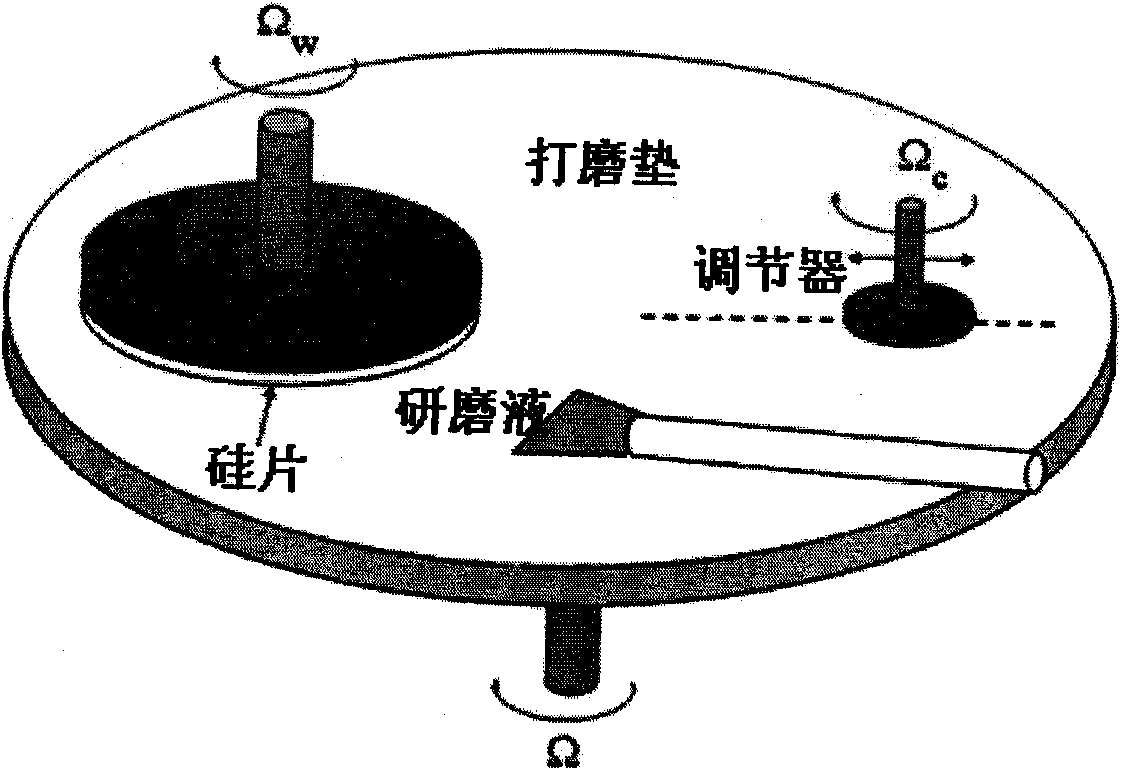
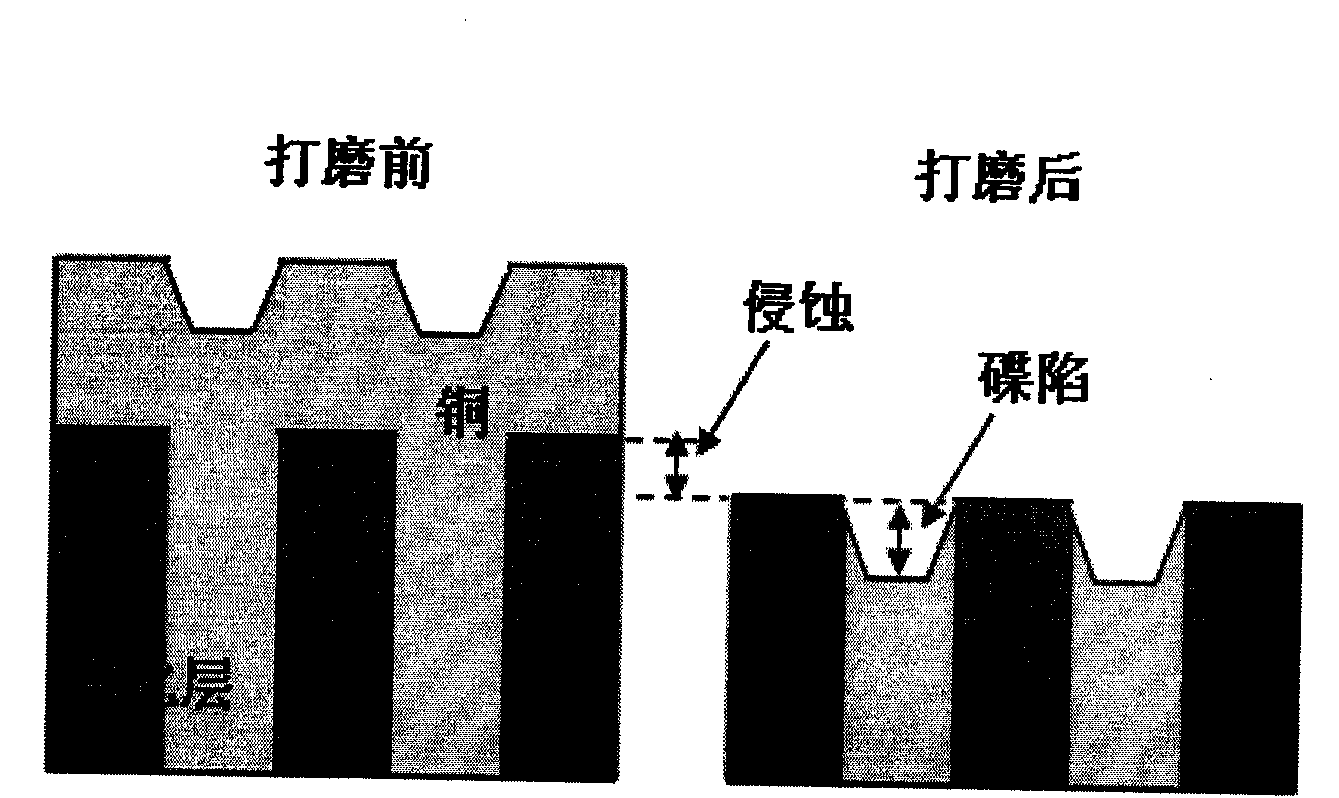
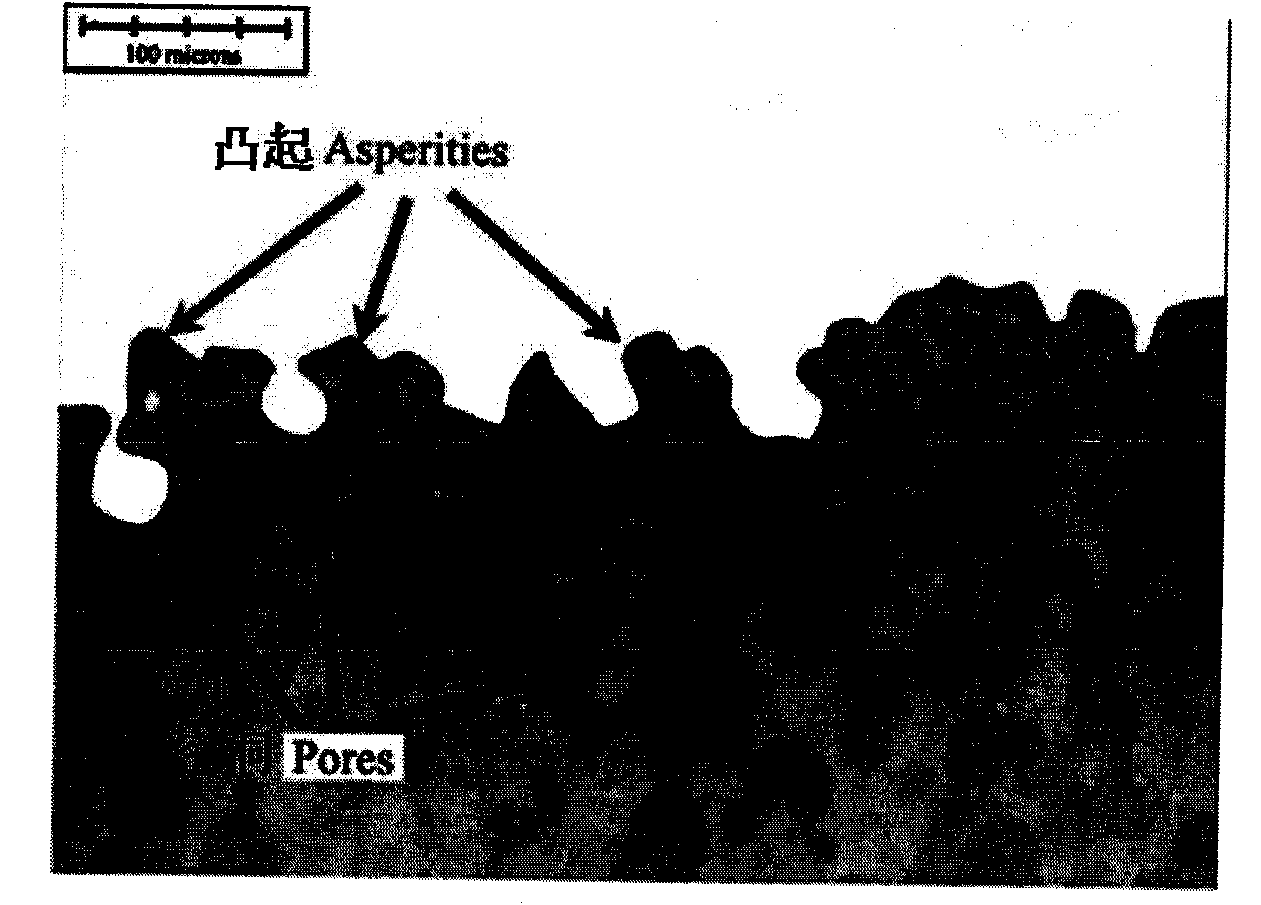
Method for establishing copper interconnection chemical mechanically mechanical polishing process model
A chemical-mechanical and process model technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to deal with non-Gaussian distribution, ignoring the lateral random characteristics of the polishing pad surface, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0140] Comparison between polishing results obtained by the model of the invention and actual experimental measurements
[0141] In this embodiment, the layout of the chip to be polished is a group of interconnection patterns with a line width plus line spacing of 250um and a line density varying from 10% to 90%. The standard down pressure is 28kPa, the copper removal rate is 15nm / s and the oxide removal rate is 5nm / s under the standard down pressure. The Young's modulus of the polishing pad is 29MPa, and the Poisson's coefficient is 0.2. The probability density function of the height of the sanding pad surface is assumed to be a Gaussian distribution, and the correlation function takes the following form
[0142] R ( x ) = e - x 2 η 2 - - ...
Embodiment 2
[0146] Comparison of polishing results for abrasive pads with two different surface distributions, Gaussian and non-Gaussian
[0147] In this embodiment, the layout of the chip to be polished is a pattern with a line width of 20um and a line density of 20%. The total polishing time is 100s, the standard down pressure is 28kPa, the copper removal rate under the standard down pressure is 15nm / s, the oxide removal rate is 5nm / s, the Young's modulus of the polishing pad is 29MPa, Poisson The coefficient is 0.2. where the non-Gaussian probability density function is
[0148] pdf 1 ( x ) = 2 2 π ( σ 1 + ...
Embodiment 3
[0154] In this embodiment, the chip to be polished is a pattern with a line width of 20um and a line density of 20%. The total polishing time is 500s, the standard down pressure is 28kPa, the copper removal rate under the standard down pressure is 15nm / s, the oxide removal rate is 5nm / s, the Young's modulus of the polishing pad is 29MPa, Poisson The coefficient is 0.2. The height of the sanding pad surface is assumed to have a Gaussian distribution.
[0155] Figure 11(A) shows the effect of changing the pad surface topography parameters (variance and correlation length) on dishing and erosion. Among them, dishing increases with the variance of the surface height of the polishing pad, while erosion decreases slightly with the variance, as shown in Fig. 11(B). The reason is that the variance of the surface height becomes larger, which means that the surface roughness increases, and the protrusions on the surface of the polishing pad are more likely to touch the bottom of the s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Young's modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com