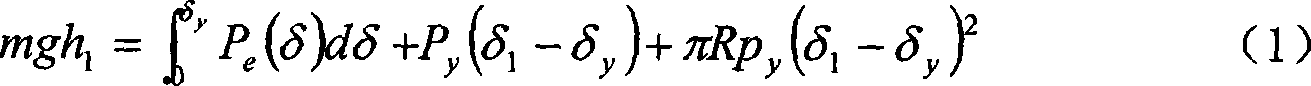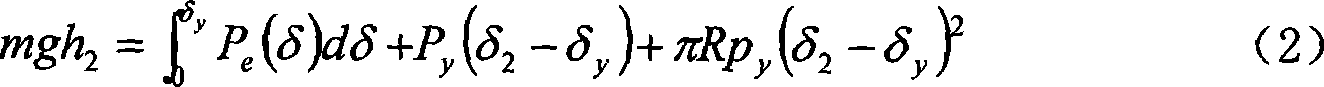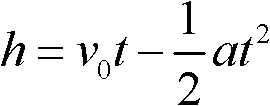Patents
Literature
52 results about "Contact mechanics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. A central distinction in contact mechanics is between stresses acting perpendicular to the contacting bodies' surfaces (known as the normal direction) and frictional stresses acting tangentially between the surfaces. This page focuses mainly on the normal direction, i.e. on frictionless contact mechanics. Frictional contact mechanics is discussed separately. Normal stresses are caused by applied forces and by the adhesion present on surfaces in close contact even if they are clean and dry.
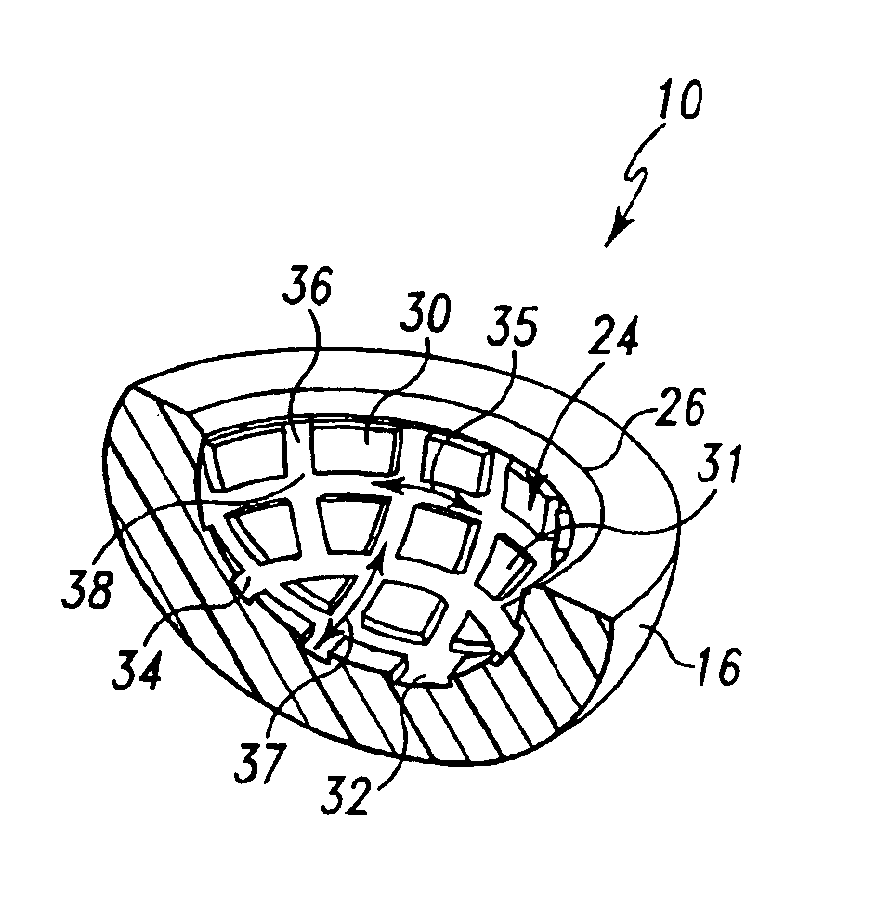
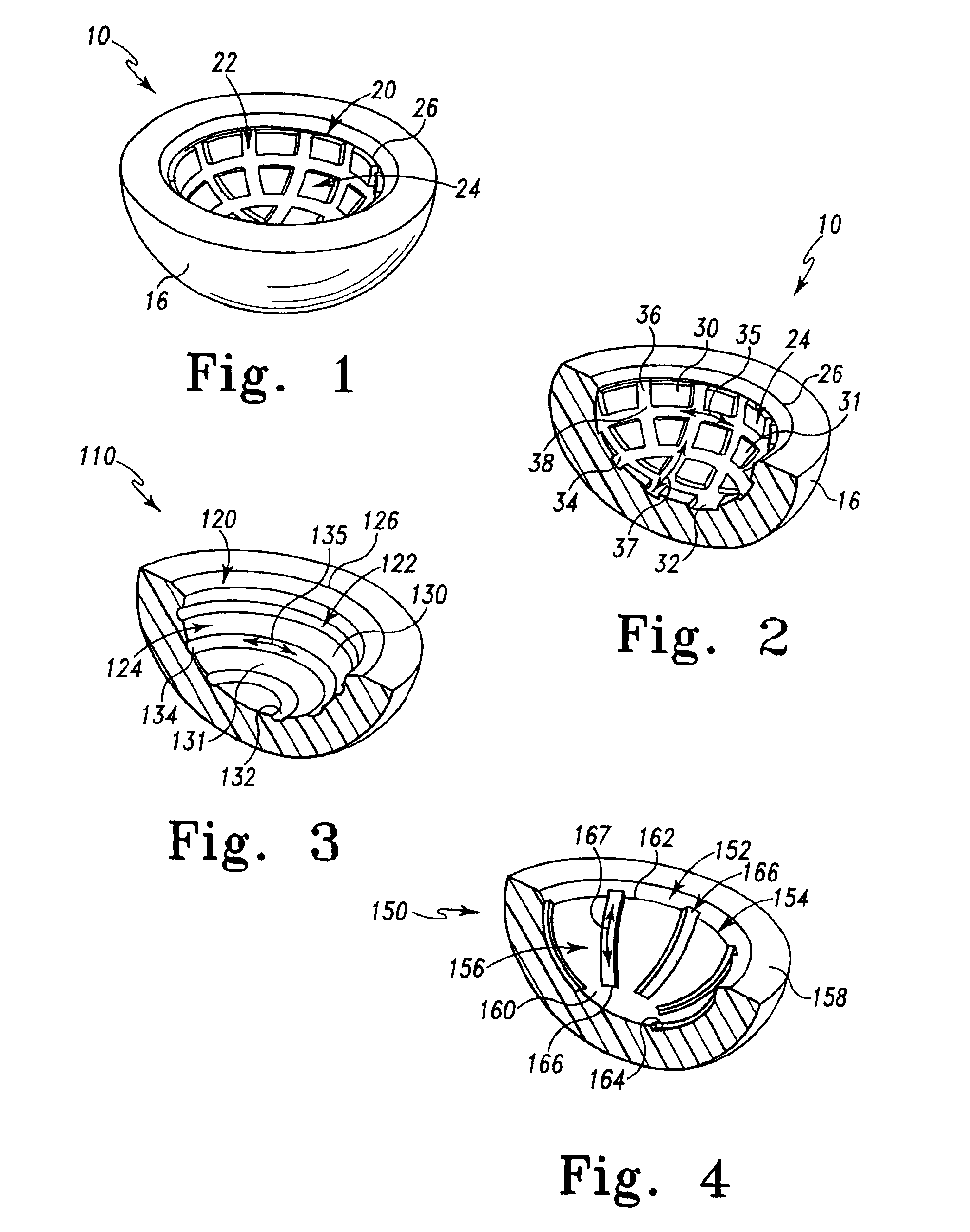
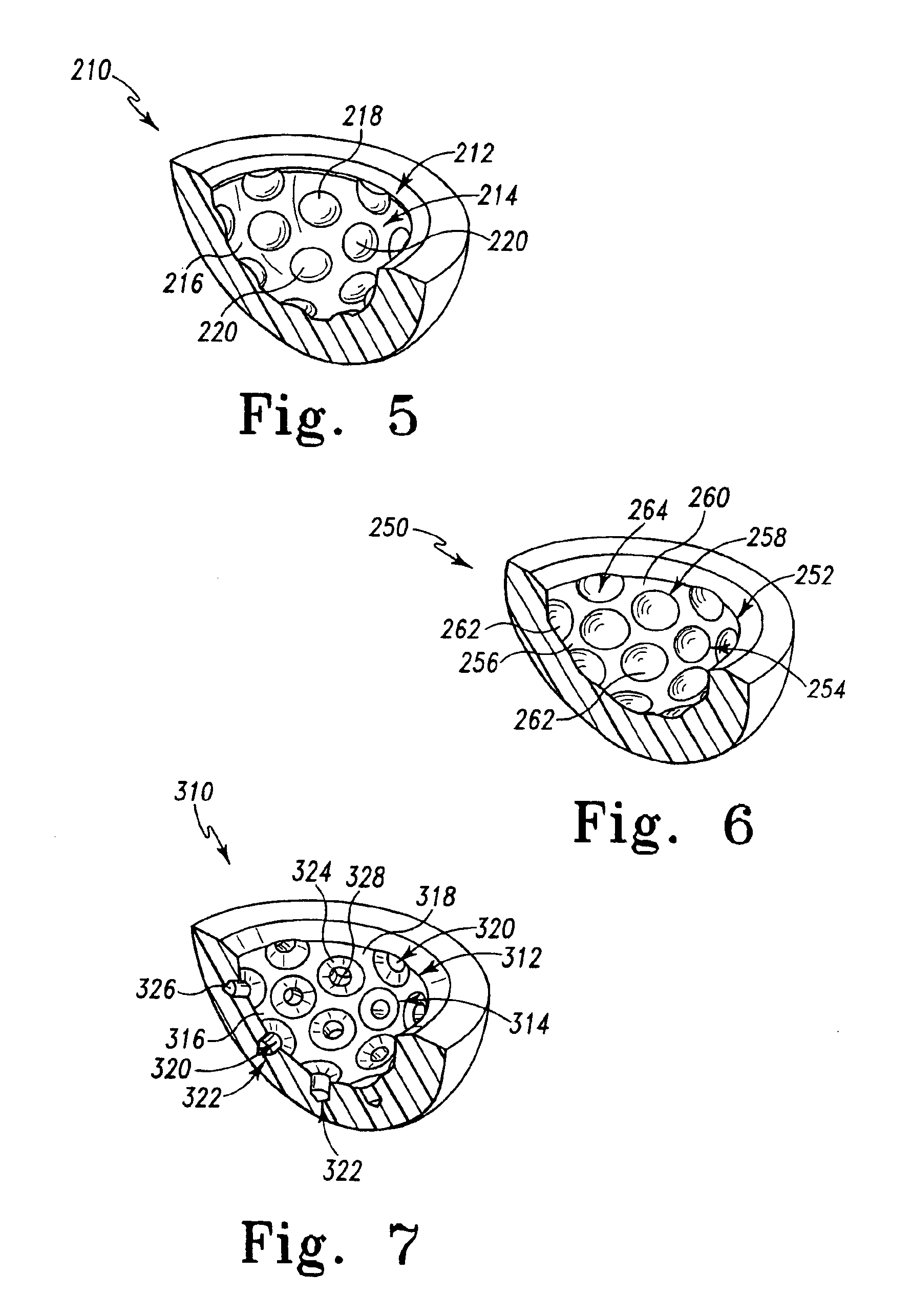
Prosthetic joints having reduced area bearing surfaces and application thereof to a range of sizes of prosthetic joints
InactiveUS6866685B2Reduce frictional torqueReduce wearWrist jointsAnkle jointsRange of motionProsthesis
A prosthetic component is configured to have intentional interruptions in an articulating face thereof. The intentional interruptions are configured to yield an optimum contact area or bearing surface, particularly with regard to low wear and greater lubricity through the application of lubrication and contact mechanics theory for the particular prosthetic component. Such optimization is applied to a wide range of prosthetic component sizes of the particular prosthetic component. The optimum range of percentage area of relief or interruptions, defined as a percentage of a baseline uninterrupted bearing surface area to be removed by the features of the interrupted bearing surface configuration is from 0.3% to 73.7% for hard-on-hard bearing components and from 5.7% to 83.2% for polyethylene-on-hard bearing components. The range for both hard-on-hard and polyethylene-on-hard implants translates to a relieved area ranging from 0.3% to 31.9% of the area of the entire articulating surface, depending on the size of the implant. For both hard-on-hard and polyethylene-on-hard bearing combinations, optimally decreasing the contact area or bearing surface by interruptions in the articulating surfaces will allow for the benefits of larger diameter prosthetic components with an increased range of motion and decreased potential for dislocation, and the low frictional torques and lower wear of smaller diameter components.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
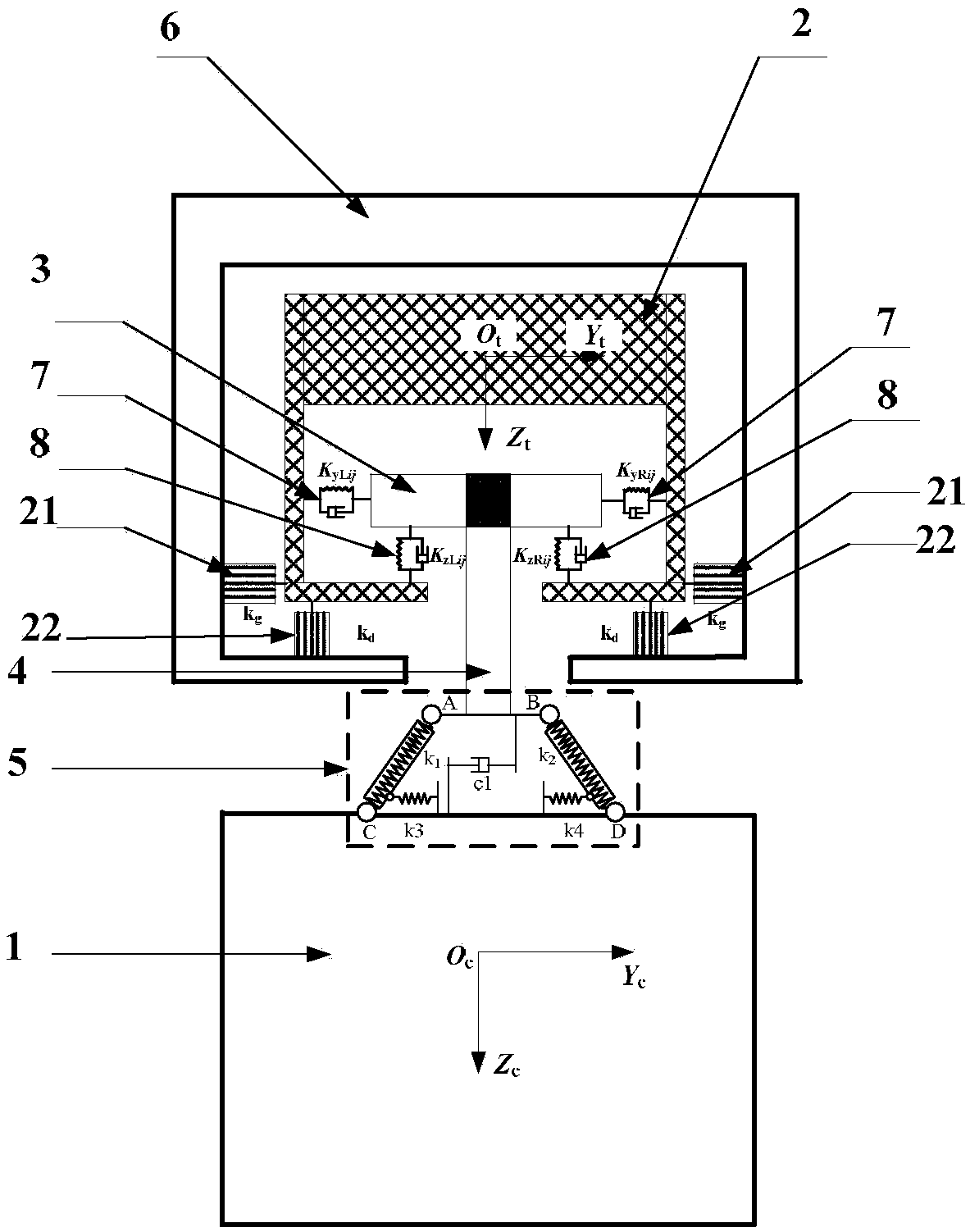
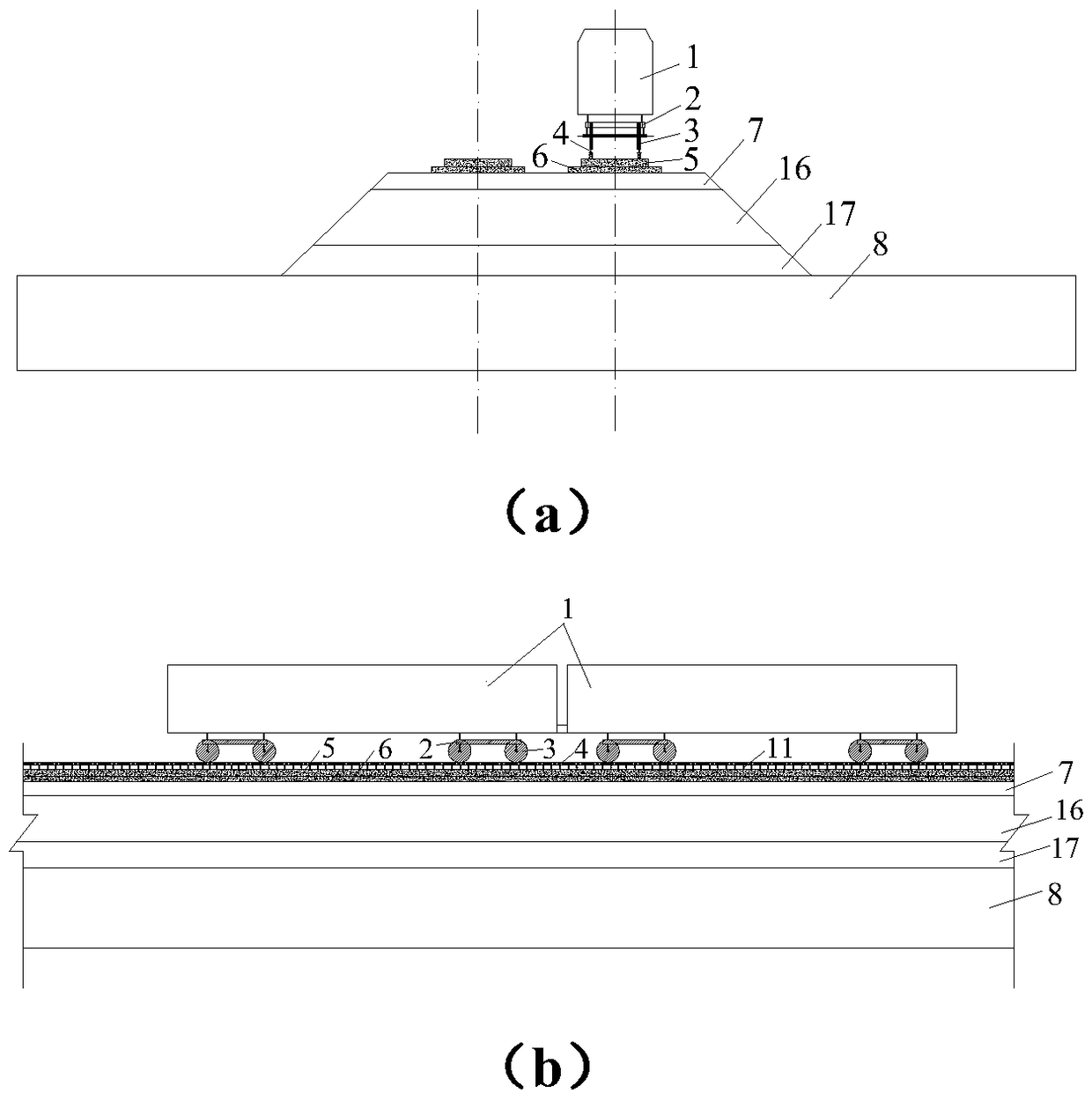
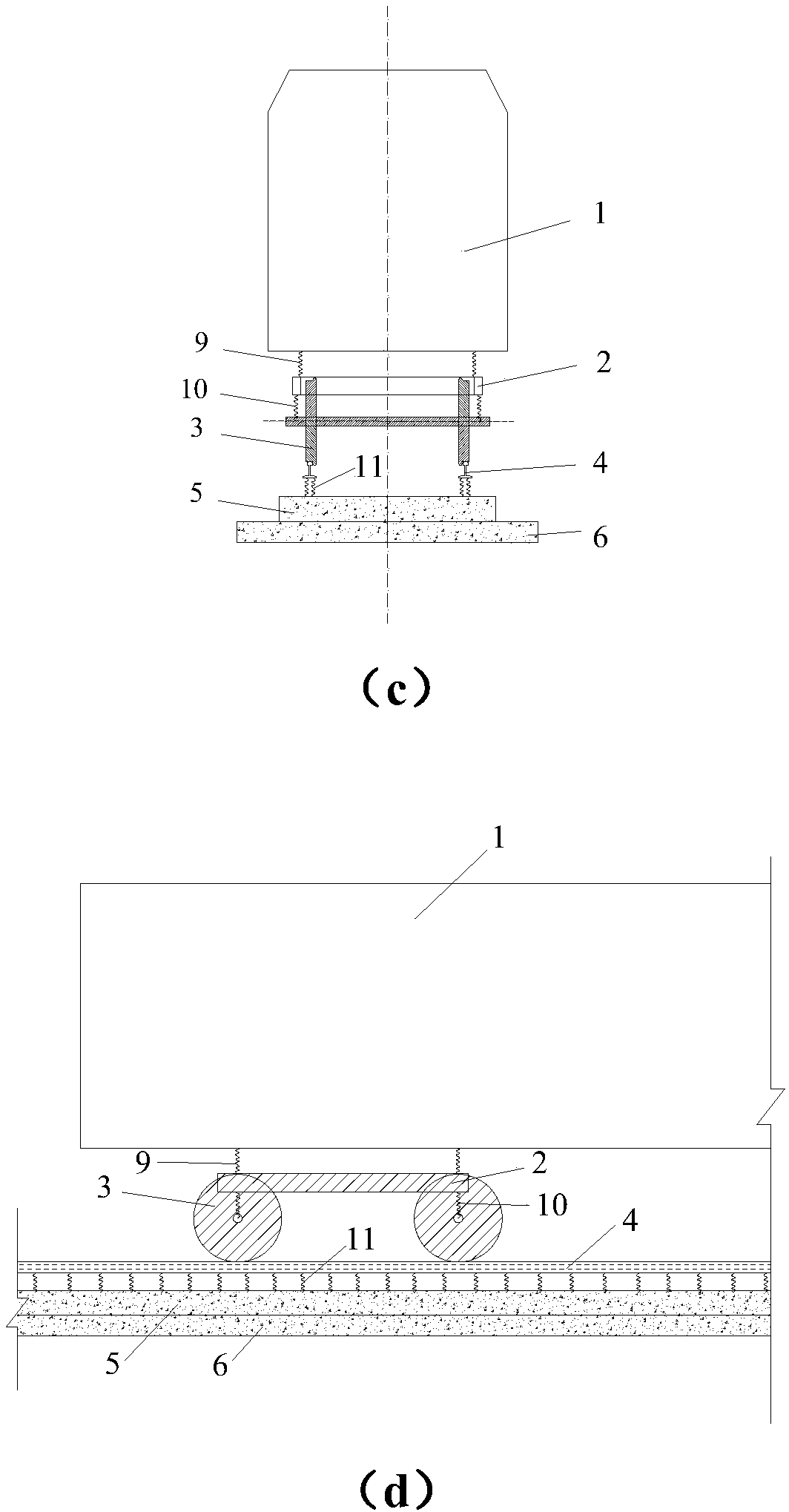
Suspension type monorail vehicle coupling dynamic simulation system and method
ActiveCN108256278ASolve decouplingReduce simulation errorSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationVehicle dynamicsDynamic models
The invention discloses a suspension type monorail vehicle dynamic model and a vehicle-bridge coupling power simulation method, belongs to the technical field of rail traffic and aims to solve the technical problem that an existing suspension type monorail dynamics simulation device is large in simulation result errors during rail beam local vibration research. By providing the suspension type monorail vehicle system dynamic model, a rubber wheel-rail surface contact mechanical model, a rail beam bottom plate and web equivalent surface force application method and a vehicle and rail beam coupling dynamic model building method, a suspension type monorail vehicle-rail beam coupling dynamic simulation system is built. By the model, the system and the method, suspension type monorail vehicle system suspension mechanism decoupling and equivalent treatment are achieved, and the technical problems that the existing suspension type monorail dynamics simulation device is large in simulation result errors during the rail beam local vibration research, rail beam dynamic stress and strain results are hard to extract, rail beam local strength destroying cannot be evaluated accurately and the like are solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
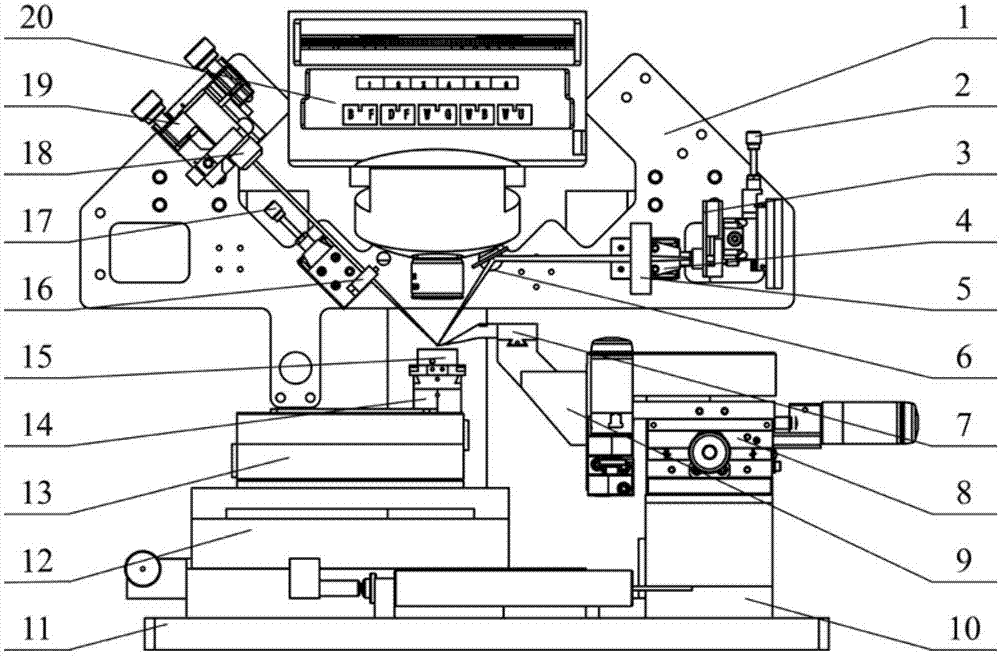
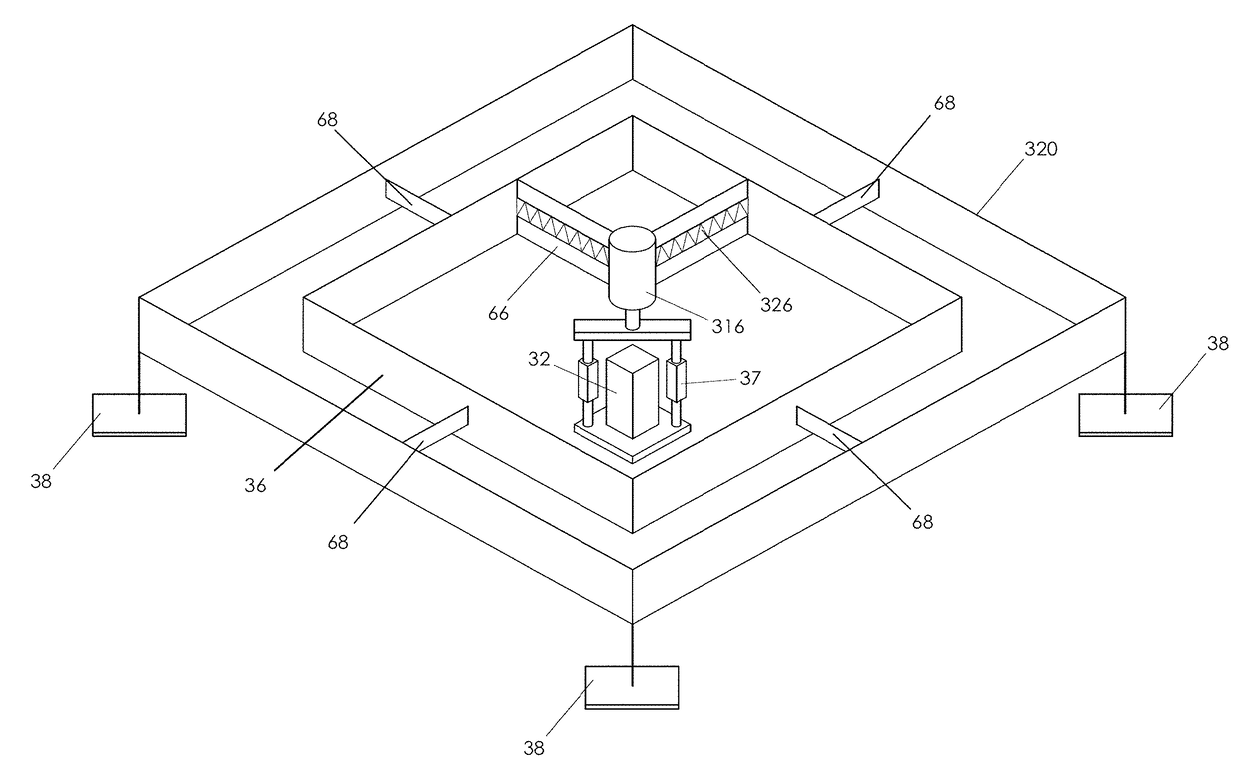
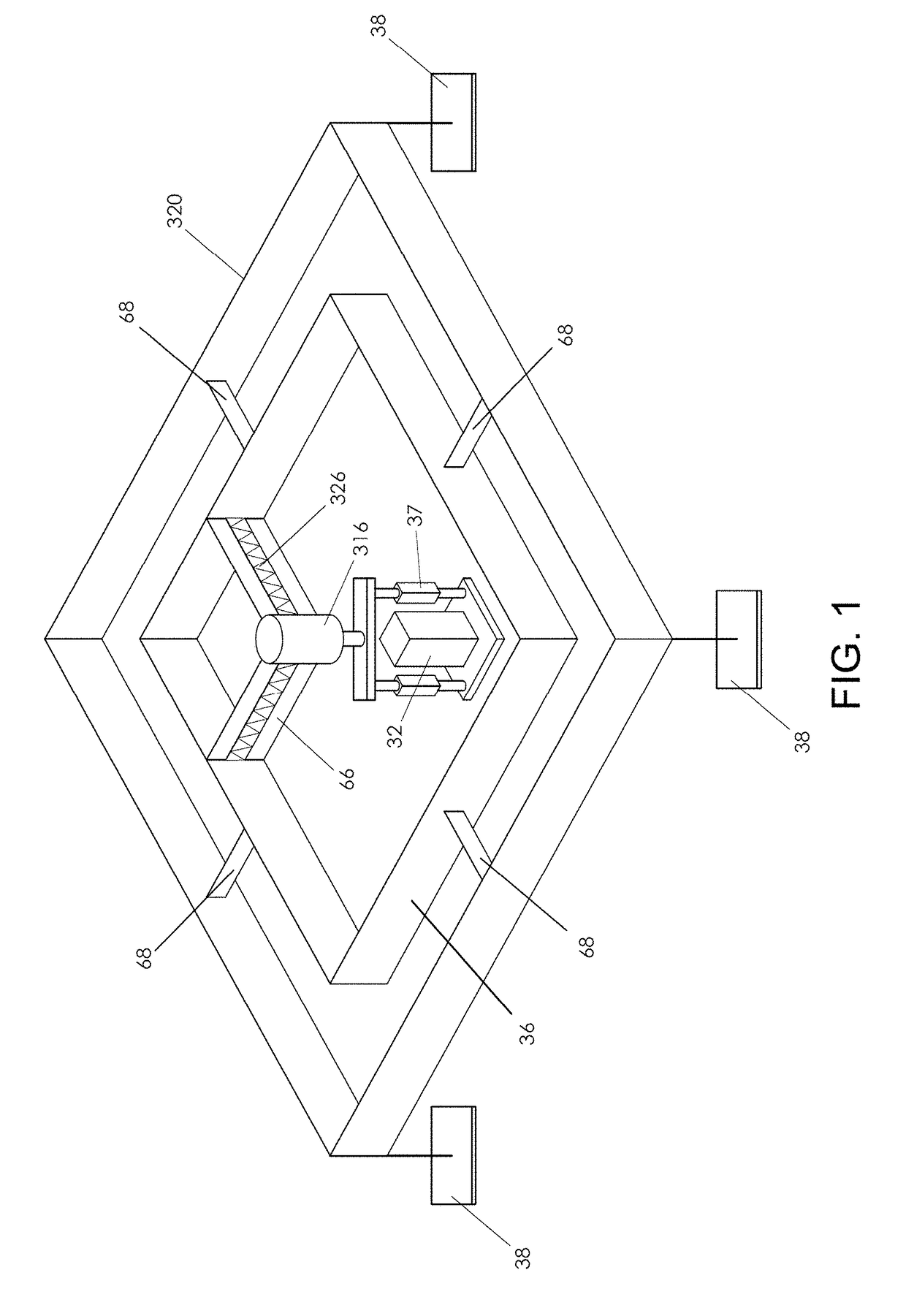
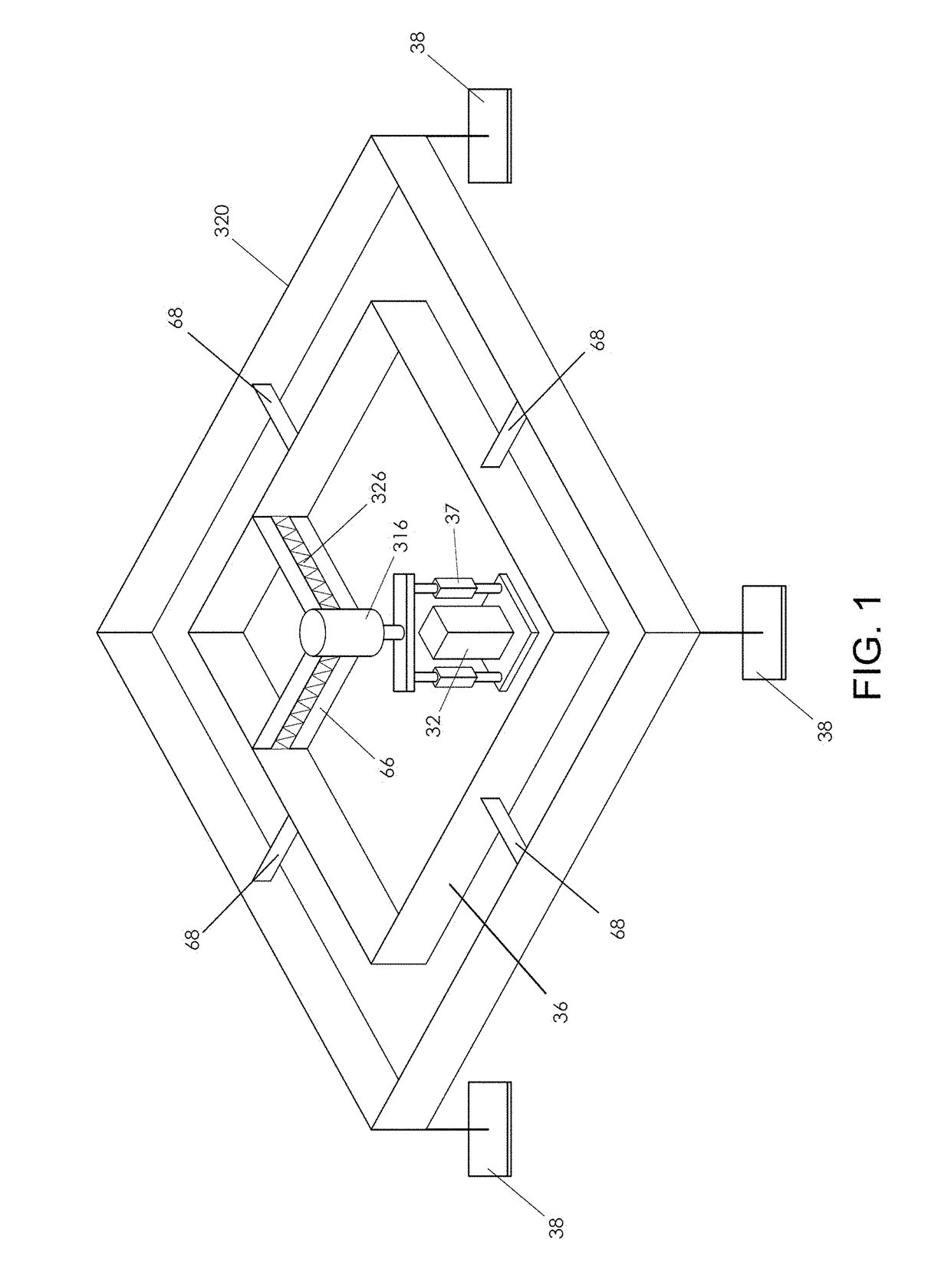
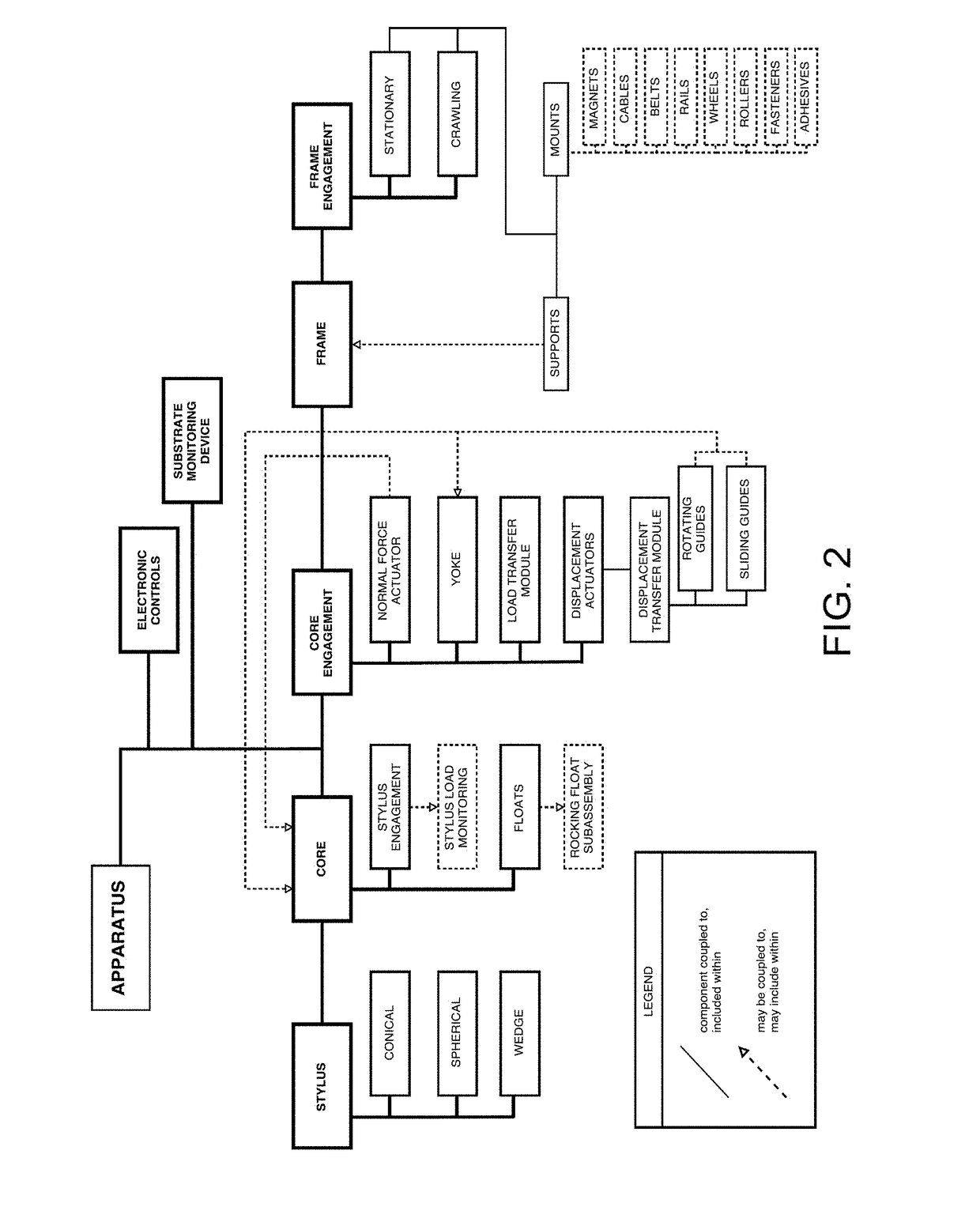
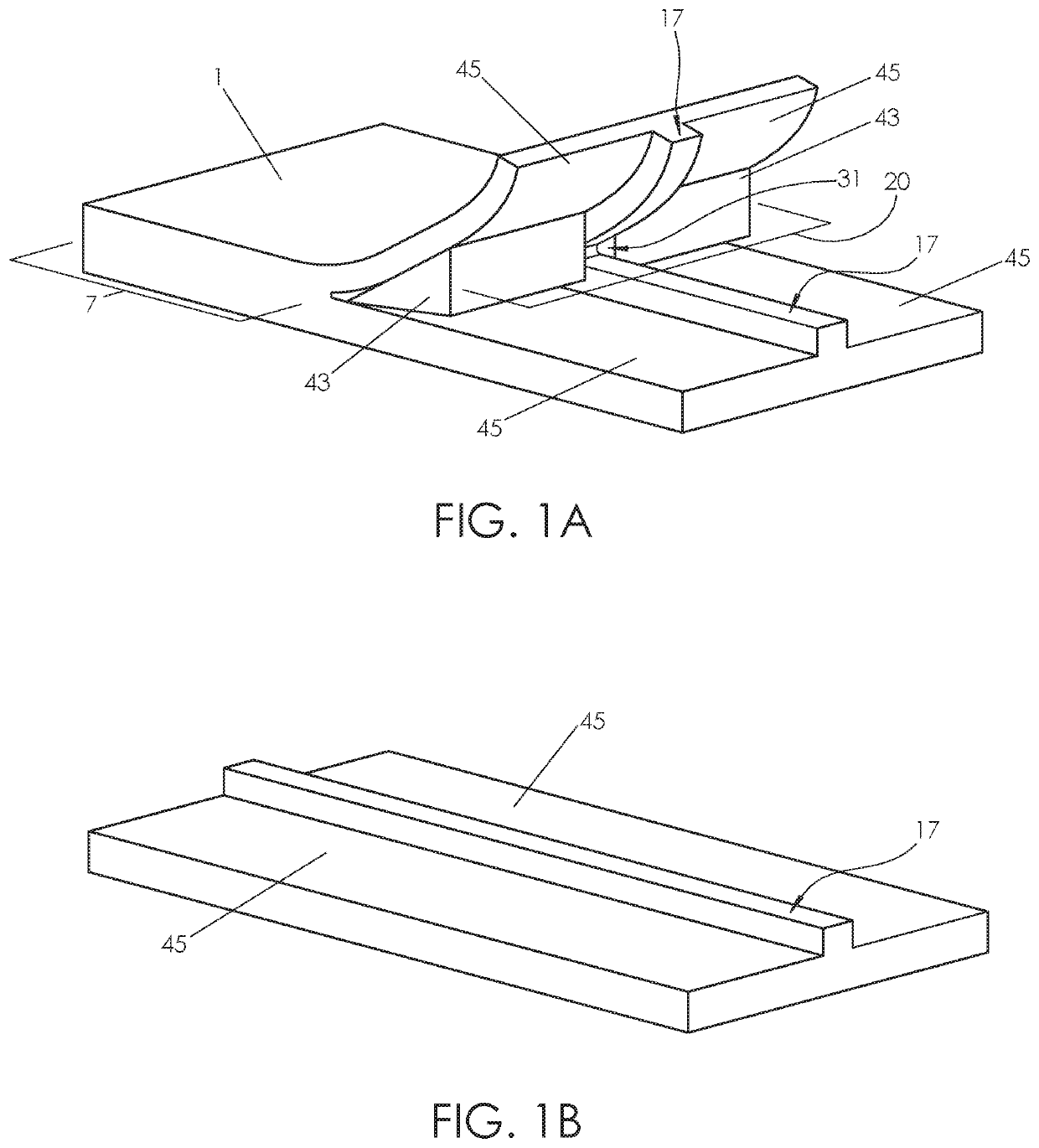
Contact Mechanic Tests using Stylus Alignment to Probe Material Properties
ActiveUS20160258852A1Design optimisation/simulationAerodynamics improvementDevices fixationEngineering
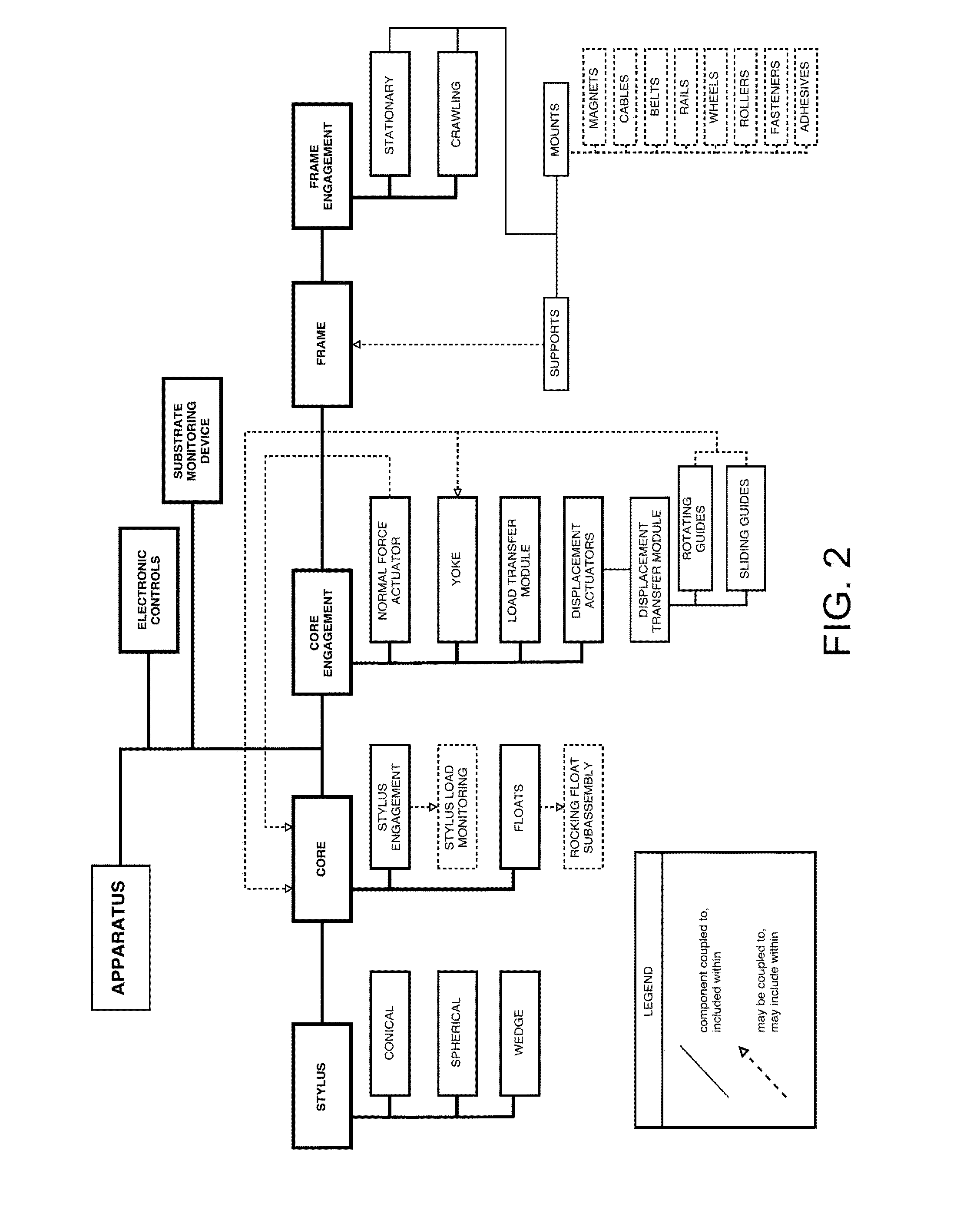
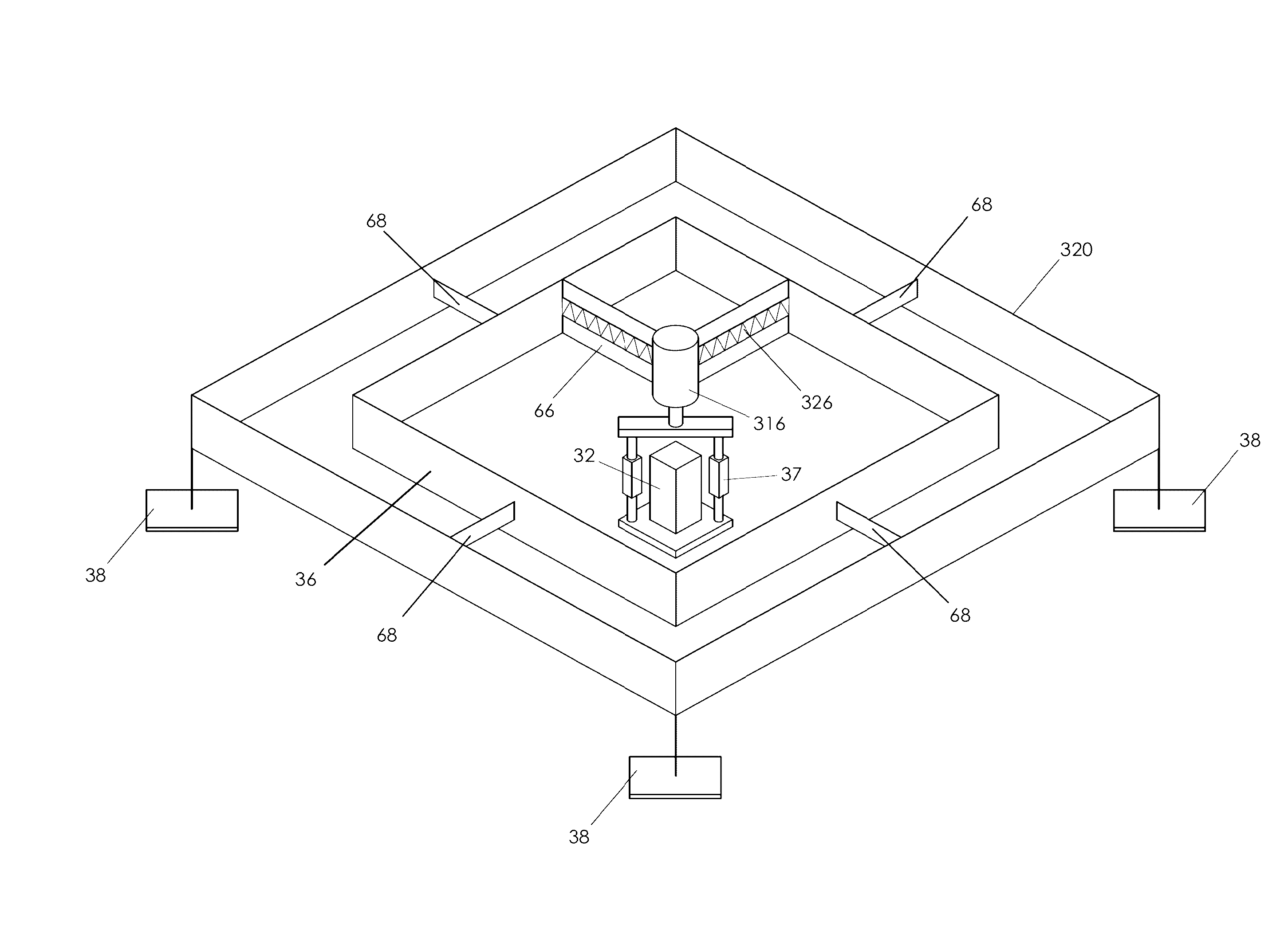
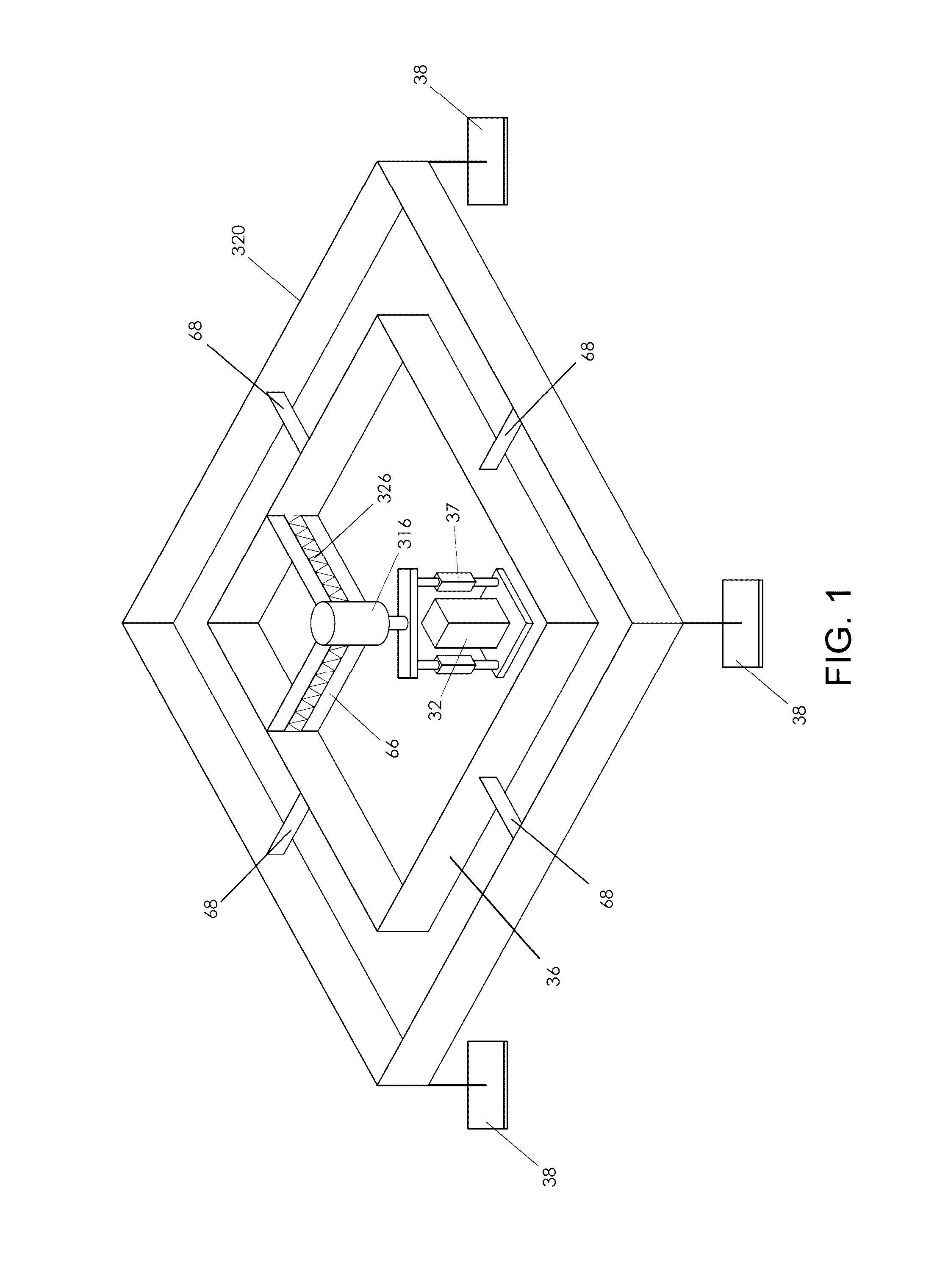
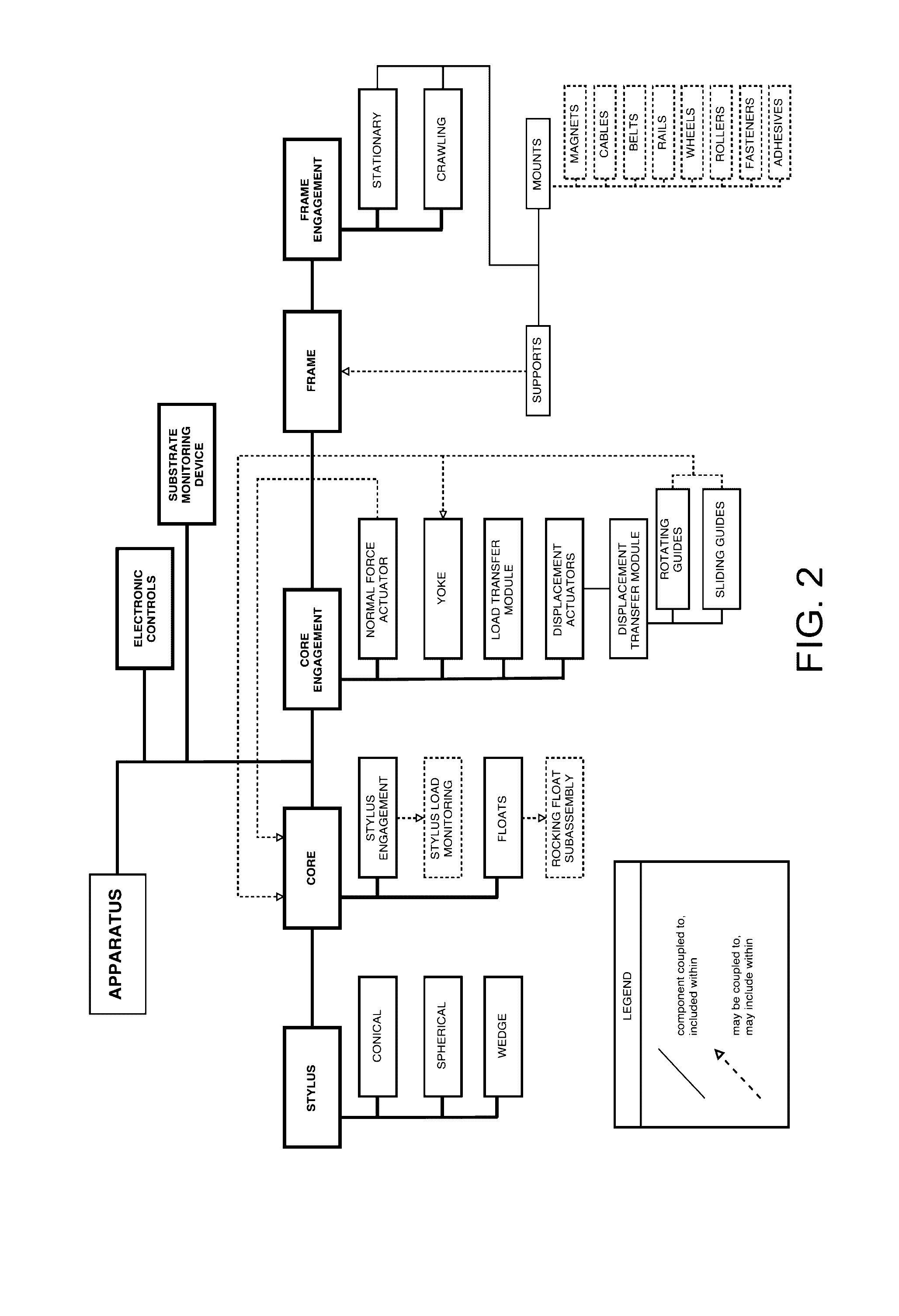
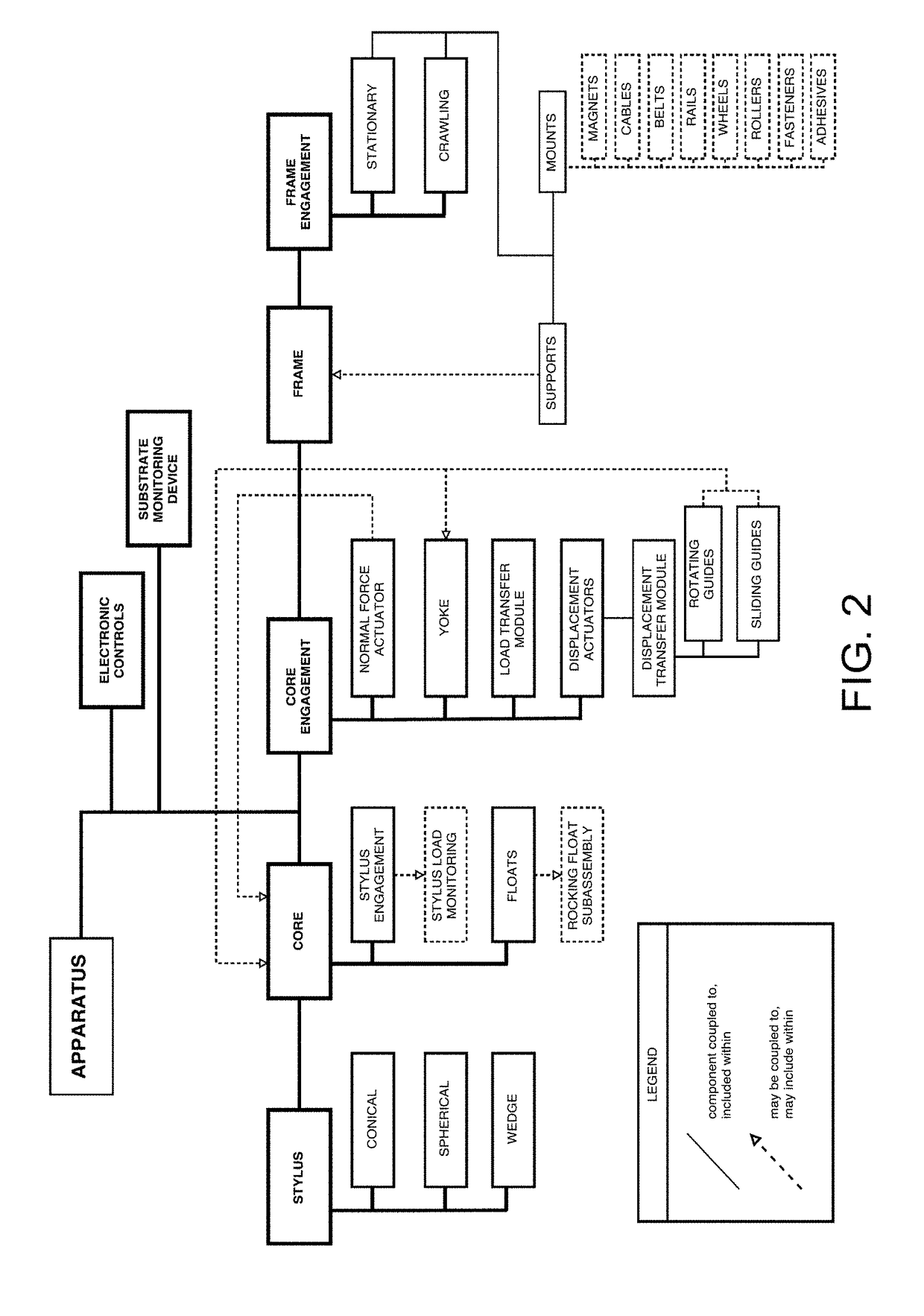
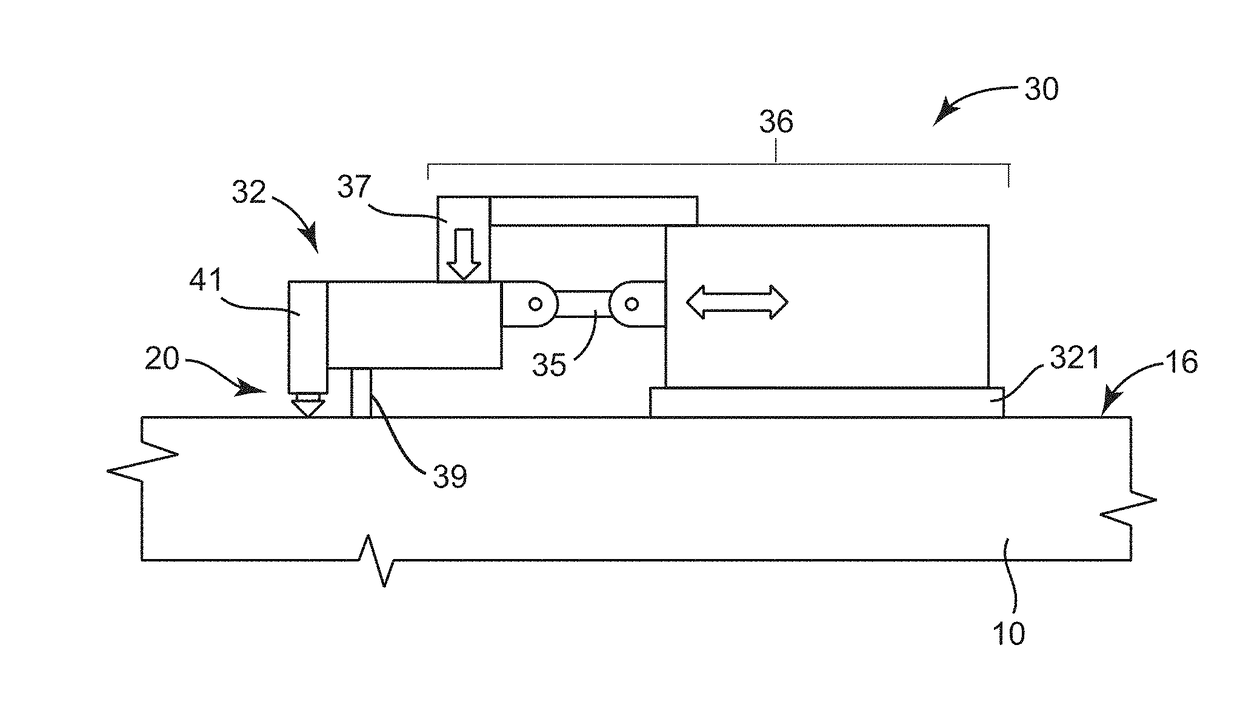
An apparatus for performing a contact mechanics test on a substrate includes a stylus, a core configured to engage the stylus against the substrate, a stylus engagement mechanism configured to induce a contact load or a penetration depth to the stylus, a core engagement mechanism configured to maintain contact of the core and to move the core along the substrate surface, a frame configured to be fixed with respect to the apparatus or to be moved together with the core engagement mechanism as an assembly, a frame engagement mechanism configured to engage the frame with the substrate surface; and a substrate monitoring device configured to measure characteristics of substrate contact response and / or collect material machined from the substrate. Methods of performing a contact mechanics test are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS MATERIALS TECH
Method for rapidly testing in situ foundation bearing capacity and deformation modulus
InactiveCN101250866ALower acquisition costsSimple test equipmentIn situ soil foundationDeformation modulusEngineering
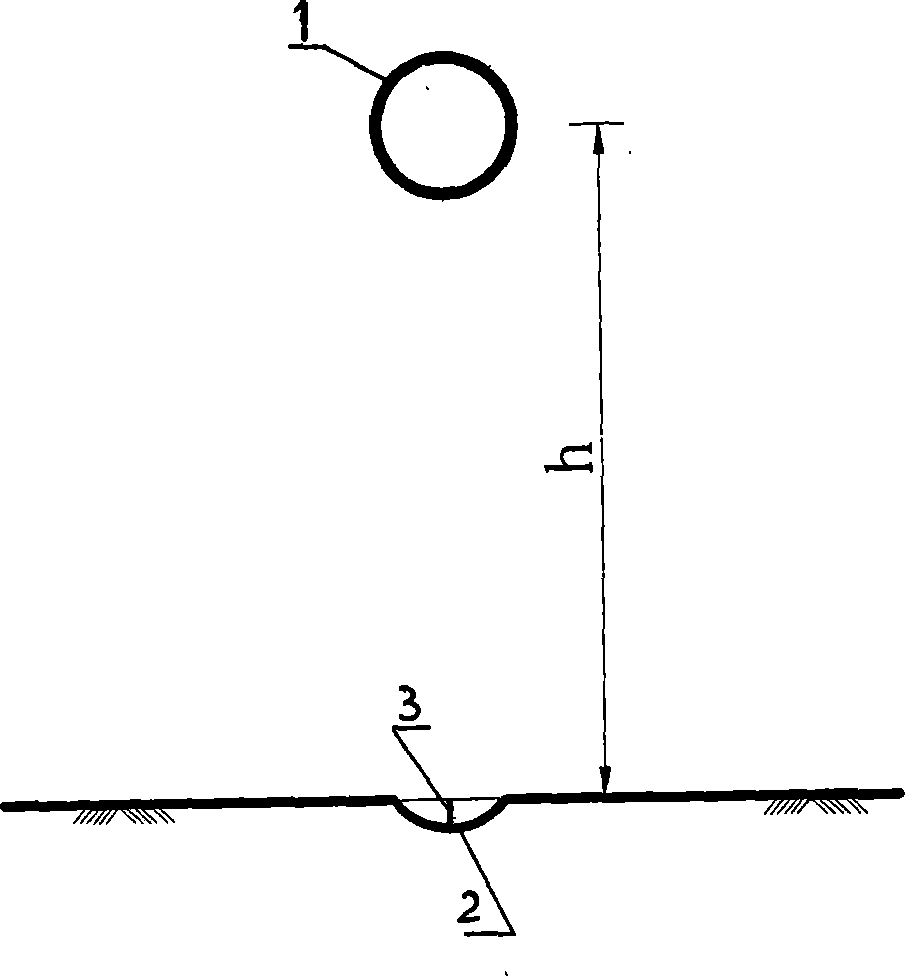
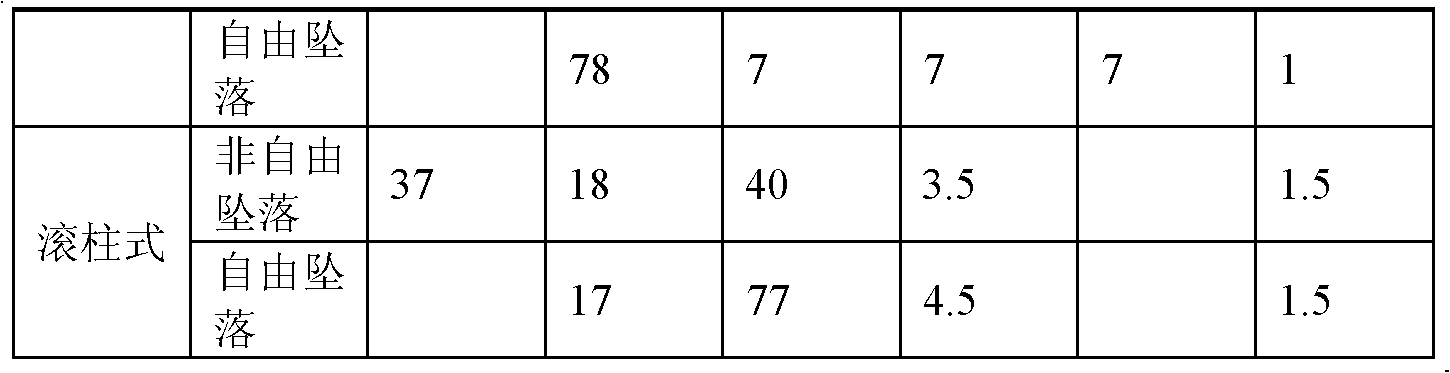
The invention relates to a rapid original position testing method of foundation bearing capacity and deformation modulus, which comprises the following step: a steel ball whose weight is m is lifted to a certain height by a tripod and freely falls, and then the depth delta that the steel ball is compacted to press into the ground is tested. The test is repeated three times or more in a same field, the falling height of each time is different, and the indentation depth values of different depth indentations which are formed when the steel ball falls in each time are correspondingly tested, then the ultimate bearing capacity and the deformation modulus of foundation soil are calculated through the contact mechanical basic theory. The rapid original position testing method is an economical, rapid, convenient and accurate original position testing method, and is capable of rapidly screening the foundation bearing capacity of a large area site.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
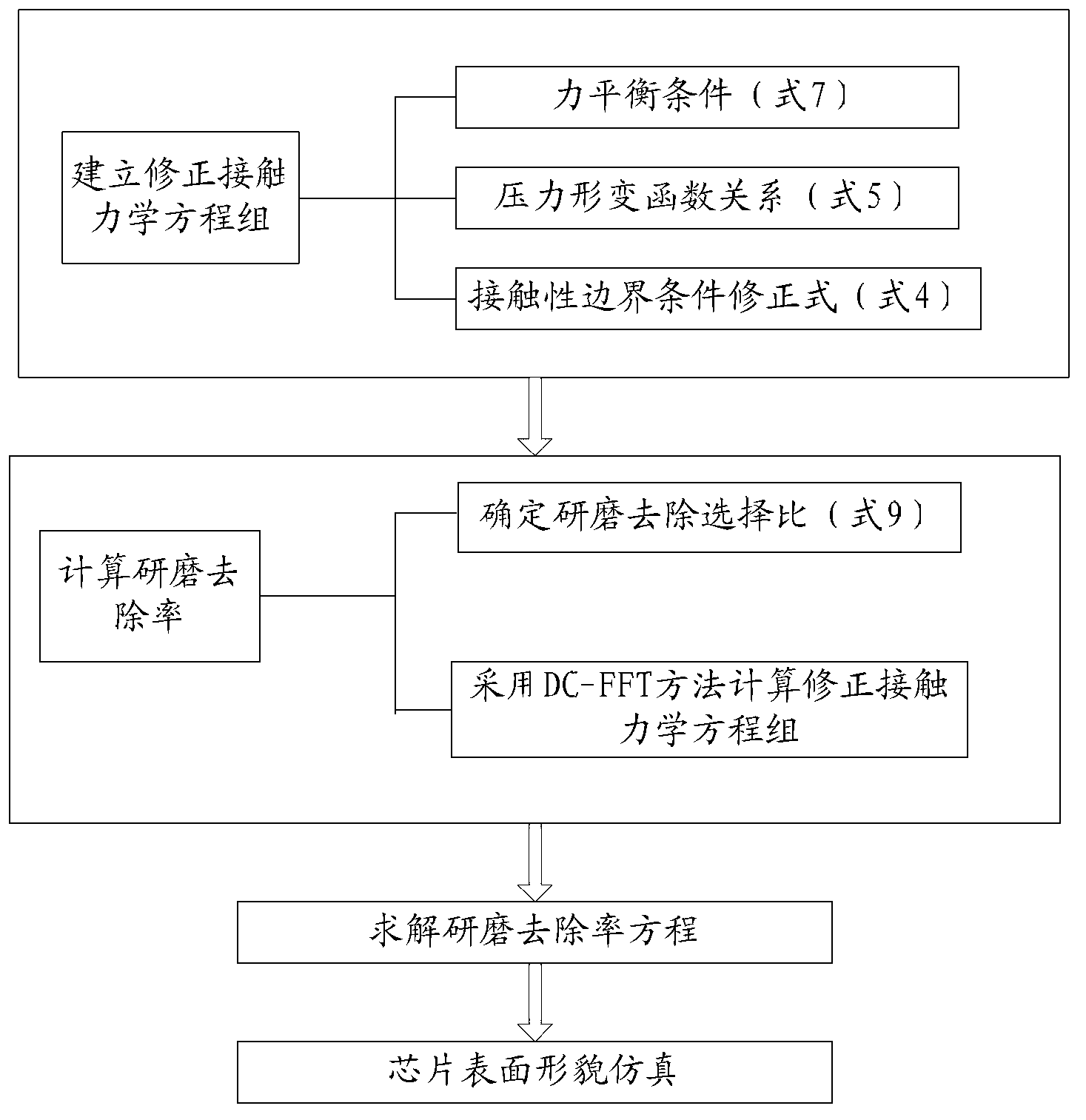
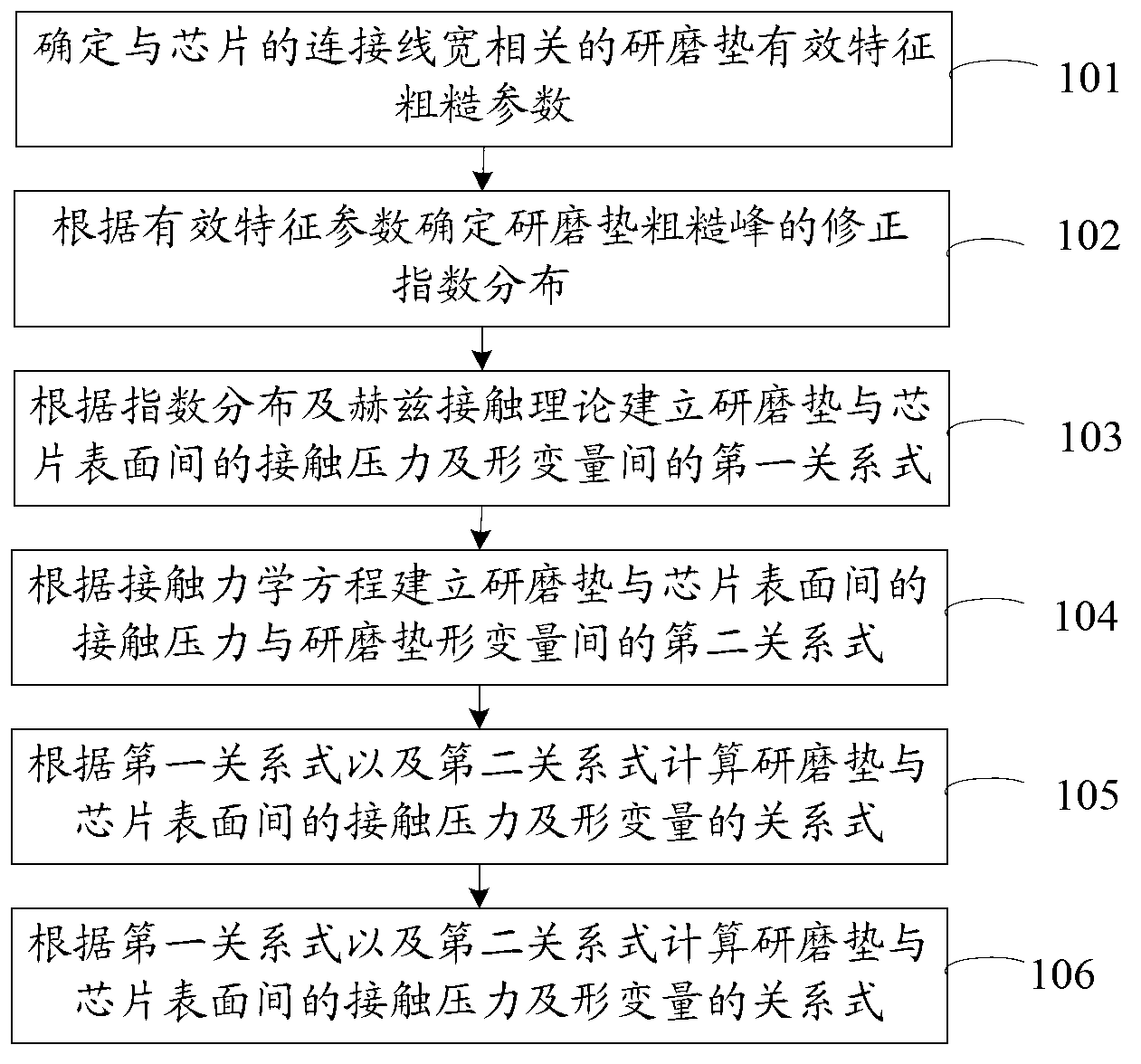
Simulation method and device for chip surface morphology
ActiveCN103226627AAvoid false conclusionsImprove forecast accuracySpecial data processing applicationsContact pressureContact mechanics
The invention discloses a simulation method and device for chip surface morphology, which are used for solving the problem that errors are bigger during simulation of GW model chip surface morphology. The method comprises the steps as follows: determining effective feature roughness parameter of a polishing pad relevant to a chip connecting linewidth; determining modified index distribution of a polishing pad rough peak according to the effective feature roughness parameter; establishing a first relation between the surface contact pressure of the polishing pad and the chip and polishing pad deformation according to the index distribution and the Hertz elastic theory; establishing a second relation between the polishing pad and the chip surface contact pressure and the polishing pad deformation according to a contact mechanics equation; calculating the relation between the polishing pad and the chip surface contact pressure and the polishing pad deformation according to the first relation and the second relation; and performing chip surface morphology simulation by using the relation of contact pressure and the deformation of the chip. The technical scheme provided by the invention avoids the wrong solution of the GW model in small linewidth CMP (chemical mechanical planarization) processing simulation, and improves the simulation and prediction accuracy of the GW model.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic drive peak force modulated atomic force microscope and multi-parameter synchronous measurement method thereof
ActiveCN107449939ALarge signal to noise ratioImprove signal-to-noise ratioScanning probe microscopyMicro nanoMechanical models
The invention provides a magnetic drive peak force modulated atomic force microscope and a multi-parameter synchronous measurement method thereof, relates to the technology of measurement of the material surface topography and mechanical properties under the micro-nano scale, and aims at solving the problems that the driving frequency range of the probe in the conventional method based on the force-displacement curve is limited and integrally driving the probe interferes the movement of the probe cantilever and influences the measurement accuracy under the liquid environment. A coil is arranged in a sample table. The probe tip is provided with magnetic particles which are magnetized along the length direction of the probe or have the magnetized component of the direction. Firstly the PSD voltage curve U<free> of vibration of the probe in the free state is acquired, then the PSD voltage curve U<inden> of the tip position when the probe intermittently contacts the sample is acquired, the voltage curve U<Force> of the probe under stress is acquired by U<free> and U<inden>, and the force-displacement curve is acquired according to all the curves so as to acquire the mechanical properties of the material through combination of the corresponding contact mechanical model. The driving frequency range of the probe is wide and the measurement accuracy is high so as to be suitable for the research of polymer composite material or biological cells.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
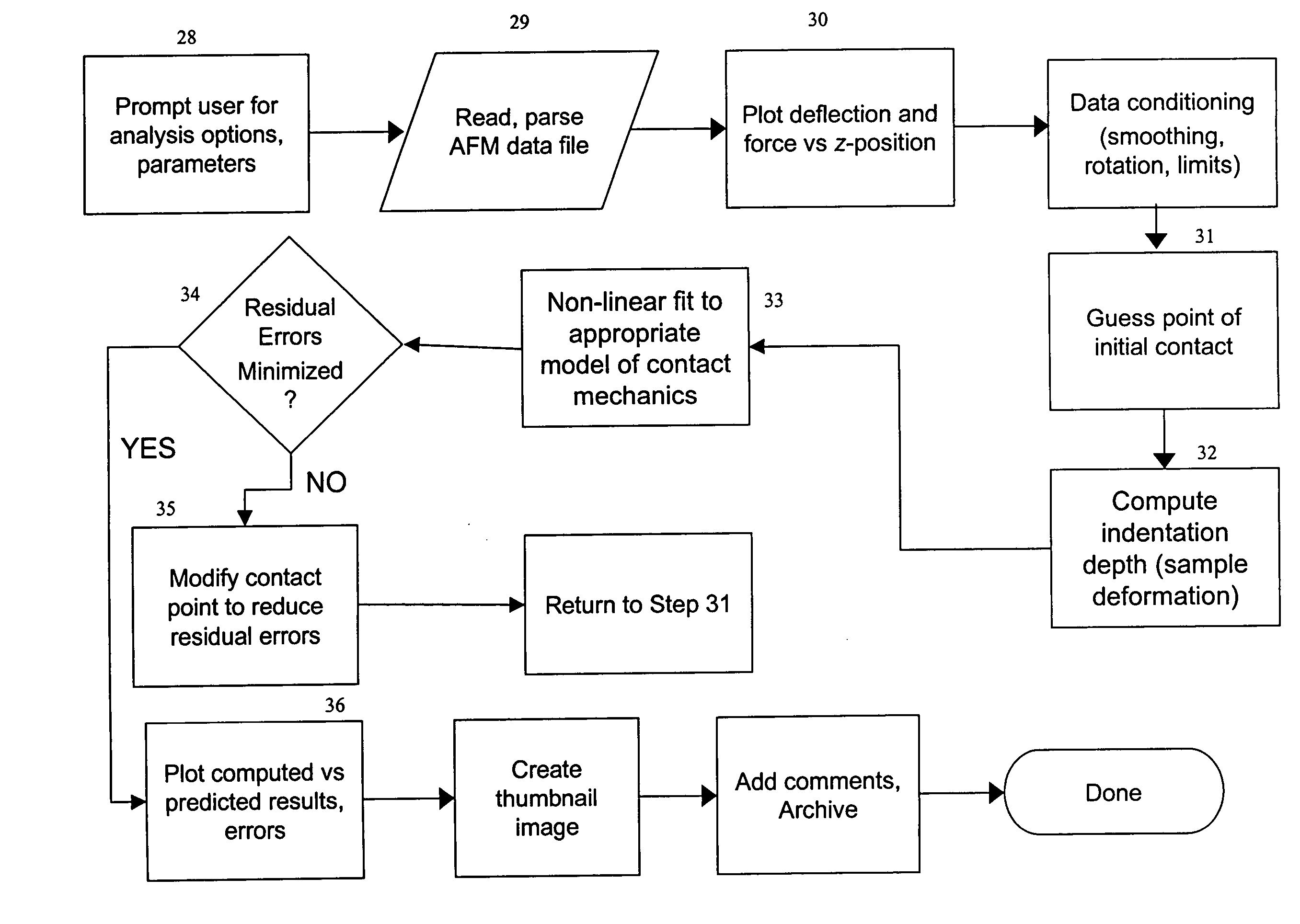
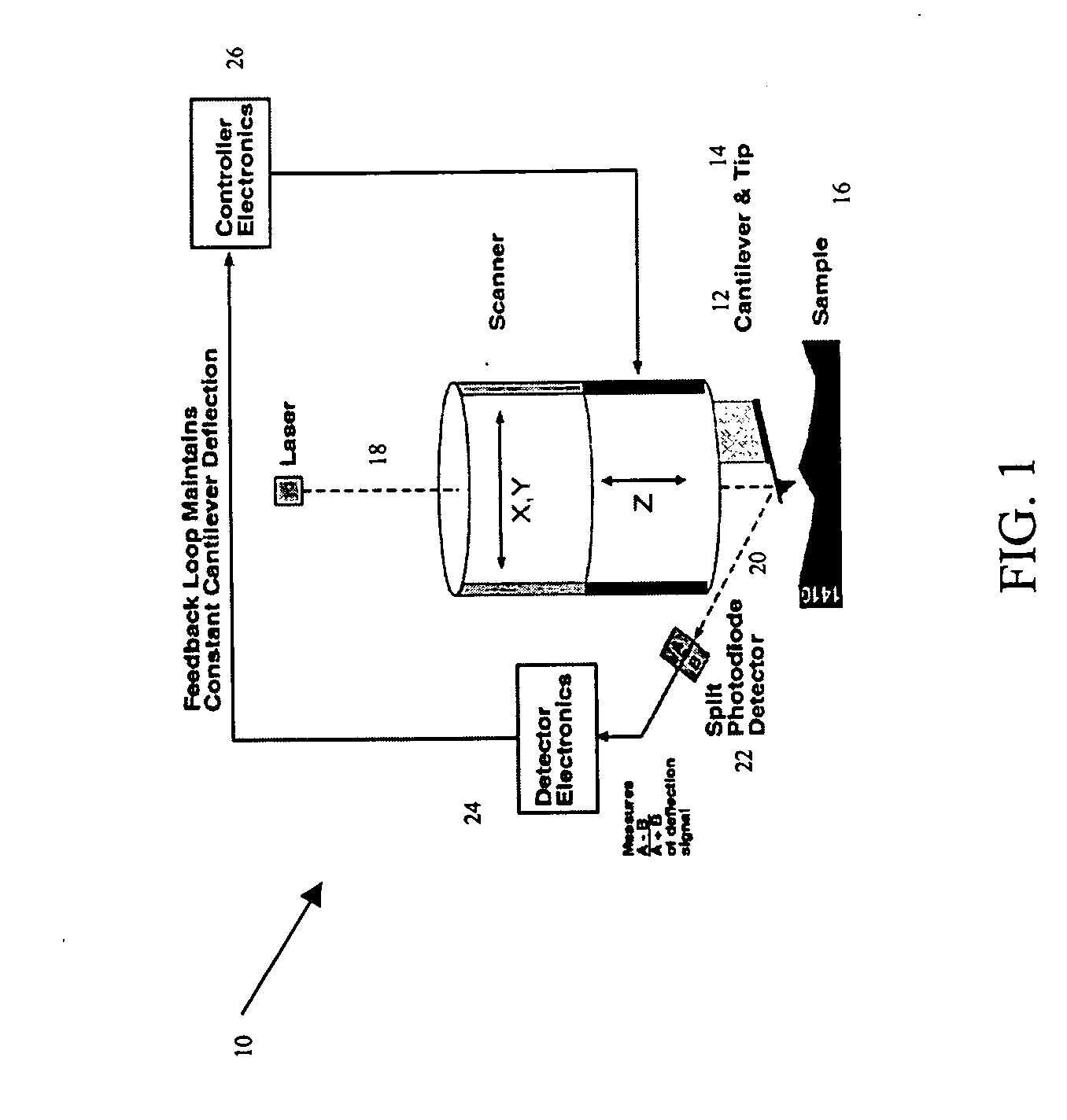
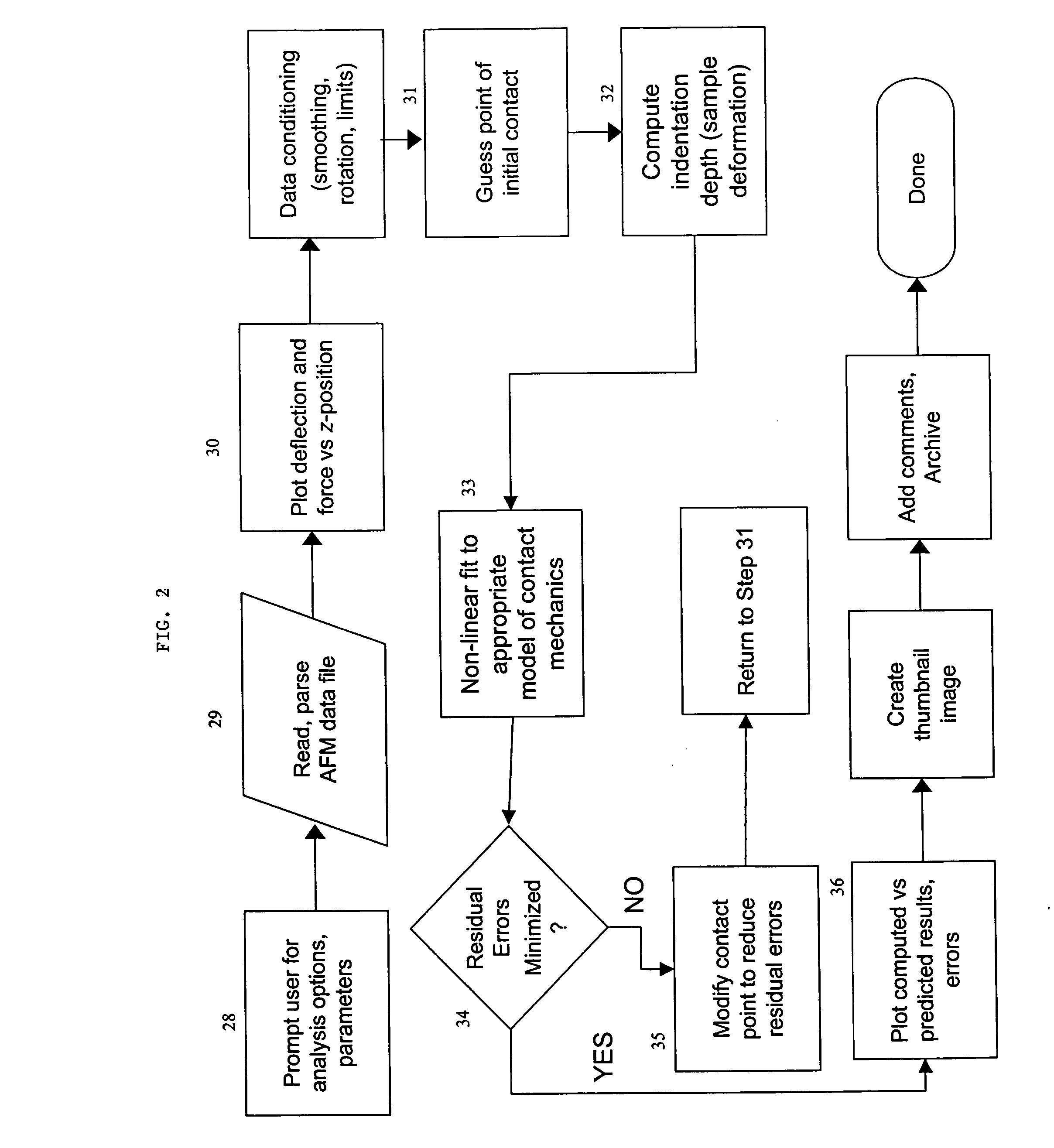
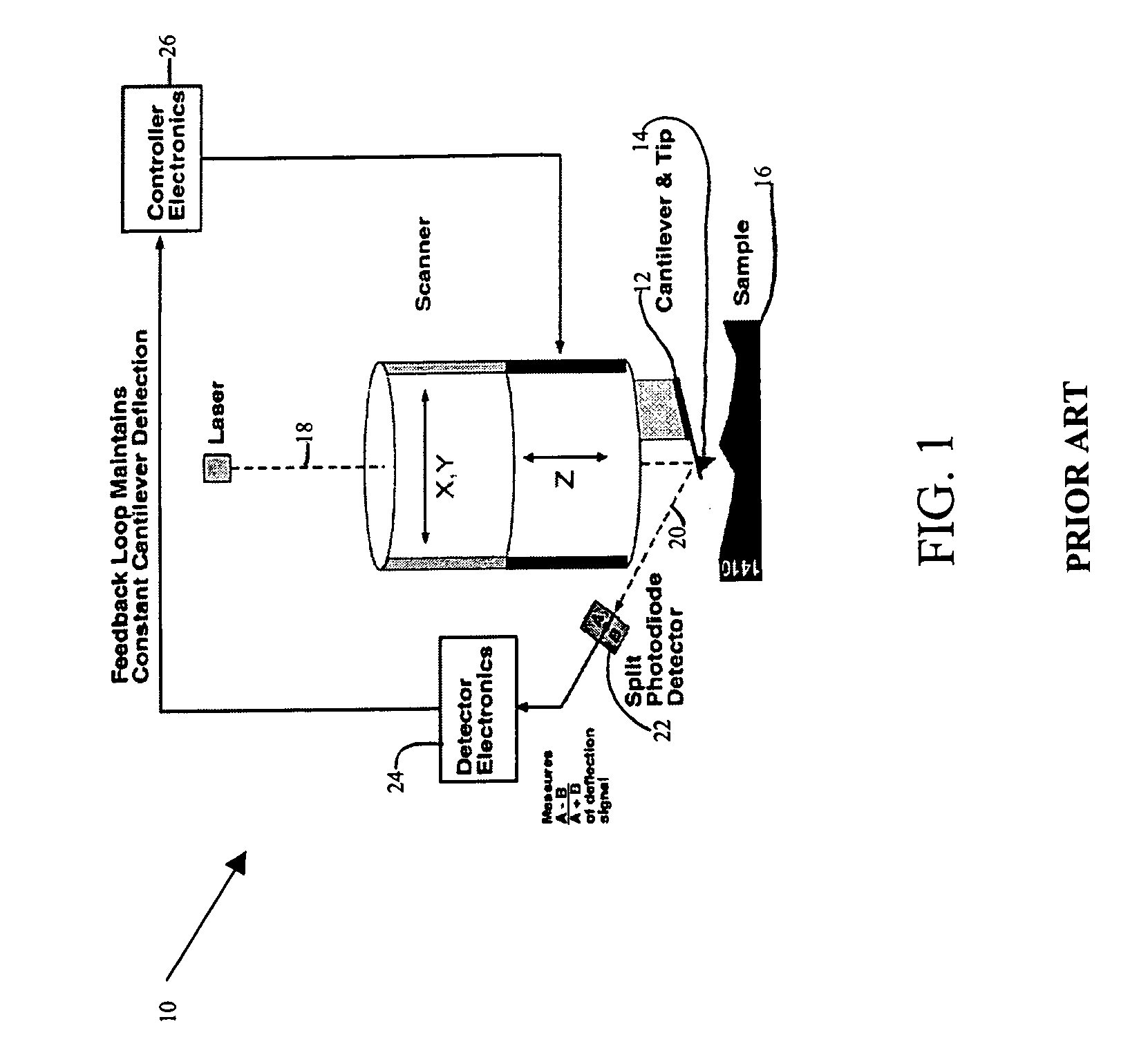
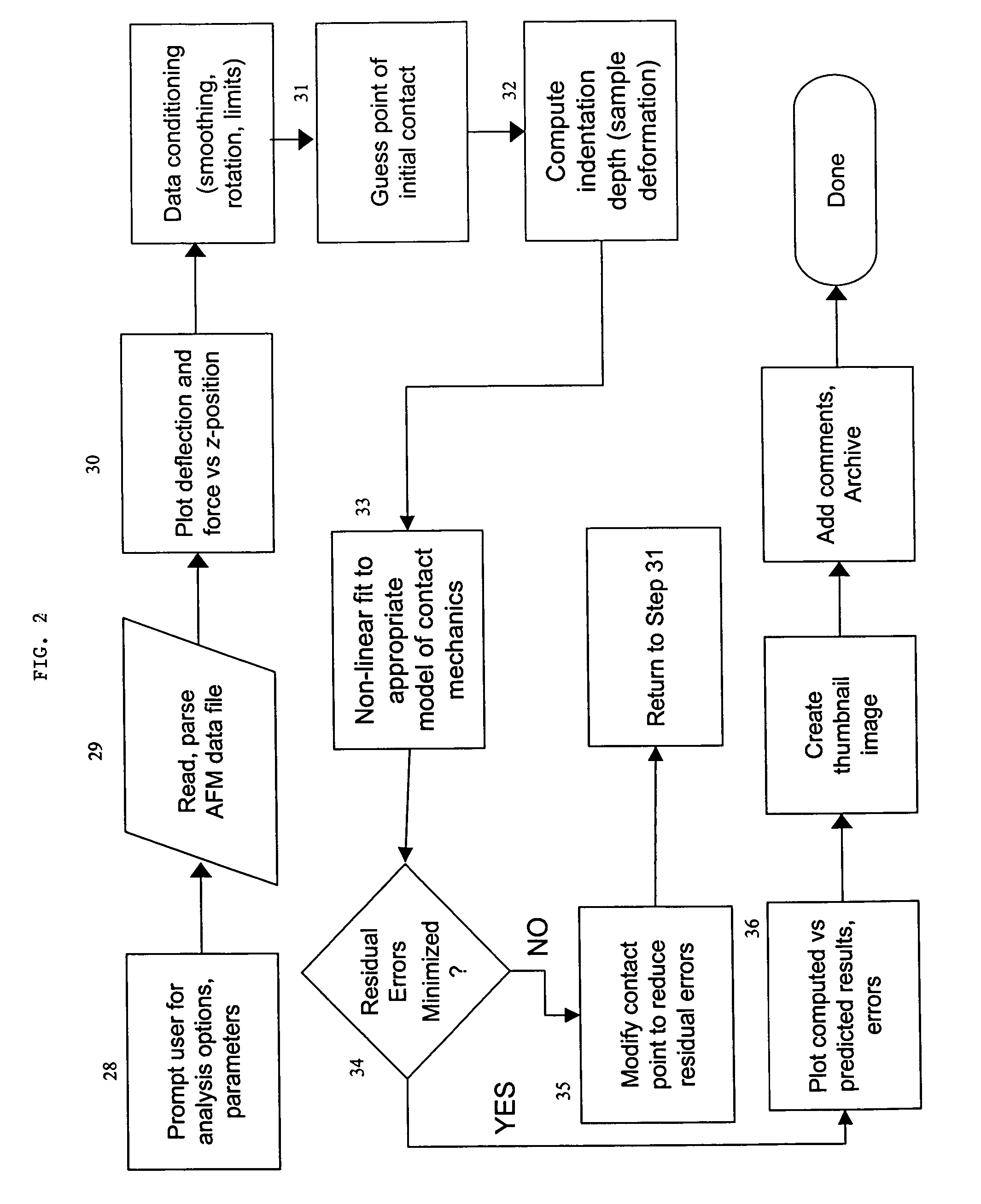
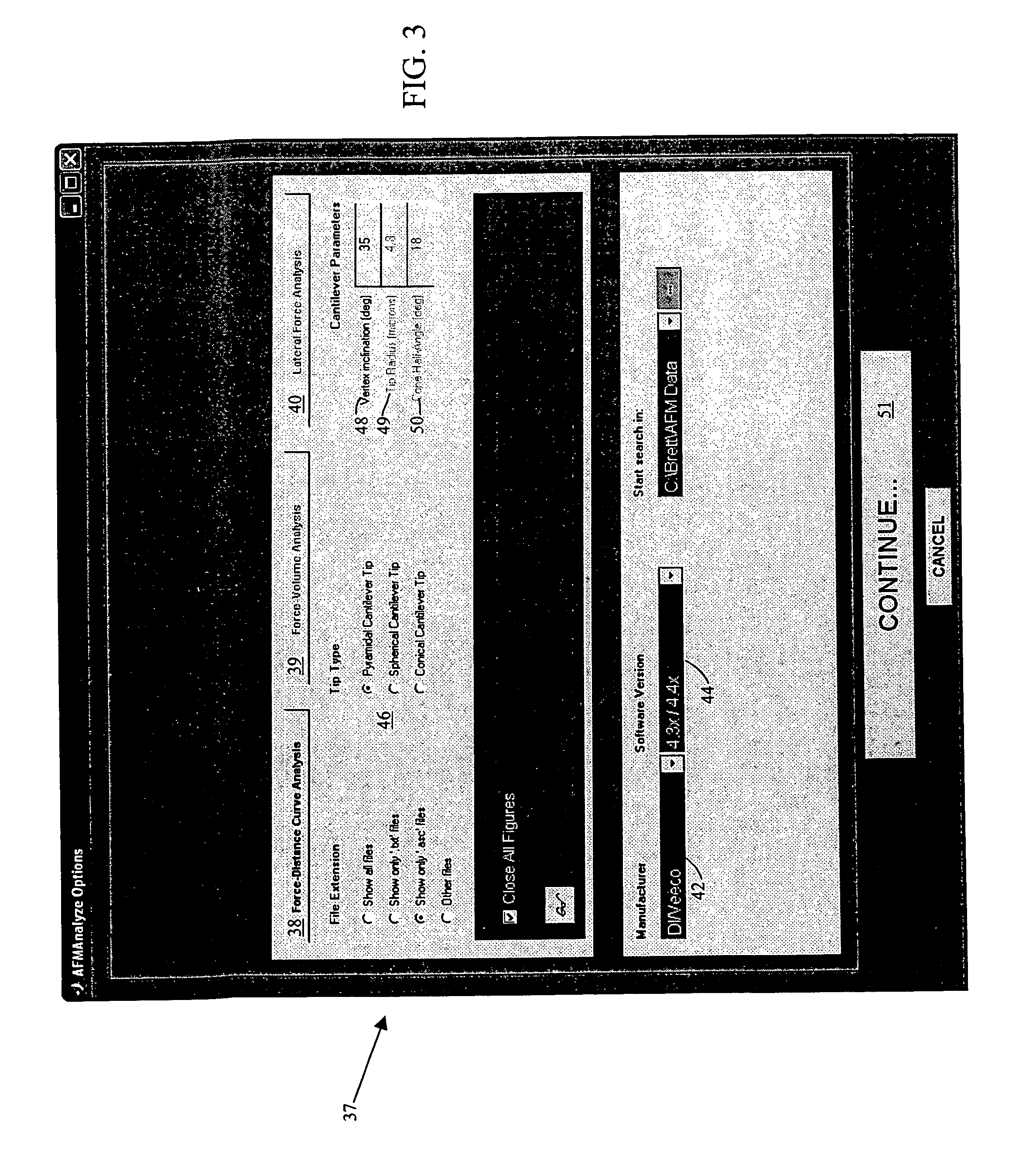
System and method for the analysis of atomic force microscopy data
InactiveUS20050081608A1NanotechAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAtomic force microscopyAnalysis data
A system and method for the analysis of AFM data is provided. The system and method can be used in conjunction with an atomic force microscopy (AFM) system including a cantilever with a tip used to analyze a sample, the AFM outputting an AFM data file. An exemplary embodiment of the invention includes a computer readable medium storing computer readable program code for causing a computer to receive user input regarding an analysis to be performed and analysis parameters; parse the AFM data file based on the user input to obtain a deflection of the cantilever; determine an indentation depth of the tip into the sample based at least in part on the deflection; select a model of contact mechanics based on the user input; solve the selected model of contact mechanics based on the input analysis using the determined indentation depth; and determine a residual error.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
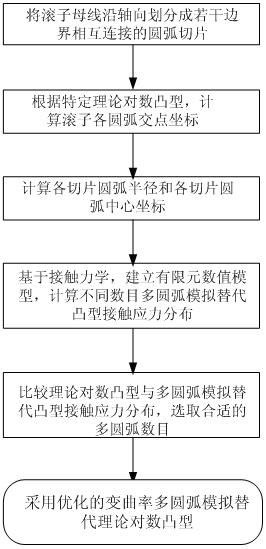
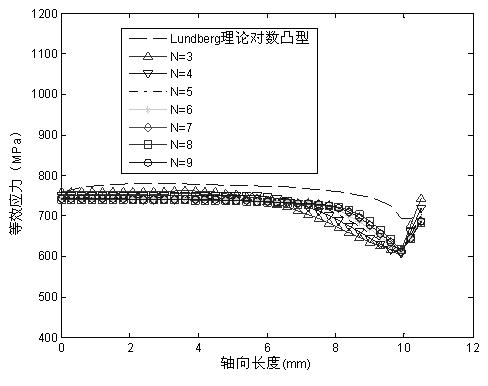
Cylindrical roller multi-circular-arc variable curvature profile engineering simulation method
InactiveCN102644663AOvercoming boundary stress concentration effectsLow processing and manufacturing costsBearing componentsStress distributionEdge effects
The invention relates to a cylindrical roller multi-circular-arc variable curvature profile engineering simulation method. In the method, a cylindrical roller is divided along the axial line direction into plural circular arc sections connected with each other, the intersection point coordinate value of the boundary of each section is calculated according to a given special logarithmic curve, the radius value of each segment of circular arc is calculated by use of adjacent circular arc segments and line of centers of two circular arc segments, and contact stress distribution along the axial line direction of the roller is calculated and analyzed under the condition of different-number variable curvature circular arc profile based on the theory of contact mechanics, and compared with theoretical logarithmic profile contact stress distribution to therefore select an optimal number of proper variable curvature circular arcs. The invention adopts variable curvature multi-circular-arc combination simulation to substitute for theoretical logarithmic curve, realizes low manufacturing cost for variable curvature multi-circular-arc profile roller, overcomes the stress edge effect of a conventional straight generatrix shaped roller end part, provides a theoretical foundation for generalization of roller crowned design technology, and is applicable for crowned design of cylindrical roller and tapered roller as well as roller inner and outer rings.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
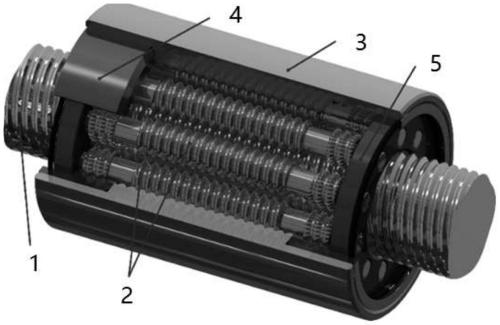
Extraction method of load spectrum of ball screw pair
ActiveCN107357967AAccurately determineDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic CADPower flowNonlinear systems of equations
The invention belongs to the field of contact mechanics and relates to an extraction method of a load spectrum of a ball screw pair. The method comprises the following steps: setting up a load distribution model of a single-nut ball screw pair; setting up a nonlinear system of equations for load distribution of the single-nut ball screw pair based on a hertz contact theory according to the principle of deformation compatibility; solving the nonlinear system of equations for contact load of a single-ball model; setting up a solving model for dynamic contact characters of high-speed motion state of the ball screw pair and solving value of the nonlinear system of equations; calculating the change rule between contact load of the screw nut pair and positions based on relations of working positions and torque current of a servo motor with time; and working out the load spectrum of the ball screw pair. The extraction method of the load spectrum of the ball screw pair utilizes precisely-determined load spectrums of all components of the screw nut pair to provide reference for reliability design of a feeding system.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
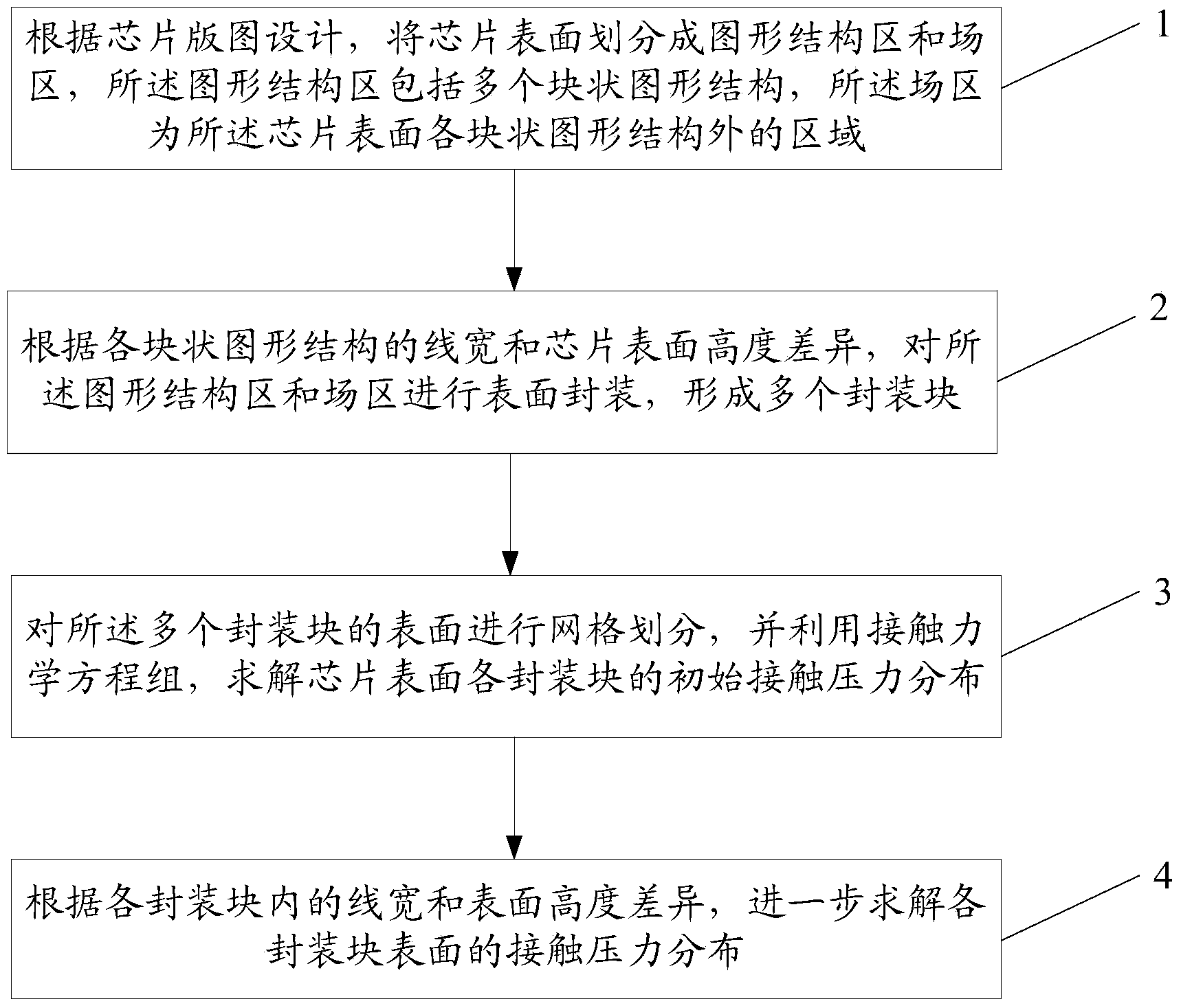
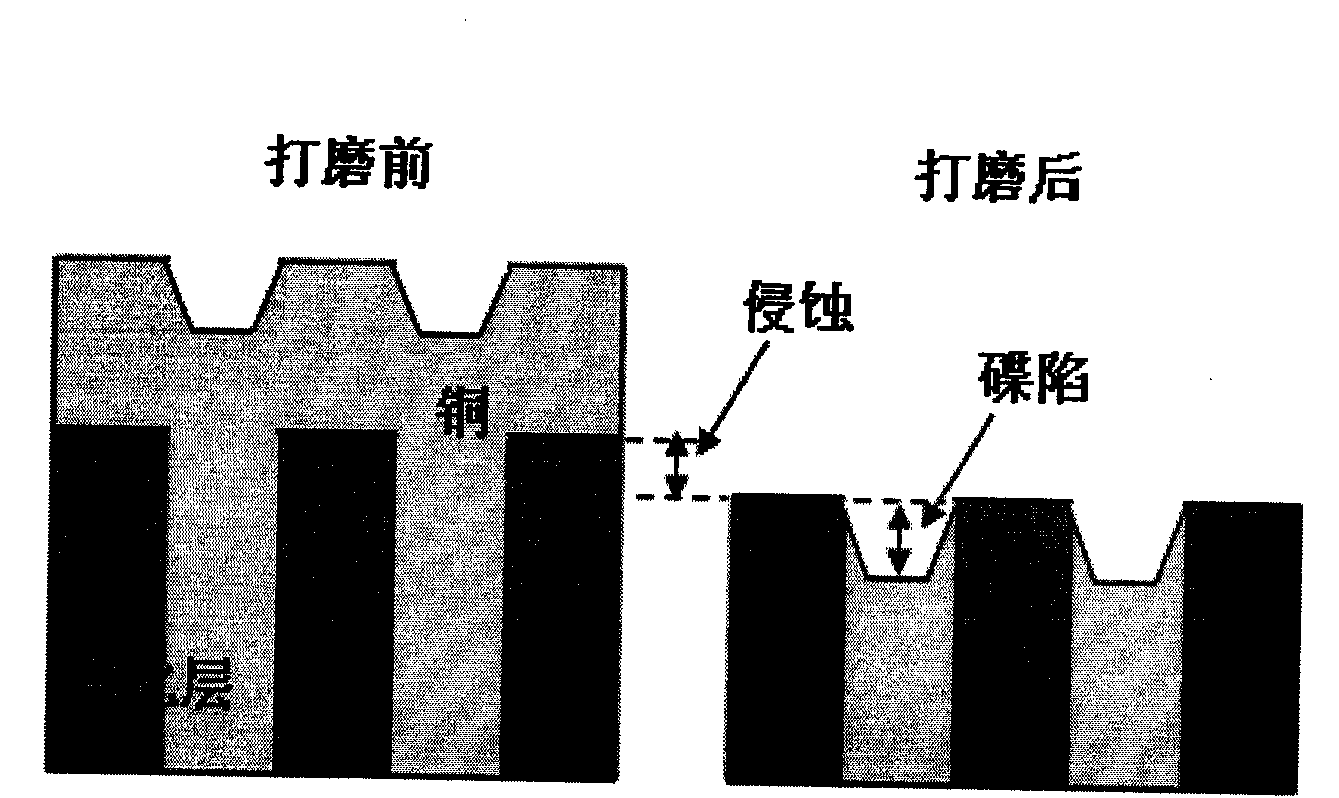
Method for calculating contact pressure between grinding pad and surface of chip in CMP simulation model
ActiveCN104021247AImprove completenessGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsBlock graph
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for calculating the contact pressure between a grinding pad and the surface of a chip in a CMP simulation model. The method includes the first step of dividing the surface of the chip into a graph structural region and a field region according to the layout design of the chip, wherein the graph structural region comprises multiple block graph structures, and the field region is the region in the surface of the chip except all the block graph structures, the second step of conducting surface packaging on the graph structural region and the field region to form multiple package blocks according to line widths of all the graph structures and the height difference of the surface of the chip, the third step of conducting grid division on the surfaces of the multiple package blocks and solving initial contact pressure distribution of each package block on the surface of the chip through a contact mechanic equation set, the fourth step of further solving the contact pressure distribution of the surfaces of all the package blocks according to the widths of lines in the package blocks and the surface height difference of the package blocks. Through the method, the calculation efficiency and calculation accuracy can be achieved simultaneously, so that the method has generality and university.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
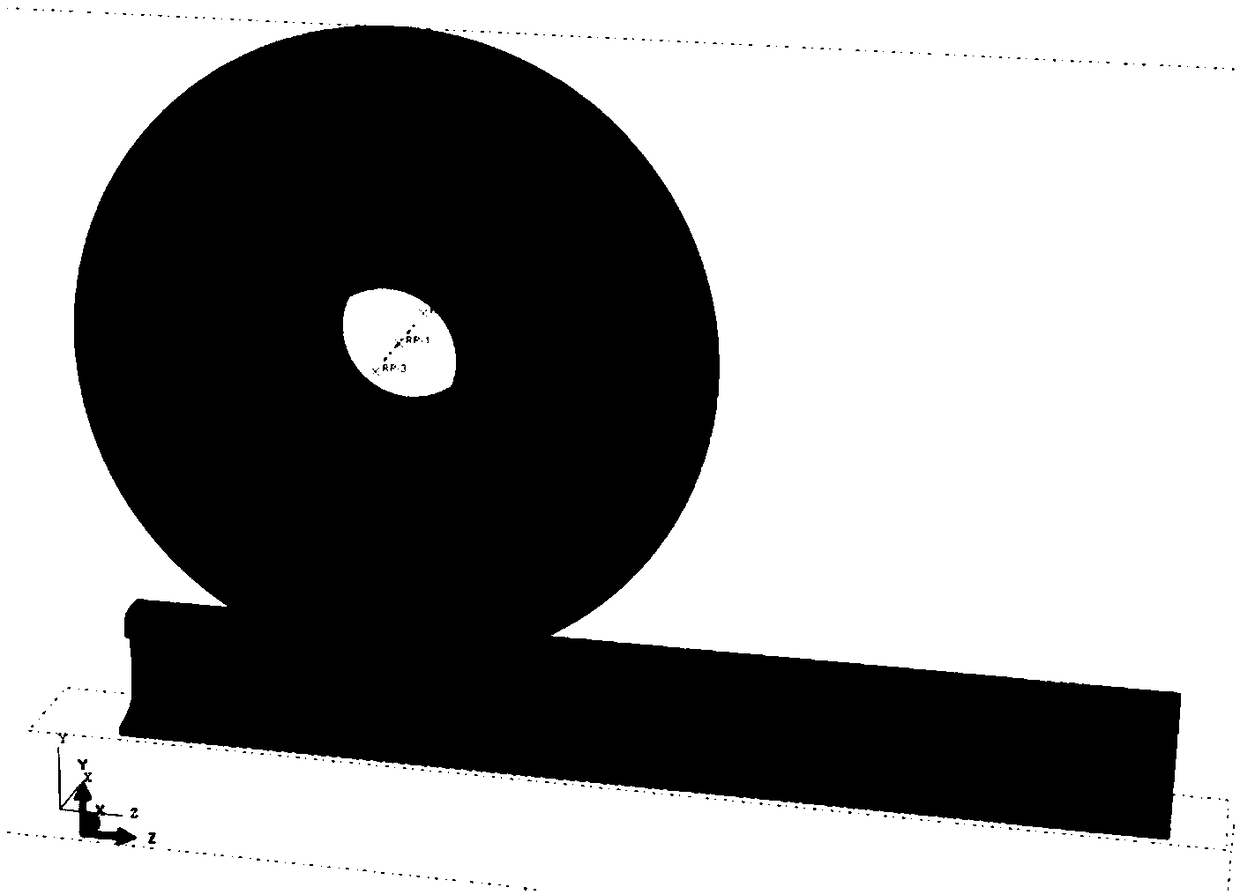
Considering wheel-rail rolling contact, the coupling modeling analysis method of high-speed railway subgrade
ActiveCN109376503AHigh precisionModel settings are reasonable and comprehensiveGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationKinematic couplingTracking model
The invention provides a high-speed railway roadbed coupling modeling analysis method considering wheel / rail rolling contact, By building a vehicle model, Track model and roadbed structure model are used to simulate the secondary suspension system of the vehicle, spring damping element is used to simulate the force transfer fastener between rail and ballastless track slab, and kinematic coupling constraint combined with the predefined field of initial velocity is used to simulate the rolling contact mechanics behavior between wheel rim surface and rail surface. At the same time, the coupling effect of roadbed reflects the mechanical response of wheel / rail under the rolling contact between wheel set and rail surface. It is a 3D finite element modeling analysis method which is closer to thereal driving process of high-speed railway. The analysis model of the high-speed railway roadbed established by the invention can obtain the calculation results of each structure which are more in line with the actual mechanical characteristics, and can effectively guide the analysis and calculation of the dynamic response of the high-speed railway roadbed and the reasonable design of the roadbedstructure.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Finite element simulation-based wheel-track contact cyclic loading-unloading simulation analysis method
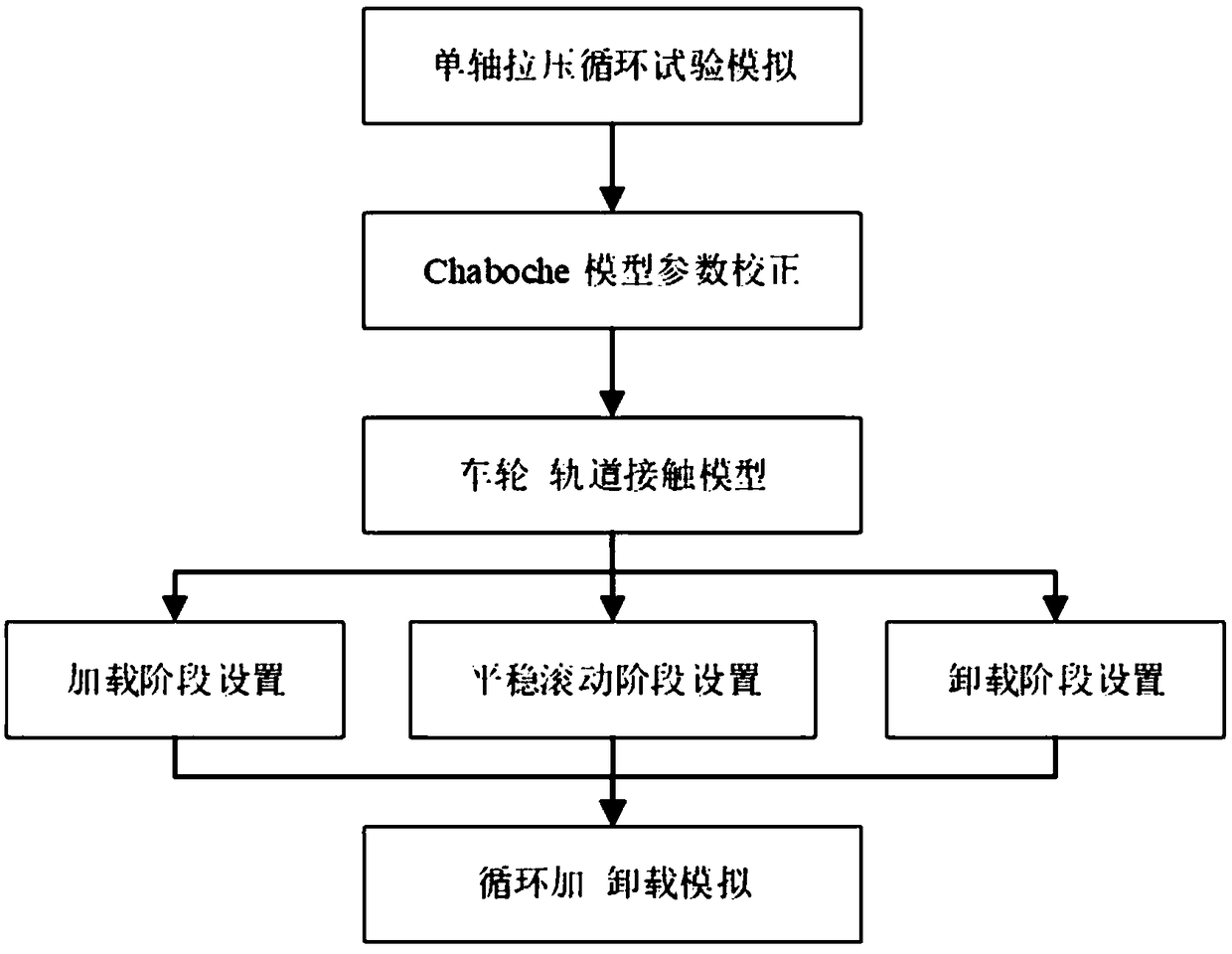
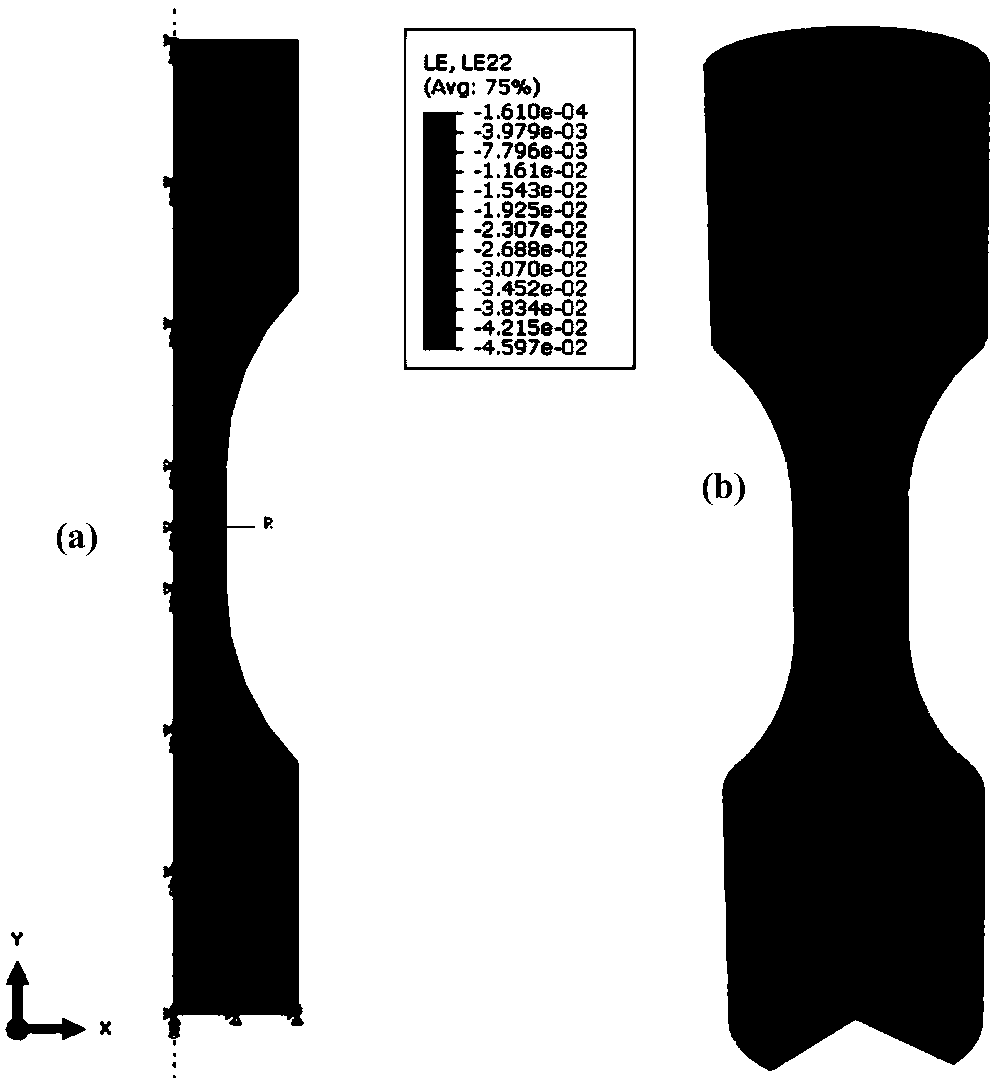
InactiveCN108664707ASolve the defects of cyclic load descriptionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime cyclesSymmetric model
The invention discloses a finite element simulation-based wheel-track contact cyclic loading-unloading simulation analysis method. The method comprises the following main steps of (a) building a uniaxial tension and compression axial symmetric model by utilizing finite element software ABAQUS; (b) performing uniaxial tension and compression cyclic test simulation, and according to an indoor test result and a Chaboche model, performing correction on a nonlinear hardening parameter of a material; (c) building a wheel-track contact model, and setting material parameters and contact parameters; (d) decomposing a single-time cycle into three stages including a loading stage, a stable rolling stage and an unloading stage, and setting a loading condition, a constraint condition, a contact condition and a boundary condition; and (e) by utilizing a restart mechanism, importing a previous calculation result, performing wheel track contact loading-unloading simulation based on this, and storing an unloading stage result to serve as an initial condition of the next cycle. Based on a nonlinear finite element simulation method and a contact mechanic theory, cyclic loading and unloading behaviorsof wheel track fatigue, damage and the like can be subjected to simulation analysis.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
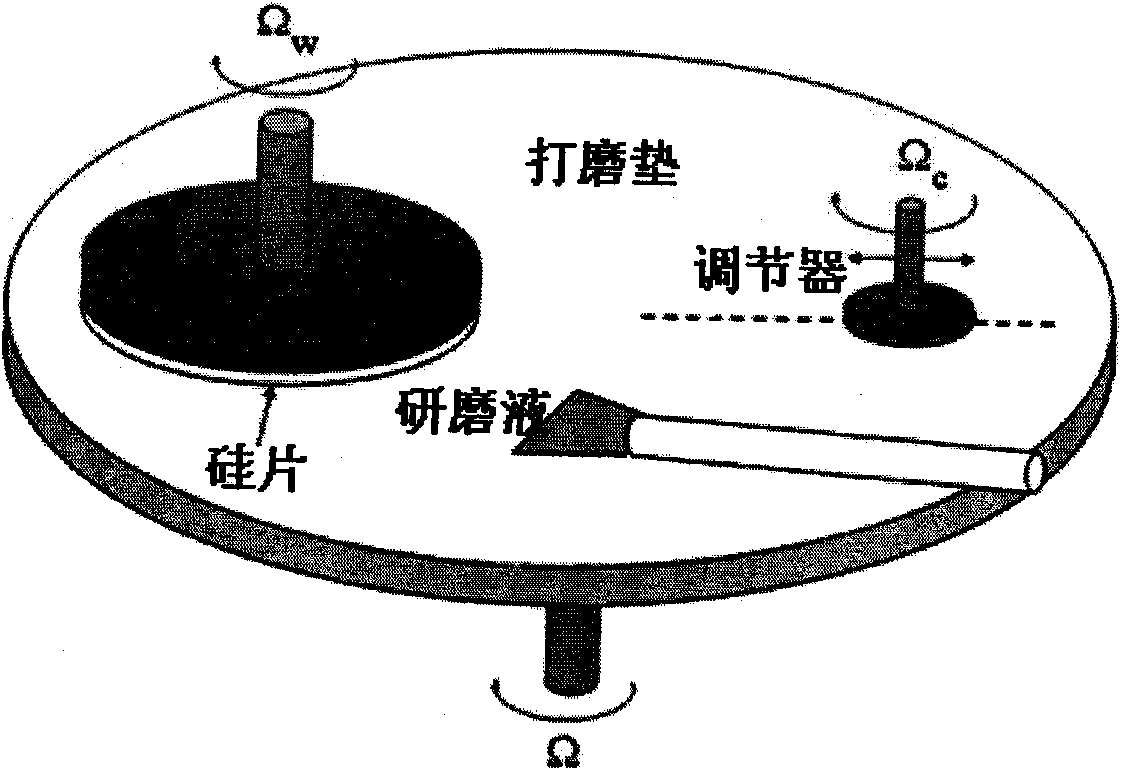
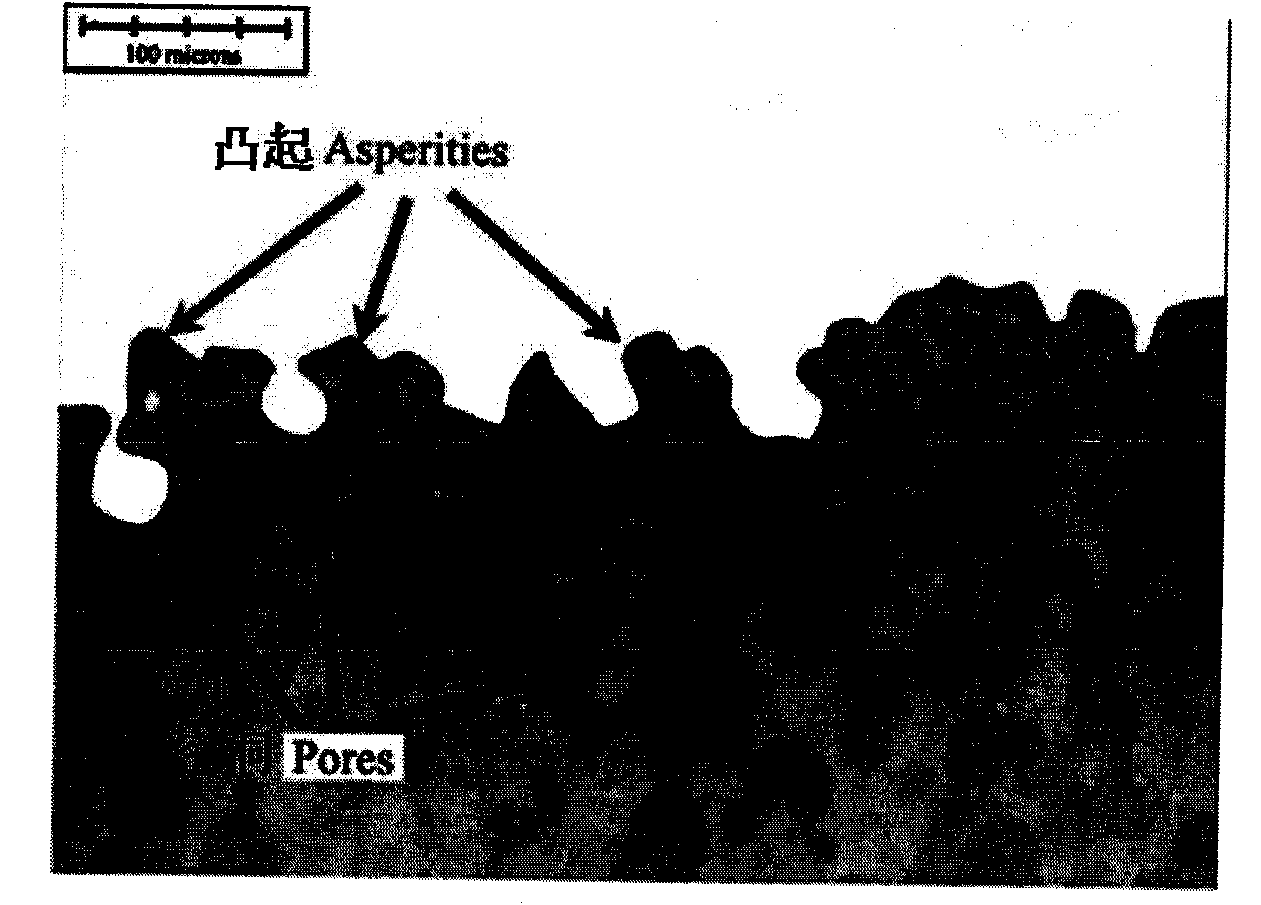
Method for establishing copper interconnection chemical mechanically mechanical polishing process model
ActiveCN101887467ASolve Contact Problems ExactlyImprove flatnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceCompound (substance)
The invention belongs to the field of a copper interconnection chemical mechanically mechanical polishing process, and in particular relates to a method for establishing a copper interconnection chemical mechanically mechanical polishing process model. In the method, a probability density function represents the height characteristic of the surface of a polishing pad, an autocorrelation function represents the traverse characteristic of the surface of the polishing pad, and the rough surface of the polishing pad according with the specific probability density characteristic is generated by adopting a spectral method and a nonlinear transform method. In the method, the surface of the polishing pad is not needed to be geometrically simplified and approximated, and the randomly distributed geometric characteristics of the surface of the polishing pad can be strictly represented. The contact problem of the rough surface of the polishing pad and the surface of a chip is accurately solved by utilizing a contact mechanics function, so the modeling of the whole mechanically mechanical polishing process is realized and the model can be used for detecting results of the mechanically mechanical polishing process.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
System and method for the analysis of atomic force microscopy data
InactiveUS6993959B2NanotechAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAtomic force microscopyUser input
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Prediction method of leakage rate of contact mechanical seal
ActiveCN102411669AGuarantee safety and reliabilityLow cost operationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringStress relaxation
The invention relates to a prediction technology of a leakage rate of an existing contact mechanical seal. By utilizing a seal interface topography evolvement rule in the wear process of a movable ring and a stationary ring, and a contact compression stress variation rule of primary and secondary seal interfaces due to the wear-down of the movable ring and the stationary ring and the stress relaxation of an O-shaped ring, the topography parameters of the seal interfaces and loads on the movable ring and the stationary ring seal interfaces, the O-shaped ring and the internal diameter and external diameter contact interfaces of the O-shaped ring are determined after the mechanical seal runs for a certain time, and the characteristic sizes of percolation channels between the movable ring and the stationary ring seal interfaces and the O-shaped ring and the internal diameter and external diameter contact interfaces of the O-shaped ring are obtained by a percolation theory, a contact mechanics theory and a fractal theory at the moment, the effect of surface tension and centrifugal force of the sealed medium is considered, and then the leakage state of the existing contact mechanical seal is predicated by a Navier-Stokes equation. The method is simple and practical, the accident problems caused by frequent replacement or expiration of the mechanical seal can be effectively solved, and the safety and reliability of equipment are improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
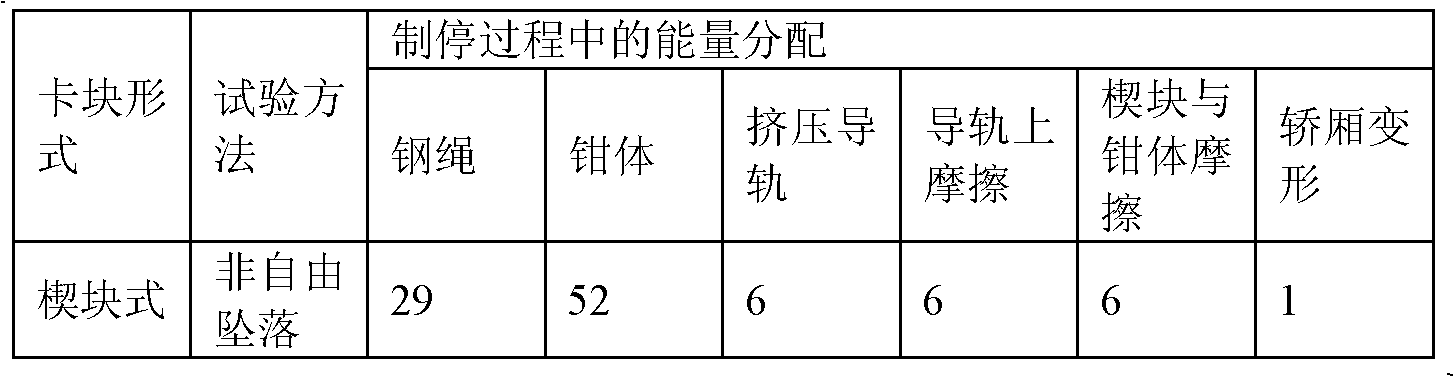
Heat flux density improved method for safety tongs of explosion-proof elevator
ActiveCN102426632AAccurate and reliable measurement resultsSpecial data processing applicationsHeat fluxNumerical models
The invention relates to the design technology of safety tongs of an explosion-proof elevator, and in particular relates to a heat flux density improved method for safety tongs of the explosion-proof elevator. In the method, time average effect is taken out, and the spatial average effect still exists at the same time so as to obtain a conservative temperature rise evaluation; analysis is performed from the point of view of contact mechanics, a complete finite element numerical model is established for stopping the safety tongs, the lift car mass is equivalent to the safety tongs block body material with extra-high density, the working pressure and initial stopping speed same as the actual working condition are applied, finite element simulation is carried out aiming at the stopping process of the safety tongs, the influences from the friction coefficient, stopping working pressure, initial stopping speed, safety tongs block material and plastic deformation of safety tongs blocks in the stopping process on the maximum stopping temperature rise can be researched by simulation analysis, the above research result is verified through a drop stopping test and is compared with a simulation result so as to ensure the measurement result to be more accurate and credible.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & TECHN RES +1
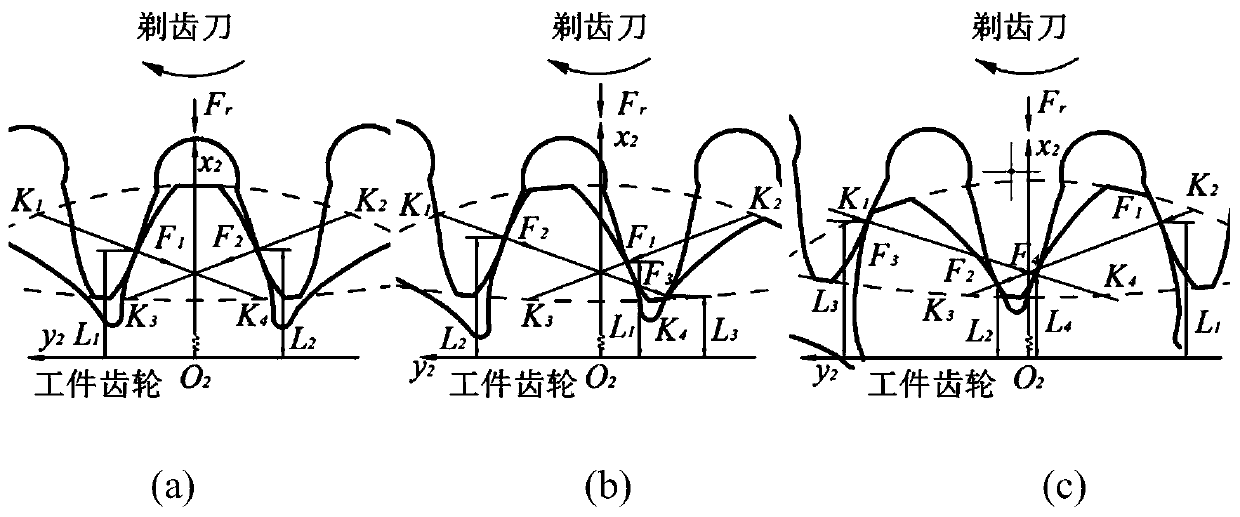
A gear shaving tooth profile error prediction method
ActiveCN109710969AControl or counteract tooth profile errorsHigh precisionForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsElastic plasticProcess guidance
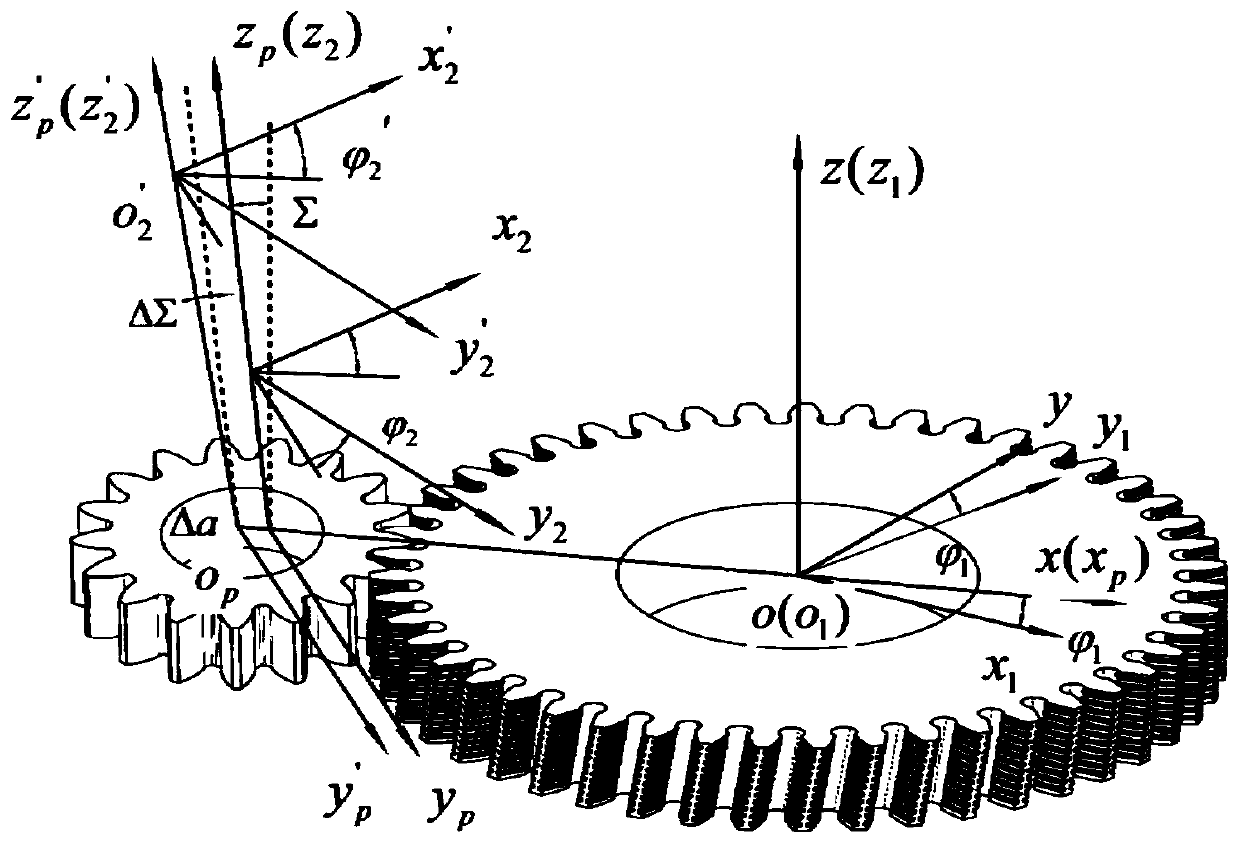
The invention discloses a gear shaving profile error prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: introducing a gear shaving mounting error into a gear shaving motion coordinate system,constructing new coordinate conversion, deducing and calculating a compensation displacement amount caused by the gear shaving mounting error, and enabling the mode of the compensation displacement amount at a normal component vector of a contact point to be a tooth profile cut depth caused by the gear shaving mounting error. And elastic-plastic press-cutting deformation of gear shaving surface contact is given based on the contact mechanics, and the actual press-cutting deformation of gear shaving is calculated by comparing the ultimate strength of the material. And comprehensively considering the gear shaving installation error tooth profile cutting depth and the gear shaving actual pressing and cutting deformation to establish a gear shaving tooth profile error prediction model. By means of the method, prediction of the gear tooth form error of the shaved workpiece can be accurately achieved, the tooth surface precision and the machining efficiency can be effectively improved, and targeted technological guidance is provided.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
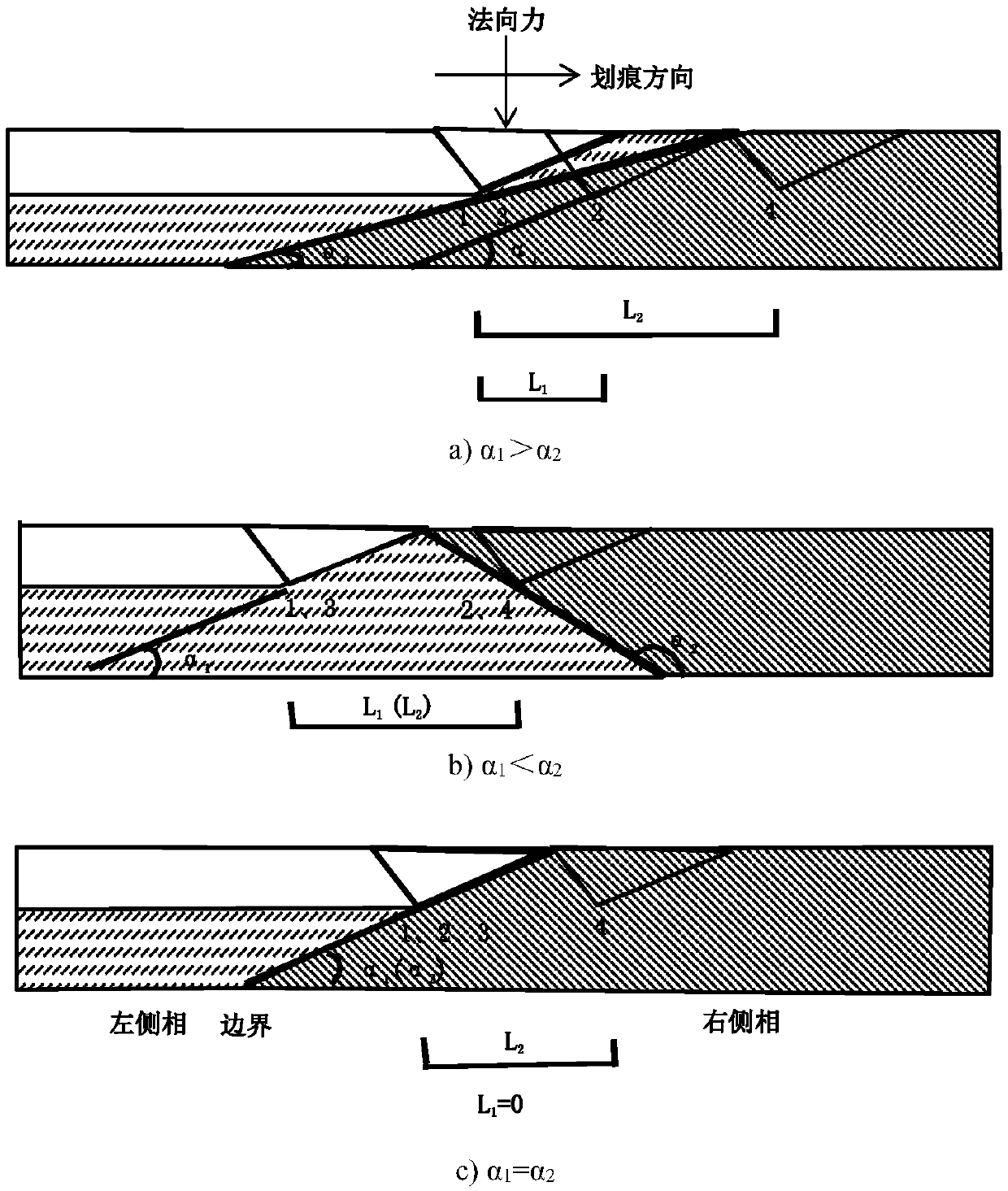
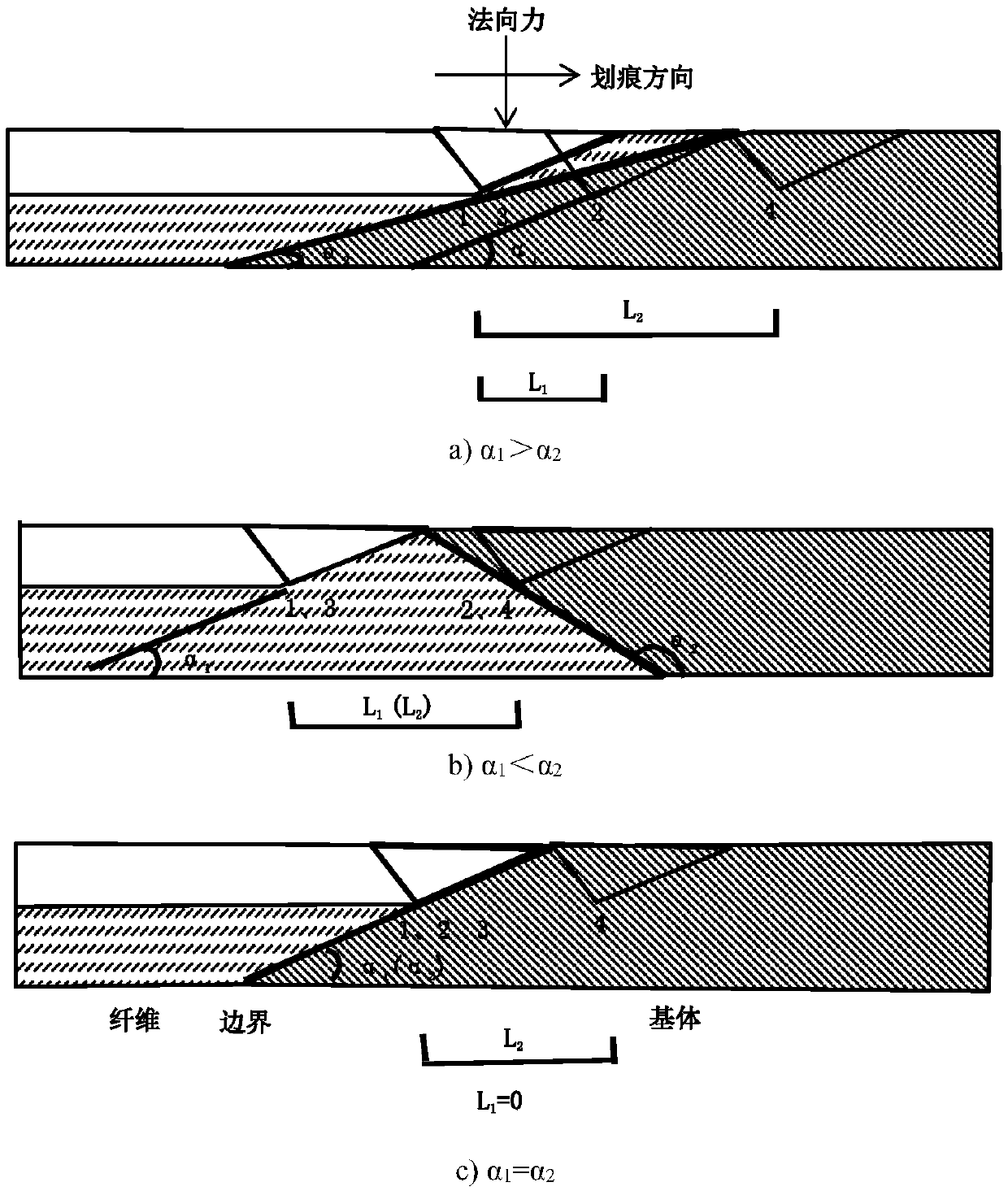
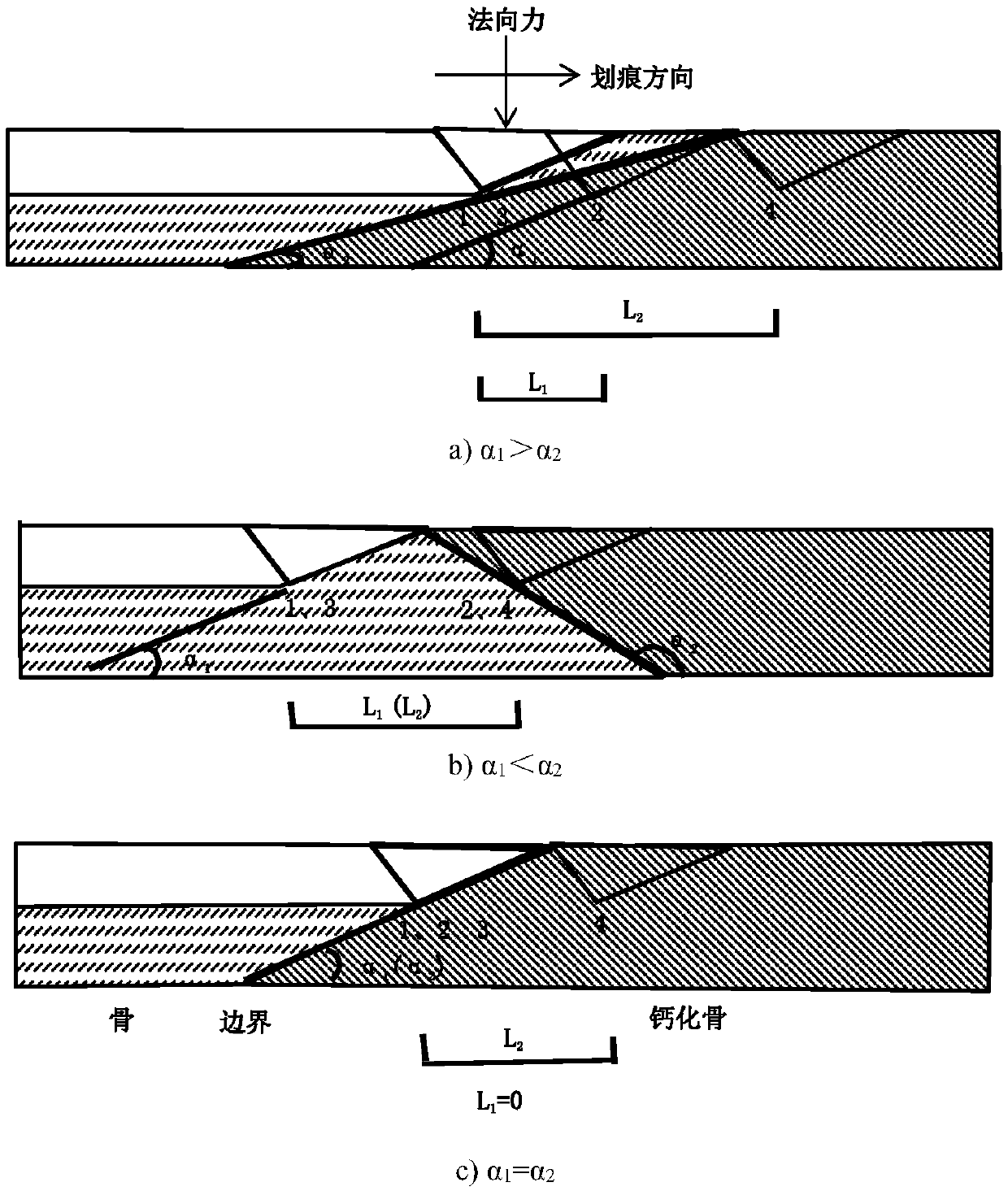
Method for testing performances of all components in heterogeneous material based on nano-scratch technology
ActiveCN107941638AEffective Judgment WidthJudgment widthInvestigating material hardnessTest performanceMicro nano
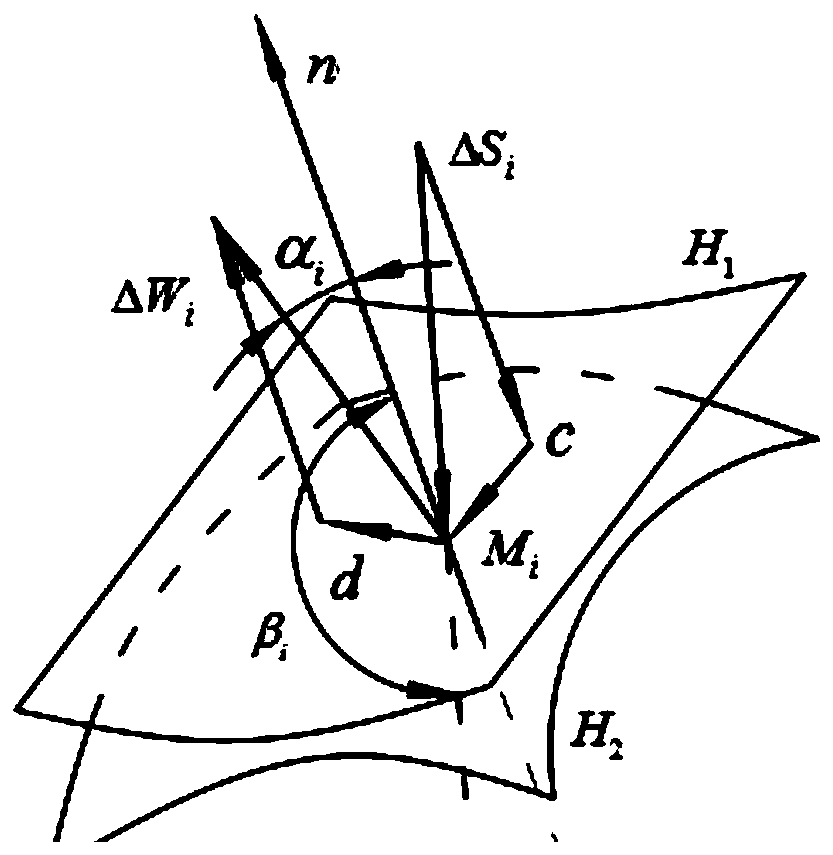
The invention discloses a method for testing the performances of all components in a heterogeneous material based on a nano-scratch technology, and belongs to a method for testing the performance of micro-nano scale materials. The method comprises the following steps: inlaying, grinding and polishing the measured heterogeneous material to produce a sample for nano-indentation and nano-scratch; keeping a pressure head at a constant scratching depth through a feedback adjustment technology, and carrying out scratch operation in a parallel manner, an equal interval manner and an equal depth manner to make the pressure head sequentially scratch into a left phase, a boundary phase and a right phase; obtaining the starting point position and the end point position of every scratch transition area according to a contact mechanics judgment criterion; and adopting the reciprocal of the measured contact stiffness as the ordinate, drawing all points through origin, linearly fitting all the points, and calculating the reciprocal of the obtained straight slope to obtain the elastic modulus of the right phase. The method has the advantages of effectiveness in judgment of the width of the boundary phase at a certain depth in a typical area, avoiding of the influences of the boundary phase, improvement of the experiment precision, and obtaining of the performances of all the components in theheterogeneous material, not affected by the circumference effects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
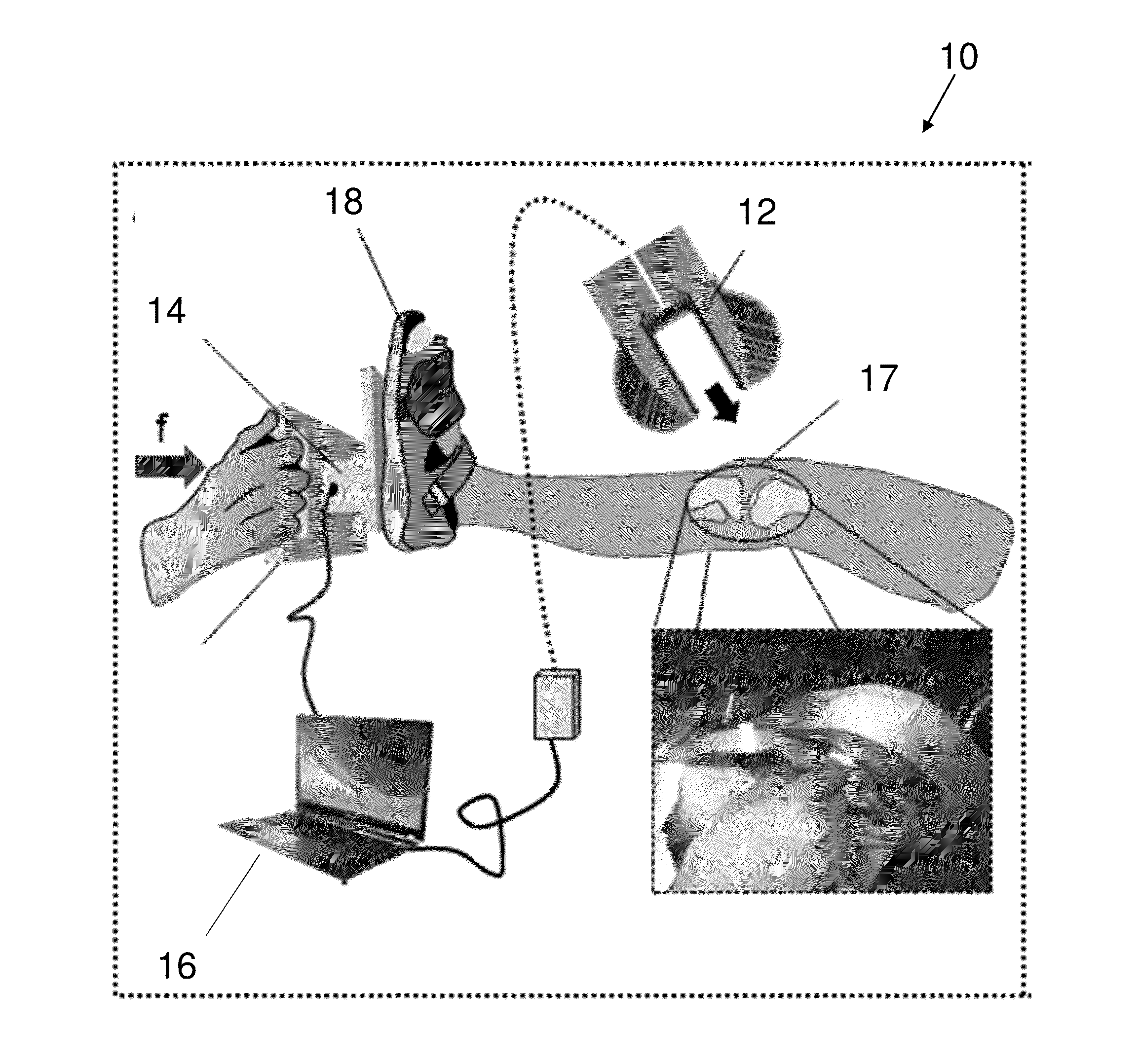
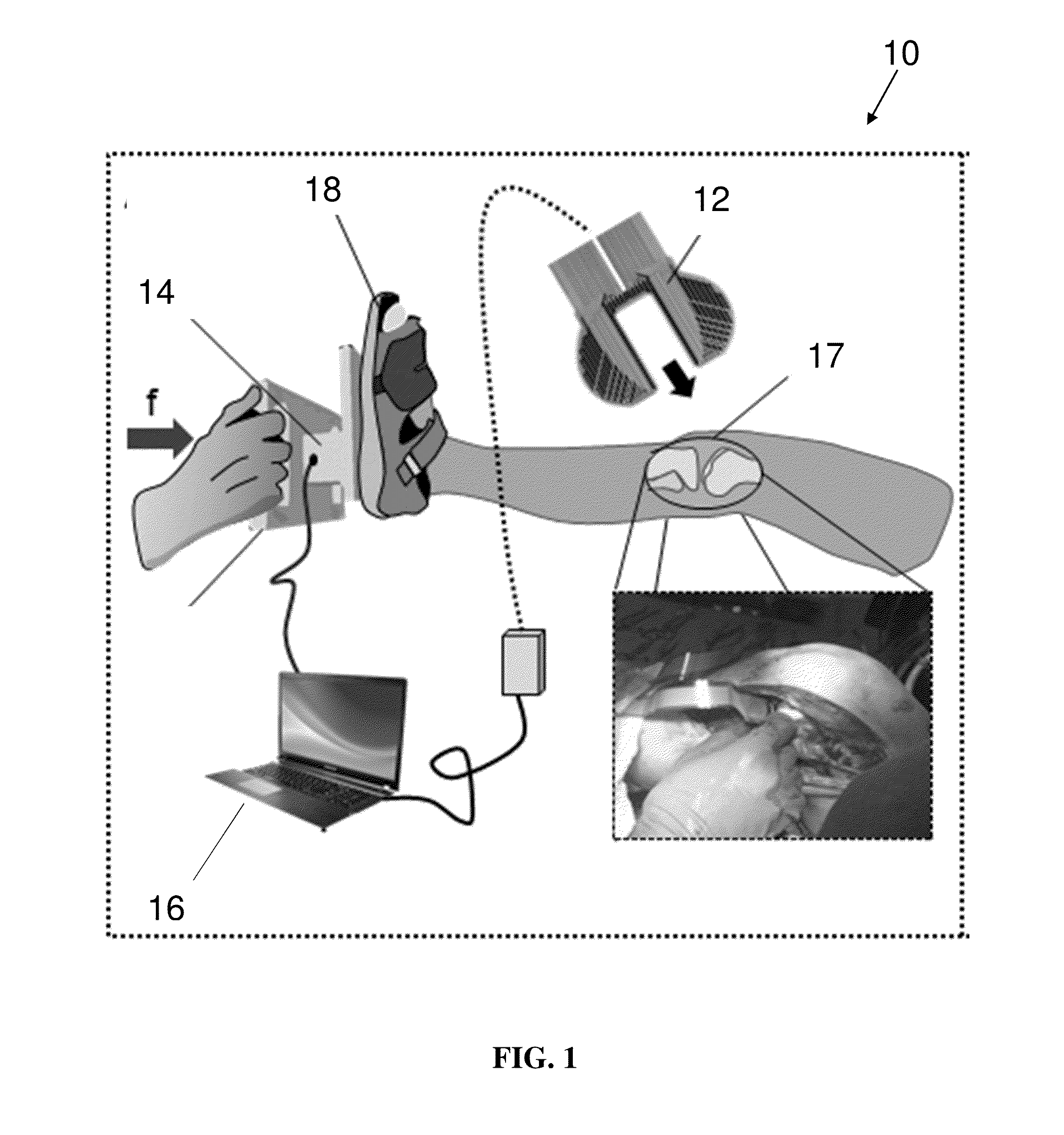
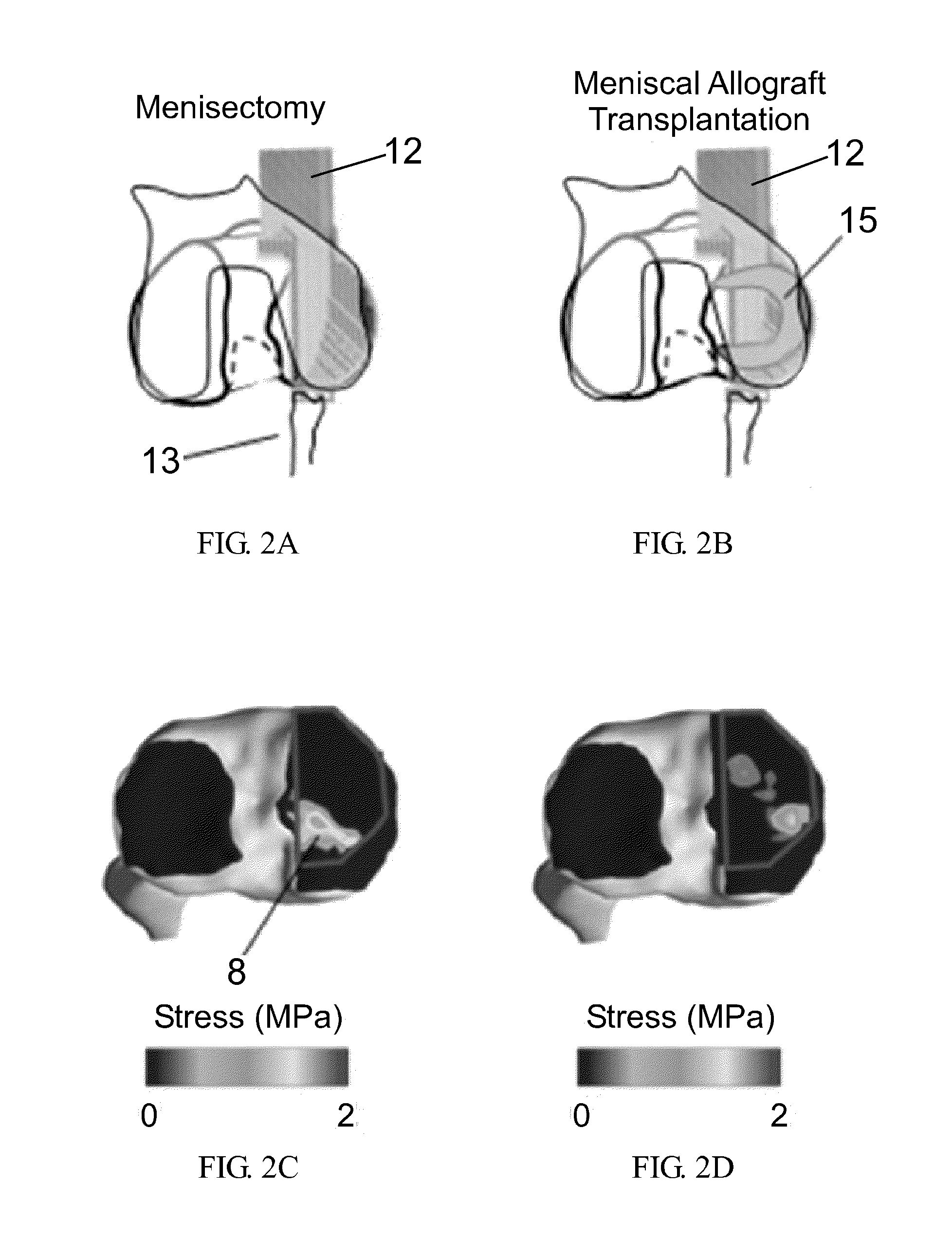
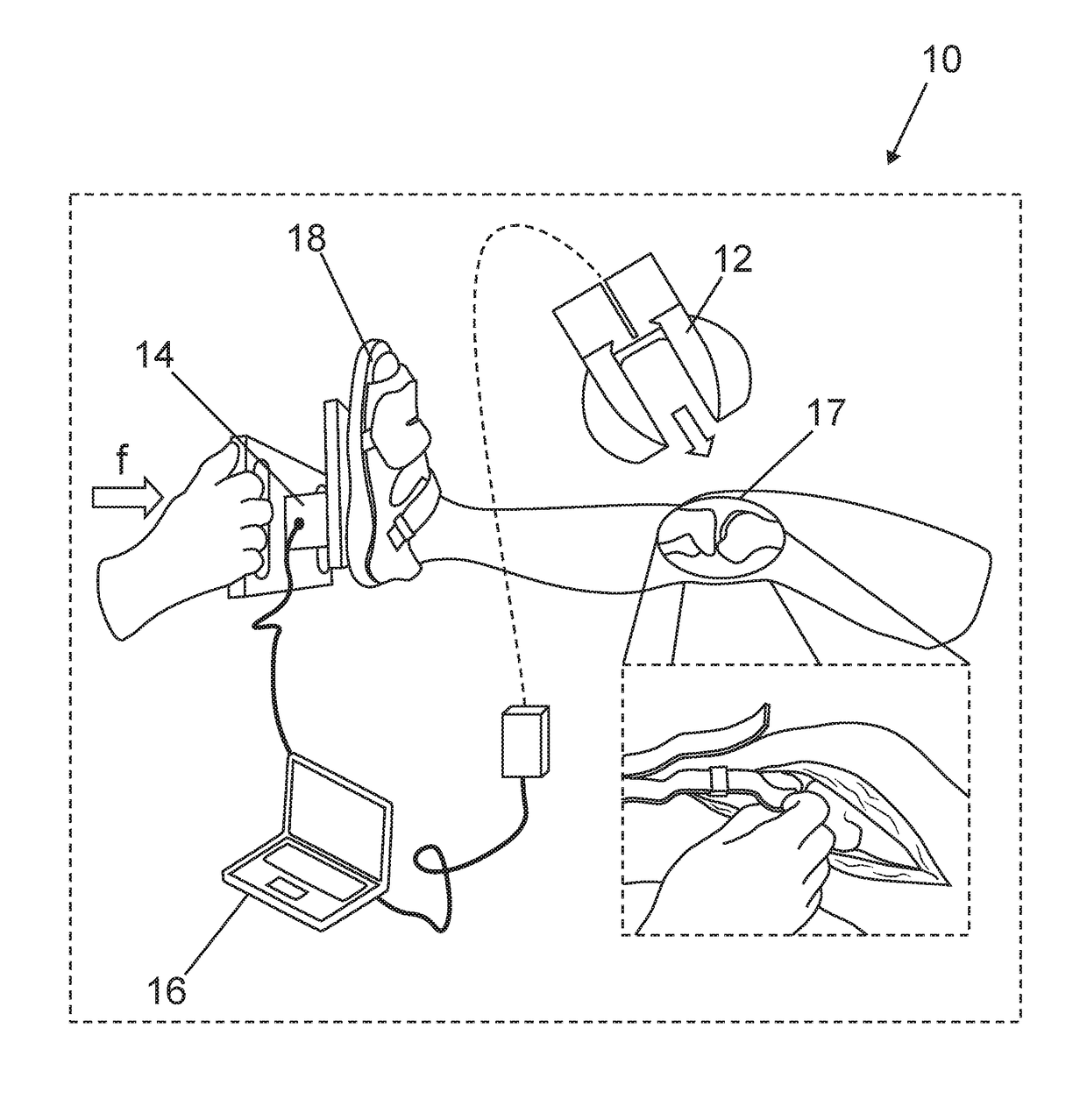
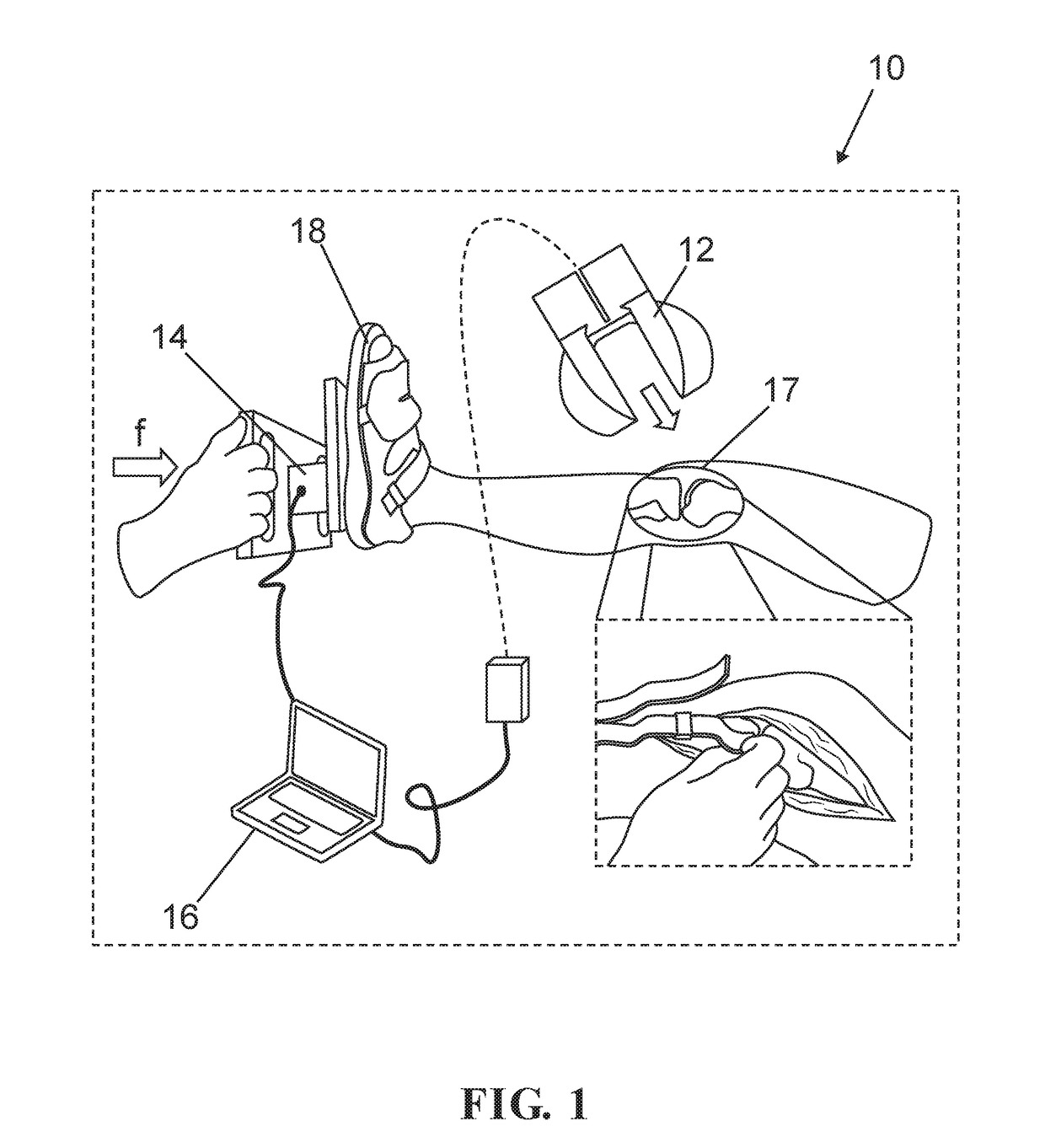
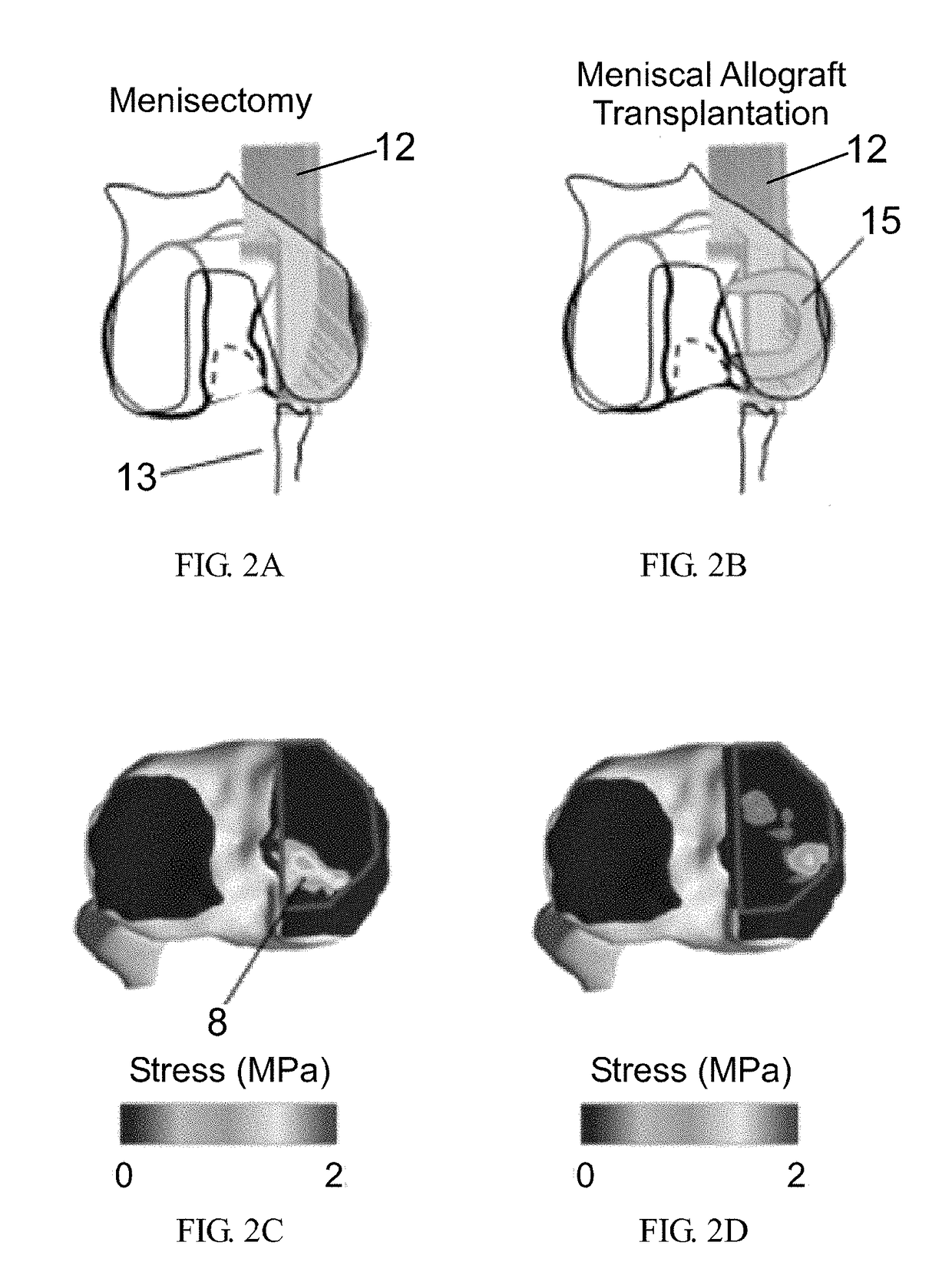
System and method for intraoperative joint contact mechanics measurement
A method for intraoperatively measuring joint contact mechanics of a patient's joint is provided. The method includes inserting a sensor between first and second bones of a joint. Then a predetermined force is applied to one of the first and second bones. Afterwards, contact mechanics such as, contact stresses, contact areas and / or forces are measured between the first and second bones in response to the applied predetermined force.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
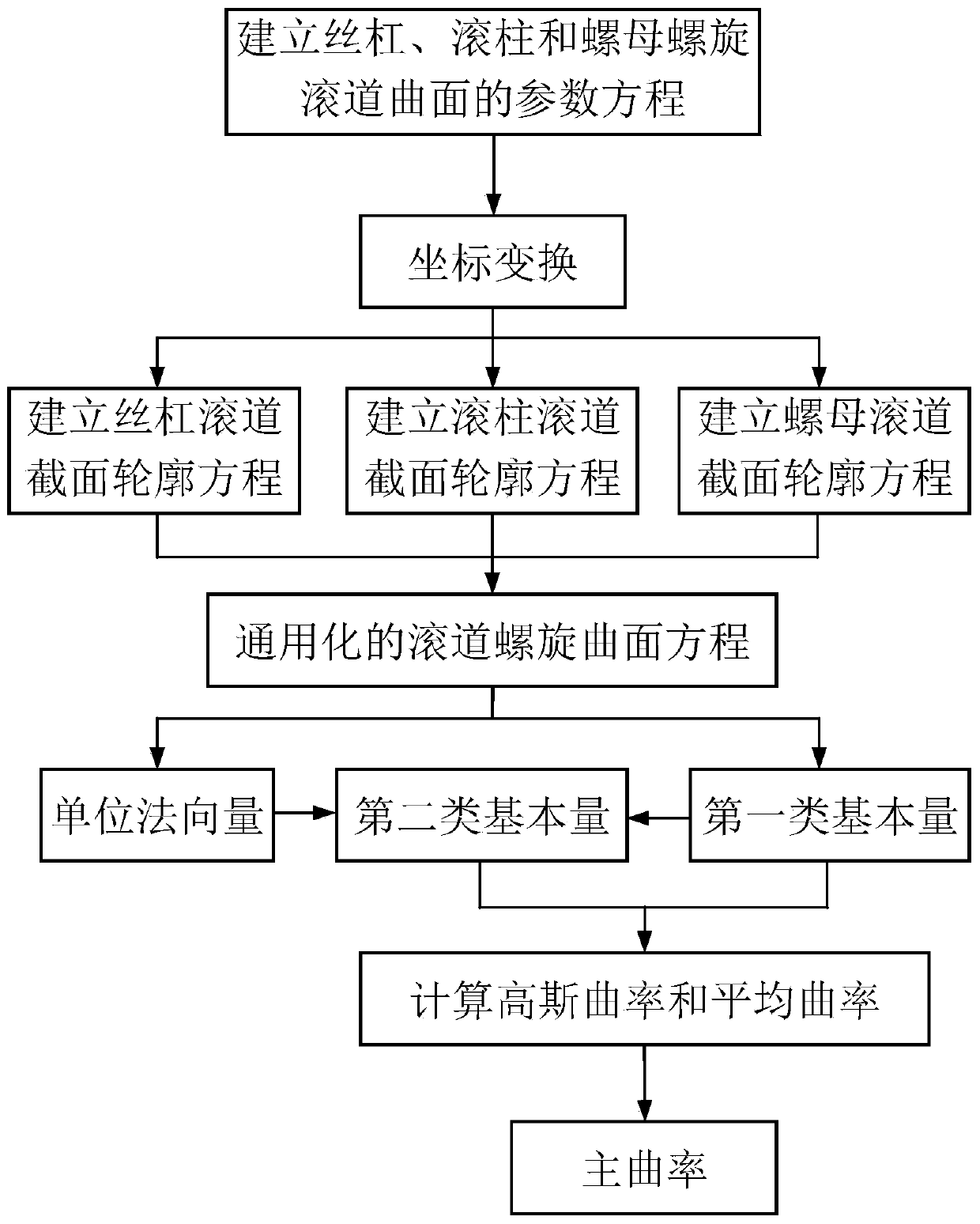
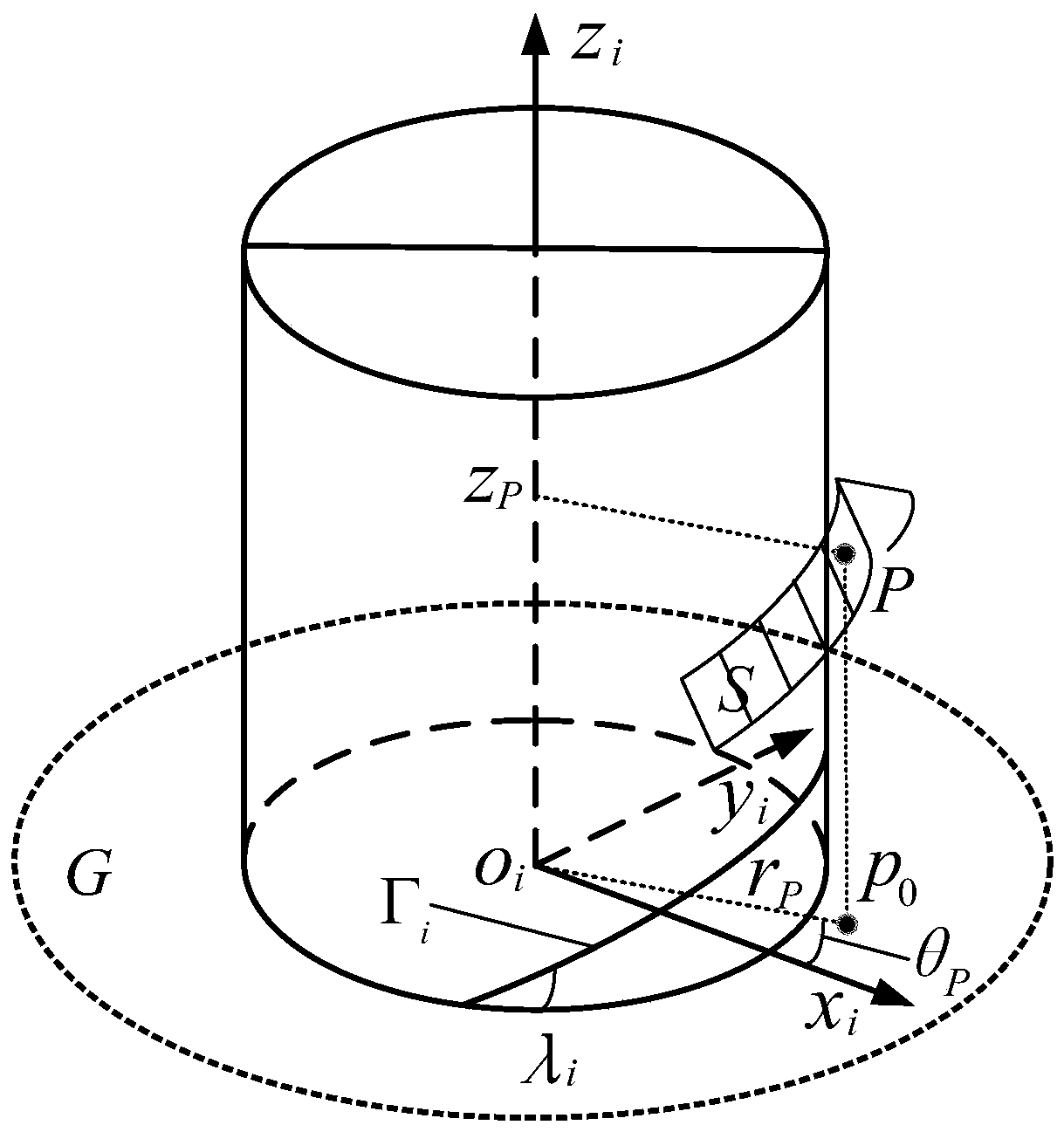
Main curvature calculation method for contact rolling path of planetary rolling column lead screw pair
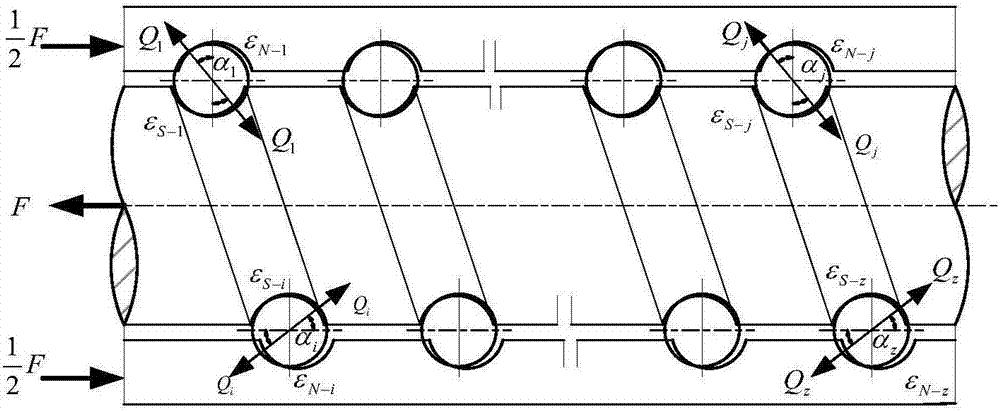
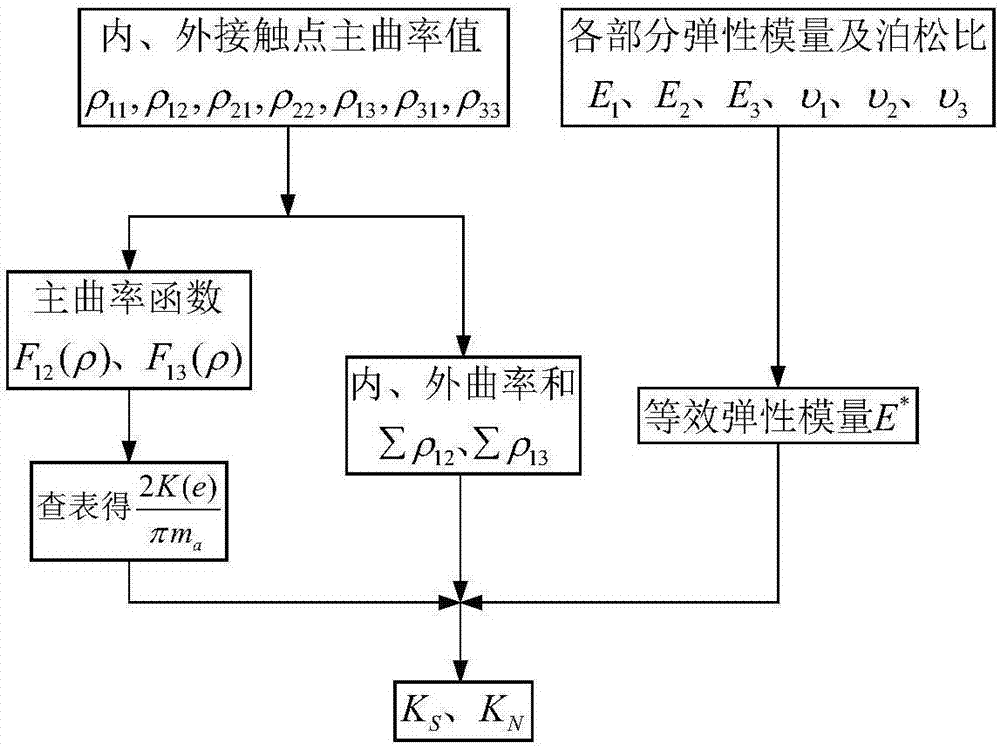
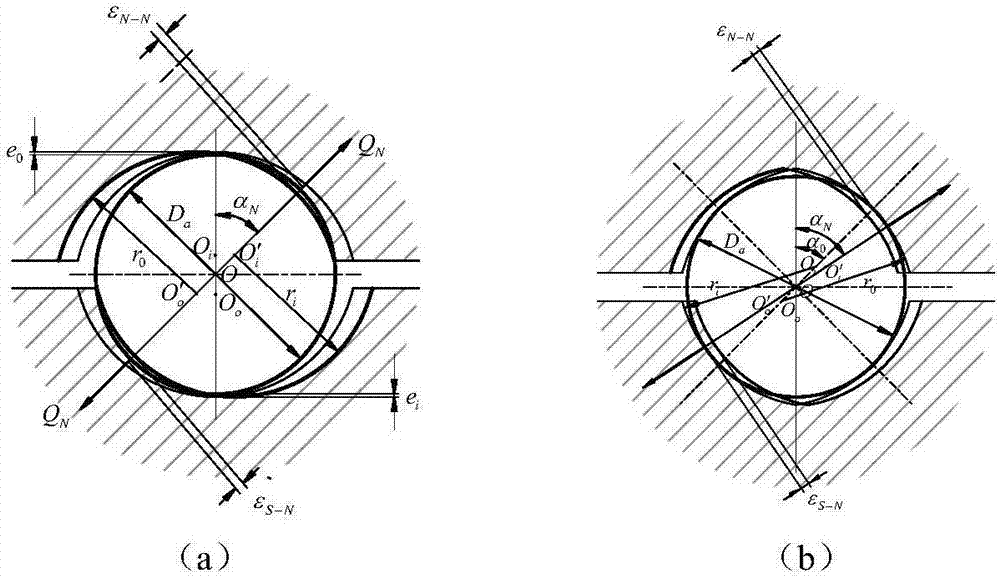
ActiveCN111199013AAccurate descriptionIncrease flexibilitySustainable transportationGearingEngineeringContact mechanics
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Contact Mechanic Tests using Stylus Alignment to Probe Material Properties
ActiveUS20160370272A1Design optimisation/simulationInvestigating material hardnessDevices fixationContact mechanics
An apparatus for performing a contact mechanics test on a substrate includes a stylus, a core configured to engage the stylus against the substrate, a stylus engagement mechanism configured to induce a contact load or a penetration depth to the stylus, a core engagement mechanism configured to maintain contact of the core and to move the core along the substrate surface, a frame configured to be fixed with respect to the apparatus or to be moved together with the core engagement mechanism as an assembly, a frame engagement mechanism configured to engage the frame with the substrate surface; and a substrate monitoring device configured to measure characteristics of substrate contact response and / or collect material machined from the substrate. Methods of performing a contact mechanics test are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS MATERIALS TECH
Micro-nano indentation experiment method for fiber-reinforced composite
ActiveCN107907436AEffective Judgment WidthImprove experimental precisionInvestigating material hardnessMicro nanoTest sample
The invention discloses a micro-nano indentation experiment method for a fiber-reinforced composite and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano mechanical testing. A fiber-reinforced composite under test is subjected to embedding prior to grinding and polishing so as to obtain a test sample of nano indentation and nano scratch; a start of scratch is a center point of a circular area; a constant scratch depth is kept for a presser by means of feedback adjustment; a series of equal depth scratches are made from the center point of the circular area sequentially through fiber, an interfacialphase and a base. Start and end point positions of the interfacial phase of each scratch are acquired through contact mechanics judging rules; the start and end points of the interfacial phase are sequentially connected by lines, and accordingly morphology of the interfacial phases is acquired. The method of the invention has the advantages that interfacial phase width of a typical area under certain depth can be effectively judged; when the indentation depth is less than the scratch depth, entry of the indentation in the interfacial phase is avoided, experiment precision is improved, and micro-nano indentation properties of the fiber-reinforced composite with no influence of peripheral effect are acquired.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Contact mechanic tests using stylus alignment to probe material properties
ActiveUS9933346B2Design optimisation/simulationInvestigating material hardnessContact mechanicsPenetration depth
An apparatus for performing a contact mechanics test on a substrate includes a stylus, a core configured to engage the stylus against the substrate, a stylus engagement mechanism configured to induce a contact load or a penetration depth to the stylus, a core engagement mechanism configured to maintain contact of the core and to move the core along the substrate surface, a frame configured to be fixed with respect to the apparatus or to be moved together with the core engagement mechanism as an assembly, a frame engagement mechanism configured to engage the frame with the substrate surface; and a substrate monitoring device configured to measure characteristics of substrate contact response and / or collect material machined from the substrate. Methods of performing a contact mechanics test are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS MATERIALS TECH
Contact mechanic tests using stylus alignment to probe material properties
An apparatus for performing a contact mechanics test on a substrate includes a stylus, a core configured to engage the stylus against the substrate, a stylus engagement mechanism configured to induce a contact load or a penetration depth to the stylus, a core engagement mechanism configured to maintain contact of the core and to move the core along the substrate surface, a frame configured to be fixed with respect to the apparatus or to be moved together with the core engagement mechanism as an assembly, a frame engagement mechanism configured to engage the frame with the substrate surface; and a substrate monitoring device configured to measure characteristics of substrate contact response and / or collect material machined from the substrate. Methods of performing a contact mechanics test are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS MATERIALS TECH
System and method for intraoperative joint contact mechanics measurement
A method for intraoperatively measuring joint contact mechanics of a patient's joint is provided. The method includes inserting a sensor between first and second bones of a joint. Then a predetermined force is applied to one of the first and second bones. Afterwards, contact mechanics such as, contact stresses, contact areas and / or forces are measured between the first and second bones in response to the applied predetermined force.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Method for testing mechanical performances of calcified bone based on nano-indentation and nano-scratch
ActiveCN107941588AObtaining nanoindentation mechanical propertiesAvoid pressingPreparing sample for investigationInvestigating material hardnessMicro nanoRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a method for testing the mechanical performances of a calcified bone based on nano-indentation and nano-scratch, and belongs to a method for testing micro-nano mechanics of biological materials. The method comprises the following steps: placing a bone cartilage in a metal sample cup, and obtaining the starting point position and the end point position of every scratch transition area according to a contact mechanics judgment criterion; establishing a rectangular coordinate system including all scratch with the summit of the left bottom of a rectangular area as the zeropoint, and sequentially connecting the start points and the end points of the transition areas to form a line; and summing up the calculated structural flexibility and the structural flexibility of aninstrument frame to obtain a corrected frame flexibility, and afresh calculating a bone and calcified bone elastic modulus to obtain the corrected bone and calcified bone elastic modulus. The bone-calcified bone interface influence area is effectively judged at a certain depth, and the pressed depth is smaller than the scratch depth, the indentation is effectively prevented from being pressed inthe bone-calcified bone composite phase, and the mechanical performances of the nano-indentation of the calcified bone are obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Measurement of material properties under local tensile stress through contact mechanics
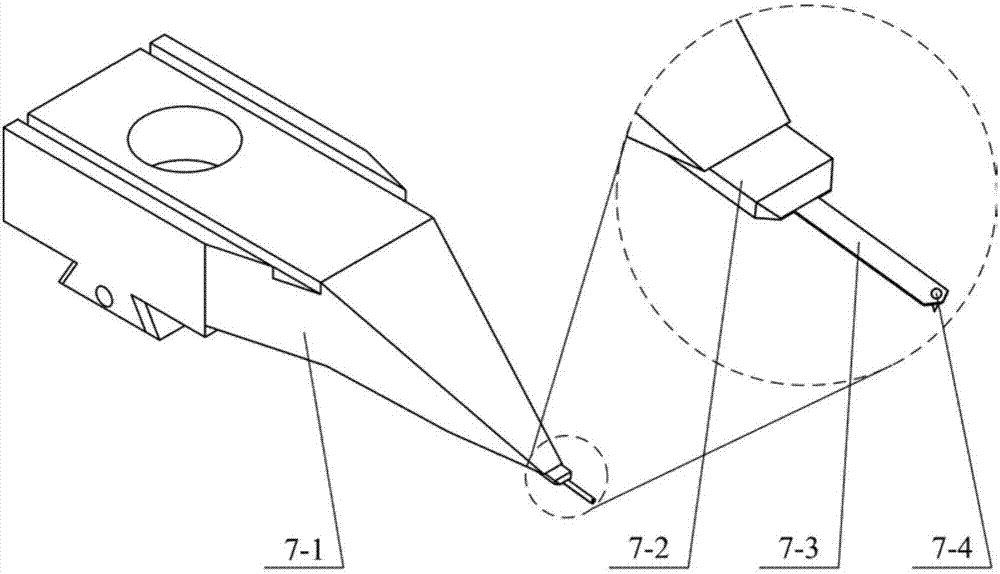
ActiveUS11378502B2Promote generationPromote tensile stressUsing mechanical meansInference methodsEngineeringContact element
An apparatus for performing a contact mechanics test in a substrate includes a stylus having at least two contact elements. Each contact element has a contact profile, and the contact elements are disposed in the stylus to define a stretch passage therebetween. The stylus is configured to deform the substrate so as to cause the substrate to flow between the contact elements and induce tension in the substrate in order to generate and preserve micromodifications in the substrate. Methods of performing a contact mechanics test using the apparatus are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS MATERIALS TECH
Method for in situ performance test of all components in particle reinforced composite material
ActiveCN107941689AReduce test efficiencyUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisMicro nanoRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a method for in situ performance test of all components in a particle reinforced composite material, and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano mechanical test. The method comprises the following steps: inlaying, grinding and polishing the tested particle reinforced composite material to prepare a sample used for nano-indentation and nano-scratch; keeping a pressure head at a constant scratching depth through a feedback technology to complete a series of scratches; establishing the rectangular coordinate system of every scratch path with the center point of a circular area as a zero point, and importing the coordinates of acquisition points on the scratch paths into origin; and obtaining the positions of the starting point and the end point of every scratch boundary phase according to a contact mechanics judgment criterion, and sequentially connecting the starting points and the end points of the boundary phases to obtain the morphology of the boundary phases. The width of the boundary phase at a certain depth in a typical area can be effectively judged during the nano-indentation experiments of the micro-nanoscale material in order to obtain the in situ performances of all the components in the particle reinforced composite material, not affected by the circumference effects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Chip surface contact pressure calculation method and variable-scale manufacturability design method
ActiveCN105631082AImprove calculation accuracyAvoid design failureSpecial data processing applicationsContact pressureMechanical equation
The invention discloses a chip surface contact pressure calculation method and a variable-scale manufacturability design method. The calculation method comprises the steps of performing grid division on a wafer surface where a chip is to obtain a plurality of first grids; calculating a contact pressure of each first grid by utilizing a contact mechanical equation set to obtain contact pressure distribution of the wafer surface, and marking the contact pressure distribution as first contact pressure distribution; dividing each first grid into a plurality of second grids; calculating a contact pressure of each second grid by utilizing the contact mechanical equation set to obtain contact pressure distribution in each first grid, and marking the contact pressure distribution as second contact pressure distribution; and according to the line width in each second grid, calculating contact pressure distribution in each second grid, marking the contact pressure distribution as third contact pressure distribution, and obtaining contact pressure distribution of the chip surface. According to the chip surface contact pressure calculation method provided by the invention, the calculation efficiency and the calculation precision can be considered simultaneously, thereby providing premise and guarantee for manufacturability design optimization.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for optimizing local finite element model of aircraft cabin door and fuselage contact area
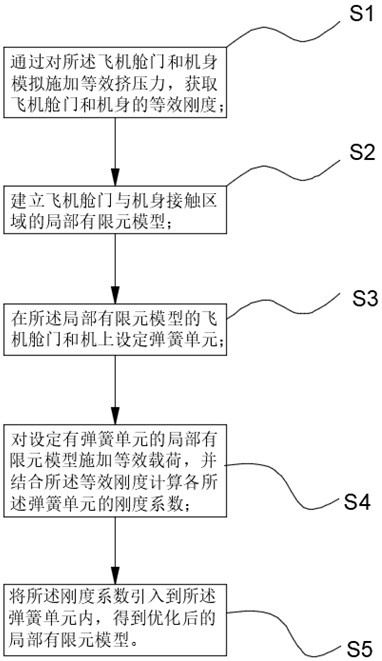
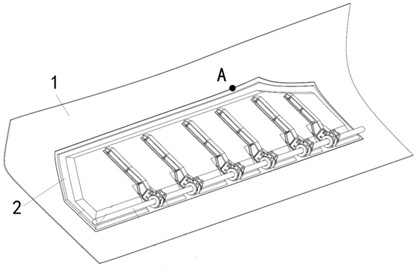
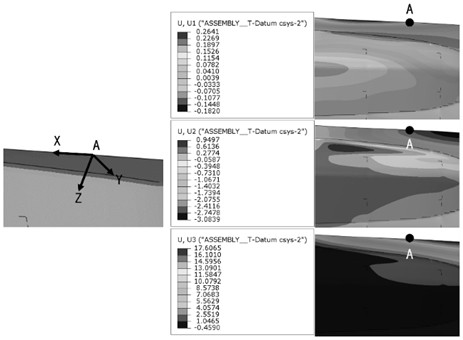
ActiveCN114692469AAchieve optimizationImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStiffness coefficientElement model
The invention discloses an optimization method for a local finite element model of a contact area of an aircraft cabin door and a fuselage, and the optimization method comprises the steps: firstly obtaining the equivalent stiffness of the aircraft cabin door and the fuselage, then building the local finite element model of the contact area of the aircraft cabin door and the fuselage, and setting a spring unit in the local finite element model; simulating and applying an equivalent load to the local finite element model, and comparing the deformation with the equivalent stiffness to obtain a stiffness coefficient of each spring unit; and finally, adding a stiffness coefficient into the local finite element model to realize optimization of the local finite element model. By introducing the equivalent stiffness of the aircraft cabin door and the fuselage, organic combination of the overall structural characteristics of the aircraft cabin door and the fuselage and the stress state of the aircraft cabin door and the fuselage at the contact point is realized, so that the overall structural stiffness of the aircraft is inherited and reflected in local stress analysis; and the calculation precision of aircraft cabin door and fuselage assembly contact mechanics is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com