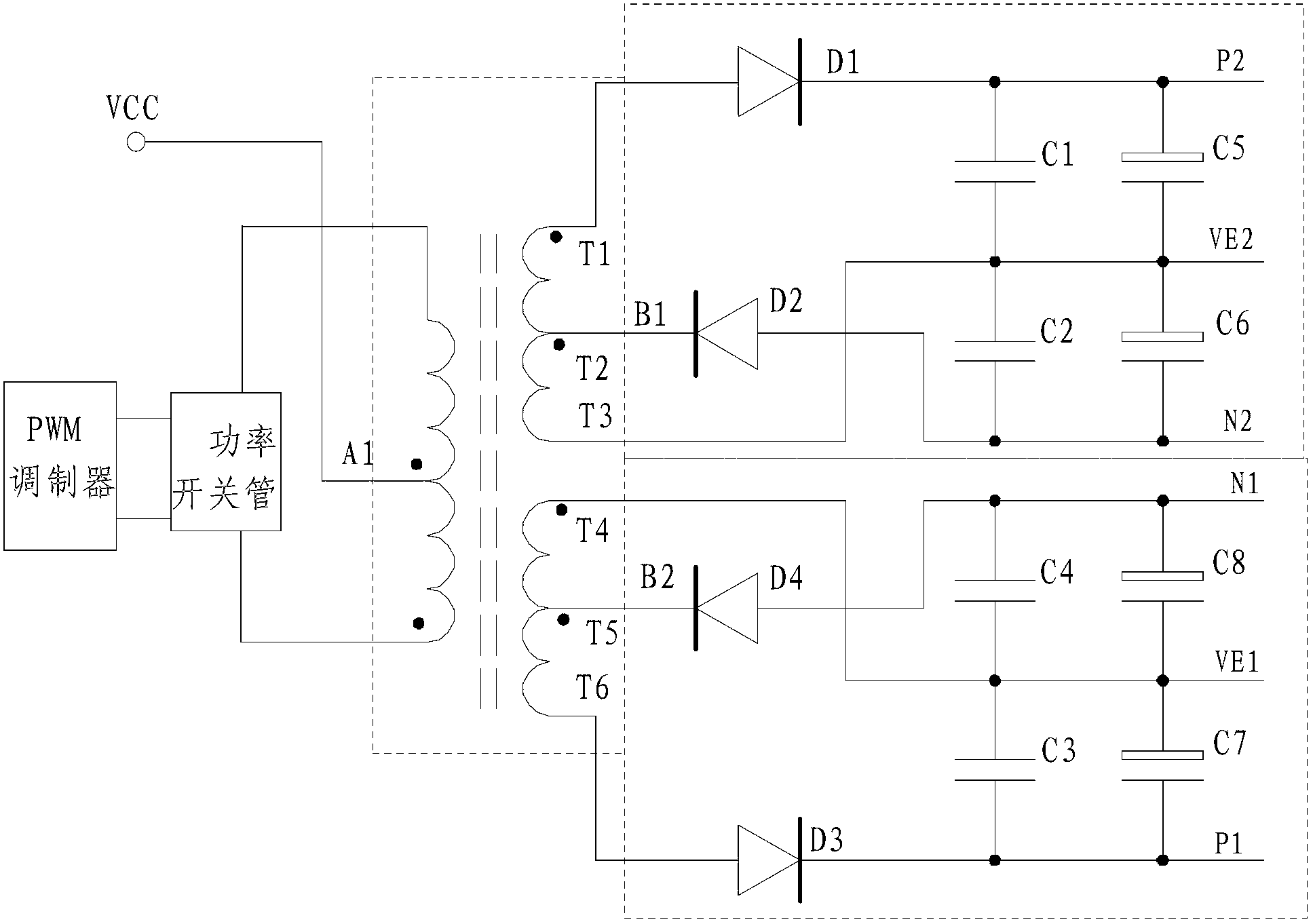Patents
Literature
169 results about "Pwm modulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
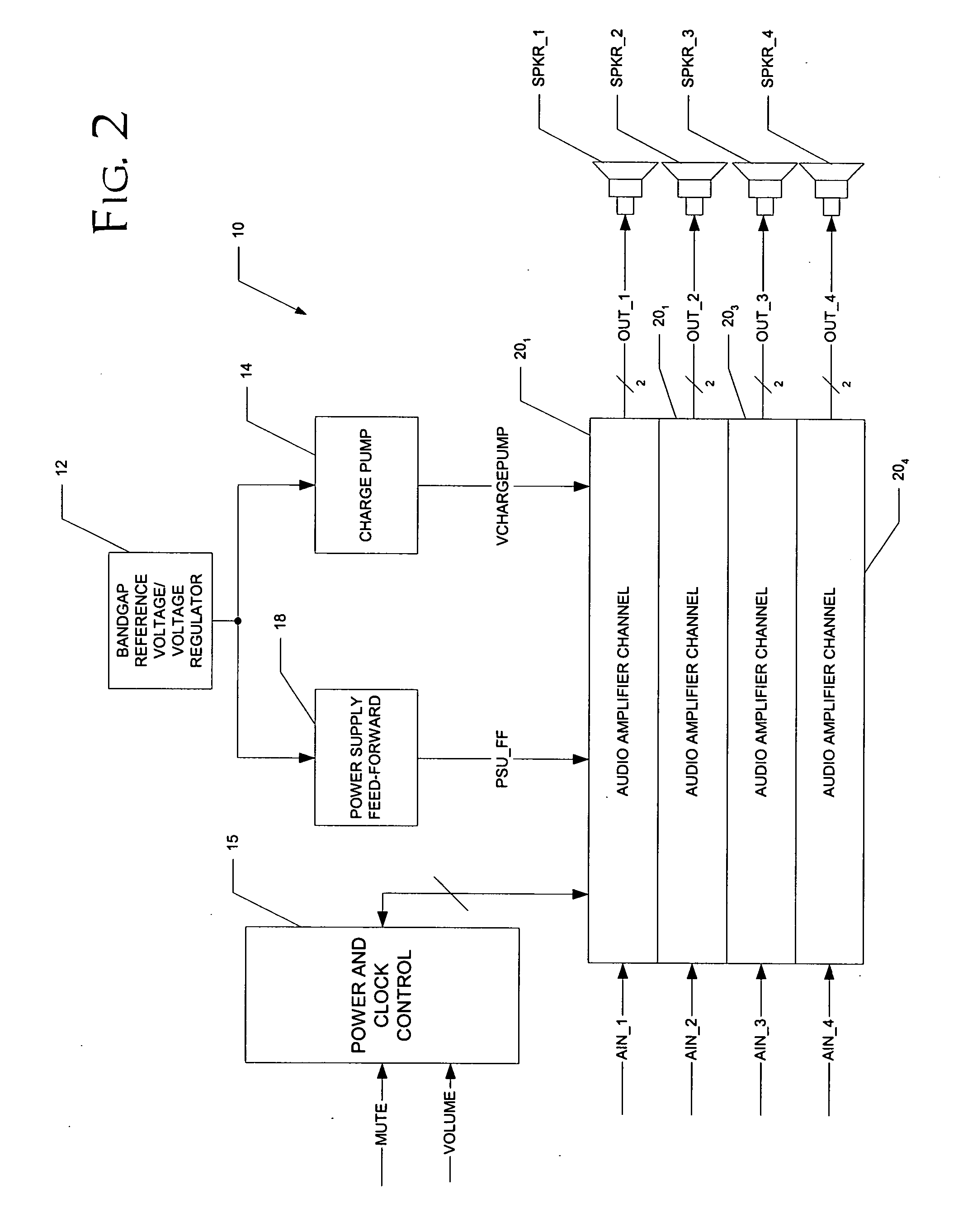
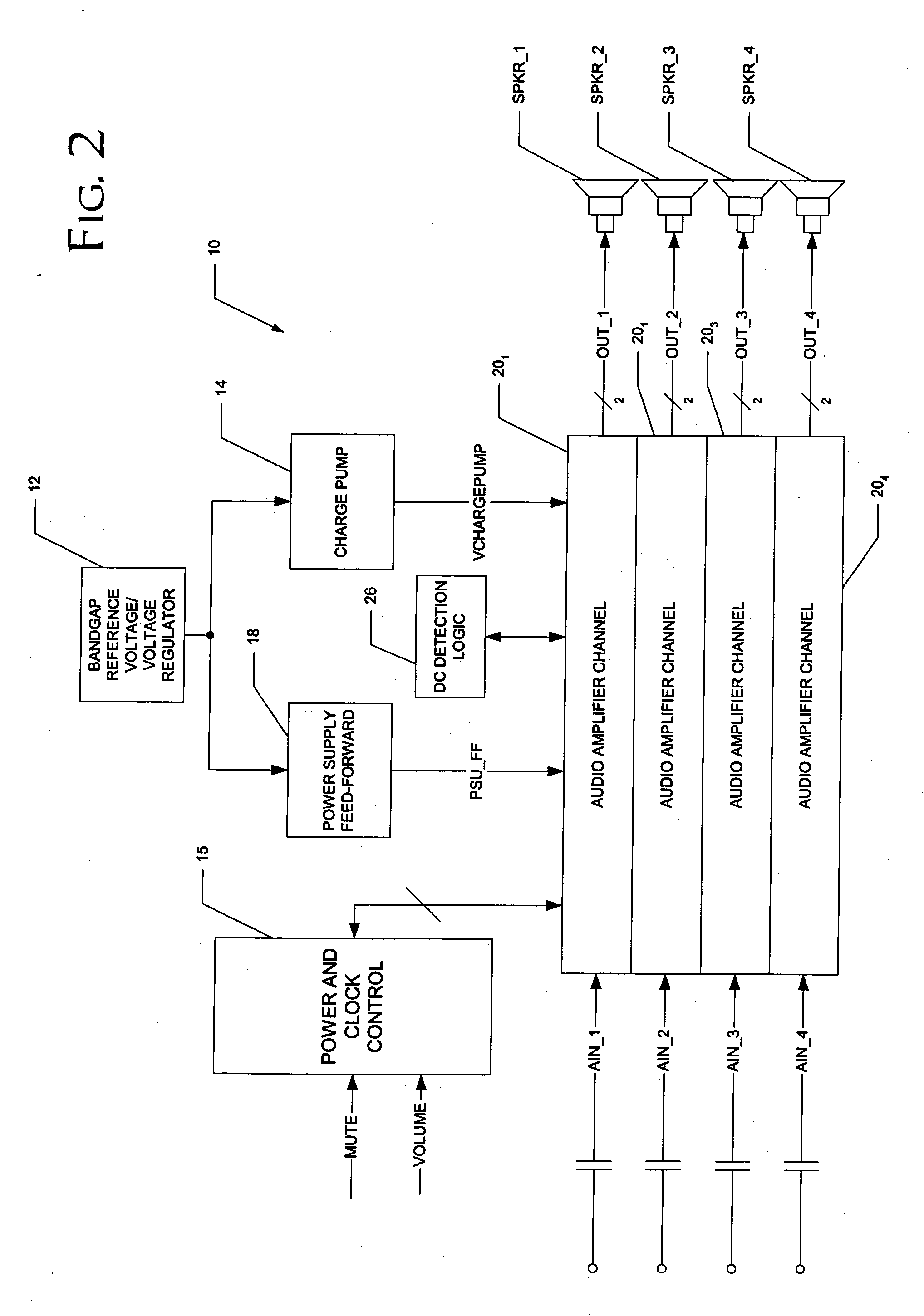
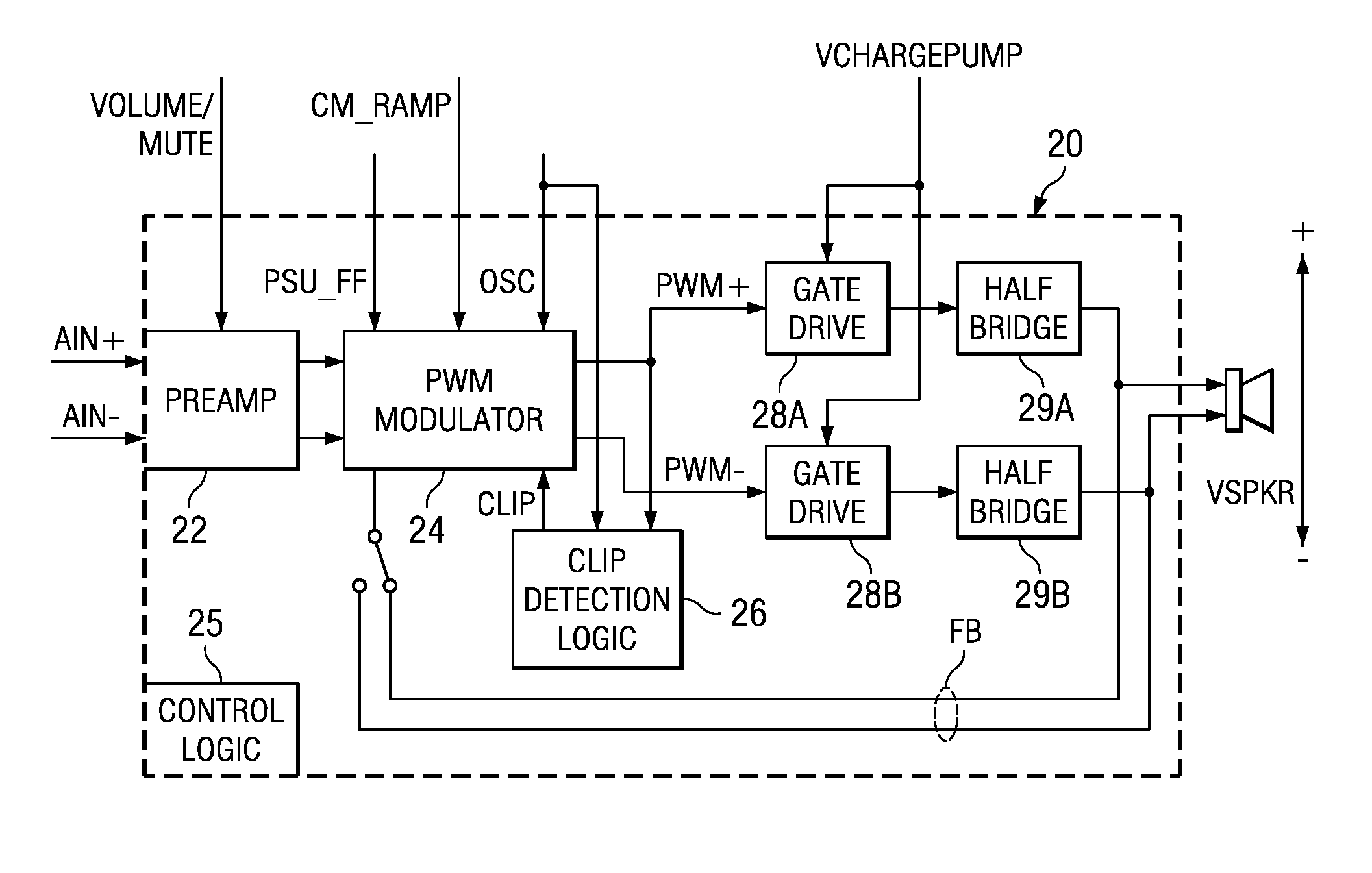
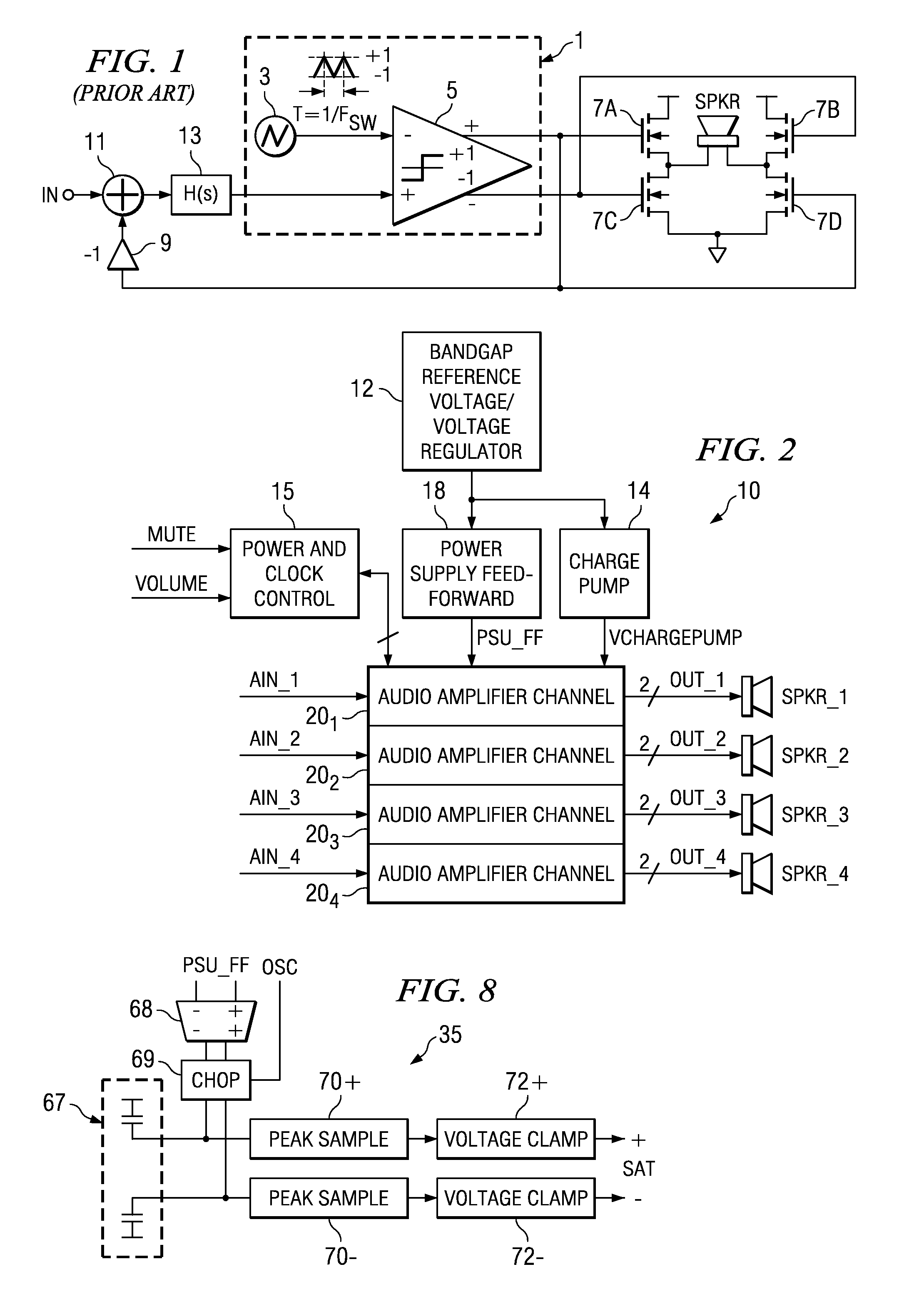
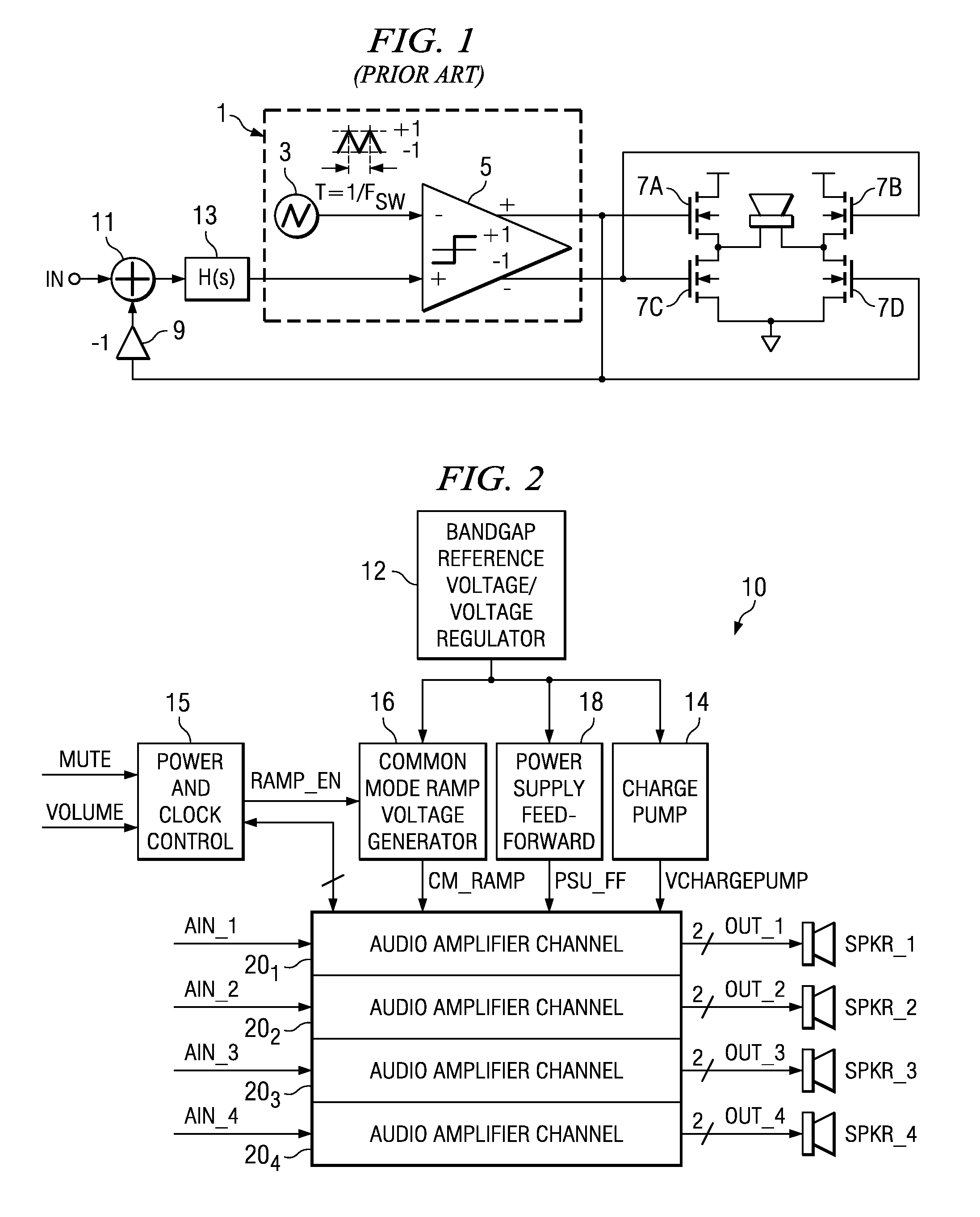
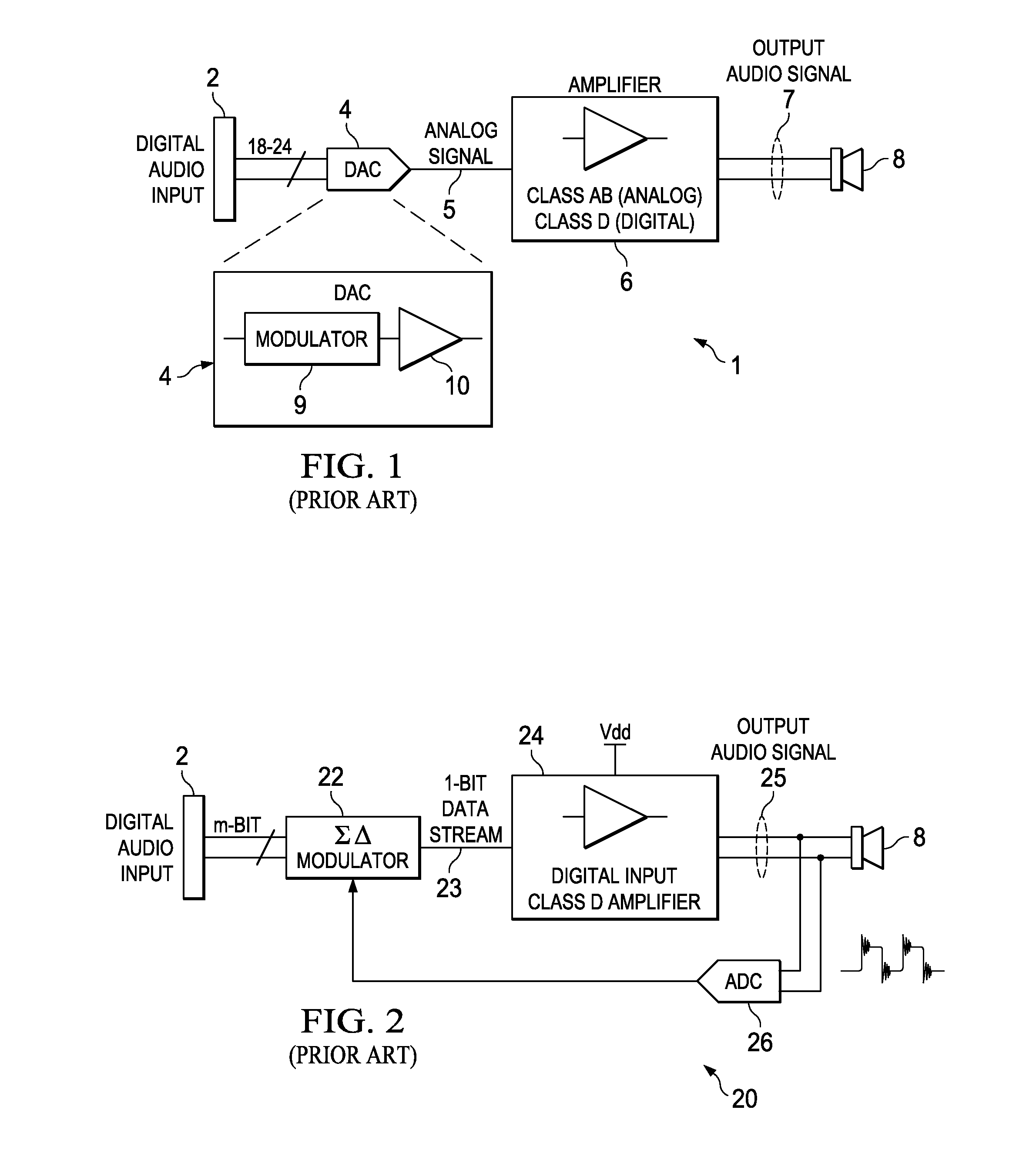
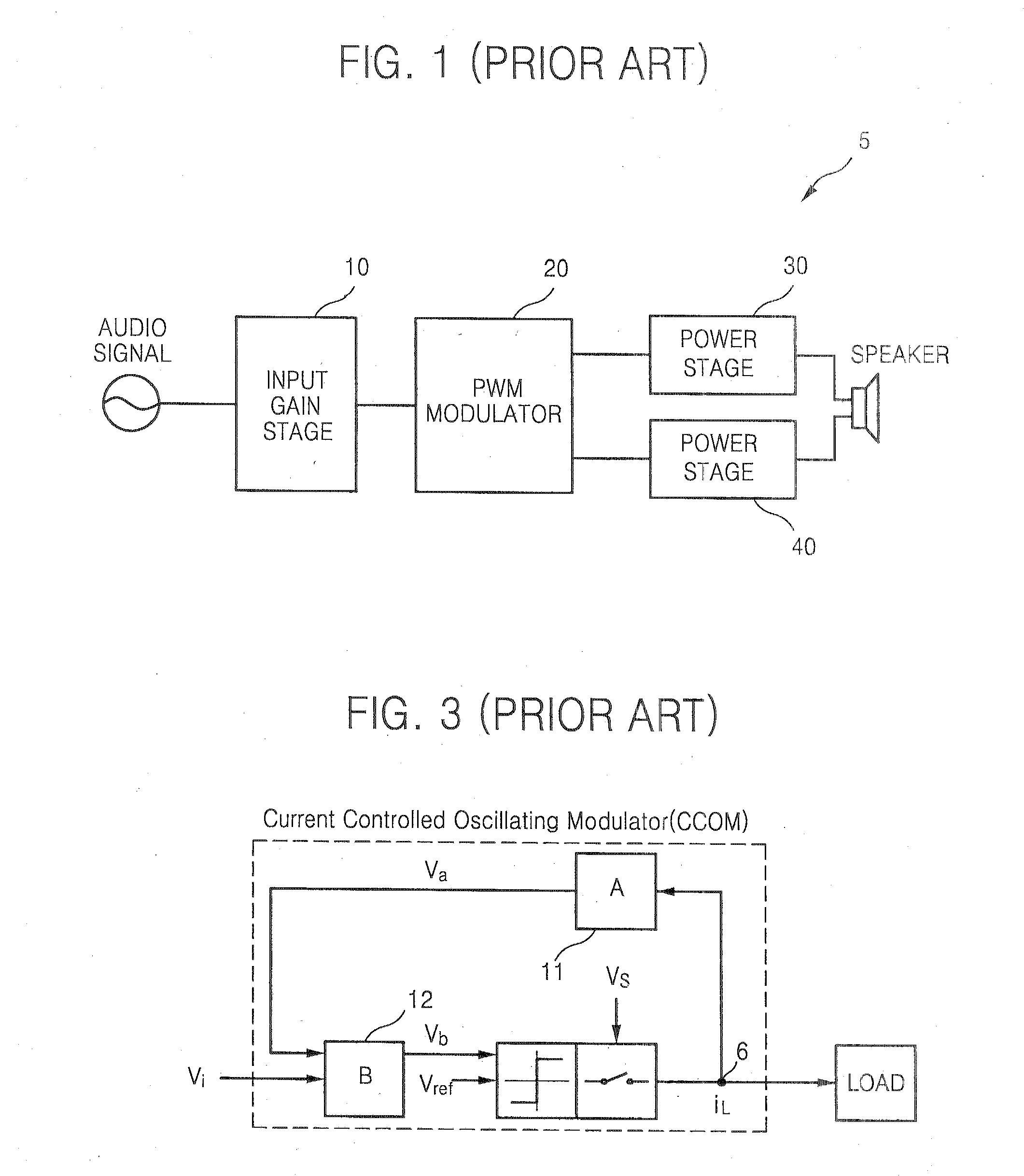
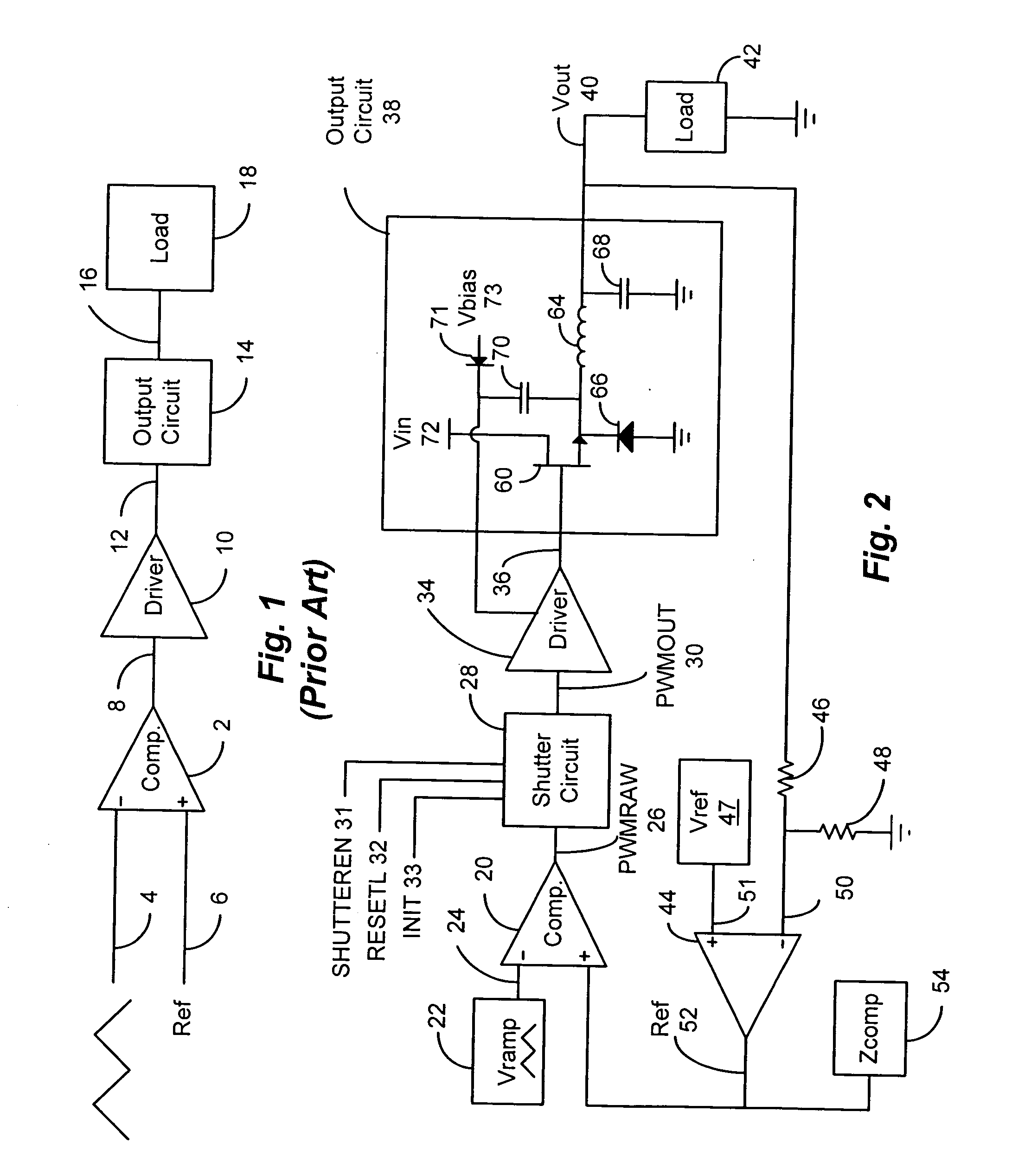
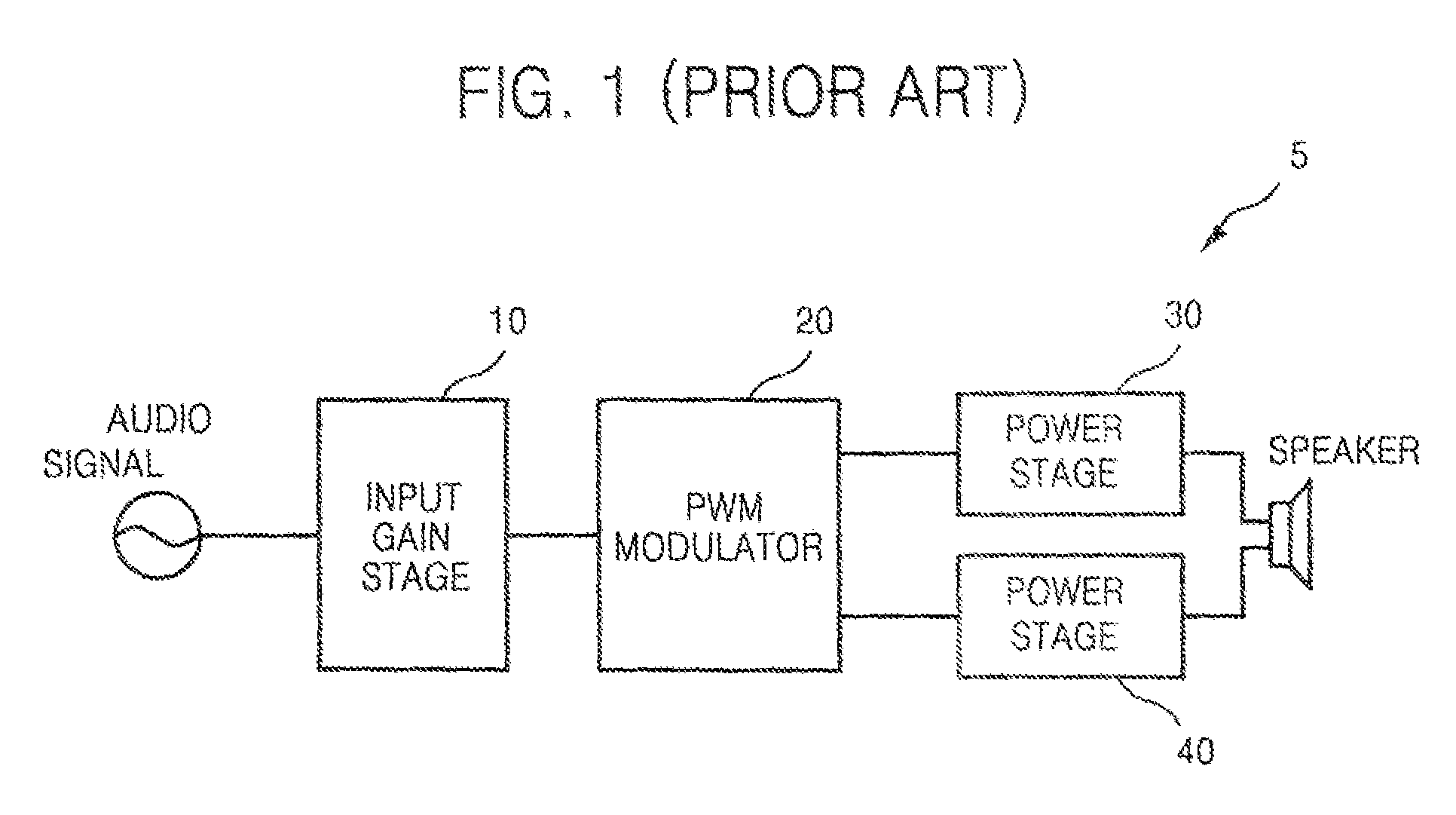
Detection of DC output levels from a class D amplifier
ActiveUS7078964B2Simple analog portionLow cutoff frequencyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationUnsafe conditionAudio power amplifier
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
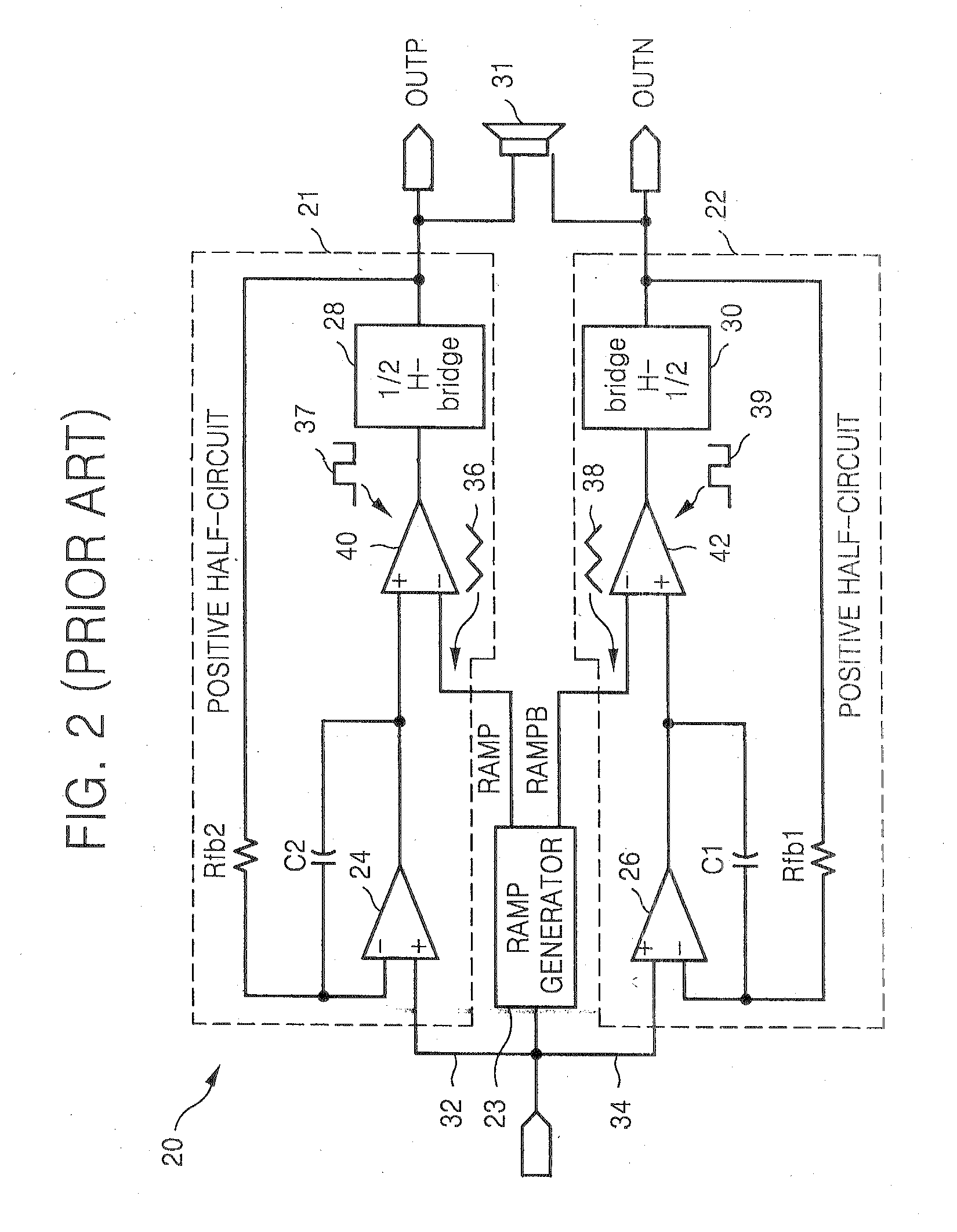
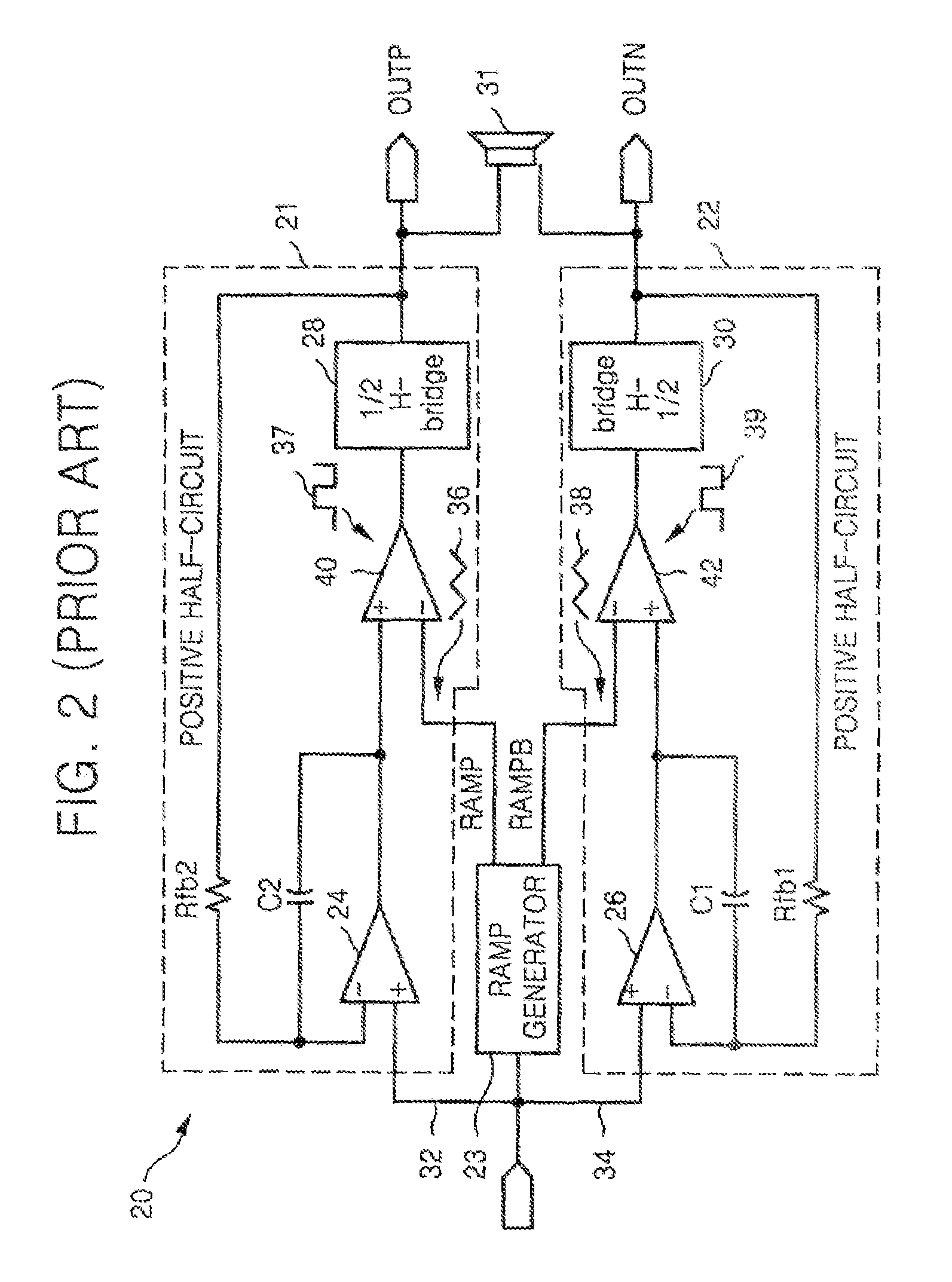
Soft transitions between muted and unmuted states in class D audio amplifiers
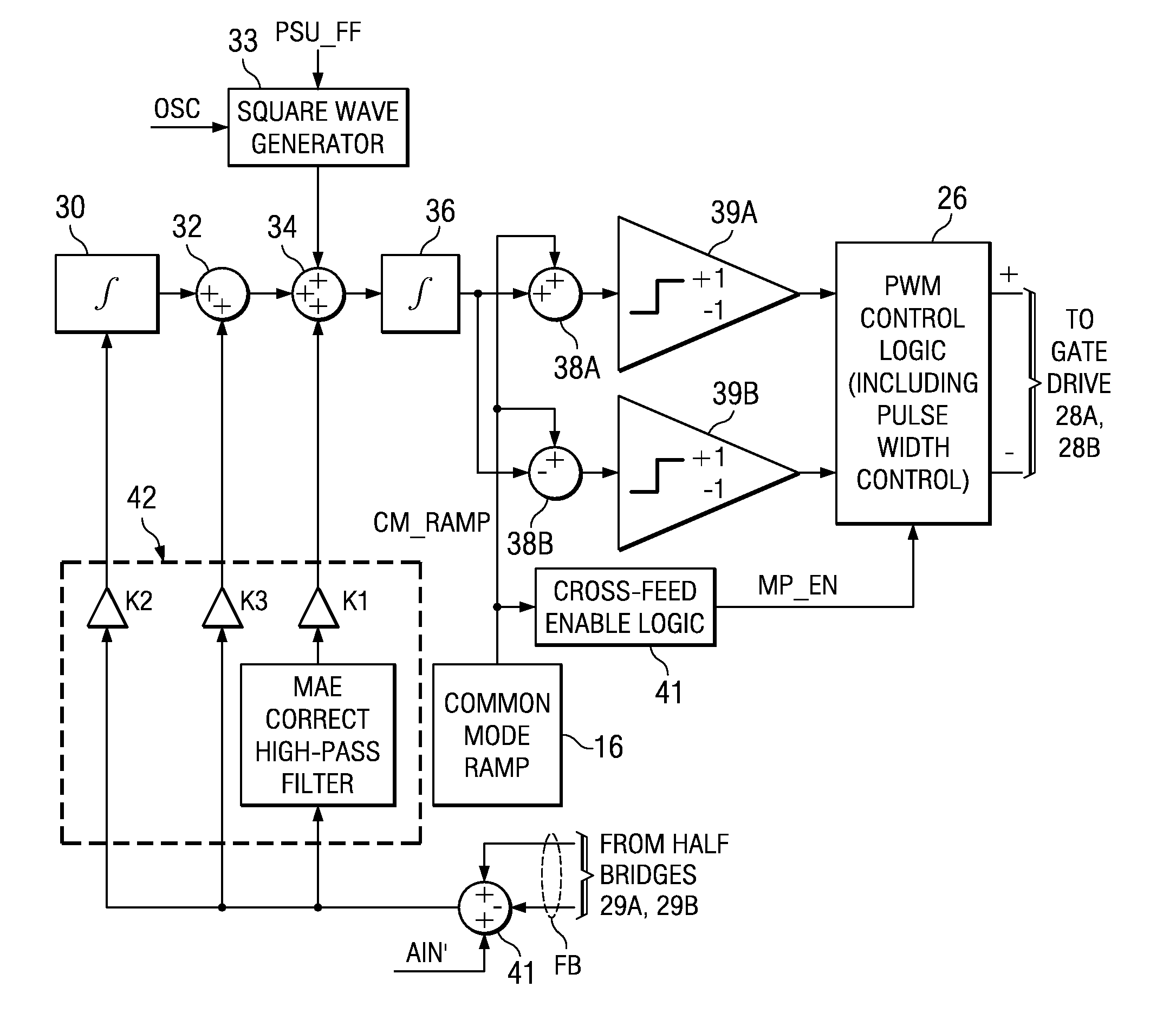
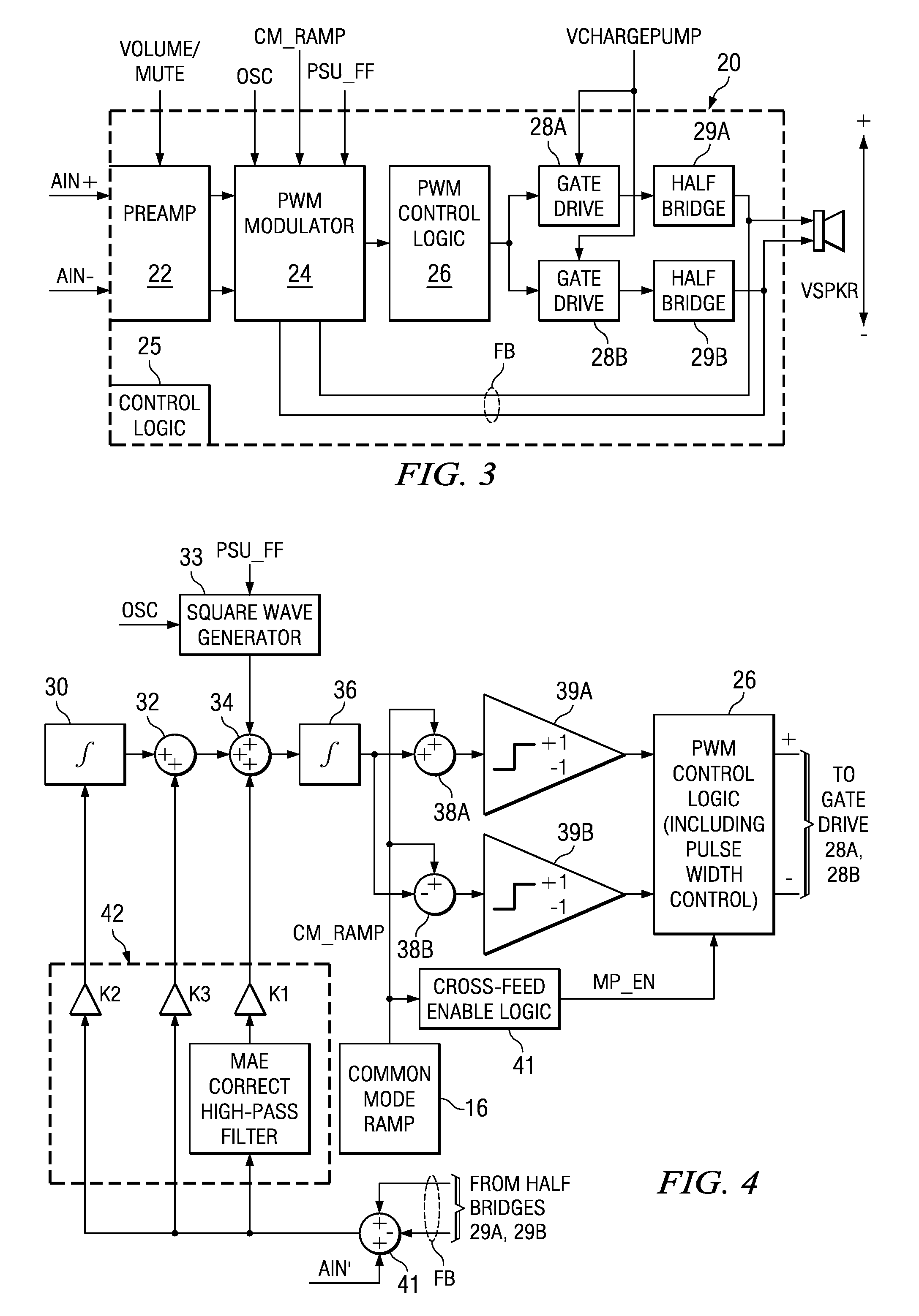
ActiveUS20050083115A1Weaken energyReduce audible sideband noiseDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorAudio power amplifierEngineering
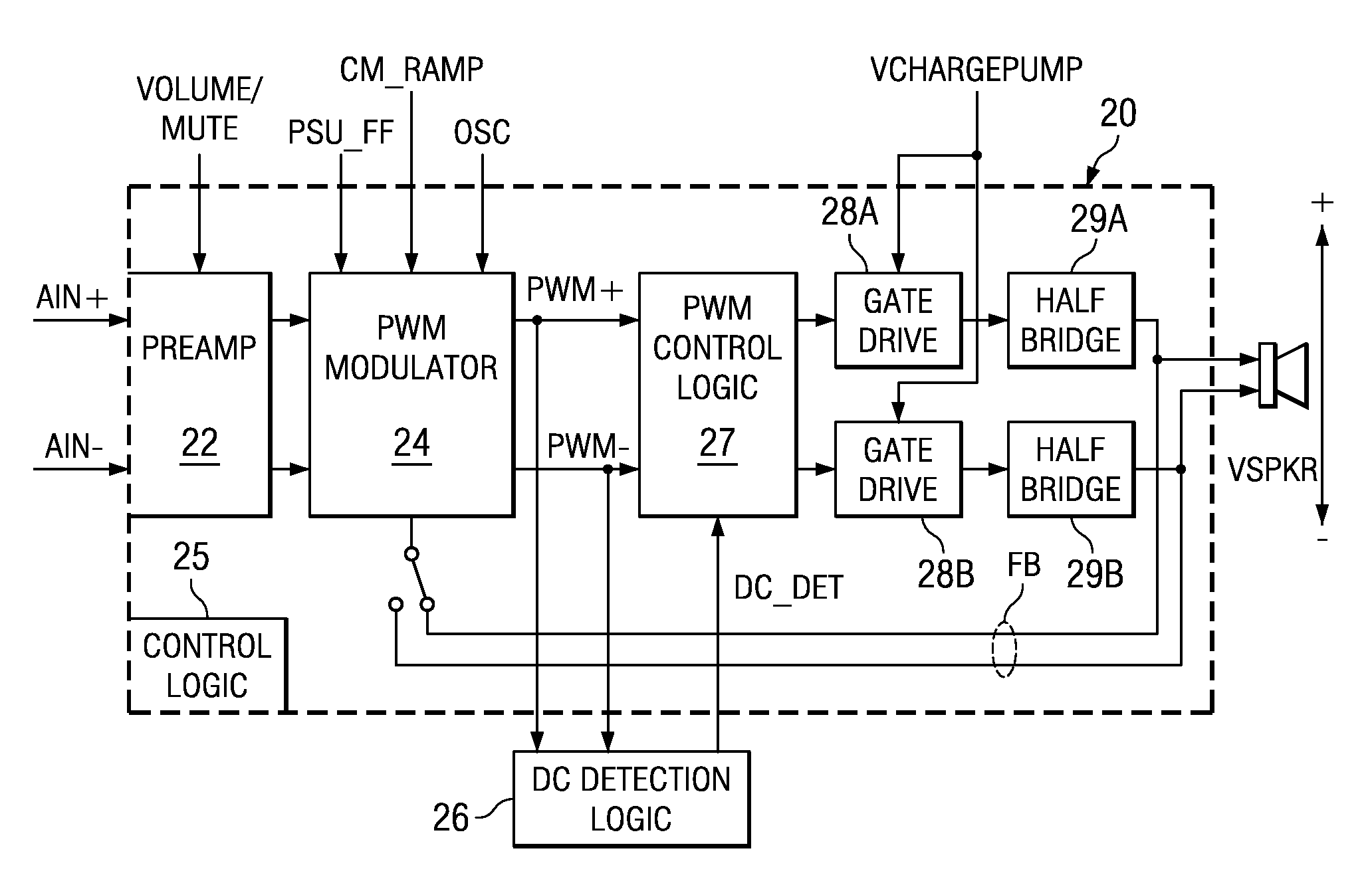
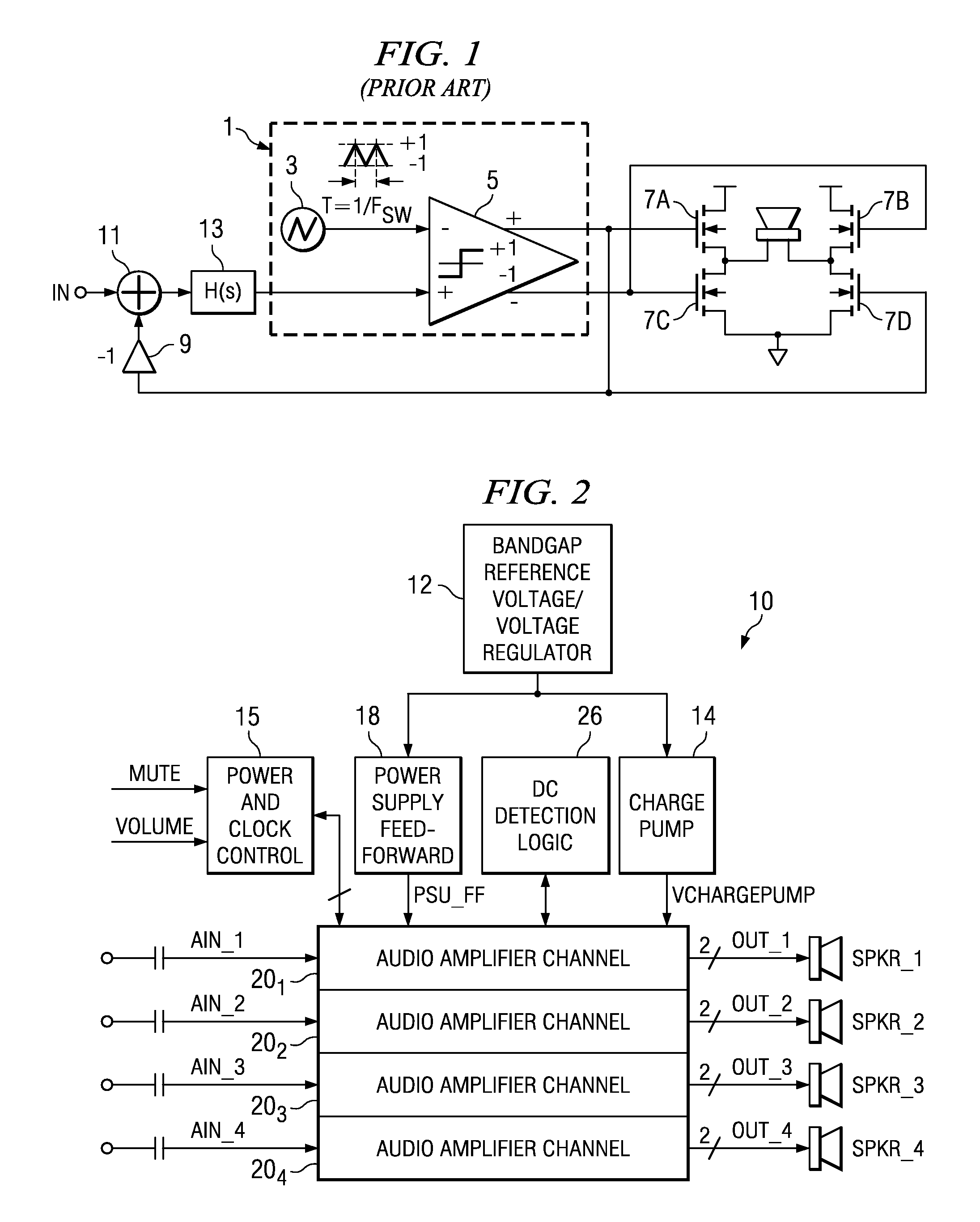
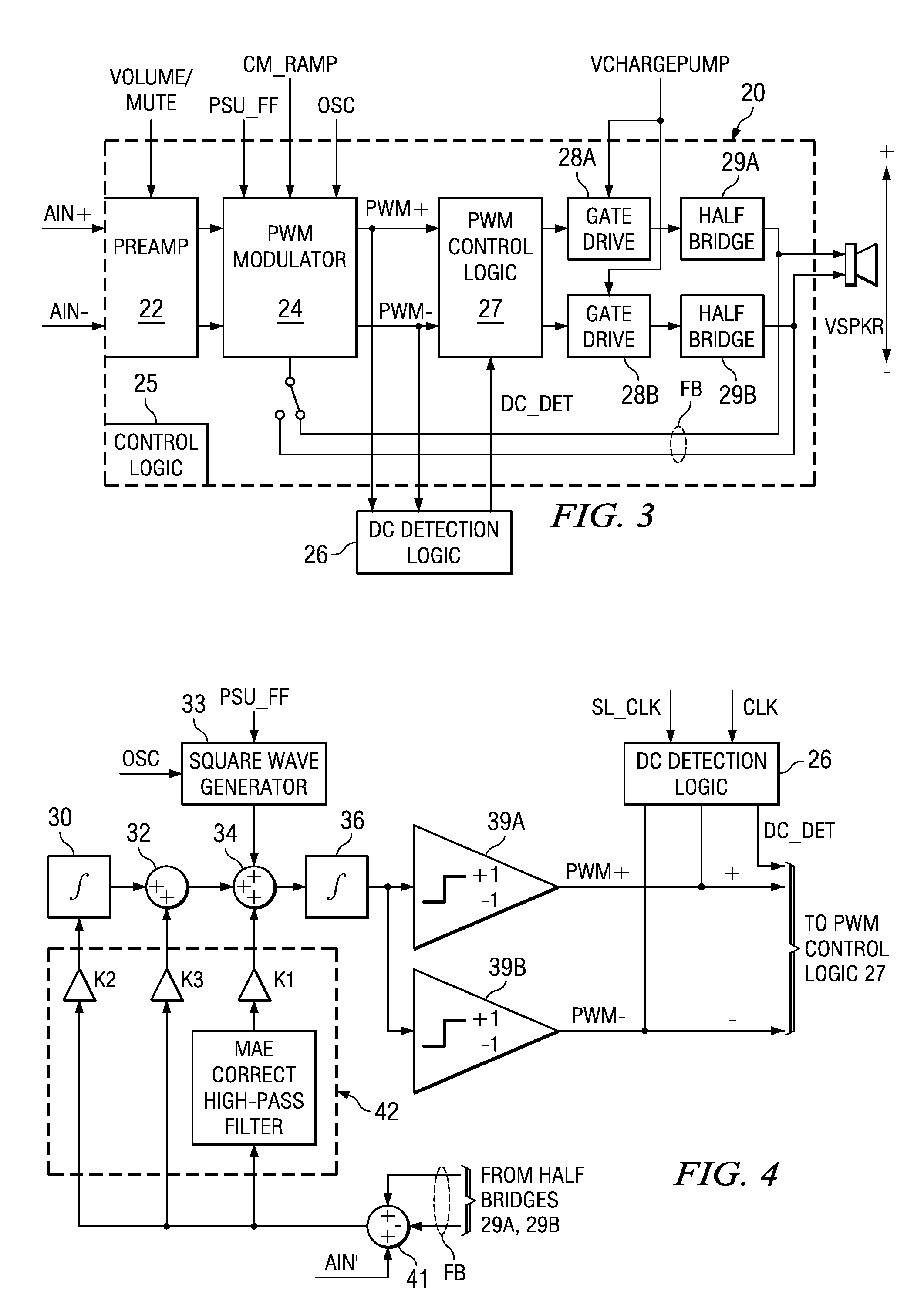
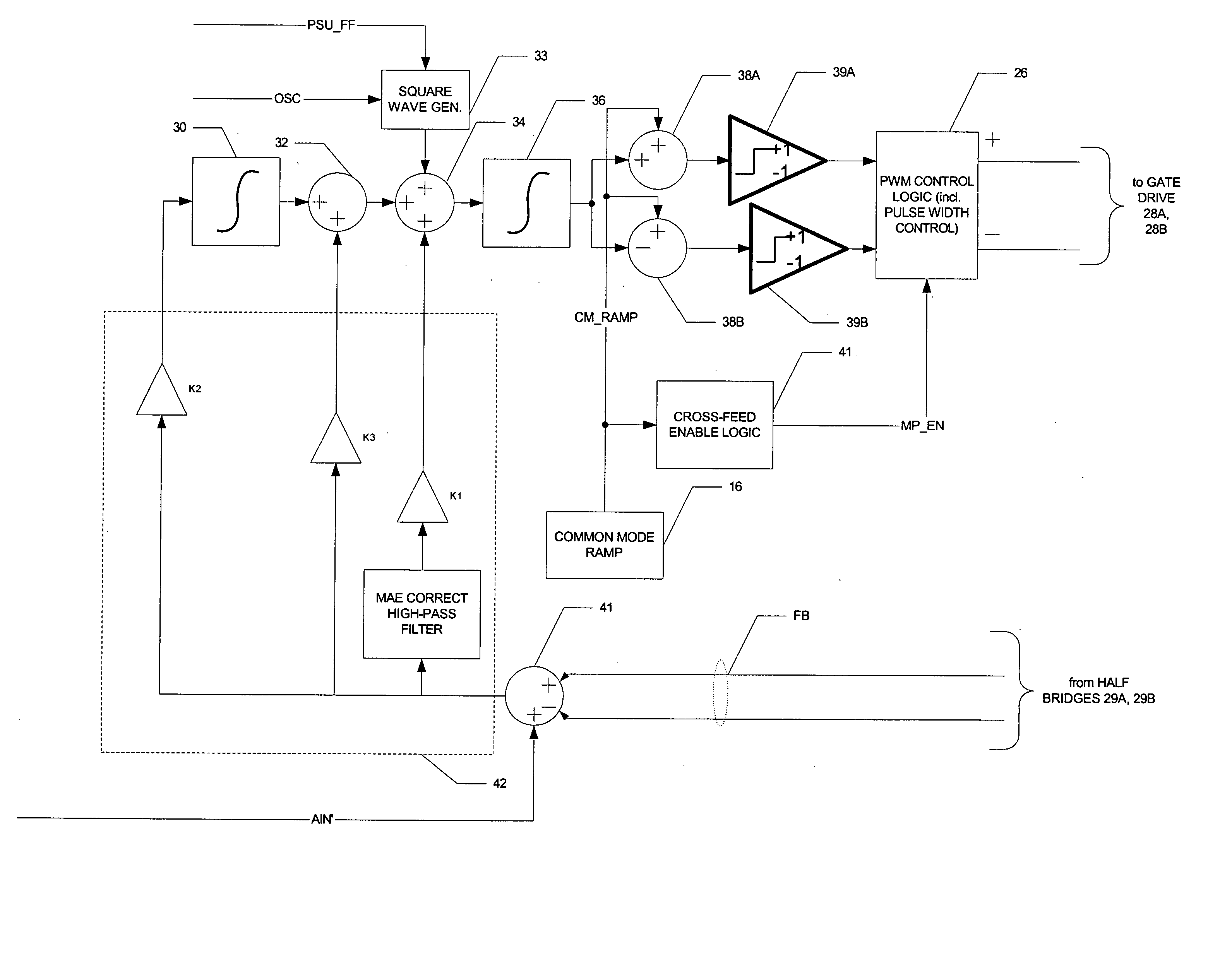
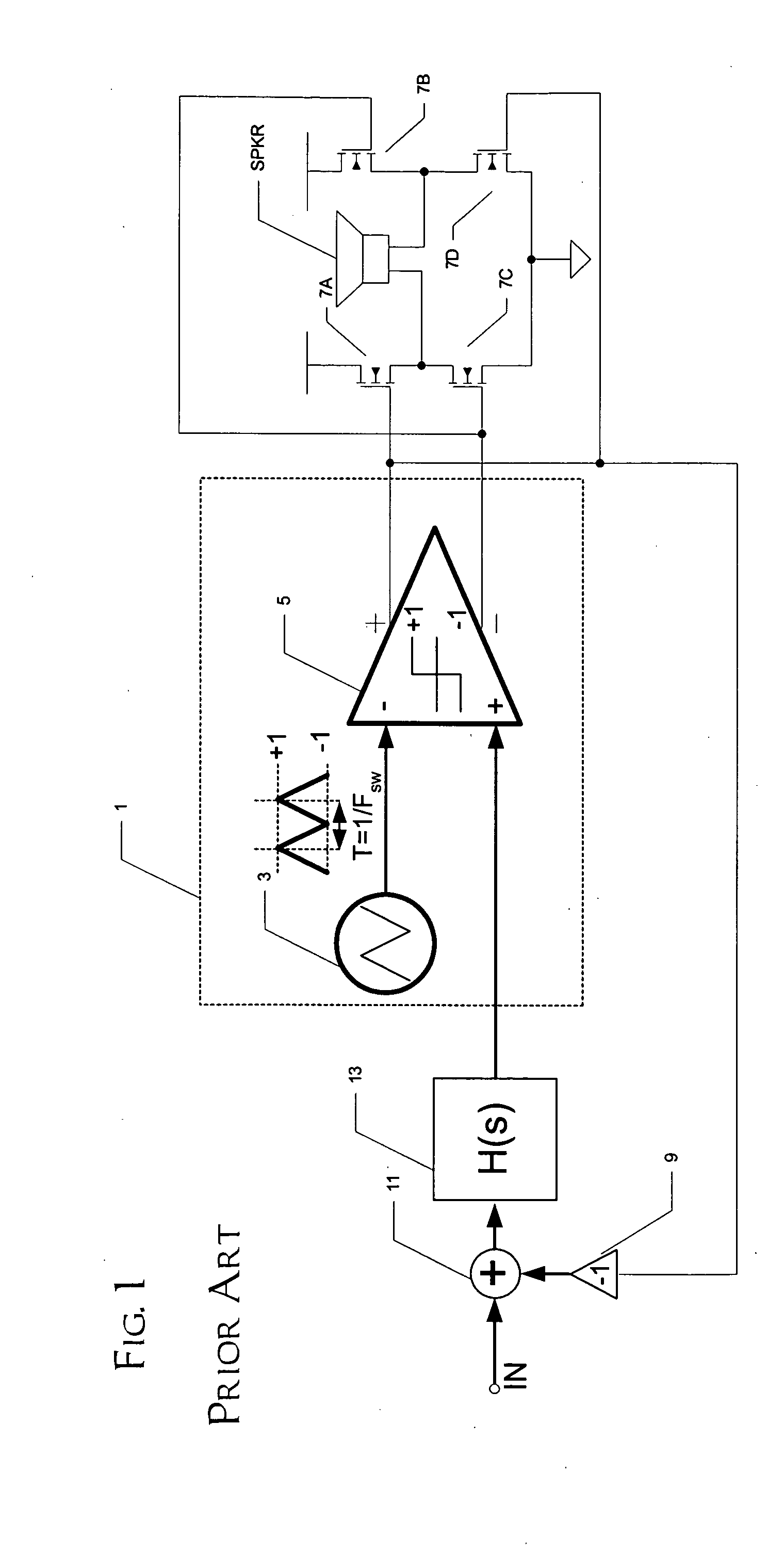
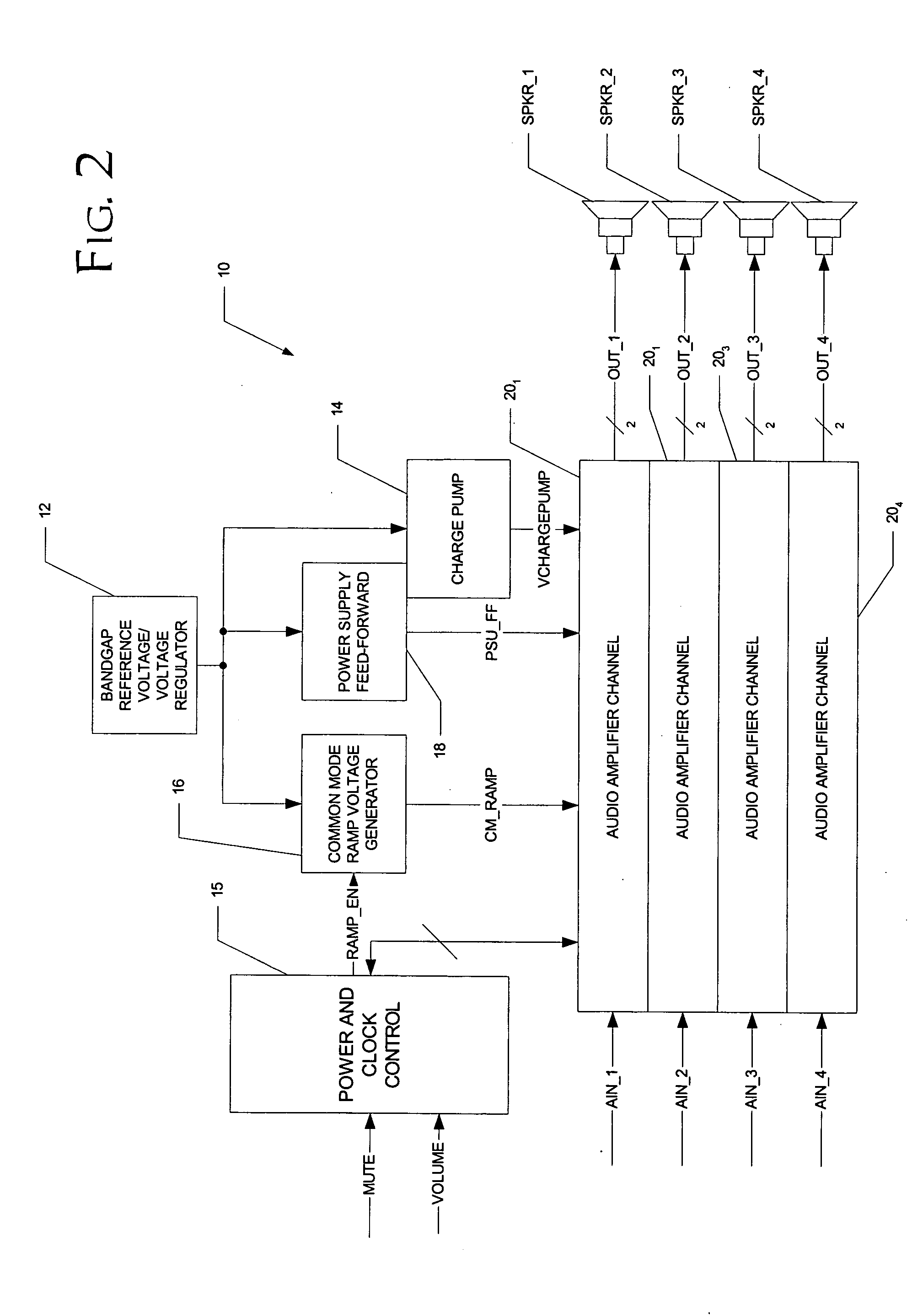
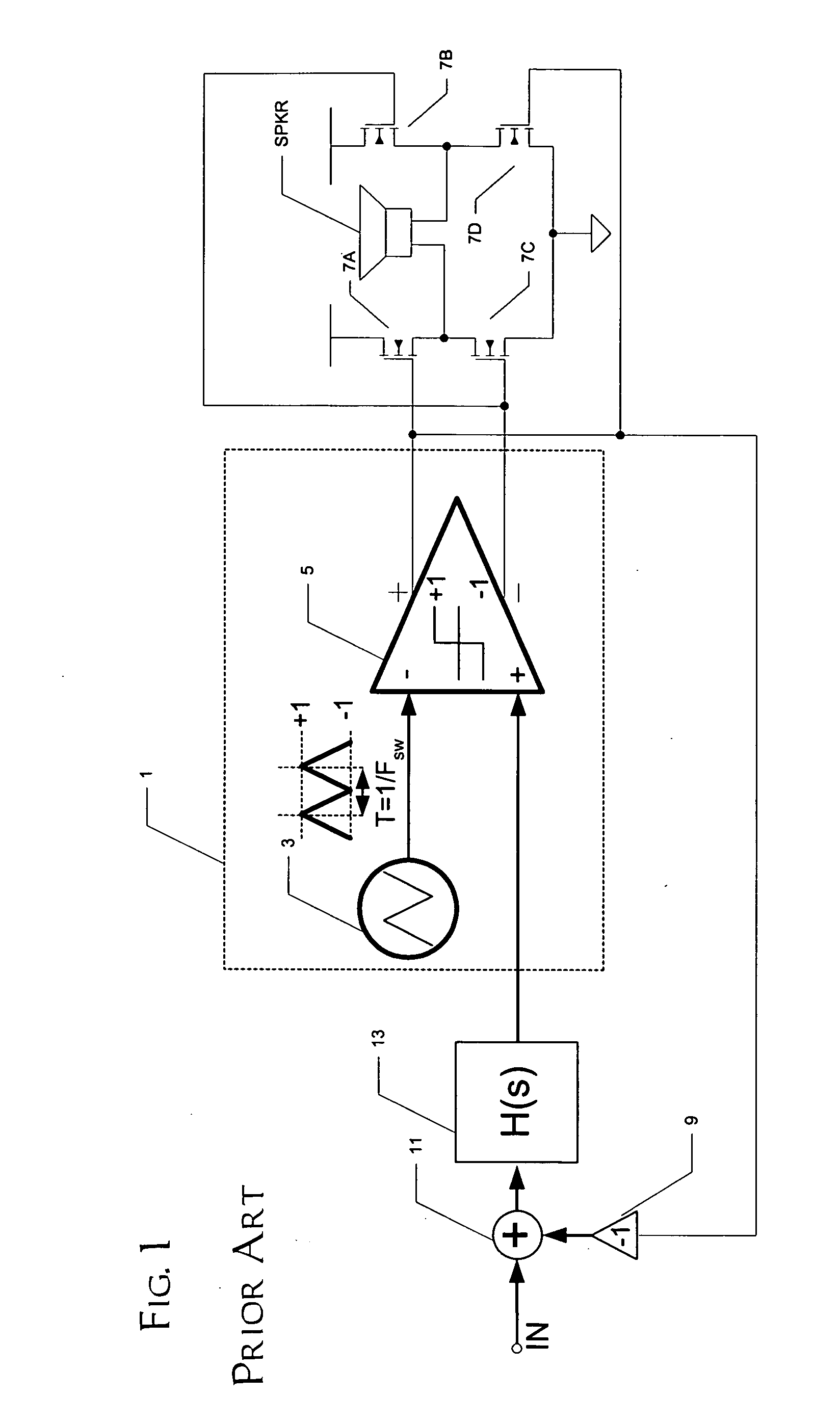
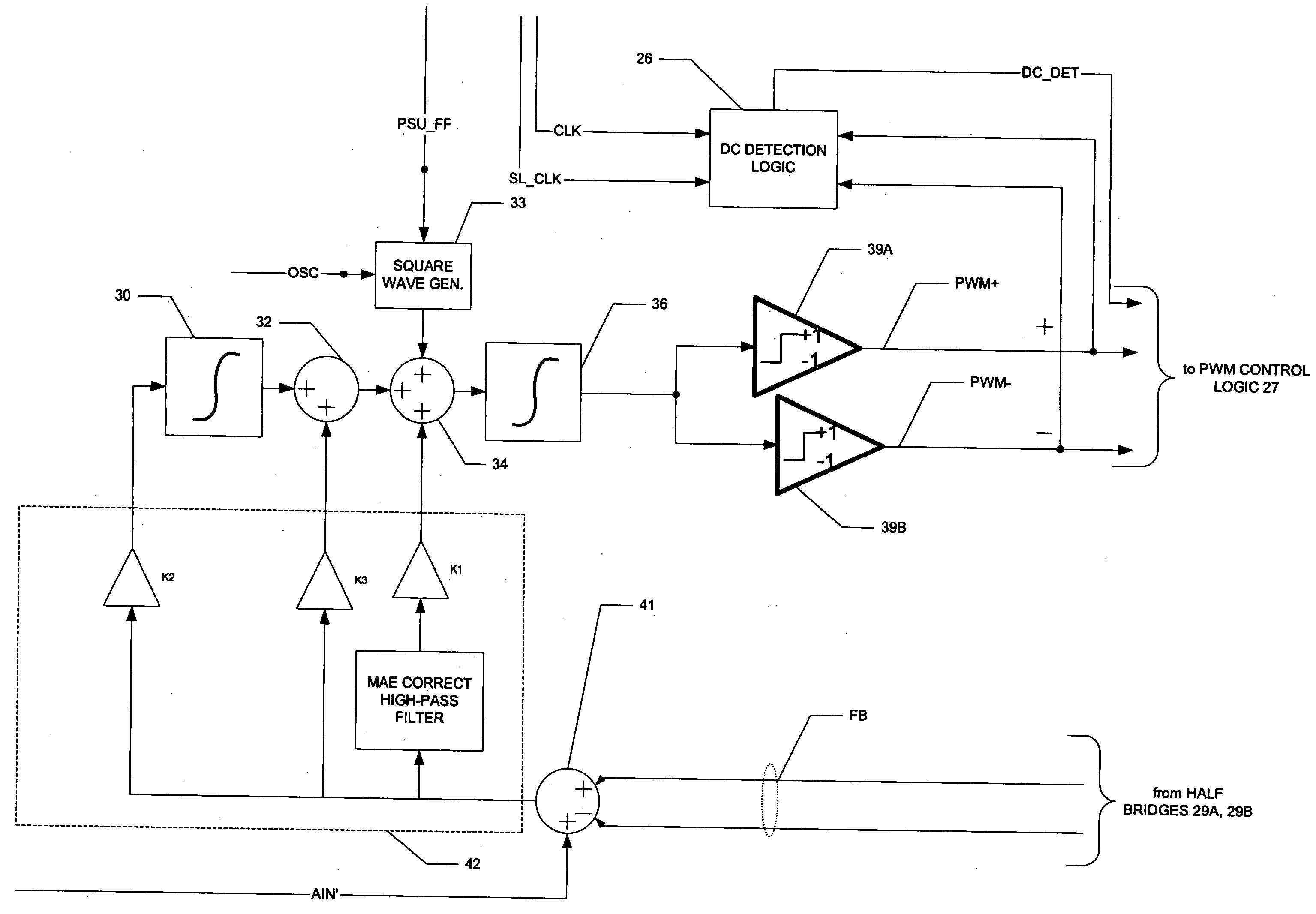
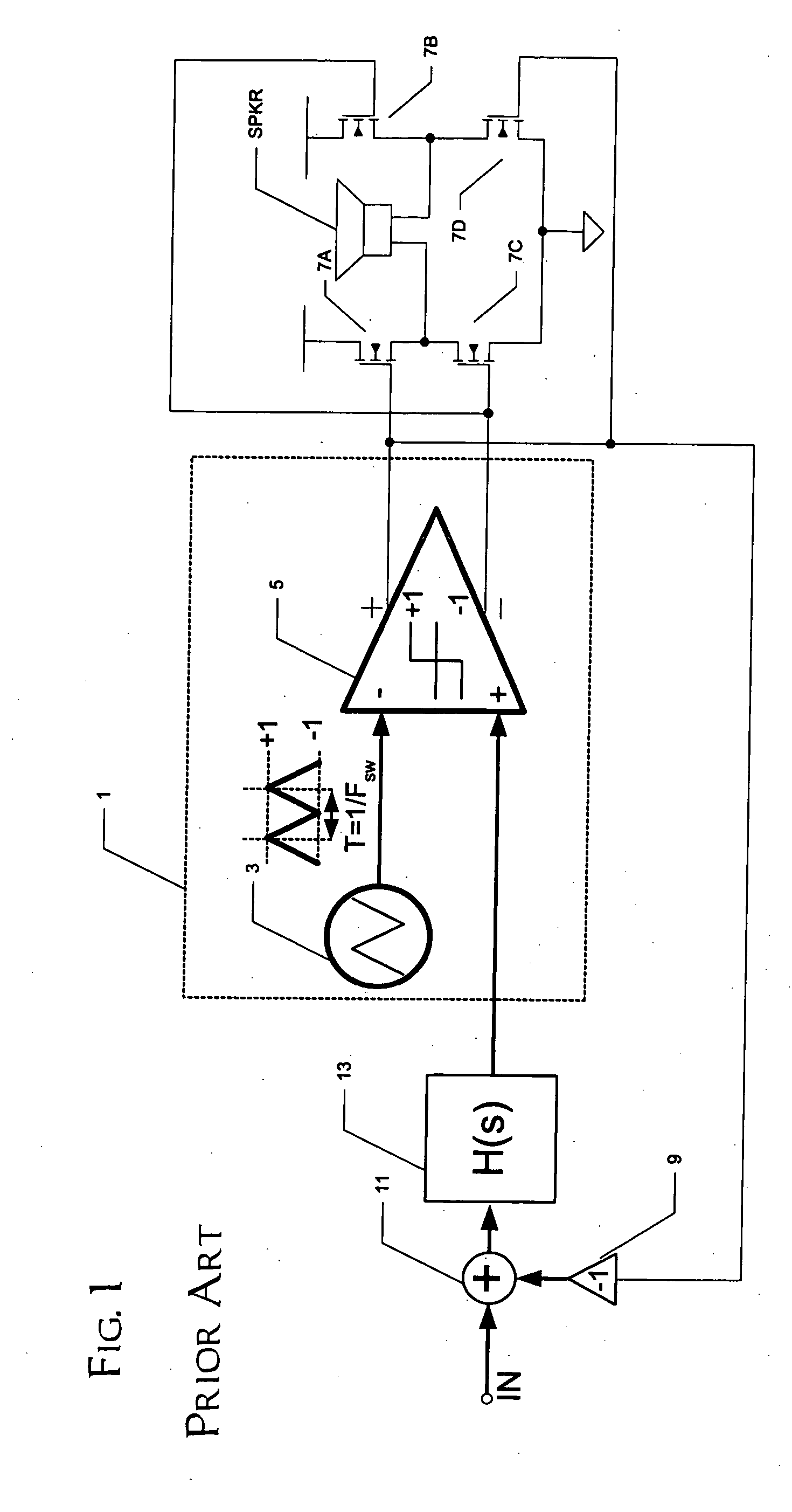
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with reduced noise capability in muting and unmuting events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. When the system is muted, a common mode voltage (CM_RAMP) is applied to the inputs of the comparators (39A, 39B; 52+ 52−) to suppress the duty cycle at the amplifier output, preferably to a zero duty cycle. In the transition from a muted state to an unmuted state, the common mode voltage (CM_RAMP) is ramped from the suppressing voltage to zero common mode voltage, permitting the duty cycle of the complementary PWM signals to gradually increase, thus reducing clicks and pops. The converse operation is performed in the transition from unmuted to muted. Pulse-width-modulation control logic (26) is also included to ensure that that the PWM “on” and “off” pulses are of at least a minimum duration, and also to generate compensating pulses on the complementary PWM line at low duty cycles.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
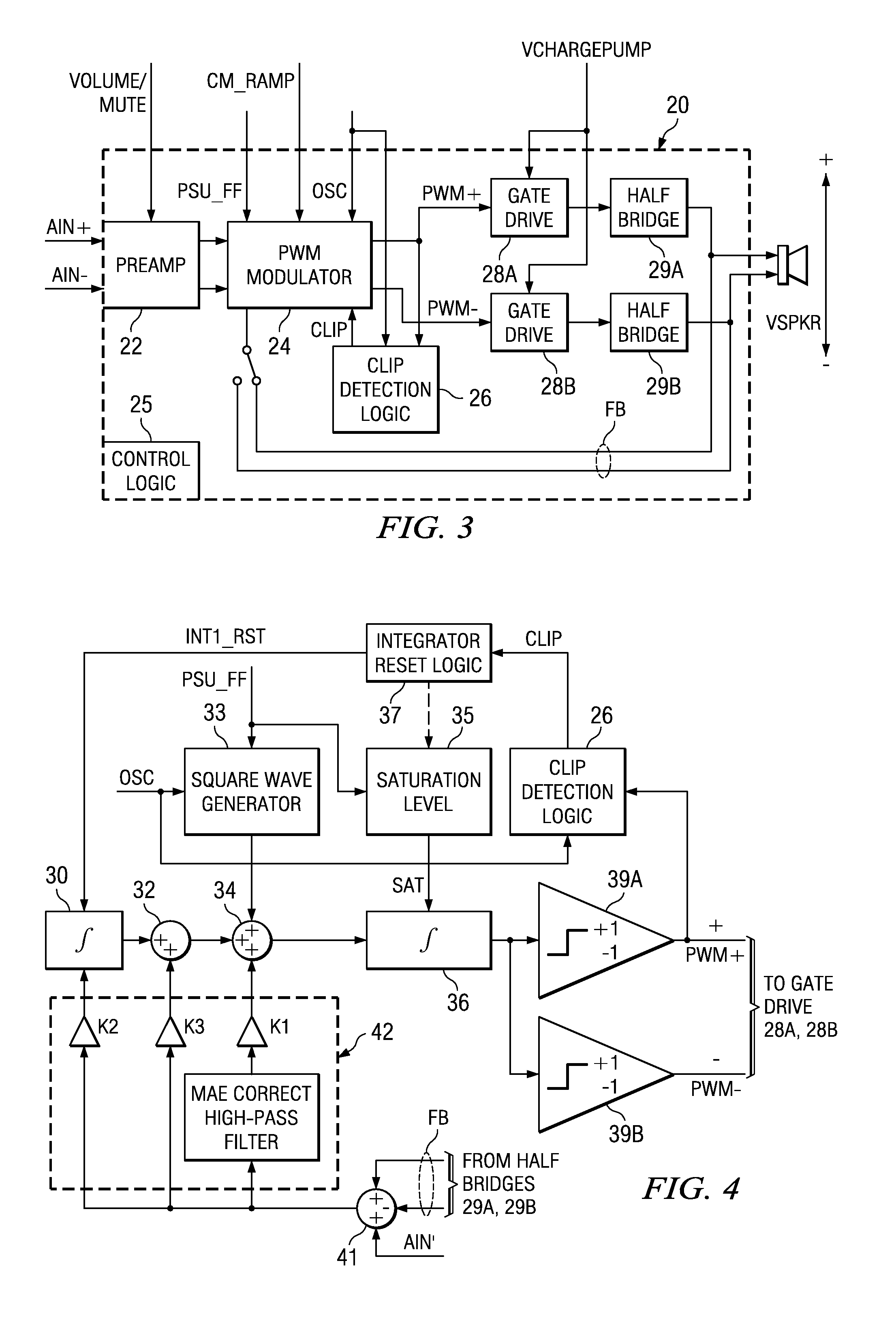
Recovery from clipping events in a class D amplifier
ActiveUS20050083114A1Shorten recovery timeAmplifier combinationsDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorLoop filterIntegrator
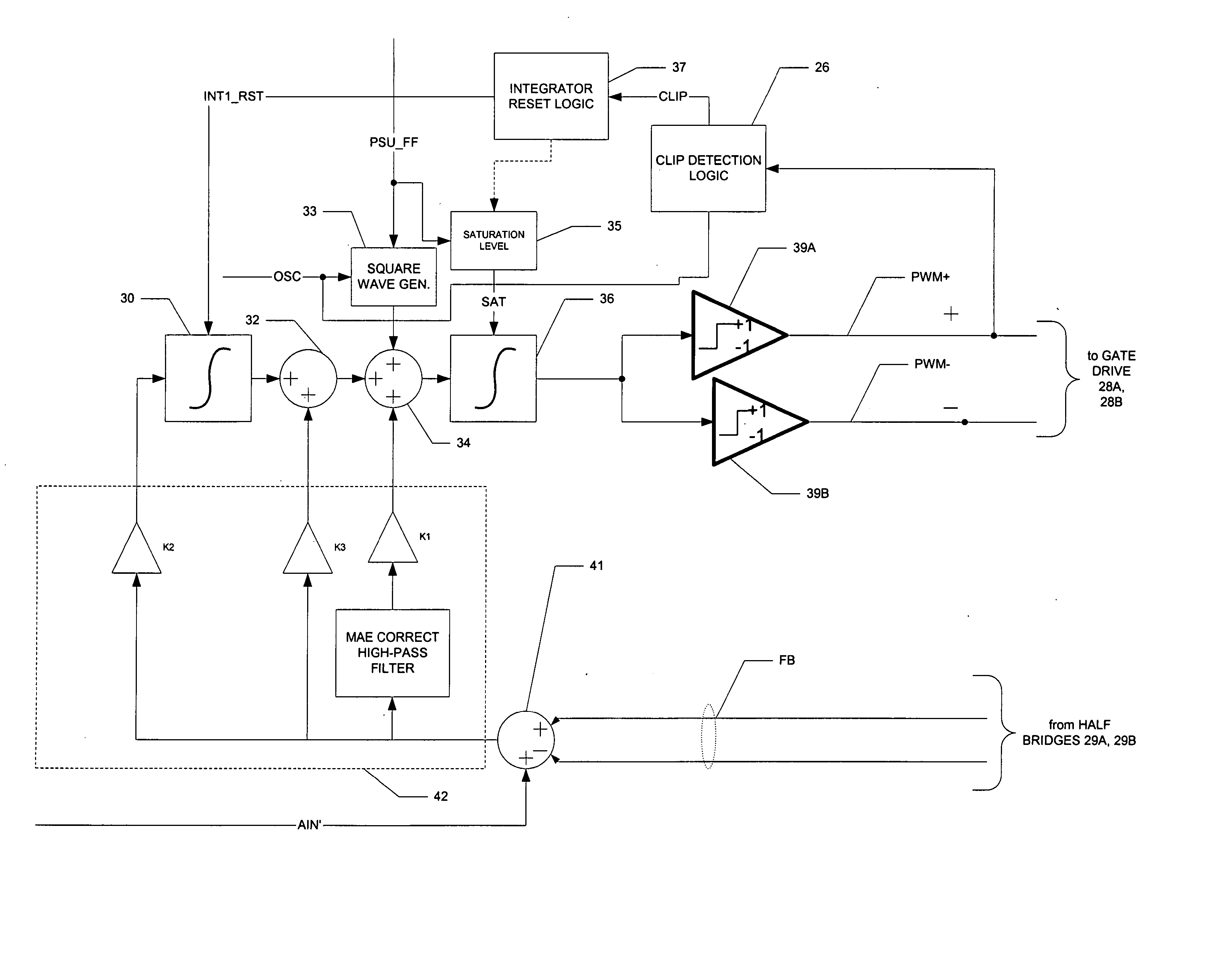
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with improved recovery from clipping events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. Clip detection logic (26) is provided to detect clipping at the output of the channel (20), preferably by detecting successive edges of the reference waveform without an intervening edge of a PWM output signal. In response to detecting clipping, a first integrator (30; 45) is reset to remove residuals and to eliminate the first integrator (30; 45) from the loop filter of the modulator (24). A saturation level circuit (35) applies a clamping voltage, preferably in both clipping and non-clipping situations, to a second integrator (36; 47). As a result, the loop filter is prevented from entering extreme conditions during clipping, which greatly reduces the clipping recovery time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Detection of DC output levels from a class D amplifier
ActiveUS20050083116A1Simple analog portionLow cutoff frequencyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationUnsafe conditionAudio power amplifier
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with DC output detection logic (26) is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which includes a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The DC detection logic (26) includes a sigma-delta modulator (60) and a digital low-pass filter (62) that monitors the PWM output signals from the PWM modulators (24). The sigma-delta modulator (60) operates at a first clock frequency, while the low-pass filter (62) operates at a much lower clock frequency, so that AC audio components, PWM harmonics, and sigma-delta quantization error is suppressed from the DC detection. The modulated filtered signal is compared against a threshold level (THRSH) to determine whether the amplitude of a DC component at the PWM output is sufficiently high to constitute a fault. If so, a fault detection signal (DC_DET) is issued, and the PWM modulators (24) are disabled to prevent unsafe conditions in the system (10).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
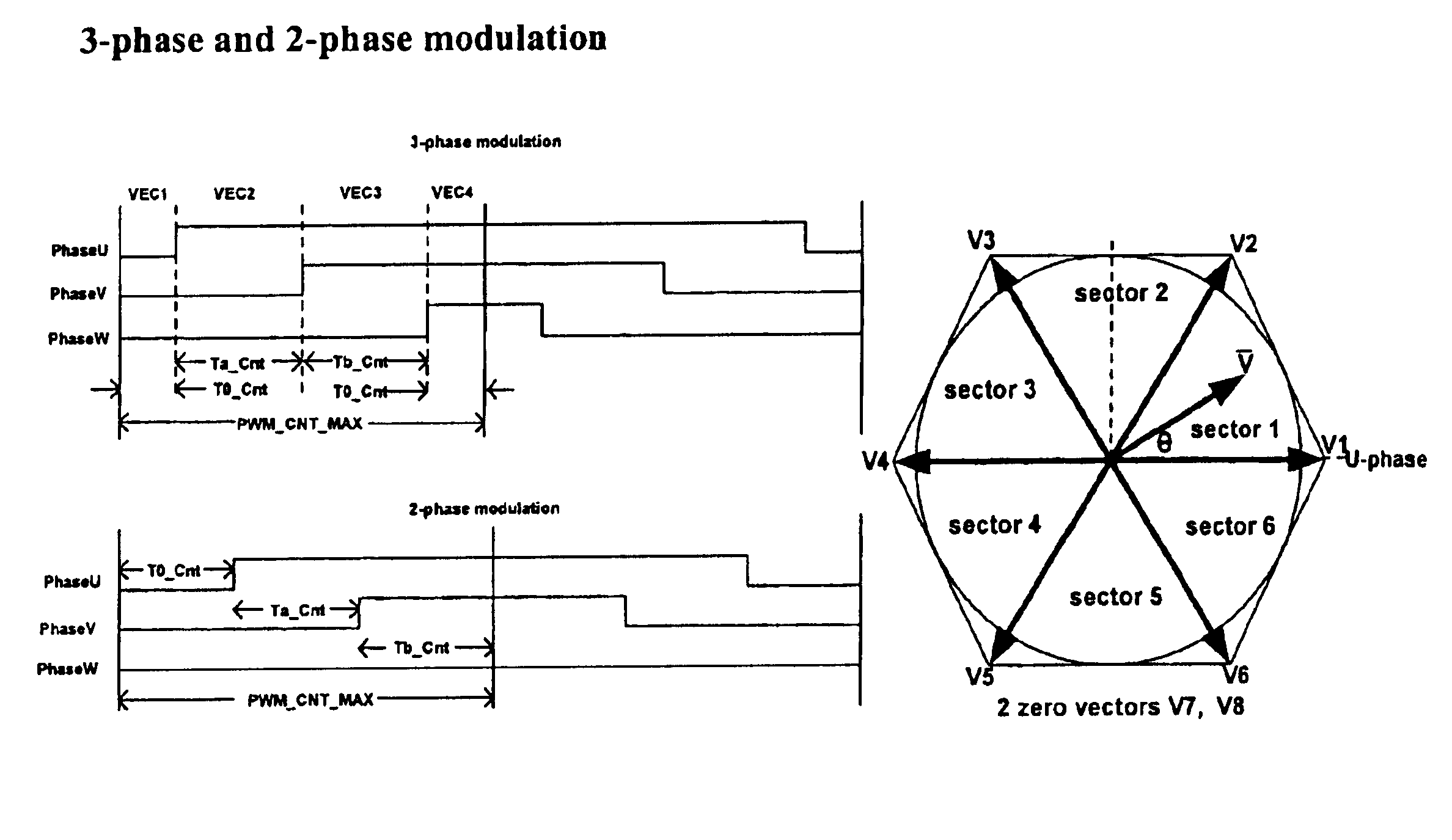
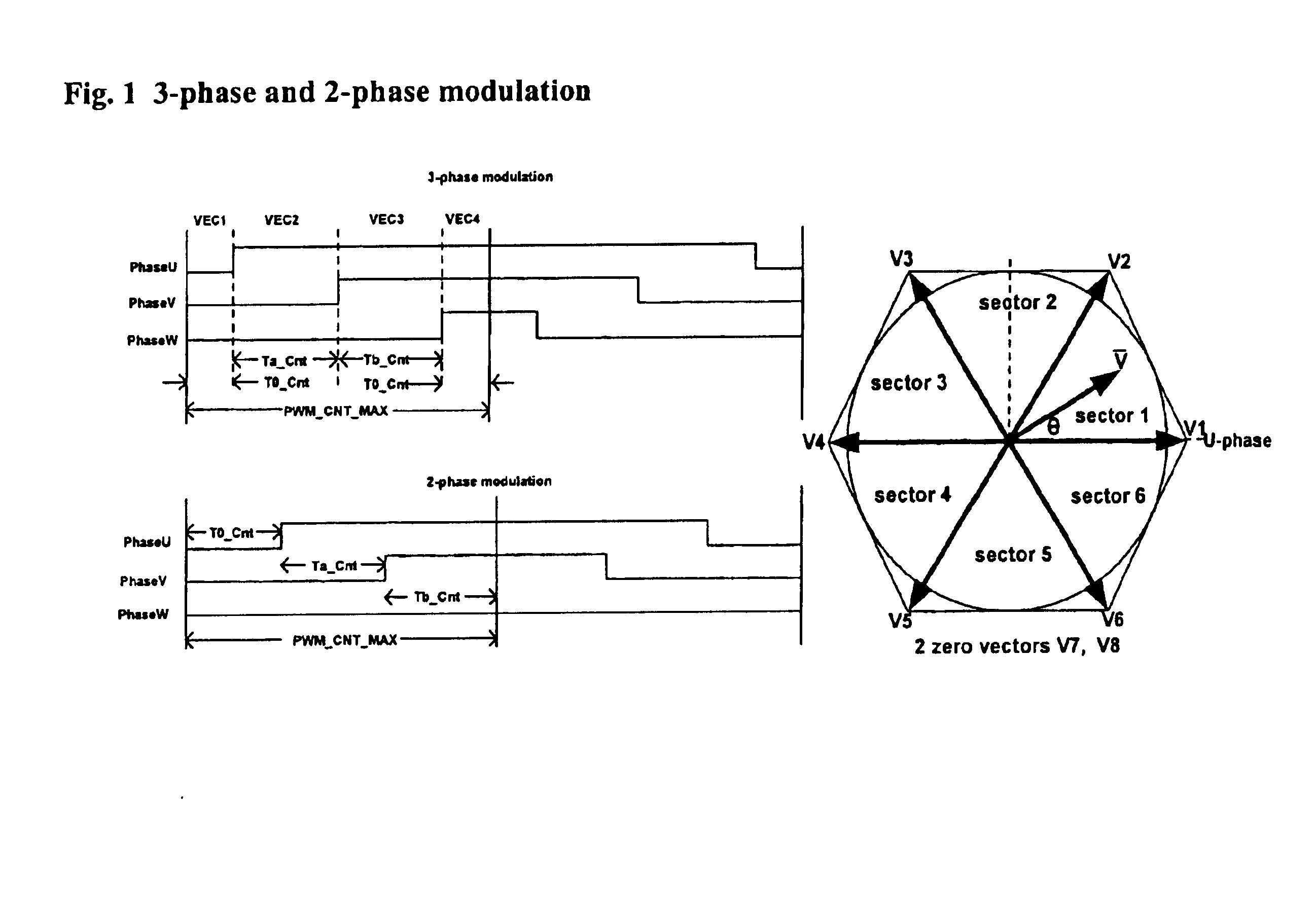
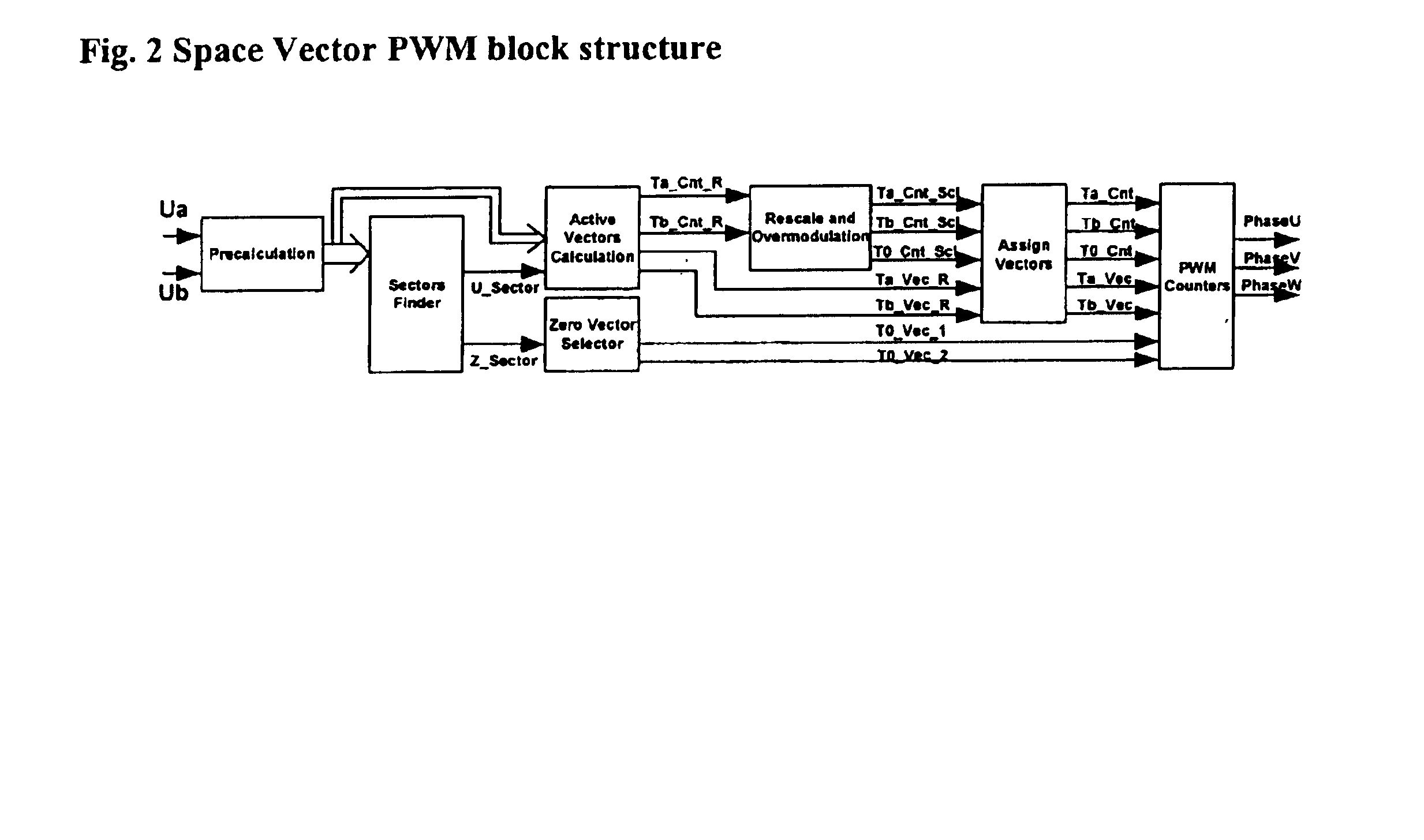
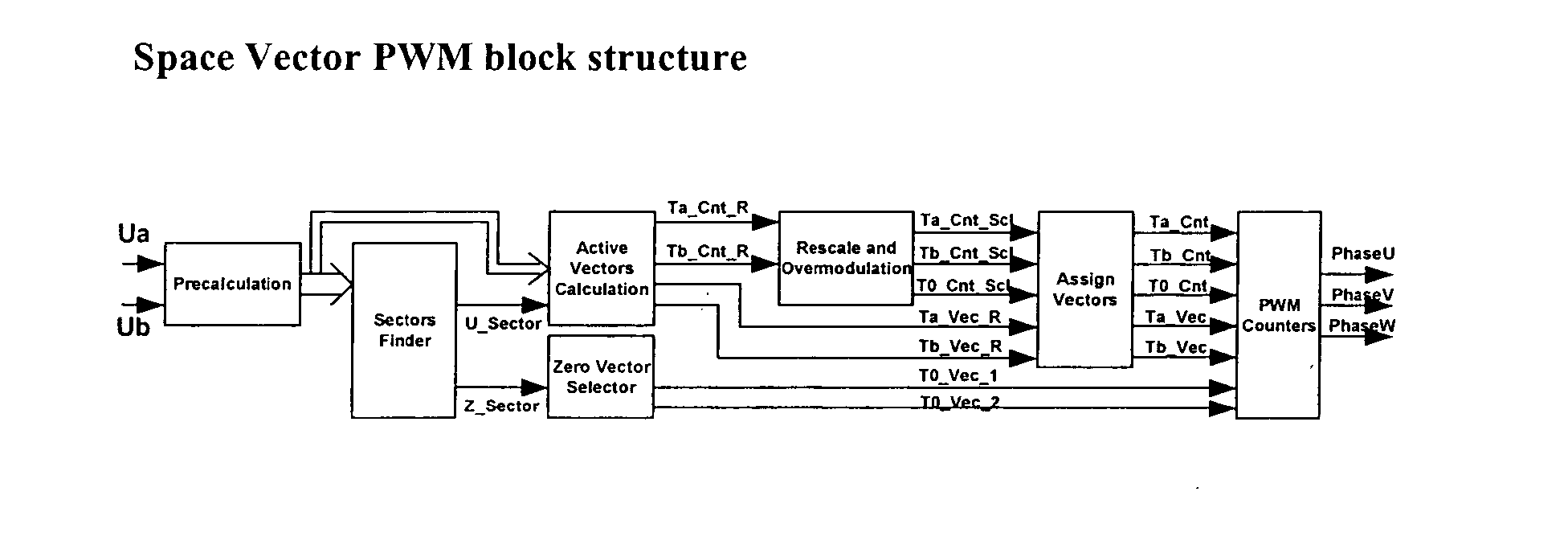
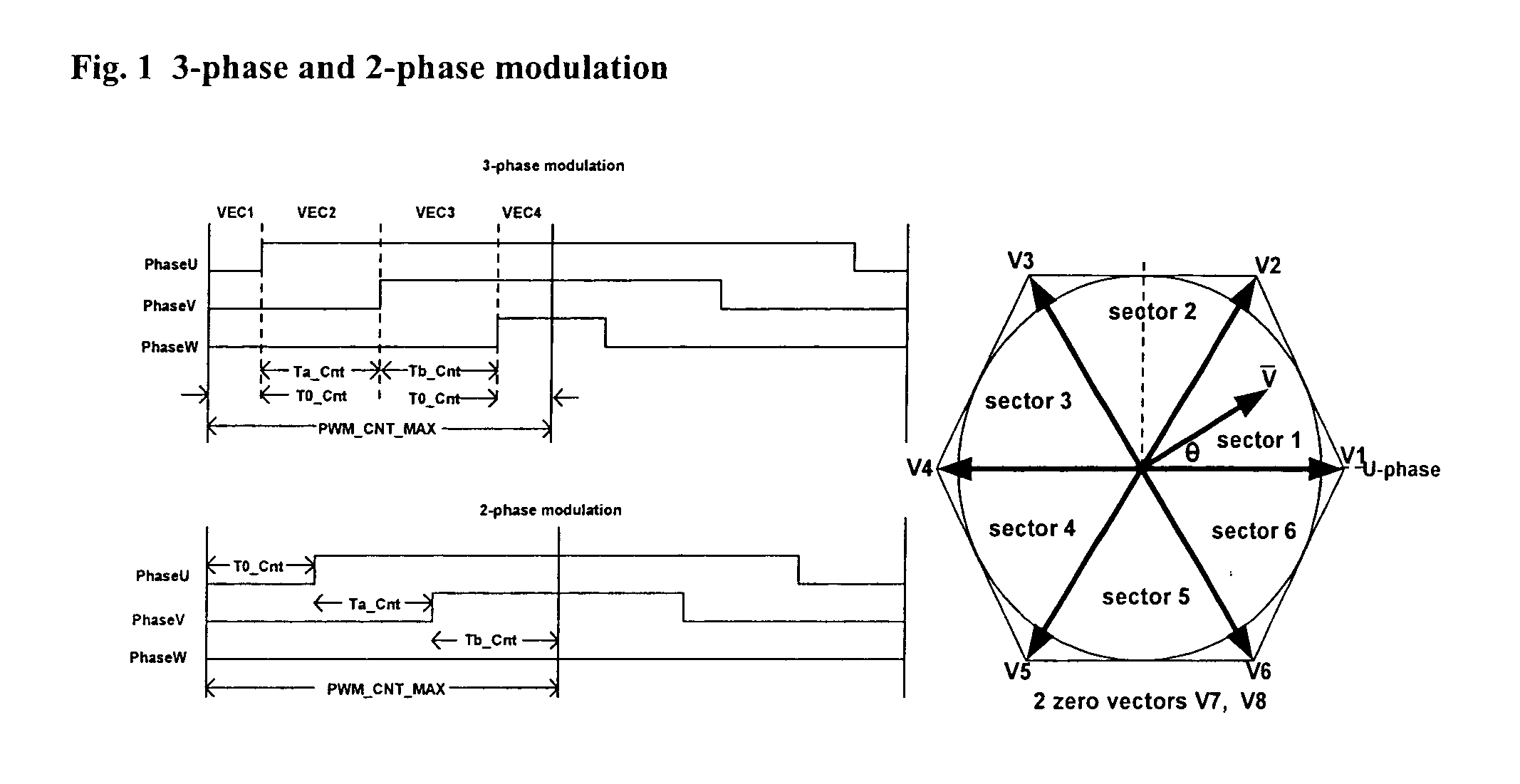
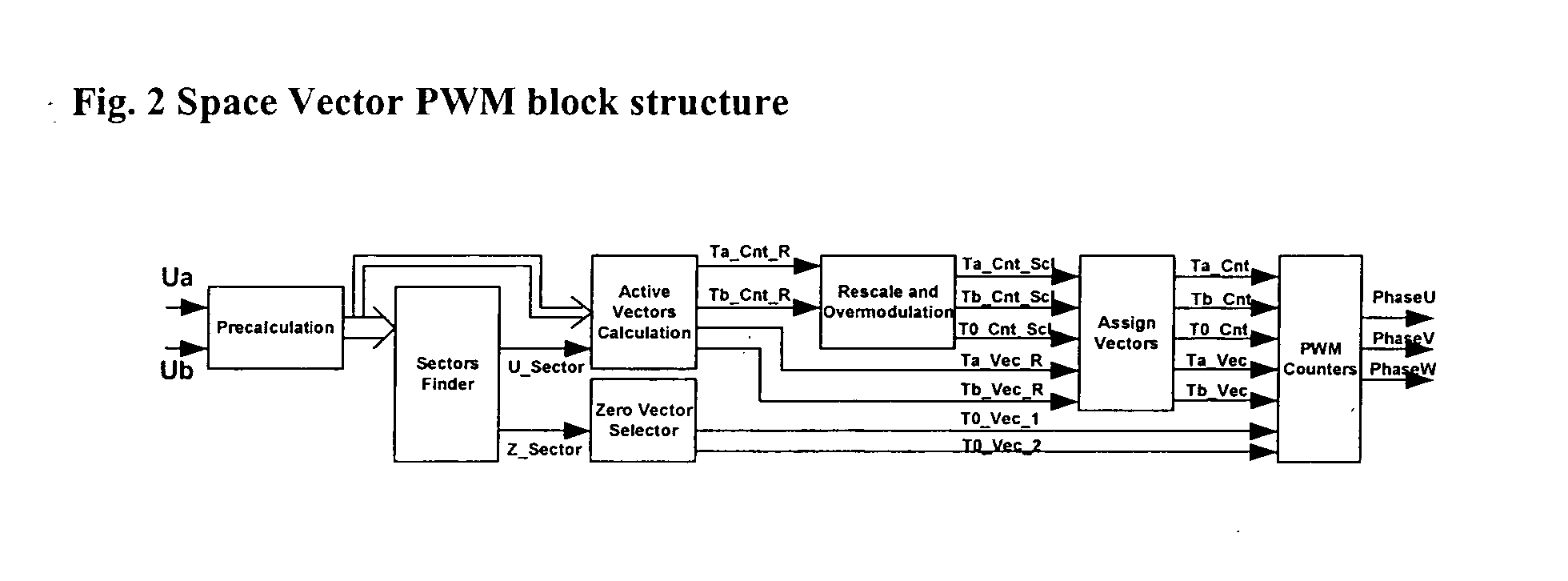
Space vector PWM modulator for permanent magnet motor drive
A space vector pulse-width modulator (SVPWM) and a method implemented by the modulator. A precalculation module accepts Ua and Ub modulation indexes and in response thereto, outputs modified Ua and Ub information; a sector finder has a U module which receives the modified Ua information and outputs a U sector; and a Z module which receives the U sector and the modified Ub information and outputs a Z sector. The U sector and the Z sector are 2-phase control signals for implementing 2-phase modulation. For 3-phase modulation, the SVPWM and method further possess an active vectors calculation module and an assign vectors module which receive the modified Ua and Ub information and the U sector, and which calculate active vectors for 3-phase modulation; a zero vector selector which receives the Z sector and calculates zero vectors for 3-phase modulation; and a PWM counter block which receives the active vectors and zero vectors and outputs 3-phase control signals for implementing 3-phase modulation. The SVPWM and method may have a symmetrical PWM mode, an asymmetrical PWM mode, or both. Advantageously there may also be a rescale and overmodulation module which receives duration information corresponding to the vectors and in response thereto, detects the occurrence of overmodulation. Overmodulation may be detected in response to a negative zero vector time. The module may respond to overmodulation by clamping the zero vector time to zero and rescaling the active vector times to fit within the PWM cycle. The rescaling may restrict a voltage vector to stay within hexagonal boundaries on the space vector plane, while preserving voltage phase.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Recovery from clipping events in a class D amplifier
ActiveUS7142050B2Shorten recovery timeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLoop filterAudio power amplifier
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with improved recovery from clipping events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. Clip detection logic (26) is provided to detect clipping at the output of the channel (20), preferably by detecting successive edges of the reference waveform without an intervening edge of a PWM output signal. In response to detecting clipping, a first integrator (30; 45) is reset to remove residuals and to eliminate the first integrator (30; 45) from the loop filter of the modulator (24). A saturation level circuit (35) applies a clamping voltage, preferably in both clipping and non-clipping situations, to a second integrator (36; 47). As a result, the loop filter is prevented from entering extreme conditions during clipping, which greatly reduces the clipping recovery time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
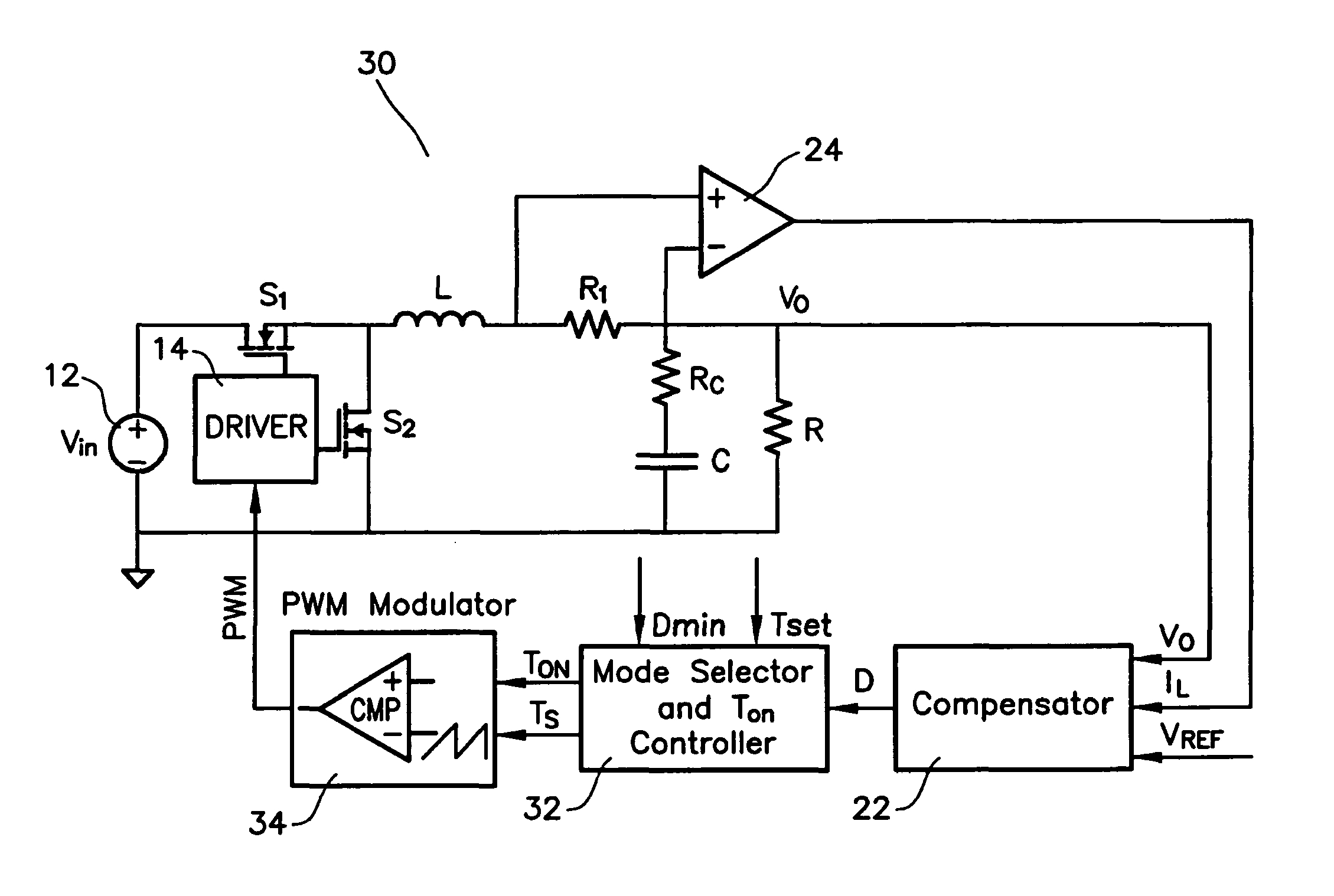
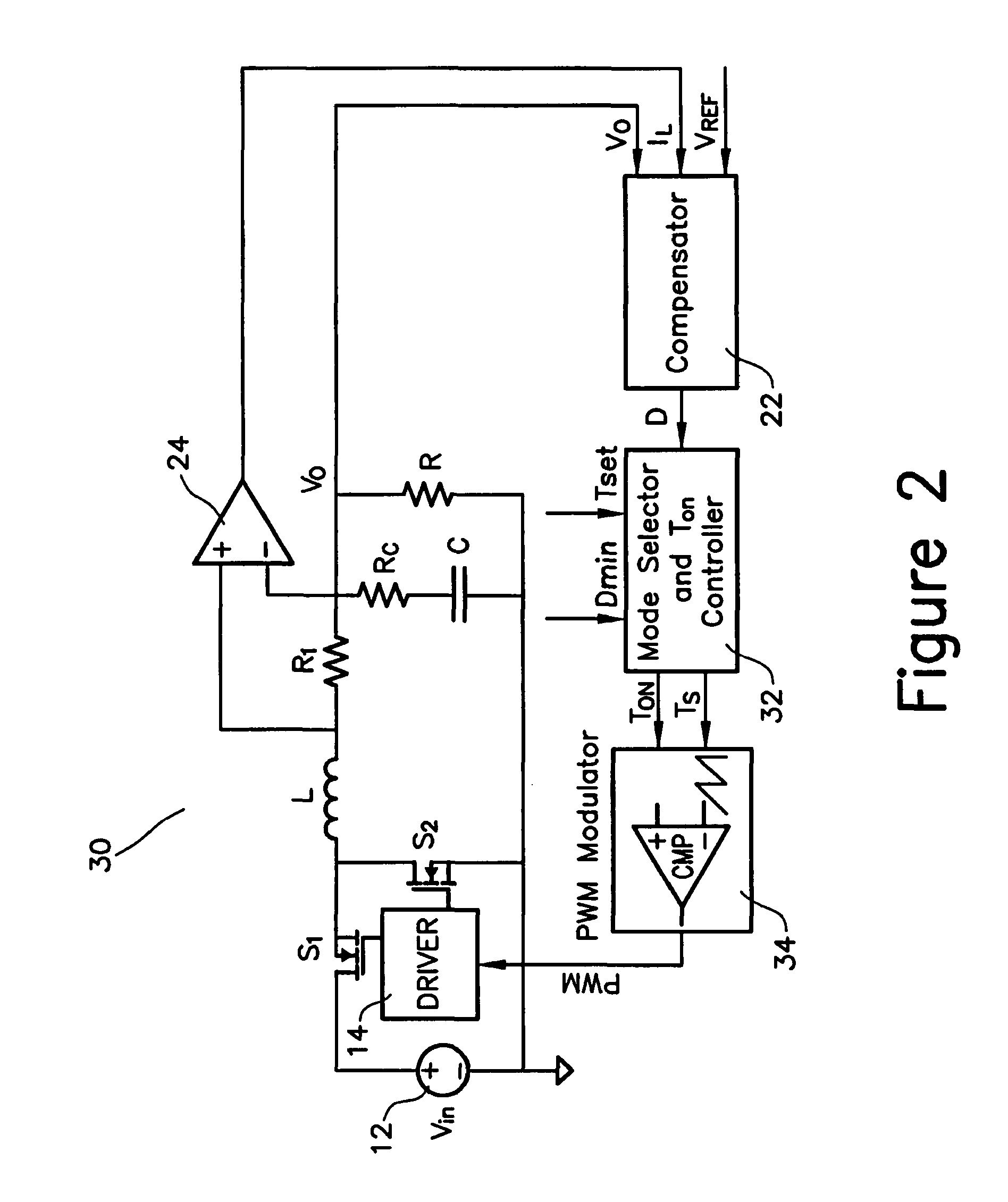
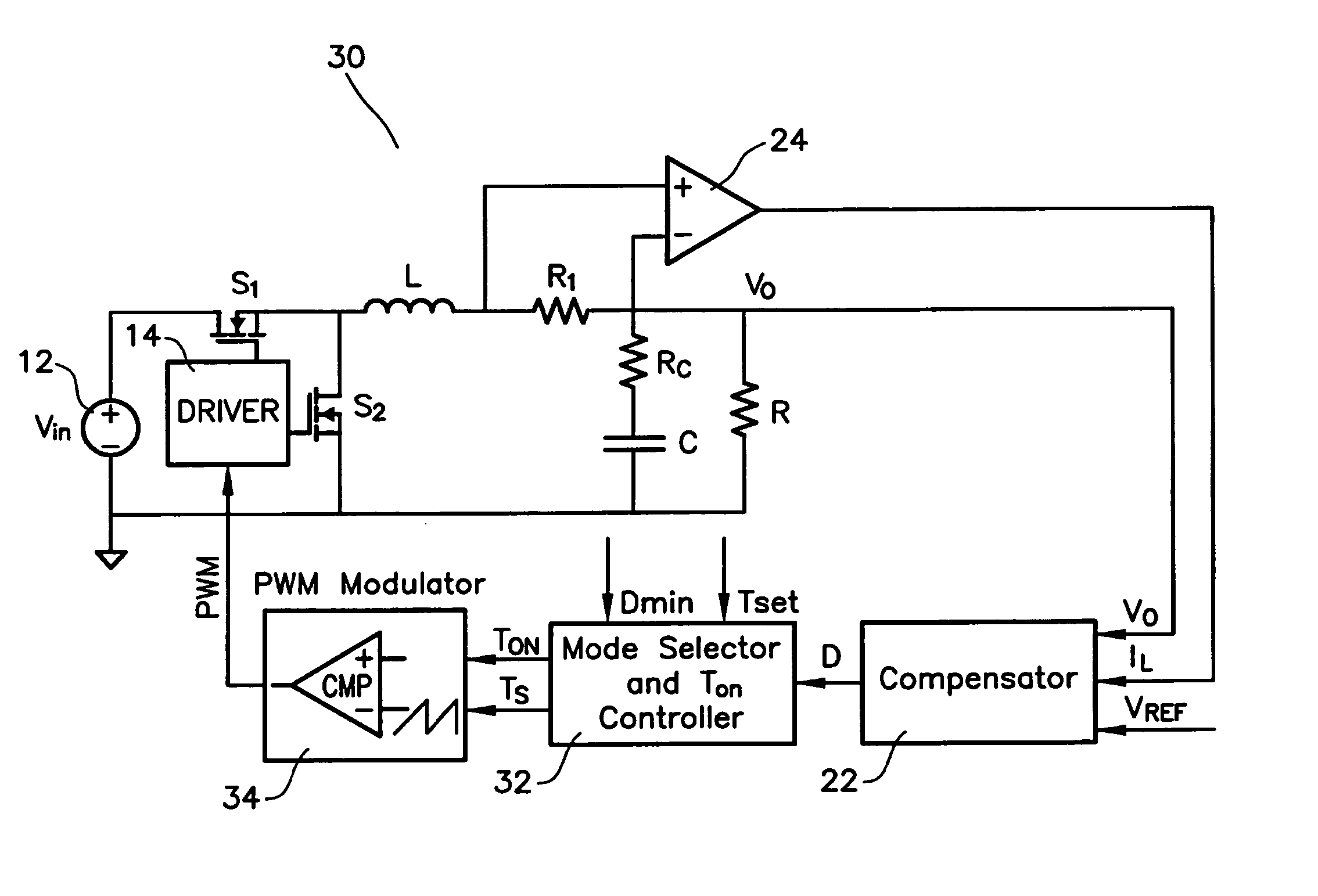
Multi-mode switching control circuit and method for improving light load efficiency in switching power supplies
ActiveUS7755342B2Improve performanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConstant frequencySwitching frequency
A circuit for transitioning between a discontinuous and a fixed frequency continuous conduction mode (DCM) and (CCM) of a power converter having a driver receiving PWM signals and controlling a switching stage comprises a control switch and a sync switch connected at a common switching node for driving a load. The circuit including a PWM modulator for providing PWM signals; and a mode selector for receiving a duty cycle value, a preset switching period, and a duty cycle at a critical conduction point having a switching frequency equal to the preset switching period and providing an on-time of the control switch and a switching period to the PWM modulator, wherein if the duty cycle value is greater than the duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the CCM with constant-frequency duty cycle control, and if the duty cycle value is less than duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the DCM by turning off the sync switch when a load current becomes negative.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Soft transitions between muted and unmuted states in class D audio amplifiers
ActiveUS7378904B2Clicking and popping is greatly reducedAvoid instabilityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with reduced noise capability in muting and unmuting events is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which can be constructed to include a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The PWM modulator (24) includes a pair of comparators (39A, 39B; 52+, 52−) that generate complementary PWM output signals based upon the comparison between a filtered difference signal and a reference waveform. When the system is muted, a common mode voltage (CM_RAMP) is applied to the inputs of the comparators (39A, 39B; 52+ 52−) to suppress the duty cycle at the amplifier output, preferably to a zero duty cycle. In the transition from a muted state to an unmuted state, the common mode voltage (CM_RAMP) is ramped from the suppressing voltage to zero common mode voltage, permitting the duty cycle of the complementary PWM signals to gradually increase, thus reducing clicks and pops. The converse operation is performed in the transition from unmuted to muted. Pulse-width-modulation control logic (26) is also included to ensure that that the PWM “on” and “off” pulses are of at least a minimum duration, and also to generate compensating pulses on the complementary PWM line at low duty cycles.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
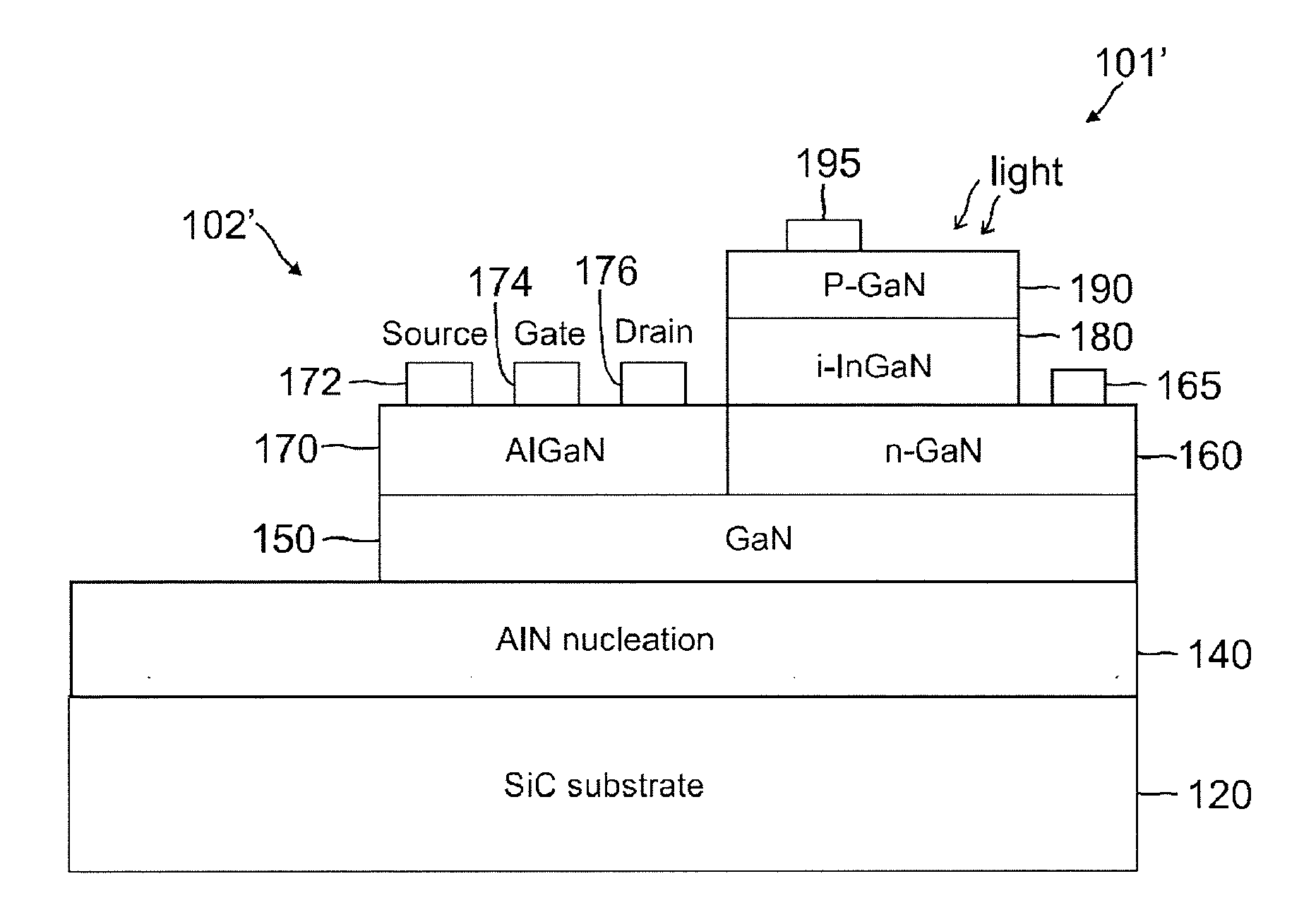
MONOLITHIC InGaN SOLAR CELL POWER GENERATION WITH INTEGRATED EFFICIENT SWITCHING DC-DC VOLTAGE CONVERTOR
ActiveUS20130074907A1Improve efficiencyDecrease in generated voltagePV power plantsDiodeEngineeringSolar cell
A single monolithic integrated circuit (10) containing a solar cell (or cells) with a DC-DC converter includes: a substrate (120, 220); the solar cell (101) or a solar cell array (100, 100′) on the substrate for generating an output voltage; and the DC-DC converter (102) integrated on the substrate for receiving the output voltage to generate a converted voltage, which may be higher or lower than the solar generated voltage. The substrate may be a silicon <111>, silicon carbide, or sapphire substrate. A GaN RF power amplifier and a CMOS controller including PWM modulator may also be monolithically integrated with an InGaN solar cell array and a GaN DC-DC converter. GaN switches (113, 115, 117, 119) may be used to couple InGaN solar cells (101) in series or parallel within the solar cell array (100, 100′) to yield improved or optimal voltage and current levels as required by the load.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
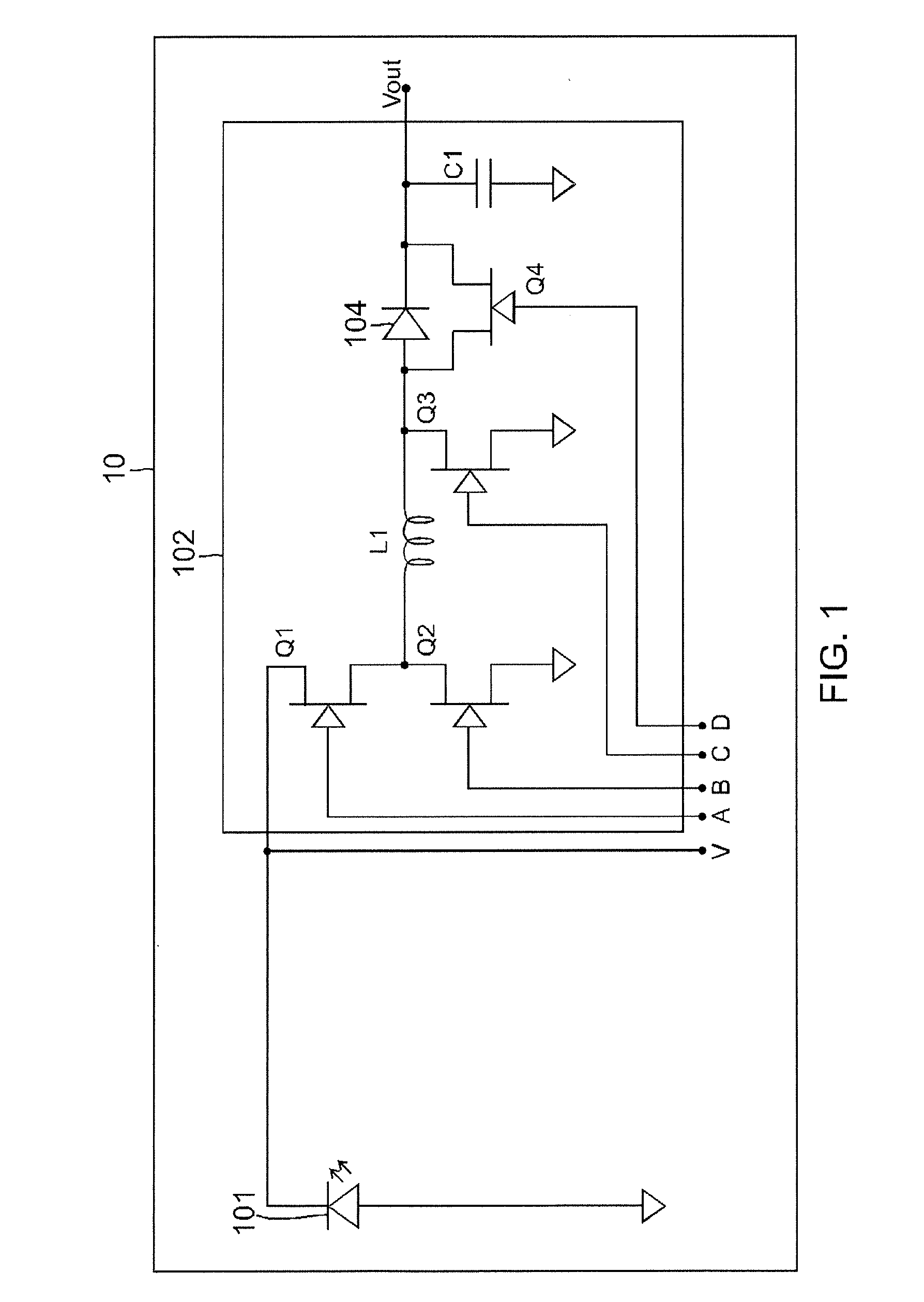
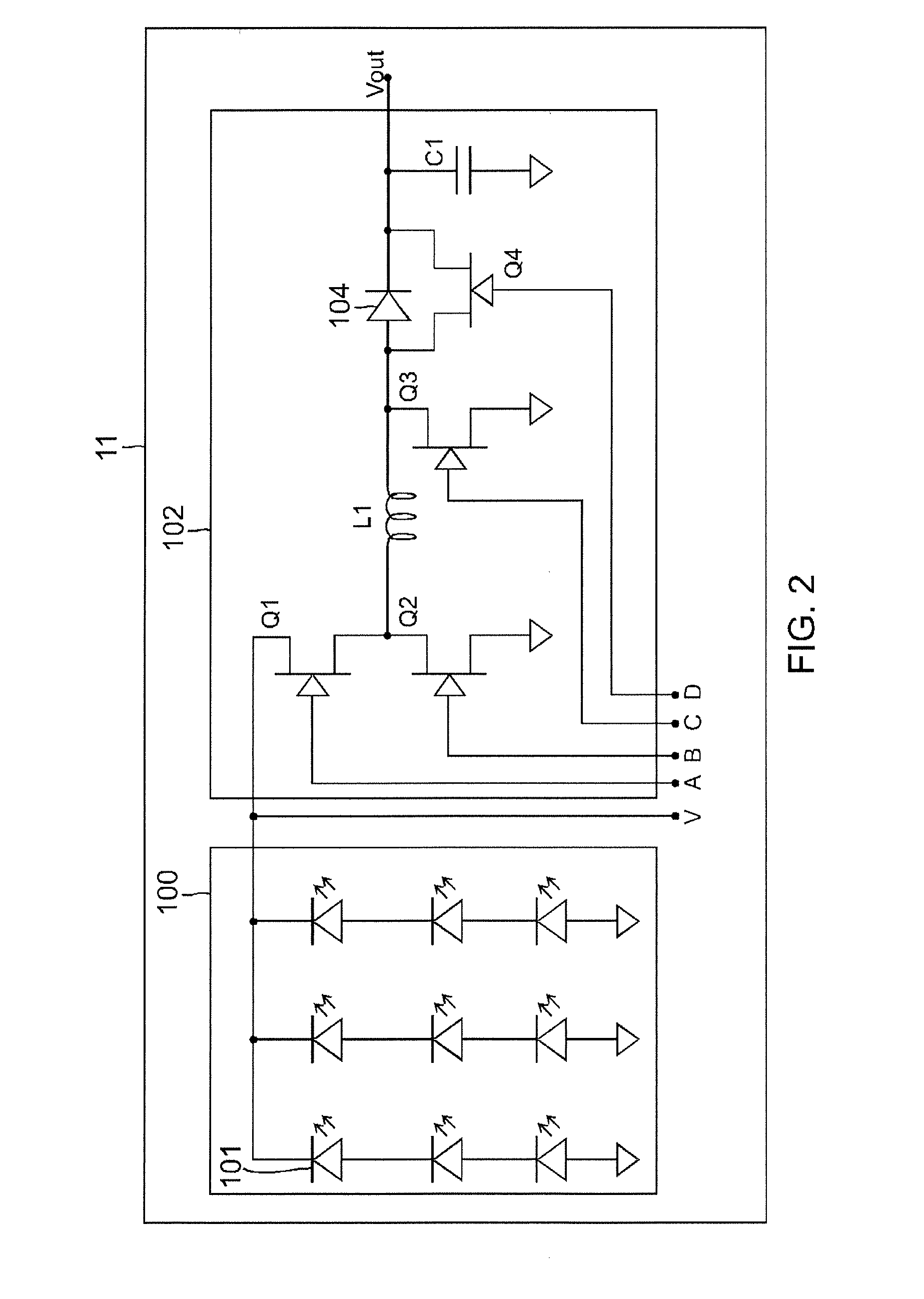
Electrical system and control method
ActiveUS20100156192A1Dc network circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityWave shape
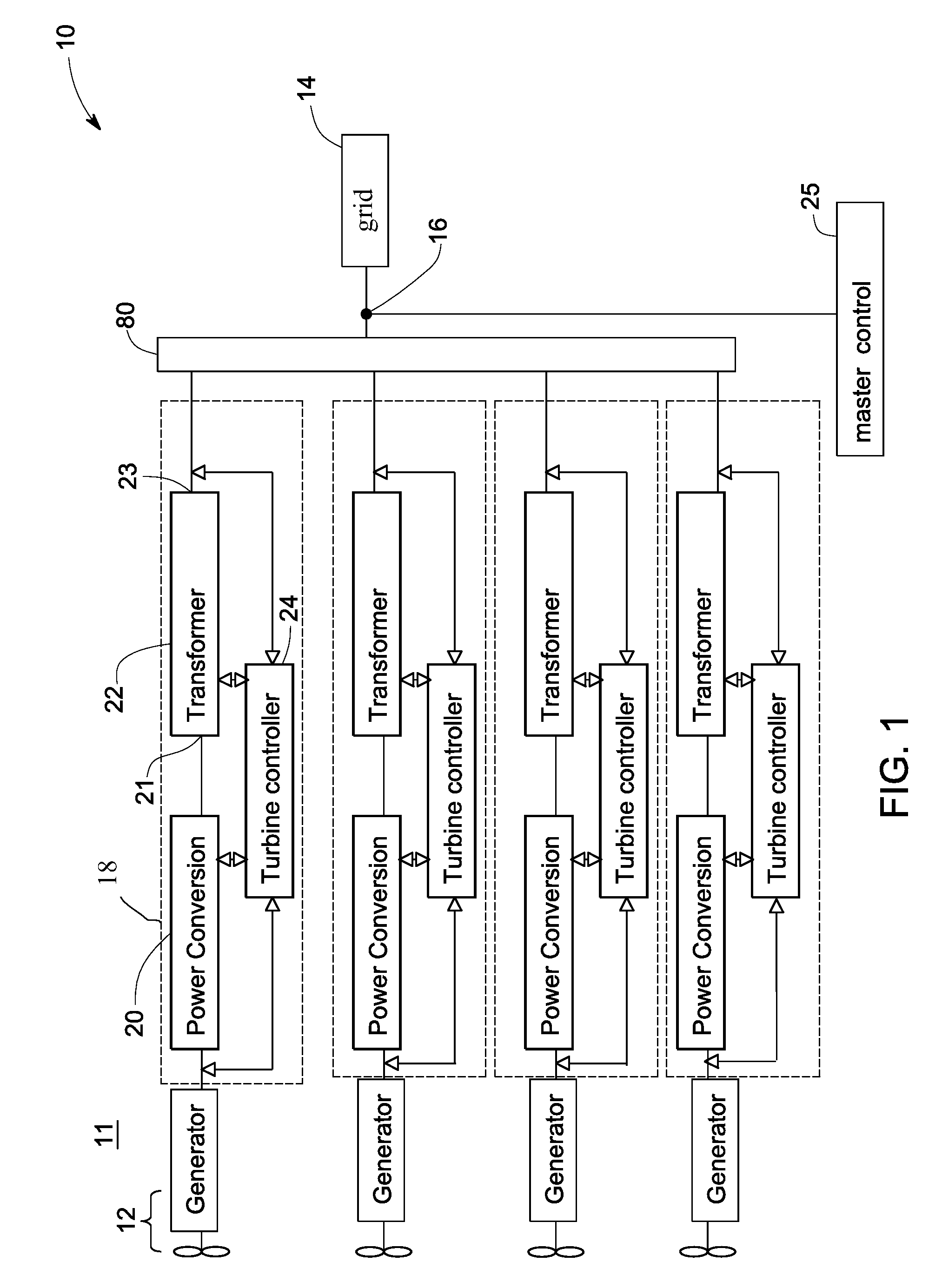
A power generation system comprises at least two electrical systems connected at an electrical connection point. Each electrical system comprises a power conversion system comprising a converter including a plurality of switches for converting direct current power into alternating current power. The power generation system comprises a control system including at least two pulse width modulation (PWM) modulators, each PWM modulator for obtaining a fundamental waveform and a carrier signal, using the fundamental and carrier signals to generate a PWM pattern, and for providing the PWM pattern to a respective converter for driving the switches of the respective converter. The control system is configured to interleave carrier signals, fundamental waveforms, or a combination of carrier signals and fundamental waveforms of the at least two electrical systems to generate interleaved PWM patterns respectively for the at least two converters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
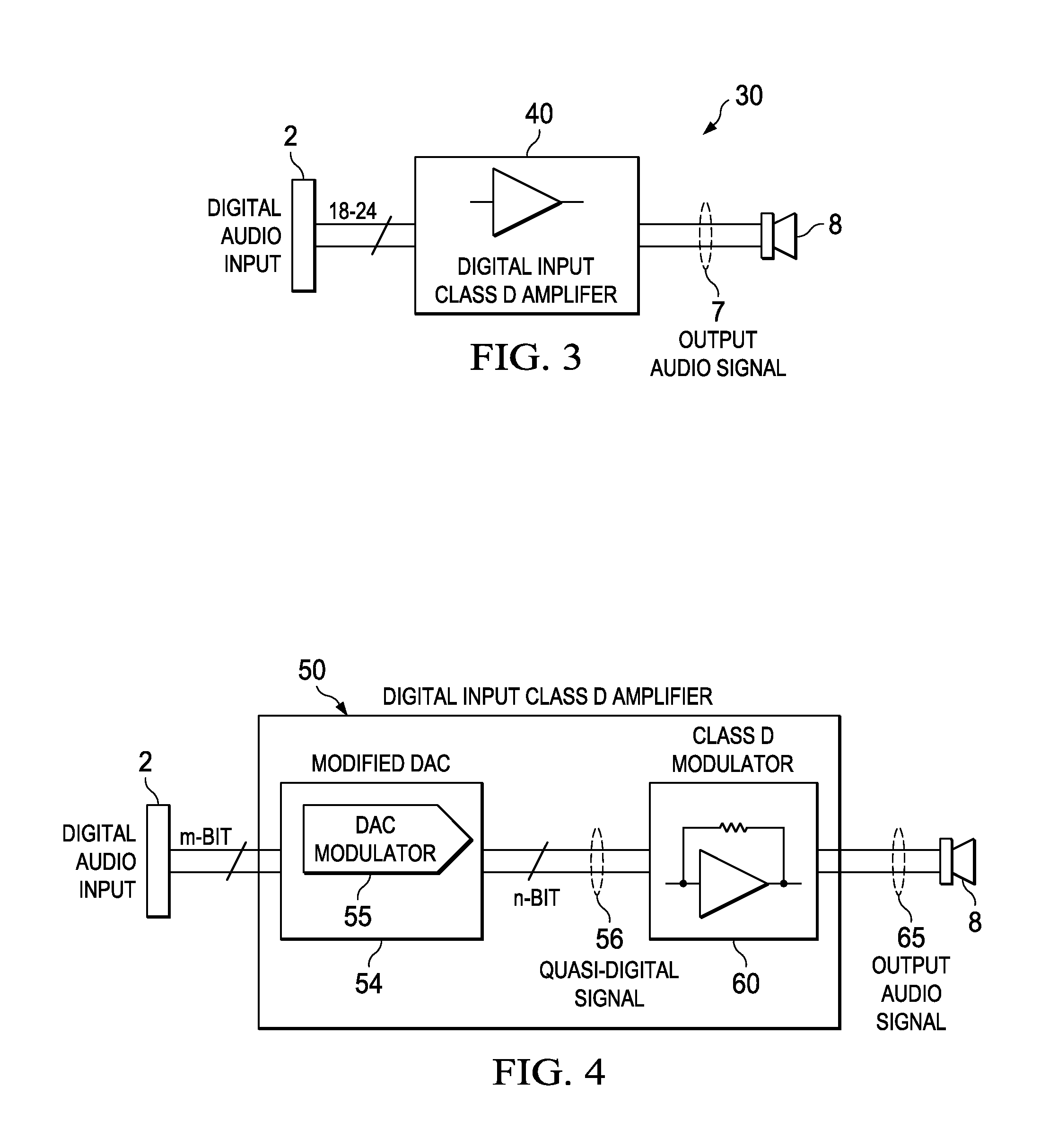
Digital Input Class-D Audio Amplifier
ActiveUS20130223652A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow frequency amplifiersAnalog feedbackAudio power amplifier
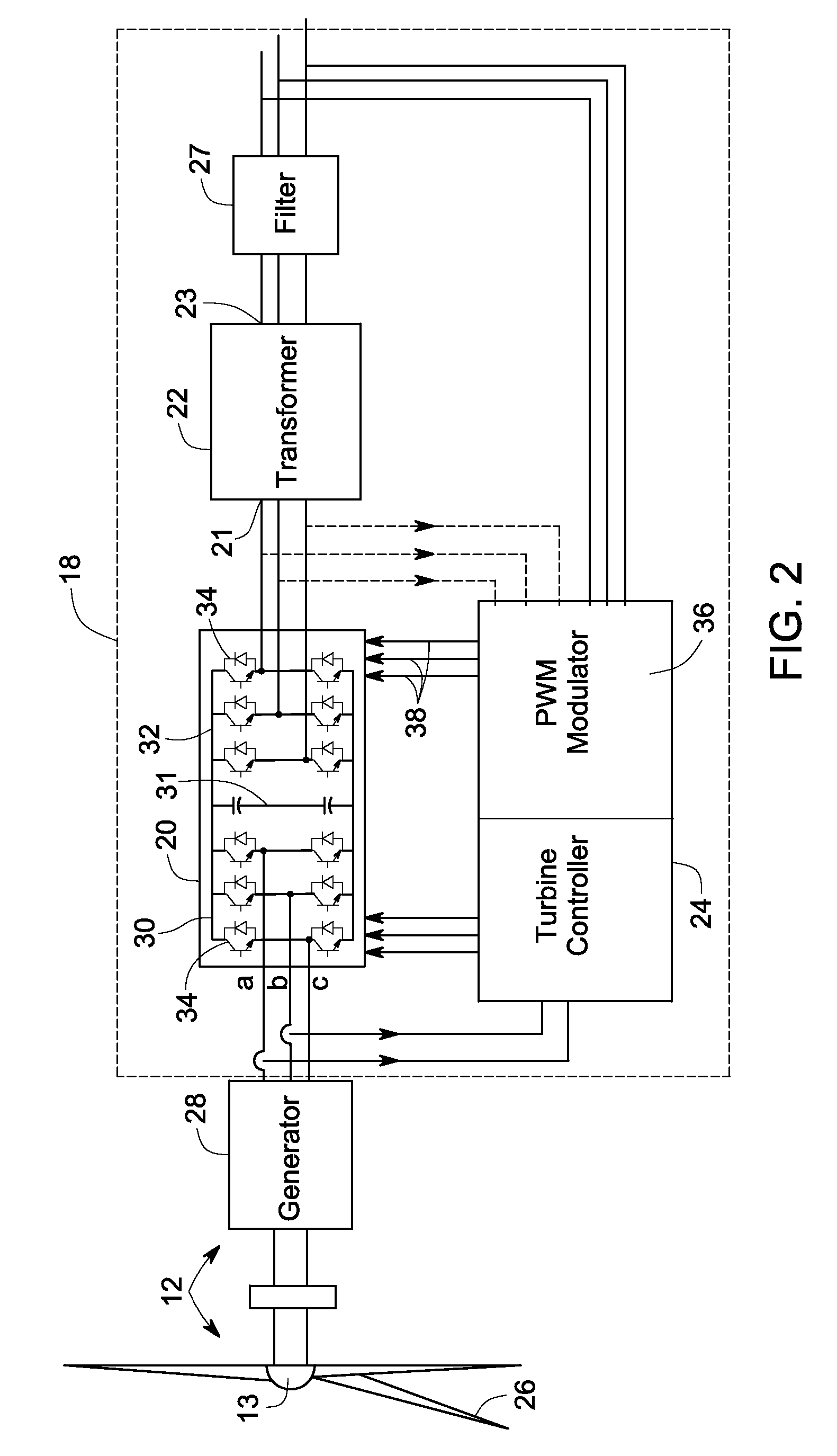
An audio amplifier receiving a digital input audio signal and generating an output audio signal for driving a speaker includes a digital input class D amplifier configured to receive the digital input audio signal and to generate the output audio signal. The digital input class D amplifier includes a first modulator configured to receive the digital input audio signal and to generate a quasi-digital signal in n-bit, and a class D modulator configured to receive the n-bit quasi-digital signal and to generate the output audio signal, the class D modulator implementing an analog feedback loop. In some embodiments, the class D modulator is implemented using a PWM modulator. In other embodiments, the PWM modulator incorporates enhanced features to improve the output noise characteristics.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for improving light load efficiency in switching power supplies
ActiveUS20080042709A1Improve performanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConstant frequencySwitching frequency
A circuit for transitioning between a discontinuous and a fixed frequency continuous conduction mode (DCM) and (CCM) of a power converter having a driver receiving PWM signals and controlling a switching stage comprises a control switch and a sync switch connected at a common switching node for driving a load. The circuit including a PWM modulator for providing PWM signals; and a mode selector for receiving a duty cycle value, a preset switching period, and a duty cycle at a critical conduction point having a switching frequency equal to the preset switching period and providing an on-time of the control switch and a switching period to the PWM modulator, wherein if the duty cycle value is greater than the duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the CCM with constant-frequency duty cycle control, and if the duty cycle value is less than duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the DCM by turning off the sync switch when a load current becomes negative.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
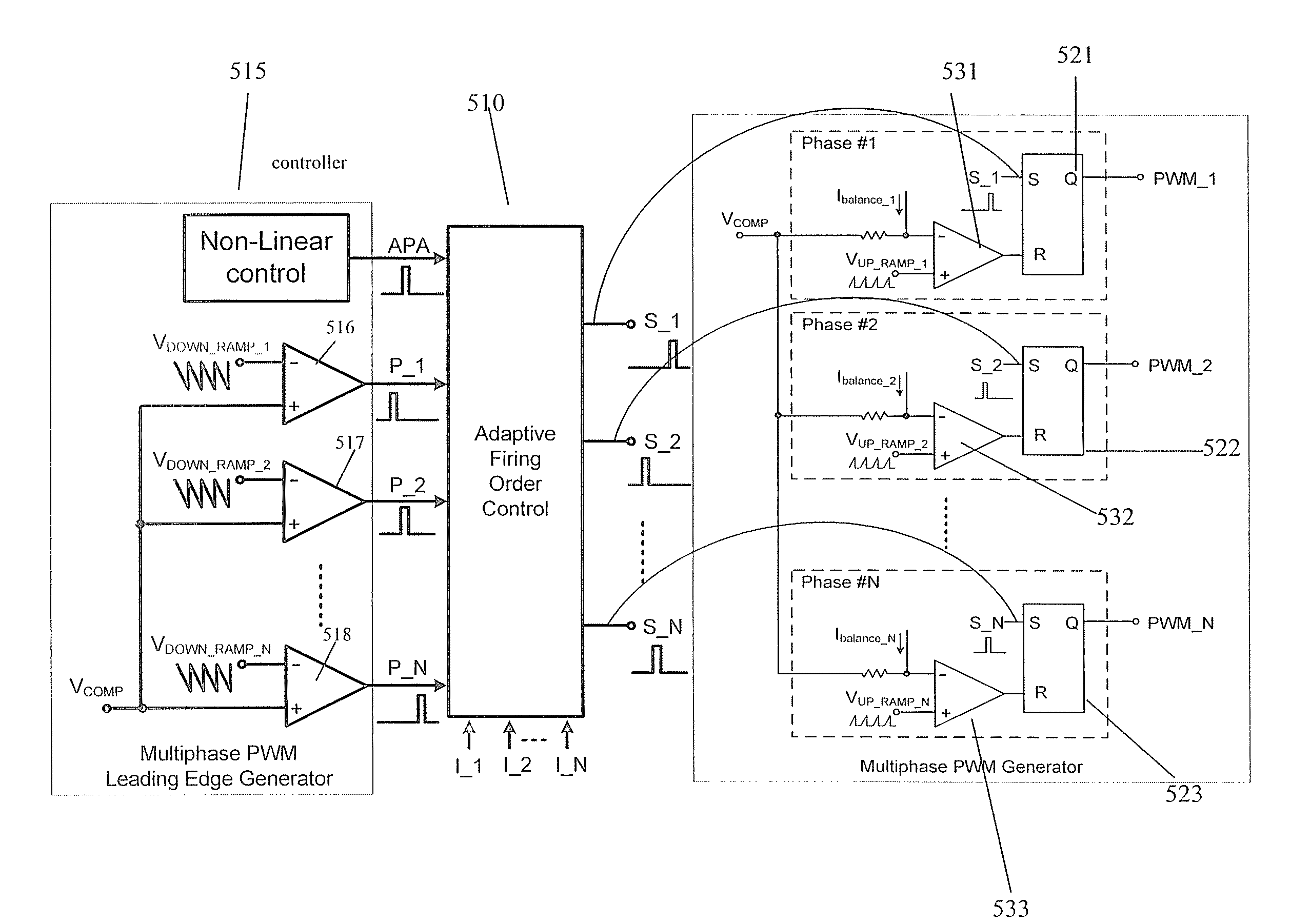
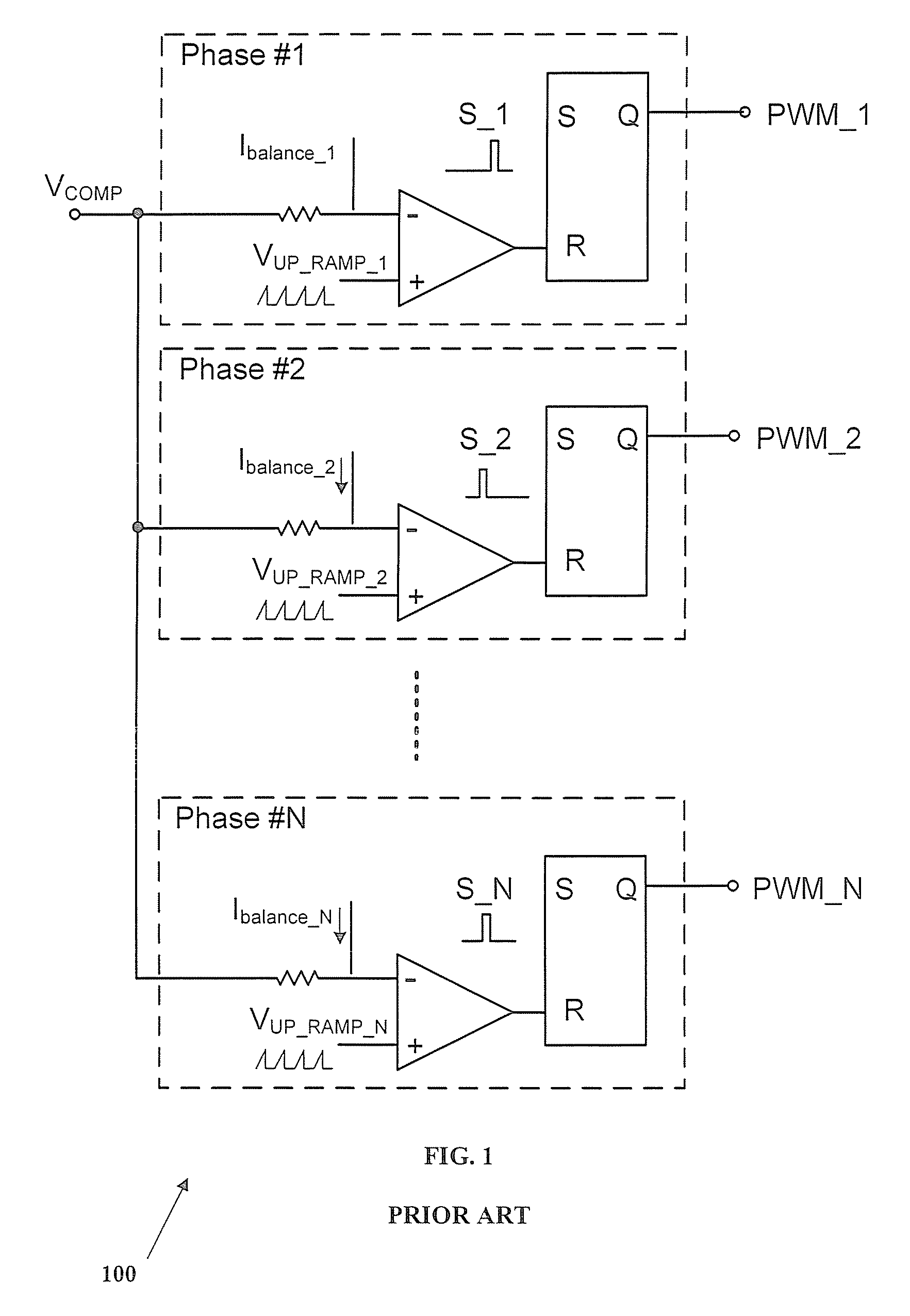
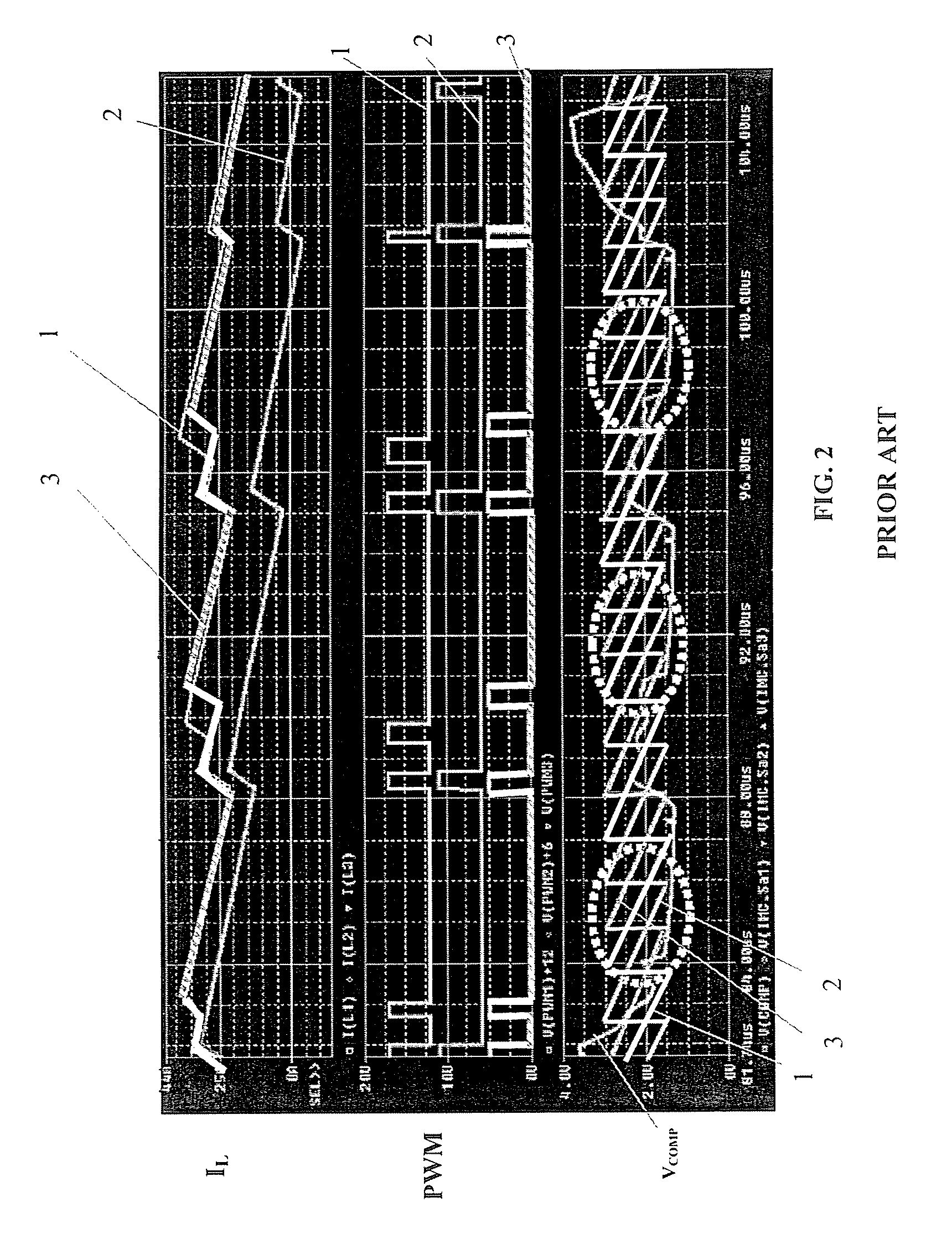
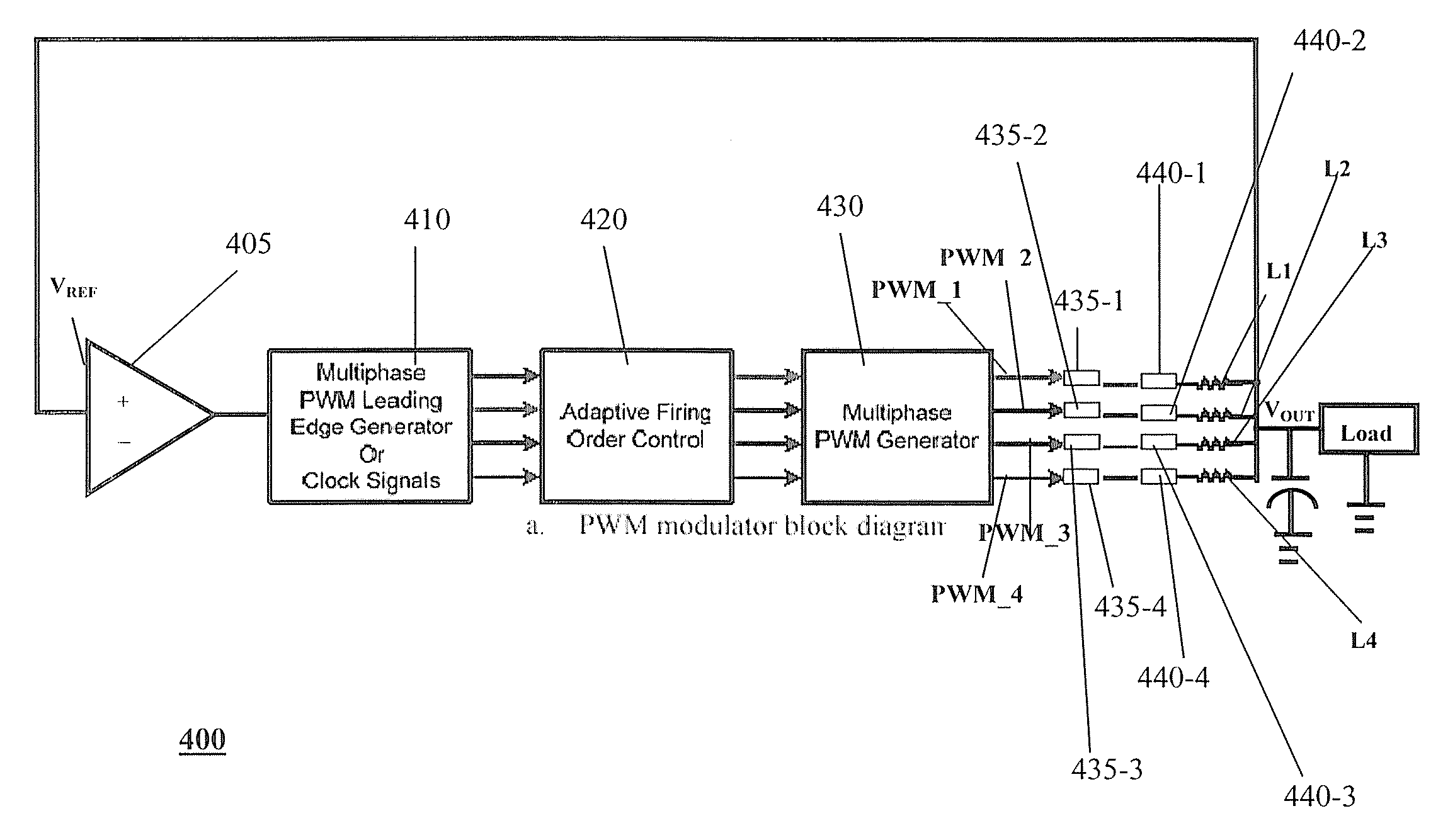
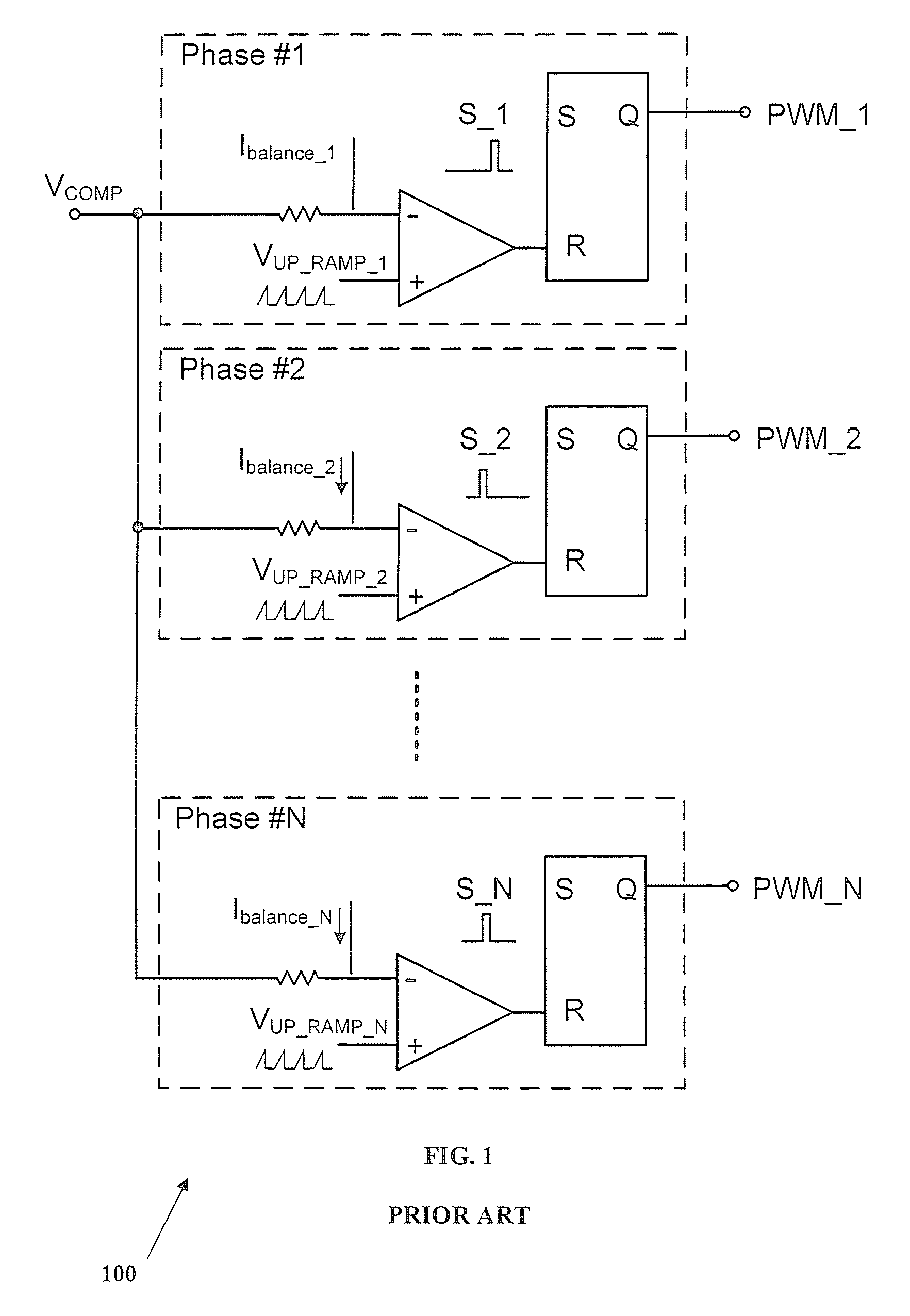
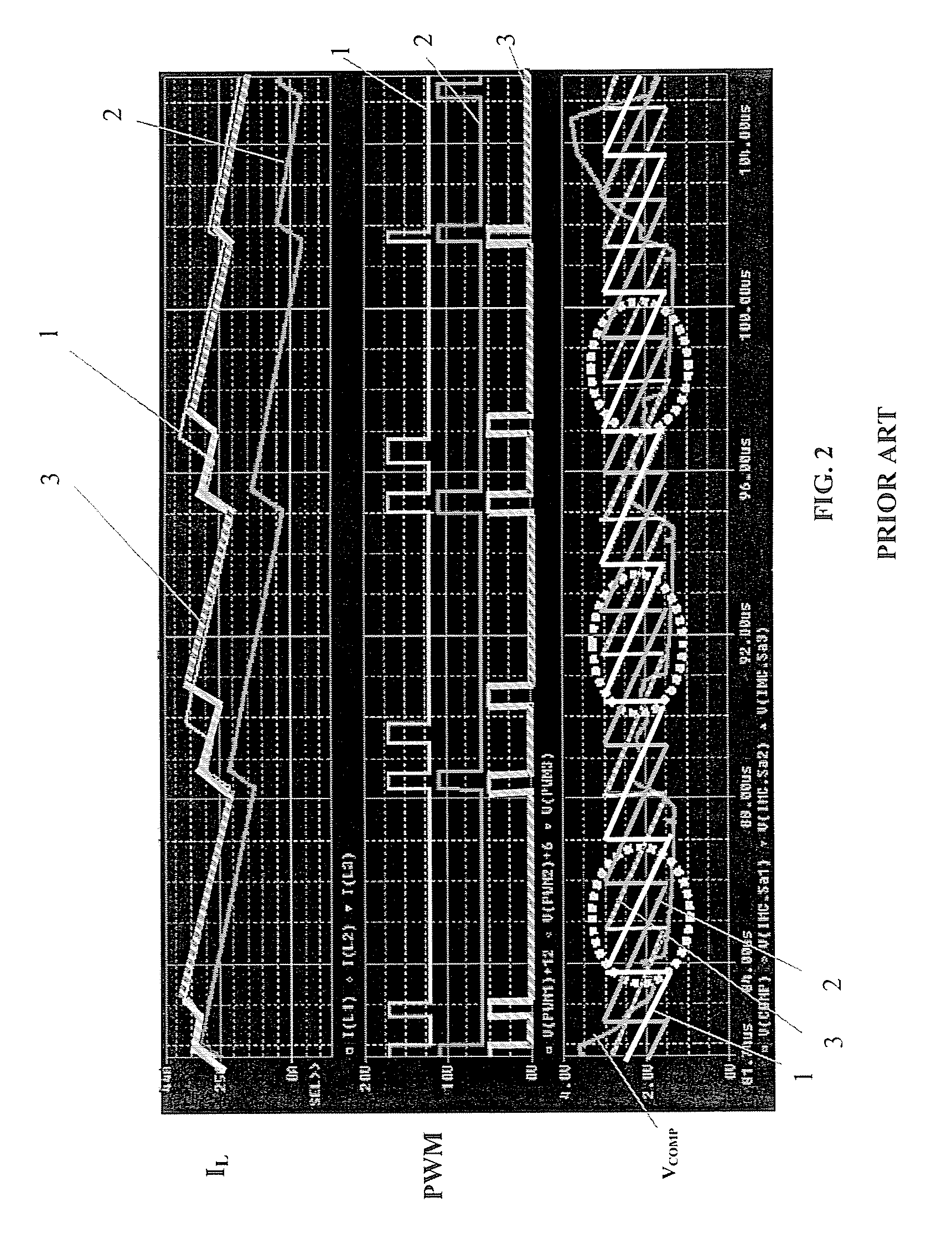
Adaptive firing order control for dynamic current balance of multiphase voltage regulators
A pulse width modulation (PWM) modulator for a multiphase power converter and related adaptive firing order (AFO) method includes a multiphase leading edge generator having pulse generating circuitry associated with each of the regulator phases, wherein the pulse generating circuitry generates phase pulses associated with each of the phases. An adaptive firing order (AFO) controller having circuitry including a mixer receives and sums the phase pulses into a summing signal and uses the summing signal to generate a series of turn-on pulses therefrom. A multiphase PWM generator has inputs coupled to an output of the AFO controller coupled to receive the series of turn-on pulses, the multiphase PWM generator having circuitry for generating said PWM signals therefrom. An adaptive firing order (AFO) controlled multi-phase power converter includes a plurality of parallel connected regulator phases controlled by respective pulse width modulation (PWM) signals provided by the PWM modulator.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
High Linearity Modulation System and Modulation Method
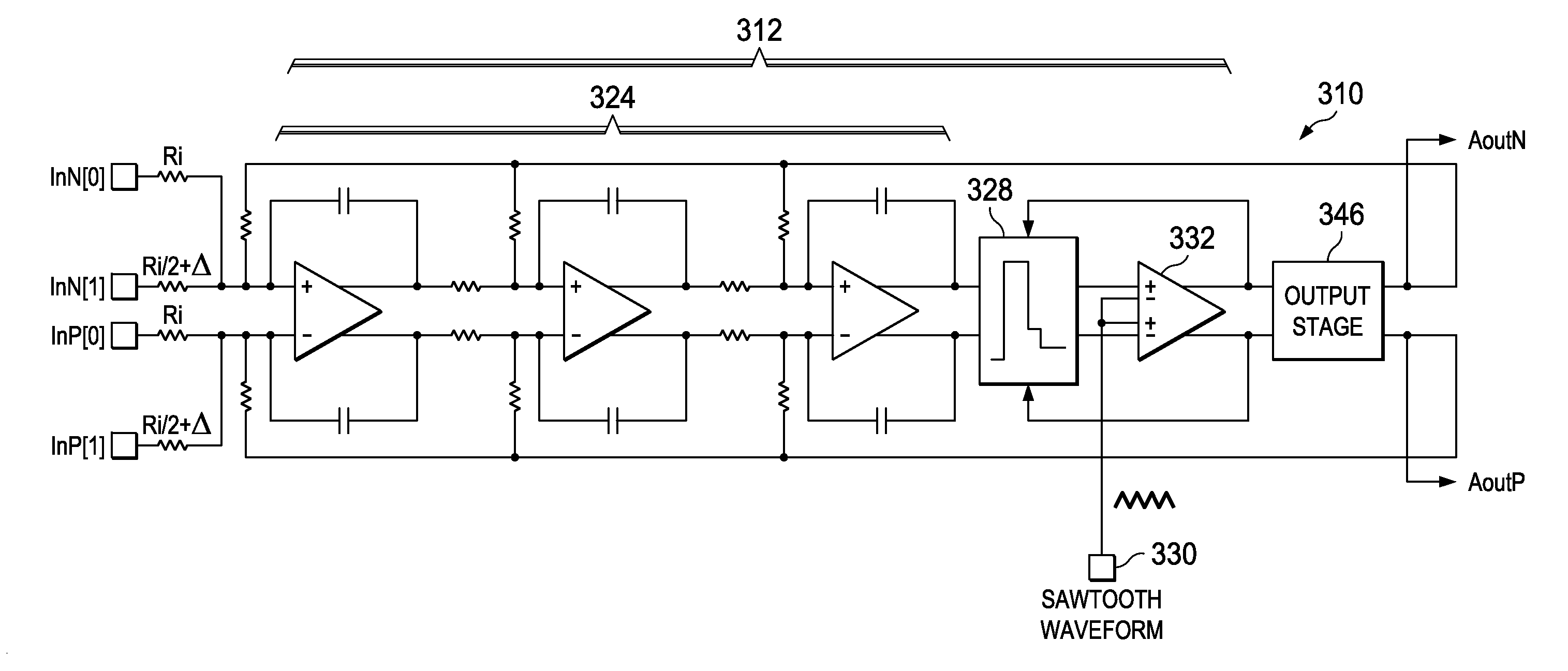
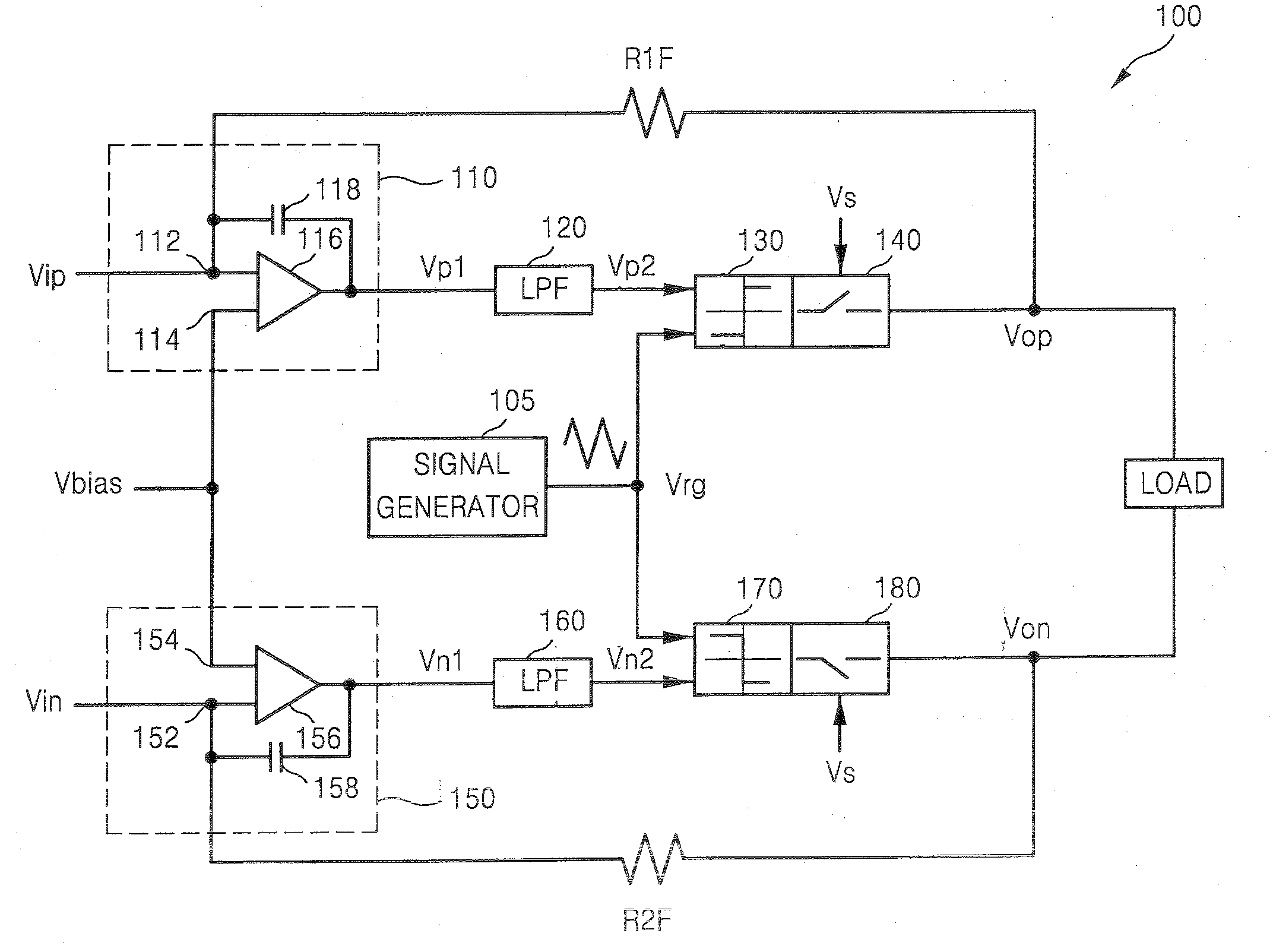
InactiveUS20070279127A1Improve linearityAudio amplifierPulse duration/width modulationIntegratorLow-pass filter
A modulation system and method having a high linearity. The system is a PWM modulator or a class D amplifier and includes an integrator, a low pass filter (LPF), a comparator, and an output circuit. The LPF is located before the comparator. Jitter noise produced by the comparator and / or switching noise of the output circuit are removed by feedback to the input. Thus, the linearity of the modulation system is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
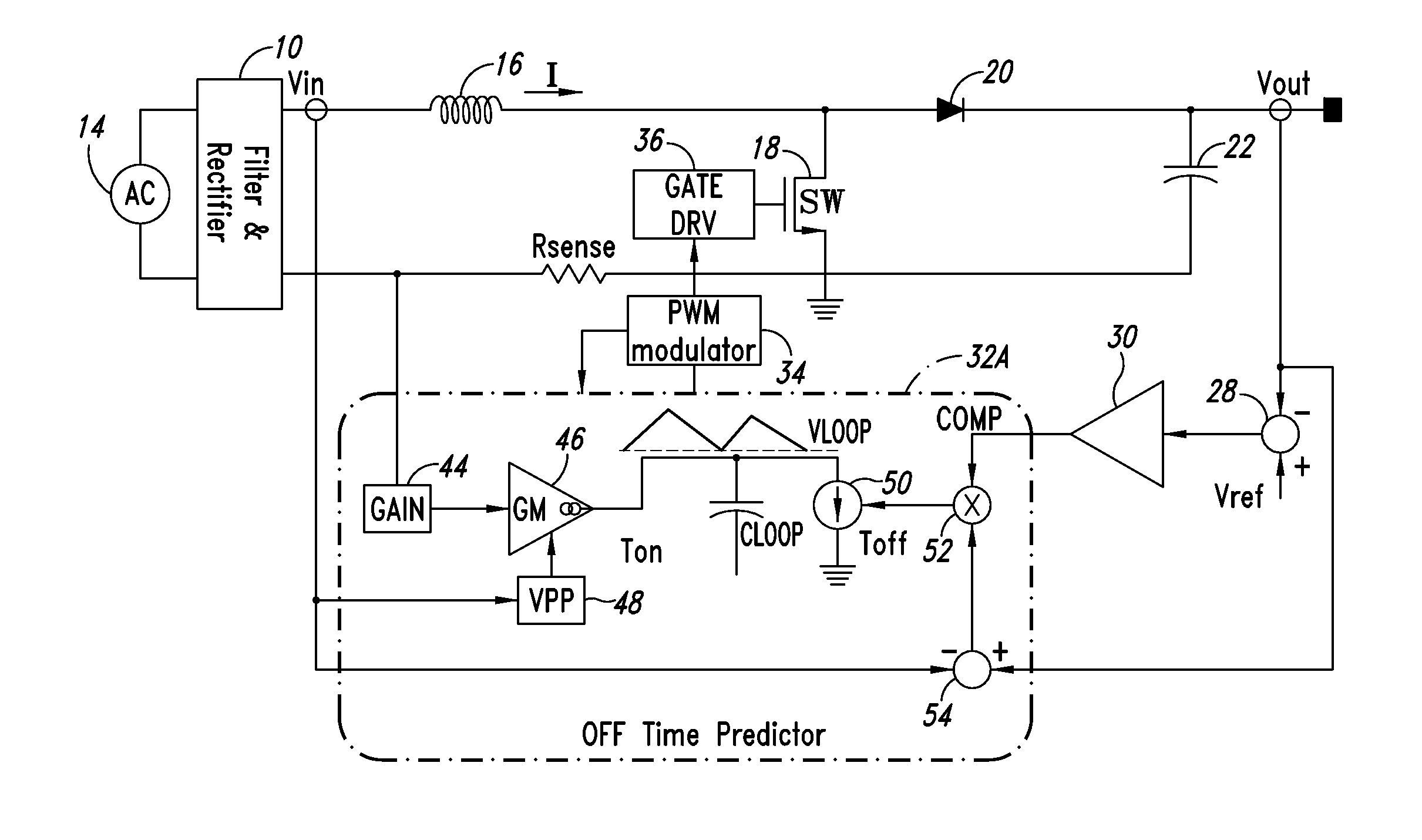
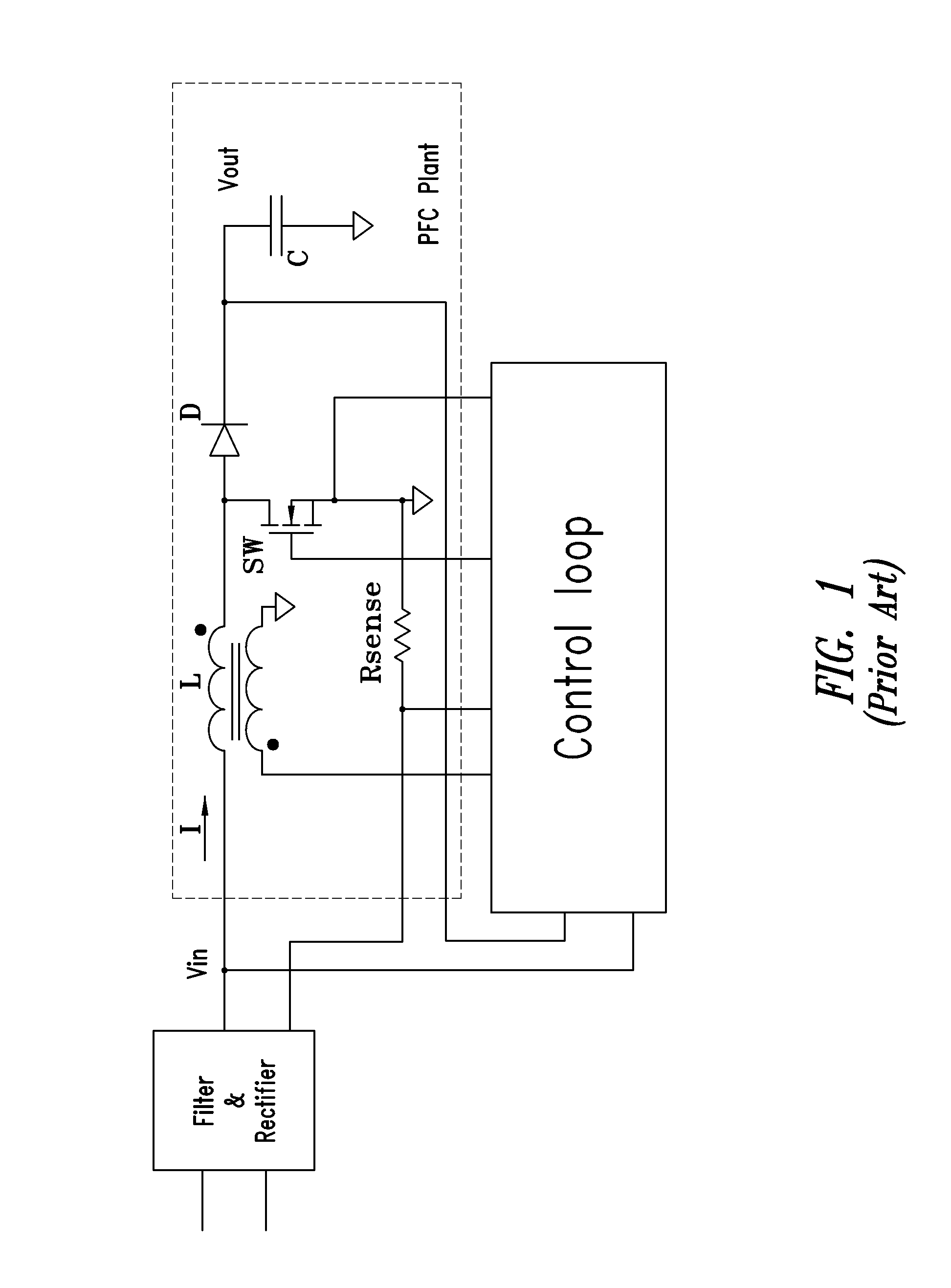
Control circuit implementing a related method for controlling a switching power factor corrector, a pfc and an ac/dc converter
ActiveUS20160020692A1Simple and low-cost circuit implementationGood body shapeAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPeak valueEngineering
A control circuit controls a switching power factor corrector based on switch off-time modulation by controlling the input electric charge during on-time. The circuit includes a charge current generator that generates charge current as a replica of a current sense signal amplified with a gain corresponding to the square of peak value of a rectified input voltage, a loop capacitor charged with the charge current during on-time intervals and discharged with a discharge current during off-time intervals, a discharge current generator that generates the discharge current proportional to a product of a comparison voltage and a difference between a regulated output voltage and the rectified input voltage, and a PWM modulator that senses a charge voltage of the loop capacitor, turns on the switch for an on-time duration in response to detecting that the charge voltage nullifies, and turns off the switch when the on-time duration has elapsed.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
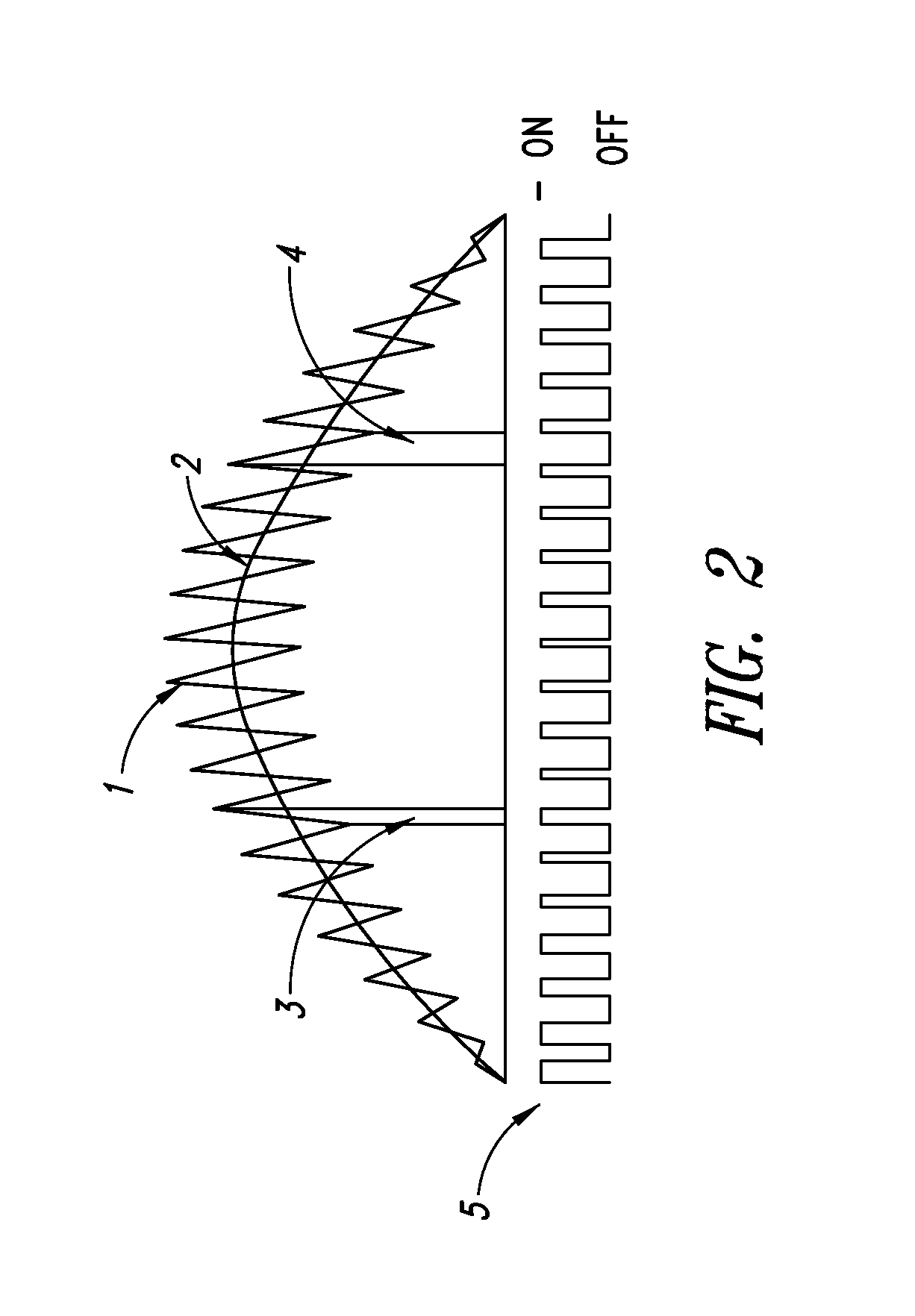
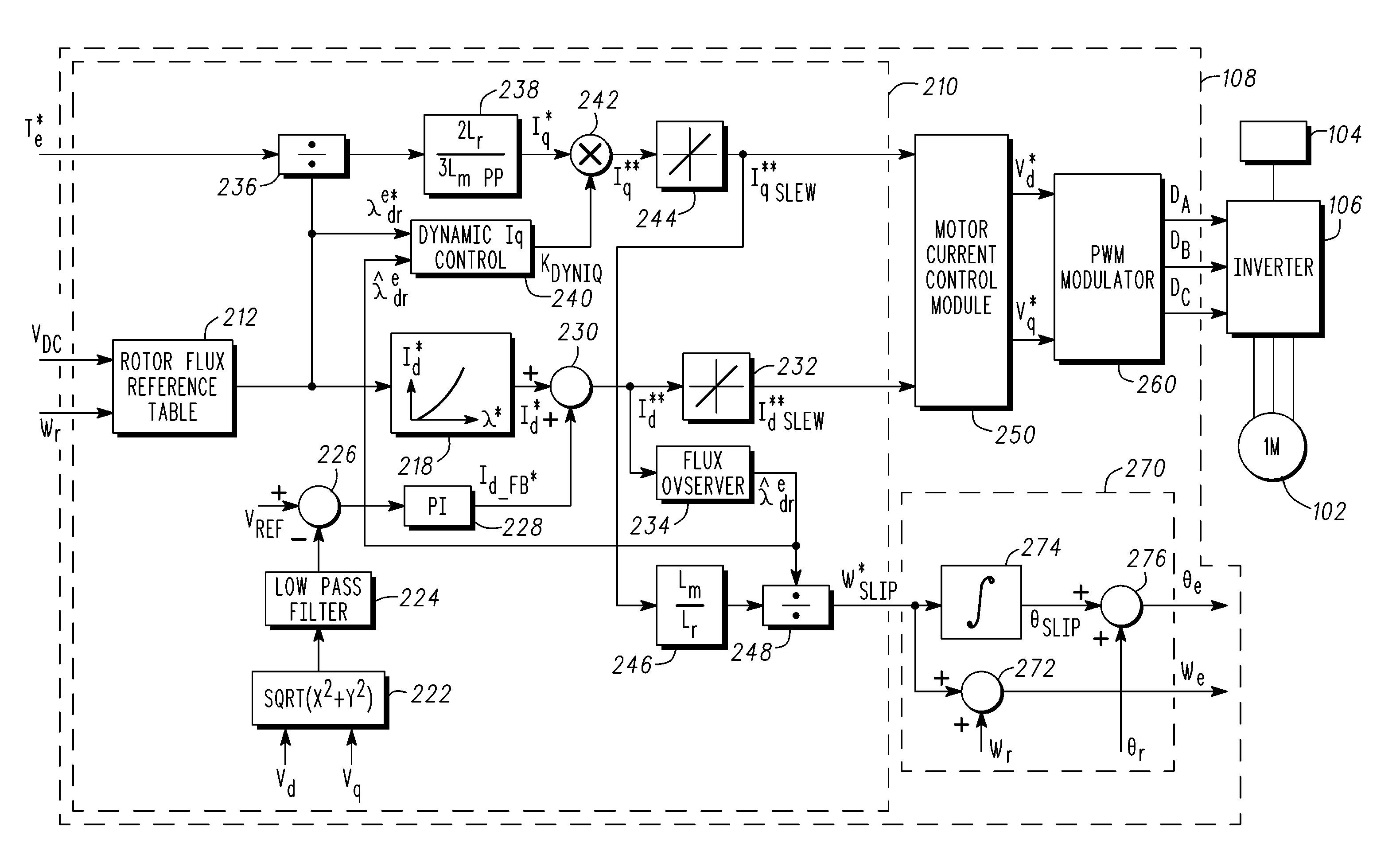
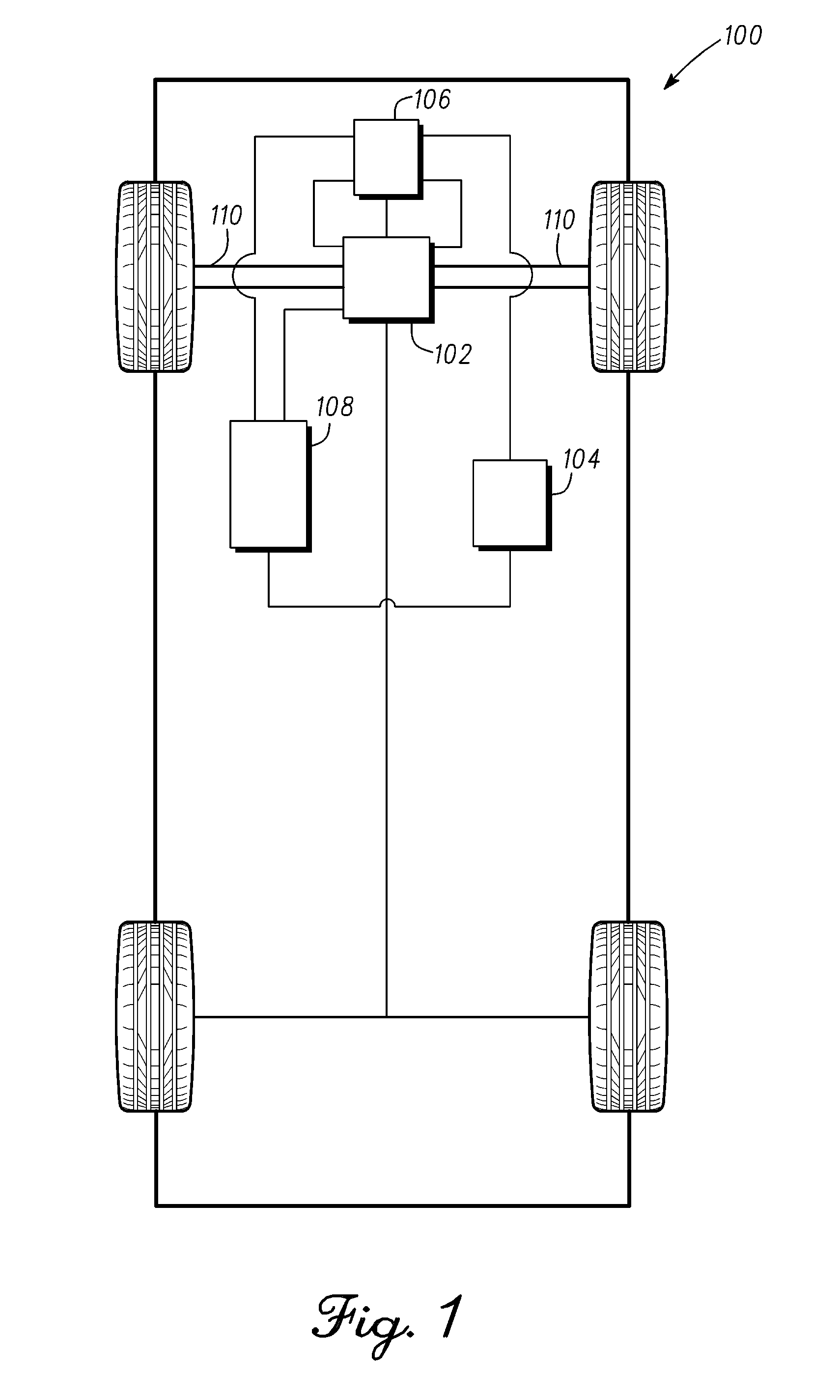
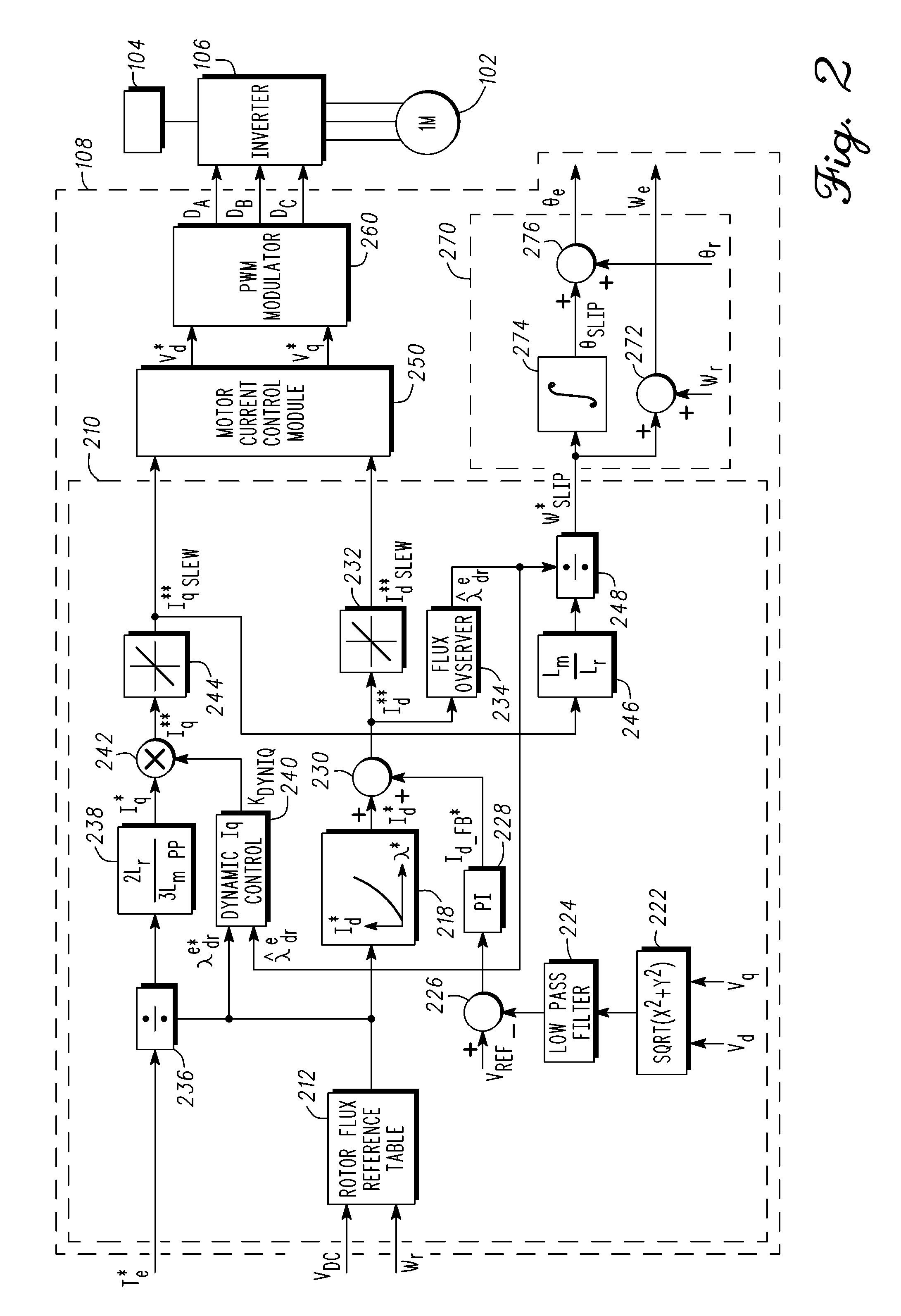
Induction motor control systems and methods
ActiveUS20110163709A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl systemControl theory
A control system is provided for an inverter assembly associated with an induction motor. The system includes a current determination module configured to generate q- and d-axis current commands based on a torque command. The current determination module is further configured to generate the q-axis current command based on an observed flux linkage and a flux linkage command. The system further includes a motor current control module coupled to the current determination module and configured to generate q- and d-axis voltage commands based on the q- and d-axis current commands generated by the current determination module and a PWM modulator coupled to the motor current control module configured to generate duty cycle signals for operating the inverter assembly based on the q- and d-axis voltage commands generated by the motor current control module.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
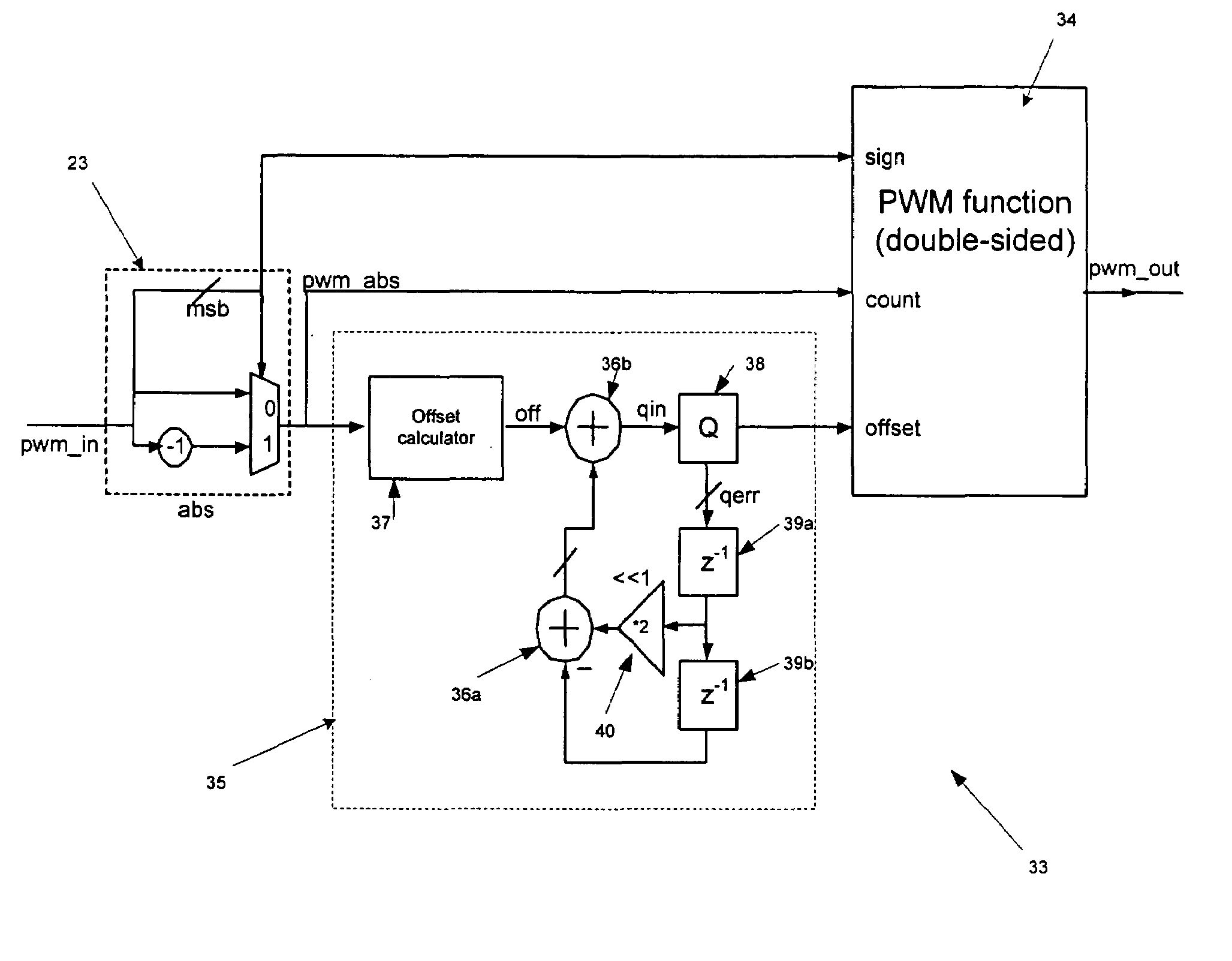
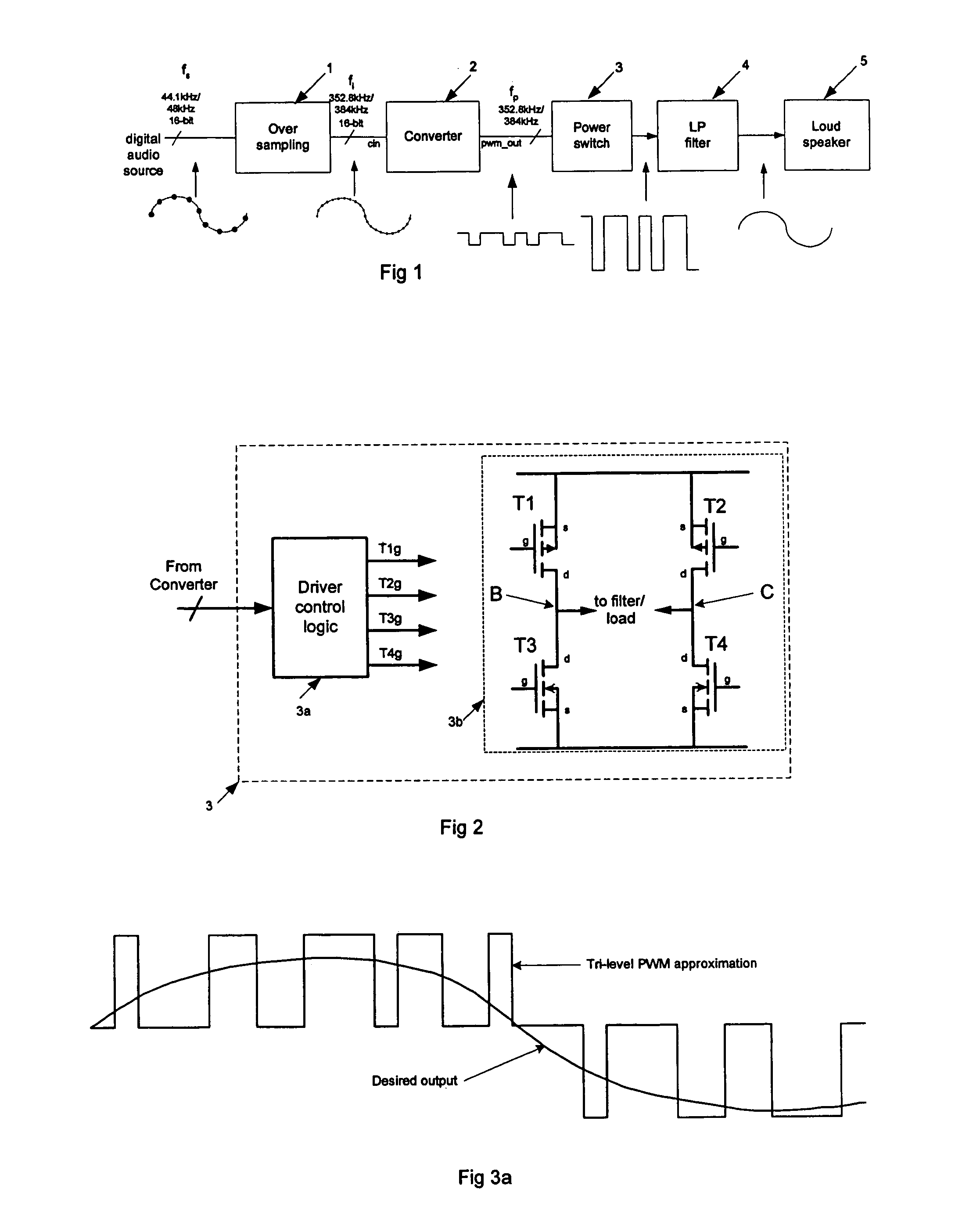
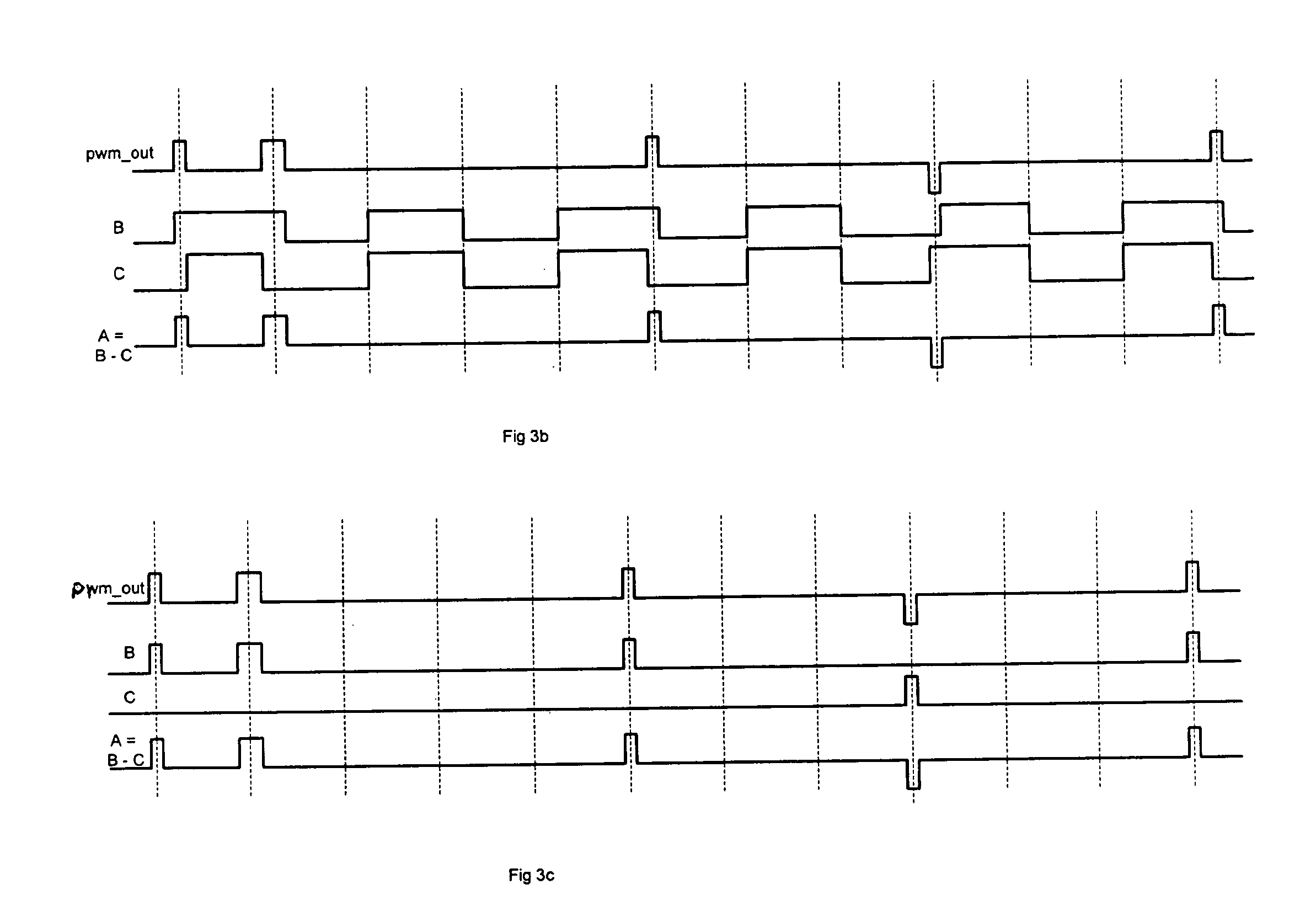
Pulse width modulator quantisation circuit
ActiveUS7205917B2Lower Level RequirementsLess distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionPower switchingPulse-code modulation
The present invention relates to pulse width modulation (PWM) modulators, especially but not exclusively for digital audio applications; and to quantizers and power switching for the same. The present invention provides a pulse width modulation (PWM) modulator or converter having a guard band quantizer arranged to block low level signal inputs to the modulator in order to prevent narrow width output pulses. This arrangement is particularly advantageous when applied to tri-level PWM modulators, but can also be applied to other level PWM modulators such as bi-level for example. Quantization noise can be reduced by implementing the quantizer in a noise shaper circuit (or possibly a SDM) having loop feedback.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Adaptive firing order control for dynamic current balance of multiphase voltage regulators
InactiveUS20080197824A1Improved dynamic current balanceDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringPwm signals
A pulse width modulation (PWM) modulator for a multiphase power converter and related adaptive firing order (AFO) method includes a multiphase leading edge generator having pulse generating circuitry associated with each of the regulator phases, wherein the pulse generating circuitry generates phase pulses associated with each of the phases. An adaptive firing order (AFO) controller having circuitry including a mixer receives and sums the phase pulses into a summing signal and uses the summing signal to generate a series of turn-on pulses therefrom. A multiphase PWM generator has inputs coupled to an output of the AFO controller coupled to receive the series of turn-on pulses, the multiphase PWM generator having circuitry for generating said PWM signals therefrom. An adaptive firing order (AFO) controlled multi-phase power converter includes a plurality of parallel connected regulator phases controlled by respective pulse width modulation (PWM) signals provided by the PWM modulator.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Space vector PWM modulator for permanent magnet motor drive
InactiveUS20040130918A1Electronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorControl signal
A space vector pulse-width modulator (SVPWM) and a method implemented by the modulator. A precalculation module accepts Ua and Ub modulation indexes and in response thereto, outputs modified Ua and Ub information; a sector finder has a U module which receives the modified Ua information and outputs a U sector; and a Z module which receives the U sector and the modified Ub information and outputs a Z sector. The U sector and the Z sector are 2-phase control signals for implementing 2-phase modulation. For 3-phase modulation, the SVPWM and method further possess an active vectors calculation module and an assign vectors module which receive the modified Ua and Ub information and the U sector, and which calculate active vectors for 3-phase modulation; a zero vector selector which receives the Z sector and calculates zero vectors for 3-phase modulation; and a PWM counter block which receives the active vectors and zero vectors and outputs 3-phase control signals for implementing 3-phase modulation. The SVPWM and method may have a symmetrical PWM mode, an asymmetrical PWM mode, or both. Advantageously there may also be a rescale and overmodulation module which receives duration information corresponding to the vectors and in response thereto, detects the occurrence of overmodulation. Overmodulation may be detected in response to a negative zero vector time. The module may respond to overmodulation by clamping the zero vector time to zero and rescaling the active vector times to fit within the PWM cycle. The rescaling may restrict a voltage vector to stay within hexagonal boundaries on the space vector plane, while preserving voltage phase.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
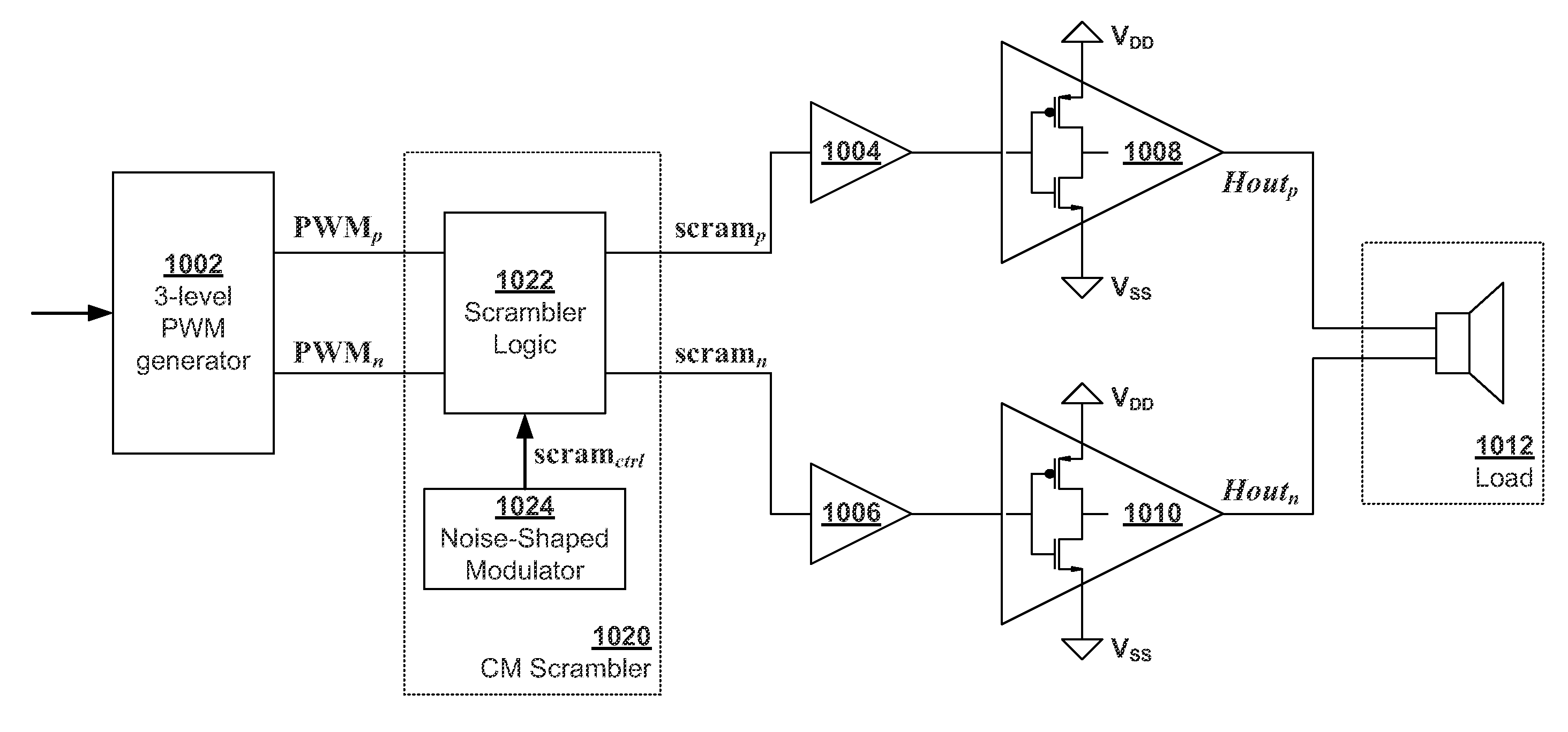
Noise-Shaped Scrambler for Reduced Out-of-Band Common-Mode Interference
ActiveUS20110050467A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsThree levelAudio power amplifier
Class-D amplifiers have evolved from using binary pulse-width modulation (PWM) modulators to three-level PWM modulators. Three-level PWM drivers for audio applications offer the benefits of eliminating costly elements at the output of an audio system. However, they also introduce increased common-mode interference. Three-level PWM generates three states, but one state has two interchangeable representations which can be scrambled in order to shape the common-mode output spectrum.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
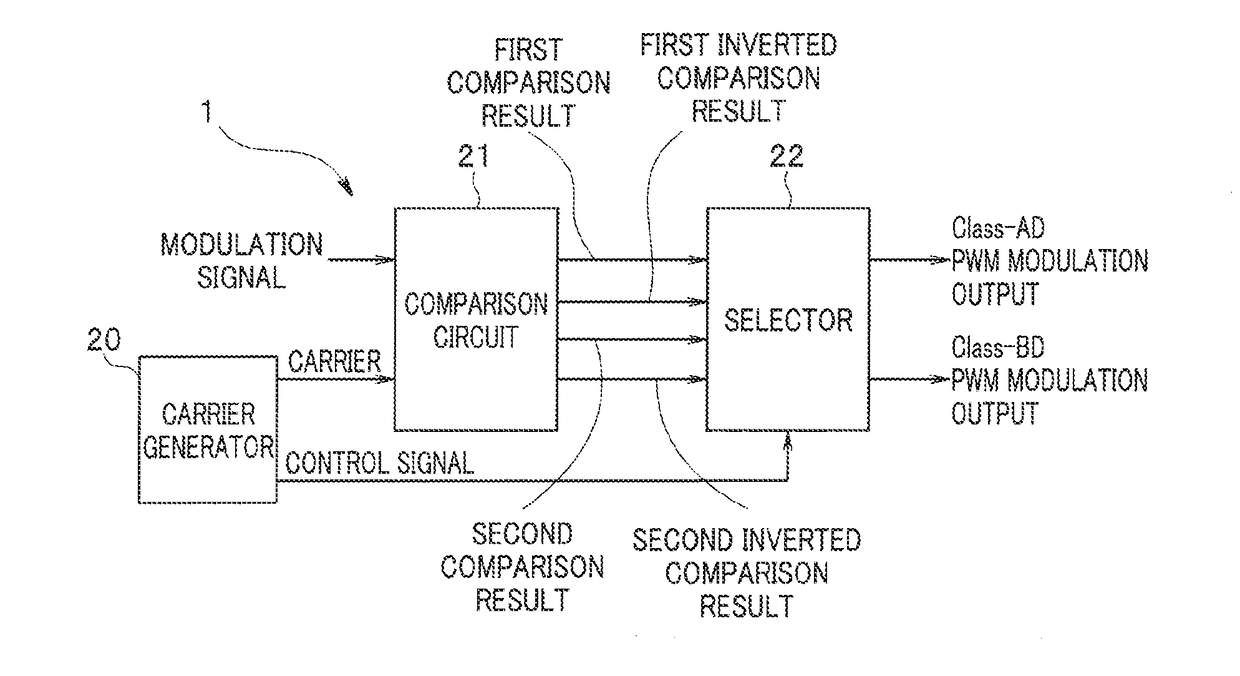
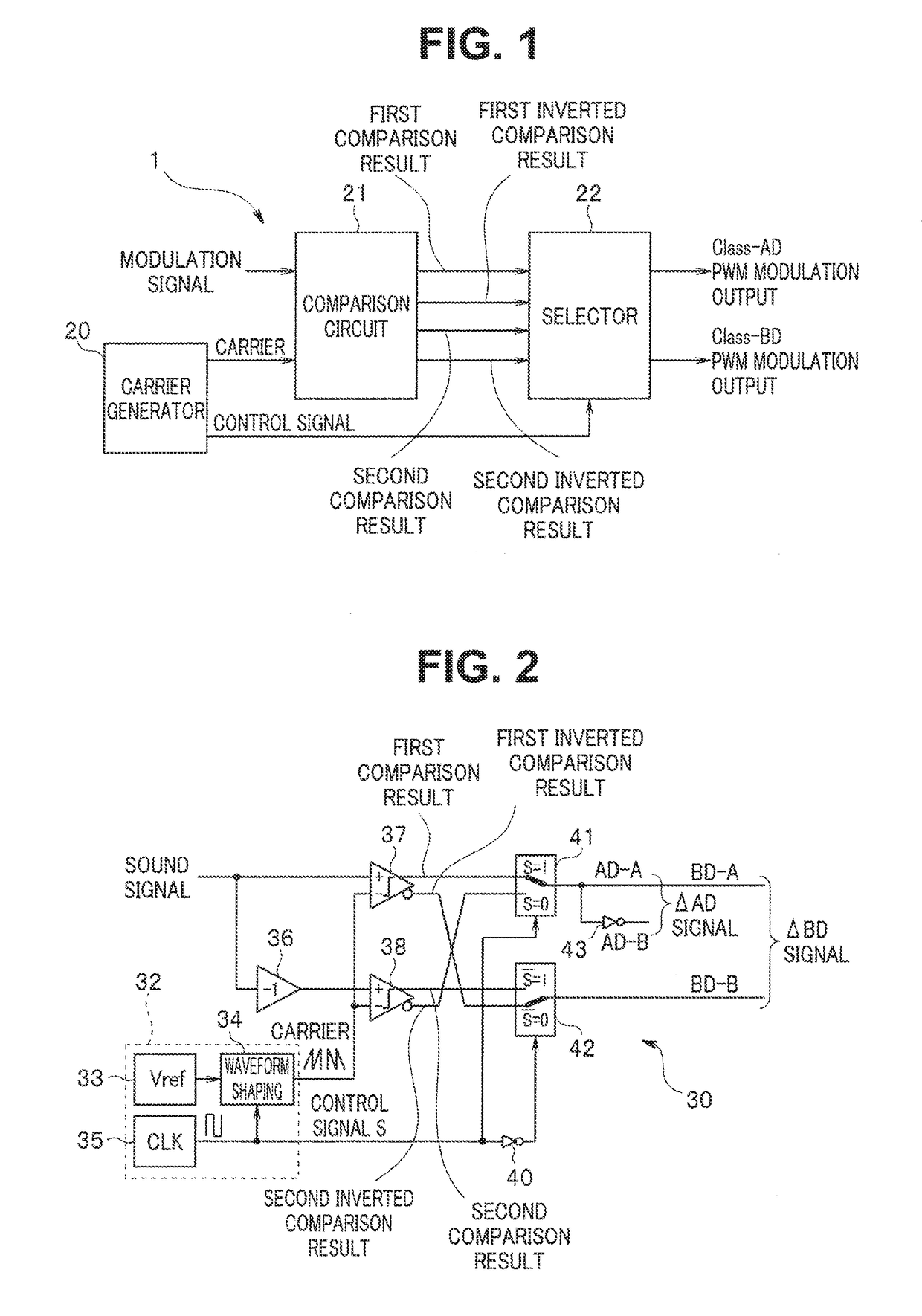
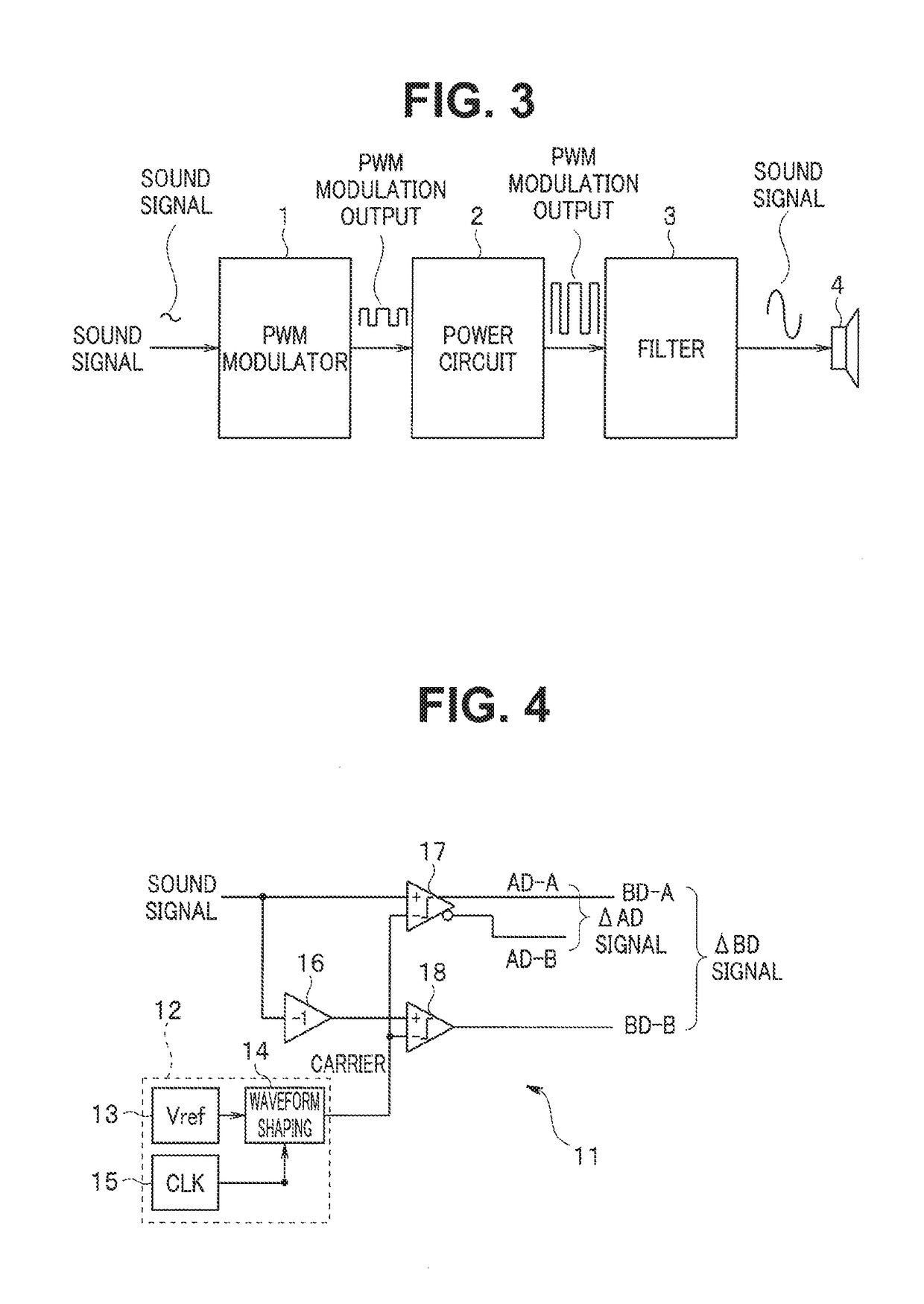
Pwm modulator
ActiveUS20180076806A1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLow frequency amplifiersOutput compareComparator
A PWM modulator according to an embodiment includes a first comparator configured to compare a first input signal with a first carrier and output a comparison result, a second comparator configured to compare a second input signal with a second carrier and output a comparison result, and a selector configured to output the comparison result while switching between the comparison result of the first comparator and the comparison result of the second comparator in a cycle according to a cycle of the first or the second carrier.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
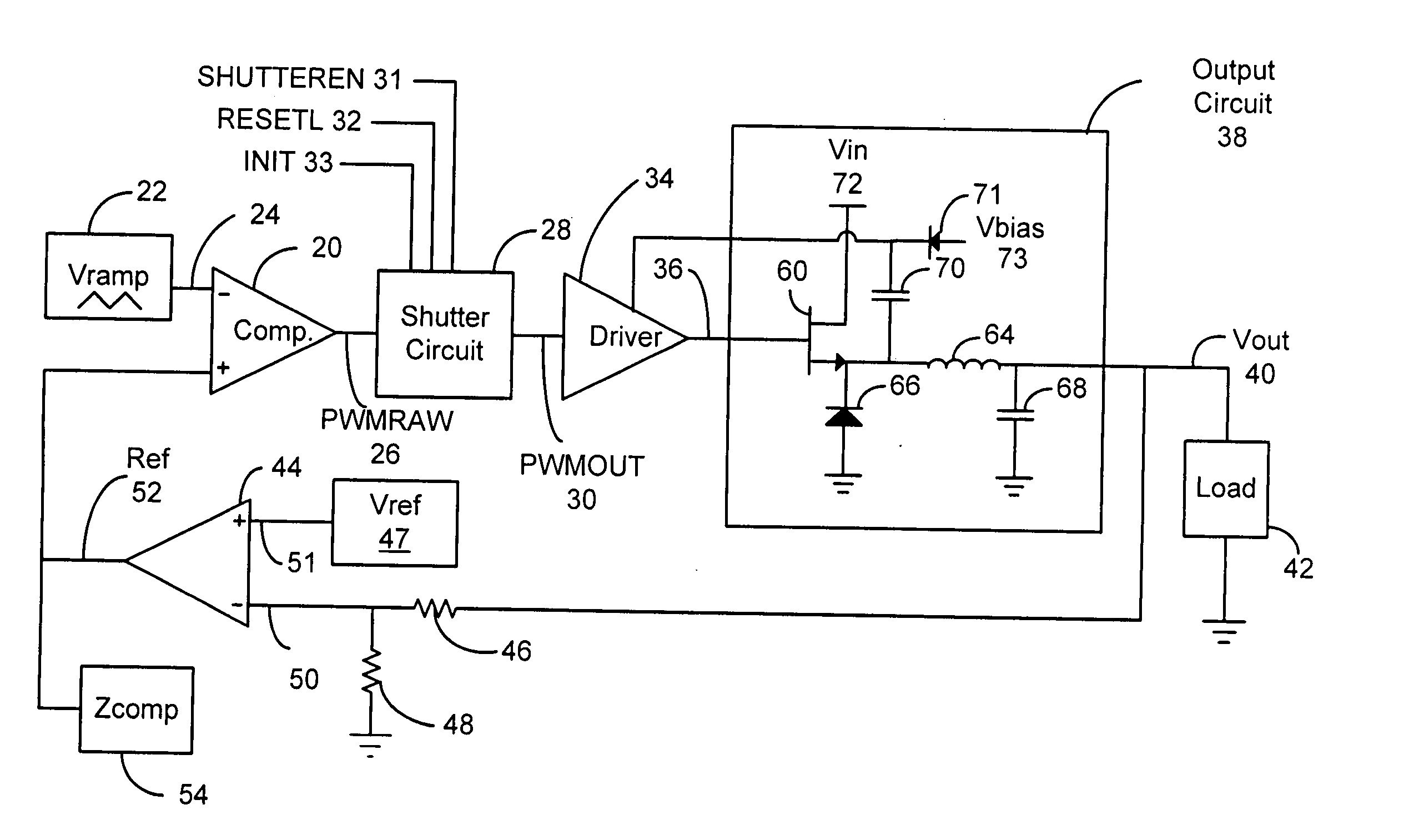
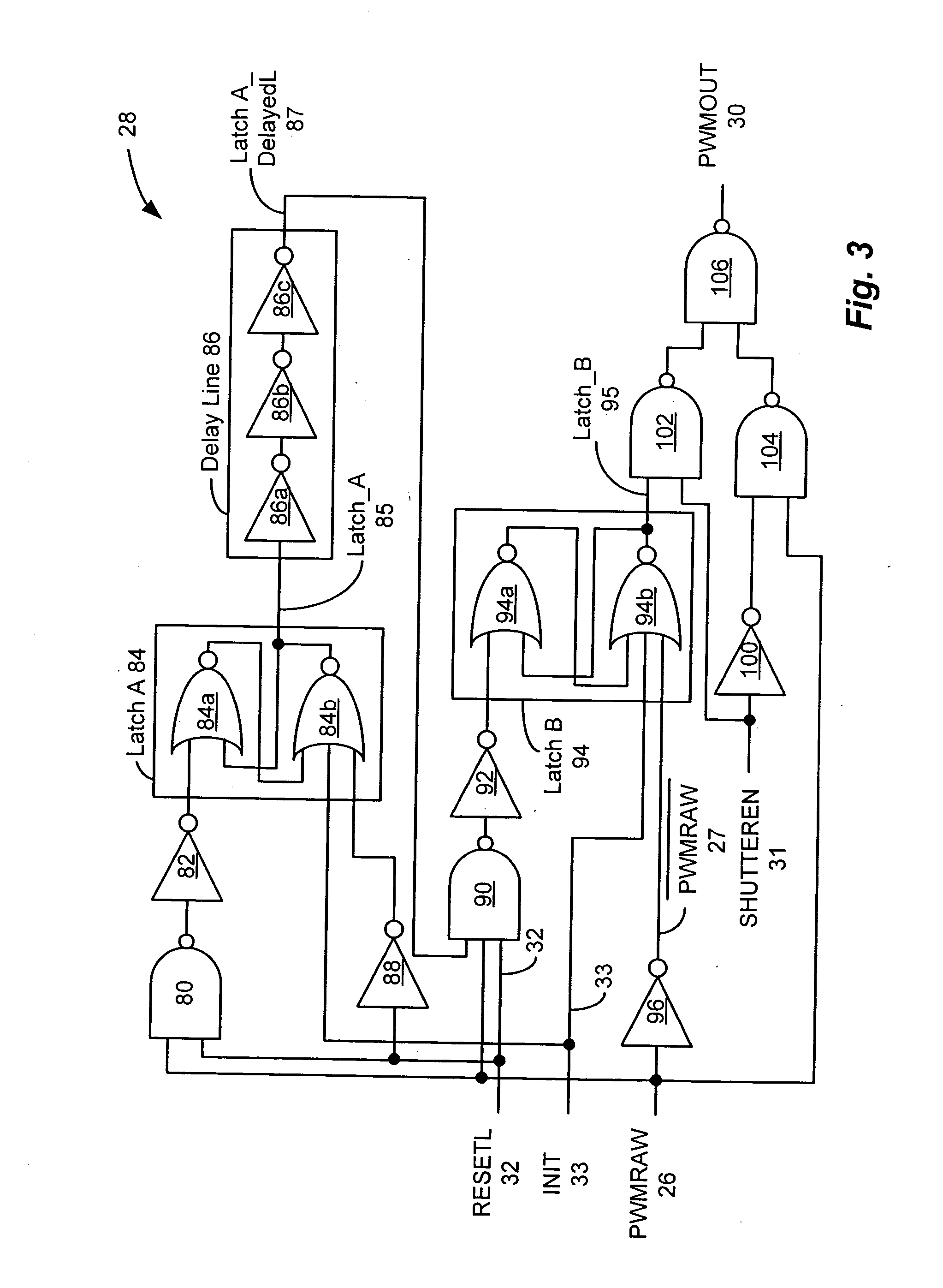
Pulse width modulation controller with double pulse immunity
ActiveUS20050134244A1Eliminates double pulsingDc-dc conversionElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitControl theory
A pulse width modulation (PWM) controller includes a shutter circuit interposed between a PWM modulator and a driver circuit. The shutter circuit receives a raw PWM output signal from the PWM modulator and processes the raw PWM signal to eliminate double pulsing that may be present on the raw PWM signal. Bypass logic responsive to a switch or software controlled enable input is provided to permit the shutter circuit to be included in the PWM controller or alternatively, to be bypassed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
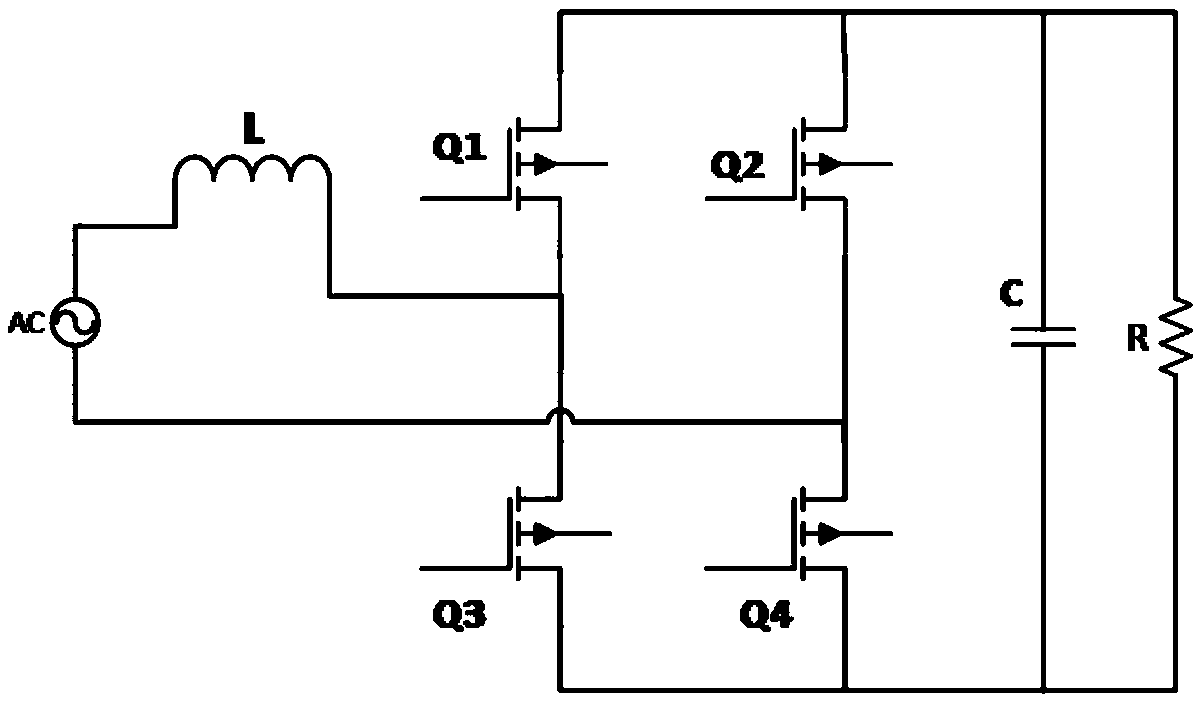
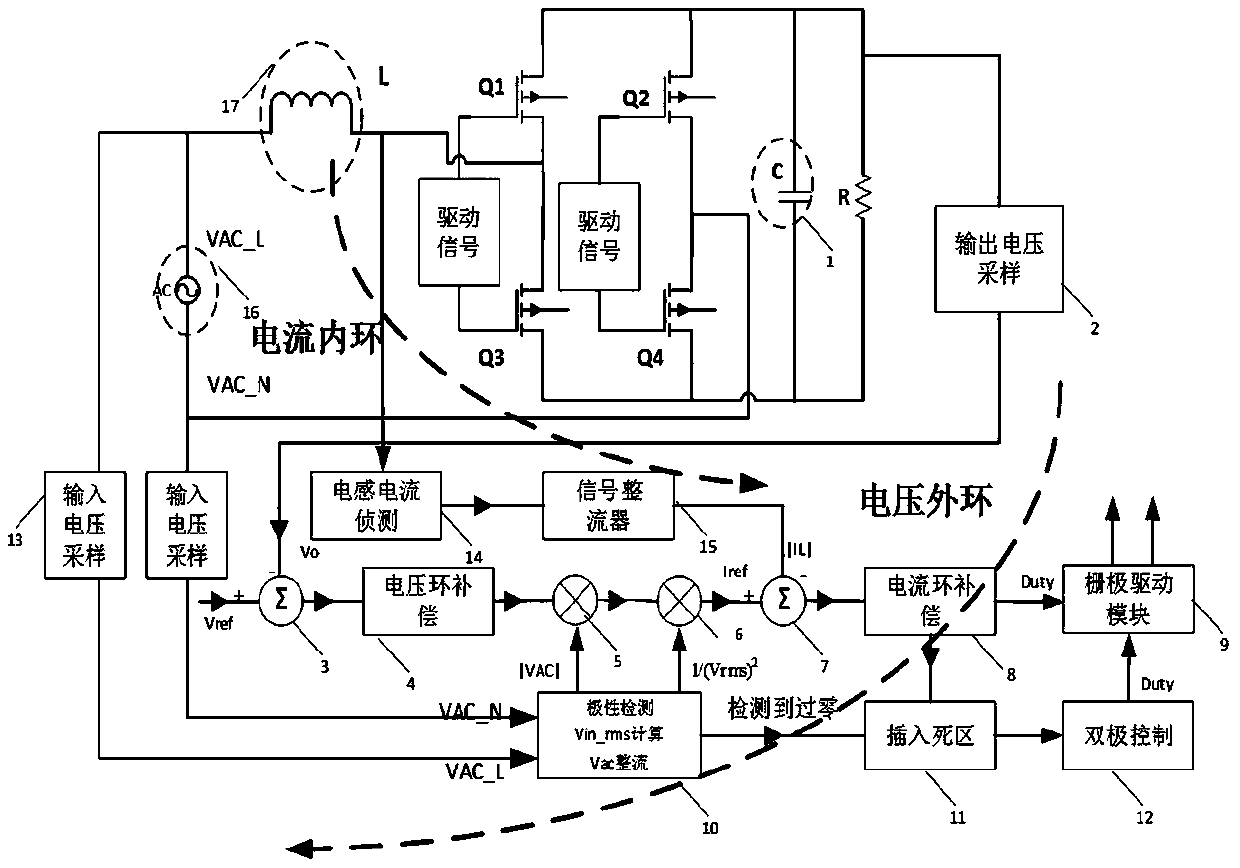
Method and device for controlling voltage zero crossing point current distortion of totem-pole PFC
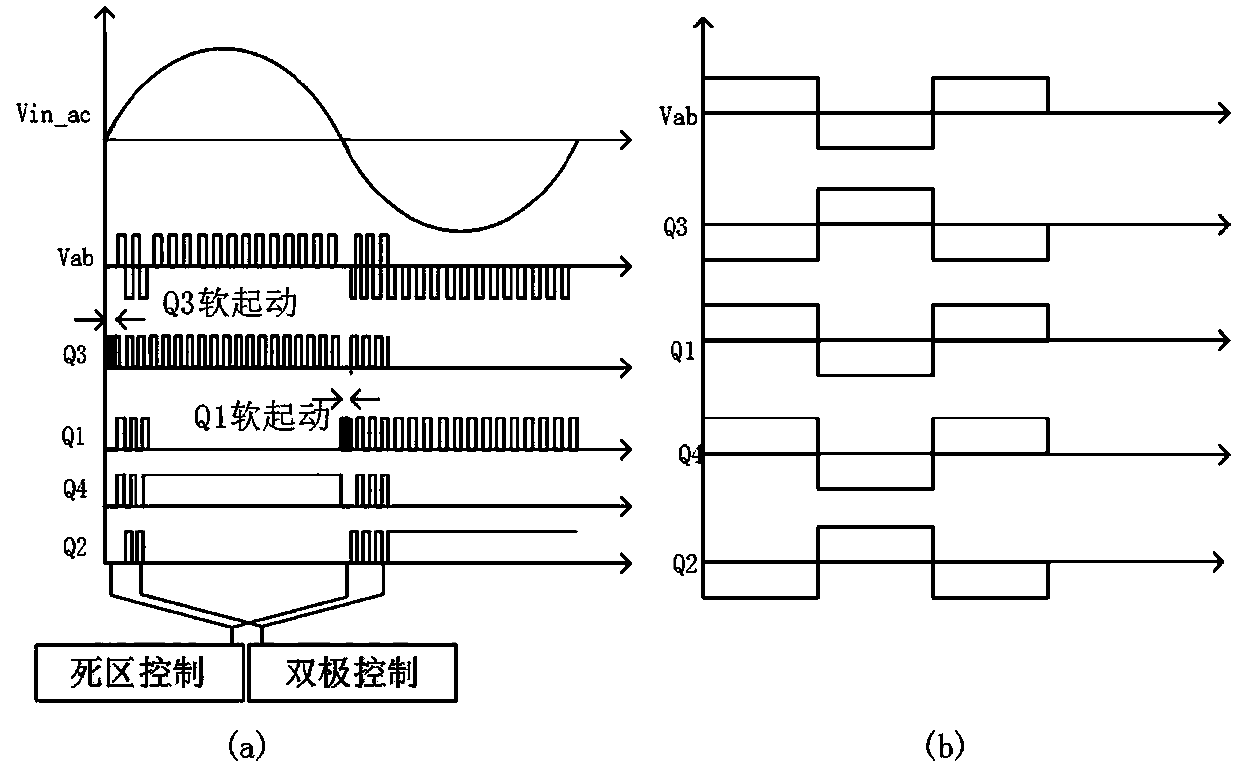
InactiveCN109617387AEliminates positive pulsesReduce Harmonic PollutionEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsTotal harmonic distortionPower factor
The invention relates to a method and a device for controlling voltage zero crossing point current distortion of a totem-pole PFC. Input and output voltage information and inductance current information are sampled through a sampling module; error signals are compensated and adjusted through a voltage outer loop adjusting unit and a current inner loop adjusting unit; and finally the processed error signals are sent to a PWM modulator to generate a gating signal. The zero crossing point state of the input voltage of each half of the power frequency period is detected to be inserted into dead zone control and bipolar control; soft start of a main switch tube of a high-frequency bridge arm in the dead zone control stage is completed, and the inductance current is constrained without generating a pulse peak; and in the bipolar control stage, the current constraint condition also can be established under the condition that the input voltage is relatively low, so that the input current can be more effectively corrected to enable the input current to follow the input voltage. The device can be stably operated in a CCM control mode, and the problem of zero crossing point pulse is solved, so that the overall power factor value is improved, and the total harmonic distortion amount of the whole system is reduced.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for inhibiting second harmonic current of preceding-stage inverter of two-stage inverter and control circuit of preceding-stage inverter of two-stage inverter
InactiveCN102843020ASecond Harmonic Current SuppressionRaise the cutoff frequencyPower conversion systemsBand-pass filterVoltage reference
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting second harmonic current of a preceding-stage inverter of a two-stage inverter and a control circuit of the preceding-stage inverter of the two-stage inverter. By the method, the low-frequency pulse current of the preceding-stage direct current inverter can be inhibited obviously, the dynamic performance can be improved and the dynamic response speed is increased. The control circuit of the preceding-stage inverter consists of a band-pass filter, a voltage regulator, a summator, a power-width modulation (PWM) modulator and a driving circuit. The work principle is as follows: a voltage sampling circuit detects intermediate bus voltage, compares the intermediate bus voltage with a voltage reference signal to generate an error signal and transmits the error signal to the voltage regulator; a current sampling circuit detects the inductive current of the preceding-stage direct current inverter; the inductive current of the preceding-stage direct current inverter, an output signal of band-pass filter and an output signal of the voltage regulator are added by the summator to generate a modulation signal; the modulation signal is transmitted to a PWM modulation circuit; and a driving signal of a switch tube is acquired by the driving circuit, so that operation of the preceding-stage direct current inverter is controlled.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
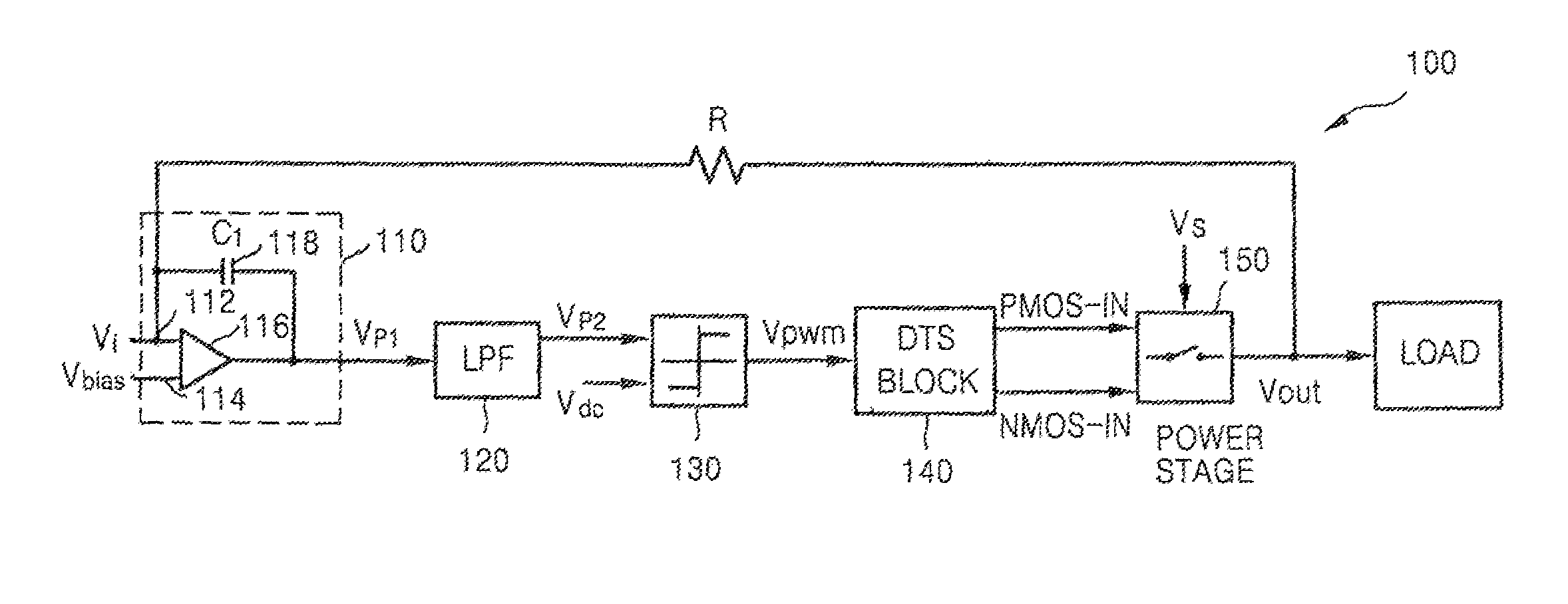
PWM modulator and class-D amplifier having the same
ActiveUS7417497B2EMI can be reducedPulse duration/width modulationDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorIntegratorAudio power amplifier
A pulse width modulation (PWM) modulator includes an integrator generating an integrated signal based on an input signal and an output signal, a low pass filter (LPF) receiving the integrated signal and performing low pass filtering, a comparator receiving an output signal of the LPF and a predetermined reference signal, comparing the received signals, and outputting a PWM signal, a dead time setup block outputting a first signal and a second signal having a predetermined phase difference therebetween based on the PWM signal, and a power stage buffering the first and second signals and generating the output signal based on a result of buffering. In the PWM modulator and a class-D amplifier having the PWM modulator, EMI can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
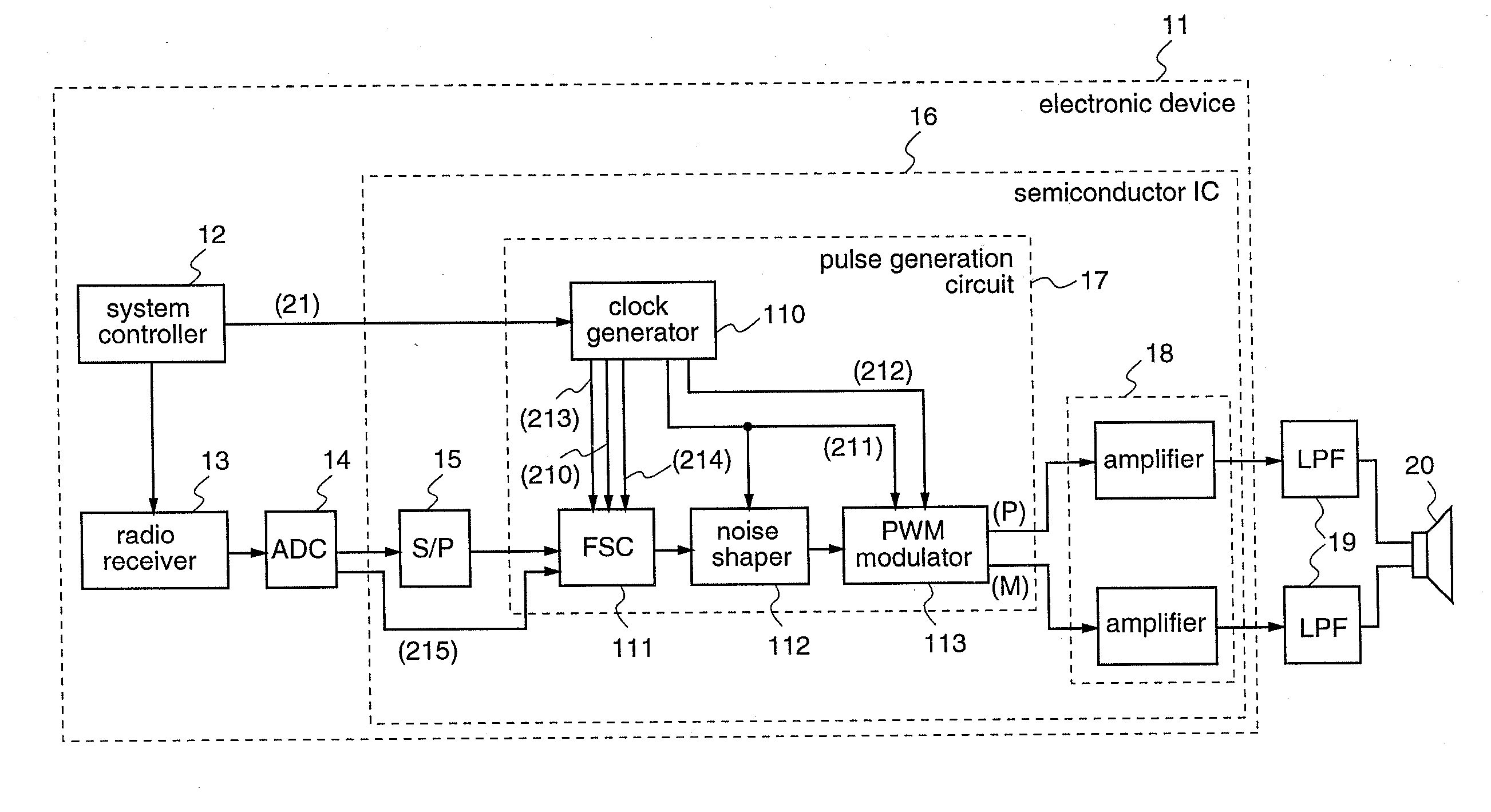
Semiconductor integrated circuit and electronic device
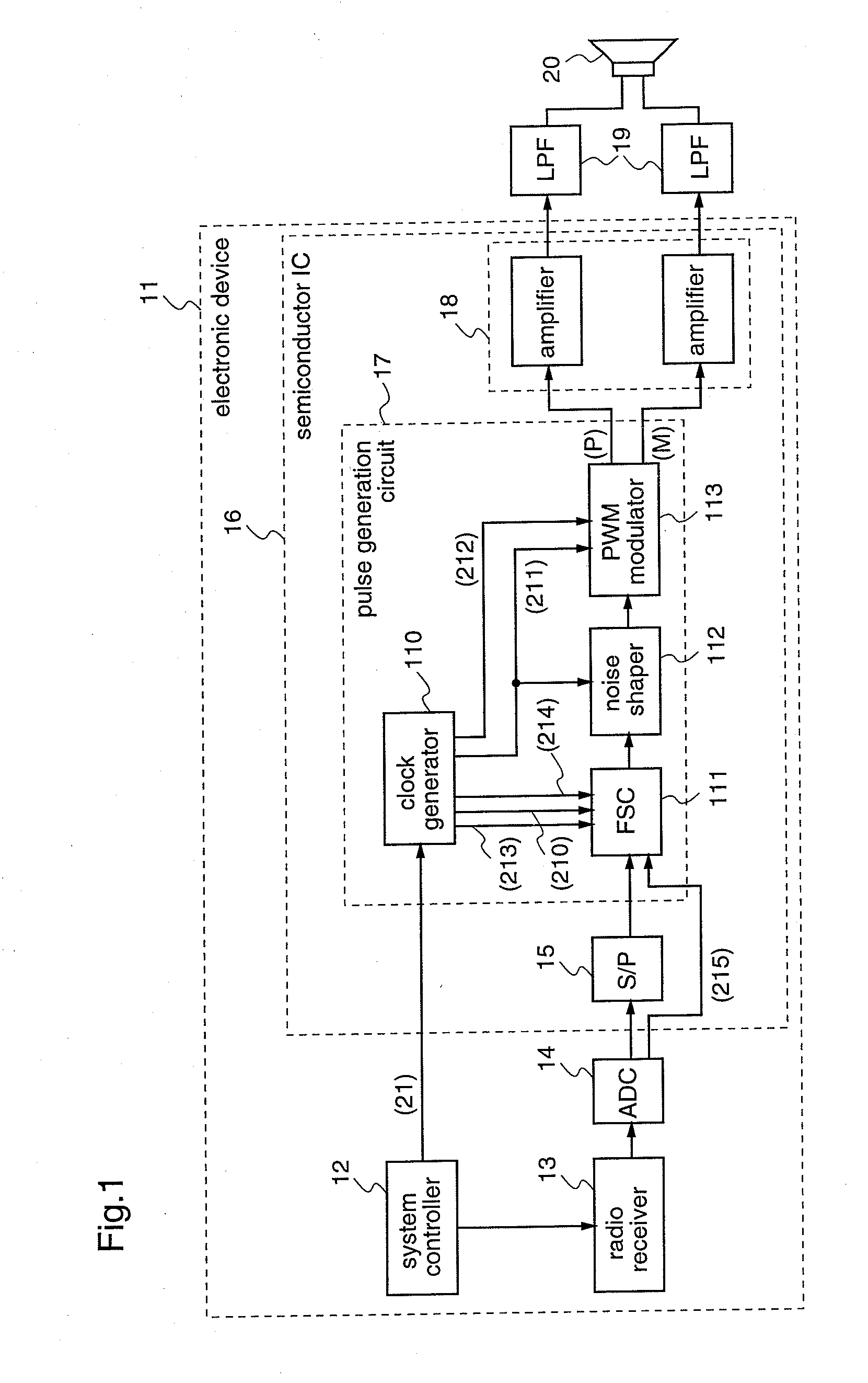
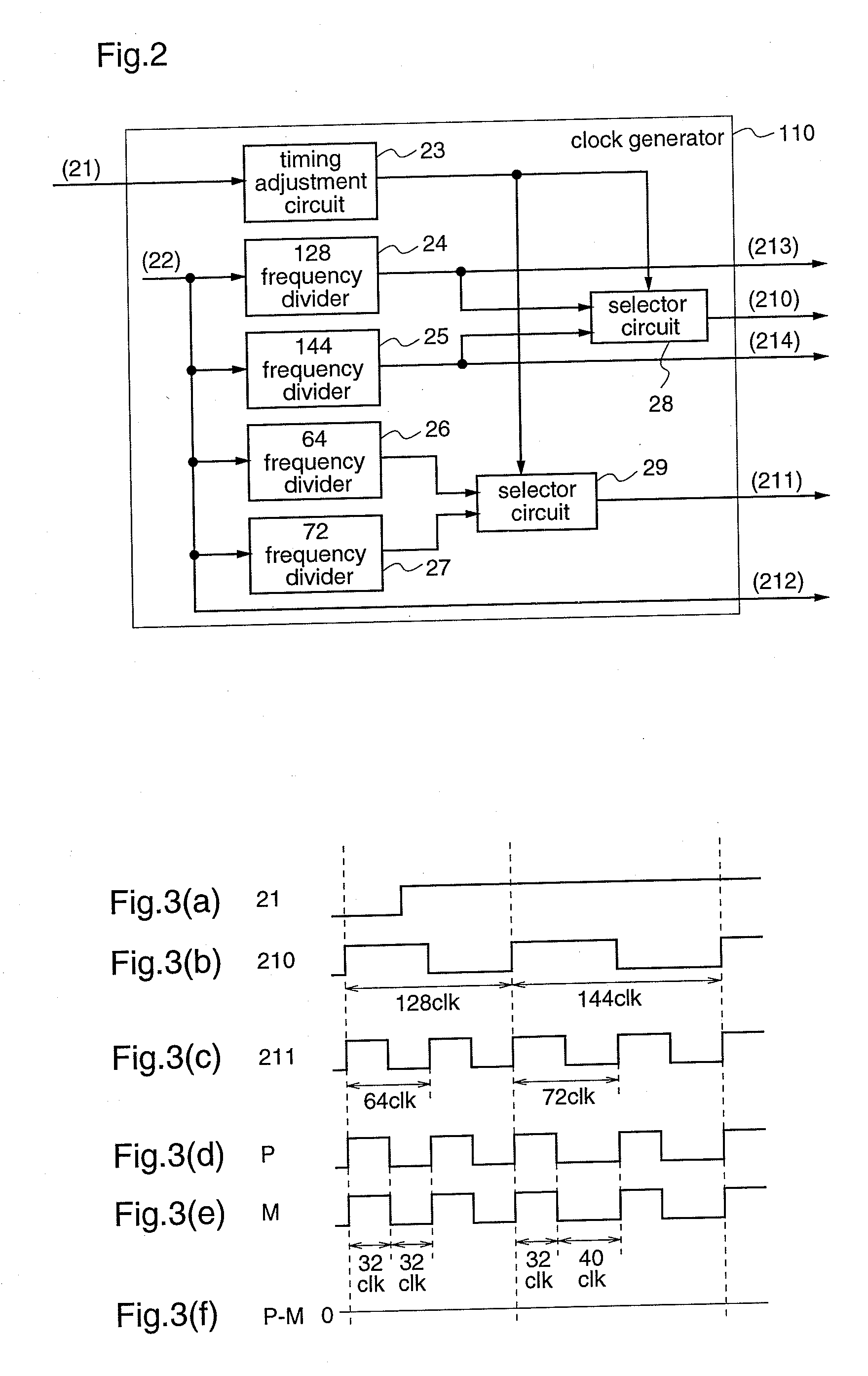
InactiveUS20090135897A1Avoid interferenceSuppress mutationAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationRadio receptionRadio receiver
An electronic device (11) according to the present invention includes a semiconductor integrated circuit (16) on which a pulse conversion circuit (17) for converting an acoustic signal received by a radio receiver (13) into a pulse signal is integrated. The pulse conversion circuit (17) includes a clock generator (110) which generates plural clocks and selects word clocks (210,211) according to the reception frequency of the radio receiver (13), an FSC (111) which performs sampling frequency conversion so as to make a sample sequence of an A / D converted acoustic signal have the same frequency as that of the word clock (210), a noise shaper (112) for performing noise shaping to the sample sequence outputted from the FSC (111) using the word clock (211), and a PWM modulator (113) for generating a pulse signal from the output of the noise shaper (112) using the word clock (211). Therefore, it is possible to avoid radio reception interference which may caused by the pulse signal when driving a speaker with the pulse signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
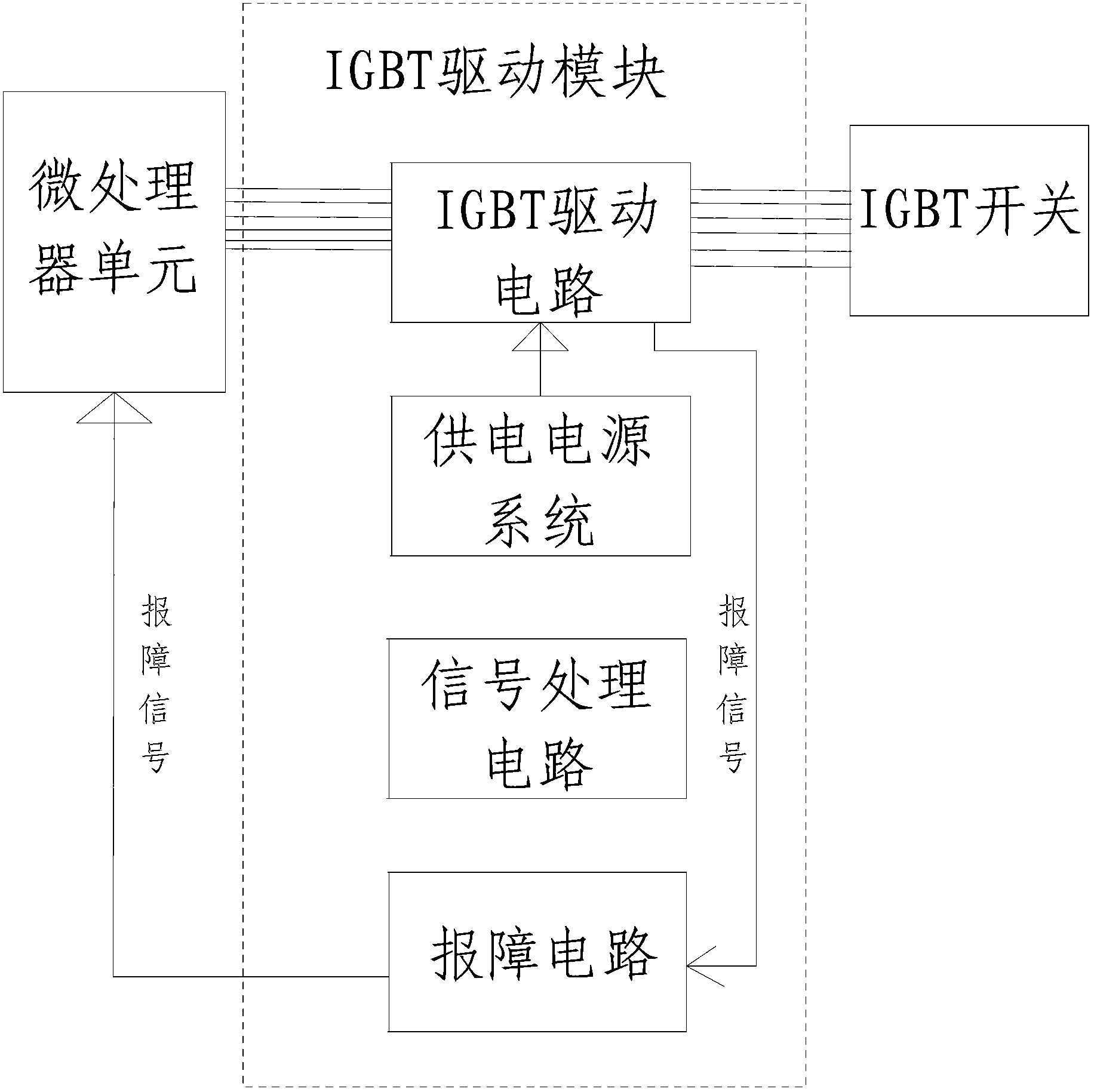
Power supply system of IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) drive module
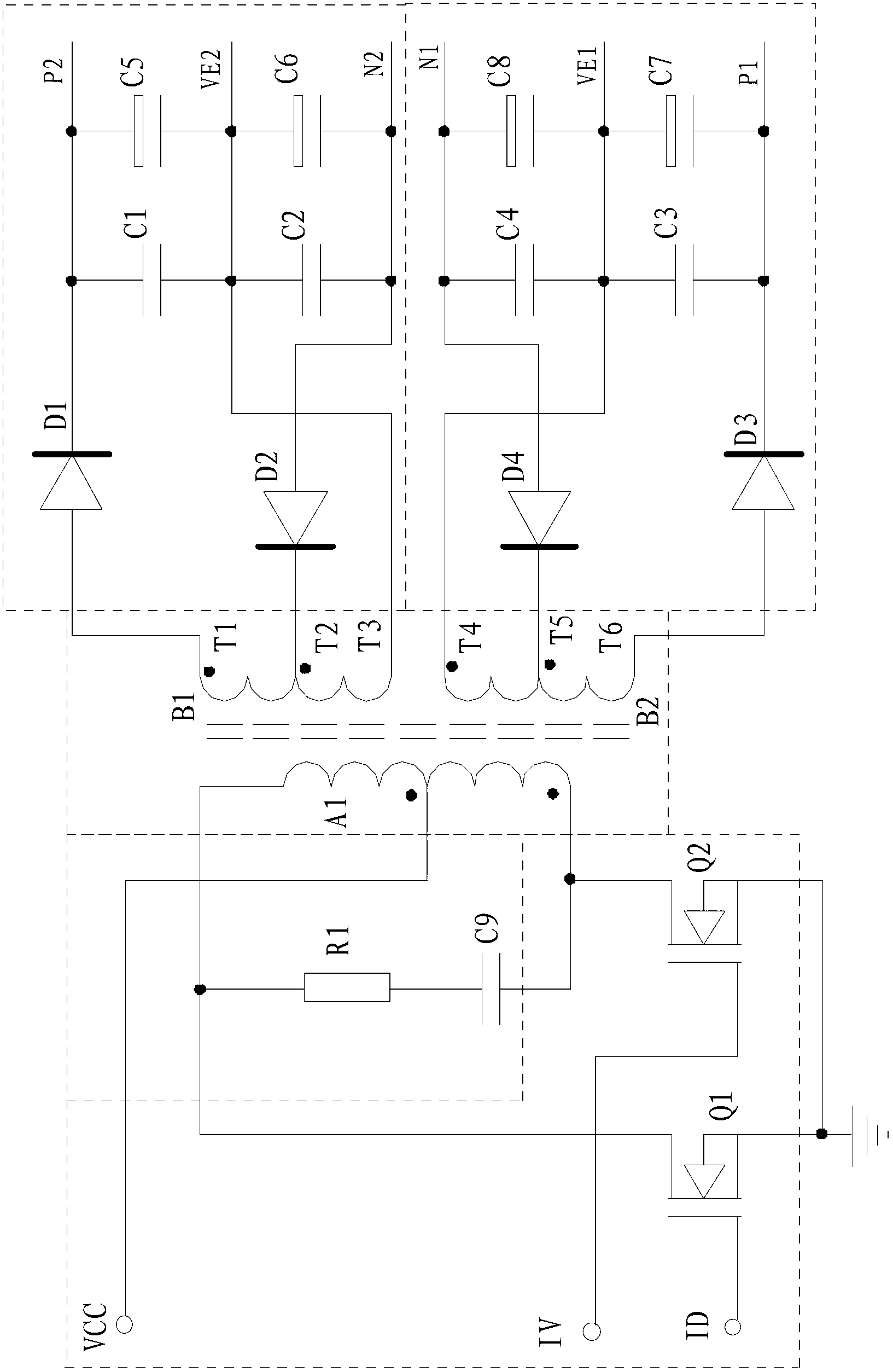
ActiveCN103219890AExtend working lifeWork reliablyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceTransformer
The invention discloses a power supply system of an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) drive module. The power supply system comprises a PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) modulator, a power switch tube and an inverter transformer, wherein a first initial end tap (T1) of a secondary first coil (B1) is connected with an anode of a first rectification diode (D1); a cathode of the first rectification diode (D1) is connected with one end of a first energy-storage capacitor (C1); the other end of the first energy-storage capacitor (C1) is connected with a first tail end tap (T3); a first middle tap (T2) is connected with a cathode of a second rectification diode (D2); an anode of the second rectification diode (D2) is connected with one end of a second energy-storage capacitor (C2); the other end of the second energy-storage capacitor (C2) is connected with the first tail end tap (T3); and the layout of a rectification and energy-storage capacitor of a secondary second coil (B2) is symmetrical with that of the secondary first coil (B1). According to the power supply system, positive and negative output voltages are mutually isolated in an inverting way, and do not interfere mutually, so that the problem of unbalance of magnetic flow of a transformer is solved, the aim of balance of magnetic flow is achieved, the stability of the power supply system of the IGBT drive module is ensured, and the interior demand of an electric automobile is met.
Owner:上海汽车电驱动有限公司 +1
Rapid dynamic compensation control apparatus and control method of voltage control type DC/DC converter
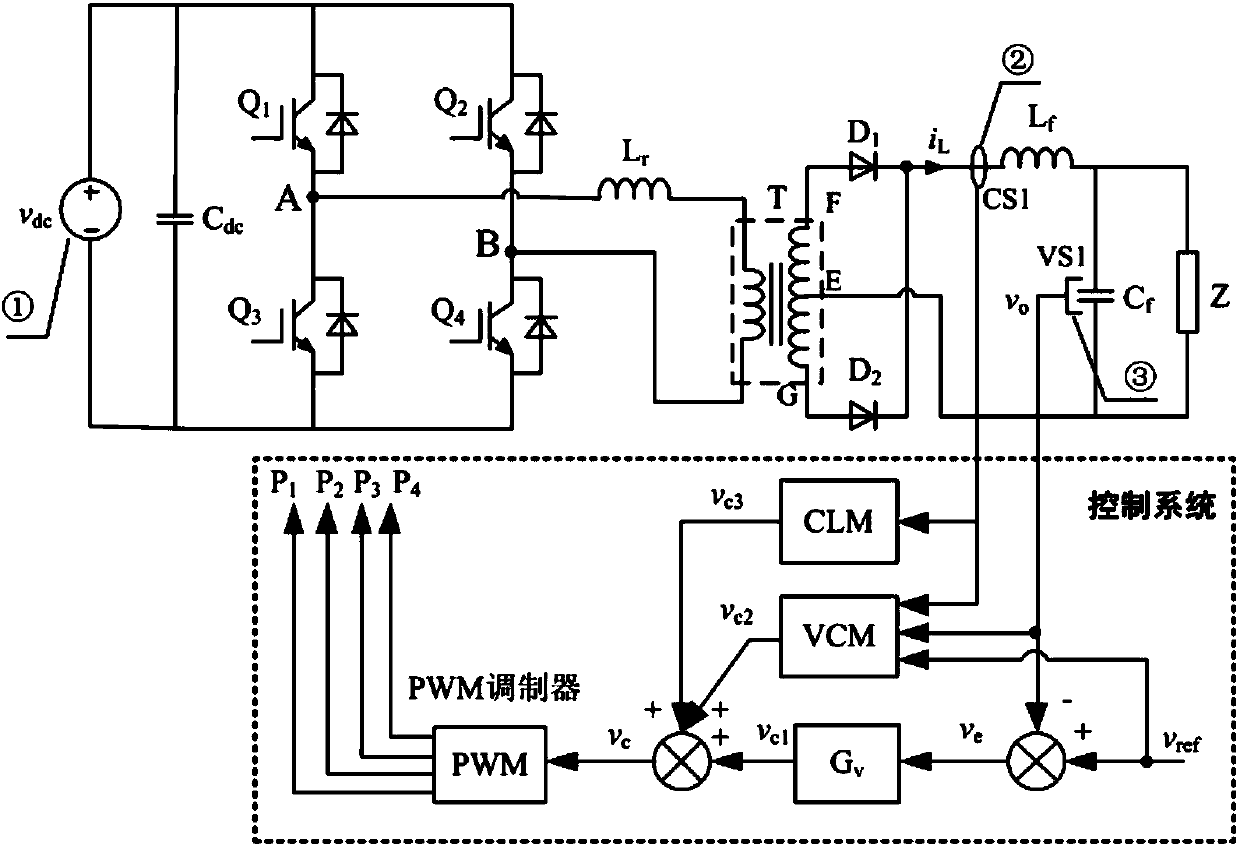
ActiveCN104184325AFast dynamic responseSmooth switchingApparatus with intermediate ac conversionLoop controlClosed loop
The invention provides a rapid dynamic compensation control apparatus and control method of a voltage control type DC / DC converter. The rapid dynamic compensation control apparatus comprises a voltage controller (Gv), a voltage compensation module (VCM), a current limiting module (CLM) and a PWM modulator. Due to the restriction of the switching frequency of a power switch device, the bandwidth of the control loop of a medium and large-power converter is quite low, under general voltage closed loop control, and in case of a load abrupt change, quite large fluctuations are caused to output voltages. Direct correction is carried out on a digit control amount which adjusts a duty ratio in a control system according to the inherent open loop characteristic of a tested converter itself, such that the purpose of rapid compensation is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
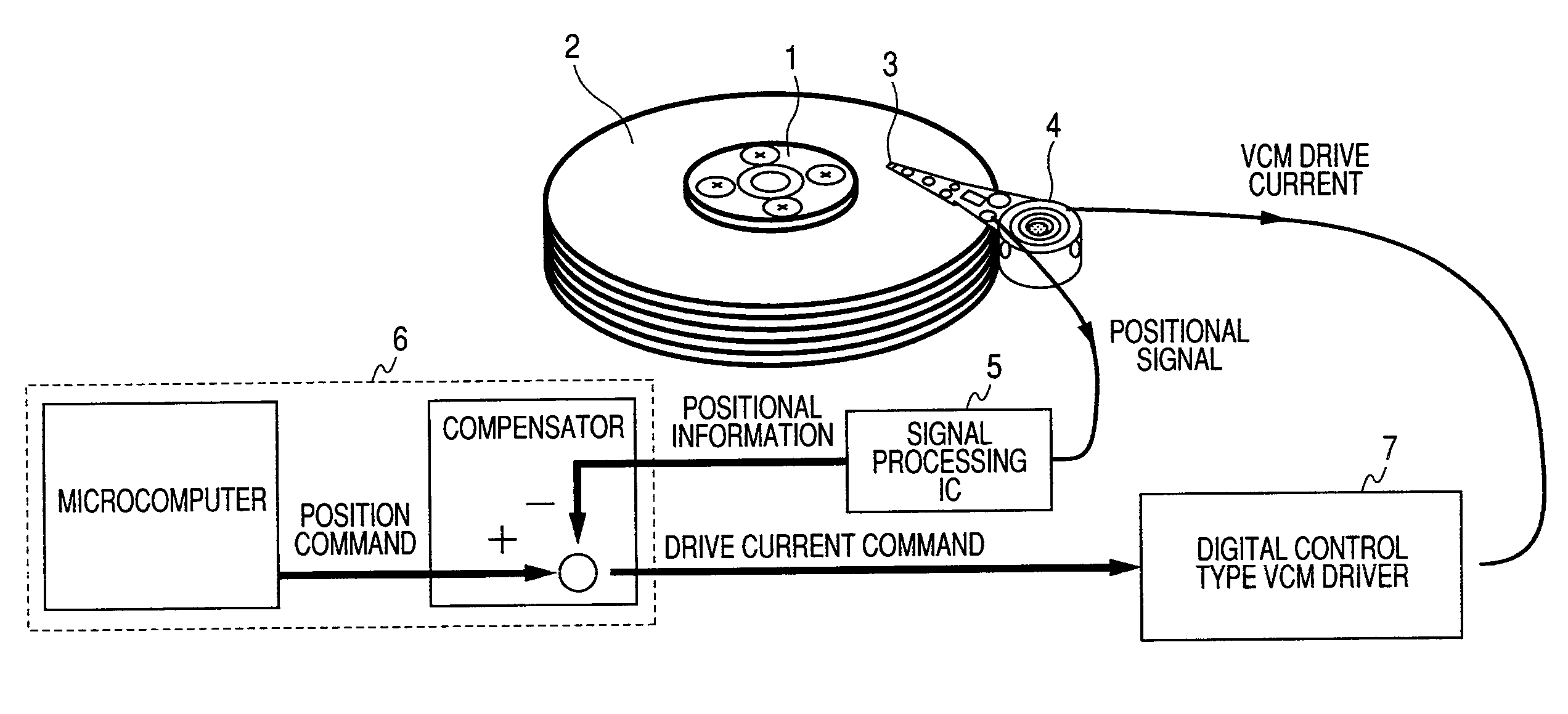
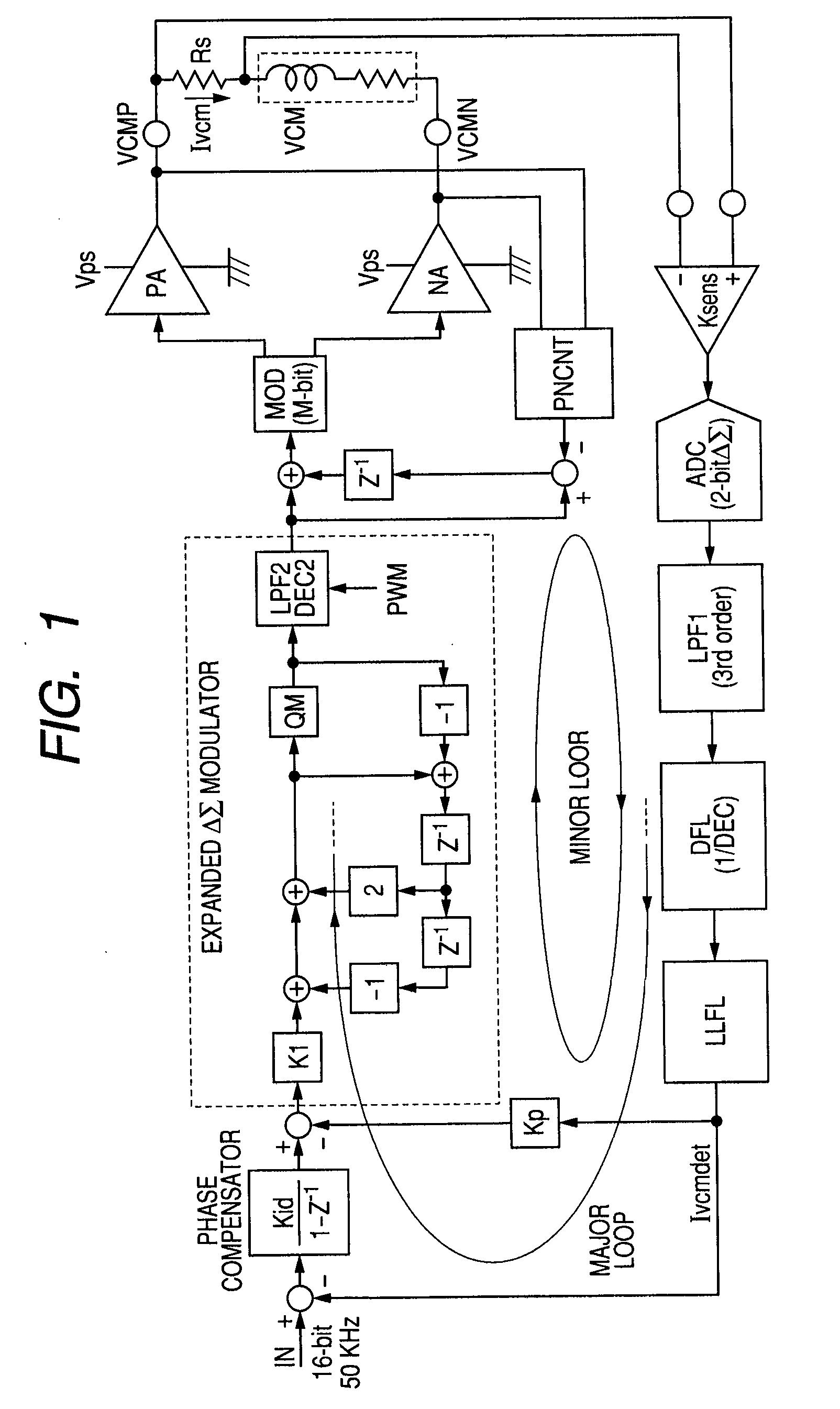
Vcm driver and pwm amplifier
InactiveUS20090080115A1Reduce errorsReduce switchingDisposition/mounting of recording headsAC motor controlAudio power amplifierLow-pass filter
The present invention provides a VCM driver realizing low power consumption and high accuracy and a PWM amplifier compensating a dead time distortion. A phase compensator, a ΔS modulator receiving an output signal of the phase compensator and converting the output signal to a control code of predetermined bits, a PWM modulator receiving the control code to produce a PWM signal, and an output circuit receiving the PWM signal to drive a voice coil constitute a forward path. A sense amplifier sensing a current of the voice coil, an ADC receiving an output signal of the sense amplifier, a low-pass filter receiving an output signal of the ADC, and a decimation filter receiving an output signal of the low-pass filter constitute a feedback path. An output signal of the decimation filter is fed back to the input side of the phase compensator to form a major feedback loop having a first-order characteristic loop gain. An output signal of the decimation filter is fed back to the output side of the phase compensator to form a minor feedback loop having a loop gain which is flat until a target band frequency when viewed from the output side of the phase compensator.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
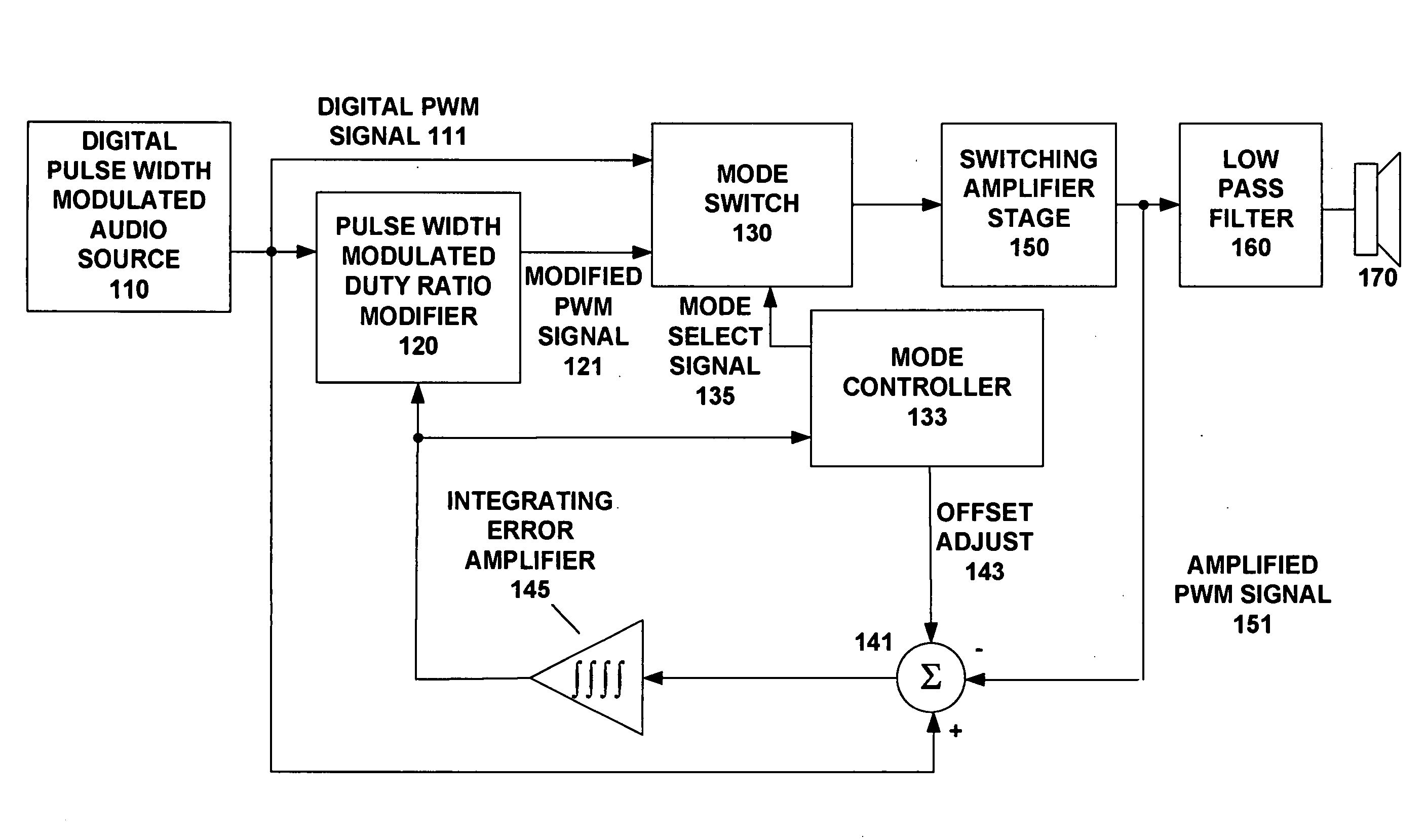
Quiet power up and power down of closed loop digital pwm modulators
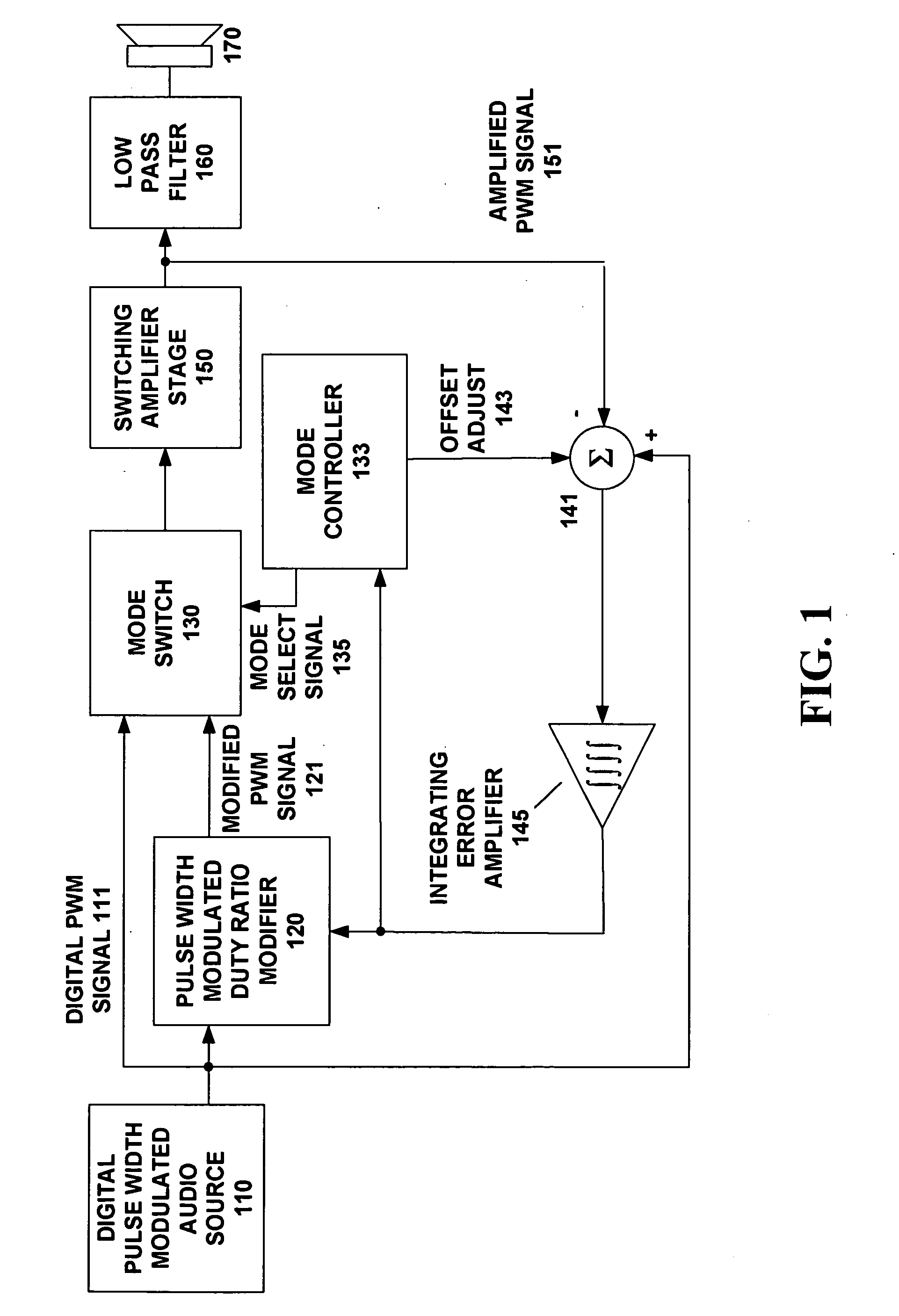
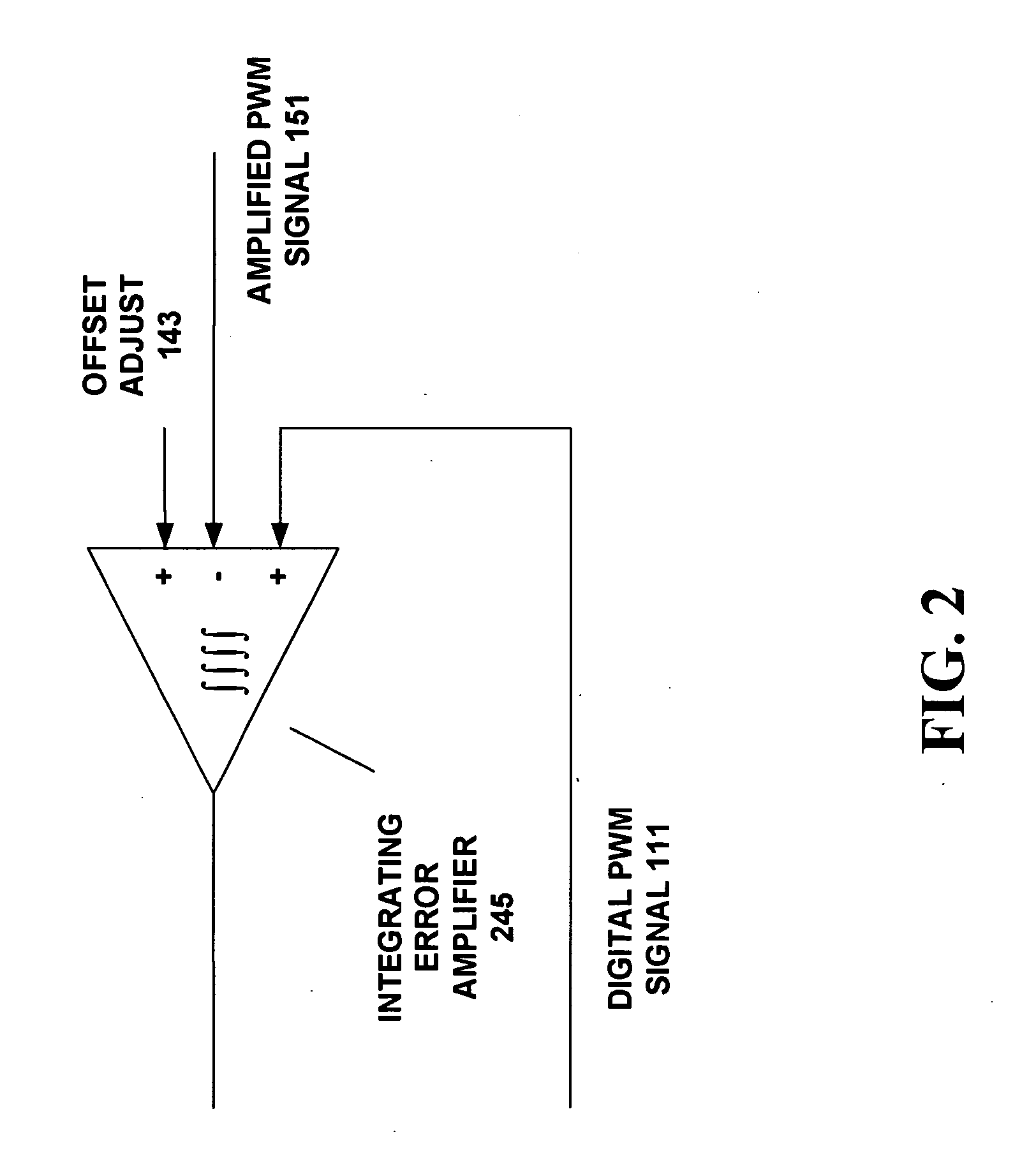
A switching audio amplifier circuit drives a switching audio amplifier stage using a digital PWM signal from an audio source. A PWM duty ratio modifier modifies an edge timing of the digital PWM signal to produce a modified digital PWM signal. A mode switch switches between the digital PWM signal and the modified digital PWM signal in a way that masks audible noise such as clicks and pops at power-up and power-down of the switching audio amplifier. An integrating error amplifier compares a difference between the digital PWM signal and an amplified PWM signal and integrates the difference to control the edge timing modified by the PWM duty ratio modifier. A mode controller can apply an offset signal to the integrating error amplifier and can control the switching of the mode switch.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com