Lattice material with function gradients
A functional gradient and lattice technology, applied in building components, earthquake resistance, construction, etc., can solve problems such as high porosity, achieve excellent impact resistance, strong designability, and light weight of the structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
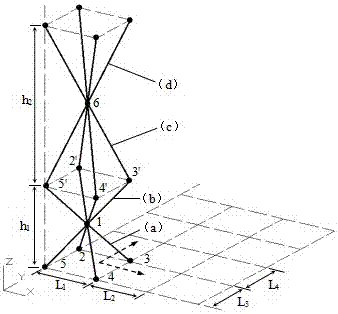
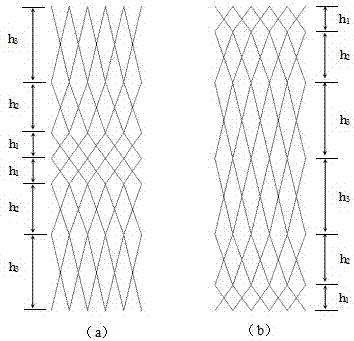
[0024] 1) if figure 1 As shown, this embodiment is a pyramid-shaped unit cell gradient function lattice material, which has a gradient function in the Z direction, and 1-6 is the endpoint of the pyramid-shaped unit cell rod, (a) is a pyramid-shaped unit cell , the endpoints on the bottom surface of the unit cell lie on the X-Y plane. The pyramid-shaped unit cell (a) is mirror-symmetrically extended and arranged with the X-Y plane where the vertex 1 is located as the symmetric plane to form the unit cell (b), and then the pyramid-shaped unit cell (c) is arranged with the X-Y plane where the vertex 6 is located. The plane is a symmetrical plane, and the mirror symmetrical extension arrangement is carried out to form a unit cell (d), and so on, to form a multi-layer spatial lattice structure, and the height of each layer is
[0025] 2) The unit cells are extended and arranged in the X and Y directions, and the distance between the end points on the bottom surface of the unit c...
Embodiment 2
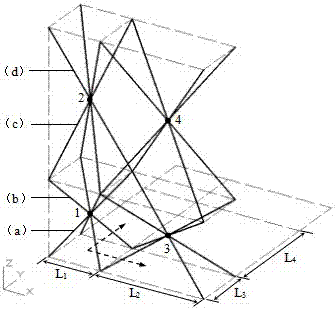
[0027] 1) if image 3 As shown, this embodiment is a pyramid-shaped unit cell gradient function lattice material, which has gradient functions in the X, Y, and Z directions. The mirror symmetrical continuation arrangement forms the unit cell (b), and then the pyramidal unit cell (c) takes the X-Y plane where the vertex 2 is located as the symmetry plane for mirror symmetric continuation arrangement to form the unit cell (d), with By analogy, a multi-layer spatial lattice structure is formed.
[0028] 2) The unit cells are extended and arranged in the X and Y directions, and the distance between the end points on the bottom surface of the unit cells changes during the extension process, that is, L 1 ≠ L 2 , L 3 ≠ L 4 , forming X, Y and Z direction functional gradient lattice materials.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com