Voltage regulator that operates in either PWM or PFM mode
a voltage regulator and pwm technology, applied in the field of voltage regulators, can solve the problems of impracticality of pfm mode and lower and achieve the effect of reducing the gate-drive power dissipation of pfm mode and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
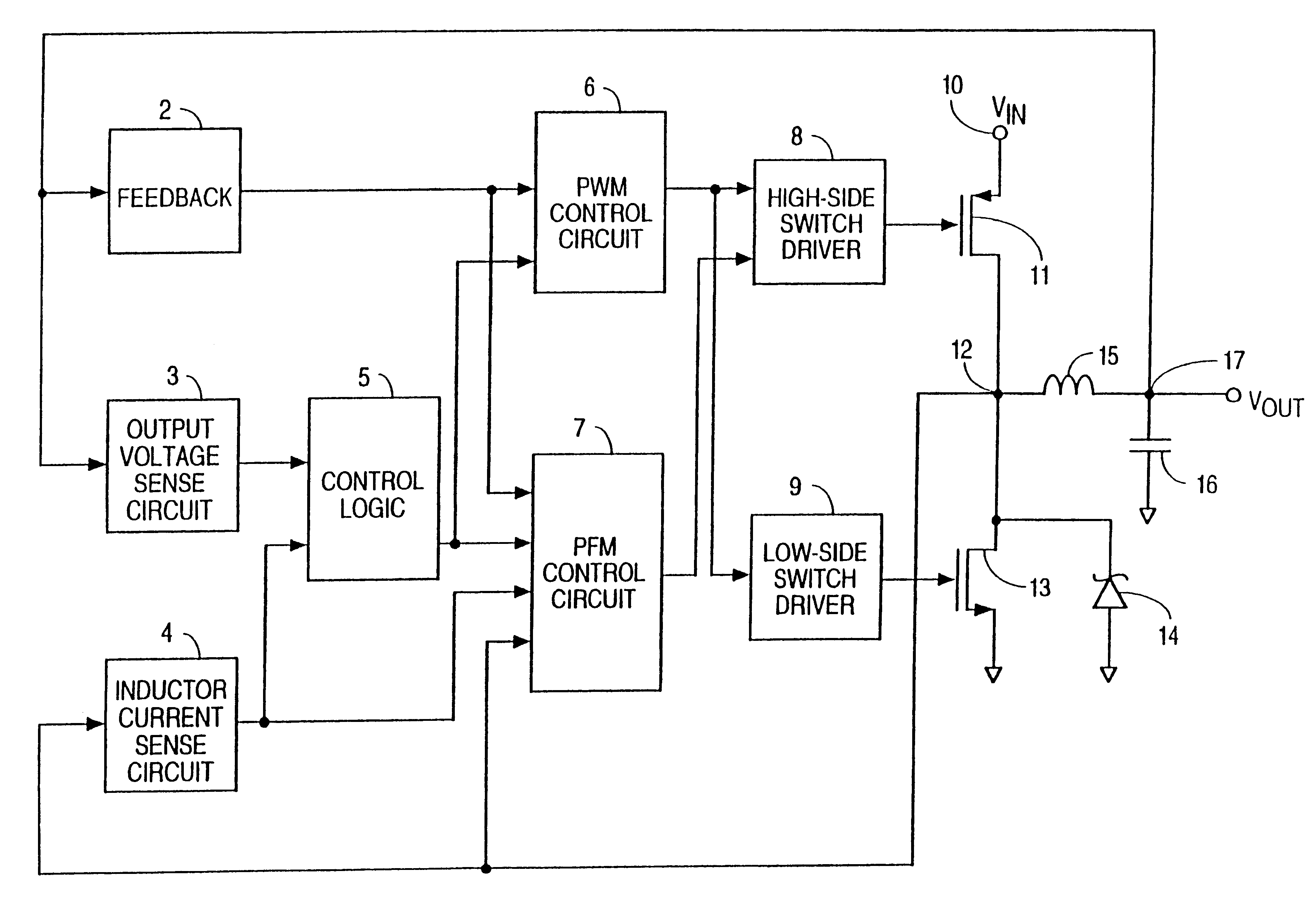
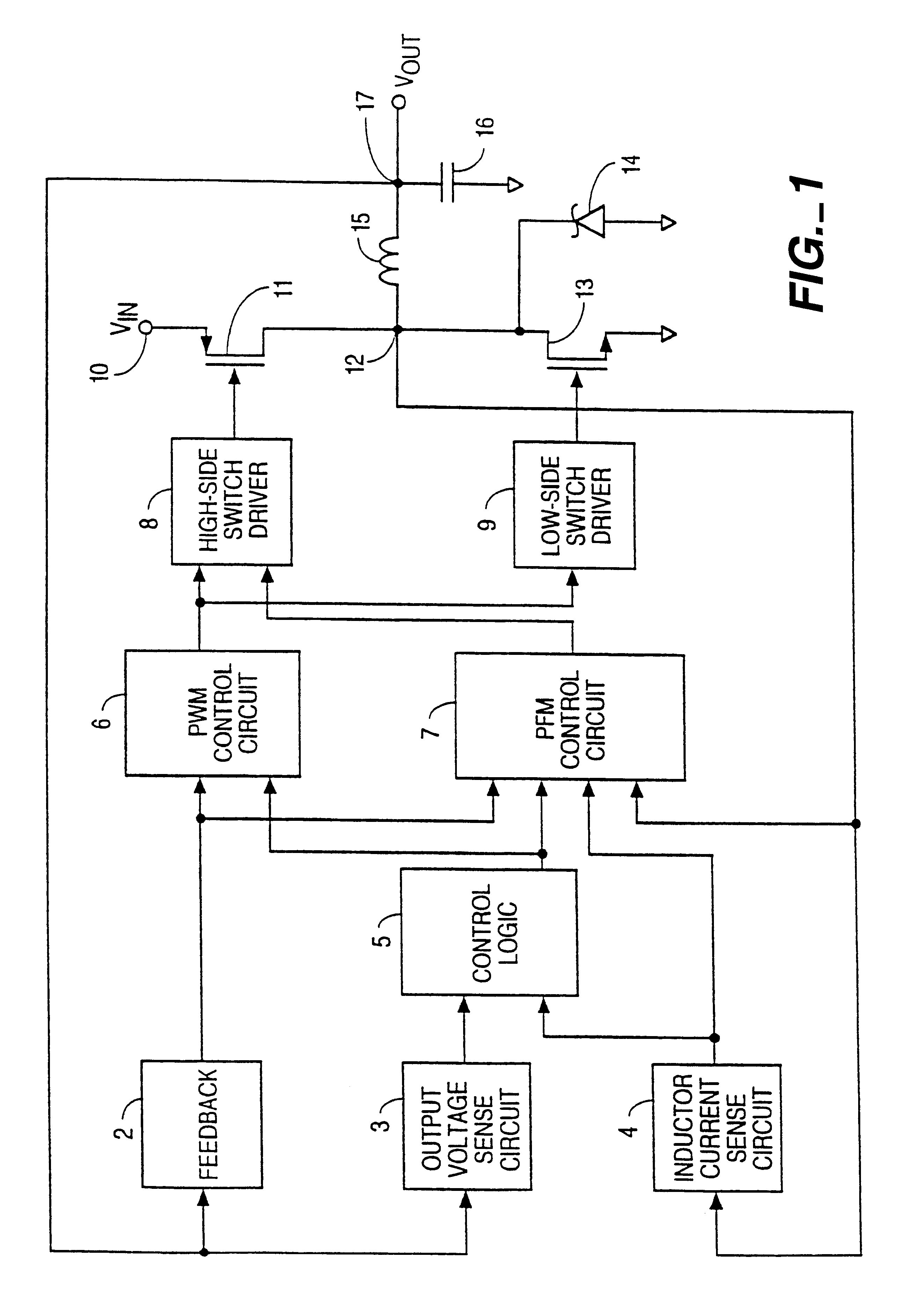
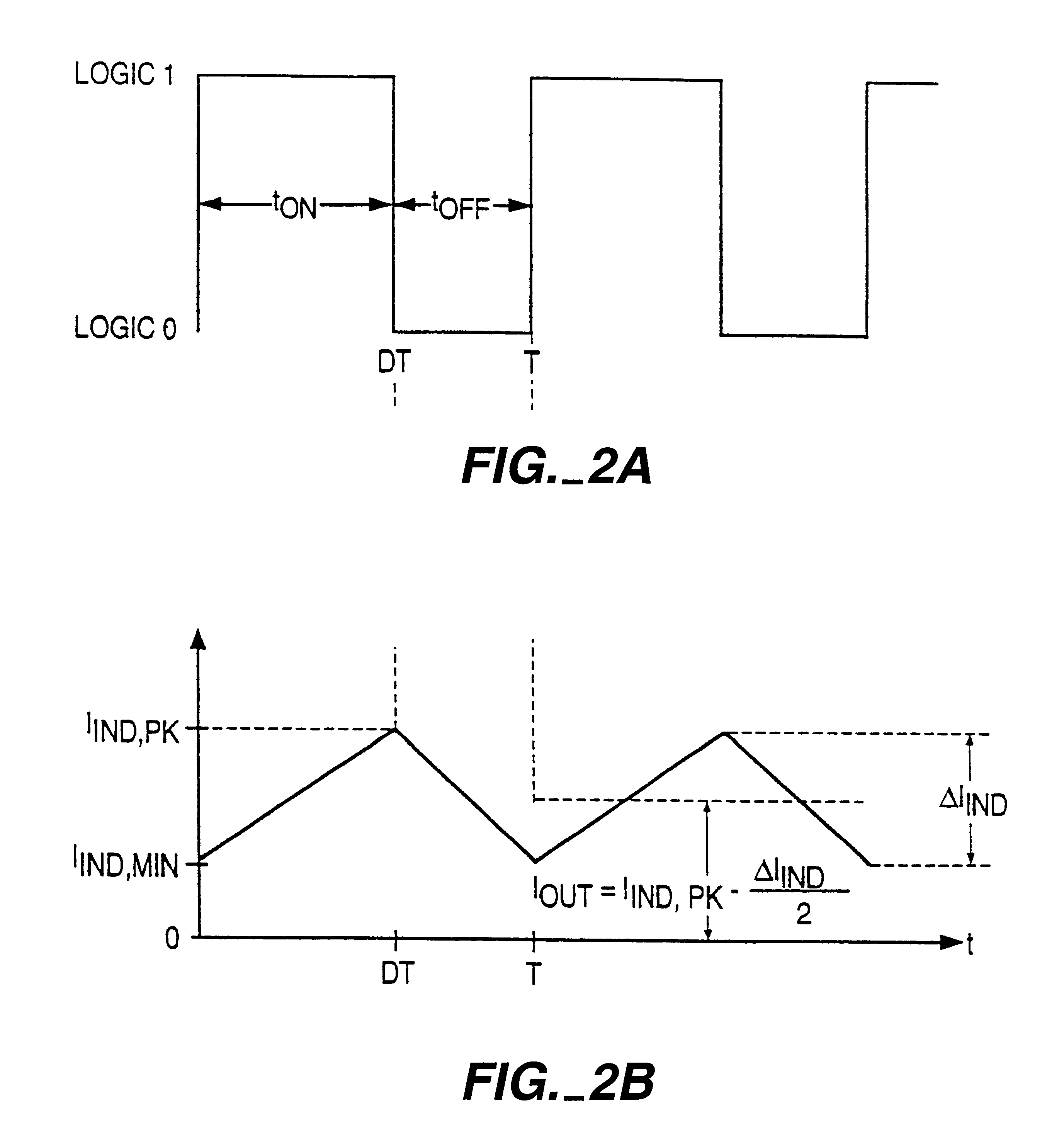
FIG. 1 is a simplified block diagram of an embodiment of the present invention. The voltage regulator of FIG. 1 includes a feedback circuit 2, output voltage sensing circuit 3, inductor current sensing circuit 4, control logic circuit 5, PWM control circuit 6, PFM control circuit 7, high-side switch driver 8, low-side switch driver 9, input terminal 10, high-side switch 11, switching node 12, low-side switch 13, schottky diode 14, inductor 15, capacitor 16, and output terminal 17.
High-side switch 11 is preferably a P-channel MOSFET that has a first terminal connected to input terminal 10 and a second terminal connected to a terminal (switching node 12) of inductor 15. The other terminal of inductor 15 is connected to output terminal 17.
PWM control circuit 6, which includes a PWM signal generator, has an output terminal connected to a first input terminal of the high-side switch driver 8. The output terminal of PWM control circuit 6 is also connected to the low-side switch driver 9. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com