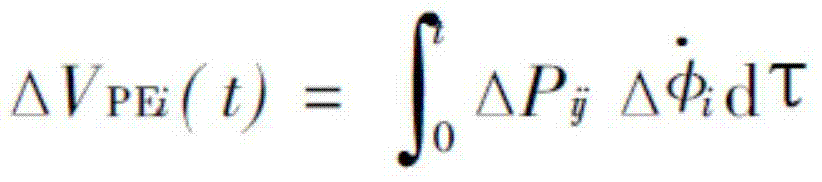Patents
Literature
134 results about "Forced oscillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
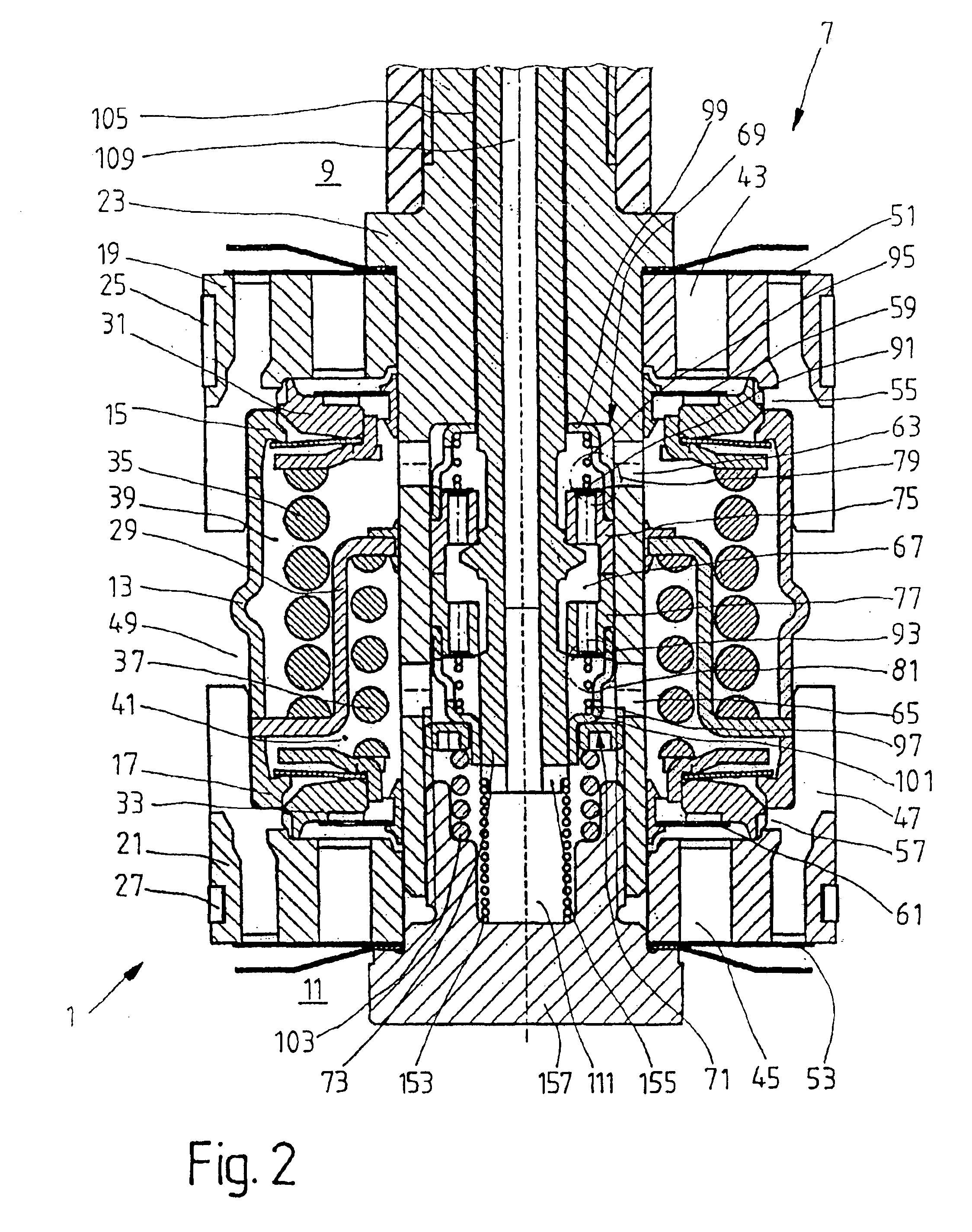
Wave energy conversion device for desalination, ETC
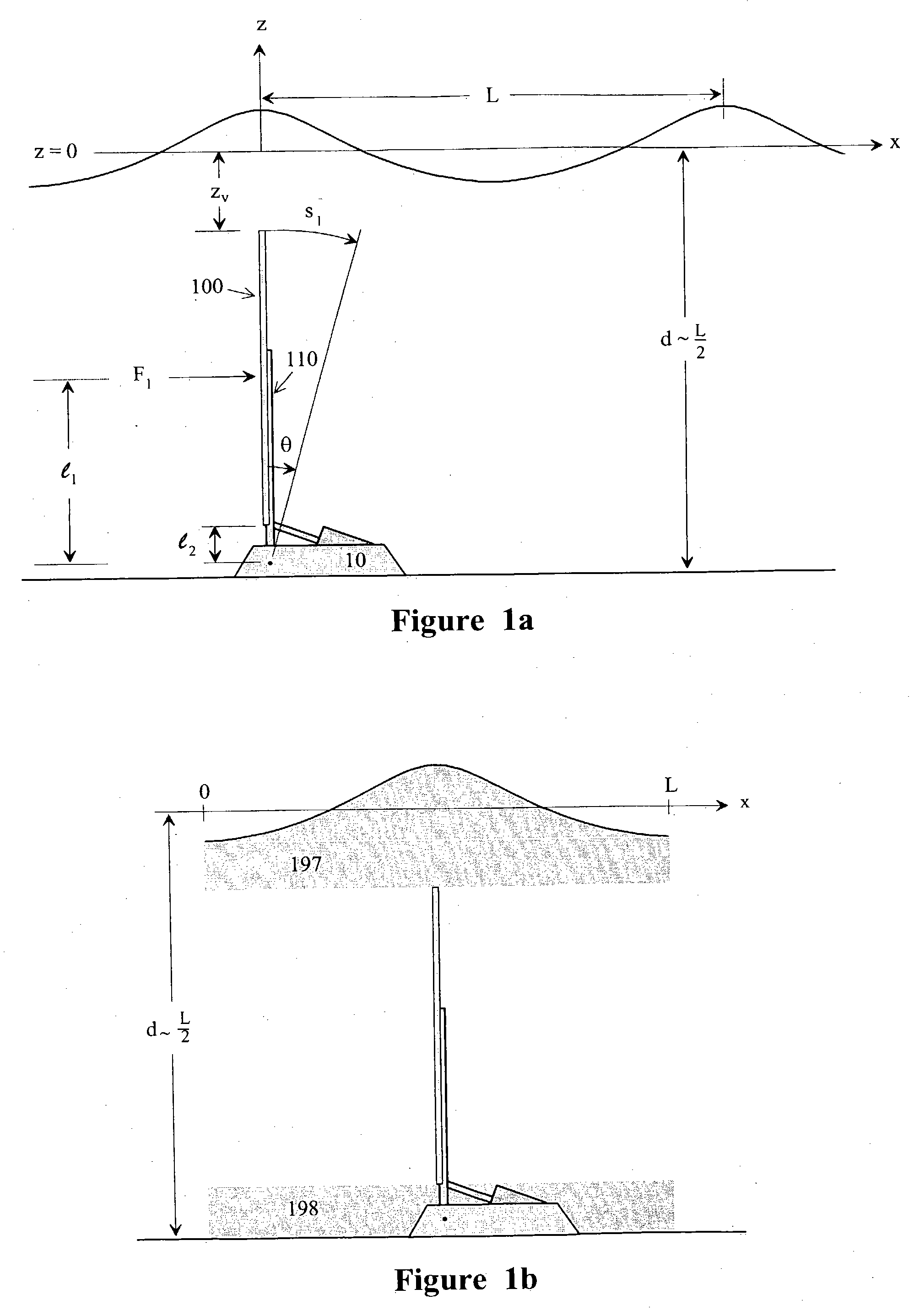
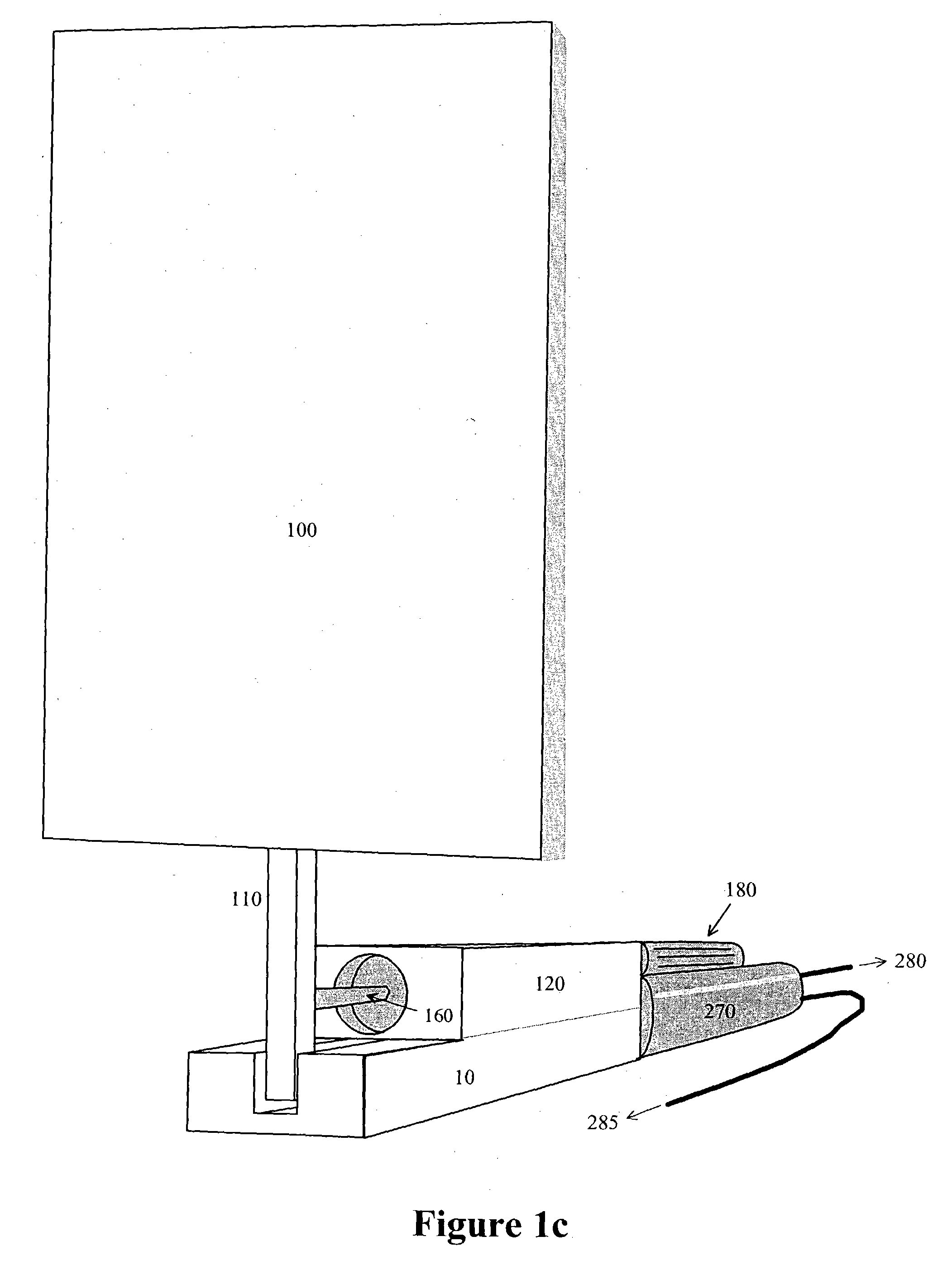
InactiveUS7023104B2Improve efficiencyEasy to operateWind motor controlGeneral water supply conservationWater qualityEngineering
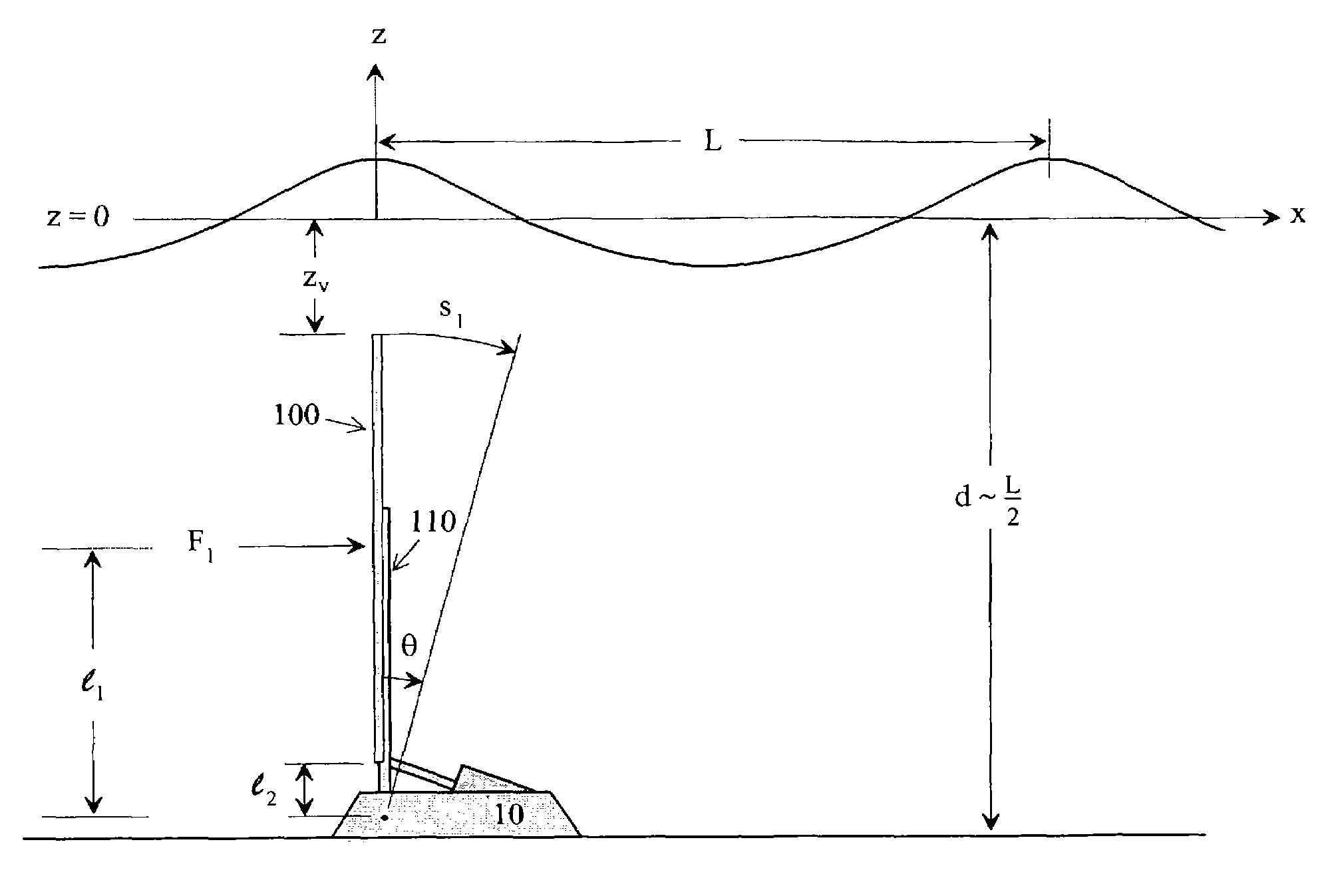
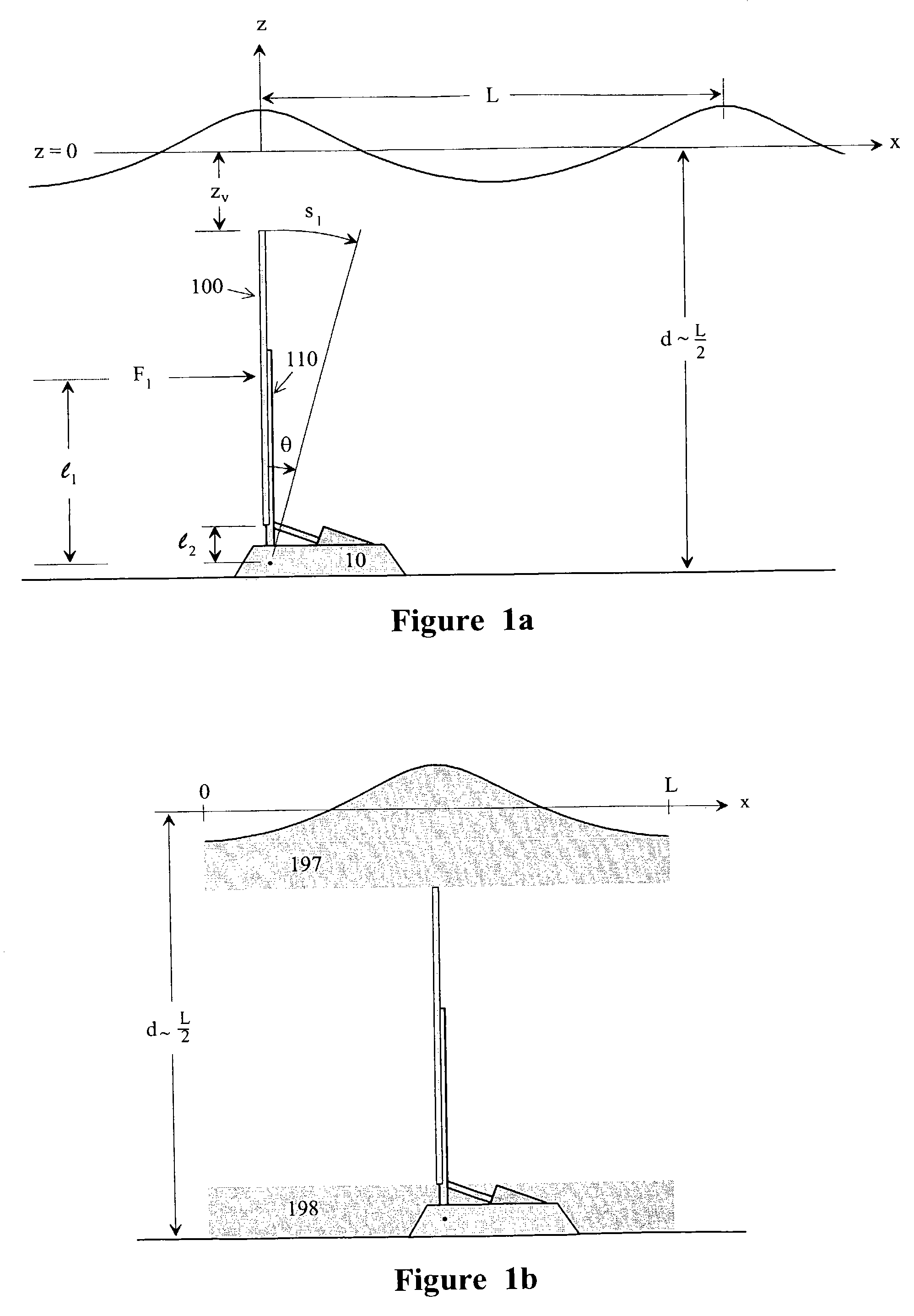
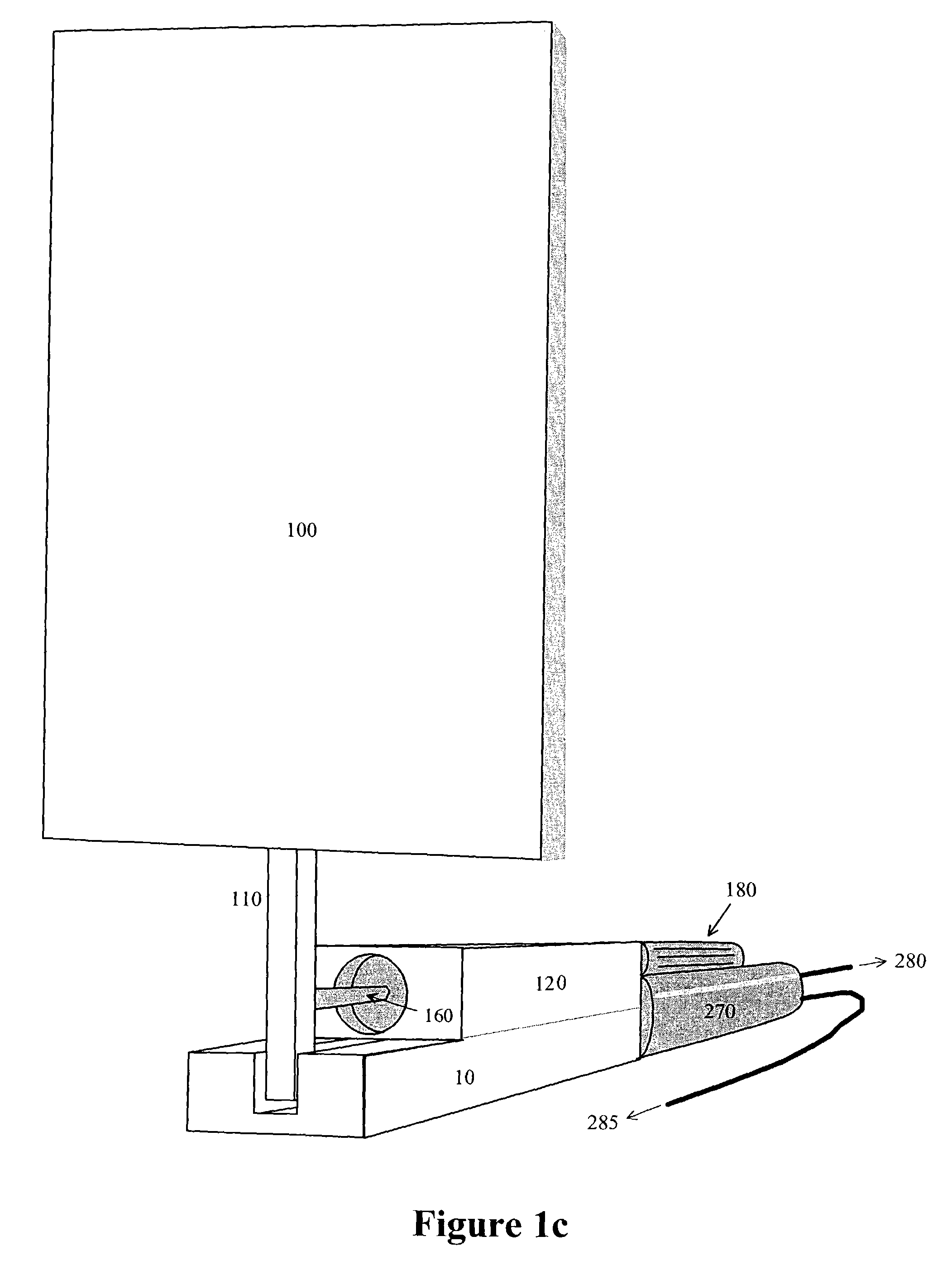
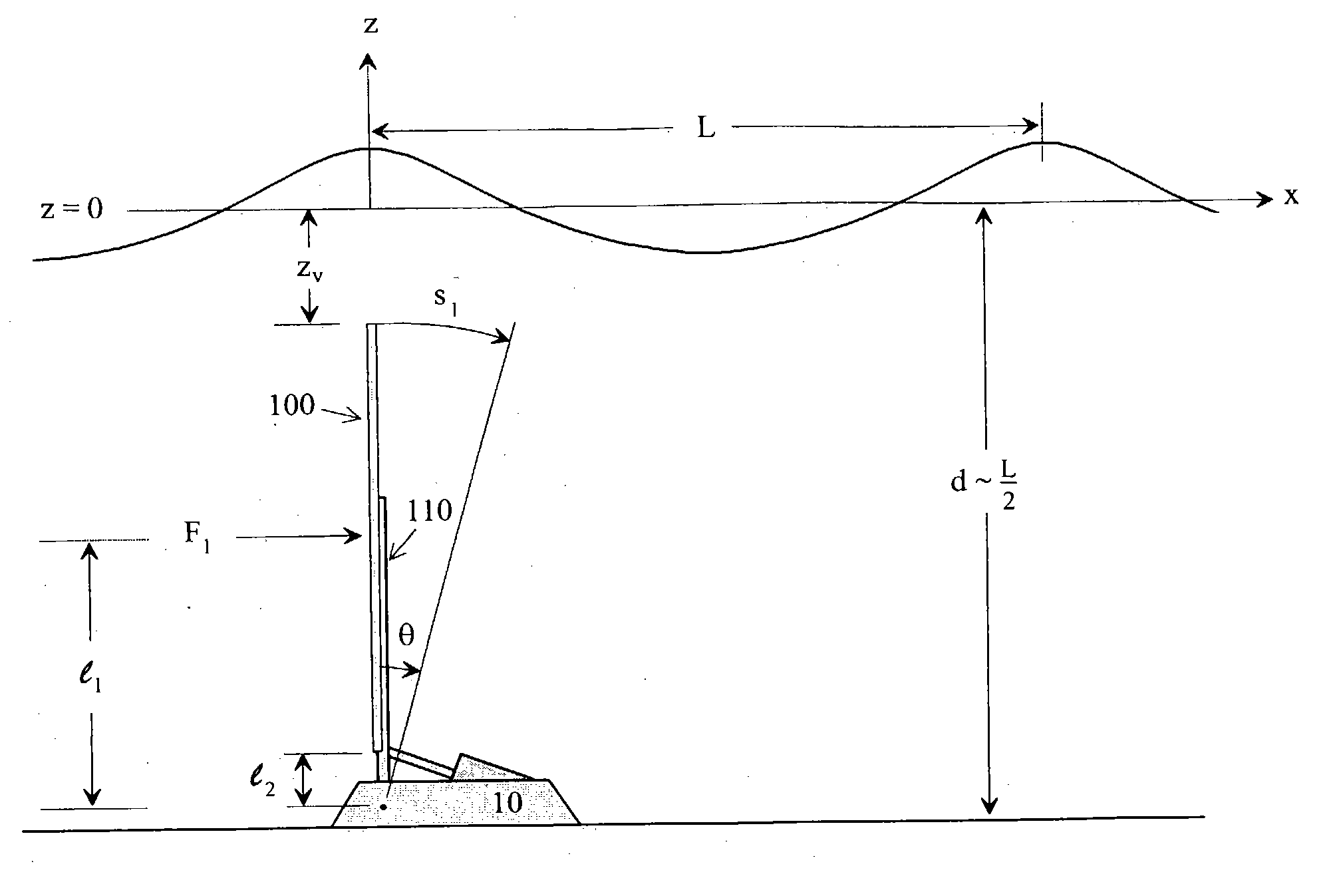
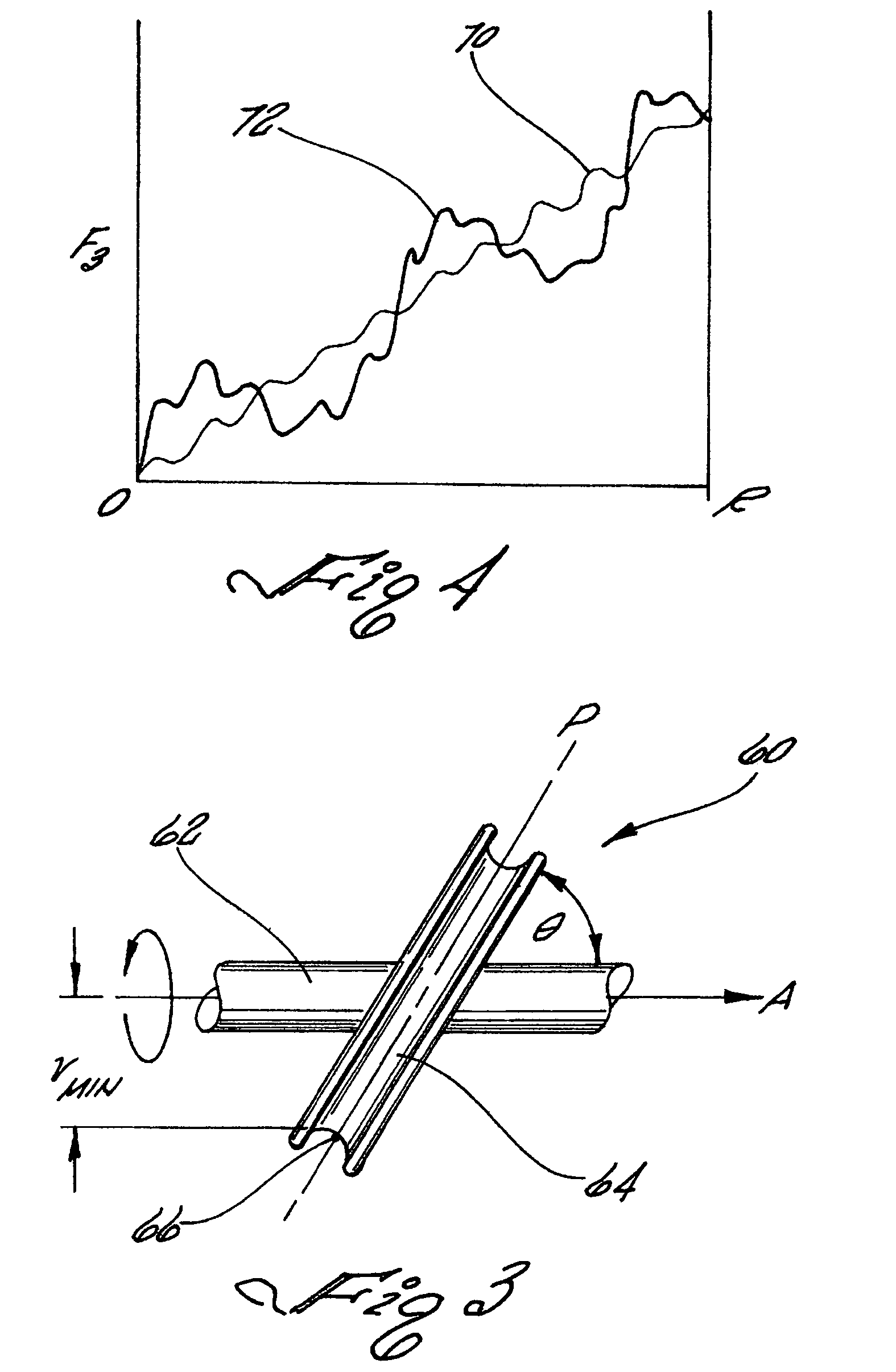
An impulse-type “wave motor” employs a seabed-mounted or supported structure mounting a wave energy absorbing panel on a hinged lever arm for reciprocation motion to obtain optimal absorption of wave energy from wave motion in the sea. For deepwater wavelengths of L, the panel is optimally positioned in a region within L / 2 depth from the sea surface. The panel motion is coupled by a connecting rod to a fluid pump which generates a high-pressure fluid output that may be used to drive a reverse osmosis desalination unit or to produce other useful work. Seawater or brackish water may be desalinated through reverse osmosis membranes to produce water quality for consumption, agricultural, or other uses. The submerged operating environment of the device in a region of one-half the design wavelength provides the maximum available energy flux and forced oscillations. The pump may be of the positive-displacement piston type, plunger type, or multi-staging driver type, or a variable volume pump.
Owner:KOBASHIKAWA ALVIN +1
Wave energy conversion device for desalination, ETC
InactiveUS20040007881A1Minimize exposureLow profileWind motor controlGeneral water supply conservationWater qualityWave motor
An impulse-type "wave motor" employs a seabed-mounted or supported structure mounting a wave energy absorbing panel on a hinged lever arm for reciprocation motion to obtain optimal absorption of wave energy from wave motion in the sea. For deepwater wavelengths of L, the panel is optimally positioned in a region within L / 2 depth from the sea surface. The panel motion is coupled by a connecting rod to a fluid pump which generates a high-pressure fluid output that may be used to drive a reverse osmosis desalination unit or to produce other useful work. Seawater or brackish water may be desalinated through reverse osmosis membranes to produce water quality for consumption, agricultural, or other uses. The submerged operating environment of the device in a region of one-half the design wavelength provides the maximum available energy flux and forced oscillations. The pump may be of the positive-displacement piston type, plunger type, or multi-staging driver type, or a variable volume pump.
Owner:KOBASHIKAWA ALVIN +1
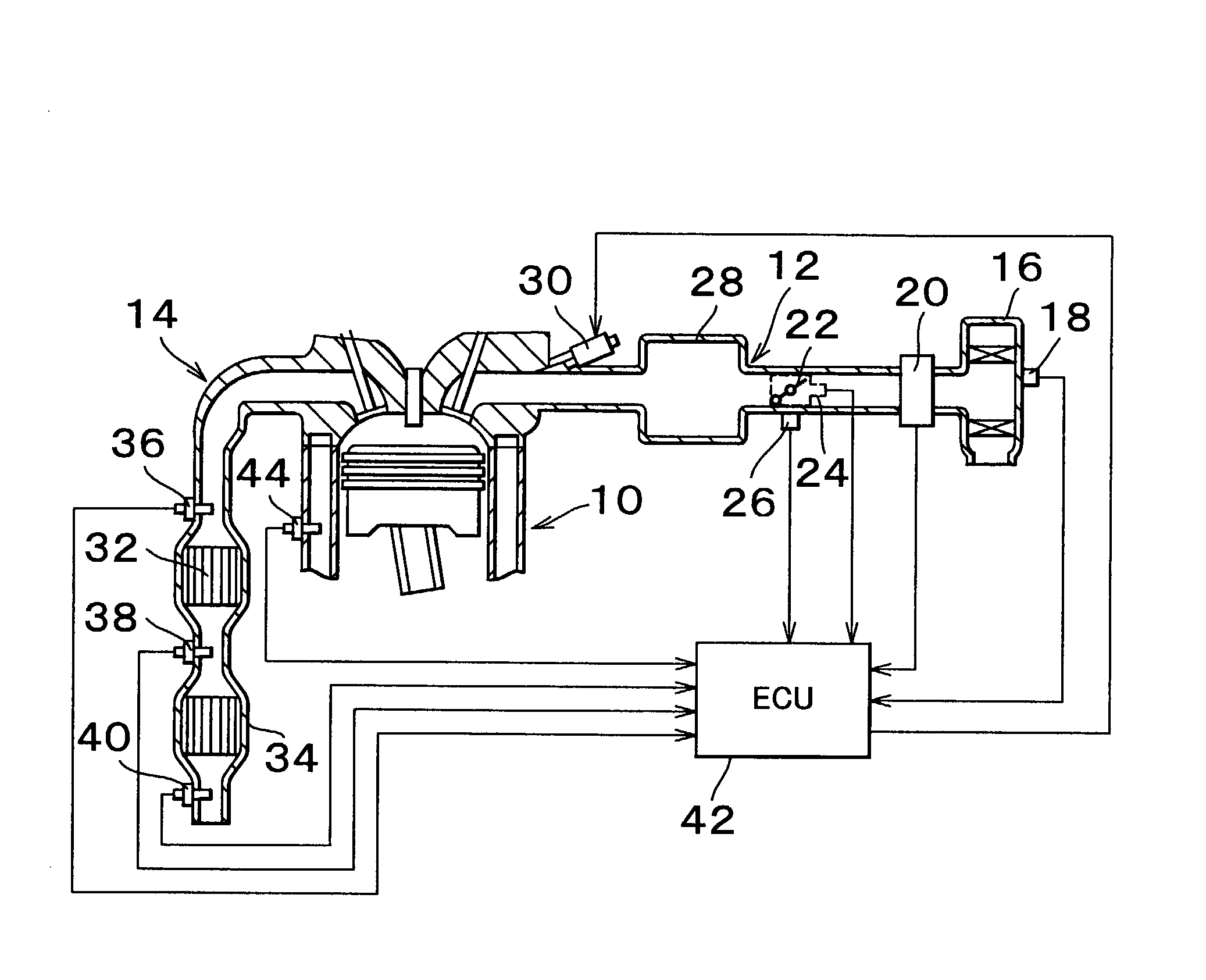
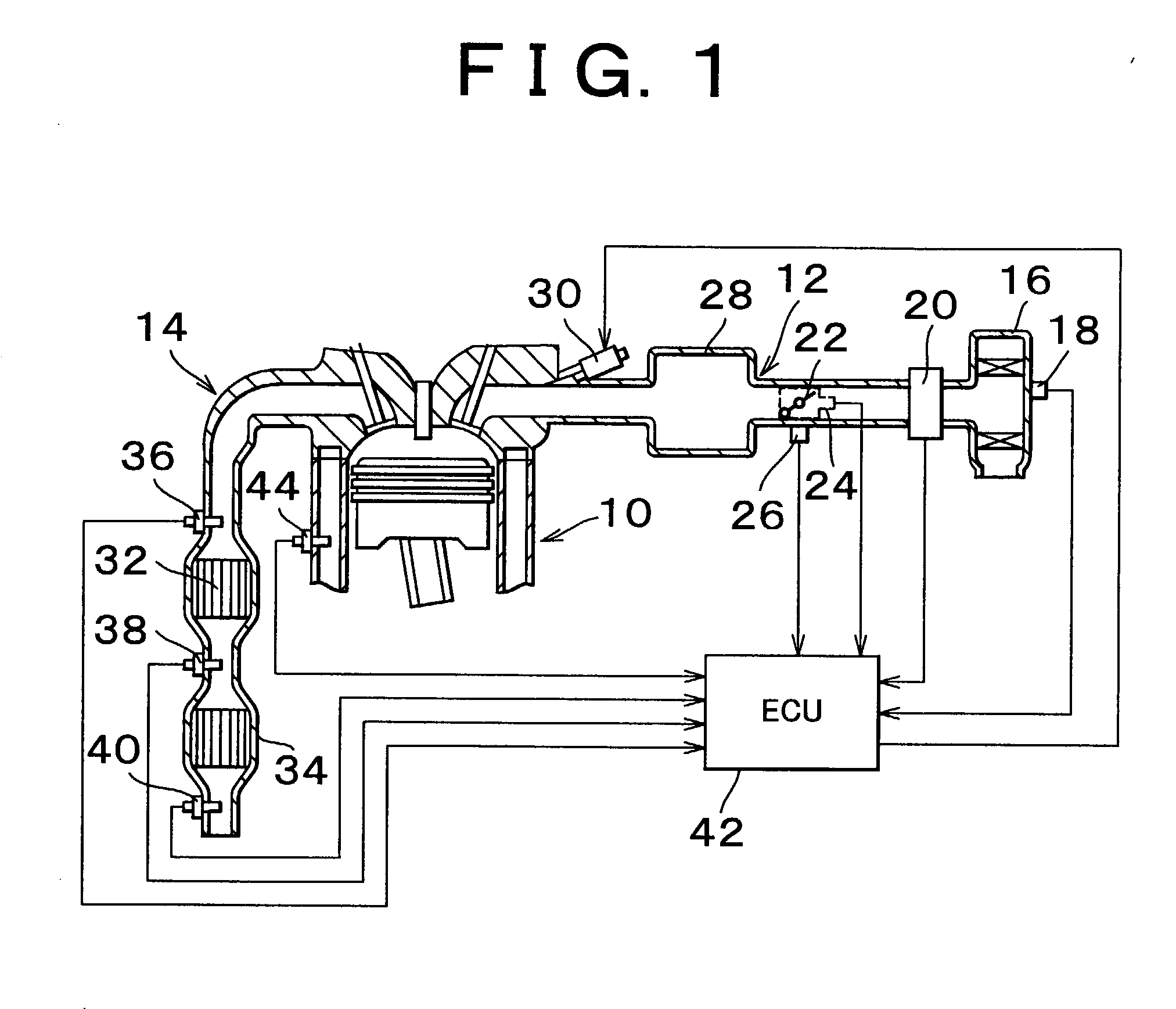
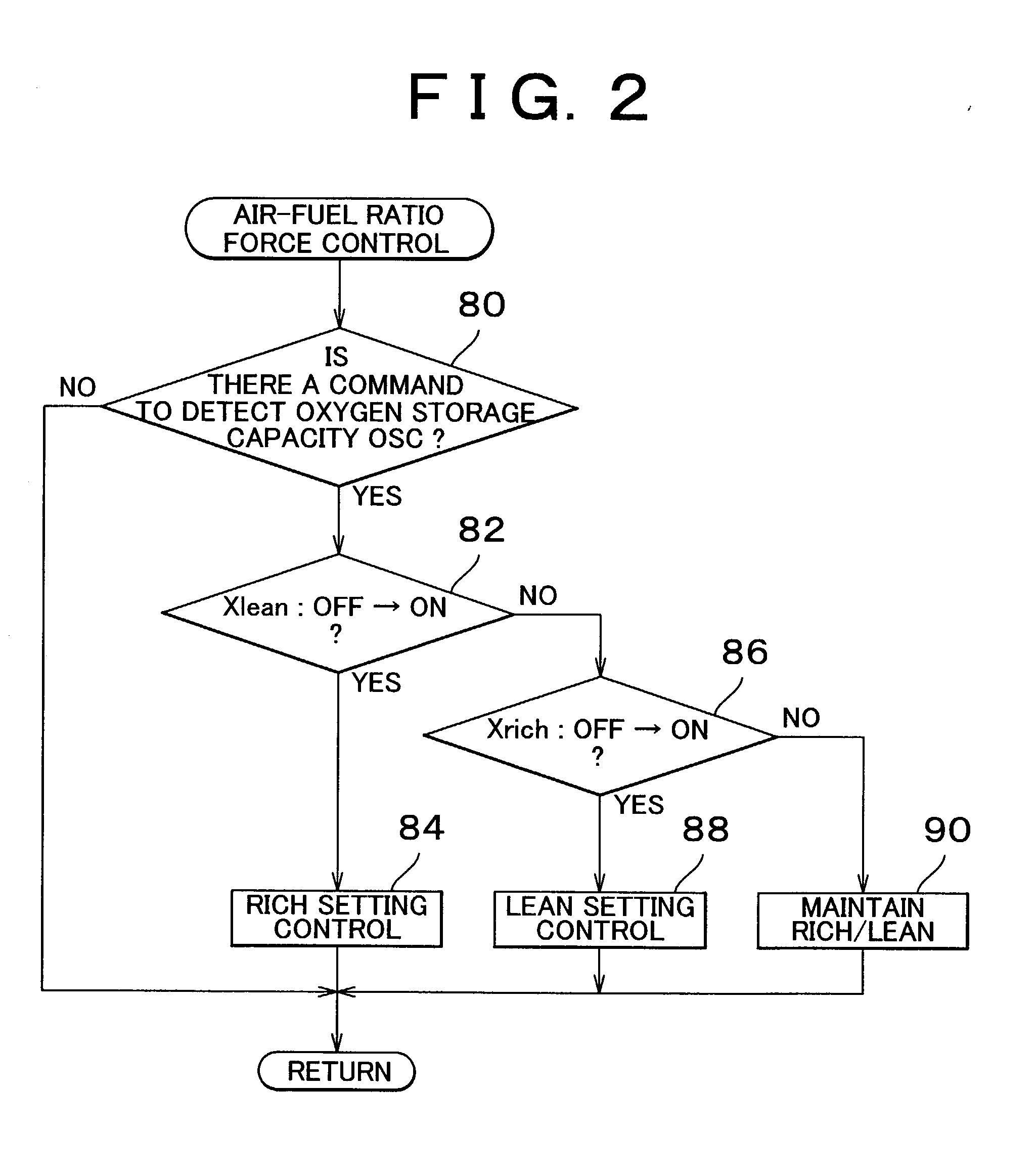
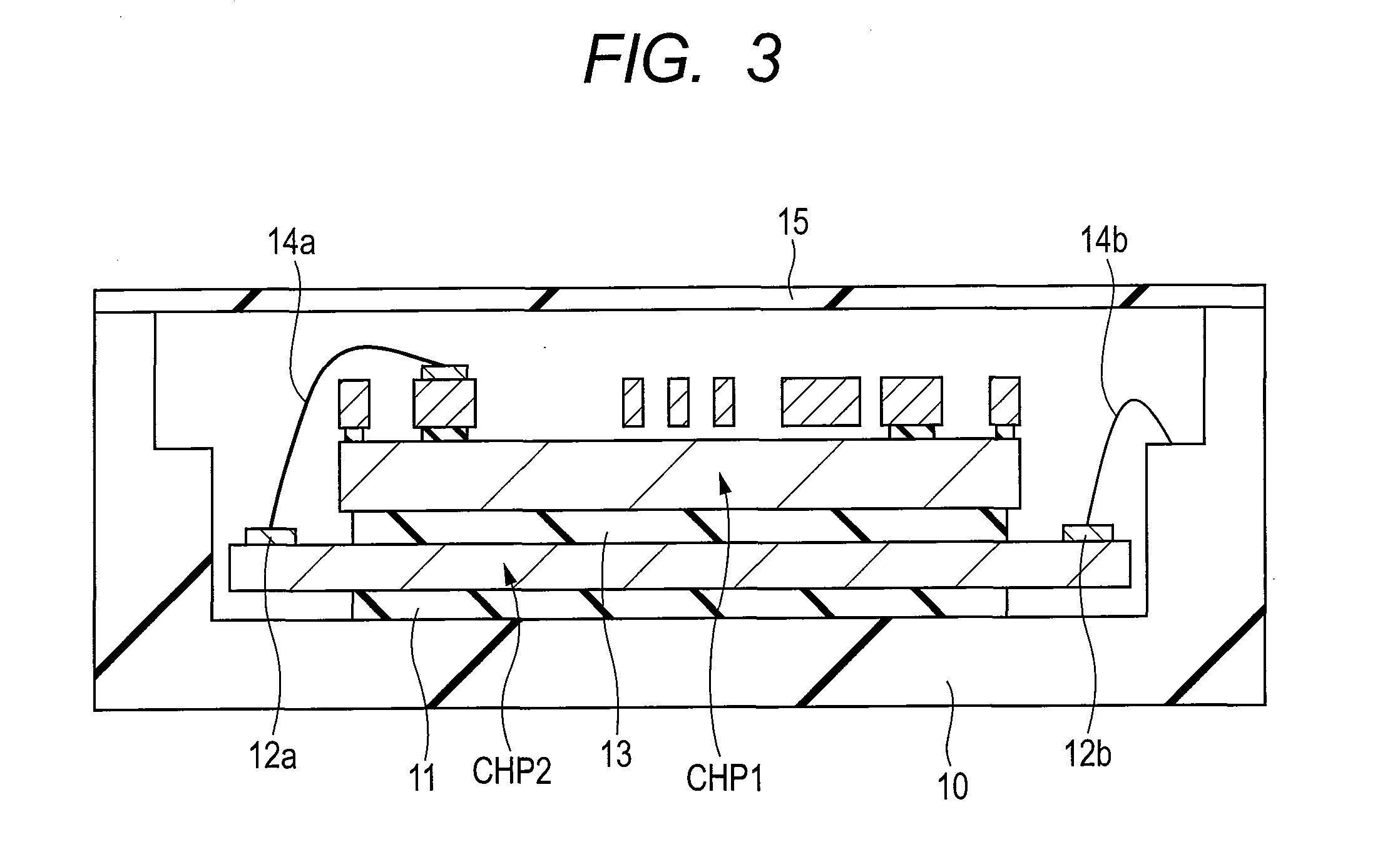
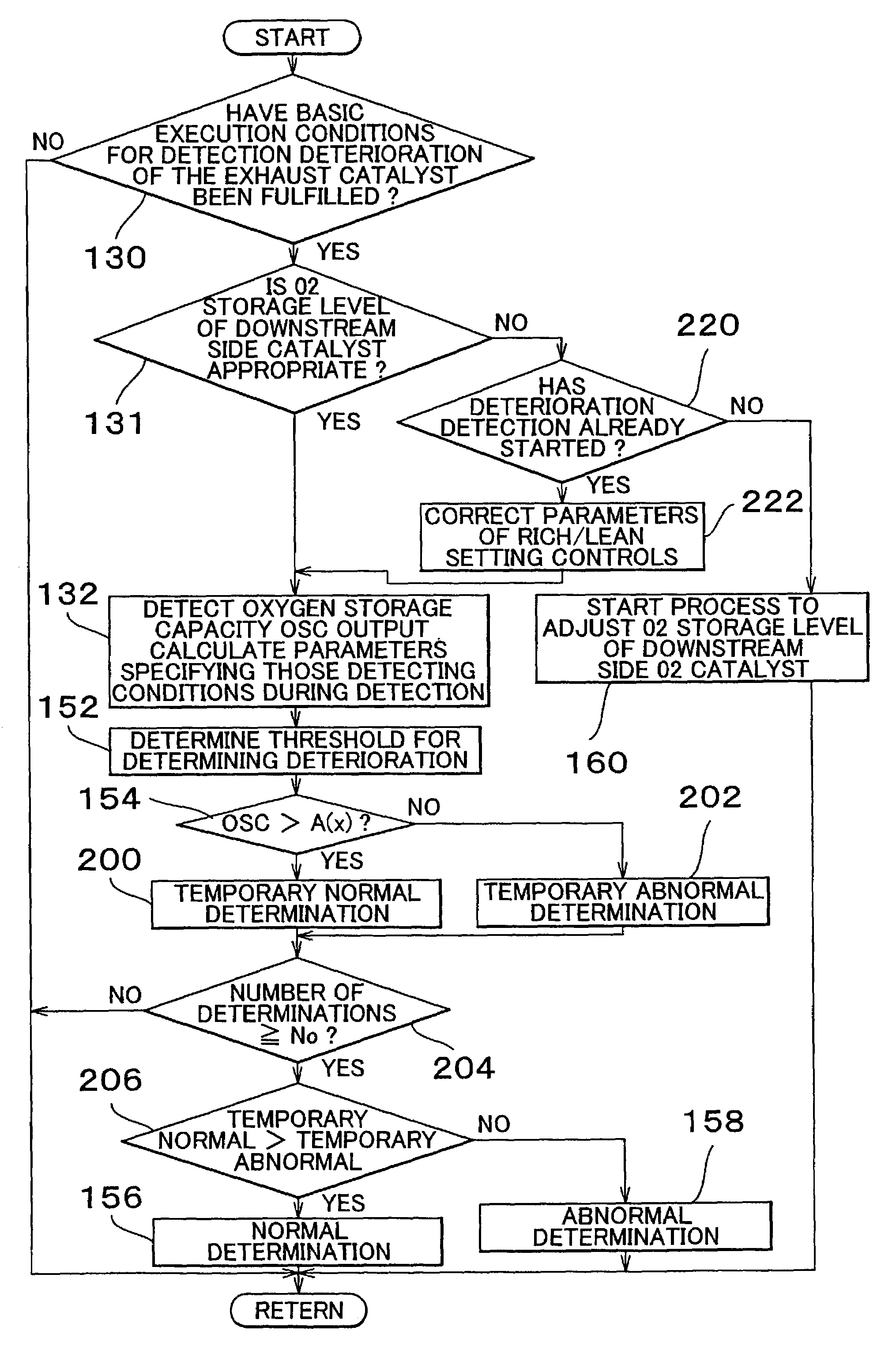
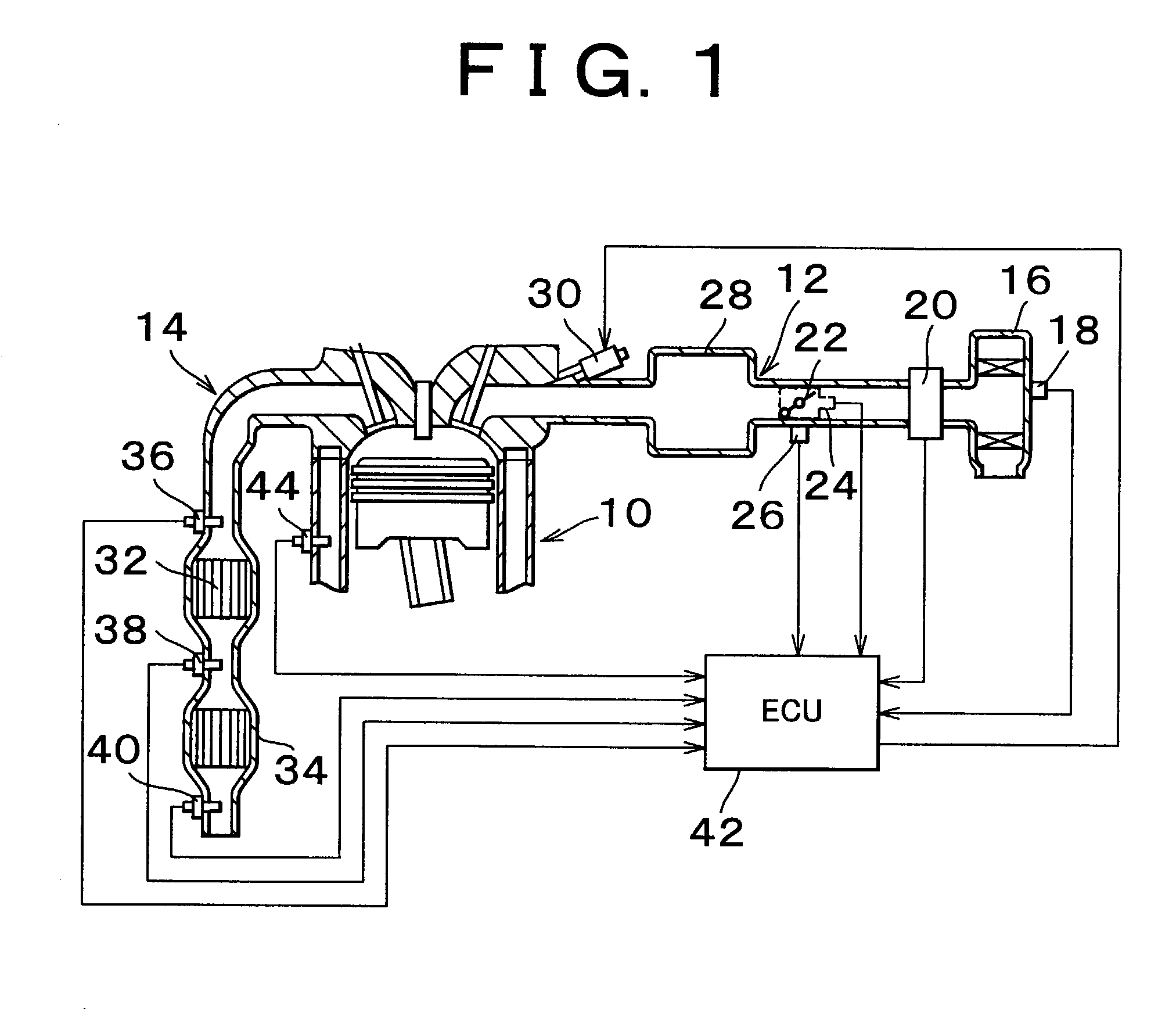
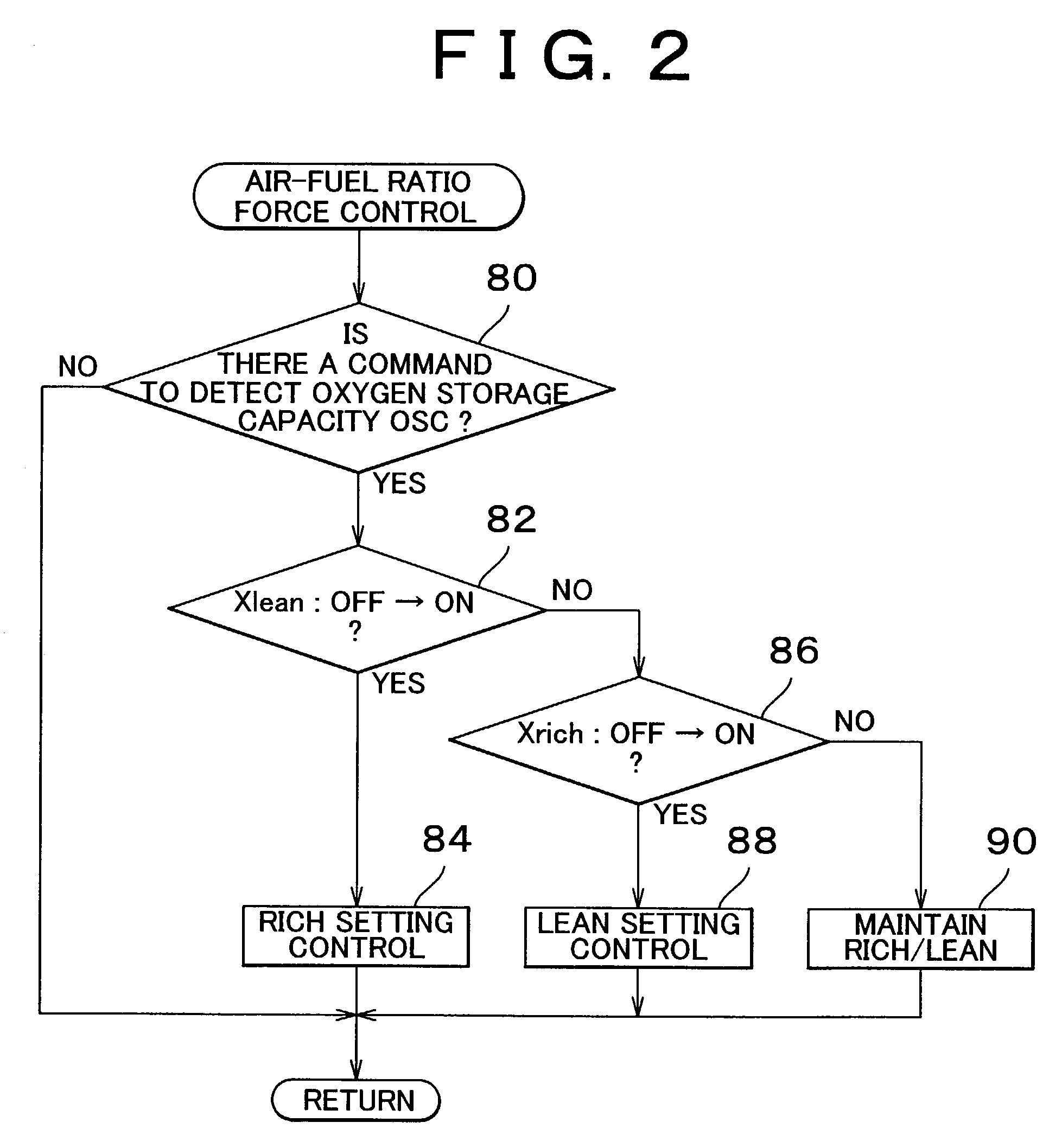
Catalyst deterioration detecting apparatus and method
InactiveUS20030017603A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesOxygen sensorEnvironmental engineering
An upstream side catalyst and a downstream side catalyst are disposed in an exhaust passage. A first oxygen sensor is disposed between these two catalysts and a second oxygen sensor is disposed downstream of the downstream side catalyst. The air-fuel ratio is forcibly oscillated and the oxygen storage capacity of the upstream side catalyst is detected. Deterioration of the upstream side catalyst is then detected based on whether this oxygen storage capacity is larger than a predetermined value. The forced oscillation of the air-fuel ratio is performed only when the oxygen storage state of the downstream side catalyst is appropriate.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
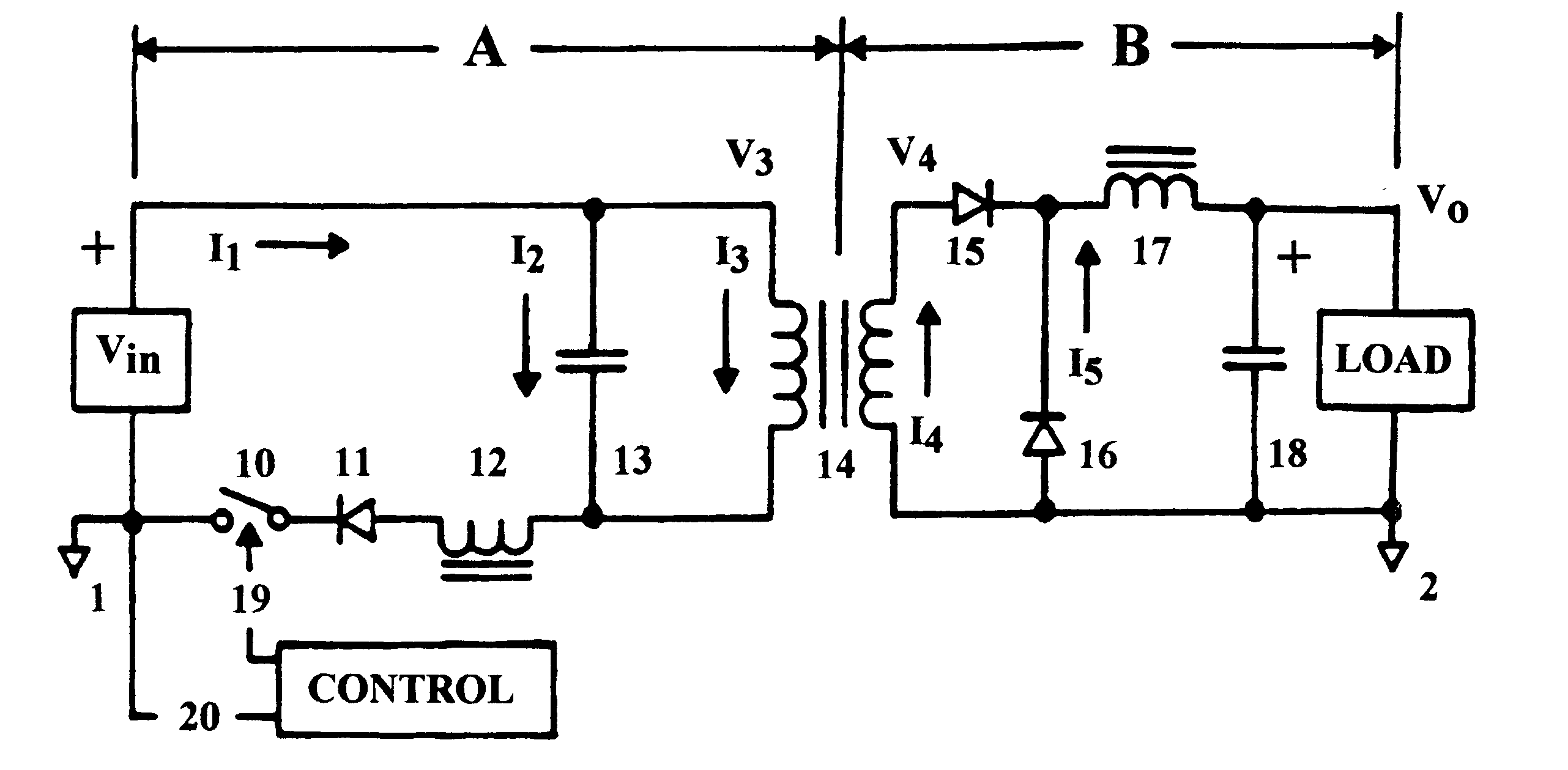
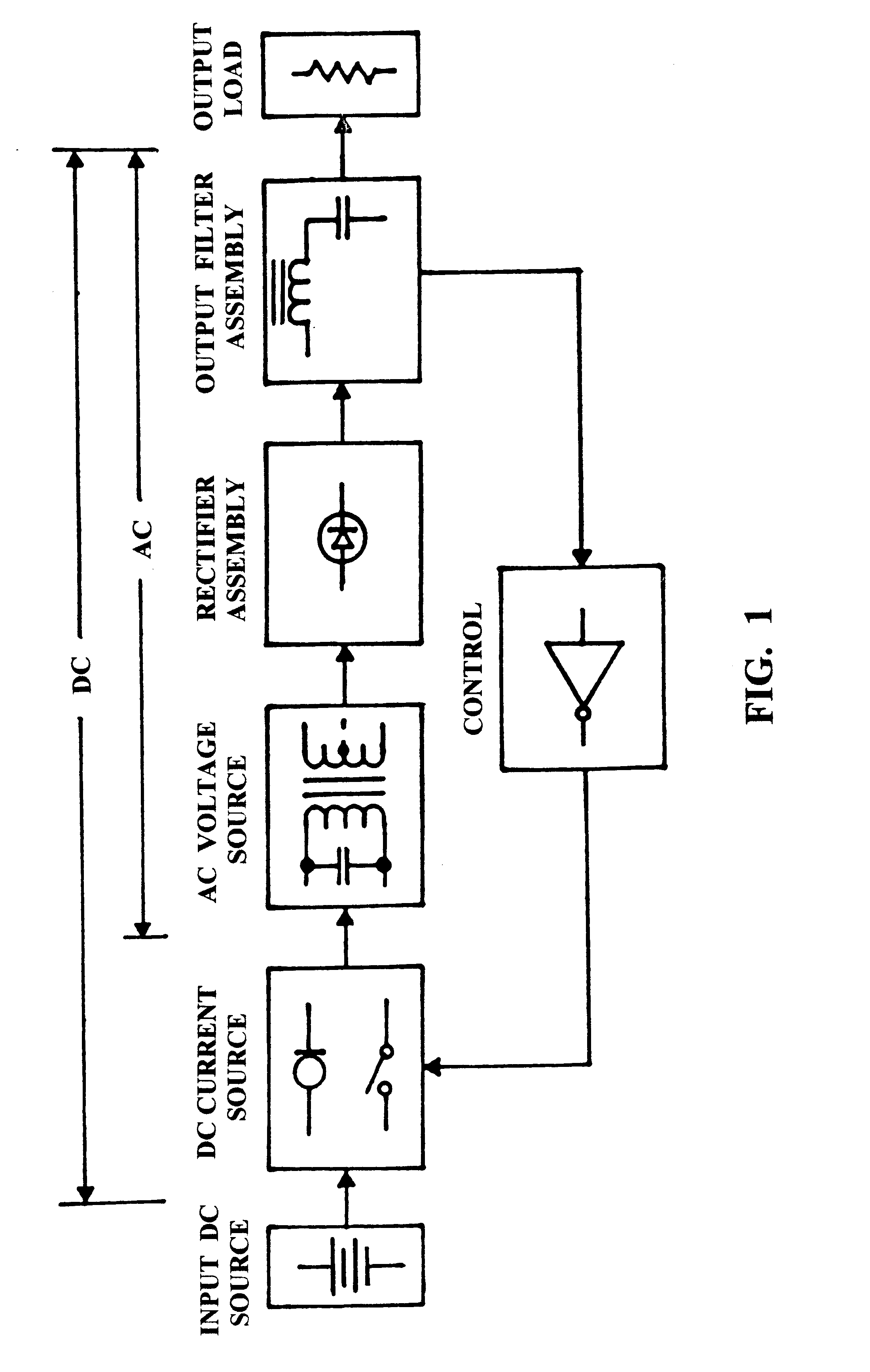
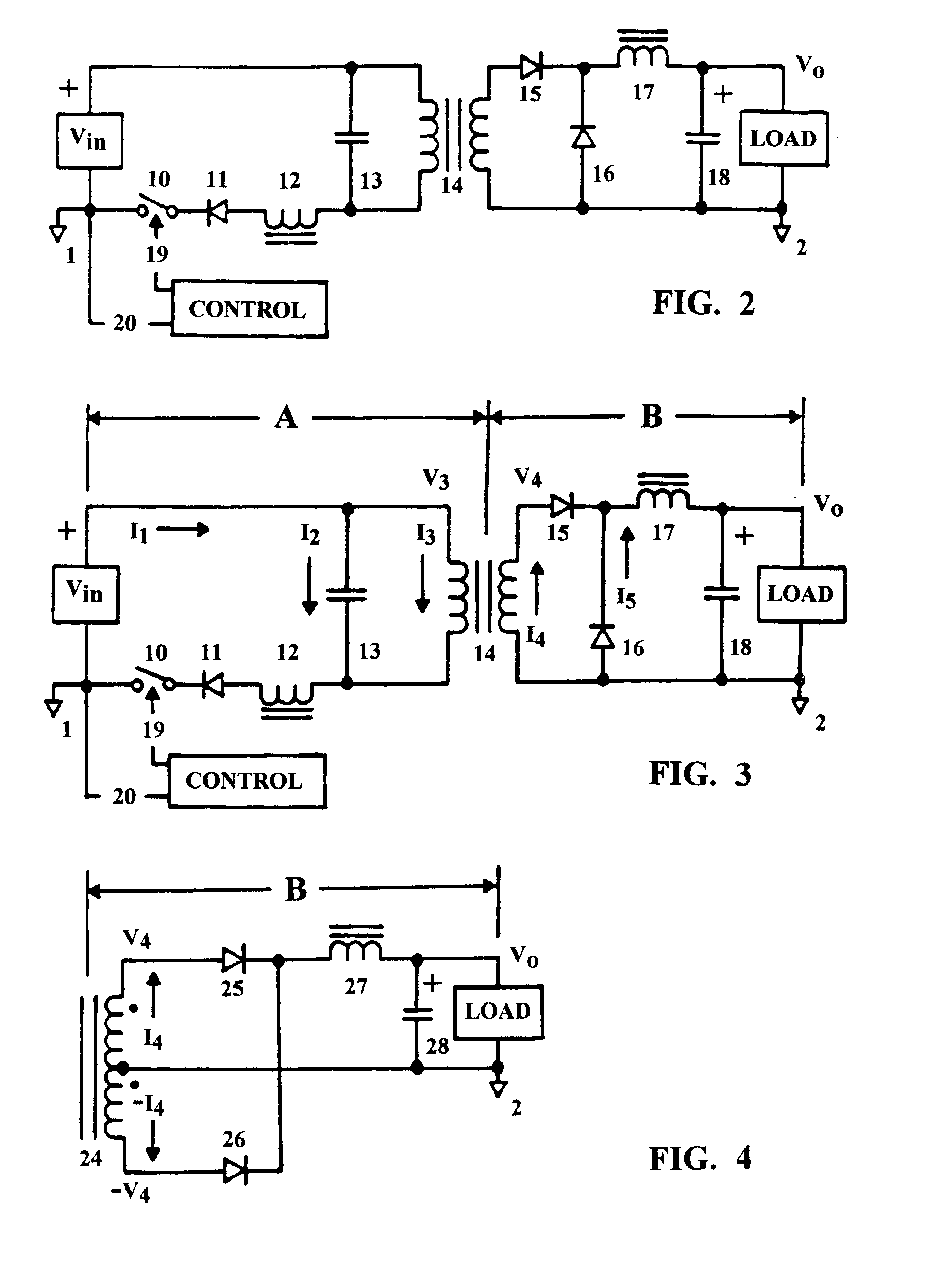
Resonant power converter with primary-side tuning and zero-current switching
InactiveUS6490177B1Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceDc current
A DC power converter consisting of a series-resonant branch used to transform a DC voltage source into a DC current source exhibiting, a uni-polar, zero-current-switching characteristic. Frequency of the series-resonant branch, acting in concert with reflected load parameters, provides a forced oscillation frequency, Fo, component to an AC voltage source generated across the input winding of a power transformer by the resonant capacitor. Complex load parameters allow AC input current, displaced by 90° from the AC voltage source, to flow in the transformer primary winding throughout a composite, carrier-frequency cycle. Another component of the carrier-frequency consists of a resonant, natural oscillation frequency, Fn, resulting from resonance by the AC voltage source capacitance with the open-circuit inductance of the primary winding on the input power transformer. The composite carrier-frequency, Fo+Fn, transported through the input power transformer is directed to a rectifier / filter assembly and applied as a DC voltage to an output load. Thus, the uni-polar DC series-resonant branch is converted into an AC power transfer function, fully isolated from the input power switch, by the AC voltage source capacitor. The power transfer function characterizing a bi-polar power inverter requires a single power switch referenced to the input power return bus.
Owner:FIGUEROA SALVADOR
Oscillation damper with adjustable damping force
InactiveUS20030029684A1Easy constructionReducing torque peaksSpringsShock absorbersSpring forceActuator
Oscillation damper with variable damping force, comprising a valve device, in which an actuator for adjusting the valve device performs a rotary motion against the spring force of a torsion spring, the position of the valve device being determined from the manipulated variable of the actuator and the reaction force of the torsion spring.
Owner:ZF SACHS AG
Fluid treatment system
ActiveUS20050263716A1Reducing velocity of fluid flowingIncrease fluid velocityLiquid separation by electricityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWastewaterForced oscillation
The present invention relates to a fluid treatment system comprising: an inlet; an outlet; and a fluid treatment zone disposed between the inlet and the outlet. The fluid treatment zone has disposed therein: (i) an elongate first radiation source assembly having a first longitudinal axis, and (ii) an elongate second radiation source assembly having a second longitudinal axis. The first longitudinal axis and the second longitudinal axis are non-parallel to each other and to a direction of fluid flow through the fluid treatment zone. The present fluid treatment system has a number of advantages including: it can treat large volumes of fluid (e.g., wastewater, drinking water or the like); it requires a relatively small “footprint”; it results in a relatively lower coefficient of drag resulting in an improved hydraulic pressure loss / gradient over the length of the fluid treatment system; and it results in relatively lower (or no) forced oscillation of the radiation sources thereby obviating or mitigating of breakage of the radiation source and / or protective sleeve (if present). Other advantages are discussed in the specification.
Owner:TROJAN TECH
Capacitance Sensor
ActiveUS20110100126A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityEngineering
A technique in which a false detection and a wrong diagnosis can be suppressed in a capacitance sensor represented by an acceleration sensor is provided. A first capacitative element and a second capacitative element, which configure a capacitance detection unit, and a third capacitative element and a fourth capacitative element, which configure a forced oscillation generation unit, are electrically separated from each other. That is, the diagnosis movable electrode that configures the third capacitative element and the fourth capacitative element is formed integrally with the movable part. On the other hand, the diagnosis fixed electrode and the diagnosis fixed electrode are electrically separated from the detection fixed electrode and the detection fixed electrode.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Catalyst deterioration detecting apparatus and method
InactiveUS7198952B2State of will deteriorateElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesOxygen sensorEnvironmental engineering
An upstream side catalyst and a downstream side catalyst are disposed in an exhaust passage. A first oxygen sensor is disposed between these two catalysts and a second oxygen sensor is disposed downstream of the downstream side catalyst. The air-fuel ratio is forcibly oscillated and the oxygen storage capacity of the upstream side catalyst is detected. Deterioration of the upstream side catalyst is then detected based on whether this oxygen storage capacity is larger than a predetermined value. The forced oscillation of the air-fuel ratio is performed only when the oxygen storage state of the downstream side catalyst is appropriate.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fluid treatment system
ActiveUS7408174B2Reduce the average velocityIncrease fluid velocityLiquid separation by electricityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWastewaterForced oscillation
The present invention relates to a fluid treatment system comprising: an inlet; an outlet; and a fluid treatment zone disposed between the inlet and the outlet. The fluid treatment zone has disposed therein: (i) an elongate first radiation source assembly having a first longitudinal axis, and (ii) an elongate second radiation source assembly having a second longitudinal axis. The first longitudinal axis and the second longitudinal axis are non-parallel to each other and to a direction of fluid flow through the fluid treatment zone. The present fluid treatment system has a number of advantages including: it can treat large volumes of fluid (e.g., wastewater, drinking water or the like); it requires a relatively small “footprint”; it results in a relatively lower coefficient of drag resulting in an improved hydraulic pressure loss / gradient over the length of the fluid treatment system; and it results in relatively lower (or no) forced oscillation of the radiation sources thereby obviating or mitigating of breakage of the radiation source and / or protective sleeve (if present). Other advantages are discussed in the specification.
Owner:TROJAN TECH
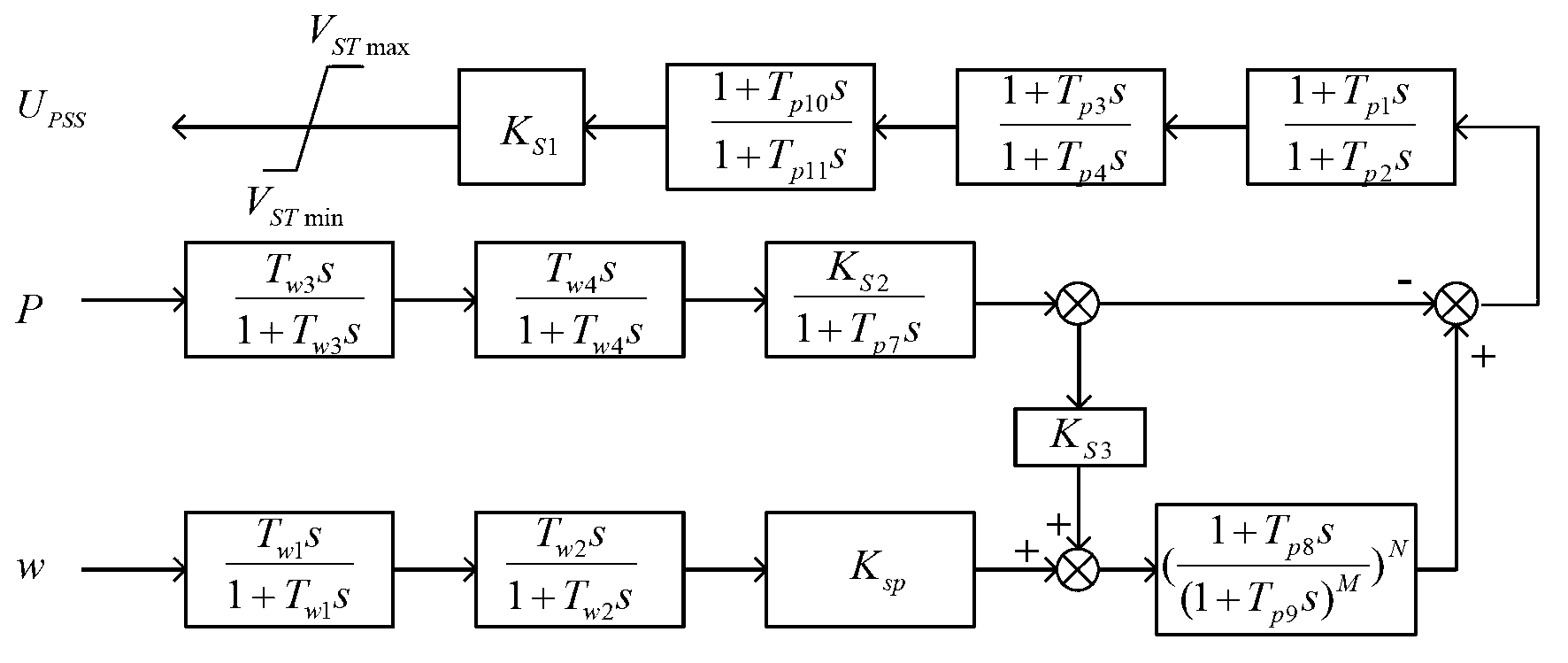
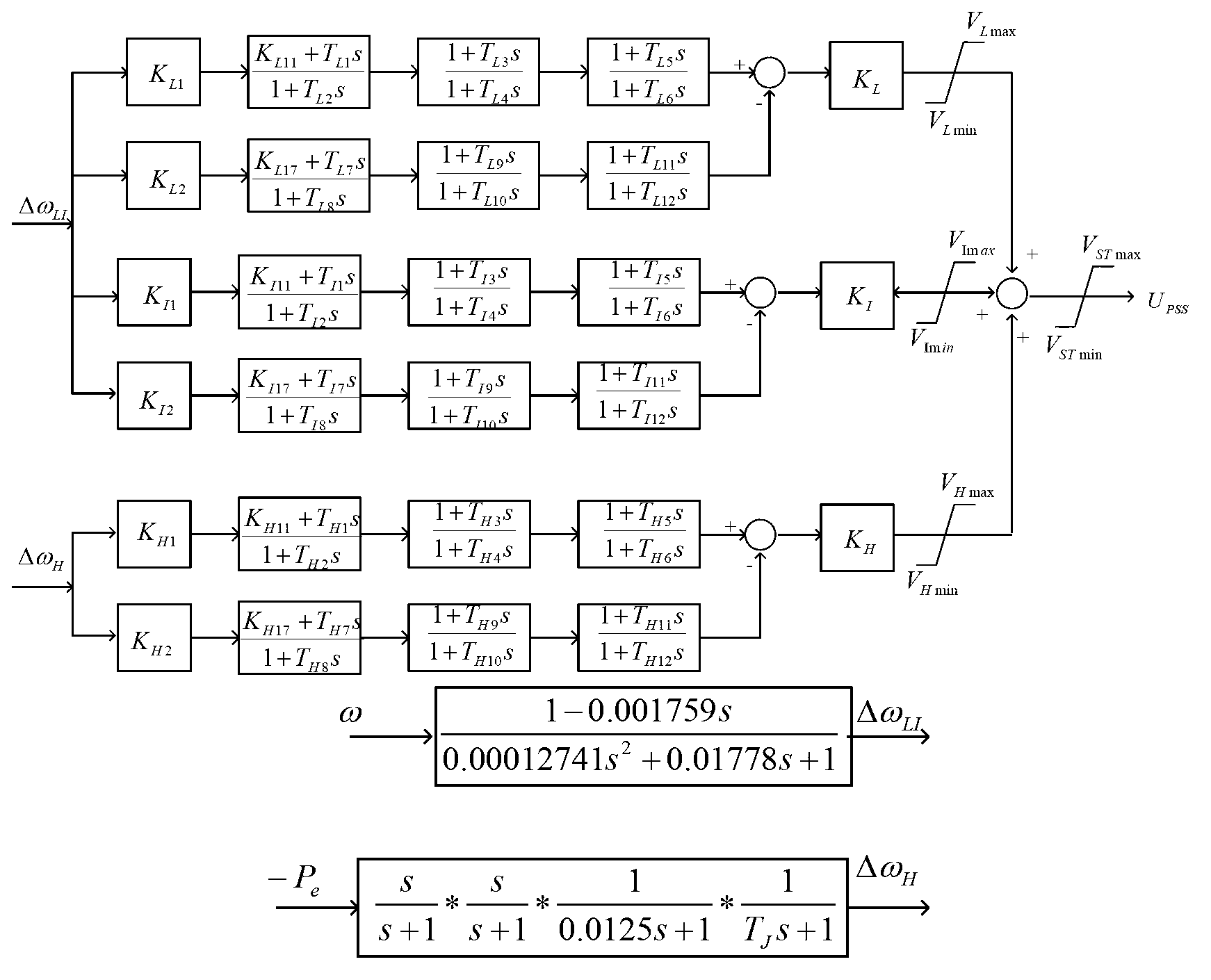
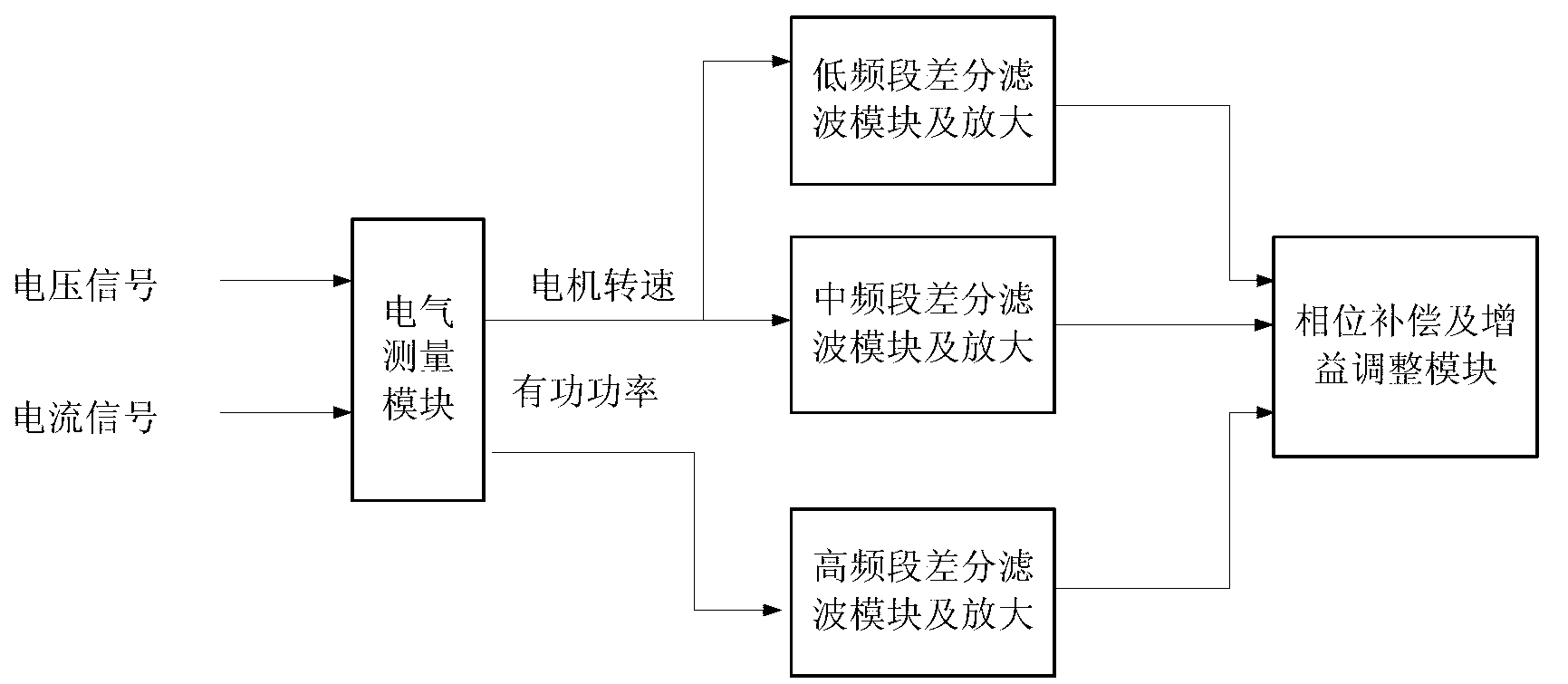
Method for implementing power system stabilizer
ActiveCN103296688ASolution rangeSolve the problem of conflicting effectsPower oscillations reduction/preventionPhase shiftedDifferential signaling
The invention discloses a method for implementing a power system stabilizer. The method includes steps of acquiring a rotation speed variable quantity via a blocking filter link according to the rotation speed and active power of a rotor of a power generator, and respectively acquiring low-band differential signals, medium-band differential signals and high-band differential signals via a differential filter; parallelly adding the low-band differential signals, the medium-band differential signals and the high-band differential signals together to acquire rotation speed variation comprehensive signals of the power generator; measuring phase-shift characteristics of the rotation speed variation comprehensive signals and the rotation speed and uncompensated phase-shift characteristics of an excitation control system of the power generator by a forced oscillation process, computing required phase-shift characteristics among the rotation speed variation comprehensive signals and the power system stabilizer, designing multi-order lead-lag link phase-shift parameters which are serially multiplied by one another, performing phase compensation to meet the required phase-shift characteristics; finally outputting signals of the power system stabilizer and superposing the signals of the power system stabilizer on a reference voltage of an excitation regulator of the power generator. The method has the advantage that active power low-frequency oscillation of the synchronous generator can be effectively suppressed.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Oscillation damper with adjustable damping force
Oscillation damper with variable damping force, comprising a valve device, in which an actuator for adjusting the valve device performs a rotary motion against the spring force of a torsion spring, the position of the valve device being determined from the manipulated variable of the actuator and the reaction force of the torsion spring.
Owner:ZF SACHS AG
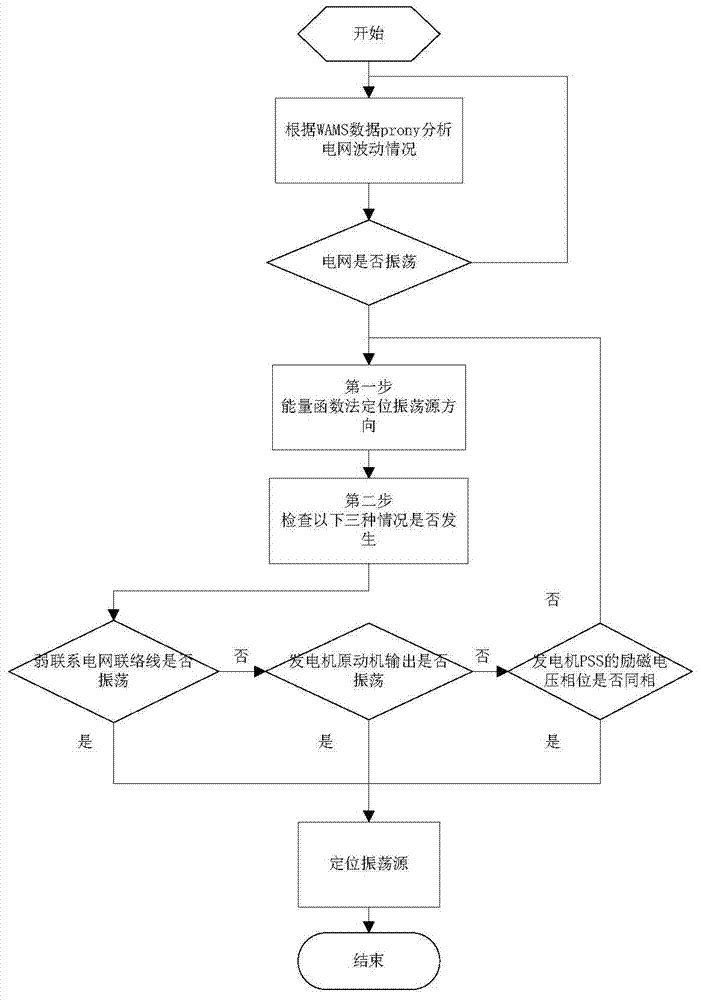
WAMS (wide area measurement system) and SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) integrated data based grid forced oscillation source positioning method
ActiveCN104242462ASolve defects that cannot be located correctlyAvoid major accidentsCircuit arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsWide areaData acquisition
The invention provides a WAMS (wide area measurement system) and SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) integrated data based grid forced oscillation source positioning method. Oscillation sources are positioned rapidly and accurately by comprehensive utilization of data of the WAMS and SCADA. According to a main principle, the method includes: firstly, positioning general directions of the oscillation sources by adopting an energy flow function method based on 500kV grid WAMS data, then adopting different accurate oscillation source positioning methods according to properties of three common oscillation sources, computing tie lines of a local weak tie network by adopting an SCADA data based oscillation extreme point judgment method, and judging whether oscillation exists in the weak tie network or not; adopting WAMS data of generator excitation voltage phase to judge whether oscillation is caused by a generator excited system or not; adopting an extreme point computation method of SCADA data of valve or guide vane opening of a generator set to judge whether grid oscillation is caused by a unit prime mover or not.
Owner:CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID COMPANY +1
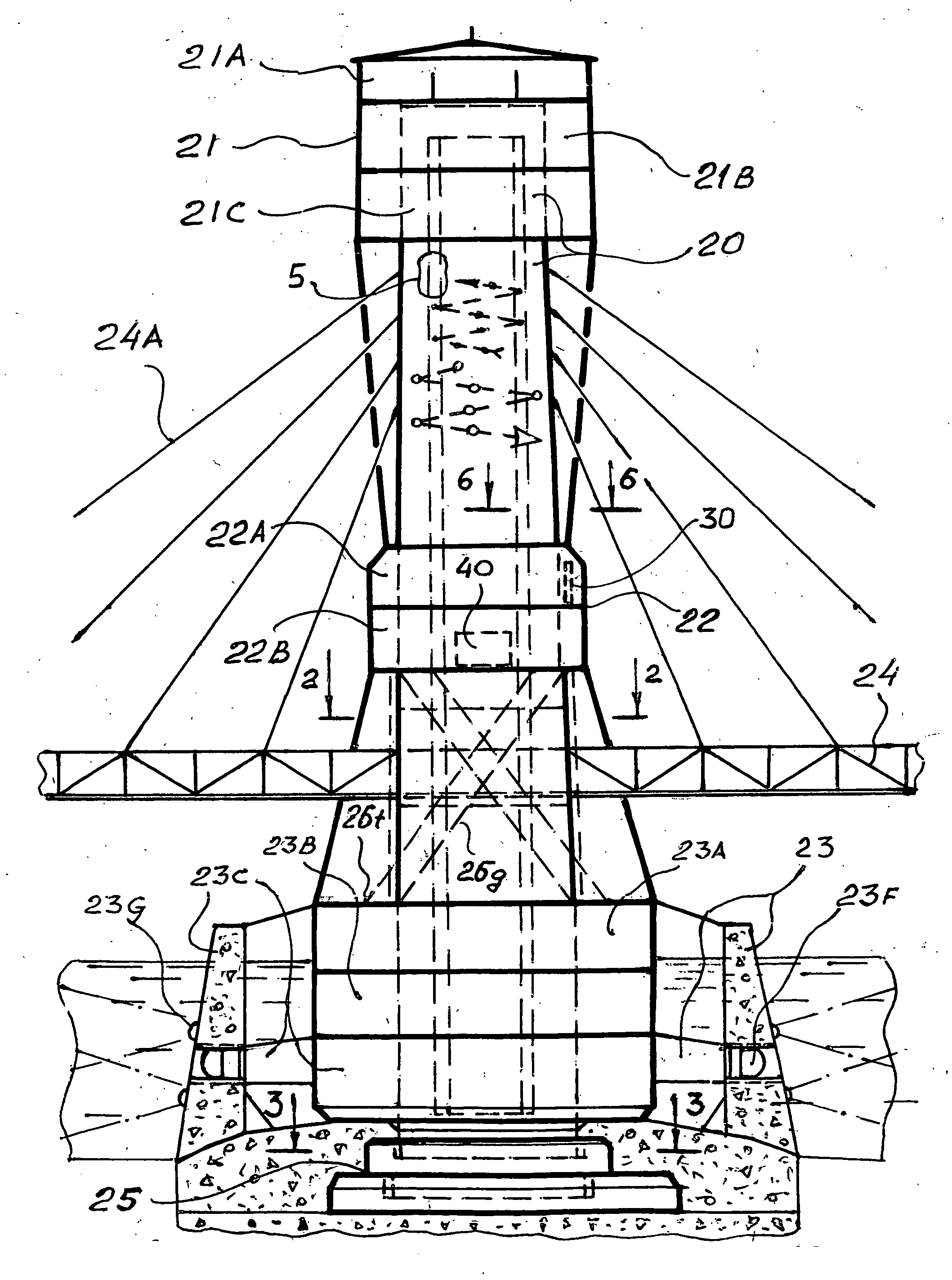
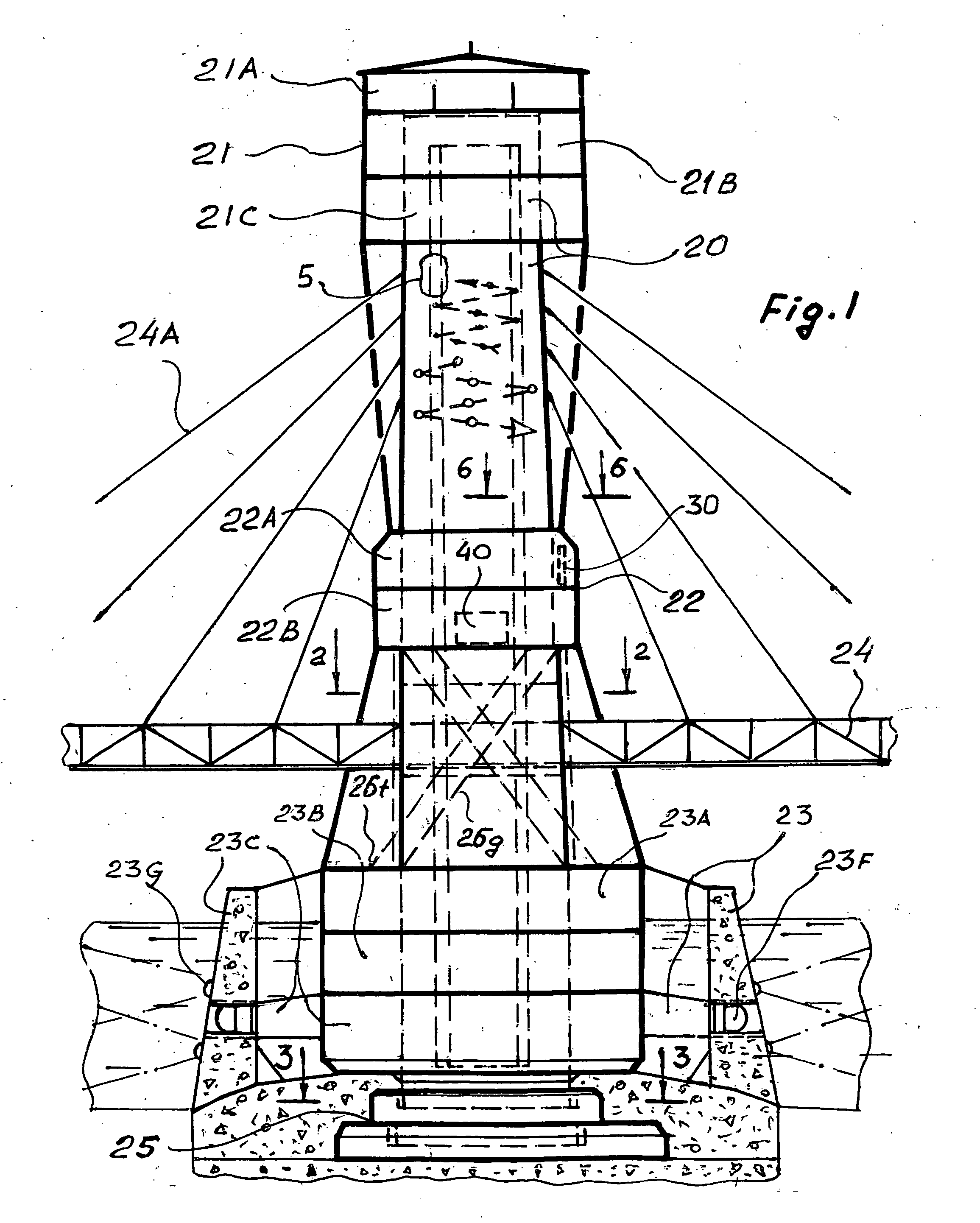
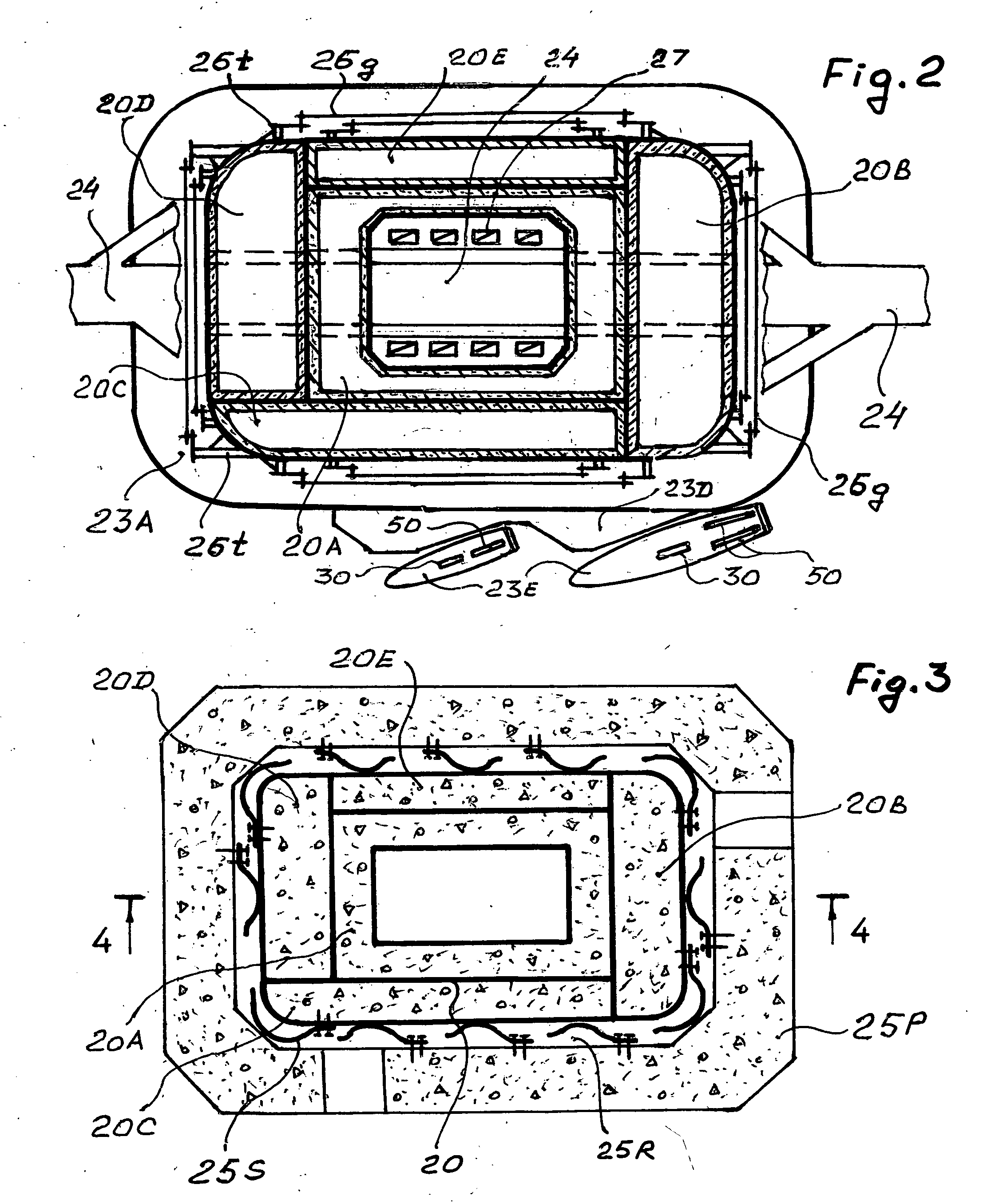
Bridge tower vast utilities
The Bridge Tower Vast Utilities comprise:multilevel blocks of recreation and pleasant entertainment arenas by usage the unique qualities of bridges as attracting, uniting structures which people always like to visit and enjoy,high-efficient energy contributors,reliable technological protection from forced oscillations, caused with gusty winds, traffic vibroeffects, earthquakes, by self-dampening flexible anti-resonance structures of the combined bridge tower column and poly flexible foundation.The swimming pools, observation lots, orchards, children centers, aquarium, jet-yacht station, parking lots, ramps, elevators, infrastructures are combined with regular transportation and architectural means of civil bridges into an integrated system. This proposal provides much shorter and faster rate period of investment returns by effective and full serving for customers and owners with natural unique substance and attractive utilities of new and reconstructed civil bridges, which could be converted into well-desired and high-profit structures.
Owner:LAZAR BERELI M
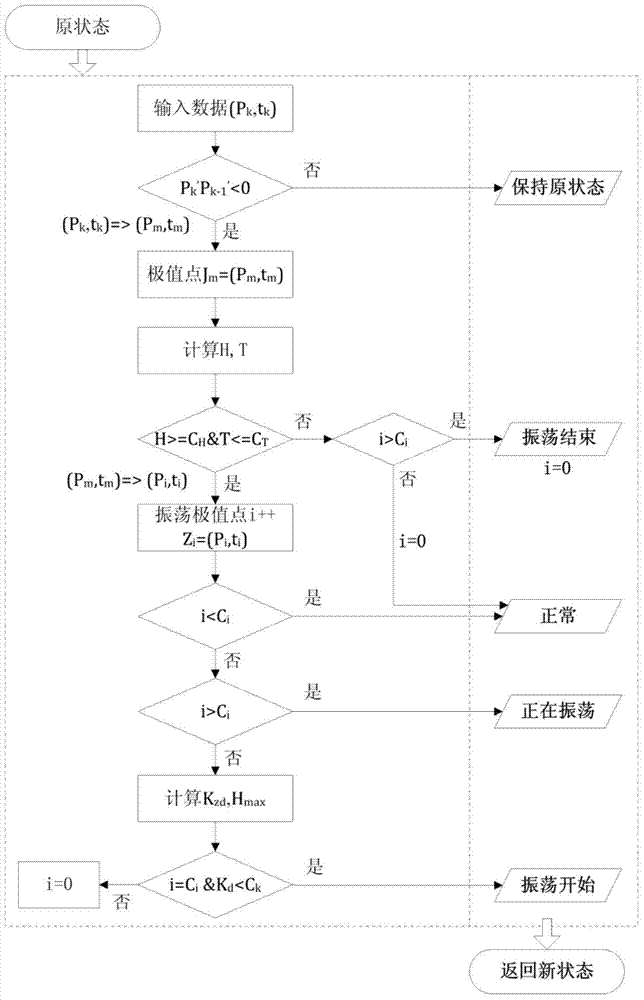
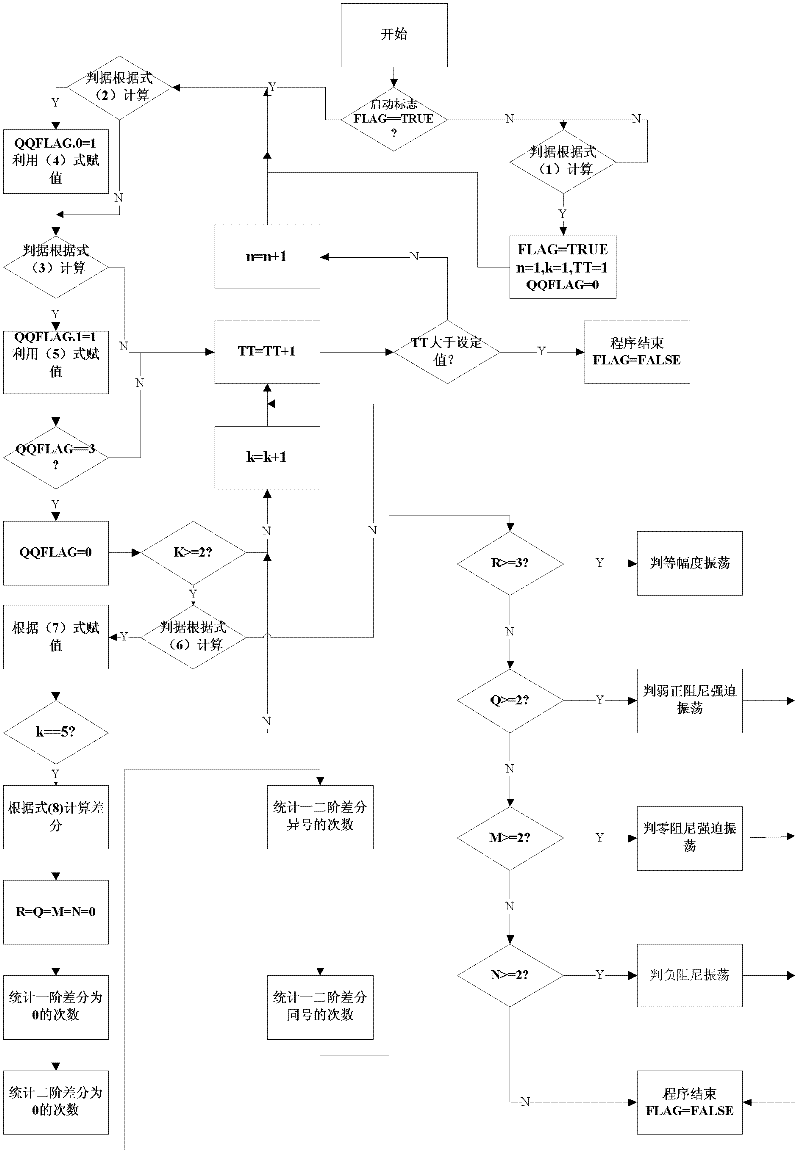
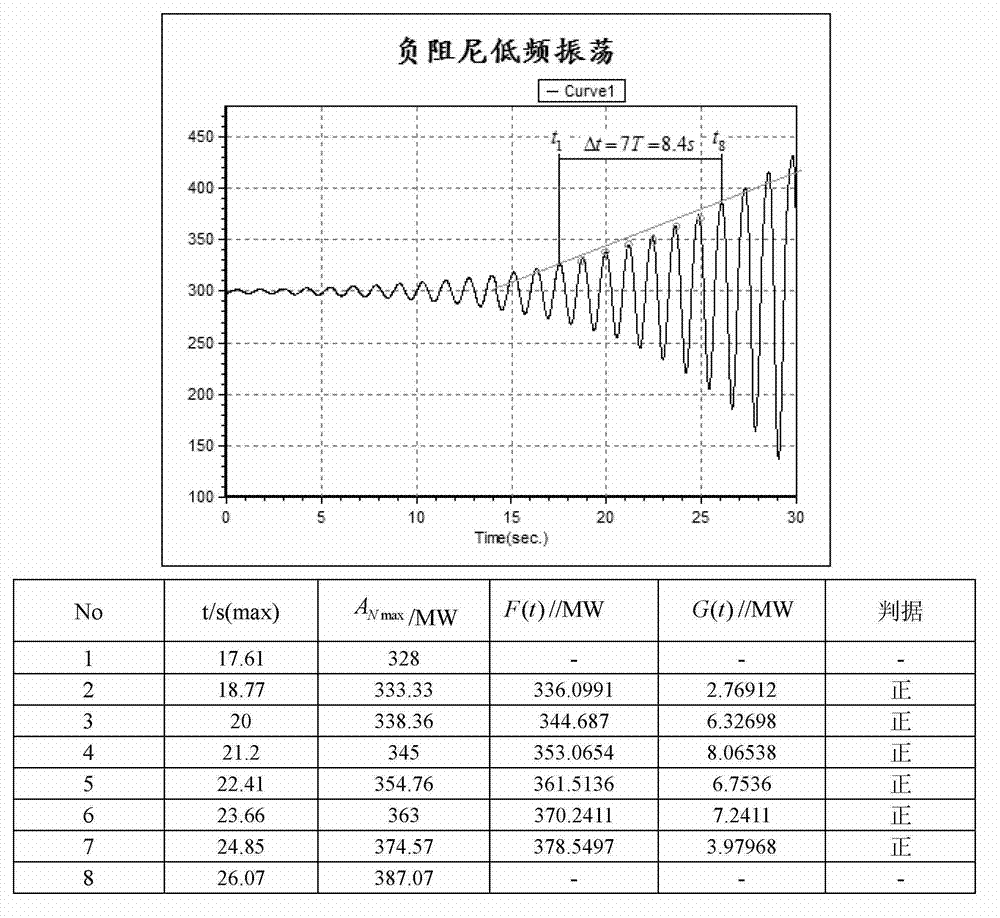
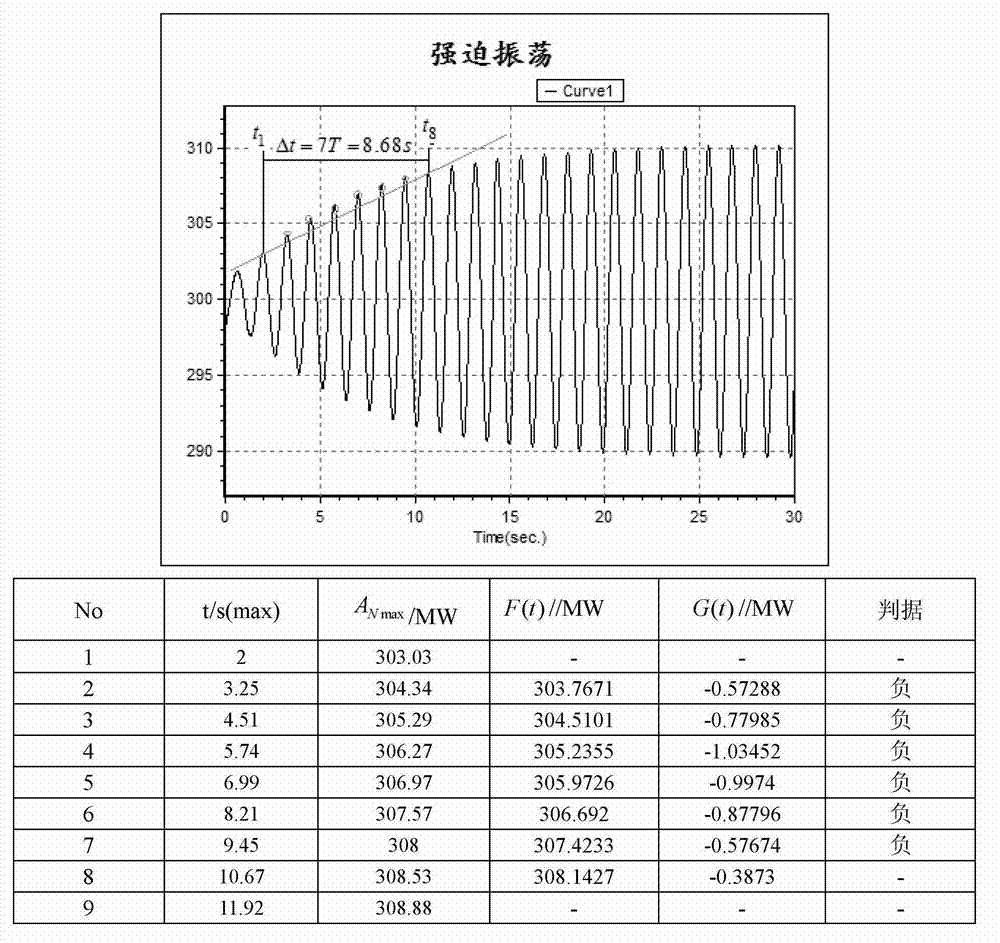
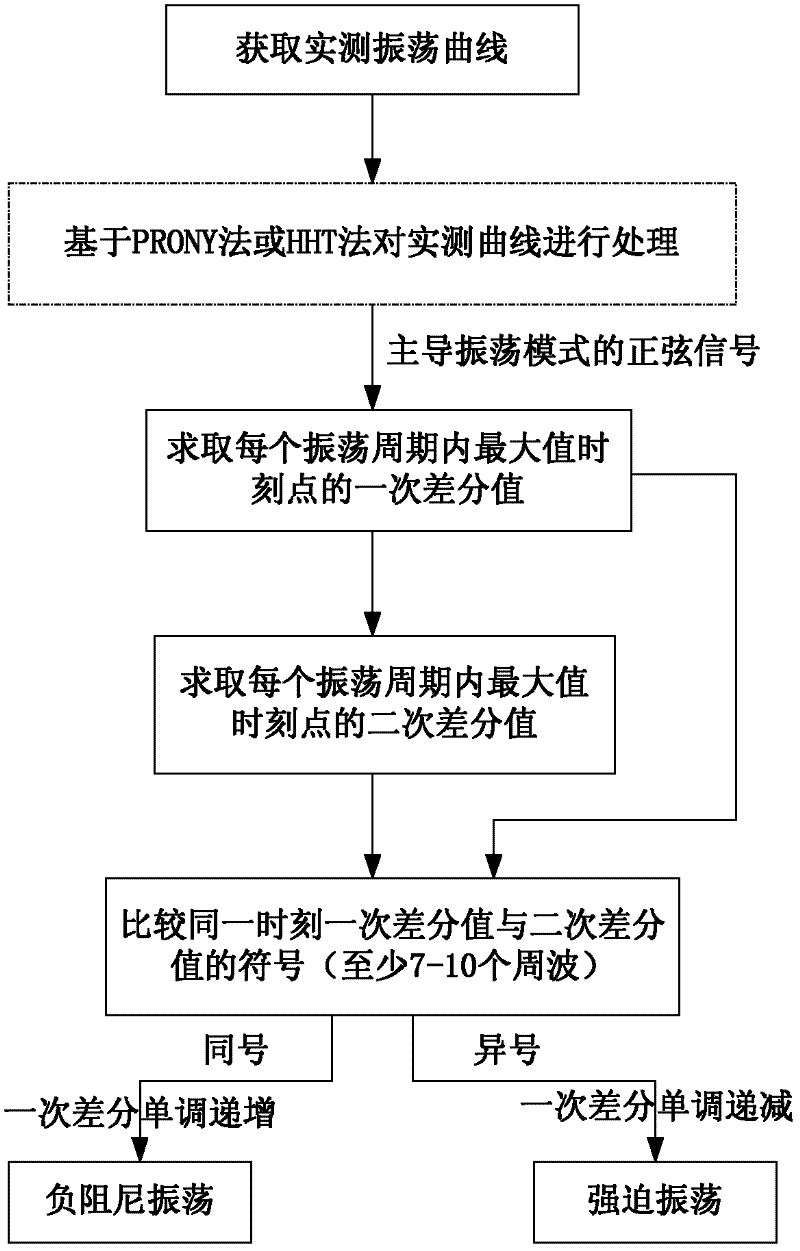
System and method for judging negative damping oscillation and forced oscillation based on second order difference method
ActiveCN102650657ASolve the problem of difficult identification of oscillation propertiesElectrical testingPower measurement by digital techniquePower gridPeak value
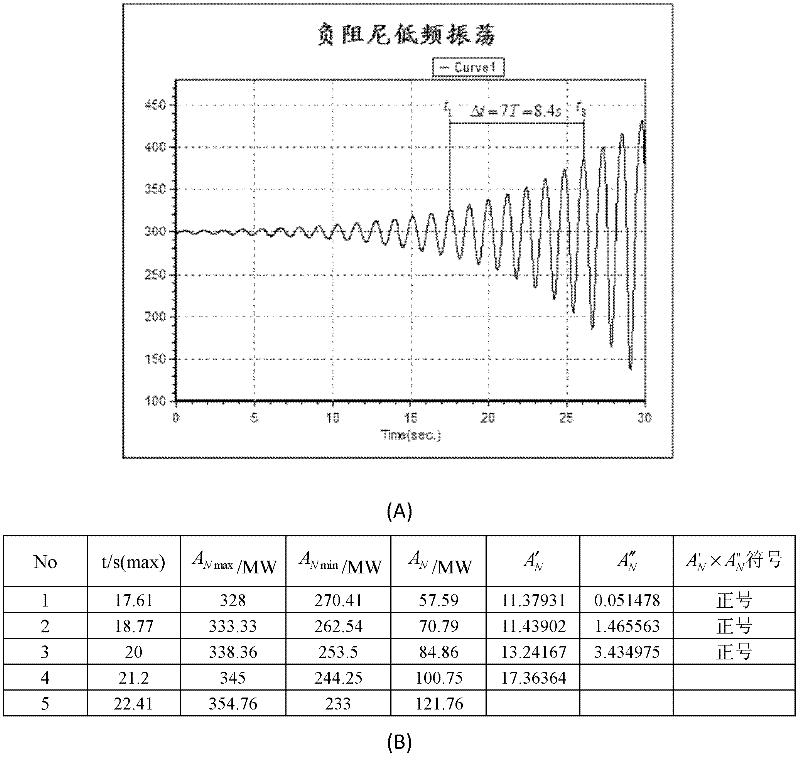
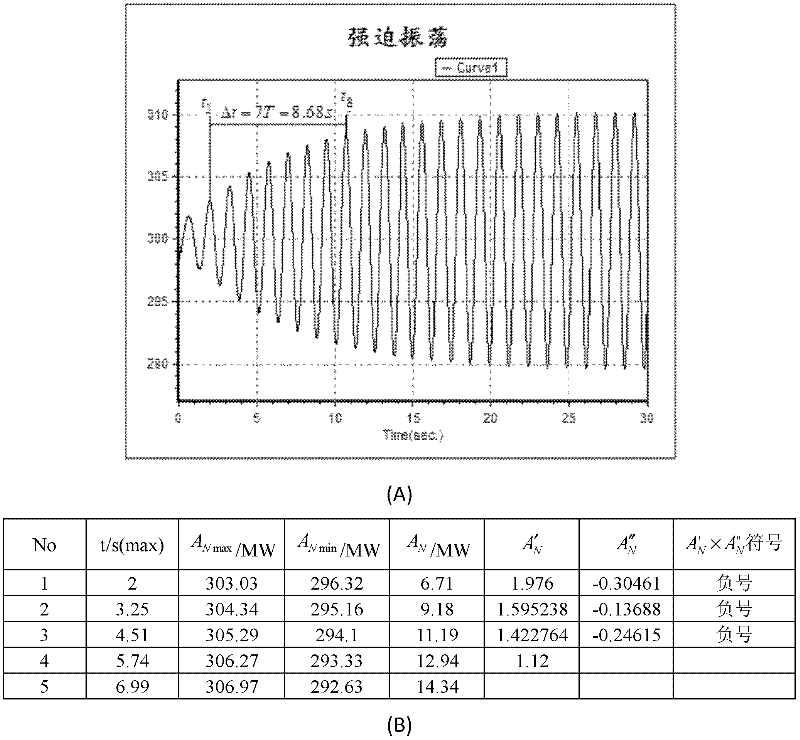
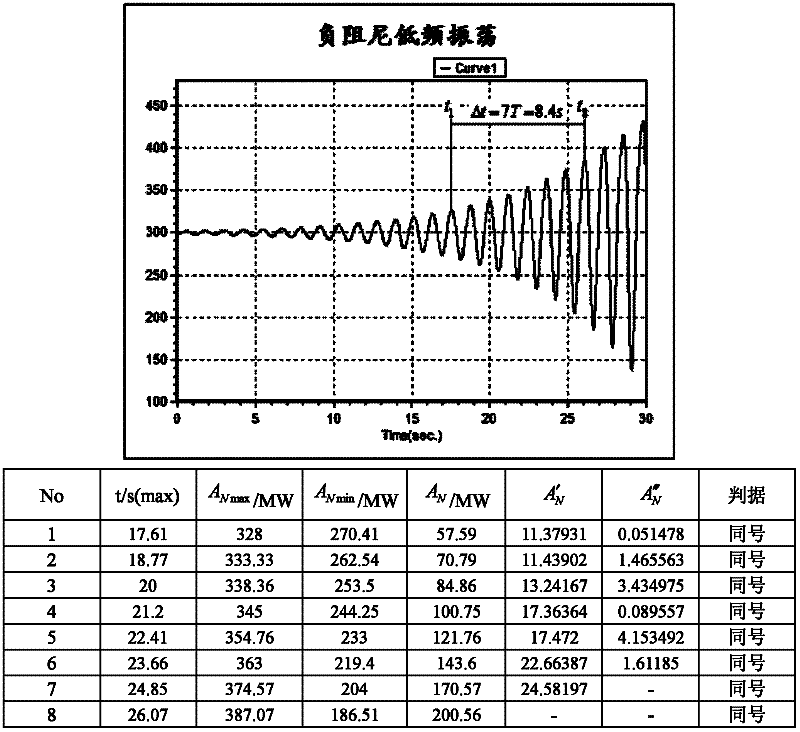
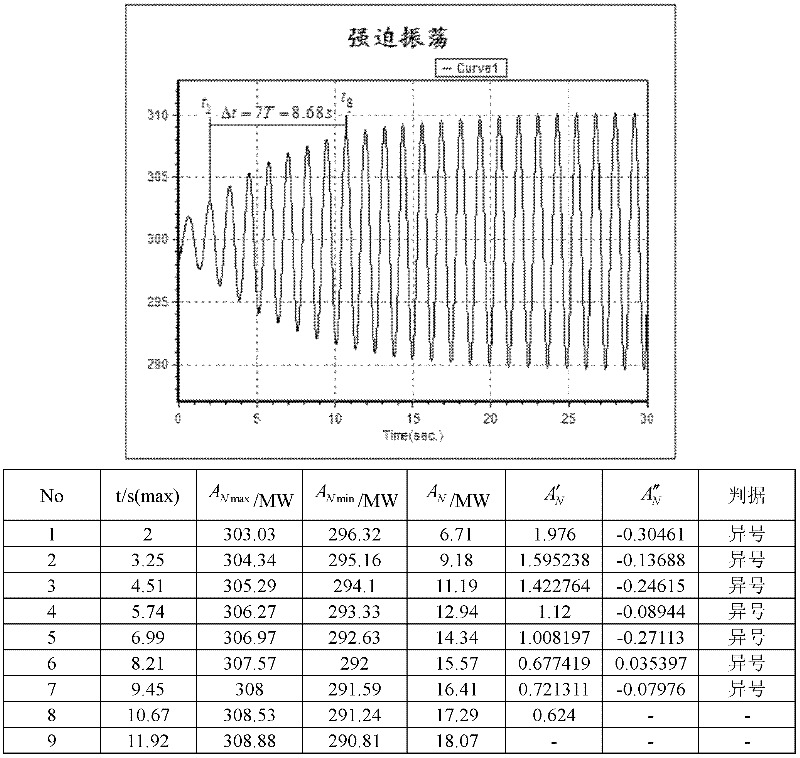
The invention provides a system and method for judging negative damping oscillation and forced oscillation based on a second order difference method. The method for judging the negative damping oscillation and the forced oscillation based on the second order difference method mainly comprises the following steps of: triggering start calculation according to an active power signal curve for hinge nodes, the frequency of transformer substation bus voltage or connecting lines, generator outlets and active power signals of the generator outlets through break-variable of current; finding out peaks of the signal curve by a sampling comparison method; calculating a first order difference value and a second order difference value of peak power in the first several or more than a dozen of cycles at the beginning of increasing oscillation, and comparing the symbols of the first order difference value and the second order difference value; if the first order difference value and the second order difference value are same in symbol, judging to be the negative damping oscillation; and if the first order difference value and the second order difference value are different in symbol, judging to be the forced oscillation. A corresponding alarm signal is given by a monitoring host according to the property of the oscillation so as to dispatch operating personnel to rapidly take the measure of restraining low-frequency oscillation, or a command of the measure of restraining the low-frequency oscillation is directly given, thereby, the safe and reliable runnability of a power grid is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Circulation control device and method of induction electric power transmission system
ActiveCN102157991ACirculation control method is simpleElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionFrequency compensation
The invention discloses a circulation control device and a method of an induction electric power transmission system, which belong to the field of induction electric power transmission control. The circulation control method provides a method for obtaining frequency difference and frequency compensation direction between a forced oscillation frequency and an inherent resonance frequency accordingto a circulation duration time and a voltage peak value, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: obtaining the circulation duration time through a first current transformer and a first comparator; then obtaining a circulation peak value by means of FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array); obtaining the frequency difference compensation direction through a second current transformer and a second comparator; judging whether the bidirectional circulation is mutated trough a differentiating circuit and a third comparator by means of FPGA, wherein when the bidirectional circulation is mutated, an AD (Average Deviation) collector is controlled to collect the voltage peak value which is corresponding to the bidirectional circulation by means of FPGA; and then recording the times for reaching to the circulation peak value in two close times by the FPGA, and obtaining the frequency difference by calculating according to the circulation peak value and the voltage peak value. The circulation control device and method of an induction electric power transmission system provided by the invention have the advantages that the purpose for accurately controlling the circulation in an induction electric power transmission system is achieved by the using of a circulation control device with low hardware requirement and a sample circulation control method.
Owner:重庆前卫无线电能传输研究院有限公司
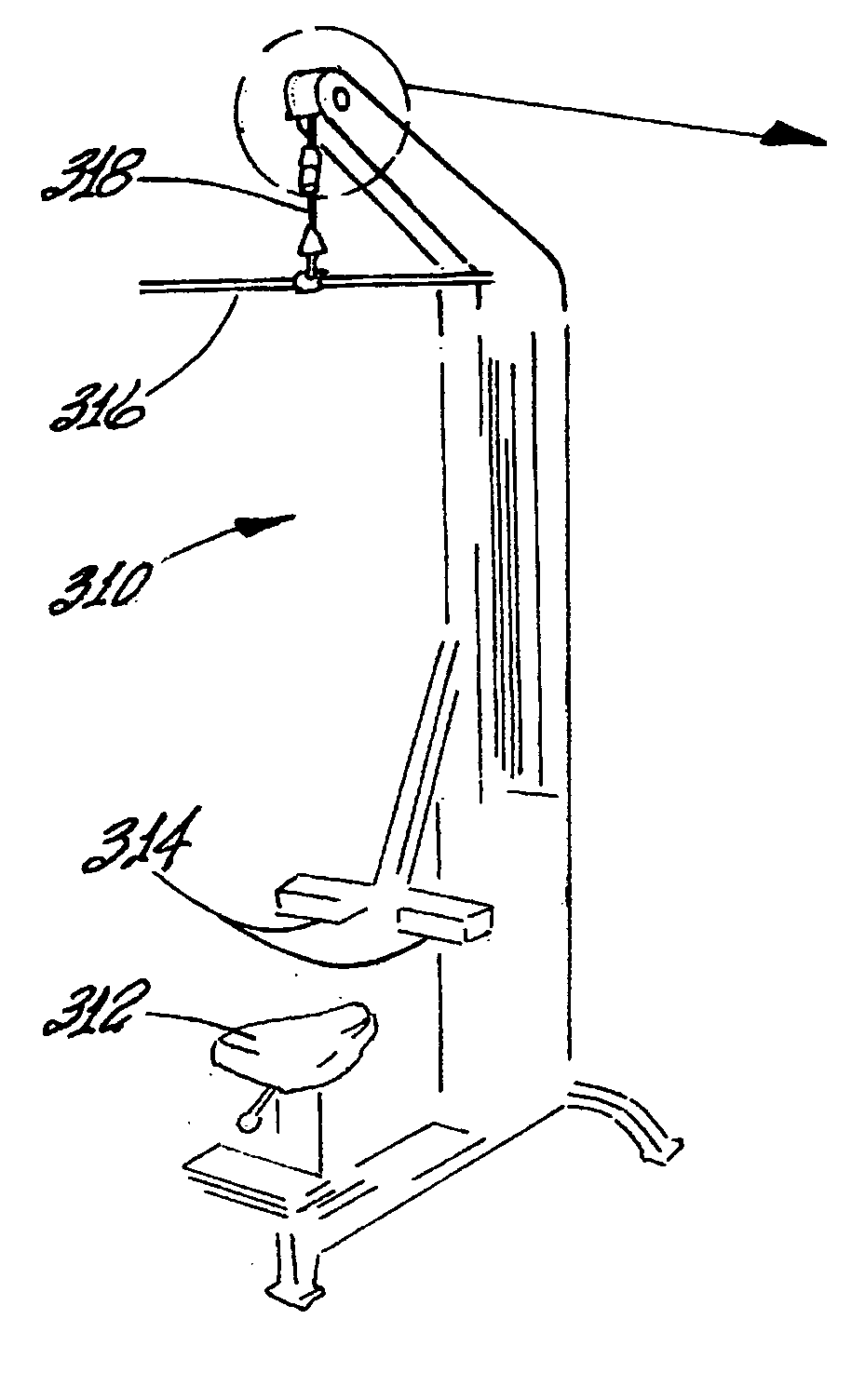
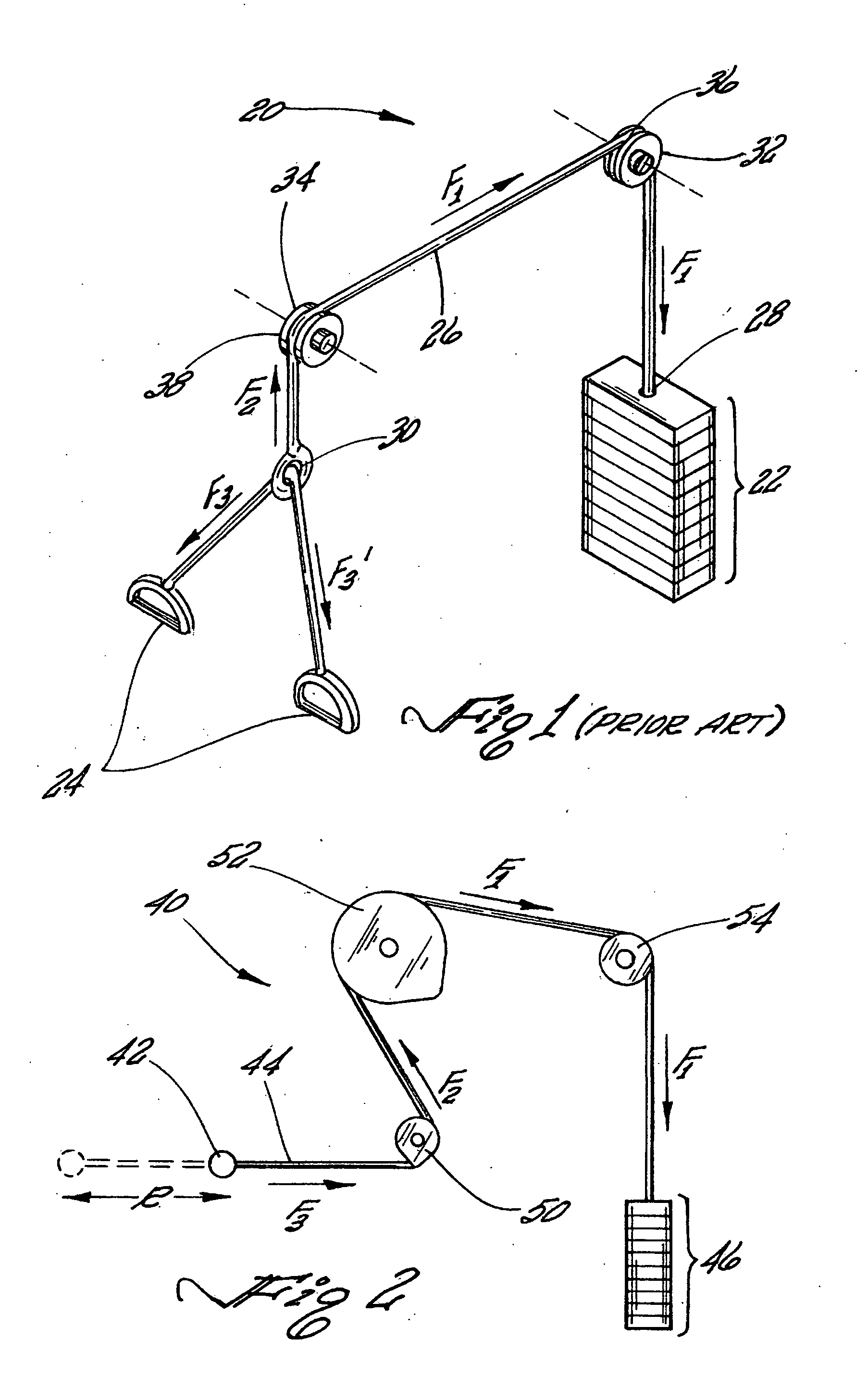
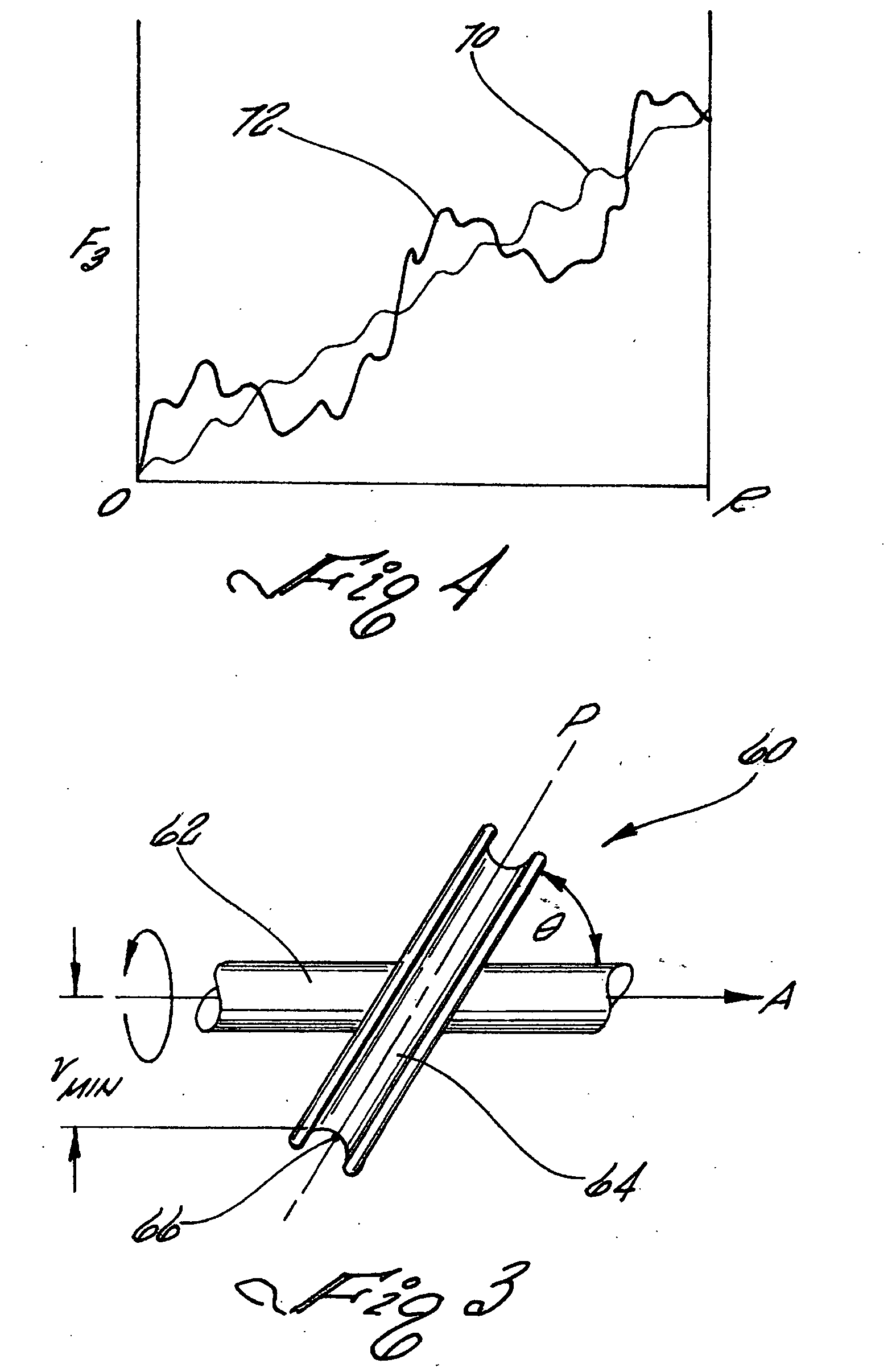
Oscillatory resistance exercise device and method
InactiveUS20070207902A1Increase the itineraryIncrease the number ofMuscle exercising devicesSpherical bearingMuscle contraction
A method for exercising one or more muscles of the body wherein one or more muscle(s) are contracted to move a limb through a range of motion in opposition to an oscillating resistive force. During a muscular contraction, the direction and / or the magnitude of the resistive force changes in an oscillatory fashion thereby inducing perturbations in the musculature. The oscillations in the magnitude and / or the direction of the resistive force include a plurality of cycles during a single repetition of muscular contraction. The waveform and frequency of the oscillations may vary during a repetition or remain constant. Embodiments of devices providing an oscillatory resistive force are presented. The embodiments provide means for enabling an exerciser to perform resistance-type exercises in accordance with the method. A guided spherical bearing may be used for rotating a lead pulley or a rigid arm to create lateral resistive force oscillations. Non-circular lead pulleys may be used to fluctuate the resistive force magnitude. The oscillations in magnitude and / or direction of the resistive force may be periodic or randomized such that during subsequent repetitions the oscillations occur at differing points.
Owner:TIAHRT LEIF K
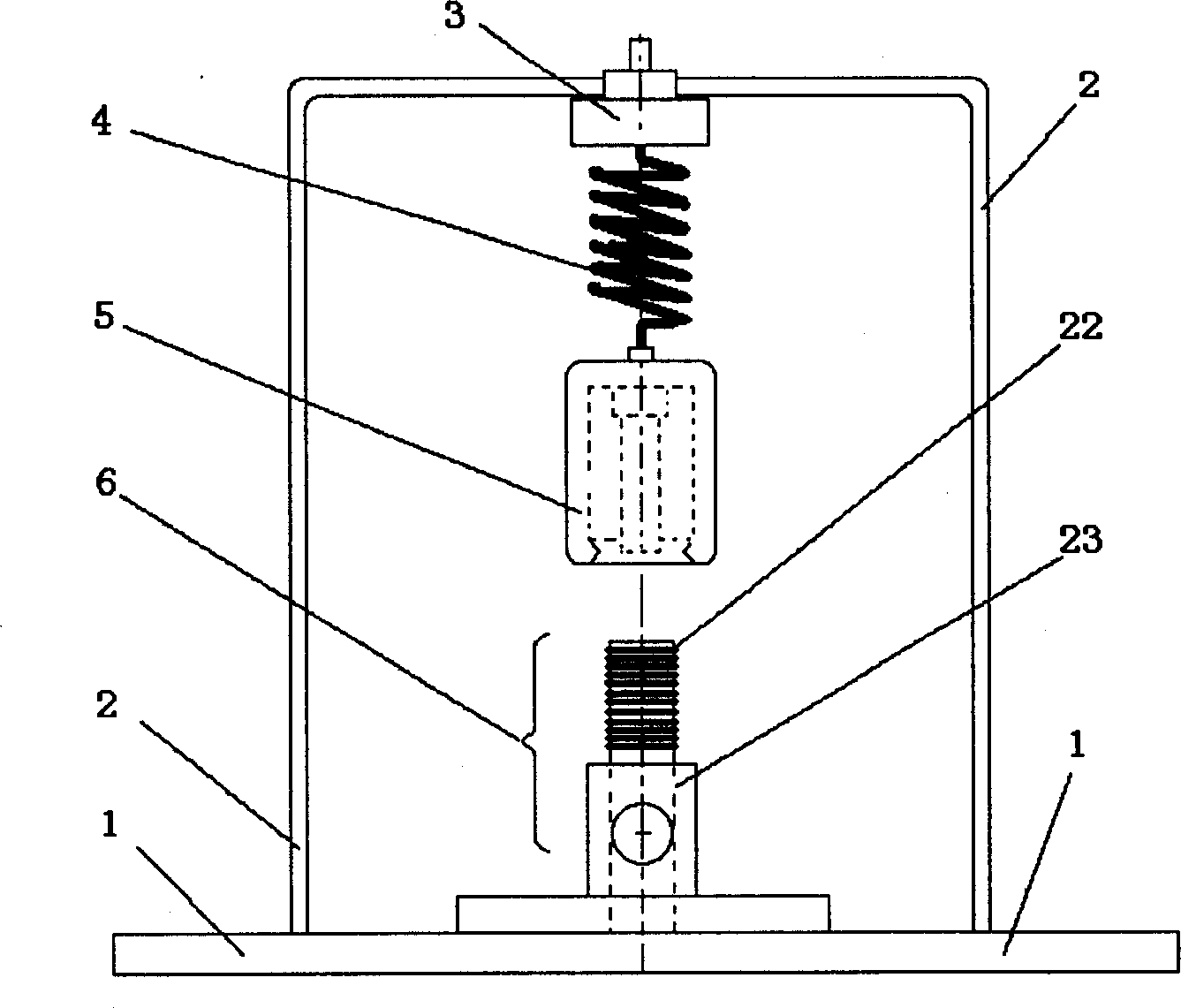
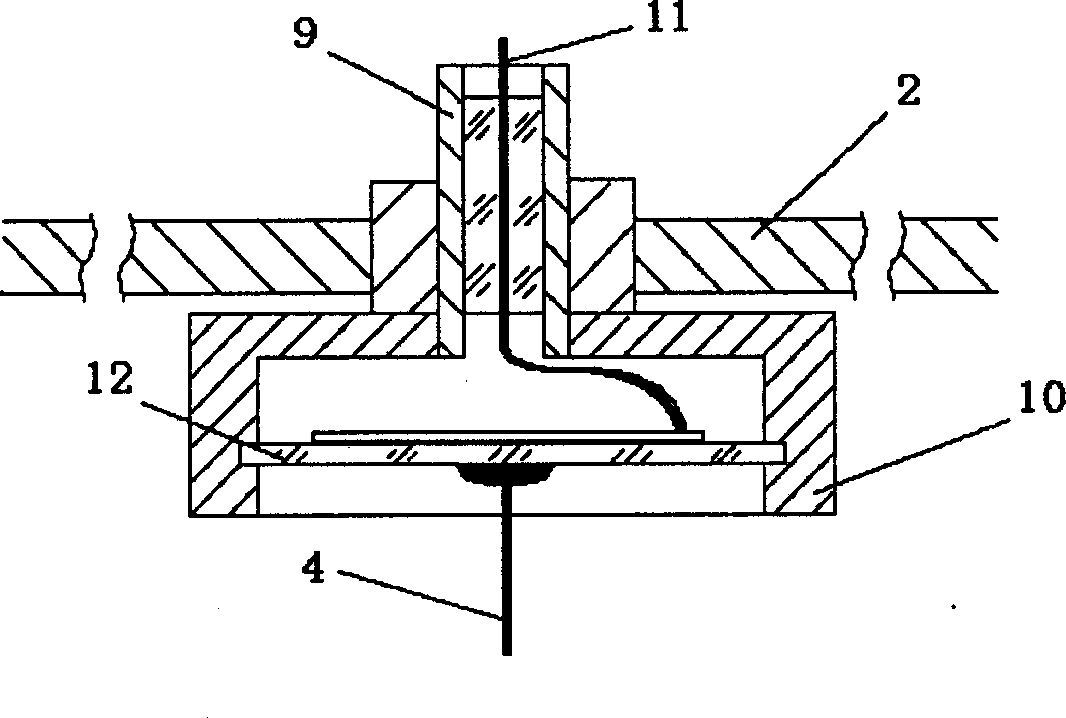
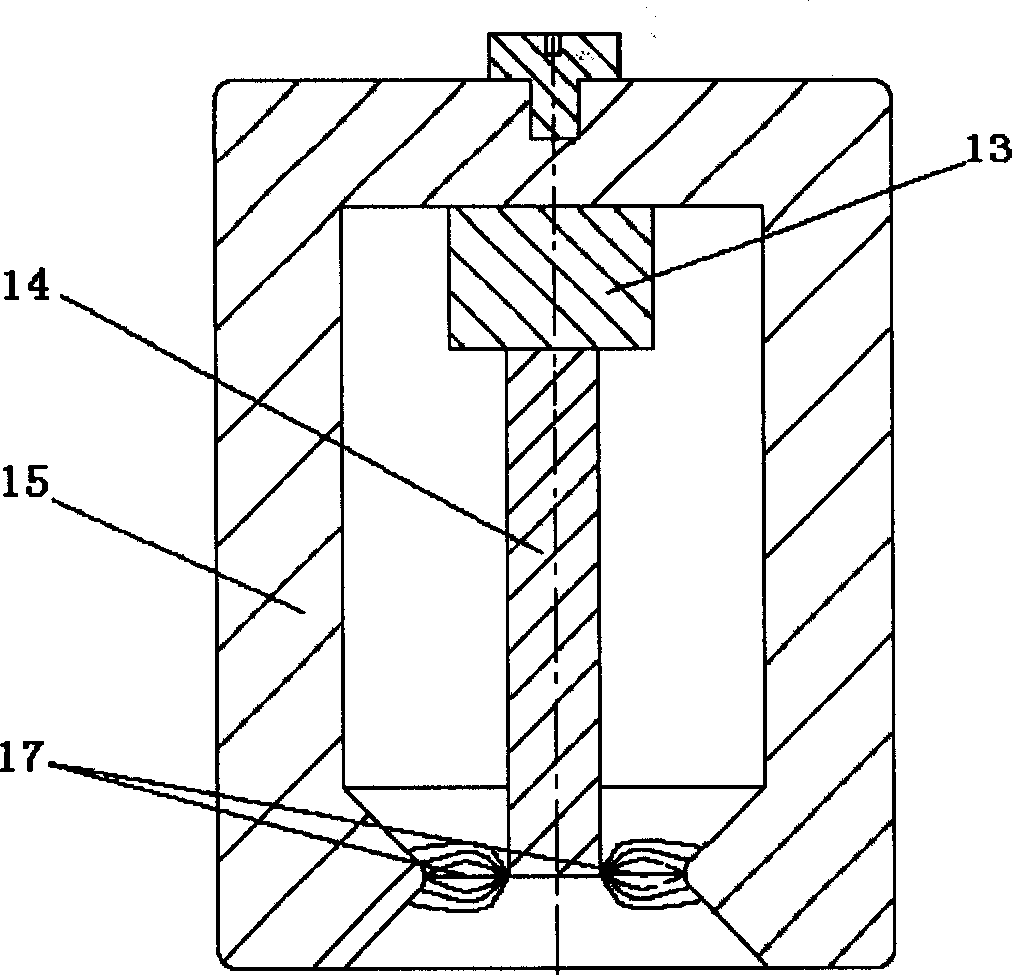
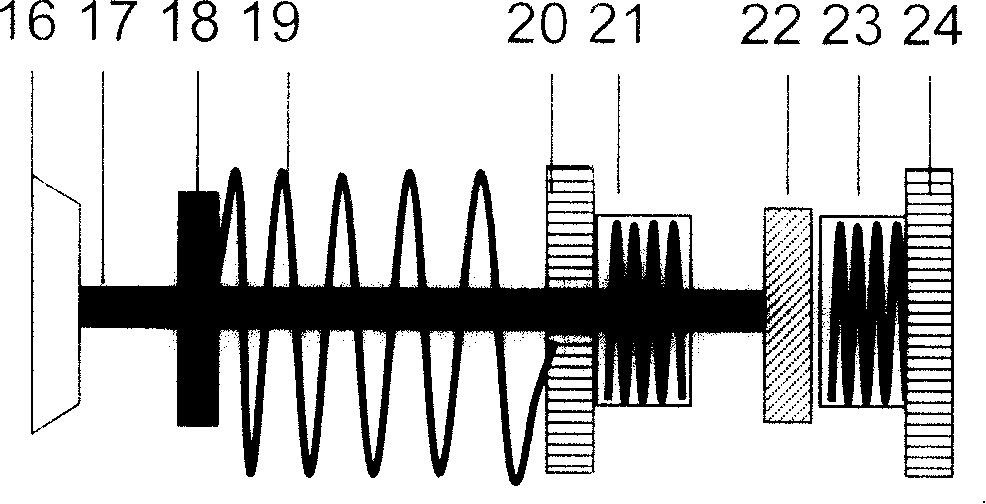
Forced vibration demonstration experiment instrument
InactiveCN1485805AIngenious ideaSimple structureEducational modelsElectrical resistance and conductancePull force
A forced oscillation demonstration test instrument comprising a base frame, a displacement sensor, a spring oscillator (spring and mass block) and a propulsion unit, wherein the voltage between the two poles of the spring oscillator is in proportional to the tension force, and the spring tension force is proportional to the displacement of the oscillator mass. When the coil is powered by alternating current, the counteracting force of the ampere force exerted on the coil will be the driving force for the excitation of spring oscillator oscillating, the driving force signal can be represented by the voltage on the resistor in series connection with the coil.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
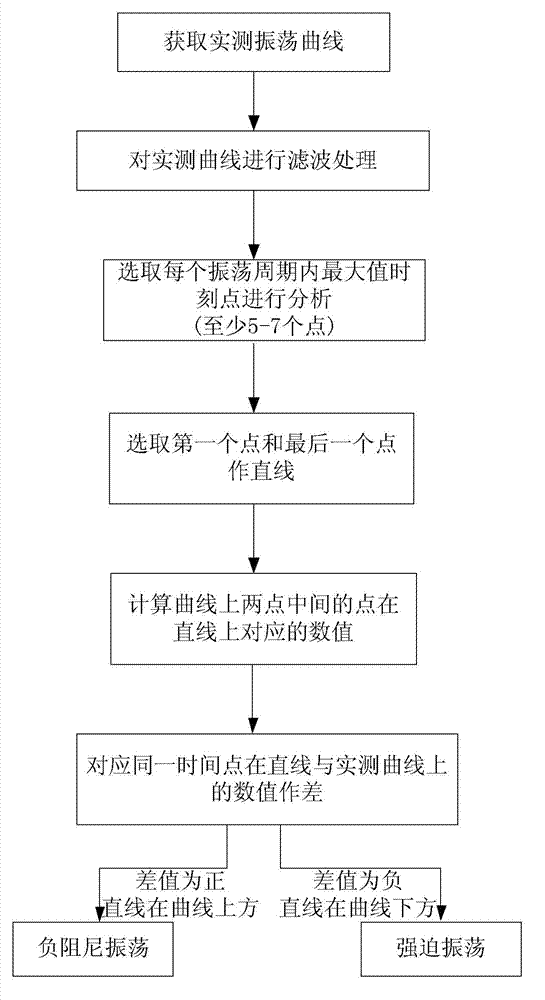
Method for judging negatively-damped oscillation and forced oscillation on basis of straight line method
InactiveCN102928695ASolve difficult to identifyEasy to implementRate of change measurementElectrical testingPower Management UnitLow-frequency oscillation
The invention provides a method for judging negatively-damped oscillation and forced oscillation on the basis of a straight line method. The method comprises the steps: (1) acquiring an actually-measured oscillation curve; (2) selecting the maximum moment point in each oscillation period for analysis; (3) confirming the oscillation as increasing oscillation; (4) selecting two points, the spacing of which is greater than four oscillation periods, to form a linear equation; and (5) calculating difference to numerical values on the straight line and the actually-measured curve at the same one time point one by one, and judging the type of oscillation according to the obtained result. According to the method for judging negatively-damped oscillation and forced oscillation on the basis of the straight line method, through the data of a PMU (Power Management Unit) or a WAMS (Wide Area Measurement System), that certain low-frequency oscillation is of low-frequency negatively-damped oscillation caused due to damp lack of the system, or the forced oscillation caused due to a forced disturbance source existing in the system can be judged so as to fast take measures to restrain the low-frequency oscillation.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Forced oscillation direct-action power generation, buffering accumulated energy and electric drive automobile
InactiveCN101214788AStable jobRealize compression ignition operationHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingCapacitanceMagnetic tension force
The invention discloses a vehicle system of optimizing the compression ratio of a motor, reducing the mechanical losses, enhancing the fuel efficiency under the wide range of conditions. The vehicle system can directly uses the line movement of the plug of a reciprocate motor to drive a coil or a magnet to produce current to generate. The plug and the coil (or) use a mechanical spring((or a magnet) to form a vibration system; during the non working stroke process, the plug is driven by the magnetic force of the vibration system and the coil; the current produced by a generator drives the motor to move via the current buffering; the vehicle system realizes the optimization of the plug stroke and the compression ratio via controlling the coil current of the generator by a controlling center; the power is adjusted by controlling the air inlet volume via controlling operating cylinders numbers and inlet air stroke distance; the driving of a gas gate also use the magnetic vibration system (or the mechanical vibration system ) and the magnetic force to force the air gate to open and close correctly, thus supplementing the energy of a forced vibration system by using the magnetic force; the vehicle system can conveniently adjust the compression ratio and suit for the compression-igniti work of a plurality of fuels.
Owner:TIANJIN CHANGING POWER TECH
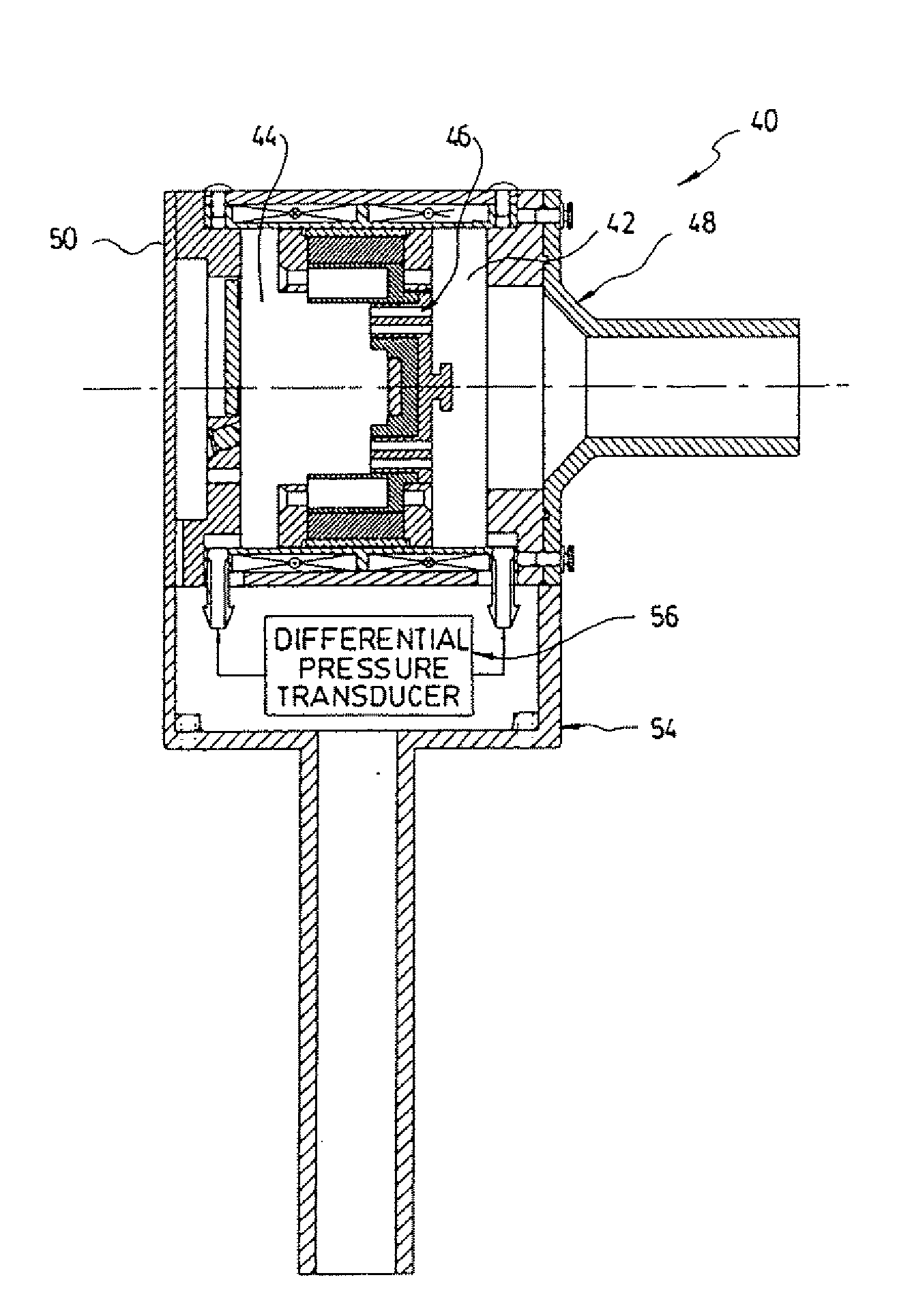
Self-actuated cylinder and oscillation spirometer
ActiveUS20090253994A1Meet actual needsServomotor componentsMagnetsPulmonary mechanicsInput impedance
A self-actuated cylinder comprising a cylinder housing comprising electro-magnetic force generating means to generate electro-magnetic forces, and a piston within the cylinder housing, wherein the electro-magnetic forces act directly on the piston to displace the piston within the cylinder housing. The self-actuated cylinder can be used as an oscillation spirometer to determine air flow, an input impedance or Forced Oscillation pulmonary mechanics.
Owner:THORASYS THORACIC MEDICAL SYST INC
Dynamic response testing device for deep-sea elongated vertical pipe under vertical forced oscillation
ActiveCN104406753ARealize vortex induced vibration testImprove securityVibration testingVertical tubeSurface ocean
The invention discloses a dynamic response testing device for a deep-sea elongated vertical pipe under vertical forced oscillation. By the dynamic response testing device, vortex-induced vibration testing of the vertical pipe under vertical forced oscillation action can be realized, safety coefficient in large pipe mounting can be increased by fully utilizing a lifting pedestal of an oceaneering deepwater pool, real Reynolds number vortex-induced vibration of the large pipe can be simulated by fully utilizing depth of the oceaneering deepwater pool, realtime monitoring equipment can be arranged around the large pipe by fully utilizing width of the oceaneering deepwater pool, and shape of a model can be adjusted according to different needs. Due to adoption of modularized design, the dynamic response testing device has the advantages that the dynamic response testing device is convenient to mount, upgrade and modify and meets different functional requirements.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
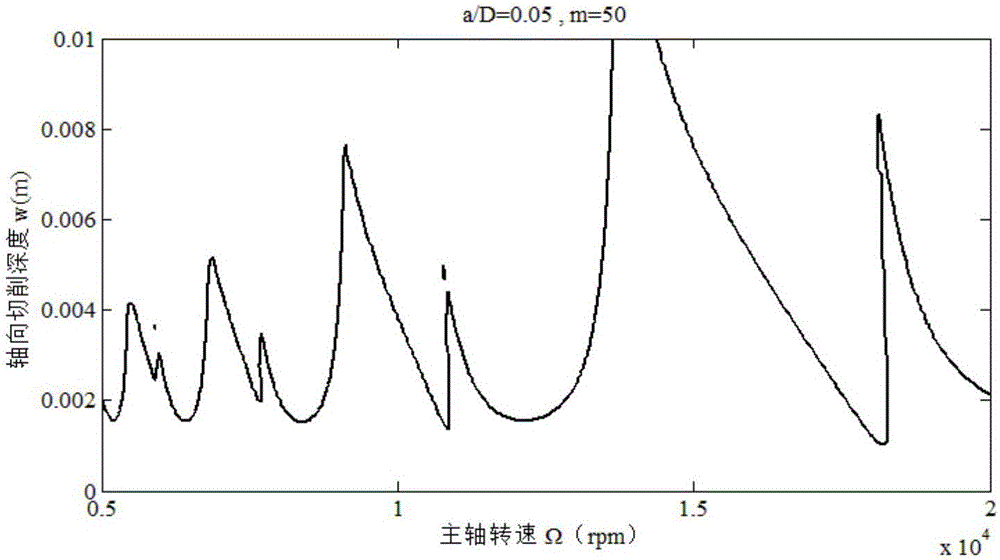
Hamming formula-based milling stability predicting method
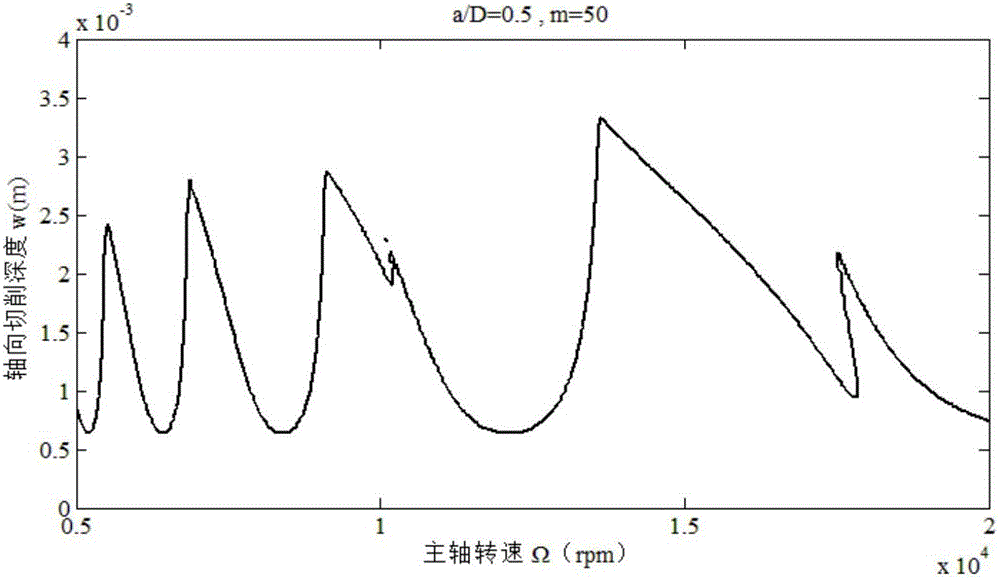
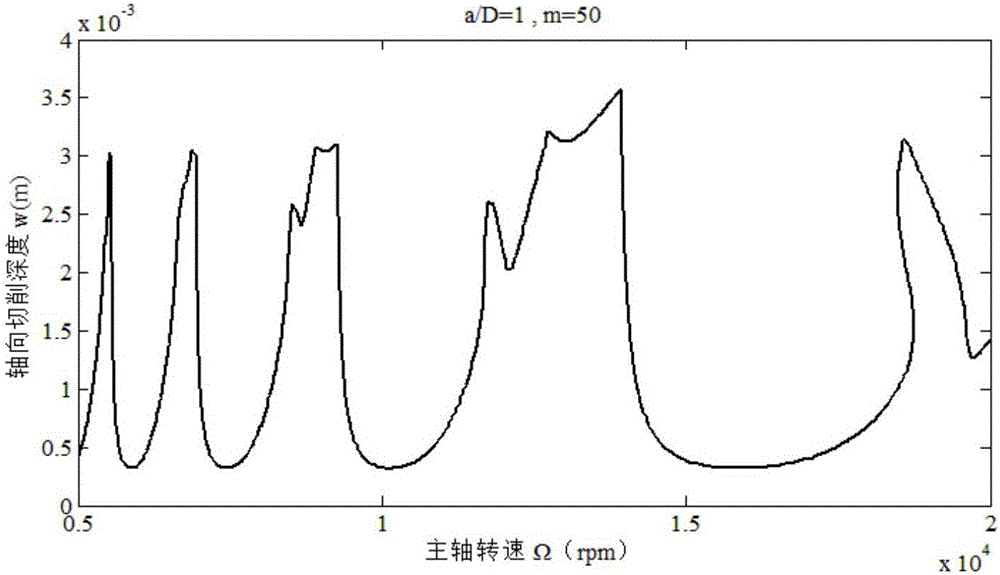
InactiveCN106843147AAvoid vibration phenomenonImprove surface qualityProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlTransfer matrix
Disclosed is a Hamming formula-based milling stability predicting method. The Hamming formula-based milling stability predicting method is mainly applied to selecting reasonable milling parameters for part machining. The Hamming formula-based milling stability predicting method is characterized by comprising dispersing a forced oscillation period into evenly-spaced intervals through the Hamming formula to obtain the transfer matrix of a milling system, and determining the characteristic value of the transfer matrix of the milling system according to the Fourier theories to predict the stability of the milling system. During high-speed numerical controlled machining processes, the Hamming formula-based milling stability predicting method can help select reasonable milling parameters according to a stability labe graph to ensure achieve high-speed and high-efficiency machining without oscillation, thereby optimizing machining parameters, ensuring high surface quality and achieving precise machining.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
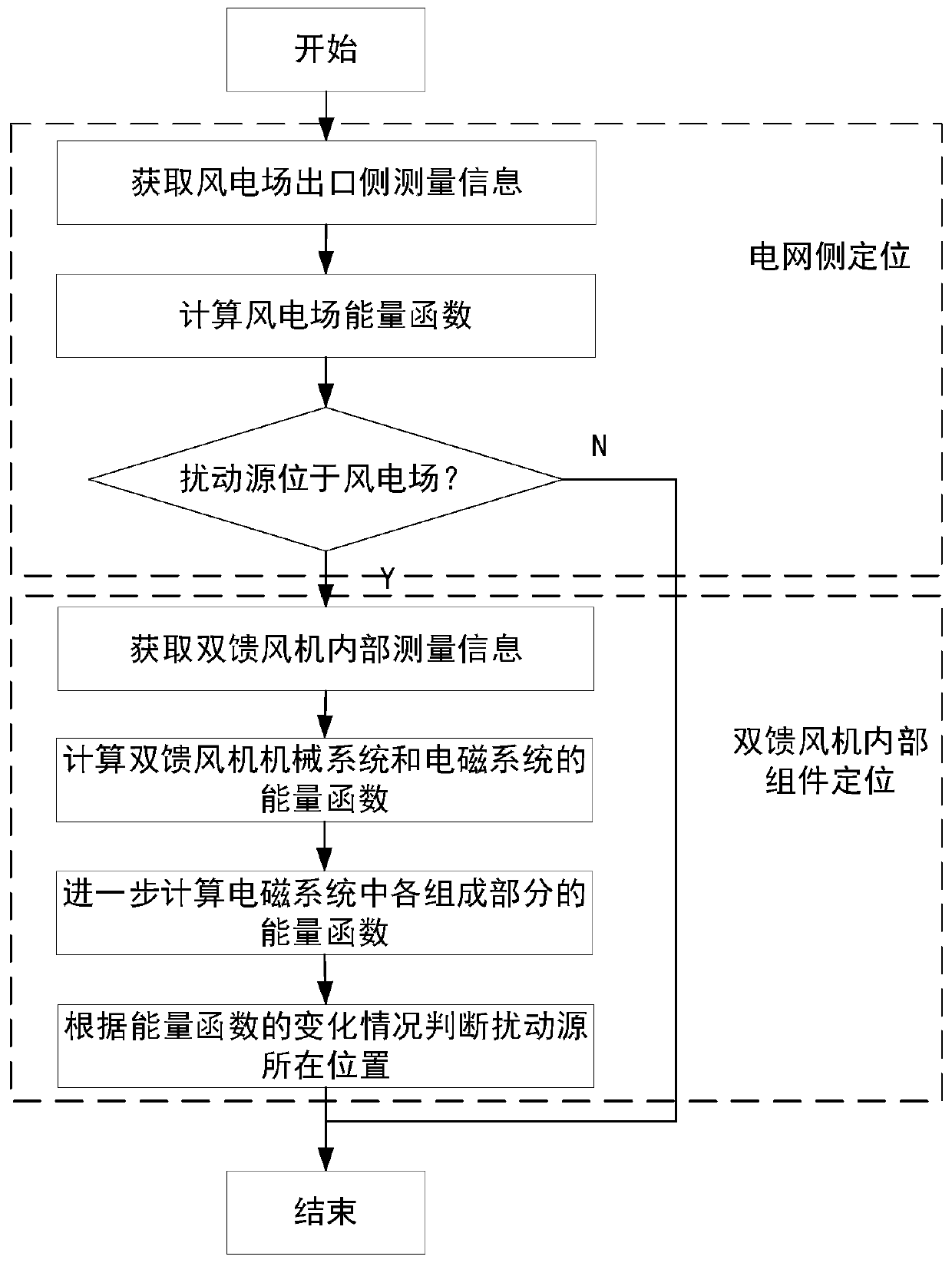
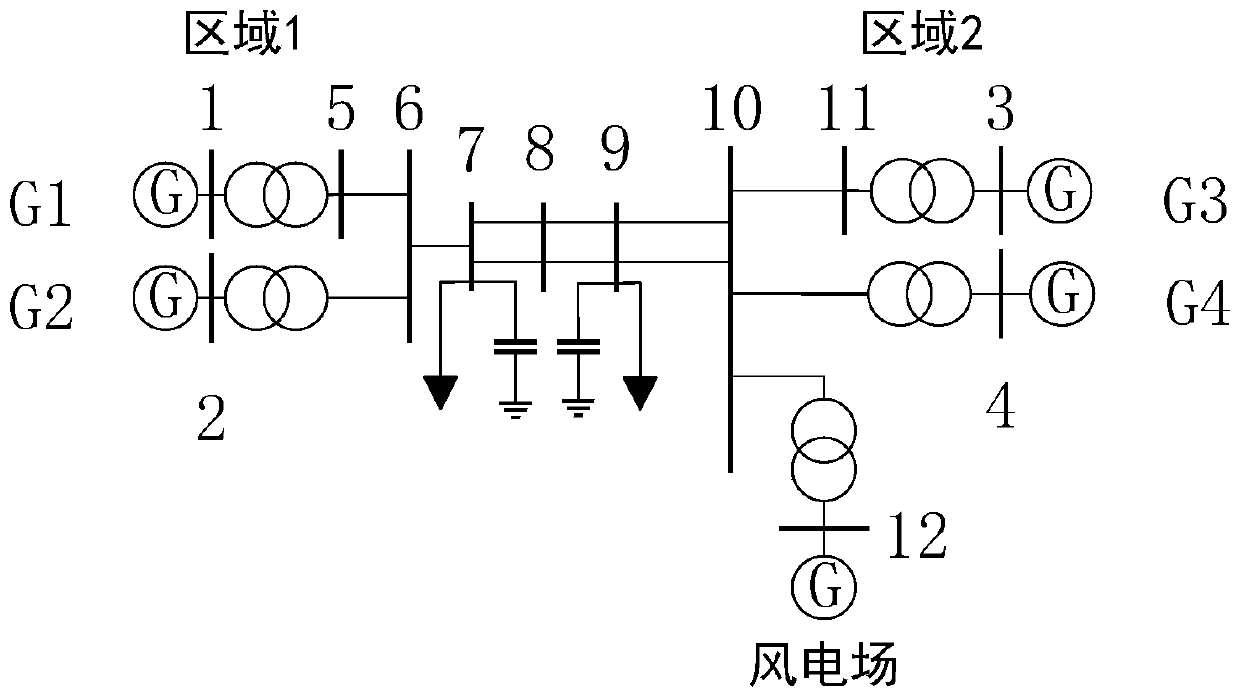
Method for locating forced oscillation disturbance source in doubly-fed wind farm
ActiveCN110011357AVarious control methodsVersatilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsFault location by conductor typesWind drivenElectricity
The invention discloses a method for locating a forced oscillation disturbance source in a doubly-fed wind farm. The method constructs an energy function of a doubly-fed wind-driven generator, can determine whether a disturbance source is located on the doubly-fed wind-driven generator, and can further determine the position of the disturbance source inside the generator if so. The method can locate the disturbance source inside the doubly-fed wind-driven generator just by providing the structure and parameter information of an induction generator without the information such as a control modeand the structure of the wind-driven generator, and has a certain universality in a context where various wind-driven generator control modes are provided and a prime mover is complicated in structure. The method can accurately determine the position of the disturbance source inside the wind-driven generator, reflects the situation that each component inside the wind-driven generator participatesin the forced oscillation, and provides convenience for optimizing the structure and control mode of the wind farm.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
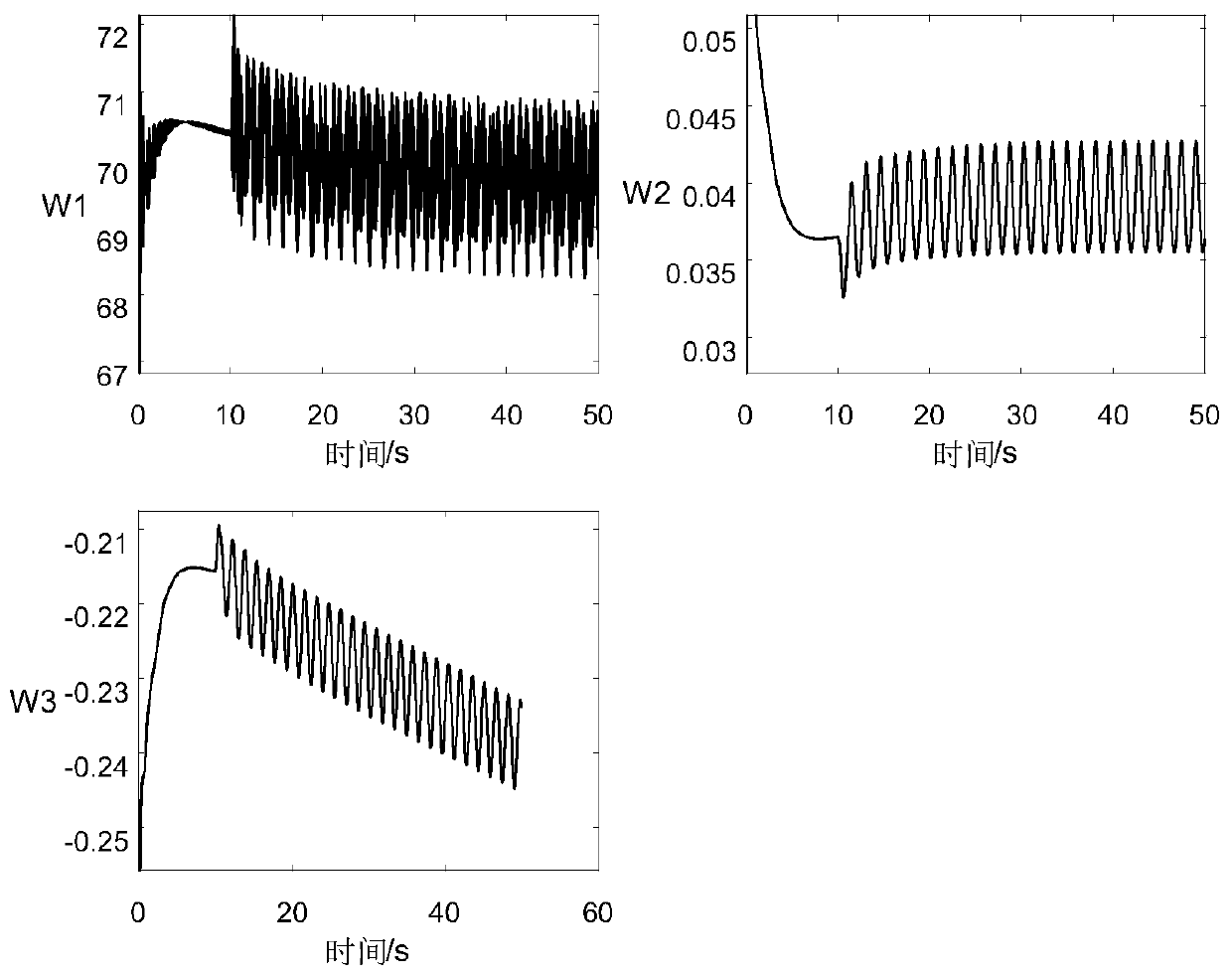
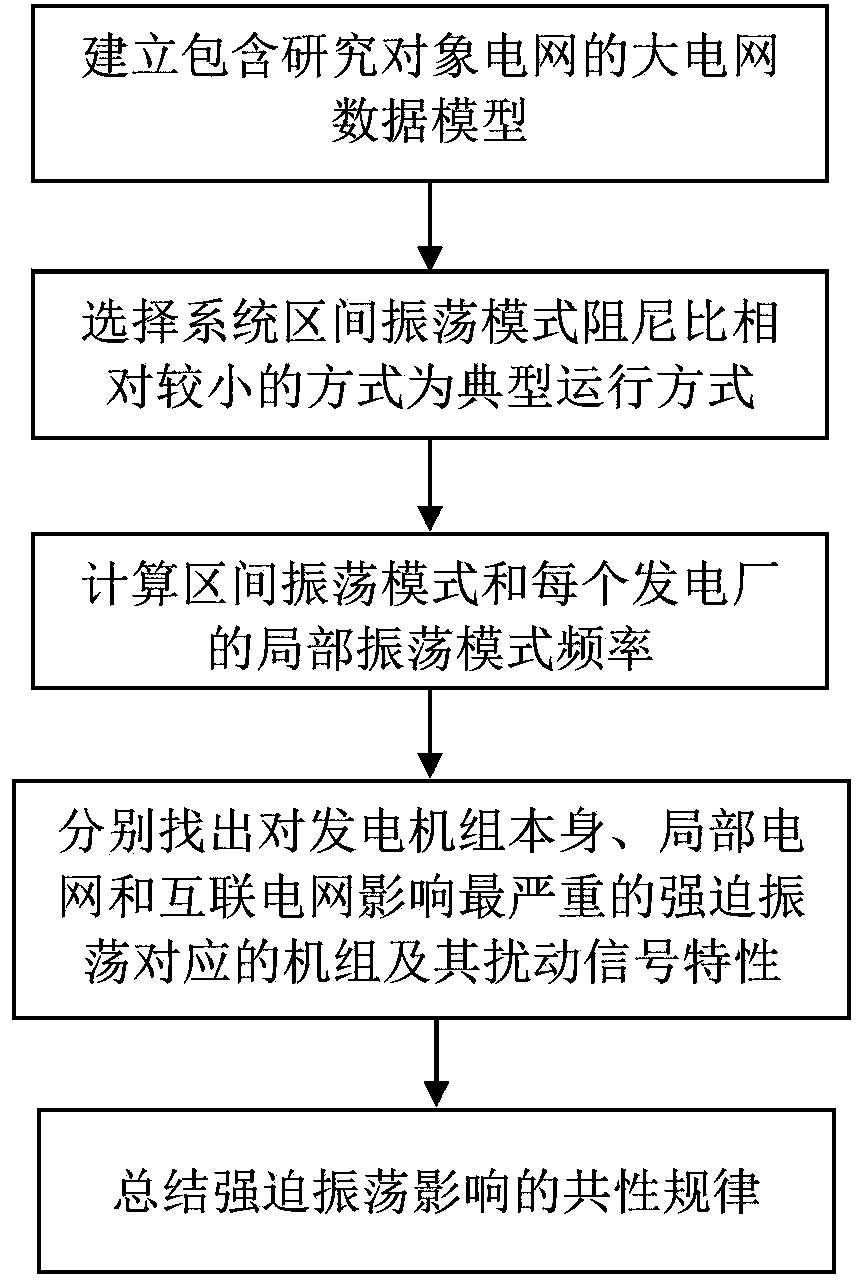
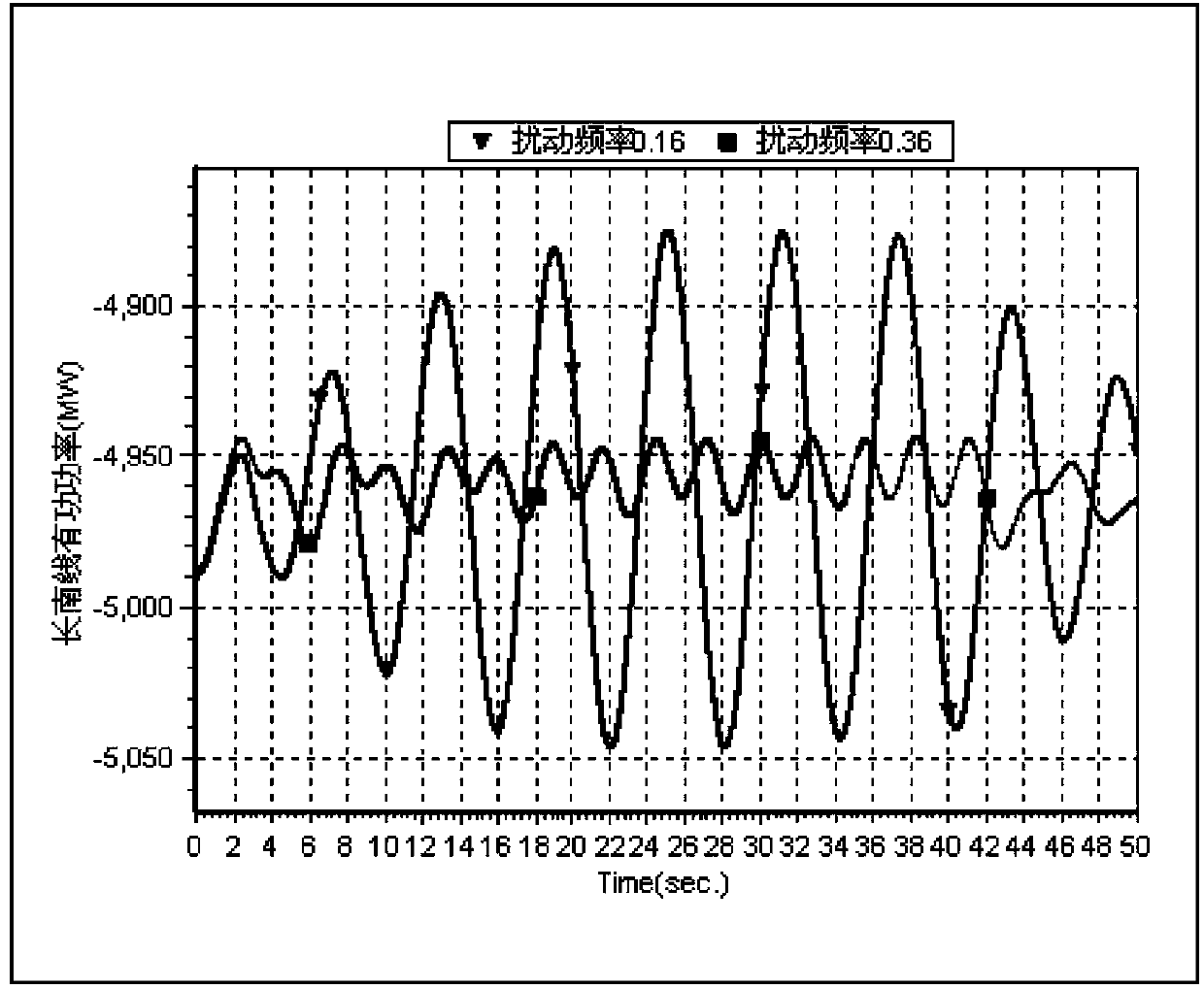
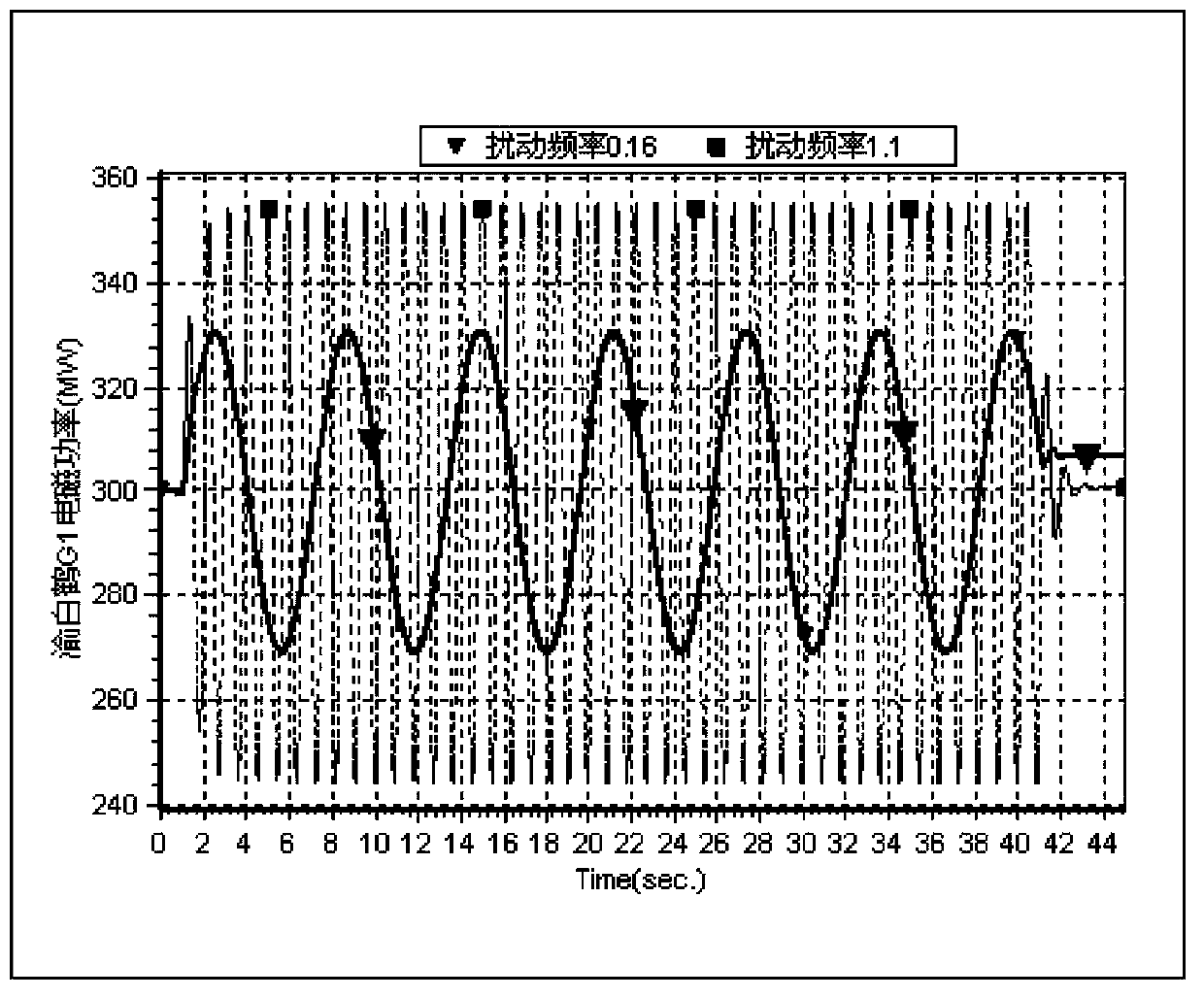
Method for evaluating forced oscillation influence in interconnected large power grid
ActiveCN103390899APrecise positioningComprehensive considerationPower oscillations reduction/preventionSpecial data processing applicationsPower gridOperation mode
The invention relates to a method for evaluating forced oscillation influence in an interconnected large power grid. The method includes the following steps: A. determining a typical operation mode of a power system; B. obtaining an oscillation mode of a power grid to be researched and a characteristic of the oscillation mode; C. finding out units corresponding to forced oscillation having the largest influence on a generator set, a local power grid and the interconnected power grid and disturbing signal characteristics of the units; D. summarizing a general characteristic rule of the forced oscillation influence. By means of the method, the defect that the existing evaluating method only considers section low-frequency oscillation frequency and only aims at influence of the forced oscillation on a large power grid is overcome, stable parameters of the generator set can be checked by combining practical recording data, the method has the advantages of being good in generality and adaptation, comprehensive in considering factors and reasonable in scheme, facilitating fast decision making and the like and has high practical value and good market prospects.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
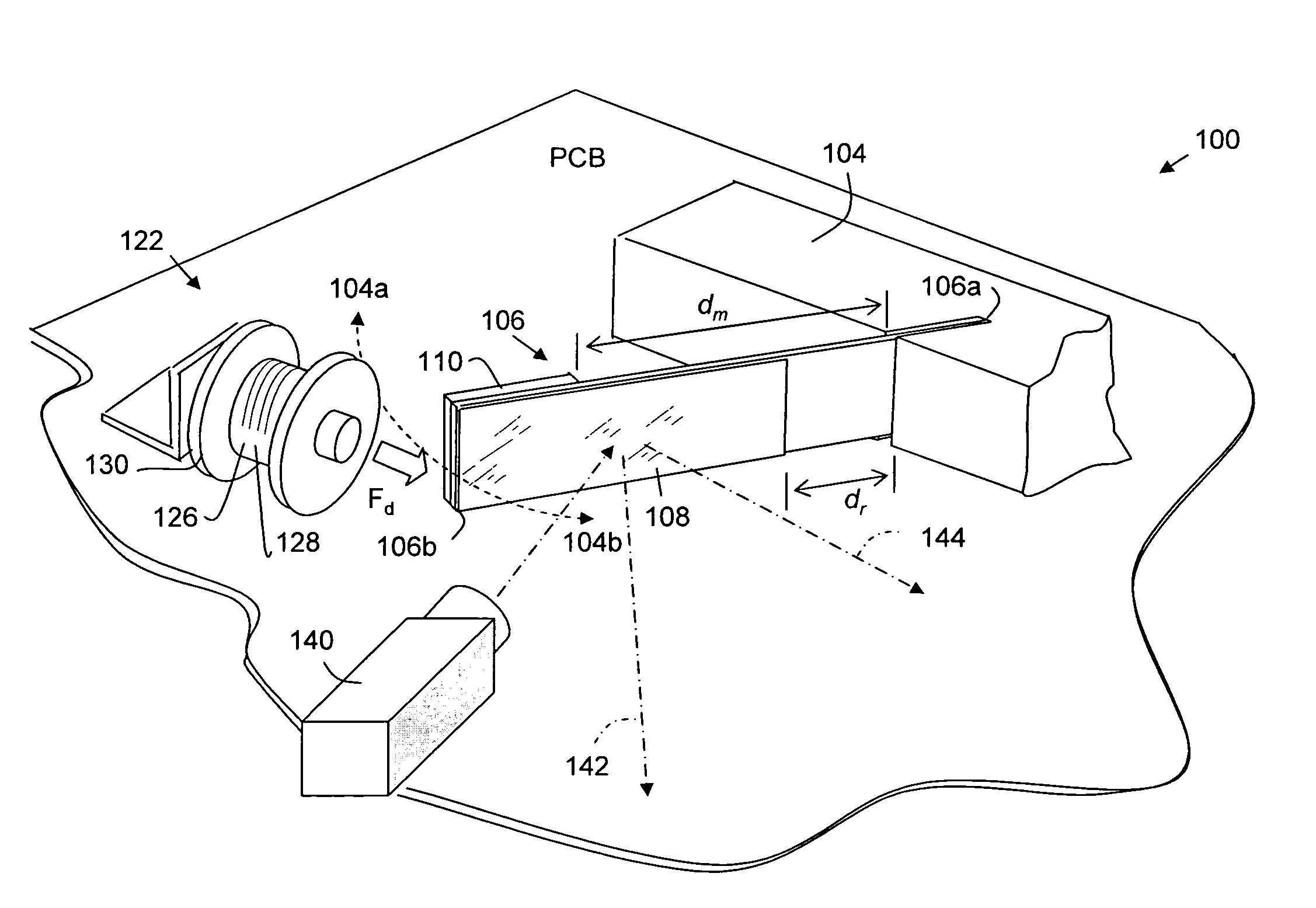
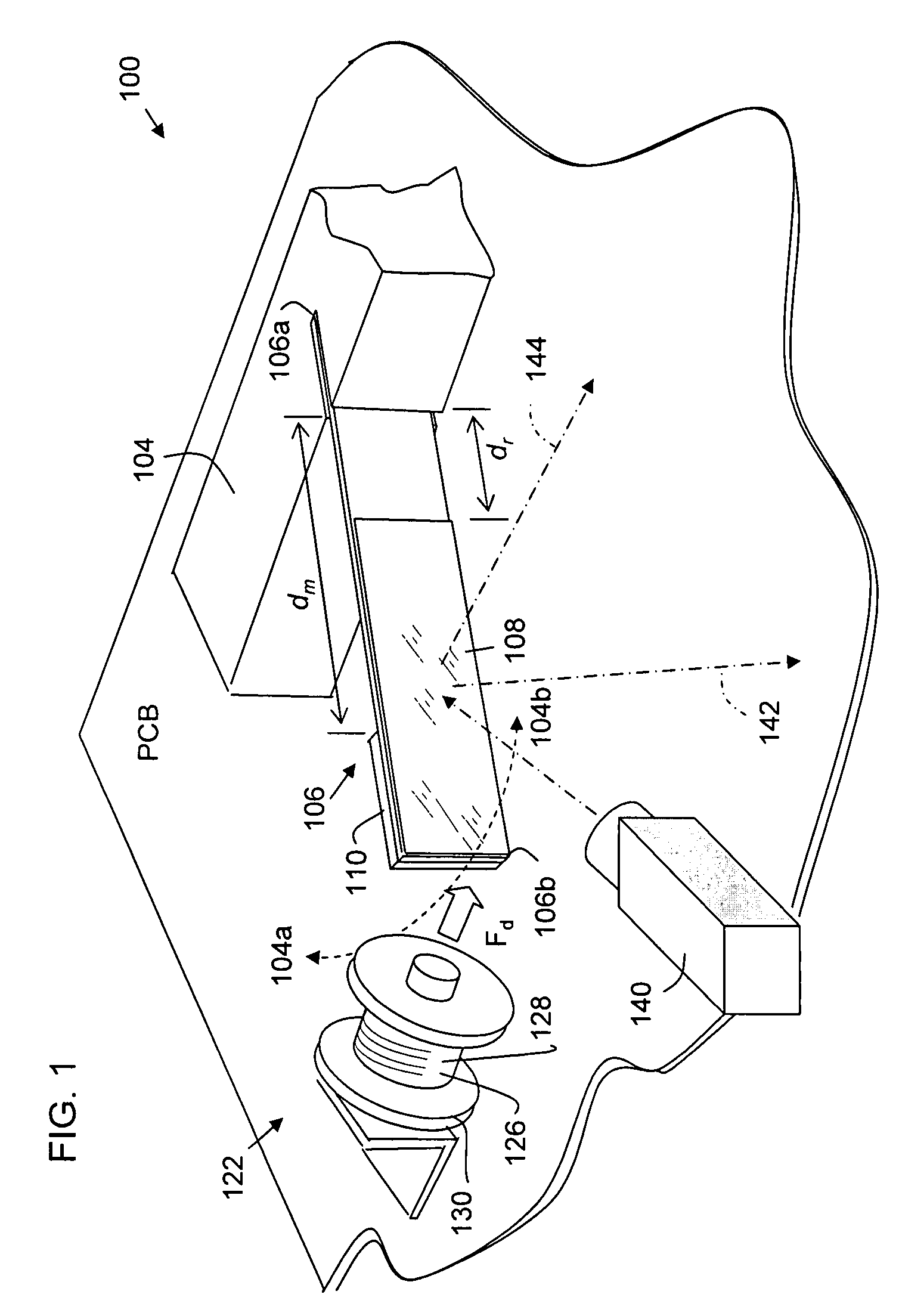
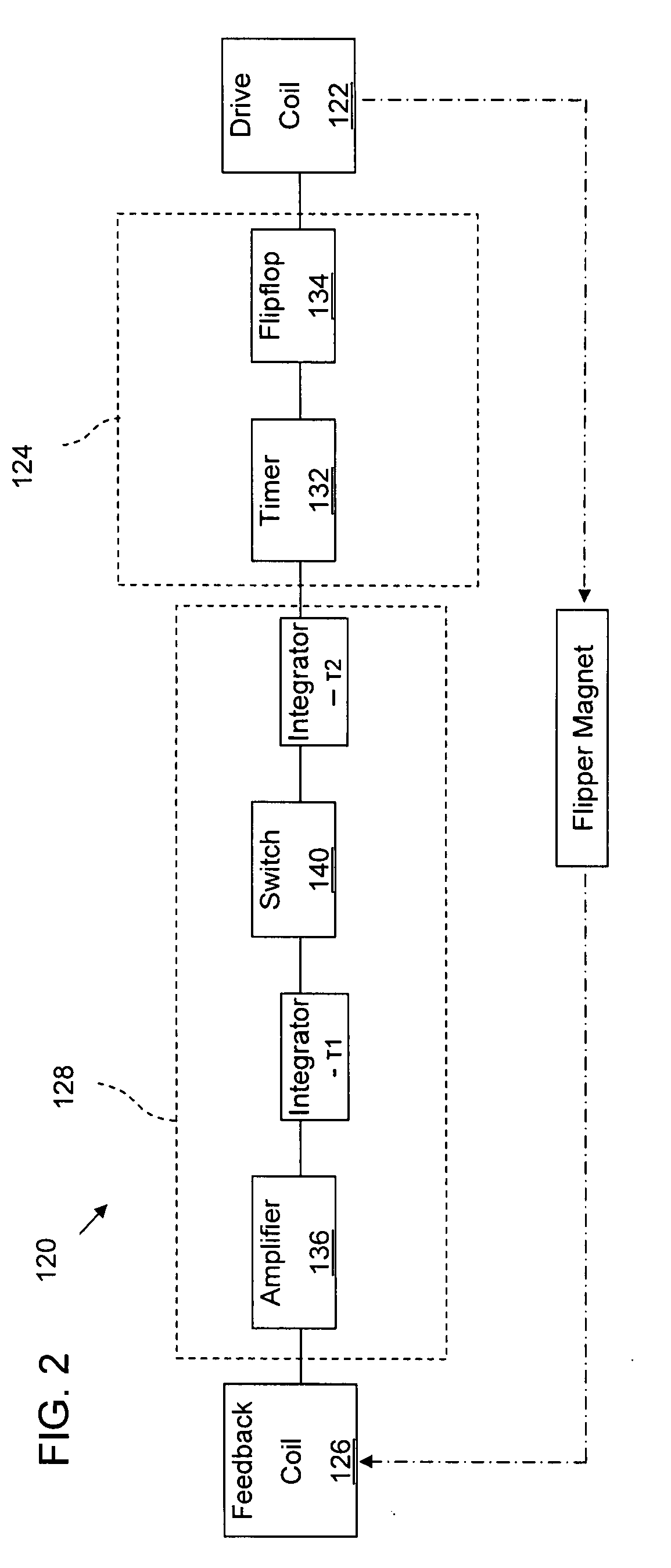
Feedback drive for resonant oscillation of scanner mechanism
InactiveUS20090086300A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansNatural resonanceIntegrator
A drive for oscillating a reflector in a beam scanner, and for other similar oscillating devices, forms a feedback loop synchronized to the natural resonance of a resiliently movable flipper strip carrying the reflector. A magnet on the free end of the flipper generates a current in a sensing coil coupled to an amplifier upon passage of the magnet. The triggering signal is phase delayed by one or more integrators or timers, whereupon a driving current is generated, for example in a different winding on the same spool as the sensing coil. The driving current is applied at a phase delay that maintains oscillation up to a high operational frequency in a range. Synchronizing the drive to the natural frequency and phase of the flipper substantially reduces power consumption compared to forcing oscillation to a different reference.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Radiation curable inkjet printing methods
InactiveUS20100309268A1Economical and versatileDuplicating/marking methodsInksPolymer substrateEngineering
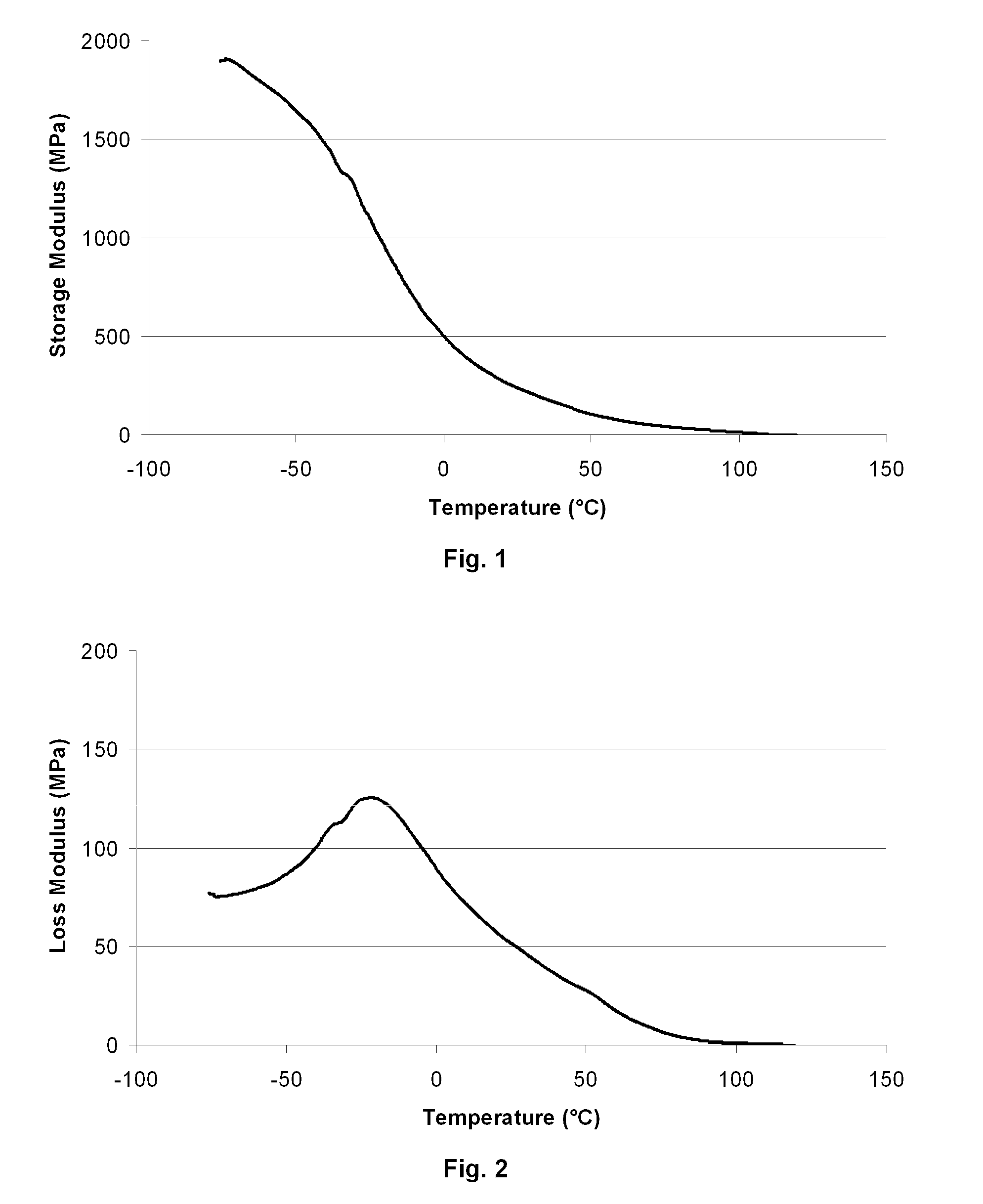
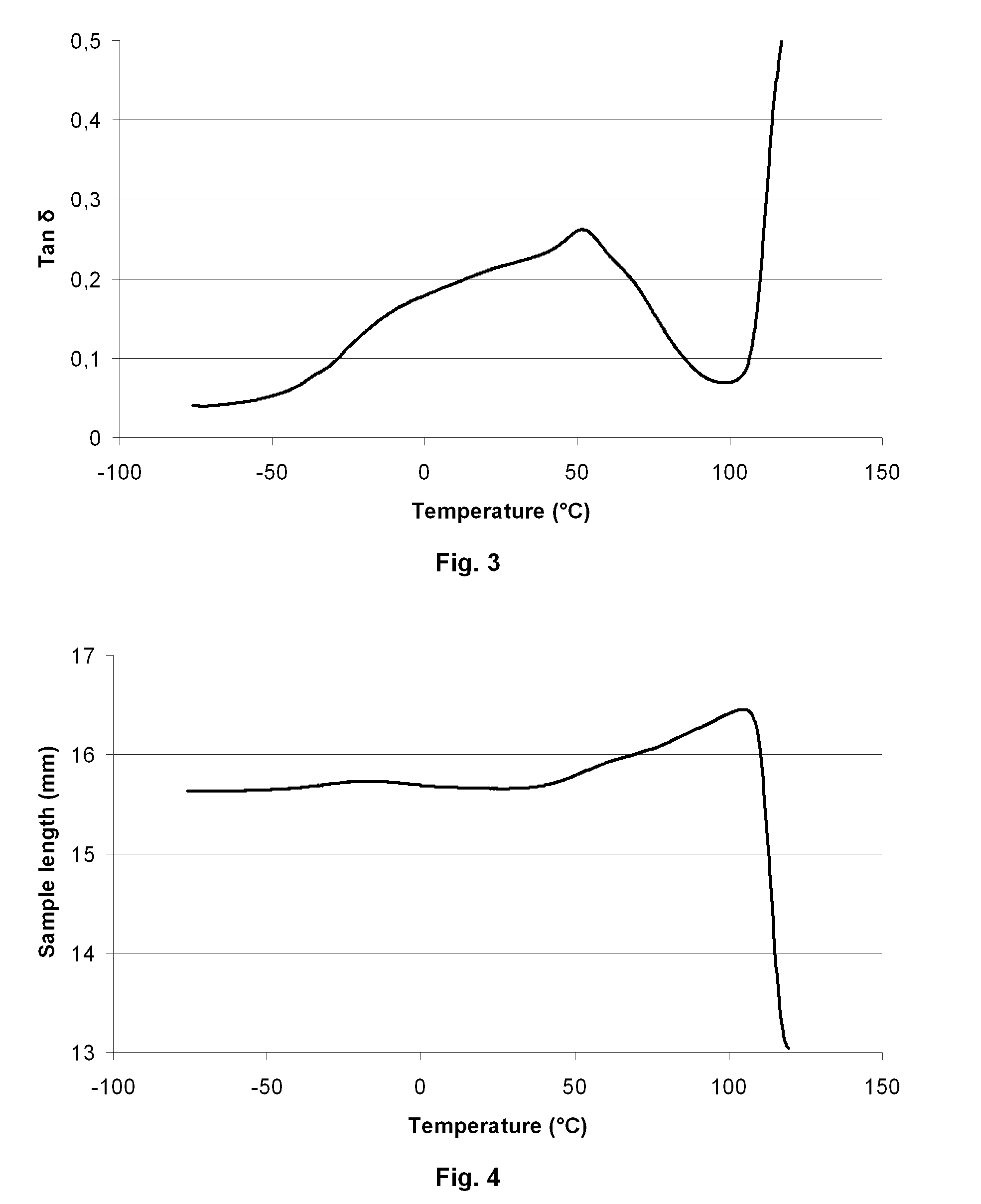
A radiation curable inkjet printing method for producing printed flexible foils and plastic bags includes the steps of a) providing a web-like polymeric substrate having a maximum value for Tan δ between 40° C. and 110° C.; b) providing a single pass inkjet printer having at least one page-wide printhead or at least one set of staggered printheads, a transporting device arranged to transport the web-like recording medium, and a curing device; c) jetting onto the web-like polymeric substrate having a surface energy Ssub, a non-aqueous radiation curable inkjet liquid having a surface tension SLiq, wherein SLiq is smaller than SSub by at least 4 mN / m; and d) curing the radiation curable liquid on the substrate at a surface temperature equal or higher than the temperature of the maximum value for Tan δ and smaller than the melting point of the polymeric recording medium. The maximum value for Tan δ is determined by dynamic mechanical analysis at a temperature ramp of 3° C. / min using forced oscillation with a cycle of 1 second and an amplitude of 100 μm. Also, a single pass inkjet printer for performing the method.
Owner:AGFA NV
Varying force vector exercise device for inducing musculature perturbations
InactiveUS7695414B2Increase the itineraryIncrease the number ofMuscle exercising devicesMuscle contractionSpherical bearing
Owner:TIAHRT LEIF K
Wide scope oxygen sensor aging monitoring system for vehicle and fault diagnosis method
ActiveCN106837569AImplement aging monitoringImplement diagnosticsInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusOxygen sensorDiagnosis methods
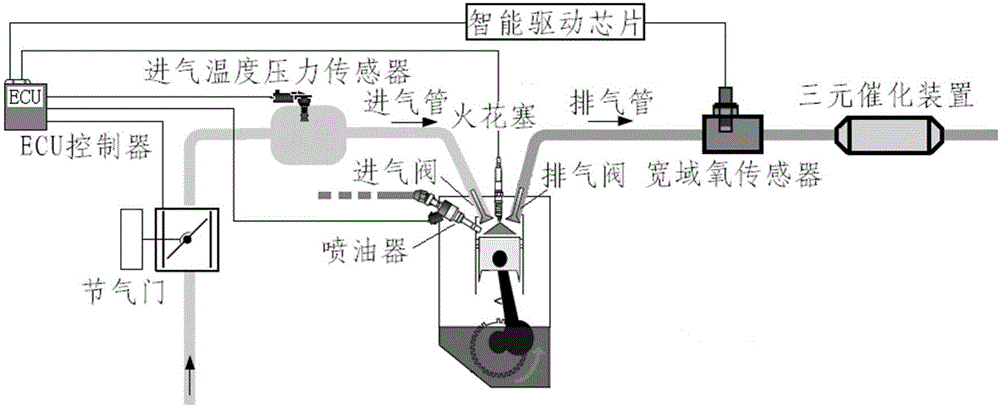
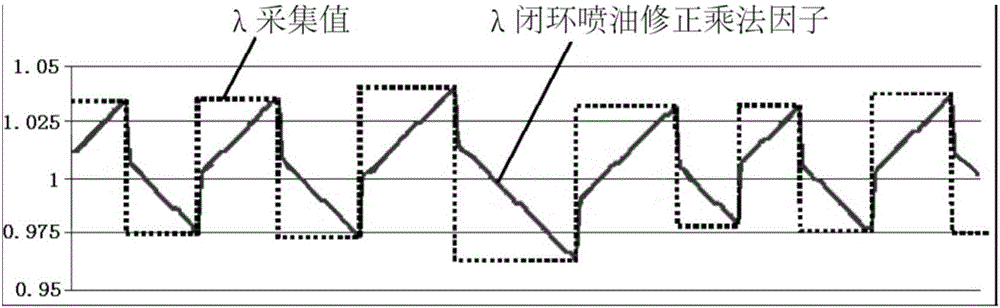
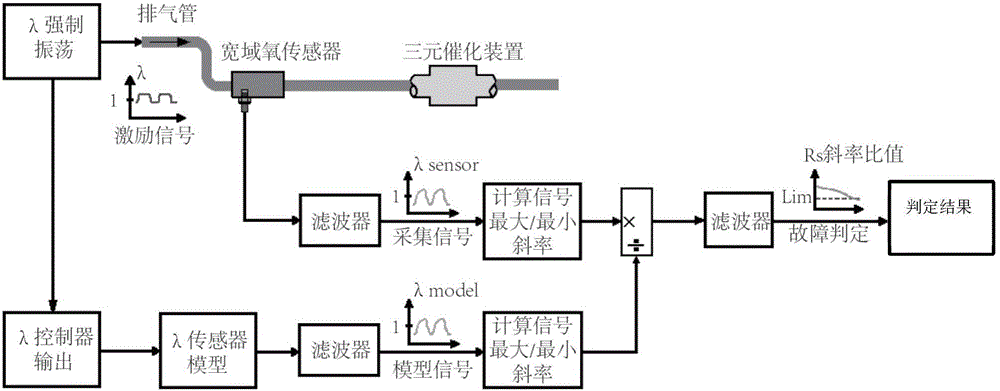
Provided are a wide scope oxygen sensor aging monitoring system for a vehicle and a fault diagnosis method. An engine and a sensor executor, an ECU and a wide scope oxygen sensor intelligent driver chip and the like thereof are utilized, and aging monitoring is performed on a wide scope oxygen sensor. The ECU is responsible for detecting and determining aging faults of the wide scope oxygen sensor, utilizing forced oscillation to compare lambda signals and lambda reference signals actually collected from the wide scope oxygen sensor, a minimum slope ratio between the lambda signals and the lambda reference signals is compared, and whether the wide scope oxygen sensor has the aging faults is determined according to the slope ratio. The system can accurately detect the aging faults of the wide scope oxygen sensor and is applicable to all vehicles where the wide scope oxygen sensor is installed.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Forced oscillation disturbance source identification and splitting method based on oscillation starting characteristic
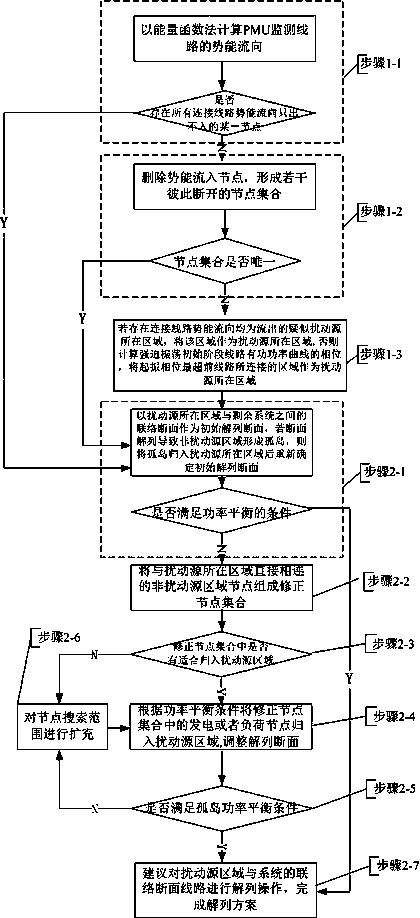
ActiveCN104269866ASafe and stable operationGuaranteed uptimeFault location by conductor typesPower oscillations reduction/preventionIslandingElectric power system
The invention discloses a forced oscillation disturbance source identification and splitting method based on an oscillation starting characteristic and belongs to the technical field of emergency adjustment and control in an electric power system. According to the method, the oscillation starting characteristic of forced oscillation and a disturbance source location energy function method are combined, the correct position is identified from a plurality of suspected disturbance source areas, and if the disturbance source area meets the condition of electric energy supply and demand balance and no island exists in the non-disturbance source areas, a connection fracture surface line between the area where a disturbance source is located and a system can be split; otherwise, the identified area where the disturbance source is located serves as an initial island, adjacent nodes of the island are searched for, and the connection fracture surface is adjusted till the requirement for electric energy supply and demand balance is met and the condition that power grids remaining after splitting are connected is met. The method solves the problem about positioning of the disturbance source in forced oscillation control. Through the method, splitting control measures can be given in real time when oscillation is detected, and the method has great significance in suppressing oscillation and guaranteeing stable running of interconnected electric power systems.
Owner:STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER +2
Method for judging negative damping oscillation and force oscillation based on second order difference method
ActiveCN102650666ASolve difficult to identifyImprove accuracyElectrical testingPower Management UnitClassical mechanics
The invention provides a method for judging negative damping oscillation and force oscillation based on a second order difference method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1-, acquiring an actual measurement oscillation curve; 2-, respectively solving a first order difference value and a second order difference value at the maximum time point in each oscillation period; and 3-, comparing symbols of the first order difference value and the second order difference value at the same time, and judging a mode of the oscillation curve according to a comparison result. According to the method for judging the negative damping oscillation and the force oscillation based on the second order difference method, whether certain low frequency oscillation is the negative damping low frequency oscillation caused by the reason that a system is lacking of damping or is the force oscillation caused by a forced disturbance source existing in the system can be rapidly identified in the more than a dozen of initial cycles through the data of a power management unit (PMU) or a wide area measurement system (WAMS), so that a measure of restraining the low frequency oscillation is rapidly taken.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com