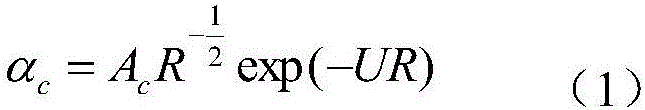Patents
Literature
78 results about "Rayleigh backscattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
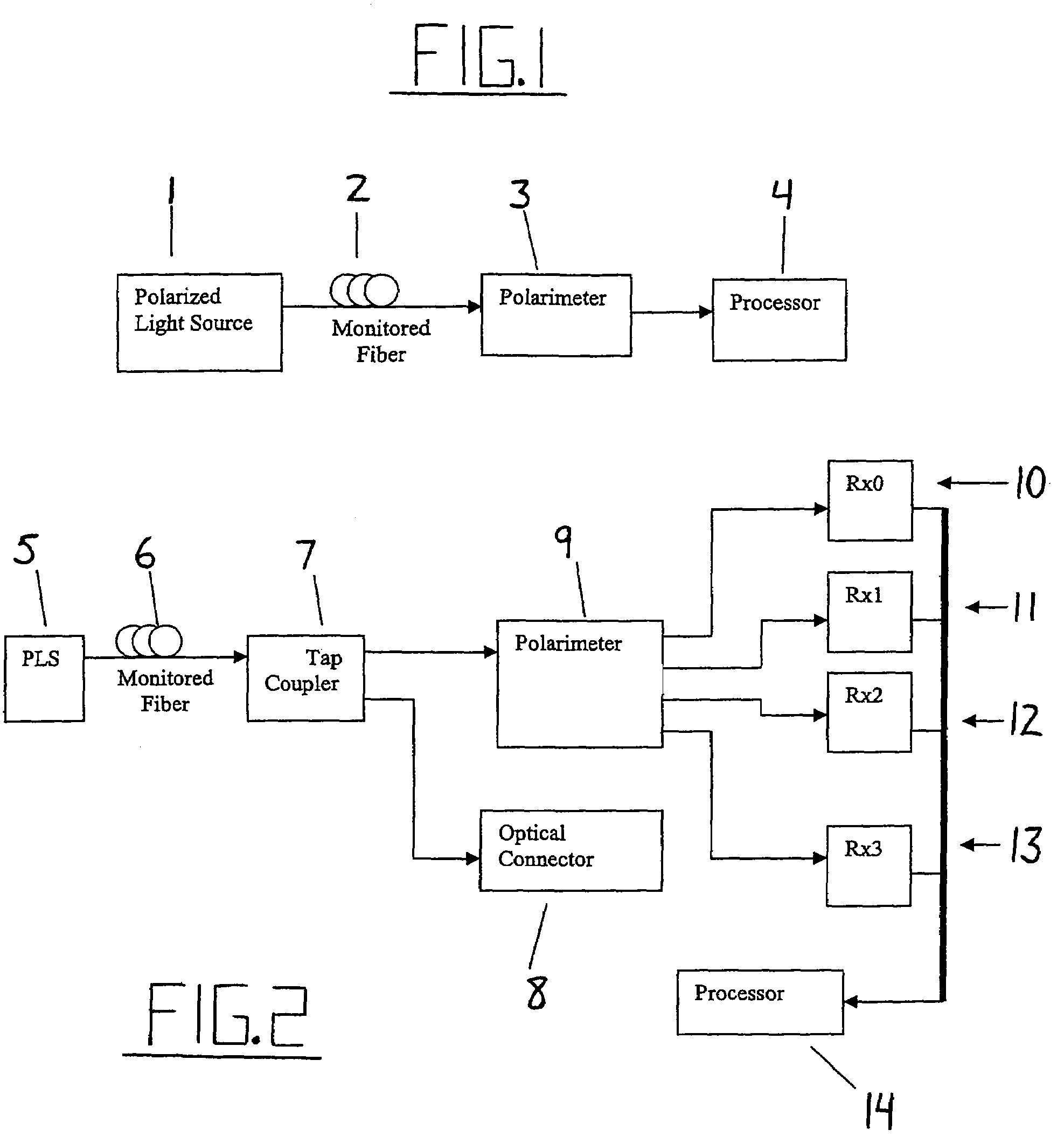
FIBER-OPTICS TEST & MEASUREMENT: Rayleigh backscatter reflectometry boosts fiber characterization. Optical backscatter reflectometry (OBR) is a powerful tool to characterize optical fiber and component properties, identifying small faults in these optical systems that can lead to failures in the field and improving the overall QC process.
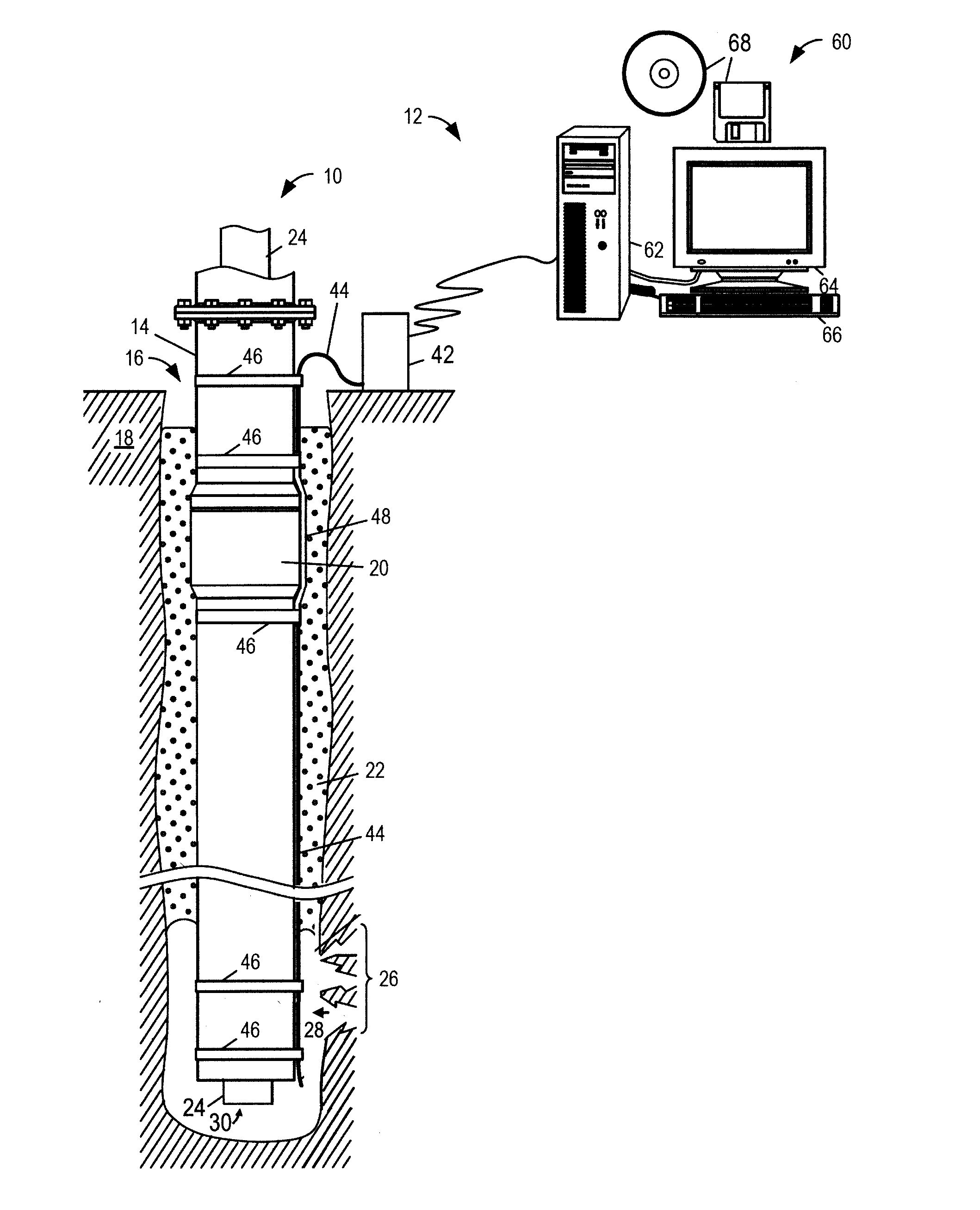
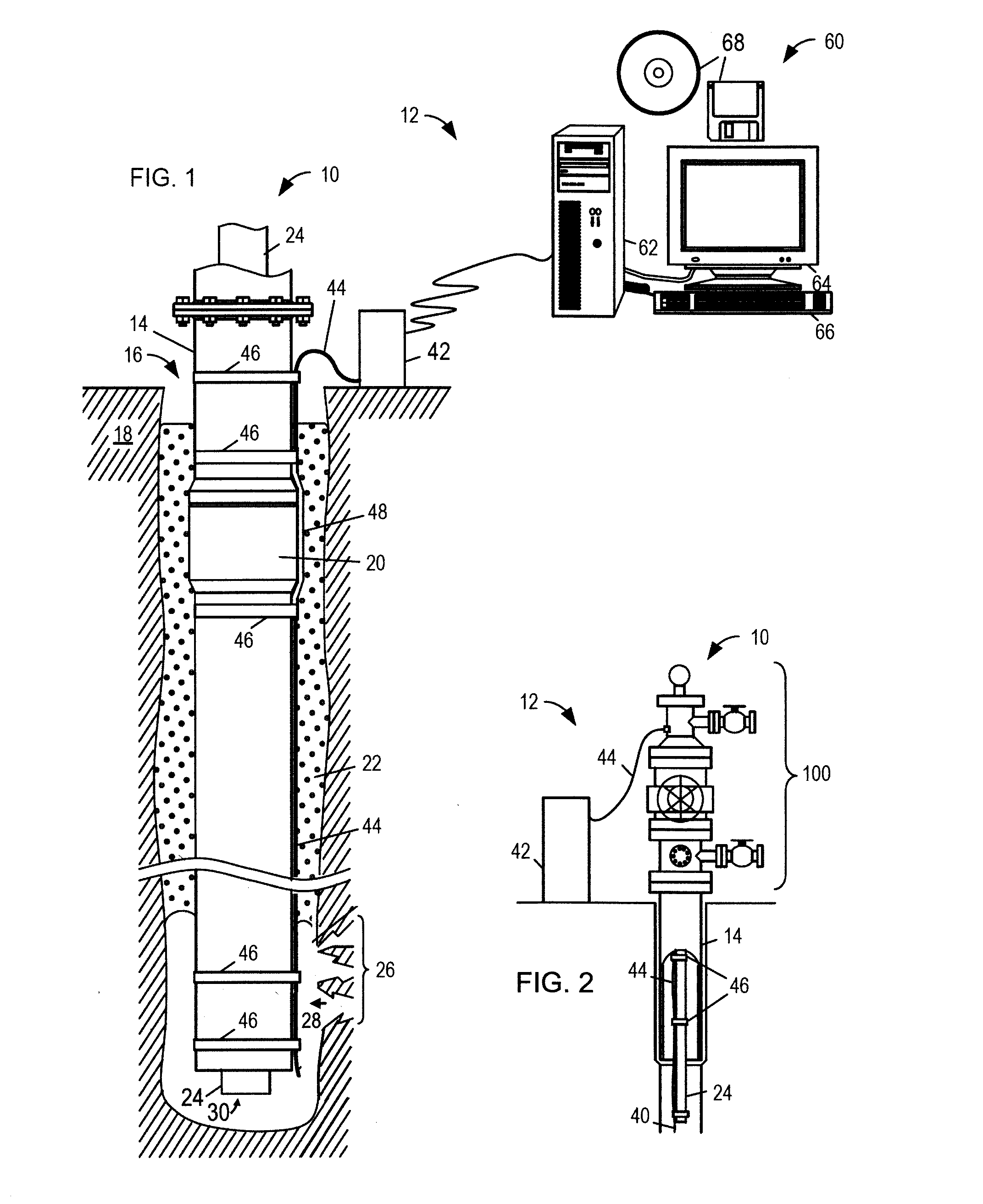
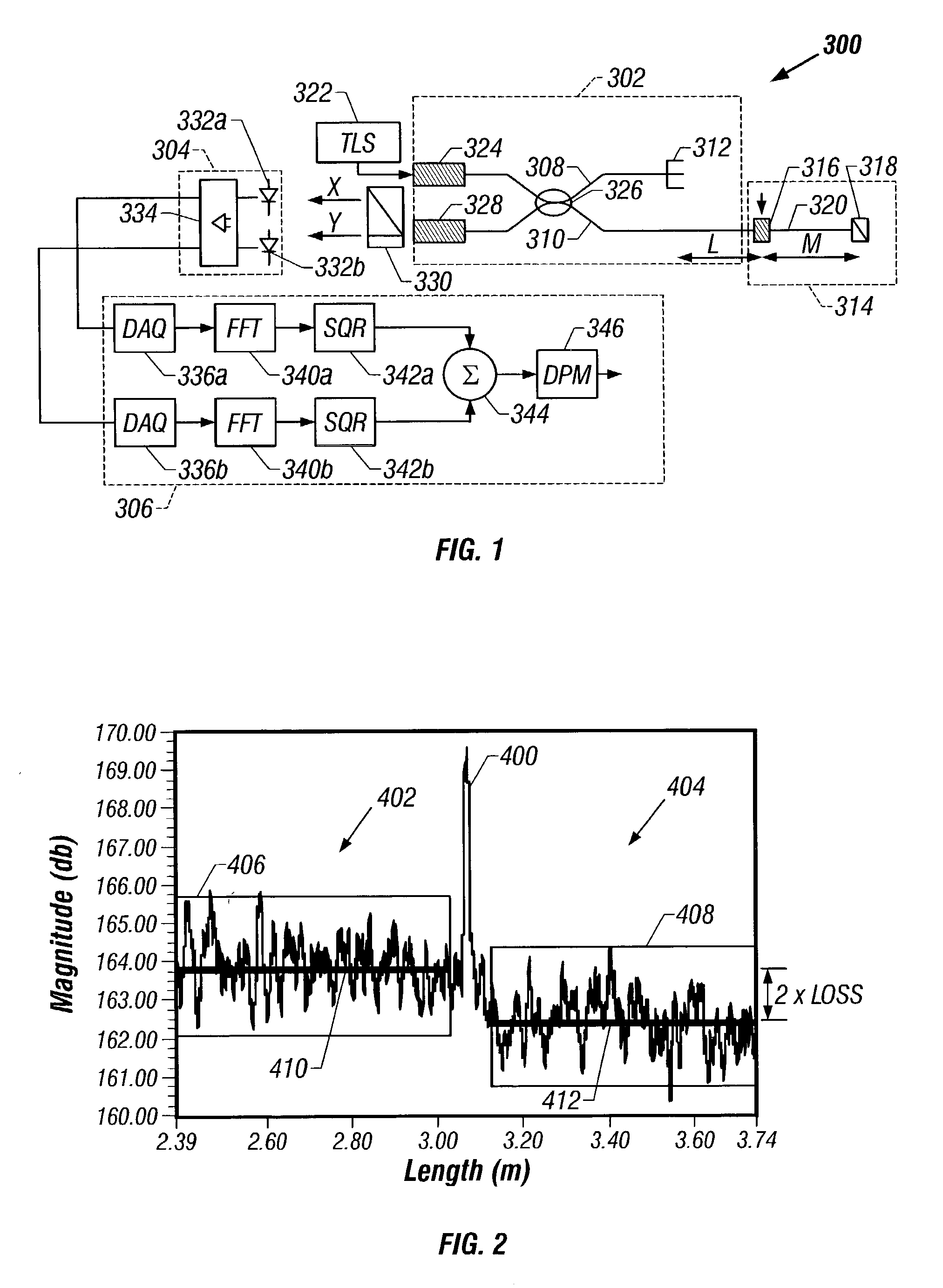
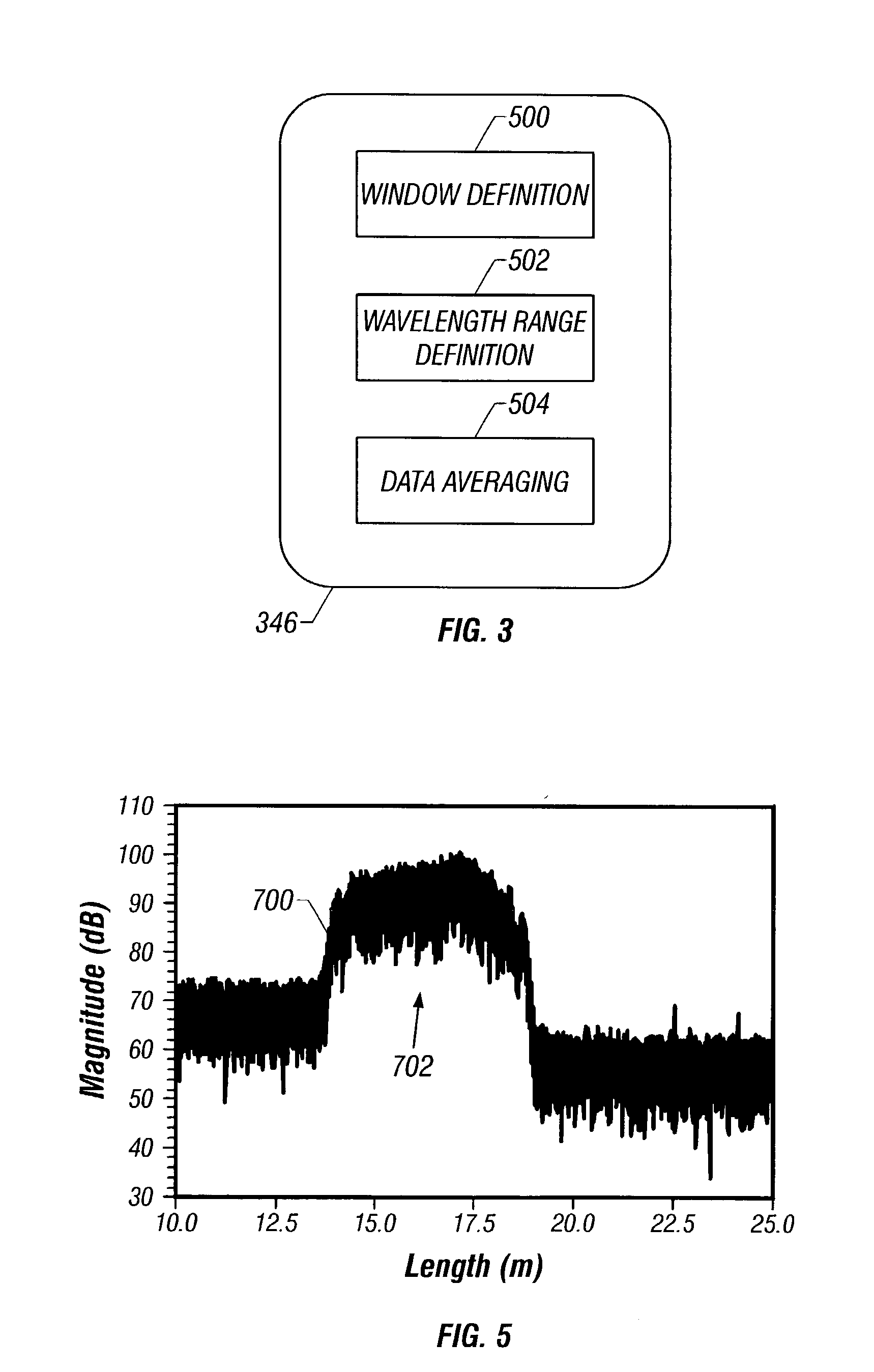
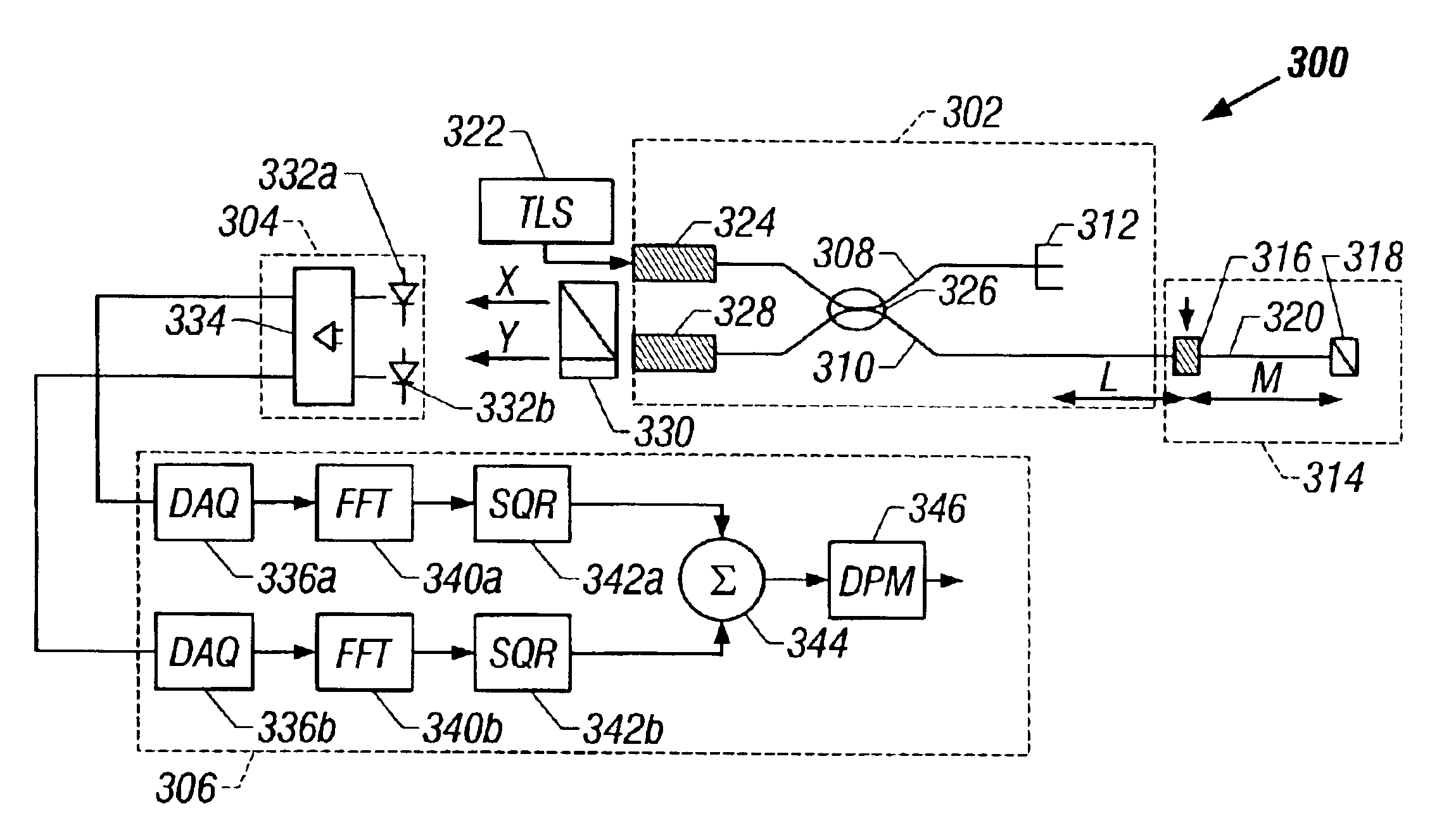
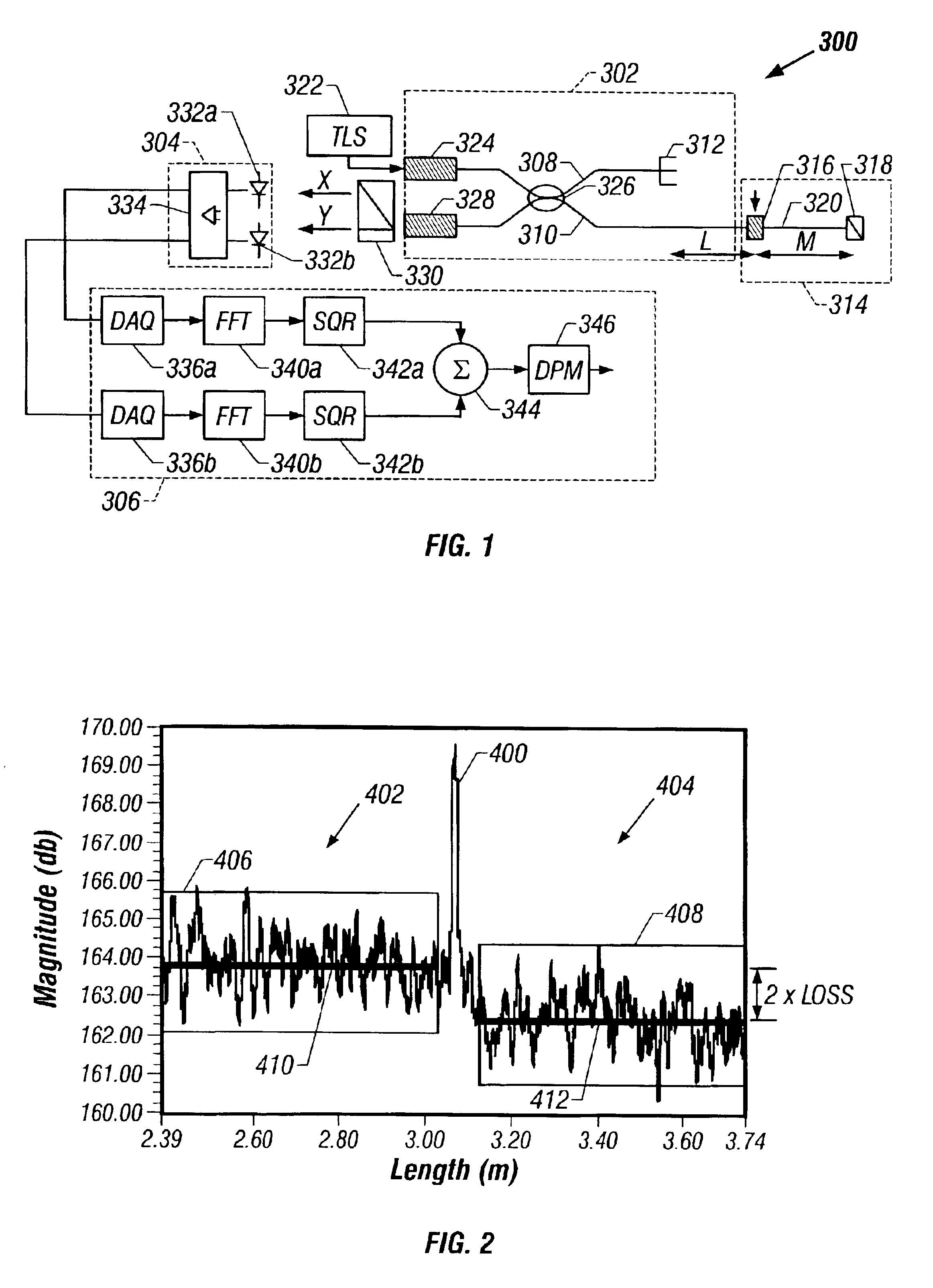
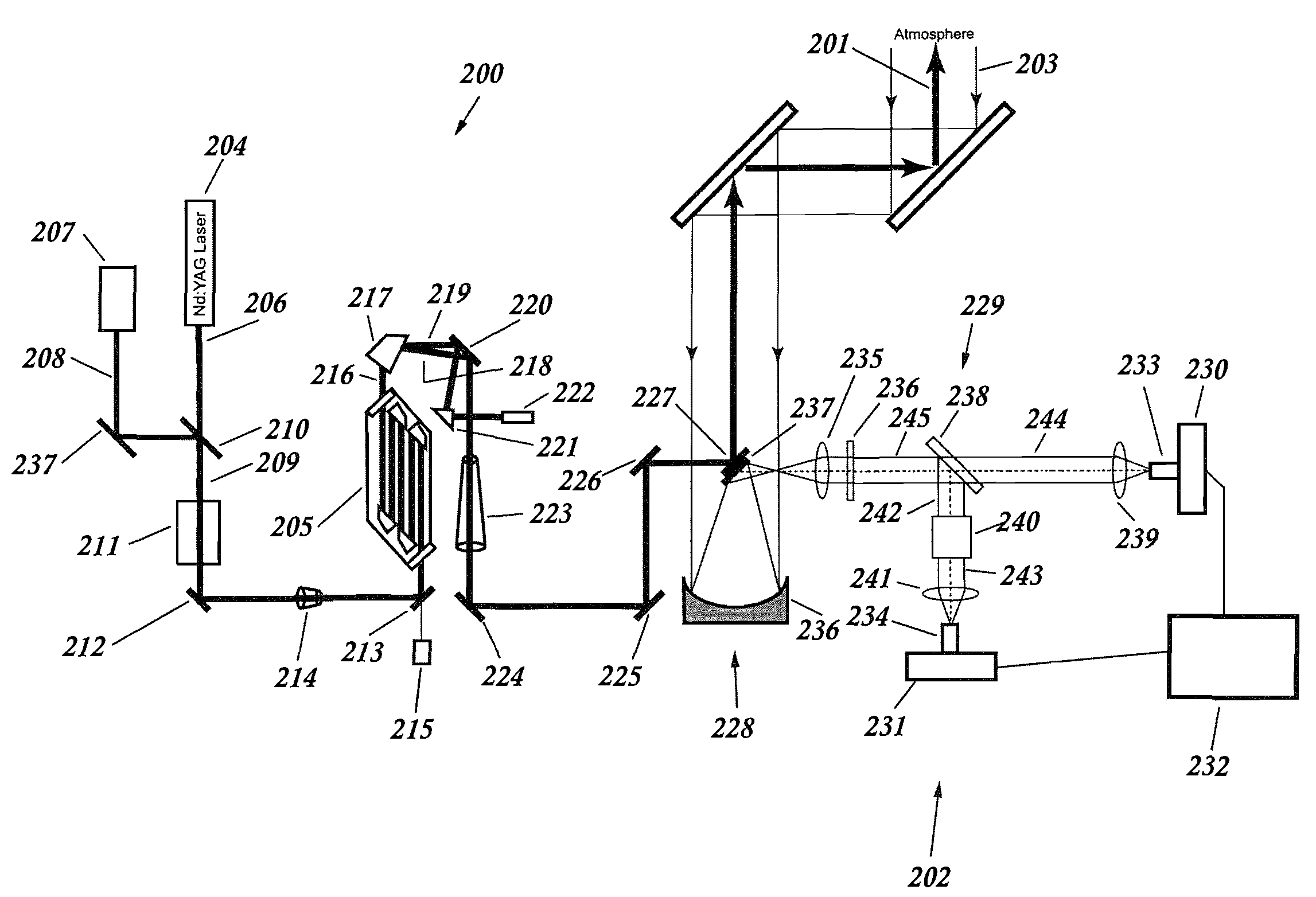
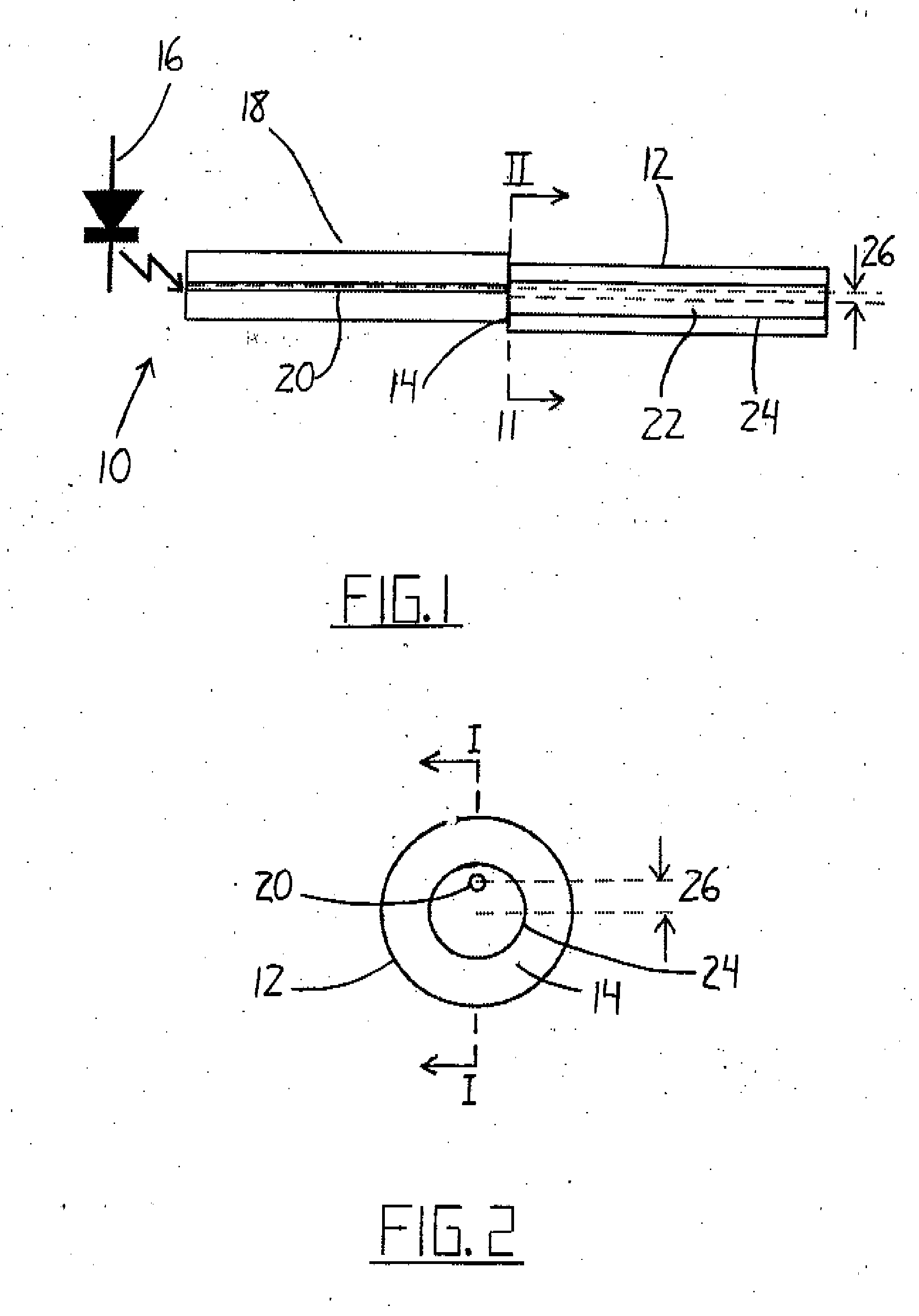
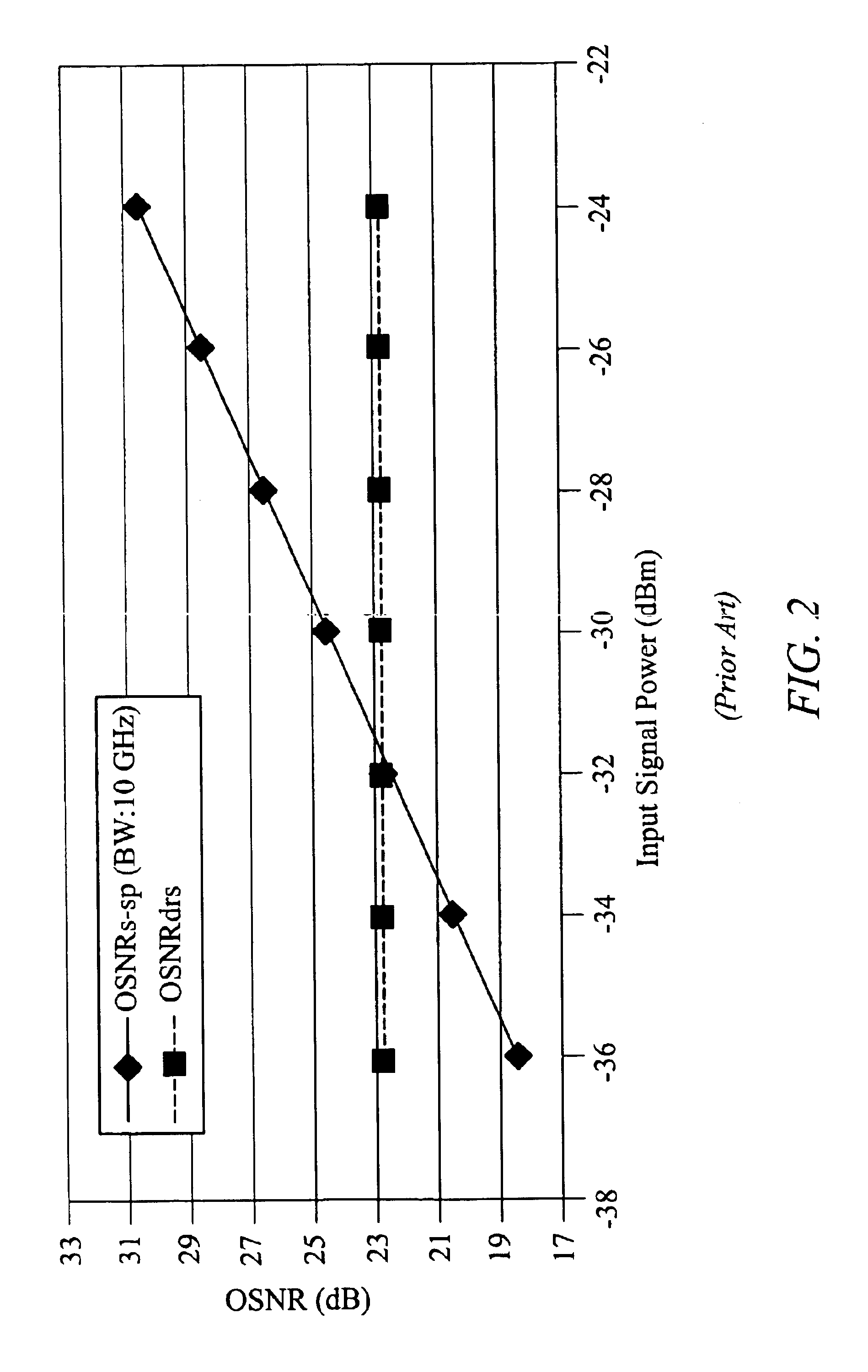
De-embedment of optical component characteristics and calibration of optical receivers using rayleigh backscatter
InactiveUS6947147B2Accurate analysisIncrease the number ofPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringFiber
Method and system are disclosed for de-embedding optical component characteristics from optical device measurements. In particular, the invention uses frequency domain averaging of the RBS on both sides of an optical component to determine one or more of its optical characteristics. Where the RBS has a slope (e.g., as in the case of a lossy fiber), a frequency domain least square fit can be used to determine the optical component characteristics. In addition, the invention uses a reference DUT to correct for variations in the frequency response of the photoreceiver. A reference interferometer is used in the invention to correct for sweep non-linearity of the TLS. The optical component characteristics are then de-embedded from optical device measurements to provide a more precise analysis of the optical device.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
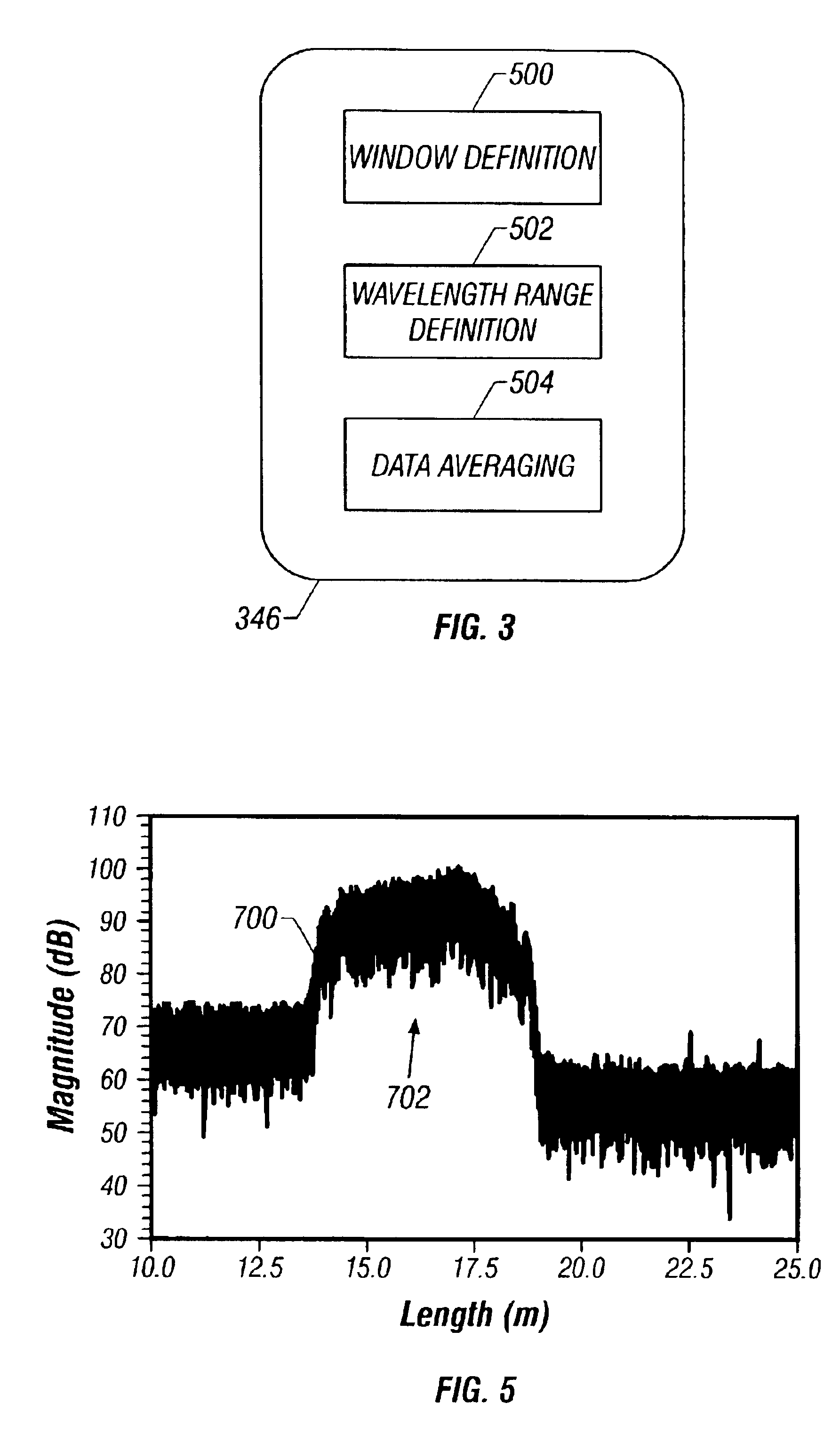
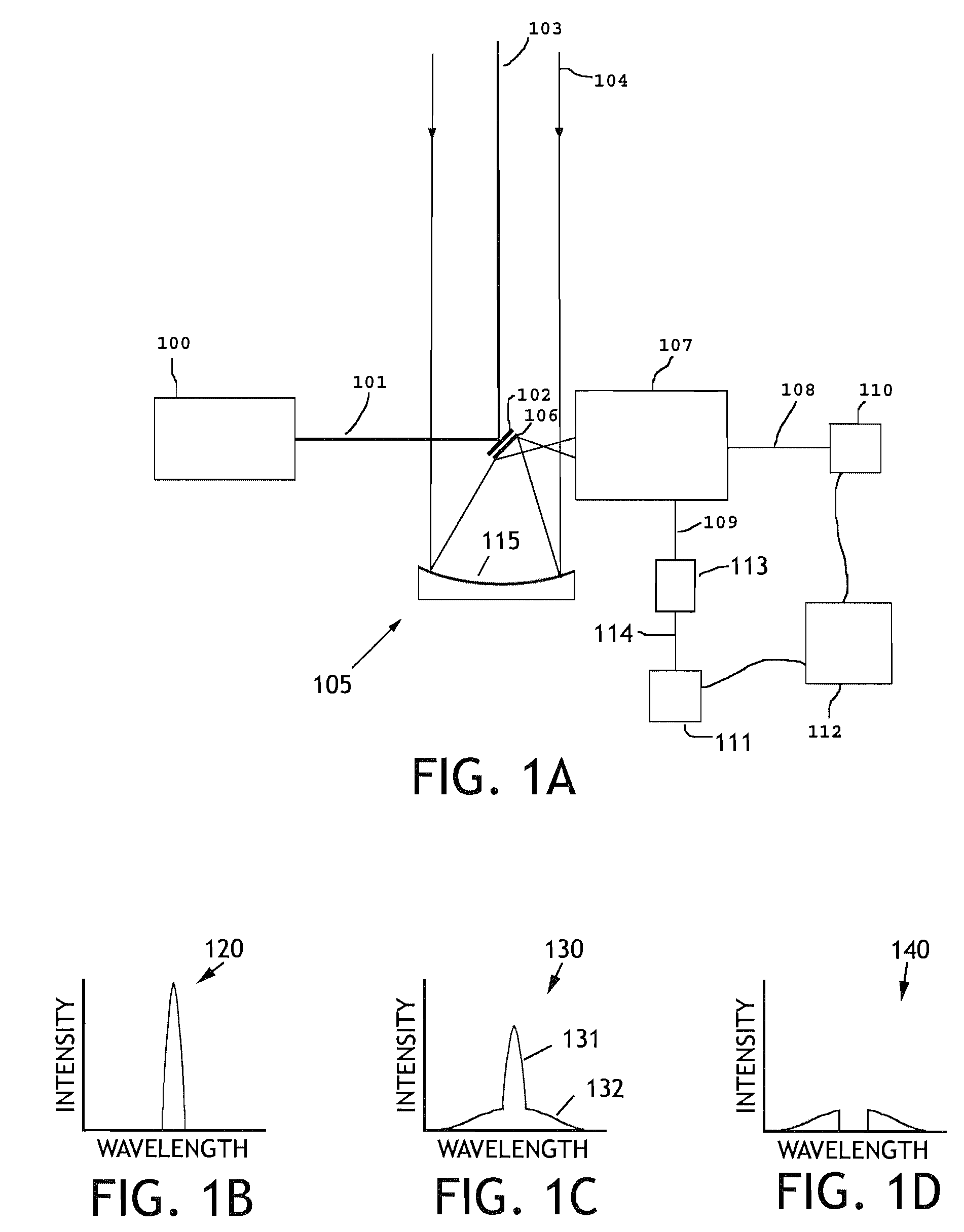
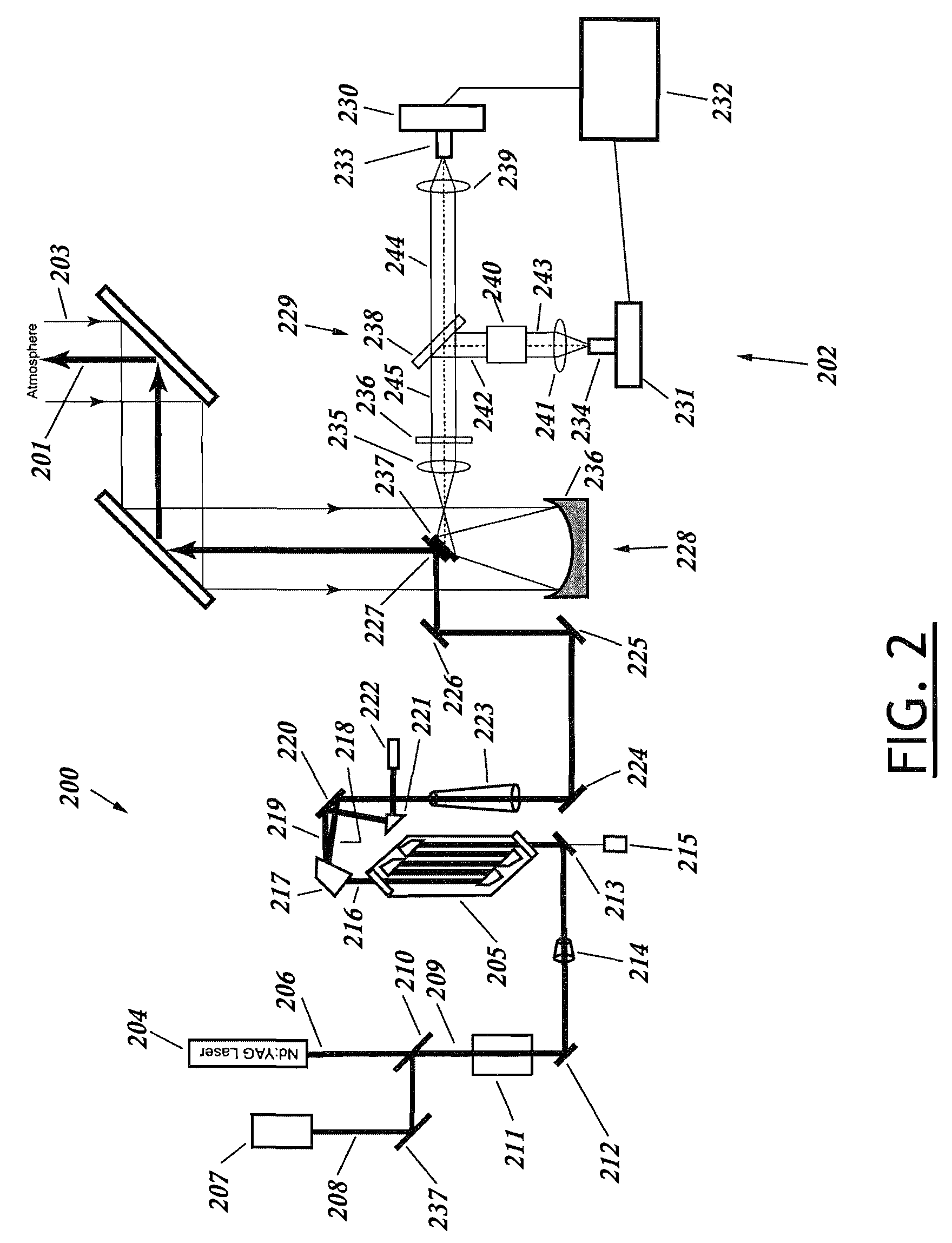
Lidar system for remote determination of calibrated, absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients
ActiveUS7656526B1Effort directedSafely and quickly and efficiently identifyRaman scatteringParticle size analysisBeam splitterAerosol backscatter
A lidar system capable of remotely identifying calibrated absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients of atmospheric aerosol particles by transmitting a beam of light and spectrally separating the intensity of Rayleigh and Mie backscattering is disclosed. The transmitter features high pulse energy to generate sufficient Rayleigh backscattering, enabling atmospheric scanning in a timely manner. The transmitter employs a seeded Nd:YAG laser and a seeded stimulated Raman scattering wavelength shifter to achieve narrow bandwidth, eye-safe laser pulses. The receiver employs a telescope, collimating lens, beam splitter, molecular absorption filter, focusing lenses, and avalanche photodiodes. Mie backscattering is blocked by the molecular absorption filter to provide a Rayleigh signal, which is used with knowledge of atmospheric density to calibrate the Mie signal. The system is intended for atmospheric research and aerosol monitoring applications where calibrated Mie scattering intensity is necessary to measure the optical depths of aerosol structures such as plumes, clouds, and layers.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
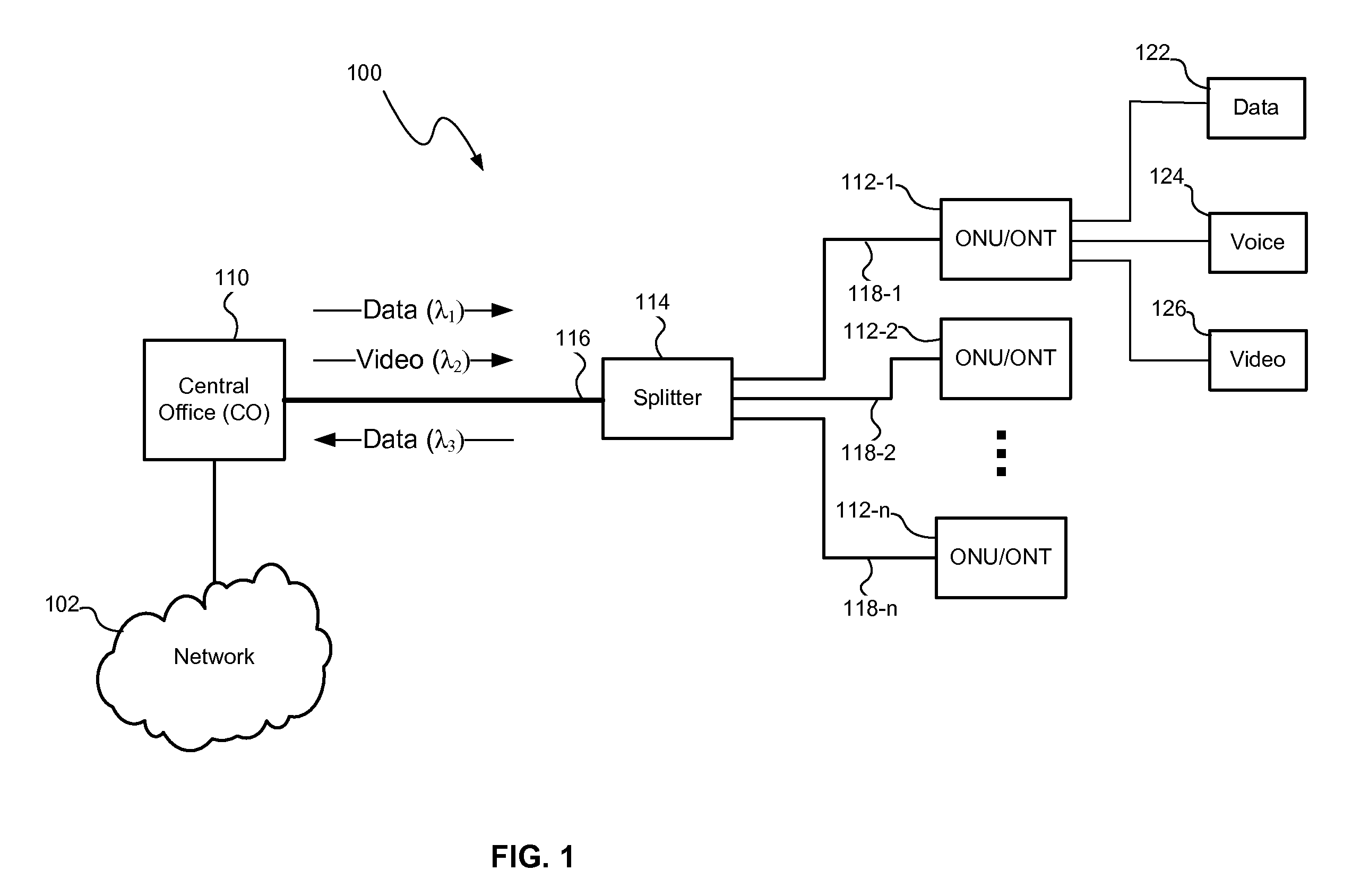
Dynamic intelligent bidirectional optical access communication system with object/intelligent appliance-to-object/intelligent appliance interaction
ActiveUS20110158653A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsPersonalizationSoftware modules
Reduced Rayleigh backscattering effect enables a longer-reach optical access communication network-thus it eliminates significant costs. Furthermore, a wavelength to an intelligent subscriber subsystem can be dynamically varied for bandwidth on-Demand and service on-Demand. A software module renders intelligence (and context awareness) to a subscriber subsystem and an appliance. An object can sense / measure / collect / aggregate / compare / map and connect / couple / interact (via one or more or all electrical / optical / radio / electro-magnetic / sensor / bio-sensor communication network(s) within and / or to and / or from an object) with another object, an intelligent subscriber subsystem and an intelligent appliance utilizing an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) and its subsequent versions.A construction of a near-field communication (NFC) enabled intelligent micro-subsystem and / or intelligent appliance with key applications (e.g., an intelligent, location based and personalized social network and an intelligent, location based and personalized direct and peer-to-peer marketing) are also described.
Owner:MAZED MOHAMMAD
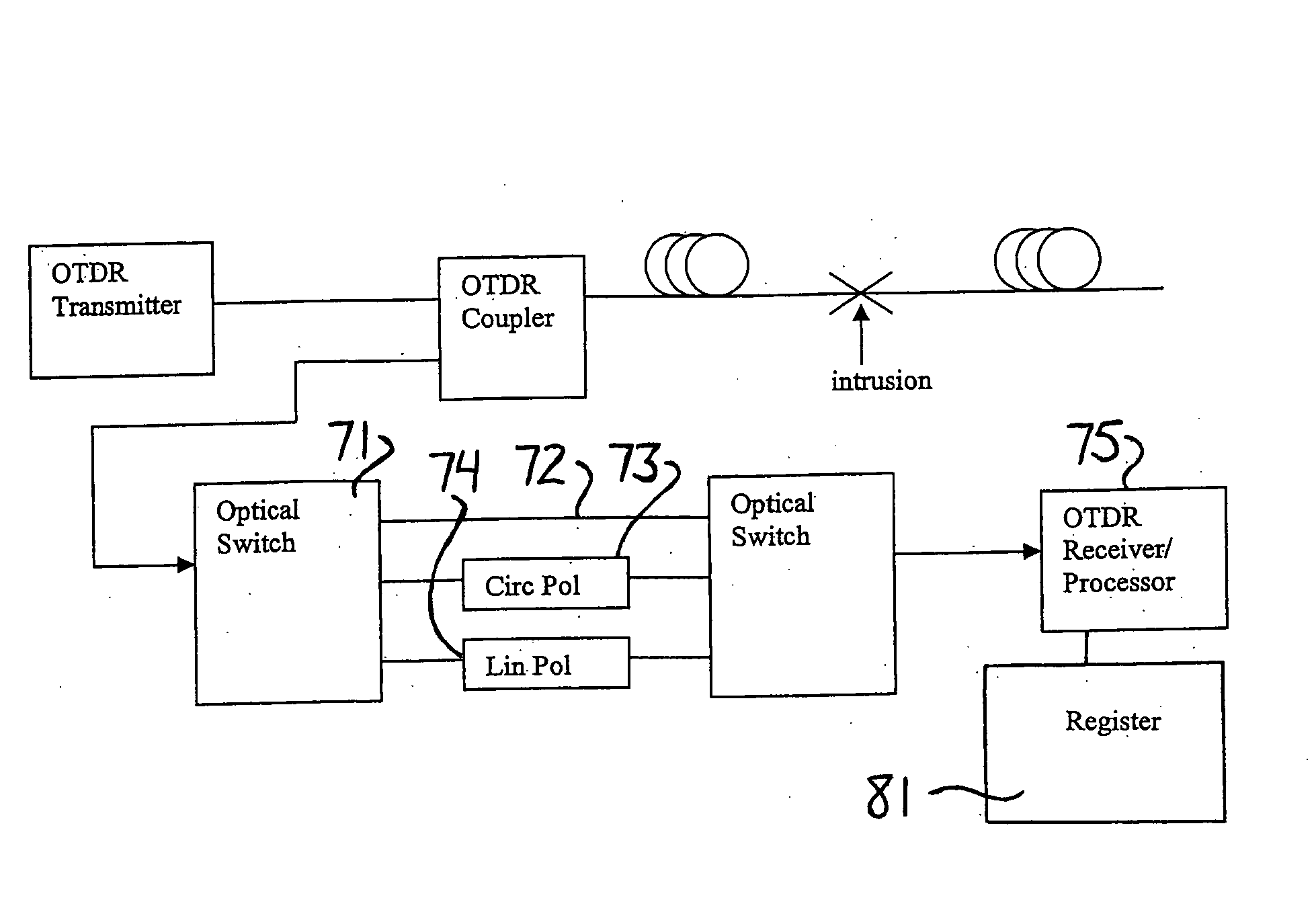
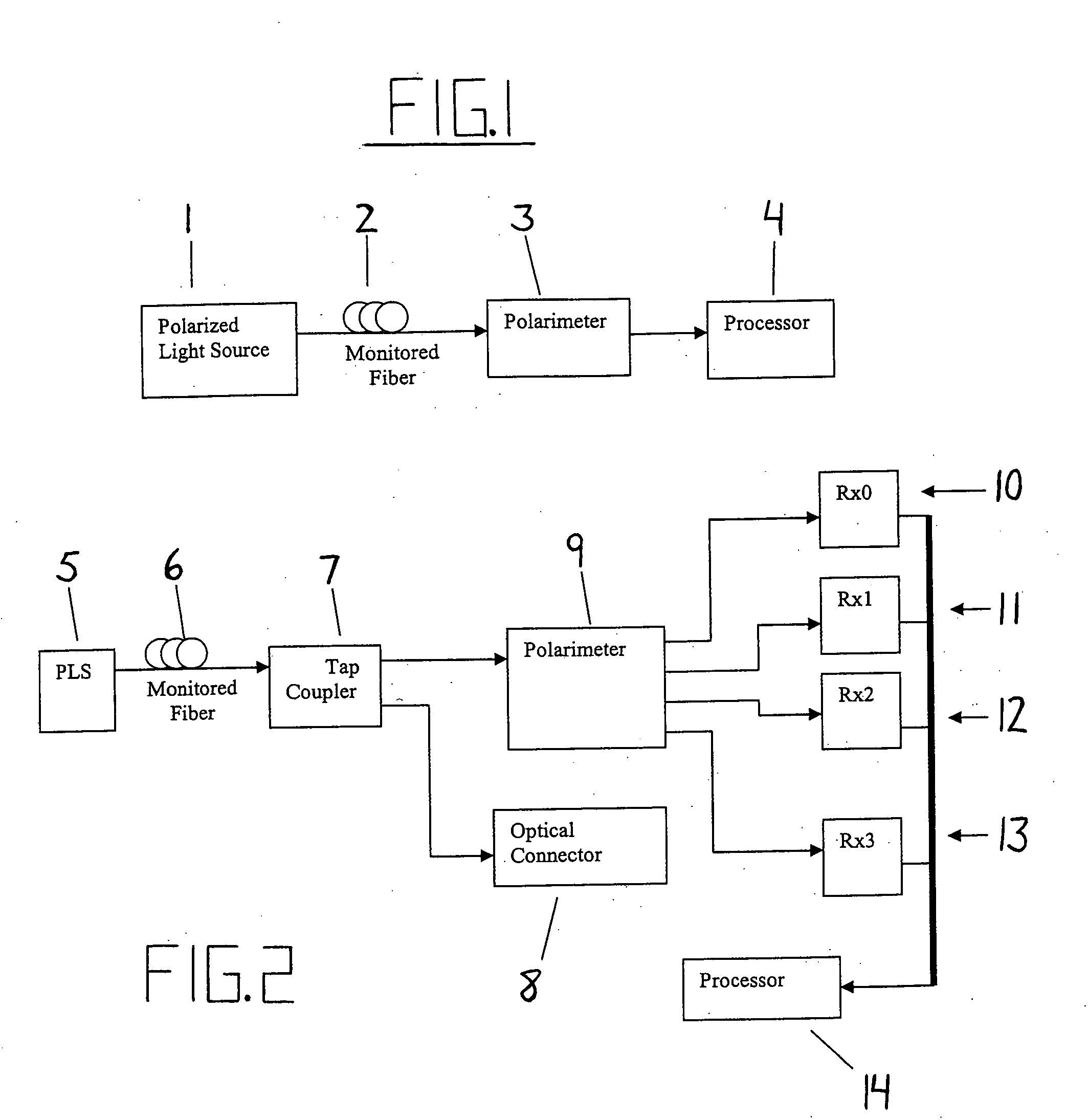
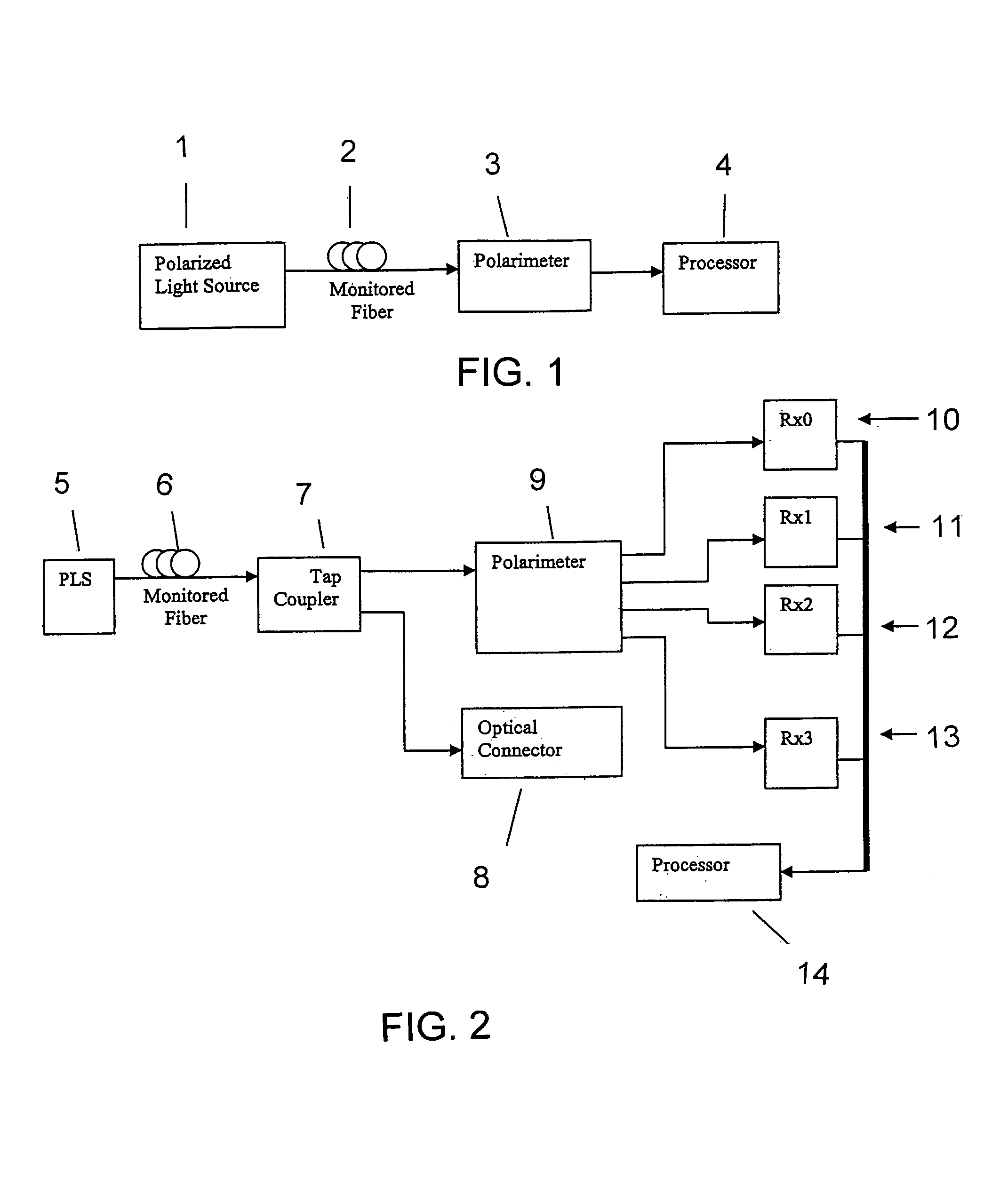
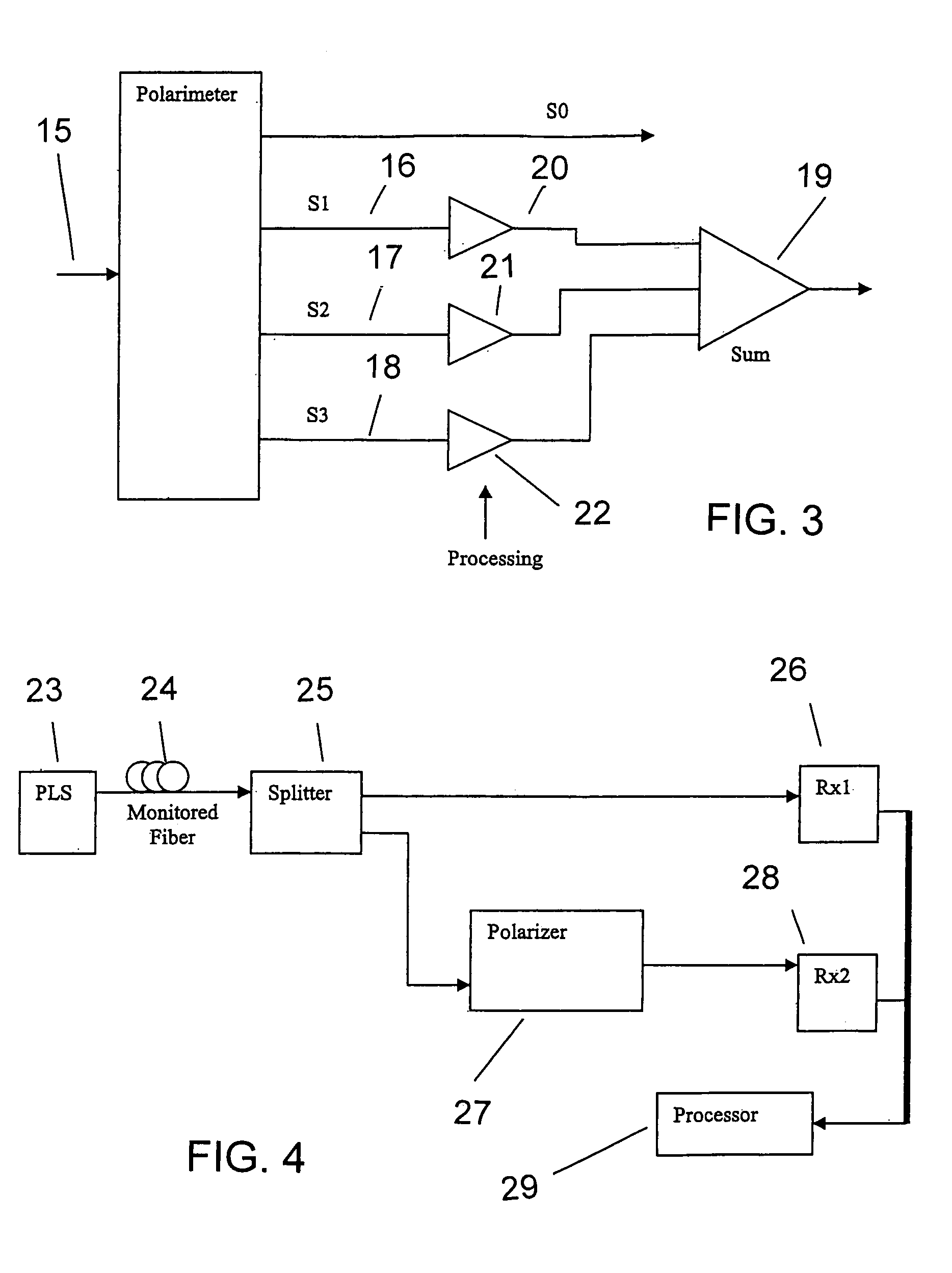
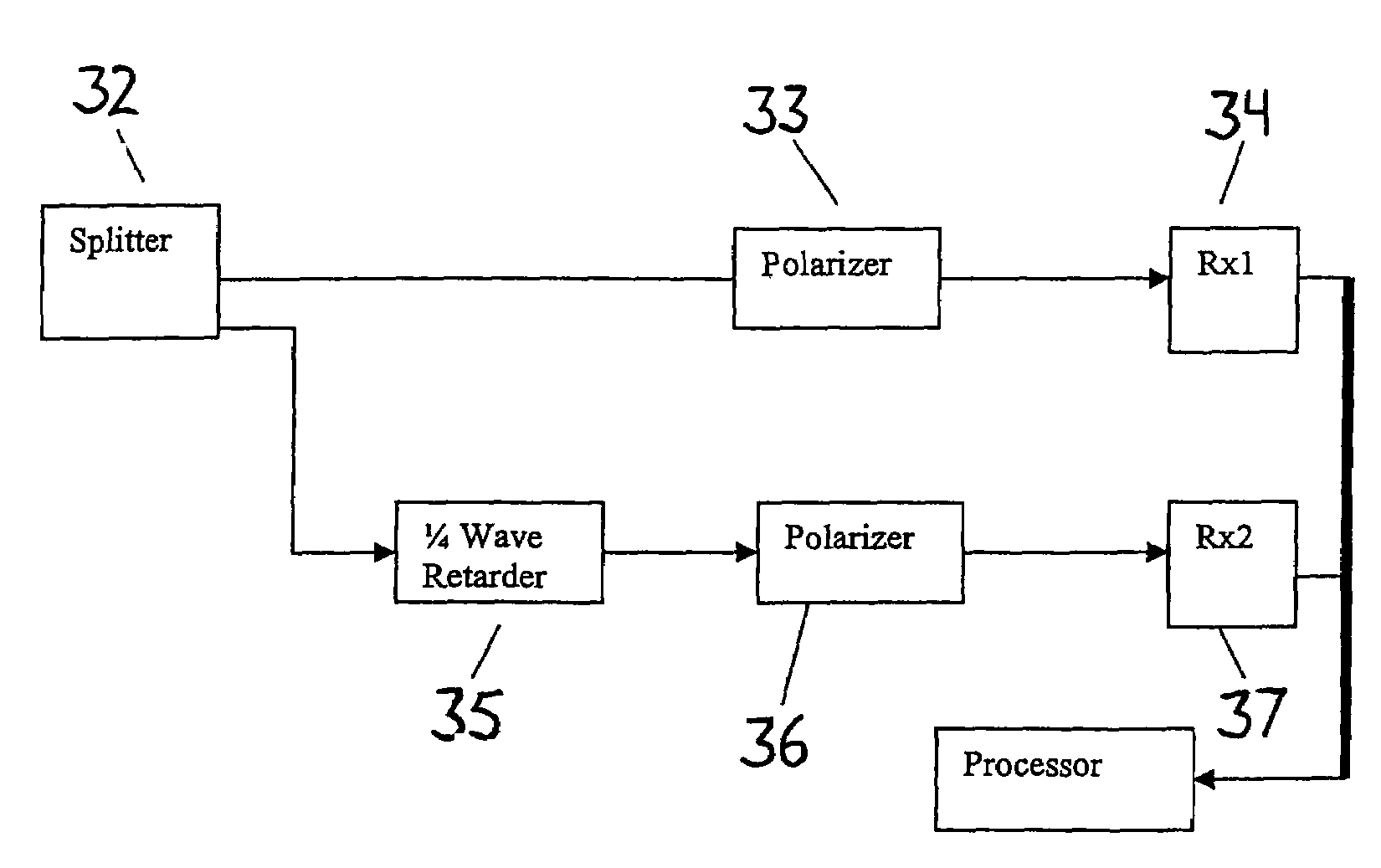
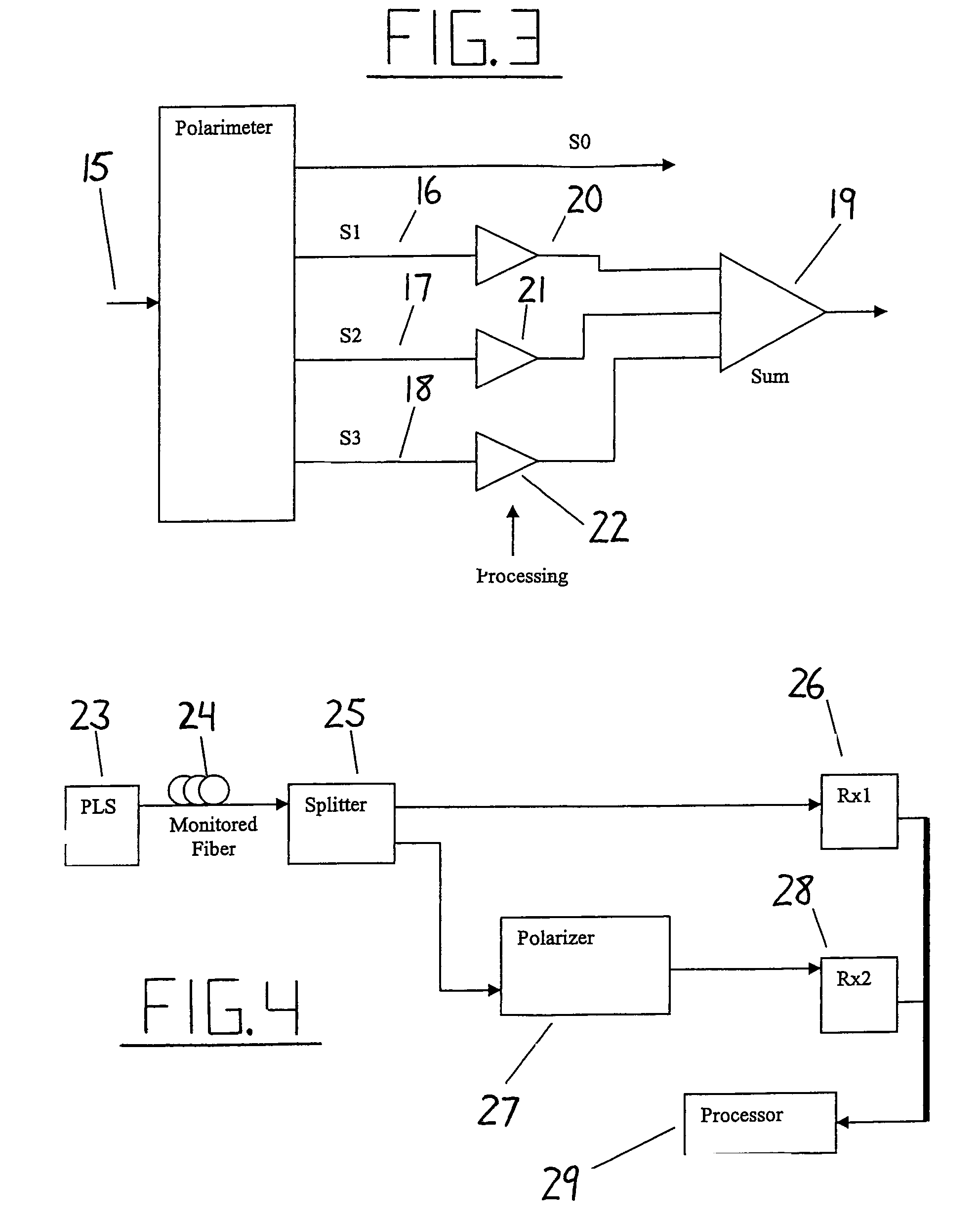
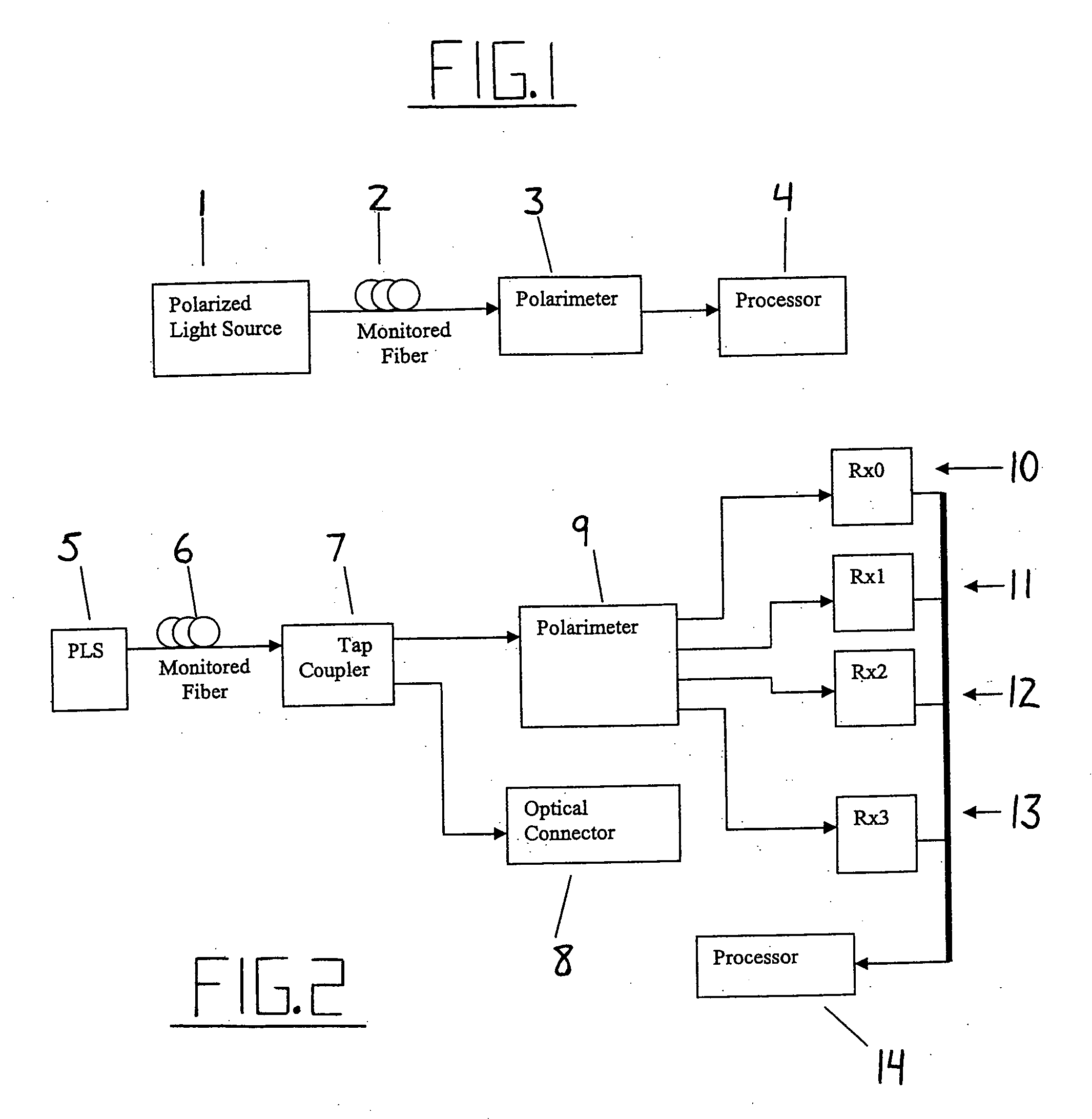
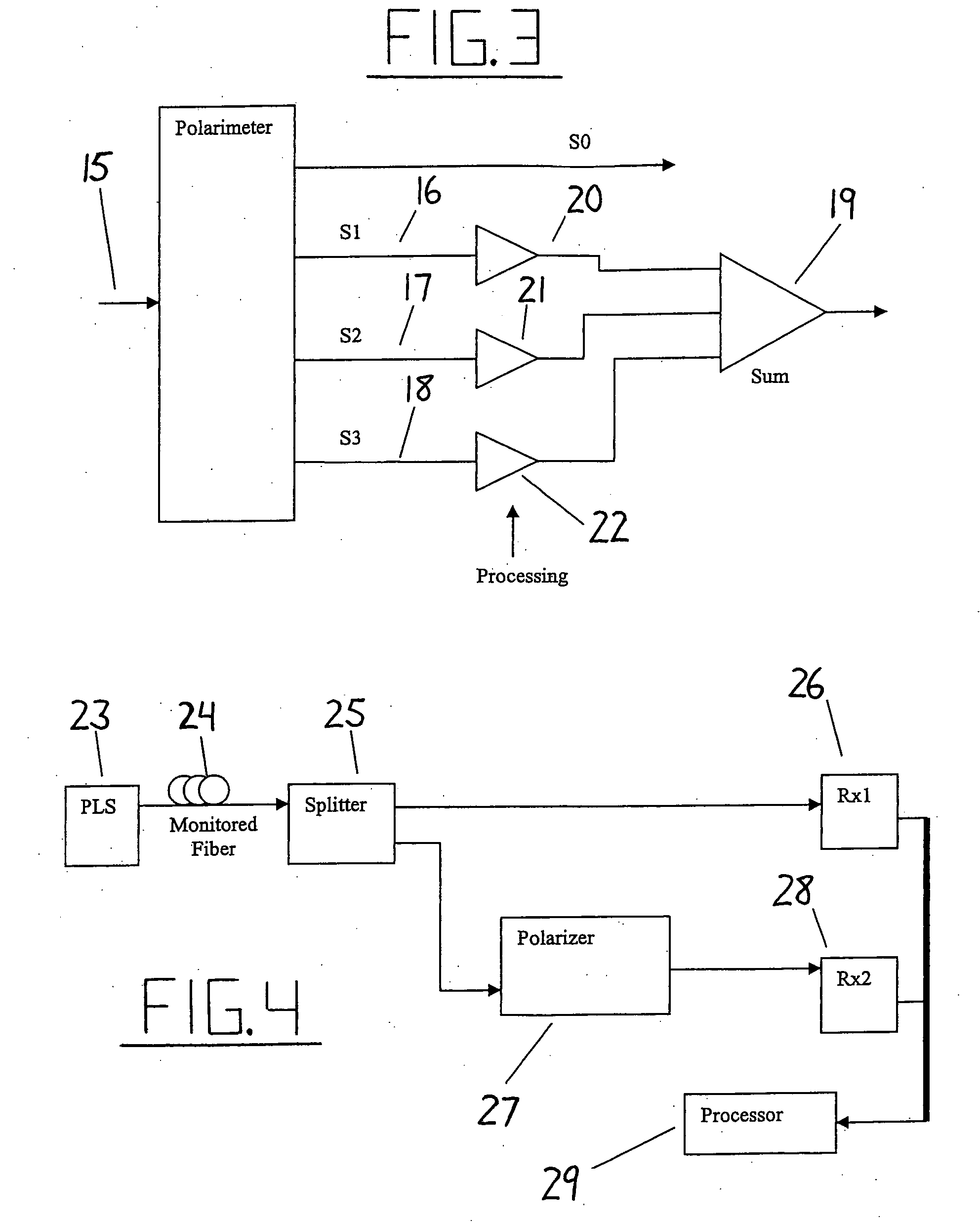
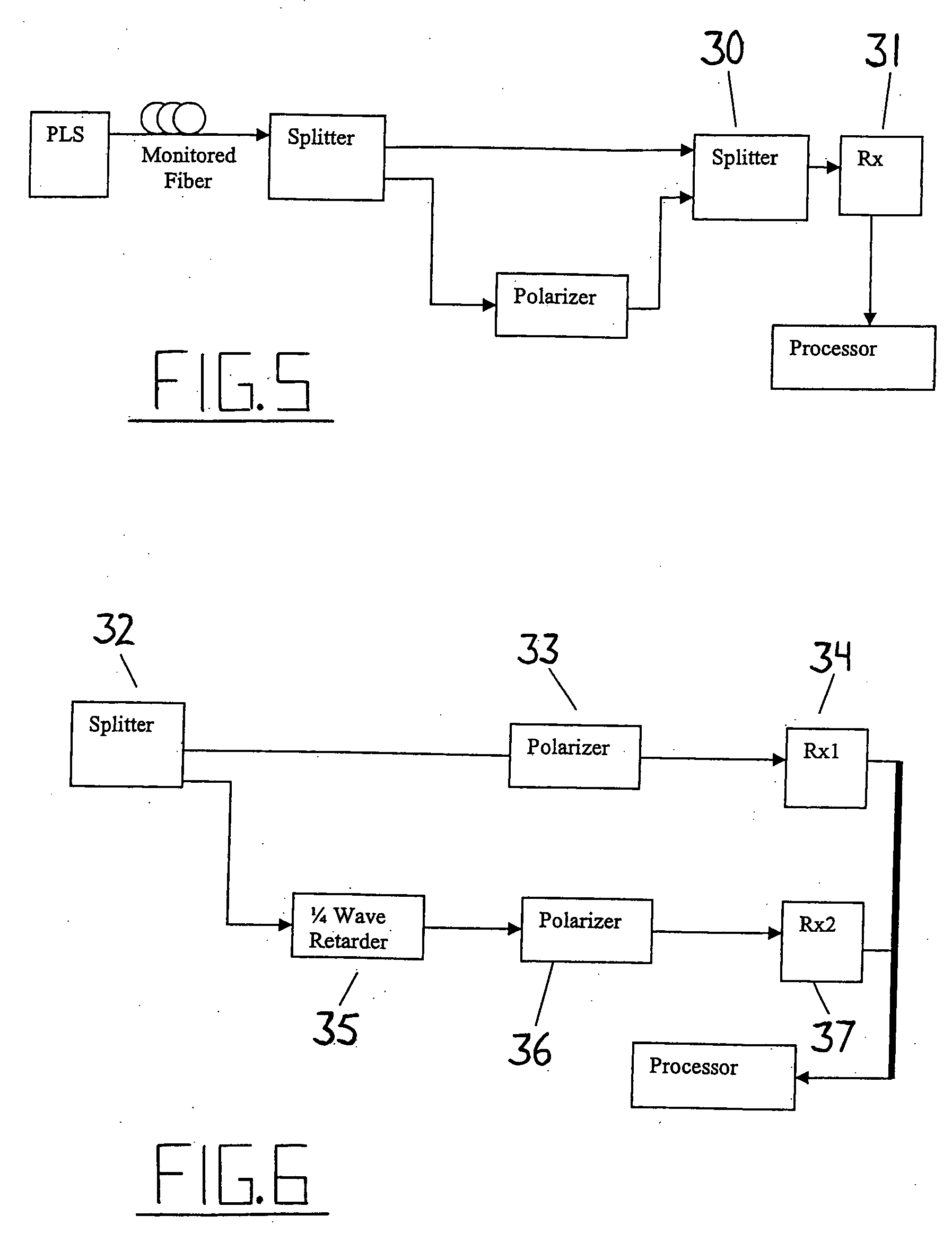
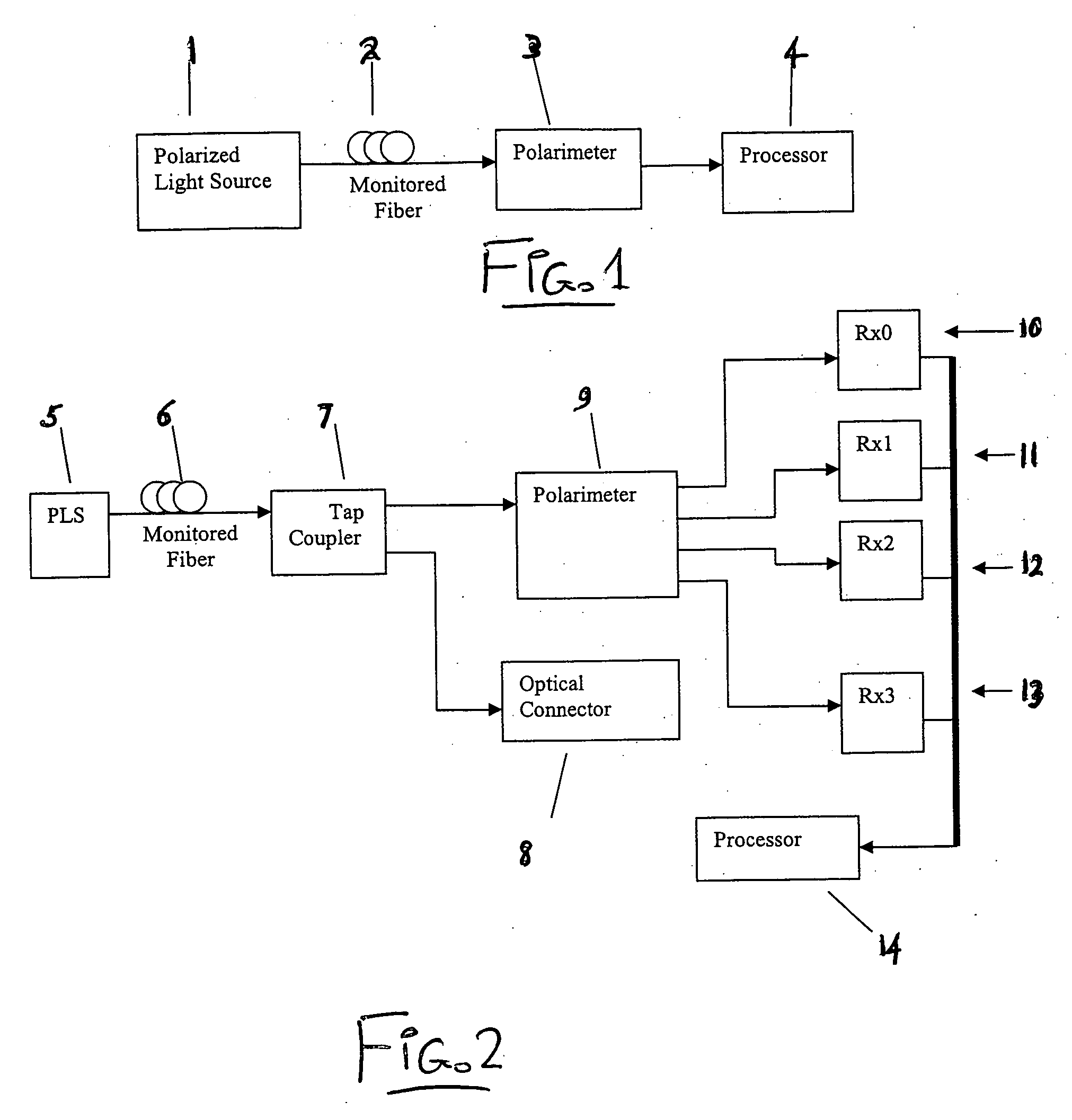
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a simplified polarimeter
ActiveUS20060153491A1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsLight polarisation measurementPolarimeterPolarizer
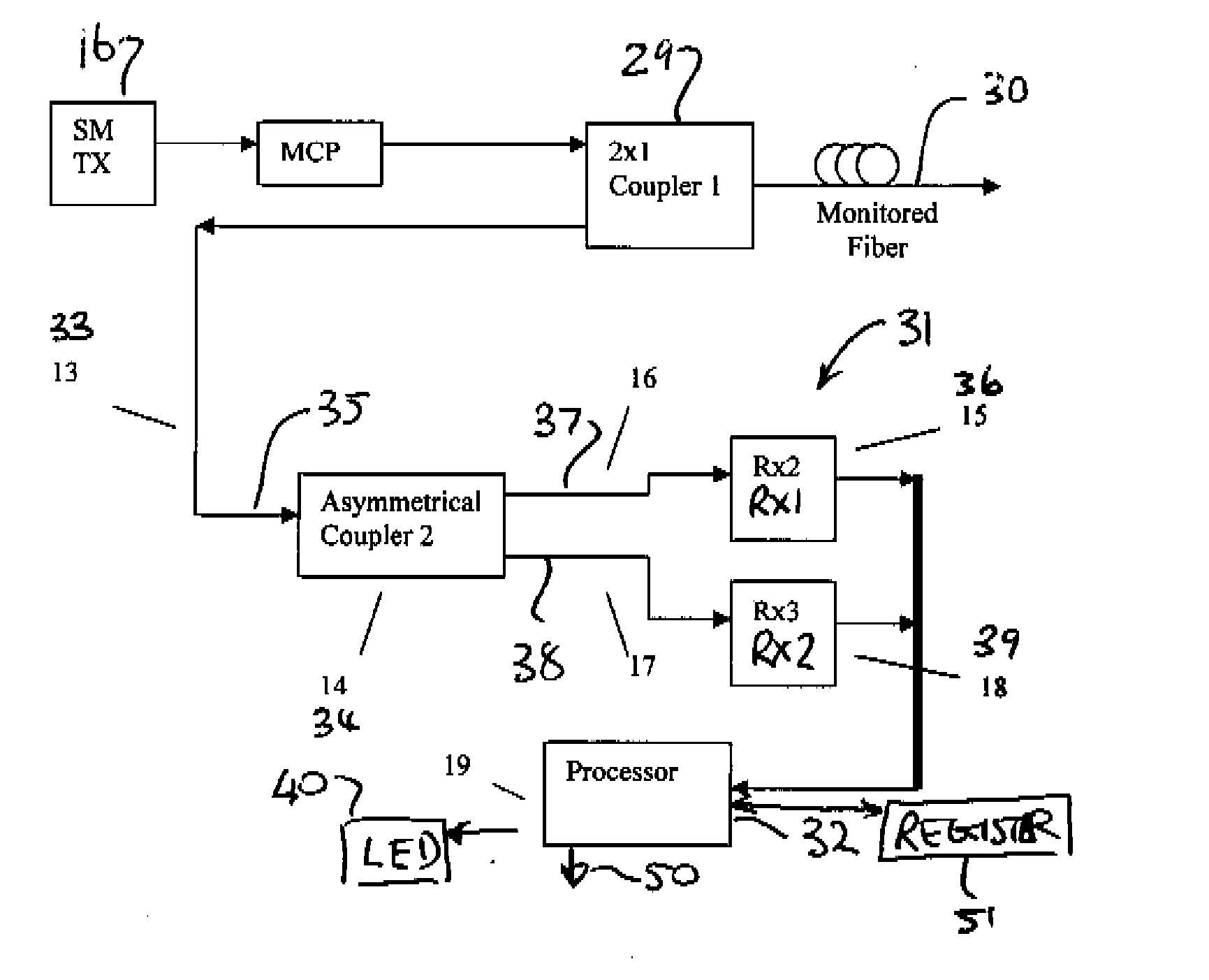
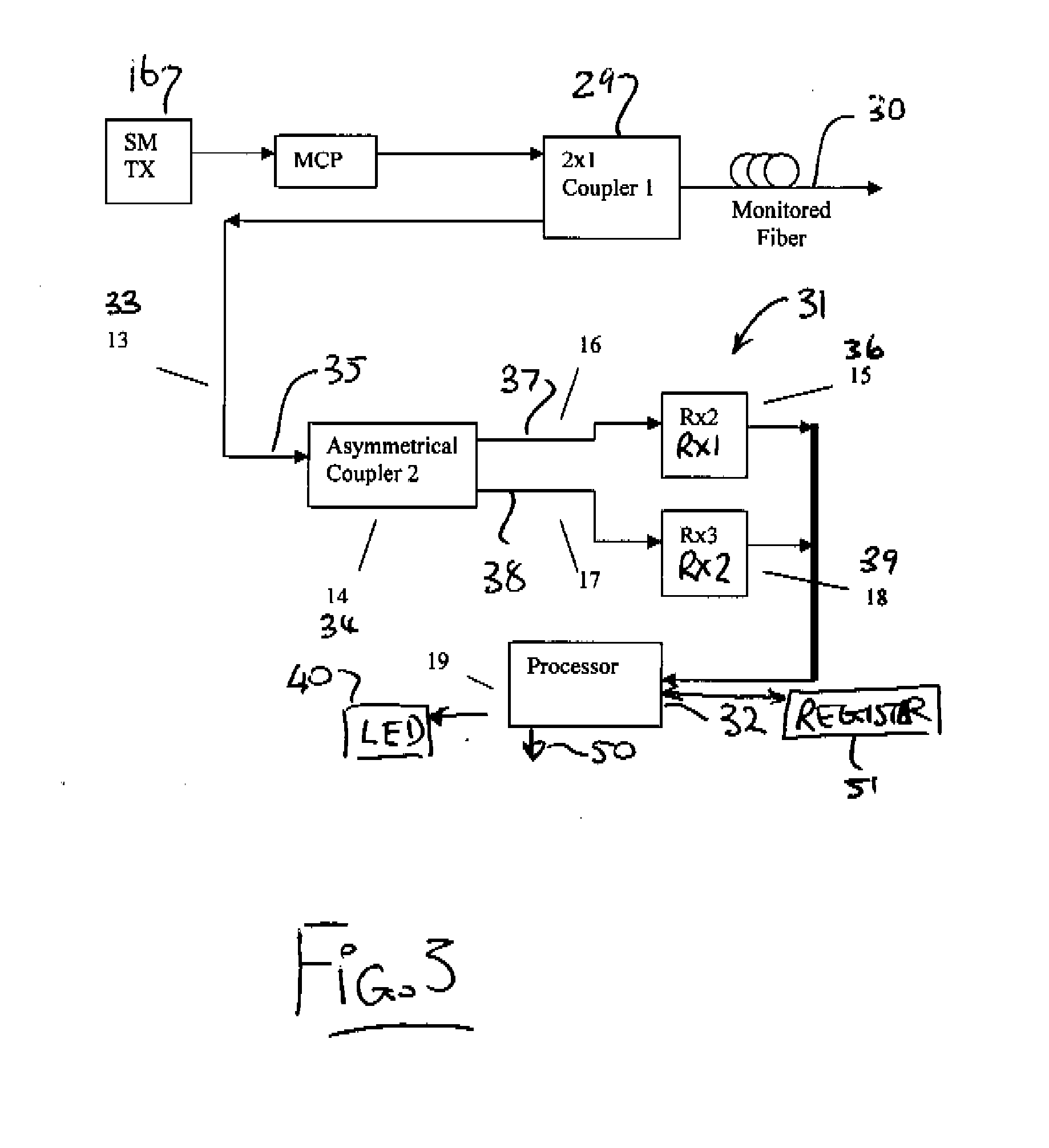
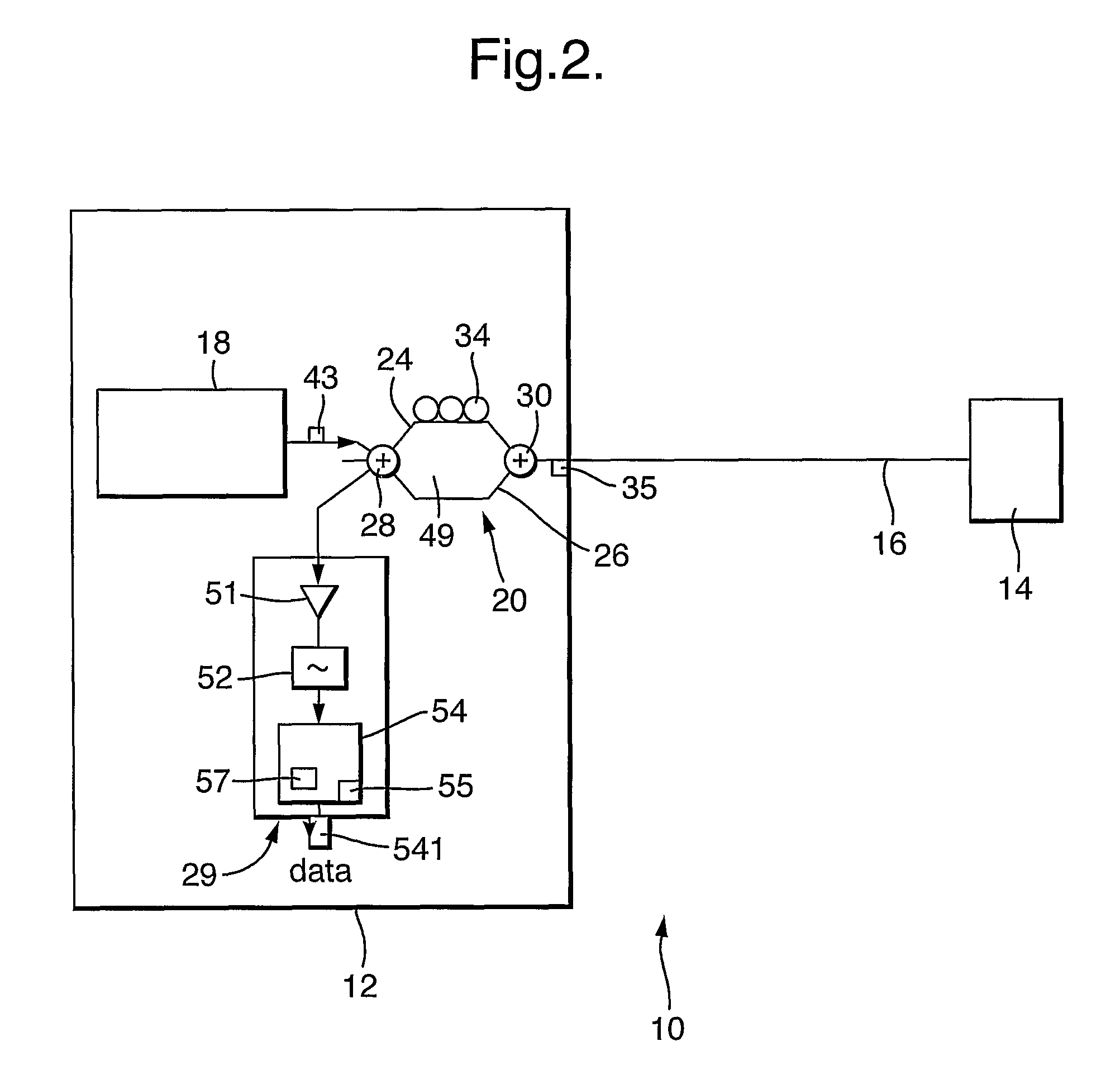
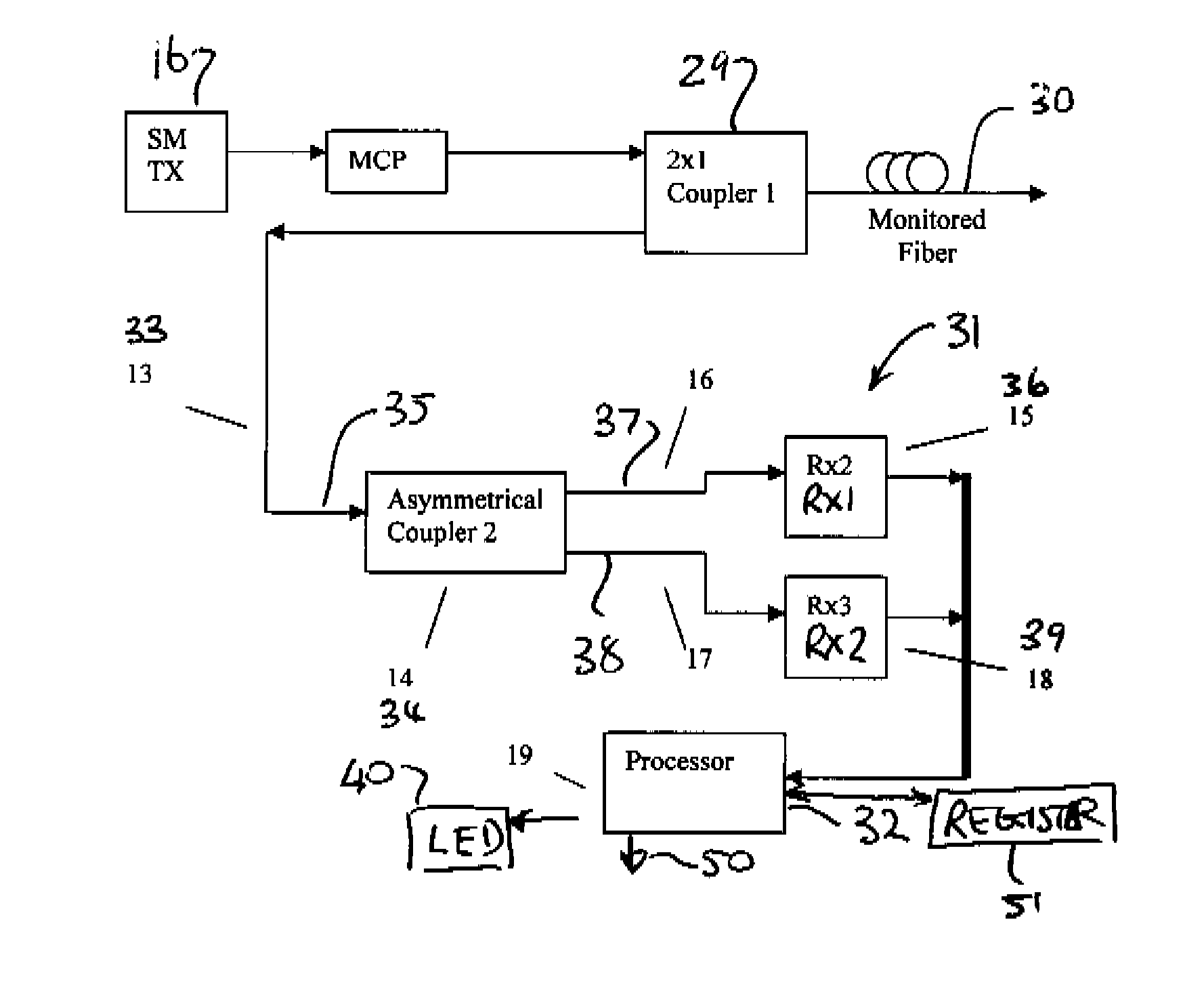
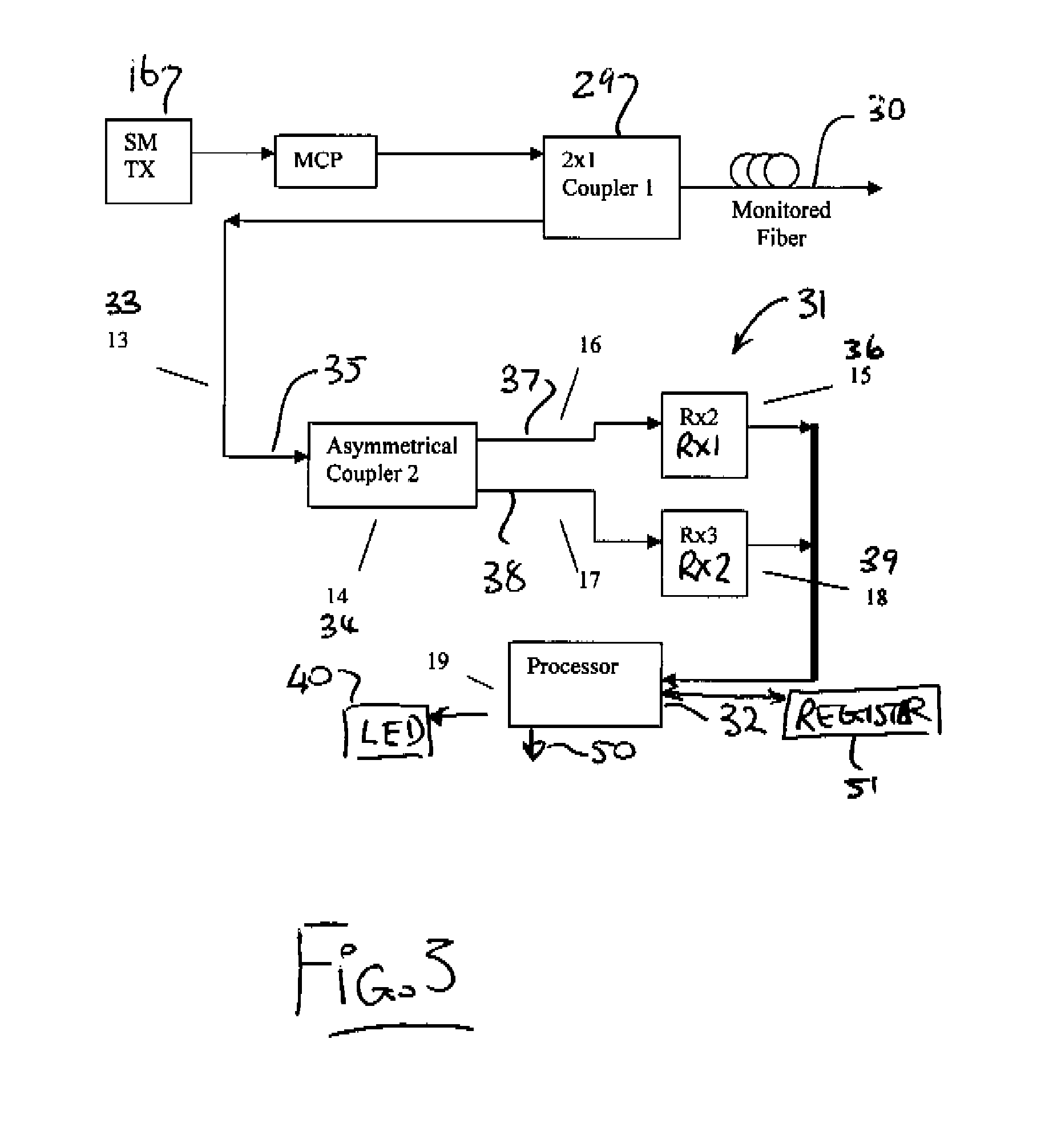
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a storage register for data
ActiveUS7142737B1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationCoupling light guidesProcessor registerPolarimeter
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
Controlling optical signal transmission to reduce optical signal degradation
InactiveUS20080031621A1Transmission monitoringOptical multiplexStimulate raman scatteringRayleigh backscattering
An optical transmission system and method may control optical signal transmission in an optical network, such as a passive optical network (PON), to reduce degradation of one or more optical signals traveling over the same optical waveguide. In particular, optical signal transmission may be controlled to reduce carrier to noise ratio (CNR) degradation of an optical signal (e.g., a multichannel video signal) resulting from the effects of stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and / or double Rayleigh backscattering (DRBS). The CNR degradation may be reduced by controlling transmission of one or more of a plurality of optical signals in the optical network based on various parameters affecting the contribution to CNR degradation by SRS and / or DRBS and affecting the performance of the optical transmission system. The optical signal transmission may be controlled by adjusting a preemphasis and / or transmitted power of the optical signal(s).
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
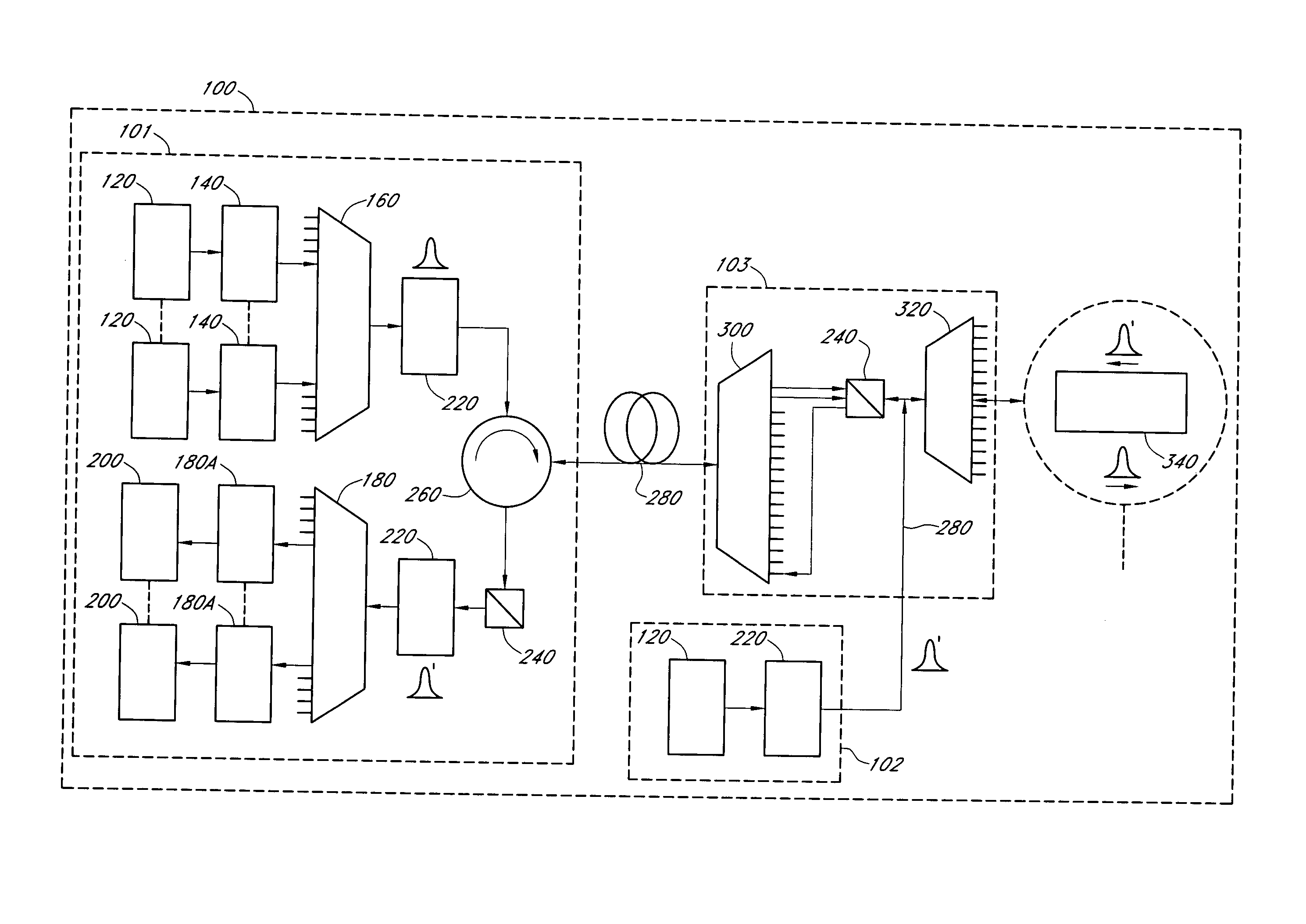
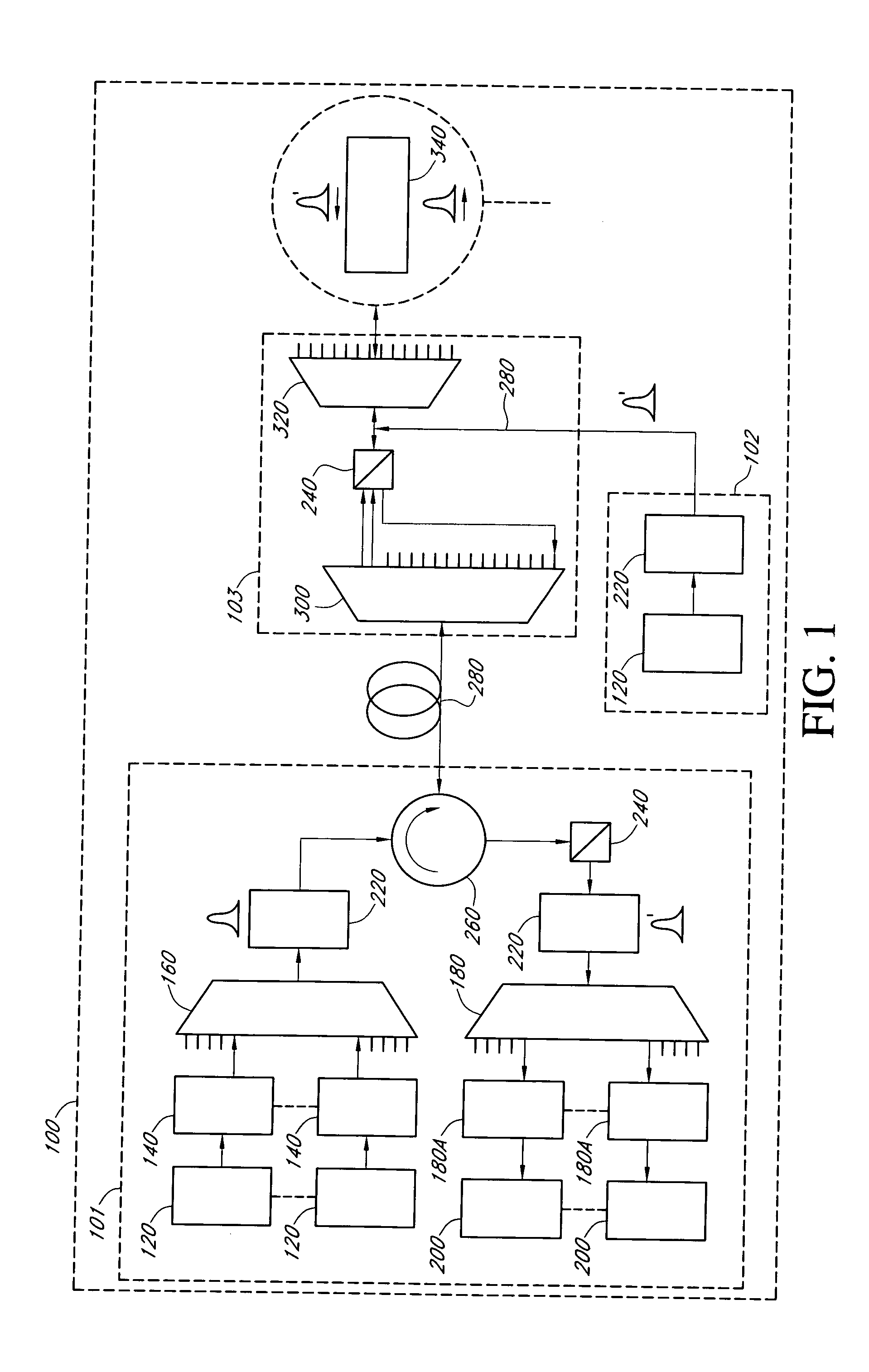
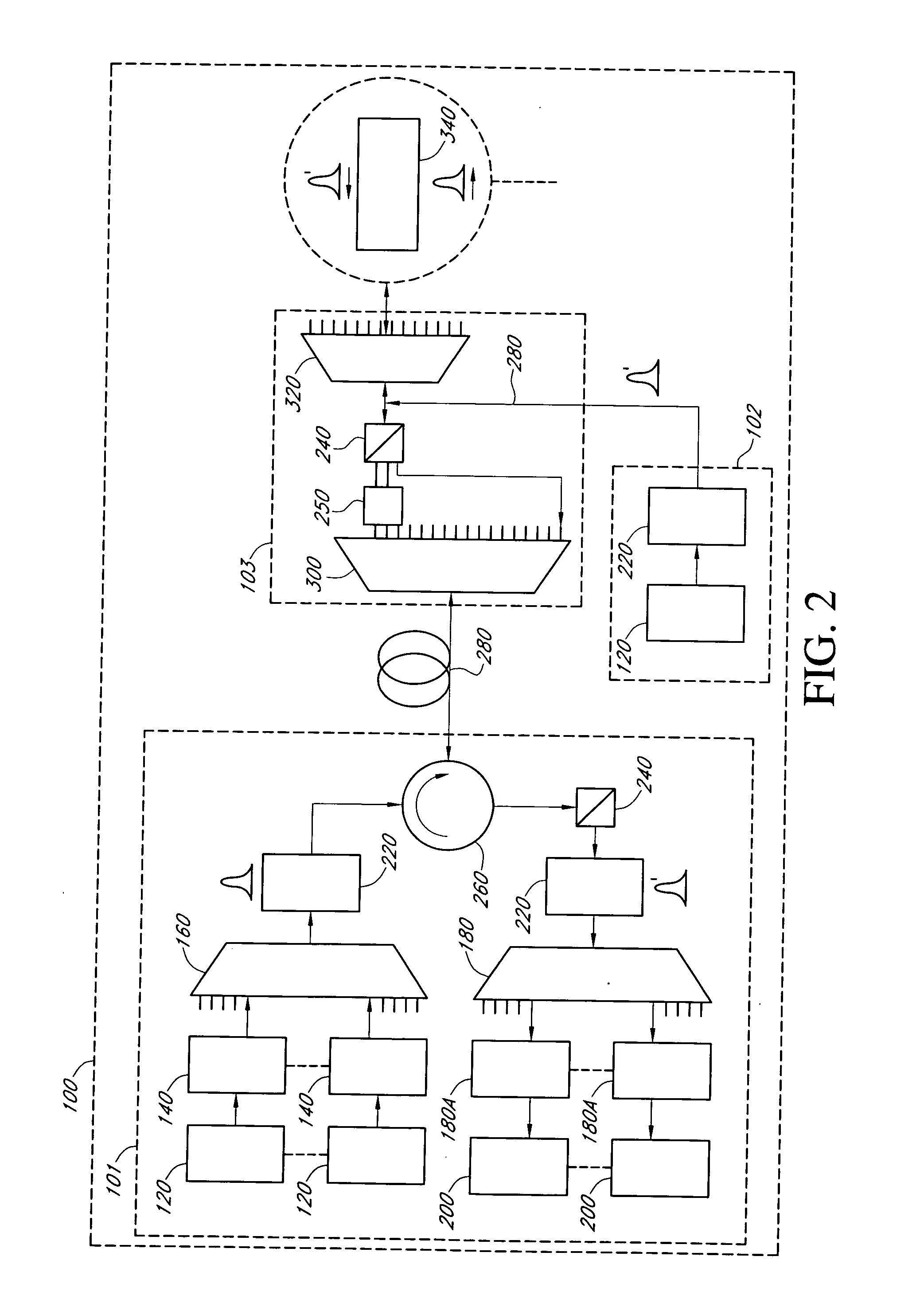
Intrusion detection and location system for use on multimode fiber optic cable
ActiveUS20070133922A1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionFiberSpectral width
A telecommunications multimode optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. Pulses are injected using a launch arrangement which generates a narrow spectral width, under-filled, non-uniform mode field power distribution in the multimode optical fiber and Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering from the pulse are detected at the transmit end to monitor the modal power distribution in the fiber which changes on manipulation of the fiber. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a modal power distribution detection system which includes an optical coupler to tap off a portion of the light which contains the higher order signal modes.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
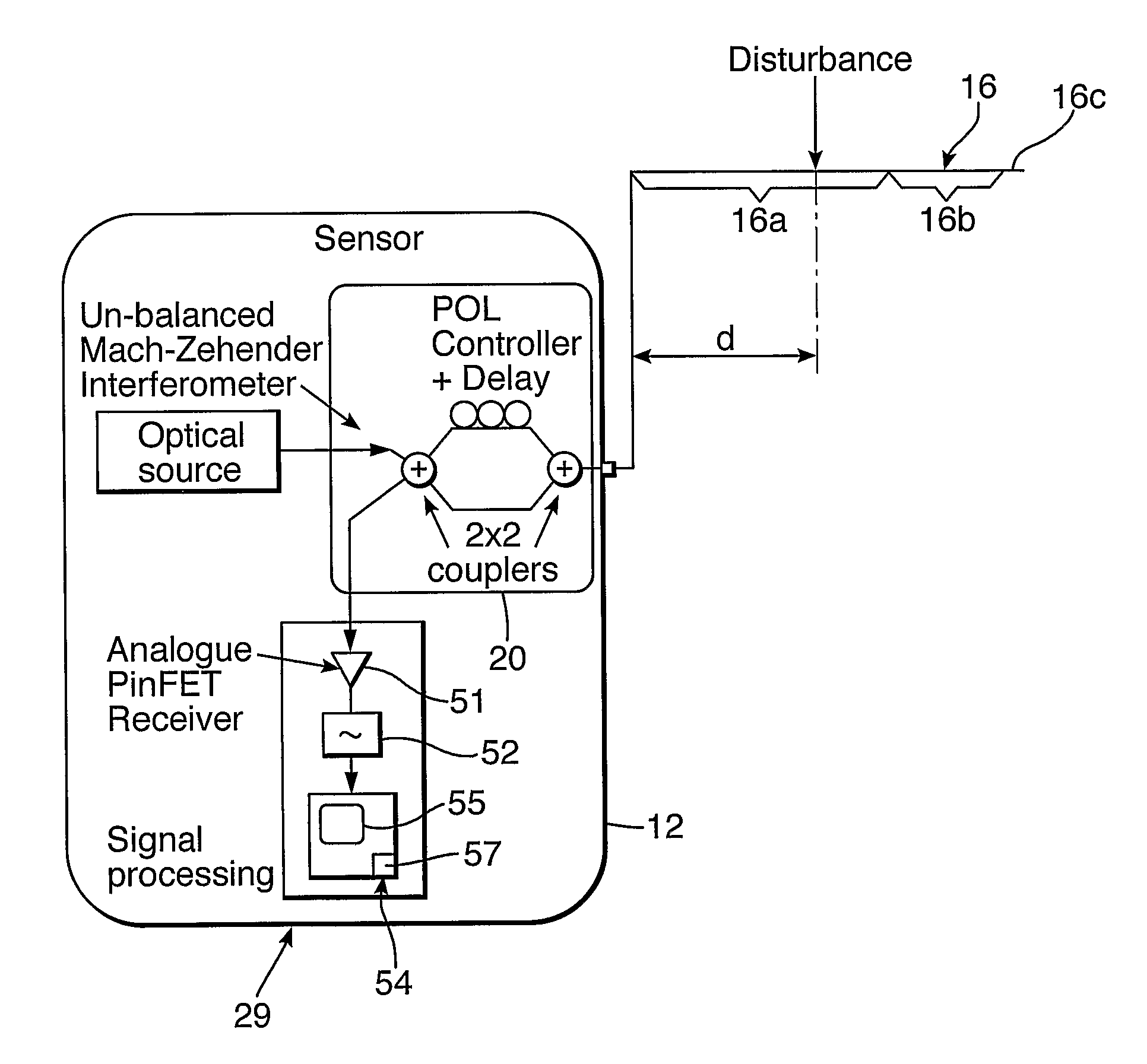
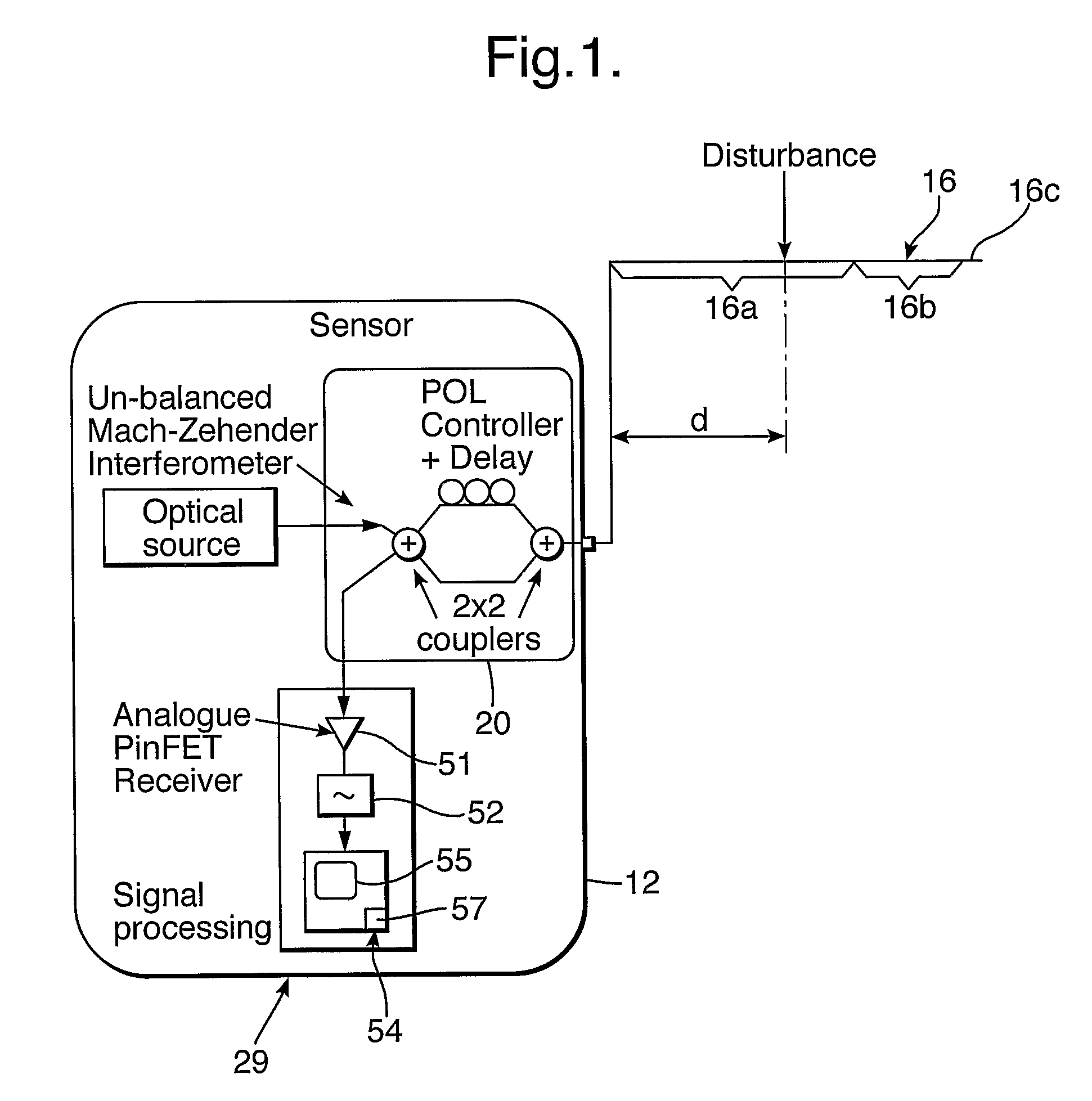
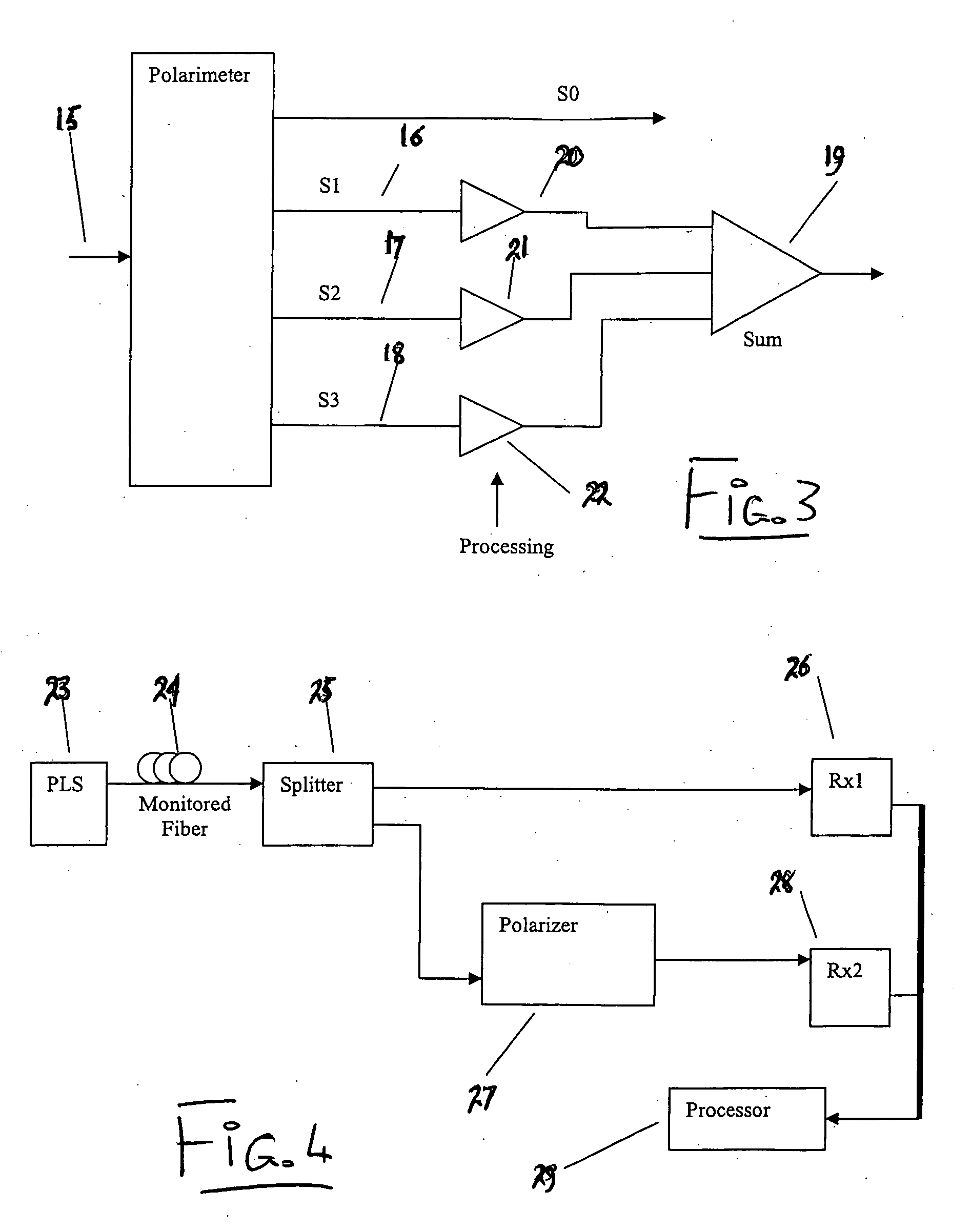
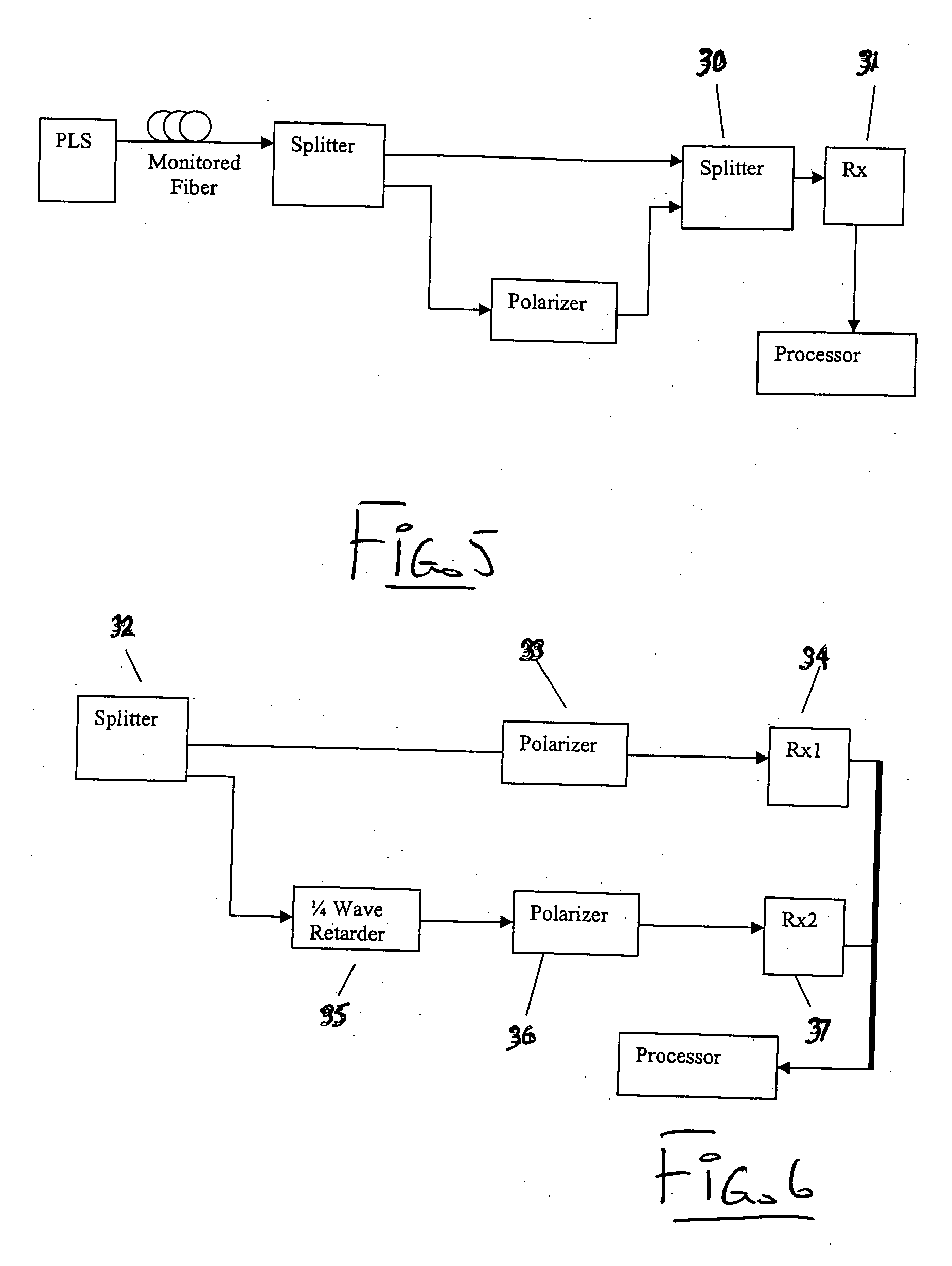
Method and apparatus using polarisation optical time domain reflectometry for security applications
InactiveUS7173690B2Detection of fluid at leakage pointWave based measurement systemsPolarizerRayleigh backscattering
A preferred apparatus and method is presented in which a distributed fiber optic sensor is used in order to detect a disturbance along its length. A pulse of polarized light is launched into an optical fiber; as the pulse propagates along the optical fiber, it continuously loses a small portion of its energy due to Rayleigh backscatter. The Rayleigh backscattered light is analyzed using a polarization sensitive element such as a fiber polarizer. The dynamics of the time dependence of the polarization analyzed backscattered light is used to ascertain if there has been a disturbance along the length of the optical fiber. This technique can be used for applications in areas such as fiber optic telecommunications, perimeter security, fire detection, and pipelines.
Owner:SENSTAR CORP
Distributed backscattering
ActiveUS7995197B2Advantage in useReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansTelecommunications linkEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for detecting or inferring a physical disturbances on a communications link, in particular by using distributed backscattering. The method includes the steps of: transmitting test signals onto a link; receiving test signals returned from a remote portion of the link; performing a function on the returned test signals; and in dependence on at least one characteristic of the combination signal, inferring the presence of a disturbance. The test signal are returned by a process Rayleigh backscattering along the fibre, so existing fibre installations can be used without requiring a mirror to be specifically introduced.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Intrusion detection and location system for use on multimode fiber optic cable
ActiveUS7333681B2Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionFiberSpectral width
A telecommunications multimode optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. Pulses are injected using a launch arrangement which generates a narrow spectral width, under-filled, non-uniform mode field power distribution in the multimode optical fiber and Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering from the pulse are detected at the transmit end to monitor the modal power distribution in the fiber which changes on manipulation of the fiber. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a modal power distribution detection system which includes an optical coupler to tap off a portion of the light which contains the higher order signal modes.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
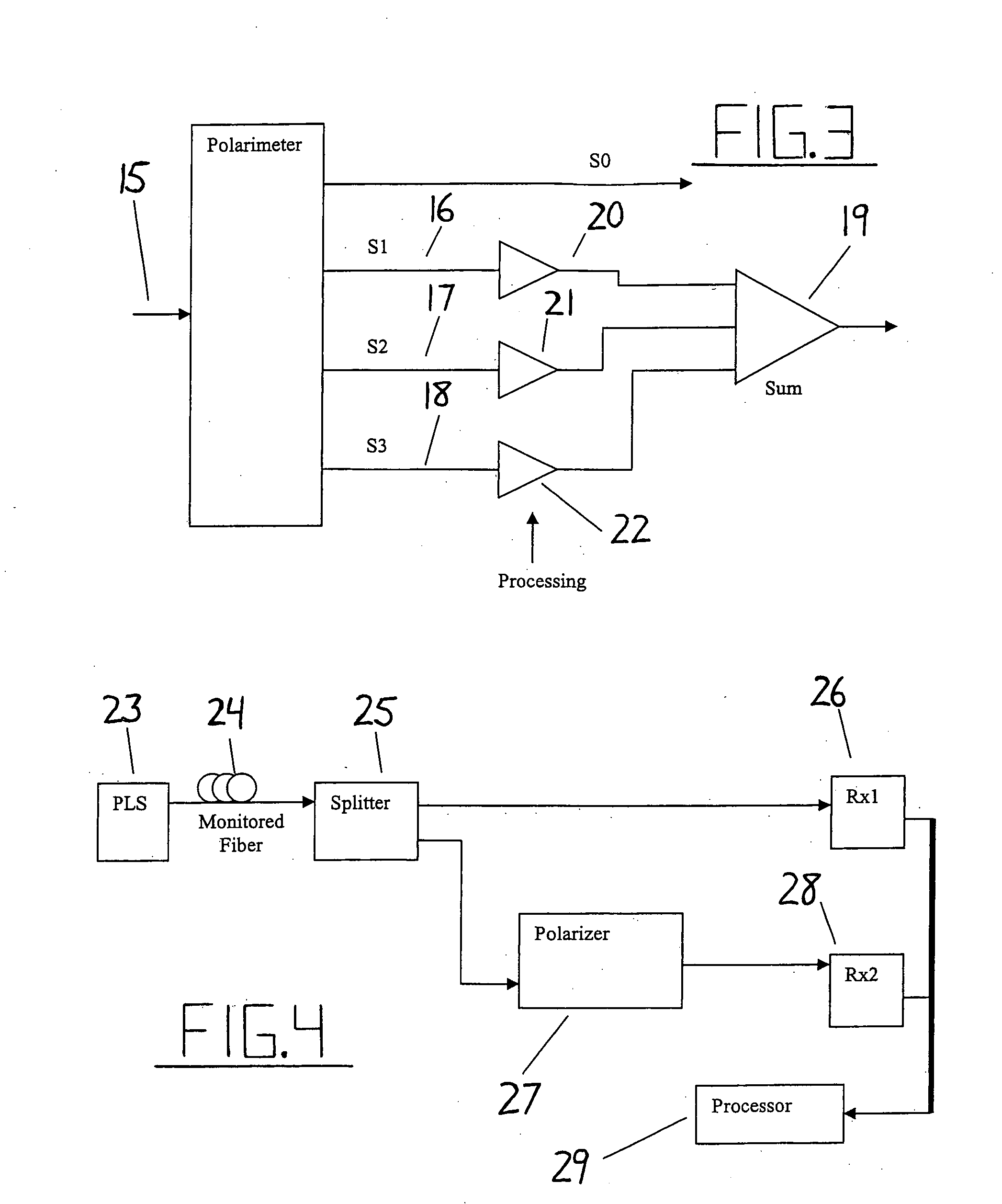
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a polarimeter
ActiveUS7206469B2Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityNon-electrical signal transmission systemsElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsProcessor registerPolarimeter
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
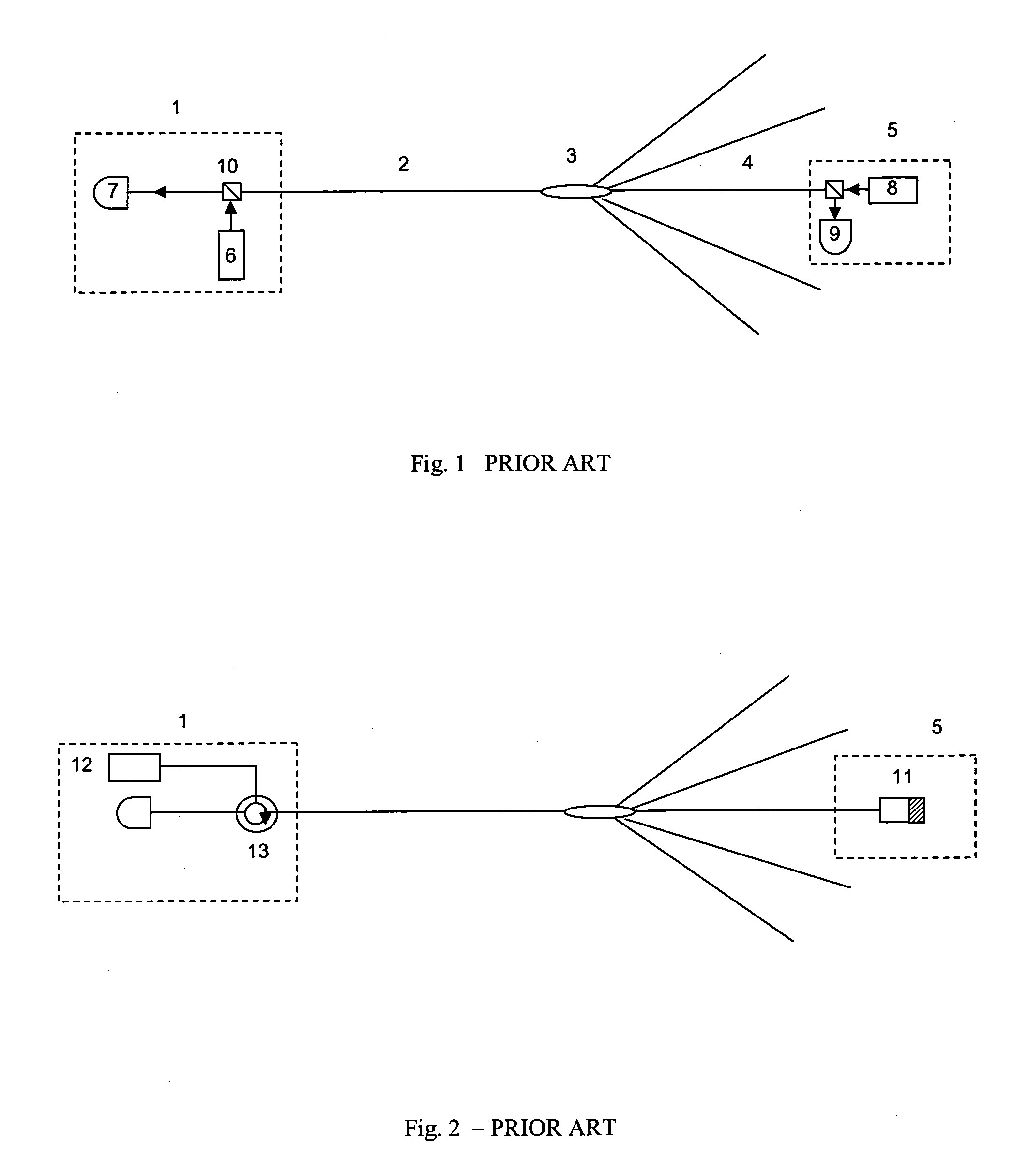
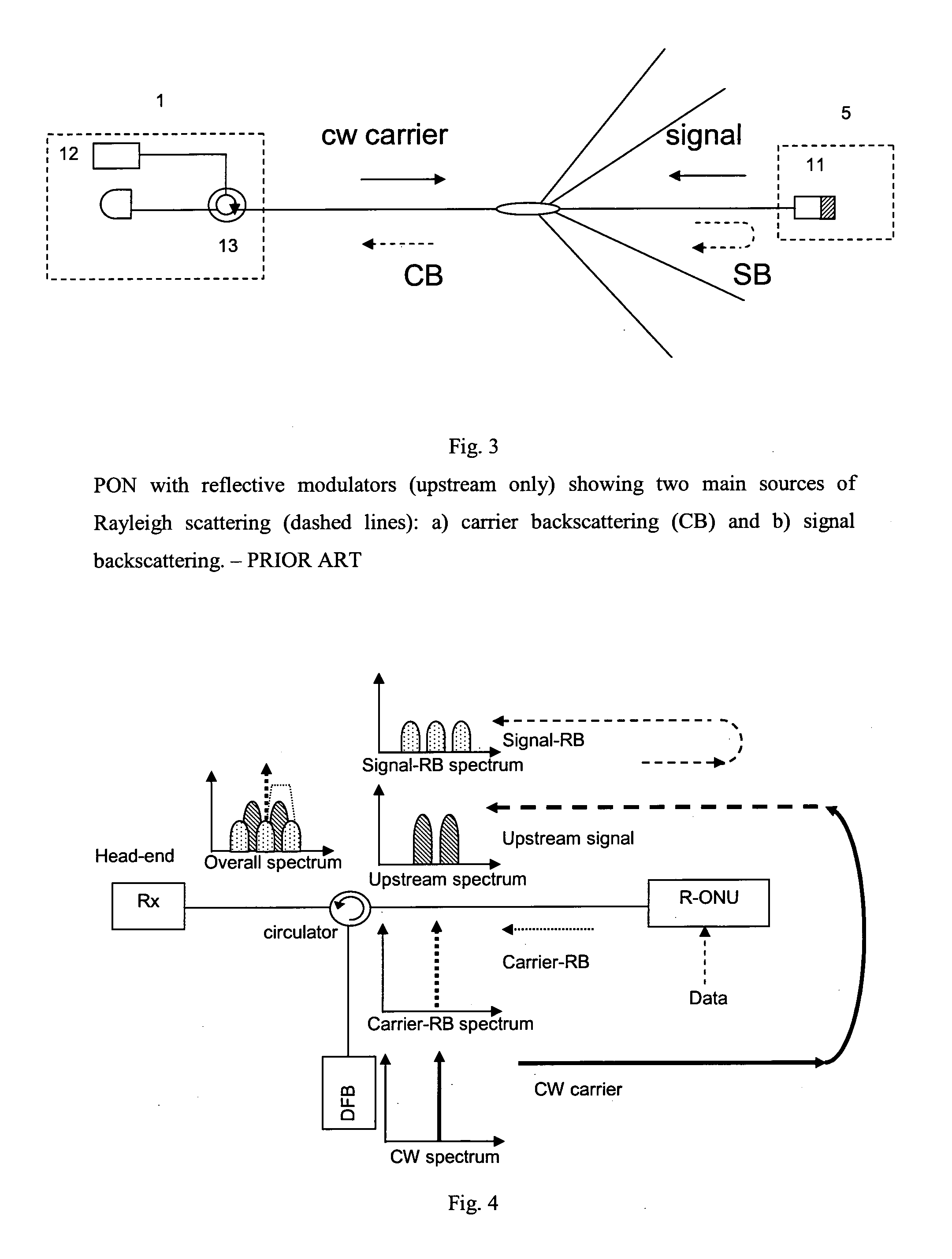
Optical communication system
InactiveUS20100111543A1Avoid noiseReduce disturbing noiseElectromagnetic transmittersMultiple station single light sourceData streamCarrier signal
An optical transmitter is of the reflective modulation type and has a means of generating reflection, a mixer for mixing a data stream and a sub-carrier, and an optical modulator for modulating an optical carrier with the output from the mixer in order to avoid optical beat-interference noise arising from, for example, Rayleigh backscattering. The modulator is in one embodiment of the interferometric type such as a Mach-Zehnder Modulator (MZM) operated to suppress the optical carrier at the transmitter output in order to reduce optical beat interference noise. The modulator preferably implements CSS-AMPSK modulation, which suppresses optical beat noise and achieves strong dispersion tolerance, enabling, for example, 10 Gb / s data transmission over 100 km distance without dispersion compensation. The transmitter may have a duobinary encoder, which encodes the data prior to mixing with the sub-carrier.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK
Dynamic intelligent bidirectional optical access communication system with object/intelligent appliance-to-object/intelligent appliance interaction
ActiveUS8548334B2Reduce impactReduced Rayleigh backscatteringMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsCommunications systemWavelength
Reduced Rayleigh backscattering effect enables a longer-reach optical access communication network-thus it eliminates significant costs. Furthermore, a wavelength to an intelligent subscriber subsystem can be dynamically varied for bandwidth on-Demand and service on-Demand. A software module renders intelligence (and context awareness) to a subscriber subsystem and an appliance. An object can sense / measure / collect / aggregate / compare / map and connect / couple / interact (via one or more or all electrical / optical / radio / electro-magnetic / sensor / bio-sensor communication network(s) within and / or to and / or from an object) with another object, an intelligent subscriber subsystem and an intelligent appliance utilizing an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) and its subsequent versions.A construction of a near-field communication (NFC) enabled intelligent micro-subsystem and / or intelligent appliance with key applications (e.g., an intelligent, location based and personalized social network and an intelligent, location based and personalized direct and peer-to-peer marketing) are also described.
Owner:MAZED MOHAMMAD
Method Of Determining Stress Variations Over Time In An Undersea Pipe For Transporting Fluids
ActiveUS20190064030A1Improve accuracyPerformed more accurately and moreForce measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesOcean bottomTemporal change
A method of determining stress variations over time in an undersea pipe for transporting fluids, the method comprising: installing along the entire length of the pipe (1) at least one distributed optical fiber sensor (2-1 to 2-4) using Rayleigh backscattering, the sensor being dedicated to measuring at least one degree of freedom of movement variation over time in the pipe at each cross section of the pipe; continuously measuring movement variation of the optical fiber sensor over time; and determining stress variations over time at each point in the pipe by time integration of the measured movement variation of the optical fiber sensor.
Owner:SAIPEM SA
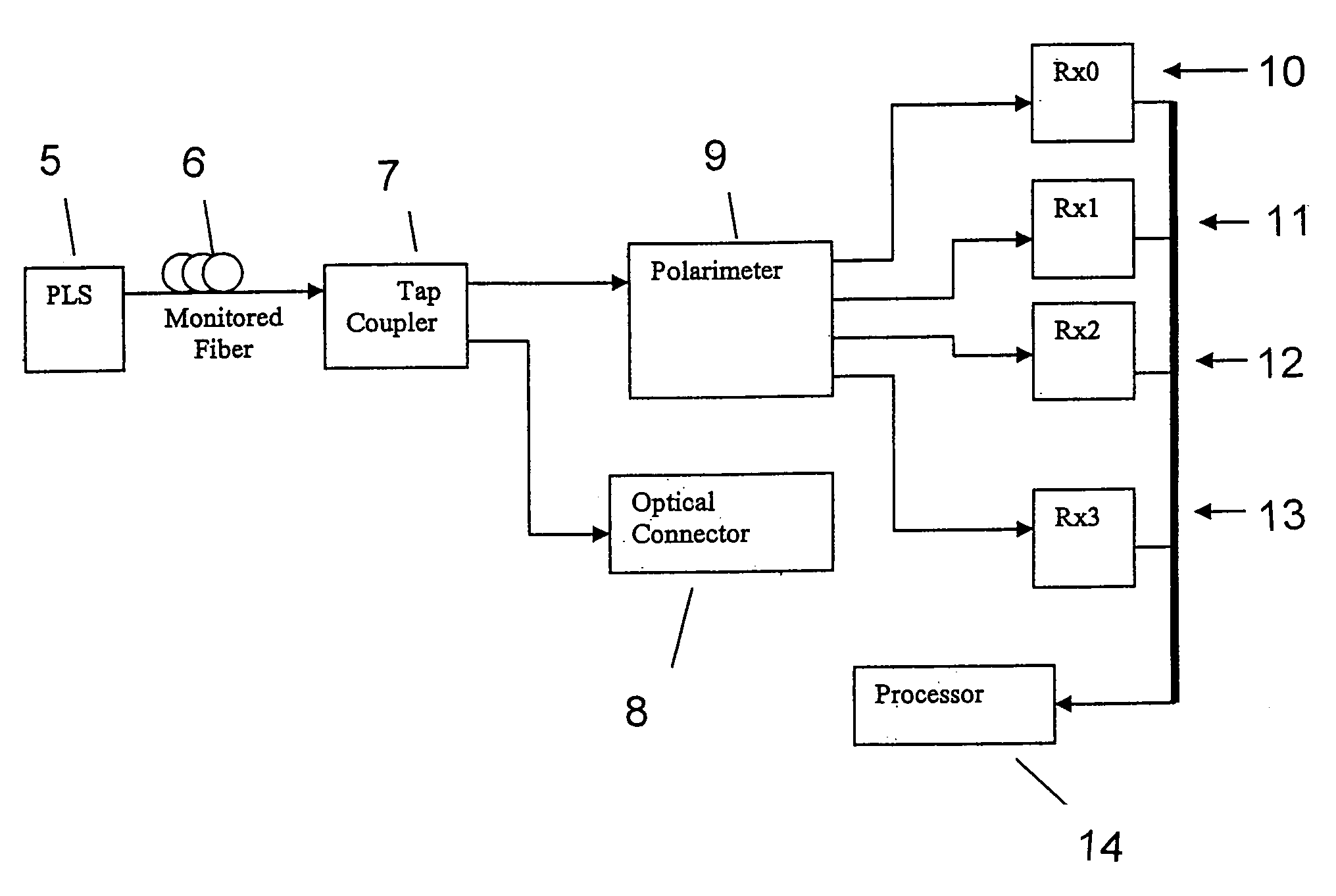
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a polarimeter
ActiveUS20060153520A1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsOptical light guidesPolarimeterPolarizer
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
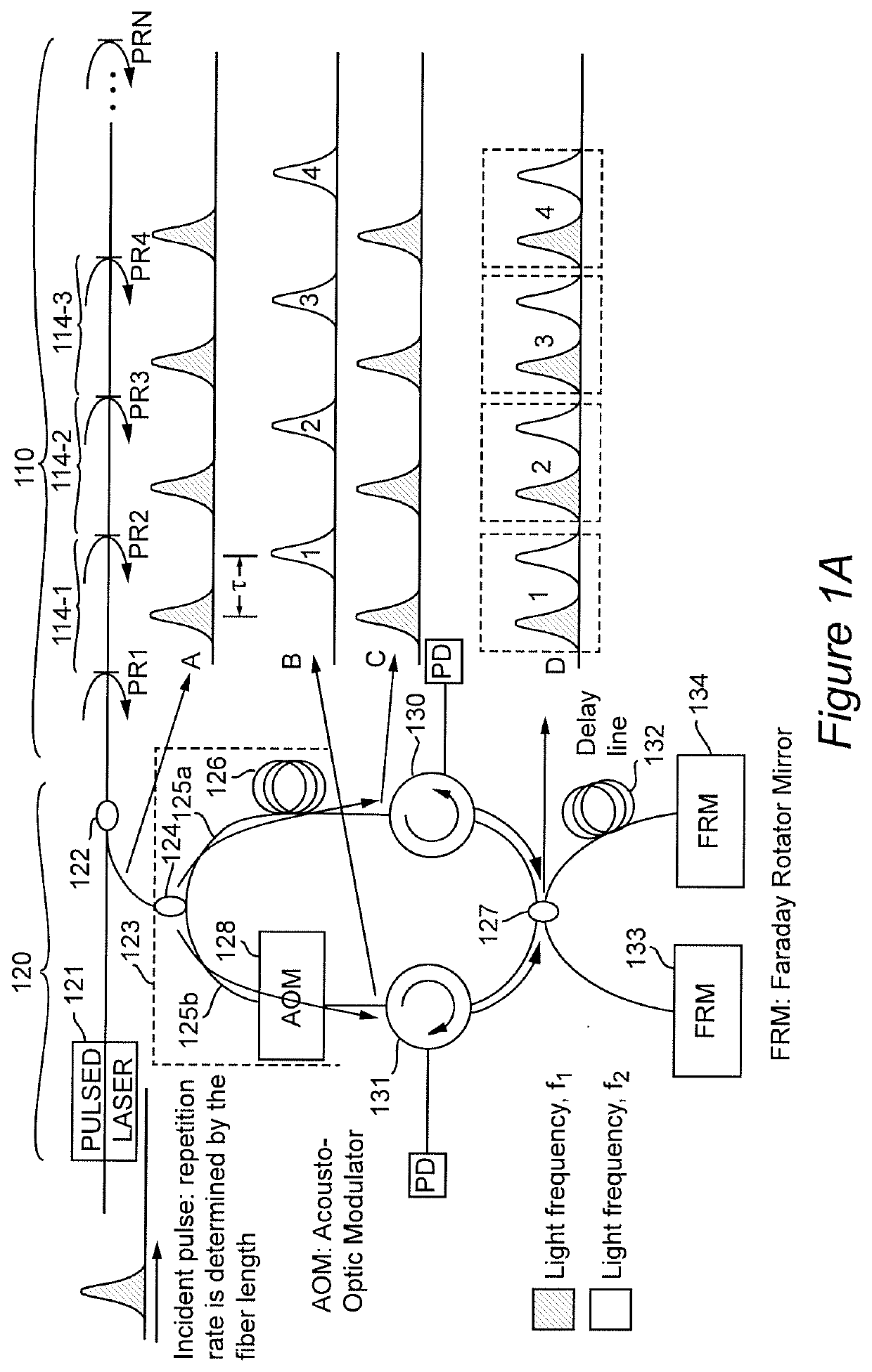
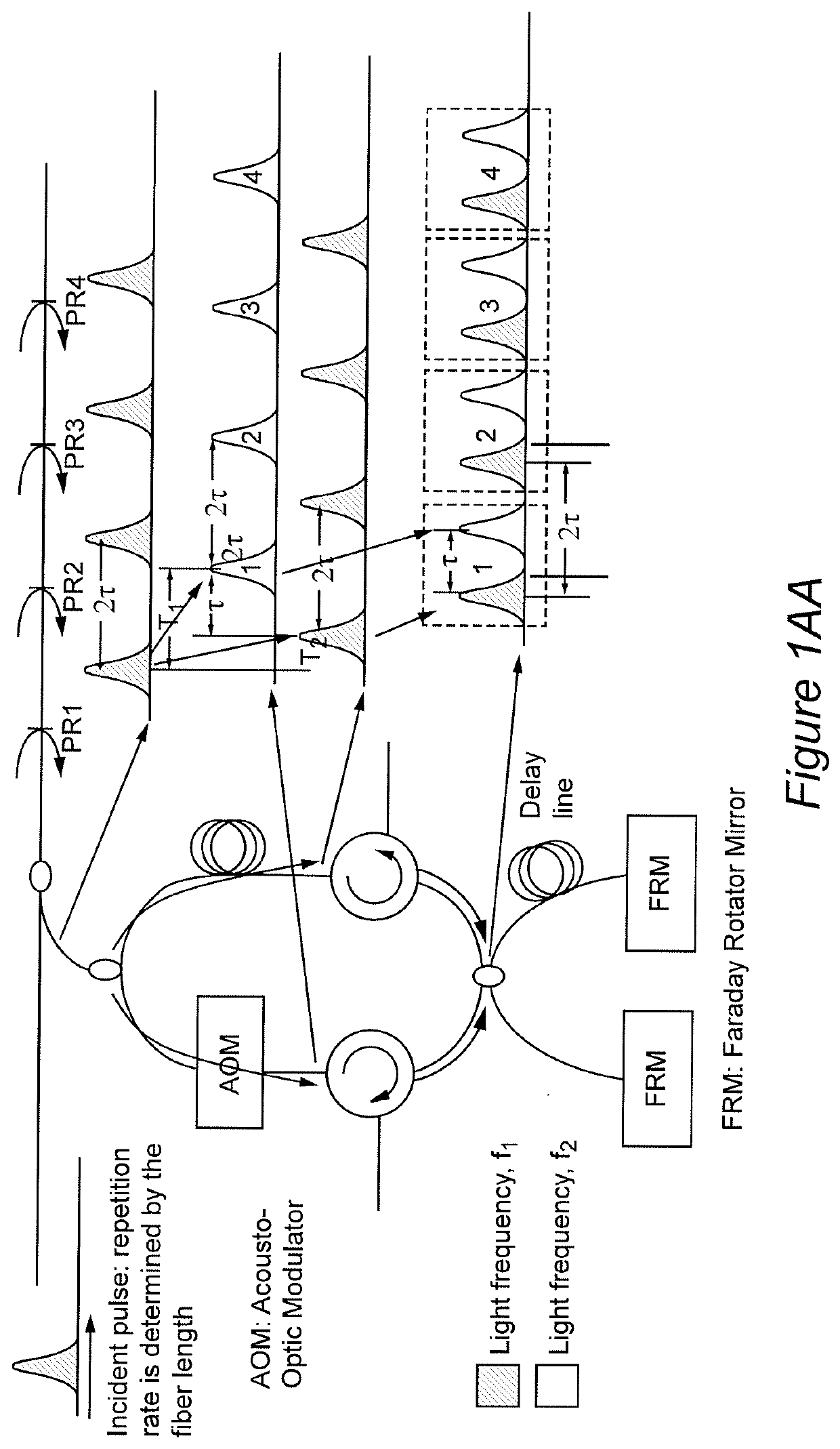
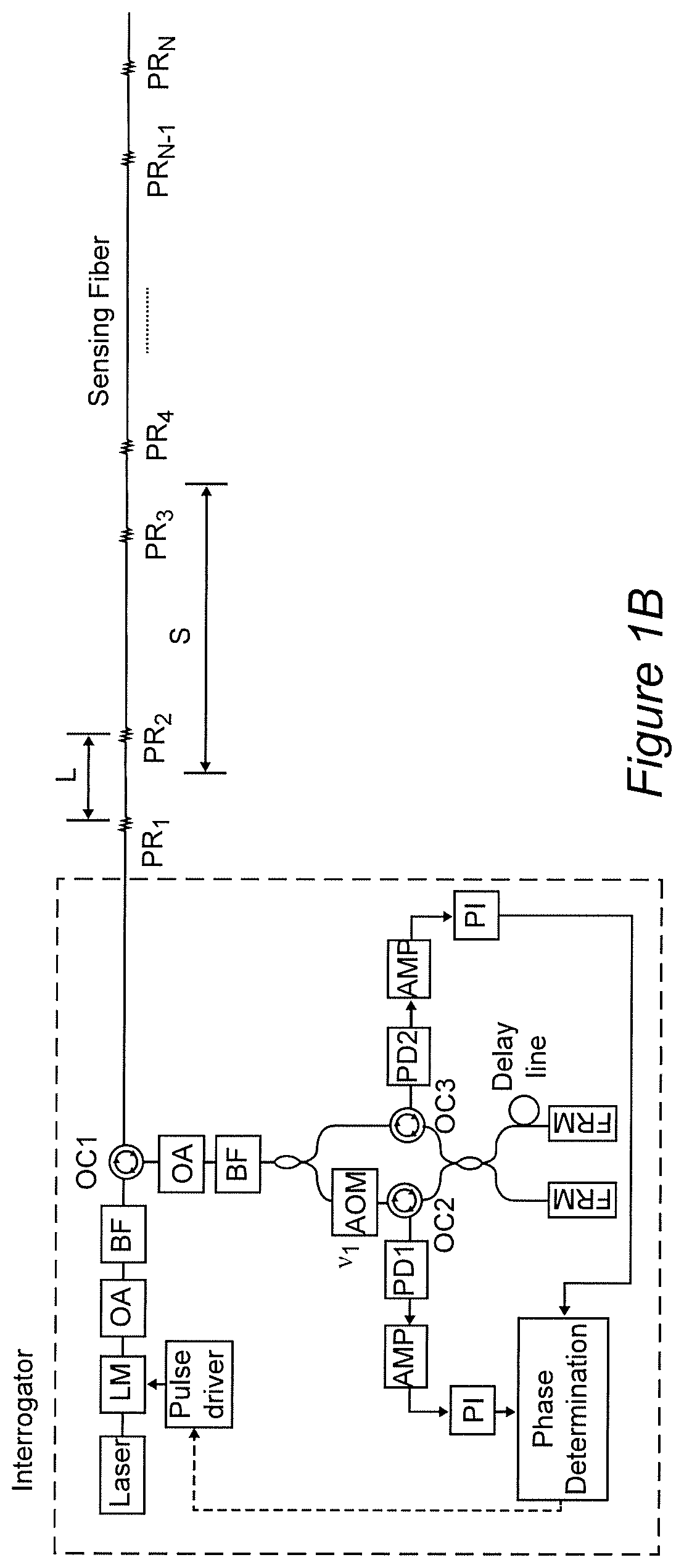
Method and apparatus for distributed sensing
ActiveUS20200249075A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansRayleigh backscatteringAcoustic wave
Forming a light pulse having a plurality of time-dependent frequency components such as a chirped light pulse or a light pulse group and superposing reflected light from different portions of an optical fiber allows detection of changes in effective optical path differences due to physical parameters in the environment of the optical fiber by sensing the optical interference pattern of each light frequency and wavelength. The development of a plurality of interference patterns from each light pulse provides sufficient information for robust demodulation by known methods to produce signals having good fidelity to variations in the physical parameters of interest, particularly vibrations and acoustic waves. The location of the measured physical parameter along the optical fiber can be determined from the time difference between injecting the light pulse and detection of a reflection or Rayleigh backscattering and diffraction index of the optical fiber.
Owner:SENTEK INSTR
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a storage register for data
ActiveUS20060291795A1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationOptical light guidesPolarimeterPolarizer
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
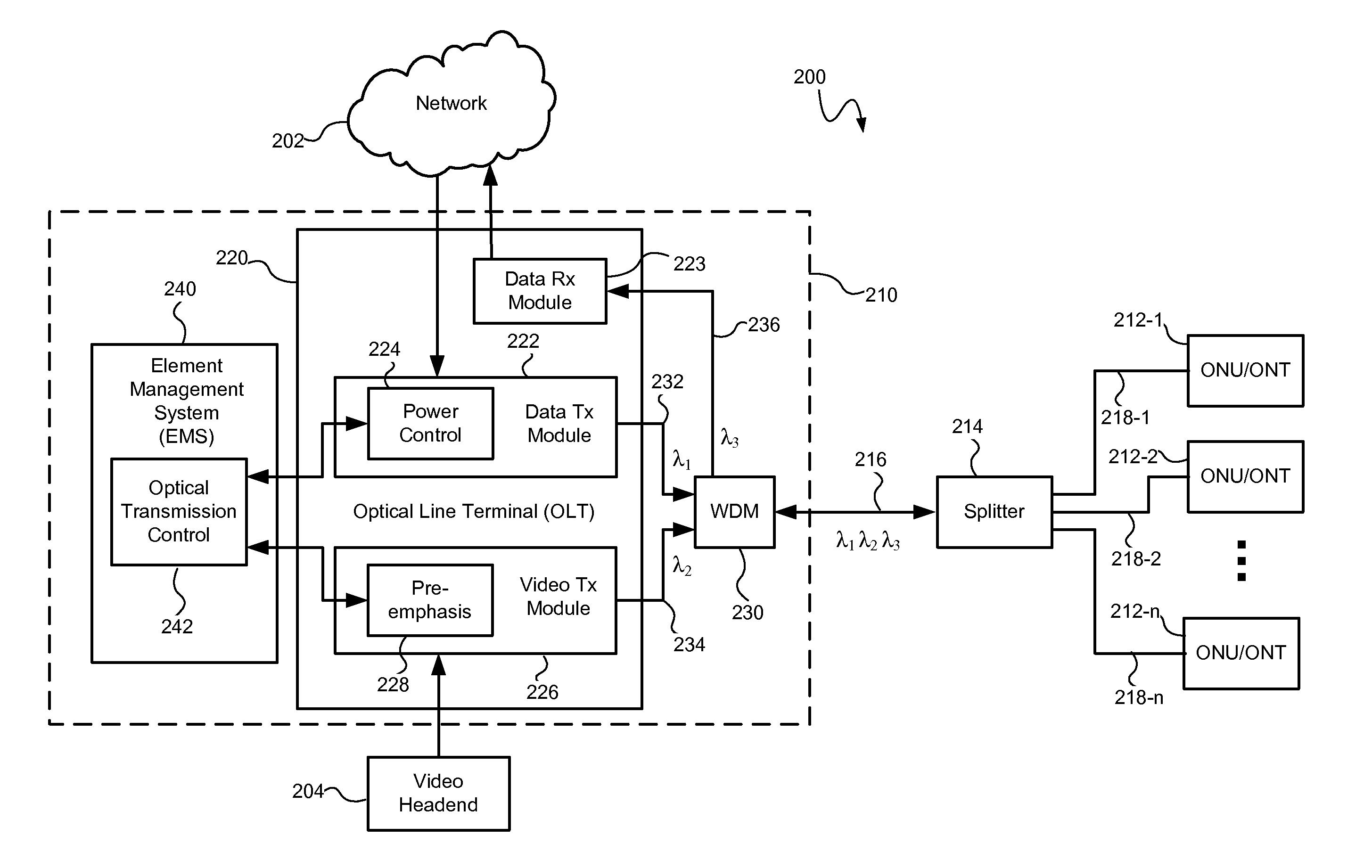
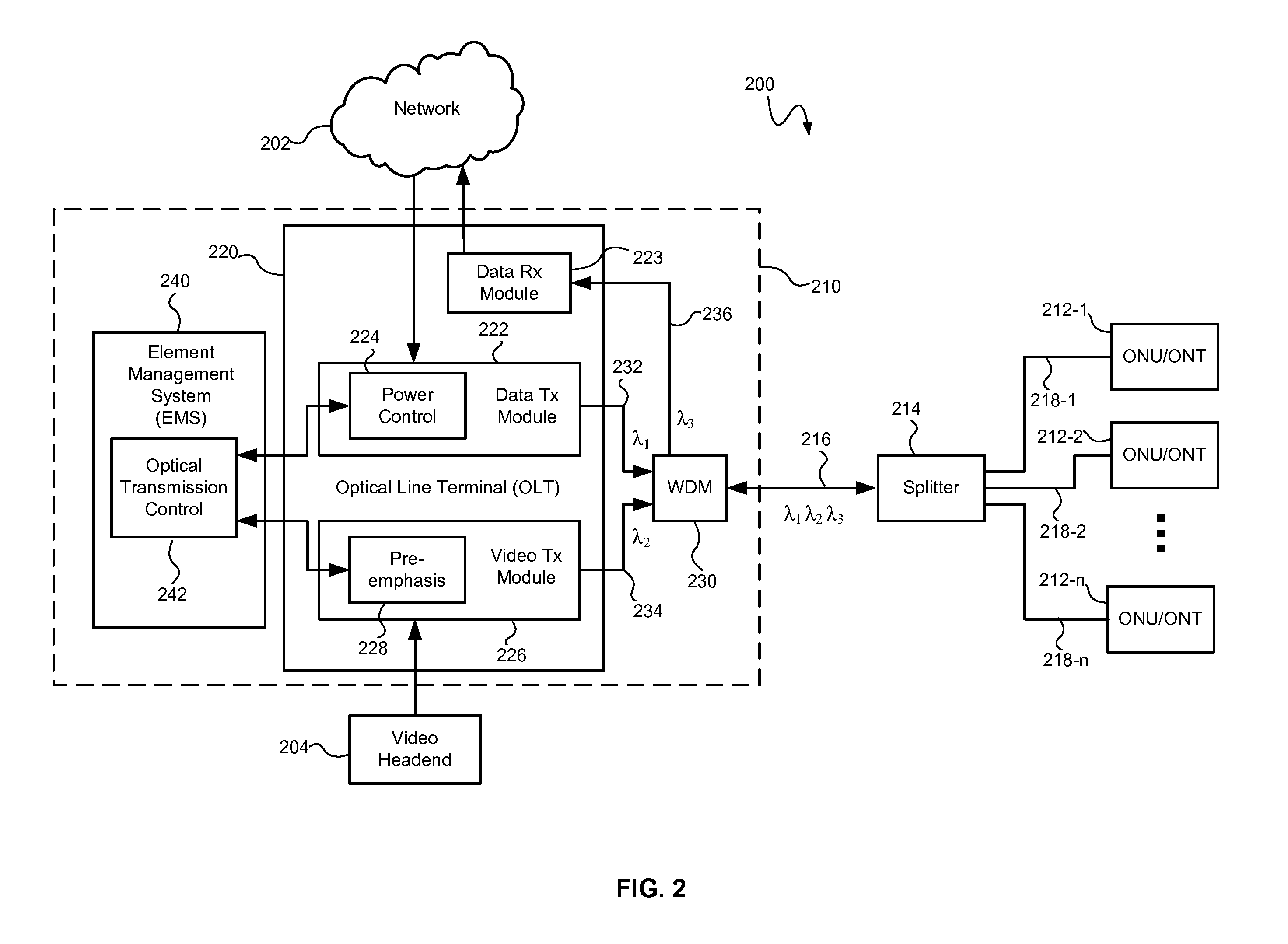
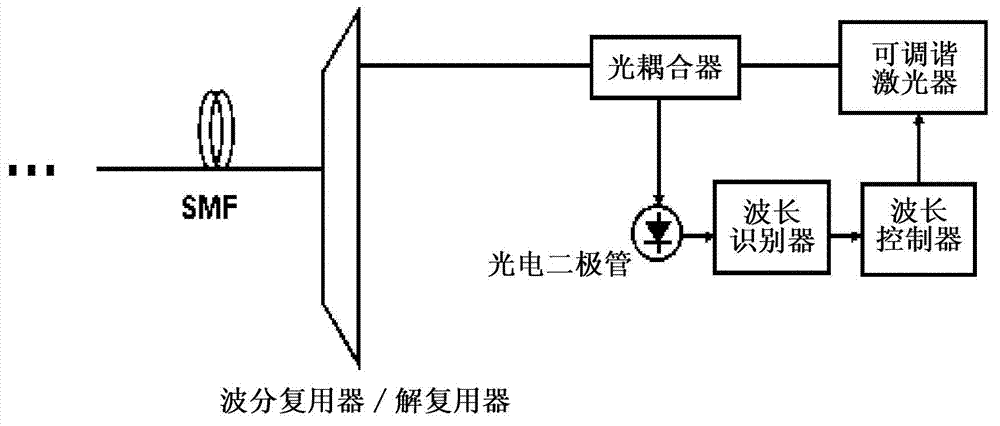
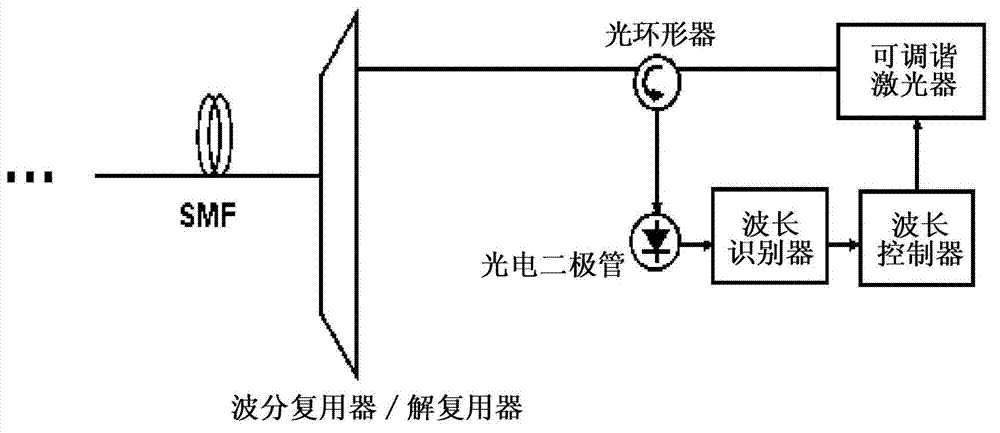
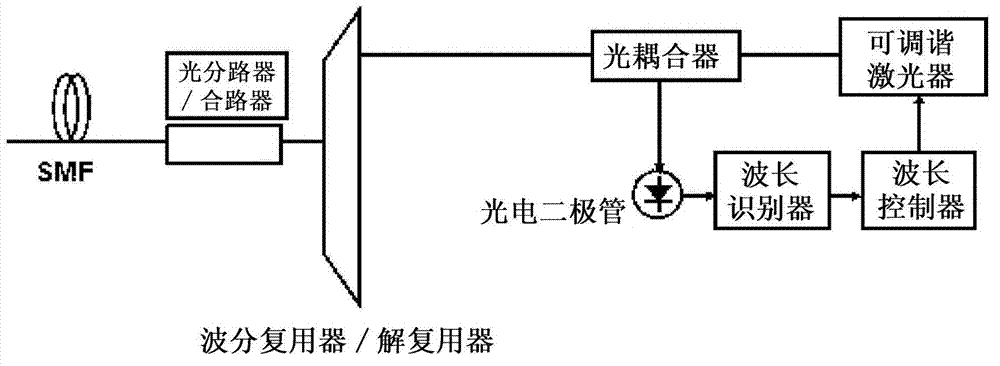
Apparatus and method for controlling the lasing wavelength of a tunable laser, and wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network comprising same
ActiveCN102771066AControl lasing wavelengthSave resourcesOptical multiplexSemiconductor lasersMultiplexerOptical power
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for controlling the lasing wavelength of a tunable laser, and to a wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network comprising same. The apparatus and method for controlling the lasing wavelength of tunable laser, and a wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network comprising same, involve controlling the lasing wavelength of tunable laser such that the lasing wavelength can automatically correspond to the transmission wavelength of a wavelength division multiplexer / demultiplexer using Rayleigh backscattering occurring in an optical fiber or the optical power characteristics or optical beating components obtained from reflected optical components, thereby improving the performance of the wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Single-ended chaotic Brillouin dynamic strain measuring device and method based on Rayleigh scattering
ActiveCN110220470AAchieve positioningImplement diagnosticsUsing optical meansContinuous lightRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a single-ended chaotic Brillouin dynamic strain measuring device and method based on Rayleigh scattering, aiming at meeting the current requirements of long-distance, high-resolution, large dynamic range and real-time and rapid application of distributed sensing and simultaneously solving the problem that a system cannot work when a breakpoint occurs because a pump light and a detection light need double-end incidence in a Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis system. A continuous light output by a light source is divided into two paths through a coupler, one pathis used as the pump light, the other path is subjected to double-sideband modulation through a high-speed electro-optic modulator, a backward Rayleigh scattering light is used as the detection lightand generates stimulated Brillouin scattering with the pump light, and a corresponding dynamic strain value is demodulated through a corresponding relation between intensity information acquired by ahigh-speed data acquisition system and strain. The single-ended chaotic Brillouin dynamic strain measuring device is simple in structure and low in cost, can effectively reduce signal power fluctuation, and realizes dynamic strain measurement with single end, high spatial resolution, long distance and good stability.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
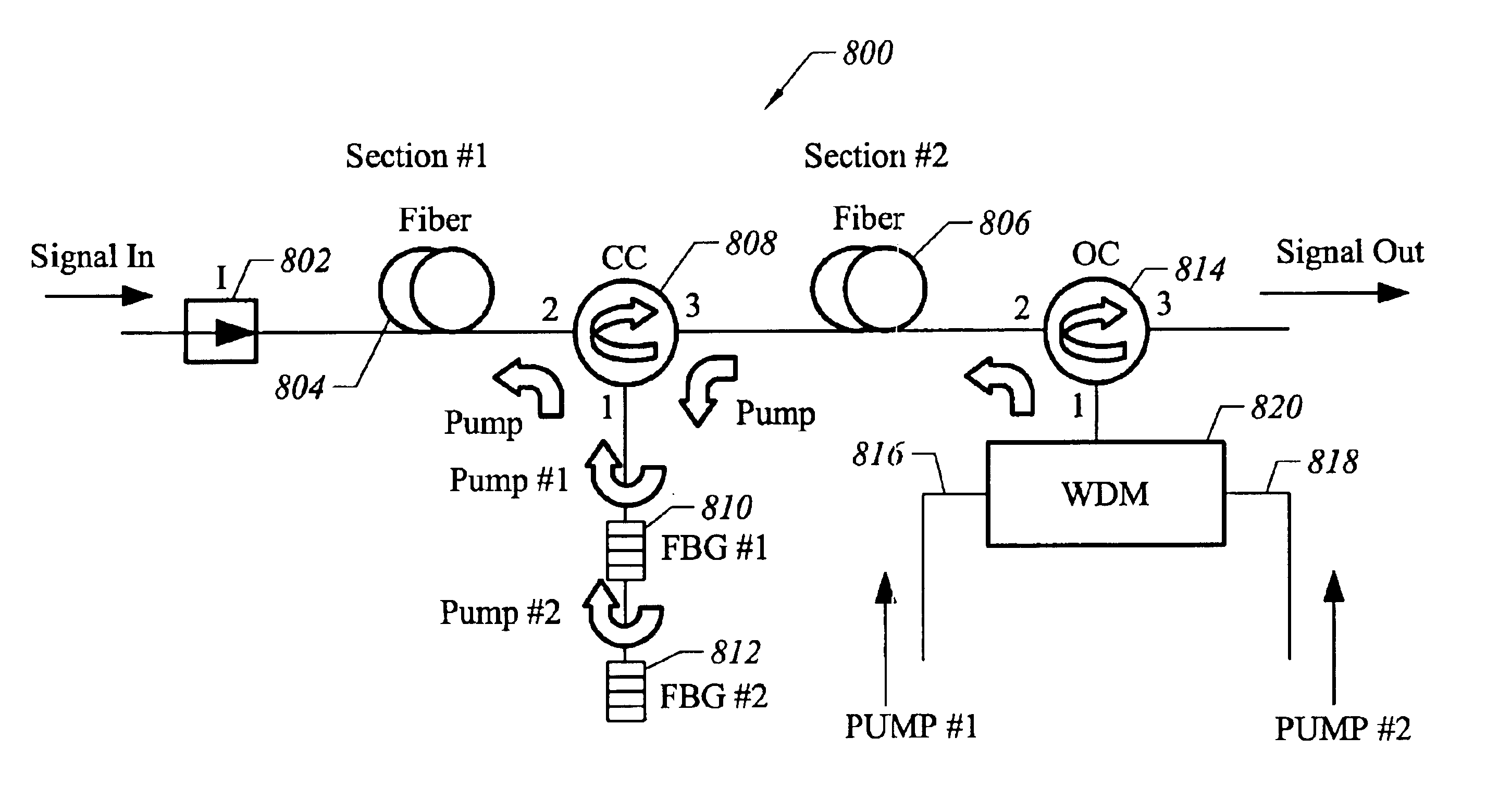
Suppression of double rayleigh backscattering and pump reuse in a raman amplifier
InactiveUS6862132B1Prevent travelGood effectLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionGratingAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods for ameliorating double Rayleigh backscattering induced impairments are provided. Raman amplification is divided among two or more stages. Optical energy from a single counter-propagating pump may traverse multiple stages while optical energy at the frequency of the signal to be amplified is permitted to propagate in the forward direction only. In this way the pump power can be effectively distributed over the entire amplifier length. The scheme may be implemented in a simple configuration employing a closed circulator and a fiber Bragg grating. Multiple wavelength pump operation may be accommodated as well as either discrete or distributed Raman amplification.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
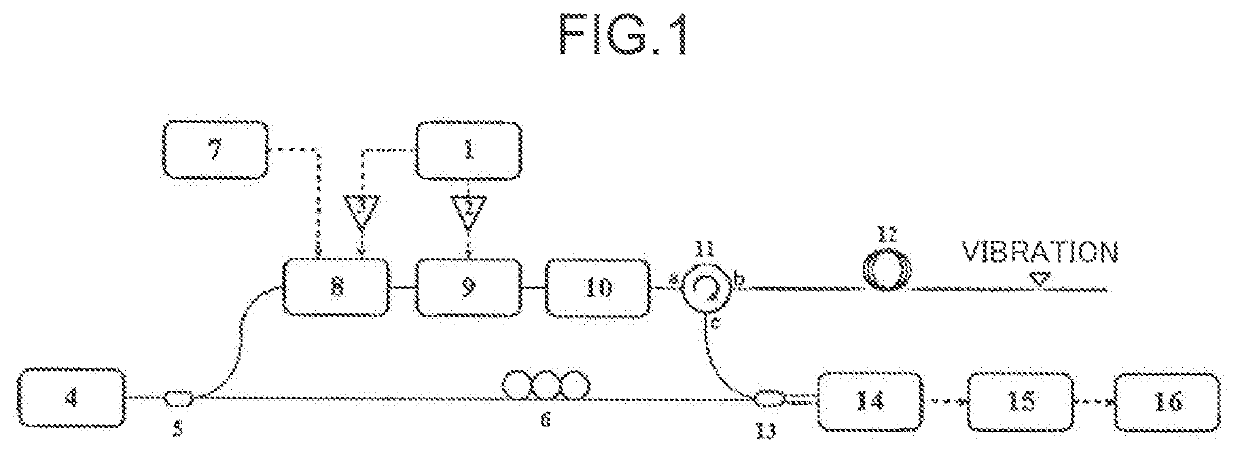
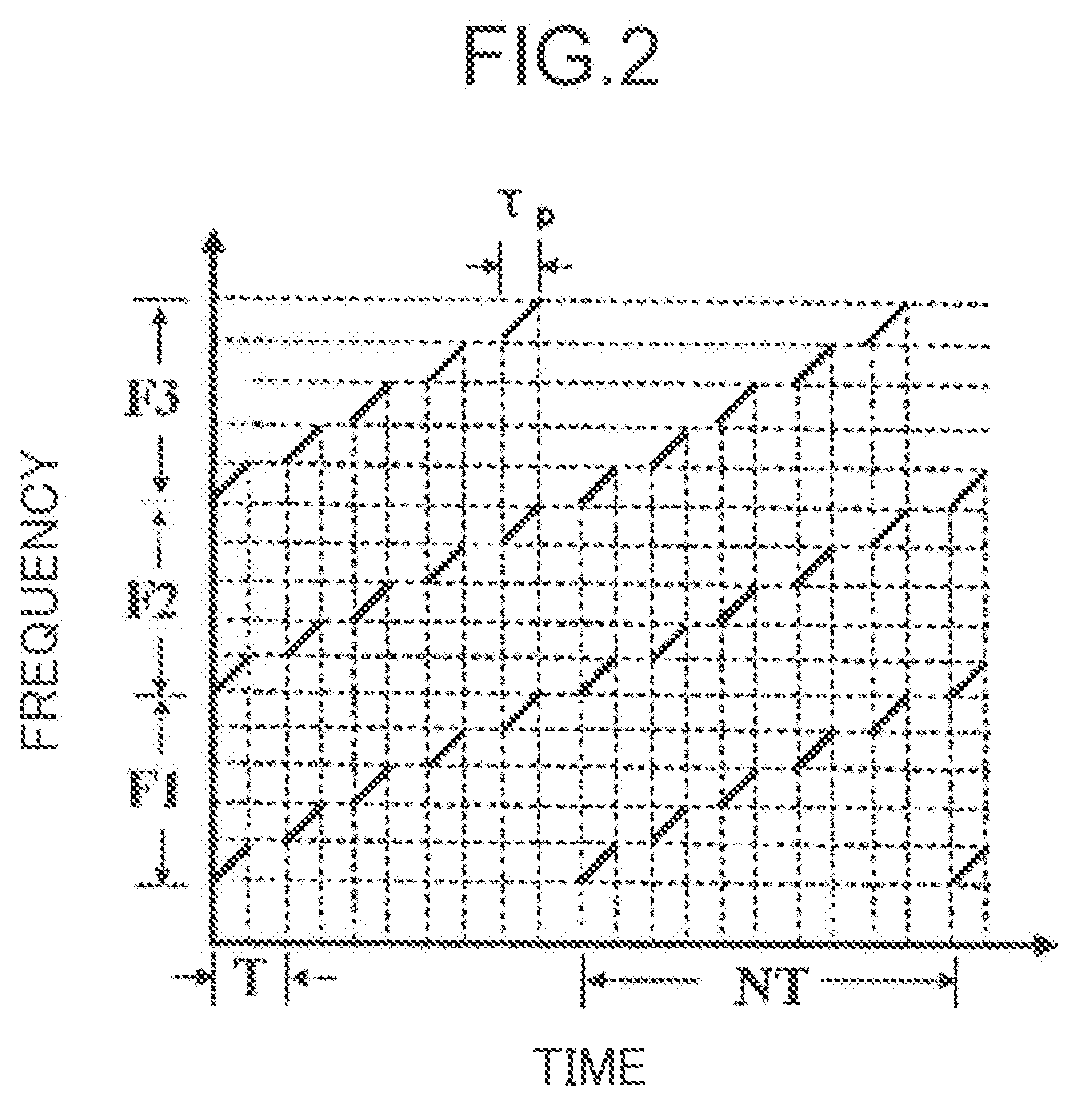
Distributed fibre sensing system and vibration detection and positioning method therefor
ActiveUS20200182685A1Improve spatial resolutionLong detection distanceSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansOptical circulatorEngineering
A distributed fibre sensing system and a vibration detection and positioning method therefor are disclosed. The system comprises: a signal generating module, a light source module, an optical frequency comb generating module, a frequency sweeping and pulse generating module, an optical circulator, a sensing fibre, an interference module, a photoelectric conversion module and a detection and position module. The method comprises: obtaining a plurality of Rayleigh backscattering signals of the sensing fibre; performing a fading elimination processing on the Rayleigh backscattering signals, thereby obtaining a plurality of averaged Rayleigh backscattering signals of non-interference fading and polarization fading; performing a phase processing on the averaged Rayleigh backscattering signals, thereby obtaining phase variance curves; and determining a vibration point according to variances in the phase variance curves, and finally obtaining a position and a vibration waveform of the vibration point.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Distributed acoustic sensing system based on space-division multiplexing with multi-core fiber
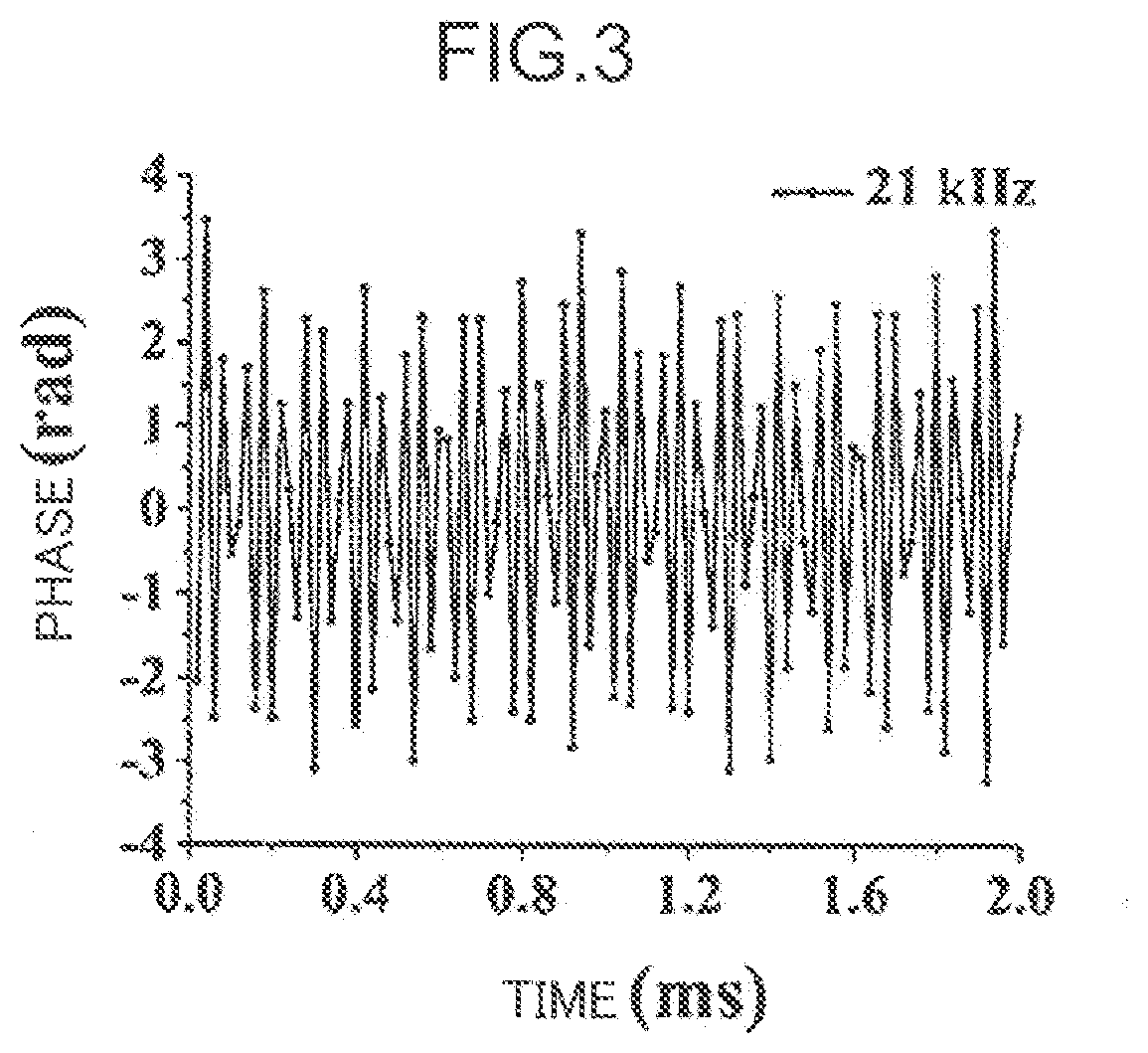
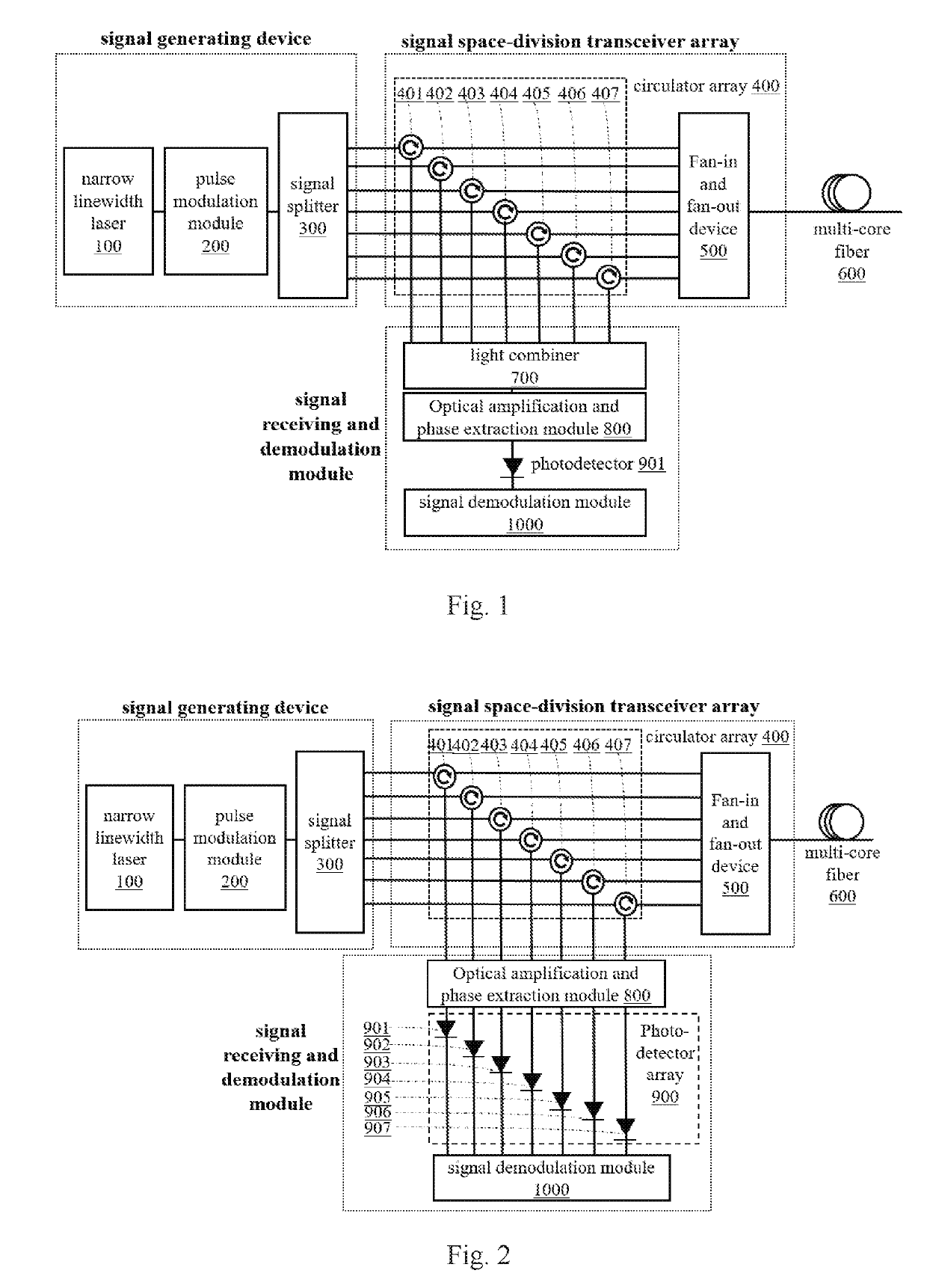
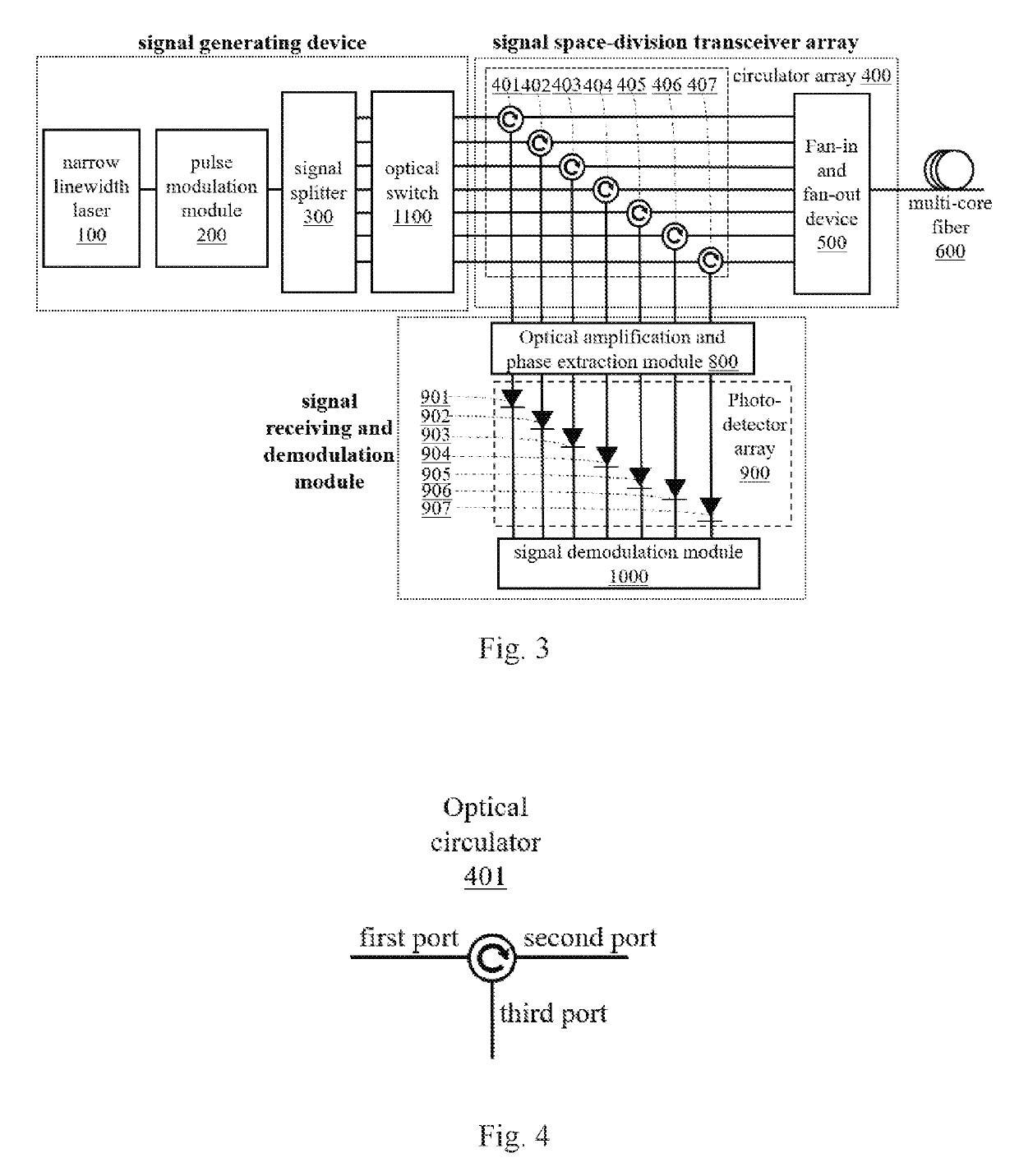
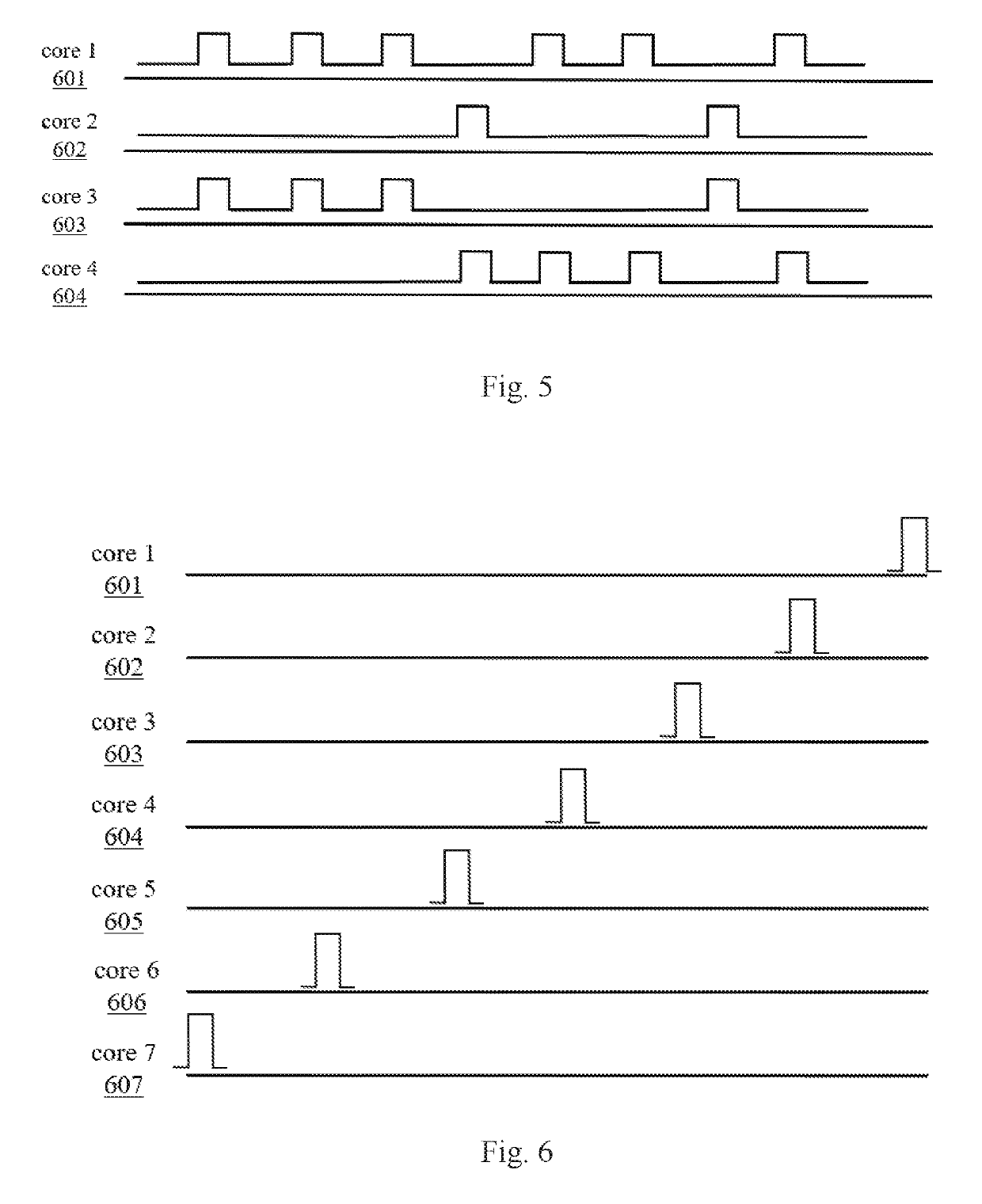
ActiveUS20190226908A1Improving strain resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementOptical mode multiplex systemsDistributed acoustic sensingTime delays
A distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) system based on space-division multiplexing with multi-core fiber (MCF) is proposed. It relates to a technical field of distributed optical fiber sensing. The present invention maintains the advantage of single-ended measurement in the standard DAS system, and realizes the intensity accumulation of the Rayleigh backscattering light within each core of the MCF, which can greatly improve the strain resolution of DAS systems. Moreover, the introduction of optical switch can make different code sequences transmit in the different core of the MCF simultaneously, which can make the single-pulse response with coding gain demodulated without sacrificing the frequency responding bandwidth. Furthermore, the utilization of space-division multiplexing can make multiple pulses with precious time delay transmit in the MCF simultaneously, which can greatly improve the frequency responding bandwidth of DAS system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
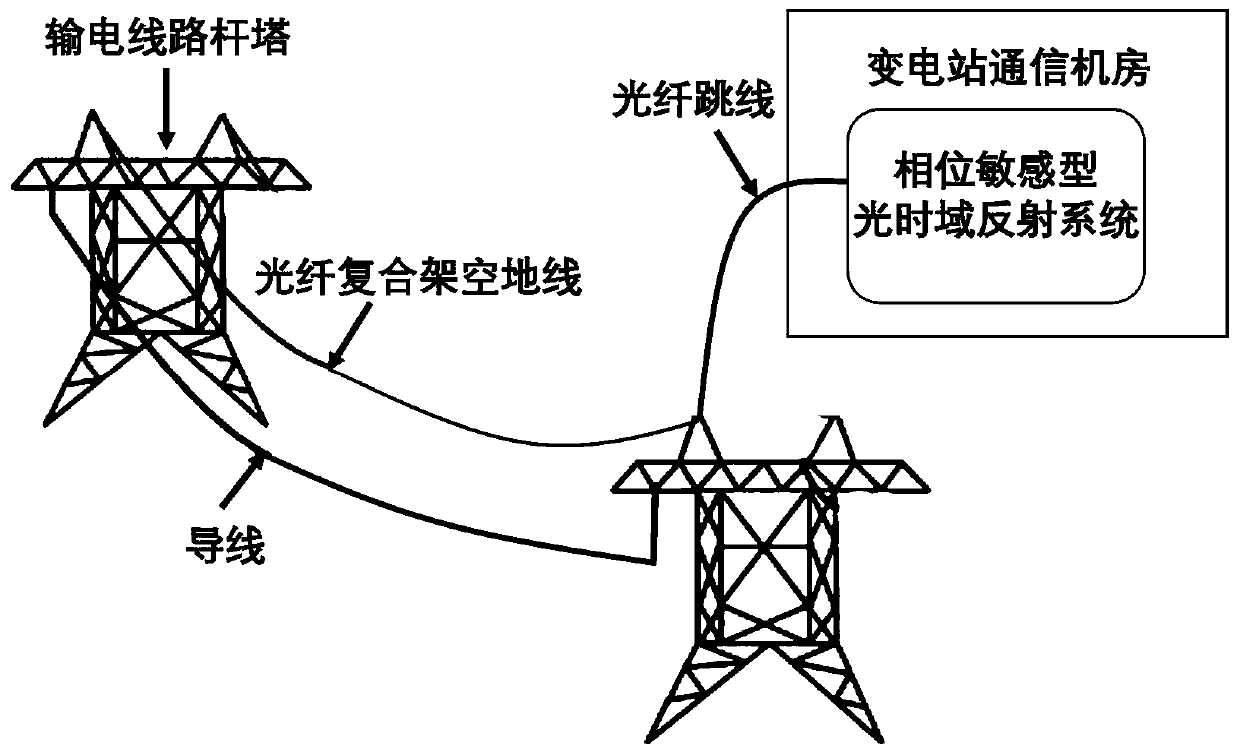
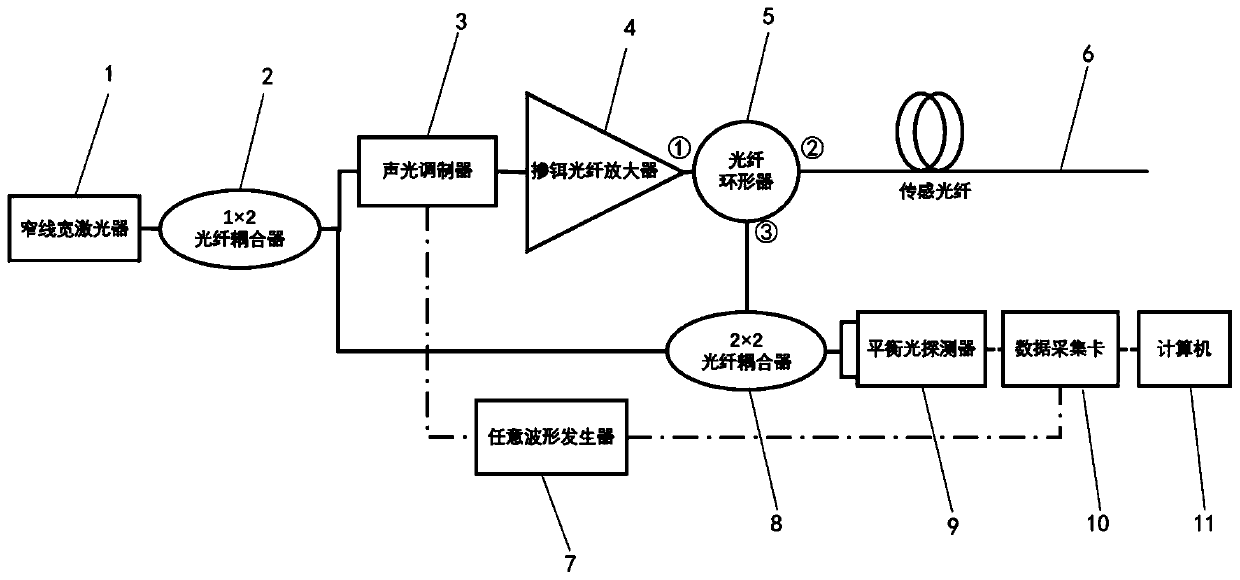
OPGW ice coating monitoring system and method based on phase sensitive type optical time domain reflection system
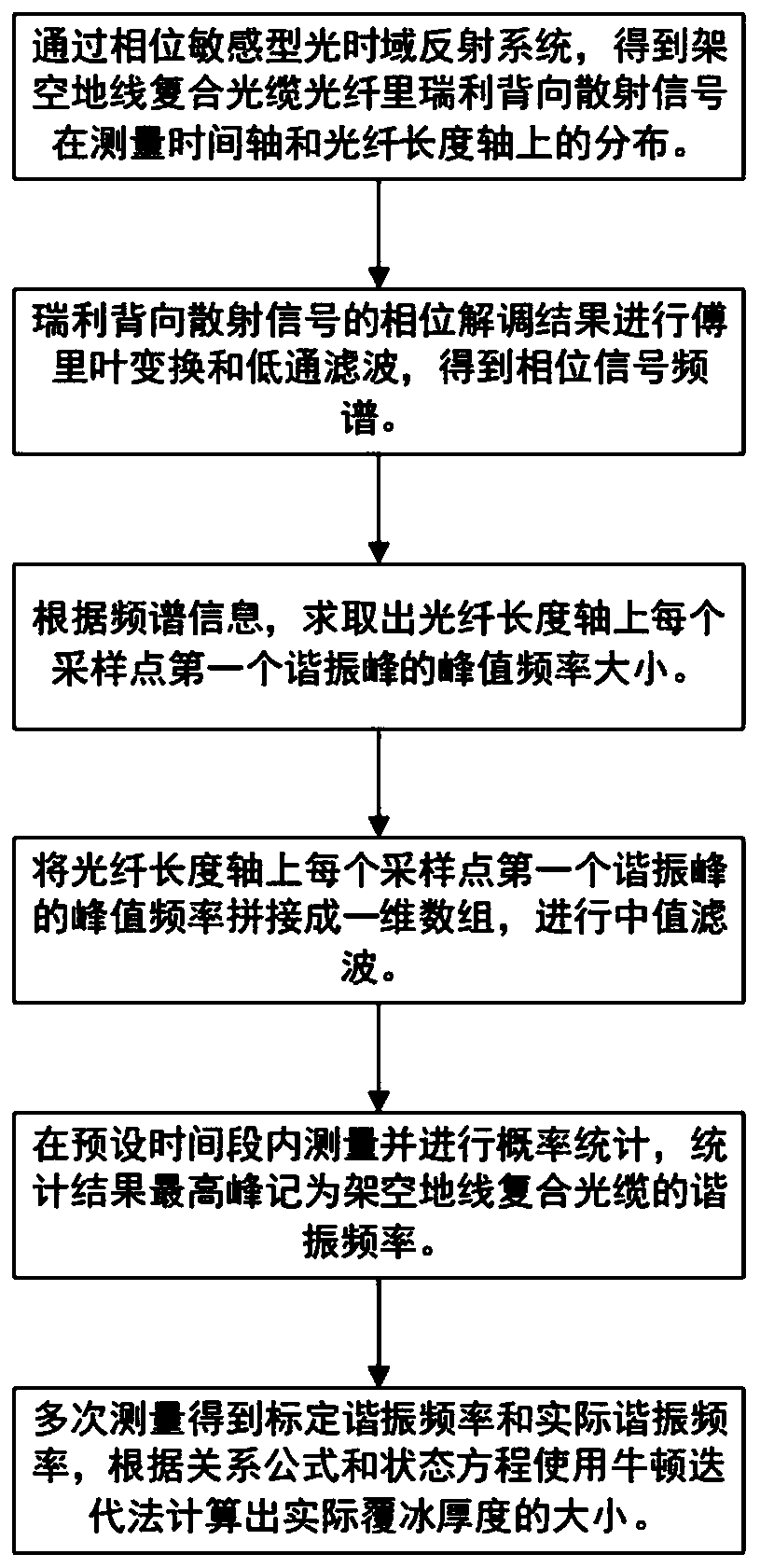
ActiveCN110686626AImprove anti-interference abilityQuick responseResonant frequencyUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansFrequency spectrumPhase sensitive
The present invention discloses an OPGW ice coating monitoring system and method based on a phase sensitive type optical time domain reflection system. A phase sensitive type optical time domain reflection system is used, to obtain distribution of a rayleigh backscattering signal in an overhead earth wire composite optical fiber cable in time and space; Fourier transformation is performed on a rayleigh backscattering signal phase demodulating result, and useless high frequency information is removed through low-pass filtering; a magnitude of a peak value frequency of the first resonance peak on each distance column is obtained according to frequency spectrum information; peak value frequencies of all distance column resonance peaks are spliced into a one-dimensional array and median filtering is performed; probability statistics is performed after long-time measurement, a frequency of a statistics result highest peak is recorded as a resonance frequency of a corresponding position, a confidence interval and a non-confidence interval are obtained according to a resonance frequency variance; a nominal resonance frequency and an actual resonance frequency are obtained through multipletimes of measurement, and an actual ice coating thickness is calculated according to the nominal resonance frequency and the actual resonance frequency calculation, so as to implement a distributed and intelligentized ice coating thickness monitoring method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
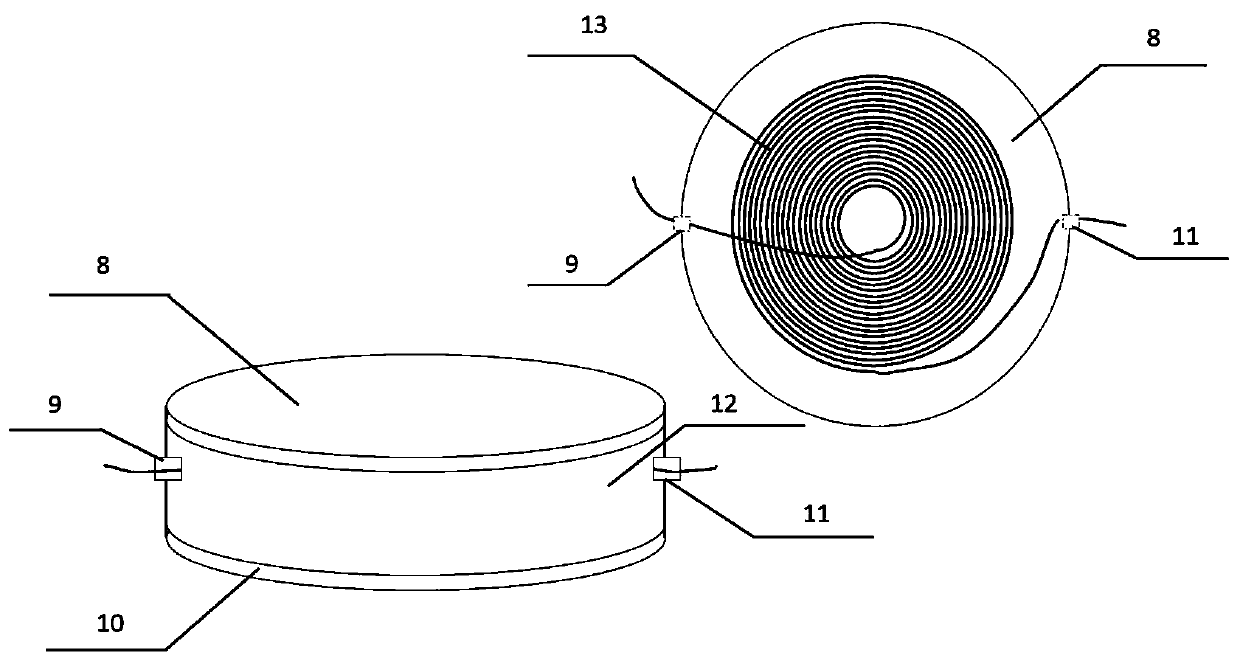
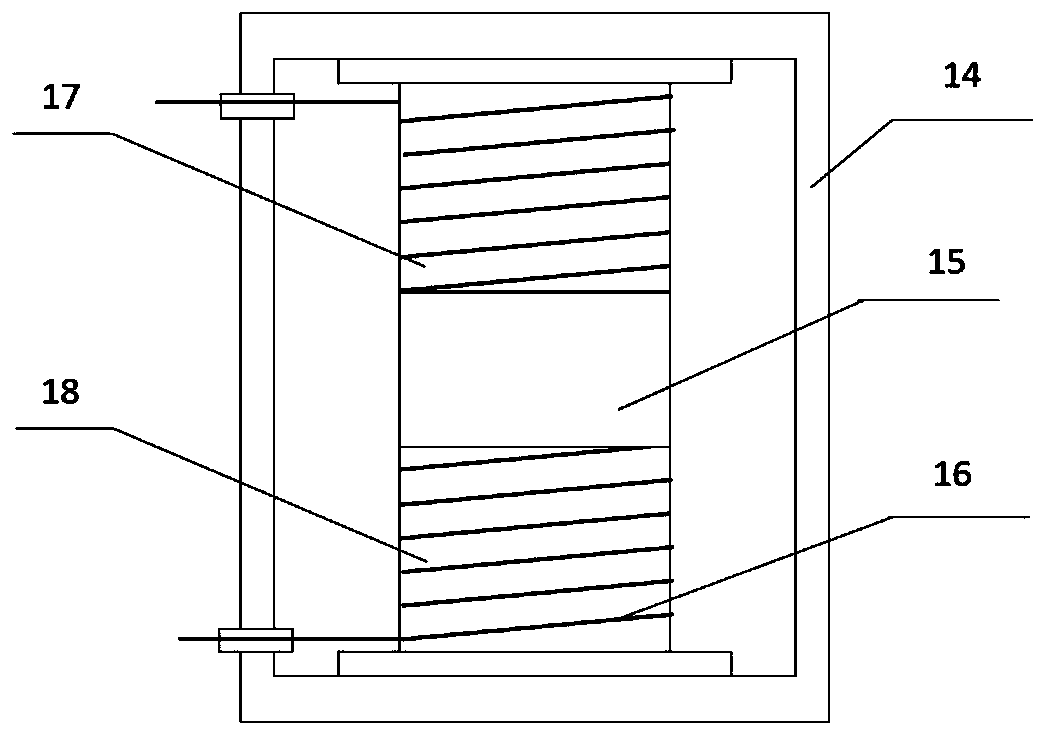
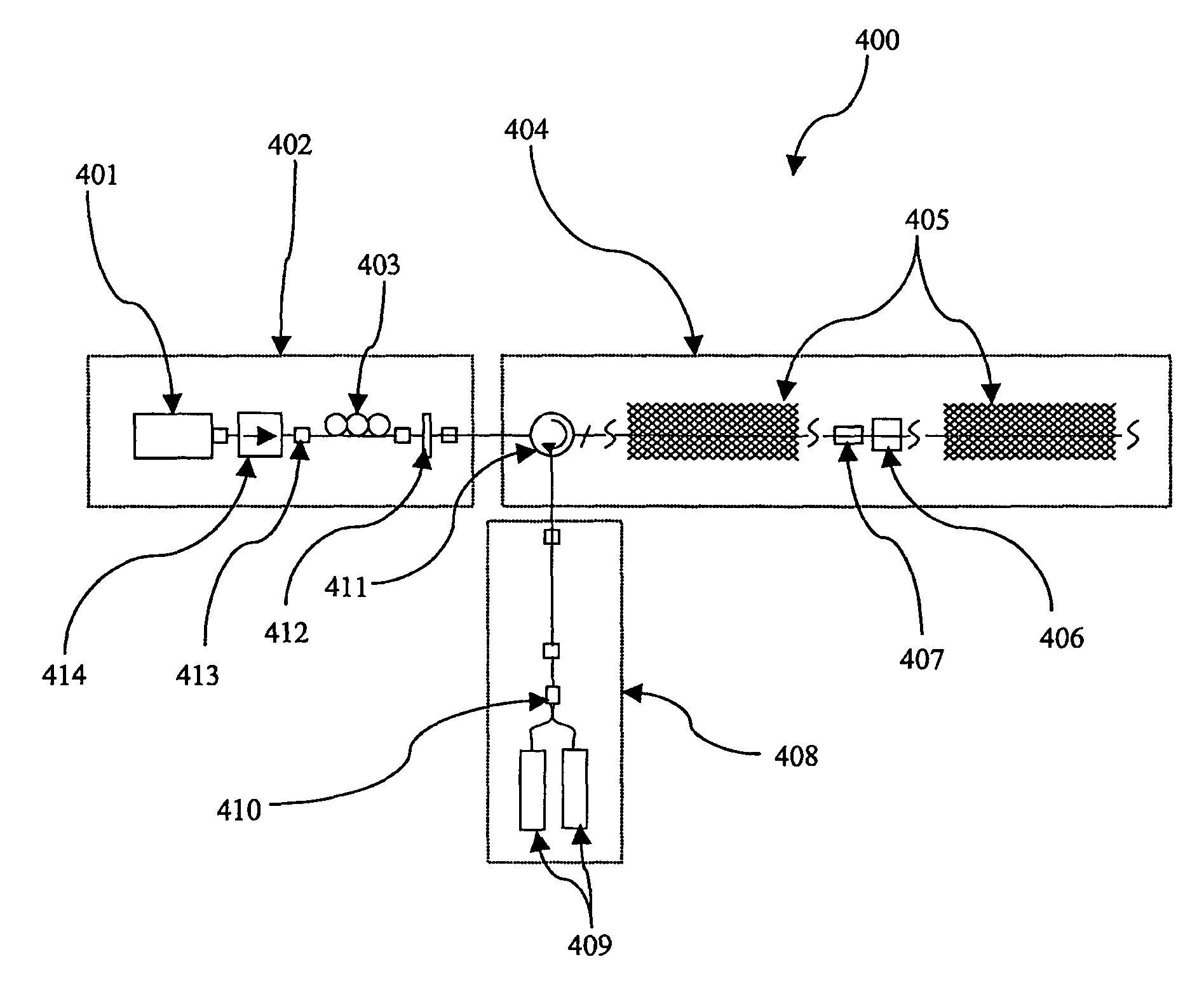
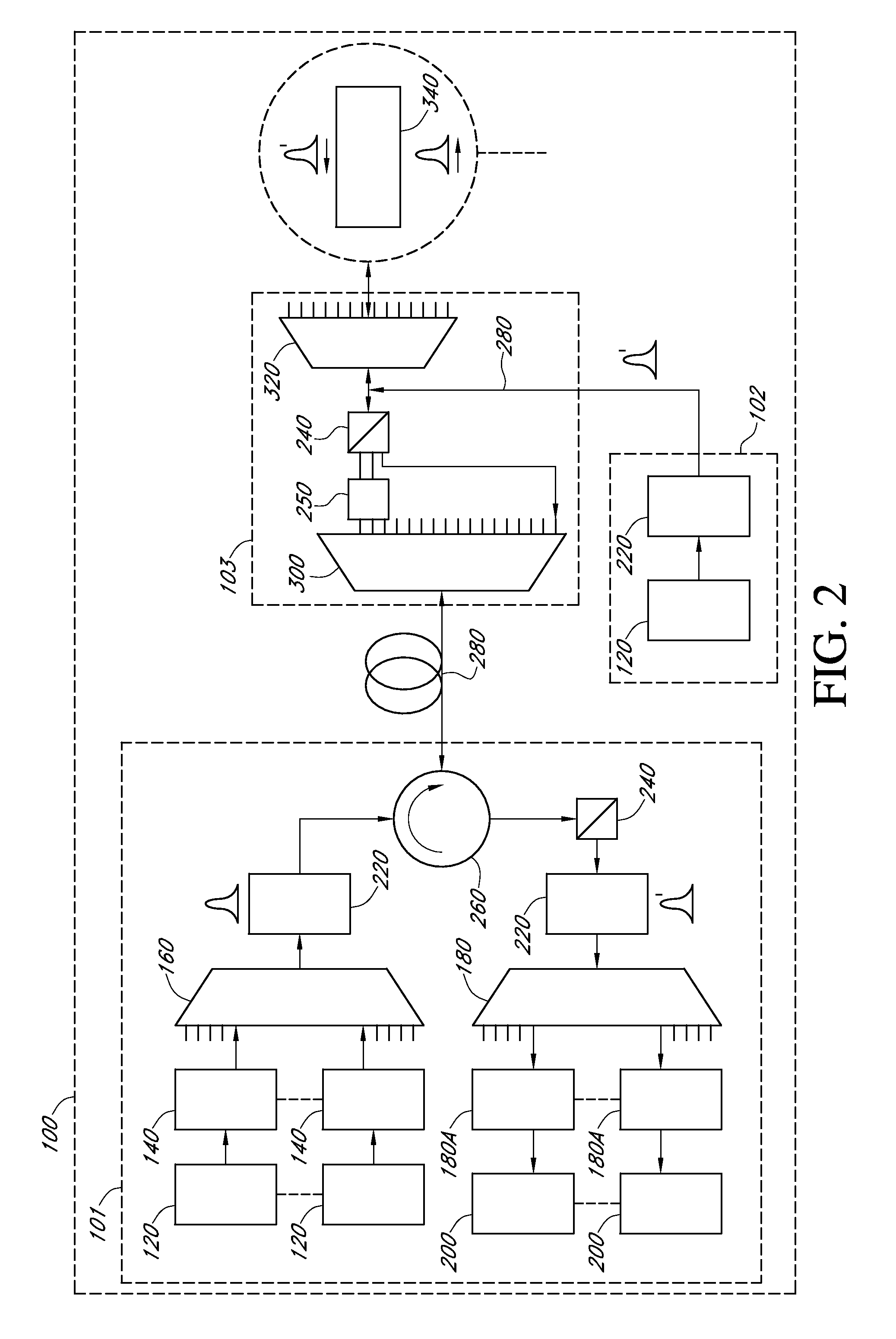
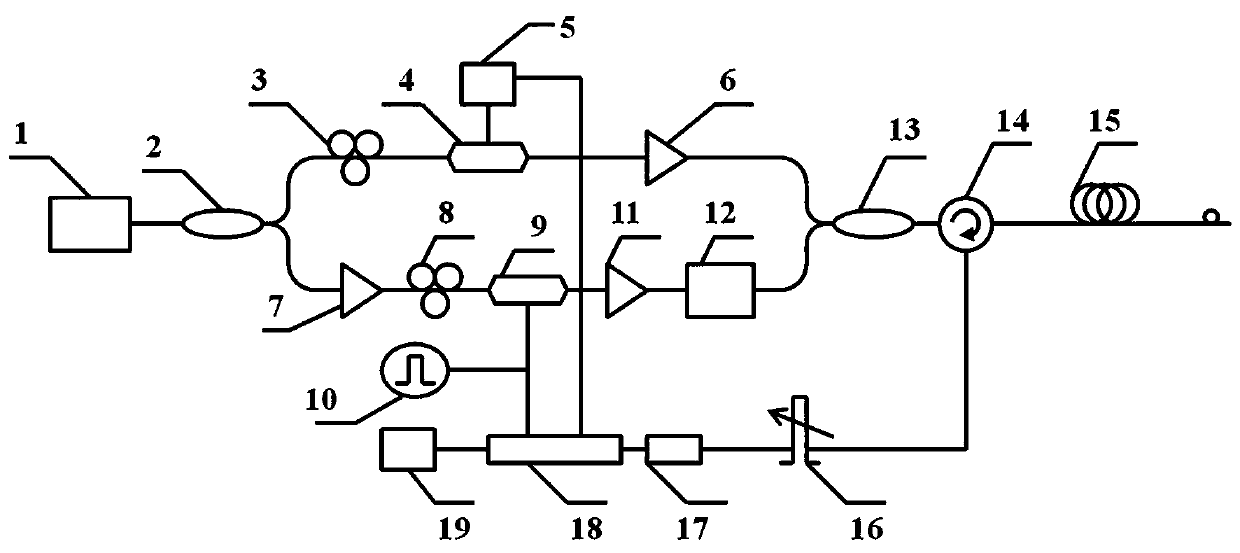
High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR
ActiveCN107727227AImprove anti-interference abilityQuick responseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansIsosceles trapezoidFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a high tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR; the method comprises the following steps: using a [phi]-OTDR system to obtain time and space distributions of Rayleigh backscattering signals in a cable; making Fourier transform so as to obtain a Rayleigh signal spectrogram; using a least square method to respectively fitting two straight lines according to end points of fundamental frequency and higher harmonic left and right edges in the spectrogram, thus obtaining an approximation isosceles trapezoid; solving the approximationisosceles trapezoid transmission line space vibration center, and determining a space segment on which ice coating waving may easily happen; stacking components from near DC to the highest frequencyin the spectrogram, continuously reading many frequency spectrums, and splicing a high frequency energy coefficient time-space diagram; extracting a high frequency energy coefficient time domain signal, smoothing and meaning the signal, making Fourier transform so as to obtain a vibration signal period, thus obtaining transmission line waving day and night change rules, and determining the ice coating waving easy happening time period. The method can timely find out and eliminate line operation safety troubles, thus preventing mass economic losses.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
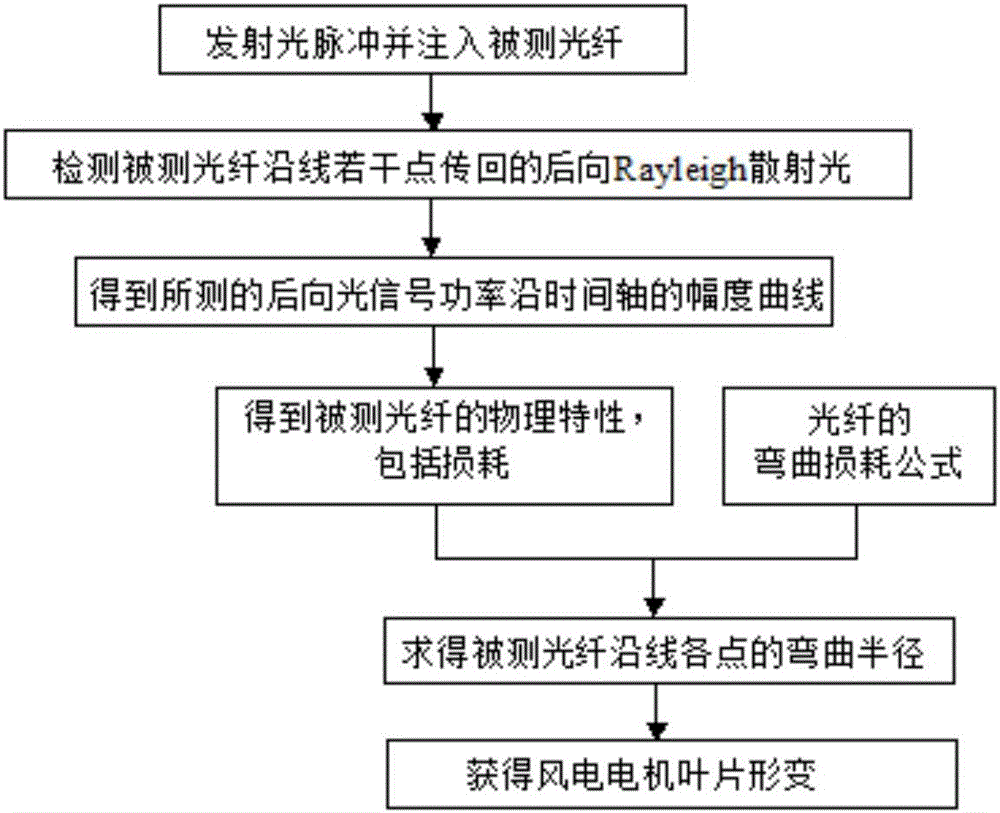
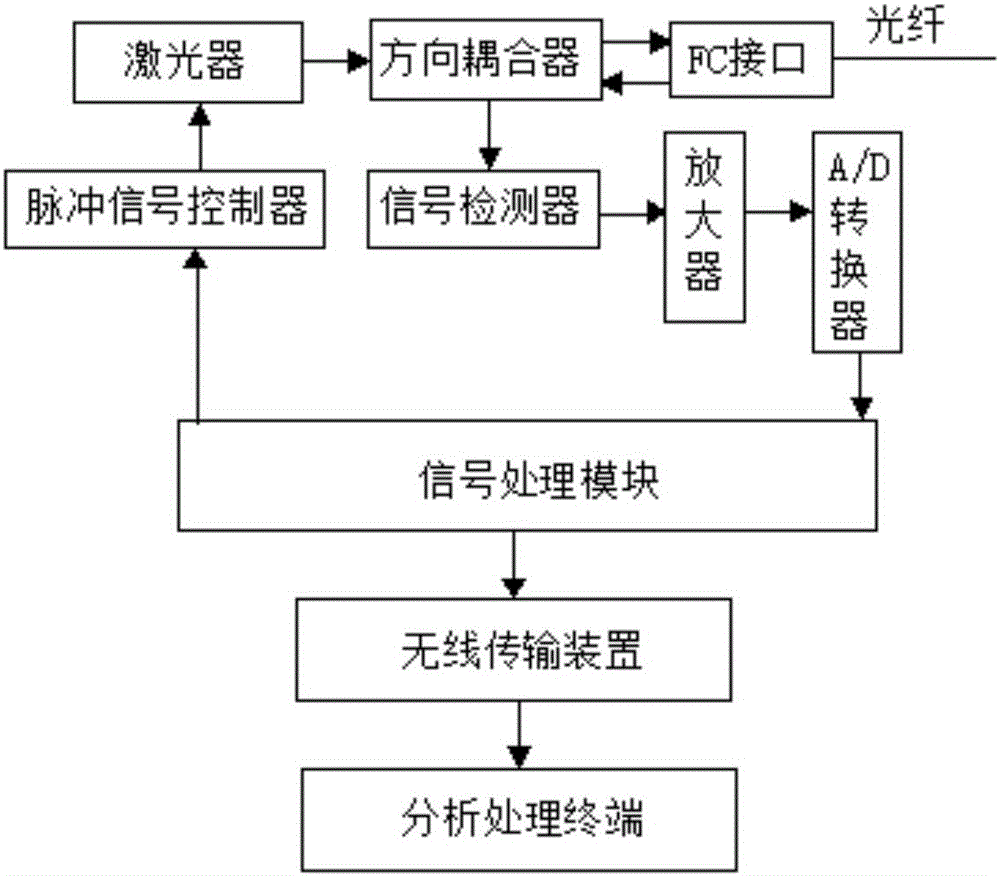
Method and system for monitoring deformation of wind power motor blade
InactiveCN105865360ADeformation dynamic real-time monitoringStrain dynamic real-time monitoringUsing optical meansRayleigh scatteringElectricity
The invention provides a method and system for monitoring the deformation of a wind power motor blade, and the method comprises the steps: transmitting a light pulse and injecting the light pulse into a detected optical fiber; detecting the Rayleigh backscattering light returned from a plurality of points of the detected optical fiber; solving the bending radiuses of all points of the detected optical fiber according to measured Rayleigh backscattering power, thereby obtaining the deformation of the wind power motor blade. The method and system employ a mode of measuring the change of the Rayleigh backscattering of the optical fiber with the bending of the optical fiber, thereby measuring the bending radiuses of all points of the wind power motor blade, and obtaining the deformation of the wind power motor blade. The method and system can carry out dynamic and real-time monitoring of the strain of the wind power motor blade, find the potential damage of the blade in advance, and employ a corresponding technical solution for avoiding a disastrous result before the blade is damaged actually.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Optical fiber ground earthquake detection method and system
ActiveCN110703316ASimple structureLow costSeismic signal receiversConverting sensor output opticallyRayleigh scatteringEarthquake detection
The present invention discloses an optical fiber ground earthquake detection method and system. The method comprises: fixing several optical fiber earthquake detectors on a sensing optical cable at intervals to form a row of sensing units, combining several rows of sensing units to form an optical fiber earthquake detector network; laser emitted by a laser device enters an optical branching deviceand is split into several rows of pulsed light signals, the pulsed light signals separately enter several circulators, and each path of pulsed light is uni-directionally transmitted to a port II by aport I in a circulator, and enters each row of sensing units; the pulsed light signals are transmitted on the detector to generate Rayleigh scattering light, the Rayleigh scattering light and Rayleigh backscattering light are transmitted to the port II of the circulator, are output by a port III of the circulator, are converted into an electrical signal after detection of a photoelectric detector, the electrical signal enters a signal processing module, and the signal process module extracts a vector or three-dimensional earthquake signal according to a demodulated vibration signal. The method and the system can implement reusing and network formation of detectors, and can implement large-range quasi-distributed vector or three-dimensional earthquake signal detection.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
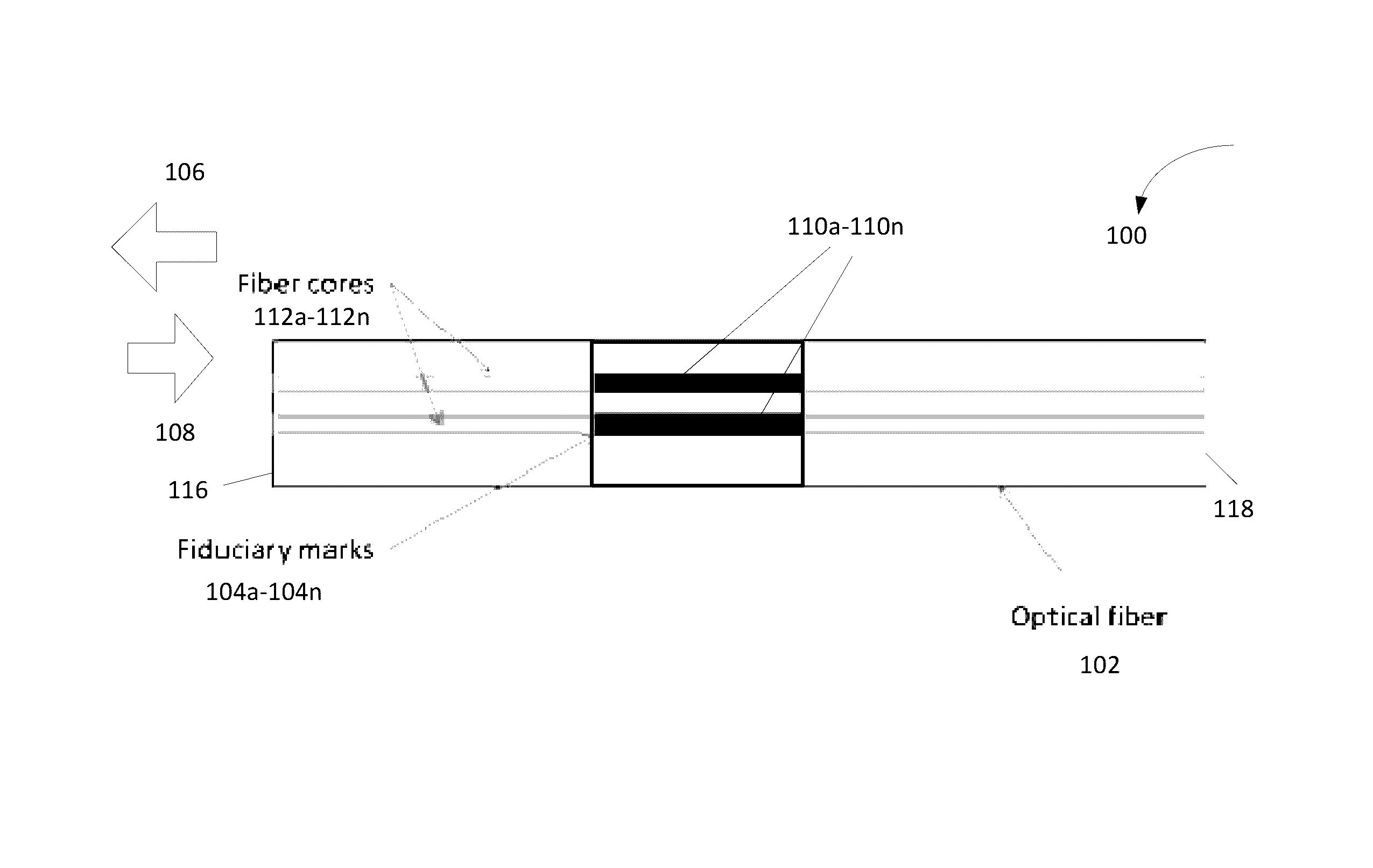
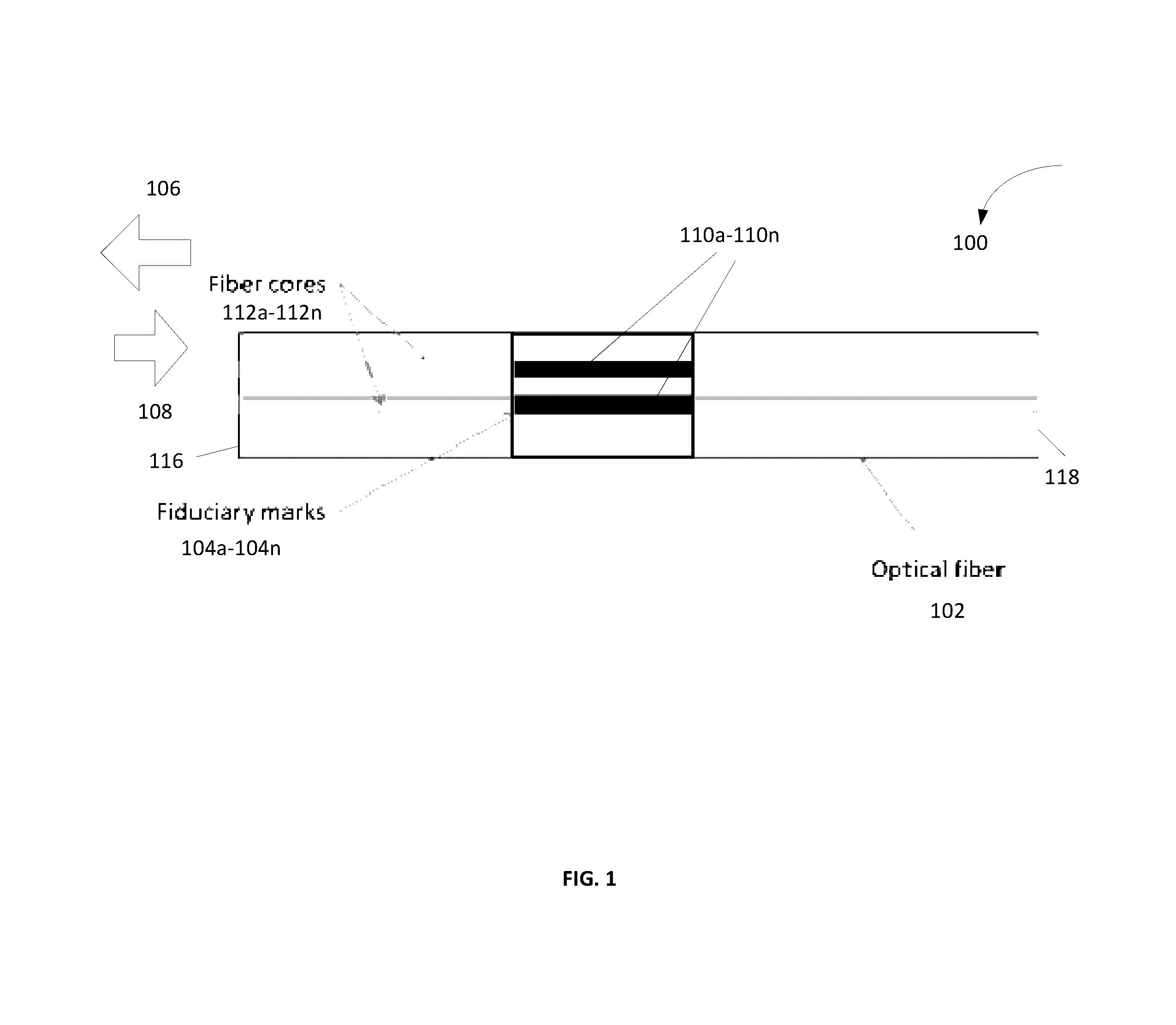
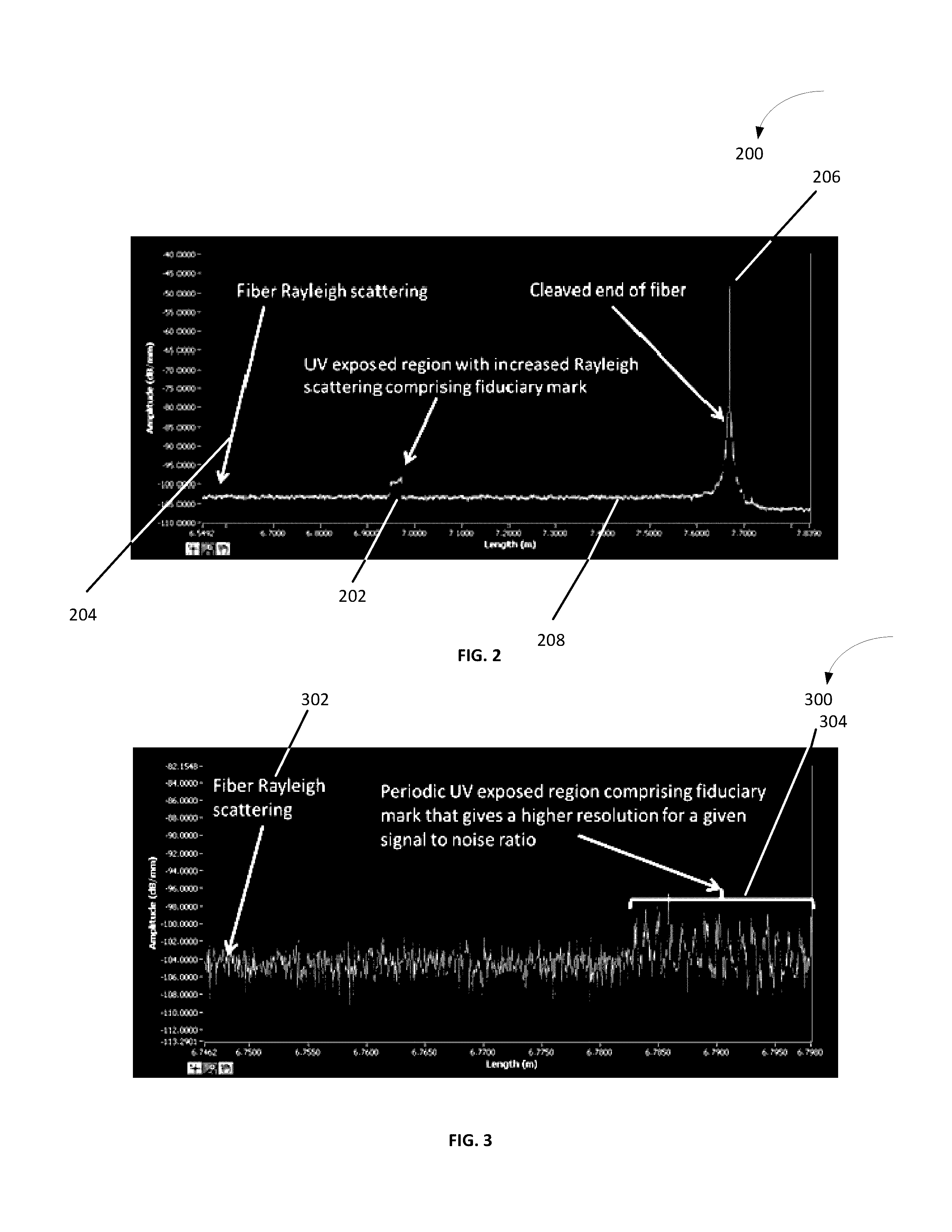
Optical sensor having fiduciary marks detected by Rayleigh scattered light
ActiveUS9470588B2Force measurement by measuring optical property variationRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
An optical fiber having at least one fiduciary mark is provided. The at least one fiduciary mark is located at one or more axial positions along the optical fiber. The at least one fiduciary mark is configured to produce at least one change in a Rayleigh backscattering signal in the optical fiber. The at least one change in a Rayleigh backscattering signal may be an abrupt change in the Rayleigh backscattering signal. The abrupt change in the Rayleigh backscattering signal occurs over a length of the optical fiber that is of the order of or less than a spatial resolution of an interrogation system employed to detect the Rayleigh backscattering signal.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
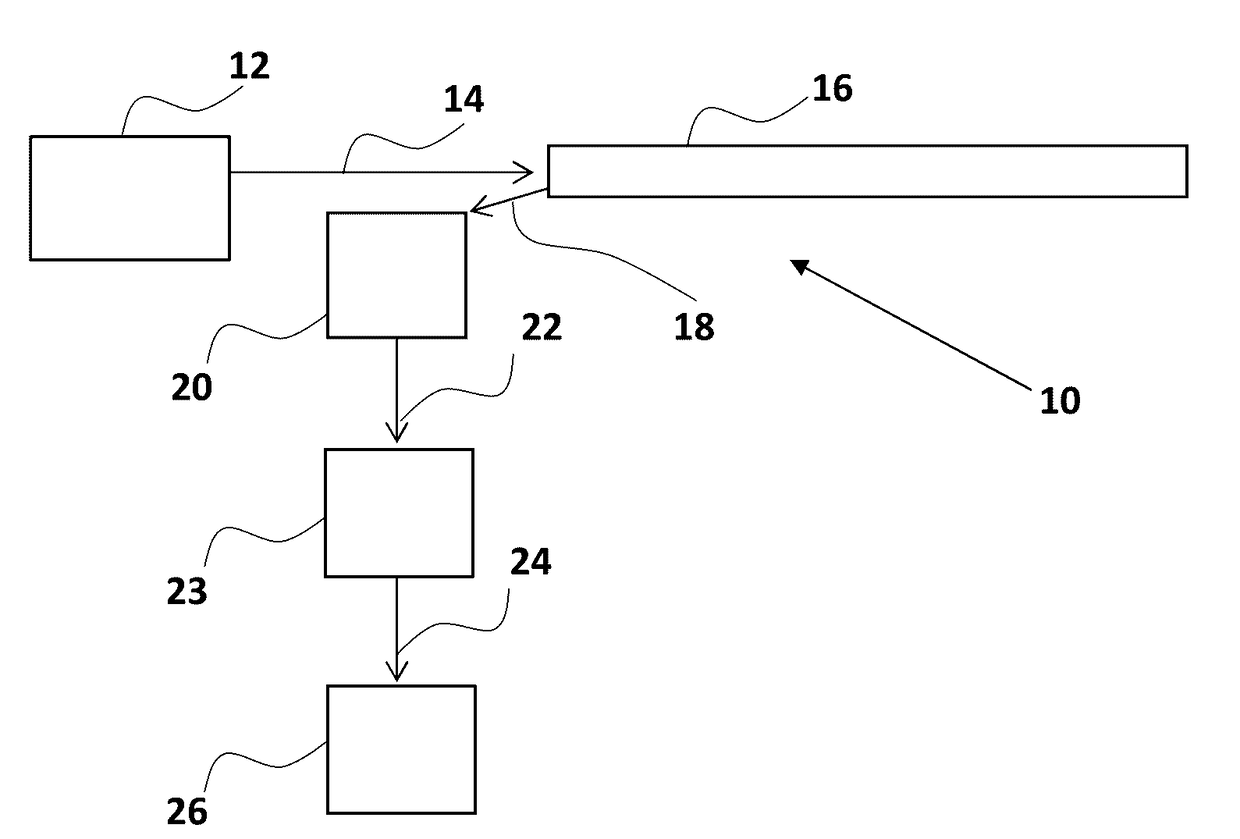
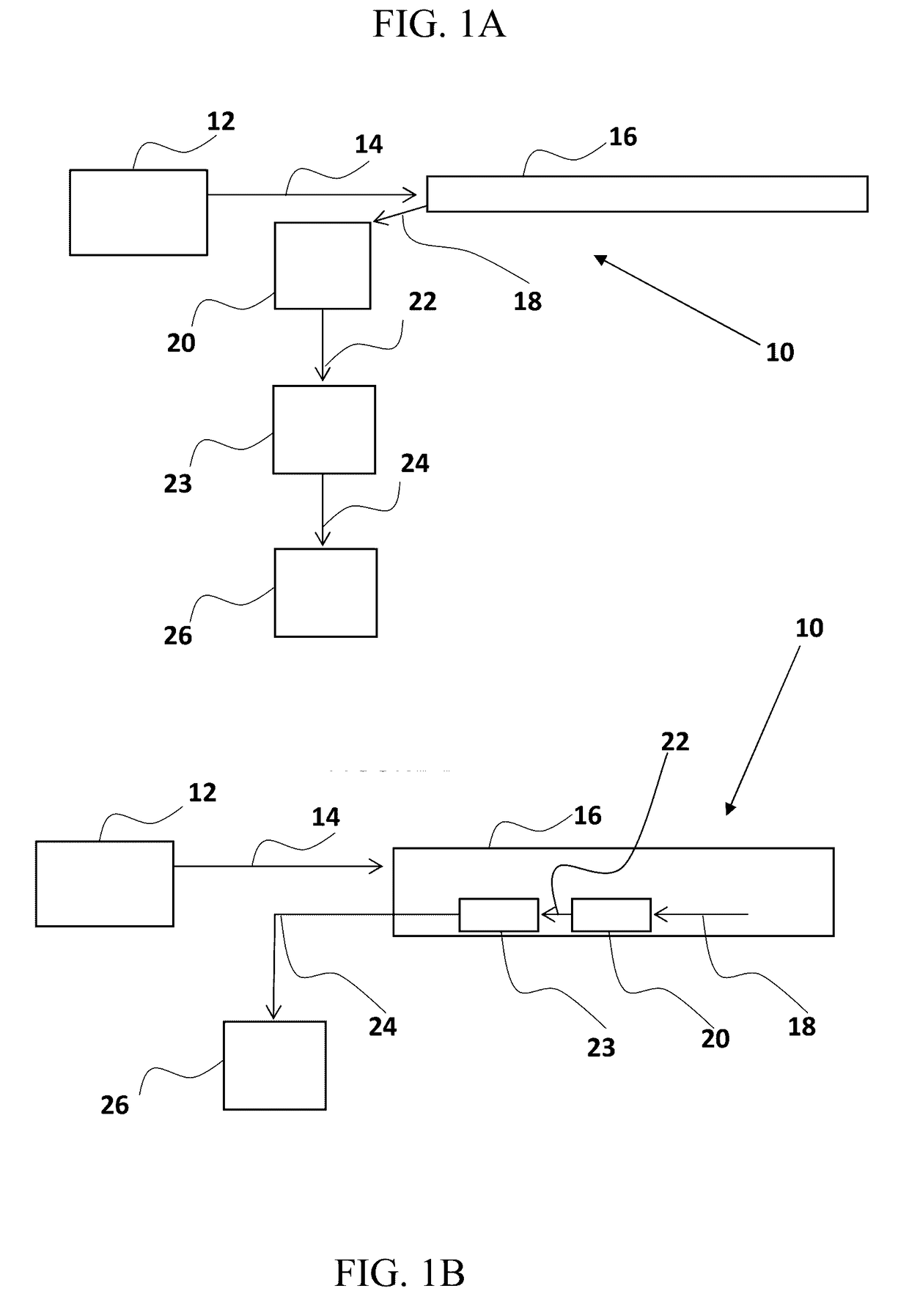
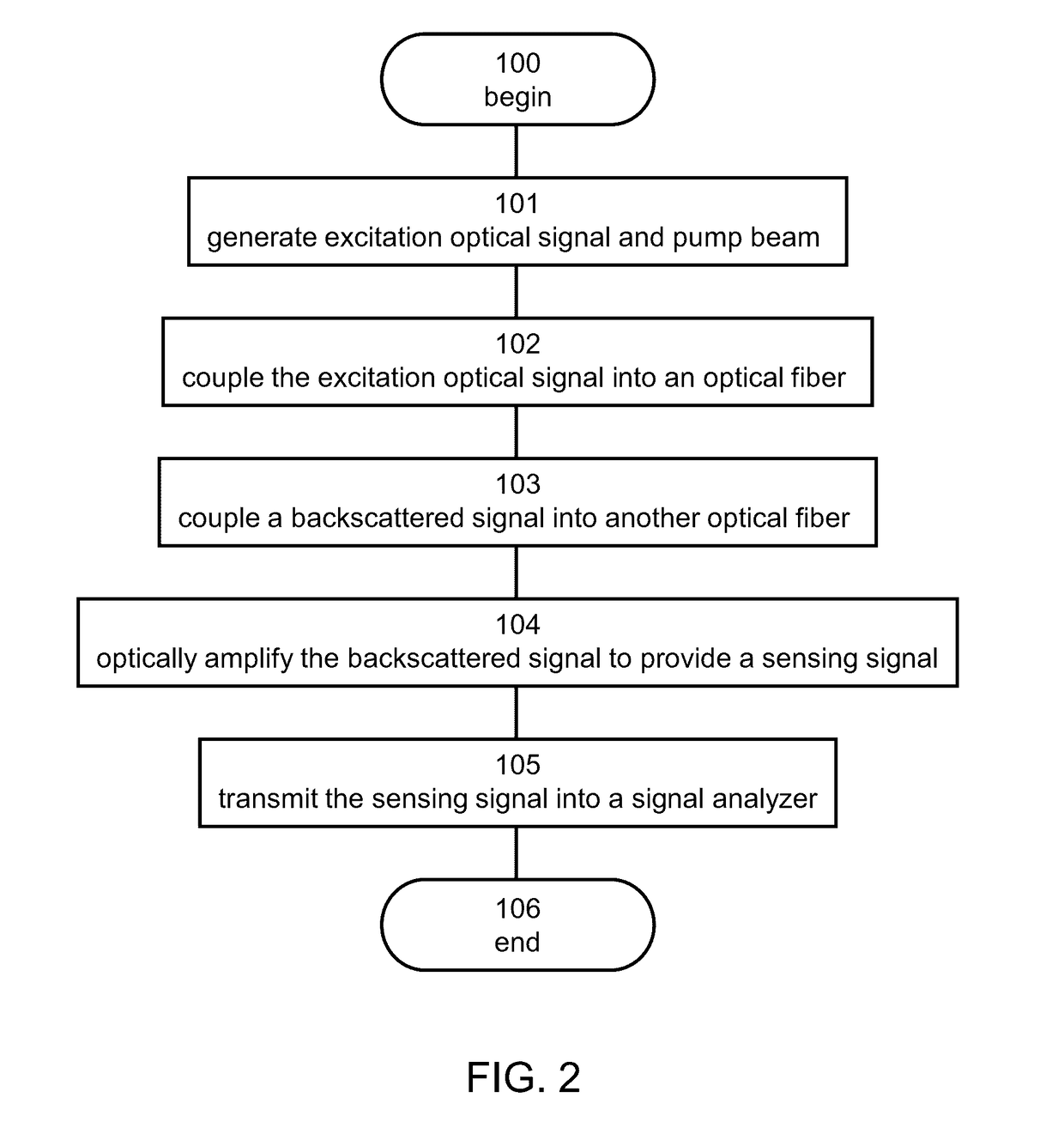
Method and system for optical fiber sensing
ActiveUS20170115138A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterLaser using scattering effectsRayleigh backscatteringOptical sensing
A method of optical sensing is disclosed. The method comprises coupling an excitation optical signal into a first optical fiber to induce Rayleigh backscattering, thereby providing a backscattered signal; coupling the backscattered signal into a second optical fiber, spatially separated from the first optical fiber; and optically amplifying the backscattered signal in the second optical fiber, thereby generating a sensing signal.
Owner:ARIEL SCI INNOVATIONS LTD
Distributed Acoustic Sensing Systems and Methods Employing Under-Filled Multi-Mode Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20160341841A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSeismic signal transmissionCoupling lossRayleigh scattering
An illustrative distributed acoustic sensing system includes a multi-mode optical fiber cable for distributed sensing and a distributed acoustic sensing interrogator coupled to the multi-mode optical fiber cable via a single mode optical fiber. The interrogator derives distributed acoustic measurements from Rayleigh backscattering light that is initiated with a substantially under-filled launch configuration that is designed to excite only the lowest-order modes of the multi-mode optical fiber. Mode conversion within the multi-mode optical fiber is anticipated to be negligible. For elastic scattering (i.e., Rayleigh scattering), it is further anticipated that the scattered light will be primarily returned in the incident propagation mode, thereby escaping the extraordinarily large coupling loss that would otherwise be expected from coupling a single-mode optical fiber to a multi-mode optical fiber for distributed sensing. Experiments with graded index multi-mode optical fiber have yielded positive results.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
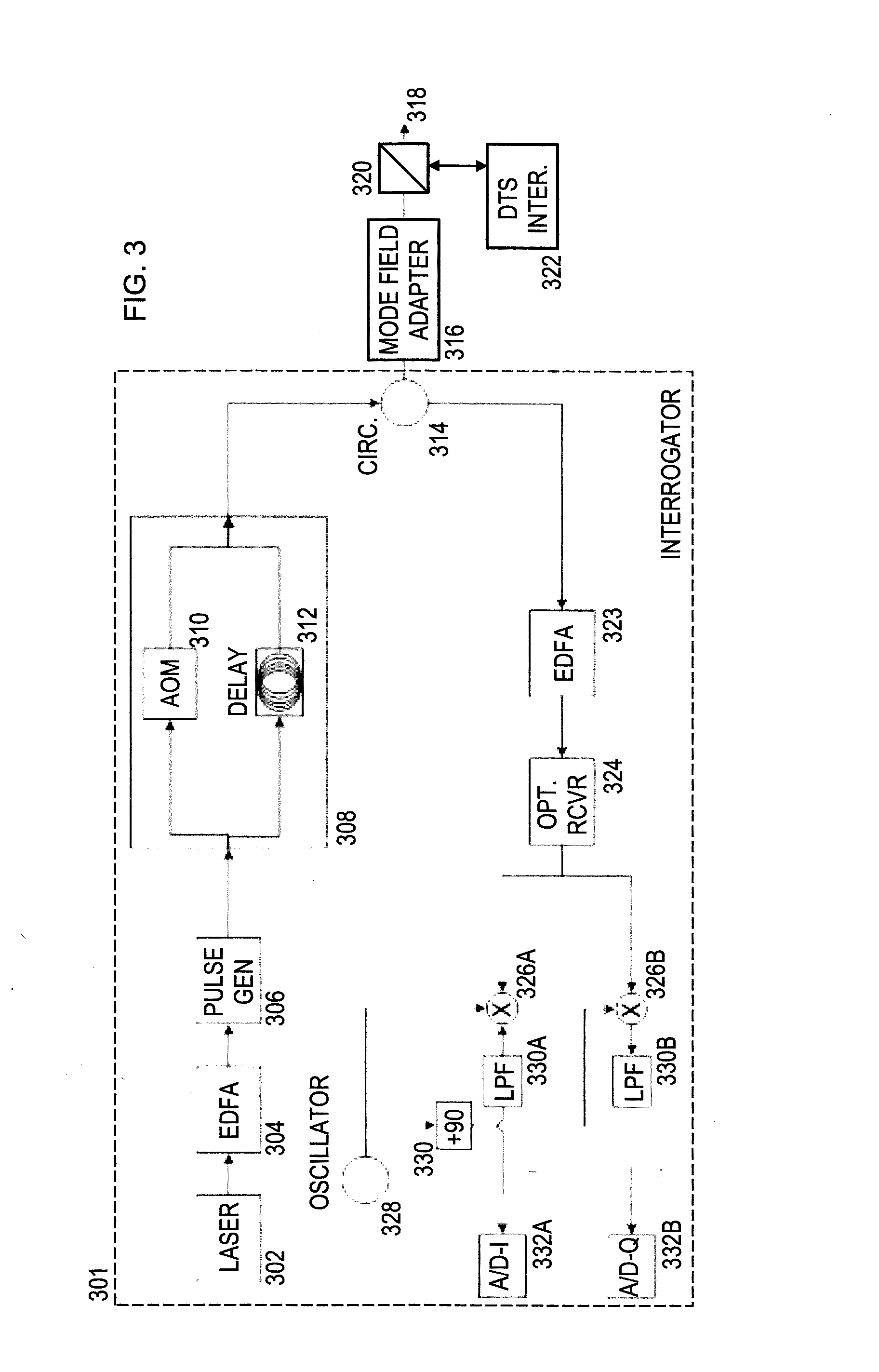
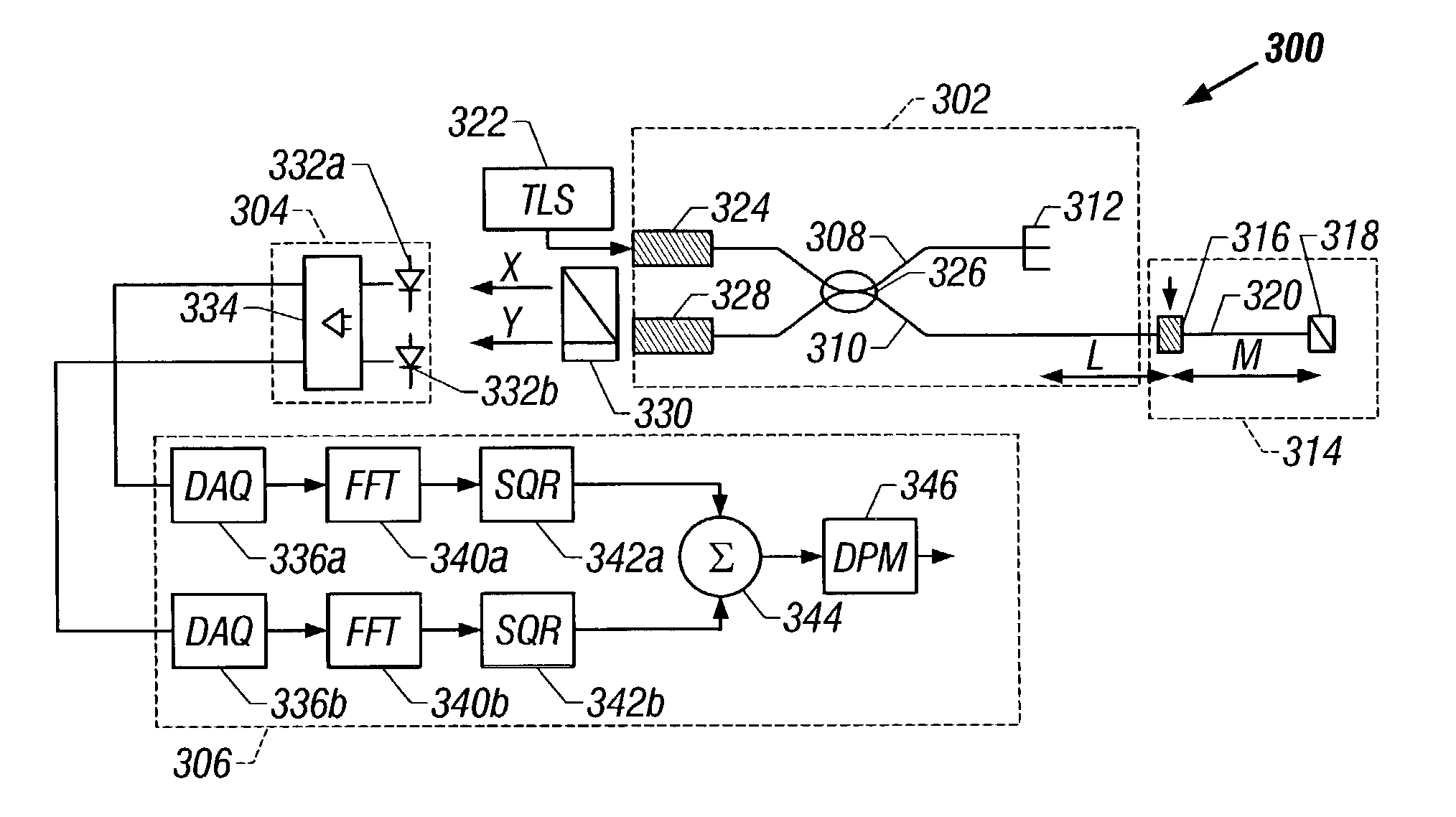
De-embedment of optical component characteristics and calibration of optical receivers using rayleigh backscatter
Method and system are disclosed for de-embedding optical component characteristics from optical device measurements In particular, the invention uses frequency domain averaging of the RBS on both sides of an optical component to determine one or more of its optical characteristics. Where the RBS has a slope (e.g., as in the case of a lossy fiber), a frequency domain least square fit can be used to determine the optical component characteristics. In addition, the invention uses a reference DUT to correct for variations in the frequency response of the photoreceiver A reference interferometer is used in the invention to correct for sweep non-linearity of the TLS. The optical component characteristics are then de-embedded from optical device measurements to provide a more precise analysis of the optical device.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1fd9e7fd-5caa-4228-8eed-4bcd47f3ed16/HDA0001426213500000011.png)
![High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1fd9e7fd-5caa-4228-8eed-4bcd47f3ed16/HDA0001426213500000021.png)
![High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR High tension transmission line ice coating waving monitoring method based on [phi]-OTDR](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1fd9e7fd-5caa-4228-8eed-4bcd47f3ed16/HDA0001426213500000022.png)