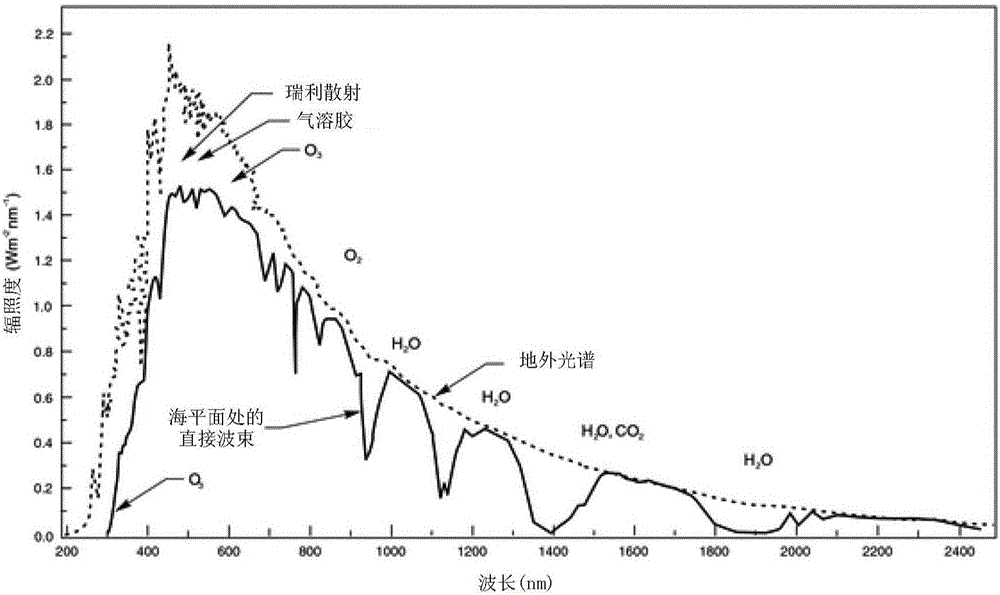
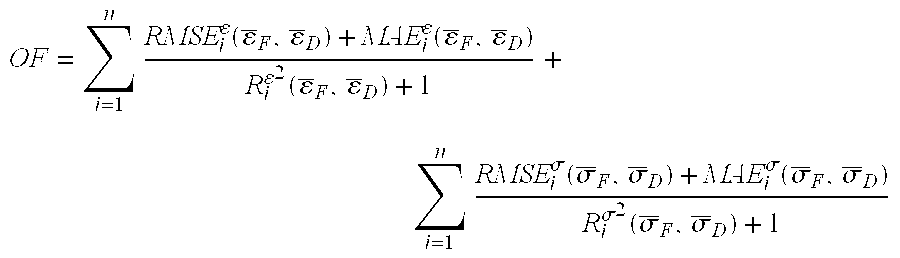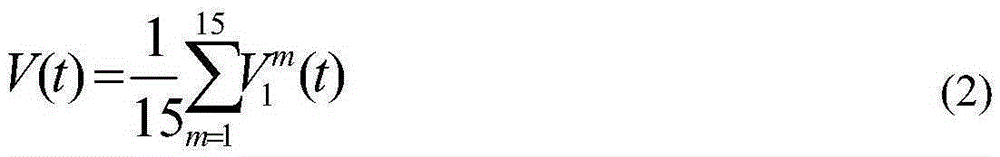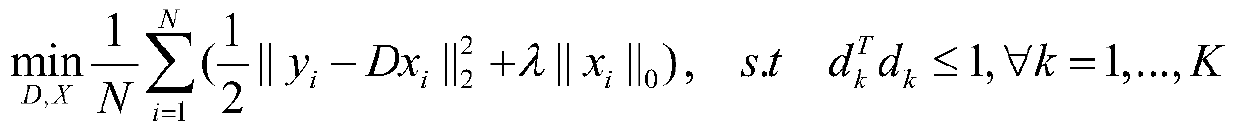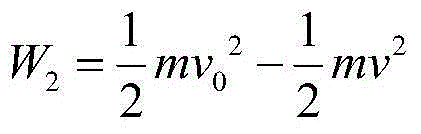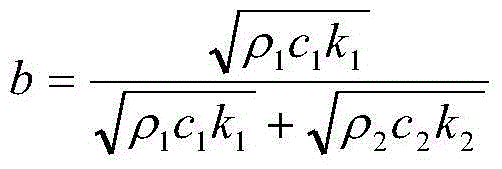Patents
Literature
32 results about "Spatial average" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spatial average. spatial average. The mathematical mean value over multiple points in space. These can be points along a line or path (line average), along a surface (area average), or within a volume (volume average).
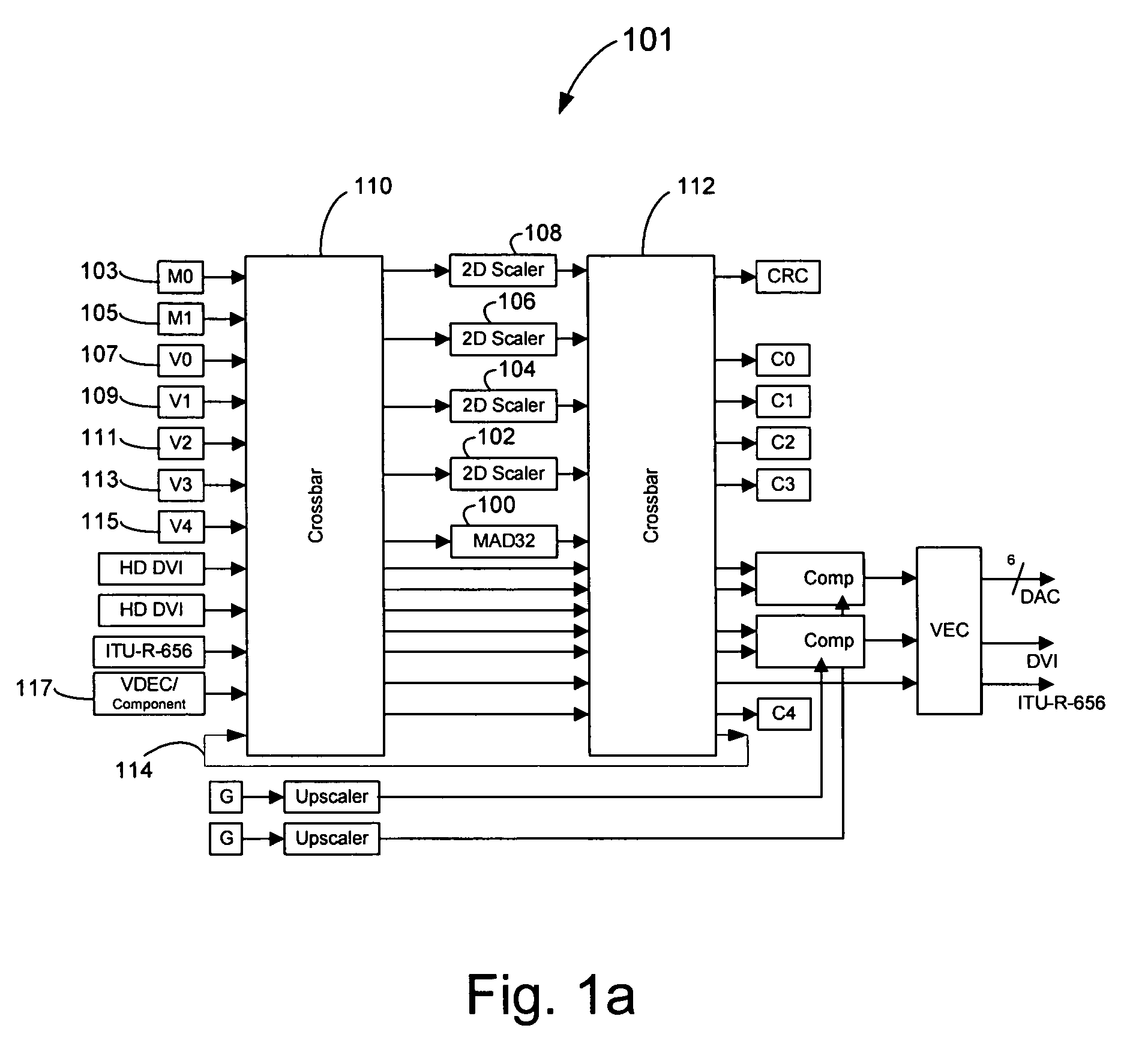
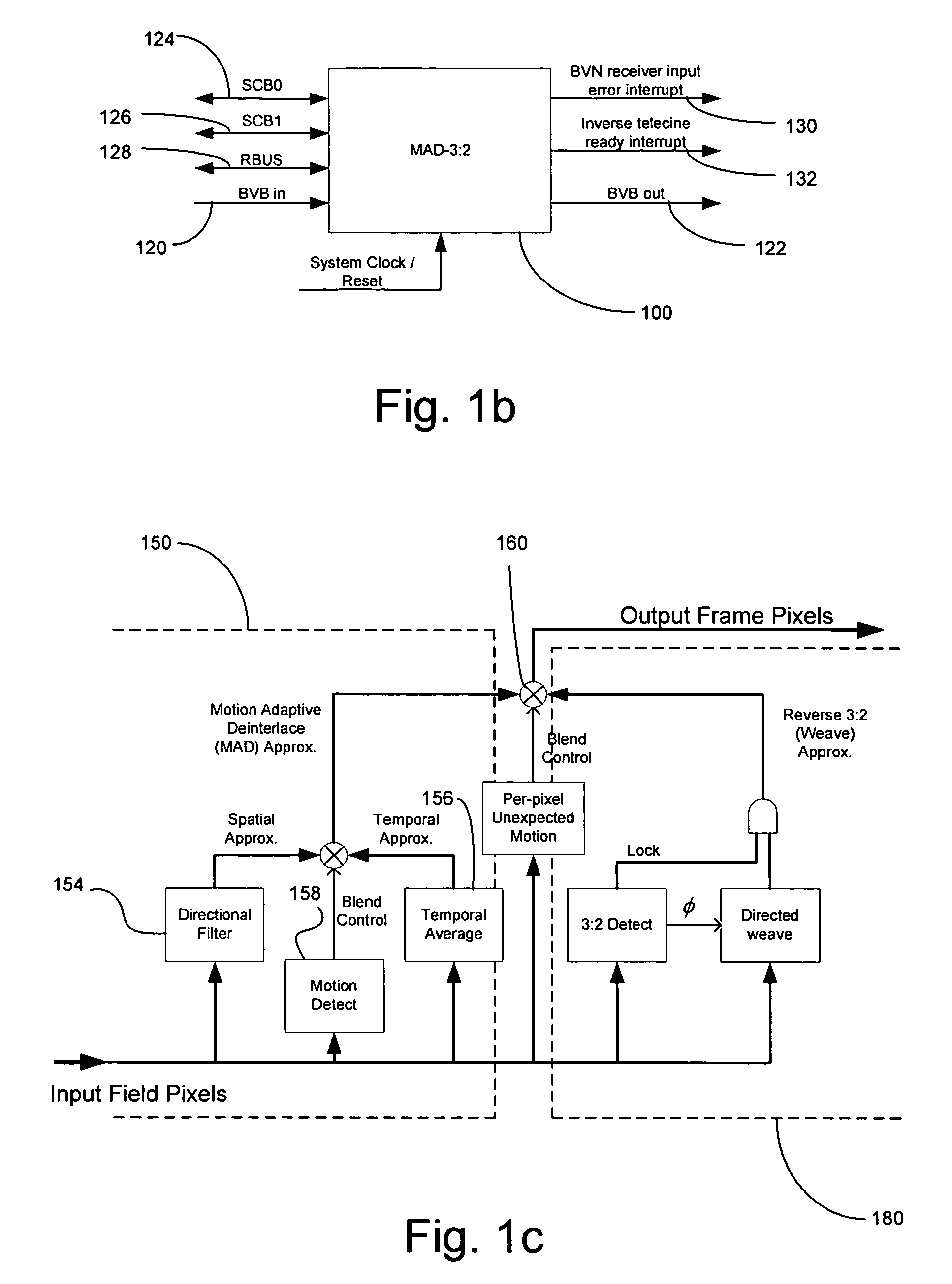
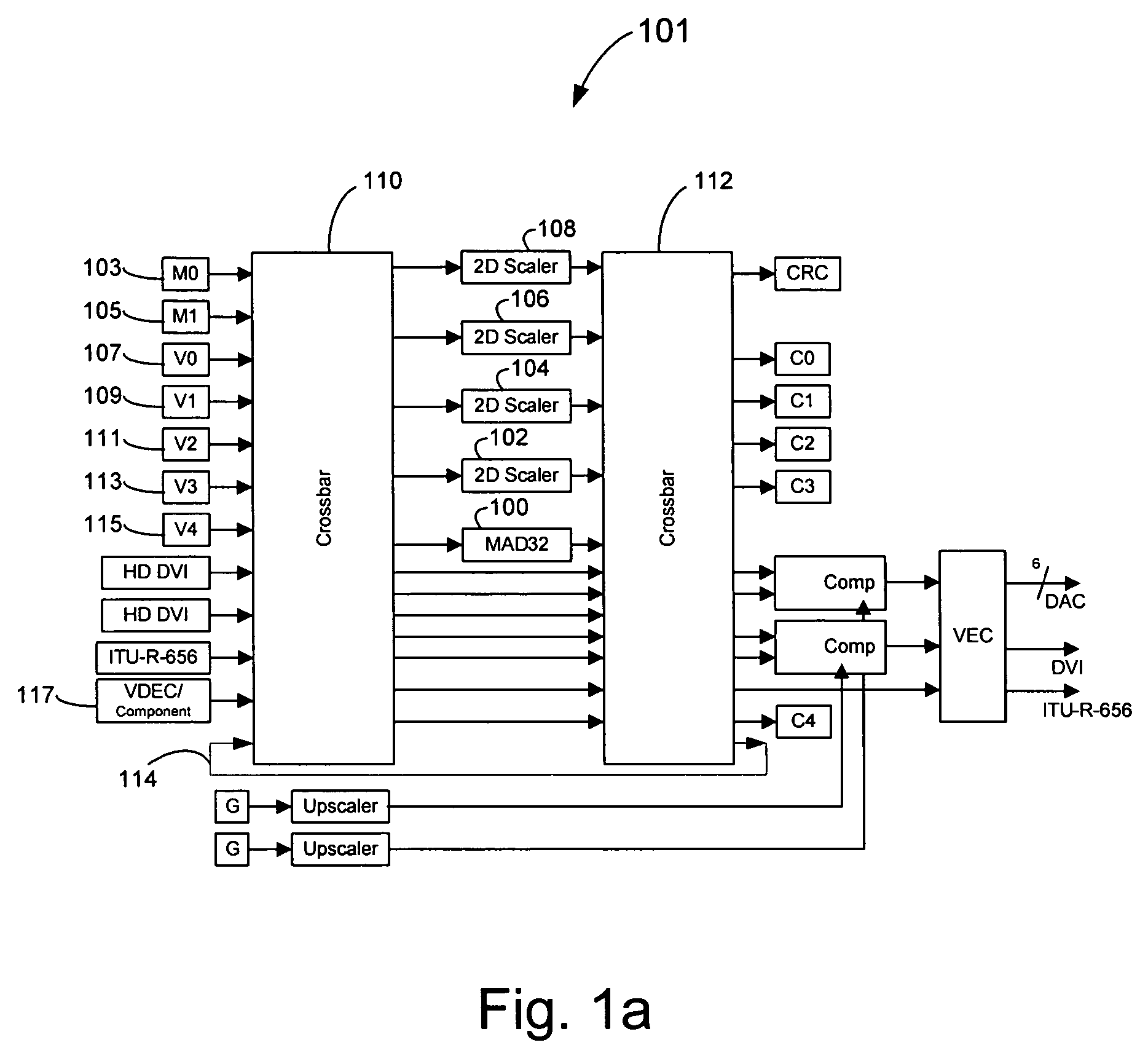
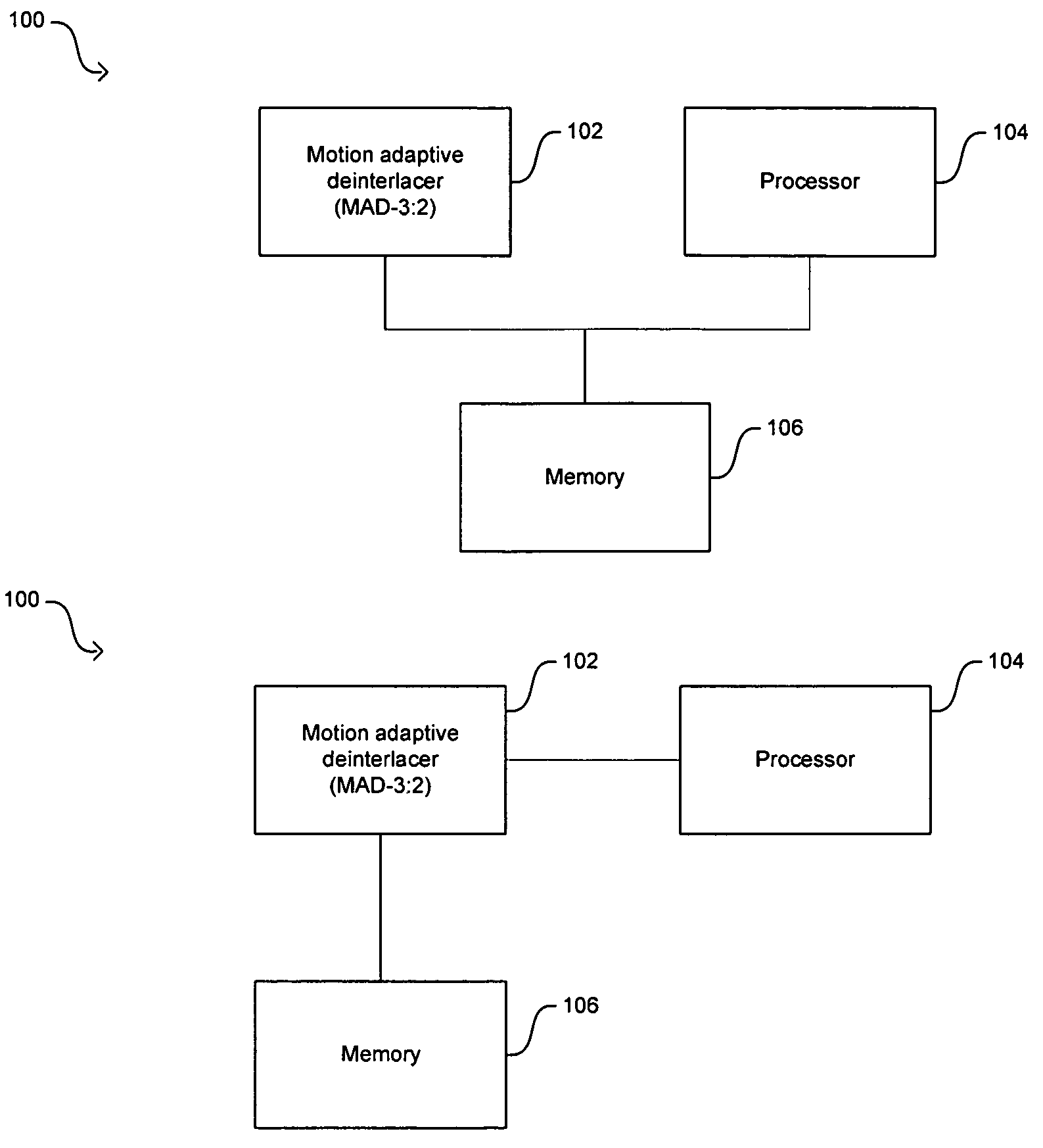
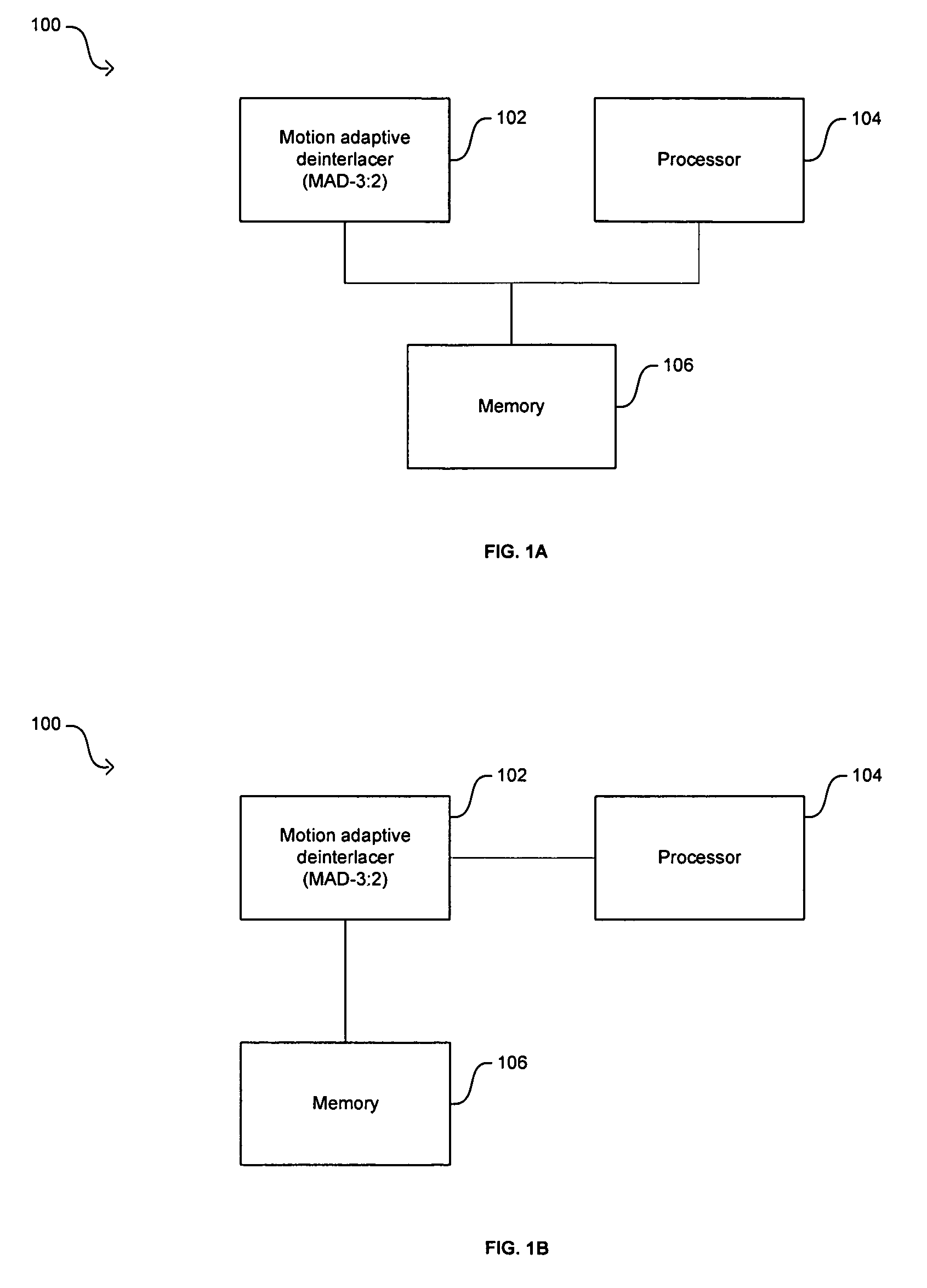
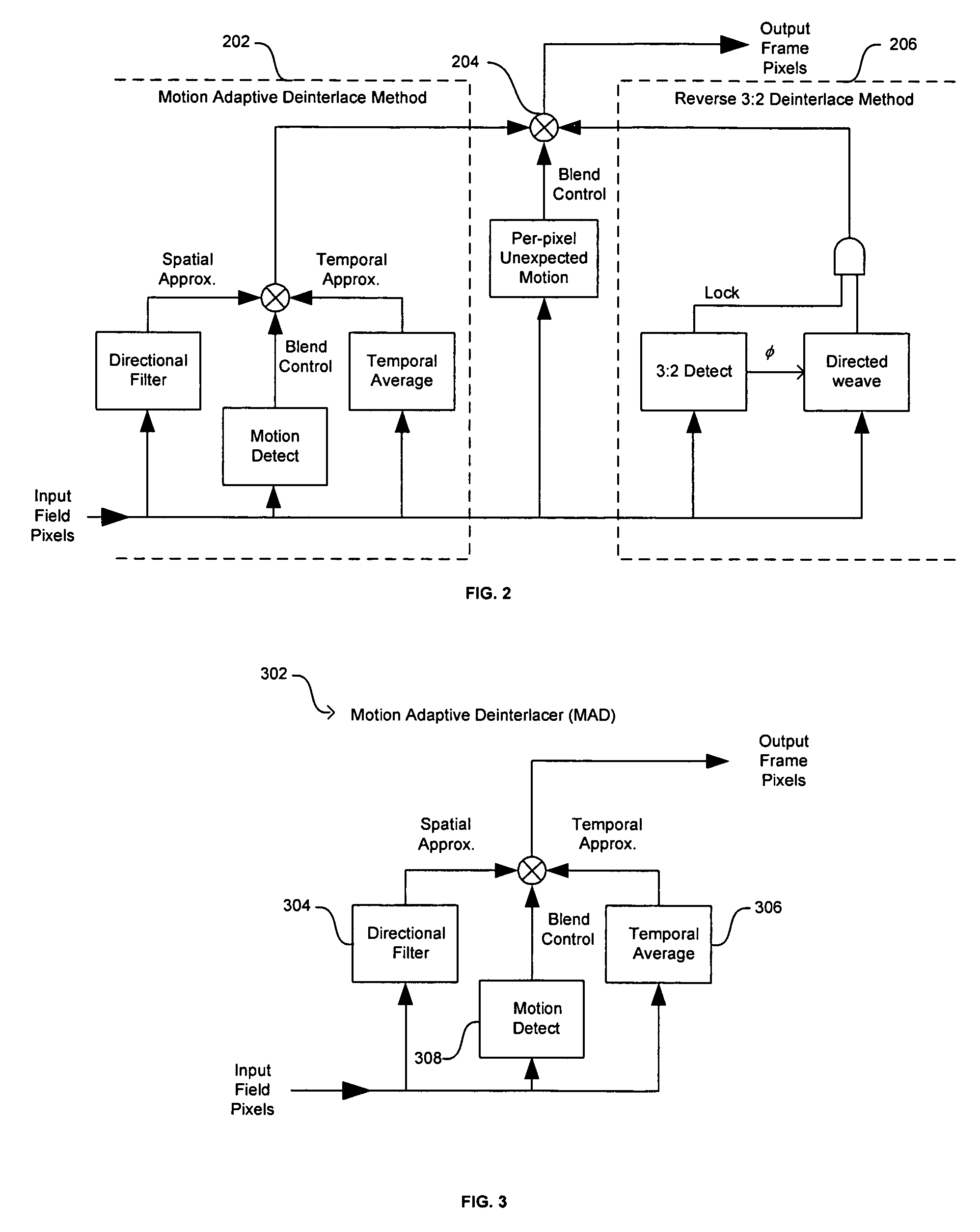
Method and system for cross-chrominance removal using motion detection
ActiveUS20050168650A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMotion detectorSpatial average
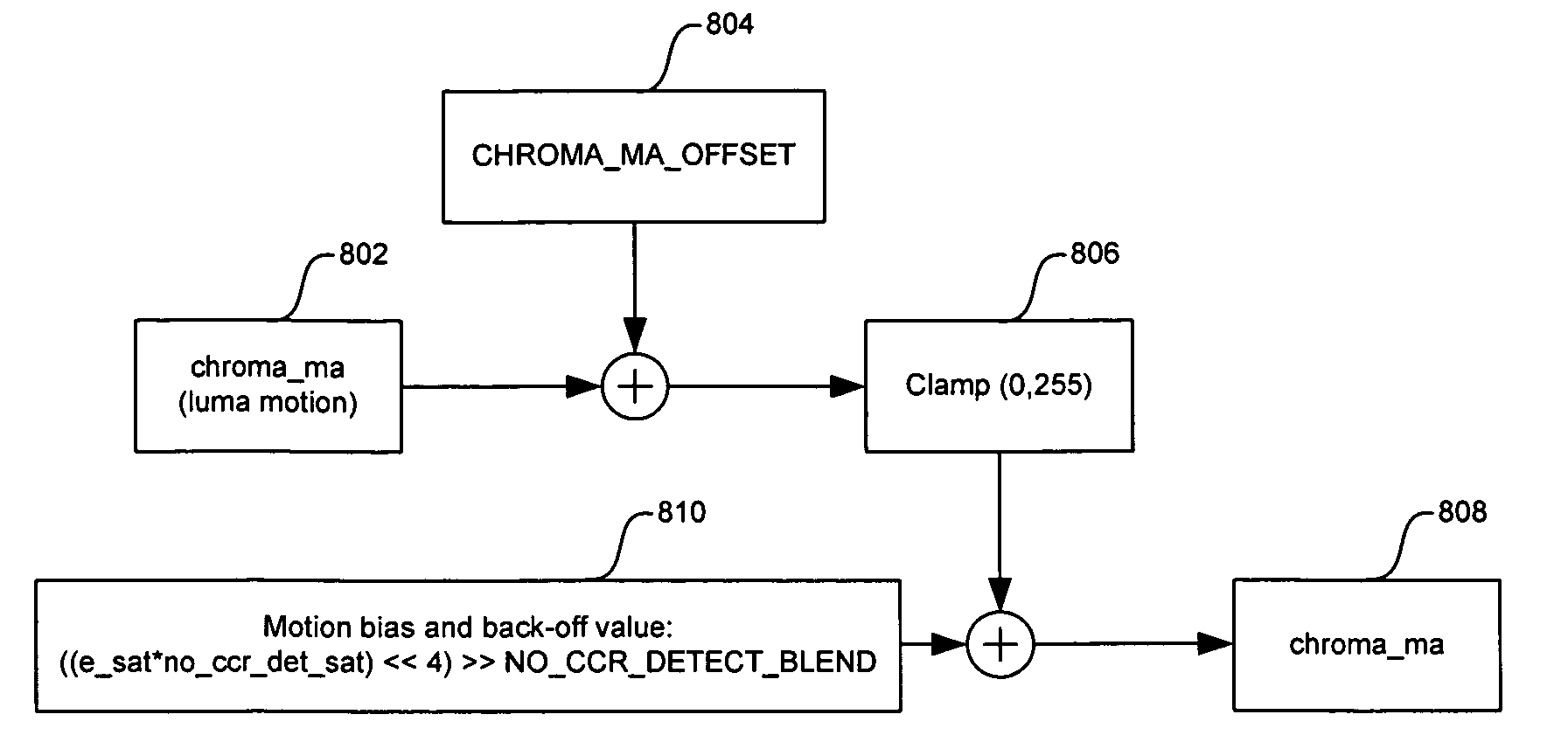
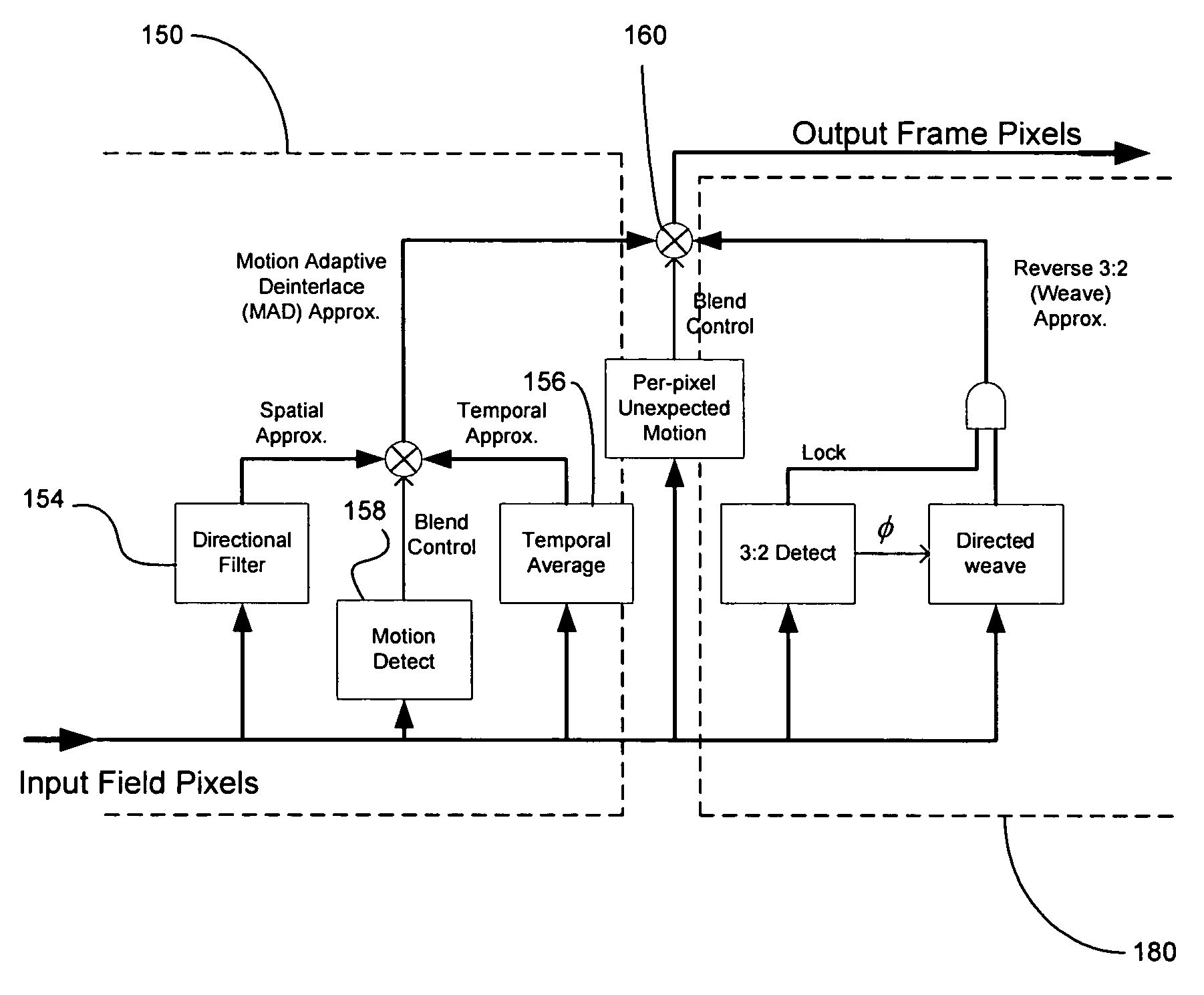
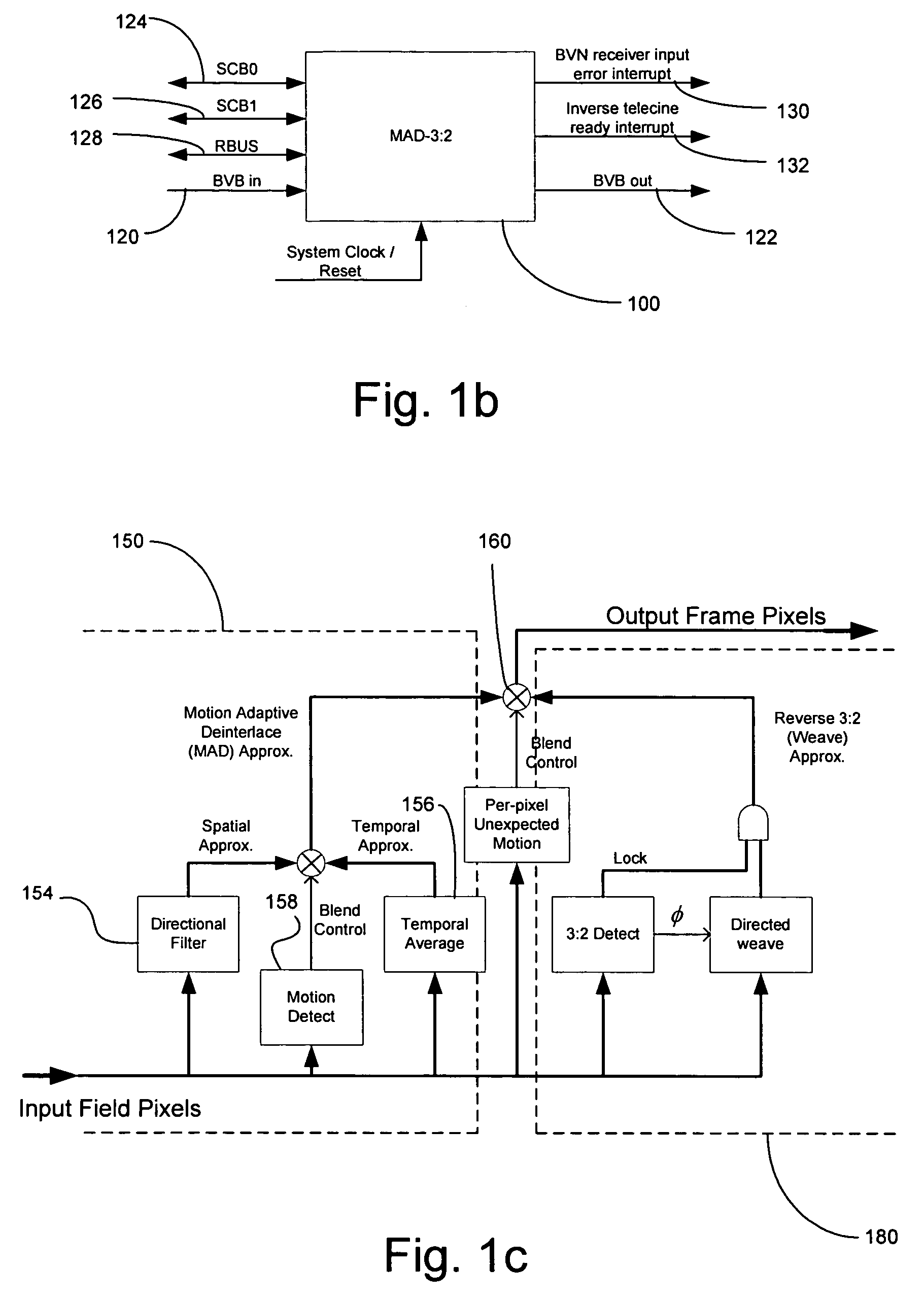
In a video system, a method and system for cross-chrominance removal using motion detection are provided. A luma motion detector in a motion adaptive deinterlacer may be used to determine a chroma current motion for a pixel in a video frame. The chroma current motion may be modified, based on a chroma motion mechanism comprising of an edge detection, a back-off, and a motion biasing, when the output pixel is found to be in a static chroma area of the video frame. A static chroma threshold parameter may be used to determine whether the output pixel is in a static chroma area. A cross-chroma reduction determined based on the current chroma motion, may be blended in the motion adaptive deinterlacer with a spatial average approximation of the output pixel to remove the cross-chrominance from the output chroma.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
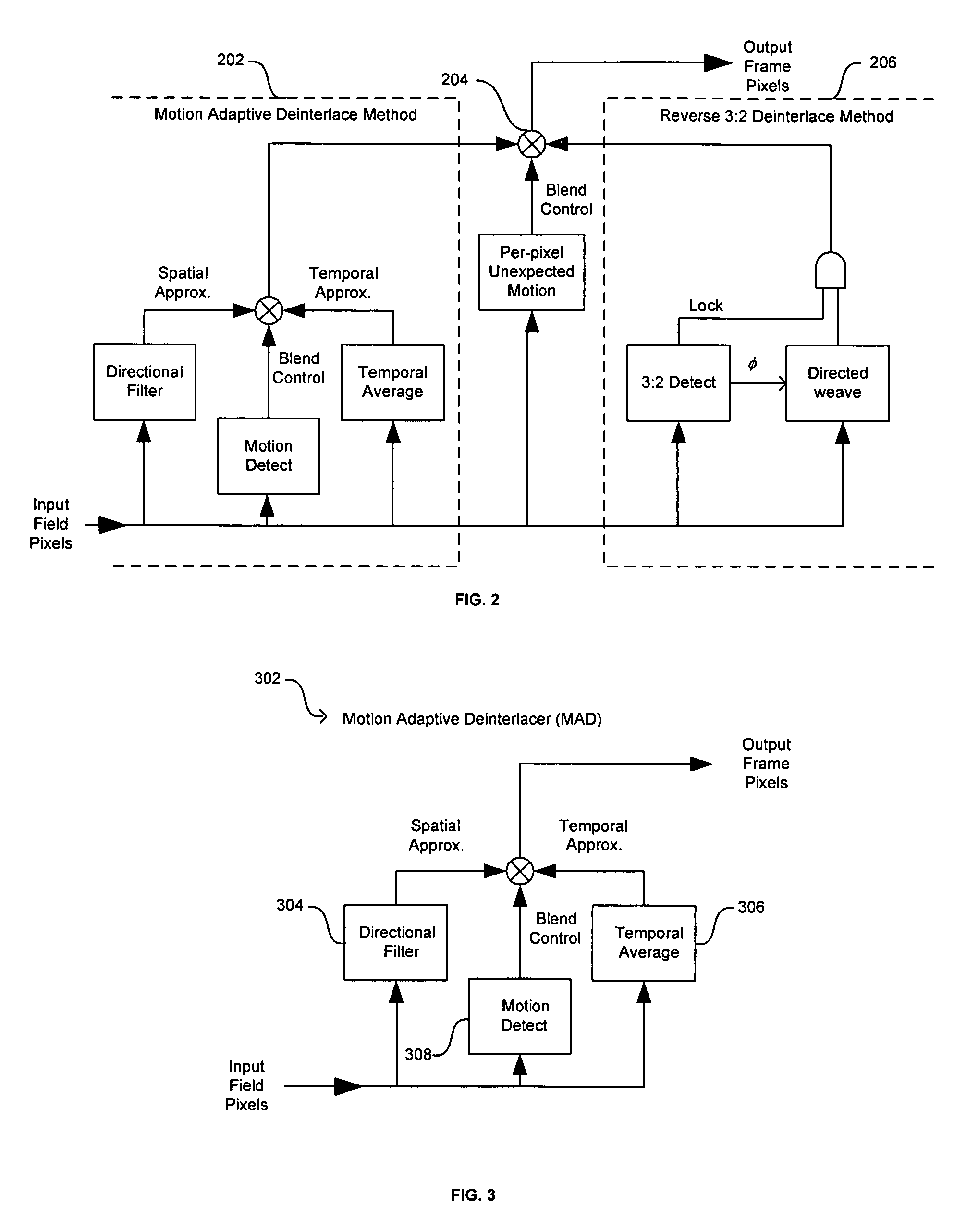
Method and system for motion adaptive deinterlacer with integrated directional filter
InactiveUS7349028B2Television system detailsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
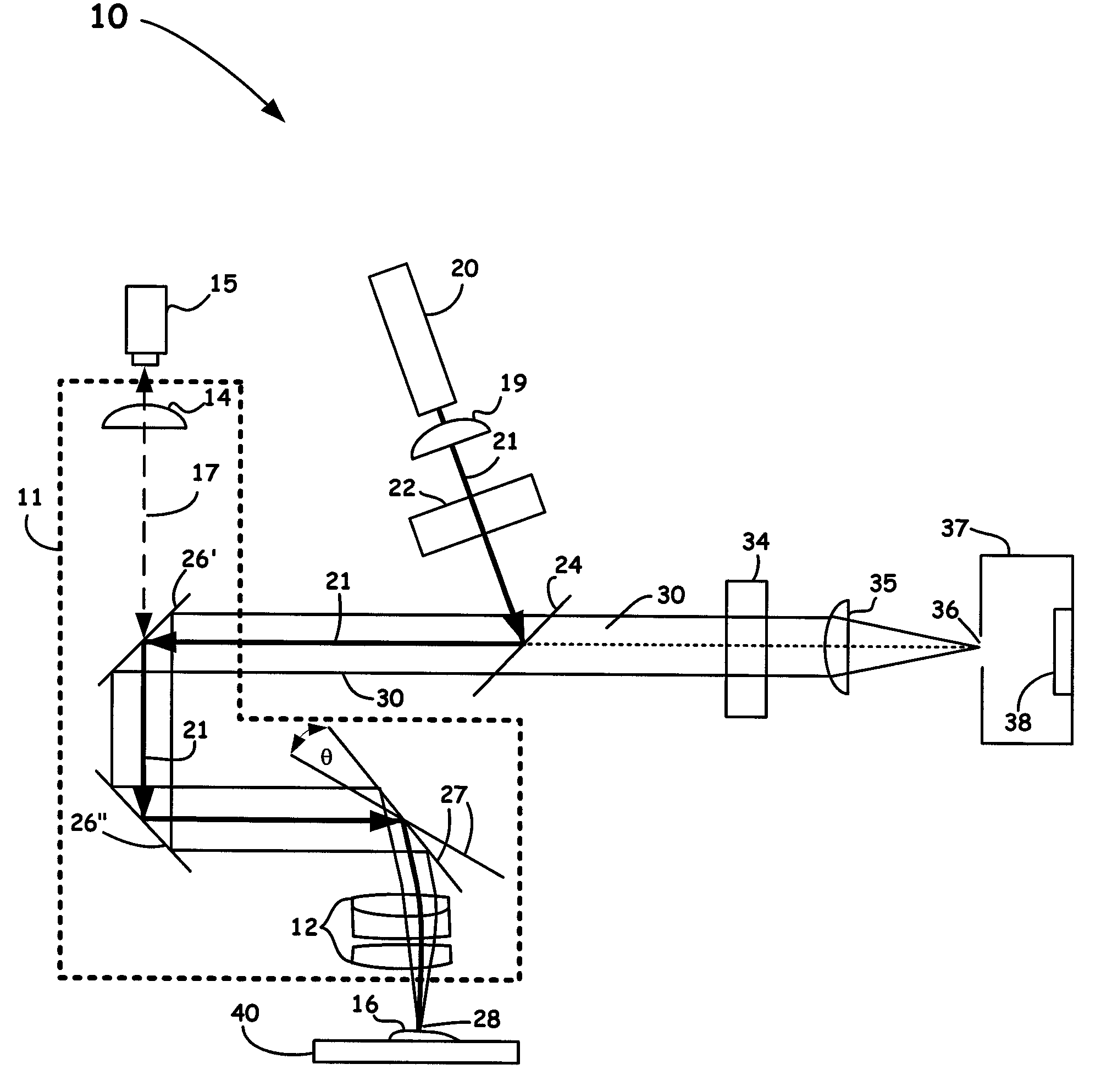
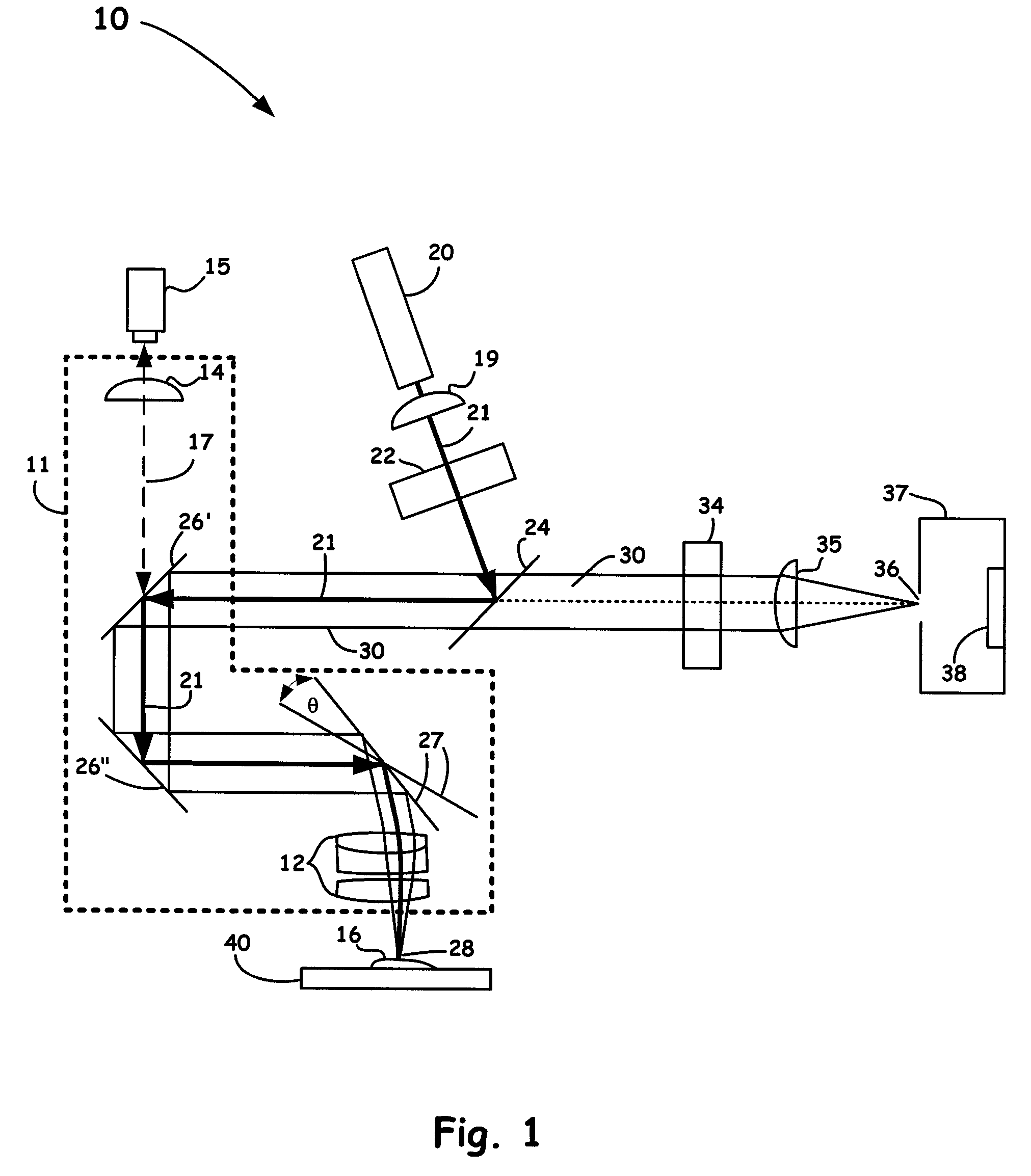
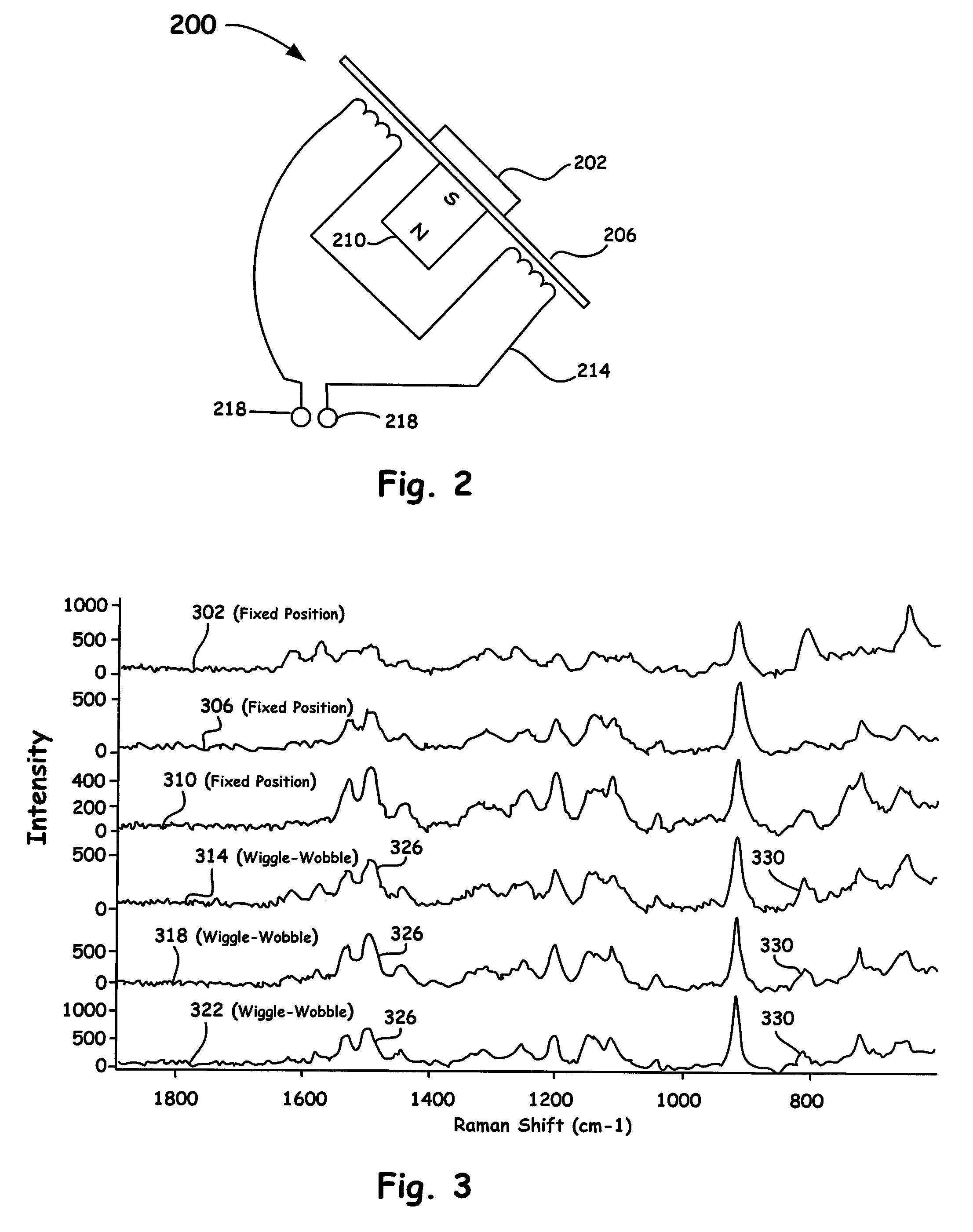
Rapid spatial averaging over an extended sample in a Raman spectrometer
ActiveUS7595873B1Rapid spatial averagingReduce sample degradationRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSpatial averageSpectroscopie raman
An optical method and apparatus is utilized to provide rapid spatial averaging over a large sample area in a Raman spectrometer, without defocusing of the optical source or the collection optics. Spatial averaging provides a representative spectrum of a sample that is inhomogeneous, either in its composition or surface characteristics. The spatial averaging configurations and methods disclosed herein also reduce sample degradation or burning resulting from the high intensity of the directed optical source. Moreover, the dimensions of the sample area of the spatial averaging methods and configurations of the present invention are adjusted to match specific sampling requirements.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRON SCI INSTR
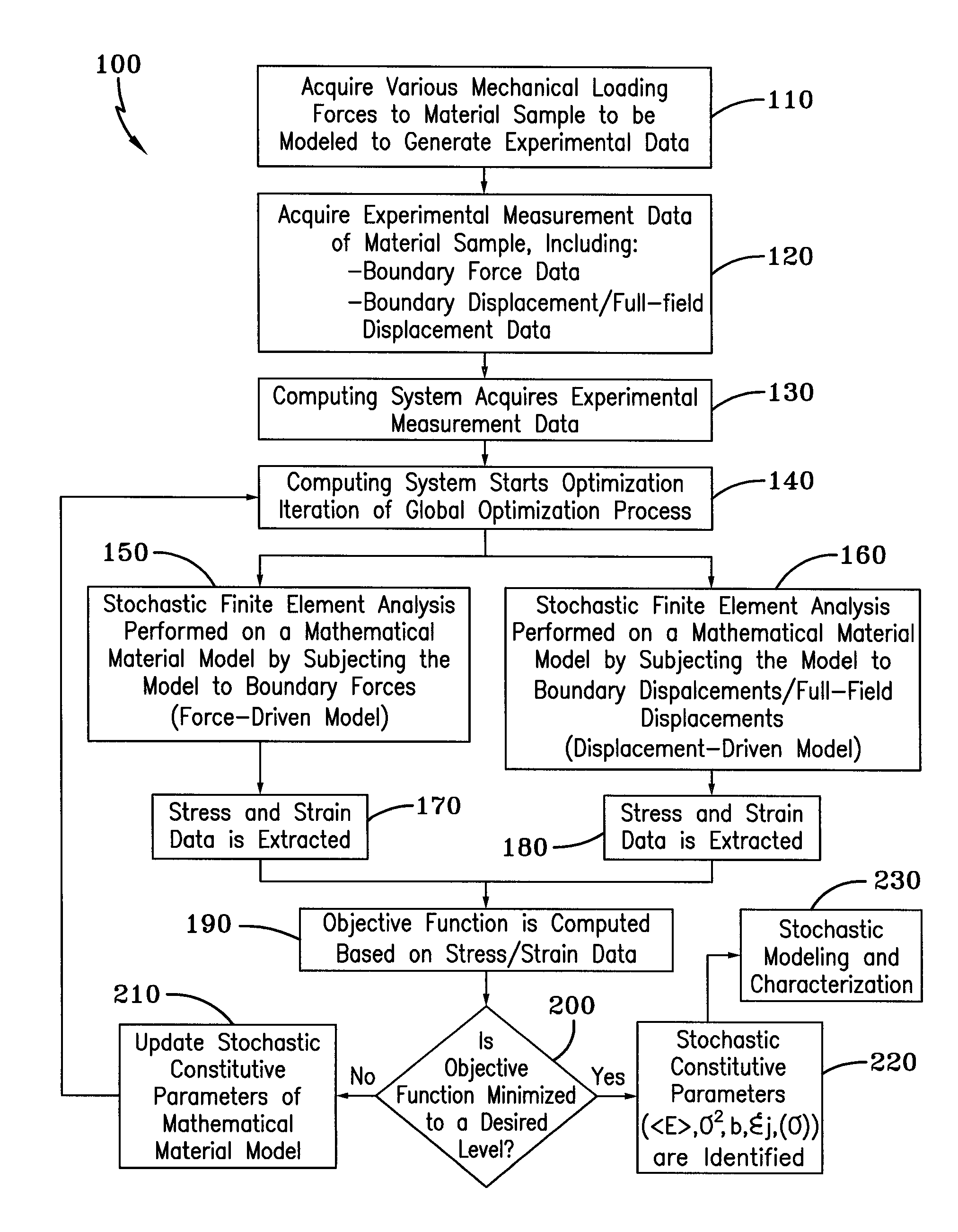
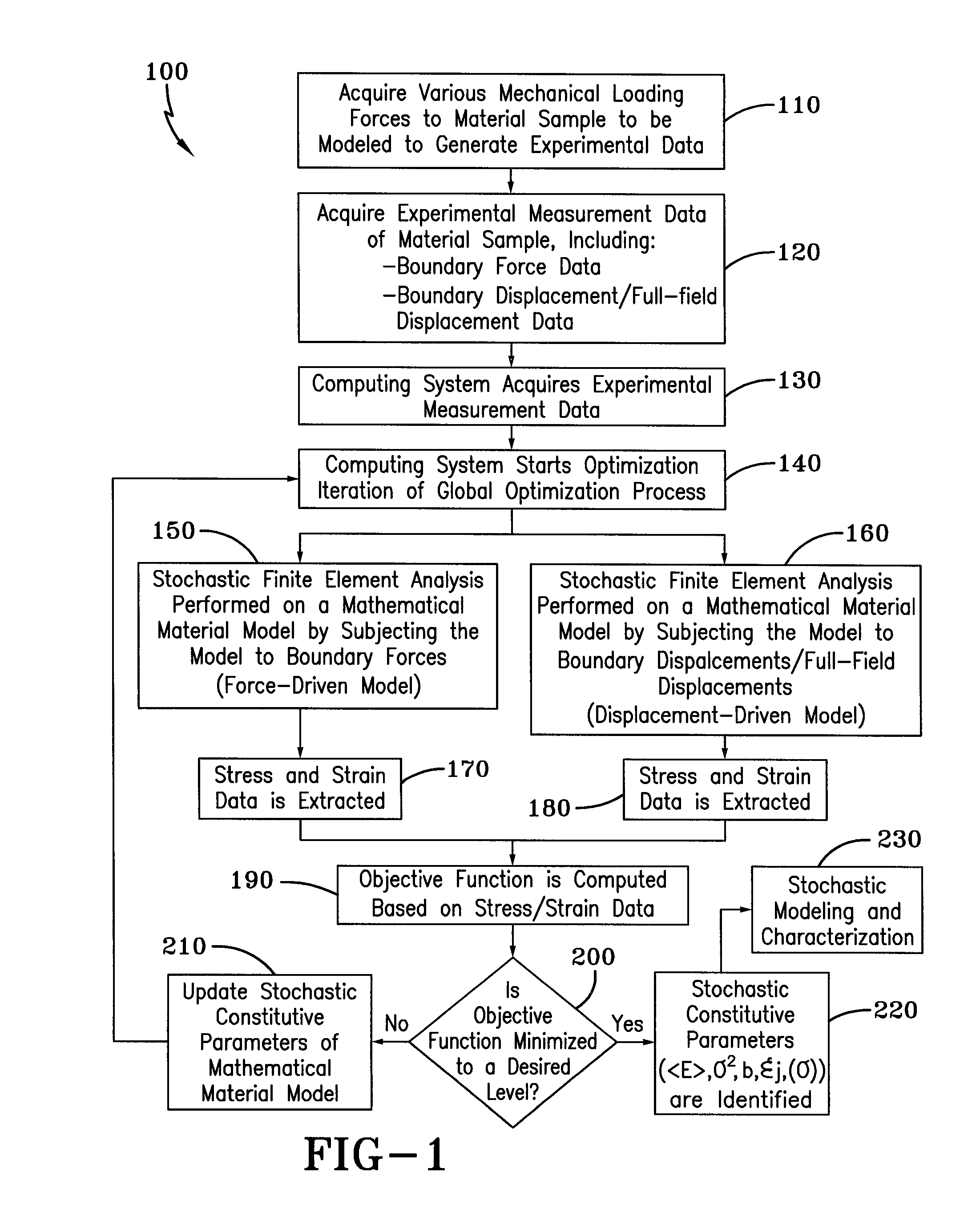
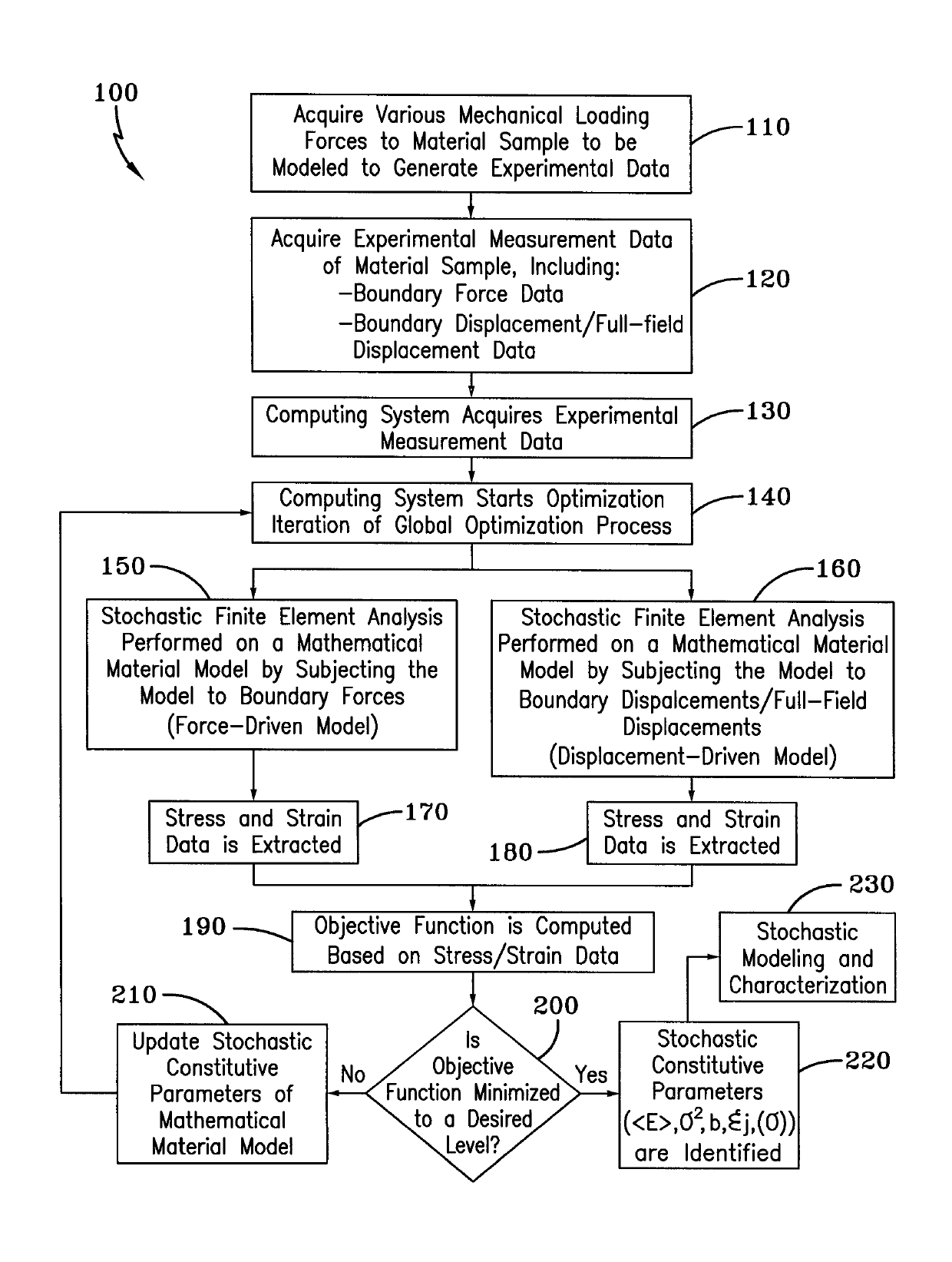
Method for Identifying Stochastic Information of Heterogeneous Materials
InactiveUS20150057988A1Minimize objective functionComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationRandom materialsElement analysis
A method for identifying stochastic information of a heterogeneous material utilizes physical loading measurements that are input into a global optimization process. The optimization process executes, in parallel, a force-driven non-linear finite element simulation and a displacement-driven finite element simulation of a constitutive model of the heterogeneous material. The constitutive models model the spatially varying random material properties (i.e. stochastic properties) using the Karhunen-Loeve expansion, thereby introducing the stochastic parameters, including spatial mean, spatial variance, and correlation length for example into the models. Stress and strain values for both the force-driven and displacement driven finite element analyses are input into an objective function, whereupon the finite element simulations are updated after each iteration of the optimization process is performed until the objective function is minimized to a desired level. This results in the identification of optimized stochastic parameters associated with the heterogeneous material under investigation.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Method and system for motion adaptive deinterlacer with integrated directional filter
InactiveUS20050168633A1Television system detailsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsInterlaced videoSpatial average
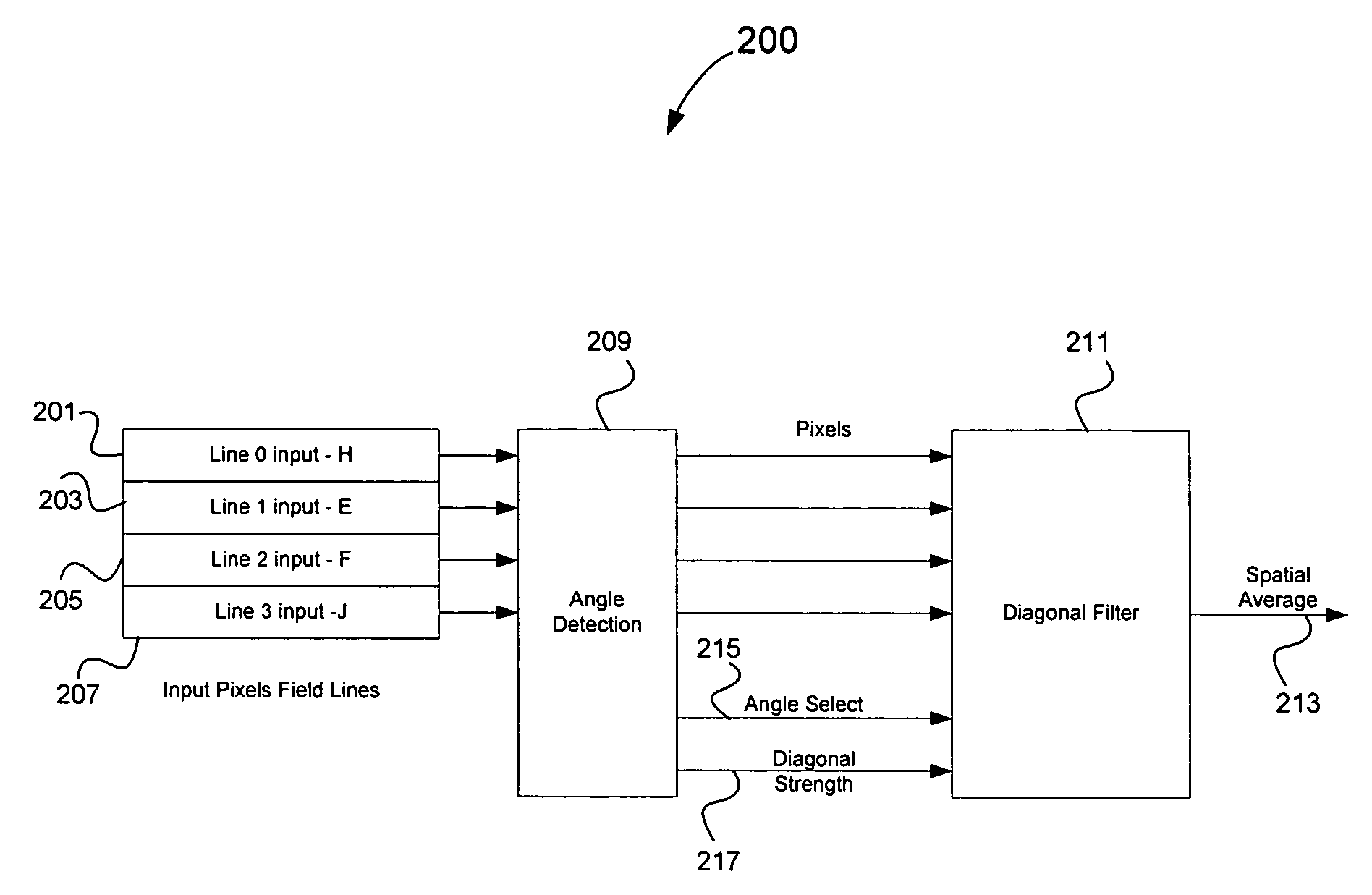
A system and method that produces a spatial average for interlaced video in a deinterlacer. The system detects edges in the video images and determines the angle at which the edges are oriented based on the gradient in the x-direction and the gradient in the y-direction. The direction of the edge is determined using the angle information of the edge. The system may also determine the strength of the edge. Based on the determined characteristics of the edge a filter may be selected to produce a spatial average of the edge in the image.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
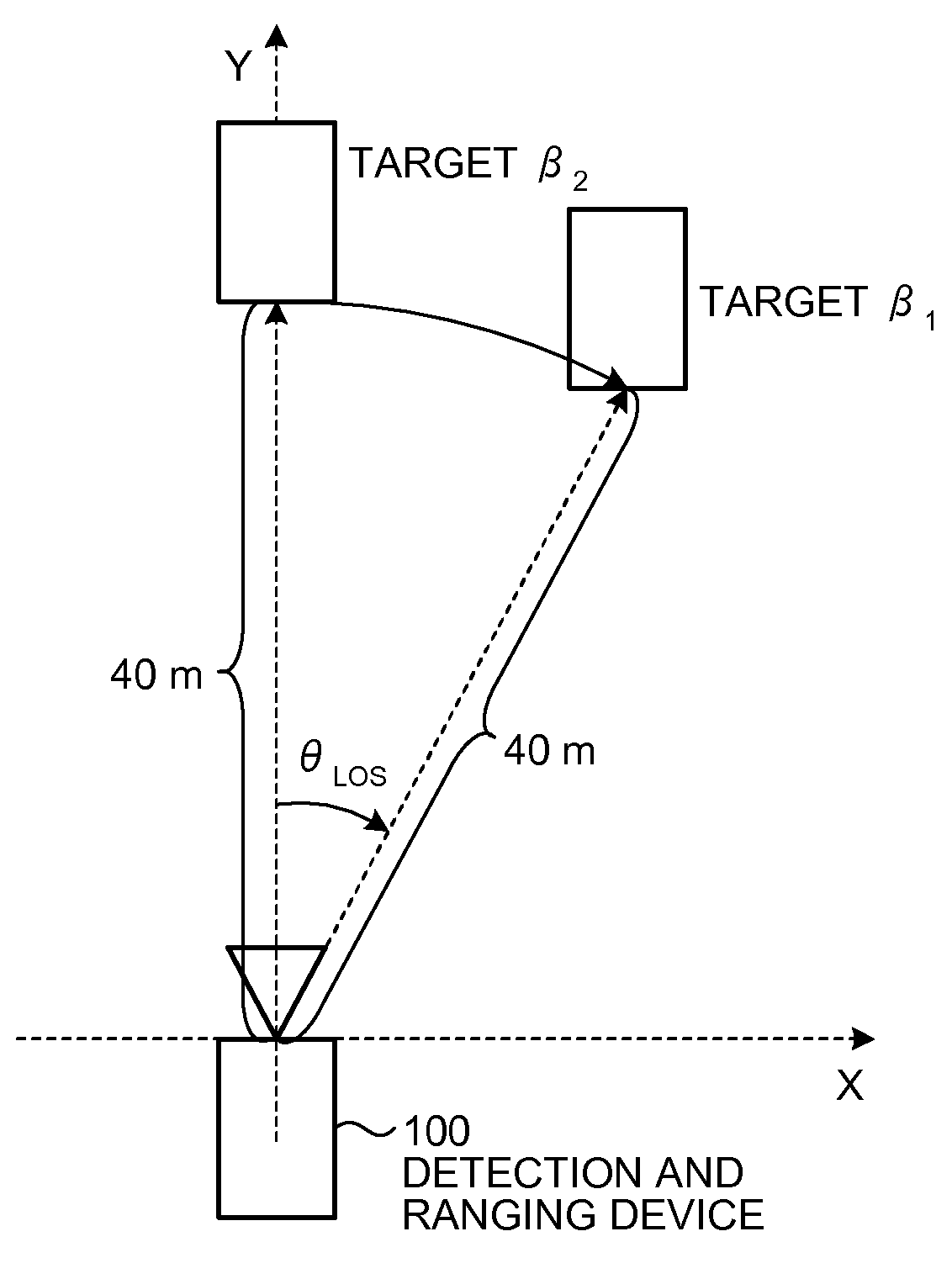
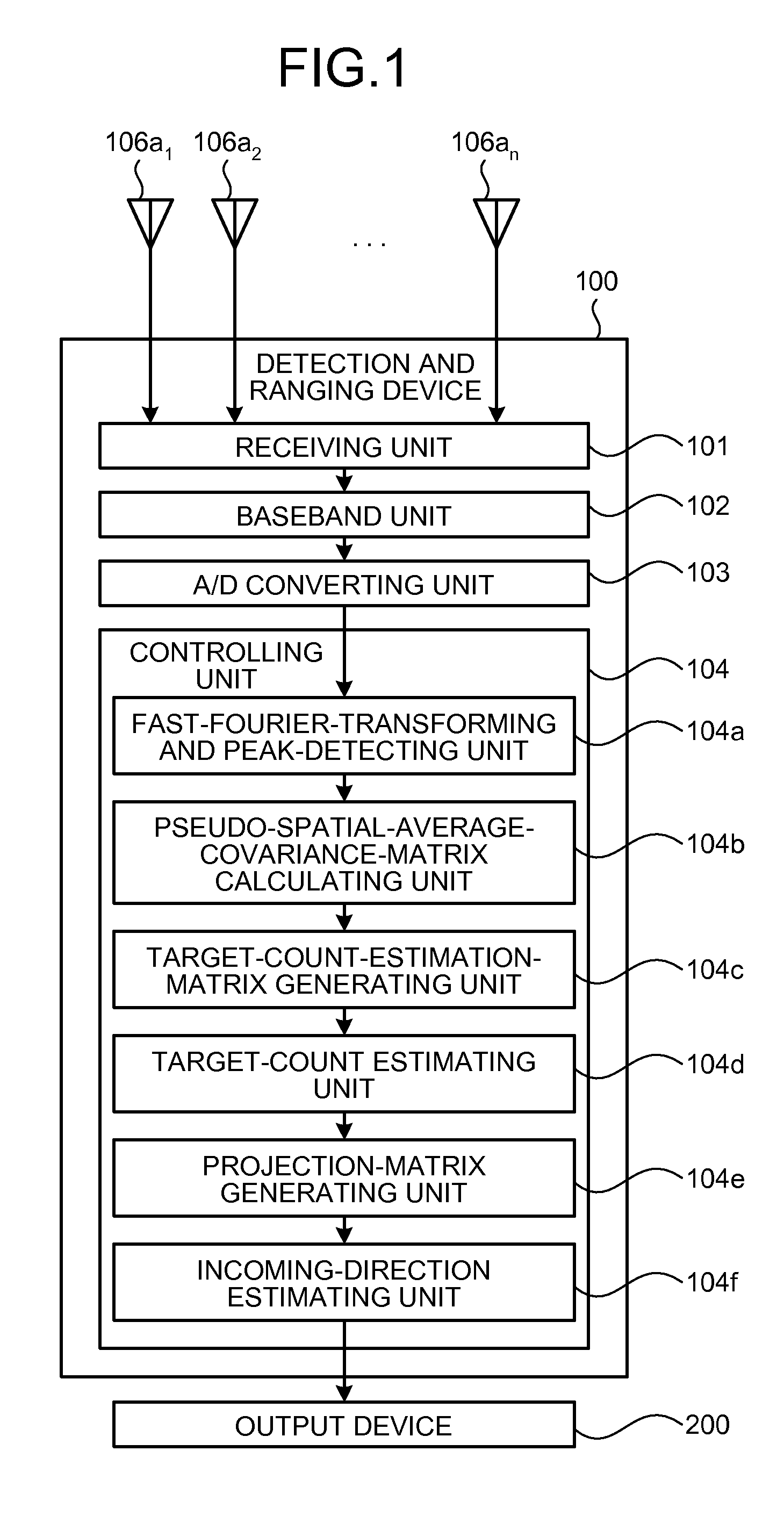
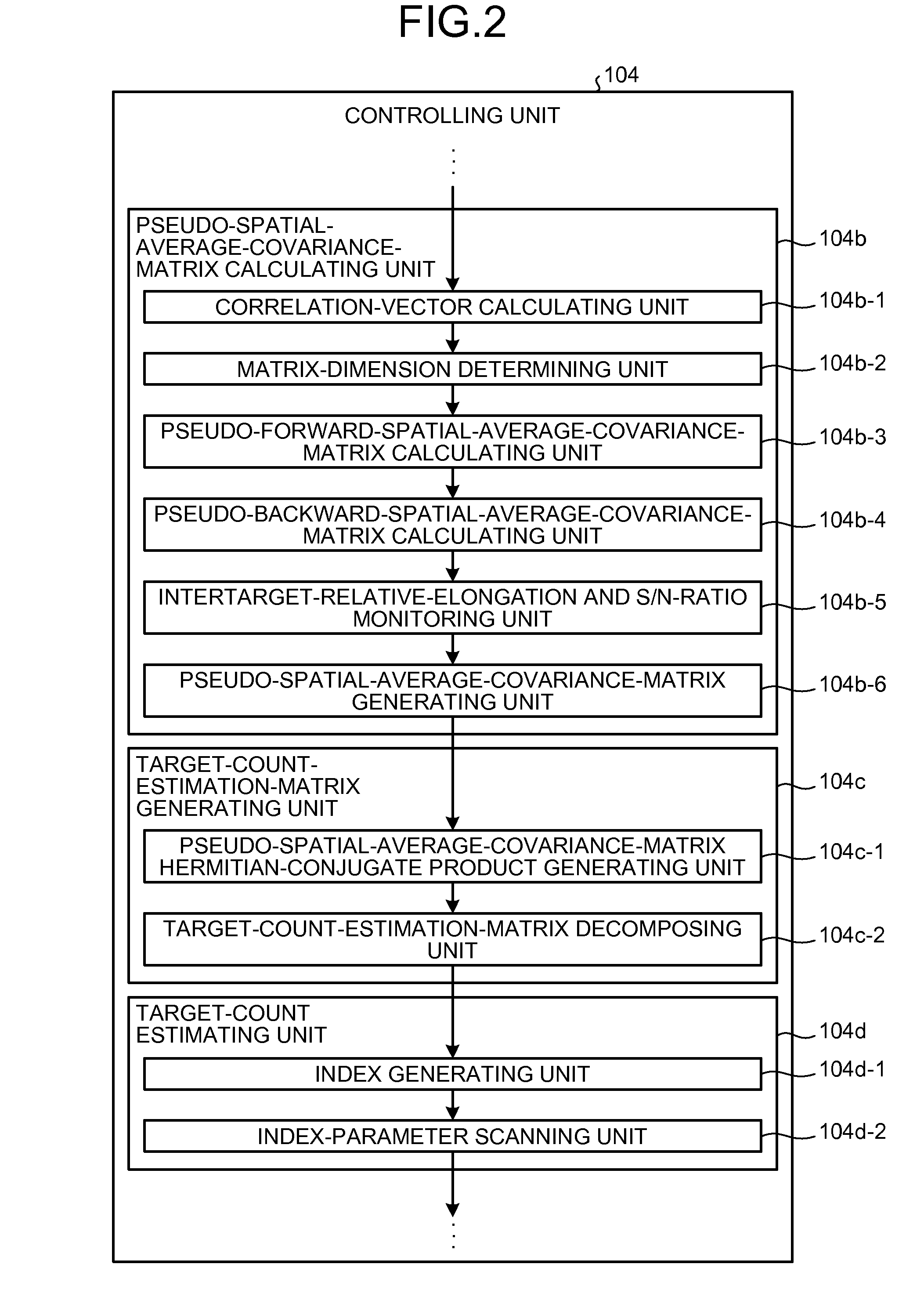
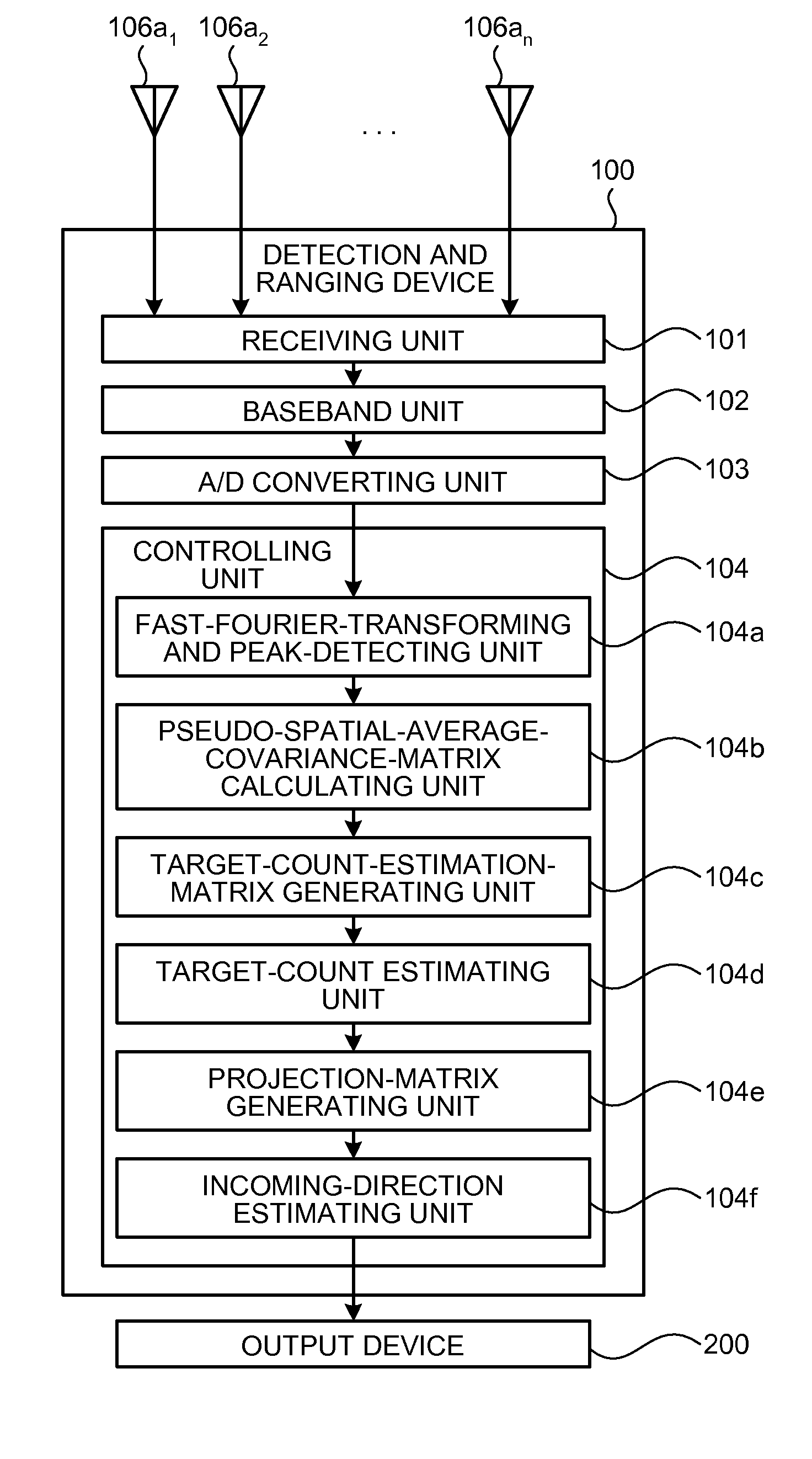
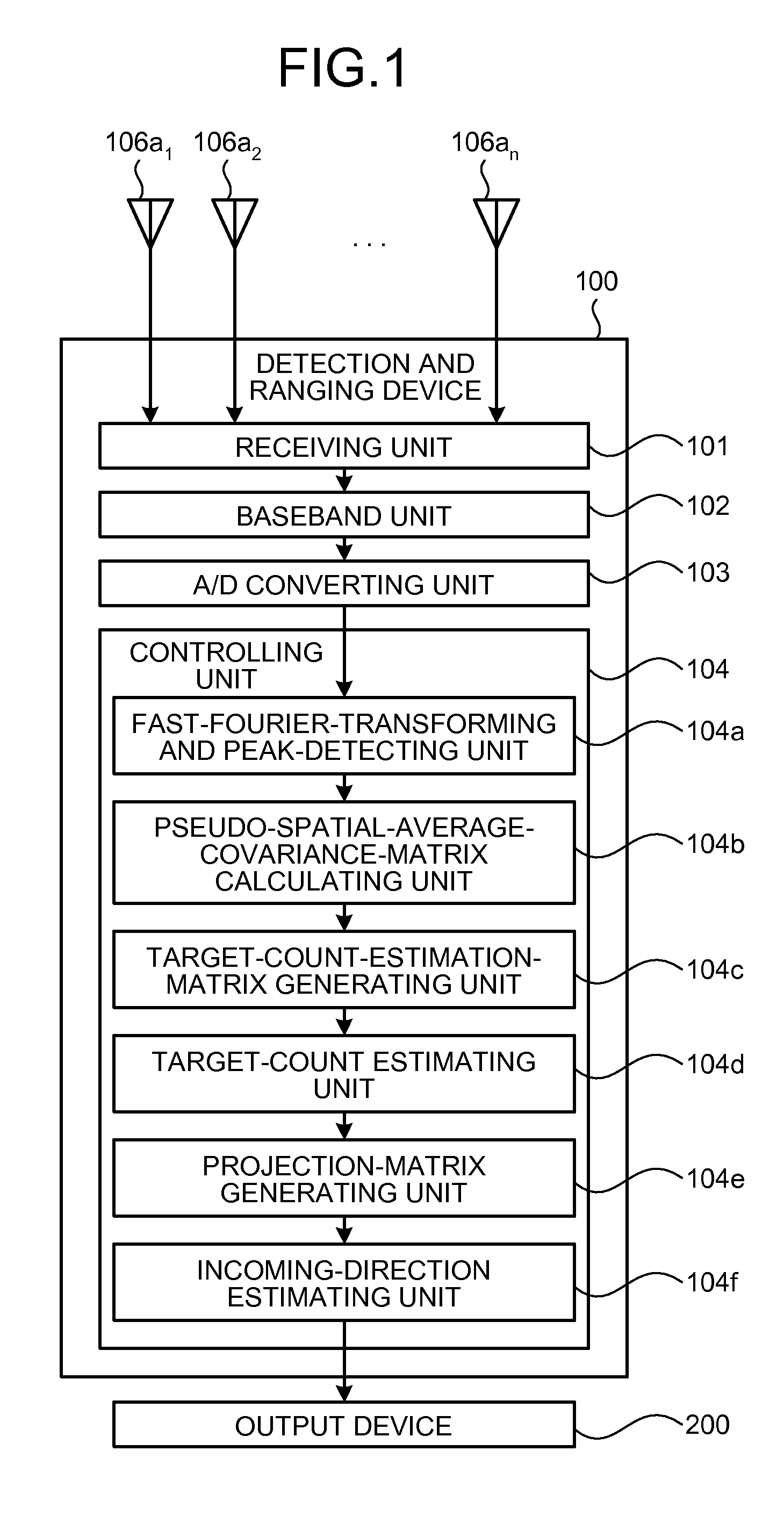
Detection and Ranging Device and Detection and Ranging Method
InactiveUS20090224978A1Solve problemsBeacon systems using radio wavesMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesSpatial averageLU decomposition
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for cross-chrominance removal using motion detection
ActiveUS7397515B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMotion detectorSpatial average
In a video system, a method and system for cross-chrominance removal using motion detection are provided. A luma motion detector in a motion adaptive deinterlacer may be used to determine a chroma current motion for a pixel in a video frame. The chroma current motion may be modified, based on a chroma motion mechanism comprising of an edge detection, a back-off, and a motion biasing, when the output pixel is found to be in a static chroma area of the video frame. A static chroma threshold parameter may be used to determine whether the output pixel is in a static chroma area. A cross-chroma reduction determined based on the current chroma motion, may be blended in the motion adaptive deinterlacer with a spatial average approximation of the output pixel to remove the cross-chrominance from the output chroma.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
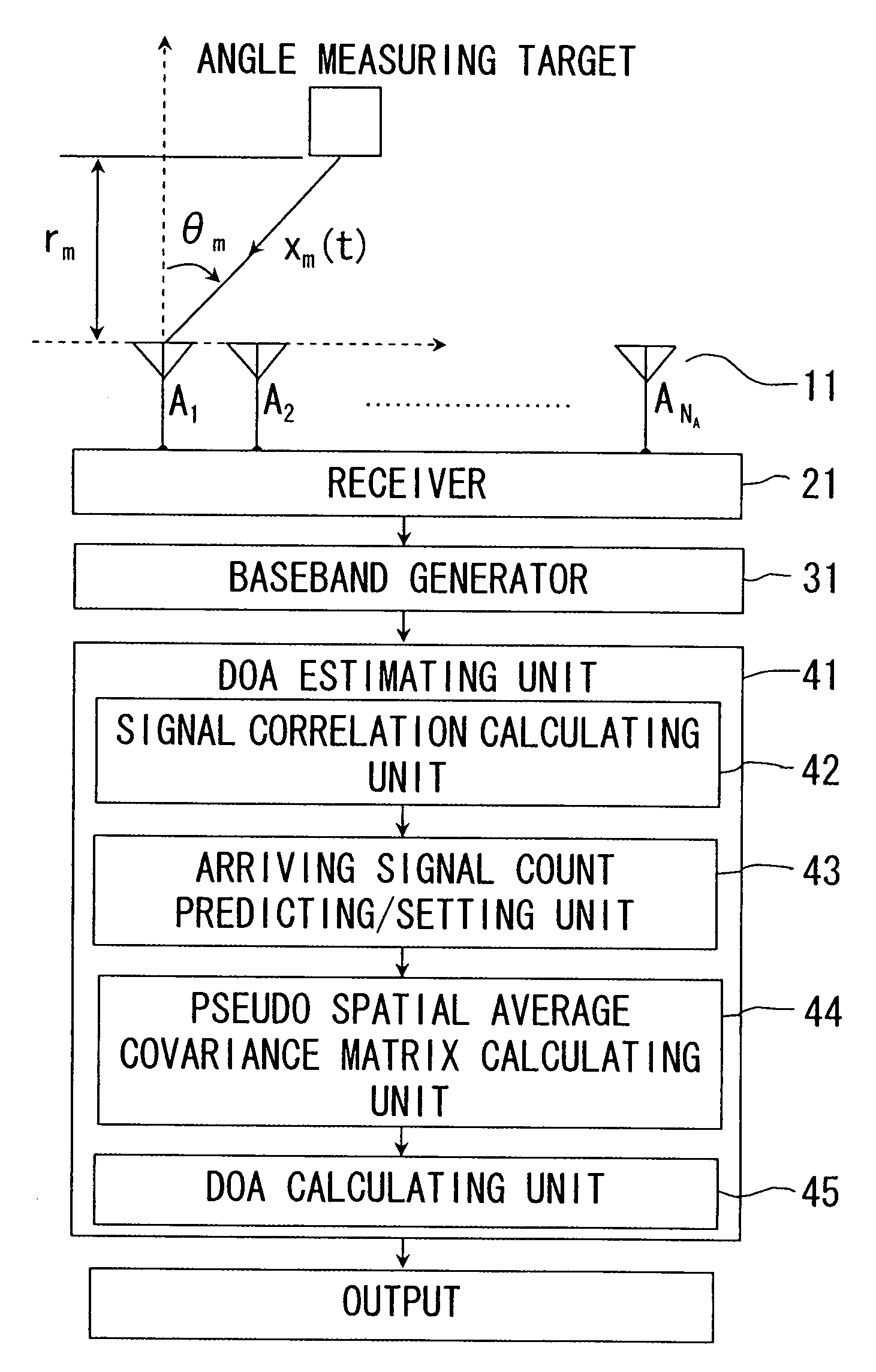
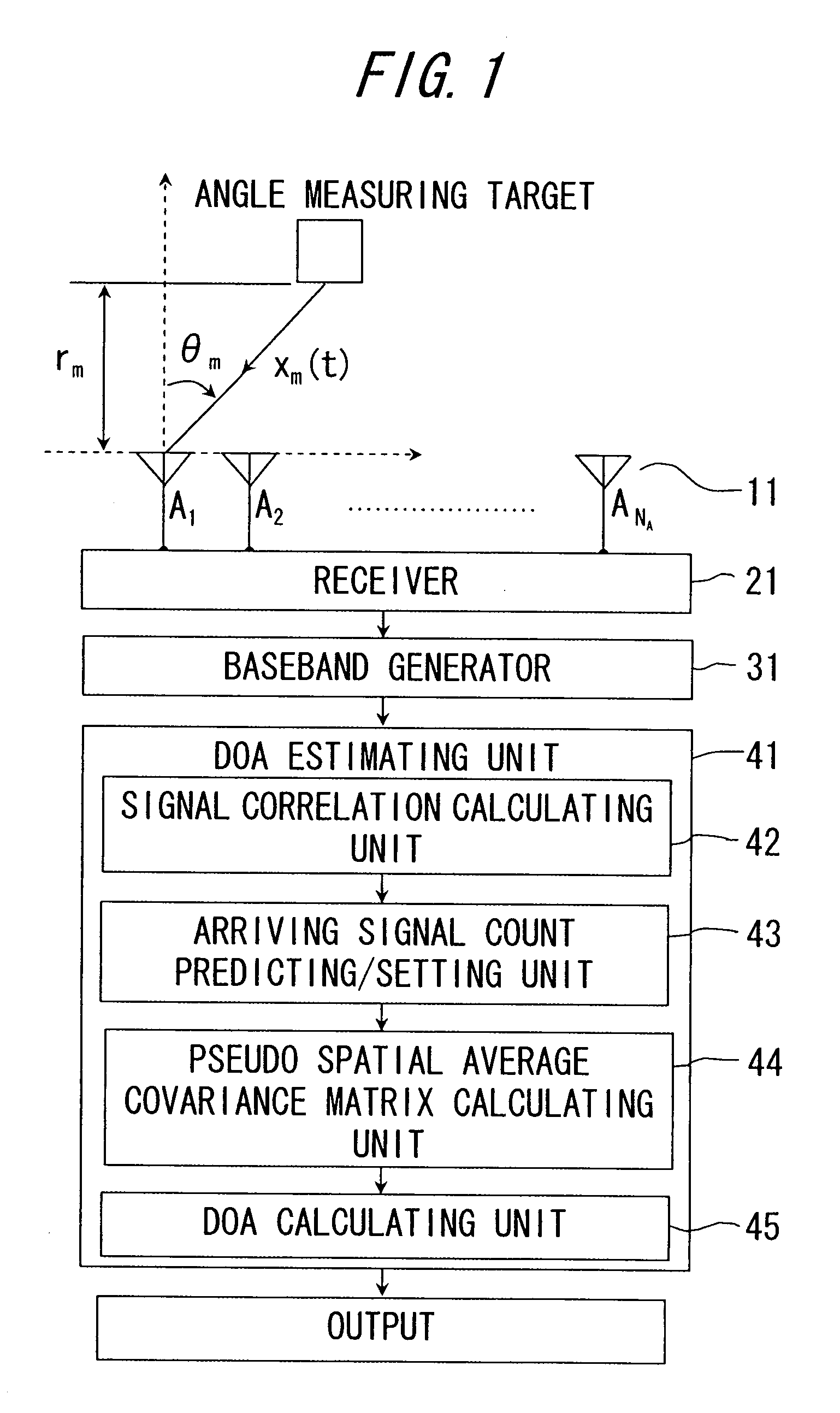
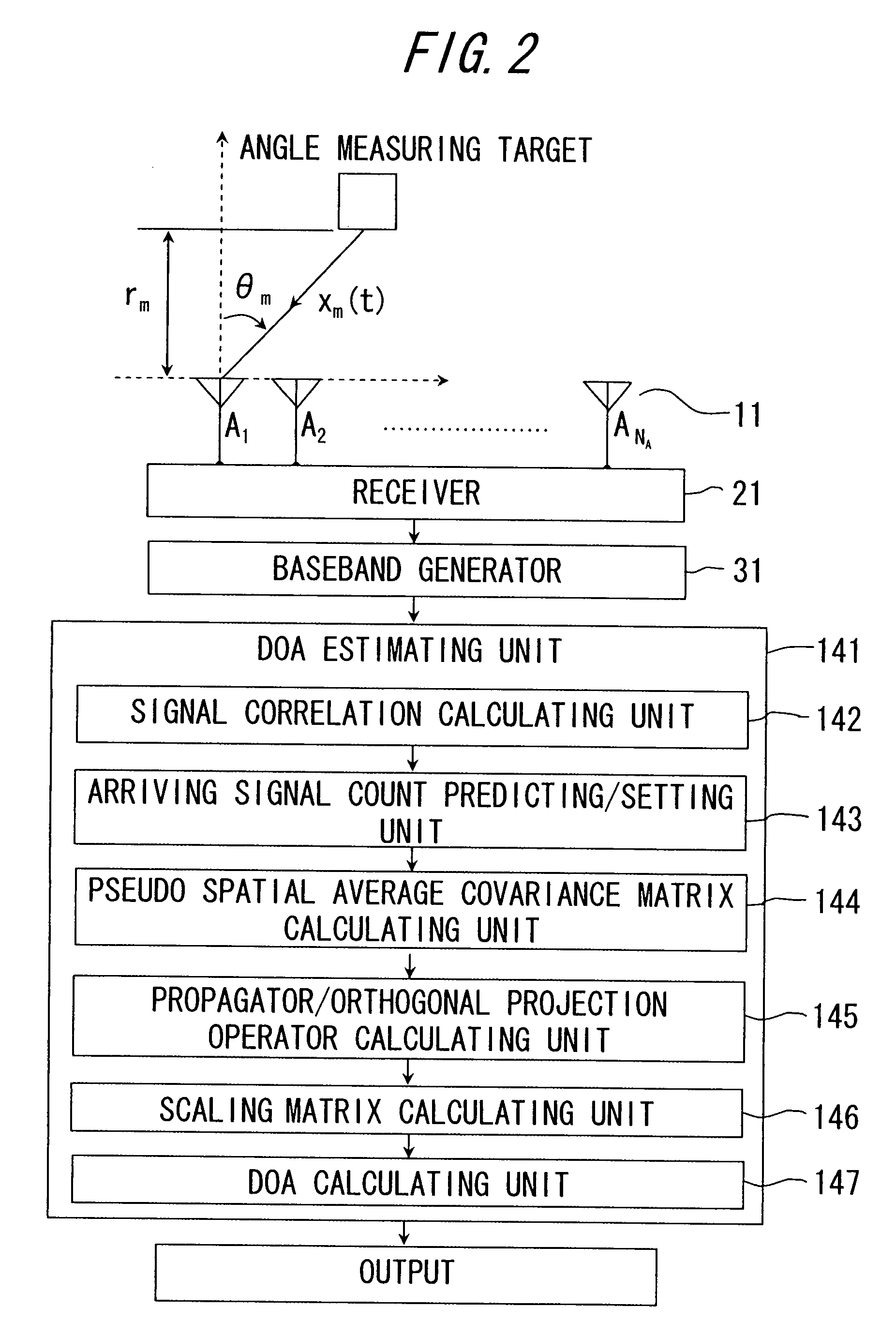
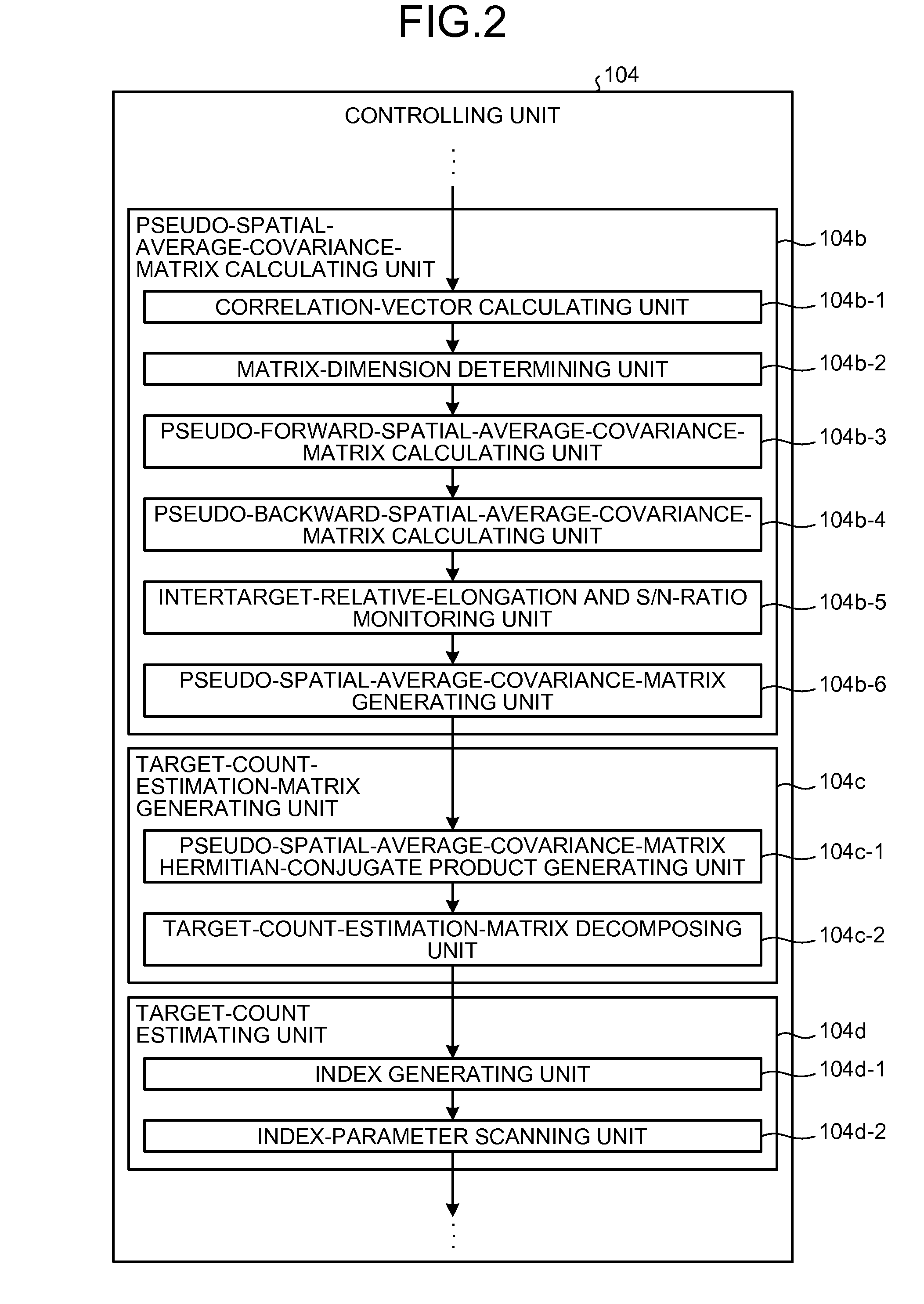
Direction-of-arrival estimating device and program
InactiveUS7847733B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationSensor arrayHat matrix
An arriving direction estimating device for estimating the arriving direction of an arriving wave with high accuracy and at high speed by using a sensor array. The arriving direction estimating device comprises a receiving section for generating a baseband signal from the arriving signals received by sensors, a matrix creating section for creating a spatial average covariance matrix R by combining the correlation vector of the baseband signal, a projection matrix creating section for creating a projection matrix Q from the matrix R depending on the number of signals of the arriving signals, a scale matrix creating section for creating a scale matrix S from a partial matrix of the matrix R, and an estimating section for estimating the arriving direction of the arriving wave from the angle distribution or an algebraic equation by using QS−1QH defined using the projection matrix Q and the scale matrix S.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for power management in an electronic device by sensing the presence and intent of an object
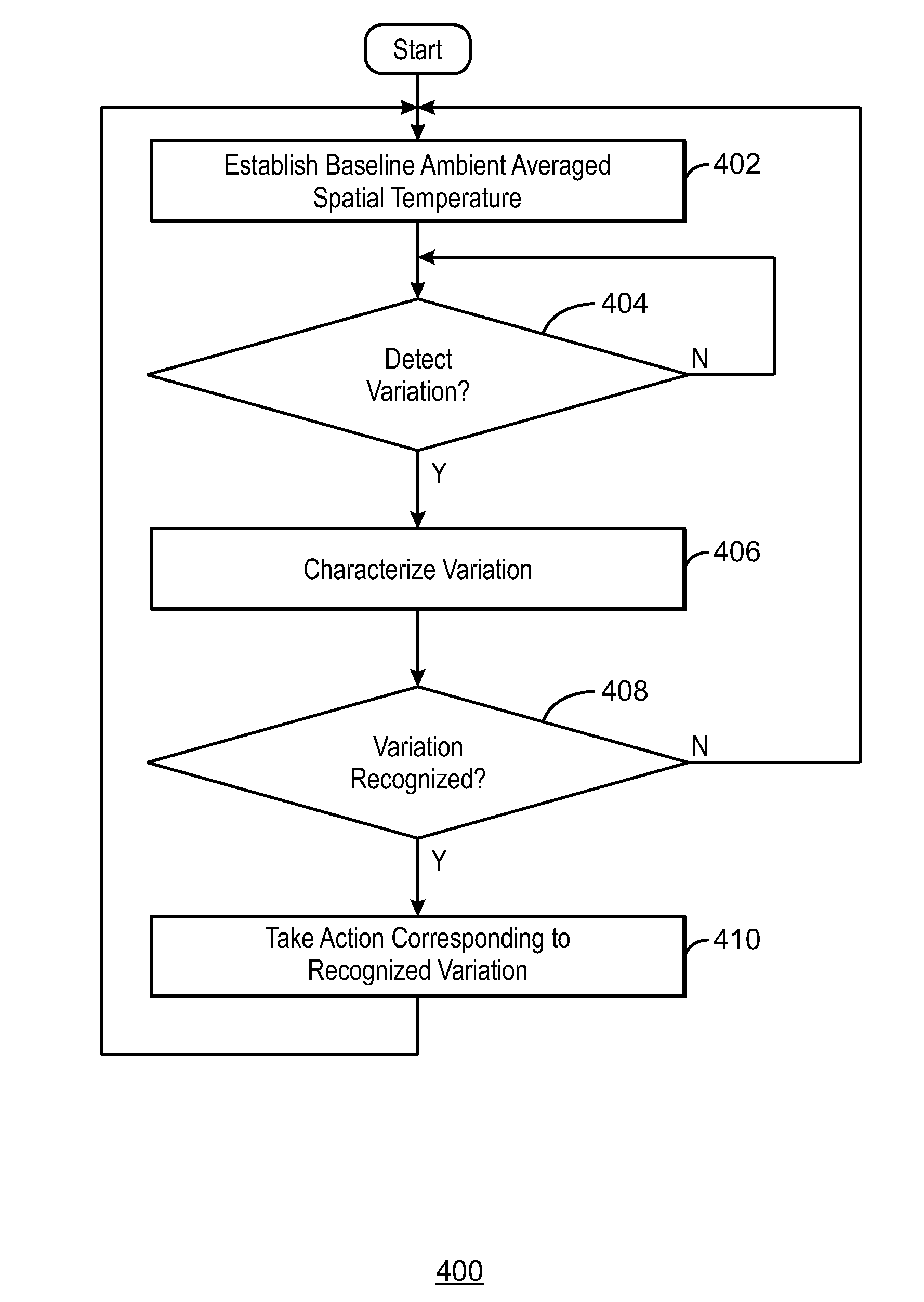
InactiveUS20150185806A1Power supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingSpatial averageElectric equipment
A method for sensing, in an electronic device, the presence and inferring therefrom an intent of an object includes sensing a baseline ambient spatial average temperature for a sensed field of view, monitoring the sensed field of view for a variation in the ambient spatial average temperature of the field of view relative to the baseline, characterizing any detected variation, determining whether the detected variation is a recognized variation, and causing the electronic device to take at least one predetermined action responsive to a recognized variation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for equalizing a loudspeaker in a room
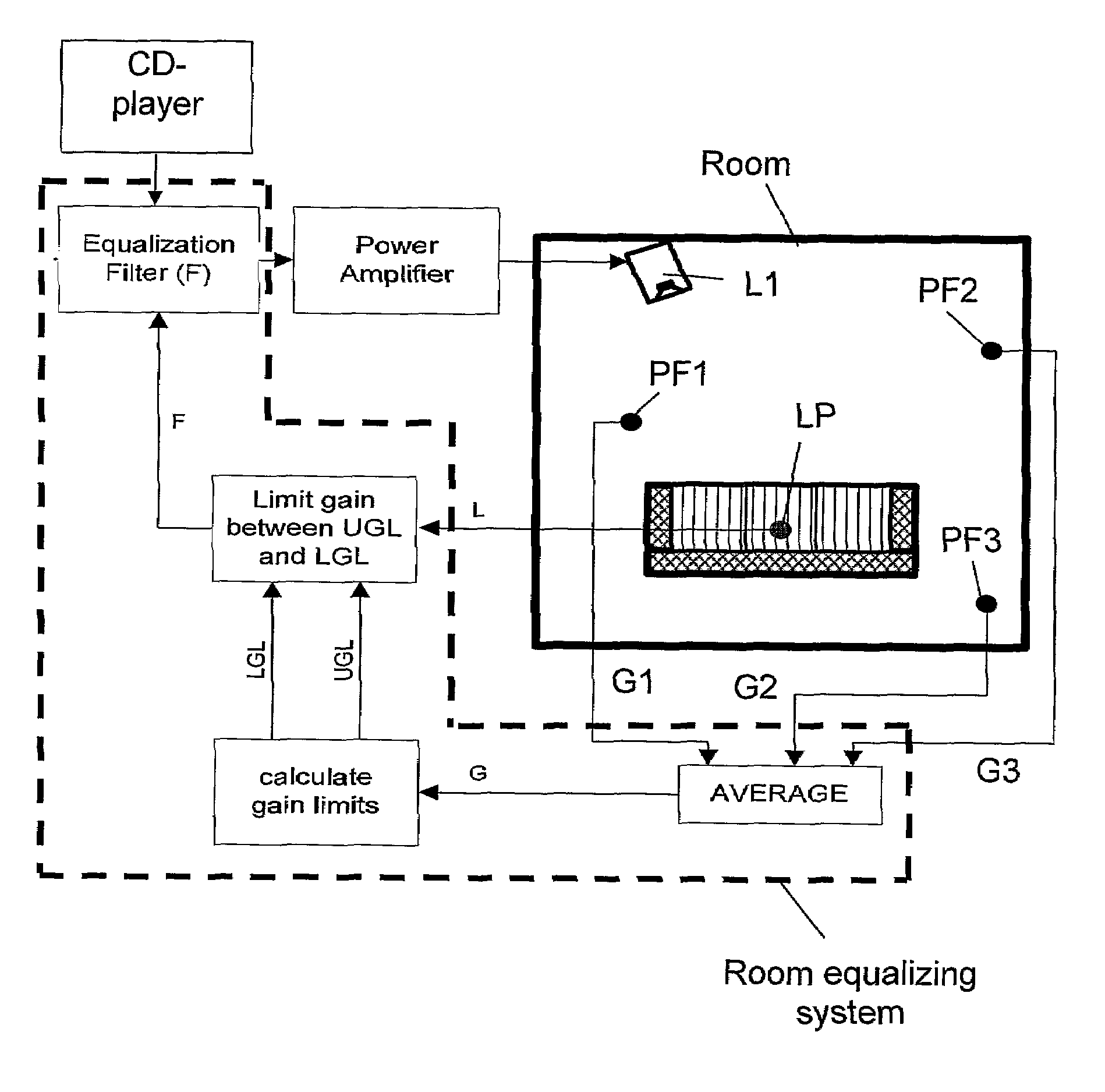
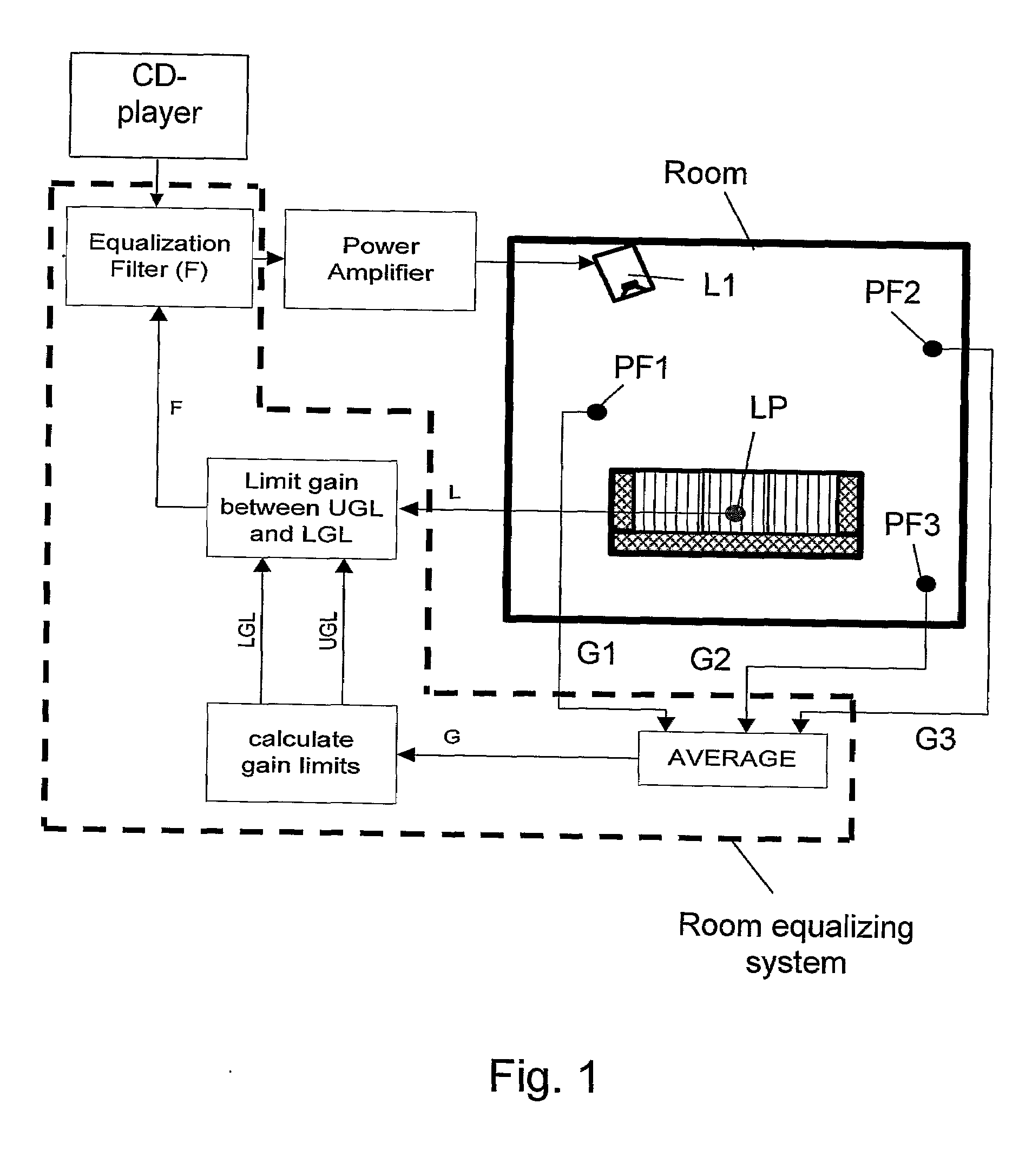
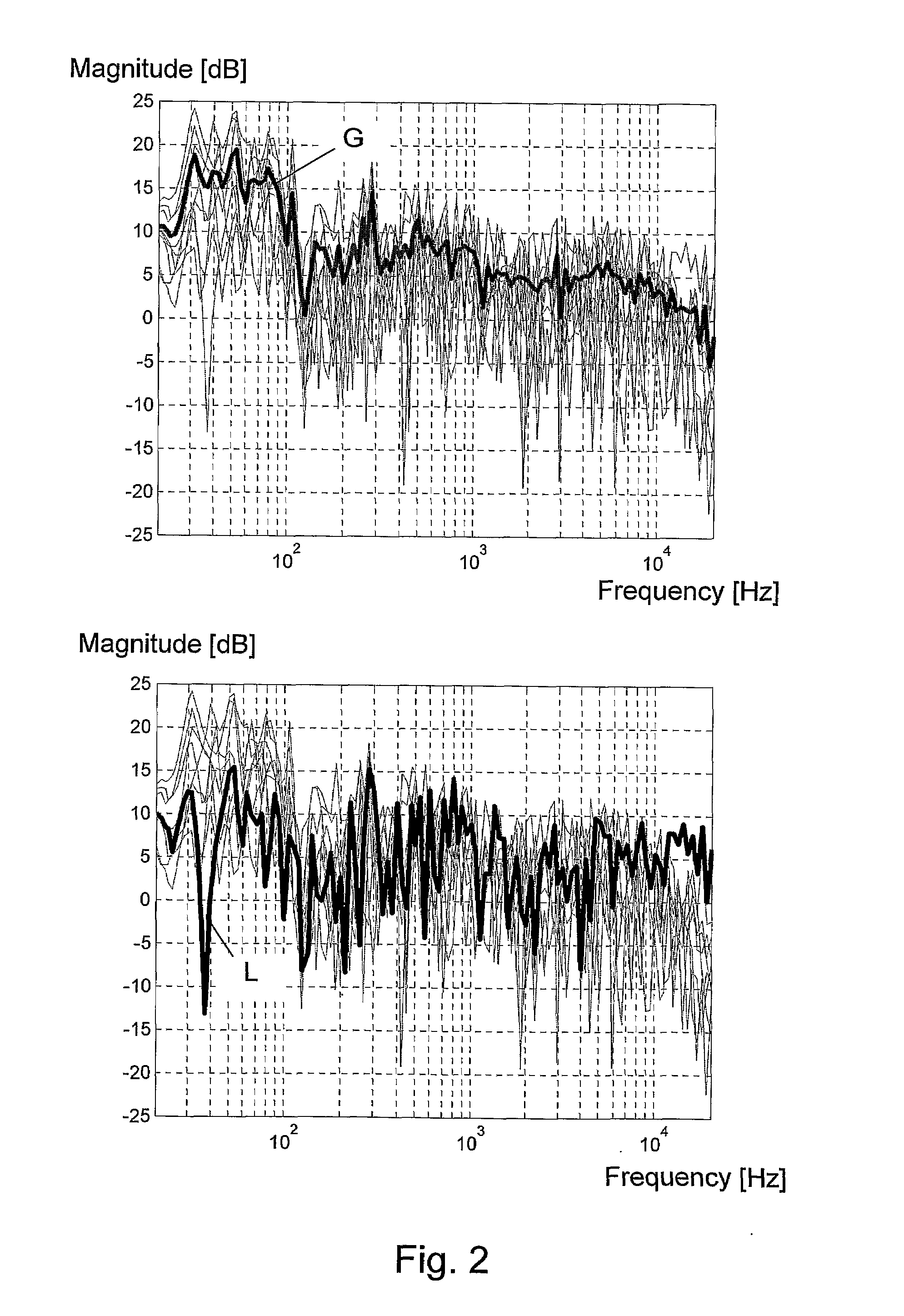
ActiveUS20090274309A1High reproduction qualityIncrease the probability of successStereophonic systemsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringLoudspeaker
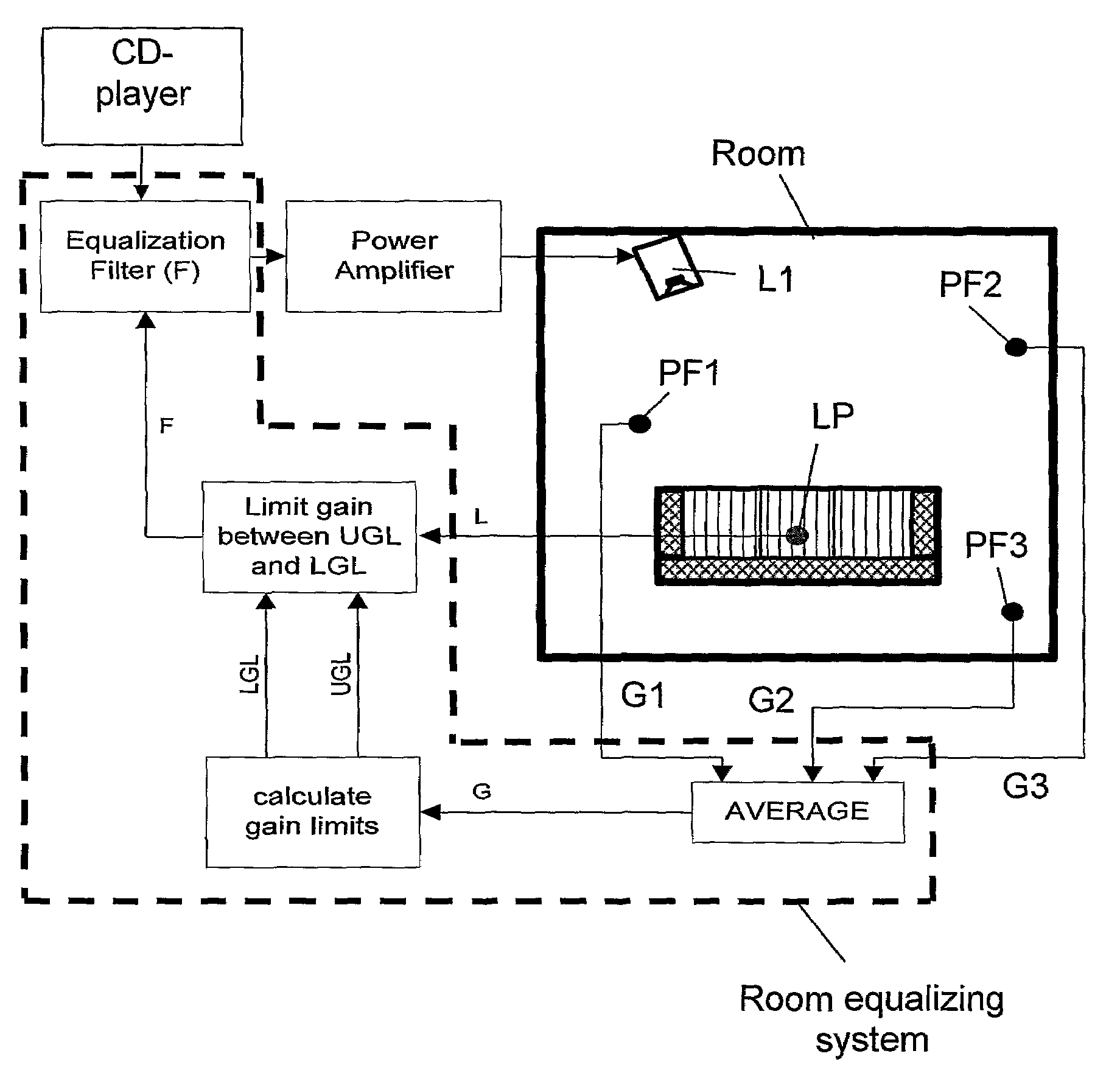
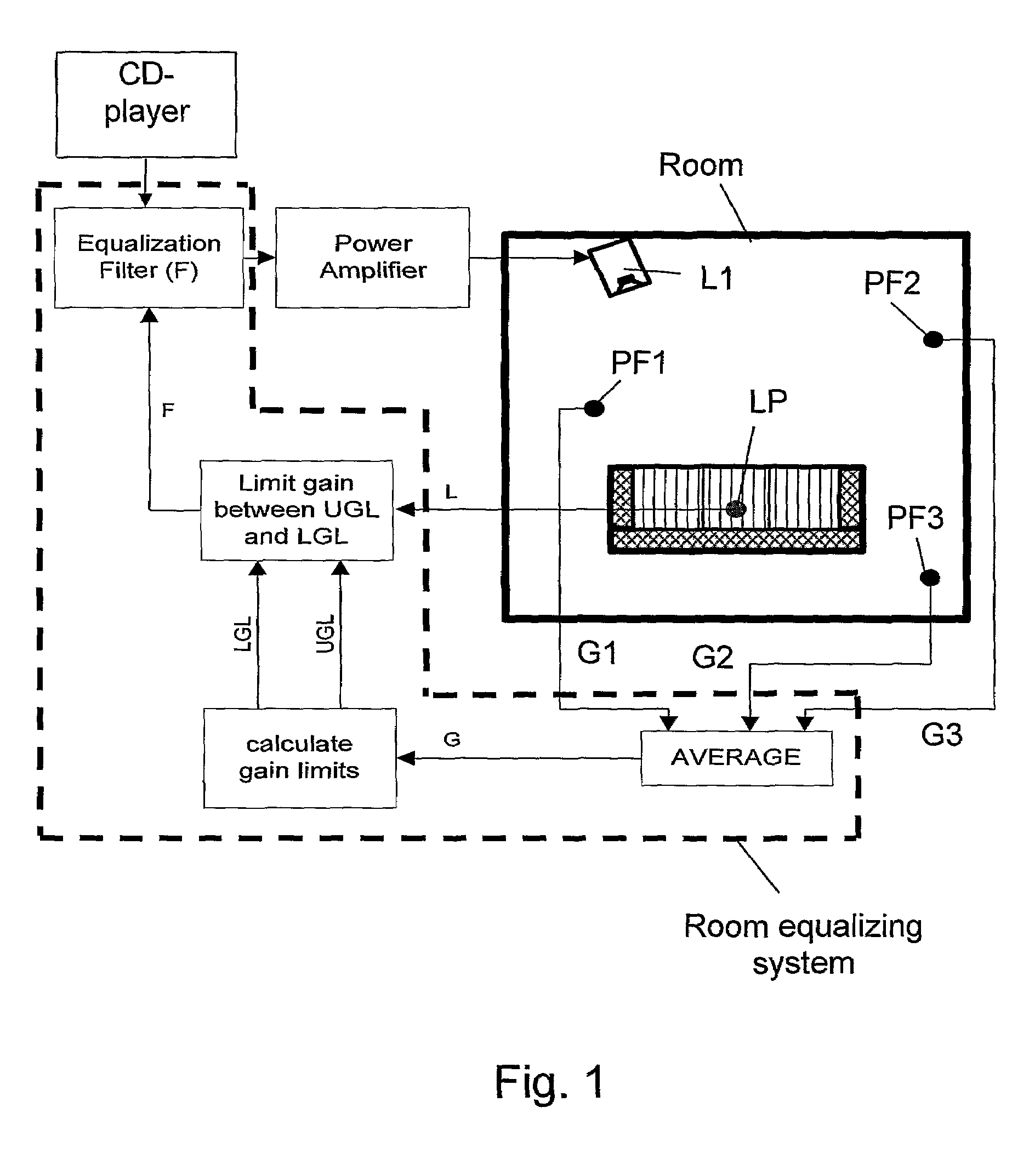
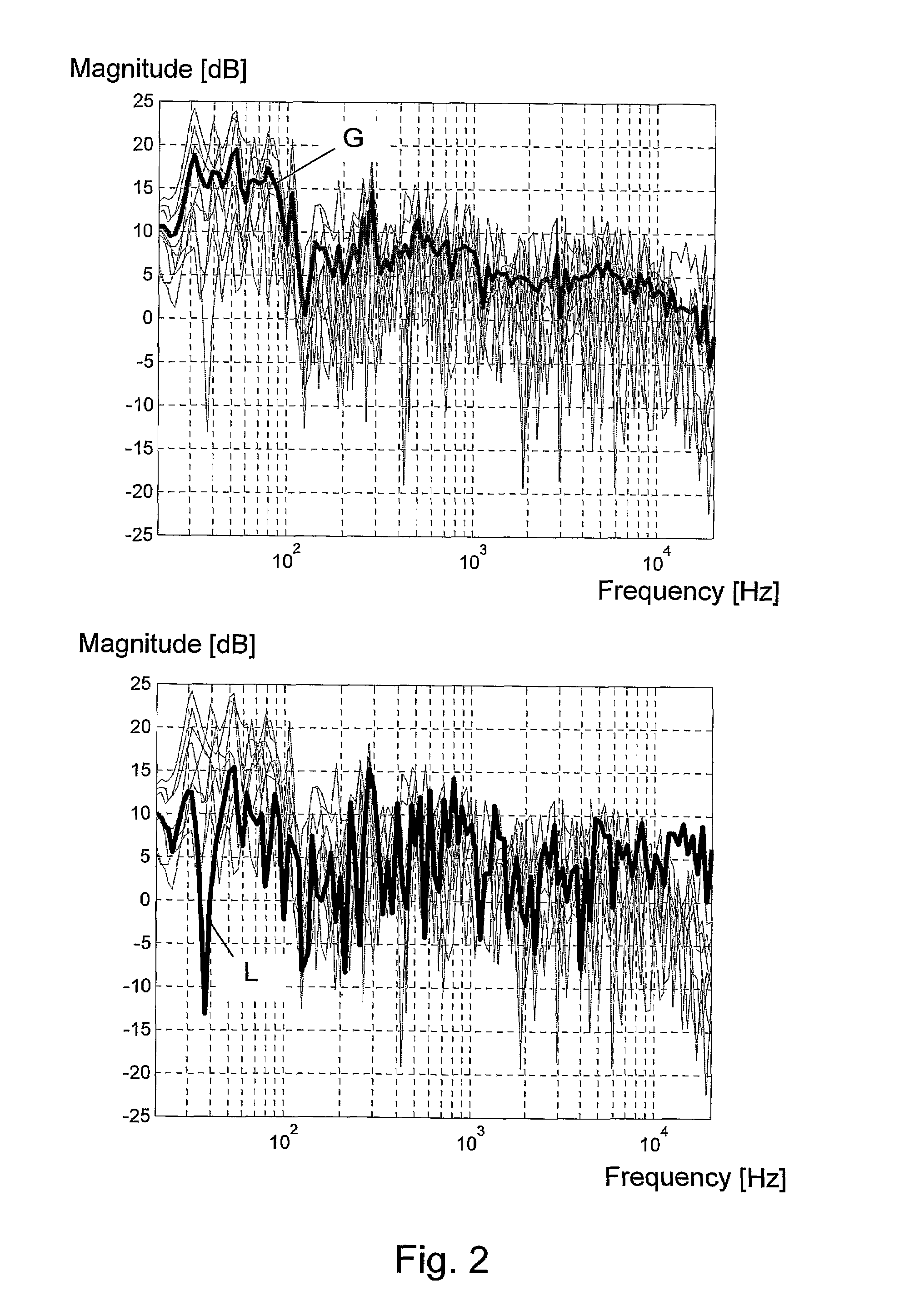
A method and a system for equalizing one or more loudspeaker(s), e.g. a hi-fi system, positioned in a room in order to compensate sound reproduction from the loudspeaker for an influence of the room. The method includes measuring a listening position transfer function (L) from electrical input of the loudspeaker (L1) to a sound pressure at a listening position (LP) in the room. A global transfer function (G) representing a spatial average of sound pressure level in the room generated by the loudspeaker (L1) is determined. This global transfer function (G) can either be determined as an average of two or more transfer functions measured in field points scattered across the room or it can be calculated based on an acoustic power output measured from the loudspeaker (L1) together with data regarding sound absorption properties of the room. An upper gain limit (UGL) as a function of frequency is then determined based on an inverse of the global transfer function (G). An equalizing filter (F) is then determined based on an inverse of the listening position transfer function (L), but with its gain being limited to a maximum gain in accordance with the upper gain limit (UGL). Finally, the loudspeaker (L1) is equalized with the equalizing filter (F), the filter (F) being implemented such as a minimum phase approximation by an FIR or an HR filter. Preferably, a lower gain limit (LGL) as a function of frequency is also determined as an inverse of the global transfer function (G), wherein a gain of the equalizing filter (F) is limited to a minimum gain in accordance with the lower gain limit (LGL). By use of the upper and lower gain limits (UGL, LGL) it is possible to implement a system capable of automatically designing the equalizing filter (F) with only simple tasks to perform for an operator of the system.
Owner:SL AUDIO
Estimating location using multi-antenna radio receiver
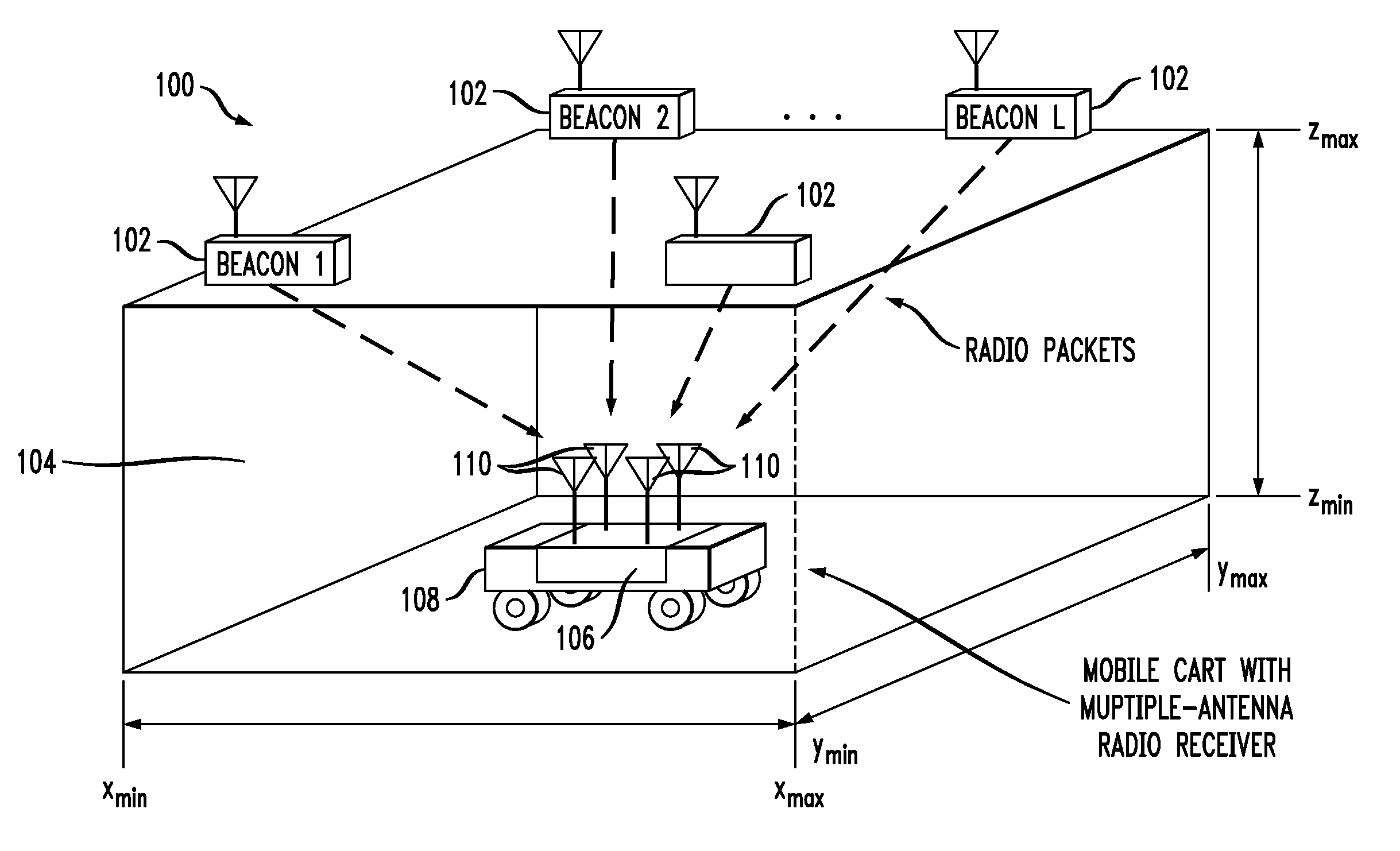
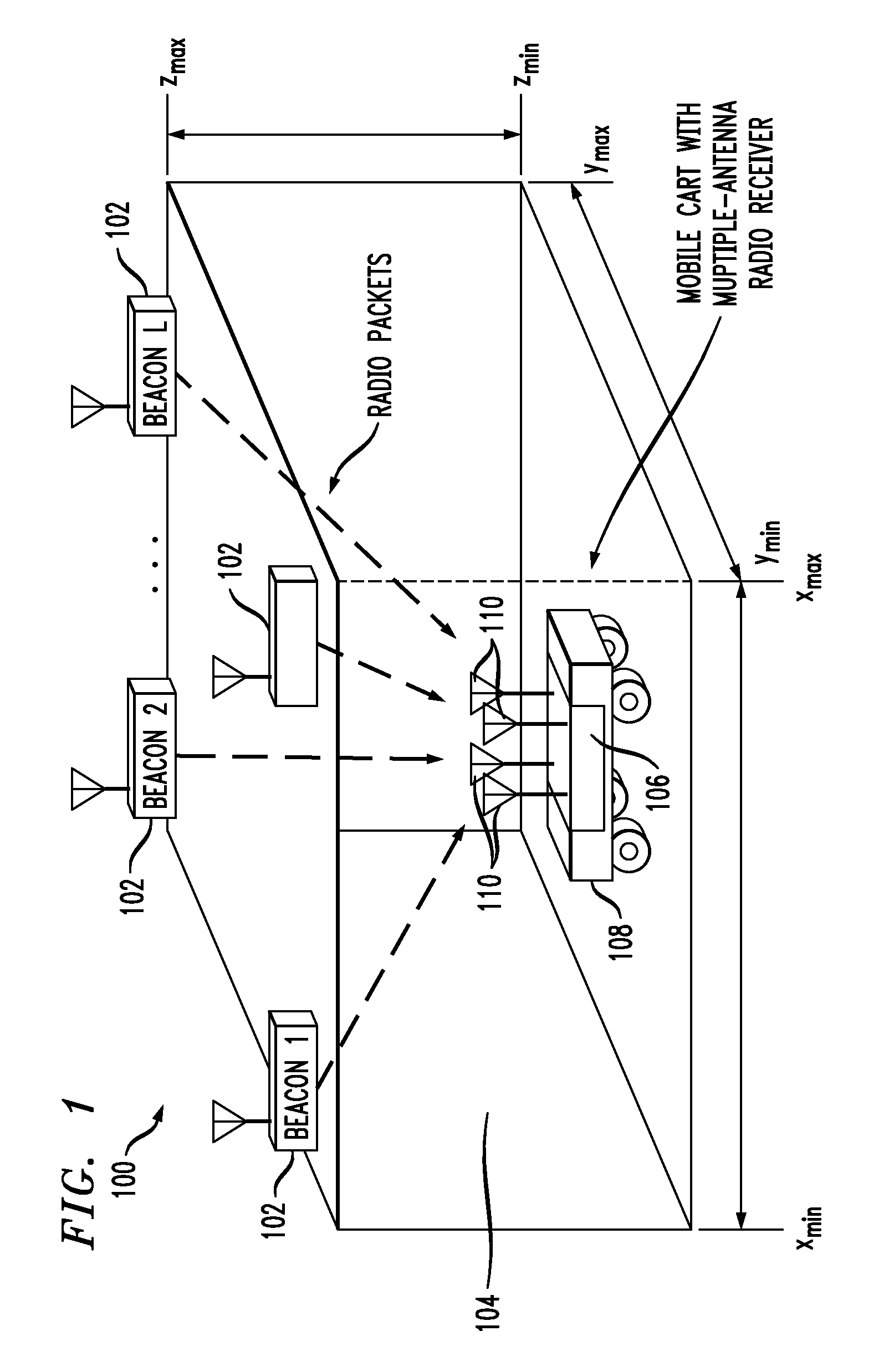
ActiveUS8086248B2Accurate estimatePosition fixationTelephonic communicationRadio receiverSpatial average
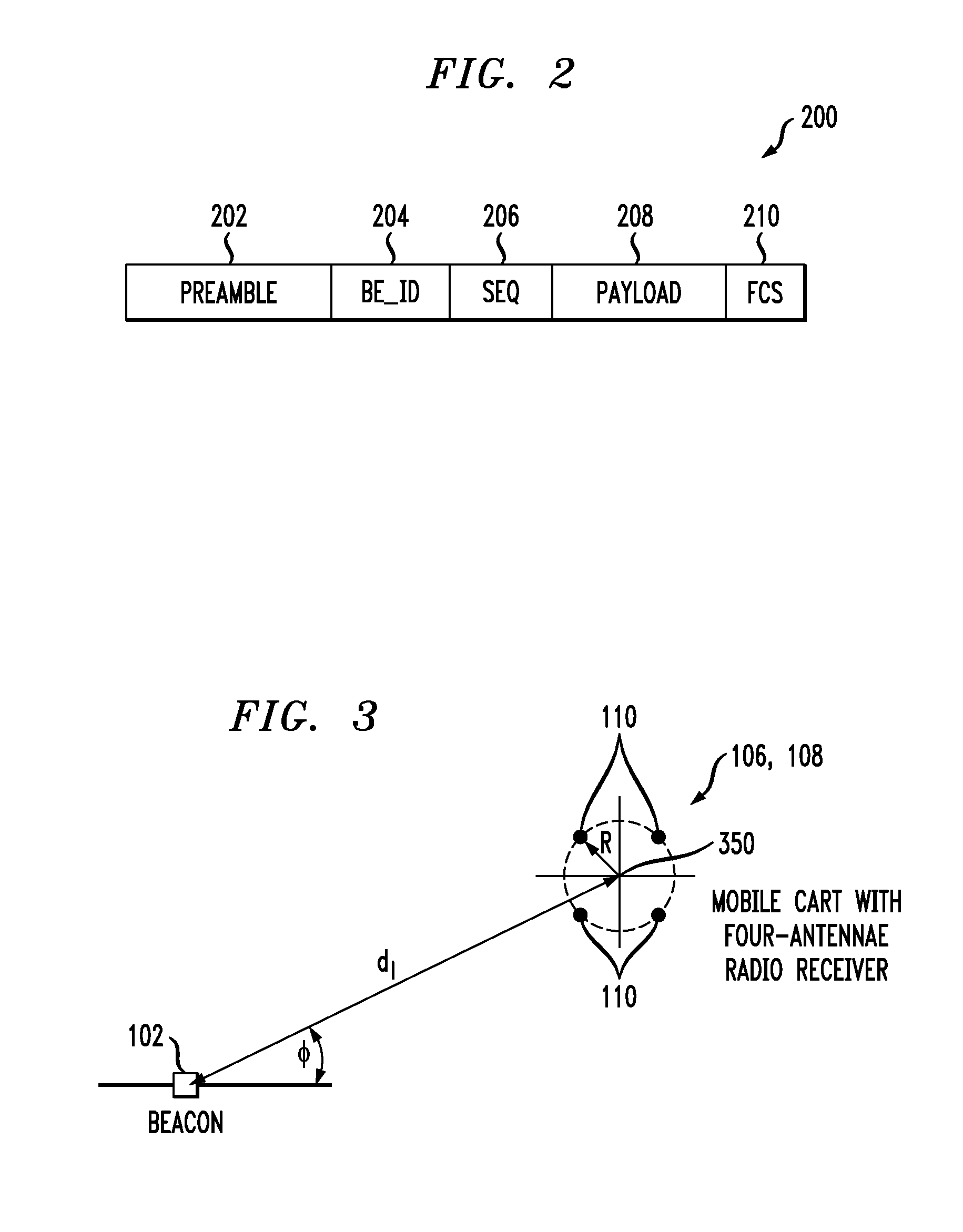
Packets are periodically transmitted by a plurality of radio beacons deployed at known positions over a location estimation area. Monitoring is conducted for incoming packets. Upon receipt of a packet from a kth one of the beacons, received signal strength, RSSI, is measured at each of the antenna outputs, the packet is decoded to obtain the unique identifier and the unique sequence number, and the received signal strength at each of the antenna outputs is spatially averaged. The measuring, decoding, and spatial averaging are repeated for additional packets from the kth one of the beacons during a pre-defined time window T. The plurality of spatially averaged received signal strengths are temporally averaged over the pre-defined time window T, to obtain a spatially and temporally averaged value of received signal strength. The distance dk from the apparatus to the kth one of the beacons is approximated based on the spatially and temporally averaged value of received signal strength. The approximate distance dk is designated as {circumflex over (d)}k. This is repeated for the K beacons that have successfully transmitted packet(s) during the pre-defined time window, k=1 to K. The location of the object is estimated as an approximate intersection of spheres with radii {circumflex over (d)}k. Each sphere is centered at the known position of the kth one of the beacons.
Owner:TERRACE LICENSING LLC
Method and system for equalizing a loudspeaker in a room
ActiveUS8094826B2High reproduction qualityIncrease probabilityStereophonic systemsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsElectricitySpatial average
Owner:SL AUDIO
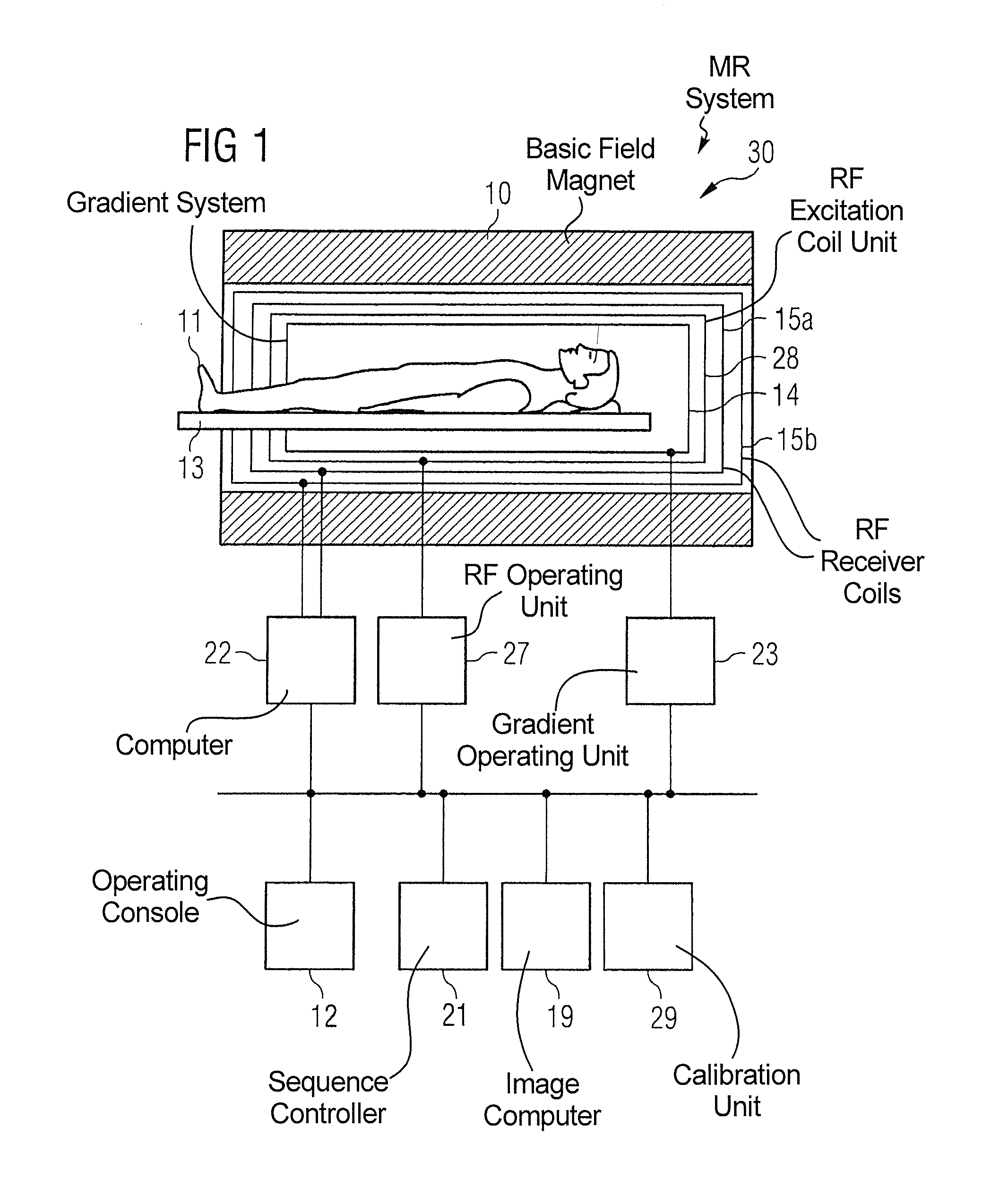
System and method of performing magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
ActiveUS20140015529A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic resonance spectroscopicSpatial average
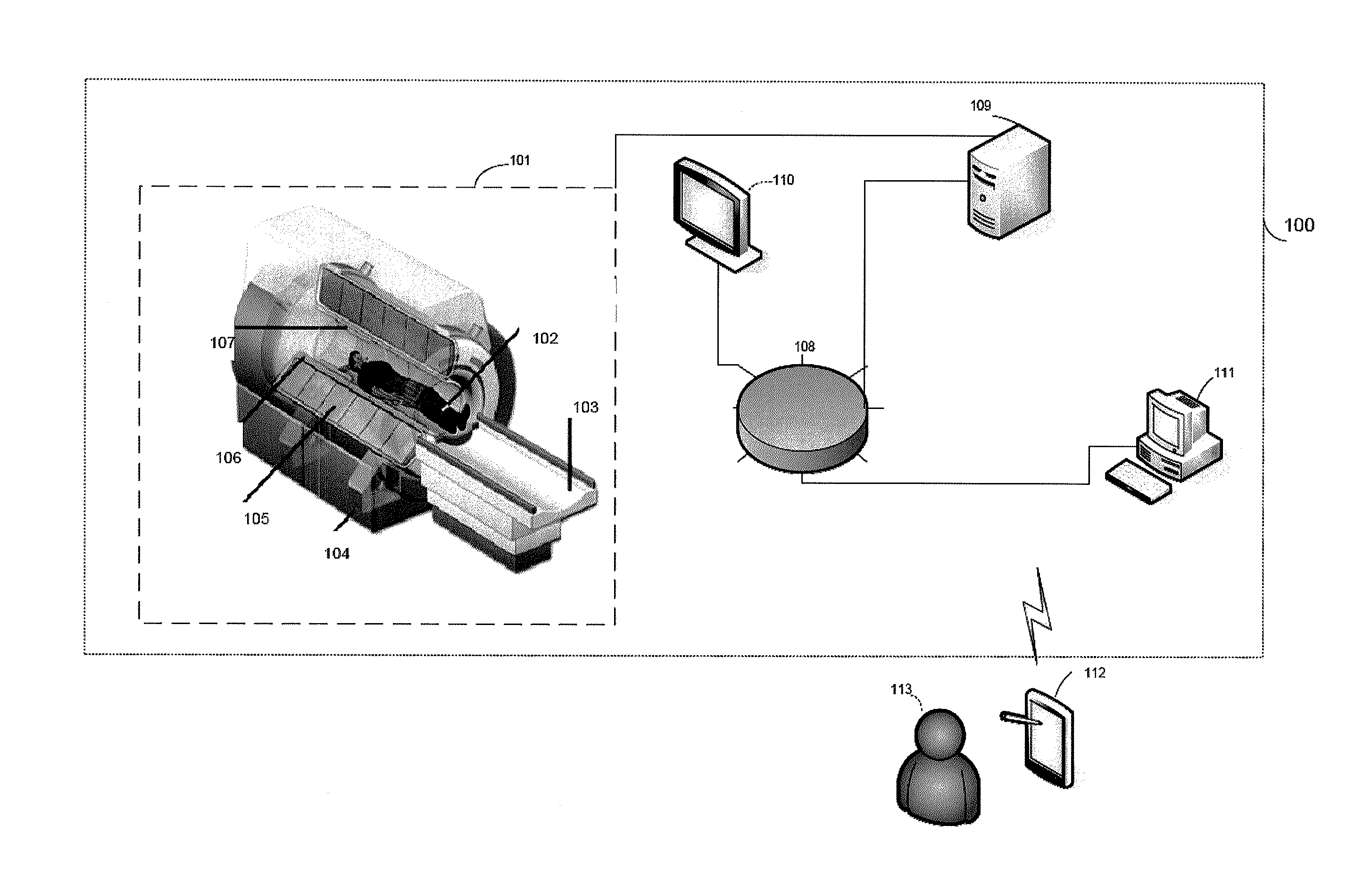
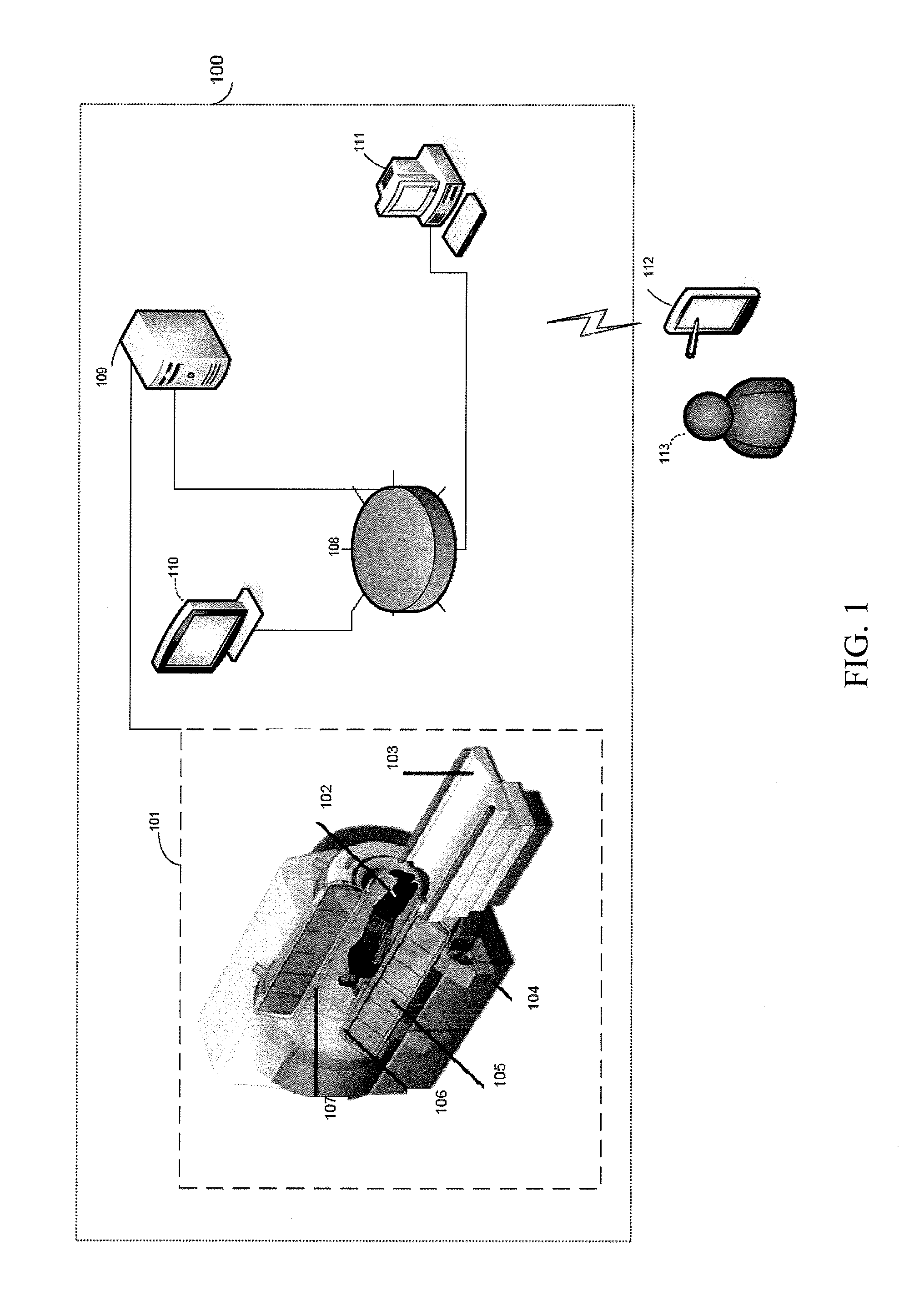
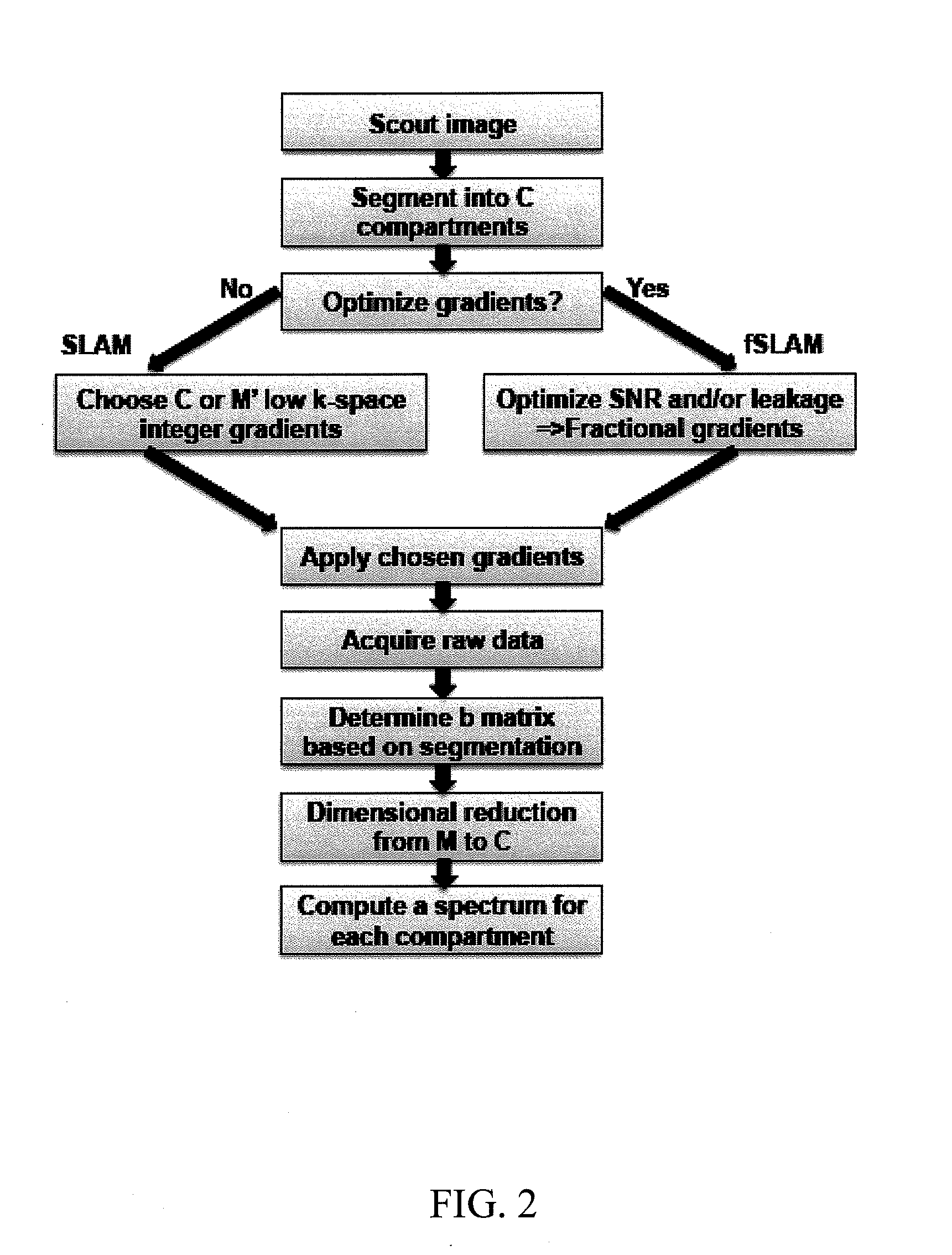
A method of performing spatially localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy includes receiving a magnetic resonance image of an object; identifying a plurality C of compartments that generate magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals in the object including at least one compartment of interest; segmenting in at least one spatial dimension the magnetic resonance image of the object into the C compartments; acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals from the compartments by applying a plurality of M′ phase encodings applied in the at least one spatial dimension, wherein M′≧C; calculating a spatially localized magnetic resonance chemical shift spectrum from the at least one compartment of interest; and rendering a spatially localized magnetic resonance spectrum that is substantially equal to a spatial average of magnetic resonance chemical shift spectra from the at least one compartment of interest. A magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging system is configured to perform the above method.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
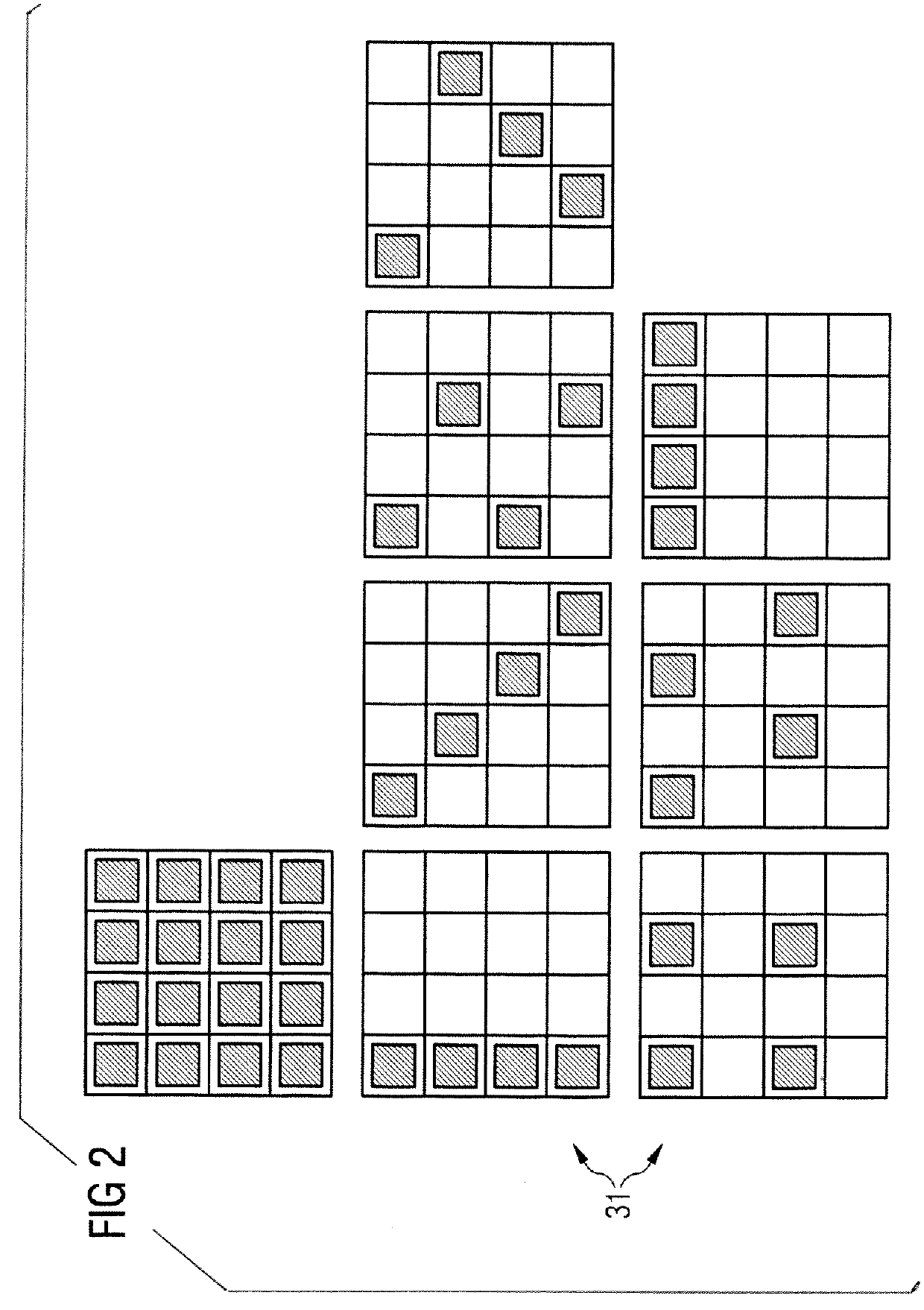
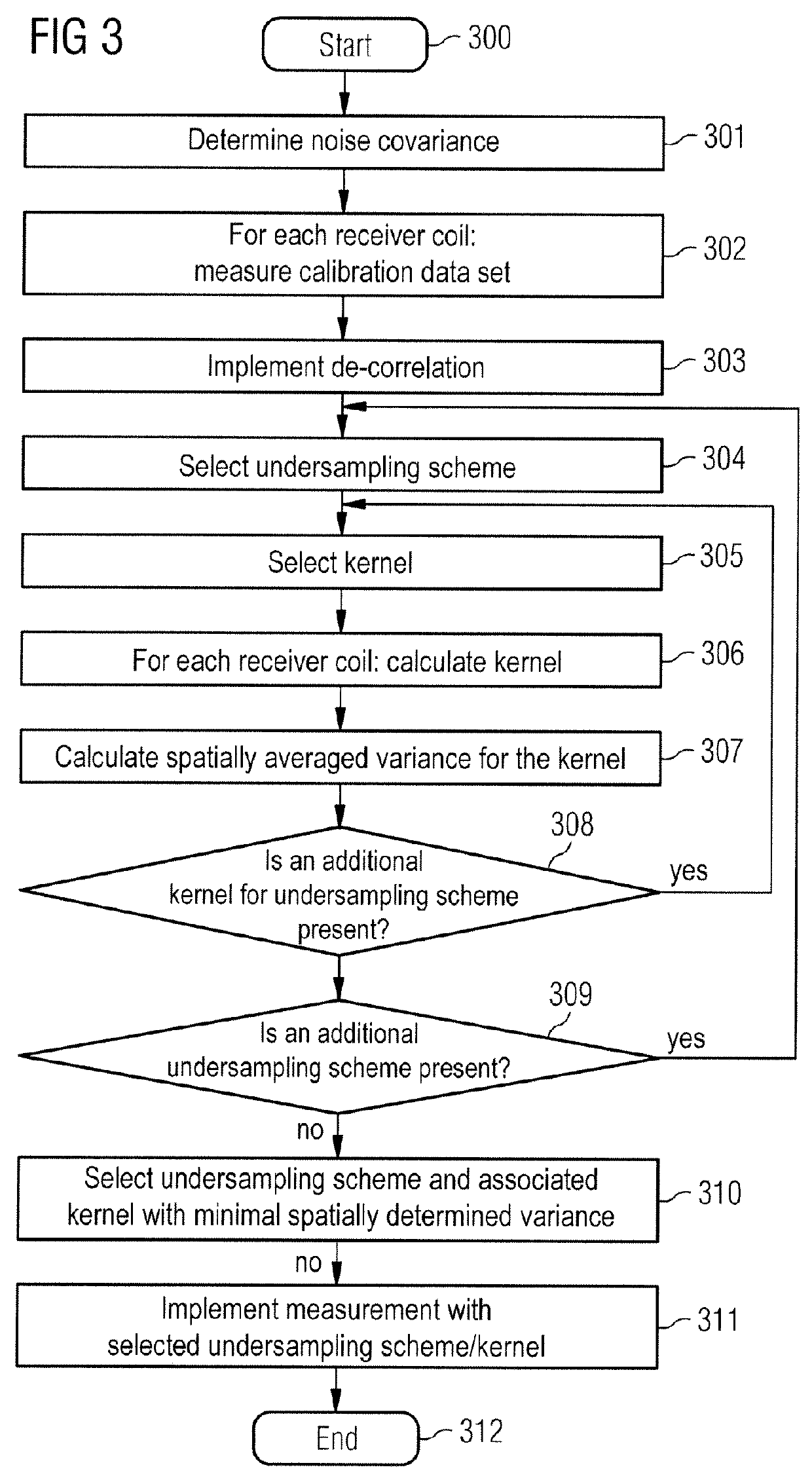
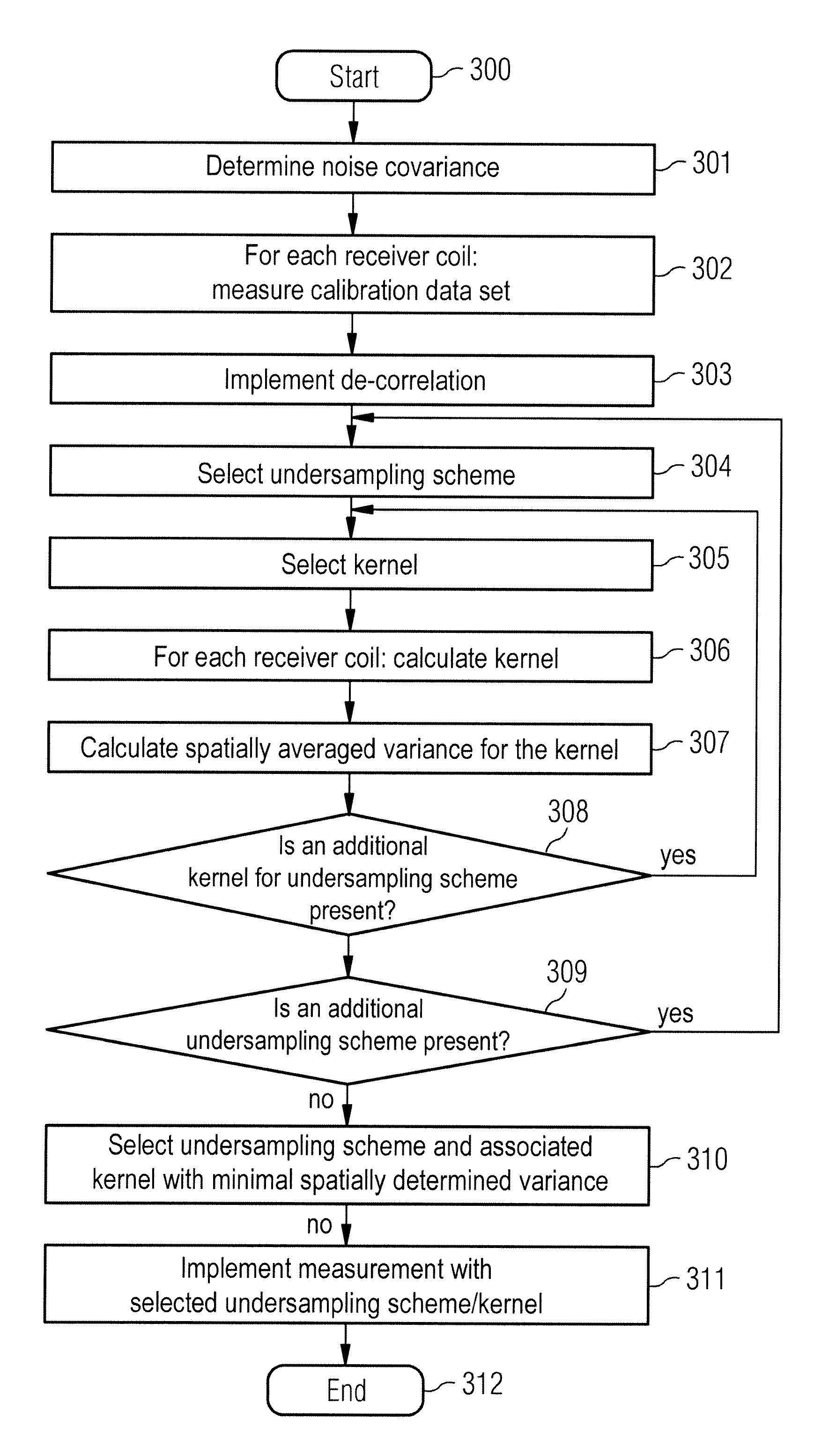
Method to select an undersampling scheme for magnetic resonance imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging method and system using such a selected undersampling scheme
ActiveUS20130076352A1Reduce dataReduce image noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setResonance
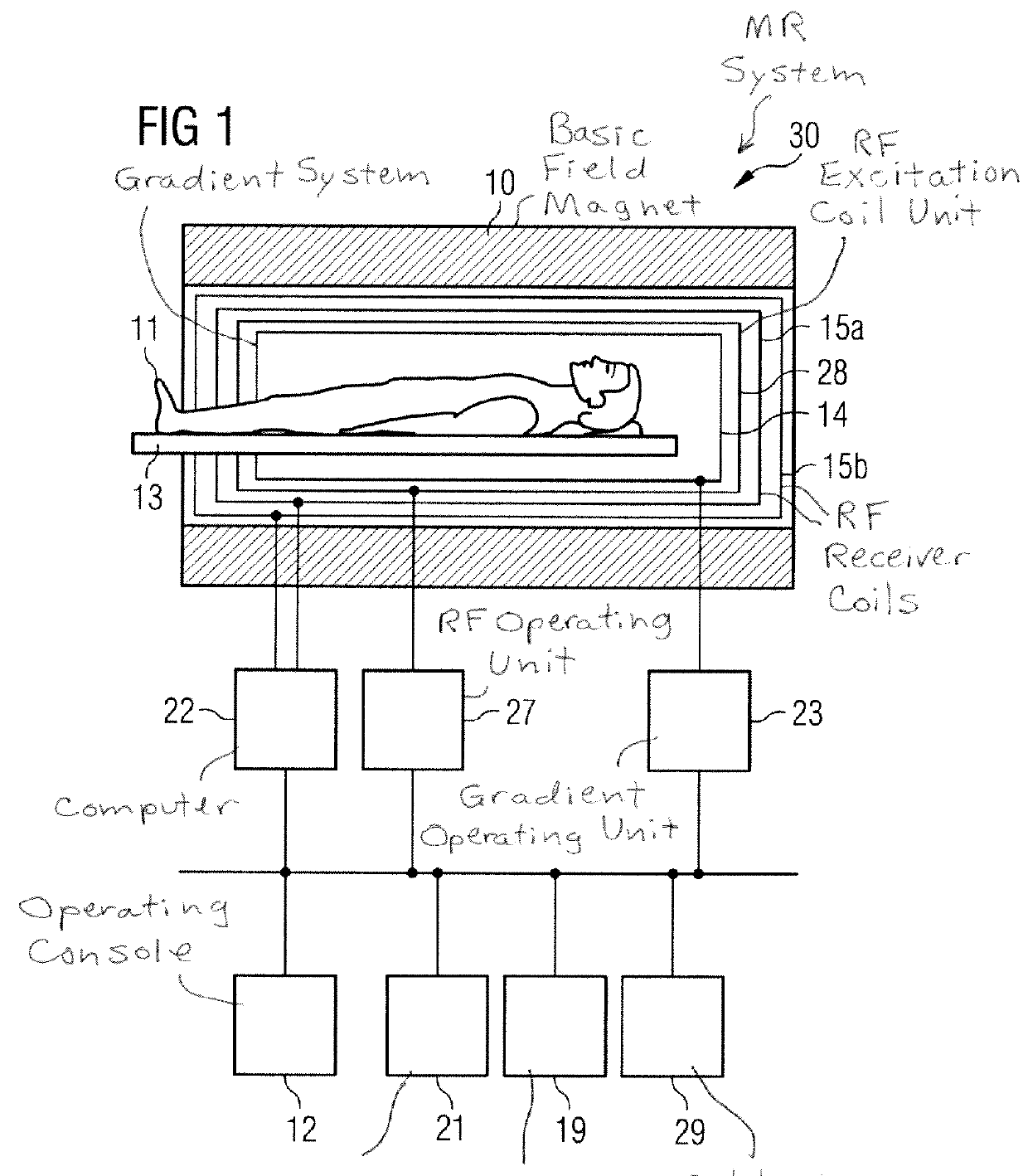
In a method to select an undersampling scheme of k-space and an associated set of reconstruction kernels to acquire reduced magnetic resonance (MR) data sets with multiple coils, a calibration data set is acquired for each of the respective coils, a noise covariance is determined from autocorrelations and correlations of the noise of the various coils. At least one set of reconstruction kernels is calculated for each of the multiple undersampling schemes from the calibration data sets of the various coils. For each set of reconstruction kernels, a characteristic value is calculated from the noise covariance and the respective reconstruction kernels of the coils, with the characteristic value being proportional to a spatial mean value of a signal noise of an MR image. A selected undersampling scheme and a selected set of reconstruction kernels are selected based on the calculated characteristic values.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
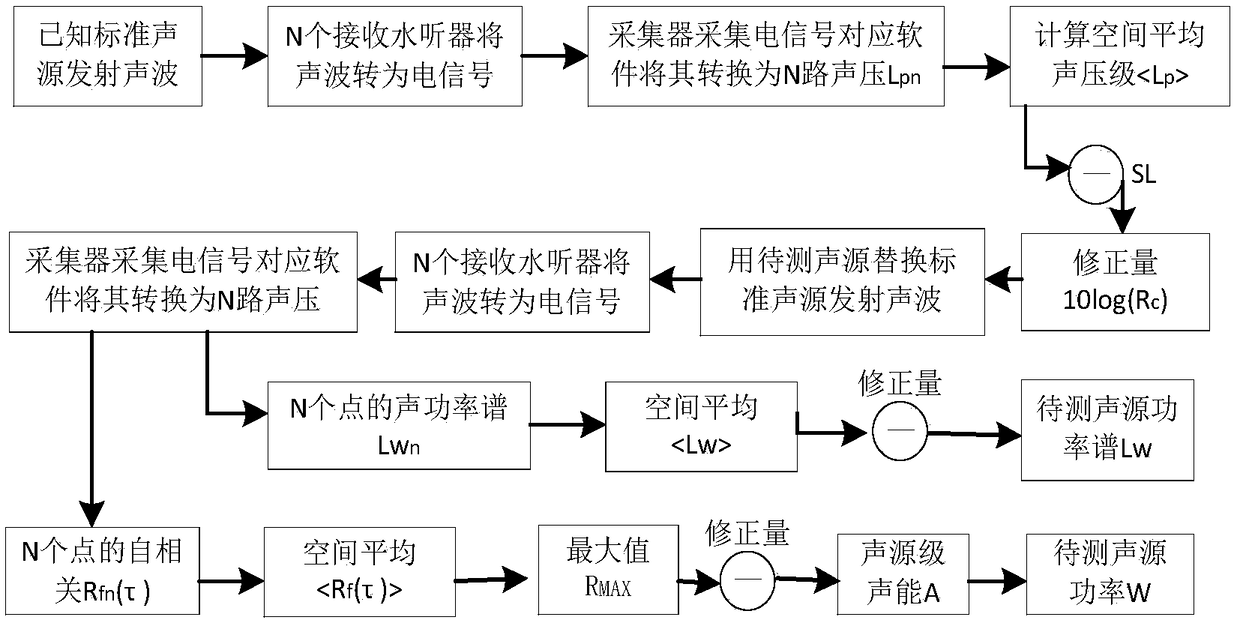
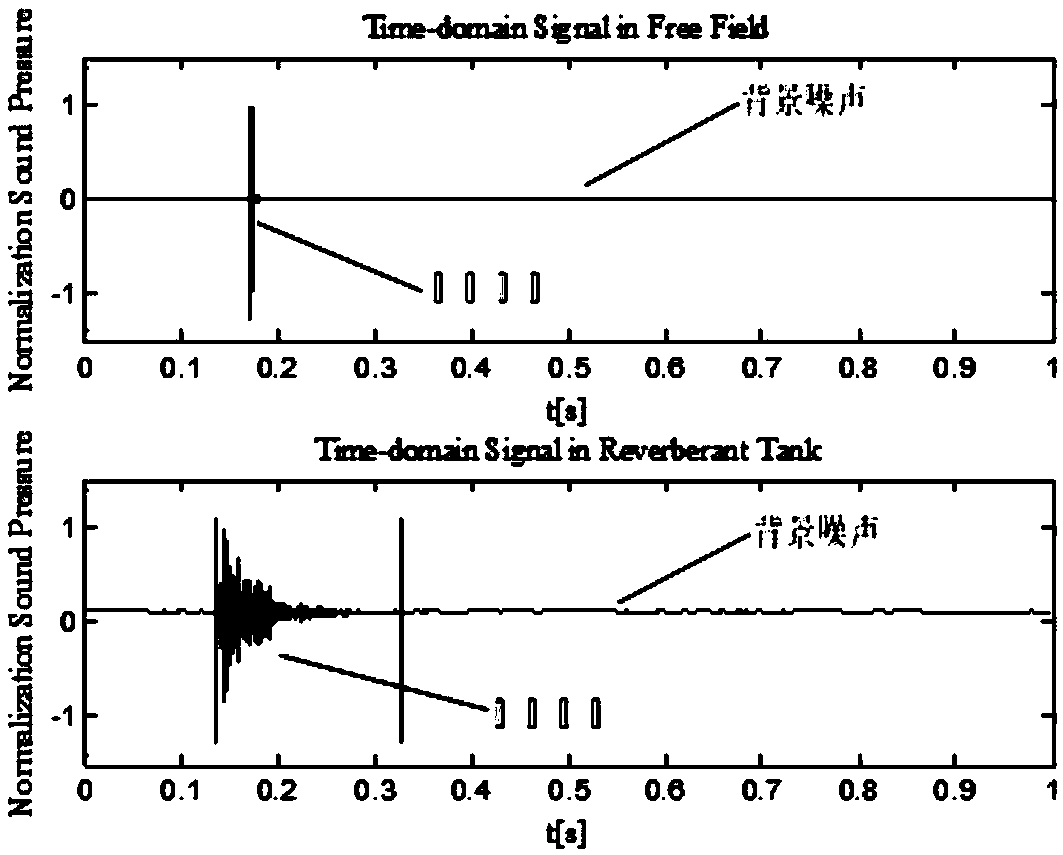
Method for measuring transient sound source characteristics in reverberation pool
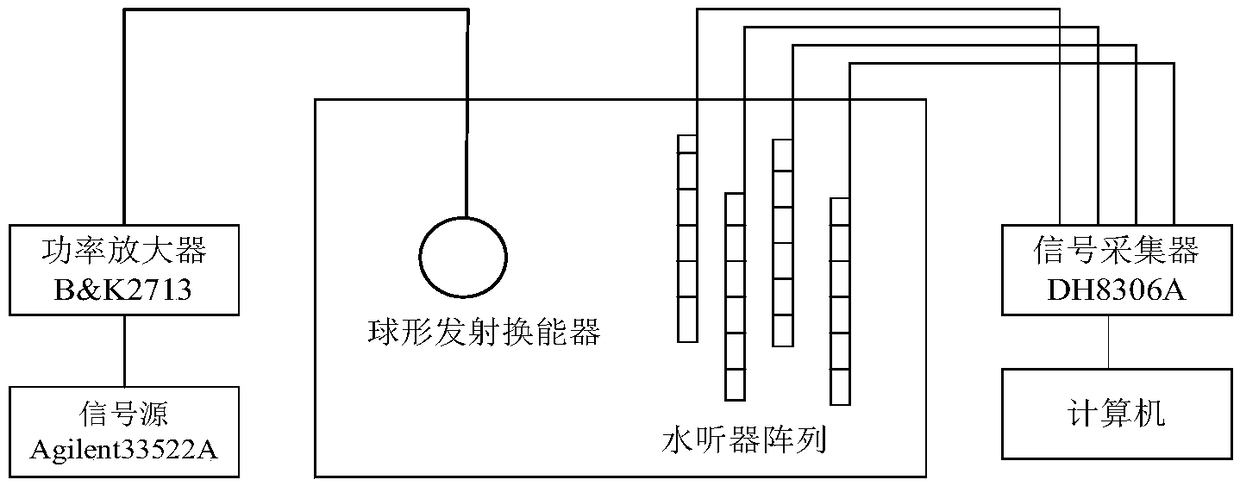
ActiveCN109238436ASuitable for quantitative acoustic evaluationEfficient measurementVibration measurement in fluidSound sourcesSelf correlation
The invention belongs to the field of acoustic measurement research, and particularly relates to a method for measuring the transient sound source characteristics in a reverberation pool. The method comprises the following steps: placing a standard sound source and a hydrophone array in the reverberation pool; placing a known standard sound source at a position having a distance with a pool wall greater than a minimal analysis frequency wavelength in the pool; placing hydrophones in a whole space in the pool, wherein the maximal distance is greater than a minimal half-wavelength, and line array placement and single placement via a bracket are adopted during the placement; causing the known standard sound source to emit a steady state broadband signal, and measuring a frequency domain soundfield correction amount of the reverberation pool; replacing the standard sound source with a transient sound source to be measured for emission, and collecting time domain sound pressure data; performing power spectrum calculation on the time domain data of all array elements to obtain a sound power level (the formula is described in the specification), and performing space average processing toobtain a spatial average sound power level (LW); and performing self-correlation processing on the time domain data fn(t) of all array elements. The invention provides a pool measurement method of transient sound characteristics, which is suitable for the quantitative acoustic evaluation of transient sound, and the method has the advantages of relatively good stability, easy implementation of measurement conditions, high measurement efficiency, etc.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method to select an undersampling scheme for magnetic resonance imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging method and system using such a selected undersampling scheme
ActiveUS9297873B2Reduce image noiseReduce measurementMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setResonance
In a method to select an undersampling scheme of k-space and an associated set of reconstruction kernels to acquire reduced magnetic resonance (MR) data sets with multiple coils, a calibration data set is acquired for each of the respective coils, a noise covariance is determined from autocorrelations and correlations of the noise of the various coils. At least one set of reconstruction kernels is calculated for each of the multiple undersampling schemes from the calibration data sets of the various coils. For each set of reconstruction kernels, a characteristic value is calculated from the noise covariance and the respective reconstruction kernels of the coils, with the characteristic value being proportional to a spatial mean value of a signal noise of an MR image. A selected undersampling scheme and a selected set of reconstruction kernels are selected based on the calculated characteristic values.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Optoelectronic measuring device
ActiveCN106646501AHigh measuring radiation powerReceivable measurement radiated powerOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansSpatial averageOptical measurements
An optoelectronic measuring device (1) for distance and / or position determination comprising radiation sources (35, 40, 75, 310) for generating optical measurement radiation (30, 36) of a first wavelength, wherein the measurement radiation (30, 36) is emitted in an oriented manner into free space. The radiation sources (35, 40, 75, 310) are designed such that the first wavelength is in the range between 1210 nm and 1400 nm and the power of the emitted measurement radiation (30, 36) is at least 14 mW in the chronological and spatial average.
Owner:HEXAGON TECH CENT GMBH
Detection and ranging device and detection and ranging method
InactiveUS7782249B2Beacon systems using radio wavesMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesSpatial averageLU decomposition
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
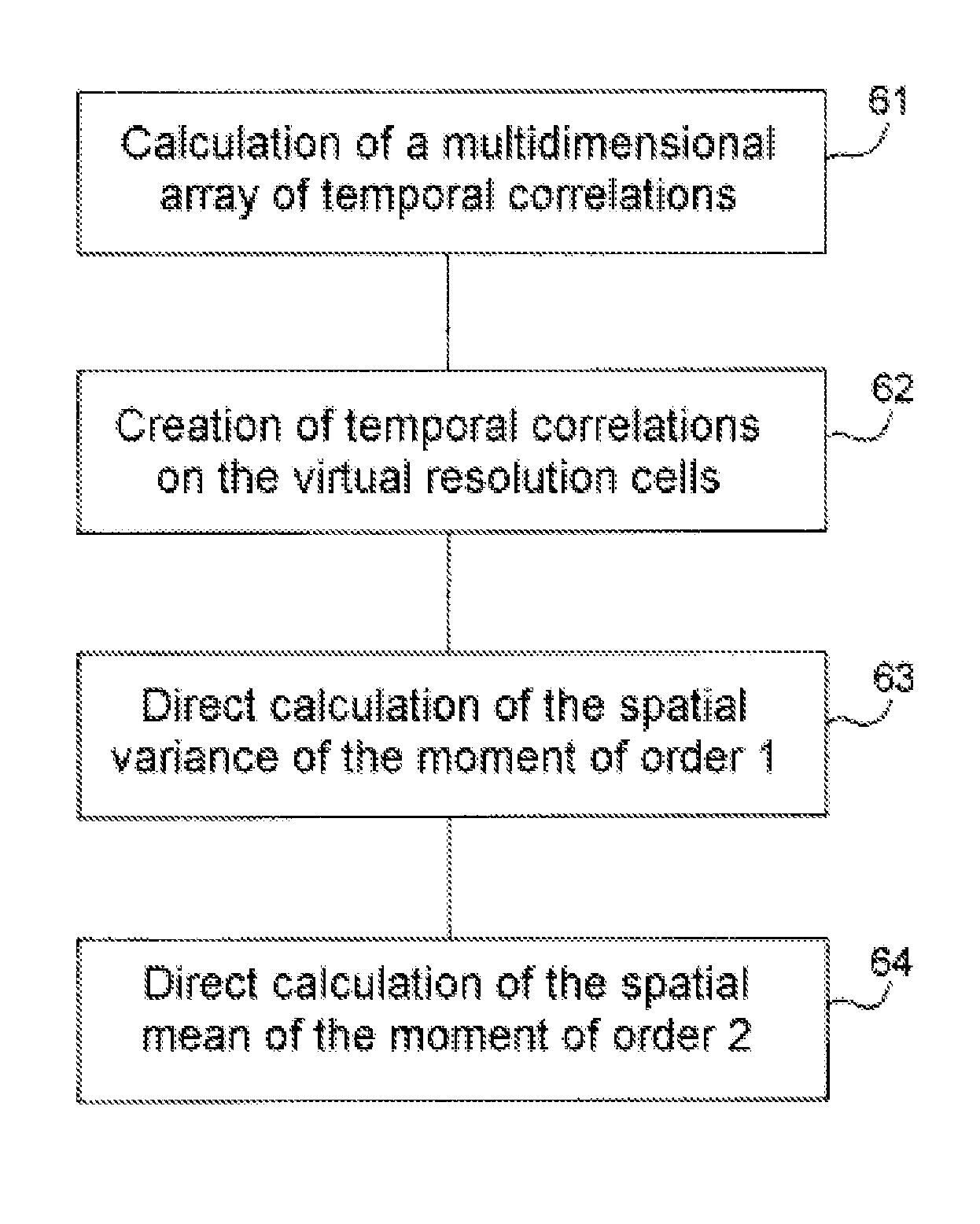
Method for characterizing an atmospheric turbulence using representative parameters measured by radar
The present invention relates to a method for characterizing an atmospheric turbulence by representative parameters measured by a radar. The emission beam of the radar carried by an aircraft scanning the zone of the turbulence, a measured parameter being the total variance of the velocity of the turbulence σU, this total variance at a point x0 inside the turbulence is the sum of the spatial variance of the spectral moment of order 1 of the signals received by the radar Var[M1({right arrow over (x)})] and of the spatial mean of the spectral moment of order 2 of the signals received Mean[M2({right arrow over (x)})], the moments being distributed as a vector {right arrow over (x)} sweeping an atmospheric domain around the point x0. The invention applies notably in respect of meteorological radars fitted to aircraft such as airliners for example.
Owner:THALES SA
Heat flux density improved method for safety tongs of explosion-proof elevator
ActiveCN102426632AAccurate and reliable measurement resultsSpecial data processing applicationsHeat fluxNumerical models
The invention relates to the design technology of safety tongs of an explosion-proof elevator, and in particular relates to a heat flux density improved method for safety tongs of the explosion-proof elevator. In the method, time average effect is taken out, and the spatial average effect still exists at the same time so as to obtain a conservative temperature rise evaluation; analysis is performed from the point of view of contact mechanics, a complete finite element numerical model is established for stopping the safety tongs, the lift car mass is equivalent to the safety tongs block body material with extra-high density, the working pressure and initial stopping speed same as the actual working condition are applied, finite element simulation is carried out aiming at the stopping process of the safety tongs, the influences from the friction coefficient, stopping working pressure, initial stopping speed, safety tongs block material and plastic deformation of safety tongs blocks in the stopping process on the maximum stopping temperature rise can be researched by simulation analysis, the above research result is verified through a drop stopping test and is compared with a simulation result so as to ensure the measurement result to be more accurate and credible.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & TECHN RES +1
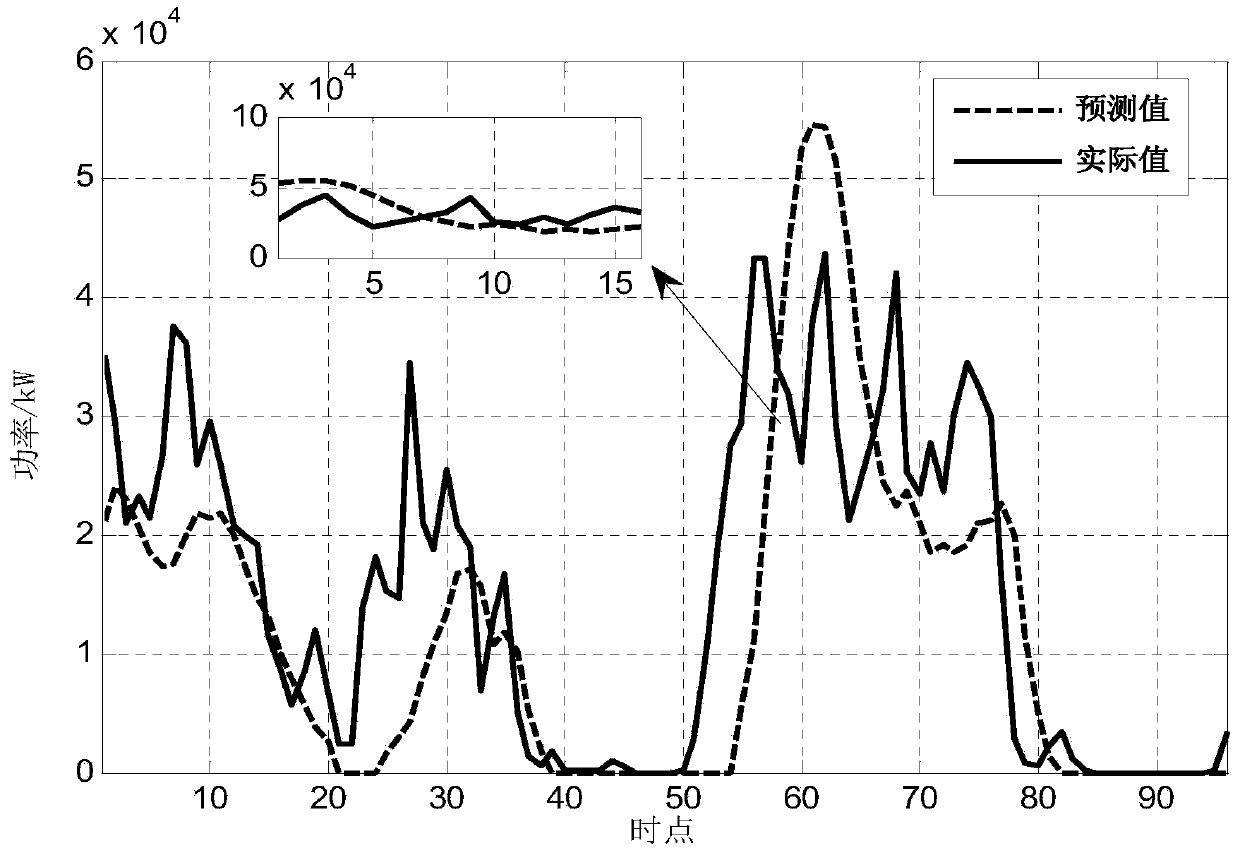
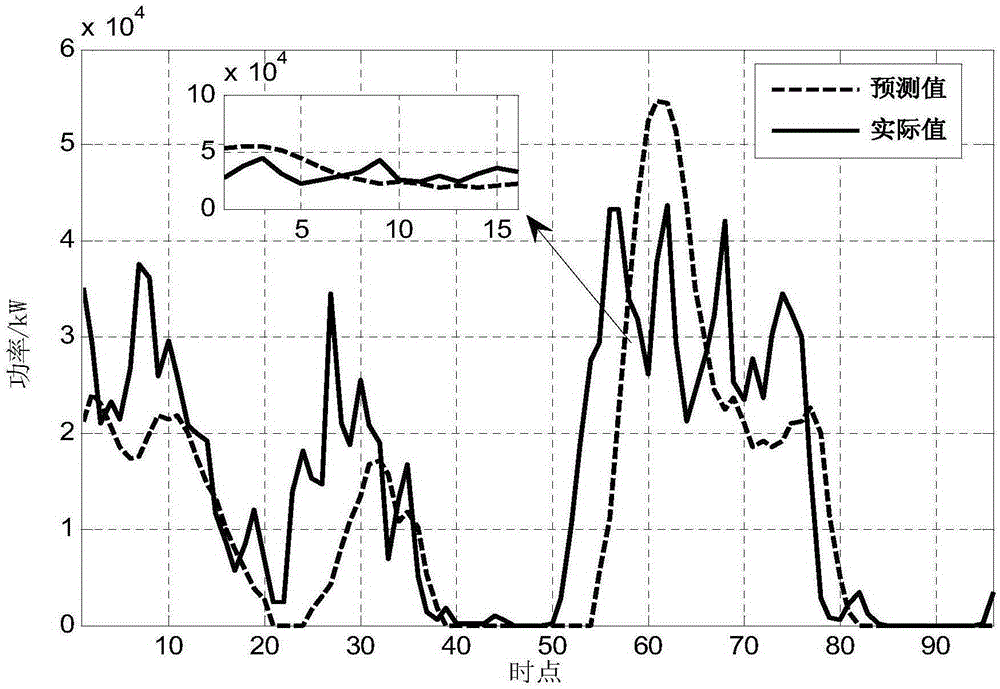
Wind power real-time prediction calculation method base on spatial average wind speed
ActiveCN104201712AMethod scienceReasonable methodClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPeaking power plantSpatial average
The invention discloses a wind power real-time prediction calculation method based on spatial average wind speed. The wind power real-time prediction calculation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: data acquisition and preprocessing: acquiring the practical wind speed value of a wind power plant needing to be predicted in one continuous hour, and eliminating poor data; data analysis and prediction: analyzing the practical wind speed data of each wind power unit of in wind power plant in an actual measurement power-on state to obtain the practical average wind speed data of the whole plant, calculating the prediction value of wind speed of the whole wind power plant in the future 4 hours through a linear regression method, and calculating the prediction value of the power of the whole wind power plant by using a wind power plant power curve; simulating calculation: inputting a simulating input quantity, and predicting the wind power in the future 4 hours; error analysis: calculating the accuracy of the calculation method according to an error evaluation standard Interim Procedures for Wind Power Plant Power Predicating and Forecasting Management issued by the National Energy Administration of the People's Republic of China in 2011. The wind power real-time prediction calculation method is scientific, reasonable and practical, and has the advantage of higher accuracy, meeting of online application requirements, and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
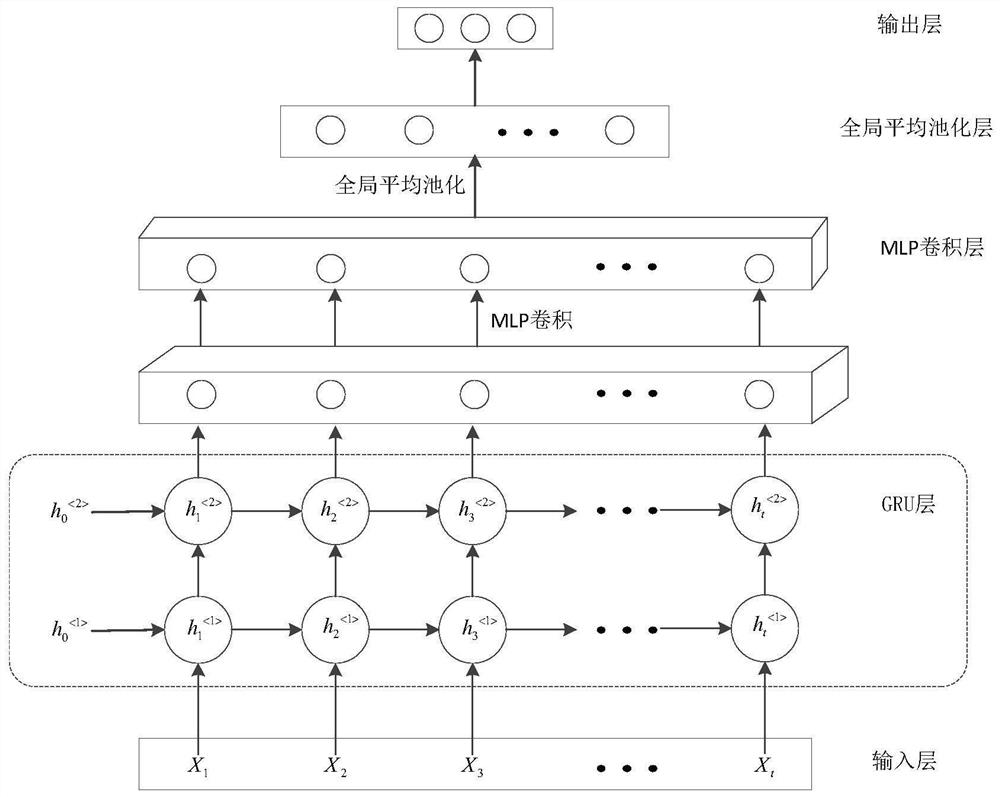
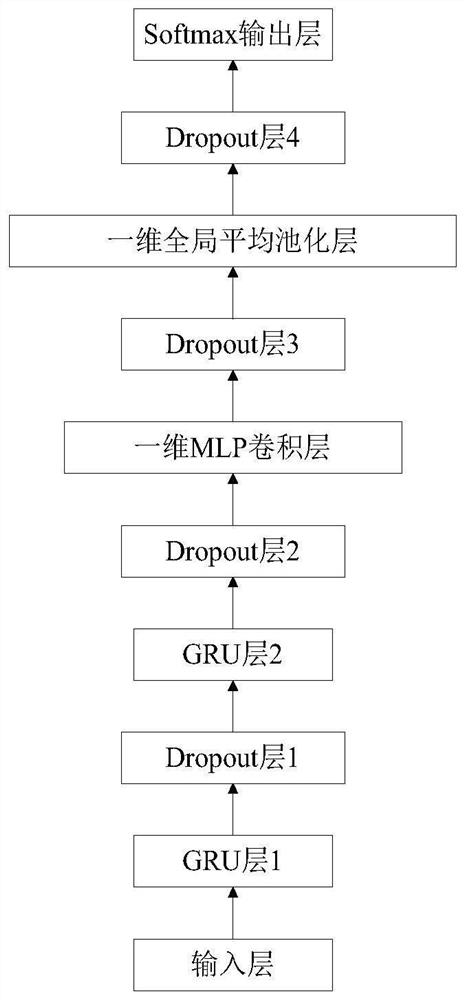
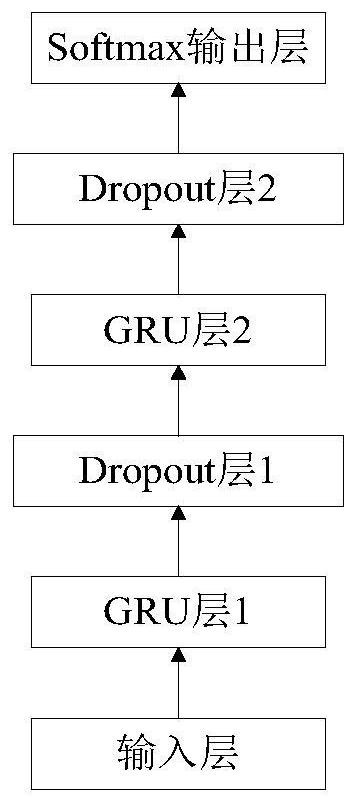
GRU-NIN model-based underwater acoustic target identification method
ActiveCN113221758AImprove the correct recognition rateEnhanced Nonlinear Fitting CapabilitiesCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature extractionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a GRU-NIN model-based underwater acoustic target identification method, which is based on a multilayer stacked GRU structure, takes implicit states output by all GRUs on the top layer of the multilayer stacked GRU structure as a multi-channel feature map input in MLP convolution operation, and through a layer of 1 * 1 convolution micro-network. integration of multi-channel feature maps obtained by different filters is realized, so that the network learns complex cross-feature map features, and GRU implicit state dimensions are compressed at the same time; the global average pooling layer is connected behind the MLP convolution layer, the spatial average of the feature map after the MLP convolution is calculated, and then the output is fed into the Softmax layer to enhance the corresponding relation between the feature map and the category. Under the framework, the model can realize feature extraction and classification recognition tasks of underwater acoustic target recognition. Experimental results show that the model has better classification and recognition performance than a multi-layer stacked GRU model.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
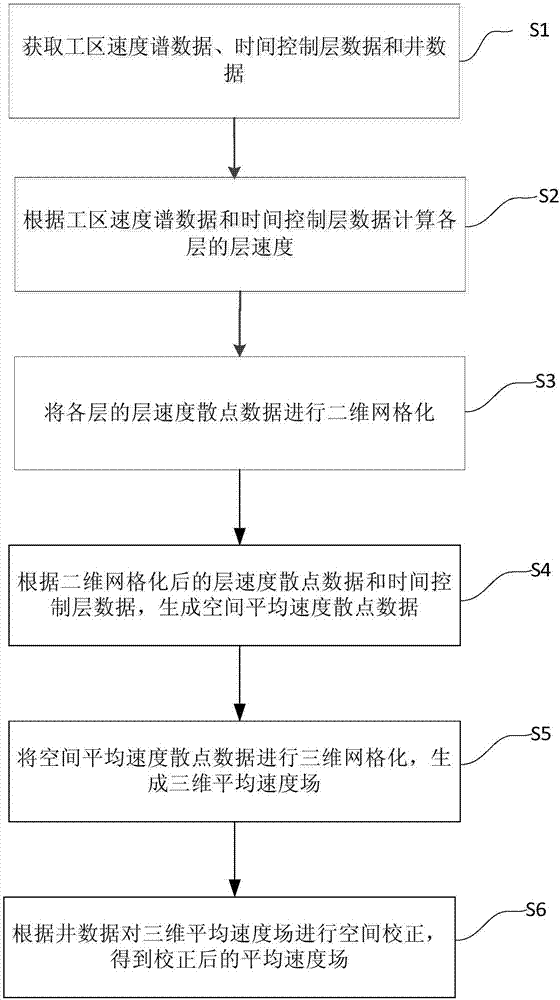
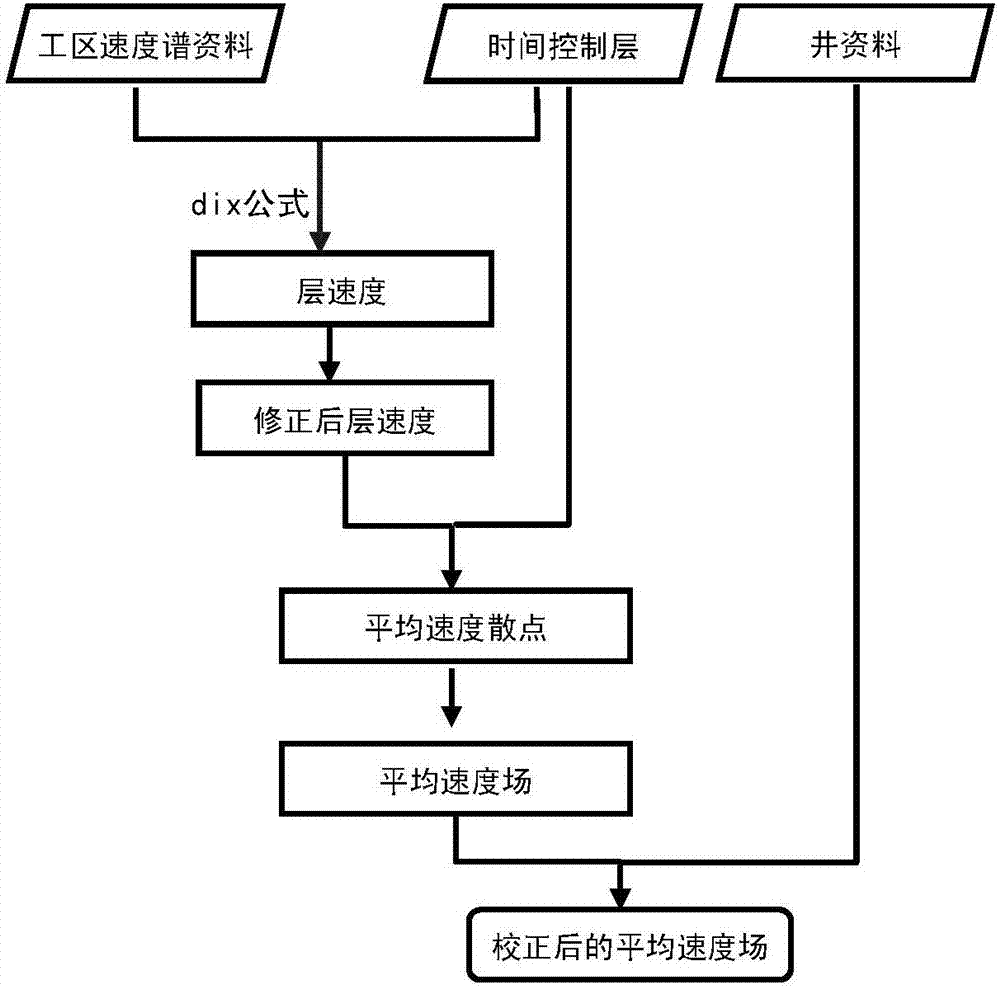
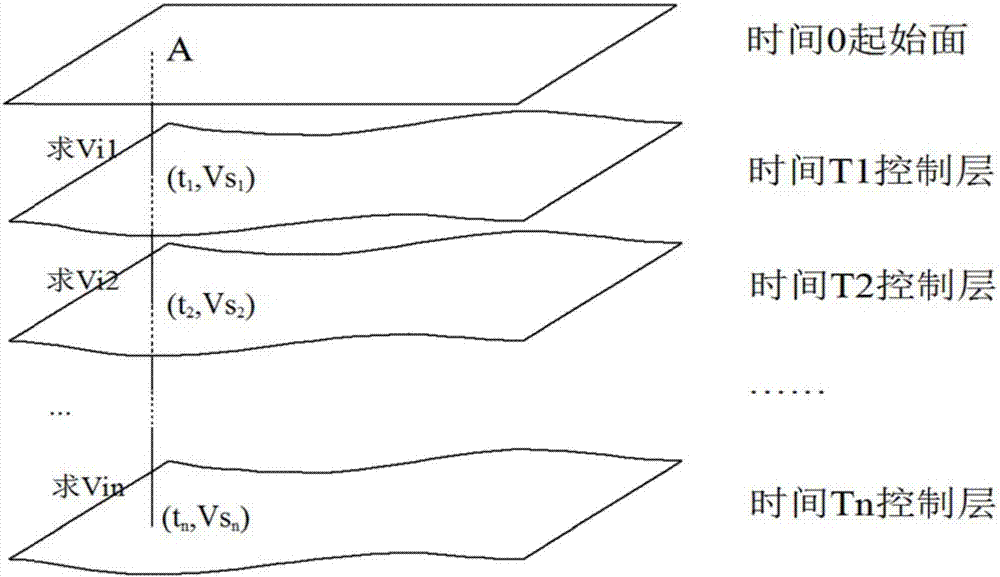
Layer speed calculating and average speed field establishing method based on position control
InactiveCN106873035AIn-depth information is reasonableImprove reliabilitySeismic signal processingSpatial averageTime control
The invention provides a layer speed calculating and average speed field establishing method based on position control. The method comprises that work-area speed spectrum data, time control layer data and well data are obtained; speeds of different layers are calculated according to the work-area speed spectrum data and the time control layer data; 2D gridding is carried out on scatter data of the speeds of the different layers; according to the scatter data of the layer speeds after 2D gridding and the time control layer data, spatial average speed scatter data is generated; 3D gridding is carried out on the spatial average speed scatter data, and a 3D average speed field is generated; and space correction is carried out on the 3D average speed field according to the well data, and a corrected average speed field is obtained. The generated average speed field is more reasonable than depth data, and approaches an expected object more.
Owner:北京金双狐油气技术有限公司
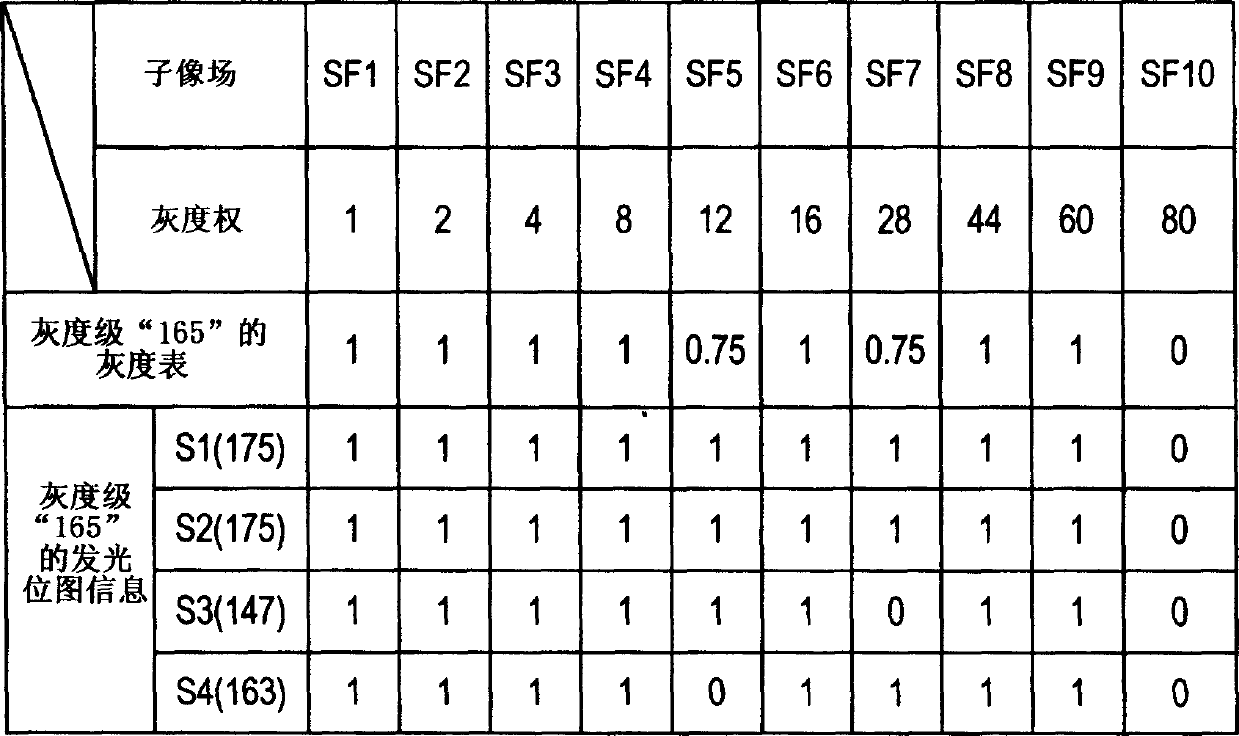
Image display method and image display apparatus
InactiveCN1717712ATelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesSpatial averageBrightness perception
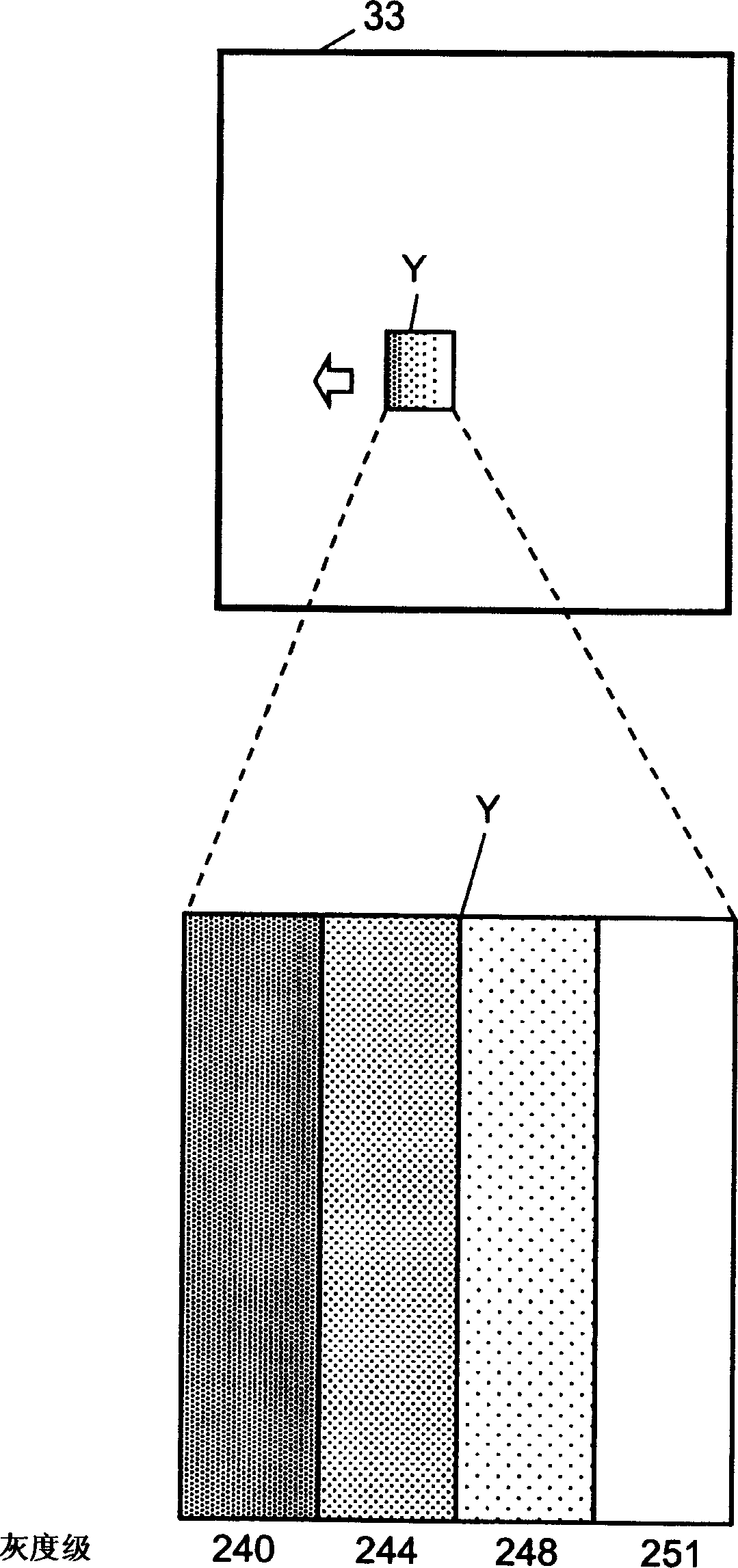
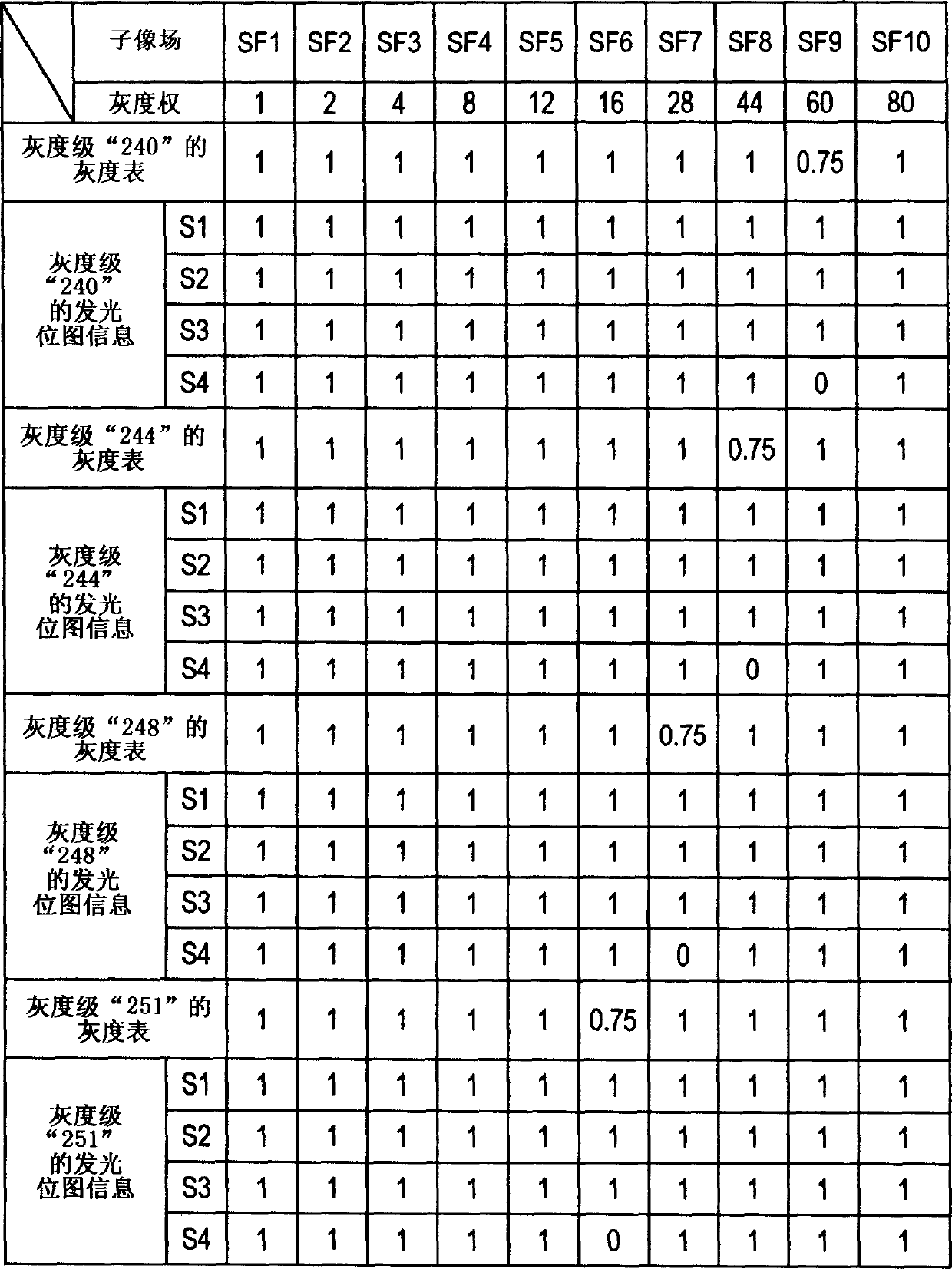
An image display method wherein a lighting pattern information generator circuit (17) in an image display apparatus (1), which divides one field into a plurality of subfields and combines lightings or non-lightings of the subfields so as to display gradations, is used to generate a plurality of lighting pattern information in which the average lighting rate of all of subfields, which have smaller brightness weights than subfields having a average lighting rate that is not zero and having the maximum brightness weight, is greater than a predetermined value, and wherein a dither generator circuit (19) is used to subject the plurality of lighting pattern information to a time average processing and a spatial average processing to display all the gradations and reduce the moving-image pseudo-contours.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
A method for real-time forecasting and calculation of wind power based on spatially averaged wind speed
ActiveCN104201712BMethod scienceReasonable methodClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsSpatial averageData acquisition
The invention discloses a wind power real-time prediction calculation method based on spatial average wind speed. The wind power real-time prediction calculation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: data acquisition and preprocessing: acquiring the practical wind speed value of a wind power plant needing to be predicted in one continuous hour, and eliminating poor data; data analysis and prediction: analyzing the practical wind speed data of each wind power unit of in wind power plant in an actual measurement power-on state to obtain the practical average wind speed data of the whole plant, calculating the prediction value of wind speed of the whole wind power plant in the future 4 hours through a linear regression method, and calculating the prediction value of the power of the whole wind power plant by using a wind power plant power curve; simulating calculation: inputting a simulating input quantity, and predicting the wind power in the future 4 hours; error analysis: calculating the accuracy of the calculation method according to an error evaluation standard Interim Procedures for Wind Power Plant Power Predicating and Forecasting Management issued by the National Energy Administration of the People's Republic of China in 2011. The wind power real-time prediction calculation method is scientific, reasonable and practical, and has the advantage of higher accuracy, meeting of online application requirements, and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Liquid crystal display device and method for driving liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20110169880A1Improve display qualityTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displaySpatial average
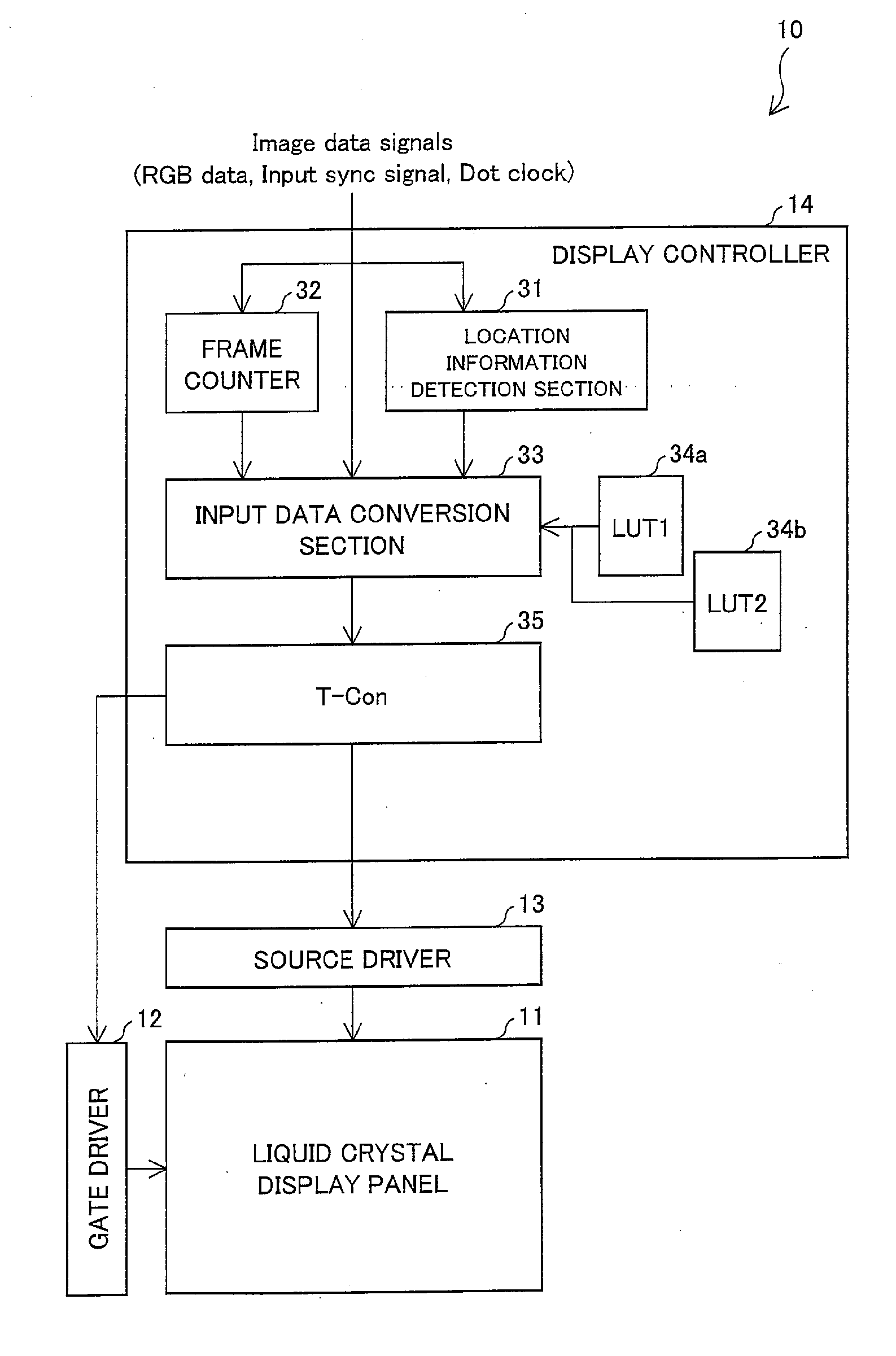
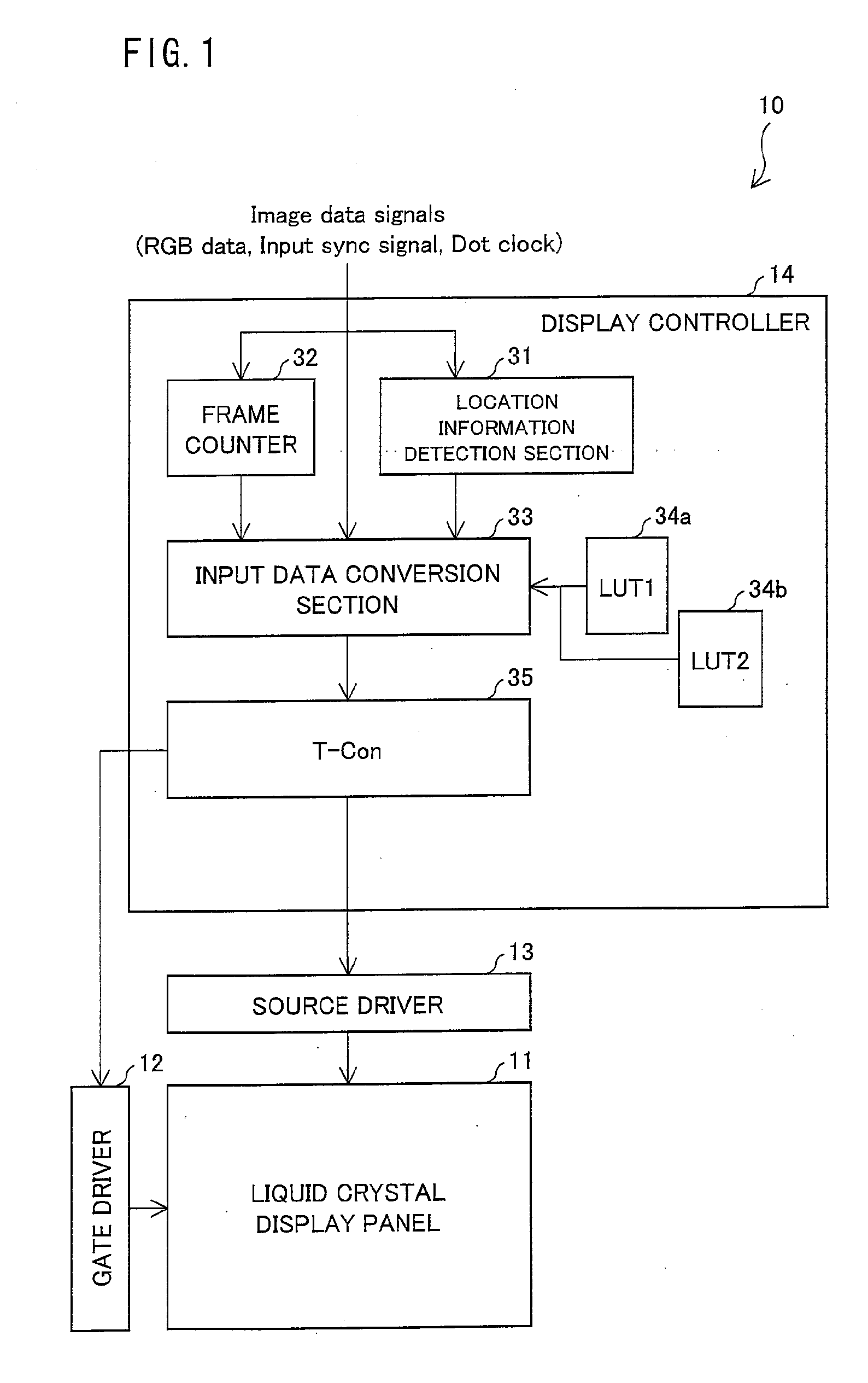
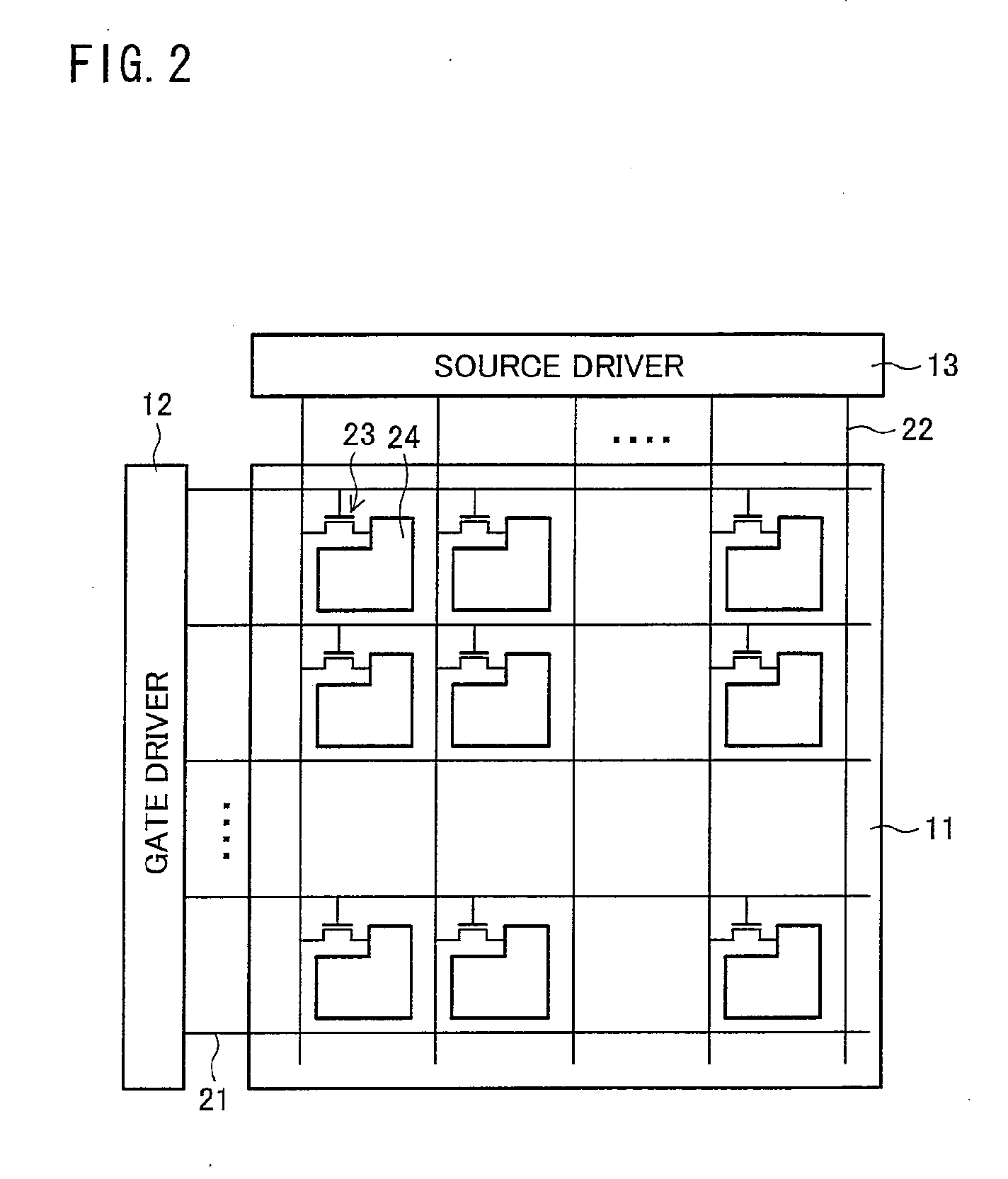
A liquid crystal display device (10) in accordance with the present invention includes a display controller (14) (display drive section) for (i) dividing dots into a plurality of units each of which includes a predetermined number of dots and (ii) supplying pieces of gray scale data, into which a piece of input gray scale data is converted and which differ from location to location, to the respective dots in each of the plurality of units. The display controller (14) carries out the conversion so that a spatial average of the pieces of the gray scale data supplied to the respective dots in each of the plurality of units causes a gray scale display based on the piece of the input gray scale data. The display controller (14) includes a location information detection section (31), an input data conversion section (33) (gray scale data conversion section), and the like.
Owner:SHARP KK
A Human Behavior Recognition Method Based on Depth Video Sequence
ActiveCN104298974BEnhance expressive abilityAvoid interferenceCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyHuman behavior
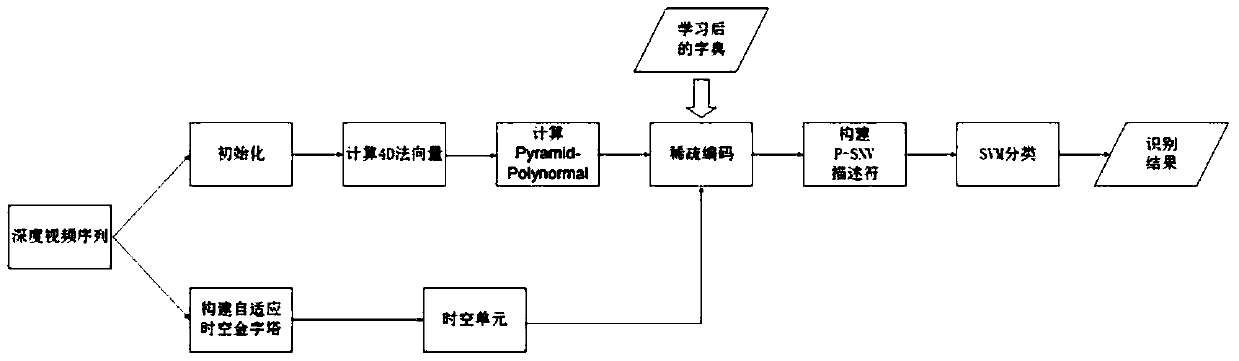
The invention discloses a human behavior recognition method based on a depth video sequence. The method calculates the four-dimensional normal vectors of all pixels in the video sequence, and extracts pixels in different layers by constructing a time-space pyramid model of the behavior sequence in different time-space domains. Based on the low-level features, the group sparse dictionary is learned based on the low-level features, and the sparse coding of the low-level features is obtained. The spatial average pooling and temporal maximum pooling are used to integrate the coding, so as to obtain high-level features as the descriptor of the final behavior sequence. This kind of descriptor can effectively preserve the spatiotemporal multi-resolution information of human behavior, and at the same time, by eliminating the similar content contained in different behavior categories, a sparse dictionary with stronger expressive power can be obtained to effectively improve the behavior recognition rate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for identifying stochastic information of heterogeneous materials
A method for identifying stochastic information of a heterogeneous material utilizes physical loading measurements that are input into a global optimization process. The optimization process executes, in parallel, a force-driven non-linear finite element simulation and a displacement-driven finite element simulation of a constitutive model of the heterogeneous material. The constitutive models model the spatially varying random material properties (i.e. stochastic properties) using the Karhunen-Loeve expansion, thereby introducing the stochastic parameters, including spatial mean, spatial variance, and correlation length for example into the models. Stress and strain values for both the force-driven and displacement driven finite element analyzes are input into an objective function, whereupon the finite element simulations are updated after each iteration of the optimization process is performed until the objective function is minimized to a desired level. This results in the identification of optimized stochastic parameters associated with the heterogeneous material under investigation.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
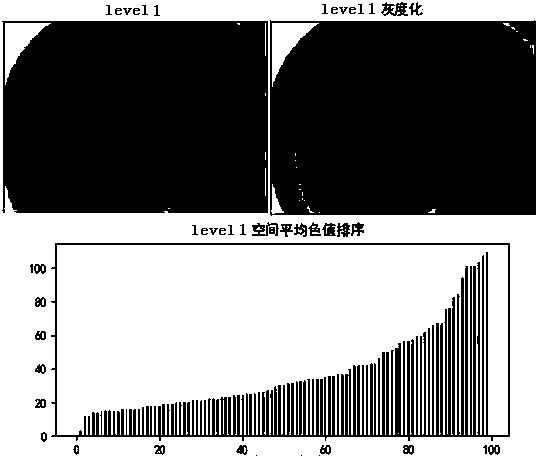
Method for automatically scoring excrement picture before colonoscopy detection
ActiveCN110070138AAccurate scoreFacilitate unified assessmentCharacter and pattern recognitionNegationSpatial average
The invention discloses a method for automatically scoring an excrement picture before colonoscopy detection. The method includes: carrying out gray scale conversion on the standard excrement pictureand the excrement picture to be scored; carrying out sub-region division on the converted gray-scale picture; calculating the spatial average color value of each sub-region and negation; inverting thespatial average color value of each sub-region and storing the inverted spatial average color value in a matrix at a corresponding position; converting the matrix into vectors; drawing a corresponding spatial average color value histogram according to the vector; fitting operation on histograms, obtaining a fitting function and a corresponding fitting vector; calculating the minimum value of thedistance between the fitting vector of the to-be-scored excrement picture and the fitting vector of the standard excrement picture, obtaining the score of the standard excrement picture correspondingto the minimum value of the distance, scoring the to-be-scored excrement picture according to the standard excrement picture. The beneficial effects of being accurate in scoring and facilitating unified evaluation are achieved.
Owner:河南省萱闱数字医疗科技有限公司
Method for computing safety tongs model node temperature using improved Heat flux density method for safety tongs of explosion-proof elevator
InactiveCN102426632BAccurate and reliable measurement resultsSpecial data processing applicationsHeat fluxNumerical models
The invention relates to the design technology of safety tongs of an explosion-proof elevator, and in particular relates to a heat flux density improved method for safety tongs of the explosion-proof elevator. In the method, time average effect is taken out, and the spatial average effect still exists at the same time so as to obtain a conservative temperature rise evaluation; analysis is performed from the point of view of contact mechanics, a complete finite element numerical model is established for stopping the safety tongs, the lift car mass is equivalent to the safety tongs block body material with extra-high density, the working pressure and initial stopping speed same as the actual working condition are applied, finite element simulation is carried out aiming at the stopping process of the safety tongs, the influences from the friction coefficient, stopping working pressure, initial stopping speed, safety tongs block material and plastic deformation of safety tongs blocks in the stopping process on the maximum stopping temperature rise can be researched by simulation analysis, the above research result is verified through a drop stopping test and is compared with a simulation result so as to ensure the measurement result to be more accurate and credible.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & TECHN RES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com