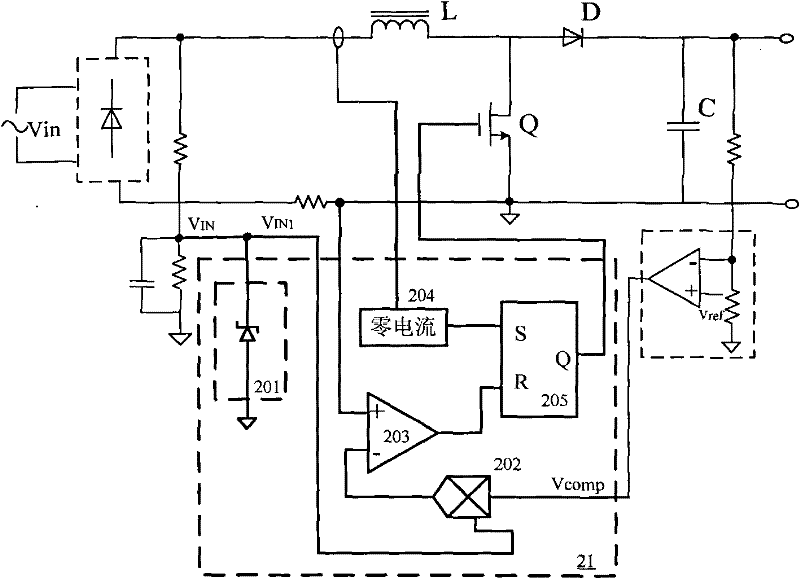
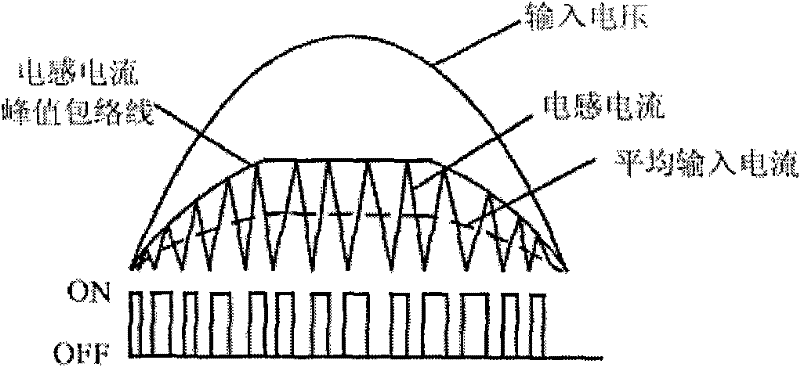
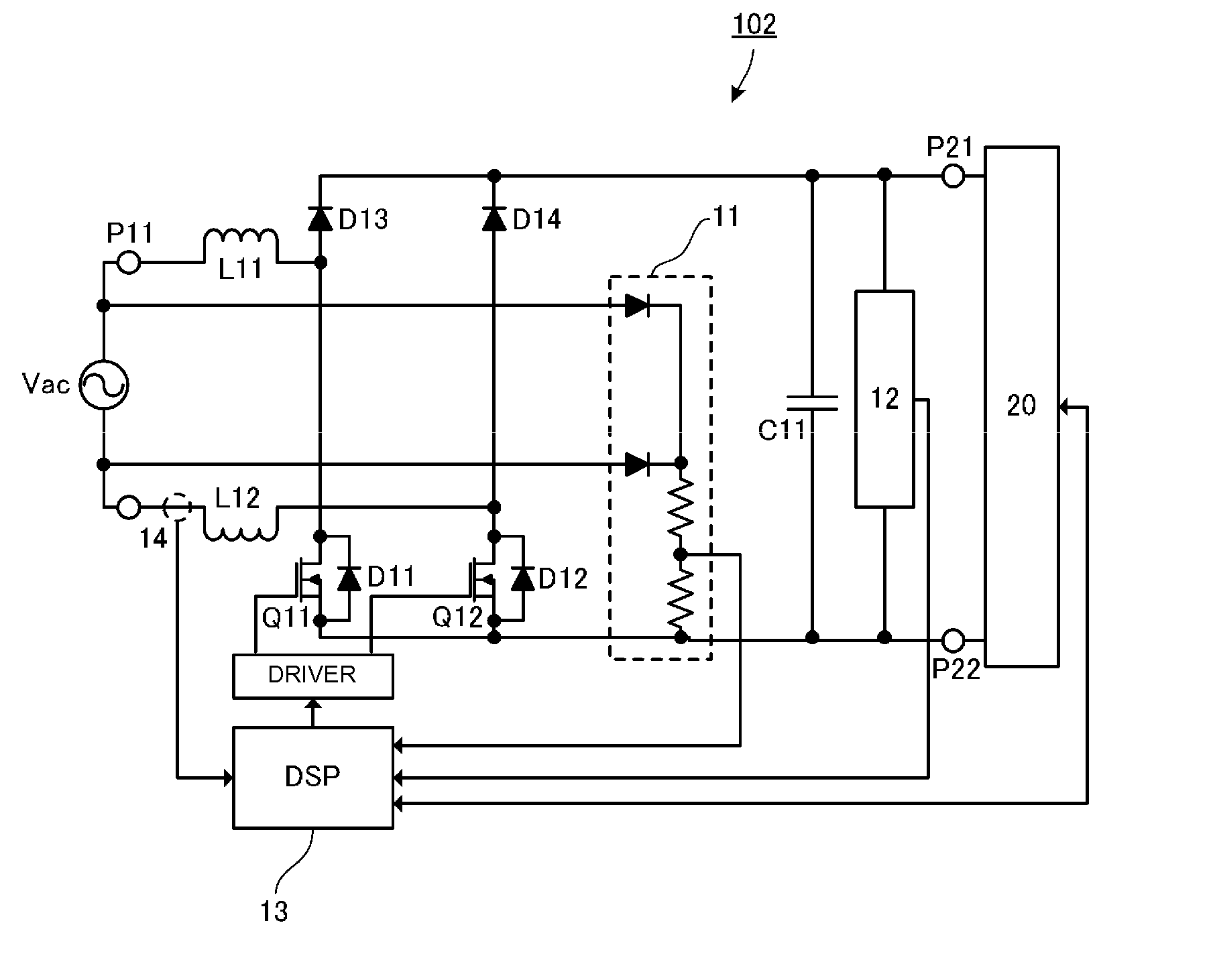
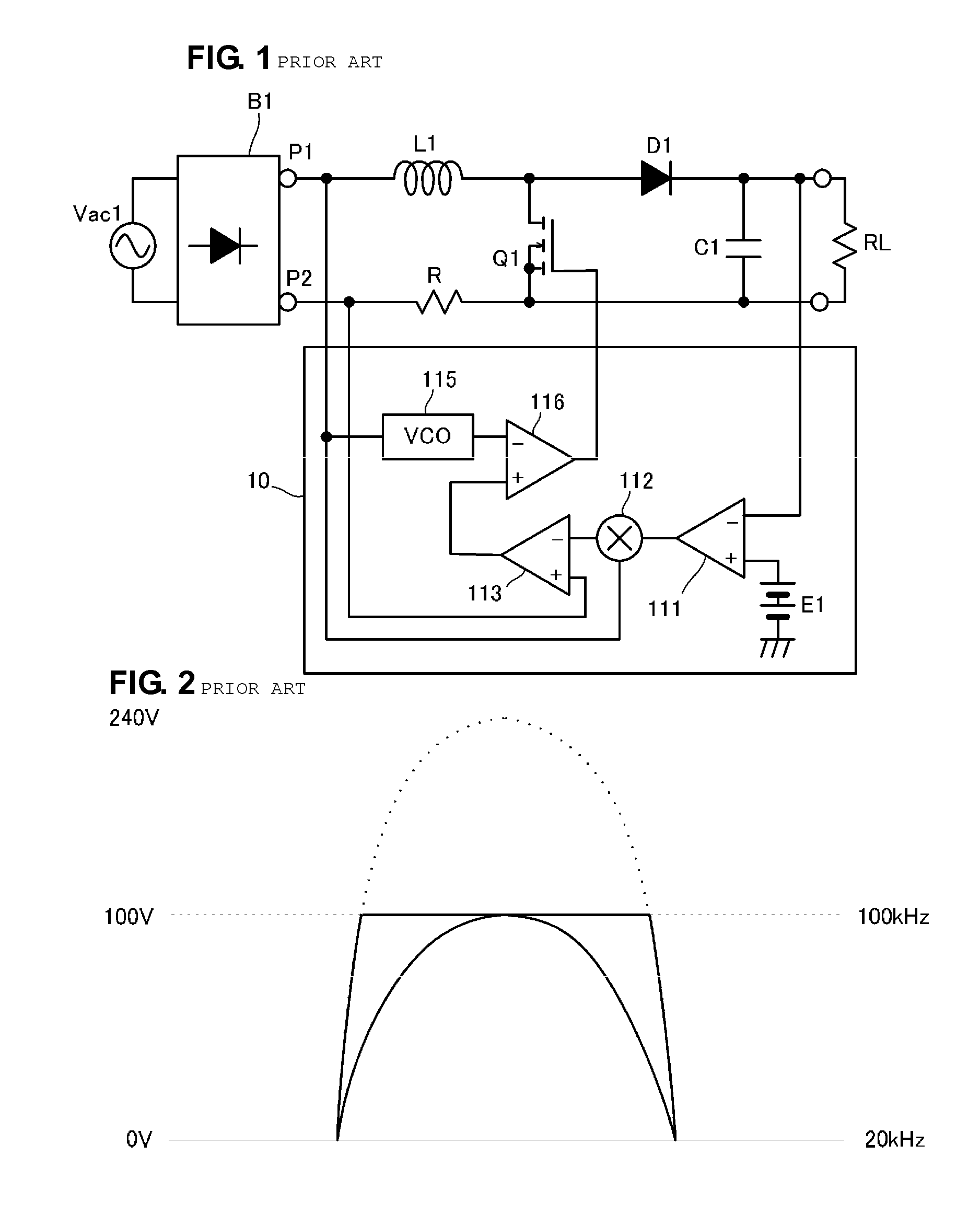
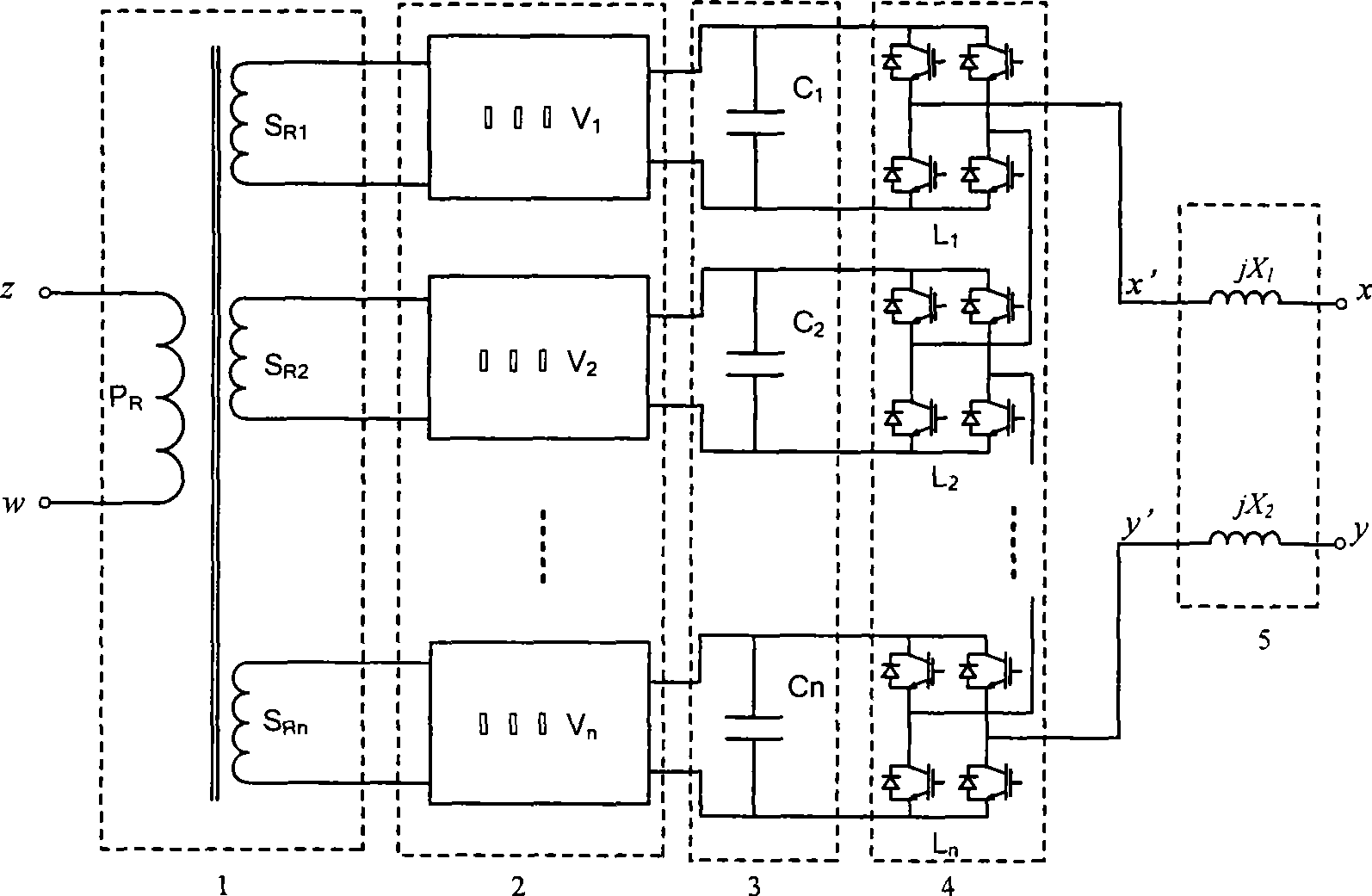
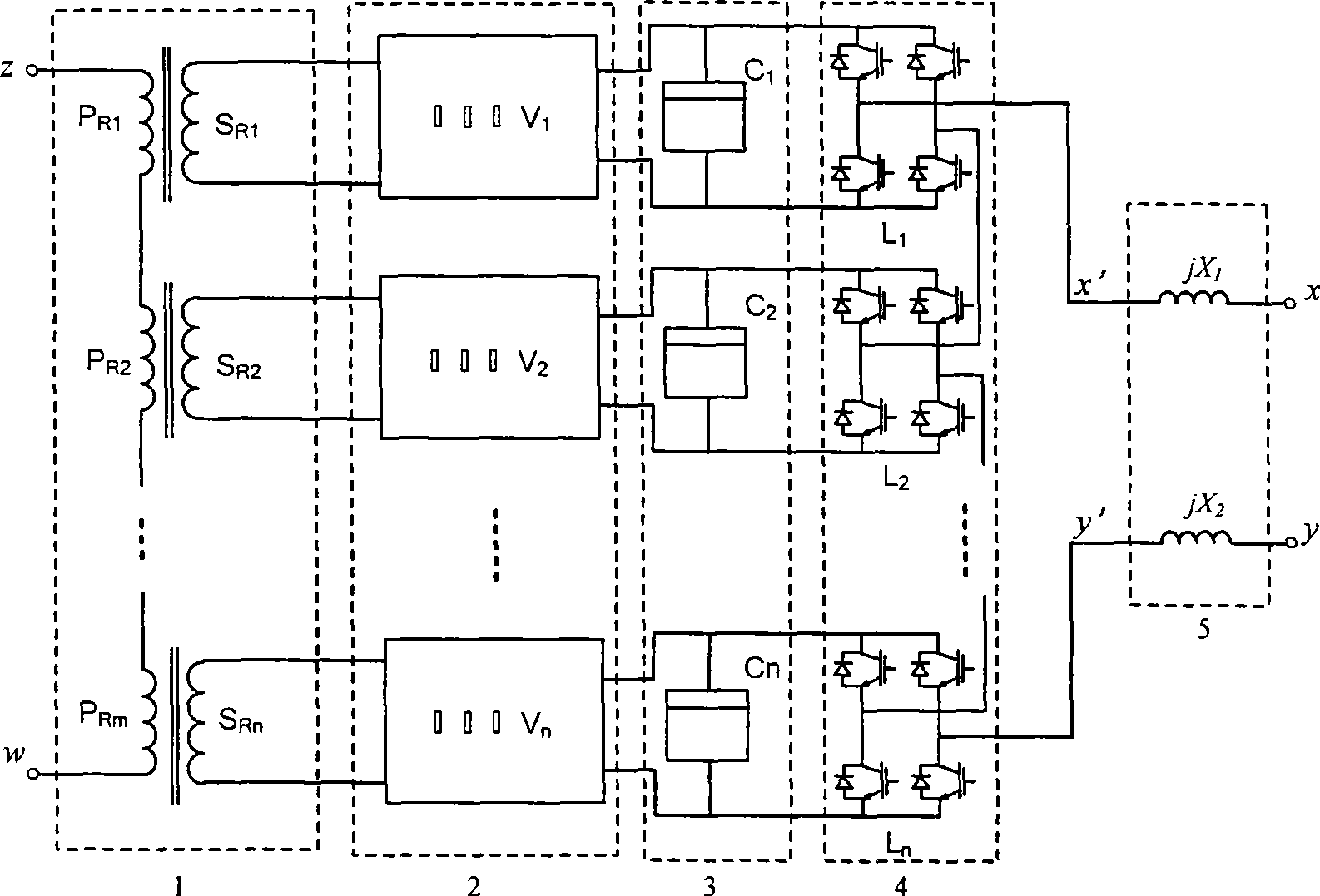
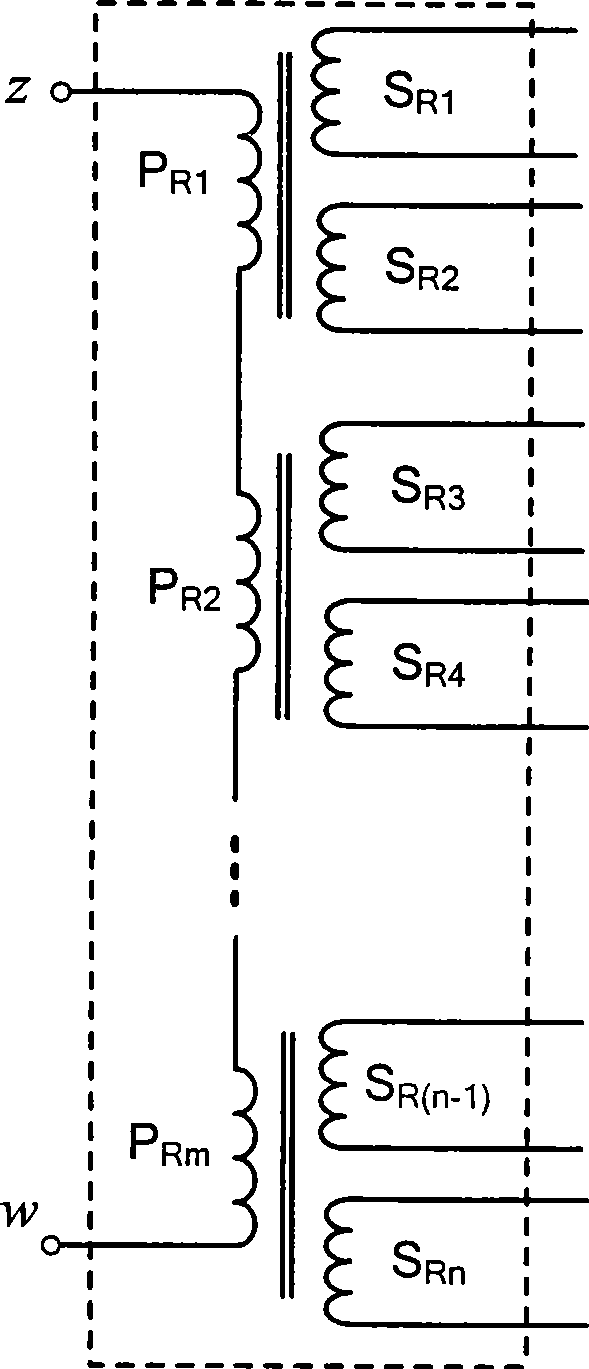
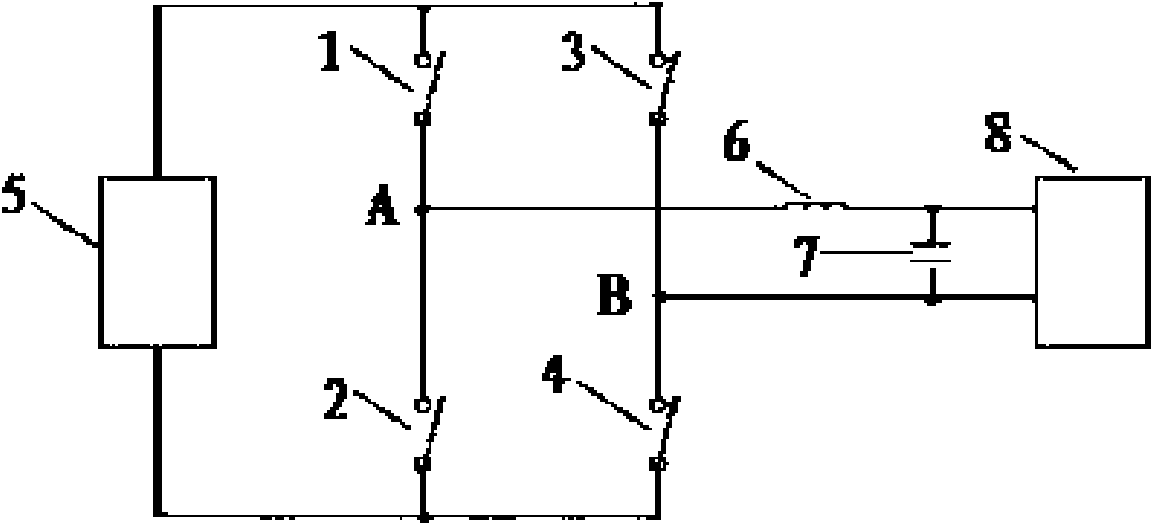
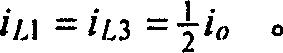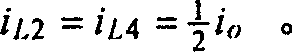Patents
Literature
658results about How to "Increase the switching frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
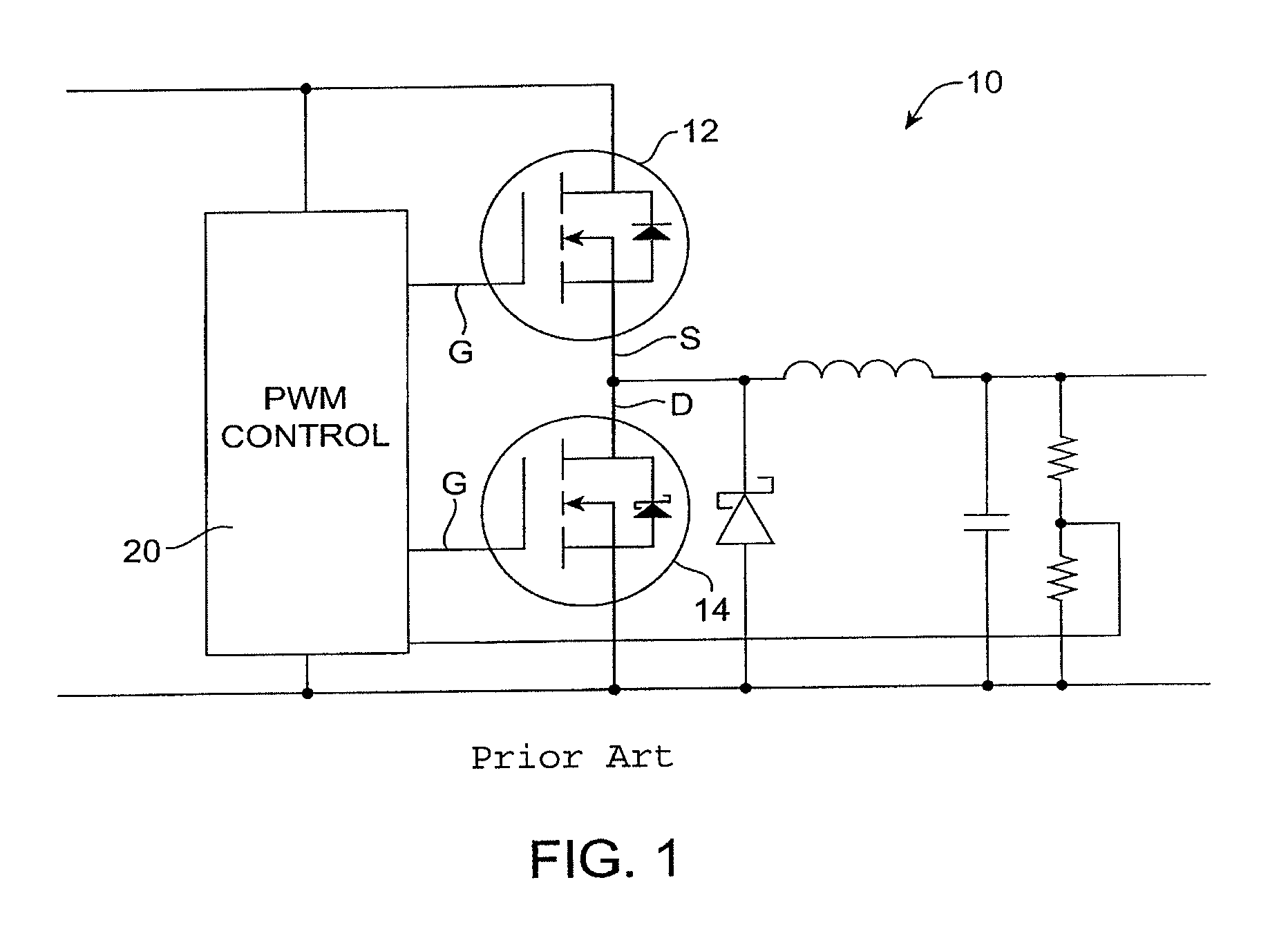
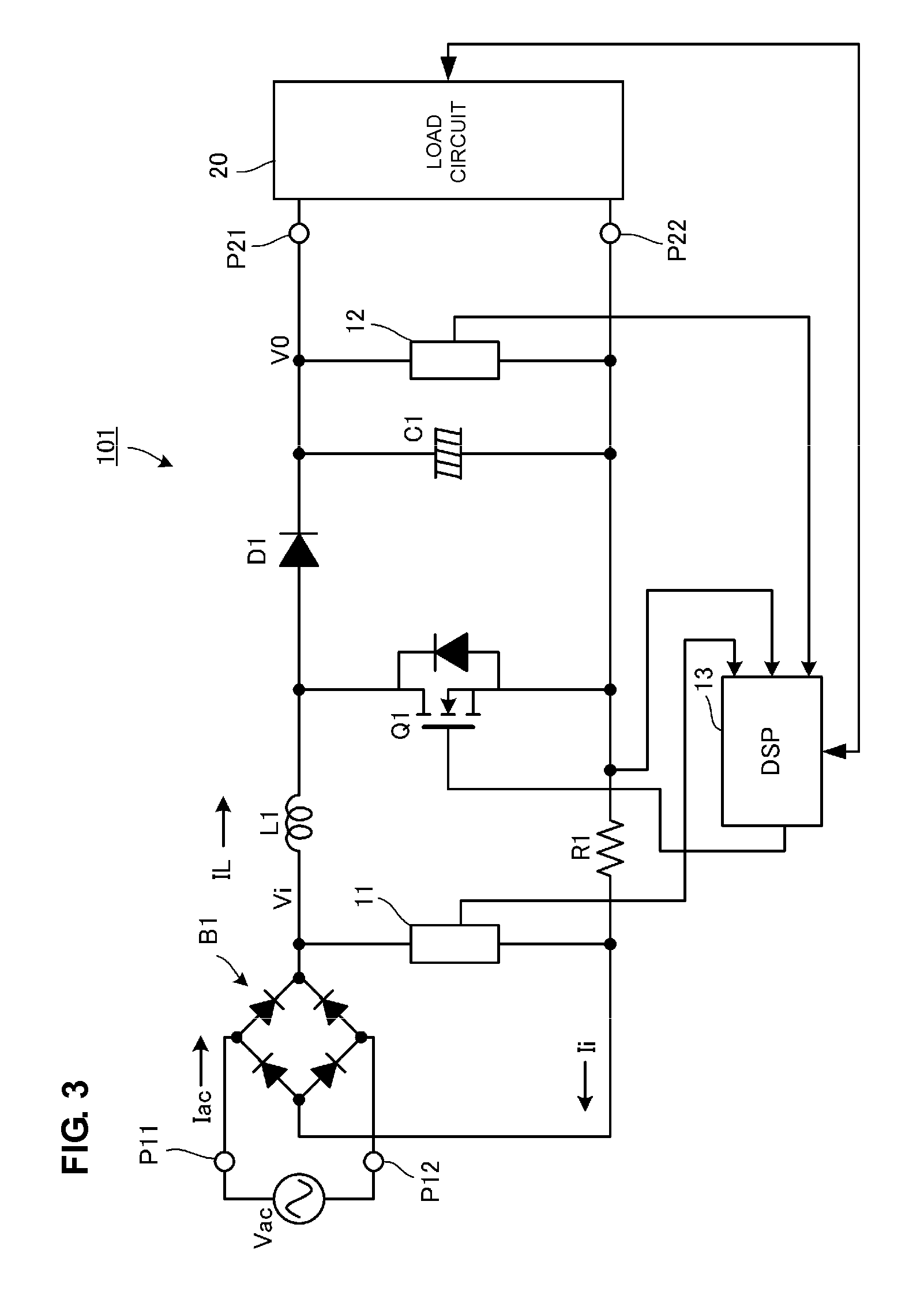
Power supplies for RF power amplifier
ActiveUS20080278136A1Increase the switching frequencyReduce switching frequencyBatteries circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersElectrical batteryEnvelope Tracking
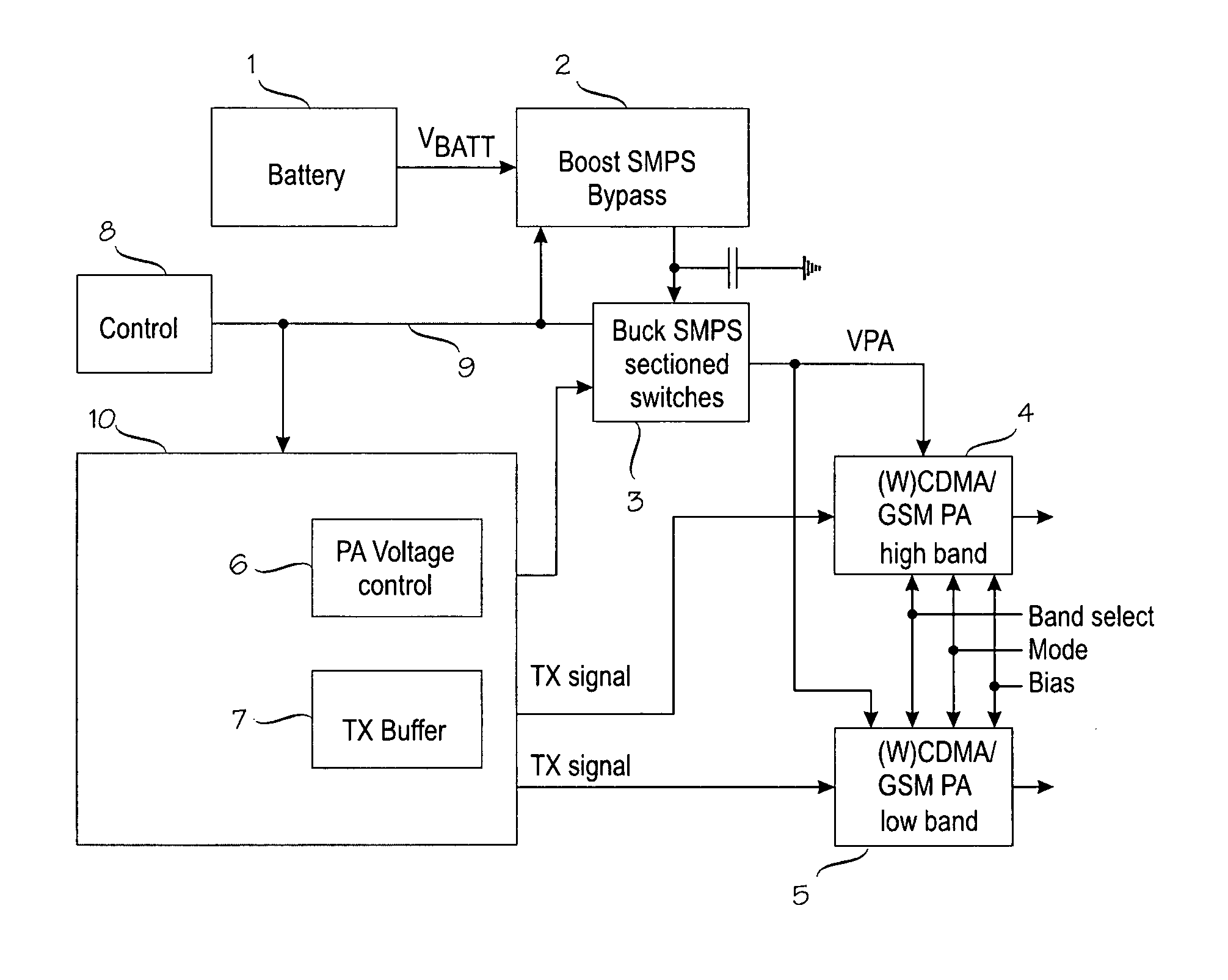
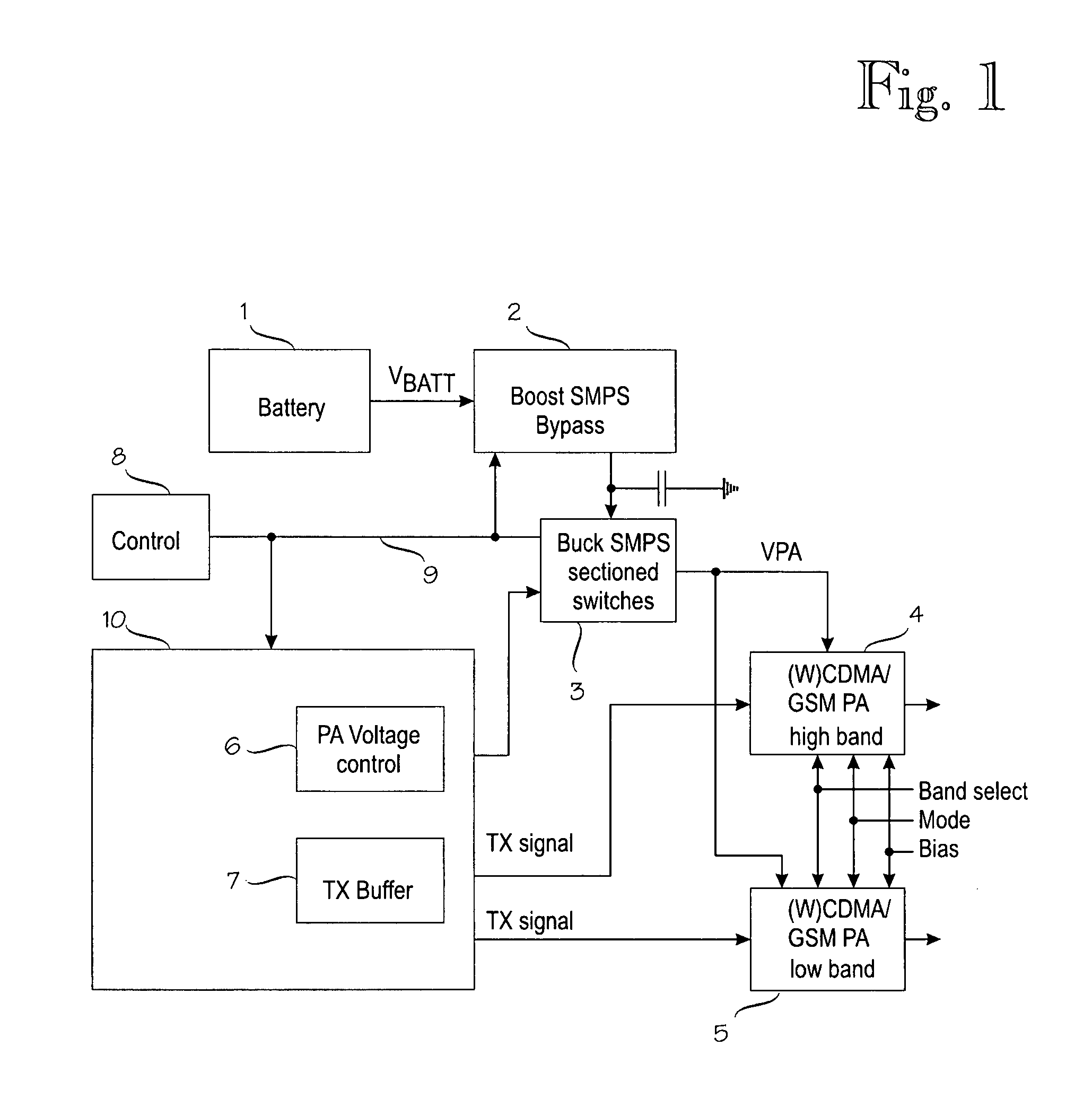
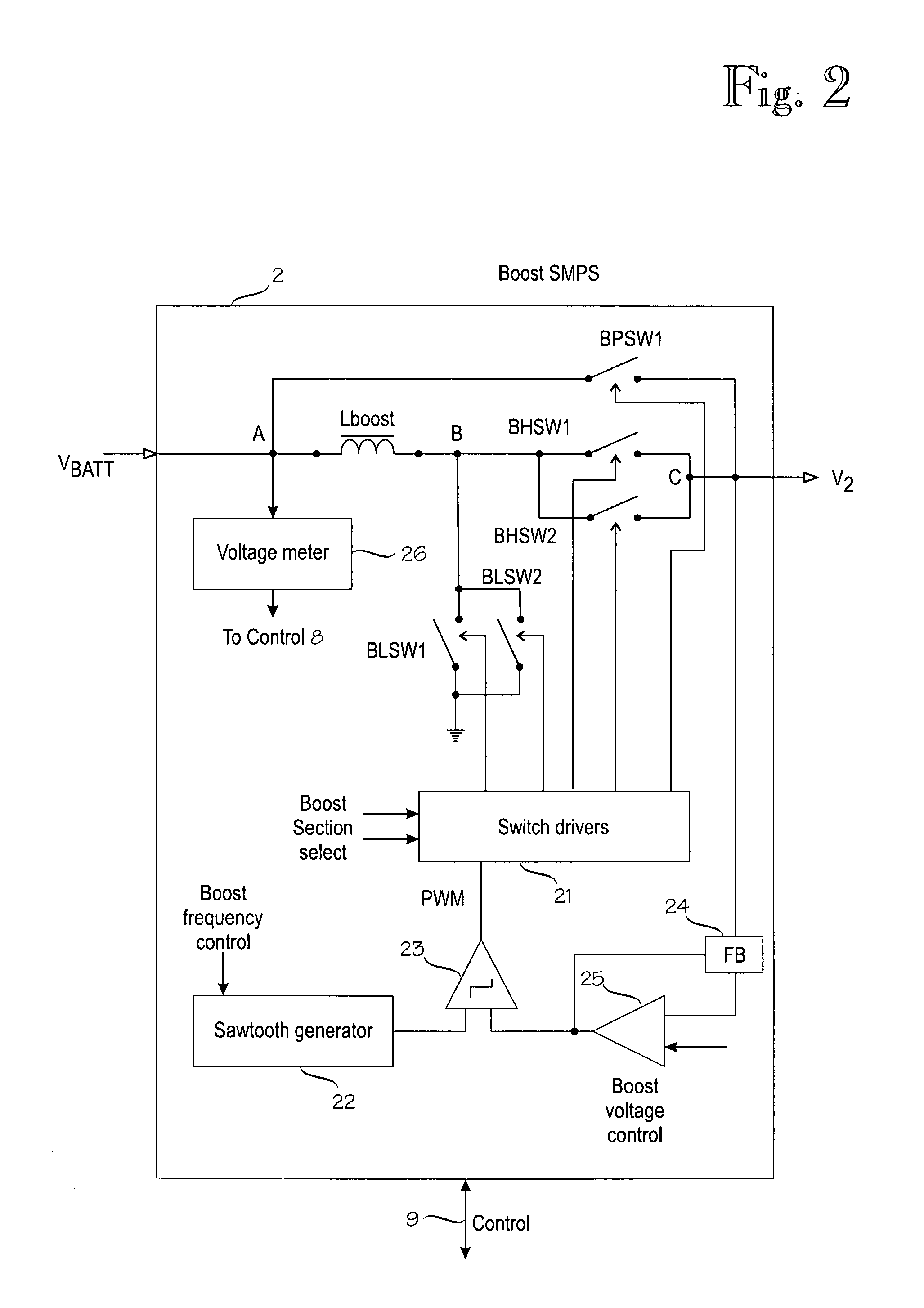
Switched-mode power supplies (SMPSs) and their control methods for radio frequency (RF) power amplifiers in battery-powered wireless transmitter devices involve a Boost-type SMPS and a Buck-type SMPS in cascade connection which are controlled so that high efficiency is maintained for various loads and transmission power levels. The Boost SMPS and the Buck SMPS can be controlled based on the mode of operation of the transmitter, such as the actual battery voltage, the needed output power, the selected frequency band, the selected RF power amplifier (PA), the selected modulation method of the transmission signal, and / or the selected PA voltage control method, such as the envelope elimination and restoration (EER) technique, the envelope tracking (ET) technique, or the power-level tracking (PT) technique.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
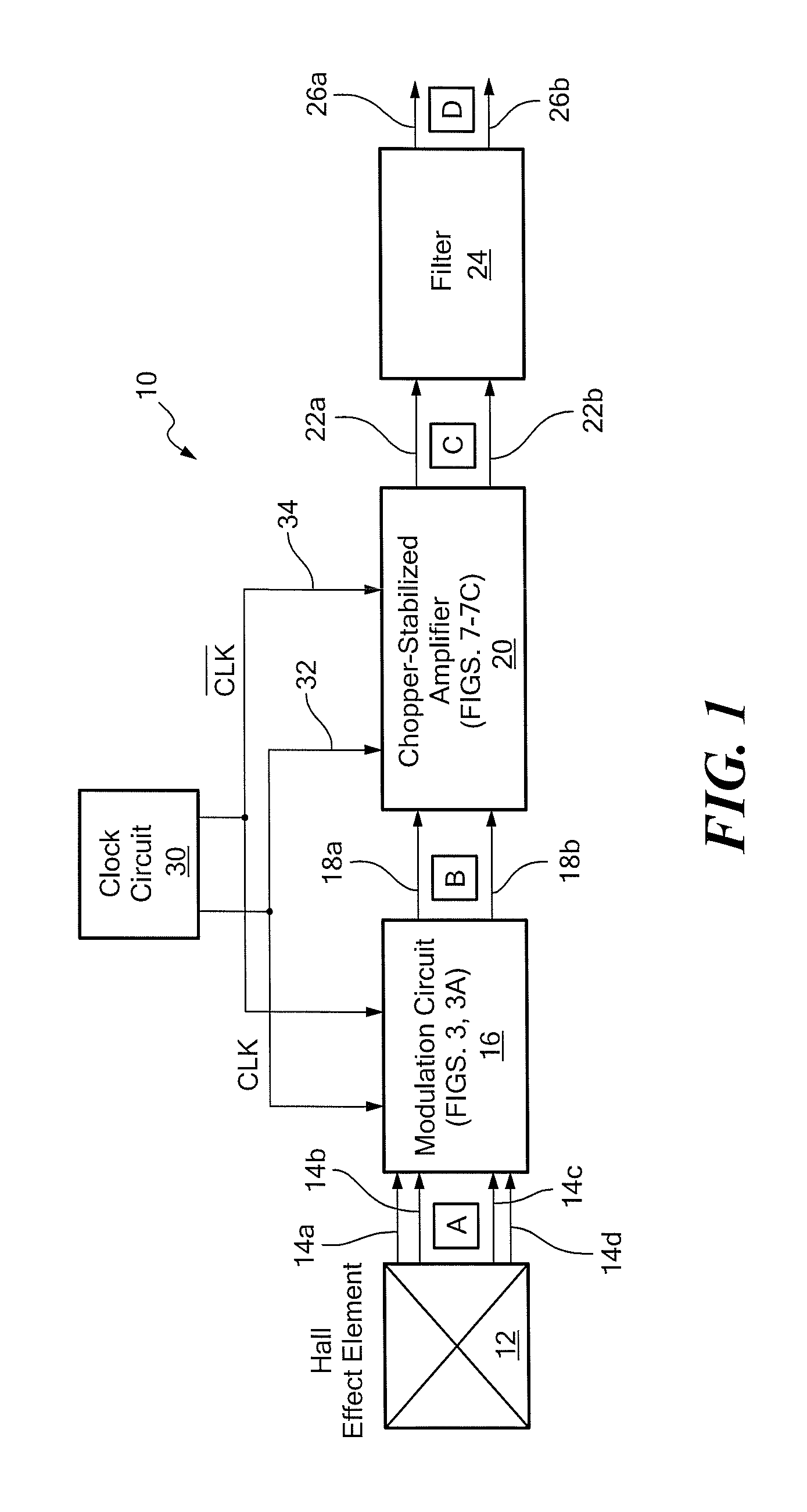
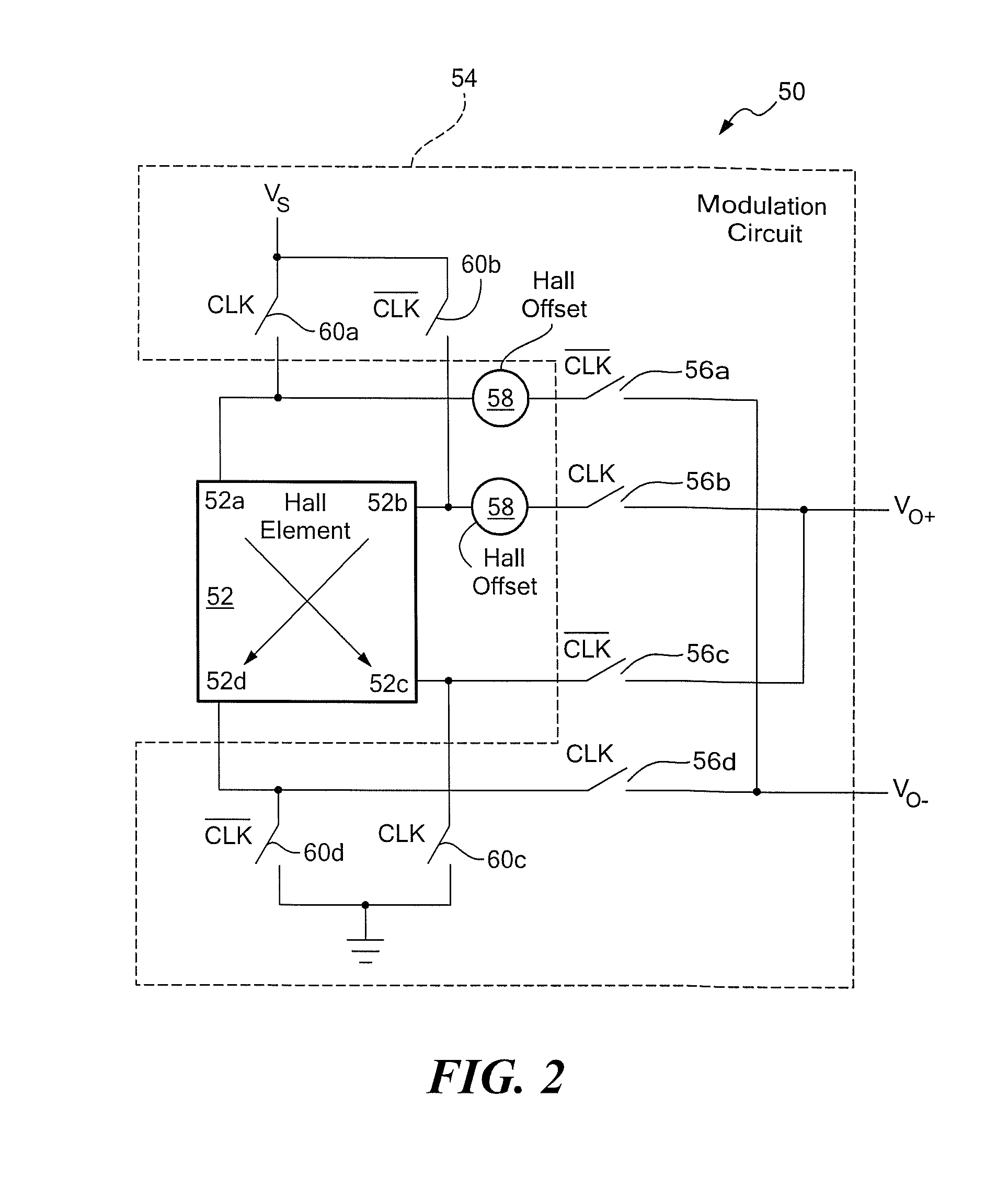
Chopper-stabilized amplifier and magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS7605647B1Reduced offset componentIncrease the switching frequencyGalvano-magnetic amplifiersMagnetic measurementsAudio power amplifierLow-pass filter
A chopper-stabilized amplifier has switching networks arranged to support a high frequency clocking signal and to provide a high common mode rejection and a high rejection of an offset component of an input signal. A magnetic field sensor includes a Hall effect element coupled to a modulation circuit. The modulation circuit provides a signal to the chopper-stabilized amplifier. The chopper-stabilized amplifier provides an output signal to a low pass filter, which provides an output signal from the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
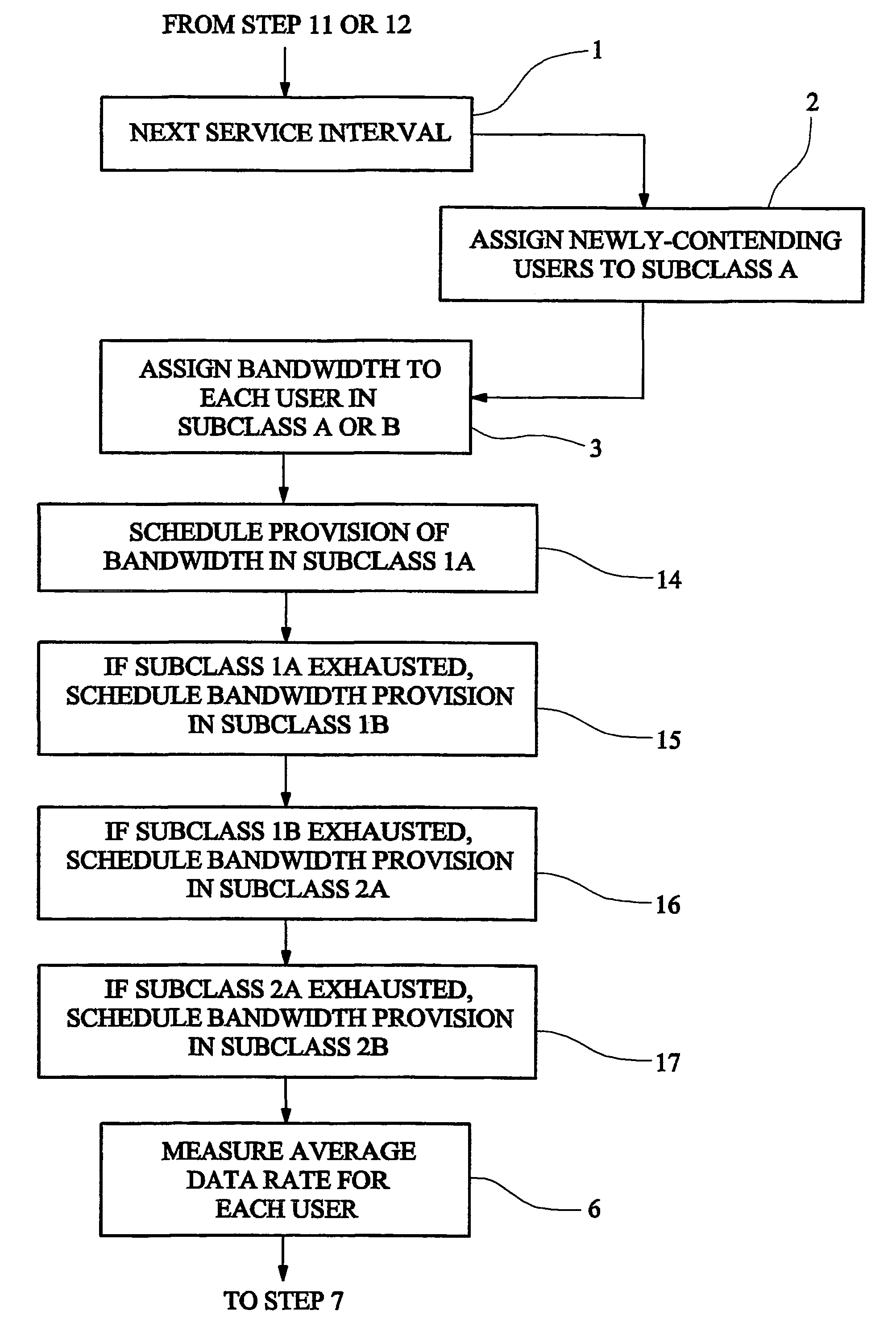
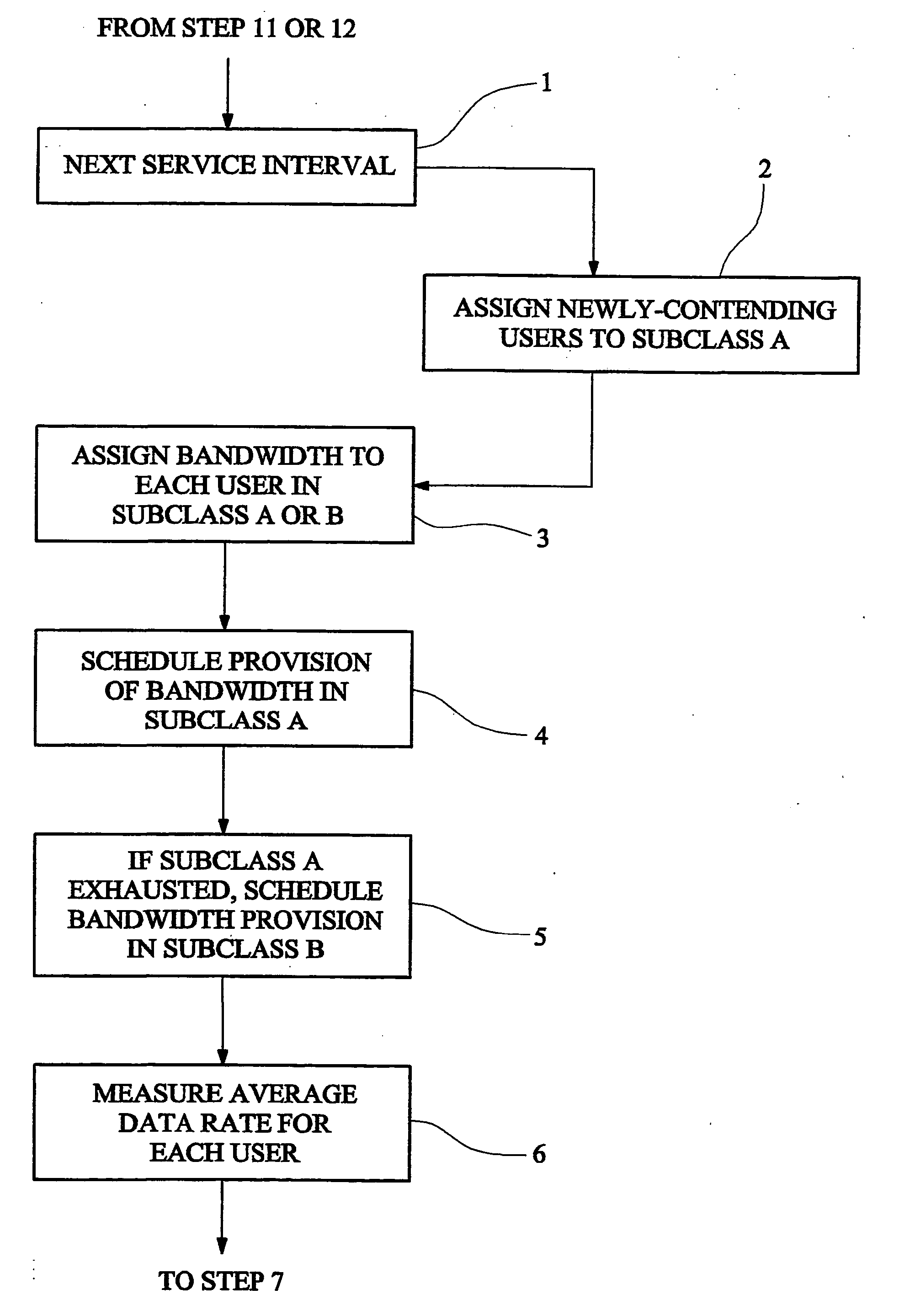
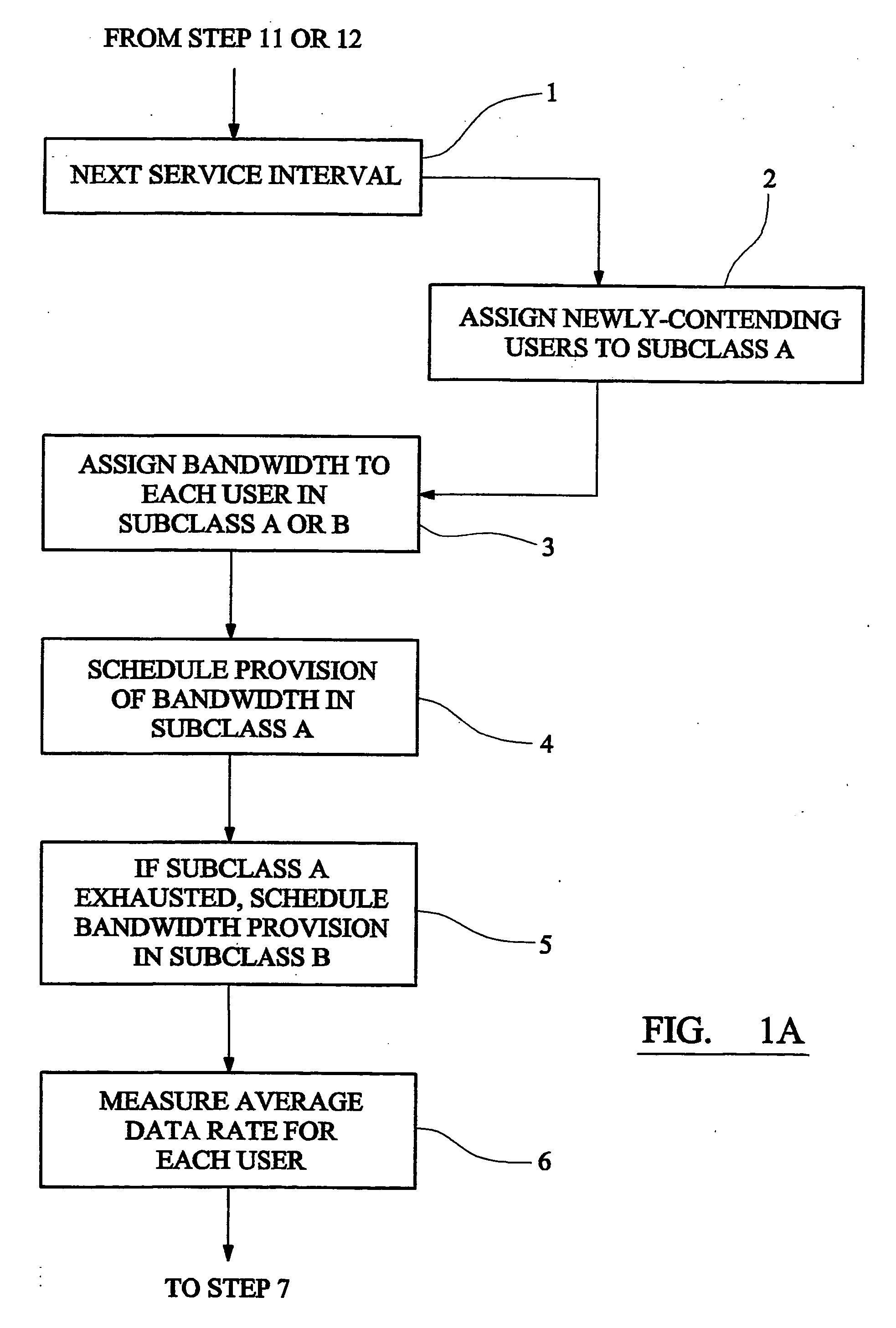
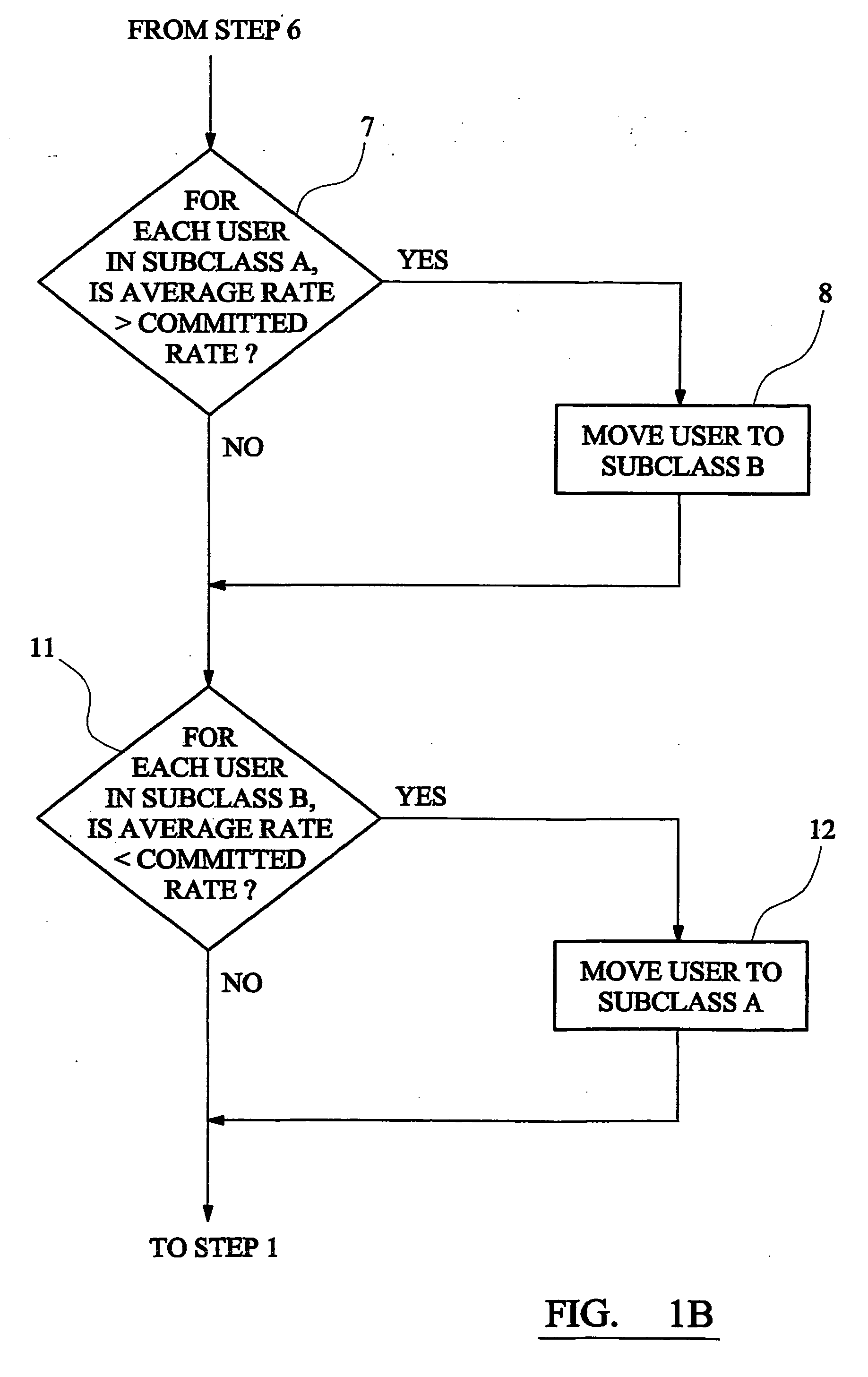
Method and apparatus for providing communications bandwidth to users having a committed data rate based on priority assignment
ActiveUS7430209B2Increase incomeHigh bandwidthData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsCommunications systemCommitted information rate
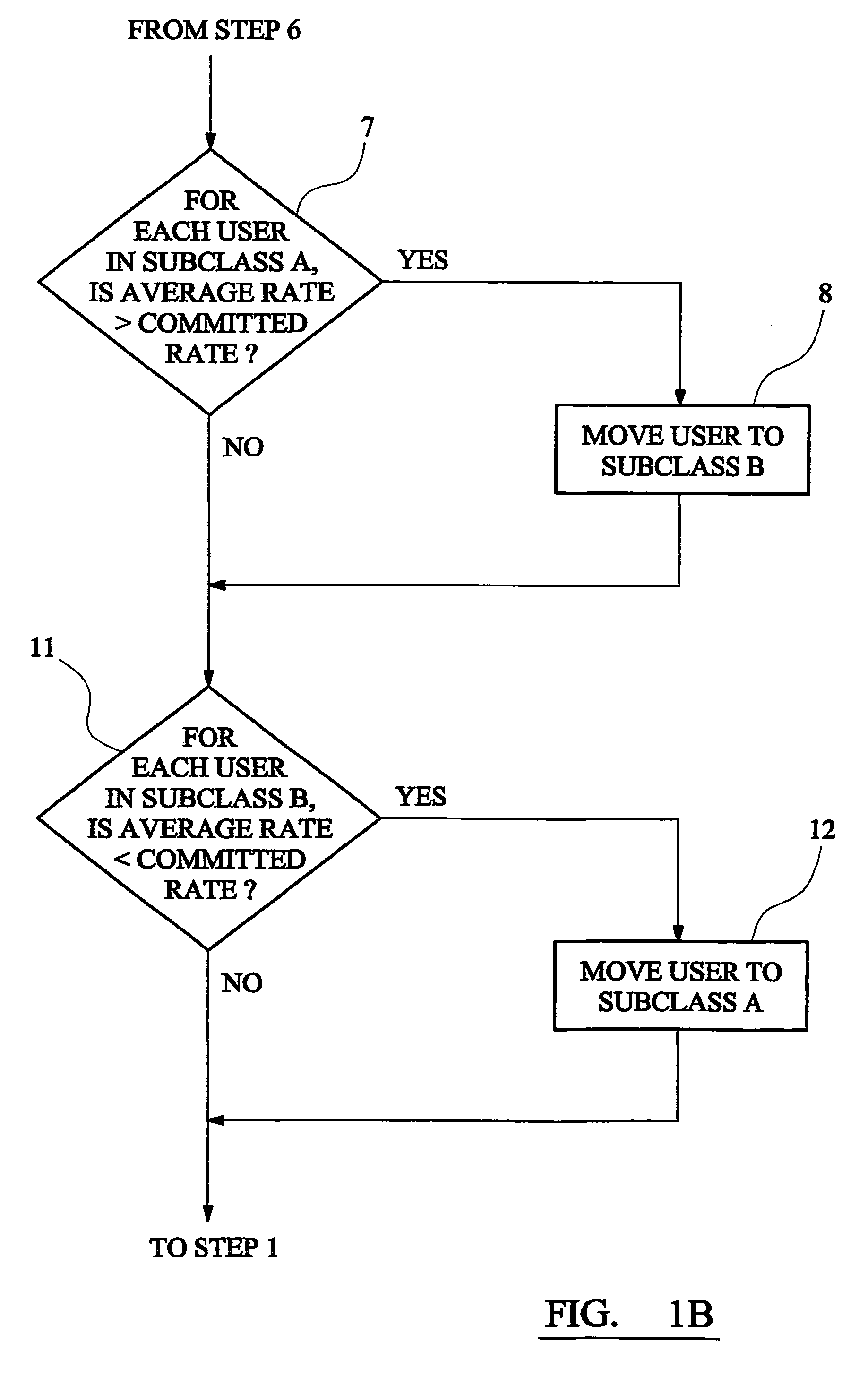
A communications system operator provides to each user of a multi-user communications system a committed information rate (CIR). When a user requests bandwidth for transmission, a system controller queues the user in a high-priority subclass A. The system controller allocates bandwidth to the user at the head of the queue as requested but if the user's bandwidth, measured as an average over a sampling time, exceeds its CIR, it is moved into a low-priority subclass B. The user can then only obtain further bandwidth after other users in the high-priority subclass have been allocated bandwidth up to their CIRs. If a user in the low-priority subclass only receives allocation of a small amount of bandwidth, so that its average inforamtion rate falls below its CIR, it is moved back in to the queue in the high-priority subclass.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE BROADBAND NETWORKS LIMITED
High switching frequency DC-DC converter with fast response time
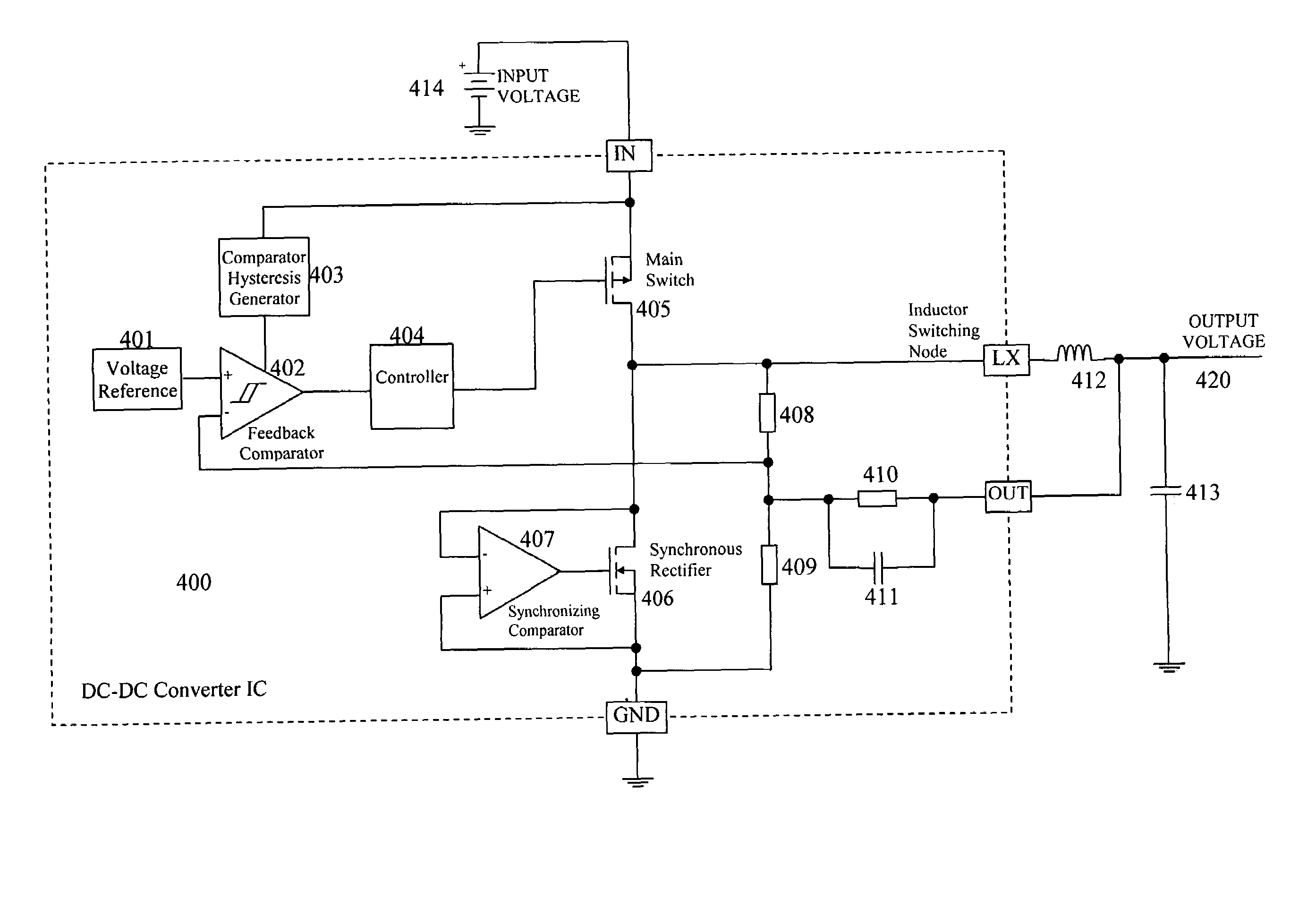
ActiveUS7279875B2Save circuit board areaShorten the timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterLoad step
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
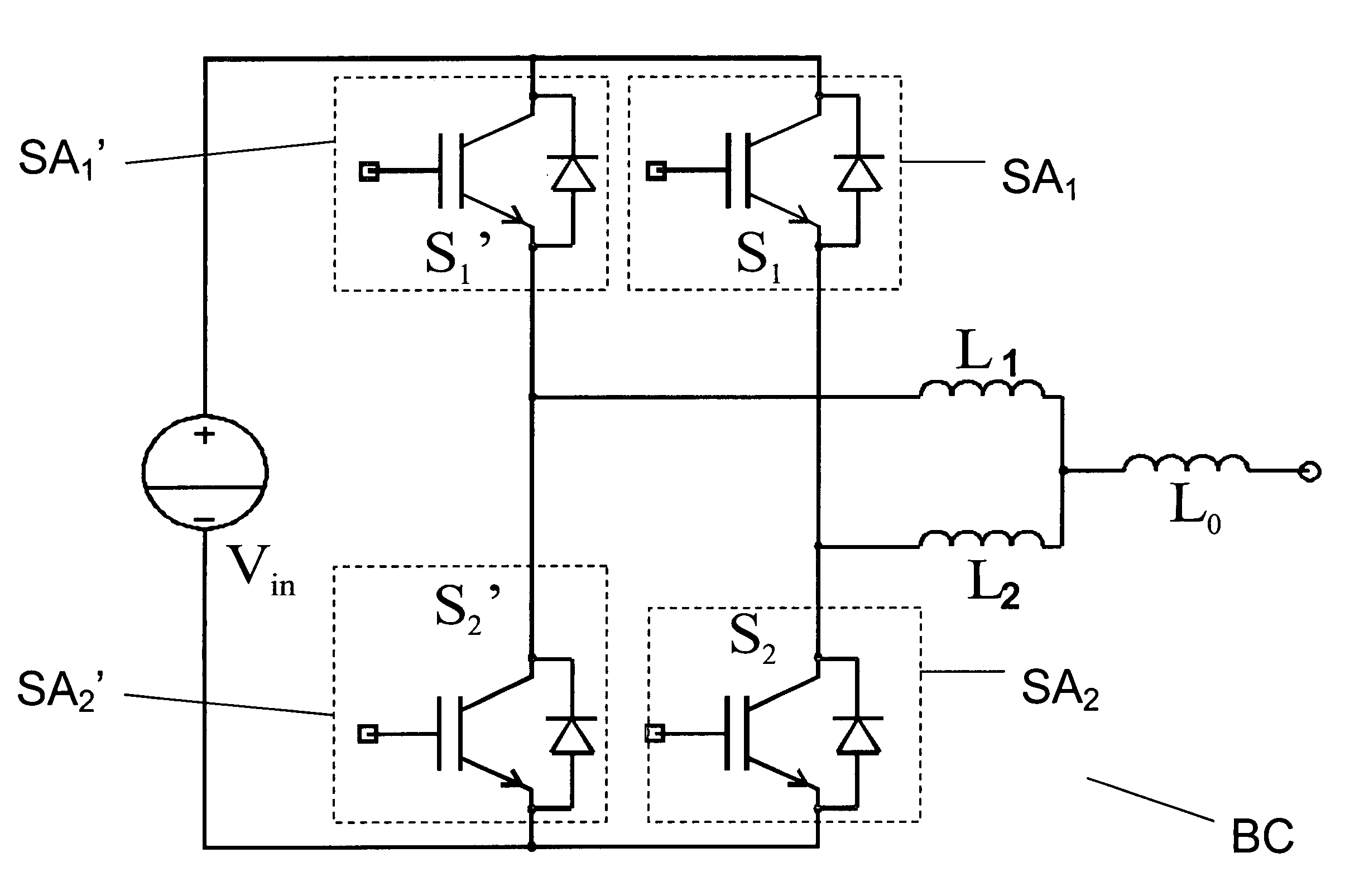
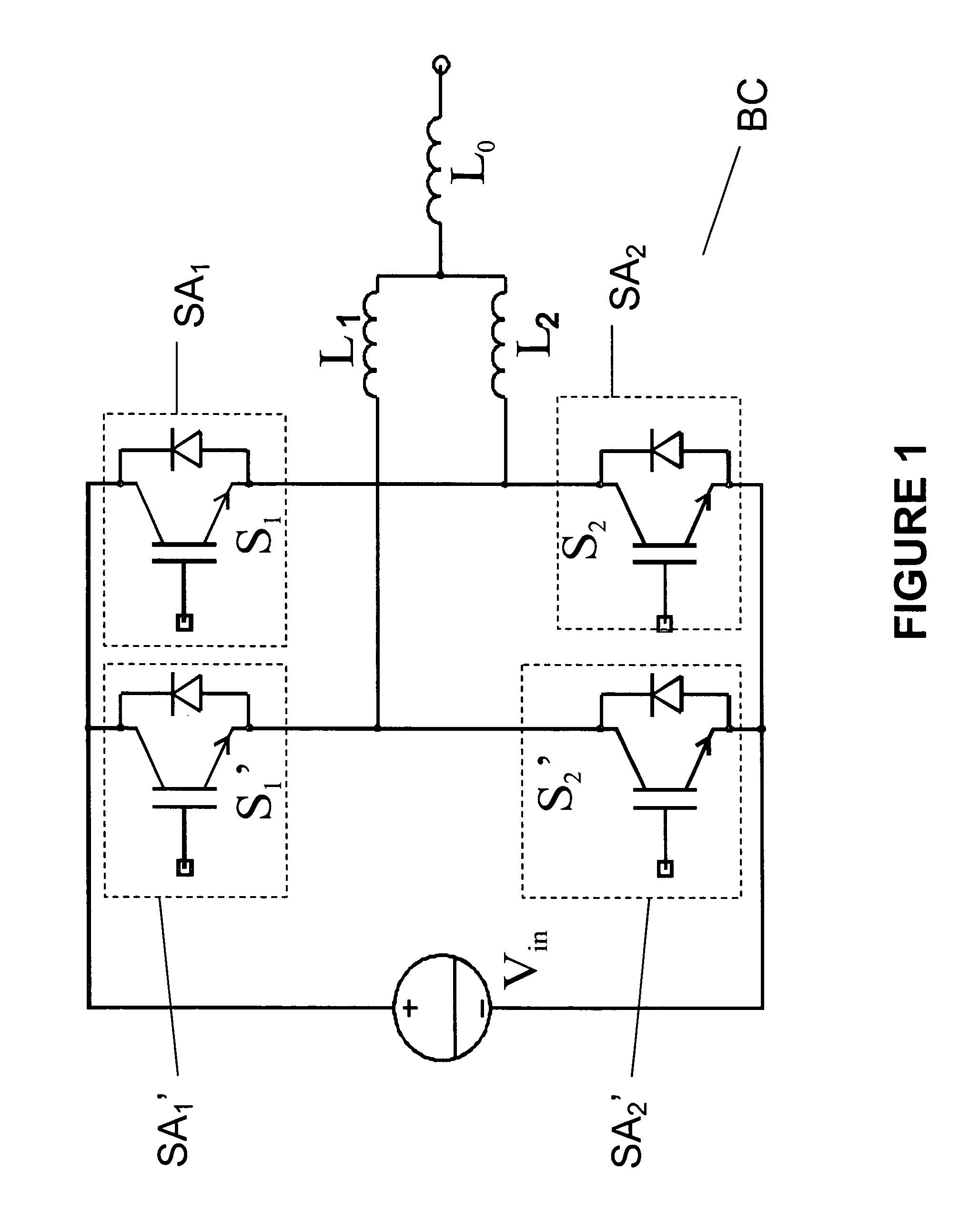
Semiconductor die package including multiple dies and a common node structure
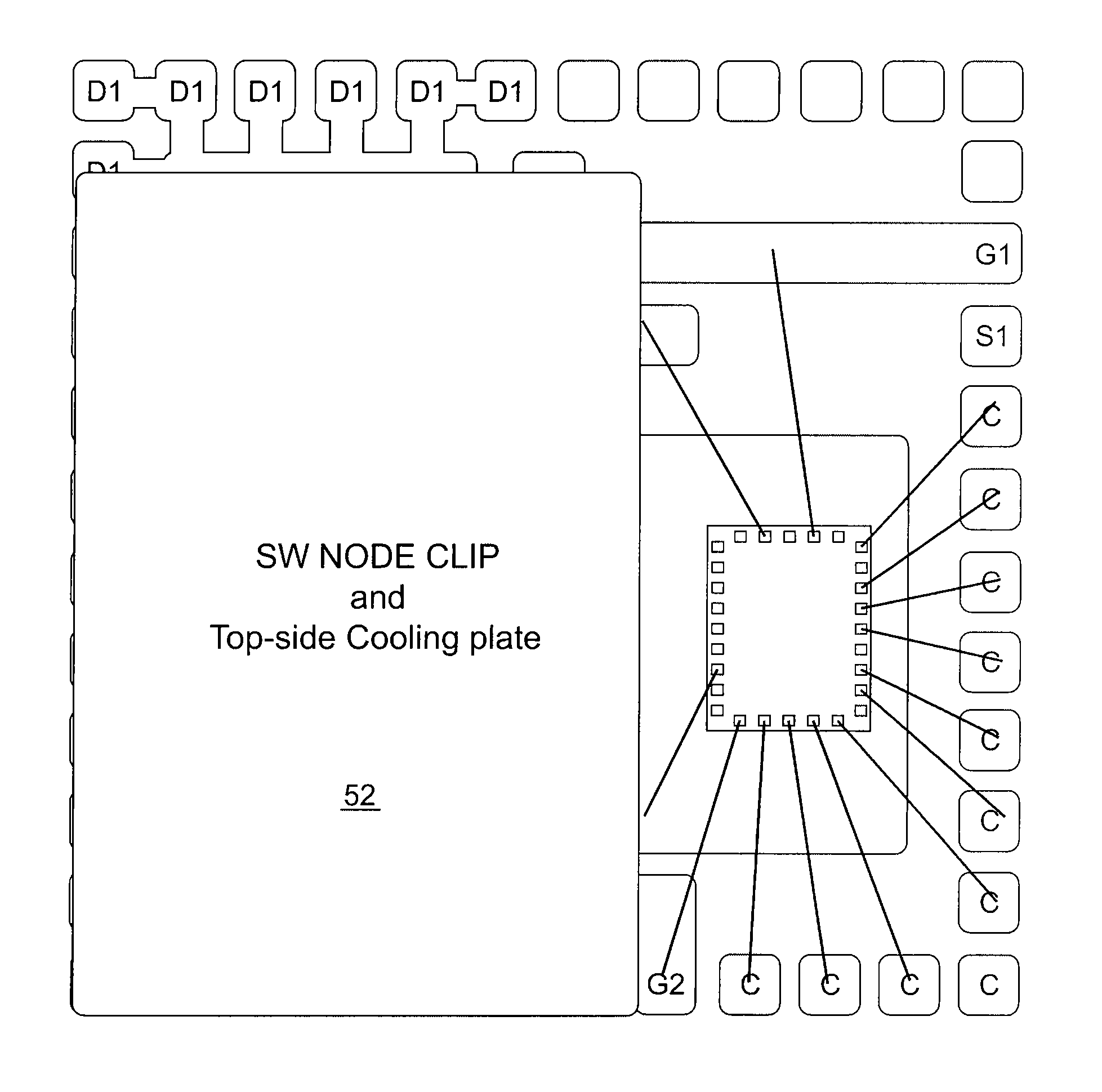
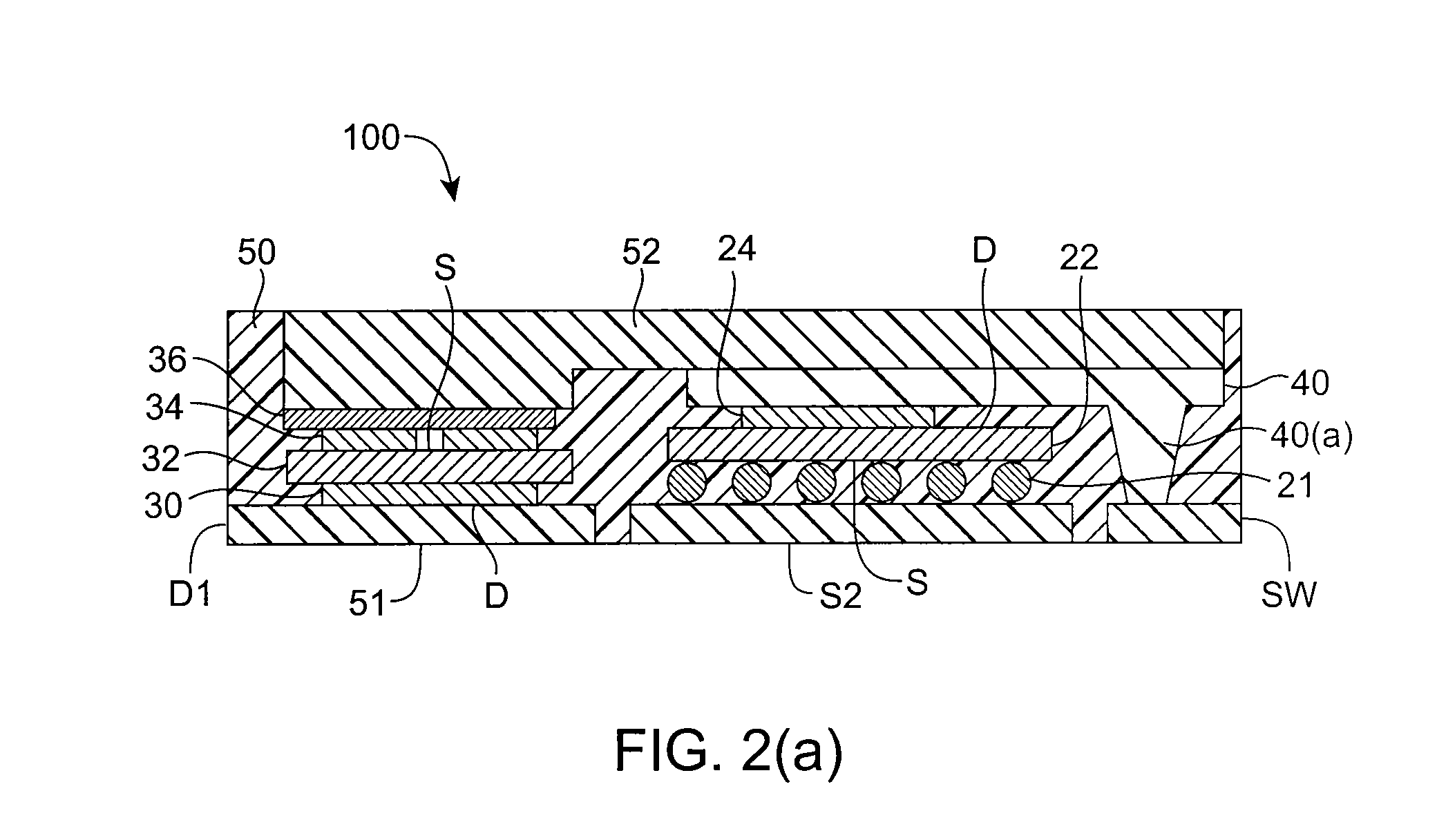
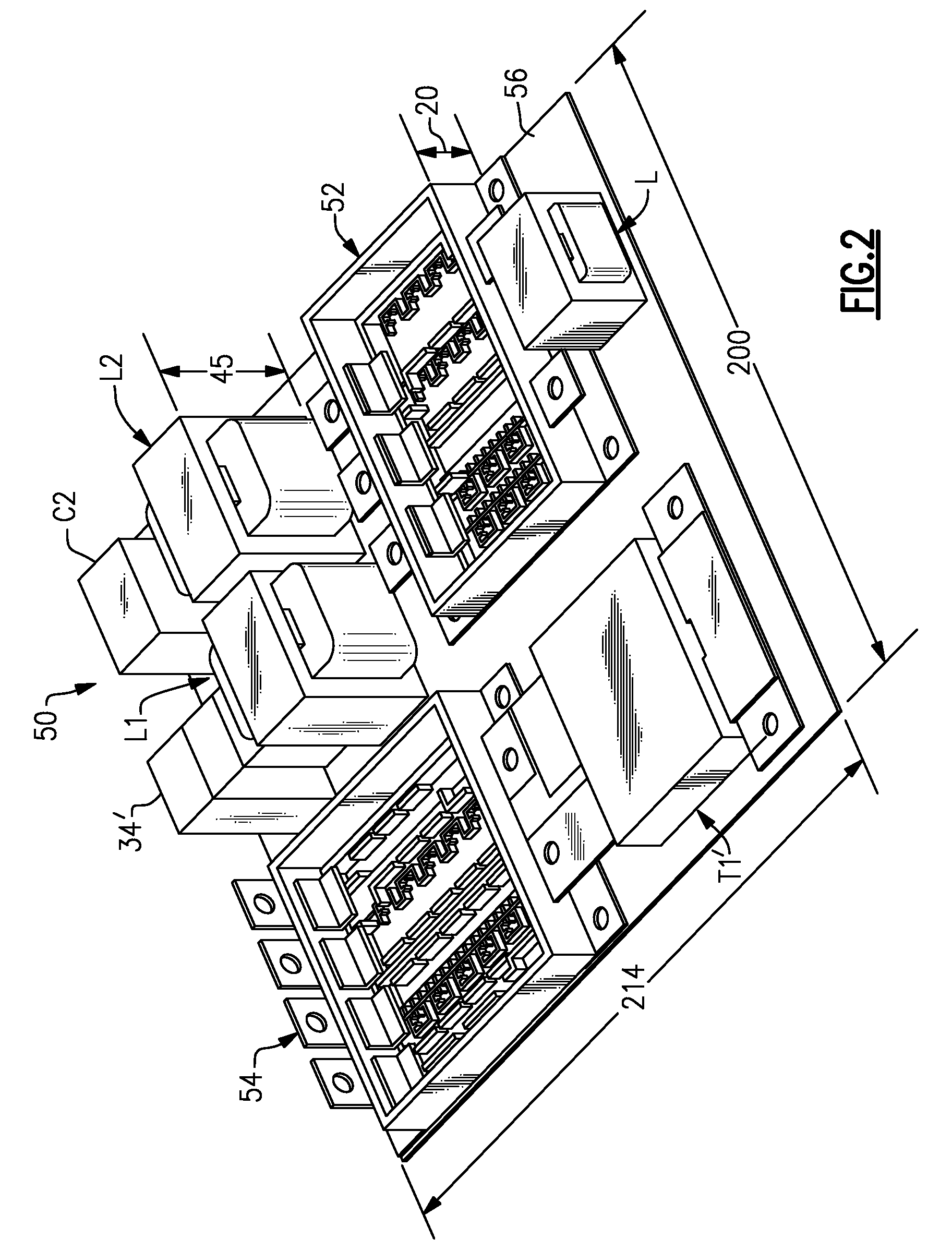
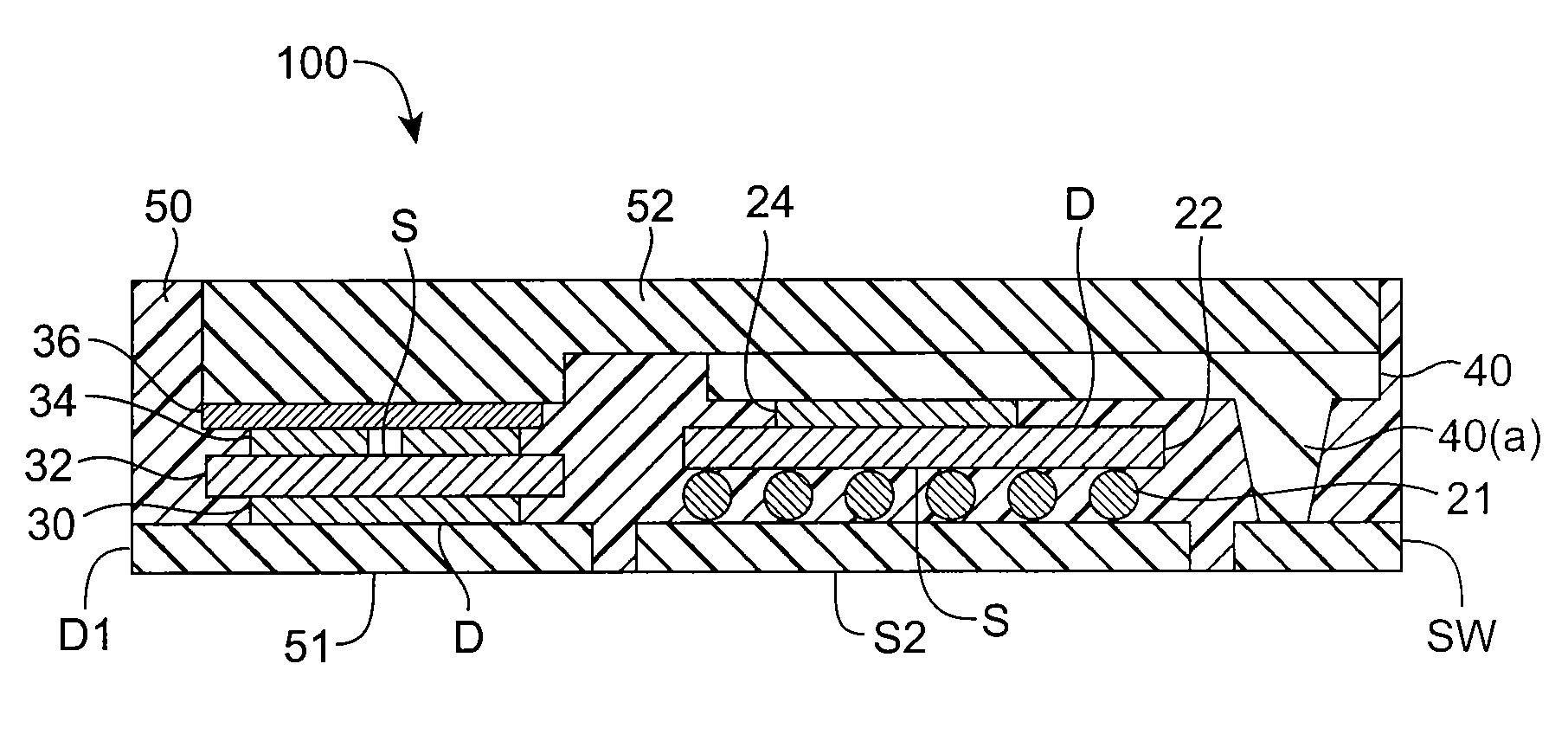
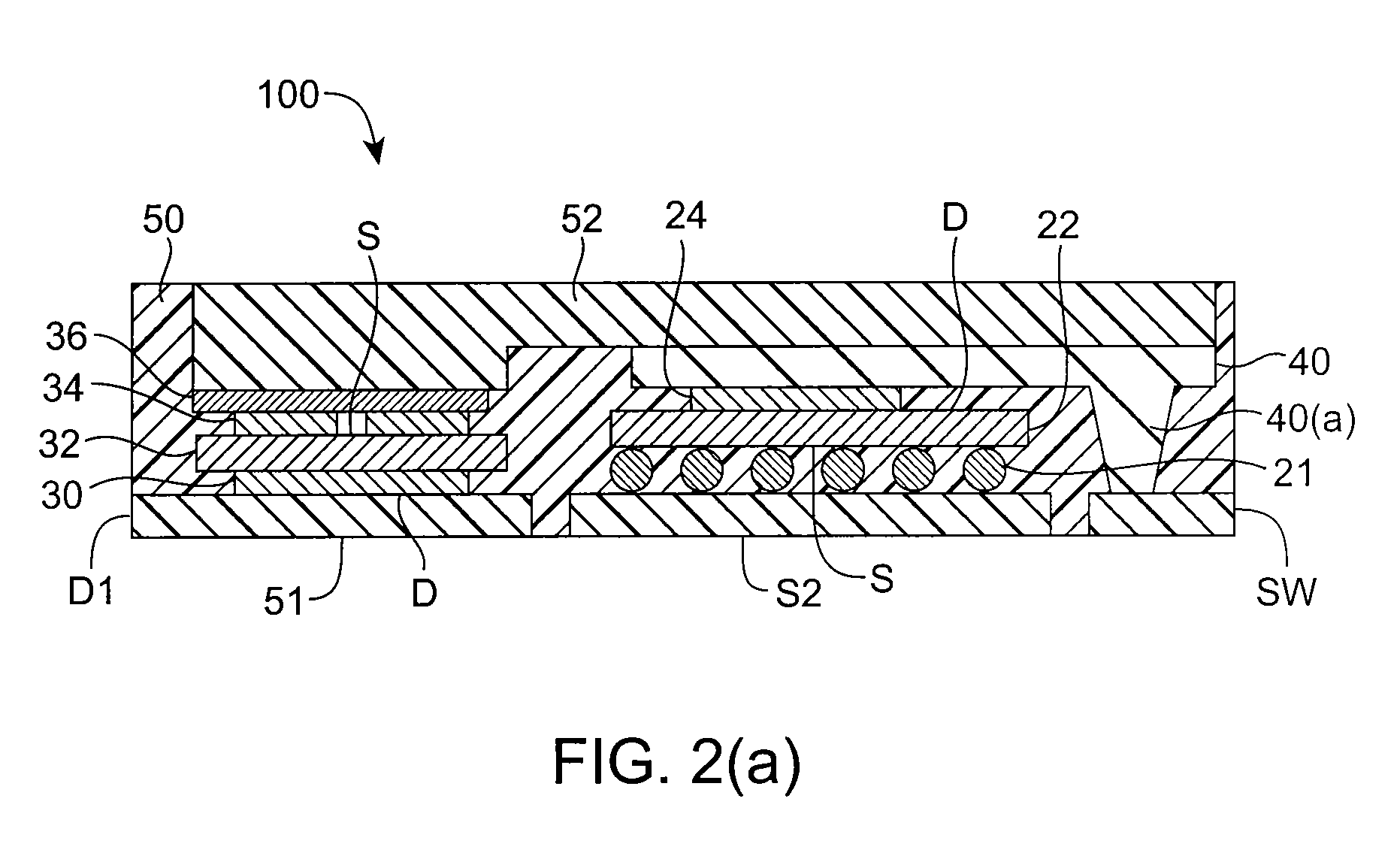
ActiveUS20070249092A1Length minimizationReducing parasitic inductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A semiconductor die package capable of being mounted to a motherboard is disclosed. The semiconductor die package includes a substrate, and a first semiconductor die mounted on the substrate, where the first semiconductor die includes a first vertical device comprising a first input region and a first output region at opposite surfaces of the first semiconductor die. The semiconductor die package includes a second semiconductor die mounted on the substrate, where second semiconductor die comprises a second vertical device comprising a second input region and a second output region at opposite surfaces of the second semiconductor die. A substantially planar conductive node clip electrically communicates the first output region in the first semiconductor die and the second input region in the second semiconductor die. The first semiconductor die and the second semiconductor die are between the substrate and the conductive node clip.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
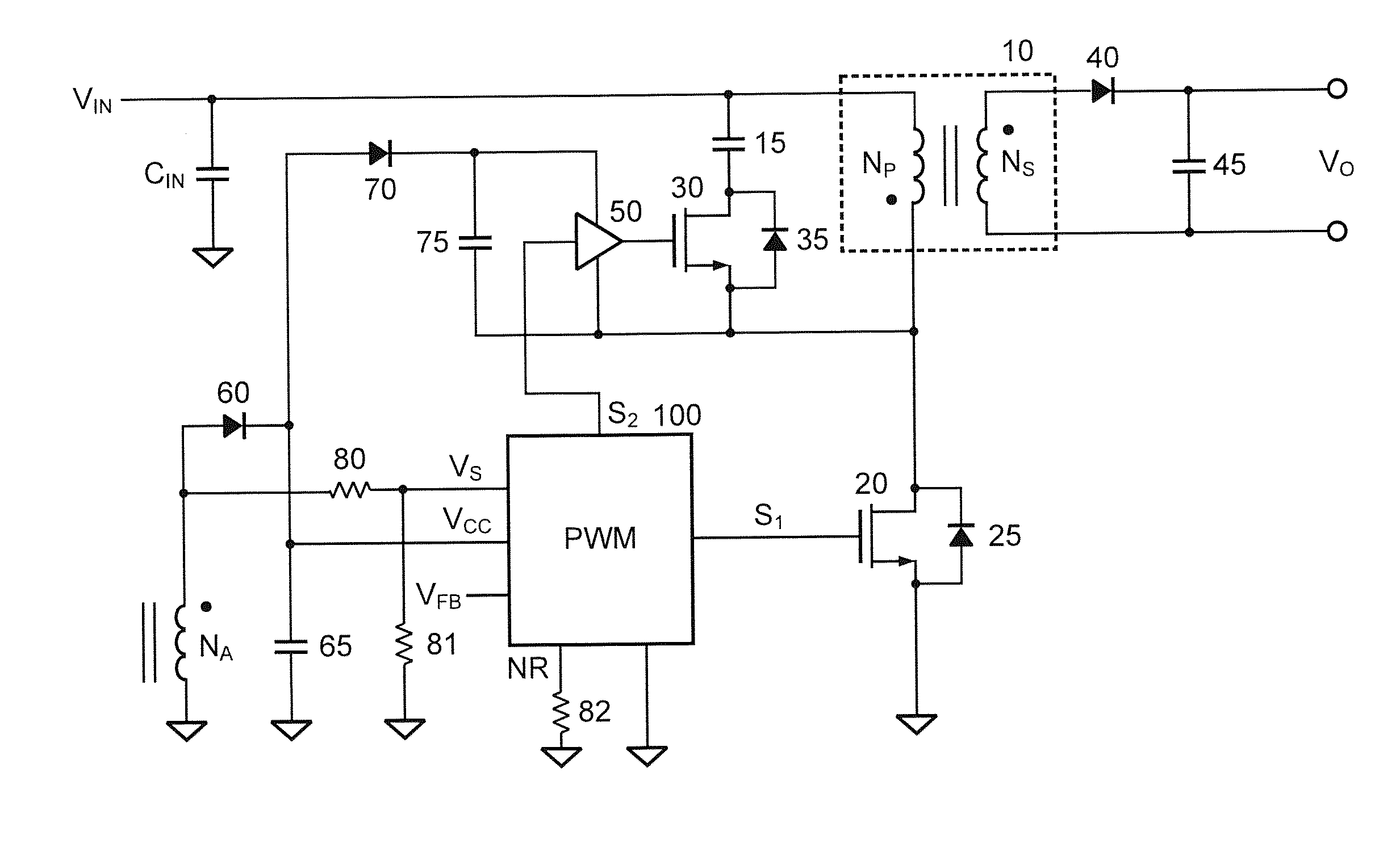
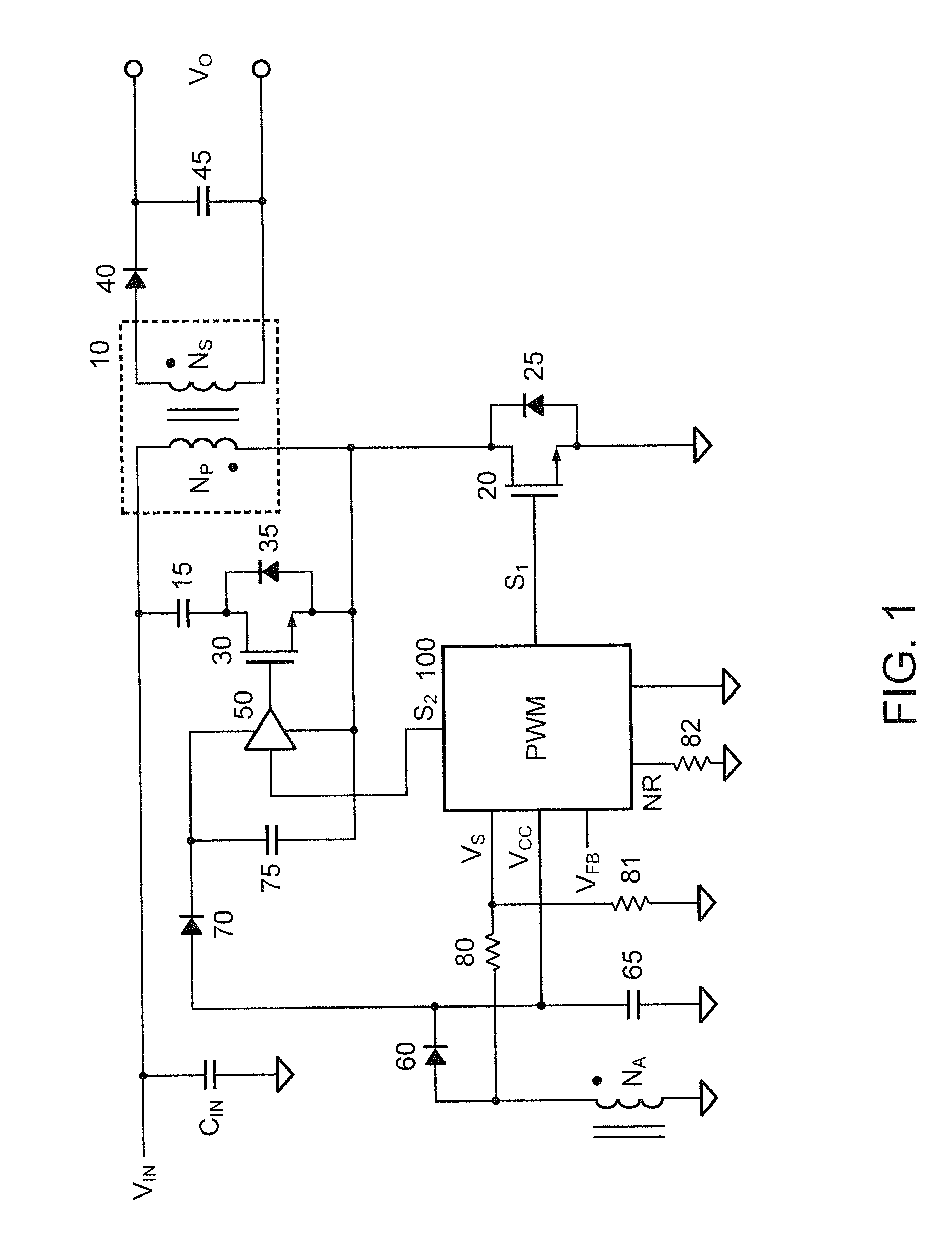
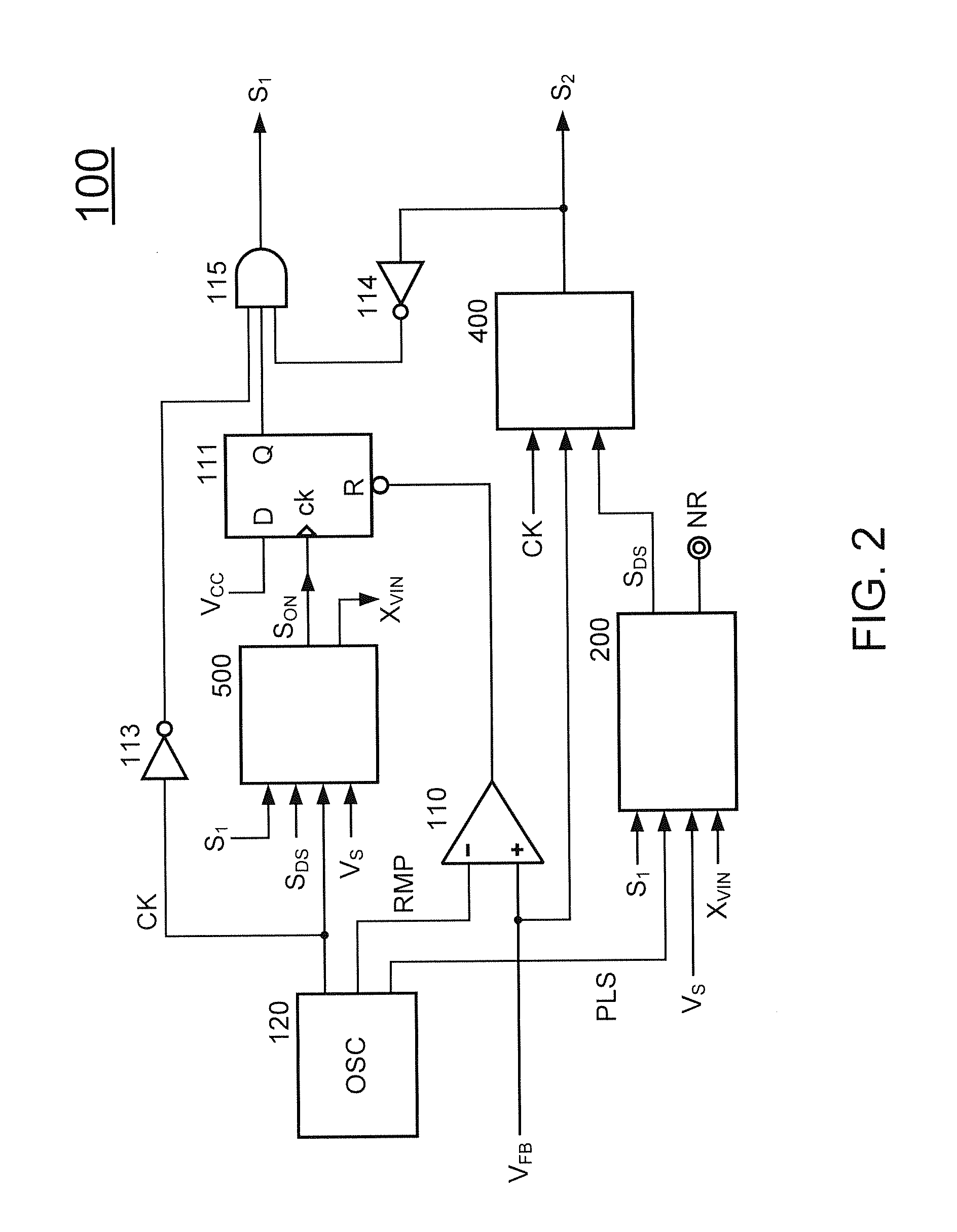
Systems and methods for regulating power conversion systems with output detection and synchronized rectifying mechanisms
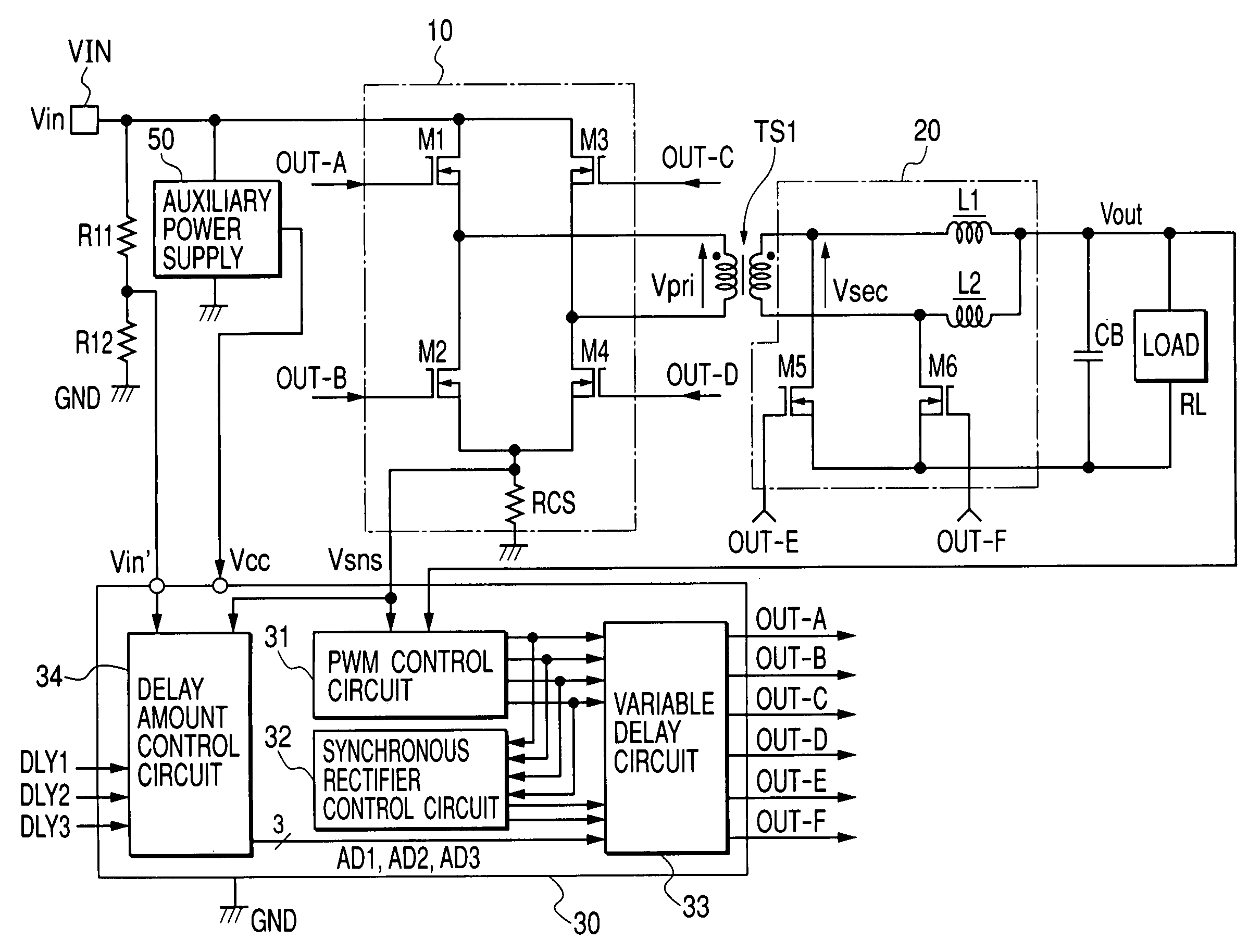
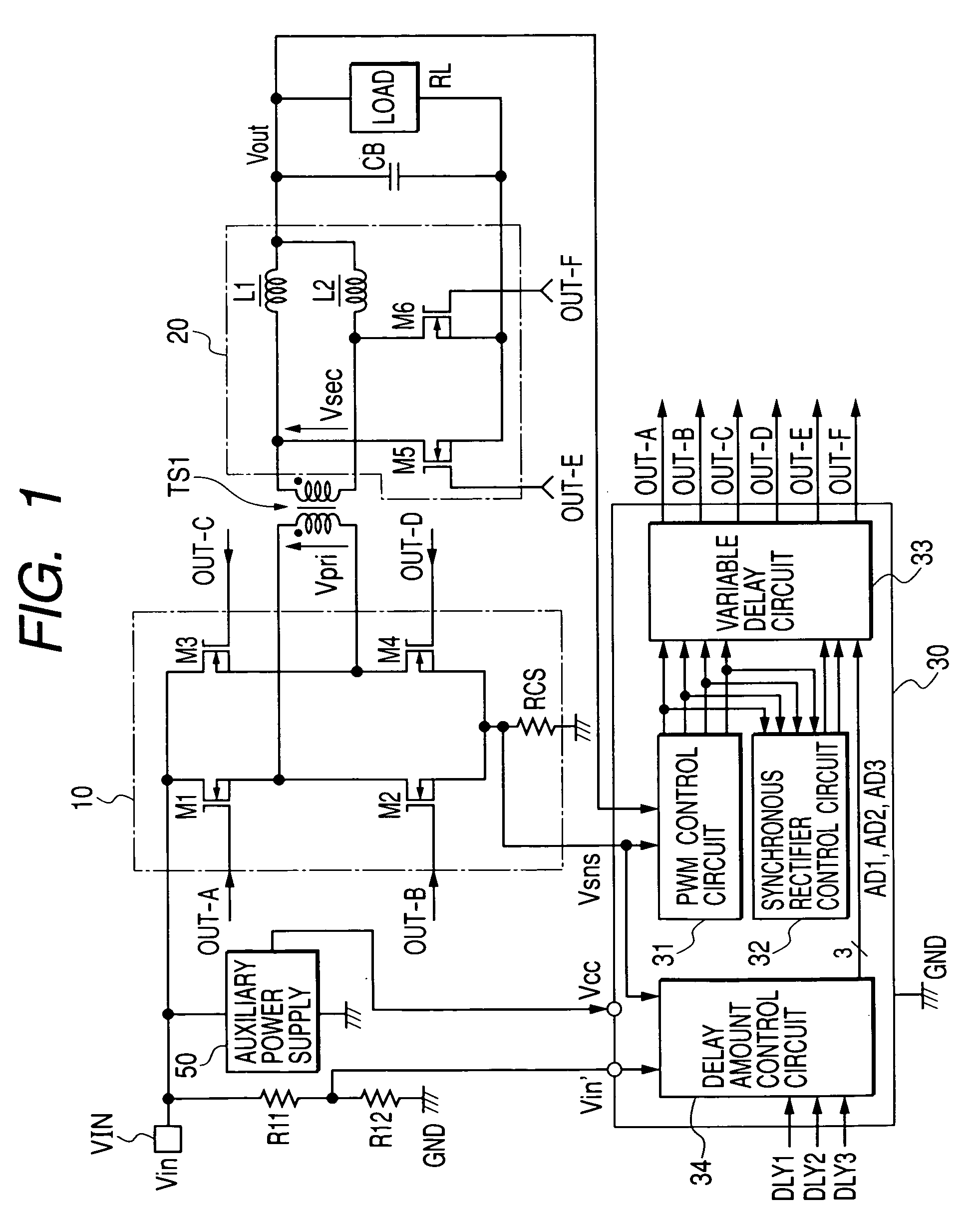
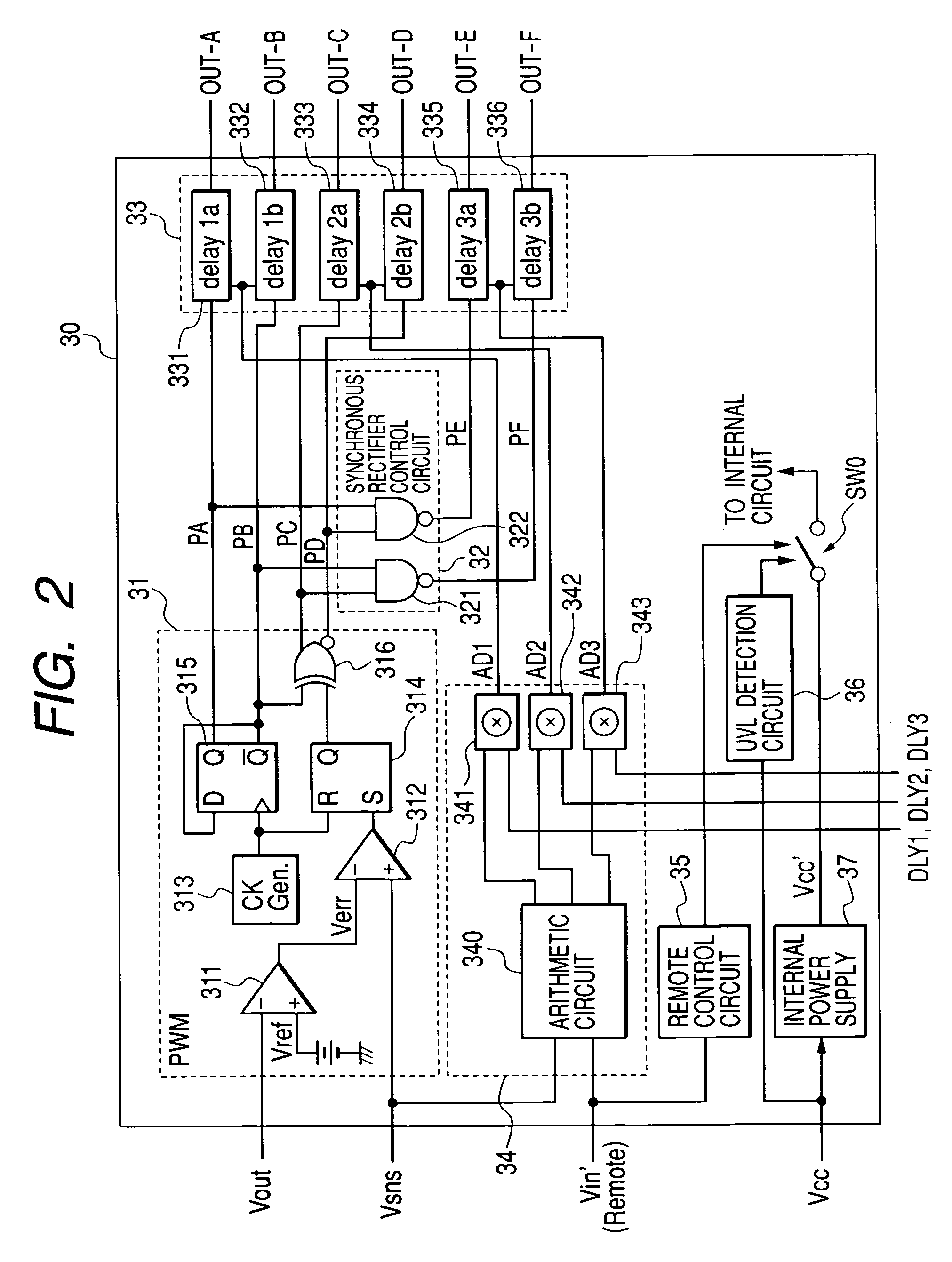
ActiveUS20140218976A1Increase the switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConductor CoilControl theory
System and method for regulating a power conversion system. An example system controller includes: a first controller terminal and a second controller terminal. The system controller is configured to: receive an input signal at the first controller terminal and generate a first drive signal at the second controller terminal based on at least information associated with the input signal to turn on or off a transistor to affect a current associated with a secondary winding of the power conversion system. The system controller is further configured to: in response to the input signal changing from a first value larger than a first threshold to a second value smaller than the first threshold, change the first drive signal from a first logic level to a second logic level to turn on the transistor.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Semiconductor power converting apparatus
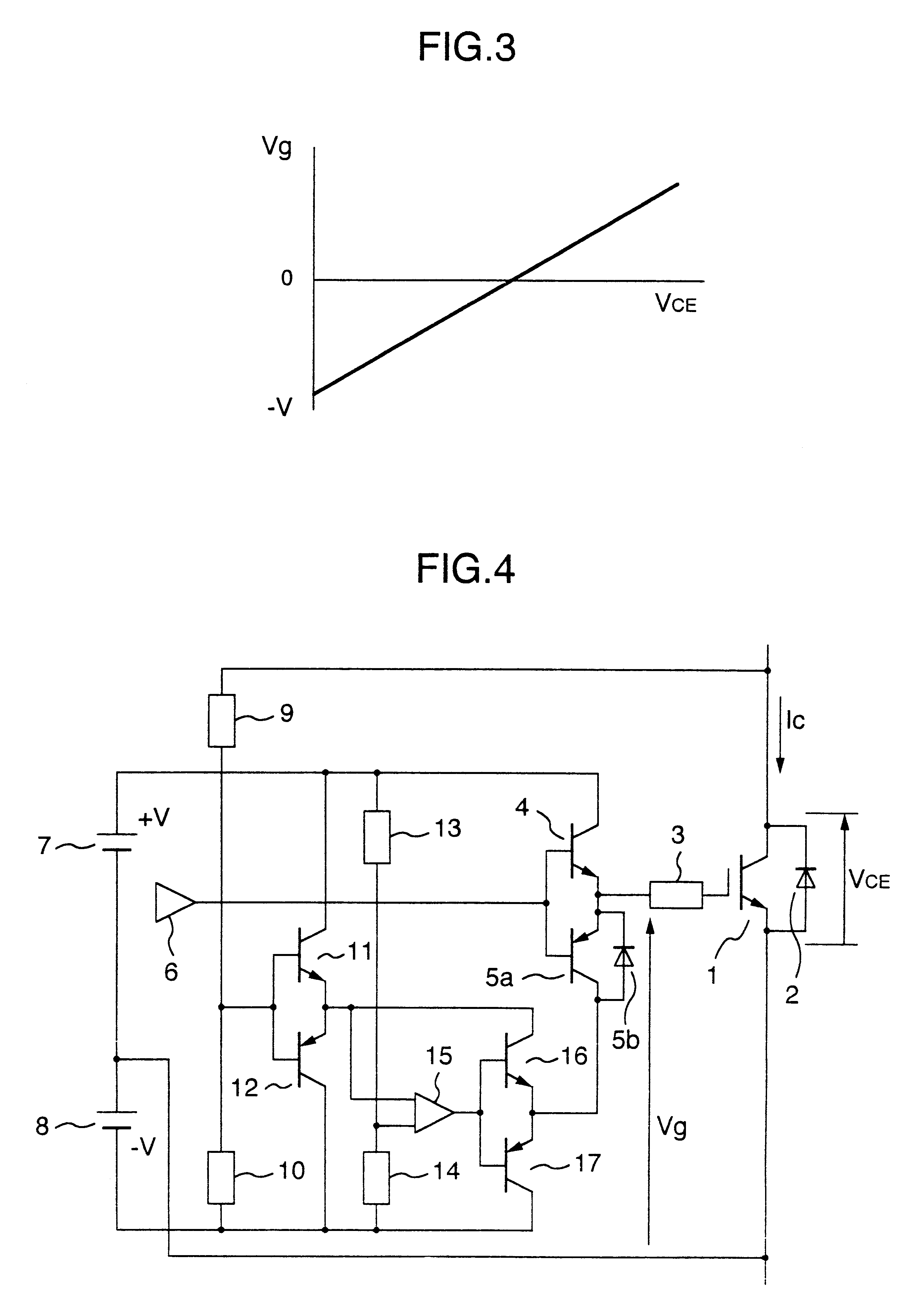
InactiveUS6380796B2Increase rate of changeEliminate the effects ofPulse generatorElectronic switchingReverse biasGate voltage
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Switching power supply device and the semiconductor integrated circuit for power supply control
InactiveUS7158392B2Reduce switching lossesReduce lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterFull bridge
It is aimed at decreasing losses not only in a synchronous rectifier circuit provided at a secondary side of a DC-DC converter, but also in a full-bridge switching circuit provided at a primary side thereof. The DC-DC converter comprises a transformer for voltage conversion, a synchronous rectifier circuit at the secondary side, and a full-bridge switching circuit at the primary side. The DC-DC converter performs synchronous rectifier control which uses switch transistors to change paths of currents flowing through the secondary coil in synchronization with switching operations at the primary side. The DC-DC converter detects currents flowing through a load at the secondary side, primary-side currents varying with the load currents, or primary-side input voltages to dynamically control off-timings of a synchronous rectification transistor at the secondary side. In addition, the DC-DC converter detects primary-side input voltages and currents flowing through the secondary-side load to dynamically control on-timings of a transistor in the primary-side switching circuit.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Capacitor-switched lossless snubber
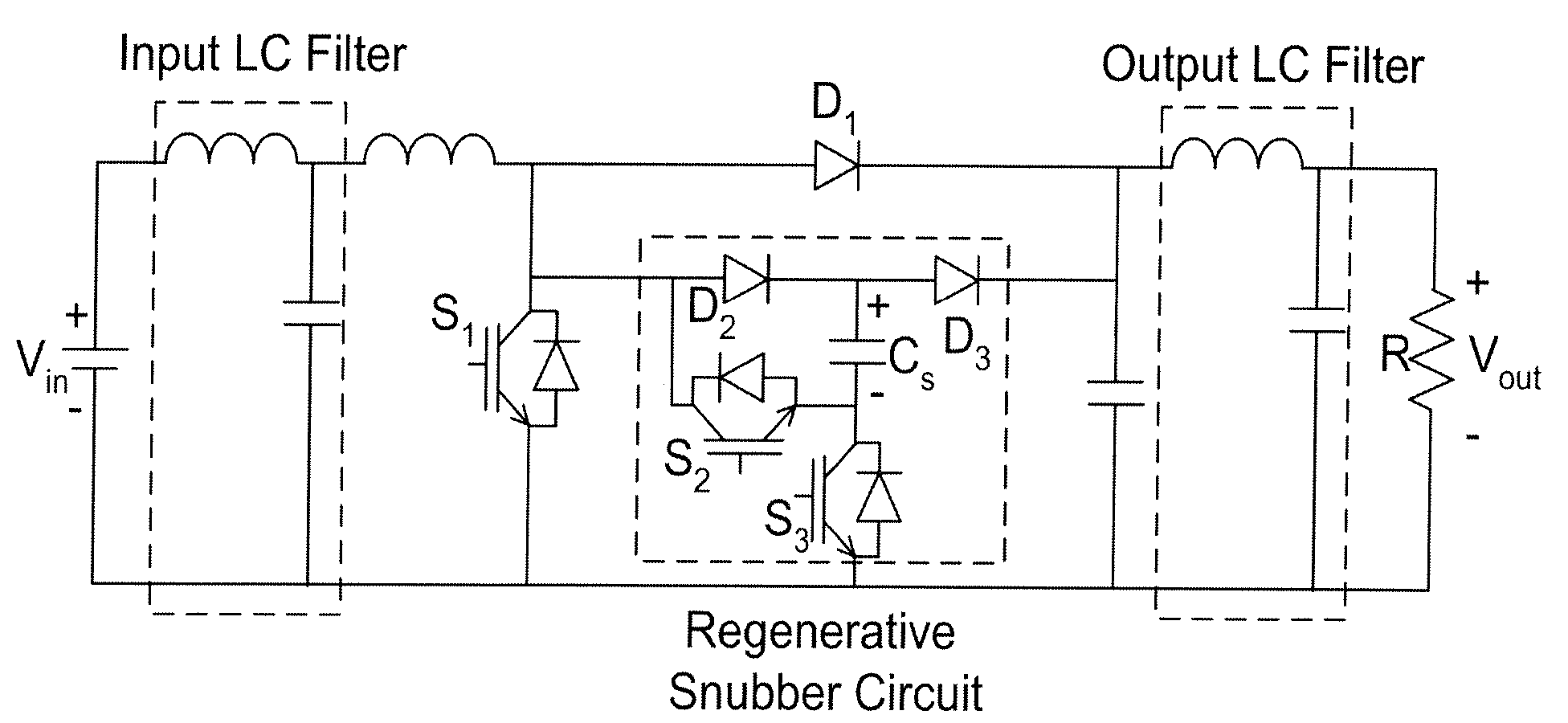
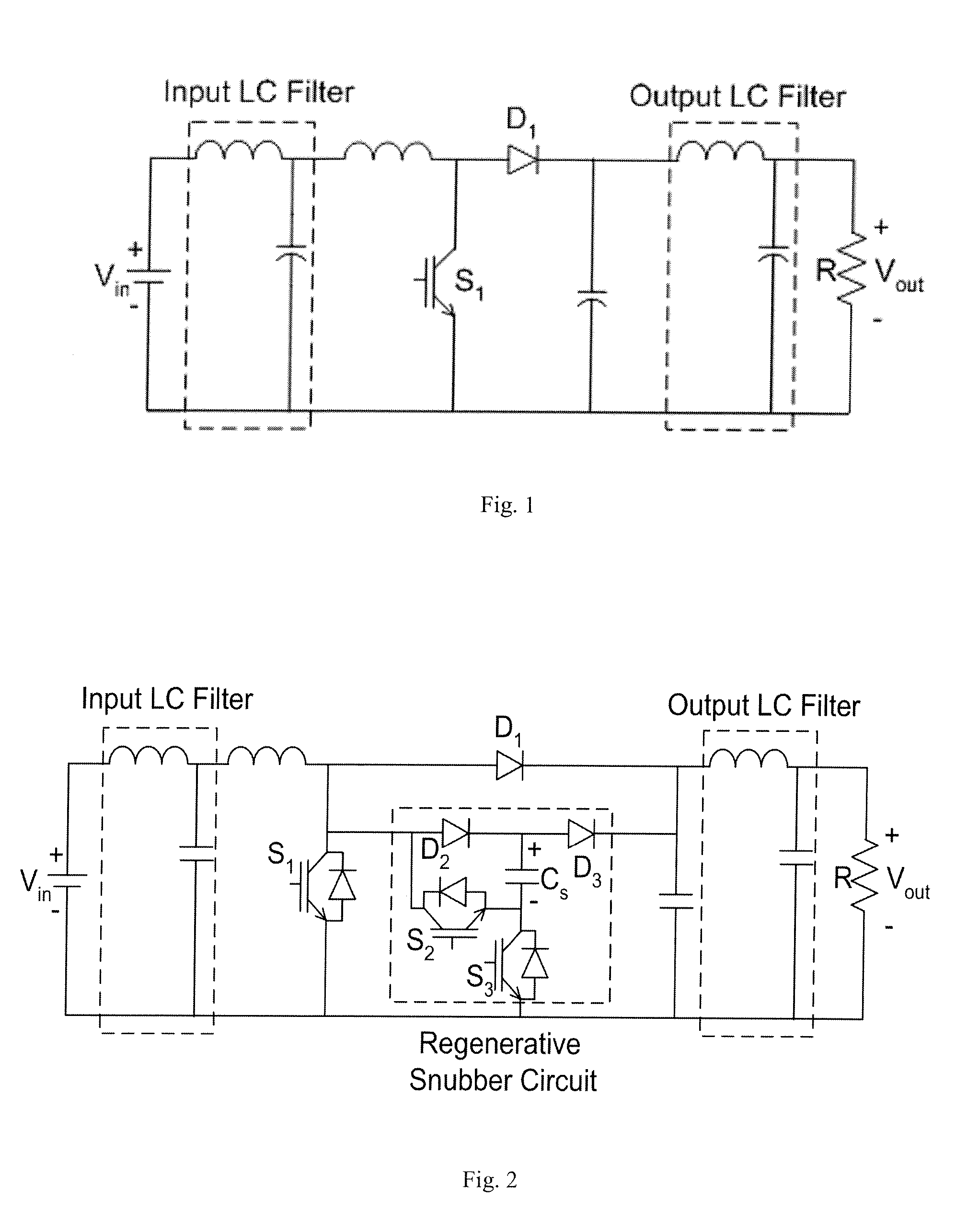
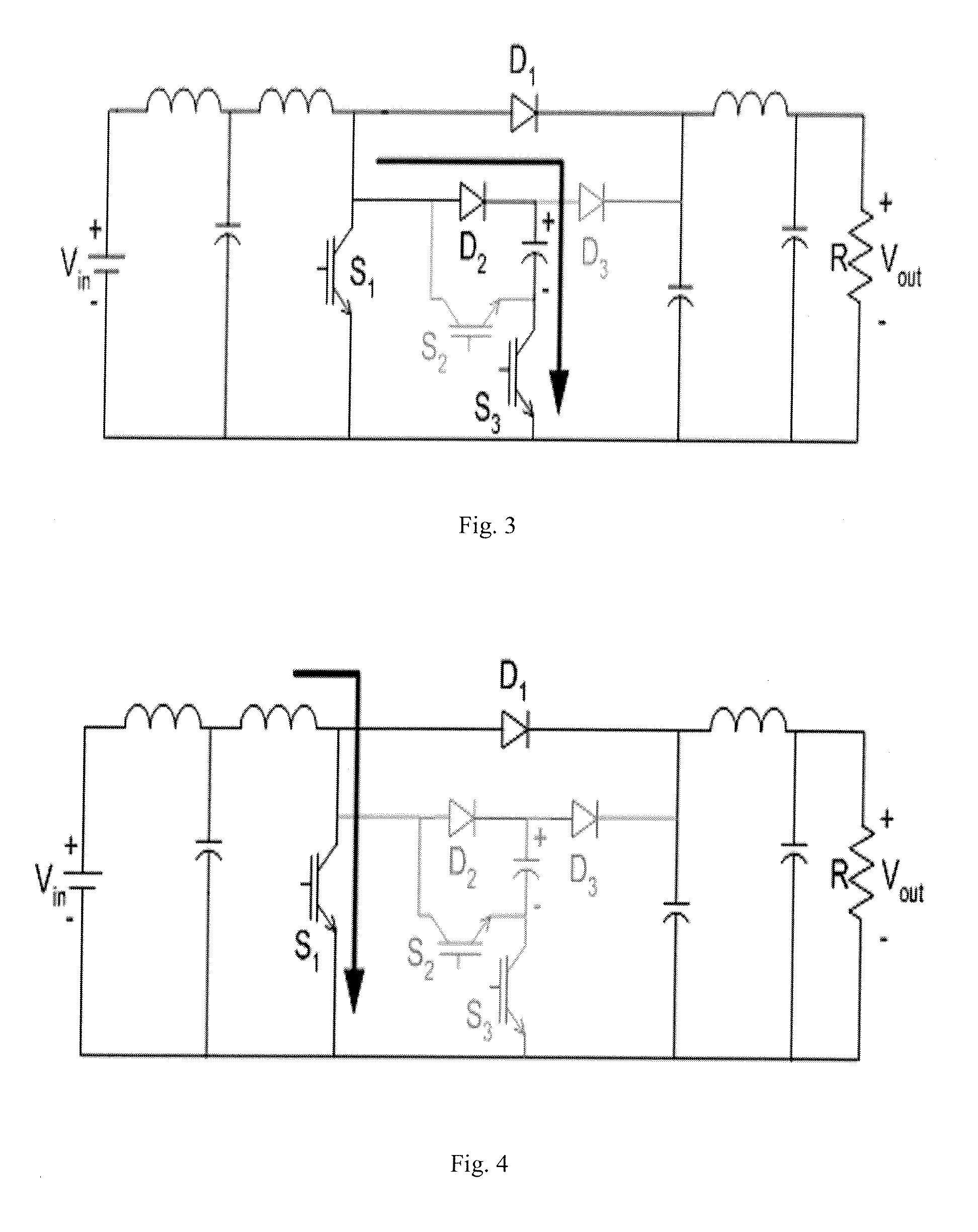
InactiveUS20080094866A1Increase the switching frequencyDesirable converter efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSnubberEngineering
A regenerative snubber circuit for a boost converter is provided which greatly reduces the switching losses of the IGBT in the converter. The circuit uses no additional magnetic components, has a simple control strategy, is relatively low-cost, and provides an increase in efficiency and decrease in size and mass of the converter.
Owner:BAUMAN JENNIFER +1
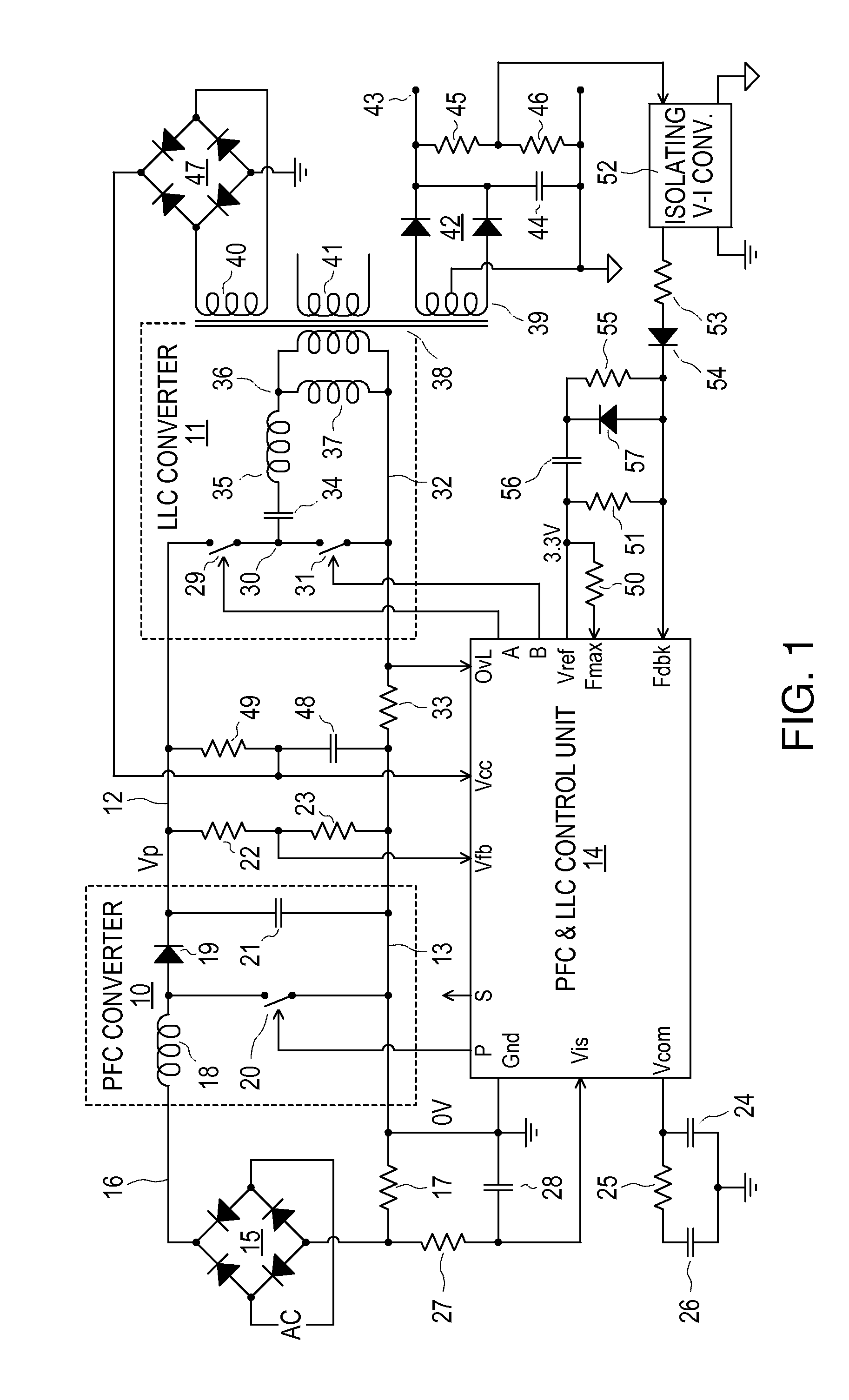
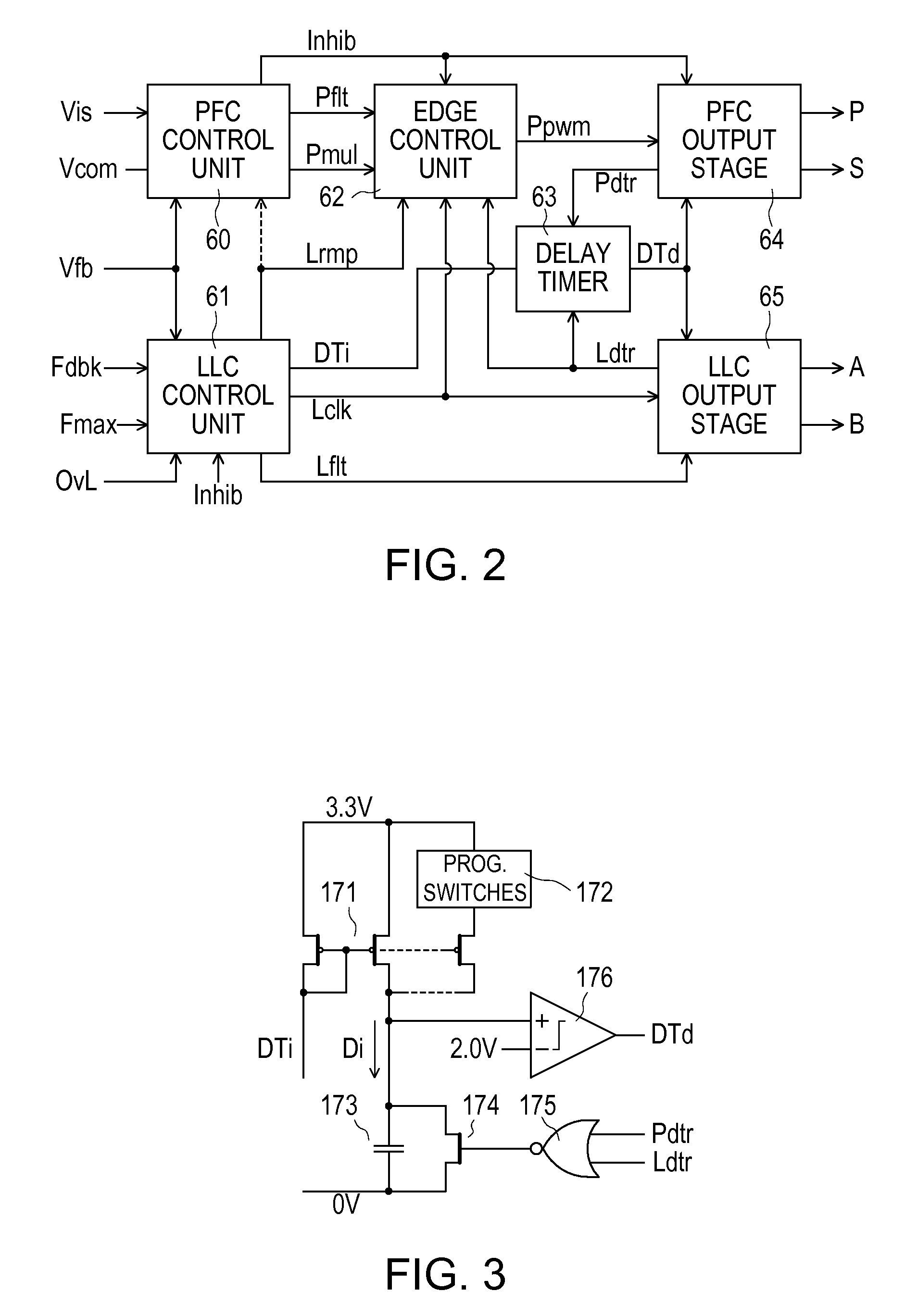
Cascaded PFC and resonant mode power converters
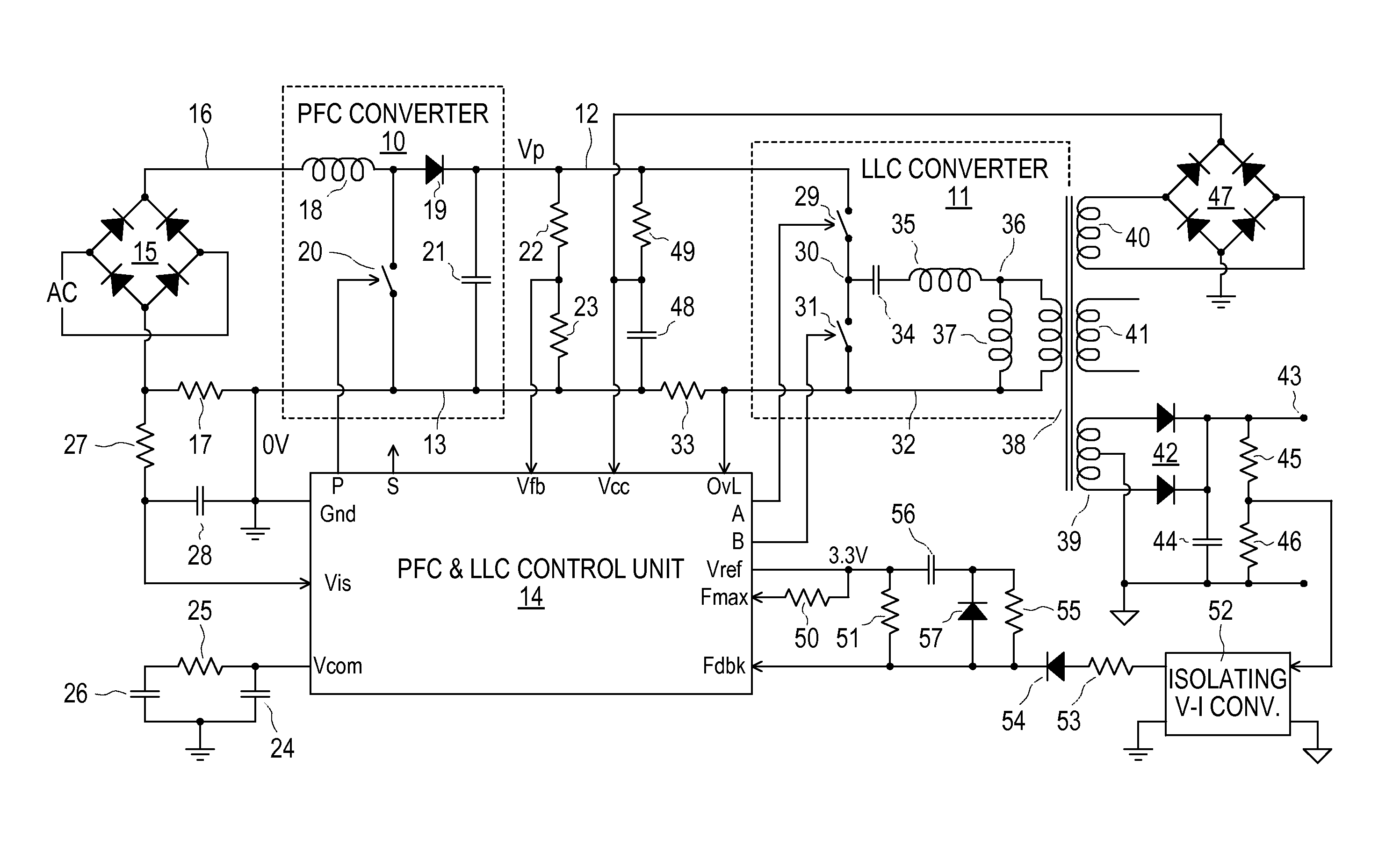
InactiveUS7885085B2Increase the switching frequencyReduce outputEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringSwitching frequency
A control unit controls cascaded PFC and LLC converters, the LLC converter having an input coupled to an output, of the PFC converter and providing an output voltage that decreases with increasing switching frequency. The control unit produces a sawtooth waveform with a linear ramp for controlling the LLC converter switching frequency, and hence its output voltage, in dependence upon a feedback signal. It also produces for the PFC converter a PWM signal with a frequency that is the same as or an integer fraction of the LLC converter switching frequency, by comparing two thresholds with the linear ramp in respective different cycles of the sawtooth waveform to turn on and off a switch of the PFC converter during these different cycles. Logic circuits prevent PFC converter switch transitions from occurring simultaneously with switching transitions of the LLC converter.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
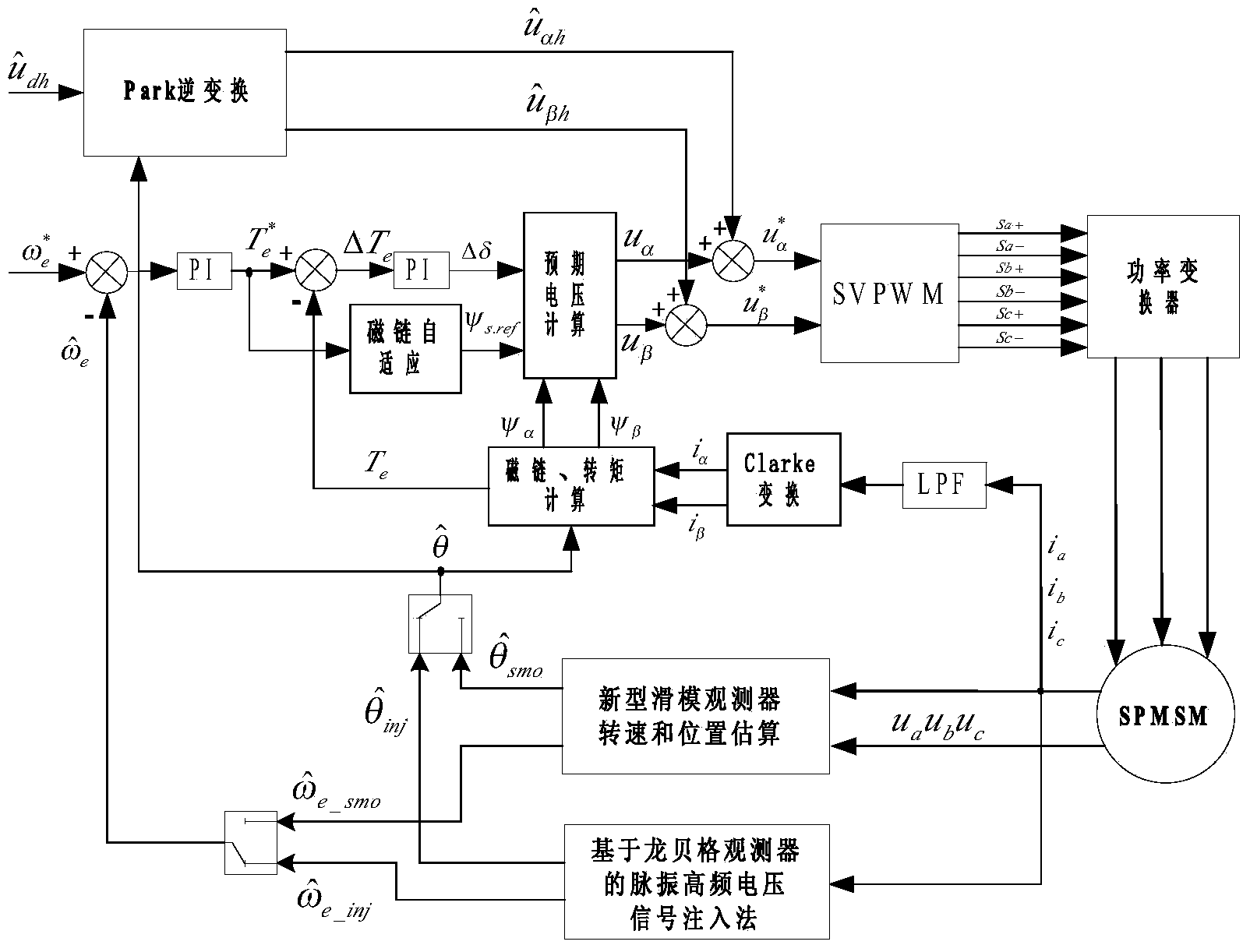
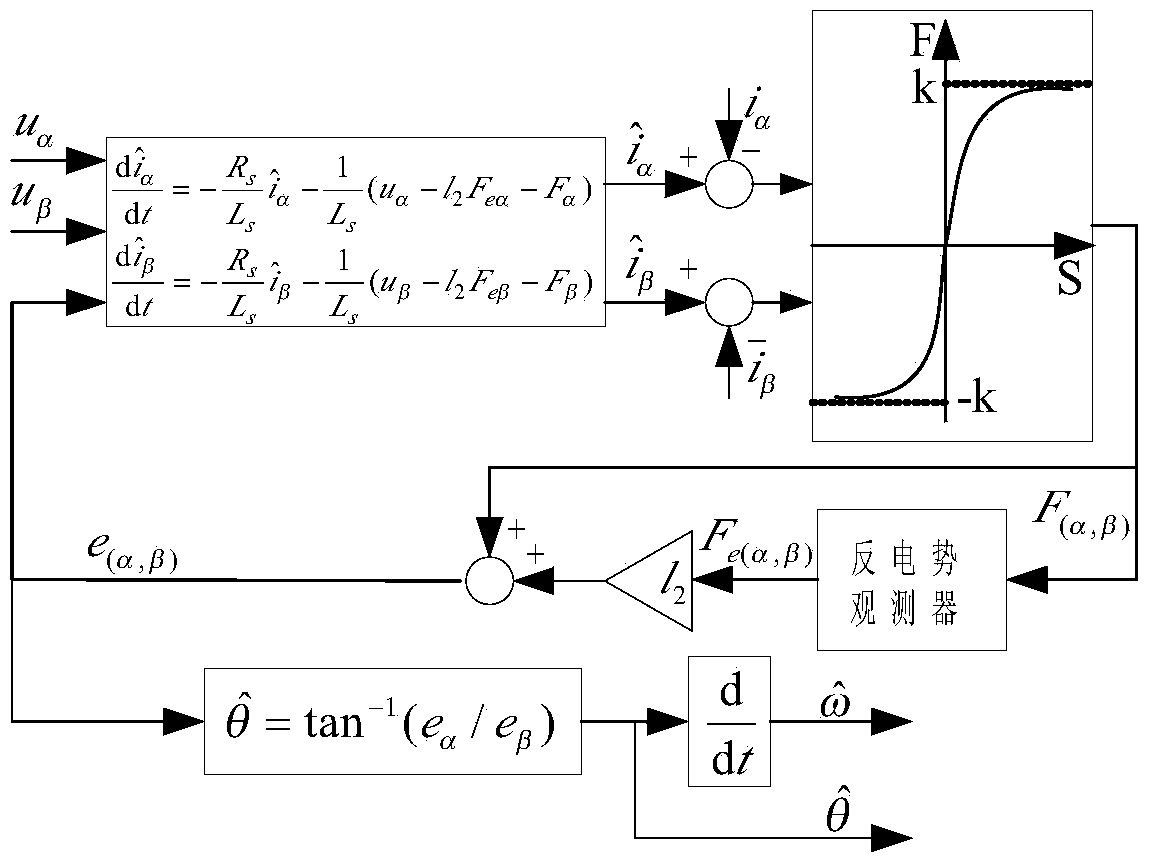
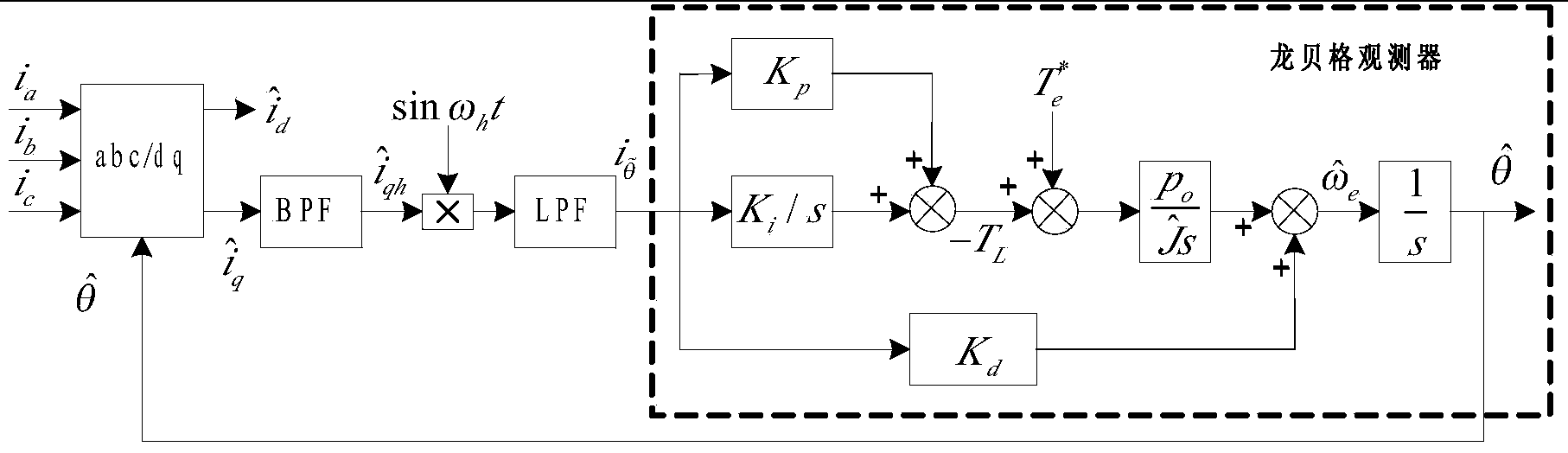
Surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor sensorless direct torque control method
InactiveCN103414423AEasy to set upReduce flux pulsationElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLow speedLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor sensorless direct torque control method. The method comprises a direct torque control method based on SVPWM and a flux linkage self-adaptive method, a novel method for estimating the positions and the rotating speed of rotors by a sliding mode observer and a novel compound control method which is suitable for self-detecting the positions of the rotors within a full speed range. According to the surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor sensorless direct torque control method, the problem that in traditional SVPWM direct torque control, straight-axis currents are large when a motor is operated in a no-load state or under the condition that the heavy load is suddenly applied is fundamentally solved, the buffeting problem of a traditional sliding mode observer is solved, the phase delay problem of the traditional sliding mode observer caused by a low pass filter is solved, and estimation accuracy of the positions of the rotors when the motor is operated is improved. In addition, the problem that the positions of the rotors are inaccurately estimated when the motor is operated in a low speed and standstill mode is further solved, and the sensorless self-starting function can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Interleaved soft switching bridge power converter
InactiveUS7423894B2Reduce switching lossesReduce recoveryConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionMotor driveReverse recovery
An interleaved soft switching bridge power converter comprises switching poles operated in an interleaved manner so as to substantially reduce turn-on switching losses and diode reverse-recovery losses in the switching pole elements. Switching poles are arranged into bridge circuits that are operated so as to provide a desired voltage, current and / or power waveform to a load. By reducing switching turn on and diode reverse recovery losses, soft switching power converters of the invention may operate efficiently at higher switching frequencies. Soft switching power converters of the invention are well suited to high power and high voltage applications such as plasma processing, active rectifiers, distributed generation, motor drive inverters and class D power amplifiers.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
High-Frequency Buck Converter that Includes a Cascode MESFET-MOSFET Power Switch
InactiveUS20080191679A1Lower on-resistanceLow off-state drain leakageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMOSFETElectrical battery
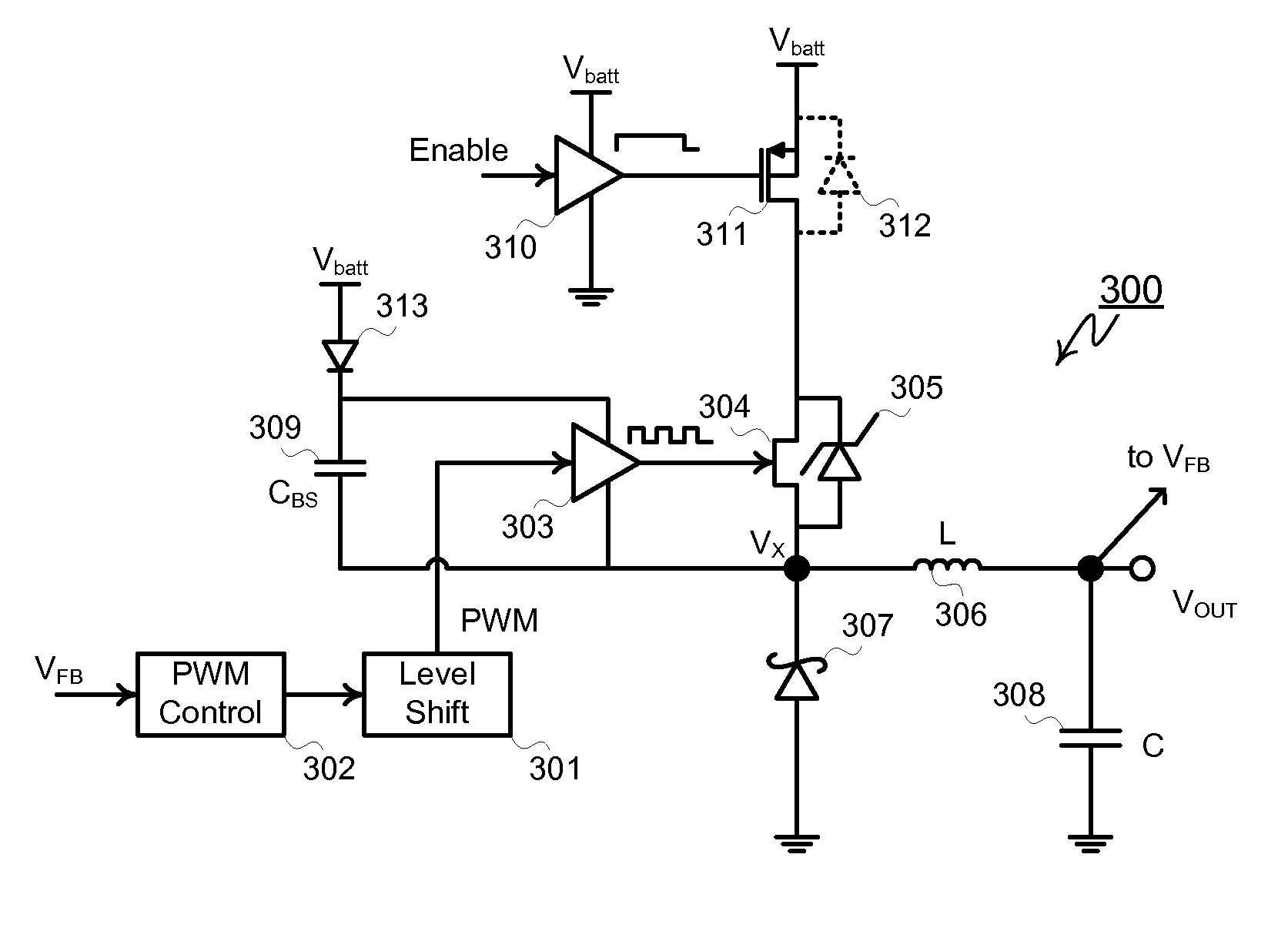
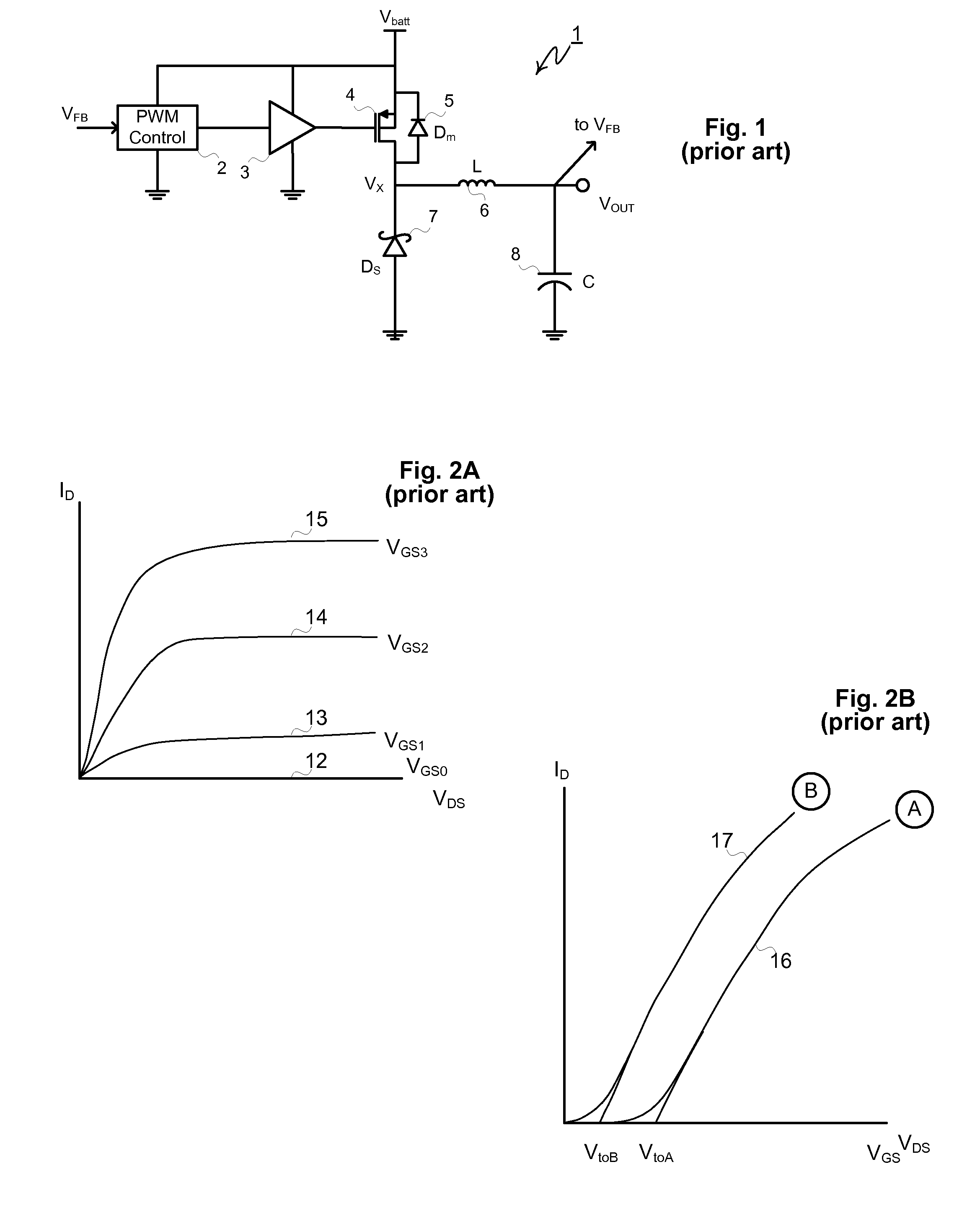
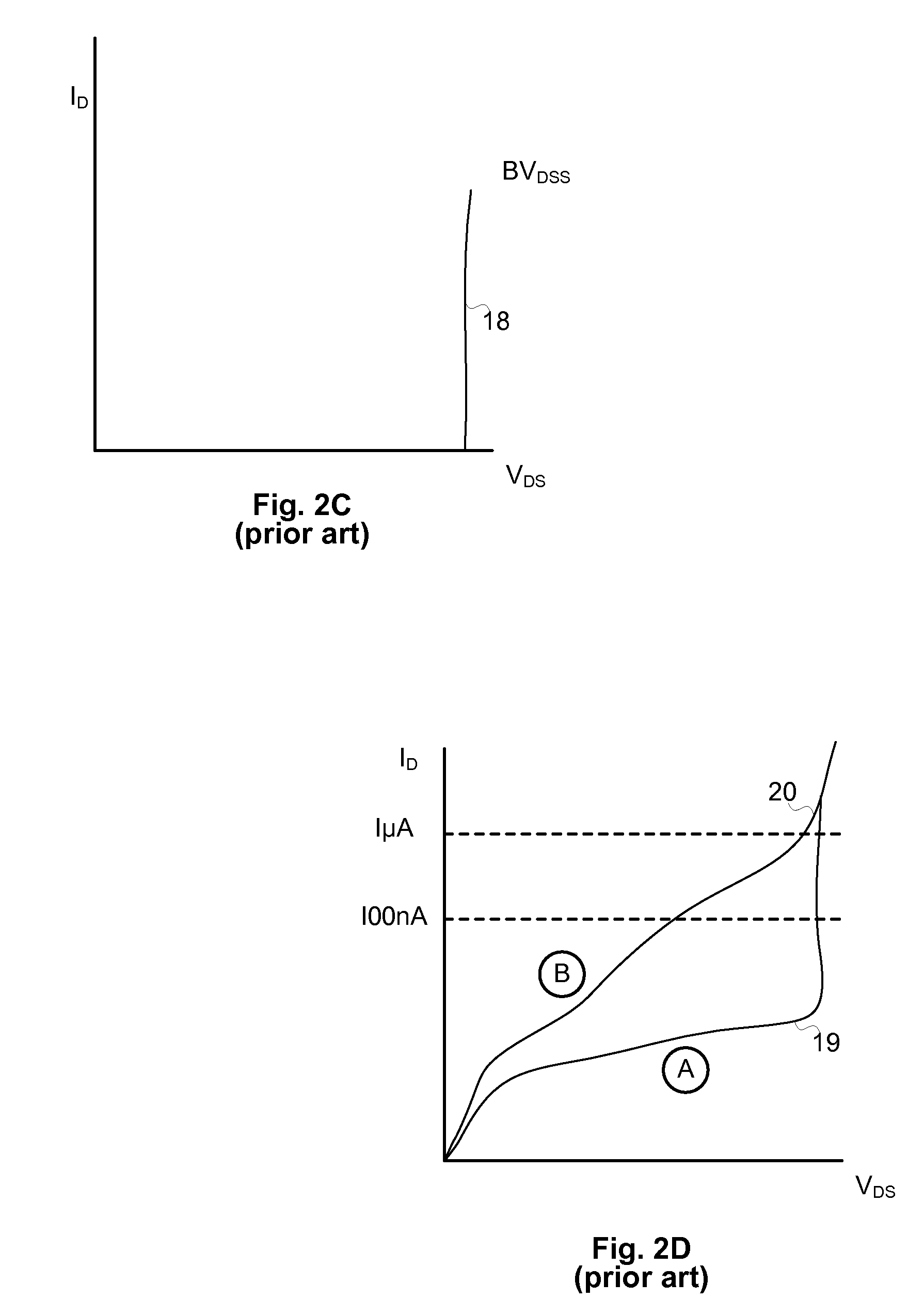
A Buck converter that includes a cascode switch comprising a series connected MESFET and MOSFET power switch. The cascode power switch is typically connected in between a power source and a node Vx. The node Vx is connected to an output node via an inductor and to ground via a Schottky diode or a second MESFET or both. A control circuit drives the MESFET (and the second MESFET) so that the inductor is alternately connected to the battery and to ground. The MOSFET is switched off during sleep or standby modes to minimize leakage current through the MESFET. The MOSFET is therefore switched at a low frequency compared to the MESFET and does not contribute significantly to switching losses in the converter.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Power factor correction control circuit for reducing EMI (electro magnetic interference)
ActiveCN102332814ALighten the filtering burdenThe maximum peak current is reducedEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryHarmonicCurrent threshold
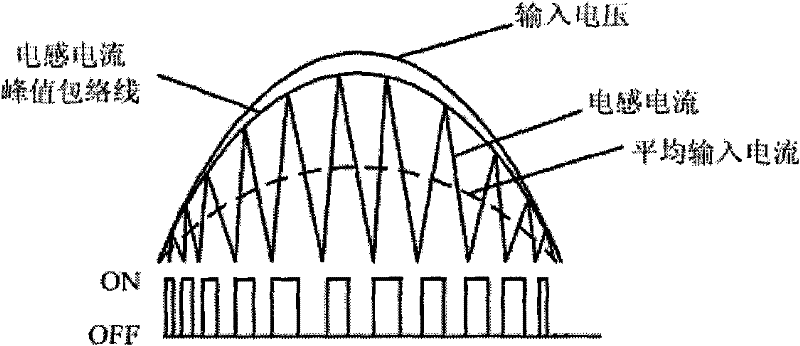
The invention discloses a power factor correction control circuit for reducing EMI (electro magnetic interference), which comprises an inductive current threshold value, wherein when an inductive current is less than the inductive current threshold value, a peak value of the inductive current is controlled to be changed along with an input voltage; and when the inductive current reaches the inductive current threshold value, the inductive current is limited to be the inductive current threshold value. In such a way, the maximum peak of the inductive current is reduced, so that an inductive ripple current is reduced; the power factor is ensured, and the EMI of the circuit is reduced simultaneously, so that circuit filtering can be carried out simply and easily; and the power factor correction control circuit is extremely suitable for occasions with middle or low power. In addition, the peak current stress of the circuit is low, so that a switch tube and other components have small loss, and the utilization ratio of a power supply is further improved. The power factor correction control circuit for reducing the EMI disclosed by the invention meets the requirements of high-power factor and IEC61000-3-2 on the harmonic of the power supply, and has low cost and a small size.
Owner:SILERGY SEMICON TECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Power factor correction converter
ActiveUS7919950B2EMI noise suppressionReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDigital signal processingFull wave
A power factor correction converter includes a diode bridge arranged to perform full-wave rectification on an AC input power supply, a switching element arranged to perform switching on an output voltage thereof, an inductor arranged to pass a current interrupted by the switching element and to accumulate and emit excitation energy, a diode, and a smoothing capacitor defining a step-up chopper circuit. A digital signal processing circuit detects a phase of an input voltage, and a switching frequency of the switching element is modulated in accordance with the phase. Accordingly, the switching frequency can be appropriately modulated without depending on an input voltage, so that a wide range of input voltages can be accepted while suppressing EMI noise with a peak generated in the switching frequency and higher-order frequency components thereof.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Variable frequency PWM controller circuit
ActiveUS7106130B2Short timeReduce frequencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionControl theoryPwm signals
The present invention discloses a circuit that generates a variable frequency pulse width modulation (VF PWM) signal. Different from the conventional PWM controller, the frequency and duty cycle of the output PWM signal vary with the error-amplified voltage of the feedback loop simultaneously in this invention. The higher the error-amplified voltage of the feedback loop is, the lower the duty cycle with lower frequency will be. A very low duty cycle PWM signal can be generated stably while its frequency is very low.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
United electric energy quality controller based on series multiplex of transformer and chain type construction
ActiveCN101453171AIncrease production capacityEasy maintenanceAc-dc conversion without reversalTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectric power systemEngineering
The invention relates to a unified power energy quality controller based on the serial-connection multiplicity of transformers and a chain structure, which belongs to the technical filed of flexible AC transmission and distribution of an electric power system and the power electronic. The unified power quality controller comprises a single-phase serial-connection multiple transformer bank and a single-phase chain H bridge converter, wherein the transformer bank consists of m single-phase transformers which form the serial-connection multiple transformer bank together with n voltage source converters connected with n secondary windings of m single-phase transformers respectively; the single-phase chain H bridge converter is provided with n chains and is formed by connecting n DC voltage supporting units and n power source converters, and an AC port of the n-chain single-phase chain H bridge converter is directly connected with the electric fence through a reactor, m and n are signless integrals equal to or more than 2, and m is less than or equal to n. The invention can realize accurate current control, has high dynamic responding speed, and can solve the problems of the traction substation of an electrified railway that the three-phase voltage is unstable and fluctuates, the power factor is low and the harmonic pollution exists, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pulse width modulation (PWM) control method for single-phase grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN101604923AEven heat dissipationIncrease the switching frequencySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc-ac conversion without reversalFull bridgePhysics
The invention discloses a pulse width modulation (PWM) control method for a single-phase grid-connected inverter, which is implemented according to the steps of: calculating to obtain single-polarity PWM wave; comparing network voltage detection with a zero crossing comparator to obtain a synchronous square wave signal, and then performing two divided-frequency on the synchronous square wave signal to obtain a synchronous square wave two divided-frequency signal; keeping only one of four power switch tubes of a single-phase full-bridge inverter in a high-frequency PWM action state, the power switch tube, which is on the diagonal of the power switch tube, of another bridge arm in a power frequency action state, and the other two power switch tubes in a shutoff state; making the four power switch tubes alternately act in a high-frequency PWM mode according to certain phase sequence; and adopting a principle that the power switch tube which conducts shuts off in advance to add dead zone time only during the zero crossing of network voltage at the same time. The method is applicable to single-phase grid-connected power generation systems, and has the characteristics of reducing the loss of switches, eliminating dead zone effect and optimizing heat dissipation.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Variable frequency PWM controller circuit
ActiveUS20050052249A1Ripple and noise be eliminateShort timeAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPwm controllerLow frequency
The present invention discloses a circuit that generates a variable frequency pulse width modulation (VF PWM) signal. Different from the conventional PWM controller, the frequency and duty cycle of the output PWM signal vary with the error-amplified voltage of the feedback loop simultaneously in this invention. The higher the error-amplified voltage of the feedback loop is, the lower the duty cycle with lower frequency will be. A very low duty cycle PWM signal can be generated stably while its frequency is very low.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Boost rectifier with half-power rated semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20050276082A1Rating of be reduceCheap deviceAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionAC powerPower semiconductor device
A rectifier has two half-controlled bridge rectifiers which are connected in parallel to provide DC power to DC bus lines. Each bridge rectifier receives AC power through inductances such as series inductors or an isolation transformer with a single primary and two secondaries. Each bridge rectifier has a full bridge of diodes, with active switching devices connected in parallel with half of the diodes in the bridge. The switching devices can be controlled to provide unity power factor at the AC input lines, allowing lower rated diodes and switching devices to be used.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Double output double step-down type half bridge inverter, and control and modulation method
The invention relates to a double-output double-buck half-bridge inverter, composed of two parallel input sides and parallel or series output sides. For eliminating the loss caused by loop current energy, it works in a semicycle operating mode, and adopts a synchronous switching semicycle SPWM method, an alternative switching semicycle SPWM method or hysteresis current source type modulation method. By selecting a different frequency voltage reference, it can realize a different frequency double-output double-buck half-bridge inverter. For the power grade, it can compose a multi-parallel double-series double-output double-buck half-bridge inverter. It has no short-circuit problem of bridge leg of a half-bridge or full-bridge double-output inverter, but has high reliability; it sustains the current by power diodes in series on the same bridge leg, beneficial to increasing switching frequency; and because of working in a semicycle operating mode, there is no loop current energy in the circuit, beneficial to increasing efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
DC-DC (direct-current to direct-current) resonant converter with automatic voltage equalizing function
ActiveCN103296882ARealize automatic pressure equalizationVoltage balanceApparatus without intermediate ac conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
The invention discloses a DC-DC (direct-current to direct-current) resonant converter with an automatic voltage equalizing function. The DC-DC resonant converter comprises a switch capacitor circuit and an LLC (logic link control) series resonant circuit. The switch capacitor circuit is formed by concatenation of a plurality of half-bridge submodules. Middle nodes of two adjacent half-bridge submodules are connected through a switch capacitor module. According to the DC-DC converter, the half-bridge submodules are in series connection before being connected in parallel at two ends of a direct-current power supply. In the ideal case, the voltage of each bus capacitor is one n-th of the direct-current voltage; two switch tubes are in series connection inside one half-bridge submodule before being connected in parallel with one bus capacitor, and accordingly turn-off voltage stress of each switch tube is half of the voltage of one bus capacitor. Switch components with low voltage and high performances can be selected for the converter, efficiency of the converter is improved, and size of the converter is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
DC/DC converter
ActiveUS7800921B2Low costImprove power densityTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionInductorTransformer coupling
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
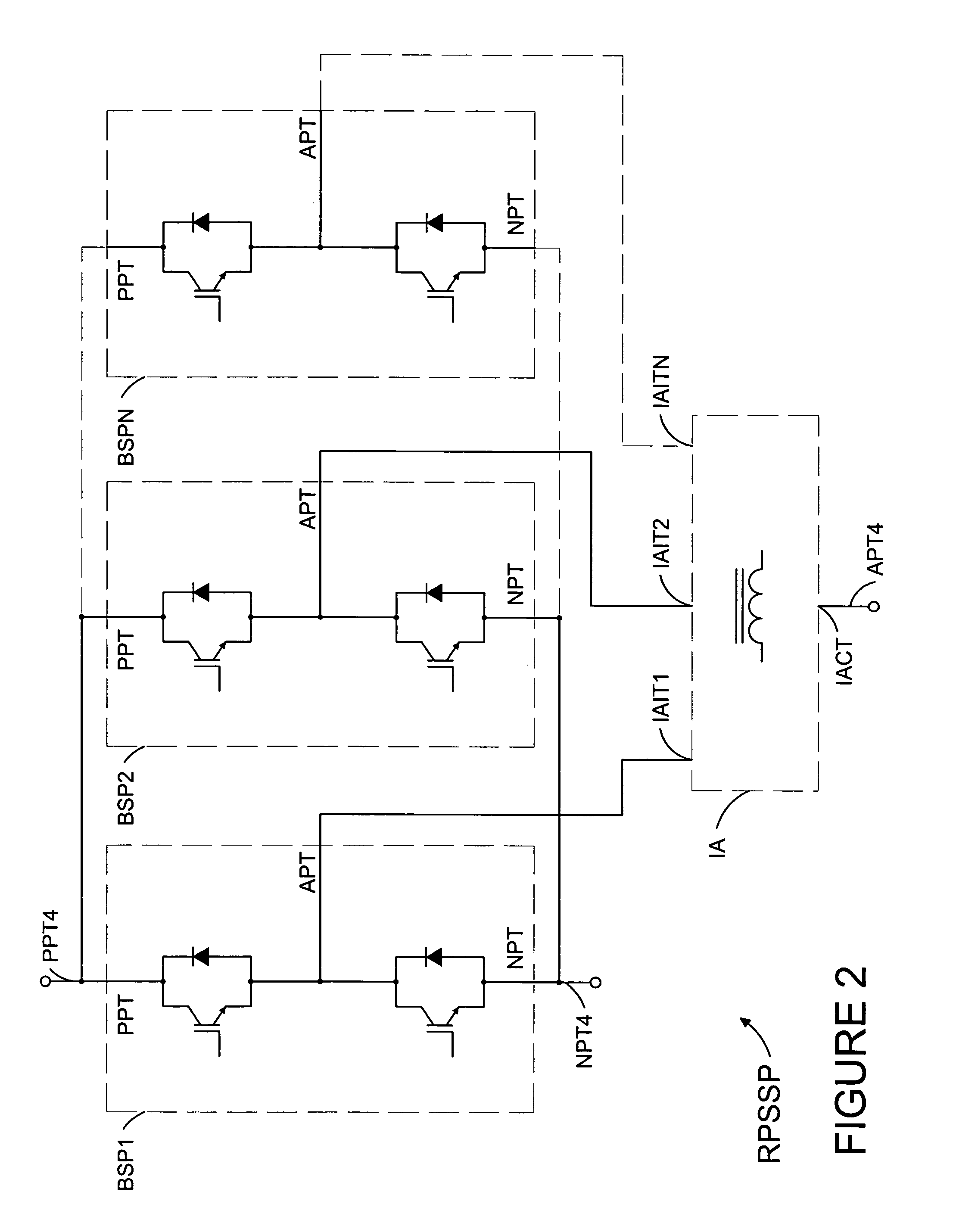
Semiconductor die package including multiple dies and a common node structure
ActiveUS7618896B2Length minimizationReducing parasitic inductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering
A semiconductor die package capable of being mounted to a motherboard is disclosed. The semiconductor die package includes a substrate, and a first semiconductor die mounted on the substrate, where the first semiconductor die includes a first vertical device comprising a first input region and a first output region at opposite surfaces of the first semiconductor die. The semiconductor die package includes a second semiconductor die mounted on the substrate, where second semiconductor die comprises a second vertical device comprising a second input region and a second output region at opposite surfaces of the second semiconductor die. A substantially planar conductive node clip electrically communicates the first output region in the first semiconductor die and the second input region in the second semiconductor die. The first semiconductor die and the second semiconductor die are between the substrate and the conductive node clip.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
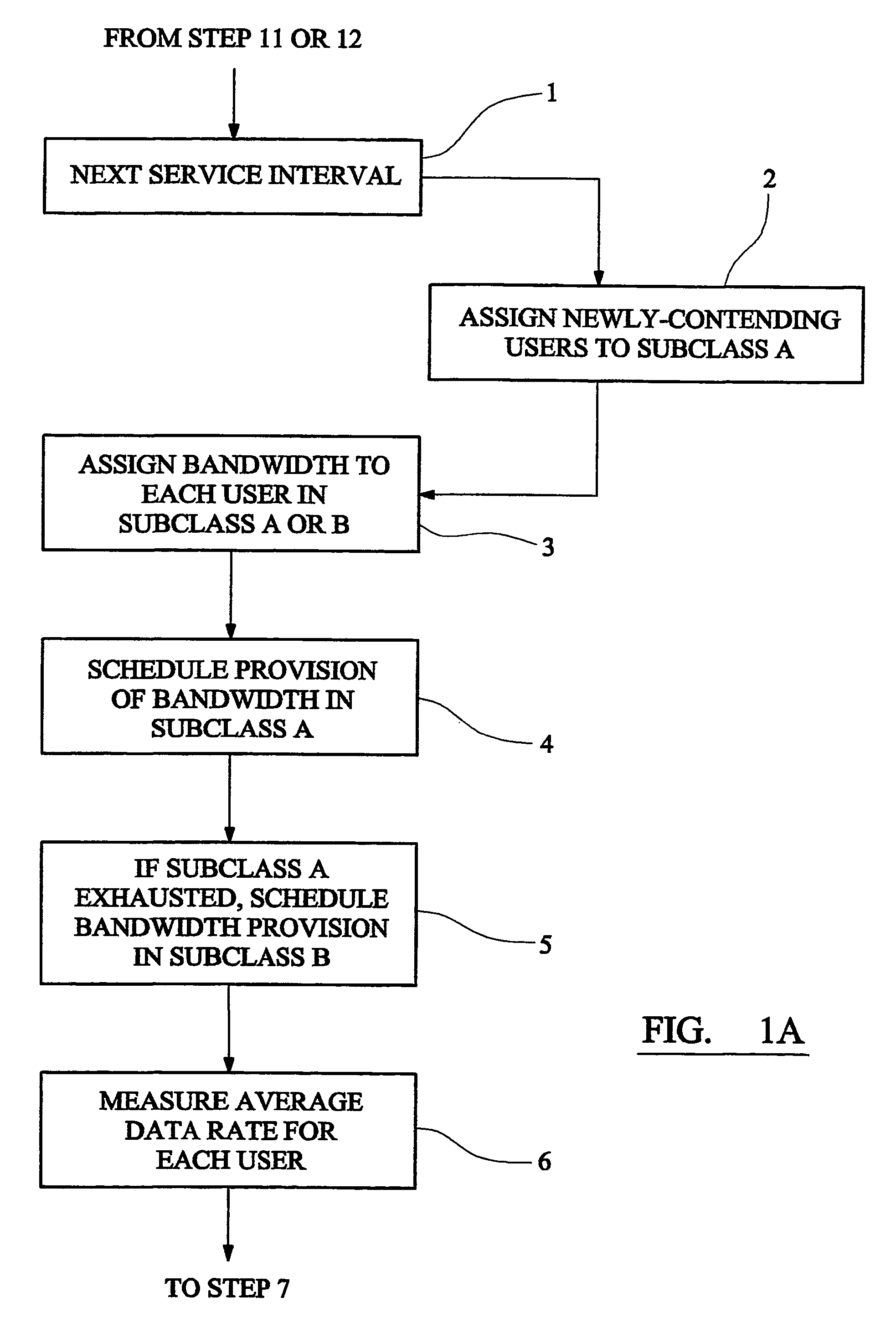
Method and apparatus for providing communications bandwidth to users having a committed data rate based on priority assignment
ActiveUS20040213259A1High bandwidthIncrease data rateData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsCommunications systemCommitted information rate
A communications system operator provides to each user of a multi-user communications system a committed information rate (CIR). When a user requests bandwidth for transmission, a system controller queues the user in a high-priority subclass A. The system controller allocates bandwidth to the user at the head of the queue as requested but if the user's bandwidth, measured as an average over a sampling time, exceeds its CIR, it is moved into a low-priority subclass B. The user can then only obtain further bandwidth after other users in the high-priority subclass have been allocated bandwidth up to their CIRs. If a user in the low-priority subclass only receives allocation of a small amount of bandwidth, so that its average information rate falls below its CIR, it is moved back into the queue in the high-priority subclass.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE BROADBAND NETWORKS LIMITED
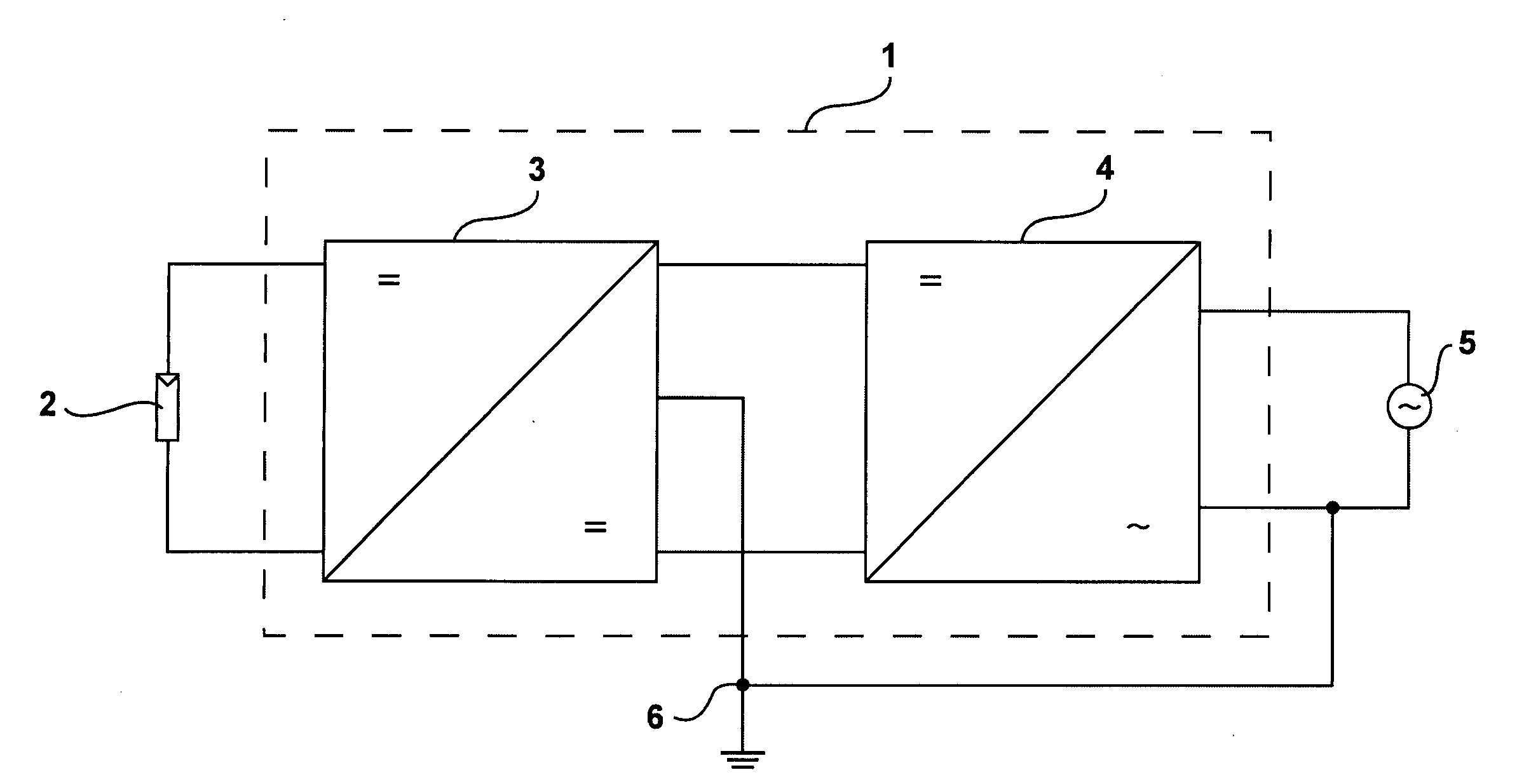
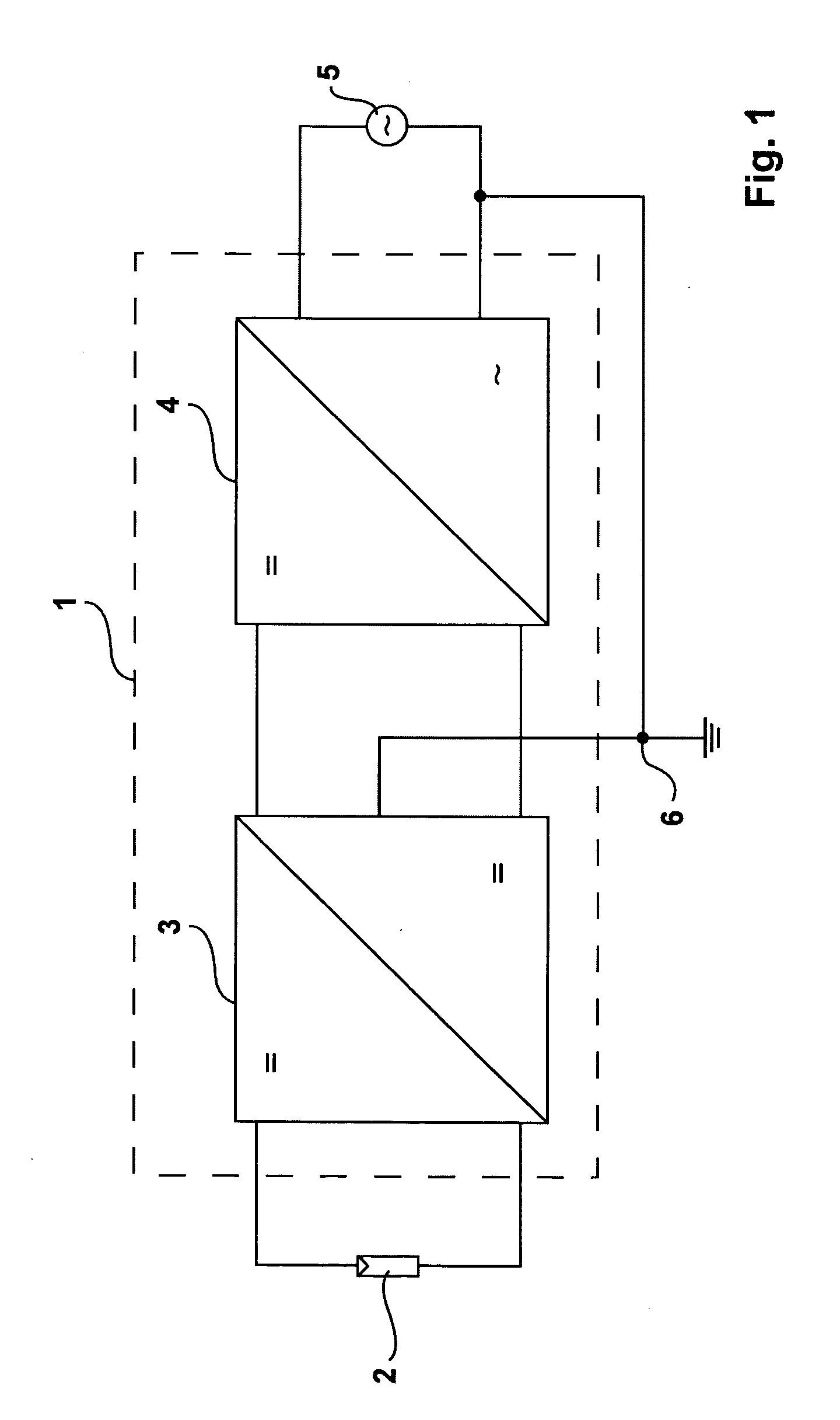
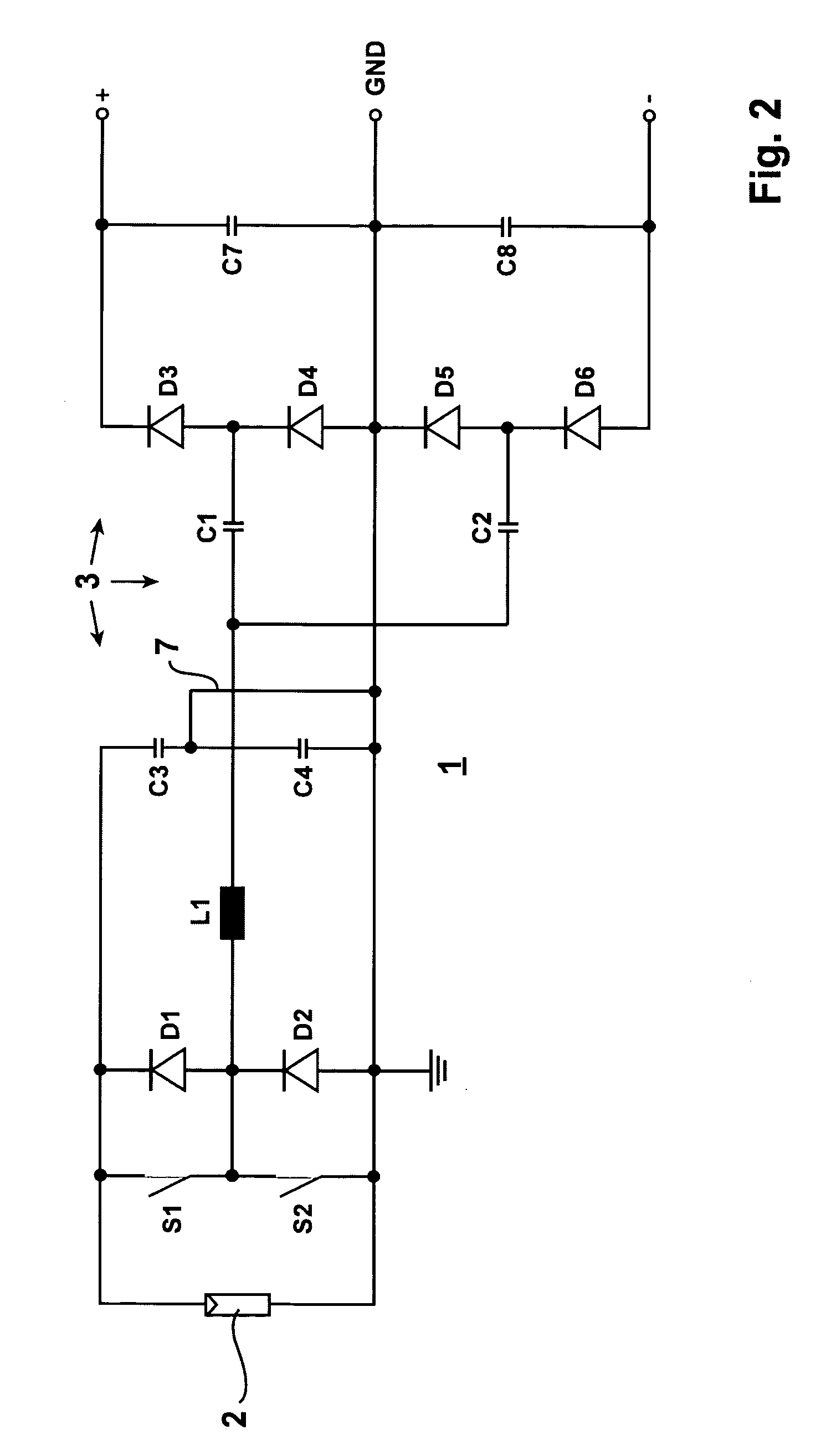
Inverter for grounded direct current source, more specifically for a photovoltaic generator
InactiveUS20090034304A1Little loadingLittle expenseBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringVoltage source
An inverter (1) for a grounded direct voltage source, in particular for a photovoltaic generator (2), a battery or a fuel cell, for converting the direct voltage into an alternative voltage with a DC-DC converter (3) and a pulse inverter that is supplied by said DC-DC converter (3), said DC-DC converter (3) being configured to be an oscillating circuit inverter and comprising a series resonant oscillating circuit, said DC-DC converter (3), which is configured to be an oscillating circuit inverter, being configured to be a series-compensated oscillating circuit inverter with a choke (L1) and a series-mounted capacitor array consisting of two or several oscillating circuit capacitors, a rectifier bridge branch including 2 diodes (D3, D4; D5, D6, . . . ), being connected to each of the partial oscillating circuit capacitors, said rectifier bridge branch being connected with its positive or its negative pole to output side intermediate circuit capacitors which are preferably connected in series so that said DC-DC converter (3) delivers at least two bipolar output voltages and is combined with the pulse inverter (4) with a divided voltage intermediate circuit that is supplied from the oscillating circuit inverter.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY
Power factor correction converter
ActiveUS20100097829A1EMI noise suppressionReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDigital signal processingFull wave
A power factor correction converter includes a diode bridge arranged to perform full-wave rectification on an AC input power supply, a switching element arranged to perform switching on an output voltage thereof, an inductor arranged to pass a current interrupted by the switching element and to accumulate and emit excitation energy, a diode, and a smoothing capacitor defining a step-up chopper circuit. A digital signal processing circuit detects a phase of an input voltage, and a switching frequency of the switching element is modulated in accordance with the phase. Accordingly, the switching frequency can be appropriately modulated without depending on an input voltage, so that a wide range of input voltages can be accepted while suppressing EMI noise with a peak generated in the switching frequency and higher-order frequency components thereof.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Intelligent control module for permanent magnet contactor
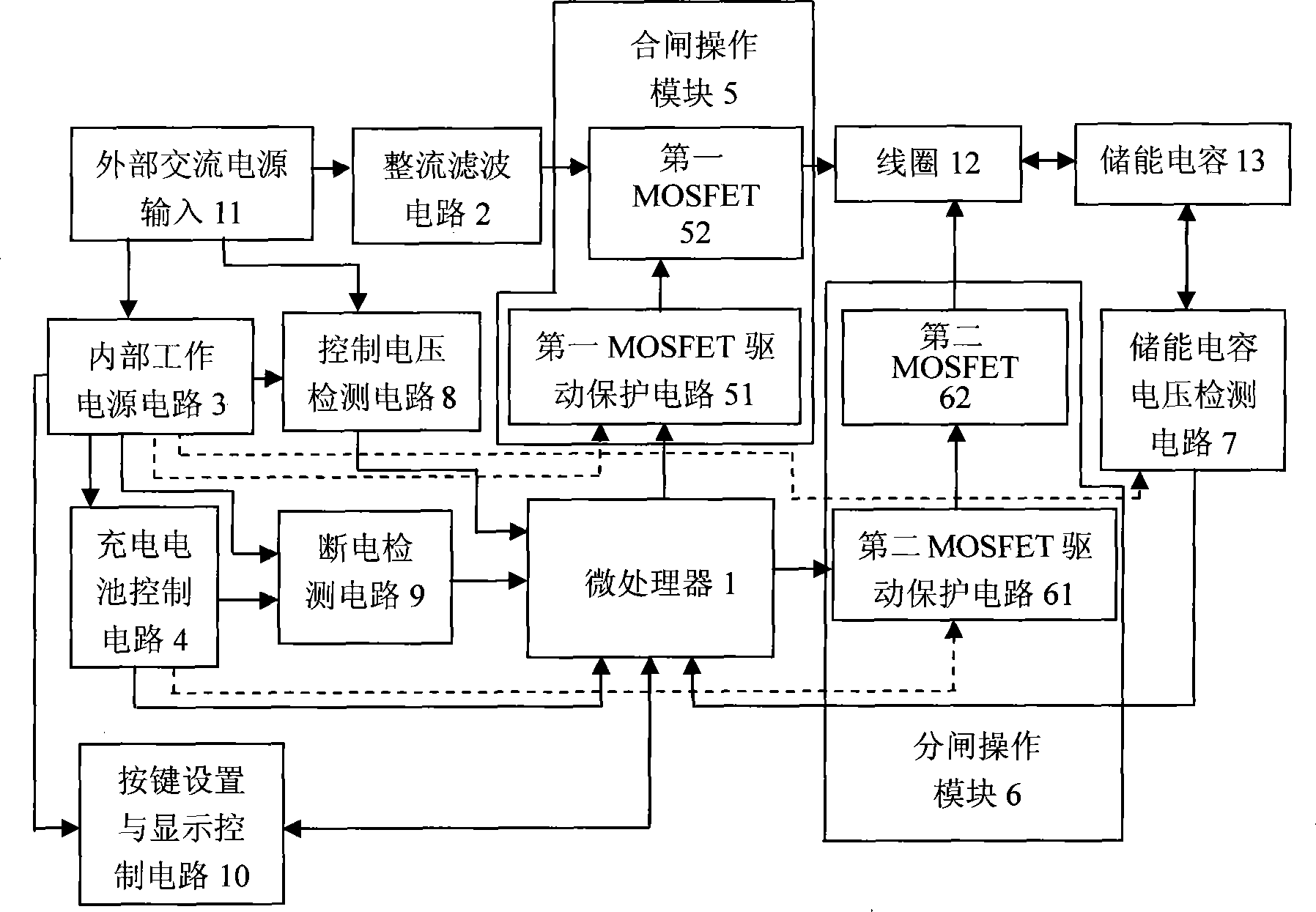
InactiveCN101477919AGuaranteed continuous operationEnsure safetyEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionRelaysContactorCapacitance
The invention discloses an intelligent control module of a permanent magnet contactor, which mainly comprises a microprocessor, a rectifier and filter, an internal working power circuit, a rechargeable battery control circuit, a closing operation module, an opening operation module, an energy-storage capacitor voltage detection circuit, a control voltage detection circuit, a power off detection circuit, and a key-press setting and display control circuit; wherein, the closing operation module consists of a first MOSFET driving protection circuit and a first MOSFET; and the opening operation module consists of a second MOSFET driving protection circuit and a second MOSFET. The intelligent control module can set delay time parameters of transient interference electricity through key-presses according to requirements of a customer, realizes delay disconnection of the permanent magnet contactor and can ensure the stable and continuous operation of equipment through staying away from influences of interference electricity; and as for conditions of requiring urgent opening operation, the intelligent control module can immediately cut off the contactor through key-press control, so as to ensure the safety of the operating equipment.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Control circuit for active clamp flyback power converter with predicted timing control
ActiveUS20140307484A1Improve efficiencyIncrease the switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionActive clampTransformer
A control circuit of a flyback power converter according to the present invention comprises a low-side transistor, an active-clamper, a high-side drive circuit, and a controller. The low-side transistor is coupled to switch a transformer. The active-clamper is coupled in parallel with the transformer. The high-side drive circuit is coupled to drive the active-damper. The controller generates a switching signal and an active-clamp signal. The switching signal is coupled to drive the low-side transistor. The switching signal is generated in accordance with a feedback signal for regulating an output voltage of the flyback power converter. The active-clamp signal is coupled to control the high-side drive circuit and the active-clamper. The active-clamp signal is generated in response to a predicted time of the transformer. The predicted time is determined in accordance with an input voltage, the output voltage and an on time of the switching signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
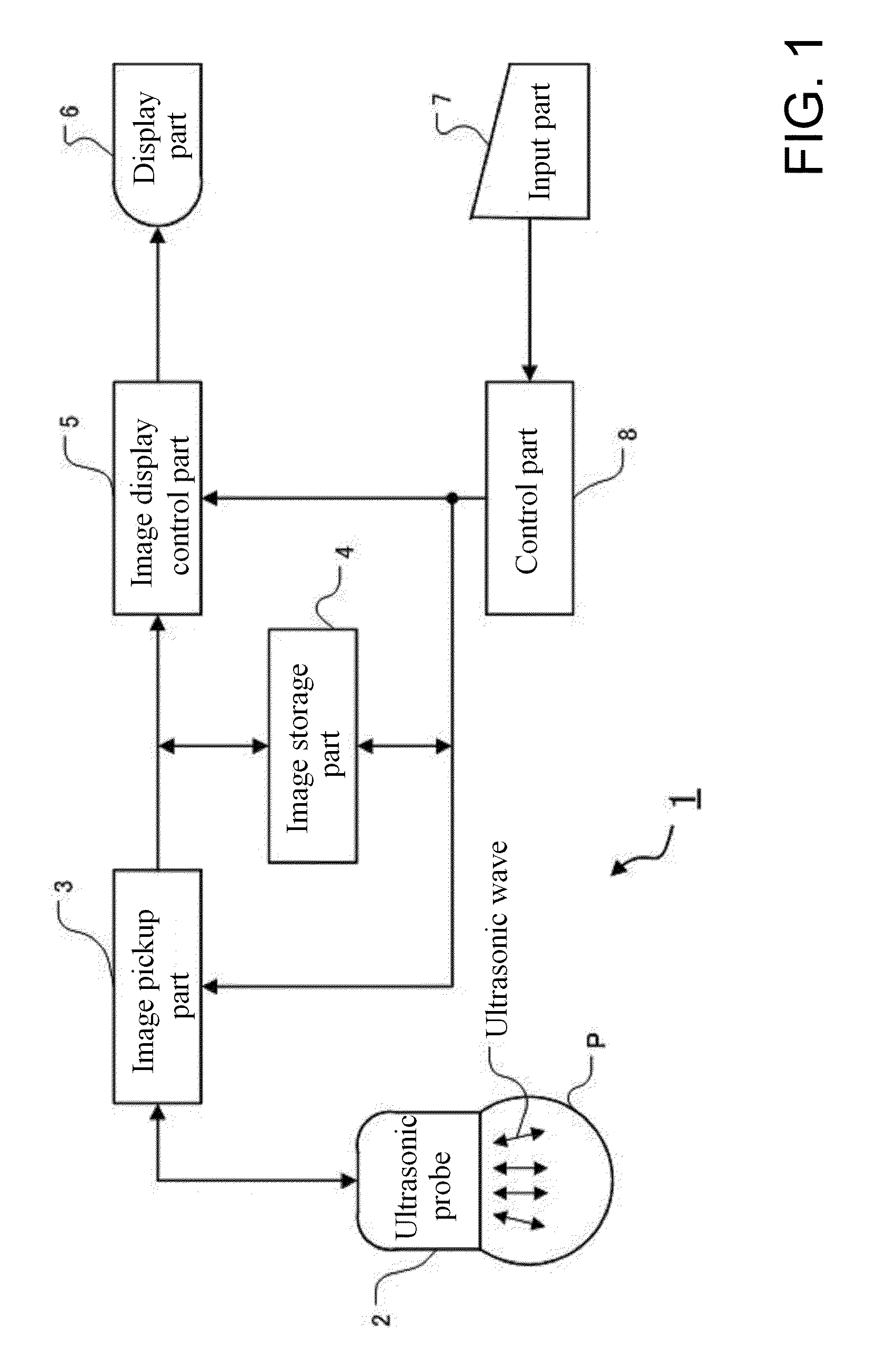
Voltage generating circuit and ultrasonic diagnosing device
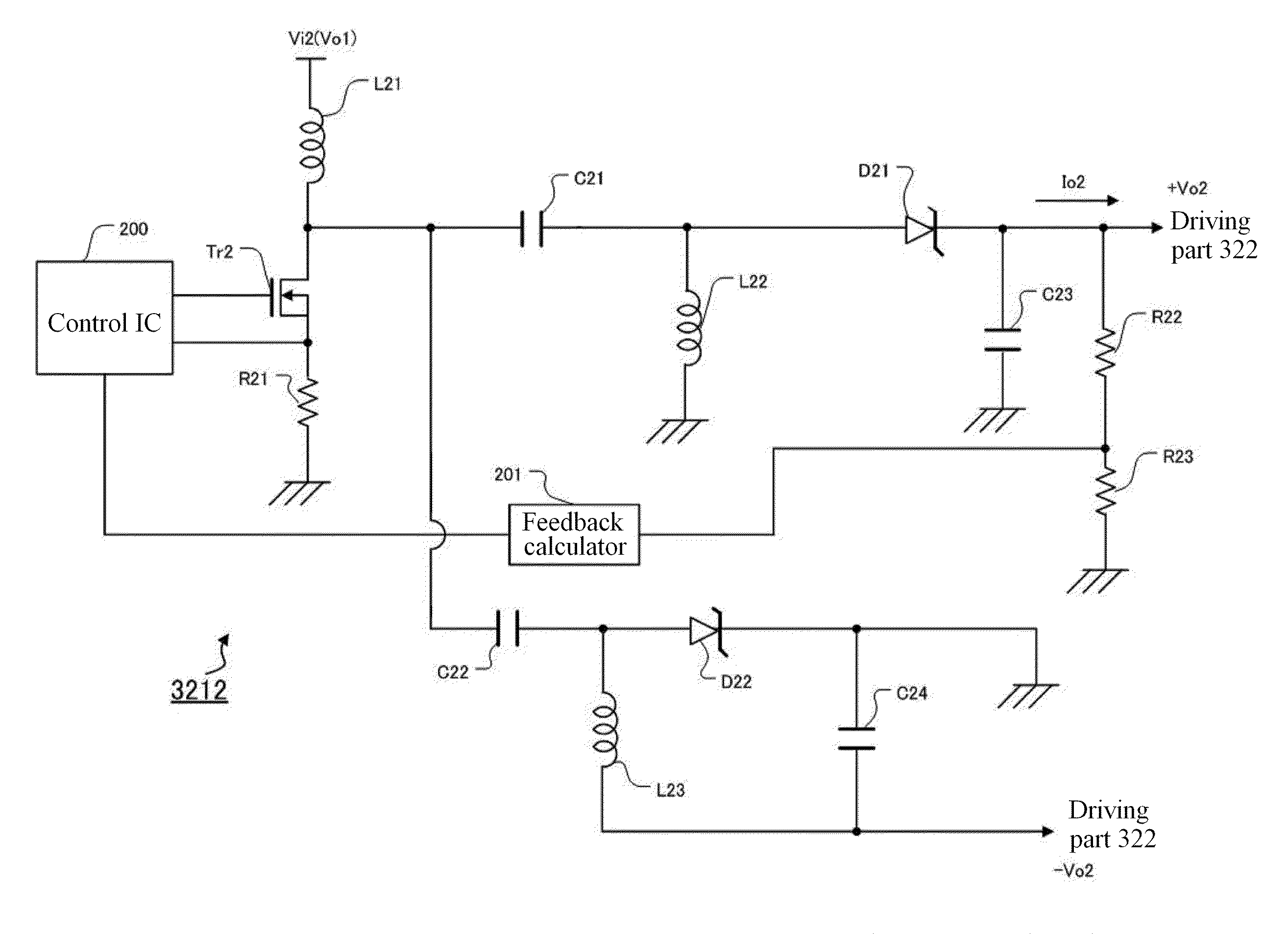
ActiveUS20100019833A1Increase the output voltageReduce input voltageBlood flow measurement devicesGenerator stabilizationTransformerEngineering
A voltage generating circuit generates a voltage for driving an ultrasonic oscillator, and includes a multi-stage connected power supply circuit without a transformer.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com