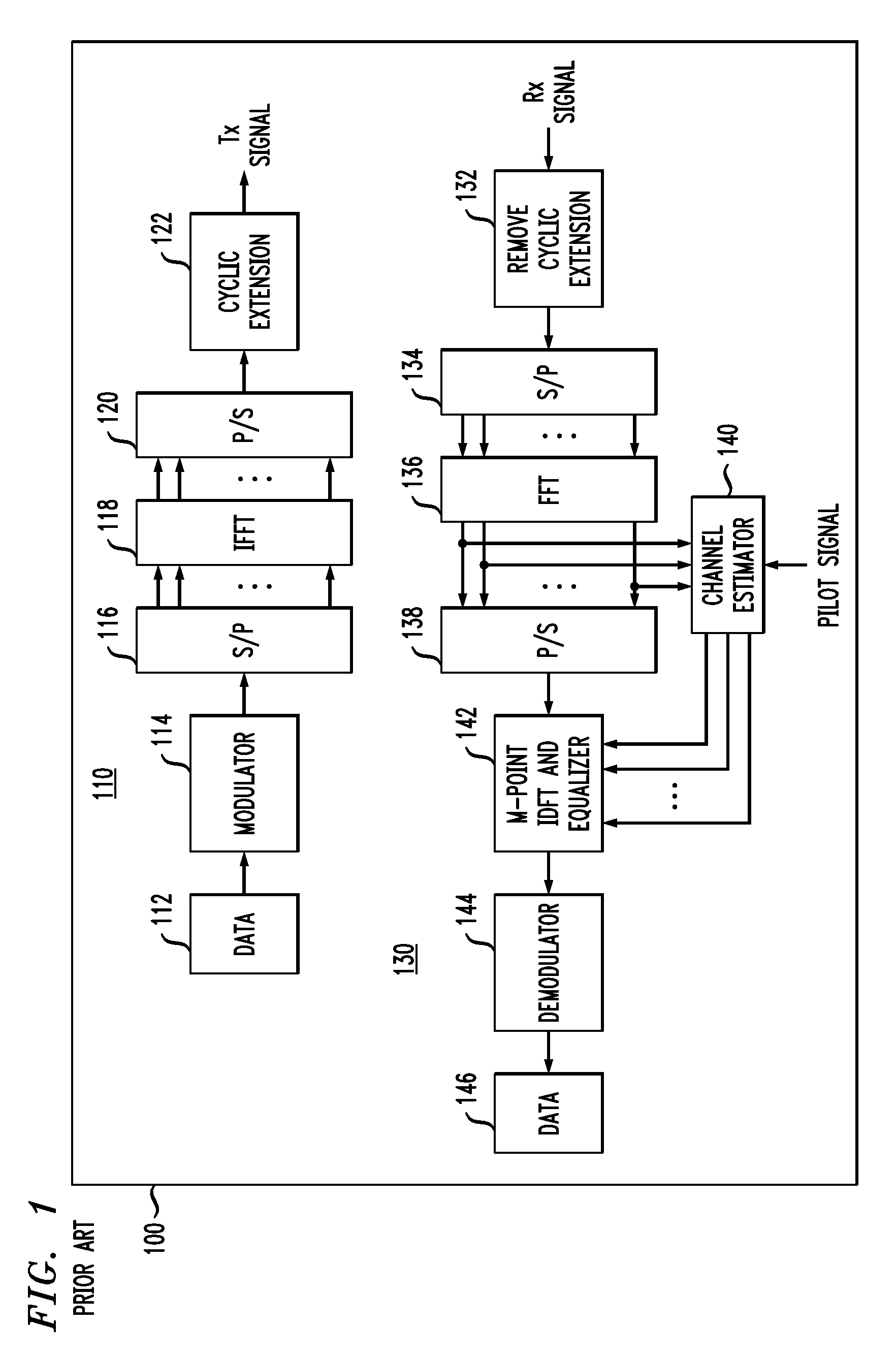
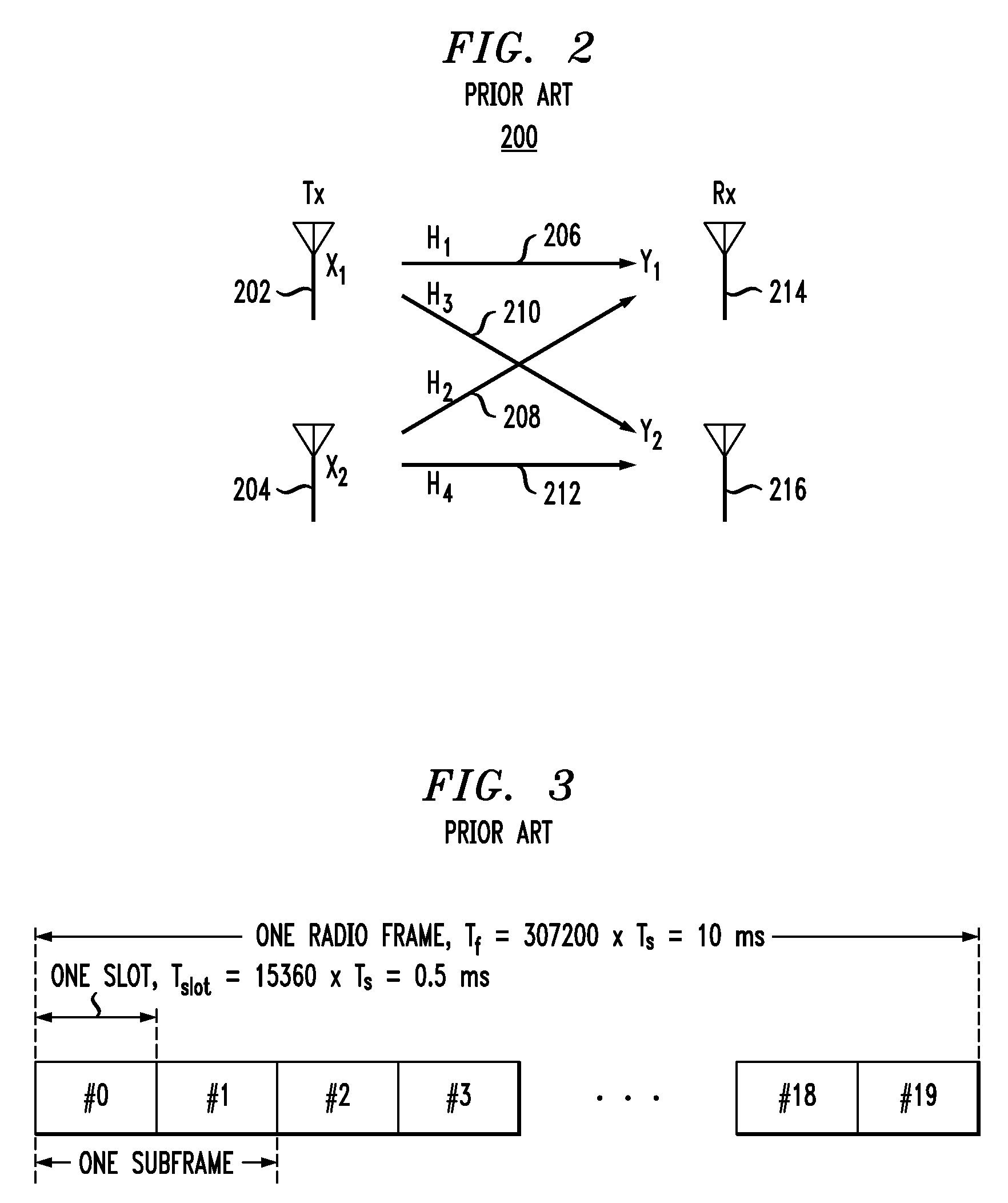
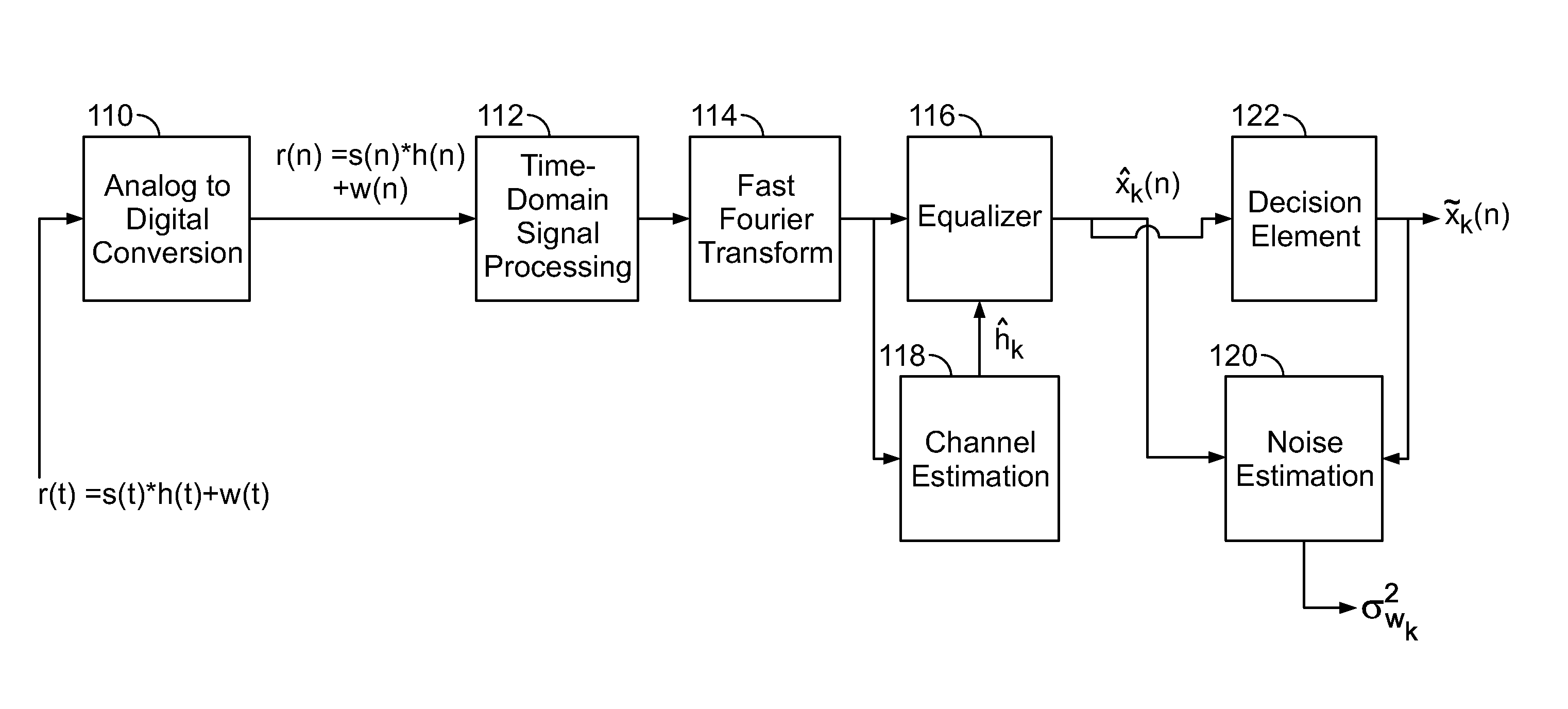
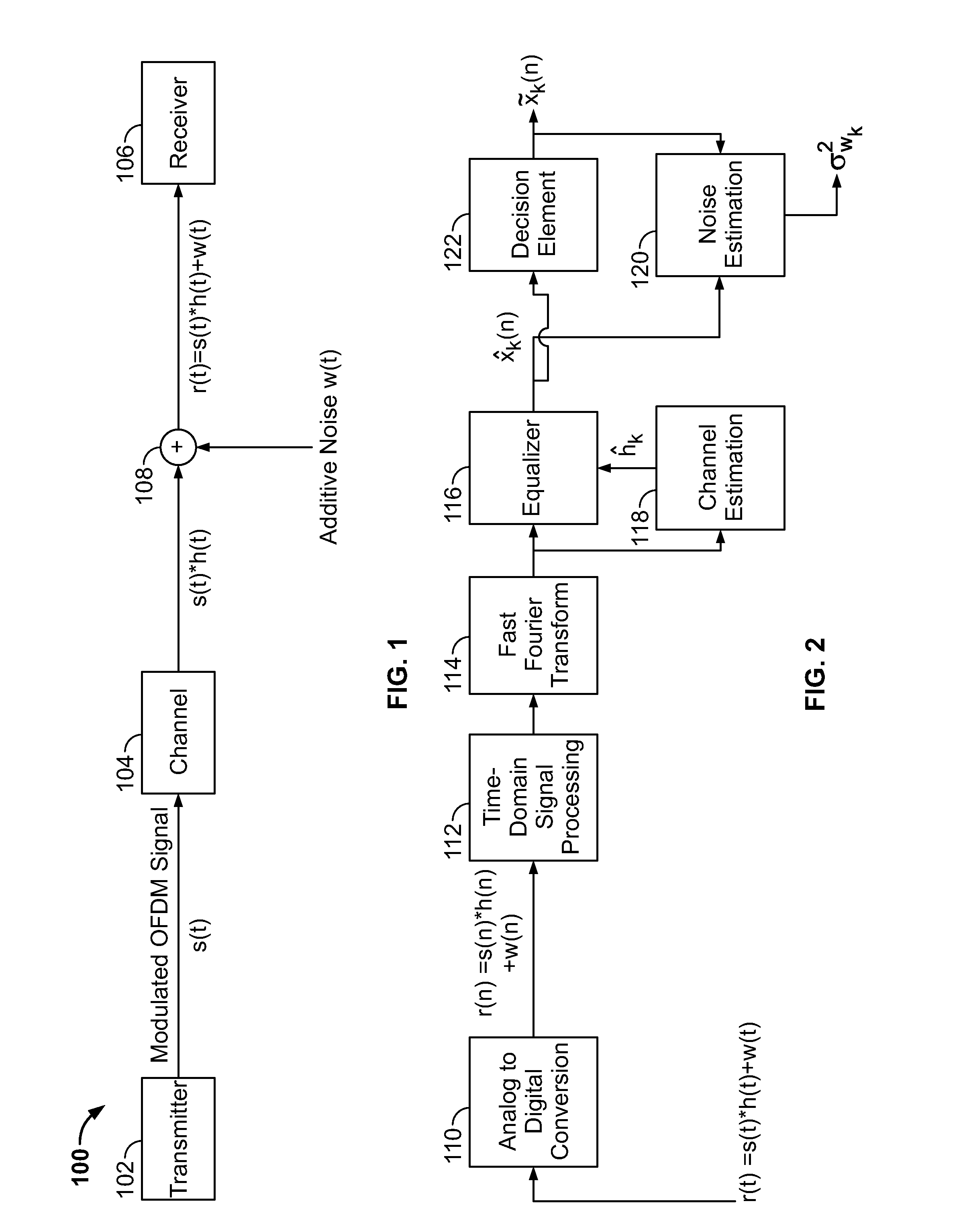
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Channel transfer function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
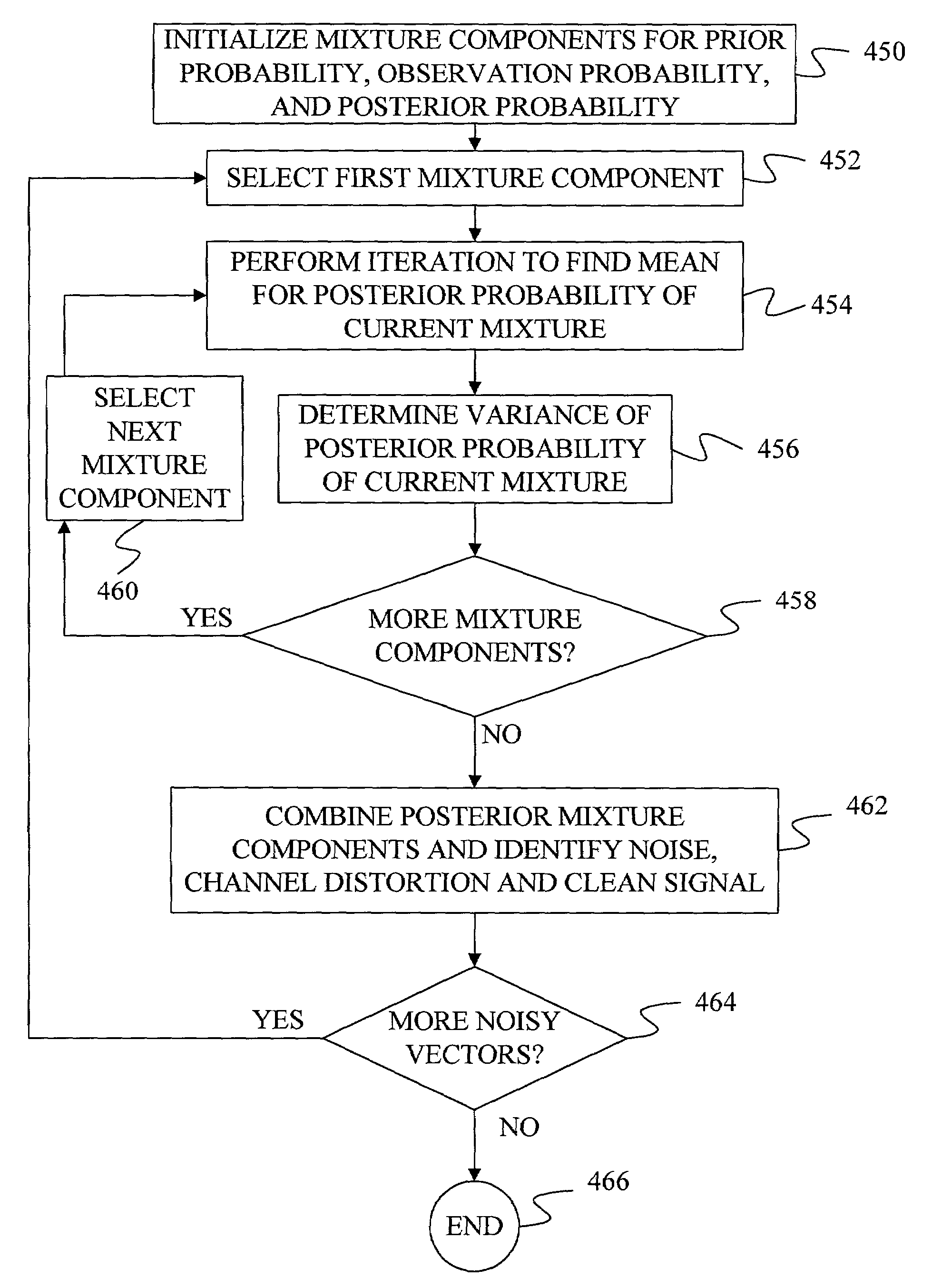
Method and apparatus for removing noise from feature vectors
A method and computer-readable medium are provided for identifying clean signal feature vectors from noisy signal feature vectors. The method is based on variational inference techniques. One aspect of the invention includes using an iterative approach to identify the clean signal feature vector. Another aspect of the invention includes using the variance of a set of noise feature vectors and / or channel distortion feature vectors when identifying the clean signal feature vectors. Further aspects of the invention use mixtures of distributions of noise feature vectors and / or channel distortion feature vectors when identifying the clean signal feature vectors. Additional aspects of the invention include using a variance for the noisy signal feature vector conditioned on fixed values of noise, channel transfer function, and clean speech, when identifying the clean signal feature vector.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
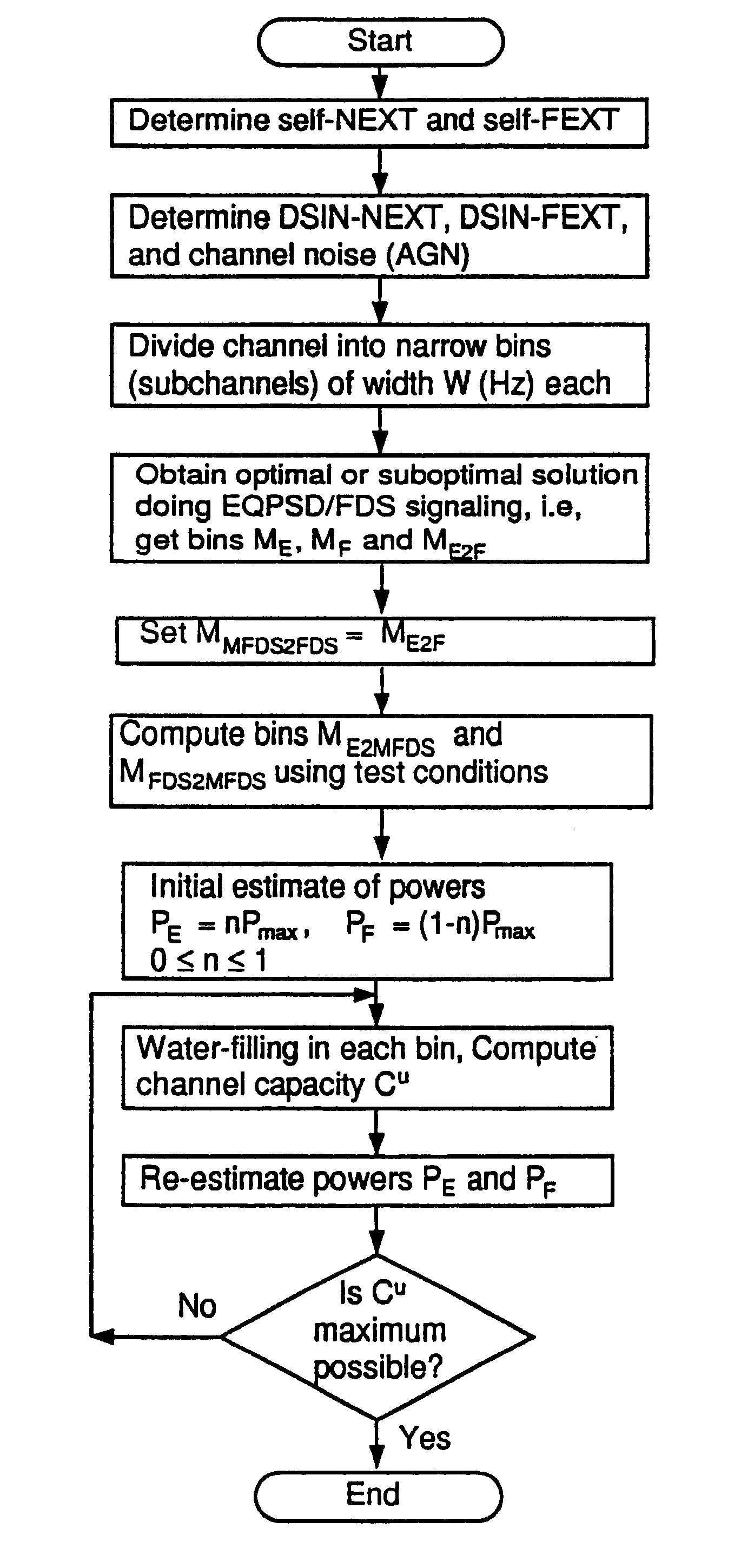
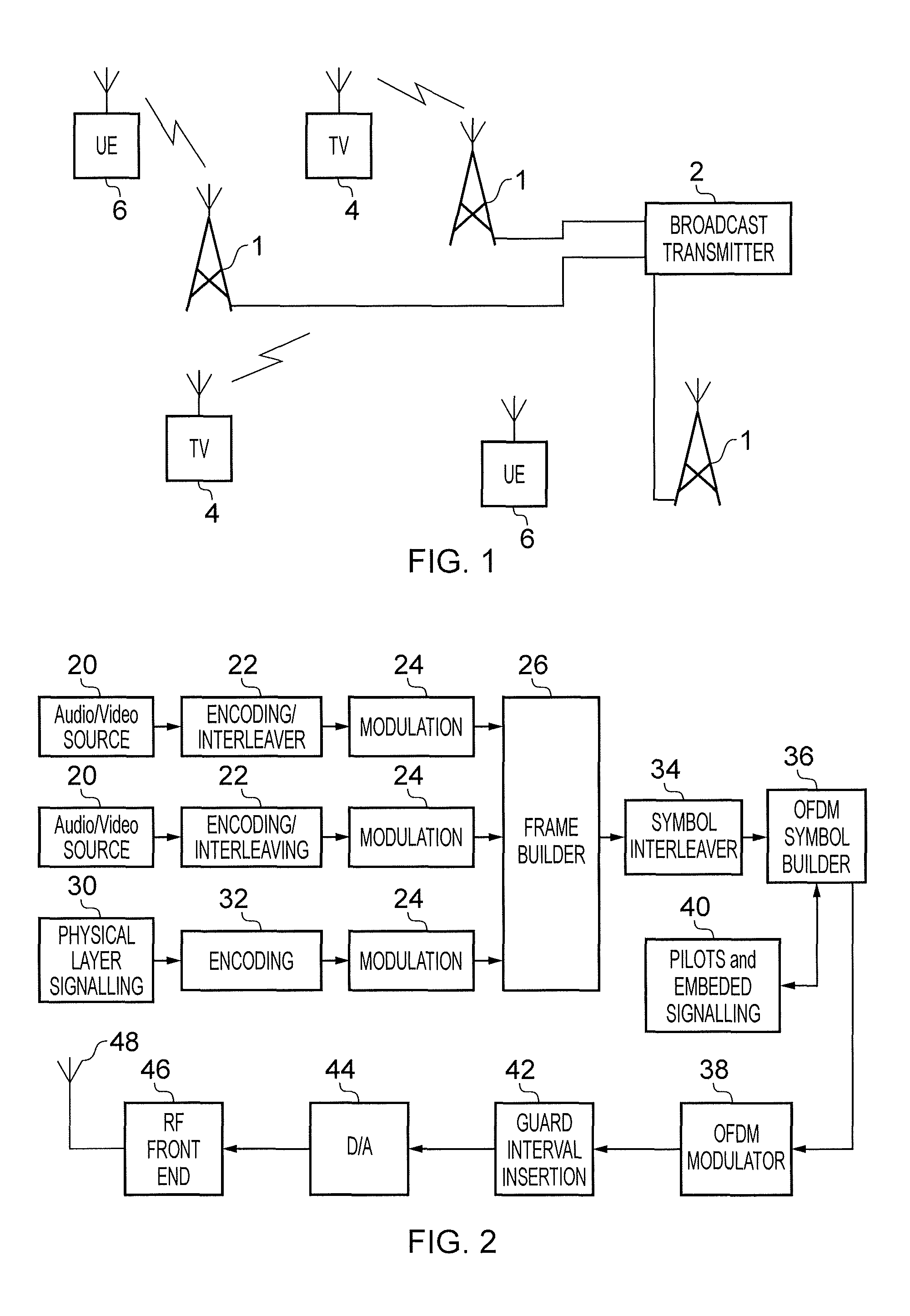
Spectral optimization for communication under a peak frequency-domain power constraint
InactiveUS6839429B1Maximize capacityMinimize effect of interferencePower managementSubstations coupling interface circuitsFrequency spectrumPeak value
System and methods for determining an optimized transmit spectra (spectral distributions of transmission power) for a set of communications channels that experience cross-talk among themselves and for transmitting data on the channels. The transmit spectra are preferably constructed so that largely contiguous frequency bands are allocated to each signaling direction (upstream / downstream) on each communications channel and / or to each channel in the set of channels. In one embodiment, each communications channel is restricted to a maximum time-averaged power. The method preferably includes steps of determining the channel transfer functions of the communications channel, determining interference characteristics of the channels, calculating substantially optimal transmit spectra for the communications channels, and redistributing the frequency bins so that they are contiguously grouped in each transmit spectra. The contiguous groupings allow wider frequency bands for signaling in the channel. In one embodiment, the channel is limited by a “peak-power constraint.”
Owner:RICE UNIV
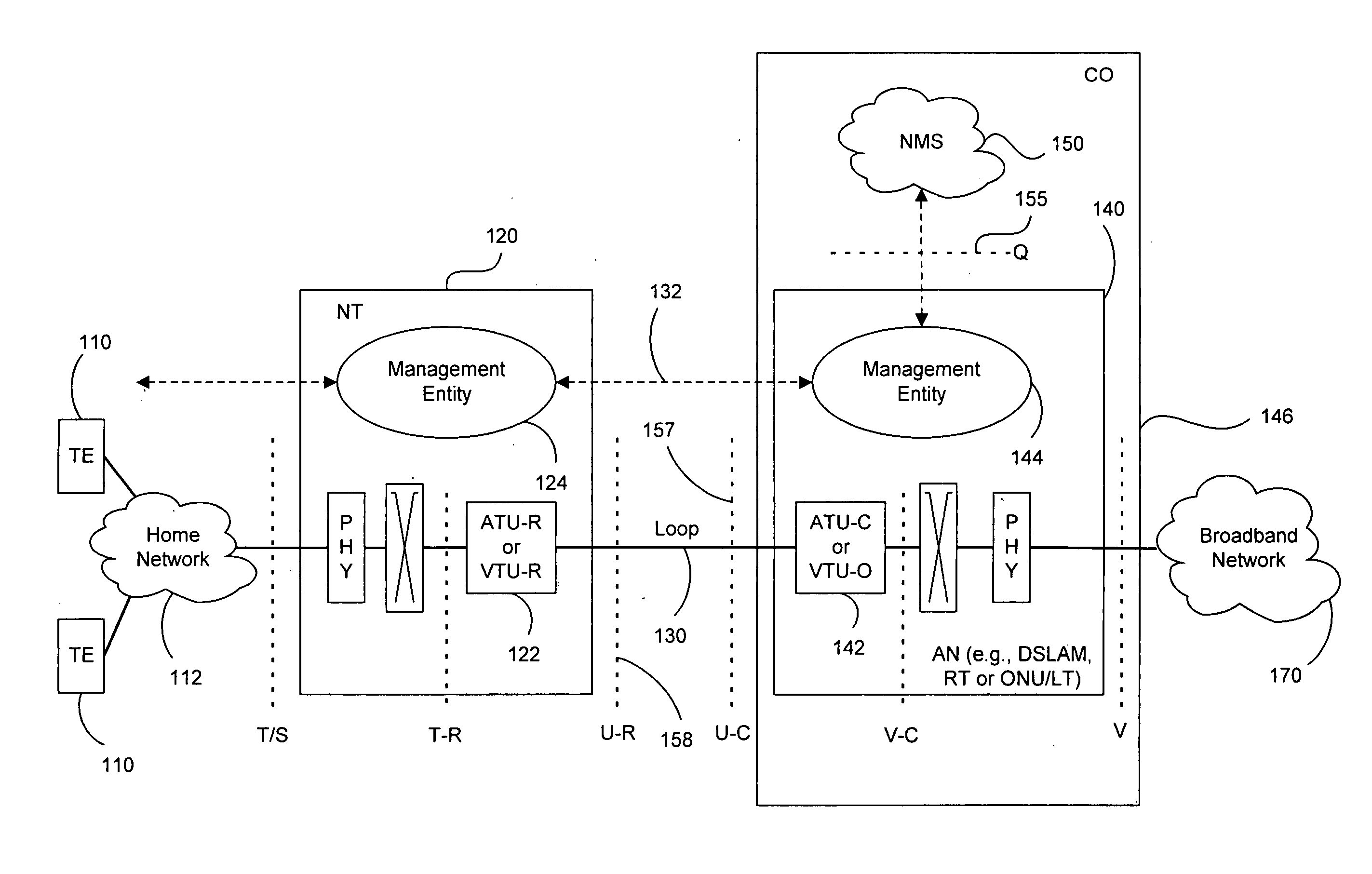
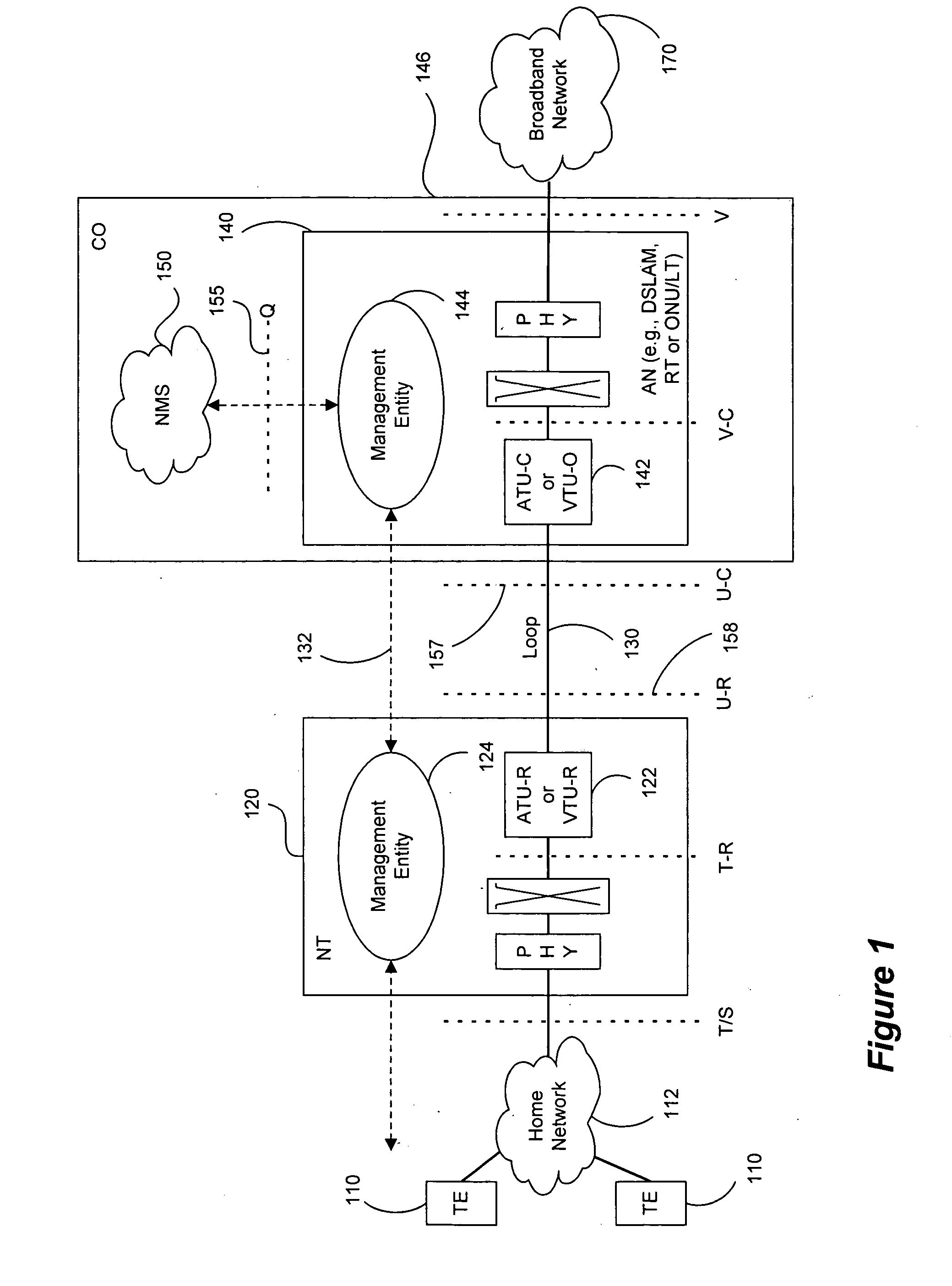
Receiver
ActiveUS20050213680A1Improve performanceReduce noiseTelevision system detailsError preventionChannel impulse responseCarrier signal
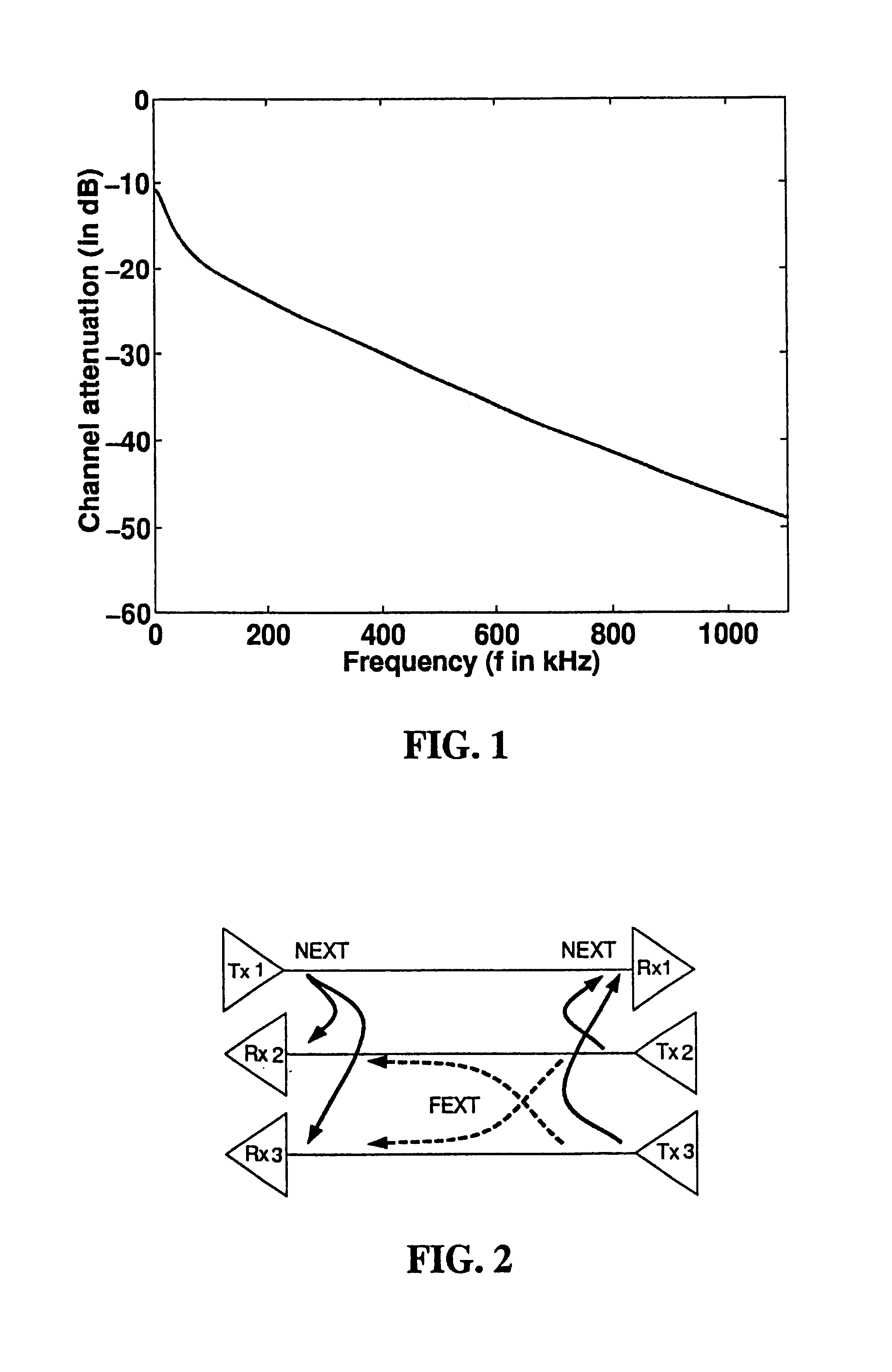
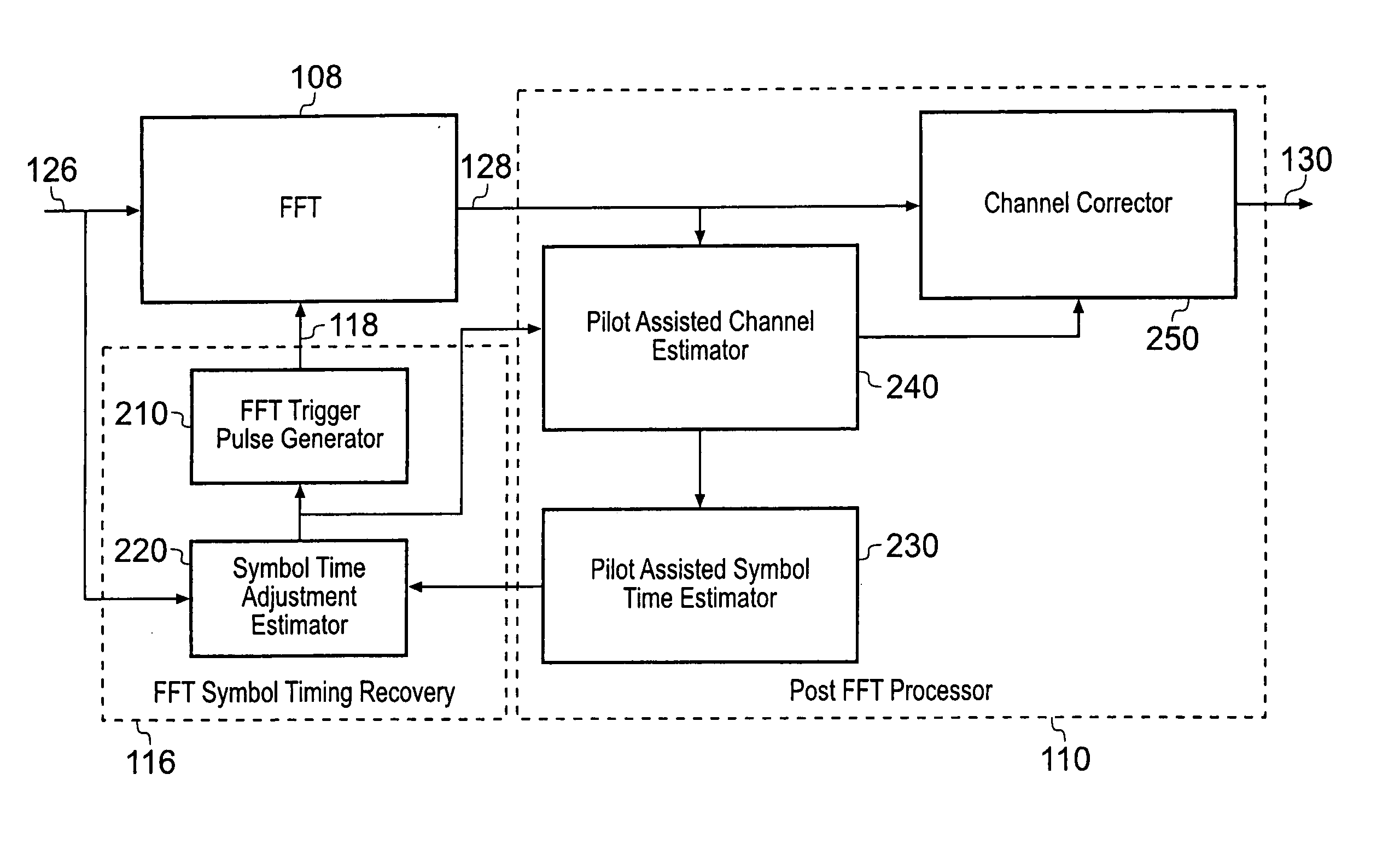
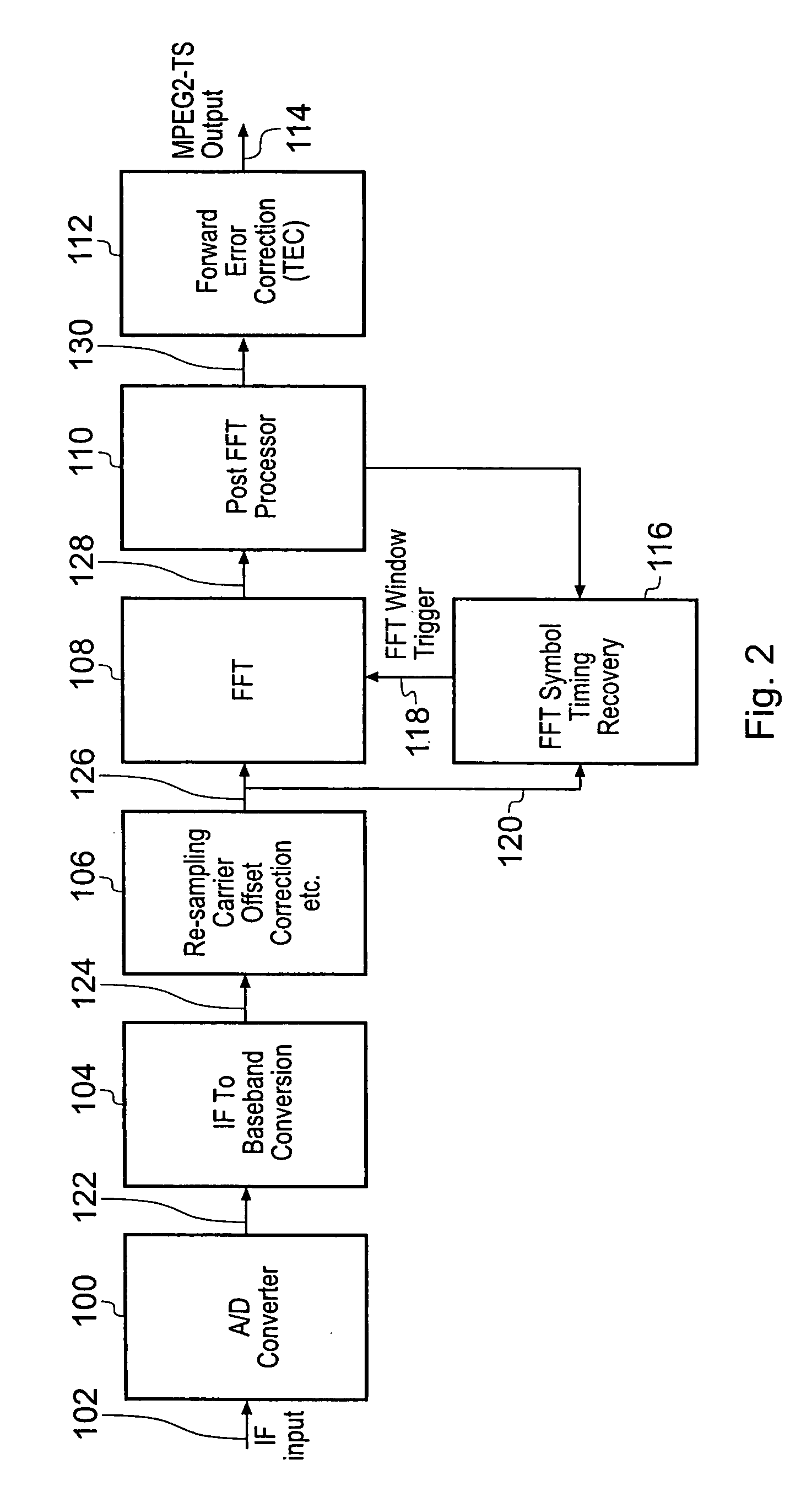
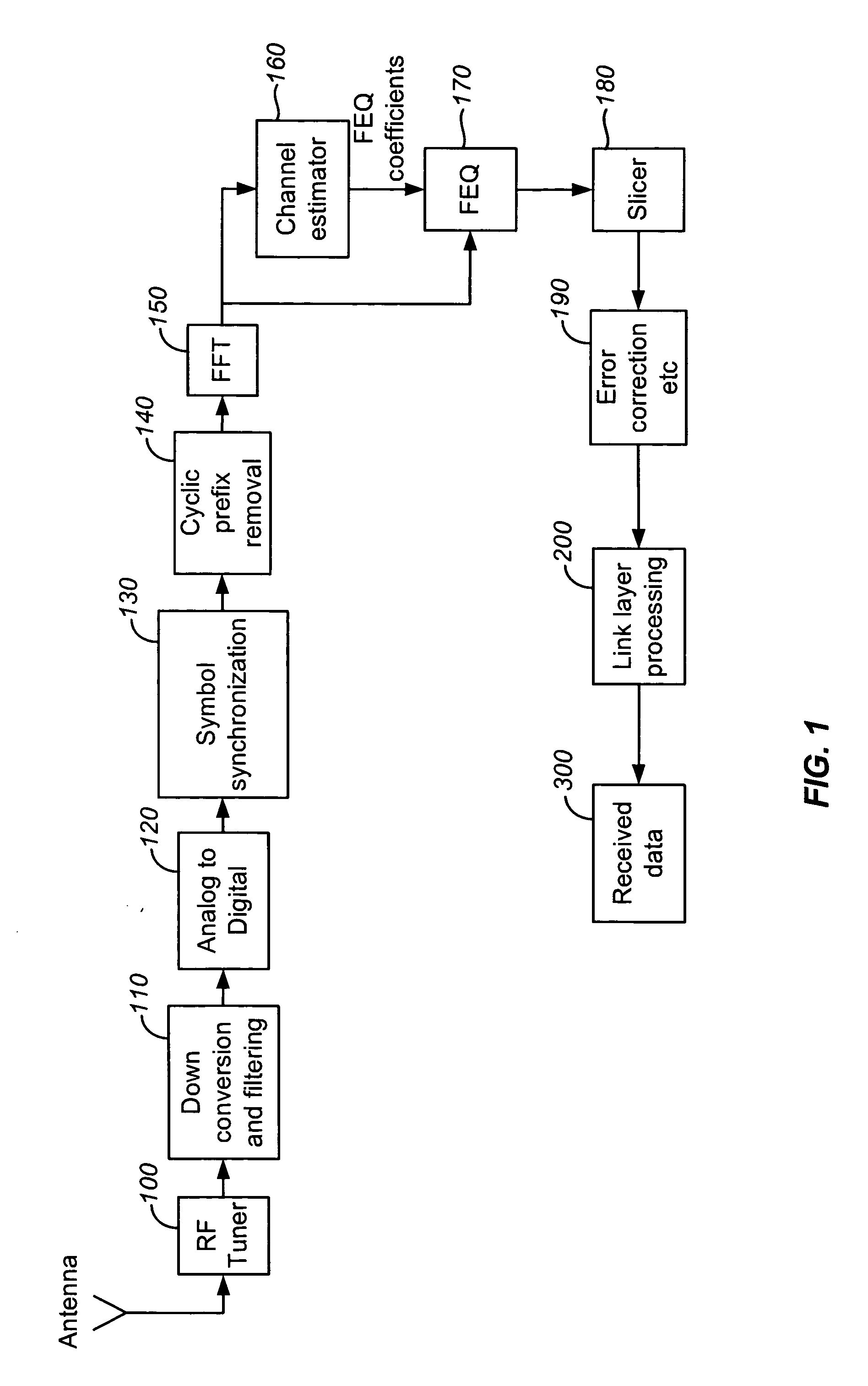
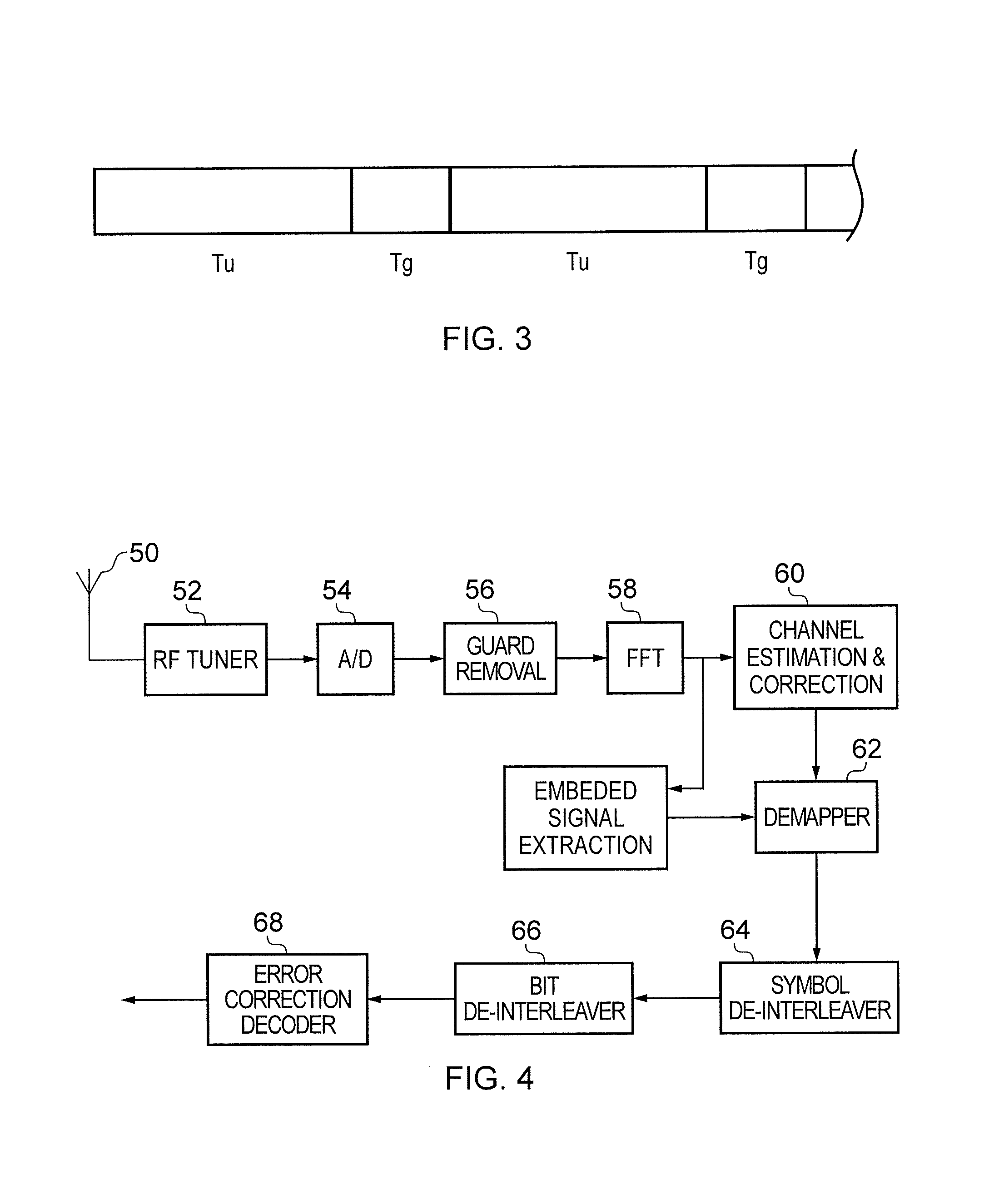
A receiver for recovering data from a symbol of signal samples generated in accordance with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing is described. The symbol may be a COFDM symbol in accordance with the DVB-T standard, and includes pilot carrier signals for use in estimating channel conditions. The receiver includes a pilot assisted channel estimator comprising a pilot extractor operable to extract the pilot carrier signals from the signal samples and to generate from the extracted pilots samples of the channel frequency response or channel transfer function estimate. The channel frequency response generator is operable to compare the extracted pilot carrier signals with a predetermined version of the pilot carrier signals. The pilot assisted channel estimator includes a frequency dimension interpolation filter operable to interpolate the pilot-derived samples of the channel frequency response in the frequency dimension, and a filter controller. The frequency response of the frequency interpolation filter has a pass bandwidth, which is adjustable, and the filter controller is operable to adjust the bandwidth of the frequency interpolation filter to the effect of reducing noise in the channel frequency response estimate. The use of an adjustable pass bandwidth for a frequency domain interpolation filter can advantageously be used to reduce noise in the channel impulse response estimate by enabling an appropriate selection of the bandwidth of the frequency domain interpolation filter according to the particular current characteristics of the channel impulse response.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC +1
METHOD AND APPARATUS USING SOUNDING PPDUs TO PROVIDE RANGE EXTENSION TO IEEE 802.11n SIGNALS
InactiveUS20100111220A1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSpatial mappingCarrier signal
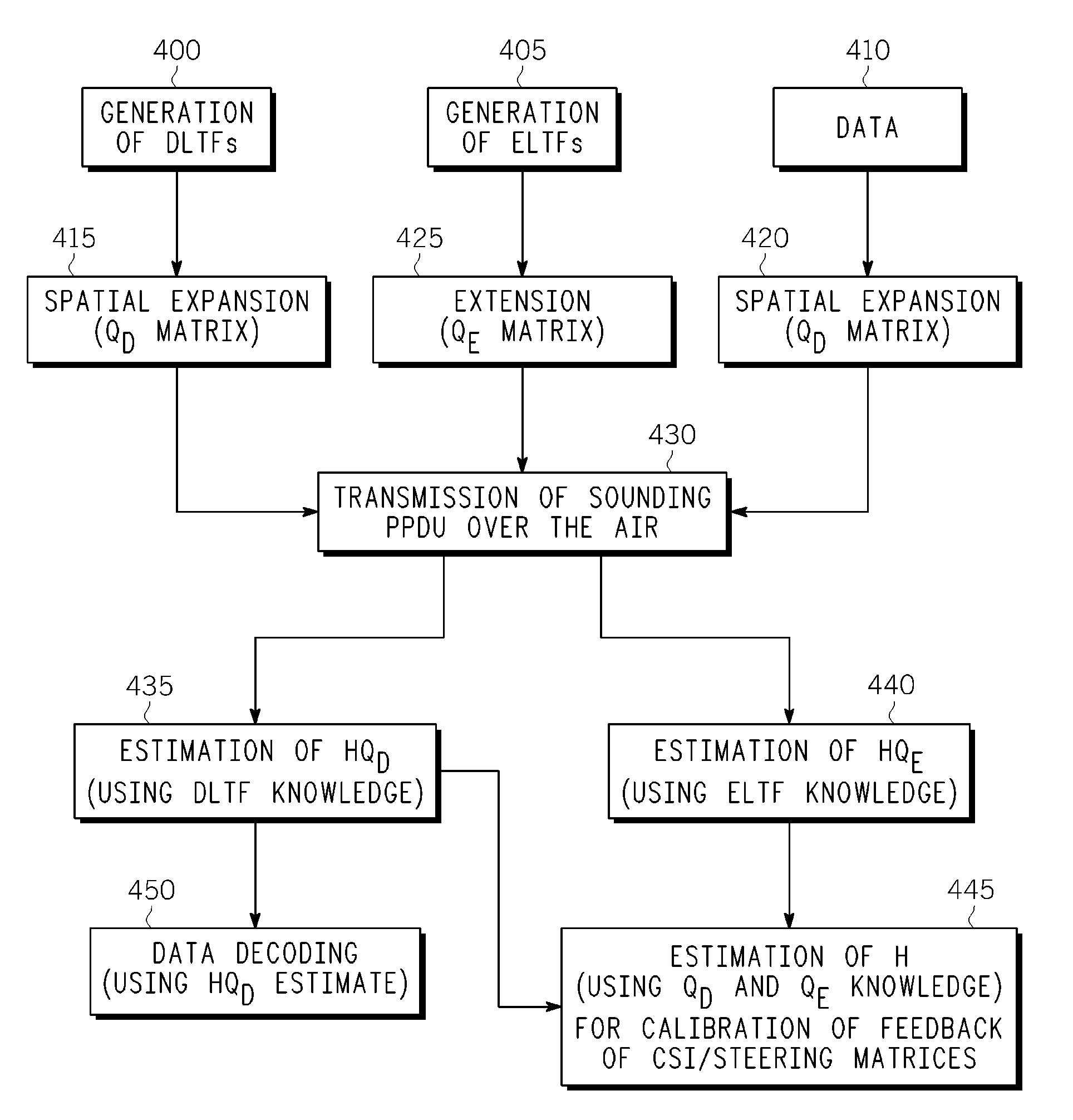
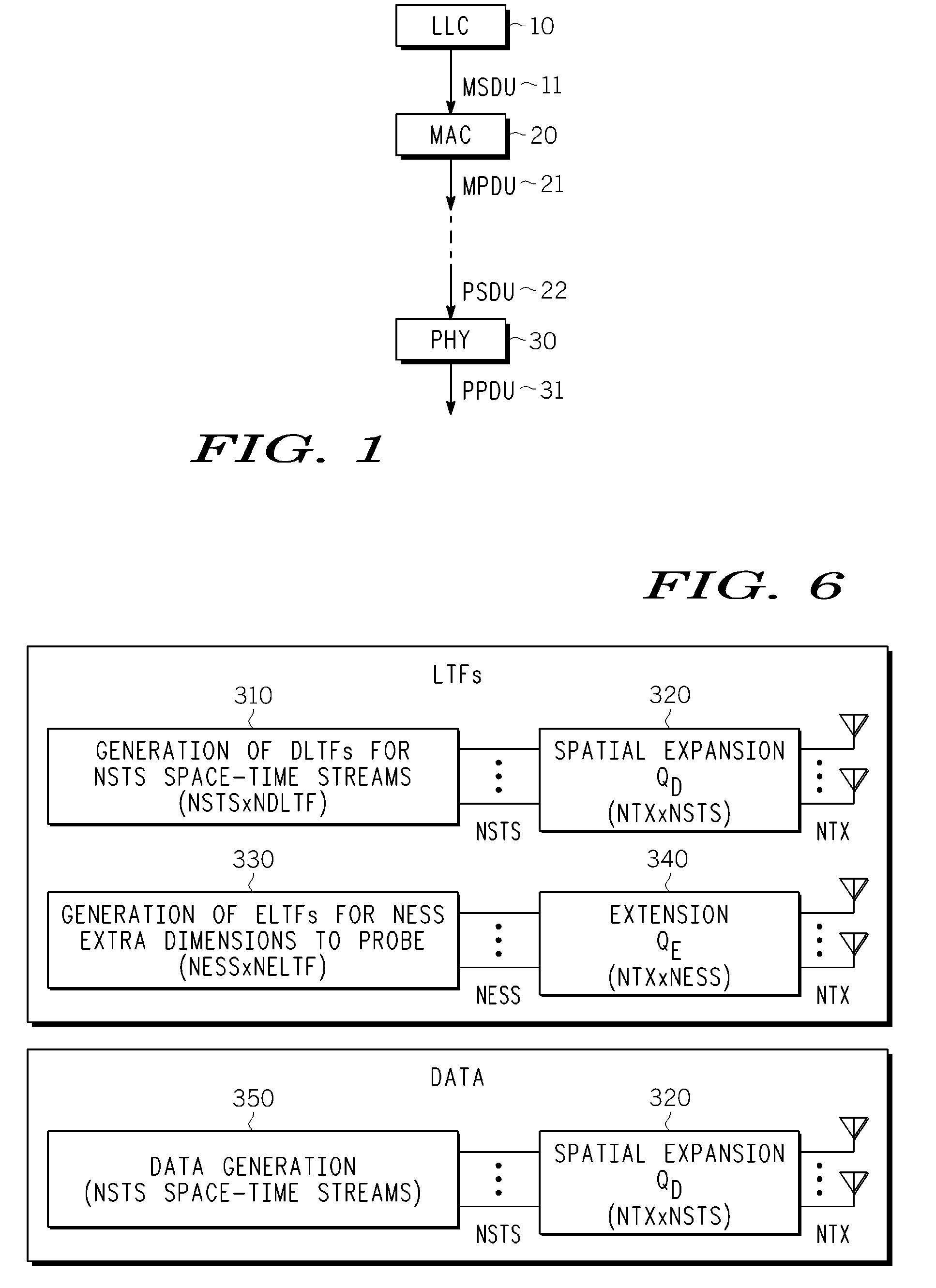
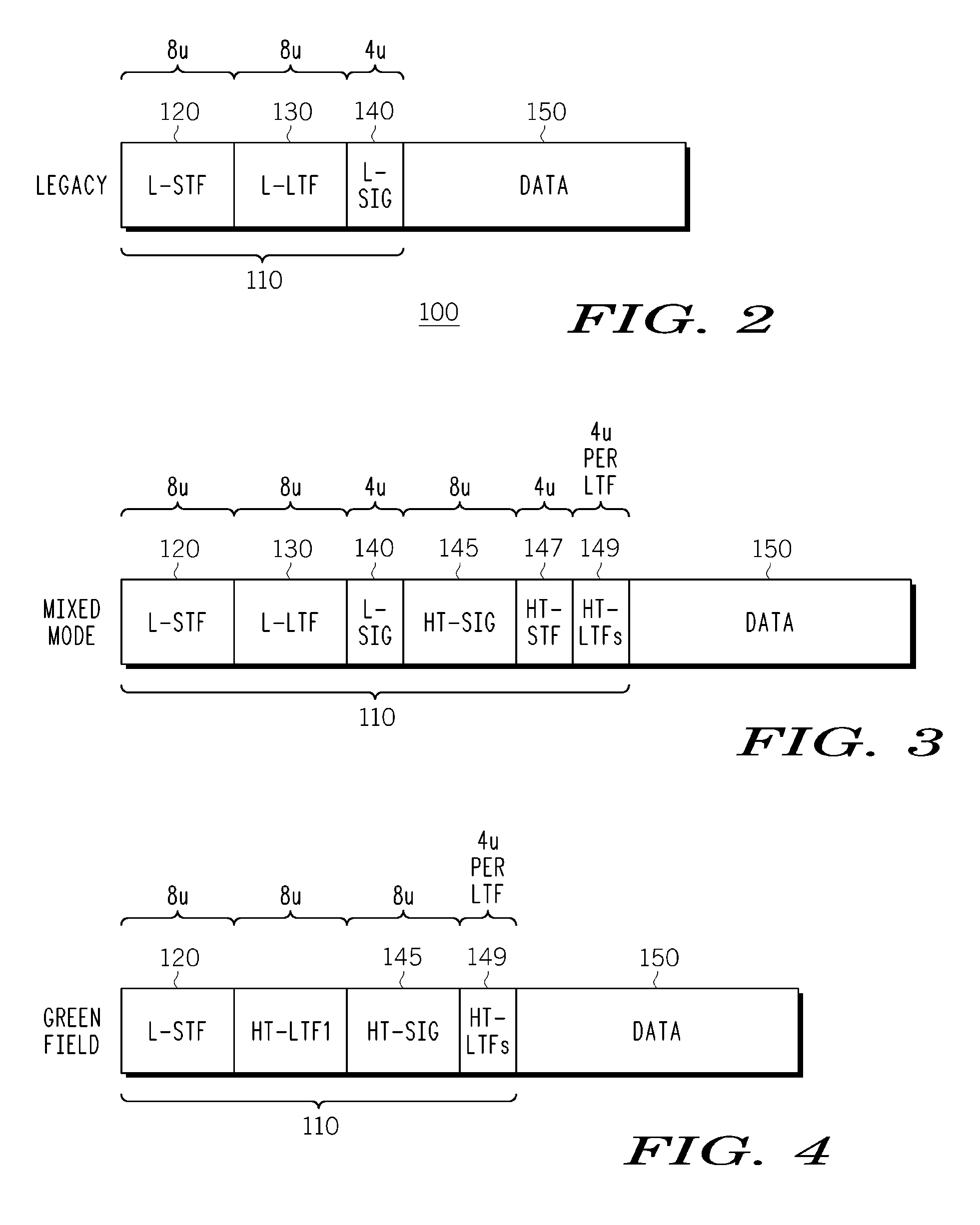
A wireless transmitter includes a stream parser for generating a plurality of spatial streams from a digital signal and a space time block coder (STBC) for mapping each of the spatial streams to a plurality of space-time streams that each include data and a preamble for estimating a channel transfer function. The transmitter also includes a spatial mapper for spatially expanding each of the space-time streams by applying a spatial expansion matrix to data and to first training symbols used in the preamble to probe a channel experienced by the data and by applying an extension matrix to second training symbols used in the preamble to probe at least one additional dimension of the channel to enable use of beamforming to achieve range extension The spatial expansion matrix and the extension matrix form an overall matrix that has at least two orthogonal columns with different norms. The wireless transmitter also includes an analog front end for modulating the spatially expanded space-time streams onto a wireless carrier.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
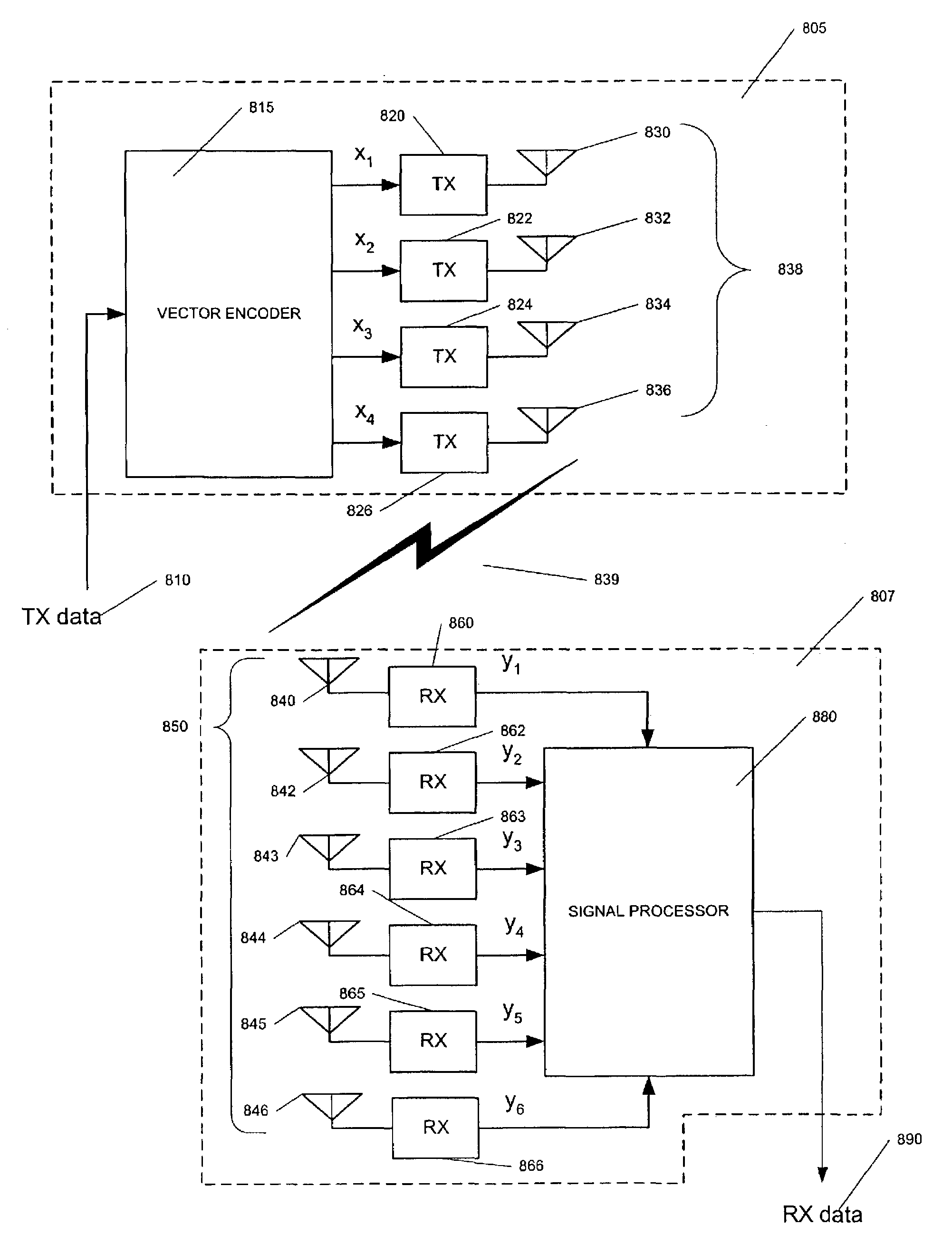
Transmit diversity wireless communication
ActiveUS7308035B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityEngineeringAntenna element
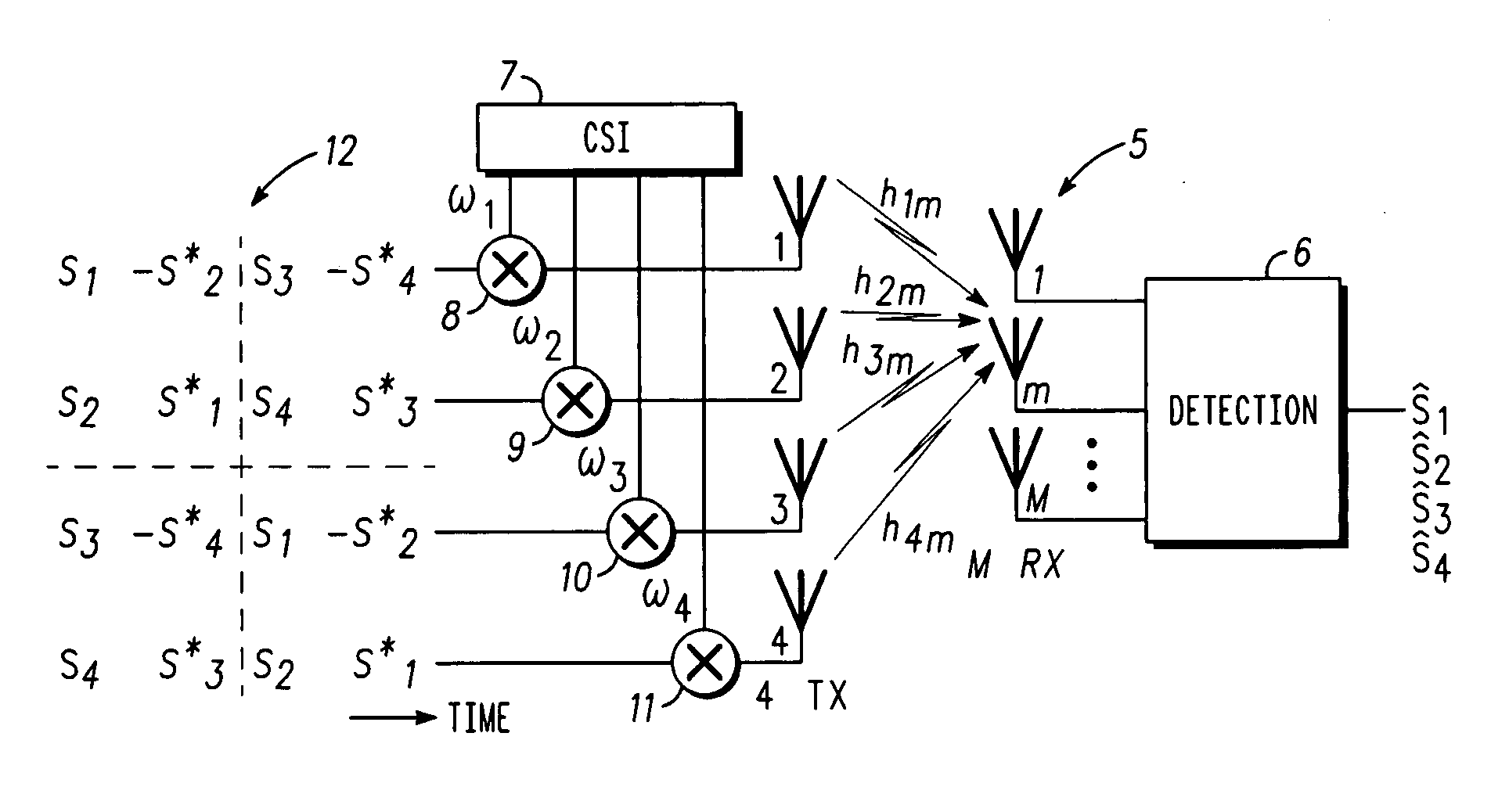
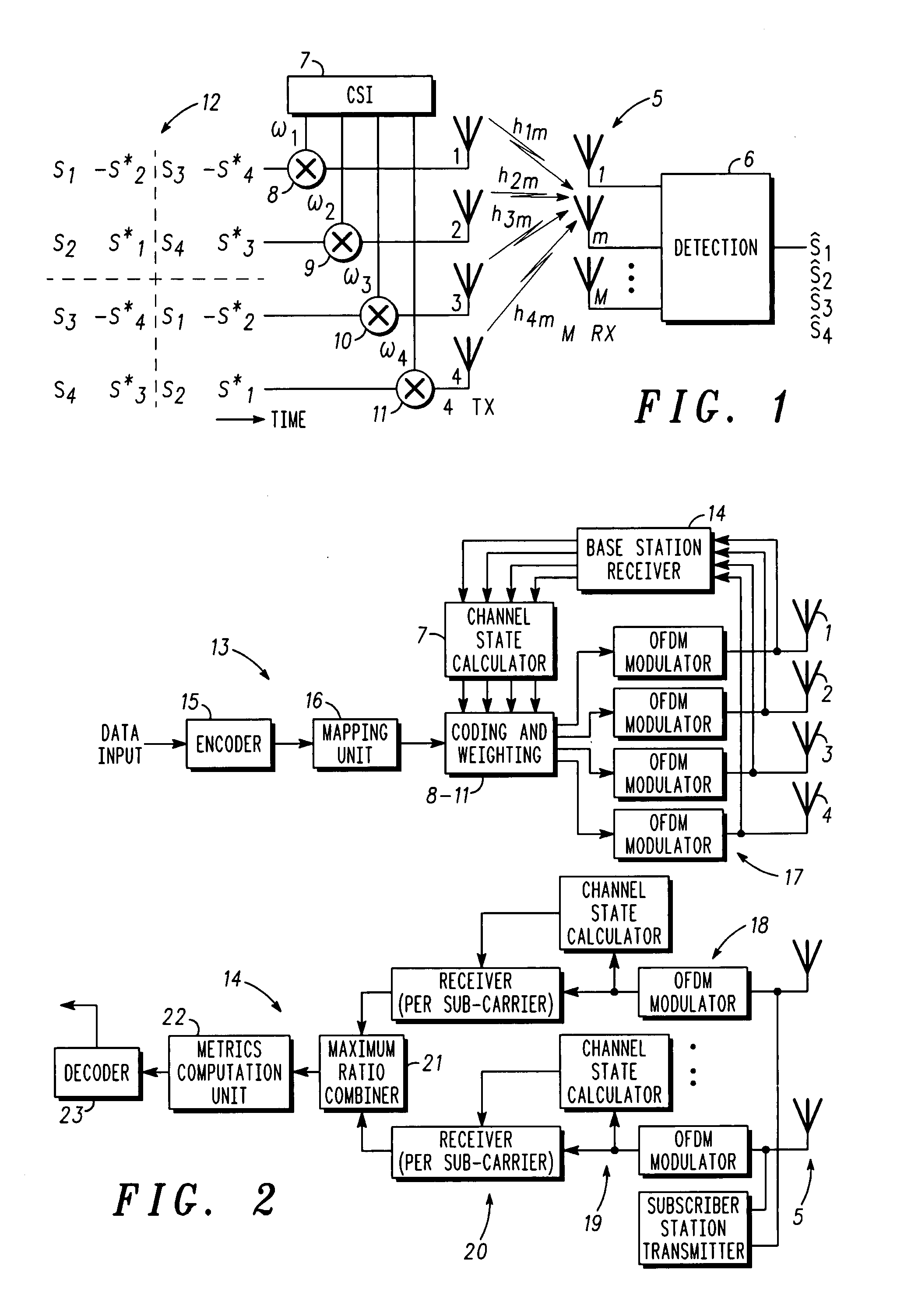
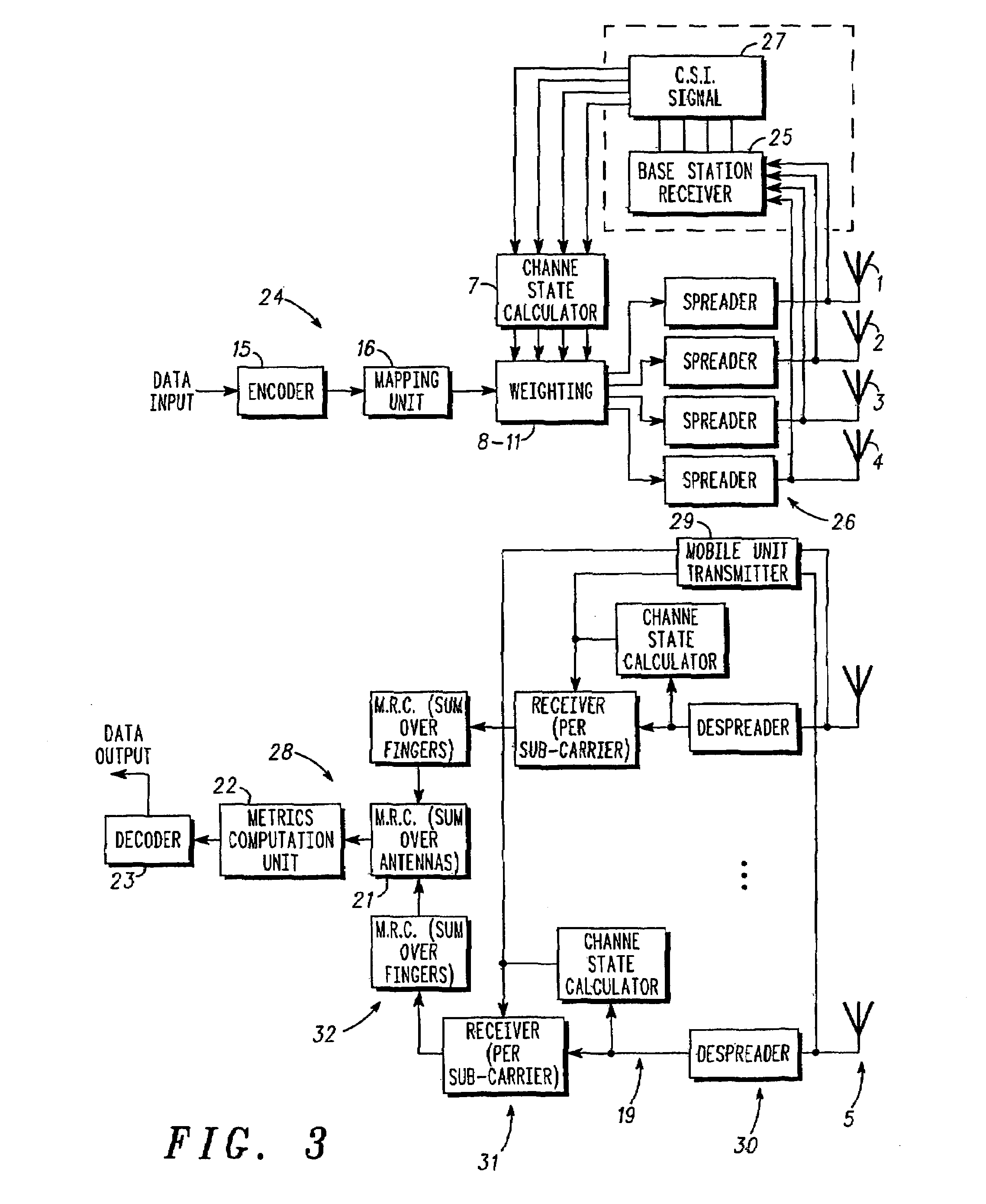
A method of transmitting data from a transmitter (13,24) to a remote receiver (14,28) using transmit diversity wireless communication, the transmitter (13,24) comprising three or more transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4). The data is encoded in symbol blocks (12), the symbols (s1,s2,s3,s4) of a block (12) being permuted within respective sub-sets of symbols between the transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4) over time with respective replications and complex conjugations and / or negations. At least one of the sub-sets of said transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4). The signals transmitted over at least one of the transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4) are modified as a function of channel information at least approximately related to the channel transfer function (h1,h2,h3 and h4) of the transmitted signals, and the sub-sets of symbols and permuted symbols are permuted over time between said sub-sets of transmit antenna elements, so that the received signal is detectable at the receiver (14,28) using an orthogonal detection matrix scheme.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Adaptive interpolator for channel estimation
InactiveUS20060269016A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTime domainCommunications system
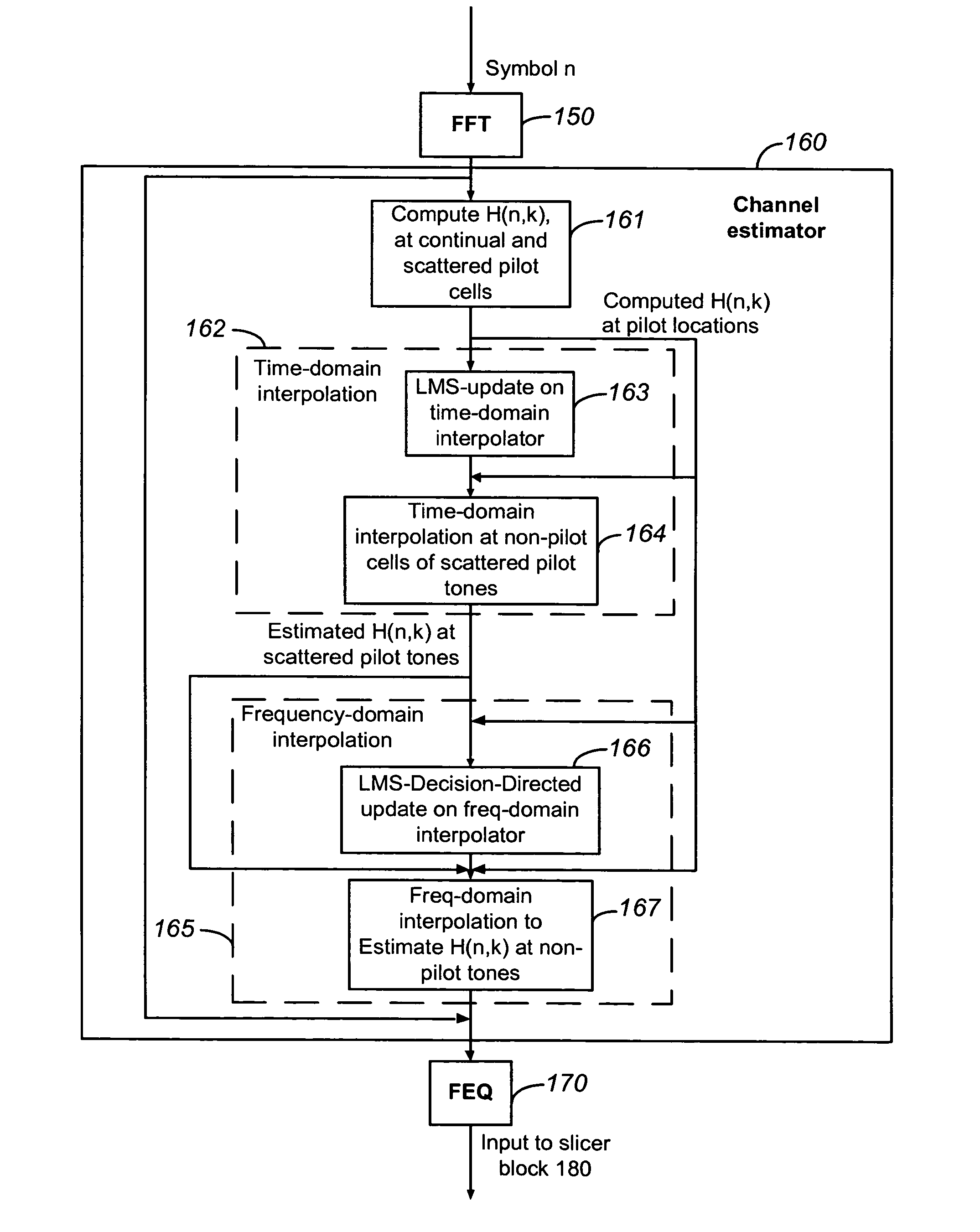
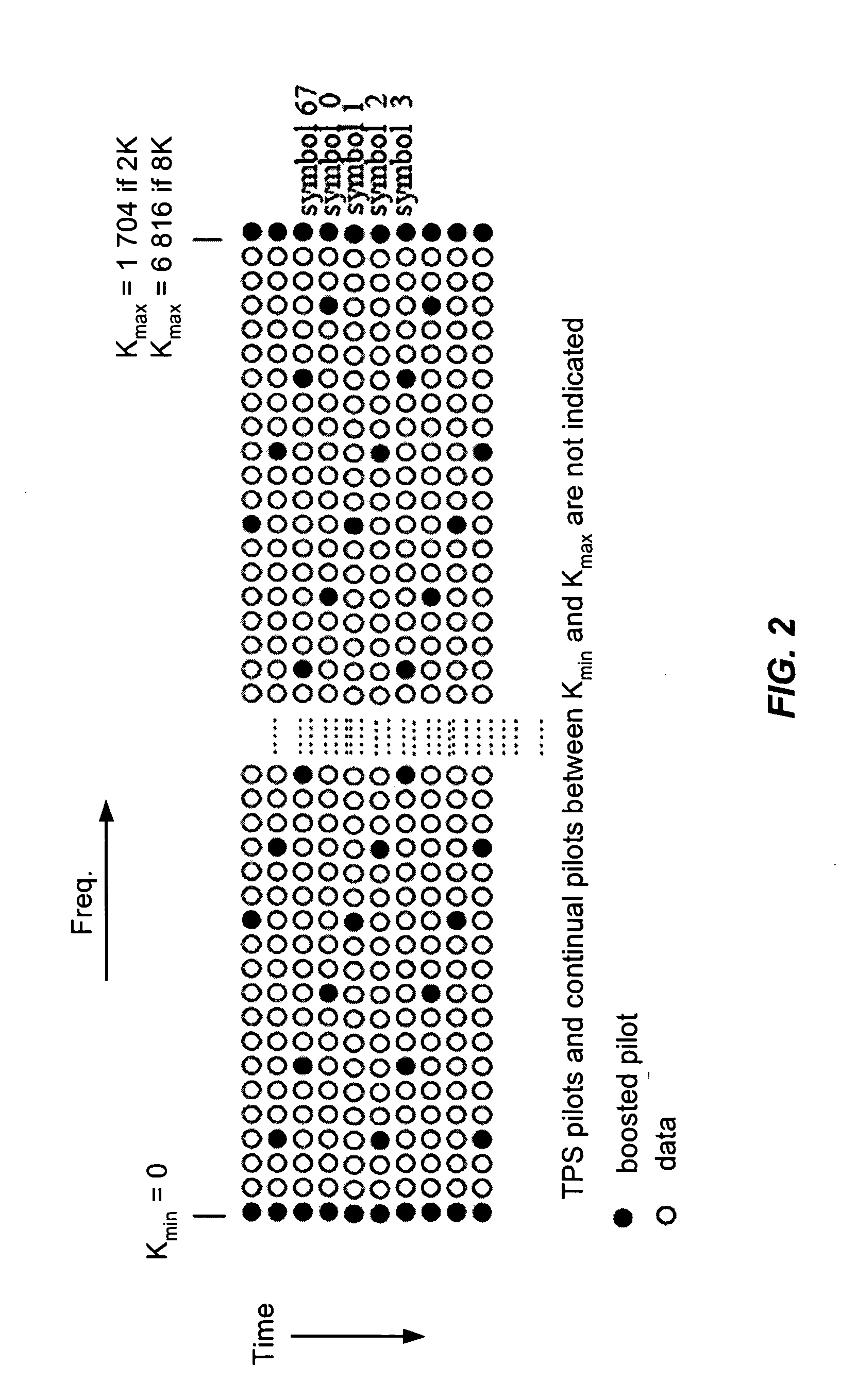
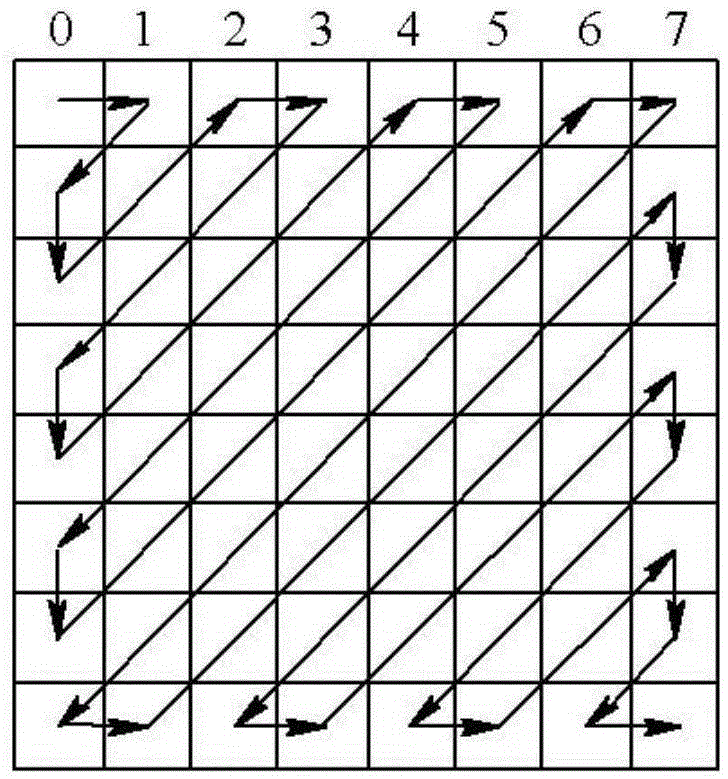
A method for channel estimation in a wireless communication system includes the following steps. Channel transfer function is computed at continual and scattered pilot cells using transmitted and received signals at the continual and scattered pilot cells. Time-domain adaptive interpolation is performed to obtain channel transfer function at non-pilot cells of the scattered pilot tones using the channel transfer function computed at continual and scattered pilot cells. Frequency-domain adaptive interpolation is performed to obtain channel transfer function at non-pilot cells of non-pilot tones using the channel transfer function computed at continual and scattered pilot cells.
Owner:MEDIAPHY CORP
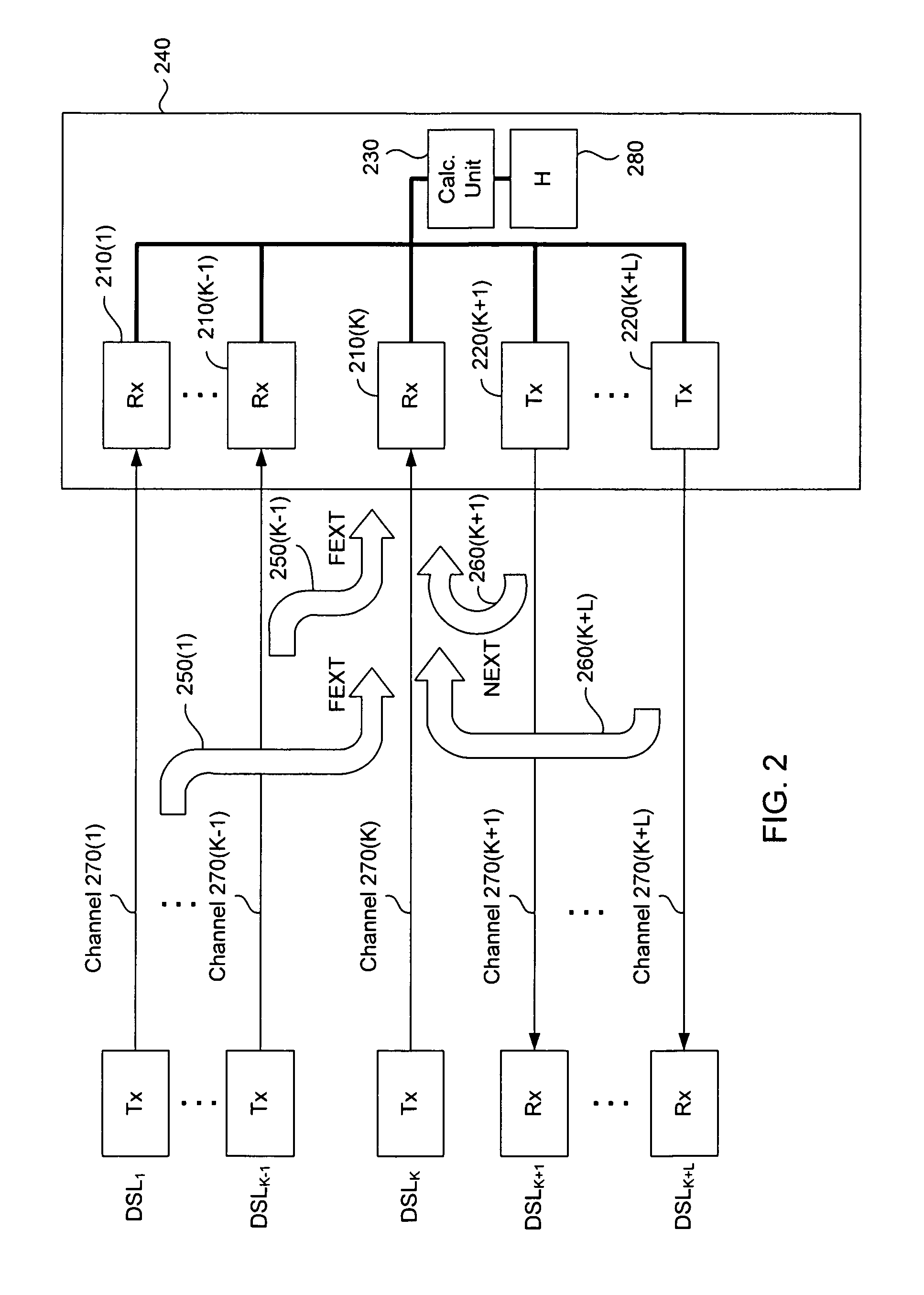
FEXT determination system
ActiveUS20050259725A1Error preventionTelephonic communicationSignal transfer functionTime-invariant system
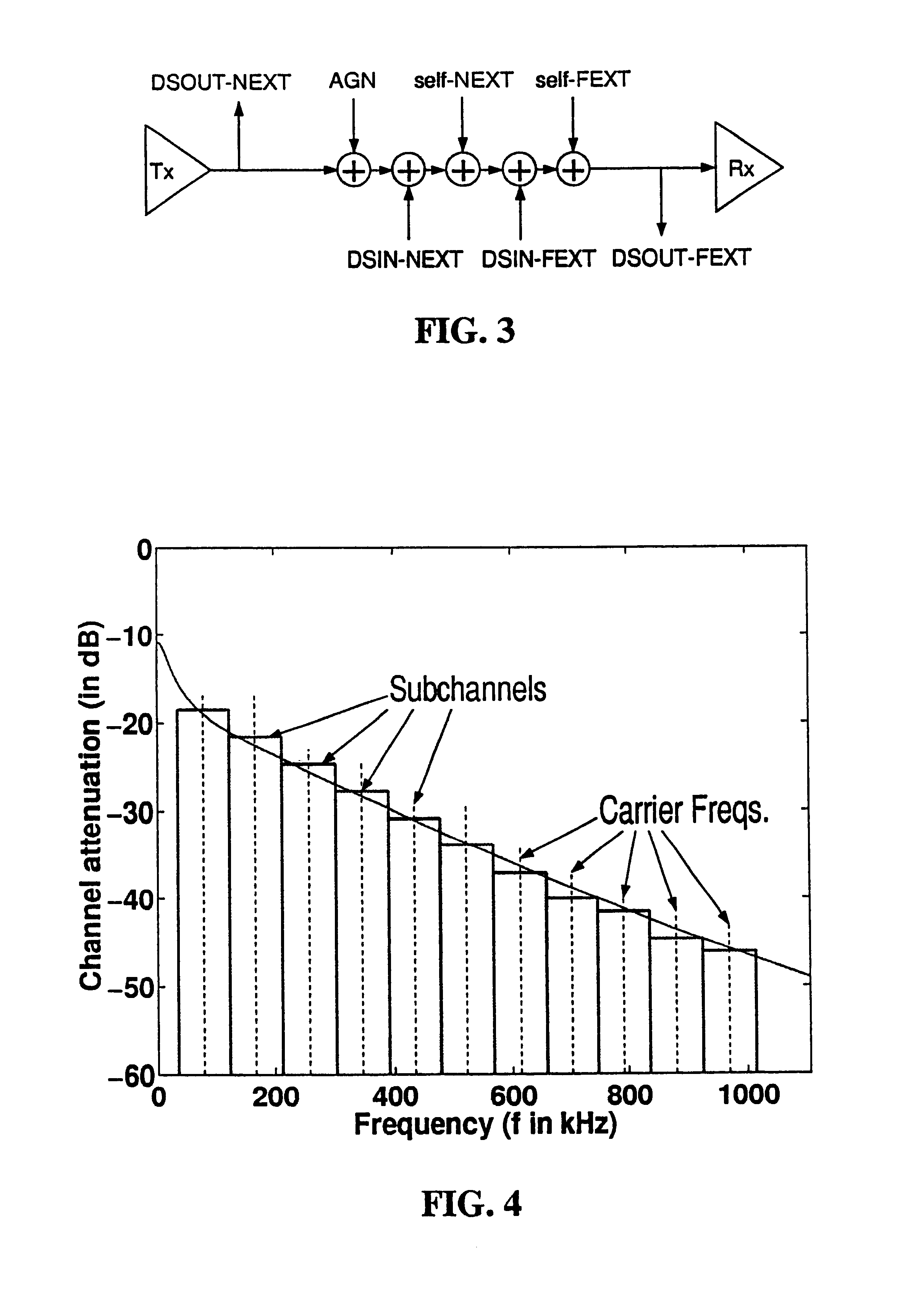
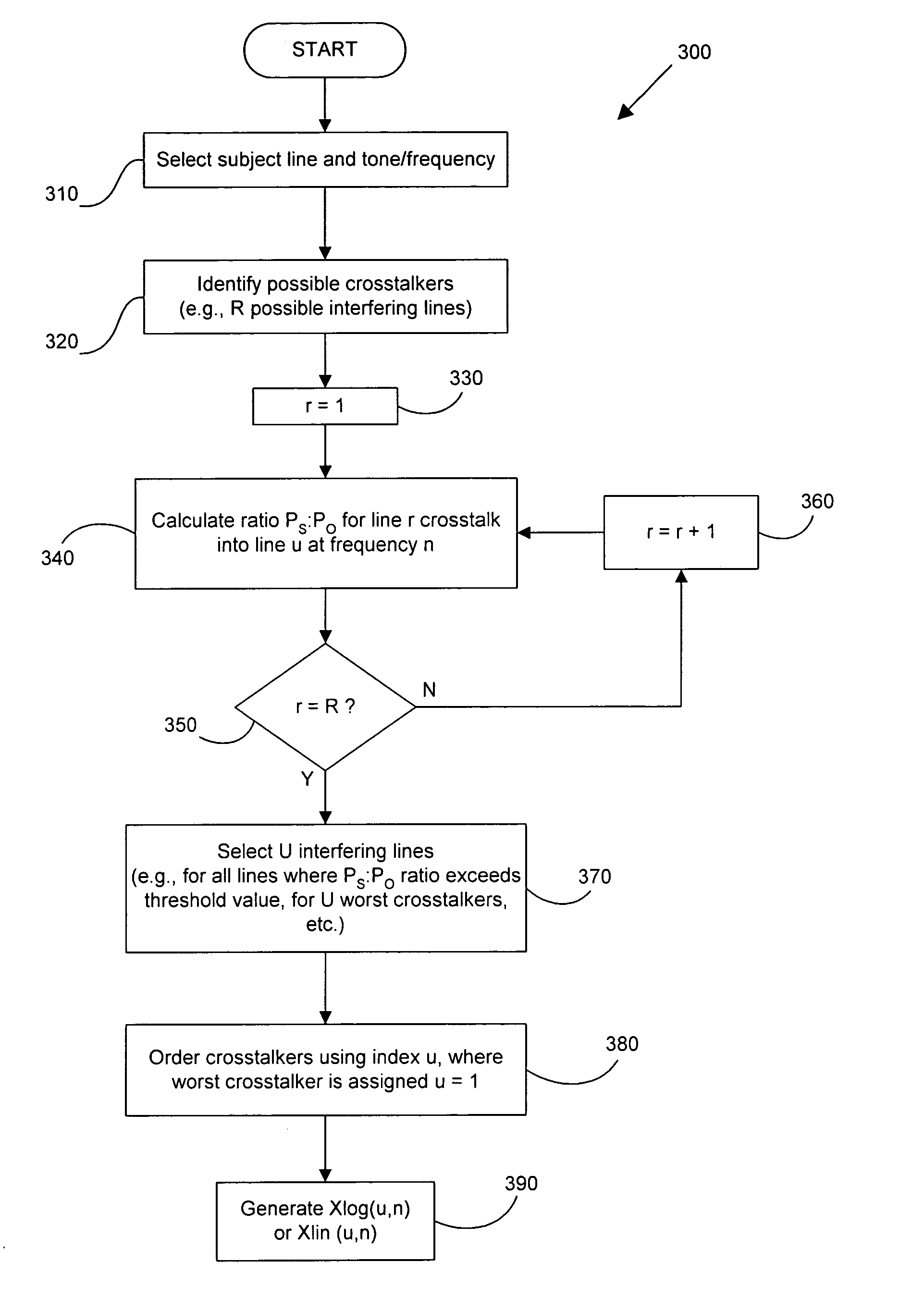
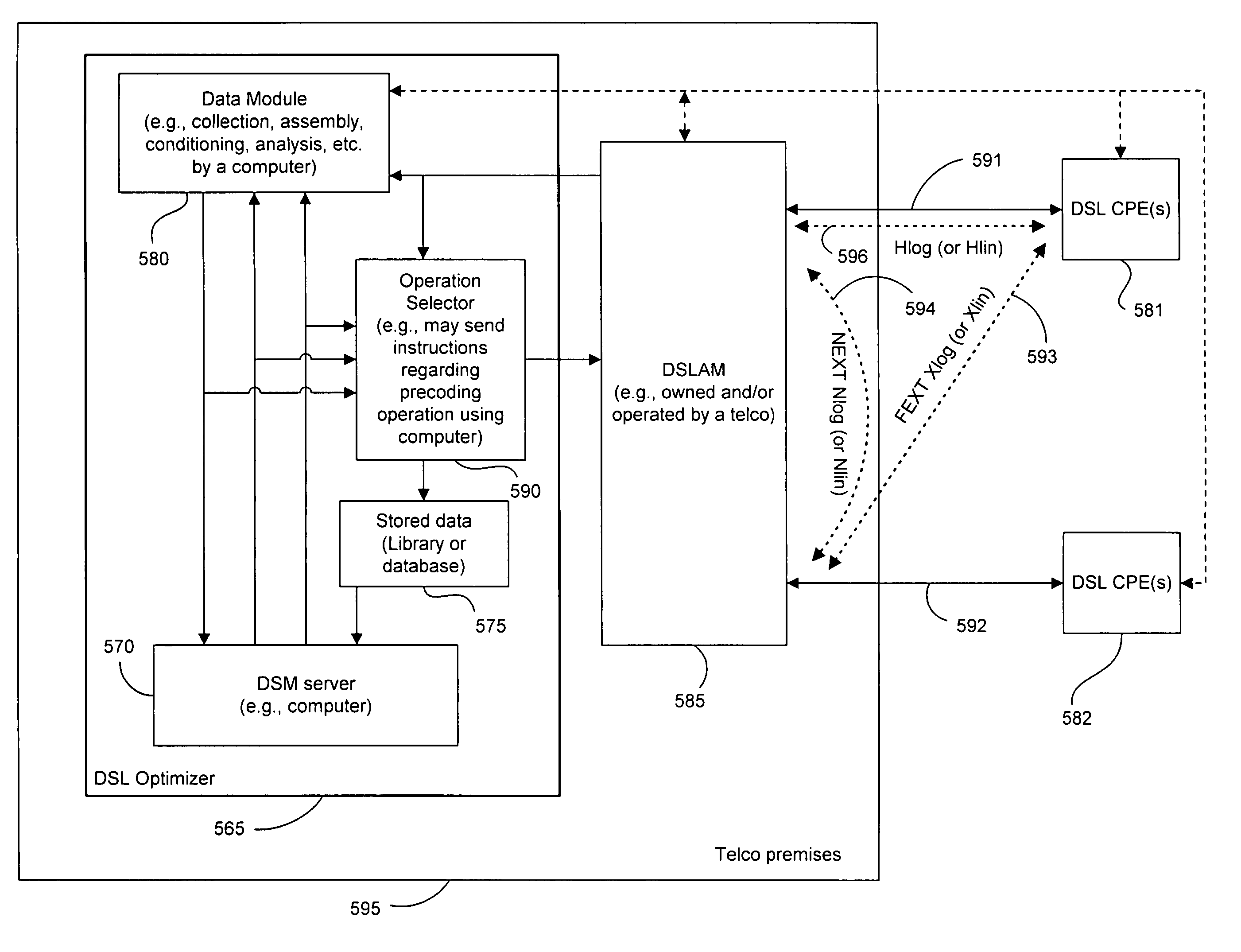
Operational data is utilized to determine the FEXT interference induced by one line into the other DSL line. FEXT interference can be calculated using the NEXT interference measured between the two lines at the upstream ends of the loops and the downstream channel transfer function of one of the loops. Because the NEXT and transfer function constitute a linear time-invariant system, as does the FEXT interference between the lines, the NEXT interference and line transfer function can be multiplied (if in linear format) or added (if in logarithmic format) to approximate the FEXT interference between the lines. The collection of data, calculations and other functions performed in these techniques may be performed by a system controller, such as a DSL optimizer. An Xlog(u,n) quantity is a decibel-magnitude representation of the insertion-loss equivalent of FEXT transfer functions and is defined as the ratio of (1) a line u's source power into a matched load of 100 Ohms when no binder is present to (2) the power at the output of the subject line when line u is excited with the same source and the binder is present. Xlin(u,n) is the linear equivalent of Xlog(u,n). The Xlog(u,n) and Xlin(u,n) quantities may be represented in specific formats that assist in their use in DSL and other systems. When defined as a line's insertion loss, Xlin (or equivalently Xlog) does not include the effect of any transmit filter.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Method and system for localization
ActiveUS20130172020A1Position fixationWireless commuication servicesComputer scienceChannel transfer function
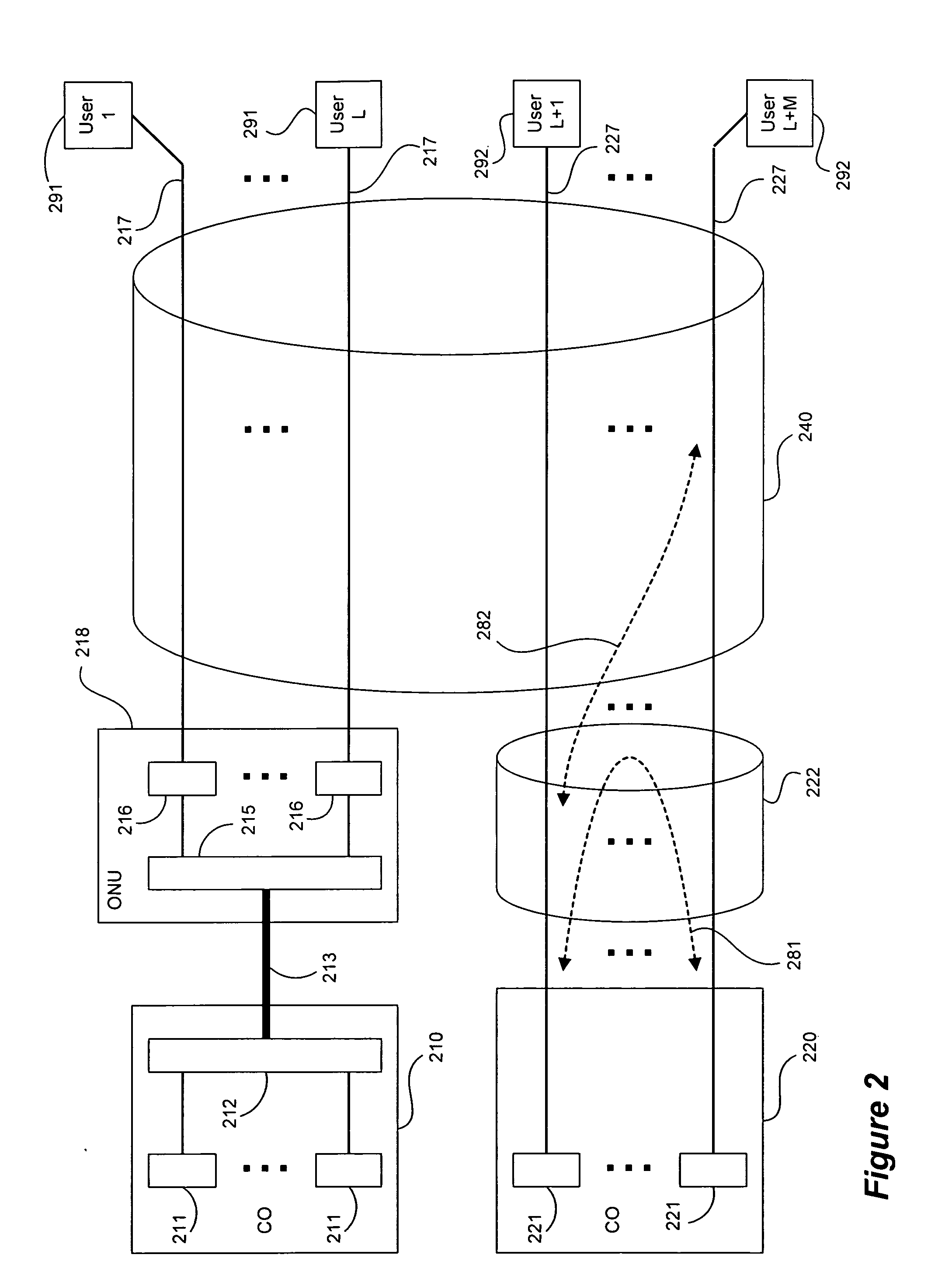
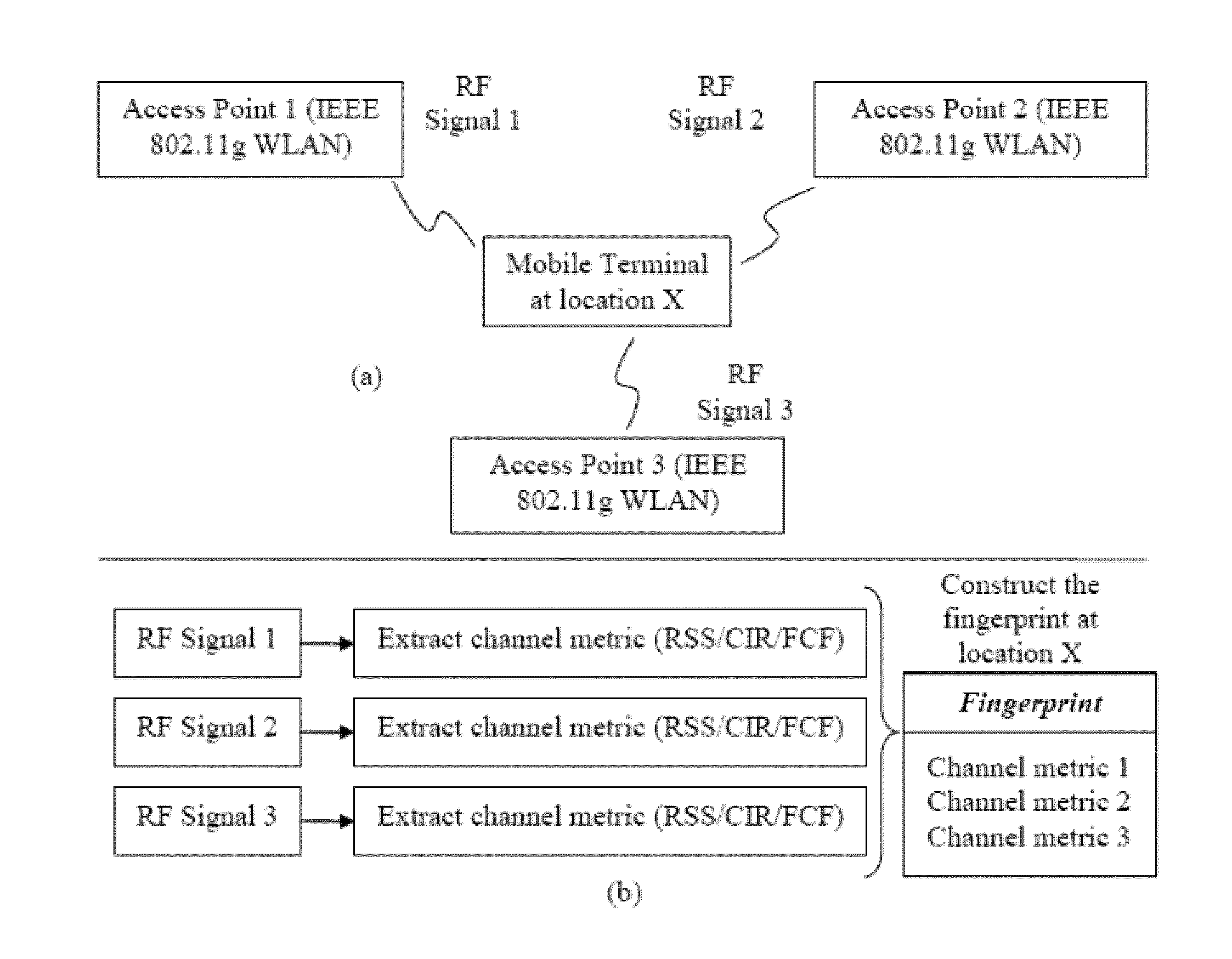
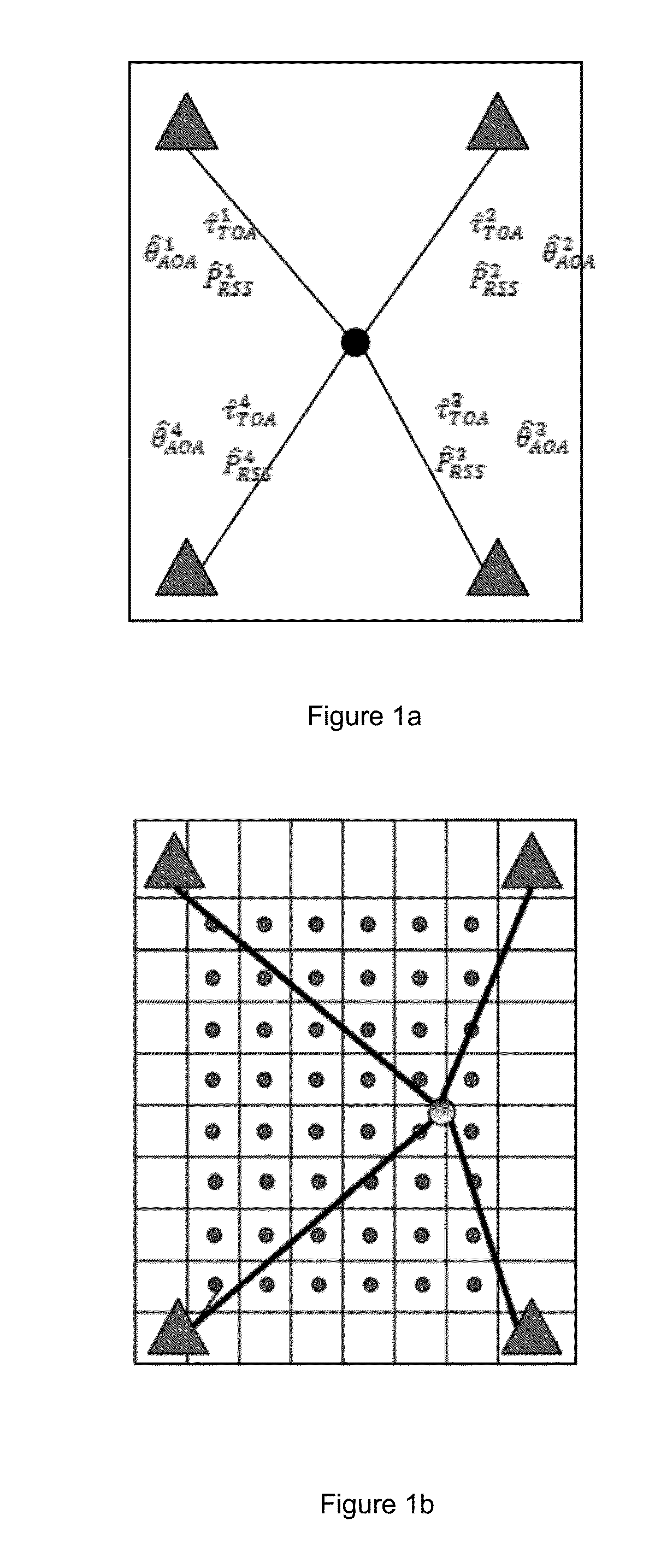
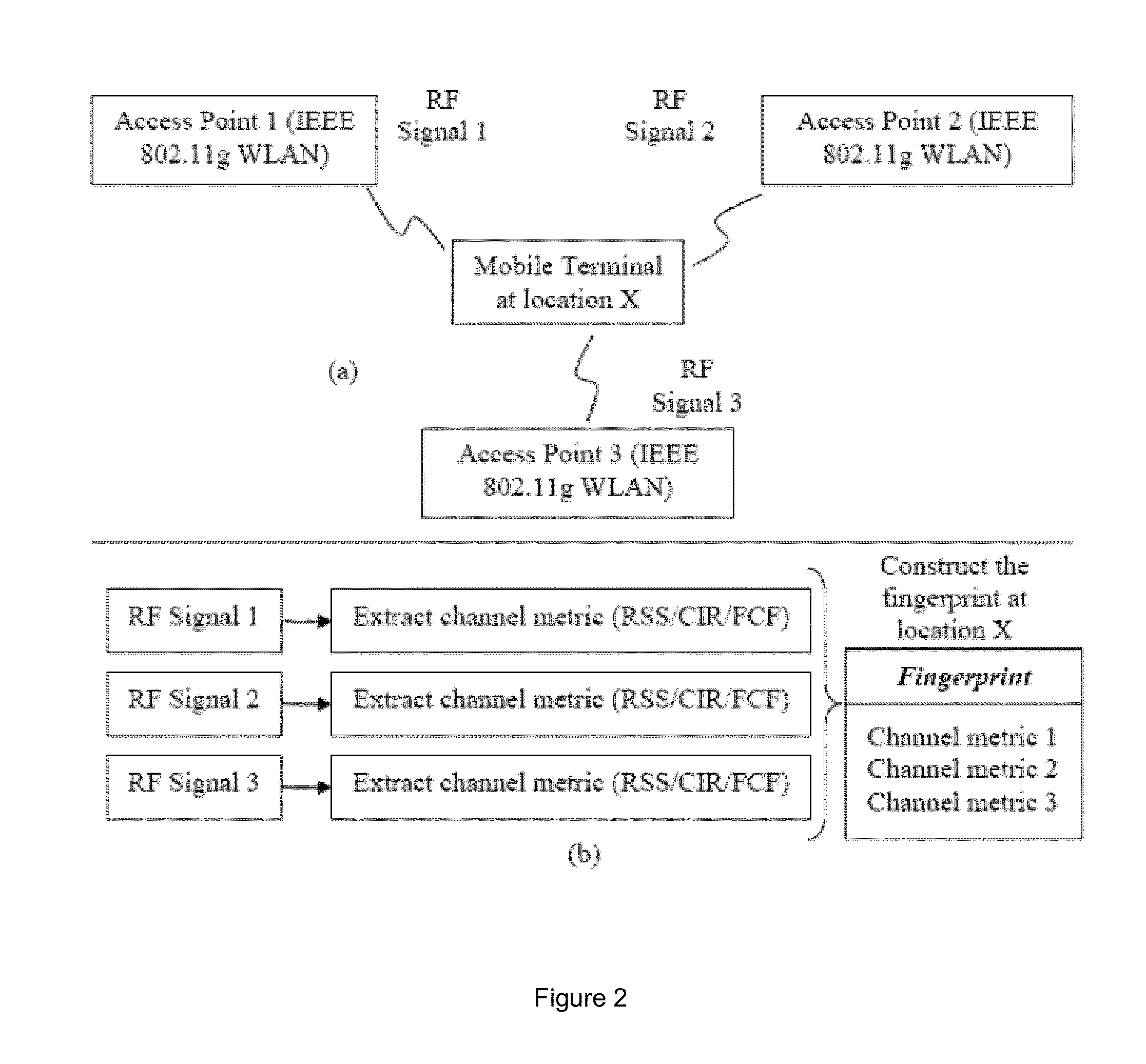
This invention relates to methods and devices for entropy-based location fingerprinting, in particular for use over wireless local-area networks (WLANs). The invention has particular application in localization for indoor environments. In embodiments of the invention, an entropy-based fingerprint is determined at a number of predetermined locations within the desired area of localization during an off-line phase and subsequently used in an on-line mode to determine the location of a receiver. In particular embodiments, the fingerprint is a vector of entropy estimates of the channel transfer function (CTF) between a mobile terminal and all access points within coverage. The invention seeks to provide a fingerprinting localization solution that has a simplicity of structure, leading to advantages in storage and pattern recognition requirements, and robustness by proving a unique measure of information that is related to the channel experienced at the location of the mobile terminal.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Multichannel voice detection in adverse environments
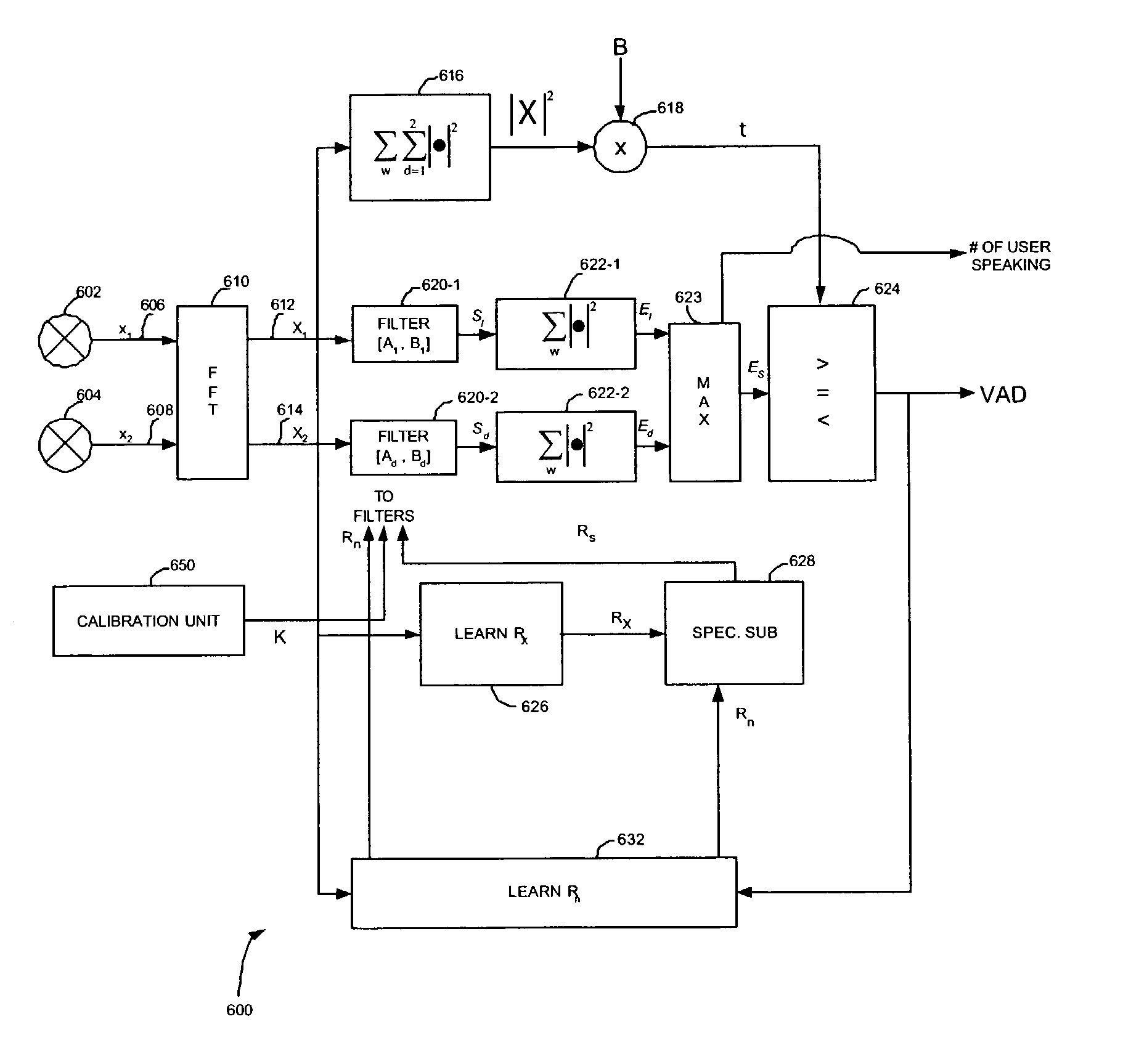
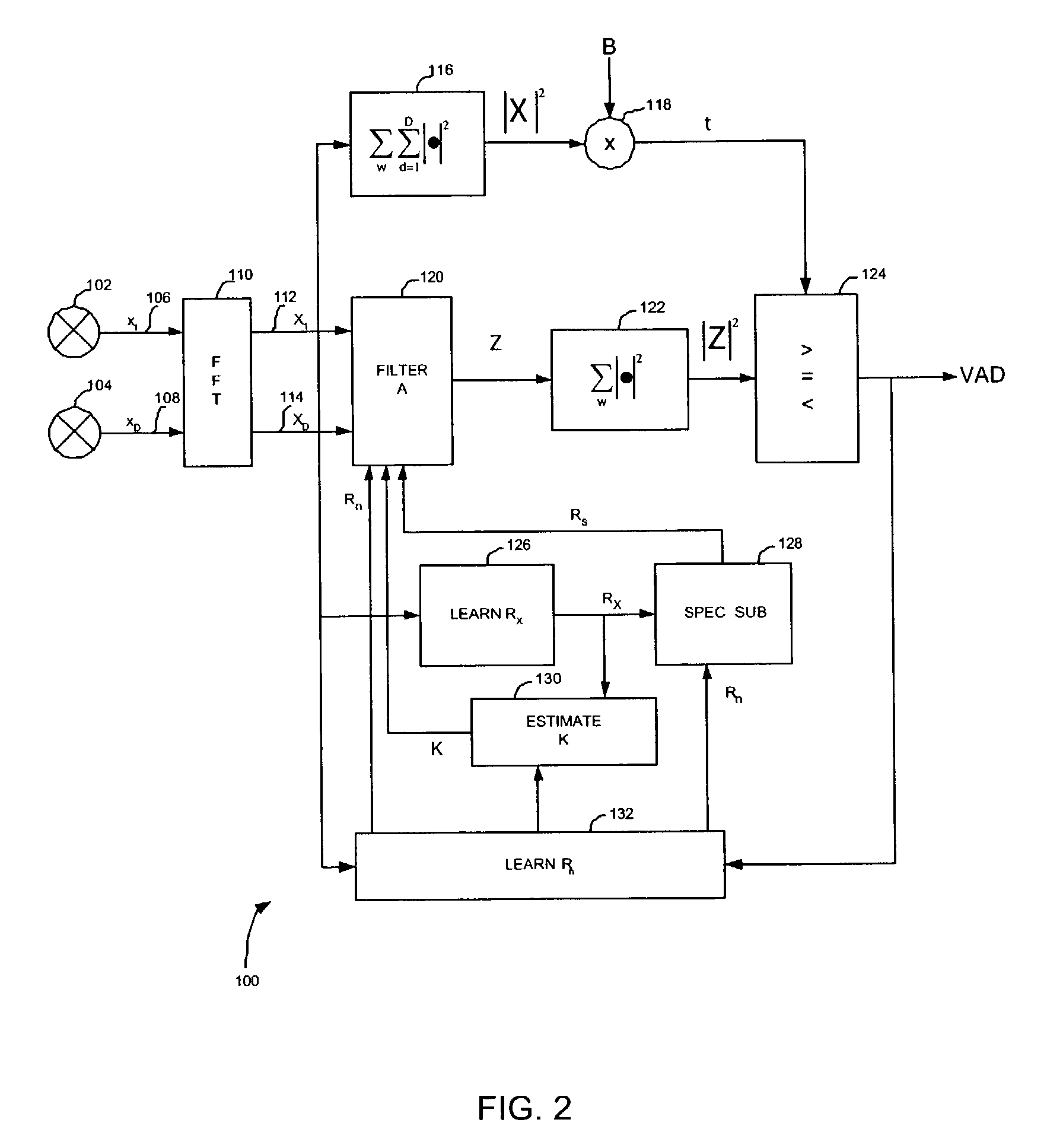
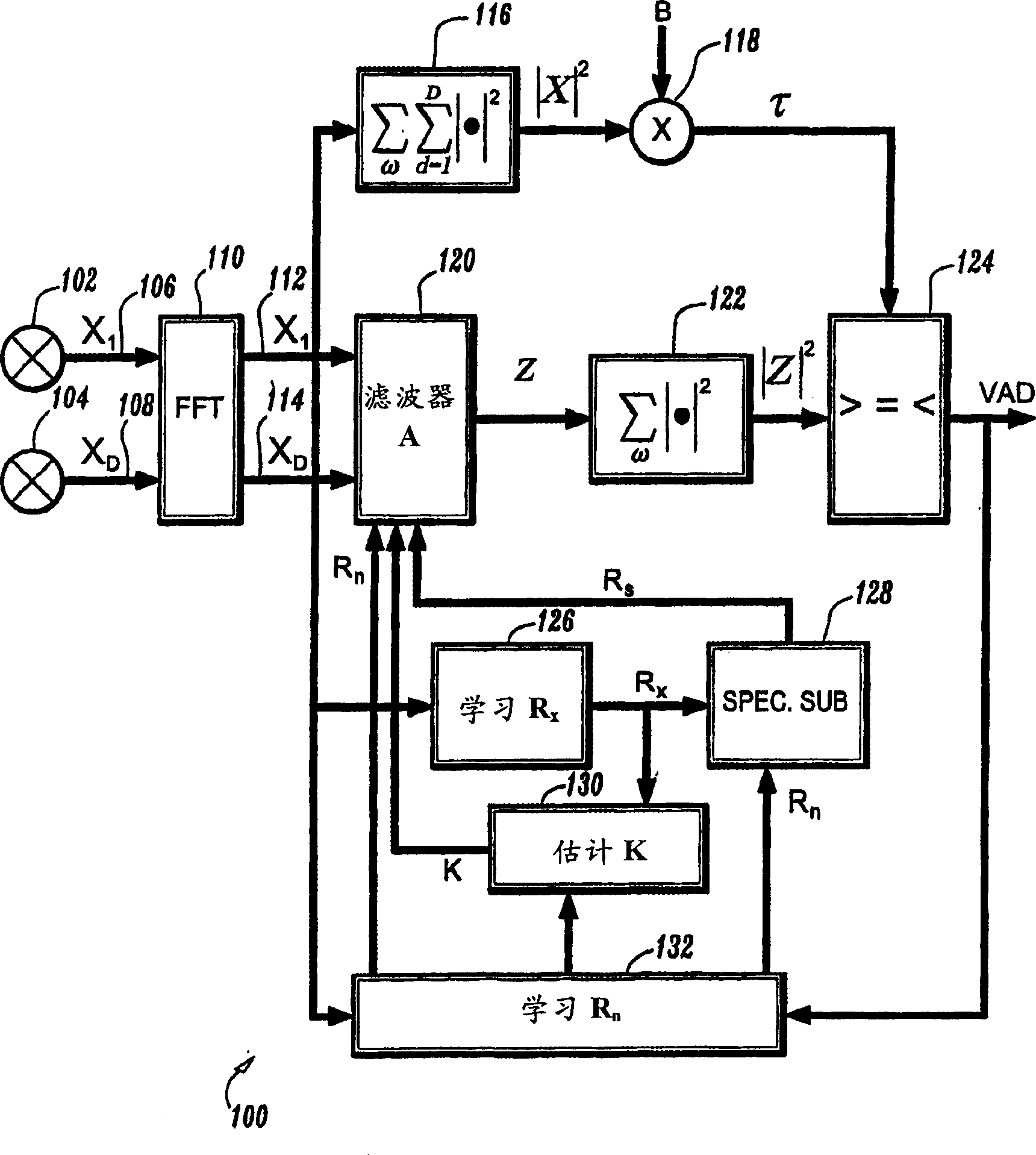
InactiveUS7146315B2Decreasing activity detection error rateEasy to identifyTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsGain controlFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
A multichannel source activity detection system, e.g., a voice activity detection (VAD) system, and method that exploits spatial localization of a target audio source is provided. The method includes the steps of receiving a mixed sound signal by at least two microphones; Fast Fourier transforming each received mixed sound signal into the frequency domain; filtering the transformed signals to output a signal corresponding to a spatial signature of a source; summing an absolute value squared of the filtered signal over a predetermined range of frequencies; and comparing the sum to a threshold to determine if a voice is present. Additionally, the filtering step includes multiplying the transformed signals by an inverse of a noise spectral power matrix, a vector of channel transfer function ratios, and a source signal spectral power.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Channel estimation for OFDM systems
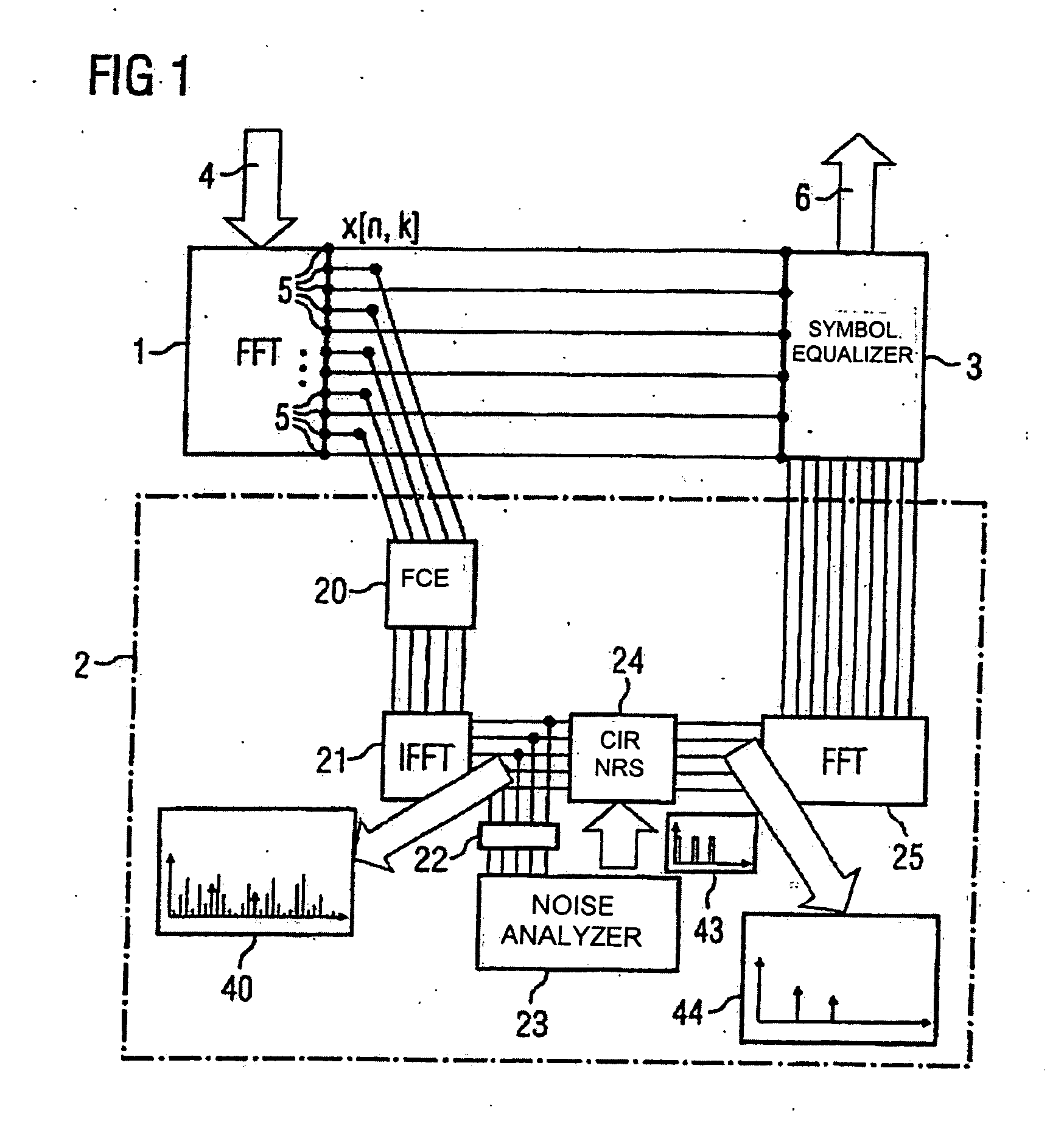
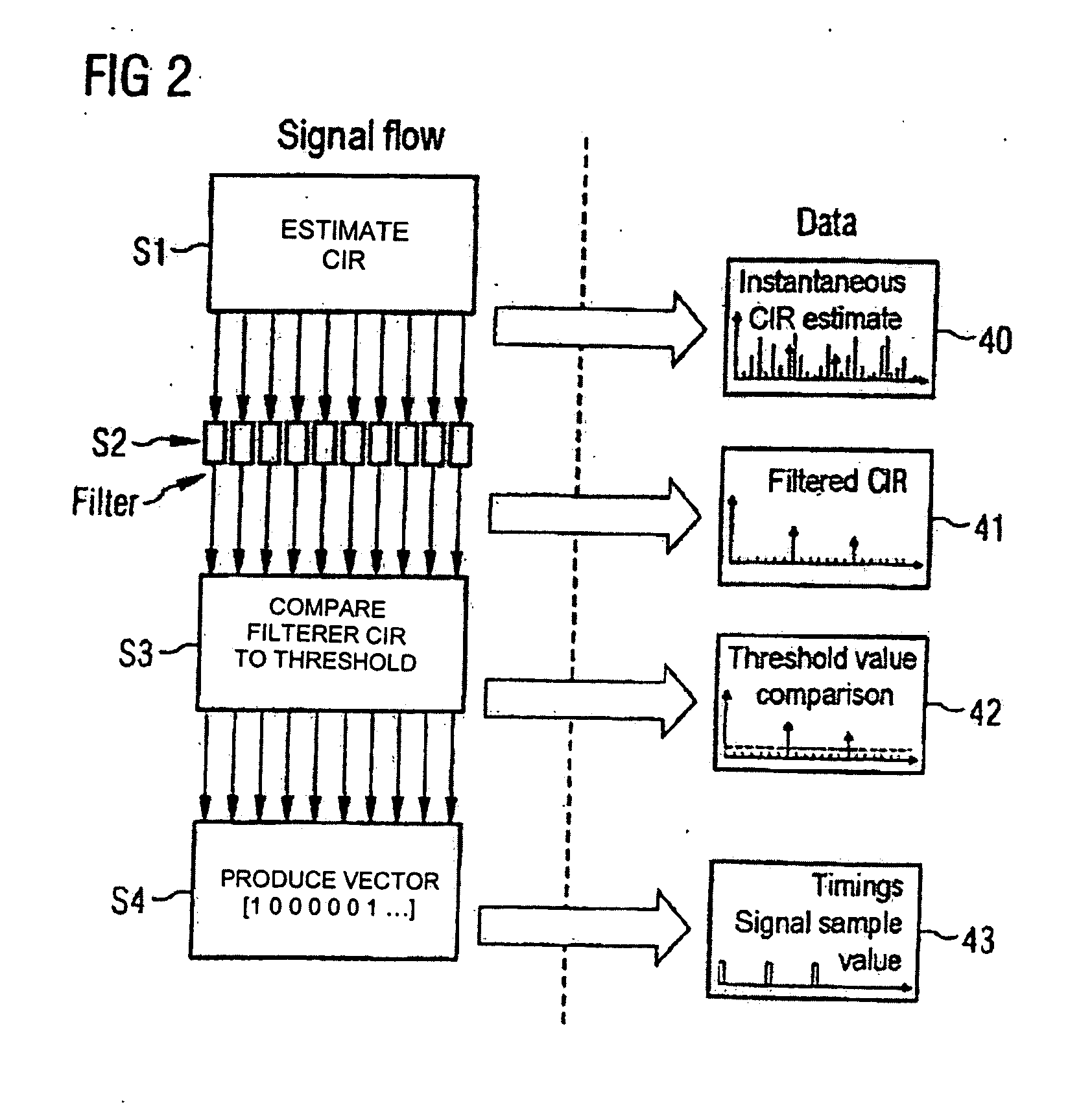
InactiveUS20080130771A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionFinite impulse responseChannel impulse response
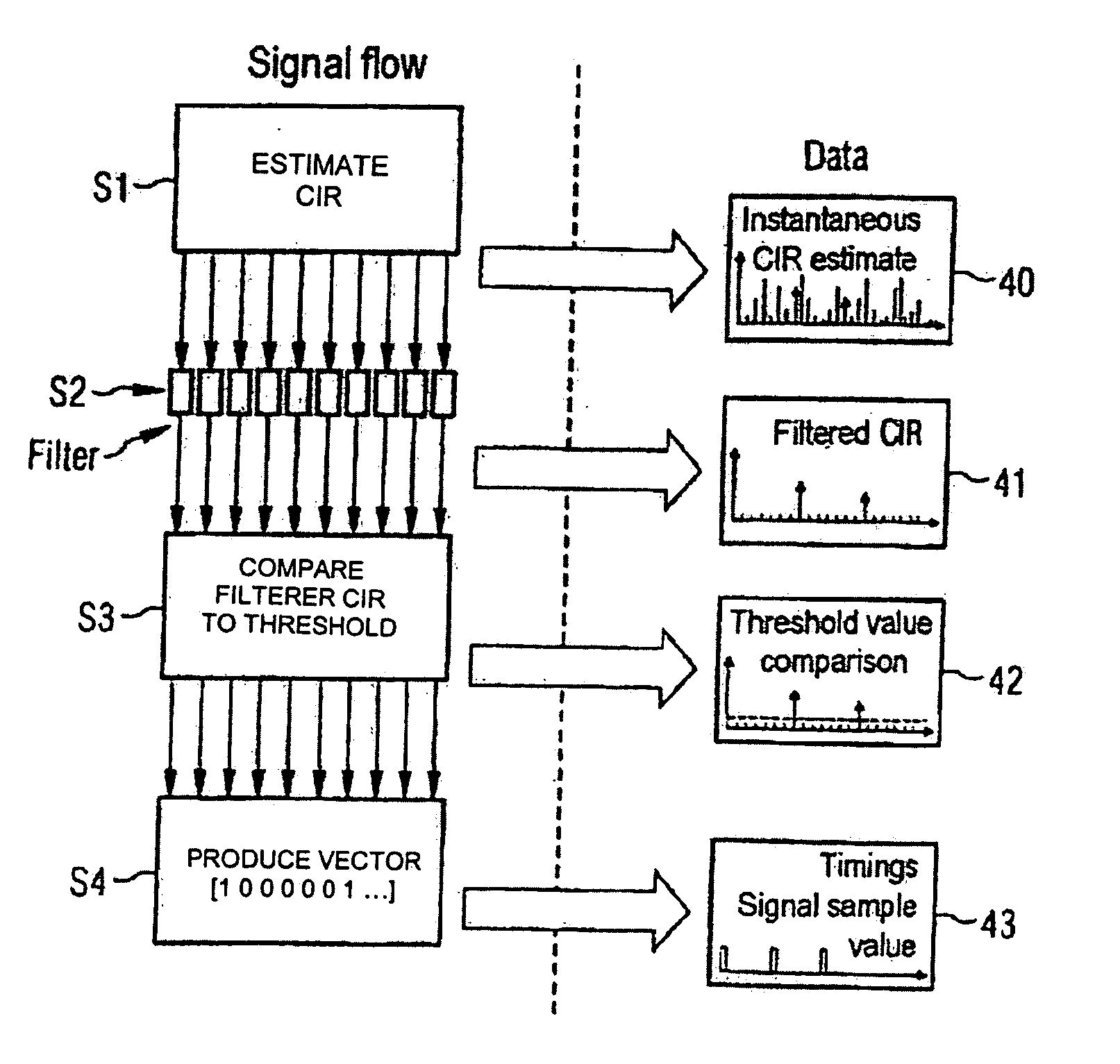
In a method for channel estimation of an OFDM signal transmitted via a channel, an initial channel transfer function is calculated by channel estimation. A channel impulse response is calculated on the basis of the initial channel transfer function. Values of the channel impulse response or of a filtered channel impulse response are classified as noise or as a signal as a function of the level of the values of the channel impulse or of the level of the values of the filtered channel impulse response. A noise-reduced channel impulse response is calculated on the basis of the channel impulse response using the classification, and a noise-reduced channel transfer function is calculated on the basis of this noise-reduced channel impulse response.
Owner:INTEL CORP
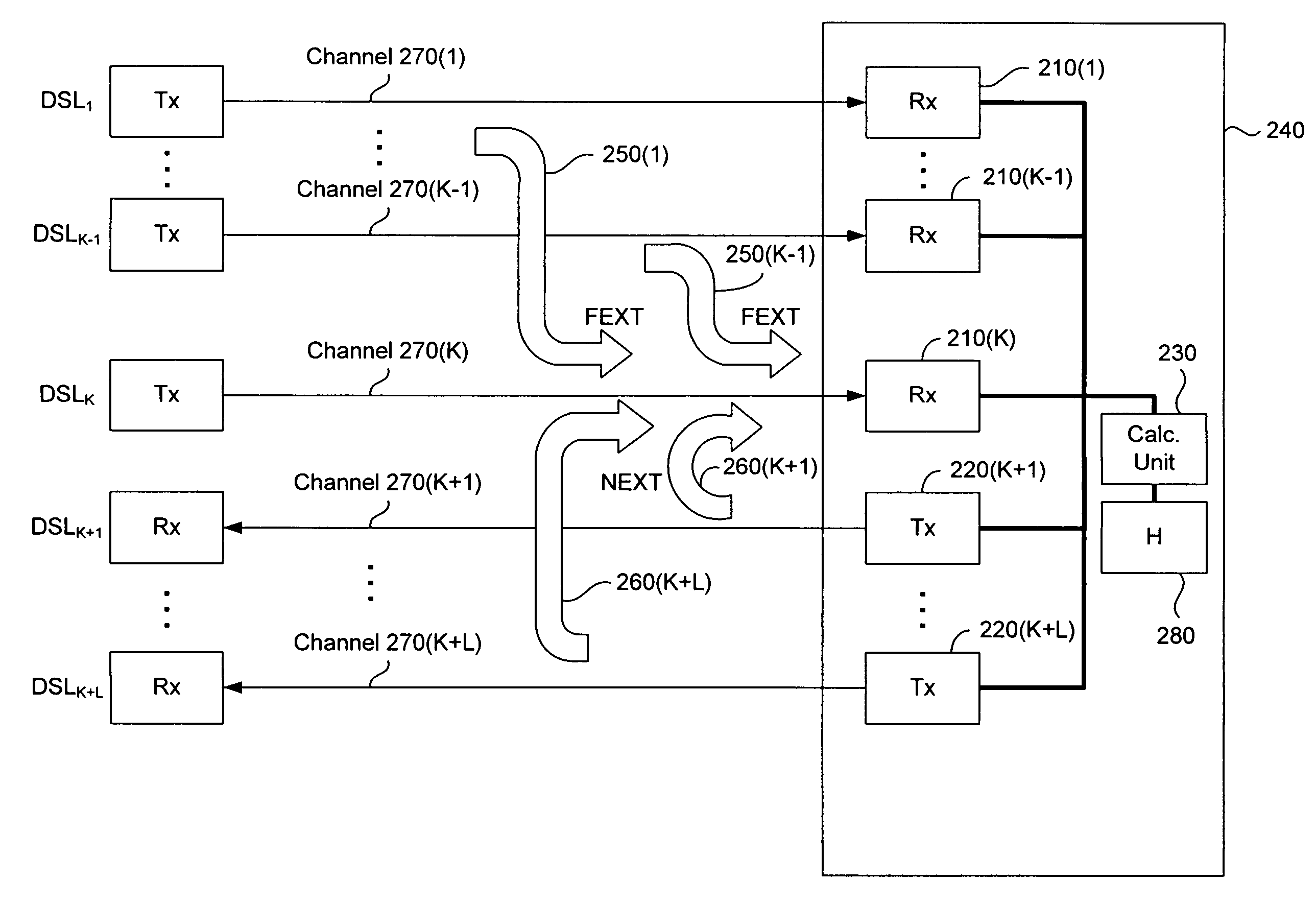
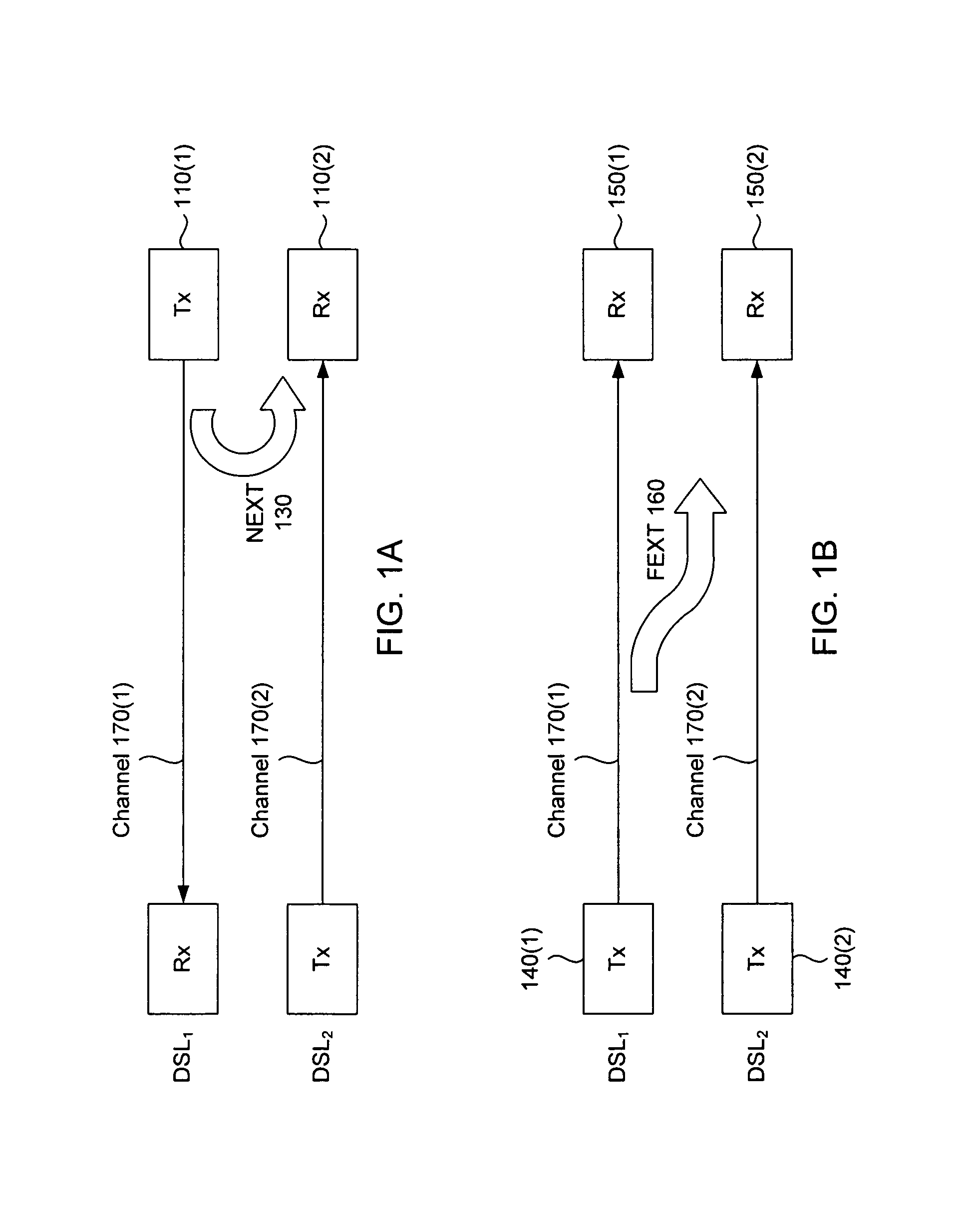
Joint reduction of NEXT and FEXT in xDSL systems
InactiveUS7394752B2Reduce signalingReduce crosstalkFrequency-division multiplex detailsCurrent interference reductionChannel dataCoupling
Methods, apparatus, techniques and computer program products for joint reduction of crosstalk in a synchronized, time division duplexed DSL systems use sequential removal of NEXT interference followed by removal of FEXT interference from a received DSL signal. Crosstalk is removed from a primary signal in a synchronized TDD DSL system having a primary channel that carries the primary signal, at least one NEXT generating channel that generates NEXT interference in the primary signal and at least one FEXT generating channel that generates FEXT interference in the primary signal. Signal data is acquired, where the signal data includes received signal data for the primary channel and at least one FEXT generating channel, transmitted signal data for at least one NEXT generating channel, and channel data comprising channel transfer function data and crosstalk coupling coefficient data for the primary channel, each NEXT generating channel and each FEXT generating channel. After the signal data is acquired, NEXT interference in the primary signal is then removed using the transmitted signal data and the channel data, followed by removal of FEXT interference in the primary signal using vectored DMT FEXT removal, the received signal data and the channel data. In another system in which FEXT generating received signals are not necessarily available, FEXT removal can be achieved using expectation cancellation, the primary signal and the channel data in connection with possible transmitted signal values.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method and arrangement for mitigation of intercell interference in a cellular communication system
ActiveUS20050232195A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCell specificCommunications system
A method (400) and arrangement (200) for mitigation of intercell and intracell interference in a 3GPP cellular communication system (100) by, in a receiver in a cell of the system, deriving for a first channel in the cell a signal, representative of first channel transfer function (A(1)); deriving for at least a second channel originating in a different cell a signal (A(2 . . . M)), representative of second channel transfer function, based on: deriving a cell specific scrambling code (s), deriving a channel impulse response (h), and deriving a channelisation code (c); and performing multi-user detection using the first and second signals. Where the channelisation code is unknown, a substitute channelisation code is preferably substituted. It will be appreciated that the technique can be applied to both downlink and uplink. This provides the advantage that both intra-cell interference and intercell interference are mitigated.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Binder identification
InactiveUS20070036340A1Reduce riskSimple designInterconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsTransceiverFrequency spectrum
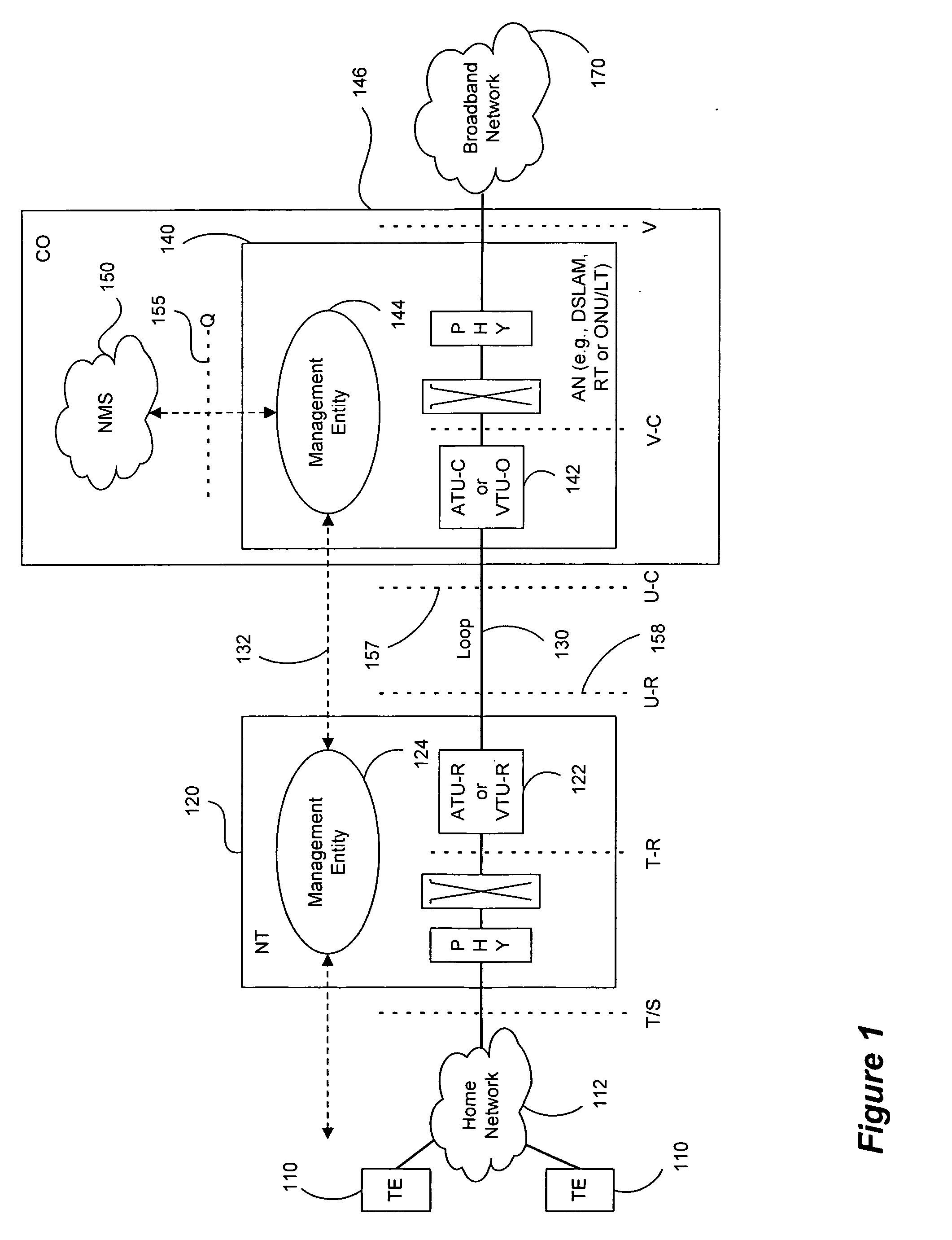
Methods, techniques and apparatus identify members and characteristics of binders and / or other groups of communication lines such as those in a DSL system. Information obtained includes the identification (for example, by scanning) of significant crosstalking “offenders” and their “victims” that are affected by the crosstalk. One or a small number of modems are instructed to transmit with preselected transmit spectra, after which evidence of crosstalk in the noise spectrum data is examined for potential victim lines. Direct evidence of noise spectrum contribution by a suspected offender line may be obtained by collecting reported noise spectrum data and / or estimated noise spectrum data from potential victim lines. Also, where such direct evidence is not available, or in addition to it, other operational data showing crosstalk interference relating to potential victim lines can be used. The transmitting modem can either be on the CO / RT side or on the CPE side. Modems other than suspected offenders might transmit zero or minimal power in one or more selected frequency bands during scanning to reduce the risk that a modem and / or line not being examined for “offender” status supplies unnecessarily complicating and / or dominant crosstalk during the procedure. For DMT modulated DSL transceivers, well designed transmit spectra can be easily enforced by manipulating line profiles where such well designed line profiles cause minimal or no interruption to existing DSL customers. The invention also can be used to identify (partially or fully) the absolute values of crosstalk channels making up a channel transfer function.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Uplink channel estimation
ActiveUS20100197264A1Simple and efficientComputationally inexpensiveError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio transmissionTime domainEngineering
In one embodiment, a receiver is provided for use in a multiple-input system that includes a receiving antenna receiving a time-domain signal corresponding to a plurality of signals transmitted from a plurality of transmitting antennas. The receiver includes: (a) a transform unit adapted to transform the time-domain signal into a frequency-domain signal; (b) a channel estimation unit adapted to estimate, based on the frequency-domain signal and a frequency-domain pilot signal, a combined transfer function corresponding to a plurality of transfer functions of respective channels between the plurality of transmitting antennas and the receiving antenna; and (c) a channel separation unit including a plurality of frequency-domain convolution units that separate the combined transfer function into a plurality of estimated channel transfer functions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Unbiased signal-to-noise ratio estimation for receiver having channel estimation error
InactiveUS20090279643A1Removing estimate of noiseTime-division multiplexFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
Apparatus and methods for estimating transmission noise in a programming information signal. Channel noise power in binary phase shift keying (“BPSK”) modulated telecommunication may be estimated. Such a method may include receiving over the channel a reference signal and a data BPSK signal. The data BPSK signal may include the programming information. The method may include formulating a channel transfer function estimate for the channel based on the reference signal. The estimate may include a channel estimation error. The data BPSK signal may be equalized using the transfer function estimate. The data BPSK signal may include noise, which may be quantified in terms of power. The data BPSK signal noise power may be estimated in such a manner that is independent of the channel estimation error.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Blast MIMO signal processing method and apparatus
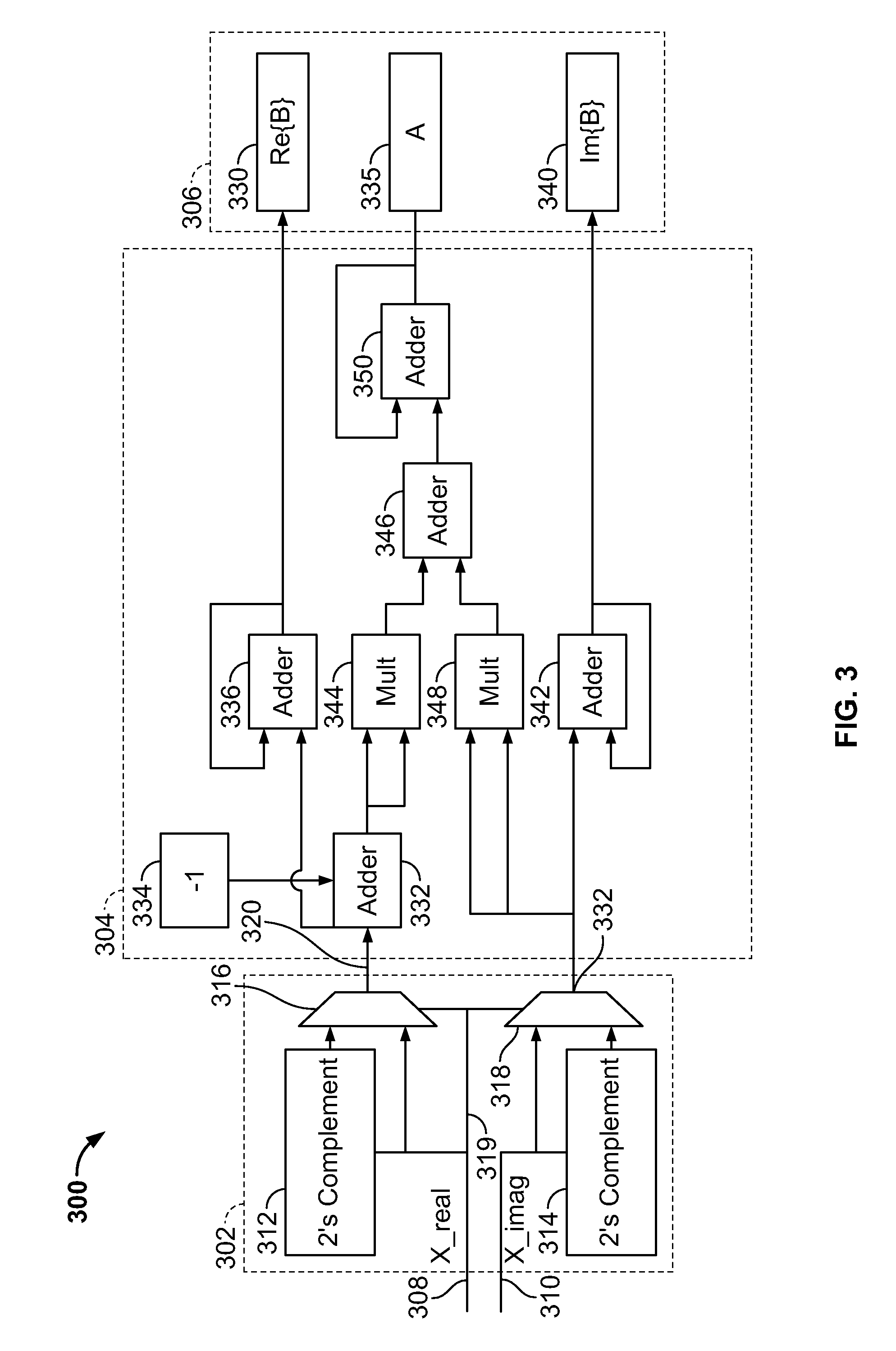
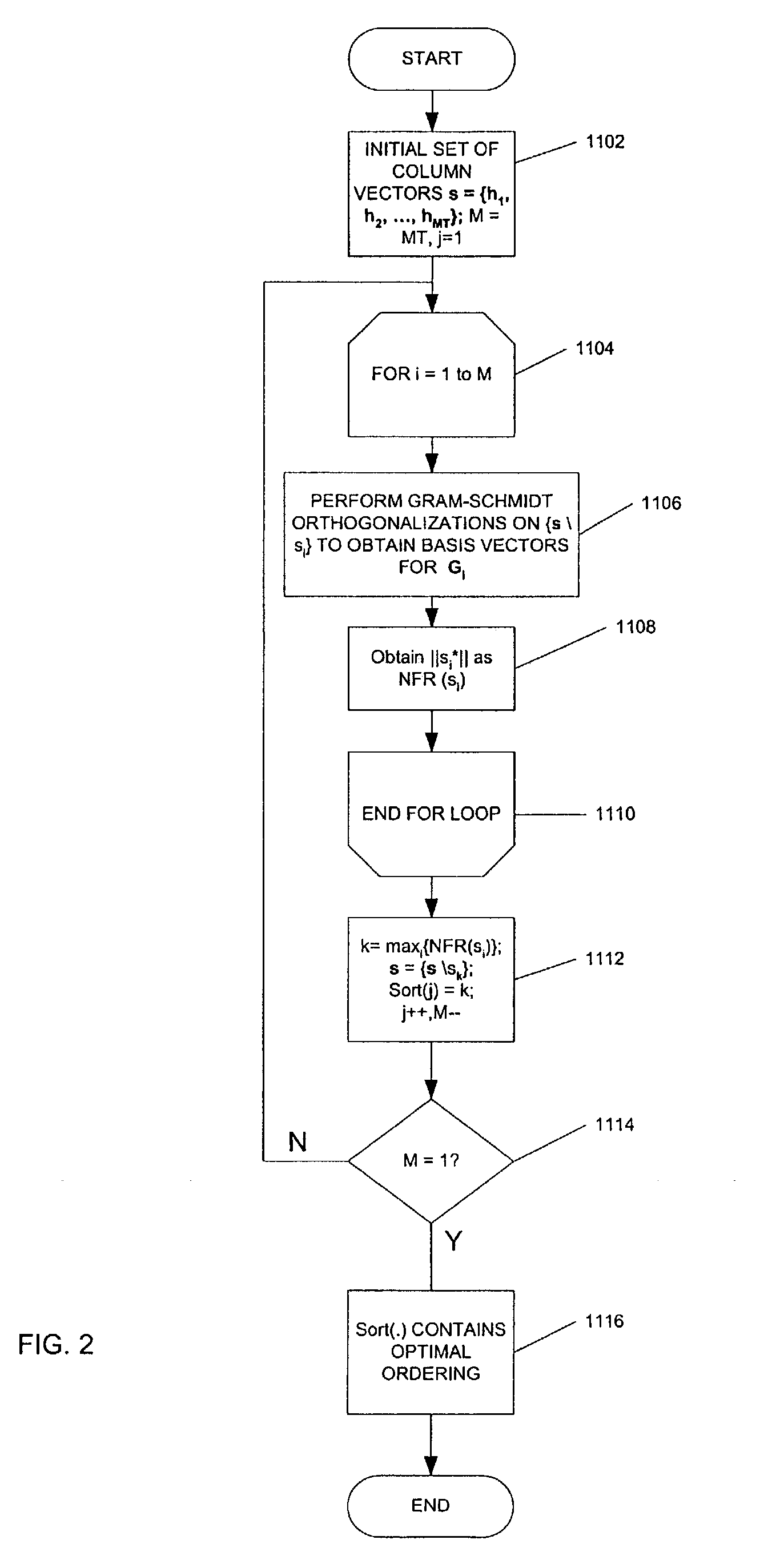
ActiveUS7209522B1Avoid the needConveniently employedSubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsTransfer function matrixLevel order
A technique for generating a demodulation ordering used in receive signal processing operations in a BLAST MIMO receiver that is based on a relative comparison of near-to-far resistance measures among vectors forming the estimated channel transfer function matrix is disclosed. This near-to-far resistance comparison provides a resulting demodulation ordering believed equivalent to that provided by conventional V-BLAST techniques without requiring computation of the pseudoinverse of the estimated channel matrix. Also disclosed is a successive interference cancellation technique which employs Multi-Staged Nested Weiner Filtering (MSNWF) to recover soft estimates of the transmitted component-symbols from the vector observed at the BLAST MIMO receiver. Employing such MSNWF estimation is believed advantageous in that it avoids the need for matrix inversion operations involving the estimated channel matrix, Covariance Level Order Recursive-MSNWF (MSNWF-COR) or MSNWF Conjugate Gradient techniques may be conveniently implemented to provide the desired MSNWF estimation.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
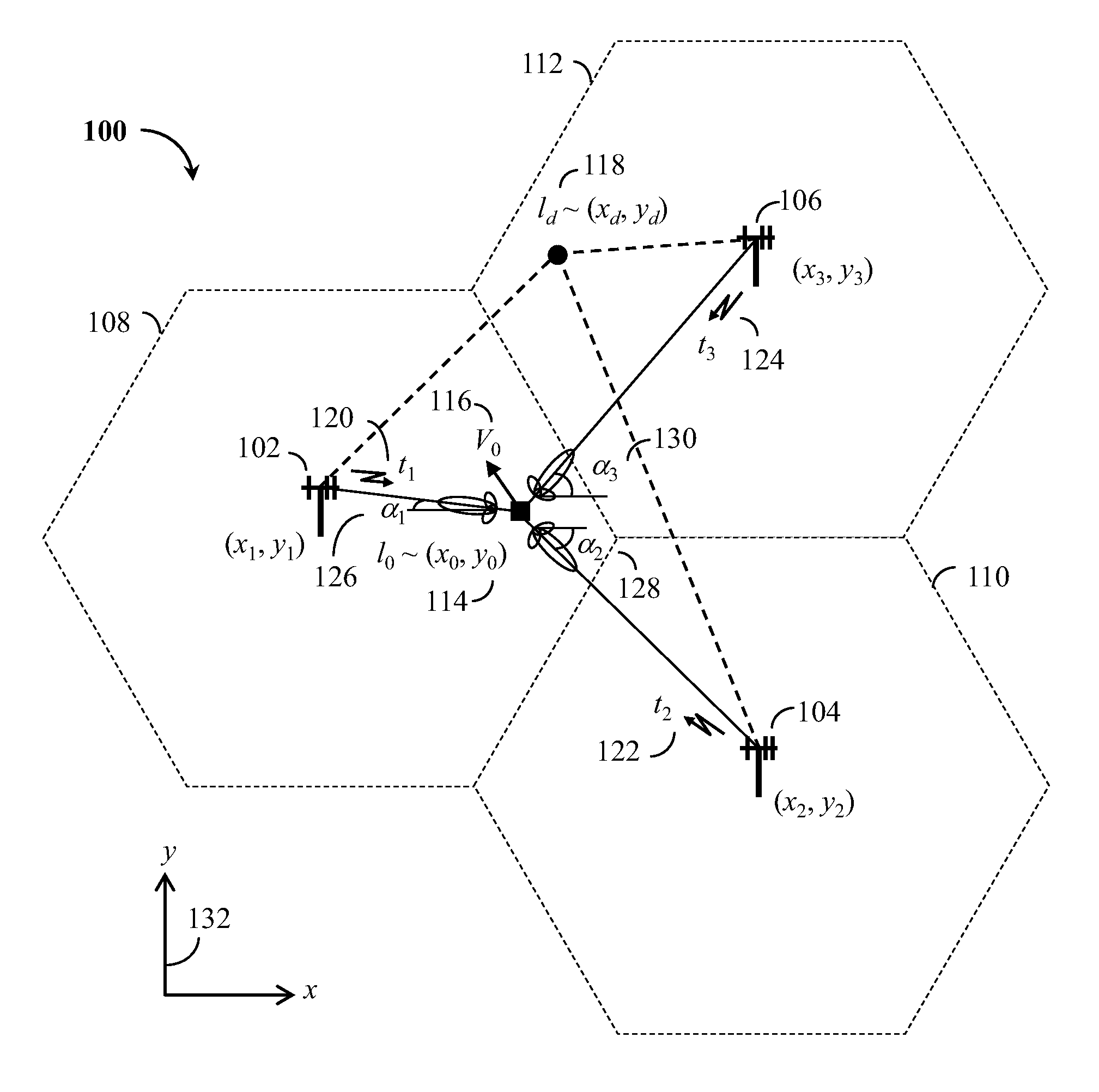
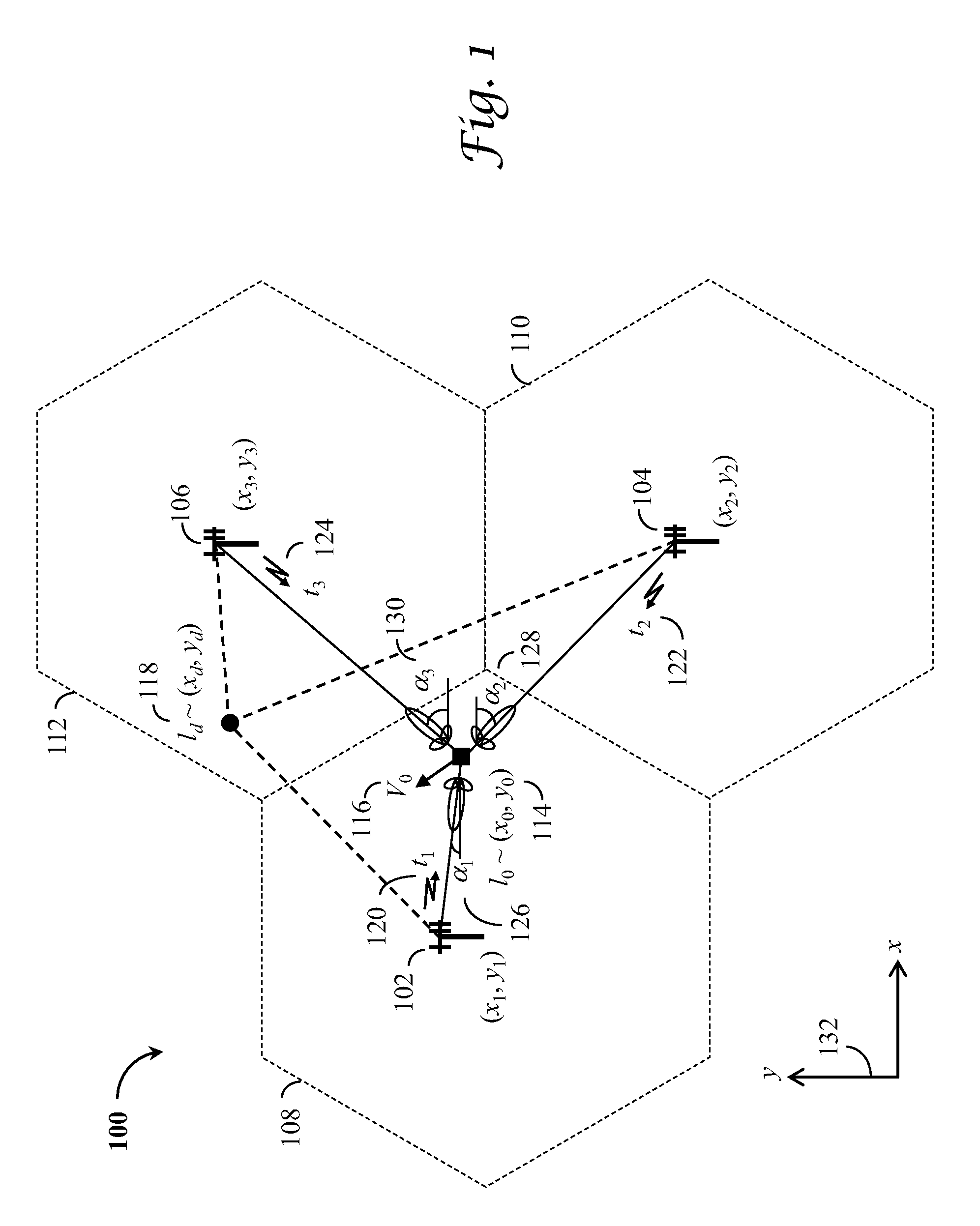
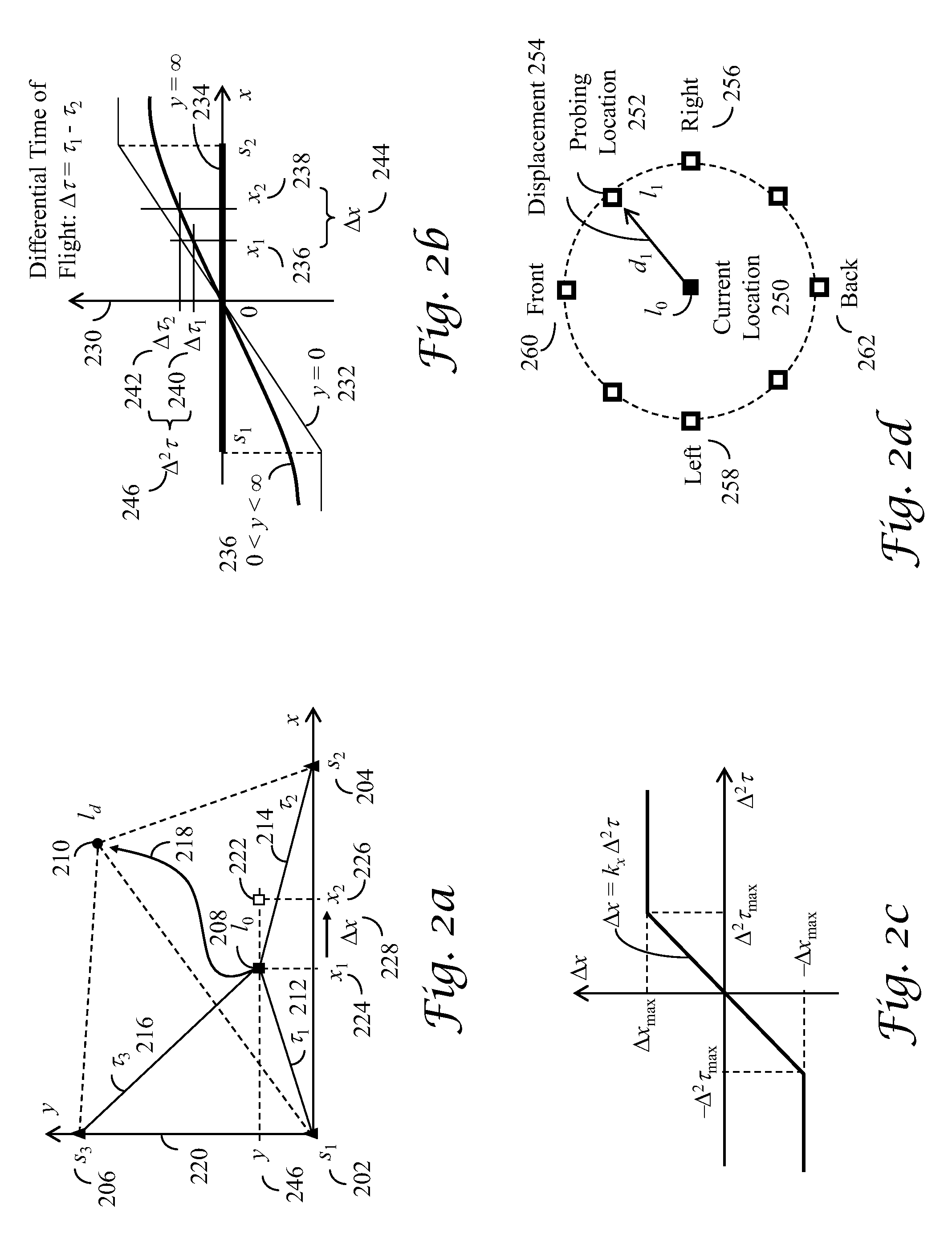
Coordinate-free measurement-domain navigation and guidance using location-dependent radio signal measurements
InactiveUS9046591B1Direction finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesTransmitterRadio signal
A system and associated methods for coordinate-free measurement-domain navigation and guidance utilizing a plurality of radio signals of opportunity, without knowing the coordinates of transmitters of said radio signals in a reference system that steers a user from an initial location to a destination without calculating coordinates in said reference system. In one embodiment, radio signal parameters comprise received signal strength indications, differential times of arrival, and sector angles from a user to at least a pair of radio sources and a combination thereof that are used for coarse navigation and guidance toward the vicinity of said destination. In another embodiment, radio signal parameters comprise temporal characteristics of radio signals, propagation channel impulse responses, radio signal power spectra, propagation channel transfer functions, and a combination thereof that are used for vernier navigation and guidance within the vicinity of said destination.
Owner:SIGTEM TECH
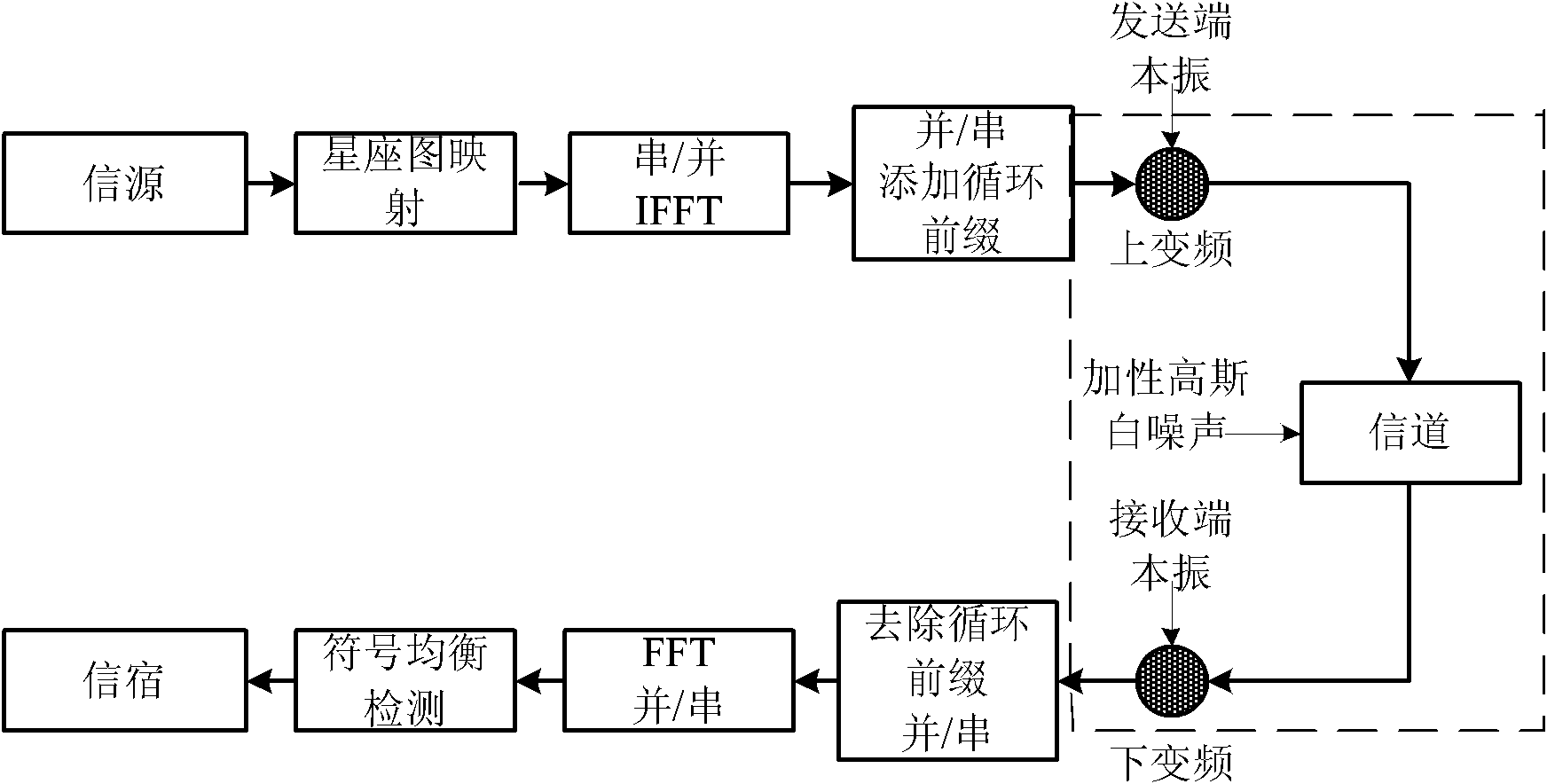
Phase noise elimination method in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
The invention discloses a phase noise elimination method in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system in the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a channel transfer function (CTF) matrix through a pretreatment matrix and a channel estimation shock response vector so as to reduce the number of channel estimation parameters from the number of sub-carriers to the number of channel time domain lengths; reducing the number of phase noise estimation parameters through a down sampling matrix; estimating CTF matrix and a phase noise matrix in a pilot frequency time slot through an iterative method to obtain an optimal estimated value of the CTF matrix, namely continuously tracking and estimating to obtain the phase noise estimated value by utilizing the optimal estimated value under the condition that the channel is invariable in adjacent pilot frequency time slots; and compensating a received signal by utilizing the phase noise estimated value so as to eliminate the noise.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
FEXT determination system
ActiveUS7593458B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal transfer functionEngineering
Operational data is utilized to determine the FEXT interference induced by one line into the other DSL line. FEXT interference can be calculated using the NEXT interference measured between the two lines at the upstream ends of the loops and the downstream channel transfer function of one of the loops. Because the NEXT and transfer function constitute a linear time-invariant system, as does the FEXT interference between the lines, the NEXT interference and line transfer function can be multiplied (if in linear format) or added (if in logarithmic format) to approximate the FEXT interference between the lines. The collection of data, calculations and other functions performed in these techniques may be performed by a system controller, such as a DSL optimizer. An Xlog(u,n) quantity is a decibel-magnitude representation of the insertion-loss equivalent of FEXT transfer functions and is defined as the ratio of (1) a line u's source power into a matched load of 100 Ohms when no binder is present to (2) the power at the output of the subject line when line u is excited with the same source and the binder is present. Xlin(u,n) is the linear equivalent of Xlog(u,n). The Xlog(u,n) and Xlin(u,n) quantities may be represented in specific formats that assist in their use in DSL and other systems. When defined as a line's insertion loss, Xlin (or equivalently Xlog) does not include the effect of any transmit filter.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
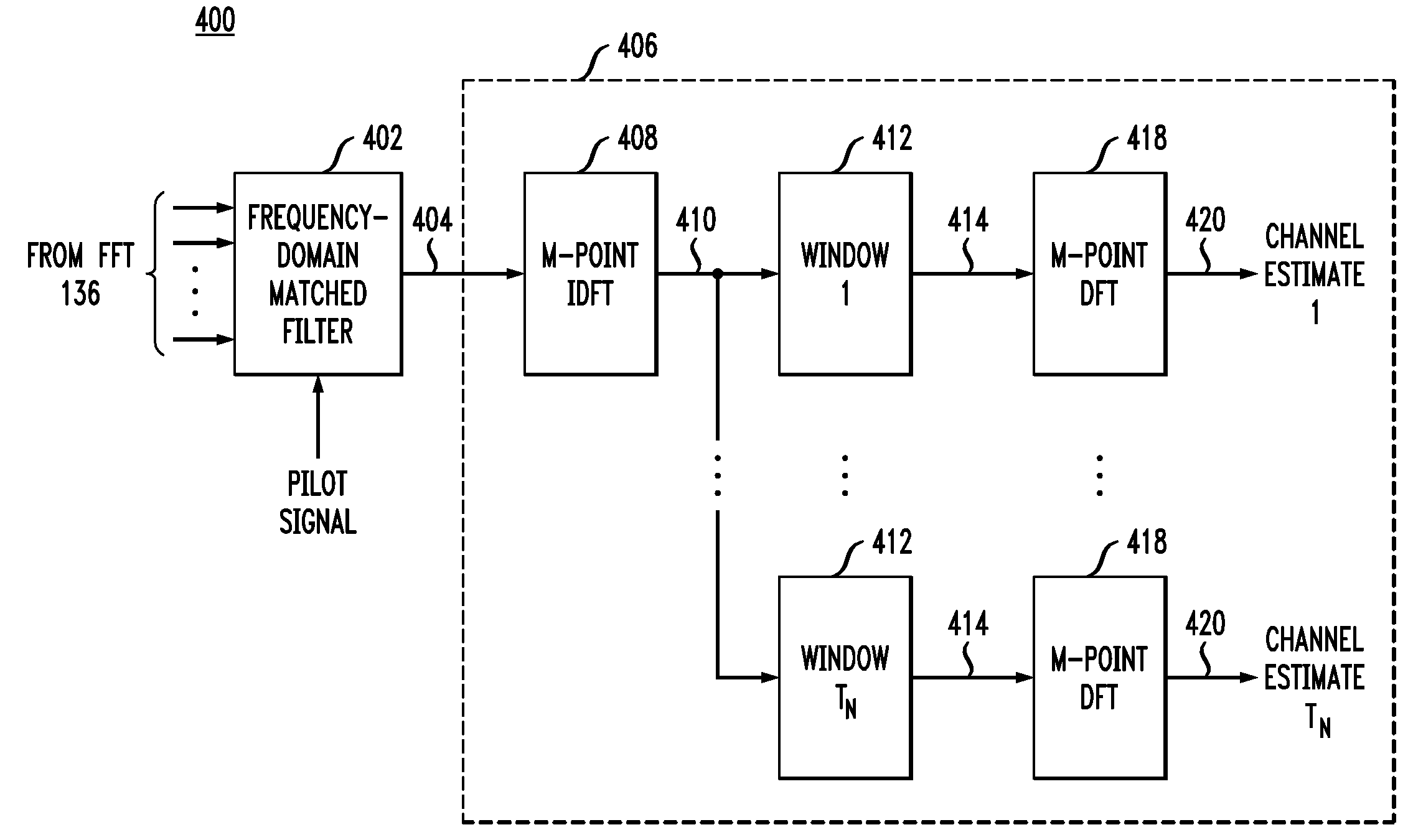
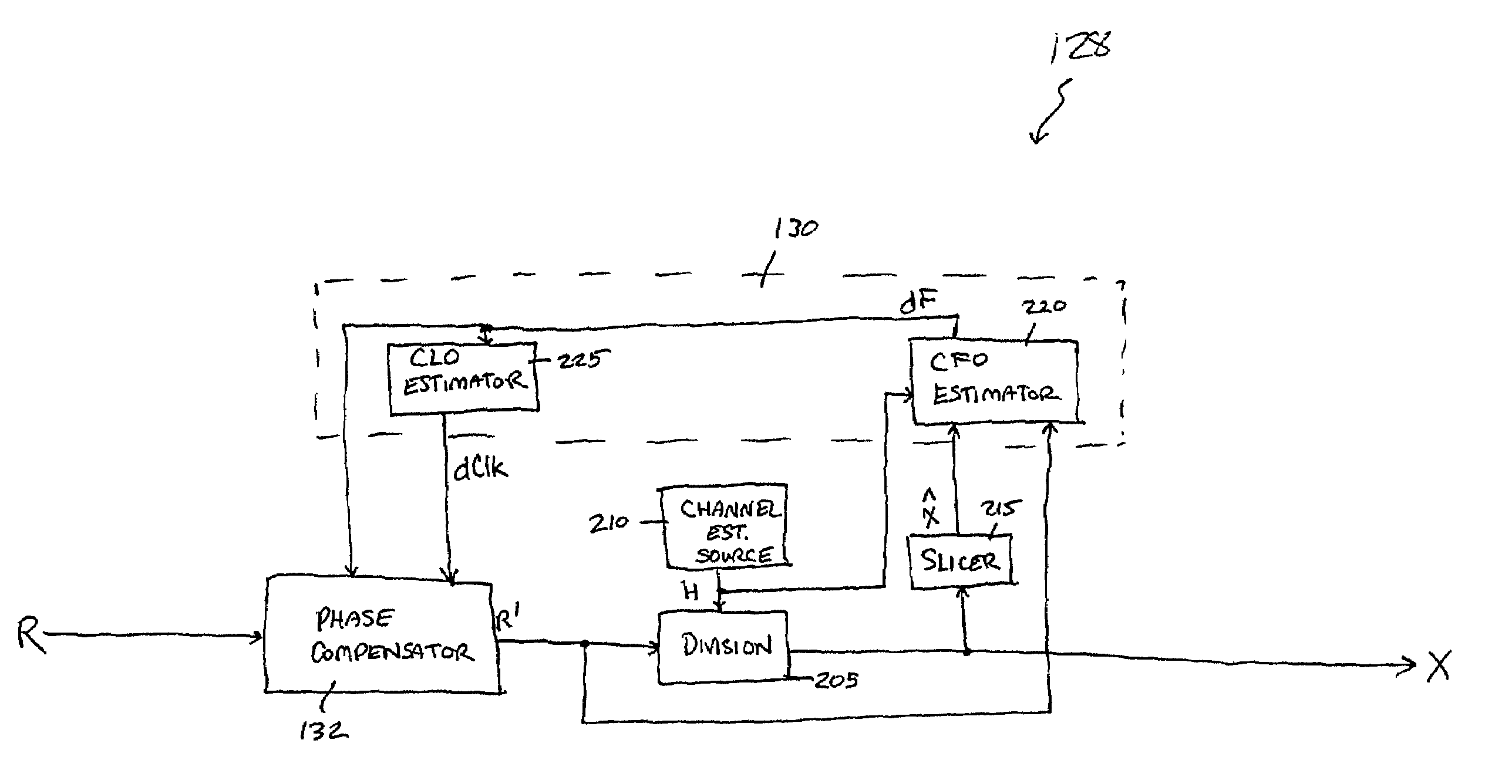
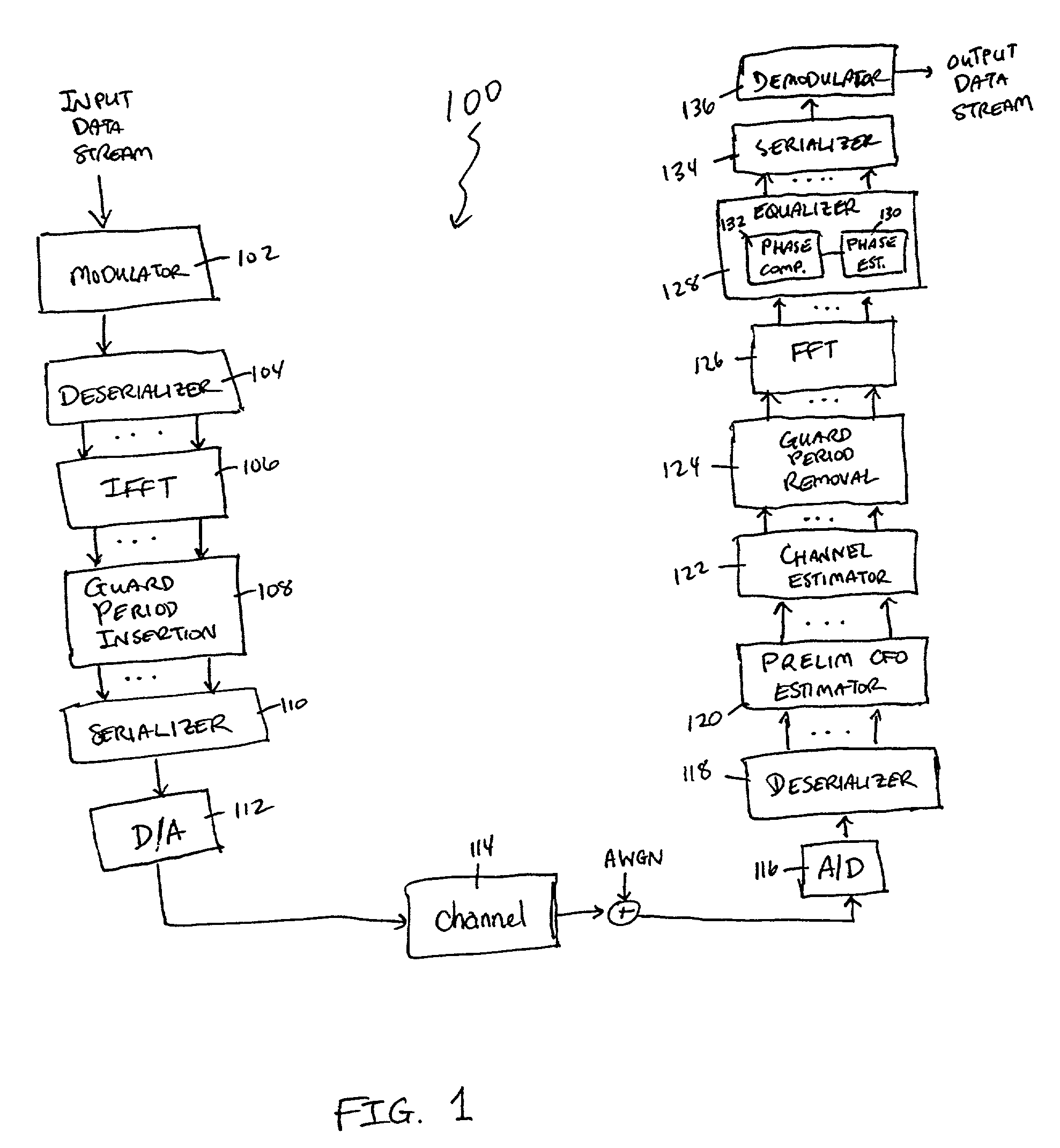
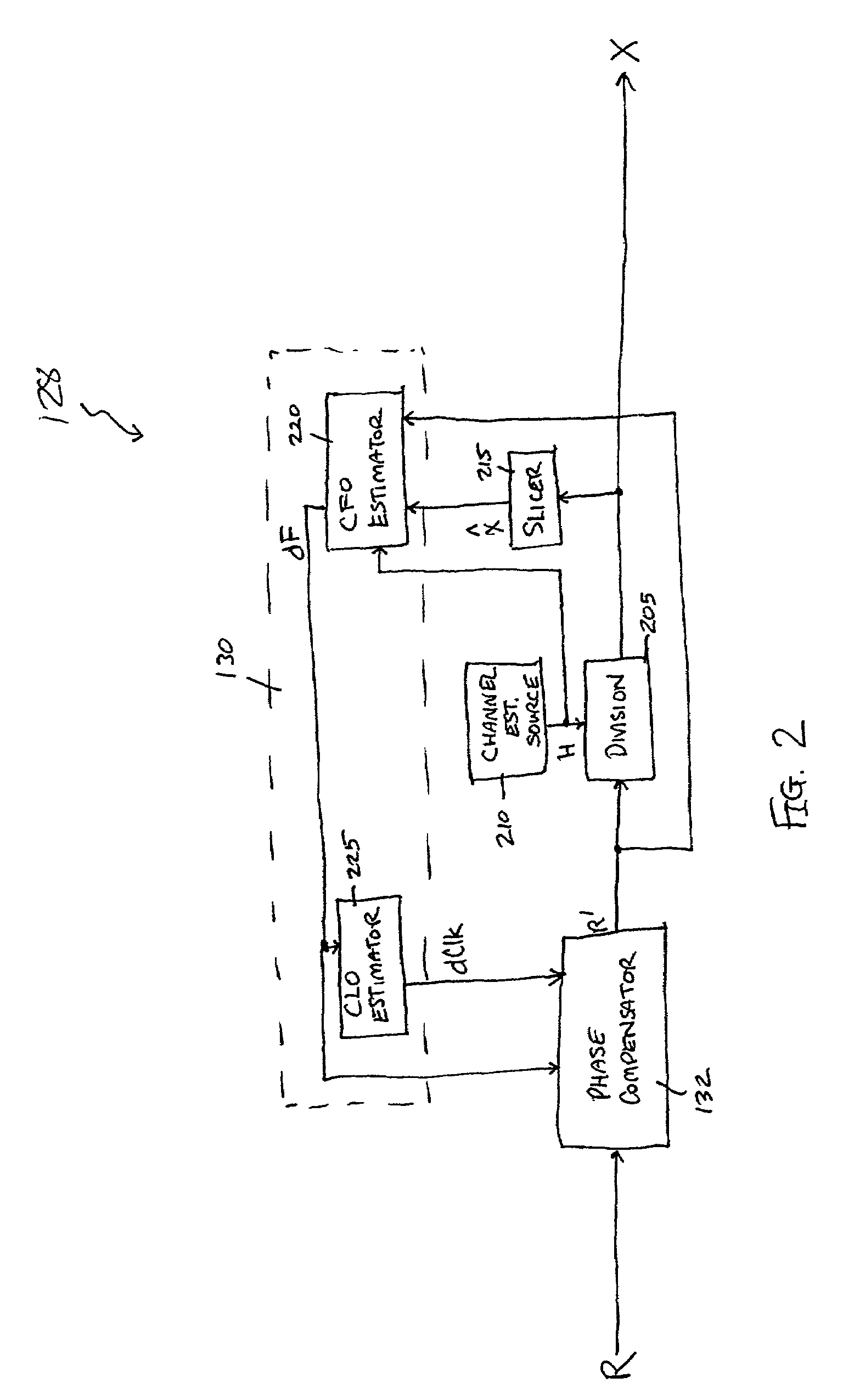
Method and apparatus for frequency-domain tracking of residual frequency and channel estimation offsets
ActiveUS7170961B2Efficient implementationReliable reproductionMultiple-port networksError preventionLow noiseCarrier frequency offset
Various methods and apparatus for frequency-domain estimation of carrier frequency offsets are provided in which the carrier frequency offset estimate is robust against non-white (frequency-dependent) noise. A carrier-specific weighting factor is associated with each carrier of a multi-carrier signal. Using the carrier-specific weighting factors, a carrier frequency offset estimate is computed from received signals and estimated channel transfer functions associated with each of the carriers. Because greater weights are given to carriers whose frequencies include lower noise and / or carriers transmitting a known sequence of symbols, the estimate of the carrier frequency offset is improved. The carrier frequency offset estimate may then be applied in a feedback loop to phase-compensate a subsequently received signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
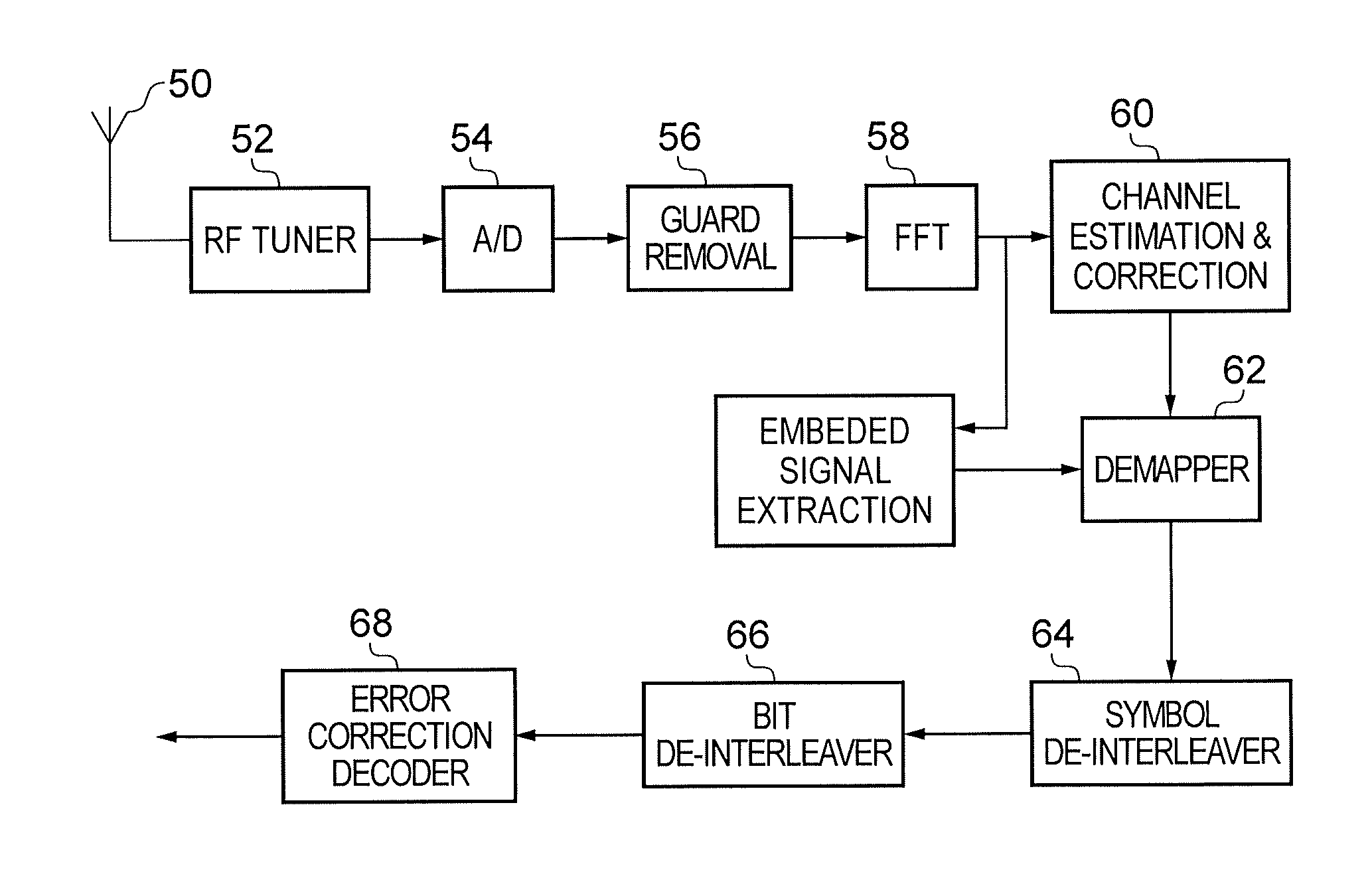
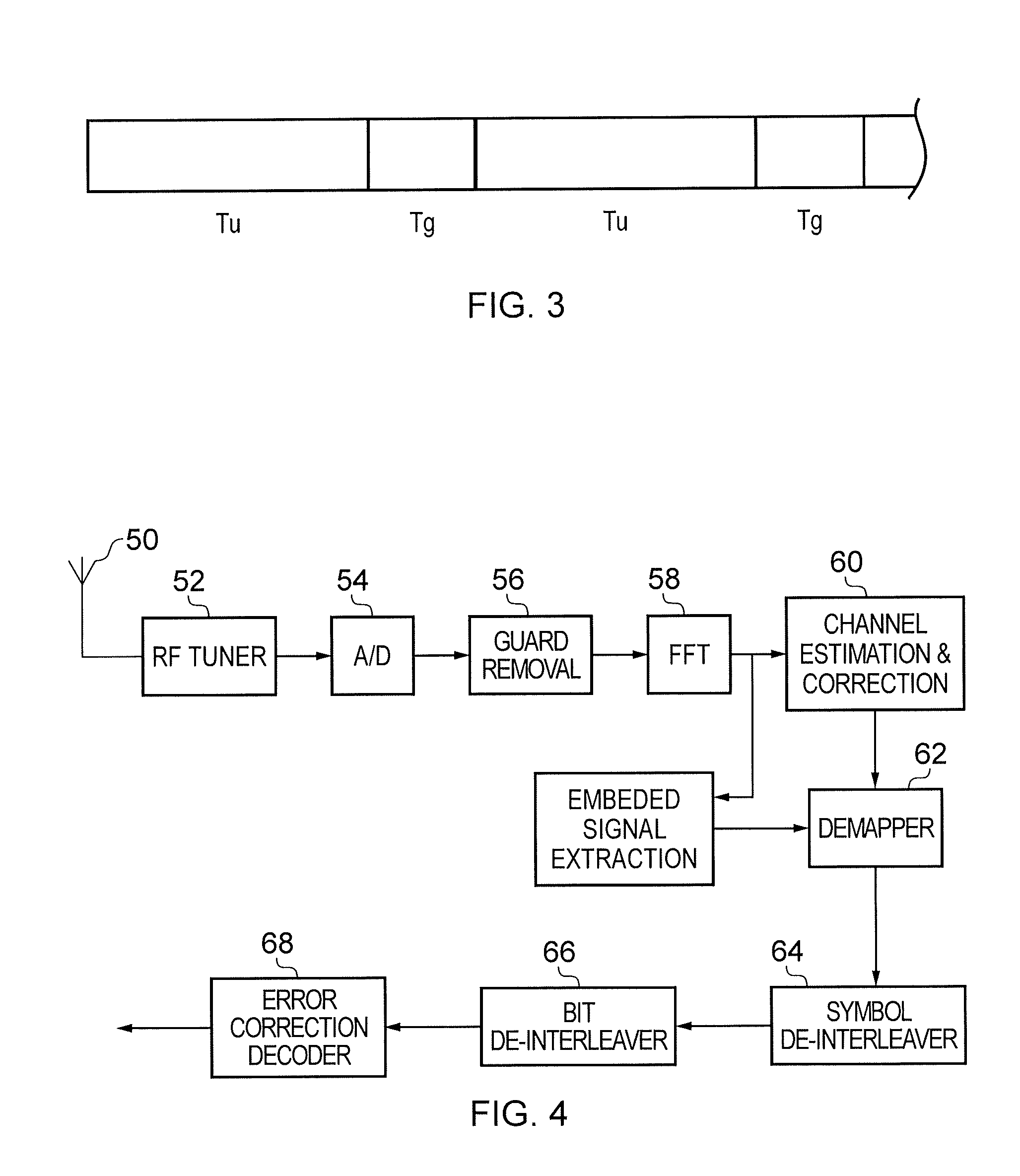
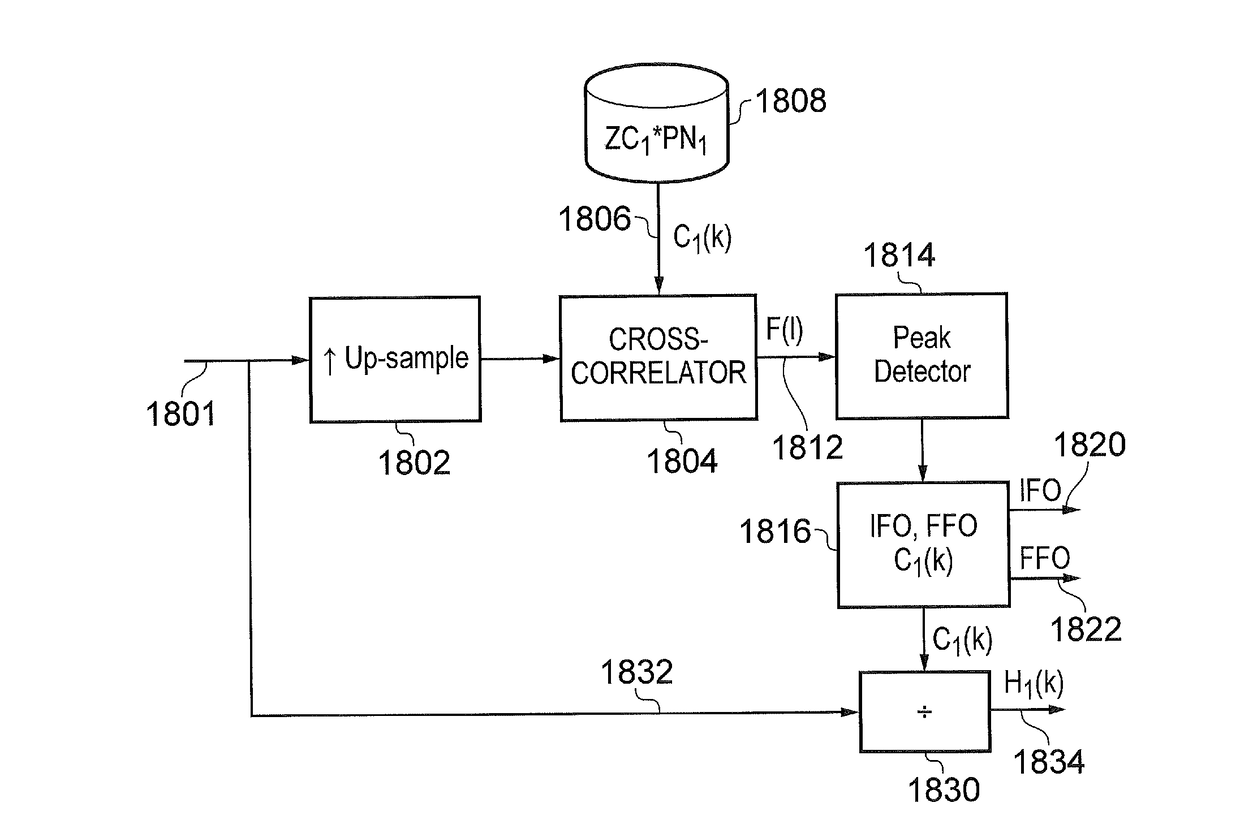
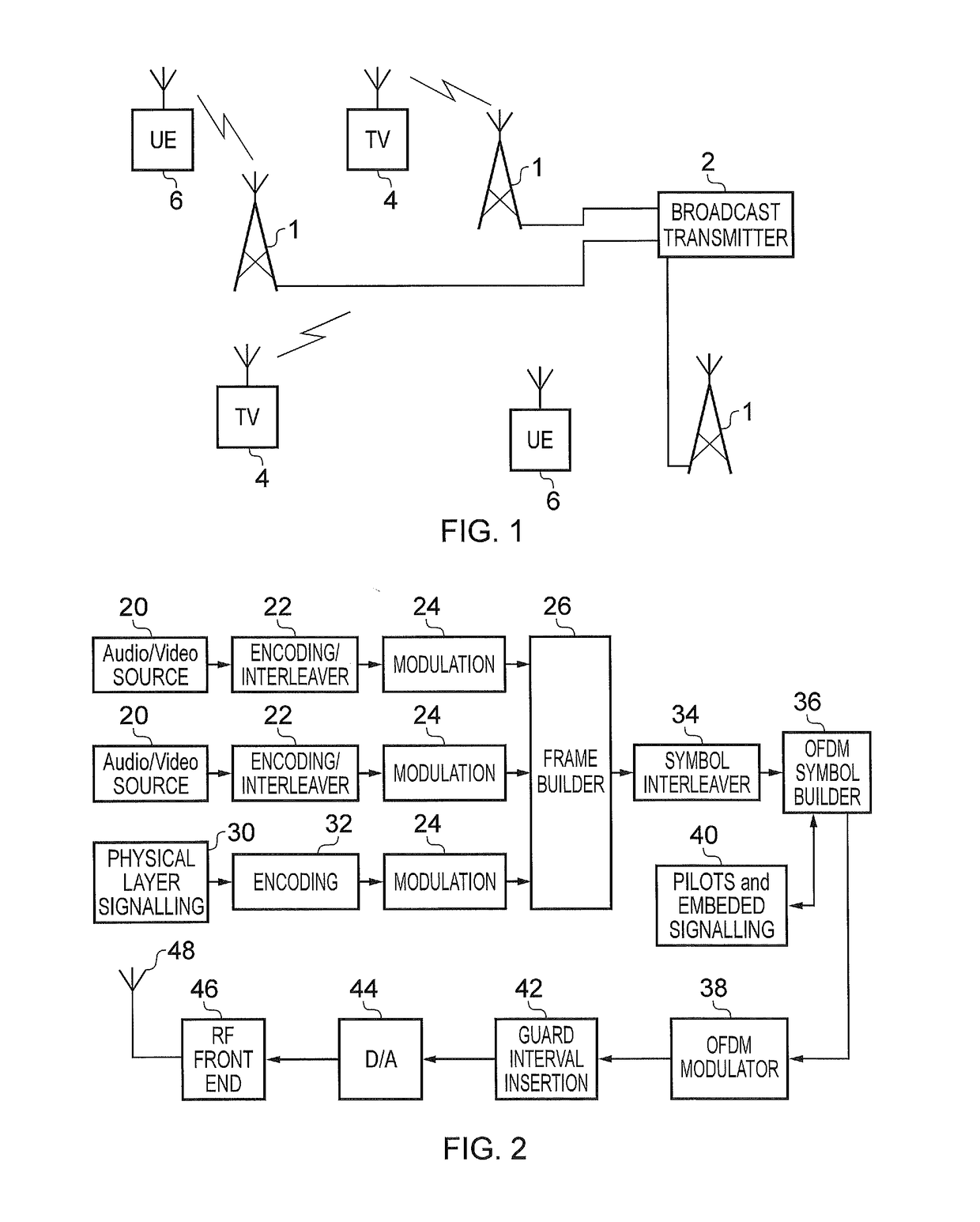
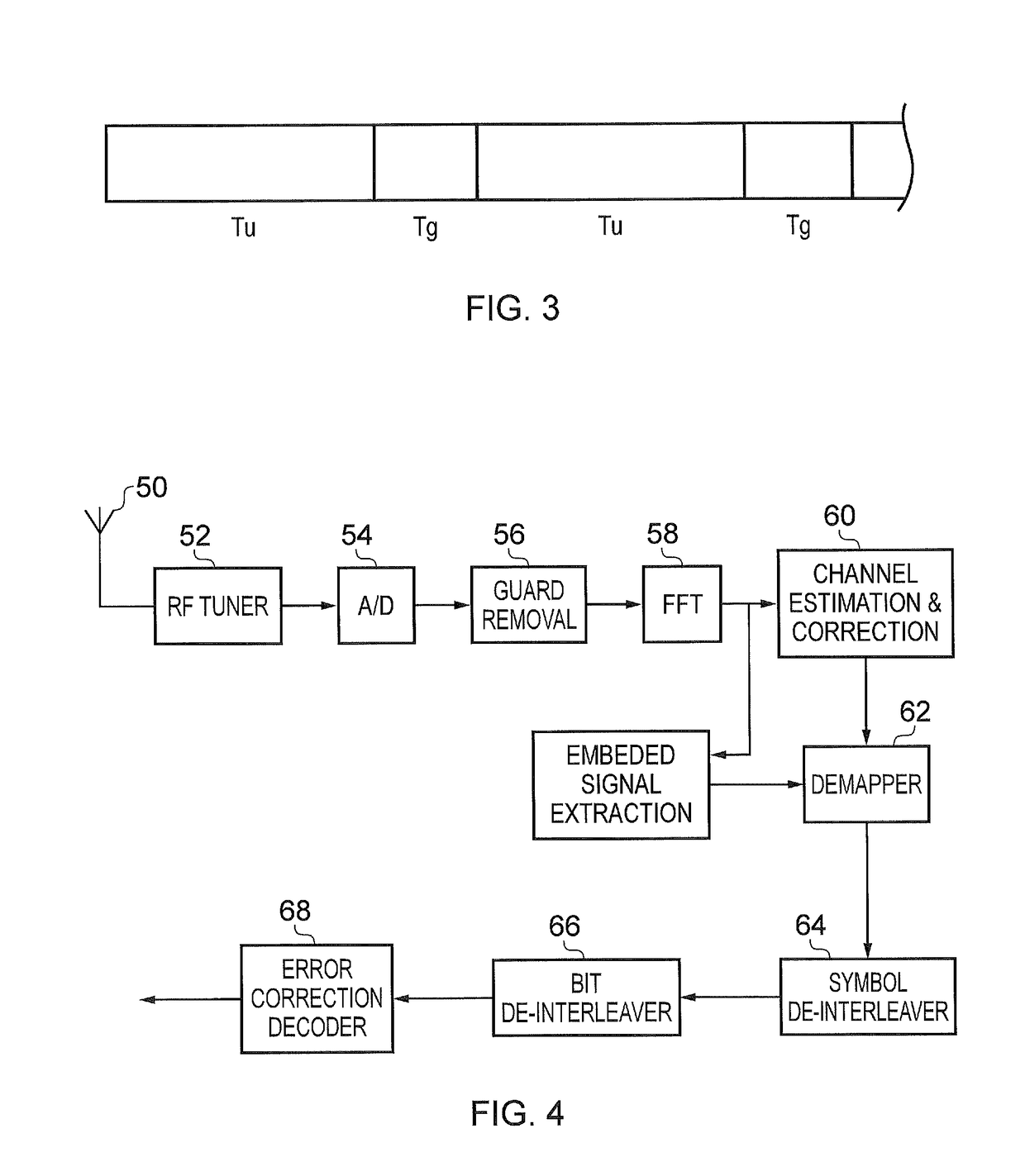
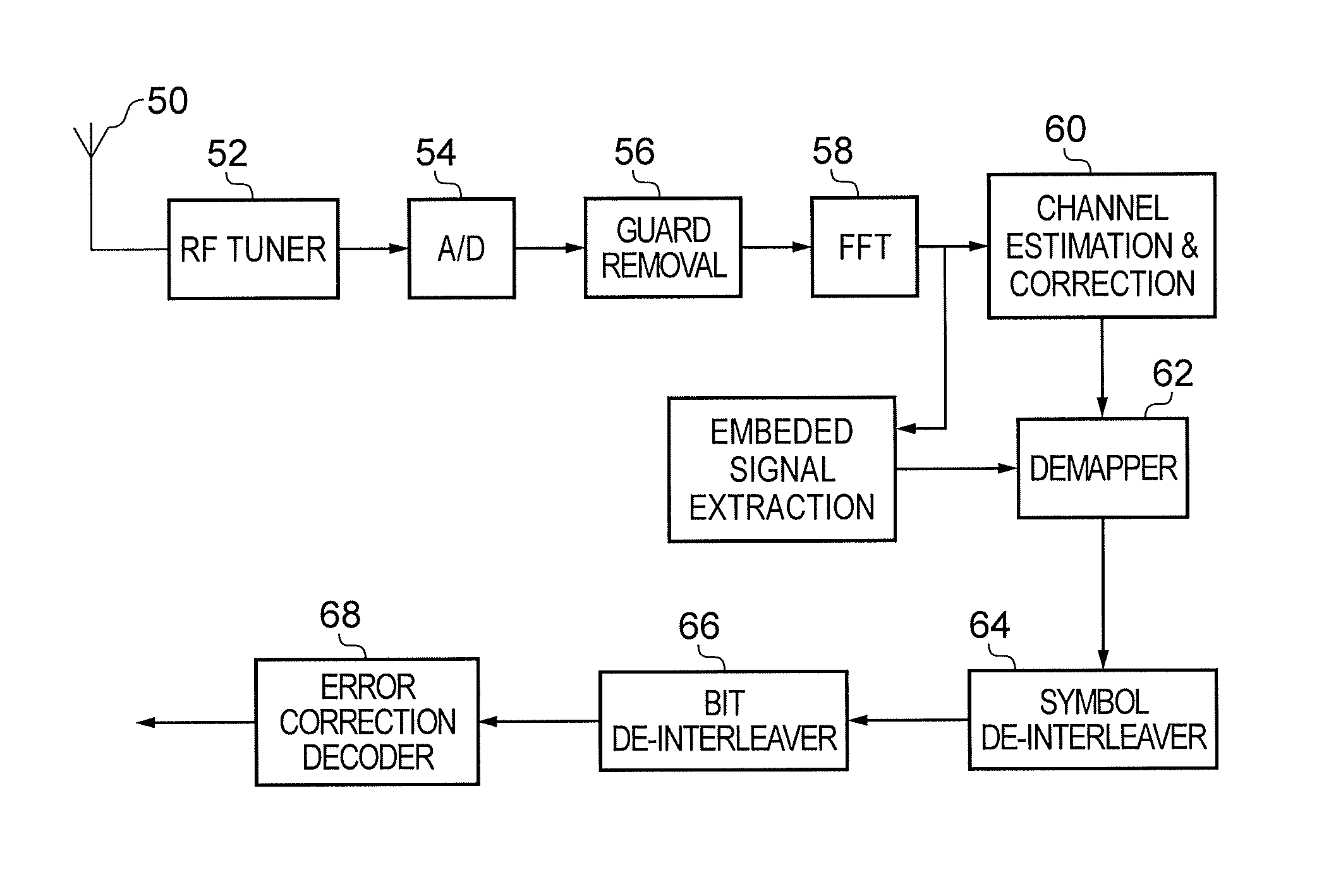
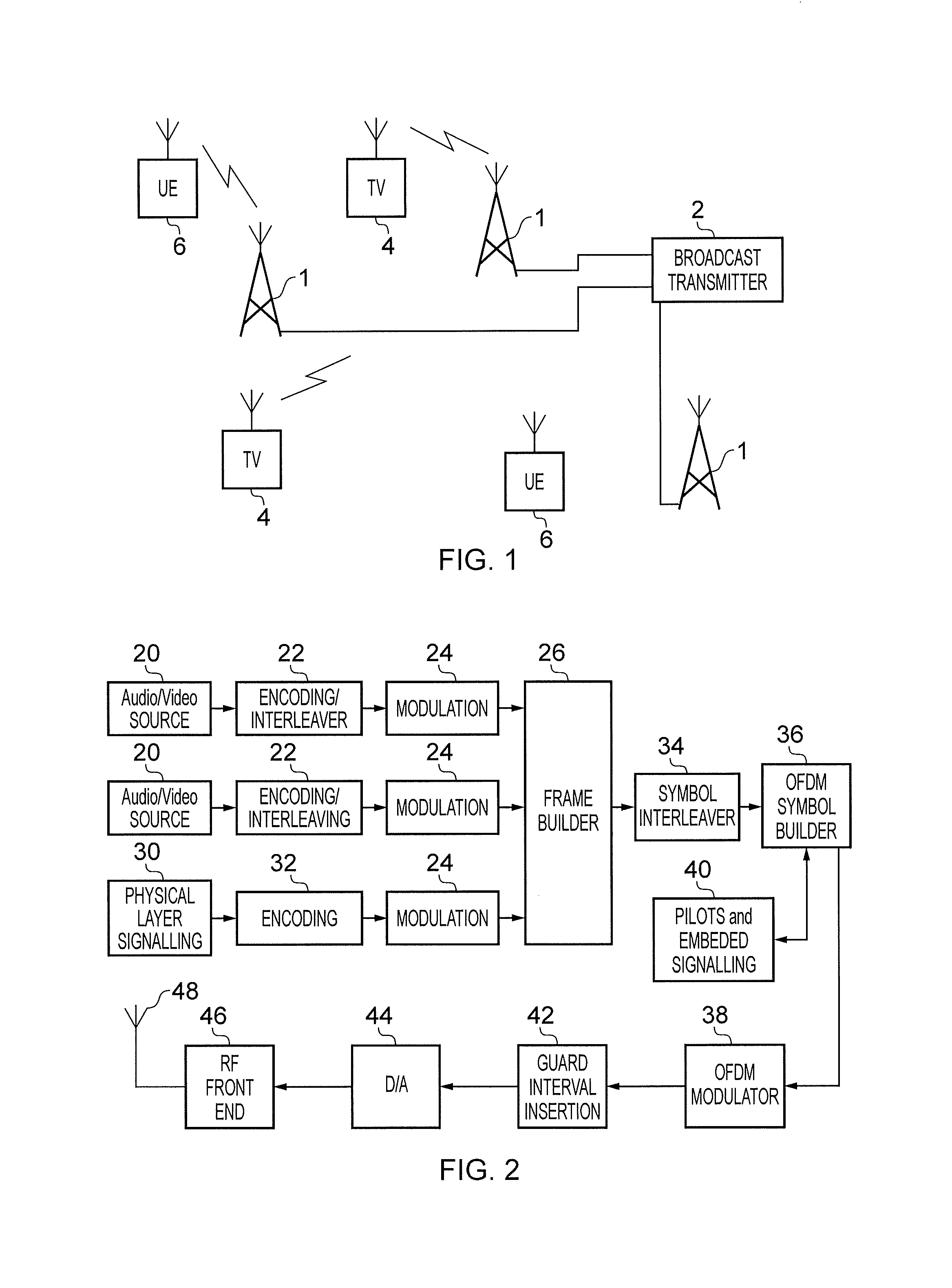
Receiver and method of receiving
ActiveUS20170026221A1Efficient implementationEfficient decodingMulti-frequency code systemsForward error control useRadio frequencyTransmitter
A receiver for detecting and recovering payload data from a received signal comprises a radio frequency demodulation circuit configured to detect the received signal. The received signal has been formed and transmitted by a transmitter to carry the payload data as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) symbols in one or more of a plurality of time divided frames, each frame including a preamble including a plurality of bootstrap OFDM symbols. One or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols of the preamble carrying signalling data represented as a relative cyclic shift of a signature sequence which has been combined with the one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols. A bootstrap processor is configured to detect the signalling data from the bootstrap OFDM symbols using an estimate of the channel transfer function determined from one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols, and a demodulator circuit is configured to recover the payload data from the payload OFDM symbols using the signalling data. The bootstrap processor comprises a channel shaper, which is configured to convolve a time domain copy of the signature sequence with the estimate of the channel impulse response to generate a channel shaped signature sequence, a cross-correlator and a cyclic shift detector. A cross-correlator is configured to cross-correlate the useful part of each of the one or more bootstrap OFDM symbols with the channel shaped copy of the signature sequence, and the cyclic shift detector is configured to estimate the signalling data conveyed by each of the one or more bootstrap OFDM symbols by detecting a cyclic shift of the signature sequence present in each of the one or more bootstrap OFDM symbols from a peak of the samples representing a result of the cross-correlation. Accordingly the signalling data can be detected by identifying the cyclic shift of the signature sequence by cross-correlating the signature sequence with the bootstrap OFDM symbols carrying the signature sequence in the time domain, which can provide a more efficient implementation.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
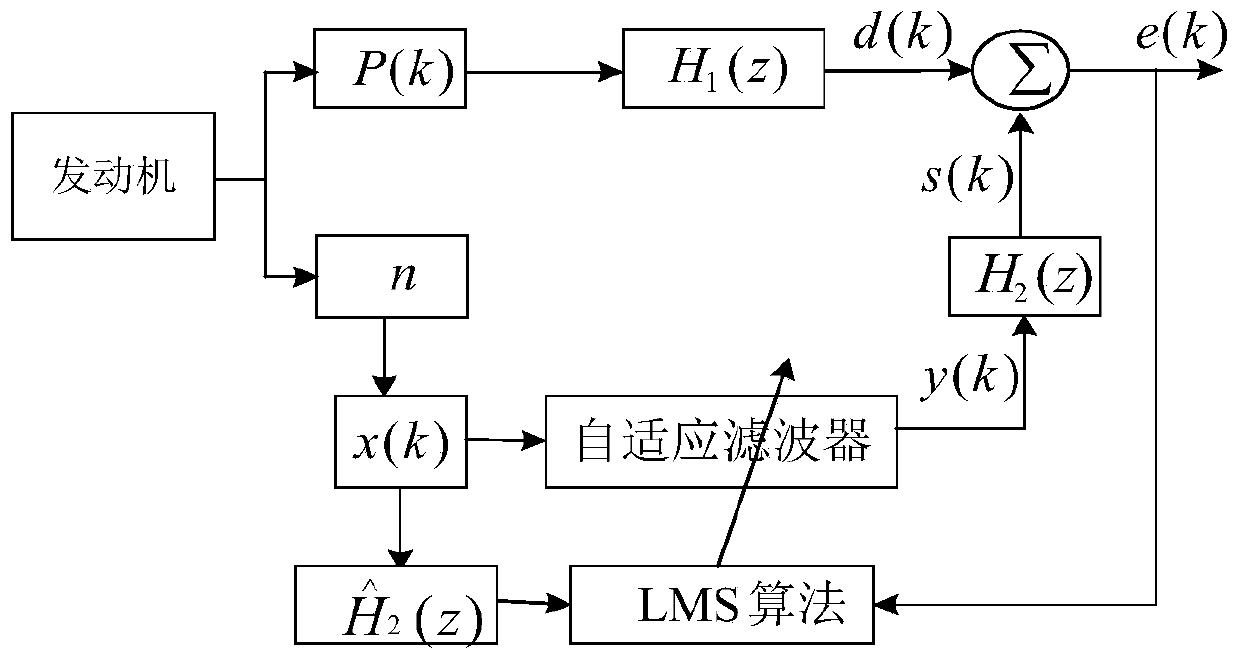
Engine noise control method based on FXLMS algorithm
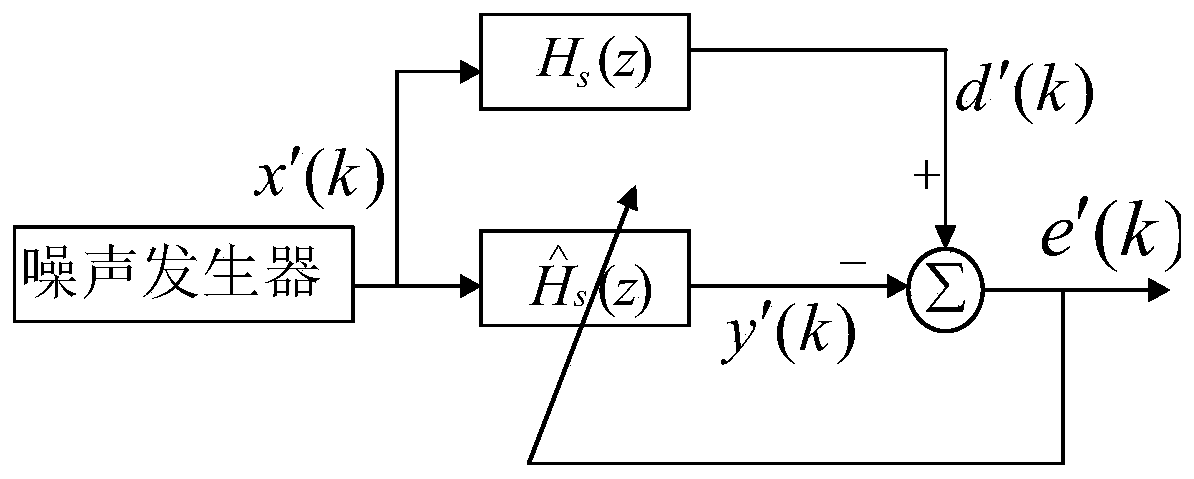
PendingCN109859733AReduce intake noiseIntake noise controlSound producing devicesNoise controlIn vehicle
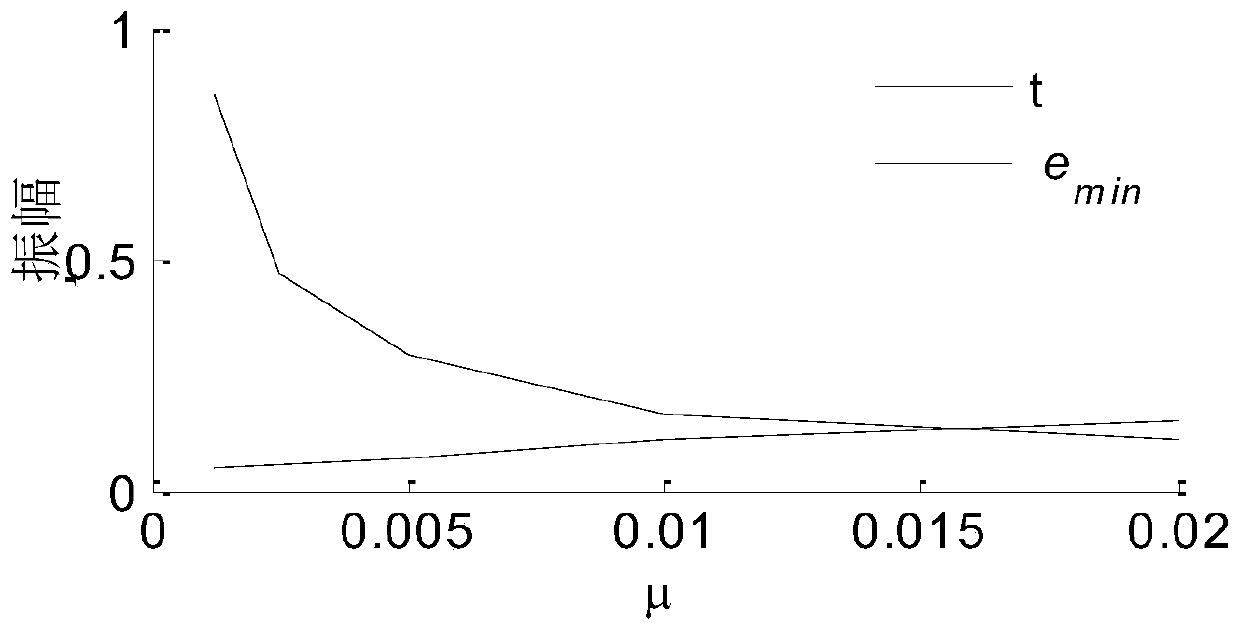
The invention provides an engine noise control method based on an FXLMS algorithm aiming at the problem of in-vehicle noise caused by an engine air inlet system, belonging to the field of noise control. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a main control system model of engine intake noise by using an FXLMS algorithm, and constructing a reference signal x (k) of the main control system model by using the rotating speed of the engine; S2, establishing an off-line identification structure, identifying a secondary channel transfer function H2(z) in an active control system model, and providing an identification result to the active control system model; and S3, controlling the engine noise by using the identified active noise control system model. In addition, an improved variable step length algorithm is proposed. The algorithm adds the parameter gamma to the step length of the normalized algorithm and replaces beta in the sine variable step length to adjust the amplitude range of the step length. The algorithm not only has the advantages of fast convergence and small steady-state error of the sine variable step length algorithm, but also has the characteristicsthat the normalized algorithm is suitable for a time-varying reference signal, and the parameter is easy to select.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multichannel voice detection in adverse environments
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Receiver and method of receiving
ActiveUS20170338994A1Improve accuracyAccurate estimateSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionDetector circuitsEngineering
A receiver detects a received signal, transmitted by a transmitter to carry payload data as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) symbols in divided frames, each frame including a preamble including plural bootstrap OFDM symbols. A detector circuit detects, from the bootstrap OFDM symbols, a synchronization timing for converting a useful part of the bootstrap OFDM symbols into the frequency domain. A bootstrap processor detects an estimate of the channel transfer function from a first OFDM symbol, and a demodulator circuit recovers the signaling data from the bootstrap OFDM symbols using the estimate. The bootstrap processor includes an up-sampler configured to receive the bootstrap OFDM symbols, to form an up-sampled frequency domain version of the bootstrap OFDM symbol, and an output processor configured to identify a peak correlation result, to determine frequency offset of the received signal from a relative position of the peak correlation result in the frequency domain.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Processing device for a pseudo inverse matrix and V-BLAST system
InactiveUS20050149596A1Effective functionEfficient processingBaseband system detailsComputation using non-contact making devicesTransfer function matrixCommunications system
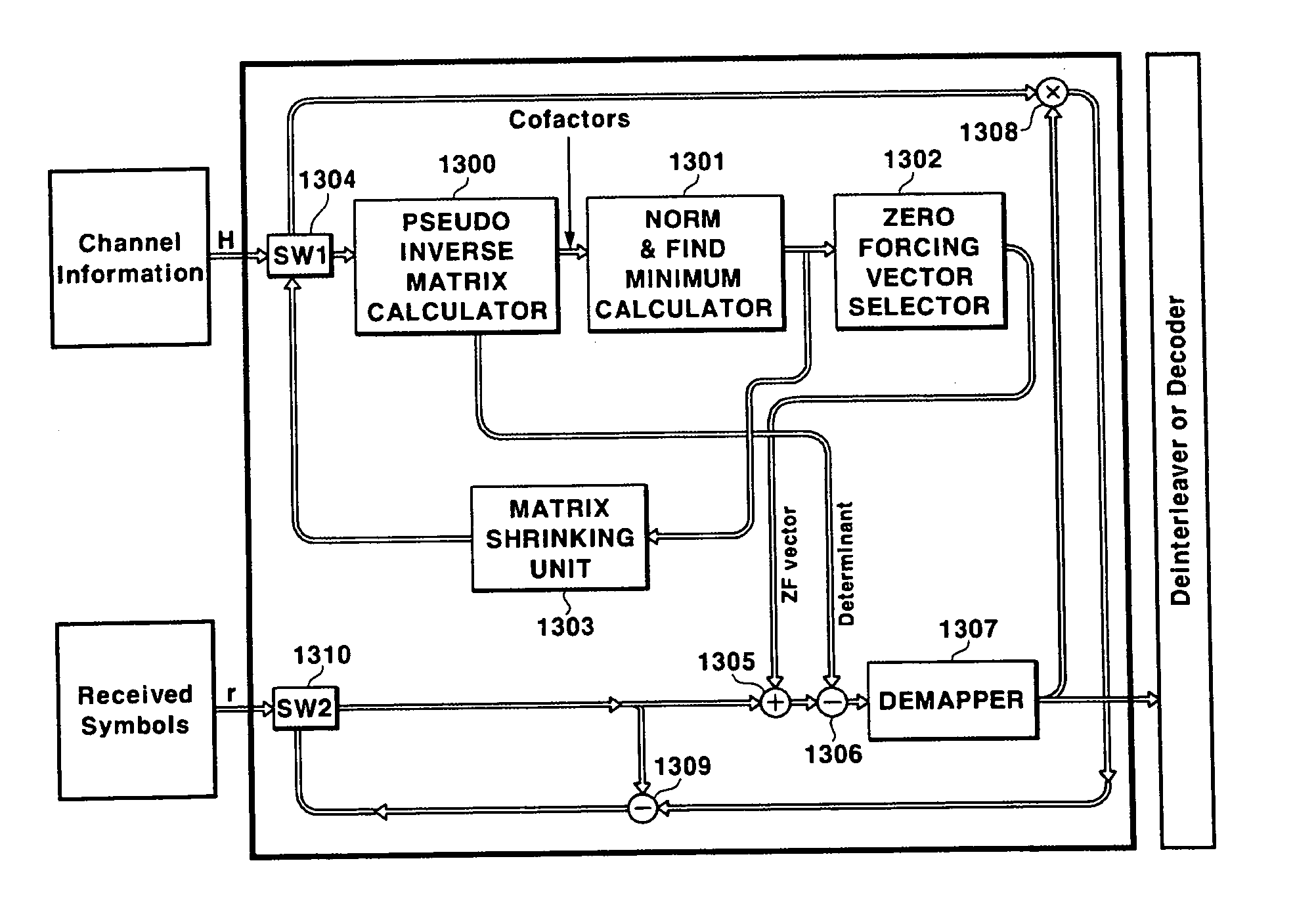
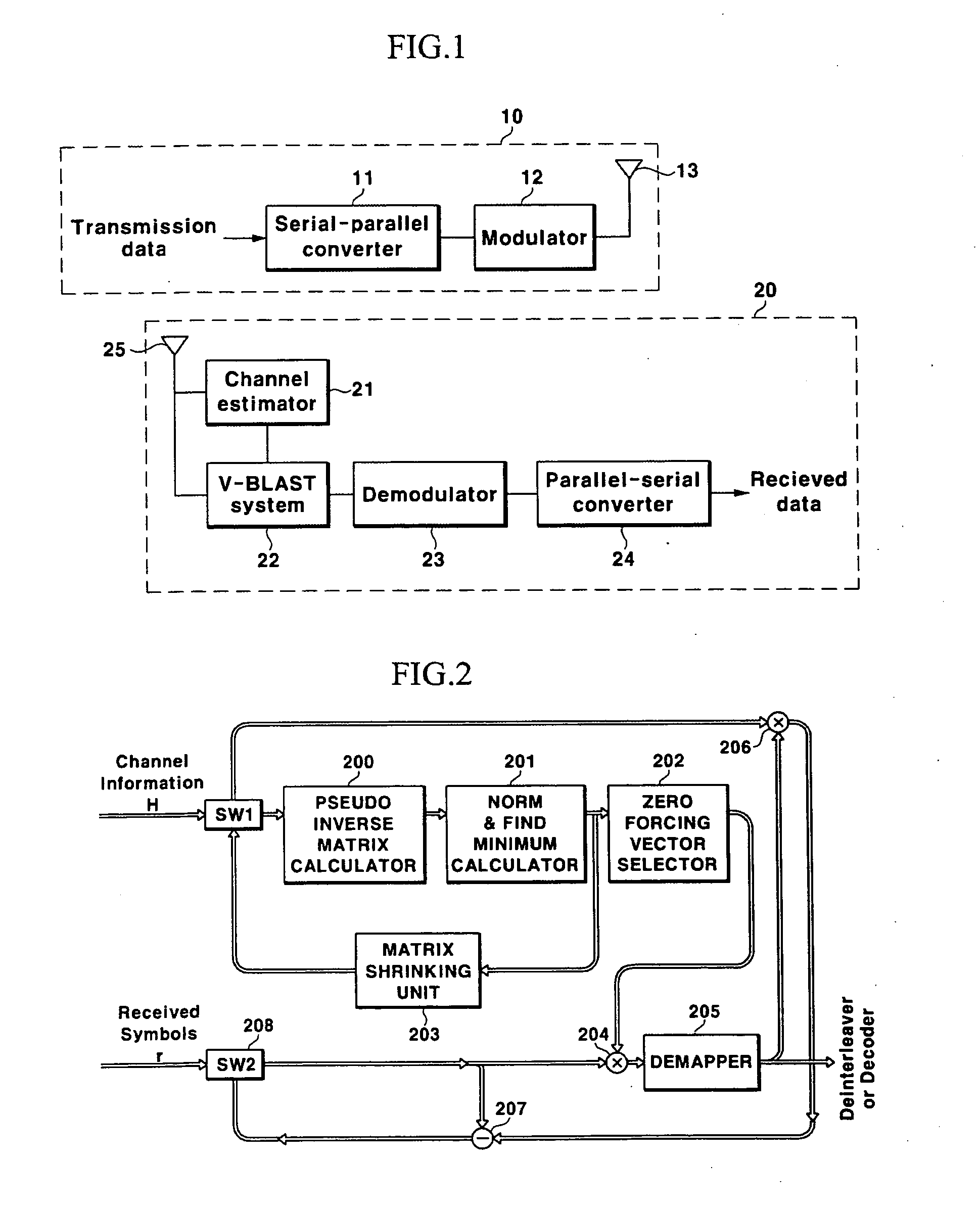
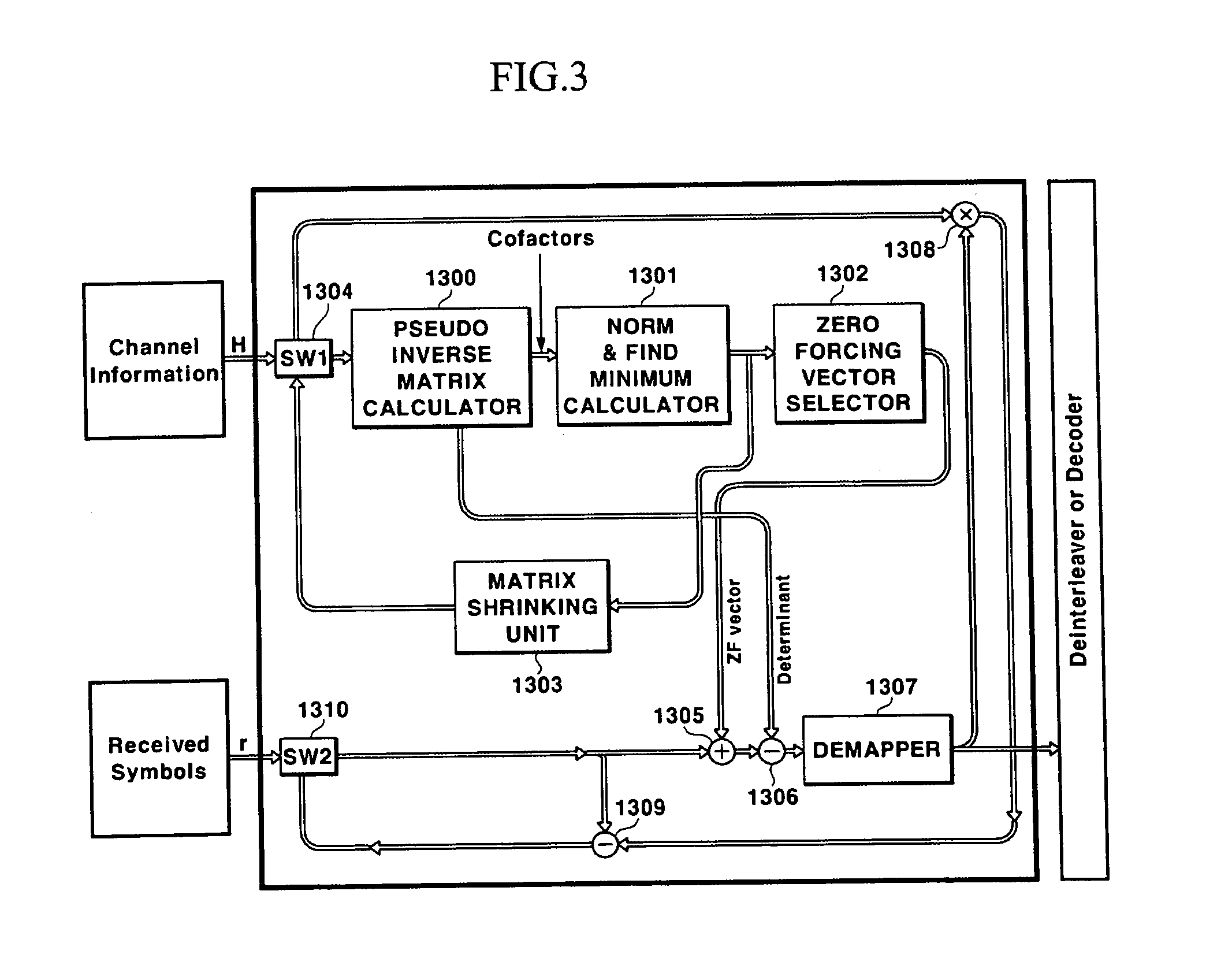
Disclosed is a V-BLAST system for a MIMO communication system. In the V-BLAST system for a MIMO communication system, a pseudo inverse matrix calculator receives a channel transfer function matrix including channel information and produces a cofactor matrix and a determinant for a pseudo inverse matrix. A norm & minimum calculator calculates a minimum index for the cofactor matrix outputted from the pseudo inverse matrix calculator, a weight vector selector selects a row vector having the minimum index and calculates a transposed matrix for the row vector; an adder adds the transposed matrix to a received input symbol, and a subtractor subtracts the determinant to the output. A demapper performs a determined function operation to the output and produces estimated information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Parameter stereo coding, decoding method based on inter-channel transfer function
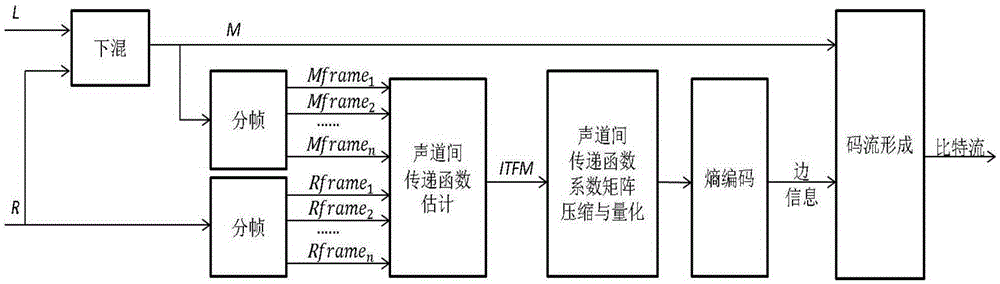
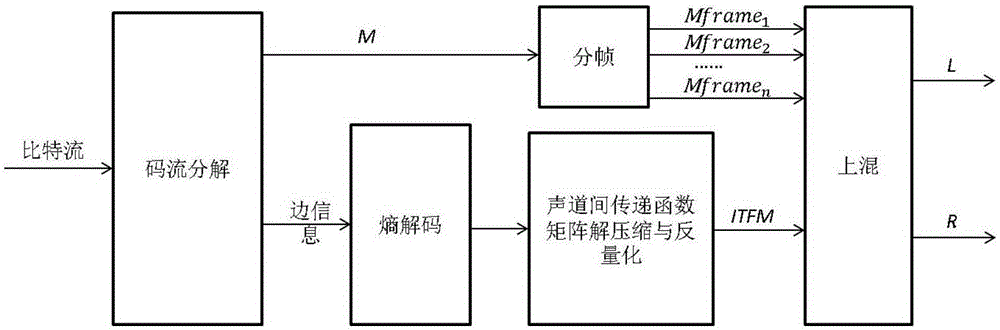
ActiveCN105405445AAchieve compressionPreserve low and high frequency spatial informationSpeech analysisDecoding methodsSide information
The invention discloses a parameter stereo coding, decoding method based on inter-channel transfer function. The parameter stereo coding, decoding method is characterized in that 1) a lower mixed signal can be generated by a coding end using a left track signal and a right track signal; 2) after the respective framing of the input lower mixed signal and the single track signal, the inter-channel transfer function coefficient of every frame can be extracted, and then the extracted transfer function coefficients can be used to form a two-dimensional matrix, and in addition, the single track signal can be the left track signal or the right track signal; 3) the two-dimensional compression, the run coding, and the entropy coding of the two-dimensional matrix can be carried out sequentially, and the coefficients of the two-dimensional matrix can be compressed to form the side information, and then the side information and the lower mixed signal can be used to form the bit stream. The lower high-power space information of the signals can be retained, and the inner-frame compression and the inter-frame compression can be realized at the same time.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Receiver and method of receiving
ActiveUS20170026220A1Signalling dataAccurate detectionChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsDetector circuitsRadio frequency
A receiver for detecting and recovering payload data from a received signal, the receiver comprising a radio frequency demodulation circuit configured to detect the received signal, the received signal carrying the payload data as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed, OFDM, symbols in one or more of a plurality of time divided frames, each frame including a preamble including a plurality of bootstrap OFDM symbols. One or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols of the preamble carry signalling data represented as a relative cyclic shift of a signature sequence carried by the bootstrap OFDM symbols, the signalling data providing an indication of parameters for detecting and recovering the payload data carried by the one or more frames. The receiver comprises a detector circuit configured to detect and to convert a useful part of the one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols into the frequency domain and a bootstrap processor. The bootstrap processor is configured to generate, using the signature sequence, an estimate of a channel transfer function from a first bootstrap OFDM symbol, and to decode the signalling information carried by one or more other bootstrap OFDM symbols using the estimate of the channel transfer function and the signature sequence. A demodulator circuit is configured to recover the signalling data from the one or more bootstrap OFDM symbols using the estimate of the channel transfer function. The bootstrap processor is configured to generate, for each of the one or more other bootstrap OFDM symbols, an updated version of the channel transfer function, to equalise each of the one or more other bootstrap OFDM symbols using the updated version of the channel transfer function for each of the one or more other bootstrap OFDM symbols, and to detect the signalling data carried by the one or more other bootstrap OFDM symbols by correlating the equalised one or more other bootstrap OFDM symbols with a reproduced version of the signature sequence. Embodiments of the present technique provide an improvement in detecting and recovering signalling data carried by the bootstrap signals by updating the channel transfer function for each bootstrap OFDM symbols.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Approach for processing data received from a communications channel to reduce noise power and optimize impulse response length to reduce inter-symbol interference and inter-channel interference
ActiveUS6996199B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceOptimize impulse response lengthAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationFinite impulse responseAdjacent-channel interference
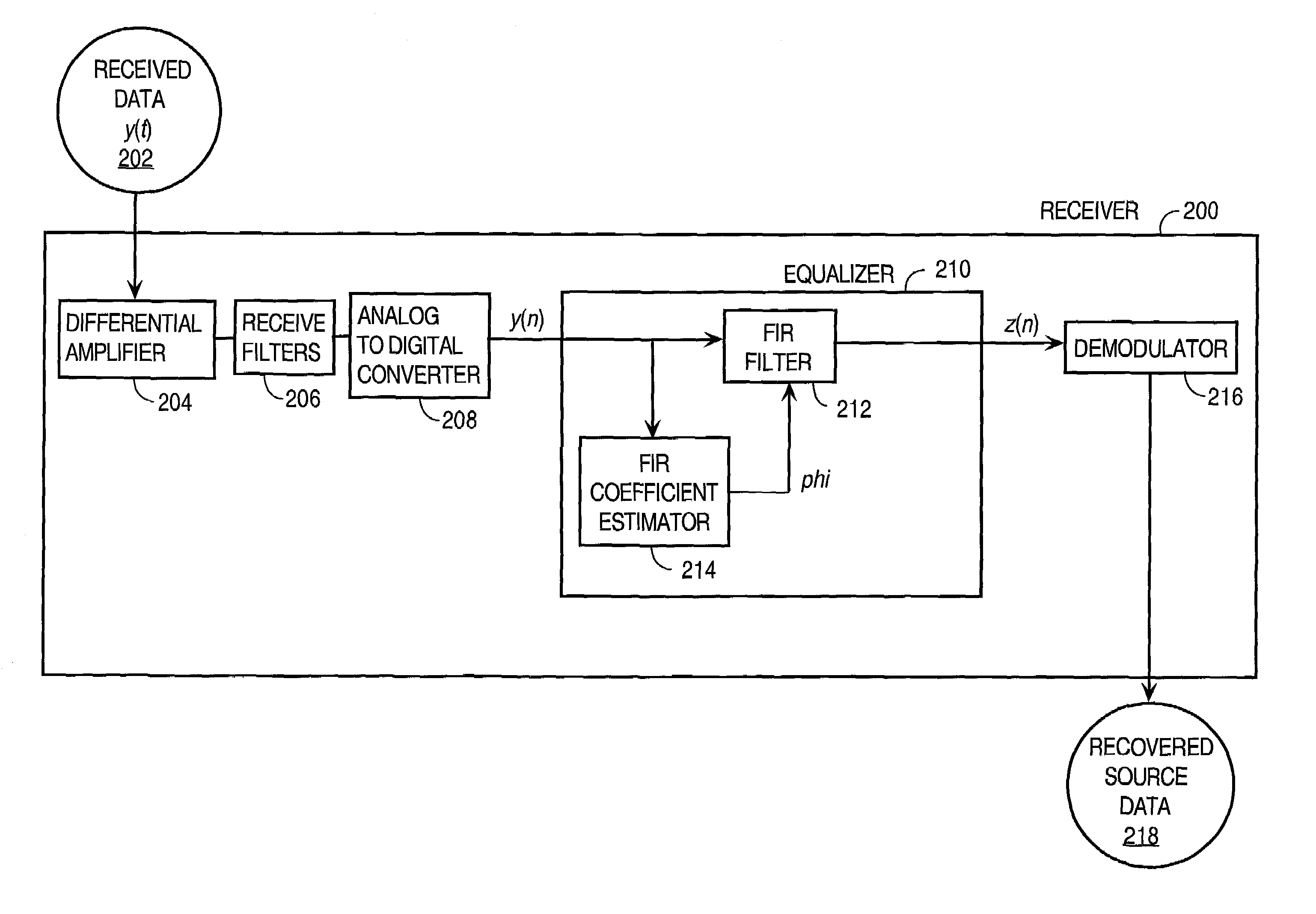
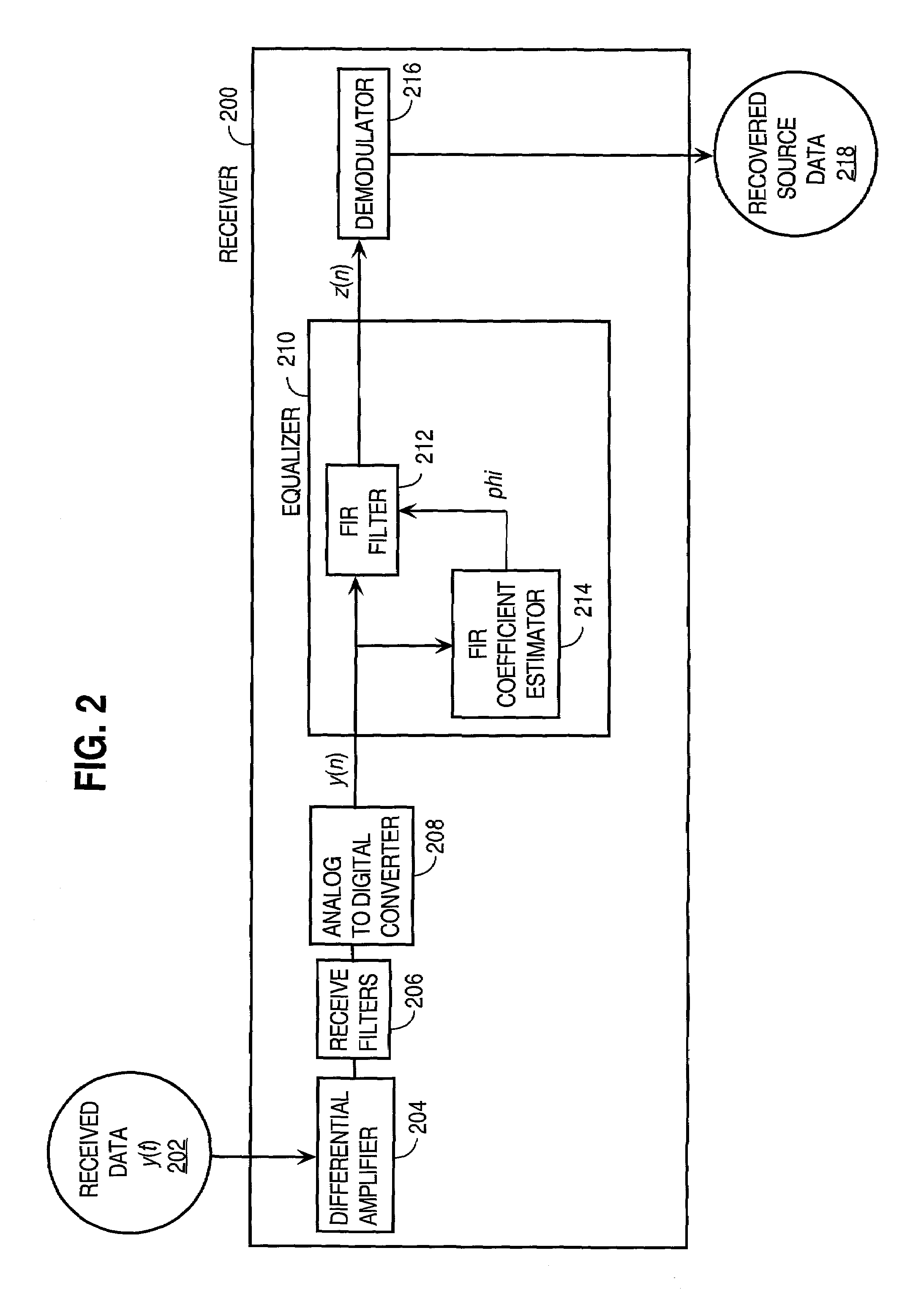
An approach for processing data received from a communications channel that minimizes noise power and optimizes impulse response length to reduce interference, such as from inter-symbol interference (ISI) and inter-channel interference (ICI), is disclosed. For example, finite impulse response (FIR) filtering may be used with FIR coefficients that are determined by optimizing a function of the impulse response length and the noise power. The impulse response length is optimized based on the communications channel transfer function to reduce interference. The noise power is minimized based on the noise covariance as determined using the total noise power density. The approach accounts for noise from a variety of interference sources besides ISI and ICI. The result is a superior equalizer for use in communications receivers employing orthogonal frequency division multiplexing or discrete multitone modulation in communications protocols employing Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, G.Lite and Very High Bit Rate DSL.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Binder identification
InactiveUS8073135B2Reduce riskSimple designInterconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsTransceiverModem device
Methods, techniques and apparatus identify members and characteristics of binders and / or other groups of communication lines such as those in a DSL system. Information obtained includes the identification (for example, by scanning) of significant crosstalking “offenders” and their “victims” that are affected by the crosstalk. One or a small number of modems are instructed to transmit with preselected transmit spectra, after which evidence of crosstalk in the noise spectrum data is examined for potential victim lines. Direct evidence of noise spectrum contribution by a suspected offender line may be obtained by collecting reported noise spectrum data and / or estimated noise spectrum data from potential victim lines. Also, where such direct evidence is not available, or in addition to it, other operational data showing crosstalk interference relating to potential victim lines can be used. The transmitting modem can either be on the CO / RT side or on the CPE side. Modems other than suspected offenders might transmit zero or minimal power in one or more selected frequency bands during scanning to reduce the risk that a modem and / or line not being examined for “offender” status supplies unnecessarily complicating and / or dominant crosstalk during the procedure. For DMT modulated DSL transceivers, well designed transmit spectra can be easily enforced by manipulating line profiles where such well designed line profiles cause minimal or no interruption to existing DSL customers. The invention also can be used to identify (partially or fully) the absolute values of crosstalk channels making up a channel transfer function.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
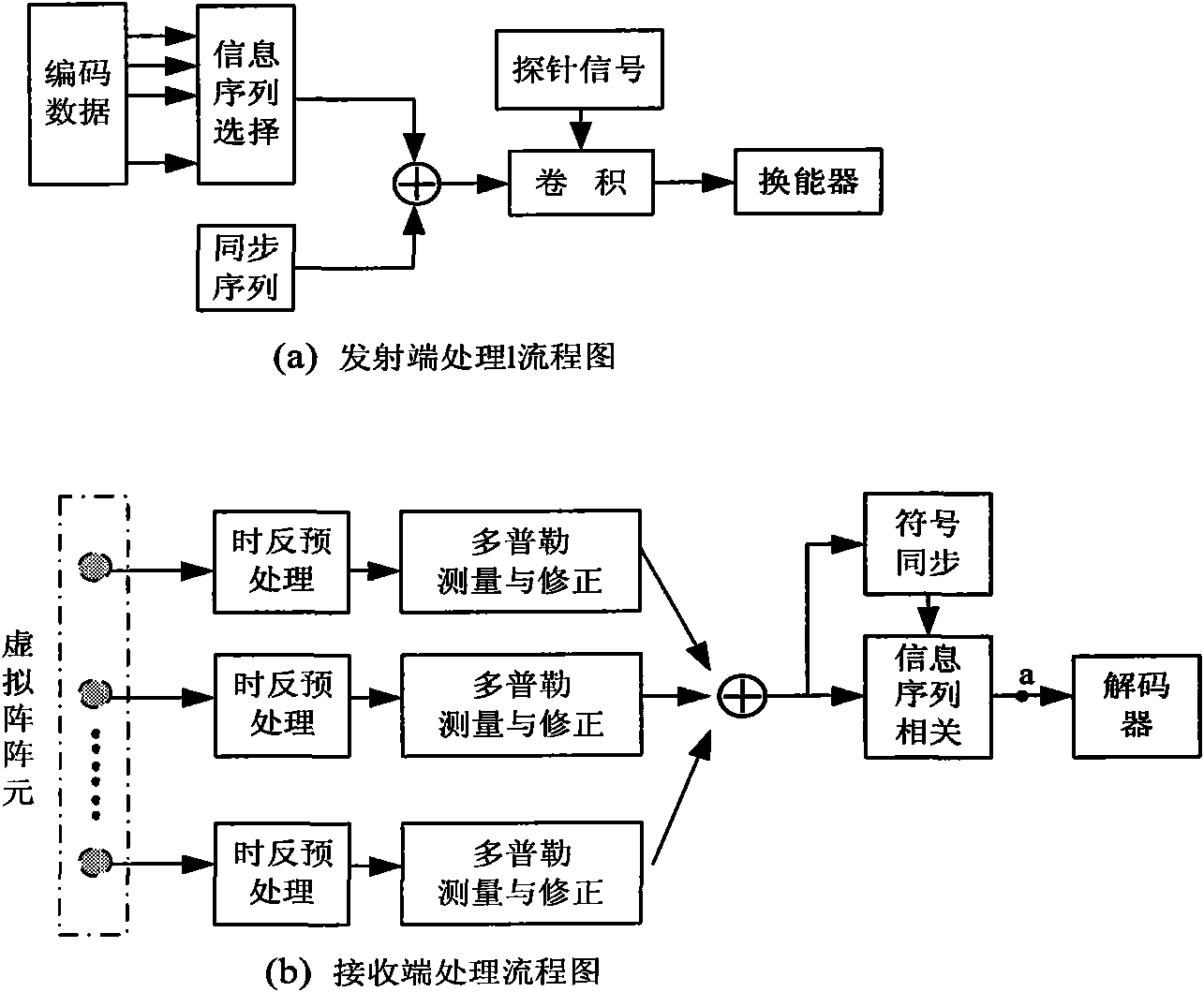
Passive time reversal underwater sound communication method suitable for mobile platform
InactiveCN102025423AGood space diversity effectGain Time Diversity GainTransmissionArray elementEngineering
The invention discloses a passive time reversal underwater sound communication method suitable for a mobile platform, wherein at least a receiver or a sender moves, the same information frame is repeatedly emitted on different position points, and channel transfer functions on different position points have lower correlation. A receiving end carries out pretreatment, such as frame synchronization, time reversal convolution, Doppler correction and the like, to a received signal, then merges a plurality of pretreated signals received on different opposite positions, and recovers emission information by operations, such as symbol synchronization, spread spectrum sequence correlation and the like. The invention has the beneficial effects that level correlation of a underwater sound communication channel is weakened by using position changes to provide a space diversity effect for time reversal treatment; the configuration of the time reversal communication system is lowered, and for the minimum configuration, the receiving end and the sending end are needed to be provided with only one real object array element respectively. Meanwhile, the same information frame is repeatedly emitted at different time points to obtain the time diversity effect, thereby obviously improving the reliability of the underwater sound communication system in the complex environment.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com