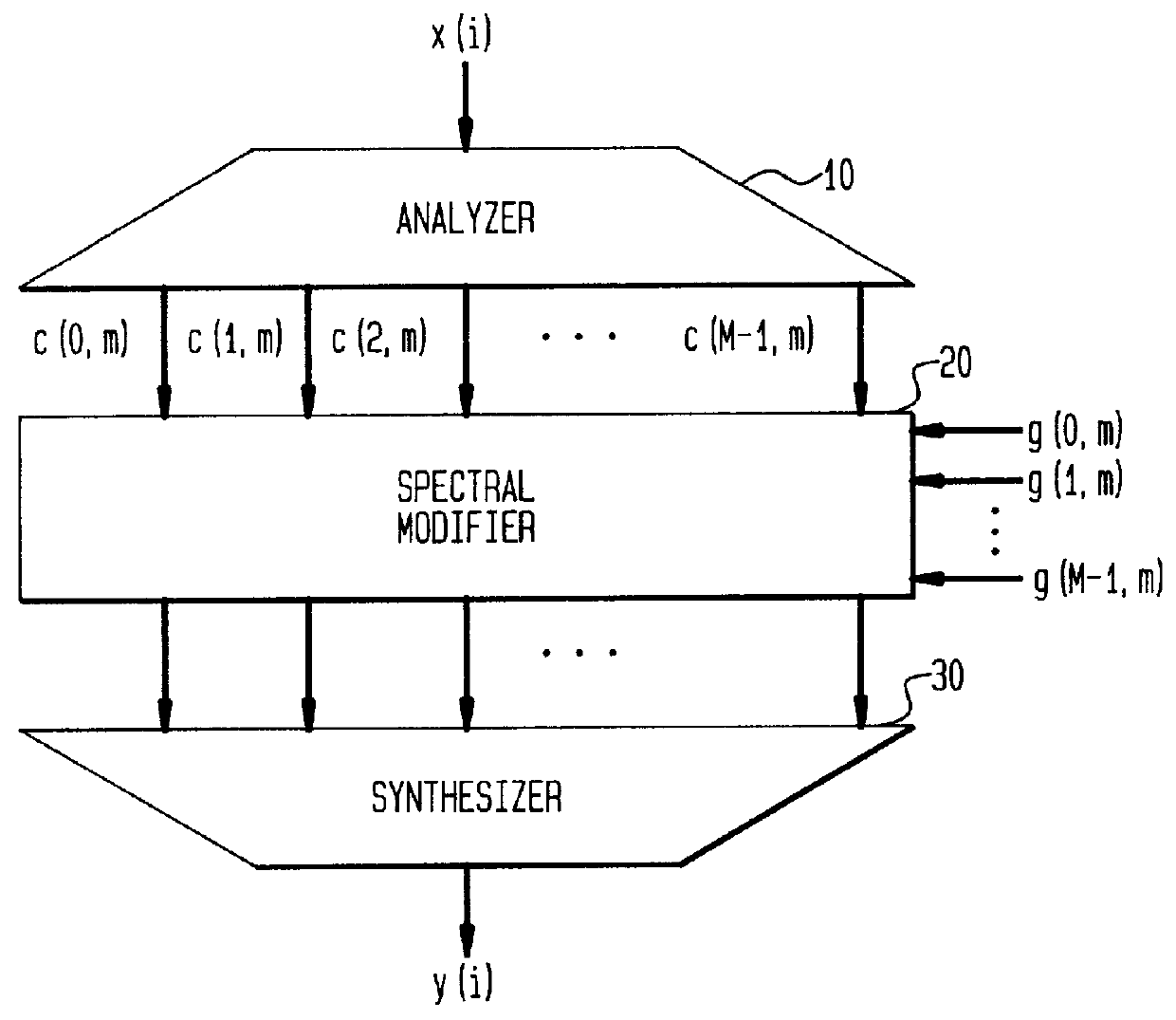
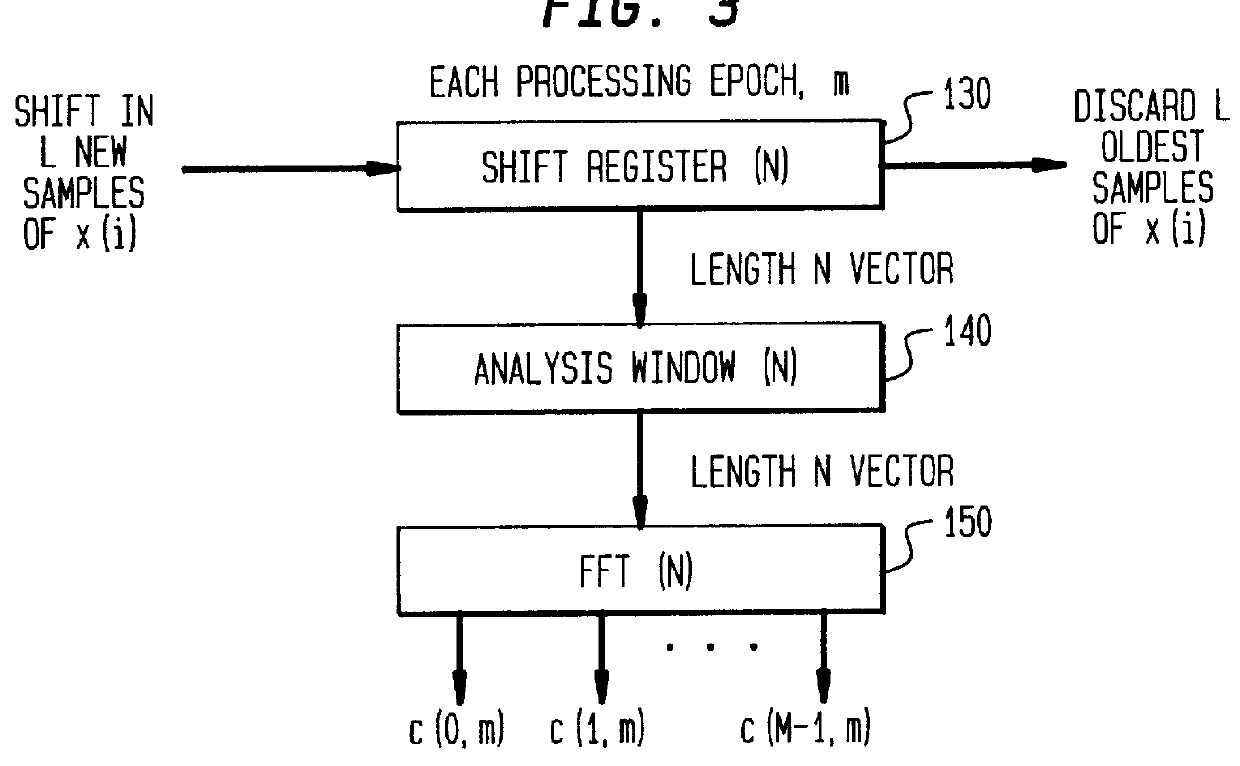
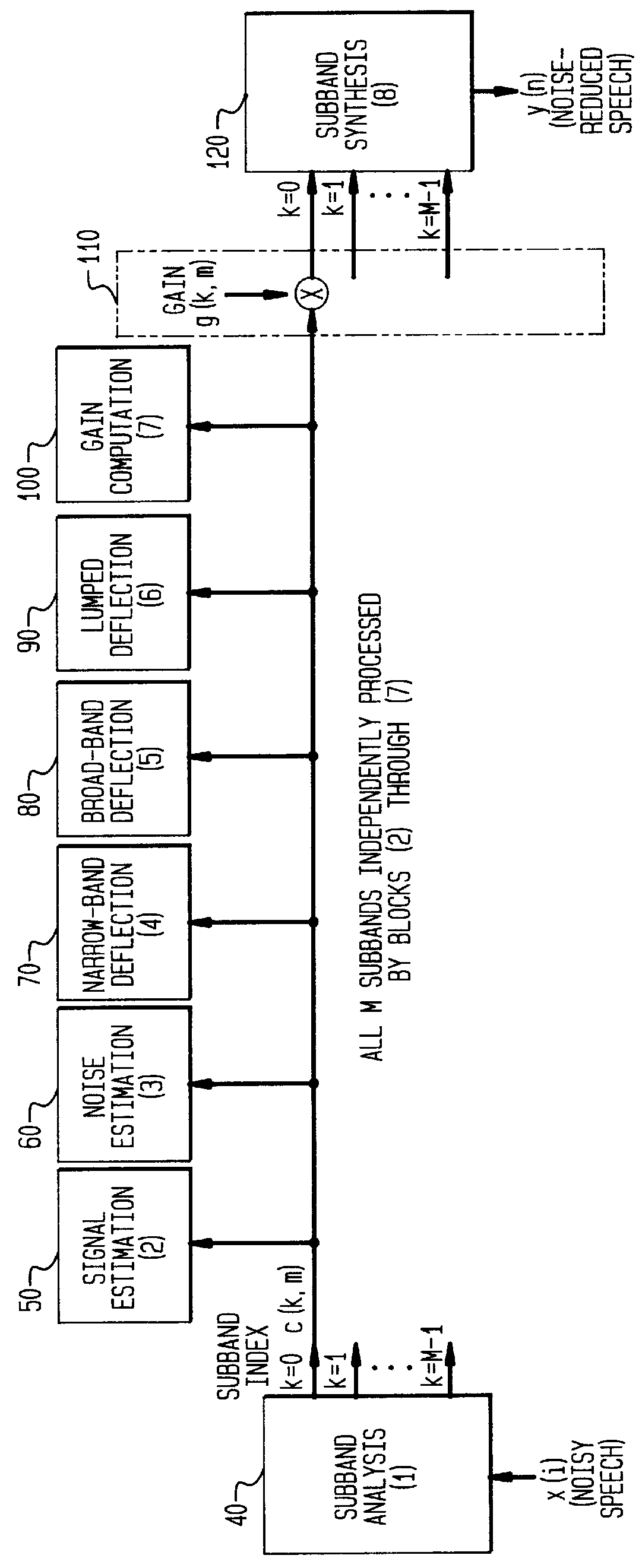
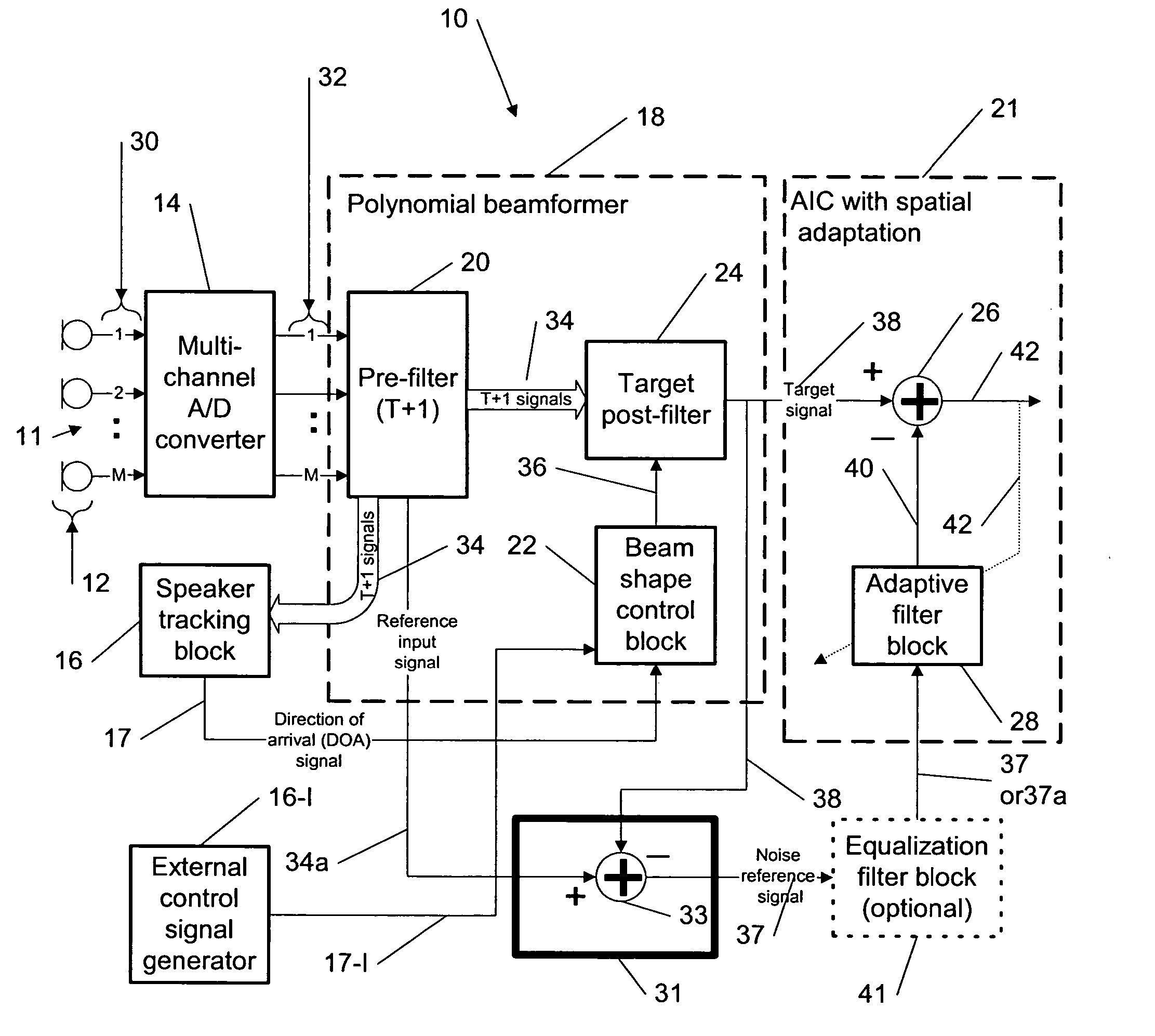
Patents
Literature
997 results about "Noise estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
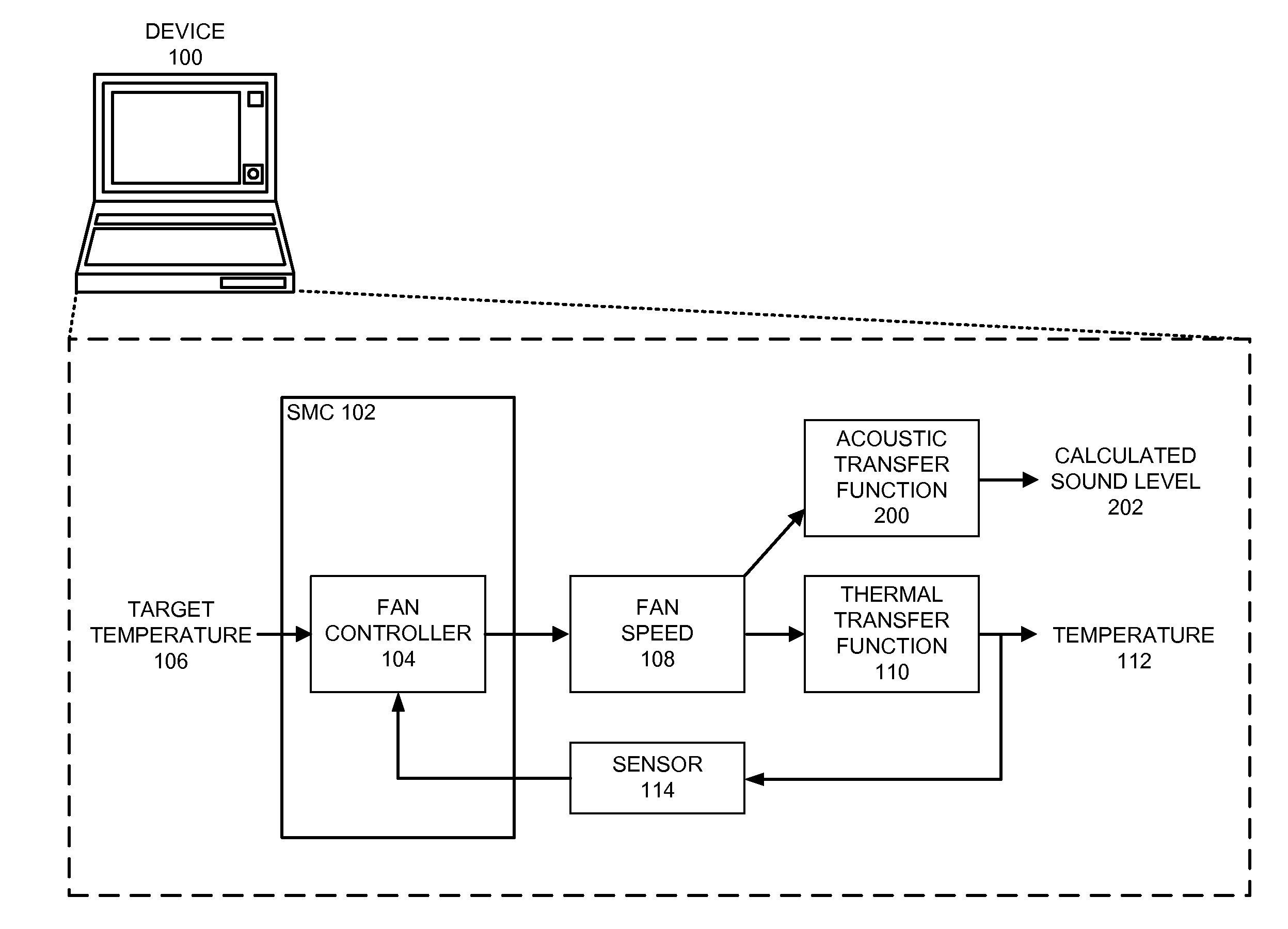
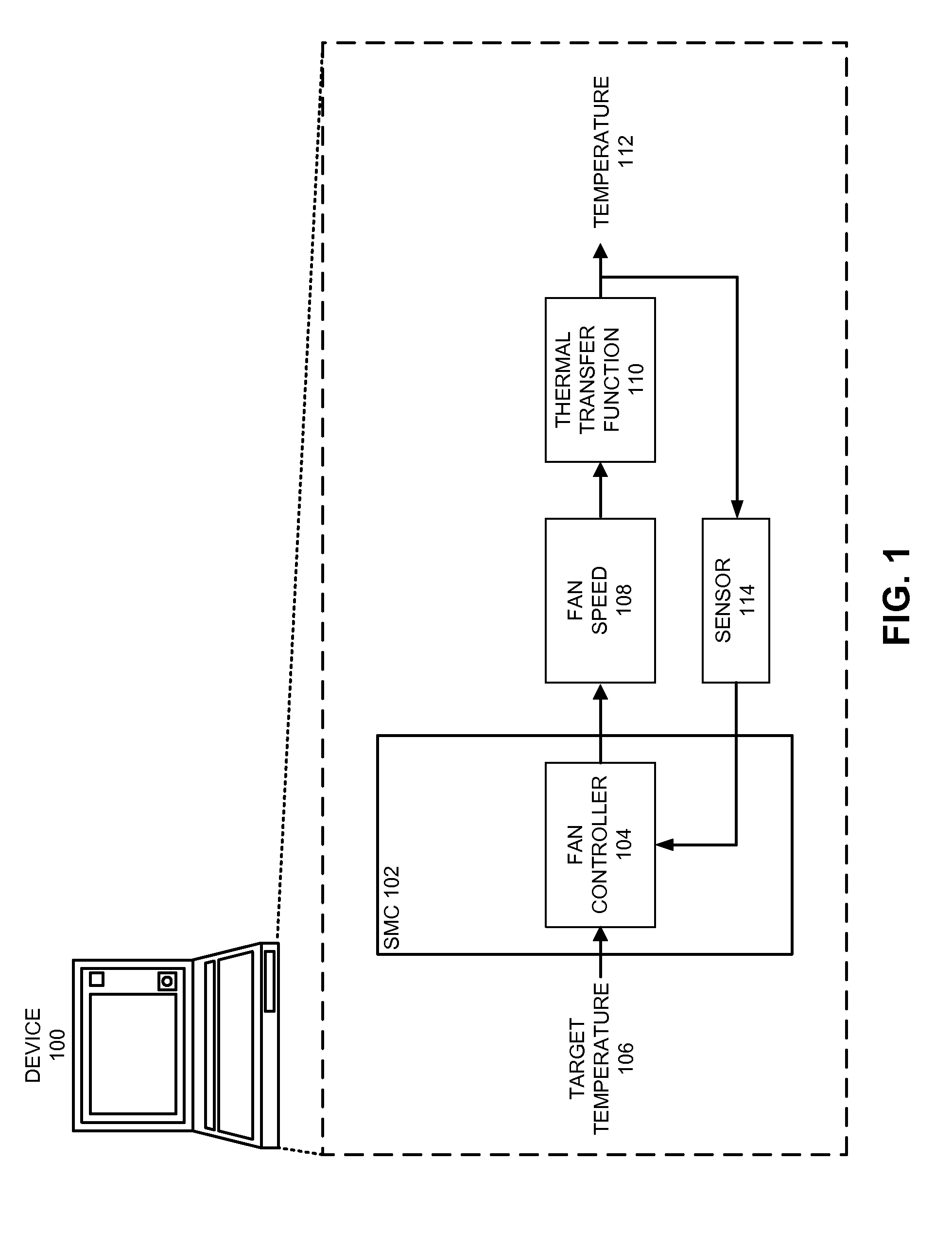
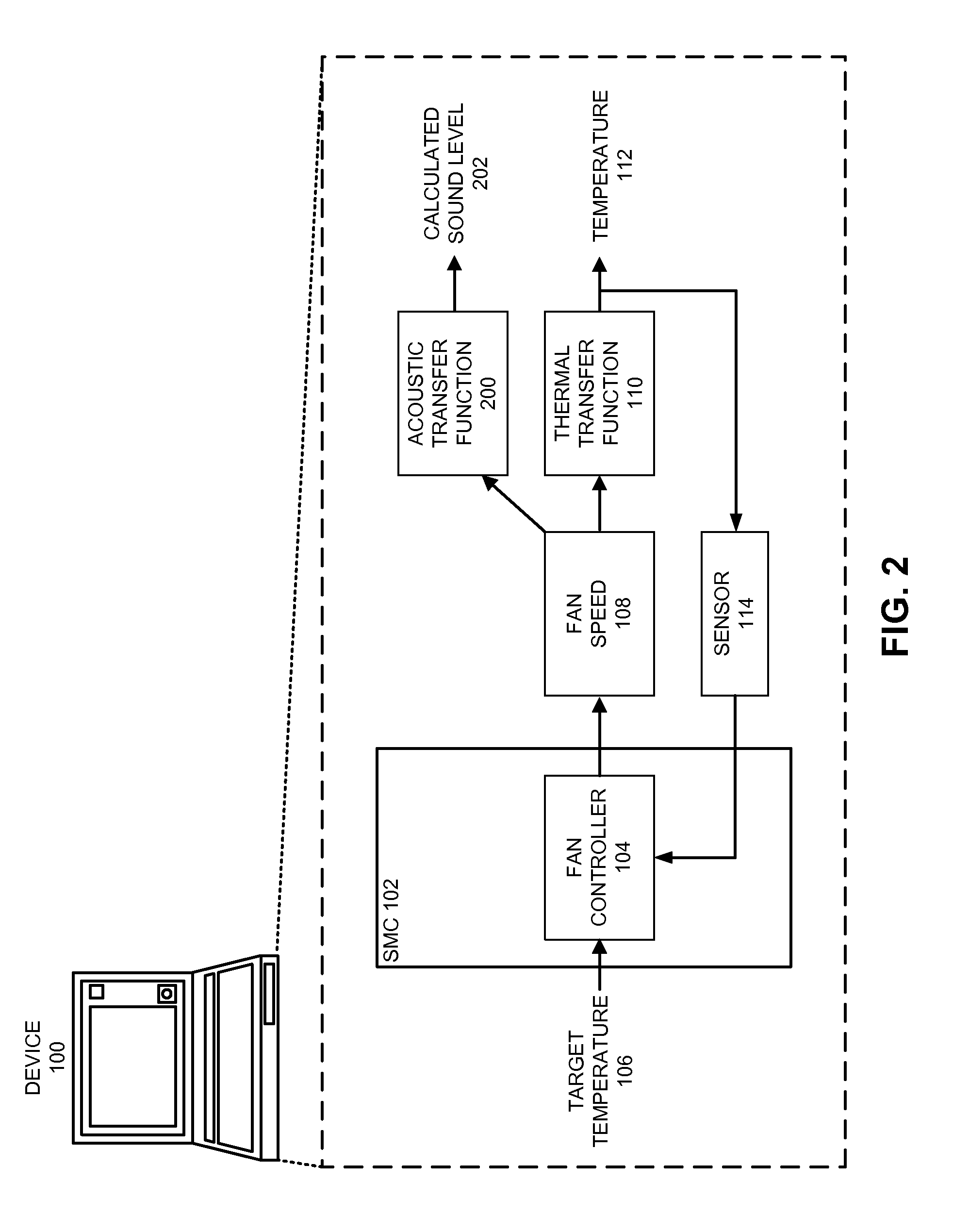
Reducing annoyance by managing the acoustic noise produced by a device
ActiveUS20090092261A1Less worryReduce user annoyanceEnergy efficient ICTEar treatmentAcousticsNoise estimation
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces annoyance by managing the acoustic noise produced by a device. During operation, the system receives a set of acoustic characteristics for noise-producing components within the device. The system then uses these acoustic characteristics to estimate the acoustic noise being generated by each of these noise-producing components. Next, the system aggregates this set of acoustic noise estimates to produce an aggregate estimate for the acoustic noise produced by the device. The system then analyzes this aggregate estimate using an acoustic annoyance model to determine the acoustic annoyance level. The system then adjusts a setting in the device to manage the acoustic annoyance level produced by the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
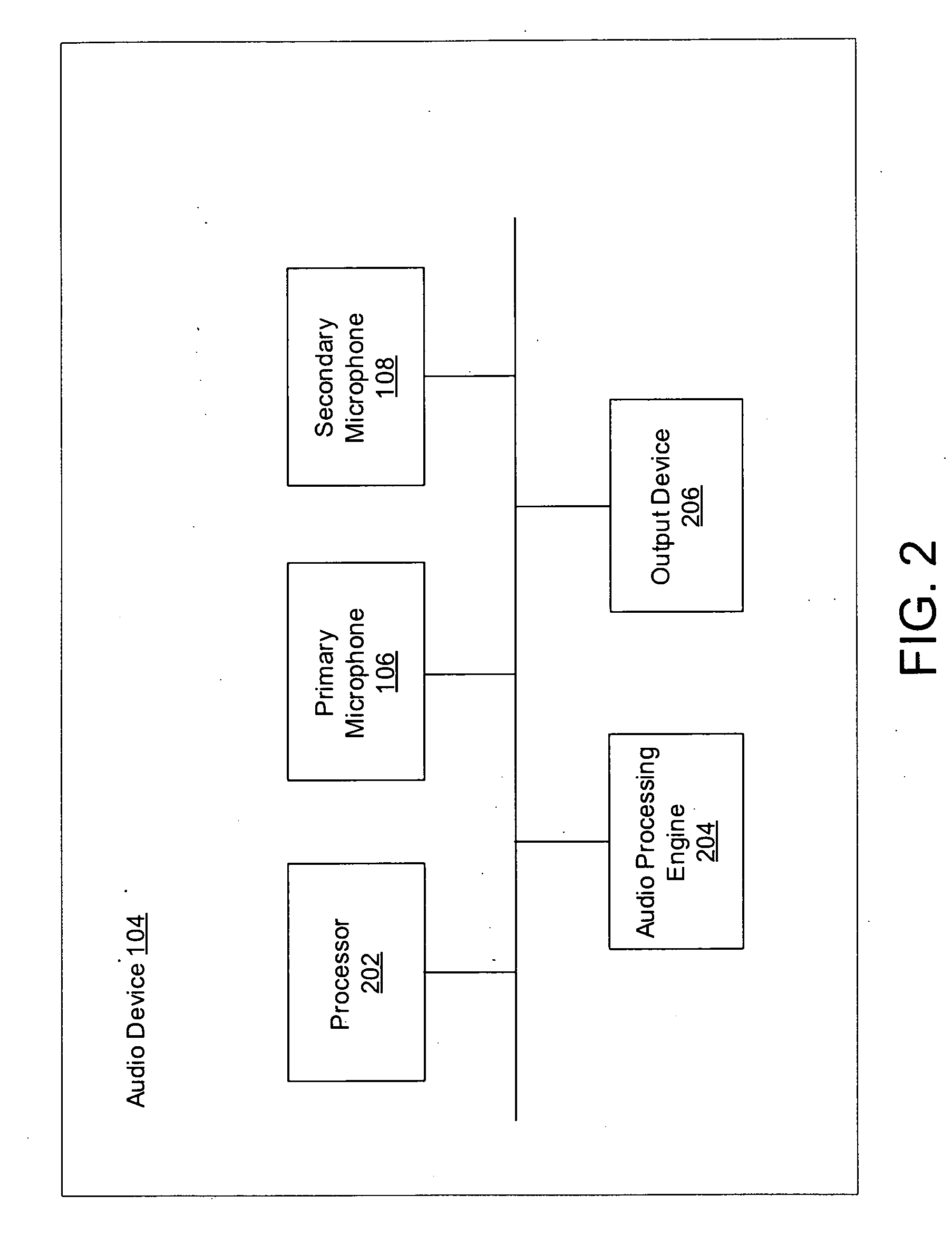
System and method for providing single microphone noise suppression fallback
Systems and methods for providing single microphone noise suppression fallback are provided. In exemplary embodiments, primary and secondary acoustic signals are received. A single microphone noise estimate may be generated based on the primary acoustic signal, while a dual microphone noise estimate may be generated based on the primary and secondary acoustic signals. A combined noise estimate based on the single and dual microphone noise estimates is then determined. Using the combined noise estimate, a gain mask may be generated and applied to the primary acoustic signal to generate a noise suppressed signal. Subsequently, the noise suppressed signal may be output.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
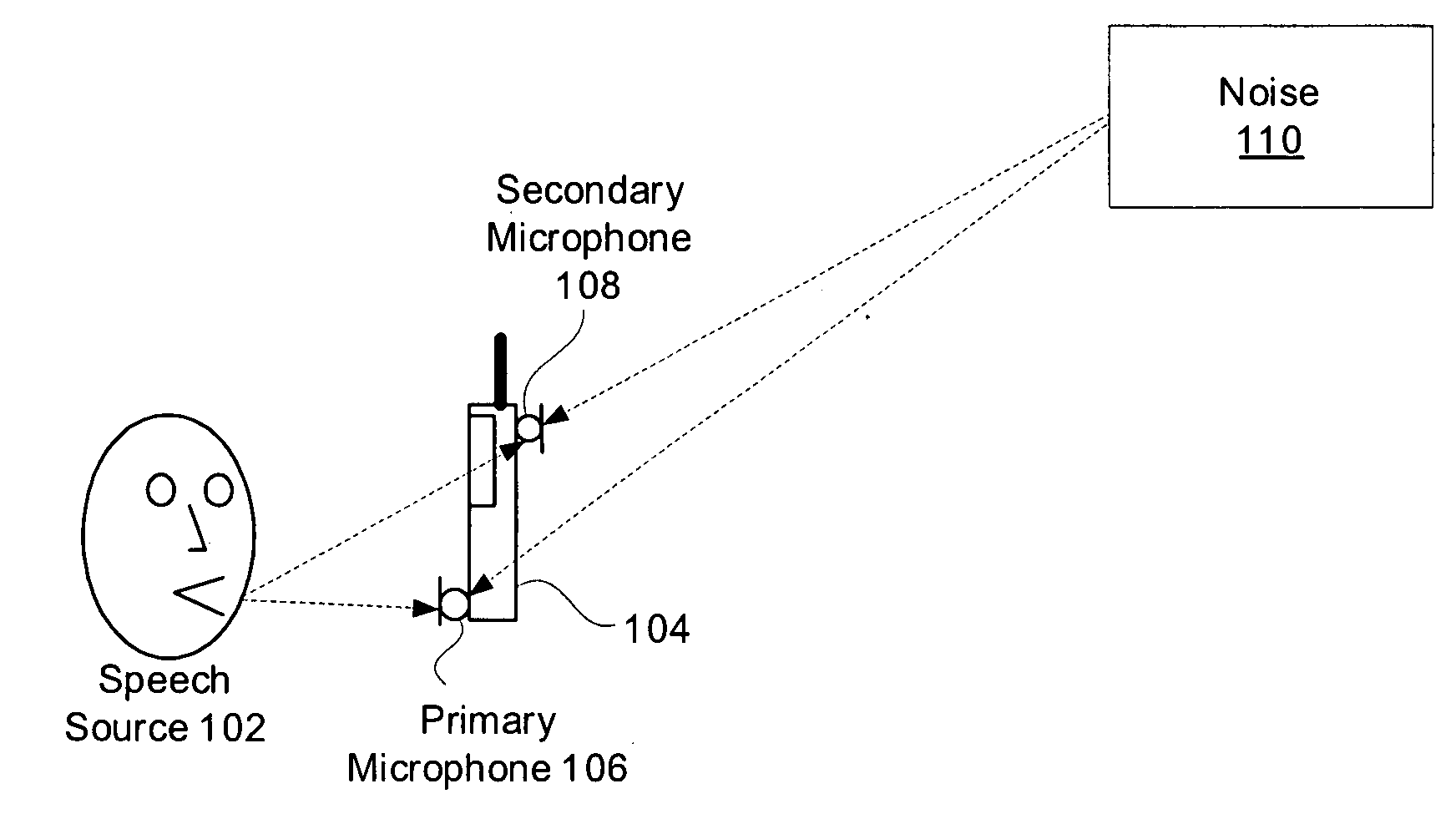
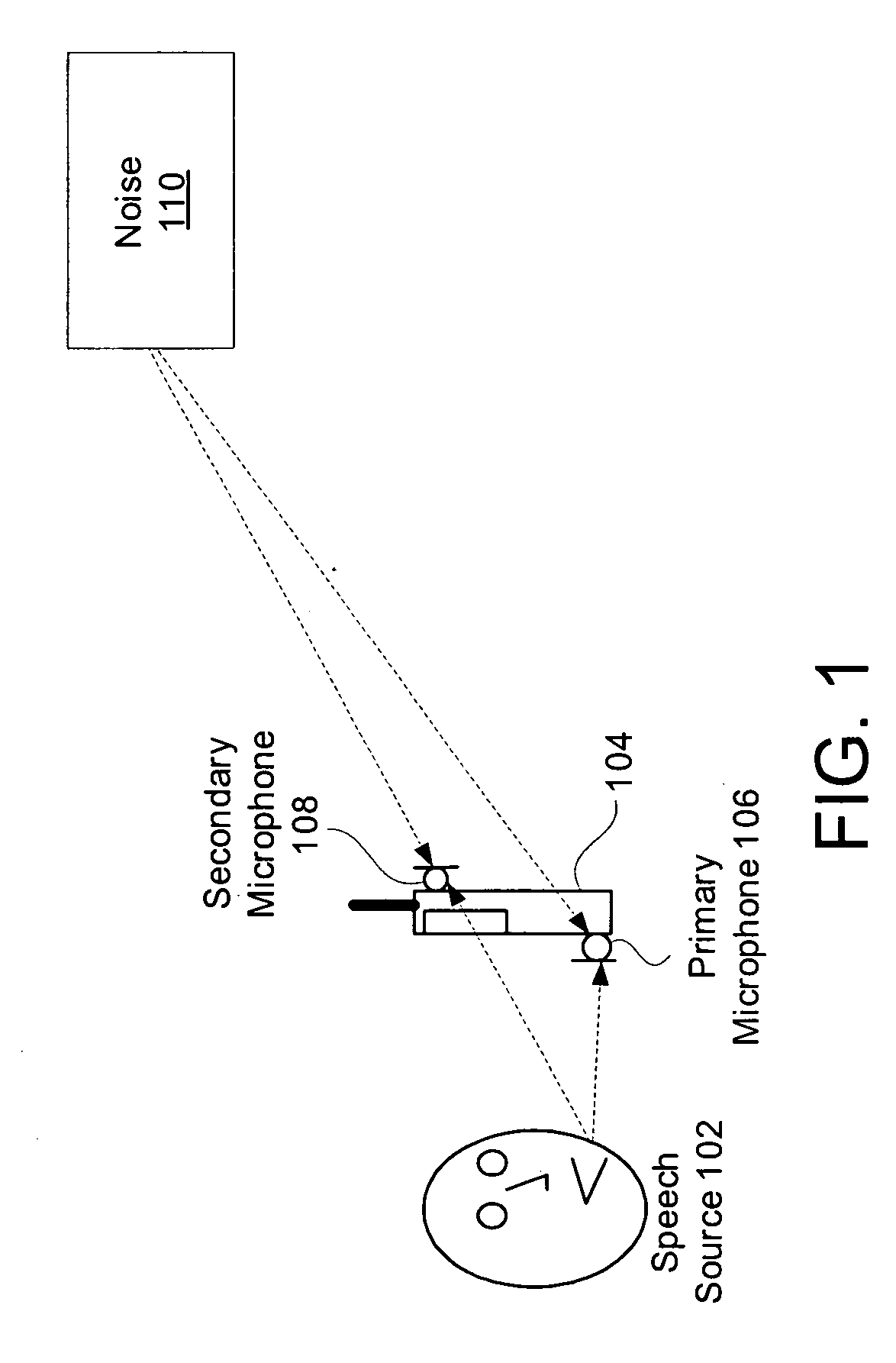
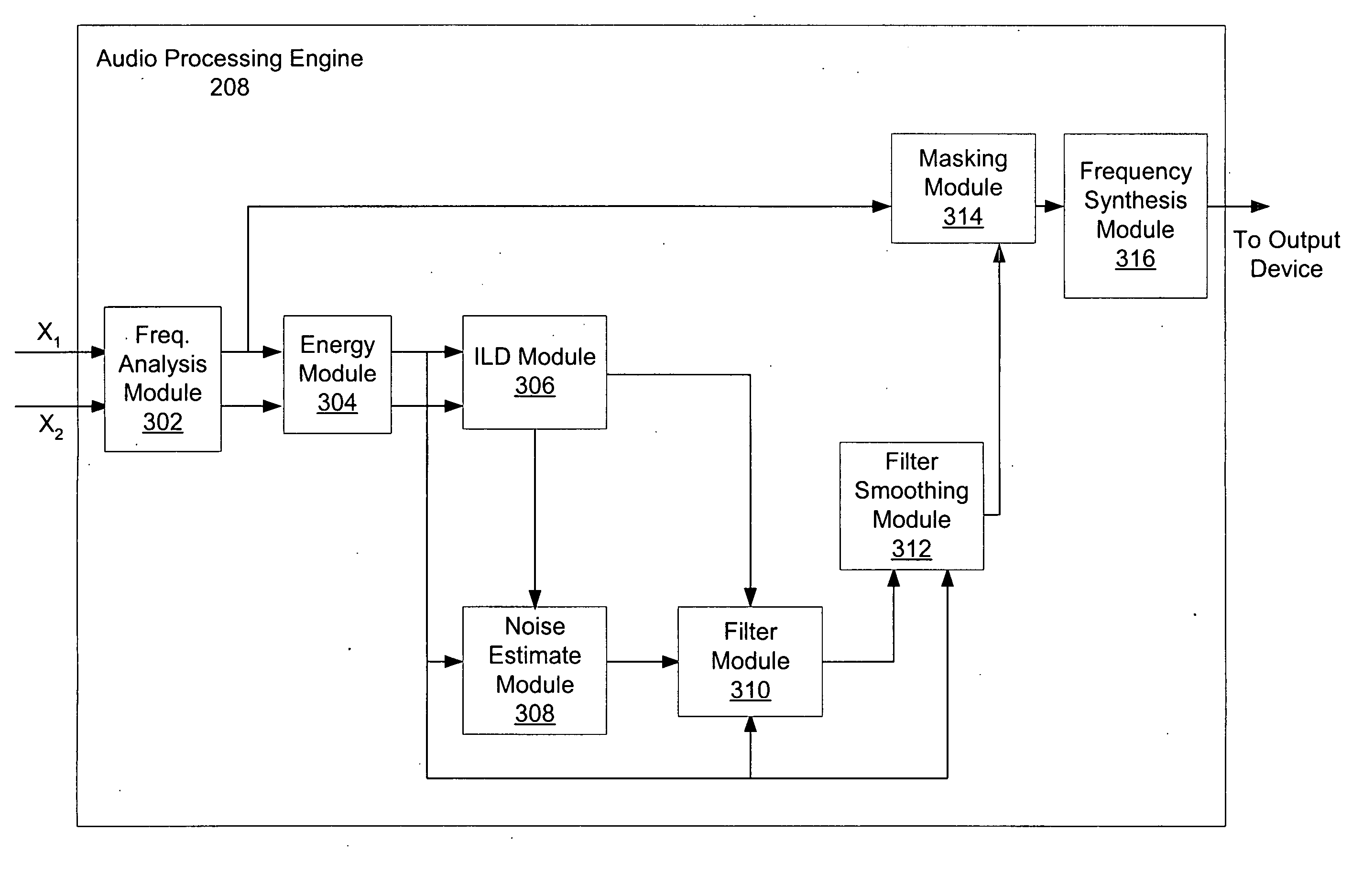
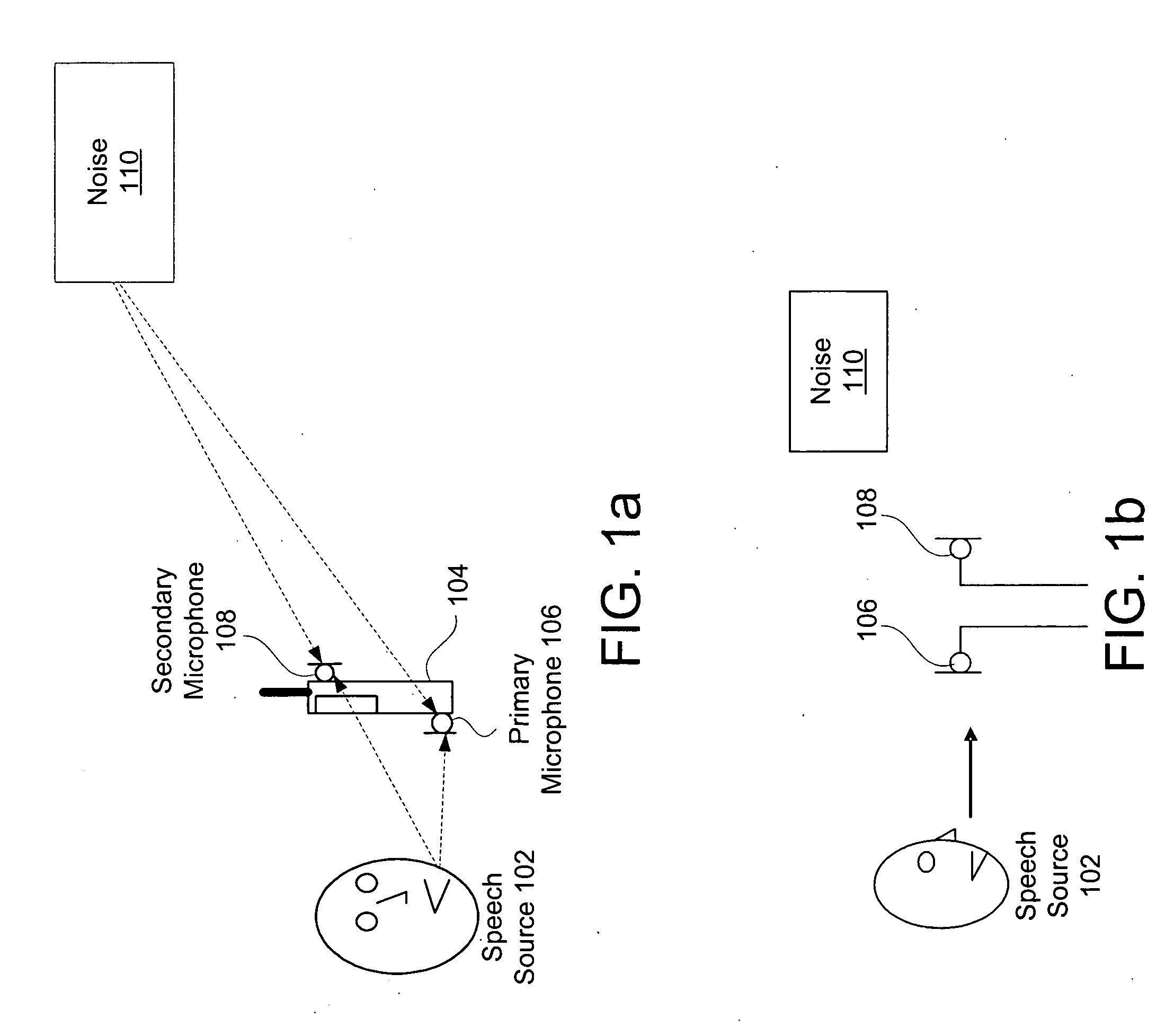
System and method for utilizing inter-microphone level differences for speech enhancement
ActiveUS20070154031A1Reduce acoustic artifactReduce artifactsMicrophonesSignal processingEngineeringNoise estimation
Systems and methods for utilizing inter-microphone level differences to attenuate noise and enhance speech are provided. In exemplary embodiments, energy estimates of acoustic signals received by a primary microphone and a secondary microphone are determined in order to determine an inter-microphone level difference (ILD). This ILD in combination with a noise estimate based only on a primary microphone acoustic signal allow a filter estimate to be derived. In some embodiments, the derived filter estimate may be smoothed. The filter estimate is then applied to the acoustic signal from the primary microphone to generate a speech estimate.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
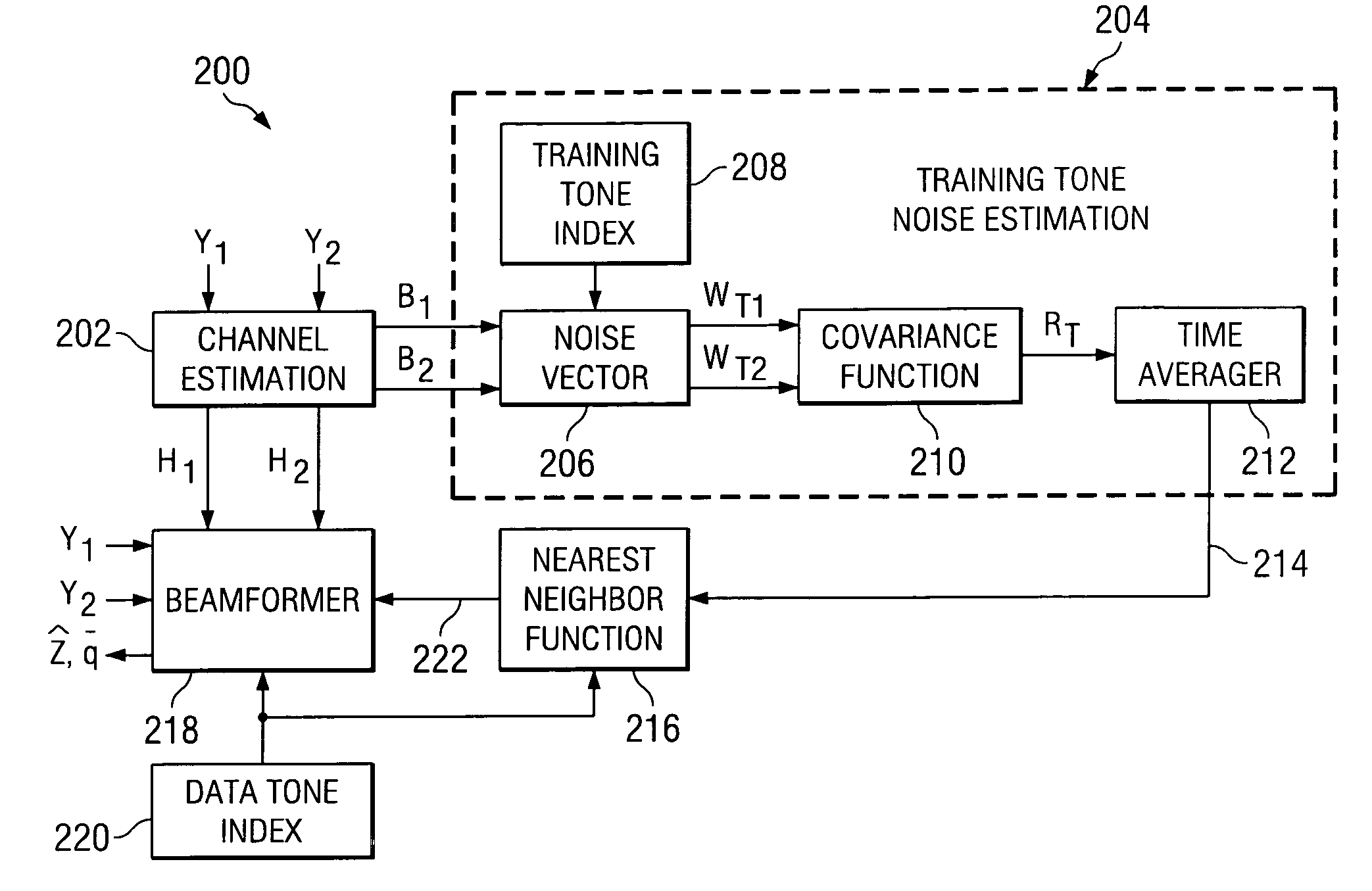
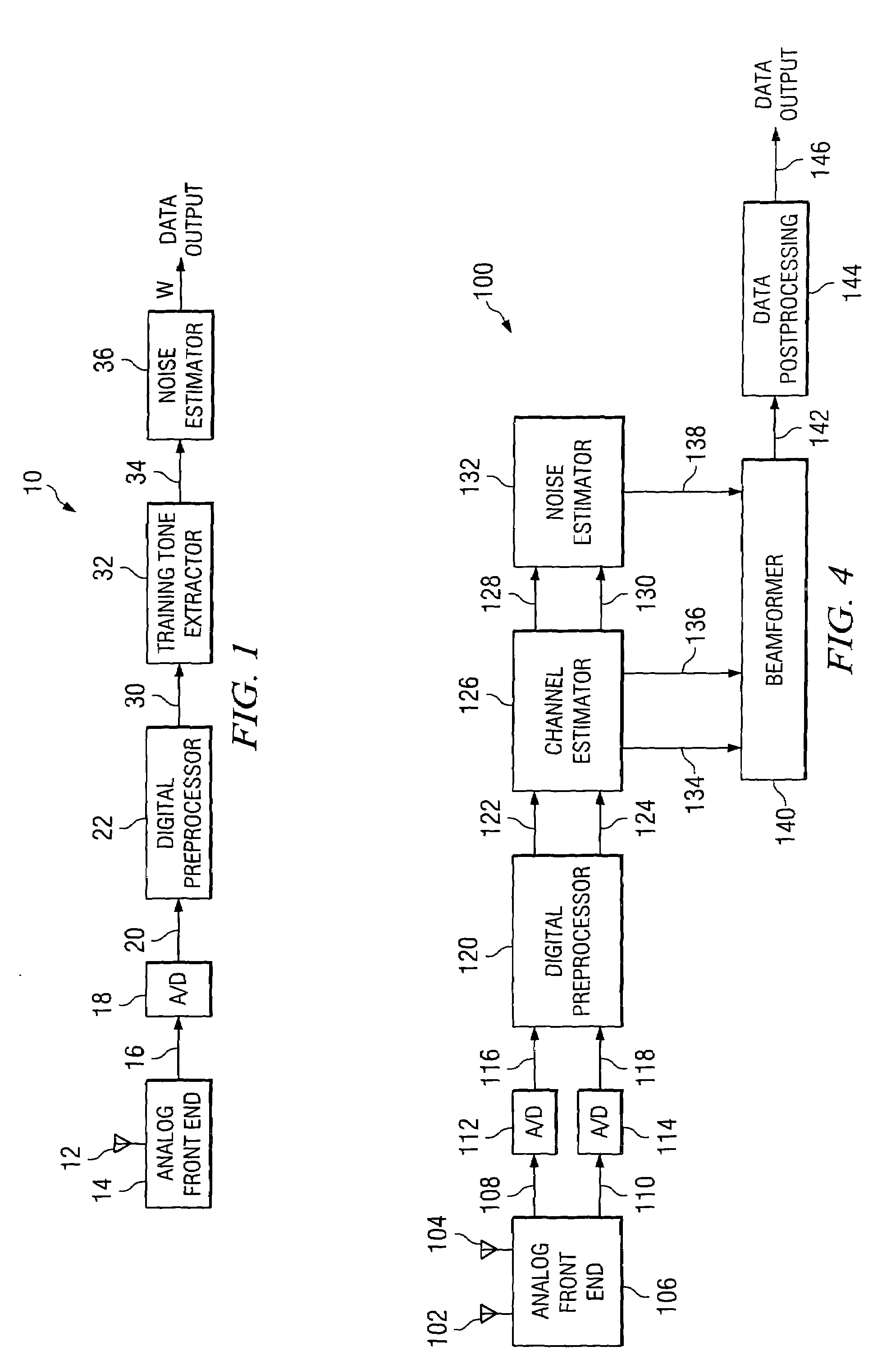
Simplified noise estimation and/or beamforming for wireless communications
ActiveUS7349667B2Simplify noise estimation computationGood indicationTransmission monitoringMulti-frequency code systemsEngineeringNoise estimation
A system and method facilitate estimating noise in a received signal. The received signal is formed of a plurality of tones, such as training tones and data tones. Noise is estimated at the training tones, which generally comprise a lesser number of the tones in the received signal than the data tones. The estimated noise at the training tones can be employed to facilitate demodulating and / or decoding data tones in the received signal. In one aspect, the estimated training tone noise can be utilized by a beamformer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
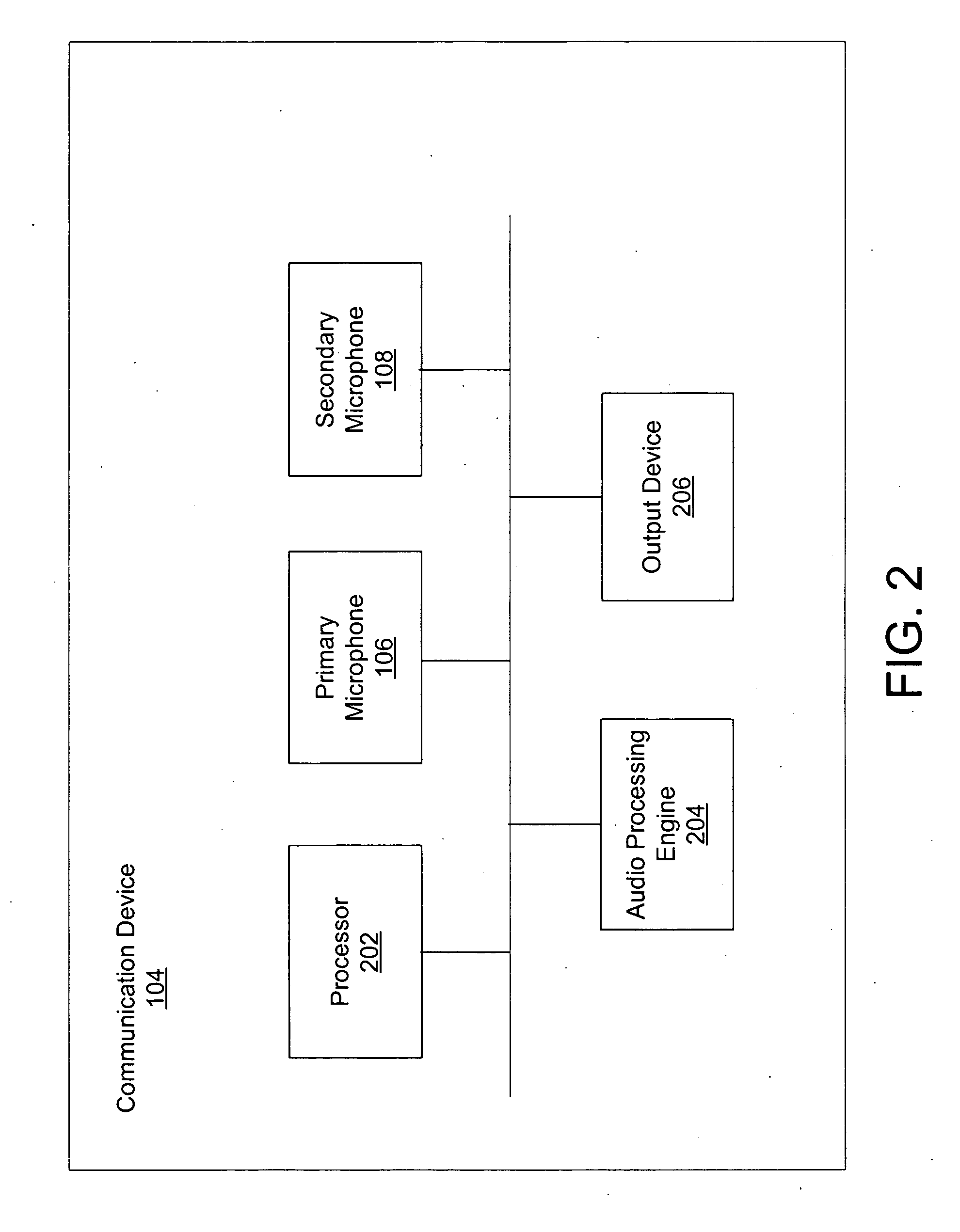
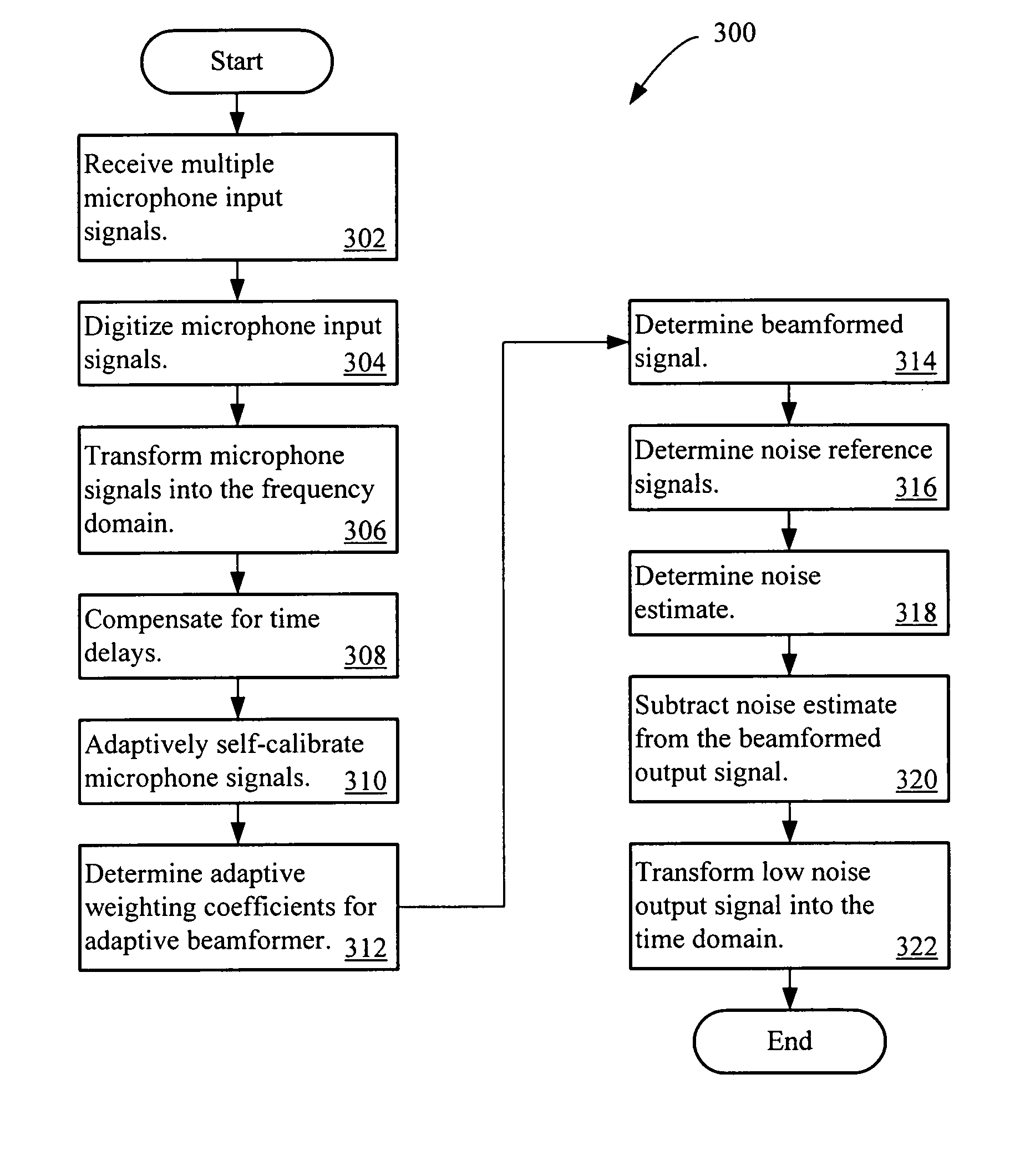
Multi-channel adaptive speech signal processing system with noise reduction
ActiveUS20060222184A1Improved speech signal clarityImprove intelligibilitySignal processingEar treatmentLow noiseHigh energy
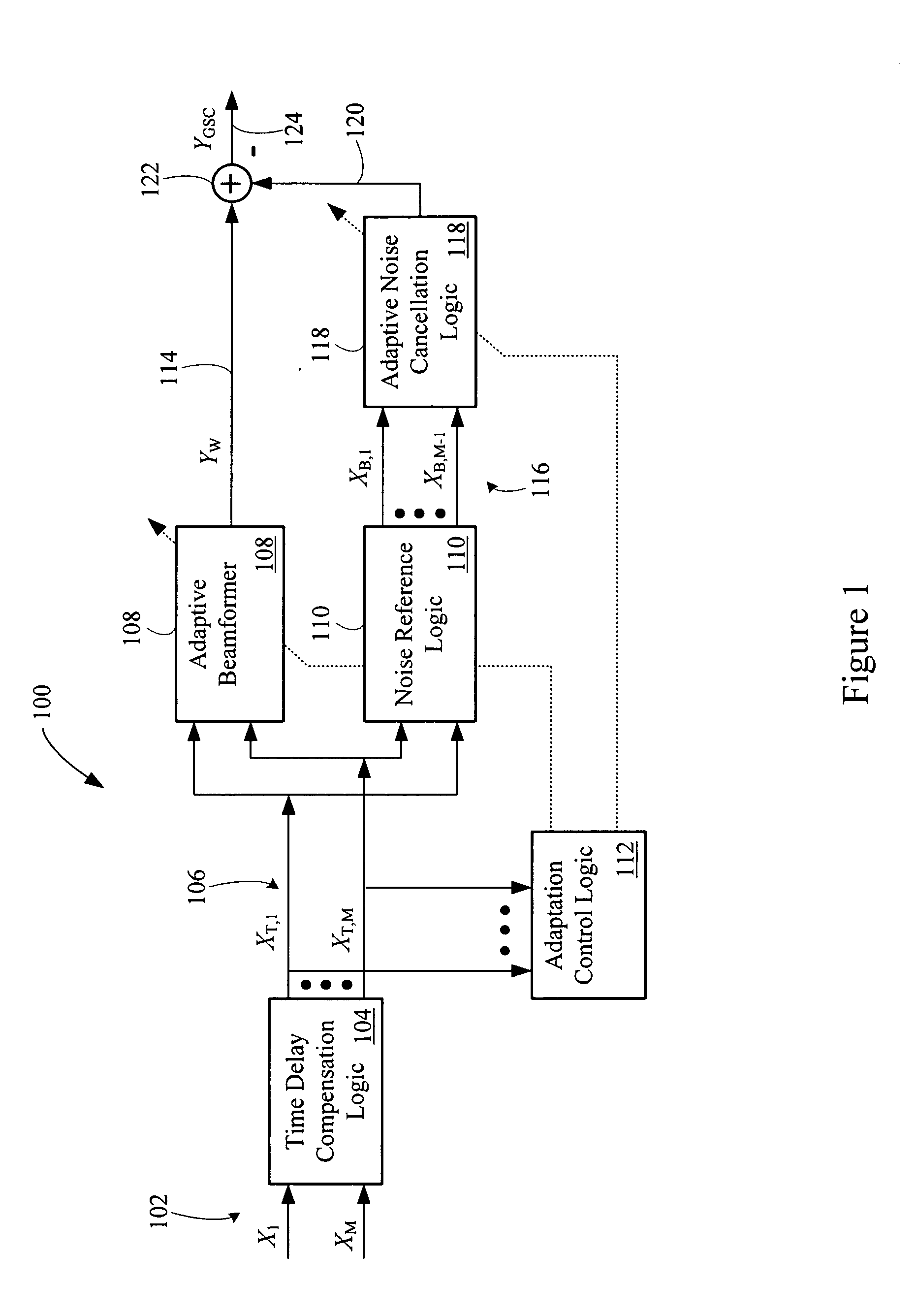
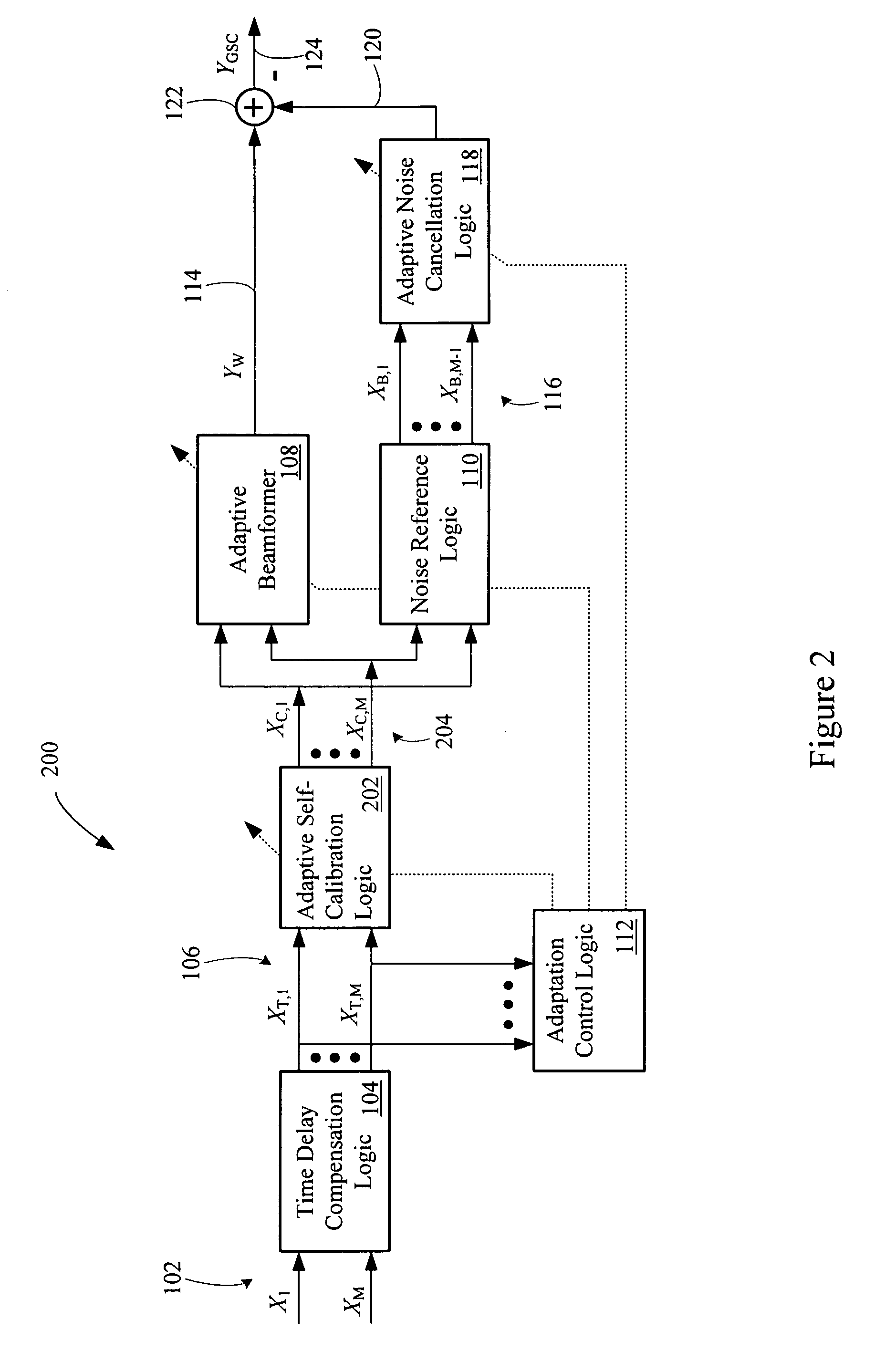
An adaptive signal processing system eliminates noise from input signals while retaining desired signal content, such as speech. The resulting low noise output signal delivers improved clarity and intelligibility. The low noise output signal also improves the performance of subsequent signal processing systems, including speech recognition systems. An adaptive beamformer in the signal processing system consistently updates beamforming signal weights in response to changing microphone signal conditions. The adaptive weights emphasize the contribution of high energy microphone signals to the beamformed output signal. In addition, adaptive noise cancellation logic removes residual noise from the beamformed output signal based on a noise estimate derived from the microphone input signals.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS
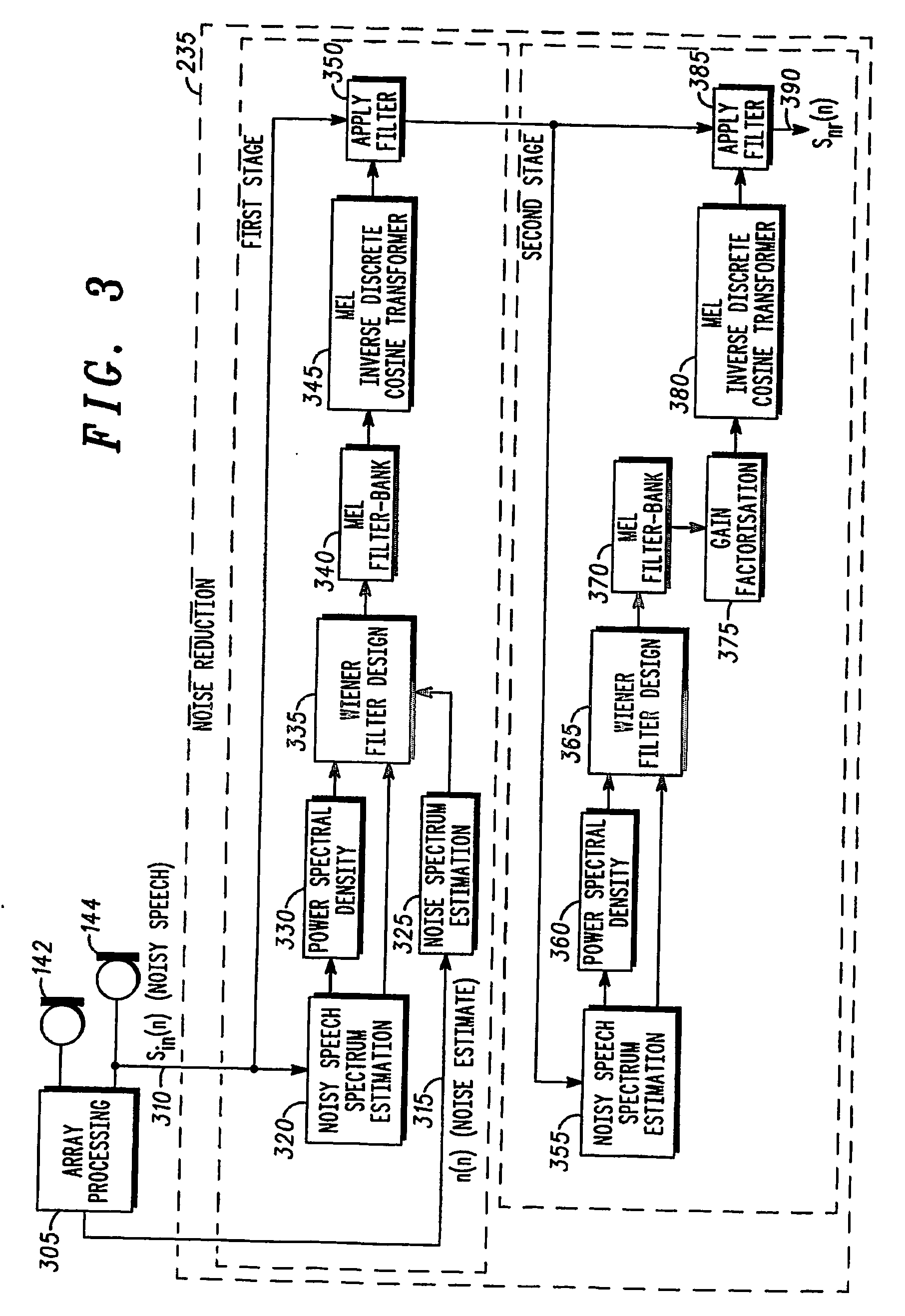
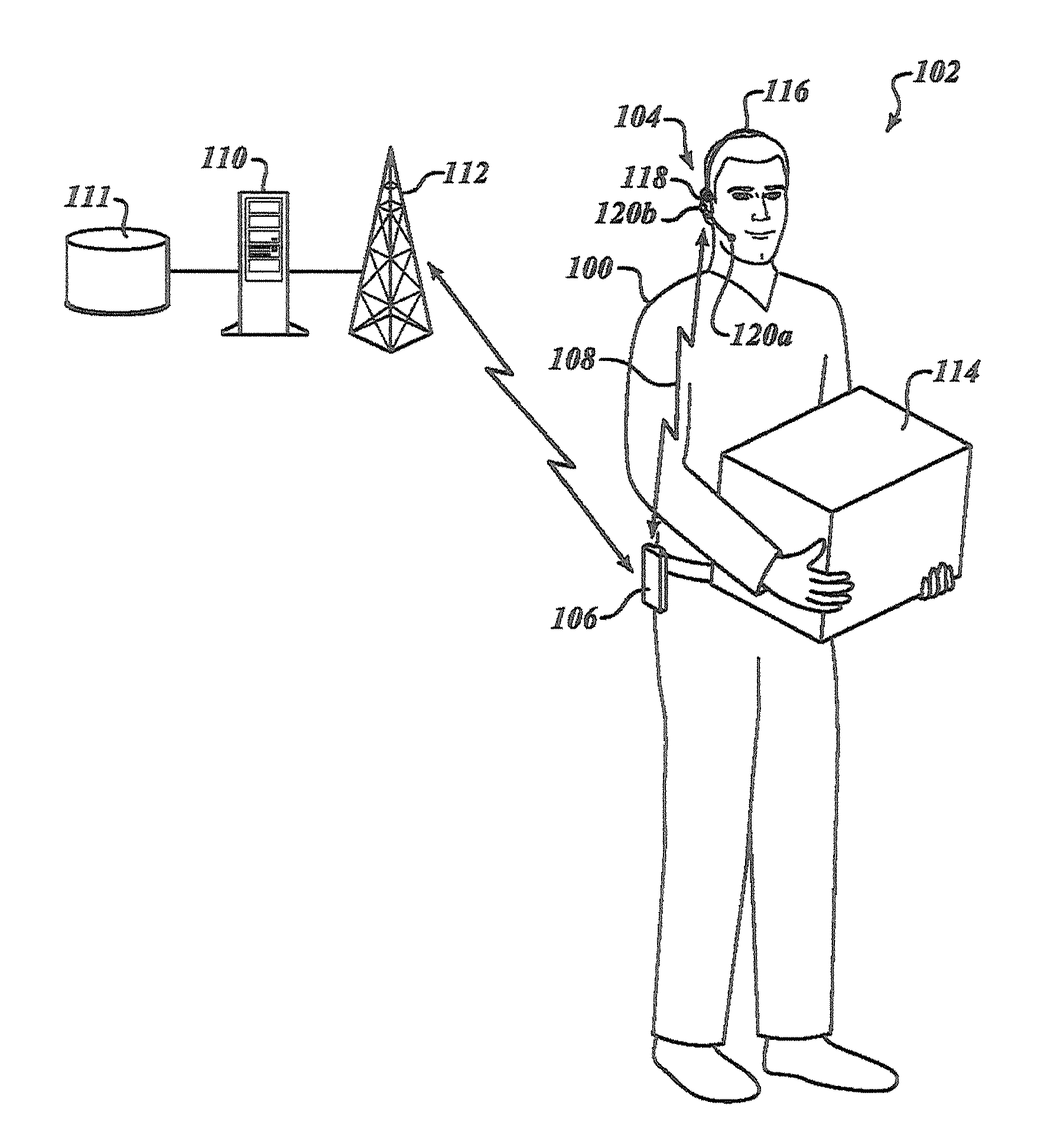
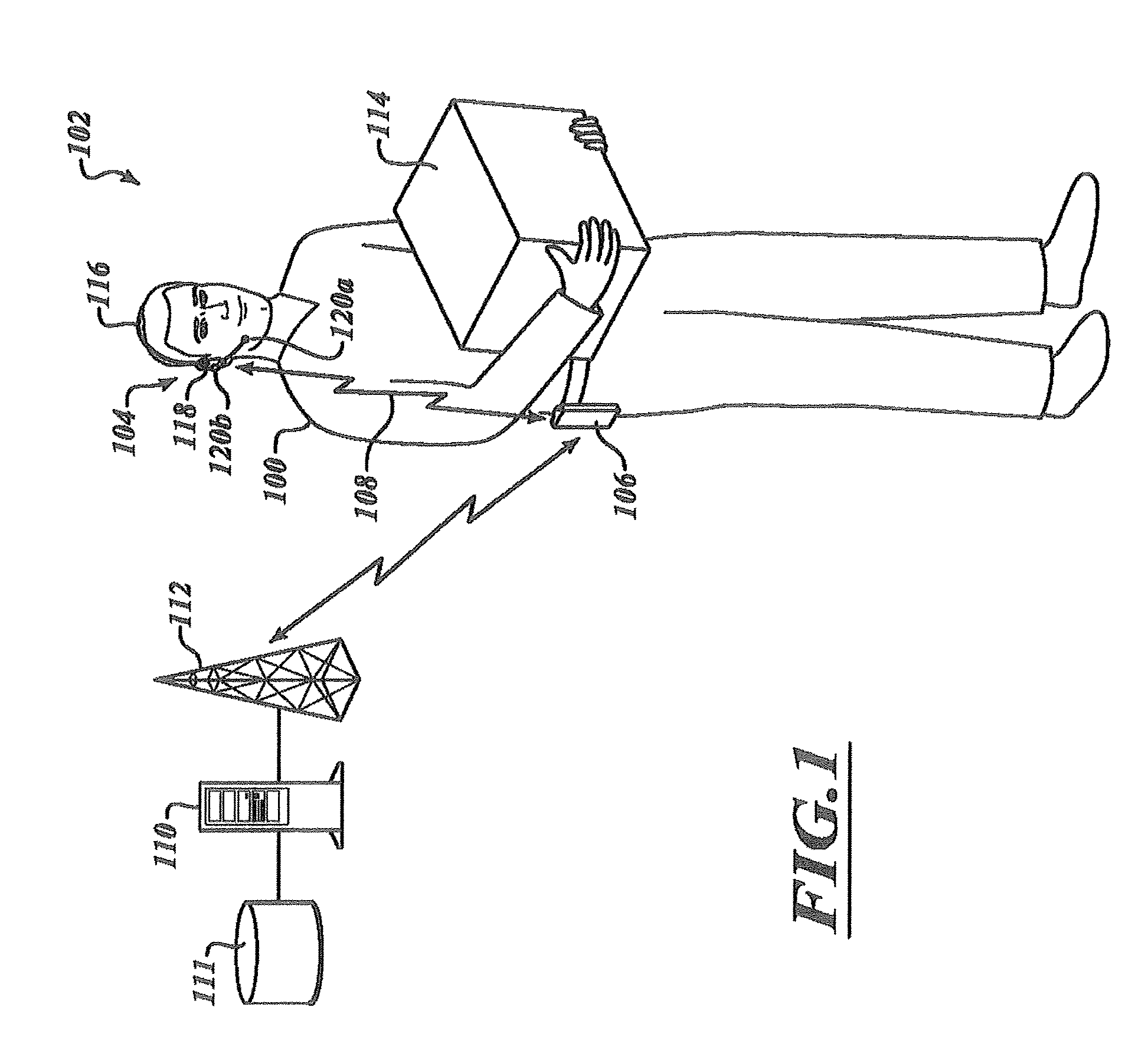
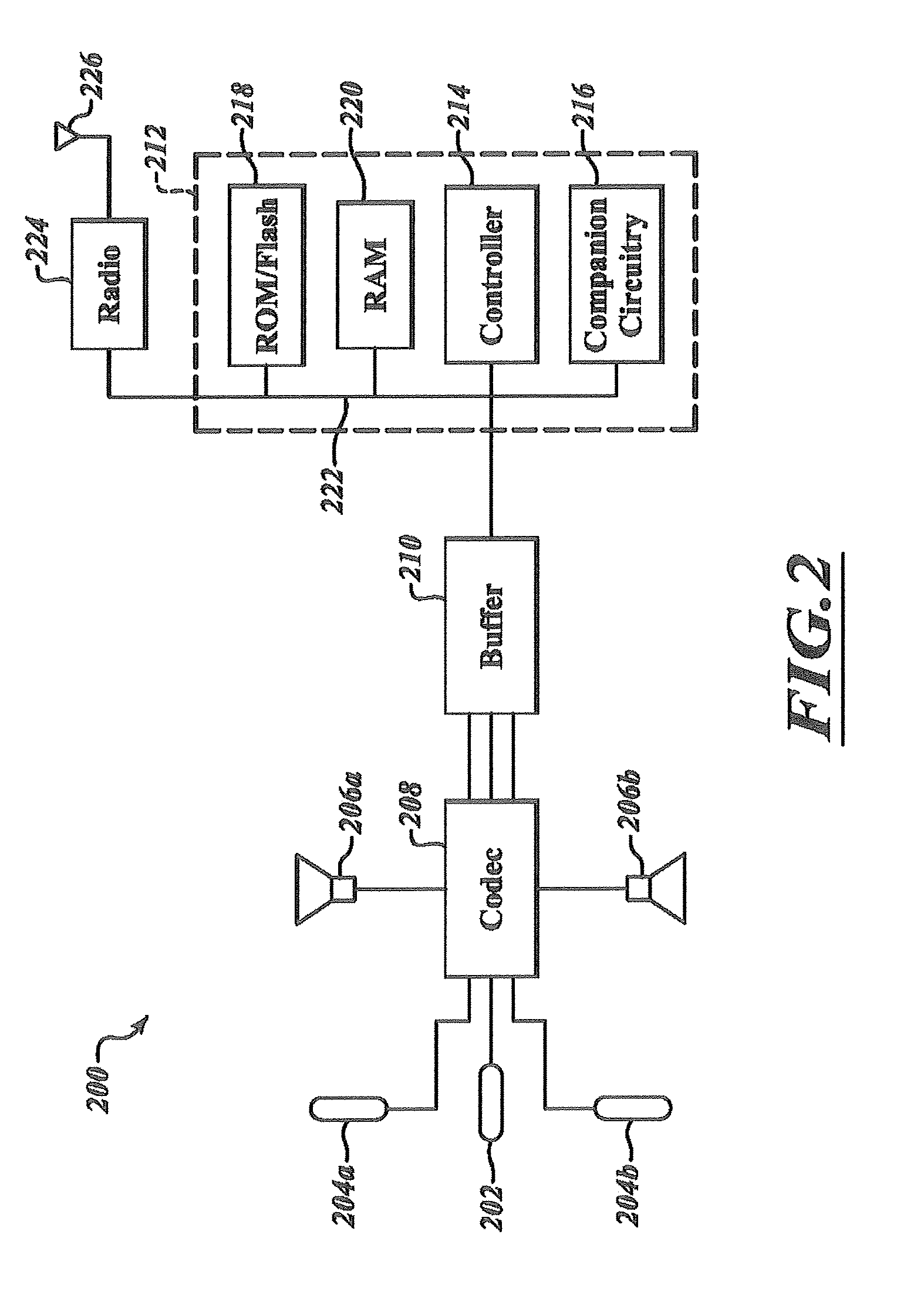
Estimation of noise in a speech signal
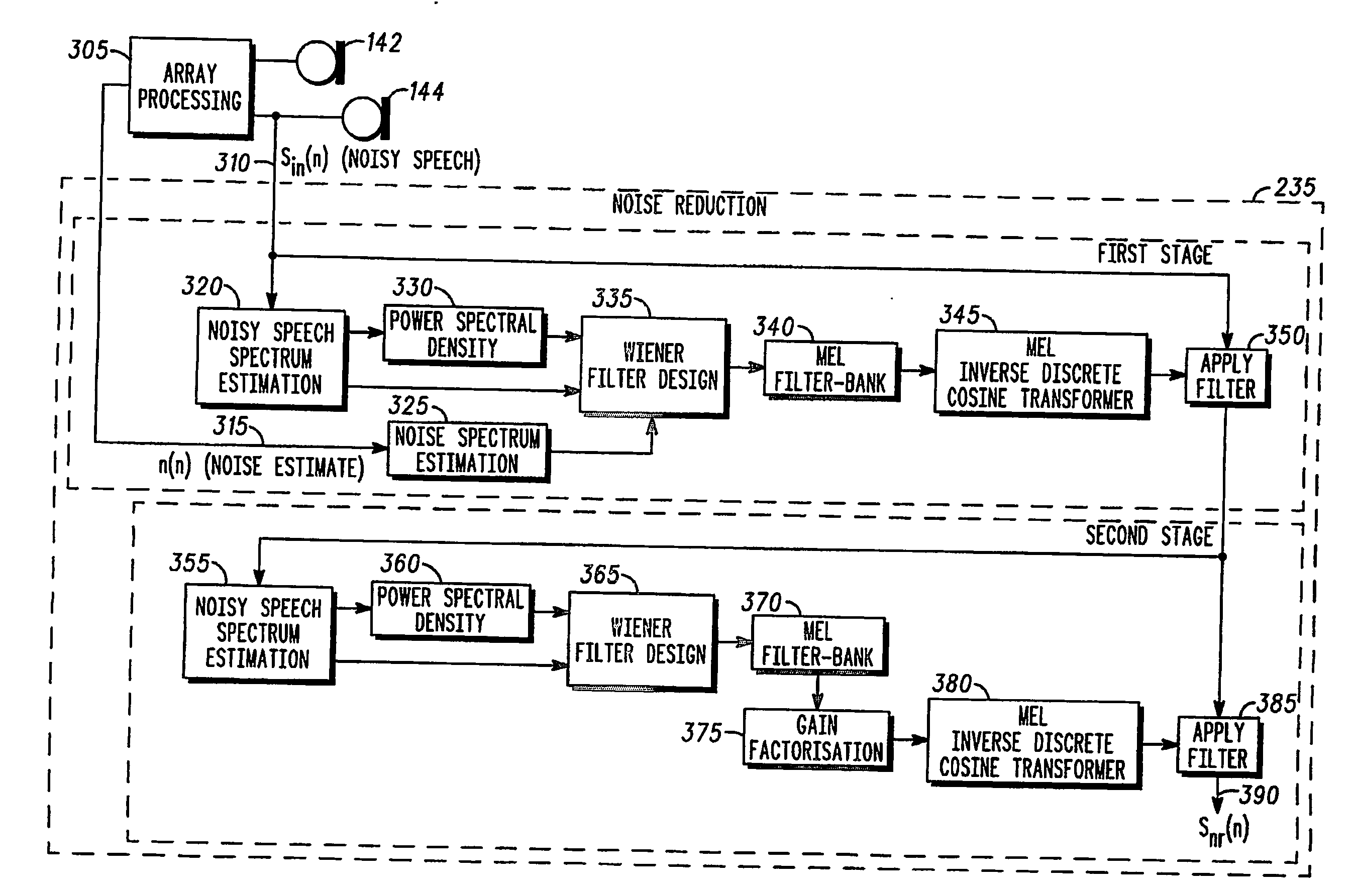
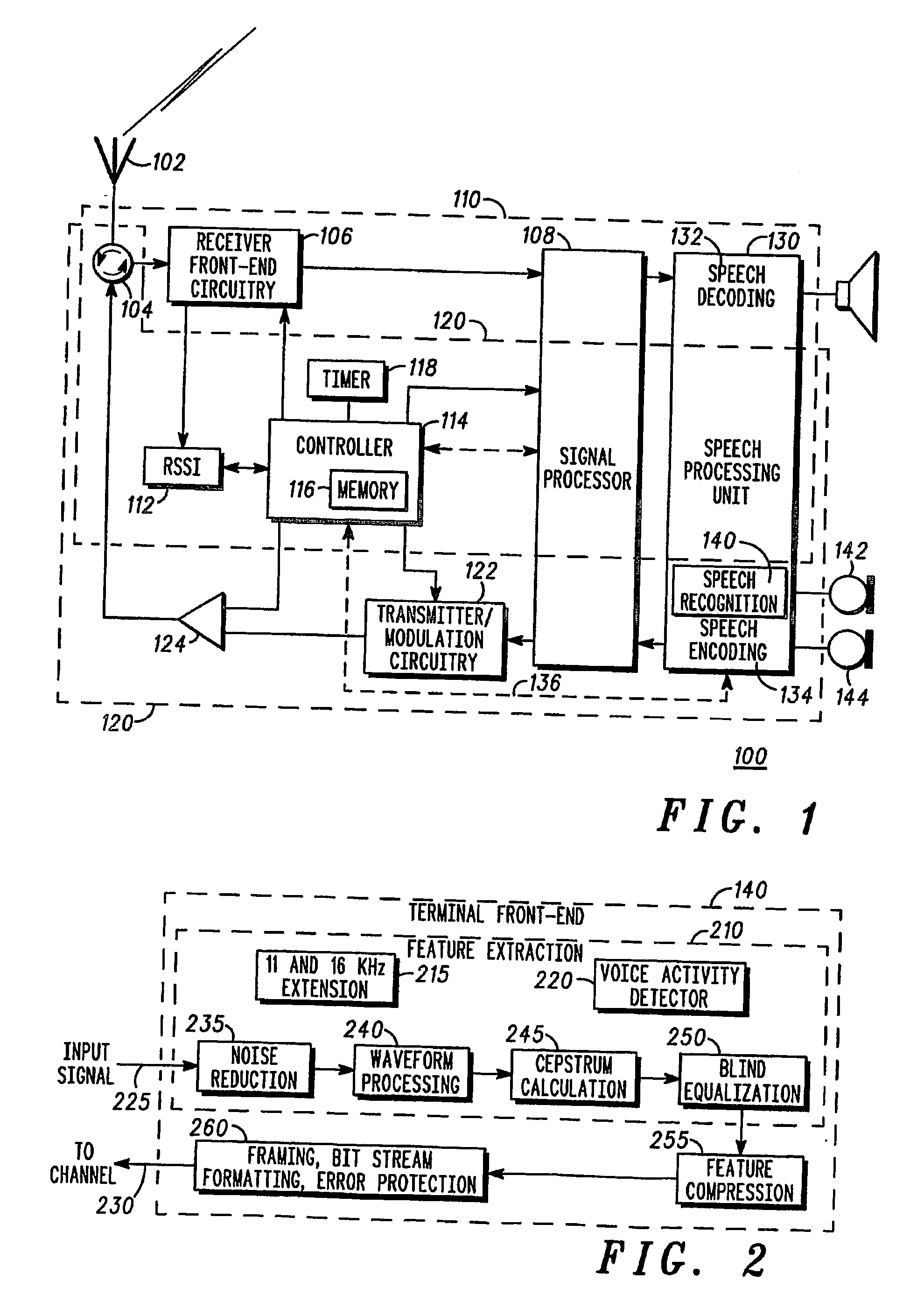
A speech communication or computing device comprises at least one speech input device for receiving noisy speech uttered by a speaker. A speech processing function comprises a voice recognition function, which comprises a noise reduction function (235) having a Wiener Filter (335) with adjustable filter co-efficients. The speech input device also comprises multiple microphones (142, 144) configured to provide a substantially continuous noise signal to a noise spectrum estimation function (325) of the noise reduction function (235) to provide a substantially continuous estimate of noise. The noise estimate is used to adjust the filter co-efficients of the Wiener Filter (335), thereby removing noise from the noisy speech. A microphone array and a method for speech recognition are also described. By using the noise estimate from, say, a microphone array, the Wiener filter coefficients can be updated substantially continuously, for example, each speech frame. This enables the noise to be tracked more closely than in known techniques. As the noise within a speech signal is tracked more closely, it can therefore be removed more effectively.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Apparatus and method to classify sound to detect speech
Audio frames are classified as either speech, non-transient background noise, or transient noise events. Probabilities of speech or transient noise event, or other metrics may be calculated to indicate confidence in classification. Frames classified as speech or noise events are not used in updating models (e.g., spectral subtraction noise estimates, silence model, background energy estimates, signal-to-noise ratio) of non-transient background noise. Frame classification affects acceptance / rejection of recognition hypothesis. Classifications and other audio related information may be determined by circuitry in a headset, and sent (e.g., wirelessly) to a separate processor-based recognition device.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
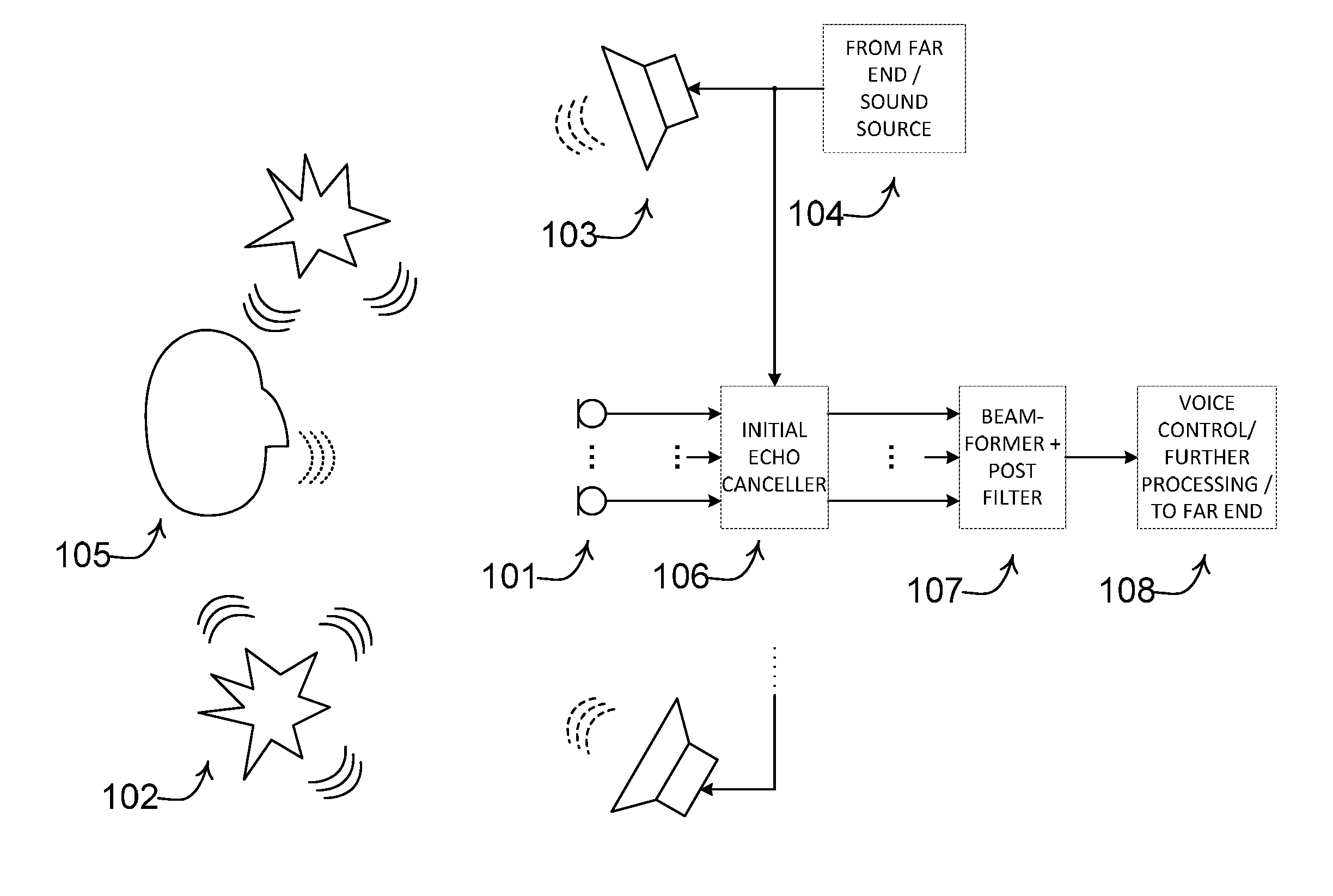
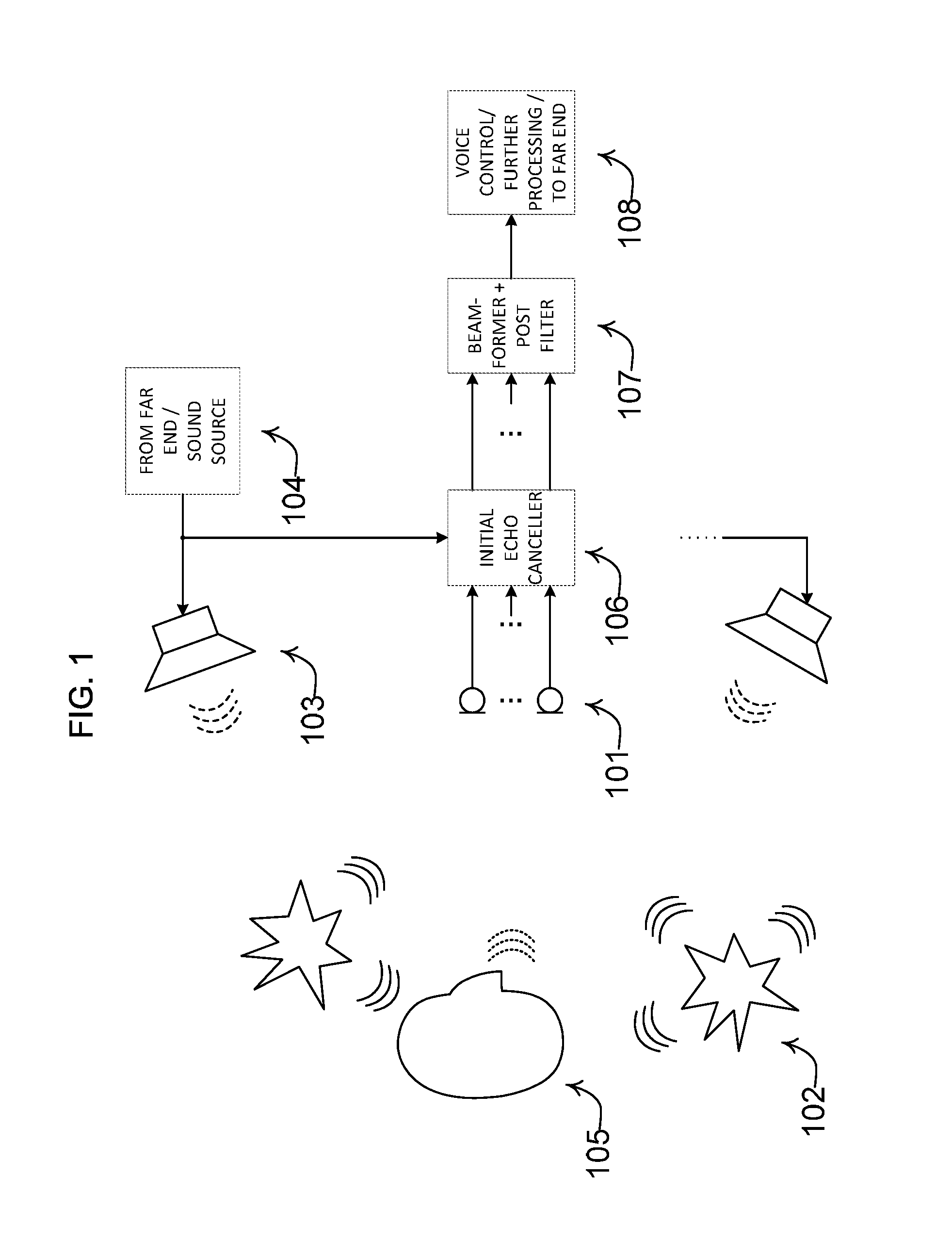
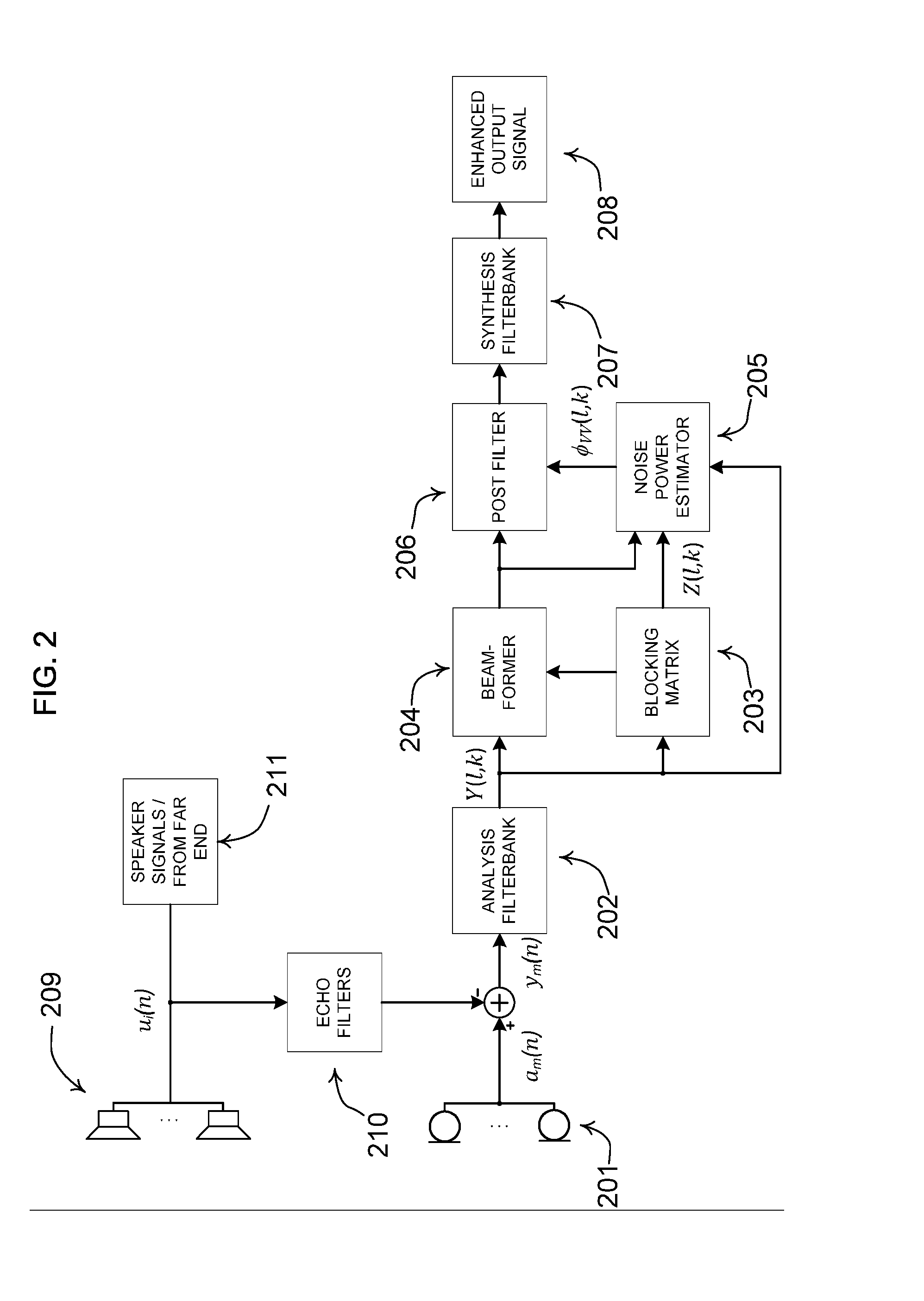
Noise estimation for use with noise reduction and echo cancellation in personal communication
ActiveUS20140056435A1Improve recognition rateImprove sound qualityInterconnection arrangementsEar treatmentNoise correctionEngineering
A method comprises processing M subband communication signals and N target-cancelled signals in each subband with a set of beamformer coefficients to obtain an inverse target-cancelled covariance matrix of order N in each band; using a target absence signal to obtain an initial estimate of the noise power in a beamformer output signal averaged over recent frames with target absence in each subband; multiplying the initial noise estimate with a noise correction factor to obtain a refined estimate of the power of the beamformer output noise signal component in each subband; processing the refined estimate with the magnitude of the beamformer output to obtain a postfilter gain value in each subband; processing the beamformer output signal with the postfilter gain value to obtain a postfilter output signal in each subband; and processing the postfilter output subband signals to obtain an enhanced beamformed output signal.
Owner:OTICON
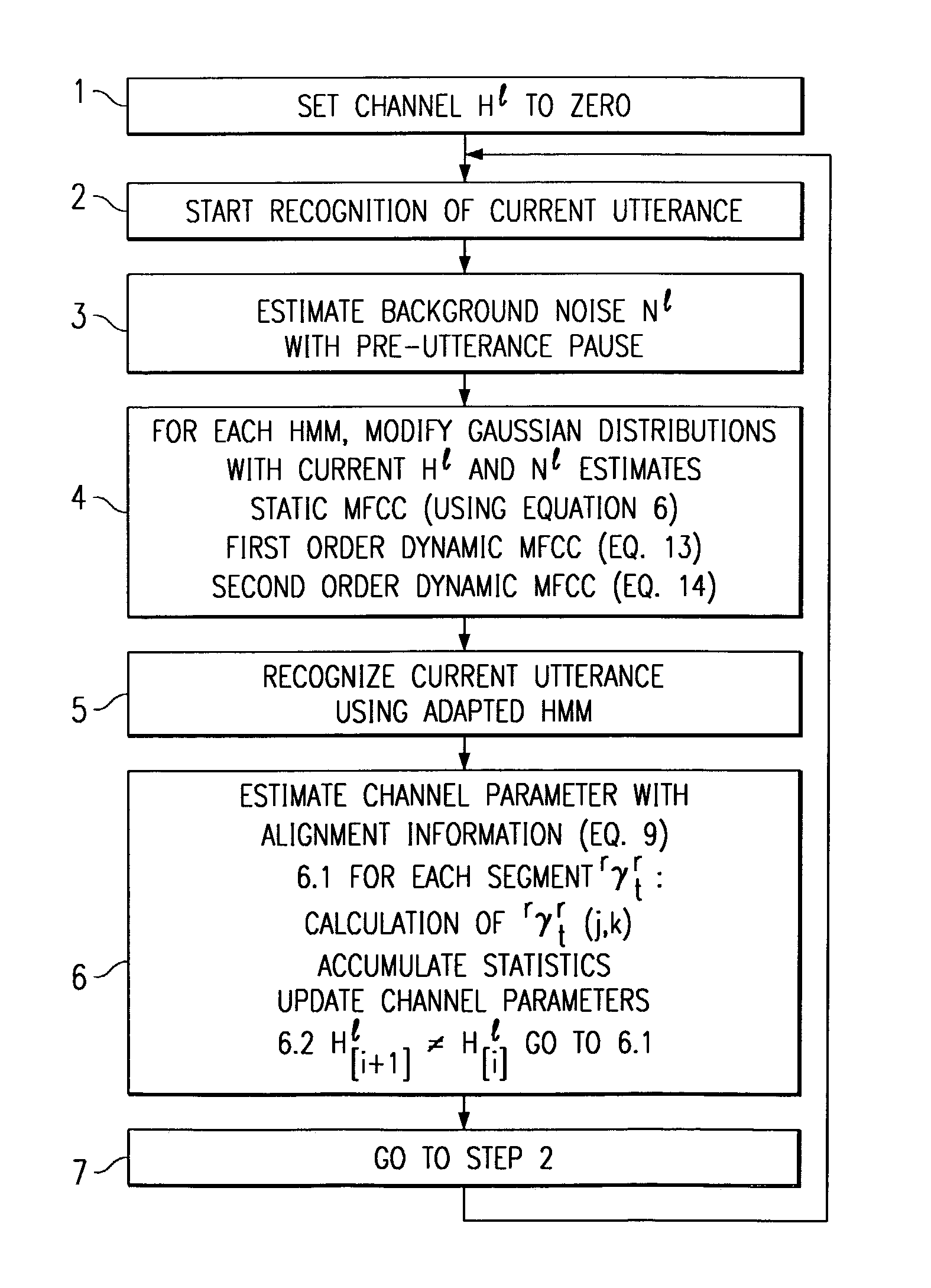
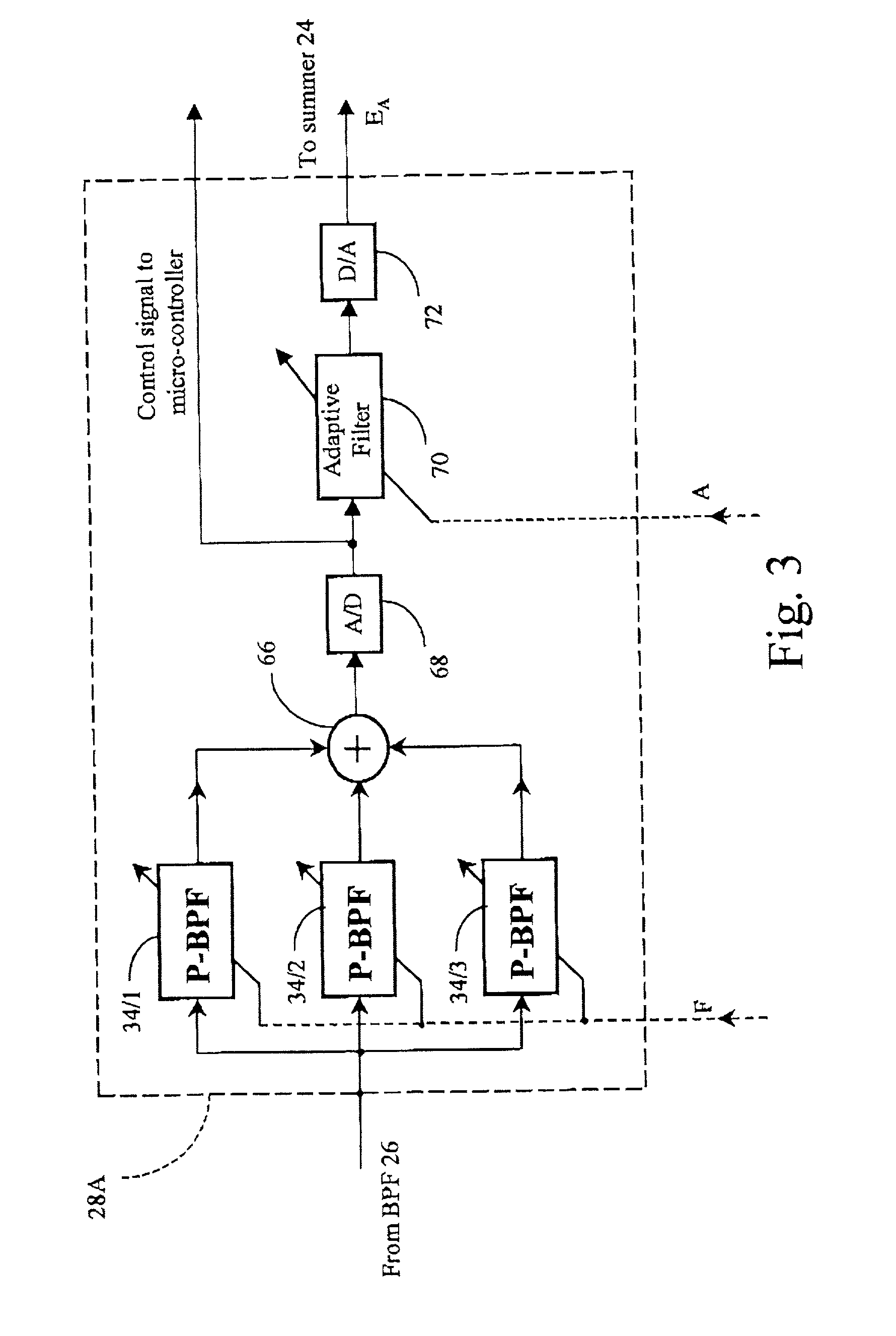
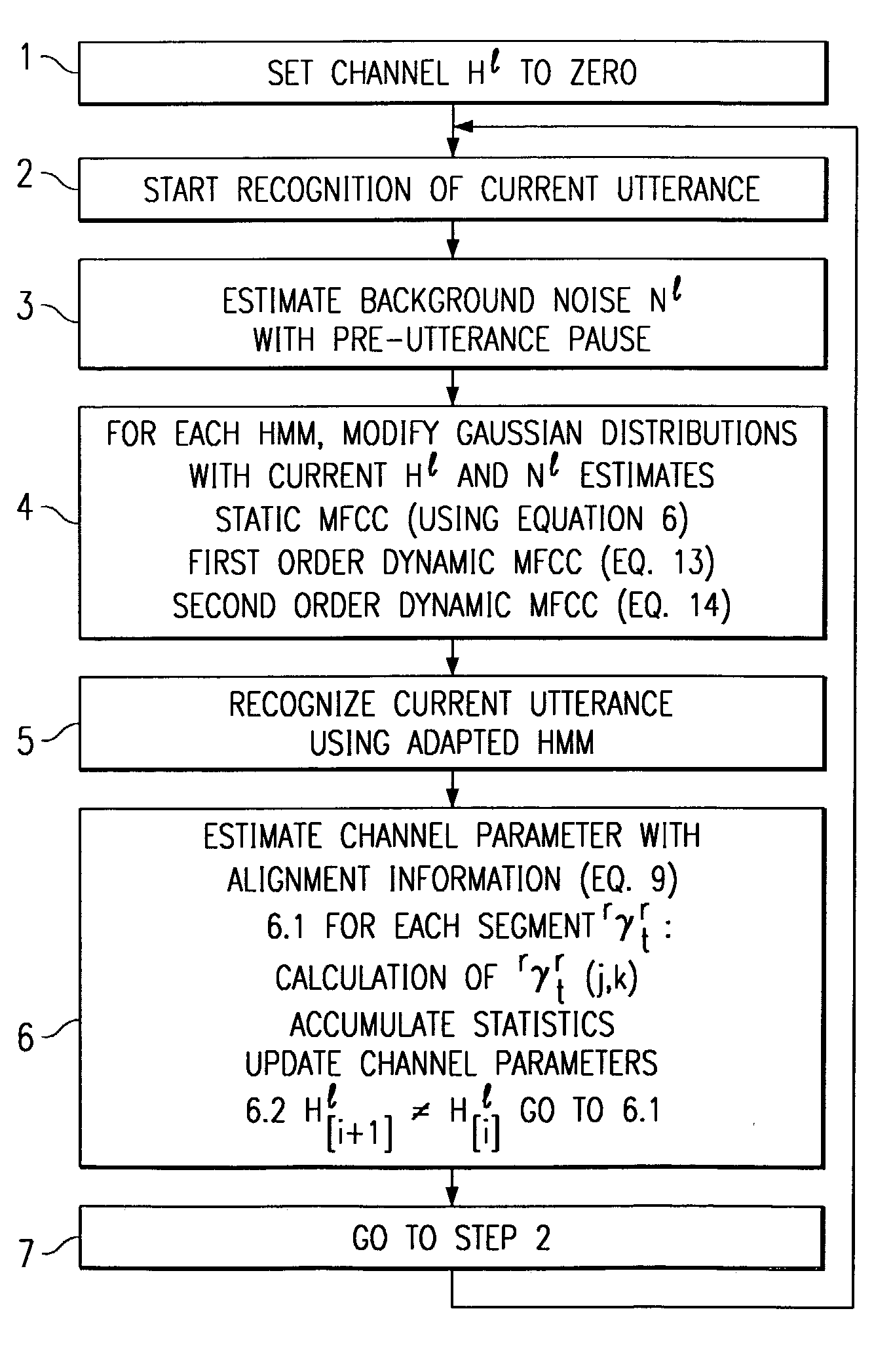
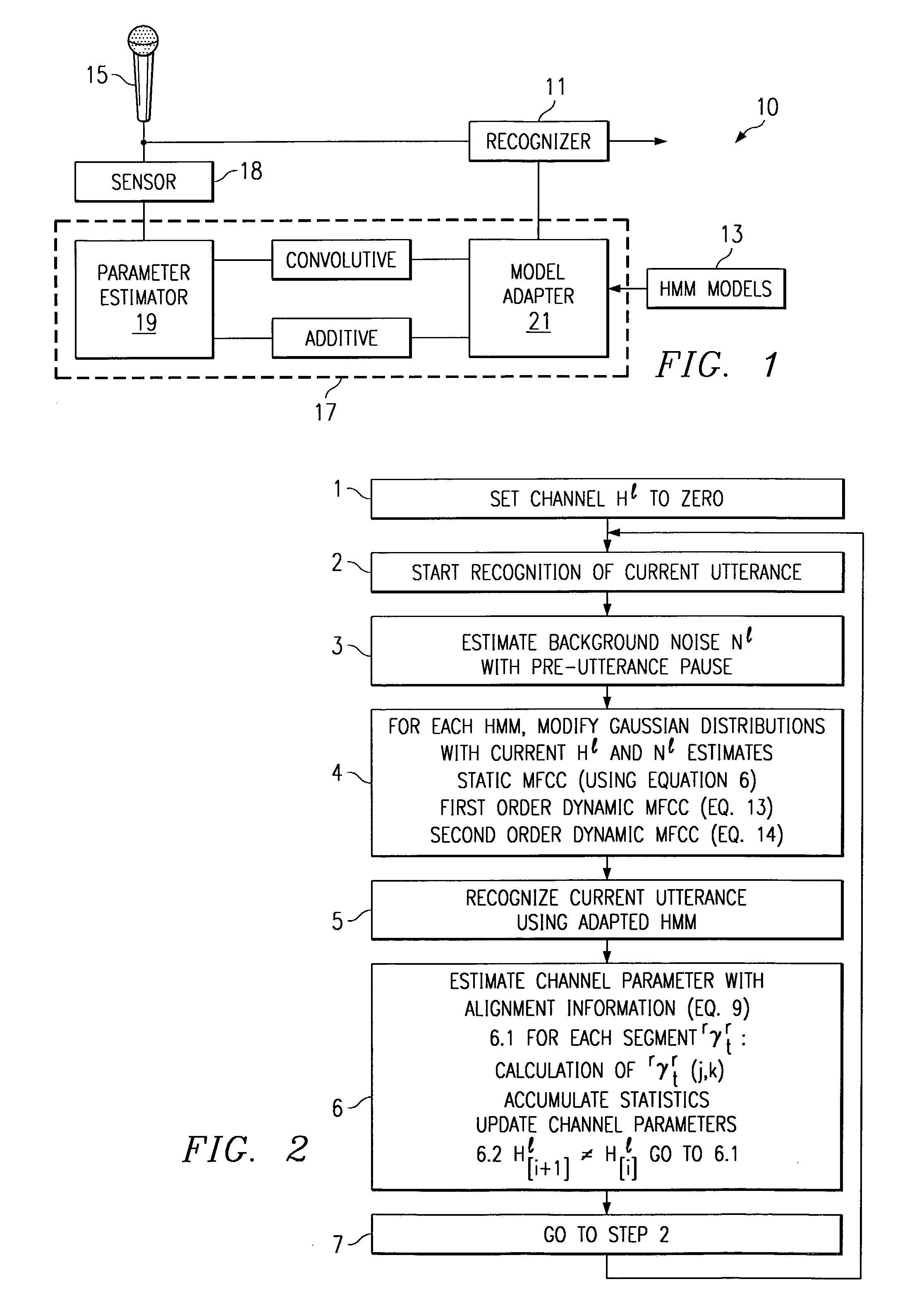
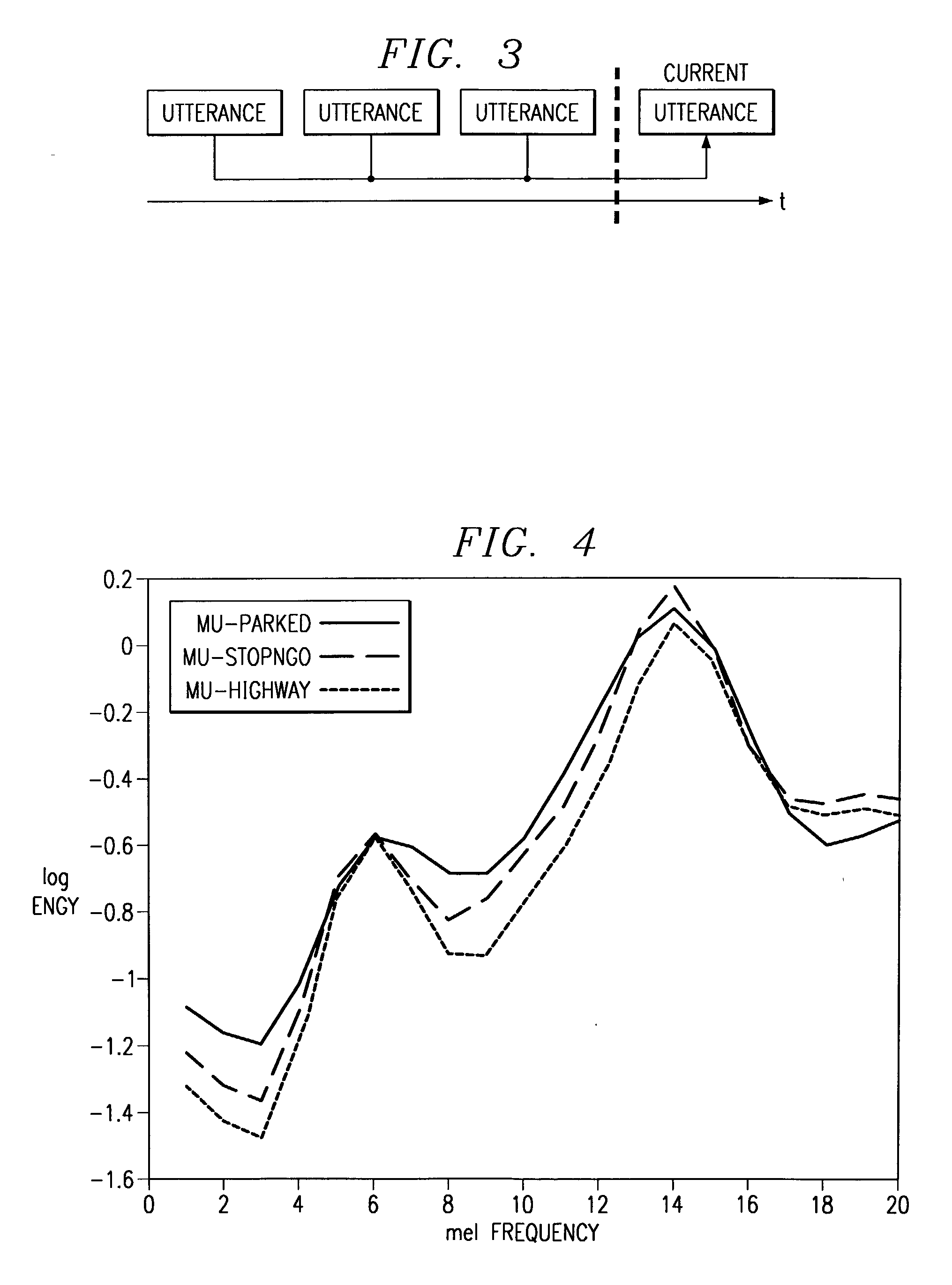
Method of speech recognition resistant to convolutive distortion and additive distortion
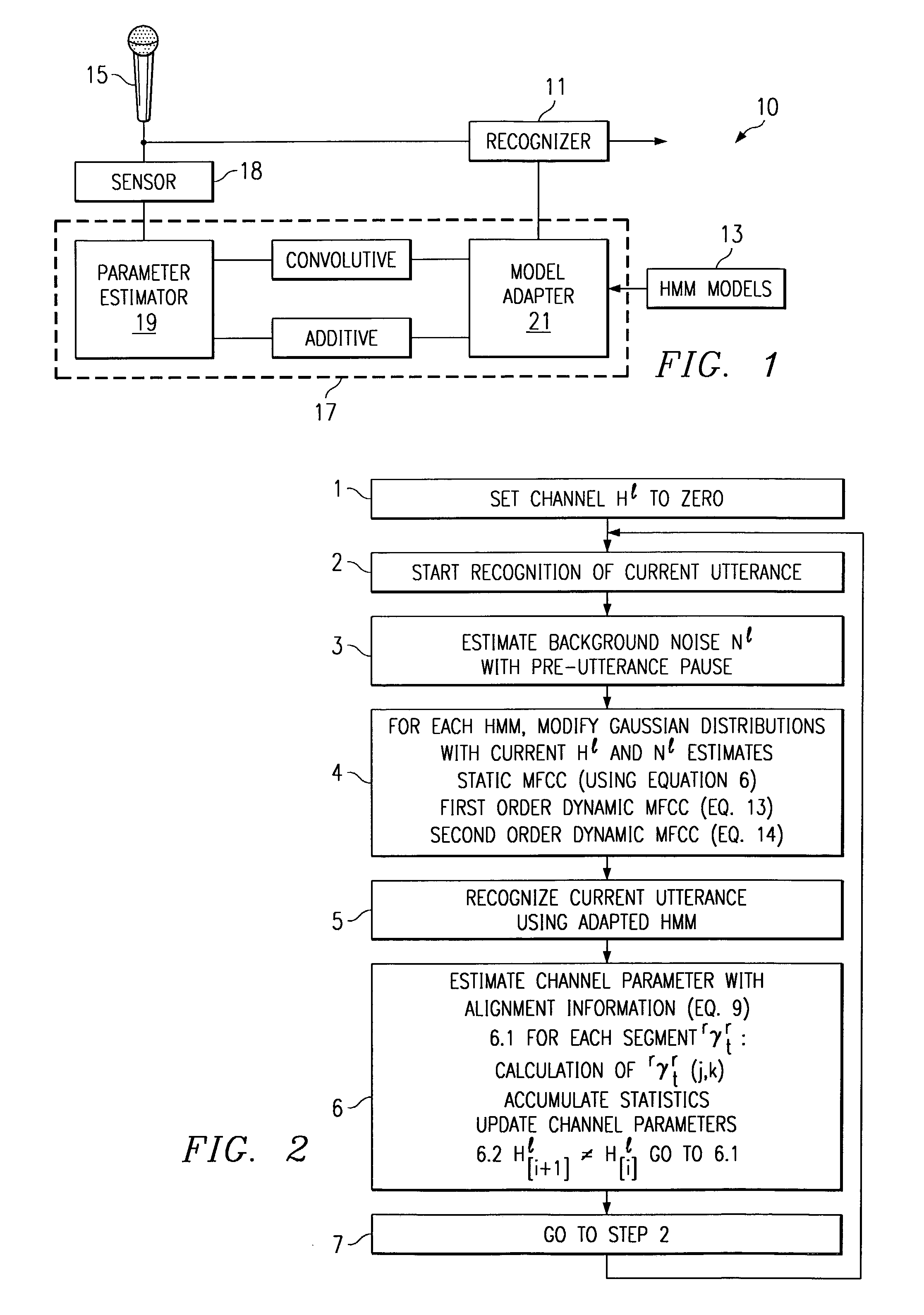
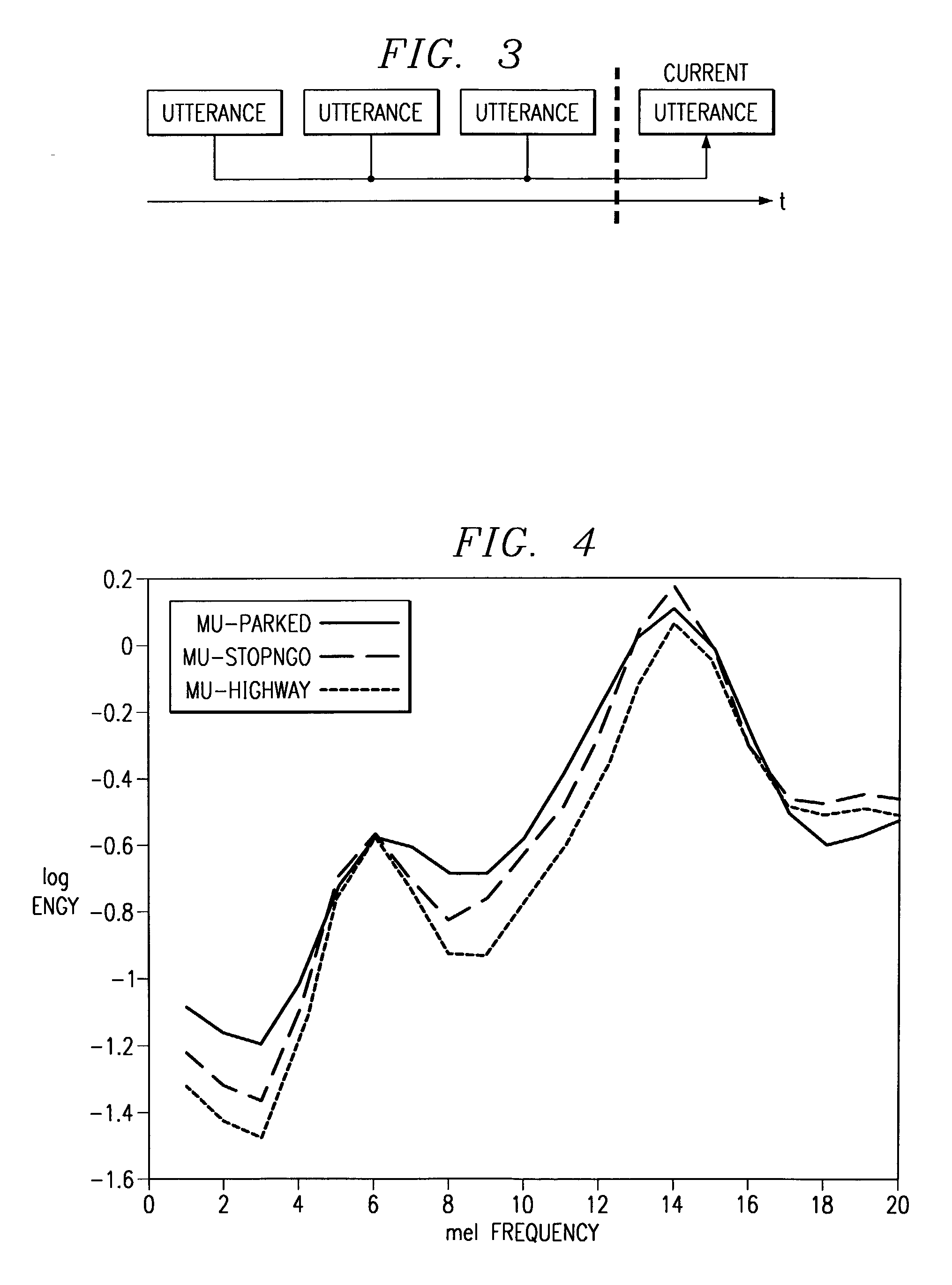
A speech recognizer operating in both ambient noise (additive distortion) and microphone changes (convolutive distortion) is provided. For each utterance to be recognized the recognizer system adapts HMM mean vectors with noise estimates calculated from pre-utterance pause and a channel estimate calculated using an Estimation Maximization algorithm from previous utterances.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Interference and noise estimation in an OFDM system
ActiveUS20050002324A1Quantity minimizationQuality improvementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringMultiuser systemCarrier signal
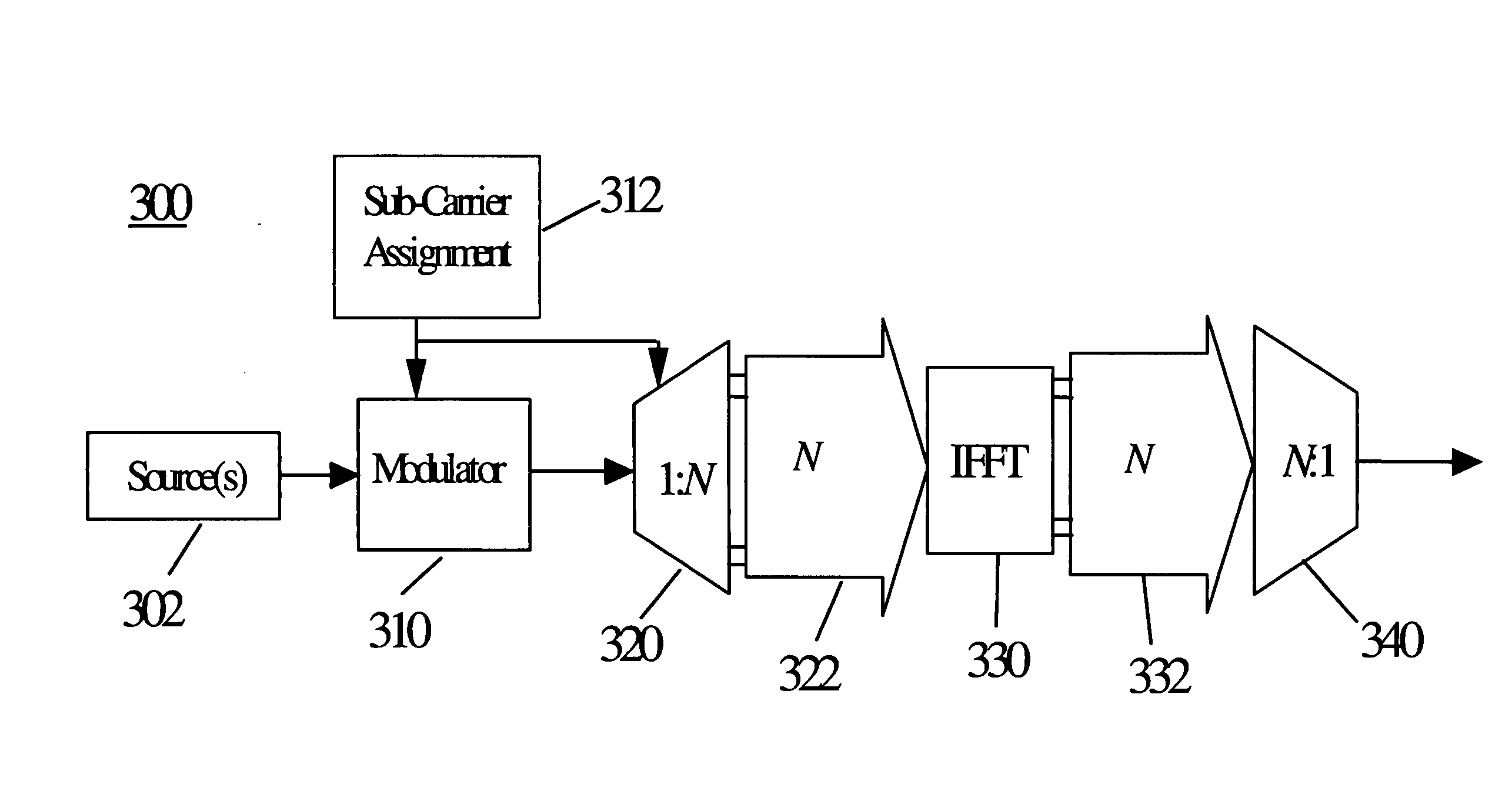
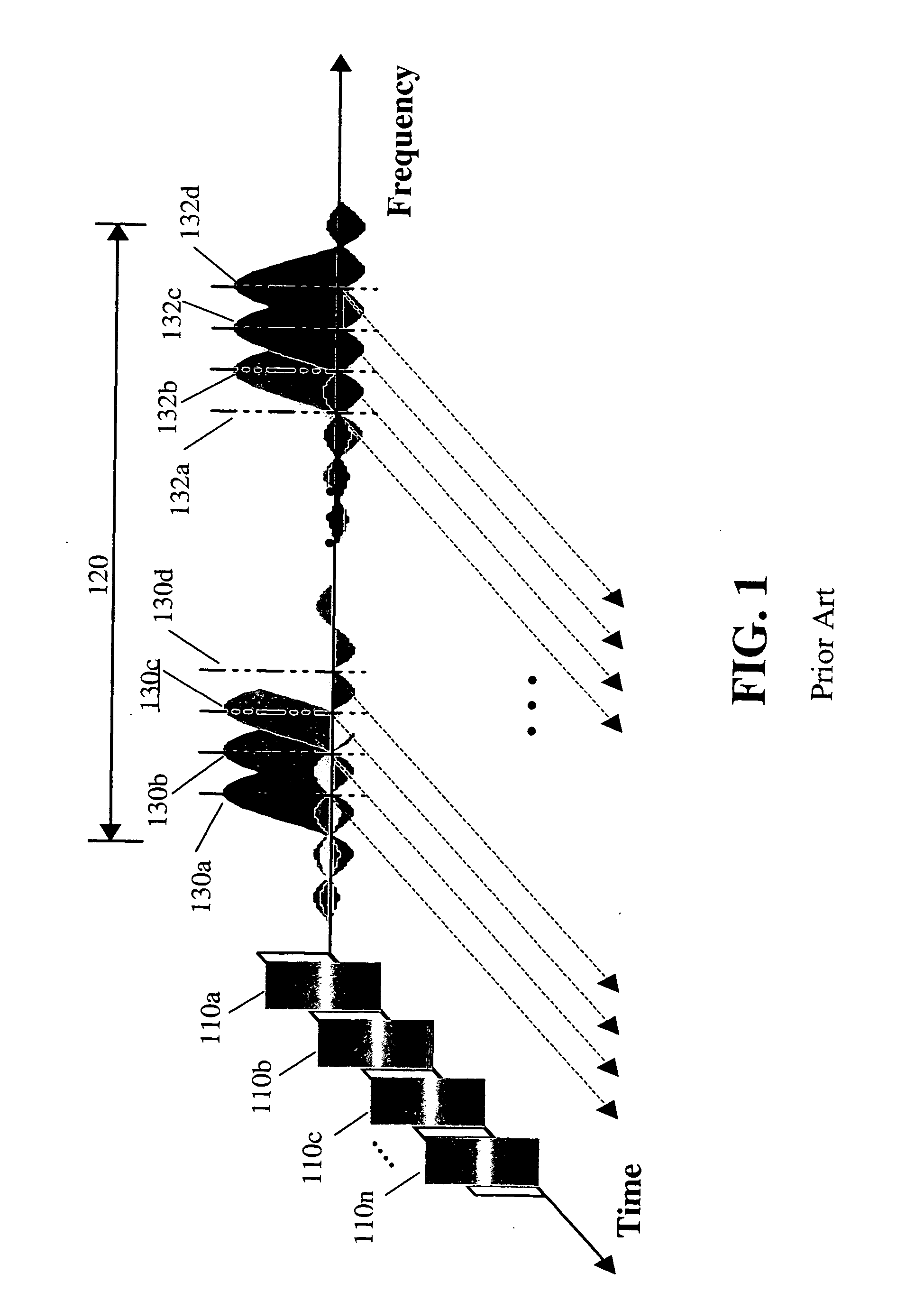
Noise and interference can be independently measured in a multiple user Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. Co-channel interference is measured in a frequency hopping, multiple user, OFDM system by tracking the sub-carriers assigned to all users in a particular service area or cell. The composite noise plus interference can be determined by measuring the amount of received power in a sub-carrier whenever it is not assigned to any user in the cell. A value is stored for each sub-carrier in the system and the value of noise plus interference can be a weighted average of the present value with previously stored values. The noise component can be independently determined in a synchronous system. In the synchronous system, all users in a system may periodically be prohibited from broadcasting over a sub-carrier and the received power in the sub-carrier measured during the period having no broadcasts.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Signal Processing Method, Signal Processing Device, and Signal Processing Program
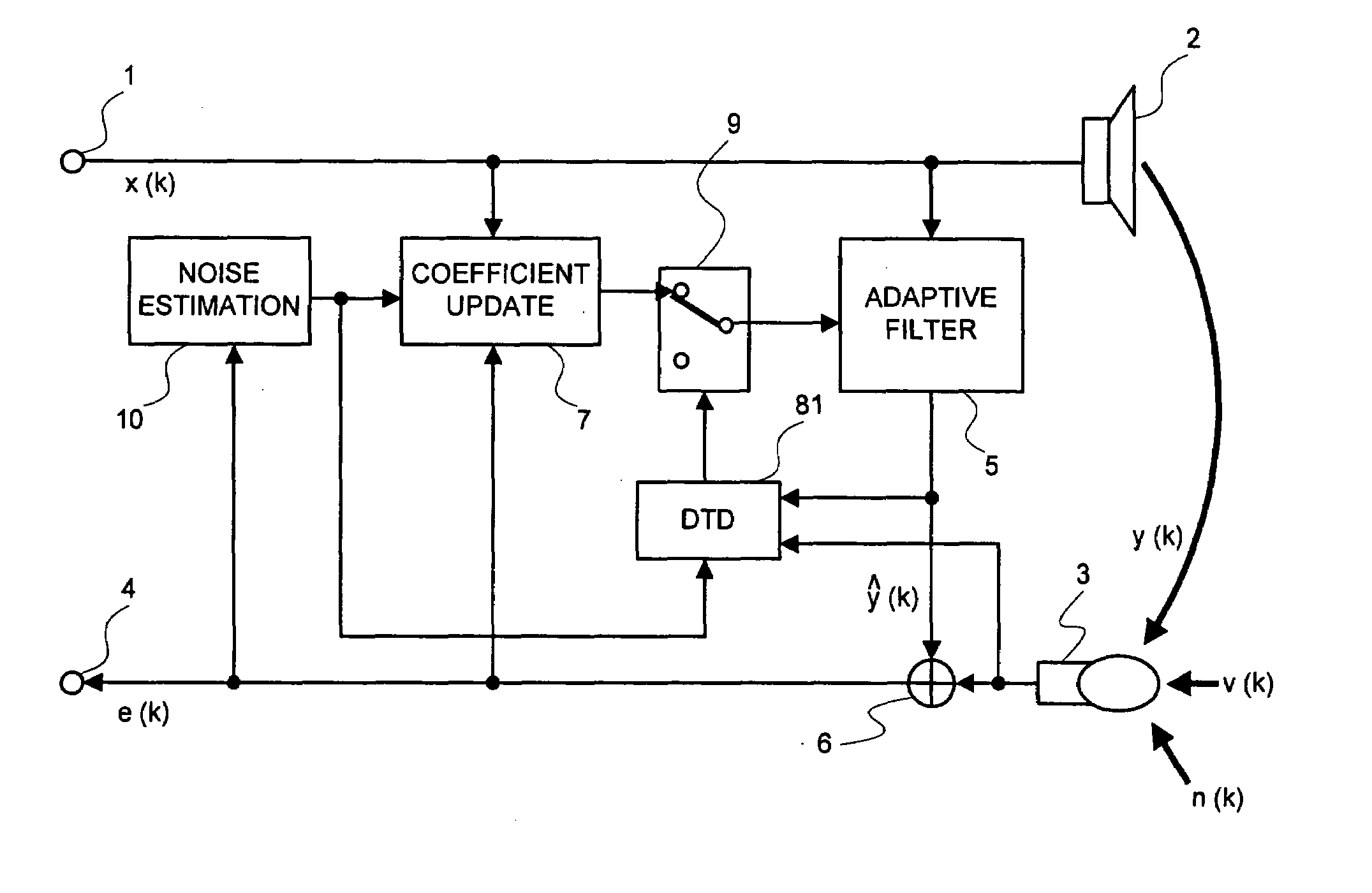
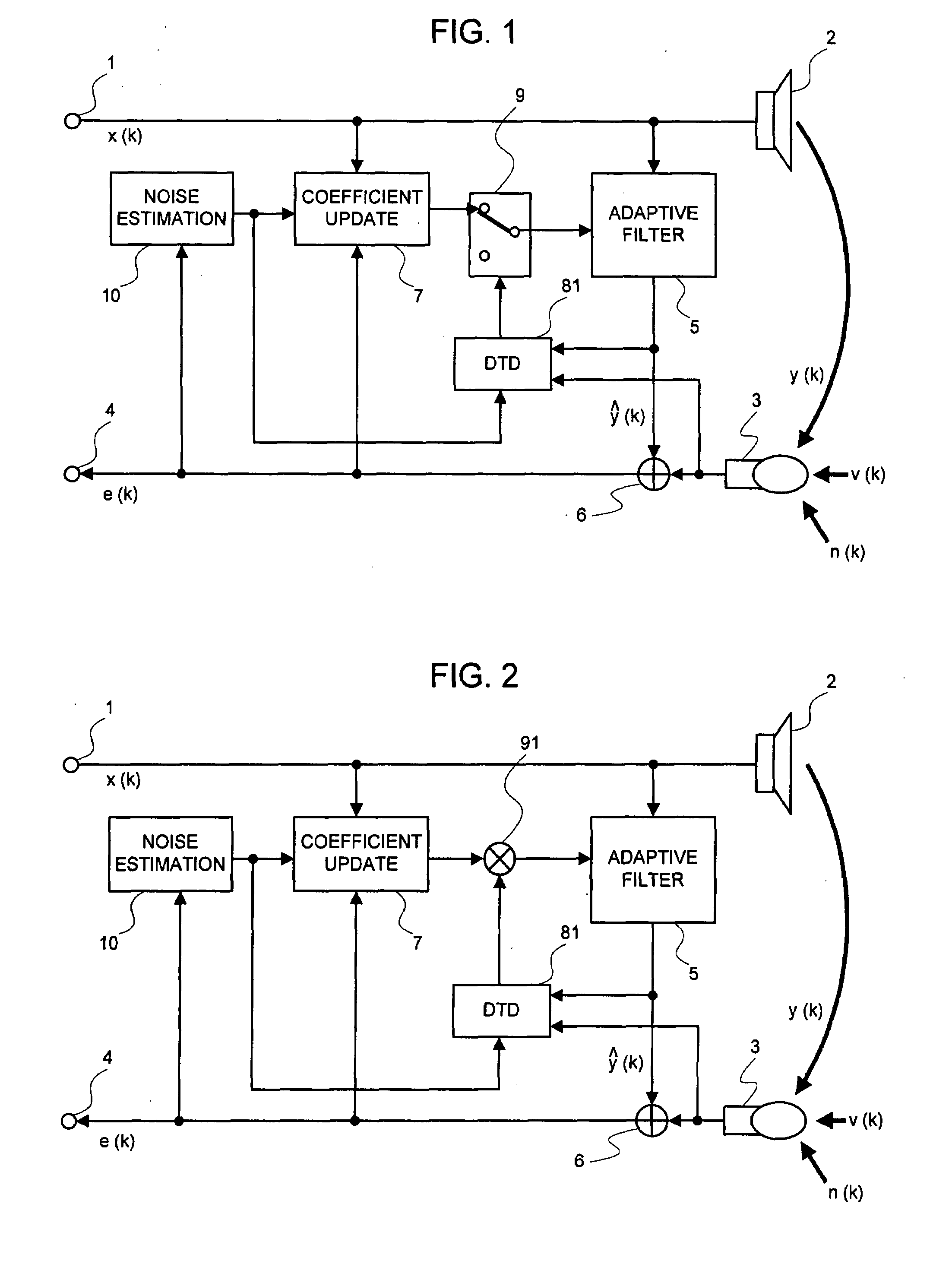
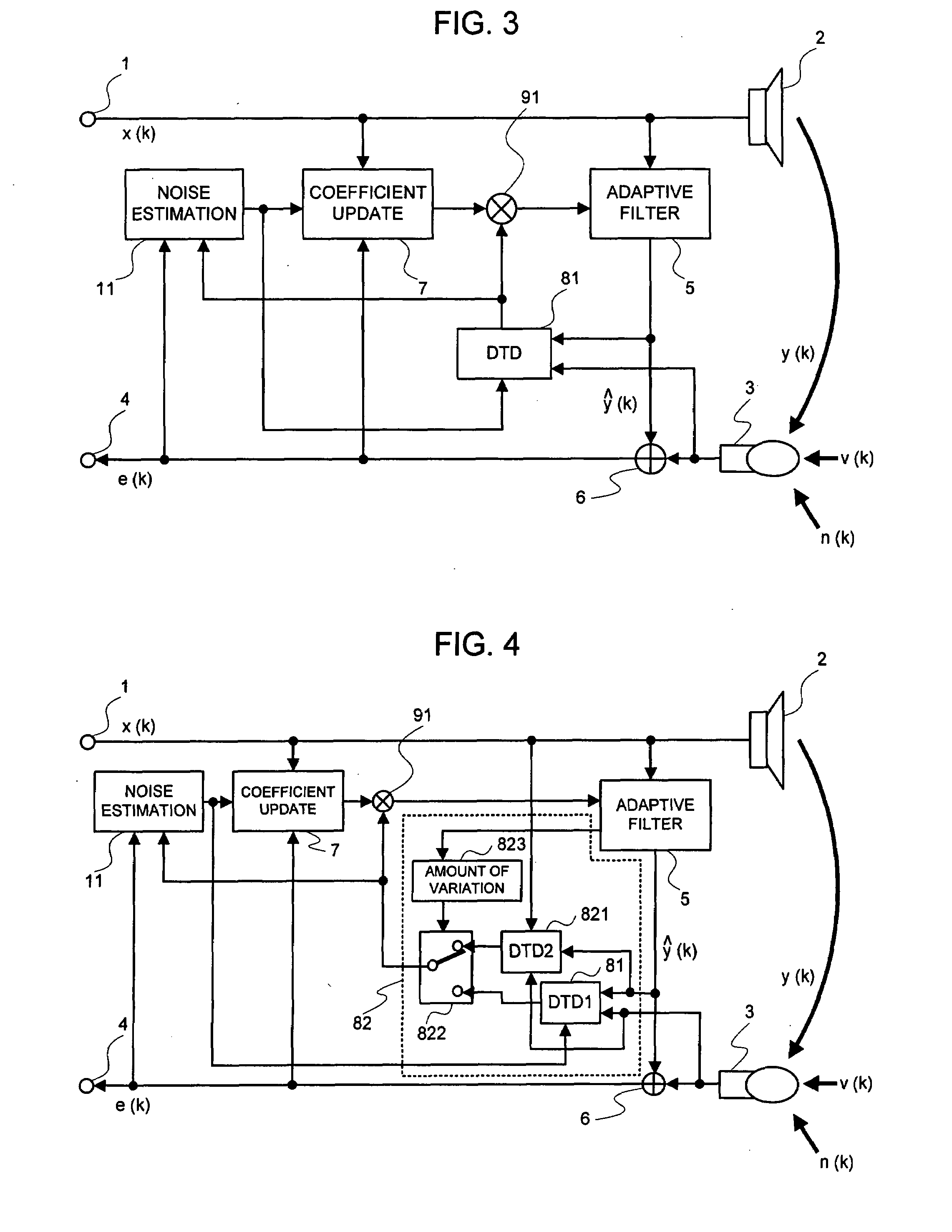
InactiveUS20080101622A1Improve performanceEasy to controlMicrophonesInterconnection arrangementsEngineeringMicrophone signal
A signal processing device includes an adaptive filter (5), a noise estimation circuit (10), and a double talk detection circuit (81) and operates so that the double talk detection circuit (81) detects a double talk by using the estimated noise obtained by the noise estimation circuit (10). The signal processing device further includes noise estimation means and detects a double talk by using an estimated noise, a microphone signal, and pseudo-echo. An echo removal method and device detect a double talk by using a reliability coefficient expressed as continuous values between 0 and 1. By using continuous values instead of two values 0 and 1, it is possible to reduce the affect of a detection error.
Owner:NEC CORP
Adaptive Noise Cancellation
InactiveUS20090012786A1Improve performanceReduce computational complexitySpeech recognitionSuppressorNoise suppression
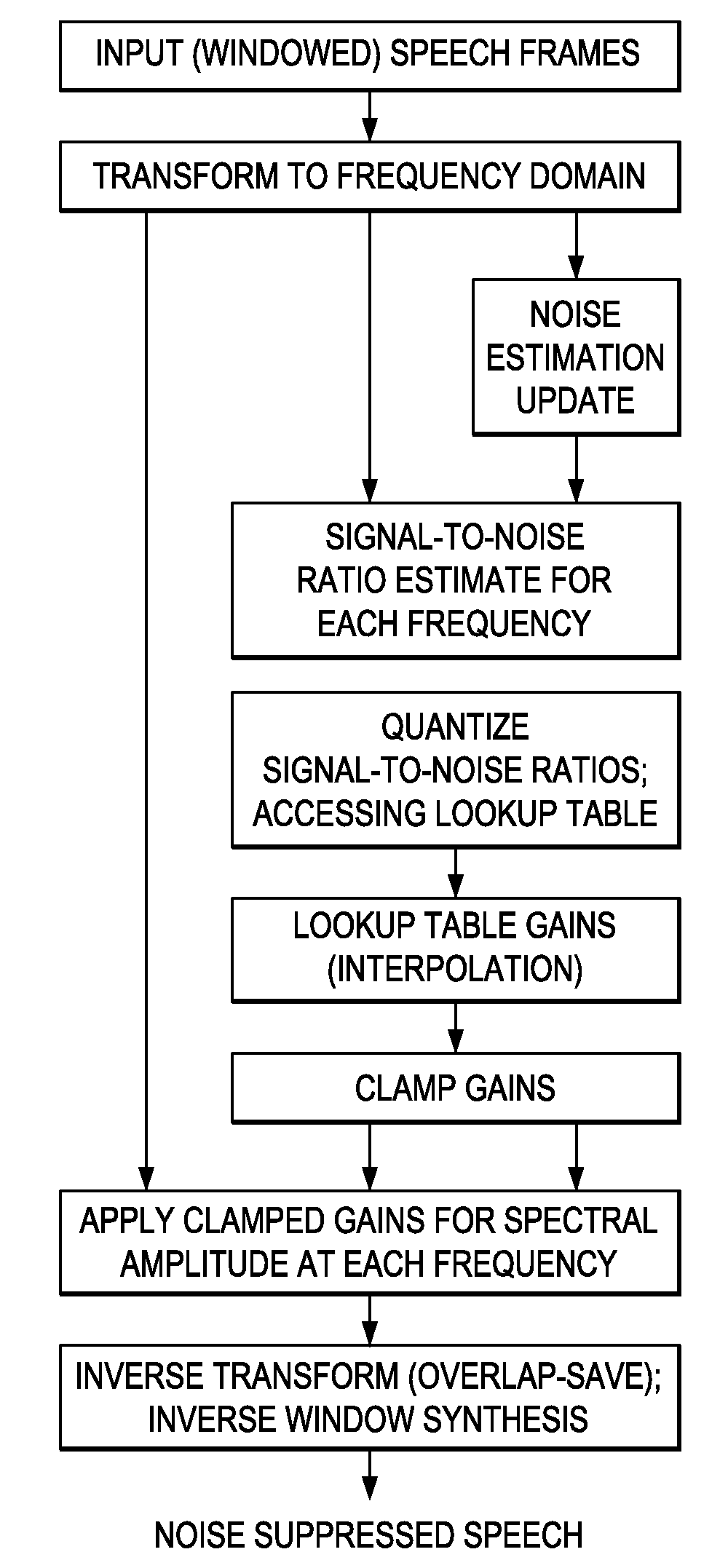
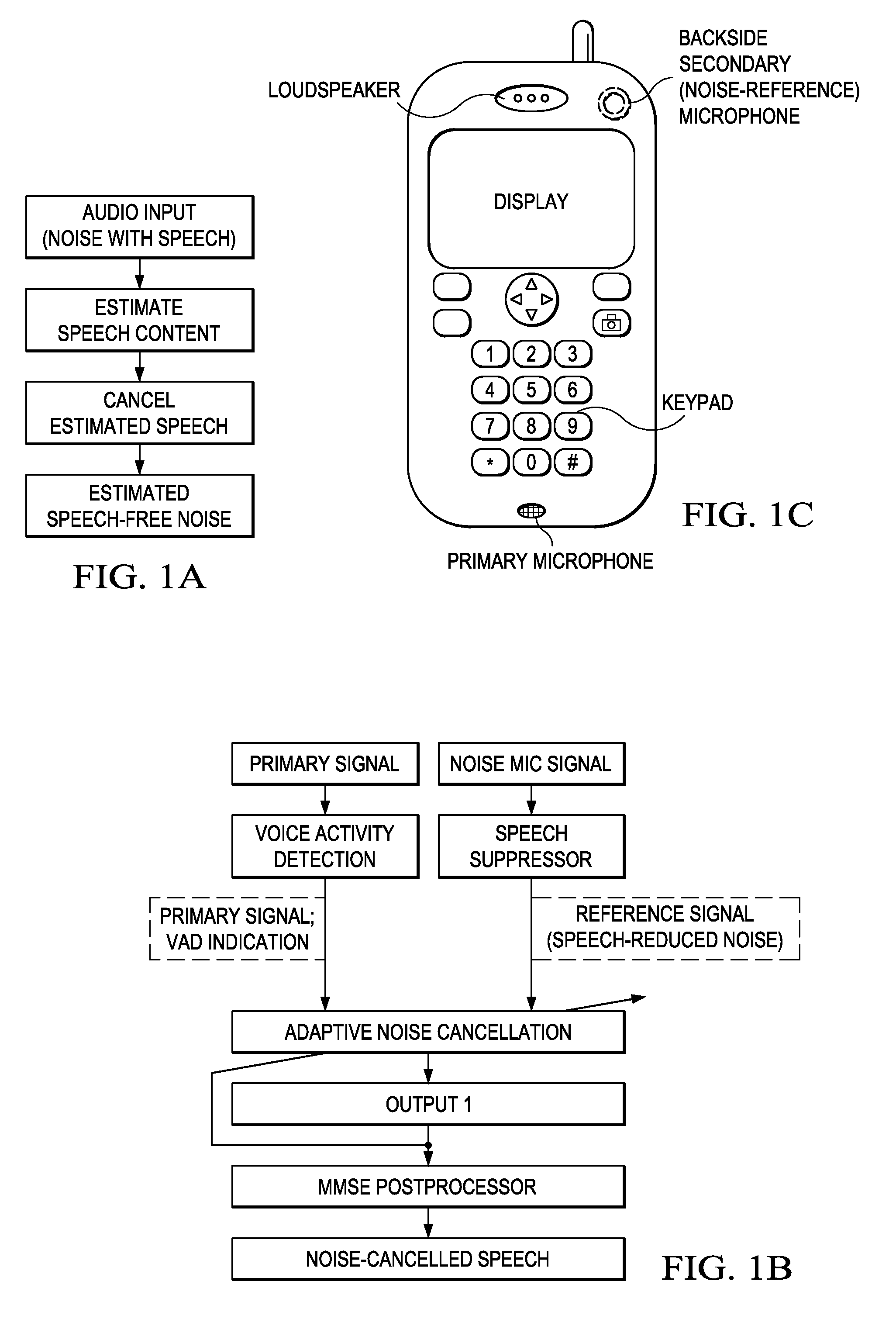
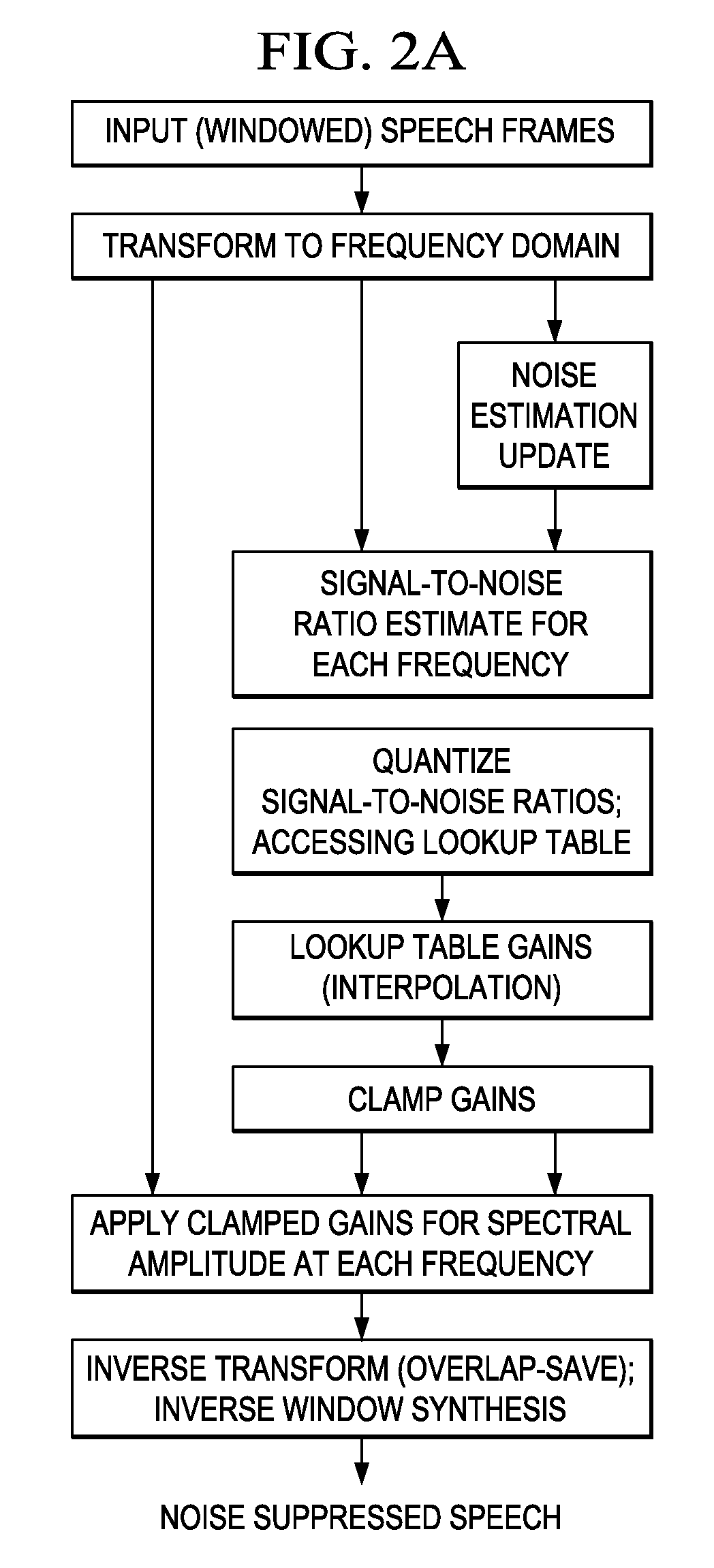
Speech-free noise estimation by cancellation of speech content from an audio input where the speech content is estimated by noise suppression. Adaptive noise cancellation with primary and noise-reference inputs and an adaptive noise cancellation filter from estimating primary noise from noise-reference input. Speech Suppressor (Noise Estimation) applied to noise-reference input provides speech-free noise estimates for noise cancellation in the primary input.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Removal of stationary noise pattern from digital images
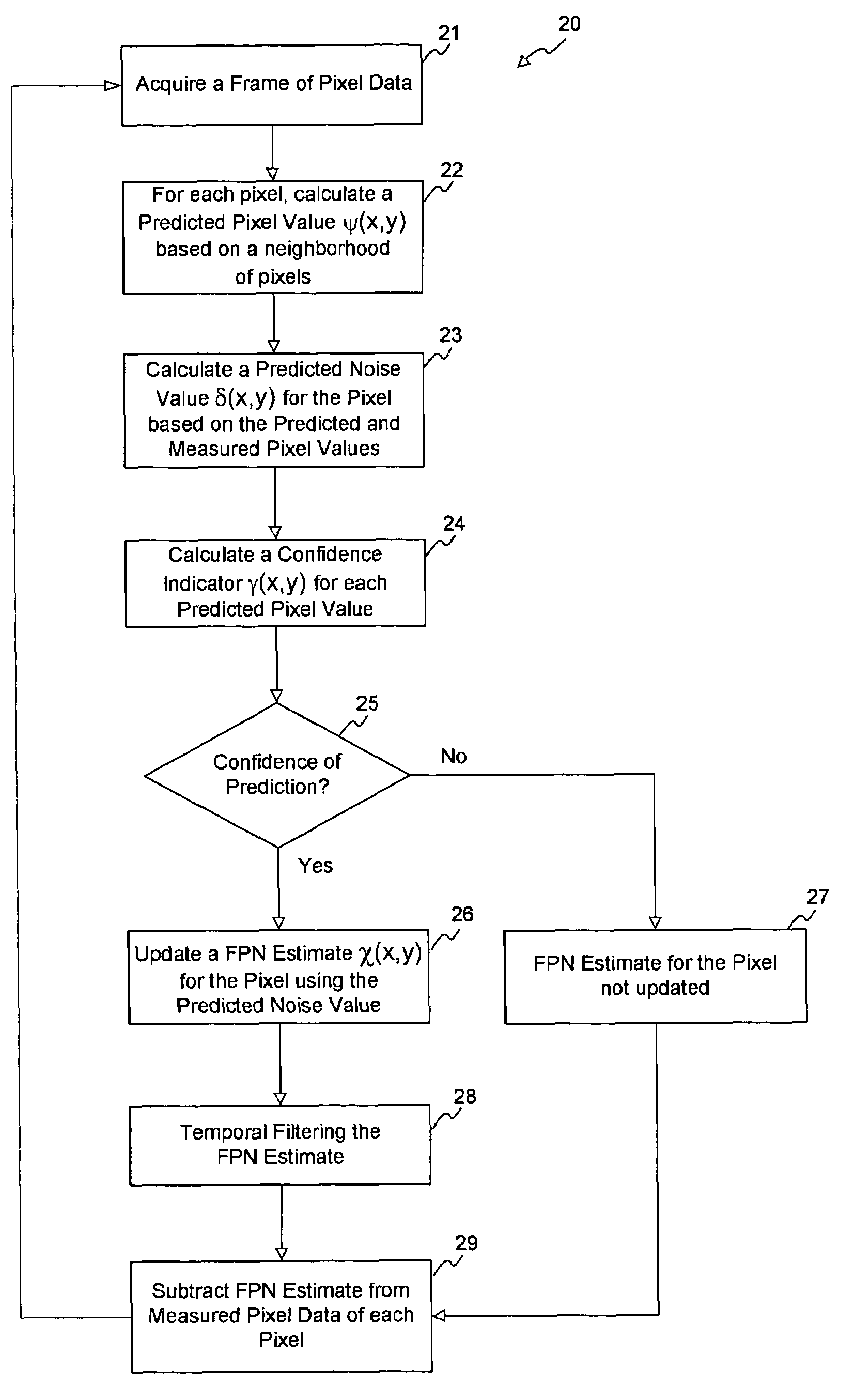
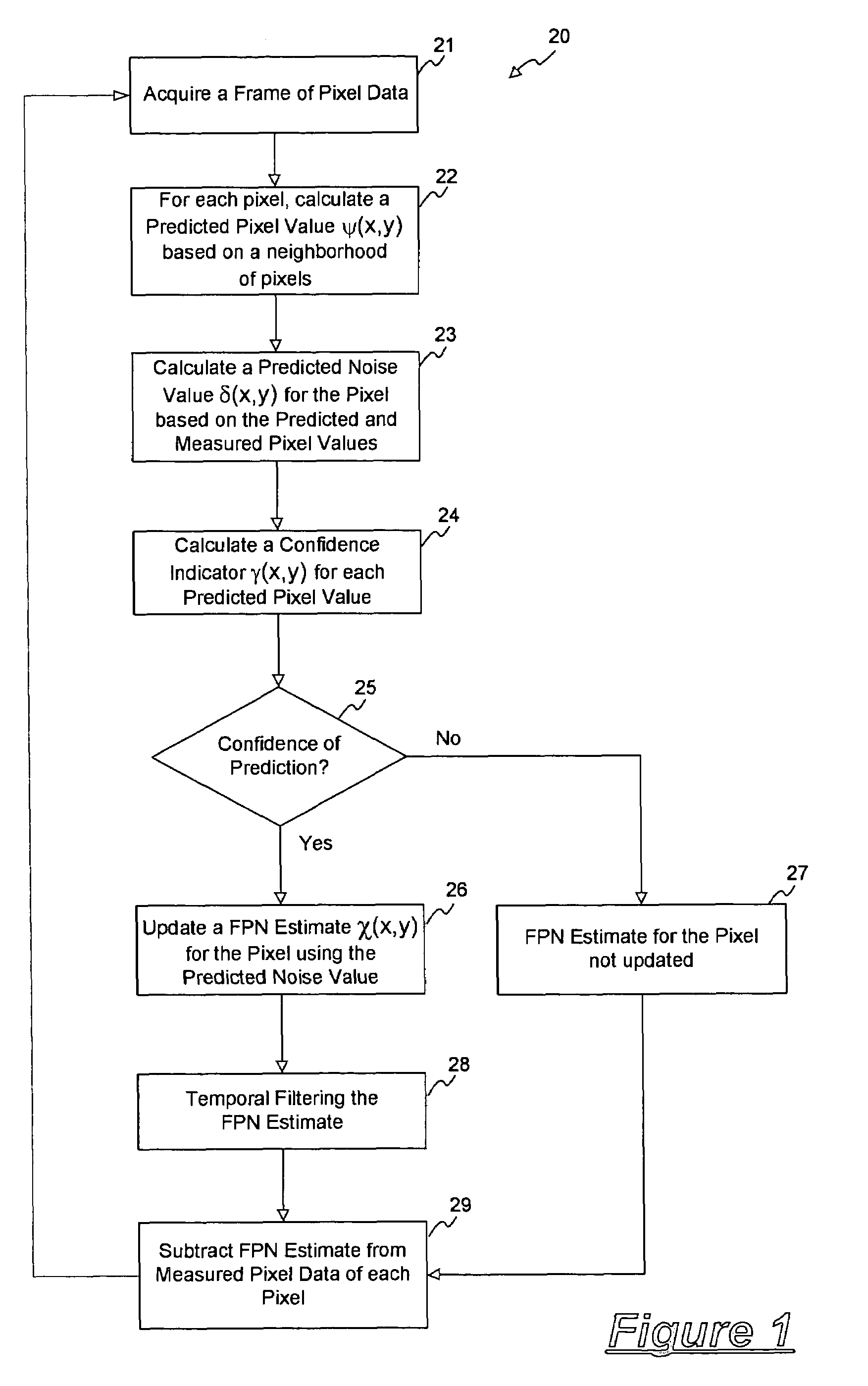
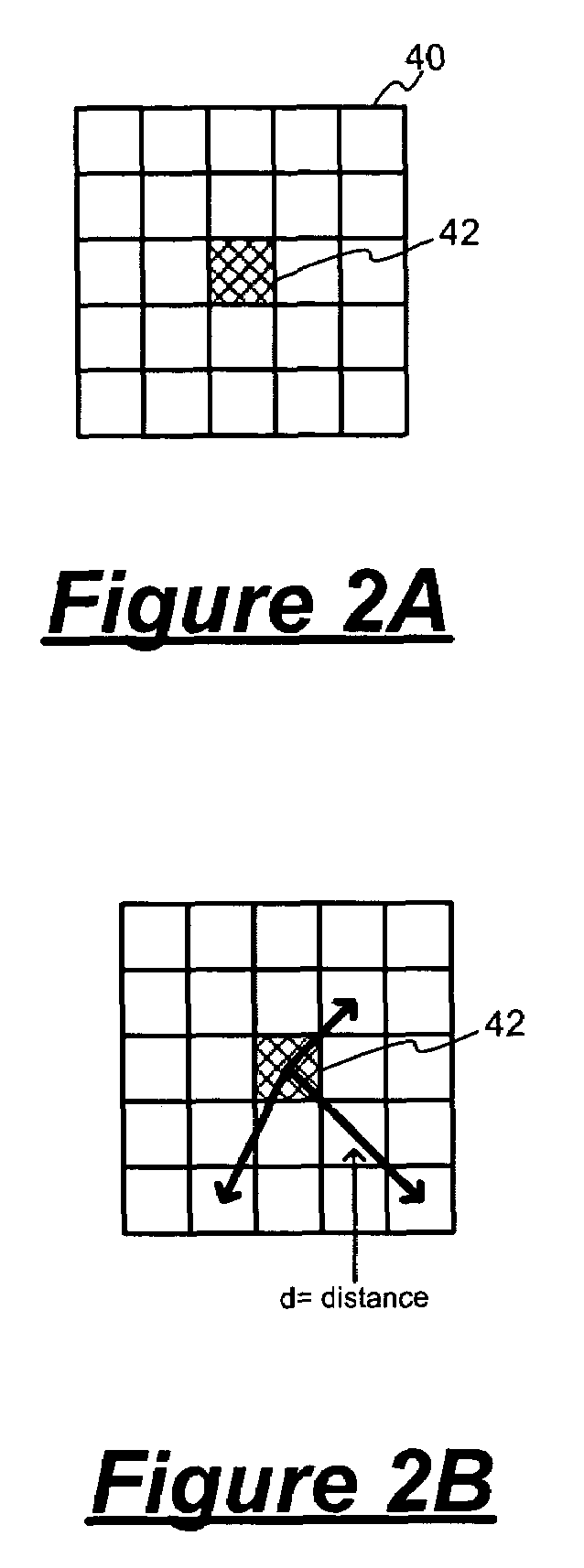
A method for removing a stationary noise pattern from digital images uses an adaptive noise estimation algorithm to calculate a prediction of the fixed pattern noise and a confidence estimate for the prediction. In one embodiment, a predicted noise value is obtained from the captured image and a predicted image derived from spatial and temporal pixel value prediction techniques. The predicted noise value is used to update a fixed pattern noise estimate only when the confidence estimate for the predicted image is high. In another embodiment, the confidence estimate is used as a weight factor for blending the noise prediction into the noise estimate. In yet another embodiment, the adaptive noise estimation algorithm is applied to a prediction area in the image for calculating scaling parameters which scaling parameters are used to calculate a noise estimate for the entire image based on a reference noise image.
Owner:PIXIM
Measuring a talking quality of a telephone link in a telecommunications nework
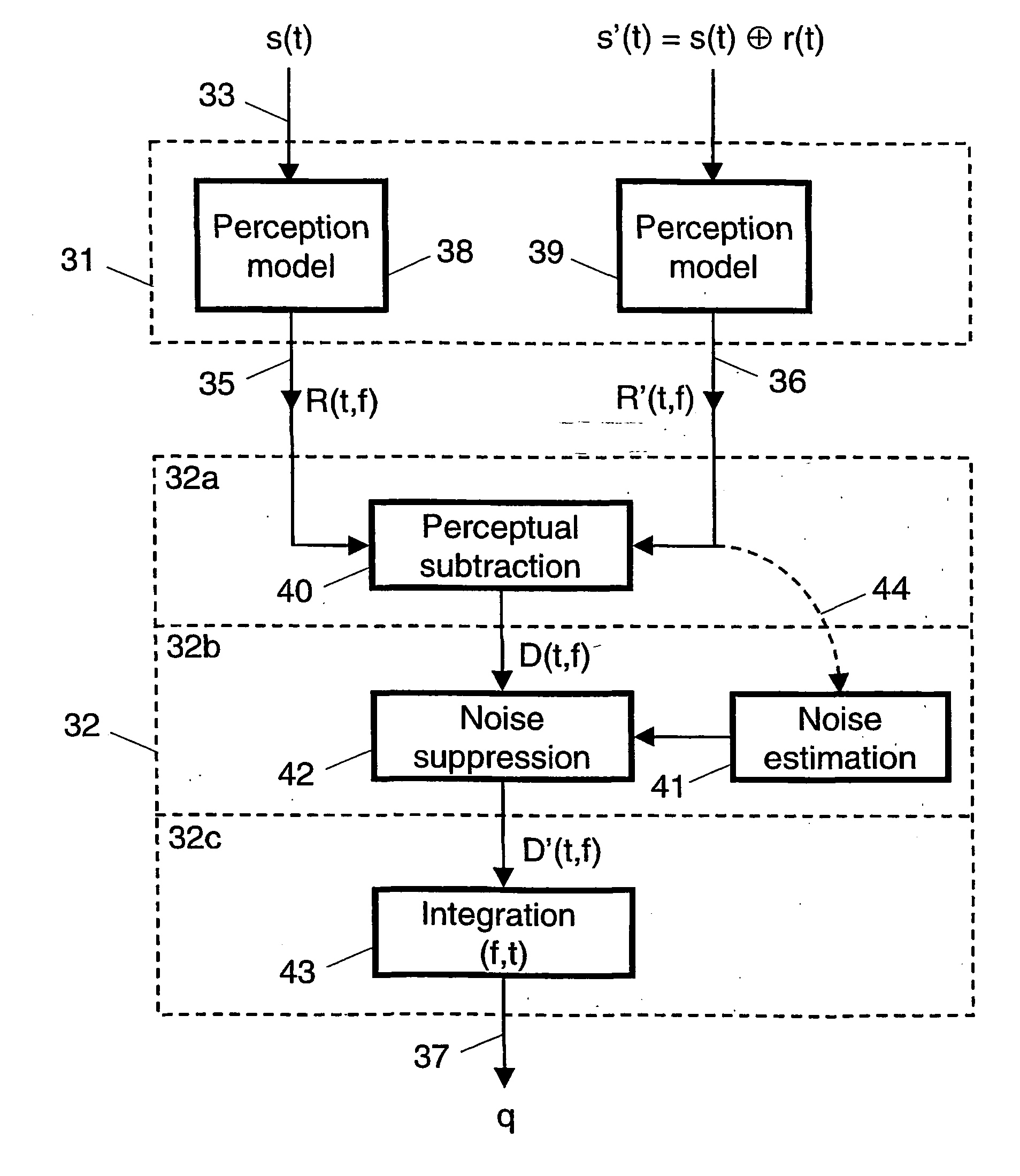
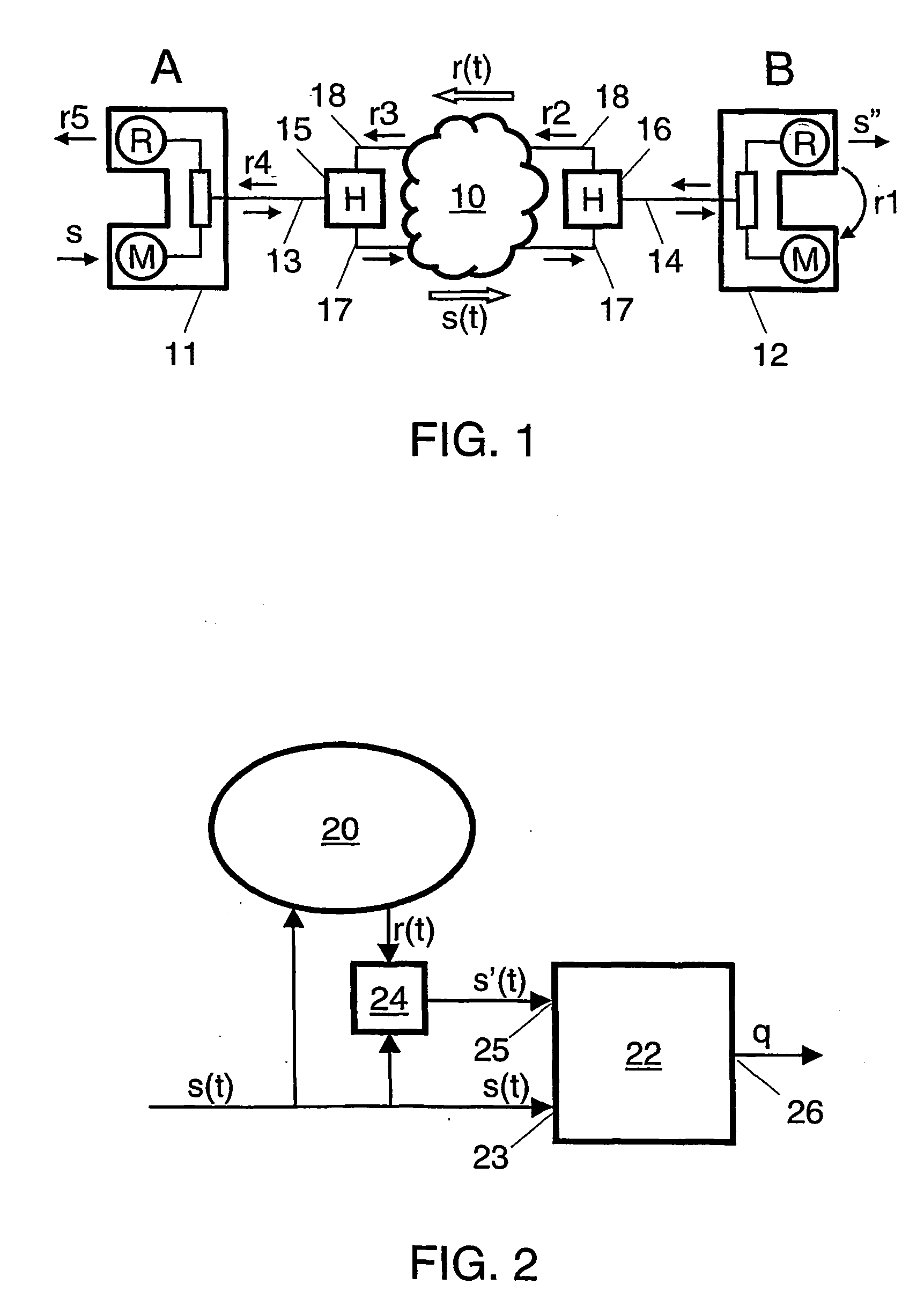
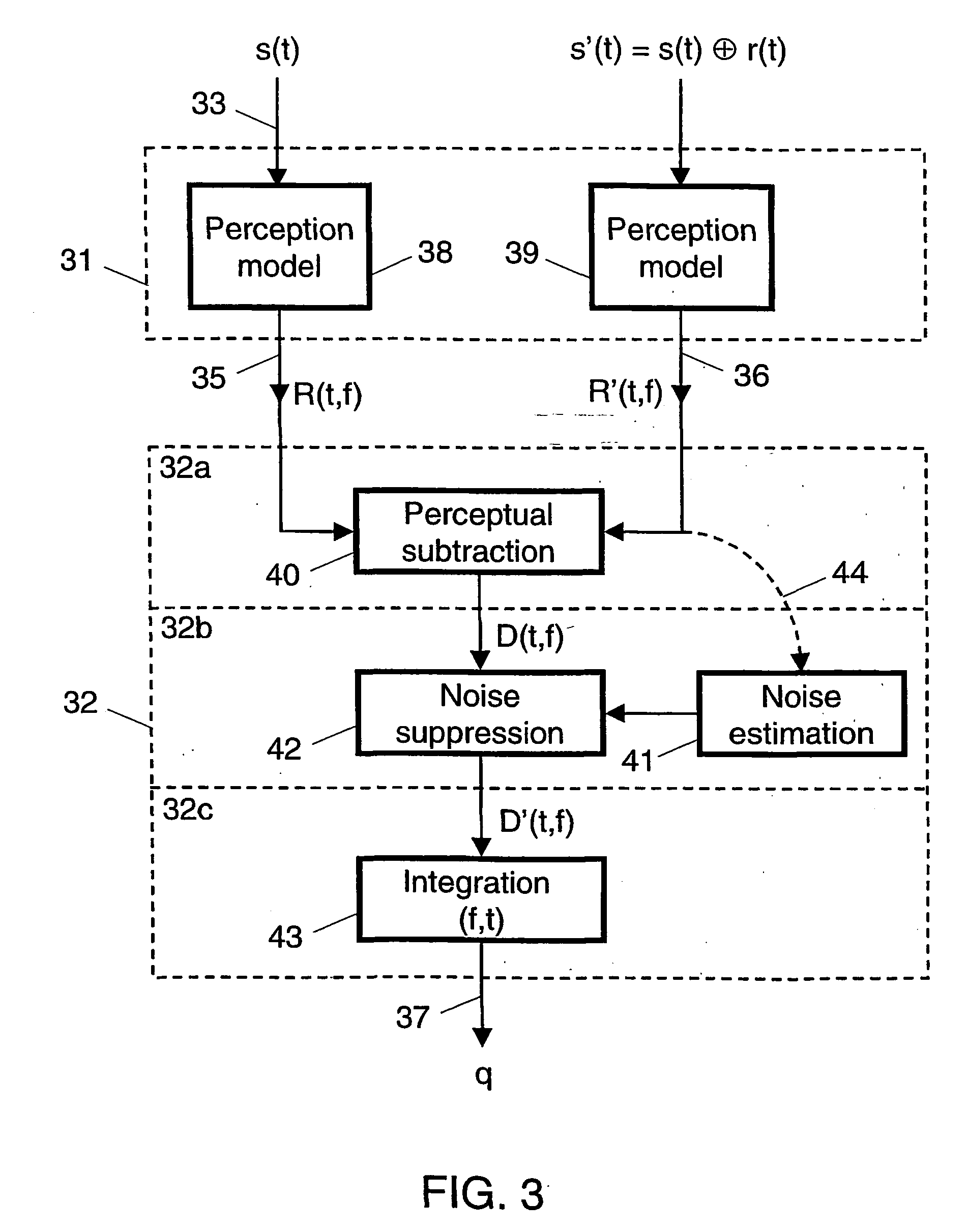
InactiveUS20040042617A1Improvement of subjectively perceived talking qualityMeasurement qualitySubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunications networkObjective measurement
For measuring the influence of noise on the talking quality of a telephone link in a telecommunications network, a talker speech signal (s(t)) and a degraded speech signal (s'(t)) are fed to an objective measurement device (22) for obtaining an output signal (q) representing an estimated value of the talking quality. The degraded signal includes a returned signal (r(t)) originating from the network during transmission of the talker speech signal over the telephone link. The objective measurement carried out by the device is a modified PSQM-like measurement, which is modified as to include a modelling (32b) of masking effects in consequence of noise present in the returned signal. Preferably the modelling includes a noise suppression (42) carried out to a difference signal (D(t, f)) in the loudness density domain using a noise estimation (41).
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
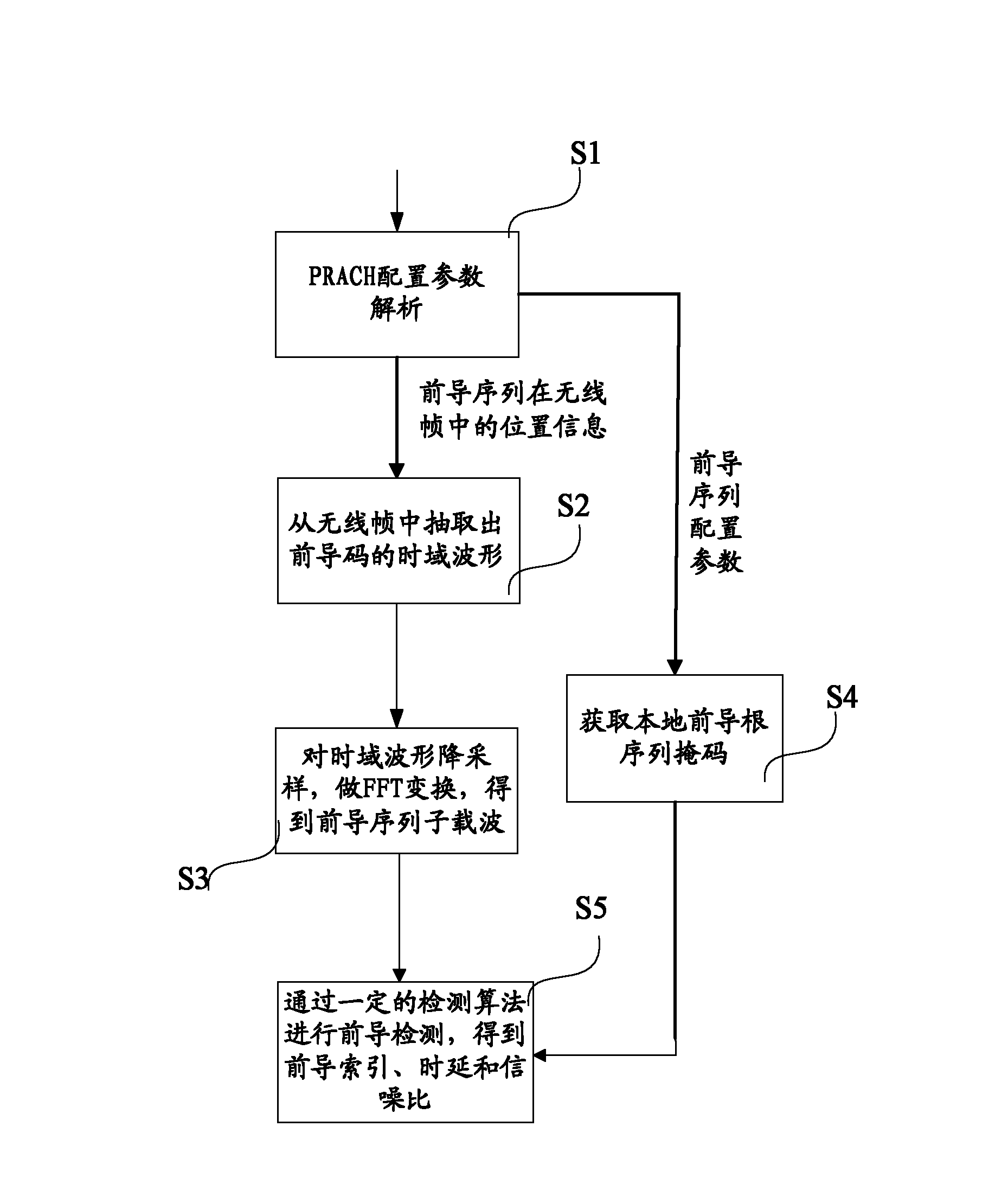
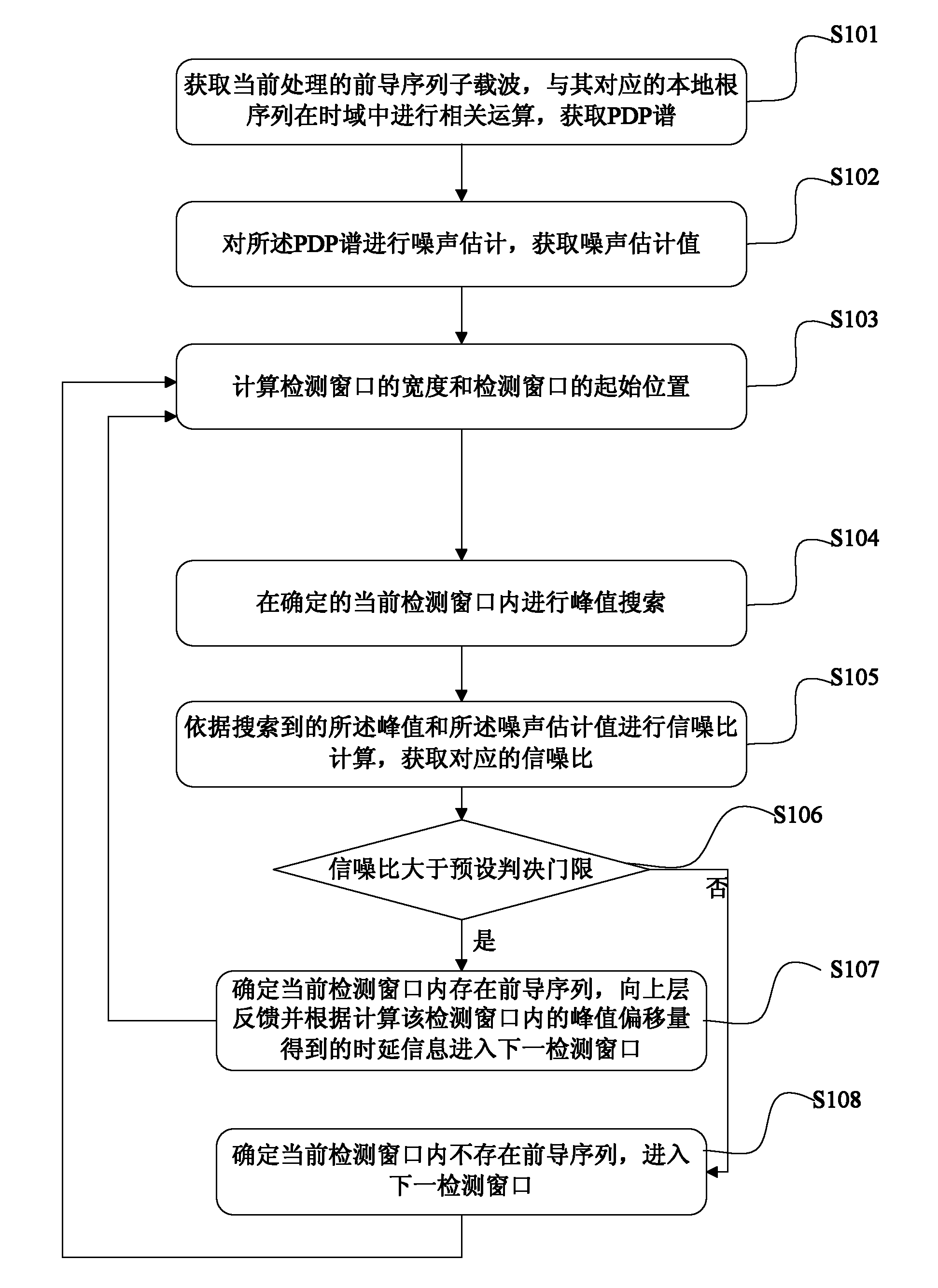
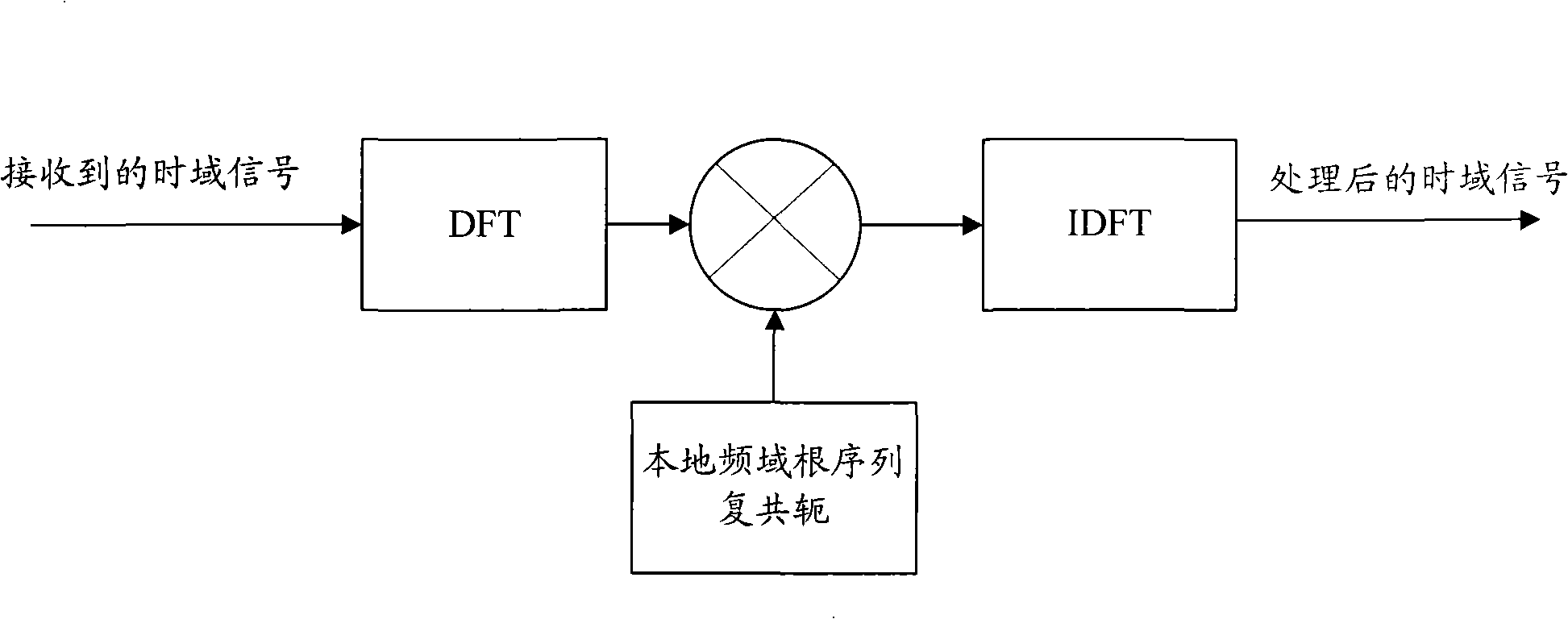
Leader sequence detection method and device for random access channel
ActiveCN102316601AReduce computationReduce complexityBaseband system detailsWireless communicationChannel powerTime delays
The invention discloses a leader sequence detection method and a device for a random access channel. The method comprises the following steps that: sub carrier waves of a leader sequence are extracted, the related operation is carried out with the corresponding local root sequence mask in the frequency domain to obtain the time domain channel power time delay spectrum power delay profile (PDP); the noise estimation is carried out on the PDP to obtain the noise estimation value; the width and an initial position of a detection window are calculated; the peak searching is carried out on the determined current detection window; the signal-to-noise calculation is carried out according to the searched peak and the noise estimation value to obtain the corresponding signal-to-noise ratio; and the signal-to-noise ratio and the judgment threshold are compared, and the detected leader sequence is determined in the current detection window when the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than the judgment threshold. The leader sequence detection method the device have the advantages that the simplification processing is respectively carried out on the relative operation, noise estimation and signal-to-noise ratio operation processes in the detection process, so the goals of reducing the operation quantity in the leader sequence detection process and reducing the processing complexity are realized.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
Expressway audio vehicle detection device and method thereof
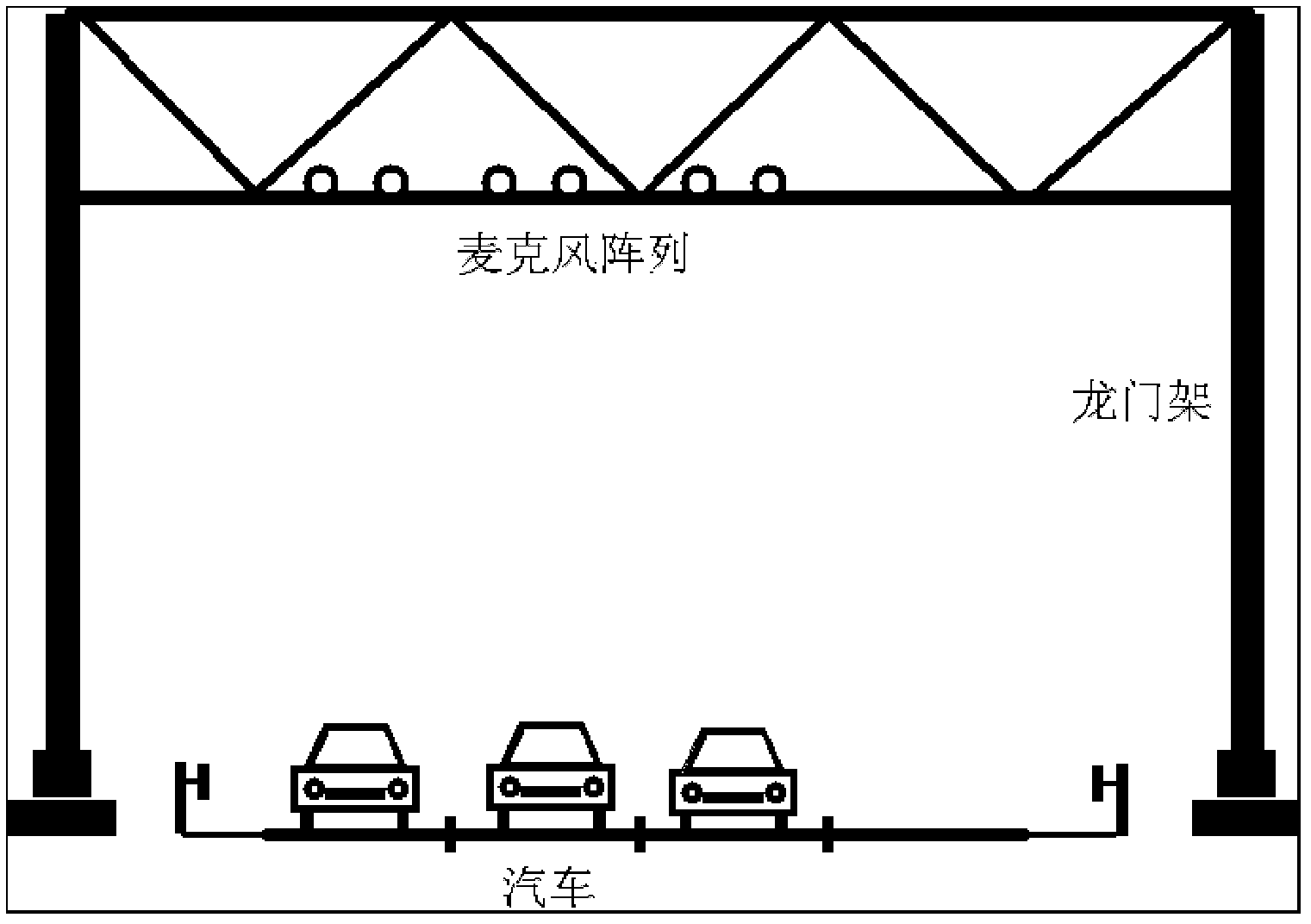
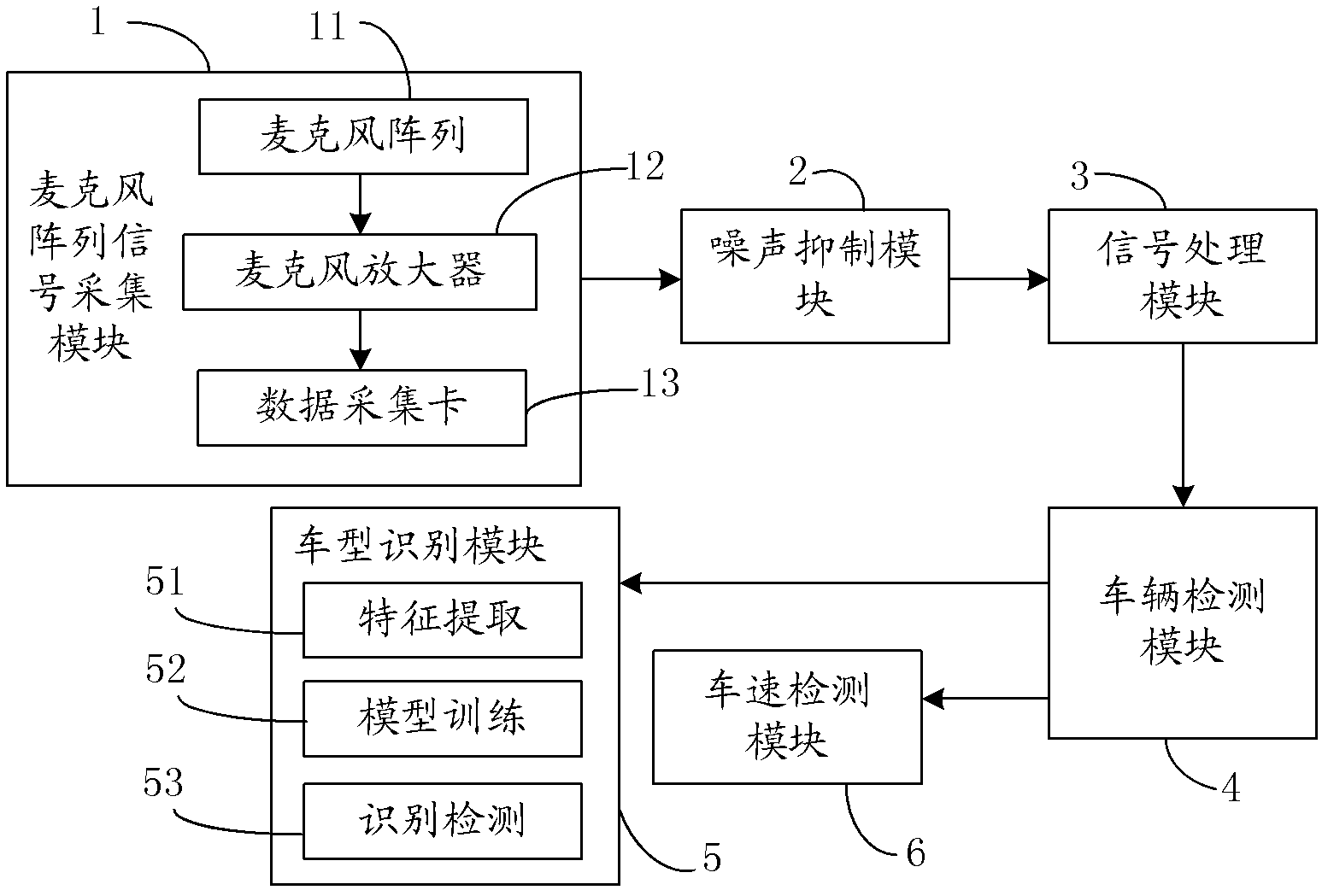
ActiveCN102682765AOvercome limitationsLow costDevices using time traversedSpeech recognitionAmplitude compressionVehicle detection
The invention relates to an expressway audio vehicle detection device and a method thereof. By the aid of the detection device, a microphone array signal acquisition module acquires an audio signal on a lane, the audio signal is subjected to band-splitting filtering and framing through a signal processing module after being subjected to de-noising processing through a noise suppression module, cross-correlation processing is conducted among sub-band signals, an audio space spectrogram is obtained, a vehicle detection module tracks a track of the maximum value on the audio space spectrogram and judges whether a vehicle passes, and the vehicle type and the vehicle speed are obtained through a vehicle type recognition module and a vehicle speed recognition module if the vehicle passes. The detection method is based on the device, a minimum statistical noise estimation method of the adaptive window length is adopted, the signal which is subjected to noise suppression processing is subjected to band-splitting filtering and framing processing, then cross-correlation processing is conducted among same sub-band signals, cross-correlation results are summed after being subjected to amplitude compression and are unfolded along a timer shaft, and an audio signal space-time spectrum is obtained. The method and the device have the advantages of being low in cost, low in energy consumption,easy to construct, interference resisting, capable of working in all weather and the like.
Owner:TAIKE HIGHWAY SCI & TECH INST BEIJING CITY +1
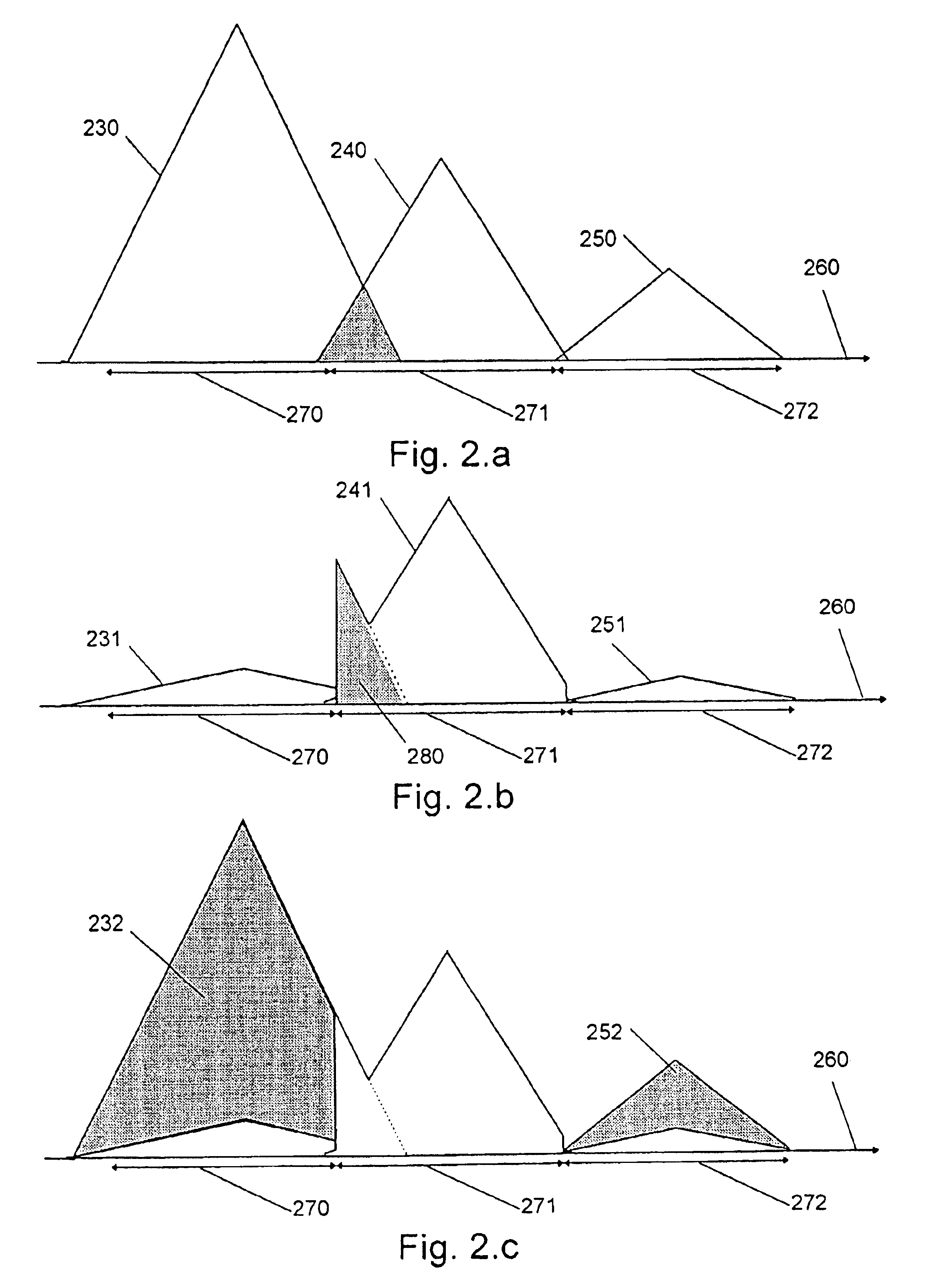
Method and an apparatus for estimating residual noise in a signal and an apparatus utilizing the method
InactiveUS6871066B1Improve performanceReduce equipment production costsTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemDigital radio
The invention relates to: A method for estimating residual noise in the frequency range (271) of a desired part (240) of a signal to a corresponding apparatus and to a mobile telephone utilizing the method.The object of the present invention is to generate a measure for the residual noise in a signal.The problem is solved in that the amplitude of the signal (114) comprising the noise is modified, and the signal (114) is combined with the modified signal (115) to create a noise estimation measure (116).The invention may e.g. be used in digital radio communications systems to contribute to the monitoring of link quality and therefore to improve payload throughput. One of the advantages of the invention is that an indication of link quality at an early stage in the receiver is provided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
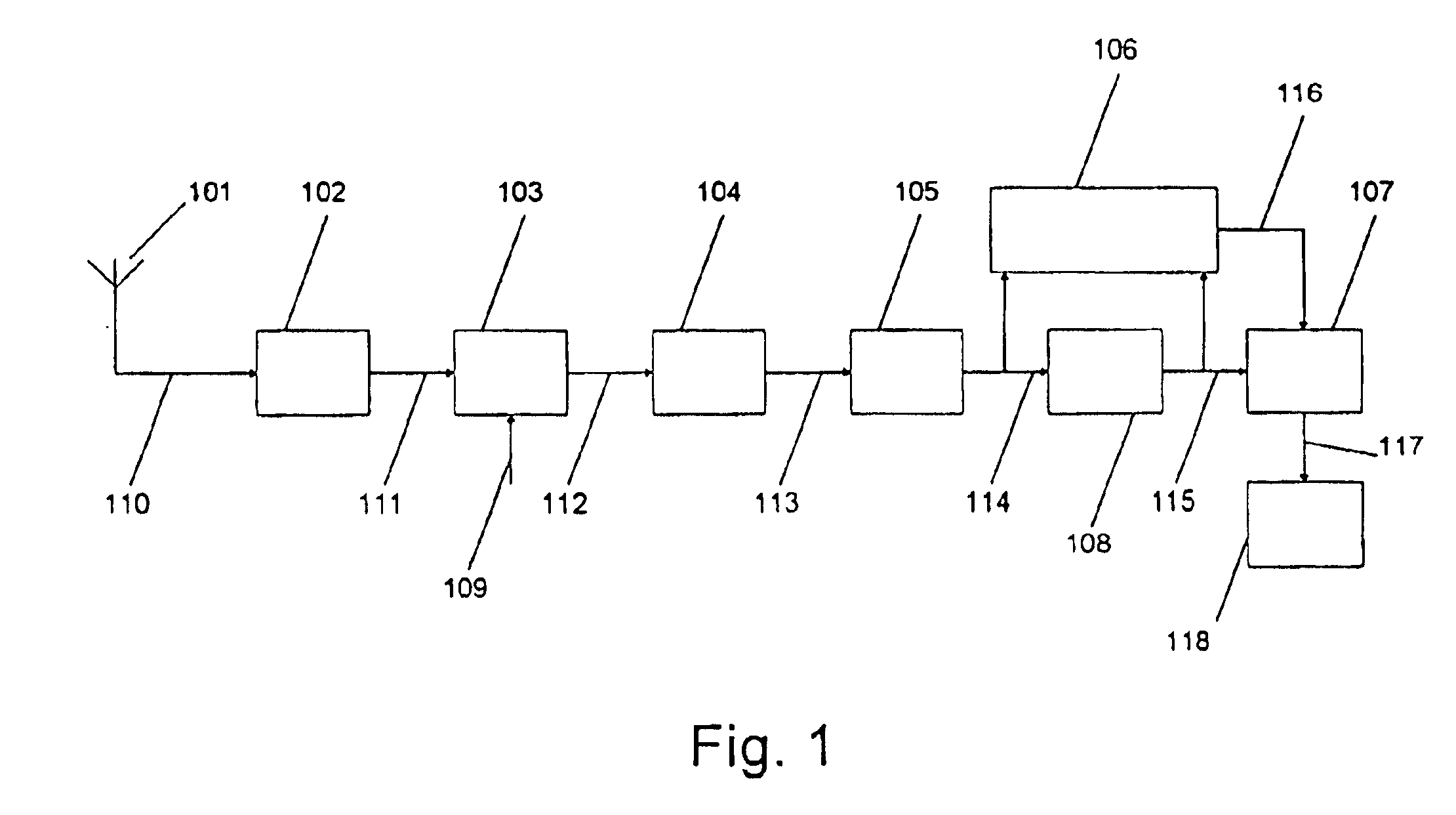
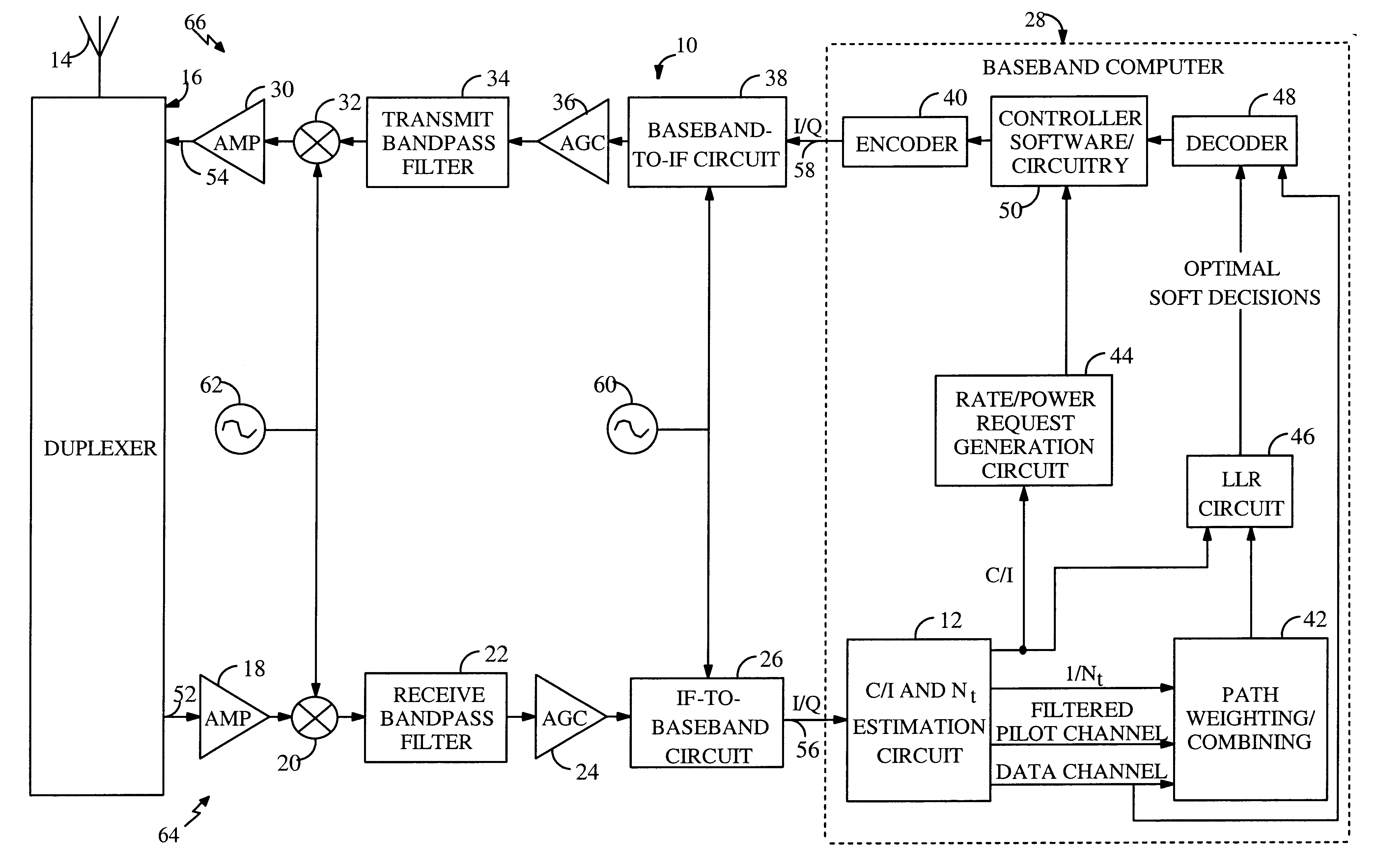
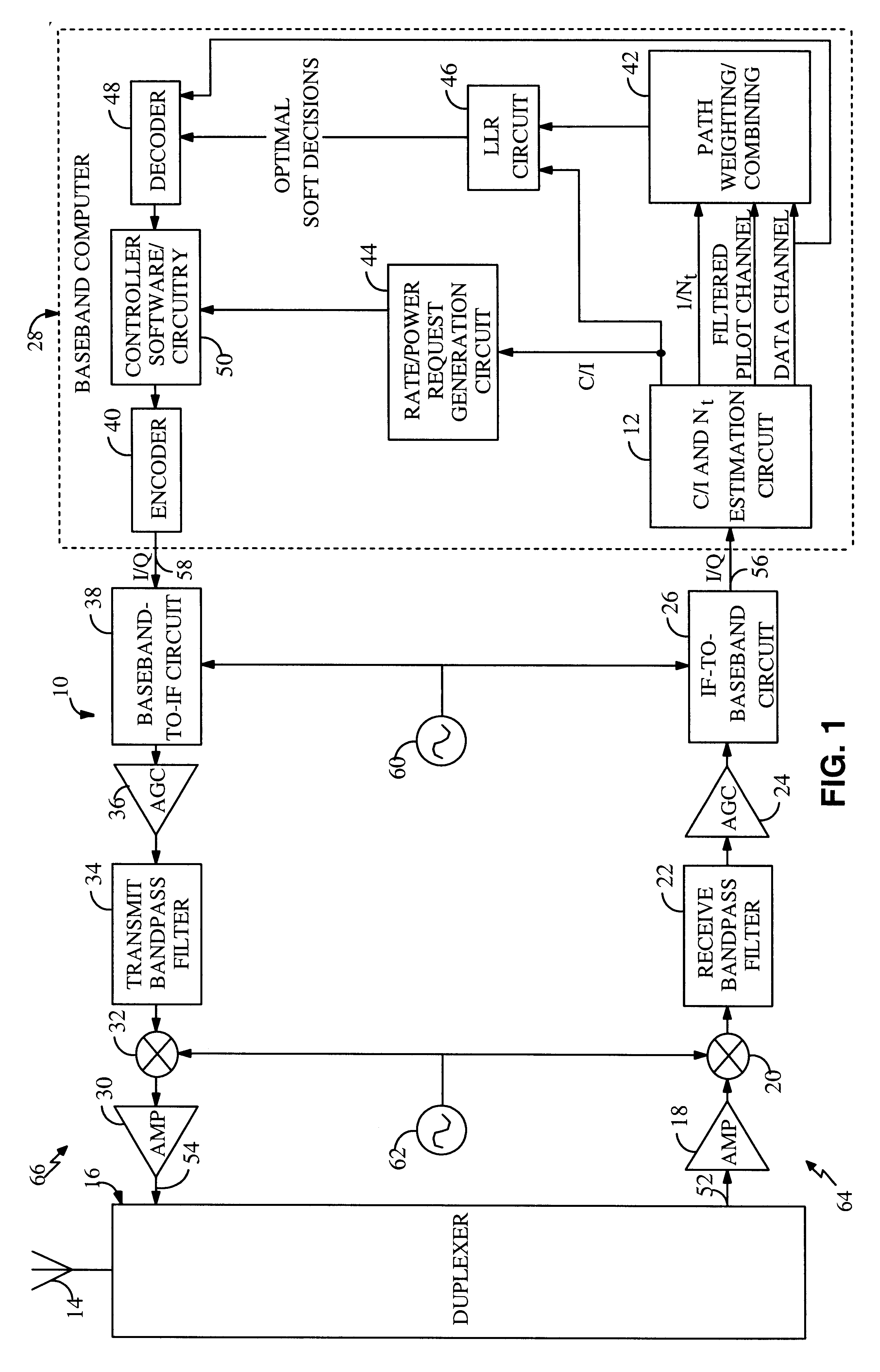
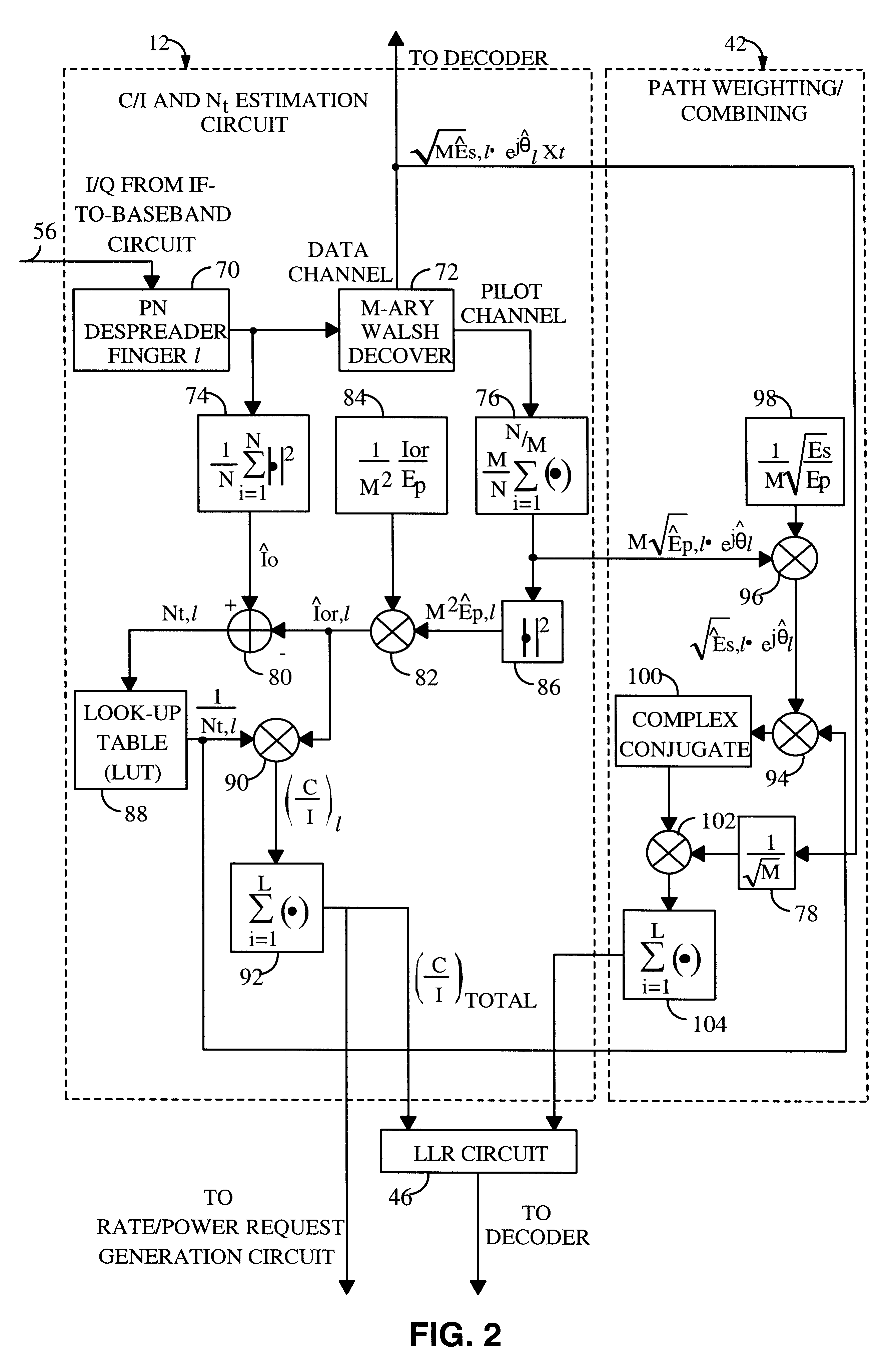
System and method for providing an accurate estimation of received signal interference for use in wireless communications systems
A system for providing an accurate interference value signal received over a channel and transmitted by an external transceiver. The system includes a first receiver section for receiving the signal, which has a desired signal component and an interference component. A signal extracting circuit extracts an estimate of the desired signal component from the received signal. A noise estimation circuit provides the accurate interference value based on the estimate of the desired signal component and the received signal. A look-up table transforms the accurate noise and / or interference value to a normalization factor. A carrier signal-to interference ratio circuit employs the normalization factor and the received signal to compute an accurate carrier signal-to-interference ratio estimate. Path-combining circuitry generates optimal path-combining weights based on the received signal and the normalization factor. In the illustrative embodiment, the system further includes a circuit for employing the accurate interference value to compute a carrier signal-to-interference ratio. An optimal path-combining circuit computes optimal path-combining weights for multiple signal paths comprising the signal using the accurate interference value and provides optimally combined signal paths in response thereto. A log-likelihood ratio circuit computes a log-likelihood value based on the carrier signal-to-interference ratio and the optimally combined signal paths. A decoder decodes the received signal using the log-likelihood value. An additional circuit generates a rate and / or power control message and transmits the rate and / or power control message to the external transceiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Noise suppression apparatus and method for speech recognition, and speech recognition apparatus and method
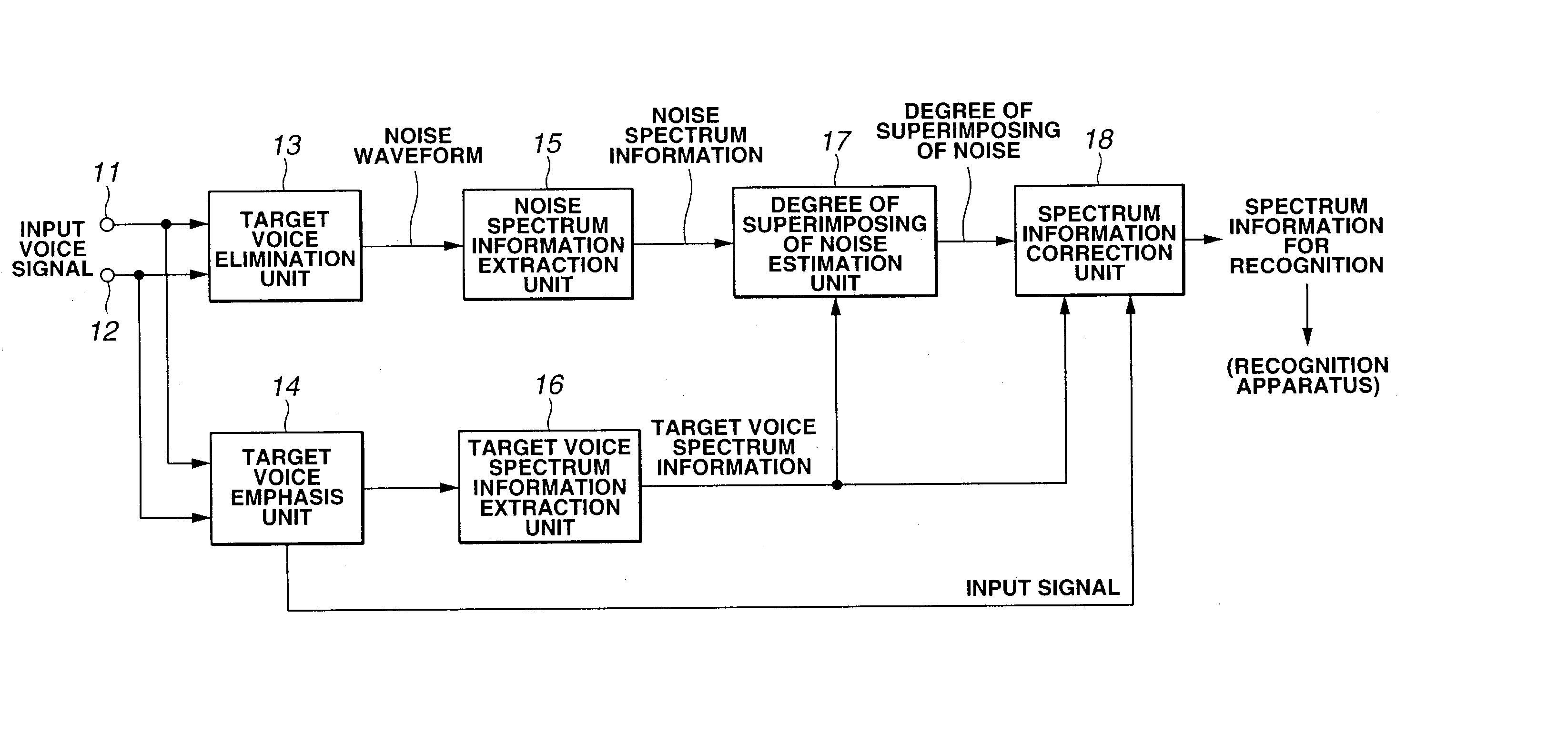
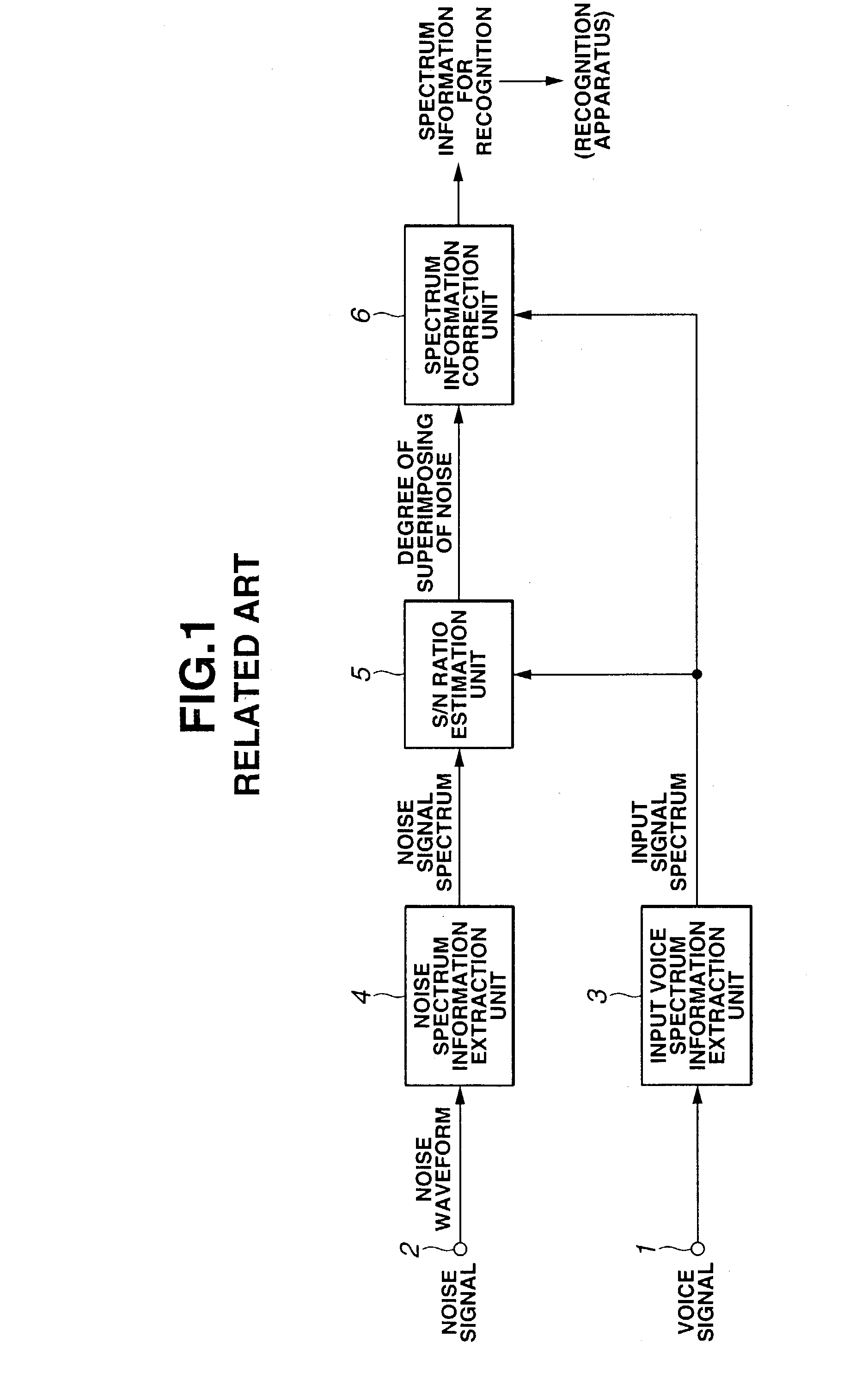
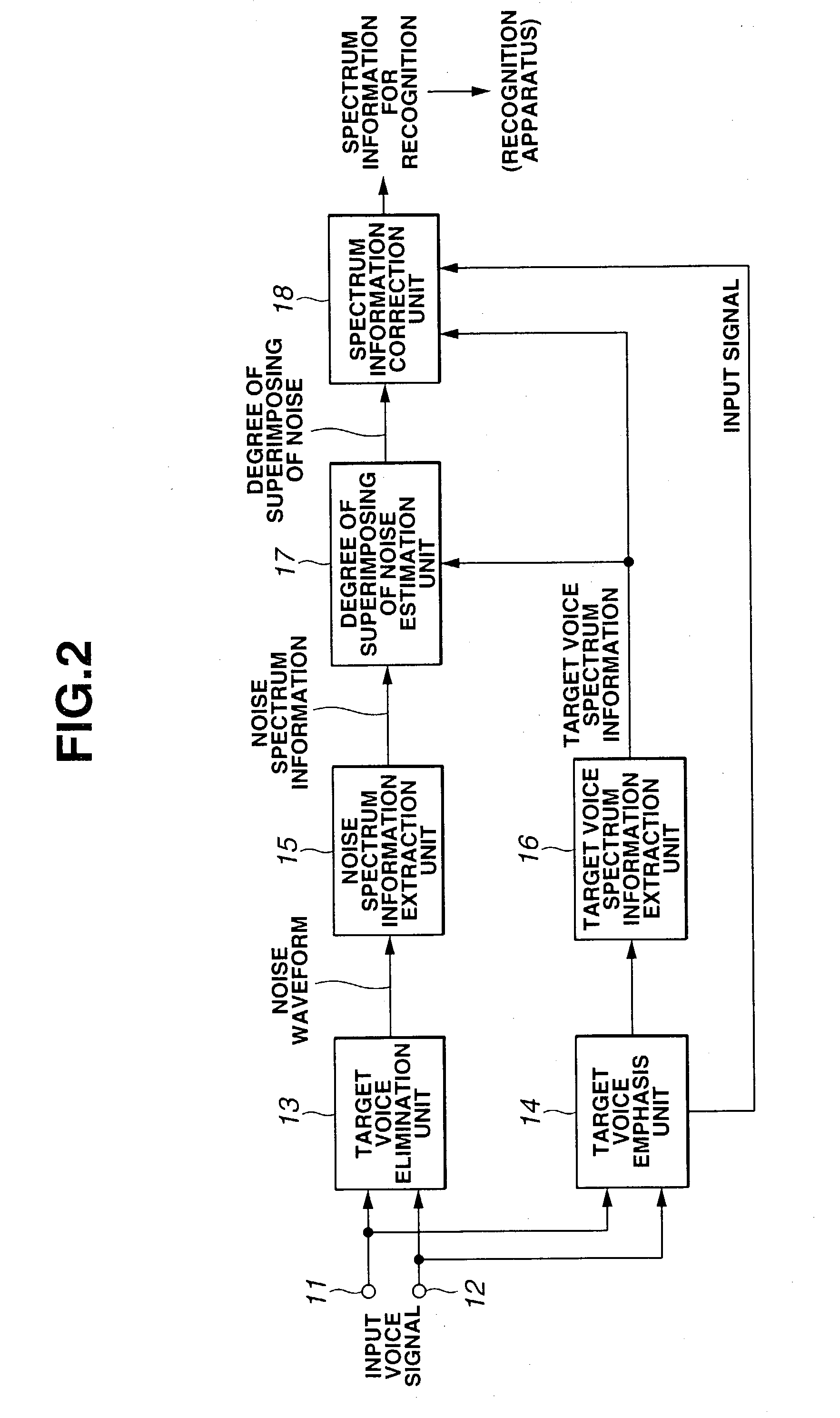
A target voice elimination unit reliably eliminates a target voice and outputs a target voice elimination signal including only a noise component. A target voice emphasis unit outputs a target voice emphasis signal from which a noise component is eliminated to some extent. A noise spectrum information extraction unit extracts noise spectrum information from the target voice elimination signal, and a target voice spectrum information extraction unit extracts target voice spectrum information from the target voice emphasis signal. A degree of multiplexing of noise estimation unit reliably detects the position where noise is superimposed and the magnitude of the noise from the noise spectrum information and the target voice spectrum information and obtains a degree of multiplexing of noise. A spectrum information correction unit reliably corrects the target voice spectrum information using the information of the degree of multiplexing of noise indicating the position and magnitude of the noise detected correctly. The influence of noise is greatly reduced in the spectrum information, thereby the accuracy of speech recognition can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for reducing noise in speech and audio signals
A method and apparatus are disclosed for enhancing, within a signal bandwidth, a corrupted audio-frequency signal. The signal which is to be enhanced is analyzed into plural sub-band signals, each occupying a frequency sub-band smaller than the signal bandwidth. A respective signal gain function is applied to each sub-band signal, and the respective sub-band signals are then synthesized into an enhanced signal of the signal bandwidth. The signal gain function is derived, in part, by measuring speech energy and noise energy, and from these determining a relative amount of speech energy, within the corresponding sub-band. In certain embodiments of the invention, the signal gain function is also derived, in part, by determining a relative amount of speech energy within a frequency range greater than, but centered on, the corresponding sub-band. In other embodiments of the invention, the sub-band noise energy is determined from a noise estimate that is updated at periodic intervals, but is not updated if the newest sample of the signal to be enhanced exceeds the current noise estimate by a multiplicative threshold (i.e., a threshold expressible in decibels). In still other embodiments of the invention, the value of the noise estimate is limited by an upper bound that is matched to the dynamic range of the signal to be enhanced.
Owner:INTEL CORP
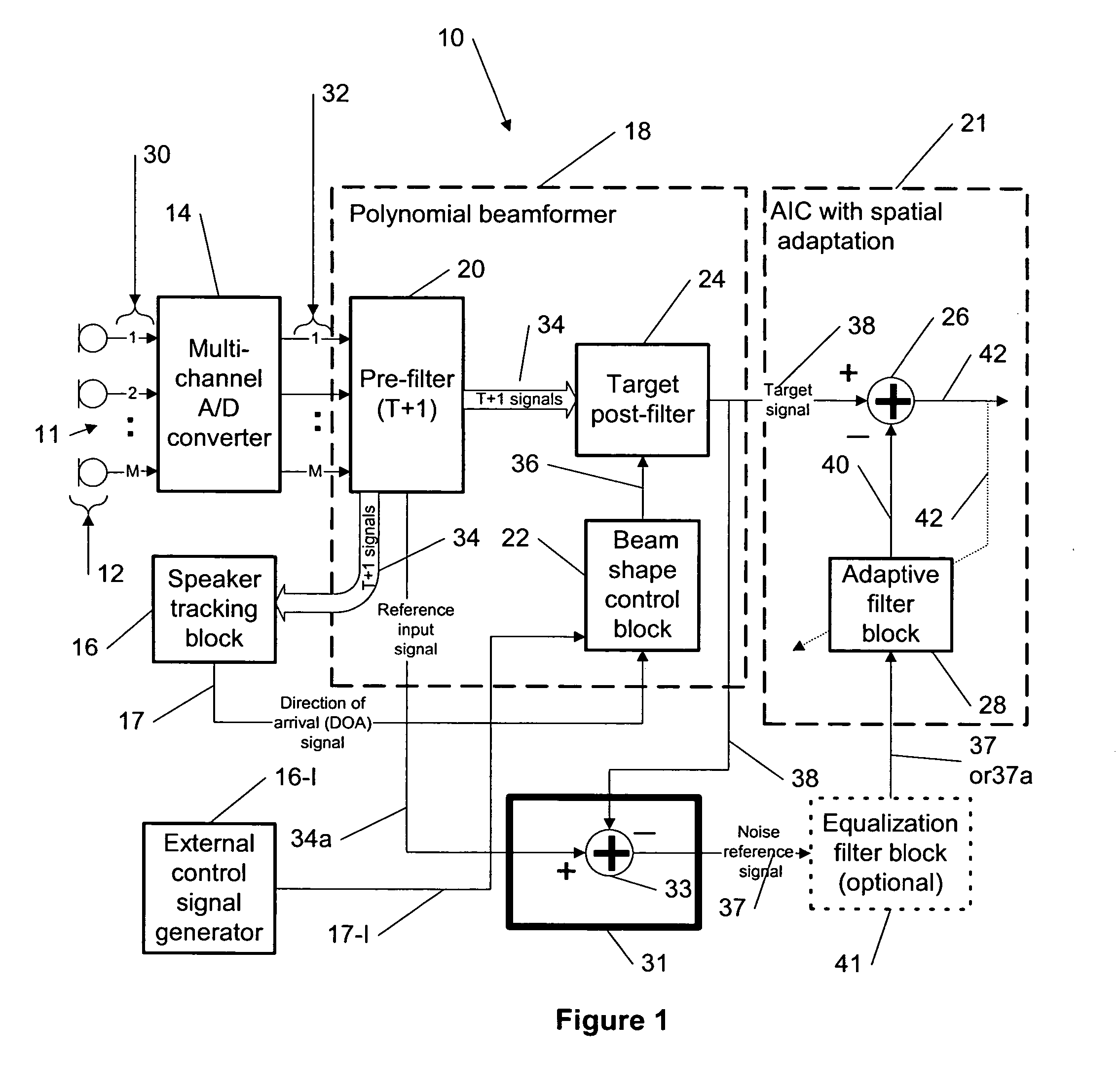
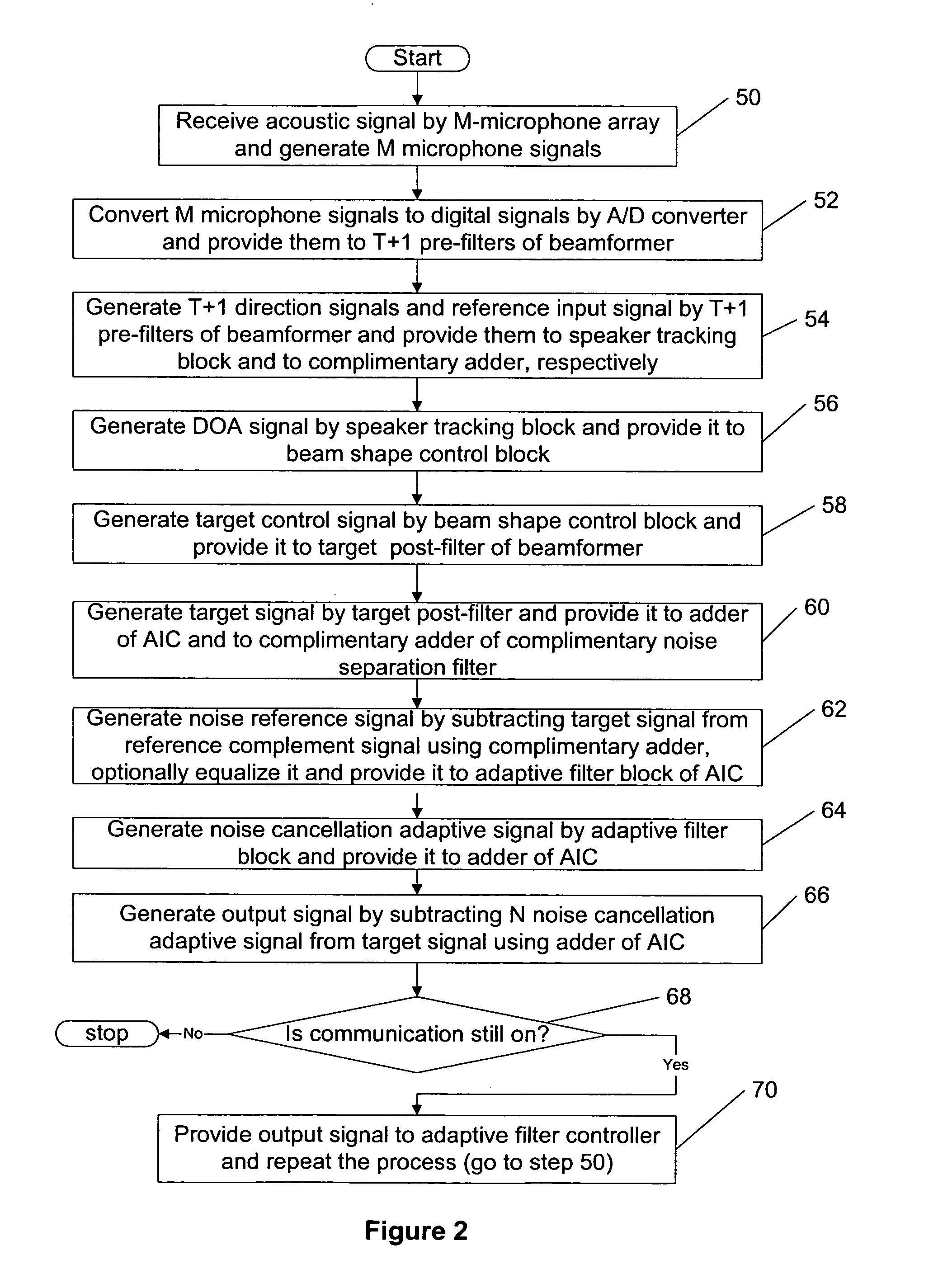
Method for efficient beamforming using a complementary noise separation filter
ActiveUS20050141731A1High computational complexityEfficient implementationSignal processingEar treatmentAdaptive filterInterference canceller
This invention describes a method for efficient beamforming for generalized sidelobe canceling using complementary noise separation filtering for generating a noise reference for adaptation performance of an adaptive interference canceller (AIC). The adaptive filter provides noise estimates to be subtracted from the desired signal path providing further noise reduction in the system output. More specifically, the present invention relates to a multi-microphone beamforming system similar to a generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) structure, but the difference with the conventional GSC method is that the complementary filter used for desired signal blocking can be realized with a simple subtraction without compromising the beam steering flexibility of the polynomial beamforming filter front end using the desired target signal and the complementary background noise estimate signal, respectively, with the complexity of one complementary filter and one sum beamformer.
Owner:III HLDG 3
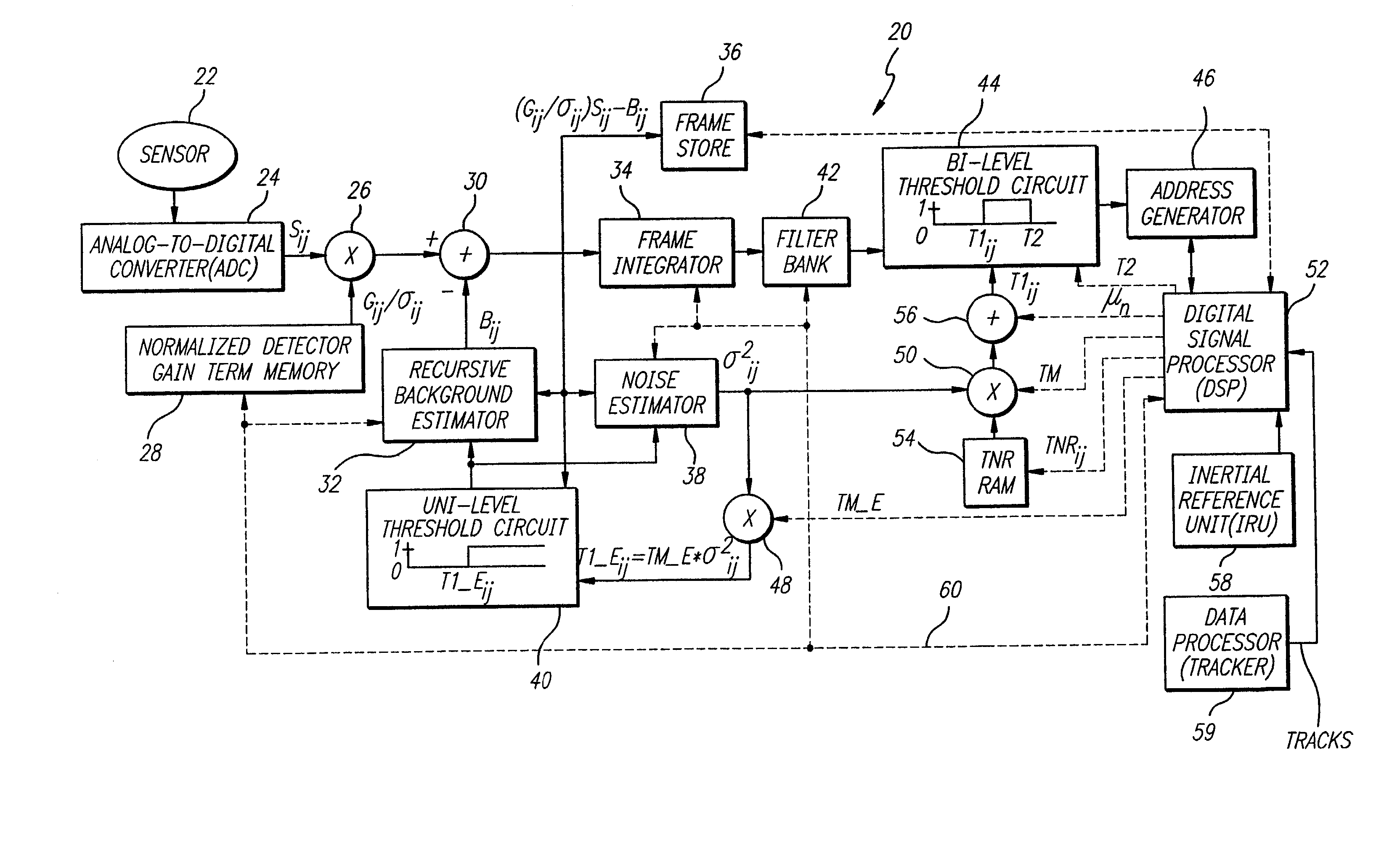
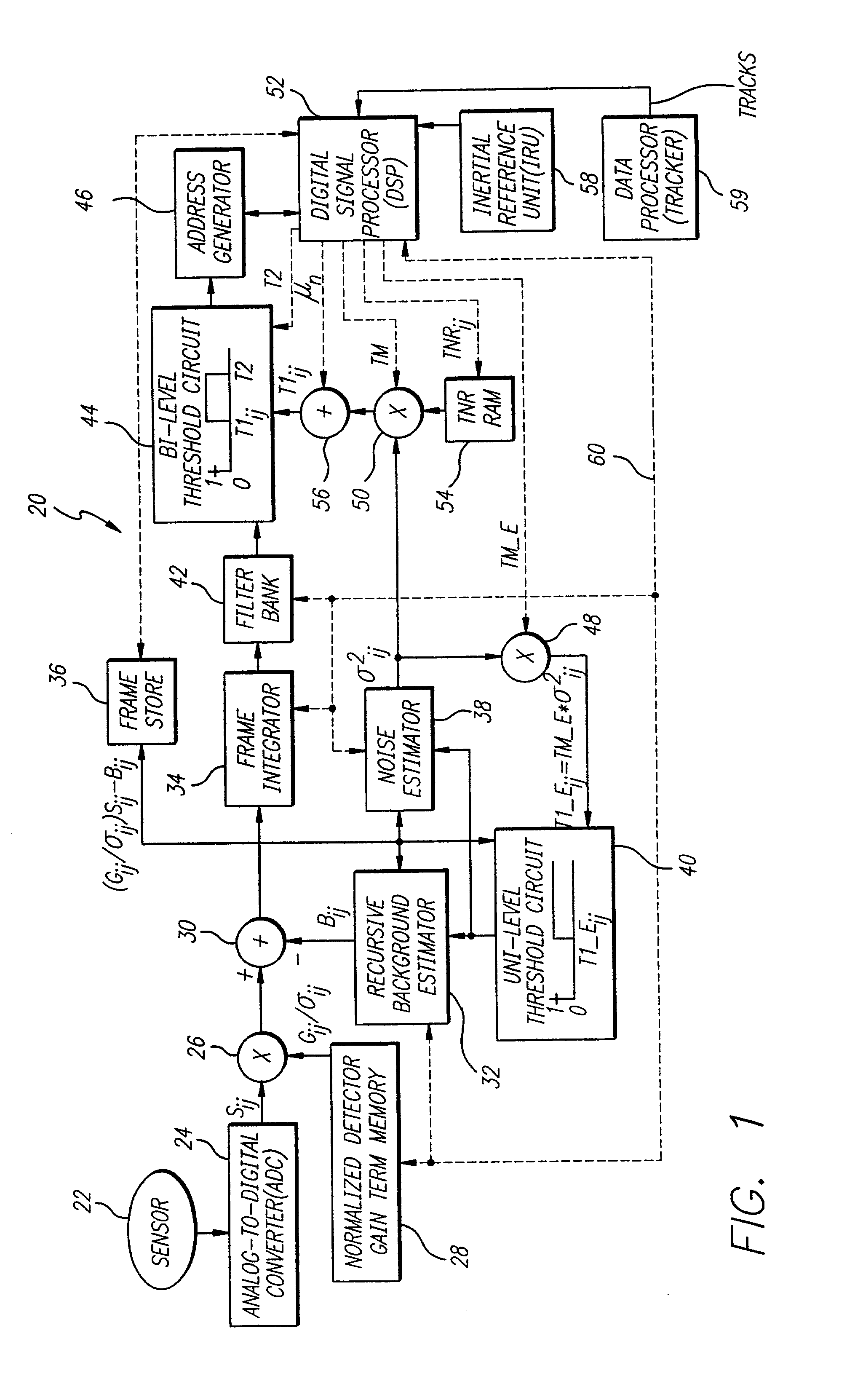
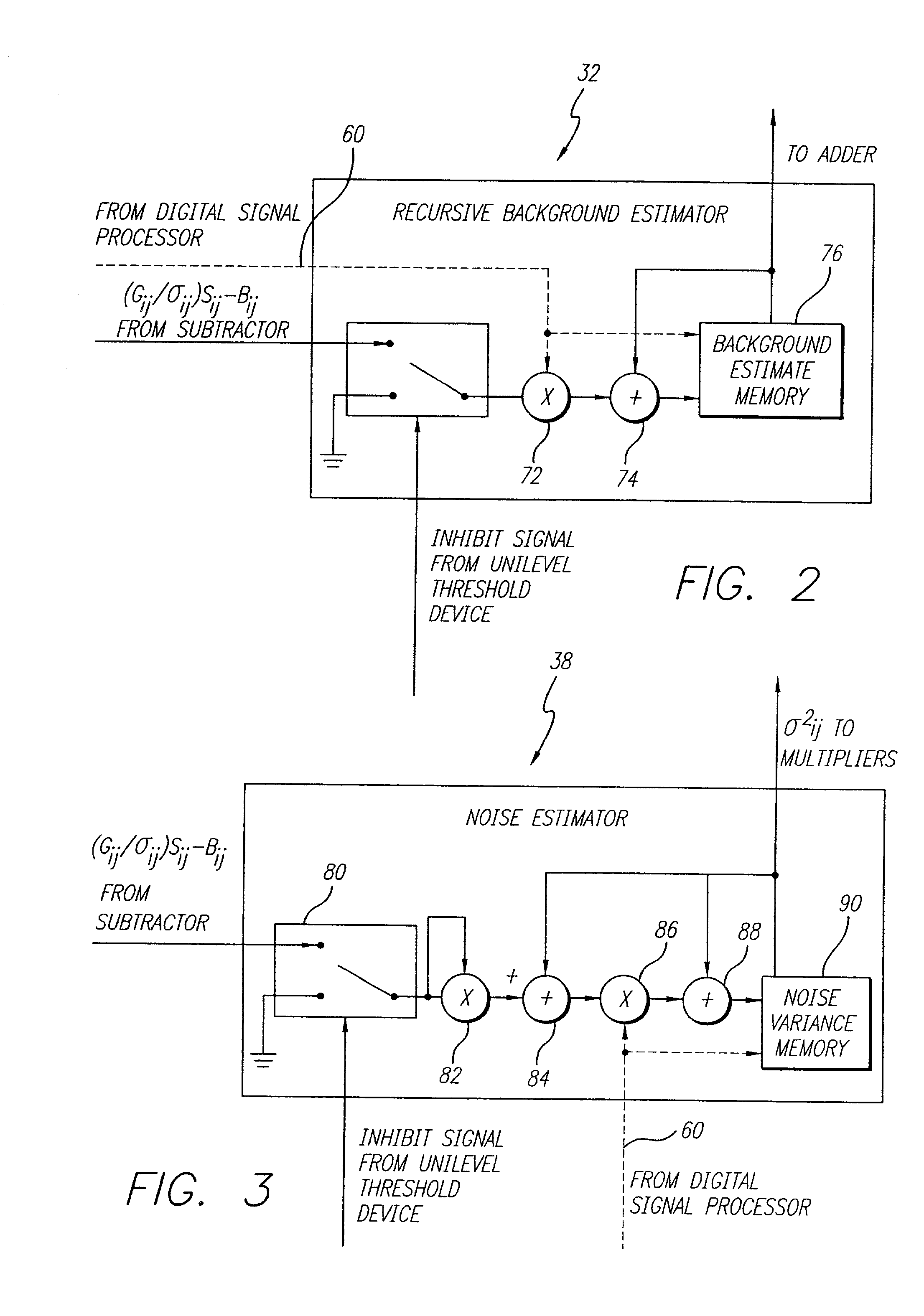
Accurate target detection system
InactiveUS20020084414A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityIntegrator
An accurate target detection system. The system includes a sensor (22) that receives electromagnetic signals and provides electrical signals in response thereto. A non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, 52) corrects non-uniformities in the sensor (22) based on the electrical signals and provides calibrated electrical signals in response thereto. A third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) determines if a target signal is present within the calibrated electrical signals and provides a target detection signal in response thereto. A fourth circuit (38, 40, 48) selectively activates or deactivates the non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, 52) based on the target detection signal. In a specific embodiment, the sensor (22) is an array of electromagnetic energy detectors (22), each detector providing an electrical detector output signal The non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, and 52) includes circuit for compensating for gain, background, and noise non-uniformities (28, 38, and 52) in the electromagnetic energy detectors. The non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, and 52) includes a detector gain term memory (28) for storing detector gain compensation values. The detector gain compensation values are normalized by noise estimates unique to each of the detectors. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, and 52) includes a signal enhancement circuit for reducing noise (34, 42) in the calibrated electrical signals. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, and 52) includes a noise estimation circuit (32, 38) that estimates noise in each of the detector output signals and provides noise estimates in response thereto. The noise estimation circuit (32, 38) further includes a noise estimator circuit (38) and a recursive background estimator (32). The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) further includes a subtractor (30) for subtracting background from the calibrated electrical signals and providing background subtracted signals in response thereto. The signal enhancement circuit (34, 42) includes a frame integrator circuit for adding frames of image data (34), each frame containing data corresponding to the background subtracted signals and providing summed frames in response thereto. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) includes a first threshold circuit (44) for comparing the filtered signal to a first threshold and a second threshold and providing a threshold exceedance signal if the filtered signal is between the first threshold and the second threshold.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
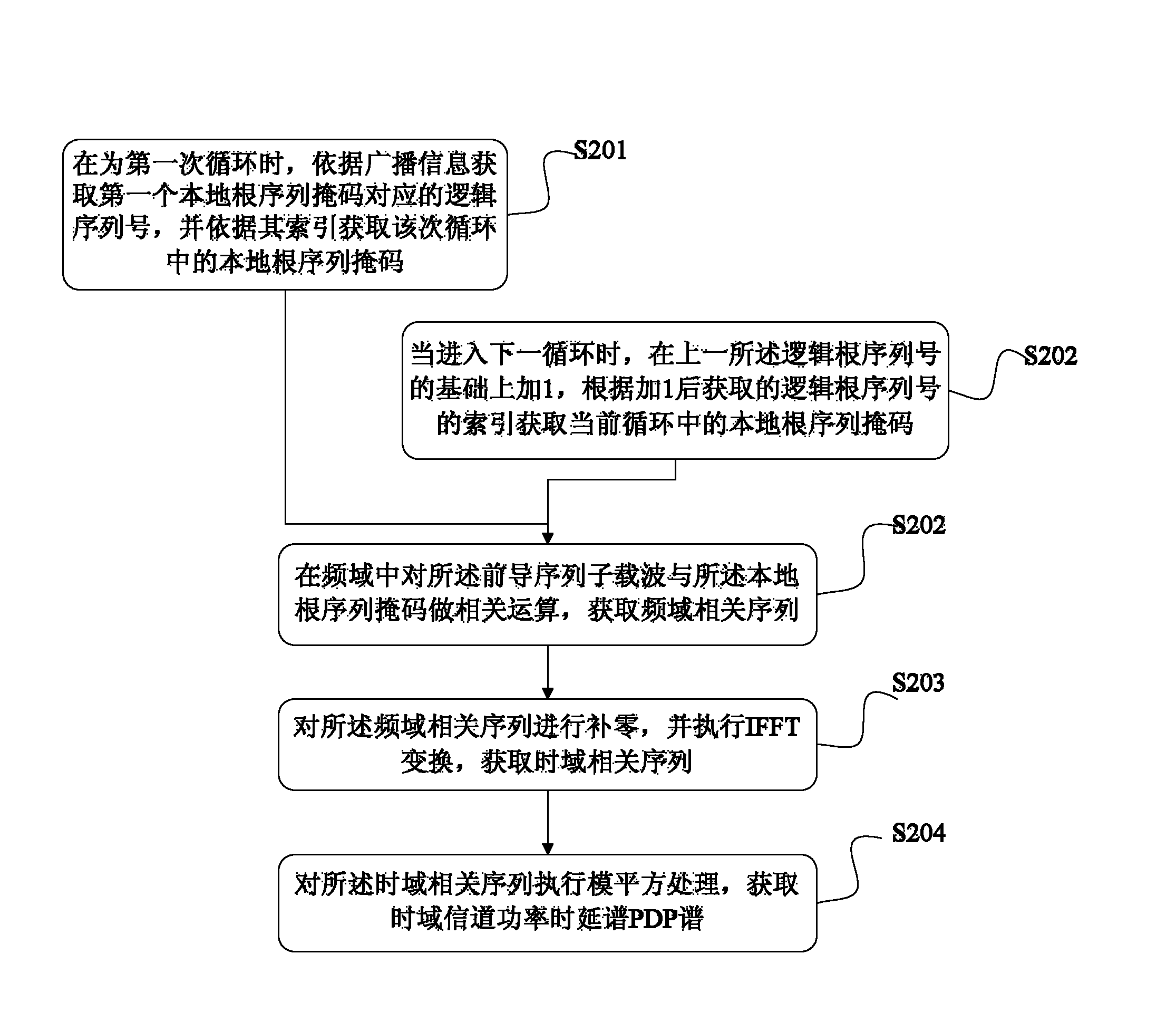
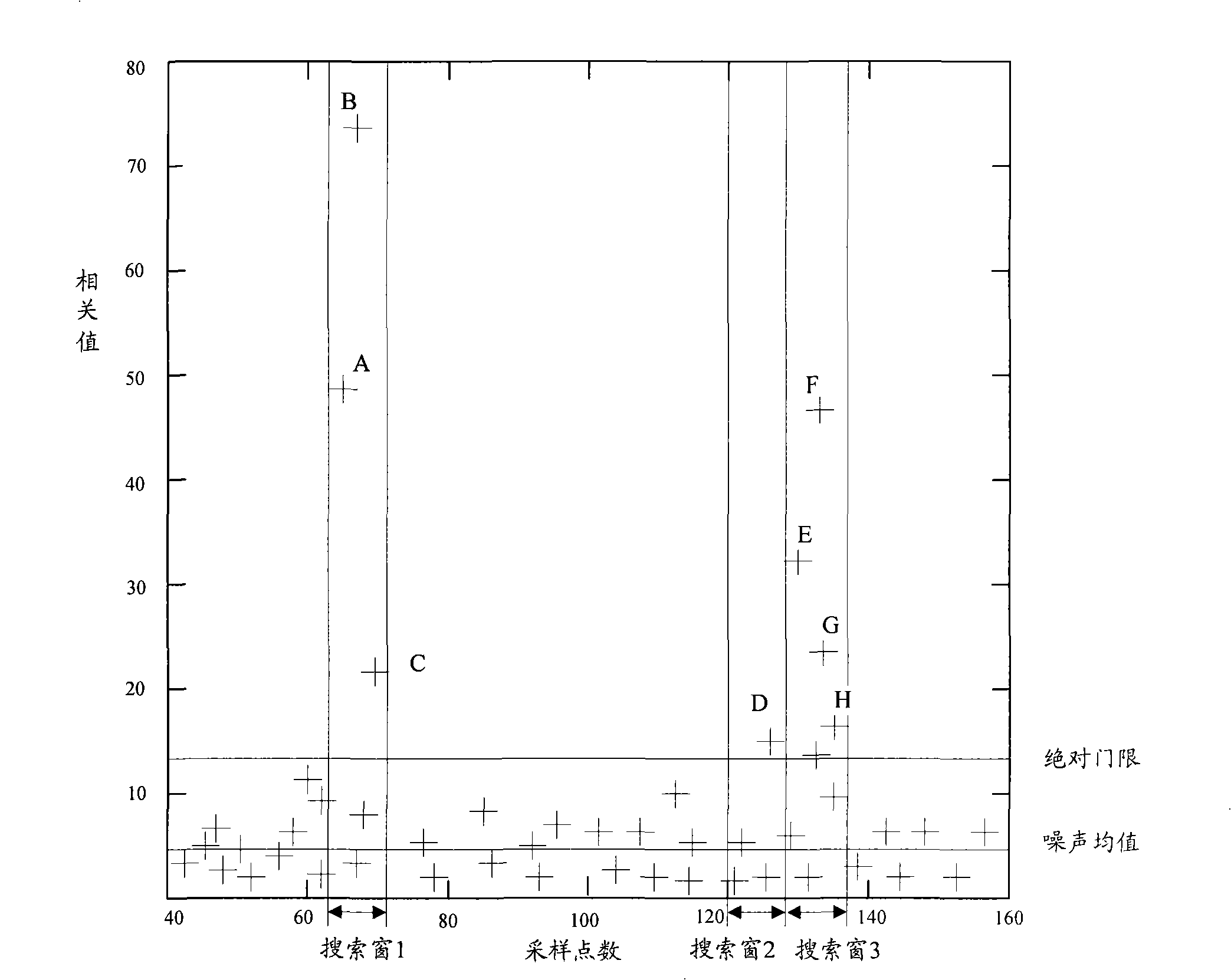
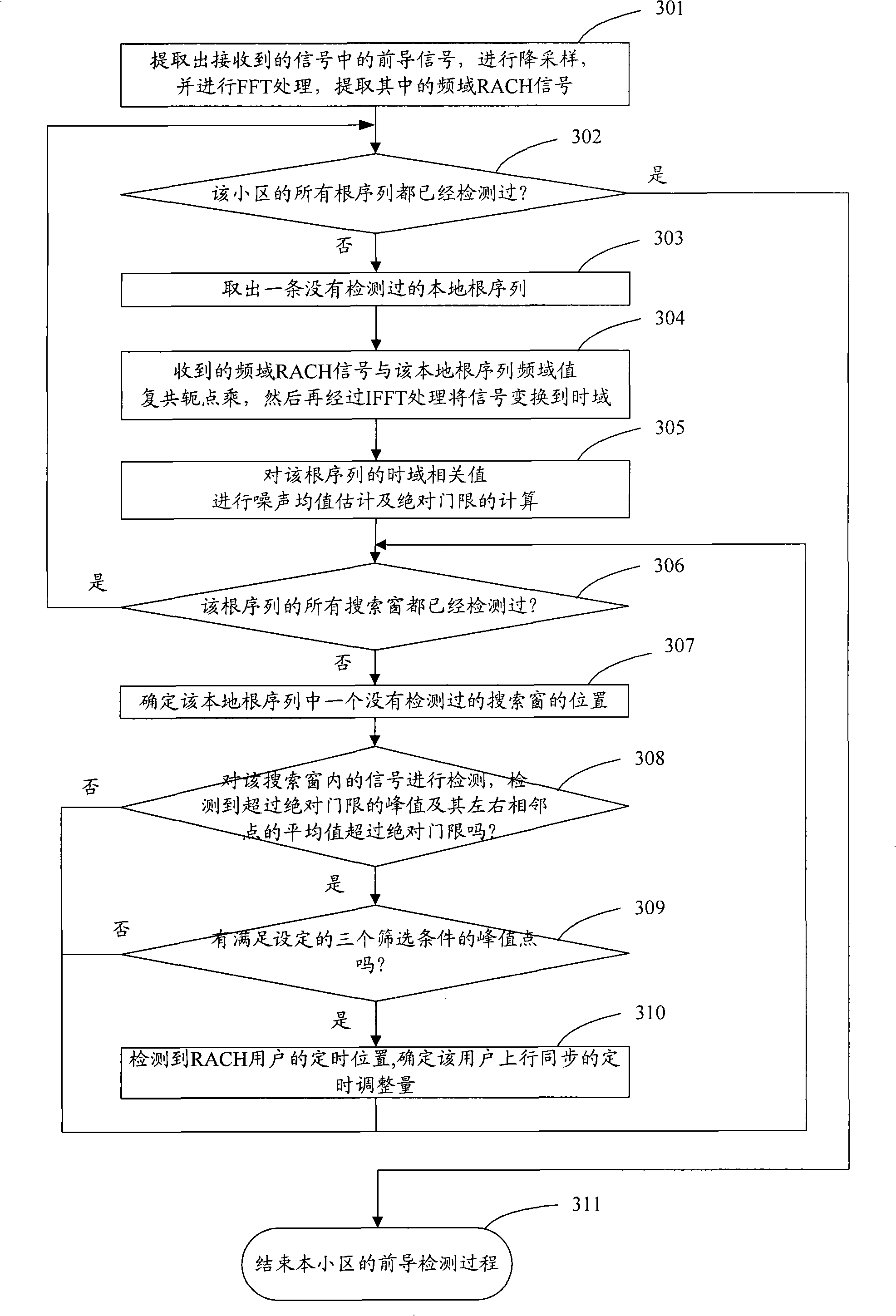
Detection method for accidental precursor access
ActiveCN101295999AReduce computationReduce the difficulty of data processingModulated-carrier systemsWireless communicationTime domainAbsolute threshold
The invention discloses a method for detecting a random access leader. After a random access channel (RACH) signal is treated with the simplified time domain-related operation, noise mean estimation is carried out to each root sequence; an absolute threshold is then detected according to a signal obtained by the noise estimation and signals in a search window are detected; the signals which exceed the detection threshold are screened and then a timing position can be determined in a fast and accurate way so as to provide reliable uplink timing adjustment information to a mobile terminal, guarantee the accuracy of the uplink synchronization and effectively eliminate the timing error due to the over-sampling and reduce the false alarm in the detection.
Owner:ZTE CORP
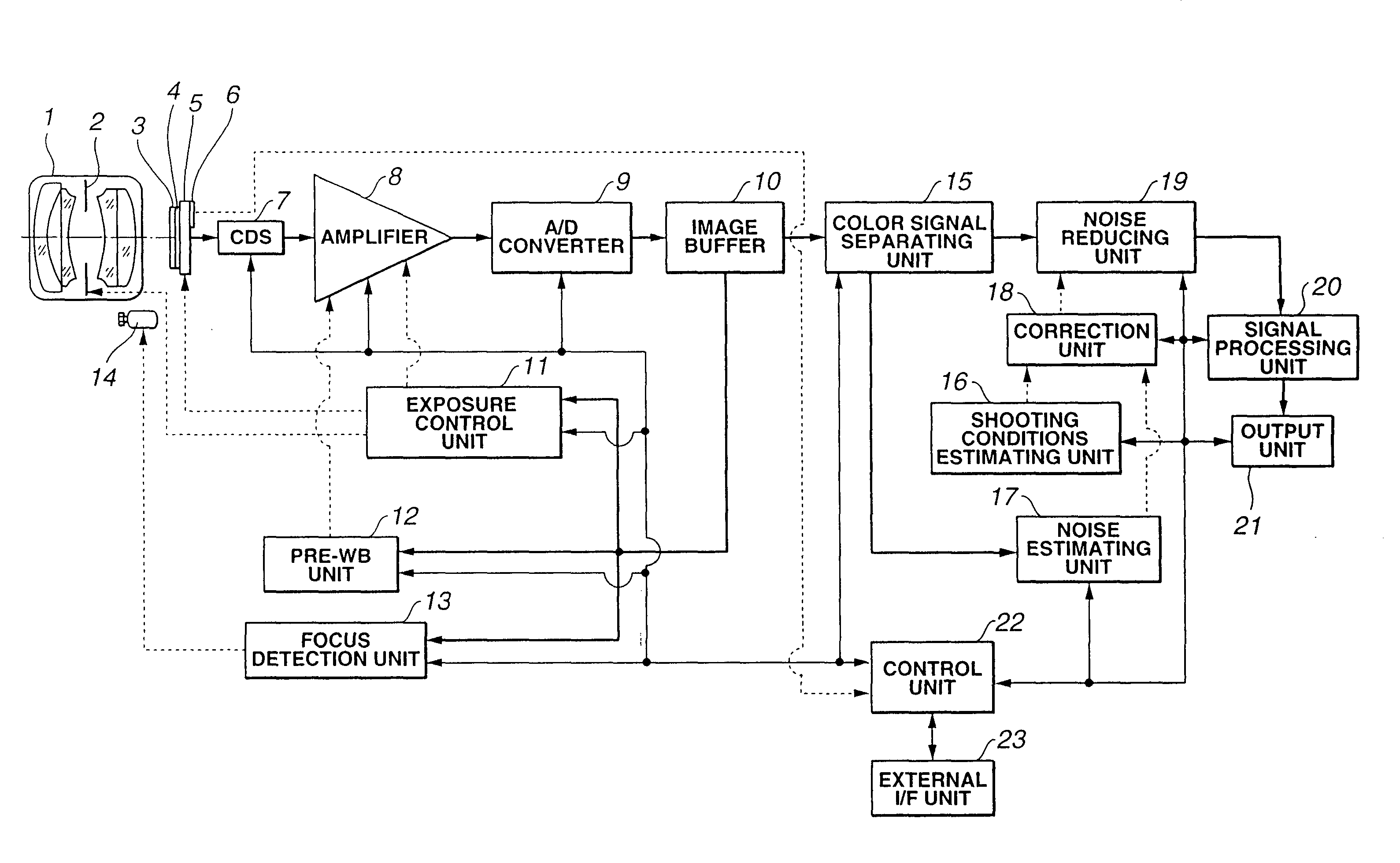
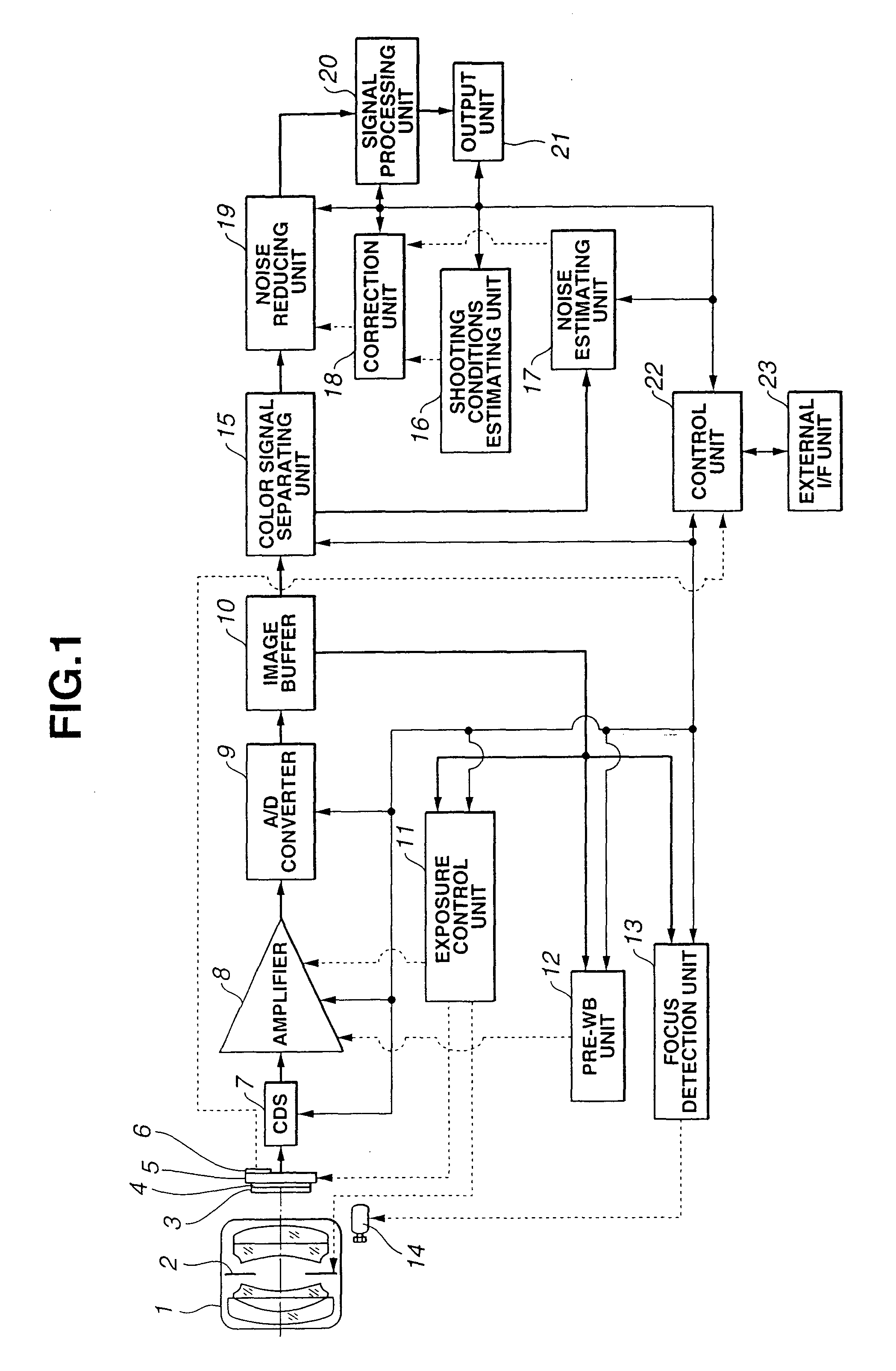
Image pickup system
ActiveUS20050099515A1Reduce noiseTelevision system detailsImage enhancementNoise estimationComputer science
An image pickup system has a noise estimating unit which estimates the amount of noise contained in a digitized signal from an image pickup element composed of an array of a plurality of pixels, either for each pixel or for each specified unit area made up of a plurality of pixels, and a shooting conditions estimation unit which estimates the shooting condition when an image based on the signal is acquired. The amount of noise estimated by the noise estimating unit is corrected on the basis of the shooting conditions estimated by the shooting conditions estimation unit, and the noise in the signal is reduced on the basis of the corrected amount of noise.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
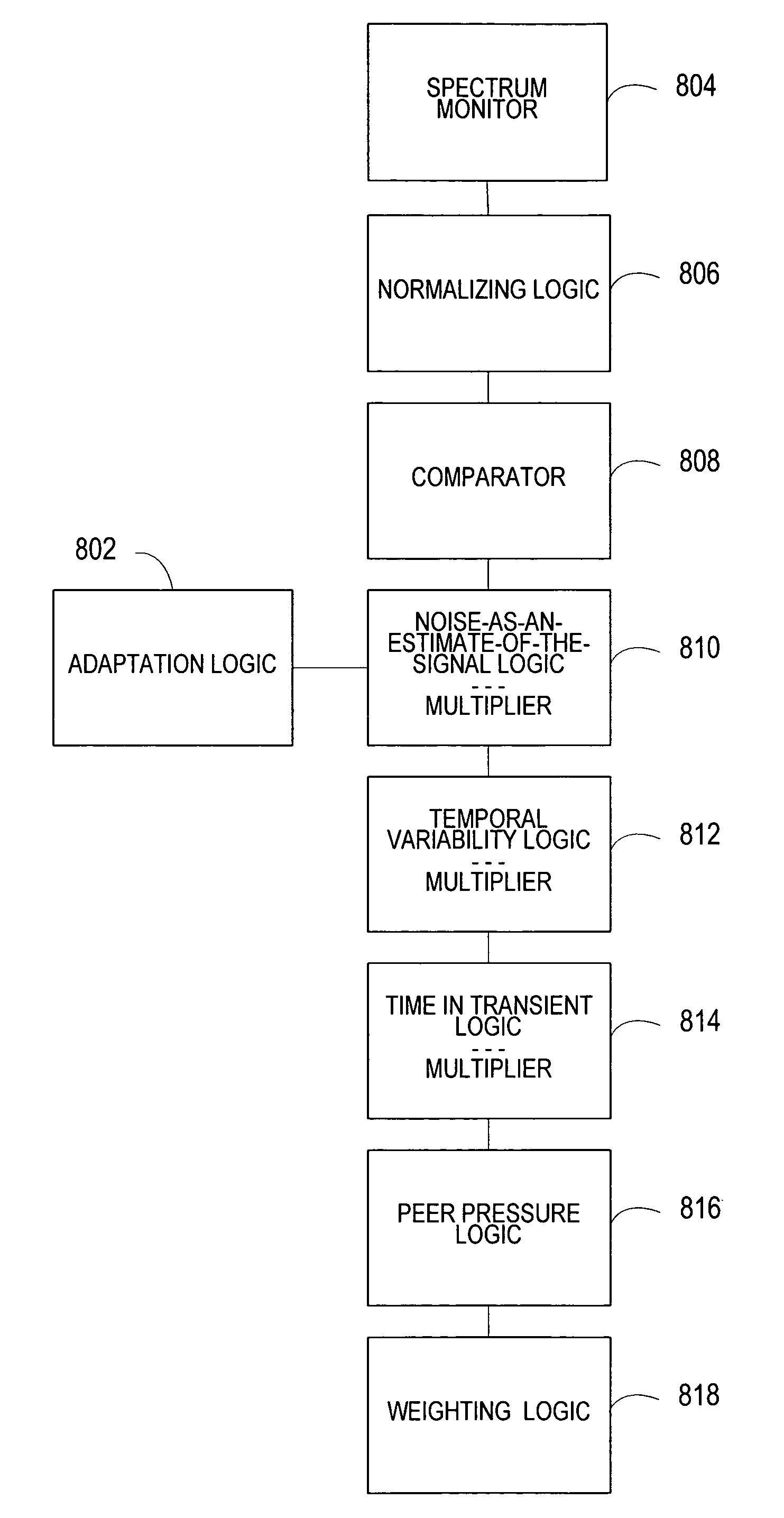
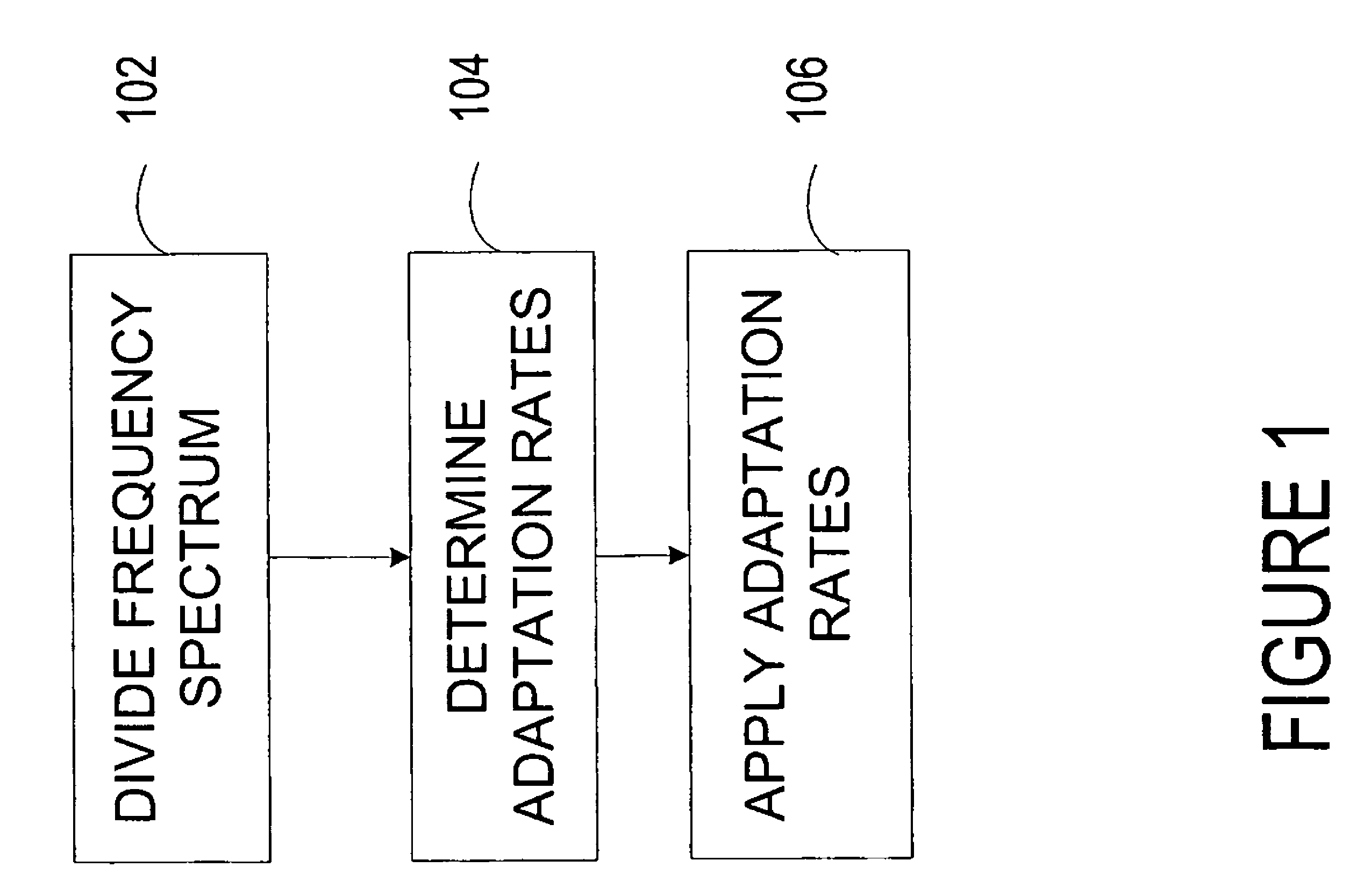
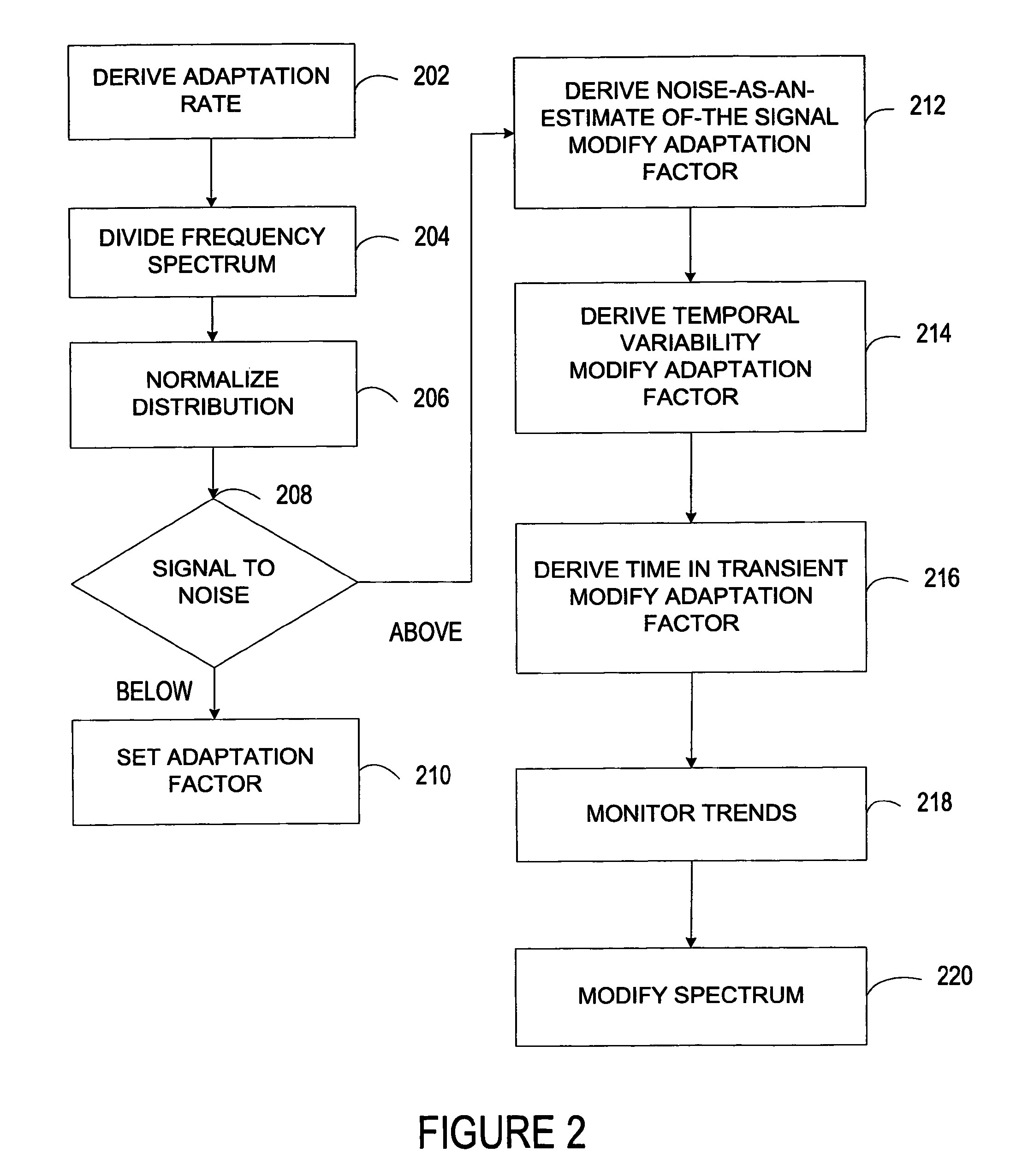
Robust noise estimation
ActiveUS7844453B2Improved noise estimationGood estimateSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumImage resolution
An enhancement system improves the estimate of noise from a received signal. The system includes a spectrum monitor that divides a portion of the signal at more than one frequency resolution. Adaptation logic derives a noise adaptation factor of the received signal. A plurality of devices tracks the characteristics of an estimated noise in the received signal and modifies multiple noise adaptation rates. Weighting logic applies the modified noise adaptation rates derived from the signal divided at a first frequency resolution to the signal divided at a second frequency resolution.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
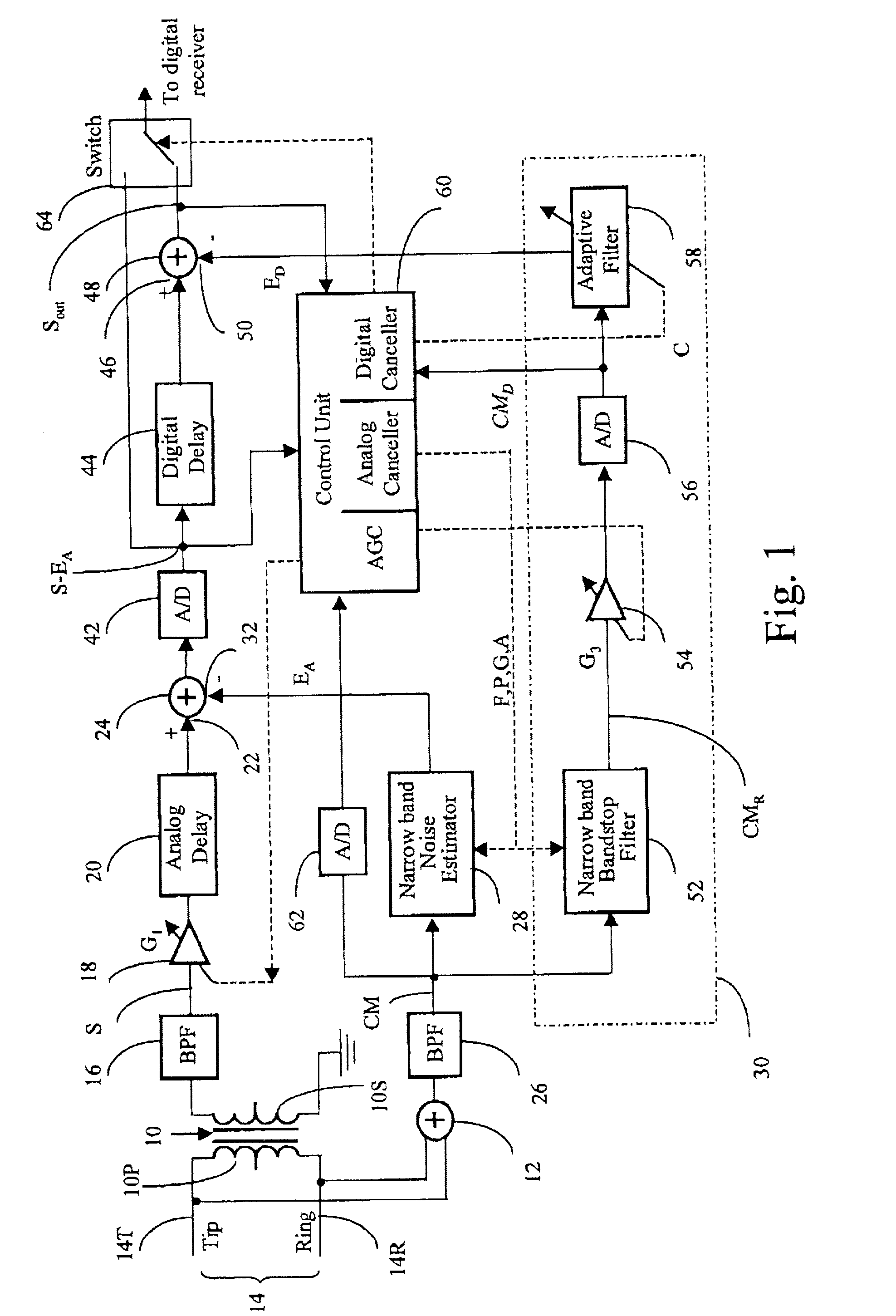
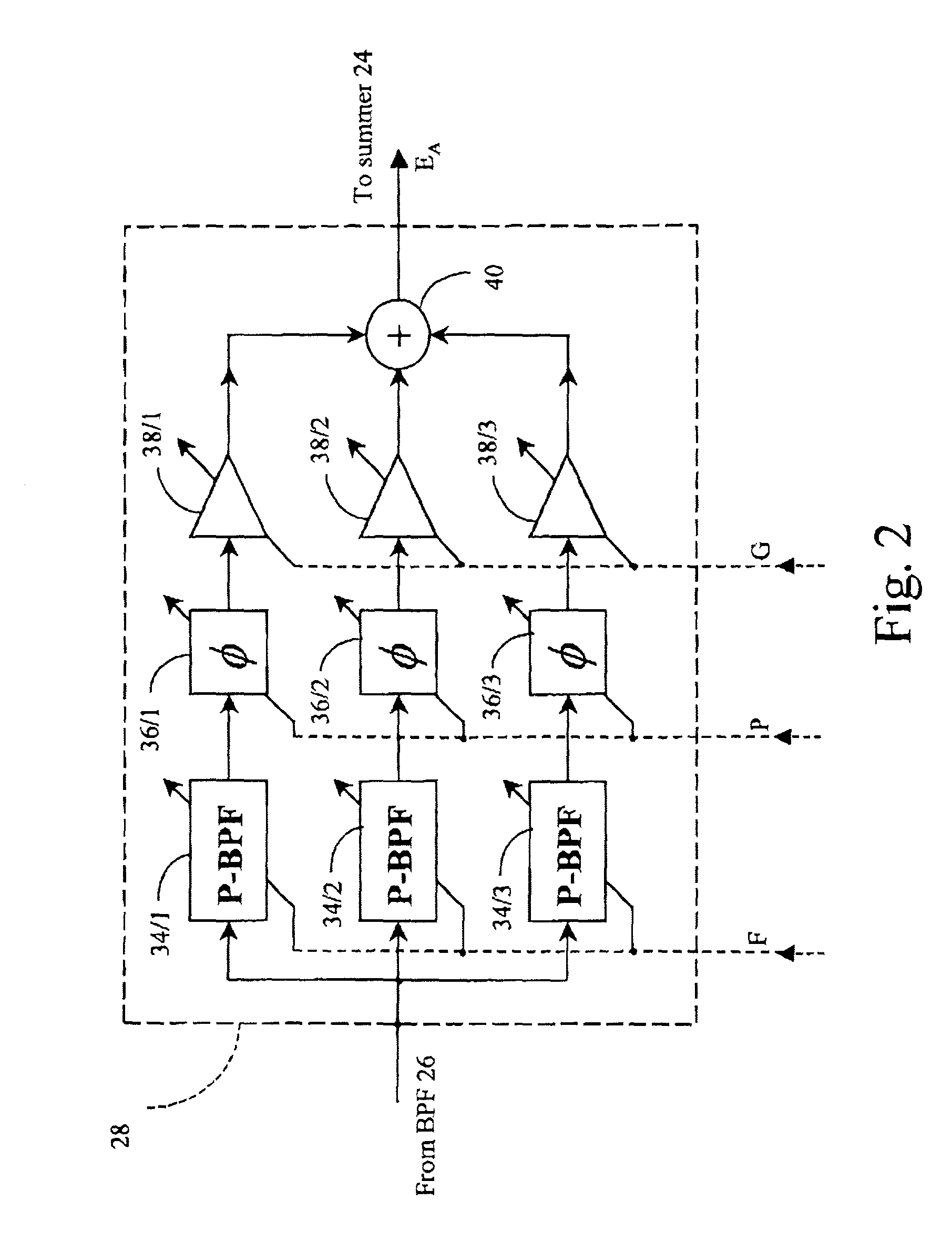
RFI canceller using narrowband and wideband noise estimators
InactiveUS20010050987A1Remove restrictionsInterconnection arrangementsError preventionBroadband noiseAdaptive filter
In an adaptive filter for cancelling common-mode noise in digital subscriber loops, a narrowband noise estimator is used to detect one or more noisy frequency bands of the common mode signal and derive therefrom a first noise estimation signal. A wideband noise estimator derives from the remainder of the common mode signal a second noise estimation signal. The first and second noise estimation signals are subtracted from the differential signal, The wideband noise estimator comprises a bandstop filter for removing the frequencies detected by the narrowband noise estimator, an analog-to-digital converter for digitizing the bandstopped signal, and an adaptive filter for deriving the second noise estimation signal from the digitized bandstopped signal and, in the process, compensating for phase and gain differences, especially attributable to the interference being injected at different points along the length of the channel.
Owner:BELL CANADA
Method of speech recognition resistant to convolutive distortion and additive distortion
A speech recognizer operating in both ambient noise (additive distortion) and microphone changes (convolutive distortion) is provided. For each utterance to be recognized the recognizer system adapts HMM mean vectors with noise estimates calculated from pre-utterance pause and a channel estimate calculated using an Estimation Maximization algorithm from previous utterances.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Methods for adaptive noise reduction based on global motion estimation
InactiveUS20070070250A1Reduce noiseEasy to adjustTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionMotion vector
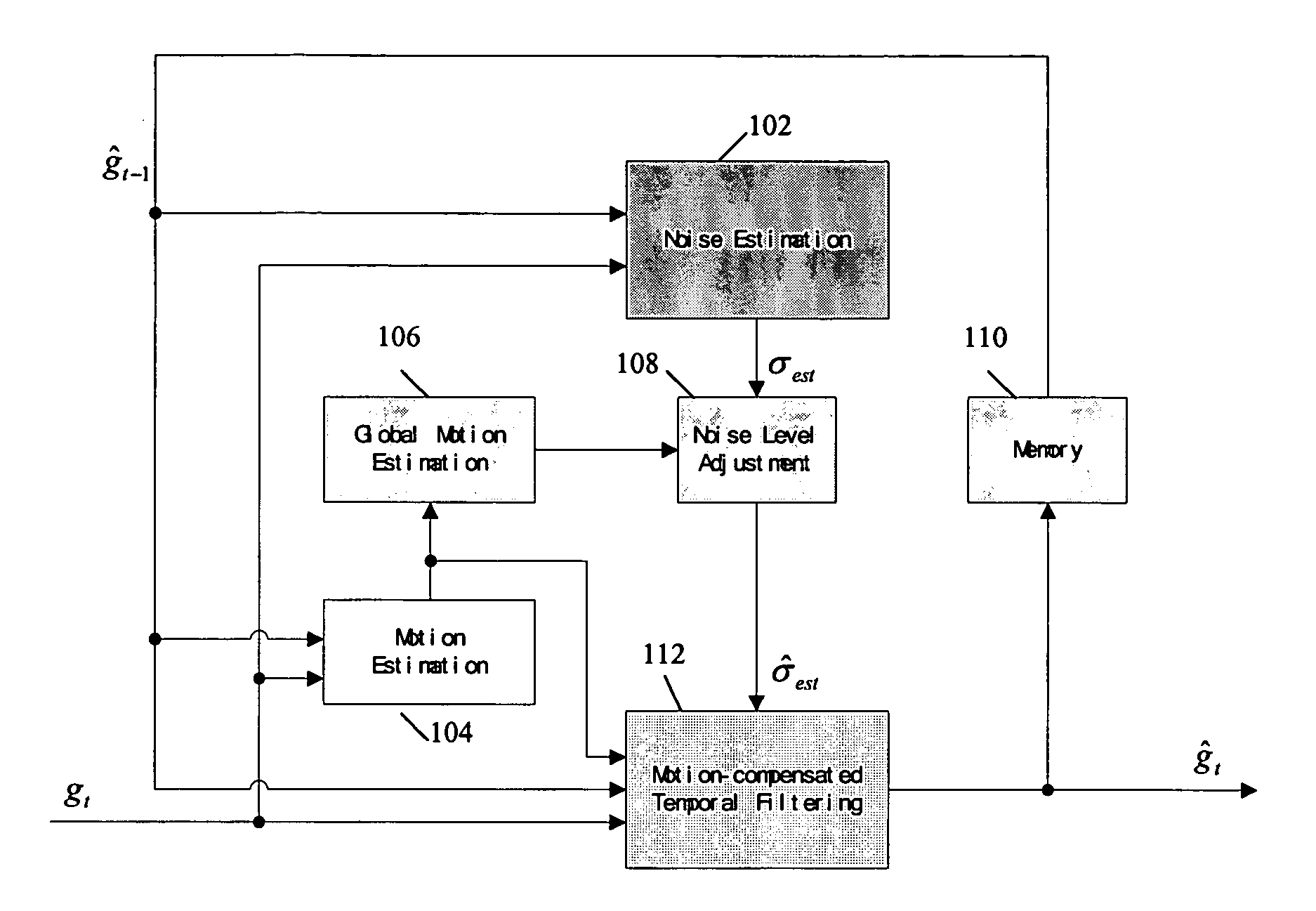
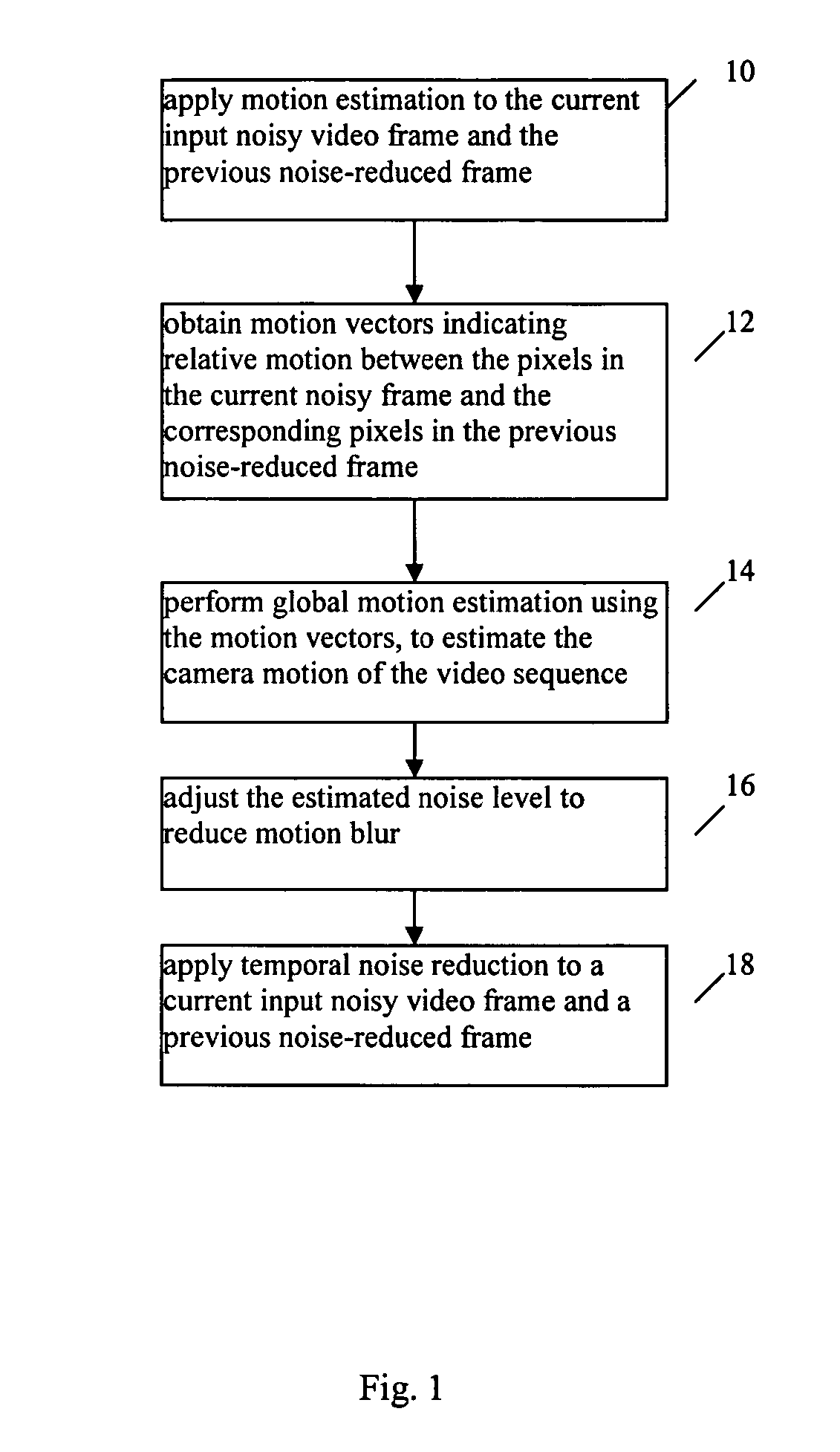
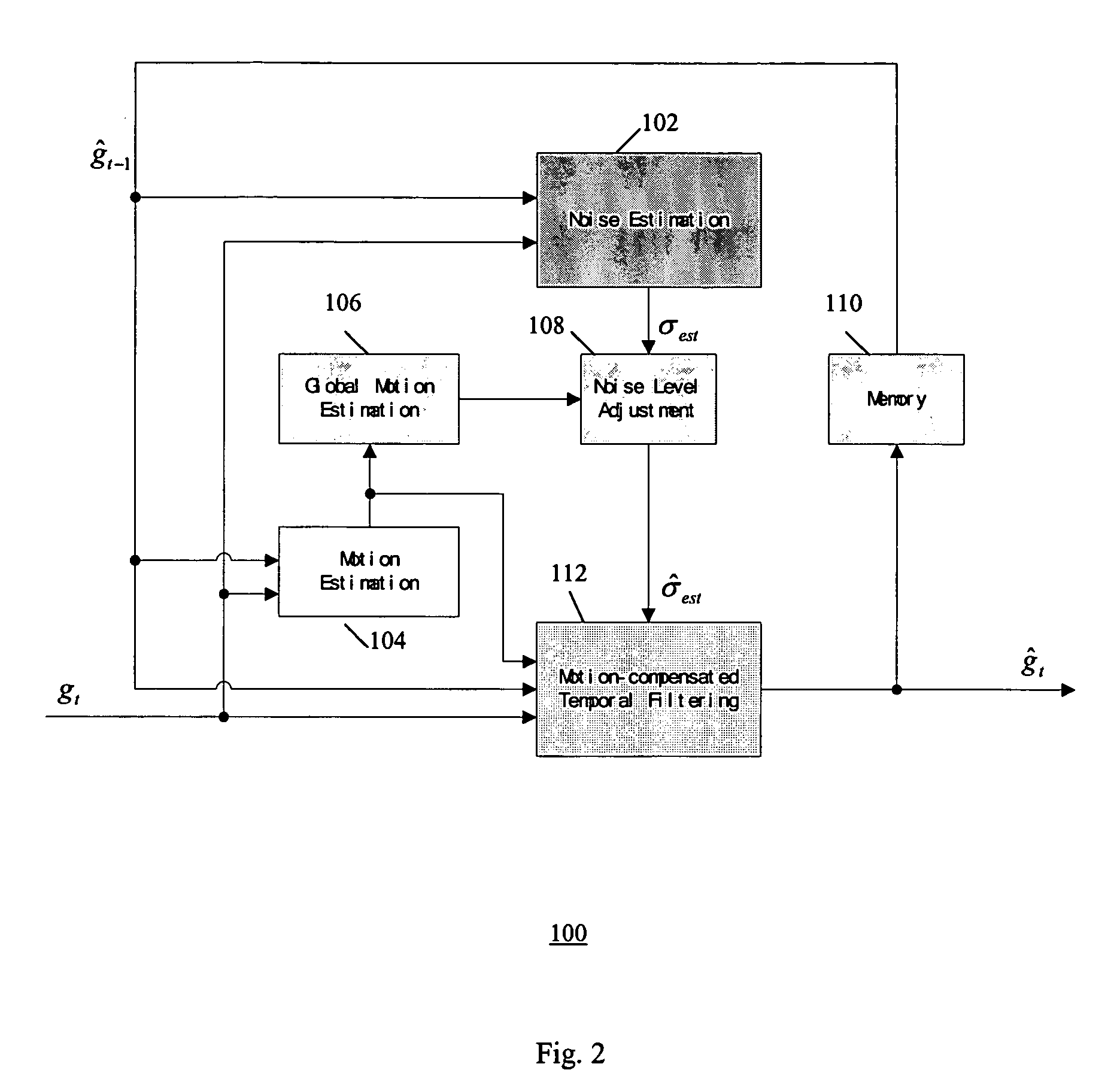
An improved temporal noise reduction method and system detects the global motion and adjusts the overall gain of the temporal filtering. Temporal noise reduction is applied to two video frames, wherein one video frame is the current input noisy frame, and the other video frame is a previous filtered frame stored in memory. In this method, noise estimation is first performed to estimate the noise variance / standard deviation in the input video sequence. Then, motion estimation is applied to obtain the motion vectors indicating relative motion between the pixels in the current noisy frame and the corresponding pixels in the previous noise-reduced frame. From such motion vectors, global motion estimation is applied to estimate the camera motion of the video sequence. If reliable global motion is obtained, the overall gain of the temporal filtering is reduced by adjusting the estimated noise level. Motion blur is thus prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coupled noise estimation and avoidance of noise-failure using global routing information
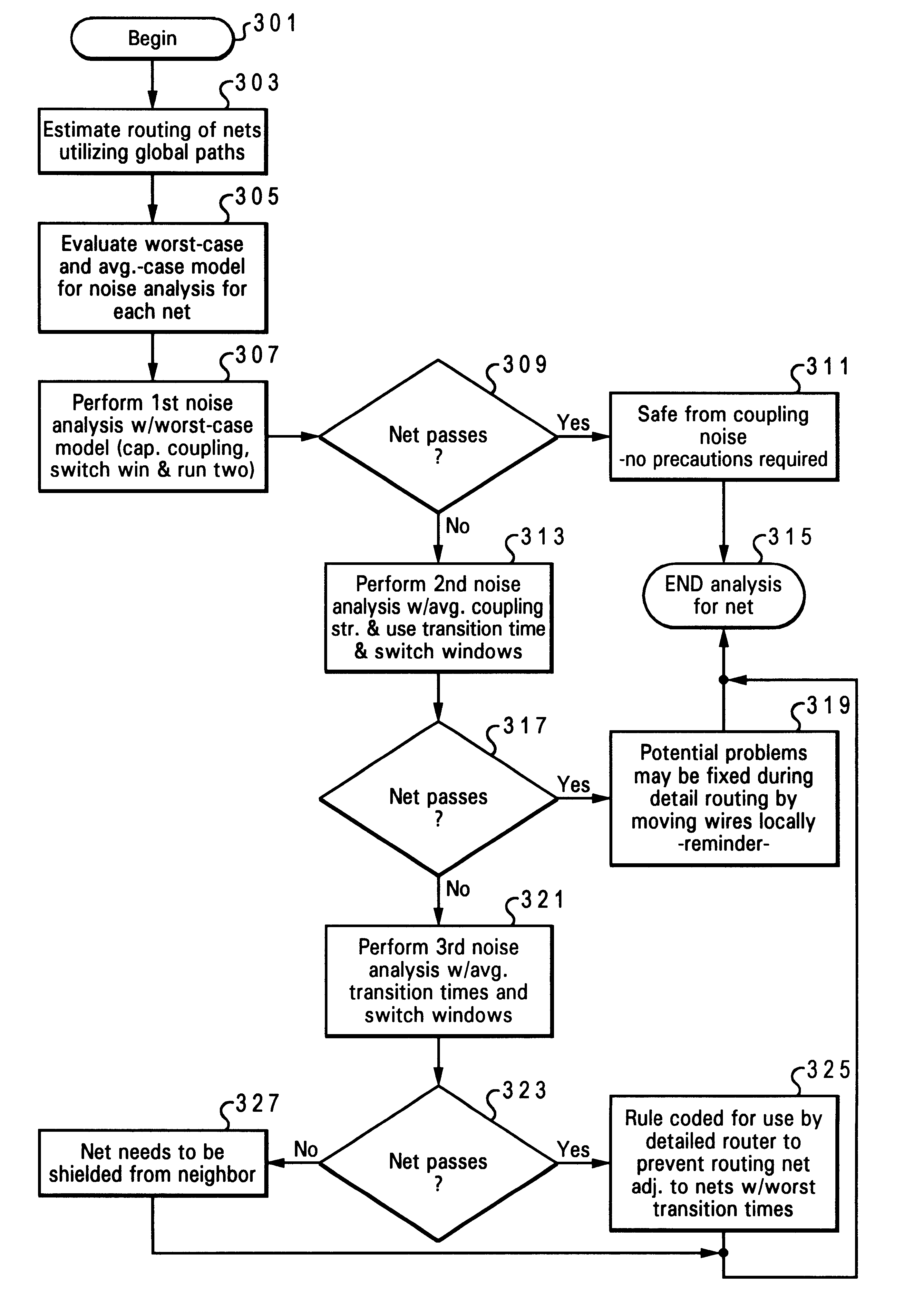
Disclosed is a method for pre-design estimation of coupling noise and avoidance of coupling noise failures in interconnects. An initial routing of a plurality of nets is estimated utilizing global paths. Then, the worst-case and average-case models for various parameters of each net are evaluated. With these models, a noise analysis is completed by which a determination is made whether coupling noise of any one of the nets is above a threshold level for noise-induced failure (i.e., a noise-failure threshold). When it is determined that the estimated coupling noise of a net falls below the noise-failure threshold, a response mechanism is triggered for later implementation during detailed routing of the nets to prevent the coupling noise from reaching the noise-failure threshold.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
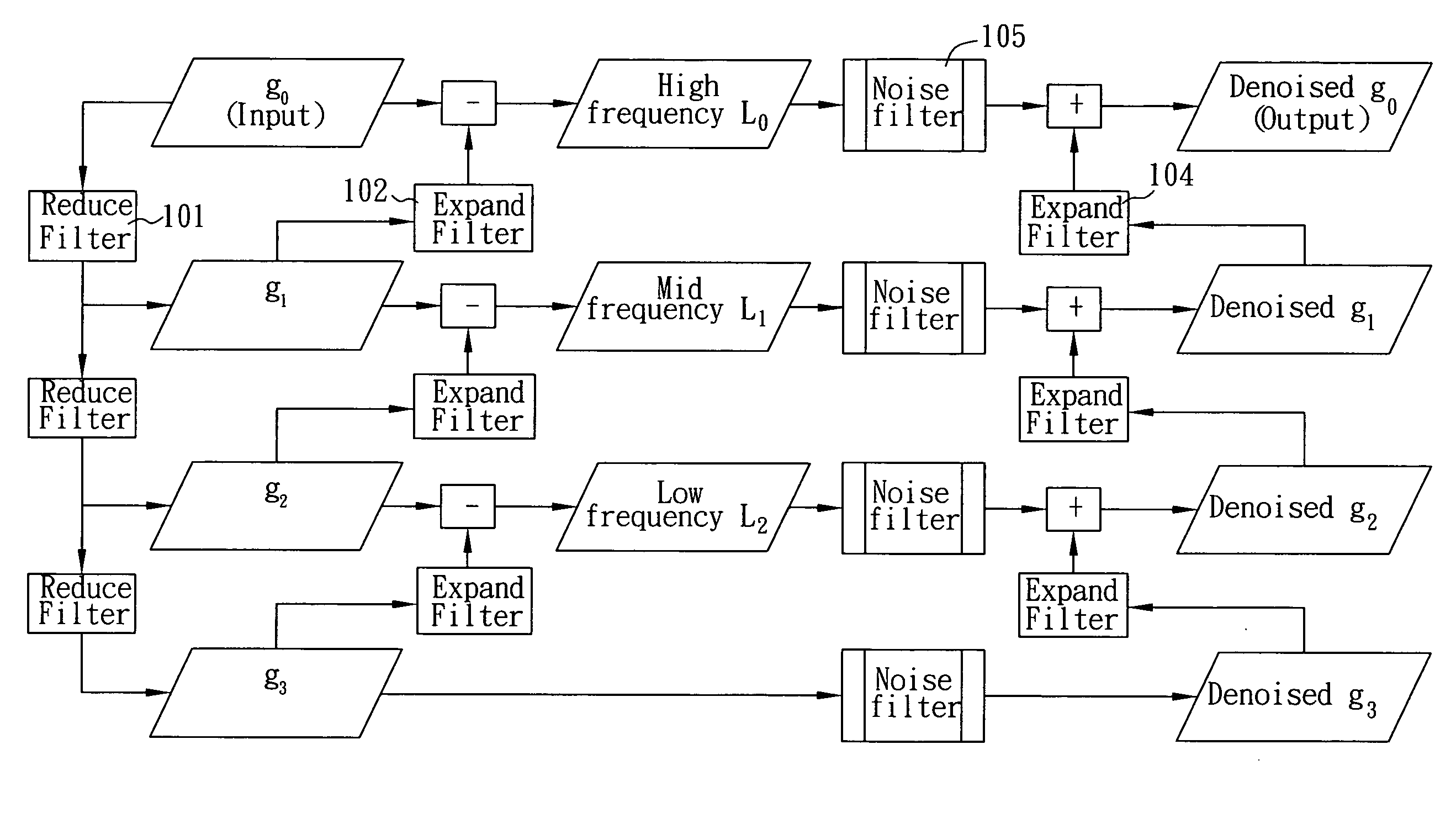
Denoise method on image pyramid
ActiveUS20080253678A1Easy to embedAvoid quality lossImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionNoise level
The present invention is to provide a denoise method on Gaussian / Laplacian image pyramid, which integrates Pyramid analysis / synthesis algorithm, MMSE (minimum mean square error) filter and NL (non local) filter on the image pyramid to reconstruct and output a denoised image of an original input image through a plurality of iterative procedures, and utilizes an auto-adaptive noise estimation algorithm to find parameter of noise level used by the NL filter, so as to be easily embedded in mobile or handheld devices for obtaining better noise removing and anti-shaking results and remove noise much faster than the conventional denoise method, but only with less quality loss.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com