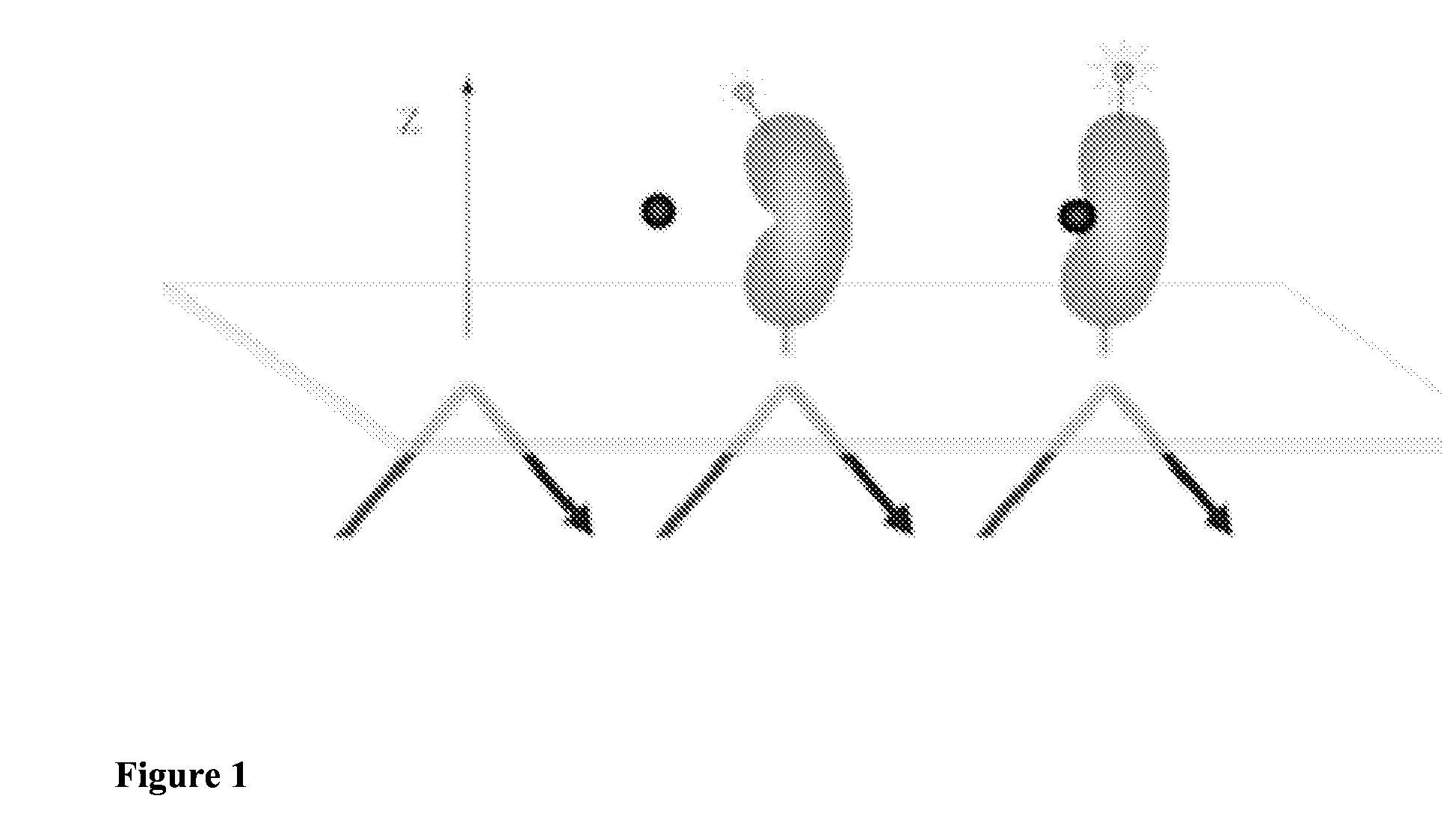
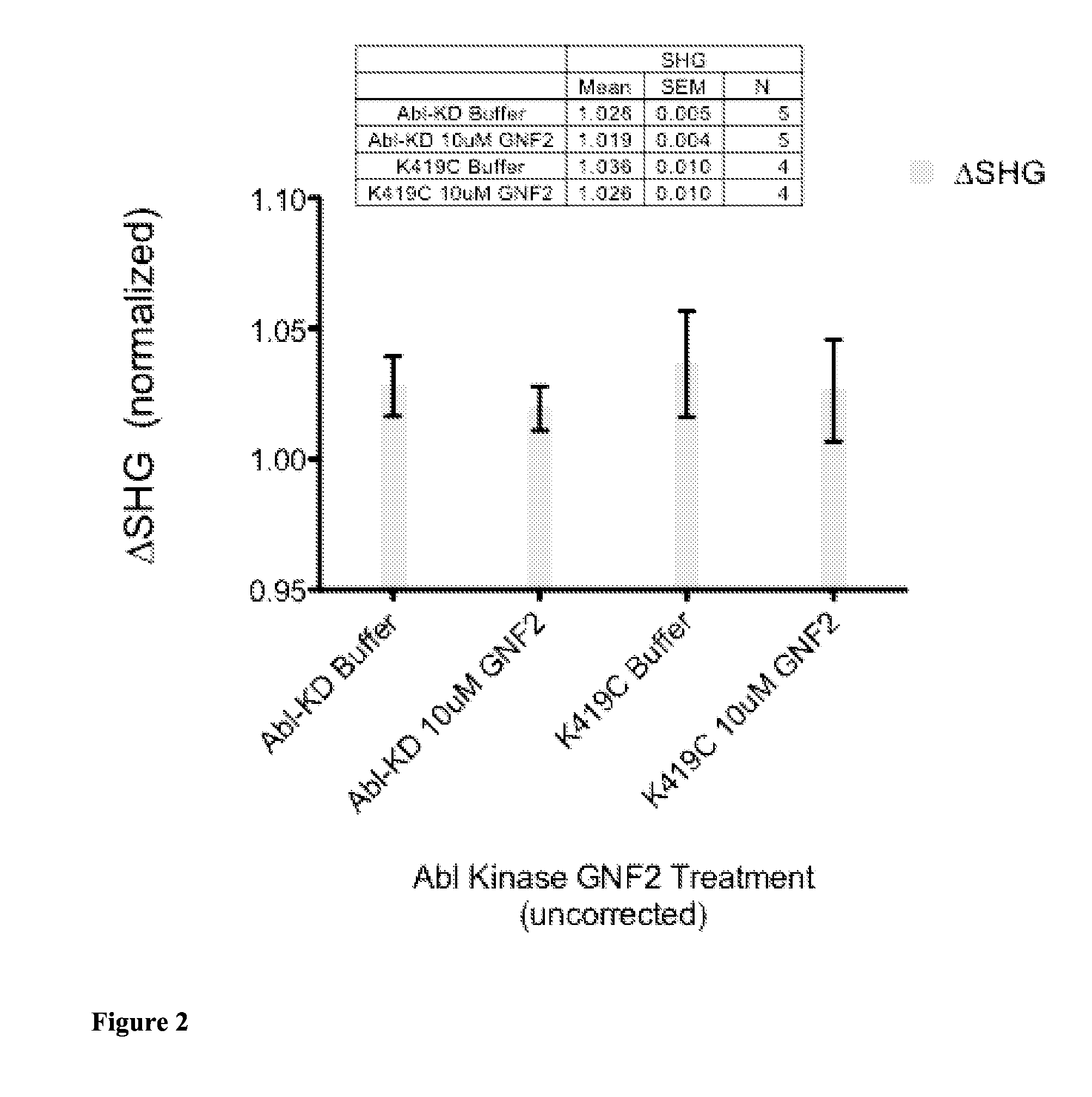
Methods for detecting allosteric modulators of protein
a technology of allosteric modulators and protein, applied in the field of molecular detection and protein detection, can solve the problems of unintended clinical side effects, difficult competition with potential drugs, and the growth of the number of approved therapies targeting the most abundantly activated cancer-related genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of Allosteric Modulators of a Kinase by Addition of a Synthetic Ligand to the Kinase Active Site
[0137]Kinases are a major class of drug targets with at least 30 distinct kinase targets currently in clinical trials. Most kinase drugs, known as type I inhibitors, bind to the kinase ATP binding site and work by mimicking and directly competing with ATP to stabilize the kinase activation loop into an active confirmation. Type II inhibitors, on the other hand, cause the activation loop of the kinase to shift into an inactive conformation by partially binding to the activation loop as well as other sites on the kinase. Type III kinase inhibitors, on the other hand, allosterically modulate kinase activity by binding to sites on the kinase other than the kinase activation loop. The identification of type III inhibitors is difficult, due to the fact that determination of the site of candidate inhibitor binding to a kinase typically requires X-ray crystallography to discern. In...
example 2
Labeling a Site Located in a Region of a Target Protein which Participates in a Partner Binding Event
[0146]Various mutations are made to insert cysteines in the region of H-Ras known to participate in PI3K effector binding. The native cysteine residue C118 can be optionally mutated to alanine or serine. The mutants are tested for an ability to be labeled by the SHG probe PyMPO-maleimide using mass spectrometry and protocols known to those skilled in the art. For example, the native residue tyrosine Y64 is known to participate in PI3K binding. Accordingly, recombinant 6×-His-tagged (N-terminal) H-Ras protein with a double mutation (C118A, Y64C) are prepared according to standard protocols (10). H-Ras is labeled using the cysteine-reactive SHG probe, PyMPO-maleimide in 0.1 M Tris pH 8.0, 20 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP, 5% glycerol and using a 12:1 dye:protein ratio for one hour at room temperature. Unreacted dye is purified away by gel filtration. Labeling of the cysteine at position 64 is c...
example 3
Labeling a Target in Two or More Different Ways, where at Least One of the Two or More Different Ways does not Involve Labeling a Native Residue
[0147]A slide with an oligo-PEG derivatization is prepared as follows: a slide-staining vessel is cleaned and dried in a vacuum oven at 75° C. / 20 inches Hg, and then allowed to cool to room temp. Enough SAT(PEG4) (N-Succinimidyl S-acetyl(thiotetraethylene glycol; Pierce) solution is added to the staining vessel to cover the entire slide (−50 mL). Ultrastick slides (amino-terminated silane derivatized slides; Thermo) are placed in a staining rack and submerged in the staining vessel. The slides are incubated in a hood at room temperature, stirring for 2-3 hrs. The slides are then removed from the SAT(PEG4) solution and transferred to a slide washing dish containing anhydrous chloroform. Sonicate the slides for 15 minutes by immersing washing dish to ⅔ its height in tap water. Transfer the slides to a second washing dish and rinse each with et...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface selective technique | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com