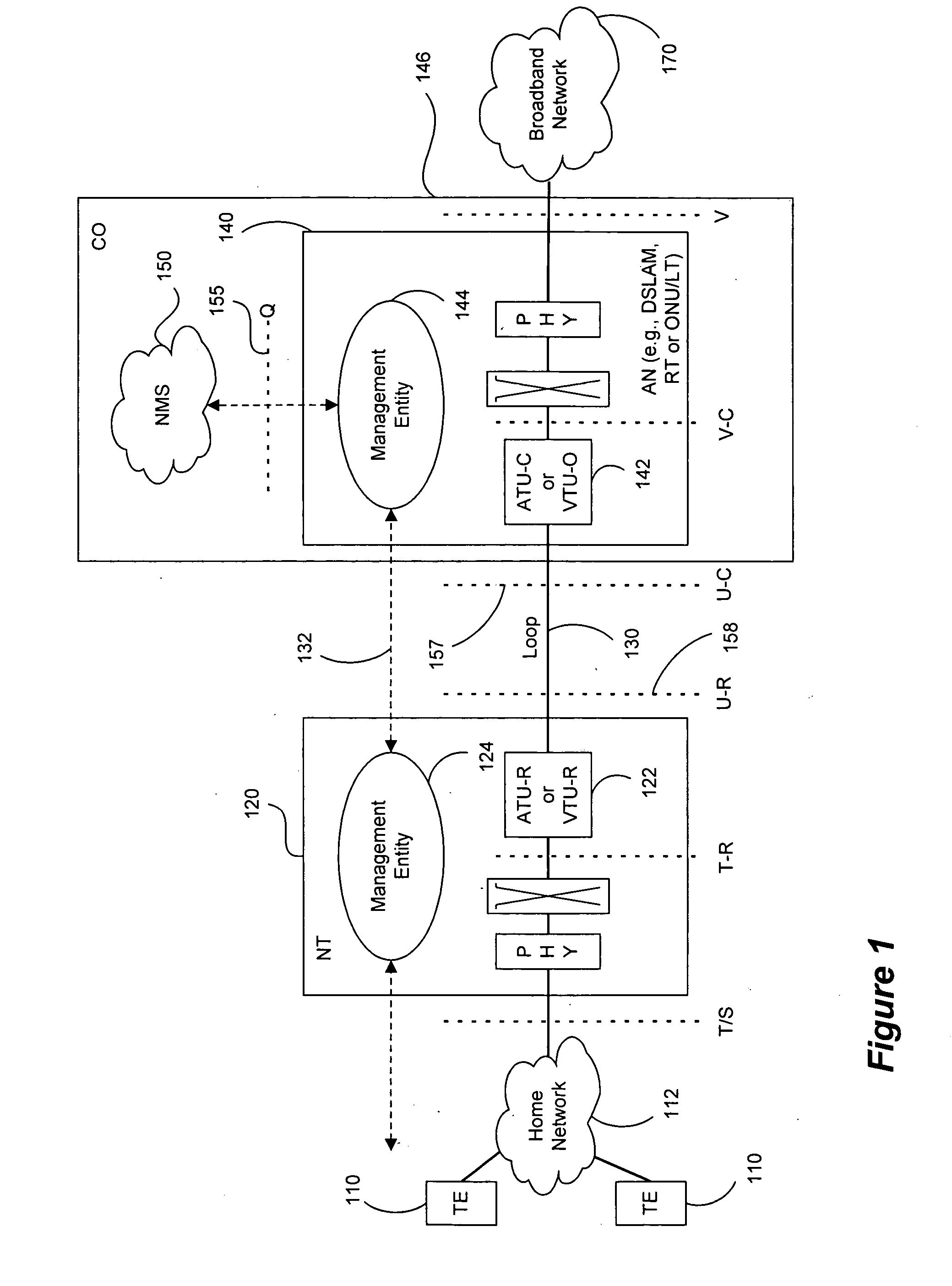
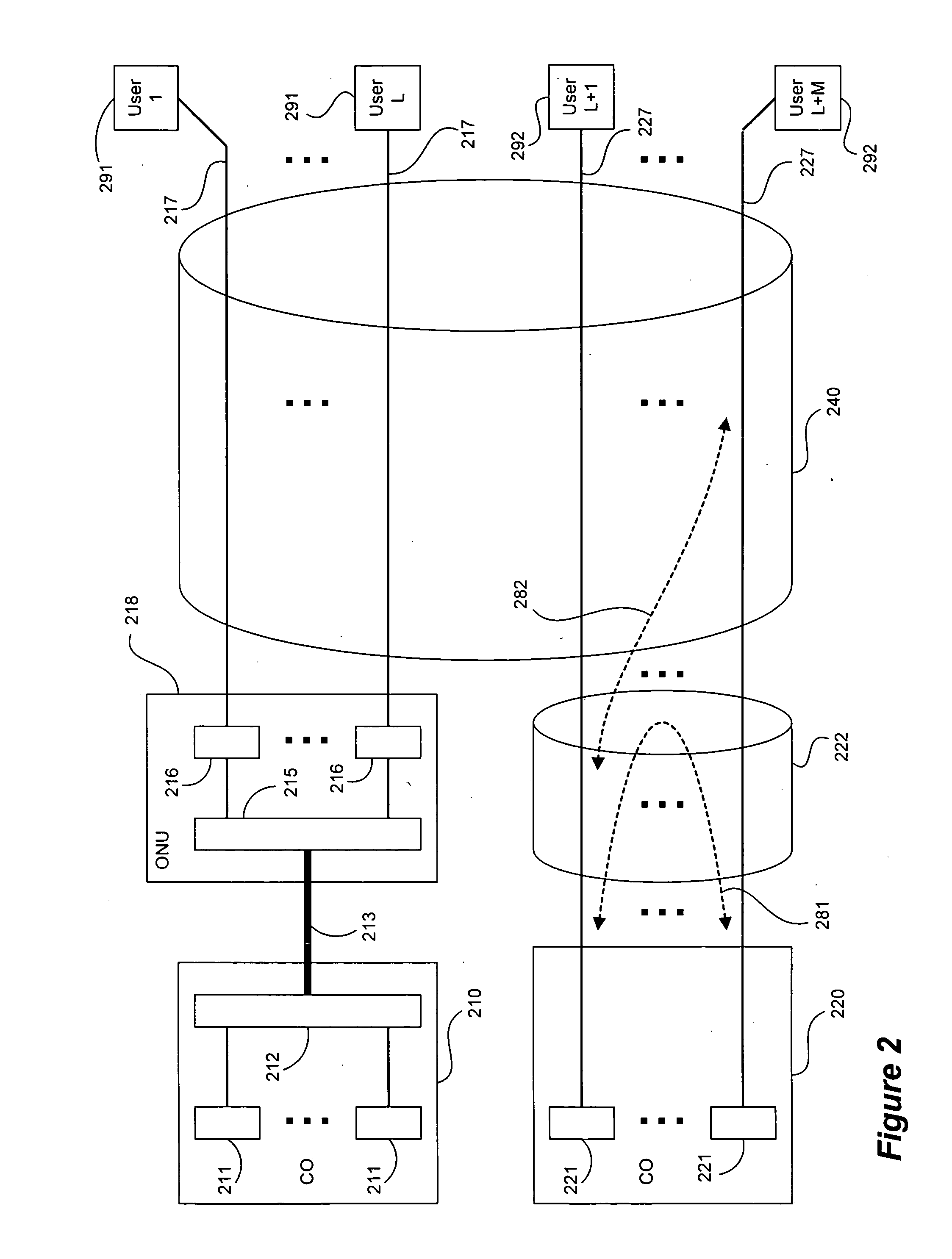
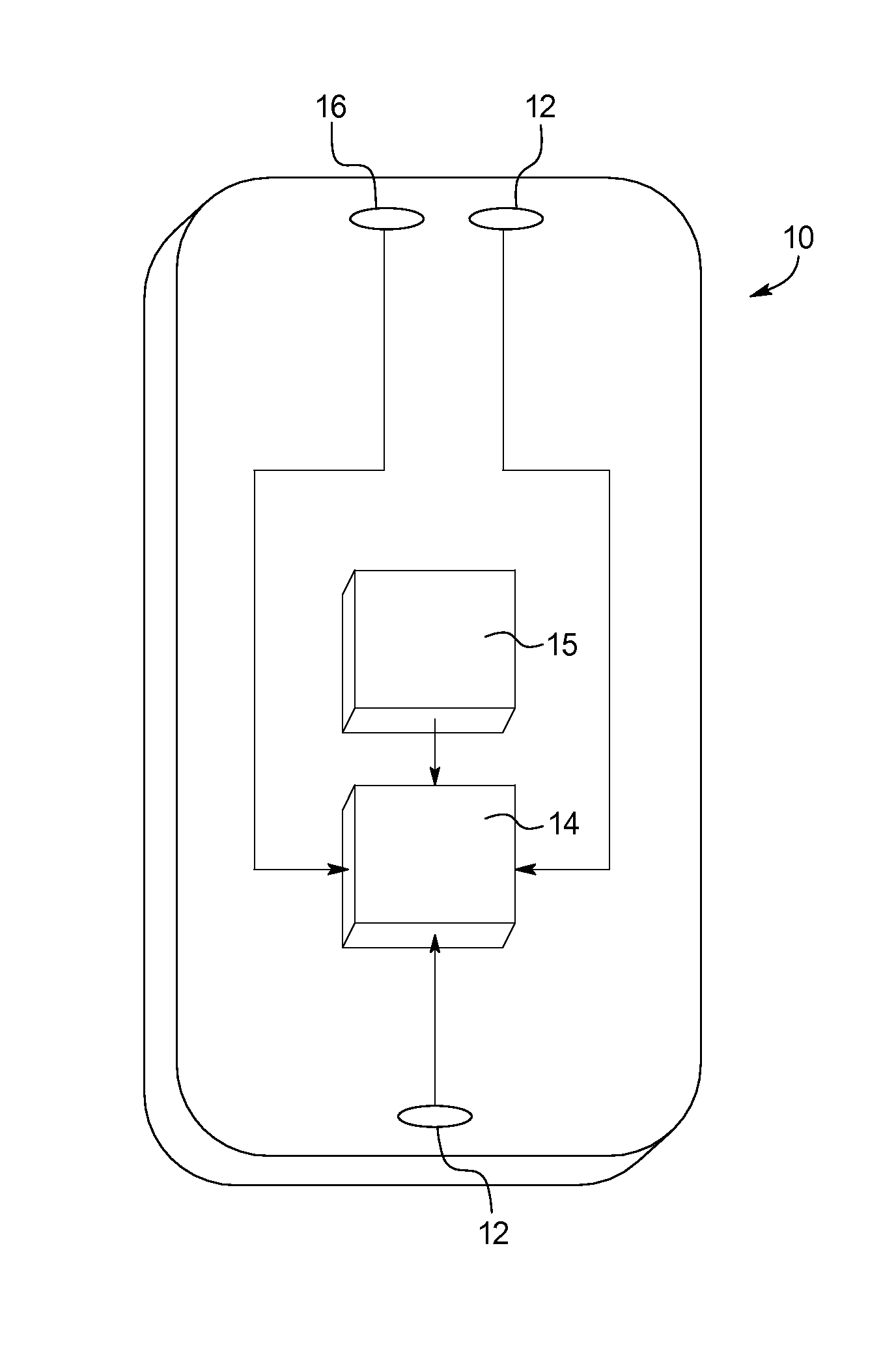
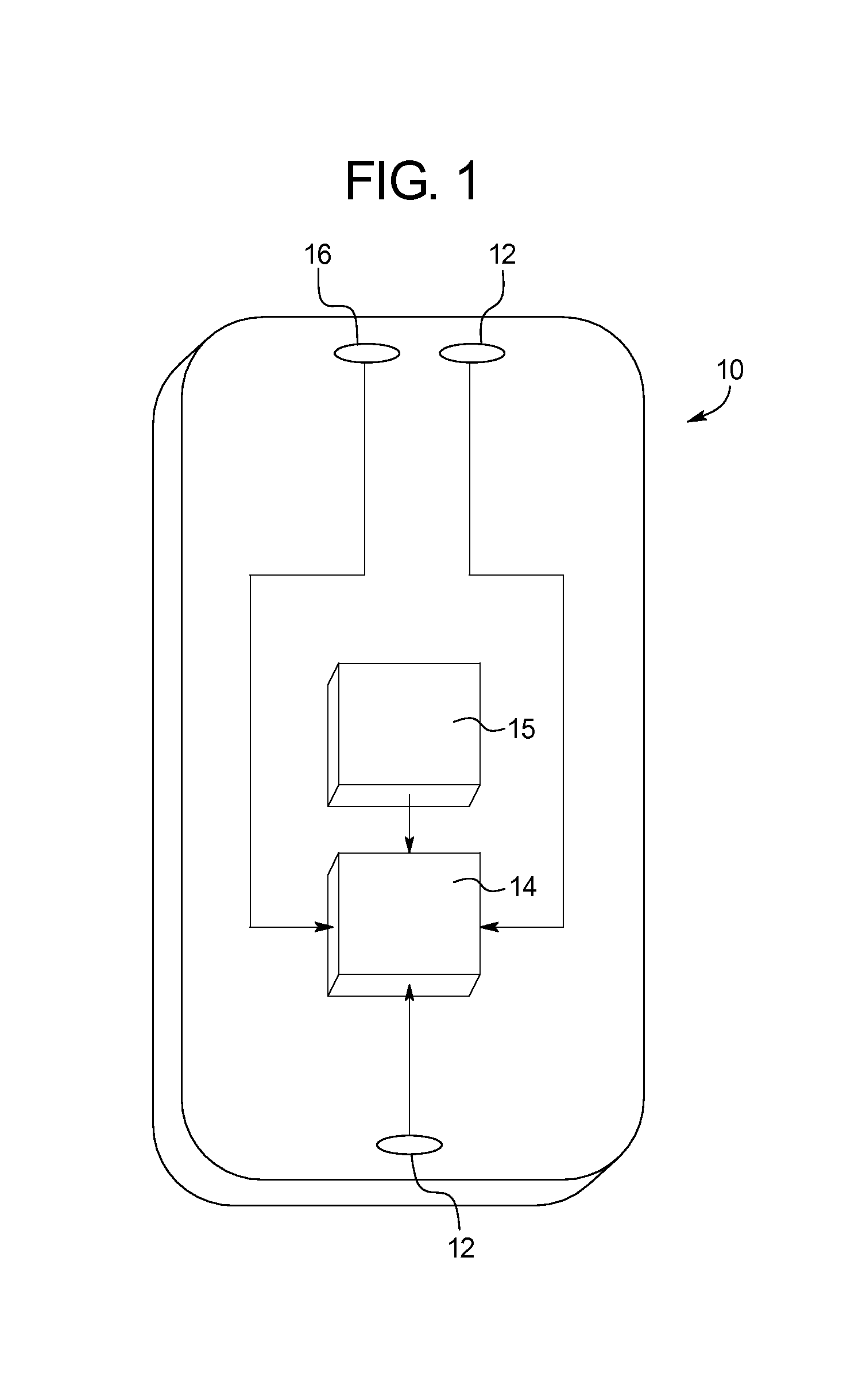
Patents
Literature
440 results about "Noise spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
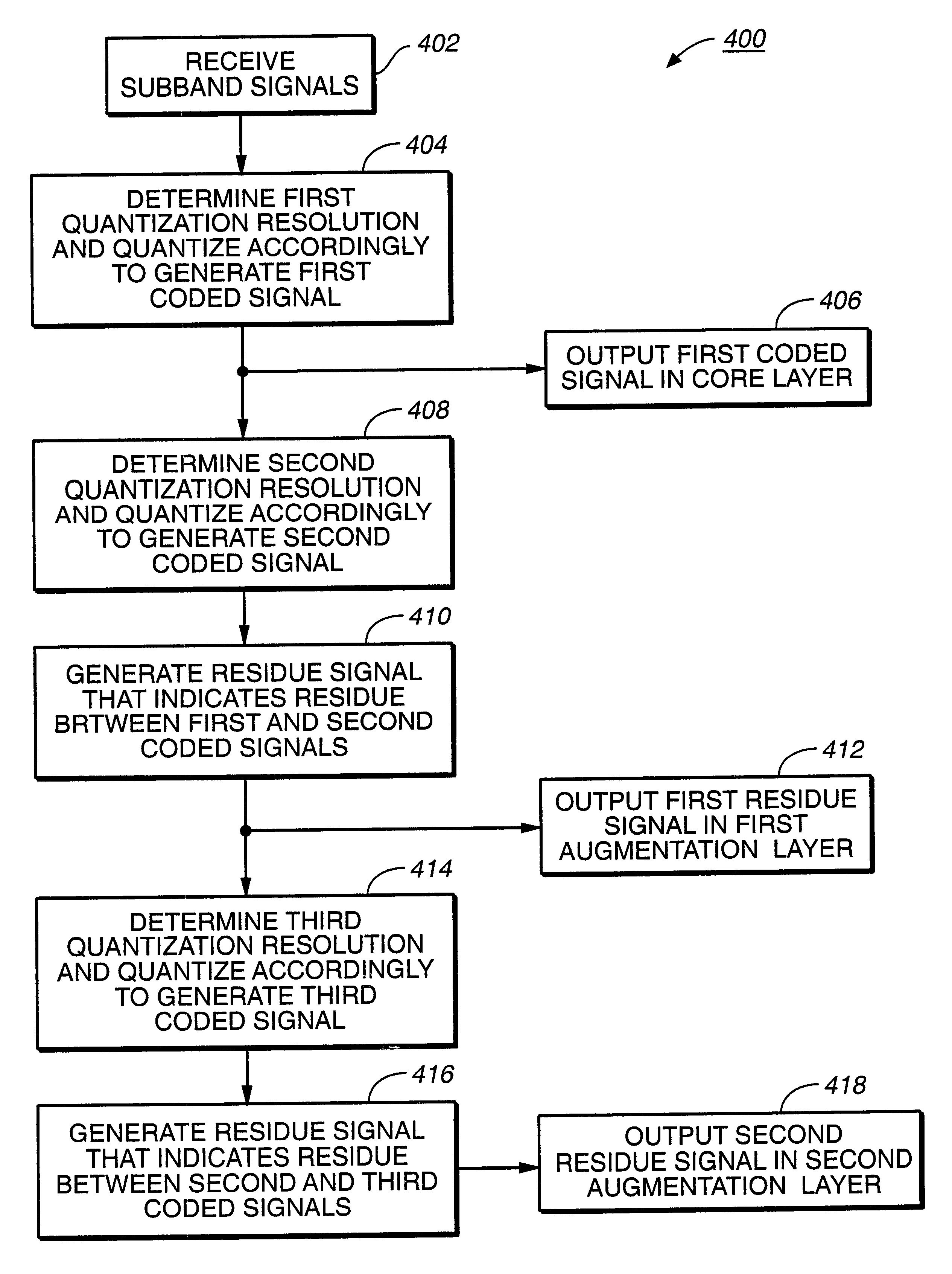
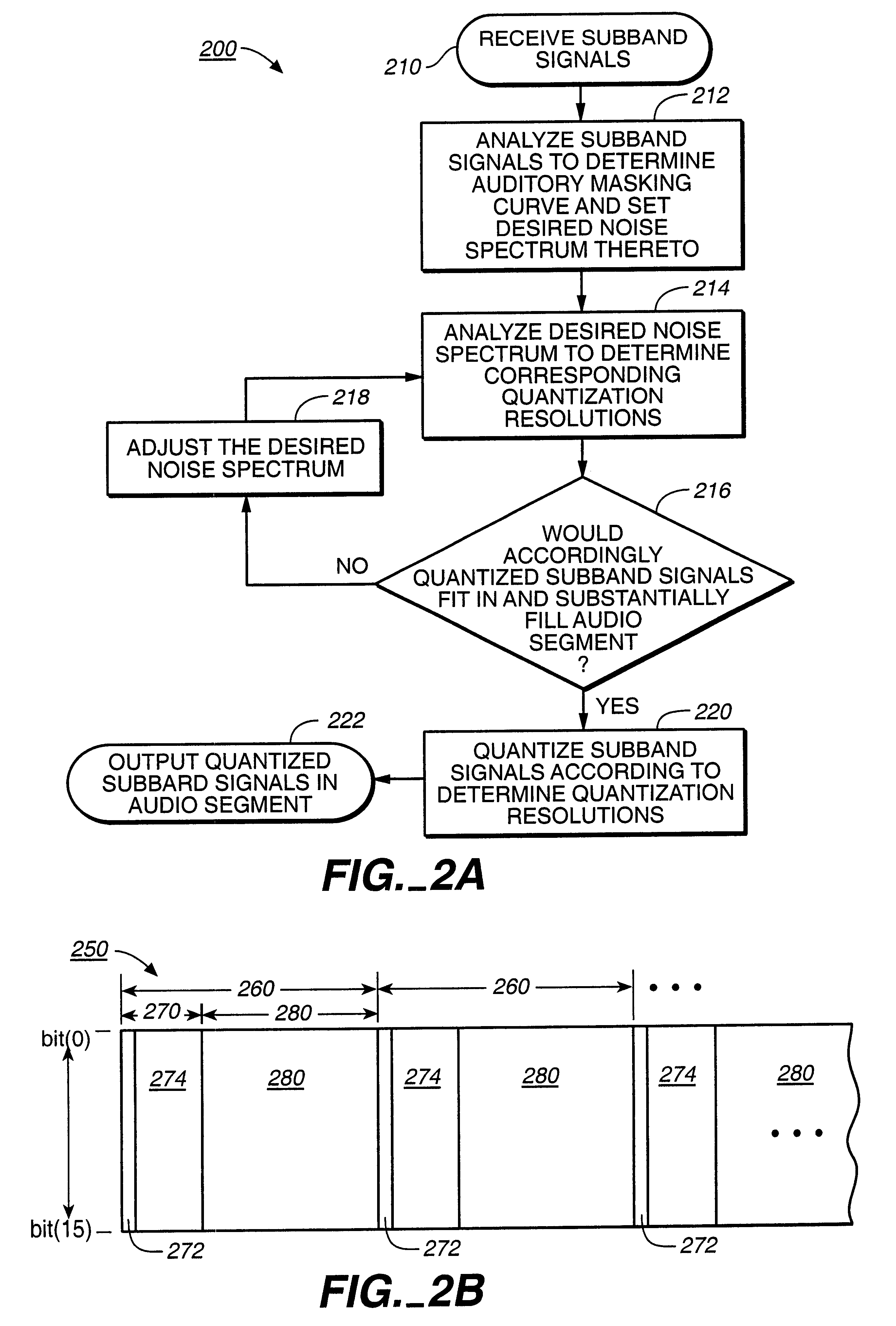
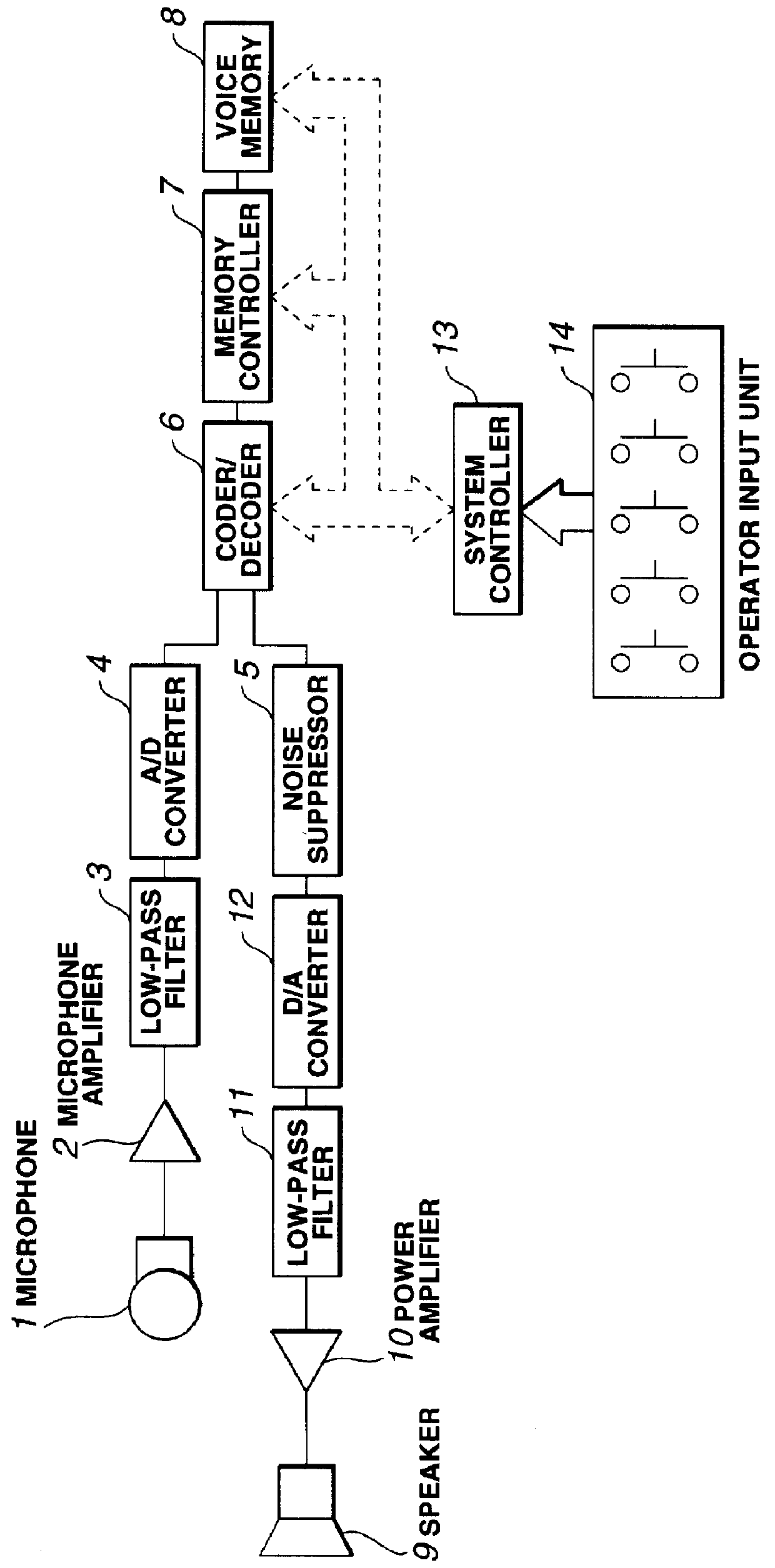
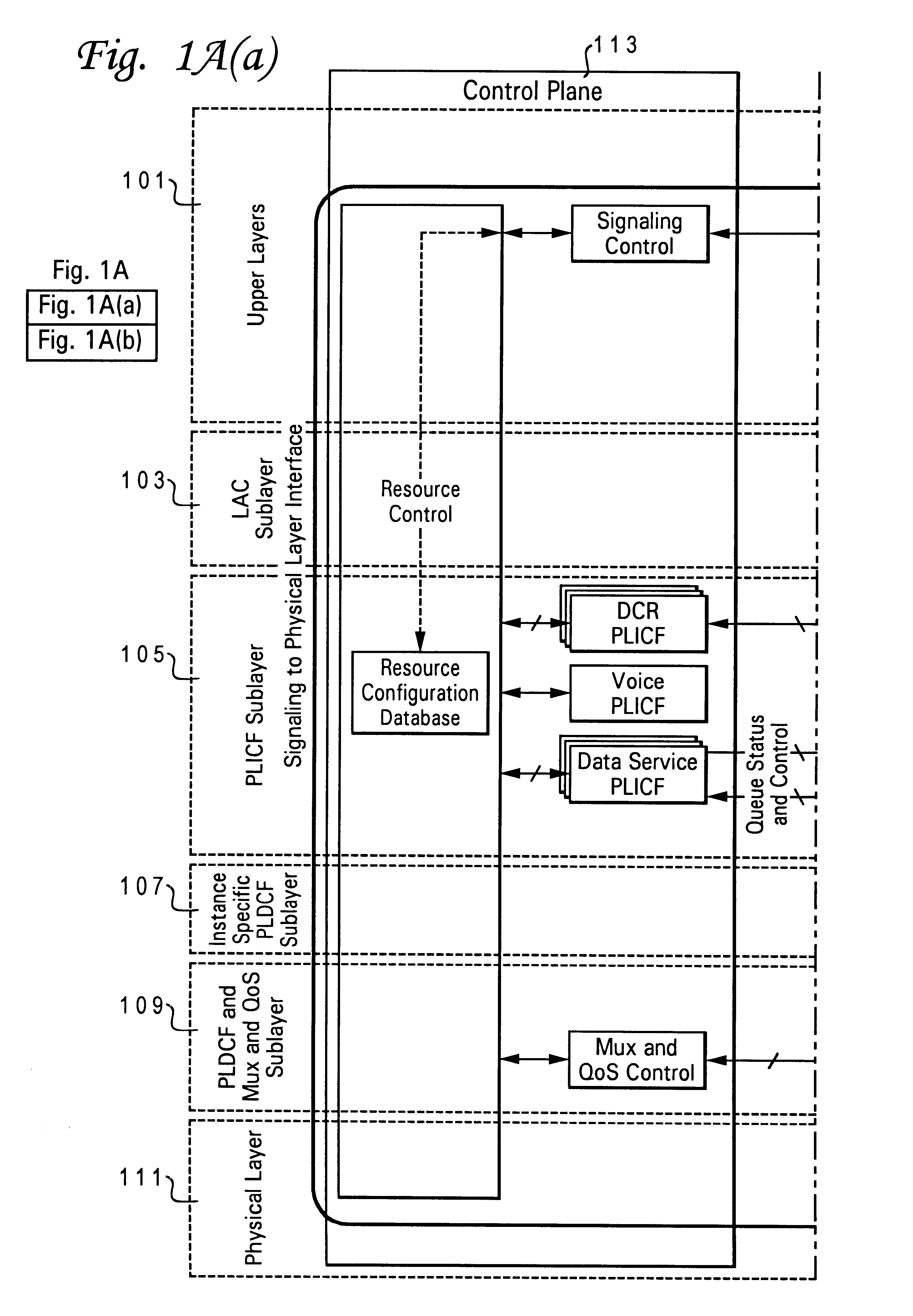
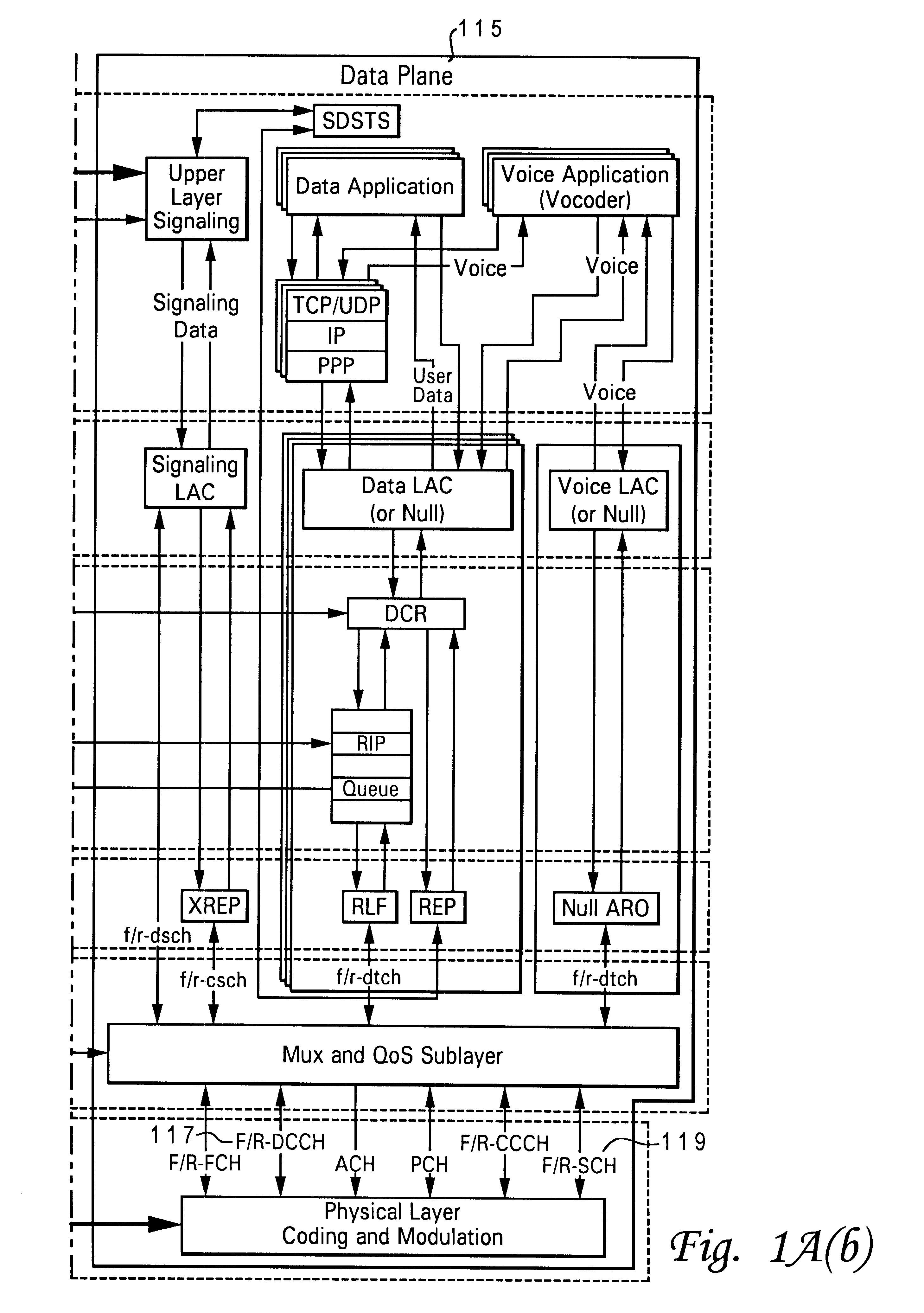
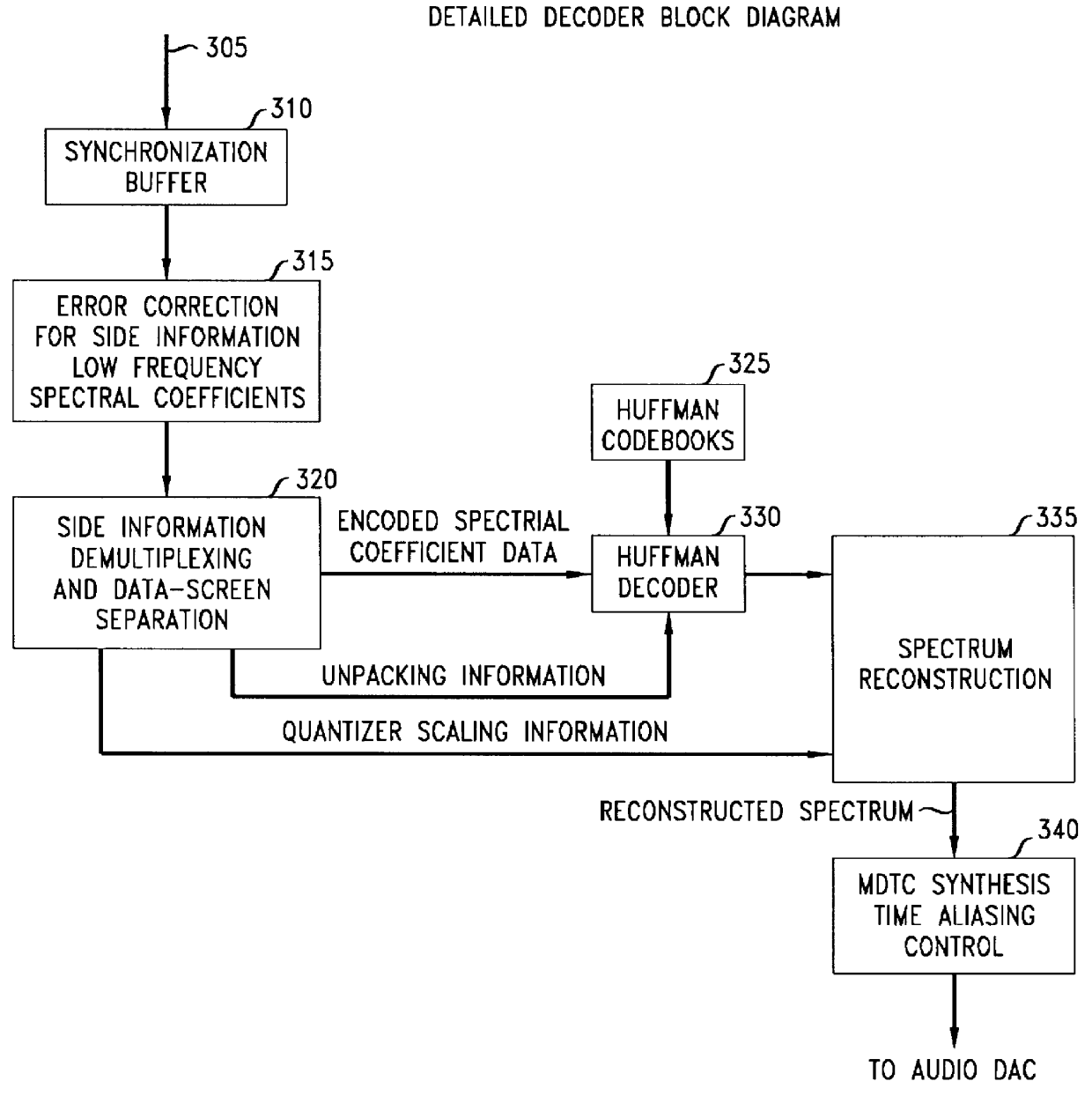
Scalable coding method for high quality audio
InactiveUS6446037B1Improve audio qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumImage resolution
Scalable coding of audio into a core layer in response to a desired noise spectrum established according to psychoacoustic principles supports coding augmentation data into augmentation layers in response to various criteria including offset of such desired noise spectrum. Compatible decoding provides a plurality of decoded resolutions from a single signal. Coding is preferably performed on subband signals generated according to spectral transform, quadrature mirror filtering, or other conventional processing of audio input. A scalable data structure for audio transmission includes core and augmentation layers, the former for carrying a first coding of an audio signal that places post decode noise beneath a desired noise spectrum, the later for carrying offset data regarding the desired noise spectrum and data about coding of the audio signal that places post decode noise beneath the desired noise spectrum shifted by the offset data.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
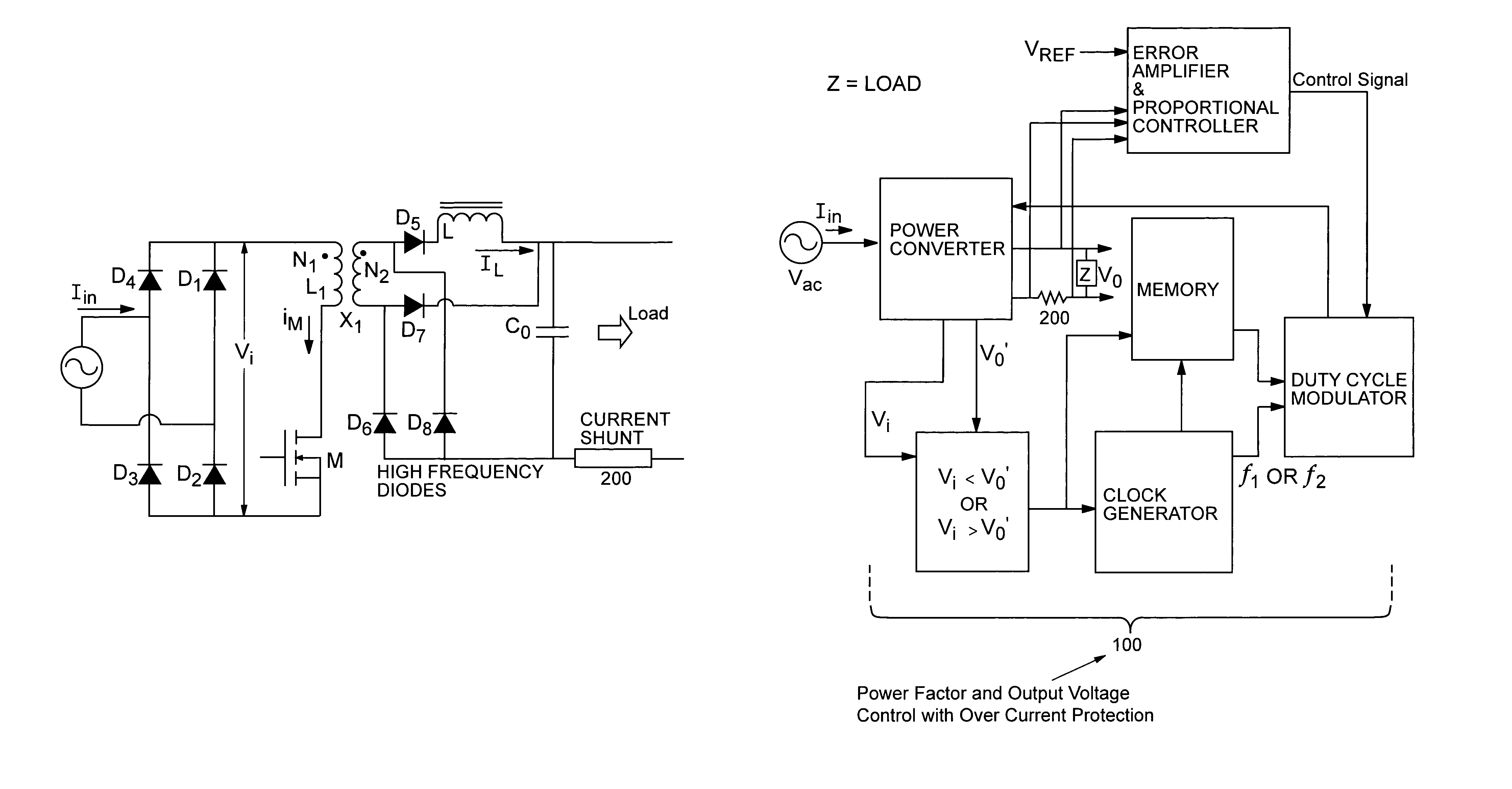
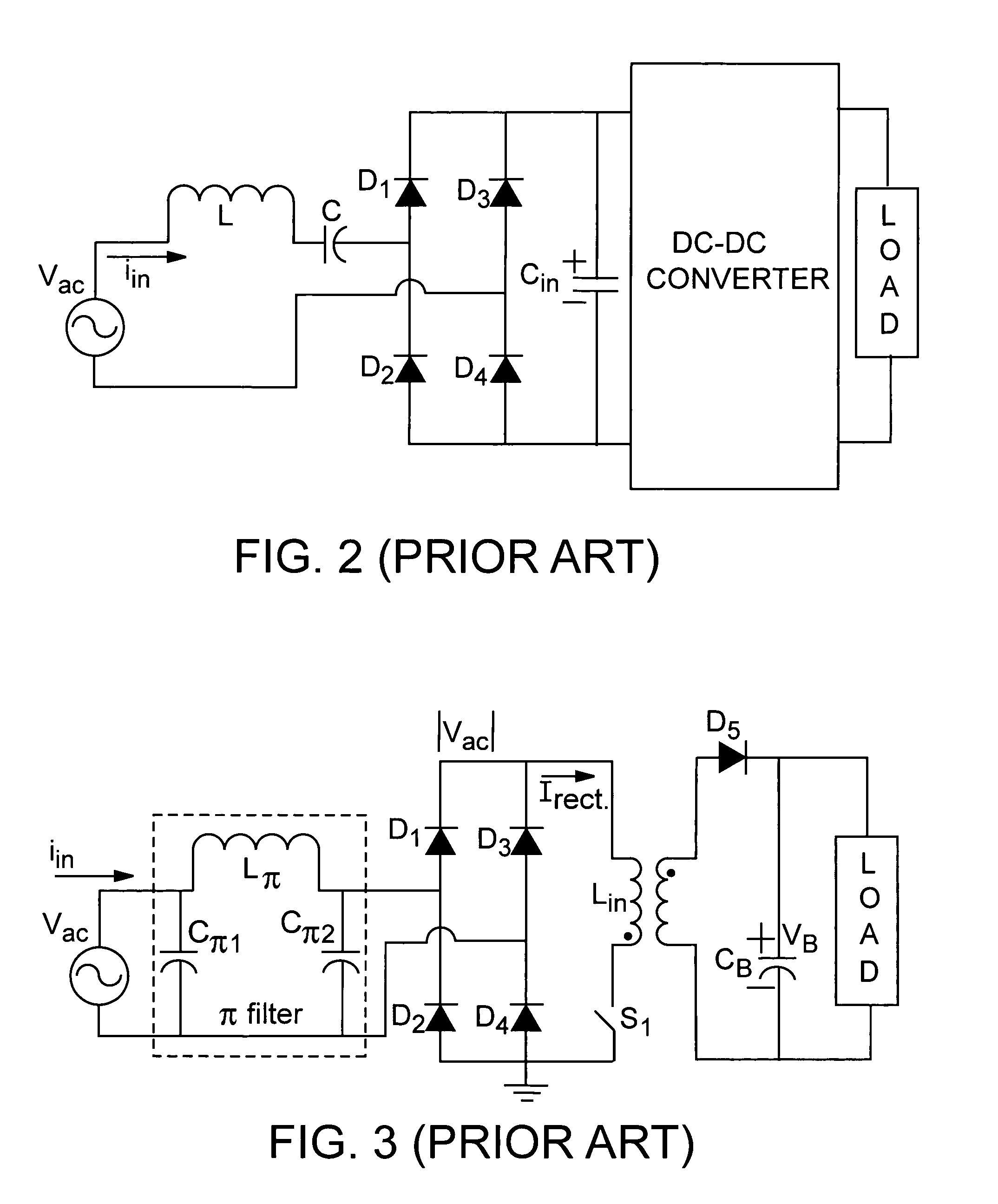
Power converter method and apparatus having high input power factor and low harmonic distortion
InactiveUS7157886B2Reduce complexityRelieve pressureAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFrequency spectrumTotal harmonic distortion
A single stage, single switch, input-output isolated converter configuration which uses a hybrid combination of forward and flyback converters is disclosed. The converter operates at a high input power factor with a regulated DC output voltage. It makes use of a novel control scheme utilizing duty cycle control at two discrete operating frequencies. Although the invention employs two frequencies, it does not use a continuous frequency variation. This configuration has the advantage of reduced peak current stresses on the components and is specifically suited for ‘buck’ applications where low DC output voltages (e.g. 24V, 48V) are needed. This configuration will be of specific interest to industries associated with battery charging and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. Apart from having several competitive features compared with prior art techniques, the dual frequency operation scheme reduces the amplitude of its noise spectrum by spreading it over a wider frequency range thus making it more electromagnetic compatible.
Owner:MICROSEMI
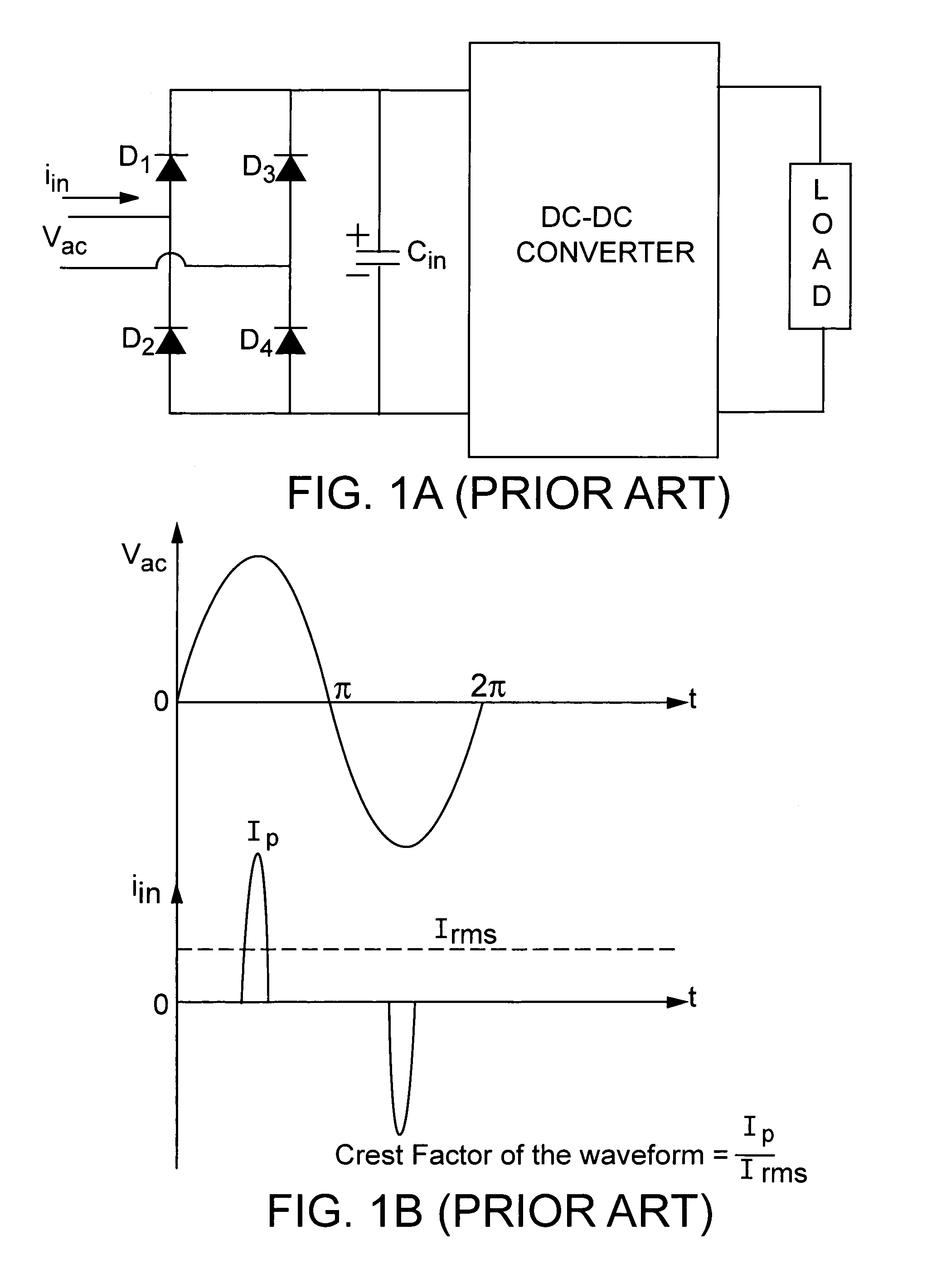
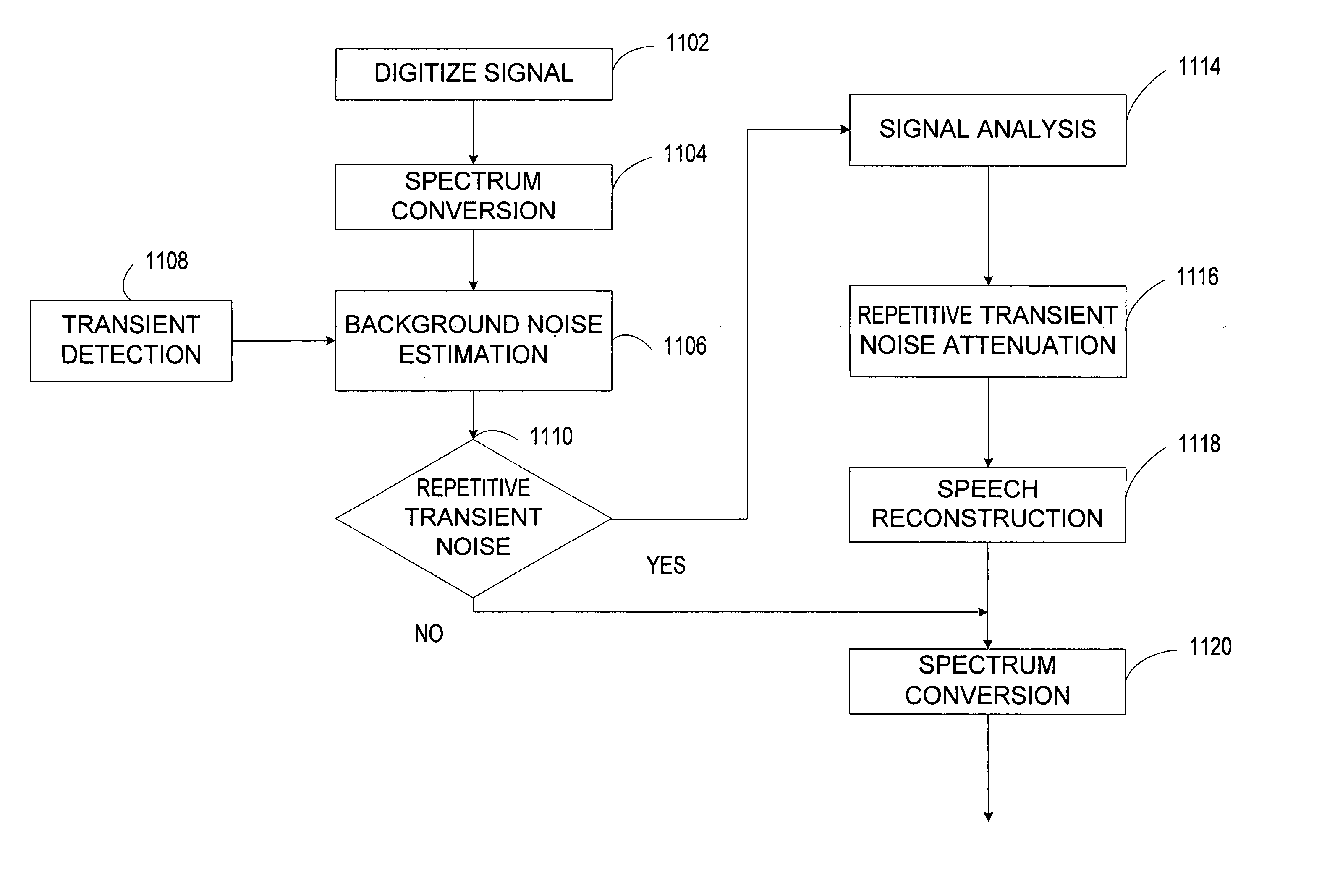
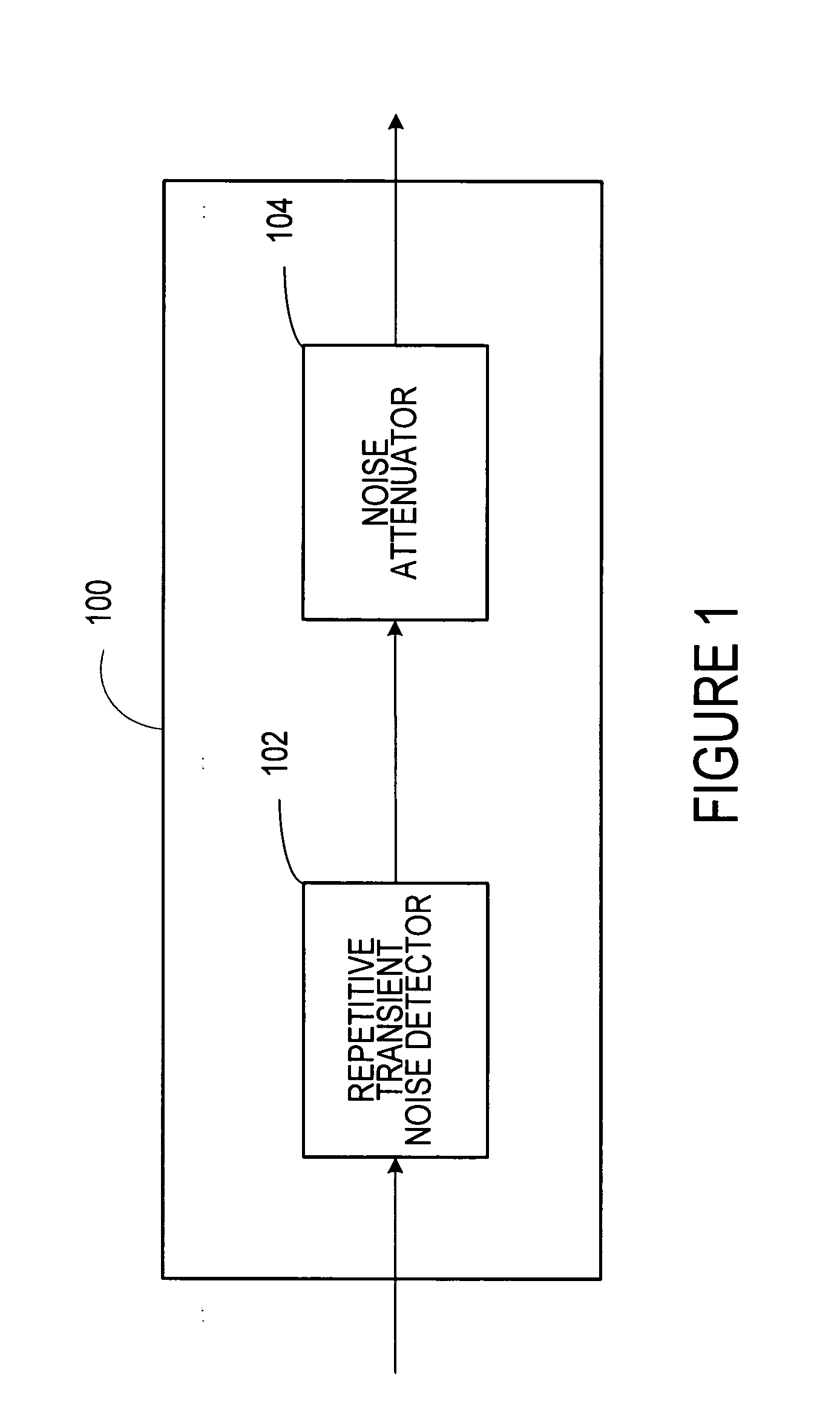
Repetitive transient noise removal
ActiveUS20060116873A1Improve voice qualityRemove and dampens repetitive transient noiseSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumHarmonic
A system improves the perceptual quality of a speech signal by dampening undesired repetitive transient noises. The system includes a repetitive transient noise detector adapted to detect repetitive transient noise in a received signal. The received signal may include a harmonic and a noise spectrum. The system further includes a repetitive transient noise attenuator that substantially removes or dampens repetitive transient noises from the received signal. The method of dampening the repetitive transient noises includes modeling characteristics of repetitive transient noises; detecting characteristics in the received signal that correspond to the modeled characteristics of the repetitive transient noises; and substantially removing components of the repetitive transient noises from the received signal that correspond to some or all of the modeled characteristics of the repetitive transient noises.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
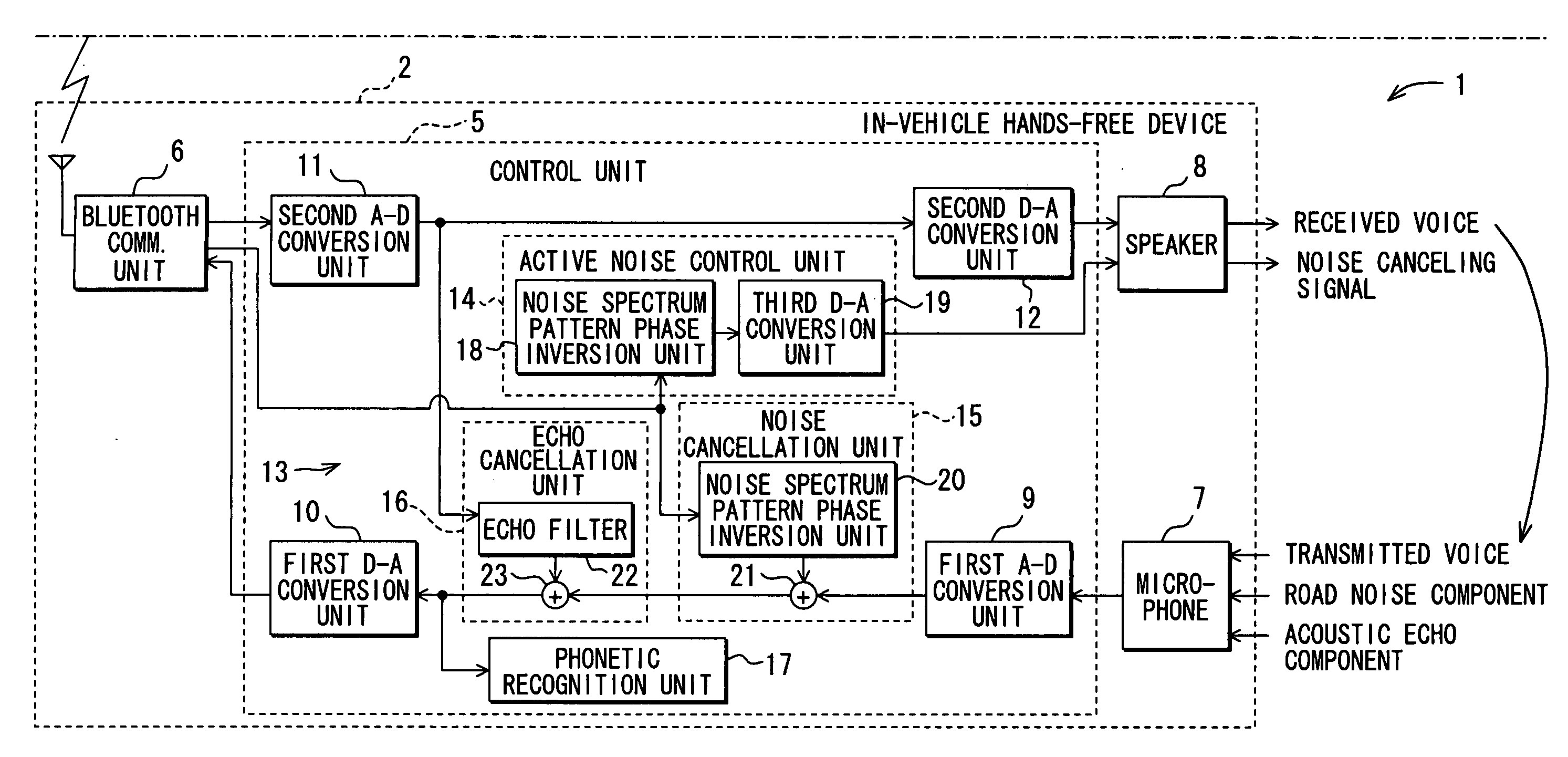
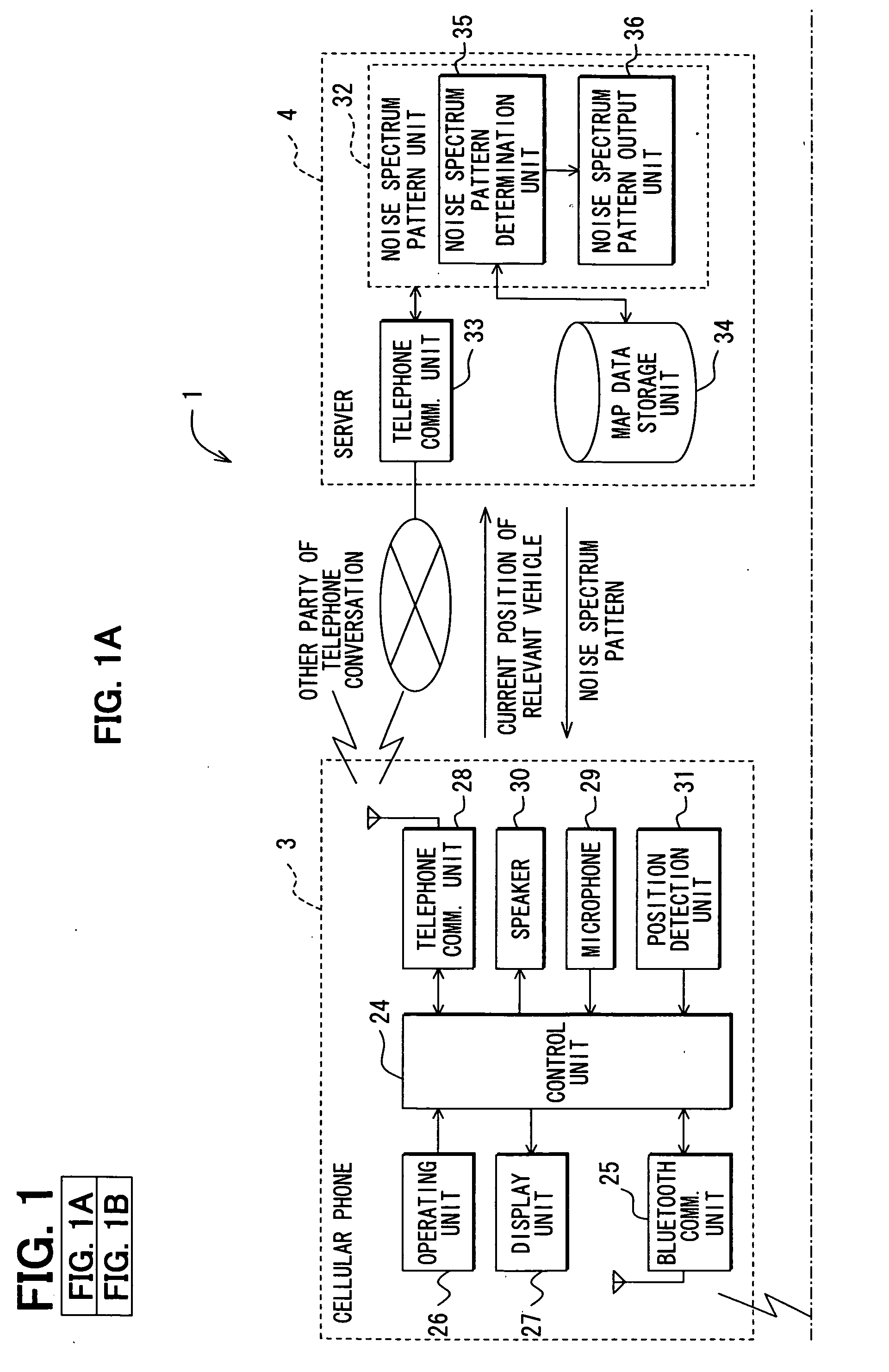
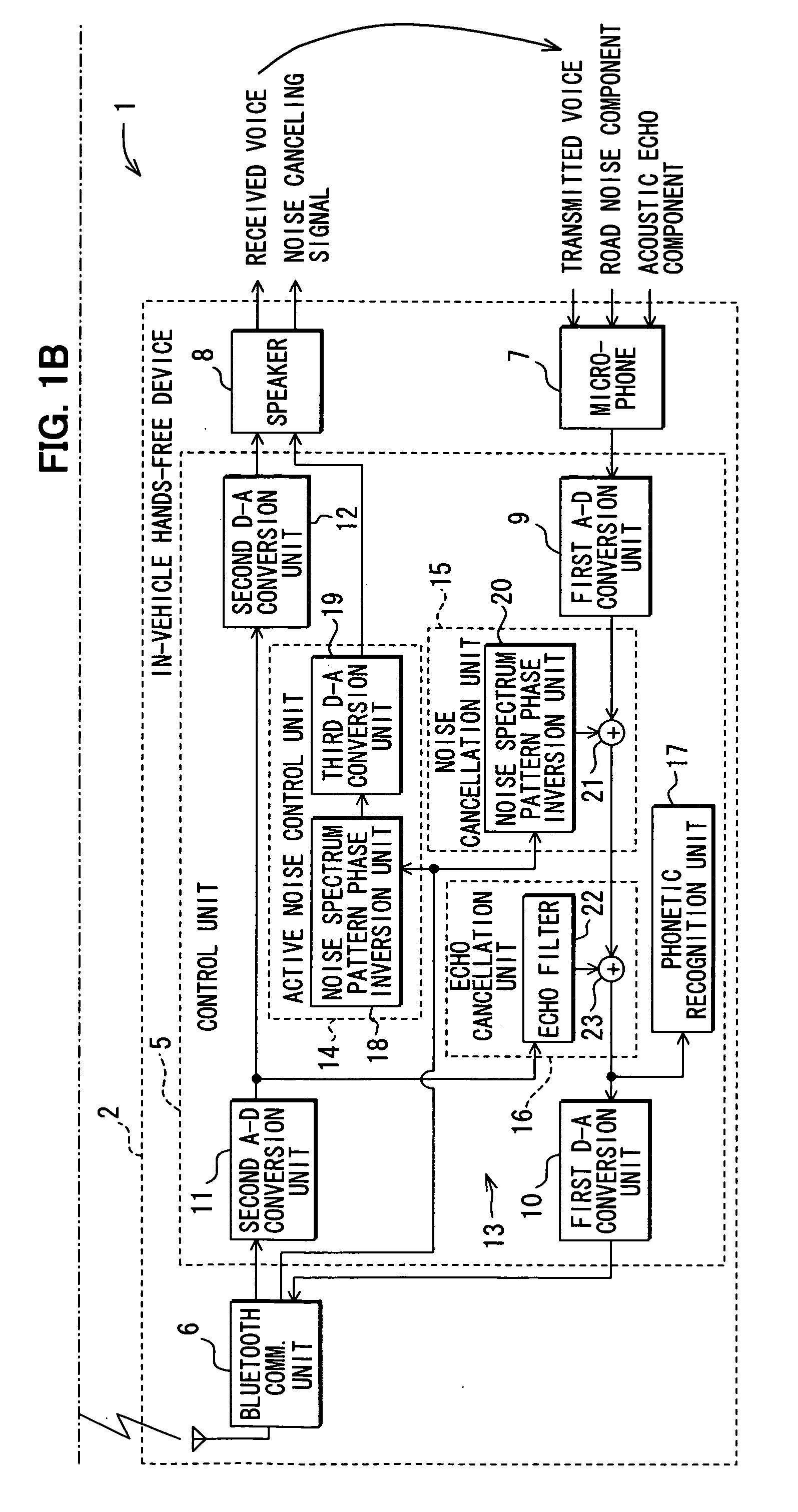
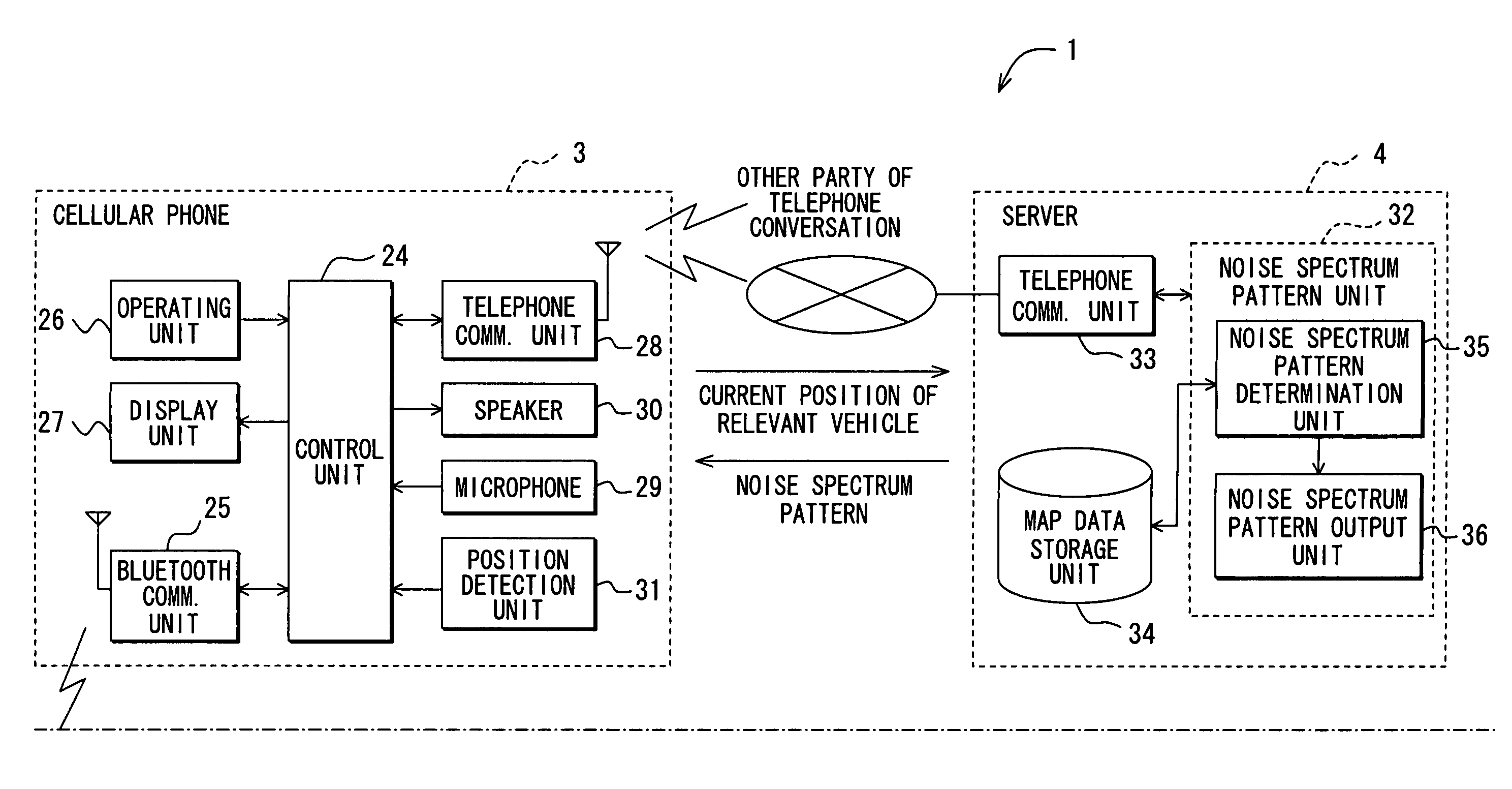
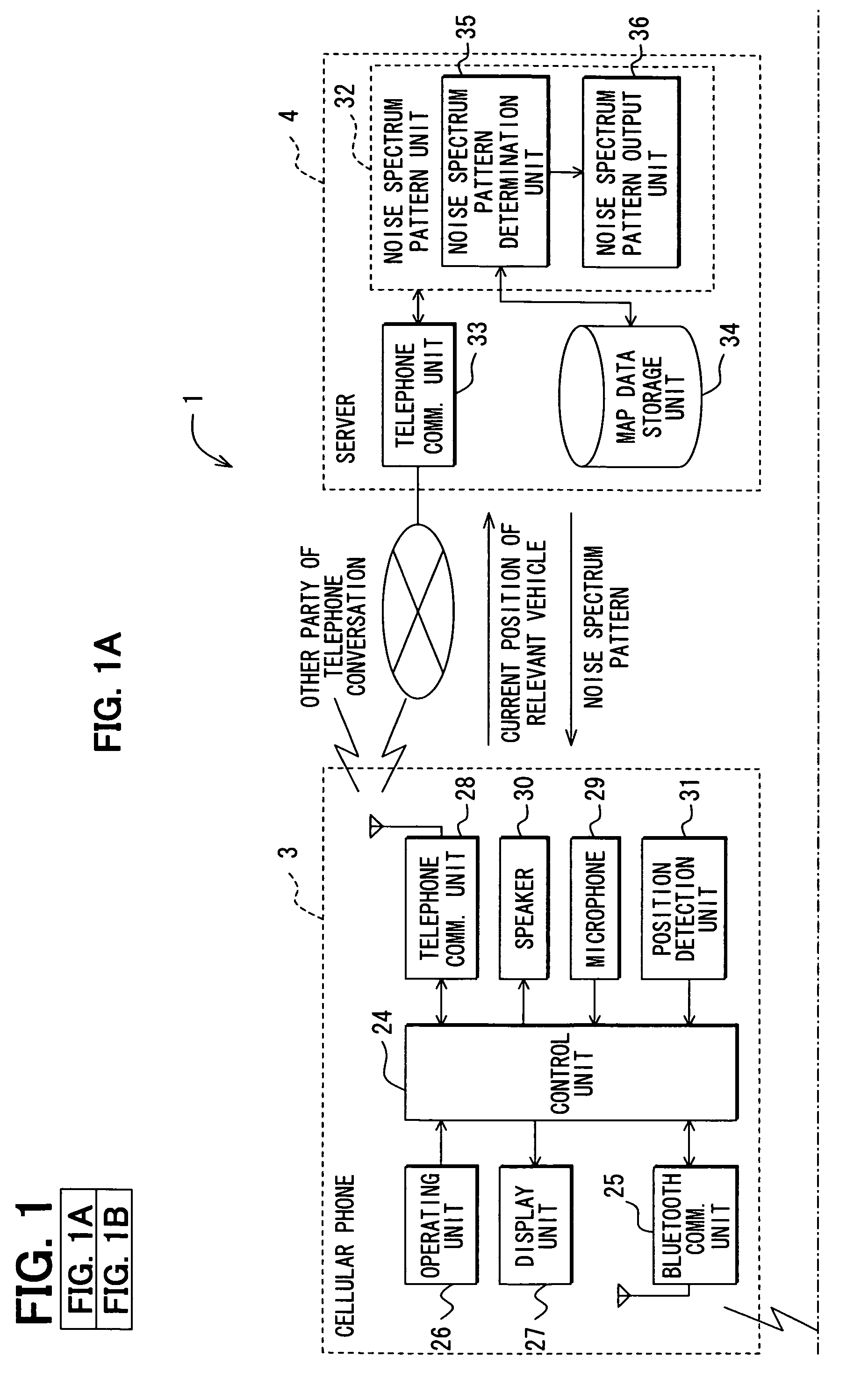
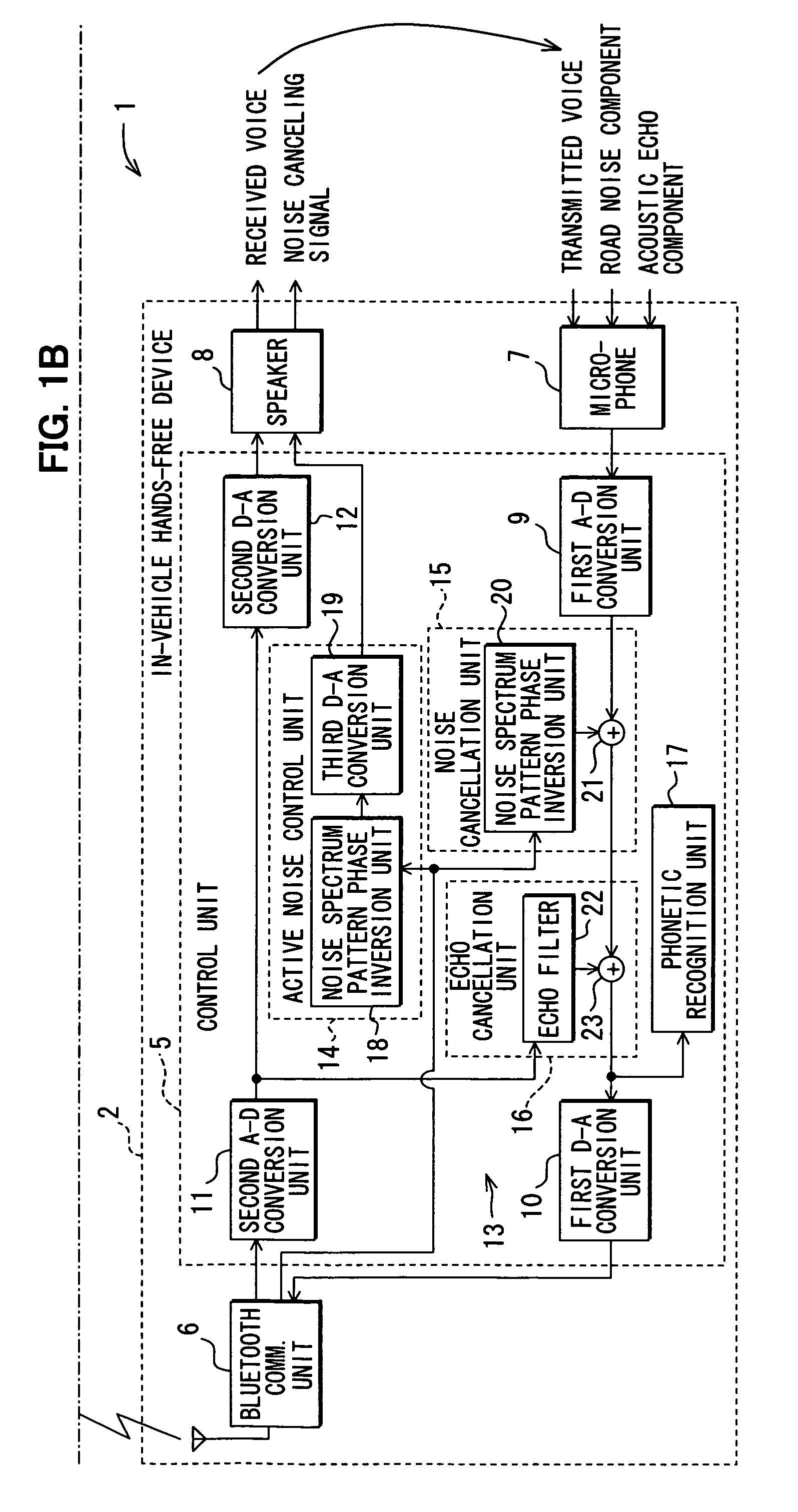
Communicating road noise control system, in-vehicle road noise controller, and server
InactiveUS20080188271A1Enhance phonetic recognition rateEar treatmentSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumControl system
Road noise is reduced without locally storing noise spectrum patterns for determination or without detecting the present position of a vehicle from the device. An in-vehicle hands-free device causes a cellular phone to detect the present position of the vehicle and transmit the position to a server. The server determines a noise spectrum pattern corresponding to the road surface on which the vehicle is presently running. The noise spectrum pattern is based on the present position of the vehicle received from the in-vehicle hands-free device and road information. The server transmits the noise spectrum pattern to the in-vehicle hands-free device whereupon a noise canceling signal is superimposed on a received signal. The noise canceling signal is based on an inverted noise spectrum pattern that is obtained by inverting the phase of the noise spectrum pattern. The resulting composite signal is output from a speaker.
Owner:DENSO CORP
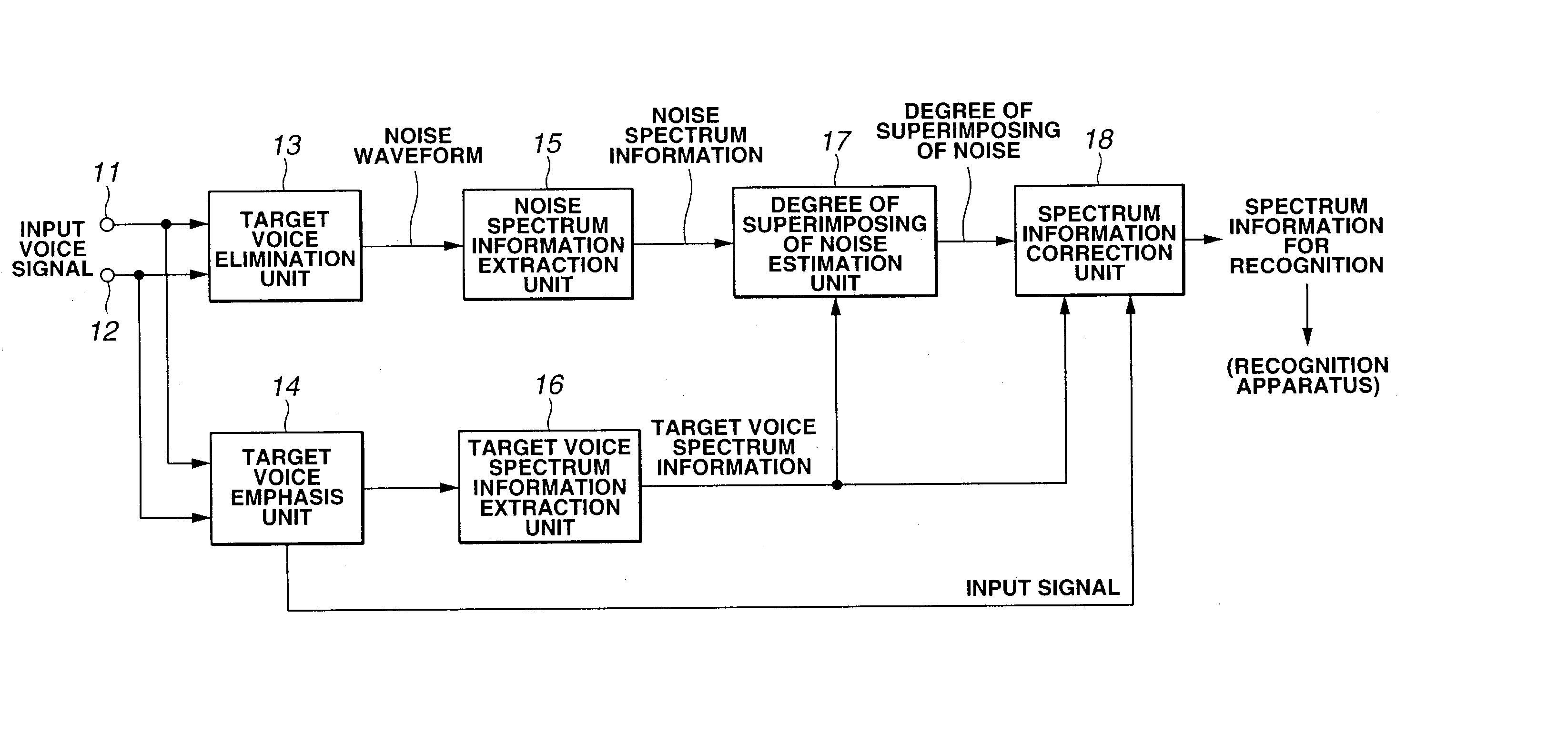
Noise suppression apparatus and method for speech recognition, and speech recognition apparatus and method
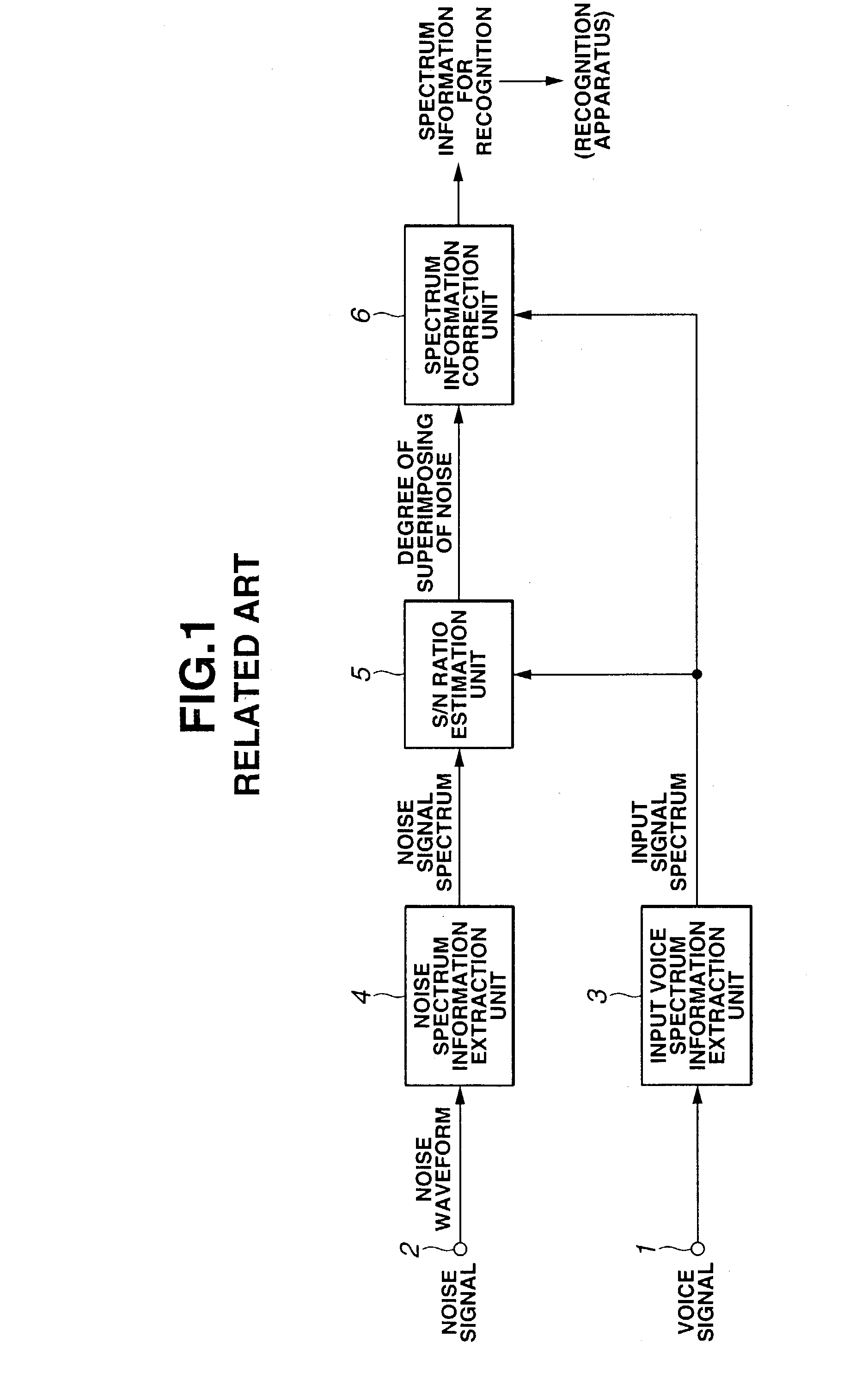
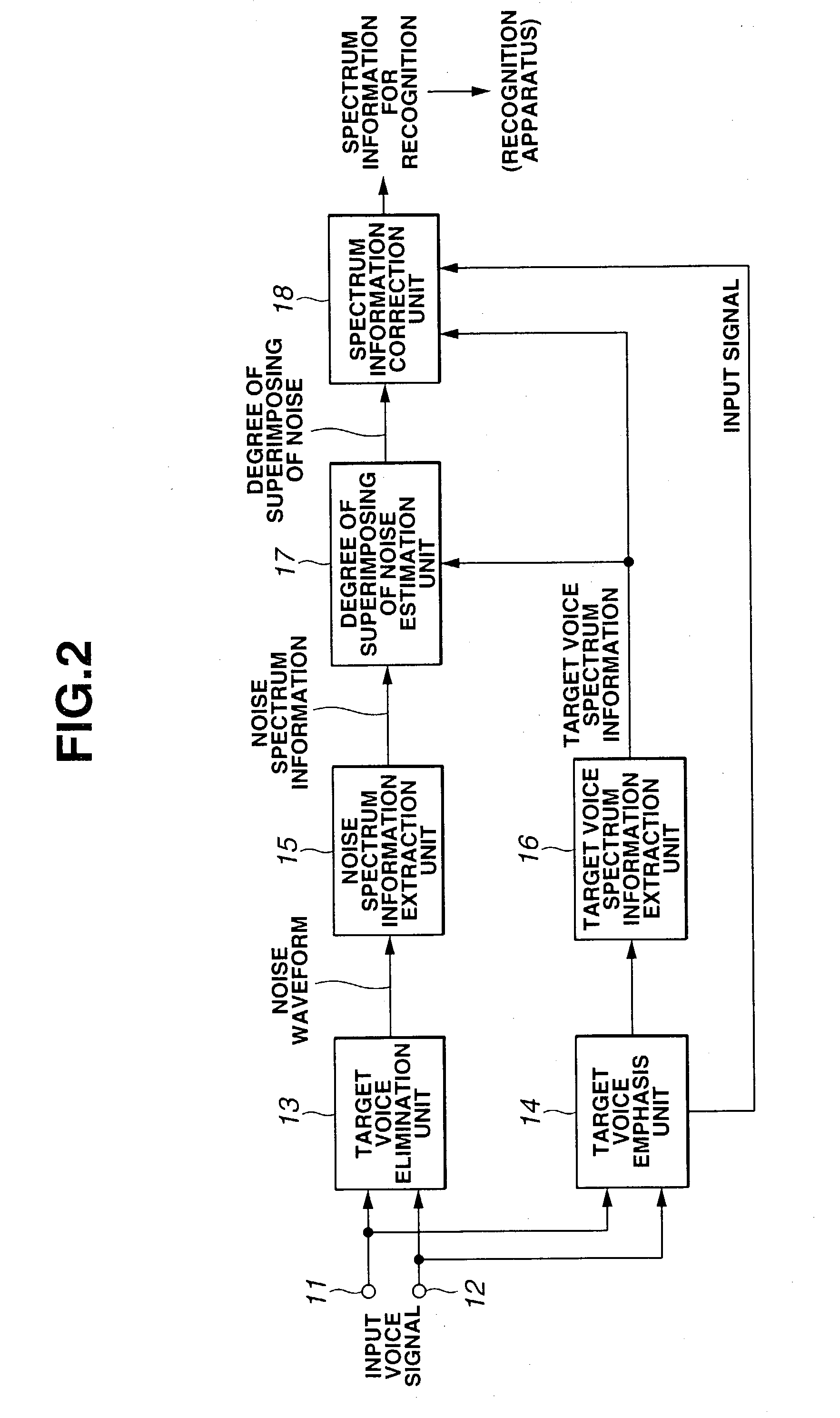
A target voice elimination unit reliably eliminates a target voice and outputs a target voice elimination signal including only a noise component. A target voice emphasis unit outputs a target voice emphasis signal from which a noise component is eliminated to some extent. A noise spectrum information extraction unit extracts noise spectrum information from the target voice elimination signal, and a target voice spectrum information extraction unit extracts target voice spectrum information from the target voice emphasis signal. A degree of multiplexing of noise estimation unit reliably detects the position where noise is superimposed and the magnitude of the noise from the noise spectrum information and the target voice spectrum information and obtains a degree of multiplexing of noise. A spectrum information correction unit reliably corrects the target voice spectrum information using the information of the degree of multiplexing of noise indicating the position and magnitude of the noise detected correctly. The influence of noise is greatly reduced in the spectrum information, thereby the accuracy of speech recognition can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and system for performing outer loop power control in discontinuous transmission mode
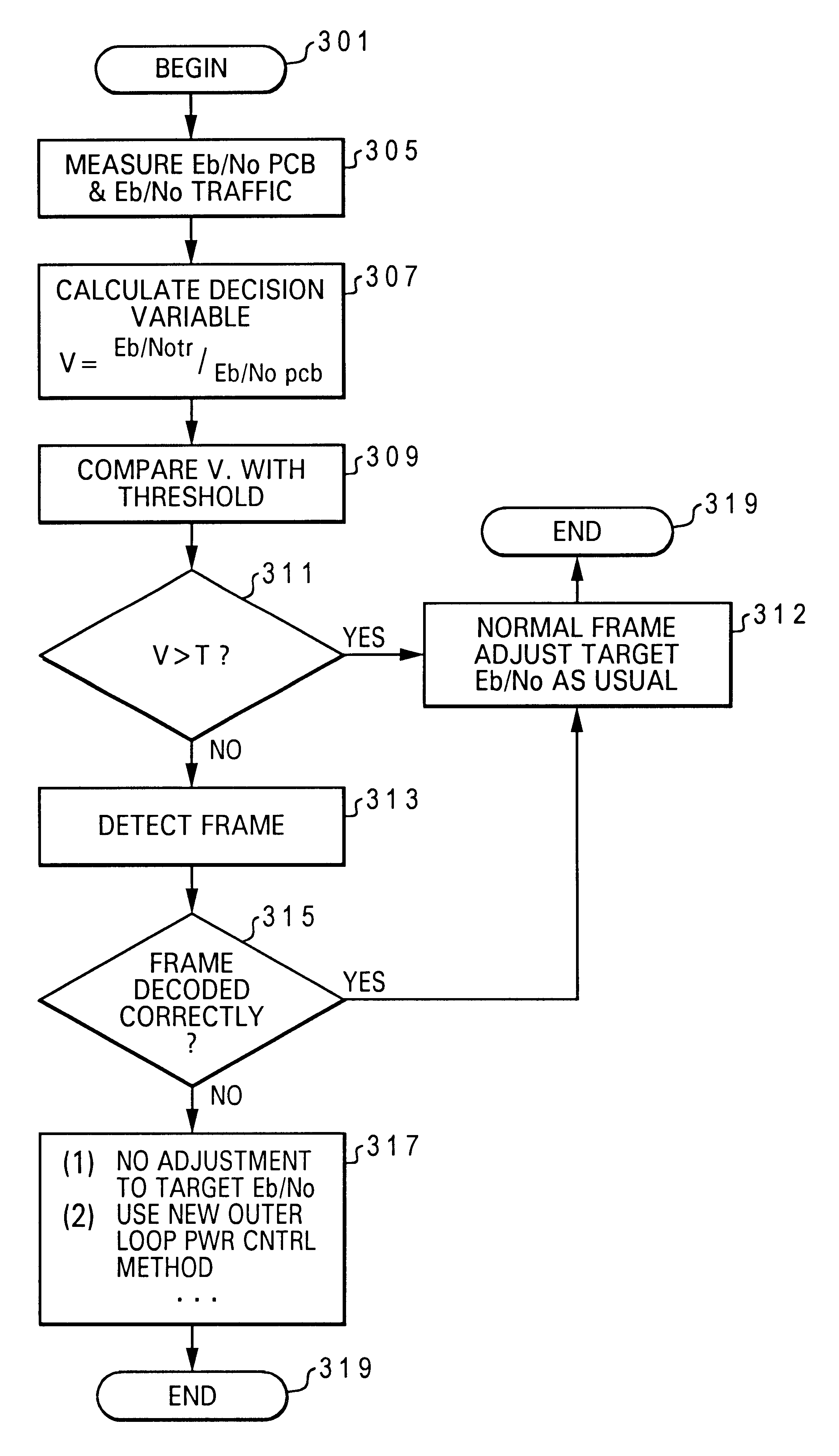
A method for controlling unnecessary power increases and call drop during discontinuous transmission (DTX) mode of a frame-based transmission system. The method comprises the steps of (1) detecting, at a receiver end of the transmission system a status of a transmitted frame indicating one of two possible transmission modes including (a) when a gating-off of the traffic channel occurs, and (b) when no gating-off of traffic occurs and normal traffic is being transmitted, and (2) controlling a change in the receiver target bit energy to noise spectrum density ratio Eb / No in response to the detection step so that a receiver target Eb / No is increased only when the detecting step does not indicate a gating-off of traffic has occurred.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Noise dependent filter
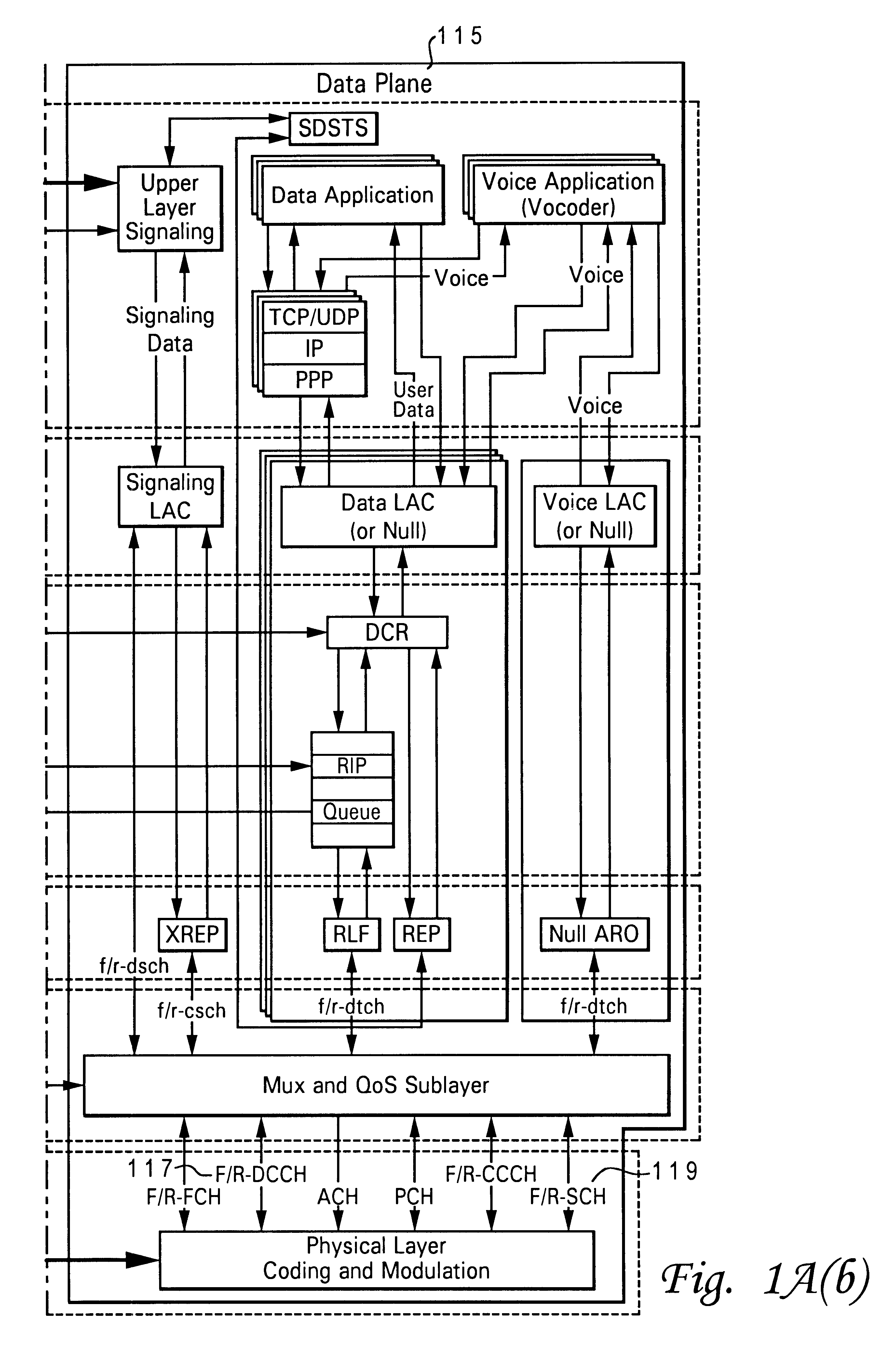
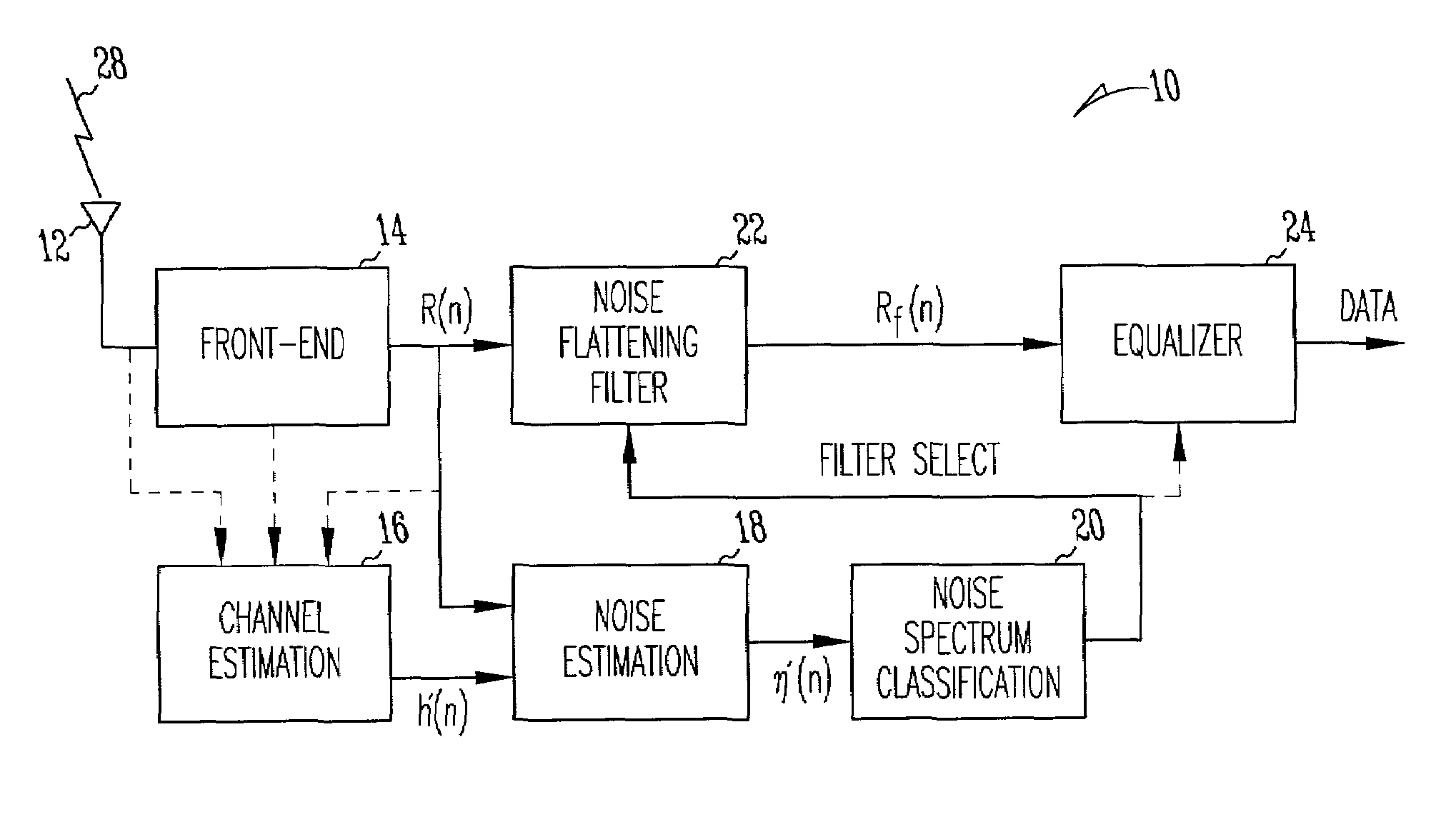
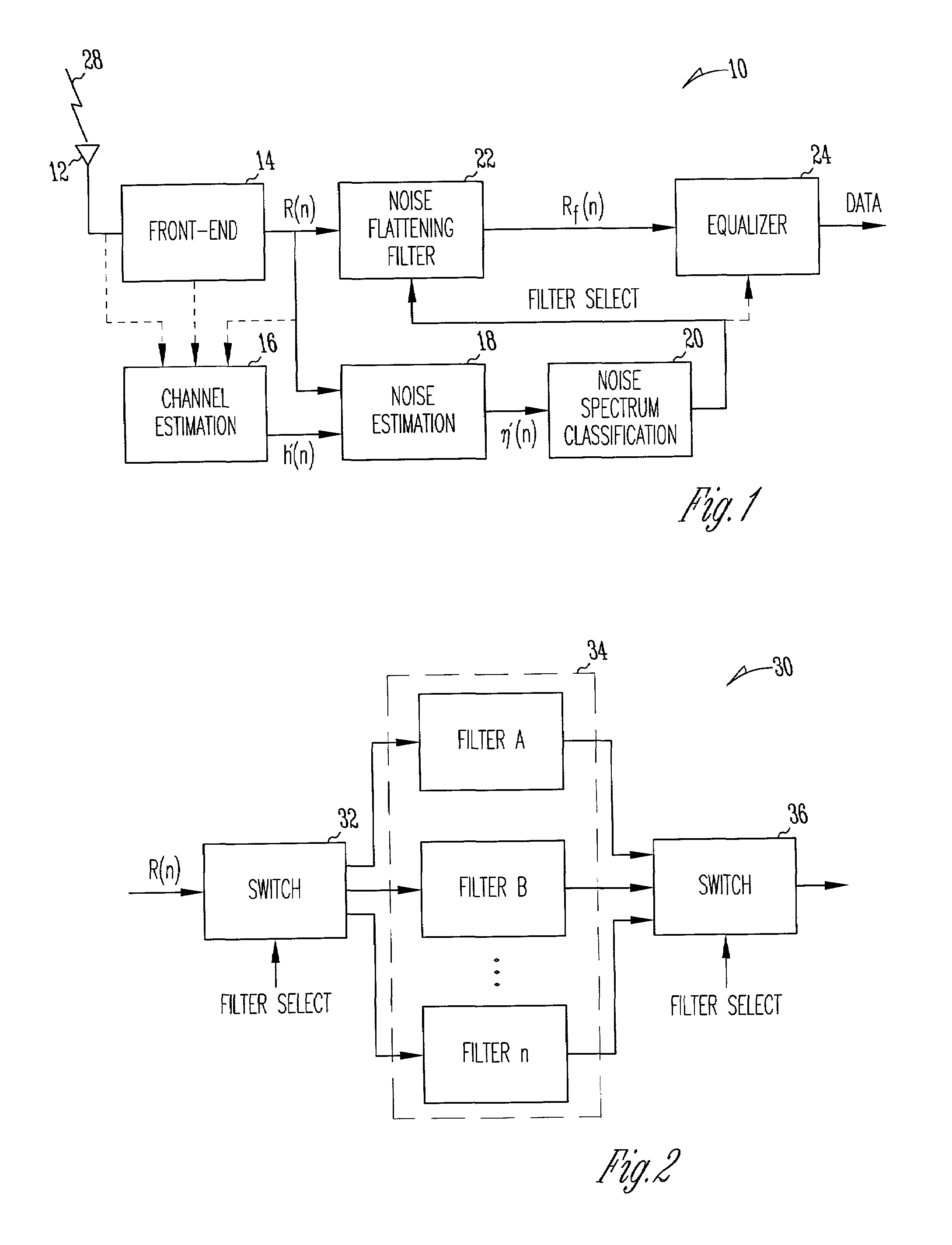
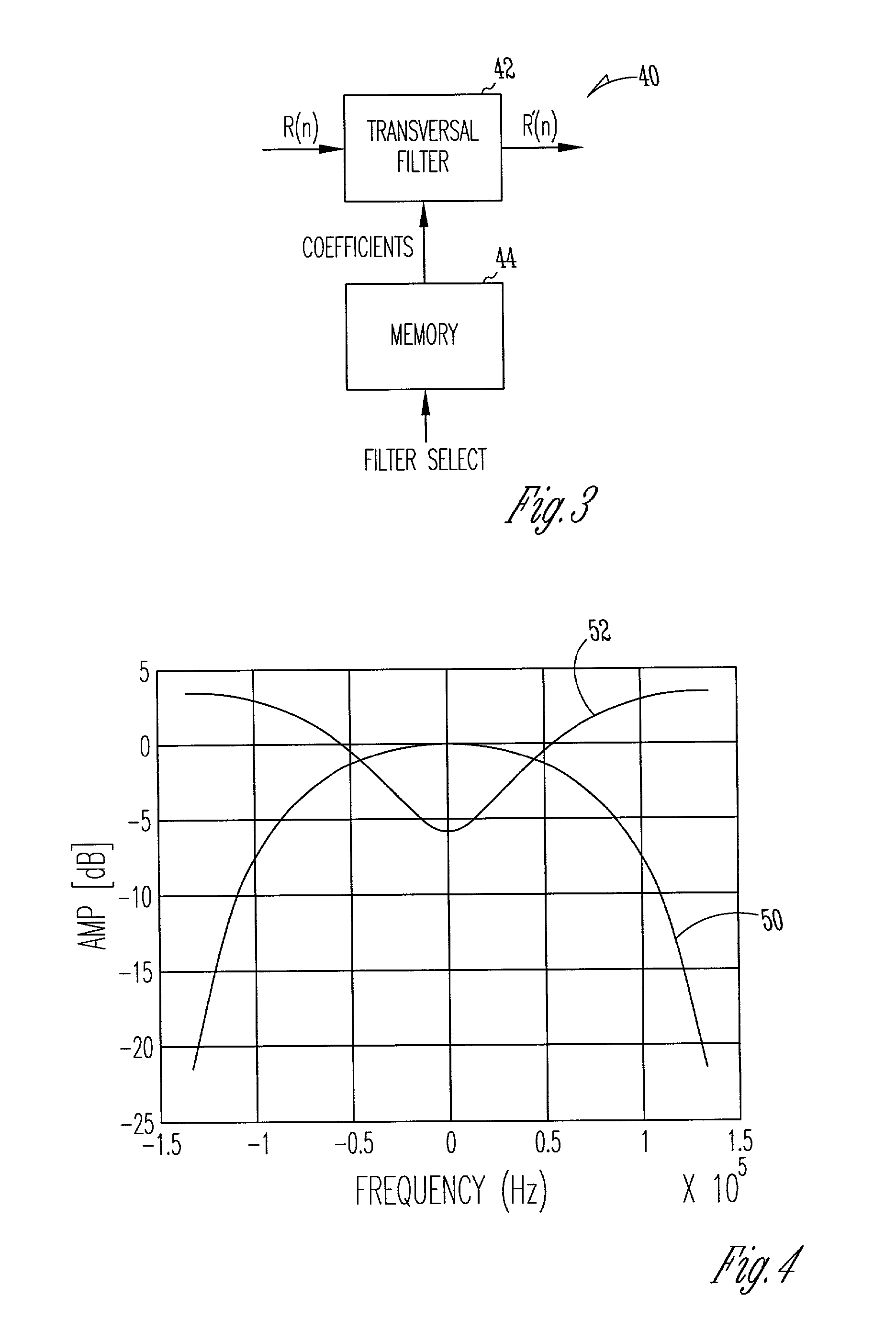
A communication device includes a noise flattening filter having a filter response that dynamically adjusts based on the current noise spectrum in a wireless channel. The noise spectrum of the wireless channel is estimated and used to determine a noise classification for the channel. A noise flattening filter response is then selected based upon the noise classification for use in filtering signals received from the channel. The filtered signals are then delivered to an equalizer for further processing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
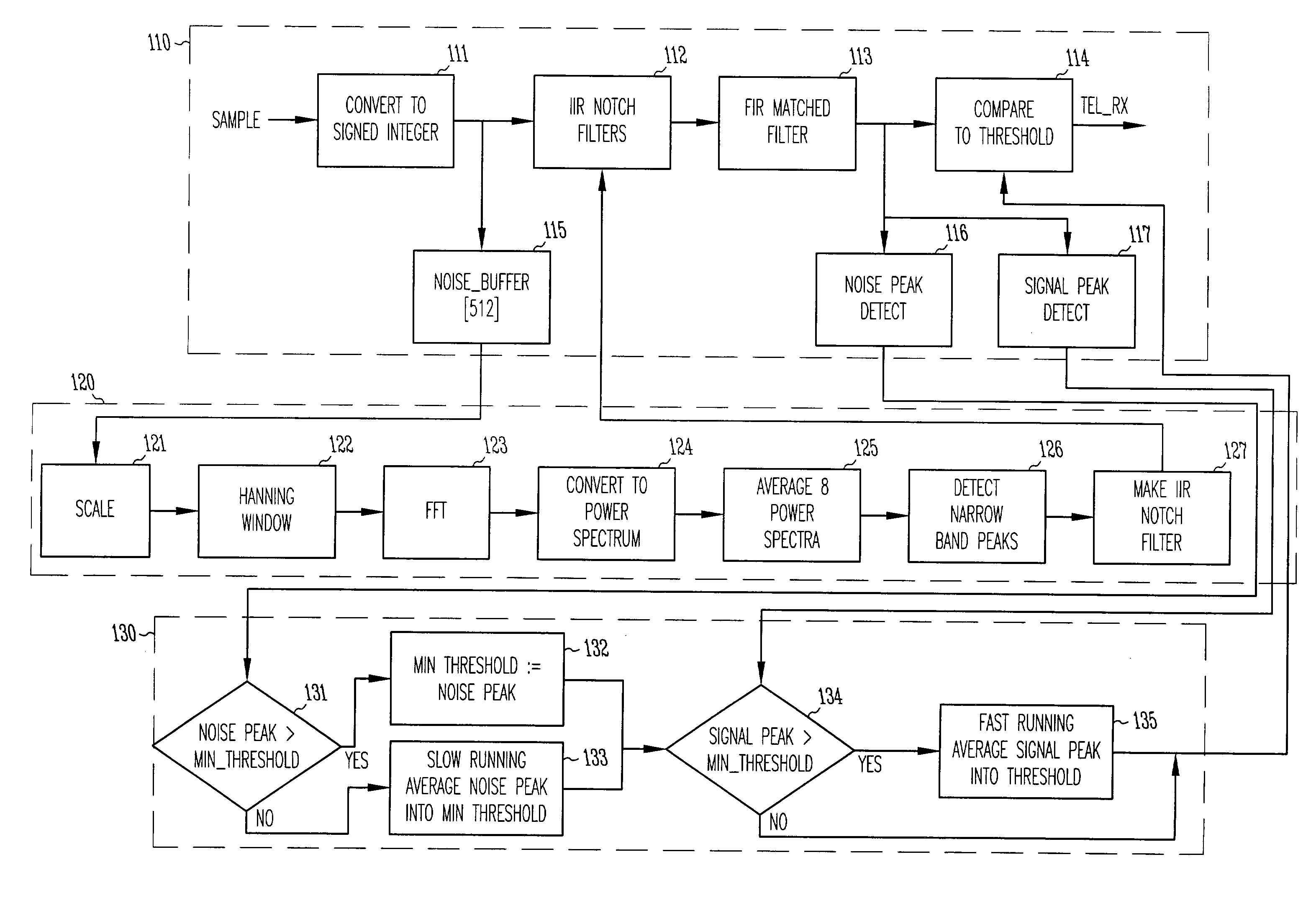
System and method for removing narrowband noise
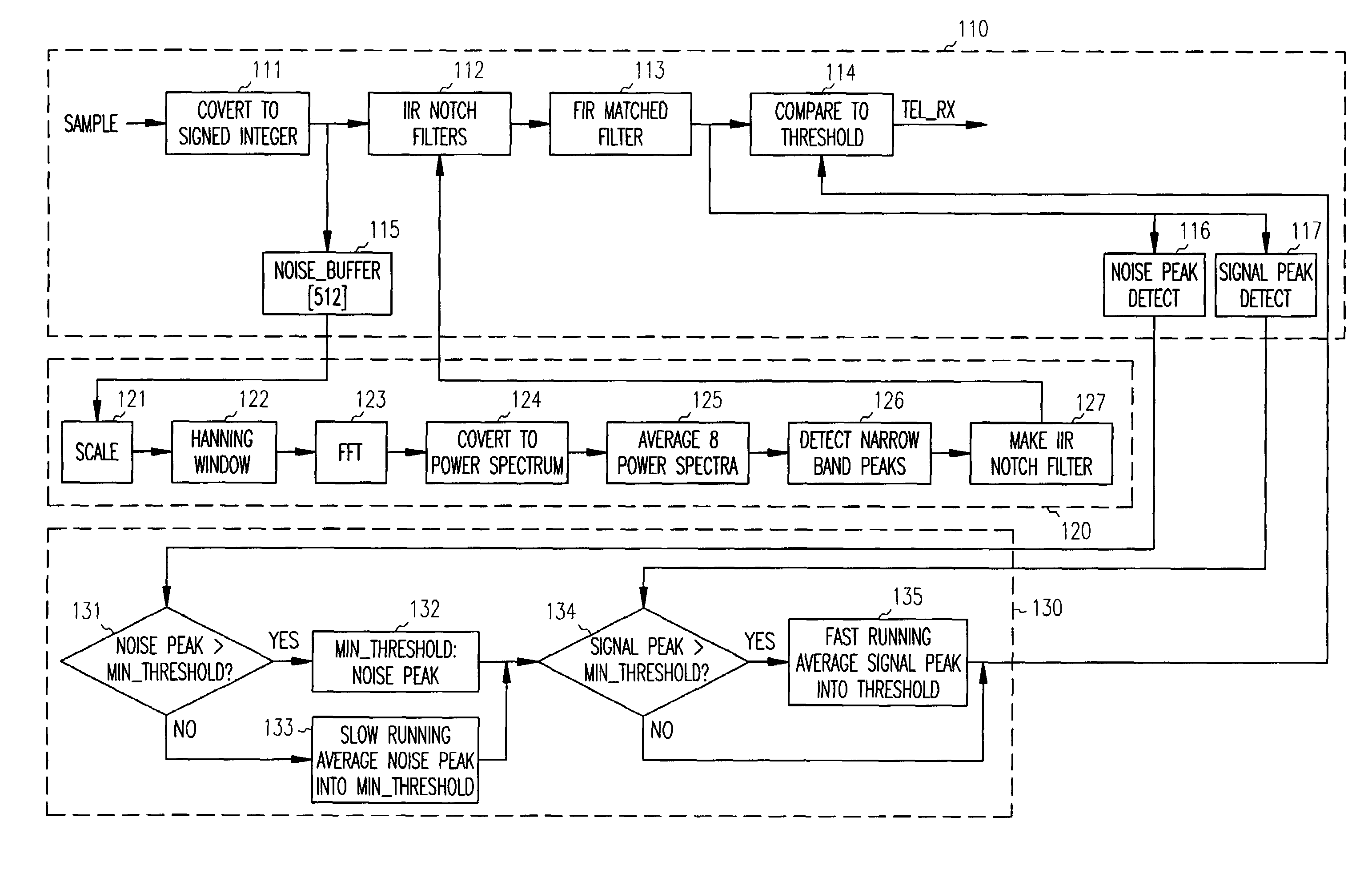
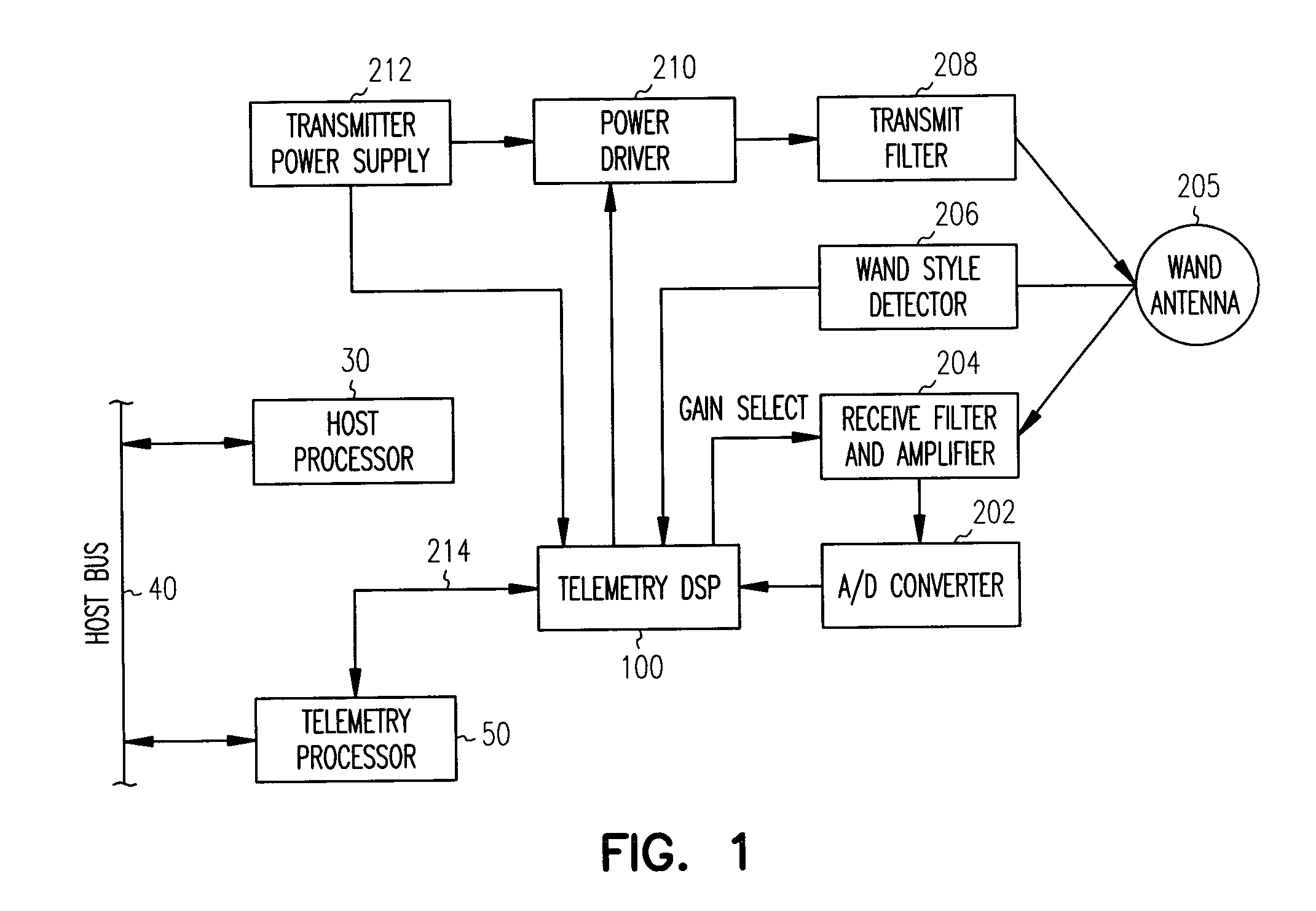
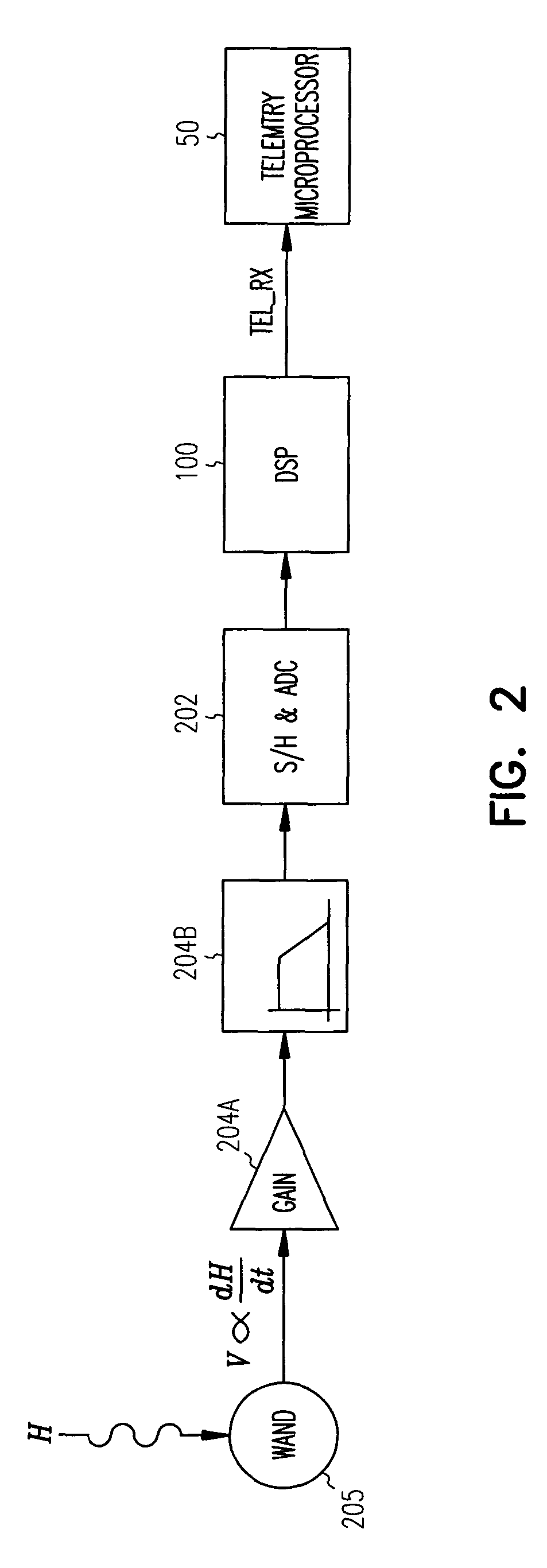
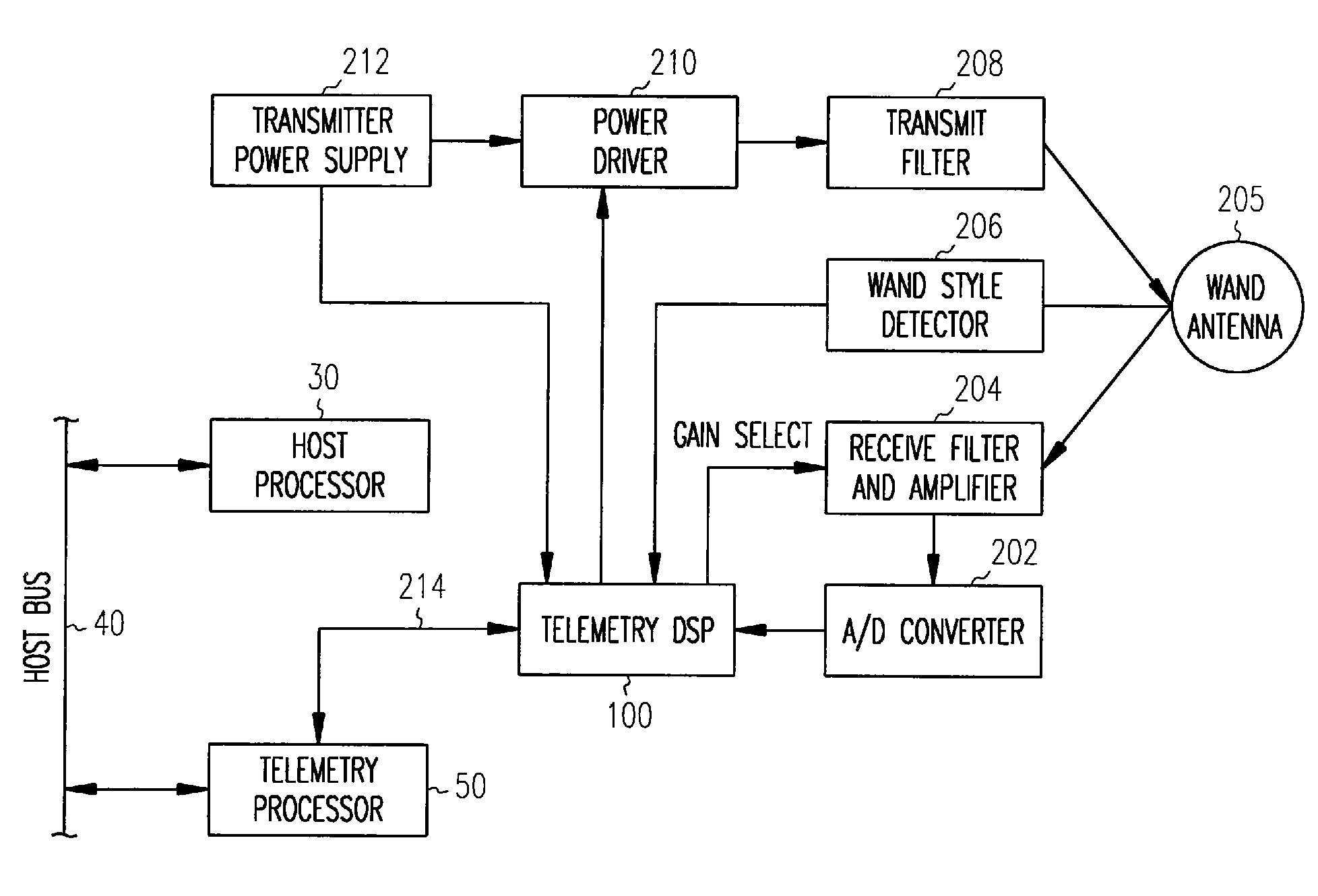
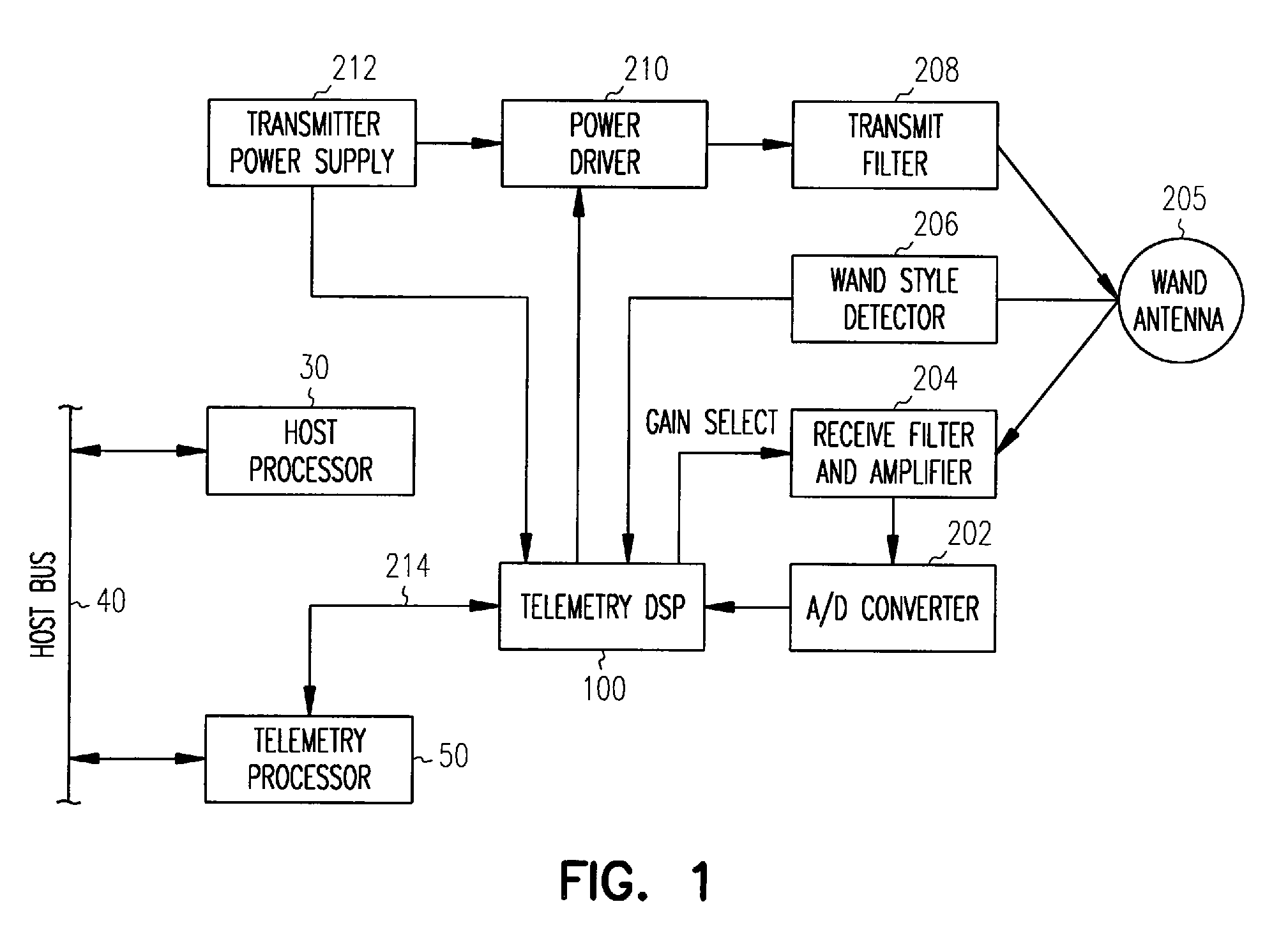
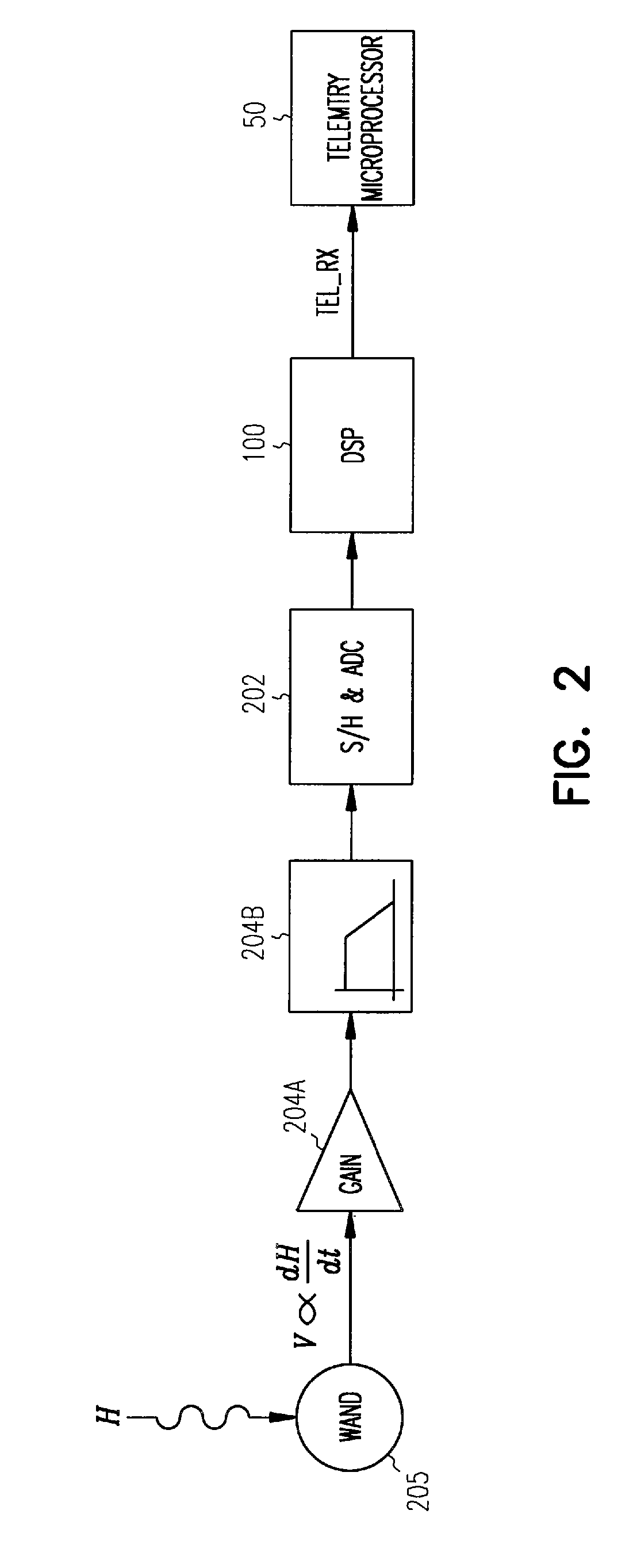
A system and method for removing narrowband noise from an input signal in which notch filters having notch frequencies corresponding to the noise are dynamically adjusted in accordance with a detected noise spectrum. The method may be applied to telemetry systems for implantable medical devices such as cardiac pacemakers to result in improved noise immunity.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
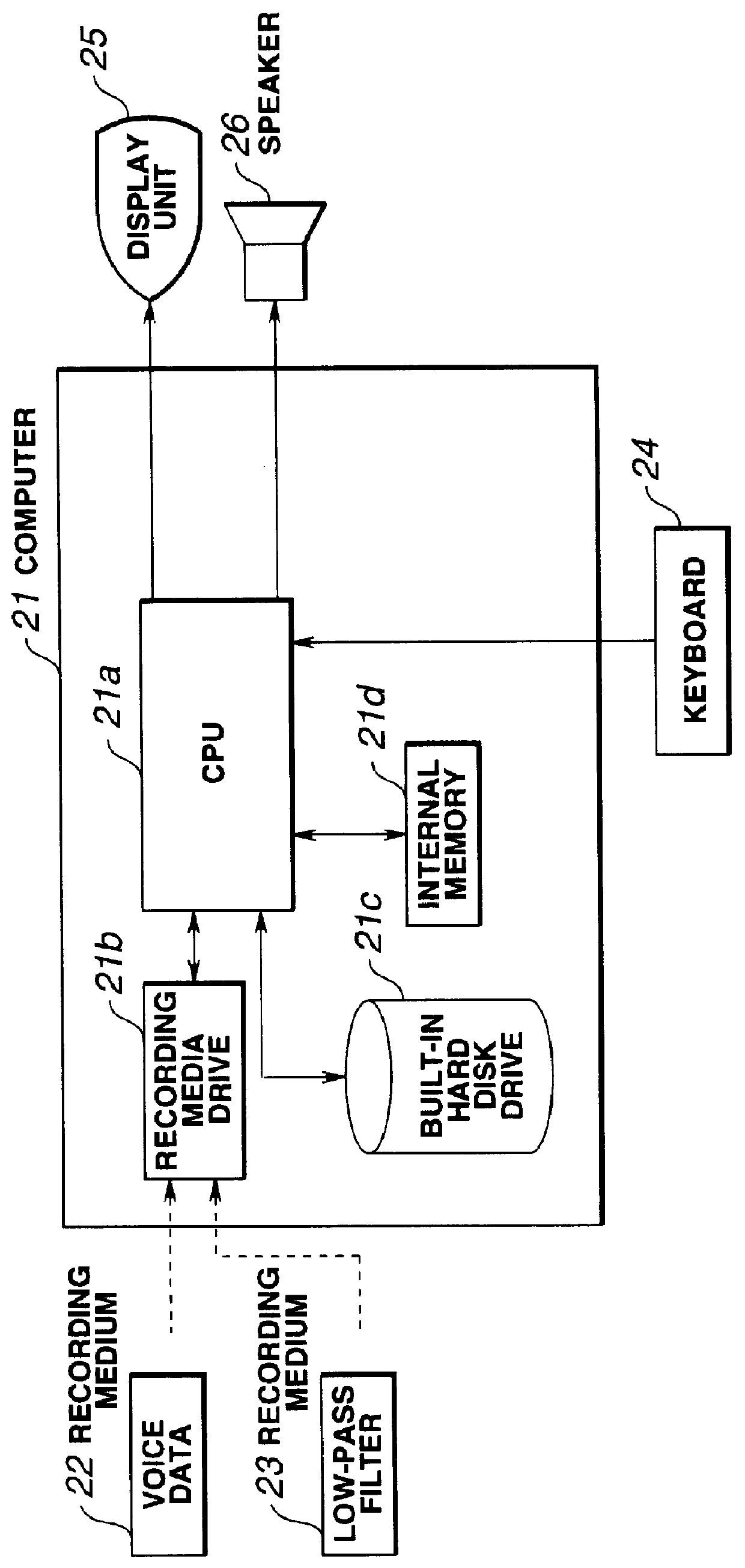
Noise suppression apparatus and recording medium recording processing program for performing noise removal from voice
InactiveUS6044341AIncreasing auditory sound qualityImprove sound qualitySpeech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionDiscriminatorFrequency spectrum
A noise suppression apparatus of the present invention includes a voice / non-voice discriminator for discriminating a frame signal divided into frames having a predetermined length; a Fourier transform unit for converting a frame signal into a spectrum; a noise spectrum estimation unit for estimating a noise spectrum of a frame judged as a non-voice signal; an amplitude spectrum subtractor for subtracting the product of an estimated noise spectrum and a predetermined coefficient from a spectrum obtained by the transform unit; an auditory correction noise adder for adding aa auditory correction noise spectrum to a spectrum outputted from the subtractor; and an inverse Fourier transform unit for performing inverse Fourier transform to an output of the adder. The noise suppression apparatus further includes a negative amplitude value counter for counting the number of frequency components in an output of the subtractor whose amplitude values are negative; a subtraction coefficient setting unit for gradually decreasing a subtraction coefficient unit the counted value becomes not more than a predetermined value; an inverse Fourier transform unit for performing inverse Fourier transform to an output of the counter; and a noise spectrum estimation unit for calculating spectrum information of noise in the frame signal using different spectrum information according to the current type of frame signal.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Communicating road noise control system, in-vehicle road noise controller, and server
Road noise is reduced without locally storing noise spectrum patterns for determination or without detecting the present position of a vehicle from the device. An in-vehicle hands-free device causes a cellular phone to detect the present position of the vehicle and transmit the position to a server. The server determines a noise spectrum pattern corresponding to the road surface on which the vehicle is presently running. The noise spectrum pattern is based on the present position of the vehicle received from the in-vehicle hands-free device and road information. The server transmits the noise spectrum pattern to the in-vehicle hands-free device whereupon a noise canceling signal is superimposed on a received signal. The noise canceling signal is based on an inverted noise spectrum pattern that is obtained by inverting the phase of the noise spectrum pattern. The resulting composite signal is output from a speaker.
Owner:DENSO CORP
System and method for receiving telemetry data from an implantable medical device
A system and method for receiving telemetry data from implantable medical devices such as cardiac pacemakers with improved noise immunity is disclosed. Ambient noise levels and signal strength are monitored and used to adaptively adjust the detection sensitivity of the receiver. Filtering of the received signal is performed to remove both broadband and narrowband noise. Removal of narrowband noise is accomplished with notch filters that are dynamically adjusted in accordance with a detected noise spectrum.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
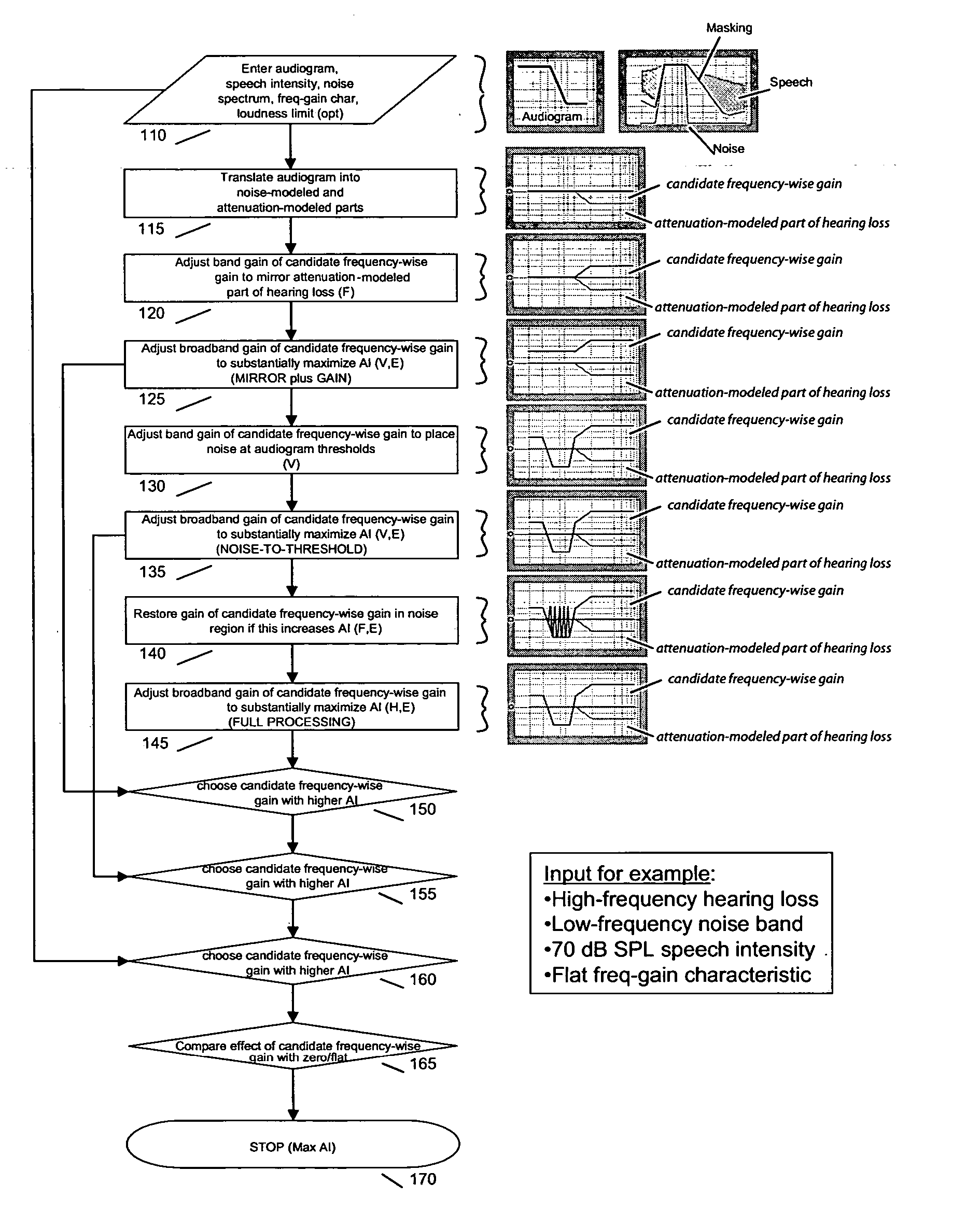
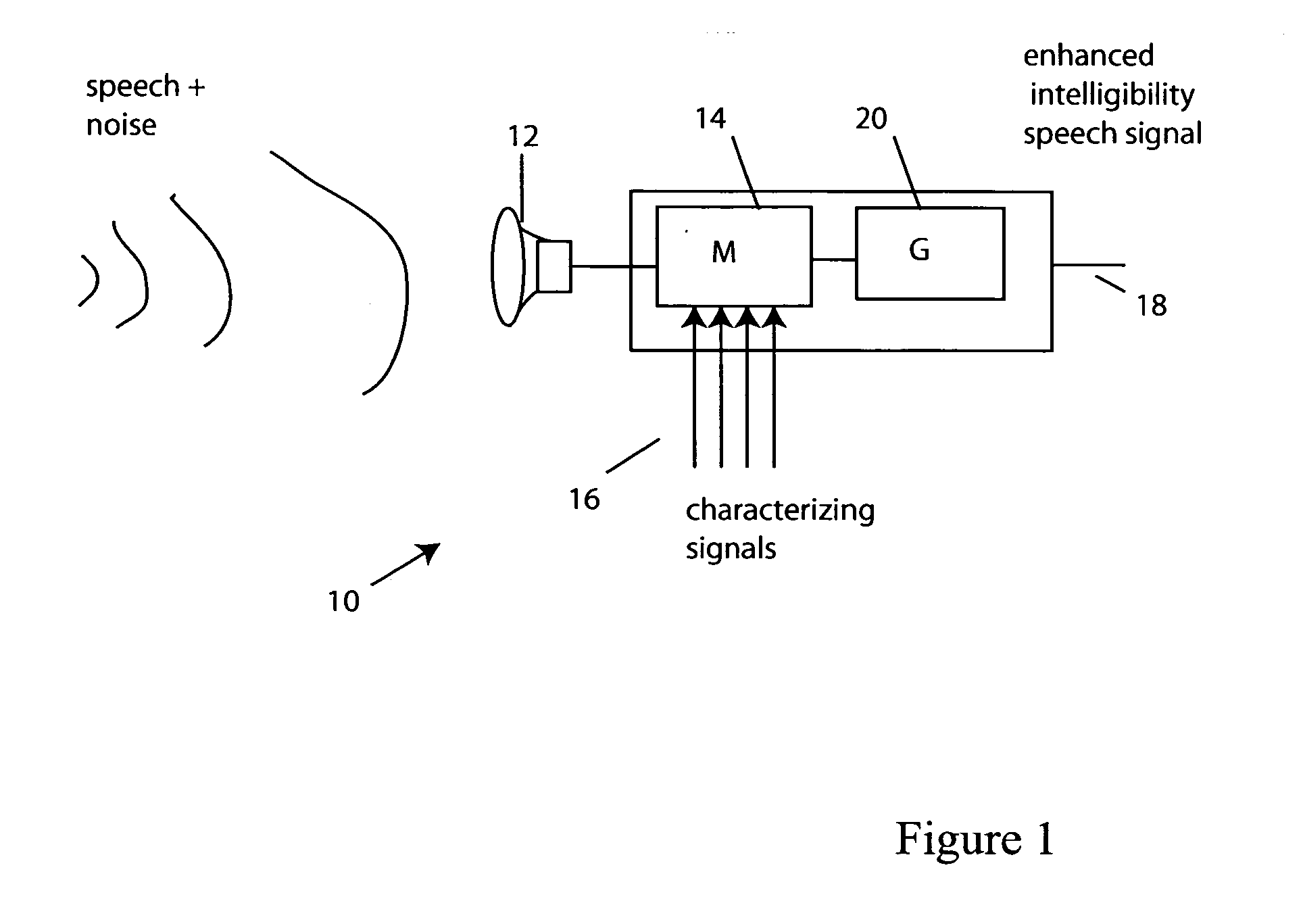
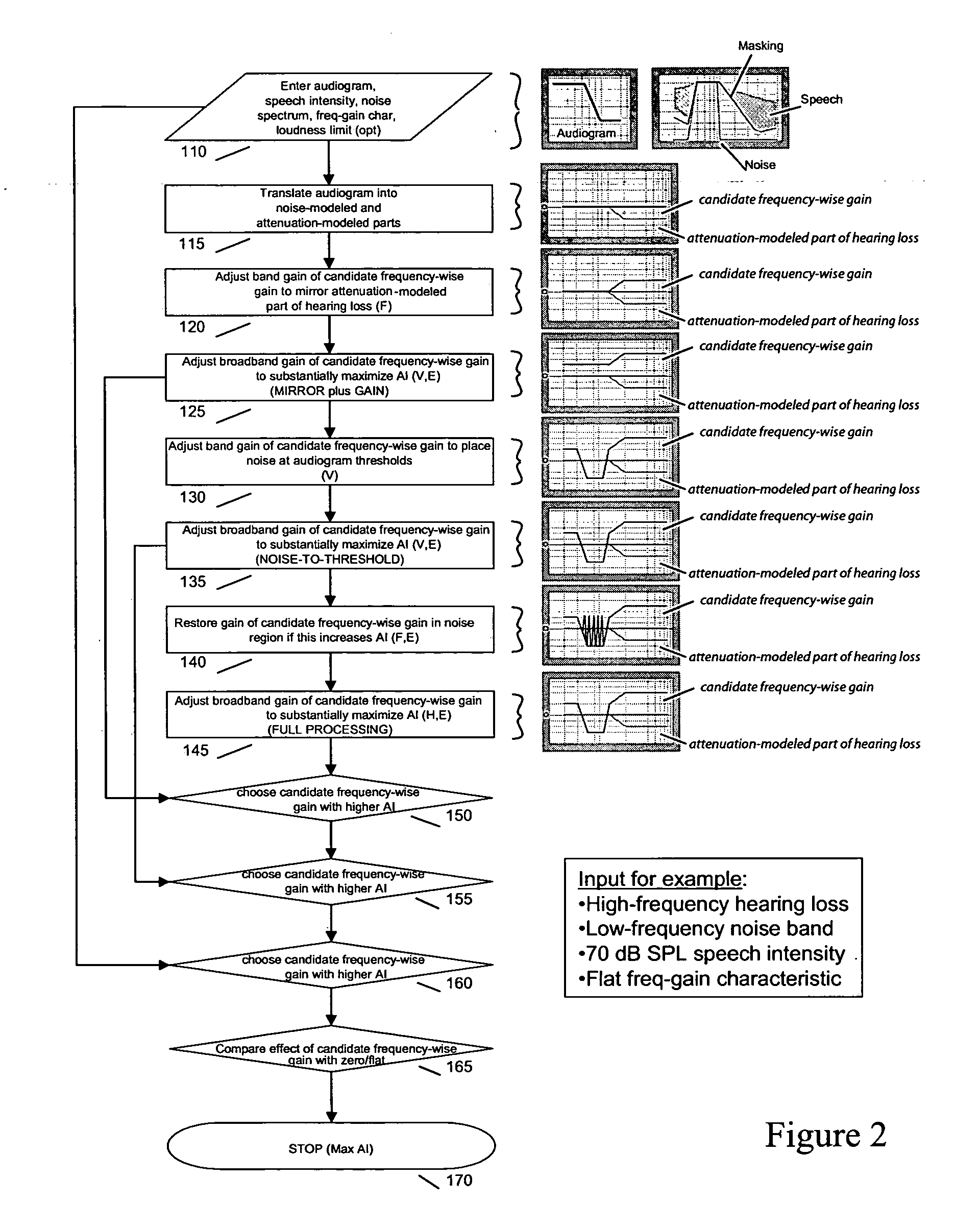
Methods and apparatus for maximizing speech intelligibility in quiet or noisy backgrounds
ActiveUS20050114127A1Improve speech clarityMaximize intelligibility metricSpeech recognitionPublic address systemHearing test
Methods and apparatus for maximizing speech intelligibility use psycho-acoustic variables of a model of speech perception to control the determination of optimal frequency-band specific gain adjustments. Speech signals (or other audio input) whose intelligibility is to be improved are characterized by parameters which are applied to the model. These include measurements or estimates of speech intensity level, average noise spectrum of the incoming audio signal, and / or the current frequency-gain characteristic of the hearing compensation device. Characterizations of listeners based on hearing test results, for example, may also be applied to the model. Frequency-band specific gain adjustments generated by use of the model can be used for hearing aids, assistive listening devices, telephones, cellular telephones, or other speech delivery systems, personal music delivery systems, public-address systems, sound systems, speech generating systems, or other devices or mediums which project, transfer or assist in the detection or recognition of speech.
Owner:ARTICULATION
Method and system for implementing outer loop power control in discontinuous transmission mode using explicit signalling
A signalling method for controlling unnecessary power increases and call drop during discontinuous transmission (DTX) mode of a frame-based transmission system. The signalling method comprises the steps of (1) detecting, at a receiver end of the transmission system a status of a transmitted frame indicating one of two possible transmission modes including (a) when a gating-off of the traffic channel occurs, and (b) when no gating-off of traffic occurs and normal traffic is being transmitted, and (2) controlling a change in the receiver target bit energy to noise spectrum density ratio Eb / No in response to the detection step so that a receiver target Eb / No is increased only when the detecting step does not indicate a gating-off of traffic has occurred.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
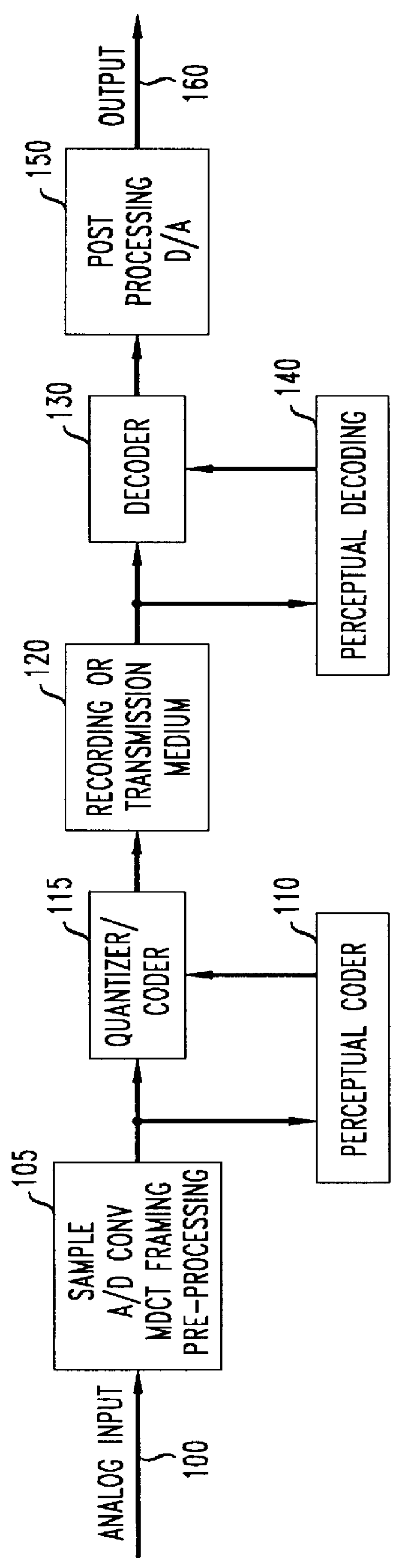
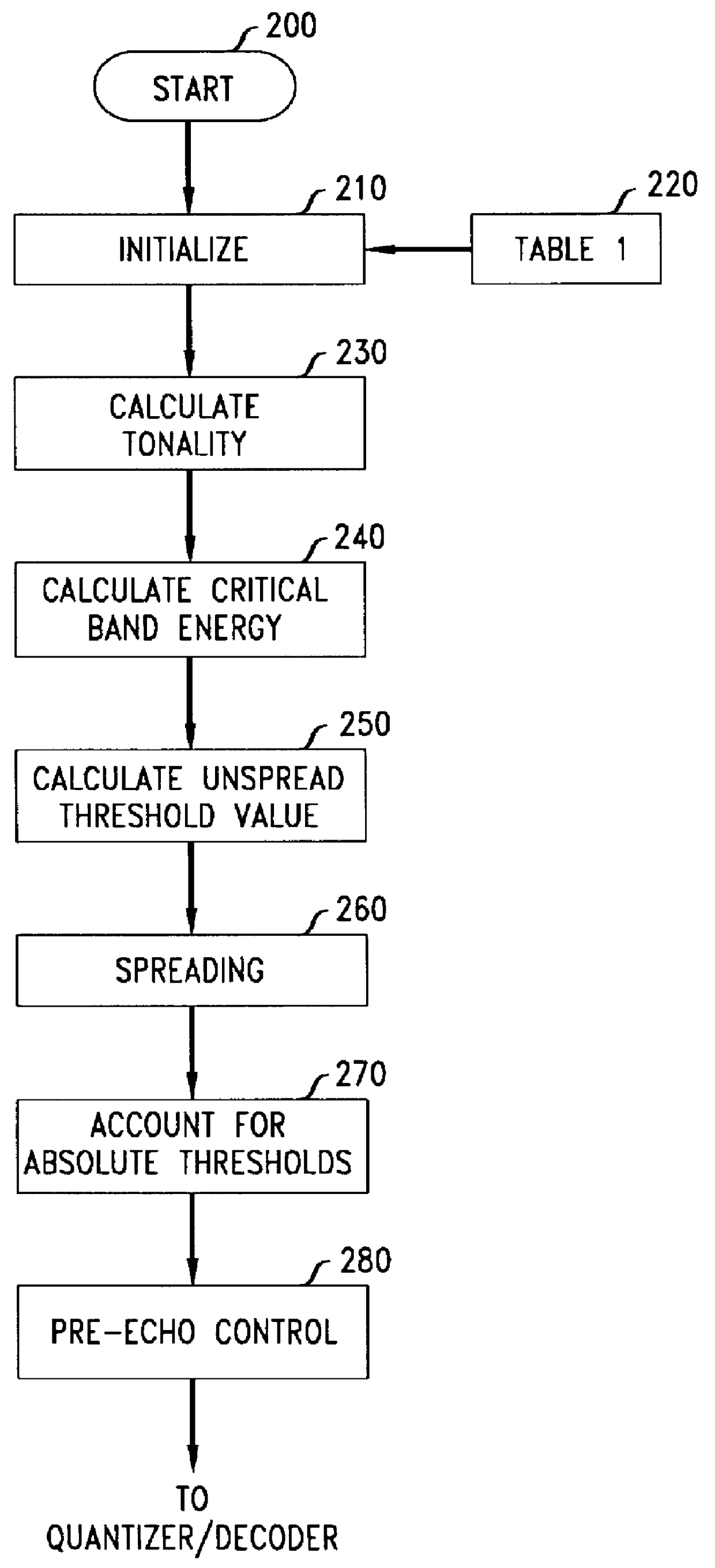
Perceptual coding of audio signals
A method is disclosed for determining estimates of the perceived noise masking level of audio signals as a function of frequency. By developing a randomness metric related to the euclidian distance between (i) actual frequency components amplitude and phase for each block of sampled values of the signal and (ii) predicted values for these components based on values in prior blocks, it is possible to form a tonality index which provides more detailed information useful in forming the noise masking function. Application of these techniques is illustrated in a coding and decoding context for audio recording or transmission. The noise spectrum is shaped based on a noise threshold and a tonality measure for each critical frequency-band (bark).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
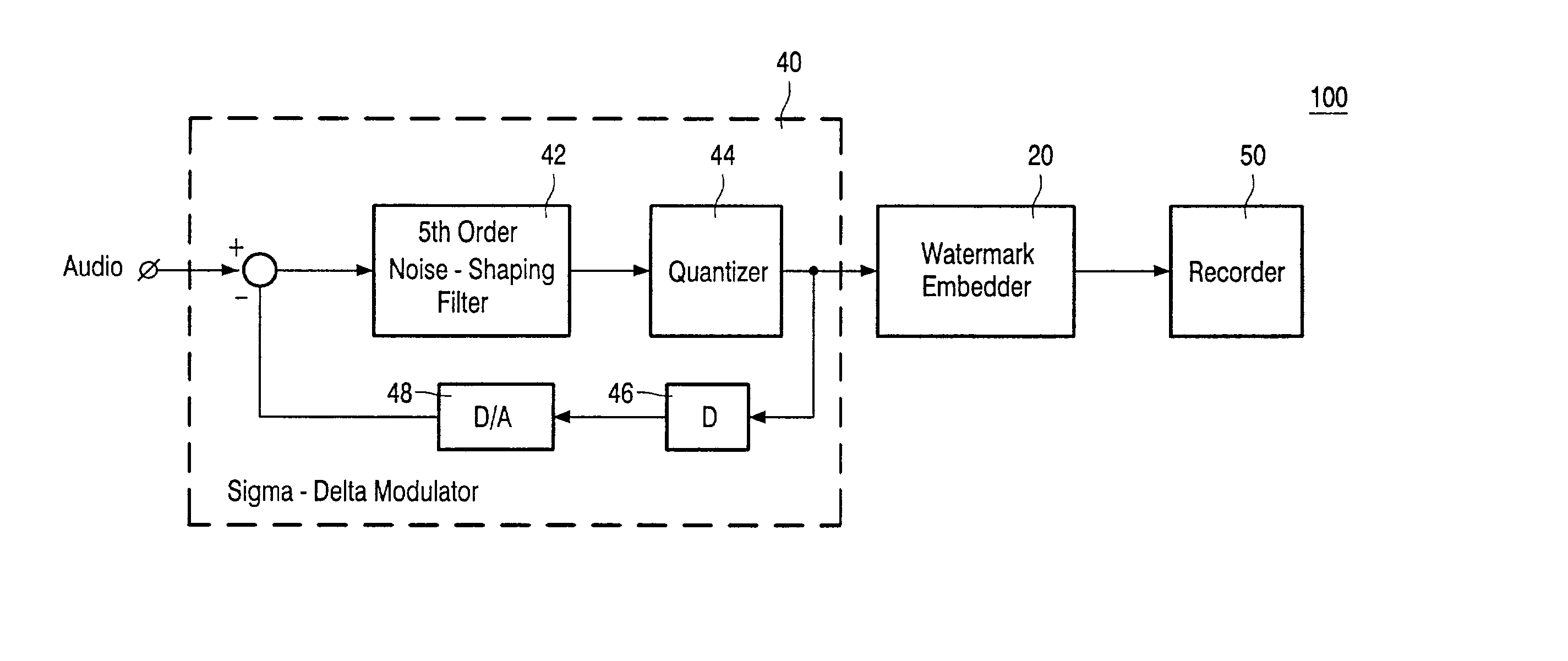
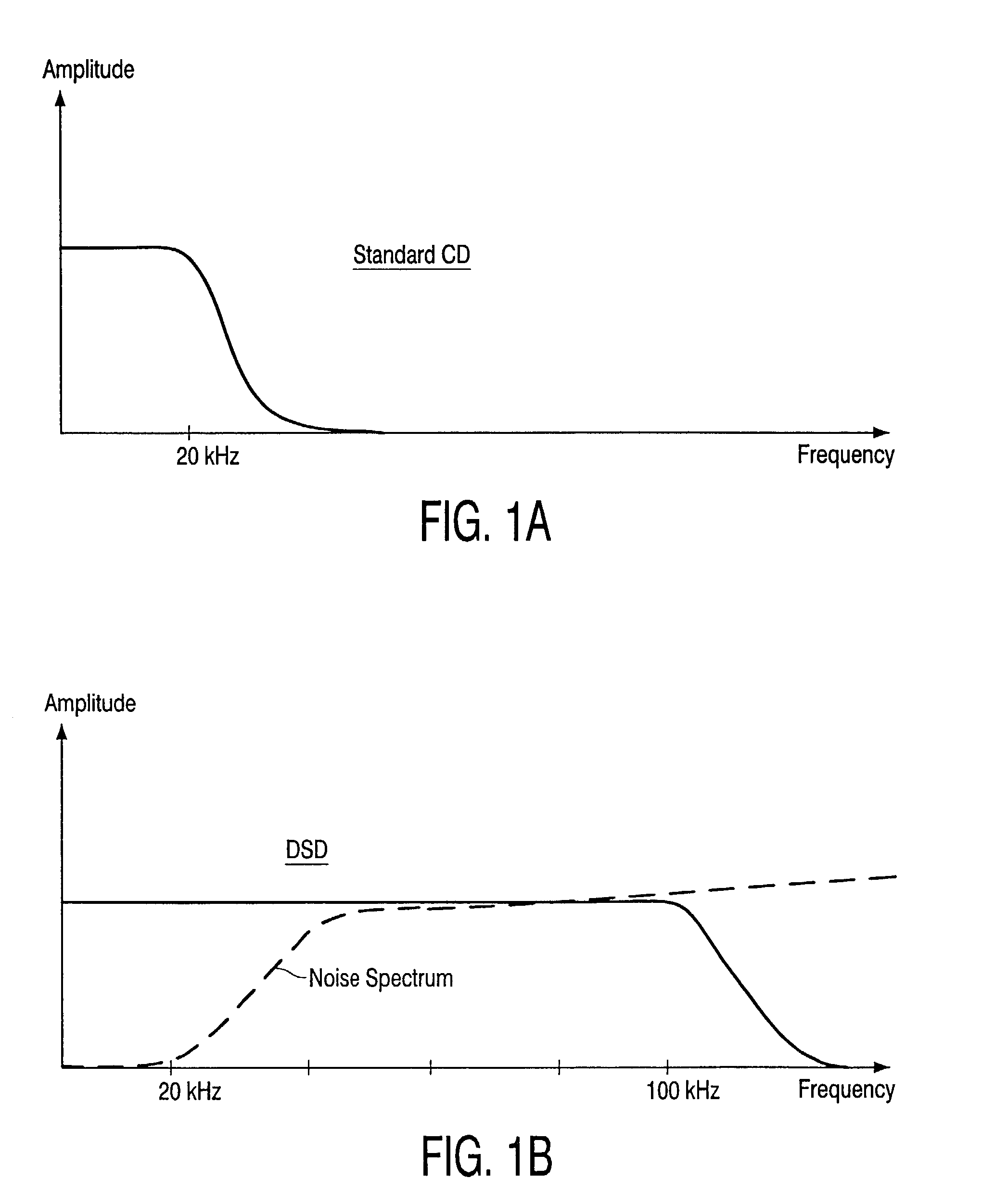
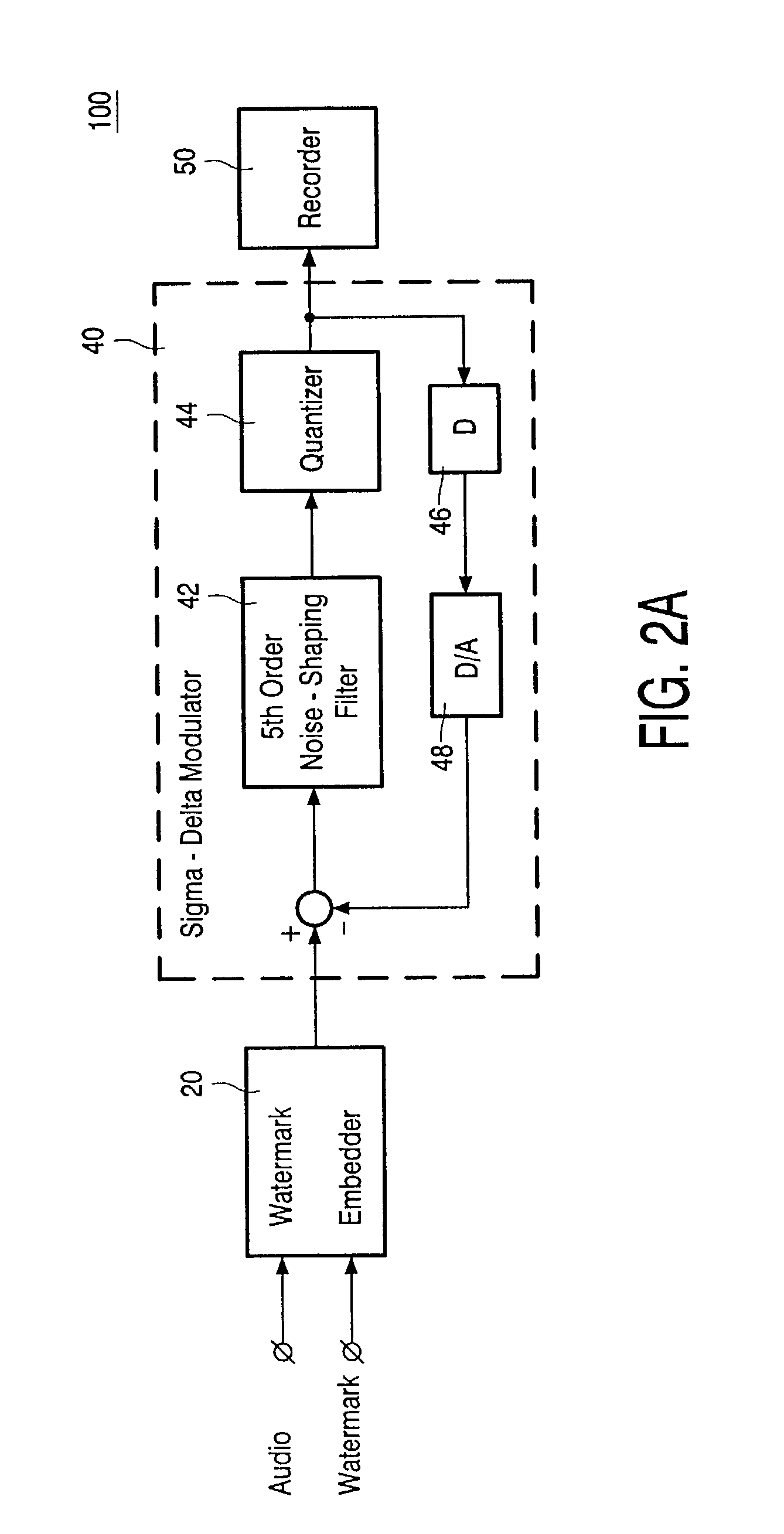
Robust watermark for DSD signals
InactiveUS20030079131A1User identity/authority verificationSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise spectrum
A robust watermark embedded into a Direct Stream Digital (DSD) audio signal including a flat frequency response in a specific frequency range which does not extend below 20 kHz or above 100 kHz. The watermark is therefore hidden in the noise spectrum of the DSD signal, such that the watermark is inaudible to a listener. Since the noise spectrum contains important information that helps provide the DSD signals with sharp transients and an accurate impulse response, the watermark cannot be removed from the DSD signal without causing significant degradation to the signal's audio quality.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
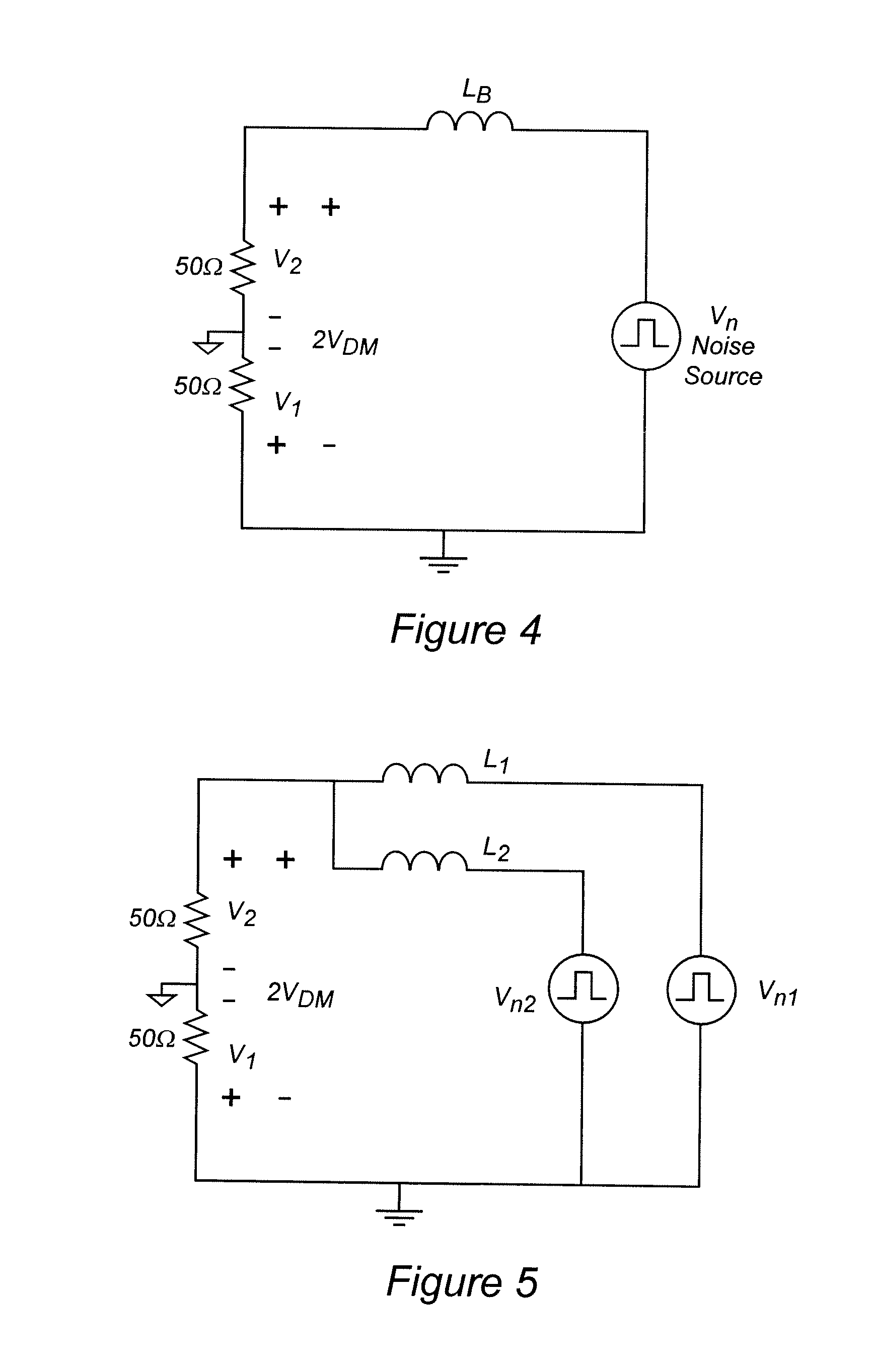
Switching power source
InactiveUS20090016087A1Increase the switching frequencyReduce noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
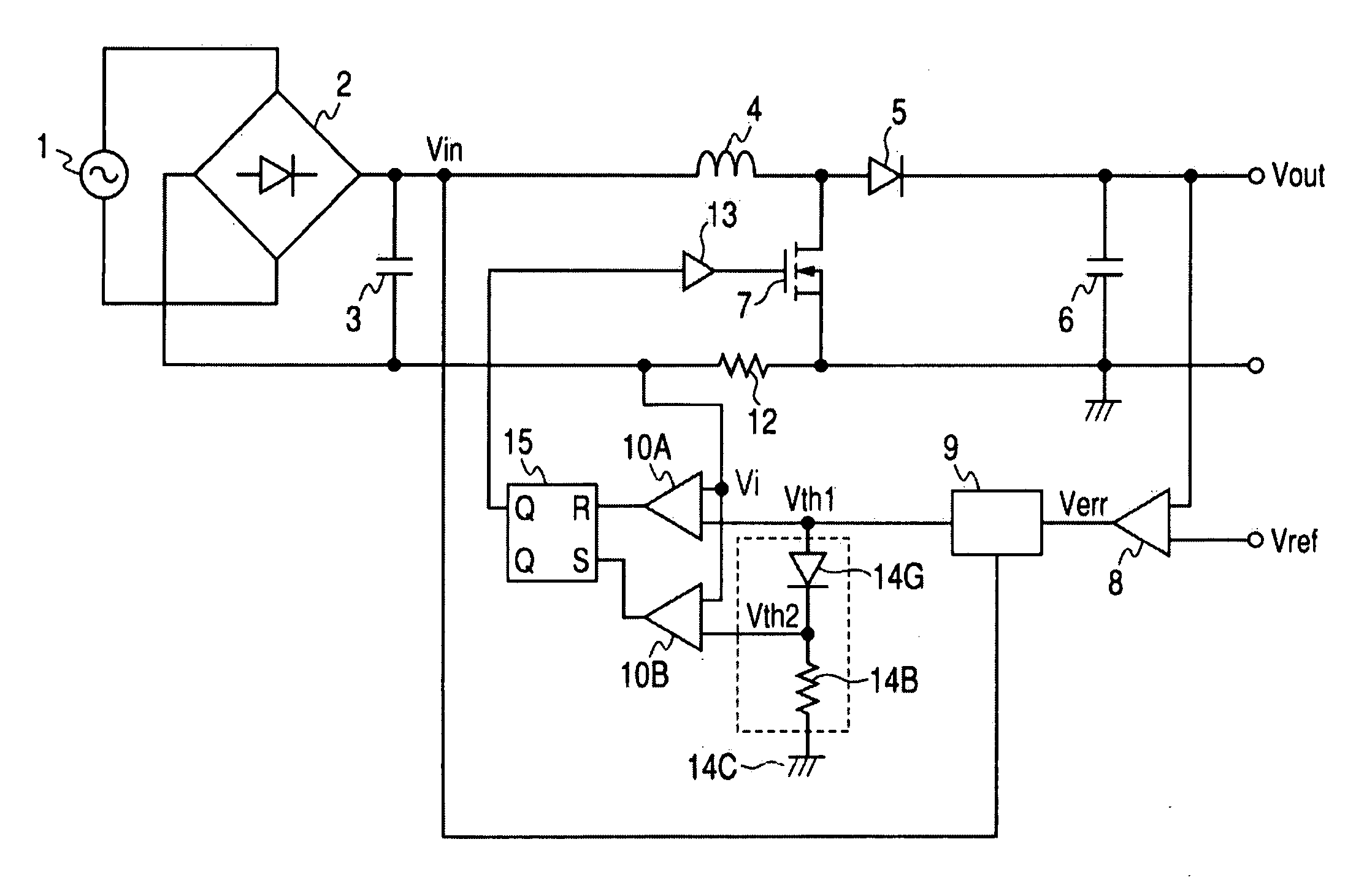
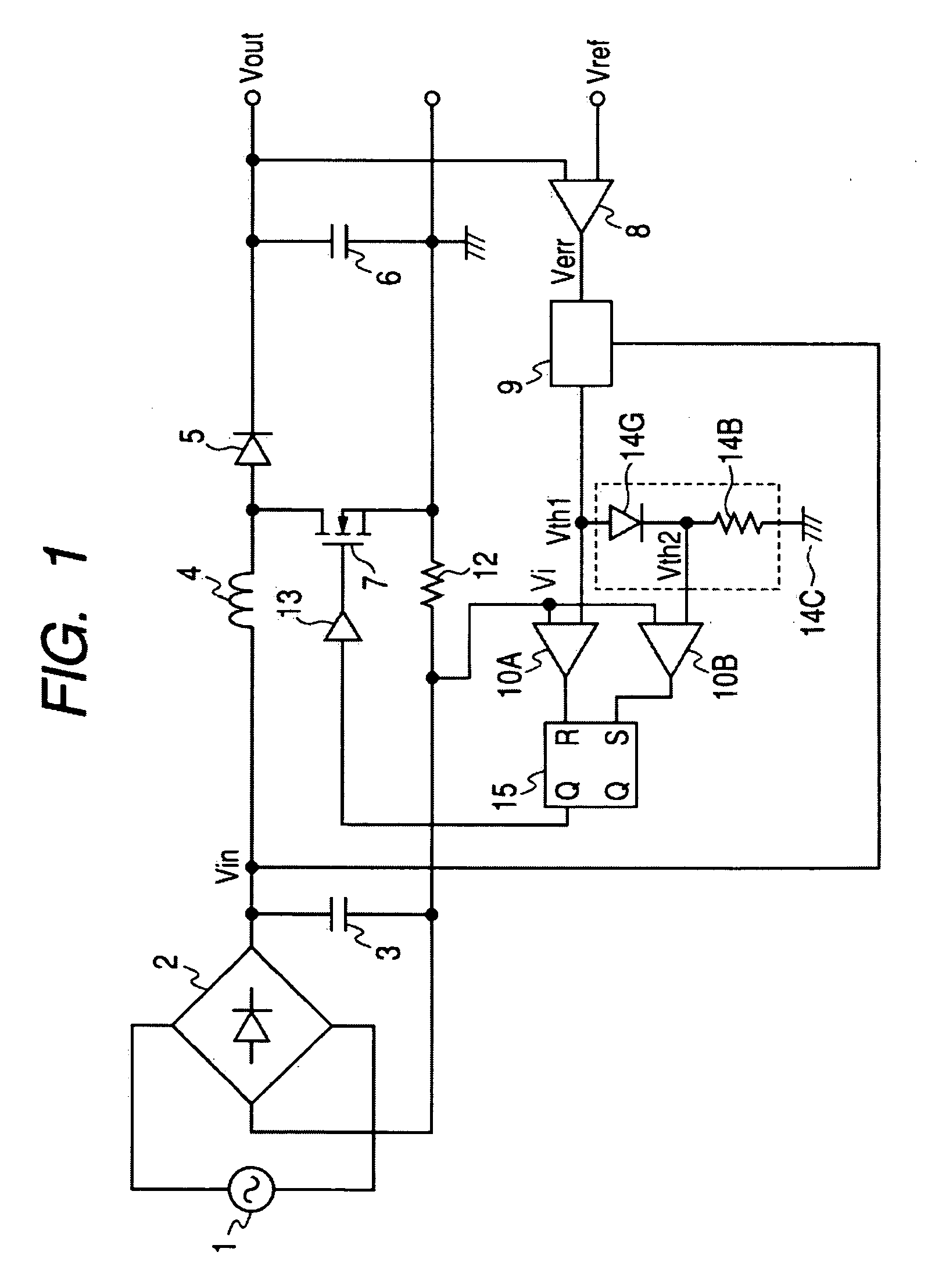
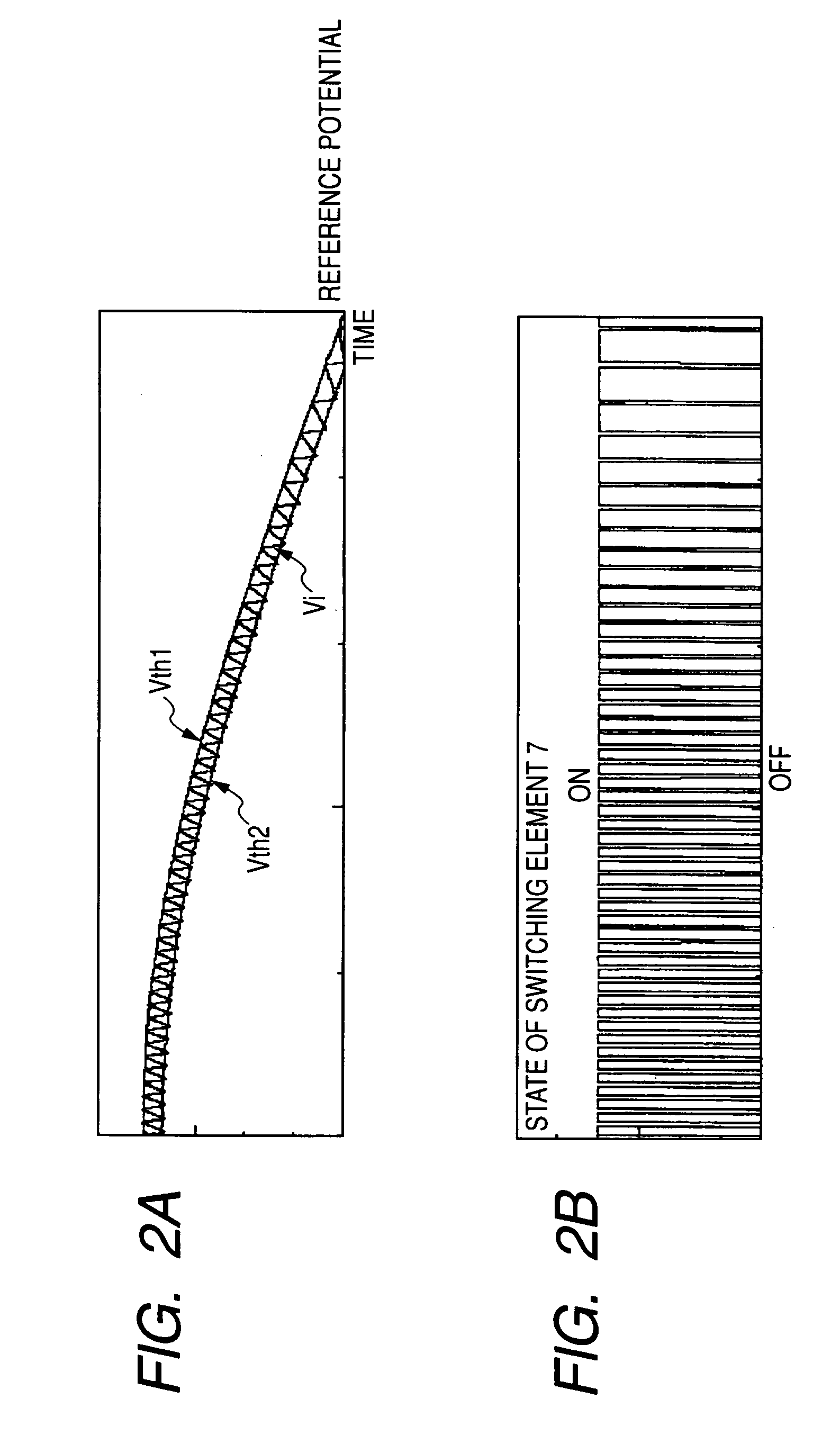
An error voltage Verr, as amplified by an amplifier, and an input voltage Vin, are multiplied together by a multiplier to generate a first threshold value signal Vth1, which is in phase with and similar in waveform to the input voltage Vin, and proportional in amplitude to the error voltage Verr. A second threshold value signal Vth2 is generated from the first threshold value signal Vth1 by a series circuit of a diode and a resistor. The power factor is increased by on / off-control of a switching element via a drive circuit, so that a current detection signal Vi, which is detected by a resistor and corresponds to an input current, falls between the two threshold value signals Vth1 and Vth2. Since the off time is not fixed, the noise spectrum is spread and increase of the switching frequency is suppressed. Noise reduction thus can be attained.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Noise suppressor and noise suppressing method
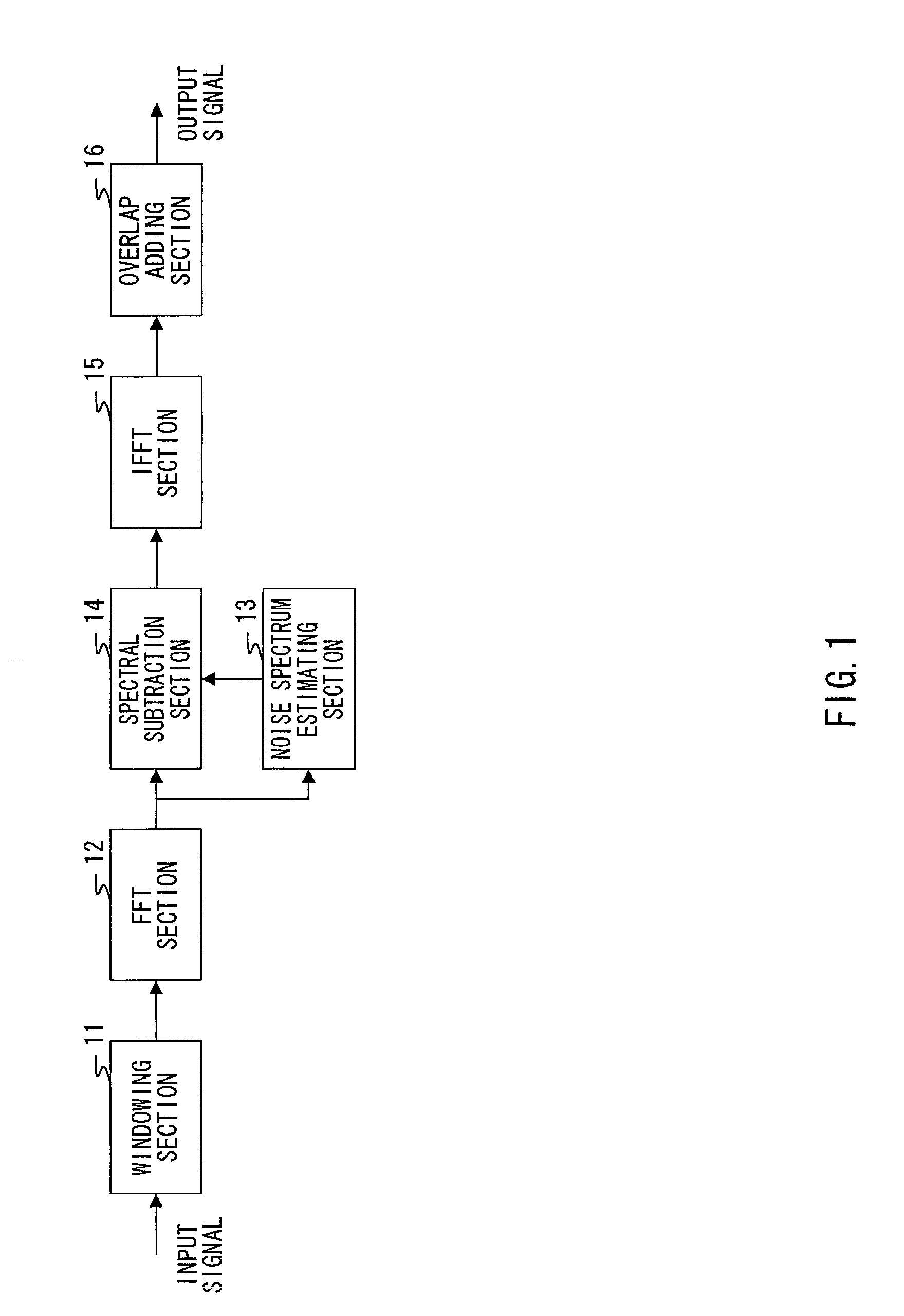
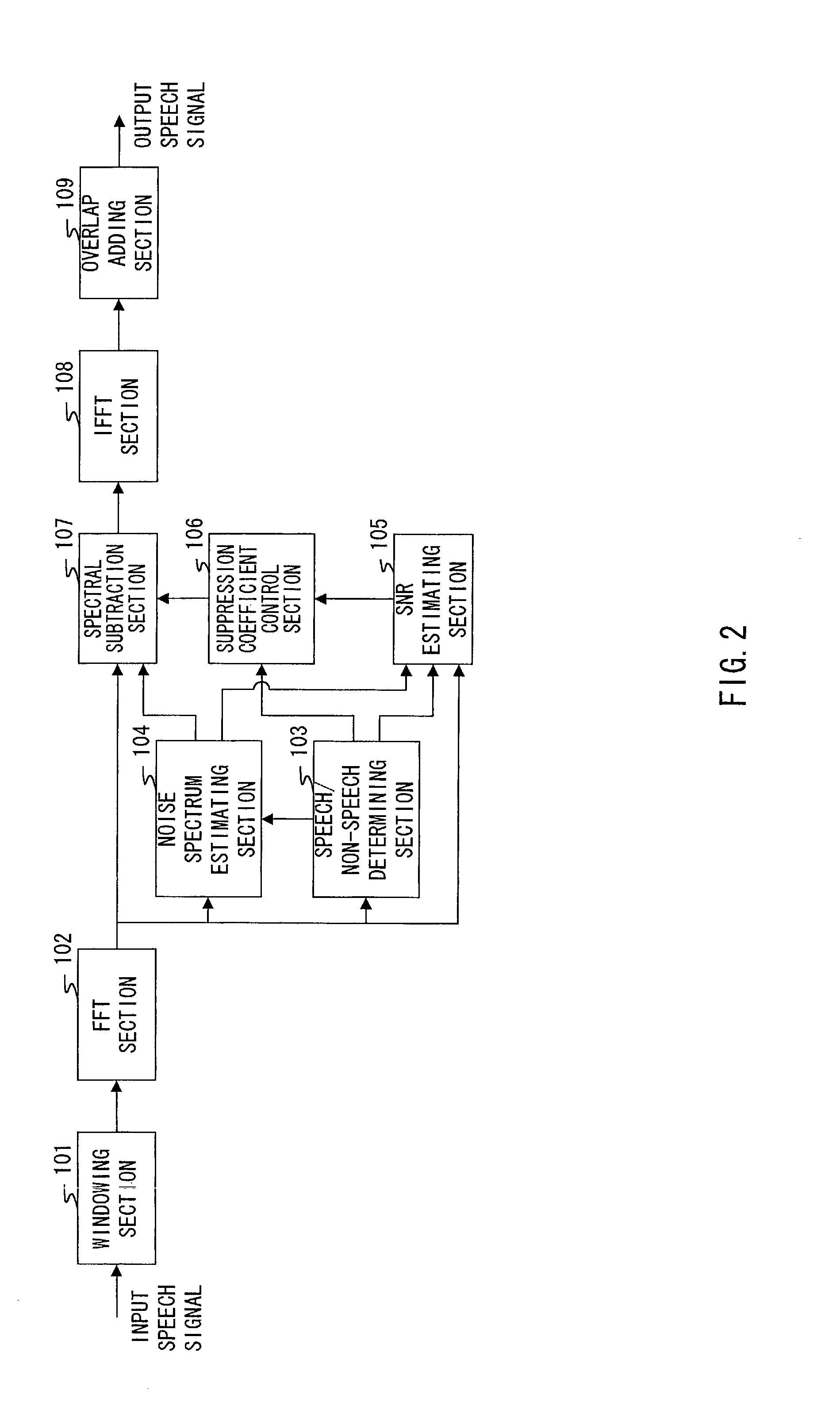
InactiveUS20020156623A1Improve efficiencyReduction of suppression distortionSubstation speech amplifiersCode conversionLower limitFrequency spectrum
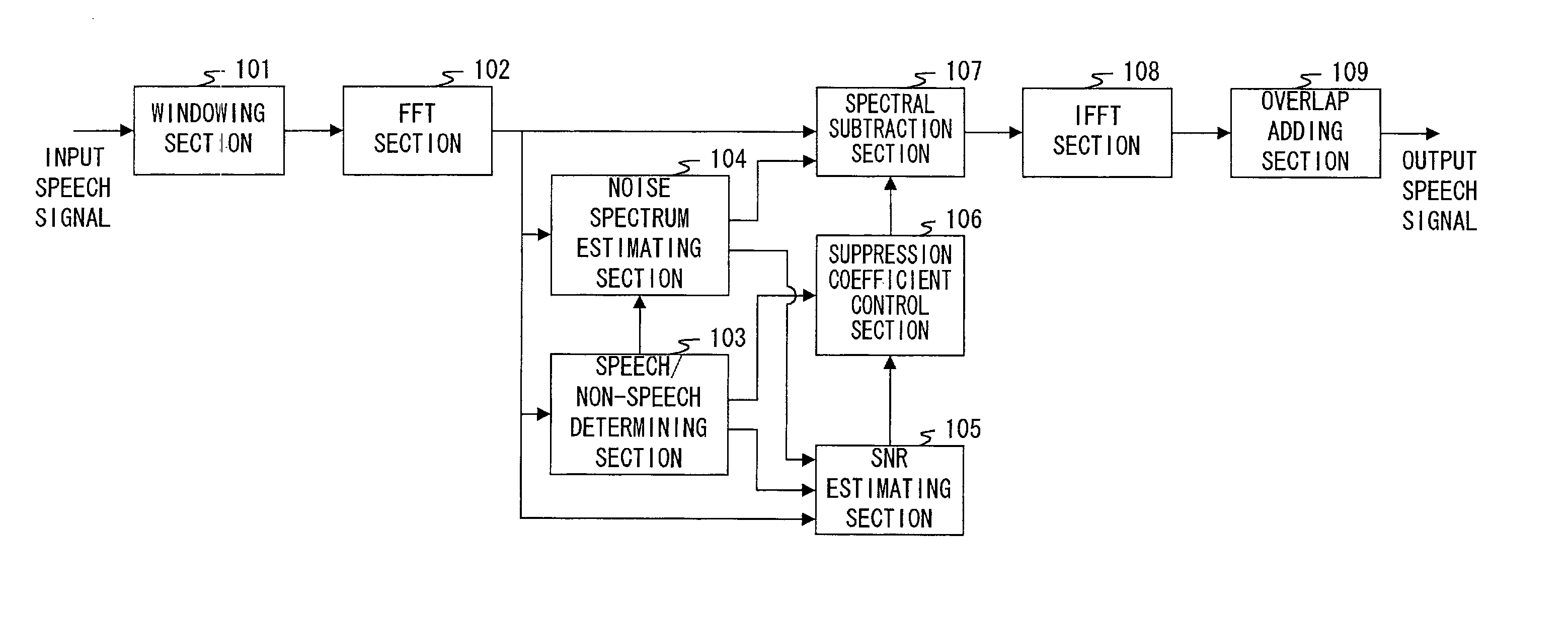
Speech / non-speech determining section 103 makes a speech / non-speech determination of whether a speech spectrum is of a speech interval with a speech included or of a non-speech interval with only a noise and no speech included. Noise spectrum estimating section 104 estimates a noise spectrum based on the speech spectrum determined as the non-speech interval. SNR estimating section 105 obtains speech signal power from the speech interval and noise signal power from the non-speech interval in the speech spectrum, and calculates SNR from a ratio of two values. Based on the speech / non-speech determination and a value of SNR, suppression coefficient control section 106 outputs a suppression lower limit coefficient to spectrum subtraction section 107. Spectral subtraction section 107 subtracts an estimated noise spectrum from the input speech spectrum, and outputs a speech spectrum with a noise suppressed.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Noise spectrum tracking in noisy acoustical signals
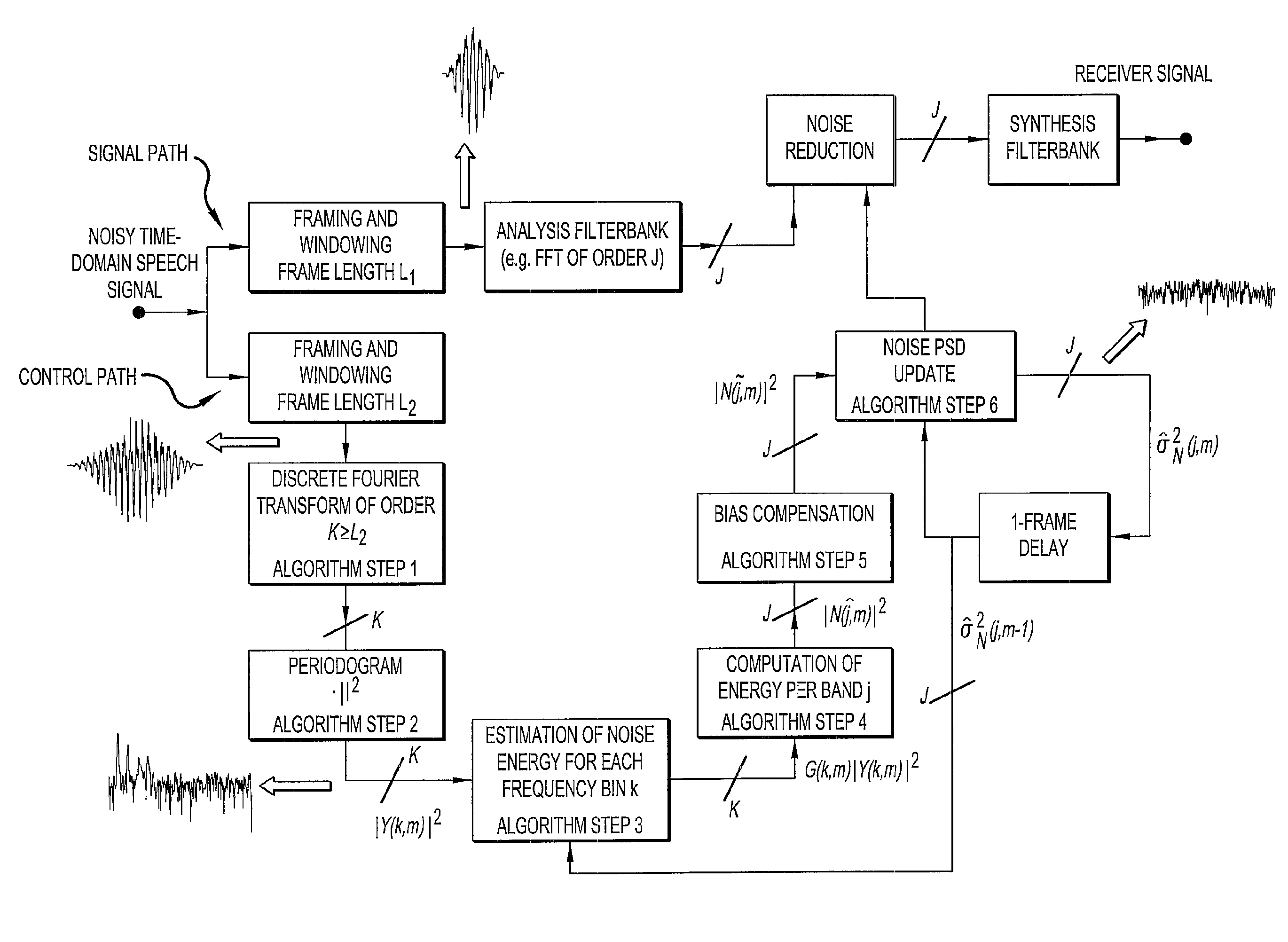
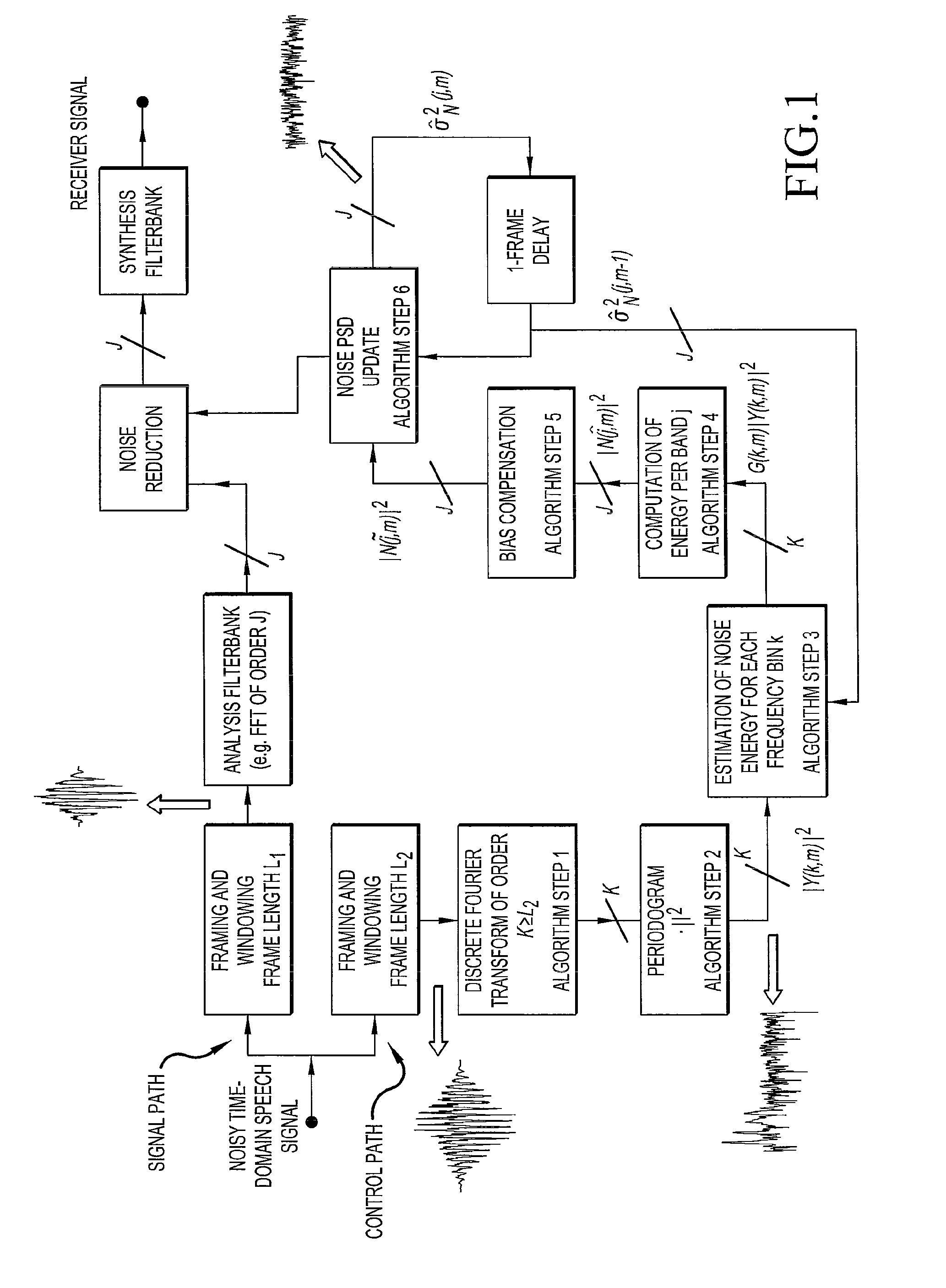
ActiveUS20100067710A1Accurate estimateReduce computational complexityElectrical apparatusSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
The invention relates to a method of estimating noise power spectral density PSD in an input sound signal comprising a noise signal part and a target signal part. The invention further relates to a system to its use. The object of the present invention is to provide a scheme for estimating the noise PSD in an acoustic signal consisting of a target signal contaminated by acoustic noise. The problem is solved by a method comprising the steps of d) providing a digitized electrical input signal to a control path and performing; d1) storing a number of time frames of the input signal each comprising a predefined number N2 of digital time samples xn (n=1, 2, . . . , N2), corresponding to a frame length in time of L2=N2 / fs; d2) performing a time to frequency transformation of the stored time frames on a frame by frame basis to provide corresponding spectra Y of frequency samples; d3) deriving a periodogram comprising the energy content |Y|2 for each frequency sample in a spectrum, the energy content being the energy of the sum of the noise and target signal; d4) applying a gain function G to each frequency sample of a spectrum, thereby estimating the noise energy level |Ŵ|2 in each frequency sample, |Ŵ|2=G·|Y|2; d5) dividing the spectra into a number Nsb2 of sub-bands, each sub-band comprising a predetermined number nsb2 of frequency samples, and assuming that the noise PSD level is constant across a sub-band; d6) providing a first estimate |{circumflex over (N)}|2 of the noise PSD level in a sub-band based on the non-zero noise energy levels of the frequency samples in the sub-band; d7) providing a second, improved estimate |Ñ|2 of the noise PSD level in a sub-band by applying a bias compensation factor B to the first estimate, |Ñ|2=B·|{circumflex over (N)}|2. The invention may e.g. be used in listening devices, e.g. hearing aids, mobile telephones, headsets, active earplugs, etc.
Owner:OTICON
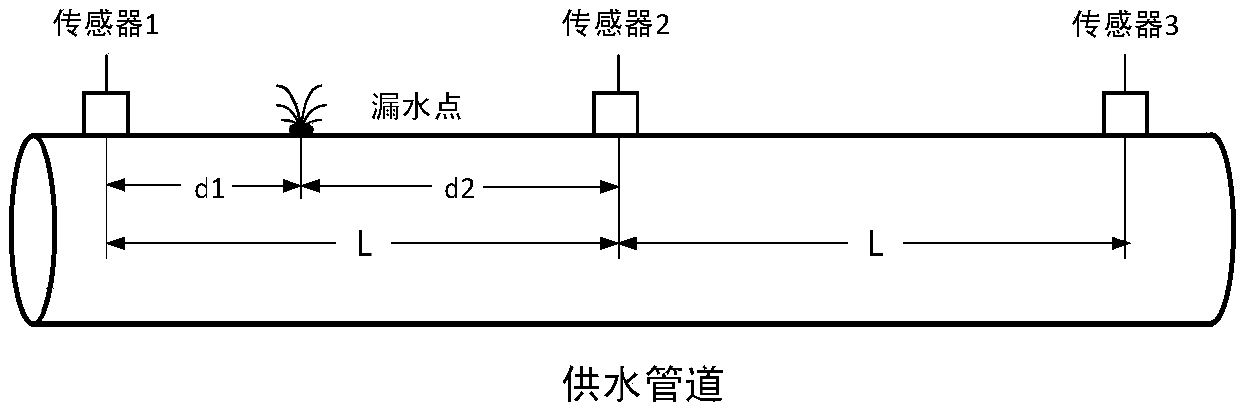
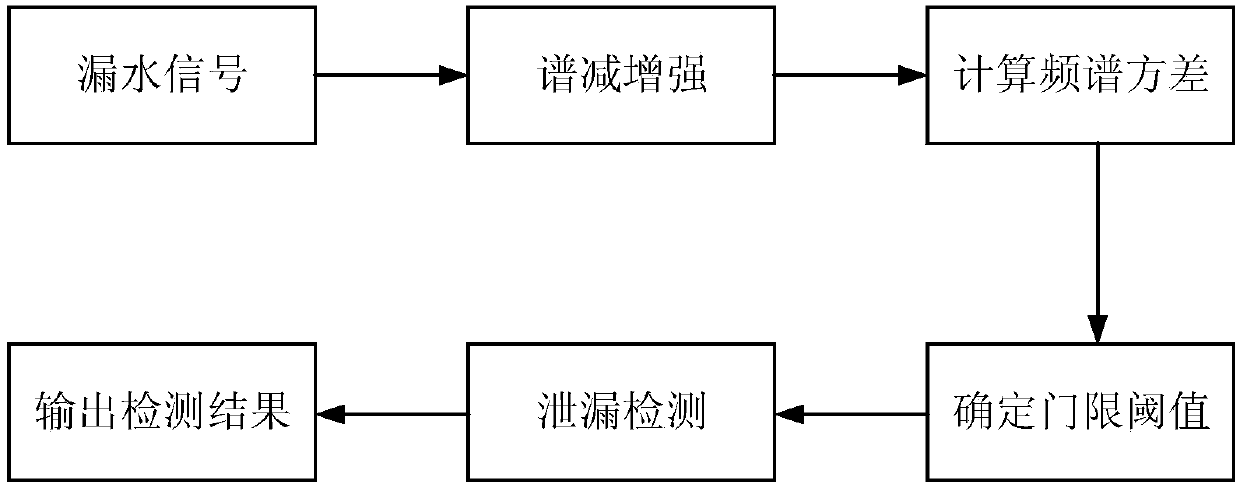
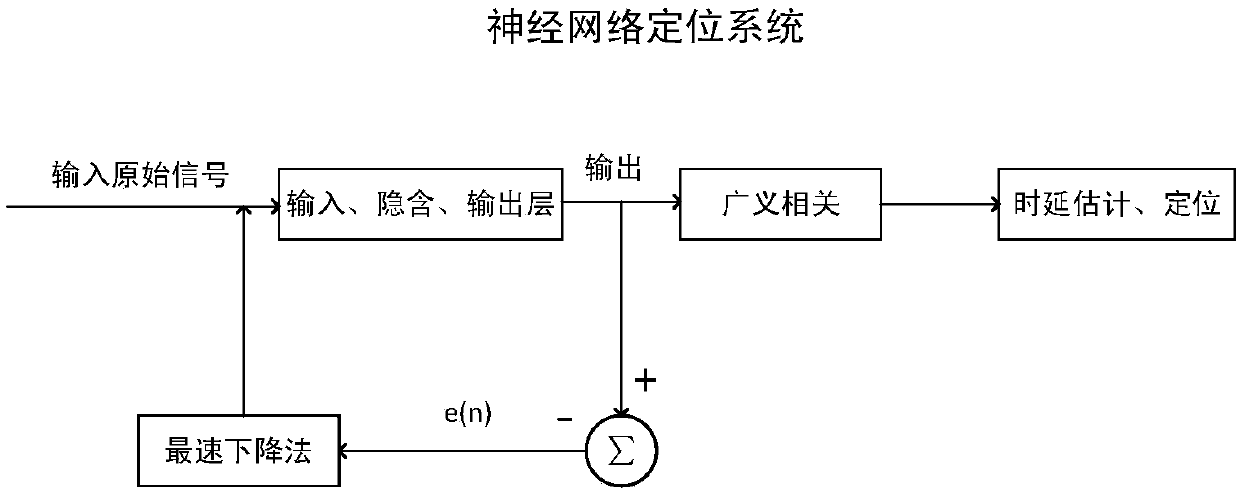
Water supply pipeline leakage detecting and positioning method
ActiveCN107061996AImprove signal-to-noise ratioIncreased effectiveness of leak detectionSpeech analysisPipeline systemsWater leakageFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a water supply pipeline leakage detecting and positioning method which is characterized in that a signal collected by a sensor is subjected to enhancement through spectral subtraction, the frequency spectrum variance of the signal after enhancement is calculated, a double-threshold method is adopted for judgment, that is, if the frequency spectrum variance is within the threshold range, which indicates that leakage occurs, the leakage point is positioned, a BP neural network is utilized to form a filter, a water leakage signal is separated from noise and subjected to generalized correlation analysis, time delay estimation is carried out according to the weight function with a good signal-to-noise ratio selectivity, three time delays of the sensor are acquired, and a water leakage positioning model is utilized for calculation to acquire water leakage point position information. According to the water supply pipeline leakage detecting and positioning method, the spectral subtraction method is adopted for signal enhancement, the double-threshold method is utilized for leakage judgment, if the frequency spectrum variance is within the threshold range, which indicates that leakage occurs, and therefore the accuracy is higher; besides, the non-leakage estimation method is adopted for estimation of the noise spectrum, the signal-to-noise ratio is increased more obviously, meanwhile the BP neural network is adopted for filtering, the generalized correlation time delay estimation accuracy is improved, and the water leakage point positioning accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
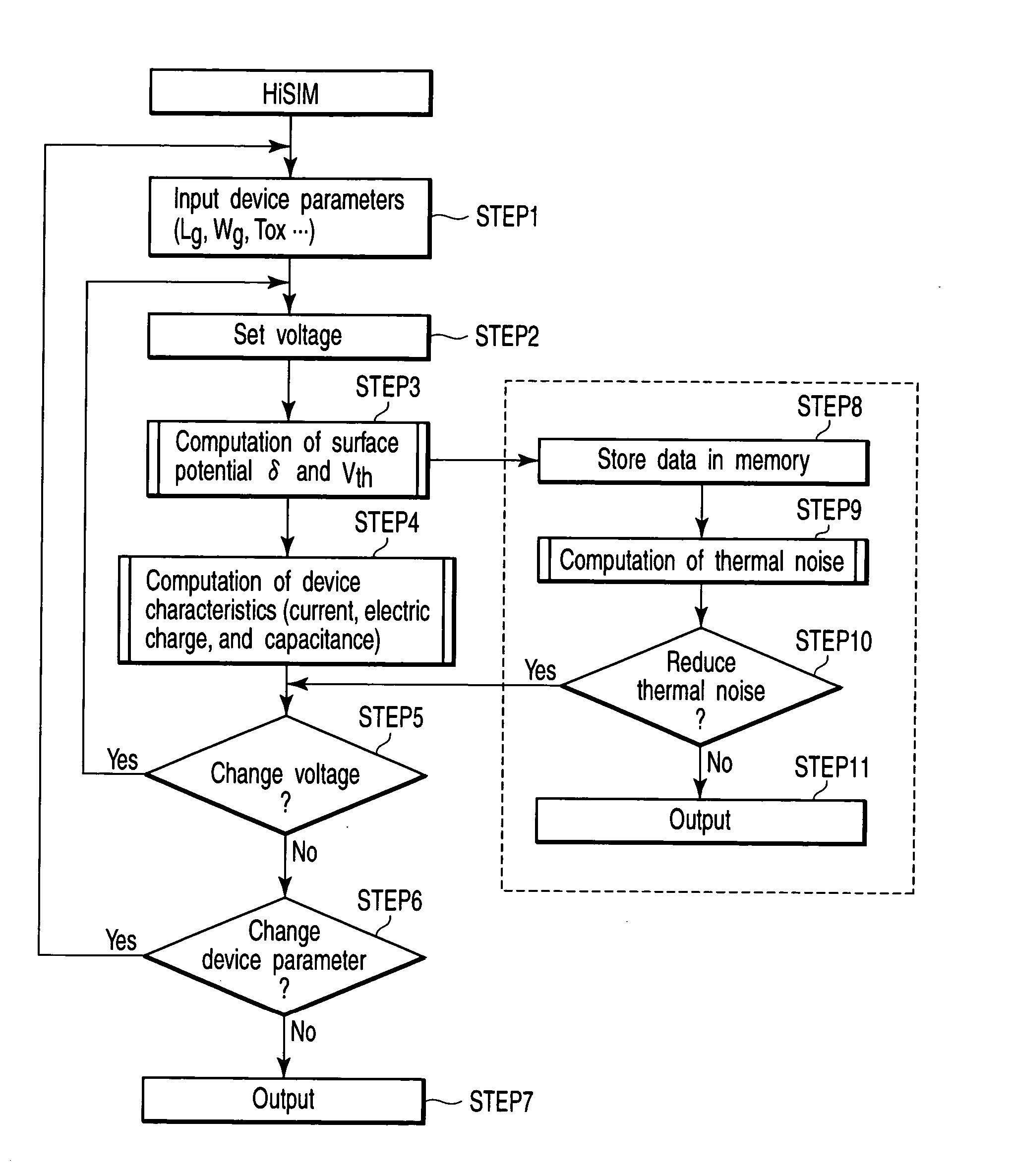
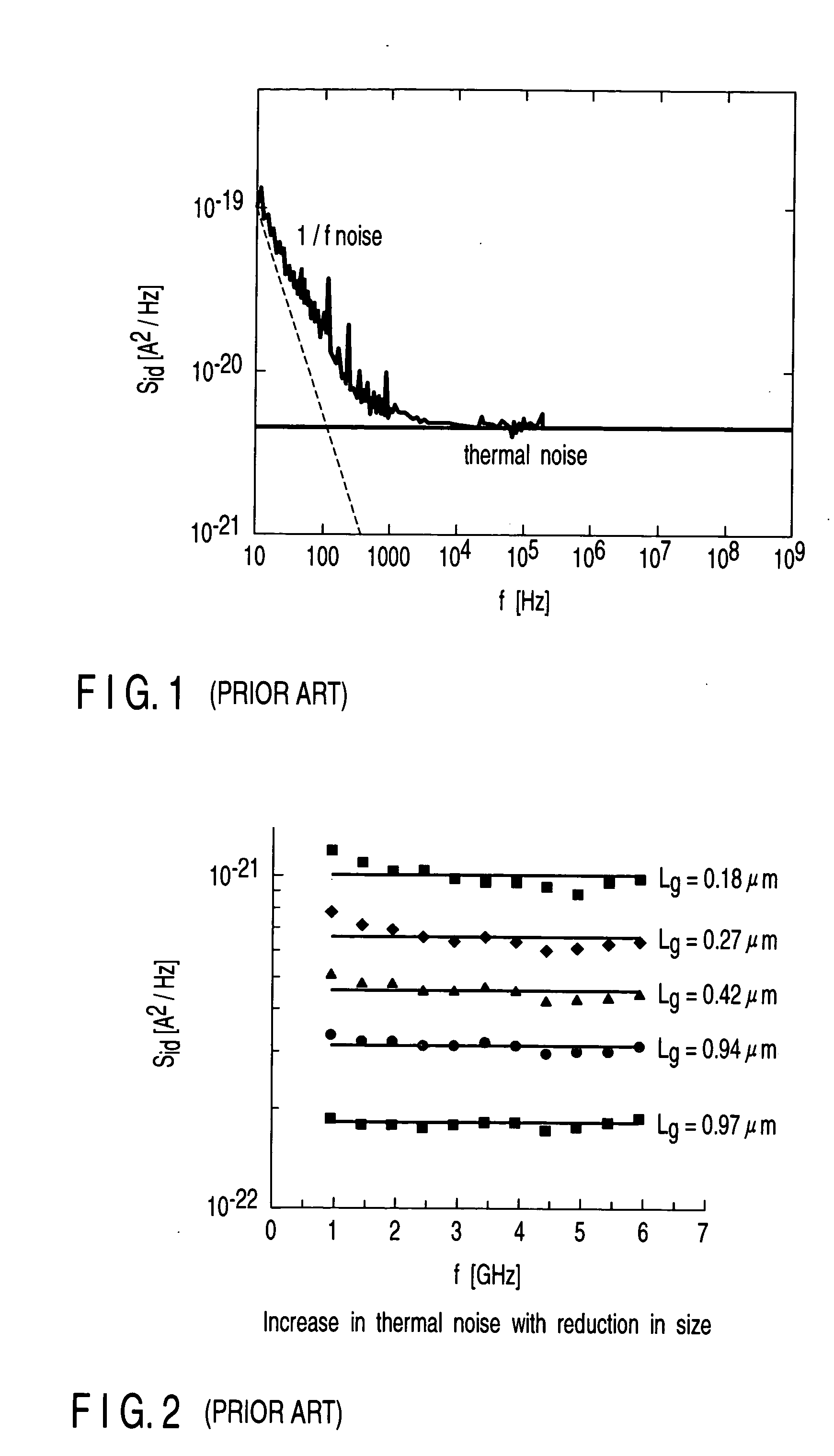
Simulation model for design of semiconductor device, thermal drain noise analysis method, simulation method, and simulation apparatus
InactiveUS20050155004A1Accurate estimateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETFrequency spectrum
A semiconductor device simulation method includes the step of storing, in a storage unit, a surface potential and threshold voltage obtained by computation, the step of computing thermal drain noise on the basis of the data of the surface potential and thermal drain noise stored in the storage unit, and the step of determining whether or not to reduce thermal drain noise, and reflecting the computation result in simulation of the model when it is determined that thermal drain noise is to be reduced. A drain current Ids of a MOSFET is calculated and substituted into a relational expression for a drain current noise spectrum density obtained from a Nyquist theorem equation, thereby calculating a thermal drain noise coefficient γ of the MOSFET by substituting the current Ids into a relational expression for a thermal drain noise spectrum density which is obtained from the Nyquist logical equation.
Owner:SEMICON TECH
Binder identification
InactiveUS20070036340A1Reduce riskSimple designInterconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsTransceiverFrequency spectrum
Methods, techniques and apparatus identify members and characteristics of binders and / or other groups of communication lines such as those in a DSL system. Information obtained includes the identification (for example, by scanning) of significant crosstalking “offenders” and their “victims” that are affected by the crosstalk. One or a small number of modems are instructed to transmit with preselected transmit spectra, after which evidence of crosstalk in the noise spectrum data is examined for potential victim lines. Direct evidence of noise spectrum contribution by a suspected offender line may be obtained by collecting reported noise spectrum data and / or estimated noise spectrum data from potential victim lines. Also, where such direct evidence is not available, or in addition to it, other operational data showing crosstalk interference relating to potential victim lines can be used. The transmitting modem can either be on the CO / RT side or on the CPE side. Modems other than suspected offenders might transmit zero or minimal power in one or more selected frequency bands during scanning to reduce the risk that a modem and / or line not being examined for “offender” status supplies unnecessarily complicating and / or dominant crosstalk during the procedure. For DMT modulated DSL transceivers, well designed transmit spectra can be easily enforced by manipulating line profiles where such well designed line profiles cause minimal or no interruption to existing DSL customers. The invention also can be used to identify (partially or fully) the absolute values of crosstalk channels making up a channel transfer function.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Multi-microphone noise reduction using enhanced reference noise signal
InactiveUS20140037100A1Improve performanceMinimal suppressionMicrophonesSignal processingFrequency spectrumNoise reduction algorithm
Systems and methods of improved noise reduction include the steps of: receiving an audio signal from two or more acoustic sensors; applying a beamformer to employ a first noise cancellation algorithm; applying a noise reduction post-filter module to the audio signal including: estimating a current noise spectrum of the received audio signal after the application of the first noise cancellation algorithm, wherein the current noise spectrum is estimated using the audio signal received by the second acoustic sensor; determining a punished noise spectrum using the time-average level difference between the audio signal received by the first acoustic sensor and the current noise spectrum; determining a final noise estimate by subtracting the punished noise spectrum from the current noise spectrum; and applying a second noise reduction algorithm to the audio signal received by the first acoustic sensor using the final noise estimate; and outputting an audio stream with reduced background noise.
Owner:QSOUND LABS
System and method for removing narrowband noise
A system and method for removing narrowband noise from an input signal in which notch filters having notch frequencies corresponding to the noise are dynamically adjusted in accordance with a detected noise spectrum. The method may be applied to telemetry systems for implantable medical devices such as cardiac pacemakers to result in improved noise immunity.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
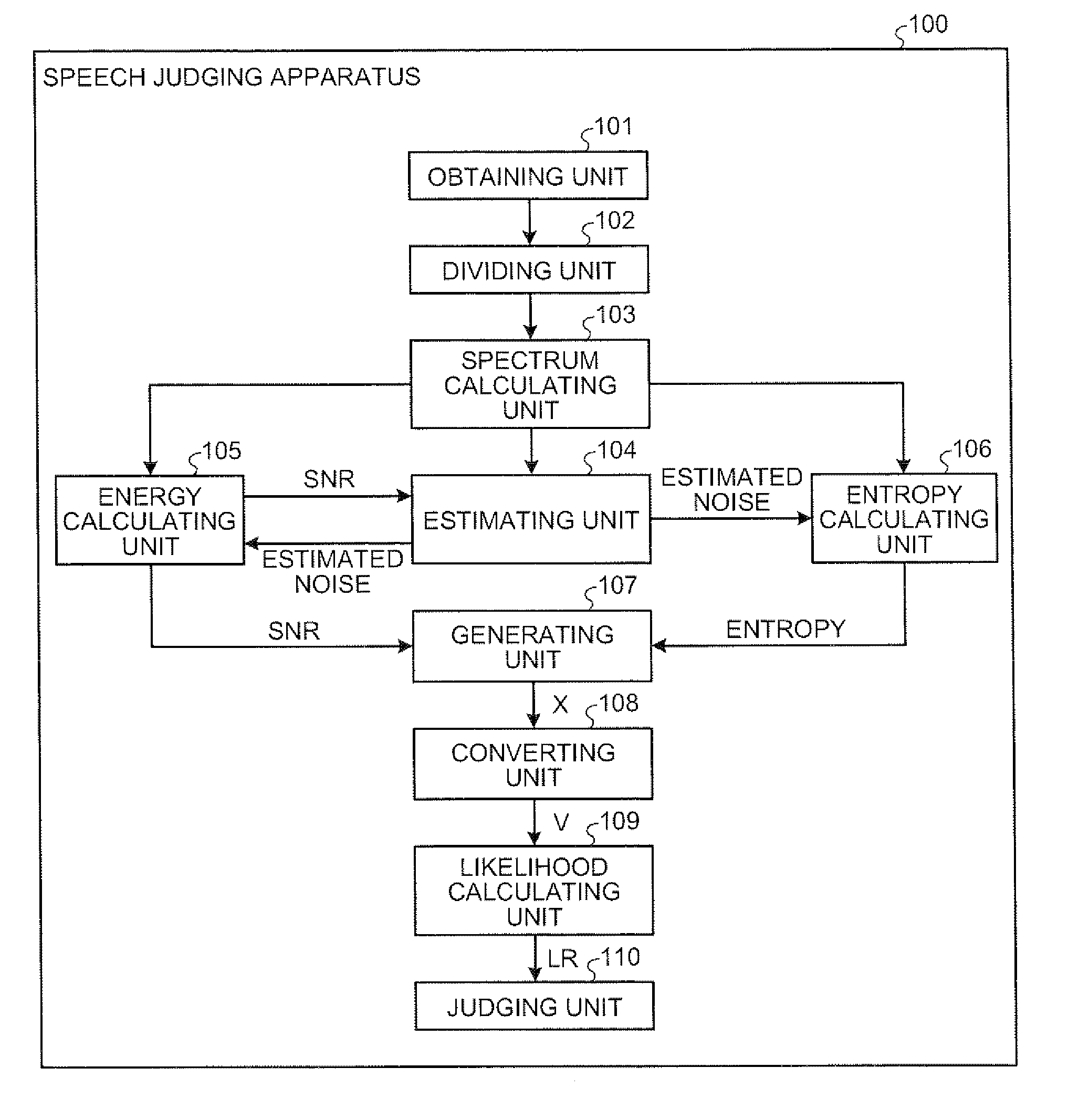
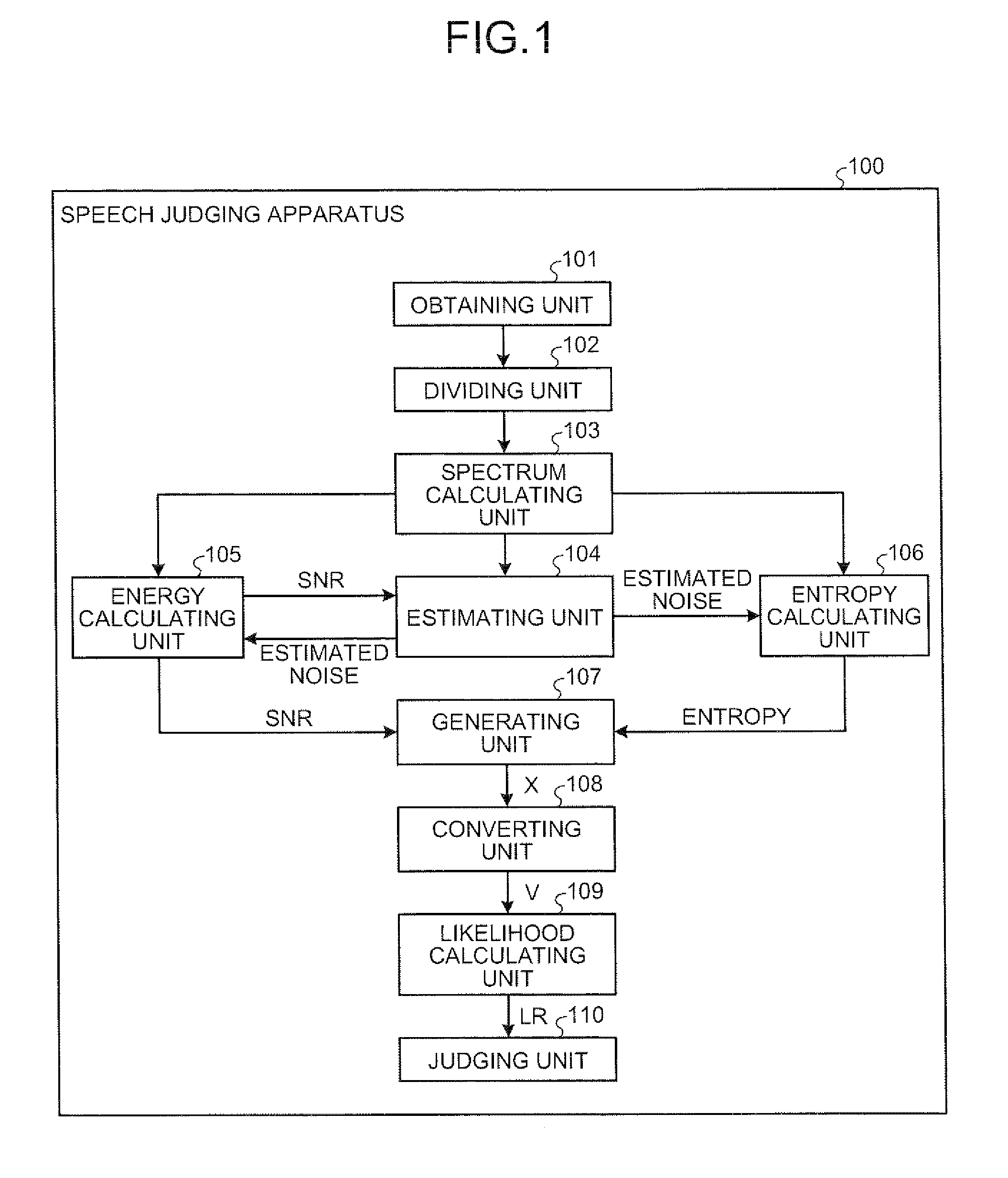
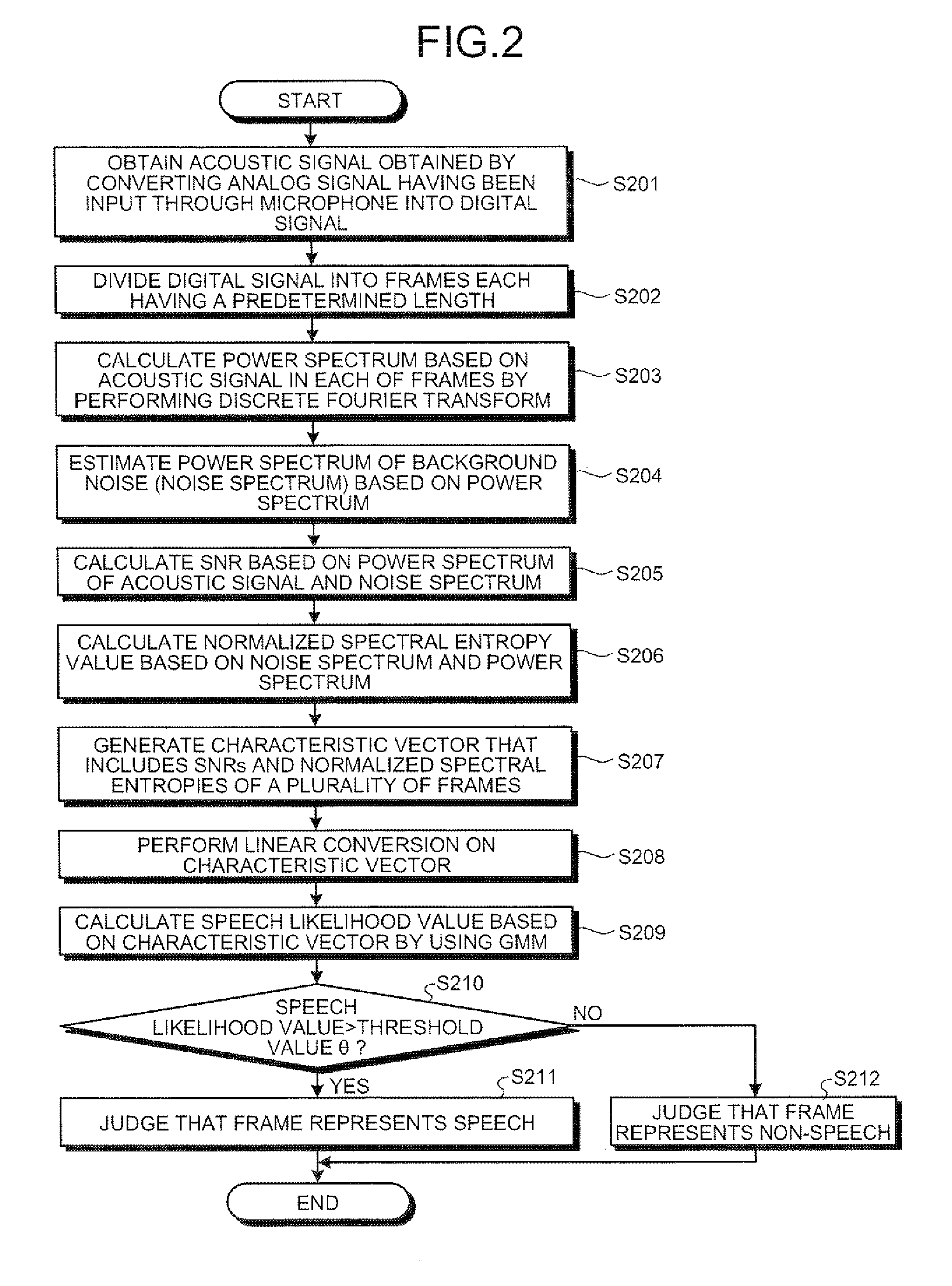
Apparatus, method, and computer program product for judging speech/non-speech
A spectrum calculating unit calculates, for each of the frames, a spectrum by performing a frequency analysis on an acoustic signal. An estimating unit estimates a noise spectrum. An energy calculating unit calculates an energy characteristic amount. An entropy calculating unit calculates a normalized spectral entropy value. A generating unit generates a characteristic vector based on the energy characteristic amounts and the normalized spectral entropy values that have been calculated for a plurality of frames. A likelihood calculating unit calculates a speech likelihood value of a target frame that corresponds to the characteristic vector. In a case where the speech likelihood value is larger than a threshold value, a judging unit judges that the target frame is a speech frame.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
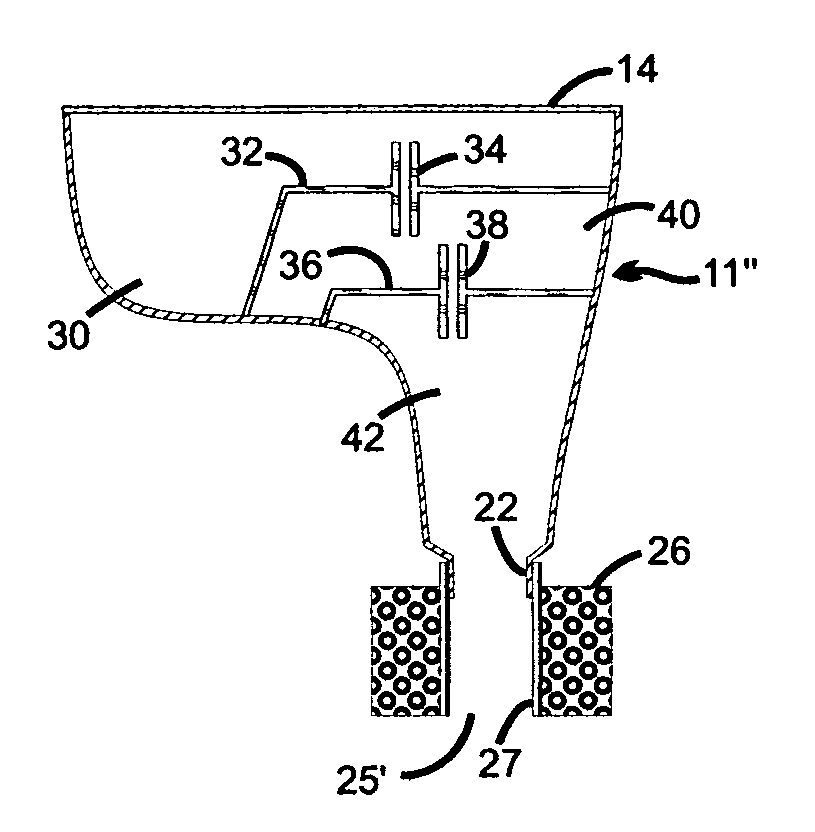
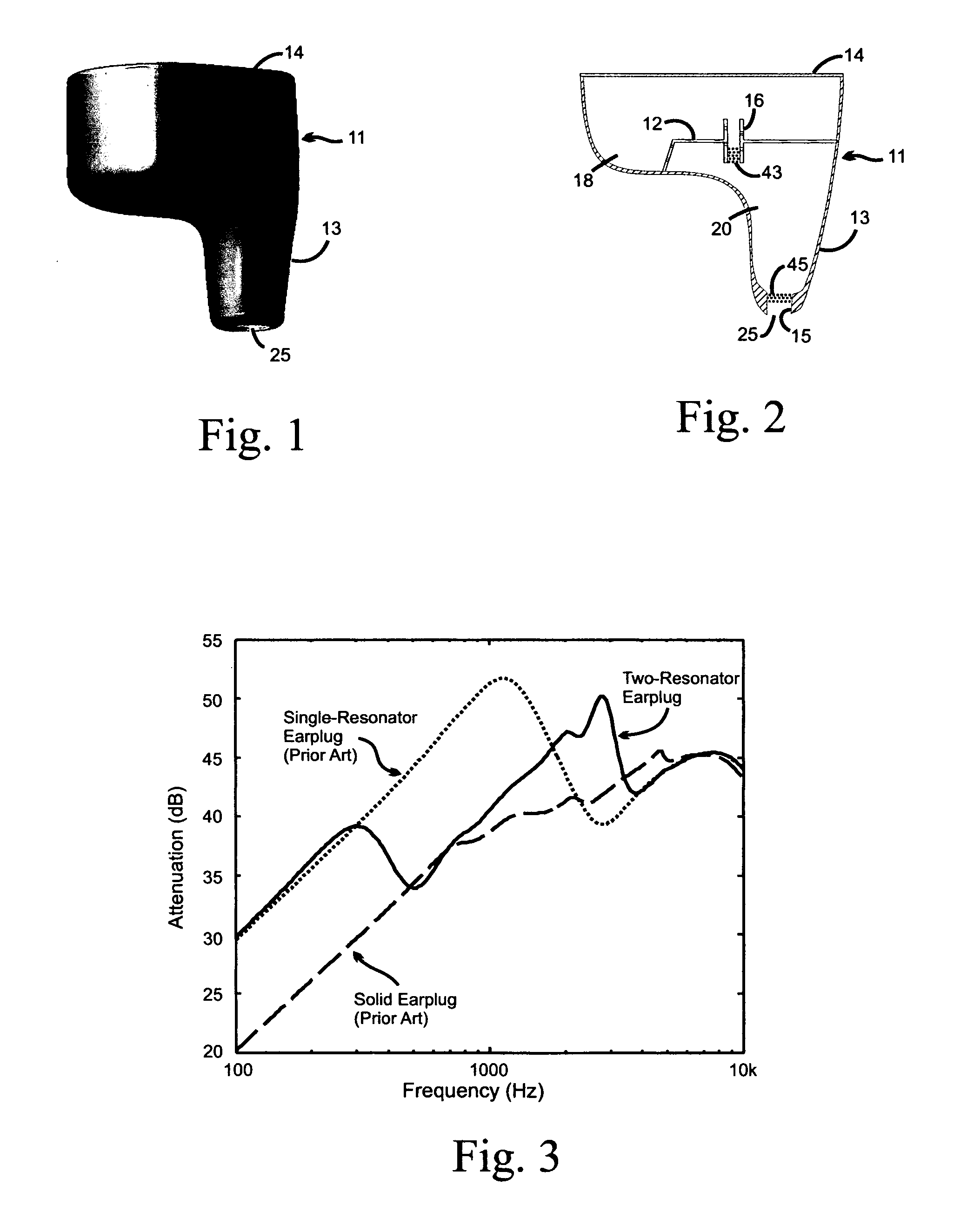
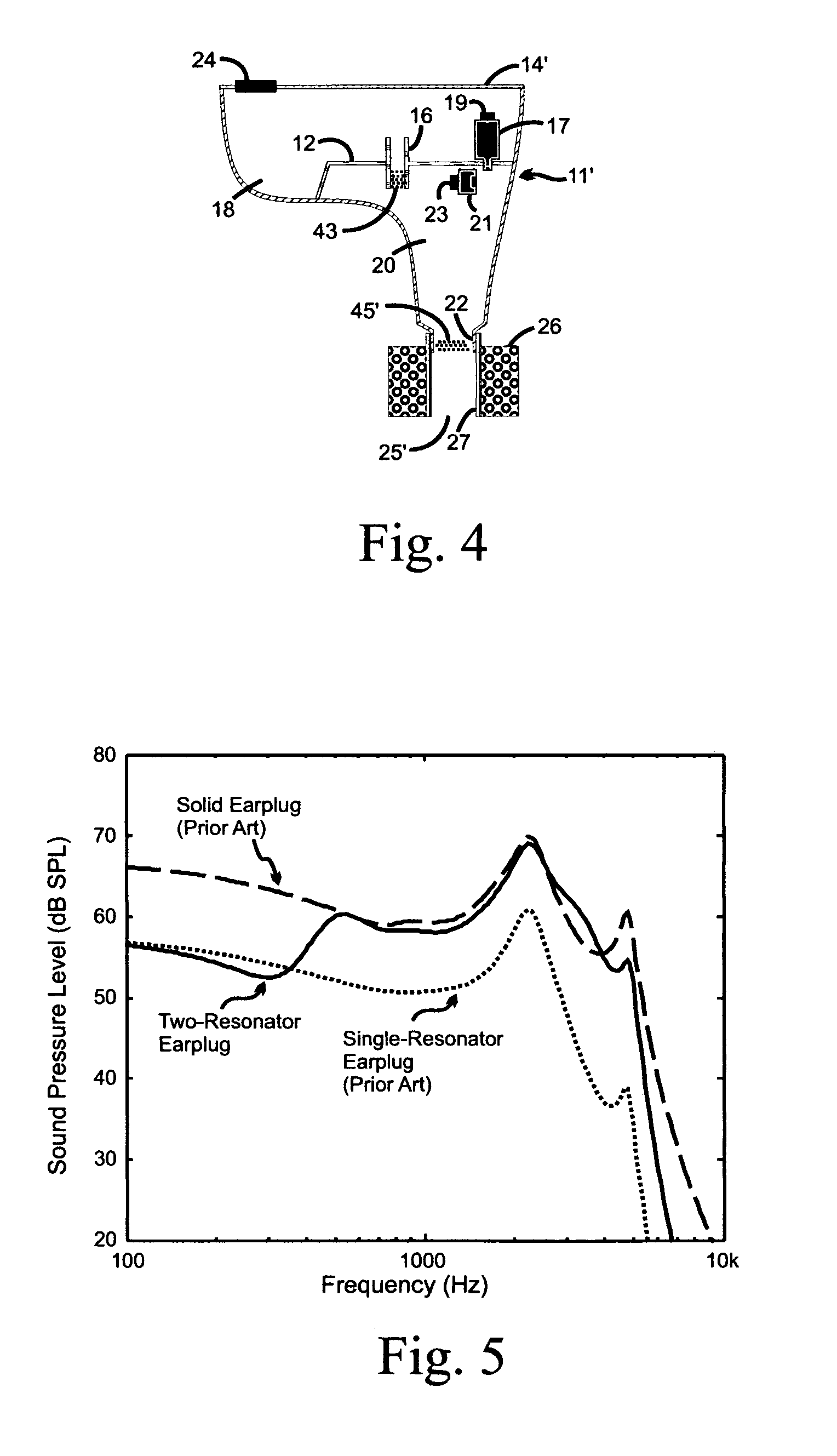
Multiple resonator attenuating earplug
InactiveUS7740104B1Enhances high-frequency communication responseEar supported setsStethoscopeNoise controlFrequency spectrum
A non-vented shell earplug for insertion into the ear canal has multiple chambers configured as coupled acoustic resonators. Each chamber is provided with an acoustic element having inertia and resistance coupling the chamber to its neighbor to form multiple resonant chambers. The dimensions of the individual acoustic elements set the frequency response of the earplug, and determine the attenuation characteristics of the resonators. Unlike the single chamber resonator of the prior art, the multiple-resonator earplug provides attenuation in both low and high frequency segments of the noise spectrum.Additionally, the present invention teaches placing loudspeaker and / or sound sensing transducer for sound communication purposes and active noise control within the earplug, with their sound field patterns directed into a chamber for coupling to the ear canal. The use of multiple resonators enhances the high frequency communications response of the earplug.
Owner:RED TAIL HAWK CORP
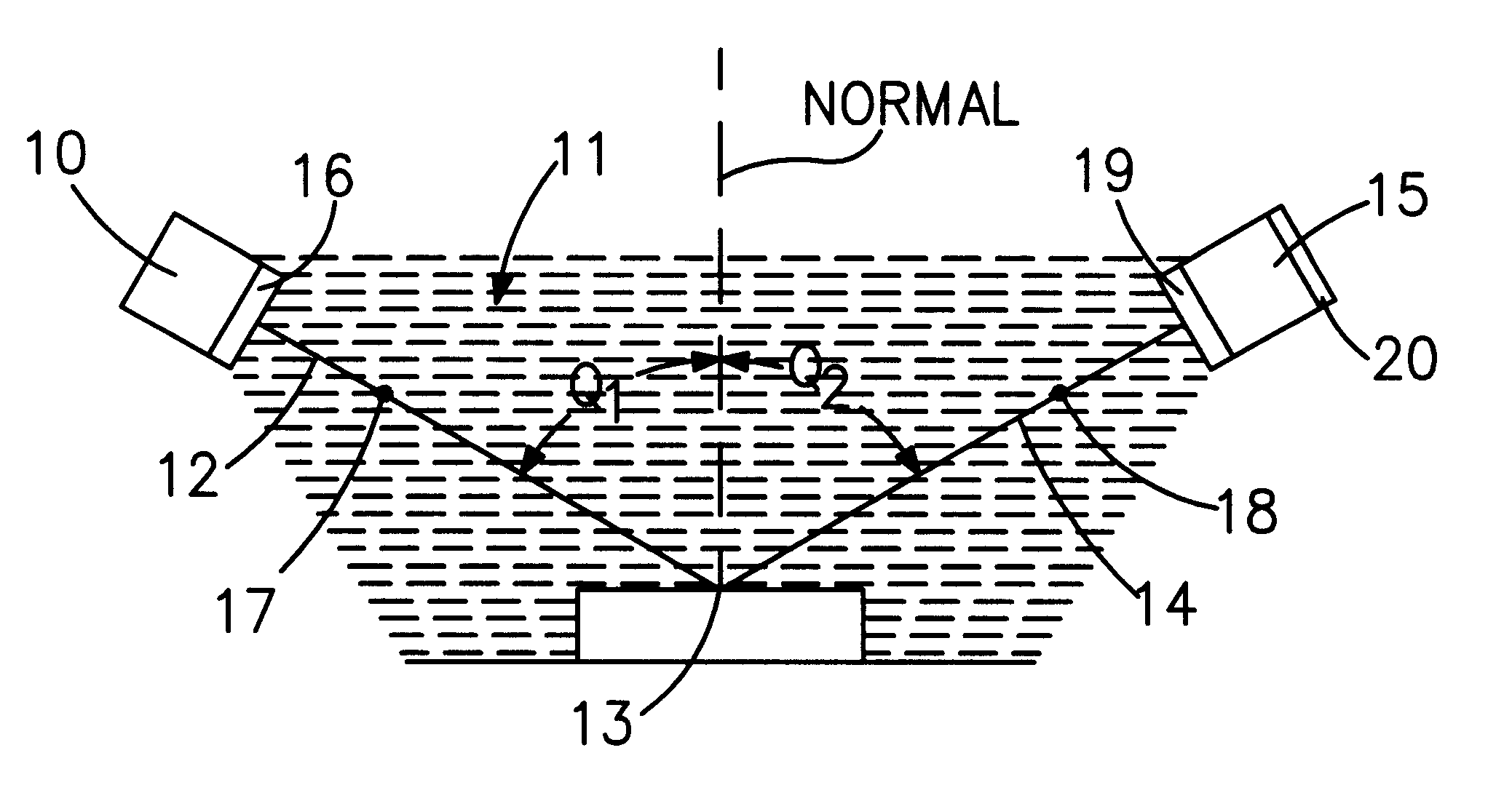
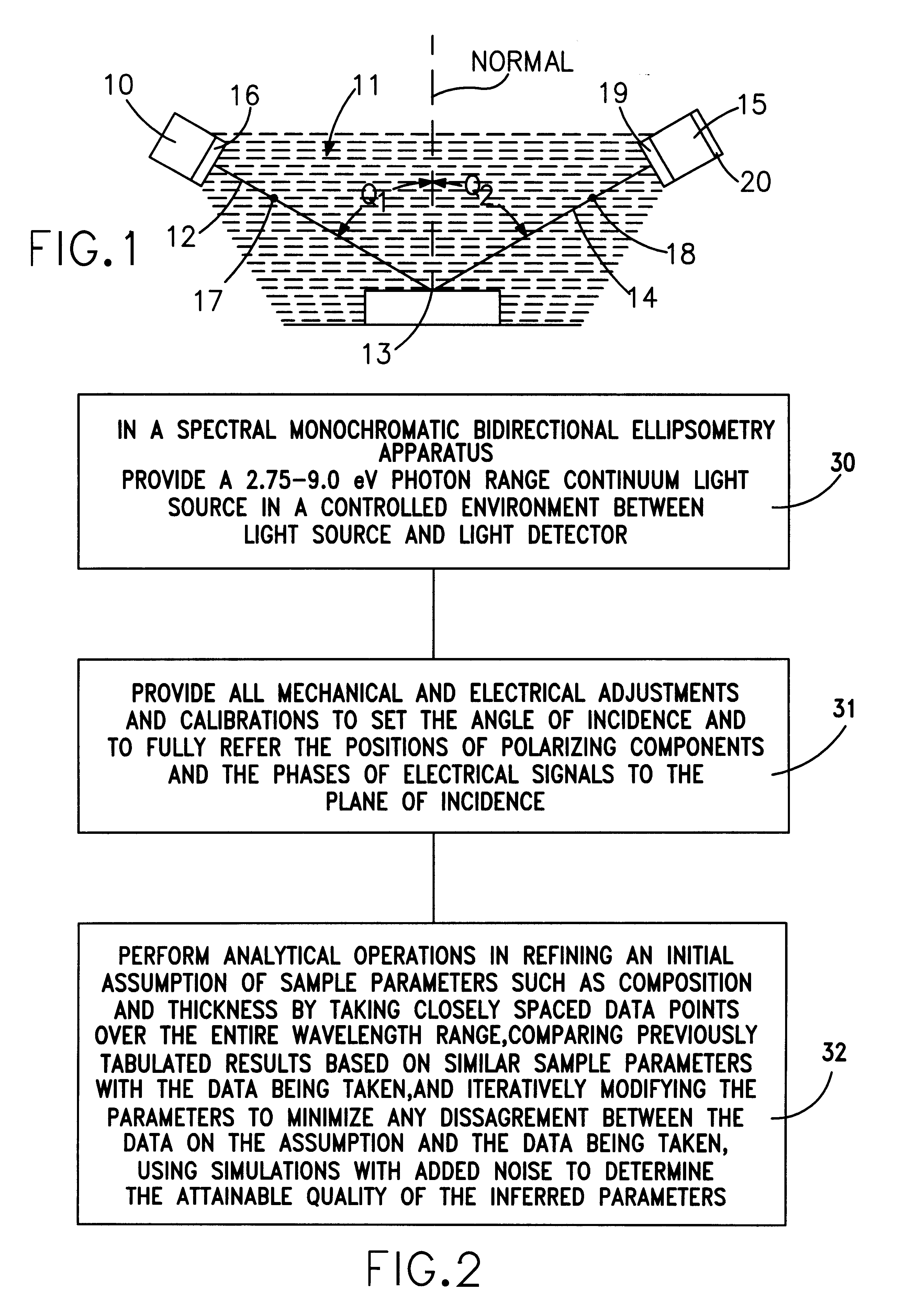
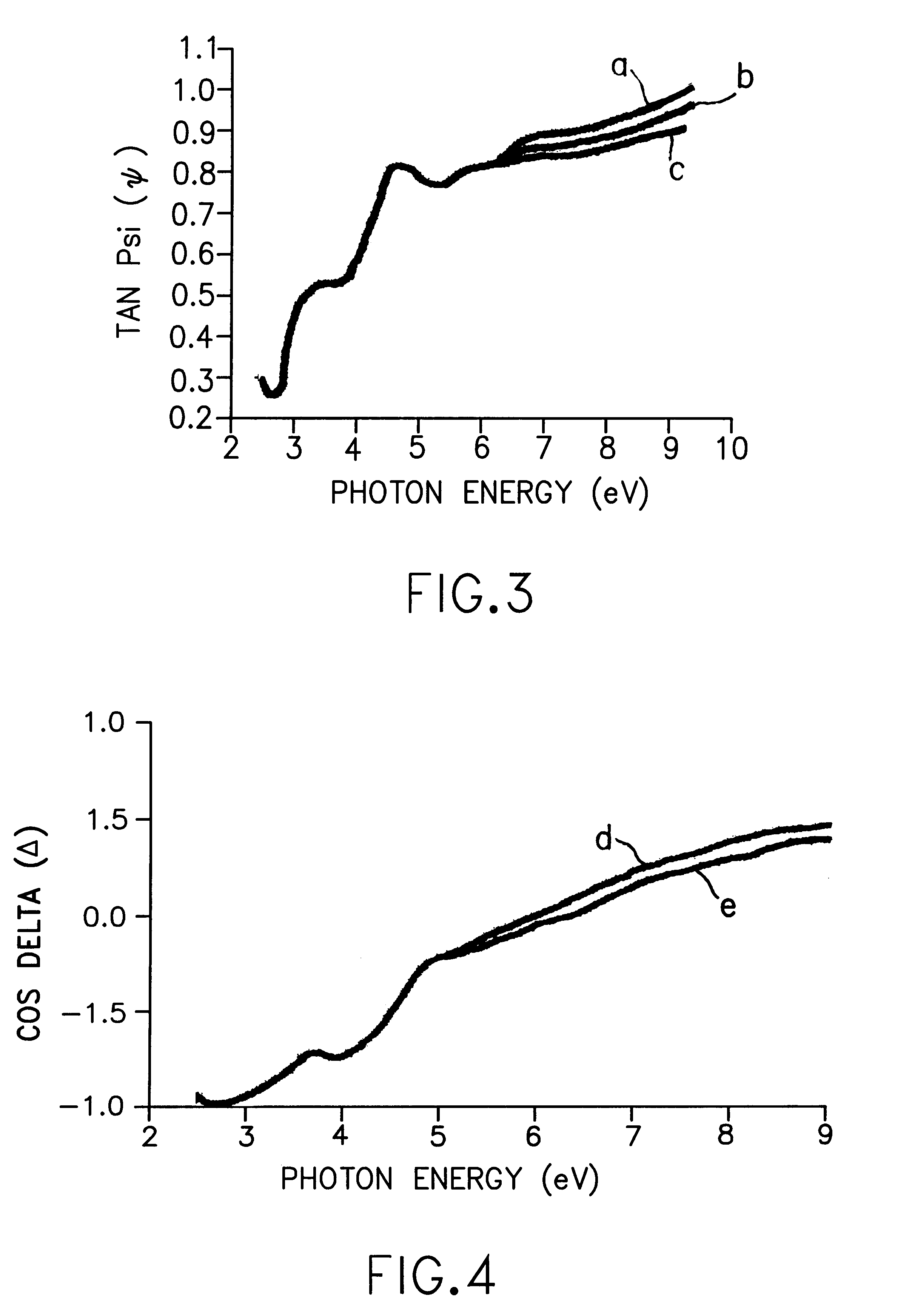
Ultrathin layer measurement having a controlled ambient of light path
InactiveUS6222199B1Polarisation-affecting propertiesInvestigating moving sheetsMetrologyFrequency spectrum
Metrology for ultrathin dielectric layers of the order of less than 10 nanometers in thickness is achieved by specular ellipsometry in a totally controlled ambient between the light source and the detector, in which, a precise 2.75 through 9.0 eV photon energy range continuum of light is employed. In the signal analysis there is the taking into consideration the effect of noise in the development of the ellipsometric parameter values and in the resulting data. In the invention the precise photon energy range operates to sharpen the identifiability of the change parameters imparted into the reflected light in the ellipsometry while minimizing absorption and signal definiteness masking; and the taking into consideration of noise in the signal analysis involves providing a simulated noise spectrum for comparison with the least squares fitting algorithm-derived parameters to determine the quality of the minimum and the reliability of the inferred parameters.
Owner:JORDAN VALLEY SEMICON
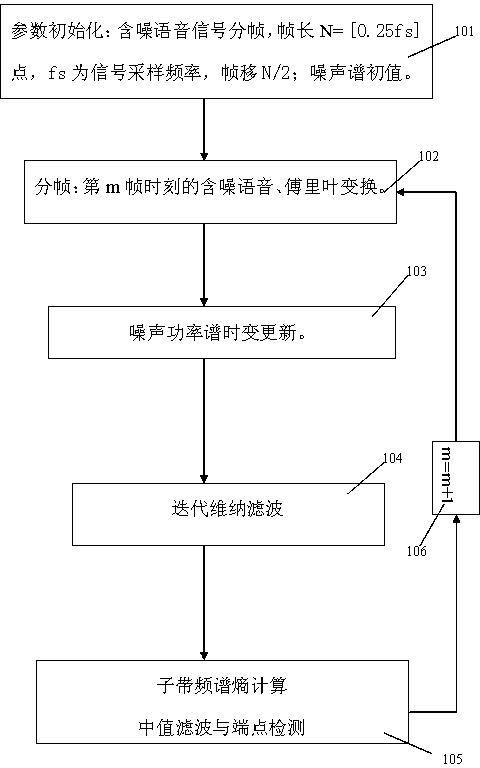
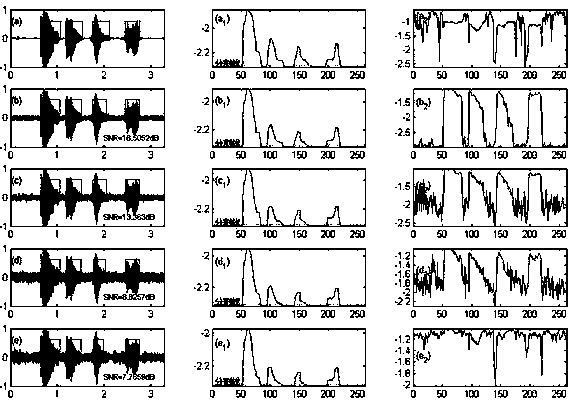
Noised voice end point robustness detection method
InactiveCN105023572AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSimple calculationSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
The invention discloses a noised voice end point robustness detection method. The method comprises the following steps of constructing an estimation method of a noise power spectrum of each frame of acoustical signals in filtering and providing a time-varying updating mechanism of a noise spectrum; firstly, carrying out iterative wiener filtering on a frequency spectrum of each frame of voices; then, dividing into several sub-band and calculating a frequency spectrum entropy of each sub-band; and then making successive several frames of sub-band frequency spectrum entropies pass through one group of median filters so as to acquire each frame of the frequency spectrum entropies; according to values of the frequency spectrum entropies, classifying input voices. By using the algorithm, the voices and noises, and a voice state and a voiceless state can be effectively distinguished. Under different noise environment conditions, robustness is possessed. The algorithm has low calculating cost, is simple, is easy to realize and is suitable for application of real-time voice signal processing system of various kinds of systems needing voice end point detection. The method is a real-time voice end points detection algorithm which adapts to a complex environment, and voice end point detection and voice filtering enhancement are completed together in a one-time state.
Owner:王景芳
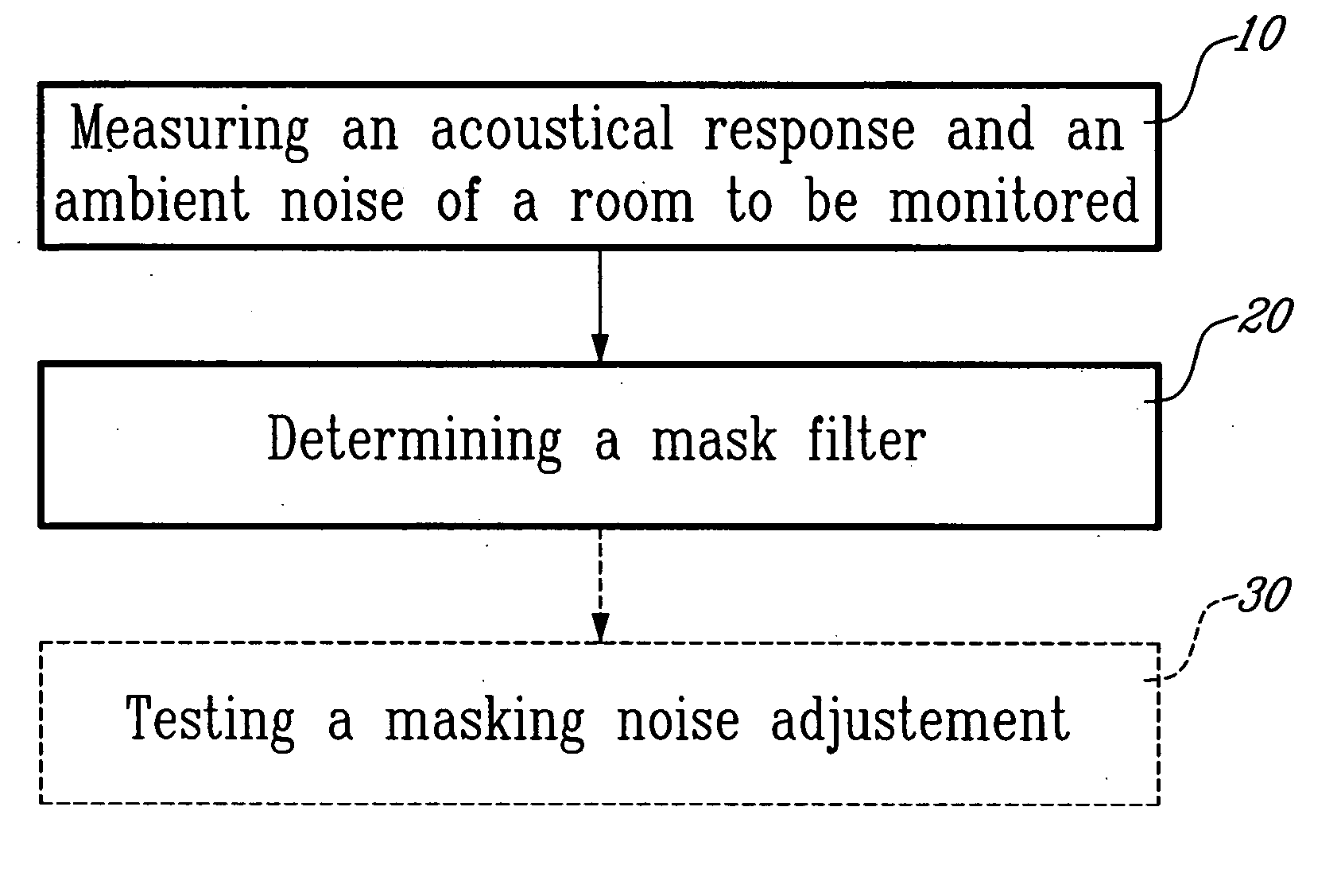
Auto-adjusting sound masking system and method
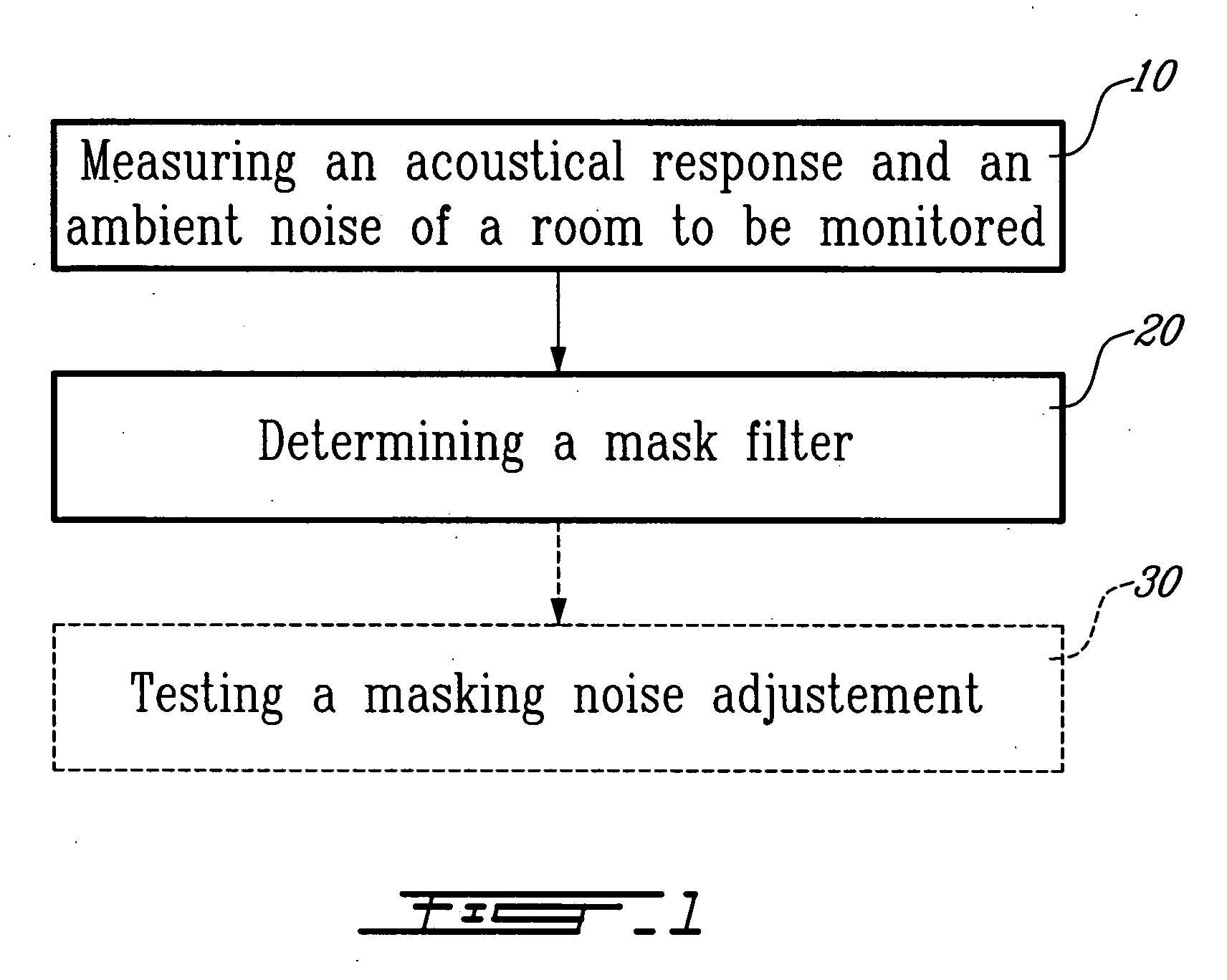
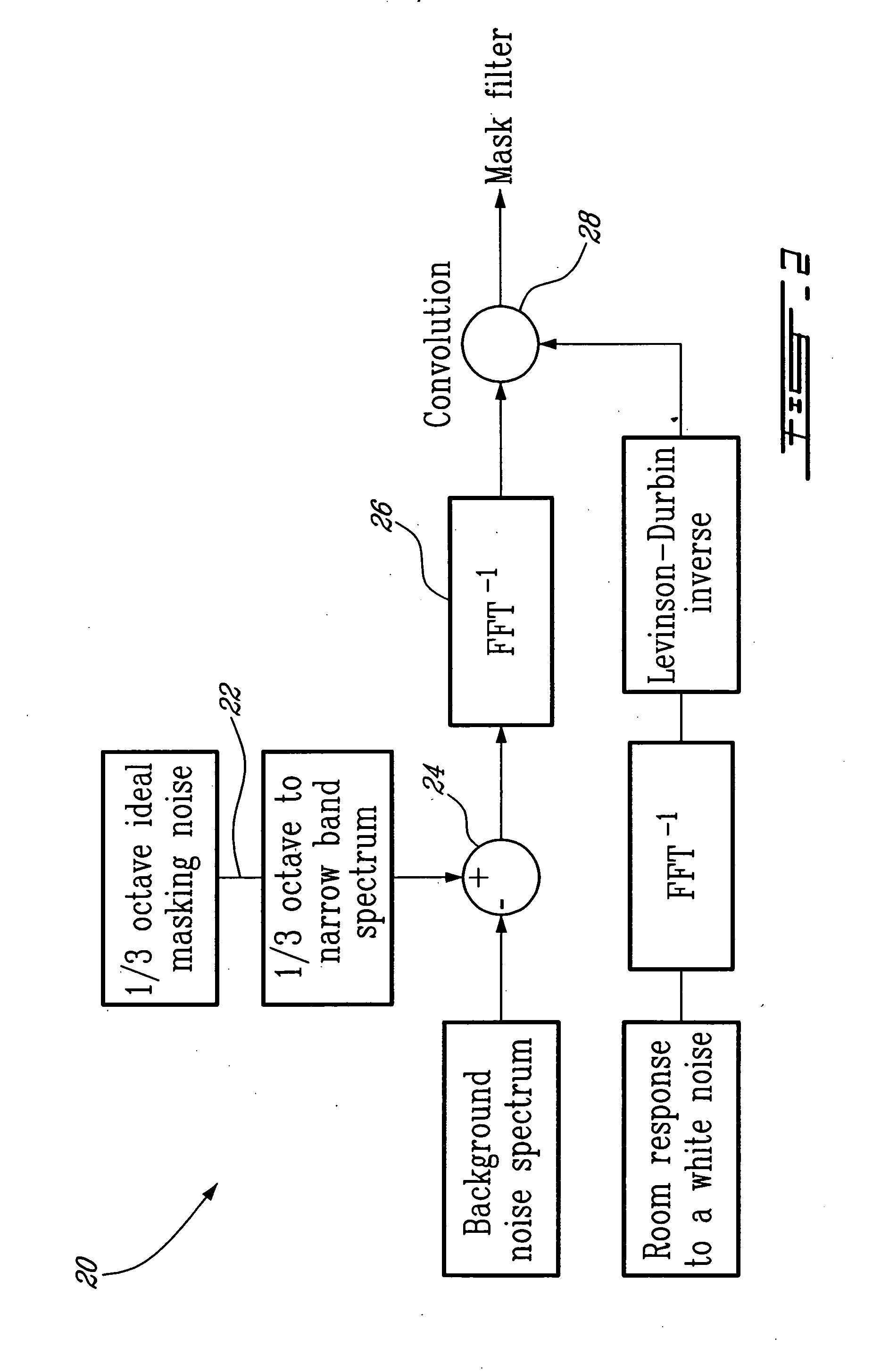
A system and method for generating a masking noise level and spectrum automatically adjusted to obtain a target masking noise spectrum in a room. The system comprises a white noise generator and a mask filter automatically determined according to a correction of an acoustical response of the room and to the target masking noise corrected by an ambient noise.
Owner:SOFT DB
Asymmetrical Interleaving Strategy for Multi-Channel Power Converters
InactiveUS20080239771A1Low costSmall sizeAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFrequency spectrumPhase shifted
In a power converter having m=two or more channels of power factor correction (PFC) circuits connected in parallel and an electromagnetic interference (EMI) filter connected in series therewith, phase shifts in switching between the respective PFC channels can allow increase of EMI filter corner frequency allowing reduction of size and cost of the EMI filter at some switching frequencies. Asymmetrical phase shifts (other than 360° / m) such as 360° / 2m and other phase shifts and variations in m allow increase of EMI filter corner frequency at switching frequencies where symmetrical, 360° / m phase shifts provide no benefit to EMI filter design by providing cancellation or partial cancellation of different harmonics of the switching noise; which cancellation may be arranged to be complementary to the EMI filter function at more than one peak of the noise spectrum. (Such asymmetrical phase shifts do not significantly increase ripple and consequent switching noise). Alteration of m and corresponding alteration of phase shift may be performed adaptively for purposes of improving efficiency at light loads and the like.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
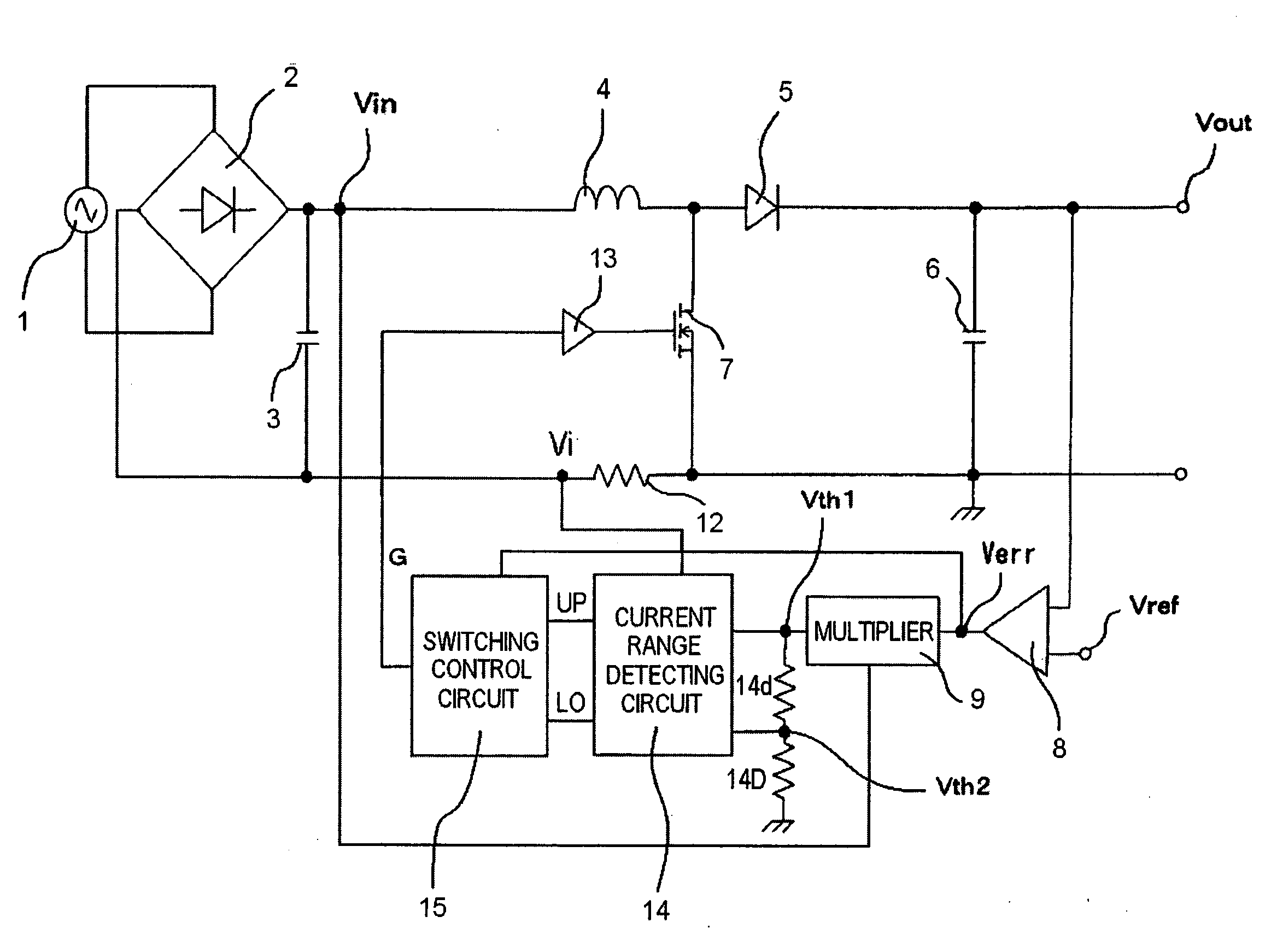
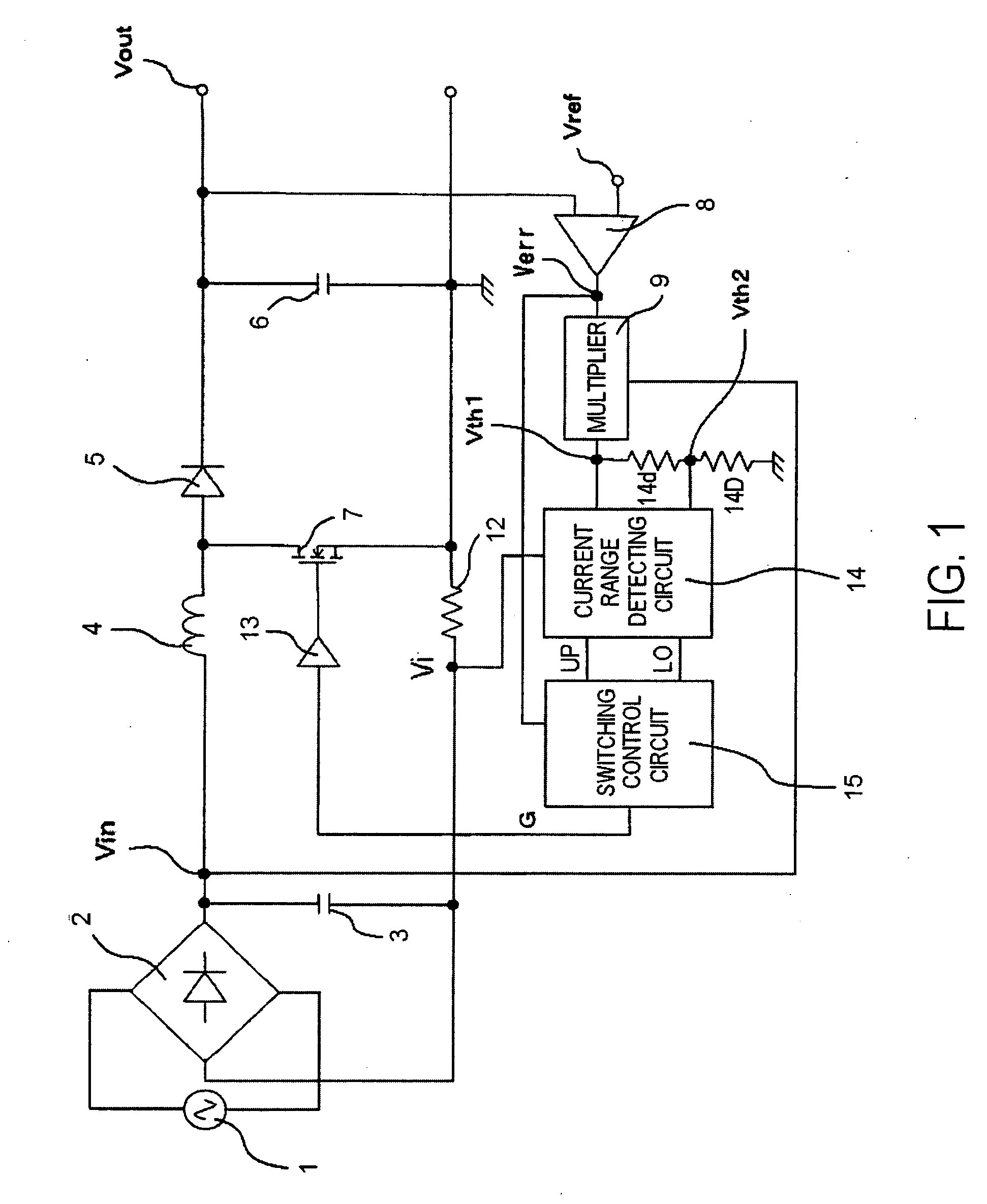
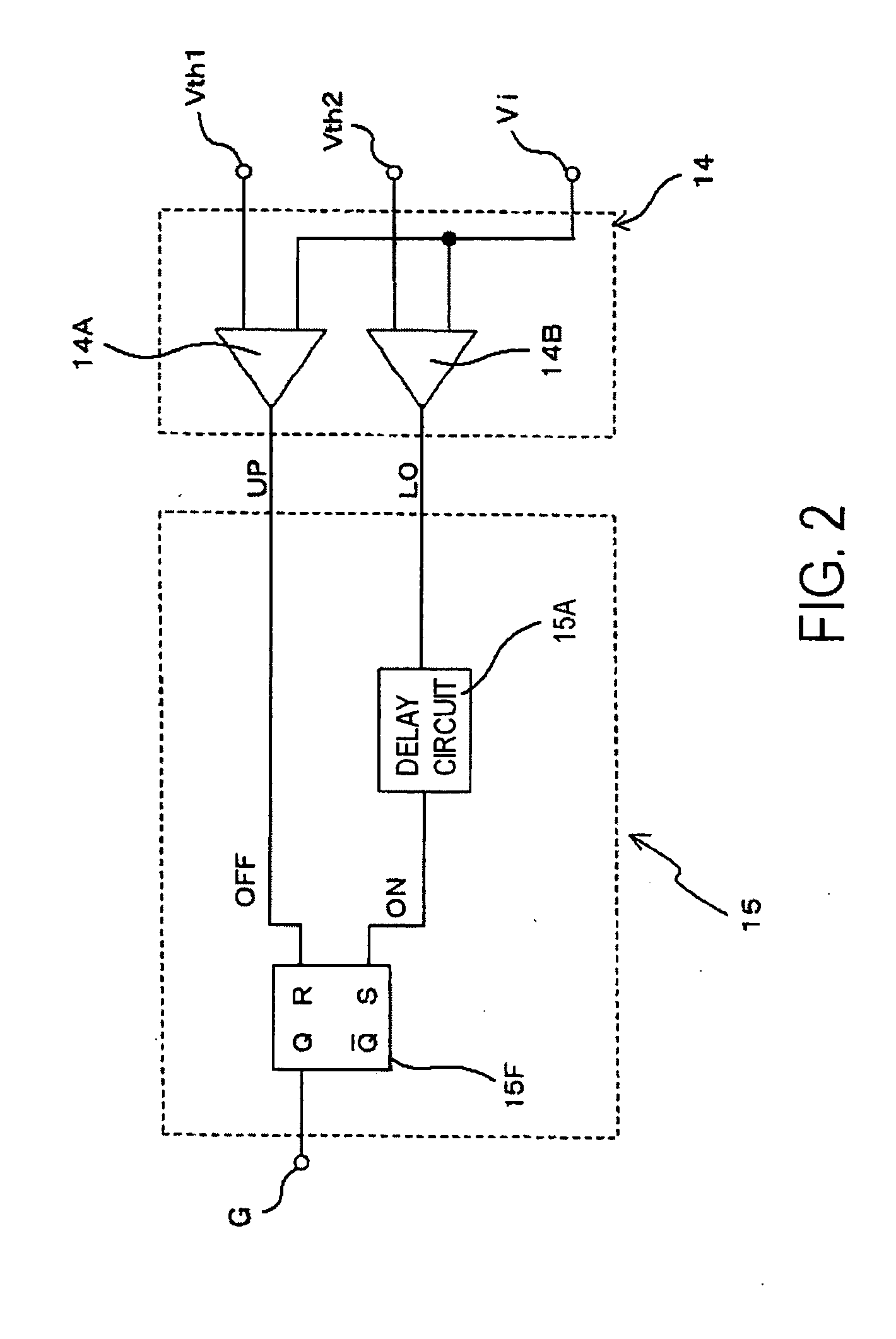
Switching power source system
ActiveUS20090303765A1Improve power factorReduce high frequency noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFrequency spectrumCurrent range
An error voltage Verr, being a difference between DC output voltage Vout and output reference voltage Vref, and an input voltage Vin are multiplied to produce first threshold voltage signal Vth1 in phase with and similar to input voltage Vin and proportional to Verr. Second threshold voltage signal Vth2 is produced from first threshold voltage signal Vth1. The input current is detected as a current detection signal Vi across a resistor 12, whether it is between the threshold value signals is detected by a current range detecting circuit, and accordingly, the timing of turning on or off switching device is controlled so that at least one of an duration on and an off duration of the switching device is limited to enhance a power factor. Unfixed off duration disperses a noise spectrum to prevent an increase in switching frequency, to reduce noise.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com