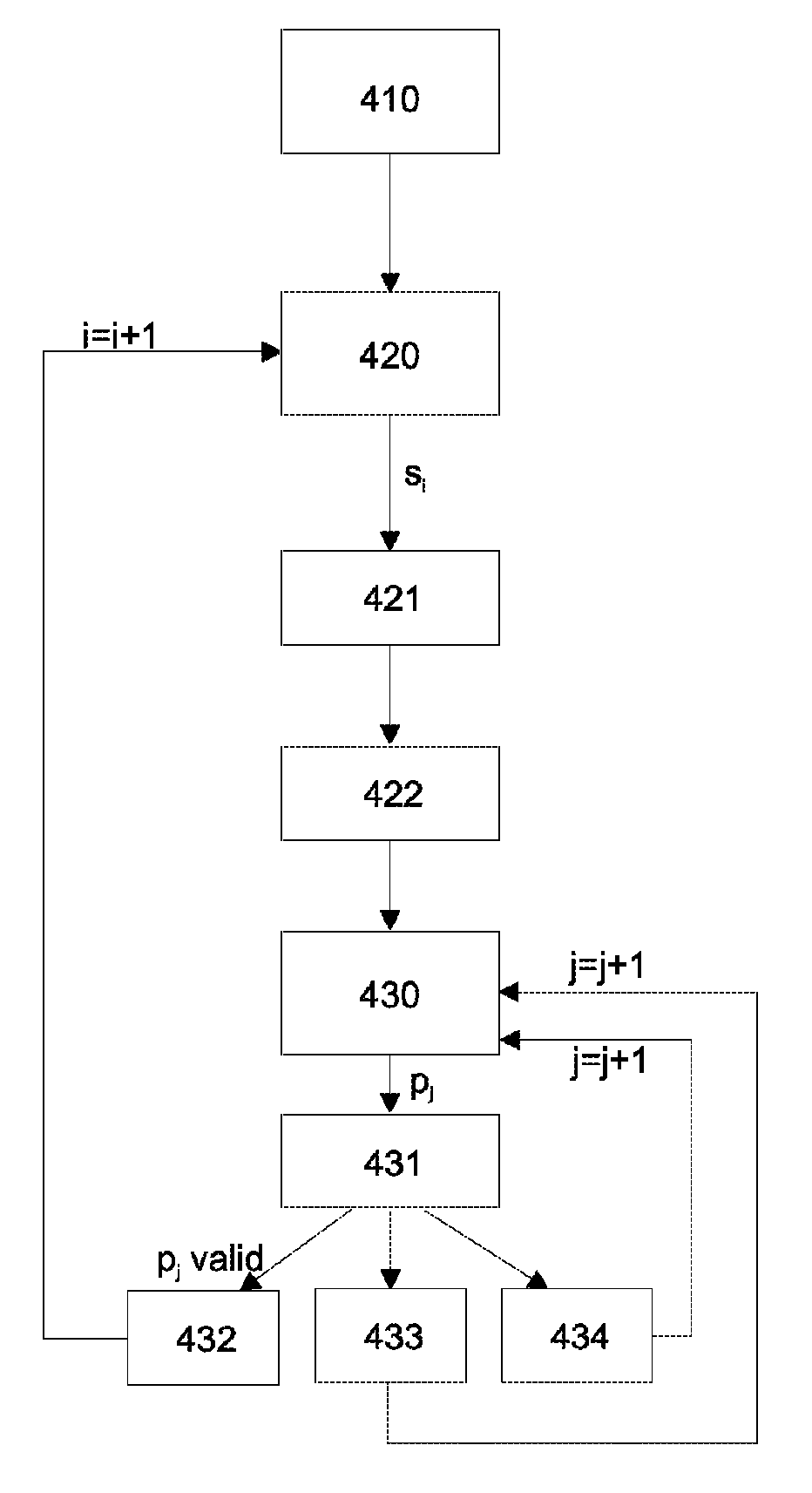
ActiveUS8701060B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designReal variableFormal specification
A method, a system and a computer readable medium for providing information relating to a verification of a digital circuit. The verification may be formal verification and comprise formally verifying that a plurality of formal properties is valid for a representation of the digital circuit. The method comprises replacing at least a first input value relating to the representation of the digital circuit by a first free variable, determining if at least one of the plurality of formal properties is valid or invalid after replacing the first input value by the first variable and indicating if the at least one of the plurality of formal property is valid or invalid. The use of a free or open variable that has not determined value can be directly in the description or representation of the digital circuit. It is not necessary to insert errors or to apply an error model.
Owner:SIEMENS ELECTRONIC DESIGN AUTOMATION GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com