Patents
Literature
7158 results about "Pwm signals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
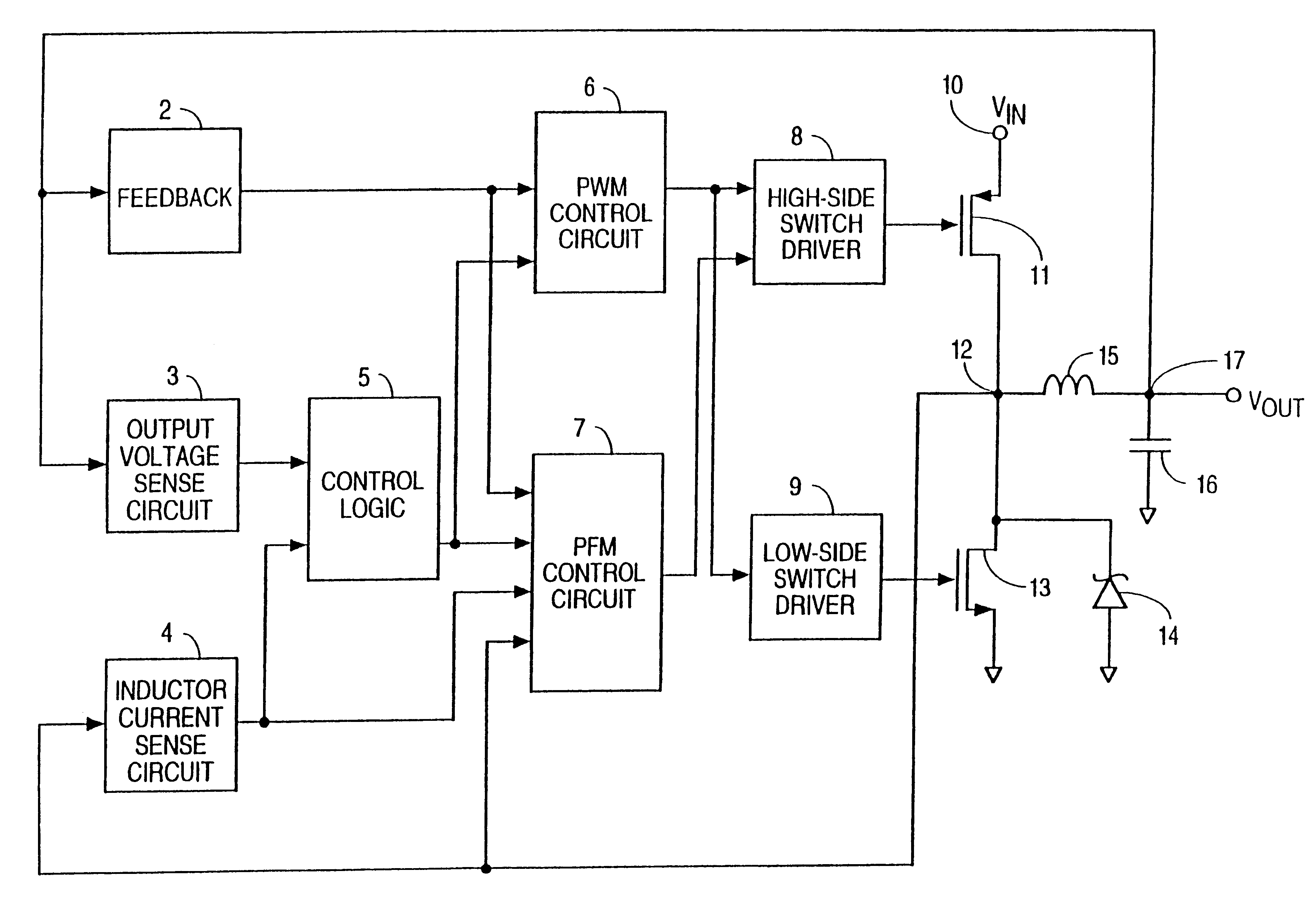
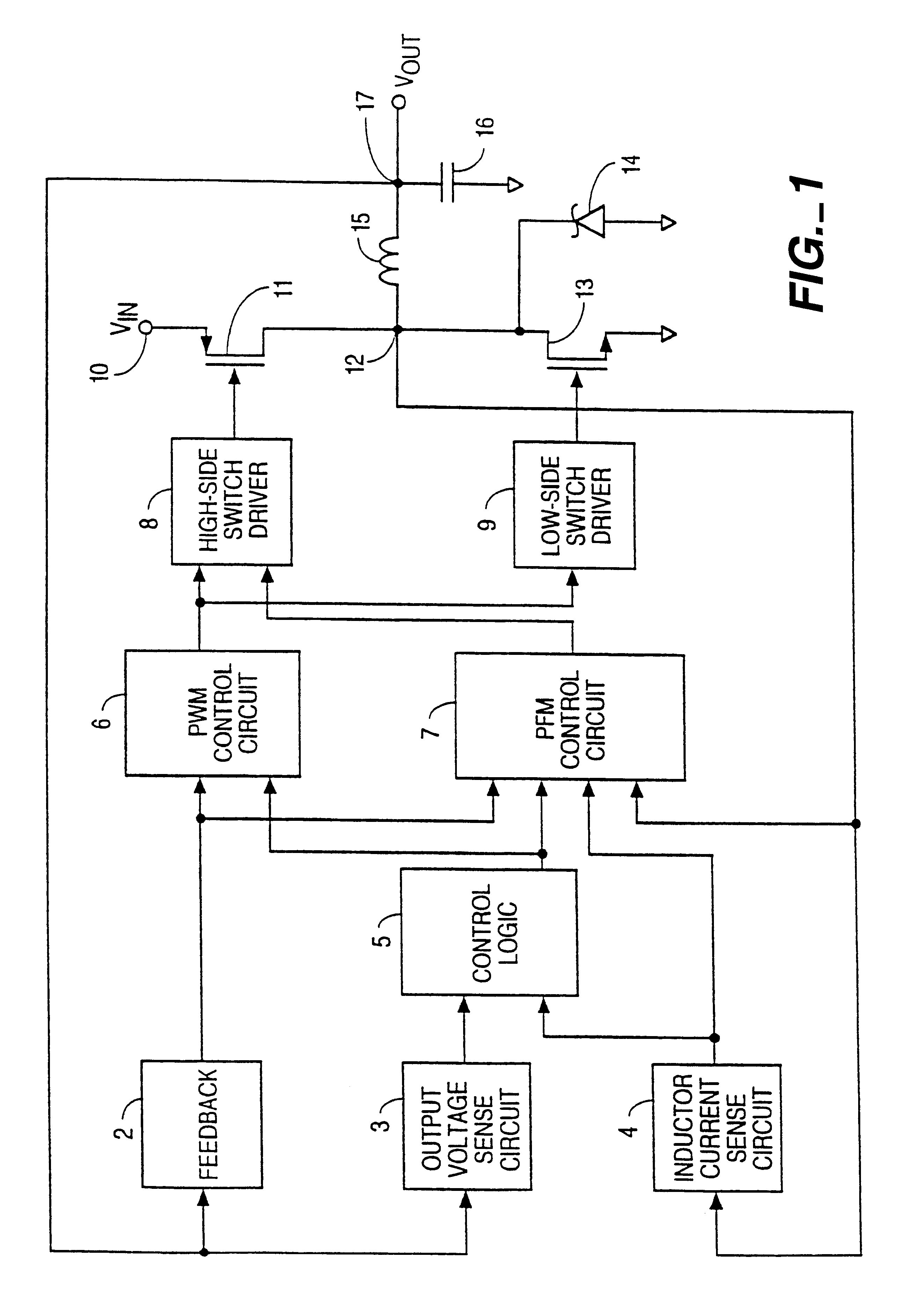
PWM signals are used for a wide variety of control applications. Their main use is for controlling DC motors but it can also be used to control valves, pumps, hydraulics, and other mechanical parts.
LED brightness control system for a wide-range of luminance control
ActiveUS6987787B1Improve the level ofReduce brightnessLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalControl system
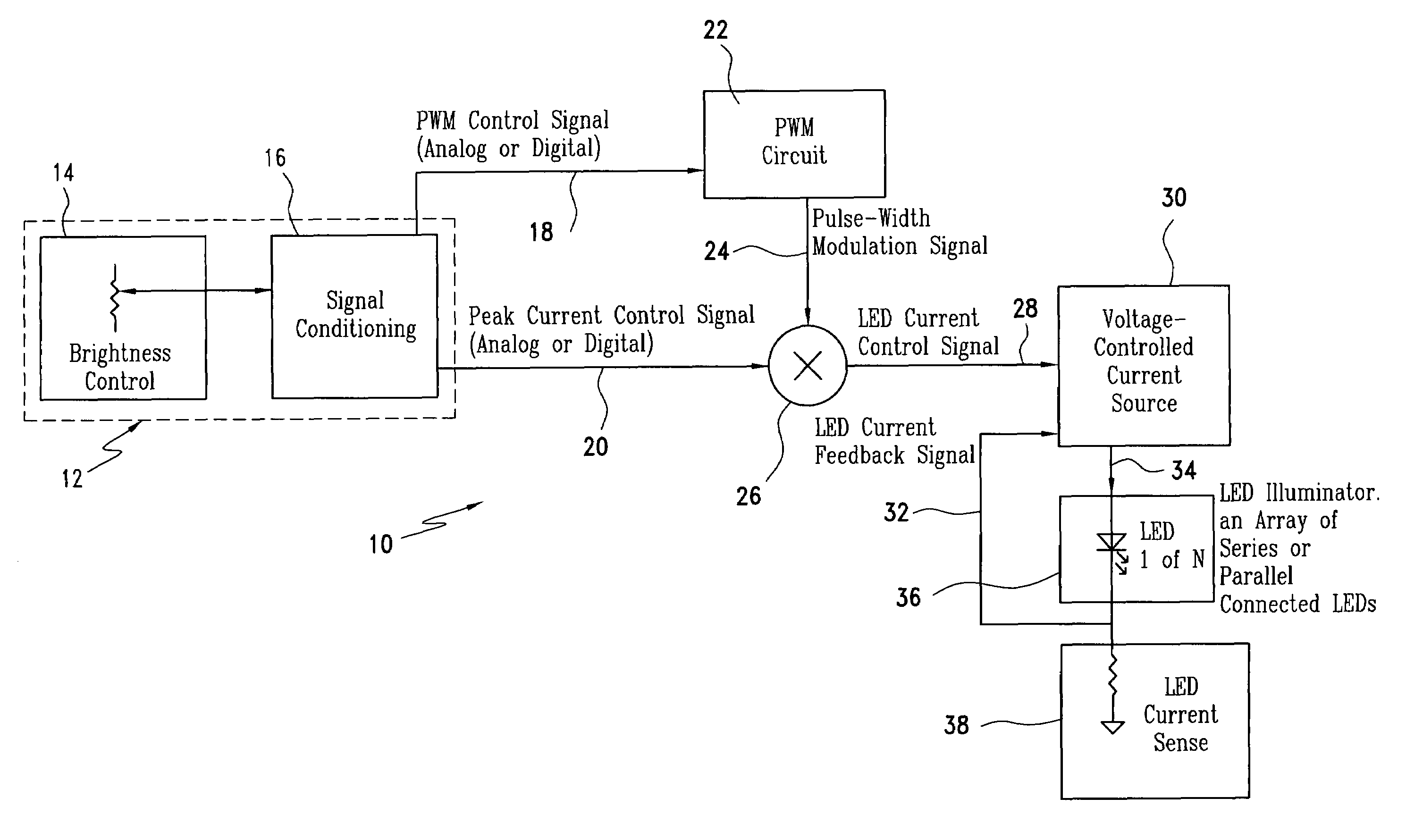
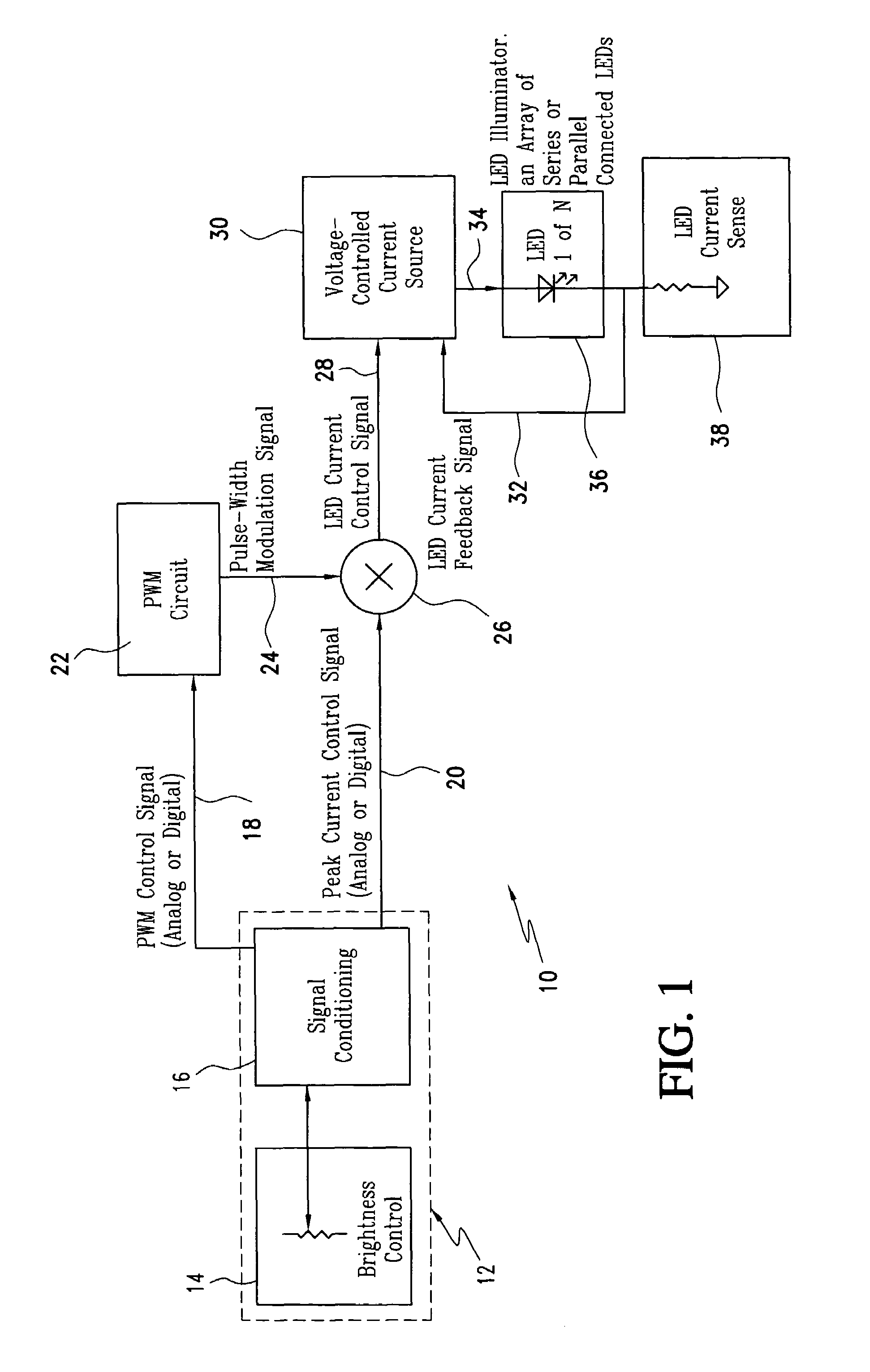
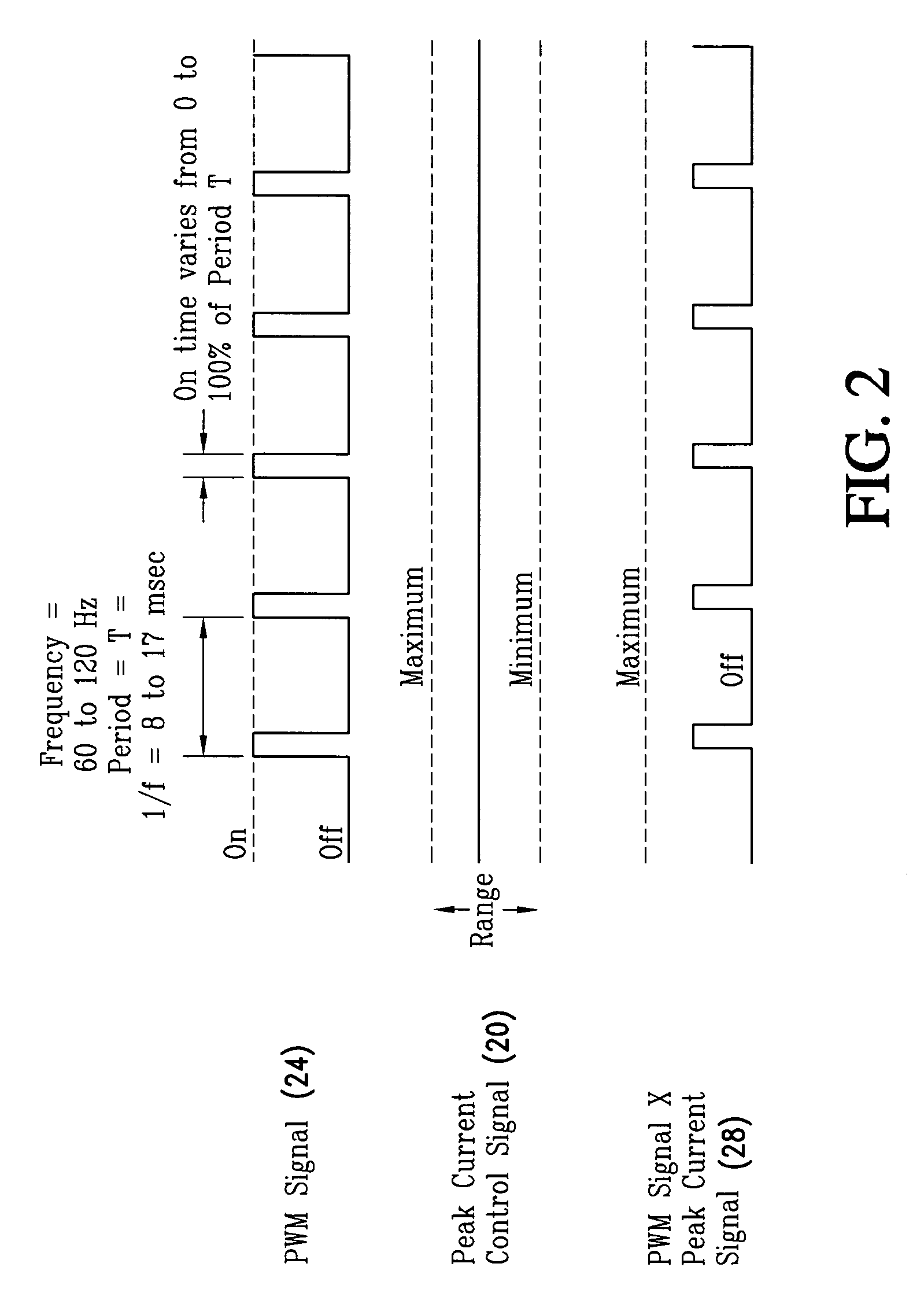
The LED brightness control system for a wide range of luminance control includes a brightness control module that provides a pulse width modulation (PWM) control signal and a peak current control signal. A pulse width modulation (PWM) converter circuit receives the PWM control signal and converts it to a PWM signal. A multiplier receives the PWM signal and the peak current control signal from the brightness control module and multiplies the same to provide a light emitting diode (LED) current control signal with a variable “on” time as well as variable “on” level. A voltage-controlled current source utilizes the LED current control signal and an LED current feedback signal for providing an LED current. An LED illuminator array receives the LED current. A current sensing element connected to the LED illuminator array for providing an LED current feedback signal representing LED peak current. The voltage-controlled current source controls a drive voltage to the LED illuminator array at a commanded level.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
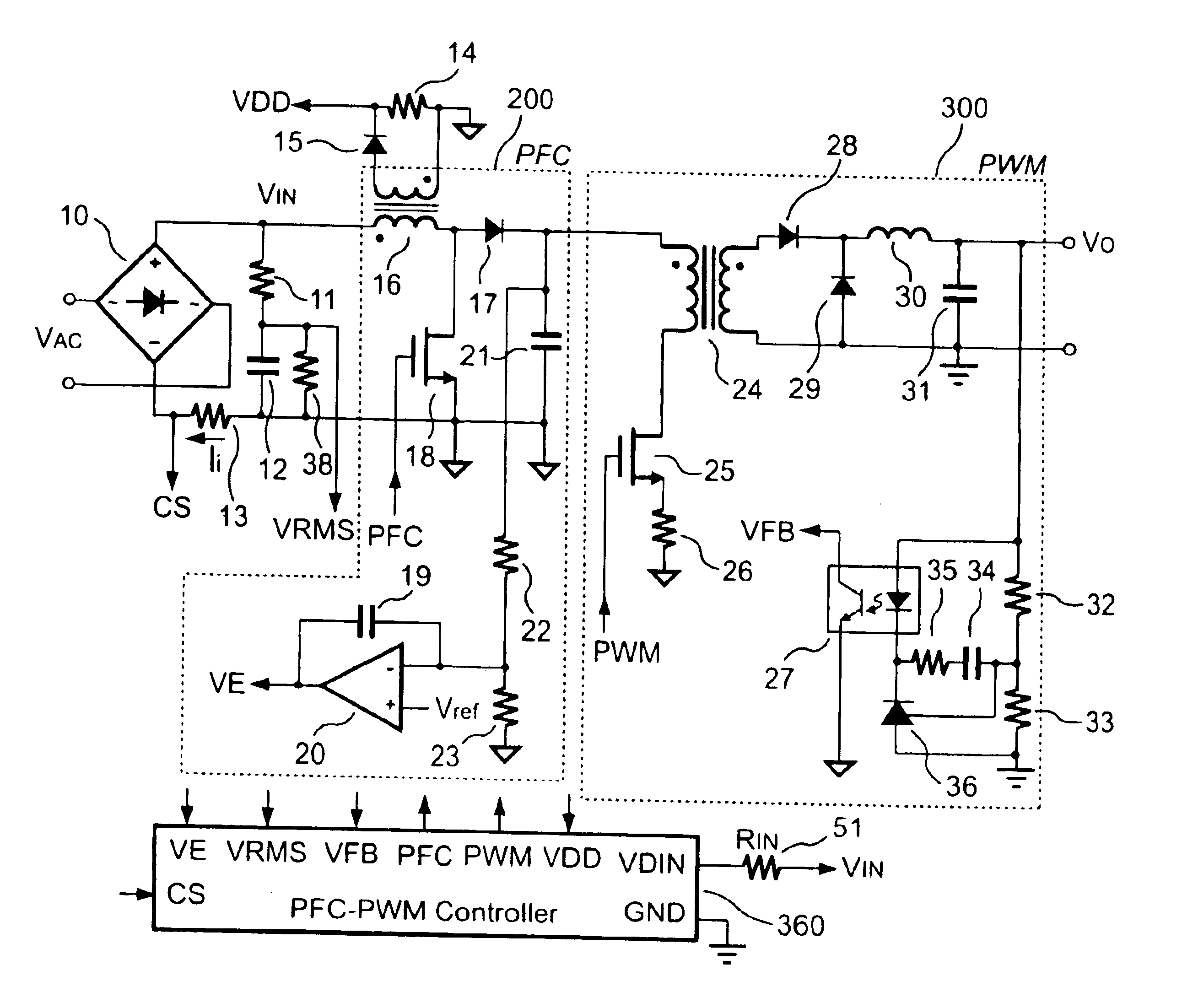
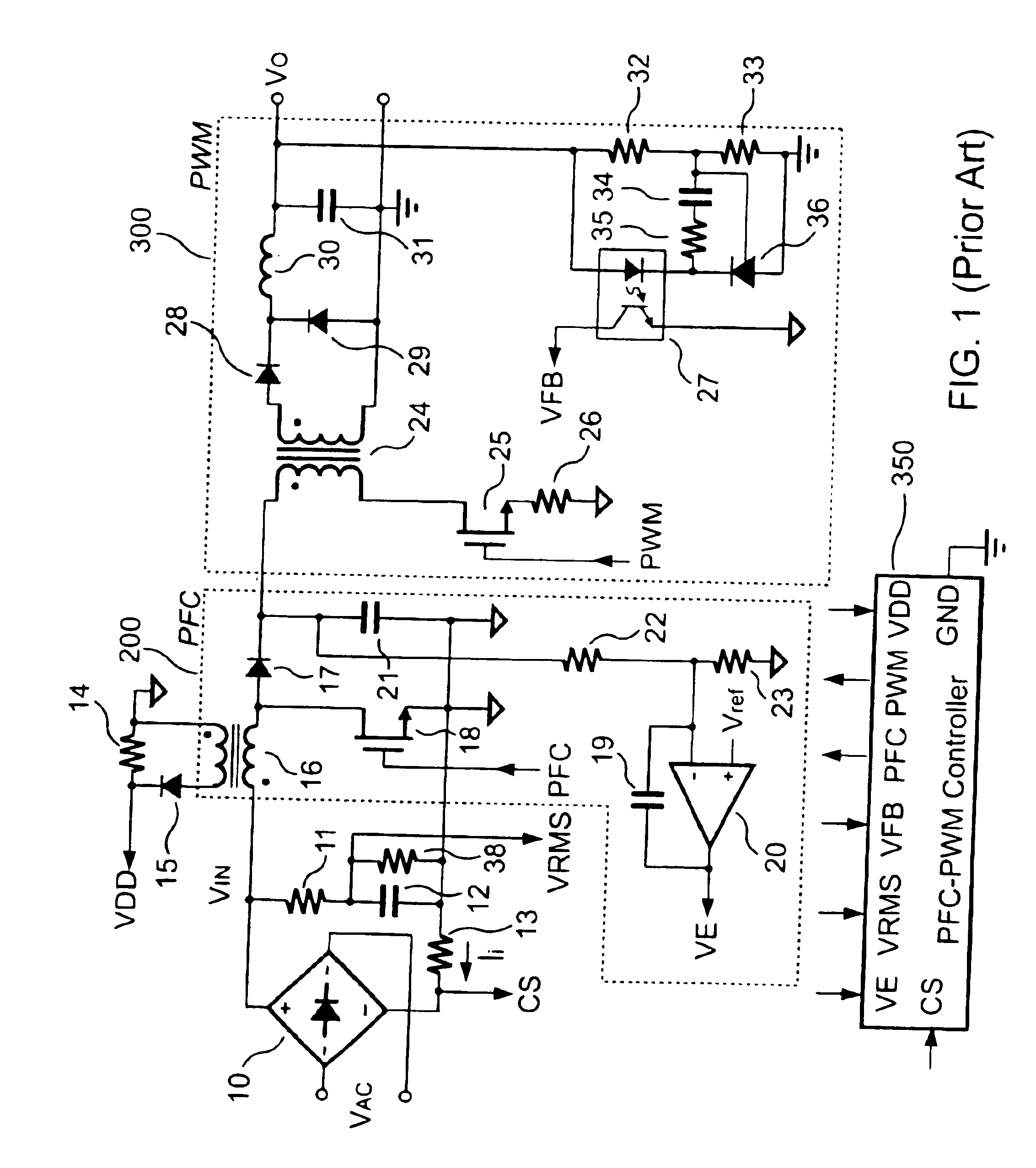
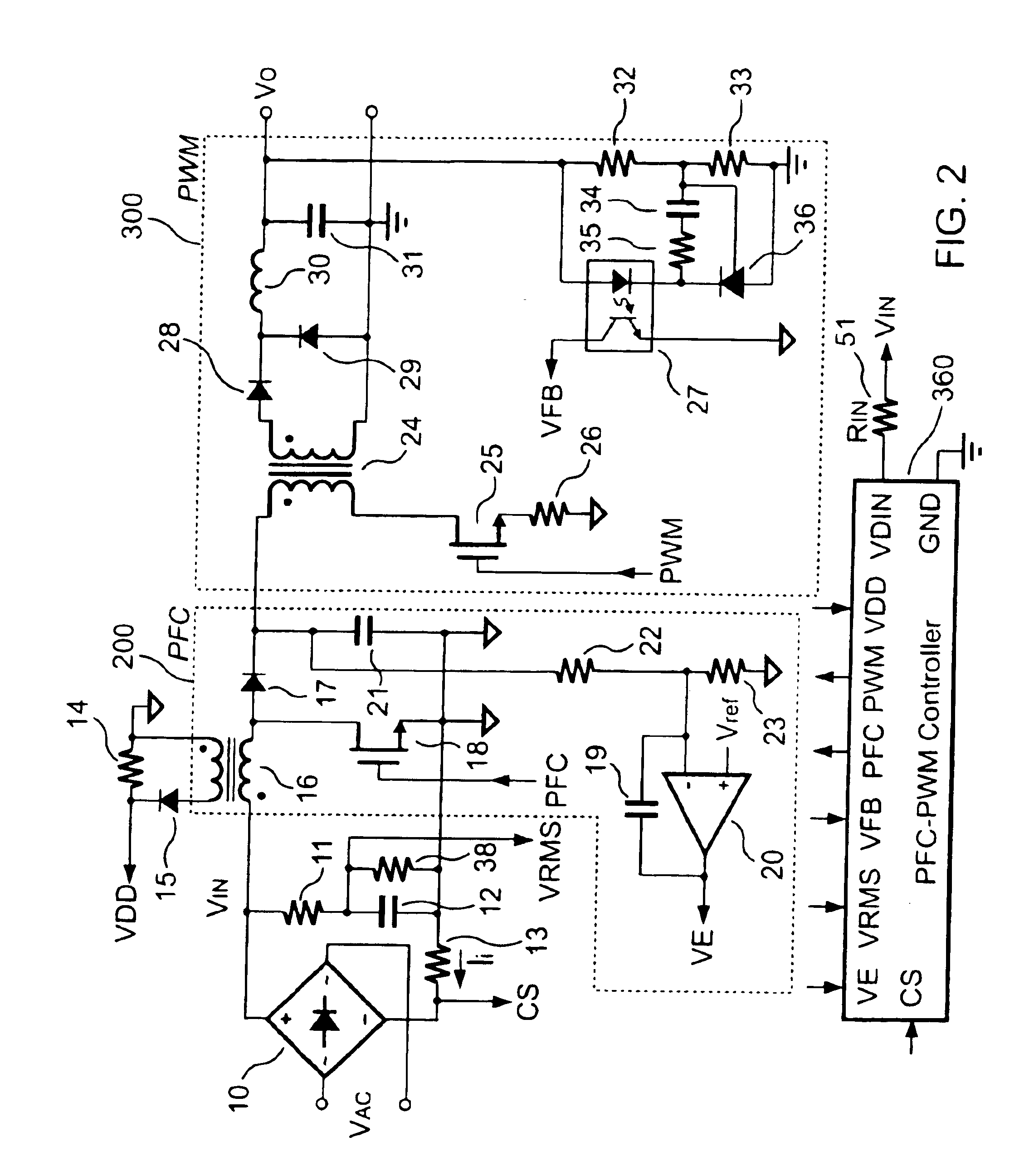
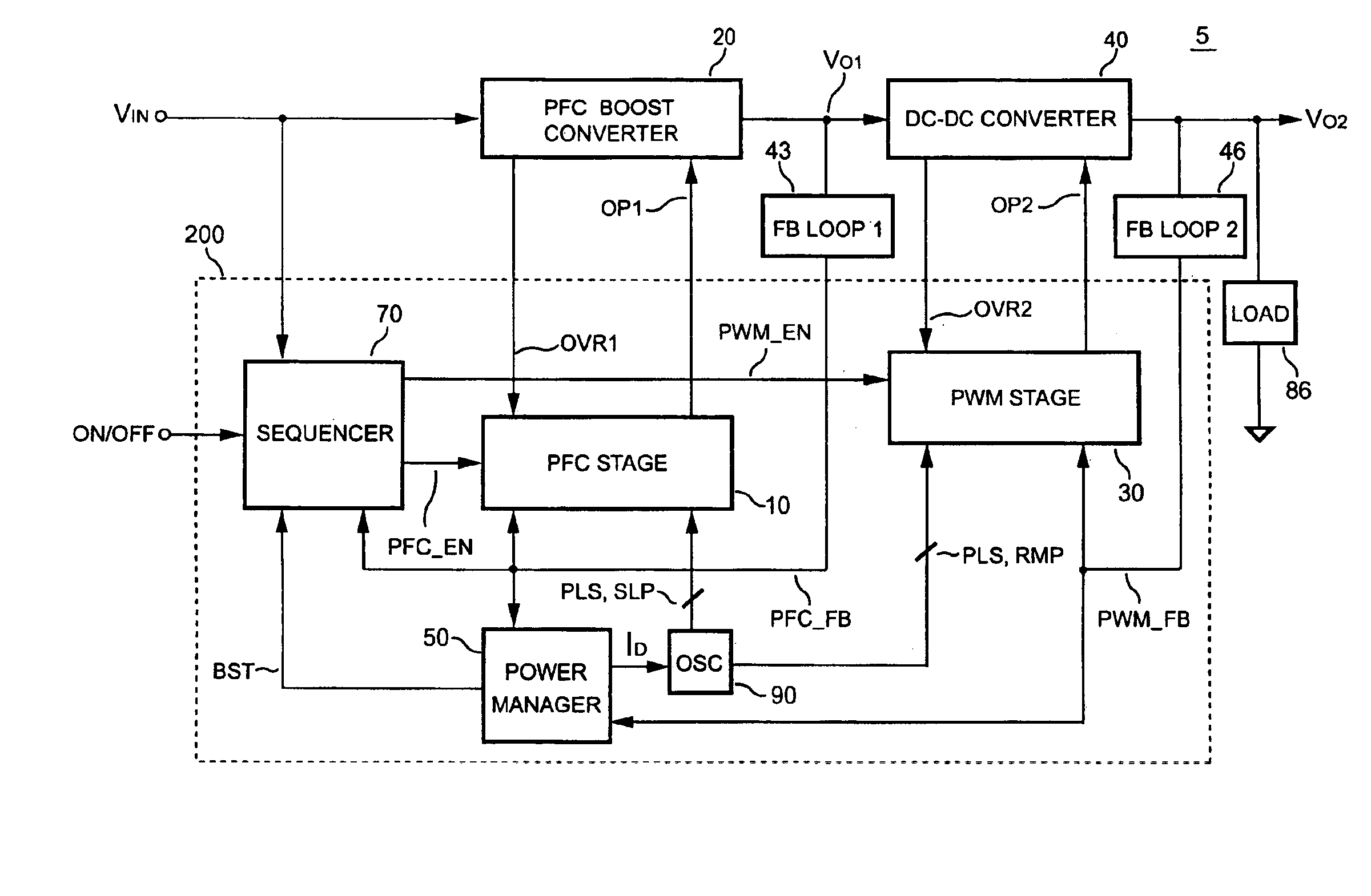
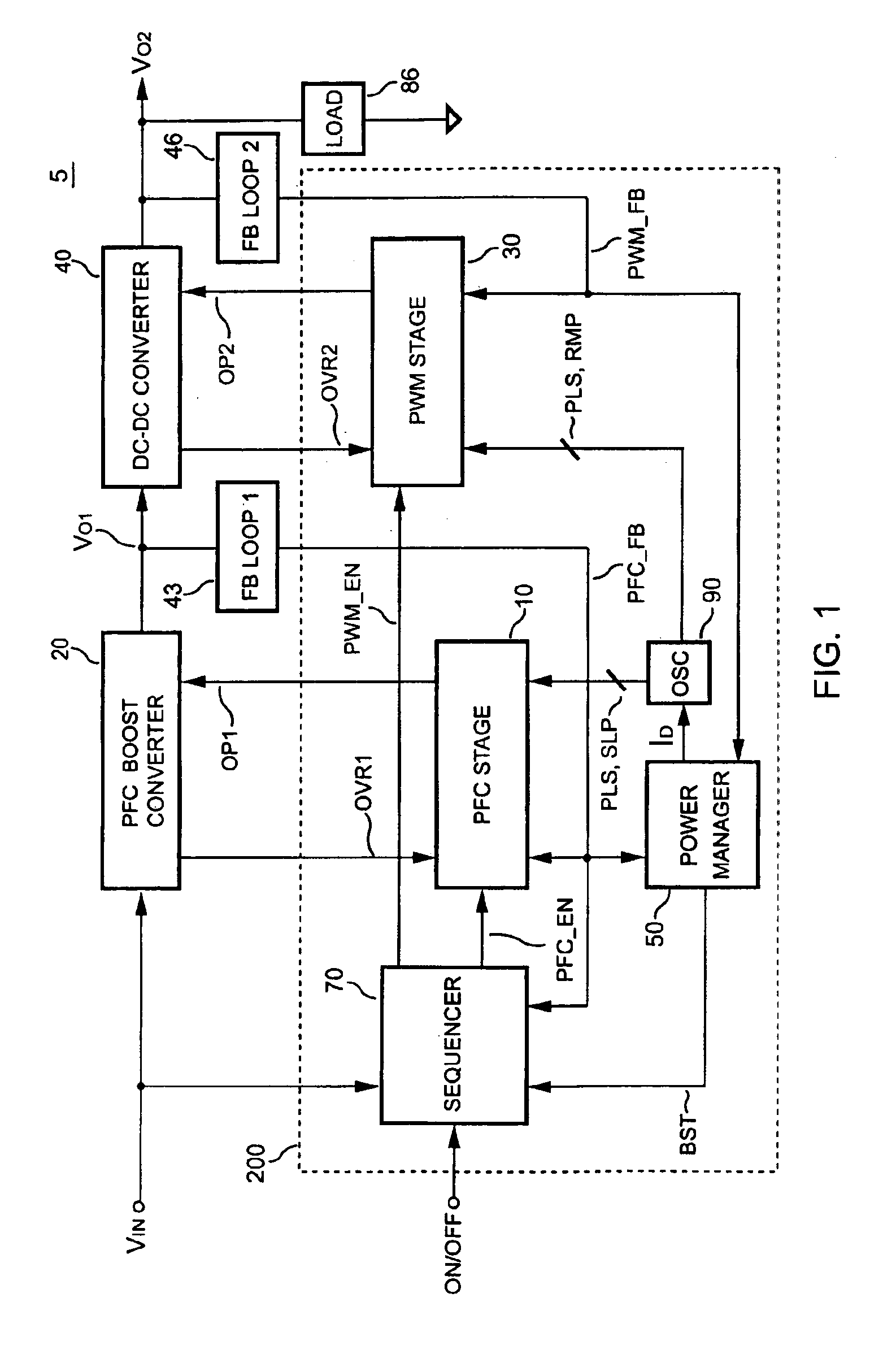
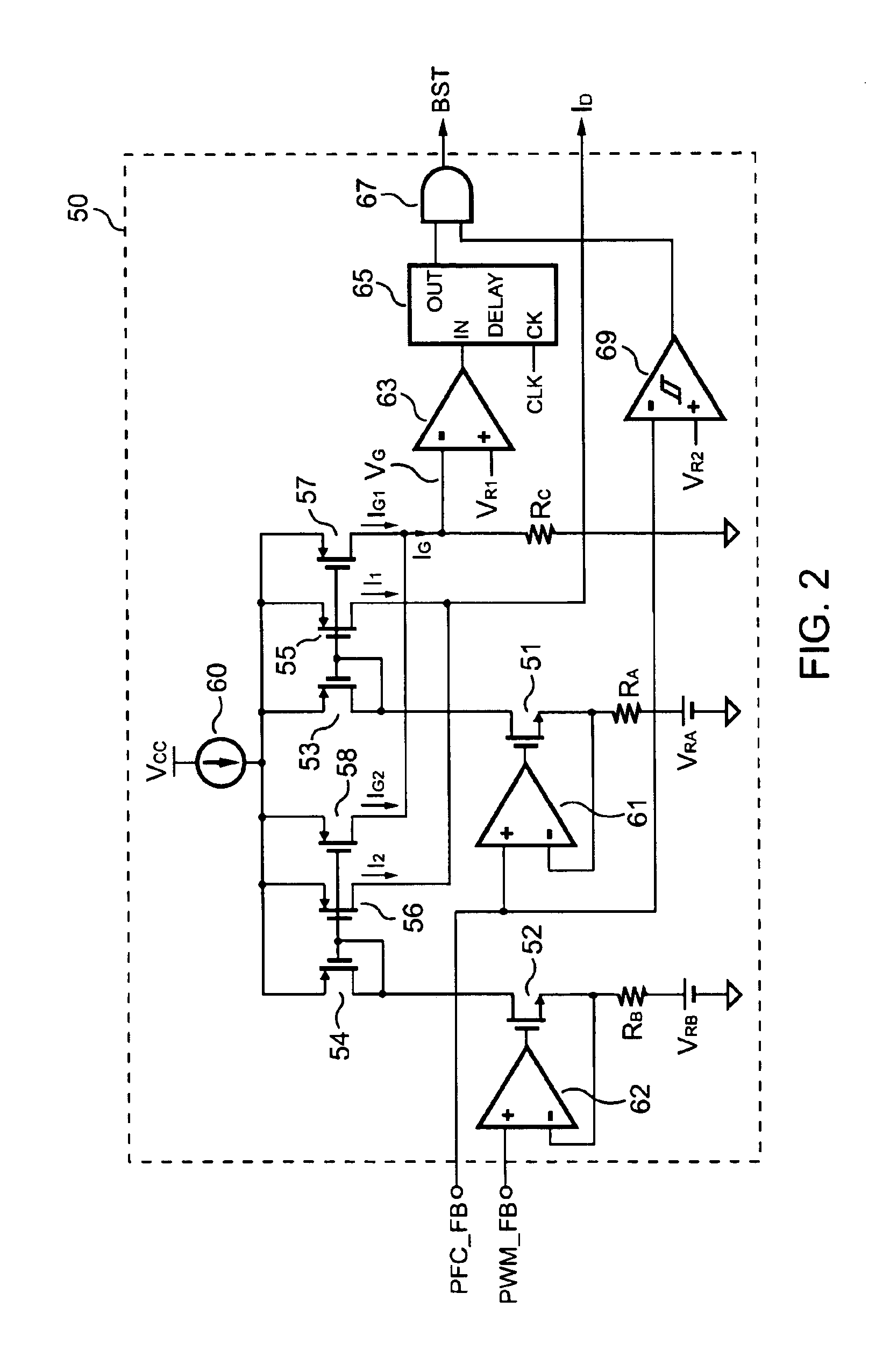
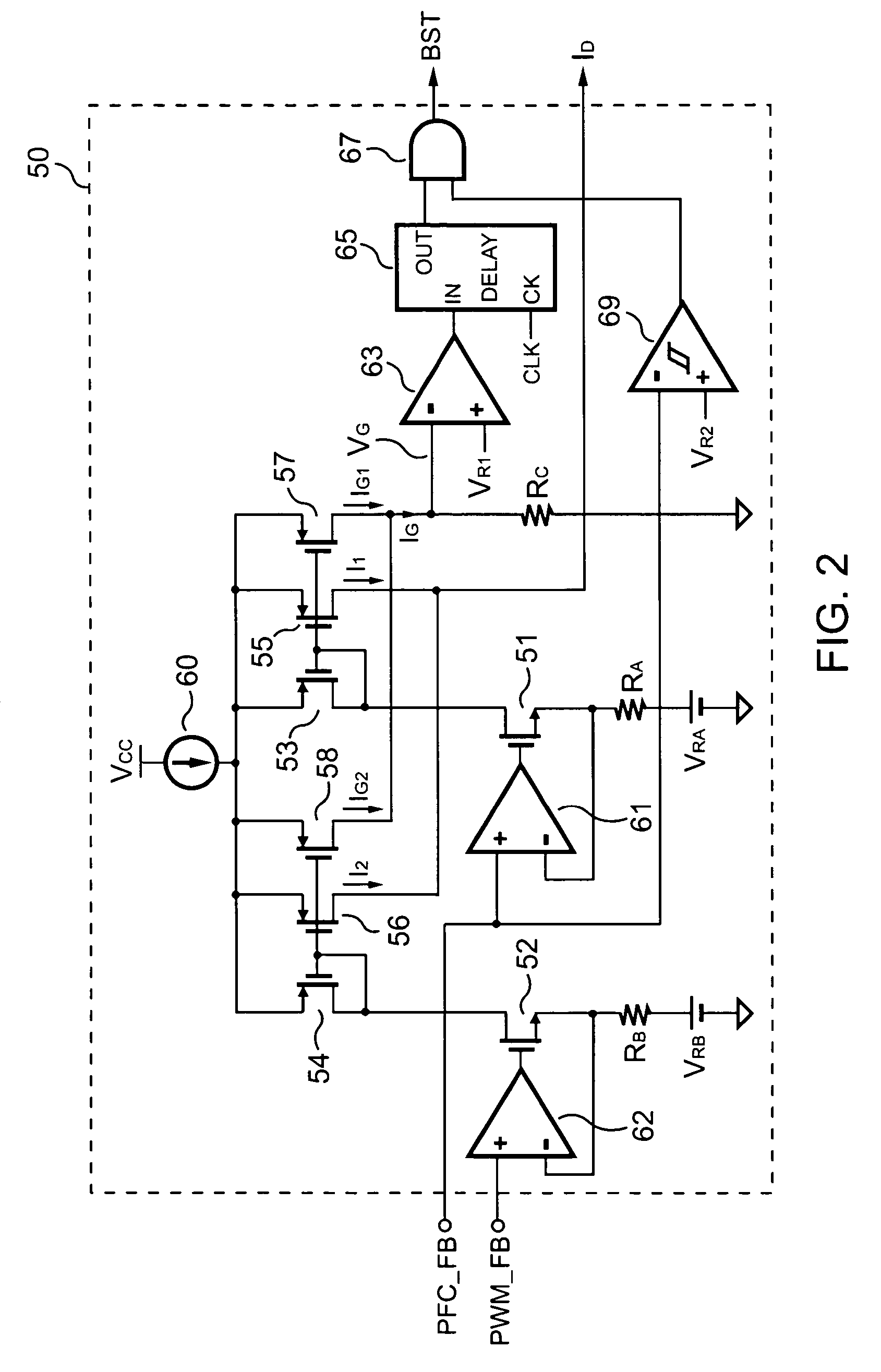
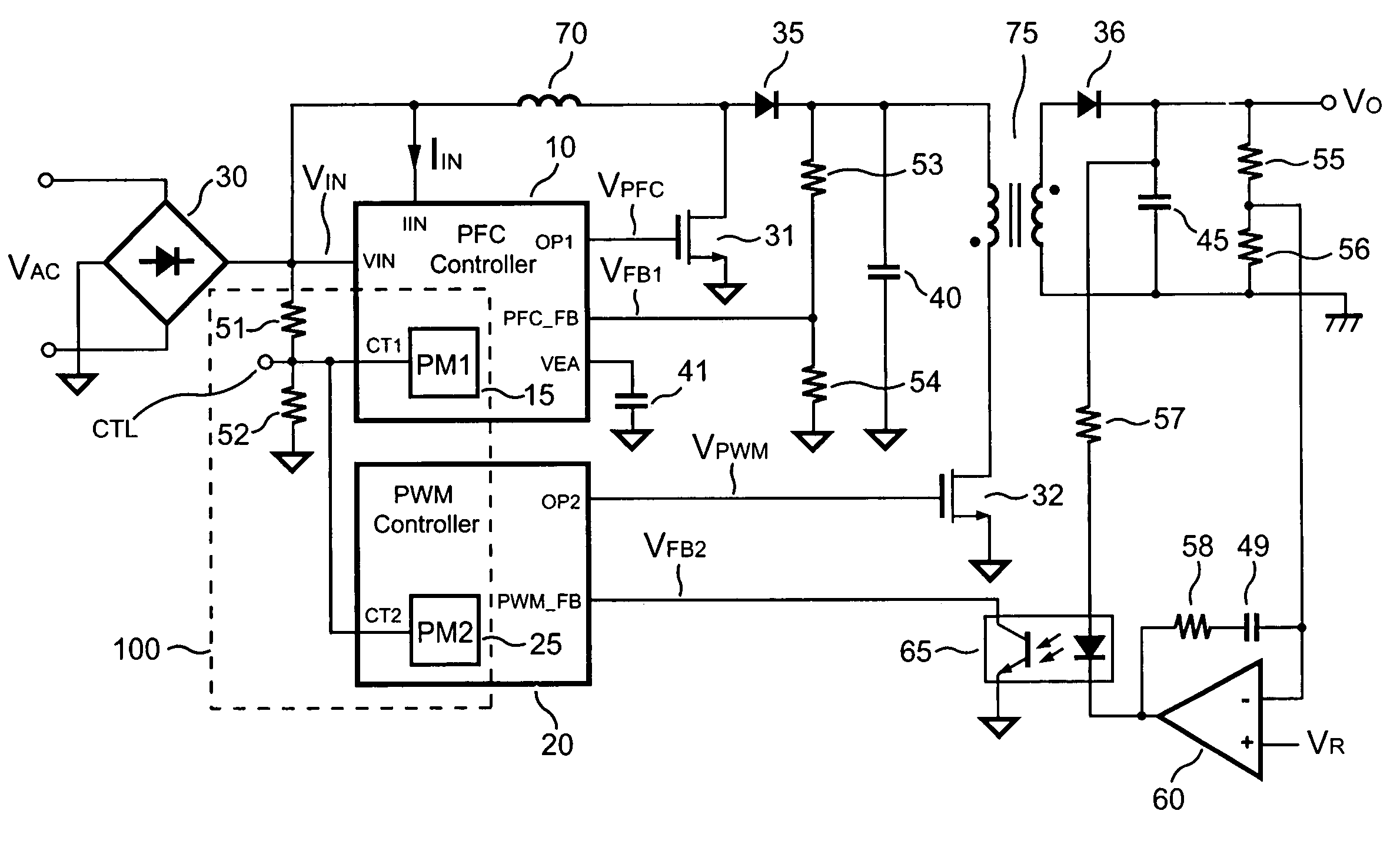
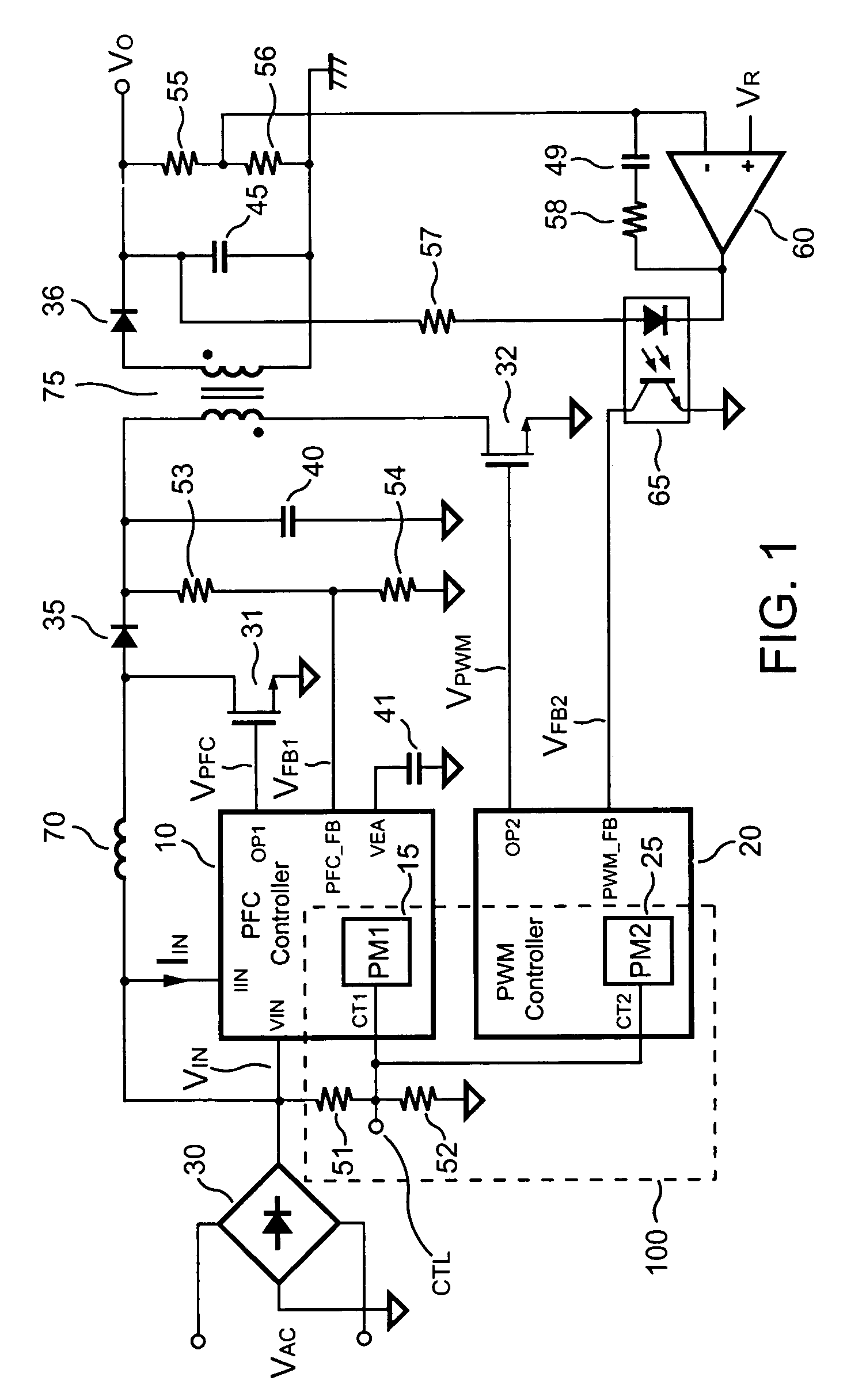
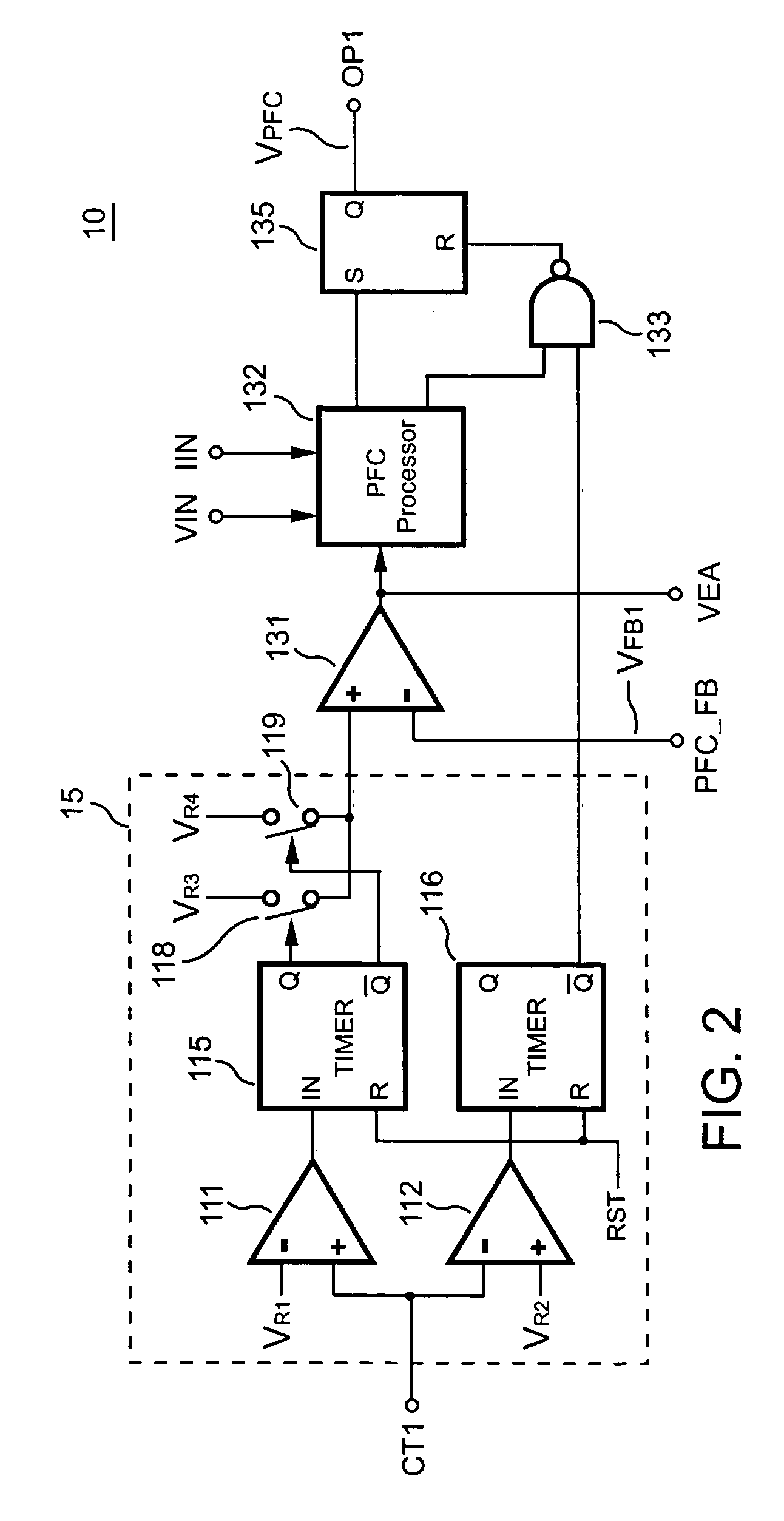
PFC-PWM controller having a power saving means
InactiveUS6839247B1Stable deliveryImprove transmission efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching signalEngineering
A PFC-PWM controller with a power saving means is disclosed. A built-in current synthesizer generates a bias current in response to feedback voltages sampled from the PWM circuit and the PFC circuit. The bias current modulates the oscillation frequency to further reduce the switching frequencies of the PWM signal and the PFC signal under light-load and zero-load conditions. Thus, power consumption is greatly reduced. The PFC and the PWM switching signals interleave each other, so that power can be transferred more smoothly from the PFC circuit to the PWM circuit. The saturation of the switching components can be avoided by limiting the maximum on-time of the PWM signal. Further, an external resistor is used to start up the PFC-PWM controller and provide an AC template signal for PFC control.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
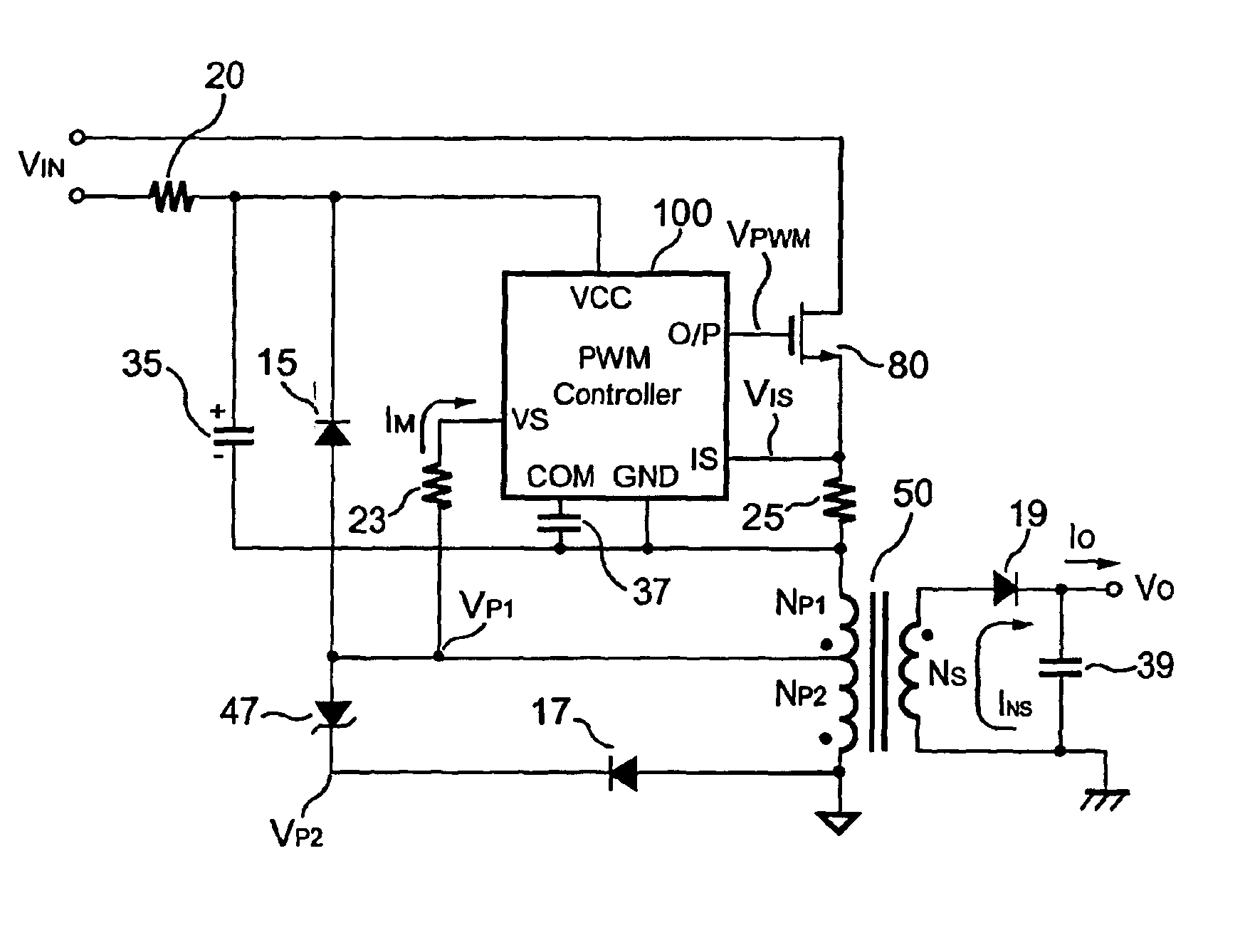
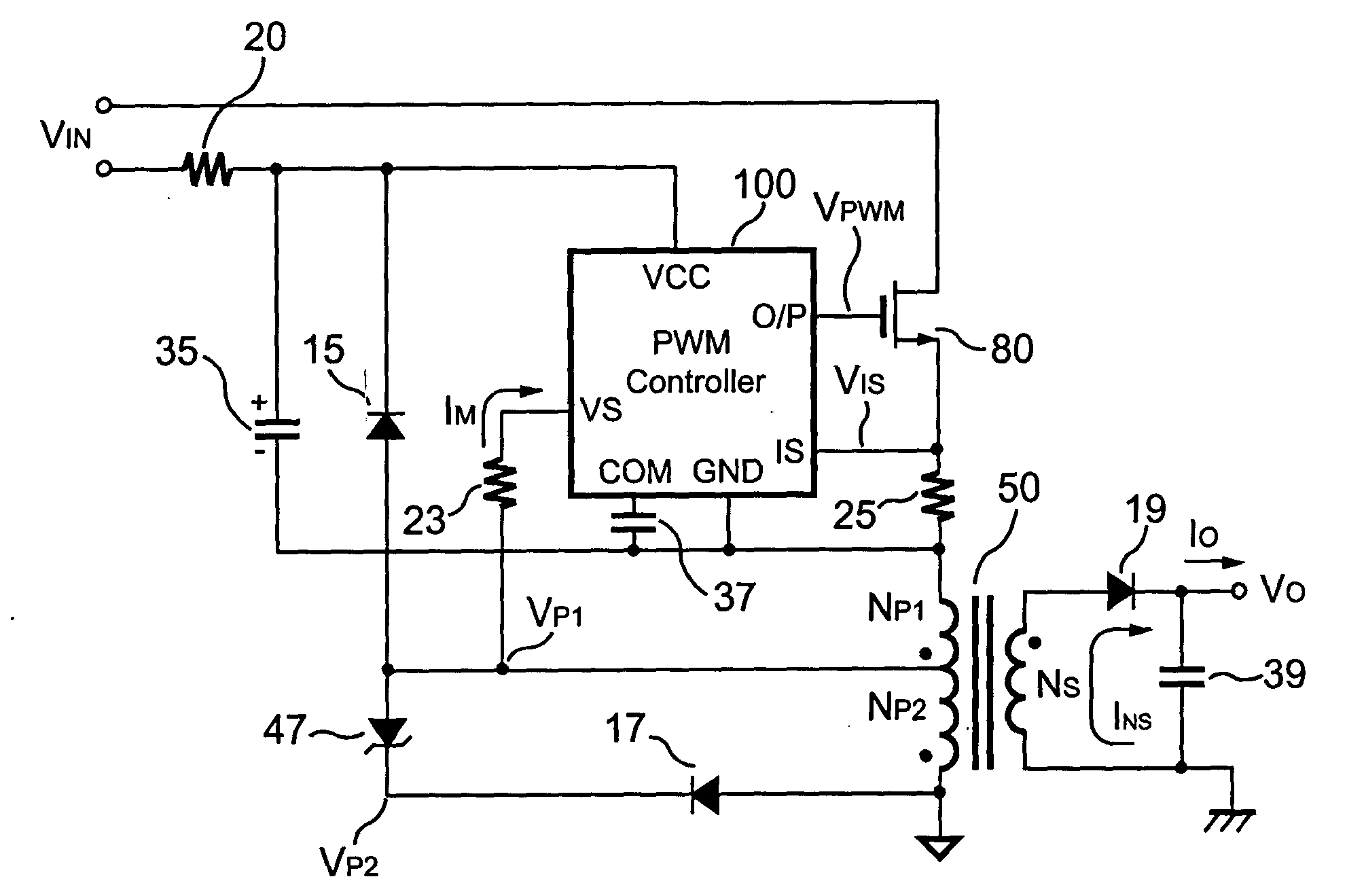
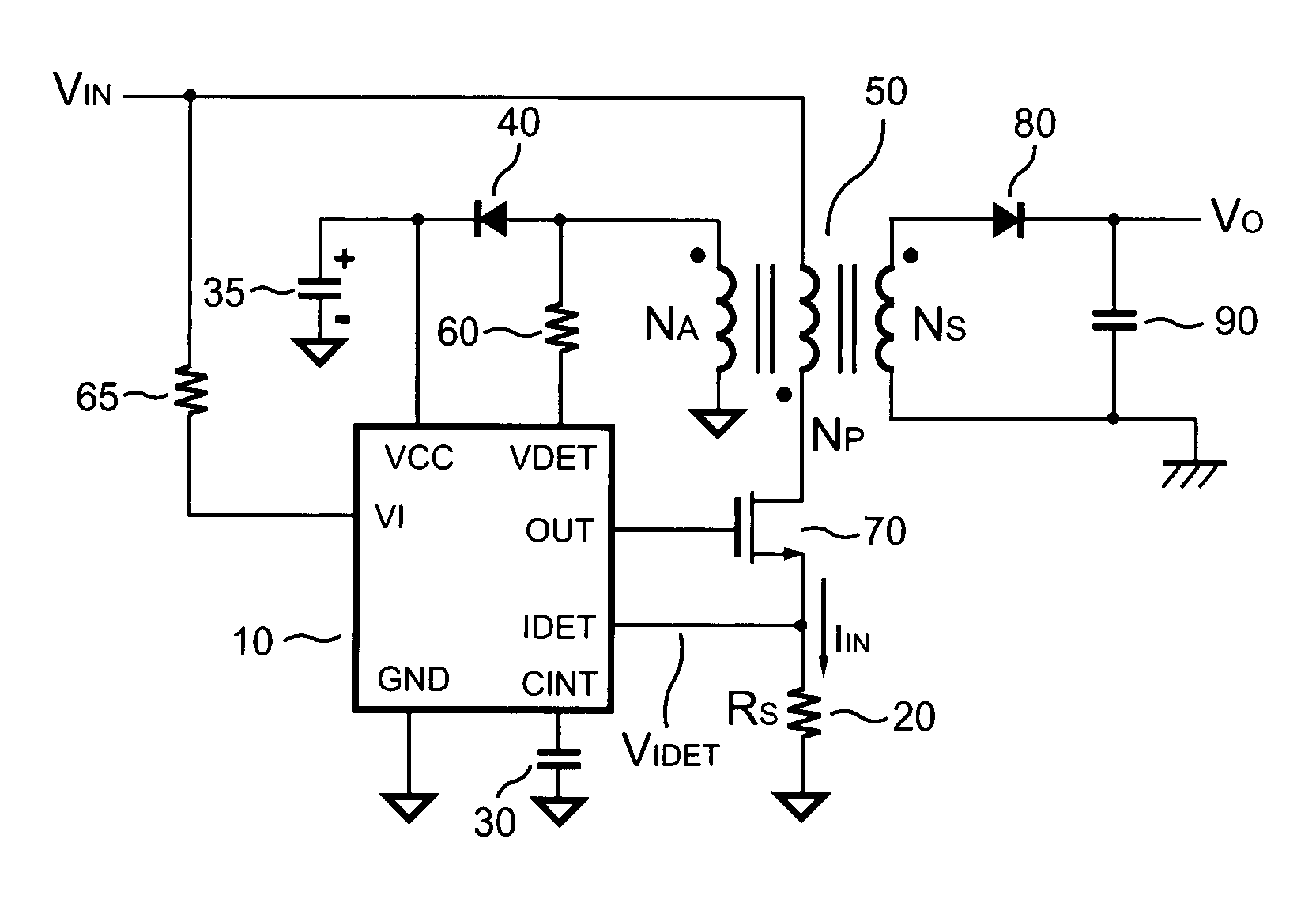
Primary-side controlled flyback power converter
InactiveUS6853563B1Low costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerSwitching frequency
The present invention provides a primary-side flyback power converter that supplies a constant voltage output and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, a PWM controller is included in the power converter in order to generate a PWM signal controlling a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage sampled from a first primary winding of the power supply transformer. Several improvements are included in this present invention to overcome the disadvantages of prior-art flyback power converters. Firstly, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller in order to reduce power consumption. A double sample amplifier samples the flyback voltage just before the transformer current drops to zero. Moreover, an offset current is pulled from a detection input of the double sample amplifier in order to generate a more accurate DC output voltage. The offset current is generated in response to the temperature in order to compensate for temperature-induced voltage fluctuations across the output rectifier. Ultimately, in order to maintain a constant output current, the PWM controller modulates the switching frequency in response to the output voltage.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
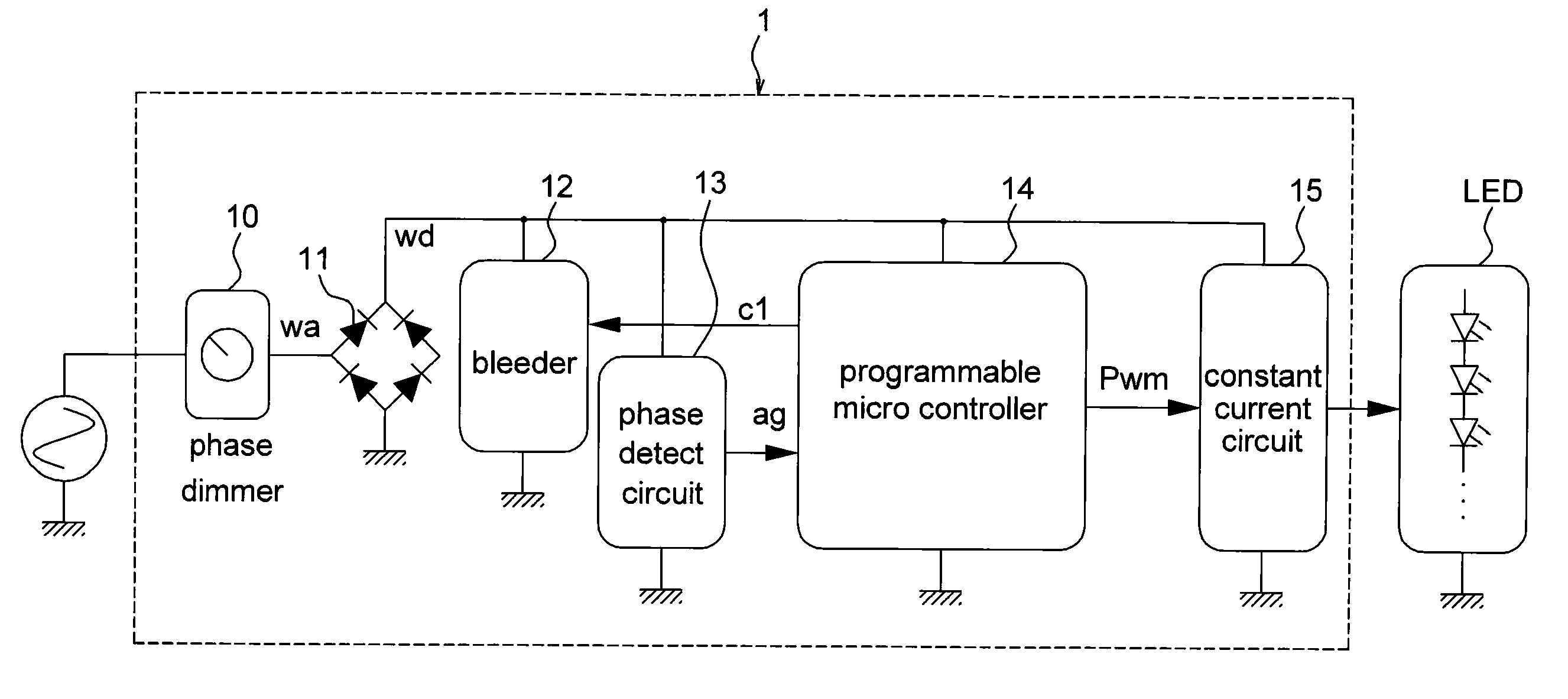
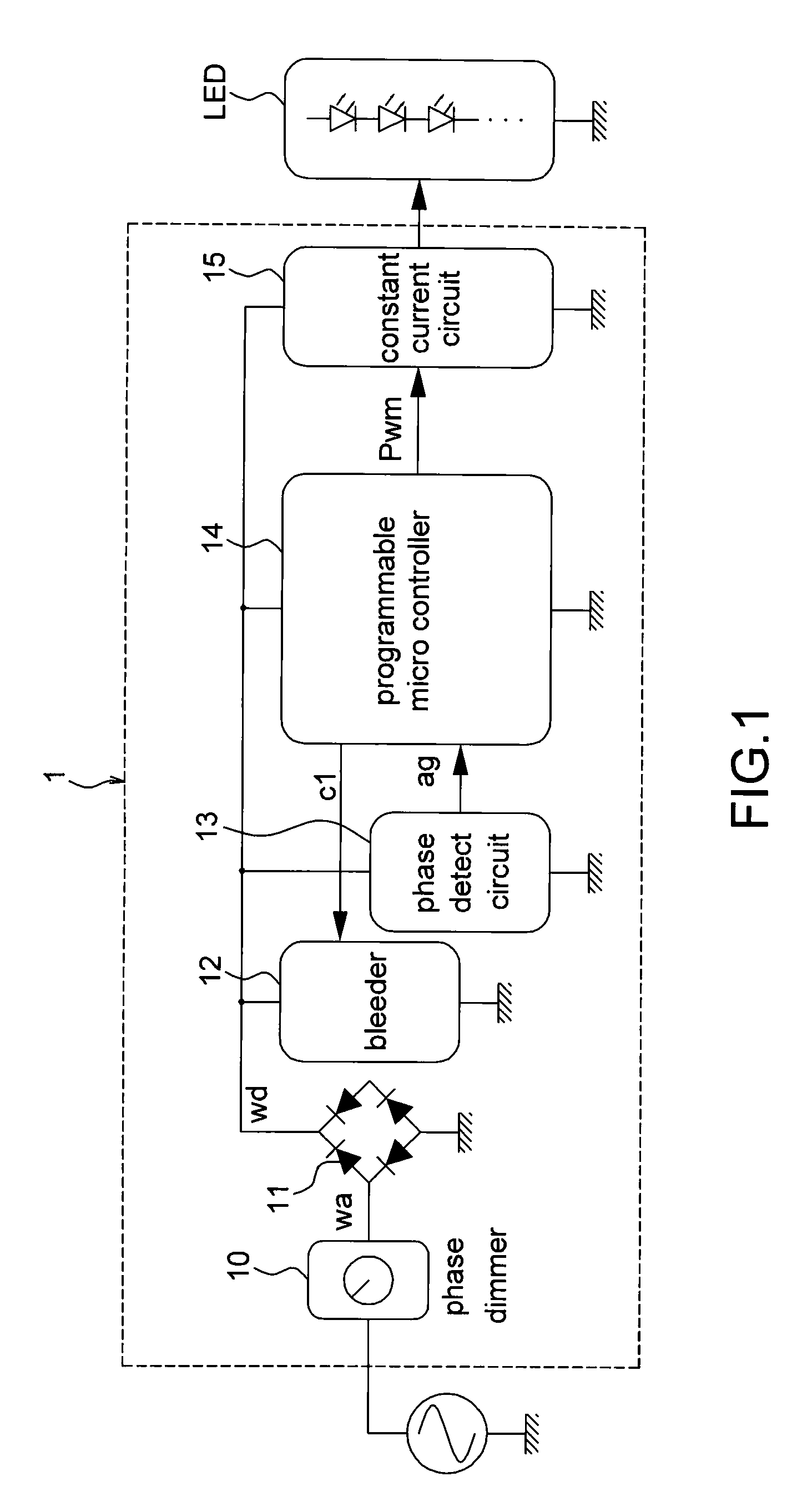
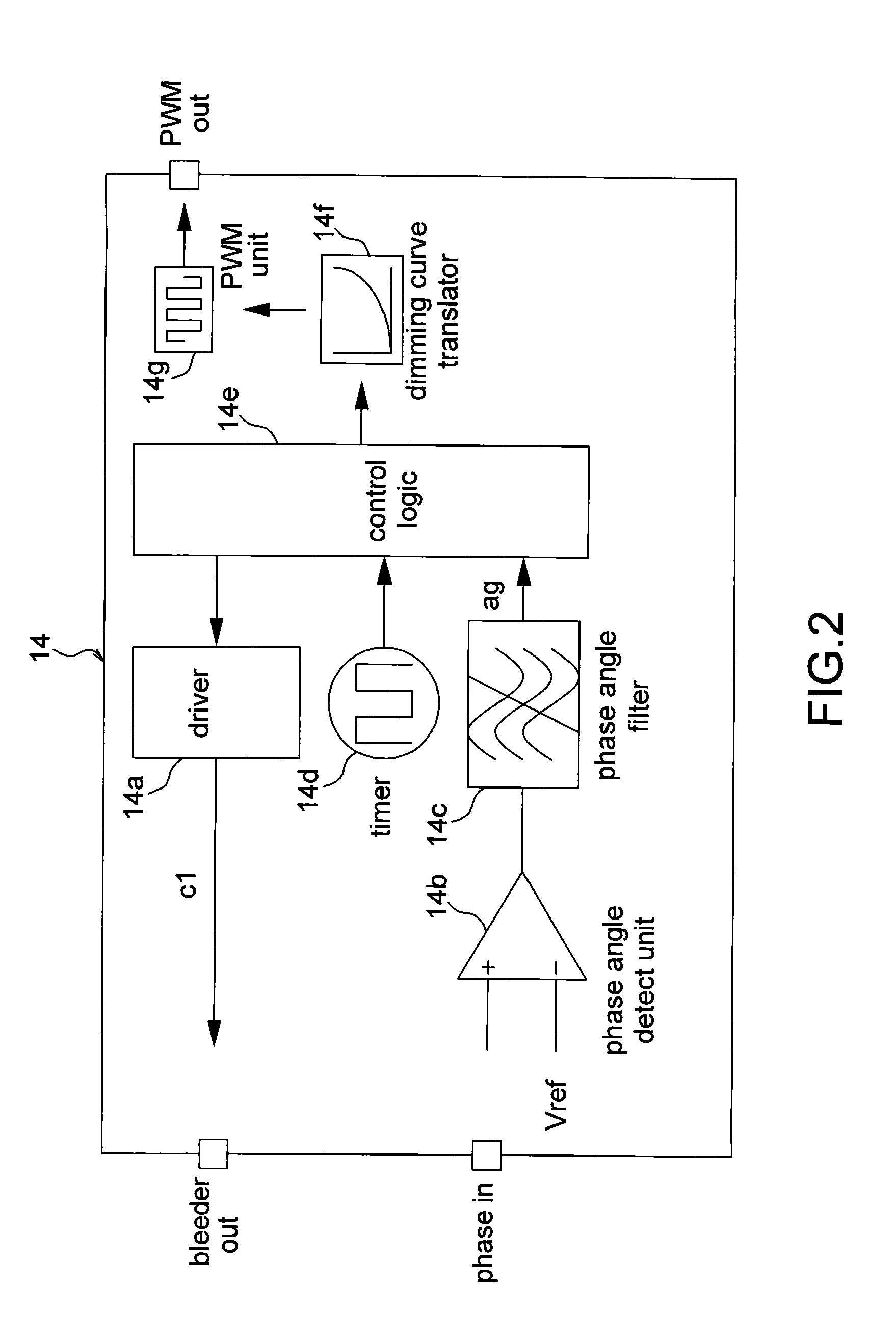
Dimmer circuit applicable for LED device and control method thereof
InactiveUS20110291583A1Improve efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesProgrammable logic controllerProgrammable Interrupt Controller
A dimmer circuit applicable for LED device and control method thereof is disclosed in the embodiments of the present invention. The dimmer circuit is applicable for controlling at least a LED device. The dimmer circuit includes a rectifier, a bleeder, a phase angle detect circuit, a constant current circuit and a programmable micro controller. The phase angle detect circuit couples to the programmable micro controller. The constant current circuit couples to the LED device The programmable micro controller generates a PWM signal according to the output signal of the phase angle detect circuit to adjust current of the constant current circuit.
Owner:UNITED POWER RES TECH CORP
Sequential burst mode activation circuit
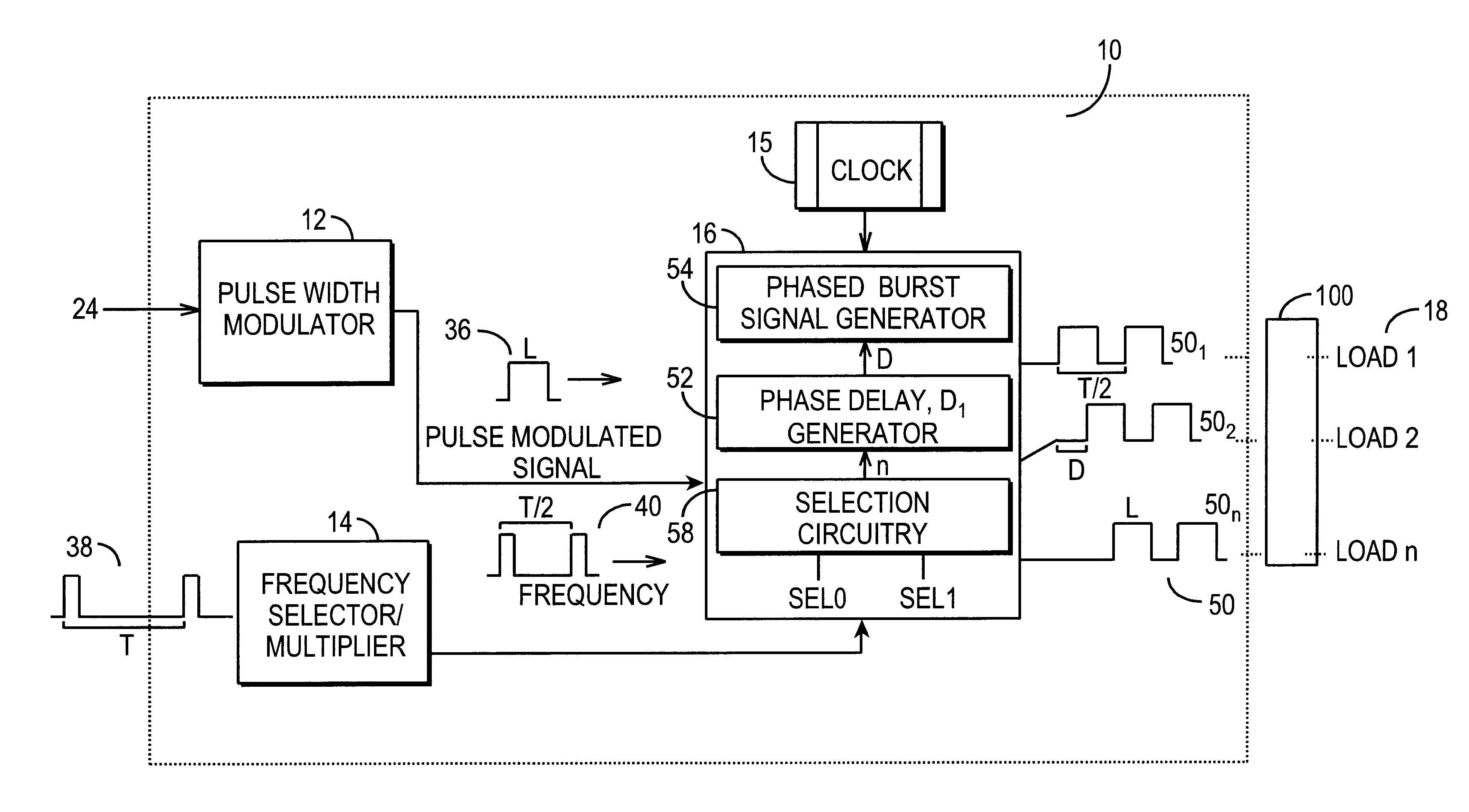
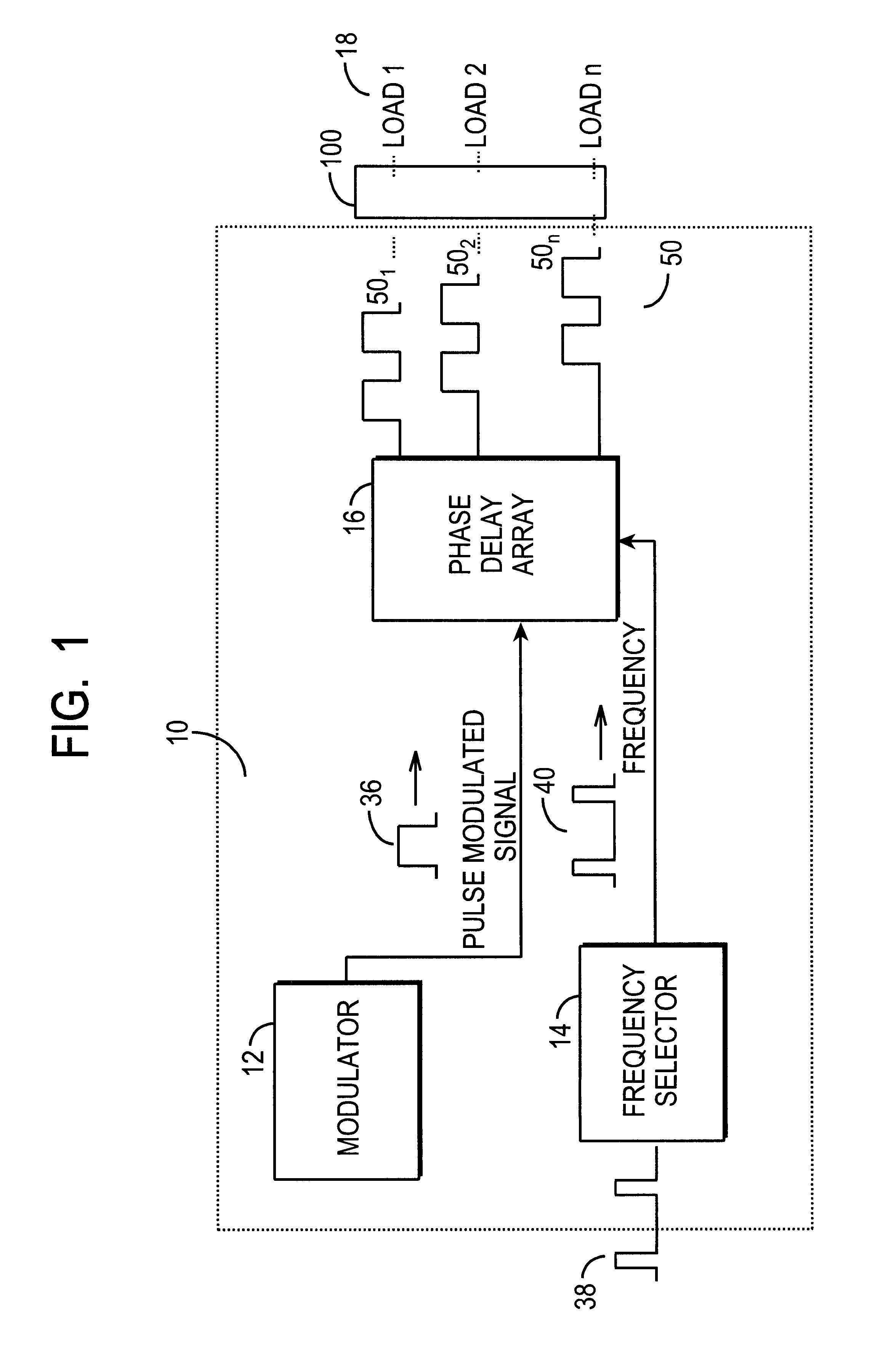
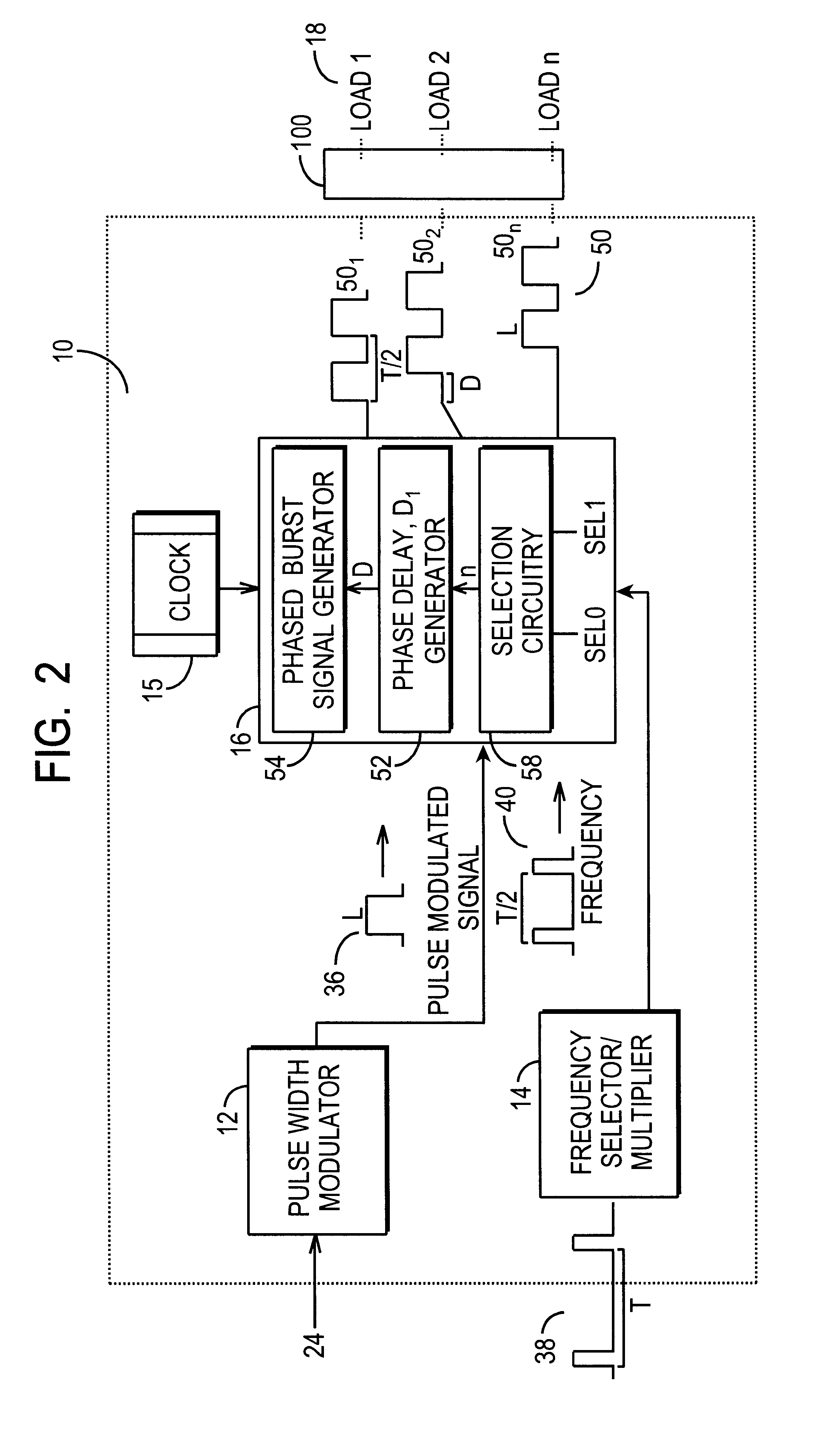
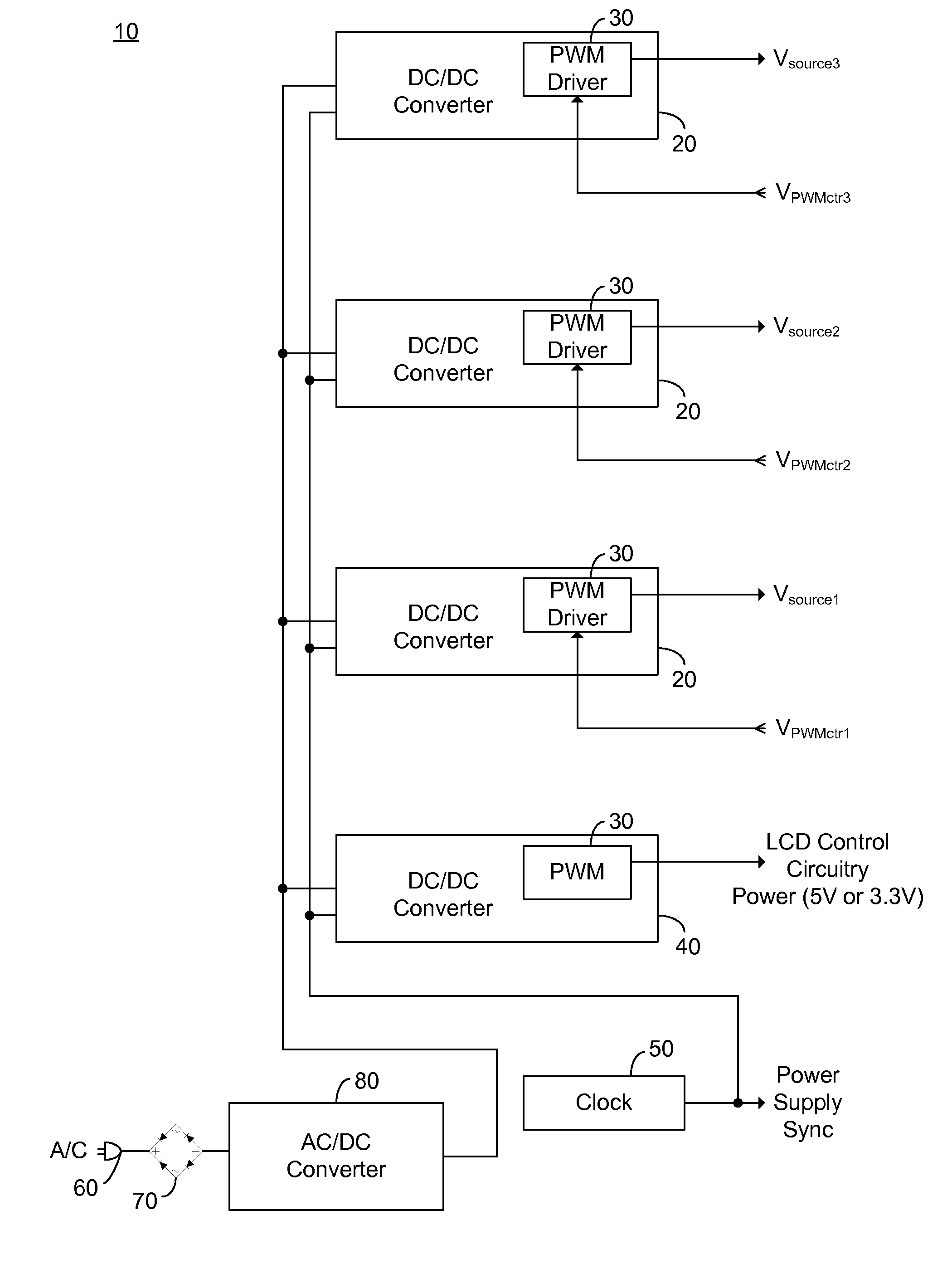
A sequential burst mode regulation system to deliver power to a plurality of loads. In the exemplary embodiments, the system of the present invention generates a plurality of phased pulse width modulated signals from a single pulse width modulated signal, where each of the phased signals regulates power to a respective load. Exemplary circuitry includes a PWM signal generator, and a phase delay array that receives a PWM signal and generates a plurality of phased PWM signals which are used to regulate power to respective loads. A frequency selector circuit can be provided that sets the frequency of the PWM signal using a fixed or variable frequency reference signal.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
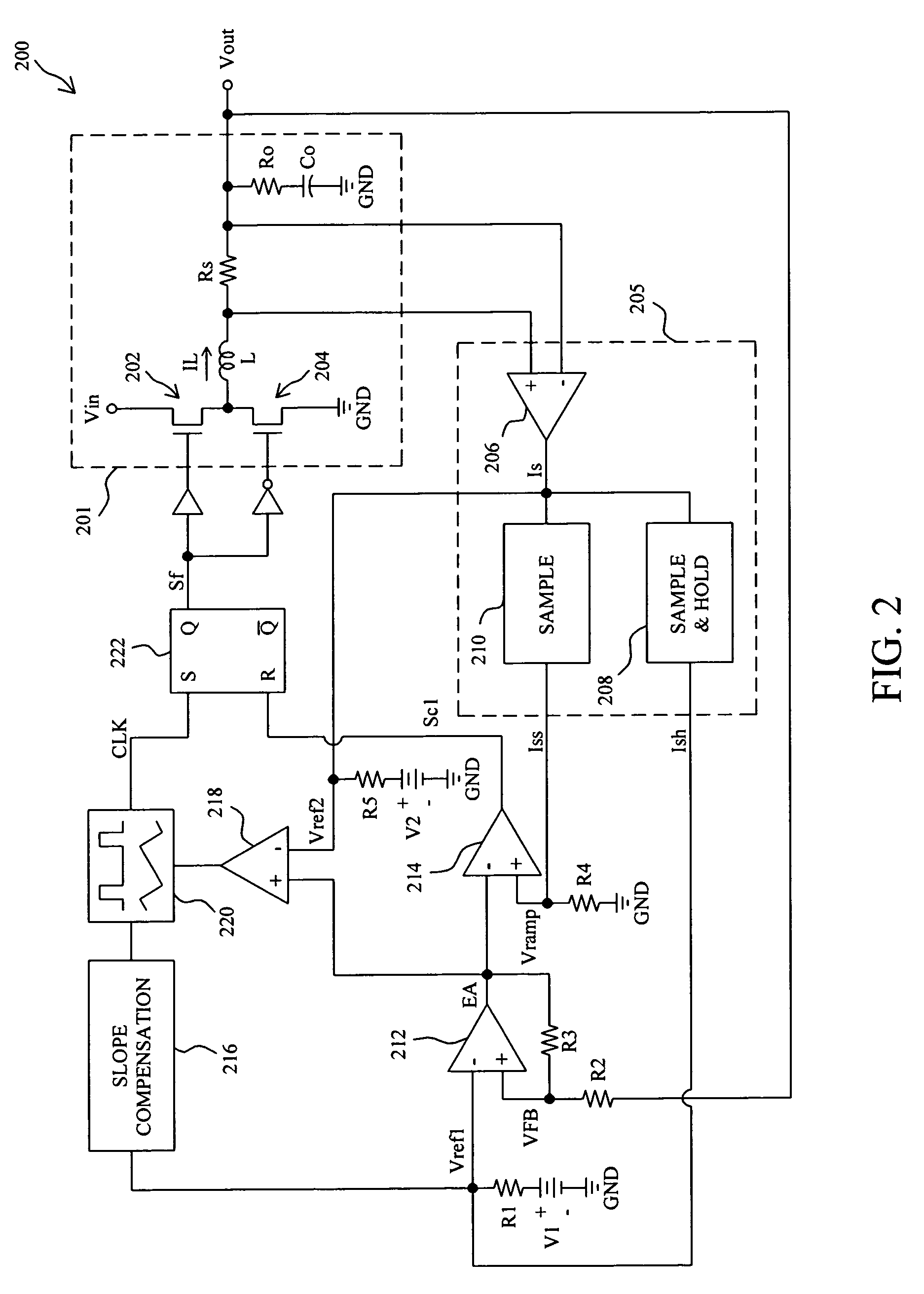
Secondary Side Post Regulation for LED Backlighting
A secondary side post regulator arrangement for a plurality of LED strings. For each secondary winding, a first electronically controlled switch is provided arranged to control the power output, and a LED string is connected thereto. A second electronically controlled switch is further connected in series with the LED string, arranged to receive a PWM signal, thereby pulsing current through the LED string. A current sensing element is further provided outputting a voltage representation of the current through the LED string, and a synchronized sampling circuit is provided arranged to sample the voltage representation during the on period of the second electronically controlled switch. The sampled and held voltage representation is compared with a reference signal and fed back to control the first electronically controlled switch. The voltage output associated with each secondary winding is controlled, responsive to the reference voltage.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
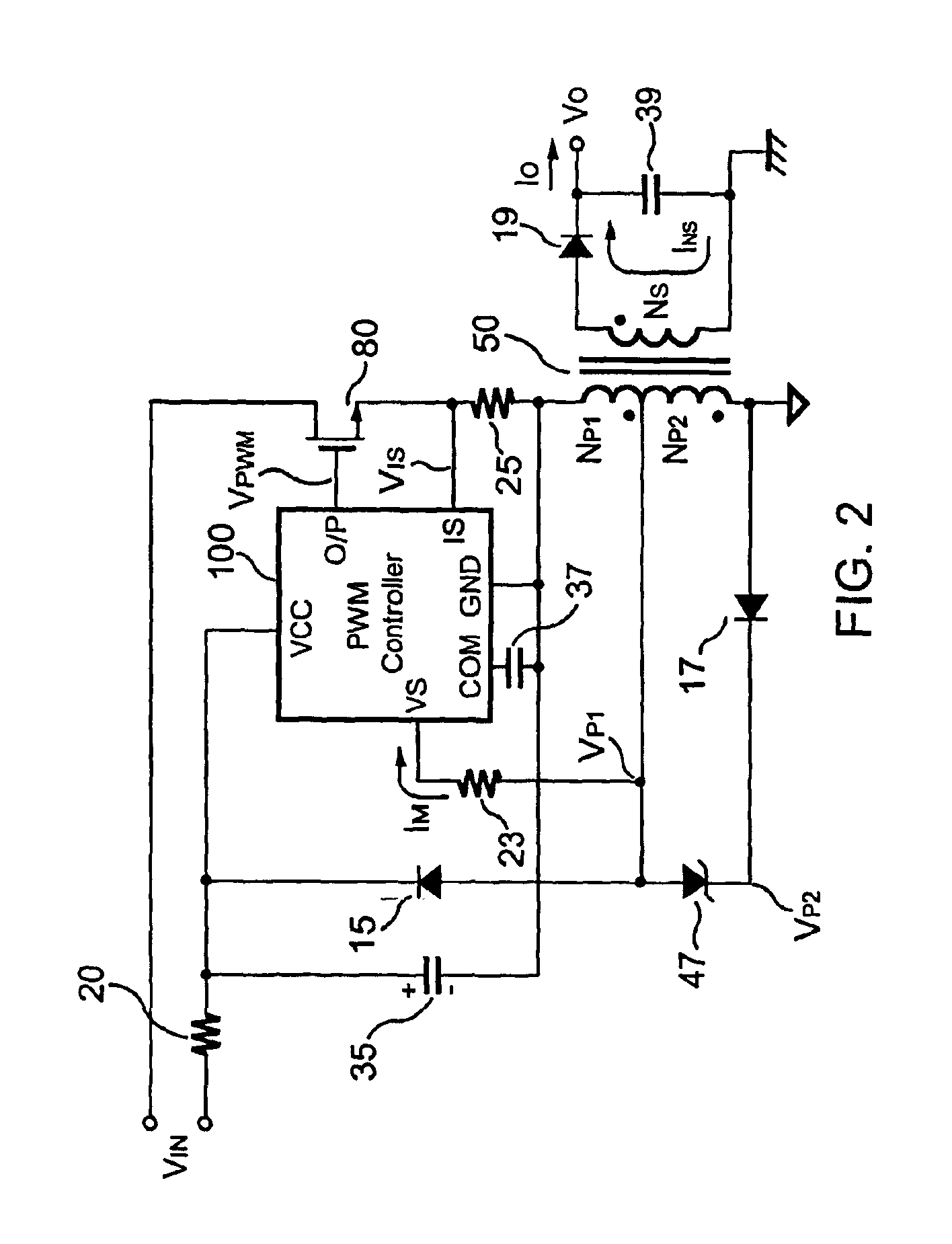
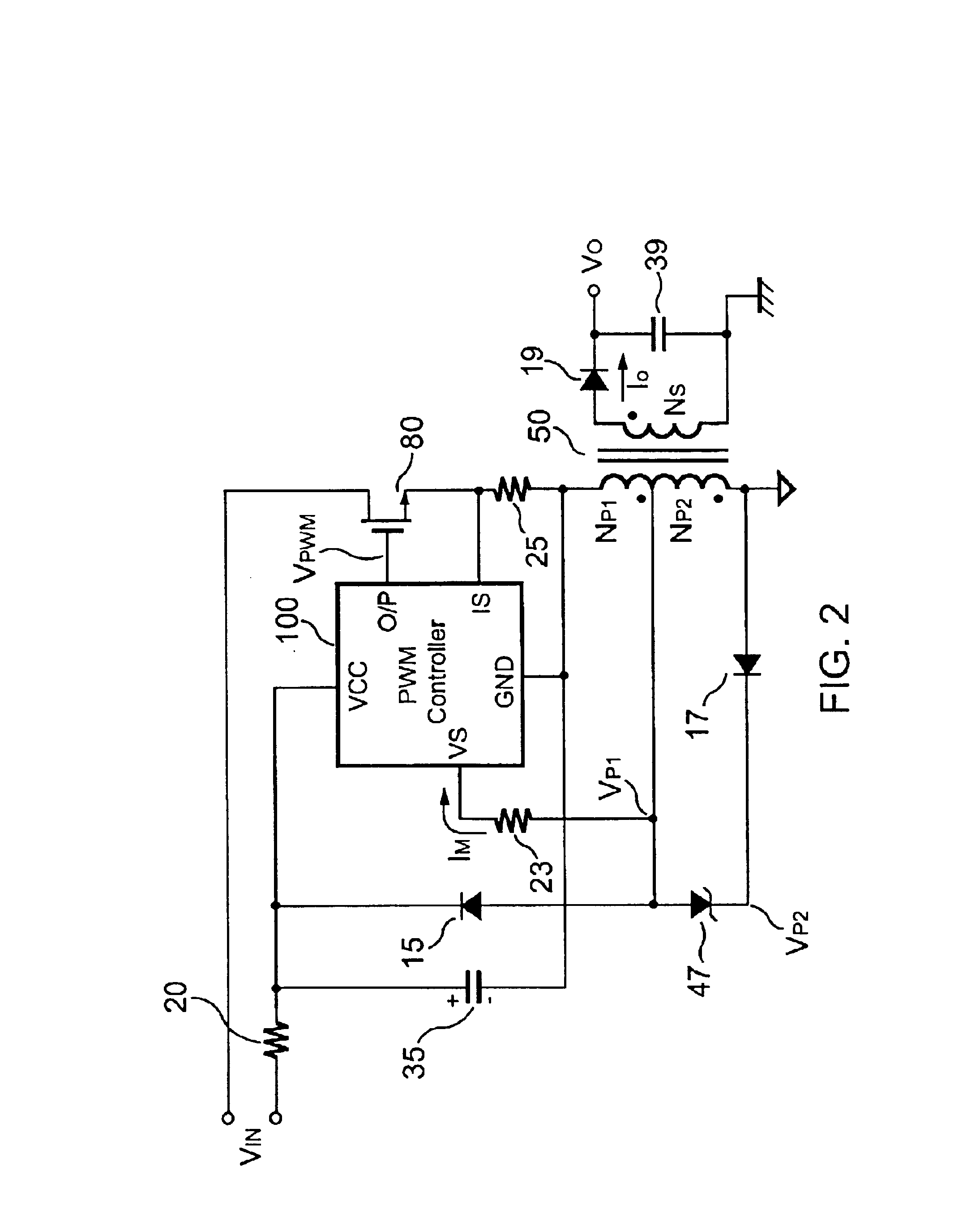
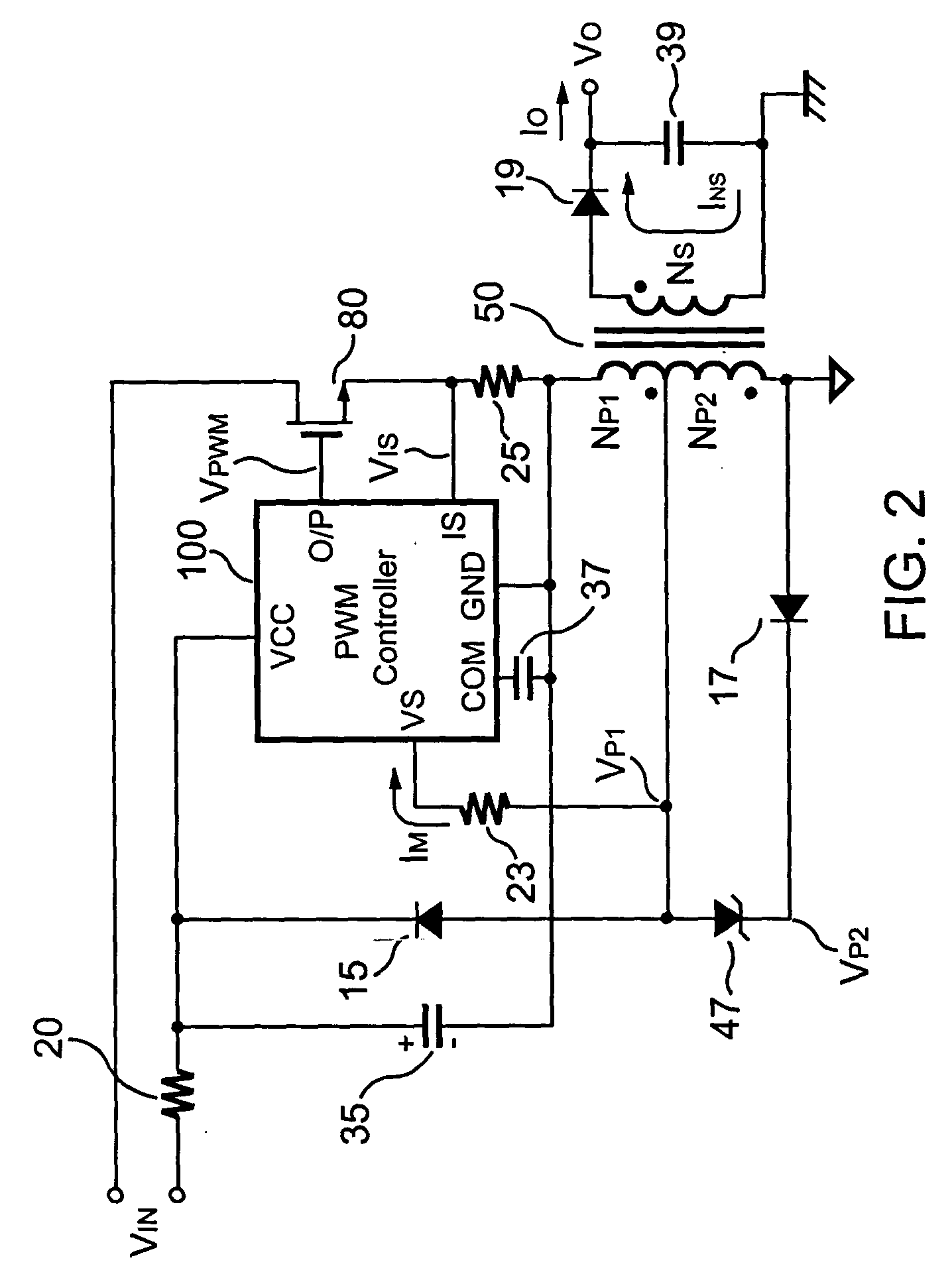
Flyback power converter having a constant voltage and a constant current output under primary-side PWM control
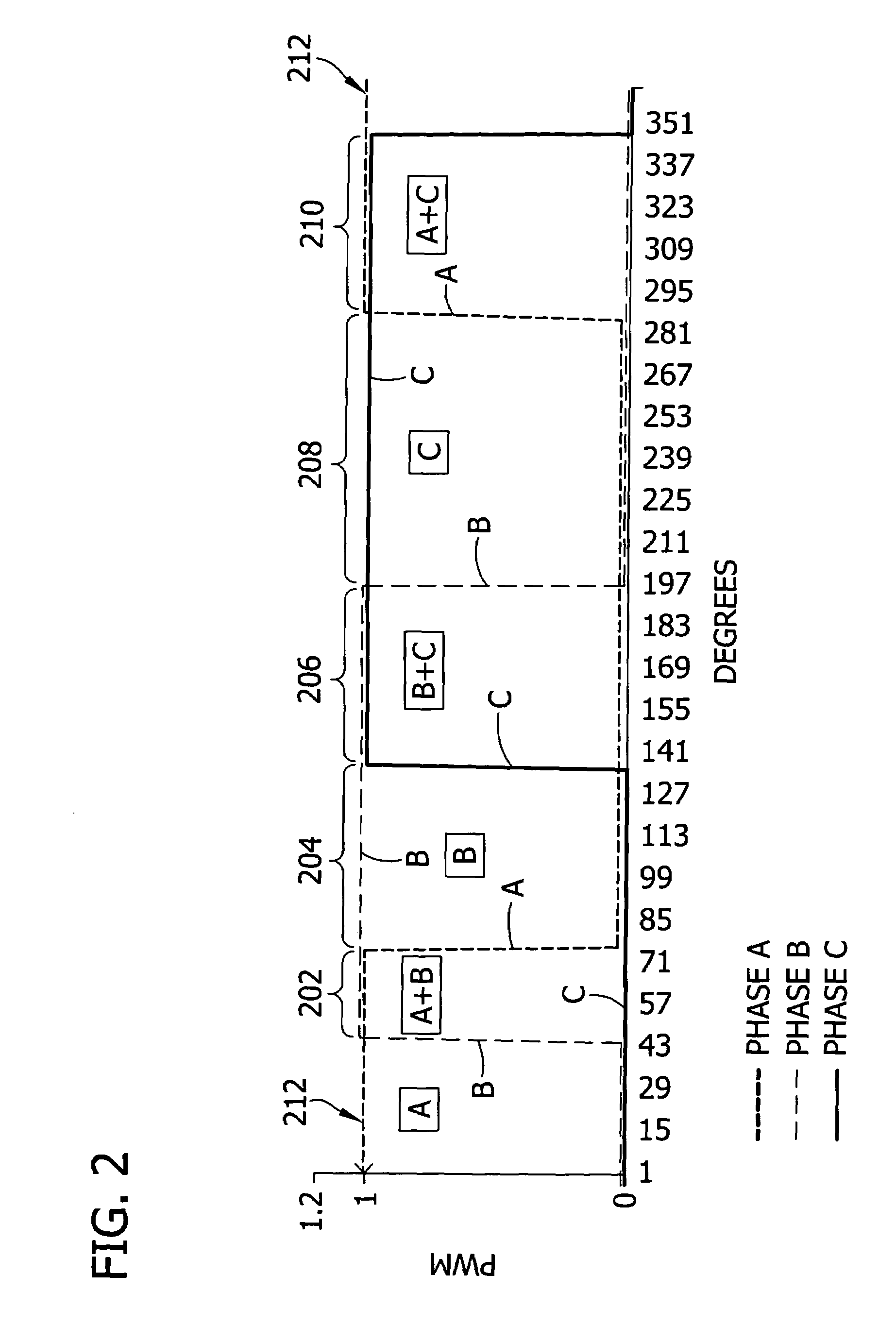
InactiveUS6862194B2Accurate supervisionSmall sizeAc-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConductor CoilPwm signals
A primary-side flyback power converter supplies a constant voltage and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, the power converter includes a PWM controller. The PWM controller generates a PWM signal to control a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage detected from the first primary winding of the power supply transformer. To reduce power consumption, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller. The flyback voltage is sampled following a delay time to reduce interference from the inductance leakage of the transformer. To generate a more accurate DC output voltage, a bias current is pulled from the detection input to form a voltage drop across a detection resistor for compensating for the voltage drop of the output rectifying diode.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
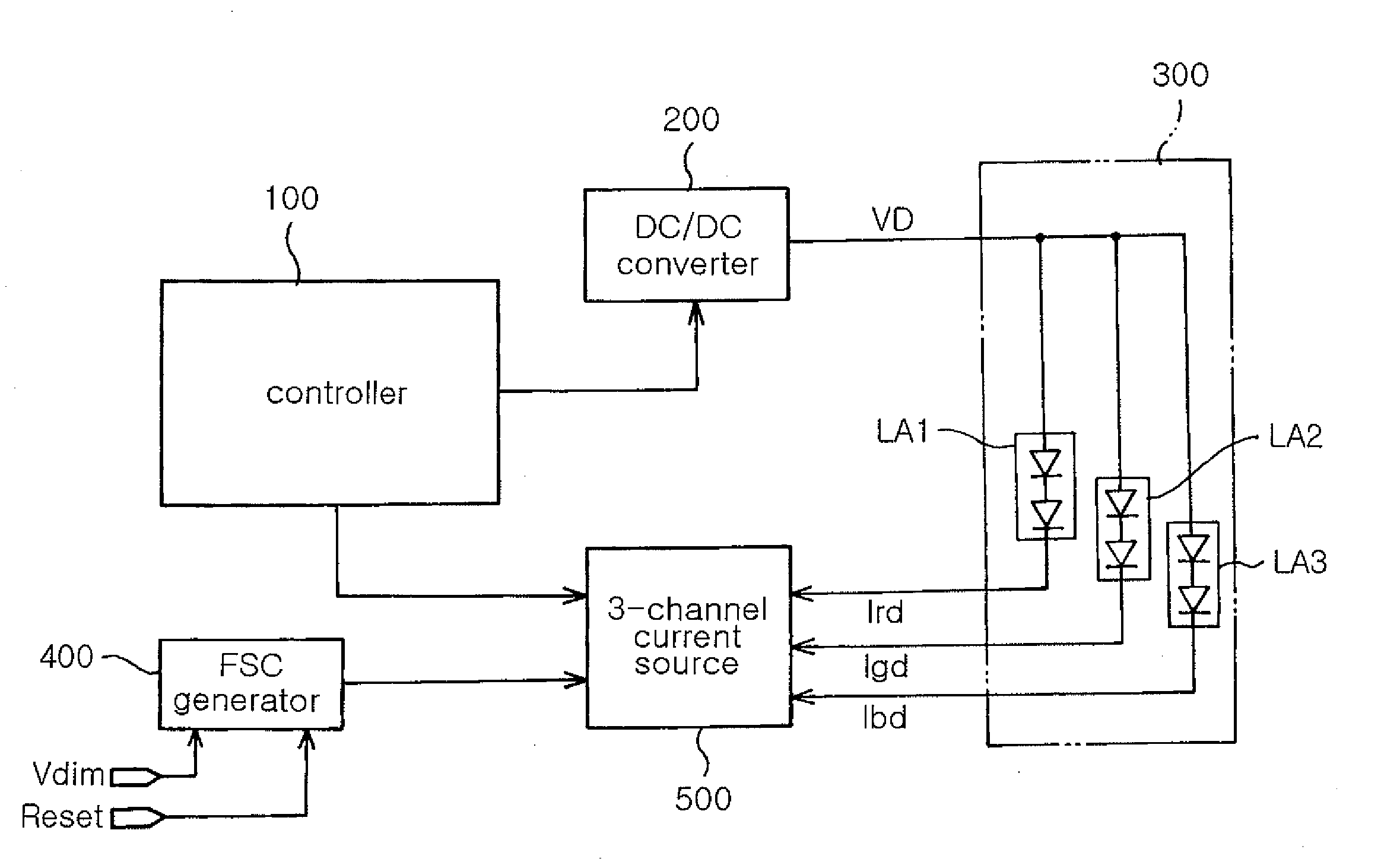
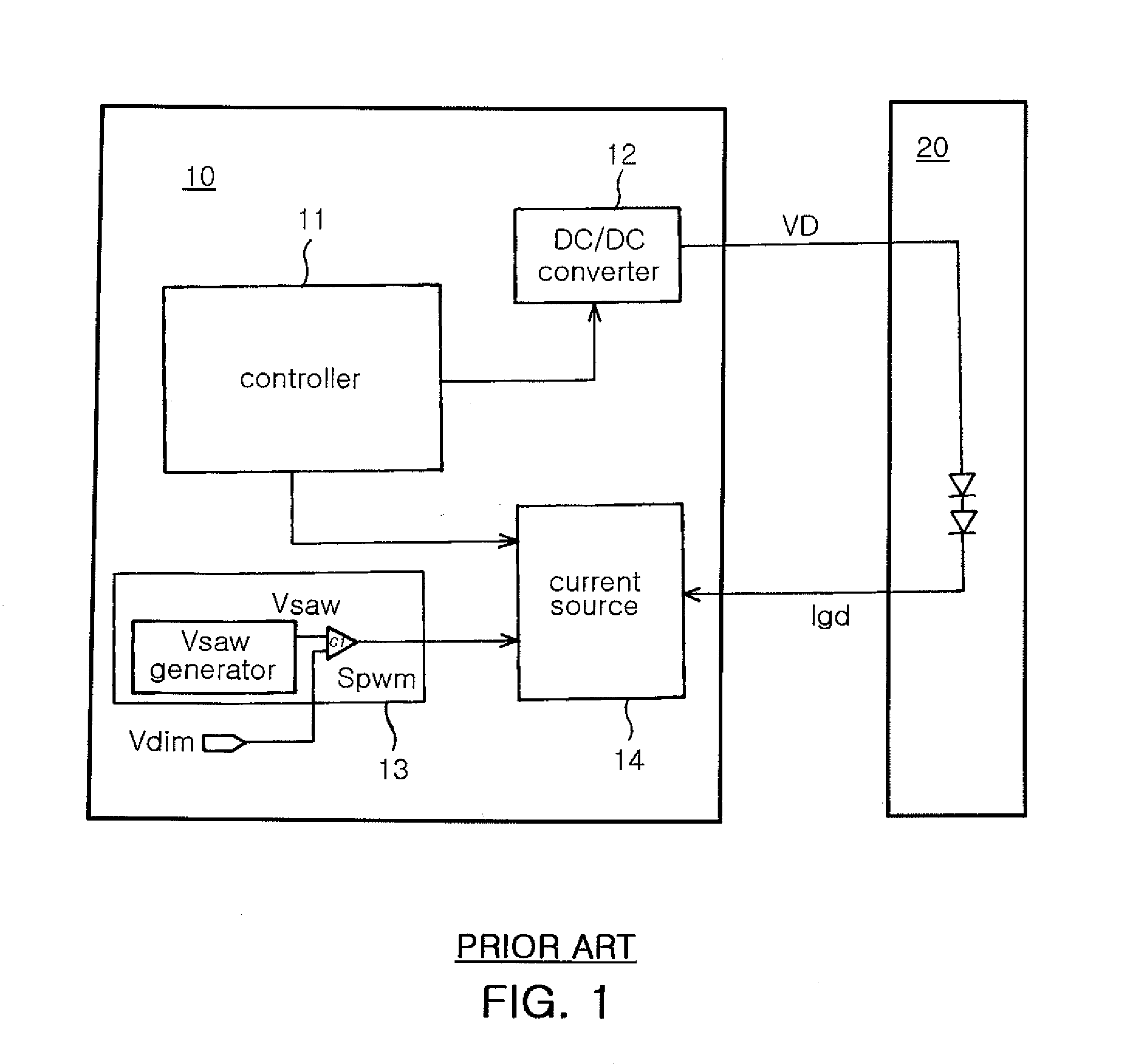
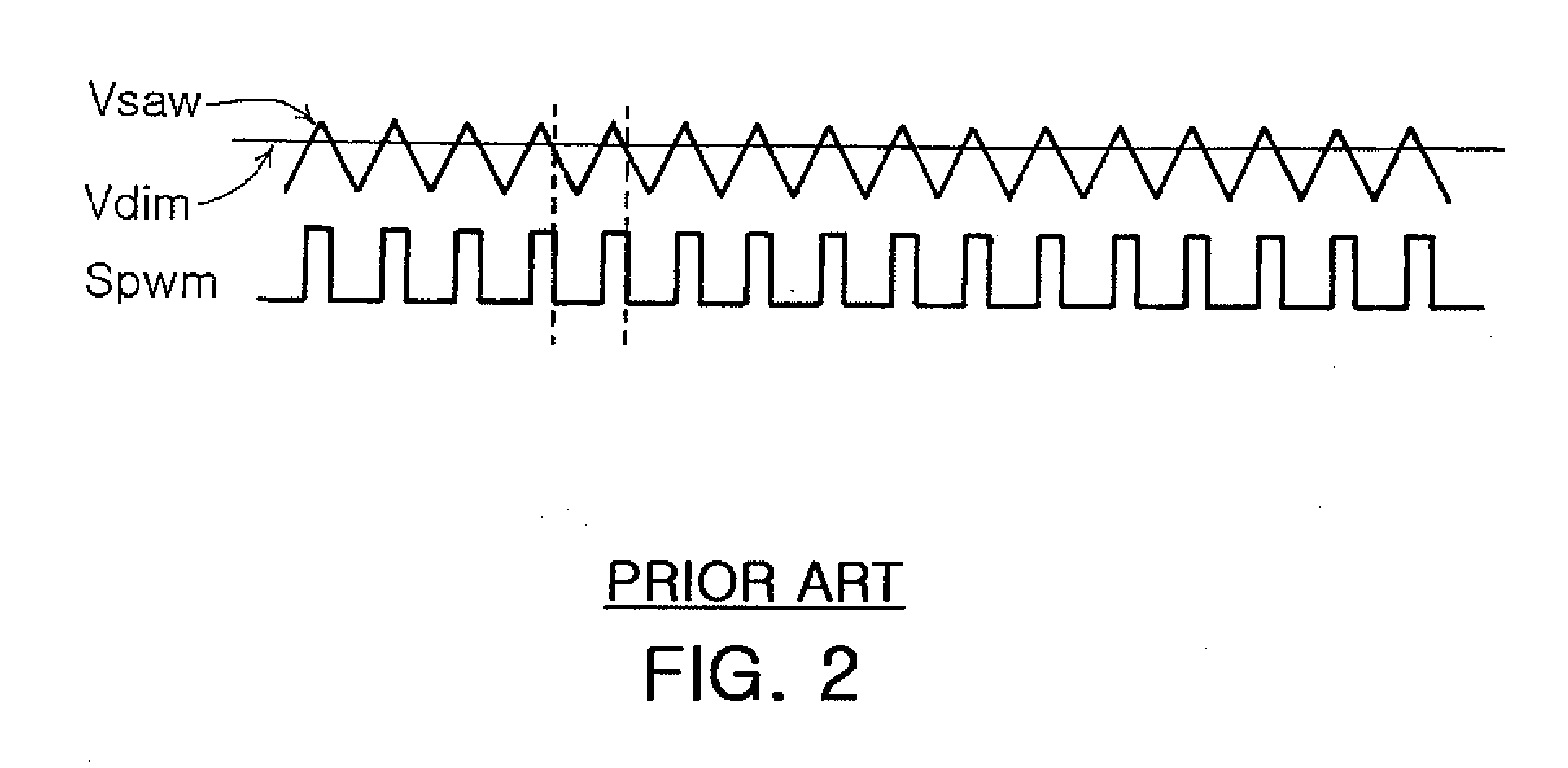
Field sequential color mode liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20070182699A1Improve luminous efficiencyReduce color distortionElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesDriving currentLiquid-crystal display
In an FSC mode LCD, a controller operates in response to an external adjustment, and a DC / DC converter converts a battery voltage into a driving voltage under control of the controller. A color LED backlight includes first, second and third color LED arrays connected in parallel, which are operated by the driving voltage. An FSC generator generates first, second and third color PWM signals according to an internal sawtooth voltage and a dimming voltage. A 3-channel current source generates first, second and third driving currents under control of the controller, and on / off switches paths of the first, second and third driving currents flowing through the first, second and third color LED arrays according to the first, second and third color PWM signals generated from the FSC generator, thereby adjusting luminance of the first, second and third color LED arrays of the color LED backlight.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching
InactiveUS6903536B2Reduce switching noiseIncrease the pulse widthEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDead timeSwitching signal
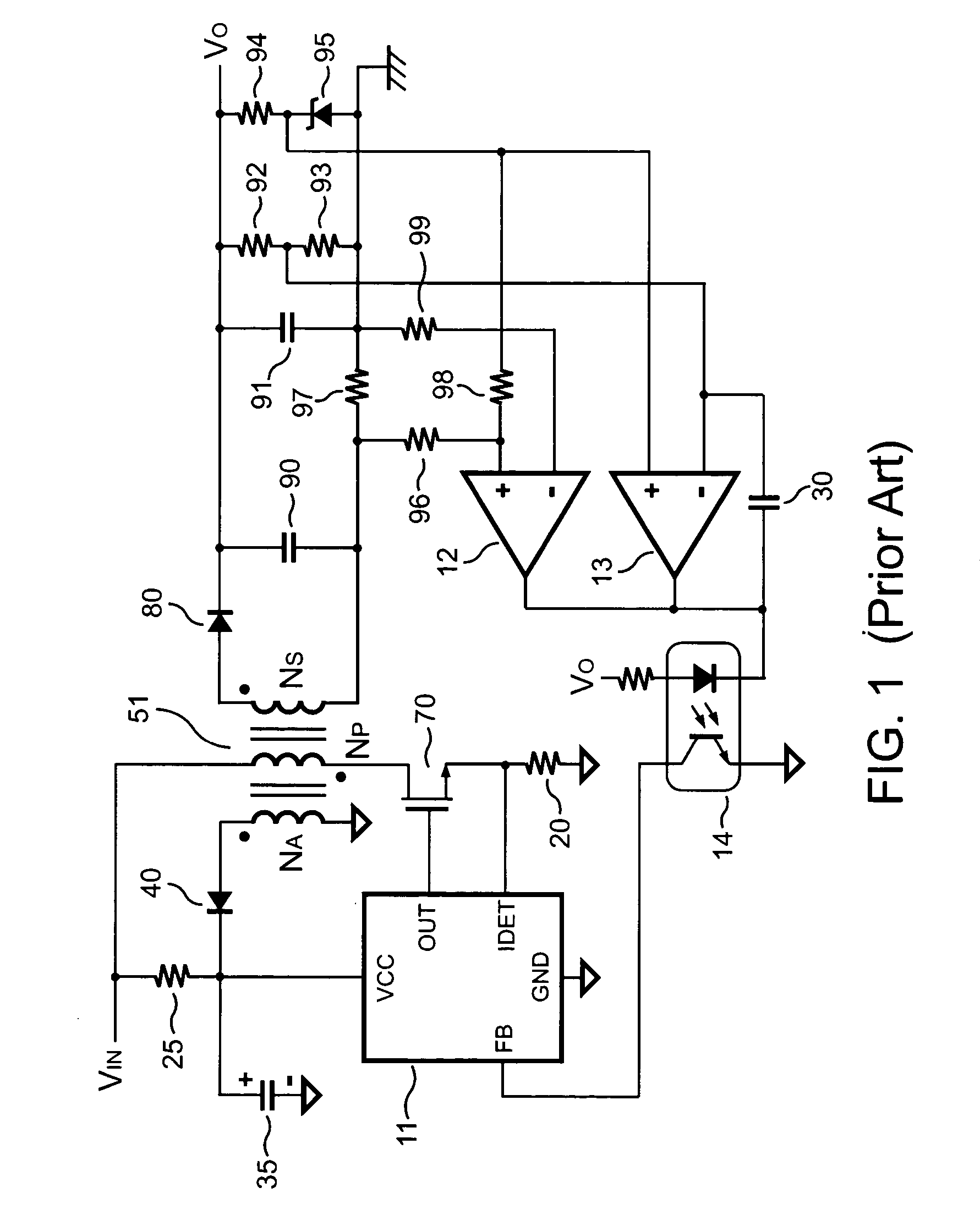
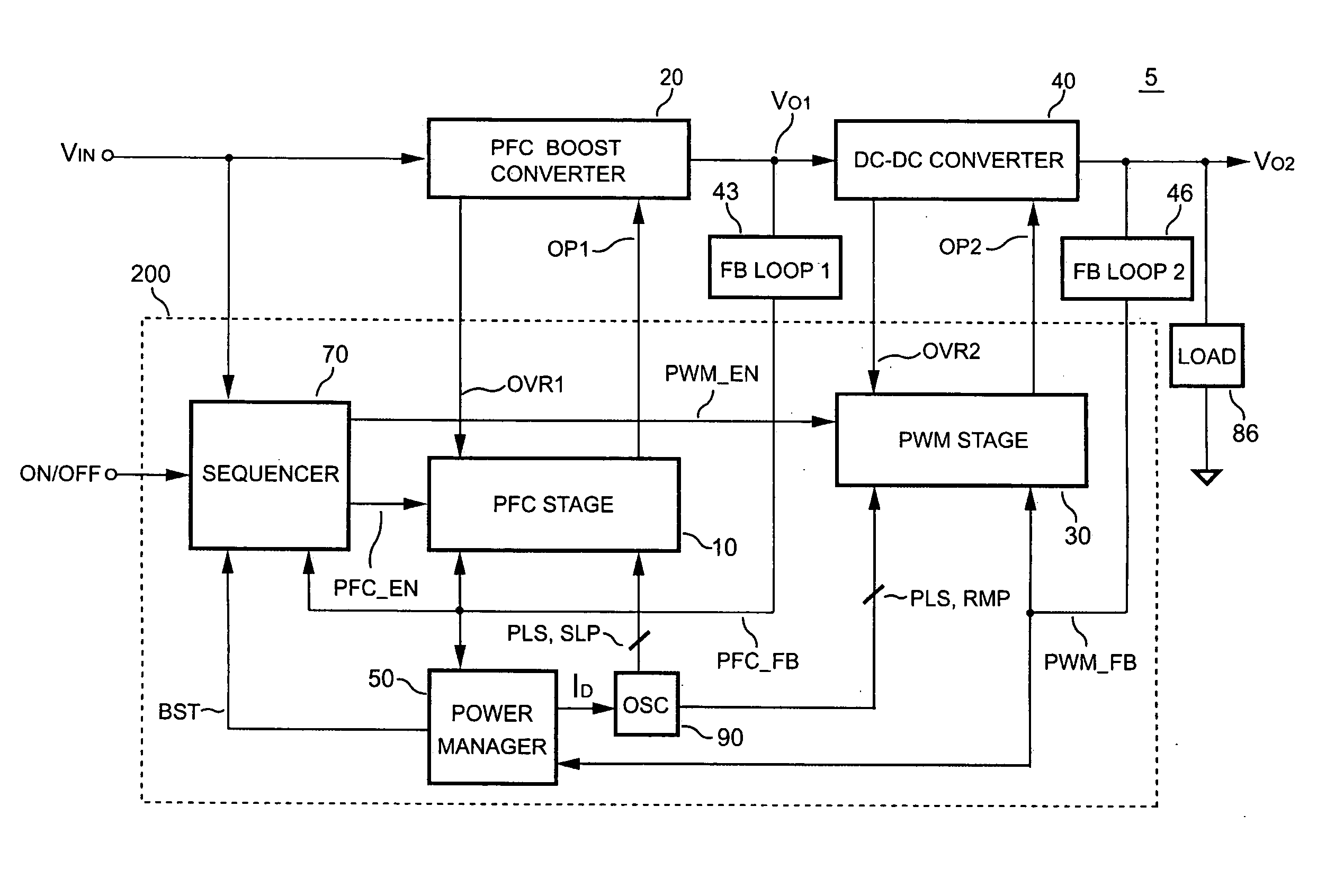
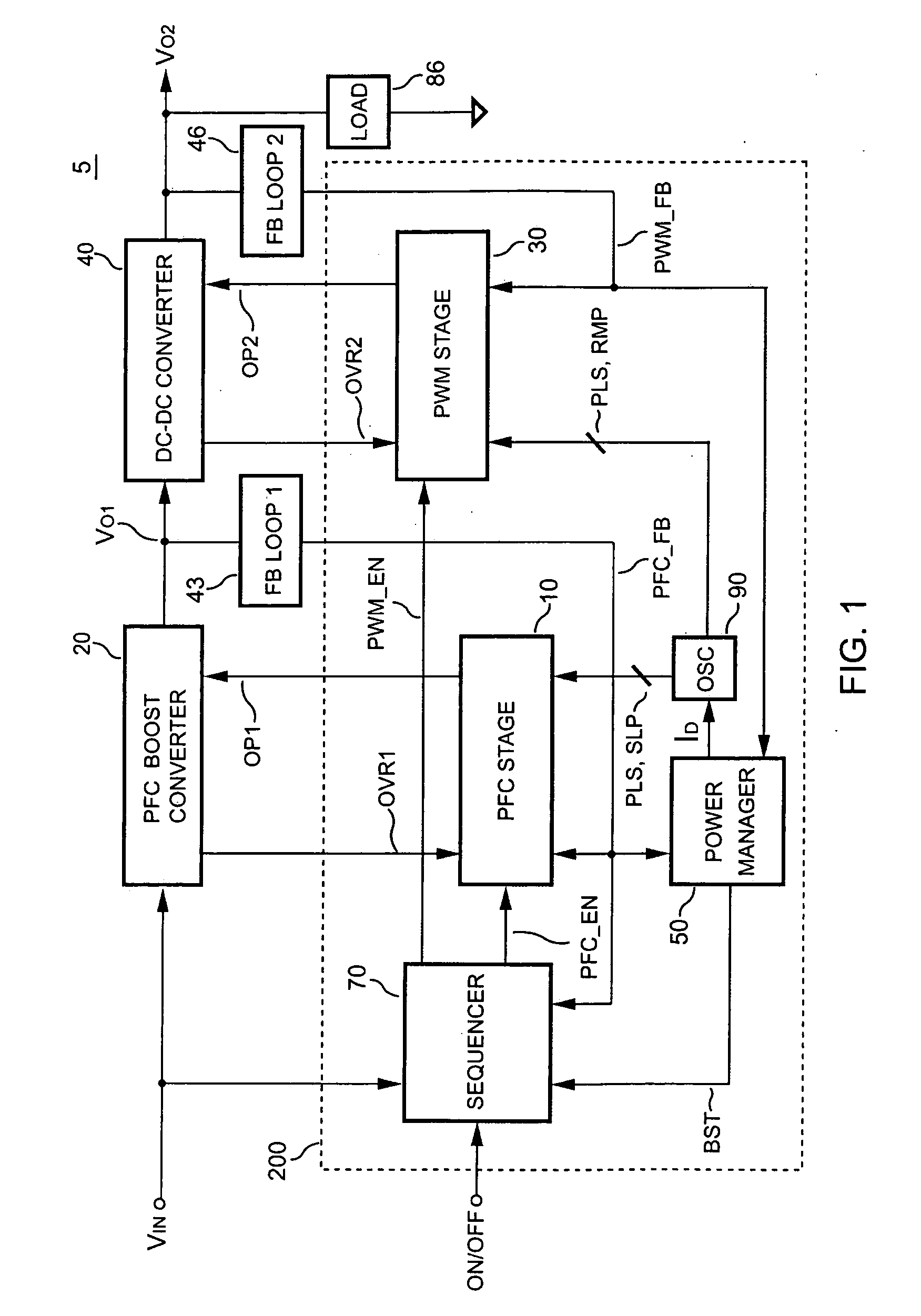
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
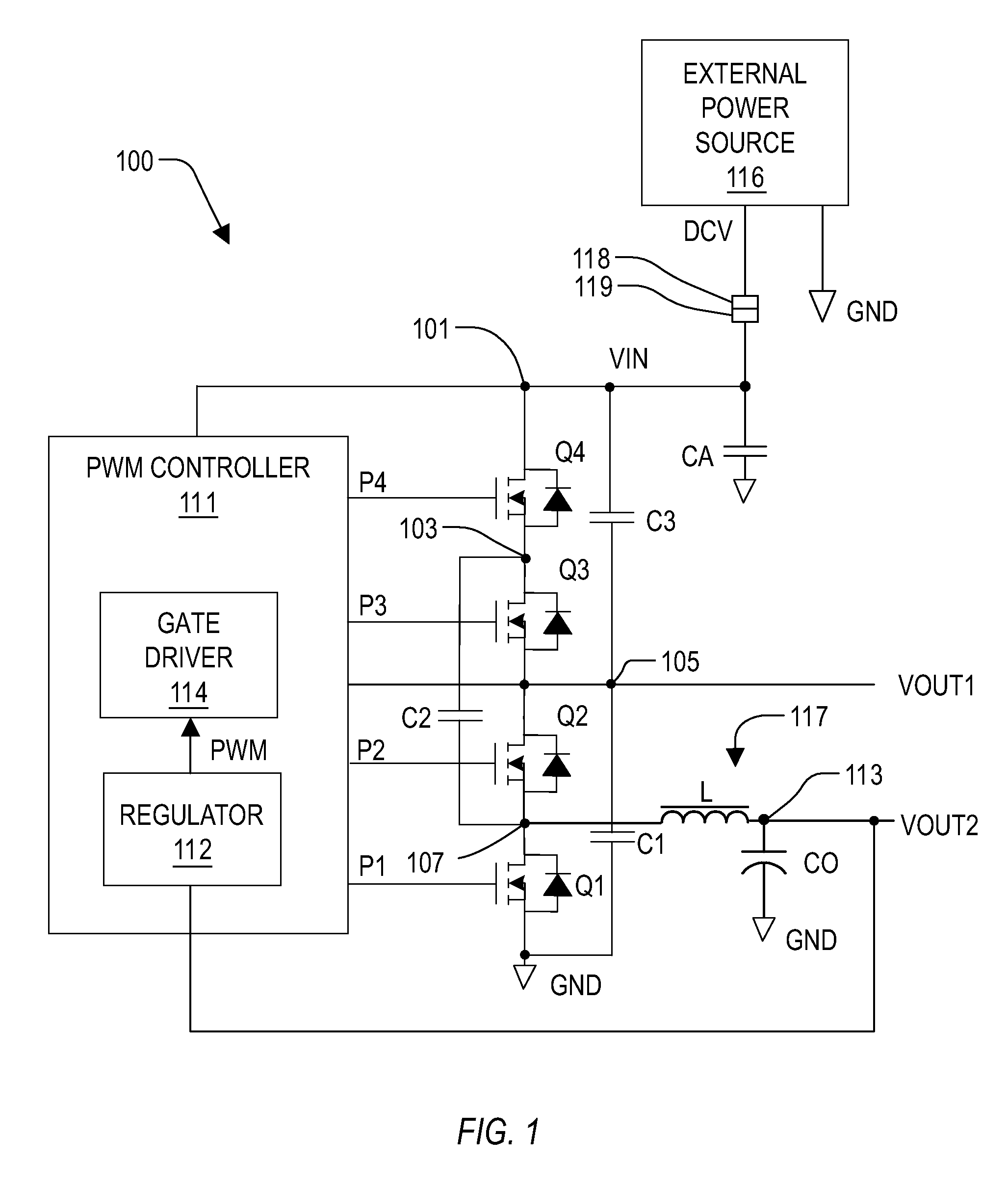
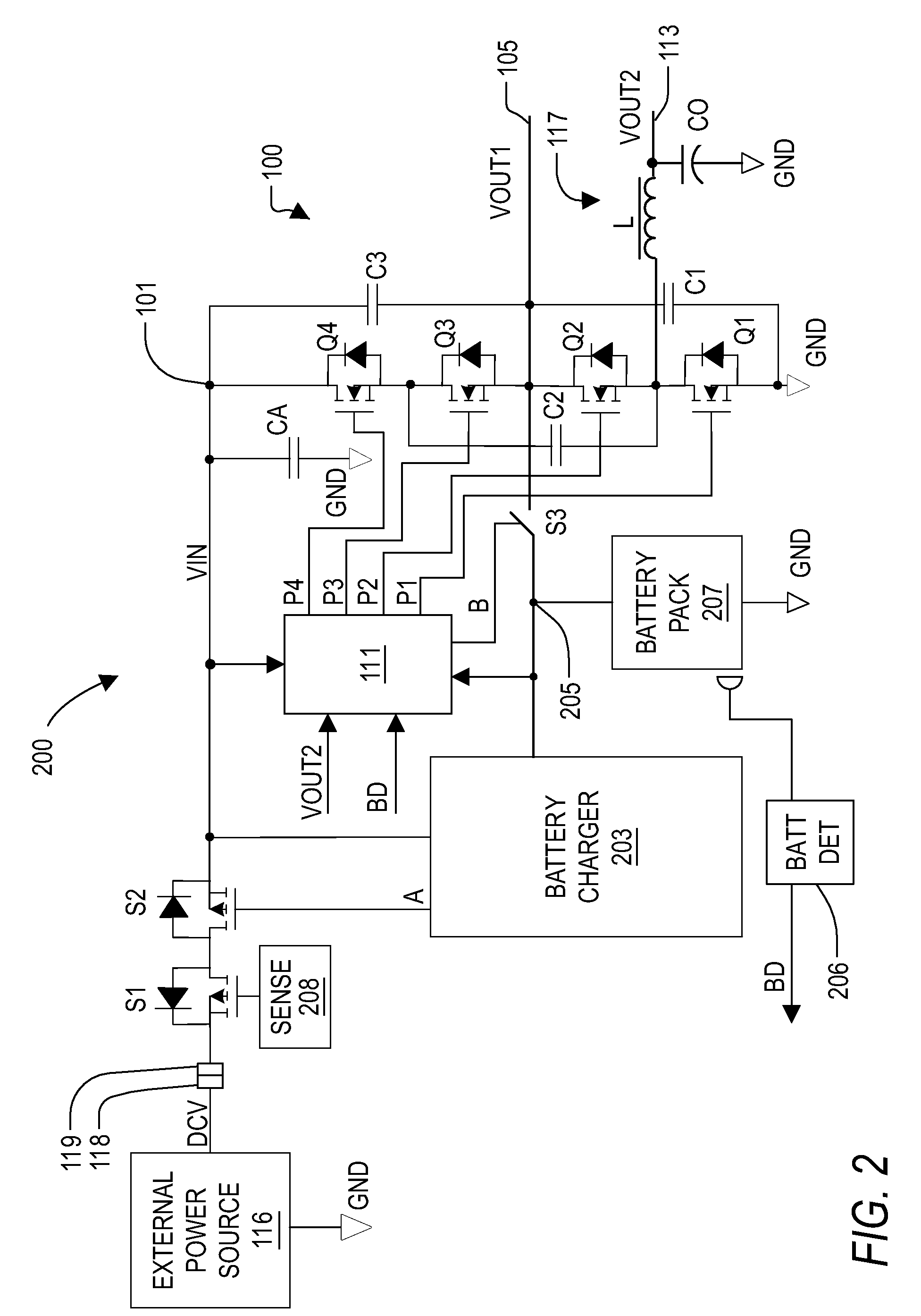
Voltage converter with combined capacitive voltage divider, buck converter and battery charger
InactiveUS20090033293A1Batteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionĆuk converterCapacitive voltage divider
A voltage converter including a capacitive voltage divider combined with a buck converter and battery charger. The converter includes four capacitors, a switch circuit, an inductor and a controller. The capacitors form a capacitor loop between an input node and a reference node and include a fly capacitor controlled by the switch circuit, which is controlled by a PWM signal to half the input voltage to provide a first output voltage on a first output node, and to convert the first output voltage to the second output voltage via the inductor. The controller controls the PWM signal to regulate the second output voltage, and provides a voltage control signal to control the input voltage to maintain the first output node between a predetermined minimum and maximum battery voltage levels. A battery charge path is coupled to the reference node and battery charge mode depends upon the battery voltage.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
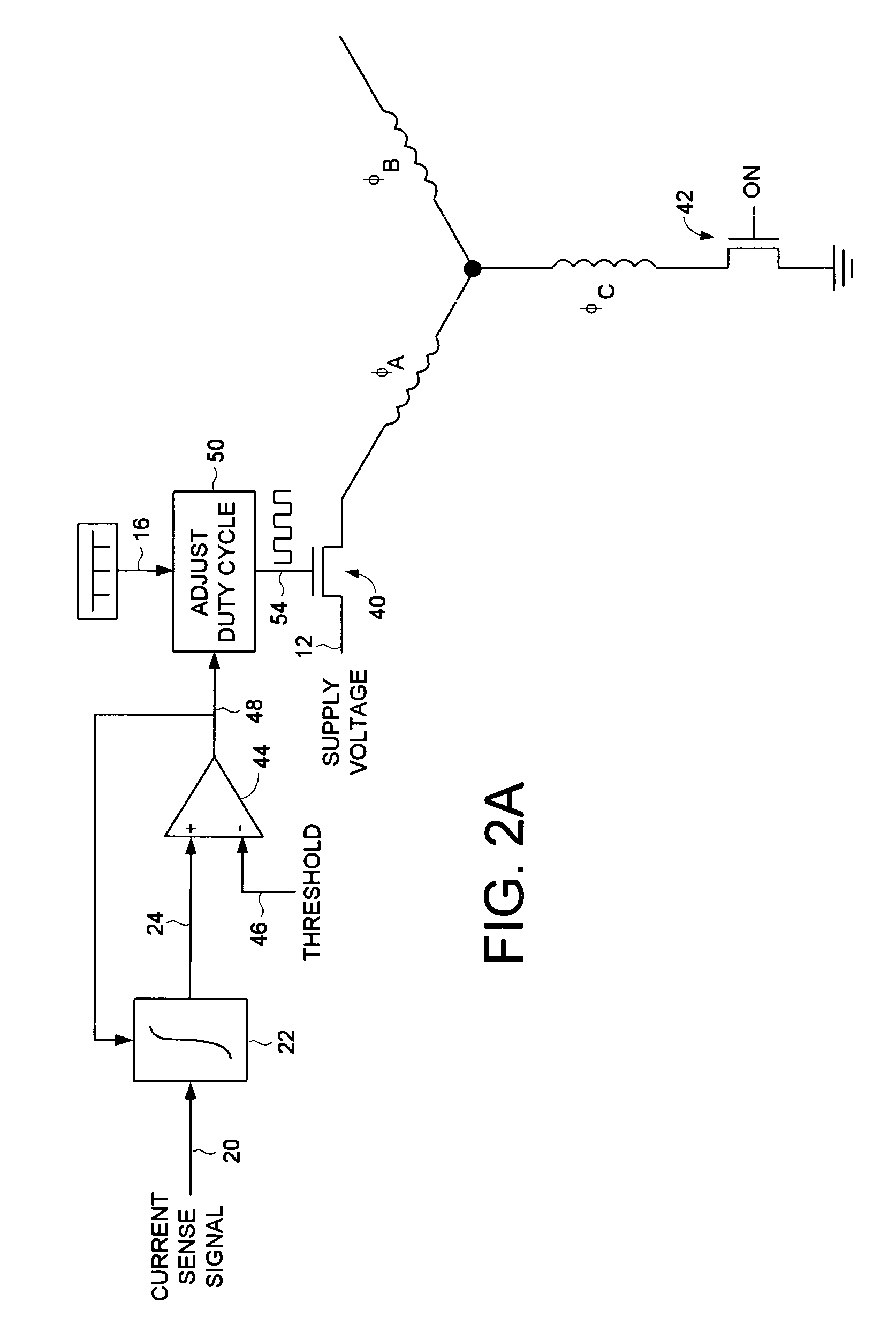
Decreasing spin up time in a disk drive by adjusting a duty cycle of a spindle motor PWM signal to maintain constant average input current
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a spindle motor for rotating a disk, wherein the current applied to the spindle motor is controlled by adjusting a duty cycle of a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal. A current sensor generates a current sense signal representing a current flowing from a supply voltage. The current sense signal is integrated to generate an integration signal. The integration signal is compared to a threshold, and the result of the comparison is used to adjust the duty cycle of the PWM signal. In this manner the disk drive draws essentially constant average input current from the supply voltage which decreases the spin up time of the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
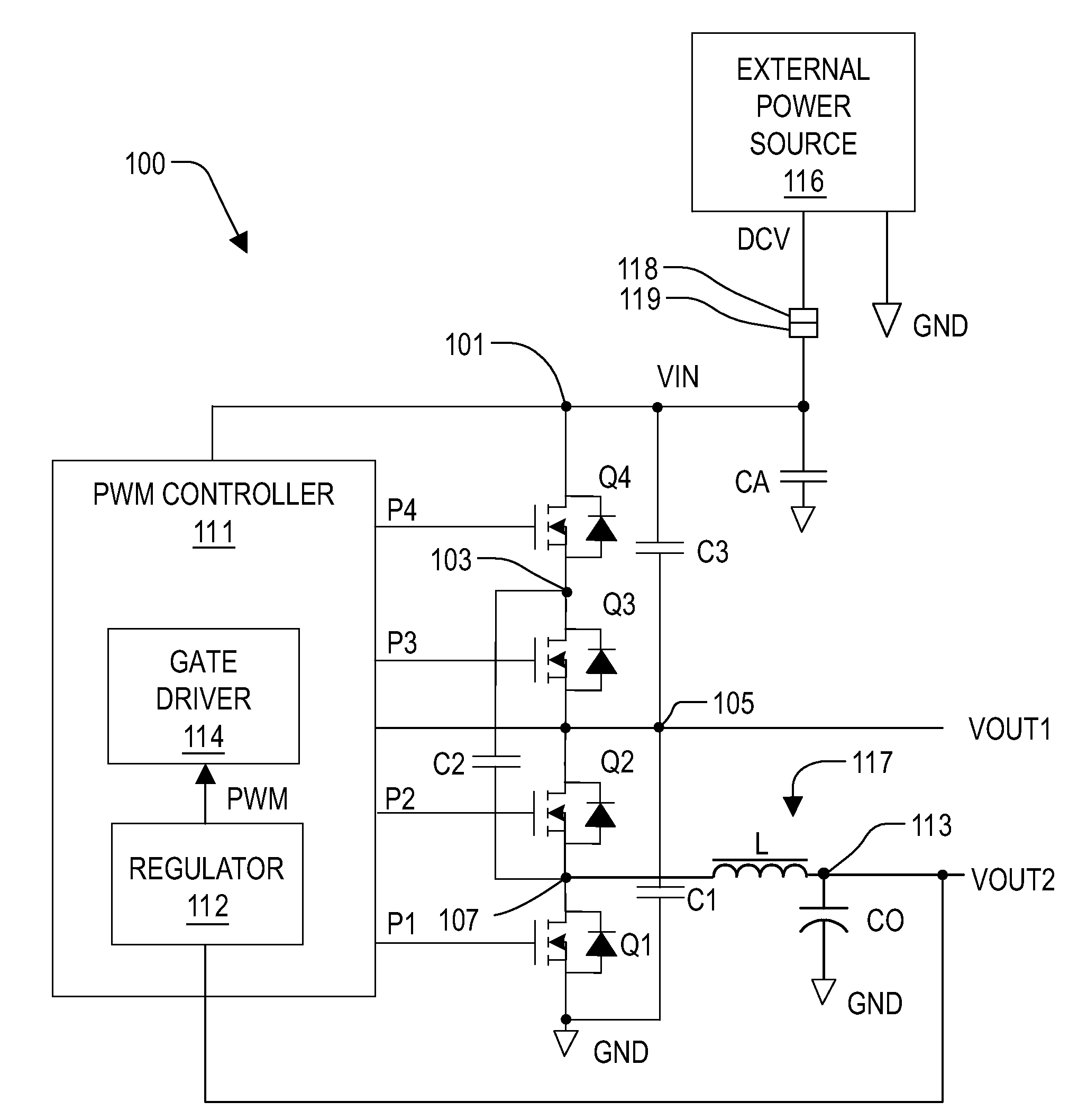
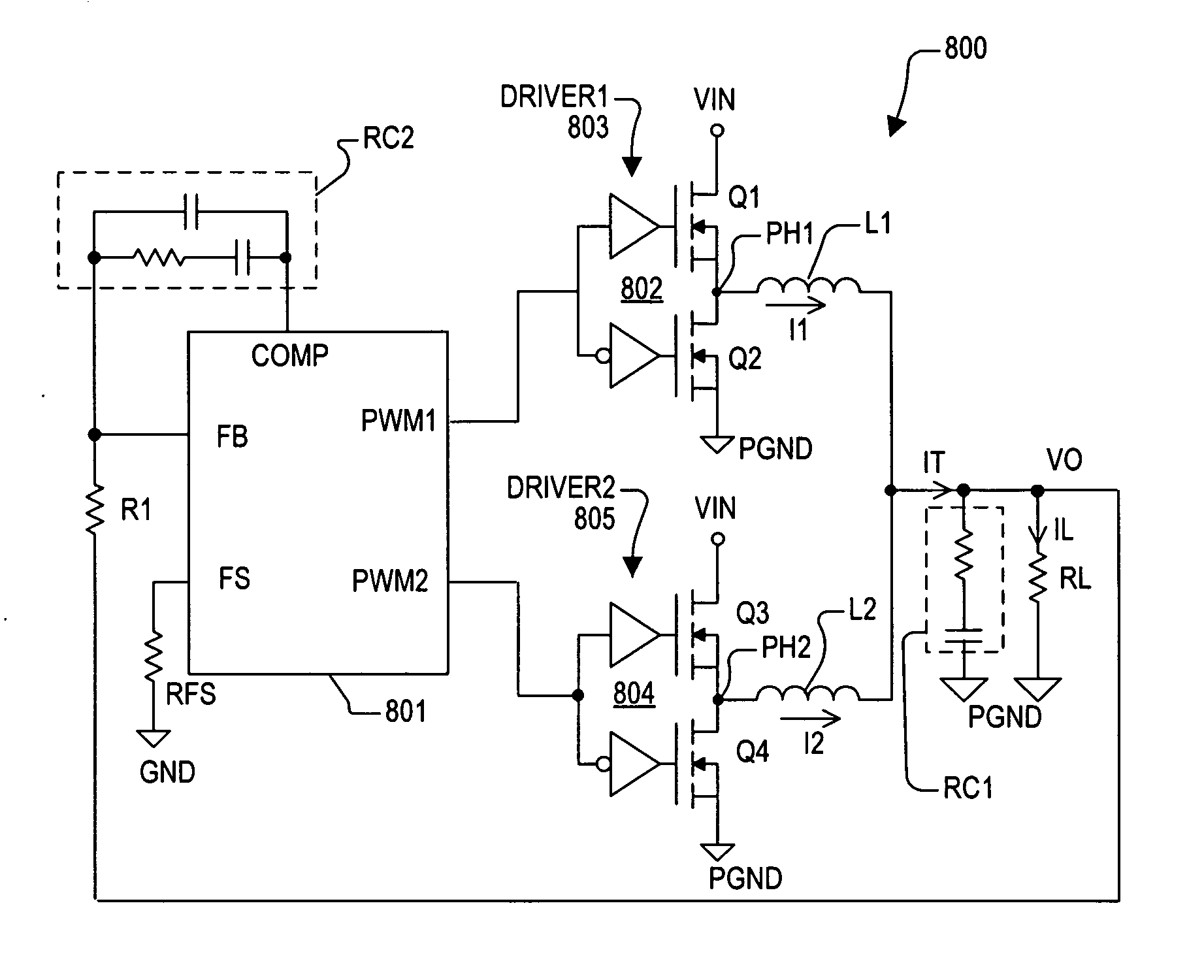
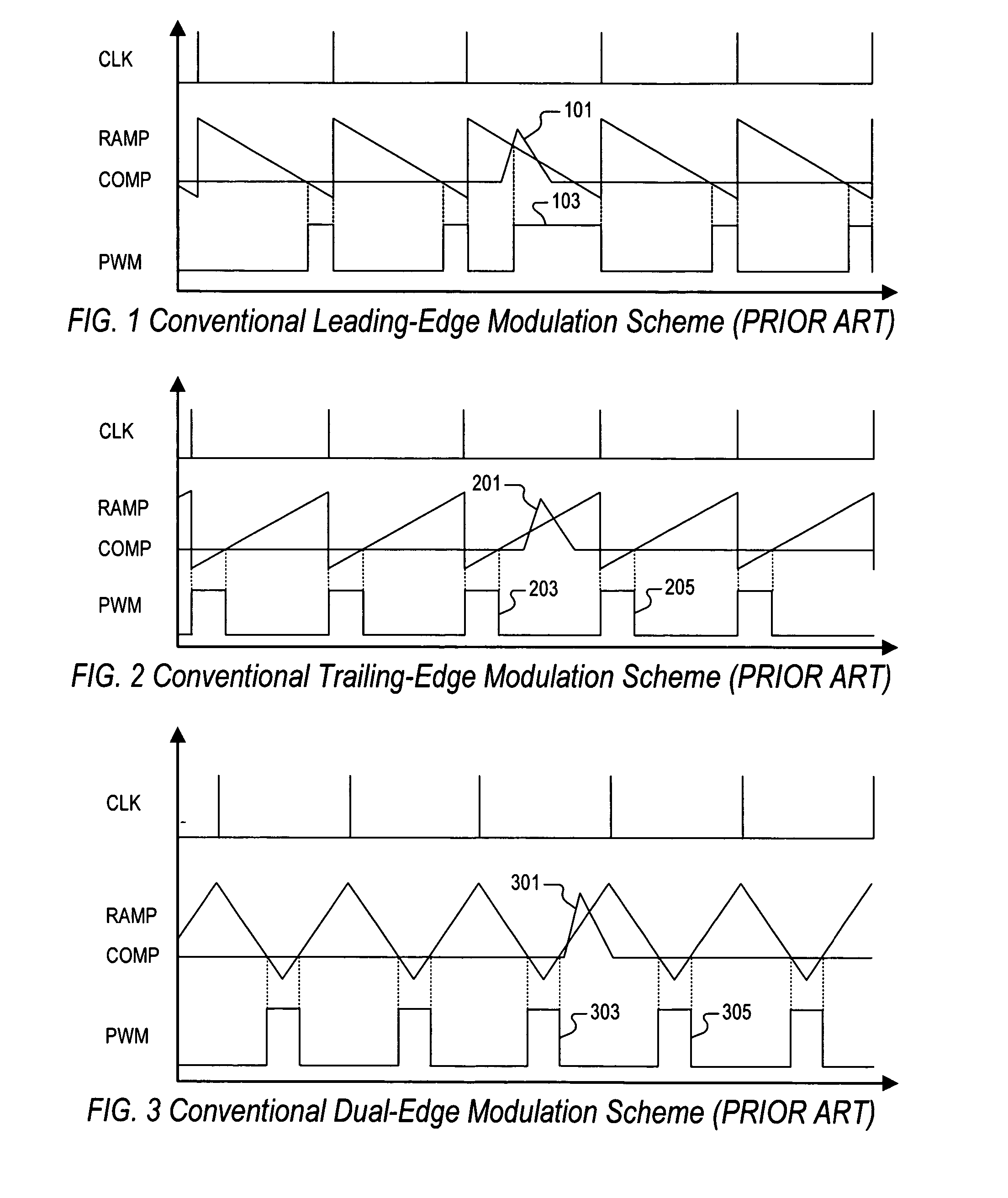
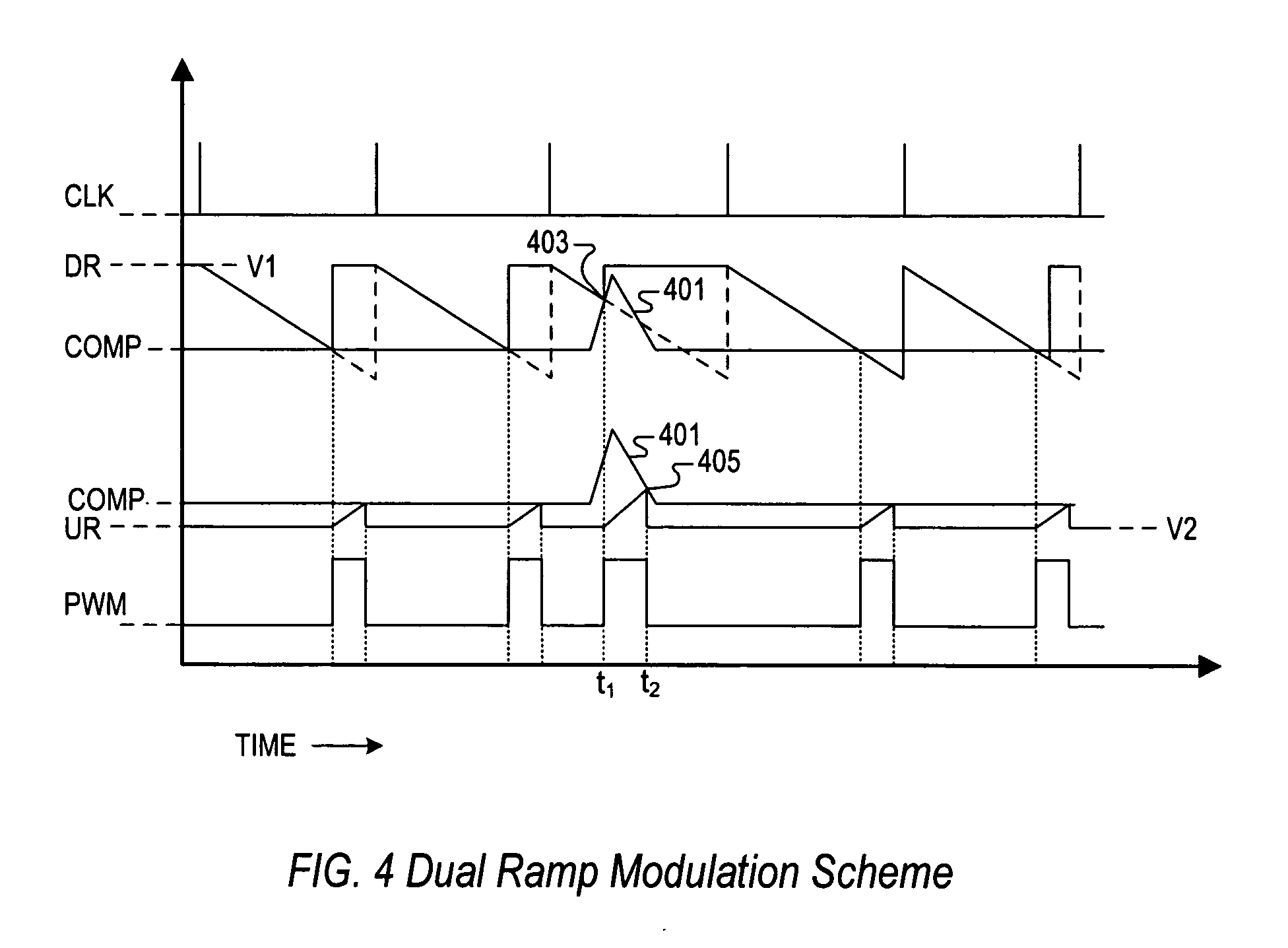
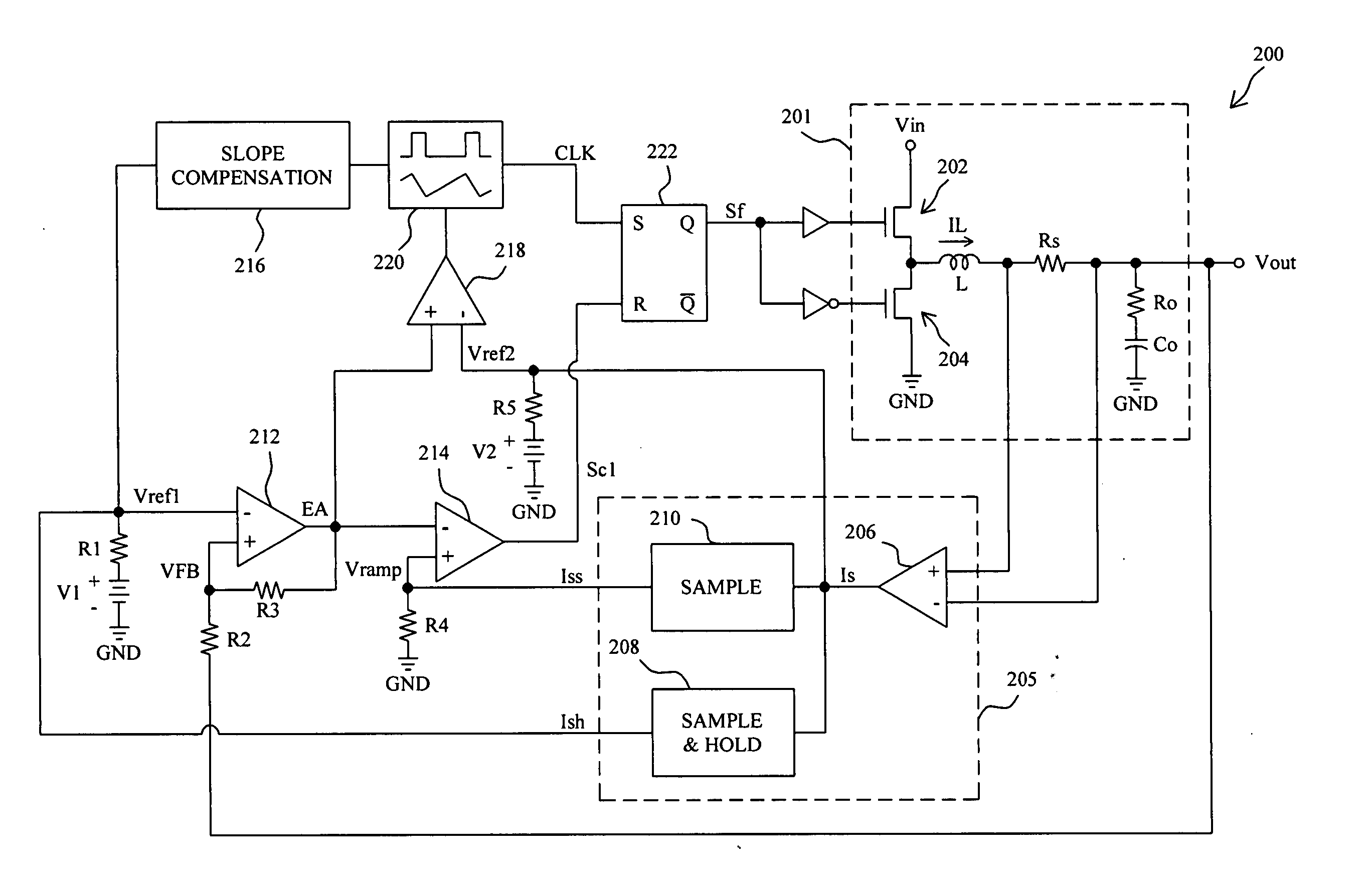
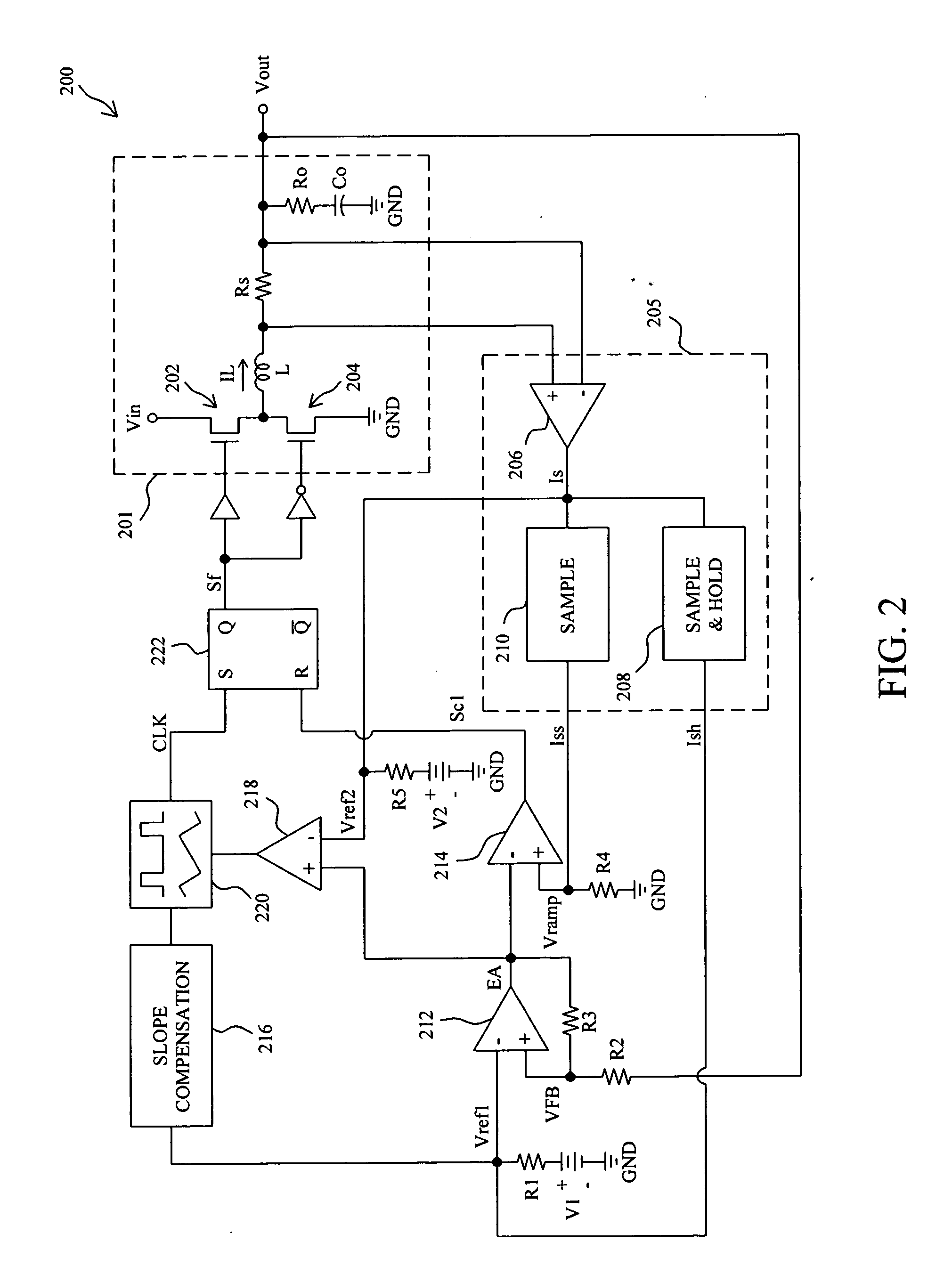
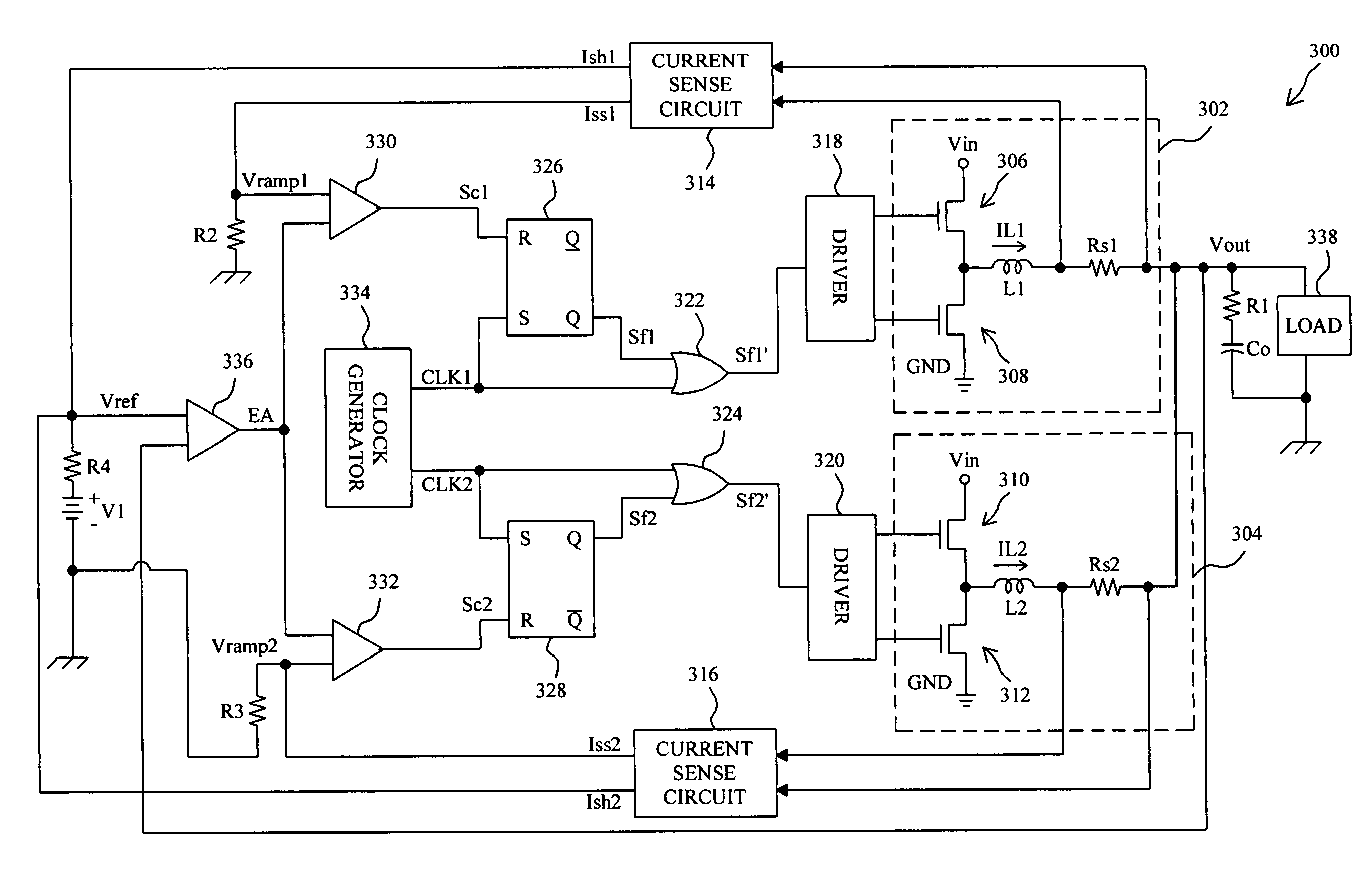
PWM controller with dual-edge modulation using dual ramps
ActiveUS20070013356A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLeading edgePulse control
A dual-edge modulation controller including first and second ramp circuits, first and second comparators, an error amplifier and pulse control logic. The first ramp circuit provides a leading-edge ramp synchronous with a clock. The error amplifier compares a feedback signal with a reference and provides a compensation signal. The first comparator compares the leading-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a set signal. The second ramp circuit provides a trailing-edge ramp that begins ramping when the set signal is asserted. The second comparator compares the trailing-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a reset signal. The pulse control logic asserts a PWM signal when the set signal is asserted and de-asserts the PWM signal when the reset signal is asserted. The controller may control multiple phases with current balancing. The slew rate of the ramps may be adjusted based on the number of PWM signal asserted.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Fixed-frequency current mode converter and control method thereof
InactiveUS20060043943A1Rapid responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationInductorCurrent mode
A fixed-frequency current mode converter comprises a power stage to produce an inductor current and an output voltage, an error amplifier to generate an error signal from the difference between the output voltage and a reference voltage varied with the inductor current, a comparator to compare the error signal with a ramp signal varied with the inductor current to generate a comparison signal, and a PWM generator to generate a PWM signal in response to a fixed-frequency clock and the comparison signal to drive the power stage. A second comparator is further comprised to compare the error signal with a second reference voltage varied with the inductor current, and generates a second comparison signal to reset the clock when the error signal is lower than the second reference voltage.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
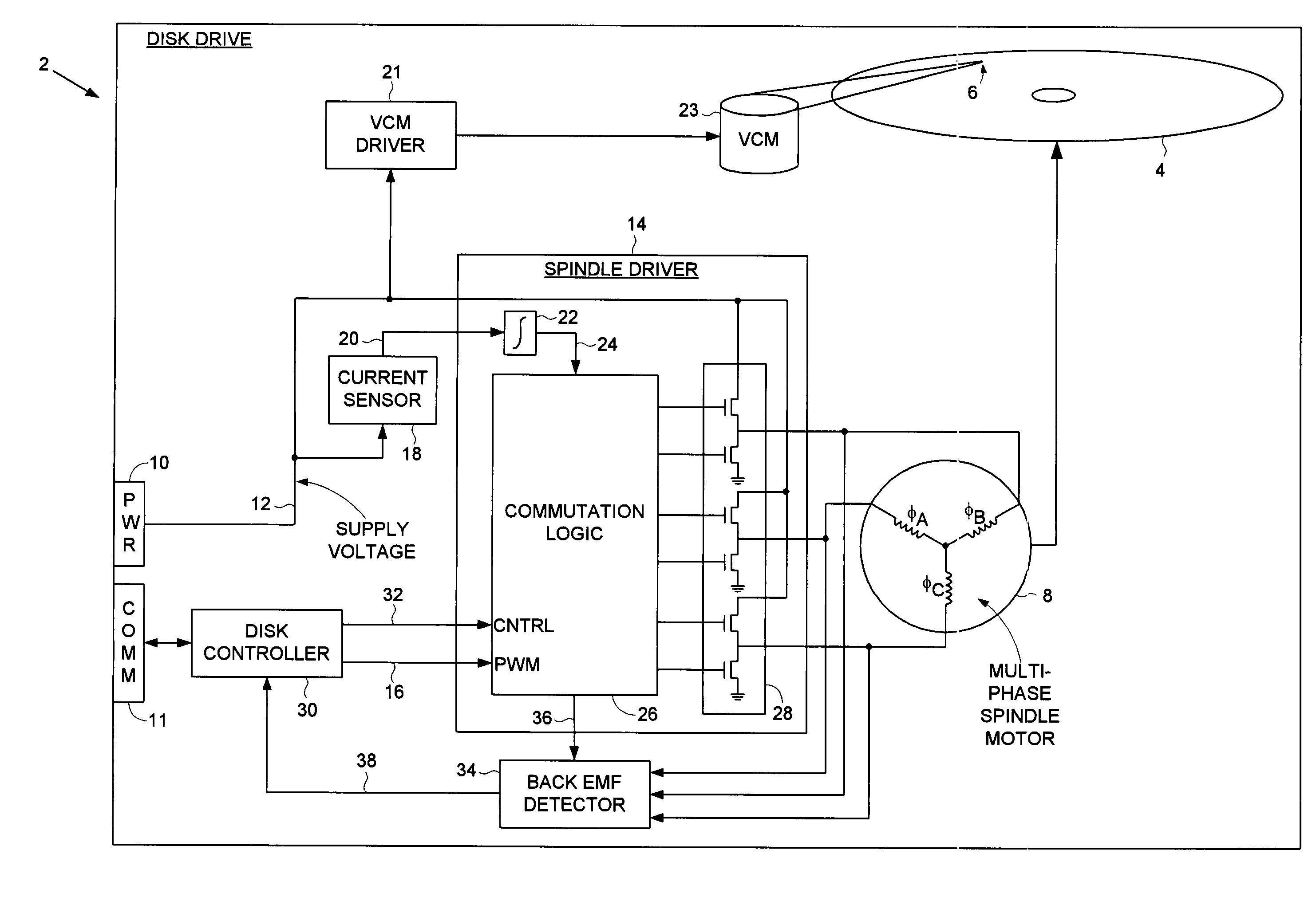
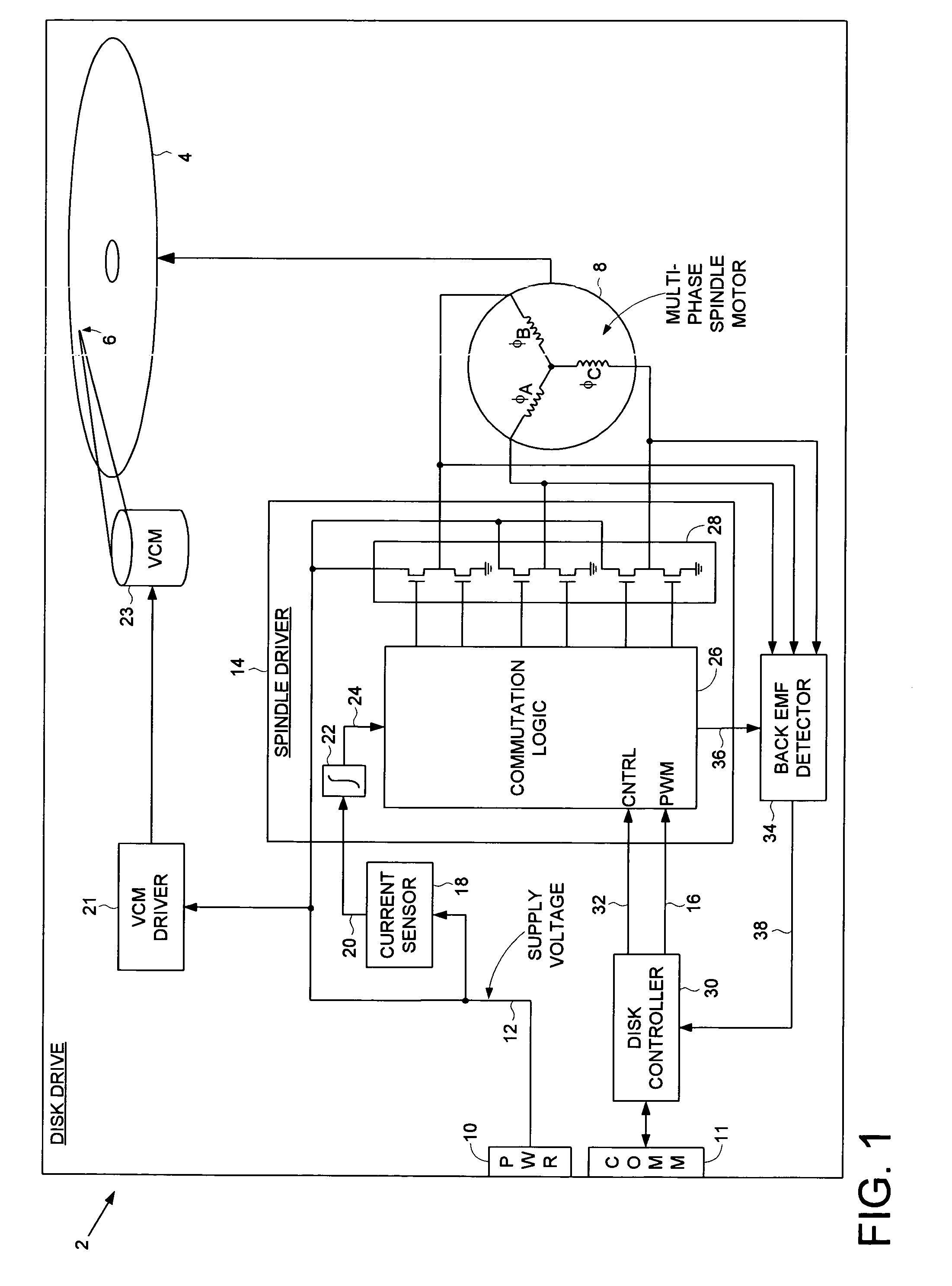
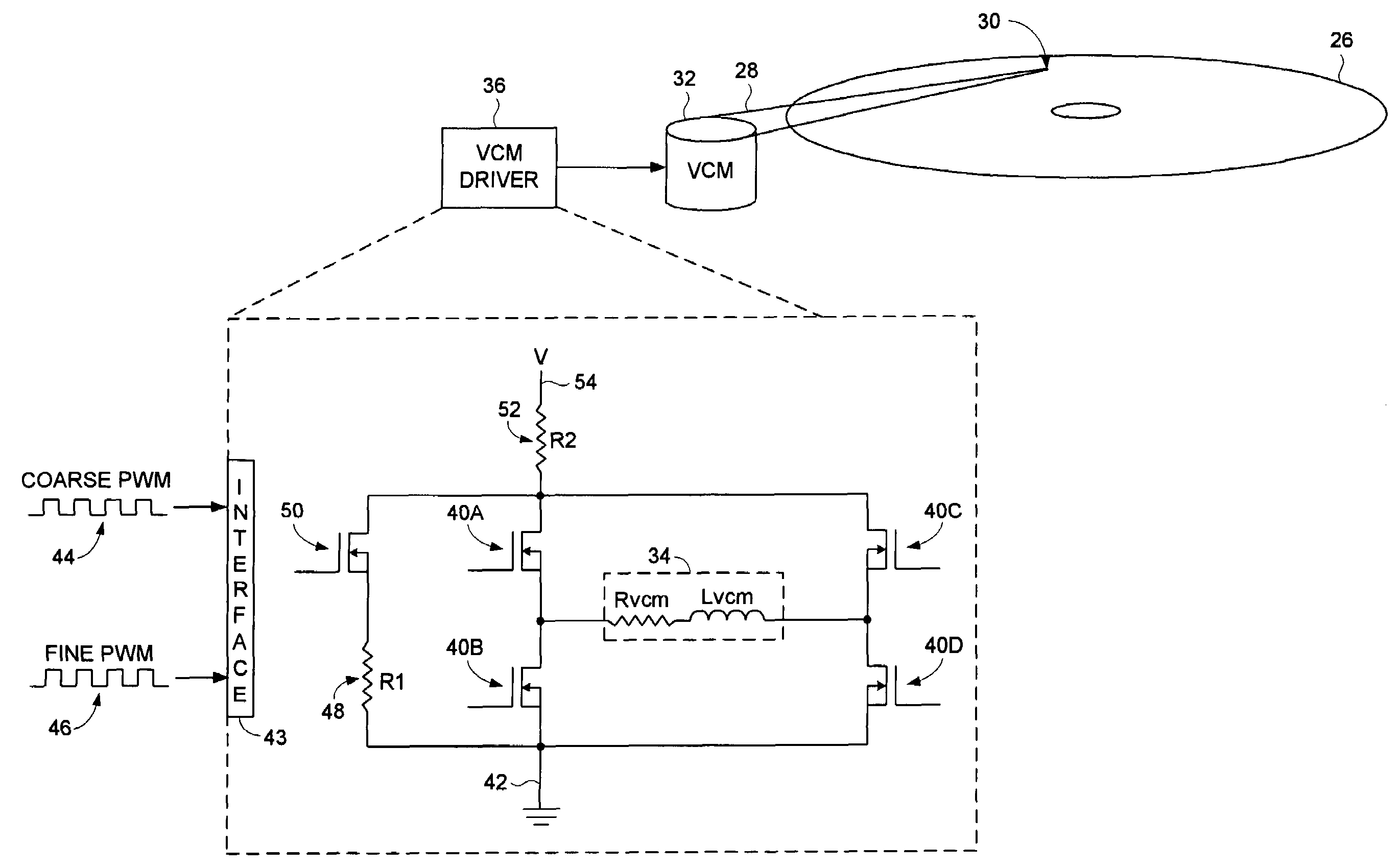
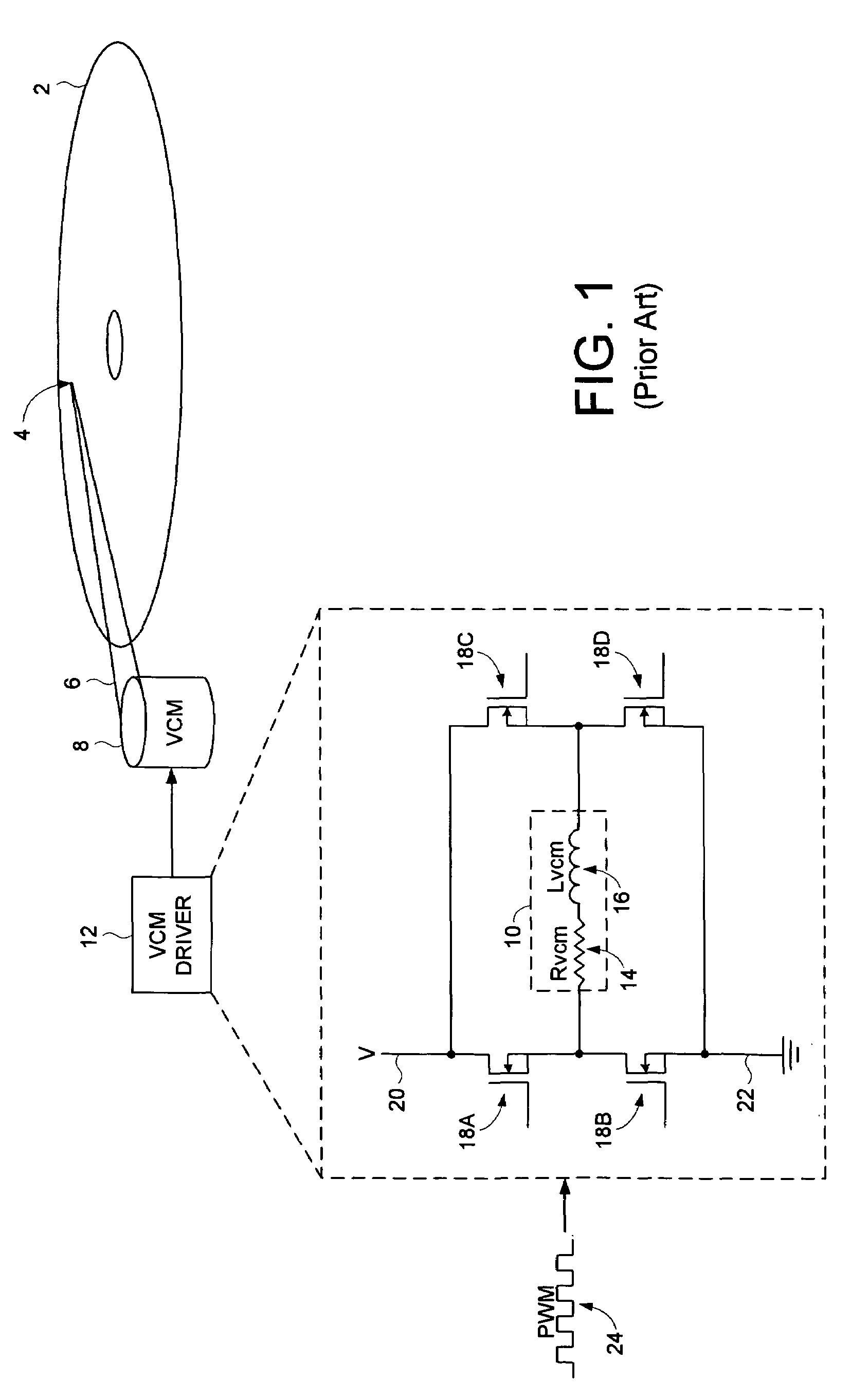
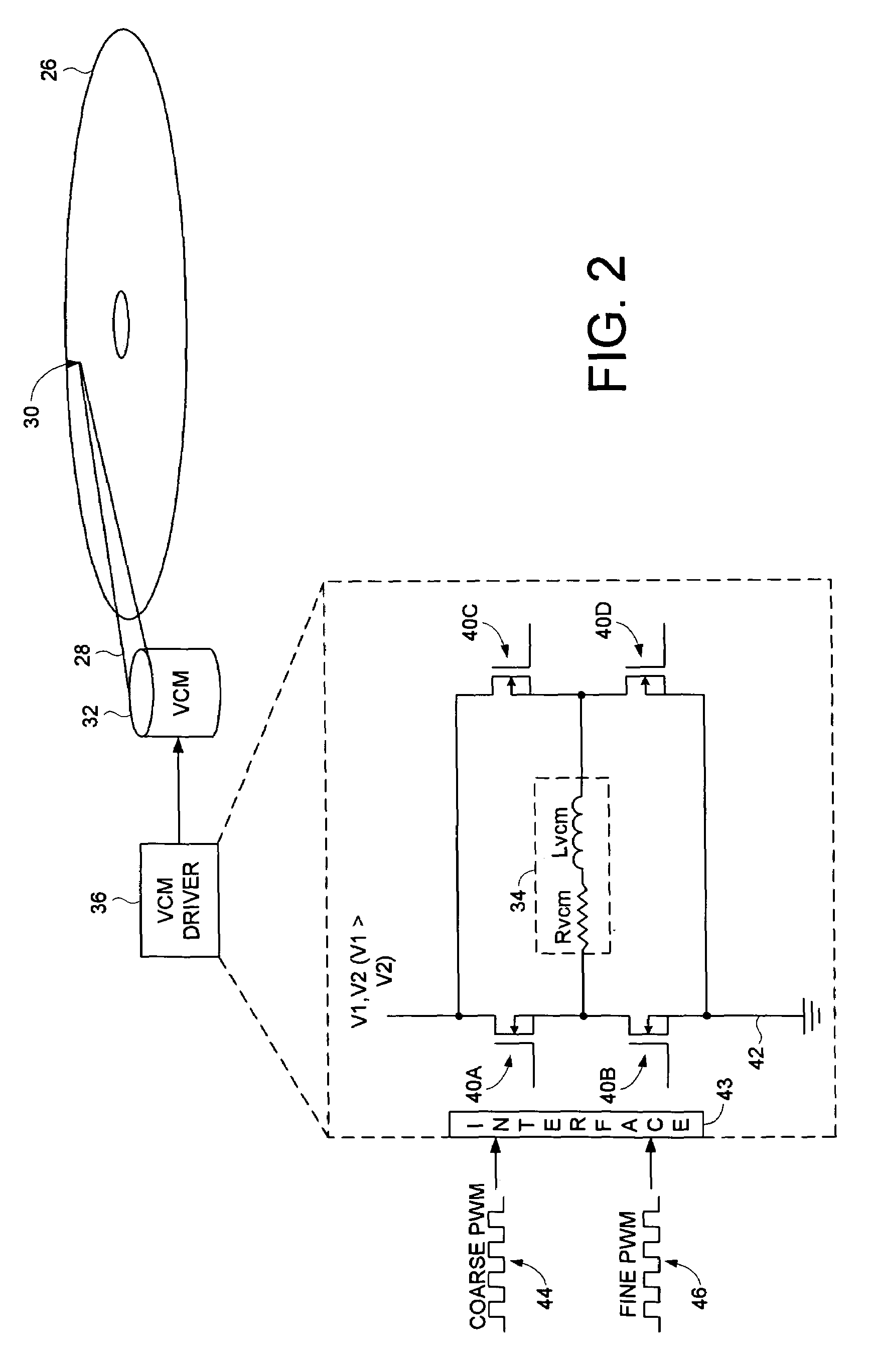
Disk drive employing a multi-stage pulse width modulated voice coil motor driver
InactiveUS7126781B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDriving currentElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a voice coil motor (VCM) having a voice coil for actuating a head over the disk. A VCM driver comprises an H-bridge driver having a plurality of driver switches for driving current through the voice coil to ground. A first pulse width modulated (PWM) signal controls a first voltage level driving the voice coil relative to a duty cycle of the first PWM signal, and a second PWM signal controls a second voltage level driving the voice coil relative to a duty cycle of the second PWM signal, wherein the first voltage level is greater than the second voltage level.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Offset PWM signals for multiphase motor
A multi phase motor includes a switching array for interconnecting a power source to each phase. A current sensor senses current supplied from the power source via the switching array to the winding and a controller generates offset PWM signals for controlling the switching array to supply power to each of the phases of the winding. The offset timing allows the individual phase currents to be determined from a single current sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Primary-side controlled flyback power converter
InactiveUS20050024898A1Save power costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerSwitching frequency
The present invention provides a primary-side flyback power converter that supplies a constant voltage output and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, a PWM controller is included in the power converter in order to generate a PWM signal controlling a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage sampled from a first primary winding of the power supply transformer. Several improvements are included in this present invention to overcome the disadvantages of prior-art flyback power converters. Firstly, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller in order to reduce power consumption. A double sample amplifier samples the flyback voltage just before the transformer current drops to zero. Moreover, an offset current is pulled from a detection input of the double sample amplifier in order to generate a more accurate DC output voltage. The offset current is generated in response to the temperature in order to compensate for temperature-induced voltage fluctuations across the output rectifier. Ultimately, in order to maintain a constant output current, the PWM controller modulates the switching frequency in response to the output voltage.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
Apparatus and method for bias modulator using zero current switching
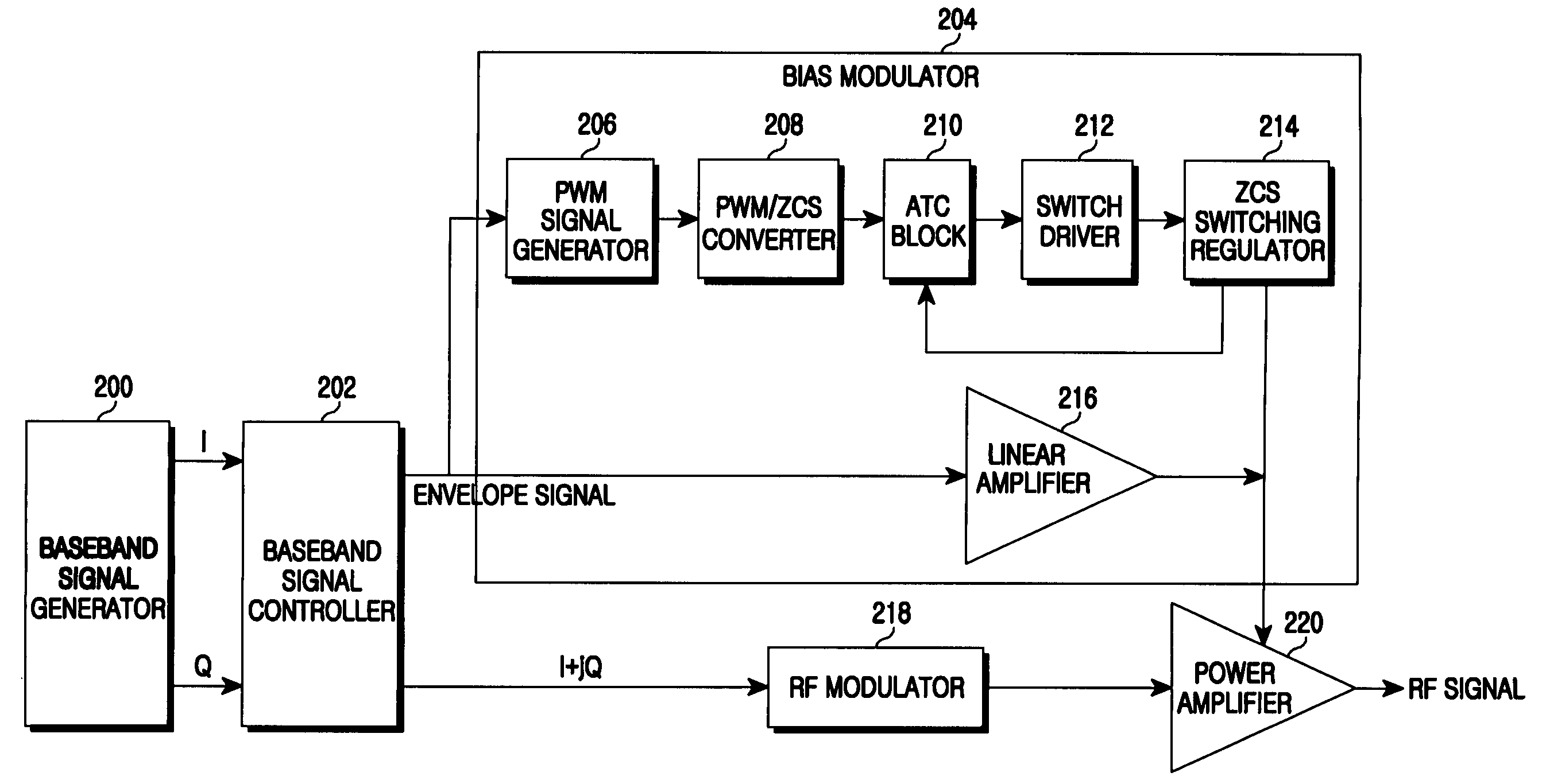
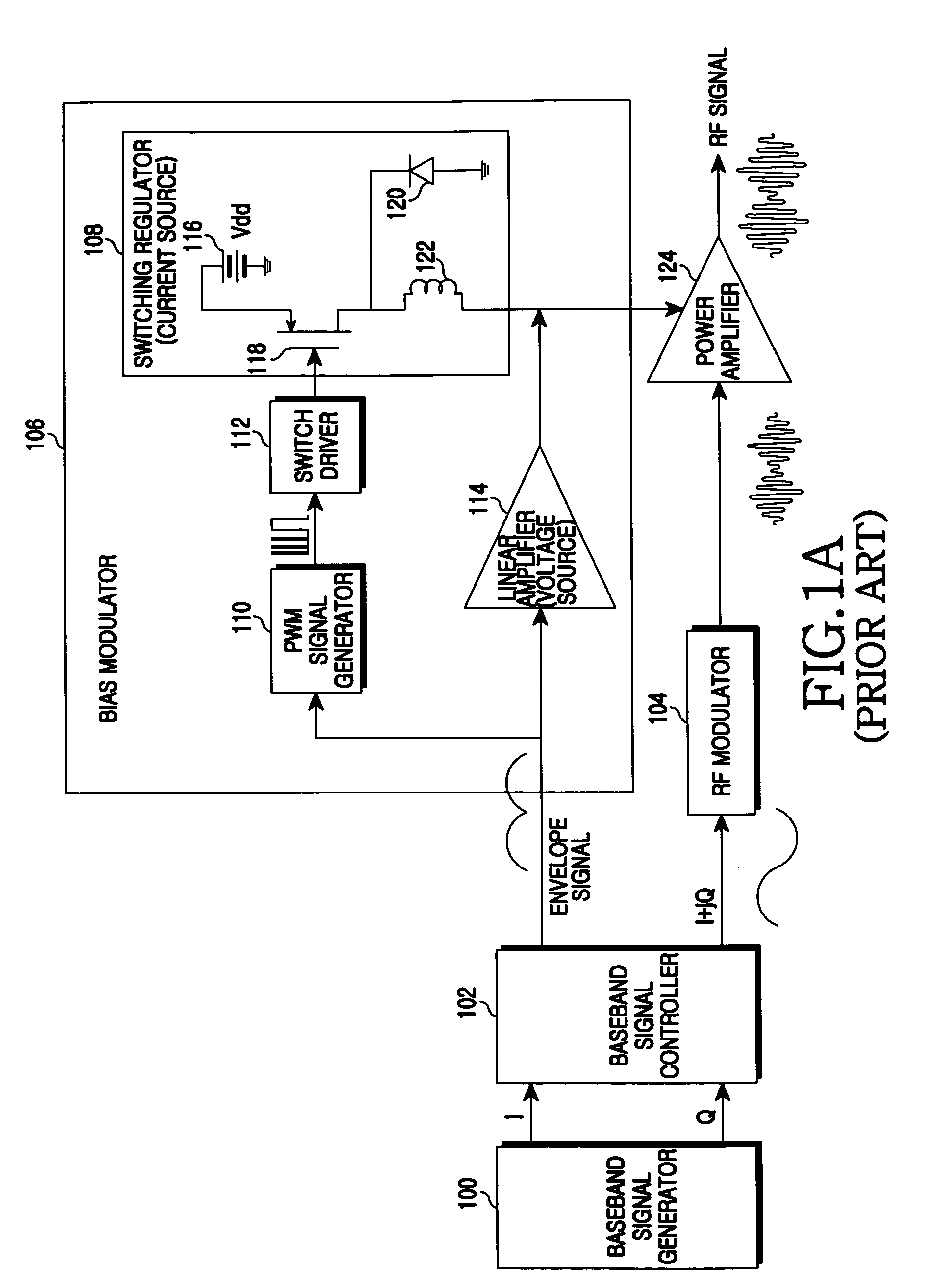
ActiveUS20090218995A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAngle modulationControl signalEngineering
An apparatus and a method for a bias modulator using a Zero Current Switching (ZCS) are provided. The bias modulator includes a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal generator for converting an input envelope signal to a PWM signal; a PWM / ZCS converter for calculating the number of ZCS control signals to be provided within an on-time duration of the PWM signal and generating at least one ZCS control signal according to the number of the ZCS control signals; and a ZCS switching regulator for generating a bias current according to the ZCS control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
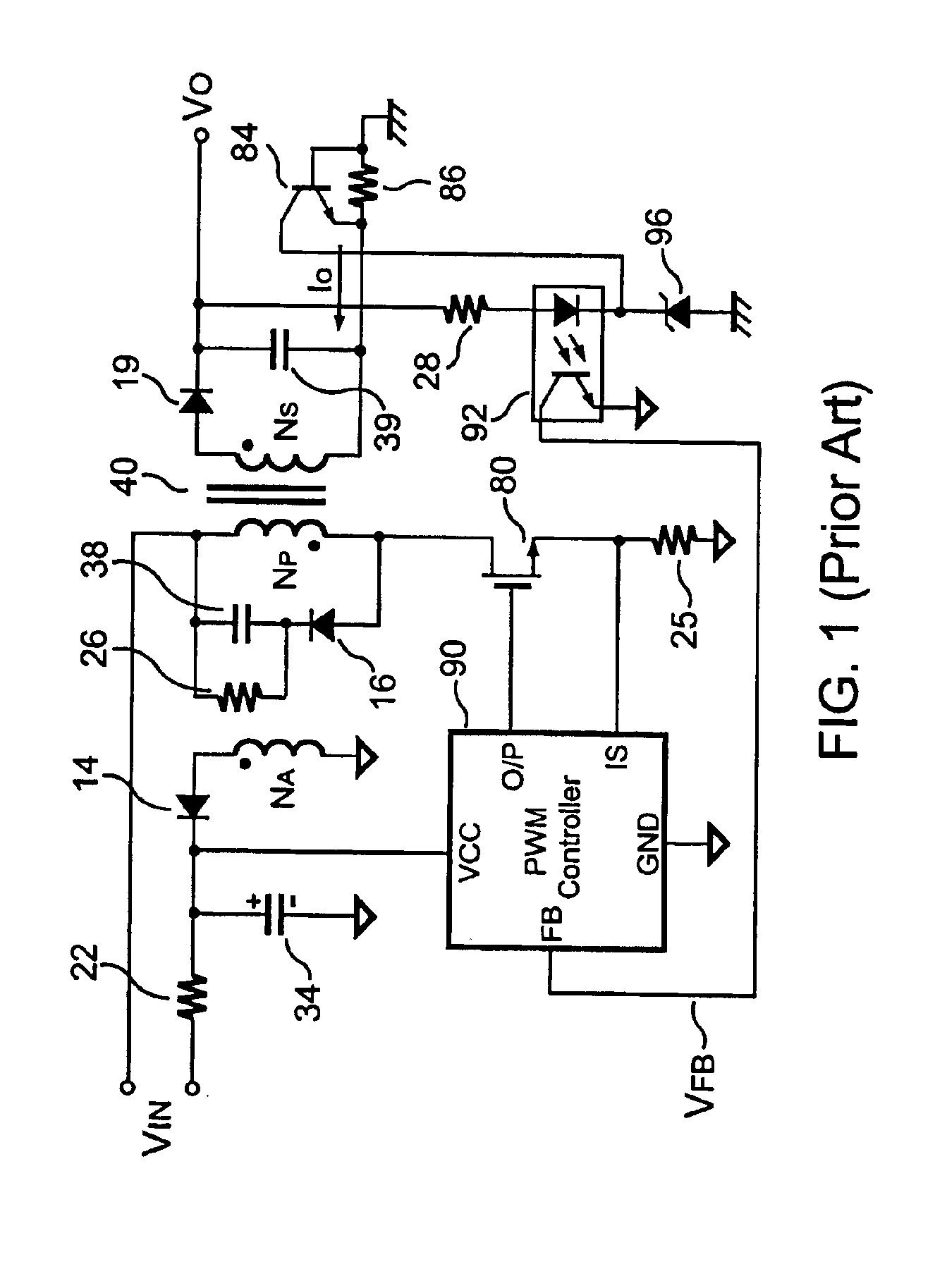
Power-mode controlled power converter
A power-mode controlled power converter is capable of supplying a constant output voltage and output current. A PWM controller generates a PWM signal in response to a voltage sampled from a transformer auxiliary winding. A programmable current-sink and a detection resistor compensate for a voltage drop of an output rectifier. A low-pass filter integrates a switching-current voltage to an average-current signal. An attenuator produces an input-voltage signal from a line-voltage input signal. The PWM controller multiplies the average-current signal with the input-voltage signal to generate a power-control signal. An error-amplifier compares the power-control signal with a power-reference voltage to generate a limit voltage. The limit voltage controls the power delivered from a primary-side circuit to a secondary-side circuit of the power-mode controlled power converter. Since the power-reference voltage varies in proportional to output voltage variations, a constant output current is therefore achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Pfc-pwm controller having interleaved switching
ActiveUS20050099164A1Reduce switching noiseImproper operationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringPwm signals
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
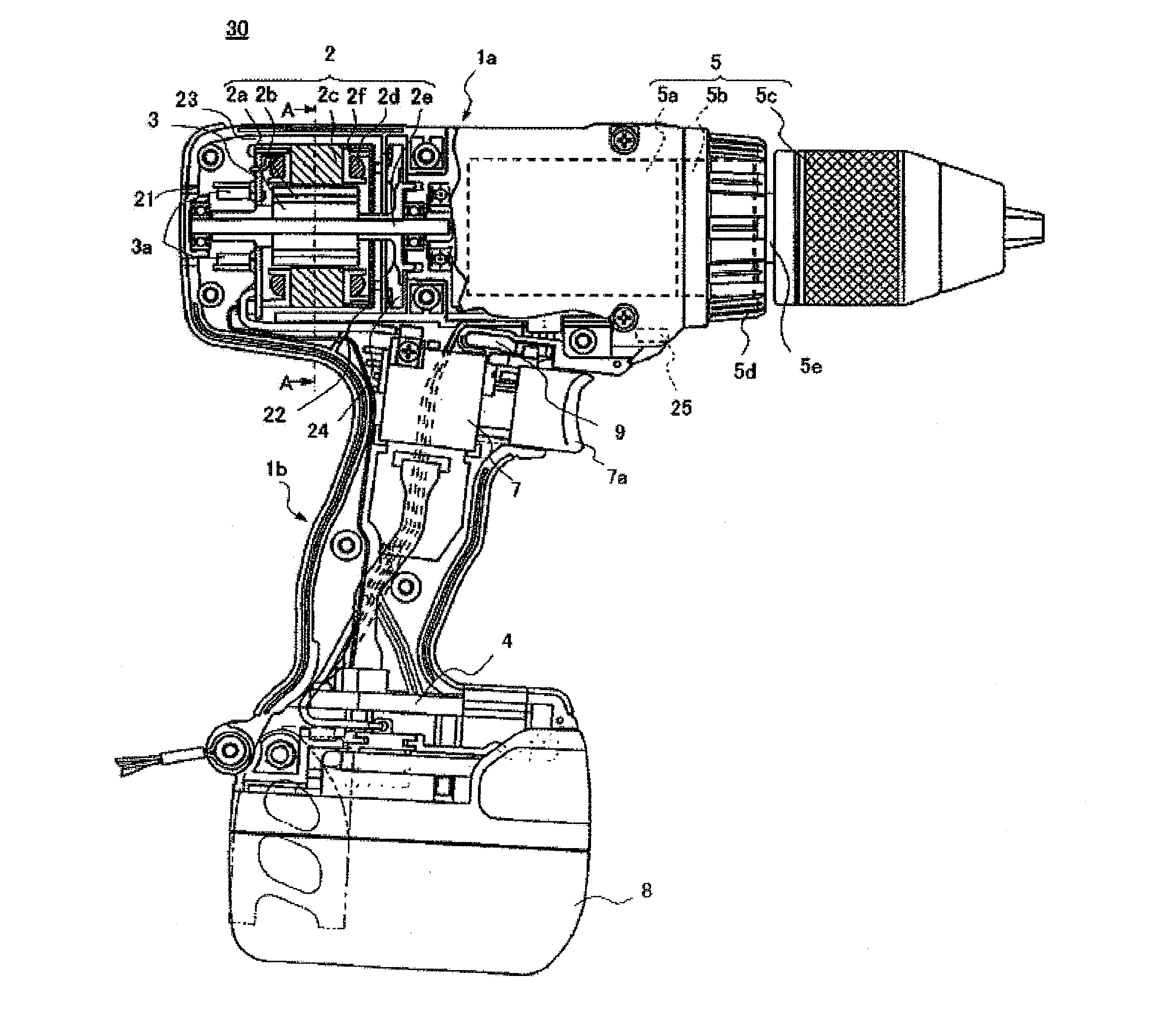
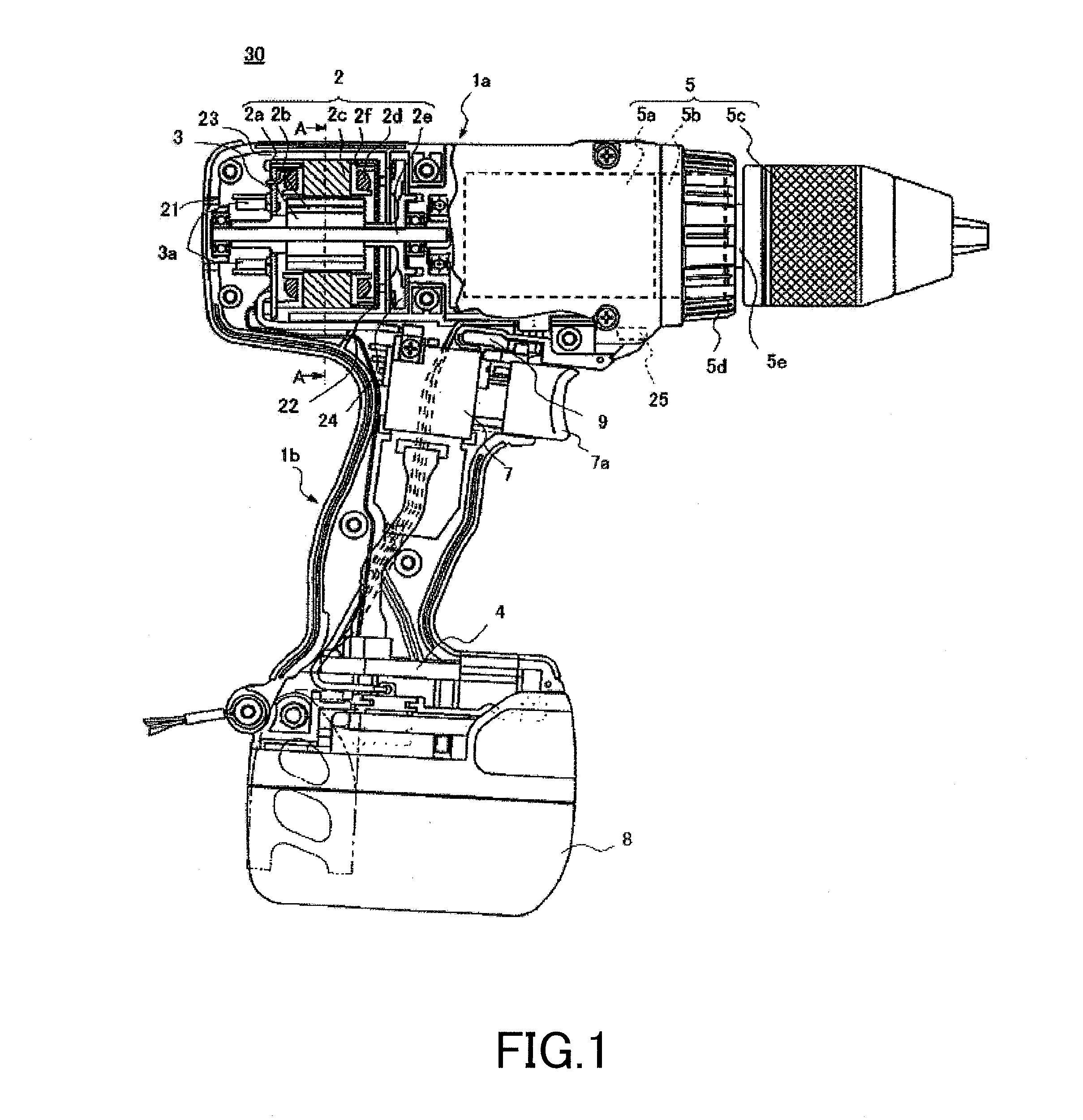
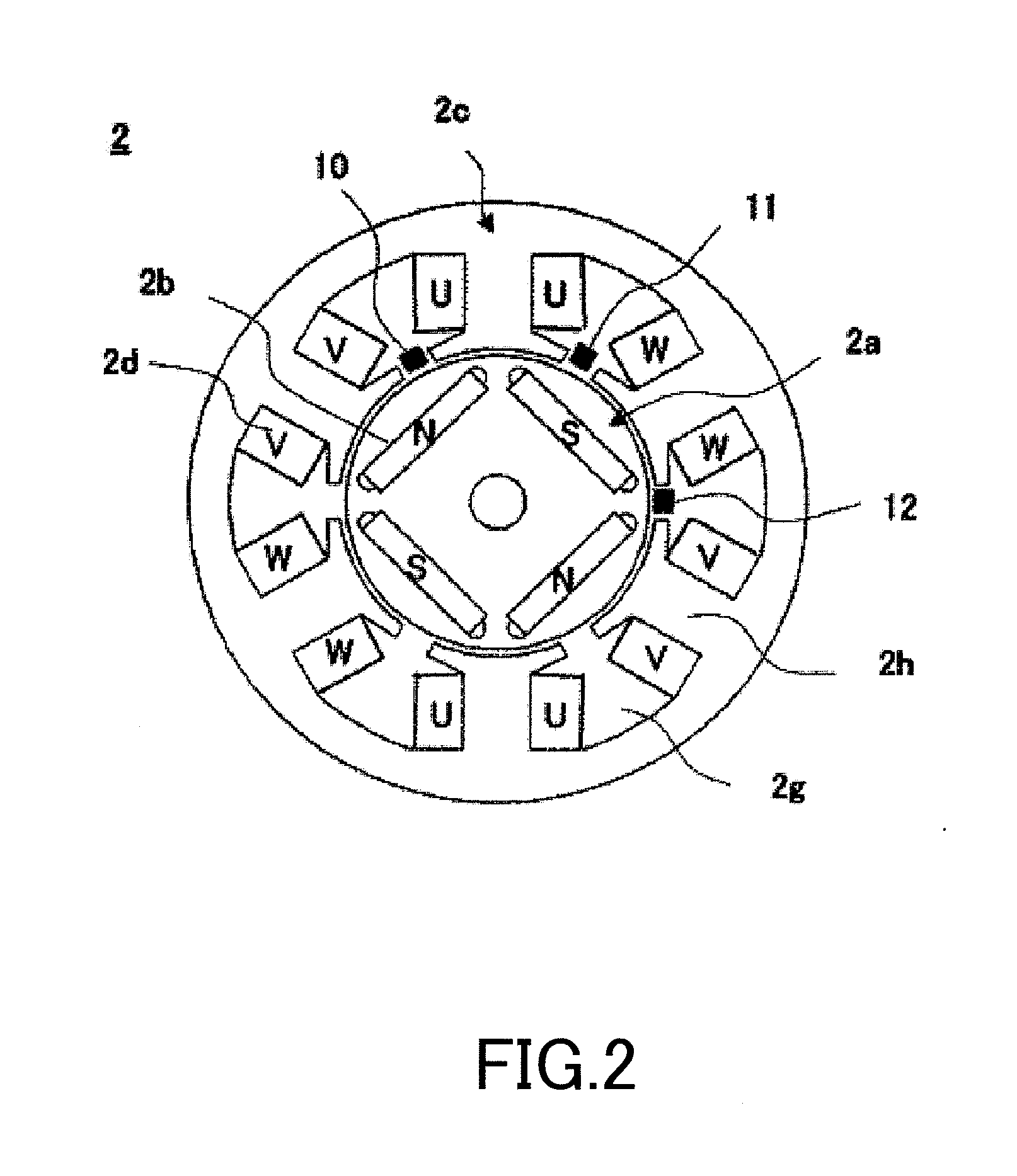
Electric Rotating Tool
ActiveUS20100307782A1Accurately and appropriately detectedAvoid partialDrilling rodsConstructionsDriving currentStator coil
A current detection circuit (18) detects that a drive current of the stator coil (2d) is exceeding a threshold value Ir. A rotation number detection circuit (17) detects that the number of rotations of a rotor (2a) is lower than a threshold value Nr. A computing part (20) outputs a PWM signal which switches a semiconductor switching element (3a) of the inverter circuit part (3). The computing part (20) changes the threshold values Ir and Nr in accordance with the PWM duty of the PWM signal determined in accordance with a pressed distance of a switch trigger (7) and detects a locked state of the motor (2) on the conditions that the motor current I is exceeding the set threshold value Ir and that the number of rotations N thereof is lower than the threshold value Nr.
Owner:HITACHI KOKI CO LTD
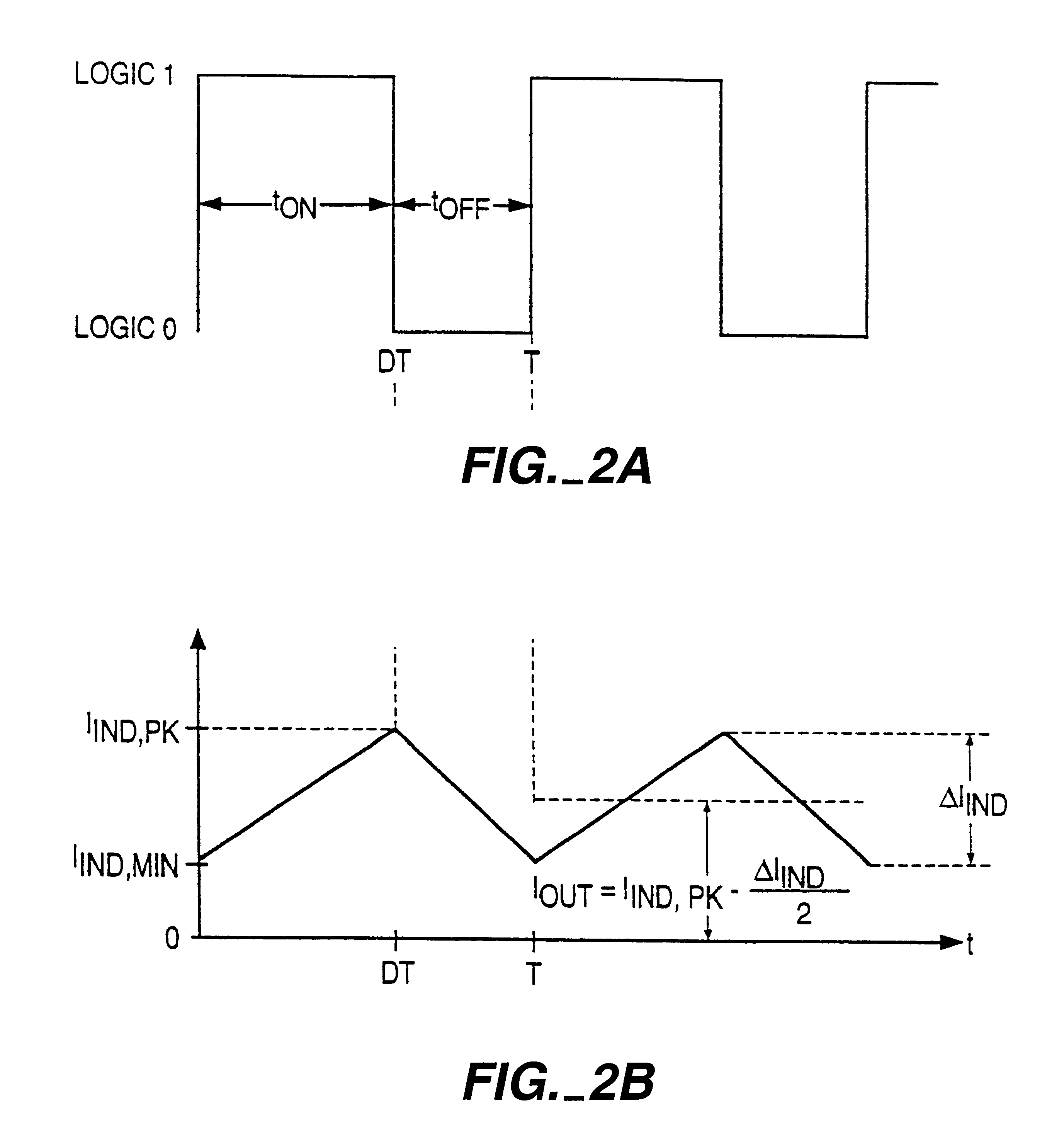
Voltage regulator that operates in either PWM or PFM mode
InactiveUSRE37609E1Improve efficiencyPower dissipationEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulationEngineering
A switching voltage regulator achieves high efficiency by automatically switching between a pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode and a pulse-width modulation (PWM) mode. Switching between the modes of voltage regulation is accomplished by monitoring the output voltage and the output current, wherein the regulator operates in PFM mode at small output currents and in PWM mode at moderate to large output currents. PFM mode maintains a constant output voltage by forcing the switching device to skip cycles when the output voltage exceeds its nominal value. In PWM mode, a PWM signal having a variable duty cycle controls the switching device. A constant output voltage is maintained by feedback circuitry which alters the duty cycle of the PWM signal according to fluctuations in the output voltage.
Owner:MICREL
Apparatus for reducing the power consumption of a PFC-PWM power converter
ActiveUS6967851B2Reduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionLow voltageEngineering
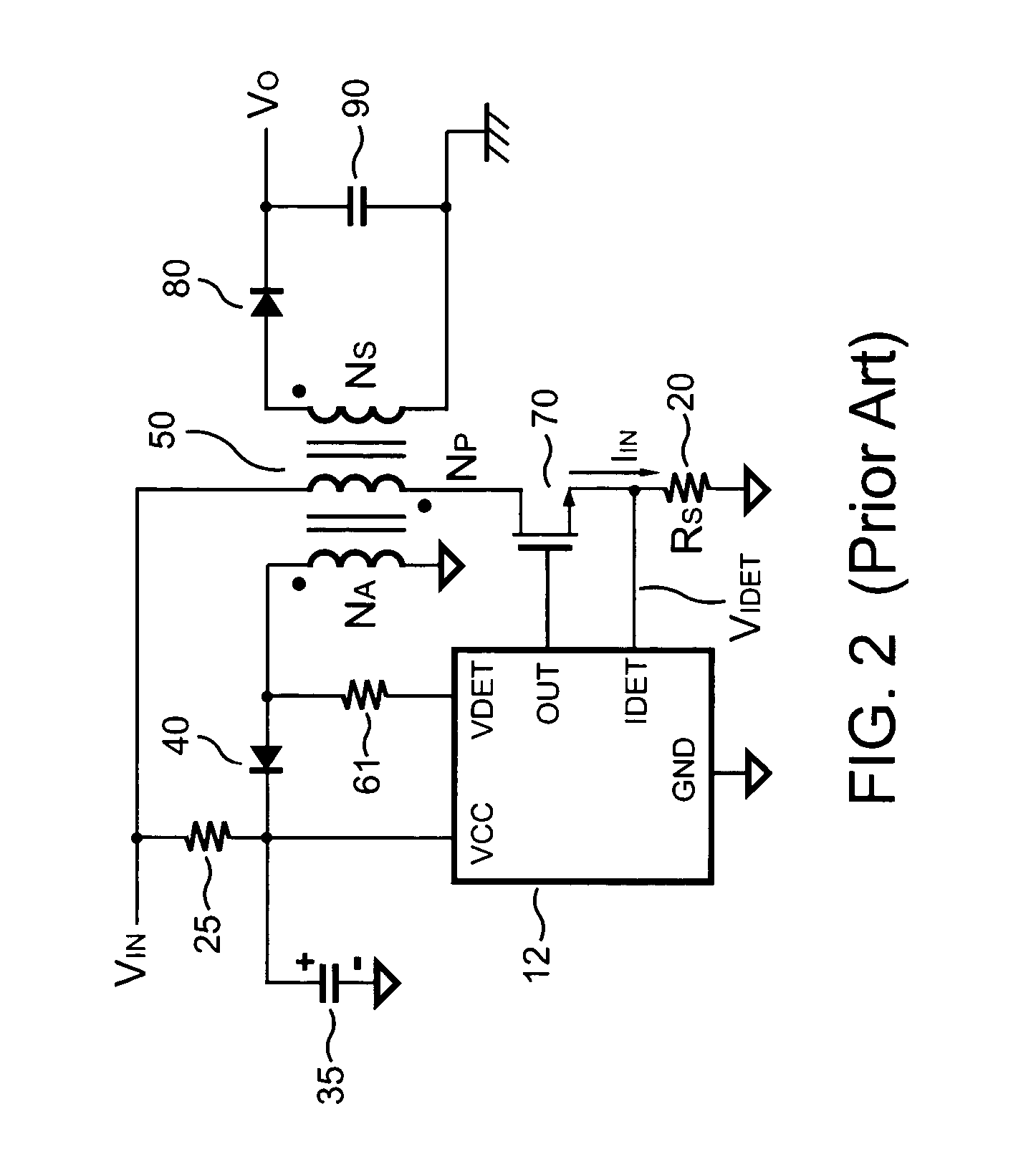
An apparatus for reducing the power consumption of a PFC-PWM power converter is described. The apparatus includes a control terminal used to detect a line-input voltage and to control a PFC signal and a PWM signal. The apparatus further includes a PFC power-manager and a PWM power-manager. The PFC power-manager of the PFC controller determines a PFC-reference voltage for an error amplifier of the PFC controller. The PFC-reference voltage is generated in response to the voltage at the control terminal. The PFC power-manager will disable the PFC signal whenever the voltage at the control terminal drops below a low-voltage threshold voltage. The PWM power-manager will disable the PWM signal whenever the voltage at the control terminal drops below a programmable threshold voltage. Furthermore, the PWM power-manager will pull the voltage at the control terminal low to disable the PFC circuitry during light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
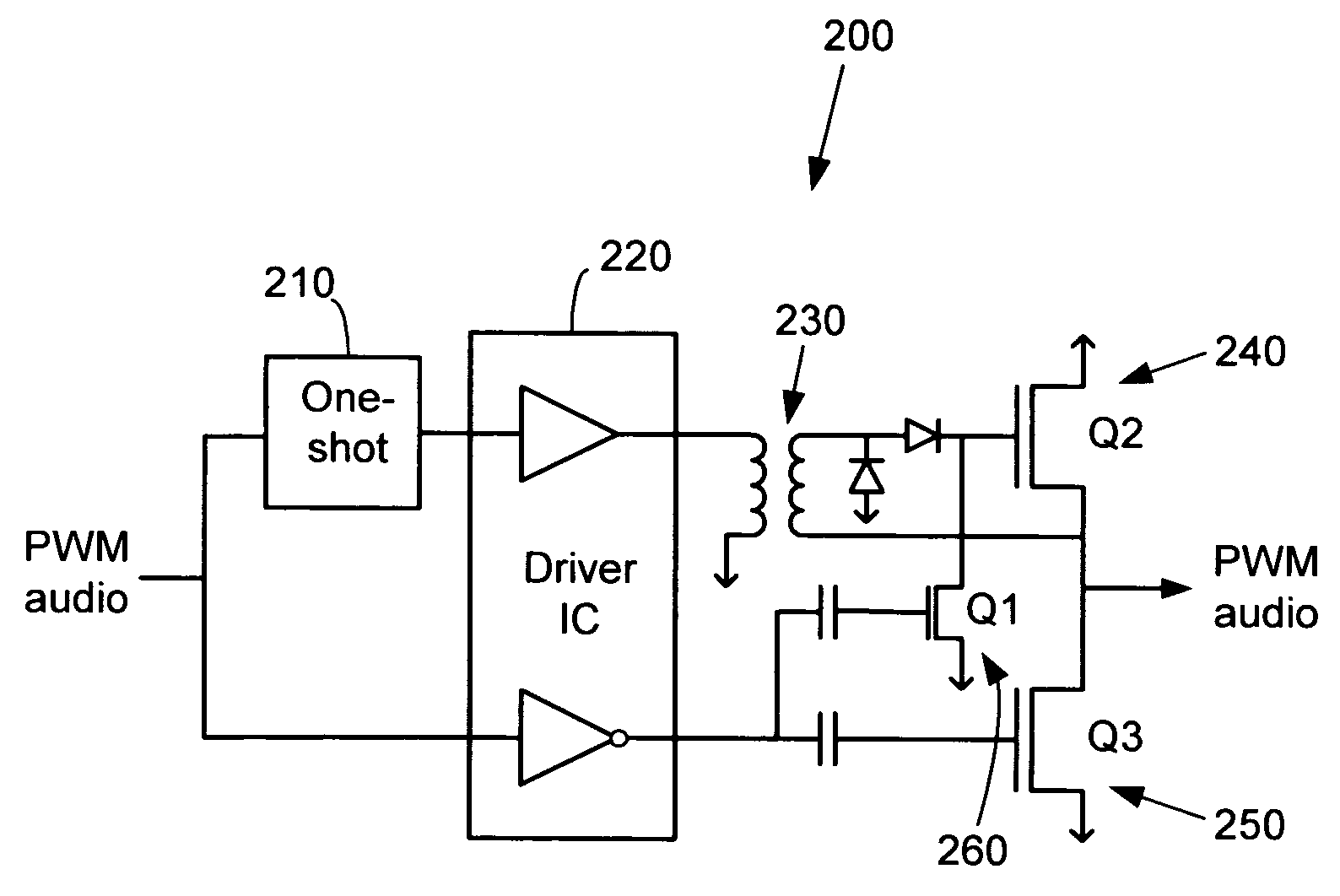
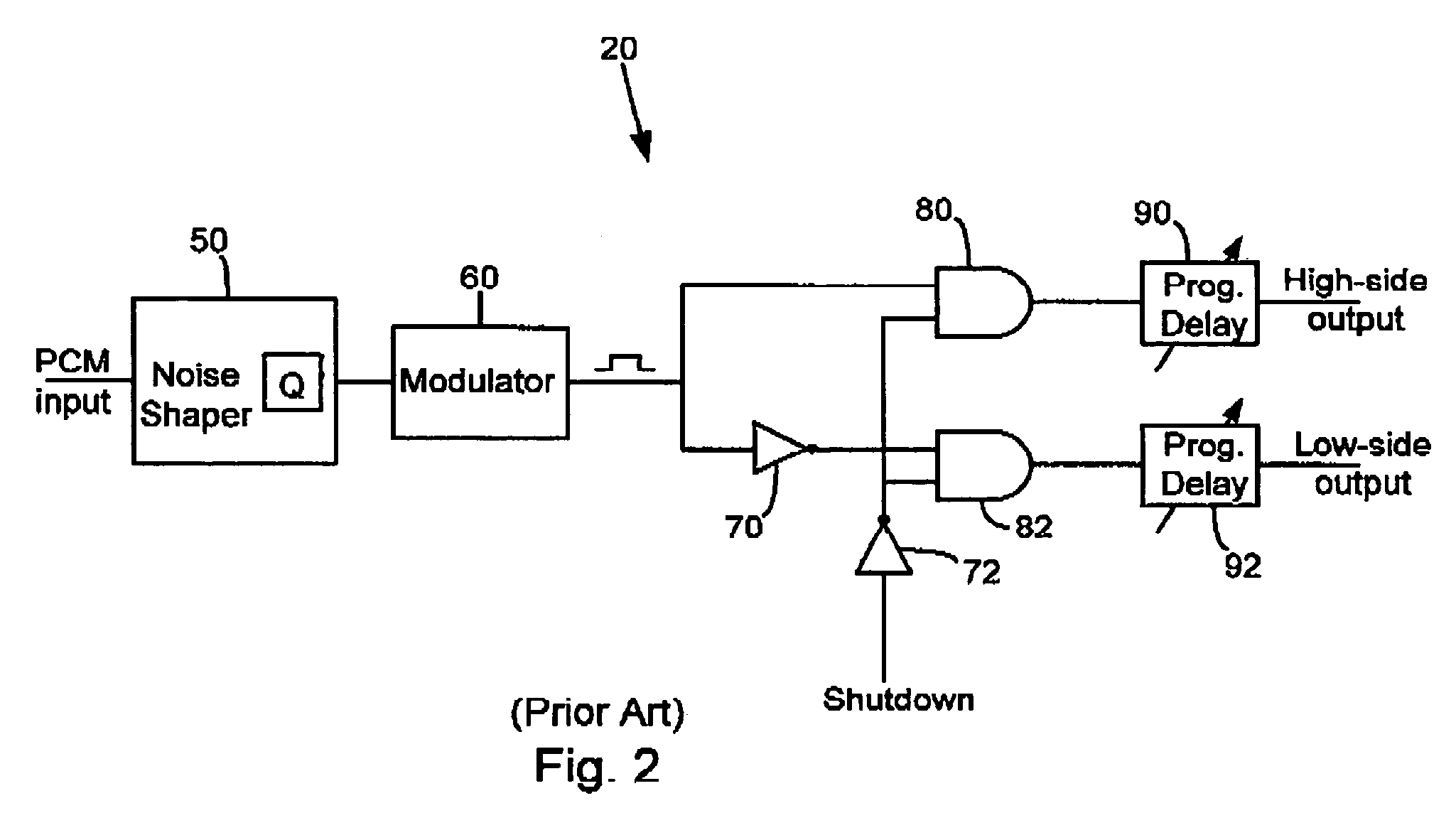
Integrated PULSHI mode with shutdown
InactiveUS7078963B1Enabling usePulse duration/width modulationDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorAudio power amplifierPulse-code modulation
Systems and methods for controlling amplification of a pair of pulse width modulated signals. In one embodiment, a system comprises an audio amplifier which is configured to receive a pulse code modulated (PCM) input signal, convert this signal to a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal in a controller, and amplify the PWM signal in an output stage. The controller separates the PWM signal into a high-side signal and a low-side signal. The controller incorporates digitally programmable delays into the processing paths for each of the high-side and low-side signals. The high-side and low-side signals are separately provided to the output stage. The separate high-side and low-side signals can be used to individually control (e.g., turn off) the high-side and low-side transistors. Circuitry is included to generate a short low-side pulse when both transistors are turned off in order to drain the gate charge from the high-side transistor.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Light-adjusting device and method of LED illuminating lamp
InactiveCN103281849APower supply impactImplement alternative upgradesElectric light circuit arrangementControl signalEngineering
A light-adjusting device of an LED illuminating lamp comprises an LED illuminating lamp brightness control single firewire setting unit, an LED illuminating lamp brightness control adjusting unit, and an LED illuminating lamp brightness control drive unit. According to a light-adjusting method of the LED illuminating lamp, a method that positive and negative half-waves of a bidirectional thyristor are controlled to be triggered in a phase shifting mode is adopted, an LED illuminating lamp brightness increasing control signal or an LED illuminating lamp brightness reducing control signal is sent out in a single firewire mode, the brightness control signal is recognized through a micro controller, and the micro controller outputs a PWM signal with an adjustable duty ratio to control the brightness of the LED illuminating lamp to change between 0% and 100% in a 1% step value. The light-adjusting device is free of a remote controller and a control wire, a power supply wire does not need to be paved again, and replacement and upgrading of a common illuminating lamp are achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Fixed-frequency current mode converter and control method thereof
InactiveUS7230406B2Faster response to load transientRapid responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringInductor
A fixed-frequency current mode converter comprises a power stage to produce an inductor current and an output voltage, an error amplifier to generate an error signal from the difference between the output voltage and a reference voltage varied with the inductor current, a comparator to compare the error signal with a ramp signal varied with the inductor current to generate a comparison signal, and a PWM generator to generate a PWM signal in response to a fixed-frequency clock and the comparison signal to drive the power stage. A second comparator is further comprised to compare the error signal with a second reference voltage varied with the inductor current, and generates a second comparison signal to reset the clock when the error signal is lower than the second reference voltage.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
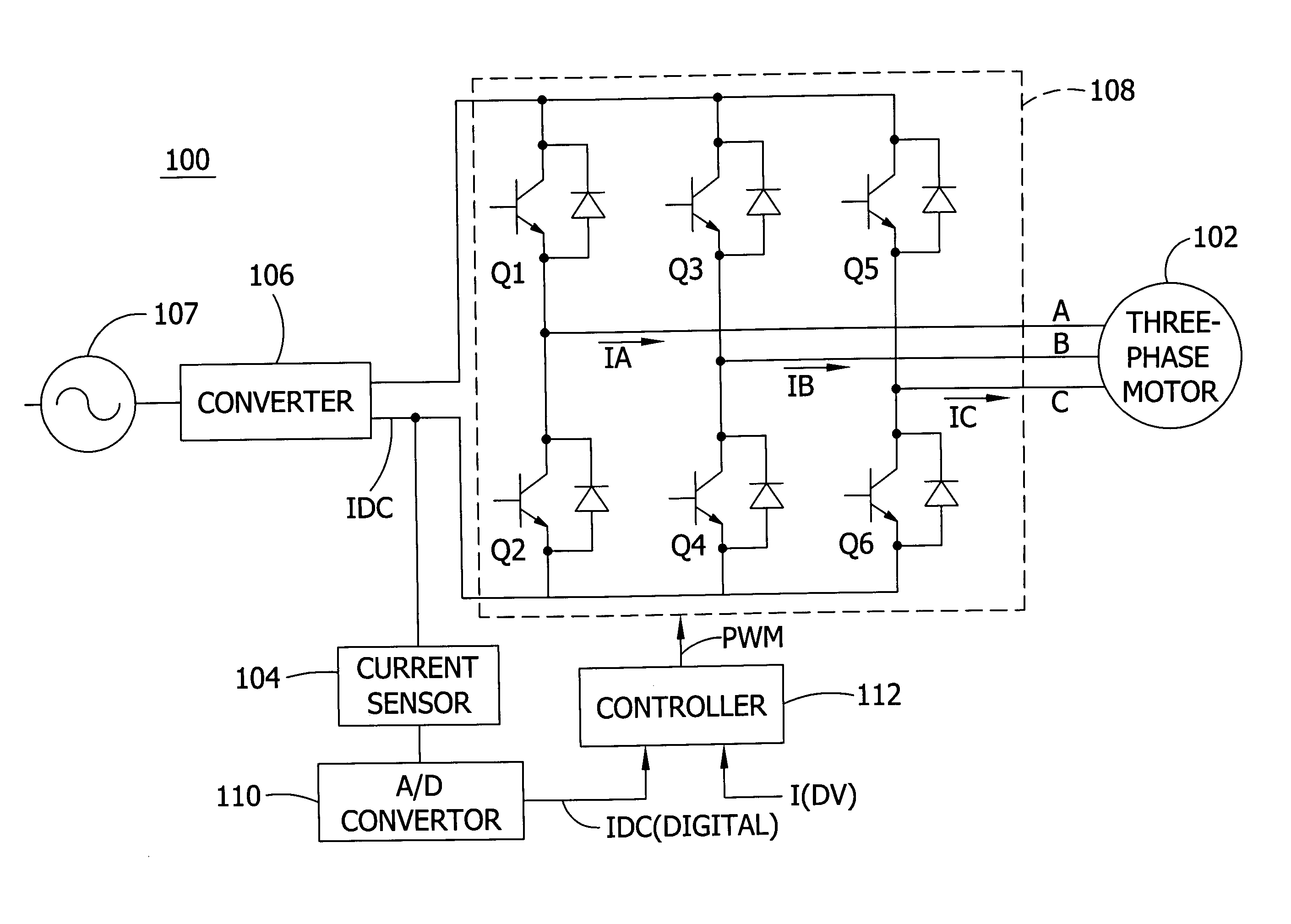
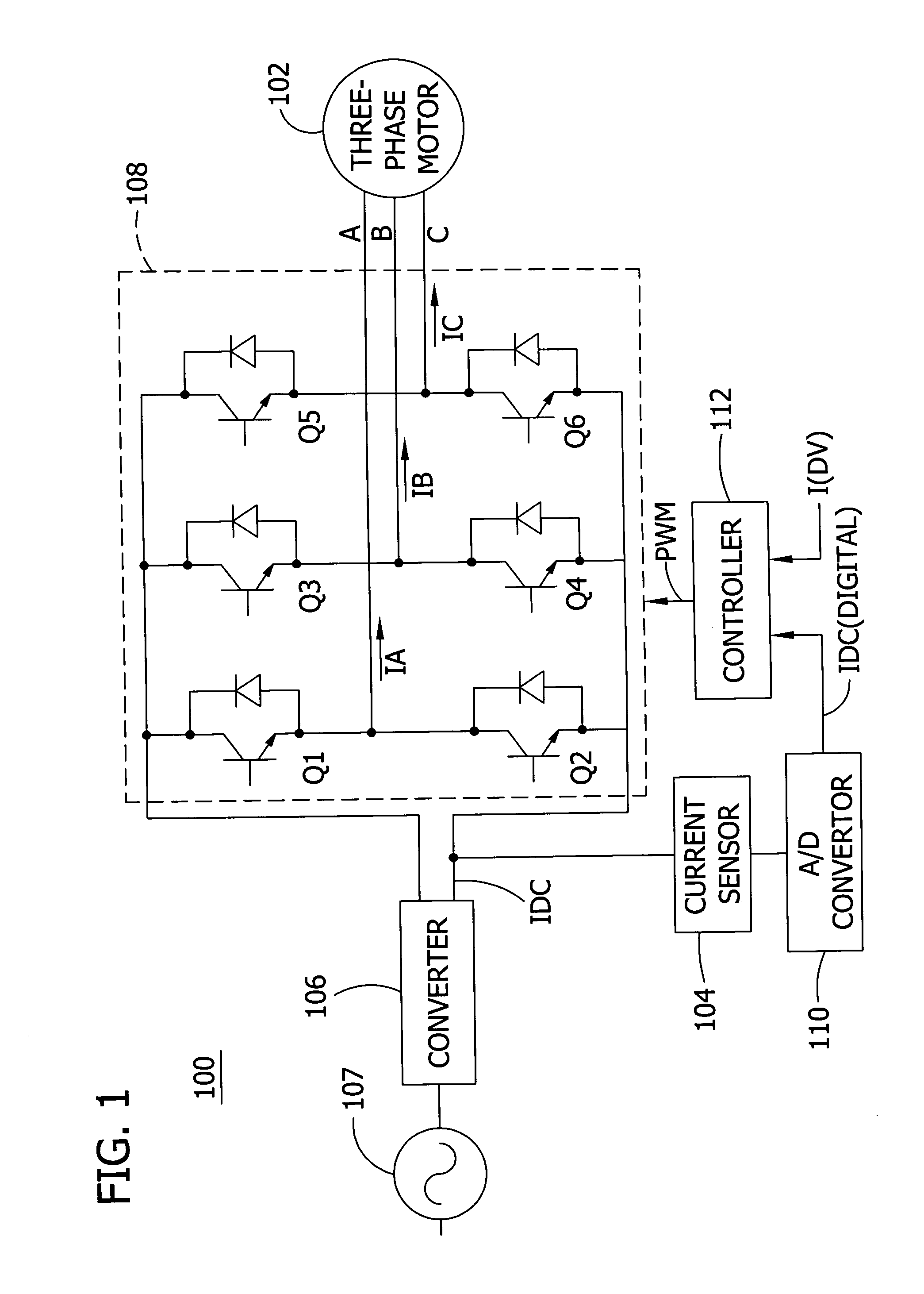
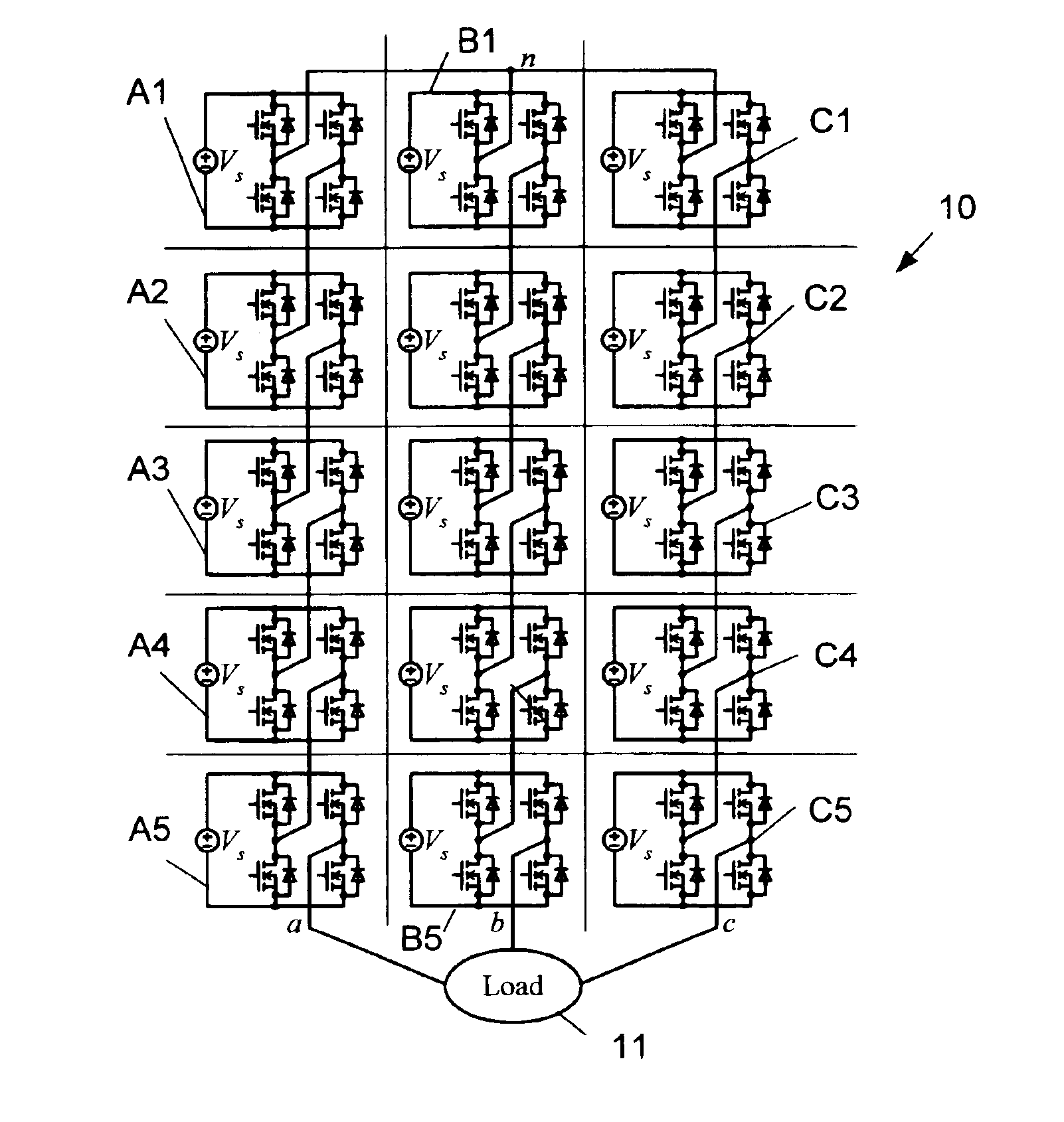
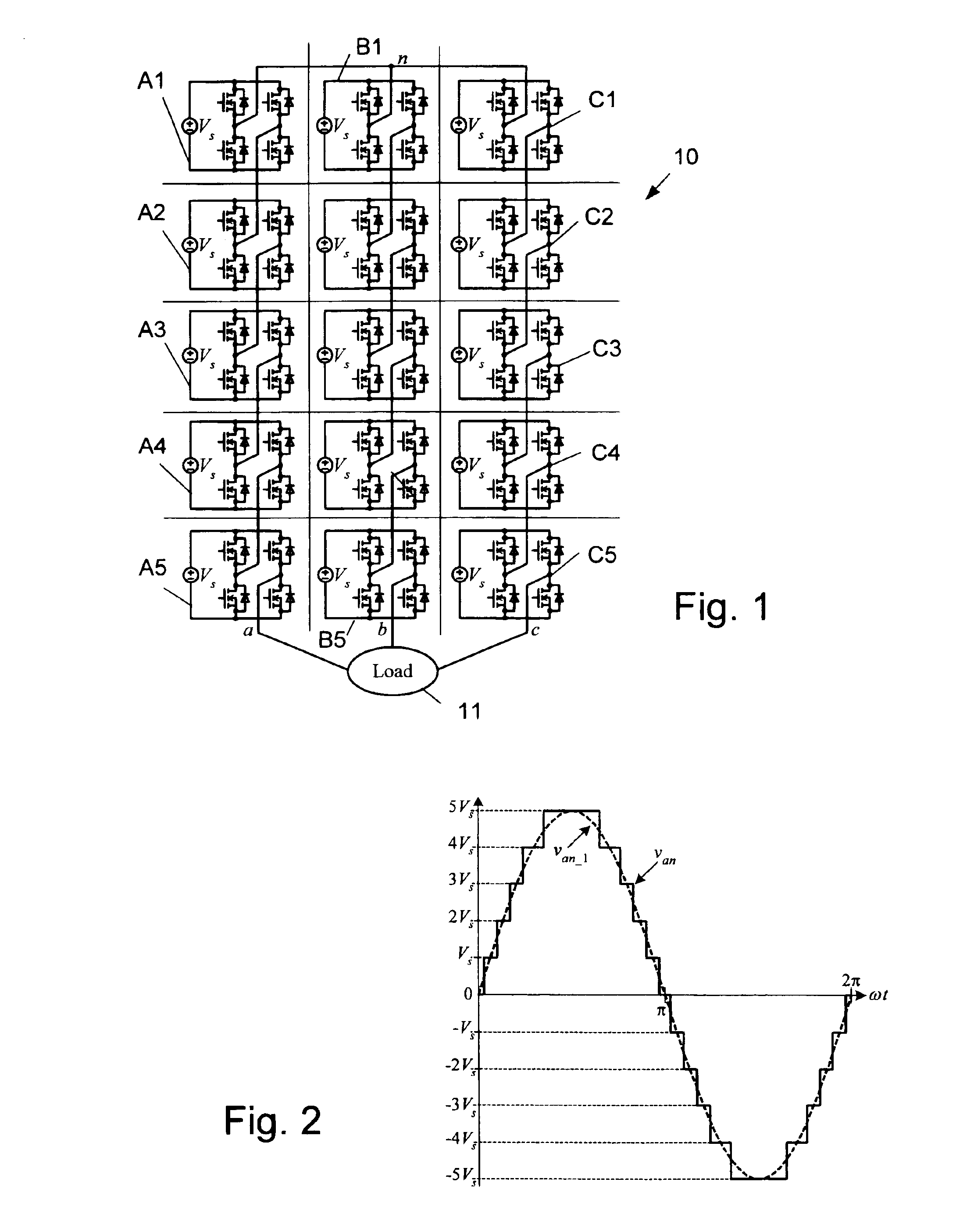
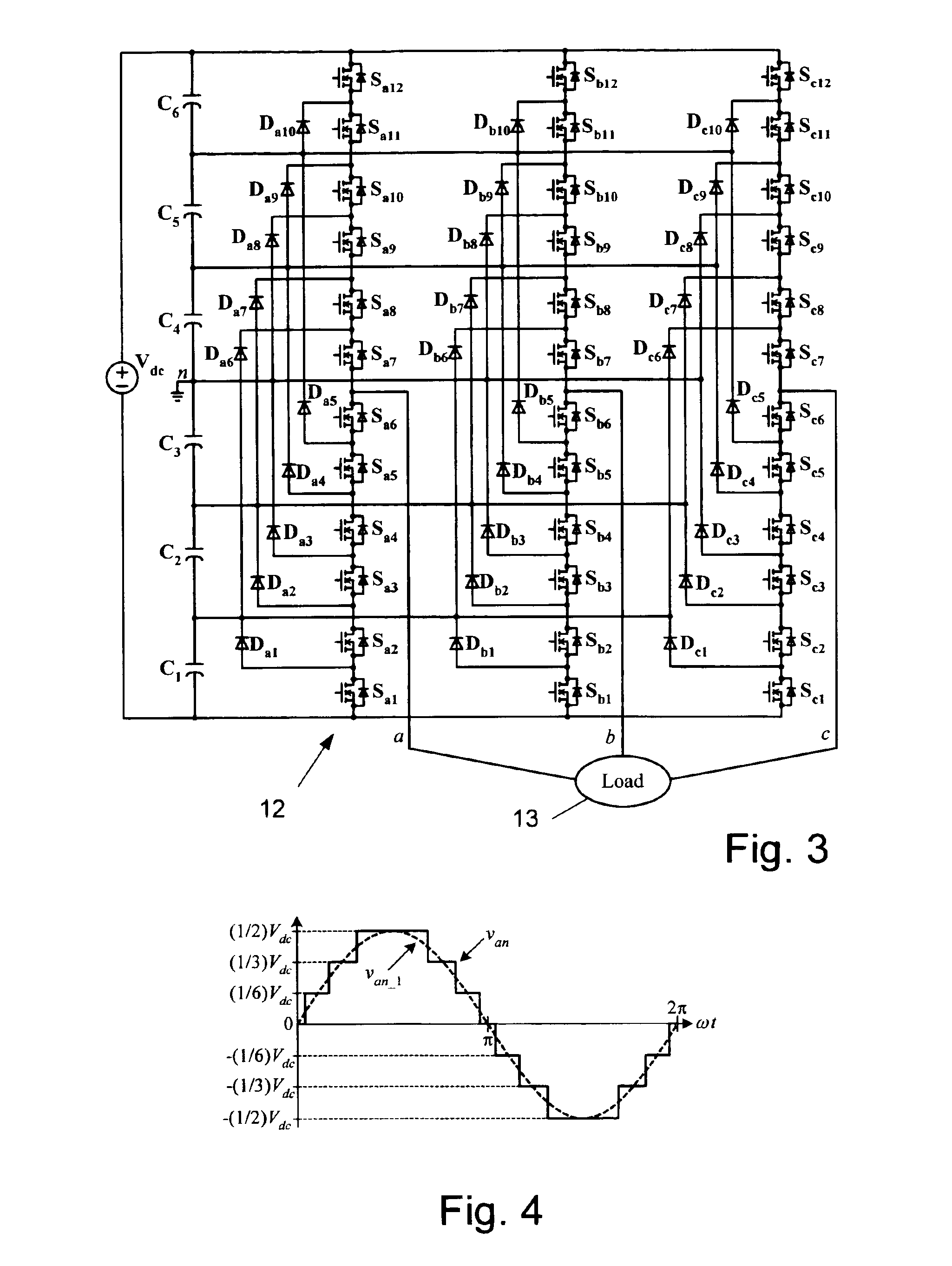
Multi-level dc bus inverter for providing sinusoidal and PWM electrical machine voltages
InactiveUS6969967B2Shorten the counting processAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlMachine controlFull bridge
A circuit for controlling an ac machine comprises a full bridge network of commutation switches which are connected to supply current for a corresponding voltage phase to the stator windings, a plurality of diodes, each in parallel connection to a respective one of the commutation switches, a plurality of dc source connections providing a multi-level dc bus for the full bridge network of commutation switches to produce sinusoidal voltages or PWM signals, and a controller connected for control of said dc source connections and said full bridge network of commutation switches to output substantially sinusoidal voltages to the stator windings. With the invention, the number of semiconductor switches is reduced to m+3 for a multi-level dc bus having m levels. A method of machine control is also disclosed.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
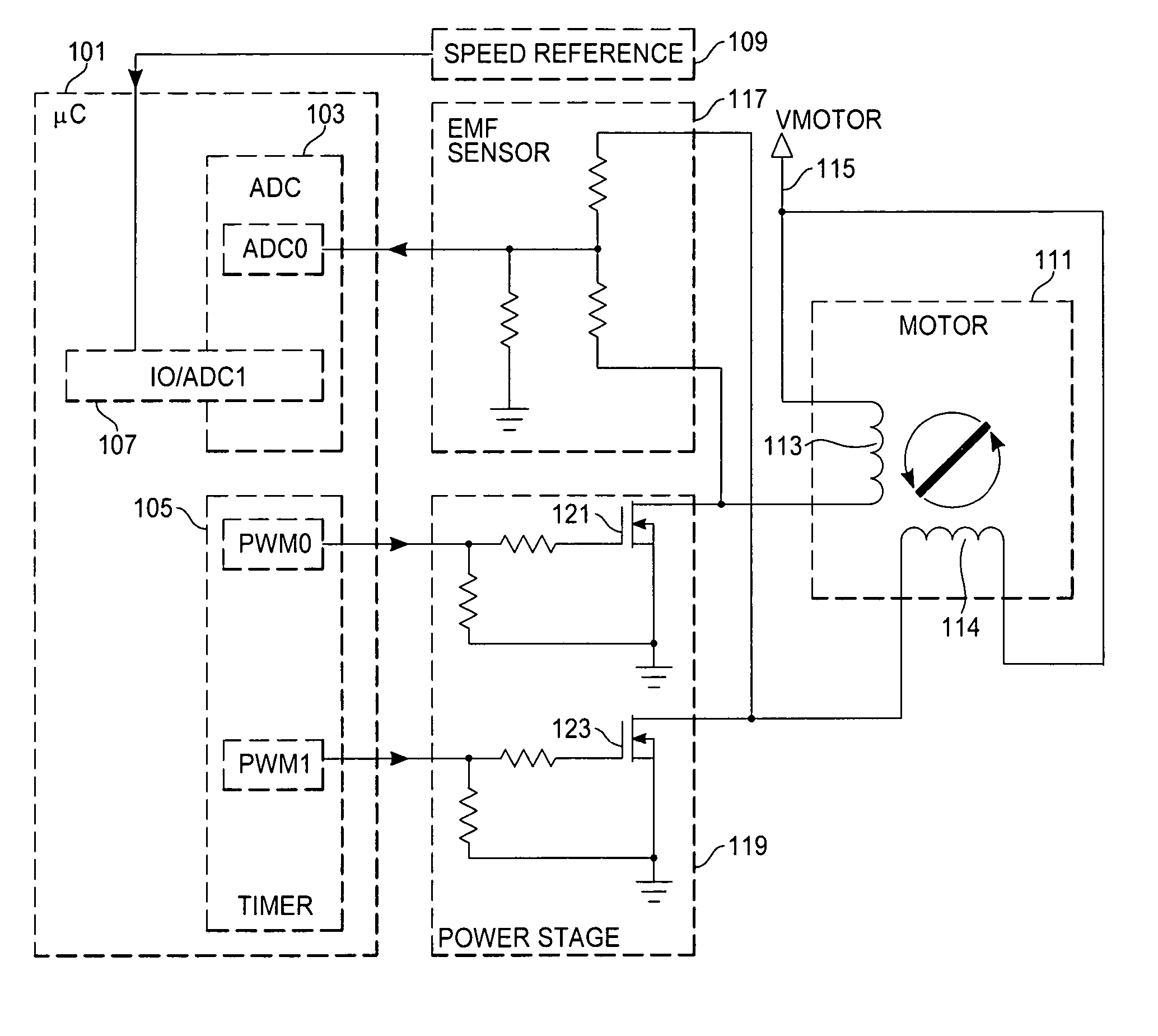
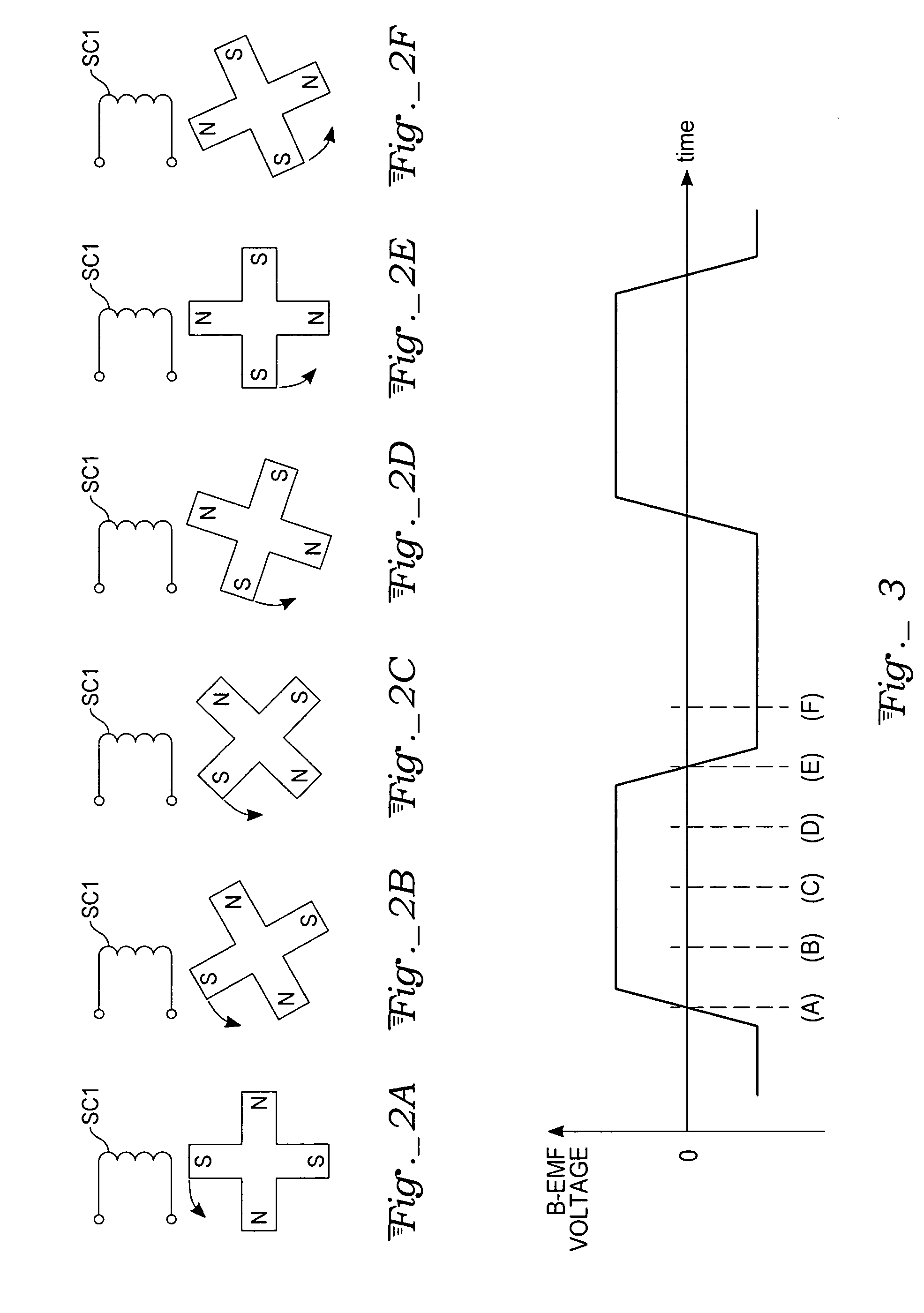
Sensorless control of two-phase brushless DC motor
A motor control system for a two-phase brushless DC motor uses measured EMF voltage from the passive set of stator coils to control commutation. A microcontroller receives the EMF voltage measurement and compares it to a threshold voltage value, which may be speed-dependent for advance commutation at high motor speeds. A match of the EMF voltage measurement with the threshold value triggers commutation of the drive to the opposite set of stator coils. The microcontroller also has an up-down counter timer whose count value is compared to an external speed reference. Each match of the count value triggers a transition in a pulse-width modulated (PWM) drive signal. The duty cycle of the PWM signal establishes an average drive voltage that controls motor speed.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Pwm method and apparatus, and light source driven thereby
InactiveUS20080048582A1Easy to driveElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageImage resolutionEngineering
The present invention provides a pulse-width modulation (PWM) method and apparatus, and light source driven thereby. In particular, the present invention provides a PWM method and apparatus for generating a PWM signal having a desired resolution and frequency using generating means traditionally limited to providing PWM signals having a lower resolution and / or frequency. The PWM method and apparatus of the present invention may be used in a number of applications where a relatively high PWM resolution and / or frequency is desired, but where selection of generating means for generating such PWM signals is relatively limited by cost and / or other such constraints. For example, a PWM signal generated by the method and apparatus of the present invention may be useful in accurately controlling the output of the one or more light-emitting elements of a light source, namely to control a dimming and / or colour level thereof, without using driving components that may be relatively costly for the application at hand.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Soft transitions between muted and unmuted states in class D audio amplifiers
ActiveUS20050083115A1Weaken energyReduce audible sideband noiseDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorAudio power amplifierEngineering
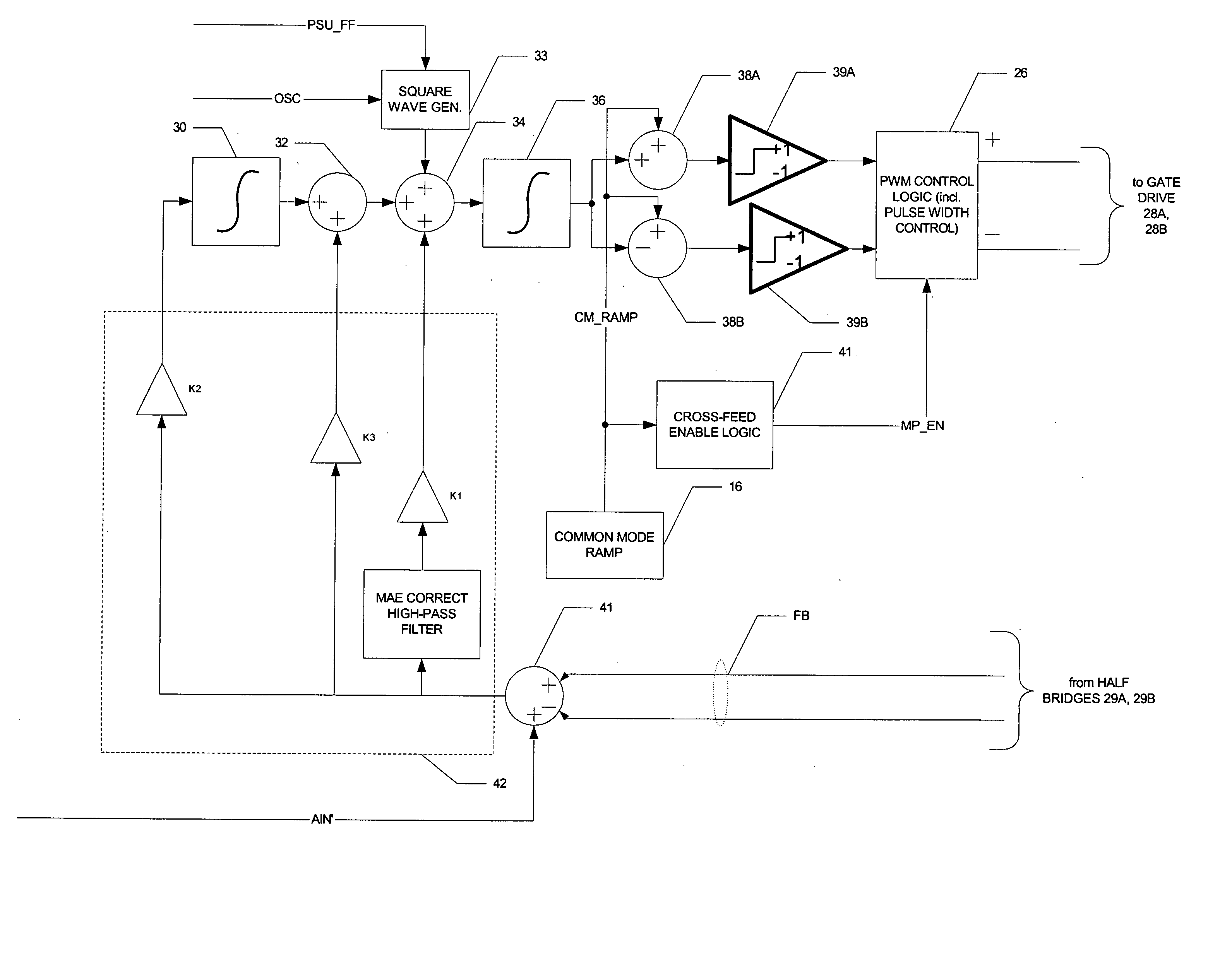
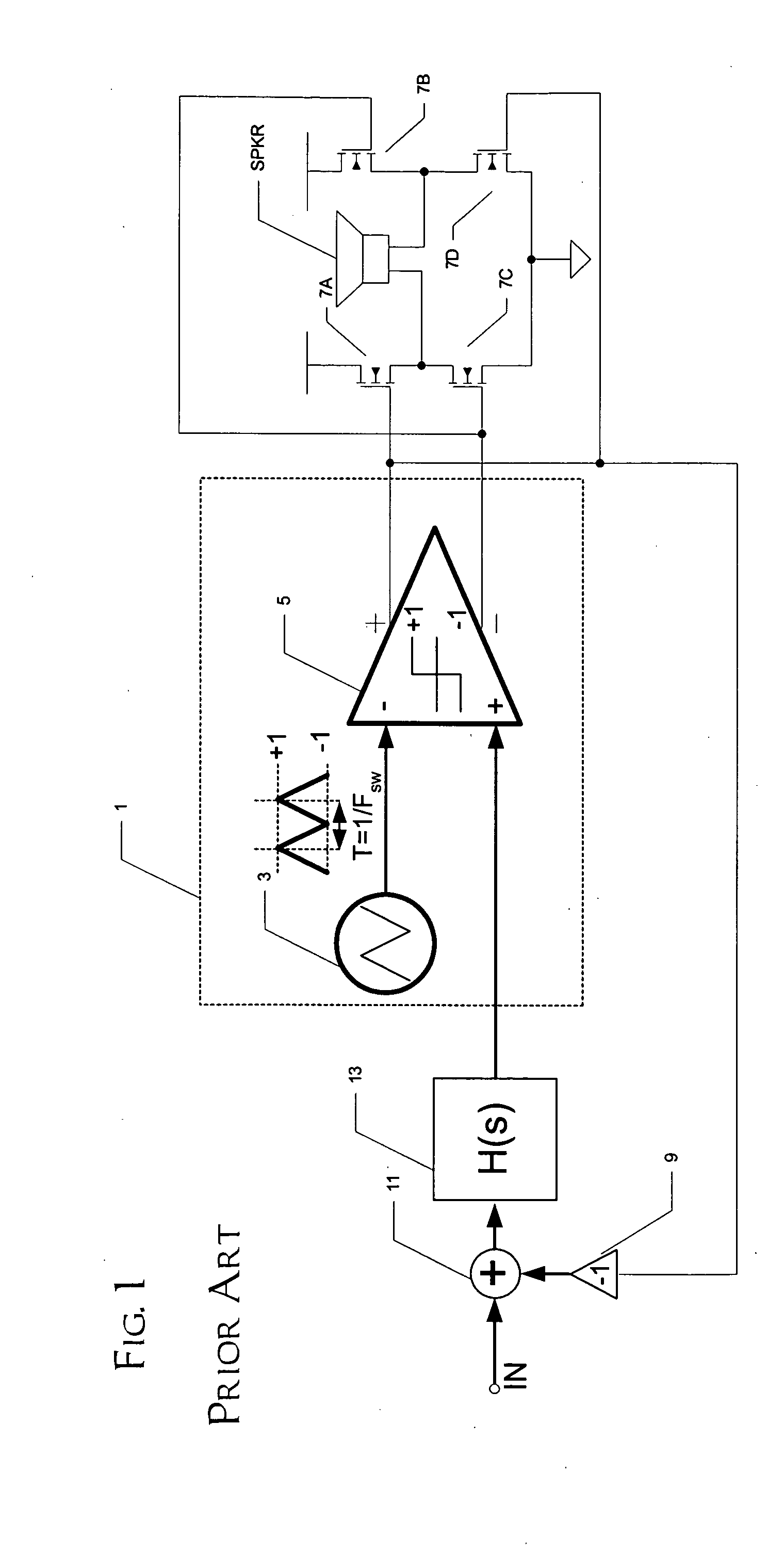
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with reduced noise capability in muting and unmuting events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. When the system is muted, a common mode voltage (CM_RAMP) is applied to the inputs of the comparators (39A, 39B; 52+ 52−) to suppress the duty cycle at the amplifier output, preferably to a zero duty cycle. In the transition from a muted state to an unmuted state, the common mode voltage (CM_RAMP) is ramped from the suppressing voltage to zero common mode voltage, permitting the duty cycle of the complementary PWM signals to gradually increase, thus reducing clicks and pops. The converse operation is performed in the transition from unmuted to muted. Pulse-width-modulation control logic (26) is also included to ensure that that the PWM “on” and “off” pulses are of at least a minimum duration, and also to generate compensating pulses on the complementary PWM line at low duty cycles.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Switching Mode Power Supply Control
InactiveUS20120153919A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching signalSwitching frequency
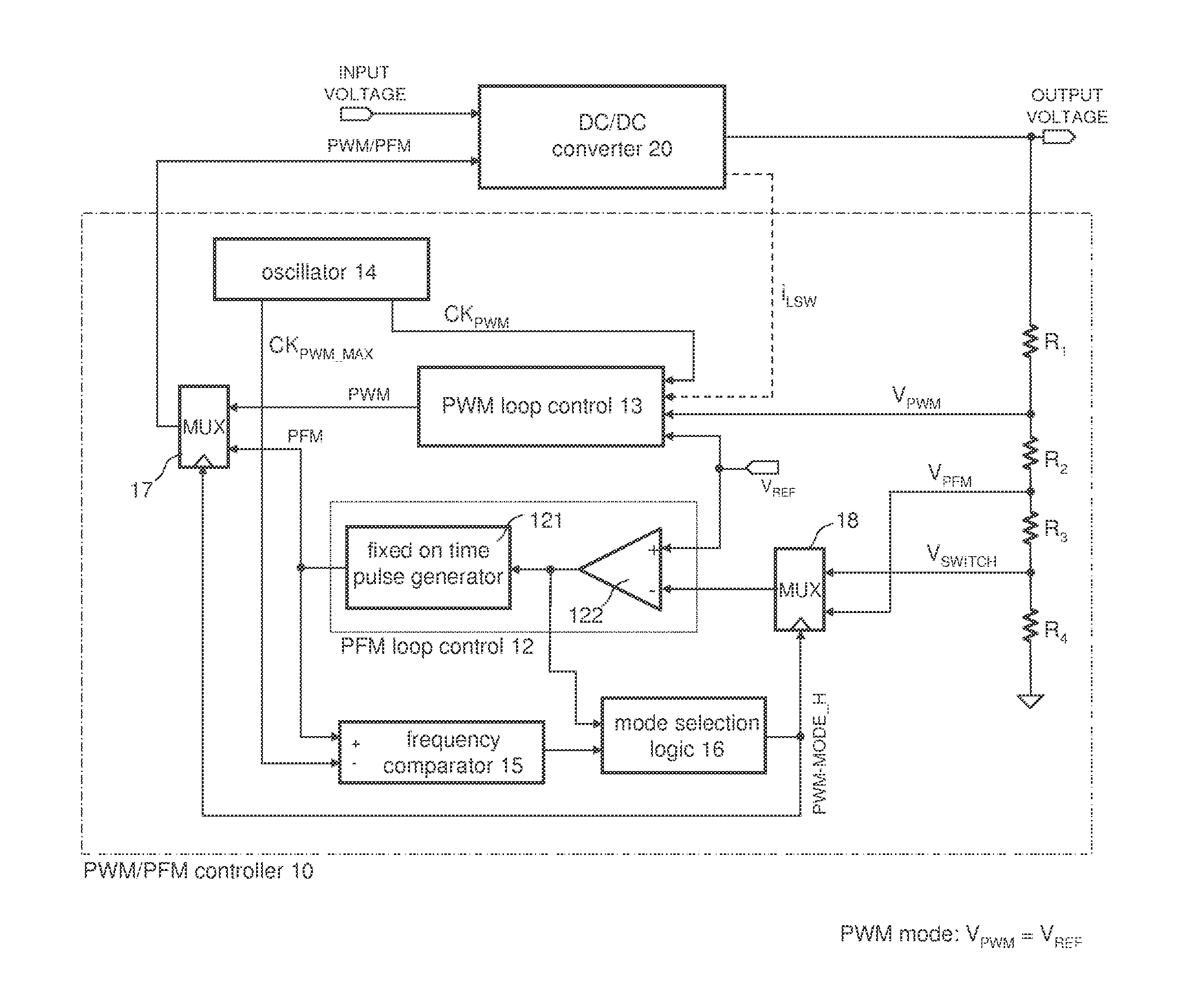
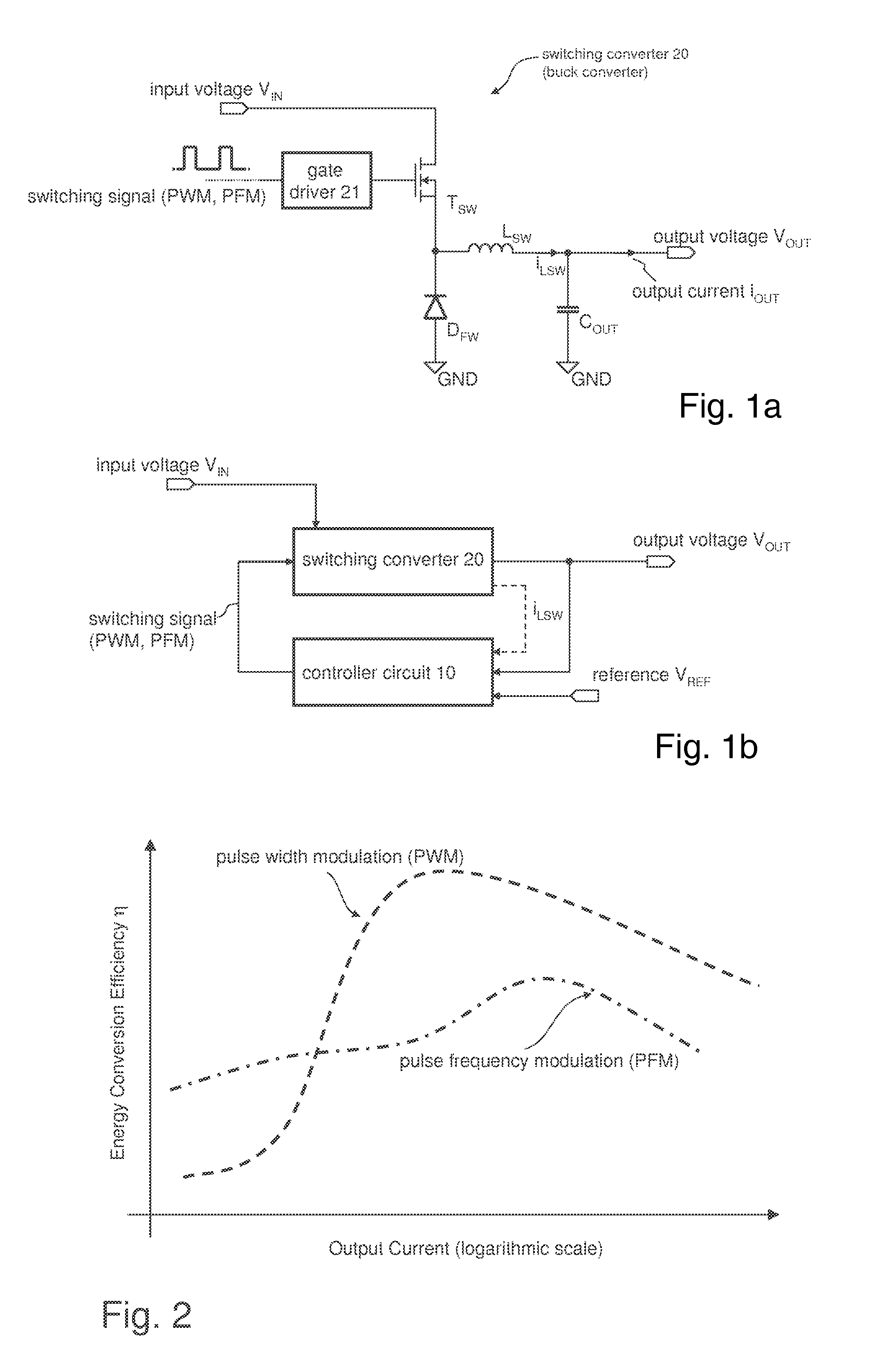
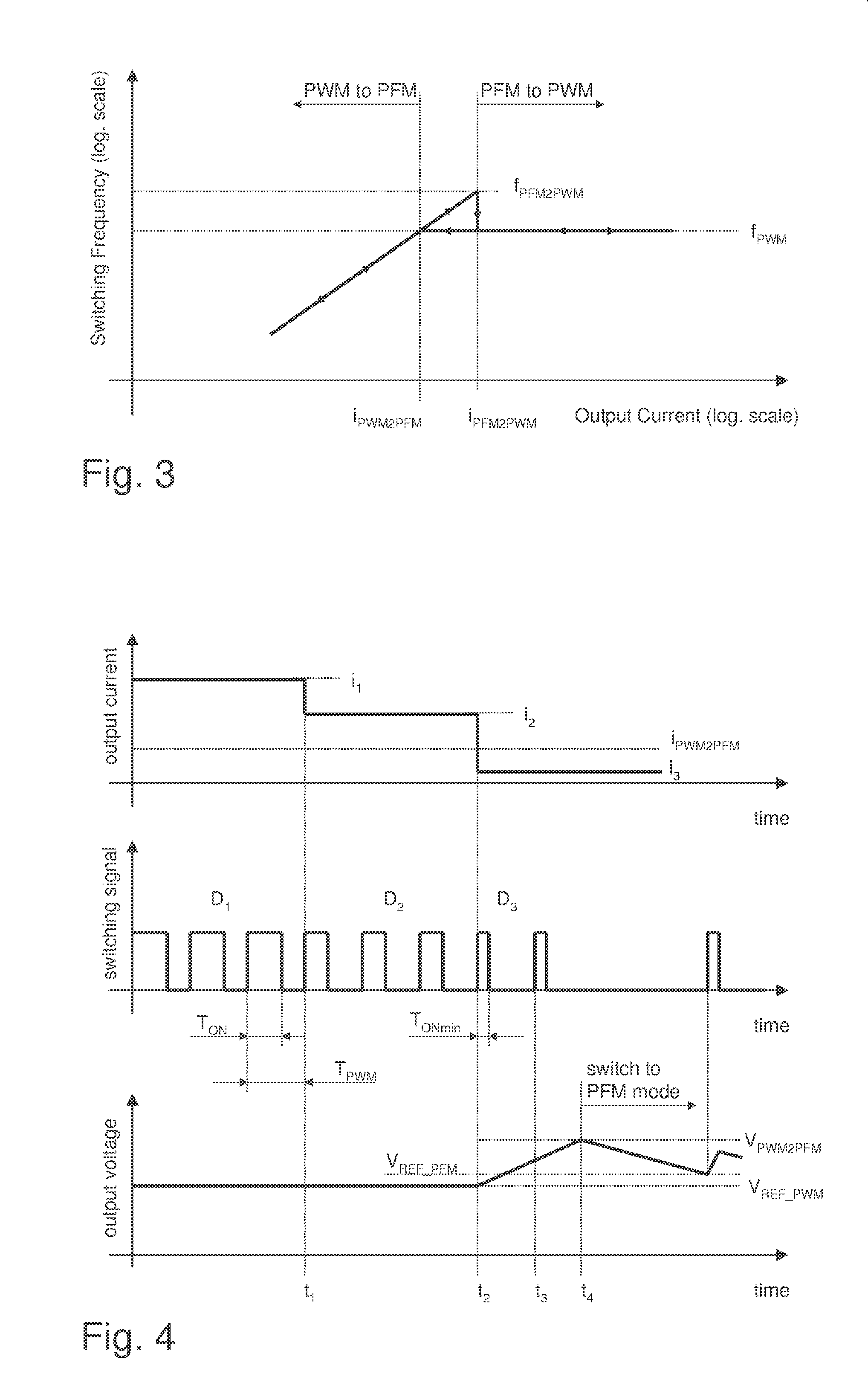
A method for controlling a switching converter is disclosed whereby the switching converter is configured to convert an input voltage into an output voltage supplied to a load in accordance with a switching signal, The switching converter is configured to operate in a pulse width modulation mode or, alternatively, in a pulse frequency modulation mode. When operating in the pulse width modulation mode, generating, as the switching signal, a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal of a pre-defined constant switching frequency. The PWM signal has a duty cycle that is regulated such that the output voltage of the switching converter matches, at least approximately, a desired output voltage under the condition that the duty cycle being regulated such that it does not fall below a predefined minimum duty cycle. The output voltage is monitored and switched over to the pulse frequency modulation mode when the output voltage exceeds a predefined first threshold. The method further comprises, when operating in the pulse frequency modulation mode, monitoring the output voltage and generating, as the switching signal, a series of pulses of a predefined constant pulse length. A pulse is generated each time the output voltage falls to a predefined second threshold and monitoring the frequency of the switching signal and switching to the pulse width modulation mode when the frequency of the switching signal exceeds a predefined frequency threshold.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com