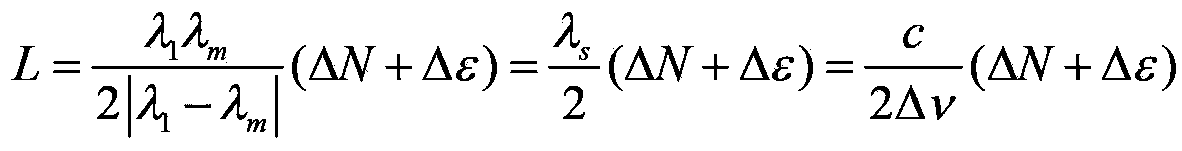Patents
Literature
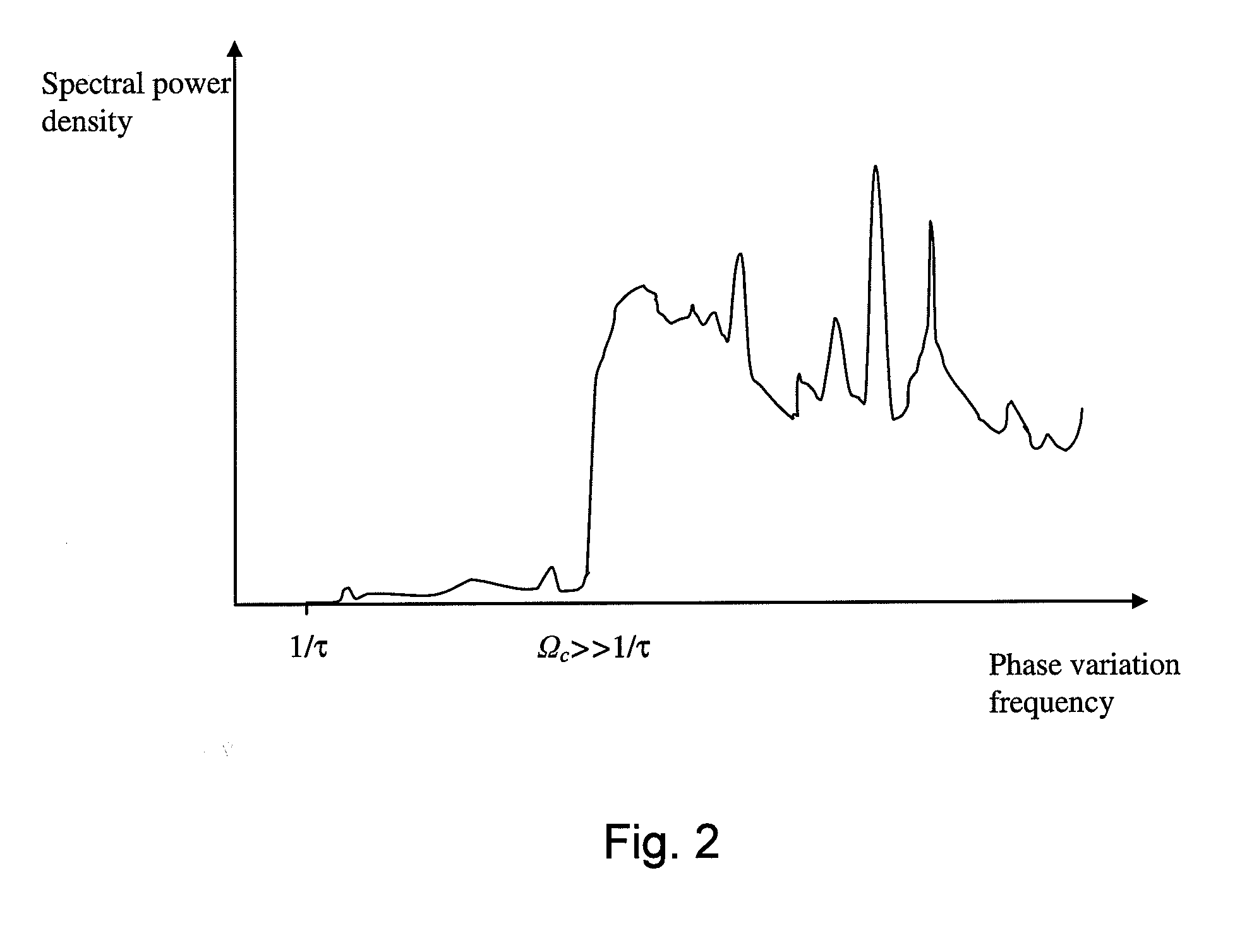
370 results about "Phase variance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A phase variance is a term applicable to phenomena or technologies that show wave-like properties.
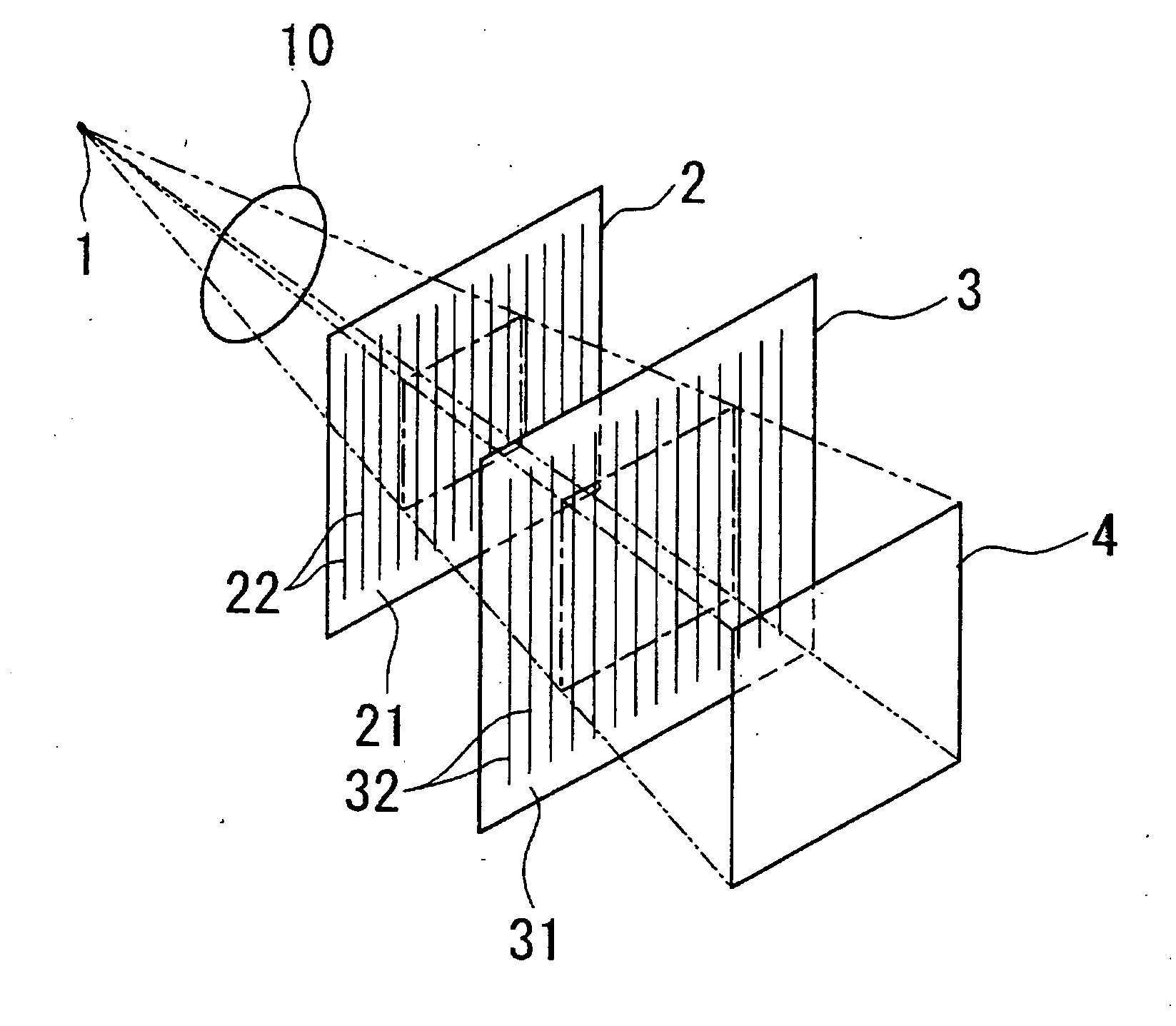
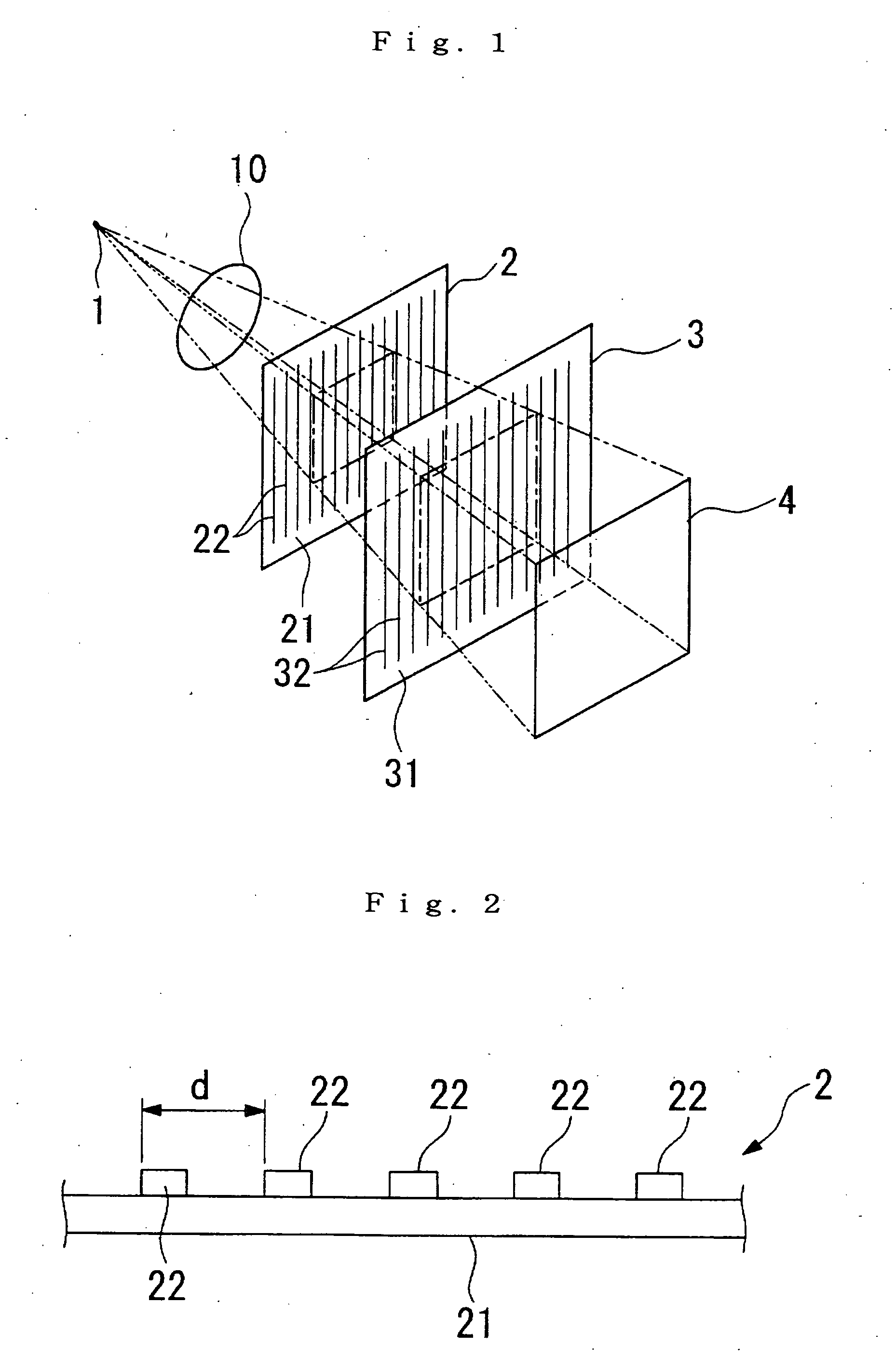
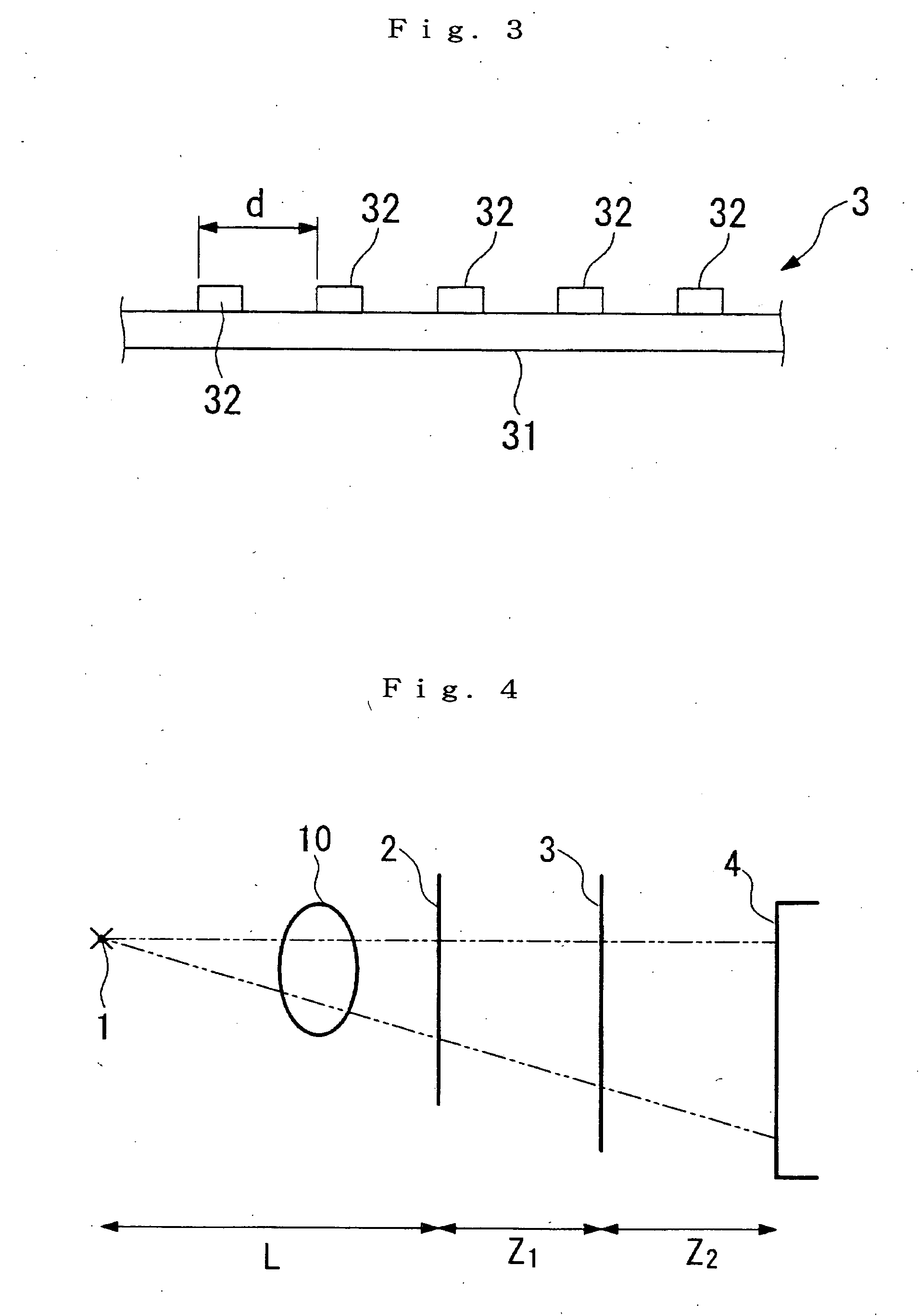
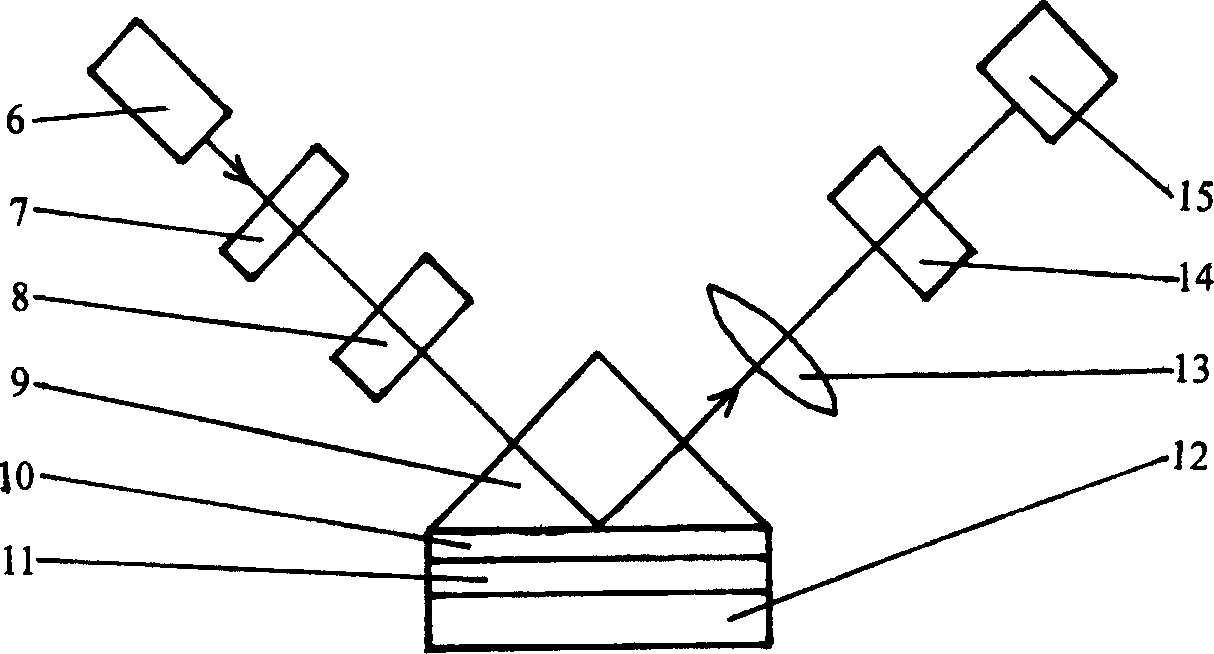
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
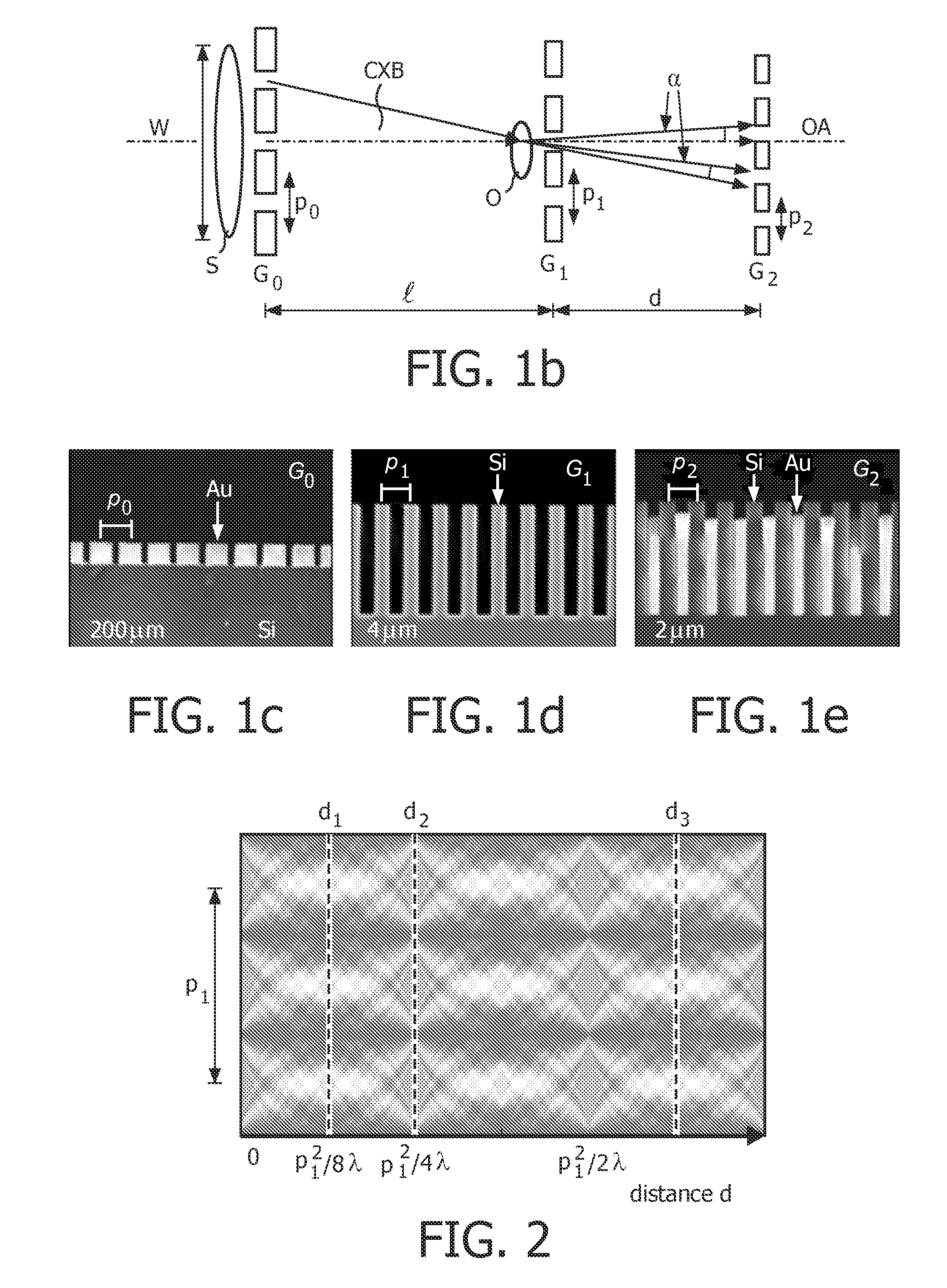
ActiveUS20050286680A1Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayImage contrast
The object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays with a simple construction. The X-ray imaging apparatus of the present invention is equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector. The first diffraction grating is constructed to generate the Talbot effect using X-rays irradiated at the first diffraction grating. The second diffraction grating is configured so as to diffract the X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is configured so as to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. By diffracting X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating, the second diffraction grating is capable of forming image contrast caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to the subject arranged in front of the front surface of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is capable of detecting X-rays creating image contrast.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
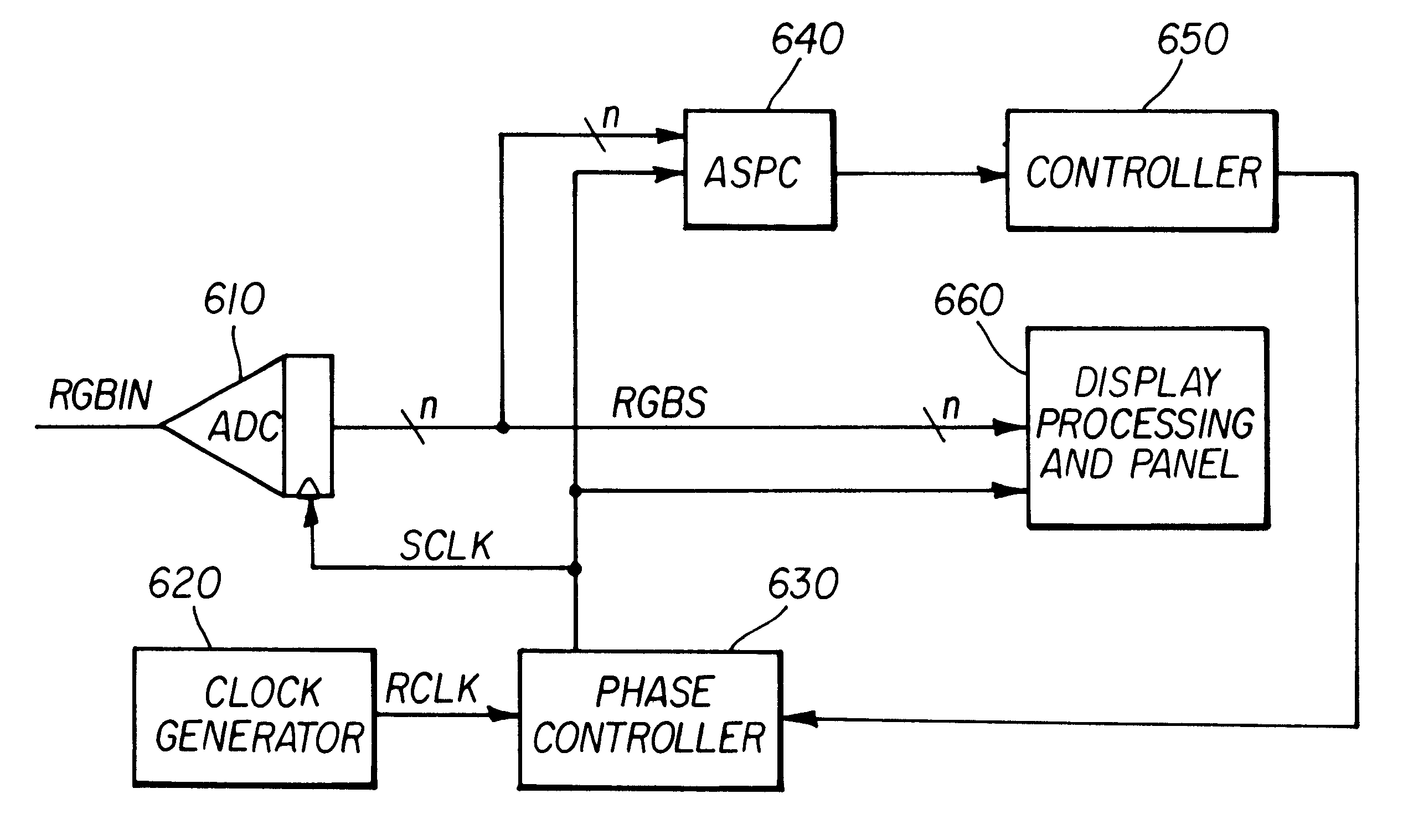
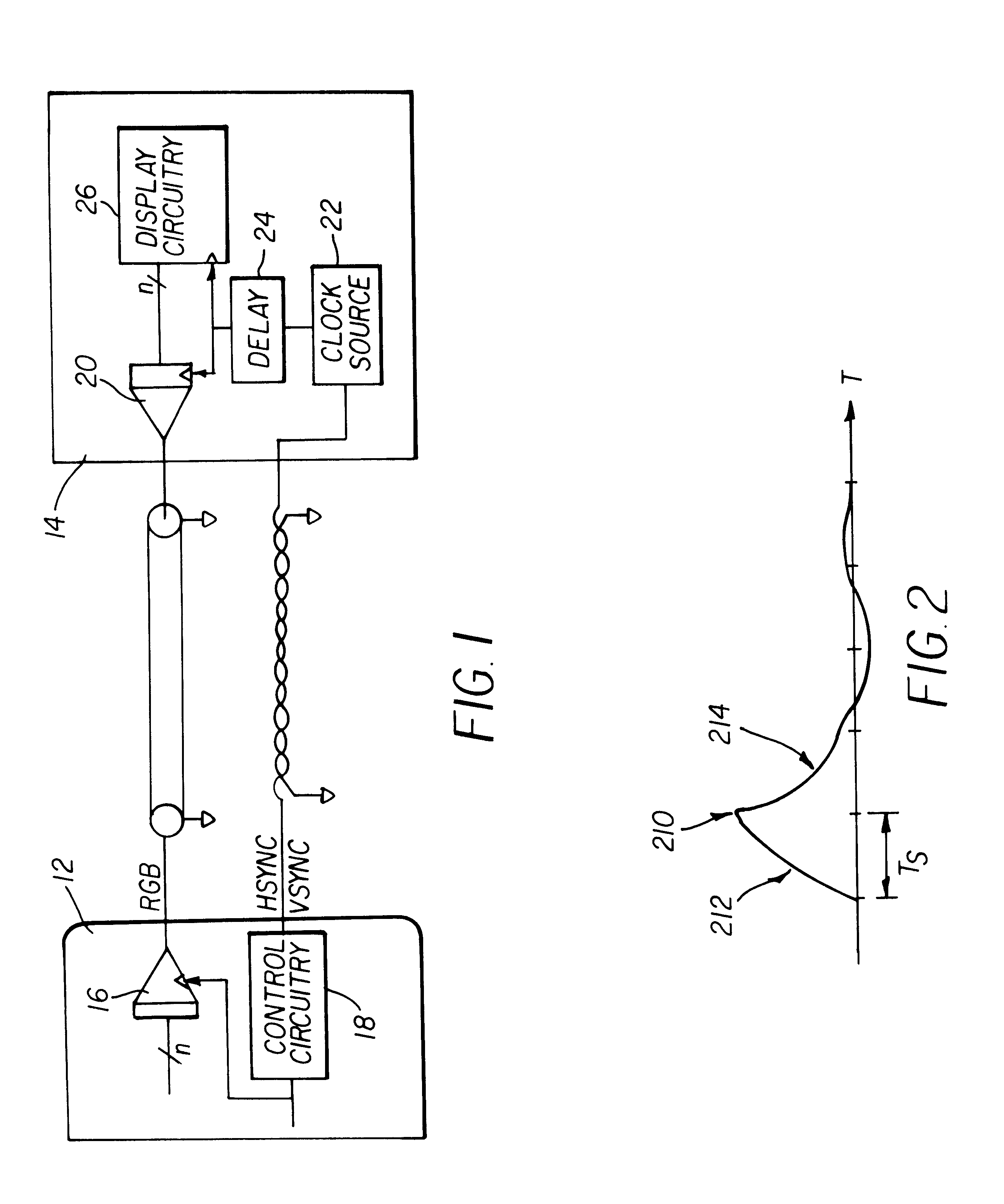
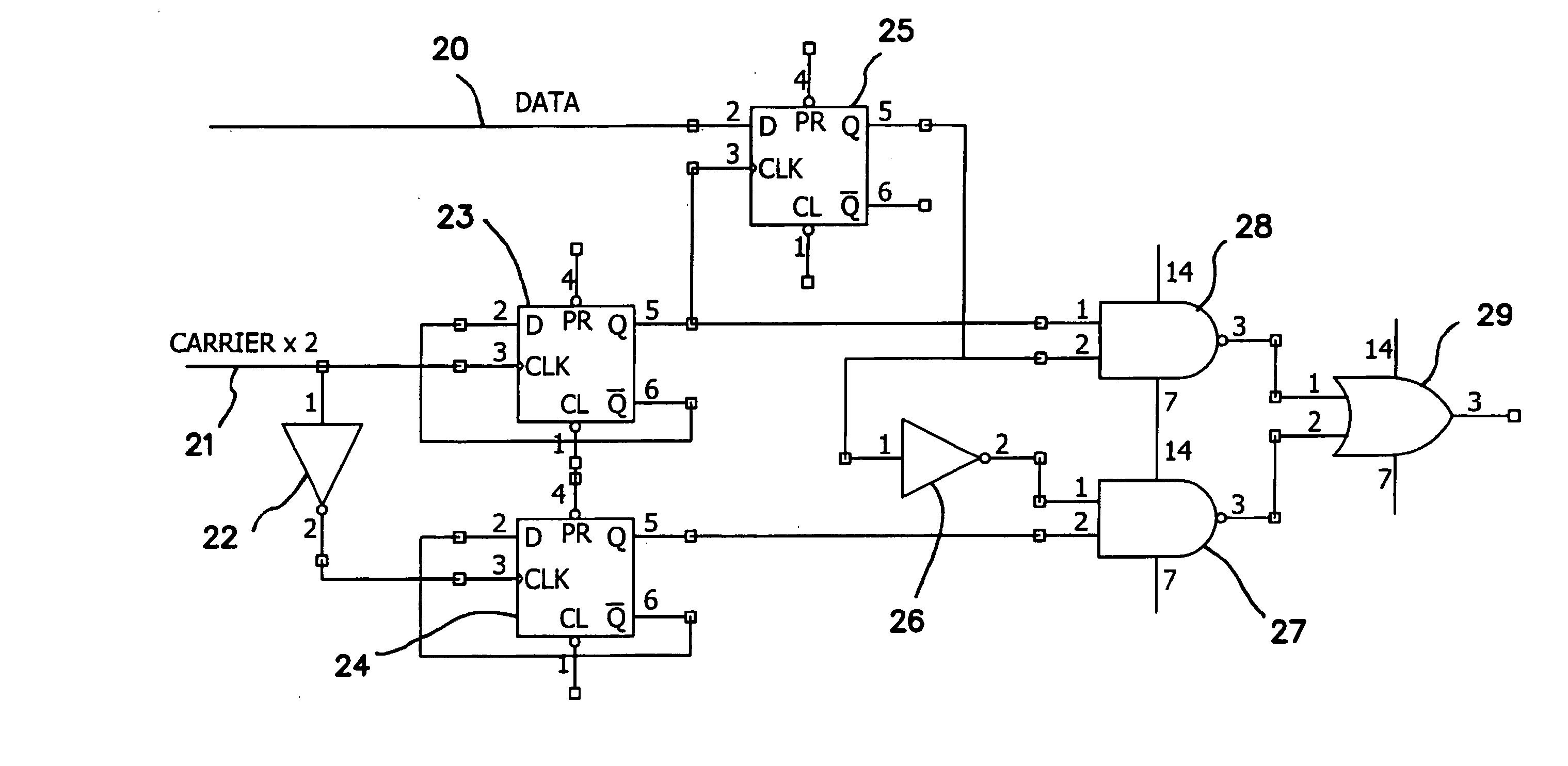
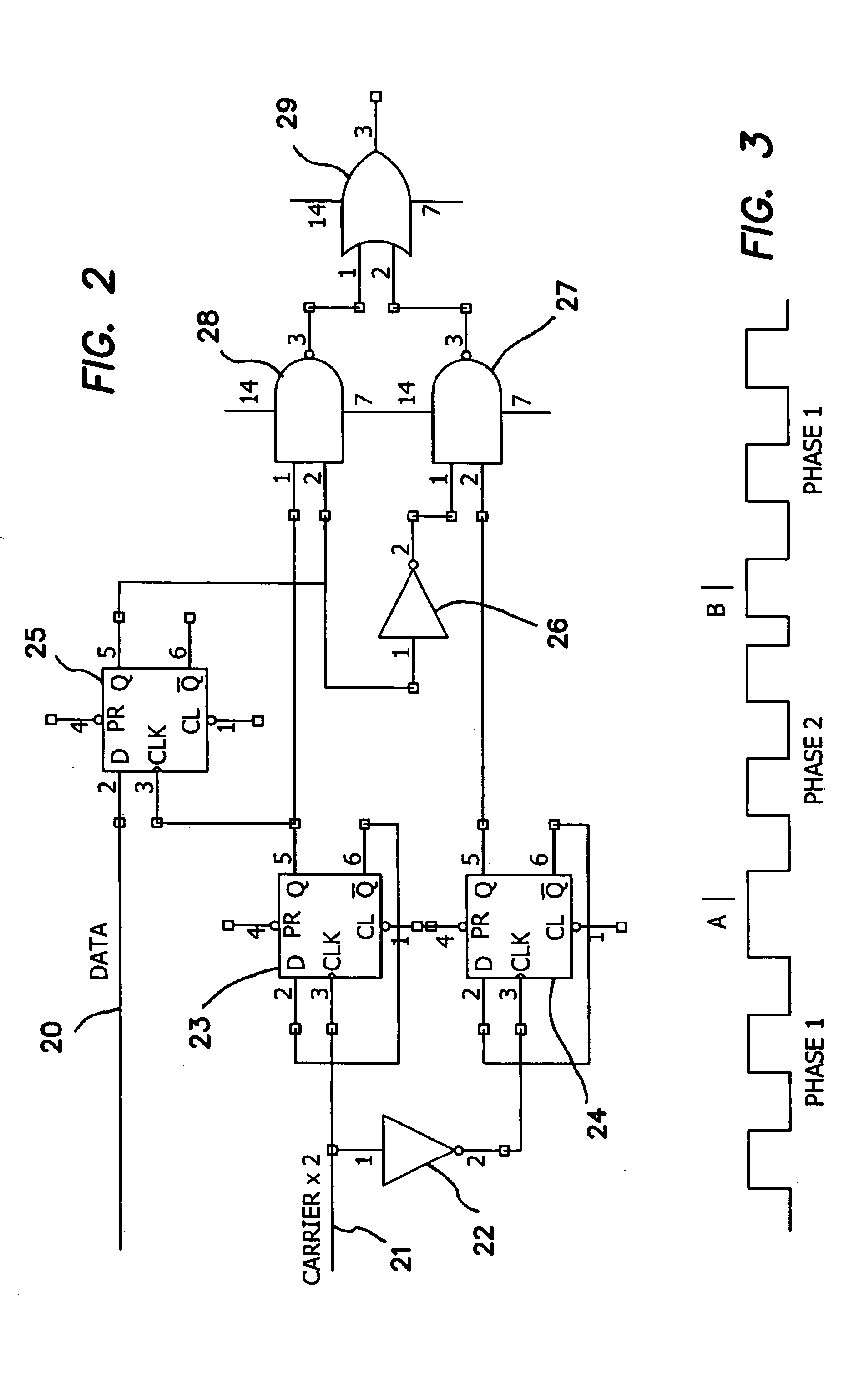
Method and apparatus implemented in an automatic sampling phase control system for digital monitors
InactiveUS6268848B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsControl systemPhase control
An automatic sampling control system for digital monitors. A clock generation circuit generates a sampling clock. A phase controller modifies the phase of the sampling clock by a phase amount. An ADC samples a frame of an analog display signal to generate digital samples. A value which is a function of the samples is generated. The function generally generates a larger value with correspondingly large sample values. The phase amount is modified for successive image frames until a maximum function value is generated. When successive image frames do not change substantially in image content, the phase amount represents the optimal phase change for the sampling clock. If the image content is changing substantially, the phase adjustment may be disabled.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
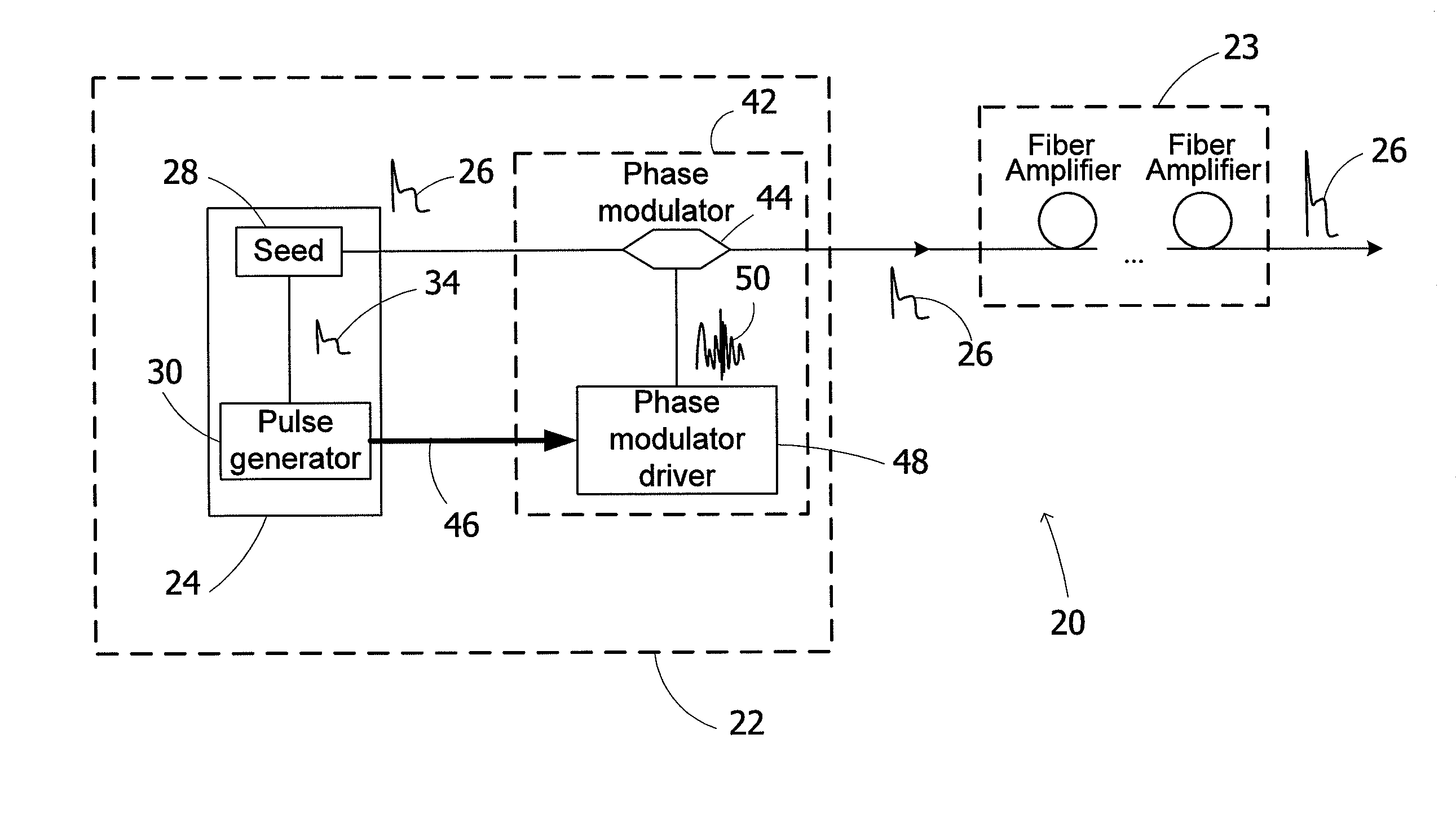
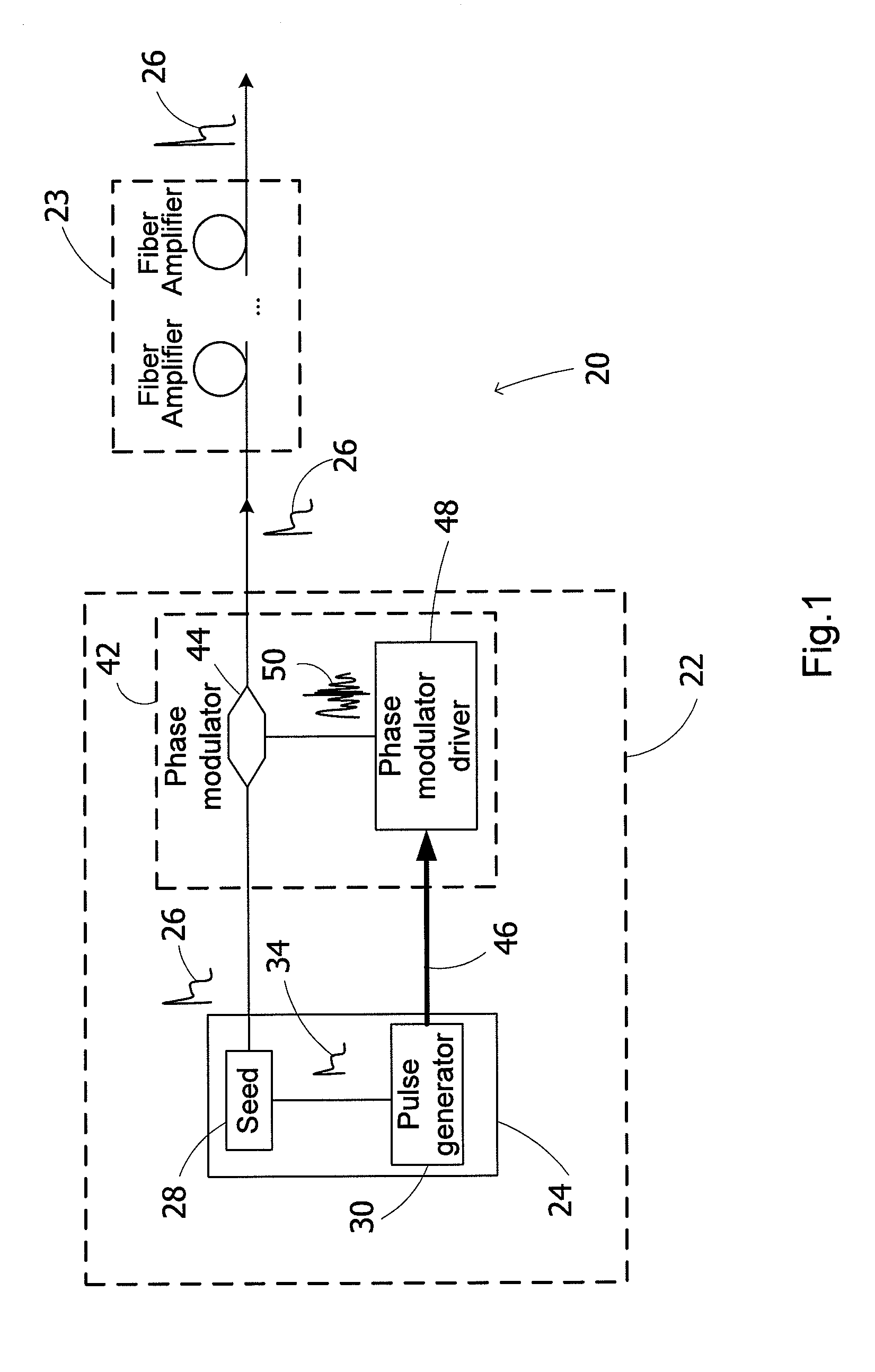
Spectrally tailored pulsed fiber laser oscillator
ActiveUS20100128744A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical devices for laserPhase variationOptical property
High power optical pulses generating methods and laser oscillators are provided. A light generating module generates seed optical pulses having predetermined optical characteristics. A spectrum tailoring module is then used to tailor the spectral profile of the optical pulses. The spectral tailoring module includes a phase modulator which imposes a time-dependent phase variation on the optical pulses. The activation of the phase modulator is synchronized with the passage of the optical pulse therethough, thereby efficiently reducing the RF power necessary to operate the device.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
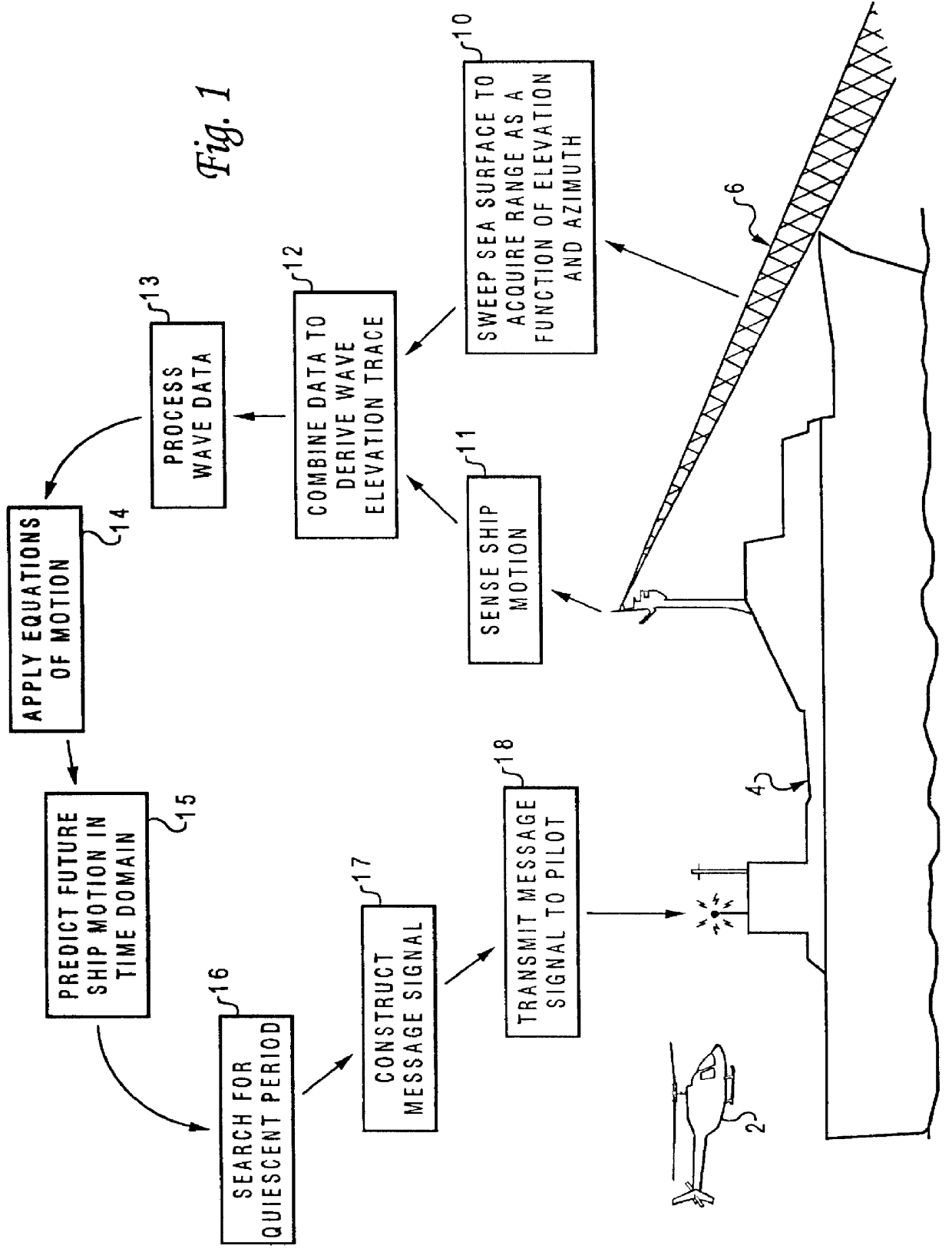
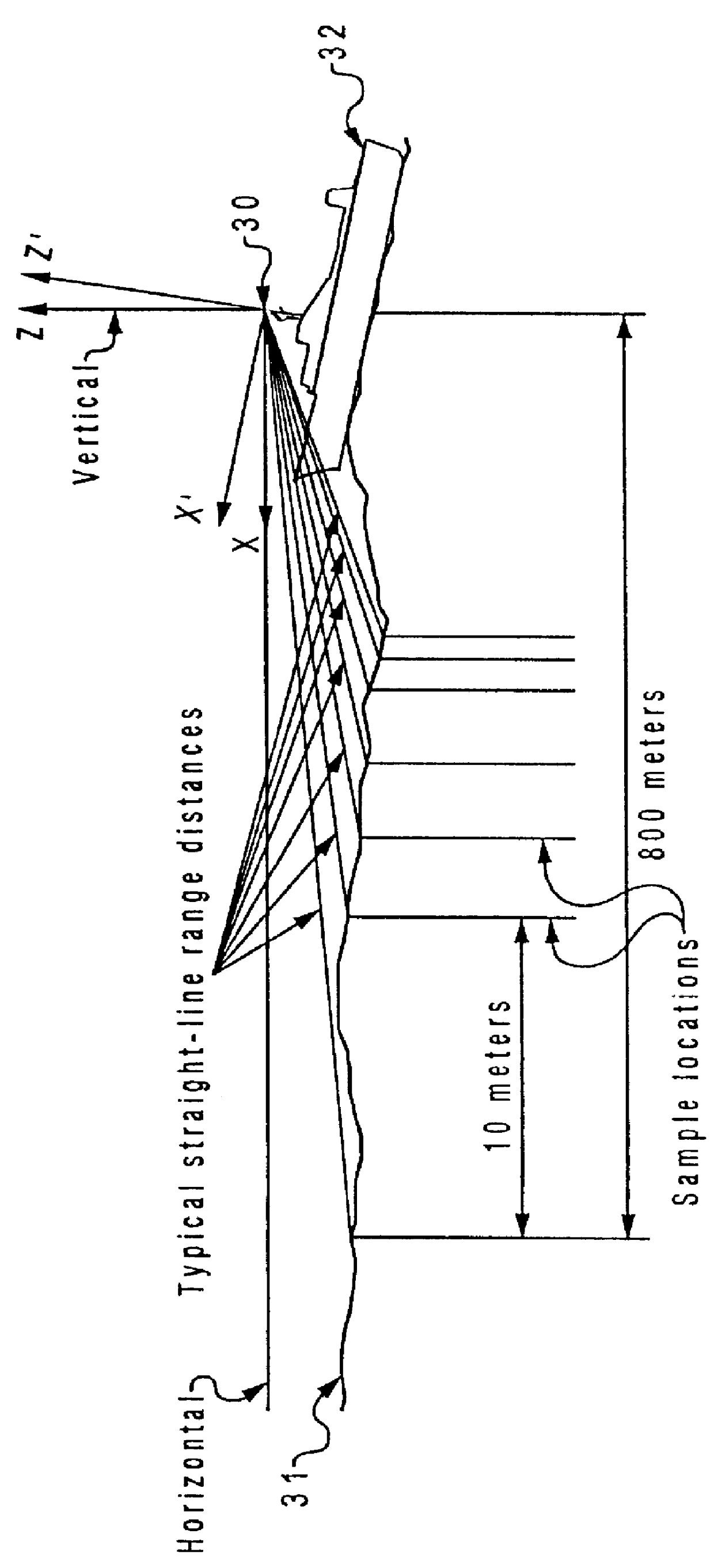
Method and system for predicting ship motion or the like to assist in helicopter landing
InactiveUS6064924AAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnchoring installationsShort termsVisual perception
A method for a short-term prediction of future ship motion in open water to furnish visual cueing information that can be remotely presented to a pilot during an aircraft landing is described. Two sets of samples of the sea surface geometry along a radial azimuth line from a ship as a function of elevation of a sensor are first acquired. These are compensated to remove the components due to the ship's motion. Two wave traces are then separately derived in Cartesian format from the two sets of acquired samples. These wave traces are subjected to a Fast Fourier Transform to detect the amplitudes and phases of the individual wavelength components. The direction of the wavelength components is determined using a measure of their phase change in the scan direction during the time interval between the two scans together with their measured wavelength. The amplitude, direction and phase of each component is utilized together with the known motion characteristics of the moving ship in order to derive a short-term prediction of future ship motion in the time domain. A quiescent period of the ship motion is located by comparing the short-term prediction with the pre-defined operating limit criteria. Finally, a message signal is transmitted to the pilot of the aircraft indicating Time-to-Land and the duration of the quiescent period.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
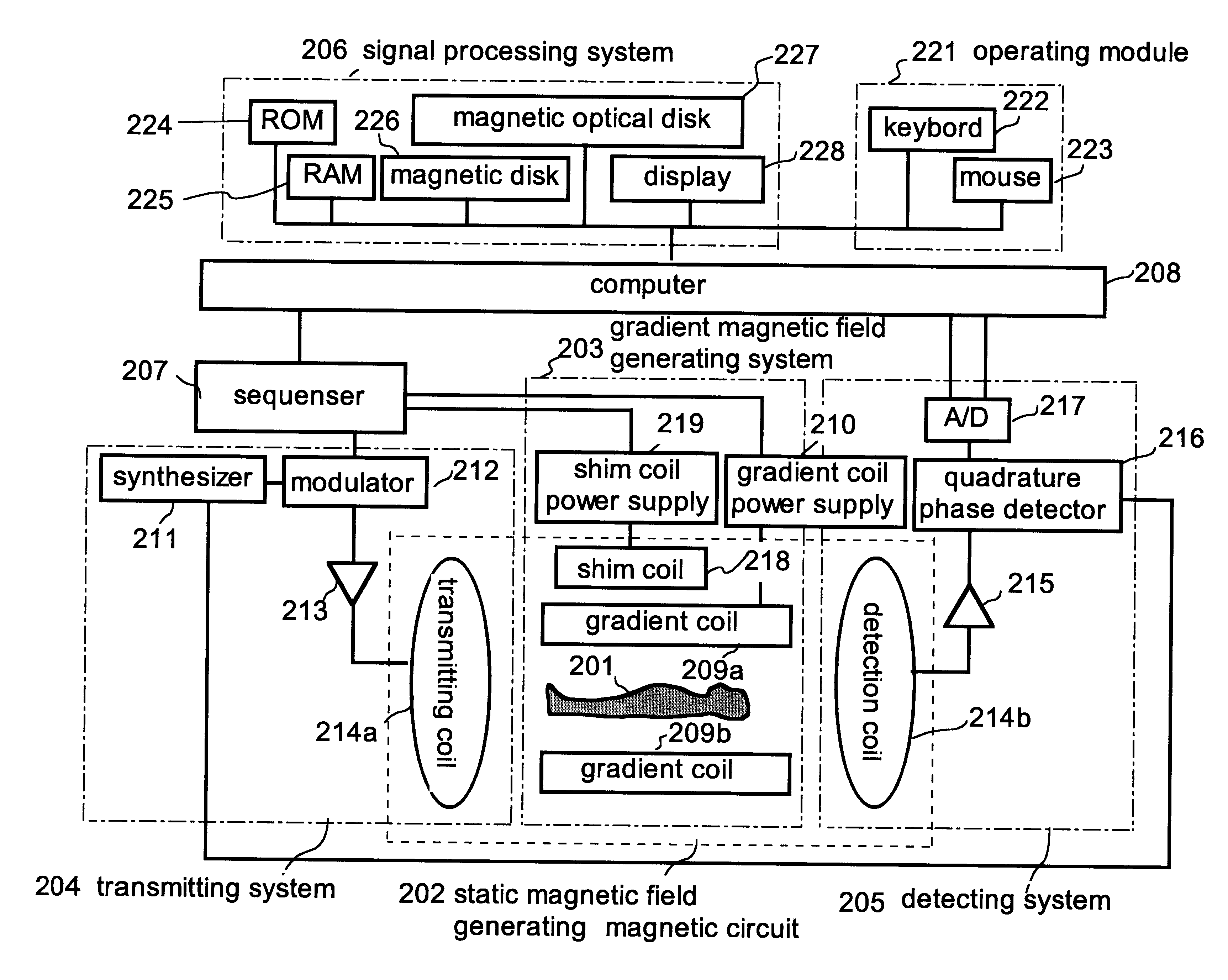
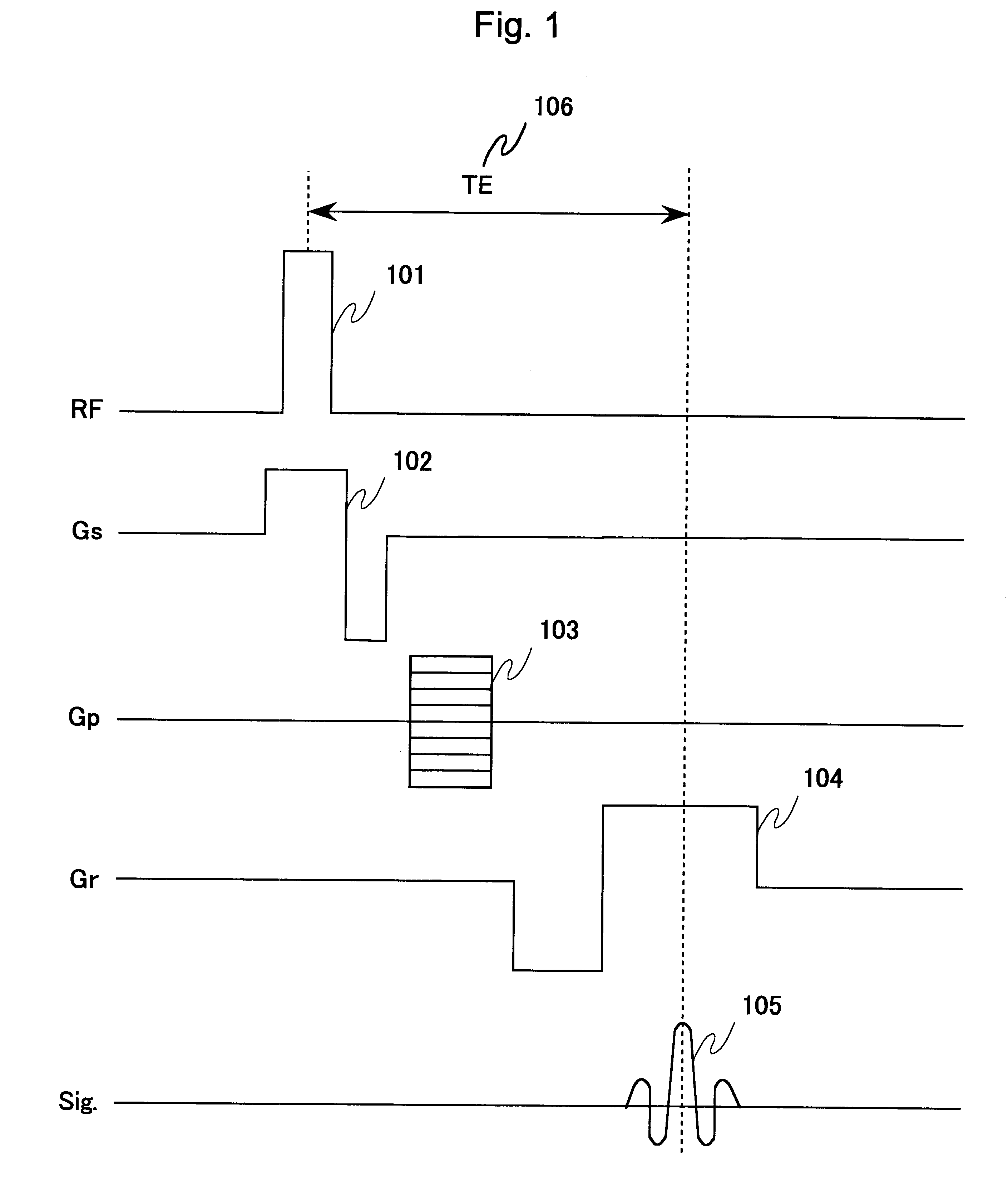
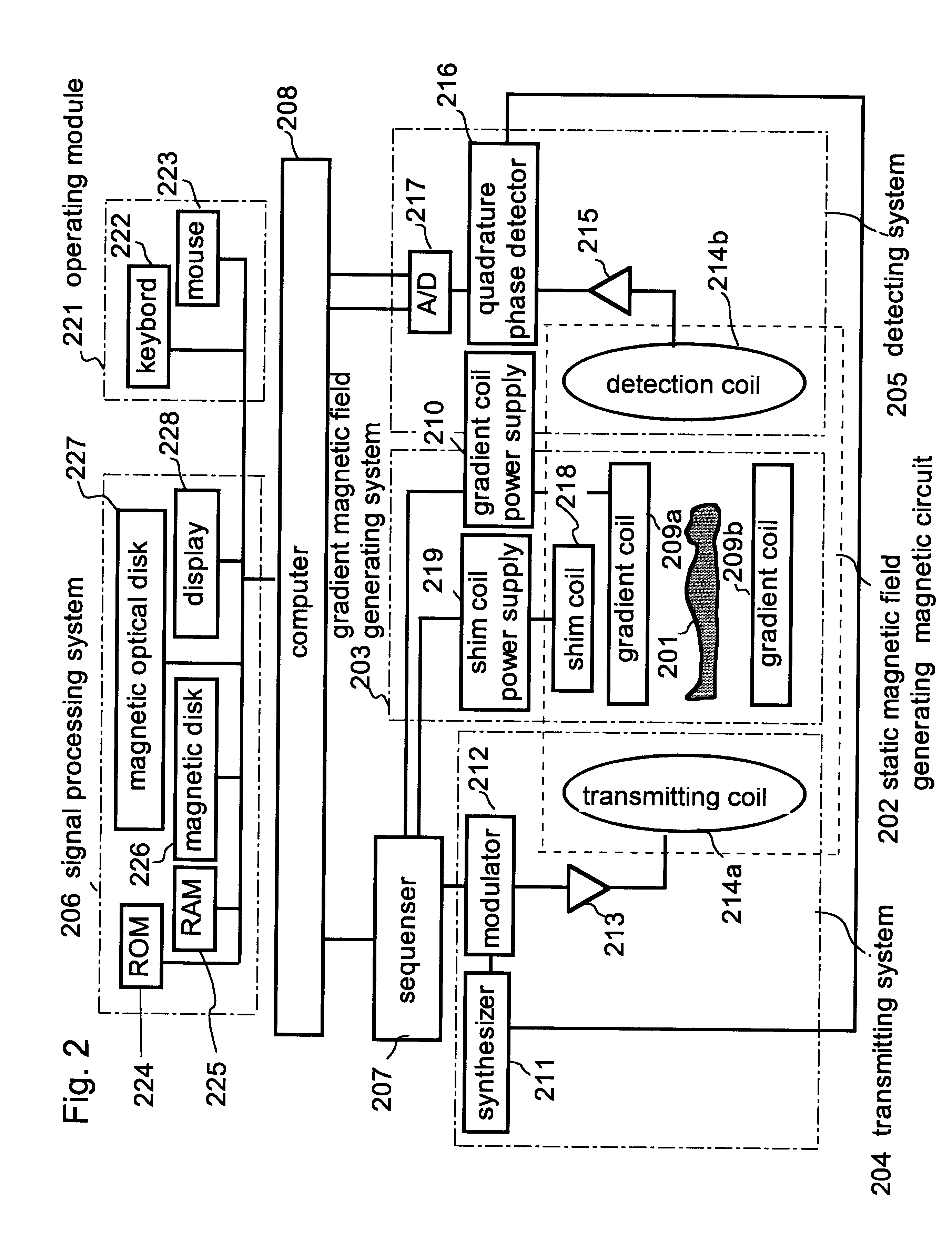
Magnetic resonance imaging device and method therefor
InactiveUS6566878B1High accurate imageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase variationCondensed matter physics
Variations in spatial phase distribution due to static magnetic field changes are corrected based on phase variations at points, specifically, at three points or a plurality of points selected by ROI, in an area where no temperature change is encountered. And a temperature distribution image is determined by using a spatial phase distribution reflecting only temperature changes after the correction, thereby high-accuracy temperature distribution image information is provided.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
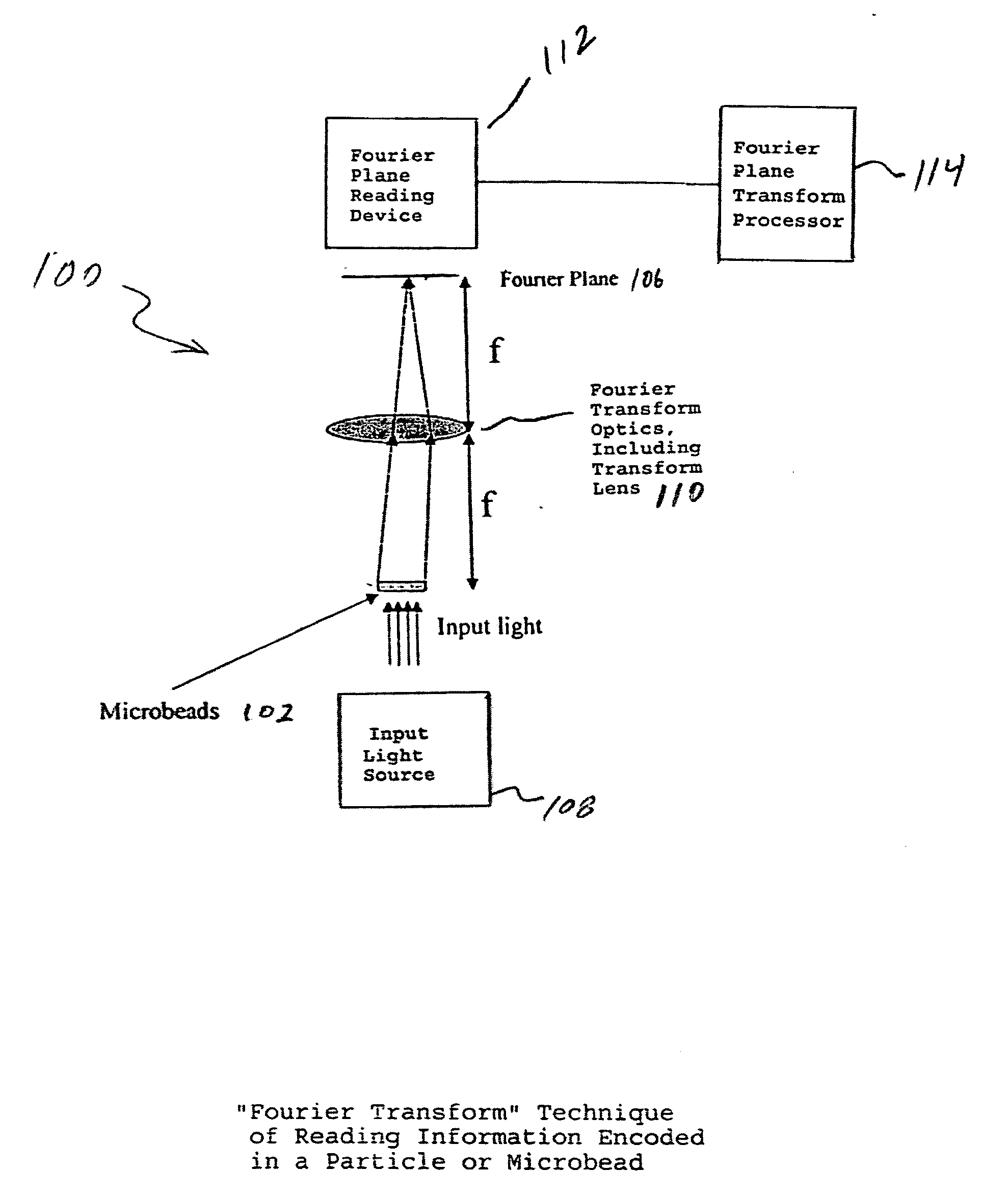
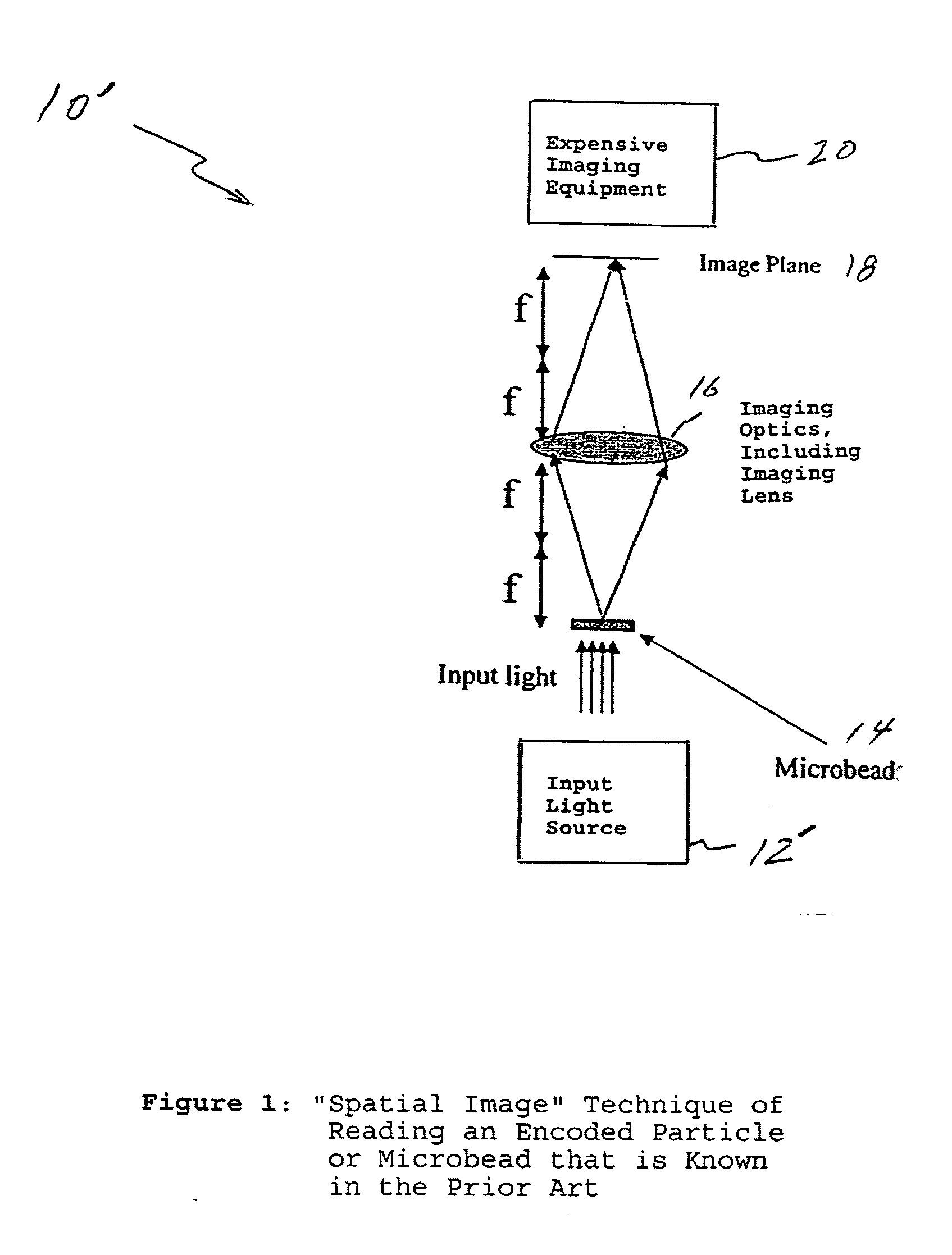
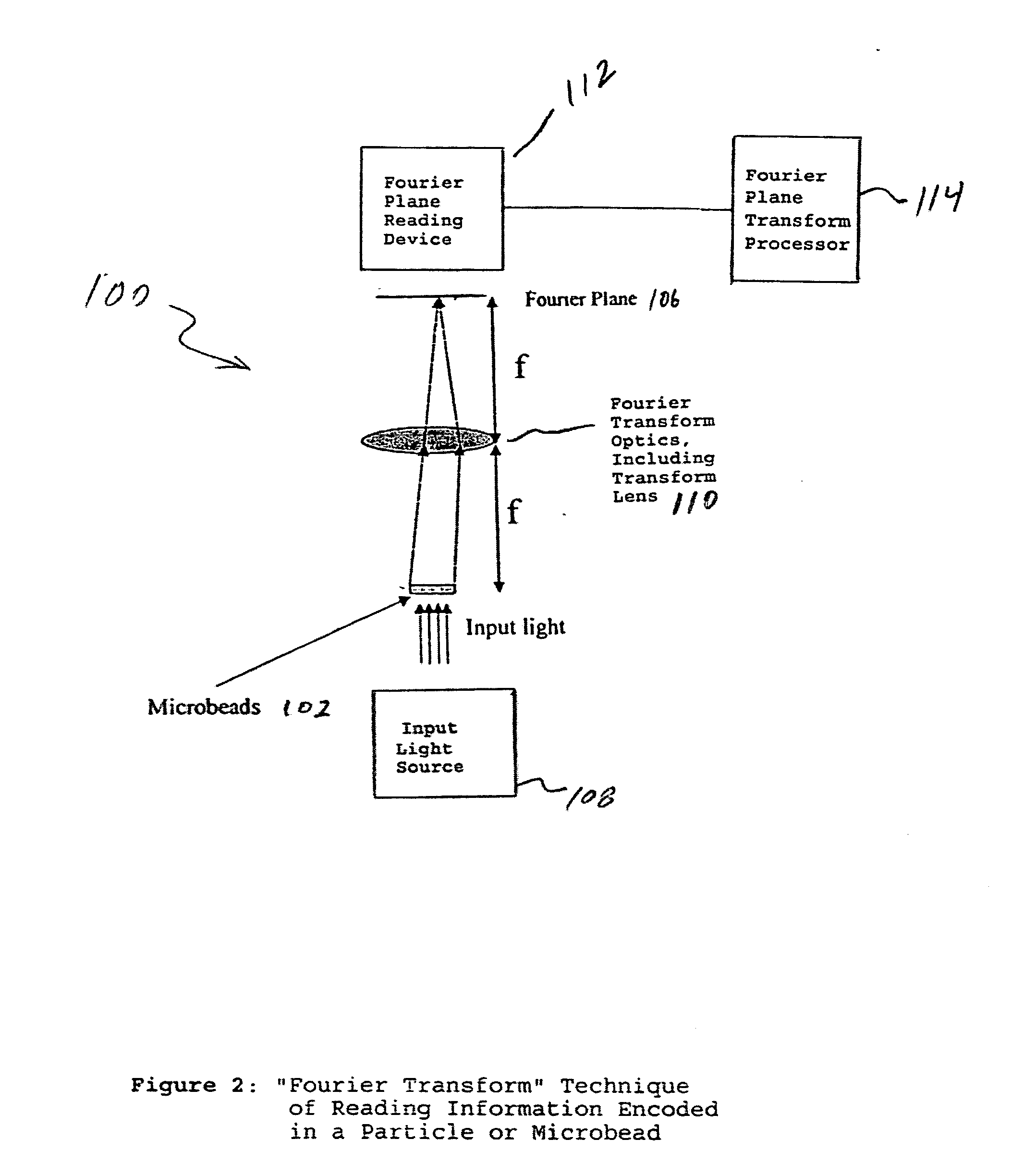
Fourier scattering methods for encoding microbeads and methods and apparatus for reading the same
ActiveUS20060119913A1Enhance the imageNanoopticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpectral patternFluorescence
A method and apparatus for reading a microbead having a code thereon is provided wherein the code is projected on and read from a Fourier plane. The microbead may be 1-1000 microns (um) or smaller in feature size. The code is projected on the Fourier plane by scattering input light off the microbead. The scattered light from the microbead is directed through an optical arrangement having a transform lens for projecting the code on the Fourier plane, and read on the Fourier plane using a charge coupled device (CCD) or other similar device. The code may include periodic layers of material having different refractivities or phase, including index of refraction differences; periodic spatial modulations having a different phase or amplitude; a periodic binary phase change used to code information in the Fourier plane; a photonic crystal used to encode the information on the microbead, wherein a pattern of holes causes interference between incident and scattered light to form spatial and spectral patterns in the far field that are unique to the pattern of holes; or may be formed in the microbead using a single photoactive inner region, a series of longitudinal holes, different fluorescence regions, or concentric rings of material in a preform.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS8855265B2Reduce impactImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
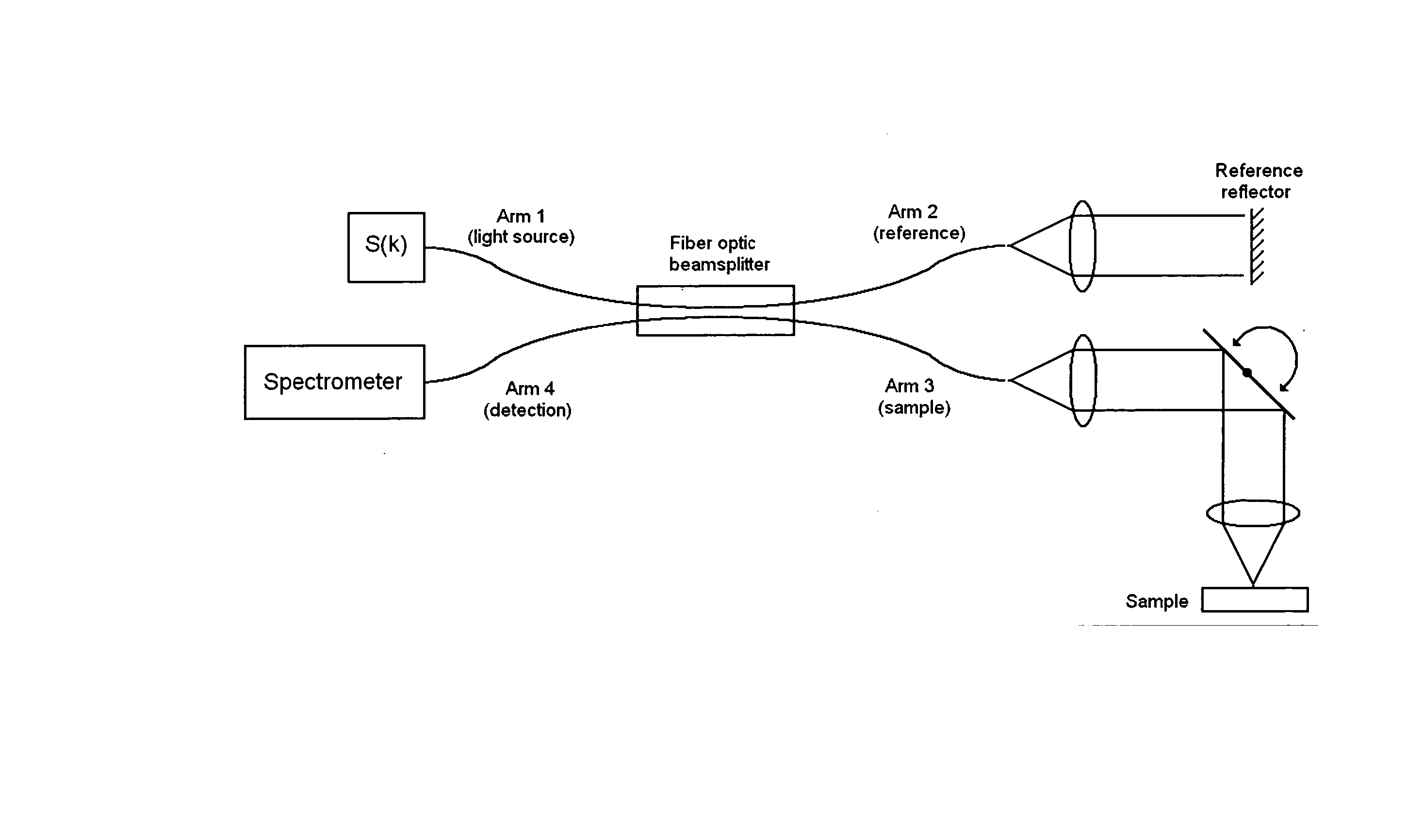
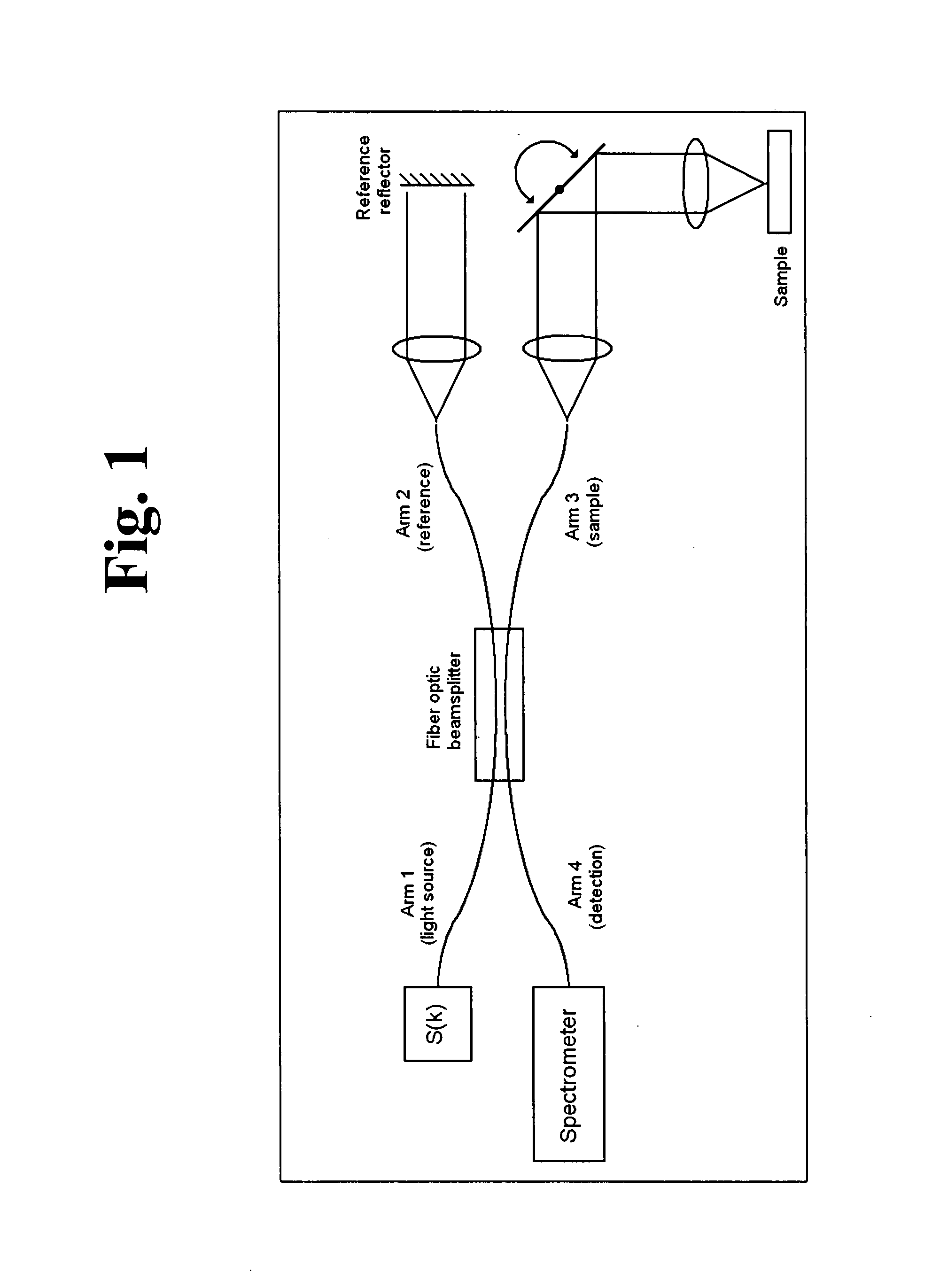
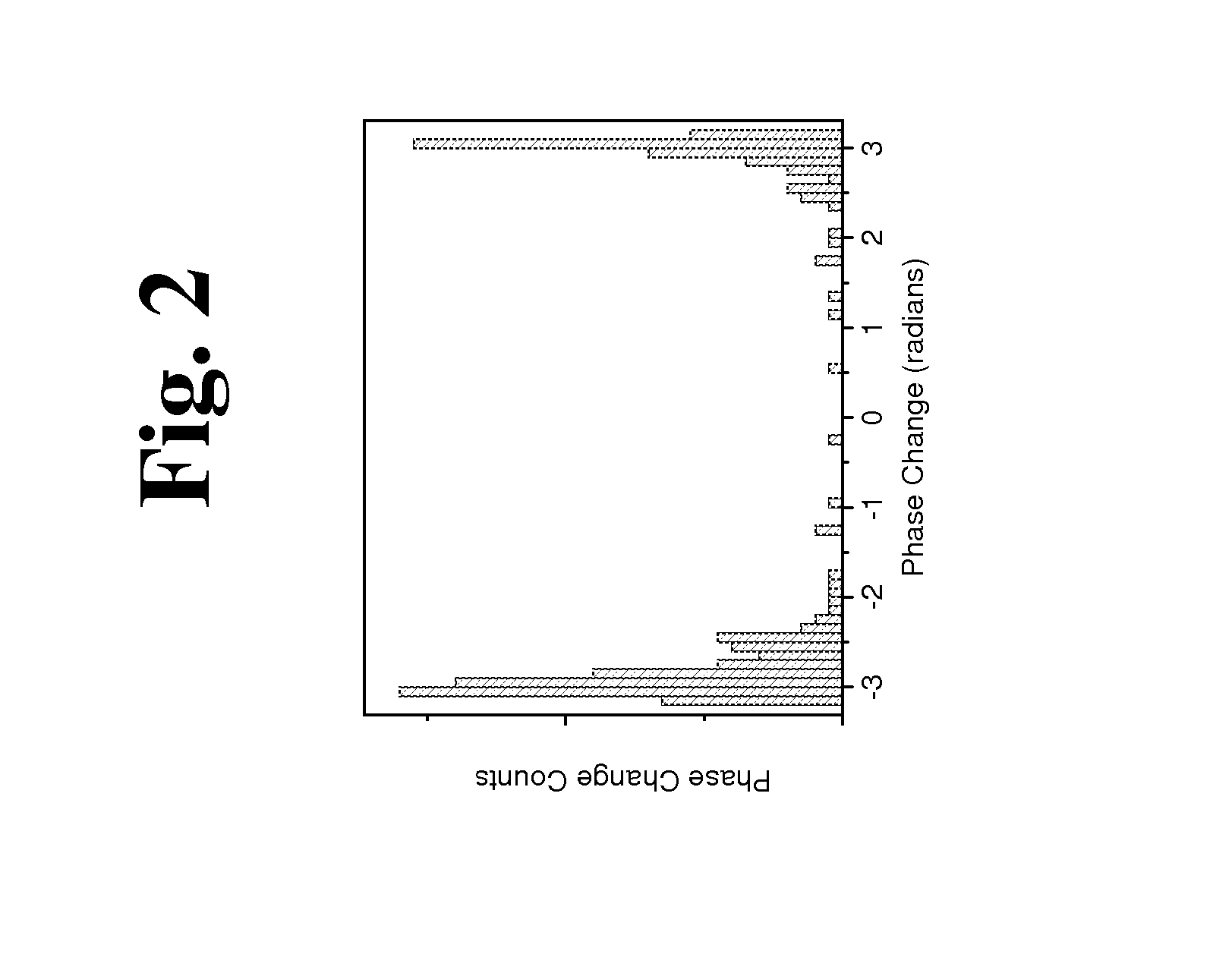
Dynamic motion contrast and transverse flow estimation using optical coherence tomography
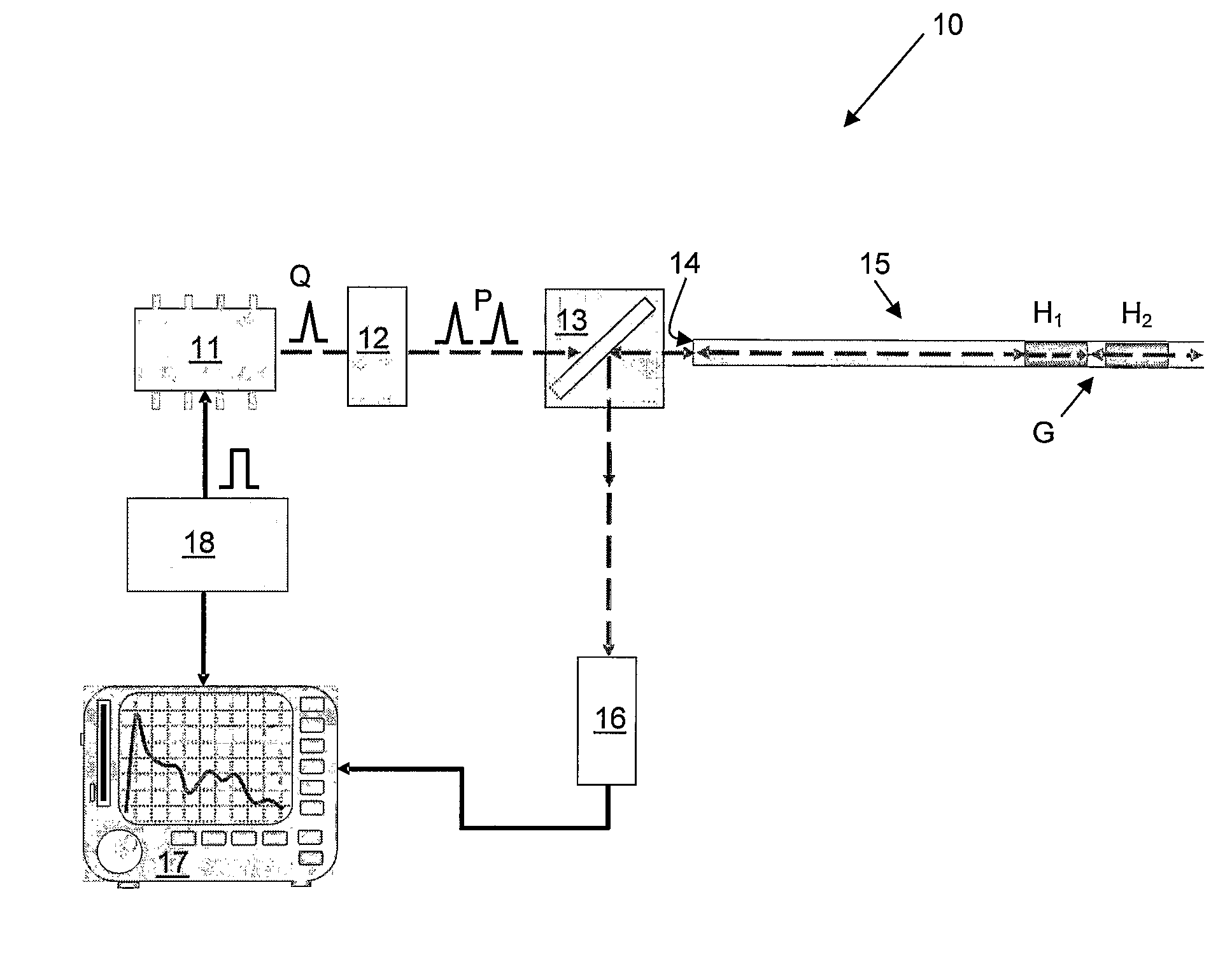
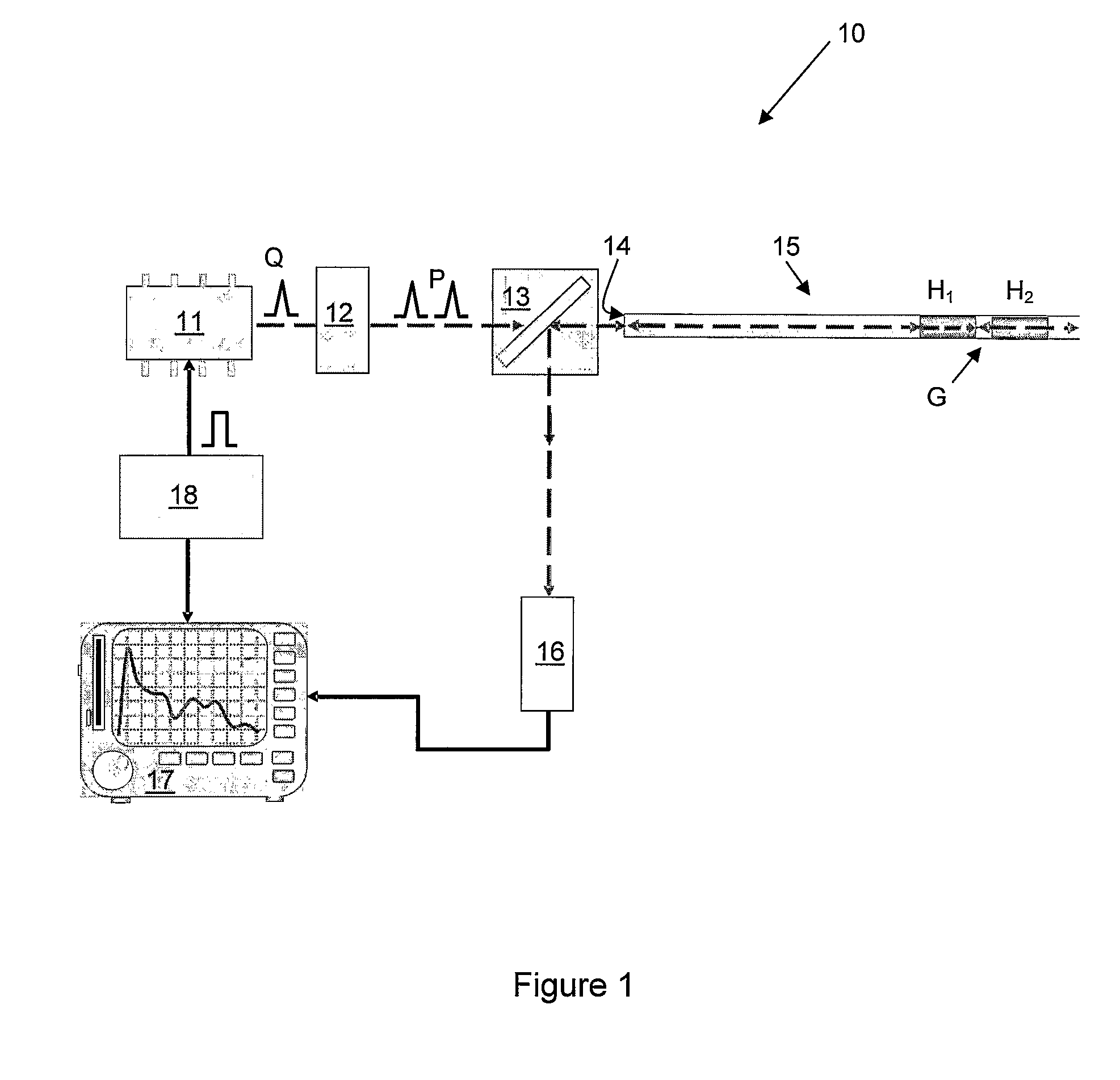
ActiveUS20080025570A1Low efficiencyHighly informativeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomographyPhase variance
The methods described herein are methods to ascertain motion contrast within optical coherence tomography data based upon phase variance. The phase variance contrast observes the nanometer scale motion of scatterers associated with Brownian motion and other non-flow motion. The inventive method of calculating motion contrast from the phase variance can differentiate regions of different mobility based on the motion contrast differences, and can use the phase information to characterize mobility properties of the scatterers. In flow regions, the inventive method for acquiring and analyzing motion contrast can identify the regions as well as characterize the motion. Furthermore, the inventive method can determine quantitative flow estimation, the index of refraction variations, and absorption variations within flow regions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
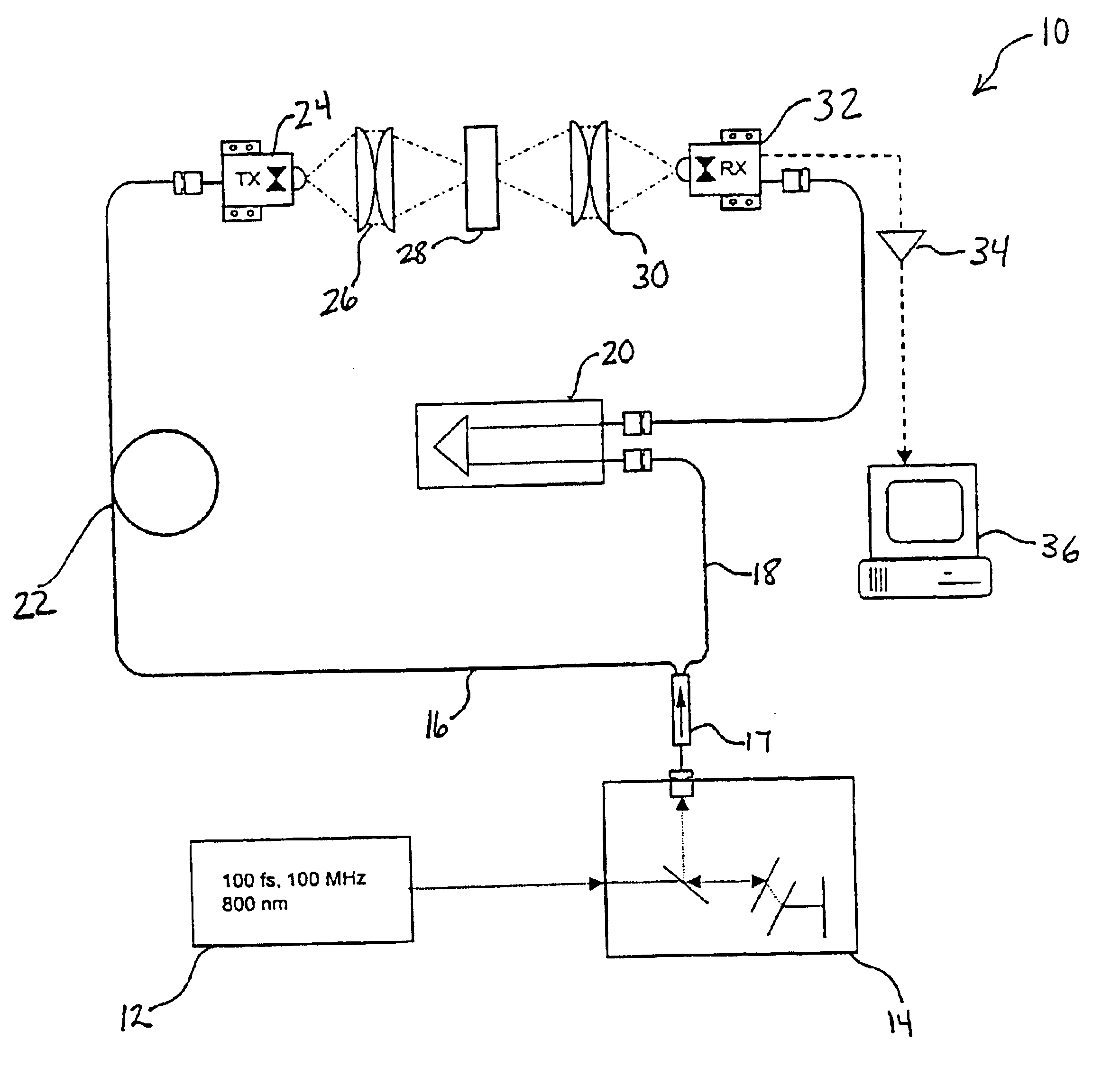
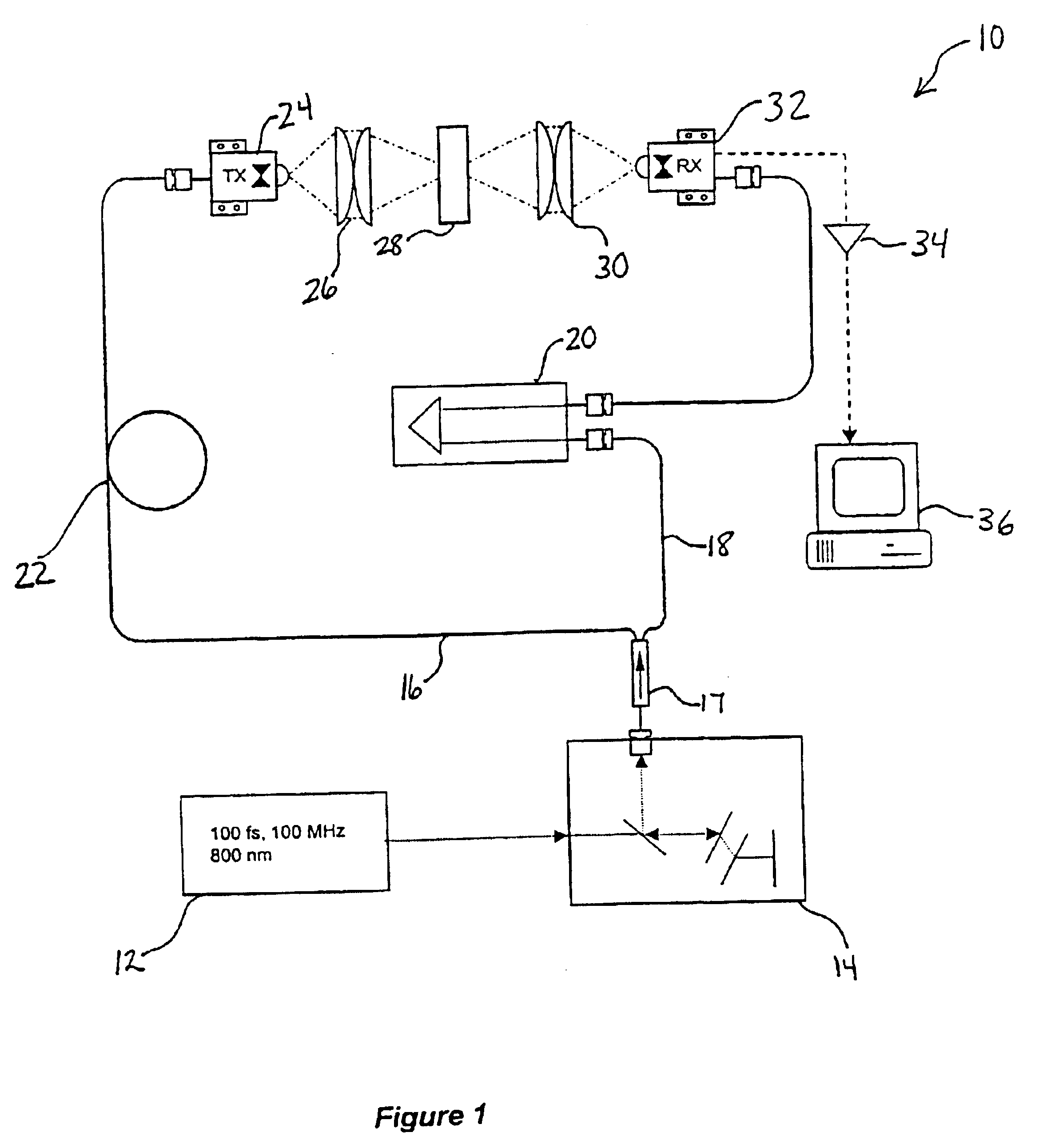
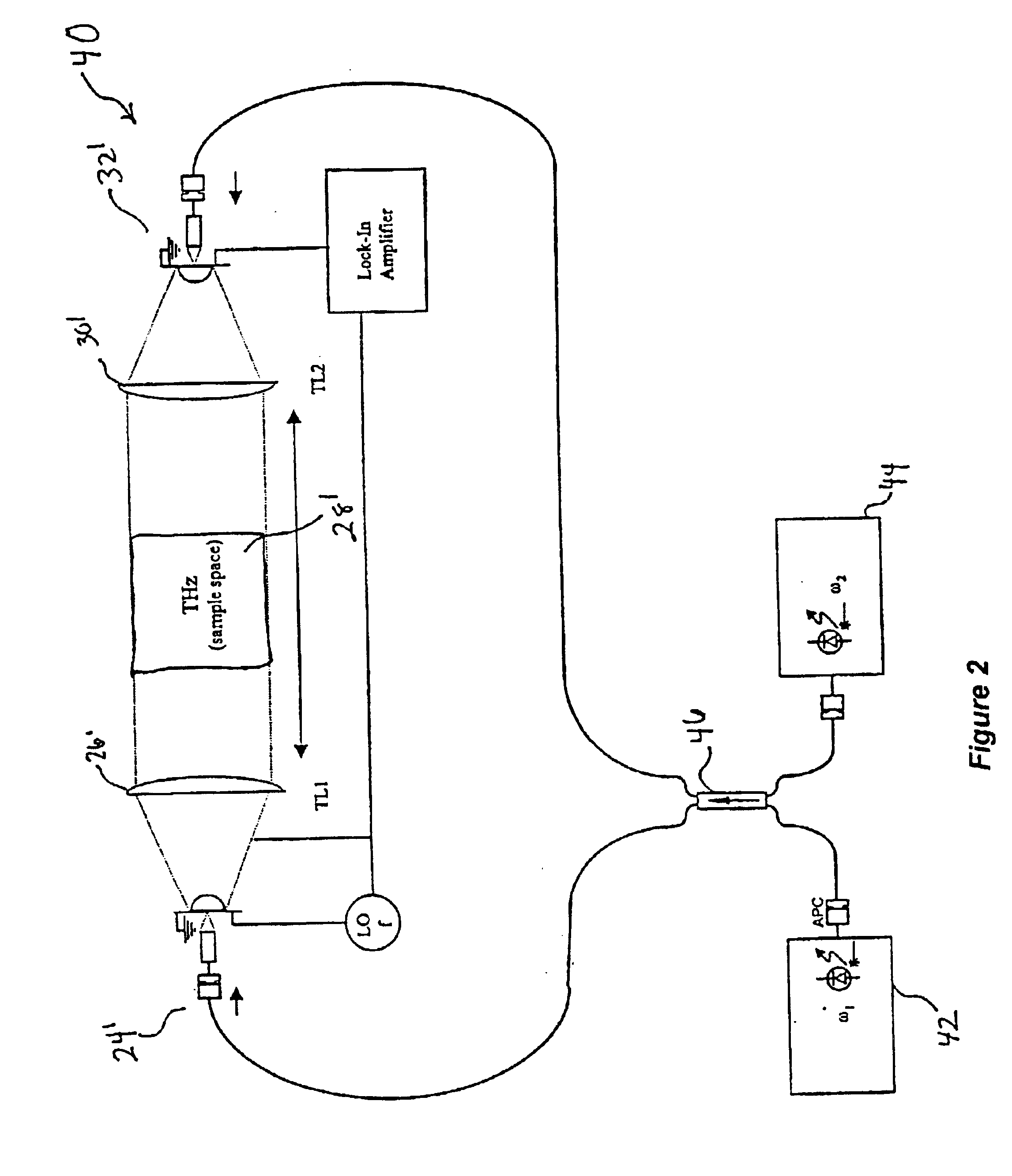
System and method for monitoring changes in state of matter with terahertz radiation
InactiveUS6849852B2Versatility and ease of useUsed in environmentLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryTerahertz radiationLiquid state
A system and method for using terahertz radiation to detect and monitor a substance undergoing a change in phase from a liquid phase to a solid phase or vice-versa is disclosed. By employing terahertz radiation in either the pulsed mode or in the continuous-wave (CW) mode, the system can non-invasively monitor these changes. The system uses the principle that matter in a liquid state will absorb and attenuate terahertz radiation to a larger degree than matter in a semisolid or solid state. Most terahertz radiation absorption occurs due to the rotational motions of molecules, i.e. either whole molecules or groups of atoms rotating about molecular bonds.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
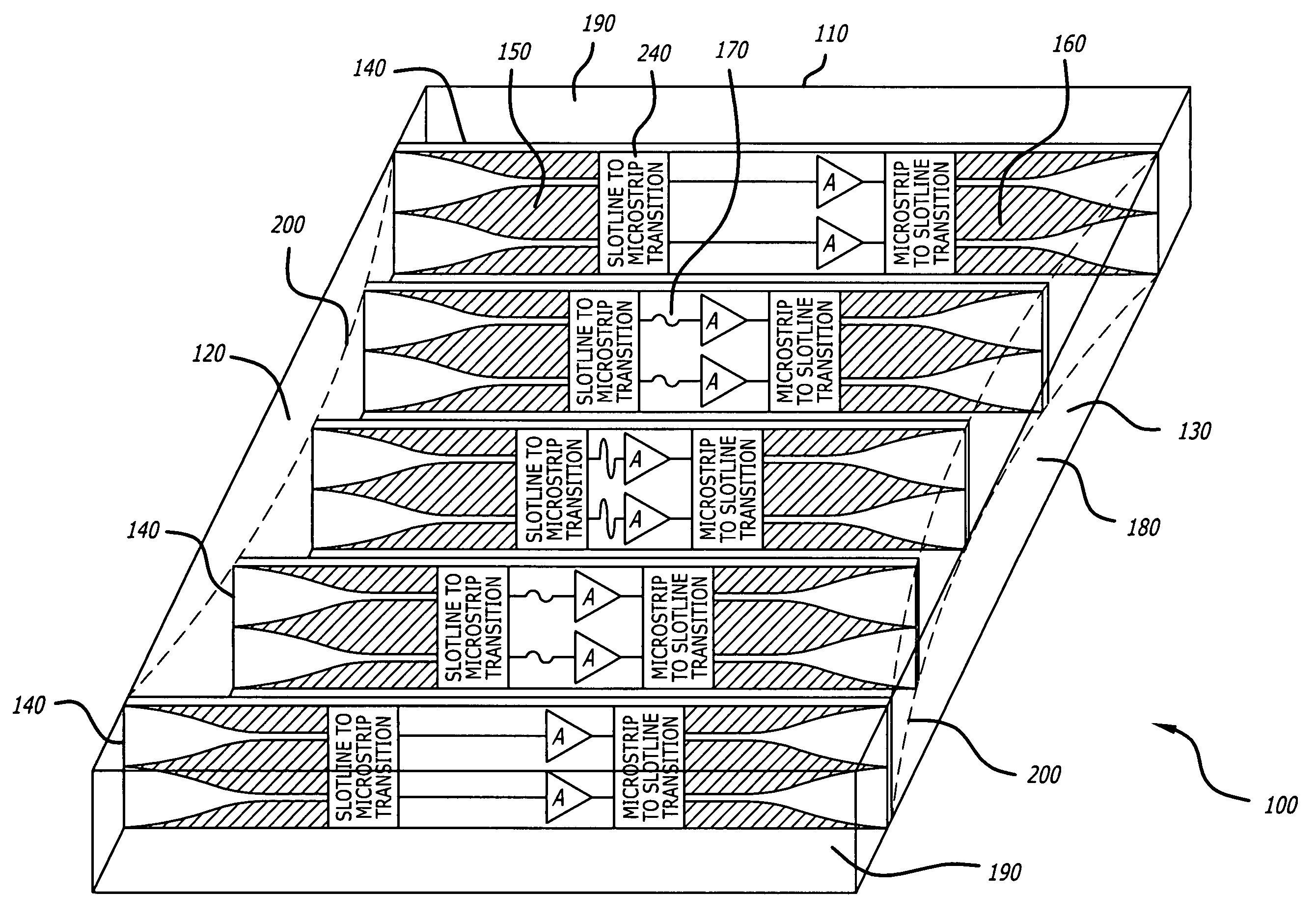
Method and apparatus for increasing performance in a waveguide-based spatial power combiner
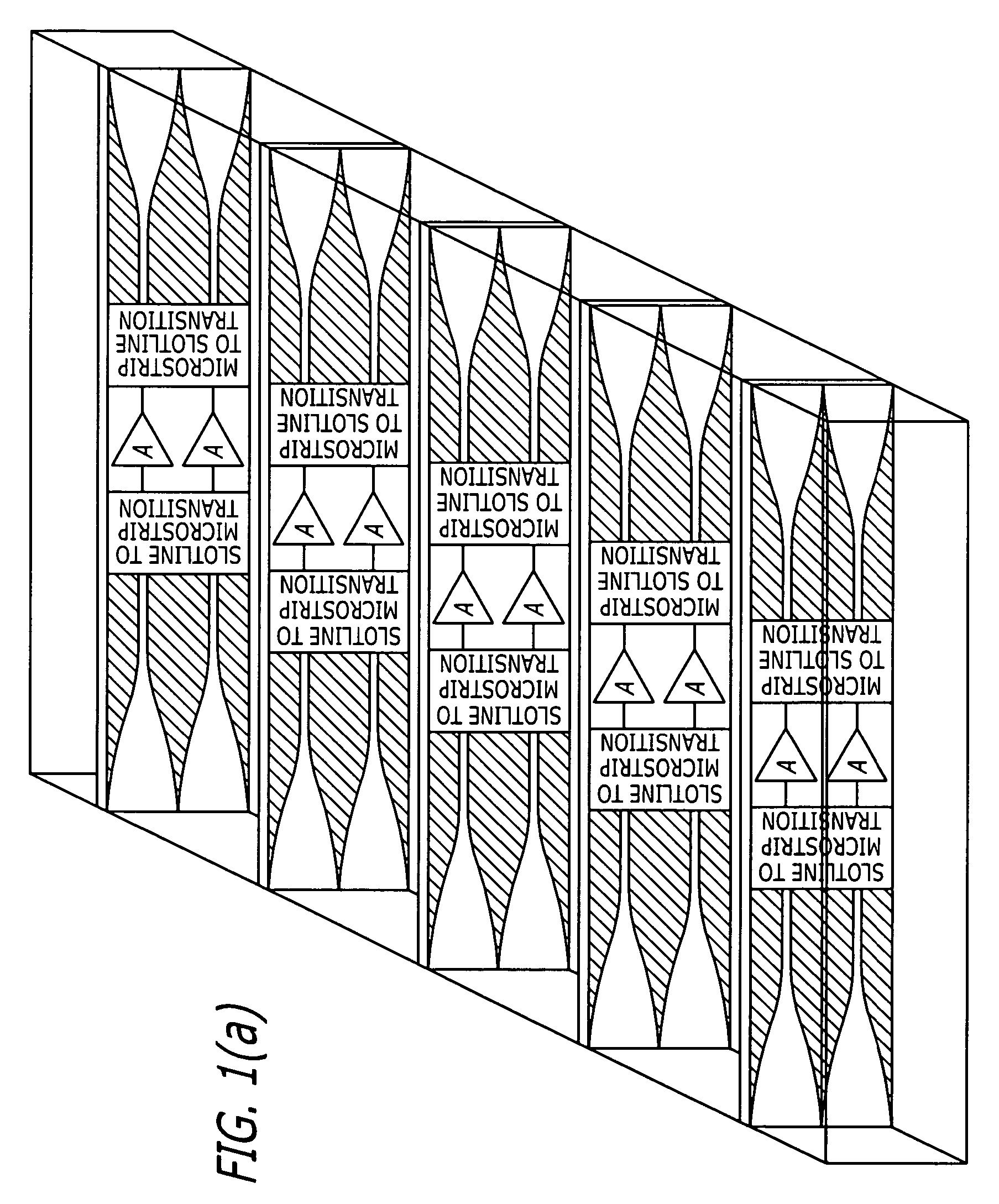
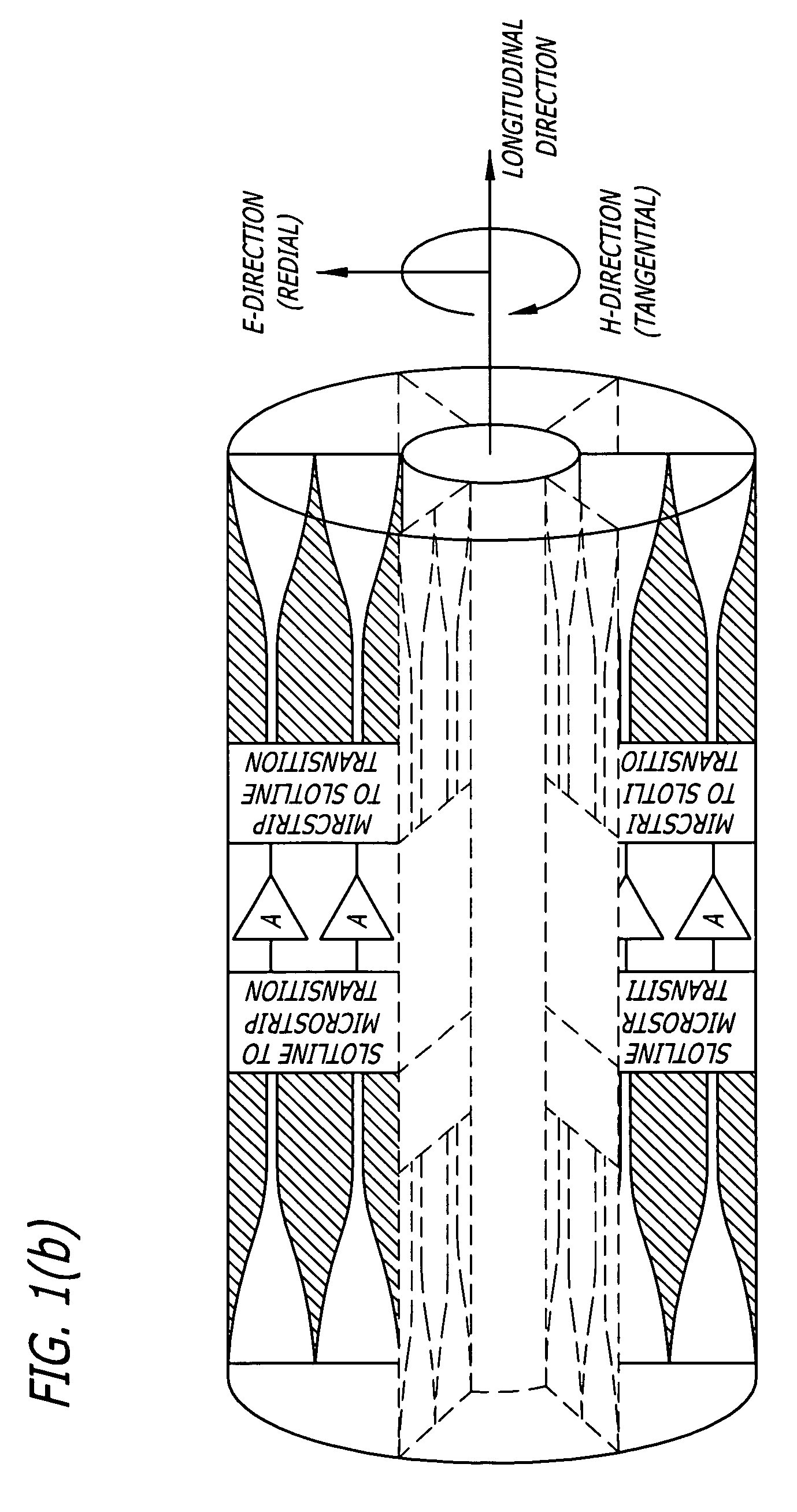
ActiveUS20060202777A1Improve performanceField intensity is weakenedAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesWaveguidesSubject matterSpatial power combiner
A power combining array and method of increasing performance in a power combining array includes a waveguide enclosure having a plurality of slotline modules disposed therein. The slotline modules include input and output antennas that have varying physical characteristics to overcome differences in field intensity across the slotline module configuration and to account for phase changes. The varying physical characteristics include differences in longitudinal position, thickness, dielectric constant, and circuit element configurations. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:WAVESTREAM CORP
Detecting a Disturbance in the Propagation of Light in an Optical Waveguide
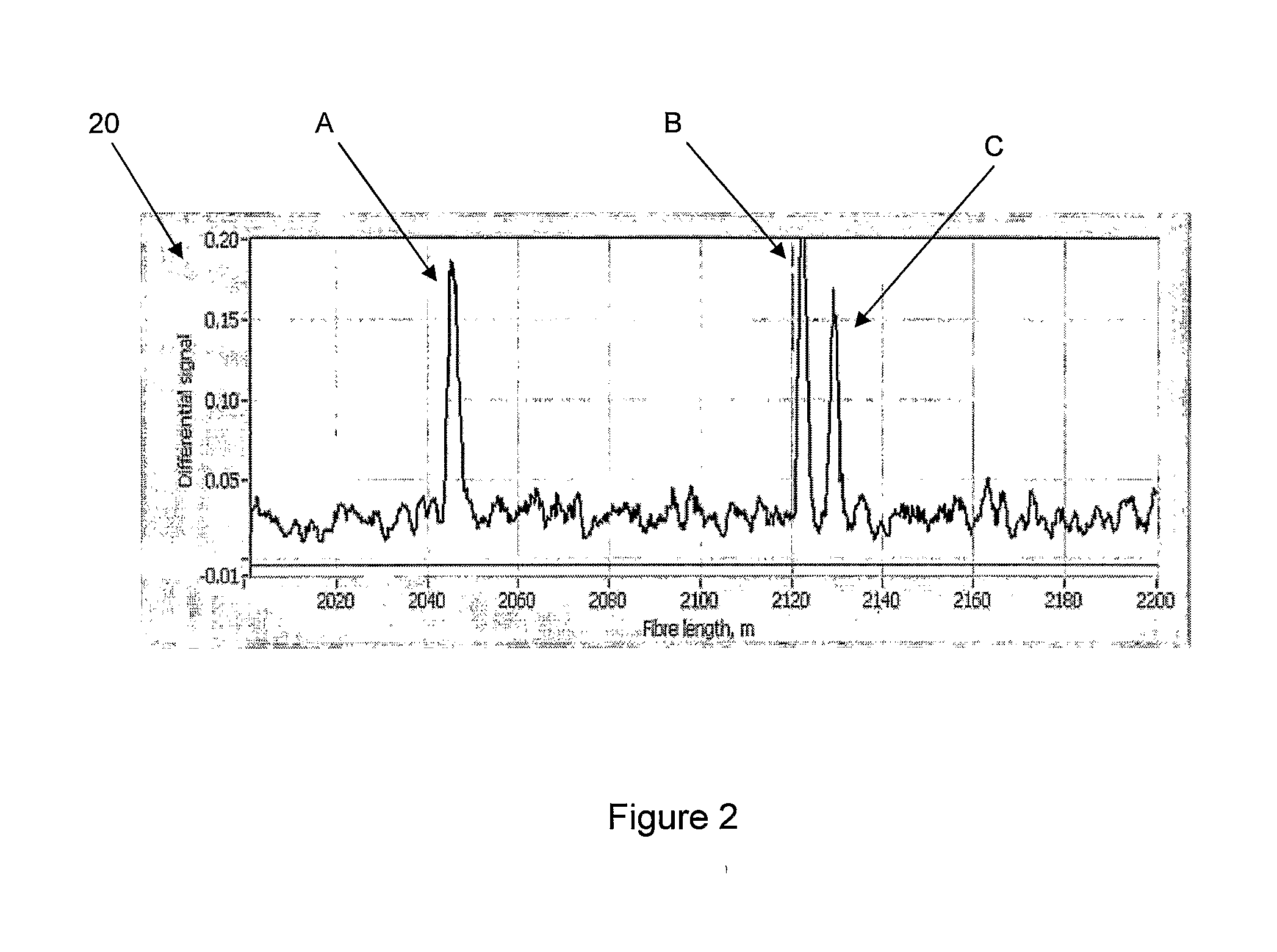
ActiveUS20080297772A1Efficient detectionAccurate detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainPhotodetectorWaveguide
An optical time domain reflectometry apparatus has a laser and light modulator for producing coherent light pulses, each having two sections of higher intensity separated by a gap of lower or substantially zero intensity. As the light pulses propagate along the optical fibre, light is continuously Rayleigh backscattered by inhomogeneities of the optical fibre. A photodetector generates backscatter signals representing the intensity of light Rayleigh backscattered in the optical fibre as each light pulse travels along the optical fibre. The PC uses these backscatter signals to derive a difference signal representing a change dI in intensity between signals generated from two successive pulses. The PC then calculates the Root Mean Square (RMS) of the difference signal averaged over the interval between the two sections of the light pulses. Next, the PC averages the backscatter signal generated from the first of the pulses over the same interval and normalises the RMS difference signal using the averaged signal to obtain a compensated difference signal that depends only on differences in the rate of change of phase of light of the light pulses as they travelled along the waveguide. This is repeated at different wavelengths to allow the compensated difference signal to be adjusted to represent the magnitude of the differences.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Method and apparatus for remote sensing of molecular species at nanoscale utilizing a reverse photoacoustic effect
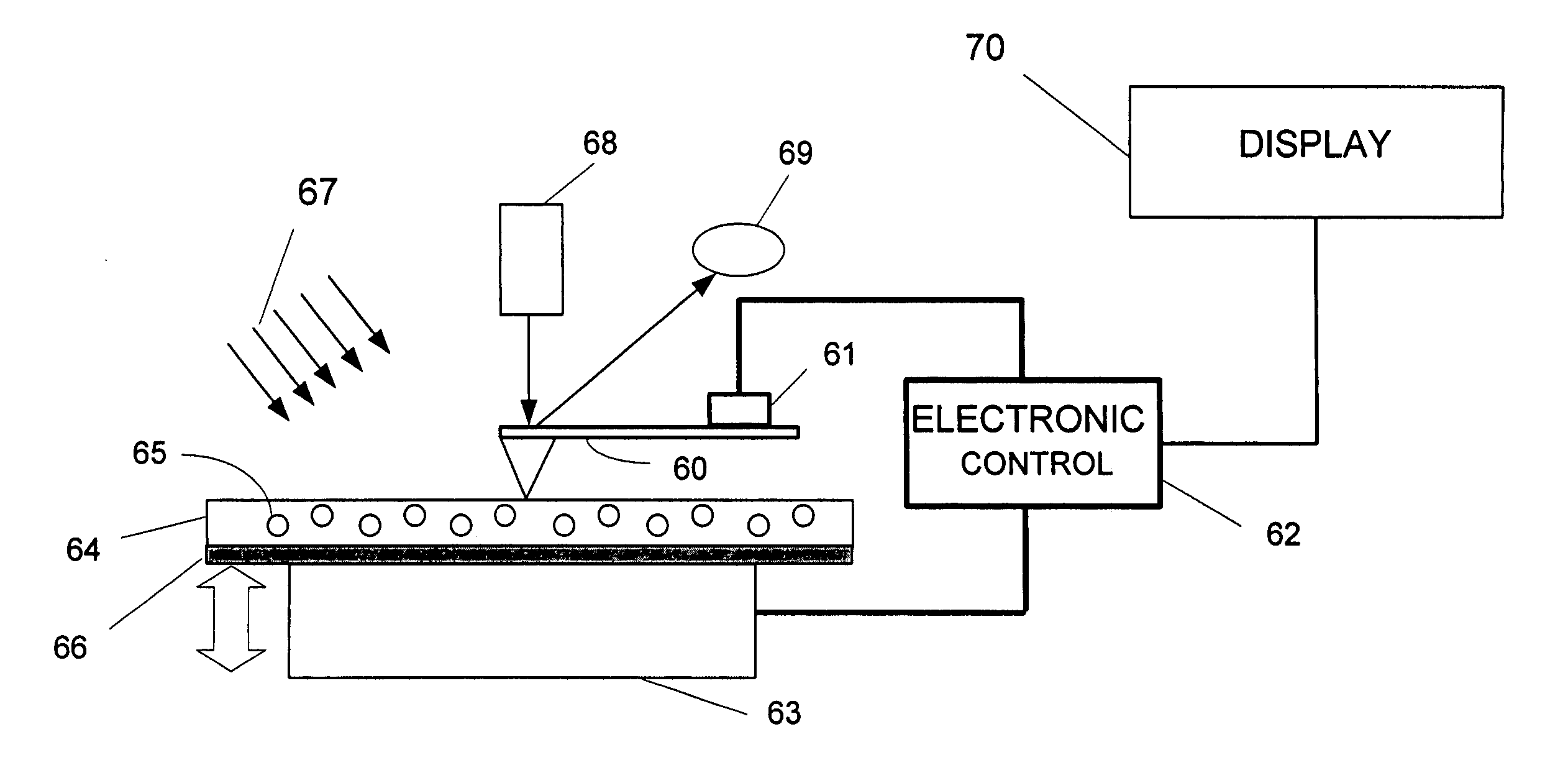
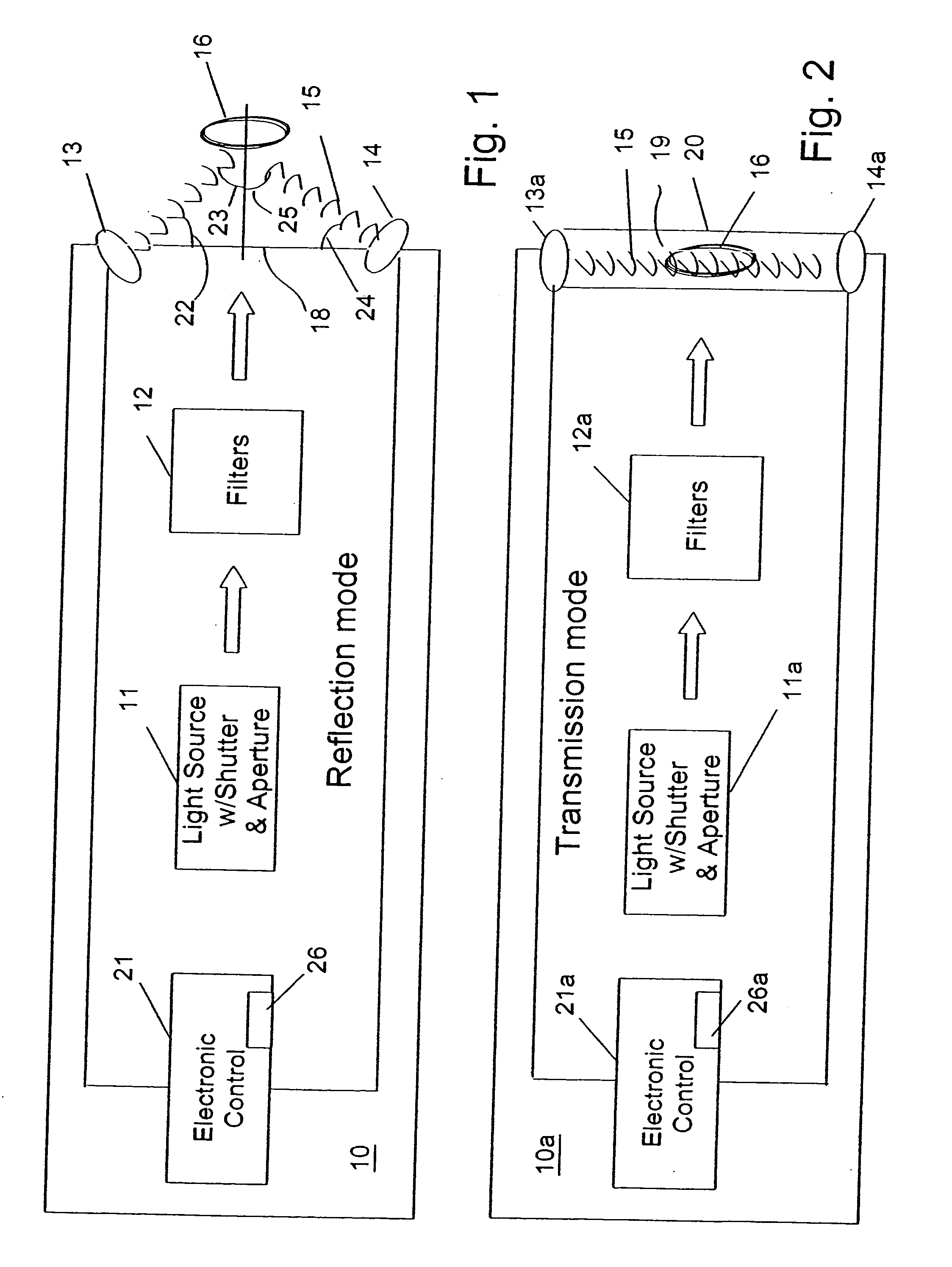
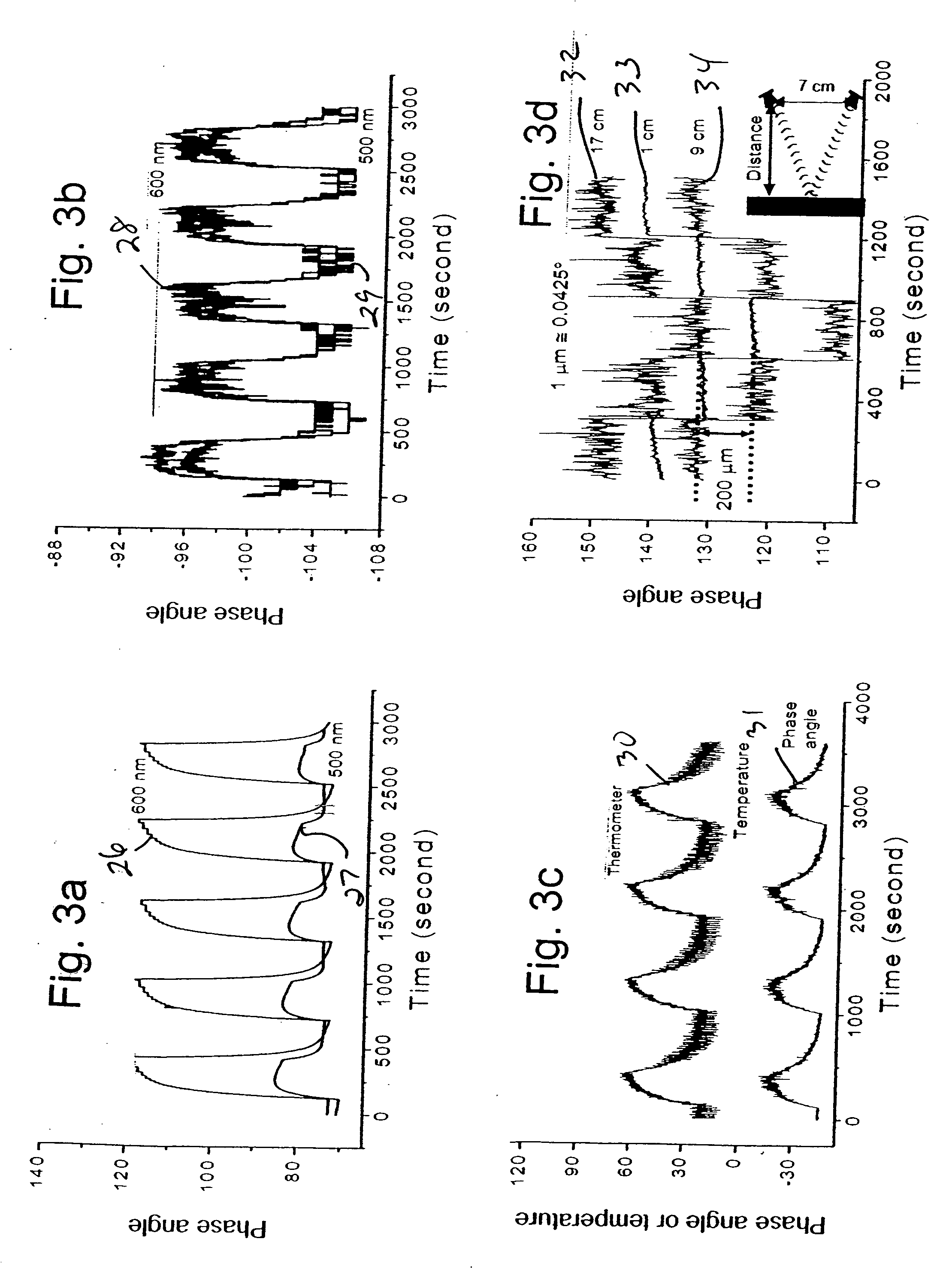
InactiveUS20070220978A1Eliminate distractionsReliable identificationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic property measurementsSignal onPhase variance
A method and apparatus for identifying a sample, involves illuminating the sample with light of varying wavelengths, transmitting an acoustic signal against the sample from one portion and receiving a resulting acoustic signal on another portion, detecting a change of phase in the acoustic signal corresponding to the light of varying wavelengths, and analyzing the change of phase in the acoustic signal for the varying wavelengths of illumination to identify the sample. The apparatus has a controlled source for illuminating the sample with light of varying wavelengths, a transmitter for transmitting an acoustic wave, a receiver for receiving the acoustic wave and converting the acoustic wave to an electronic signal, and an electronic circuit for detecting a change of phase in the acoustic wave corresponding to respective ones of the varying wavelengths and outputting the change of phase for the varying wavelengths to allow identification of the sample. The method and apparatus can be used to detect chemical composition or visual features. A transmission mode and a reflection mode of operation are disclosed. The method and apparatus can be applied at nanoscale to detect molecules in a biological sample.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
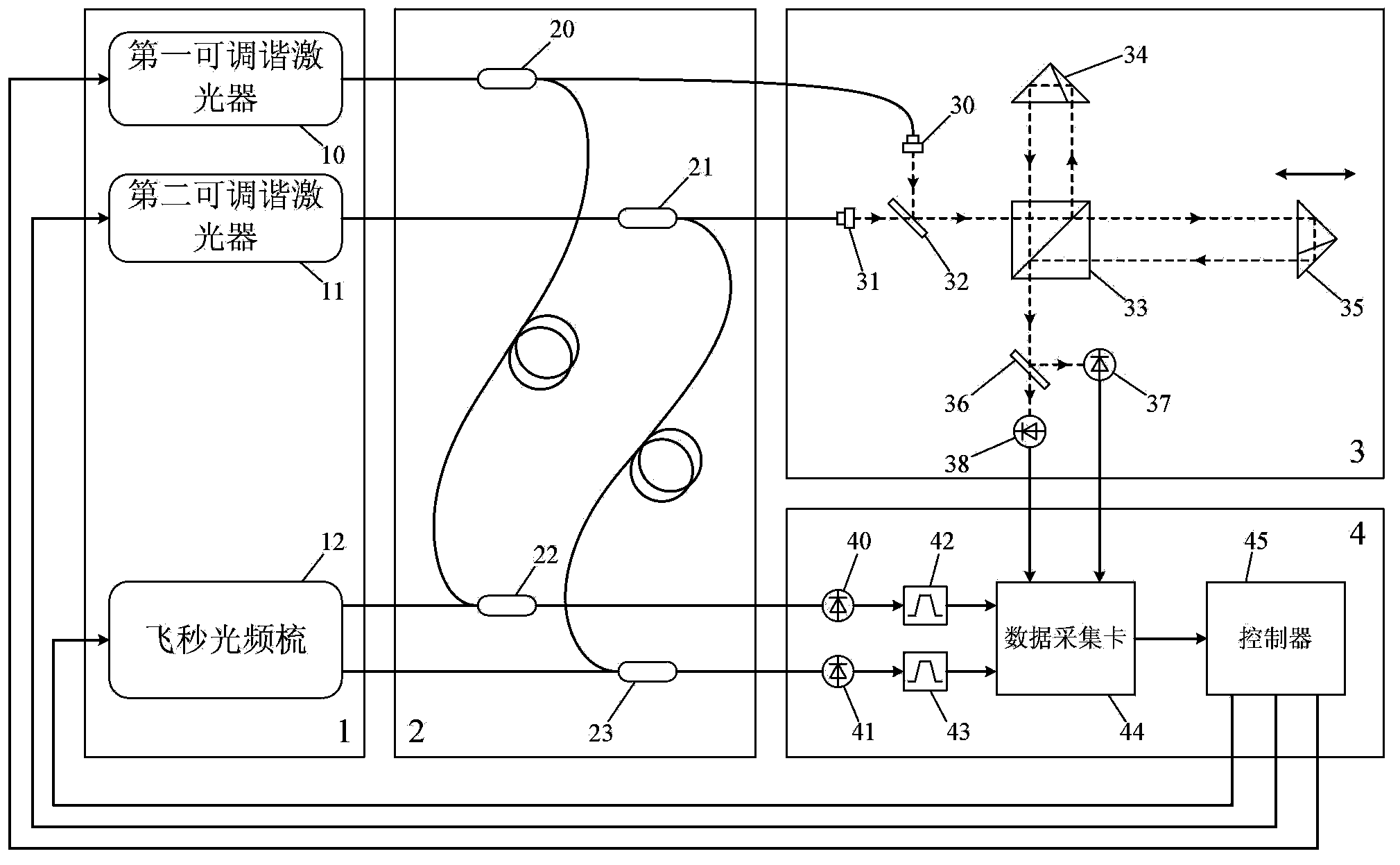
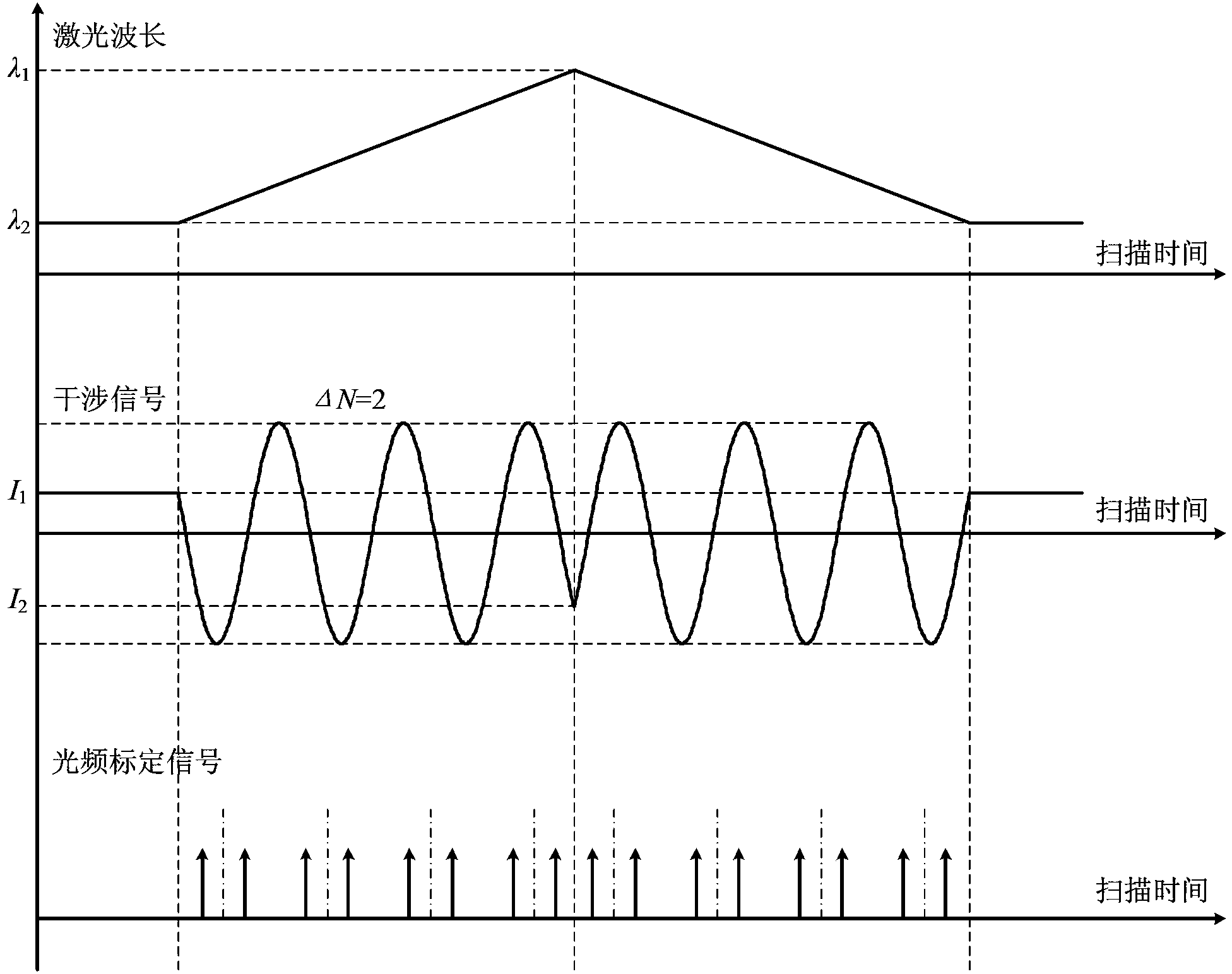
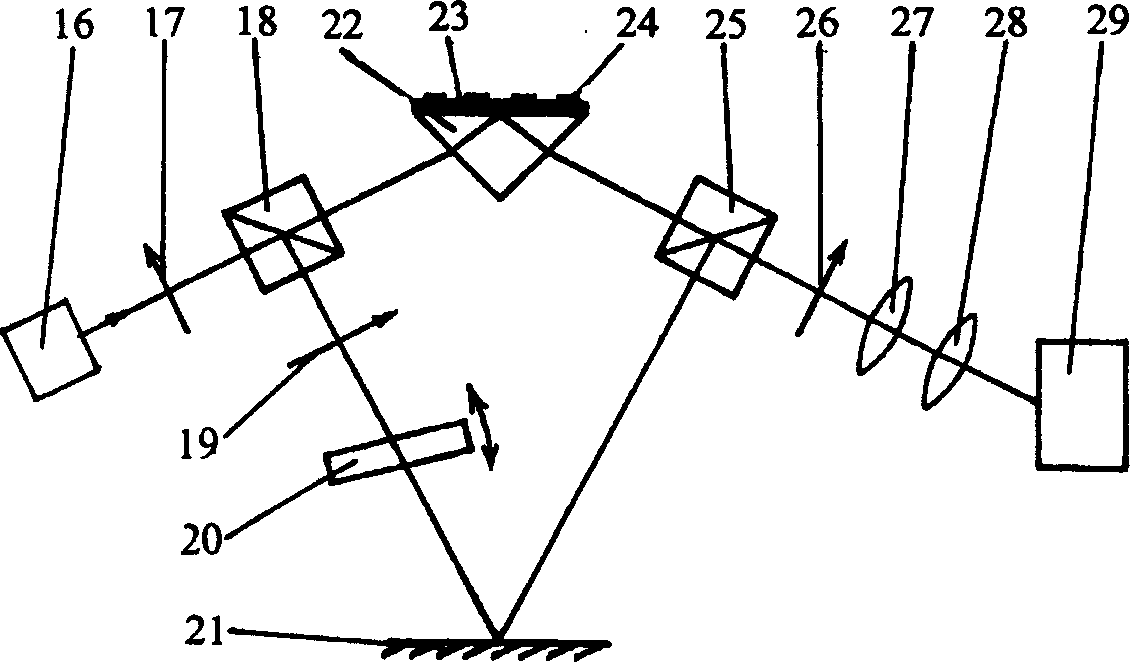
Optical frequency comb calibration-based dual-color laser scanning absolute distance measuring device and method
InactiveCN103364775AHigh measurement accuracySimple structureUsing reradiationMeasure outcomesRefractive index
An optical frequency comb calibration-based dual-color laser scanning absolute distance measuring device and a method are characterized in that the device comprises a laser light source system, a polarization-maintaining optical fiber system, a Michelson interference system and a laser frequency calibration system. The method comprises the steps of controlling two tunable lasers in the laser light source system to continuously simultaneously adjust the output light frequency without mode skips, wherein the laser frequency calibration system records the interference signal of the Michelson interference system and a beat frequency signal of the tunable lasers and the optical frequency comb; computing the scanning range of the lasers and the period integer and period decimal of the phase change of the interference signal in the scanning process according to the collected data; and finally computing to obtain the absolute distance of a to-be-measured light path refractive face. The optical frequency comb calibration-based dual-color laser scanning absolute distance measuring device and the method have the advantages of simple system structure, high measuring precision, compensating effect on air refractive index, and traceable measuring outcome, and are suitable for the measuring field of space absolute distance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
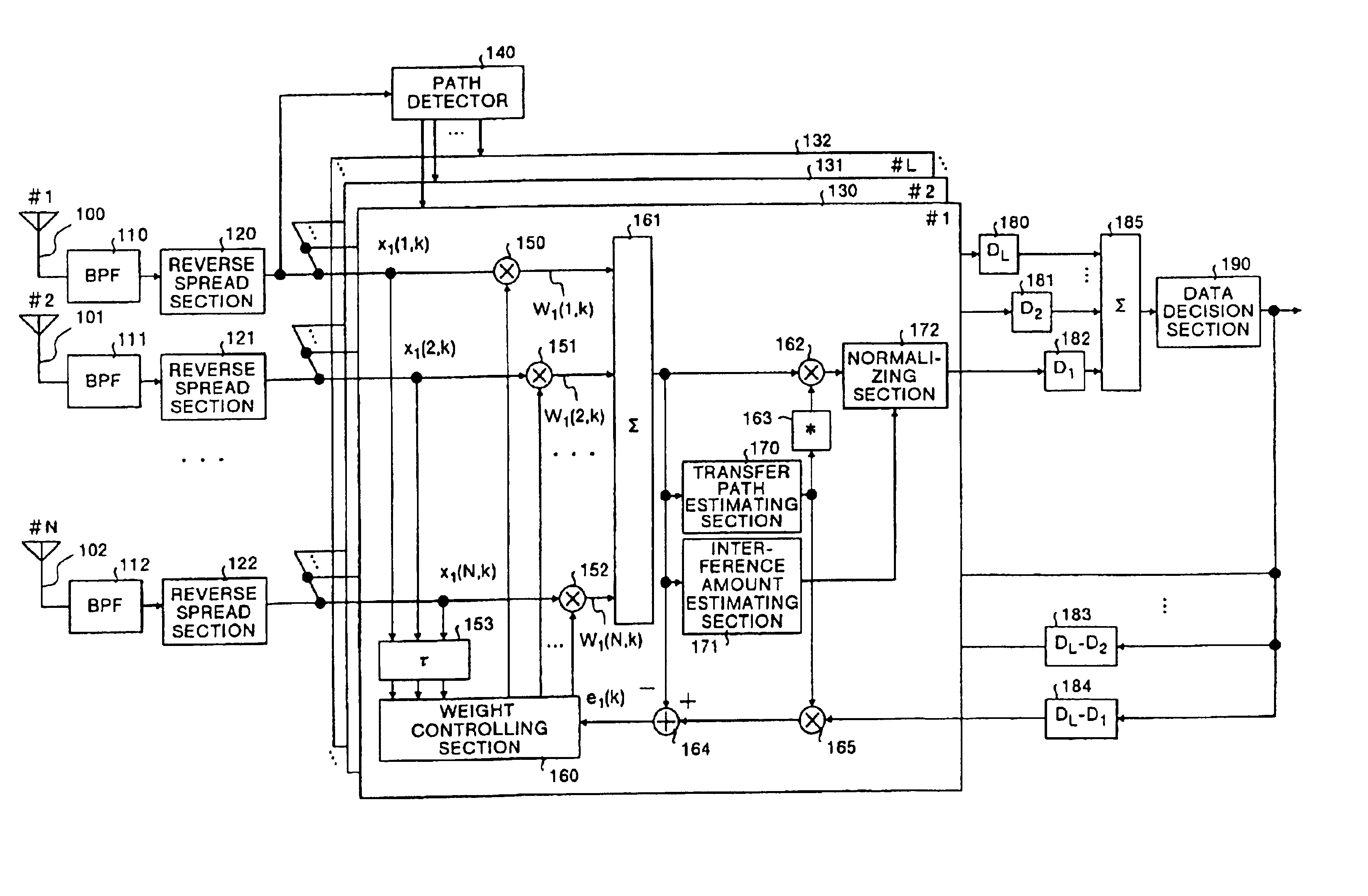
Spread spectrum receiving apparatus
InactiveUS6882681B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase variationEngineering
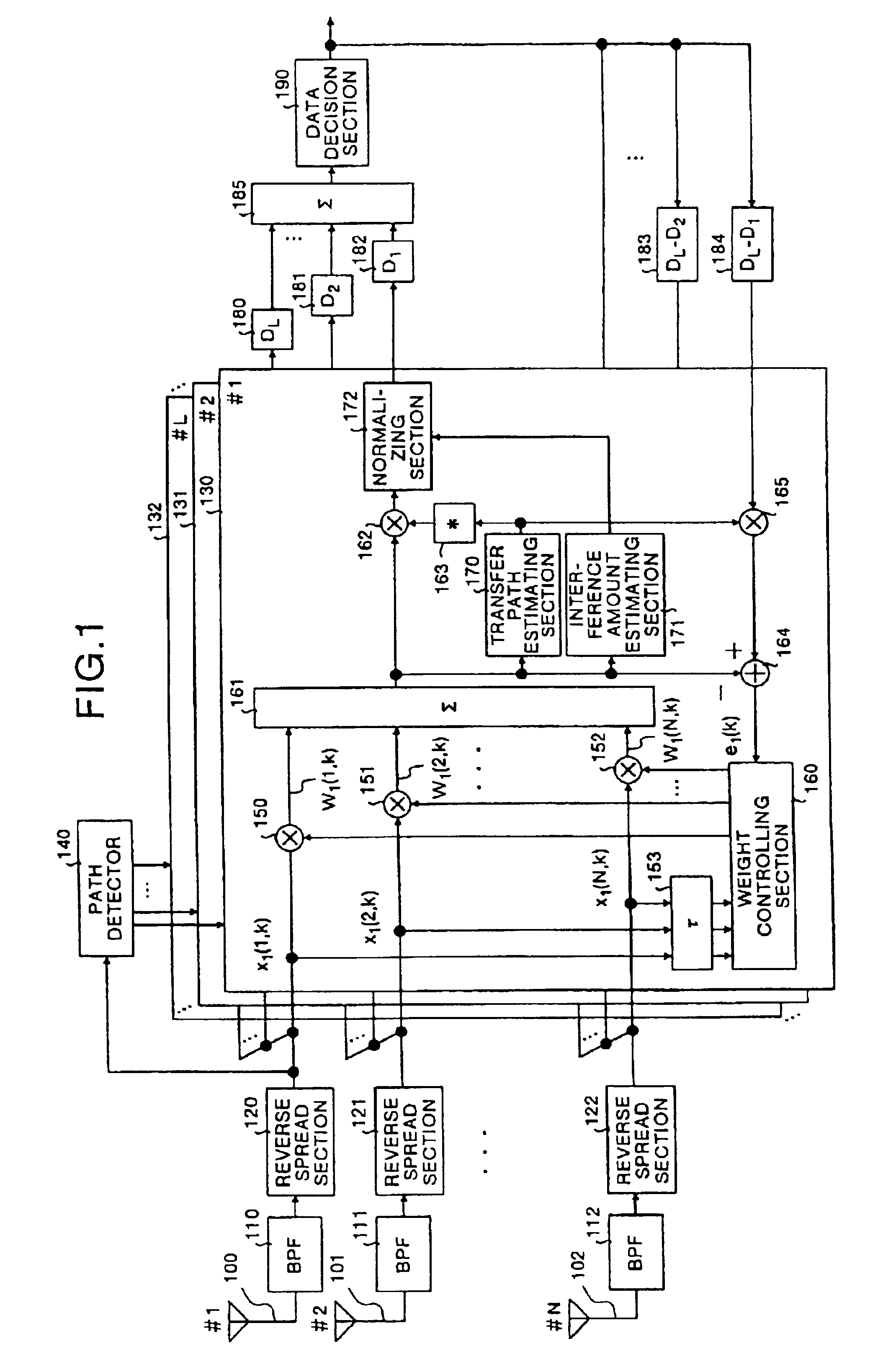
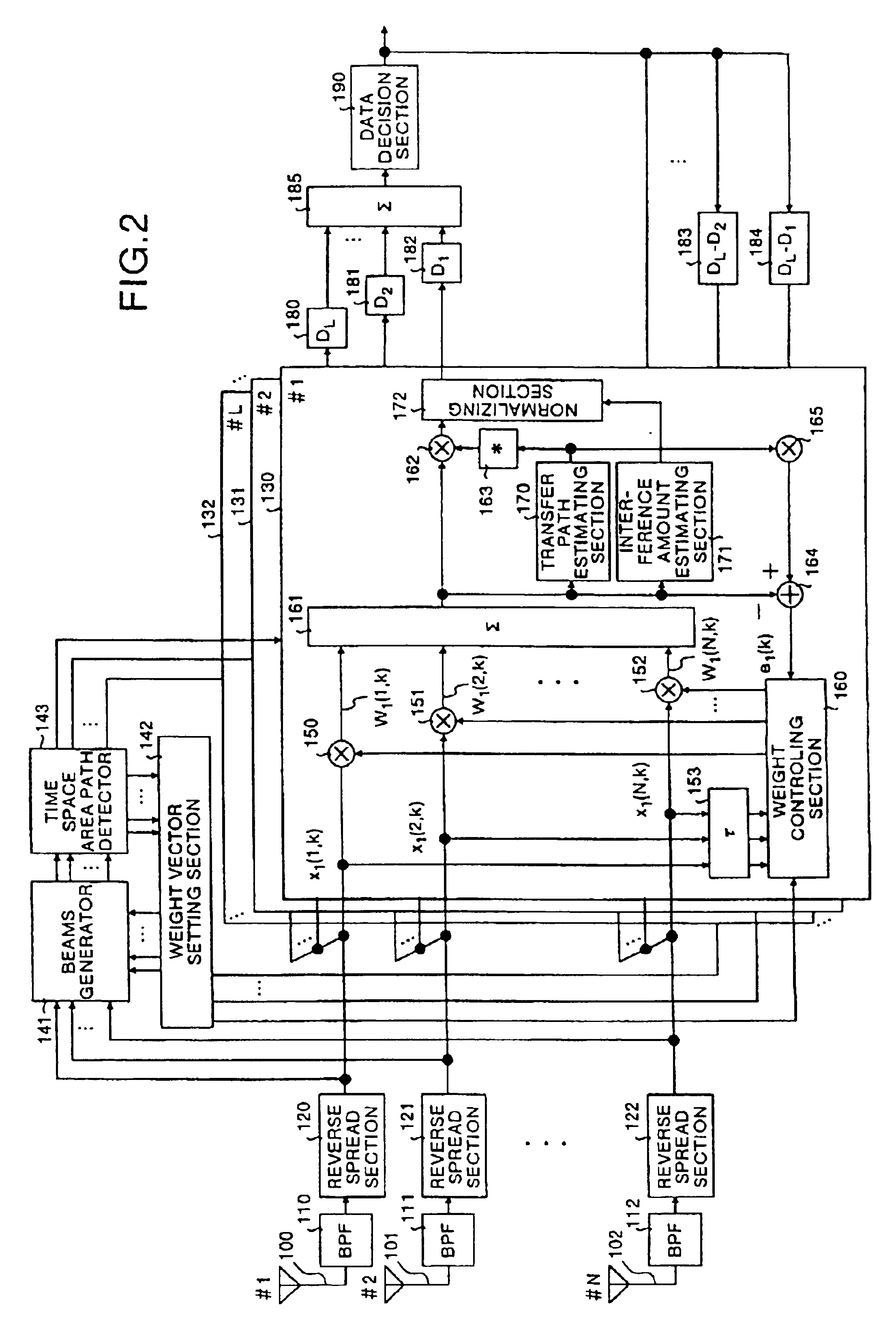
A path detector (140) detects a plurality of multi-path waves that have satisfied a predetermined standard from reverse spread signals, a plurality of adders (161) form beams on the basis of a path, a plurality of transfer path estimating sections (170) and complex conjugate calculators (163) calculate a transfer path estimation value, and based upon the result of the estimation, carry out a weighting process in accordance with the signal amplitude and a removing process of the phase variations. Moreover, a plurality of interference amount estimating sections (171) extract the amount of interference, a plurality of normalizing sections (172) normalize the signals that have been subjected to the phase variation removing process based upon the amount of interference, an adder (185) combines all the signals that have been normalized, and a data determining section (190) determines the signal that have been combined.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
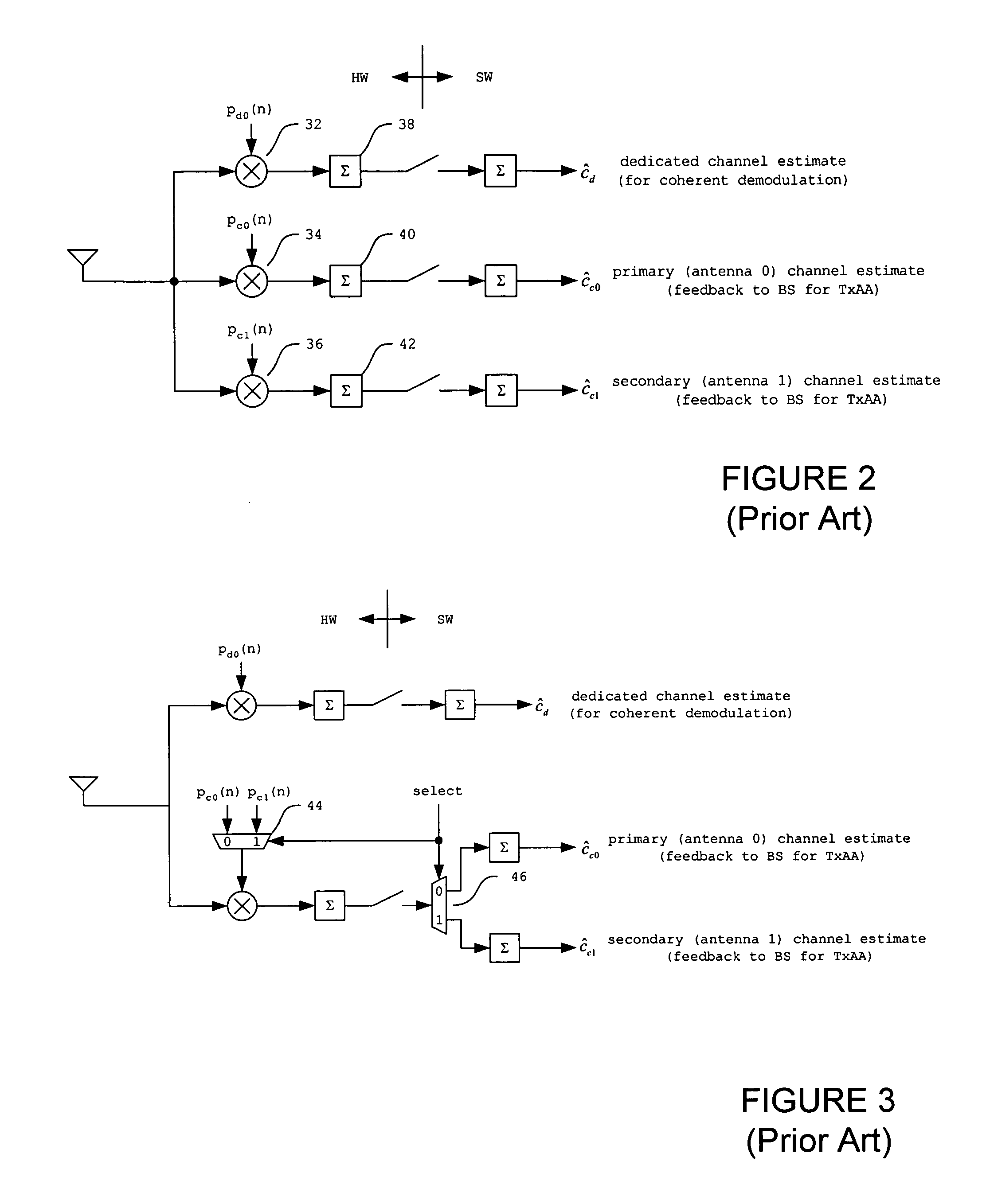
Method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel correlations in a wireless communication system
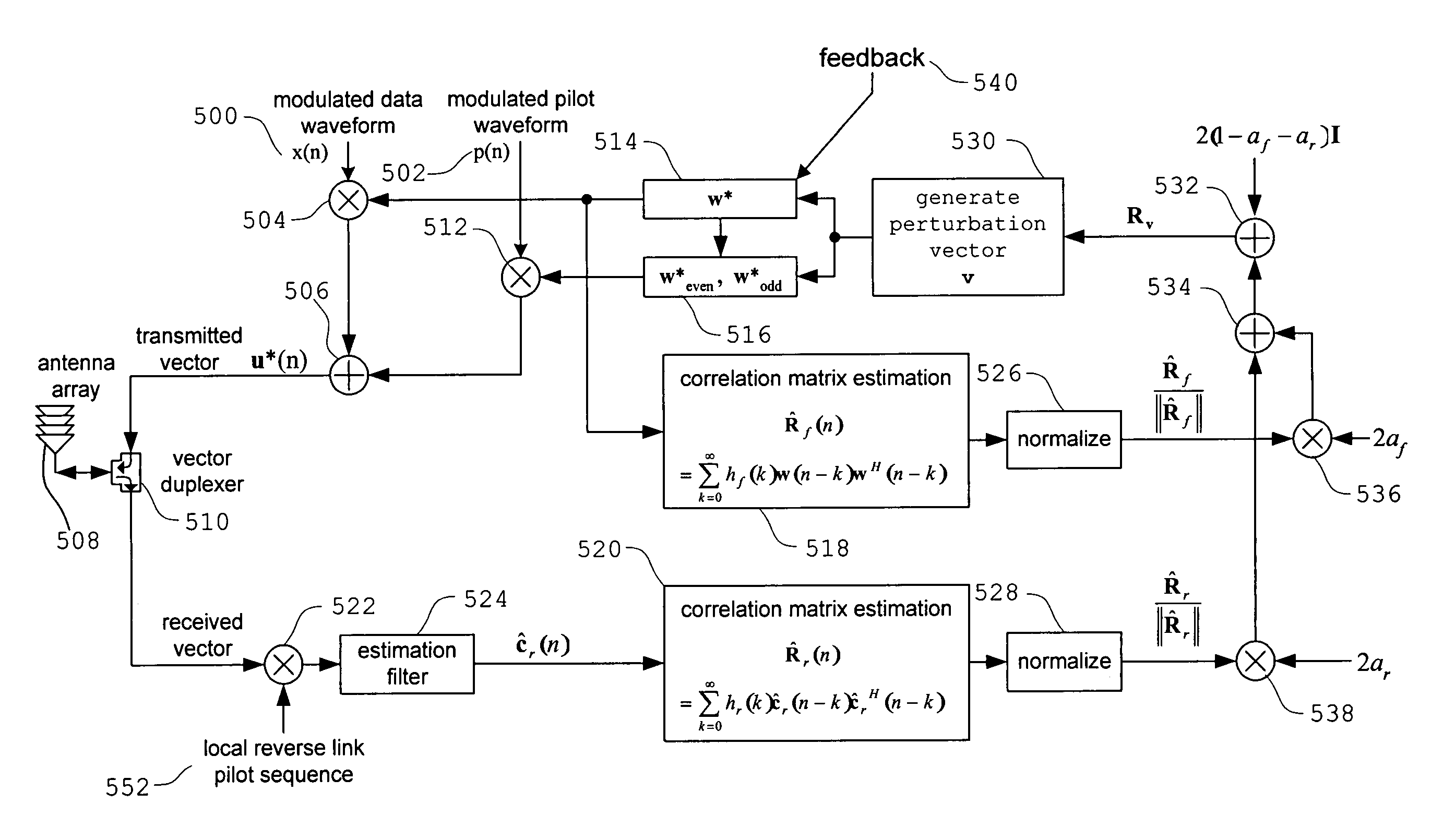
InactiveUS7236538B1Improves weight vector trackingDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPhase correlationGradient estimation
A novel method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel vector element to element correlations in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The present channel autocorrelation tracking technique utilizes the observation that tracking can be improved when a channel gain vector contains correlated elements. In a first embodiment of the autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing a perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimate and a perturbation autocorrelation matrix to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a second embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing eigendecompositions, perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimates, and perturbation autocorrelation matrices to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a third embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention reduces the phase change that can occur at receivers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
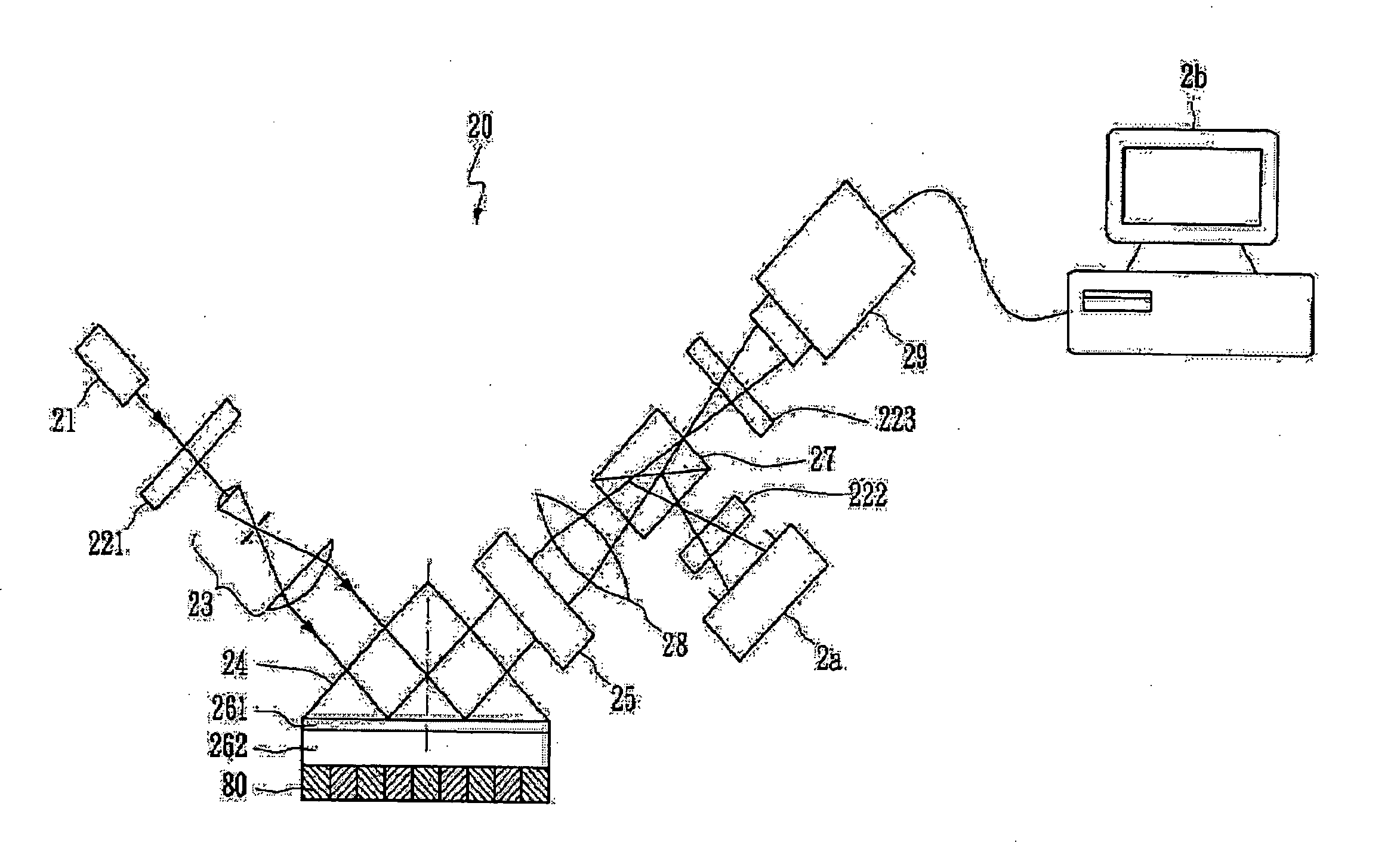
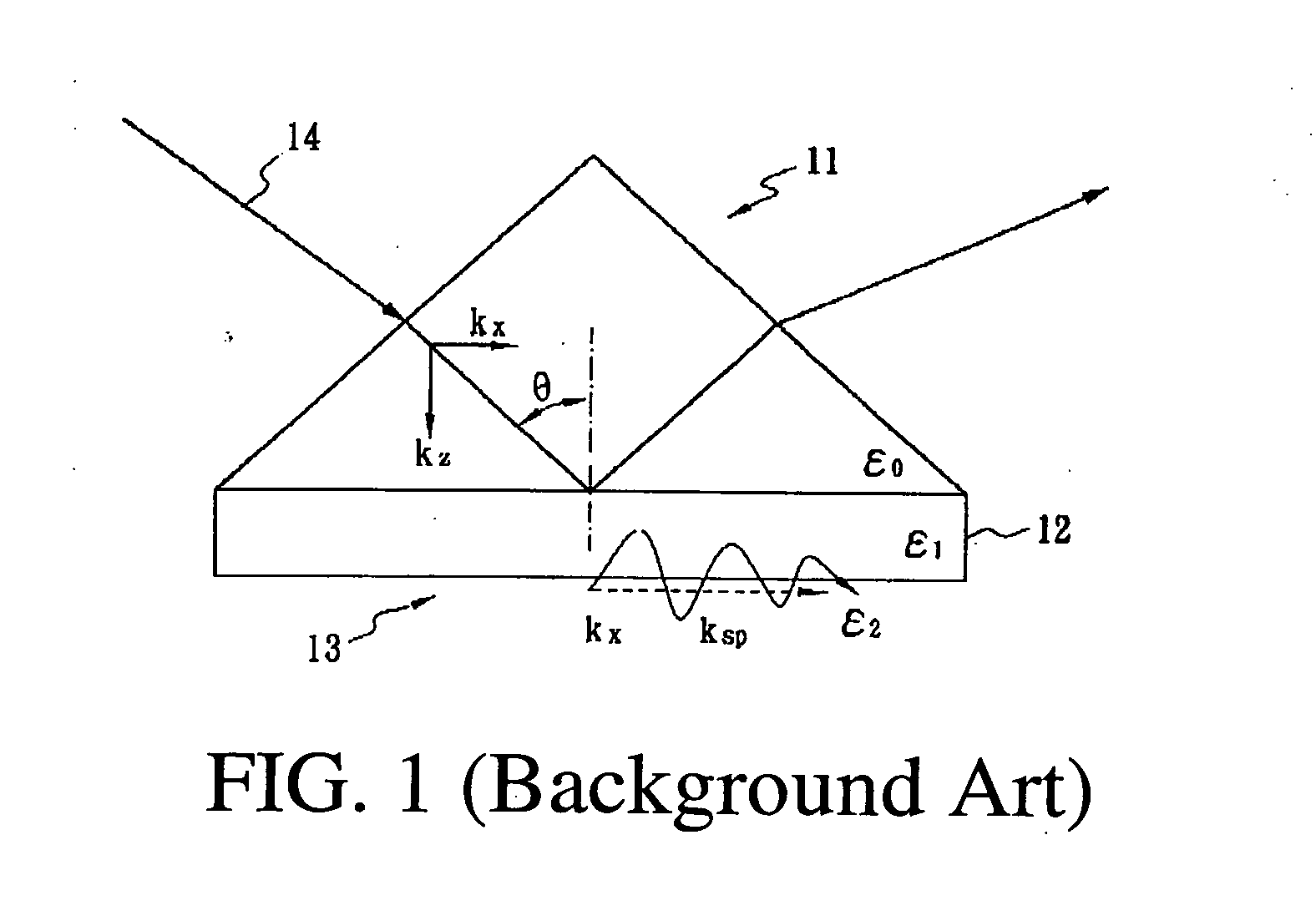
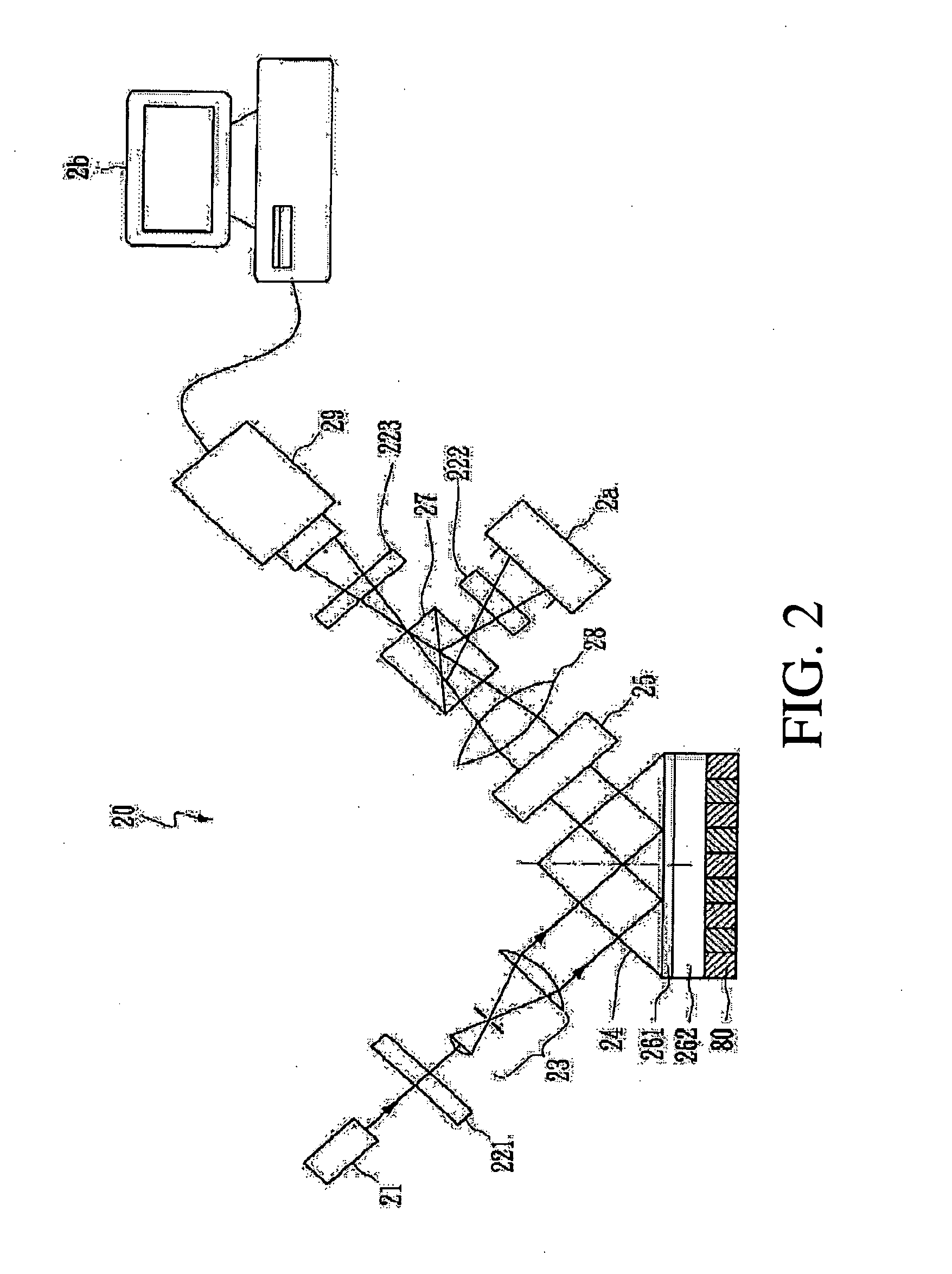
Surface plasmon resonance microscope using common-path phase-shift interferometry
InactiveUS20060119859A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexPhase shift interferometry
The present invention integrates the surface plasmon resonance and common-path phase-shift interferometry techniques to develop a microscope for measuring the two-dimensional spatial phase variation caused by biomolecular interactions on a sensing chip without the need for additional labeling. The common-path phase-shift interferometry technique has the advantage of long-term stability, even when subjected to external disturbances. Hence, the developed microscope meets the requirements of the real-time kinetic studies involved in biomolecular interaction analysis. The surface plasmon resonance microscope of the present invention using common-path phase-shift interferometry demonstrates a detection limit of 2×10−7 refractive index change, a long-term phase stability of 2.5×10−4π rms over four hours, and a spatial phase resolution of 10−3 π with a lateral resolution of 100 μm.
Owner:PHALANX BIOTECH GROUP
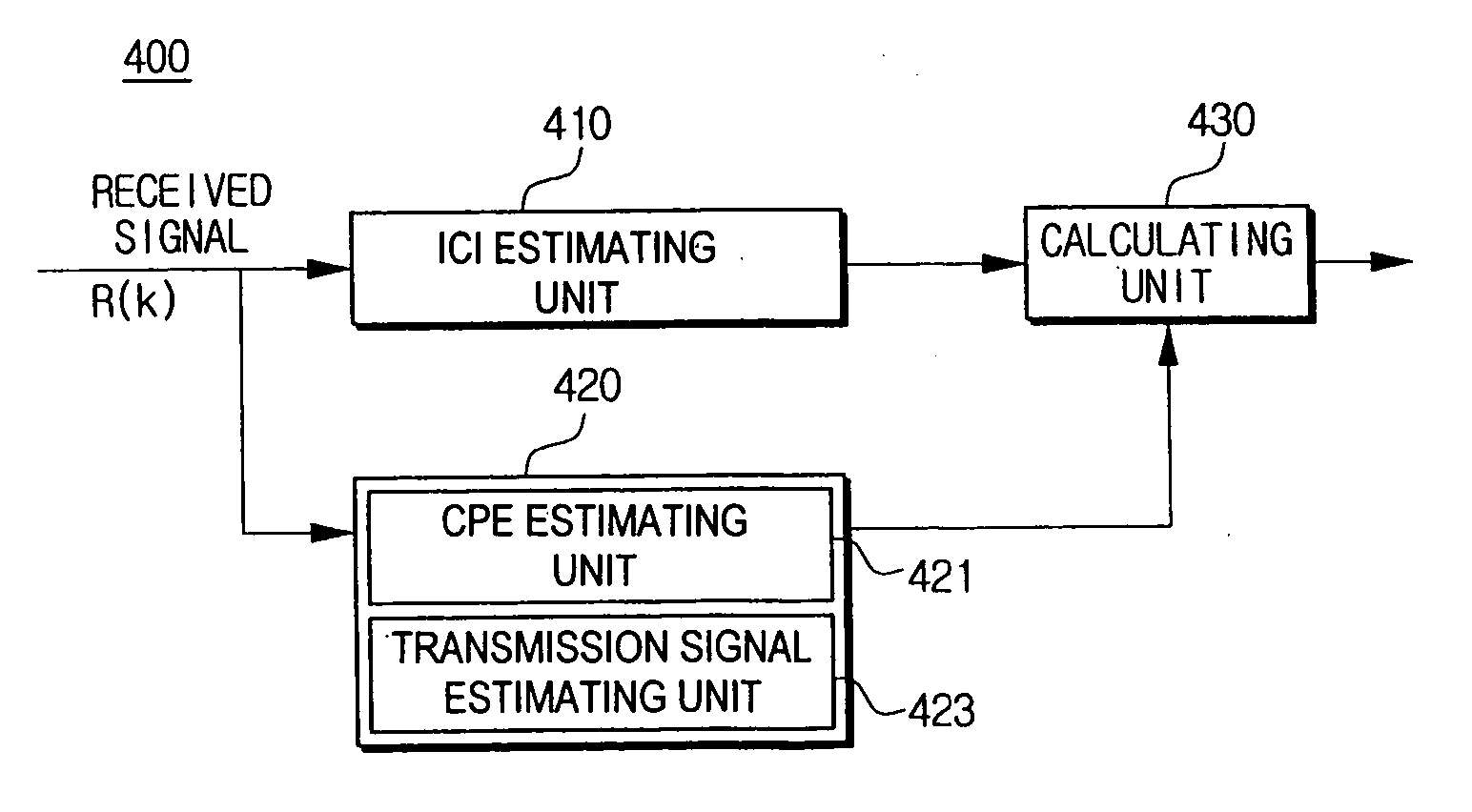
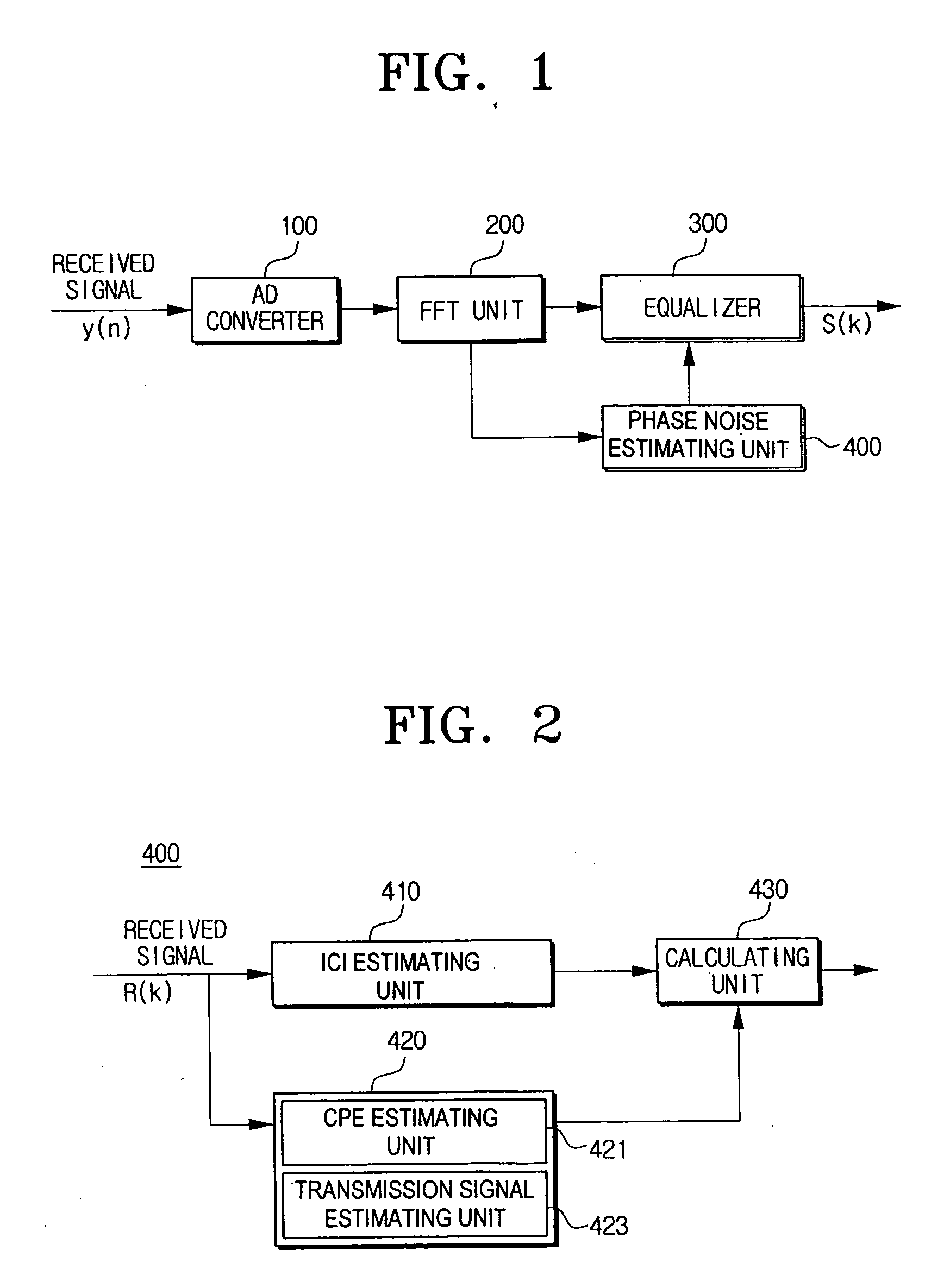
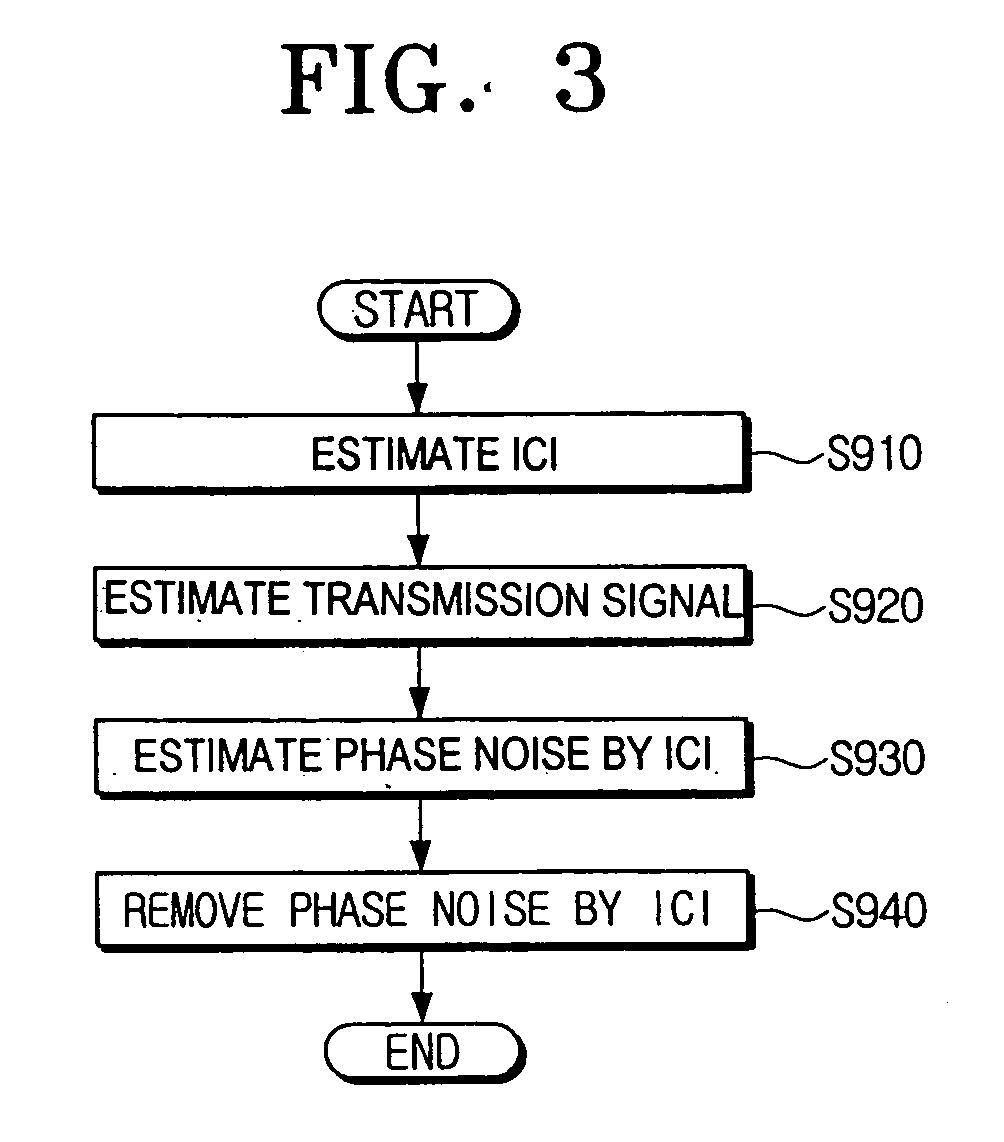
Phase noise compensation apparatus and an OFDM system having the apparatus and method thereof
Disclosed is a phase noise compensation apparatus to be applied to the OFDM system, comprising an ICI estimating unit for estimating inter carrier interference (ICI) using a pilot sub-carrier included in a reception signal, a estimating unit for estimating a common phase error (CPE), which is a phase noise from the reception signal as sampled, using the pilot sub-carrier, and estimating a transmission signal by removing the estimated CPE from the reception signal, a calculating unit for calculating phase change by the ICI in the reception signal by convoluting the ICI and the transmission signal, and an equalizer for compensating the calculated phase change by the ICI in the reception signal. Accordingly, phase noise can be exactly compensated by estimating as phase noise the result of convoluting a received signal where the CPE is removed in a frequency domain and the estimated ICI according to the present invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for detecting biological chip by space phase modulation interference array
InactiveCN1588064AHigh sensitivityImprove detection efficiencyPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsPolarizerPrism
The invention relates to a method and system of adopting space phase modulation and interference array to detect the biochip, which belongs to biological technical field. The invention aims to overcome the deficiency of current technique and provides a new biochip detecting method and system, which can detect different volumes of DAN chips and protein chips dispense with mark and real-time achieve the information about the interaction of the biomolecules. The principle of the detection by space phase modulation and interference array is: the light reflected by the biosensor unit entering wallaston prism after combined by the one dimensional magnifying lens, the contained s ray and p ray which is polarizationdirection is divided into the two rays transmitting in different direction and realizing co-lightpath space phase modulation and interference in wallaston prism; the interference fringe being converted into electrical signal through the polarizer and imaging lens, the information of real-time phase change of the each unit on the array chip being acquired after processing and be offered to the biologist and medical scientists to parse.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
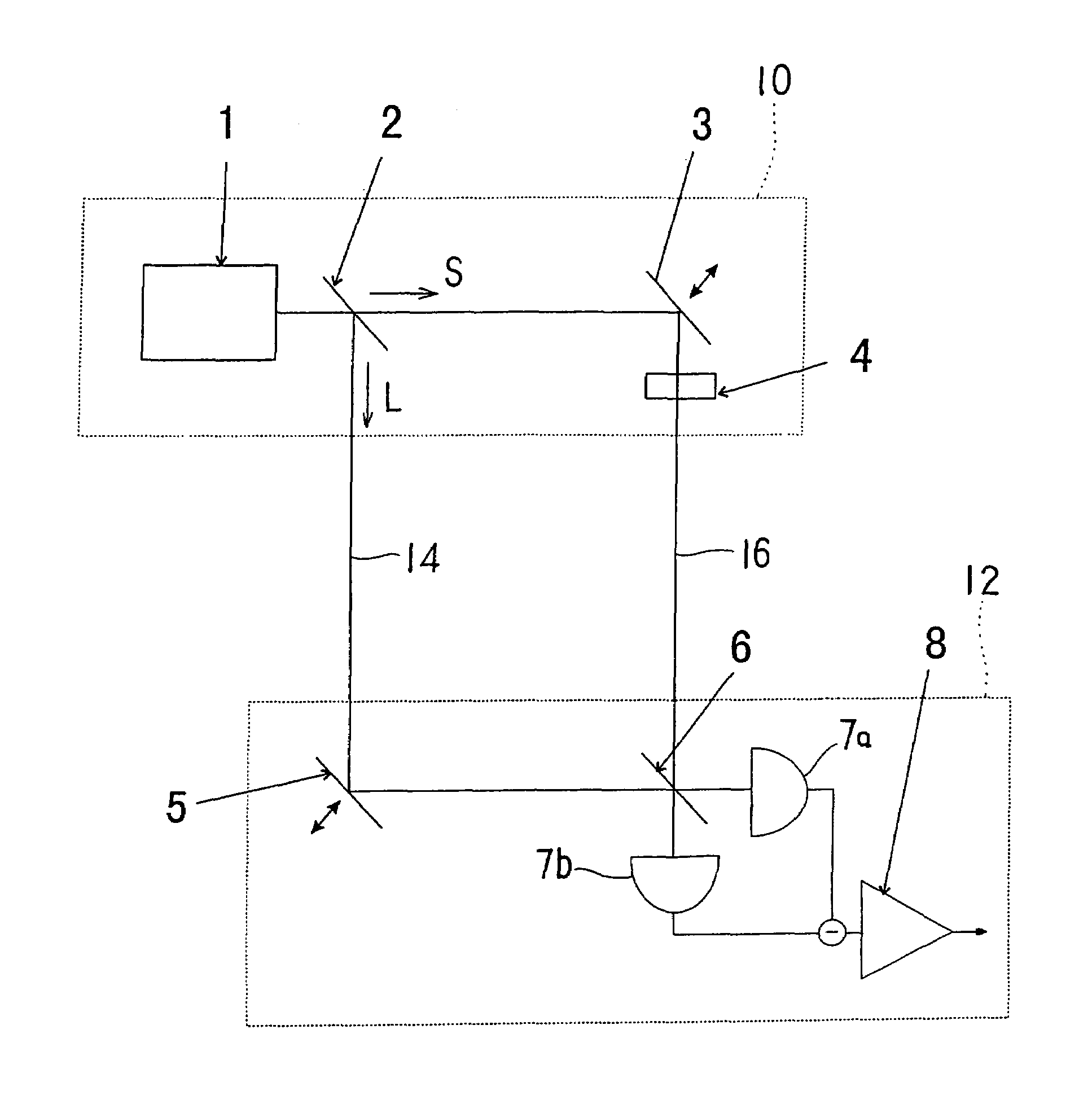
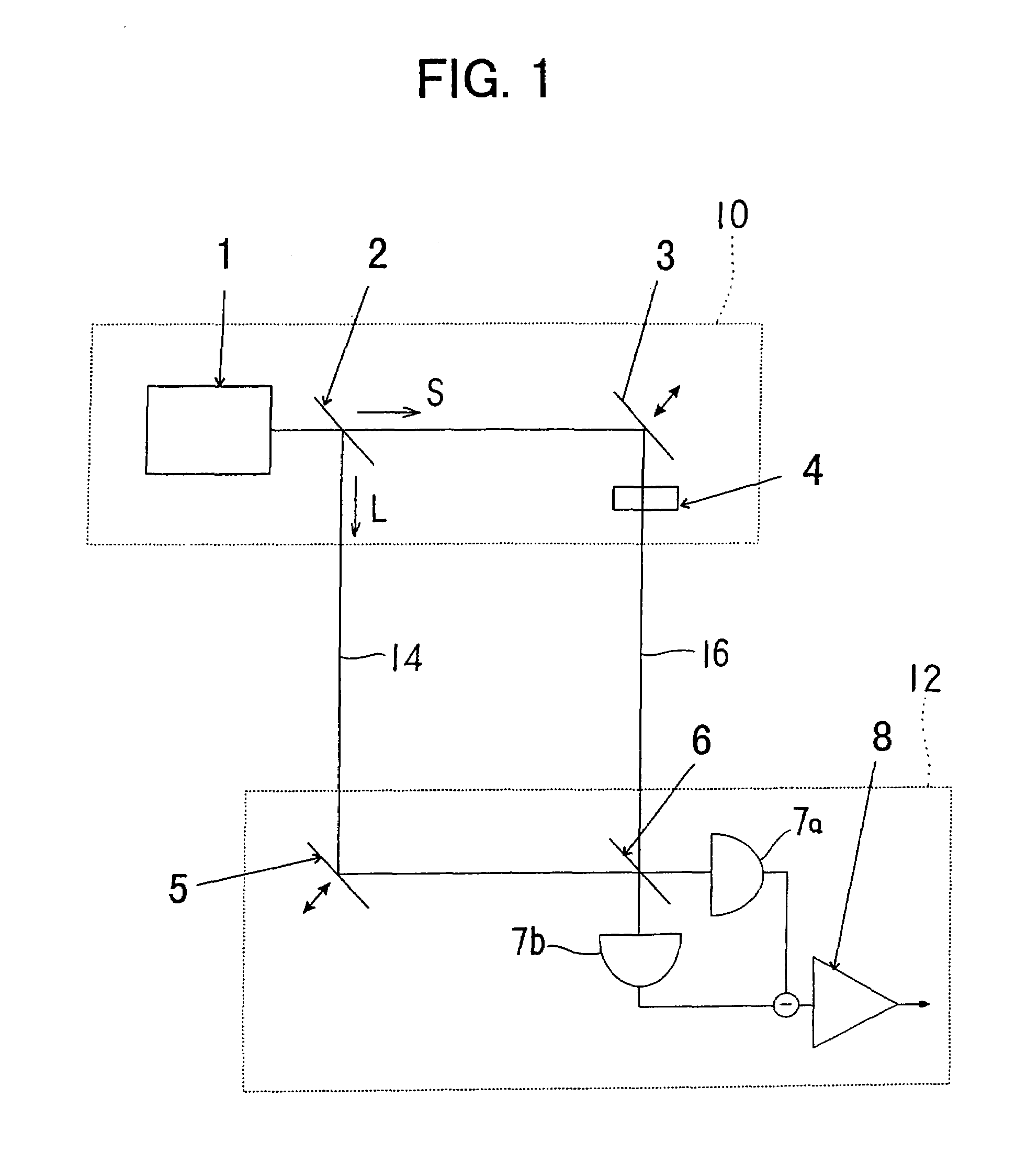
Quantum cipher communication system
InactiveUS7305091B1Improve quantum efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesBeam splittingLaser beams
A quantum cipher communication system includes a sender's apparatus, a recipient's apparatus and a transmission path. The sender's apparatus includes a beam splitting for splitting a laser beam into a weak signal light and an intense reference light, a phase modulation unit for imparting a phase change on either the weak signal light or the intense reference light. The recipient's apparatus includes a phase modulation unit for imparting a phase change on either the weak signal light or the intense reference light, a superimposing unit for superimposing the weak signal light and the intense reference light, a pair of photoconductive diodes for converting two output lights from the superimposing unit into electric signals, and an amplifying unit for amplifying a difference signal between the electric signals, wherein the recipient assigns bit values by comparing the difference signal with threshold values.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for Adaptive Complex Wavelet Based Filtering of Eeg Signals
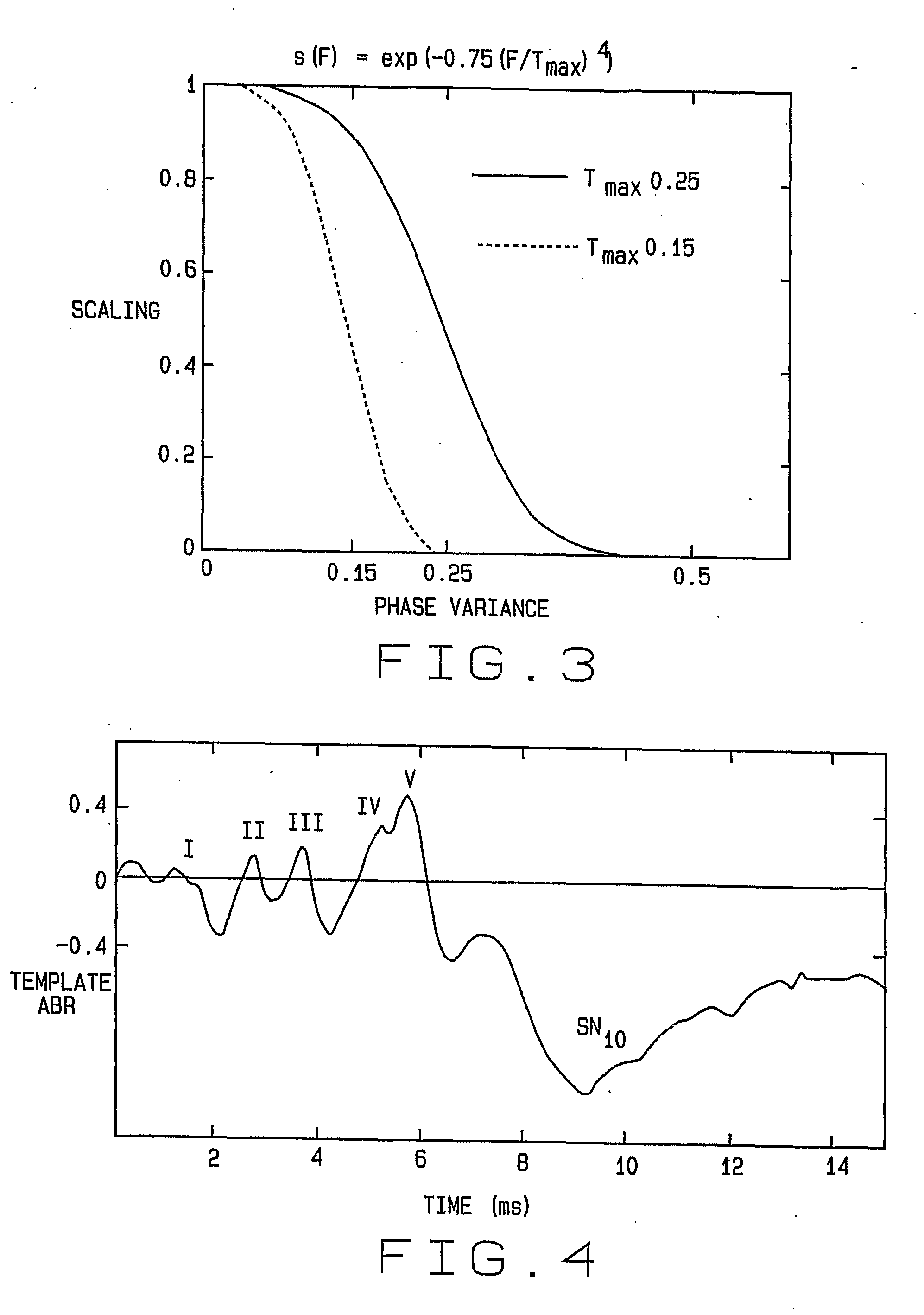
A method for adaptive filtering of EEG signals in the wavelet domain using a nearly shift-invariant complex wavelet transform. EEG signal data is segmented into a set of K “trials” or “light averages” of M-frames of data each. These trials are overlapped by a number of frames P, where P<M. A dual-tree complex wavelet transform is computed for each light average K of EEG signal data. Next, the phase variance of each resulting normalized wavelet coefficient is computed, and the magnitude of each wavelet coefficient is selectively scaled according to the phase variance of the coefficients. The resulting wavelet coefficients are then utilized to reconstruct the ABR signal extracted from the EEG data.
Owner:BRAINSCOPE SPV LLC
Radio receiving device
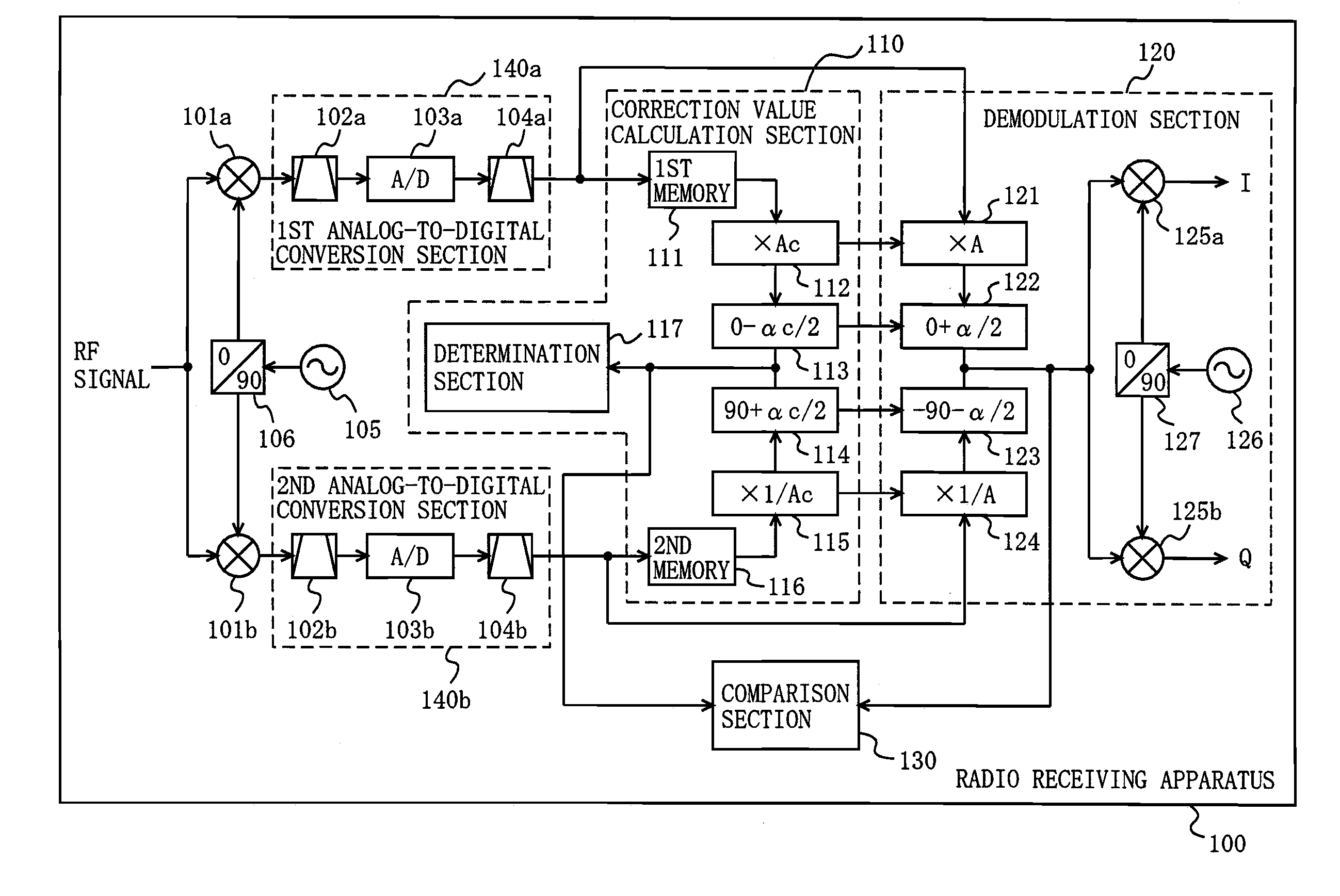
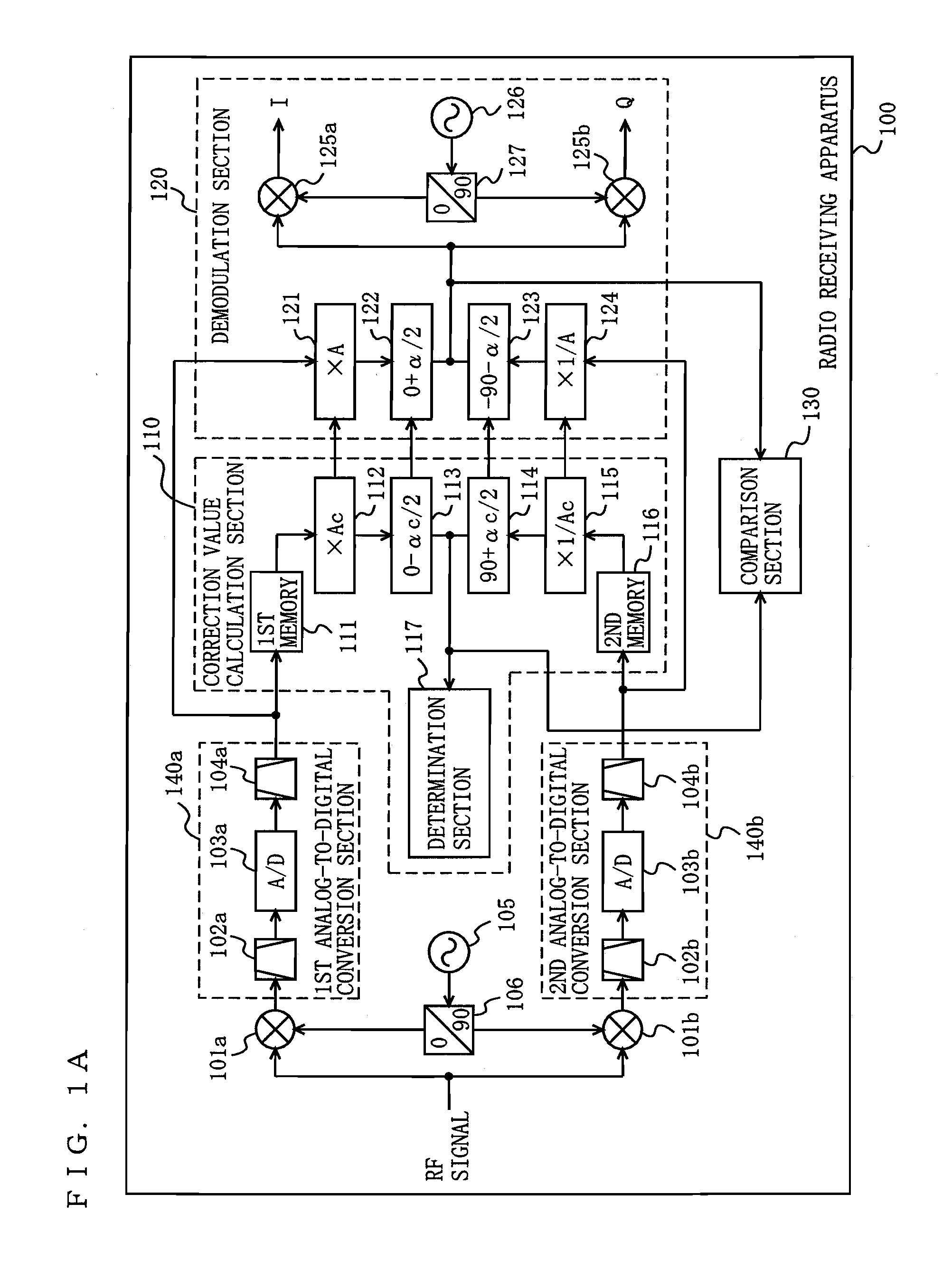
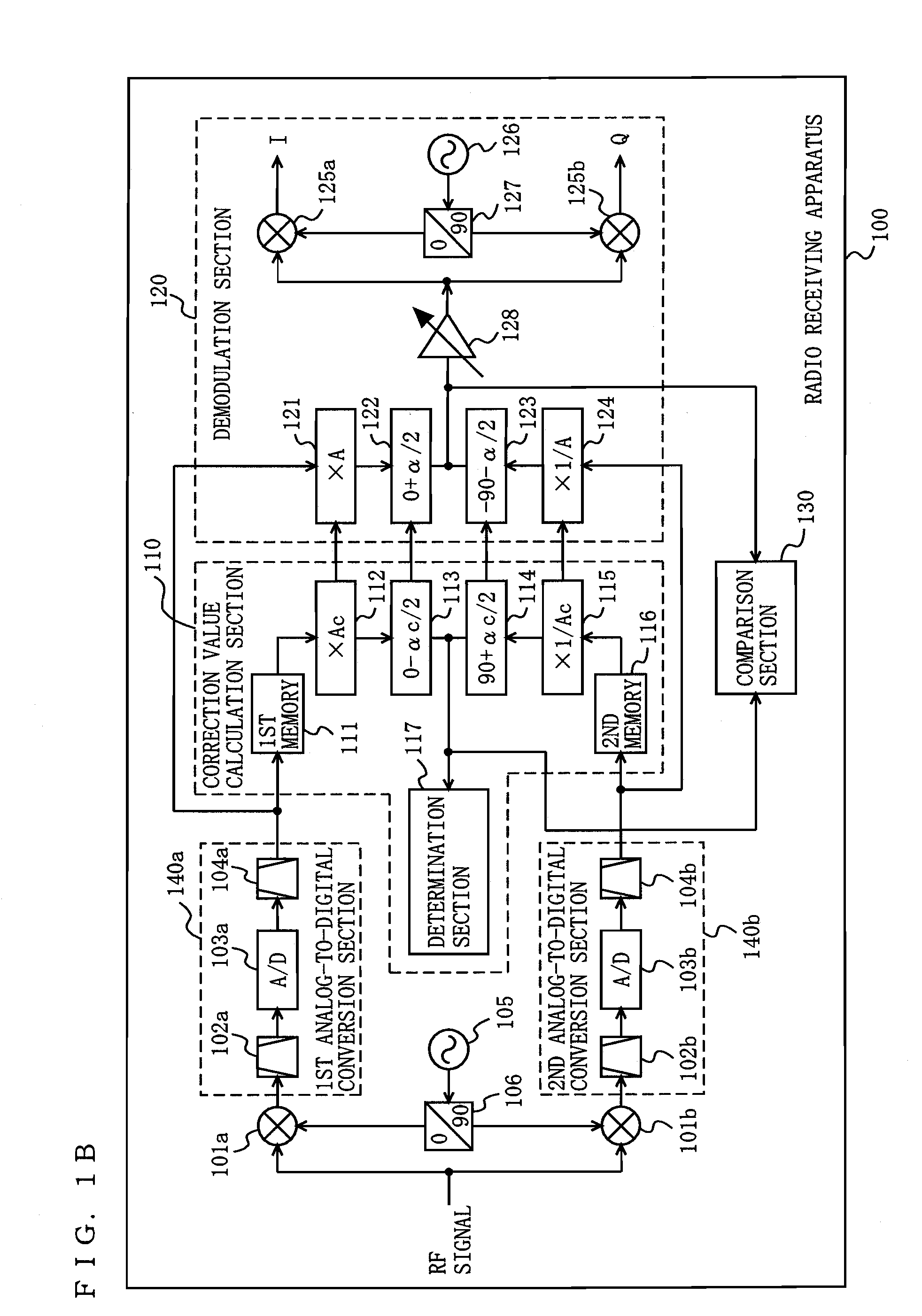
ActiveUS20100189197A1Suppress image noiseAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationPhase correctionPhase variation
A radio receiving apparatus capable of making compensation for both amplitude variations and phase variations and of suppressing image interference in a short period of time is provided.A correction value calculation section (110) combines a signal, obtained by multiplying a first digital signal by an amplitude correction candidate value and rotating the phase of the first digital signal, with a signal obtained by multiplying a second digital signal by a multiplicative inverse of the amplitude correction candidate value and performing, for the second digital signal, phase rotation which is in a quadrature relationship to phase rotation performed for the first digital signal, so as to obtain a first combined signal, obtain an inflection point of the first combined signal, and input, to a demodulation section (120), the amplitude correction candidate value and a phase correction candidate value, which correspond to the inflection point, as an amplitude correction value and a phase correction value, respectively. The demodulation section (120) makes compensation for the amplitudes and the phases and suppresses image interference, based on the amplitude correction value and the phase correction value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High sensitivity coherent photothermal interferometric system and method for chemical detection
A photo-thermal interferometric spectroscopy system is disclosed that provides information about a chemical at a remote location. A first light source assembly is included that emits a first beam. The first beam has one or more wavelengths that interact with the chemical and change a refractive index of the chemical. A second laser produces a second beam. The second beam interacts with the chemical resulting in a third beam with a phase change that corresponds with the change of the refractive index of the chemical. A detector system is positioned remote from the chemical to receive at least a portion of the third beam. An adaptive optics system at least partially compensates the light beam degradation caused by atmospheric turbulence. A focusing system is used to bring together the light passed through the chemical; the focusing system includes a multimode fiber for the light collection, The detector system provides information on a phase change in the third beam relative to the second beam that is indicative of at least one of, absorption spectrum and concentration of the chemical.
Owner:CELIGHT
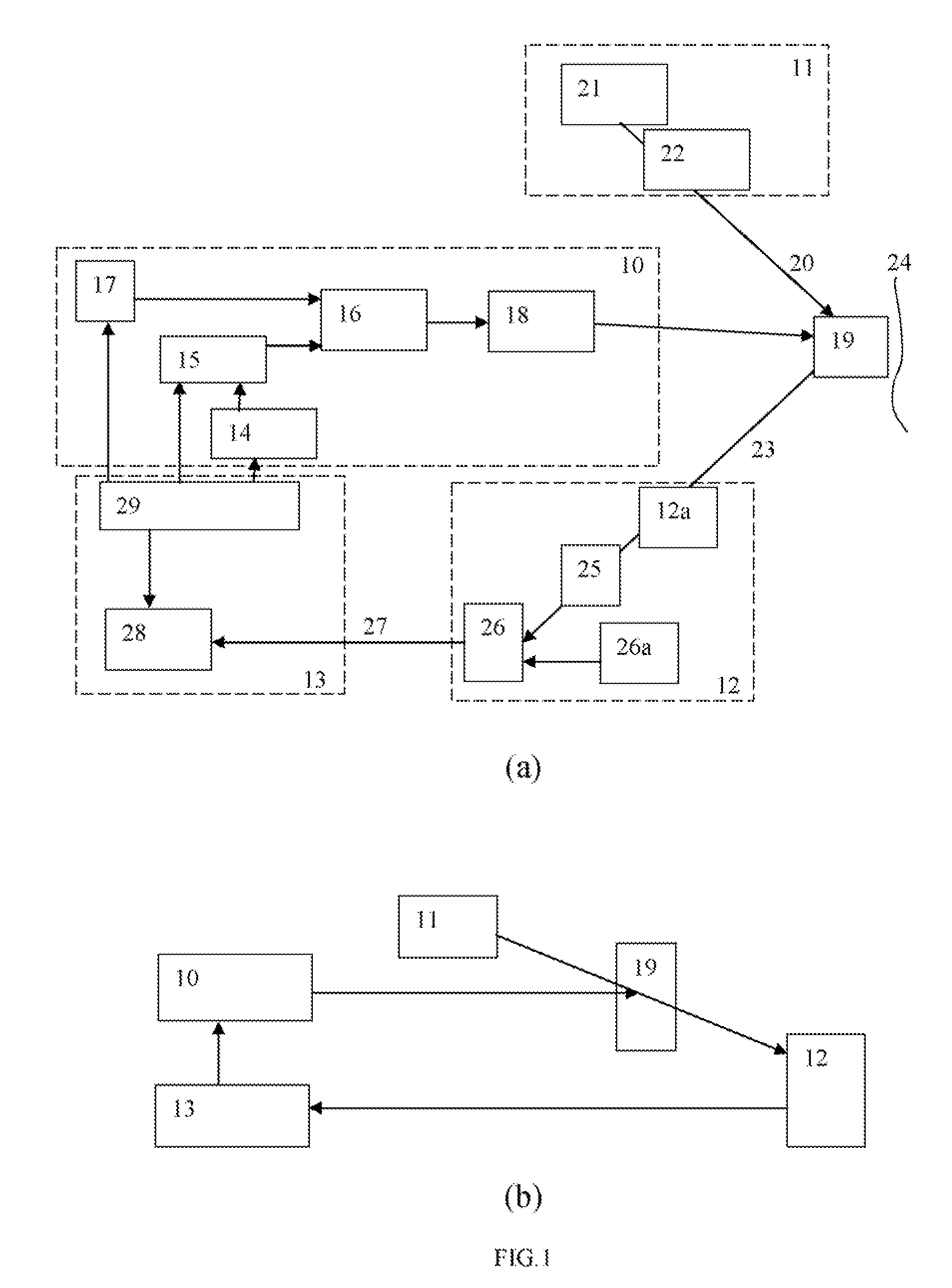
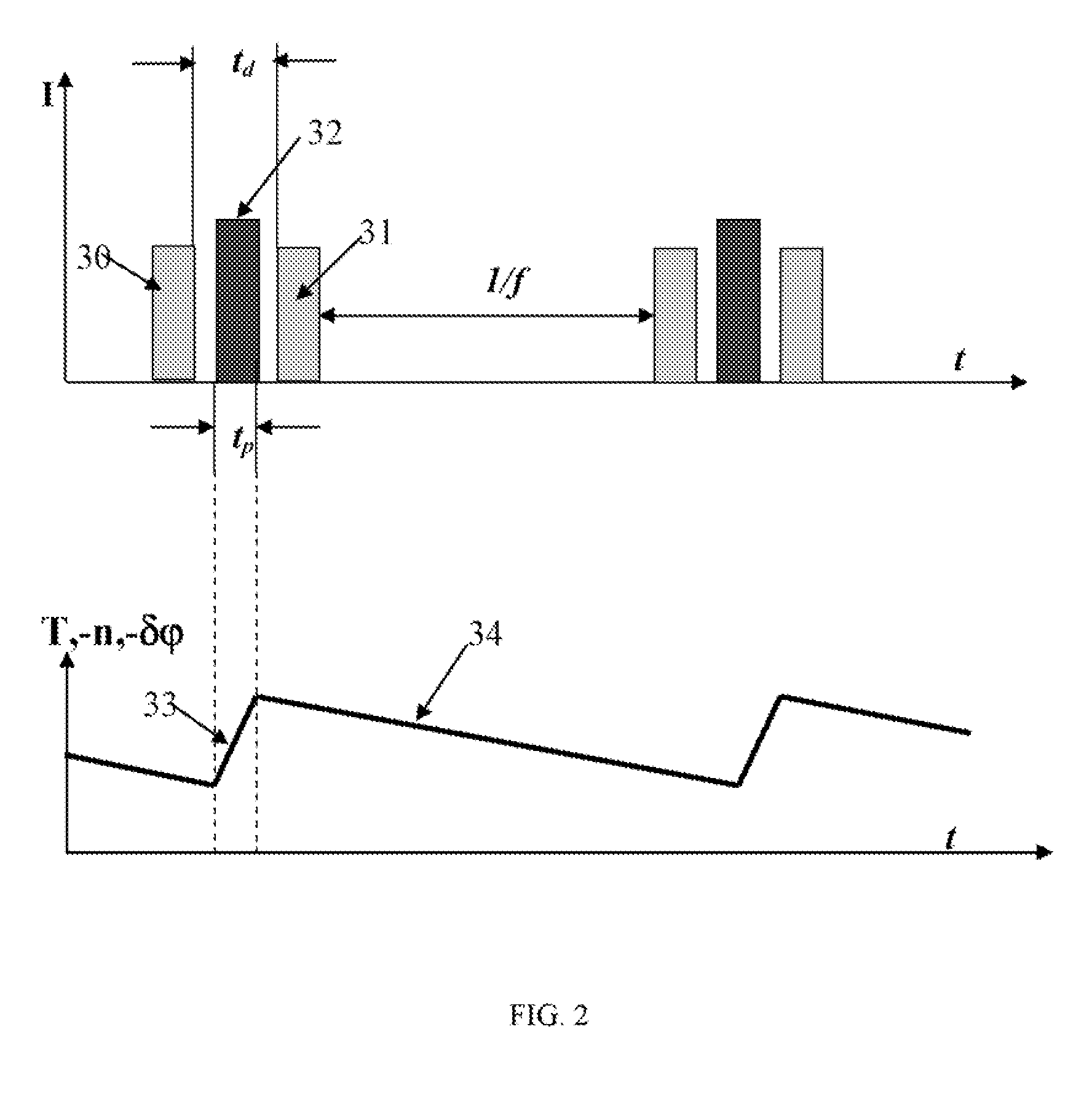
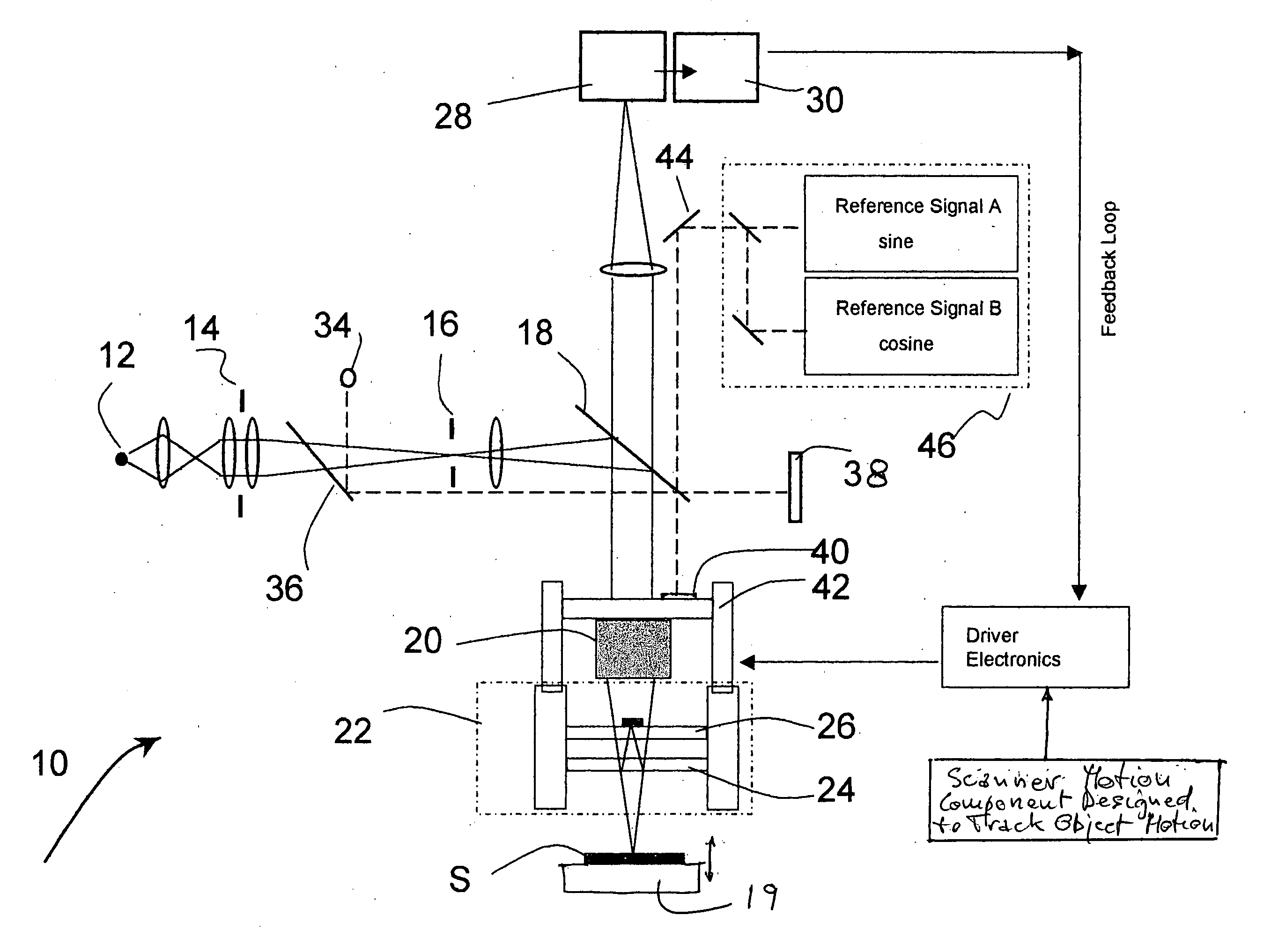
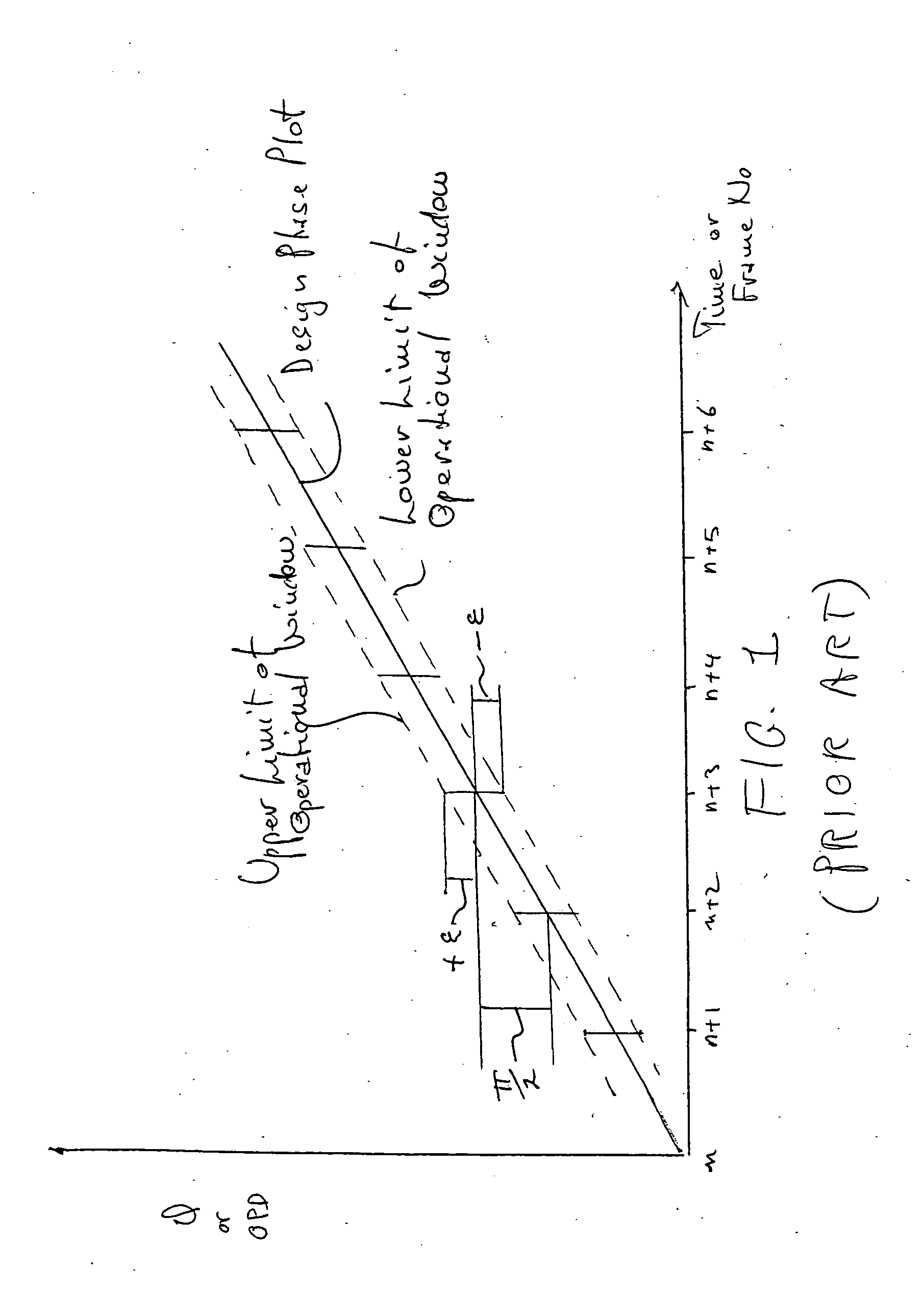
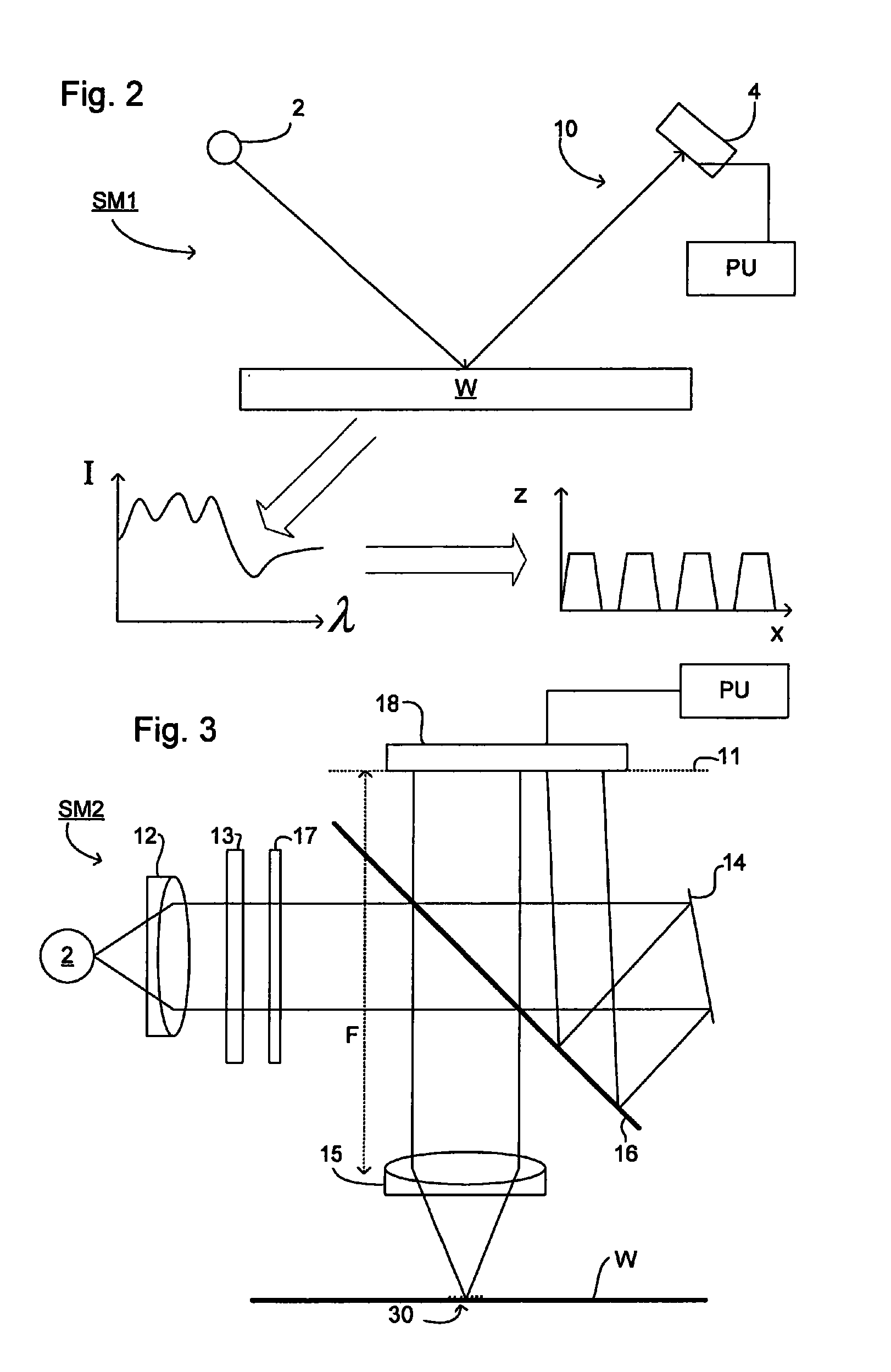
Measurement of object deformation with optical profiler
An interferometric profiler is used to measure object motion by modifying the motion of the scanner so that the phase variation at each scanning step is kept within the acceptable limits of the algorithm used to calculate phase changes. The scanner motion is so manipulated on the basis of prior knowledge about the nature of the object motion, or knowledge obtained by pre-calibration, or by real-time feedback based on current measurements. The object motion is recovered from the scanning information by subtracting the scanner position from the object position as it evolves during the scan.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Detection and location of boundary intrusion, using composite variables derived from phase measurements
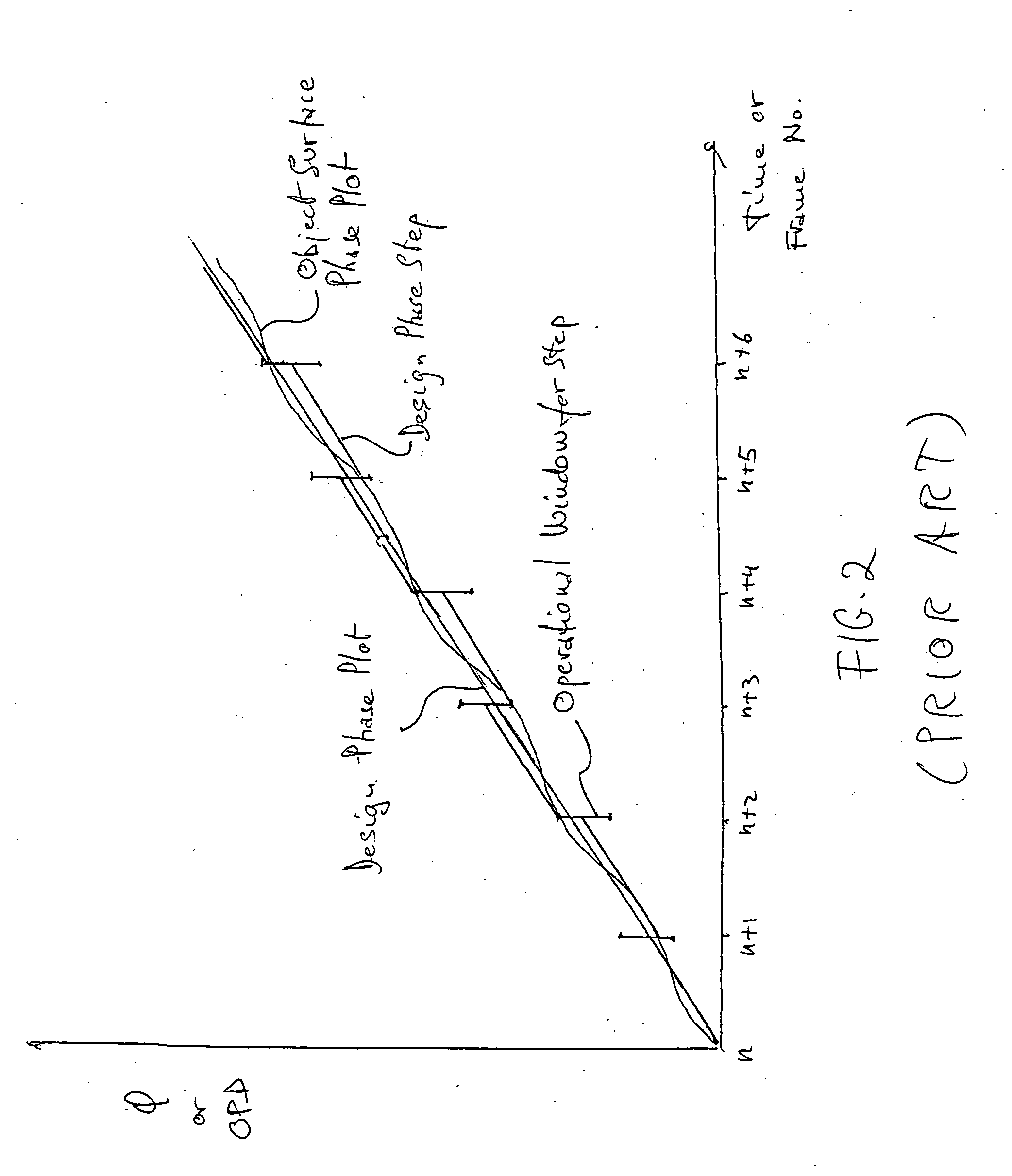
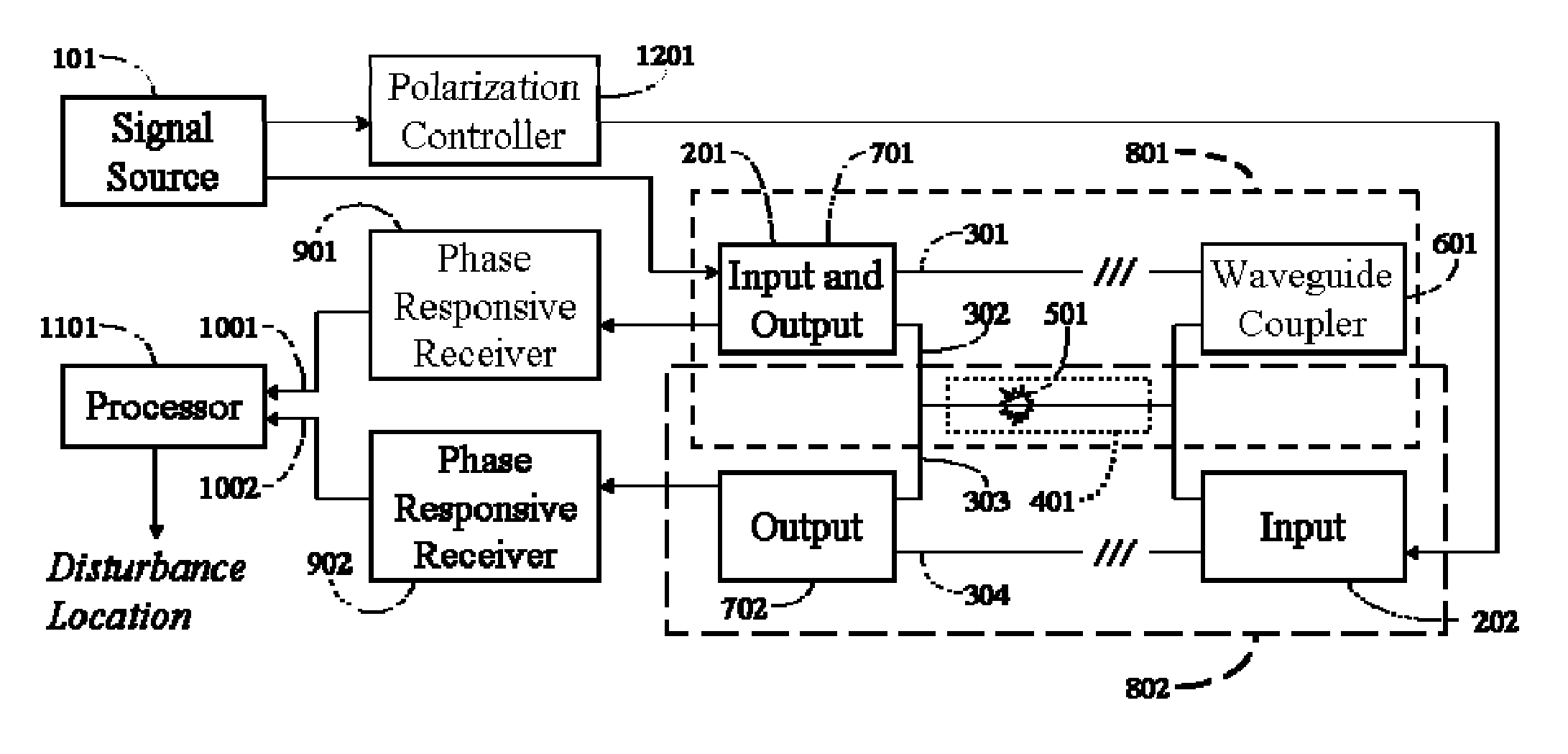
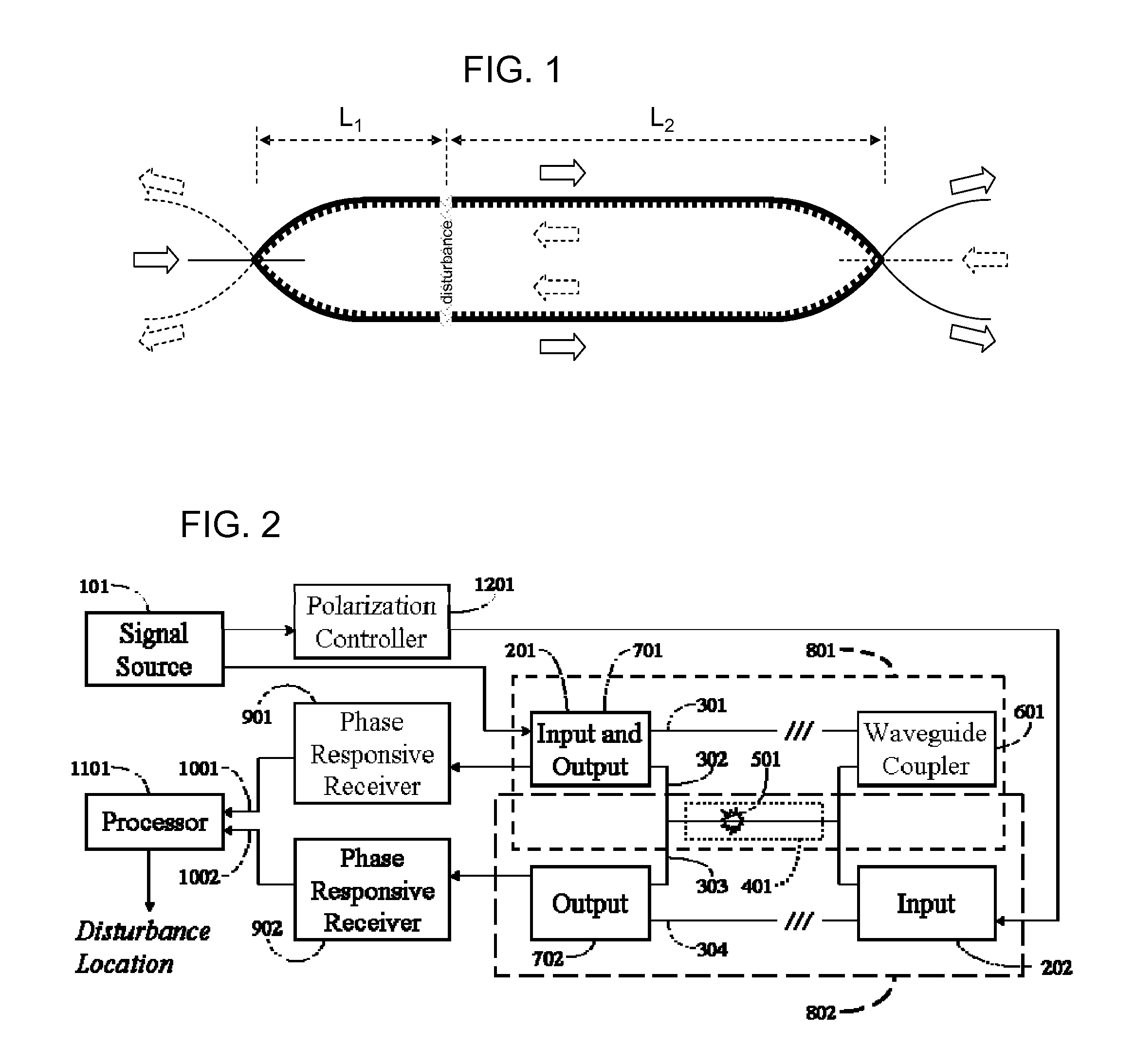
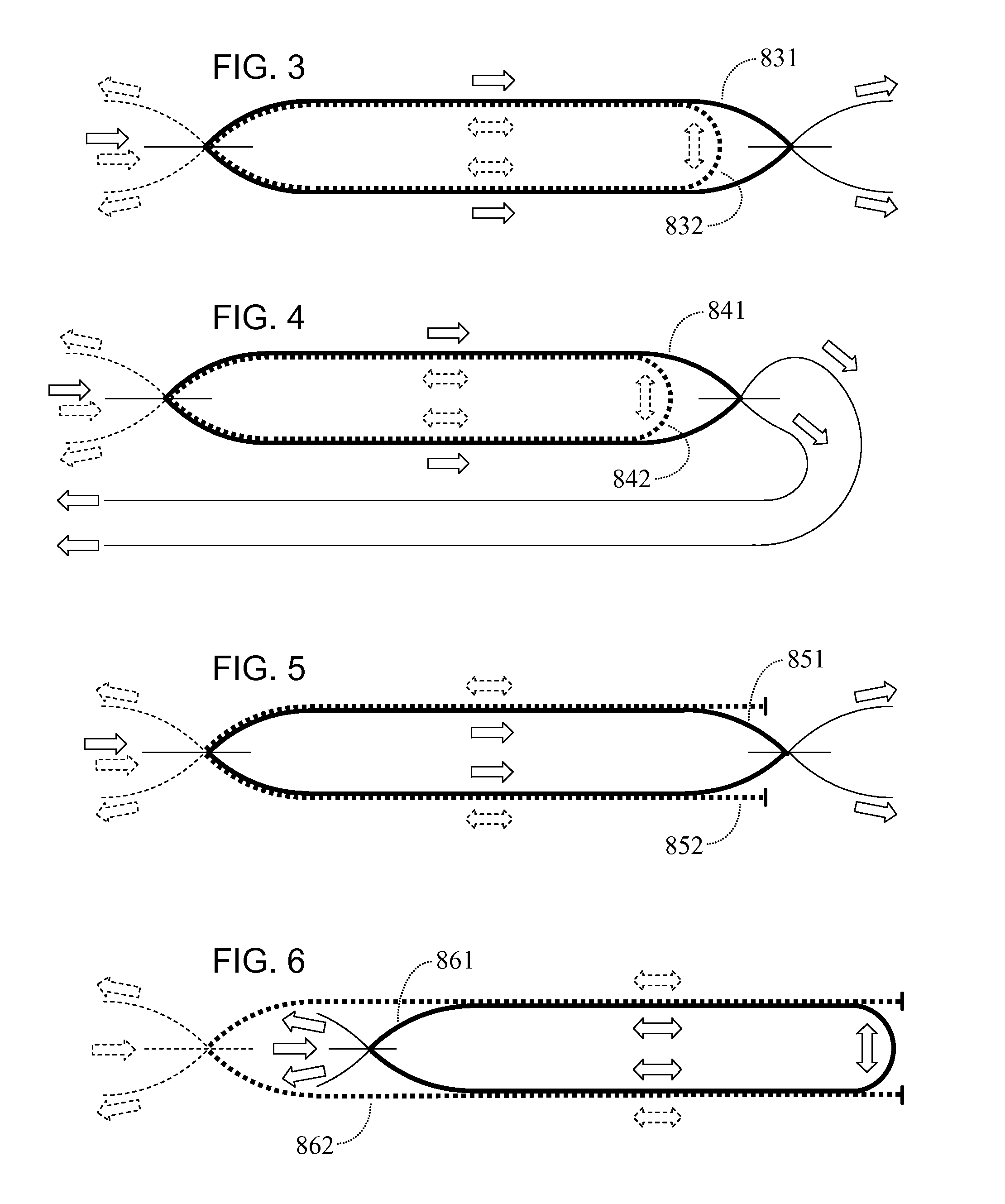
A disturbance, such as vibration from human activity, is located along a fiberoptic waveguide configuration (301-304) with two interferometers (801, 802) of the same or different types, such as Mach-Zehnder, Sagnac, and Michelson interferometers. Carrier signals from a source (101) are split at the interferometer inputs (201, 202) and re-combined at the outputs (701, 702) after propagating through the detection zone (401), where phase variations are induced by the disturbance (501). Phase responsive receivers (901, 902) detect phase relationships (1001, 1002) between the carrier signals over time. A processor (1101) combines the phase relationships into composite signals according to equations that differ for different interferometer configurations, with a time lag between or a ratio of the composite signals representing the location of the disturbance. The detected and composite values are unbounded, permitting phase displacement to exceed the carrier period and allowing disturbances of variable magnitudes to be located.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
Apparatus and method for ultra narrow band communications
InactiveUS20070237218A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce noiseMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCarrier signalEngineering
A method and apparatus for transmitting information combining abrupt phase change modulation with an ultra narrow band filter to remove unnecessary Fourier sidebands, resulting in a single frequency being transmitted to carry data. The method examines and detects the changes in the carrier phase only, after filtering to remove or reduce all sidebands, to obtain a usable signal. Only a single frequency with phase changes is transmitted. An ultra narrow band filter, having a rapid rise time and near zero group delay, passes the near instantaneous modulation changes of phase in the carrier.
Owner:WALKER HAROLD R
Inspection apparatus for lithography
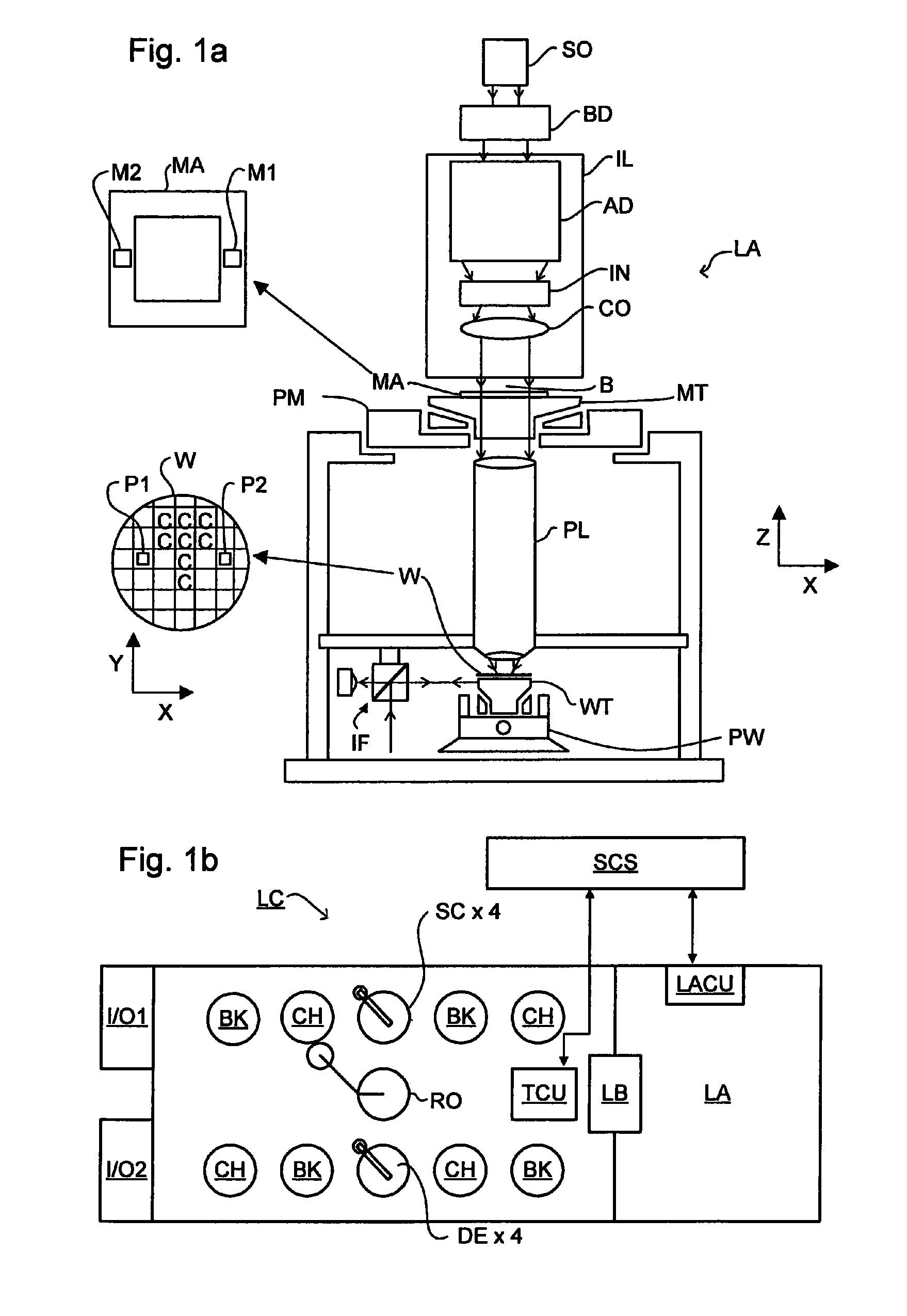
ActiveUS8681312B2Photomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansLithographic artistRelative phase
The measurement of two separately polarized beams (Ix, Iy) upon diffraction from a substrate (W) in order to determine properties of the substrate is disclosed. Circularly or elliptically polarized radiation is passed via a variable phase retarder in order to change the phase of one of two orthogonally polarized radiation beams with respect to the other of the two beams. The phase change is dependent on the wavelength of the polarized beam. The relative phases of the two radiation beams and other features of the beams as measured in a detector gives rise to properties of the substrate surface.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
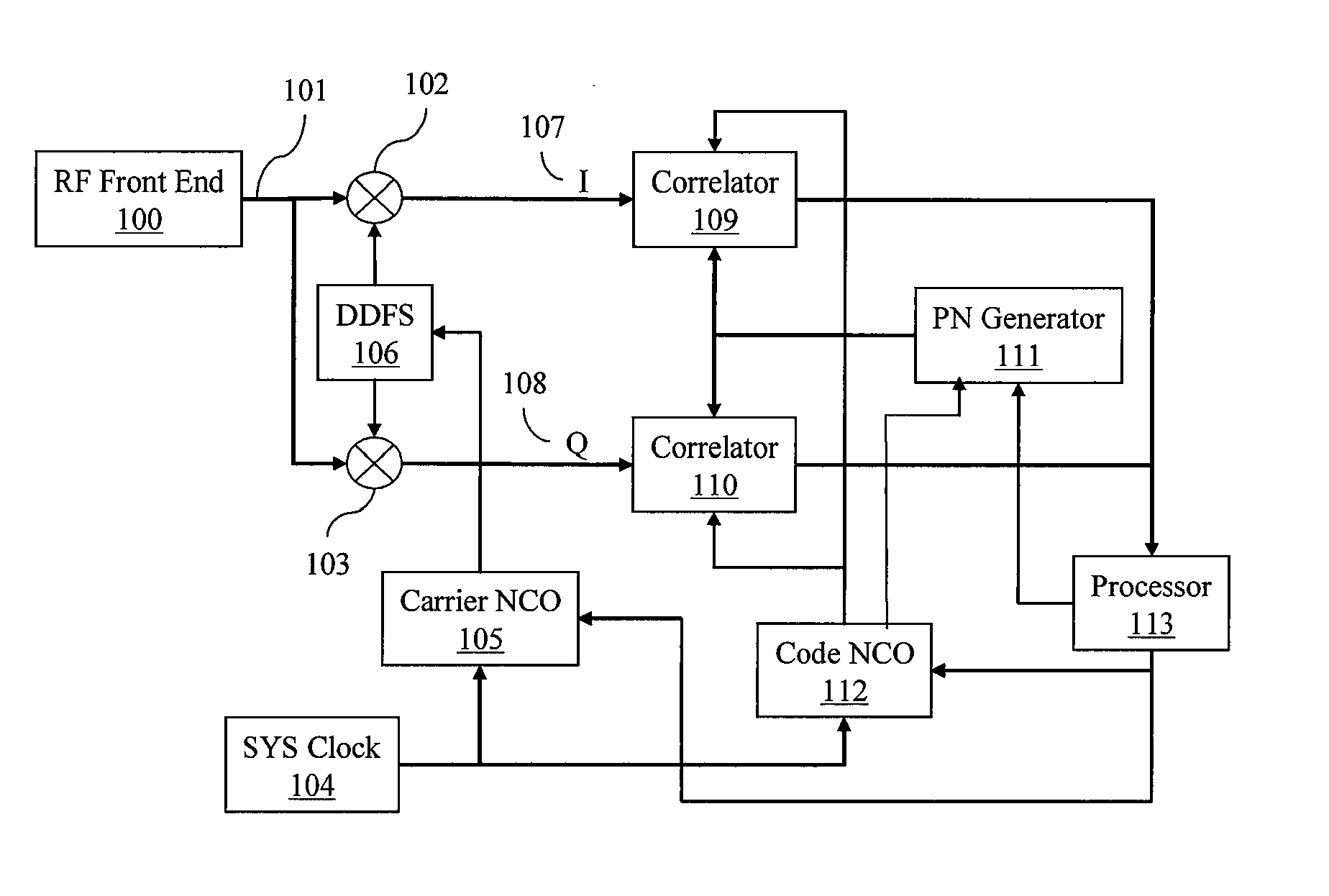
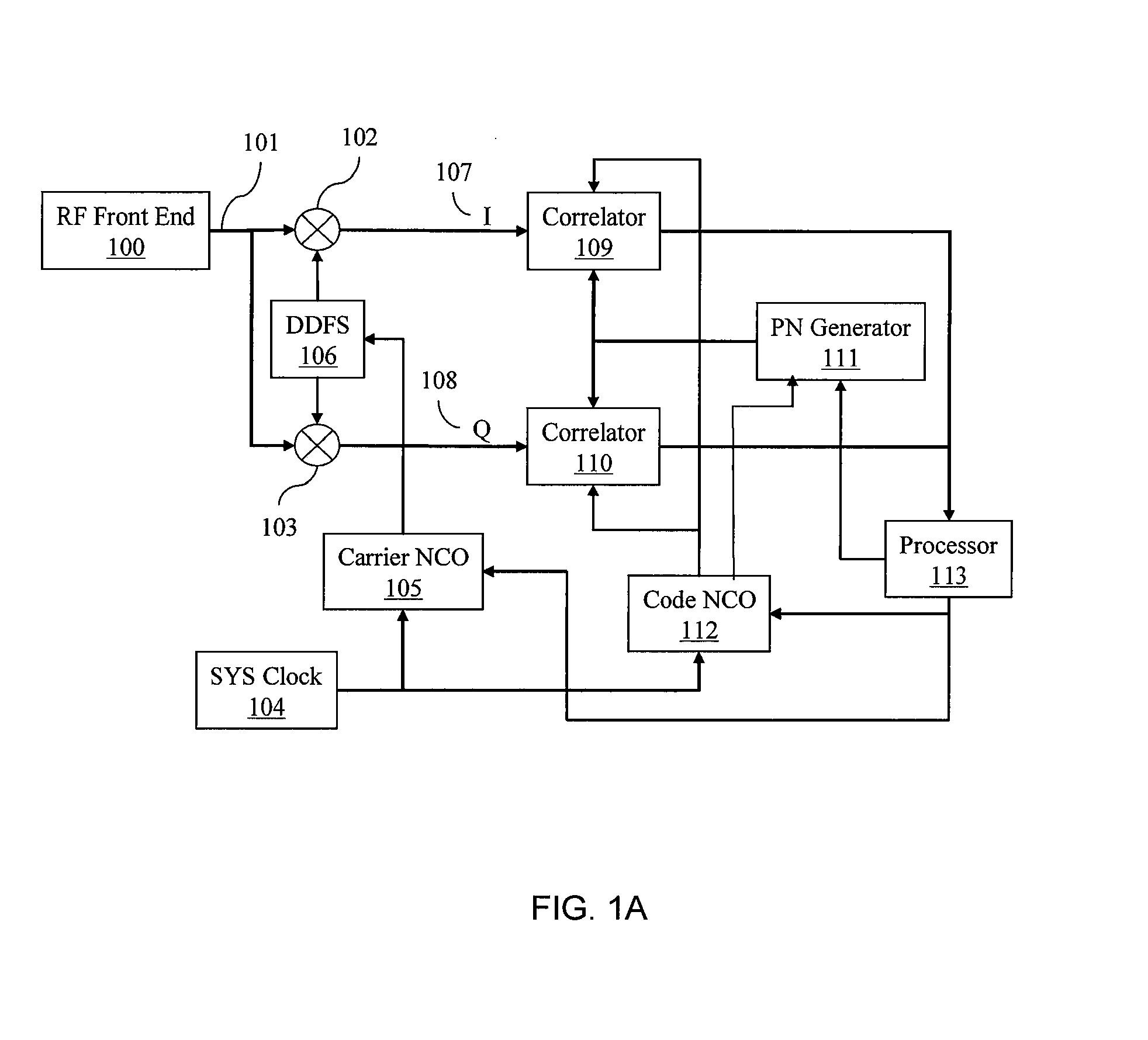
Methods and systems for acquisition, reacquisition and tracking of weak navigational signals
ActiveUS20080180321A1High sensitivityHighly accurate reference signalBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationFourier transform on finite groupsEphemeris
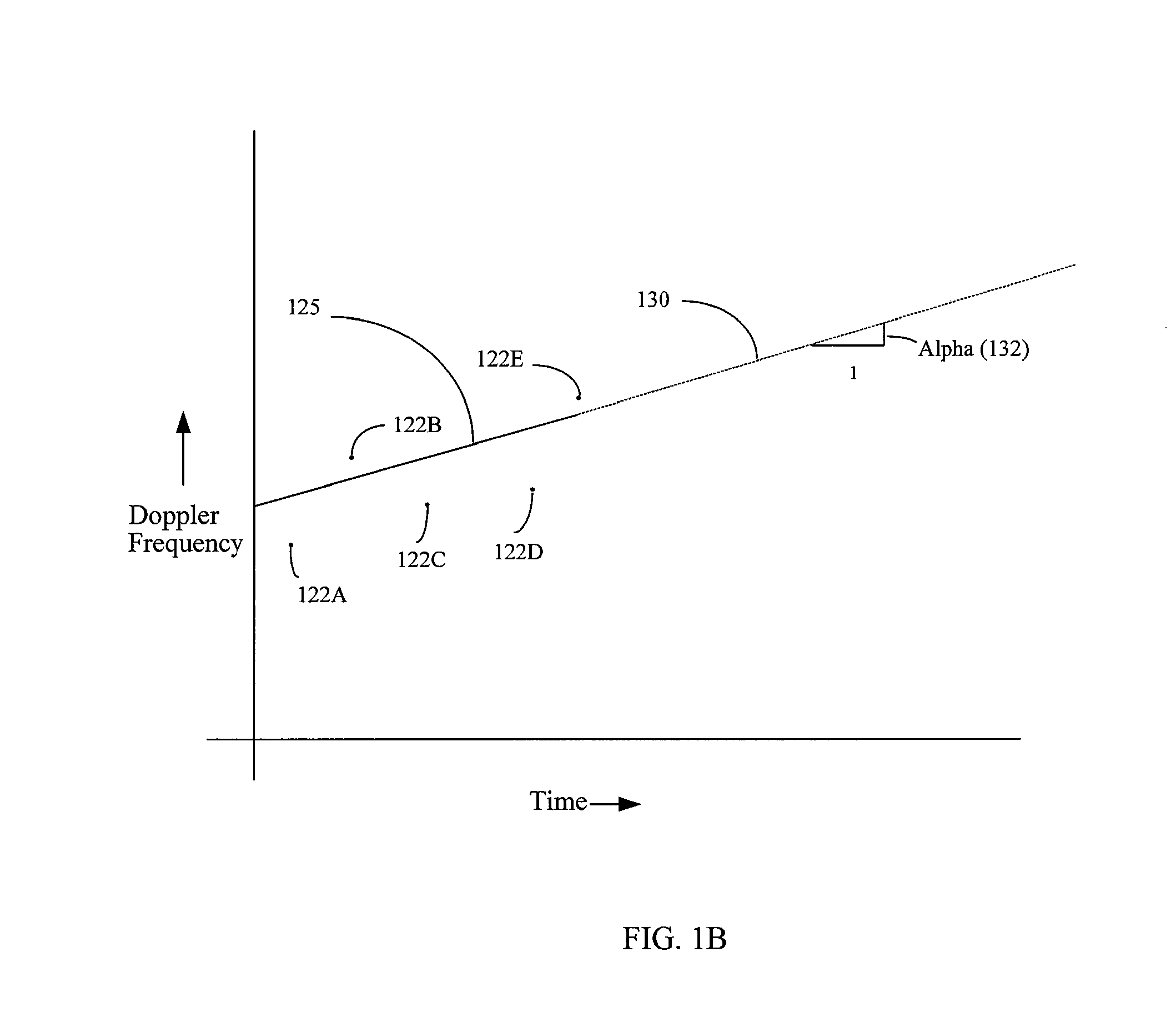
Provided herein are systems and methods for achieving long coherent integration in a navigational receiver to improve the sensitivity of the receiver and enable the receiver to acquire, reacquire and track signals under very weak signal conditions. In an embodiment, phase compensation is computed based on estimated Doppler frequency, rate of change of the Doppler frequency with time, and second order rate of change of the Doppler frequency. The Doppler frequency may be computed from an orbital model or ephemeris. This phase compensation is used to compensate samples of the input signal for changes in the phase due to the Doppler frequency. Frequency components of the phase-compensated samples are then computed using a frequency analysis such as a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The maximum frequency component is taken as an error frequency and used to compensate the samples of the input signal for residual frequency error.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Sound and ultrasonic nondestructive detection method
InactiveCN101413926AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationUltrasonic sensor
The invention discloses a sound and ultrasonic nondestructive detection method, In the method, the nondestructive detection is carried out on the performance (such as adhesion) of materials such as composites by sound and ultrasonic sensors (such as an electroacoustic transducer made of piezoelectric material, magnetostrictive material, and the like) in a way of direct contact coupling or coupling by a couplant, the single and dual electroacoustic transducers can be excited in the form of continuous waves such as variable sine, pulse or triangle wave, a Phase Sensitive Detection (DSD) technique is adopts to process the change of amplitude and phase of feedback echo, and the detection effect of removing certain interference signals (namely retaining the truth and clearing up the false) can be achieved especially by frequency mixing processing of signals which are collected by different frequencies. The application mechanism of the method adopts currently advanced multifrequency and frequency spectrum analysis technique used for eddy detection to process the information obtained by the electroacoustic transducer, thus obtaining all detection characteristics which the existing noise and vibration detecting does not have.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH
Bi-directional short pulse ring laser
InactiveUS6650682B1Reduce noiseOptical resonator shape and constructionSagnac effect gyrometersMagnetic susceptibilityRefractive index
A bi-directional pulsed ring laser that produces bi-directional light pulses that interact in such a way that they are phase conjugated. A nonlinear substance, such as a nonlinear crystal or fluid, that has an index of refraction that is dependent upon light intensity is located near a beam waist of the laser cavity to provide a self-lensing effect. Methods for reducing dead band beyond observable limits are also provided. The increased sensitivity of the bi-directional pulsed ring laser provides application in detecting magnetic susceptibility by detecting the change in phase between the arrival times of the bi-directional pulses at a modulator and the electrical signal of the modulator to determine the change in frequency of a coil that has magnetic susceptibility.
Owner:STC UNM
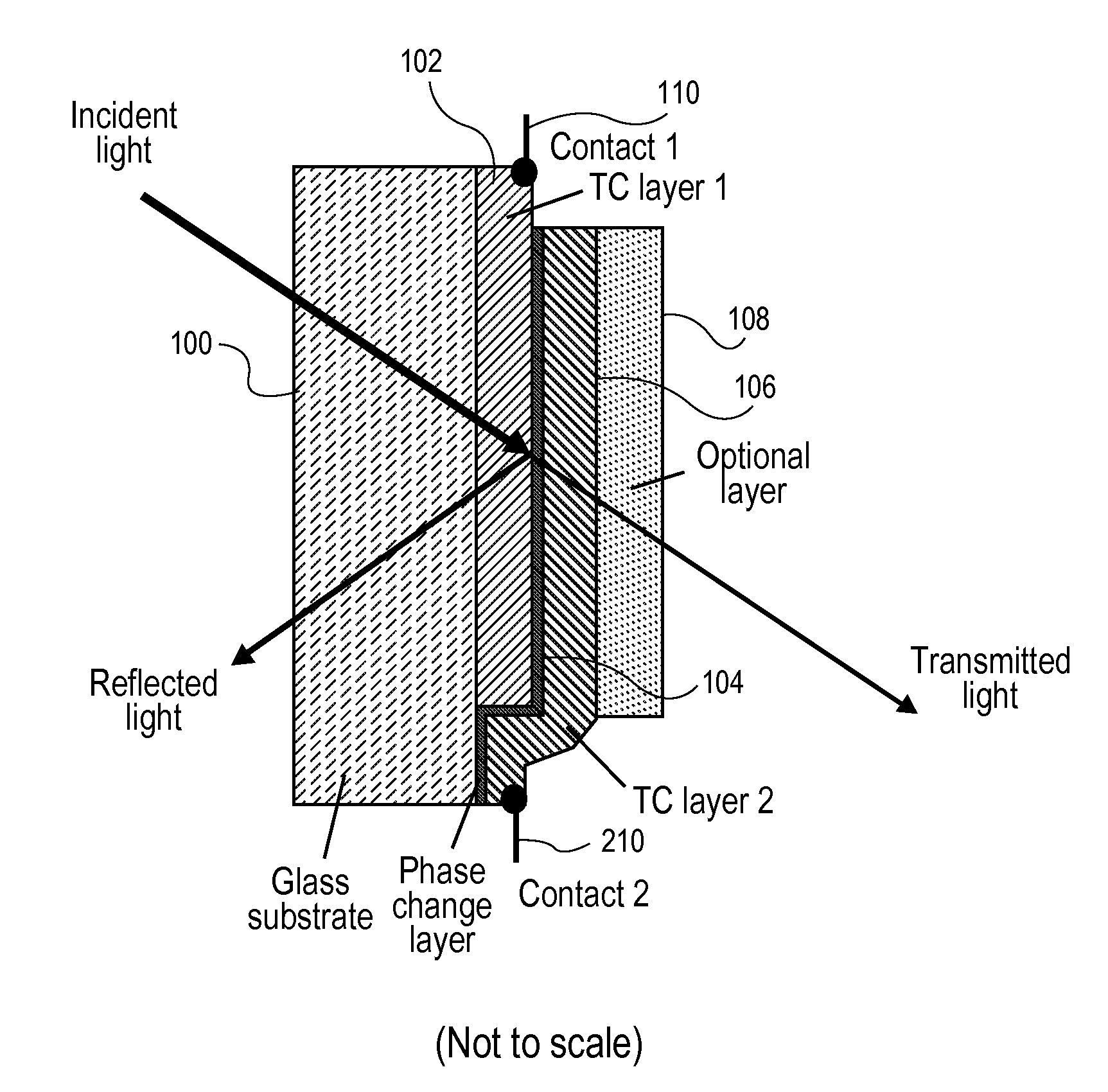
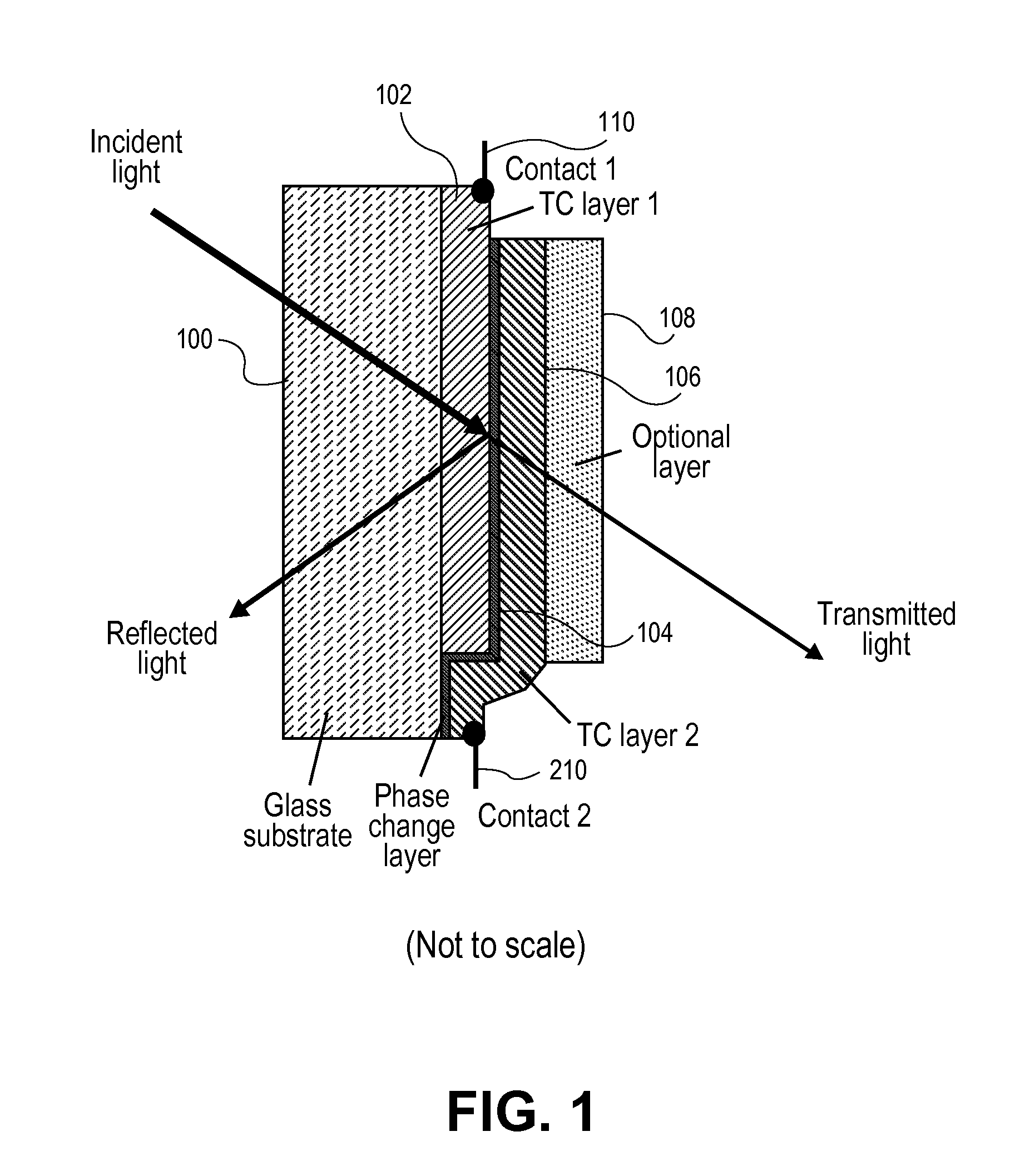
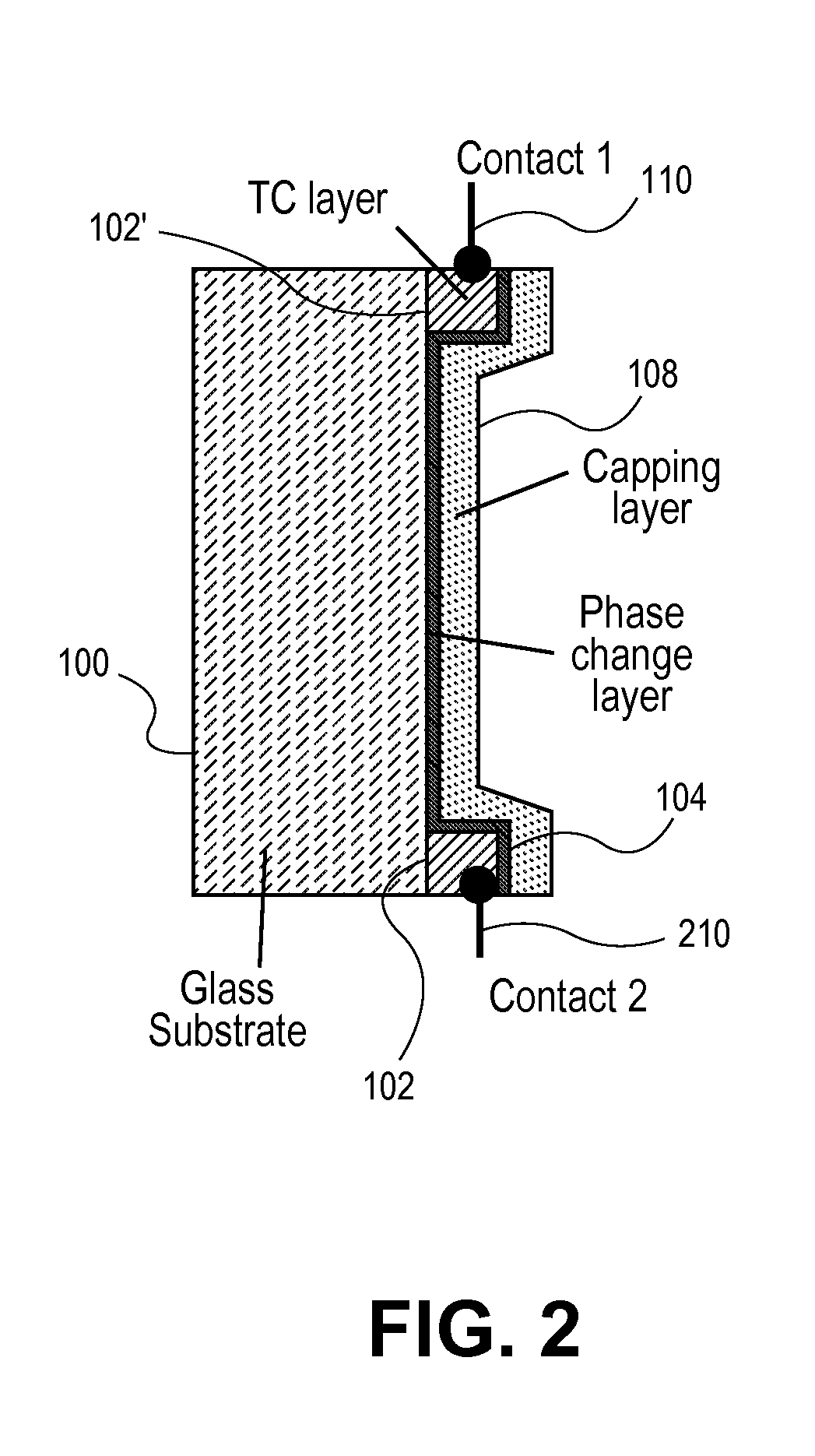
Phase change device
A phase change material is applied as a very thin film to a transparent substrate such as glass, which material when switched from the amorphous to the crystalline state and back again can affect the reflectivity / transmittance of the combined substrate-coating system. When used with glass panels in the fabrication of relatively large area window glass, the change in spectrally selective transmittance can be used to modulate the amount of sunlight passing through the glass, and thus reduce the amount of cooling required for an interior space in the summertime, and the amount of heating required of that same interior space in the wintertime, while also optimizing the use of visible daylight. Exemplary of a suitable phase change material for glass coating is GeSb or BiSn. Heating of the phase change material to initiate a change in phase can be provided by the application of electric energy, such as supplied from a pulsed power supply, or radiant energy, such as from a laser.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com