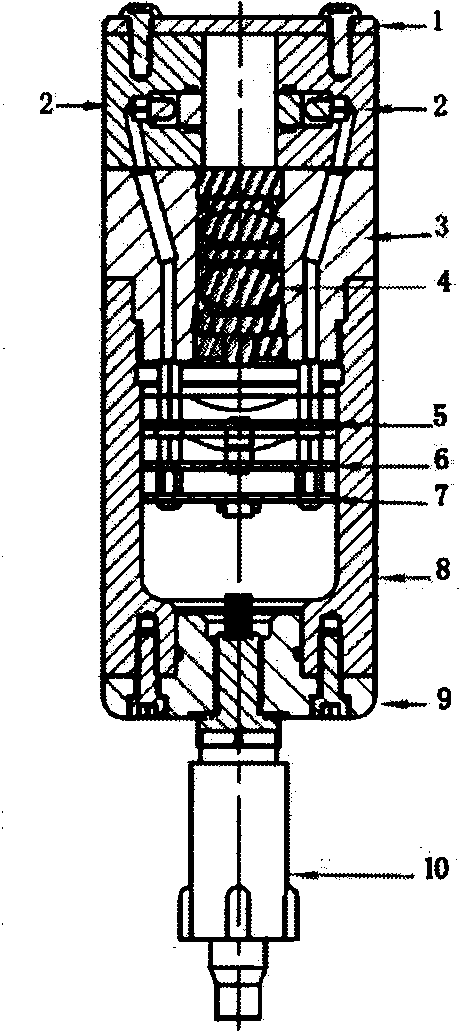
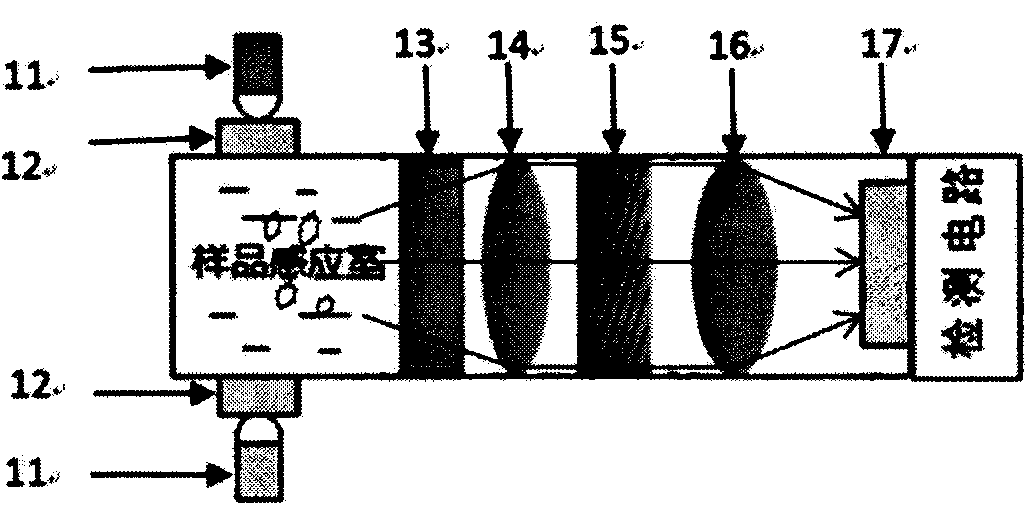
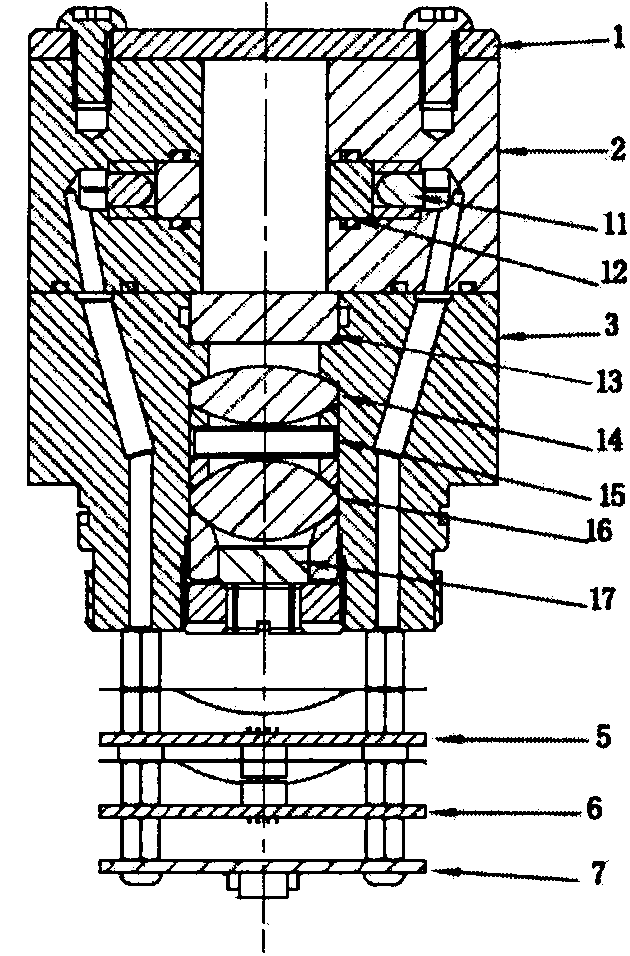
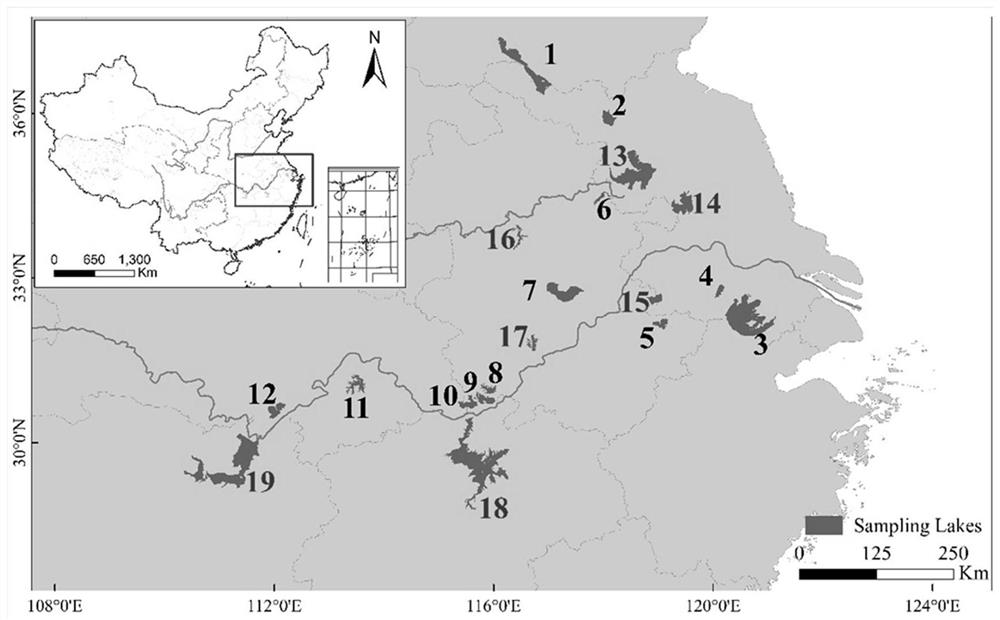
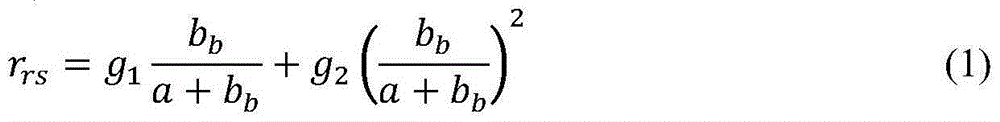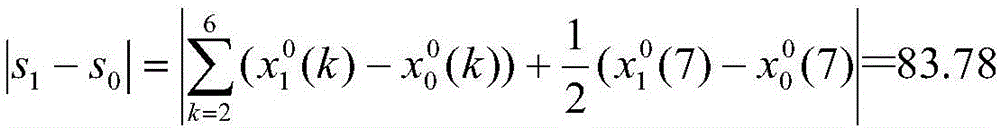Patents
Literature
140 results about "Chlorophyll concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
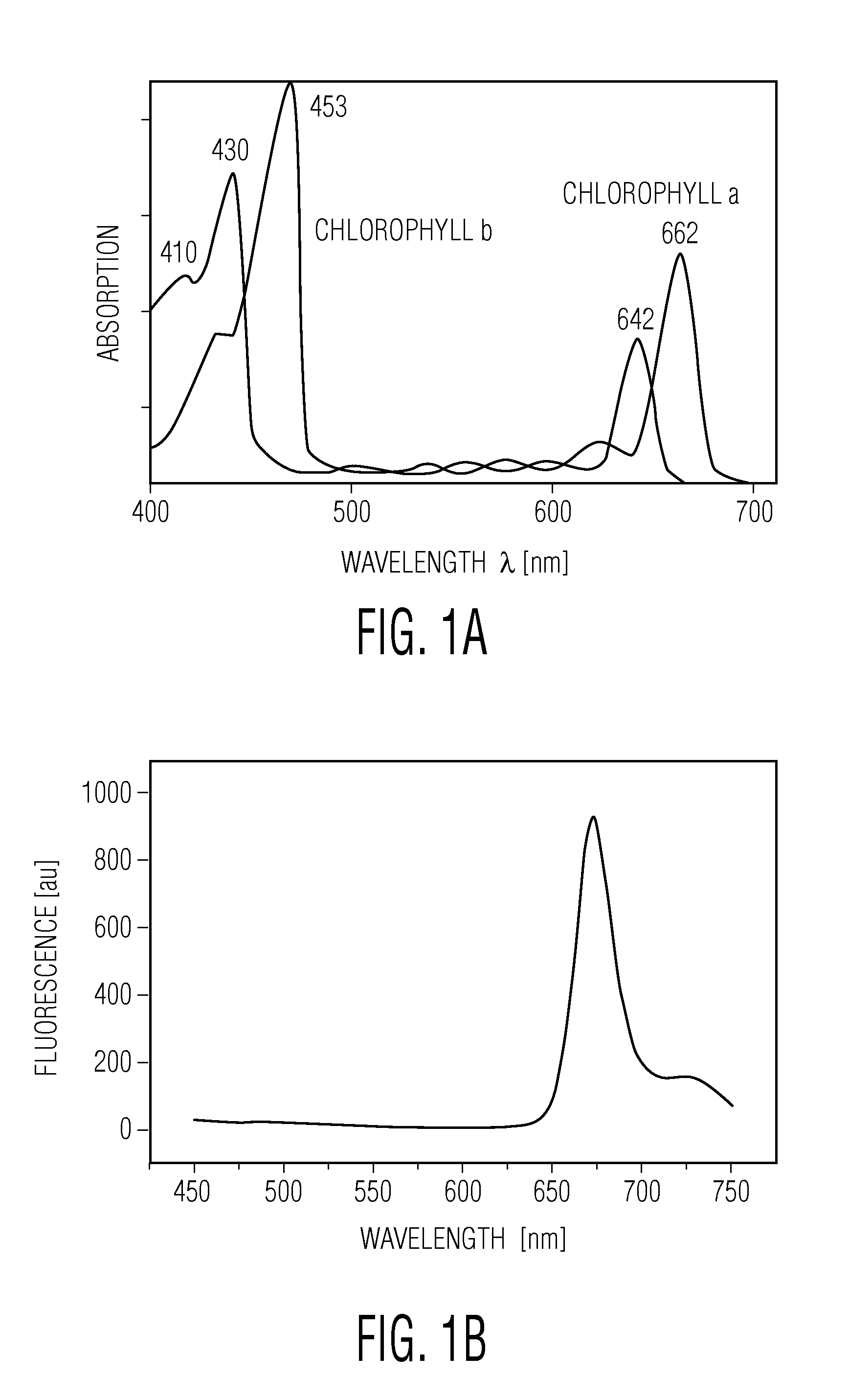
Surface chlorophyll concentration (CHL) is a measurement of the quantity of plant life in the surface layer of the ocean. Chlorophyll observations give us information about how clear the water is at a particular location and where different water masses come into contact with each other.
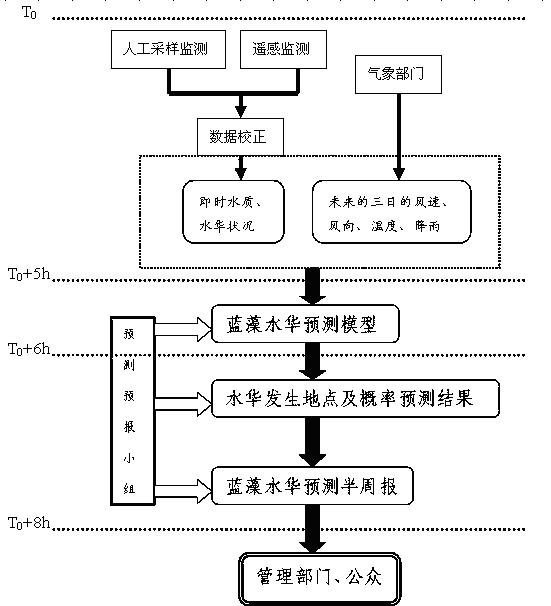
Method for forecasting blue-green algae water bloom in large-scale shallow lake within 72 hours
The invention discloses a method for forecasting blue-green algae water bloom in a large-scale shallow lake within 72 hours. The method comprises the following steps of: building a content forecasting model of chlorophyll a in a water body and a probability forecasting model of water bloom generation according to an in-situ growth rate and drift rate parameters of blue-green algae; analyzing instant content of the chlorophyll a in a monitoring water area; distributing and acquiring meteorological information data in a monitoring period; inputting the built models; and outputting a predicted value of the concentration of the chlorophyll a in the monitoring water area in the next 72 hours and the water area and the probability of water bloom generation. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of strong operability, easily acquired parameters used for forecasting and high timeliness, and can be used for rapidly and accurately predicting breakout of the blue-green algae water bloom and forecasting the blue-green algae water bloom in a waterhead site and a vital landscape water area.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
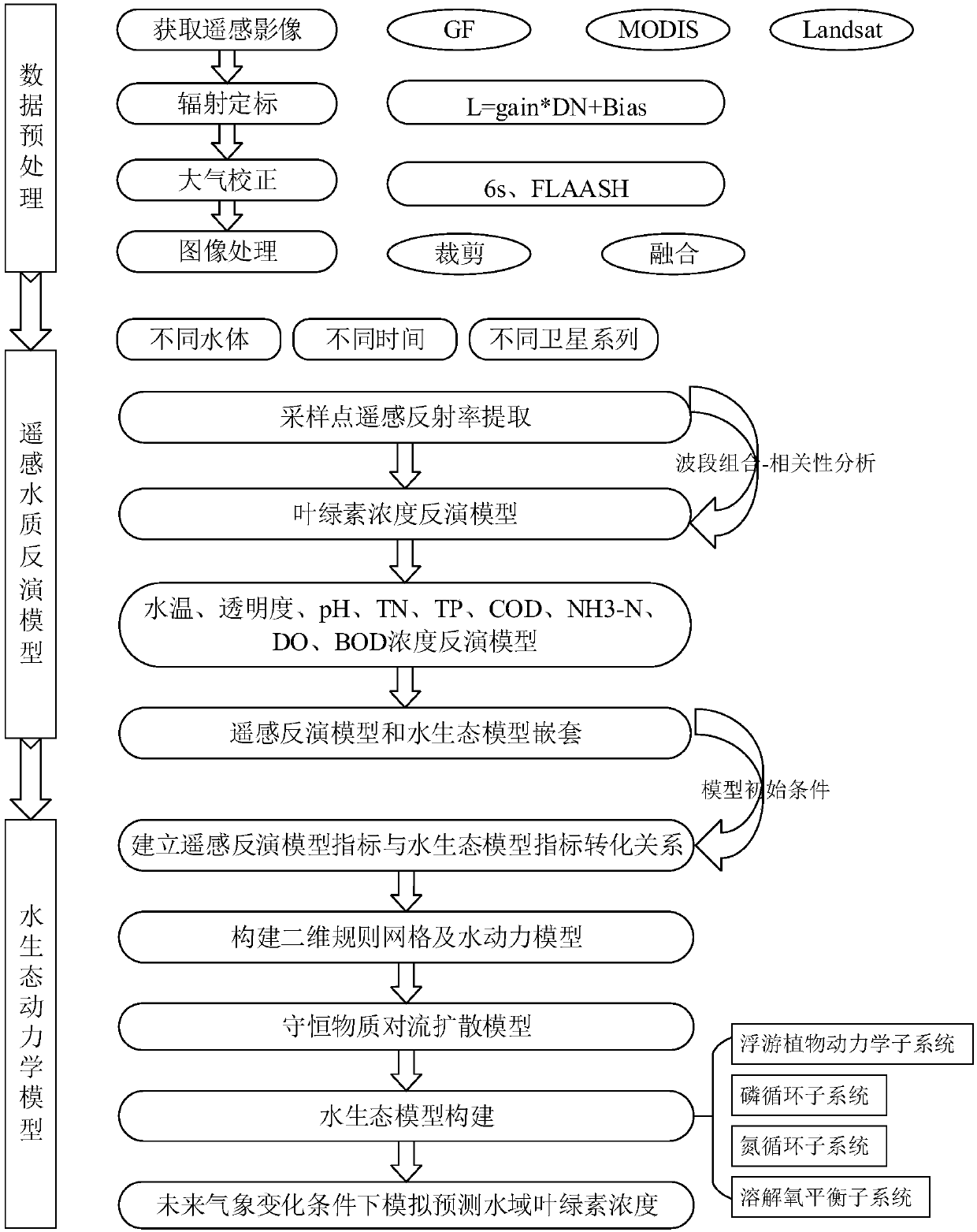
Chlorophyll calculating method based on remote-sensing images and water ecological model
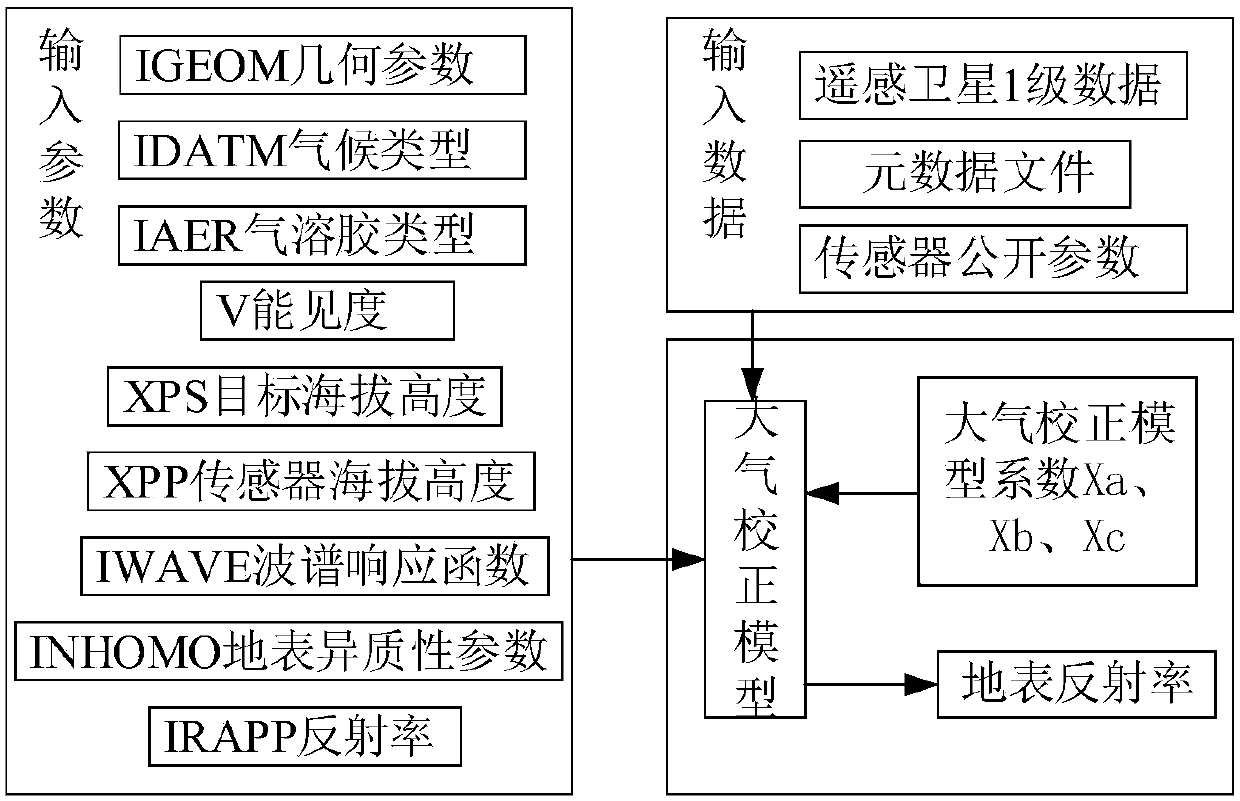
ActiveCN108038351AComprehensiveImprove applicabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSystems biologyWater qualityAtmospheric correction
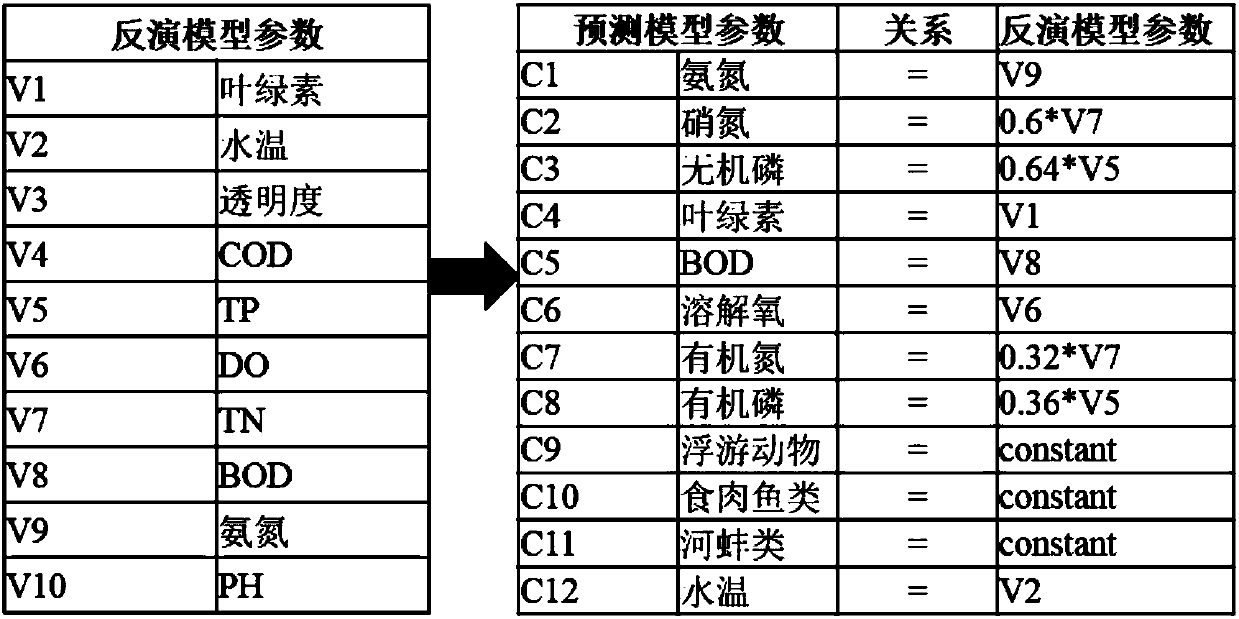
The invention discloses a chlorophyll calculating method based on remote-sensing images and a water ecological model. The method comprises the steps of 1, based on remote-sensing image data, data preprocessing like radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction and image cropping and fusing is conducted; 2, a remote-sensing water quality inversion model is constructed, and respective inversion ofindexes like water temperature and chlorophyll concentration is achieved; 3, various index concentrations and future weather change which are obtained through inversion of the remote-sensing images are regarded as input conditions of the water ecological model, and the chlorophyll concentration dynamic change process of a water area environment is simulated within a future duration caused by change like nutritive substance conversion and algae growth and death under a future weather change condition. The chlorophyll calculating method is applicable to water environment monitoring and predicting, and has popularity and high calculation precision, chlorophyll concentration prediction and simulation of a large area of a drainage basin are achieved in real time under the condition of the limited monitoring site, and an integrated chlorophyll concentration predicting system integrating the remote-sensing images and the water ecological model can be formed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Lake water body blue-green algae abundance estimation method based on remote sensing
InactiveCN103760112AIncrease contentAccurate estimateColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectanceAtmospheric correction
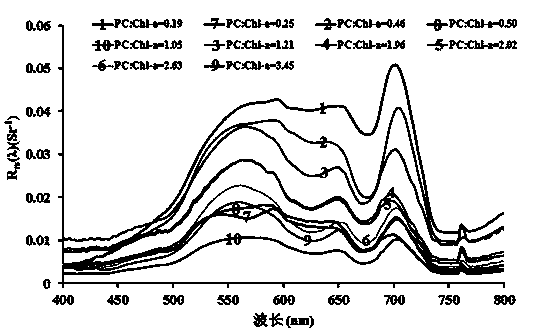
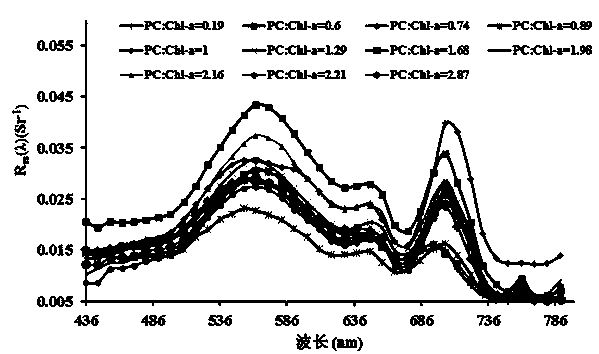
The invention discloses a lake water body blue-green algae abundance estimation method based on remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out high-spectrum remote sensing measurement on a lake water body by utilizing the concentration ratio of phycocyanin and chlorophyll to represent the blue-green algae abundance, selecting the ratio of remote sensing reflective rates of the two specific wave lengths and a function thereof as characteristics of blue-green algae, establishing an estimation model of the lake water body blue-green algae abundance, and estimating the lake water body blue-green algae abundance based on remote sensing. The method provided by the invention adopts a surface feature spectrograph or an onboard high-spectrum imager to carry out high-spectrum remote sensing on the lake water body, and the remote sensing reflective rate required for estimation can be obtained through performing radiation correction and atmospheric correction on aviation satellite high-spectrum data. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the accuracy is high, the model is simple, the remote sensing reflective rates of the two wave lengths are selected, not only can the estimation on the water body blue-green algae abundance measured by the surface feature spectrograph be realized, but also the estimation on the blue-green algae abundance by virtue of aviation high-spectrum remote-sensing images is realized.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Remote sensing retrieval method for extracting chlorophyll concentration distribution information of complex water body
InactiveCN105115941AAvoid influenceAccurate extractionScattering properties measurementsFluorescenceAtmospheric correction
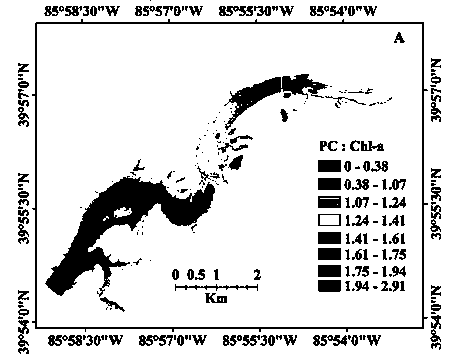
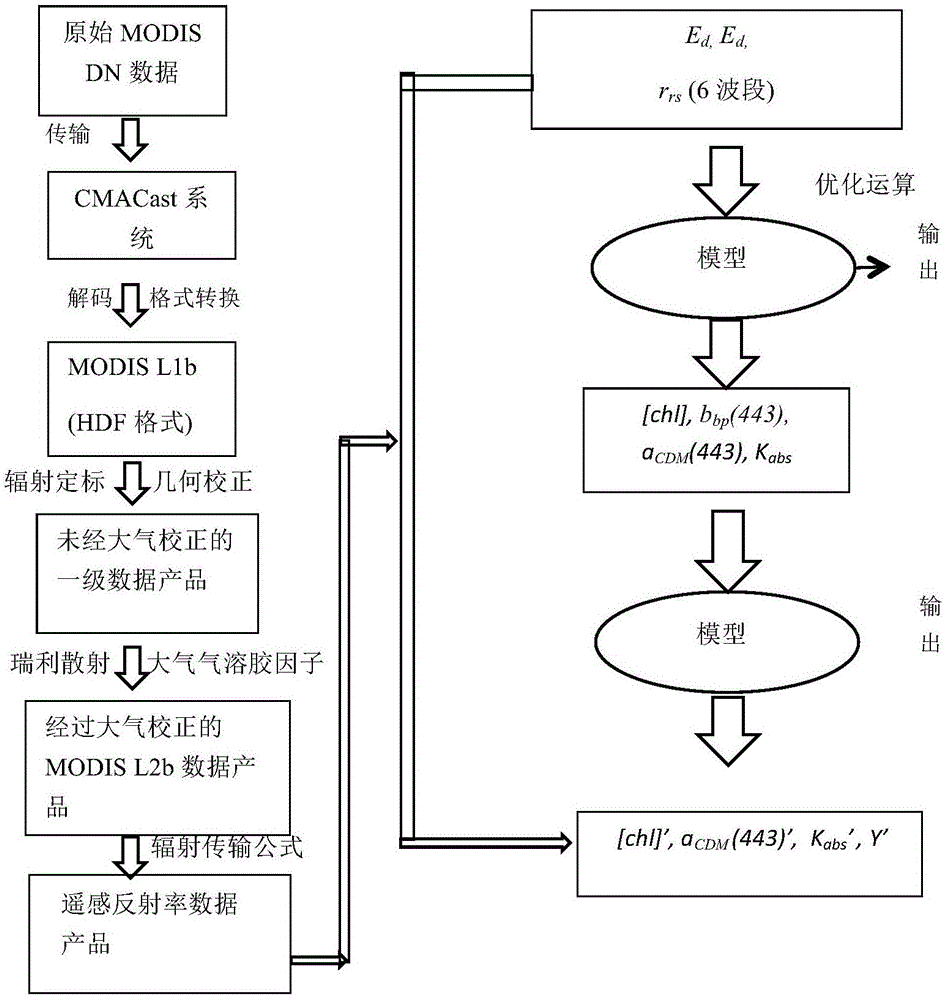
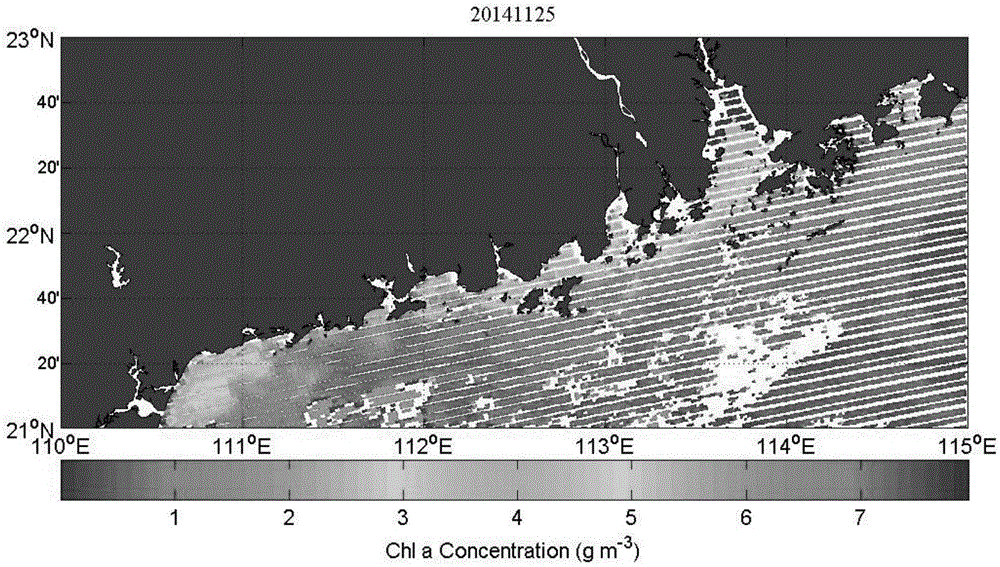
The invention relates to a remote sensing retrieval method for extracting chlorophyll concentration distribution information of a complex water body, which comprises the steps: receiving MODIS L0 data of a CMACast data transmission system in real time, and decoding to convert to a MODIS L1b data product in a hdf format; performing atmosphere correction on the MODIS L1b data product; performing dual optimization iteration chlorophyll inversion by reflection rate data subject to atmosphere correction. A GSM algorithm and a semiempirical algorithm of LI Zhongping are combined with a chlorophyll inversion algorithm, absorption scattering optical characteristics of phytoplankton are inverted by adopting twice nonlinear optimization iteration, thus avoiding influence of absorption fluorescent characteristics of CDOM on a reflection rate spectrum, more accurately extracting chlorophyll concentration information, and providing technical support for a water color remote sensing inversion algorithm.
Owner:国家海洋局南海预报中心
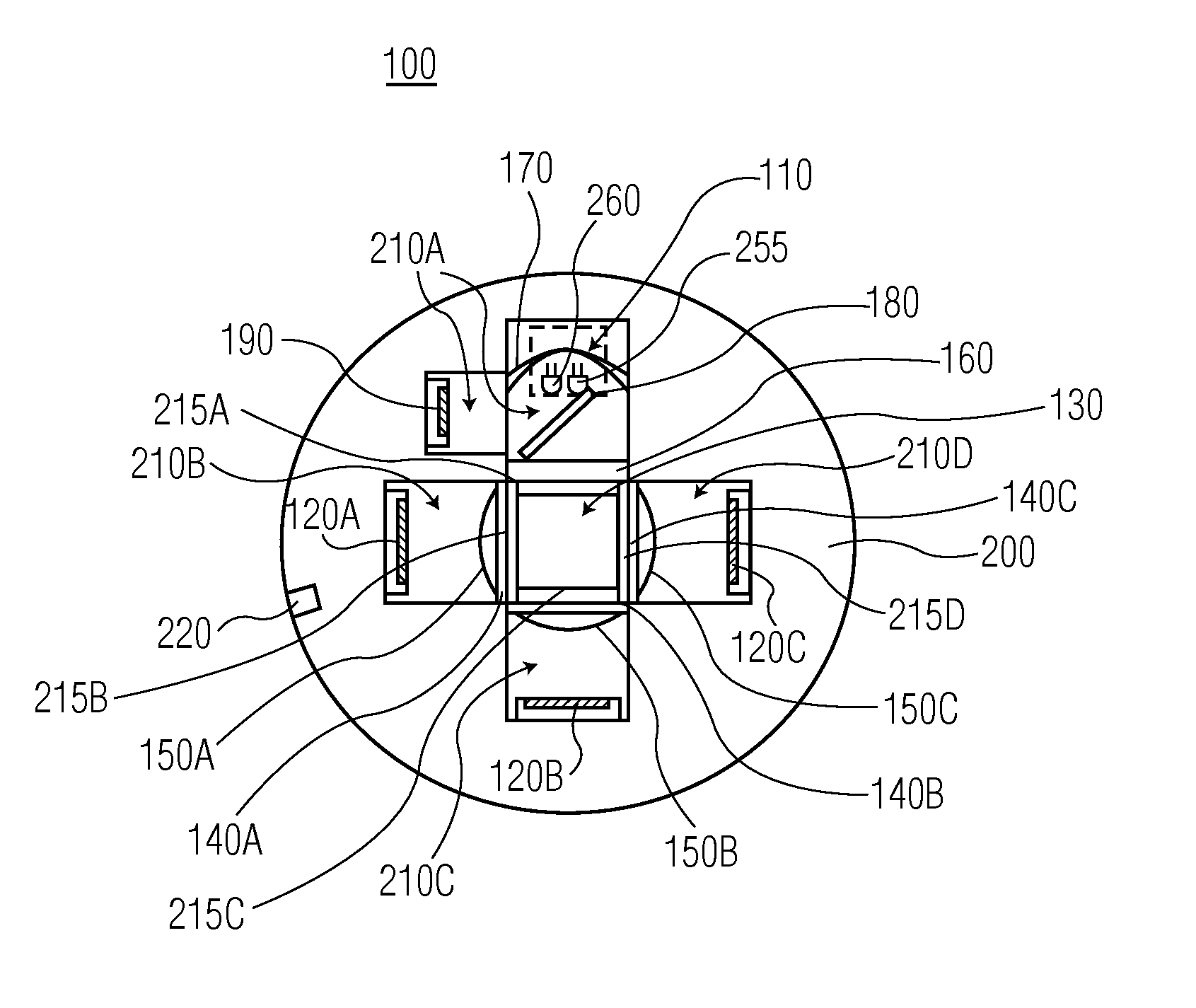
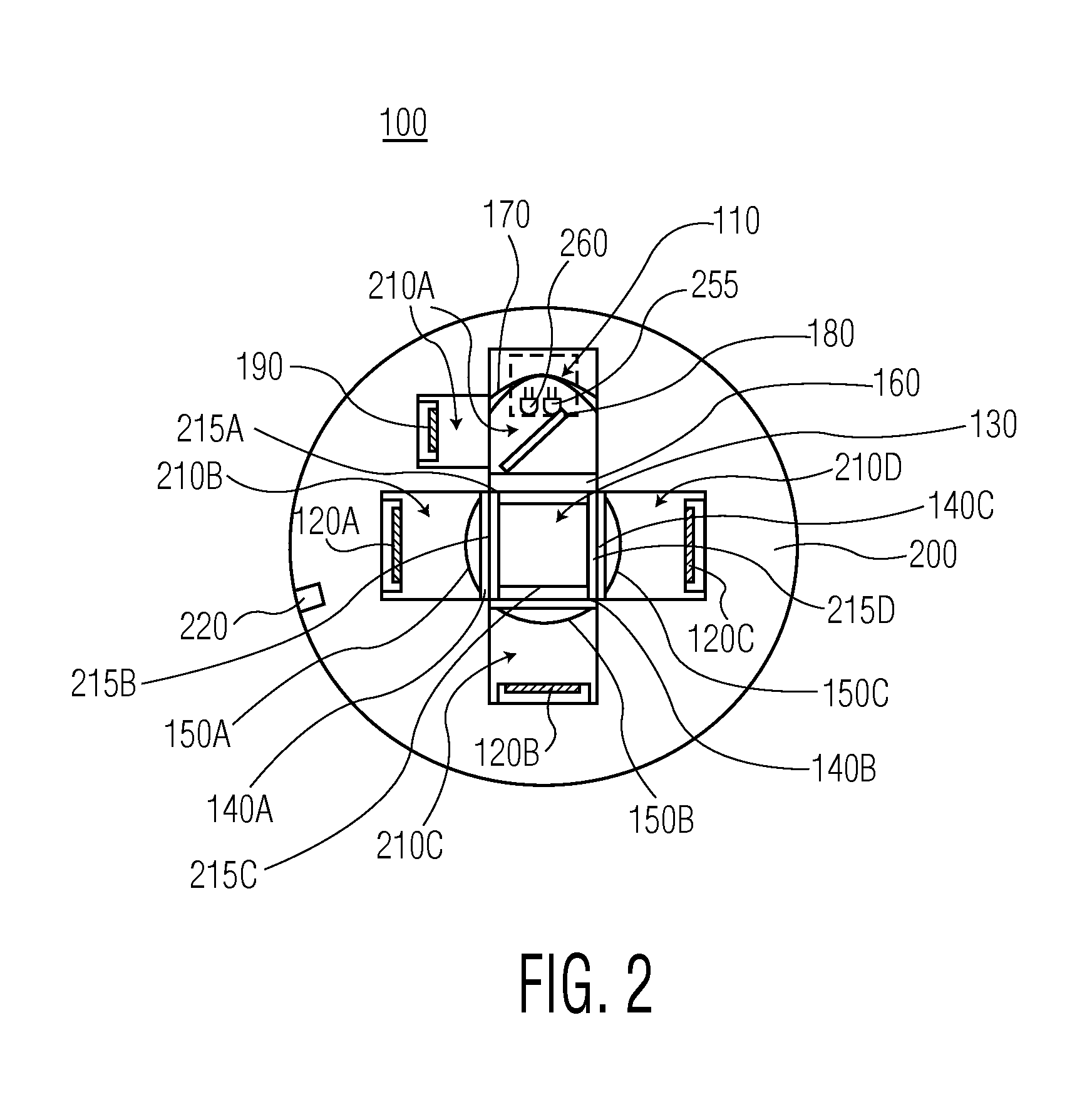
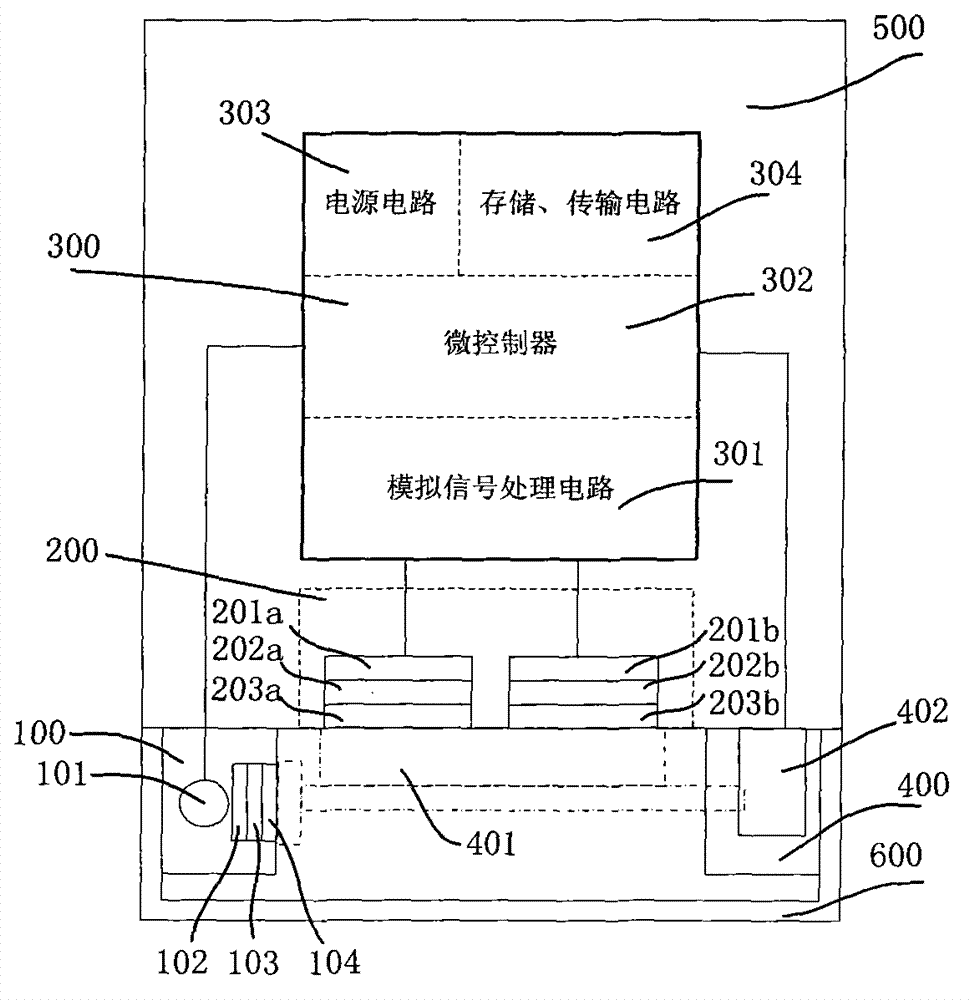
Chlorophyll and turbidity sensor system
ActiveUS20110273705A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsForward scatterOptical density measurement
A low cost sensing system that can measure both chlorophyll concentration and turbidity is provided. The system is an optical system that utilizes at least three light sensors for measuring side-scattered and forward scattered light, as well as fluorescence. The system is able to take optical density measurements, steady state fluorescence measurements and maximum fluorescence measurements, and can be configured for wireless control and data transmission. The system may also be housed in one or more fluidtight housings so as to make it submersible.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
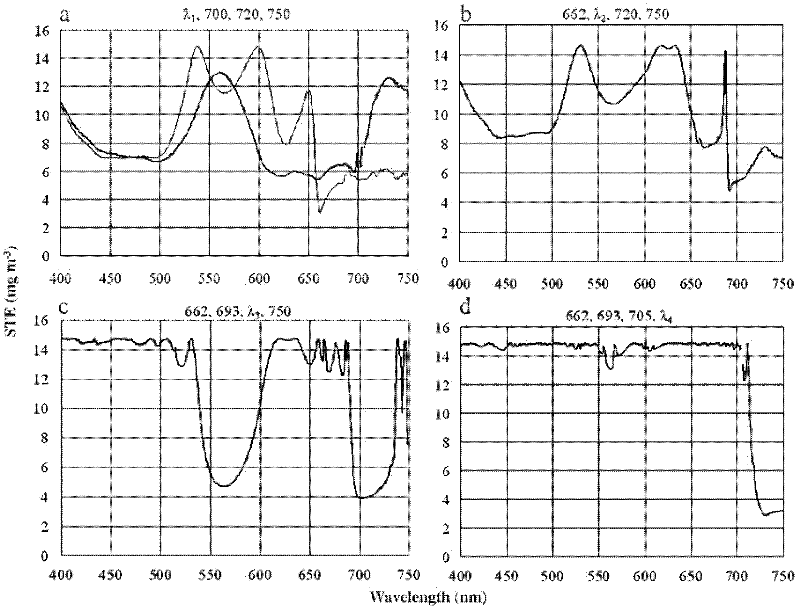
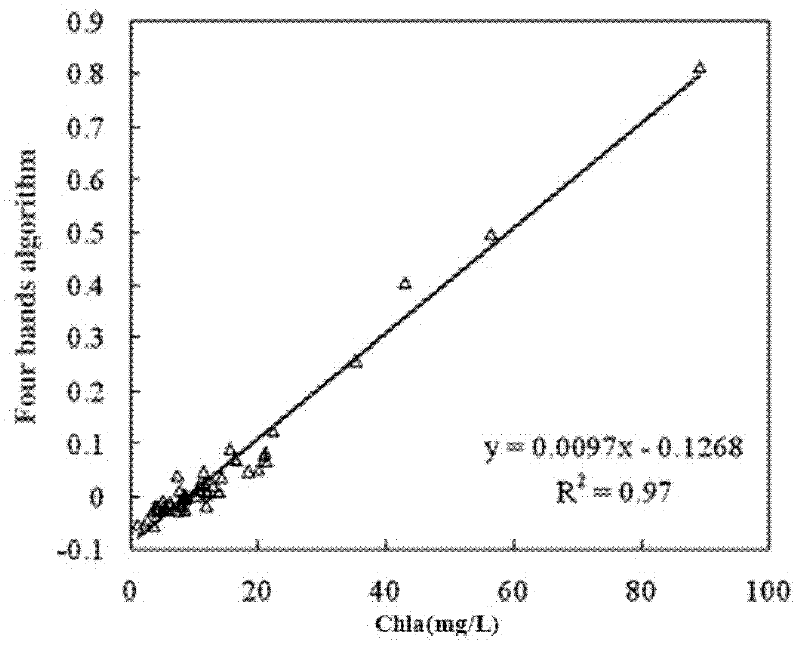
Four-band semi-analysis model for inverting chlorophyll a concentration in high-turbidity water body
InactiveCN102508959AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsParticulatesTurbidity
The invention discloses a method used for building a four-band semi-analysis model for inverting the chlorophyll a concentration in a high-turbidity water body. According to the method, a fourth band is introduced on the basis of the original three-band semi-analysis model for improvement, [Rrs-1(Lambda 4)-Rrs-1(Lambda 3)]-1 is used for replacing the Rrs(Lambda3) part in a three-band model factor and is used for reducing the backward scattering and absorption of suspension particles in the high-turbidity water body and the influence of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) on the remote sensing reflection rate, the chlorophyll a concentration characteristics are stressed, then, the positions of four corresponding bands are determined by a iteration method, influence factors are determined, and in addition, an inverting model is further obtained through linear regression. Compared with the three-band semi-analysis model, the model provided by the invention has the advantages that the chlorophyll a concentration in the high-turbidity water body is inverted, the influence of the suspension concentration and the CDOM is minimized, and the model precision is improved to a great degree.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
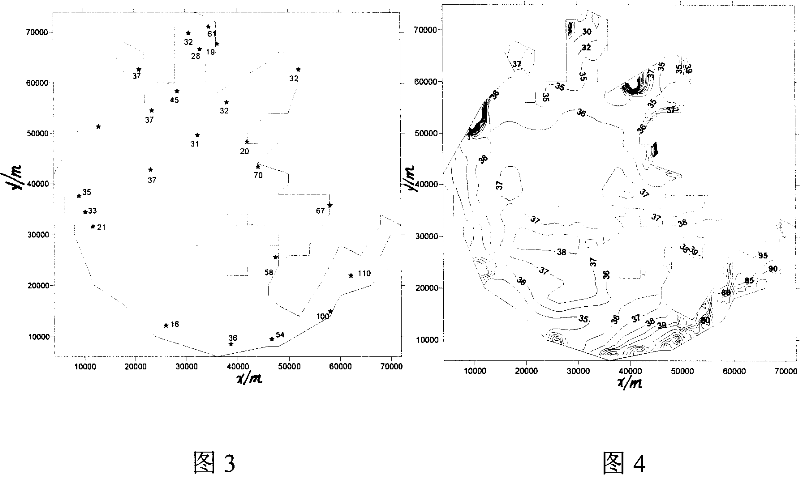
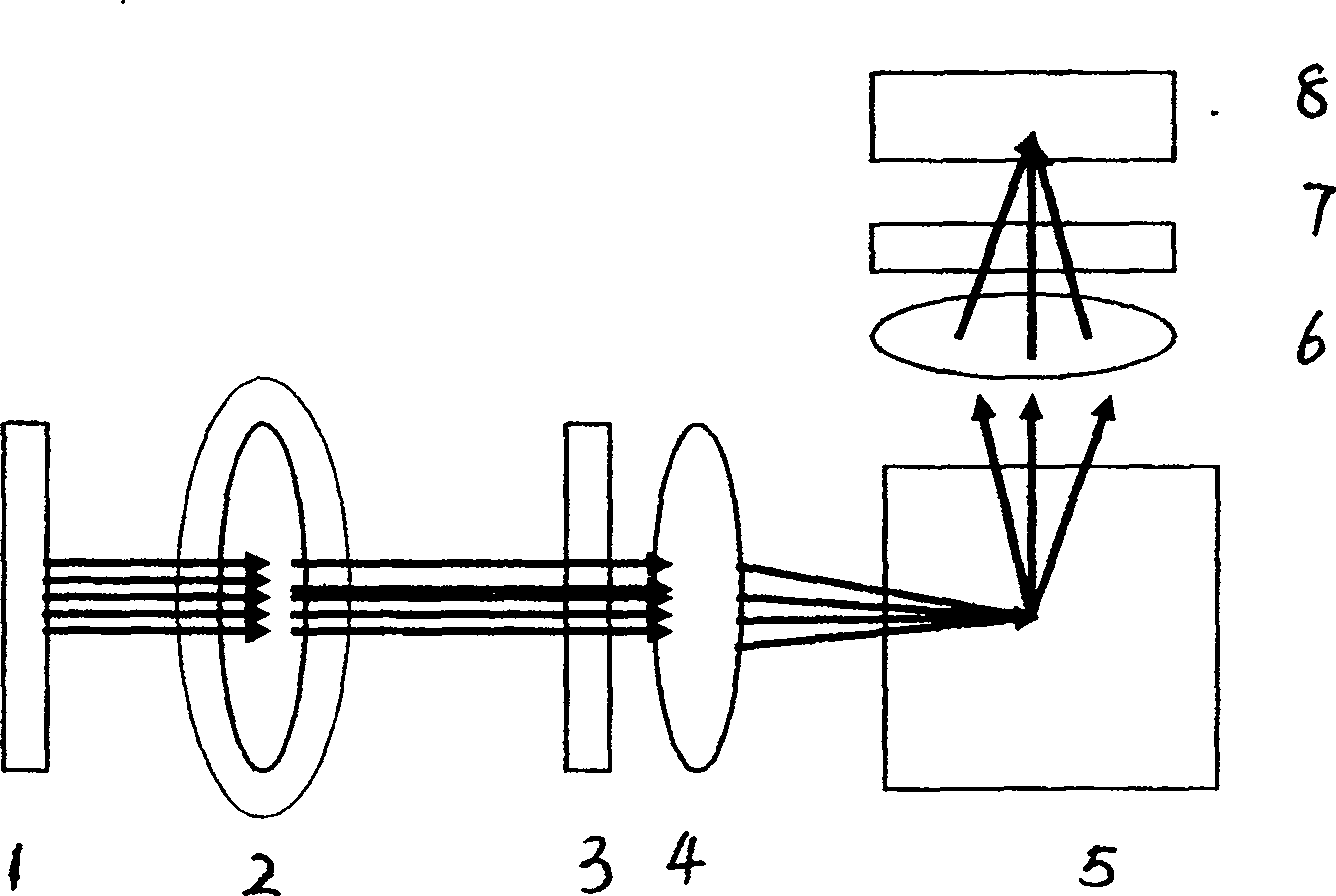
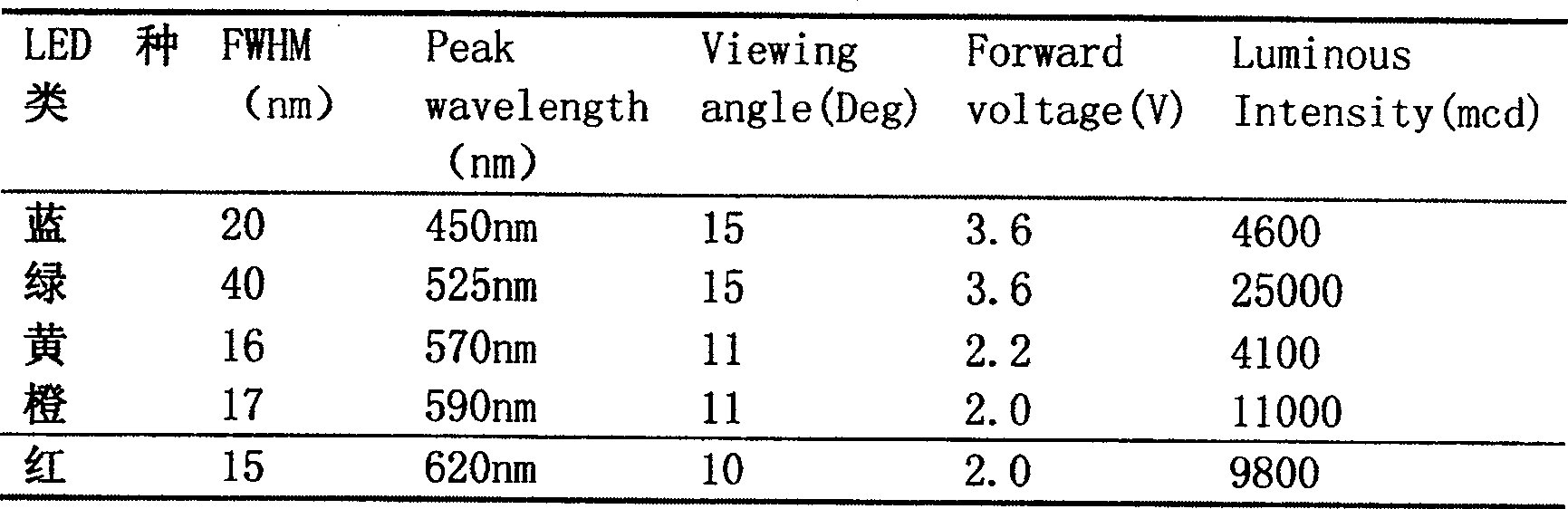
Method and device for classified detecting density of phytoplankton under water in site
ActiveCN1916604ALow costReduce volumeColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceChlorophyll aFluorescence
A method for classifying underwater original position of polytoplankton by detecting concentration of polytoplankton includes setting a groove at one side of closed pressure box and a light shading cover at external side of said box; erecting LED array formed by parallel-arranged LED with center wavelength of 450nm, 525nm, 570nm 590nm and 620nm in light path at side surface of said groove; dividing polytoplankton to be five light spectrum set as green, blue, brown, red and mixture; measuring 685nm florescent intensity of five different exciting wavelength to calculate out chlorophyll concentration of each light spectrum according to known coefficient.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
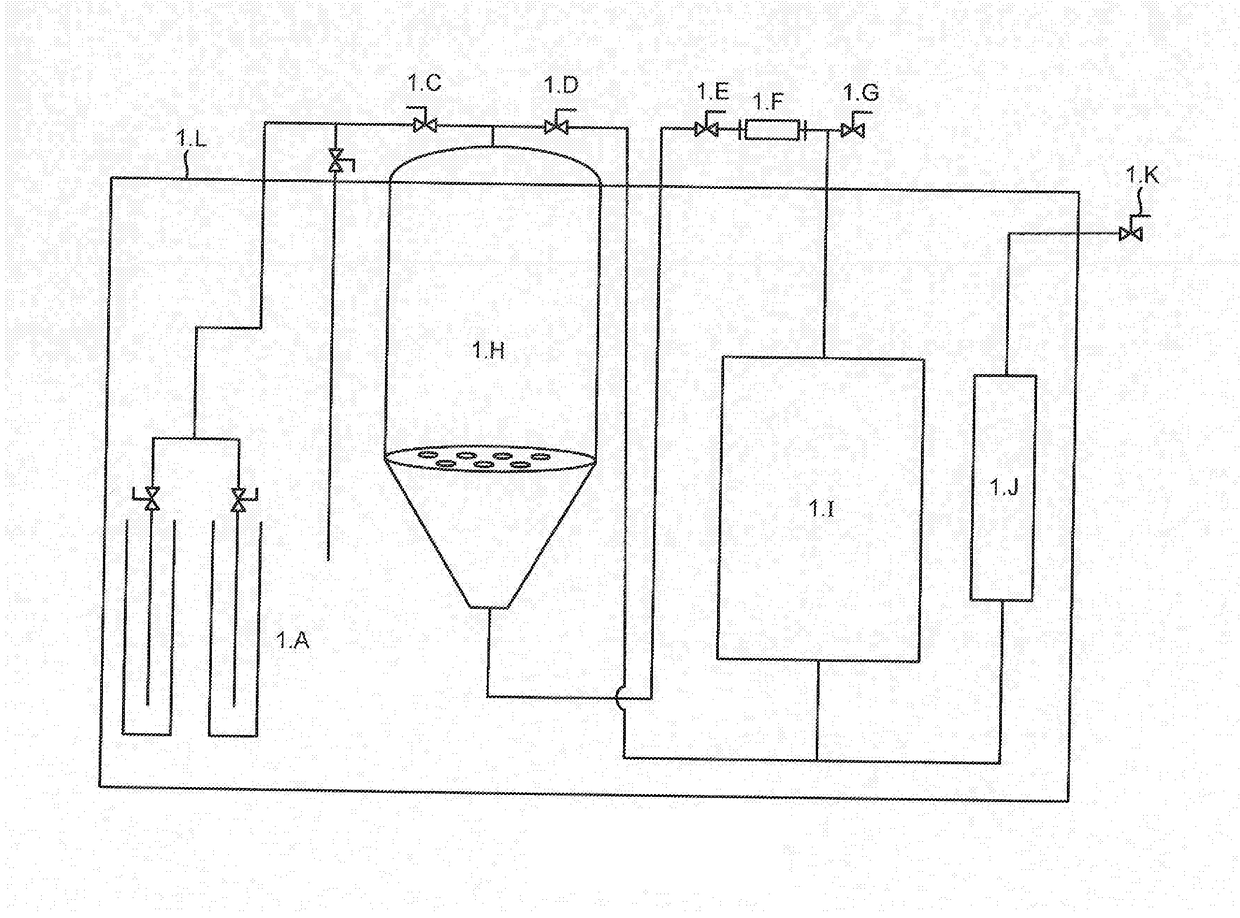
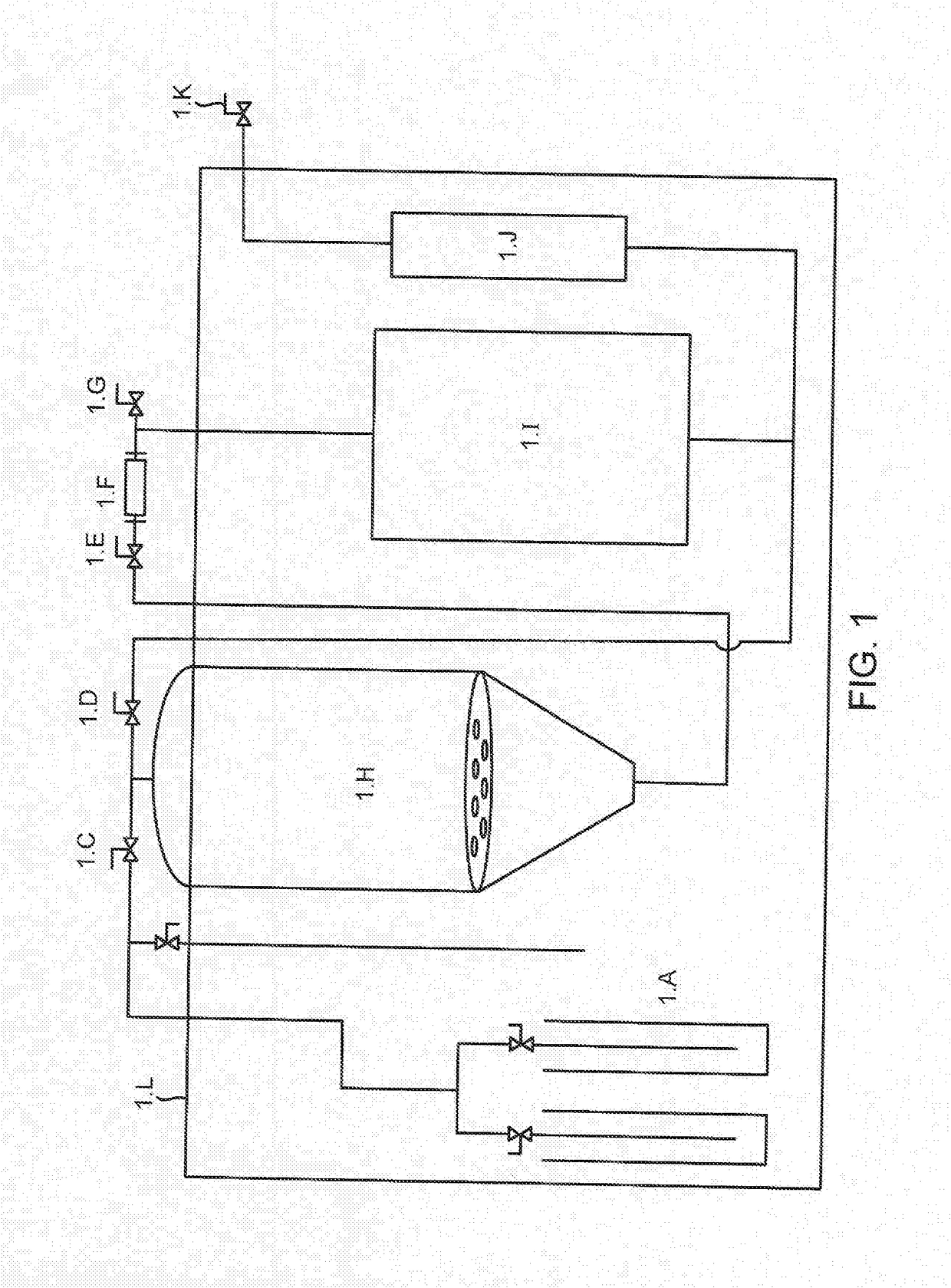
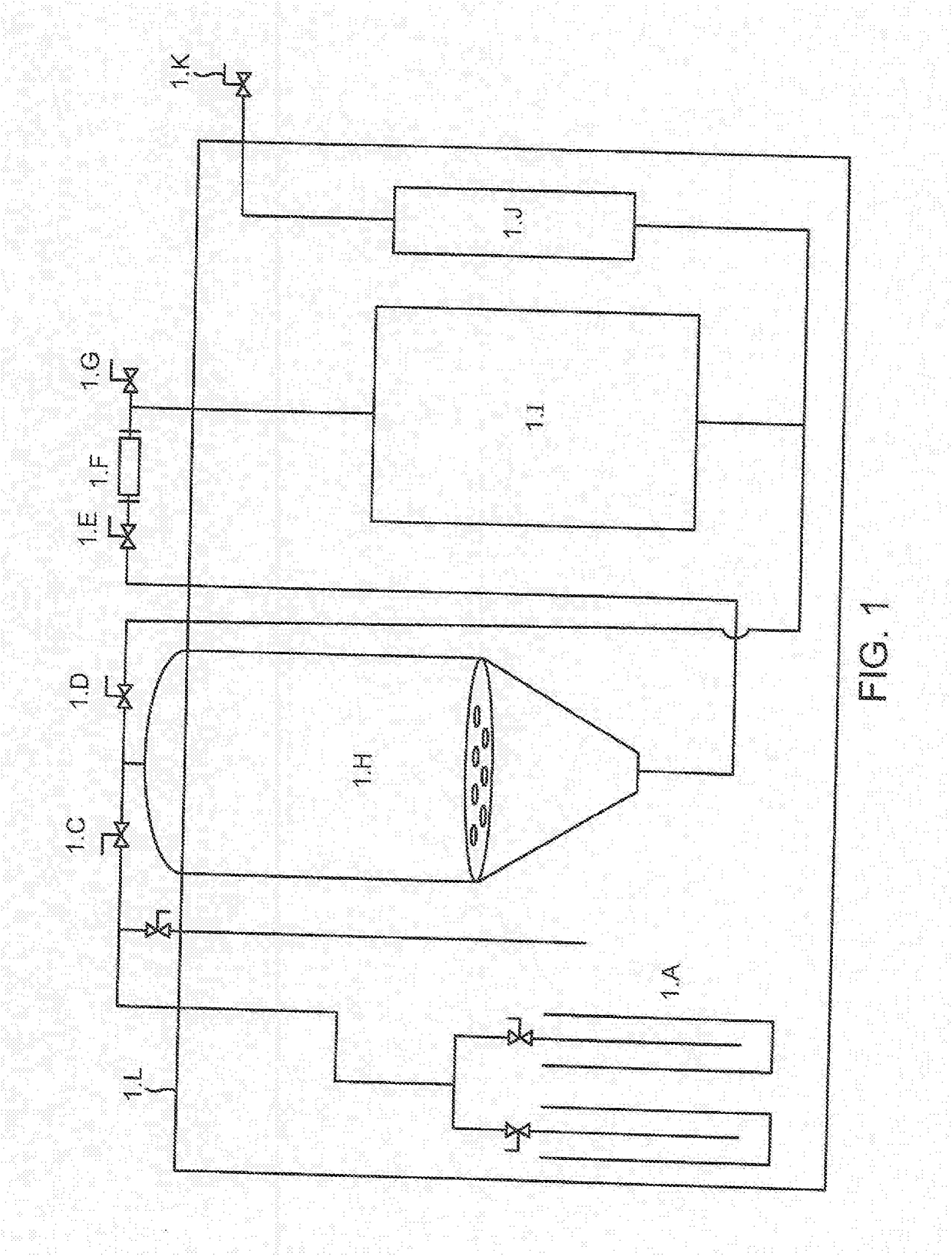
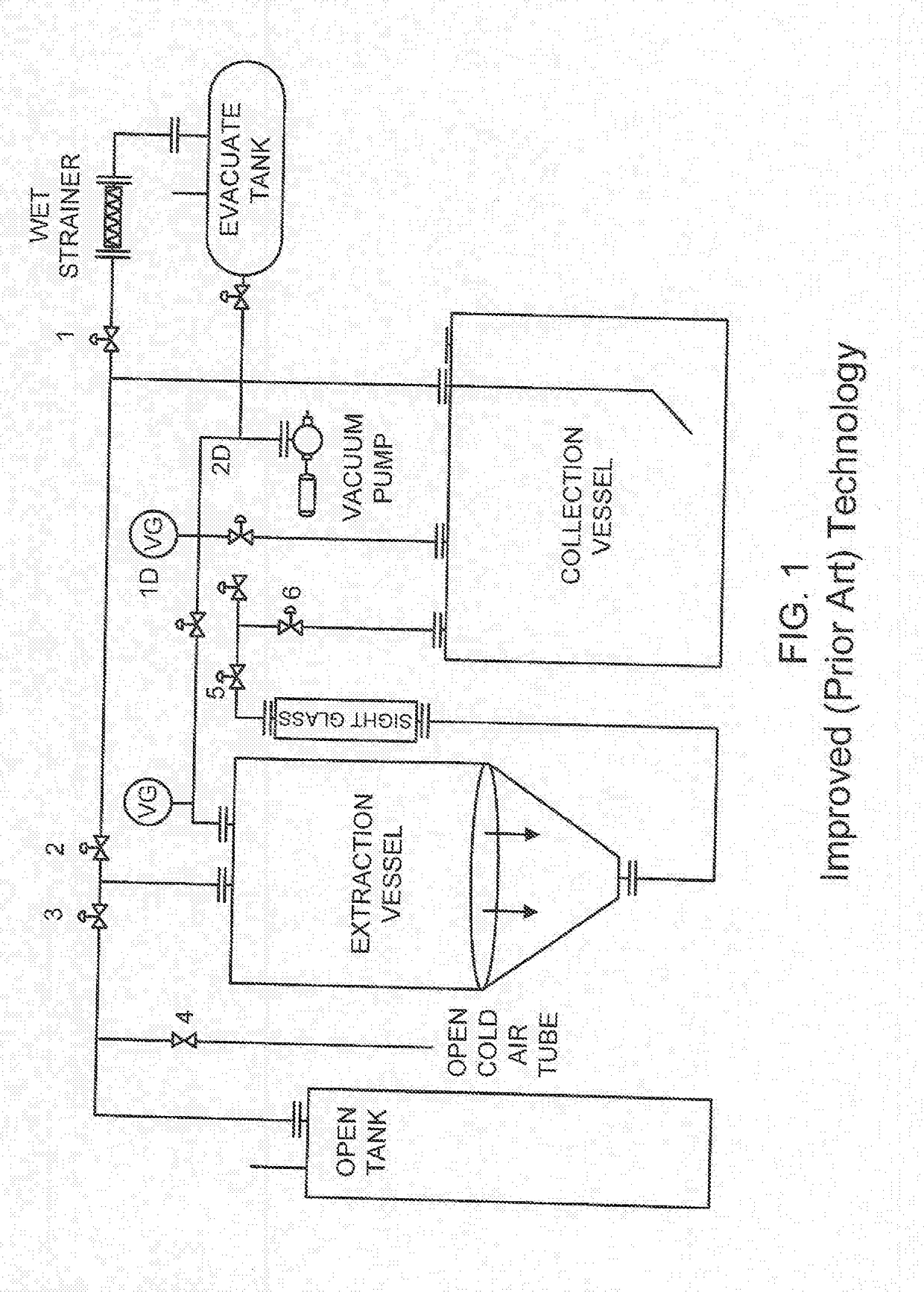
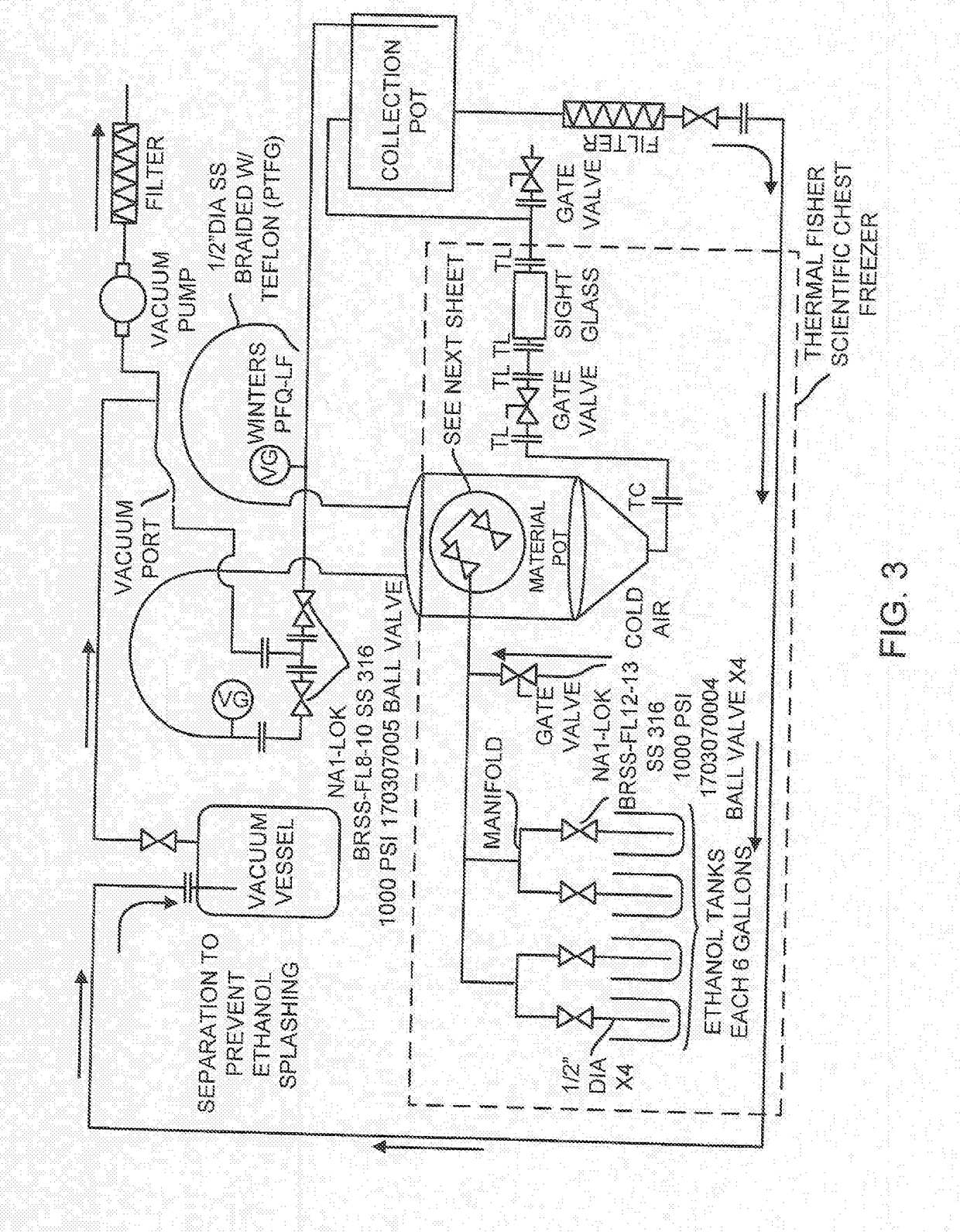
Methods to Reduce Chlorophyll Co-Extraction Through Extraction of Select Moieties Essential Oils and Aromatic Isolates
ActiveUS20170312651A1Essential-oils/perfumesCompression machines with cascade operationAlcoholChlorophyll c
A system, machines and methods for extracting select moieties, flavonoids, and essential oils from plant material without co-extracting chlorophyll, lipids and other undesirable constituents from plants. Super-cooled extraction techniques are taught. Likewise, according to embodiments methods provides 100% grain ethyl alcohol extract with a concentration of chlorophyll that is below 1%.
Owner:CAPNA IP CAPITAL LLC
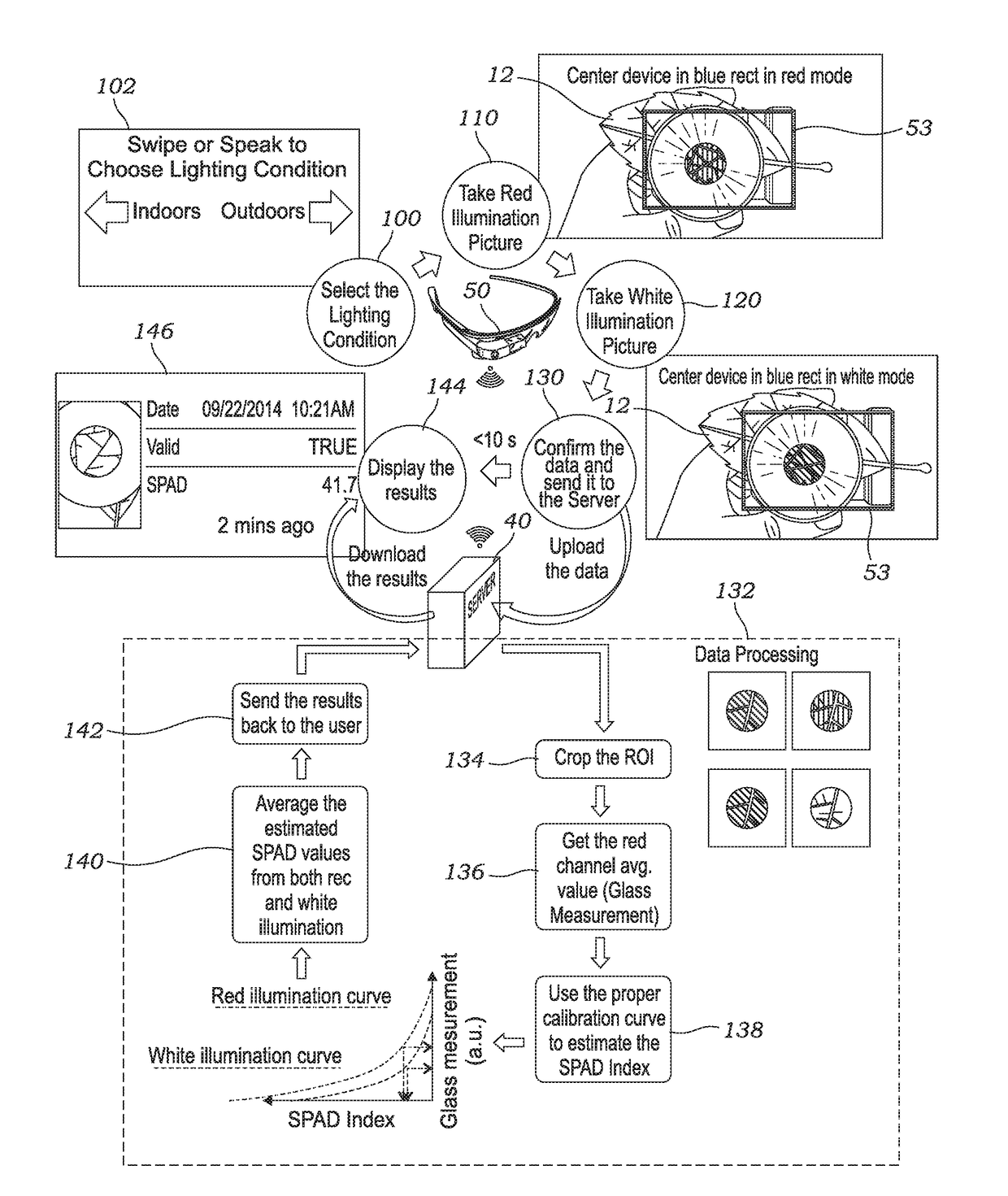
Method and device for quantification of plant chlorophyll content
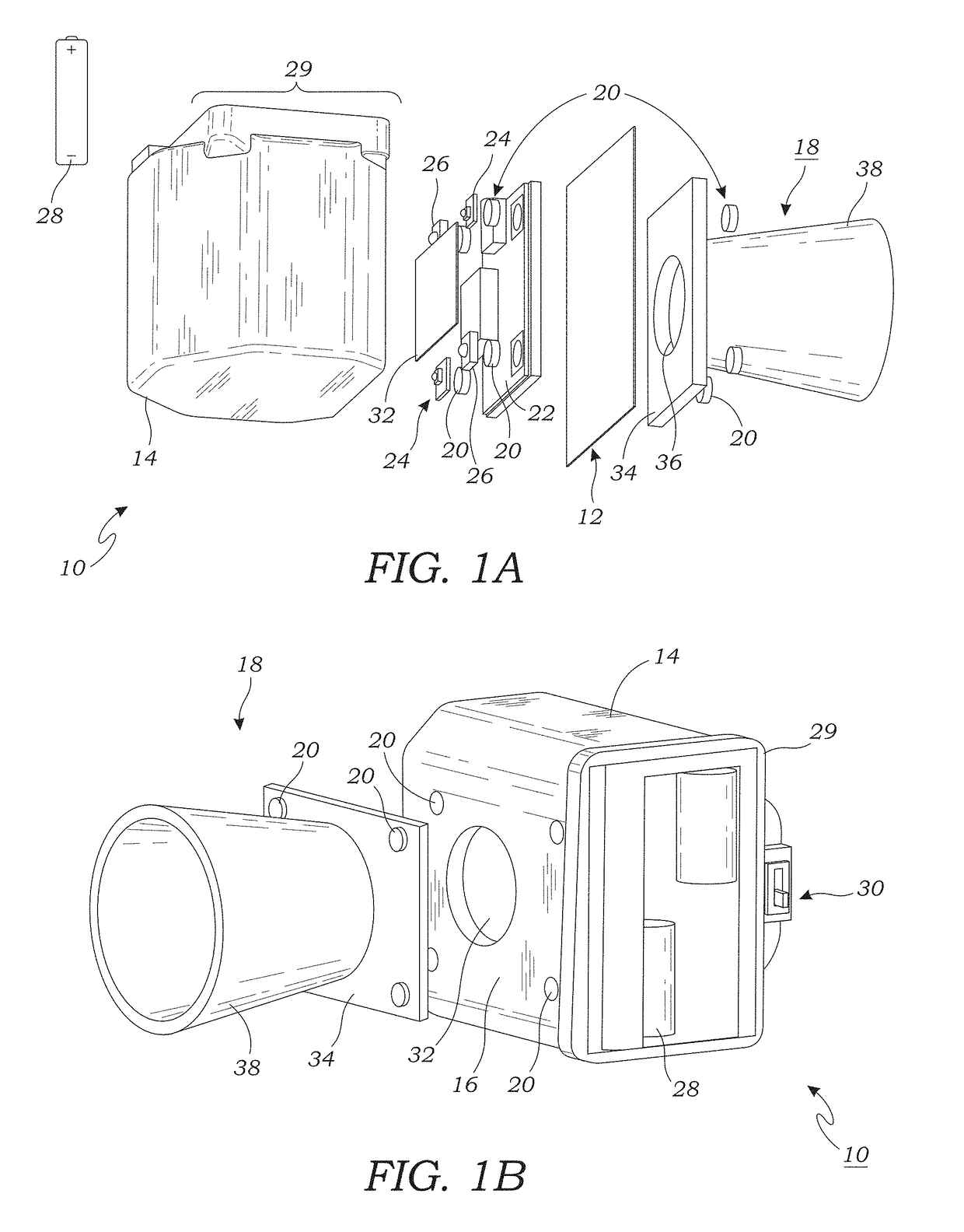
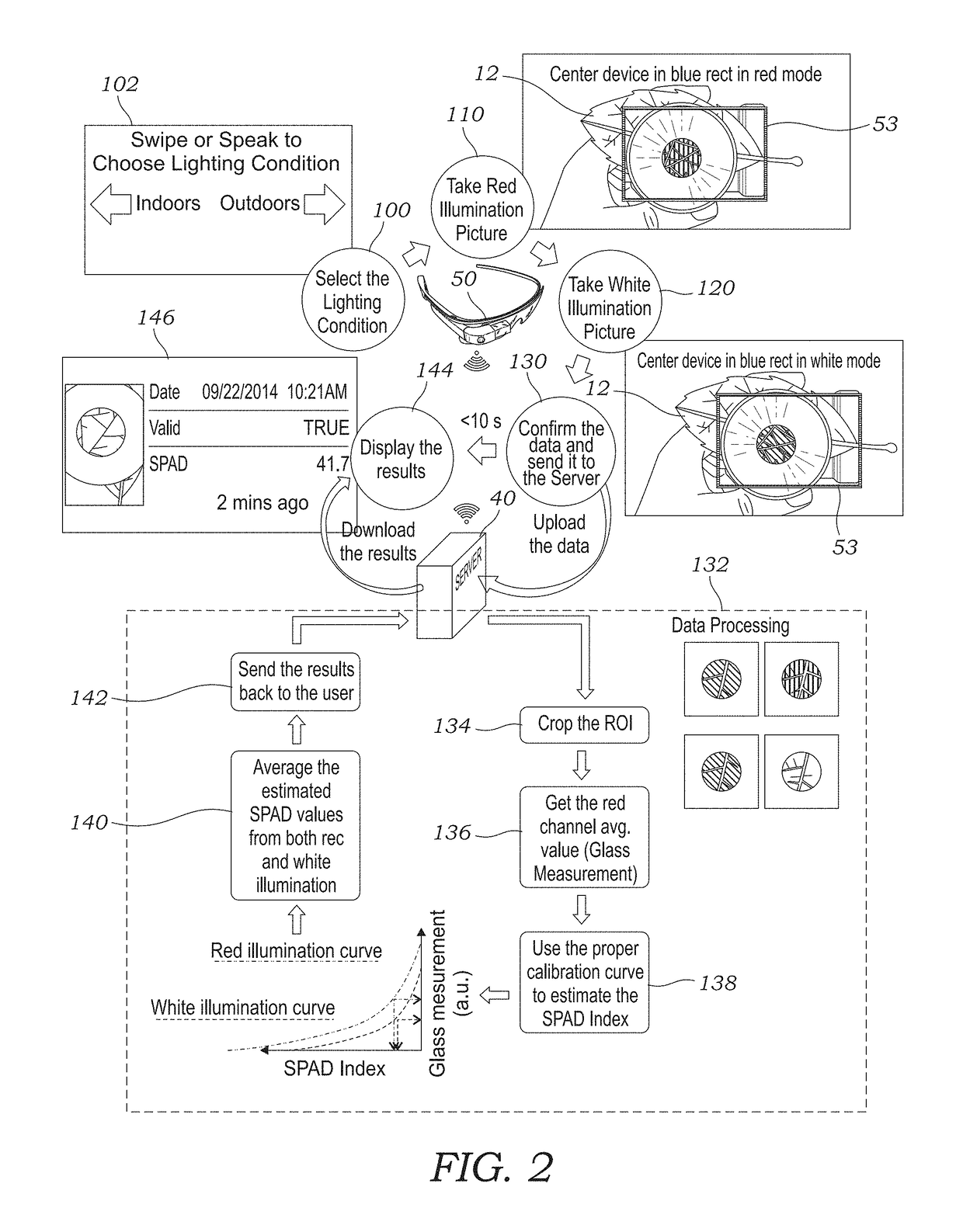
ActiveUS20180003686A1Rapid and accurate and non-destructiveRapid and non-destructiveTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsInvestigation of vegetal materialChlorophyll indexMobile electronics
A system for measuring chlorophyll concentration in a leaf sample includes a leaf-holding illuminator device with a main body containing a power source, a plurality of switchable light sources emitting light at different spectra (e.g., red and white light from a broadband light source), and a cap detachably secured to the main body using one or more fastening means. The leaf sample is interposed between the main body and the cap and held in place during imaging. The system includes a mobile electronic device having a camera configured to capture an image of the leaf illuminated by the plurality of switchable light sources, the mobile electronic device having wireless connectivity to a network and an application contained therein configured to transfer the images to a remote sever or computer via the network for data processing. A final chlorophyll index value is calculated based on the transferred images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
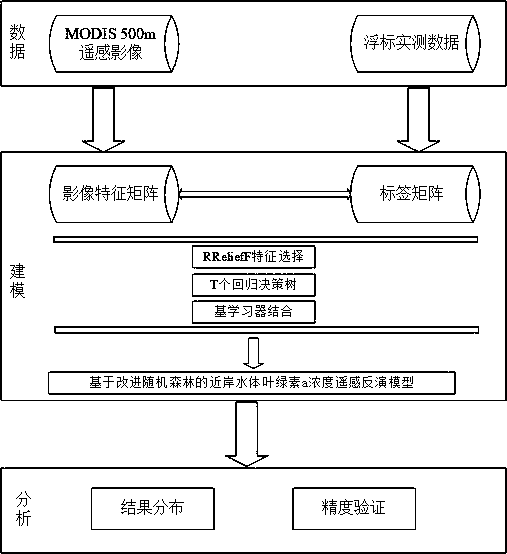
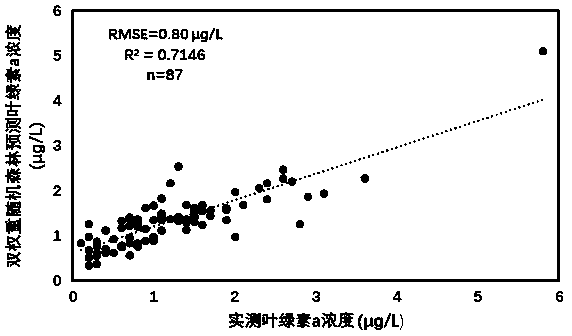
An improved random forest-based remote sensing inversion method for the concentration of chlorophyll a in an offshore water body
InactiveCN109409441AAvoid the problem of poor regression decision tree effectMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionOffshore waterBuoy
The invention relates to an offshore water chlorophyll a concentration remote sensing inversion method based on an improved random forest. remotely sensing image data by utilizing a time sequence; combining timing buoy observations, The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an intelligent remote sensing inversion model to carry out remote sensing inversion on the chlorophyll a concentration of an offshore water area by taking time continuous space sparse compensation as a modeling strategy and adopting an improved random forest-double-weight random forest method to obtain a very good inversion result, and visually and accurately displaying the spatial distribution of the chlorophyll a concentration of the offshore large range. The invention can provide a macroscopic, continuous and effective method for monitoring the concentration of chlorophyll a in the near-shore water body, can make up the deficiency of the traditional chlorophyll a concentration monitoring, and hashigher practical value.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method and device for quantification of plant chlorophyll content
ActiveUS10175215B2Reduce light changeEasy attachment/detachmentImage analysisTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsBroadband light sourceBroadband
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
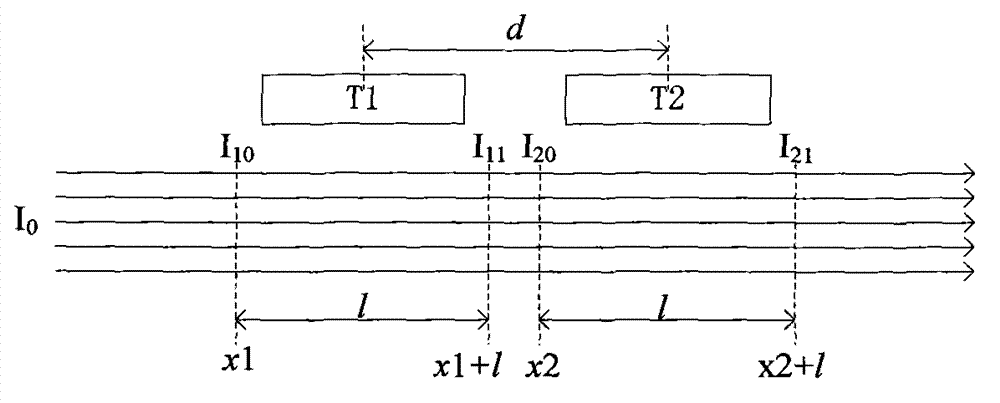
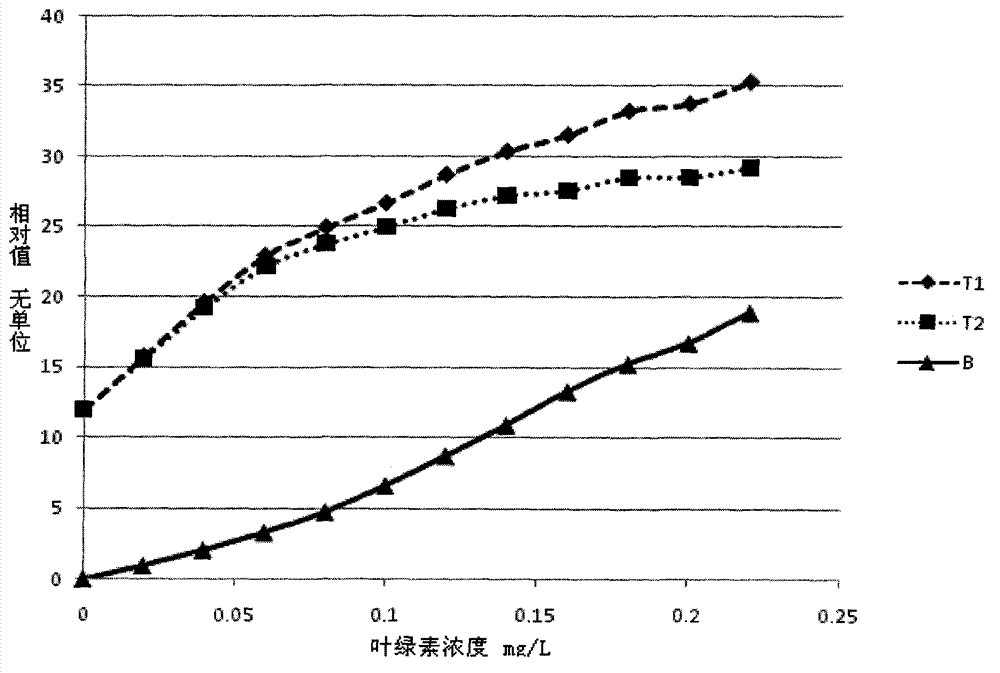
On-line detection method and device for chlorophyll concentration in water body based on two detectors
ActiveCN102928390AAvoid temperature driftHigh Common Mode Rejection RatioFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotovoltaic detectorsLight beam
The invention relates to a detection method and an in-situ detection device based on fluorescence intensity ratio of two detectors. The detection method comprises the following steps that: a light-exciting unit emits parallel light beams with certain wavelengths, and two photoelectric detectors positioned in the direction vertical to the parallel light beams and having an interval of d are used for detecting fluorescence signals; and based on the Lambert-Beer law, a proportional relation model between strength ratio of the two paths of fluorescence signals and the chlorophyll concentration in the water body is established. The detection device further comprises a signal processing unit, a window cleaning unit, a waterproof airtight cavity, an environmental protection cover unit and the like. With the adoption of the detection method and device, the influences caused by fluctuation of incident light, temperature variation, light scattering, pollution of a detection window and the like can be reduced, and the linear range of detection is expanded.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for analyzing underwater light transmission characteristic
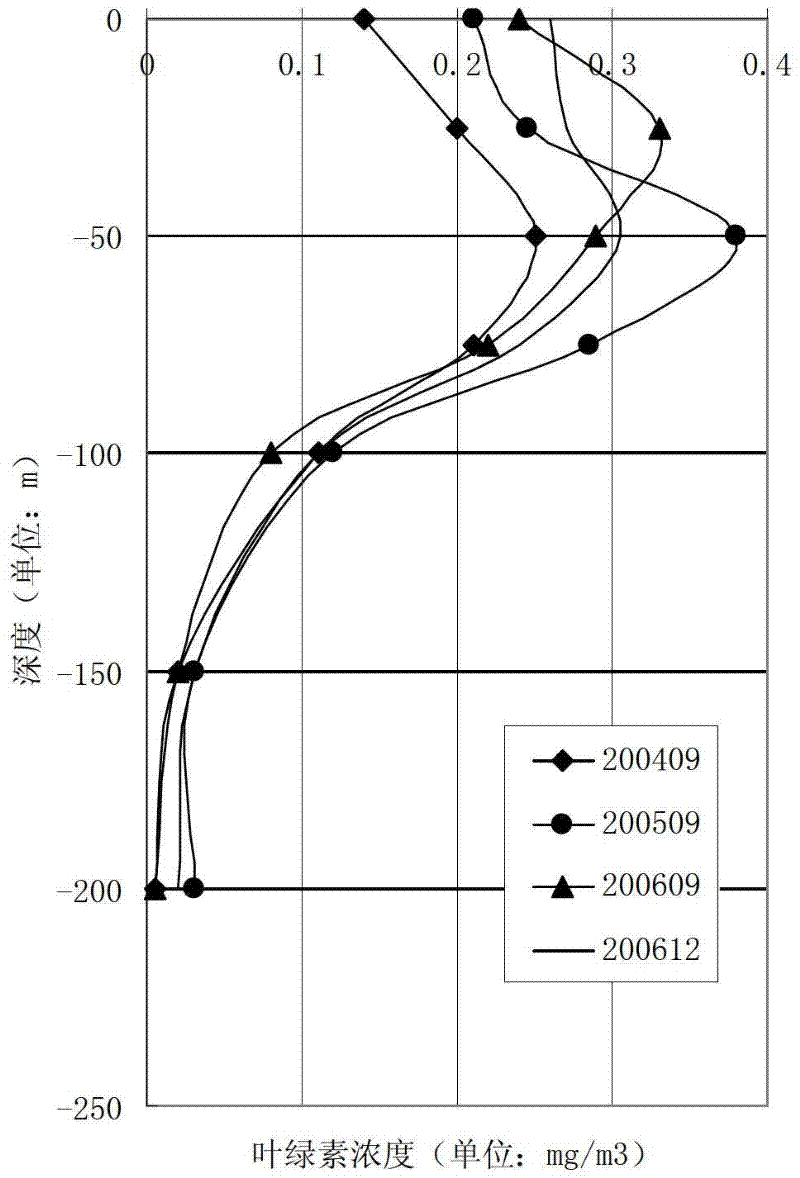
The invention discloses a method for analyzing an underwater light transmission characteristic. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, layering a water body in a depth direction, acquiring absorption coefficient values and scattering coefficient values which correspond to different layers, and calculating diffusion attenuation coefficients of the corresponding layers according to the absorption coefficient value and scattering coefficient value of each layer; 2, calculating the transmissivity of each layer according to the diffusion attenuation coefficient of each layer, multiplying the transmissivity of each layer to obtain the whole transmissivity of a water body communication channel, and correcting the whole transmissivity by adopting a truncation error to obtain the corrected whole transmissivity; and 3, outputting the transmission characteristic of the water body communication channel according to an attenuation situation of the water body. According to the method for analyzing the underwater light transmission characteristic, the communication channel transmission characteristic of light in the water is analyzed by using a vertical distribution model of chlorophyll concentration; and compared with the conventional attenuation coefficient model, the attenuation coefficient model has the advantages that the attenuation coefficients at different depths are not required to be measured through experiments, and the method is simple and is easy to apply.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Northwest Pacific Ocean ommastrephidae bartramii winter-spring stock colony abundance prediction method based on gray system
InactiveCN106203686AIncreased resource abundanceClimate change adaptationForecastingPacific oceanOcean sea
The invention discloses a northwest Pacific Ocean ommastrephidae bartramii winter-spring stock colony abundance prediction method based on a gray system. The northwest Pacific Ocean ommastrephidae bartramii winter-spring stock colony abundance prediction method comprises steps of (1) obtaining nino3.4 anomaly, PDO data, sea surface temperature SST and chlorophyll concentration ch1-a, and four sea environment and climate factors, (2) performing gray correlation analysis on four sea environment and weather factors, (3) choosing four factors having a highest association degree according to a gray association analysis result, wherein the four factors include: average sea surface temperature of an egg laying field in march, an interdecadal oscillation index of the pacific ocean in January, nino3.4 anomaly in march and average chlorophyll concentration in march; (4) establishing 8 prediction models based on the gray system according to four chosen factors; and (5) performing effective examination on 8 prediction models to choose a gray association model GM (1,4) structure as the prediction method for the northwest pacific ocean ommastrephidae bartramii winter-spring stock colony abundance. The prediction accuracy of the prediction method of the invention reaches more than 90%.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Cyanobacterial bloom prediction method based on multi-factor time sequence-random depth confidence network model
ActiveCN108416460AReduce usageImprove forecast accuracyForecastingNeural architecturesSequence analysisAlgorithm
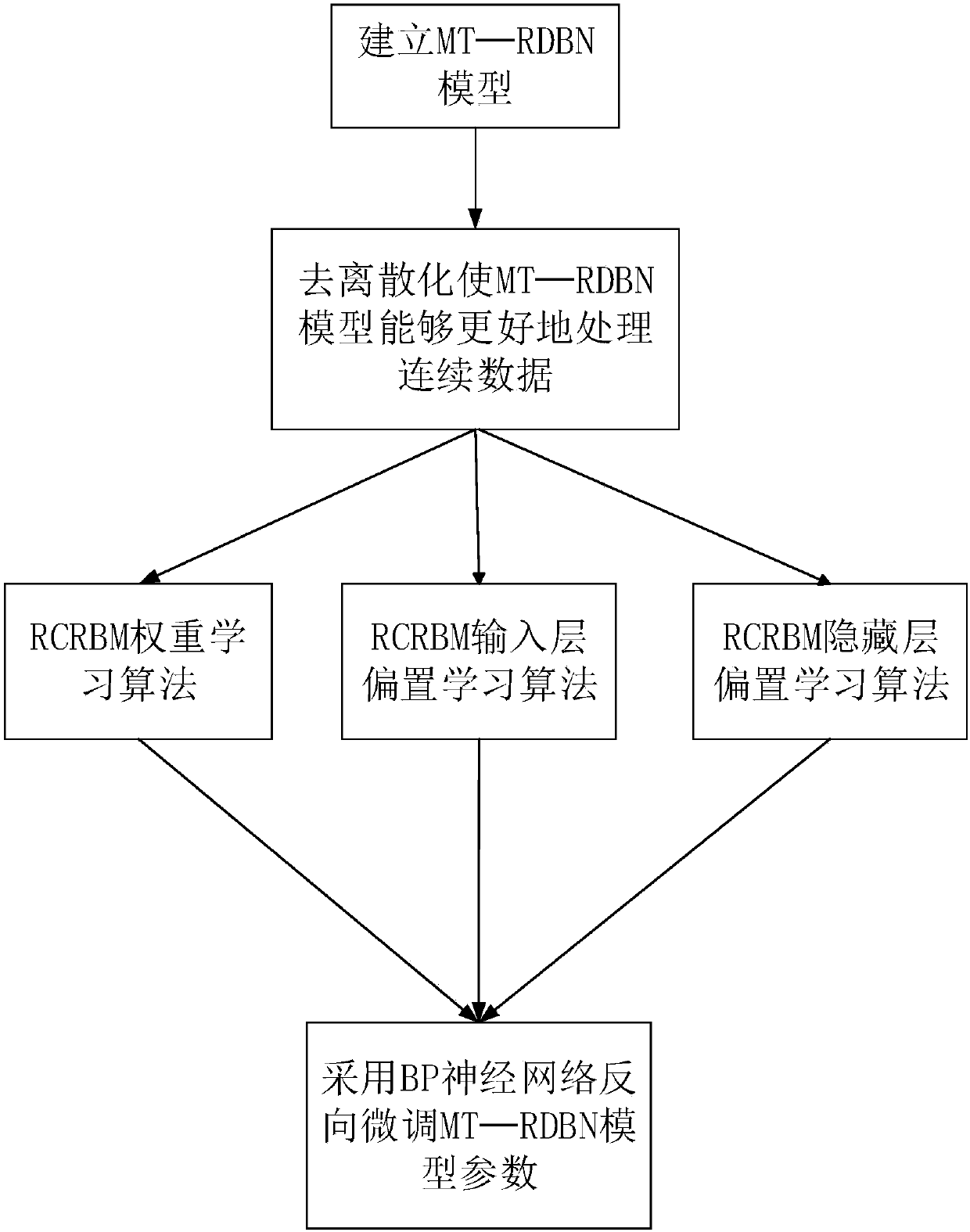
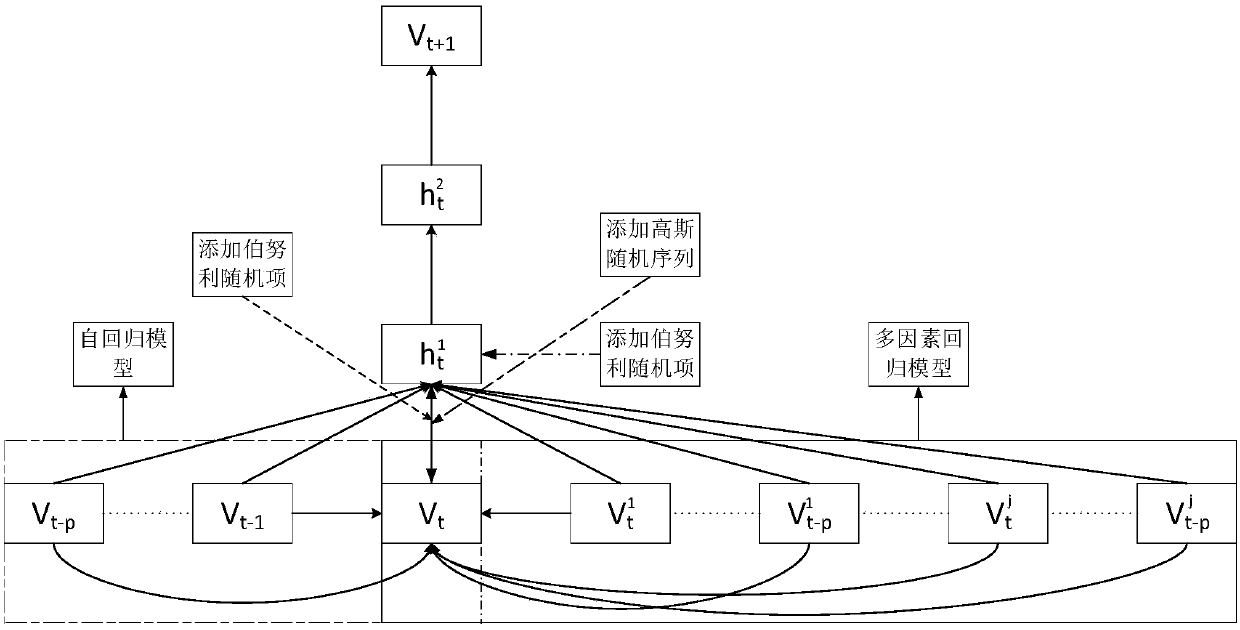
The invention discloses a cyanobacterial bloom prediction method based on a multi-factor time sequence-random depth confidence network model and belongs to the water environment prediction technologyfield. In the invention, improved depth confidence network method is combined with a multi-factor time sequence analysis method so as to construct the multi-factor time sequence-random depth confidence network model, and then, a MT-RDBN model is adopted to discretize, an RCRBM learning algorithm and MT-RDBN model parameter fine-tuning are adopted too. An autoregressive model and a multi-factor regression model in a time sequence are used when the model is established, influence factors are considered so that an MT-DBN model can predict the representation factor of a future moment through the chlorophyll concentrations and the influence factor data of a current time and a historical moments, a sample application amount is reduced and prediction precision is increased.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
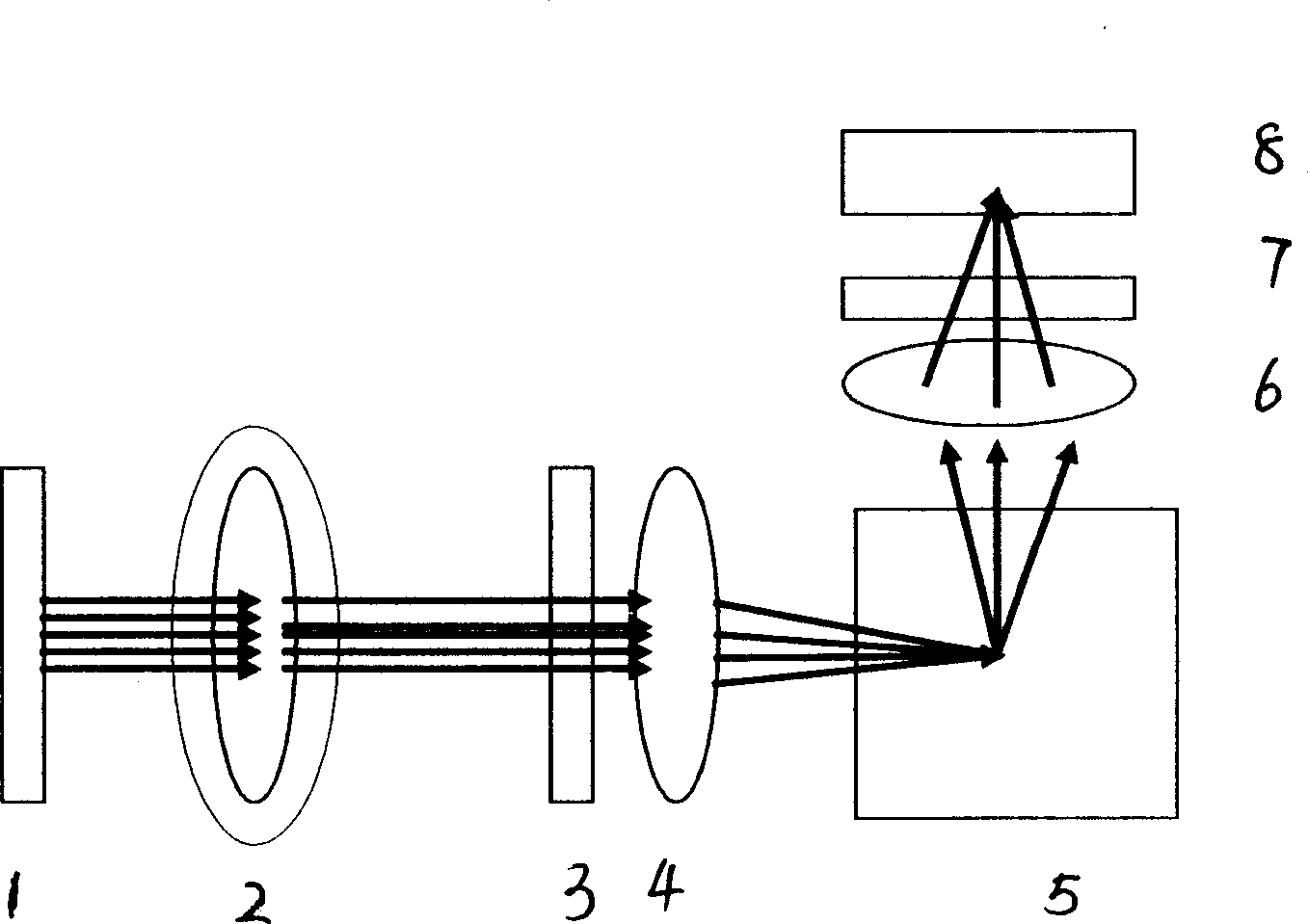
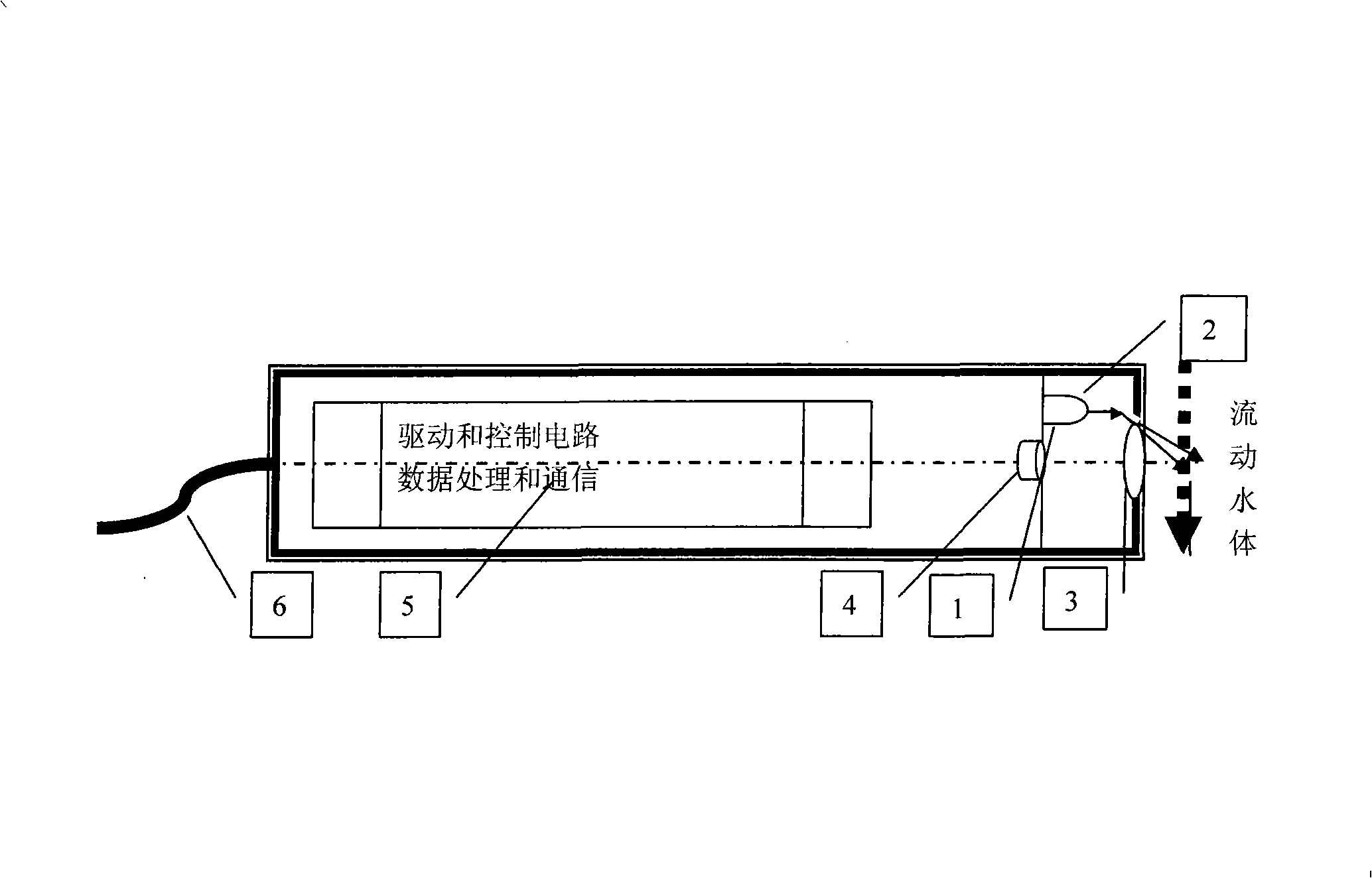
Fluorescence instrument for fast on-line measurement of water body chlorophyll concentration
InactiveCN101403695AHigh sensitivityIncrease the intensity of incident lightFluorescence/phosphorescenceData acquisitionWater quality
The invention relates to a fluorometer used for online measuring the concentration of water chlorophyll quickly, in particular to an underwater fluorometer, belonging to the water quality analysis field; wherein, the underwater fluorometer is used for the in-situ quick measurement of the chlorophyll a, thus obtaining the real-time data of a water body. The technical proposal adopted by the fluorometer is that the fluorometer comprises an LED light source which carries out output by a turning mirror, and a postpositive photodiode used for receiving the fluorescence by a condensation lens group; the output of the postpositive photodiode is sequentially output by a signal automatic gain adjustment and signal collecting circuit, a control and signal processing module, a serial port and finally an output cable to a PC or a data collection system; the signal automatic gain adjustment and signal collecting circuit, the control and signal processing module and an RS-232 serial port are arranged on a circuit board in the fluorometer; and the circuit board in the fluorometer is also provided with a light source driving circuit which is used for driving the LED light source. The fluorometer is mainly applied to the water quality analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
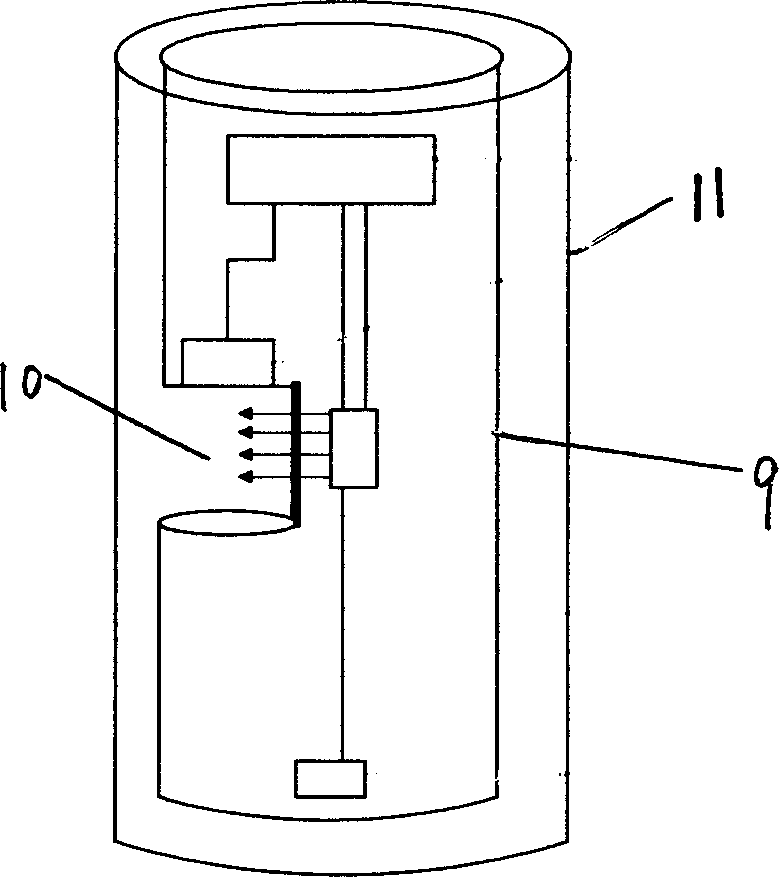
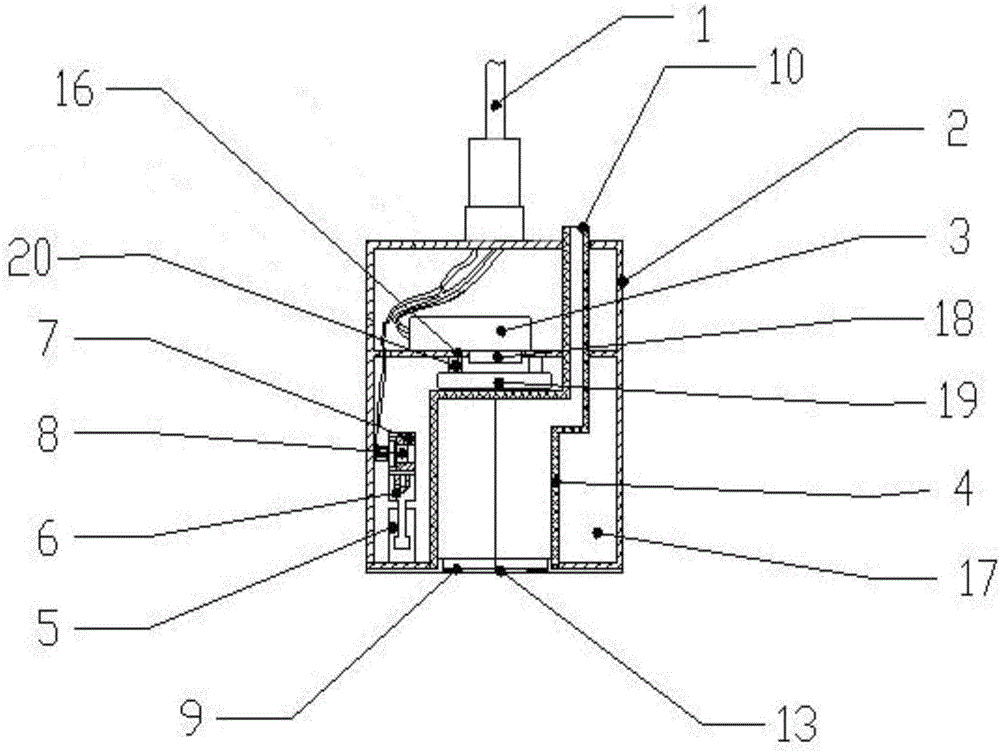
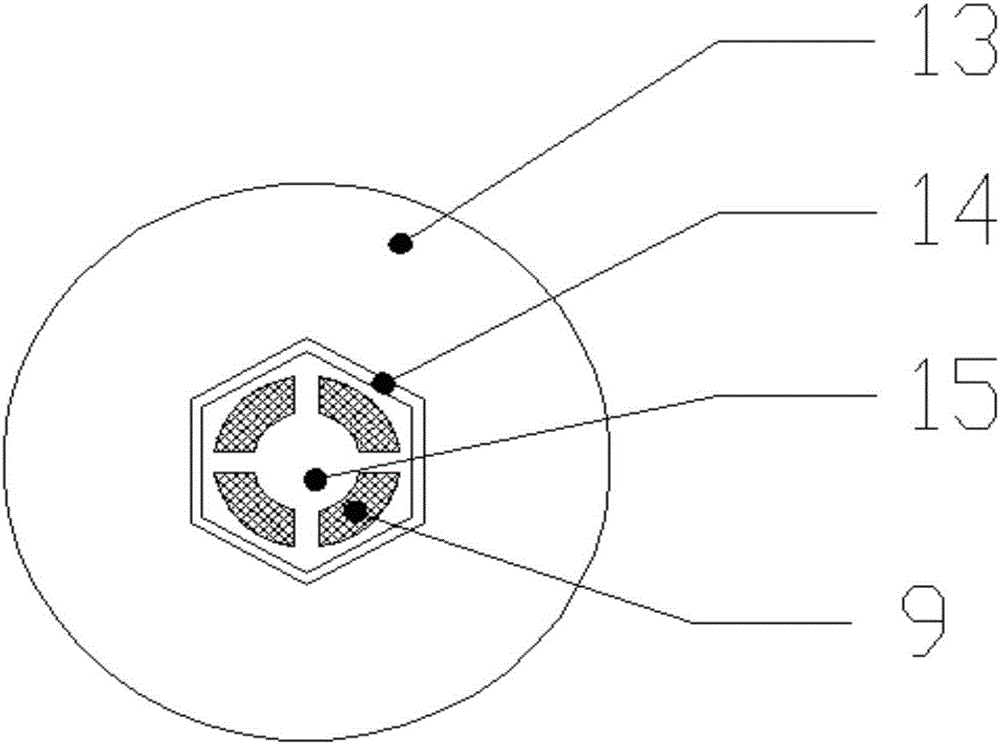
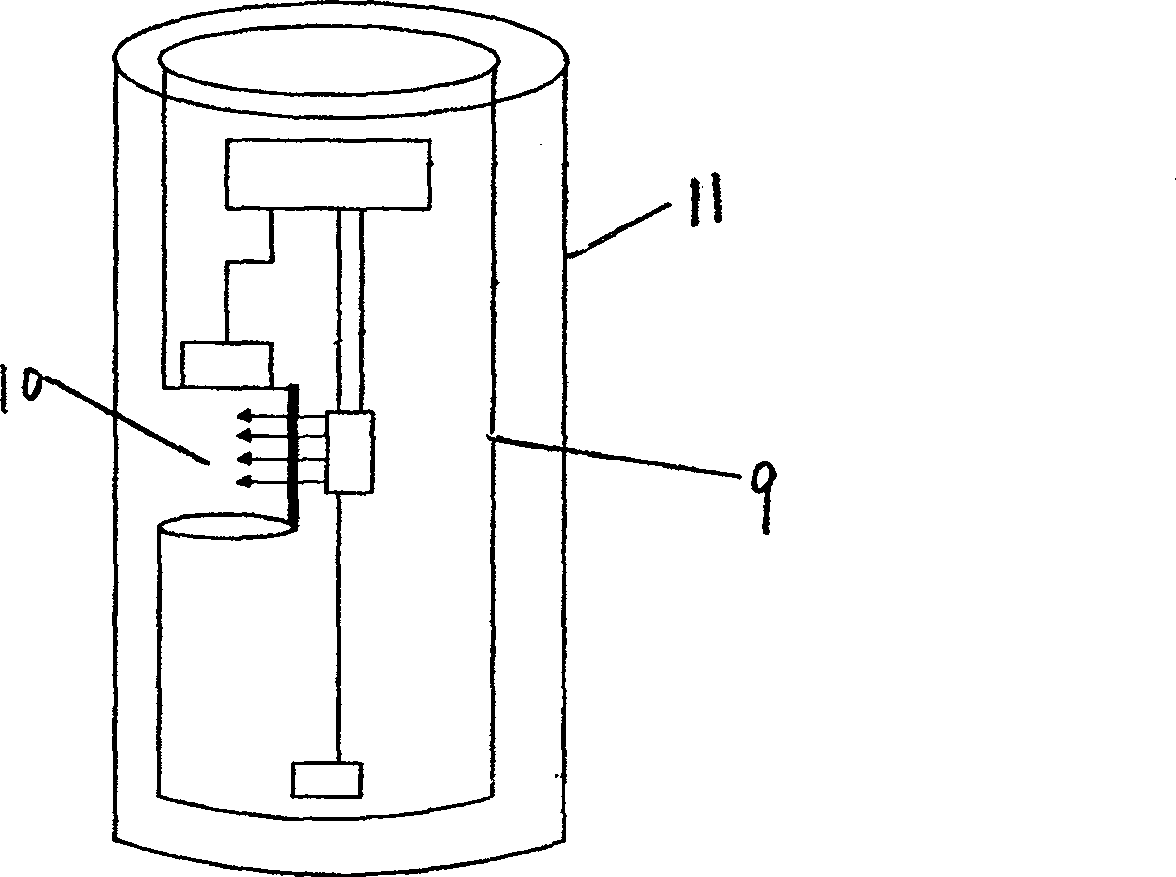
In-situ detection device for chlorophyll concentration of water and detection method of in-situ detection device
ActiveCN106092895ANo sampling requiredReduce power consumptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical pathlengthLight filter
The invention relates to an in-situ detection device for the chlorophyll concentration of water and a detection method of the in-situ detection device. The in-situ detection device and the detection method aim at solving the problems that in an existing device, the excitation light path can be not adjusted, the fluorescence intensity is low, and the fluorescence detection accuracy and sensitivity are low due to scattering generated when water contains lots of impurities. A water sample chamber water inlet device is arranged at the bottom of a quartz water sample chamber, a stainless steel shell is arranged outside the quartz water sample chamber, a detector, a light filter and a focusing lens are arranged over the quartz water sample chamber, a light source, a light source transverse adjustment support, a light source transverse adjustment mechanism and a light source direction adjustment mechanism are arranged on the side face of the quartz water sample chamber, and the detector, the light source, the light source transverse adjustment mechanism and a light source incidence angle adjustment mechanism are connected with a host through wires. The method includes the steps that water background fluorescence signals measured under the off-state of the excitation light source are collected, then water fluorescence signals under the on-state of the excitation light source are collected, and background fluorescence interference is automatically subtracted through operation.
Owner:NO 49 INST CHINESE ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP +1
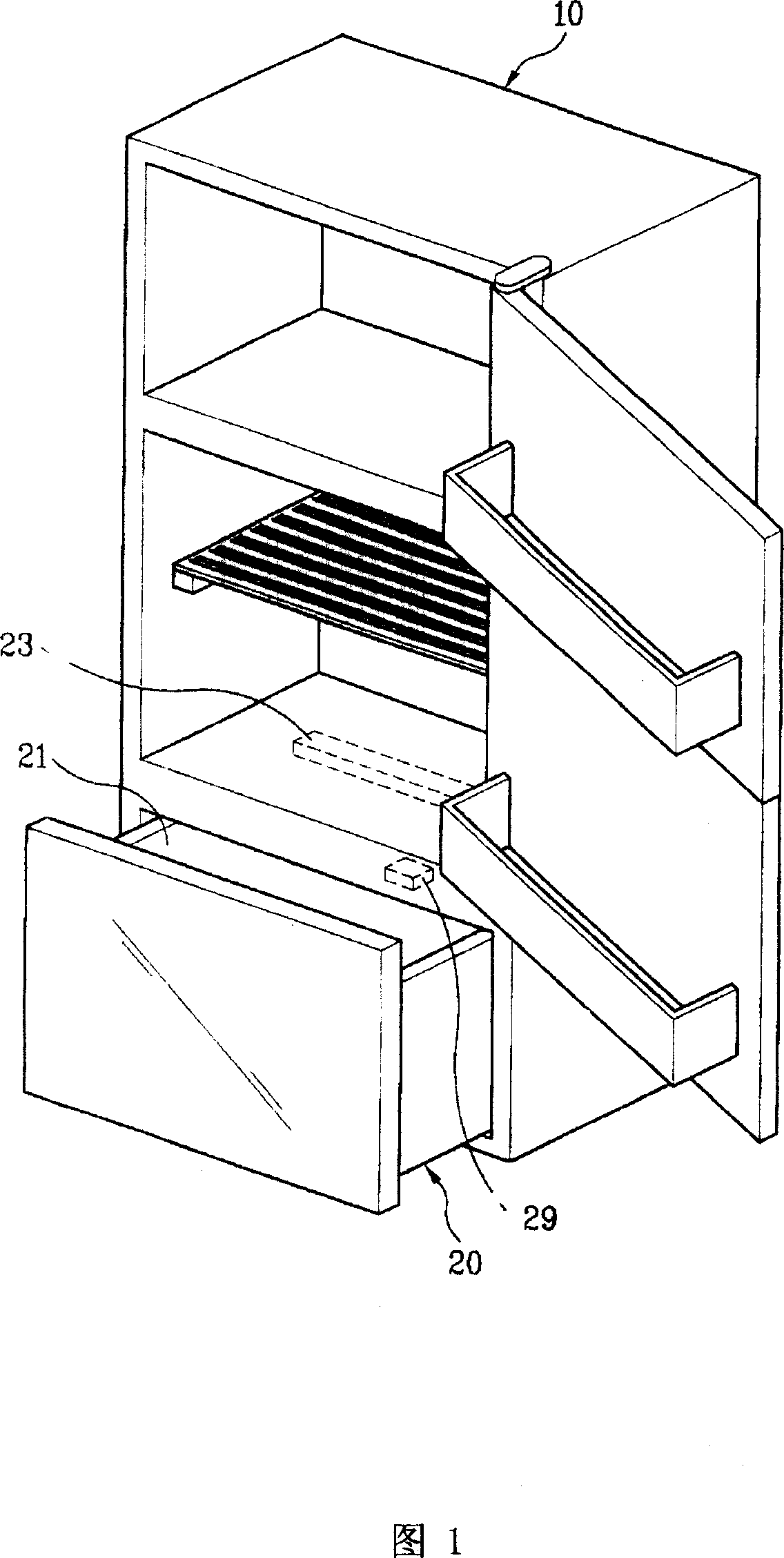
Foodstuff preserving container, refrigerator with the same and foodstuff preserving method
InactiveCN101085651AIncreased freshness maintenance effectReduce concentrationLighting and heating apparatusShock-sensitive articlesFood categoryCool storage
A food container comprises the storage chamber, emitting device reflecting visible lights into the storage chamber reflecting based on the stored food, with the storage chamber composed of ultraviolet emission device, light deruster module of the optical catalytic filter. It also provides cooling storage method. It keeps food based on the color to choose the best light to reduce the impact to chlorophyll. It obviously keeps several foods category, improved in effect. Users can choose the color of the stored goods to set the proper light.
Owner:TAIZHOU LG ELECTRONICS REFRIGERATOR CO LTD
Chlorophyll and turbidity sensor system
ActiveUS8654319B2SamplingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorForward scatterWireless control
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Apparatus and processes for photosynthetic activity measurement and mapping
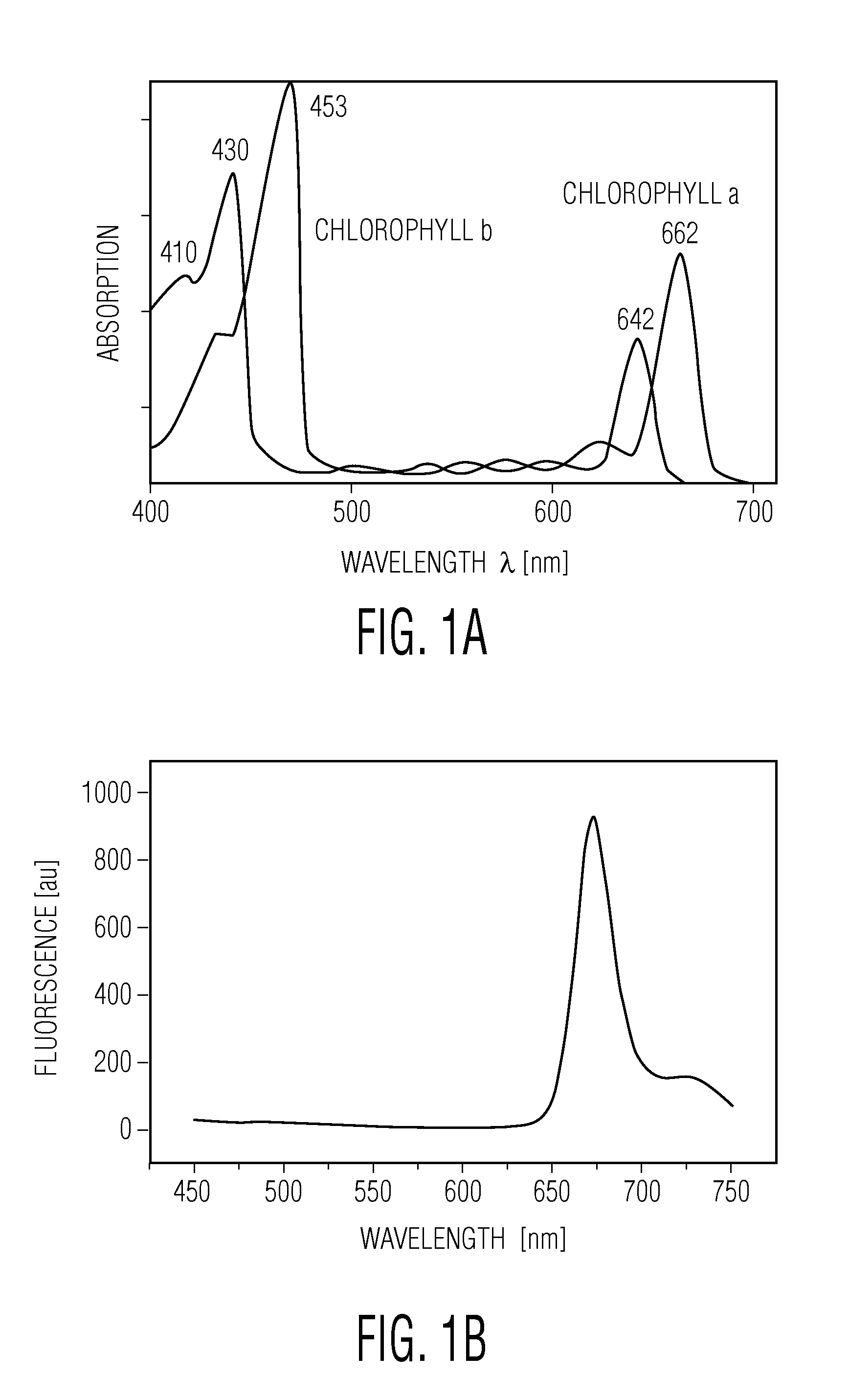
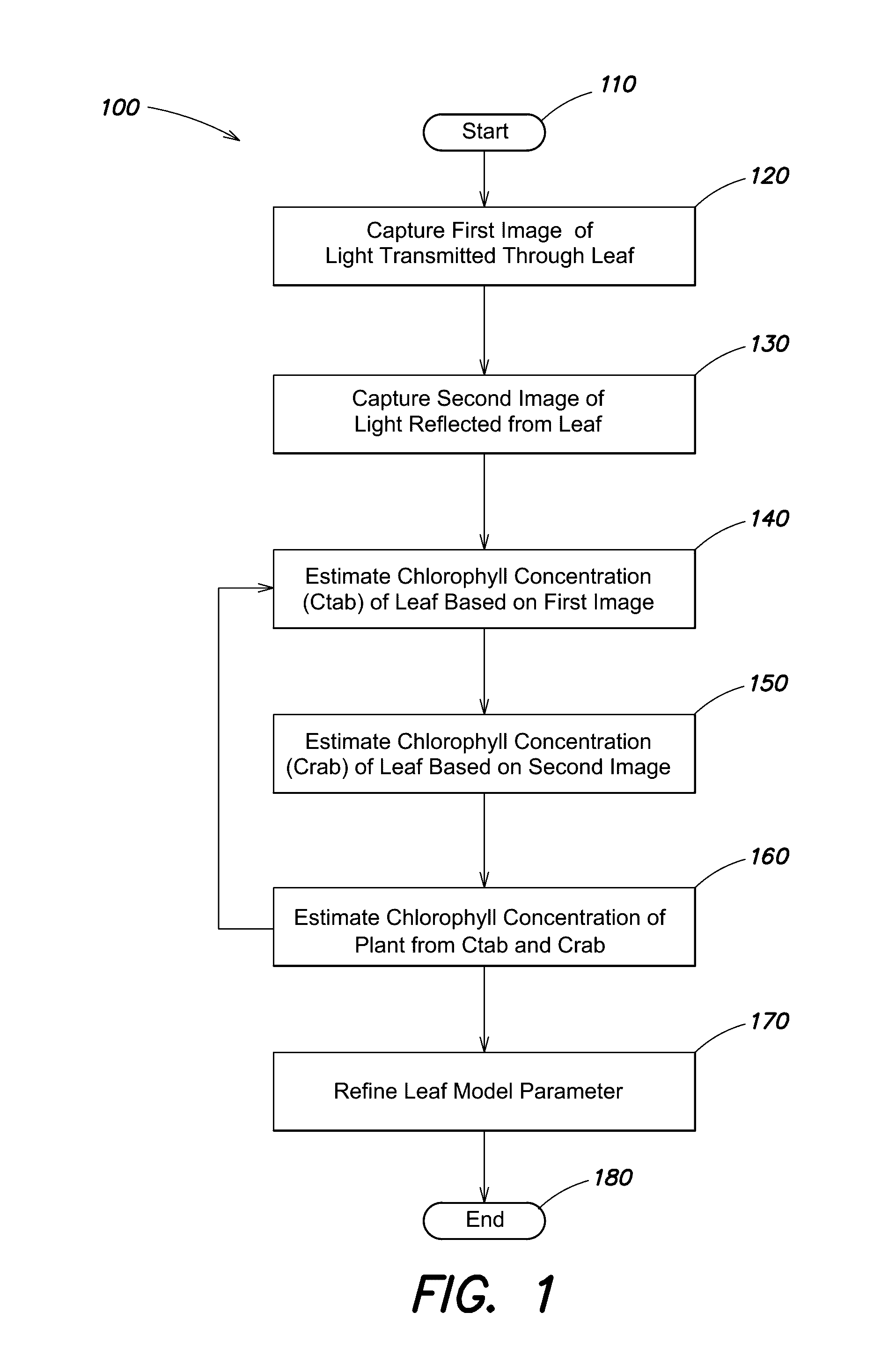
A method for determining chlorophyll content of a plant comprises capturing a first image comprising light transmitted through a leaf of a plant; capturing a second image comprising light reflected from the leaf of the plant; estimating, from a plurality of pixels in the first image, a transmissive chlorophyll concentration value of the leaf; estimating a reflectance chlorophyll concentration value for the leaf from a plurality of pixels in the second image using bidirectional reflectance parameters for which a variance of the reflectance chlorophyll concentration value across the plurality of pixels in the second image is reduced; and determining an estimated chlorophyll concentration value for the plant based at least on the transmissive chlorophyll concentration value and the reflectance chlorophyll concentration value.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
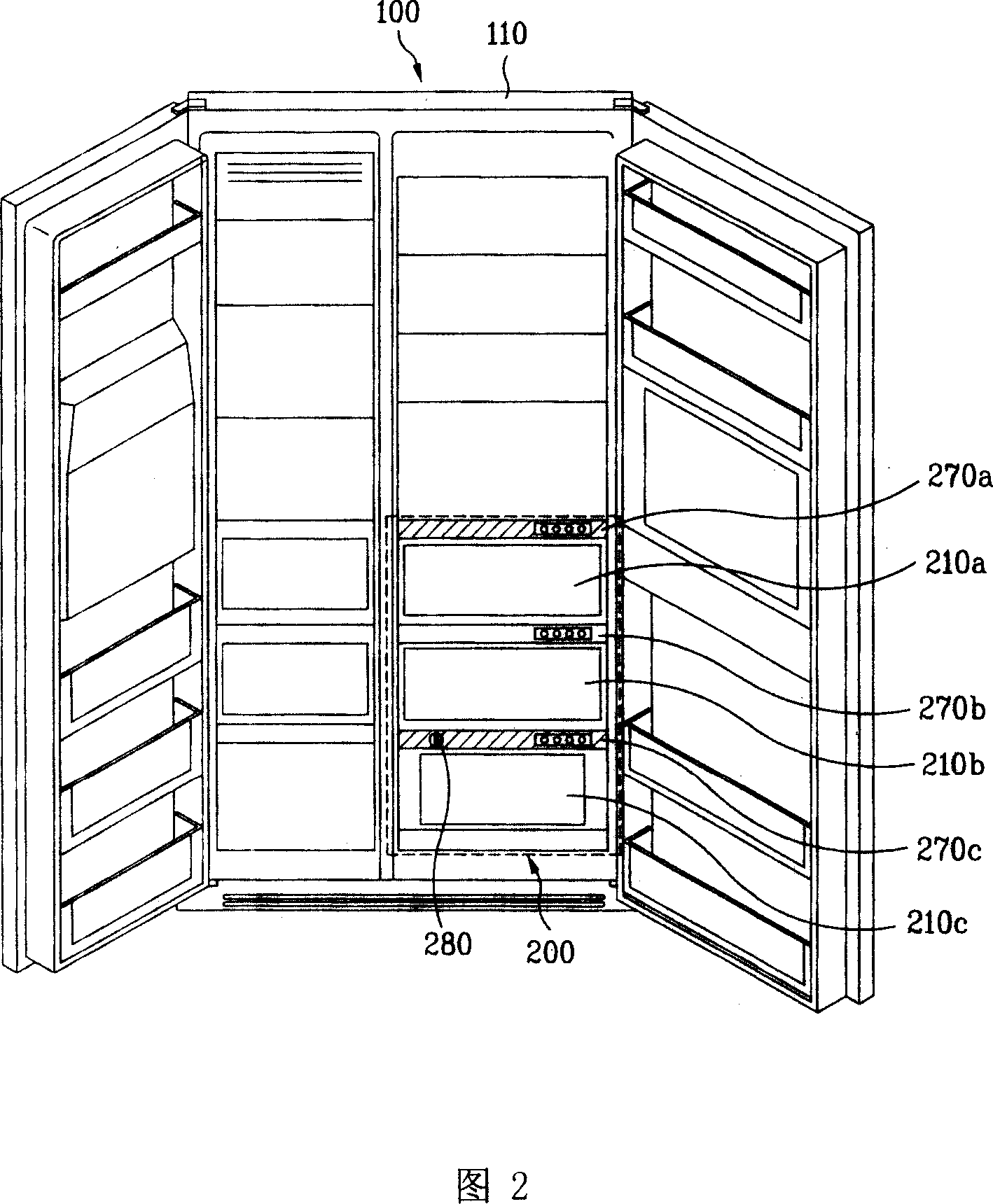
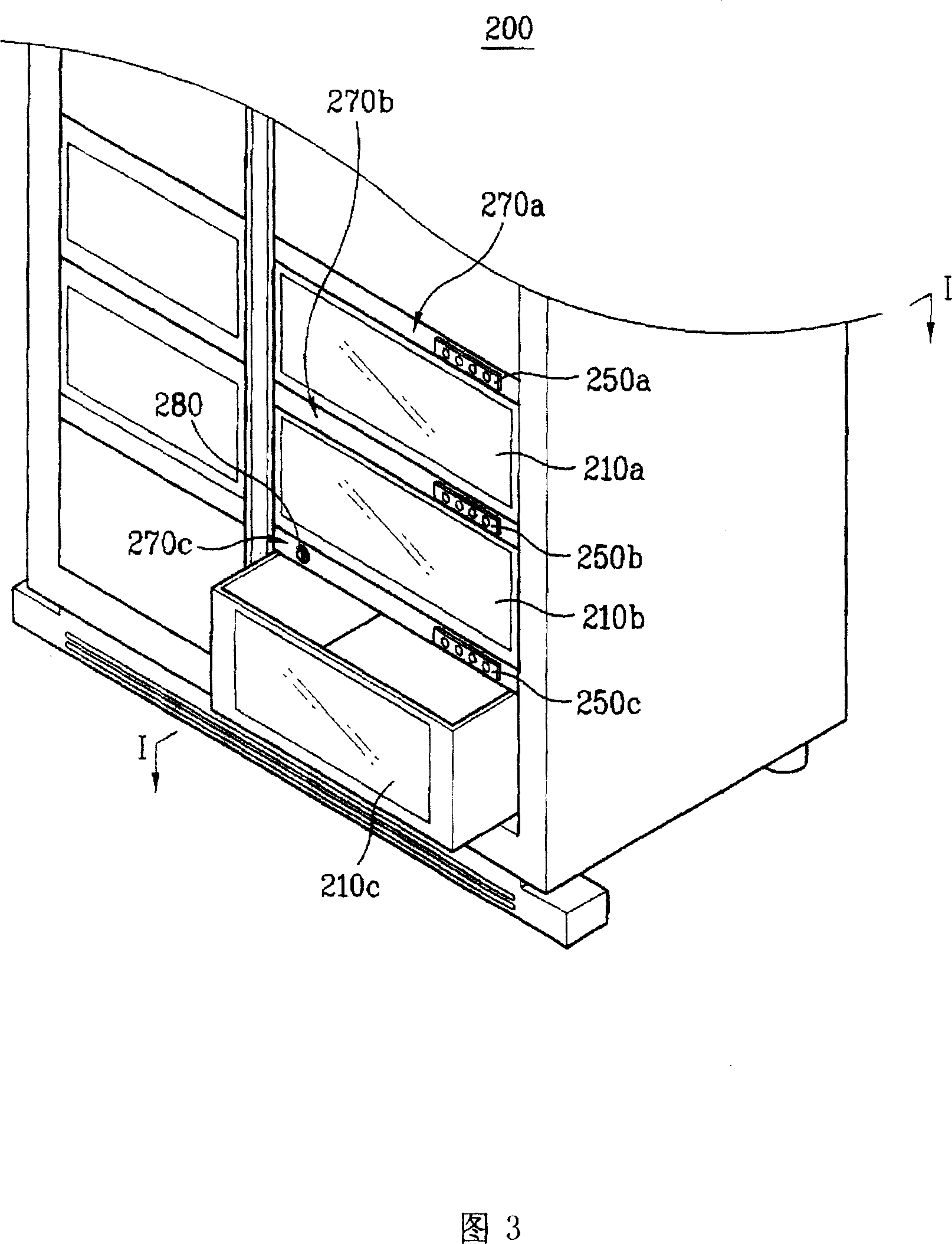
Refrigerator and food preservation method employing the refrigerator
InactiveCN101086410AGuaranteed freshnessImprove satisfactionLighting and heating apparatusLighting arrangementEngineeringFood classification
The invention discloses a refrigerator and a food saving method with the refrigerator. The refrigerator comprises the following parts: a body, a plurality of saving chambers for saving the food in the body, a lighting device for lighting the saving chamber with the visual range light with the same saving food color in the saving chamber. The refrigerator has the effect by the following: firstly, lighting the same food color light to the classified food according to the food color in order to keep the food fresh and avoid reducing the chlorophyll concentration with the lighting device; secondly, determining the basic standard guideline of the food classification in a plurality of saving chambers in order to guarantee the effect of the saving chambers; thirdly, selecting the light color which is fit for saving the food according to the saving food color by the users; fourthly, improving users' satisfactory degree for the lighting device by selecting the light color conveniently and the definite and visual selection method.
Owner:TAIZHOU LG ELECTRONICS REFRIGERATOR CO LTD
Chlorophyll inversion method suitable for sparse vegetation area
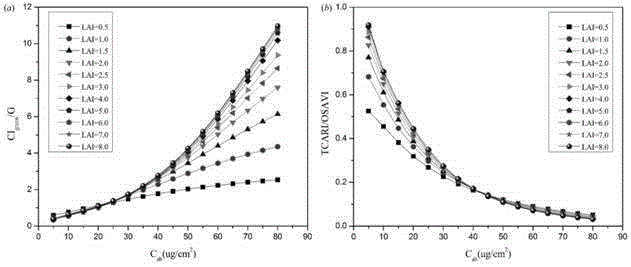
InactiveCN105352893AImprove inversion accuracyReduce the impact of inversion resultsColor/spectral properties measurementsVegetationAccuracy improvement
The present invention discloses a method for reducing soil background influence on chlorophyll inversion results by use of vegetation index combinations. Firstly, remote sensing image atmospheric correction is performed, two vegetation index combinations CIgreen / G and TCARI / OSAVI are calculated, and finally the two vegetation index combinations are introduced a model cost function for regional inversion. In low chlorophyll concentration region, the CIgreen / G is used for controlling the inversion result; in medium and high chlorophyll concentration regions, the TCARI / OSAVI is used for controlling the inversion result, and chlorophyll content subregion threshold can be determined according to the actual situation. LAI can be set to a fixed value when the method is used for chlorophyll inversion, and model execution efficiency and inversion accuracy improvement can be facilitated. The technical method has an obvious effect of reduction of soil background influence in sparse vegetation area chlorophyll inversion process.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
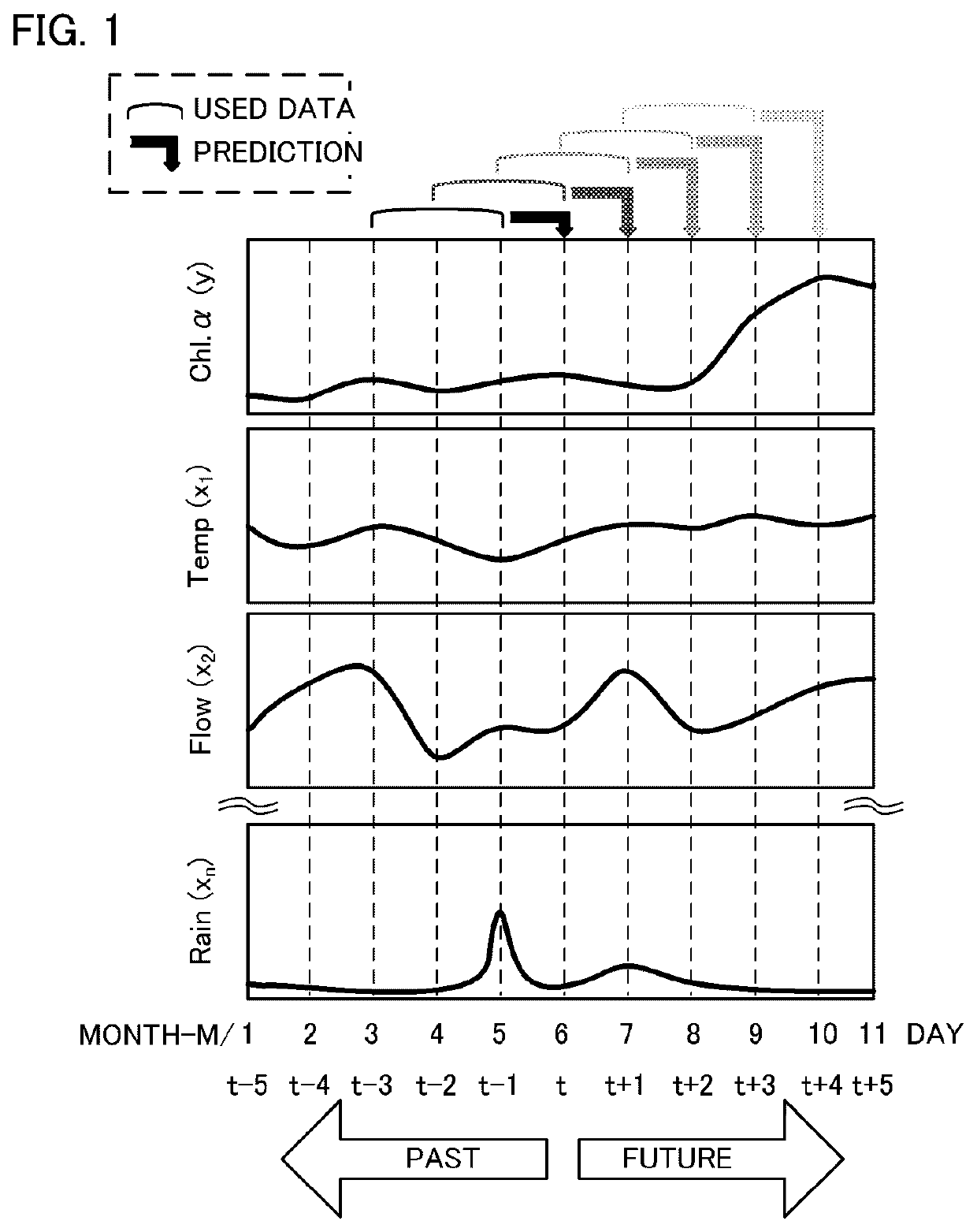
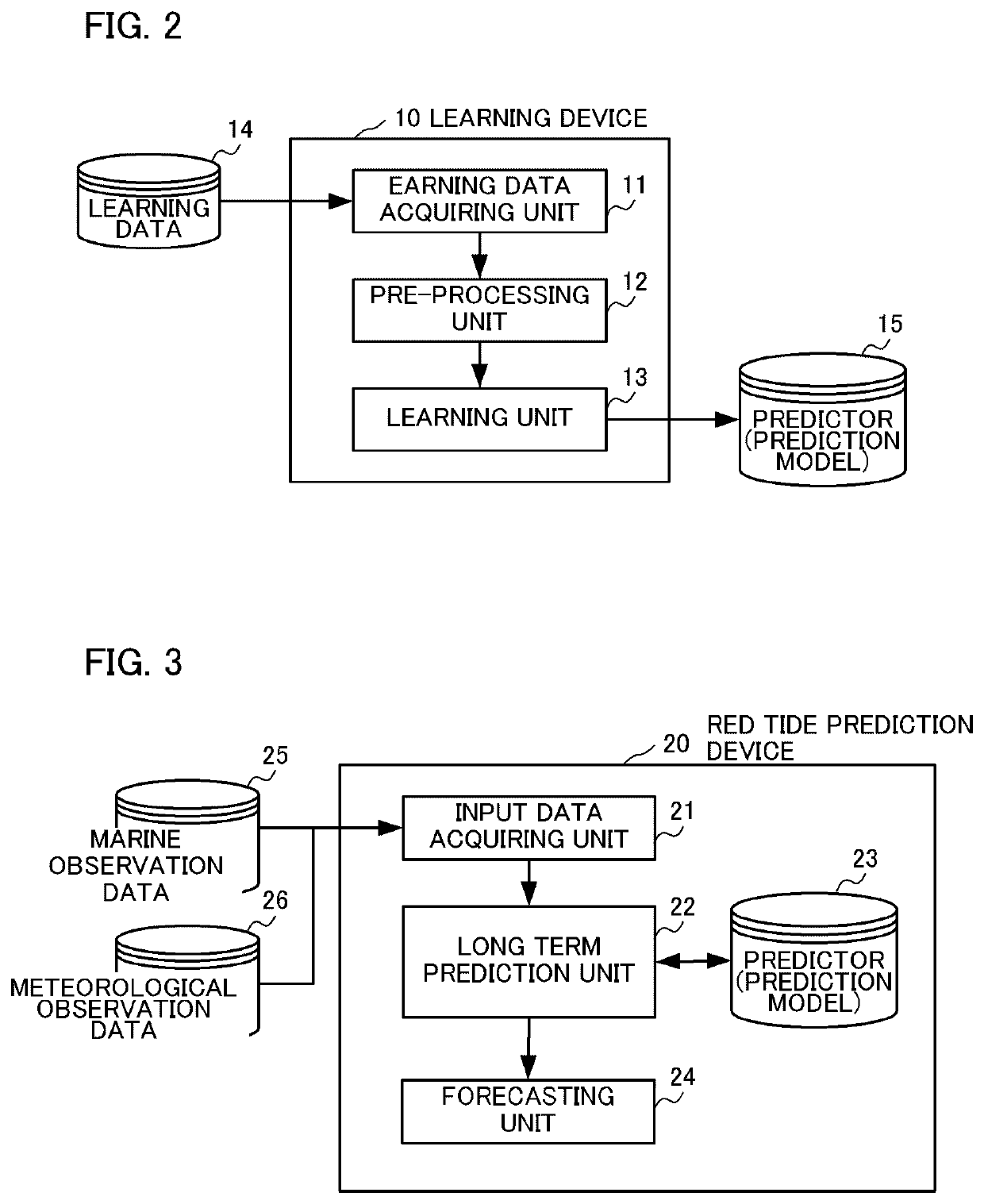
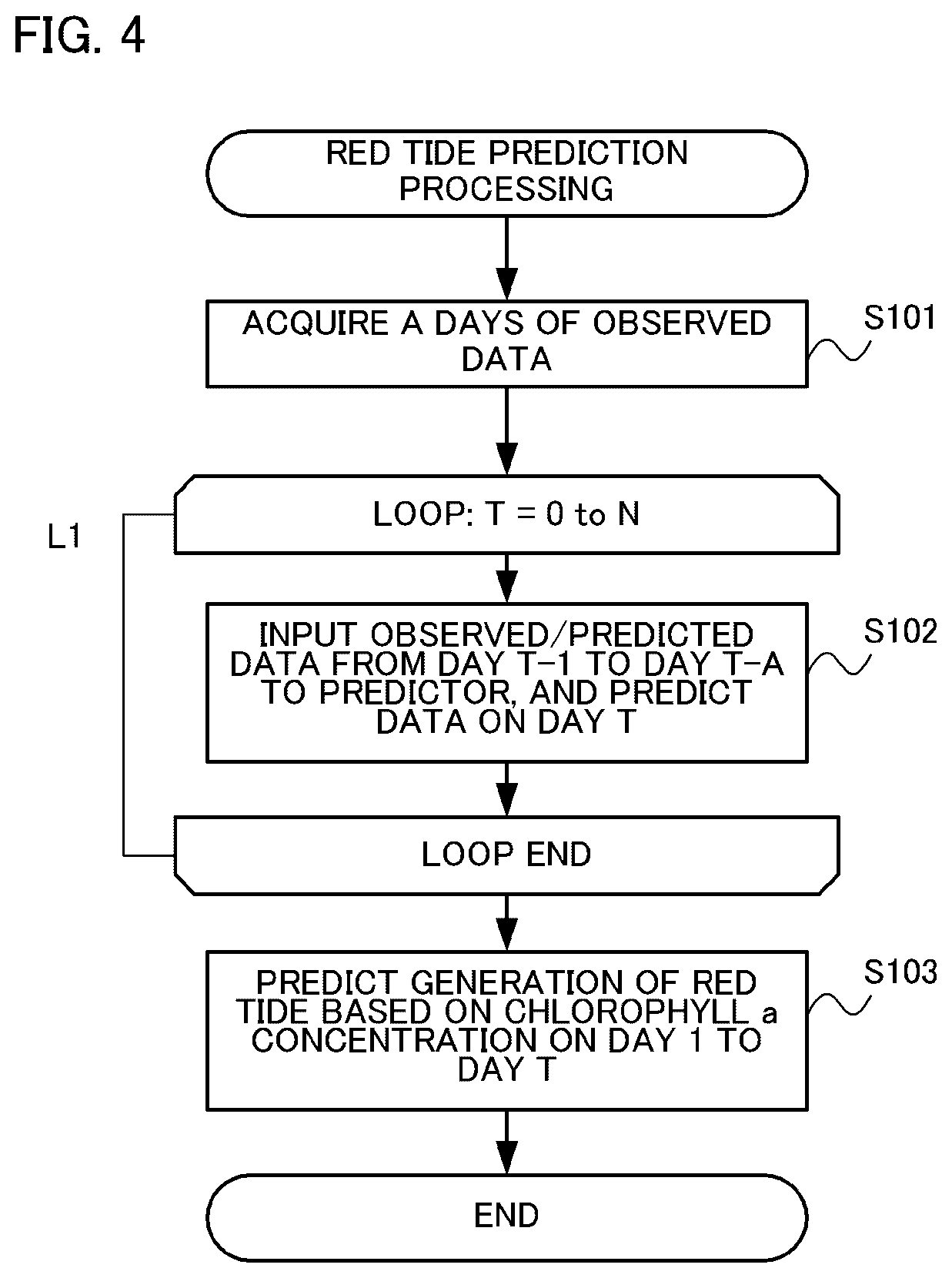
Device, method and program for environmental factor estimation, learned model and recording medium
PendingUS20220198303A1Improve accuracyIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesHydraulic engineering apparatusWater qualityAtmospheric temperature
Provided is an environmental factor prediction device that includes a predictor and predicting means. The predictor uses, as explanatory variables: water quality data in a plurality of layers in water, the data including a value corresponding to a biochrome level or a bioluminescence level (e.g. chlorophyll concentration), water temperature, salt concentration, dissolved oxygen, turbidity and flow rate; and meteorological data including atmospheric temperature, precipitation and sunshine duration, and outputs an estimated value of each item of the explanatory variables at a unit time later, based on time series data of the explanatory variables. The predicting means predicts the water quality data up to an N unit time later by repeating prediction using the estimated value acquired by the predictor as input of the predictor again. According to the present invention, the environmental factors that cause generation of red tide, blue tide or water bloom, diseases of fish, and the like, can be predicted, on a long term basis and at high accuracy.
Owner:RIKEN
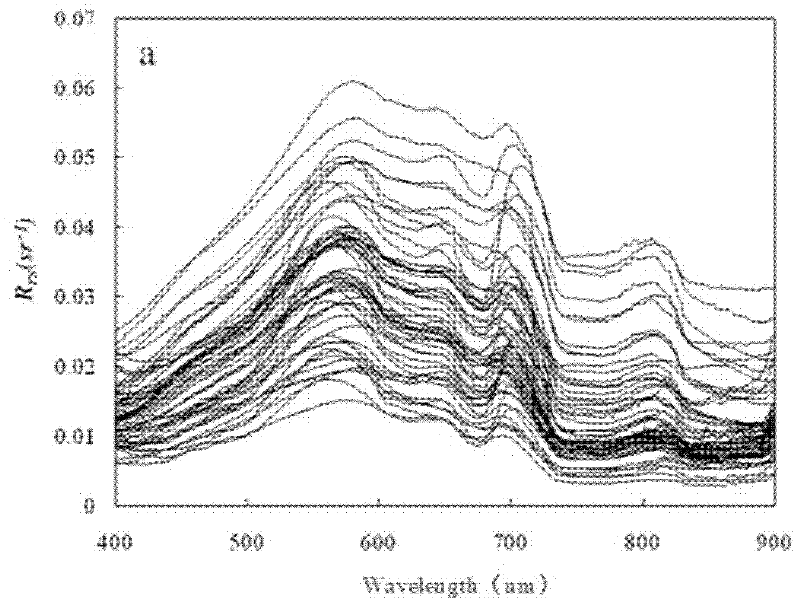
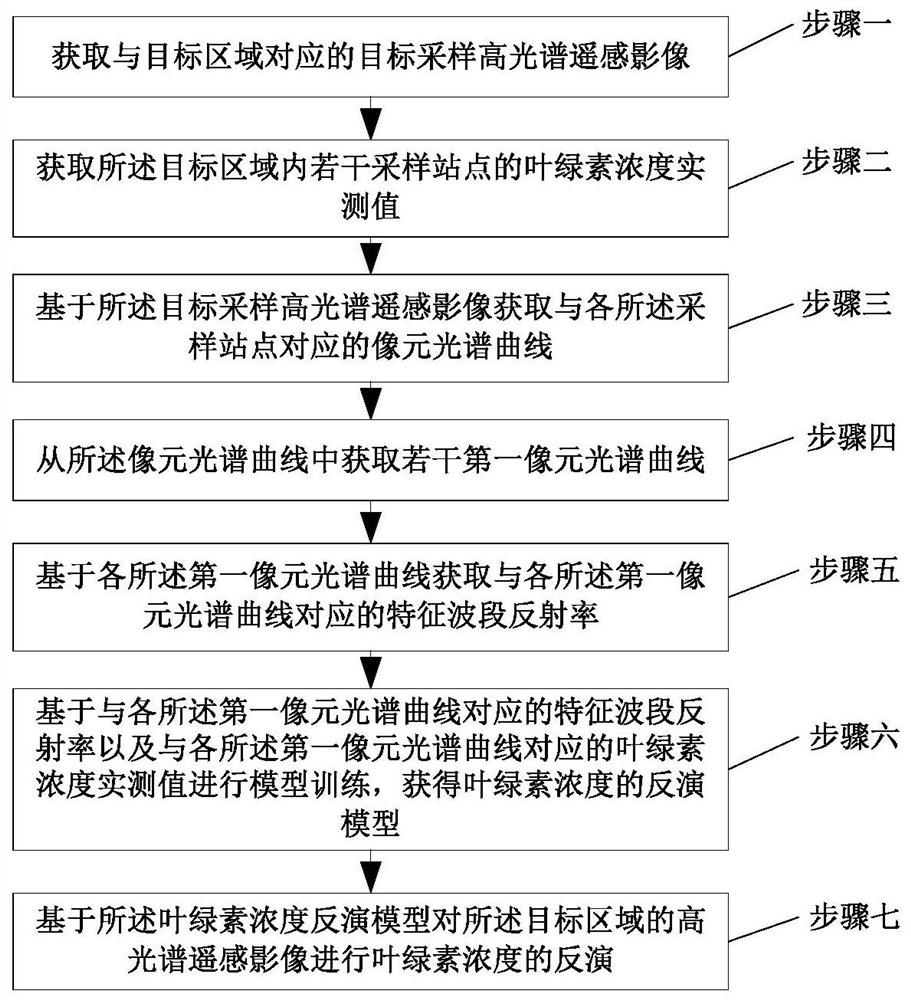
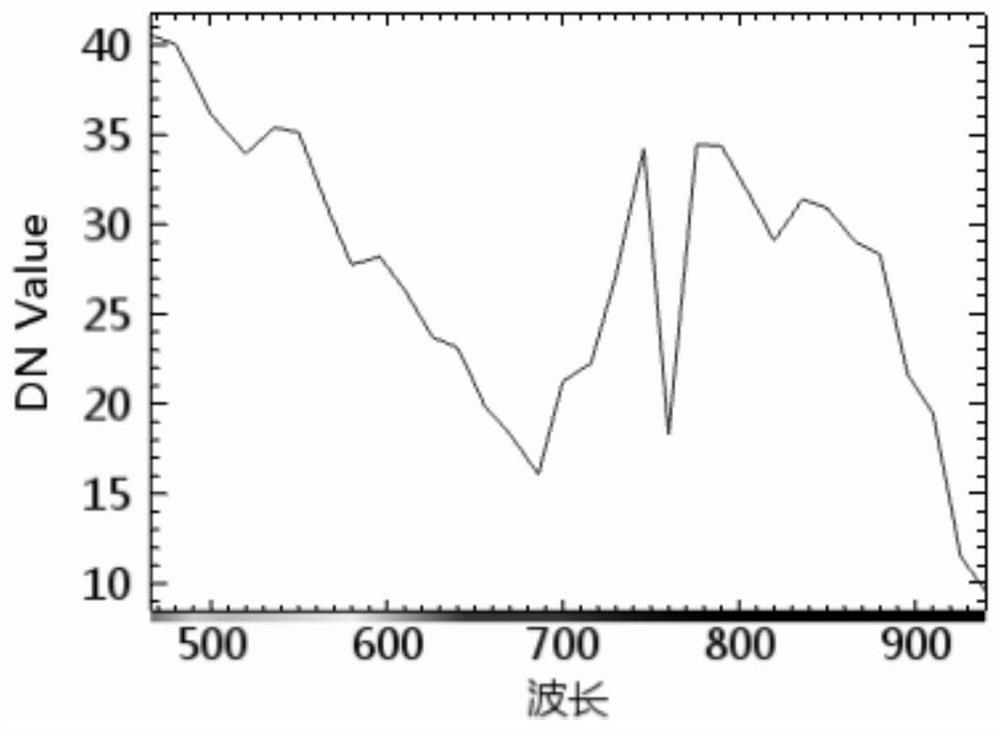
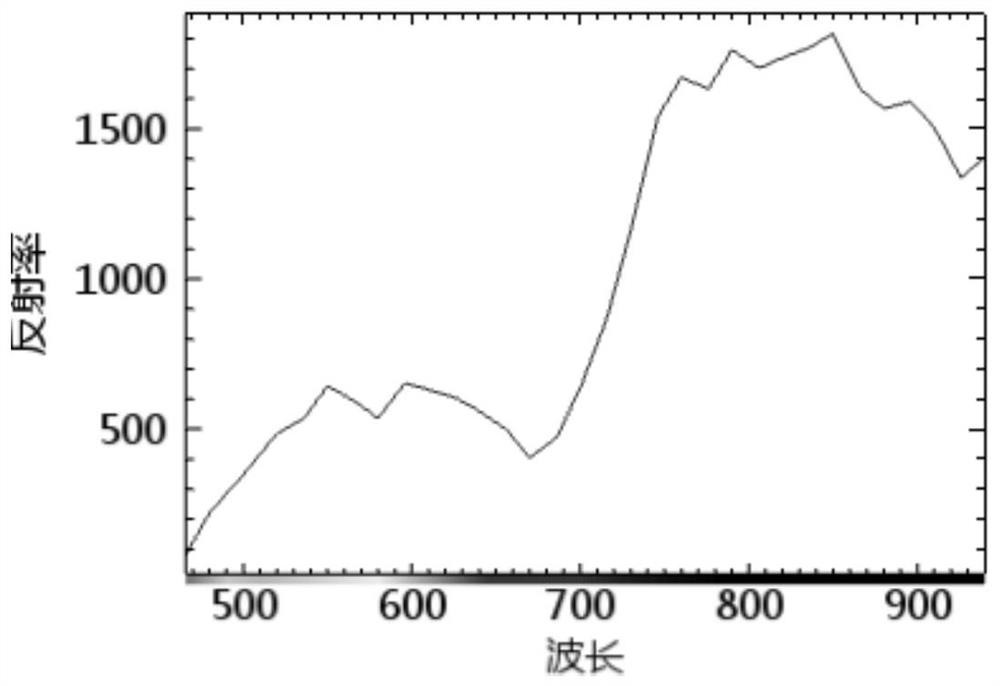
Water chlorophyll concentration inversion method and device based on hyperspectral remote sensing
PendingCN112504979AThe characteristic band reflectivity is good forAccurate acquisition of chlorophyll concentrationColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectral curveAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a water chlorophyll concentration inversion method and device based on hyperspectral remote sensing. The method comprises the steps that a target sampling hyperspectral remotesensing image corresponding to a target area is acquired; obtaining chlorophyll concentration measured values of a plurality of sampling stations in the target area; acquiring a pixel spectral curve corresponding to each sampling site based on the target sampling hyperspectral remote sensing image; obtaining a plurality of first pixel spectral curves from the pixel spectral curves; acquiring characteristic waveband reflectivity corresponding to each first pixel spectral curve based on each first pixel spectral curve; performing model training based on the characteristic waveband reflectivity corresponding to each first pixel spectral curve and the chlorophyll concentration measured value corresponding to each first pixel spectral curve to obtain an inversion model of chlorophyll concentration; and performing chlorophyll concentration inversion on the hyperspectral remote sensing image of the target area based on a chlorophyll concentration inversion model.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
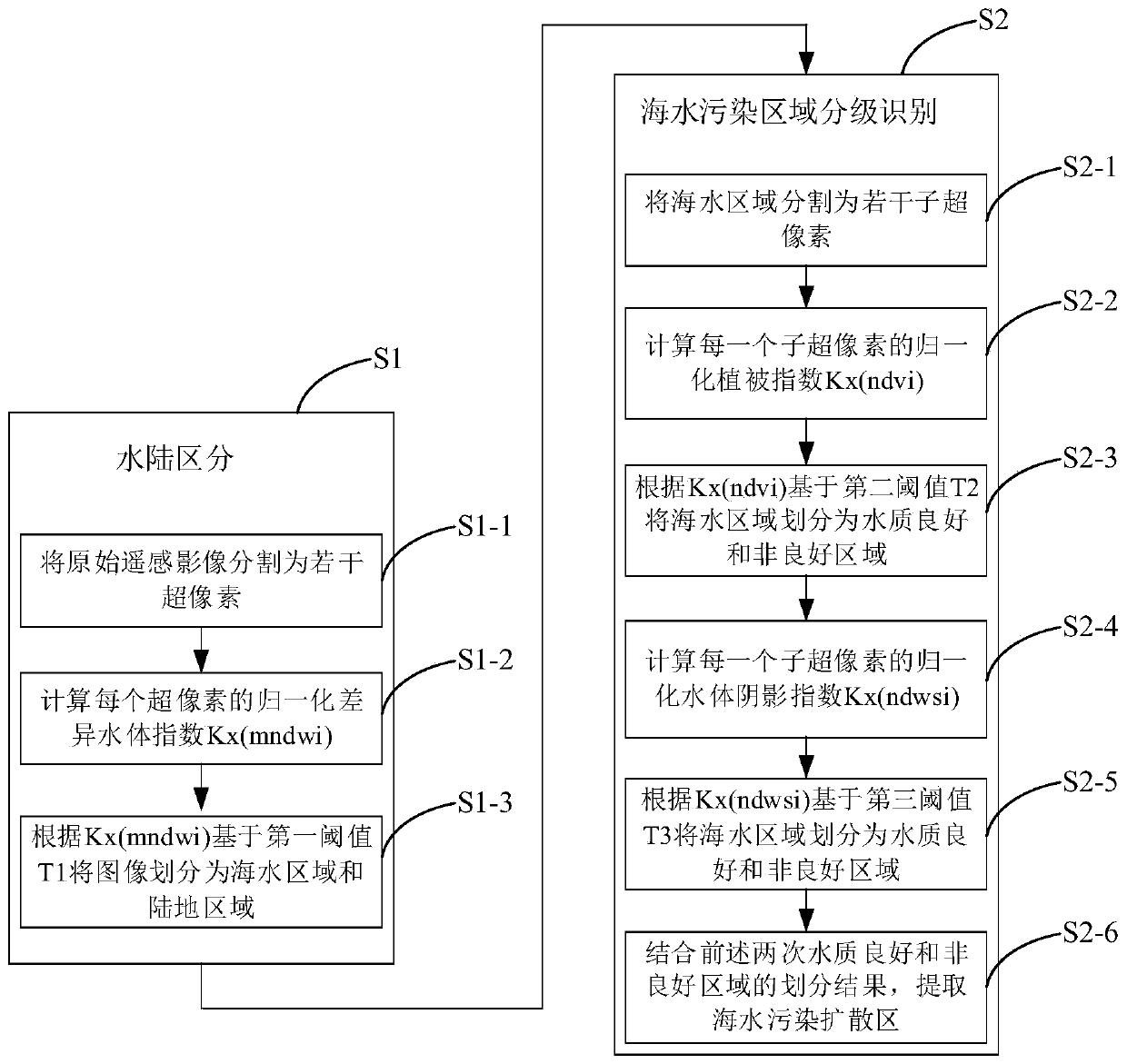
Seawater pollution area identification method and device based on high-resolution remote sensing image
ActiveCN110765941AImprove efficiencyImprove timelinessImage enhancementImage analysisImaging interpretationWater quality
The invention discloses a seawater pollution area identification method and device based on a high-resolution remote sensing image, and belongs to the field of digital image processing. The method comprises: firstly, performing sea-land automatic classification on remote sensing images through a supervised learning algorithm, a classification result can reach a high precision level through processiterative clustering, and meanwhile, compared with an existing sea-land boundary analysis and classification method, the operand being small; then, using the chlorophyll concentration difference andthe brightness difference of pollutant shadows existing between the marine pollution area and surrounding seawater; combining a normalized vegetation index related to chlorophyll, a normalized water body shadow index related to brightness, a segmentation-based image interpretation thought and a human eye vision-based saliency mechanism in remote sensing interpretation; through threshold segmentation, realizing extraction of a marine pollution area, respectively extracting an area with excellent water quality and a severely polluted area, and further obtaining a pollution transition area. The method provided by the invention provides convenient and accurate reference for marine pollution prevention and treatment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
Methods to Reduce Chlorophyll Co-Extraction Through Extraction of Select Moieties Essential Oils and Aromatic Isolates
InactiveUS20180361271A1Essential-oils/perfumesCompression machines with cascade operationAlcoholChlorophyll c
Owner:CAPNA IP CAPITAL LLC
Ocean chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor
InactiveCN103674910AImprove detection accuracyReduce power consumptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceHorizontal distributionBuoy
The invention discloses a small-size chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor capable of being used in water depth of 3000m. According to the small-size chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor, an exciting light modulation and synchronous detection technology is adopted, a system light path is optimized and a low-power-consumption circuit design is adopted, so that the small-size chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor has the advantages of high detection precision, low power consumption, ambient light interference resistance and the like. The small-size chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor can be connected with an underwater battery to carry out long-time self-contained type work or is mounted into a towed body to carry out underwater towing and vertical section investigation; the small-size chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor can be integrated to third party platforms including a multi-parameter system, an ocean buoy / a subsurface buoy, a seabed observational network and the like in a modularized manner to carry out in-situ continuous monitoring. The small-size chlorophyll fluorescence in-situ monitor can be used for conveniently and rapidly determining vertical and horizontal distribution of chlorophyll concentrations of different sea areas from off-shore areas to the ocean.
Owner:SUZHOU INDAL TECH RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lake eutrophication inversion method based on remote sensing data
PendingCN112989692AScattering properties measurementsDesign optimisation/simulationData setChlorophyllin
The invention relates to a lake eutrophication inversion method based on remote sensing data, and the method comprises the steps: dividing a lake water body into two types based on a surface reflectance product data set of a Landsat-8 inland lake and a corresponding actually measured chlorophyll a concentration, carrying out the wave band combination through combining with a baseline method, and respectively constructing inversion models of a nutrition state index TSI for the two types of water bodies. By the adoption of the method, estimation of the Landsat-8OLI in the lake nutrition state index TSI can be achieved, and the algorithm has certain universality and can be suitable for remote sensing estimation of large-scale lake eutrophication; besides, the method is used for observing small and medium-sized lakes, the limitation that a traditional medium-resolution water color satellite cannot observe is made up, lake eutrophication inversion precision and observation scale are improved, and reference is provided for lake water eutrophication monitoring and treatment and sustainable development of the lake water environment.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Method for measuring water transparency under present situation and non under present conditions
InactiveCN101038281AForecasting the Changing State of TransparencyForecast distribution change lawTesting waterParticle suspension analysisNatural factorTurbidity
The water transparency is an important index reflecting the water limpidity and turbidity extent. The present invention provides a method used for obtaining water transparency under current conditions and noncurrent conditions, which comprises steps of inputting data about water features, current features, boundary hydrology, water quality, and the like, into related formulas to work out suspended matter concentration, chlorophyl concentration and permanganate index concentration; and then inputting the suspended matter concentration, chlorophyl concentration and permanganate index concentration obtained into transparency prediction formulas to work out the water transparency values. The present invention is capable of used for detecting the water features under current conditions in a water environment, referring to detecting the water transparency; for calculating out the water environment or transparency improving effect for a variety of pollution controlling steps; and for working out the affecting extent on the water environment or transparency by nature factors.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method and device for classified detecting density of phytoplankton under water in site
ActiveCN100520365CReal-time measurementQuick measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceChlorophyll aFluorescence
A method for classifying underwater original position of polytoplankton by detecting concentration of polytoplankton includes setting a groove at one side of closed pressure box and a light shading cover at external side of said box; erecting LED array formed by parallel-arranged LED with center wavelength of 450nm, 525nm, 570nm 590nm and 620nm in light path at side surface of said groove; dividing polytoplankton to be five light spectrum set as green, blue, brown, red and mixture; measuring 685nm florescent intensity of five different exciting wavelength to calculate out chlorophyll concentration of each light spectrum according to known coefficient.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com