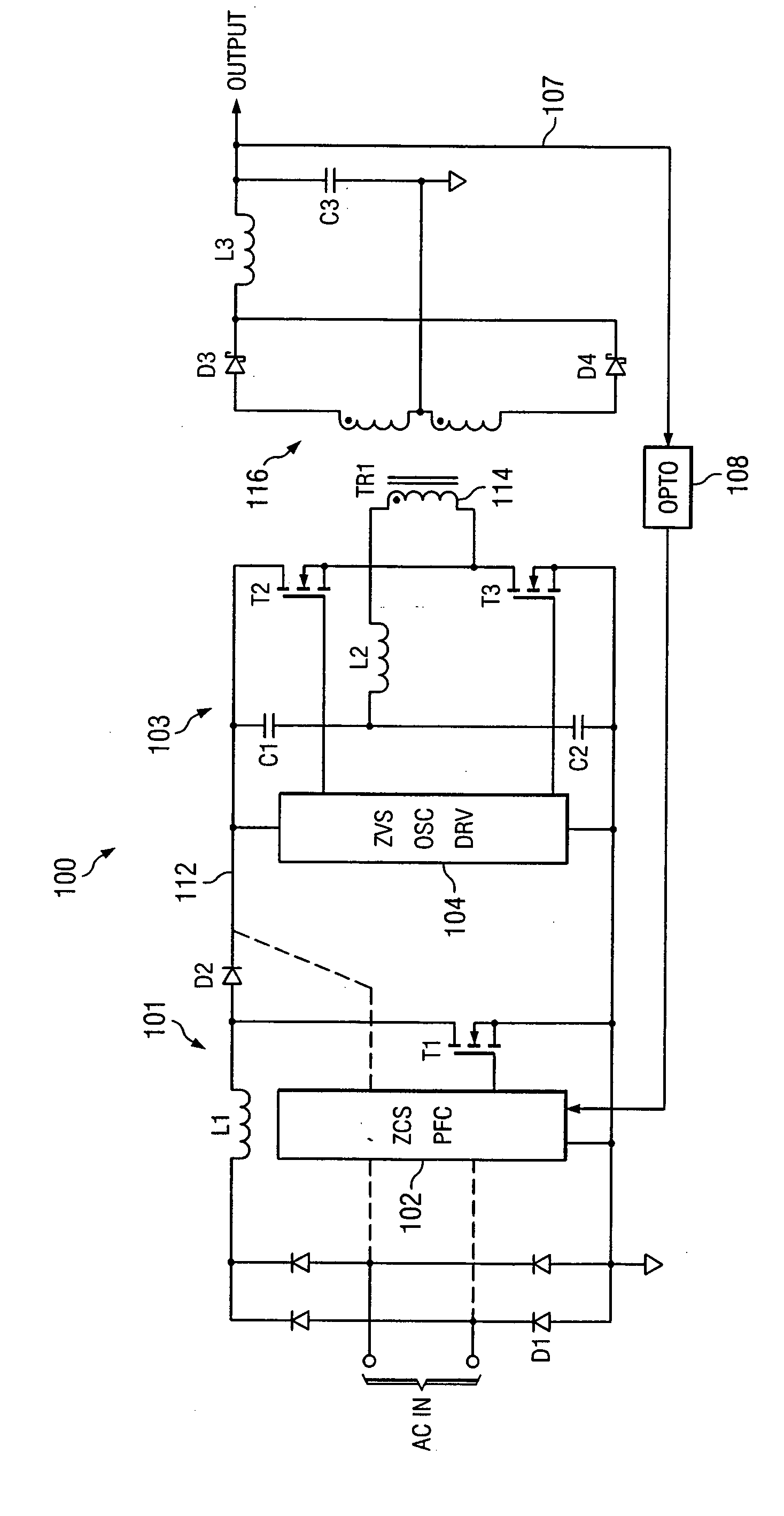
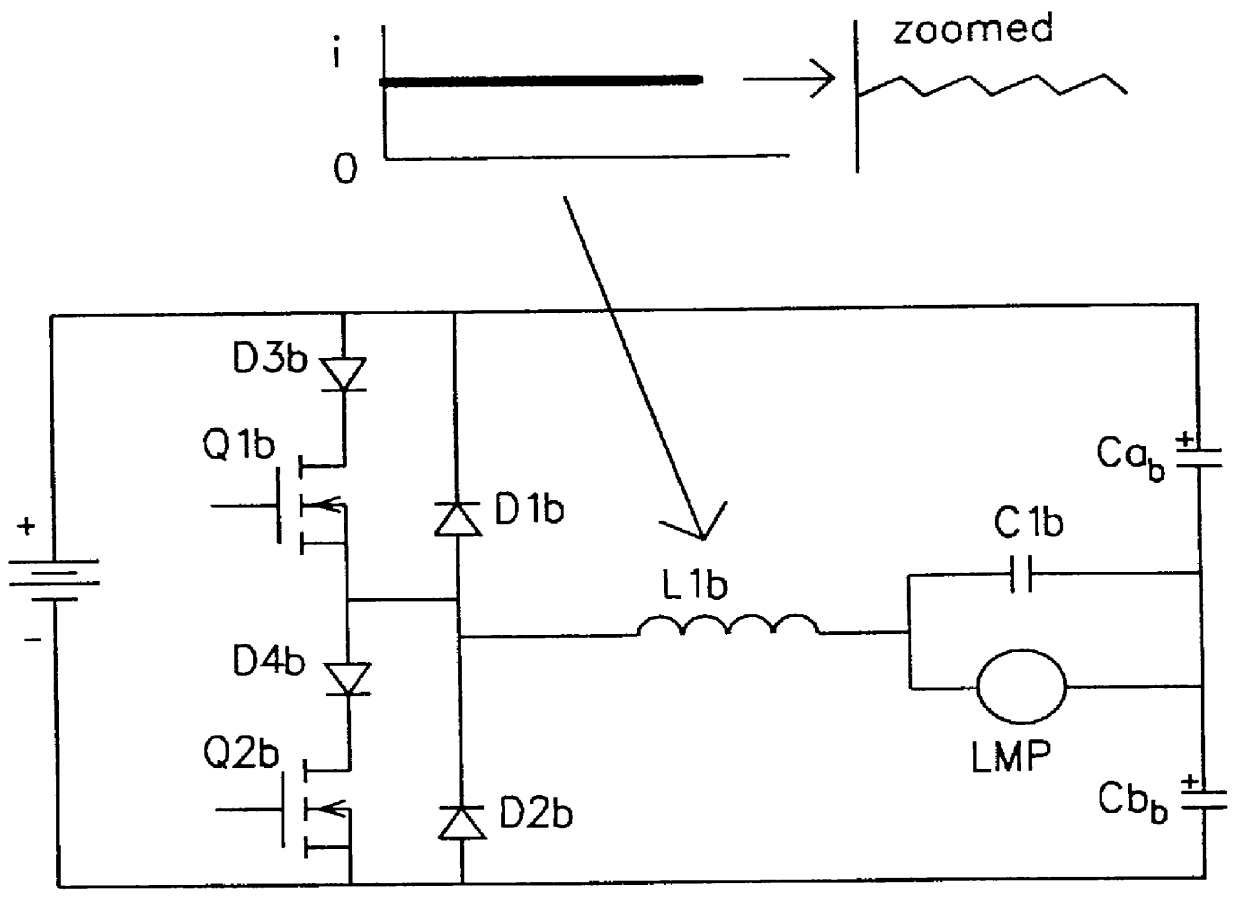
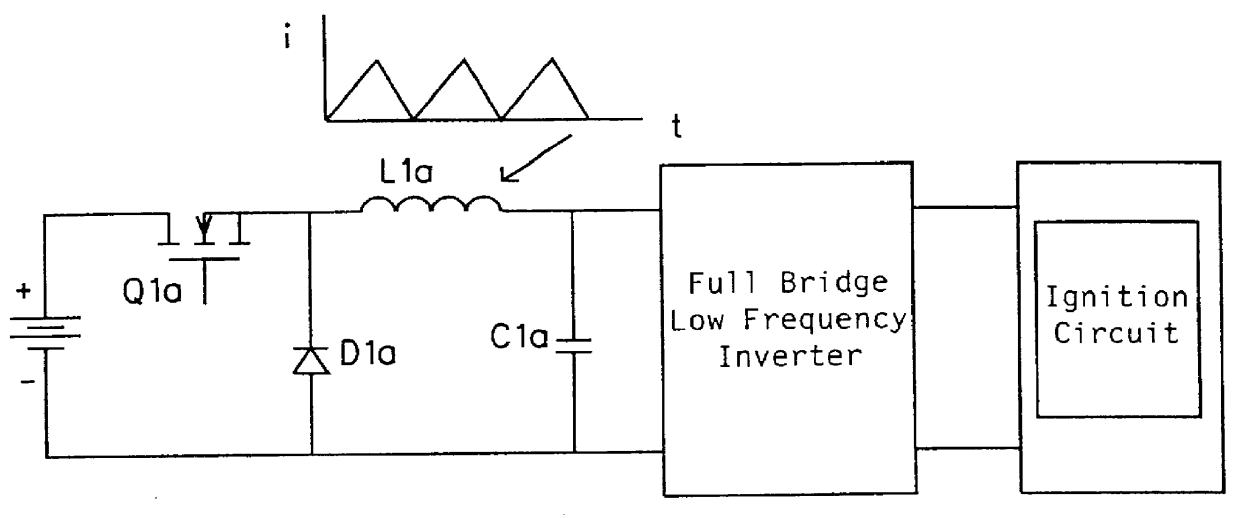
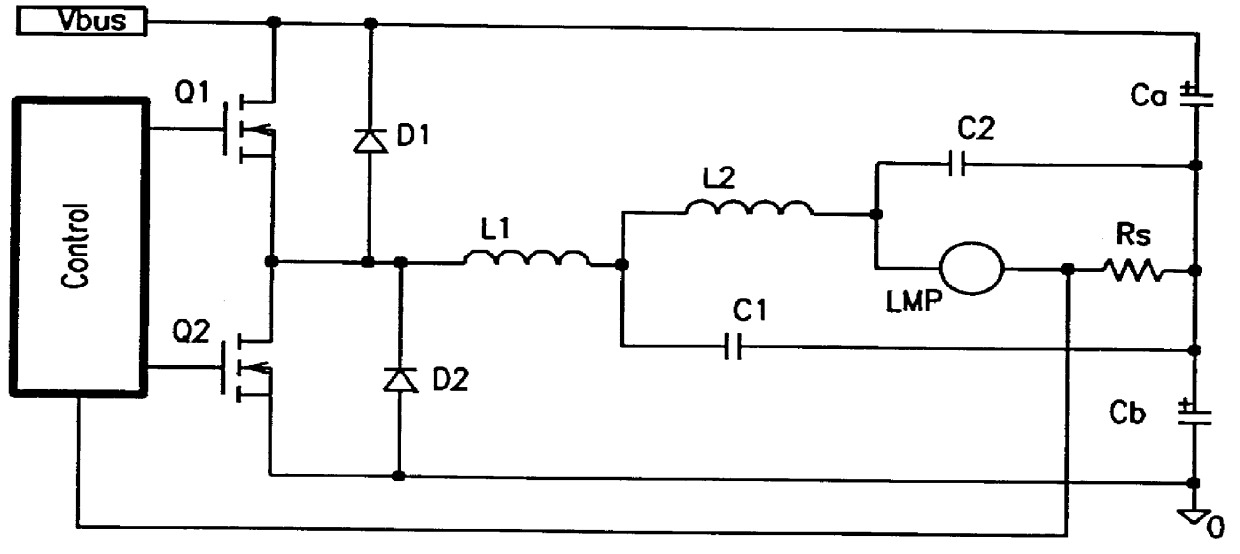
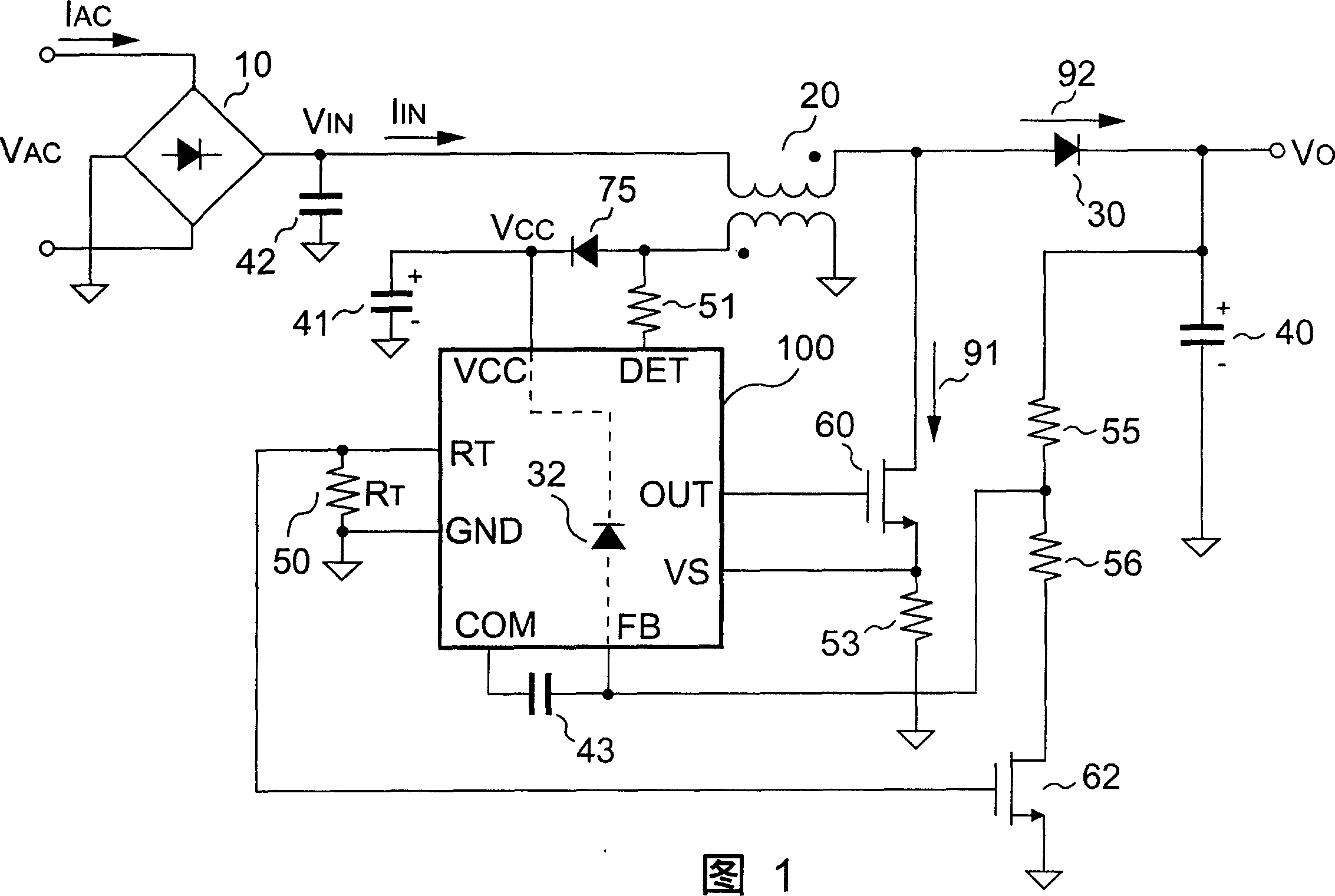
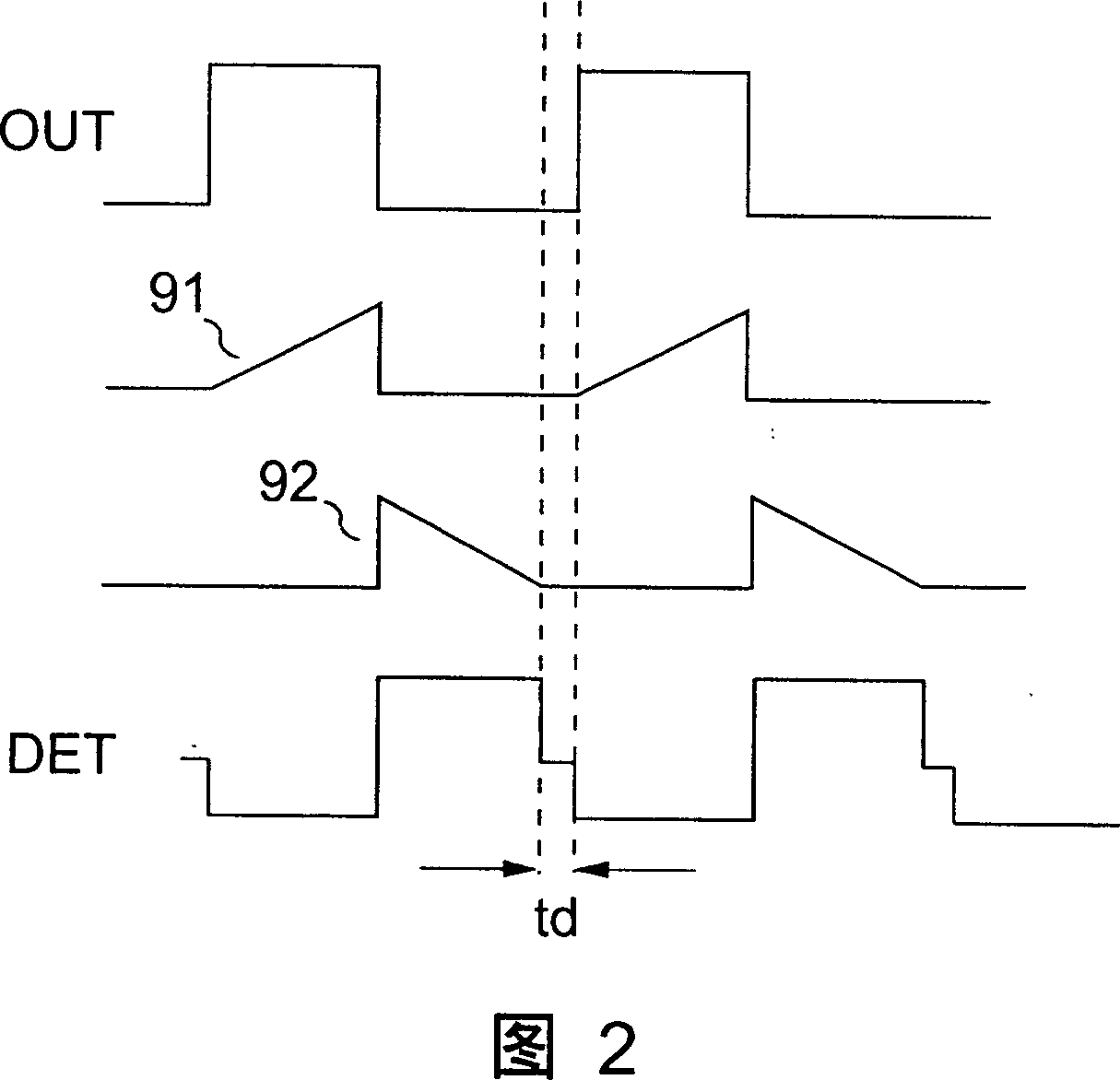
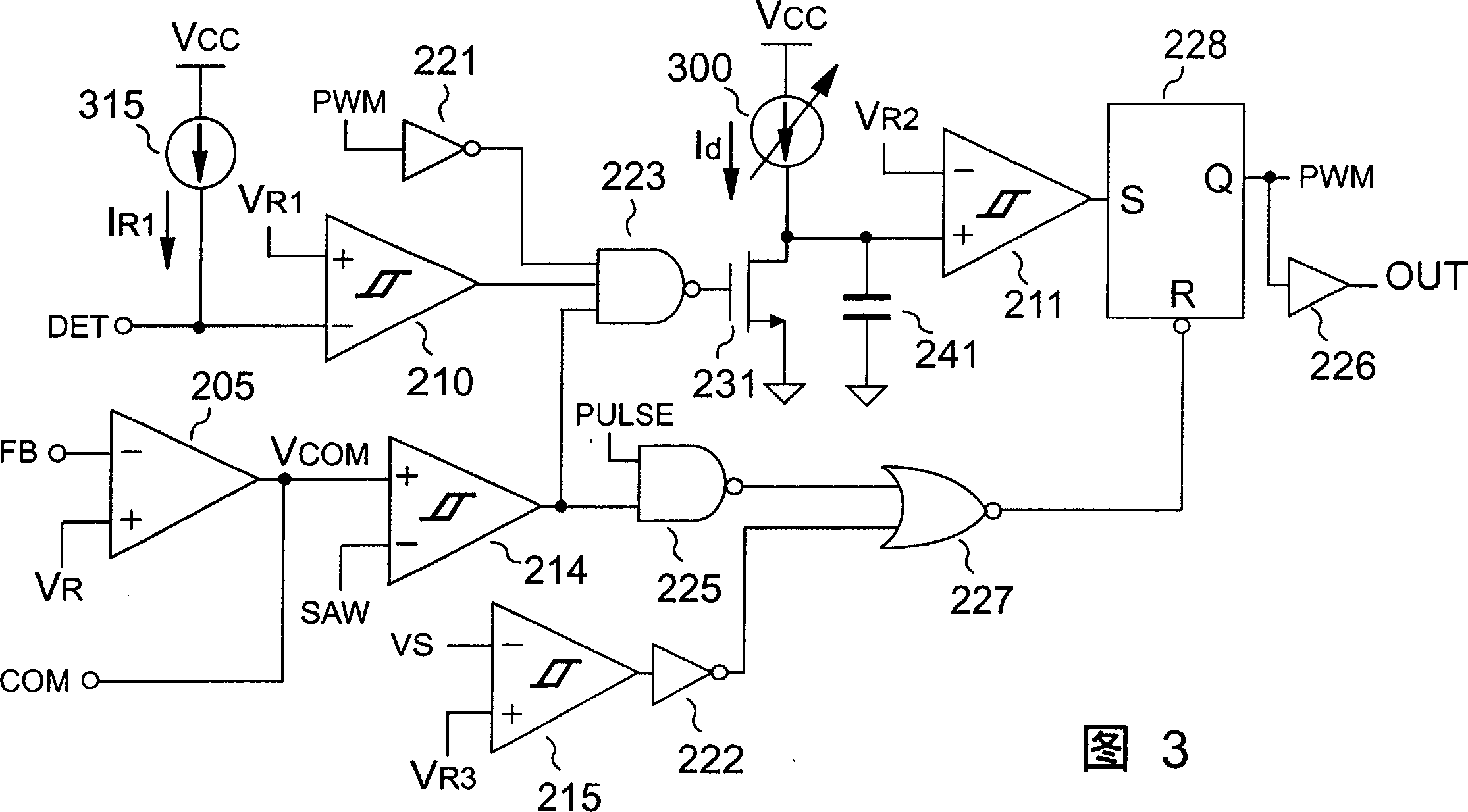
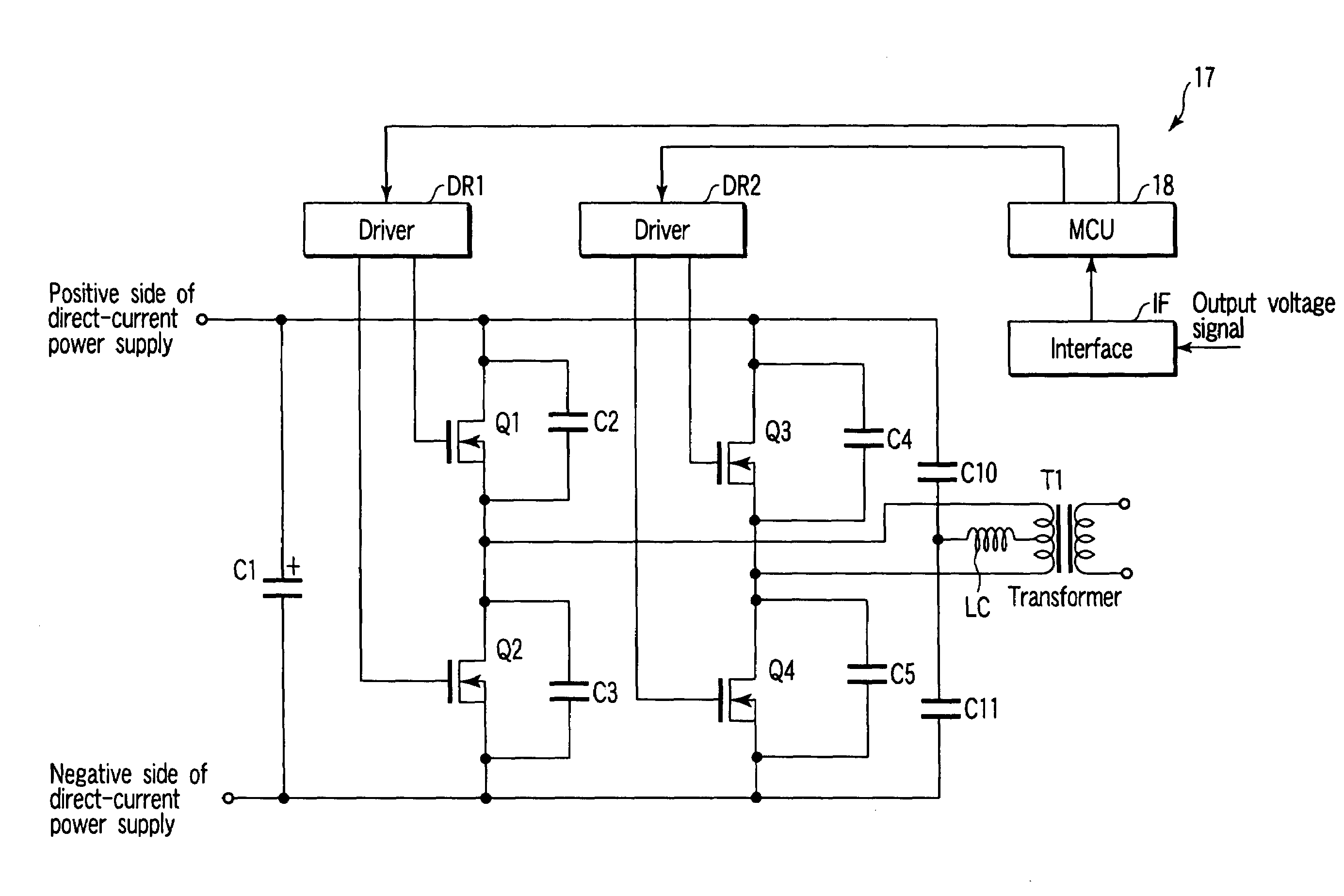
Patents
Literature
188 results about "Zero current switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zero- current switching eliminates the switching loss caused by IGBT current tailing and by stray inductances. It can also be used to commutate SCR’s. Zero-voltage switching : transistor turn-on transition occurs at zero voltage. Diodes may also operate with zero-voltage switching.
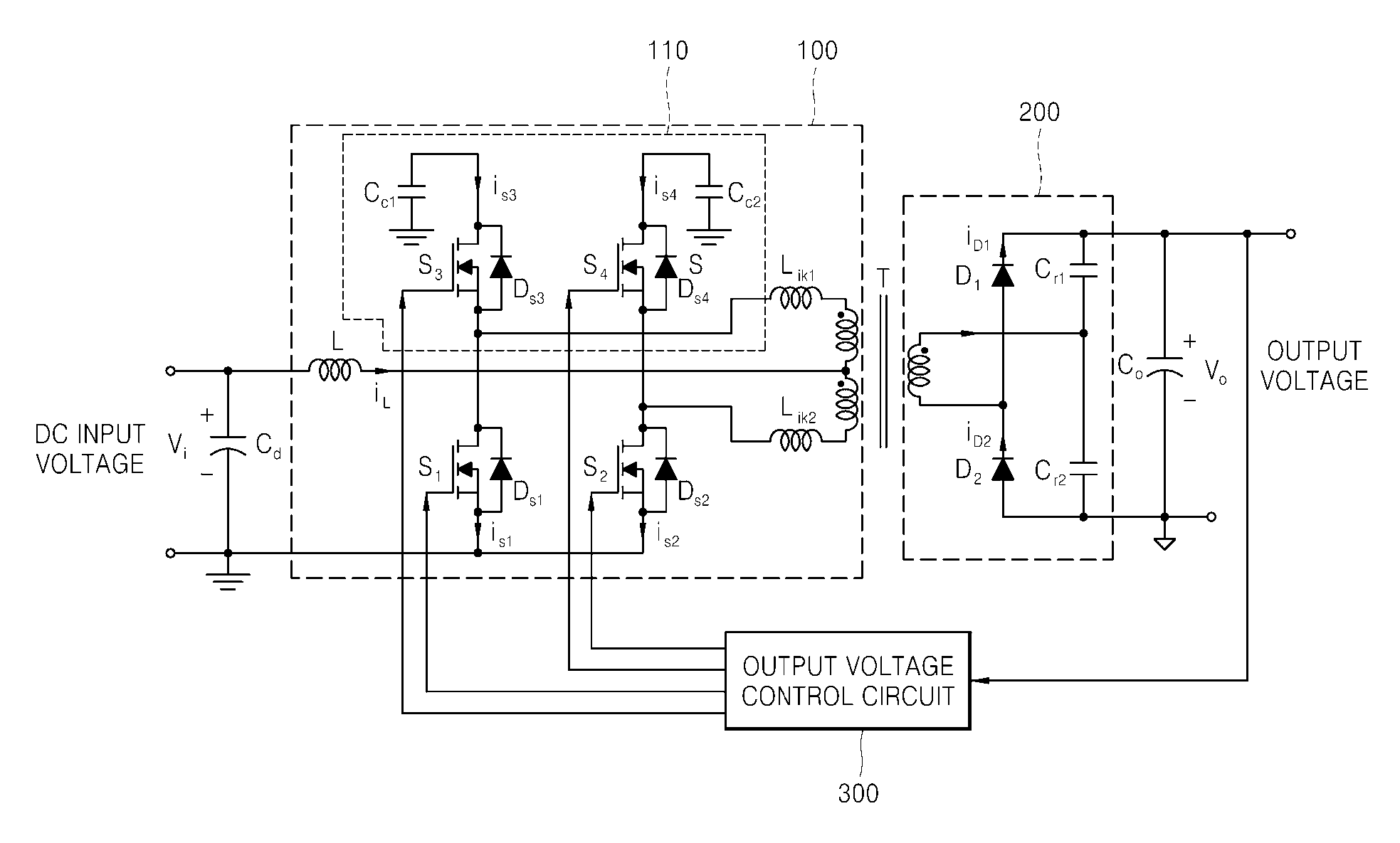
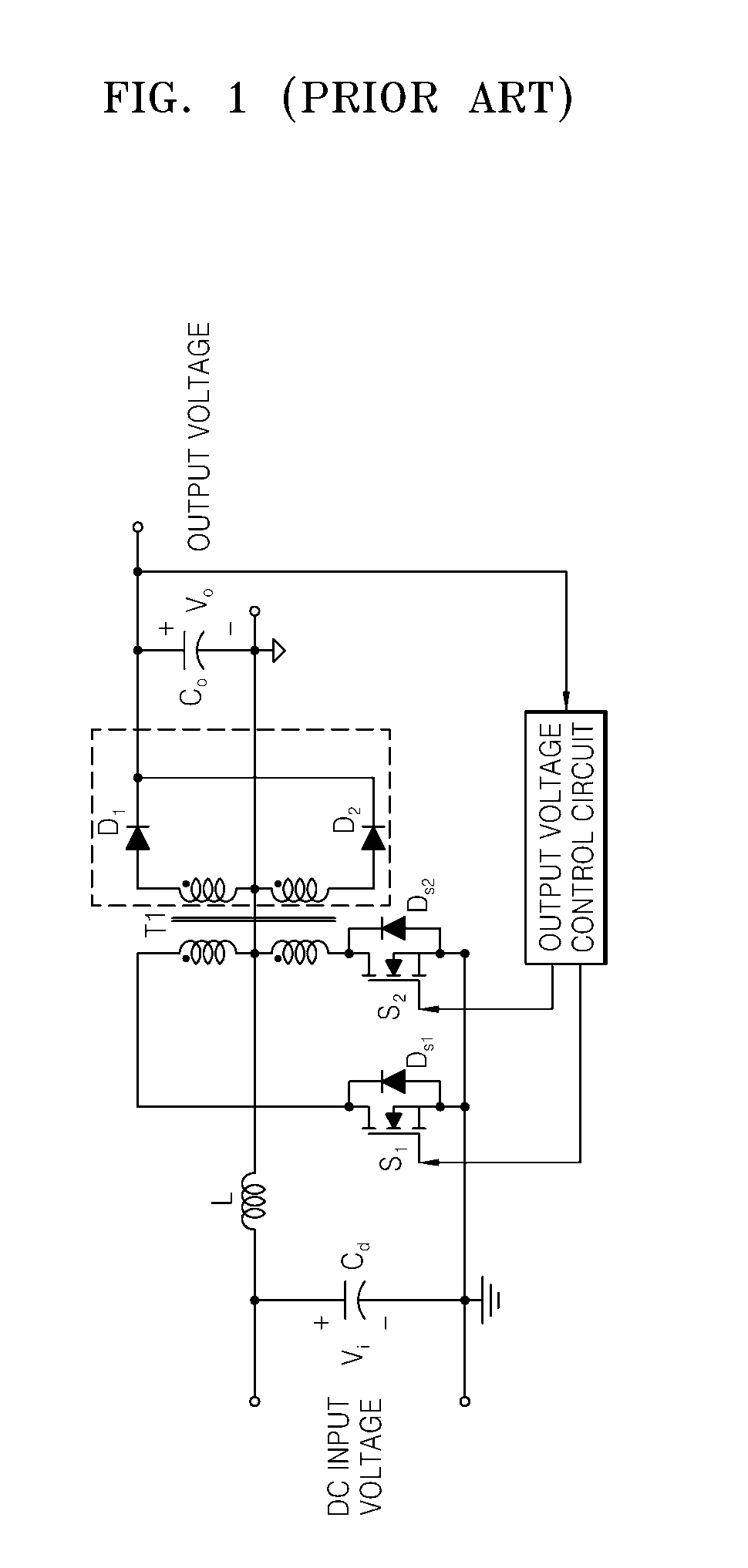
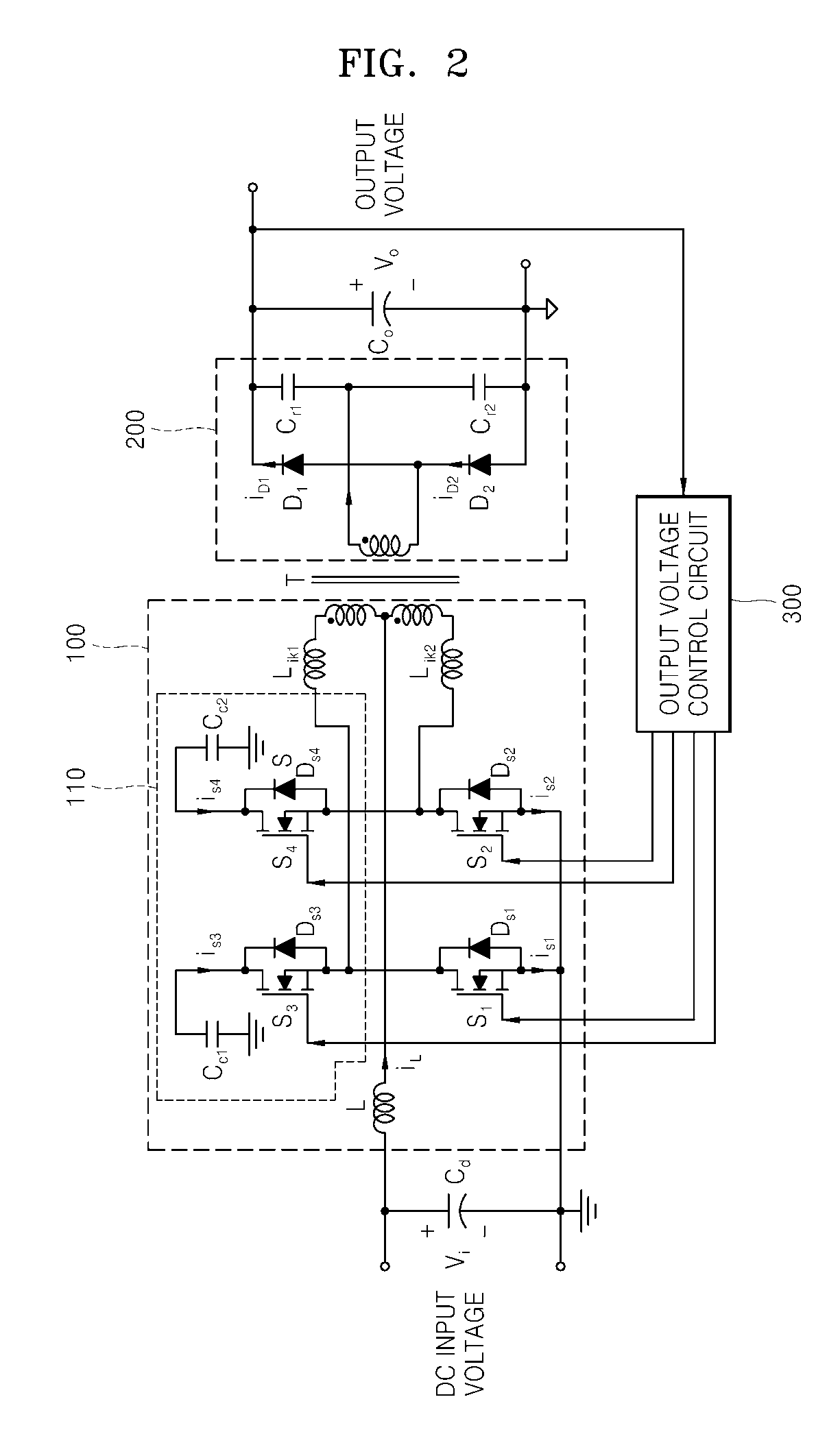
Active-clamp current-source push-pull dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20070247877A1Improve power conversion efficiencyReduce voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePush pull
Provided is a current-source push-pull DC-DC converter using an active clamp circuit for reusing energy of leakage inductances by not only diodes on a secondary side of a transformer being zero-current switched using a series-resonant full-wave rectifier, but also the active clamp circuit on a primary side of the transformer, which provides a discharge path of the energy stored in the leakage inductances, increases power conversion efficiency even for a wide input voltage range and reduces a switch voltage stress as compared to a conventional current-source push-pull circuit by operating even for a duty ratio below 0.5 by flowing a current of an input inductor through capacitors of the active clamp circuit when both main switches are off.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
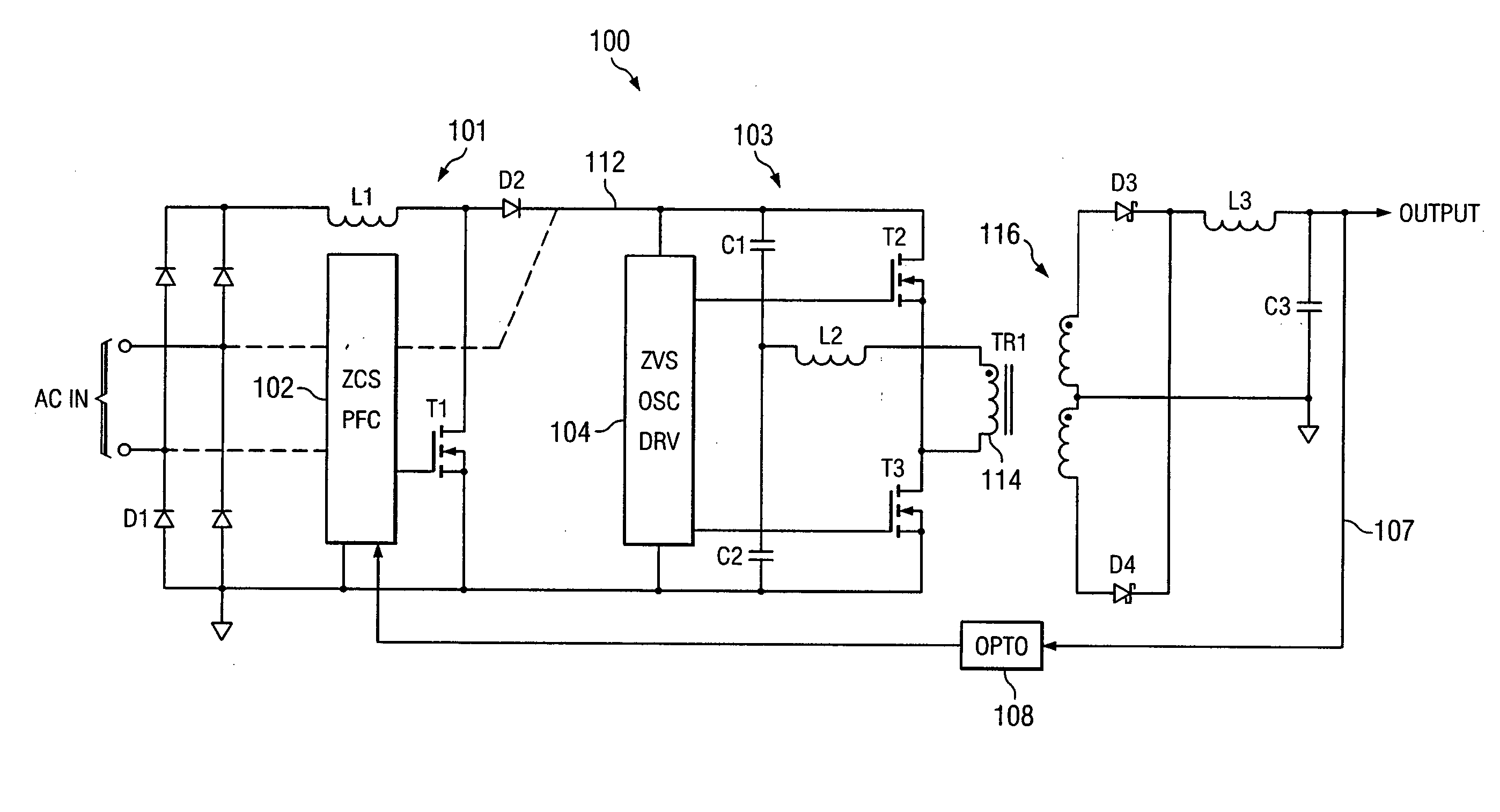
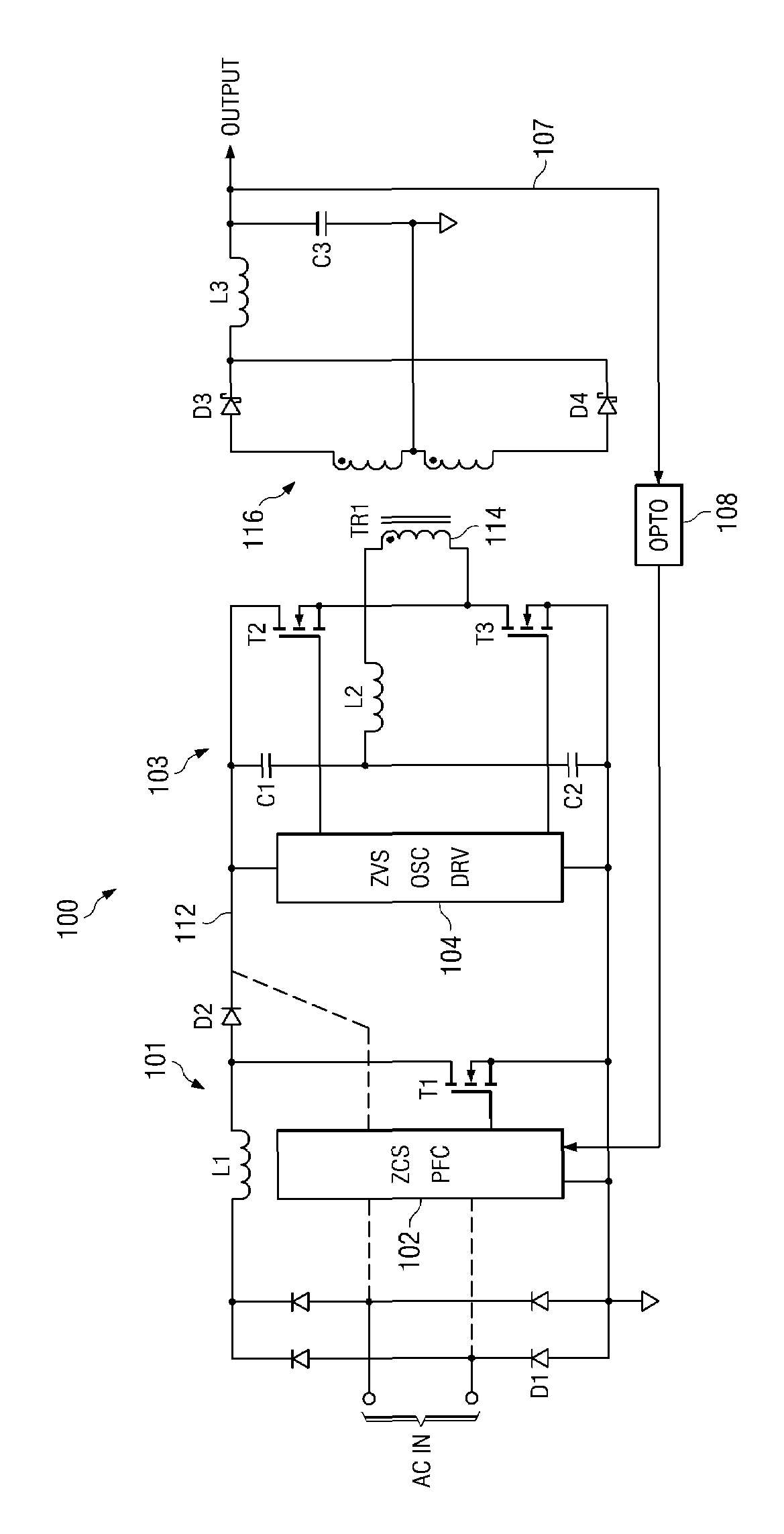
Highly efficient isolated AC/DC power conversion technique
ActiveUS20070081364A1Reduce circuit sizeReduce complexityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerEngineering
An AC-to-DC power converter that is capable of generating a regulated, isolated DC voltage output from a power factor corrected AC voltage input with improved efficiency. The AC-to-DC power converter is a two-stage power converter including a PFC stage connected in series to a power conversion stage. The PFC stage performs power factor correction using a zero current switching technique, and the power conversion stage includes a zero voltage switched half-bridge converter. The power conversion stage includes a transformer for providing the isolated DC voltage output. The AC-to-DC power converter includes a single feedback control loop for transferring error information from the DC voltage output to the PFC stage, thereby obtaining regulation of the DC voltage output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
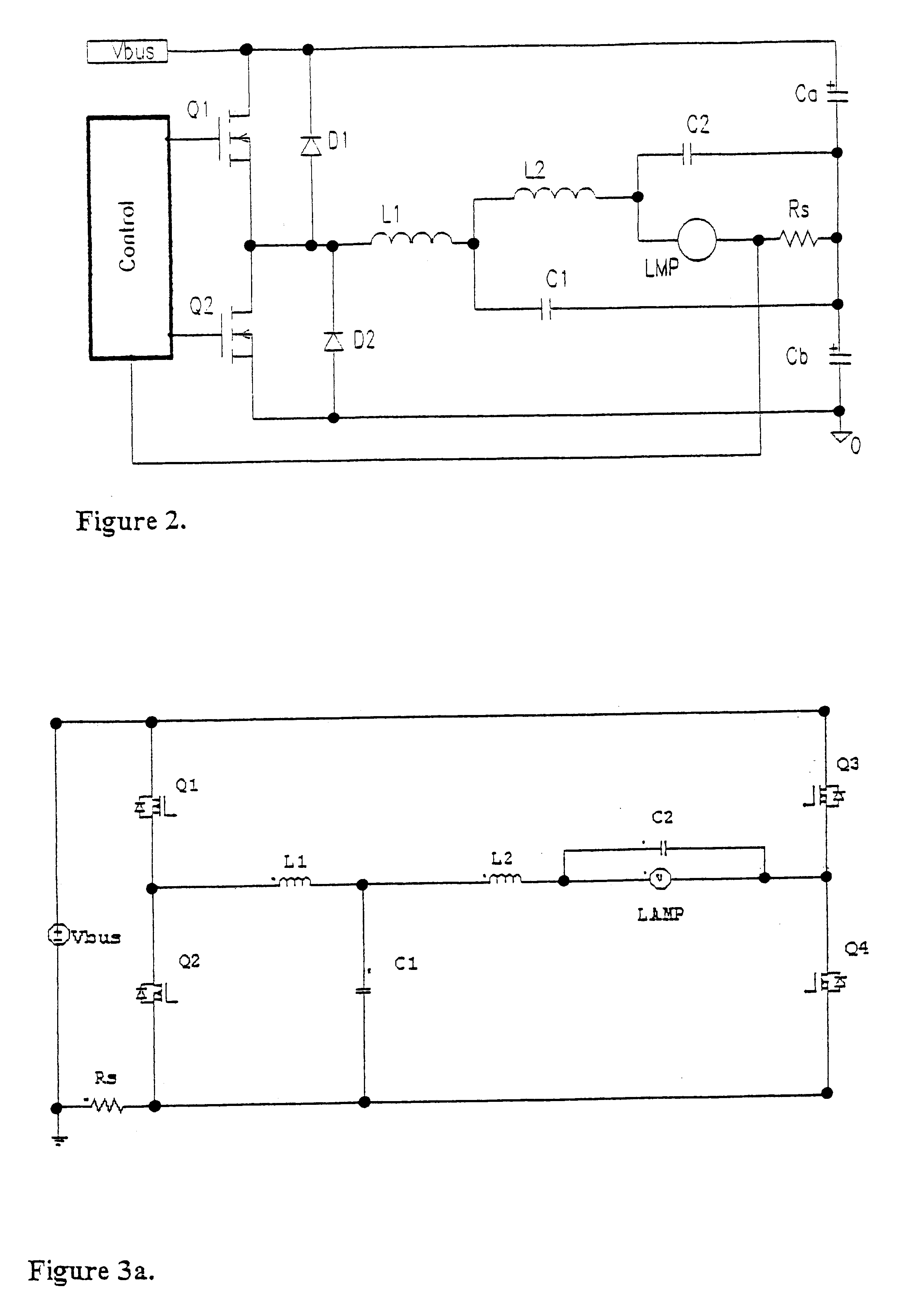
Driving circuit for high intensity discharge lamp electronic ballast
InactiveUS6020691AImprove performanceAvoiding excessive currentElectric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageLamp currentEngineering
A circuit arrangement and control thereof for igniting a high intensity discharge (HID) lamp, for reducing the high frequency ripple superimposed on the low frequency rectangular waveform lamp current after ignition, and for increased circuit efficiency. The high frequency ignition voltage is only applied to the lamp during ignition phase and is mainly generated by the second stage of the low pass (LP) filter. The first stage of the LP filter whose resonant frequency is below the second stage further attenuates the high frequency ripple current through the lamp in normal operation. The resulting lamp current is a low frequency rectangular wave with less than 10% high frequency ripple. Acoustic resonance is avoided. The inductor in the first stage of LP filter is operated in discontinuous current mode. Doing so, the active switches are in zero current switching (ZCS) to maximize the circuit efficiency.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
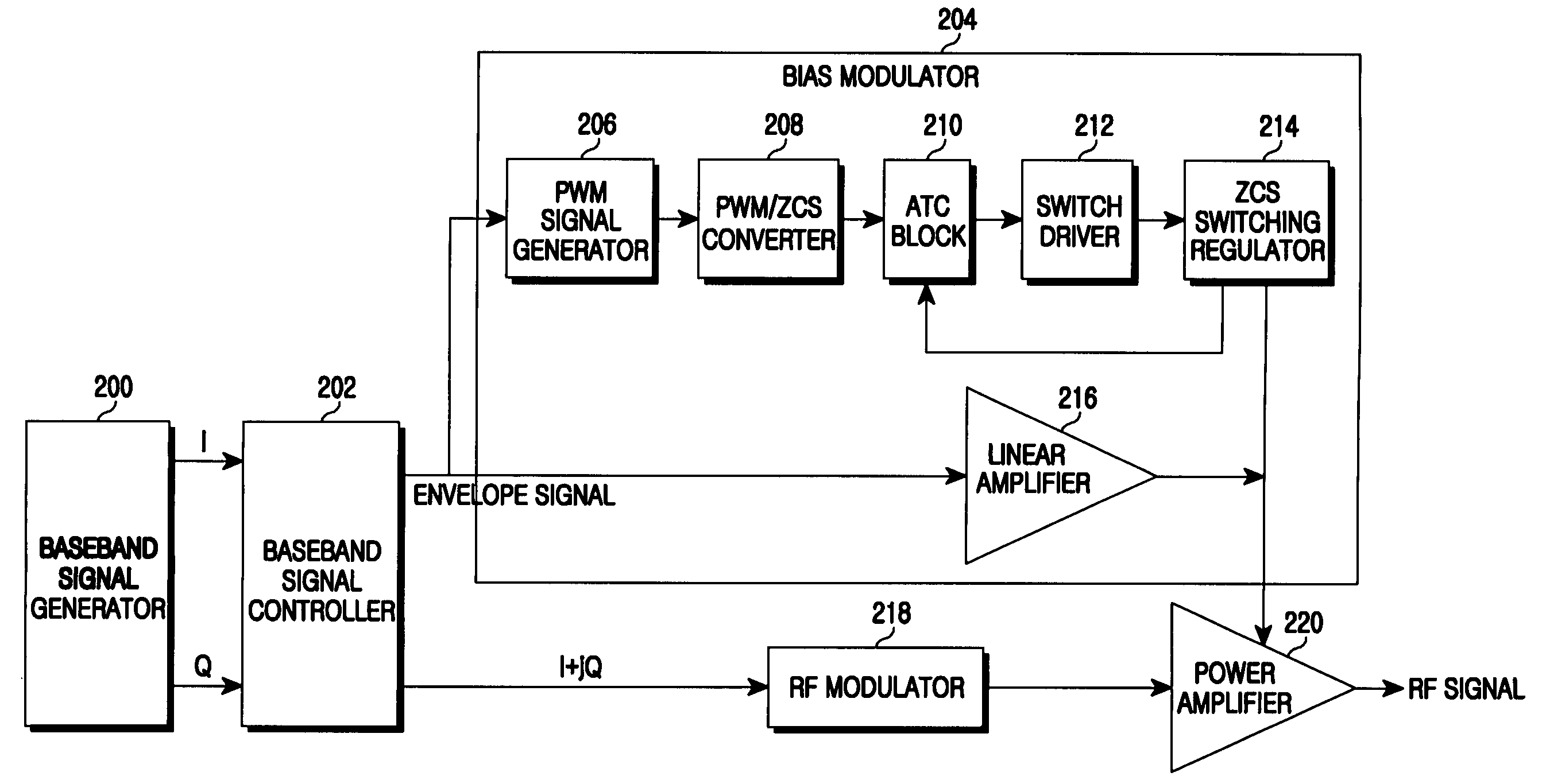
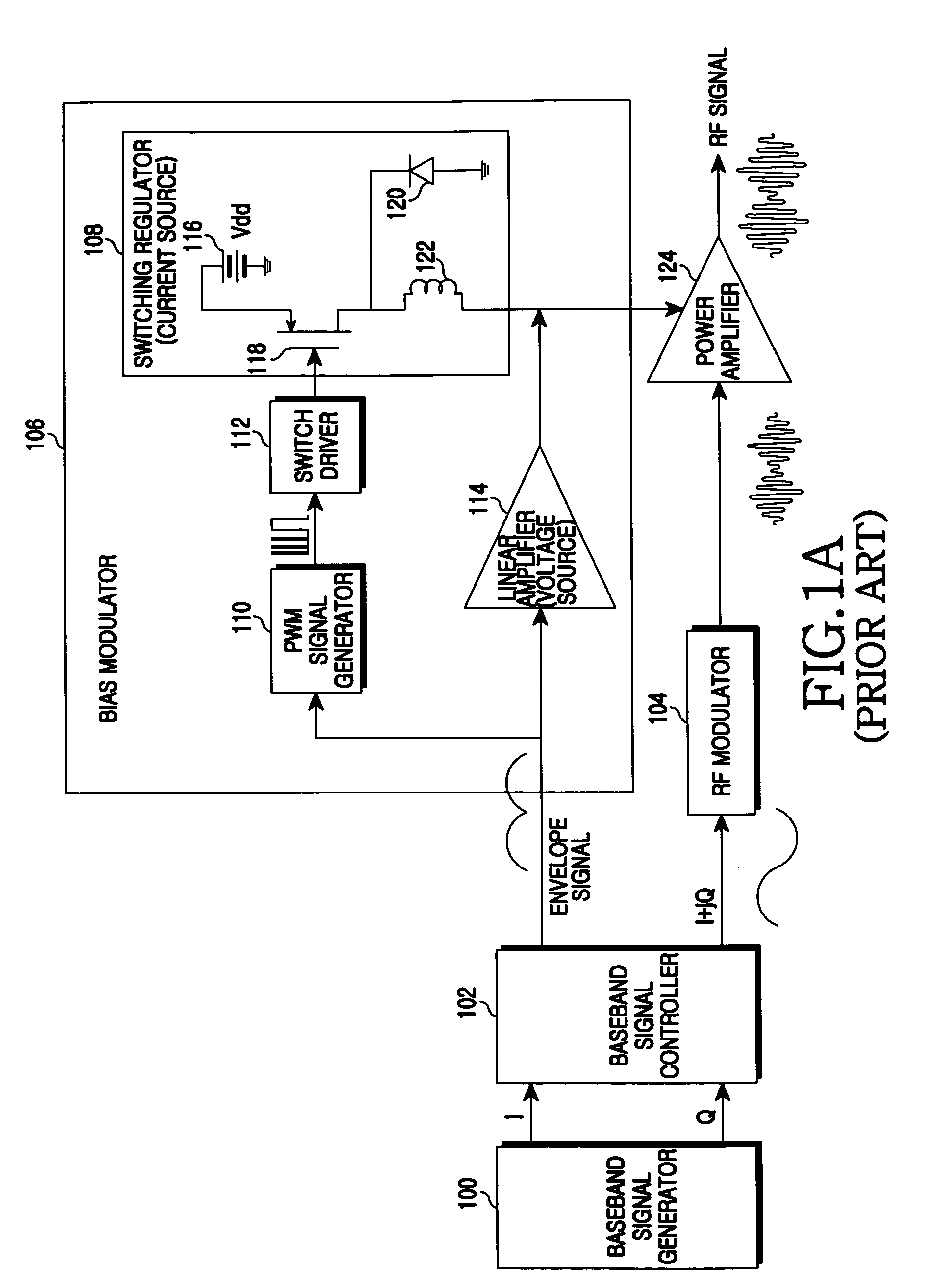
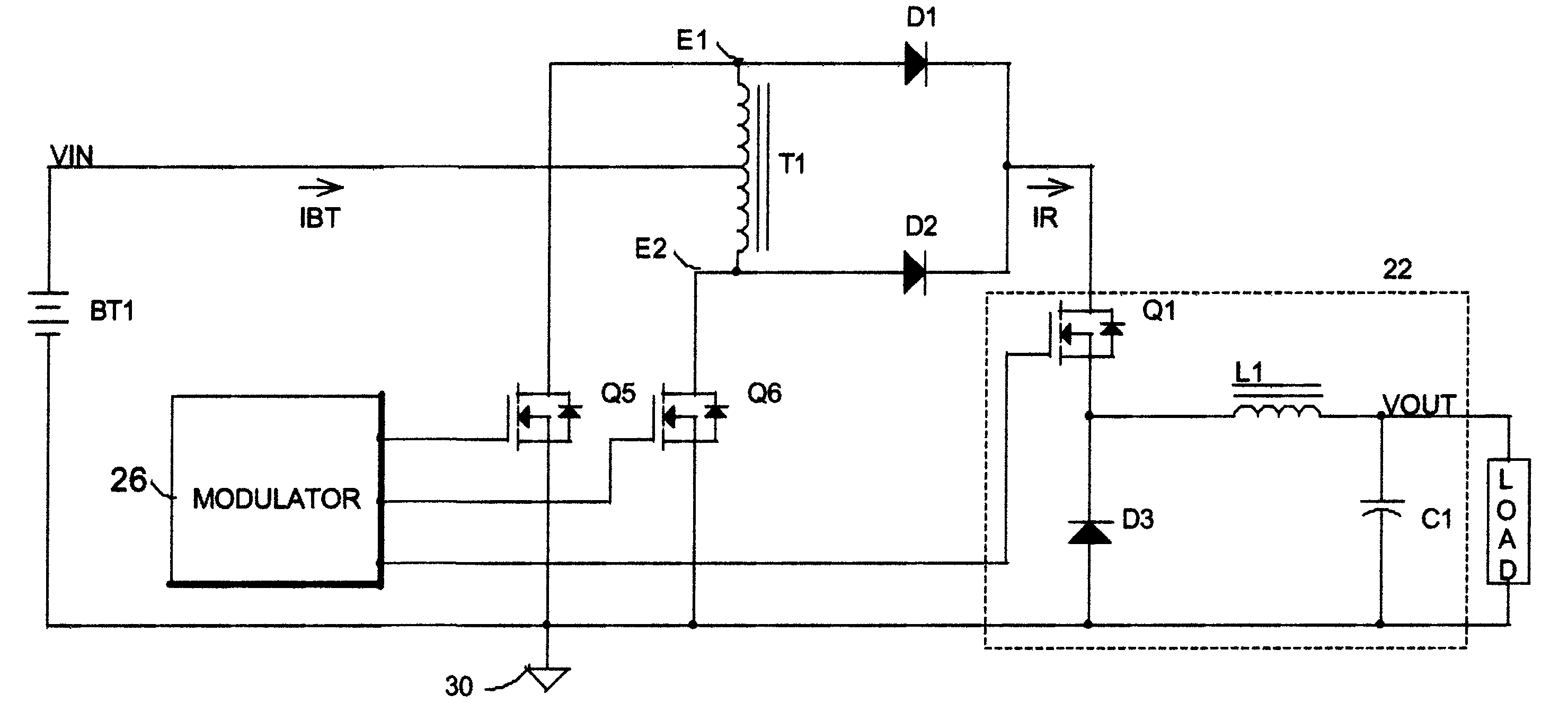
Apparatus and method for bias modulator using zero current switching
ActiveUS20090218995A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAngle modulationControl signalEngineering
An apparatus and a method for a bias modulator using a Zero Current Switching (ZCS) are provided. The bias modulator includes a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal generator for converting an input envelope signal to a PWM signal; a PWM / ZCS converter for calculating the number of ZCS control signals to be provided within an on-time duration of the PWM signal and generating at least one ZCS control signal according to the number of the ZCS control signals; and a ZCS switching regulator for generating a bias current according to the ZCS control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-efficiency power converter system
ActiveUS20080002444A1Readily apparentAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringAlternating current
In one embodiment, a power converter system includes a first input terminal and a second input terminal operable to connect to an alternating current (AC) power source, and an output terminal at which an output voltage can be provided to a load. A first inductor and a first diode are connected in series between the first input terminal and the output terminal. A second inductor and a second diode are connected in series between the second input terminal and the output terminal. A first switch is connected to the first inductor and the first diode, and a second switch is connected to the second inductor and the second diode. The first switch and the second switch alternately function as a boost switch and a synchronous rectifier for charging and discharging the first and second inductors during operation of the power converter system. An auxiliary network is operable to provide for zero voltage switching (ZVS) and zero current switching (ZCS) conditions for both the first and second switches during operation of the power converter system.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Variable structure circuit topology for HID lamp electronic ballasts
InactiveUS6380694B1Increase speedSmooth transitionElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementFull bridgeEngineering
A high intensity discharge (HID) lamp driving circuit. The HID lamp driving circuit includes a first pair of switching devices connected to a high frequency resonant filter, and a second pair of switching devices connected to a ripple reducing filter. A HID lamp is connected between the first pair of switching devices and second pair of switching devices, with a dc power supply being connected to the first pair of switching devices and the second pair of switching devices. The first pair of switching devices and the second pair of switching devices are connected to a common ground with the dc power supply. The lamp driving circuit operates in a half bridge topology during a start-up operation mode of the lamp, and operates in a full-bridge topology during a steady-state operation mode of the lamp. The HID lamp driving circuit is operated in an active zero current switching scheme.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
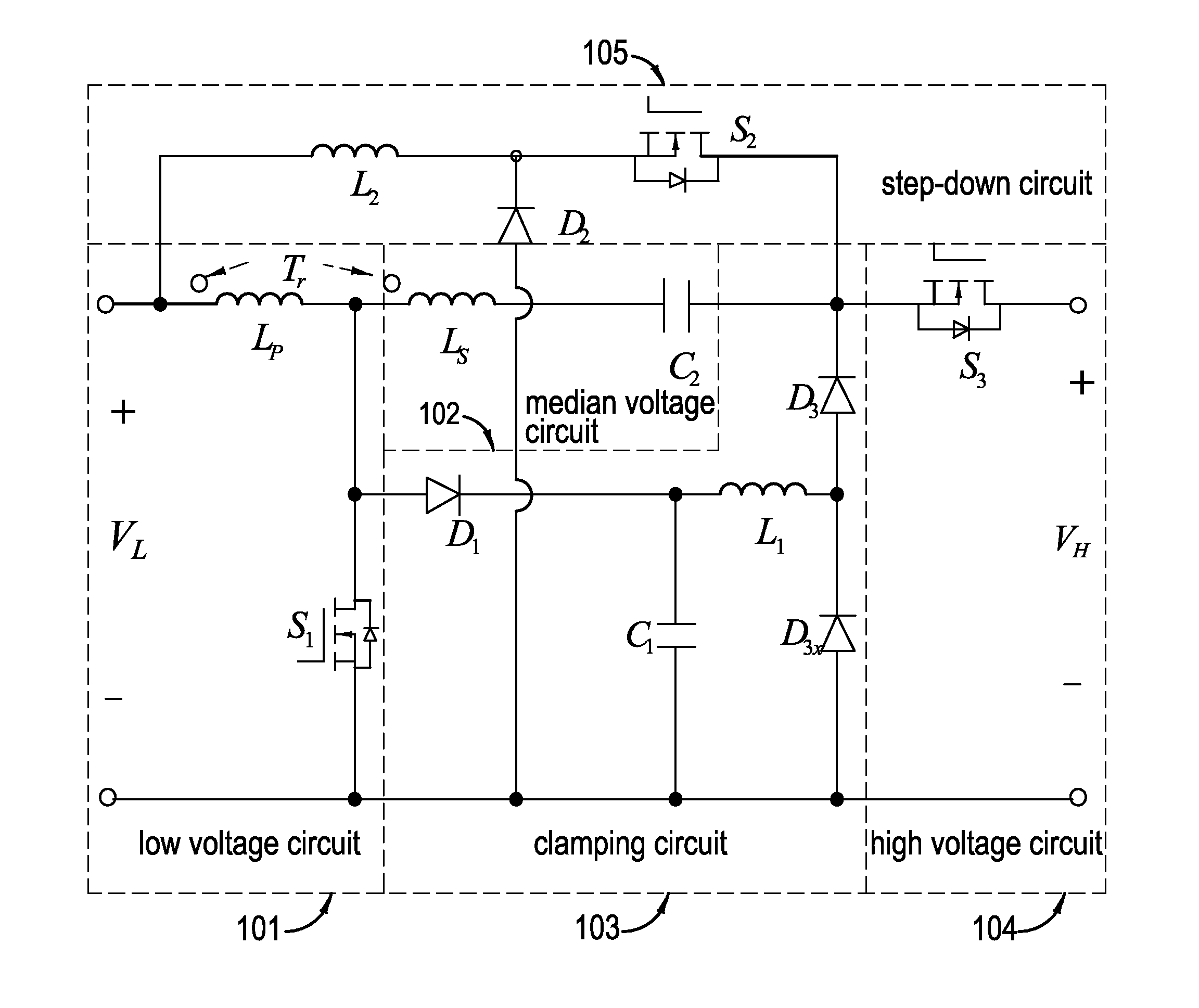
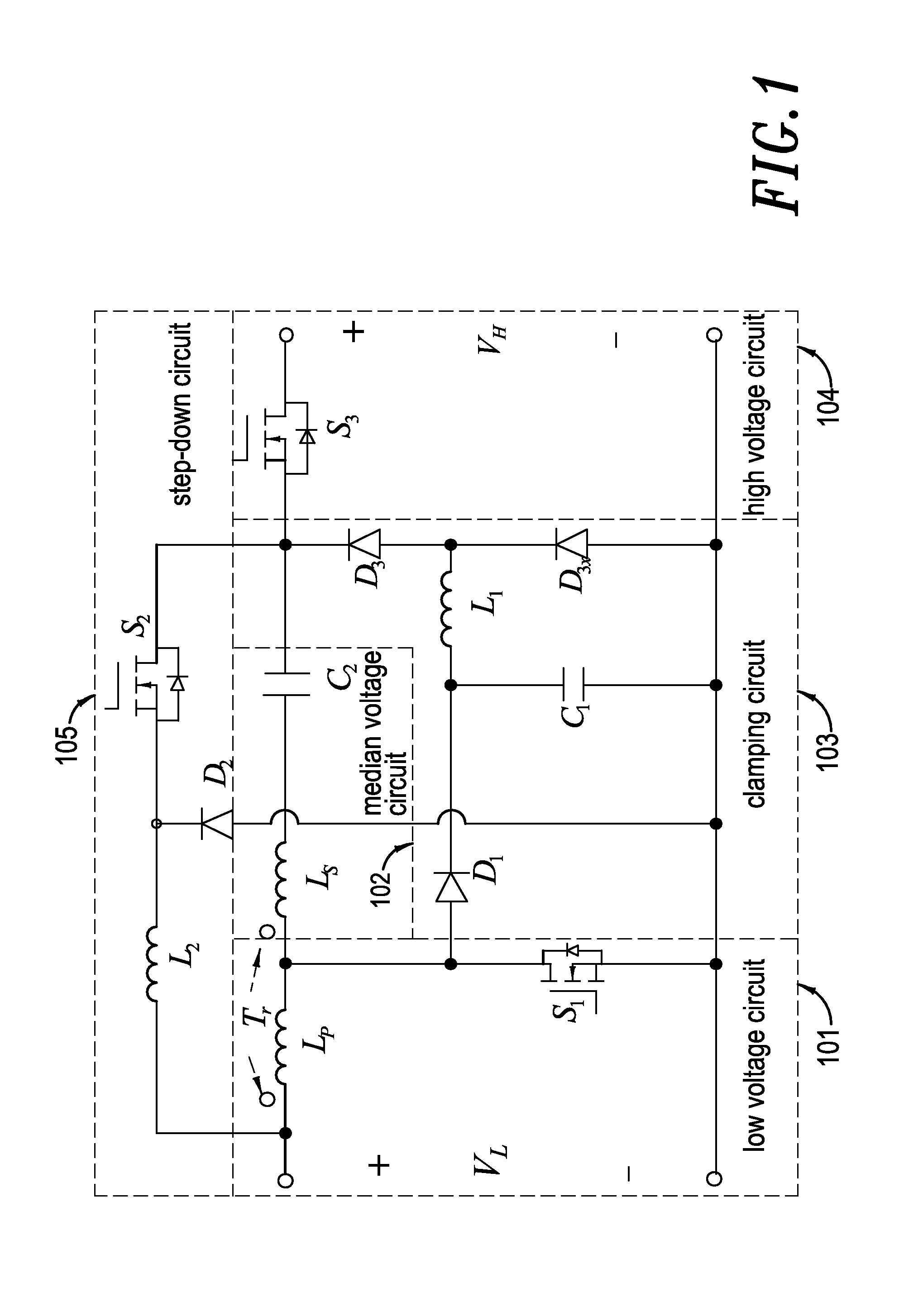
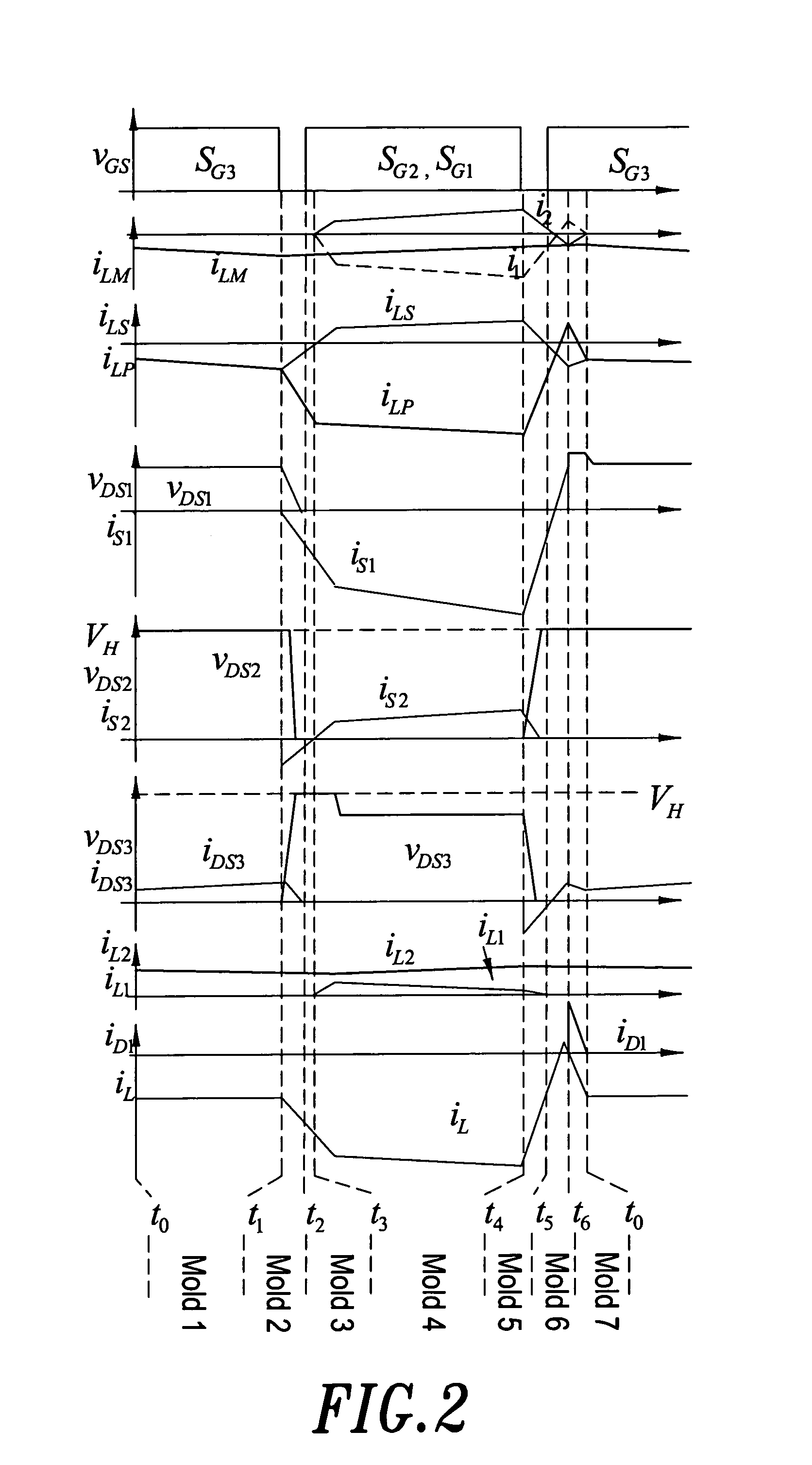
High-efficiency high-voltage difference ratio bi-directional converter
InactiveUS7382113B2Reduce conduction lossReduce voltageDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionTransformerLow voltage
The aim of this invention focuses on the development of a high-efficiency bidirectional converter for power sources with great voltage diversity. In traditional bidirectional converters, the circuit topology with transformer form is the common usual. Moreover, the soft-switching techniques including zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) or zero-current-switching (ZCS) are usually used for alleviating the corresponding switching losses. However, there are four and upward power semiconductor switches in these circuit schemes. By this way, it will result in the increase of production cost, and the degeneration of conversion efficiency. The coupled-inductor bidirectional scheme in the proposed converter only adopts three power semiconductor switches to accomplish the objective of bidirectional current control. Under the situation of non-isolation circuit topology, it still possesses the protection of electric safety for operators. Due to the characteristics of high step-up and step-down ratio, the battery module with low voltage could be injected into a high-voltage dc bus for the later utilization, e.g., high-voltage load, front-end of inverter. Since the techniques of voltage clamping, synchronous rectification and soft switching are manipulated in this circuit topology, and the corresponding device specifications are adequately performed, it can achieve the goal of high-efficiency bidirectional power conversion for power sources with great voltage diversity.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
High-efficiency high-voltage difference ratio bi-directional converter
InactiveUS20070216390A1Reduce conduction lossReduce voltageDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionLow voltageTransformer
The aim of this invention focuses on the development of a high-efficiency bidirectional converter for power sources with great voltage diversity. In traditional bidirectional converters, the circuit topology with transformer form is the common usual. Moreover, the soft-switching techniques including zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) or zero-current-switching (ZCS) are usually used for alleviating the corresponding switching losses. However, there are four and upward power semiconductor switches in these circuit schemes. By this way, it will result in the increase of production cost, and the degeneration of conversion efficiency. The coupled-inductor bidirectional scheme in the proposed converter only adopts three power semiconductor switches to accomplish the objective of bidirectional current control. Under the situation of non-isolation circuit topology, it still possesses the protection of electric safety for operators. Due to the characteristics of high step-up and step-down ratio, the battery module with low voltage could be injected into a high-voltage dc bus for the later utilization, e.g., high-voltage load, front-end of inverter. Since the techniques of voltage clamping, synchronous rectification and soft switching are manipulated in this circuit topology, and the corresponding device specifications are adequately performed, it can achieve the goal of high-efficiency bidirectional power conversion for power sources with great voltage diversity.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Highly efficient isolated AC/DC power conversion technique
ActiveUS7375994B2Improve efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerEngineering
An AC-to-DC power converter that is capable of generating a regulated, isolated DC voltage output from a power factor corrected AC voltage input with improved efficiency. The AC-to-DC power converter is a two-stage power converter including a PFC stage connected in series to a power conversion stage. The PFC stage performs power factor correction using a zero current switching technique, and the power conversion stage includes a zero voltage switched half-bridge converter. The power conversion stage includes a transformer for providing the isolated DC voltage output. The AC-to-DC power converter includes a single feedback control loop for transferring error information from the DC voltage output to the PFC stage, thereby obtaining regulation of the DC voltage output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Soft-switched power converters
ActiveUS20050226012A1Reduce switching lossesEffect efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSnubberSoft switch
A soft-switched boost converter includes an active snubber to provide soft switching of all semiconductor components. Specifically, the current (“turn-off current”) in the rectifier is switched off at a controlled rate, the main switch is closed under zero-voltage switching (ZVS) condition, and the auxiliary switch in the active snubber is opened under zero-current switching (ZCS) condition. As a result, switching losses are reduced with beneficial effects on conversion efficiency and EMC performance.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof
ActiveCN101702578AIncrease profitReduce volumeApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationClamp capacitorResonance
The invention discloses a forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof, comprising two power switch tubes, two auxiliary switch tubes, four anti-parallel diodes, a switch tube parallel capacitor, two clamp capacitors, two switch capacitors, two output diodes and two coupling inductors respectively provided with two windings. The invention realizes zero-voltage switching on of the power switch tubes through the resonance of the leakage inductance of the two coupling inductors and the switch tube parallel capacitor, absorbs the voltage peak switched off by the switch tubes caused by the leakage inductance and realizes energy lossless transfer by utilizing a clamp circuit comprising the anti-parallel diodes of the switch tubes and the two clamp capacitors, realizes the high gain output of the inverter by utilizing the serial connection of the second windings of the two coupling inductors, further improves the gain of the inverter and lowers the output voltage stress of the diodes by utilizing the switch capacitors and realizes the output zero-current switching off of the diodes by utilizing the leakage inductance of the coupling inductors.
Owner:HOYMILES POWER ELECTRONICS INC
Resonant power converter with primary-side tuning and zero-current switching
InactiveUS6490177B1Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceDc current
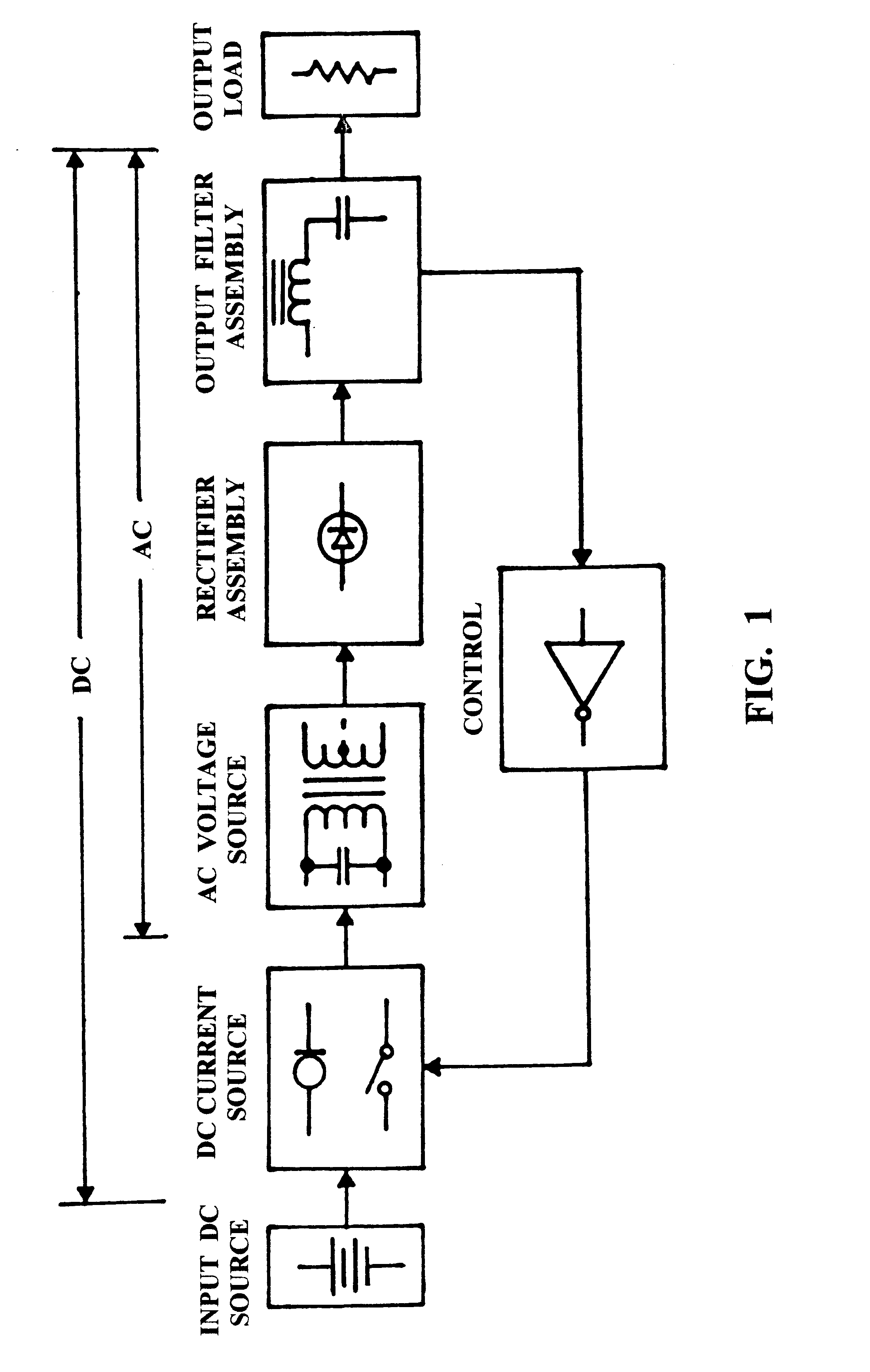
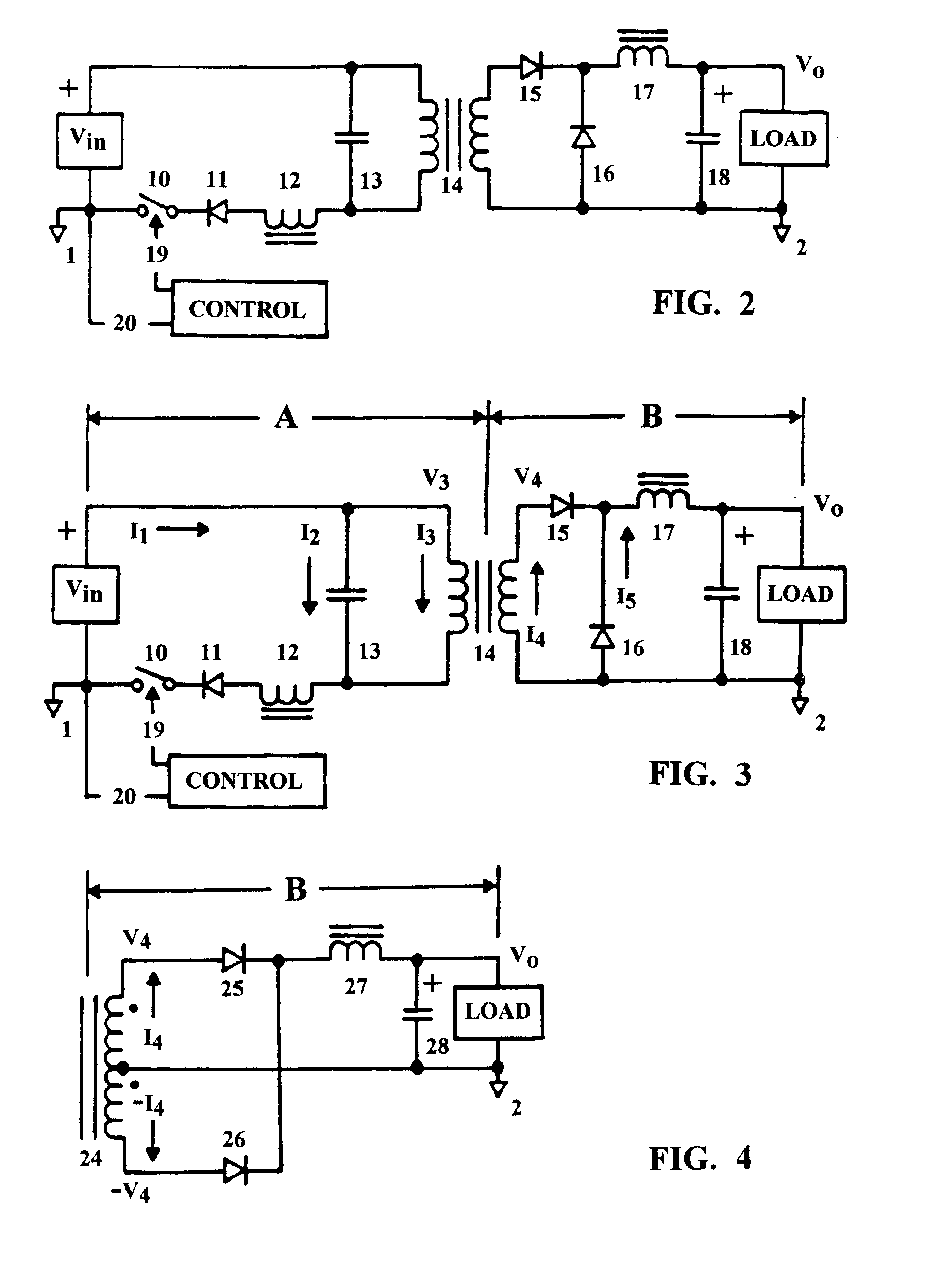
A DC power converter consisting of a series-resonant branch used to transform a DC voltage source into a DC current source exhibiting, a uni-polar, zero-current-switching characteristic. Frequency of the series-resonant branch, acting in concert with reflected load parameters, provides a forced oscillation frequency, Fo, component to an AC voltage source generated across the input winding of a power transformer by the resonant capacitor. Complex load parameters allow AC input current, displaced by 90° from the AC voltage source, to flow in the transformer primary winding throughout a composite, carrier-frequency cycle. Another component of the carrier-frequency consists of a resonant, natural oscillation frequency, Fn, resulting from resonance by the AC voltage source capacitance with the open-circuit inductance of the primary winding on the input power transformer. The composite carrier-frequency, Fo+Fn, transported through the input power transformer is directed to a rectifier / filter assembly and applied as a DC voltage to an output load. Thus, the uni-polar DC series-resonant branch is converted into an AC power transfer function, fully isolated from the input power switch, by the AC voltage source capacitor. The power transfer function characterizing a bi-polar power inverter requires a single power switch referenced to the input power return bus.
Owner:FIGUEROA SALVADOR
Soft-switched power converters
ActiveUS6987675B2Reduce switching lossesEffect efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSnubberSoft switch
A soft-switched boost converter includes an active snubber to provide soft switching of all semiconductor components. Specifically, the current (“turn-off current”) in the rectifier is switched off at a controlled rate, the main switch is closed under zero-voltage switching (ZVS) condition, and the auxiliary switch in the active snubber is opened under zero-current switching (ZCS) condition. As a result, switching losses are reduced with beneficial effects on conversion efficiency and EMC performance.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Soft-switching circuit for power supply
InactiveUS20080316775A1Reduce conduction lossReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringVoltage source
A soft-switching circuit for a power supply comprises a bridgeless rectifier circuit and an auxiliary circuit. The auxiliary circuit is connected to the bridgeless rectifier circuit, which comprises at least one filtering inductor, two main switches, two diodes and a capacitor. The filtering inductor is connected to the first diode. The first diode is connected to the second diode. The second diode is connected to the first main switch. The first main switch is connected to the second main switch. The diodes and the main switches are connected in parallel with the capacitor to reduce conducting loss. The auxiliary circuit comprises at least one resonant inductor, an auxiliary switch, at least two diodes and a voltage source circuit. The diodes are connected to the resonant inductor and further connected to the voltage source circuit. The voltage source circuit is connected to the auxiliary switch, whereby the soft-switching circuit can accomplish zero voltage switching and zero current switching to provide low conducting loss and low switching loss.
Owner:LEAD YEAR ENTERPRISE
Discontinuous mode PFC controller with energy-saving modulator and its operating method
InactiveCN1938932AReduce power lossReduce power consumptionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionSwitching cycleEngineering
The present invention discloses a ZCS discontinuous mode PFC controller having a power saving modulator. The controller turns on through the feedback resistor and the parasitic diode of the controller, thus eliminating the need for a startup resistor. To achieve ZCS, the inductor current is released to zero, while the switching signal is off, before the next switching cycle starts. In order to decrease the switching frequency for light load conditions, an off-time delay is inserted right before the start of every switching cycle. The off-time delay is modulated to be the function of the feedback voltage and supply voltage. When the supply voltage is lower than the limit voltage, the off-time delay will decrease to inhibit the decrease of a switching frequency therefore prevents a low supply voltage. The switching frequency is decreased in accordance with the decrease of the load. Consequently, the switching losses and power consumption for light load and no load conditions are reduced.
Owner:SYST GEN
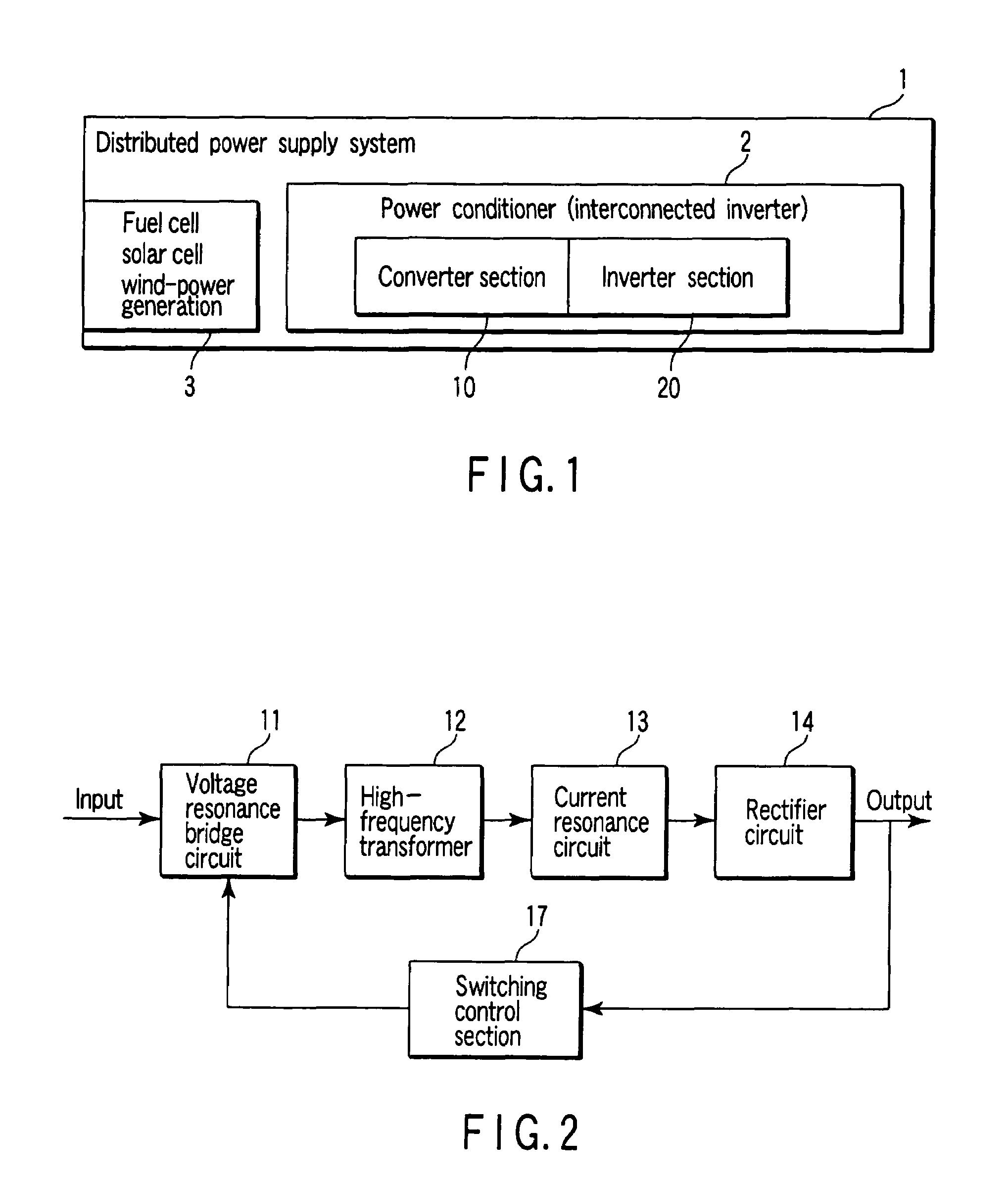
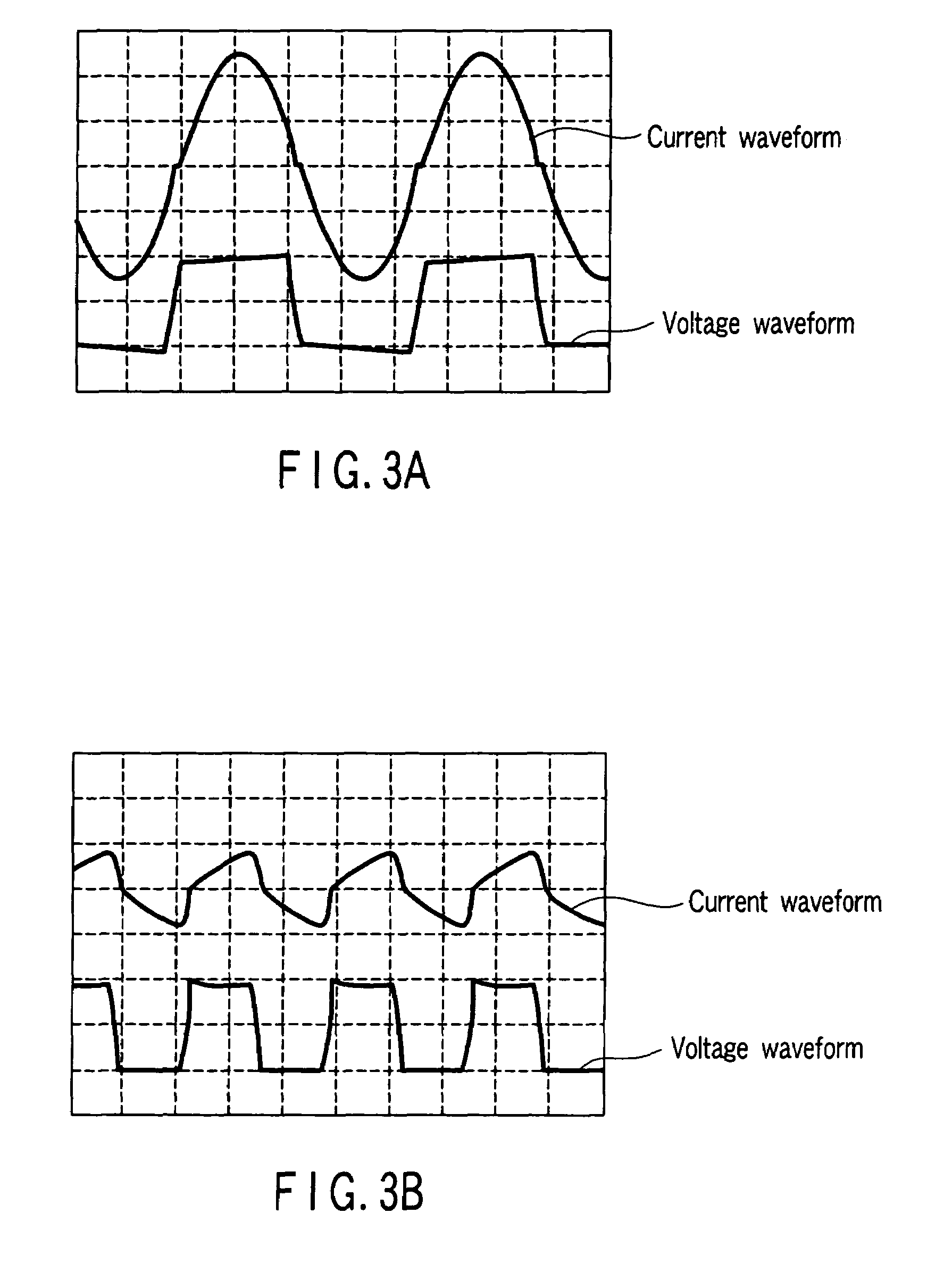
DC-DC converter
ActiveUS7333348B2Dc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalLow voltageSolar cell
There is provided a high-efficiency DC-DC converter which comprises a voltage resonance circuit to which electric power from a low-voltage direct-current power supply, including a household fuel cell and a solar cell, is input and performs DC-AC conversion by zero-voltage switching, an insulating high-frequency transformer which transmits the converted power, a current resonance circuit which is provided on the secondary side of the transformer and performs zero-current switching, a rectifier circuit which rectifies the output from the current resonance circuit, and a smoothing circuit which rectifies the output from the rectifier circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
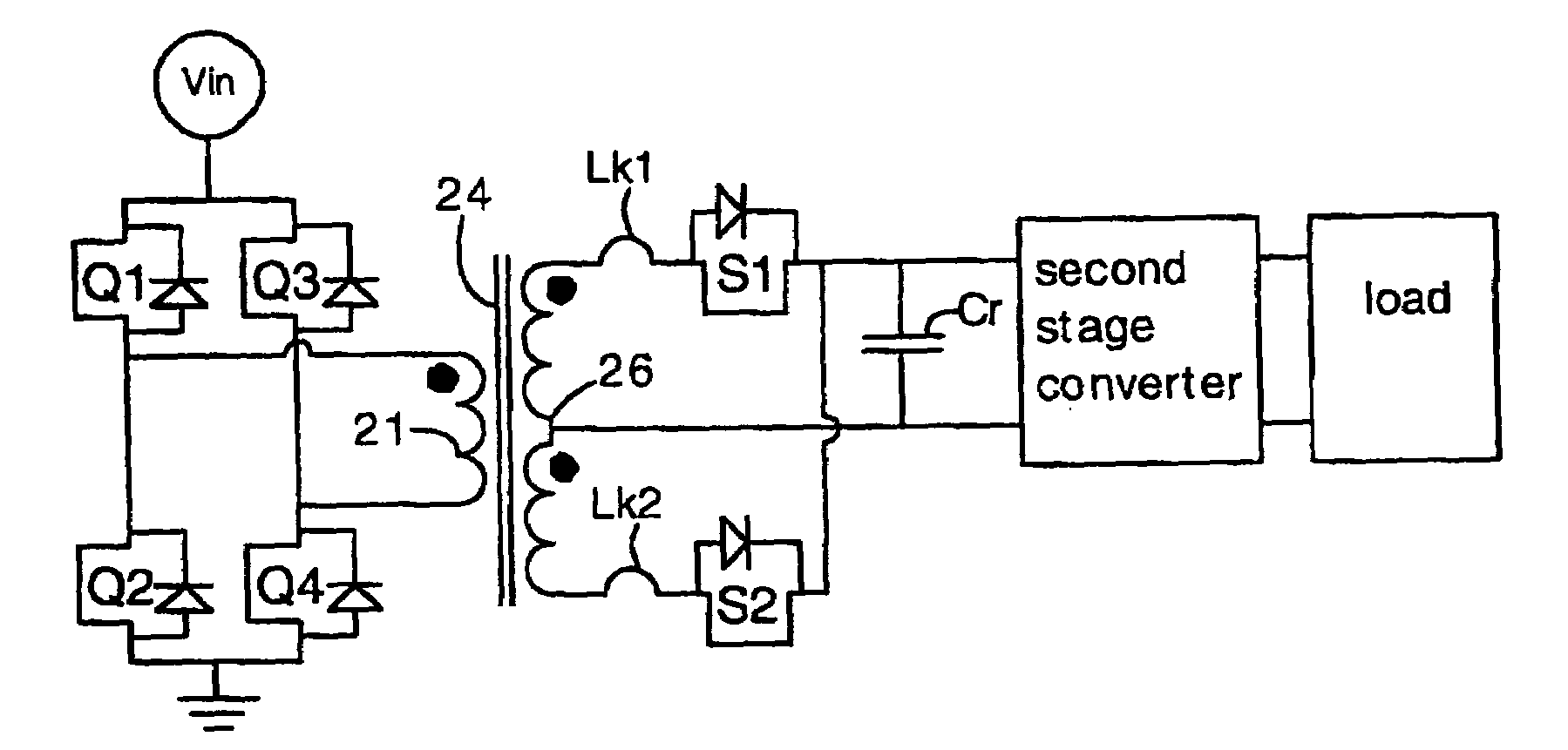
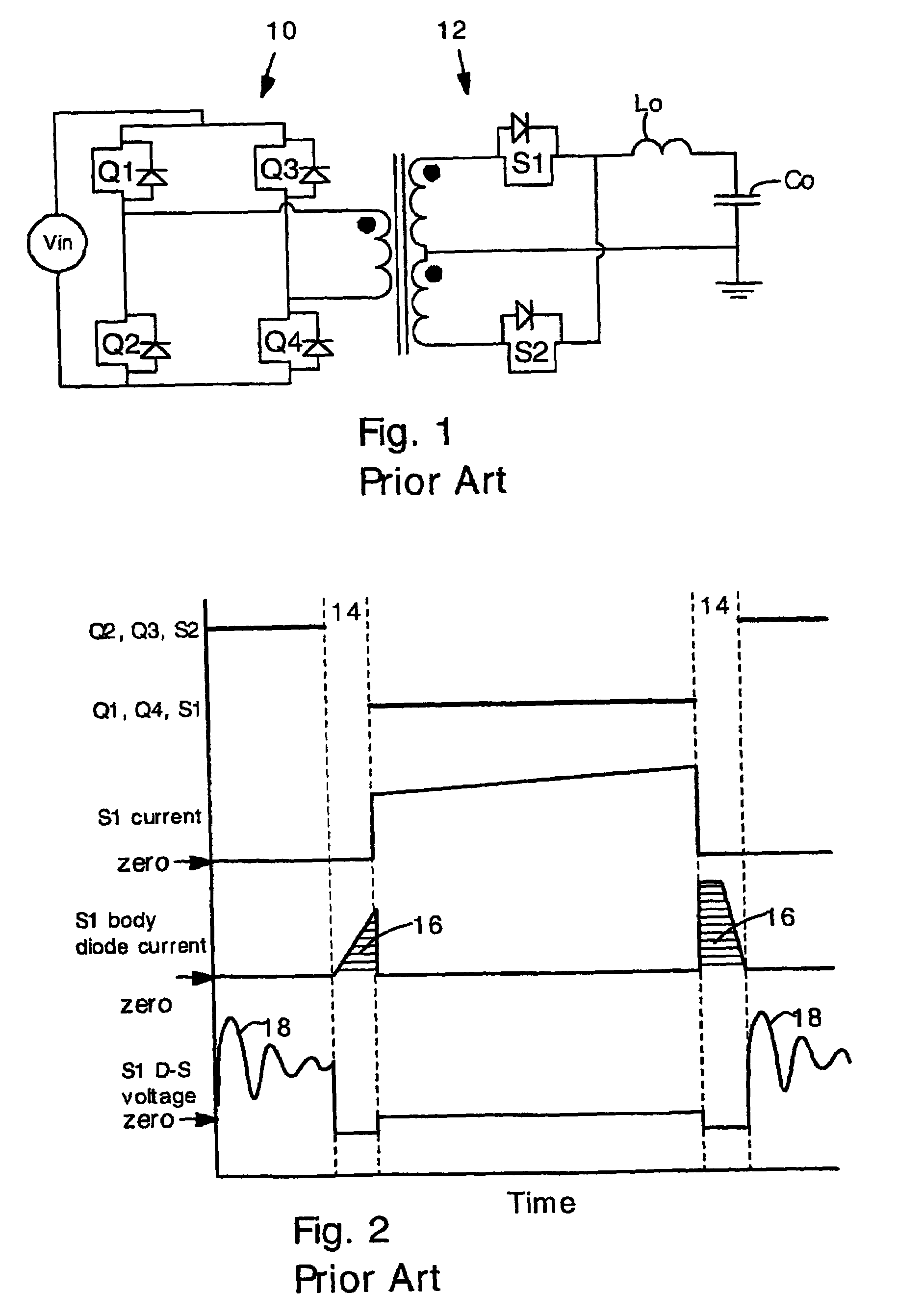
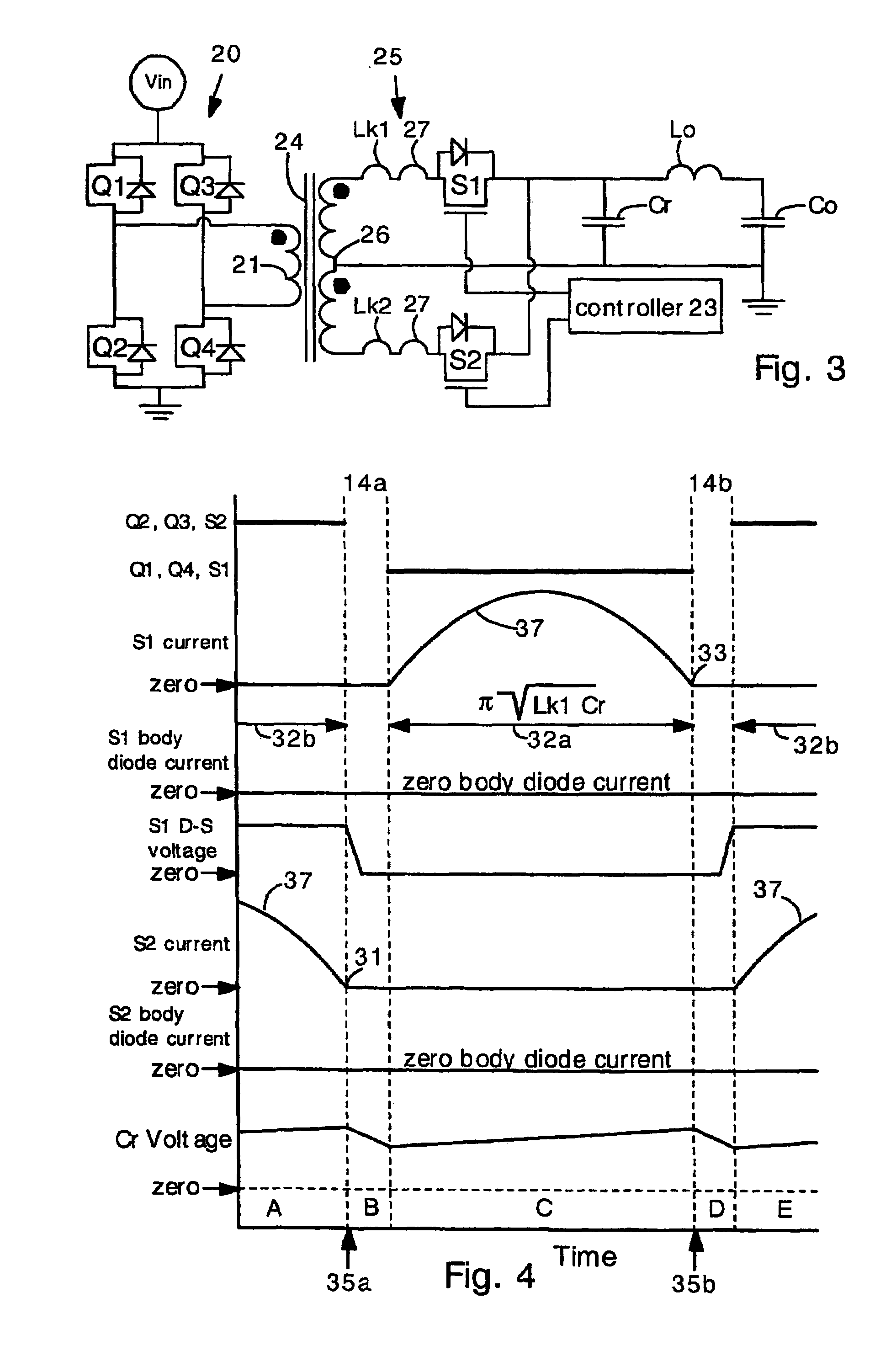
Power converters having capacitor resonant with transformer leakage inductance
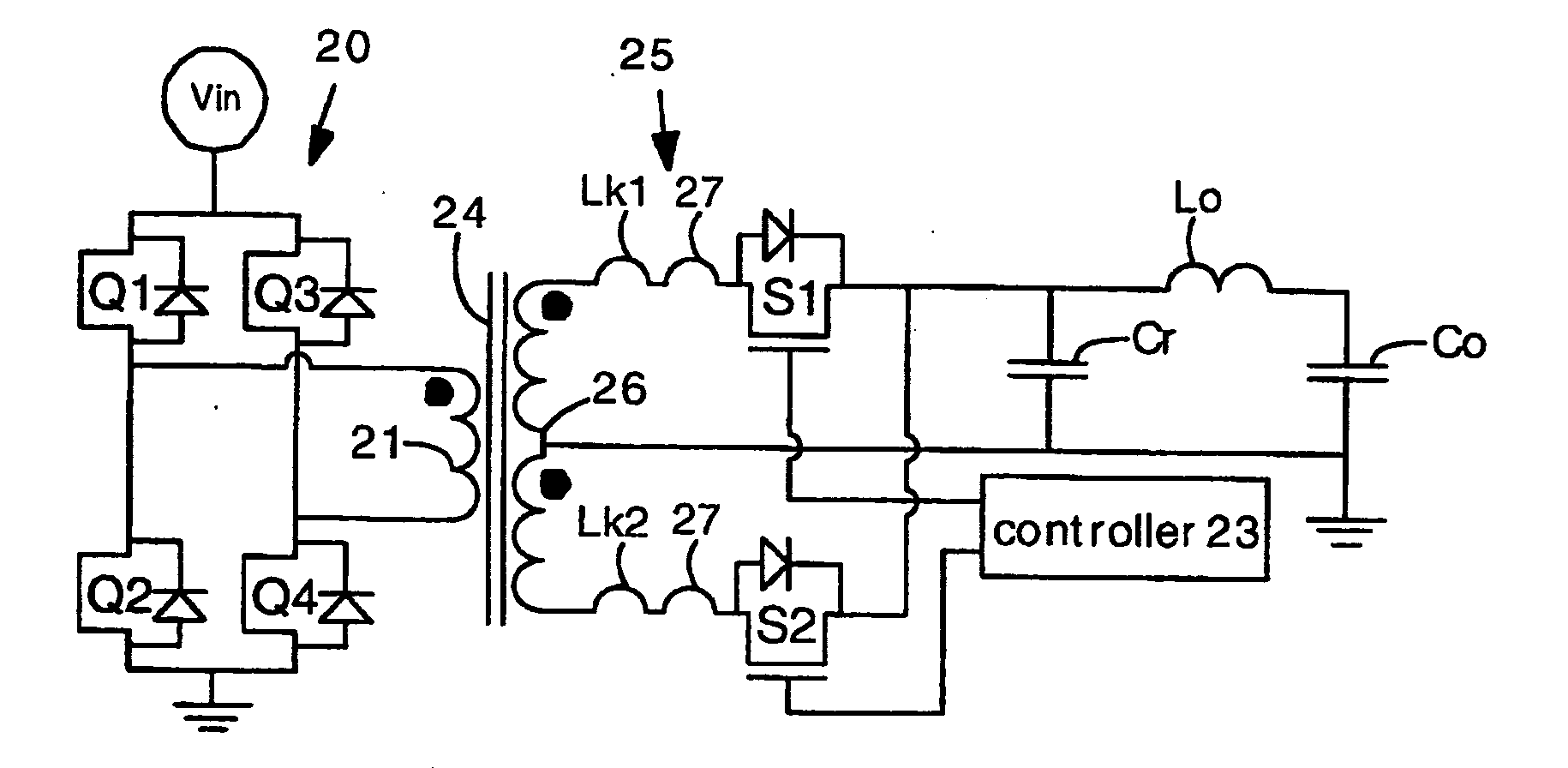
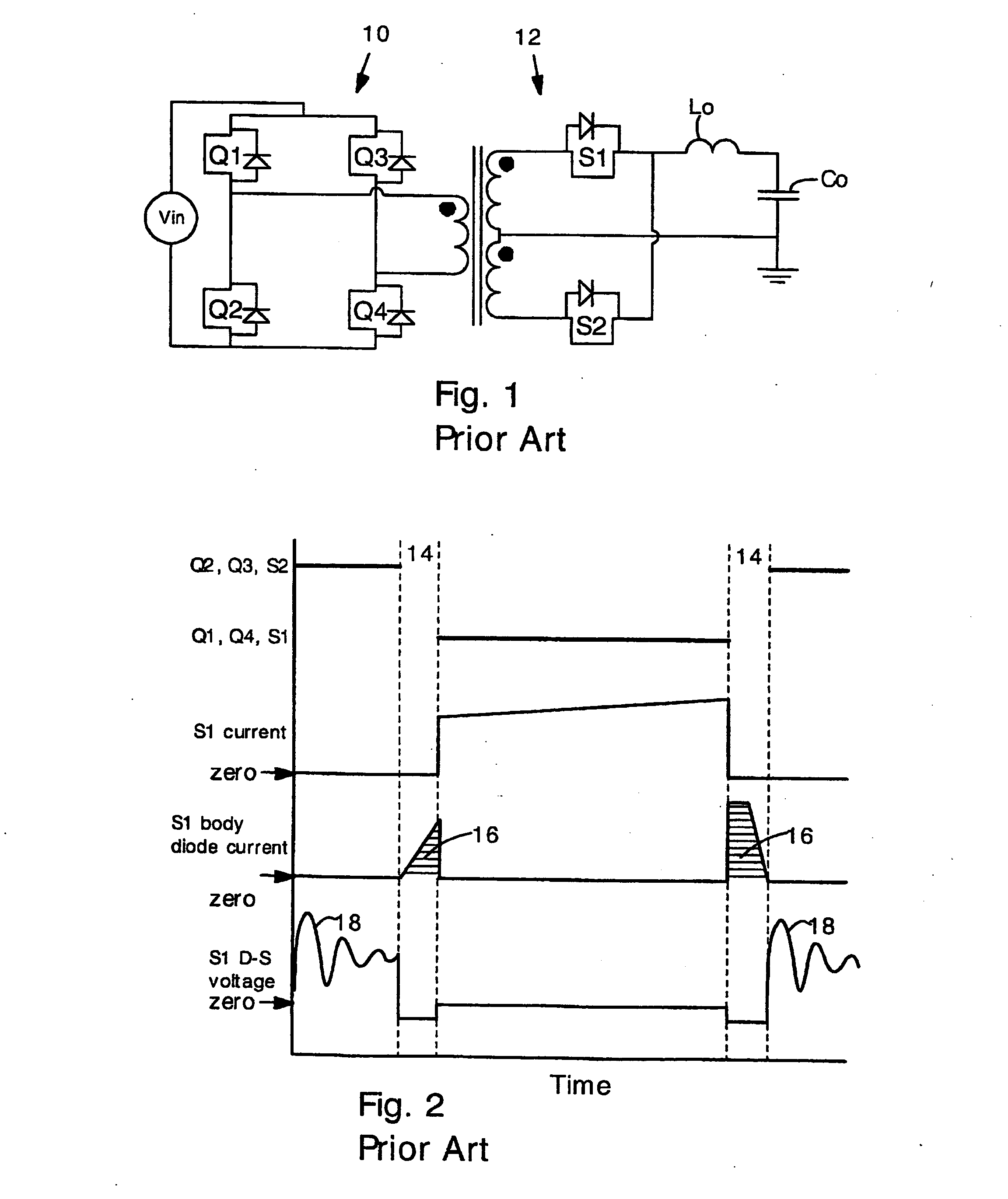
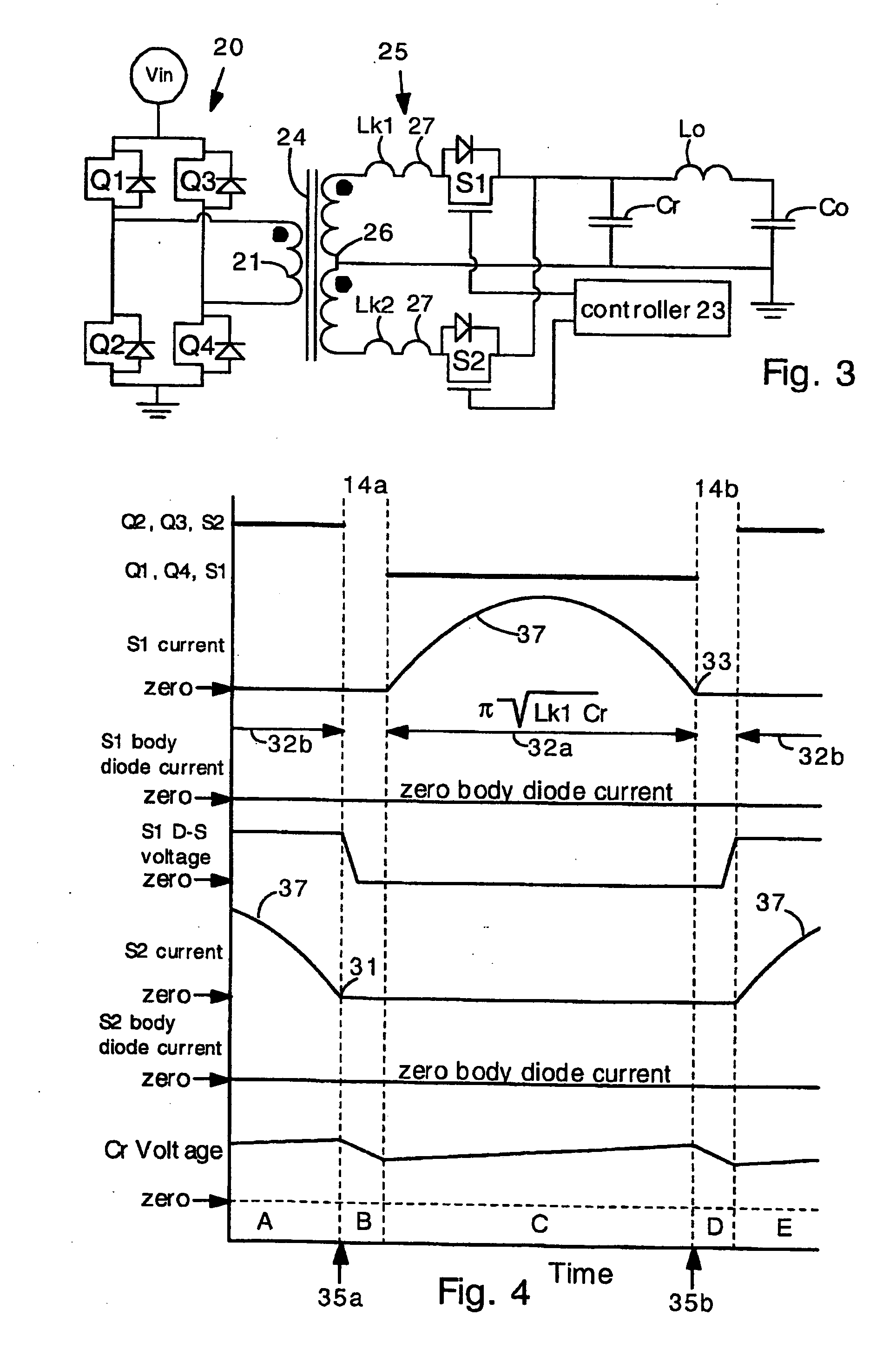
Power converters having reduced body diode conduction loss, reduced reverse recovery loss and lower switching noise, among other benefits, have a resonant capacitor Cr connected across an unfiltered output. The resonant capacitor Cr resonates with the leakage inductance Lk of the transformer. The resonant capacitor and leakage inductance are selected such that ½ a LC resonance period is equal to an ON time of each secondary switch S1 S2. The resonance provides zero current switching for secondary switches S1 S2, eliminates zero body diode conduction during dead times, and eliminates reverse recovery losses in the secondary switches. The present invention is applicable to many different circuit topologies such as full bridge, active clamp forward, push-pull forward, and center-tap secondary. The present converters provide high energy conversion efficiency and high frequency operation.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Dc/ac conversion device and ac power supply method
ActiveUS20050047176A1Easy to superviseReduce switching lossesConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric lighting sourcesTransformerFull bridge
A dc-ac converter capable of supplying a finely regulated ac drive voltage to a load is provided. For this purpose, the converter includes, in a primary winding of a transformer, a full-bridge or half-bridge type semiconductor switch circuit whose switches can be controlled by pulse-width modulation. Transformer has a secondary winding for connection with a load. Based on PWM signals and by use of adequate switching logics for controlling multiple semiconductor switches, sophisticated control including zero-current switching and penetrating current prevention can be effected. Moreover, by means of regulated burst control of the ratio of on-duty period to off-duty period together with pulse-width modulation control, power supplied to the load can be regulated over a wide range beyond the limits of control obtained by the pulse-width modulation.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Single-phase inverter
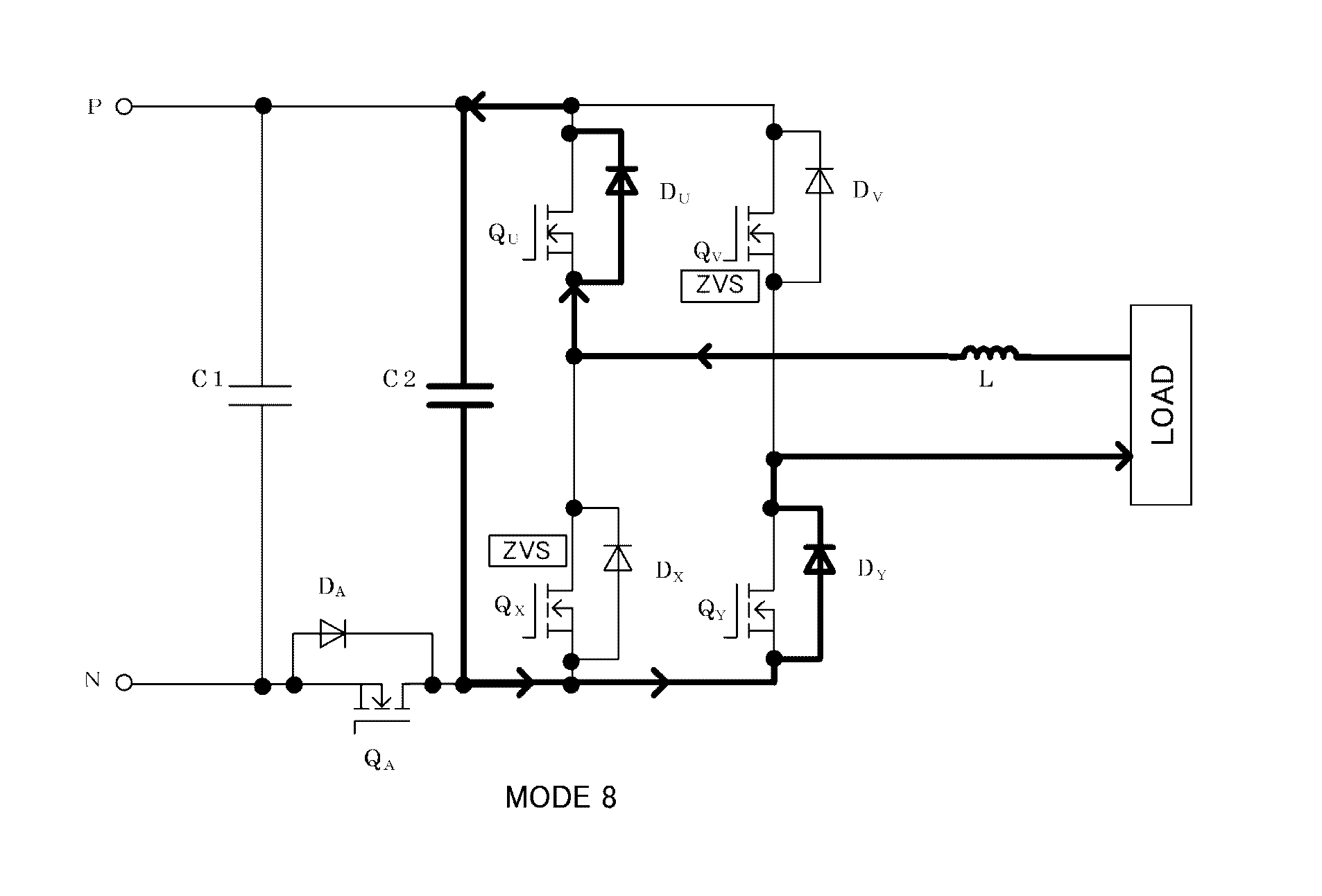
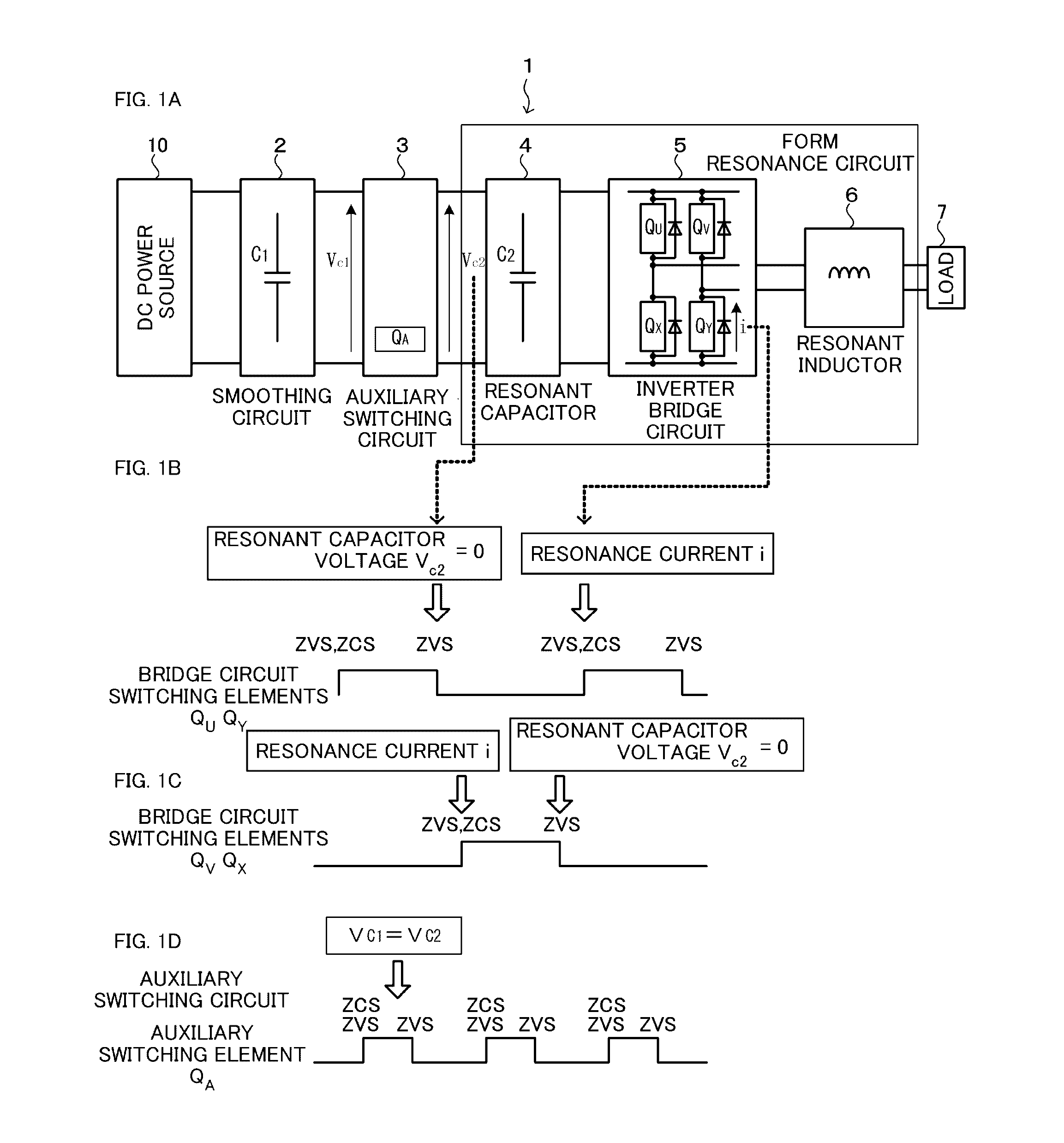
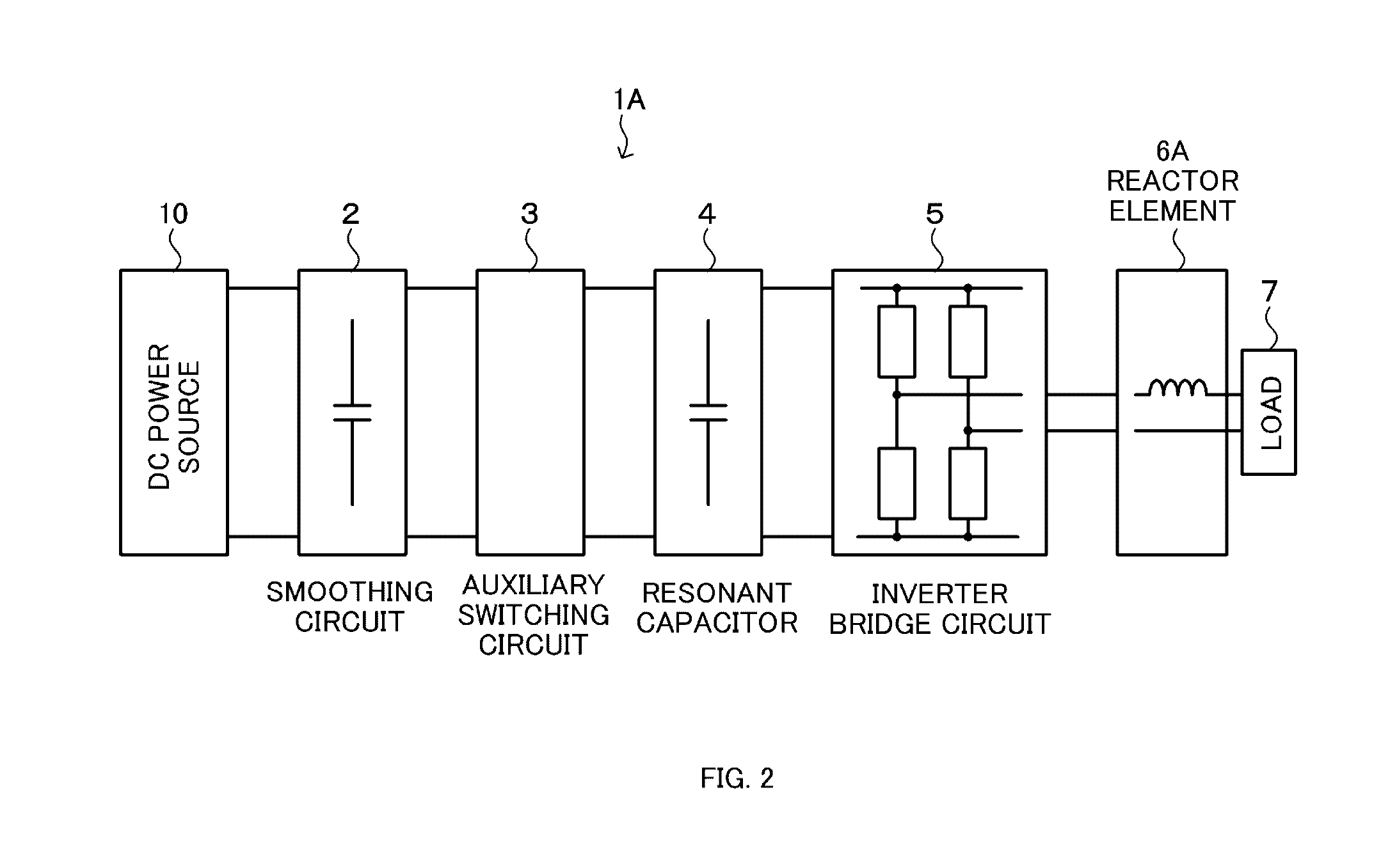
ActiveUS20160308457A1Simple configurationAvoid switching lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHemt circuitsInverter
In an inverter circuit, more particularly in a single-phase inverter, soft switching is performed with a simple configuration to prevent switching loss of a switching element. A resonance circuit is configured by a resonant capacitor provided on the power supply side of a bridge circuit constituting a single phase inverter, a resonant inductor provided on the output side of the bridge circuit, and the bridge circuit. A resonance current passing through the resonance circuit allows zero voltage switching (ZVS) and zero current switching (ZCS) to be implemented at the rising time of main switching elements constituting the bridge circuit, and the zero voltage switching is implemented by means of zero voltage of the resonant capacitor at the falling time of the main switching elements constituting the bridge circuit.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
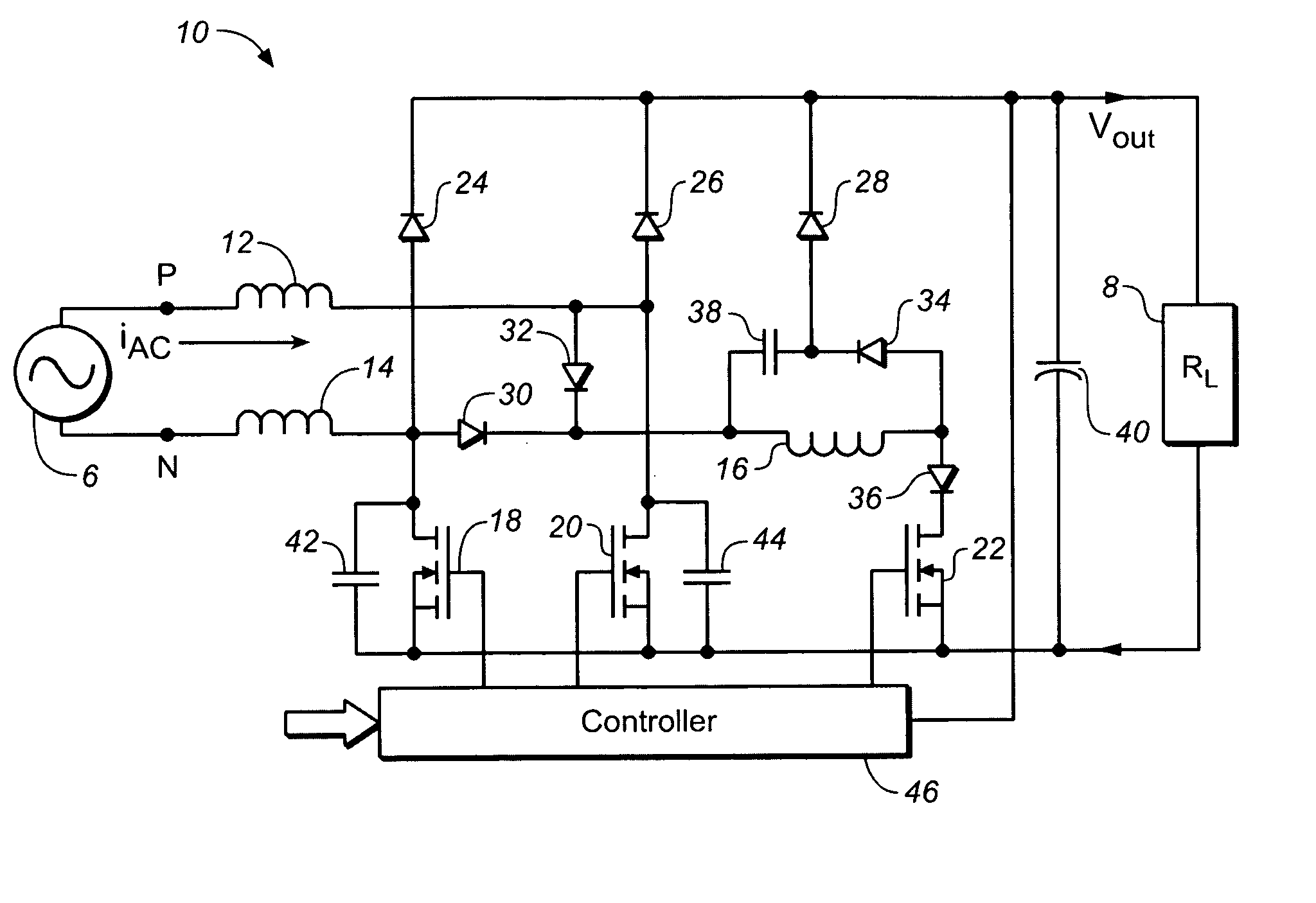
Switch-mode power supplies
InactiveUS6429629B1Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCenter tapZero current switching
A family of switch-mode power supplies with low current stresses on switches and capable of producing an output voltage higher than the input voltage, incorporating a multiple-tap transformer driven by at least one ground-referenced switch. When the transformer is center-tapped, it is driven by two ground-referenced switches. The current stress in each switch is equal to the difference between the source current and the load current. The converters can operate in zero current switching and zero voltage switching. Integrated magnetics can be used to reduce further component count.
Owner:NGUYEN TRANH TO
LC series resonance high frequency chain matrix-type inverter topology and resonance modulation method thereof
InactiveCN105915095AImprove reliabilityImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversionAc-ac conversionMatrix convertersVoltage overshoot
The present invention provides a LC series resonance high frequency chain matrix-type inverter topology and a resonance modulation method thereof. The topology comprises of a full bridge LC series resonance inverter, a high-frequency transformer T, a matrix converter and a CL-type filter which are connected in order. The modulation method is configured to process the SPWM wave through separation and link semi-excitation modulation logics to obtain driving signals of a transformer pre-stage LC series resonance inverter and a transformer post-stage matrix converter so as to allow the work duty ratio of the transformer pre-stage resonance circuit excitation resonance work state in the resonance half period to be controllable and realize the control of energy side transmission to the output load. The transformer post-stage matrix converter is modulated and decoupled to two common current-type inverters for controlling, a switch tube performs switching during the zero current outputting to realize zero current switching to avoid causing voltage overshoot problems and realize energy bidirectional flow and four-quadrant operation. The power transformation grades are few, the control method is simple, the circuit stability is high, and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
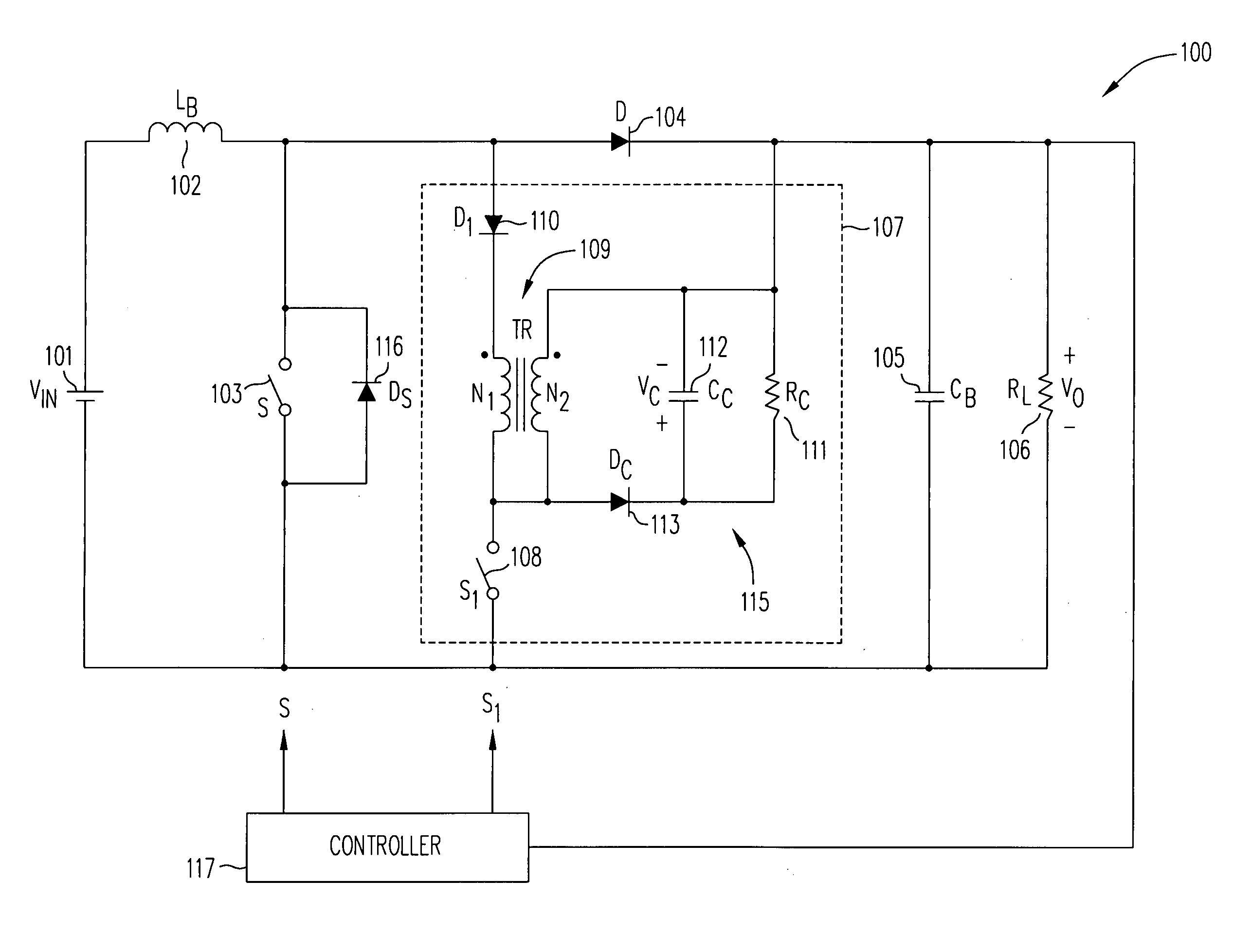
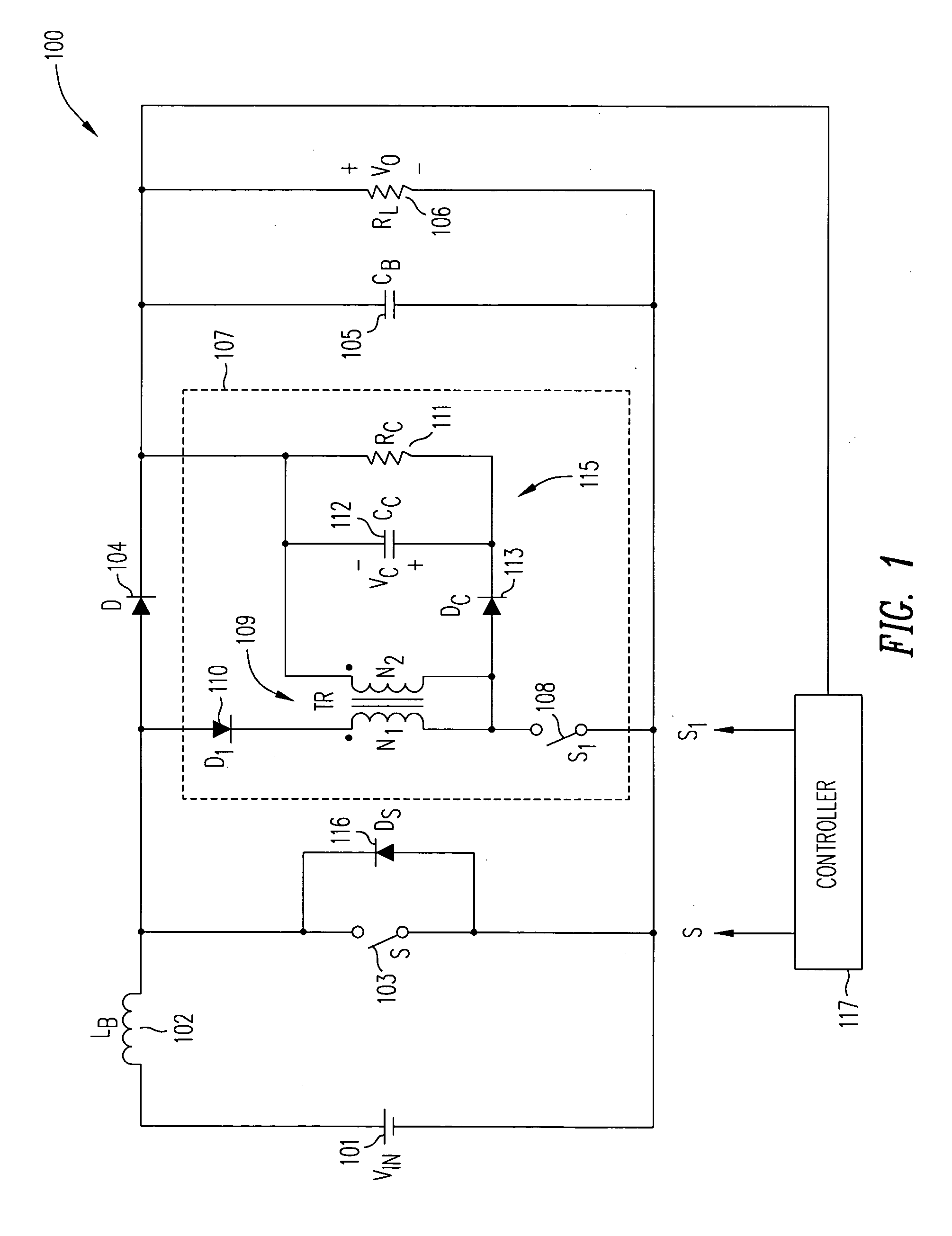
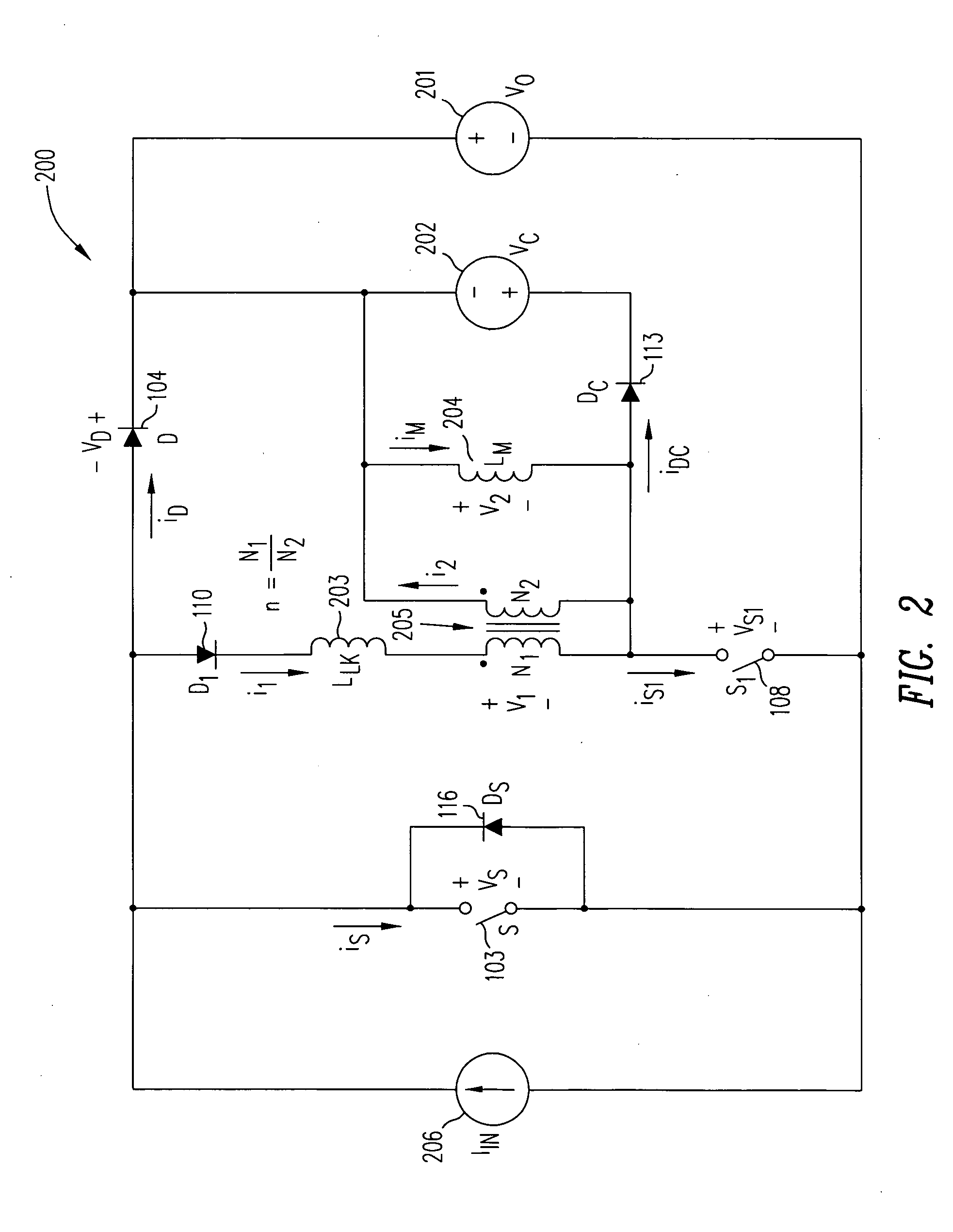
Zero-voltage switching half-bridge DC-DC converter topology by utilizing the transformer leakage inductance trapped energy
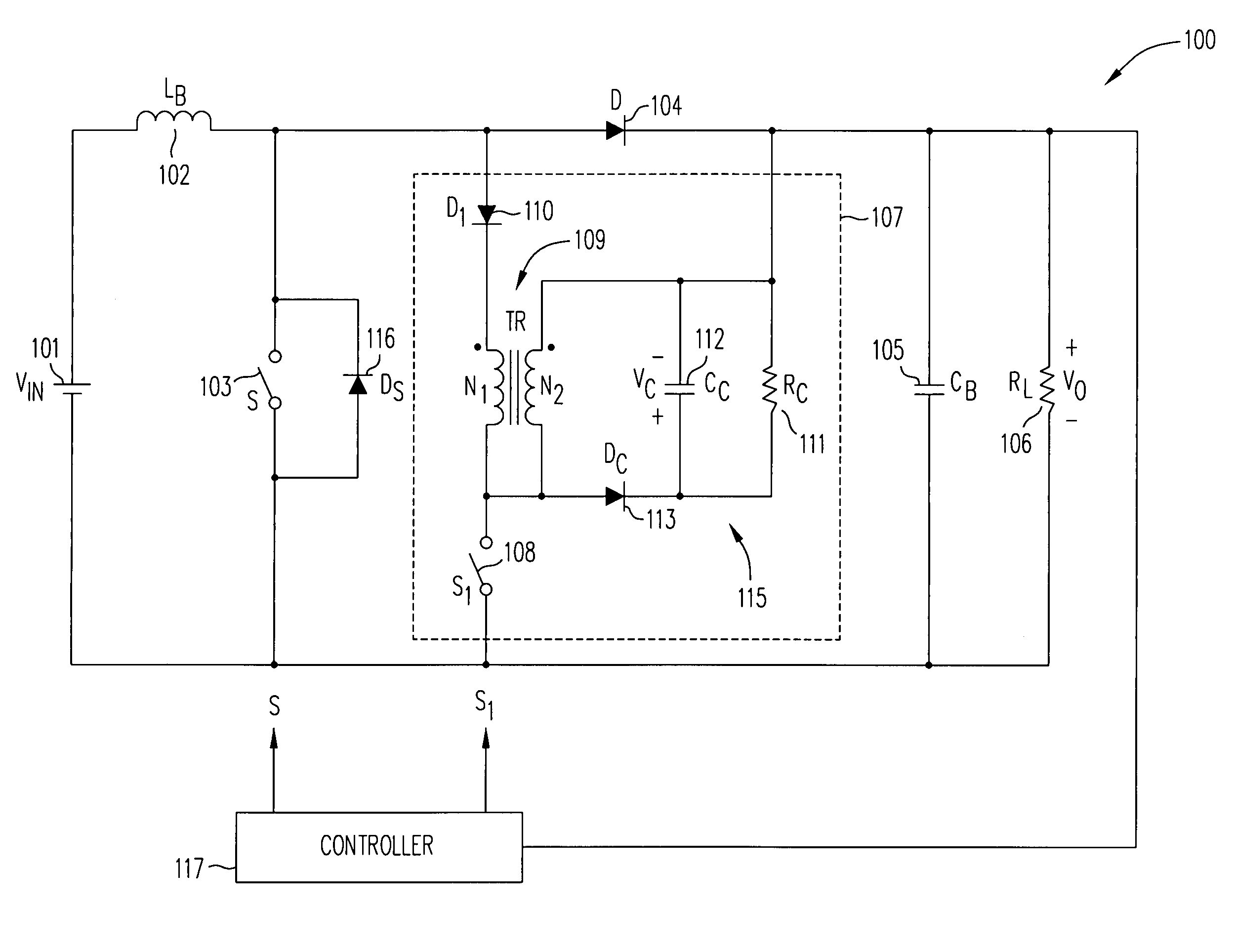
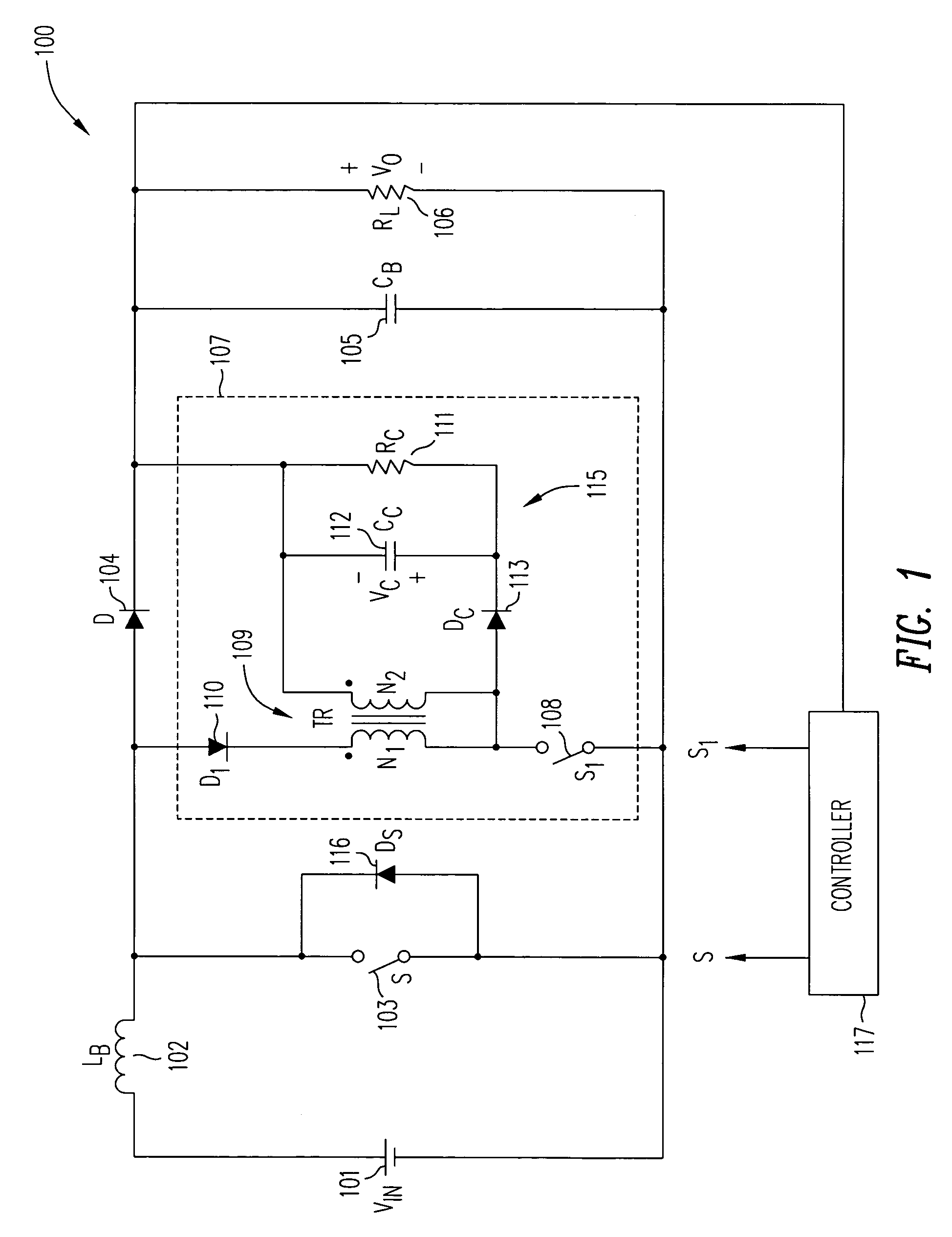
A duty-cycle-shifted pulse-width modulation controlled half-bridge zero-voltage switching DC—DC converter has a primary side, a secondary side and a transformer coupling the primary side to the secondary side. The primary side has first and second primary switches coupled to a primary winding of the transformer and an auxiliary branch having one side coupled to a junction of the first and second primary switches and a second side coupled to common. The auxiliary branch includes a grounded auxiliary switch that is switched on when one of the first and second primary switches is on to trap leakage inductance energy of the transformer when that primary switch is turned off and thereafter switched off to release the trapped leakage inductance energy to provide a zero voltage switching condition for the other primary switch. The one of the first and second primary switches that is on when the auxiliary switch is switched on may be controlled with duty-cycle-shifted pulse width modulation to provide a zero current switching condition for that primary switch.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
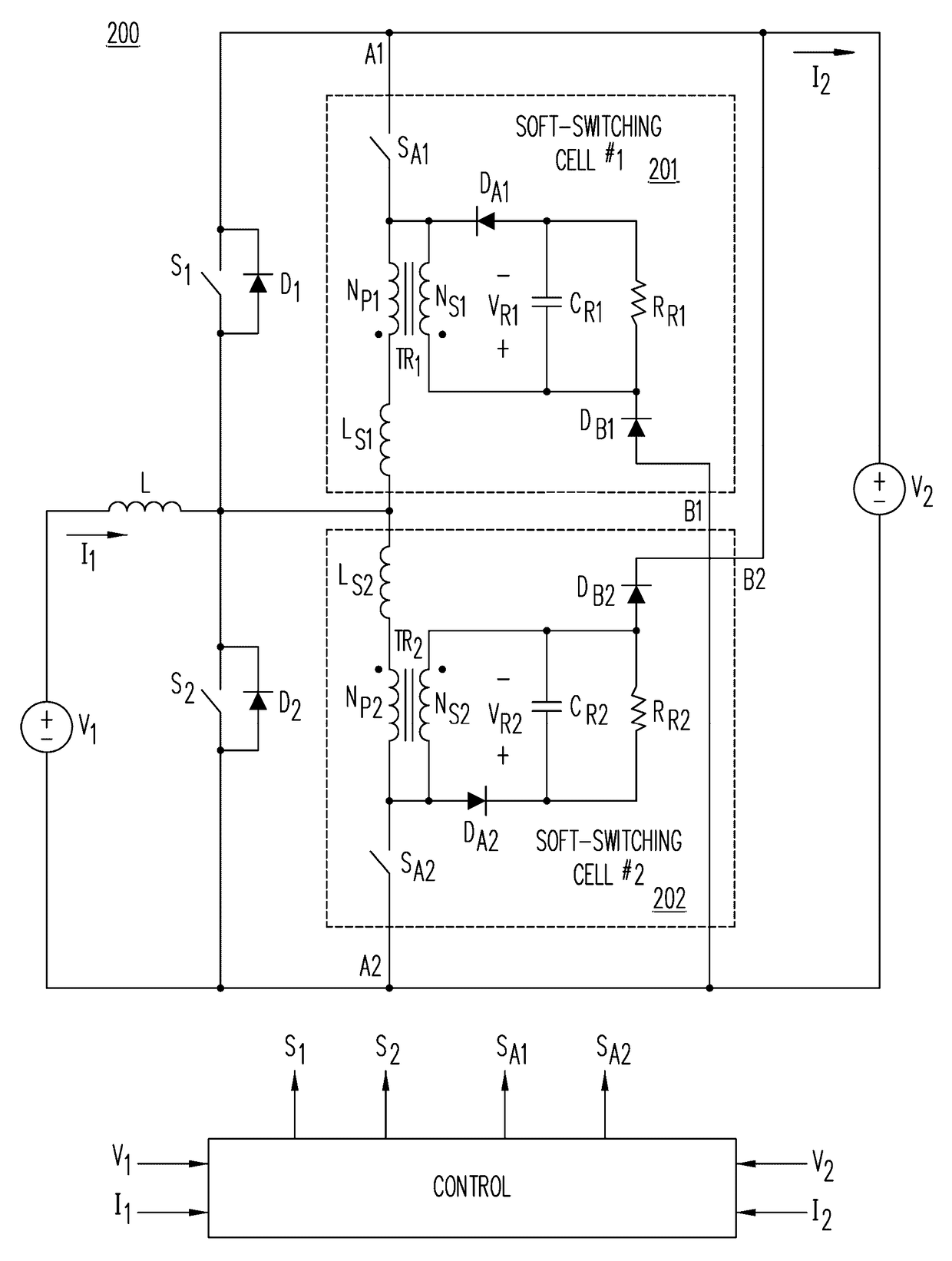
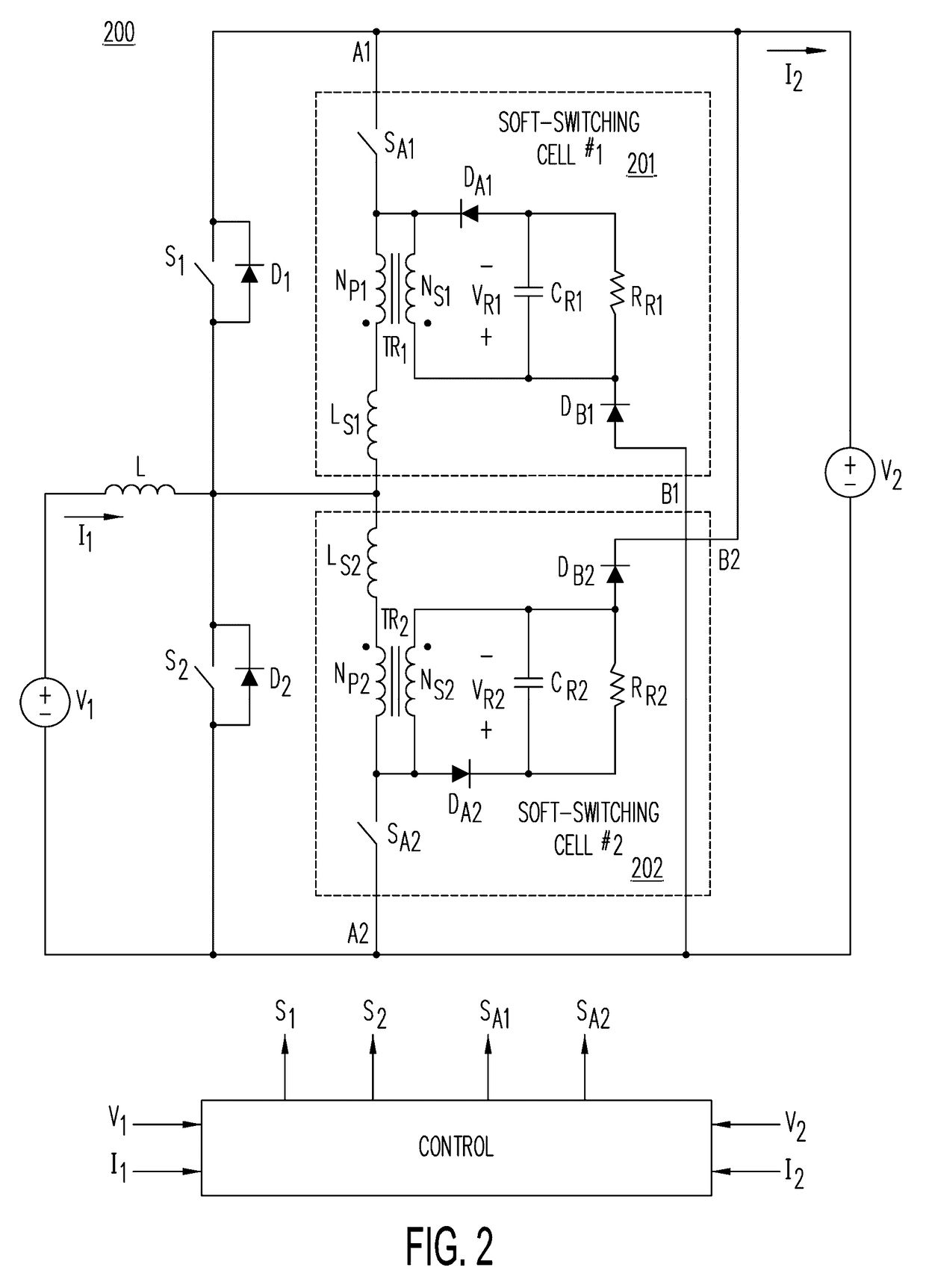
Soft-switched bidirectional buck-boost converters
ActiveUS20170163163A1Reduce switching lossesMinimize reverse-recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransformerActive switch
A bidirectional buck-boost converter includes at least one soft-switching cell to reduce switching losses by providing soft-switching of all semiconductor devices. A soft-switching cell comprises an active switch coupled in series with an inductor, a two-winding transformer, and a reset-voltage circuit. The soft-switching cells enable the buck and boost rectifiers to turn off with a controlled turn-off rate of their current to minimize their reverse-recovery losses, the power-controlling buck and boost switch to turn on with zero-voltage switching (ZVS), and the switch of the soft-switching cell to turn off with zero-current switching (ZCS).
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
High-efficiency power converter system
ActiveUS7518895B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionAlternating currentInductance
In one embodiment, a power converter system includes a first input terminal and a second input terminal operable to connect to an alternating current (AC) power source, and an output terminal at which an output voltage can be provided to a load. A first inductor and a first diode are connected in series between the first input terminal and the output terminal. A second inductor and a second diode are connected in series between the second input terminal and the output terminal. A first switch is connected to the first inductor and the first diode, and a second switch is connected to the second inductor and the second diode. The first switch and the second switch alternately function as a boost switch and a synchronous rectifier for charging and discharging the first and second inductors during operation of the power converter system. An auxiliary network is operable to provide for zero voltage switching (ZVS) and zero current switching (ZCS) conditions for both the first and second switches during operation of the power converter system.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Soft switch power converter
InactiveCN1574582AEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionEngineeringSnubber
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
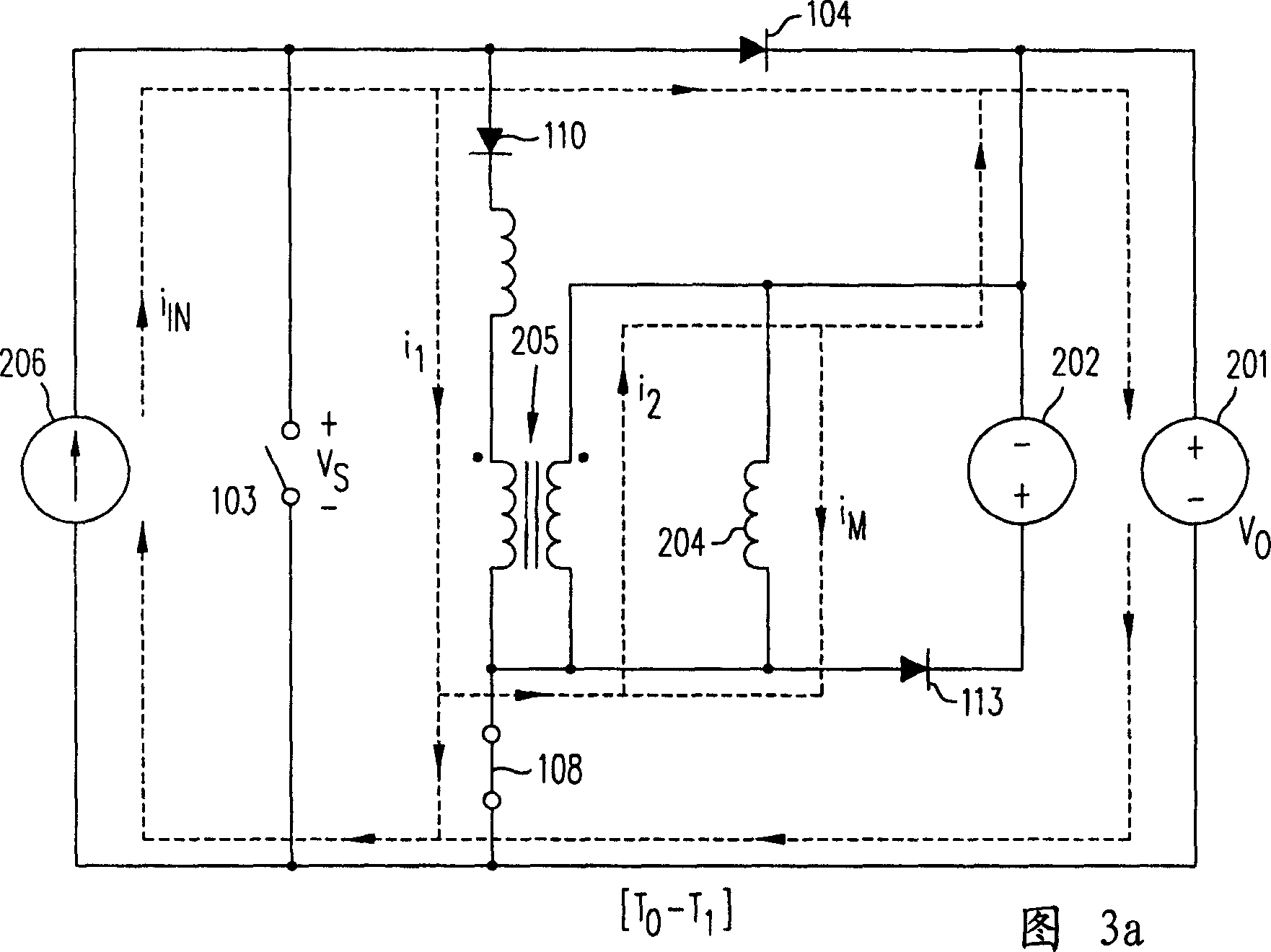
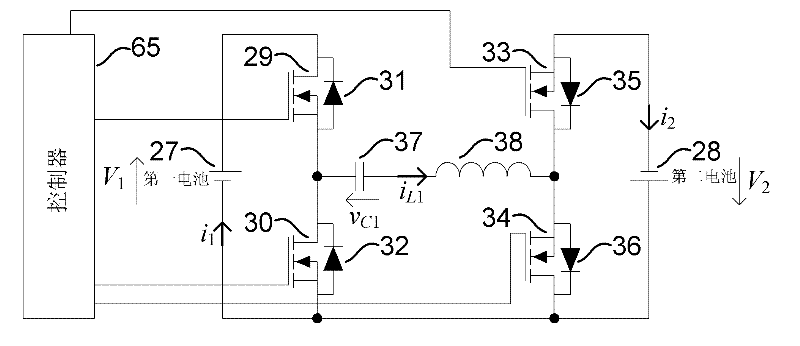
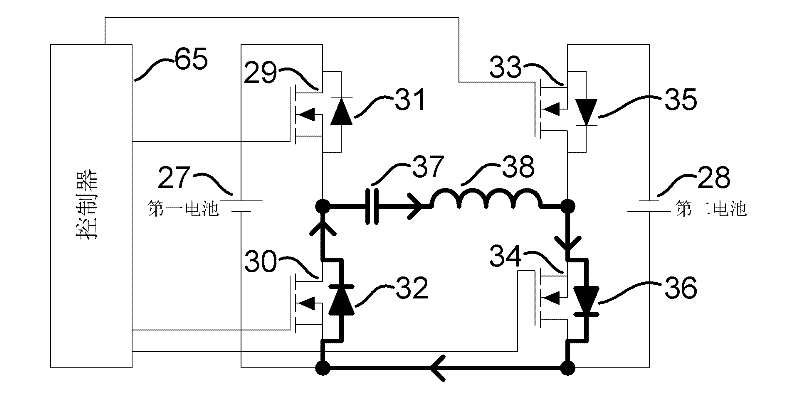
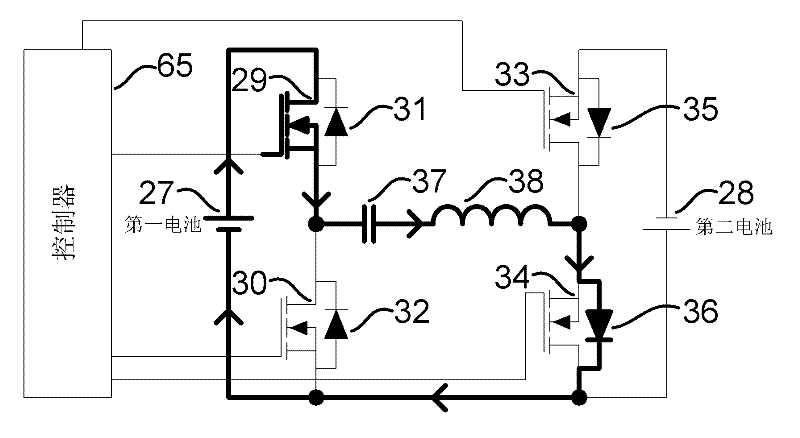
Battery energy balancing circuit
The invention relates to a battery energy balancing circuit. The battery energy balancing circuit comprises a first battery pack and a second battery pack which are sequentially connected in series for output, wherein each battery pack comprises a battery, two switch tubes and two diodes. The battery energy balancing circuit further comprises a controller and a resonant impedance. The batteries conduct periodic energy transfer through the battery energy balancing circuit. The controller is connected with the first switch tube to transfer energy of the first battery to the resonant impedance, connected with the second switch tube to transfer energy of the resonant impedance to the second battery, connected with the fourth switch tube to transfer energy of the second battery to the resonant impedance, and connected with the third switch tube to transfer energy of the resonant impedance to the first battery. The battery energy balancing circuit adopts the series resonance of the switching capacitance and the resonant inductance to achieve zero-current switching on / off of the switch tubes, has high efficiency and can not cause large energy conduction loss or switching loss during energy transfer.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Power supply with single stage converter for performing power factor correction and resonant conversion
ActiveUS20120106206A1Reduce power lossLow costEfficient power electronics conversionElectrical energyControl signalEngineering
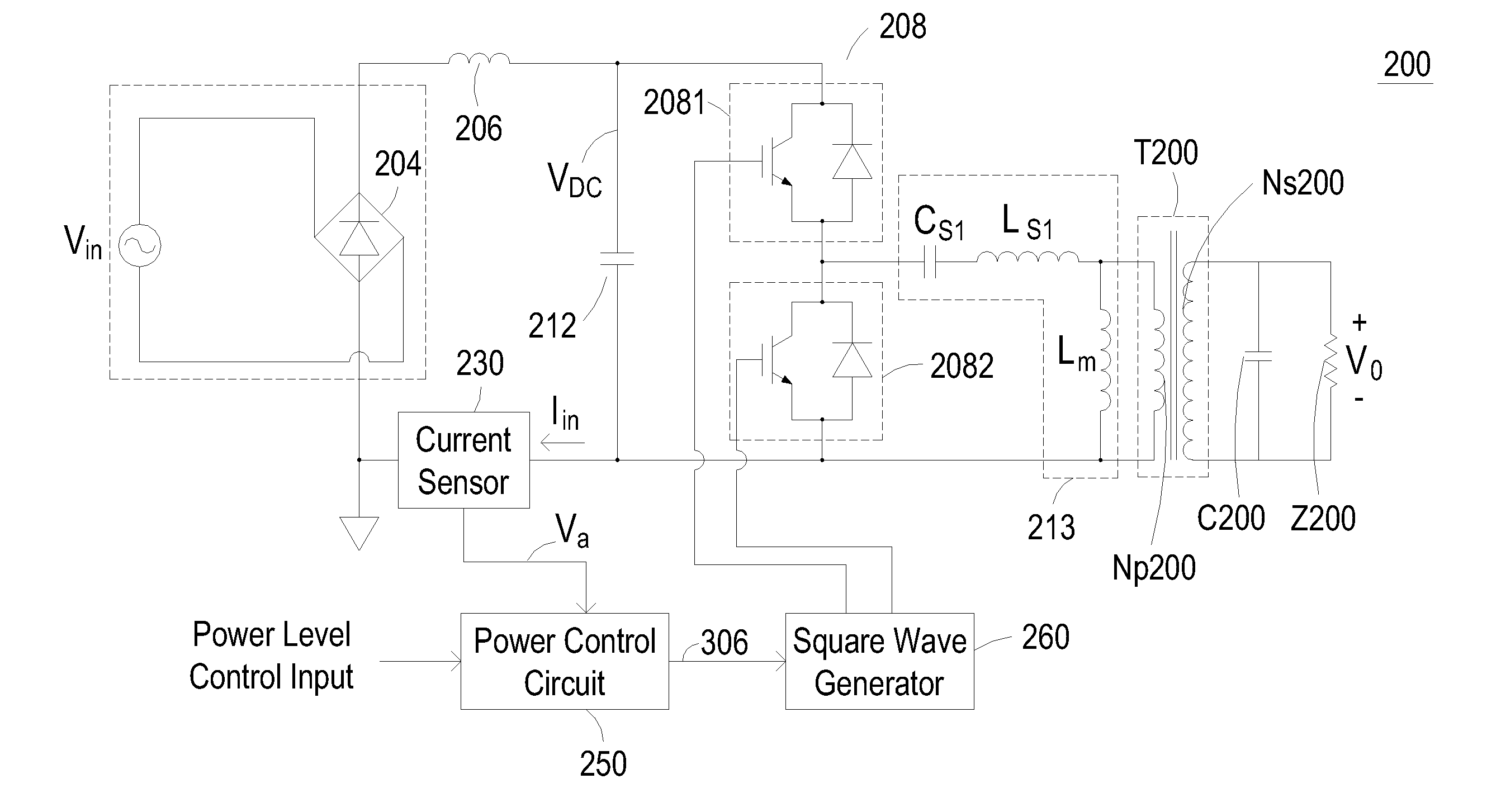
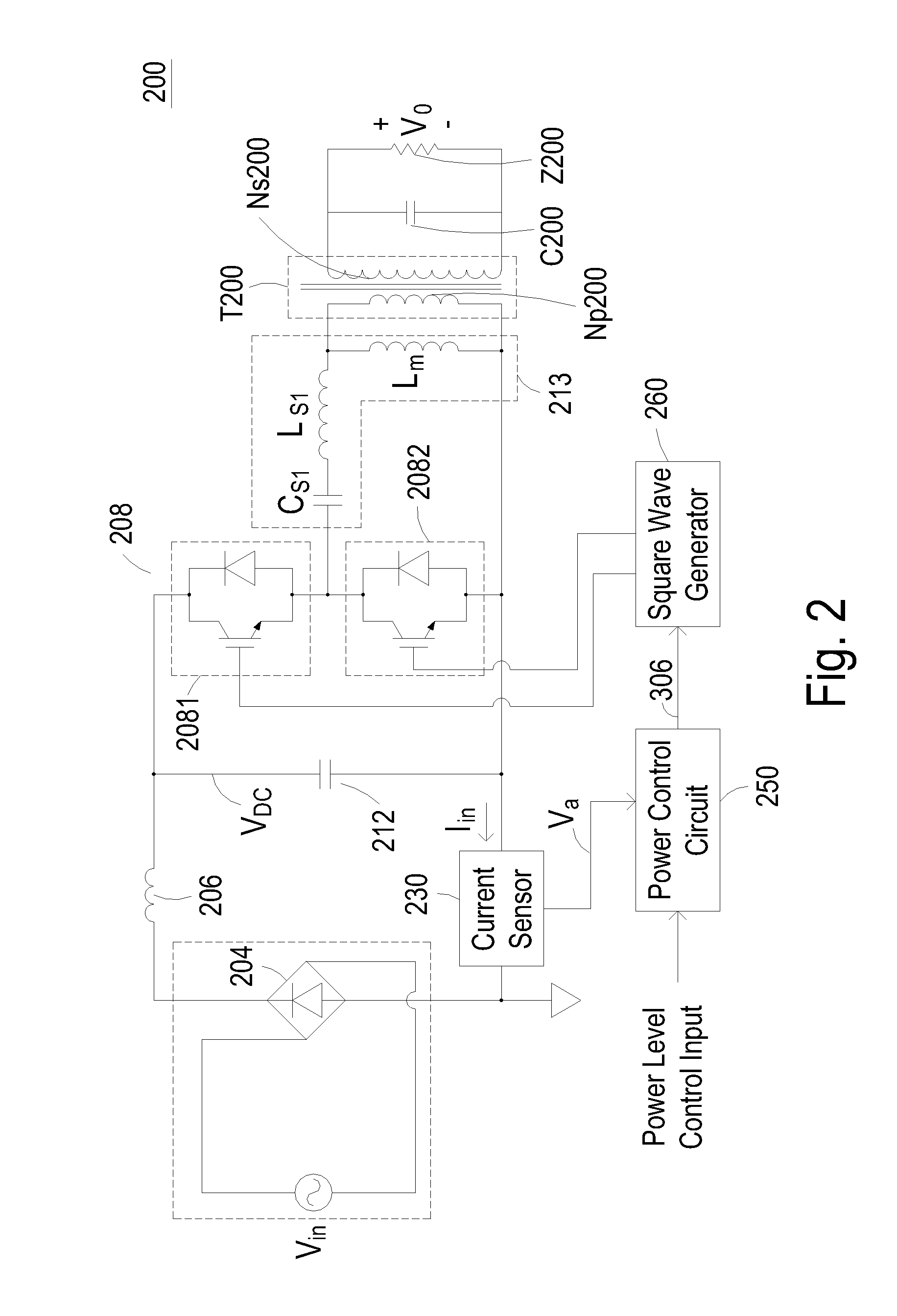
The invention discloses a power supply having a single stage converter for performing power factor correction to reduce high-frequency harmonics in the input current and performing resonant conversion to achieve zero-voltage switching or zero-current switching for power conversion. The inventive single stage converter includes a switching circuit, a resonant circuit, a power control circuit, and a square wave generator. The switching circuit includes at least one switch and the resonant circuit includes a LLC resonant tank. The power control circuit includes a proportional differential circuit such as a power amplifier configured in a negative feedback topology, and the square wave generator is configured to generate driving signals based on the frequency modulation control signal generated by the comparison of the sensed input current and a user-defined power level input, thereby allowing the square wave generator to regulate the switching operation of the switching circuit.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Dc/ac conversion device and ac power supply method
ActiveUS7095632B2Easy to superviseReduce switching lossesDc network circuit arrangementsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull bridgeTransformer
A dc-ac converter capable of supplying a finely regulated ac drive voltage to a load is provided. For this purpose, the converter includes, in a primary winding of a transformer, a full-bridge or half-bridge type semiconductor switch circuit whose switches can be controlled by pulse-width modulation. Transformer has a secondary winding for connection with a load. Based on PWM signals and by use of adequate switching logics for controlling multiple semiconductor switches, sophisticated control including zero-current switching and penetrating current prevention can be effected. Moreover, by means of regulated burst control of the ratio of on-duty period to off-duty period together with pulse-width modulation control, power supplied to the load can be regulated over a wide range beyond the limits of control obtained by the pulse-width modulation.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
DC-DC converter
ActiveUS7332897B2Reduce switching lossesElectric lighting sourcesDc-dc conversionDc dc converterControl signal
A DC-DC converter includes a main inductor connected to an input voltage, a main switching element connected in series to the main inductor, a main diode connected to the main inductor and a load, and a main capacitor connected to the main diode and the load, the DC-DC converter changing the input voltage to output a changed input voltage as an output voltage. The DC-DC converter further includes an oscillator connected between the main inductor and the main diode, an auxiliary switching element connected to the oscillator, the auxiliary switching element changing an operation state based on an externally applied control signal to control the oscillator, and a diode unit connected to the oscillator and the auxiliary switching element and controlling current flow based on operations of the oscillator and the auxiliary switching element to change the output voltage. The main switching element and the main diode are to be zero voltage switching or zero current switching in accordance with the operations of the oscillator and the auxiliary switching element.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Power converters having capacitor resonant with transformer leakage inductance
Power converters having reduced body diode conduction loss, reduced reverse recovery loss and lower switching noise, among other benefits, have a resonant capacitor Cr connected across an unfiltered output. The resonant capacitor Cr resonates with the leakage inductance Lk of the transformer. The resonant capacitor and leakage inductance are selected such that ½ a LC resonance period is equal to an ON time of each secondary switch S1 S2. The resonance provides zero current switching for secondary switches S1 S2, eliminates zero body diode conduction during dead times, and eliminates reverse recovery losses in the secondary switches. The present invention is applicable to many different circuit topologies such as full bridge, active clamp forward, push-pull forward, and center-tap secondary. The present converters provide high energy conversion efficiency and high frequency operation.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com