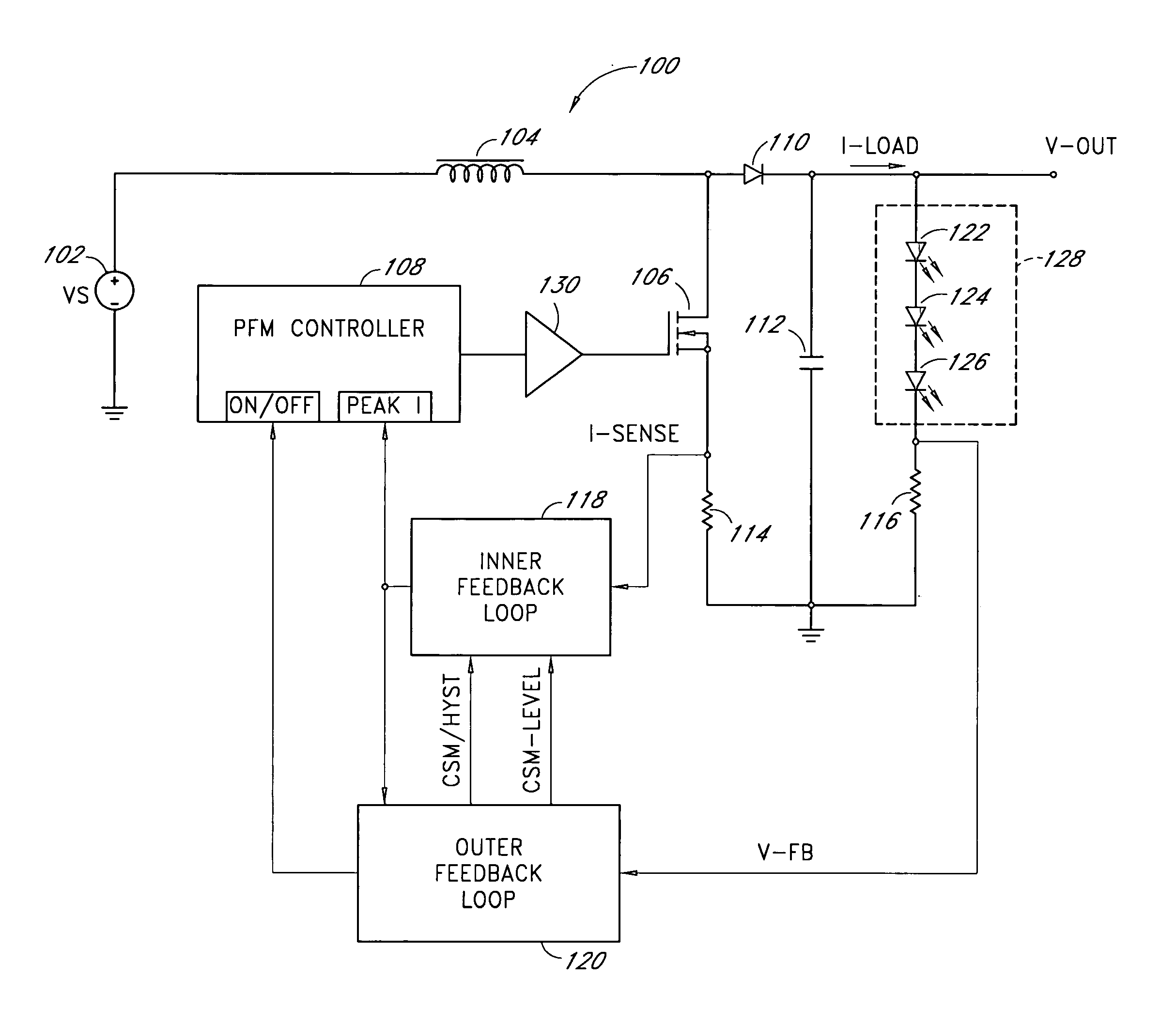
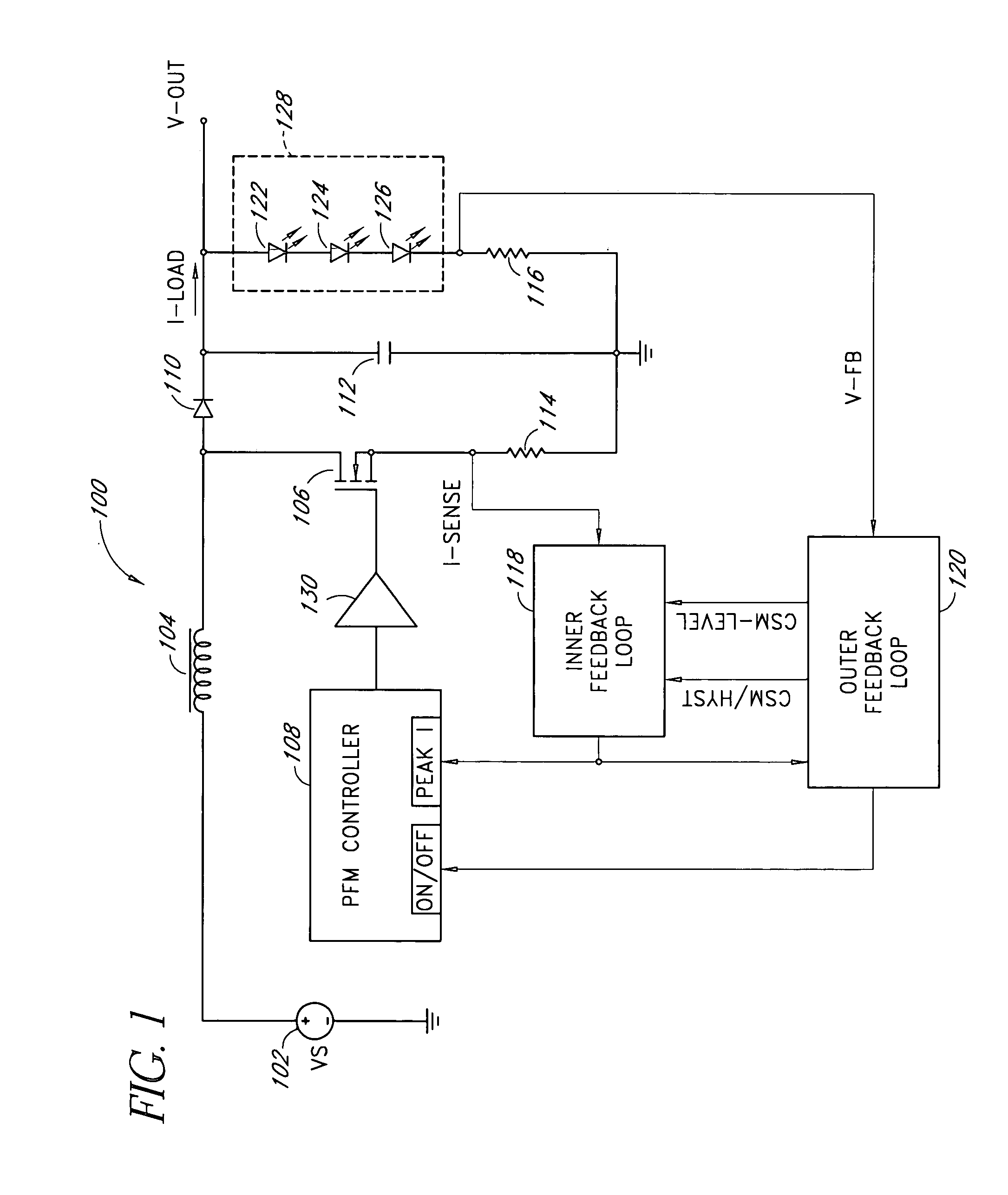
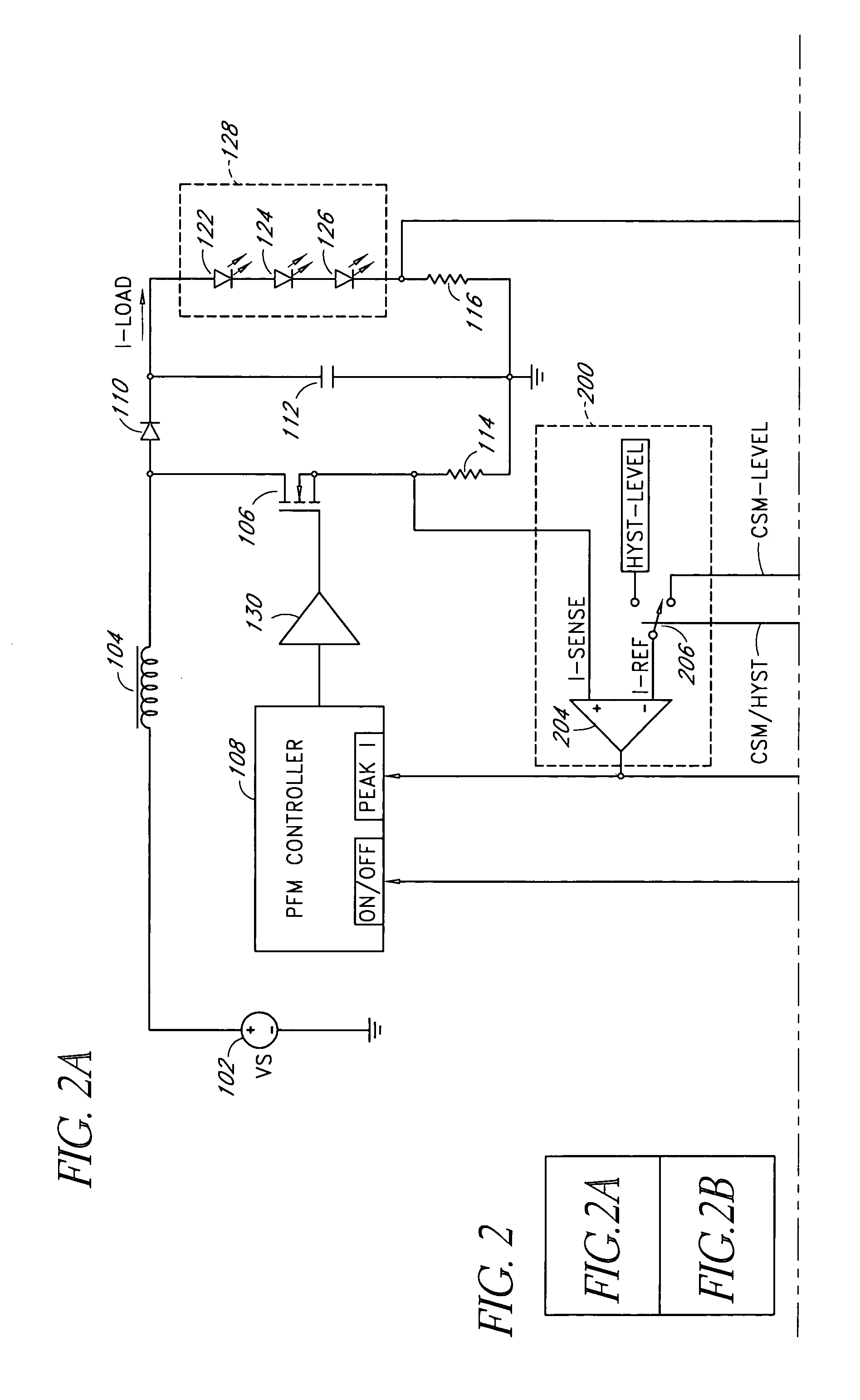
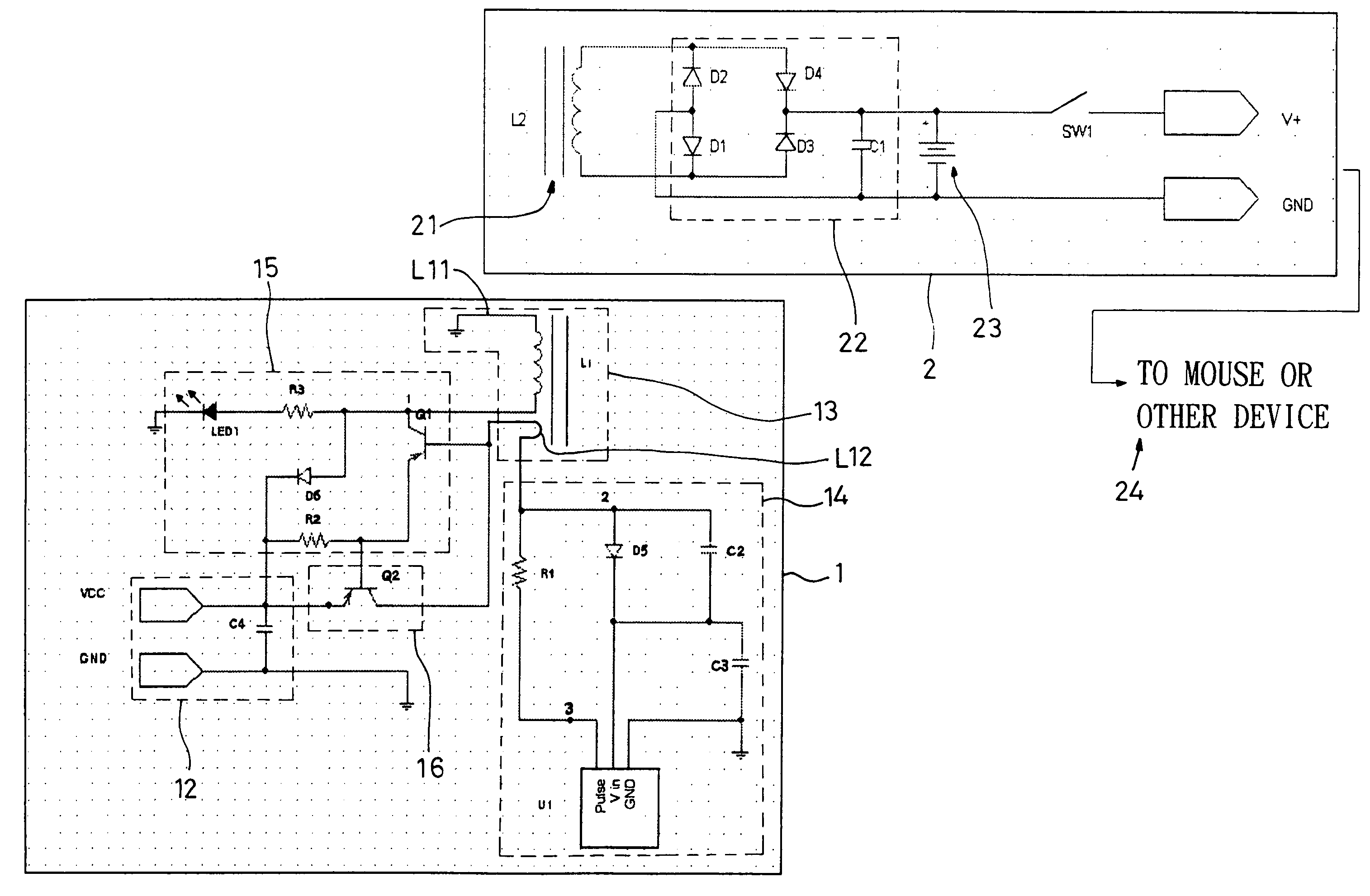
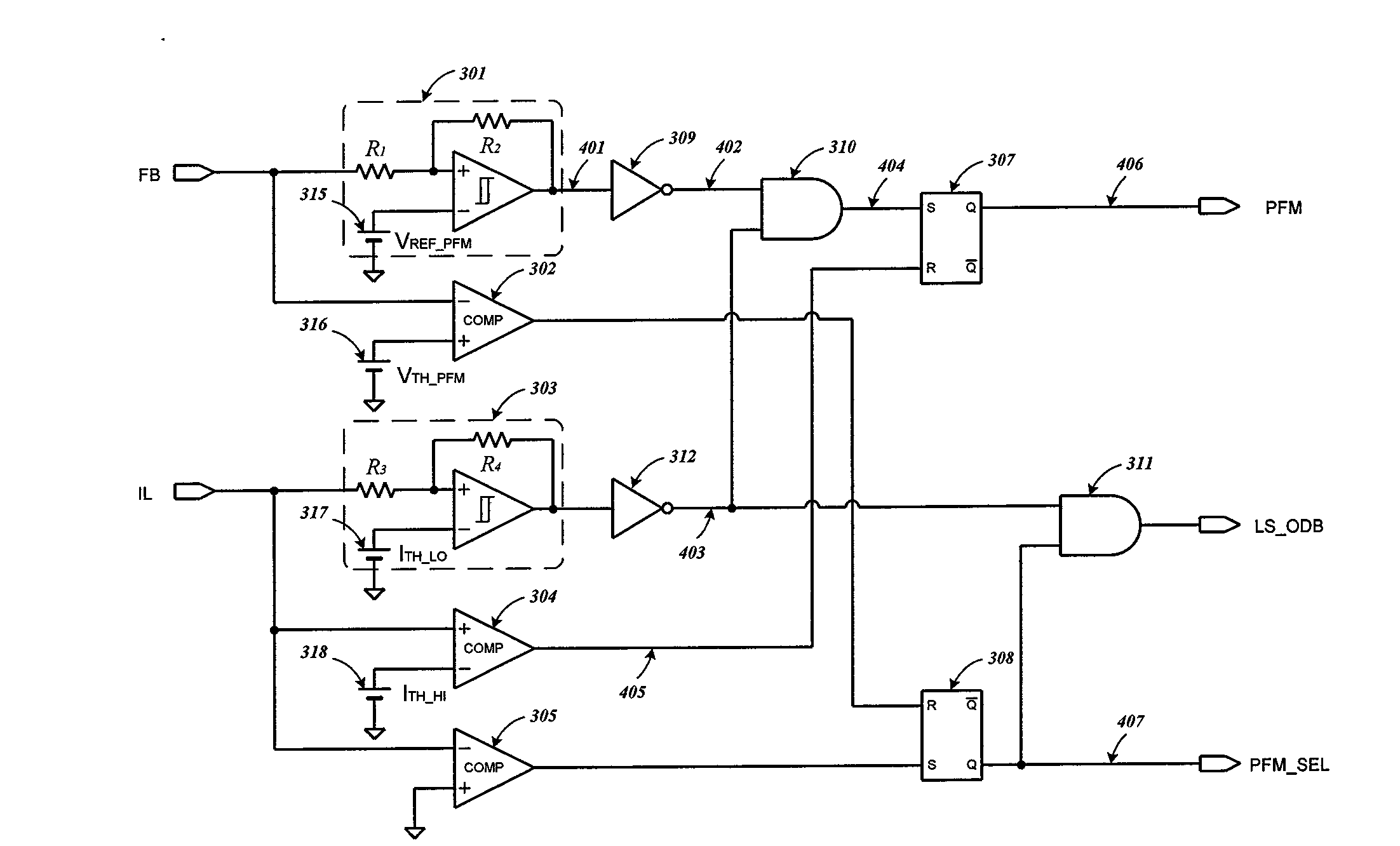
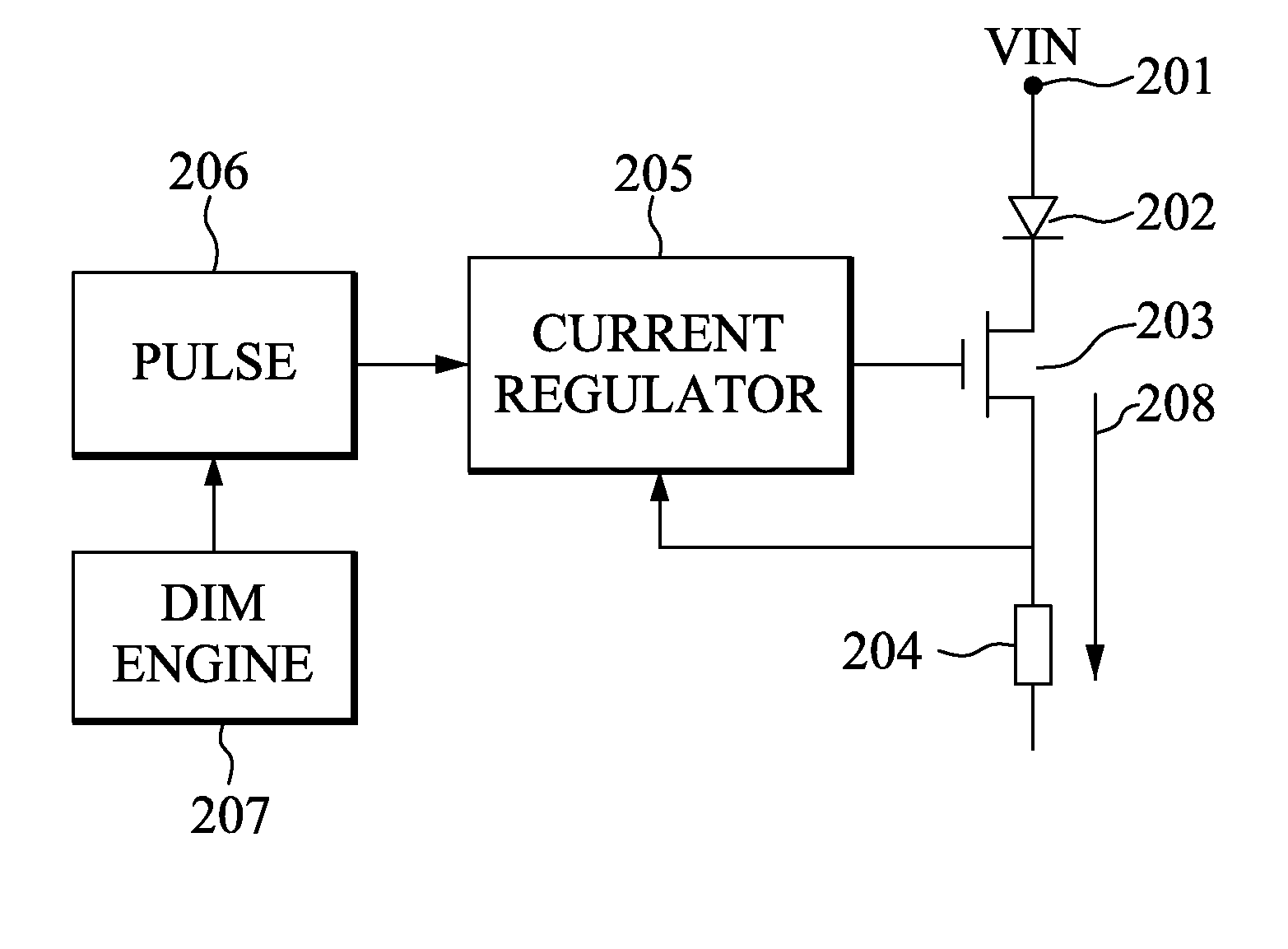
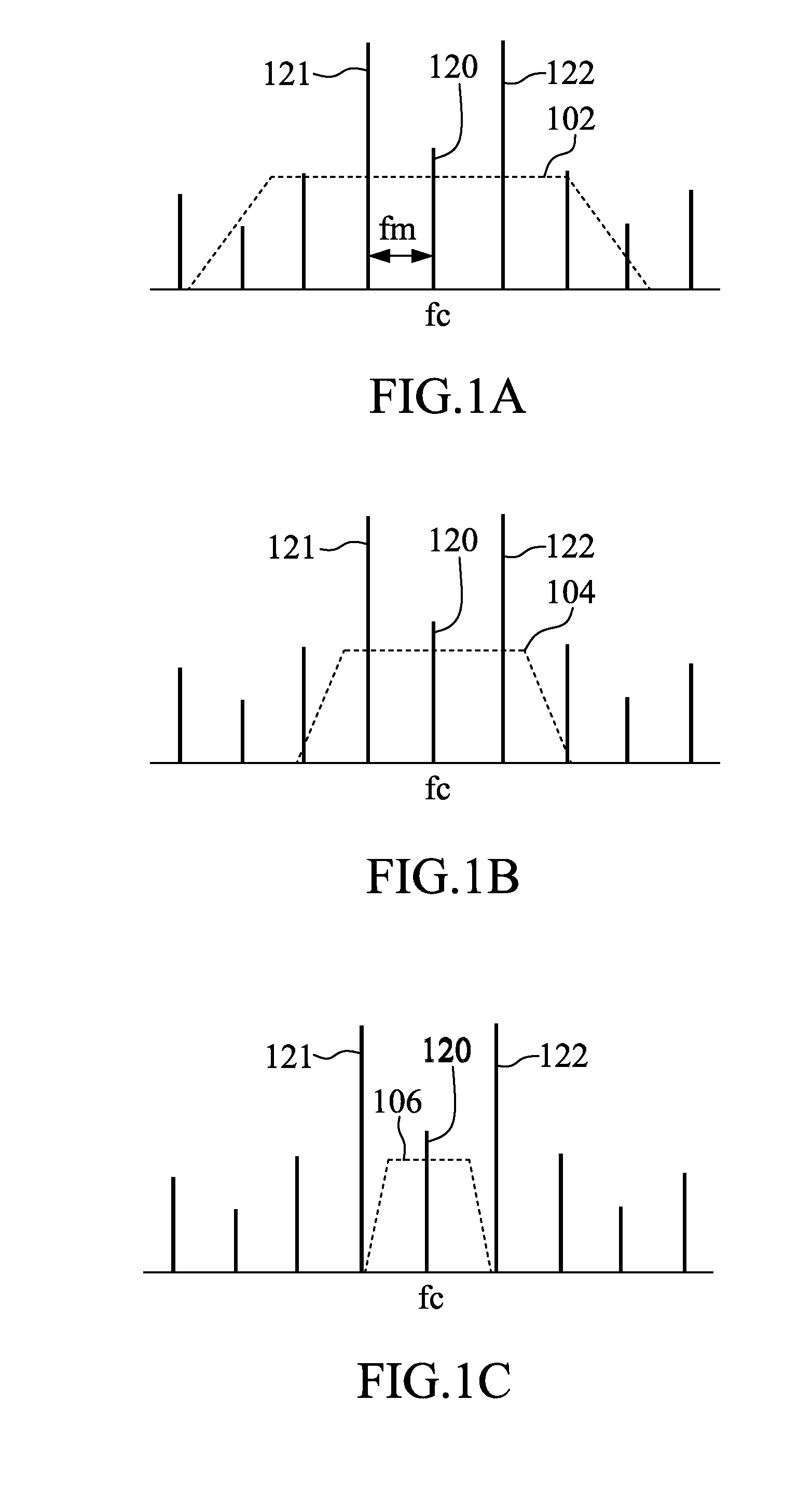
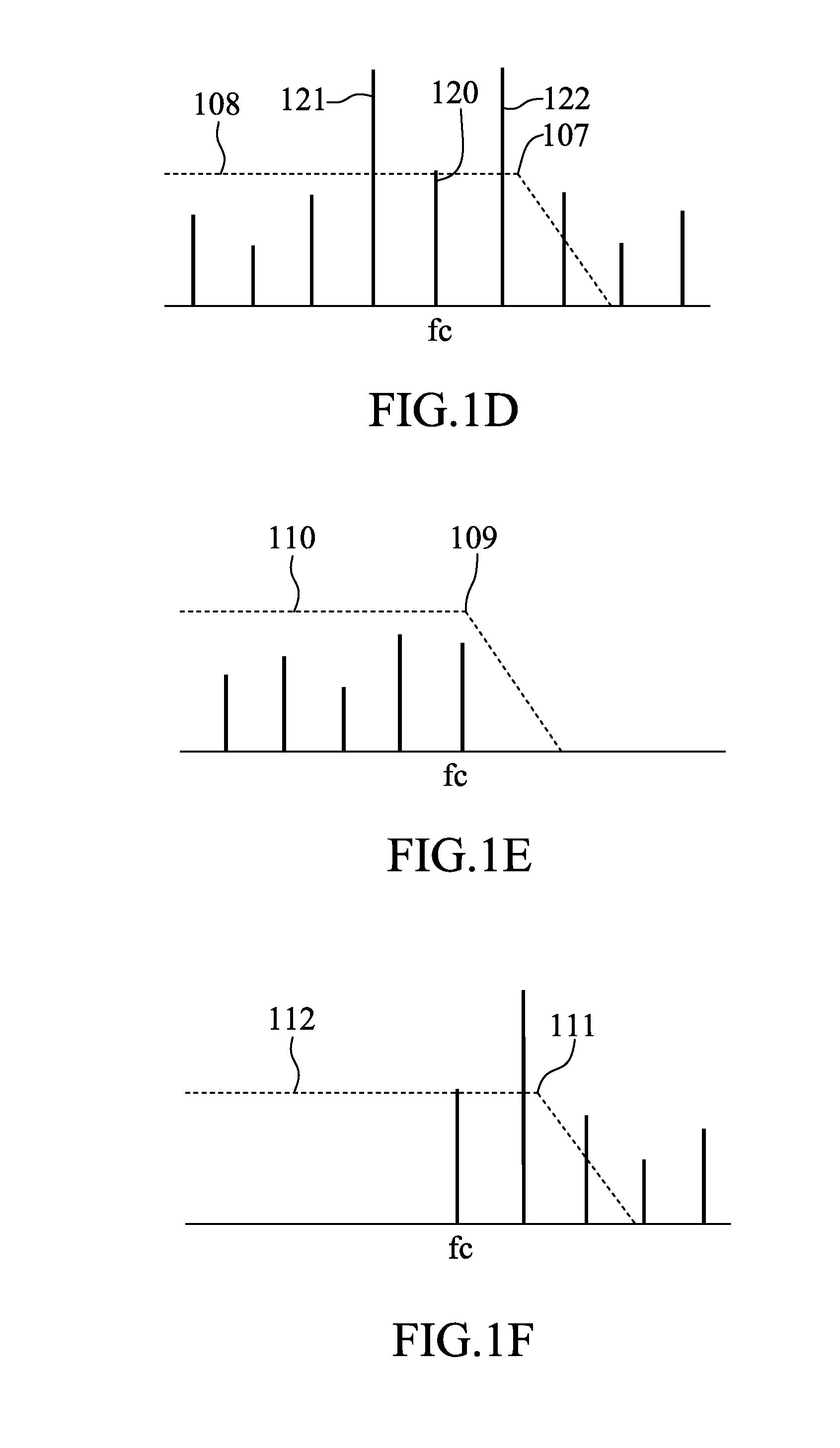
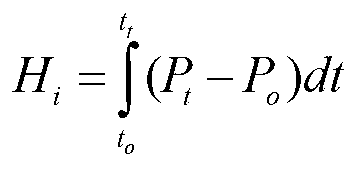Patents
Literature
902 results about "Pulse-frequency modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
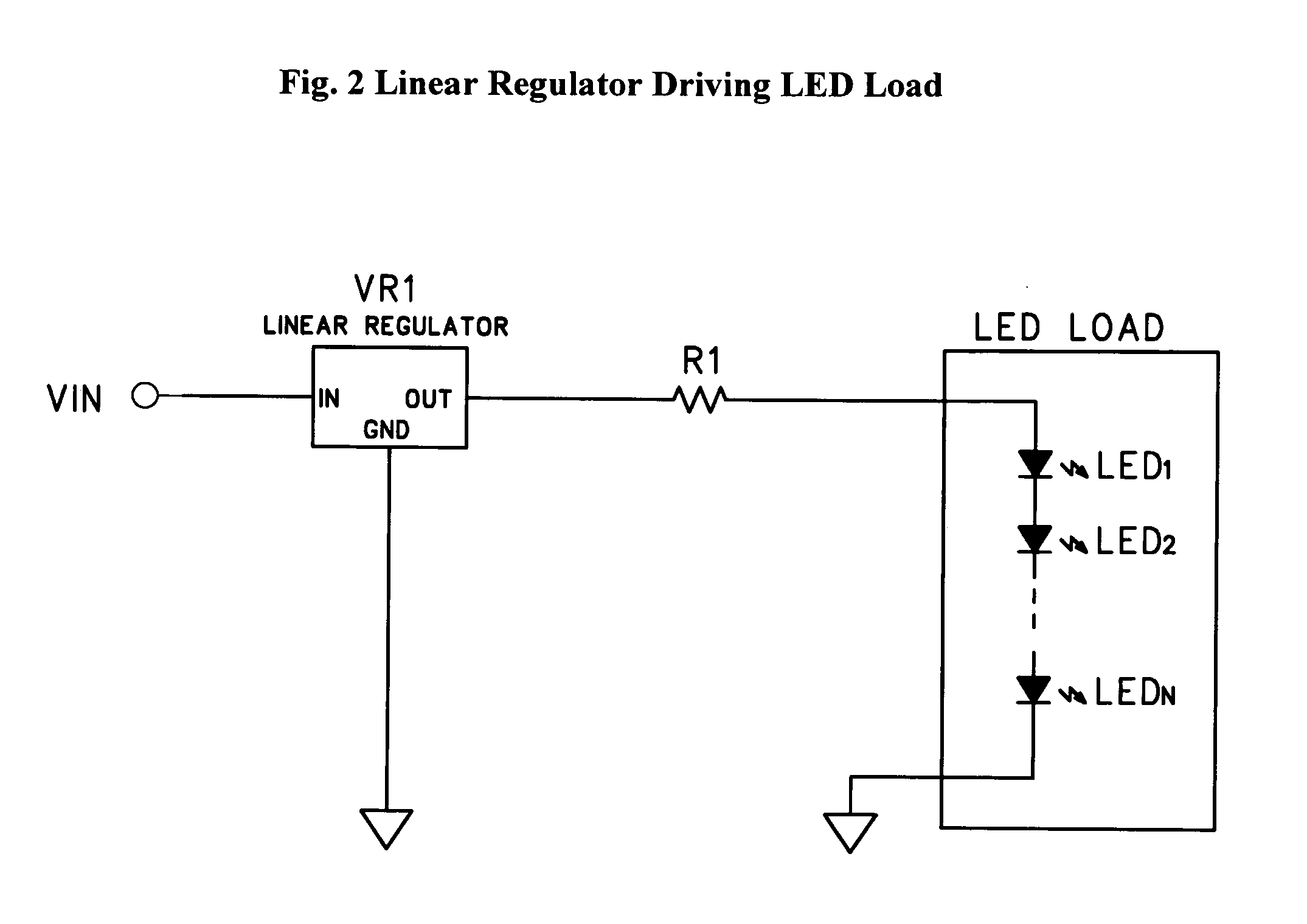
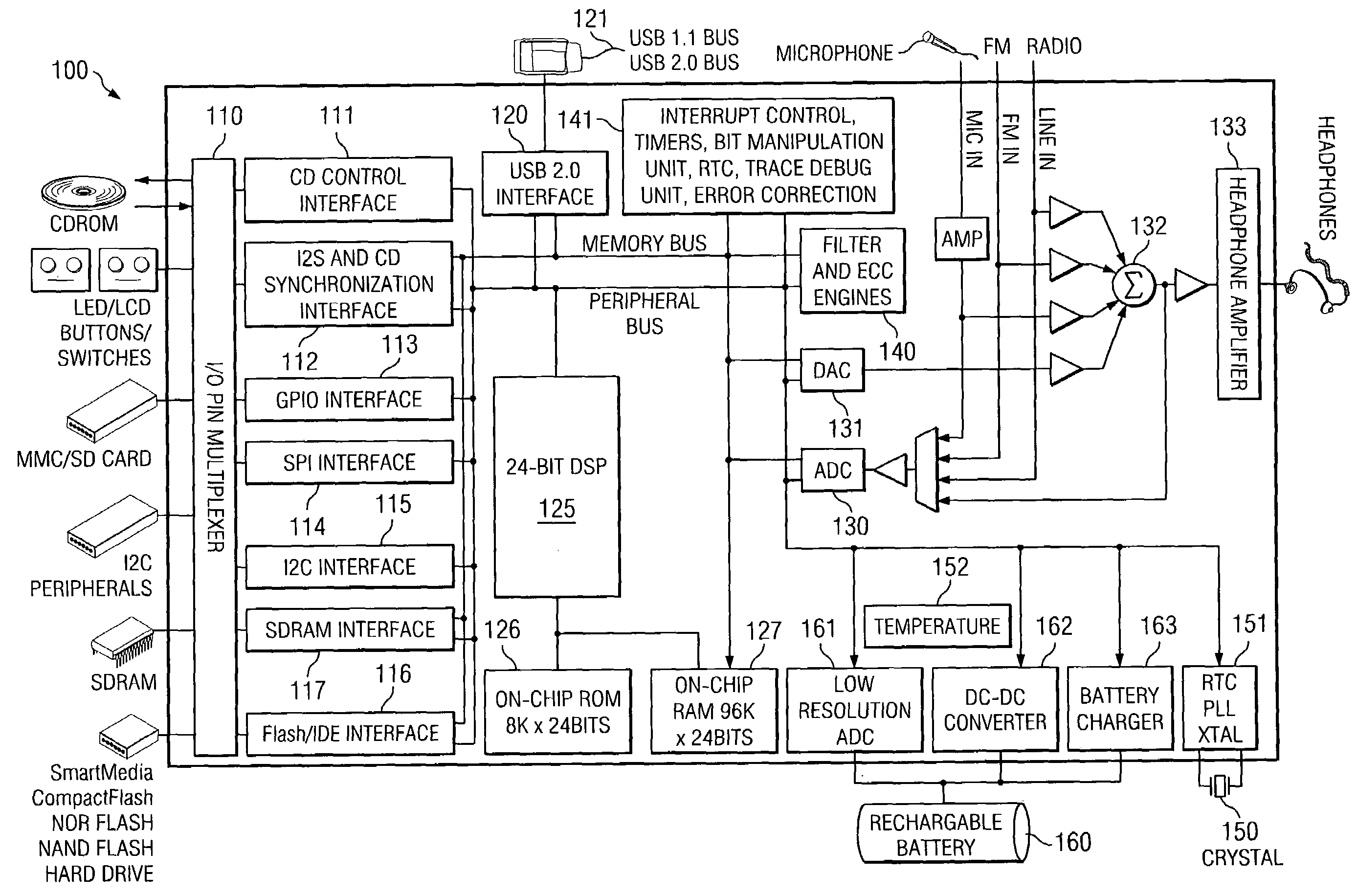
Pulse-Frequency Modulation (PFM) is a modulation method for representing an analog signal using only two levels (1 and 0). It is analogous to pulse-width modulation (PWM), in which the magnitude of an analog signal is encoded in the duty cycle of a square wave. Unlike PWM, in which the width of square pulses is varied at constant frequency, PFM fixes the width of square pulses while varying the frequency. In other words, the frequency of the pulse train is varied in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal at sampling intervals. The amplitude and width of the pulses is kept constant.
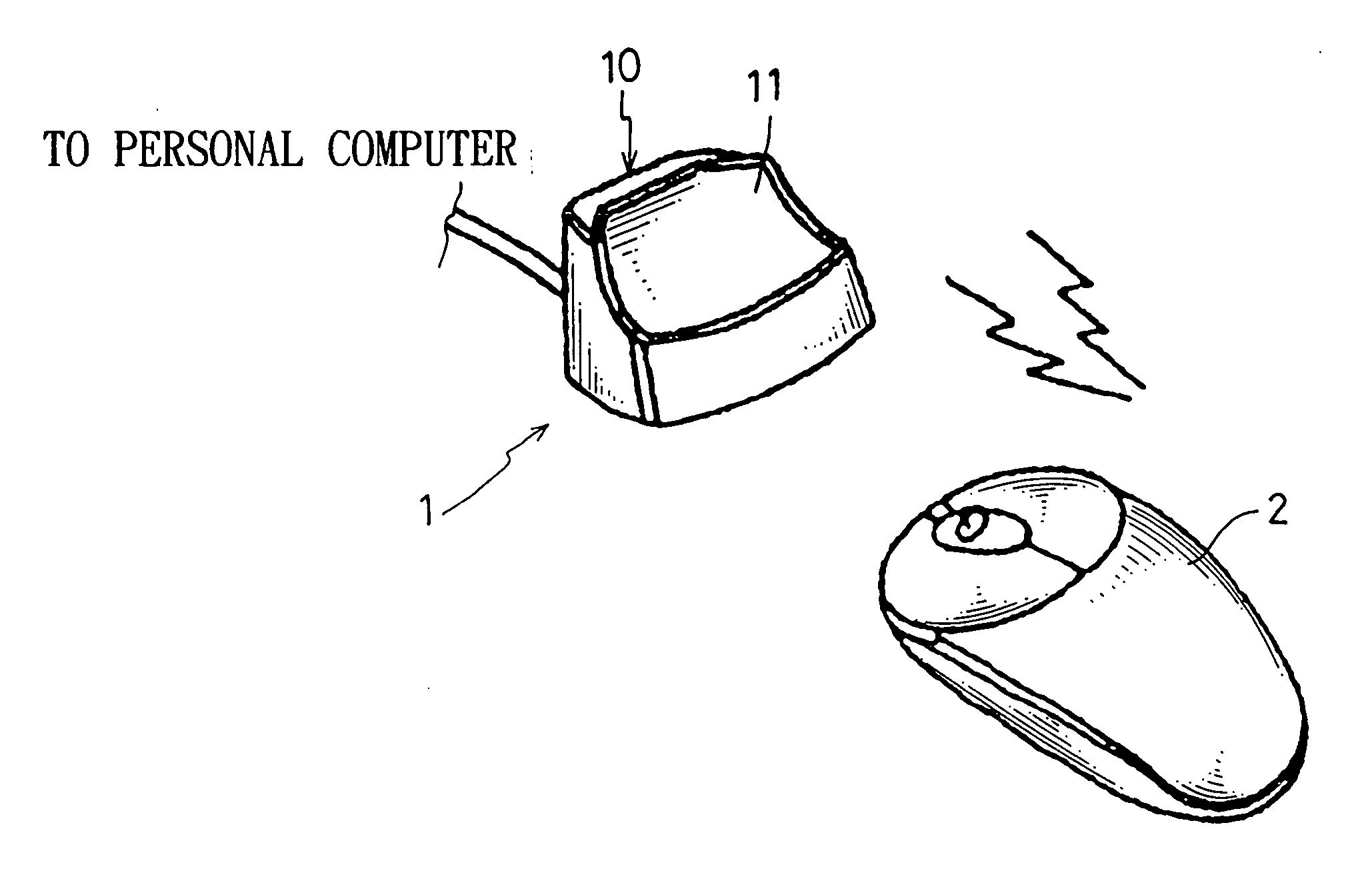
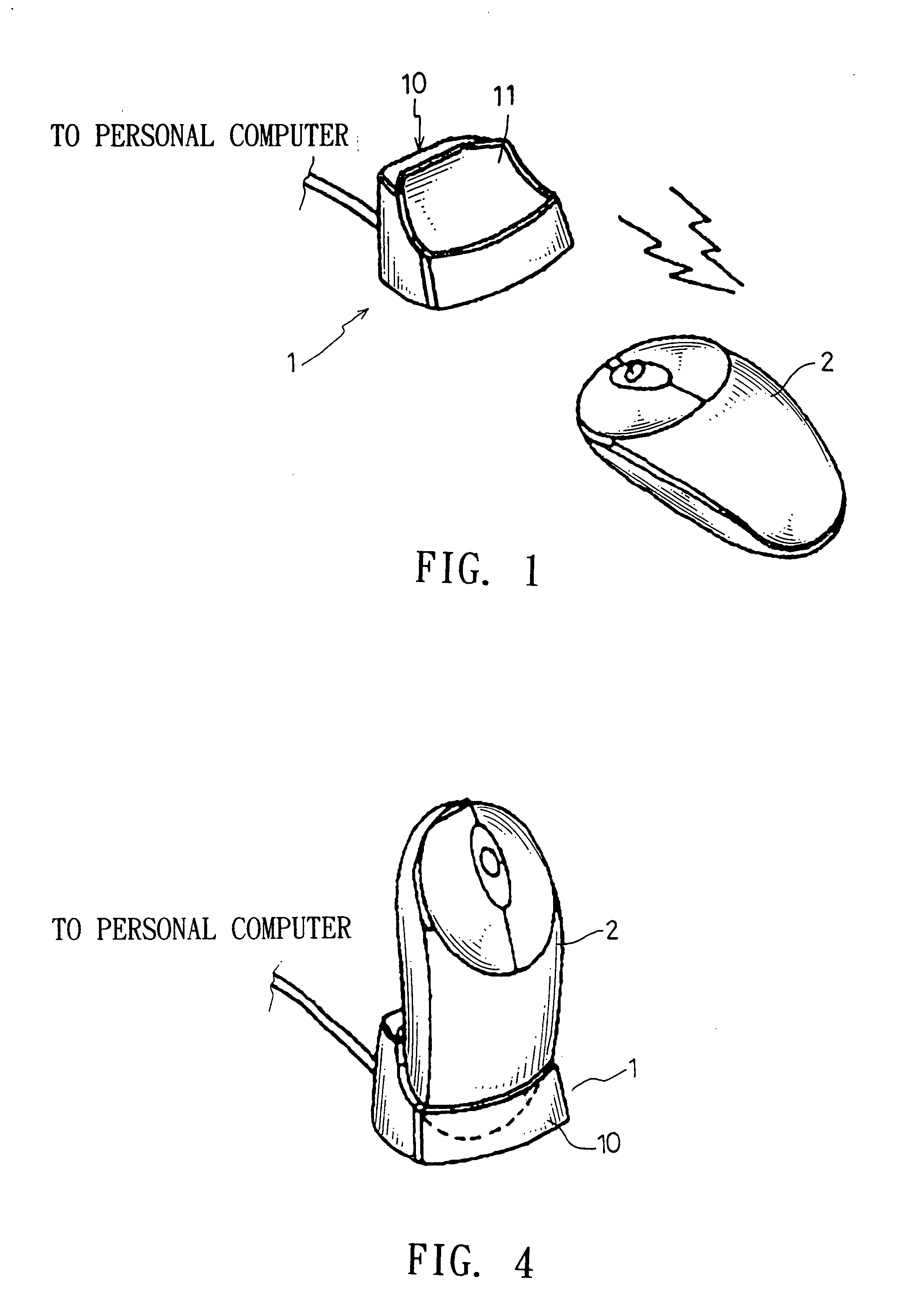
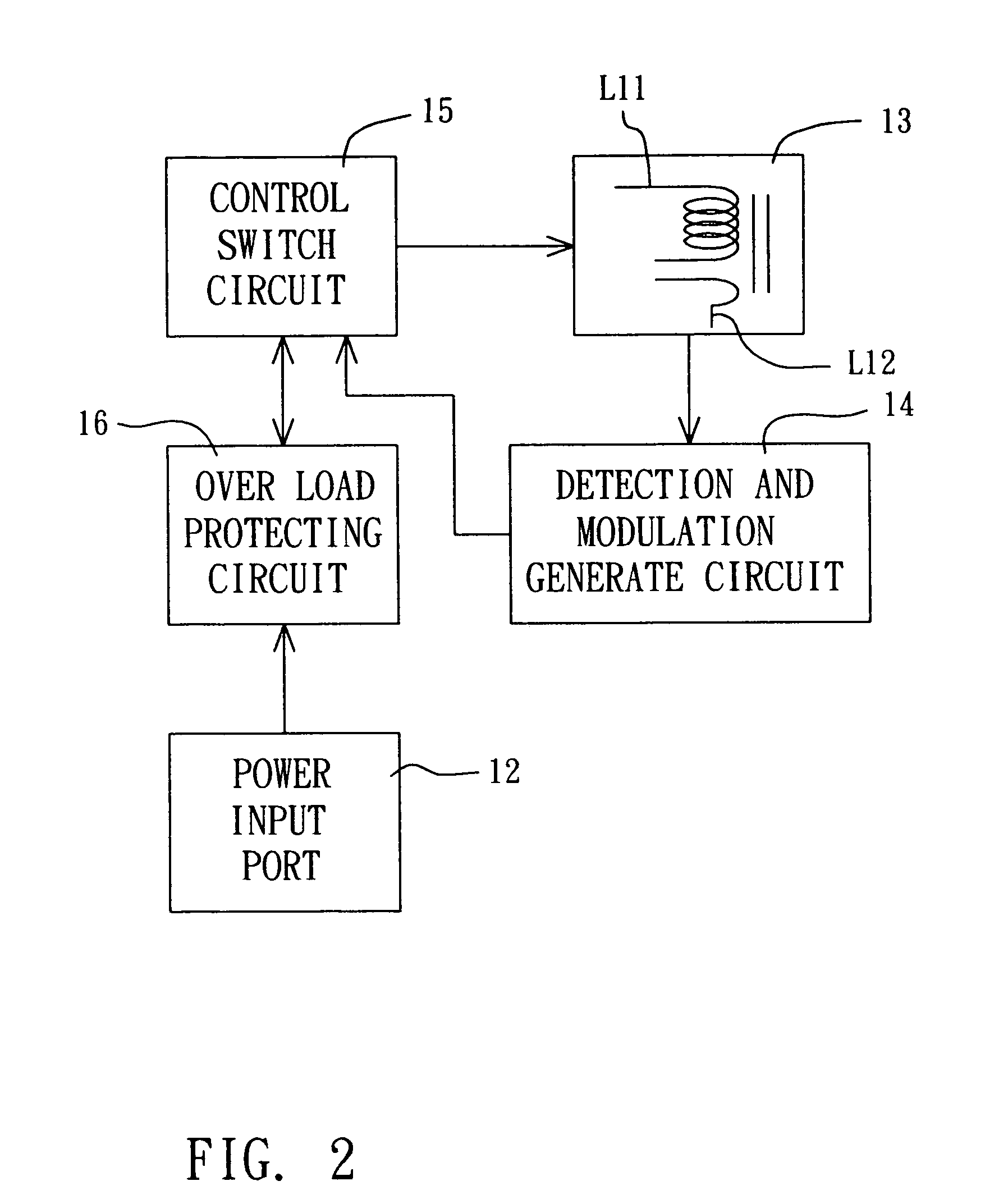
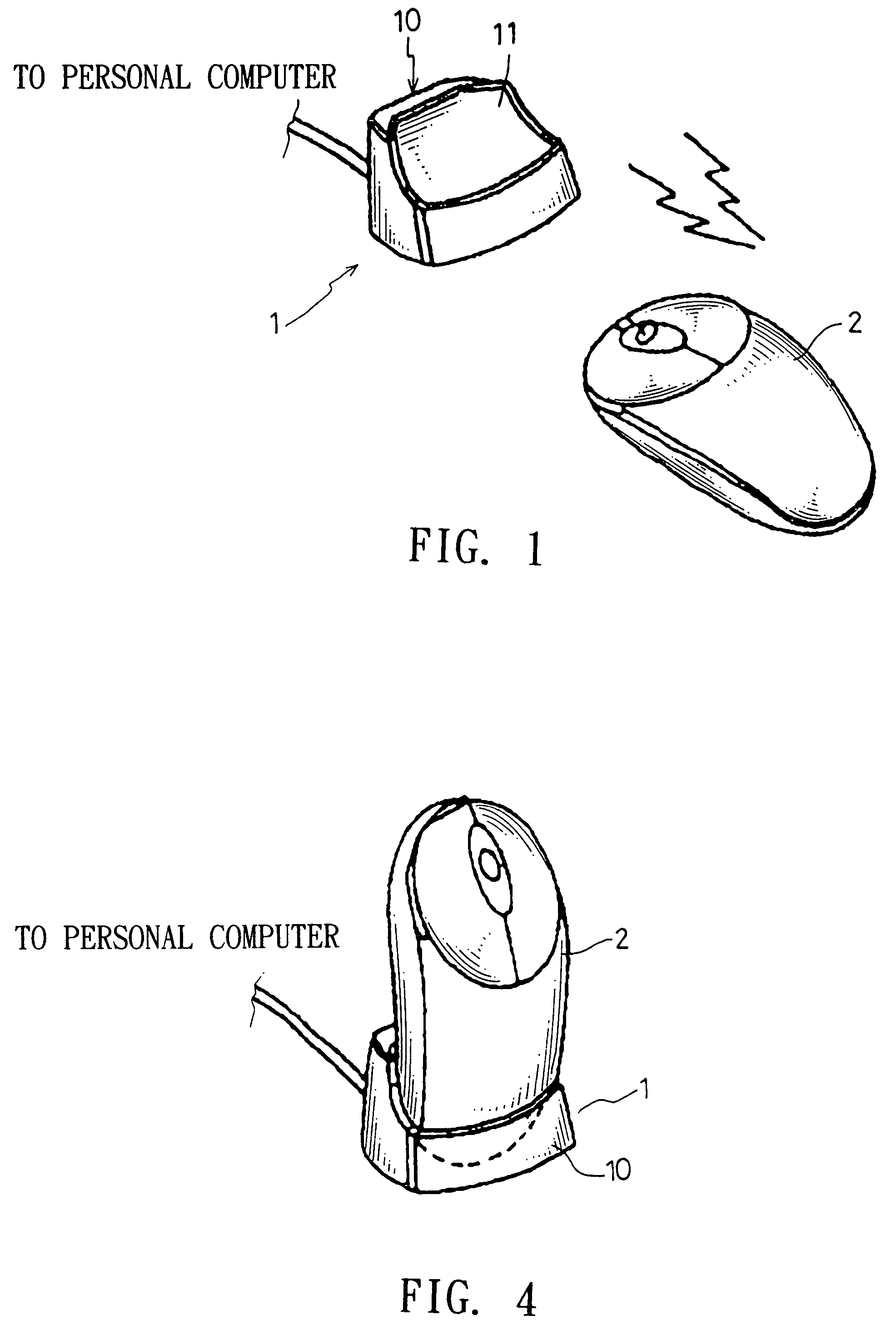
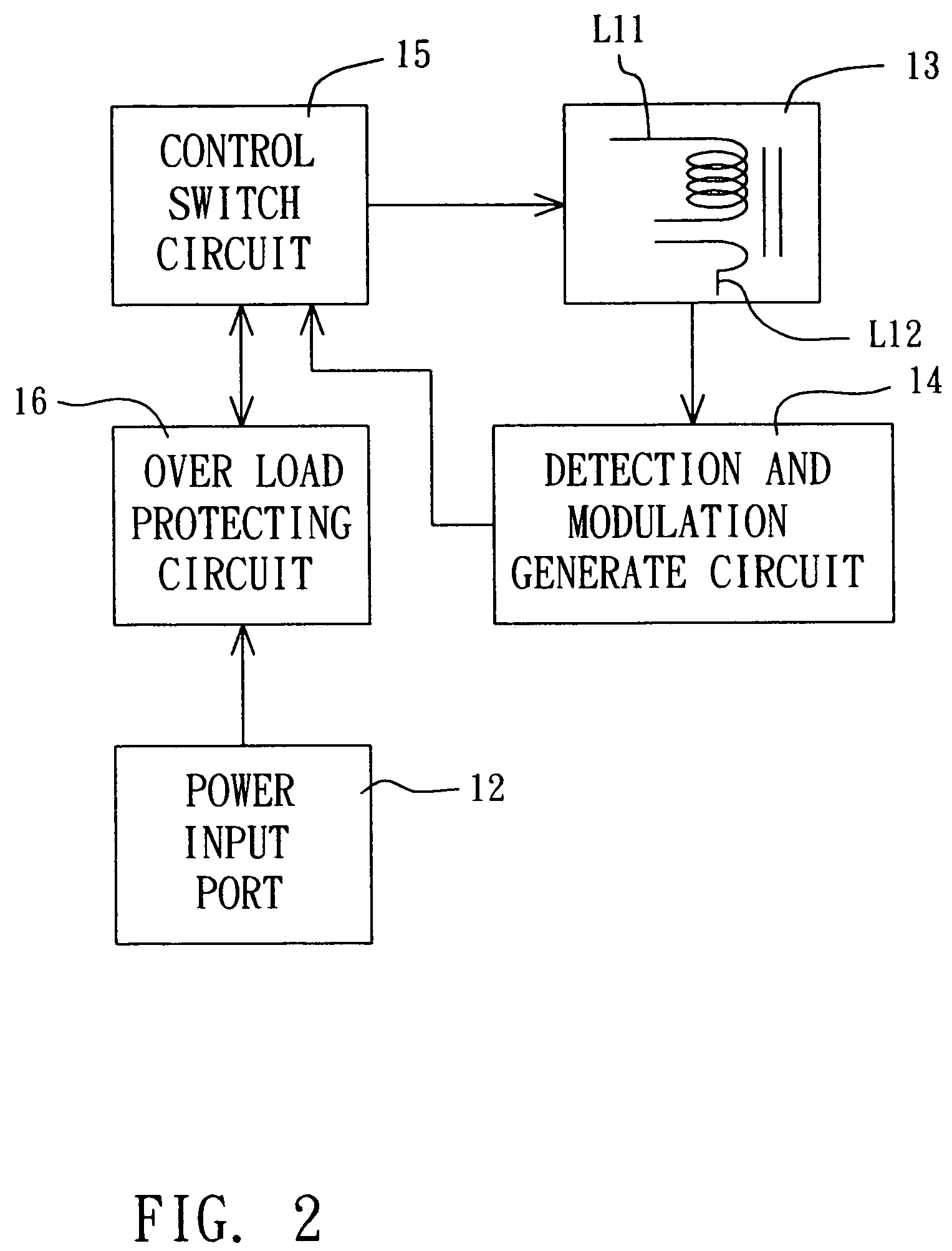
Pulse frequency modulation for induction charge device
InactiveUS20060022636A1Electric powerBattery overcurrent protectionElectromagnetic fieldControl switch
The present invention is related to a pulse frequency modulation for induction charge device, which comprises a pulse frequency modulation for induction charge device being provided to charge a portable electronic device, wherein, the portable electronic device comprises a induction coil, which comprises: an electric magnetic field generate and the secondary coil react circuit; a detection and modulation generate circuit; and a control switch circuit; whereby, the detection and modulation generate circuit could generate pulse singles with various frequencies according to the load varying generated due to distance varying between the portable electronic device and the charged device, and charge to the portable electronic device according the pulse singles so as to reach the goal of effective management the power.
Owner:KYE SYST CORP
Dual-mode PFM boost converter
InactiveUS7102340B1Conduction loss downReduce switching lossesElectric lighting sourcesDc-dc conversionSwitched currentDual mode
A dual-mode pulse frequency modulation boost converter operates in a hysteretic mode during light load currents to regulate an output voltage using a substantially fixed peak switching current and operates in a continuous mode during heavy load currents to regulate the output voltage using a variable peak switching current. The boost converter senses load power to automatically switch between the hysteretic mode and the continuous mode.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Modified dimming LED driver
ActiveUS20090261748A1Enhances dimming responseEasy to controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitEffect light
A driver circuit produces variable current output for an LED lighting system providing improved dimming capability and greater power efficiency when responding to industry standard lighting dimmers, through the use of an input voltage monitoring circuit which variably controls the current output of a switching regulator. Output current modulation methods such as analog, PWM, Pulse Frequency Modulation, or other digital modulation, and combination or hybrid methods such as that disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 7,088,059 B2 may be employed. The current invention marries such output modulation techniques with a control method which is derived through intelligent monitoring of the input voltage waveform. The circuit and method described is adapted to higher current applications such as LED lighting systems using the latest high-power LEDs.
Owner:BOCA FLASHER
Voltage regulator that operates in either PWM or PFM mode
InactiveUSRE37609E1Improve efficiencyPower dissipationEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulationEngineering
A switching voltage regulator achieves high efficiency by automatically switching between a pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode and a pulse-width modulation (PWM) mode. Switching between the modes of voltage regulation is accomplished by monitoring the output voltage and the output current, wherein the regulator operates in PFM mode at small output currents and in PWM mode at moderate to large output currents. PFM mode maintains a constant output voltage by forcing the switching device to skip cycles when the output voltage exceeds its nominal value. In PWM mode, a PWM signal having a variable duty cycle controls the switching device. A constant output voltage is maintained by feedback circuitry which alters the duty cycle of the PWM signal according to fluctuations in the output voltage.
Owner:MICREL
Method and apparatus to switch operating modes in a PFM converter
InactiveUS7102339B1Conduction loss downReduce switching lossesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitched currentDual mode
A dual-mode pulse frequency modulation boost converter operates in a hysteretic mode during light load currents to regulate an output voltage using a substantially fixed peak switching current and operates in a continuous mode during heavy load currents to regulate the output voltage using a variable peak switching current. The boost converter senses load power to automatically switch between the hysteretic mode and the continuous mode.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Pulse frequency modulation for induction charge device
The present invention is related to a pulse frequency modulation for induction charge device, which comprises a pulse frequency modulation for induction charge device being provided to charge a portable electronic device, wherein, the portable electronic device comprises a induction coil, which comprises: an electric magnetic field generate and the secondary coil react circuit; a detection and modulation generate circuit; and a control switch circuit; whereby, the detection and modulation generate circuit could generate pulse singles with various frequencies according to the load varying generated due to distance varying between the portable electronic device and the charged device, and charge to the portable electronic device according the pulse singles so as to reach the goal of effective management the power.
Owner:KYE SYST CORP
Control method and circuit of double-module modulation and mode smooth conversion switching power supply
InactiveCN101667019AReduce lossSmall rippleDc-dc conversionPulse duration/width modulationSwitching frequencyEngineering
The invention relates to a control scheme of double-module operation of a direct current switching power supply, which is used for direct current voltage stabilization and improves the efficiency whenthe power supply is in underloading. Under heavier load, a system adopts a pulse width modulation (PWM) mode. When in underloading, the system automatically enters a pulse frequency modulation (PFM)mode, and outputs stable direct current voltage according to detected current and load voltage by corresponding logic. Under the PFM mode, equivalent switching frequency of the power supply is loweredfollowing the reduction of the load, and the switching loss is reduced, thereby improving the efficiency when in underloading. When the load is jumped, the system automatically performs the smooth transition between the PFM mode and the PWM mode and ensures the rapid dynamic response of the output voltage. Under the PWM mode, the system integrates feedforward control of the input voltage and increases the capacity of resisting the jump of the input voltage by the load voltage. The invention is suitable to power supply control of a portable media player, an intelligent mobile phone, a load point power supply and the like.
Owner:徐嘉萍
LED Dimming Techniques Using Spread Spectrum Modulation
InactiveUS20100109550A1Easy to controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHarmonicFundamental frequency
Circuits and methods of LED dimming are disclosed. Frequency modulation using controlled modulation depth generates deterministic sidebands of both the fundamental frequency and its harmonics. Various filters including low-pass, band-pass, high-pass and combinations of those are used to selectively filter the deterministic frequency components generated by the frequency modulation to achieve LED dimming.
Owner:HUDA MUZAHID BIN +1
Switching Mode Power Supply Control
InactiveUS20120153919A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching signalSwitching frequency
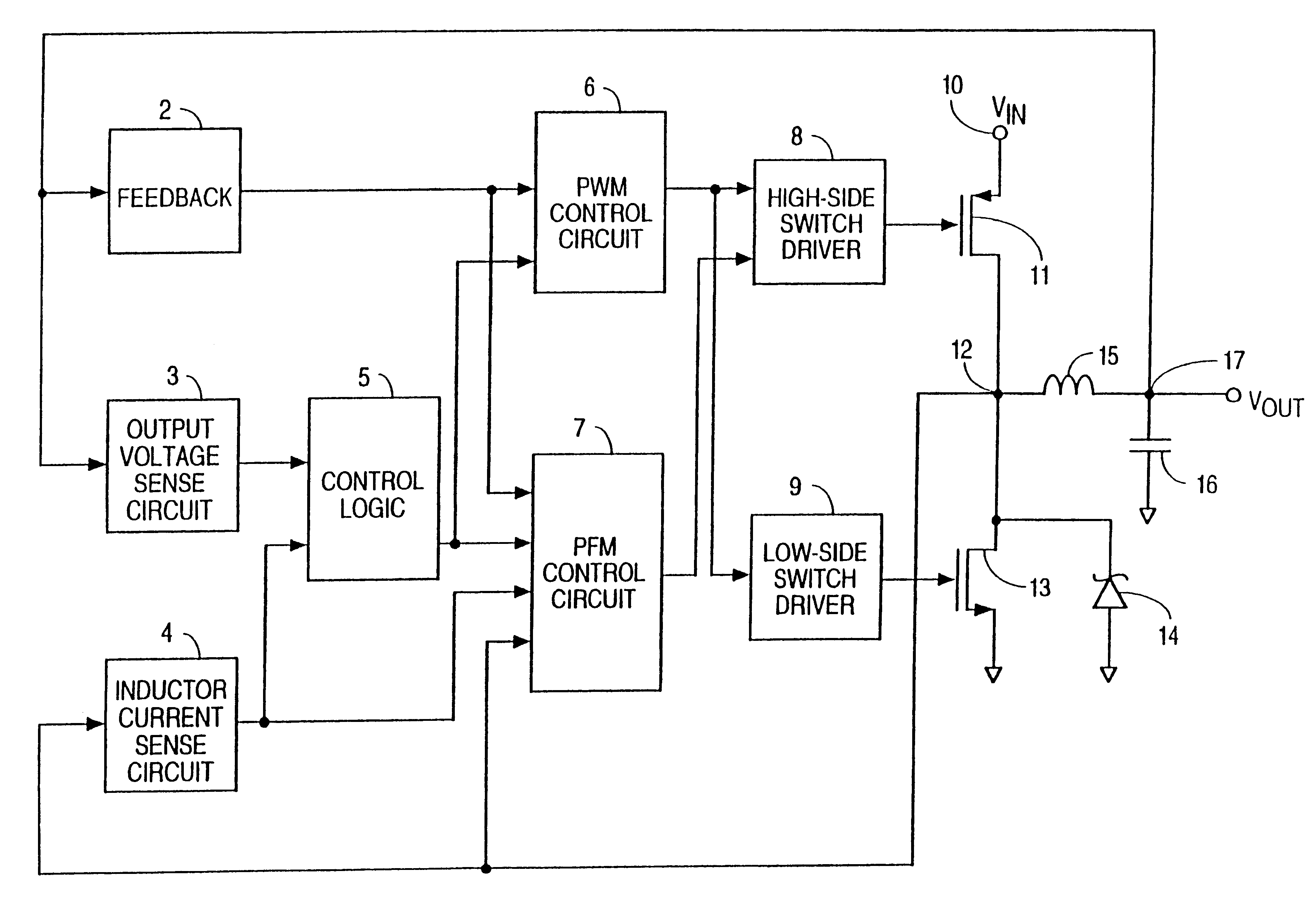
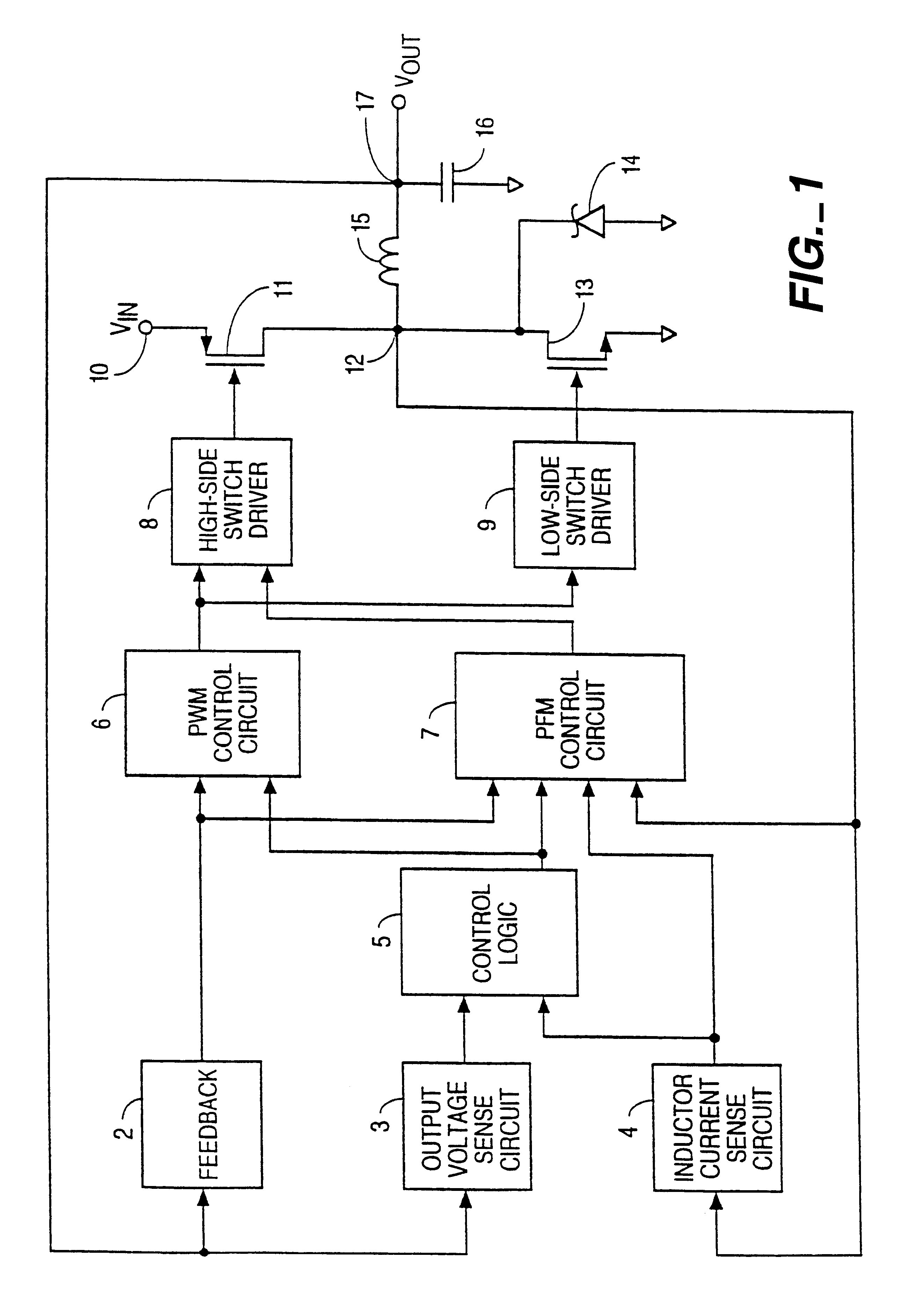
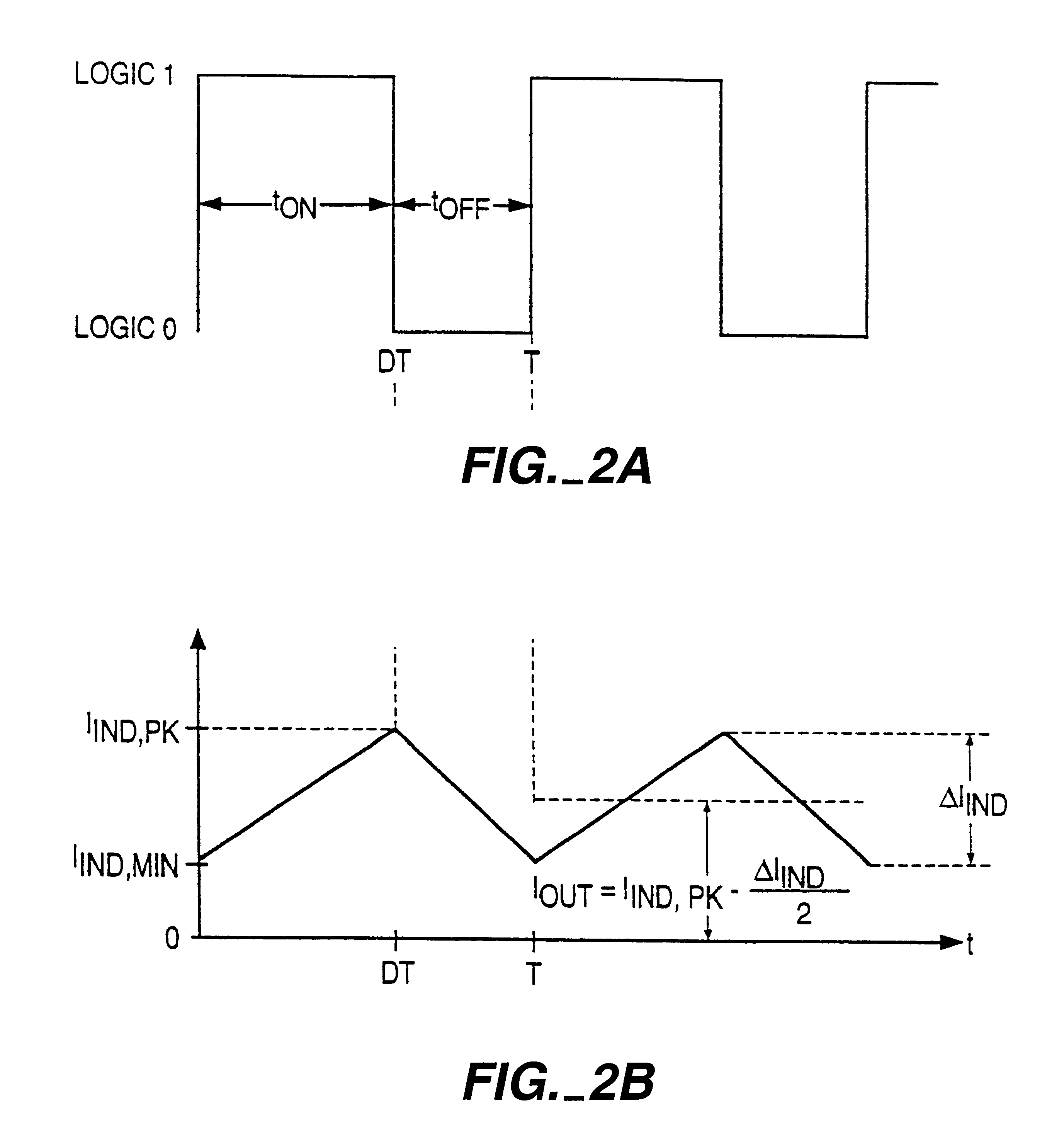
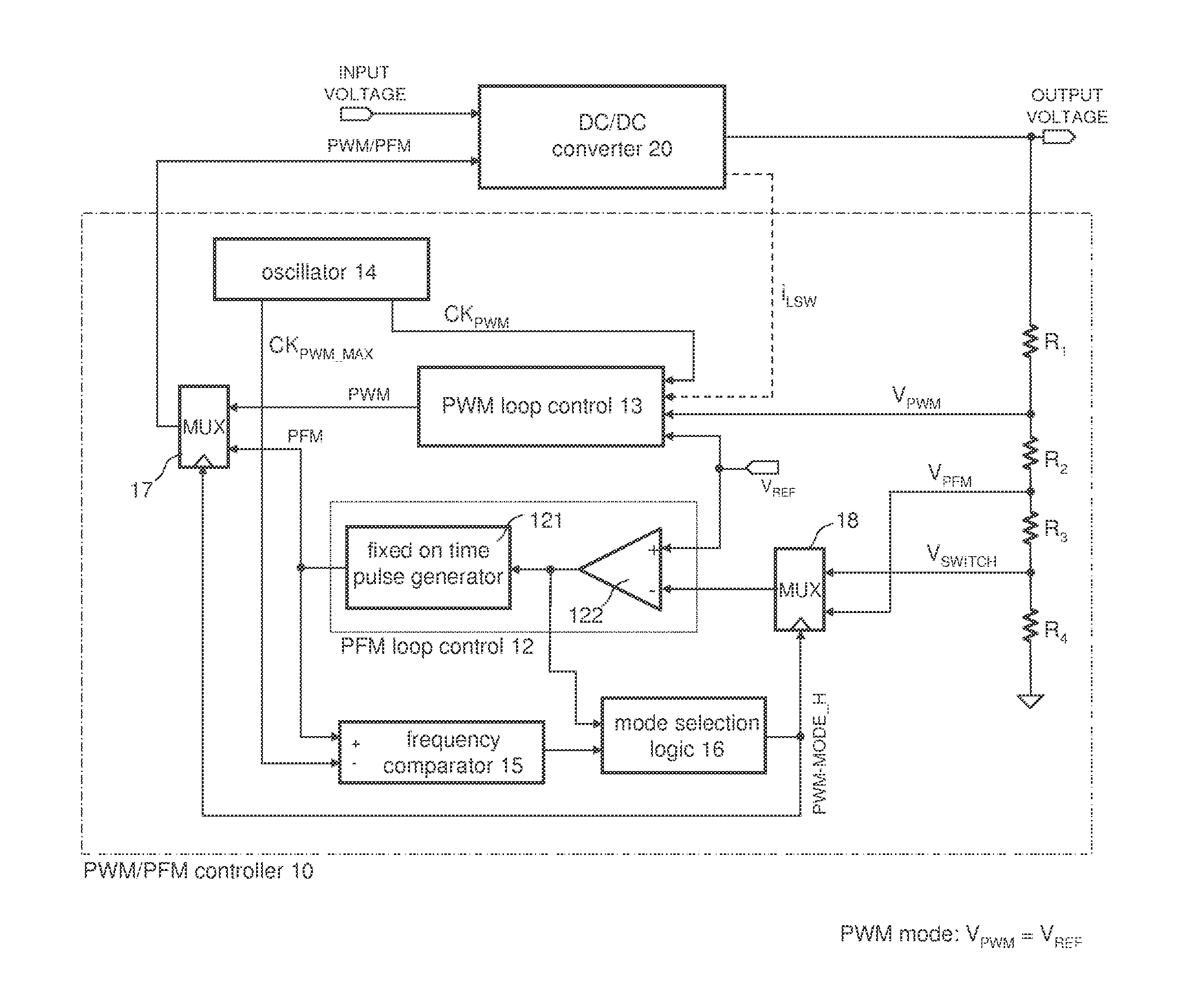
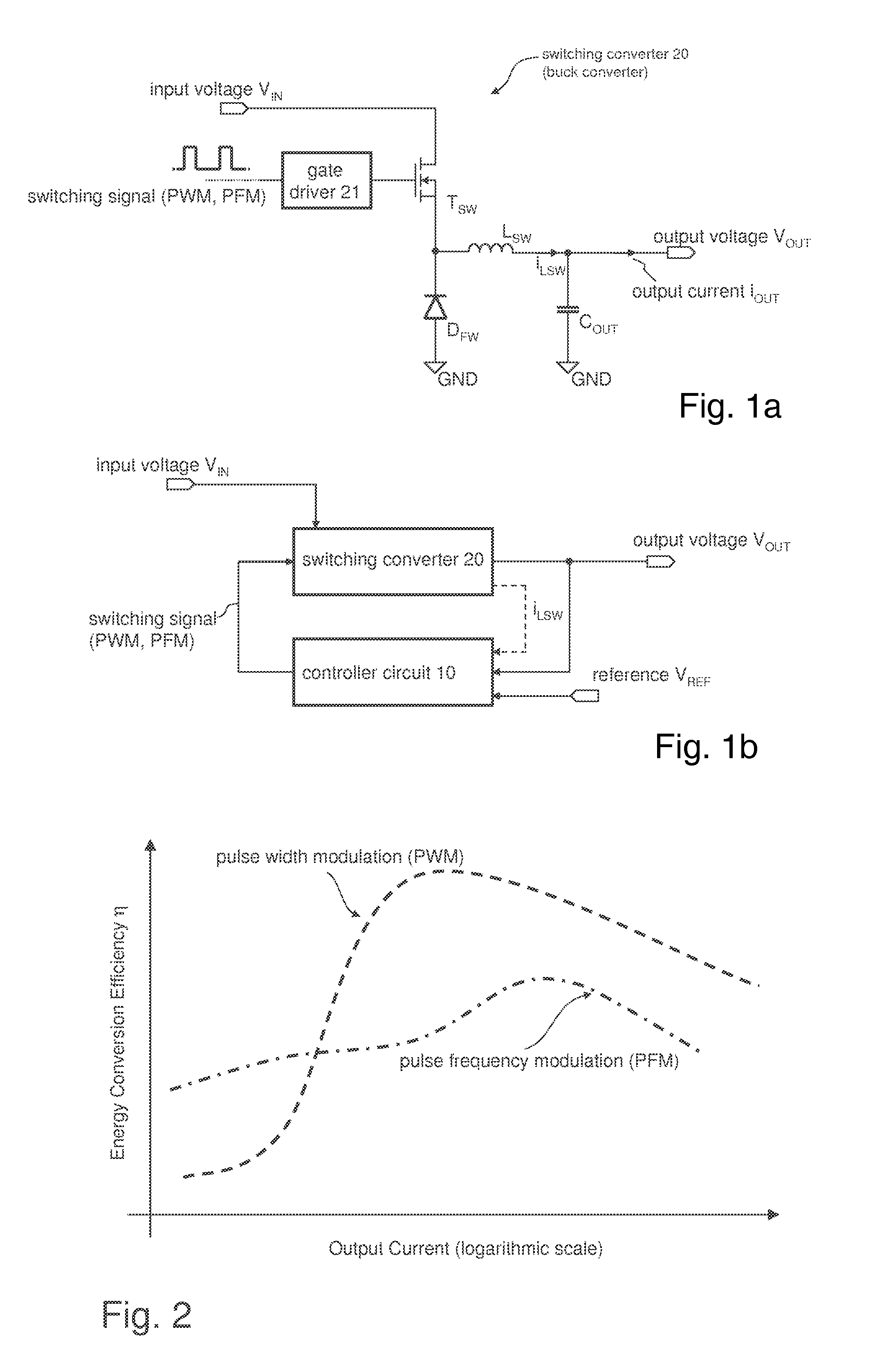
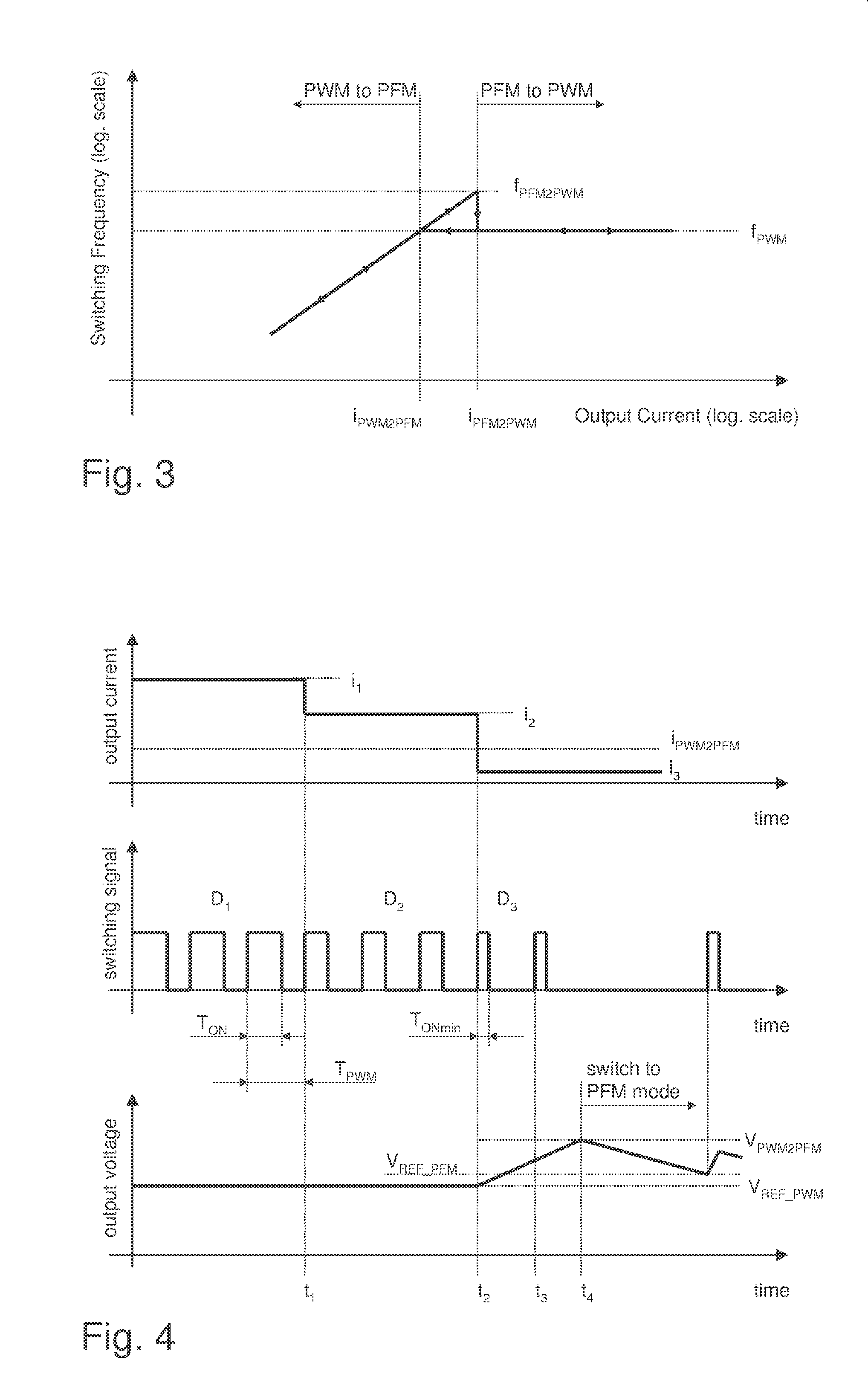
A method for controlling a switching converter is disclosed whereby the switching converter is configured to convert an input voltage into an output voltage supplied to a load in accordance with a switching signal, The switching converter is configured to operate in a pulse width modulation mode or, alternatively, in a pulse frequency modulation mode. When operating in the pulse width modulation mode, generating, as the switching signal, a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal of a pre-defined constant switching frequency. The PWM signal has a duty cycle that is regulated such that the output voltage of the switching converter matches, at least approximately, a desired output voltage under the condition that the duty cycle being regulated such that it does not fall below a predefined minimum duty cycle. The output voltage is monitored and switched over to the pulse frequency modulation mode when the output voltage exceeds a predefined first threshold. The method further comprises, when operating in the pulse frequency modulation mode, monitoring the output voltage and generating, as the switching signal, a series of pulses of a predefined constant pulse length. A pulse is generated each time the output voltage falls to a predefined second threshold and monitoring the frequency of the switching signal and switching to the pulse width modulation mode when the frequency of the switching signal exceeds a predefined frequency threshold.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes
InactiveUS7826237B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectricityPower mode
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a power system with selectable power modes. The power system includes a first terminal for outputting energy, and the first terminal is electrically coupled to a load. The system also includes a pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse frequency based on the load. The system additionally includes a pulse-width modulation (PWM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse width based on the load. The system further includes a switch that is electrically coupled to the first terminal. Also, the system includes a control component, the control component being configured to provide a control signal that is capable of causing the switch to be turned on or off. The control signal is associated with an output of the PWM component and the pulse width if an output is greater than a predetermined value. The control signal is associated with an output of the PFM component and the pulse frequency if an output is lower than a predetermined value.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Adaptive multi-mode digital control improving light-load efficiency in switching power converters
ActiveUS20100164455A1Improve switching power converter light-load efficiencyImprove light load efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFrequency levelEngineering
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR
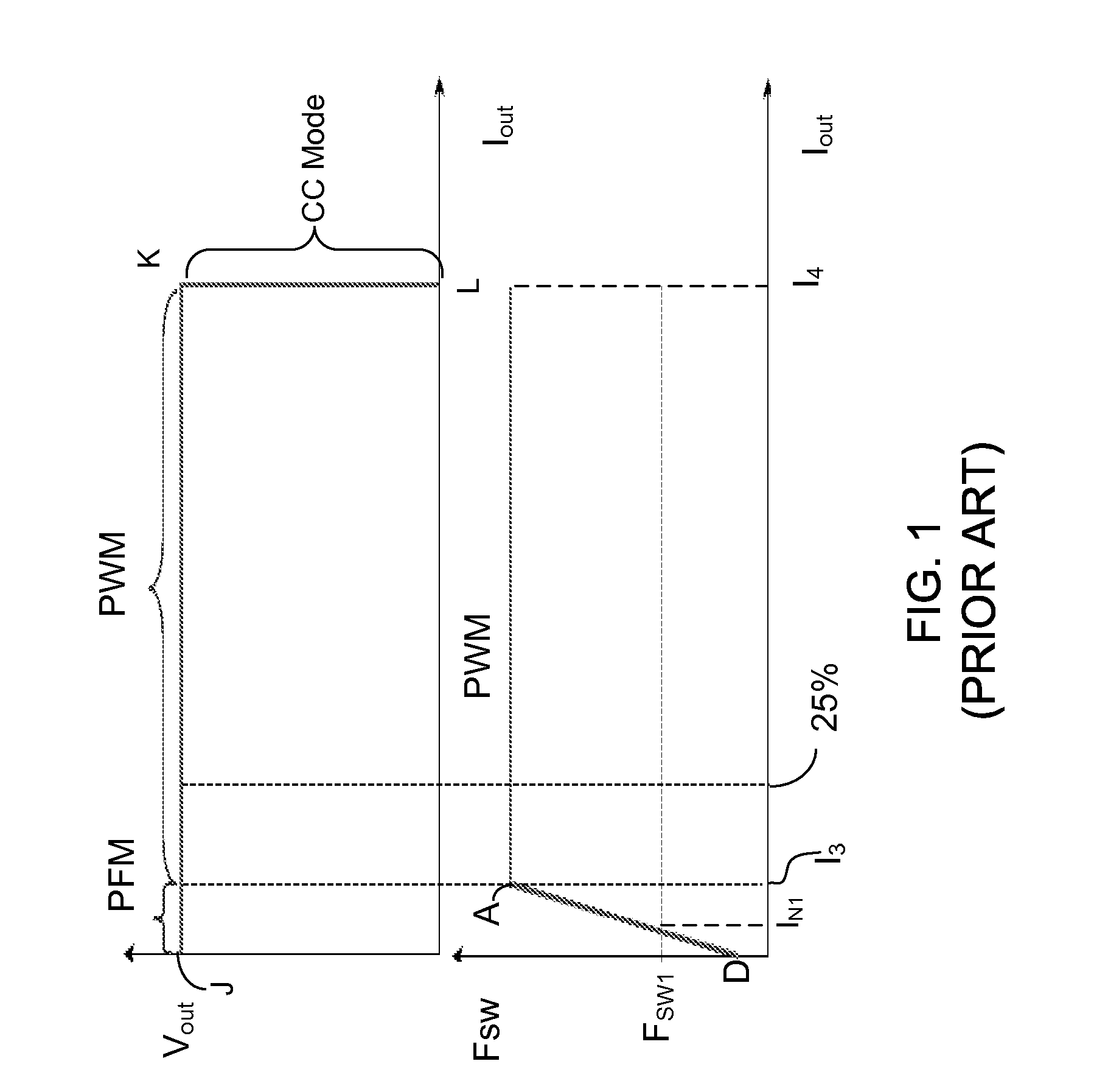
Current Mode Buck Converter with Fixed PWM/PFM Boundary
A current mode buck converter is disclosed. The buck converter operates in a pulse width modulation (PWM) mode or a pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode. To prevent an output inductor with various probable magnitudes from varying a decision boundary between the PWM mode and the PFM mode, the buck converter adaptively adjusts a triggering condition for the pulse frequency modulation mode according to an average value of an inductor current of the output inductor or AC components of the inductor current and a slope compensation current.
Owner:ANPEC ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes
InactiveUS20090206814A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEffective powerPower mode
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a power system with selectable power modes. The power system includes a first terminal for outputting energy, and the first terminal is electrically coupled to a load. The system also includes a pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse frequency based on the load. The system additionally includes a pulse-width modulation (PWM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse width based on the load. The system further includes a switch that is electrically coupled to the first terminal. Also, the system includes a control component, the control component being configured to provide a control signal that is capable of causing the switch to be turned on or off. The control signal is associated with an output of the PWM component and the pulse width if an output is greater than a predetermined value. The control signal is associated with an output of the PFM component and the pulse frequency if an output is lower than a predetermined value.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
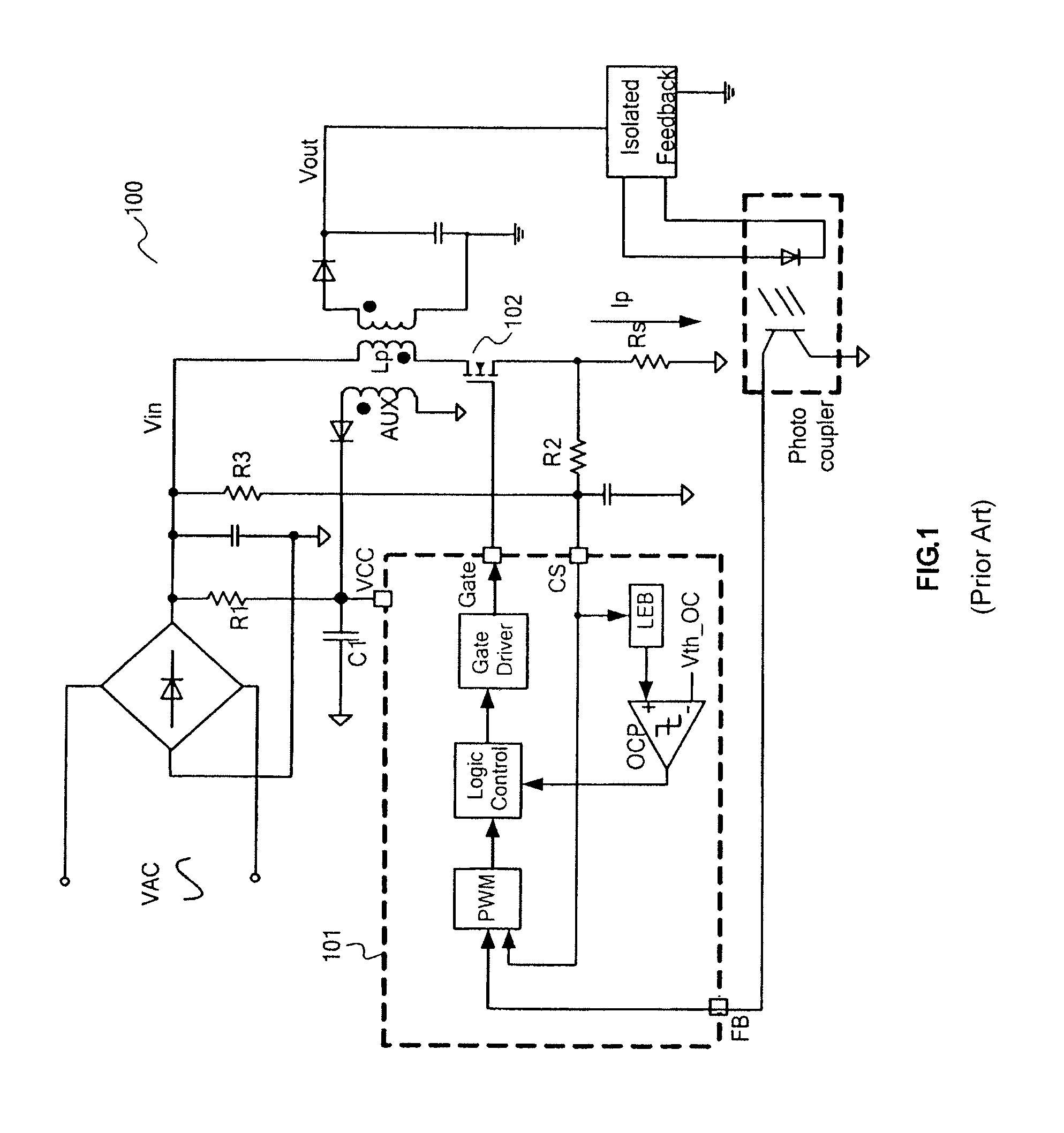
System And Method For Controlling A Current Limit With Primary Side Sensing Using A Hybrid PWM and PFM Control
ActiveUS20090059632A1Accurate constant current (CC) controlMinimizing leakage inductanceAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionEnergy transferCurrent limiting
A hybrid constant current control system that uses both pulse width modulation (PWM) and pulse frequency modulation (PFM) control. When transitioning from constant voltage mode to constant current mode the present invention can continue to control using PWM. Thereafter, when the voltage has dropped, the present invention smoothly transitions to PFM mode. The point of transition is based upon the switching frequency and the lowest rated voltage of operation. The system and method avoids very short (narrow) Ton times which ensures accurate constant current (CC) control with bipolar junction transistor (BJT) devices. The present invention also avoids acoustic noise because the switching frequency is maintained at a high enough level to avoid such acoustic noise even when the energy transferred through the transformer is still substantial and the output voltage is not too low. In addition the output current limit is insensitive to variation in the inductance-input voltage ratio, and is minimized against leakage inductance.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
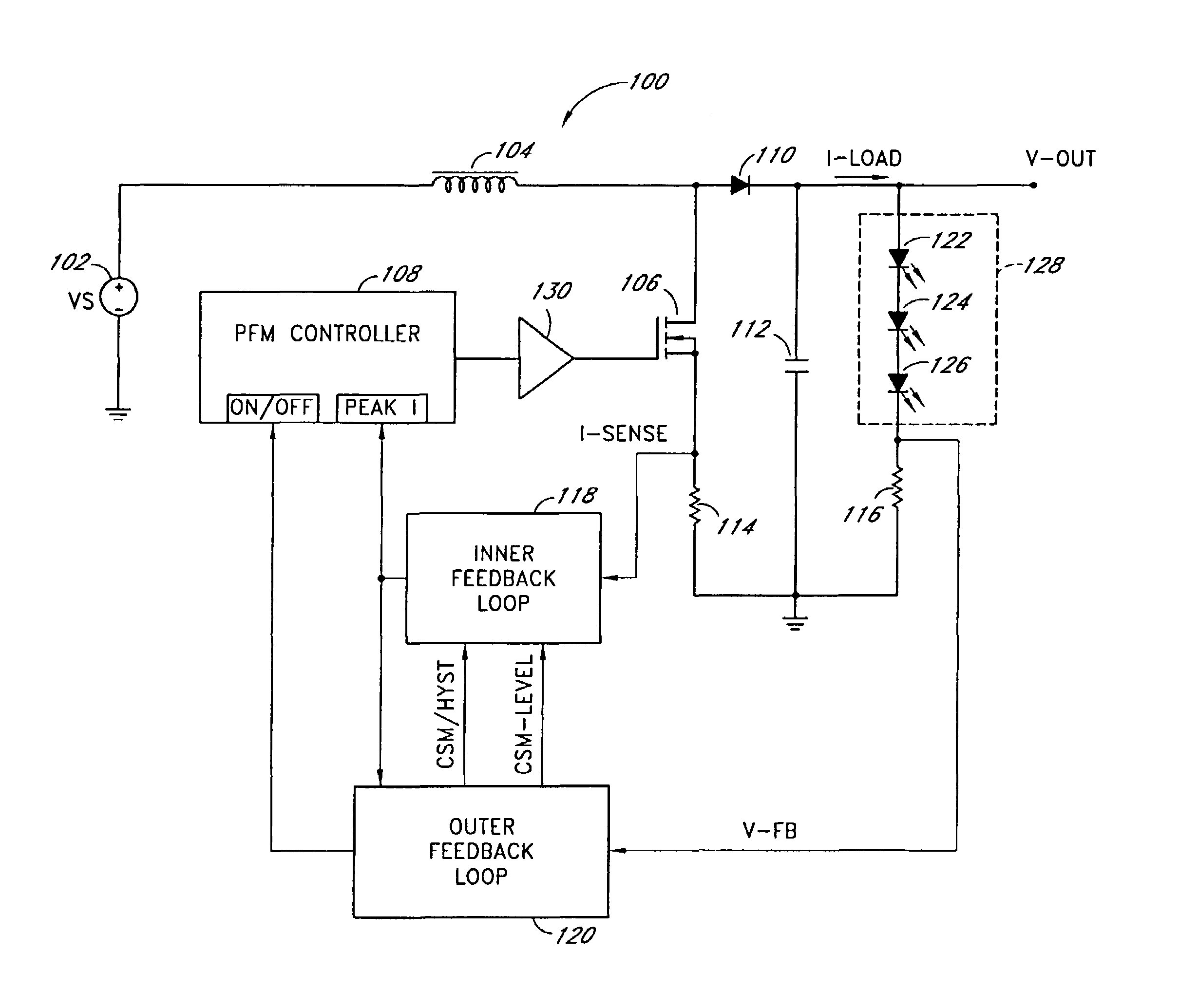
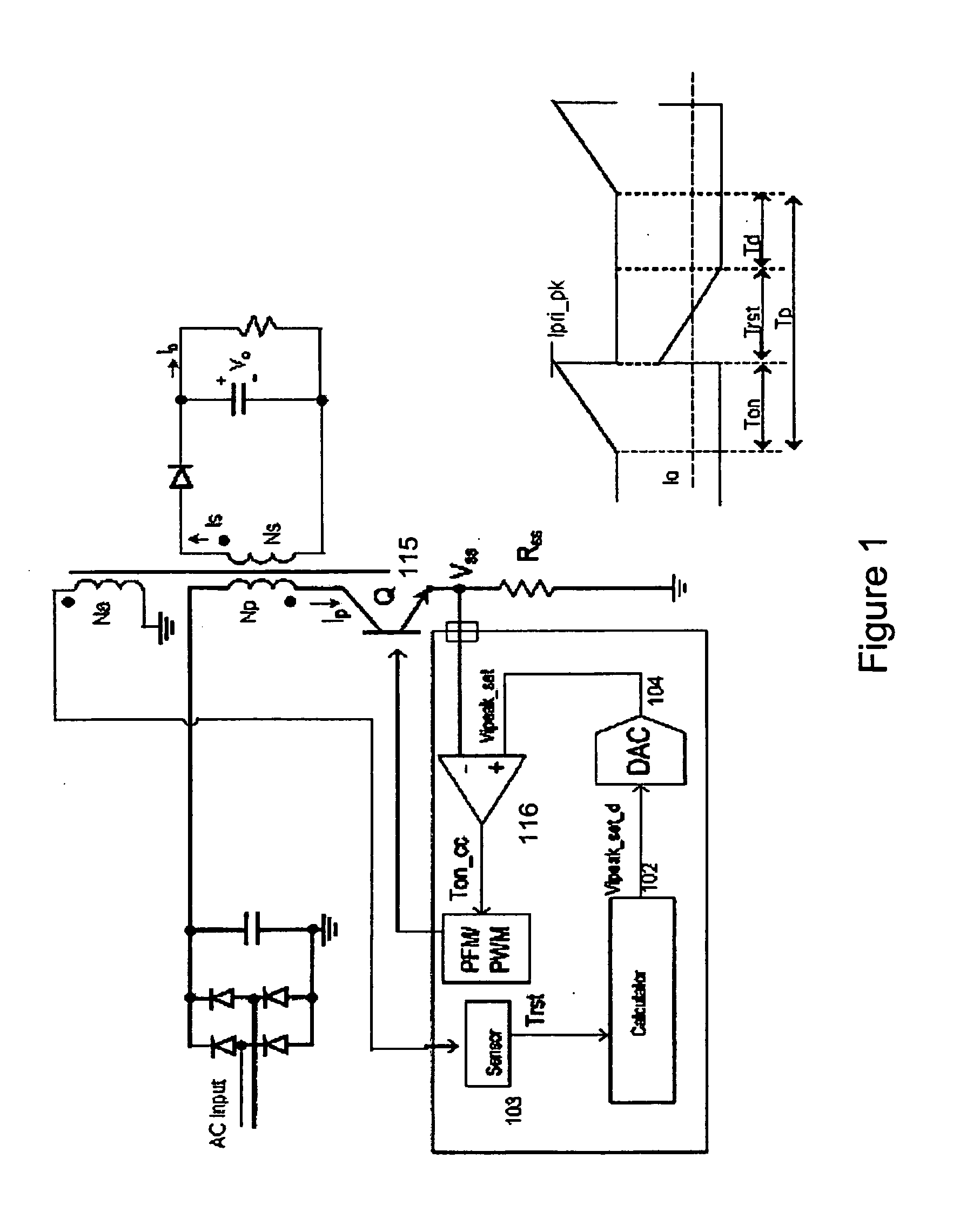
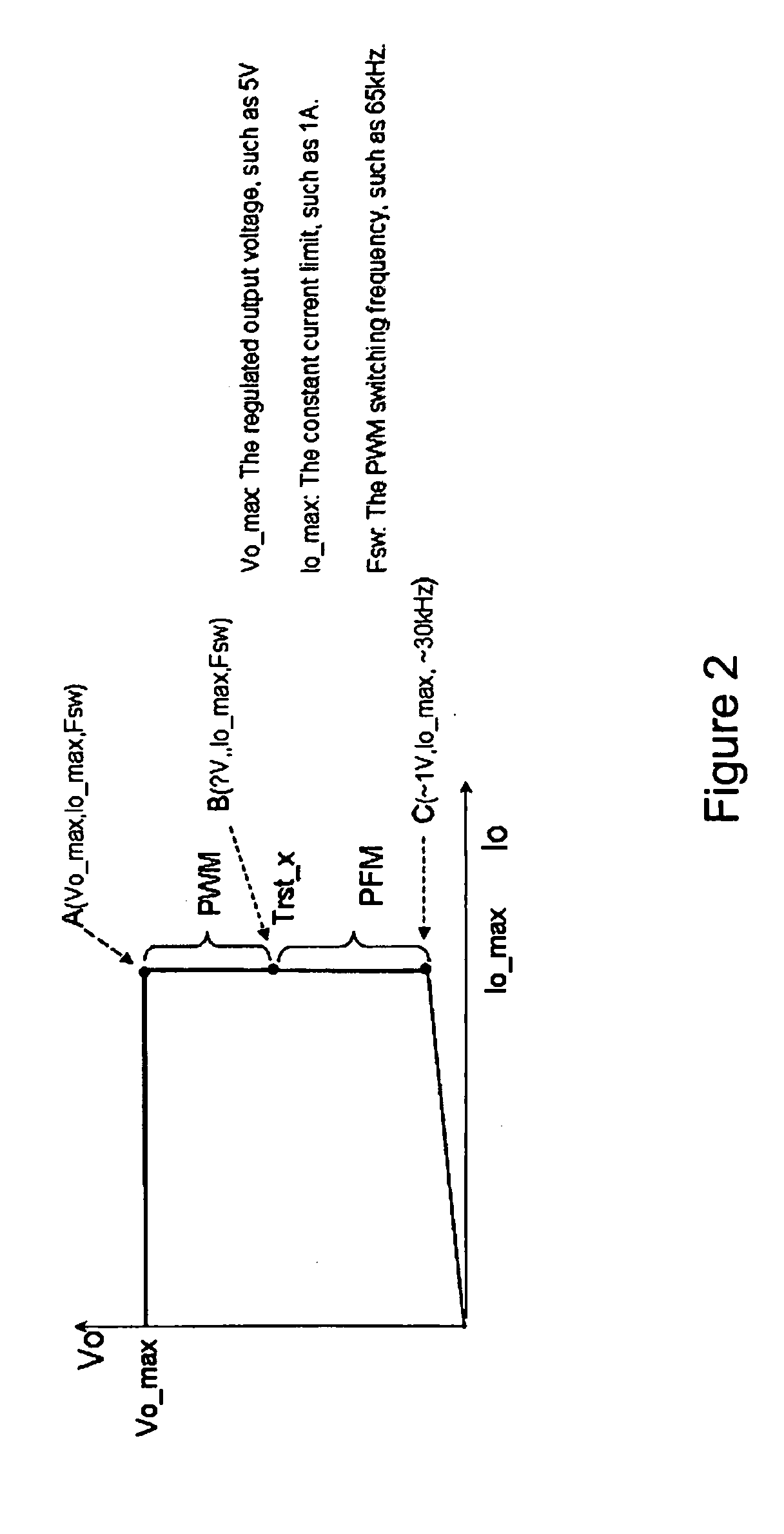
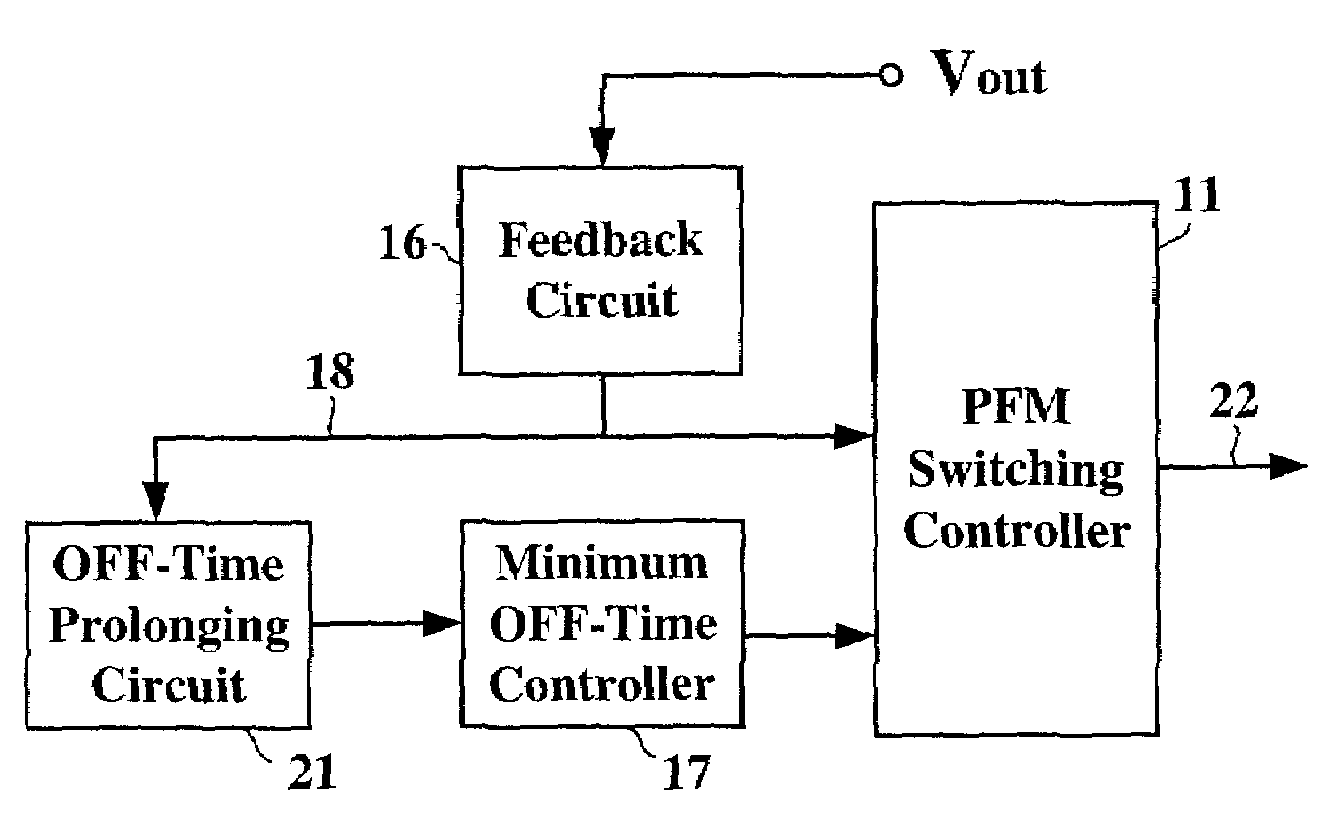
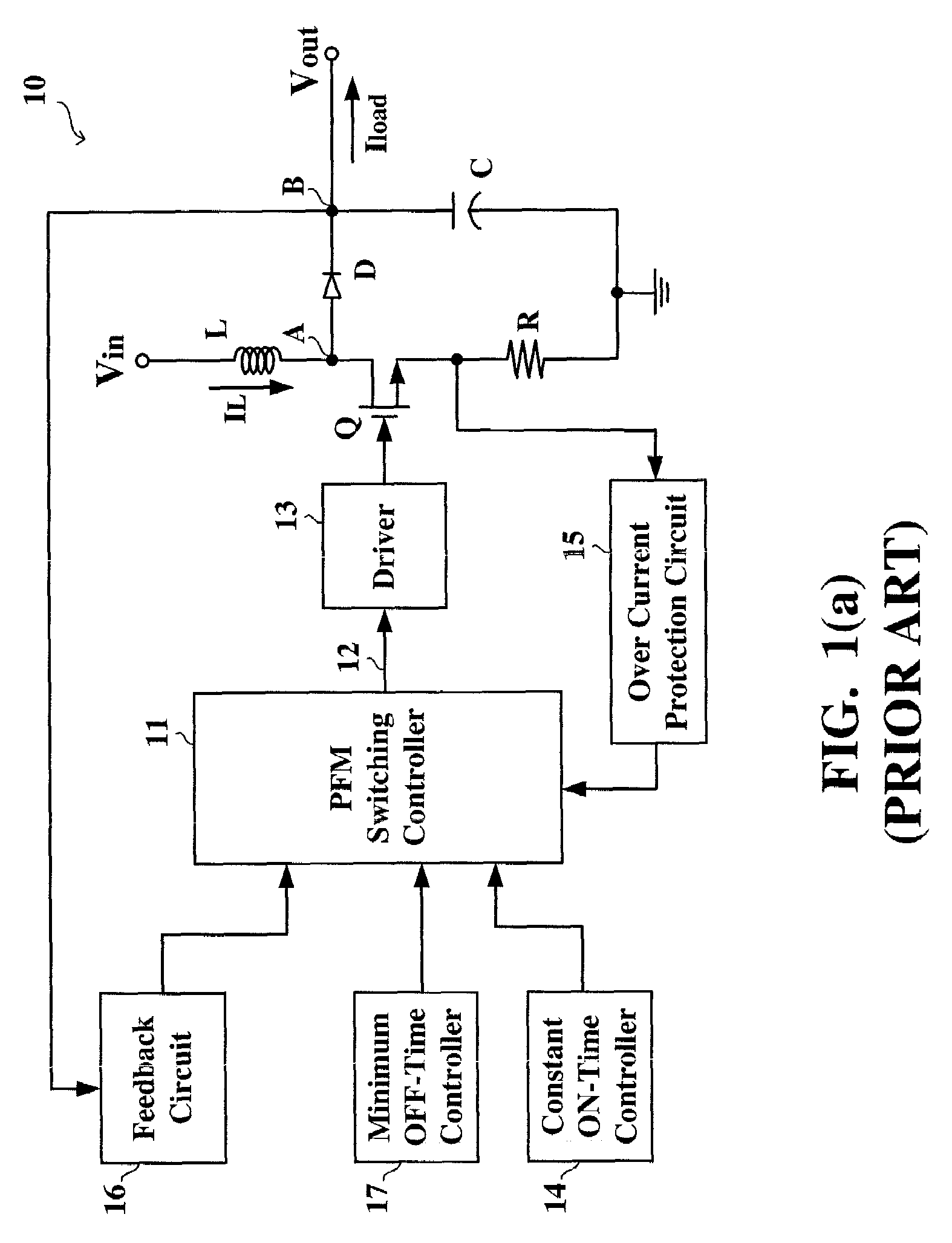
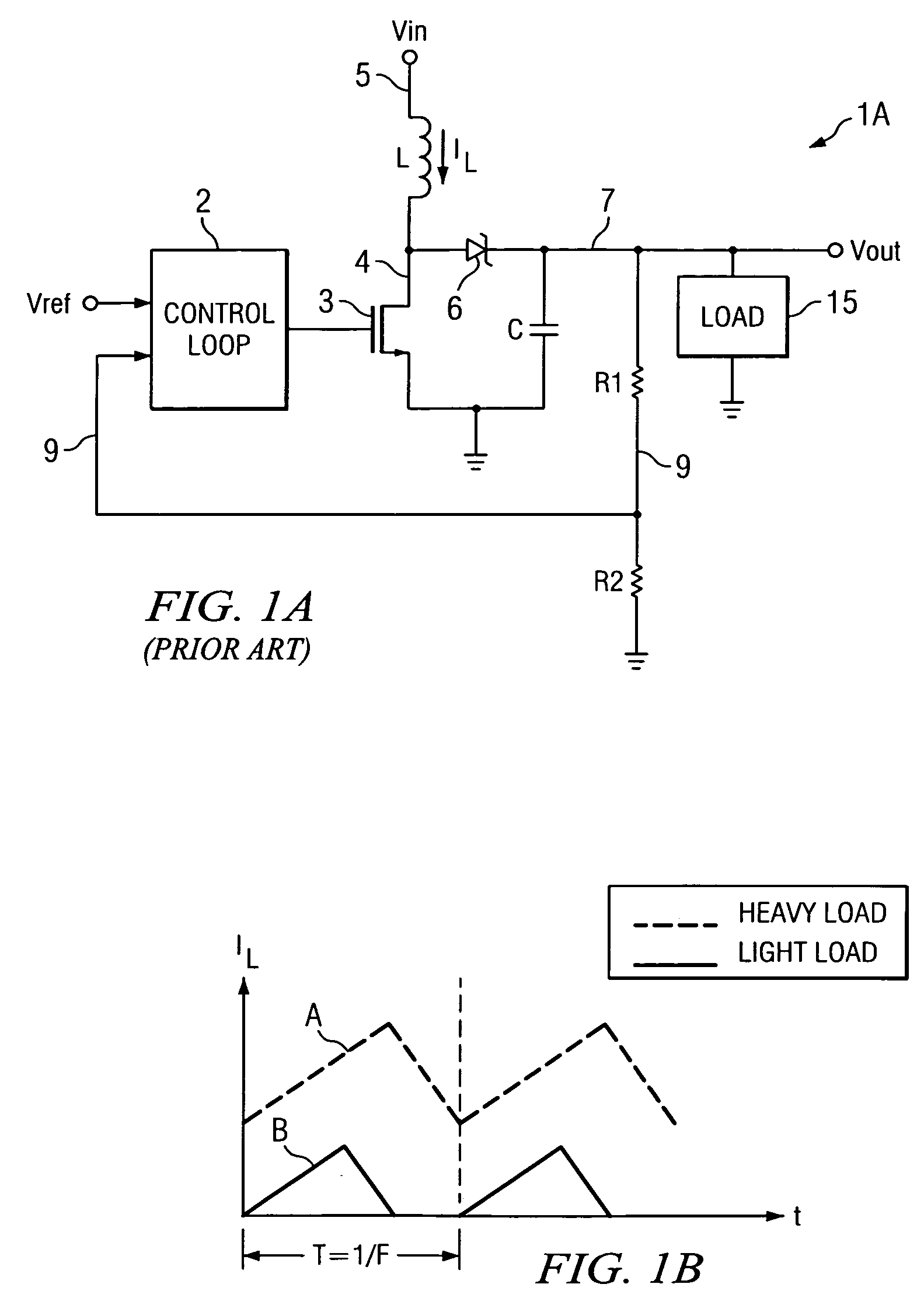
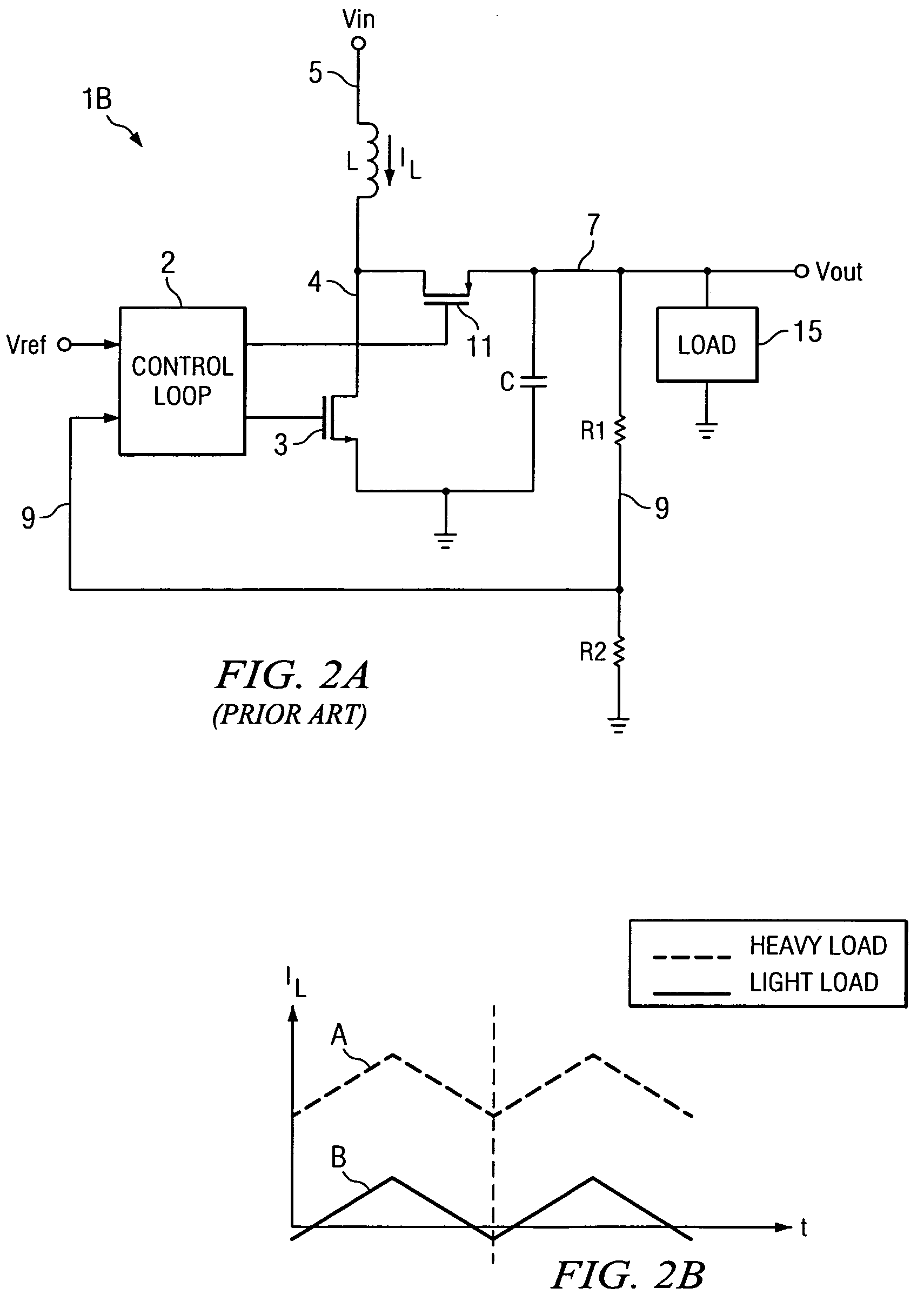
Pulse frequency modulated voltage regulator capable of prolonging a minimum off-time
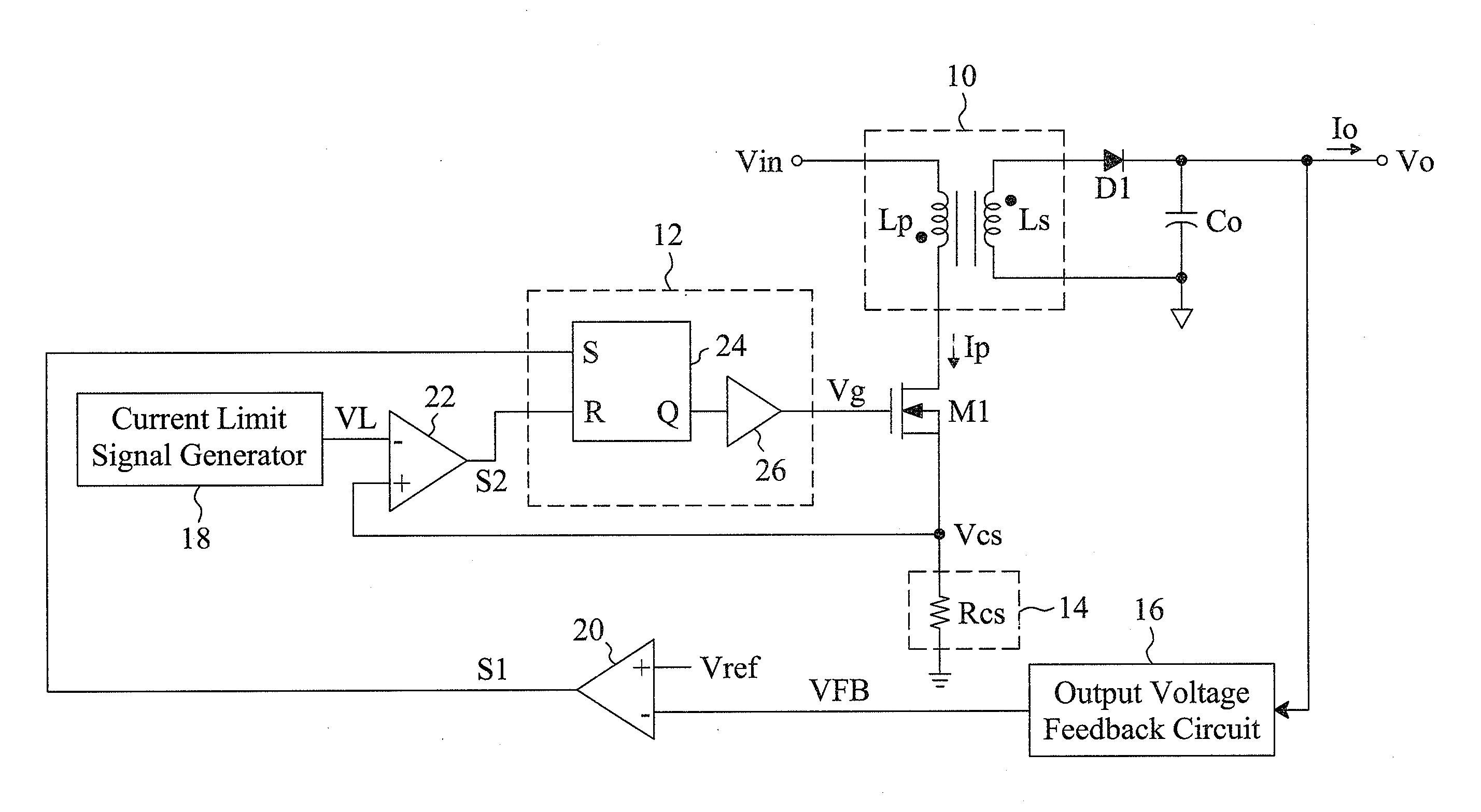
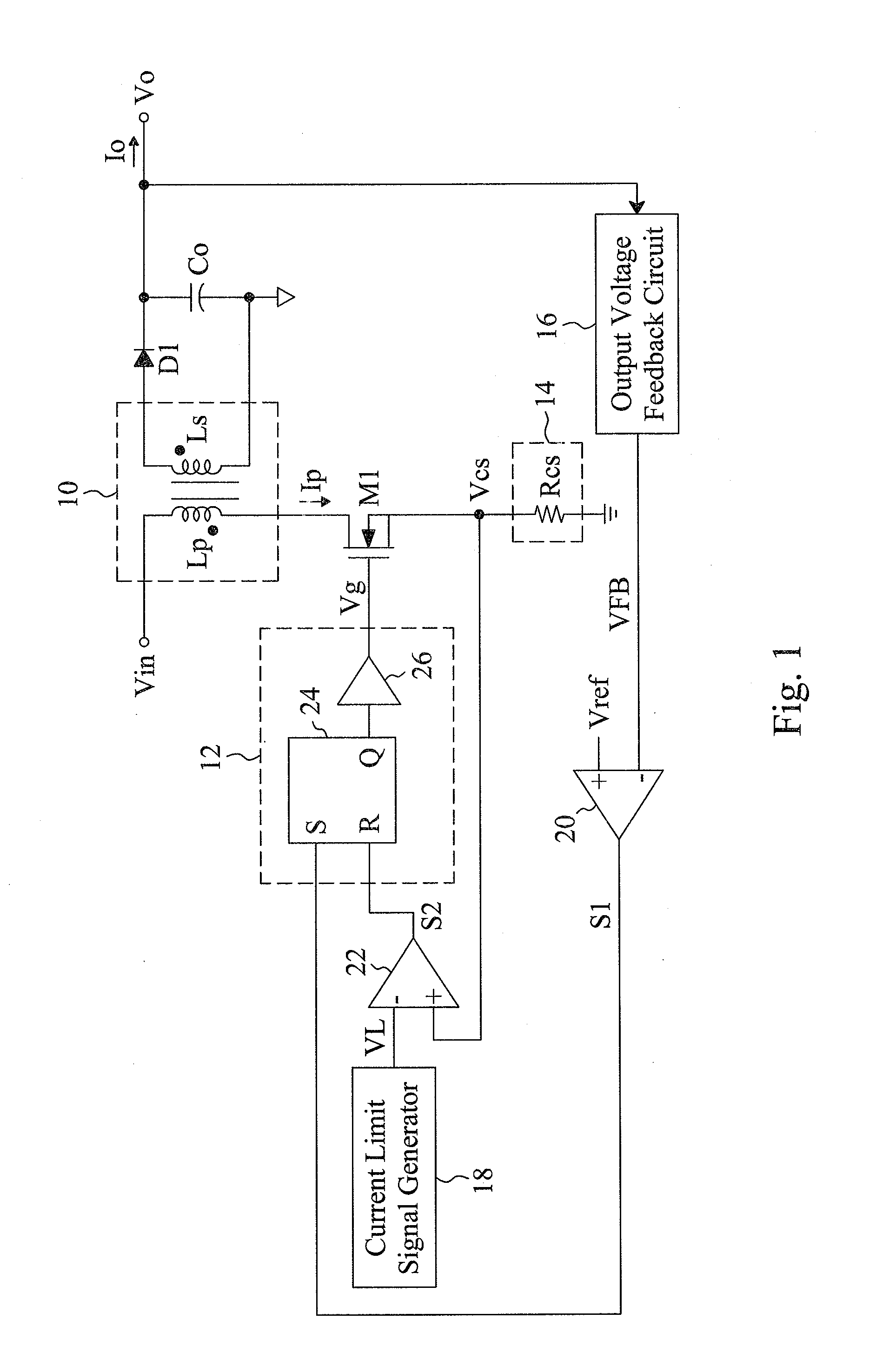
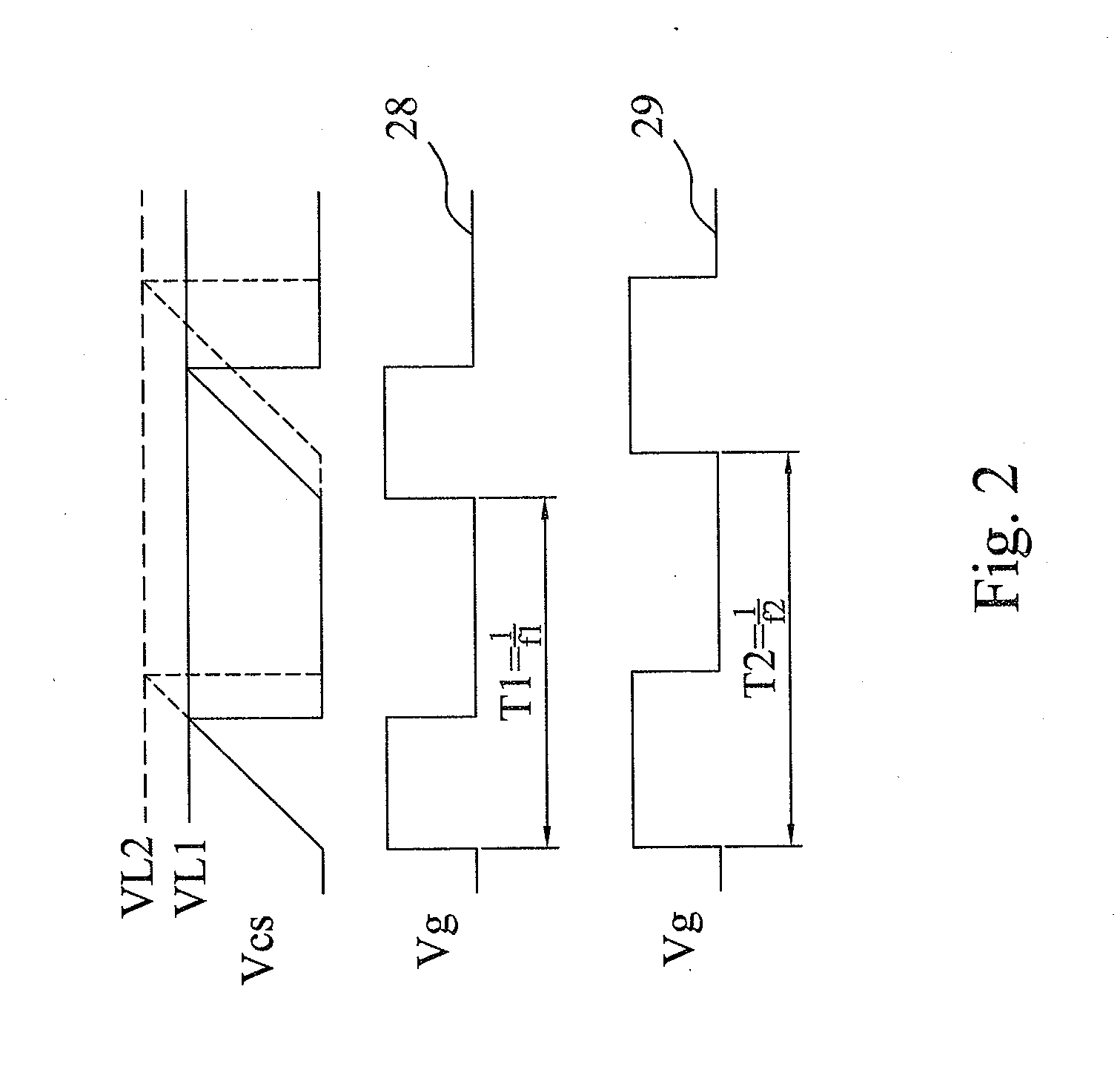
ActiveUS6972548B2Reduce rippleProlonging a minimum OFF-timeElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsTime extensionEngineering
In a pulse frequency modulated (PFM) voltage regulator, a PFM switching controller is provided to generate a PFM switching signal for converting a DC voltage source to an output voltage. A minimum OFF-time controller provides the PFM switching signal with a minimum OFF-time. In response to the output voltage, a feedback circuit generates a feedback signal. When the output voltage is lower than a predetermined target voltage, an OFF-time prolonging circuit prolongs the minimum OFF-time in response to the feedback signal. In other words, a time of delivering energy to a capacitor from an inductor may be prolonged by the OFF-time prolonging circuit. Therefore, a ripple of the output voltage is effectively reduced when the PFM voltage regulator is operated in a heavy loading condition.
Owner:GLOBAL MIXED MODE TECH
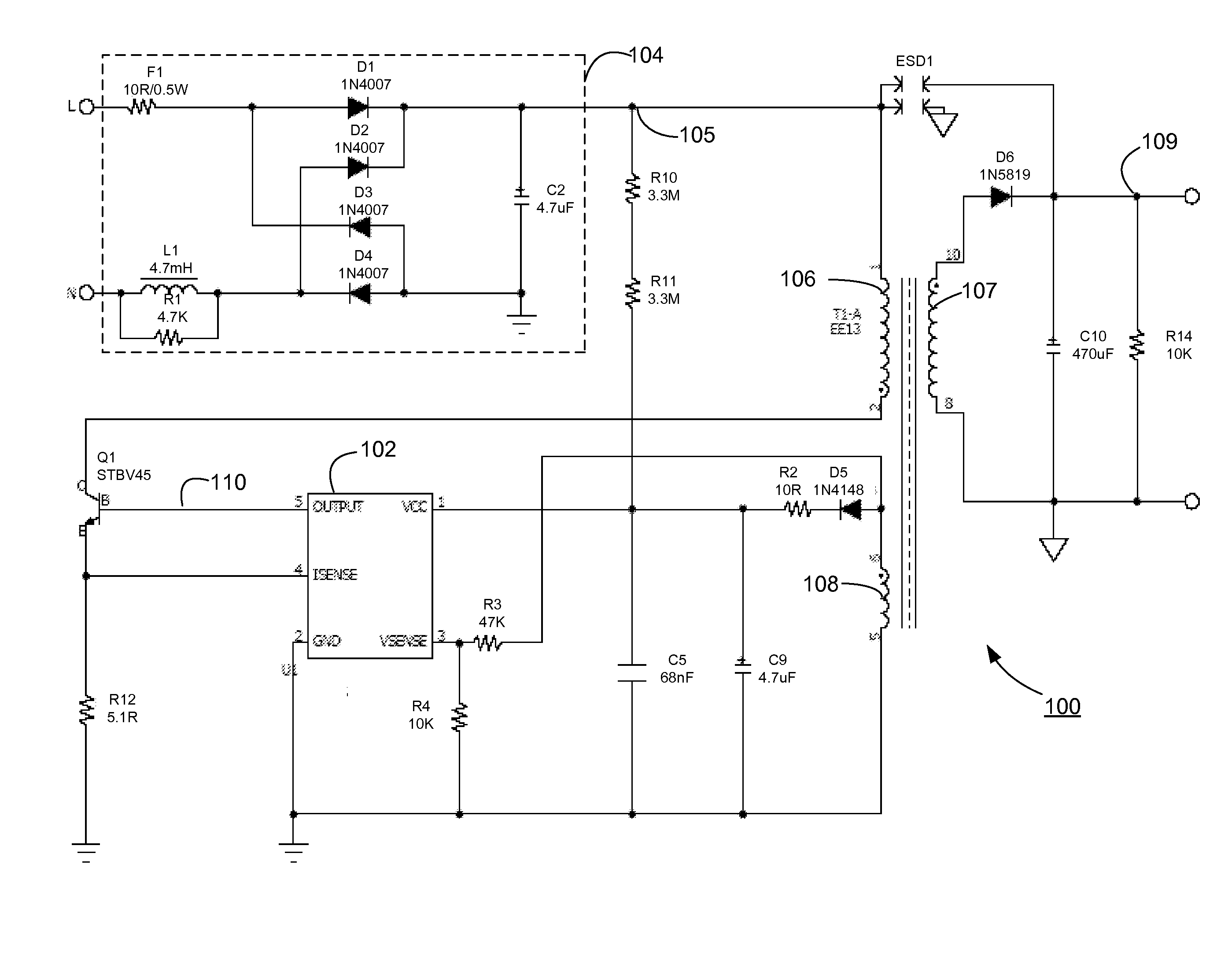
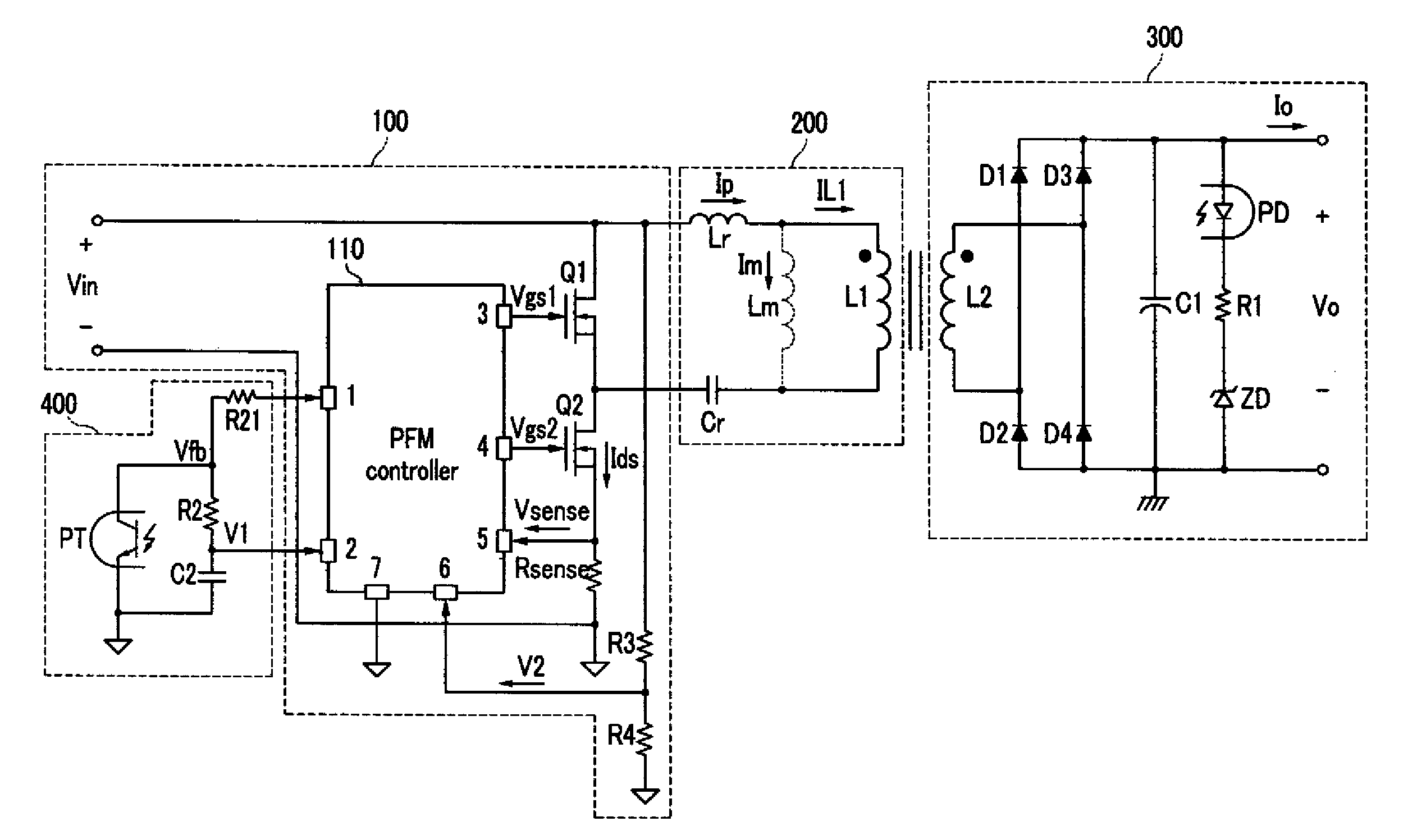
Method and system for pulse frequency modulated switching mode power supplies
ActiveUS20080310191A1Reduce conversion lossSolve the power is smallPulse generatorDc-dc conversionControl signalElectromagnetic interference
A pulse frequency modulation (PFM) controller for controlling a switching mode power supply. The controller includes an output terminal for providing a control signal to turn on and off a current in the power supply to regulate an output of the power supply. A first input terminal receives a feedback signal related to the output of the power supply, the feedback signal exhibiting a ringing waveform when the current in the power supply is turned off. The controller also includes a control circuit configured to provide the control signal in response to the feedback signal. The control signal is adapted to turn on the current in the power supply when the feedback signal is substantially at a valley of the ringing waveform of the feedback signal. In an embodiment, such a PFM controller can reduce turn-on transition loss in a power supply and provides frequency dithering to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multislice DC-DC converter
InactiveUS20030090244A1Energy efficient ICTEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceDead time
A novel monolithic step-down dc-dc buck converter that uses two or more ("n") parallel slices to achieve a high output current with a small filter capacitor is provided. Each of the n slices may be operated with a phase difference of 360° / n. Each of the converter slices may be based on a synchronous rectifier topology to avoid the excessive power losses introduced by the diode component of conventional step-down buck converters. Hysteretic control may be used (with or without pulse-width modulation and pulse-frequency modulation) to provide an internal gate-drive waveform without the need to provide a dedicated clock signal or oscillator circuit. The hysteretic control is further refined using digital control techniques to enforce a brief dead time between the activation of each slice such that undesirable circulating currents are prevented. A significant advantage of the proposed multi-slice step-down dc-dc buck converter and its associated control is that the semiconductor switches, filter inductors and capacitor, and the control circuit may be fabricated as part of a single monolithic integrated circuit.
Owner:SHAKTI SYST
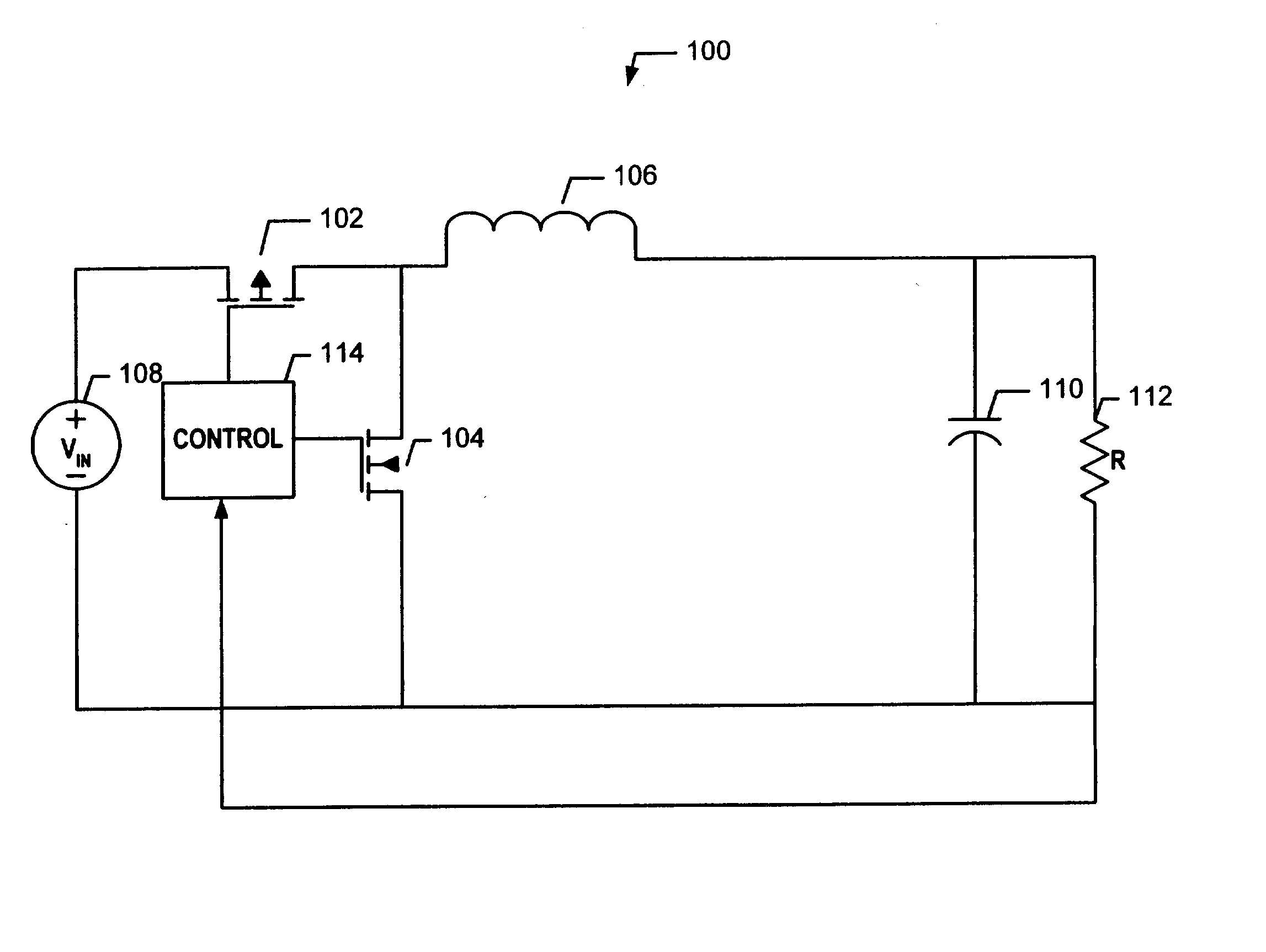
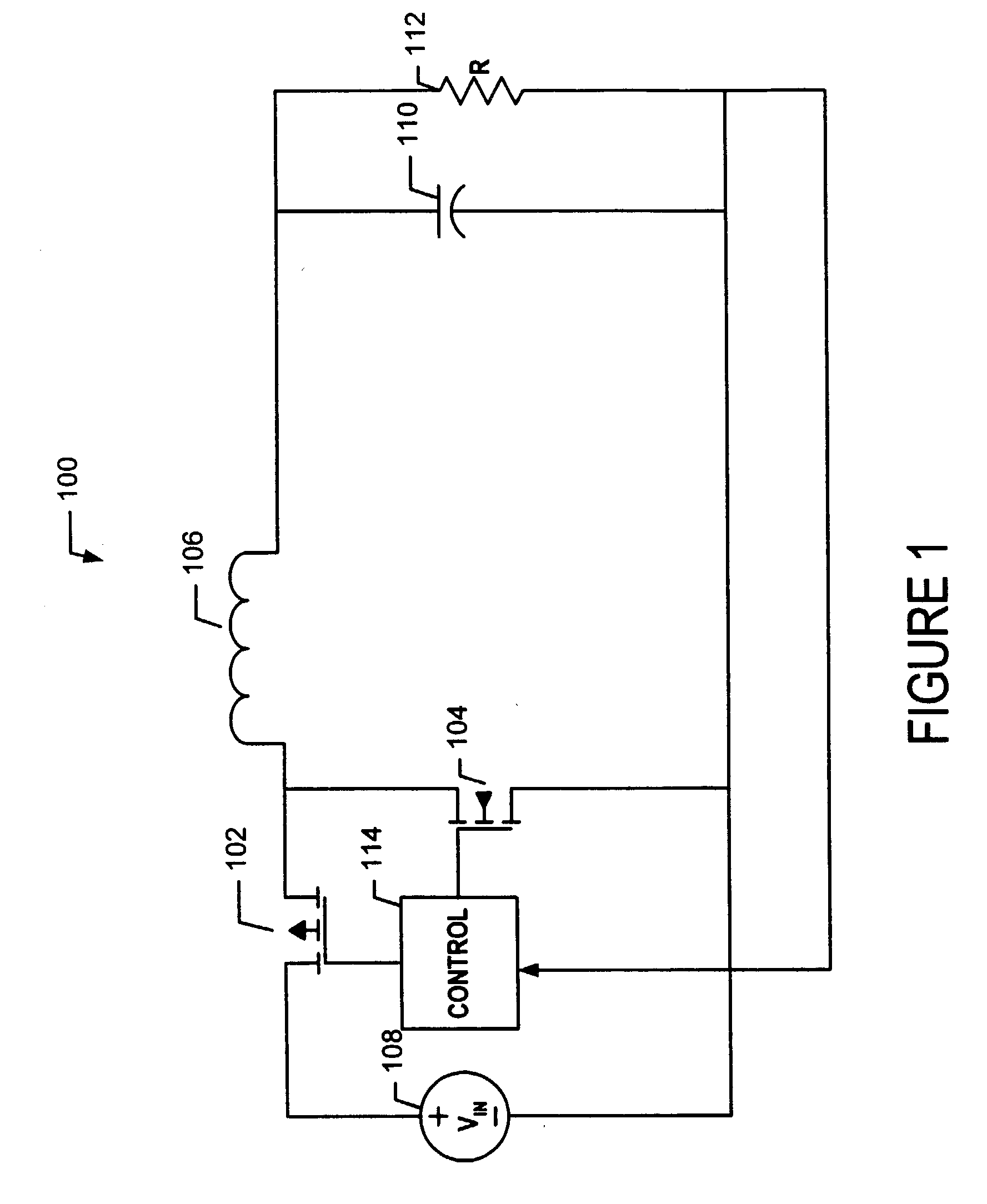
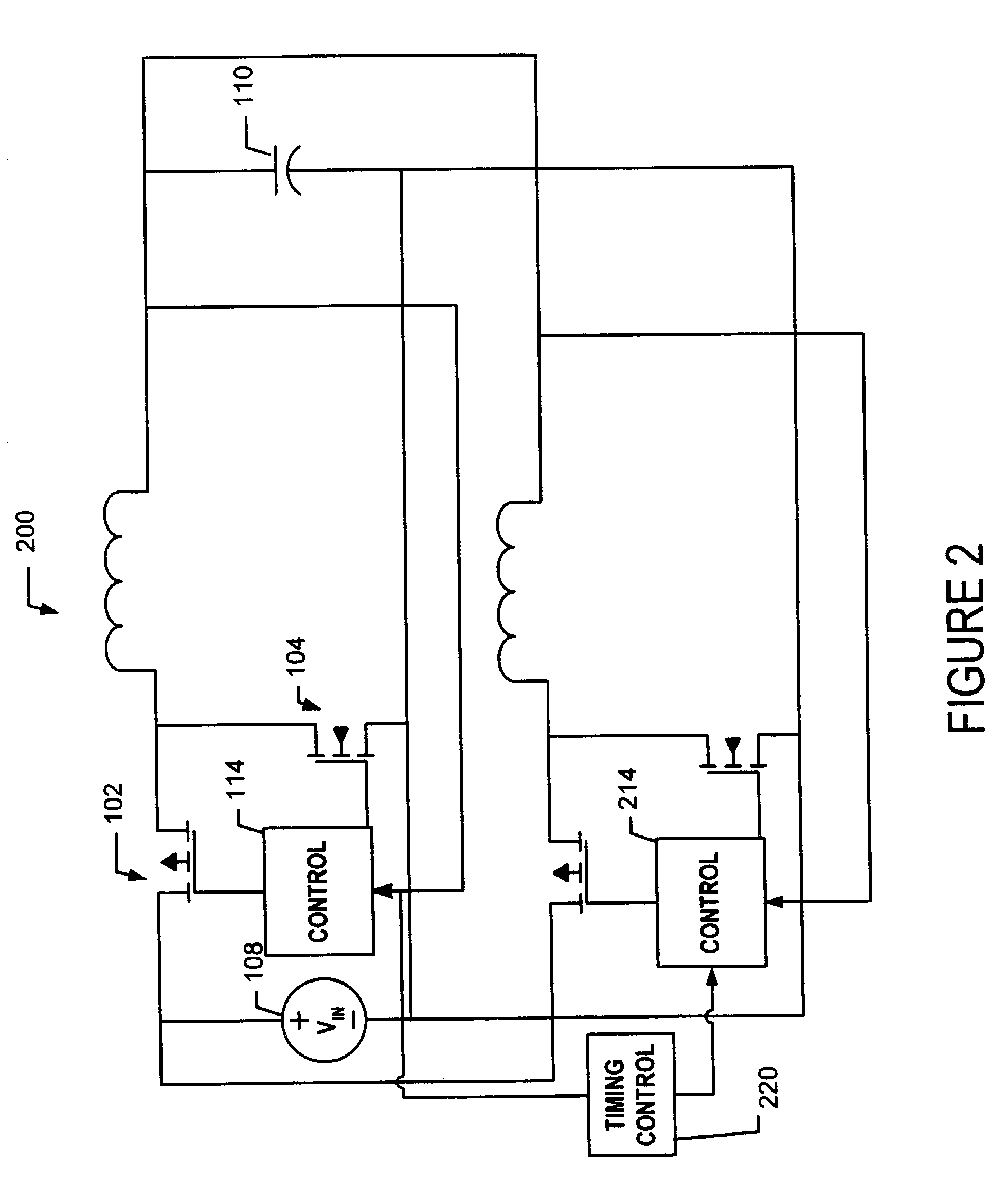
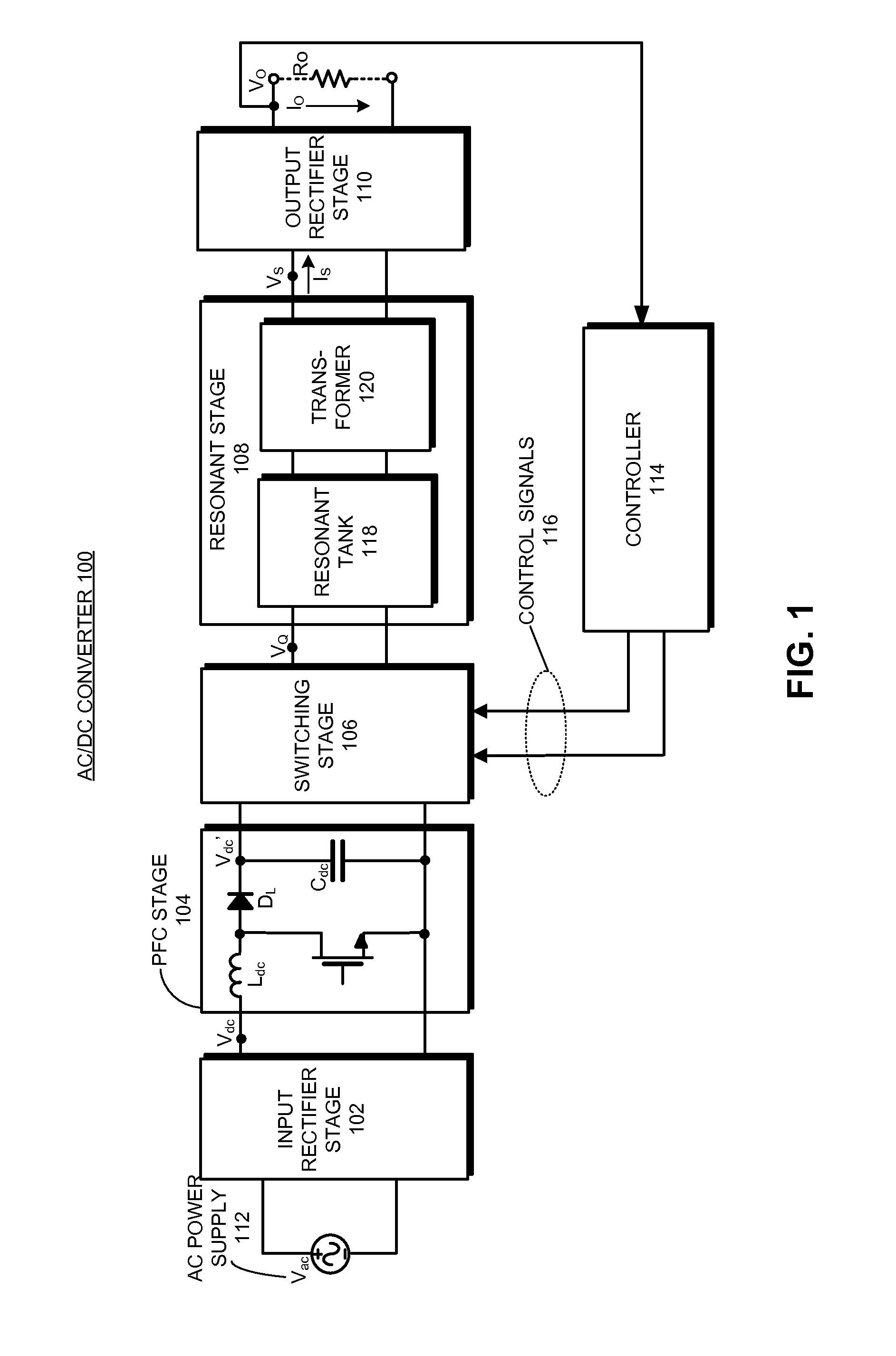
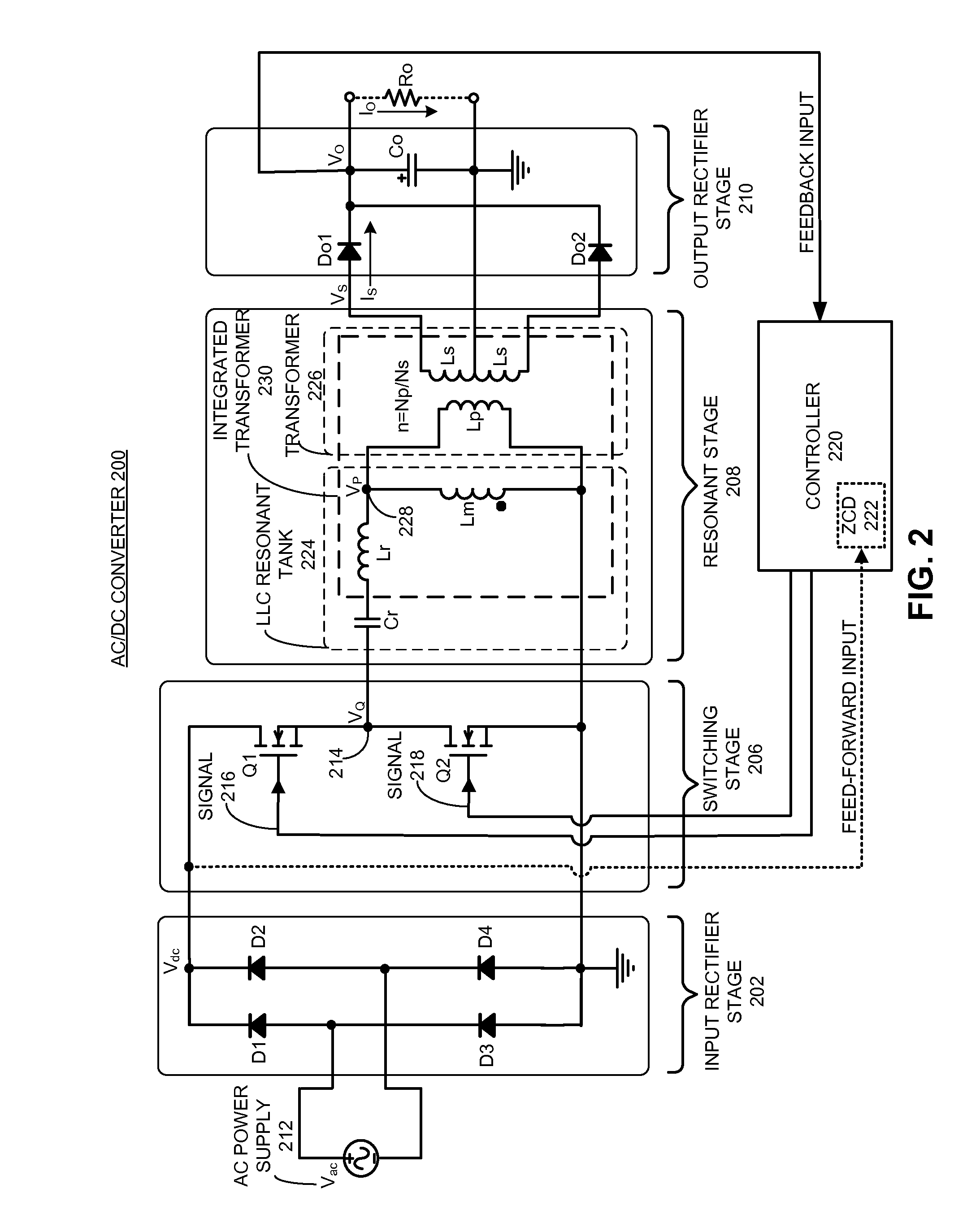
Hysteretic-mode pulse frequency modulated (hm-pfm) resonant ac to DC converter
InactiveUS20140160805A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDirect couplingAc to dc converter
The disclosed embodiments provide an AC / DC power converter that converts an AC input voltage into a DC output voltage. This AC / DC power converter includes an input rectifier stage which rectifies an AC input voltage into a first rectified voltage. The AC / DC power converter also includes a switching resonant stage which is directly coupled to the output of the input rectifier stage. The switching resonant stage converts the rectified voltage into a first high frequency AC voltage of a first amplitude. This AC / DC power converter additionally includes a transformer which is coupled to the output of the switching resonant stage and is configured to down-convert the first high frequency AC voltage into a second high frequency AC voltage of a second amplitude. Furthermore, the AC / DC power converter includes an output rectifier stage which is coupled to the output of the transformer, wherein the output rectifier stage rectifies the second high frequency AC voltage into a DC output voltage.
Owner:APPLE INC
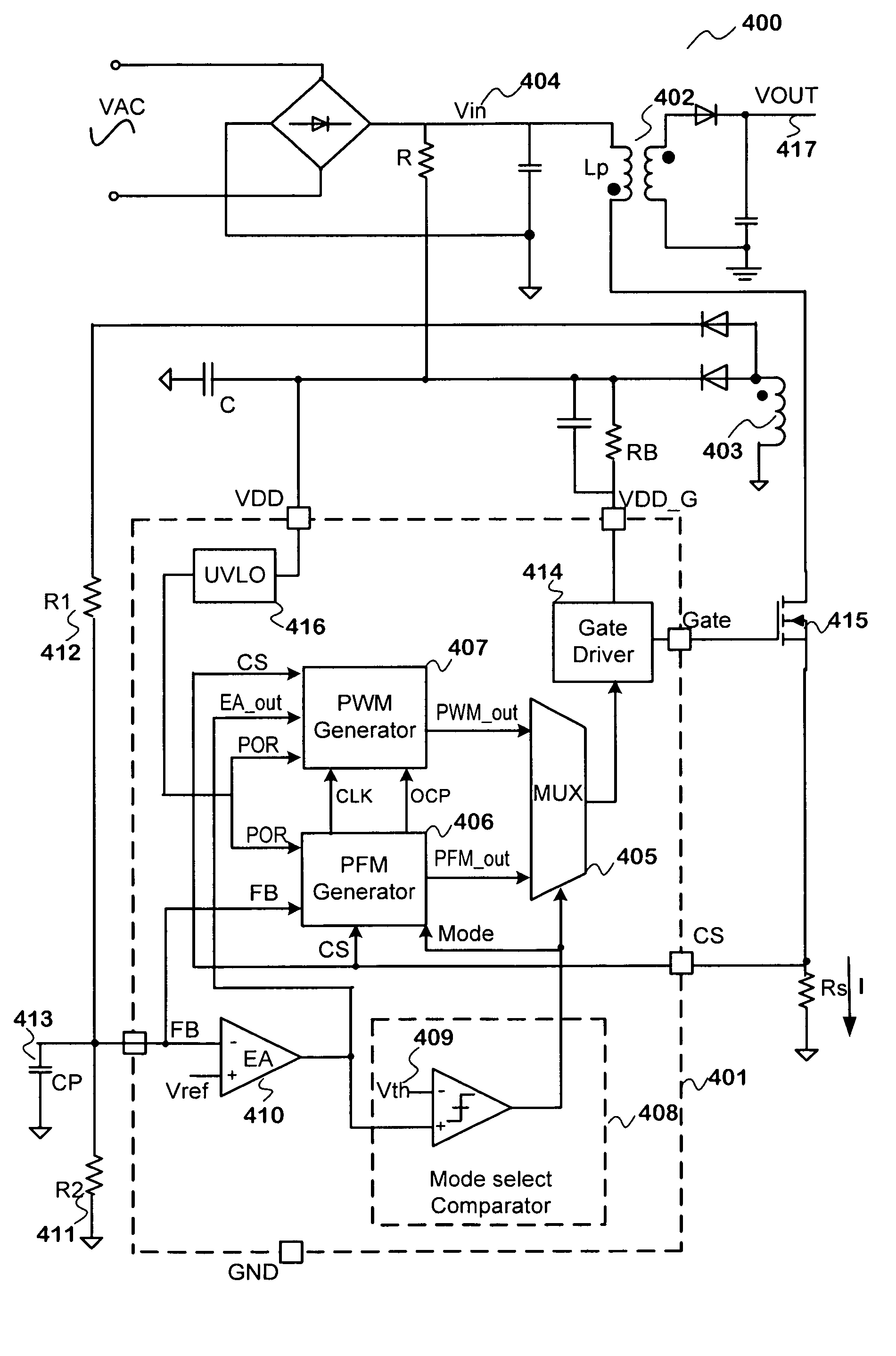
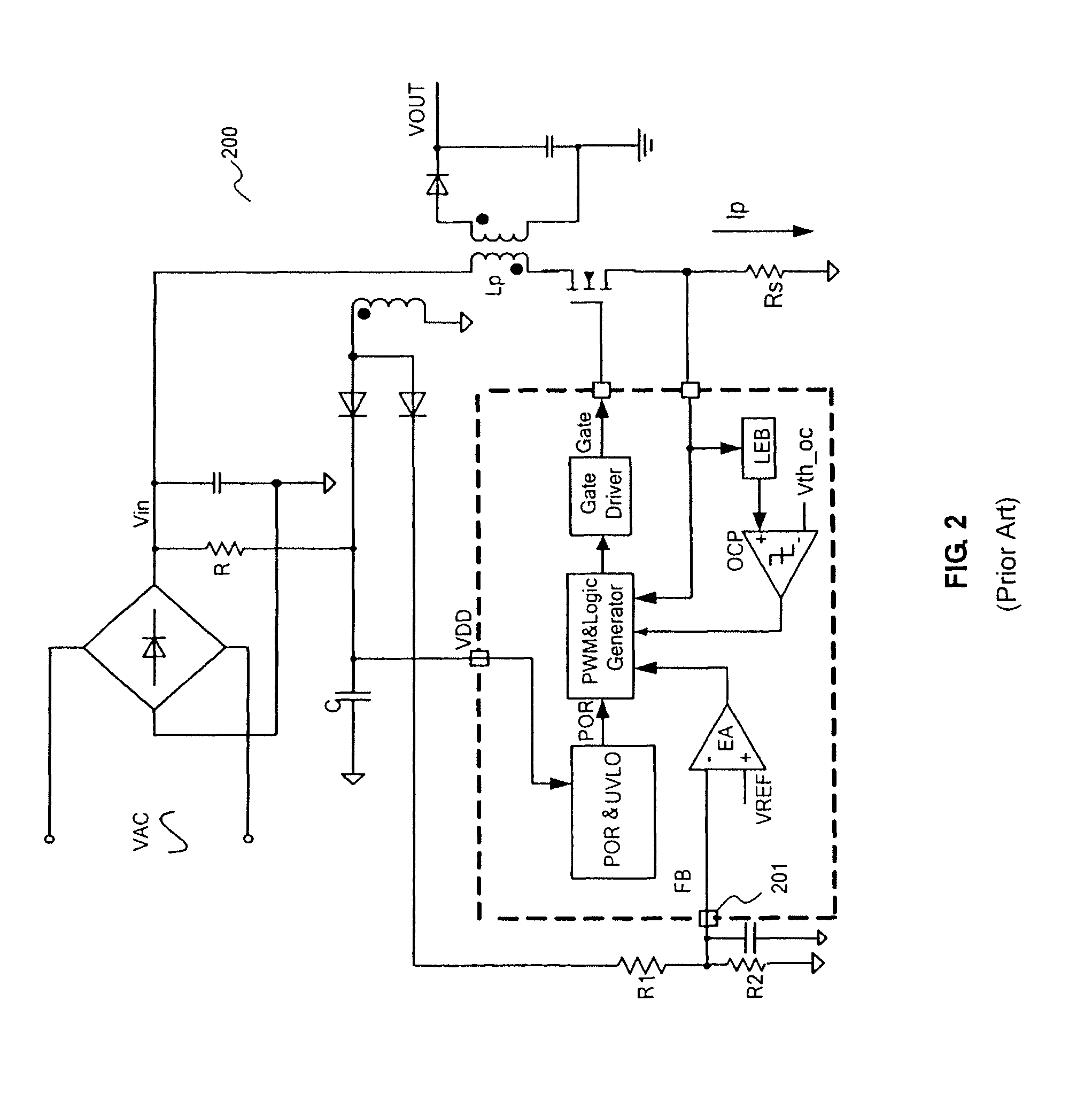
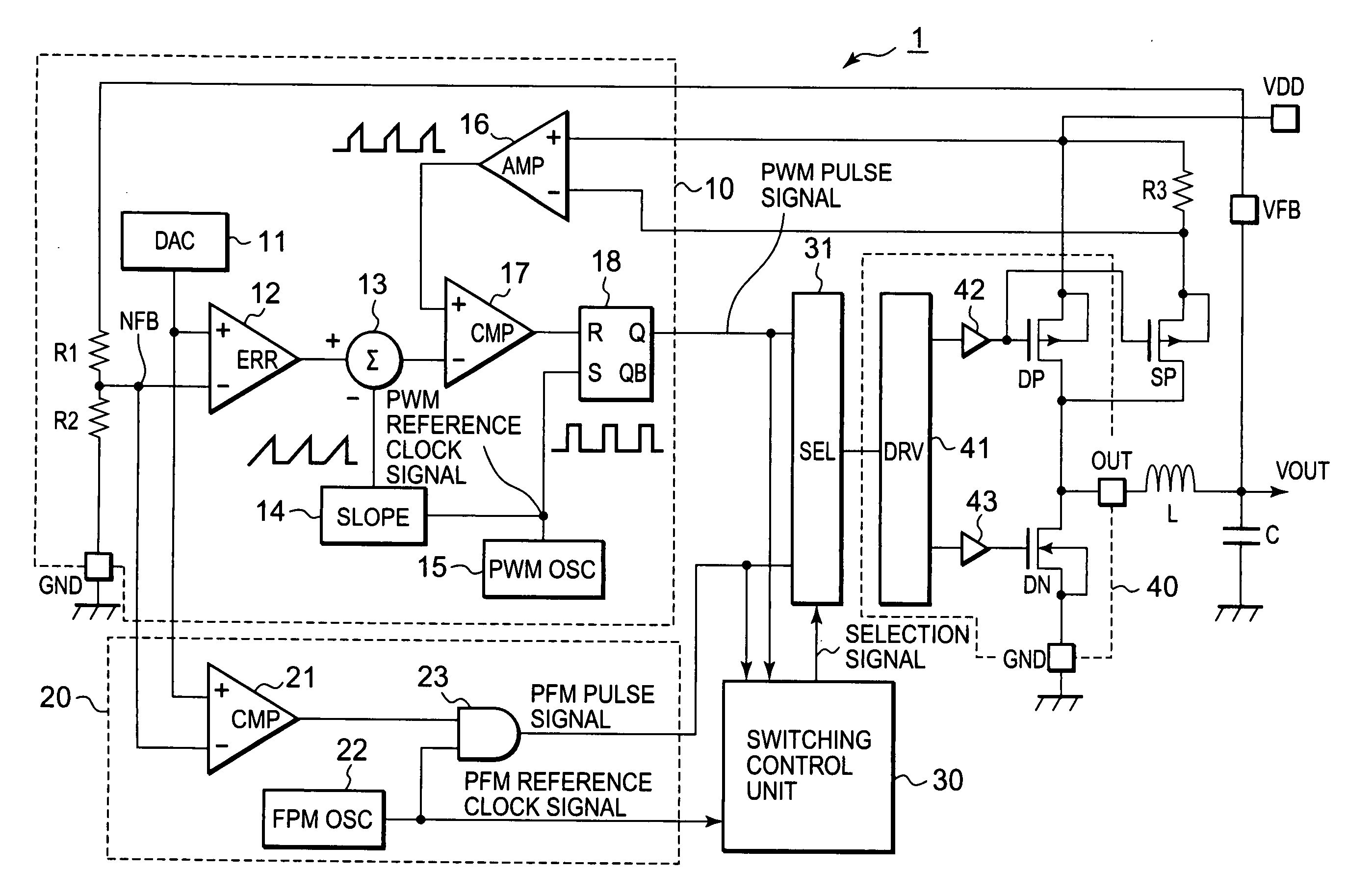
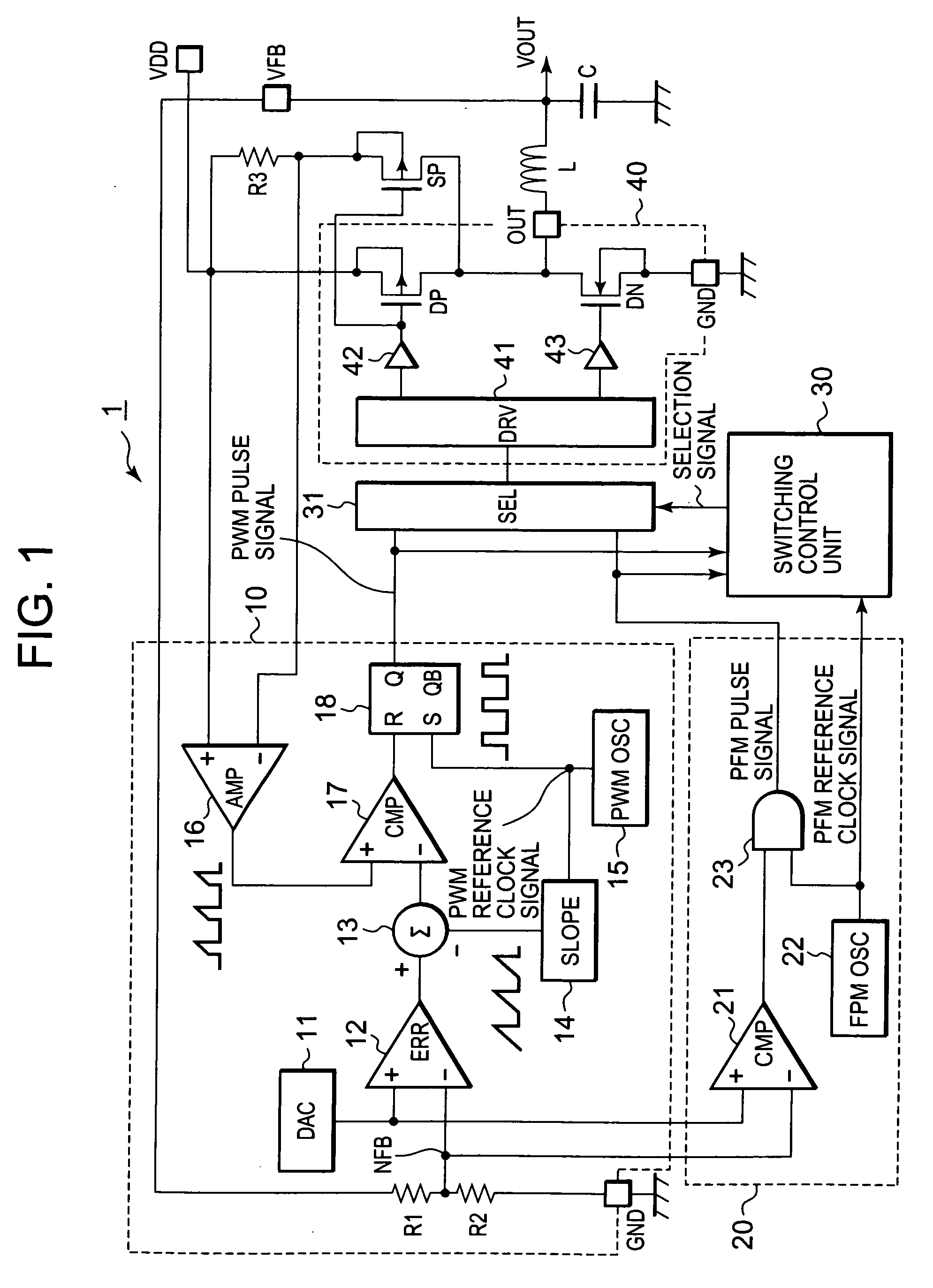
DC converter which has switching control unit to select PWM signal or PFM signal
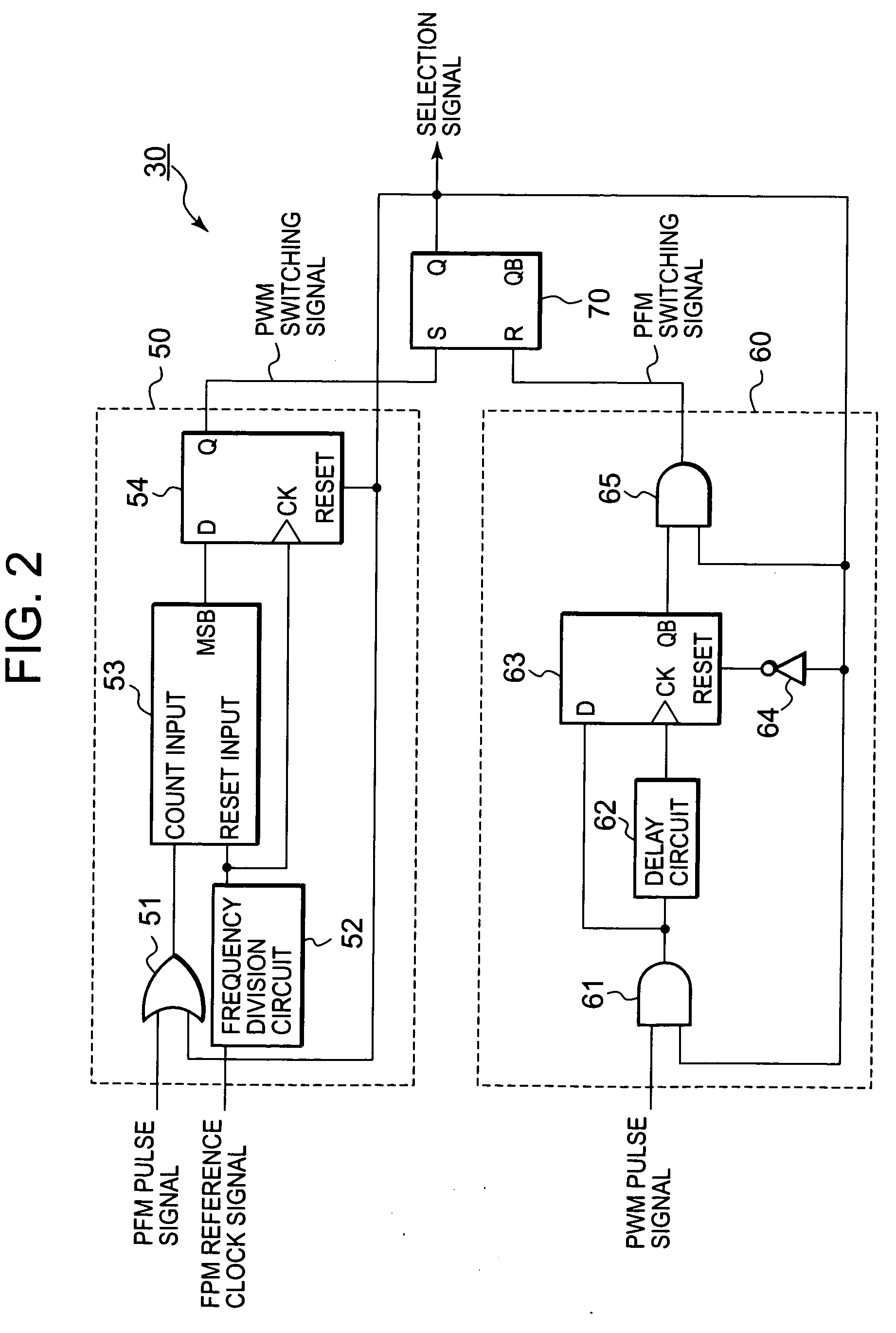
InactiveUS20090218999A1Tendency increaseTrend downDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPulse-code modulationPwm signals
A DC (direct current) converter includes a PWM (pulse width modulation) pulse generation unit outputting a PWM pulse signal whose duty ratio is controlled in accordance with an output voltage, a PFM (pulse frequency modulation) pulse generation unit outputting a PFM pulse signal whose pulse output interval is controlled in accordance with an output voltage, a selection circuit selecting and outputting any one of the PWM pulse signal and the PFM pulse signal in response to a selection signal, a drive circuit unit driving a load and generating an output voltage on the basis of a signal outputted from the selection circuit, and a switching control unit outputting the selection signal. When the selection signal is in a second state, the switching control unit detects a fact that the number of pulses of the PFM pulse signal in a measurement period increases to or above a set value of the maximum number of pulses, and switches the selection signal to a first state.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Frequency jittering control circuit and method for a pfm power supply
ActiveUS20130051089A1Apparatus with intermediate ac conversionPulse duration/width modulationControl signalSwitching frequency
A frequency jittering control circuit for a PFM power supply includes a pulse frequency modulator to generate a frequency jittering control signal to switch a power switch to generate an output voltage. The frequency jittering control circuit jitters an input signal or an on-time or off-time of the pulse frequency modulator to jitter the switching frequency of the power switch to thereby improve EMI issue.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
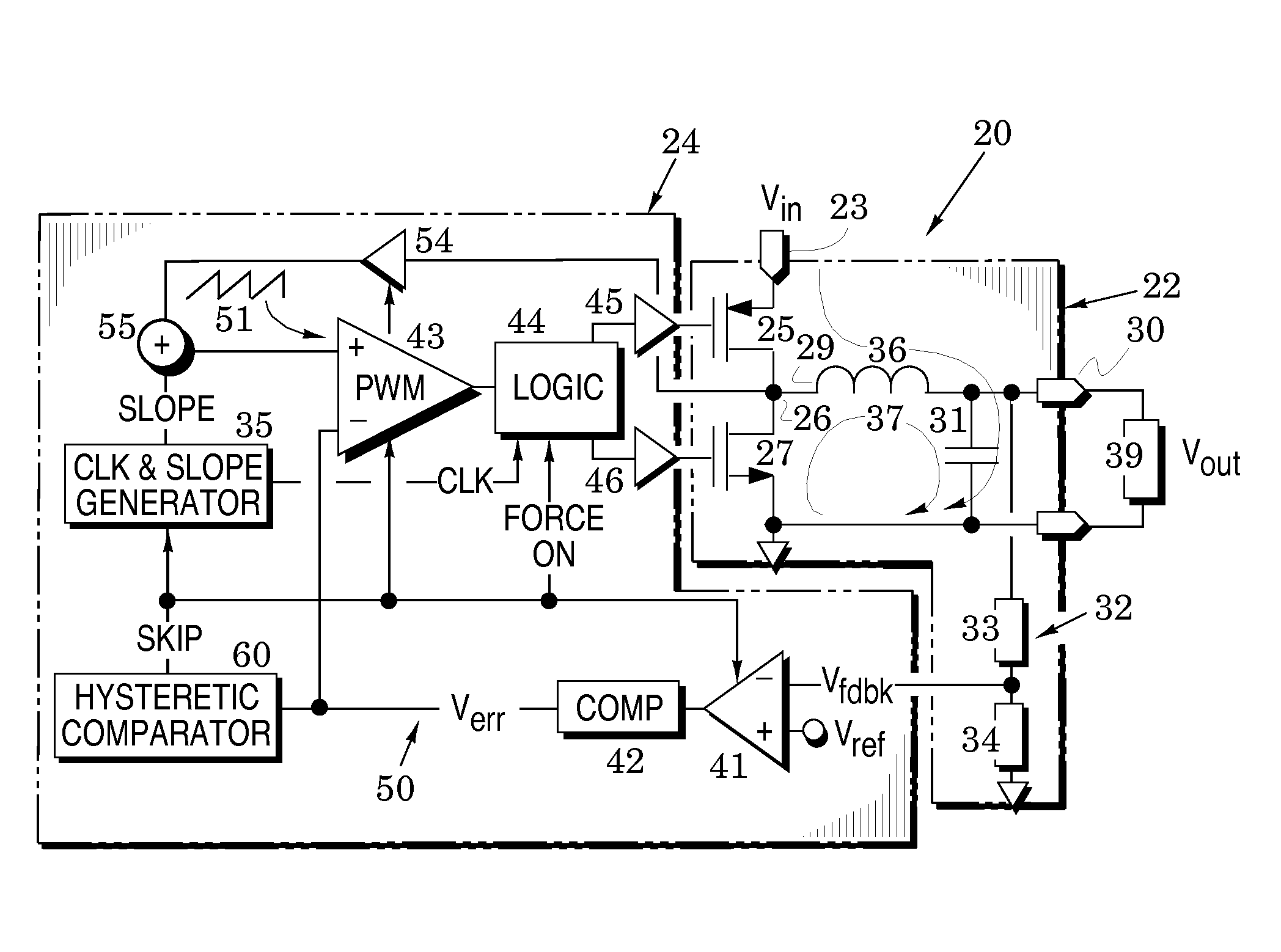
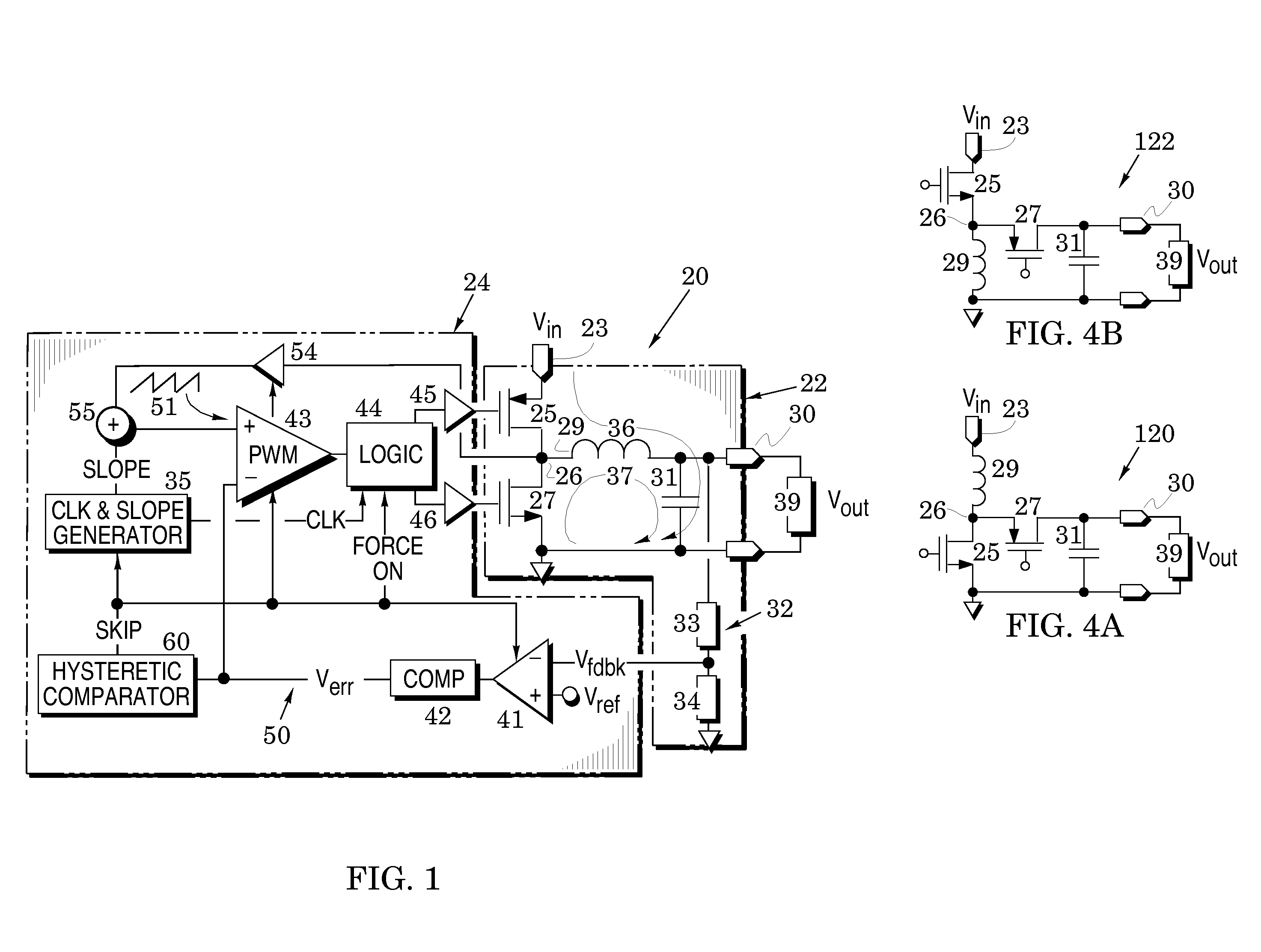
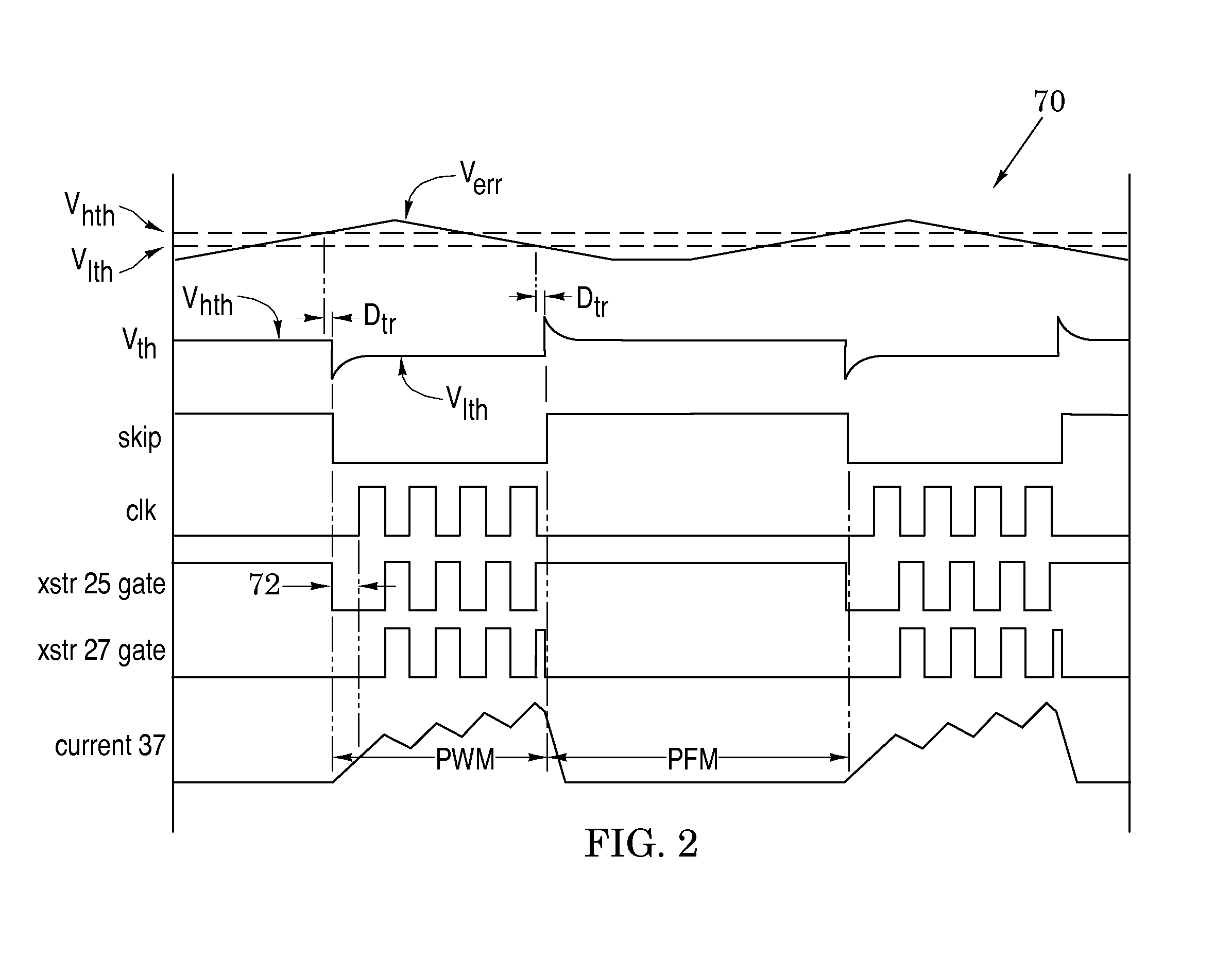
Switching voltage regulators with hysteretic control for enhanced mode-transition speed and stability
ActiveUS20120161728A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCurrent mode controlMode control
Switching voltage regulator embodiments are provided with hysteretic control to thereby switch between pulse-width modulation and pulse-frequency modulation operational modes. The switching is in response to different levels of an error voltage Verr in the feedback loop of voltage regulators. The hysteretic control is configured to provide a dc hysteretic response to changes in the error voltage Verr and also an ac hysteretic response to these changes. These two responses can be independently set to thereby enhance operational speed of the voltage regulators and also enhance immunity to transient noise signals that are generated by the mode switching. The voltage regulator embodiments facilitate instant return from the pulse-frequency modulation operational mode to the pulse-width modulation operational mode so that the stability of the feedback control of the regulator is enhanced. This feature is especially useful when the feedback loop is configured to include current-mode control as it minimizes the time duration in which the feedback loop operates in a voltage-mode control. The instant return insures that the feedback loop is immediately returned to the greater stability of the current-mode control.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
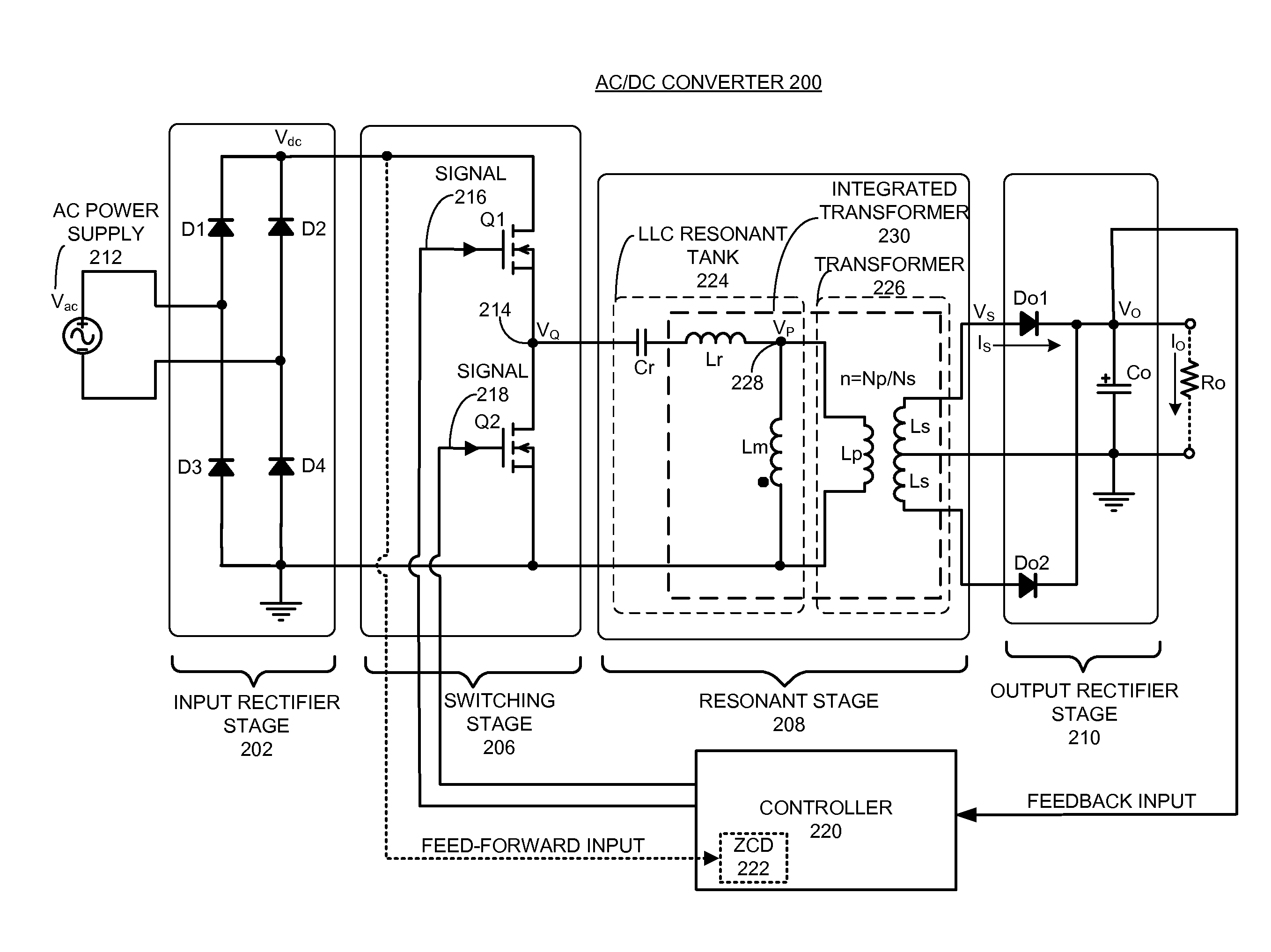
Resonant Converter
ActiveUS20090196074A1Drive stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionResonant inverterSquare waveform
A resonant converter includes a square wave generator including a first switch and a second switch, and generating a first square wave corresponding to an input voltage by alternately turning on / off the first and second switches; a resonator including a first coil of a primary coil of a transformer, and generating a resonance waveform corresponding to the first square wave; and an output unit including a second coil of a secondary coil of the transformer, and outputting a voltage corresponding to a current generated in the second coil corresponding to the resonance waveform. The square wave generator includes a pulse frequency modulation controller for turning on / off the first and second switches, comparing a first voltage linearly increased while the second switch maintains the turn-on state and a second voltage corresponding to an integration value on the time of the current flowing to the second switch when the second switch is turned off, and changing on / off drive frequencies of the first and second switches according to a comparison result. Therefore, a resonant converter driven with safety is realized.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Valley-mode switching schemes for switching power converters
ActiveUS20100165672A1Avoid powerApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationSwitching cycleLow voltage
An improved valley-mode switching (VMS) scheme and circuitry for implementing the improved VMS switching scheme in a switch-mode power converter are disclosed. For a given switching cycle, a desired switch turn-on time is determined based on a pulse width modulation, pulse frequency modulation, or other suitable power converter control scheme. Also, one or more times corresponding to local minimums (valleys) are predicted for the voltage across a power switch of the switching power converter. The power switch is turned on at a valley immediately subsequent or otherwise subsequent to the desired switch time determined according to the power converter control scheme. Thus, the improved VMS scheme enables low-voltage switch operation to reduce switching loss and EMI noise without restricting the control scheme of the power converter.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Modified dimming LED driver
ActiveUS8319445B2Enhances dimming responseEasy to controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHemt circuitsEngineering
A driver circuit produces variable current output for an LED lighting system providing improved dimming capability and greater power efficiency when responding to industry standard lighting dimmers, through the use of an input voltage monitoring circuit which variably controls the current output of a switching regulator. Output current modulation methods such as analog, PWM, Pulse Frequency Modulation, or other digital modulation, and combination or hybrid methods may be employed. The current invention marries such output modulation techniques with a control method which is derived through intelligent monitoring of the input voltage waveform. The circuit and method described is adapted to higher current applications such as LED lighting systems using the latest high-power LEDs.
Owner:BOCA FLASHER
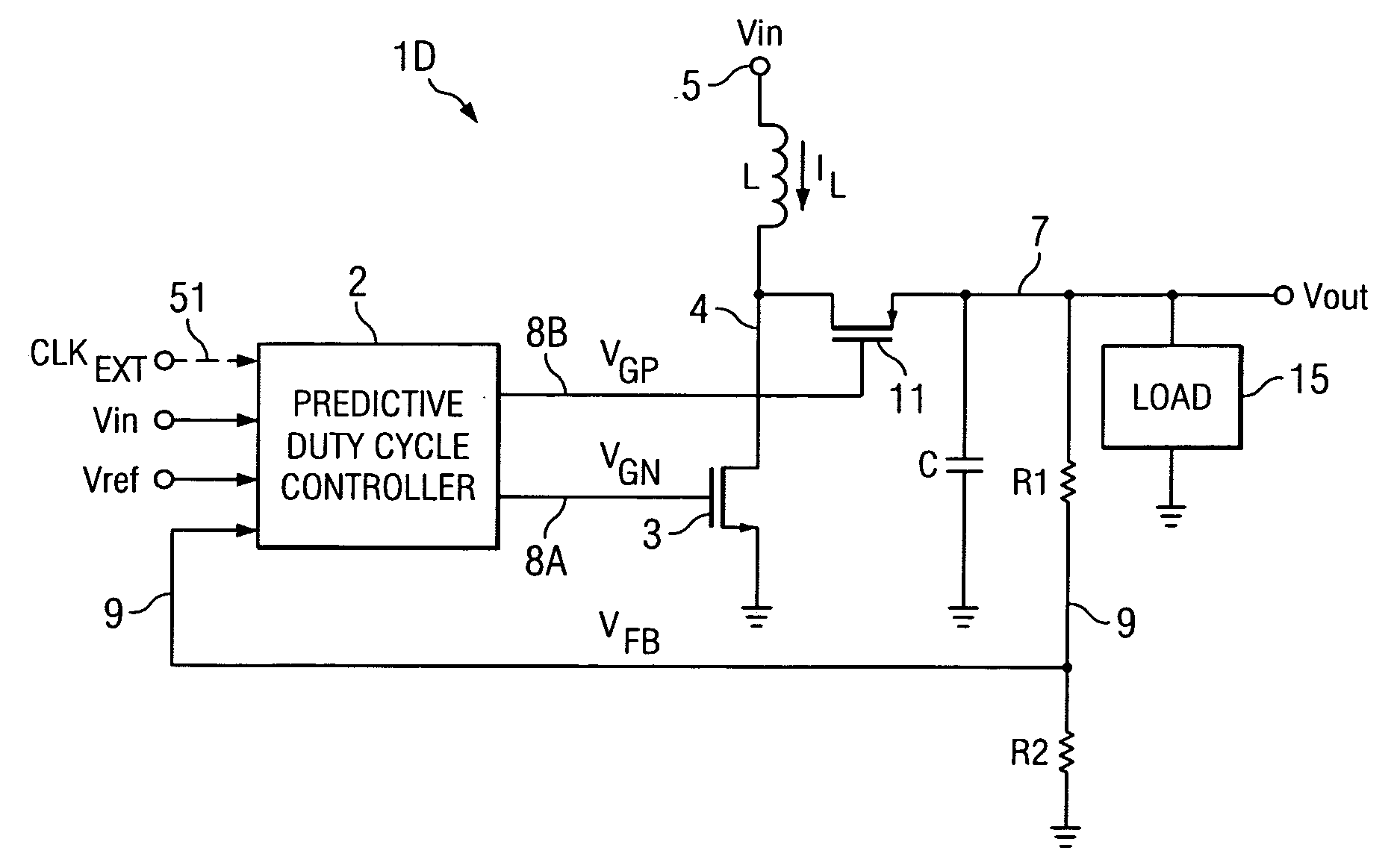
Predictive duty ratio generating circuit and method for synchronous boost converters operating in PFM mode
ActiveUS20080094861A1Inhibit transferEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectrical conductorControl signal
A synchronous DC-to-DC converter includes an inductor coupled to receive an input voltage, a first transistor having a source coupled to a first reference voltage and a drain coupled to the inductor, and a second transistor having a source coupled to an output conductor to produce an output voltage and a drain coupled to the inductor. A feedback signal representative of a value of the output voltage is generated, and a switch control signal is produced in response to the input voltage and a second reference voltage. The second transistor is turned off in response to the switch control signal each time the inductor current has decayed to zero to prevent reverse current flow through the inductor. A regulating signal indicates whether or not the feedback voltage exceeds the second reference voltage, to regulate the output voltage in a pulse-frequency modulation mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
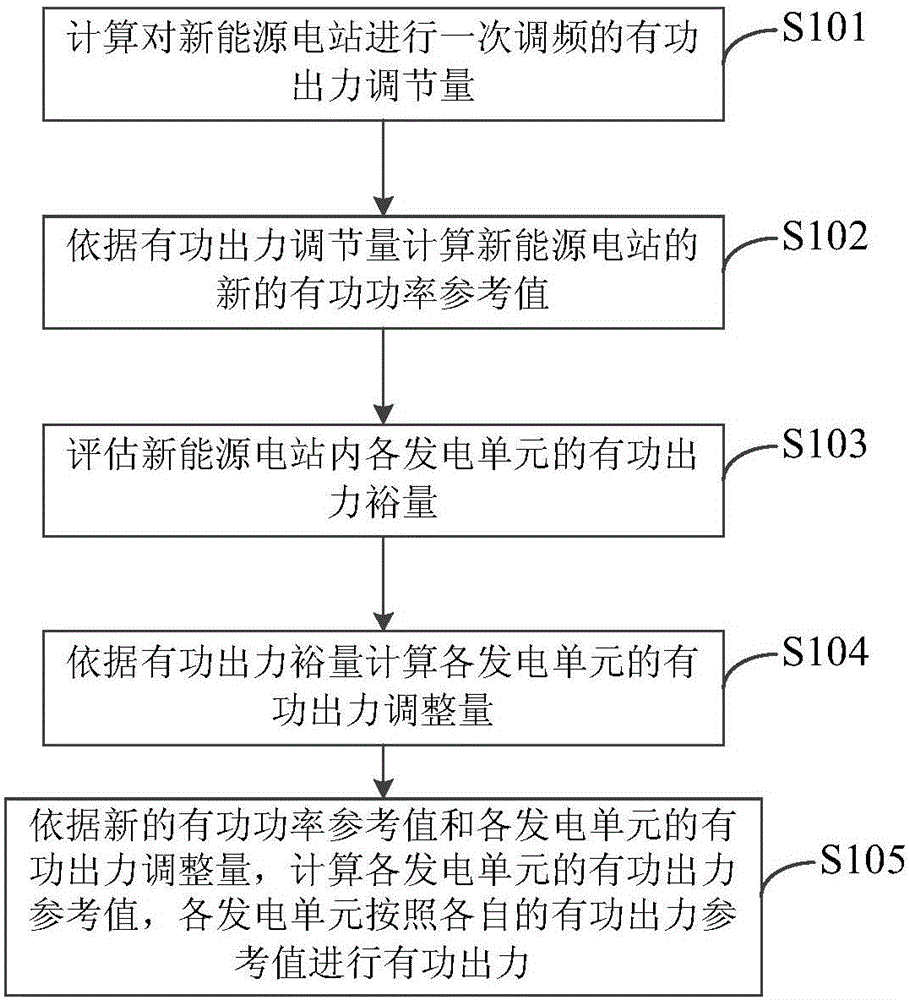
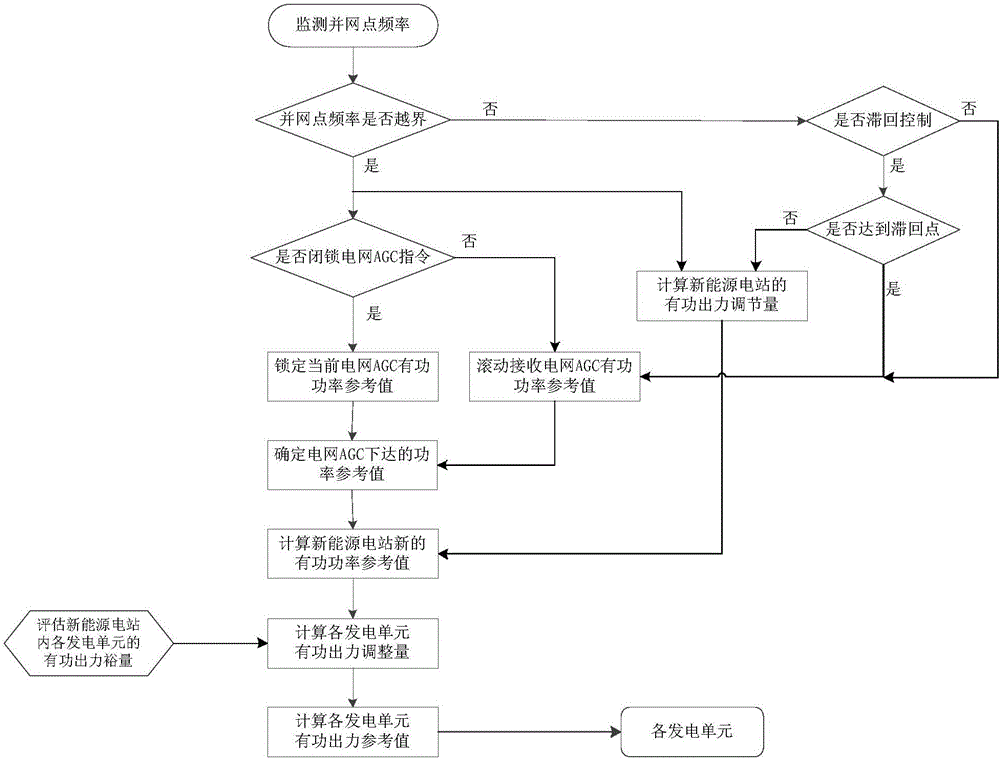
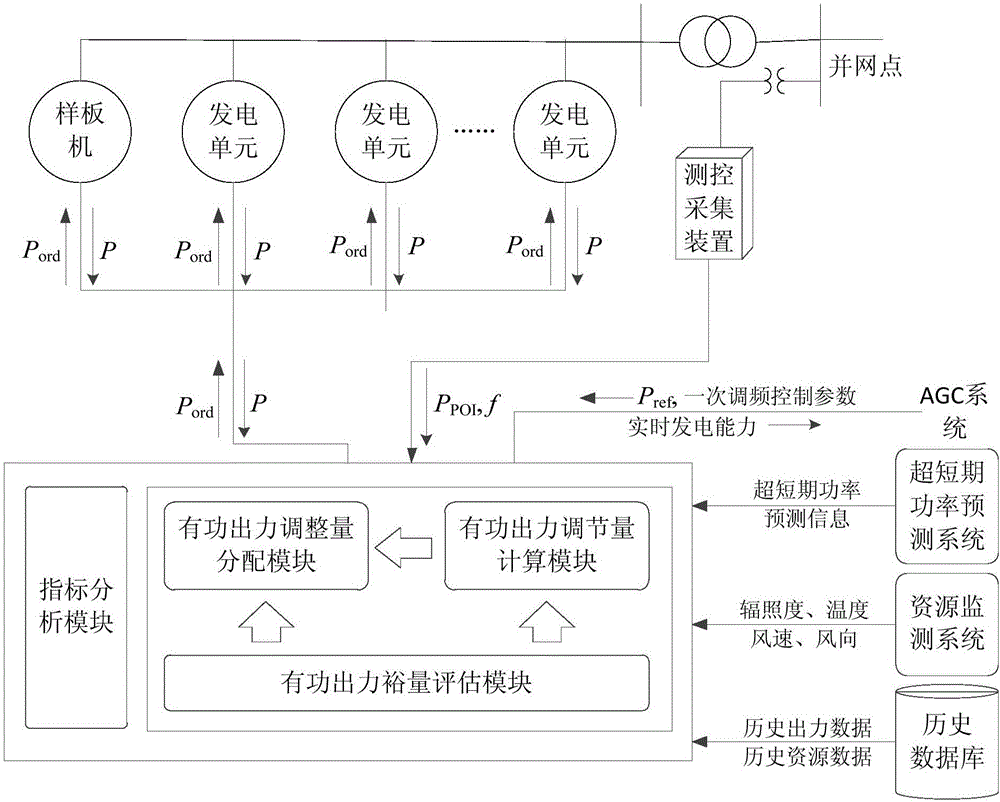
Primary frequency modulation control method and system of new energy power station
ActiveCN106300394AAdjust grid connection frequencyPower oscillations reduction/preventionPower stationNew energy
The invention provides primary frequency modulation control method and system of a new energy power station. The primary frequency modulation control method includes: calculating active power output regulating variables and new active power reference values on primary frequency modulation of the new energy power station; evaluating active power output margins of power generation units in the new energy power station; calculating the active power output regulating variables of the power generation units according to the active power output margins; according to the new active power reference values and the active power output regulating variables of the power generation units, calculating the active power reference values of the power generation units, and the power generation units performing active power output according to the active power output values. Compared with the prior art, the primary frequency modulation control method and system has the advantages that both the active power output regulating variables of the new energy power station and the active power output margins of the power generation units are taken into consideration, and grid-connection frequency of the new energy power station can be regulated under the premise of safe operation of the power generation units.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
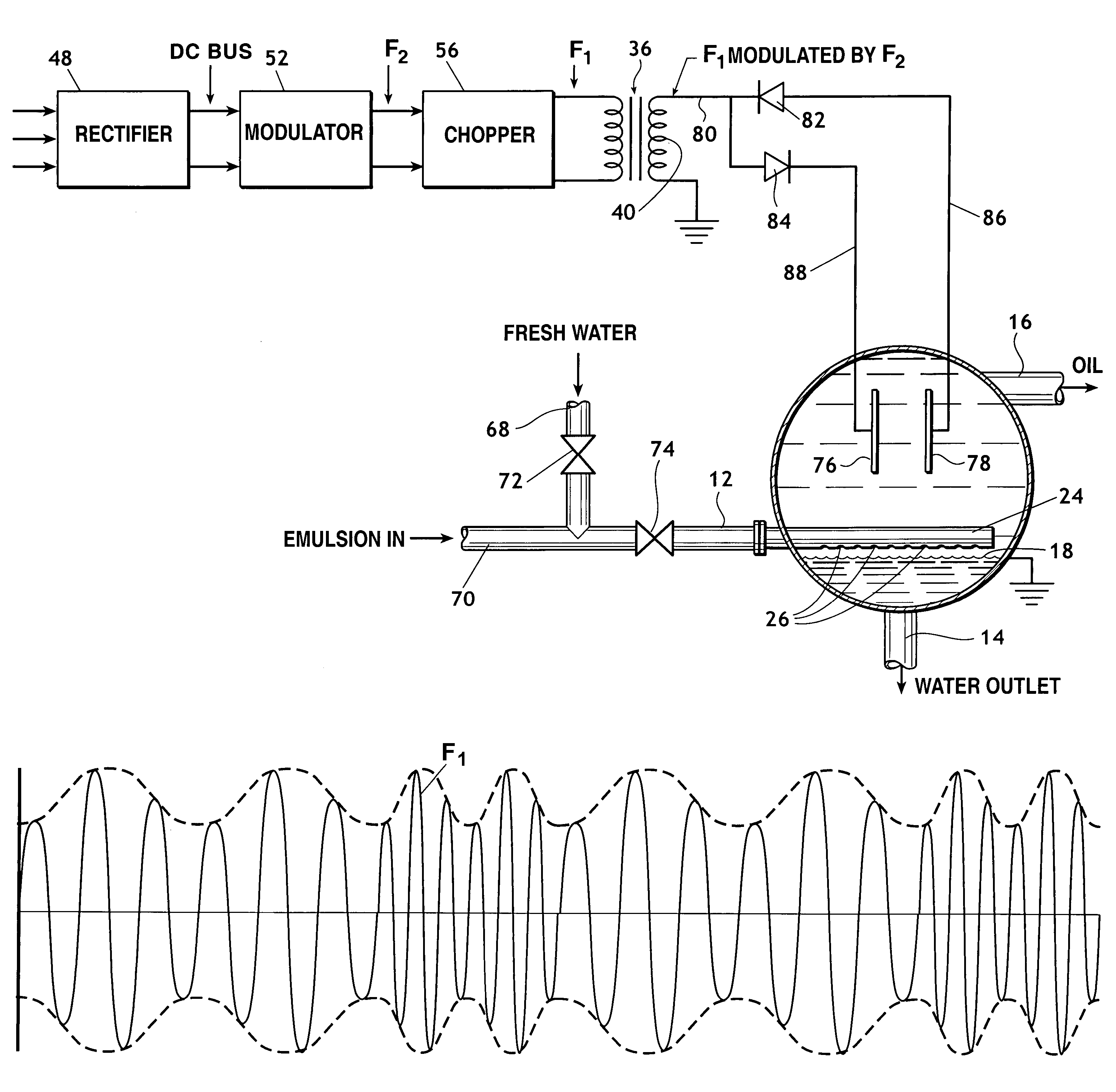
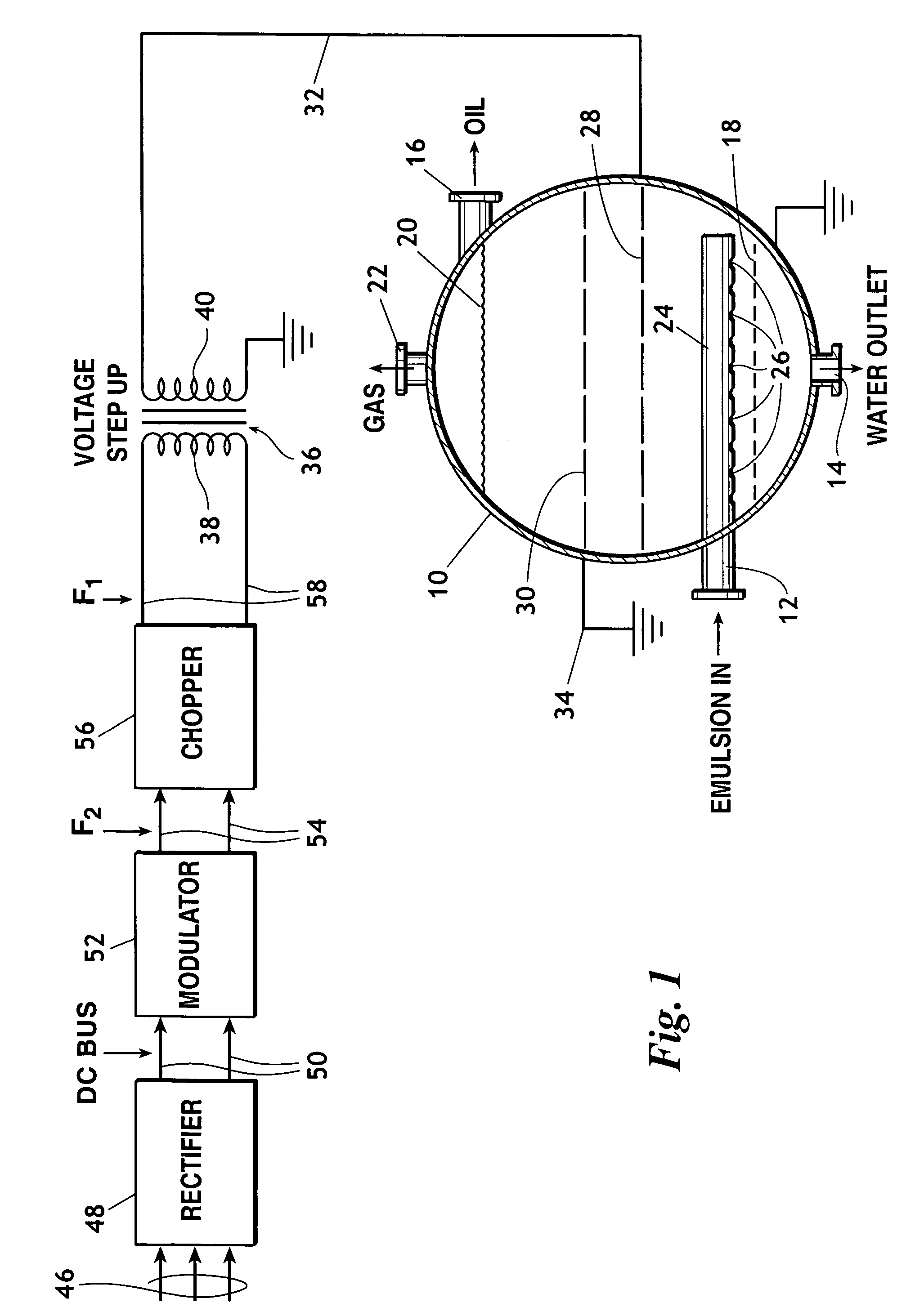
Multiple frequency electrostatic coalescence
A method of augmenting the separation of immiscible heavier and lighter components of an emulsion including the steps of conducting the emulsion into a treatment vessel, providing an AC voltage source, employing from the source an AC voltage of at least one selected frequency F1 to establish at least one electric filed within the vessel through which the emulsion passes, and cyclically modulating the AC voltage with a method of modulation selected from: (a) amplitude modulation; (b) frequency modulation; and (c) combined amplitude and frequency modulation.
Owner:NAT TANK
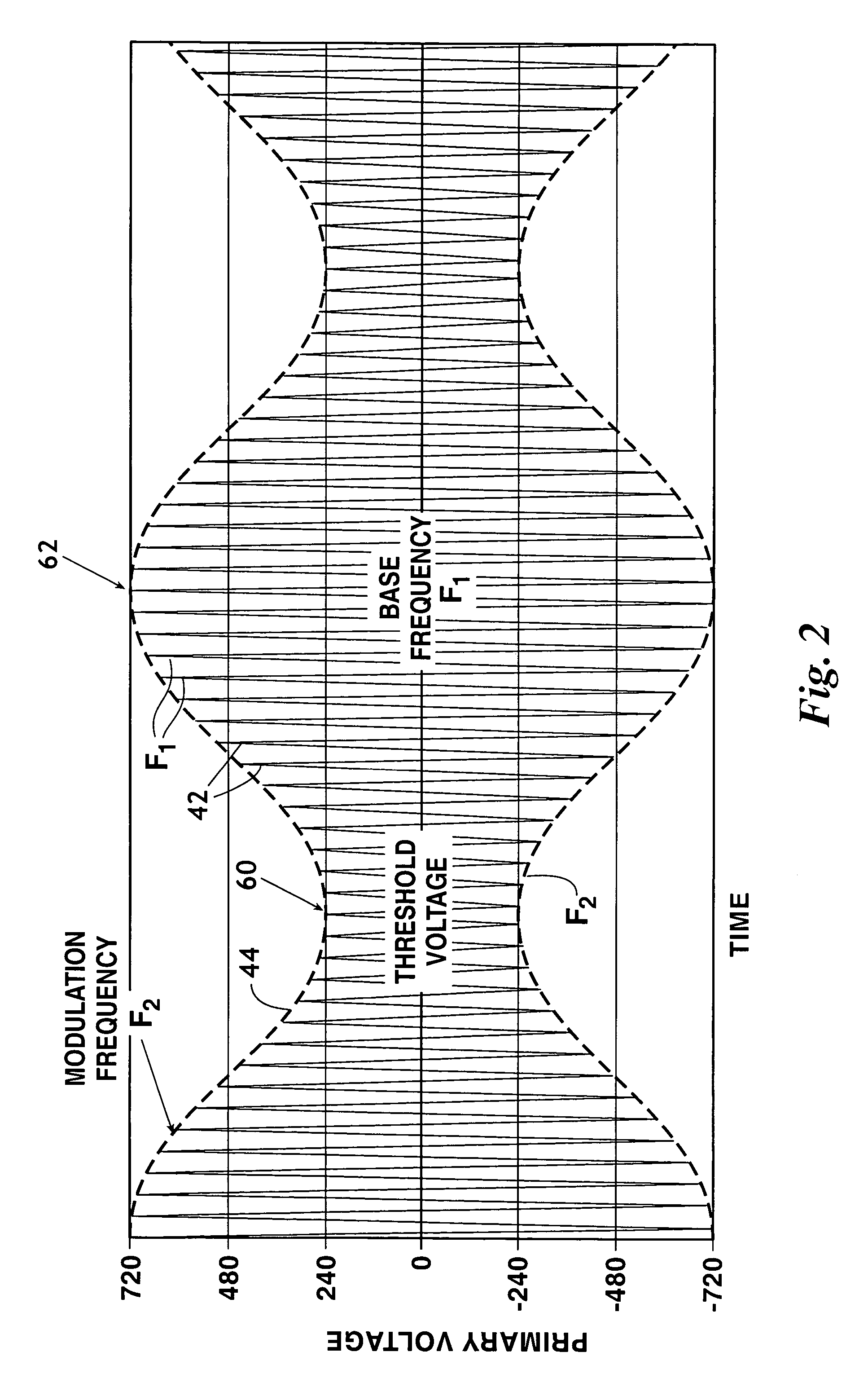
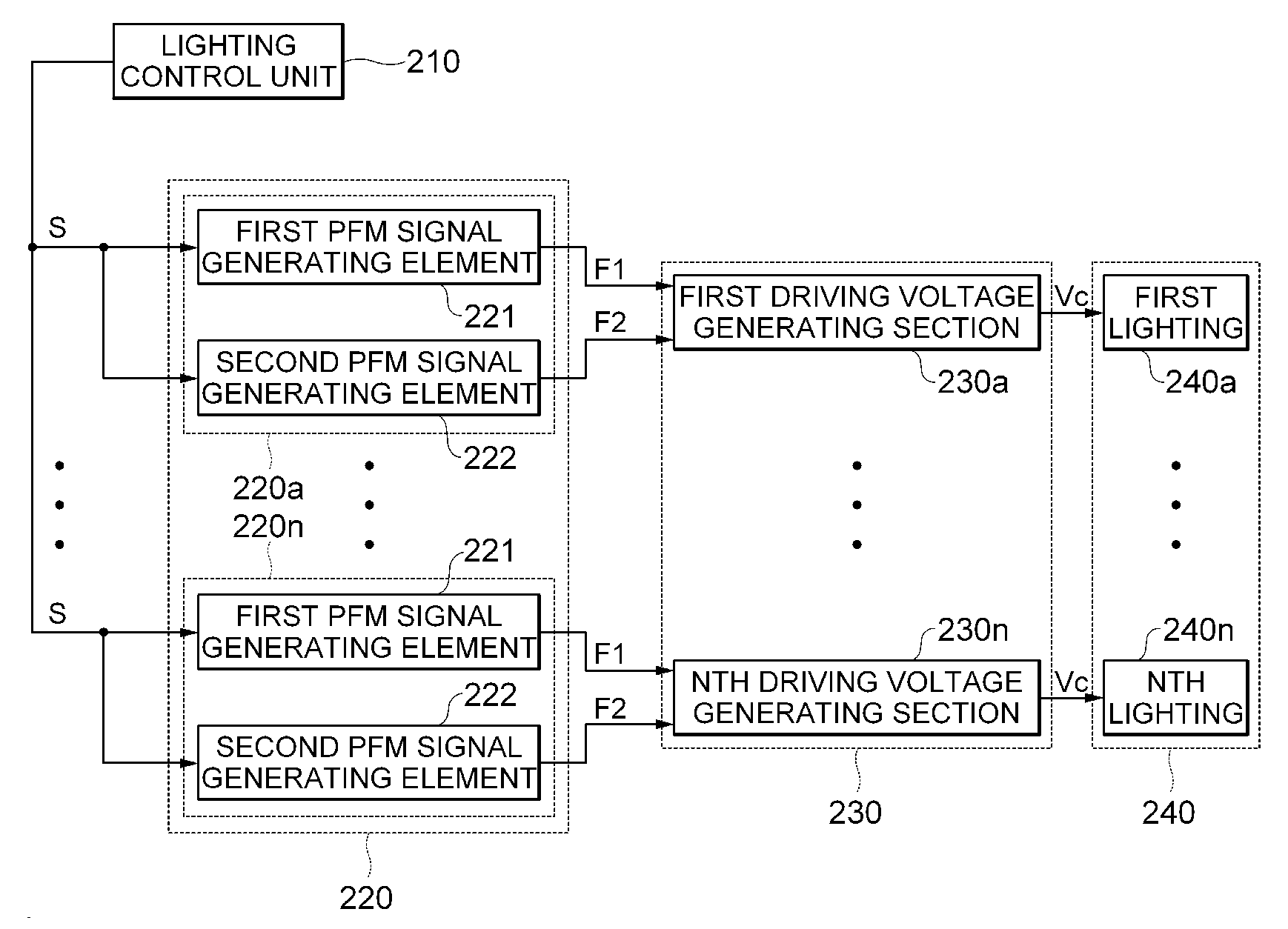
Apparatus and method for controlling lighting brightness through pulse frequency modulation
InactiveUS20090160360A1Prevent spurious signalAvoid signalingElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementControl signalEngineering
Provided is an apparatus for controlling lighting brightness through PFM, the apparatus including a lighting control unit that generates a control signal for controlling the brightness of a plurality of lightings; a PFM signal generating unit that is controlled by the control signal so as to generate a plurality of PFM signals having a different frequency from each other; and a driving voltage generating unit that composes the generated PFM signals in accordance with a preset combination, thereby generating driving voltages for driving the lightings.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Online monitoring and performance assessing method for primary frequency modulation of thermal generator set
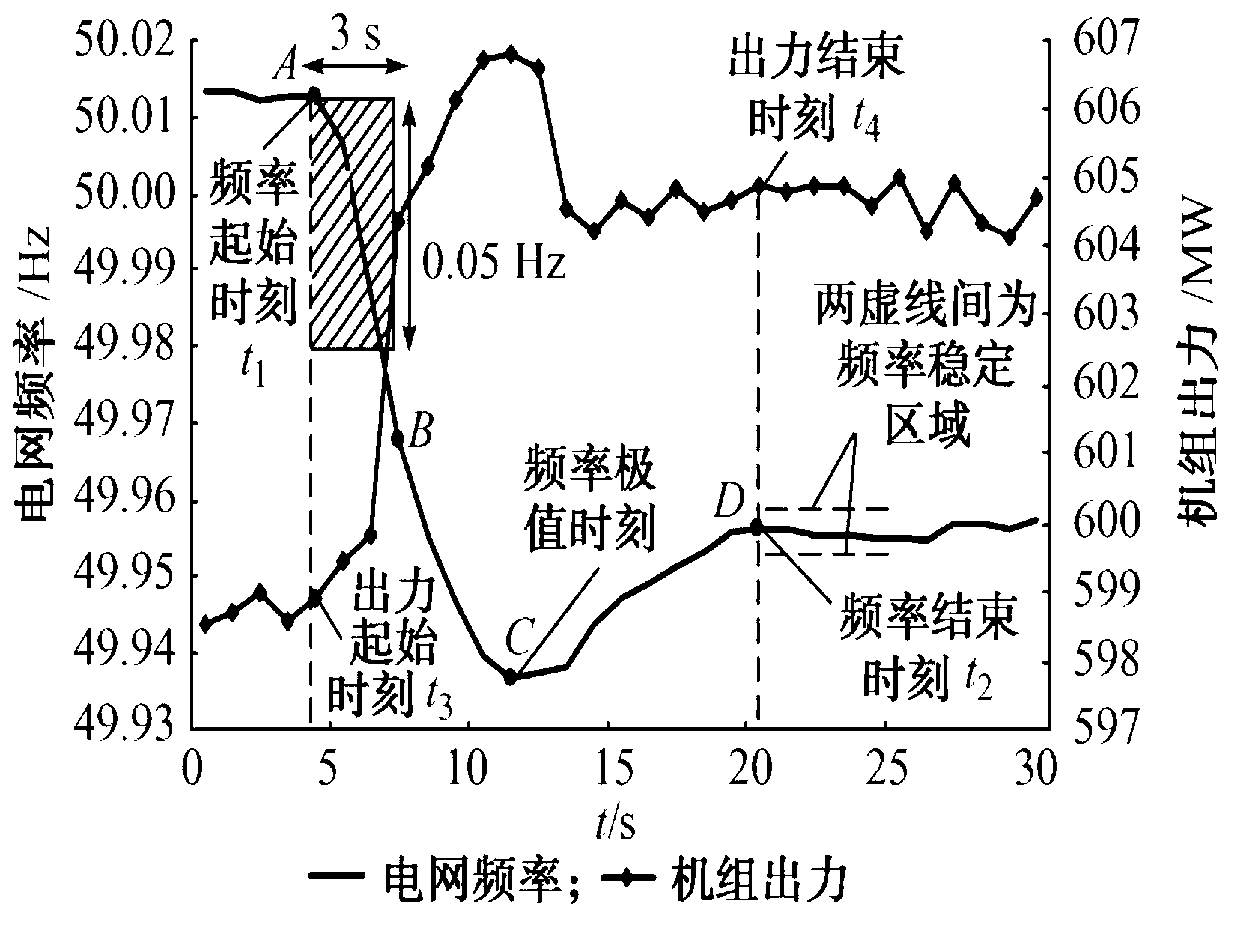
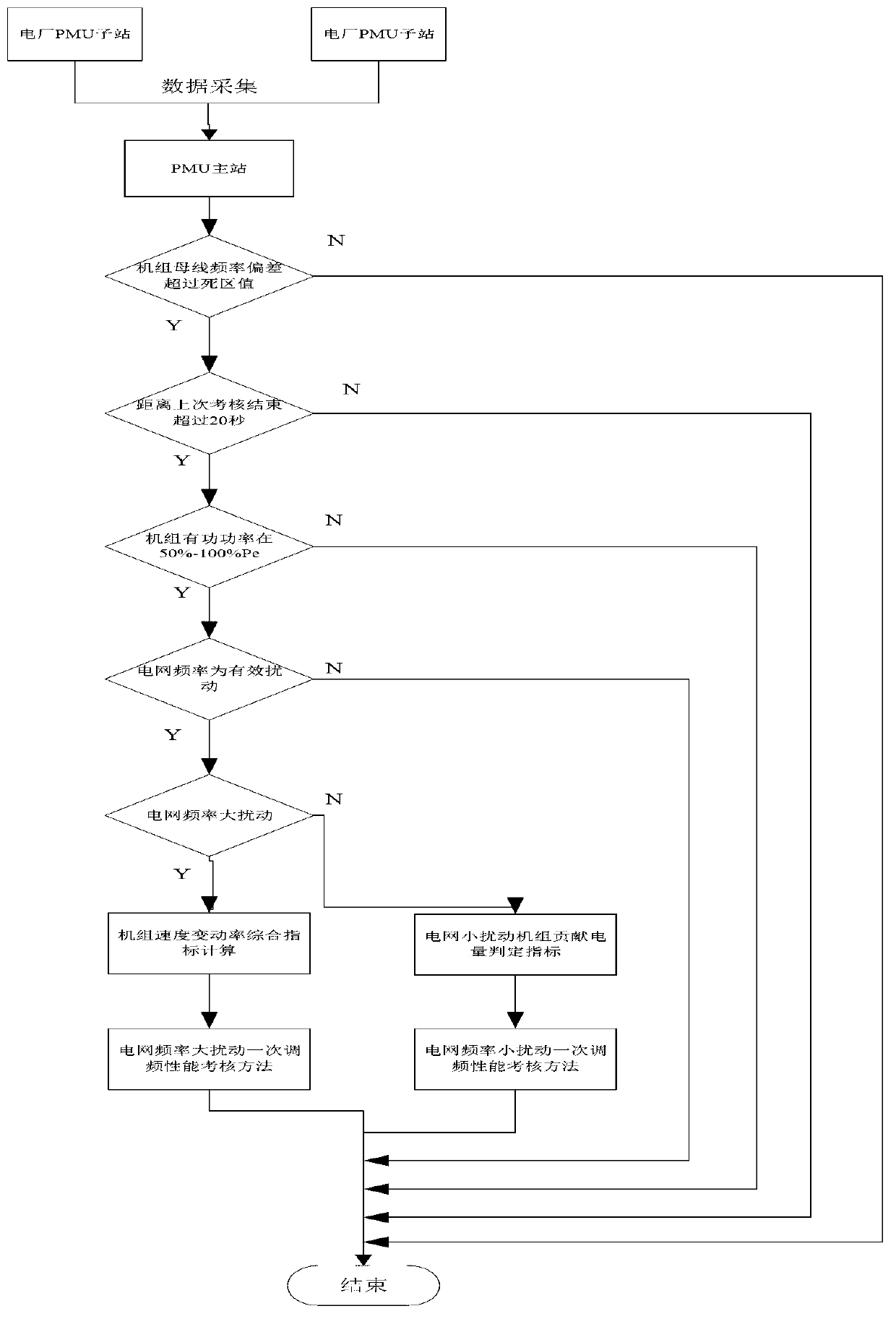
InactiveCN103346619AFully master the performance of primary frequency modulationData processing applicationsCircuit arrangementsPerformance indexEngineering
The invention discloses an online monitoring and performance assessing method for primary frequency modulation of a thermal generator set. The method divides grid frequency changes into invalid disturbance, valid disturbance, large frequency disturbance and small frequency disturbance, wherein the large frequency disturbance and the small frequency disturbance are contained in the valid disturbance. Specific performance indexes of response time, stabilization time, diversity factors of set rotating speed and the like of the primary frequency modulation of the set are quantitatively assessed, the contributed electric quantity and the correct operation rate of the primary frequency modulation under the small disturbance of the set and the diversity factors of the set rotating speed under the large disturbance of the set can be effectively calculated, and an assessing method for the performance of the primary frequency modulation of the set is further provided. The online monitoring and performance assessing method for the primary frequency modulation of the thermal generator set has the advantages that calculation and monitoring can be carried out on the operation performance of the primary frequency modulation of the set in a long period of time, the comprehensive index of the primary frequency modulation of the set is further calculated, an assessing method is quantified, and the performance of the primary frequency modulation of sets in a network can be comprehensively learned by province professionals.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Pulse-skipping PFM DC-DC converter using a voltage mode control loop
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com