Patents
Literature
1490 results about "Sub wavelength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
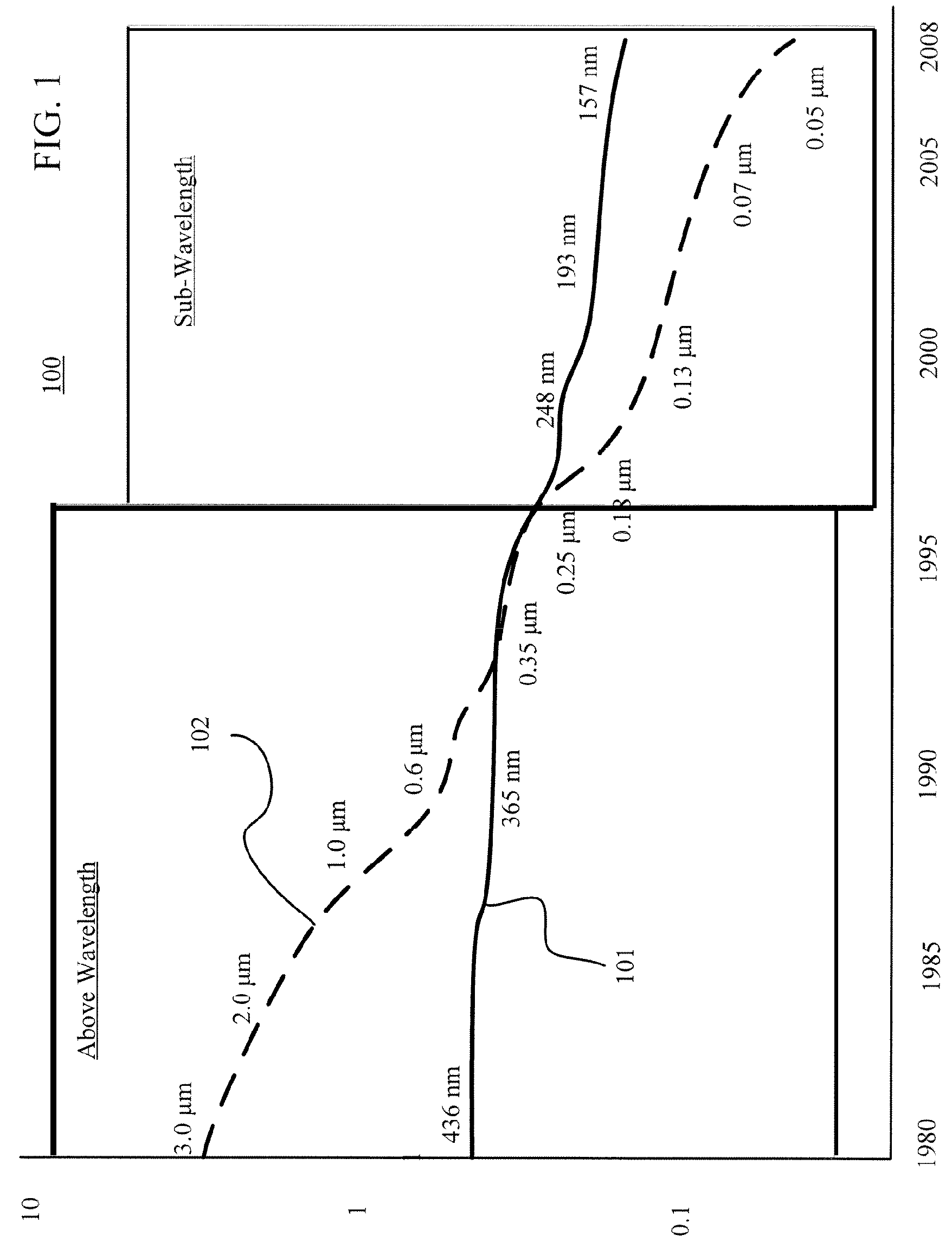
Re: Sub-wavelength. Subwavelength is a word indicating the use of dimensions below the length of the waves used. i.e. In the photolithography, if you have a dimension below that of the wavelength used then its a subwavelenth dimension.
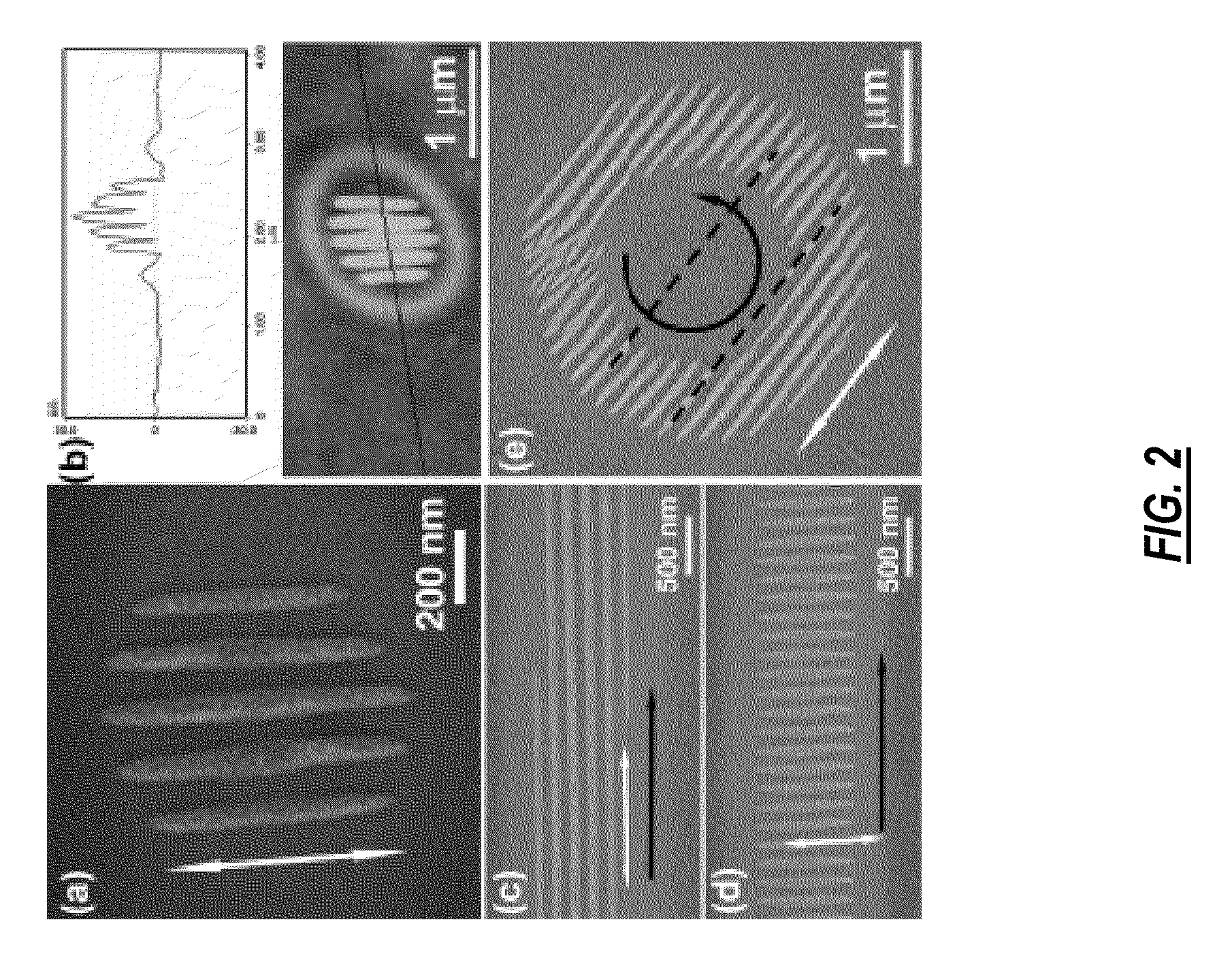
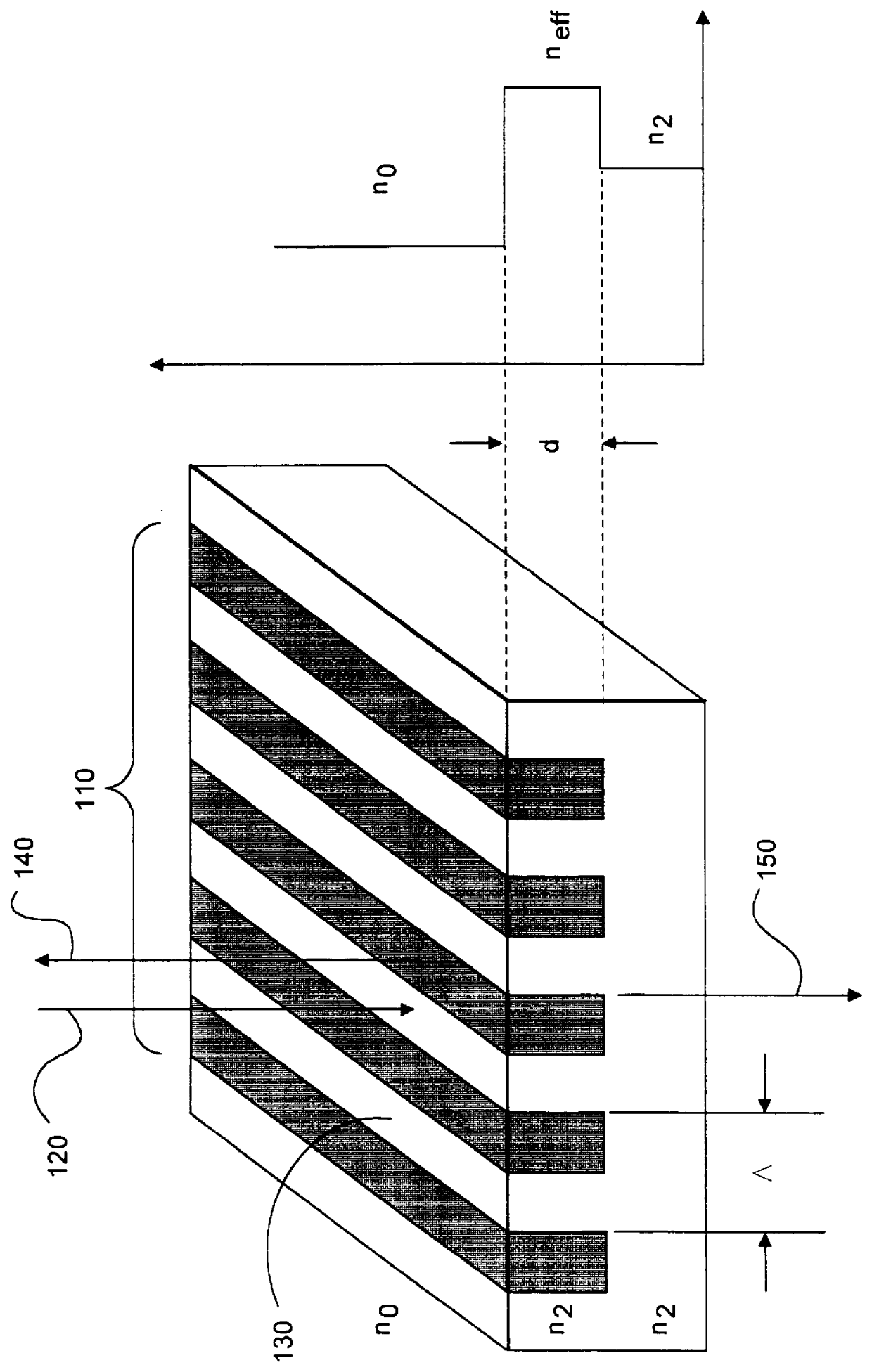
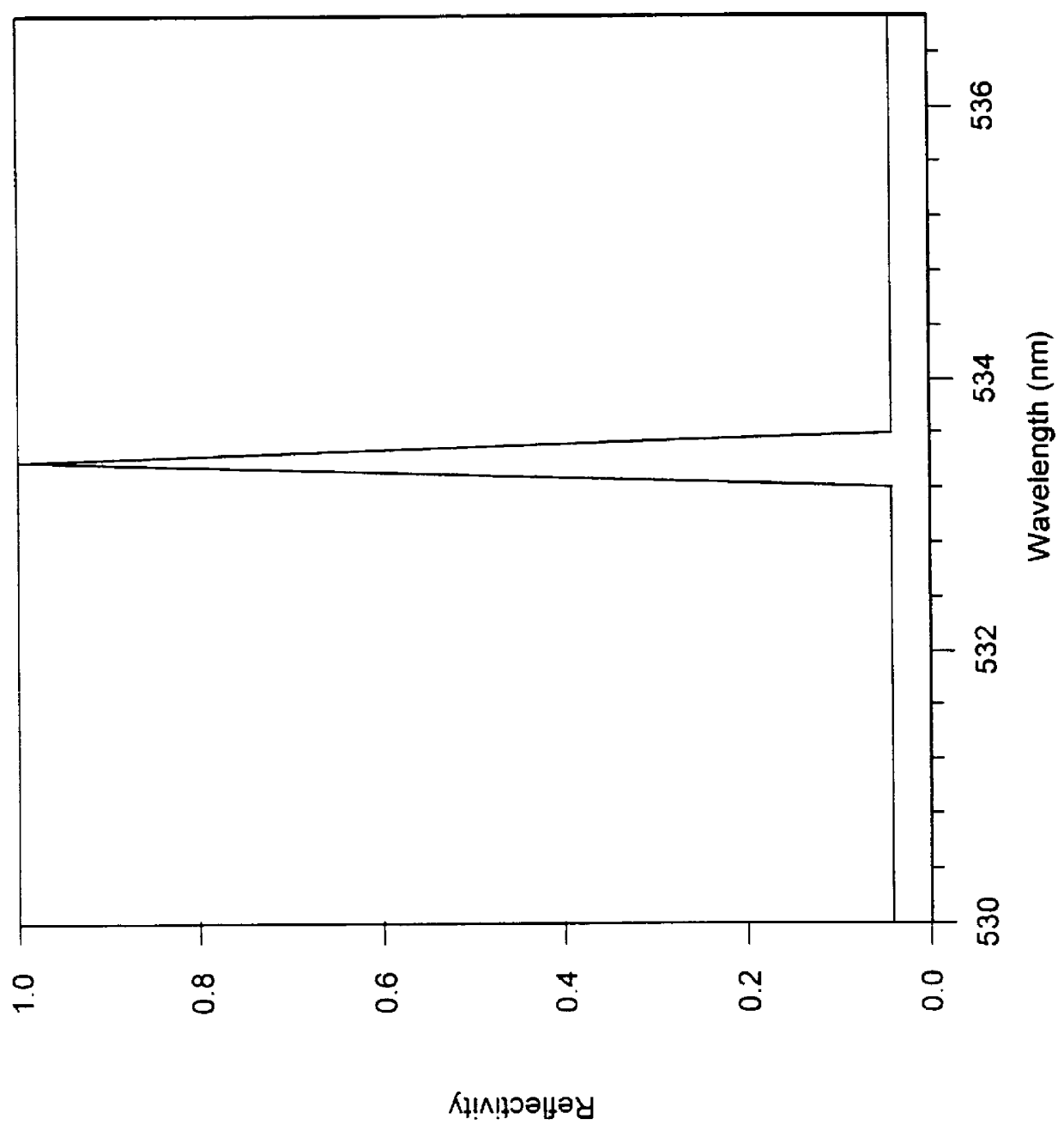
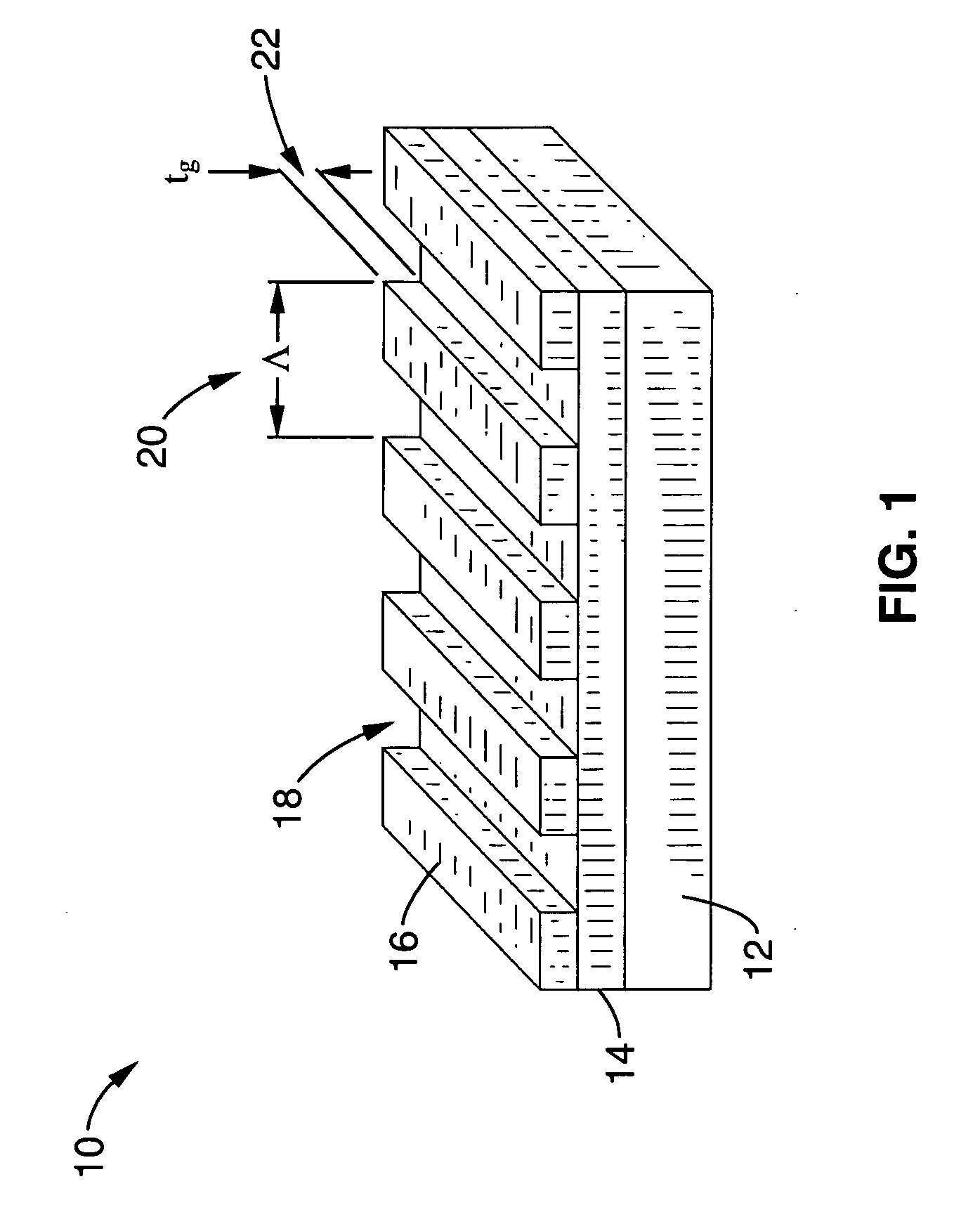
Integrated narrowband optical filter based on embedded subwavelength resonant grating structures
InactiveUS6035089ACost effectiveMinimal reflectionOptical filtersOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingWavelength
A resonant grating structure in a waveguide and methods of tuning the performance of the grating structure are described. An apparatus includes a waveguide; and a subwavelength resonant grating structure embedded in the waveguide. The systems and methods provide advantages including narrowband filtering capabilities, minimal sideband reflections, spatial control, high packing density, and tunability.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
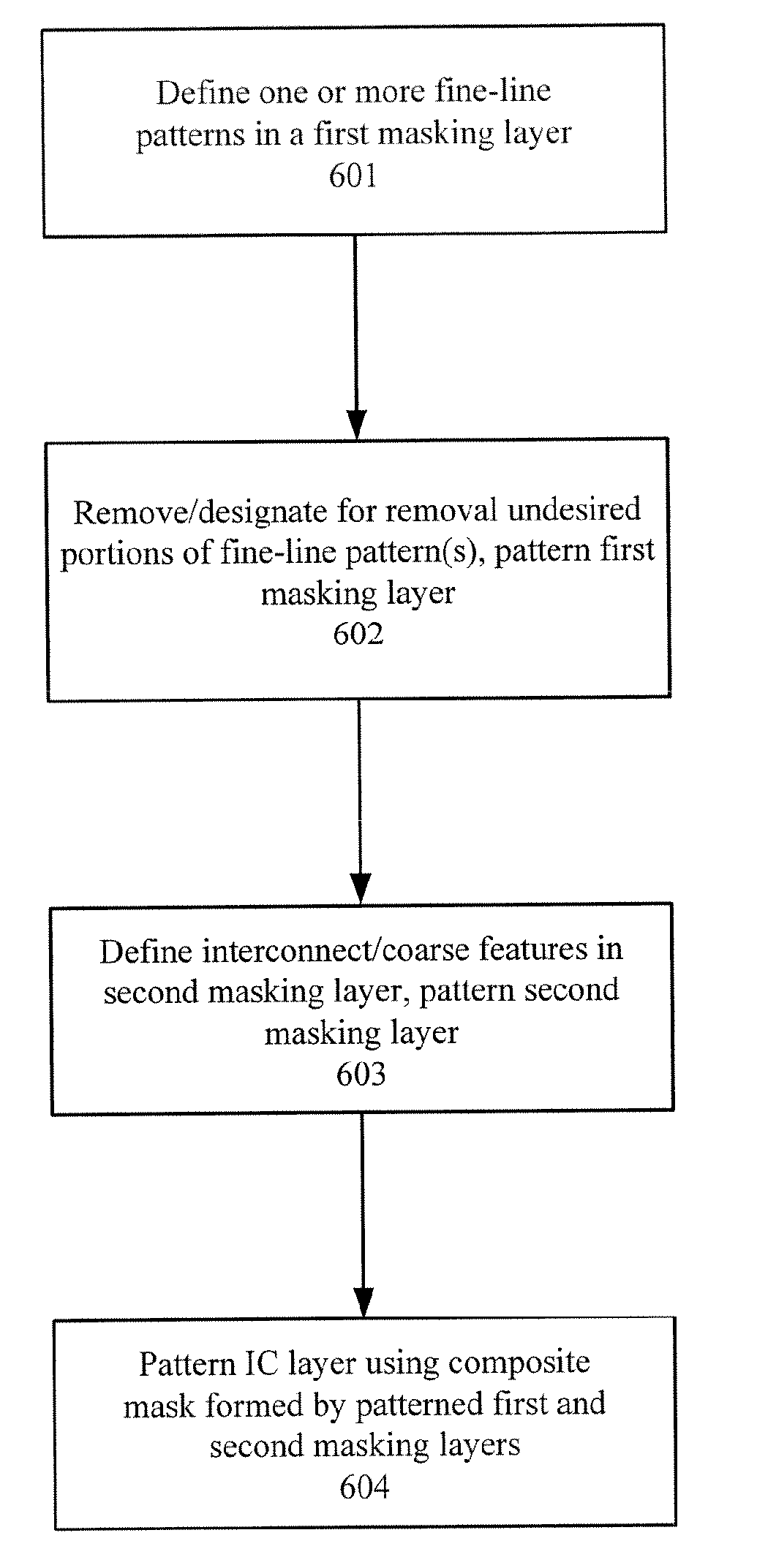
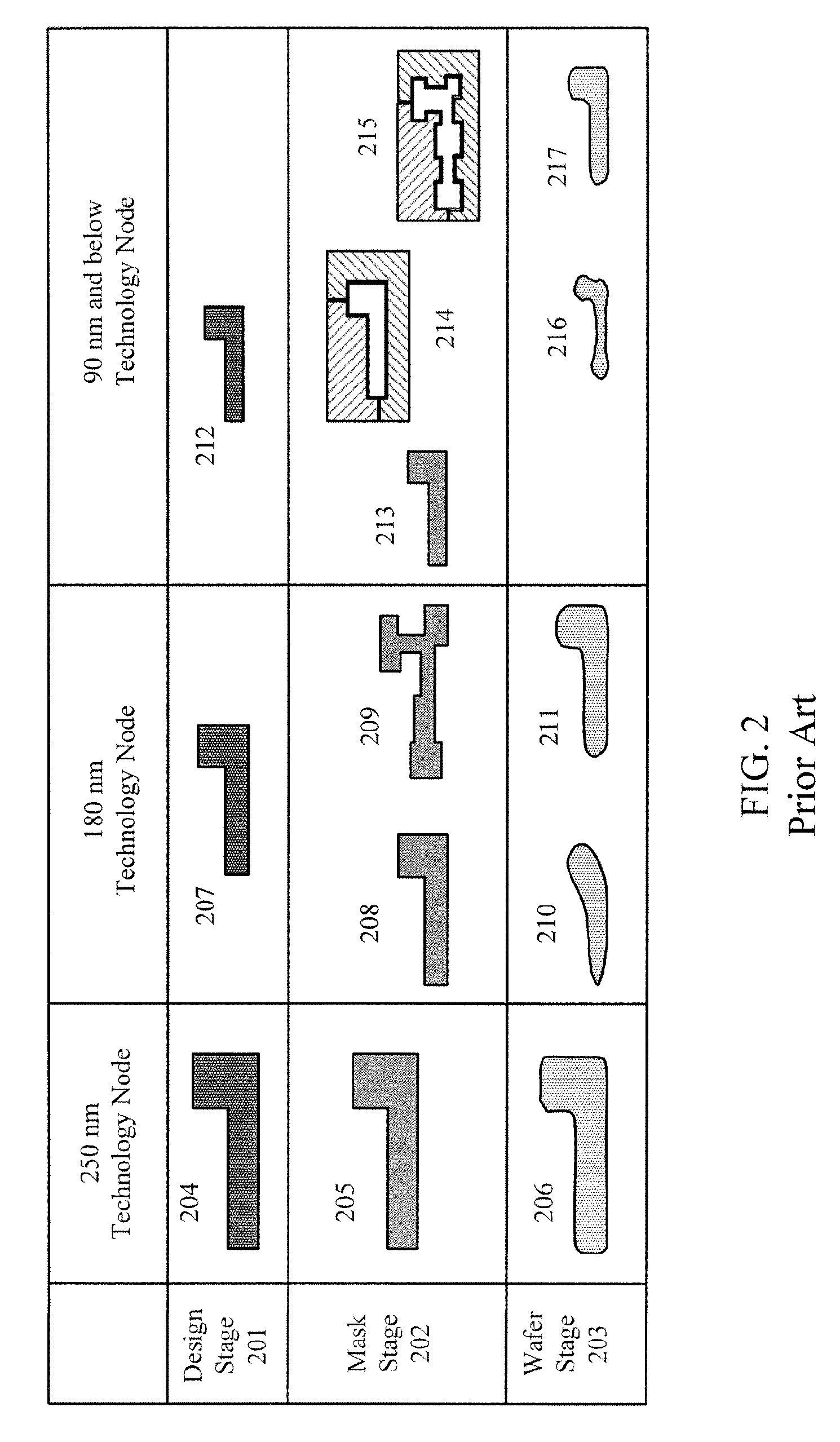
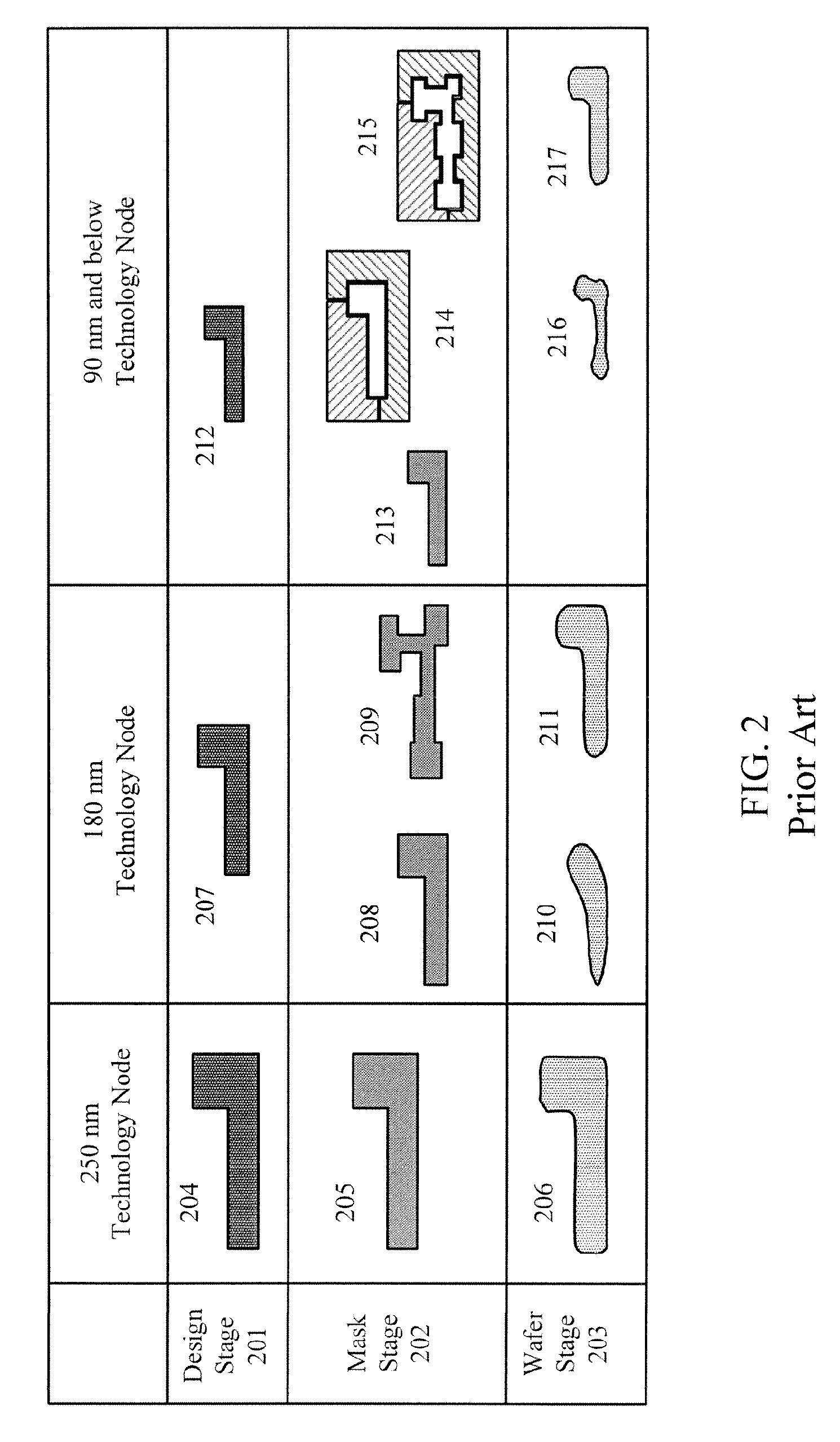
Patterning A Single Integrated Circuit Layer Using Multiple Masks And Multiple Masking Layers
ActiveUS20070275309A1Increase productionEasy to useSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResolution enhancement technologiesLength wave
A multiple mask and a multiple masking layer technique can be used to pattern a single IC layer. A resolution enhancement technique can be used to define one or more fine-line patterns in a first masking layer, wherein each fine-line feature is sub-wavelength. Moreover, the pitch of each fine-line pattern is less than or equal to that wavelength. The portions of the fine-line features not needed to implement the circuit design are then removed or designated for removal using a mask. After patterning of the first masking layer, another mask can then be used to define coarse features in a second masking layer formed over the patterned first masking layer. At least one coarse feature is defined to connect two fine-line features. The IC layer can be patterned using the composite mask formed by the patterned first and second masking layers.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Grating trim retarders
InactiveUS20070070276A1Improve image contrastEasily integrated into oneColor television detailsNon-linear opticsIn planeZeroth order
A grating trim retarder fabricated from a form-birefringent multi-layer dielectric stack including at least one anti-reflection coating and supported on a transparent substrate is provided. The form-birefringent dielectric stack includes an axially-inhomogeneous element in the form of a −C-plate grating and a transversely-inhomogeneous element in the form of an A-plate grating. Each of the −C-plate and the A-plate gratings are fabricated with dimensions to form a zeroth order sub-wavelength grating structure. Fabricating the grating trim retarder with anti-reflection coatings and / or a segment where the −C-plate and A-plate grating overlap enables the in-plane and out-of-plane retardances to be tailored independently according to the desired application.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Patterning a single integrated circuit layer using multiple masks and multiple masking layers
ActiveUS7537866B2Low costEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResolution enhancement technologiesWavelength
A multiple mask and a multiple masking layer technique can be used to pattern a single IC layer. A resolution enhancement technique can be used to define one or more fine-line patterns in a first masking layer, wherein each fine-line feature is sub-wavelength. Moreover, the pitch of each fine-line pattern is less than or equal to that wavelength. The portions of the fine-line features not needed to implement the circuit design are then removed or designated for removal using a mask. After patterning of the first masking layer, another mask can then be used to define coarse features in a second masking layer formed over the patterned first masking layer. At least one coarse feature is defined to connect two fine-line features. The IC layer can be patterned using the composite mask formed by the patterned first and second masking layers.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
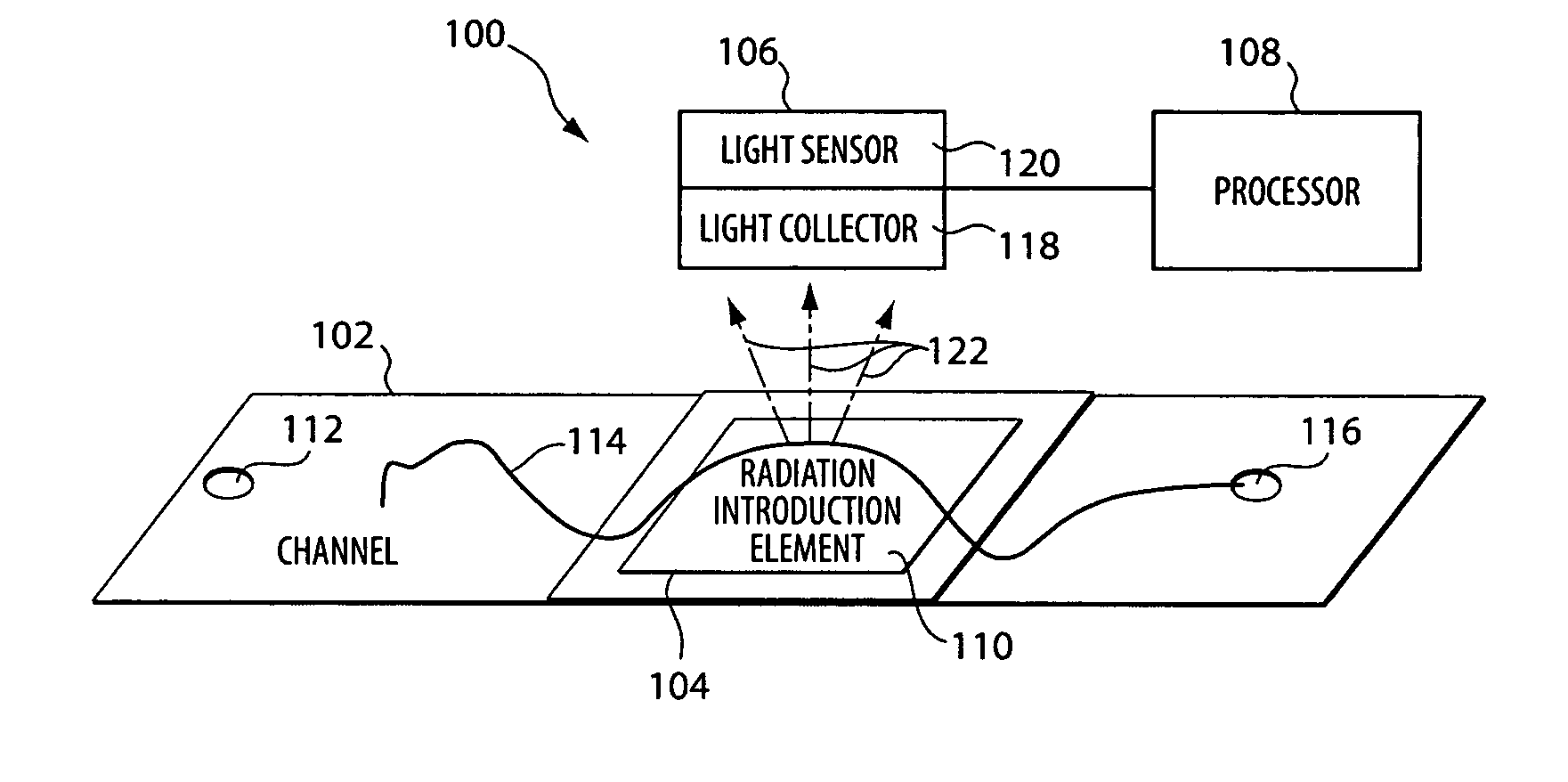
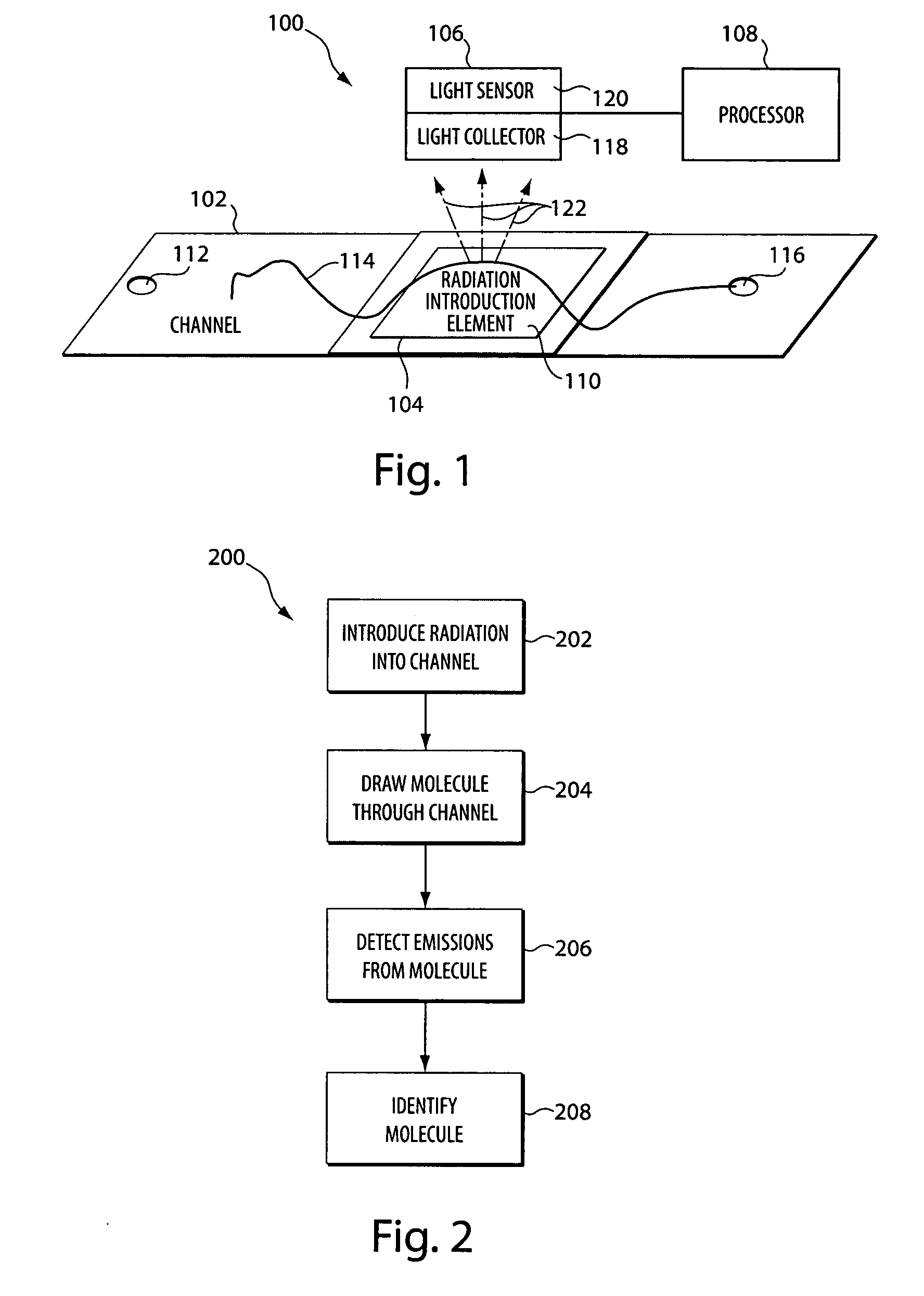
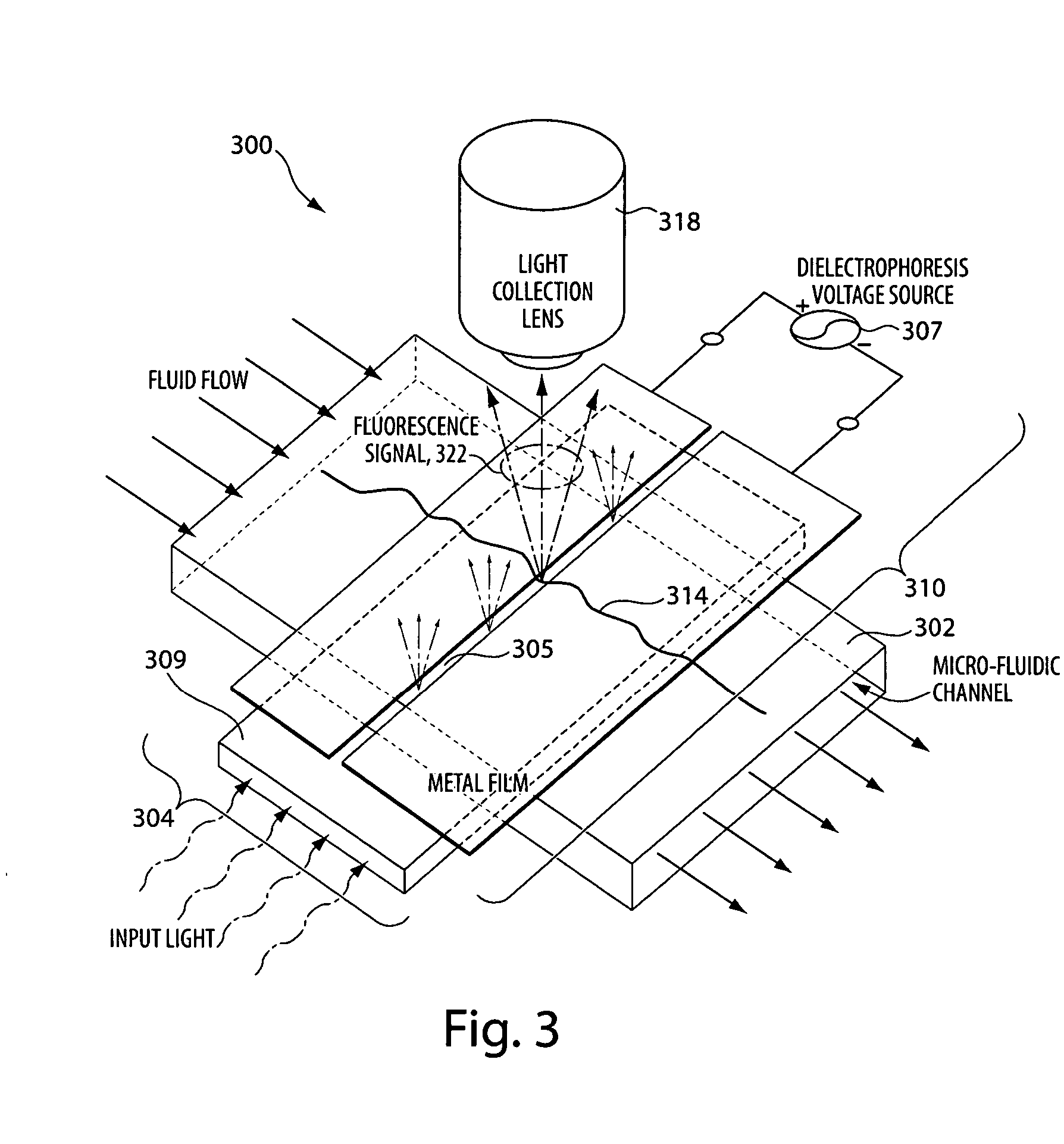
Methods and apparatus for biomolecule identification
The apparatus and methods described herein provide improved resolution, high-throughput, biomolecule identification by exciting sub-wavelength regions of biomolecules drawn through a microfluidic channel.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
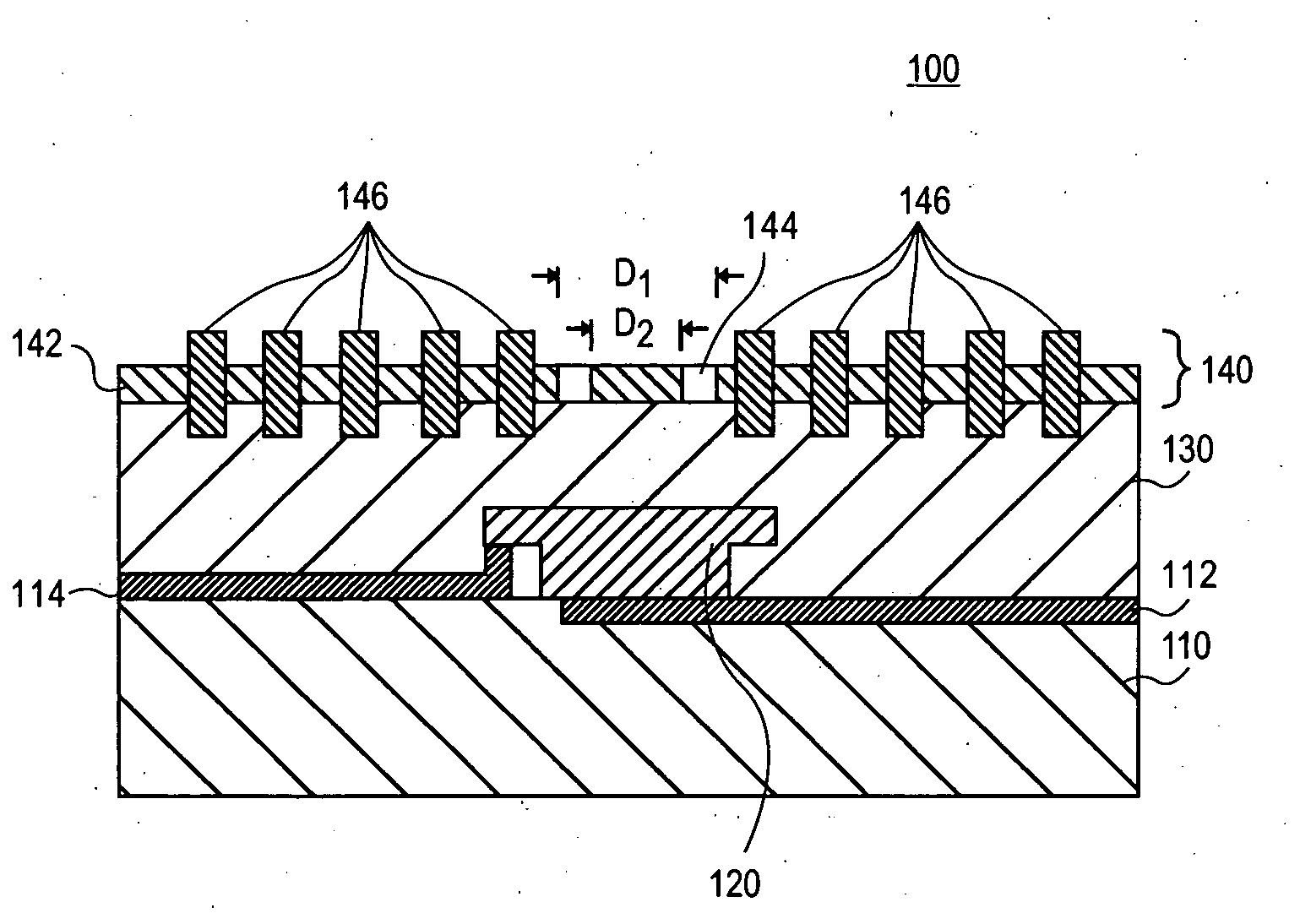
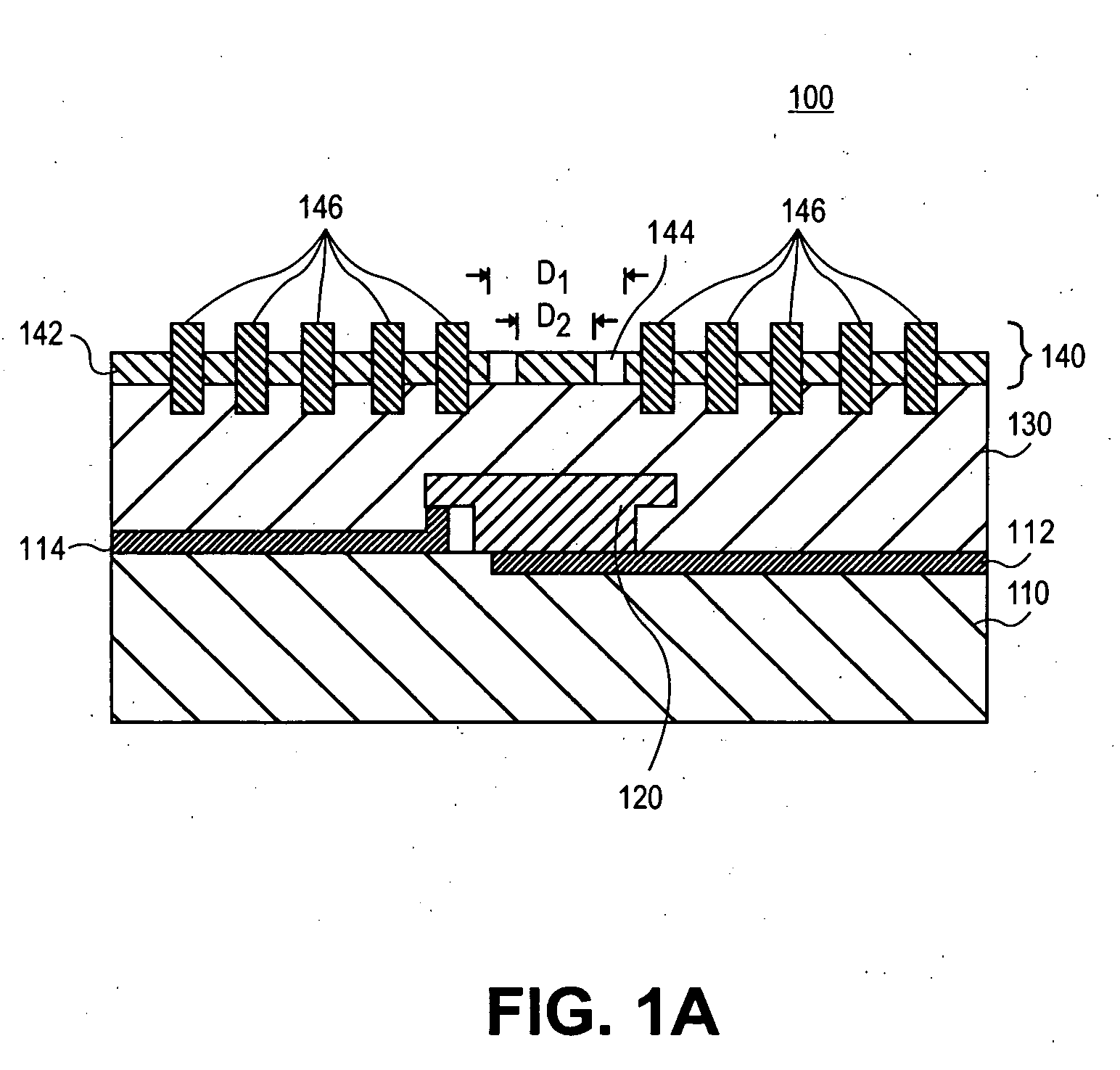
Plasmonic enhanced infrared detector element
ActiveUS20060175551A1Material analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsElectromagnetic radiationWavelength
Electromagnetic radiation detector elements and methods for detecting electromagnetic radiation, in particular, infrared radiation, are provided. The electromagnetic radiation detector element can include an electromagnetic radiation detector and a plasmonic antenna disposed over the electromagnetic radiation detector. The plasmonic antenna can include a metal film, a sub-wavelength aperture in the metal film, and a plurality of circular corrugations centered around the sub-wavelength aperture.
Owner:STC UNM
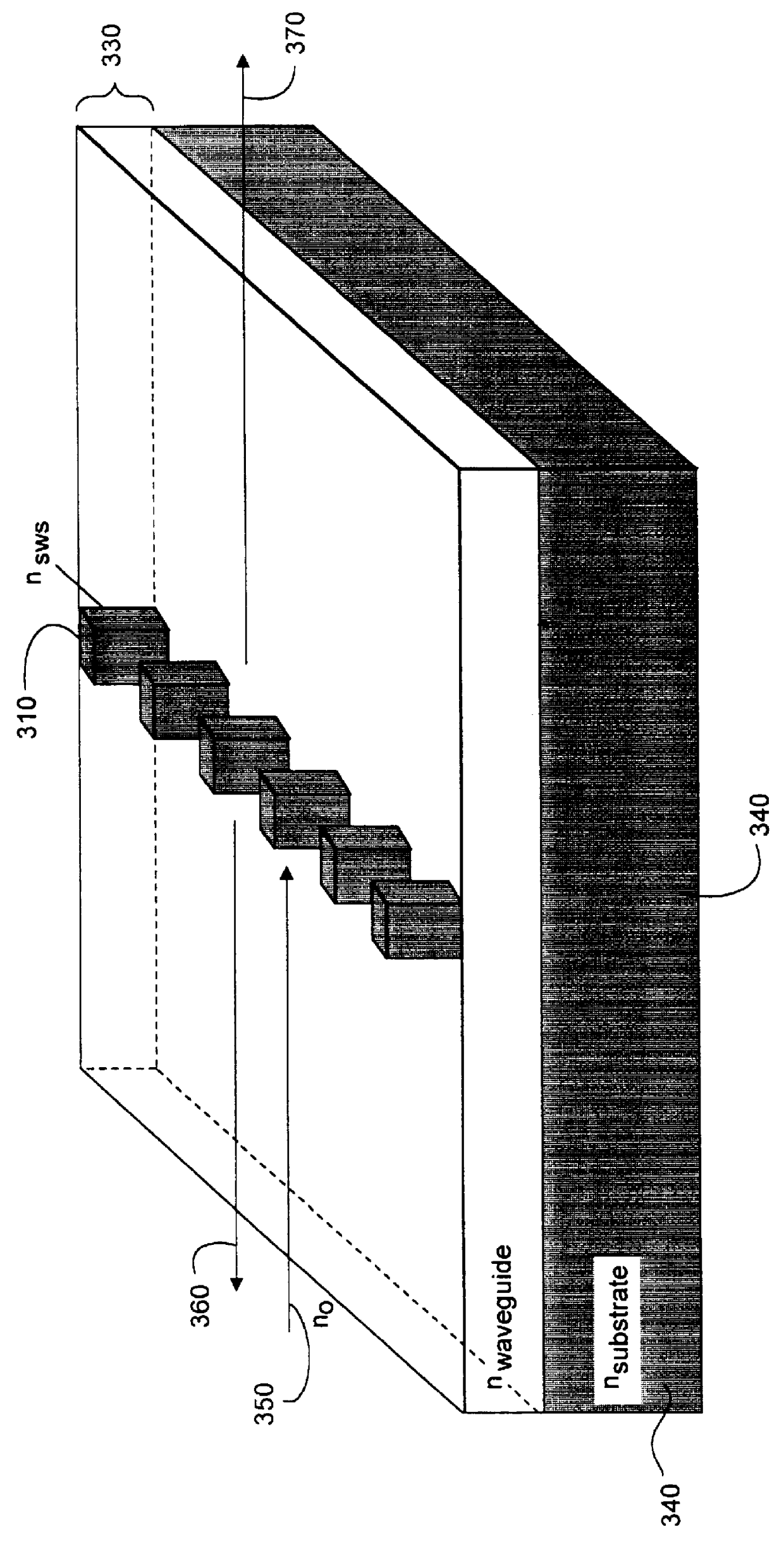
Ultra broadband mirror using subwavelength grating
ActiveUS20070115553A1Broad reflection spectrumImprove reflectivityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingRefractive index
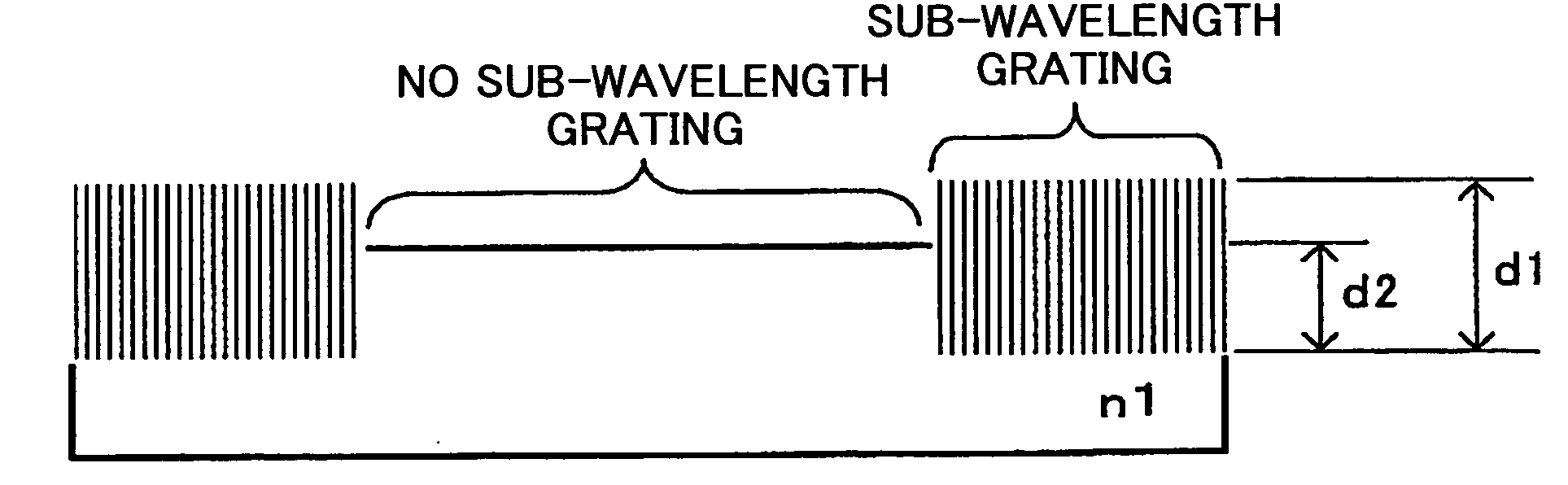
A sub-wavelength grating structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity comprising segments made of high refractive index material disposed on a layer of low refractive index material and a low refractive index material disposed above and between the segments. The index differential between the high and low index materials determines the bandwidth and modulation depth. The larger difference in refractive indices gives rise to wider reflection bands. The reflection is sensitive to parameters such as the grating period, the grating thickness, the duty cycle of the grating, the refractive index and the thickness of the low index layer underneath the grating. The design is scalable for different wavelengths, and facilitates monolithic integration of optoelectronic devices at a wide range of wavelengths from visible to far infrared. The sub-wavelength grating reflectors may be used in a variety of settings such as tunable etalon filters and as a replacement for conventional distributed Bragg reflectors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Resolution antenna array using metamaterials
ActiveUS7928900B2High resolutionSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsImage resolutionWavelength
An antenna array includes at least one transmit array comprising a plurality of metamaterial elements. The antenna array further includes at least one near-field stimulator for inputting electromagnetic signal to the transmit array so that a sub-wavelength target is illuminated with an electromagnetic wave.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
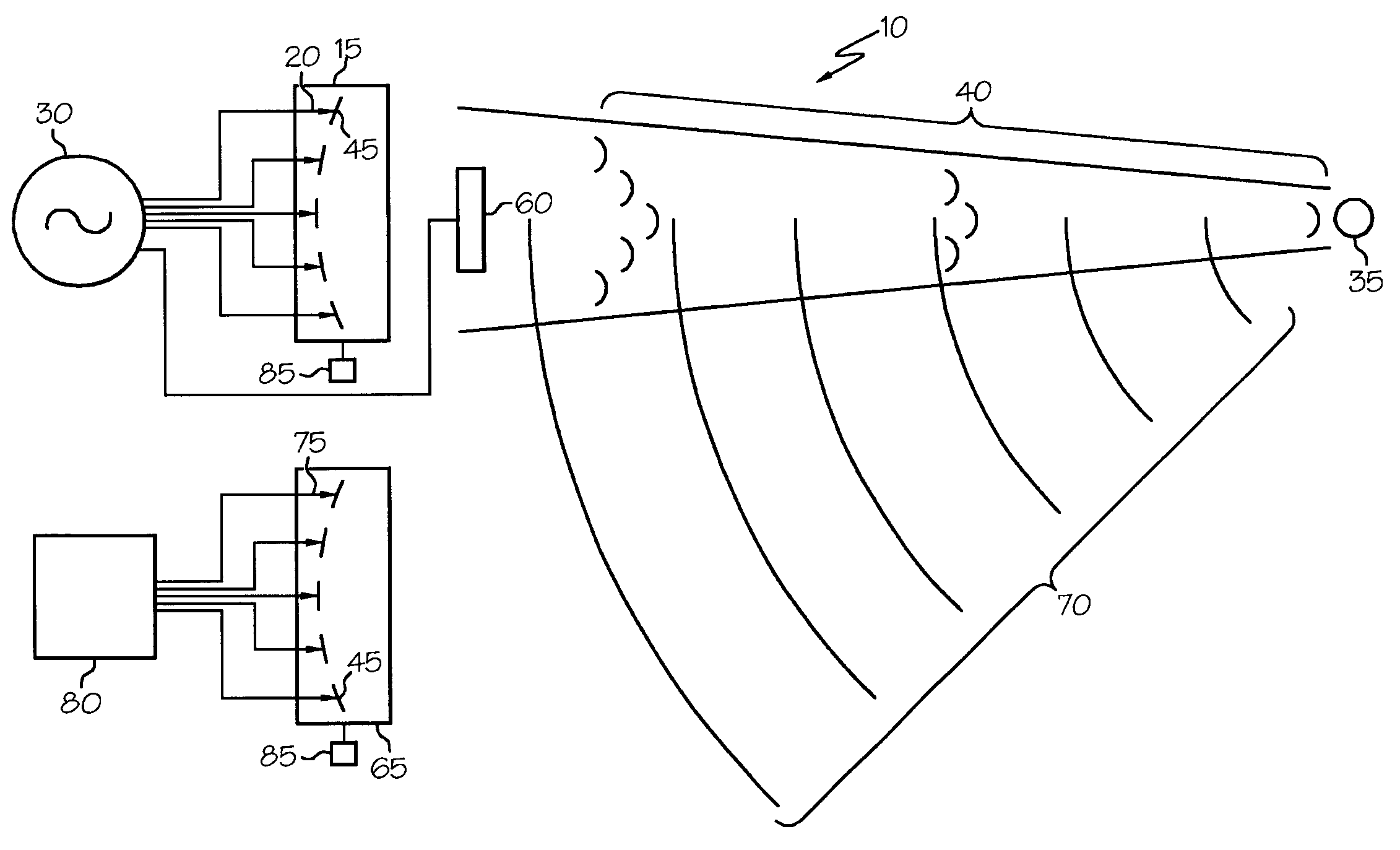
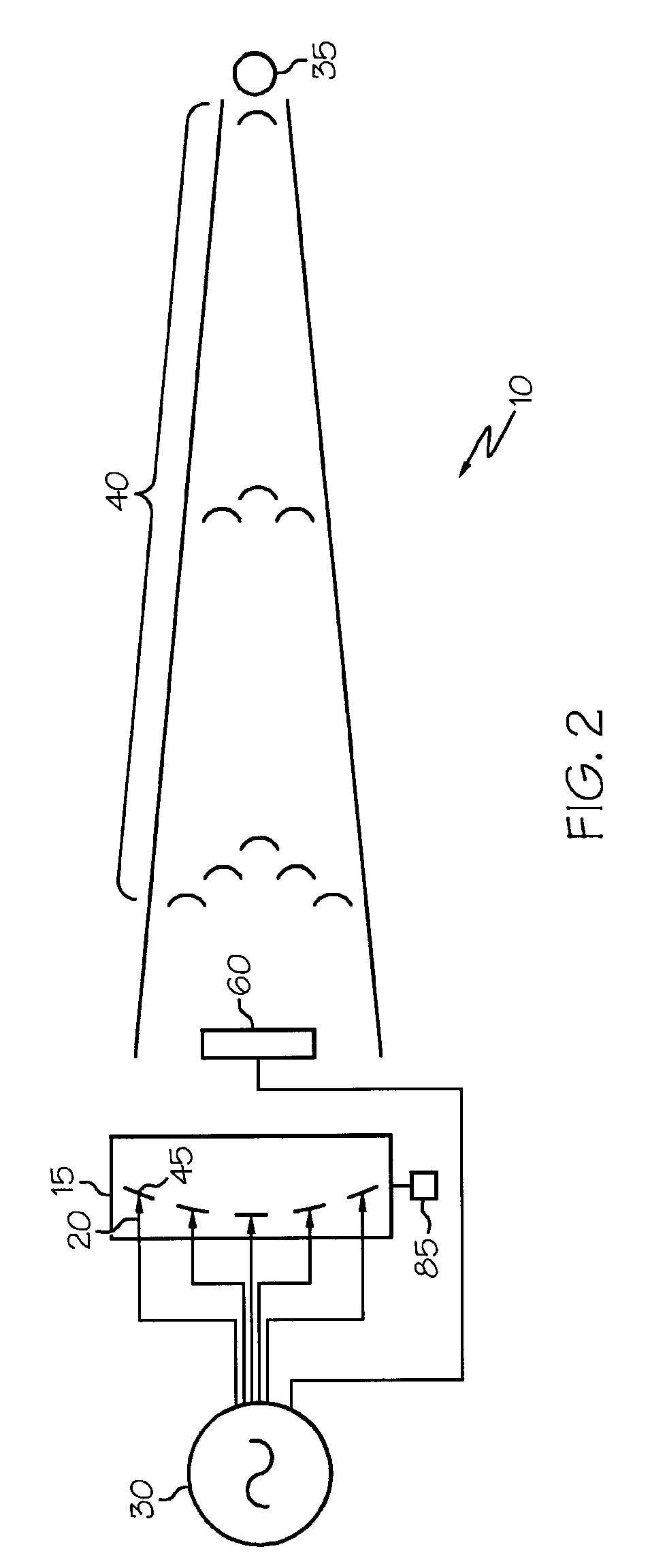
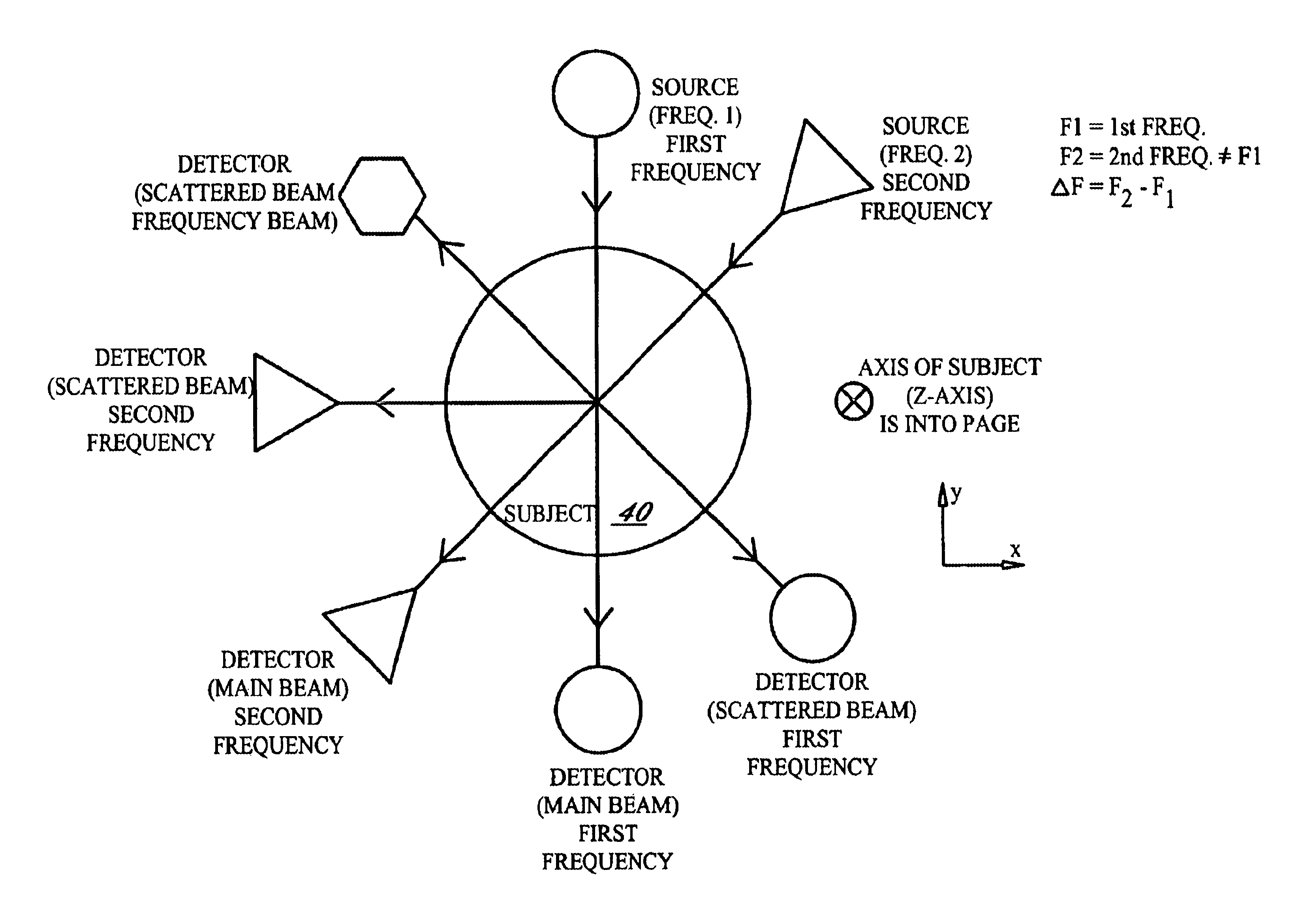
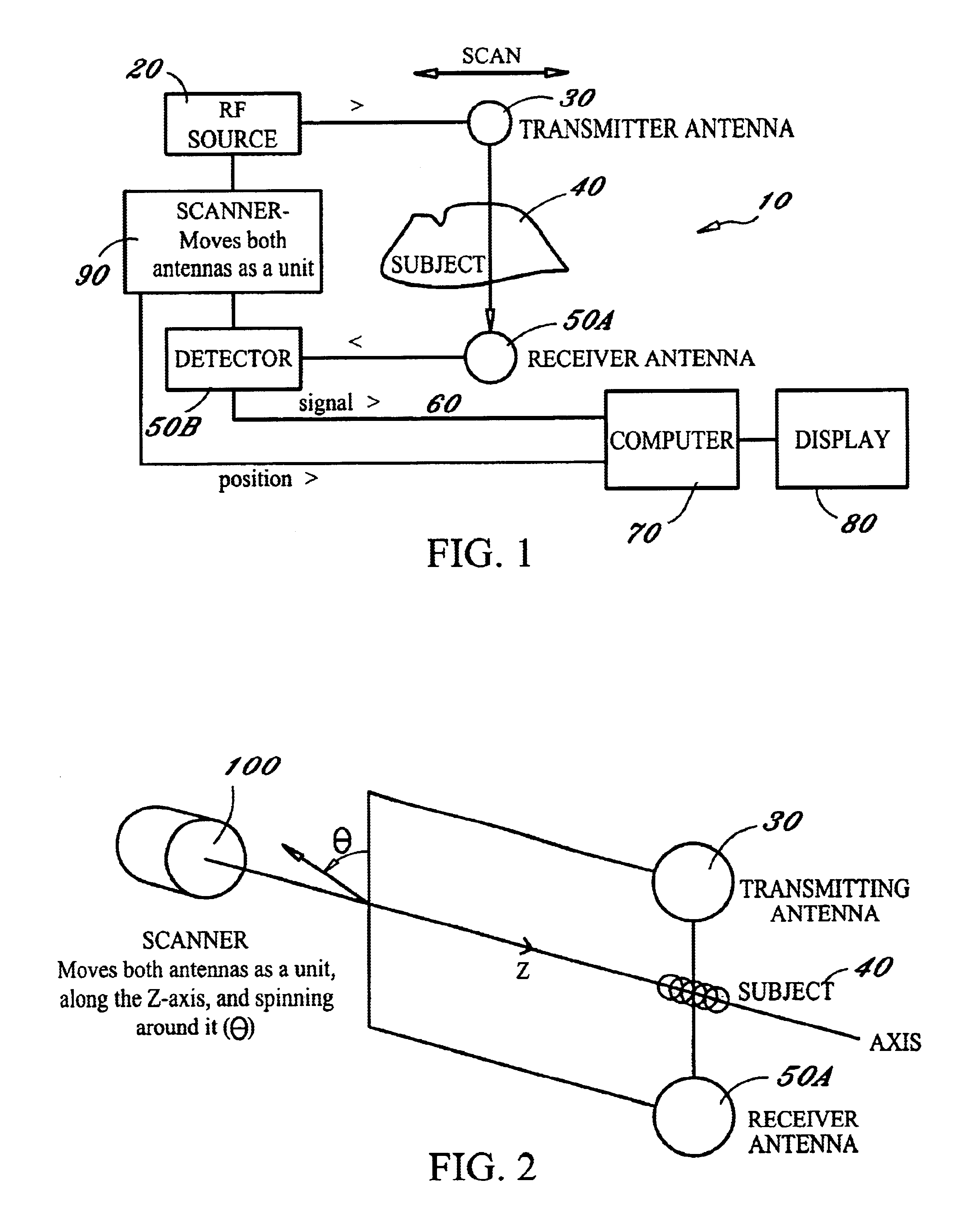
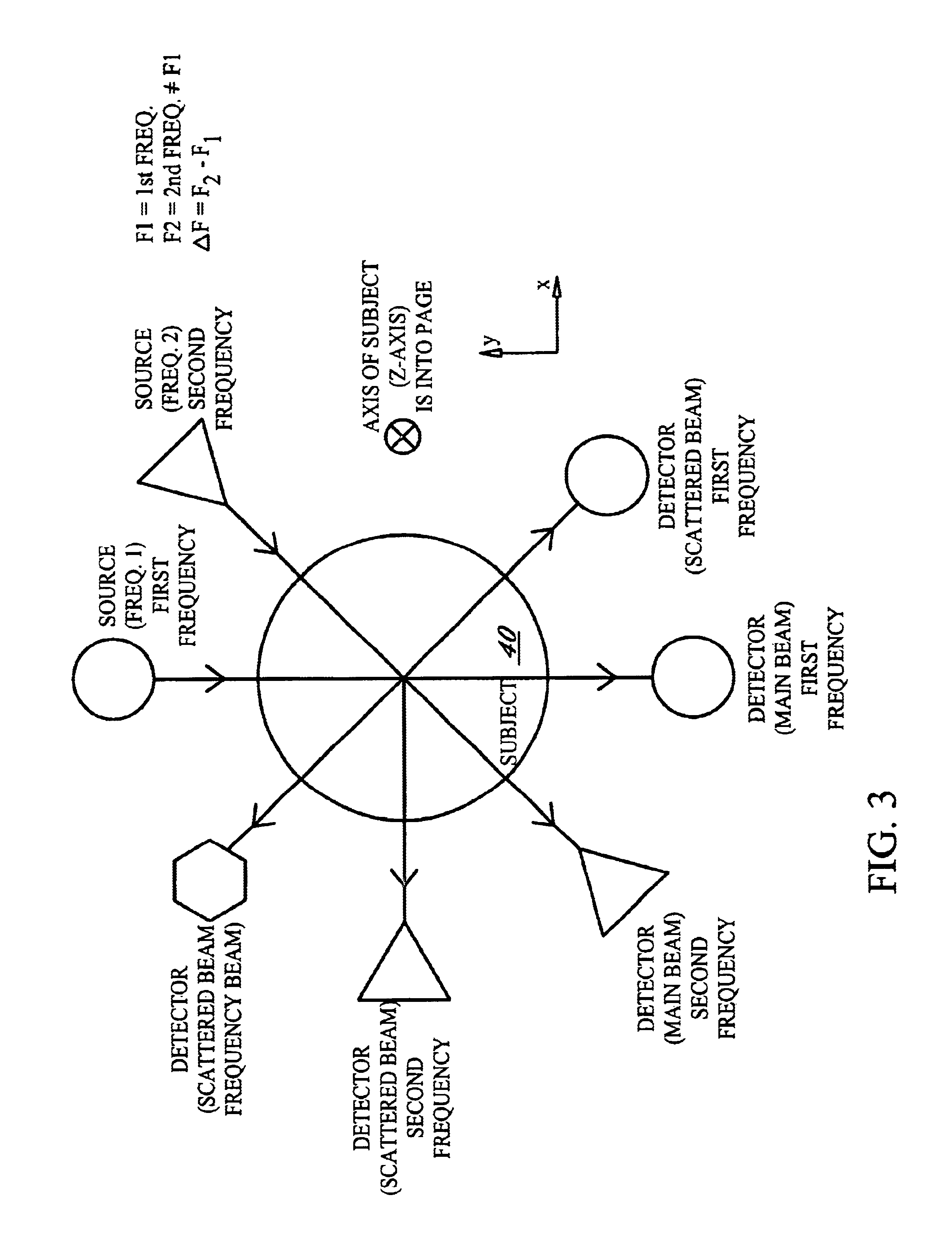
Radio-frequency imaging system for medical and other applications
InactiveUS6885191B1Easy and quick imagingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResistance/reactance/impedenceHuman bodyImage resolution
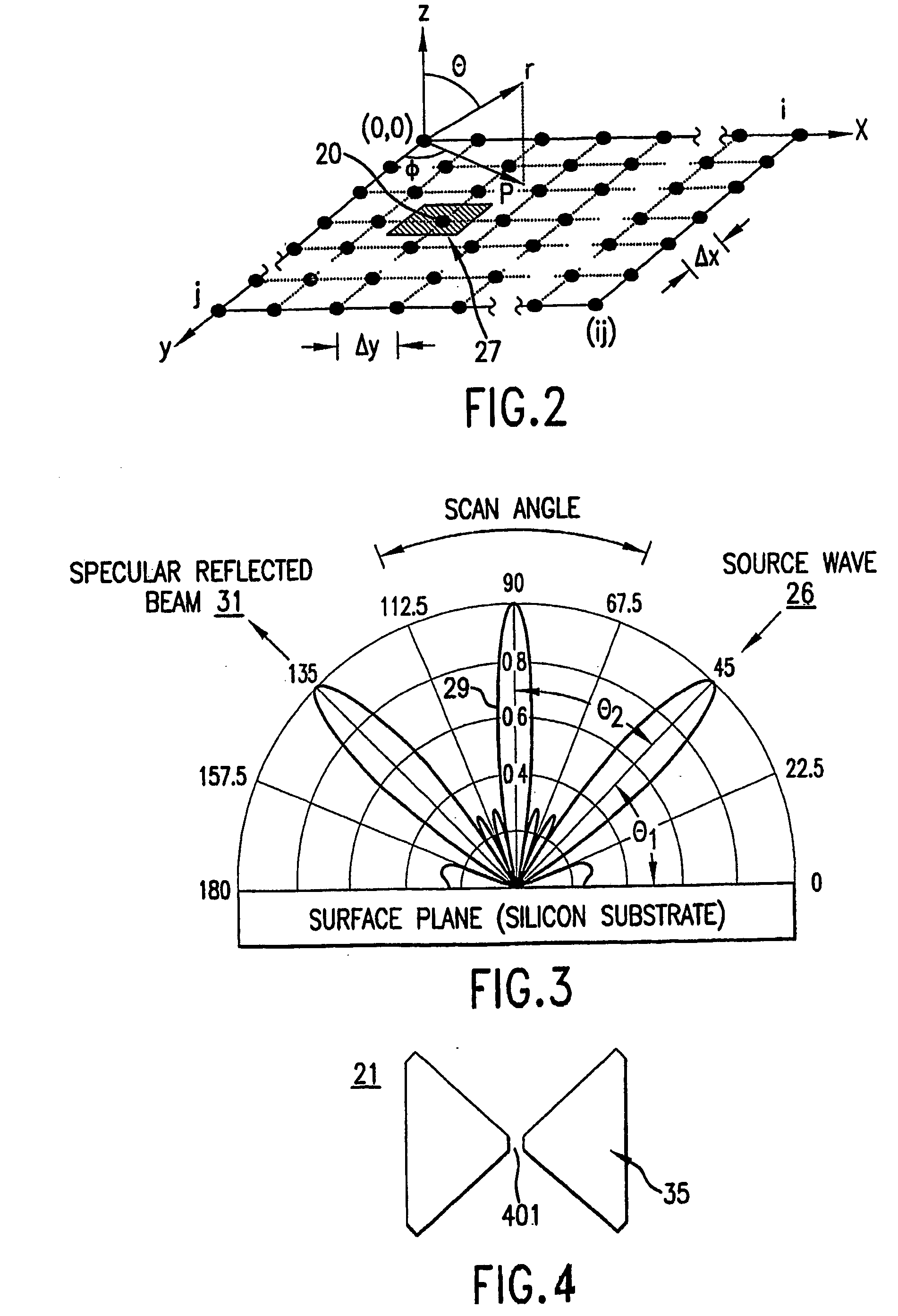
An imaging system for medical and other applications in which the internal structures of an overall object must be seen without invading or damaging the object. The system works by transmitting electromagnetic waves of single or a multiplicity of frequencies through the object (for example the human body) and measuring the absorption and scattering of these waves by the various structures and inhomogeneities of the object, using scanning sub-wavelength resolution detectors.
Owner:GLEMAN STUART M
Phononic metamaterials for vibration isolation and focusing of elastic waves
ActiveUS20130025961A1Reduce throughputMore complexity in manufacturingNon-rotating vibration suppressionSound producing devicesWaveform shapingBroadband
A methodology for designing structured metamaterials that can reflect, absorb and focus the propagation of both scalar acoustic and vector elastic waves is described. Three exemplary representative inventions based on the disclosed invention are described, illustrating i) compact ultra-wide broadband isolation, ii) sub-wavelength gaps and negative index propagation utilizing a single material platform, and iii) a fundamentally new method of producing multiple high frequency spectral gaps. Such metamaterial designs possess a wide range of potential applications, ranging from but not limited to, isolating an entity from external mechanical or acoustical vibrations, compact focusing lenses as well as cascaded high frequency filters for wave shaping and nonlinear wave propagation control.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Polarized diffractive backlight
A backlight is provided for illuminating an at least partially transmissive display. The backlight includes a light source. A light guide receives the light from an edge surface and guides the light by total internal reflection. The light is extracted from the lightguide using sub-wavelength extraction features designed on the basis of two interleaved grating structures. The emitted light, using this arrangement has a high level of polarization.
Owner:SHARP KK
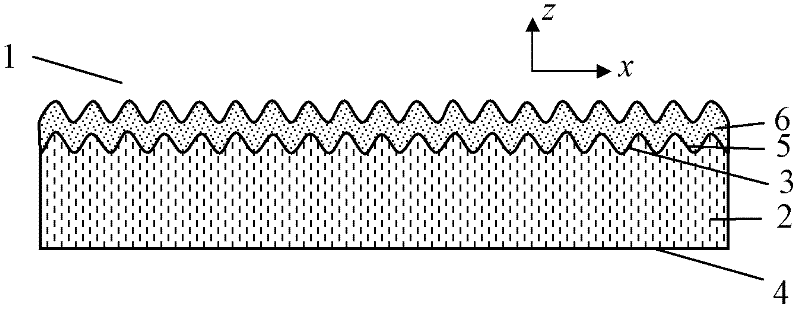
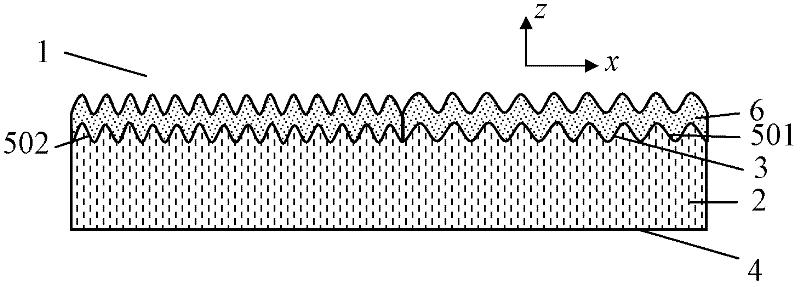
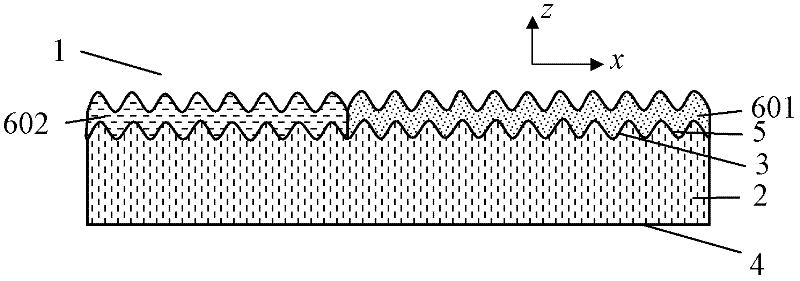
Optical anti-counterfeiting element
ActiveCN102514443AWide variety of colorsImprove anti-counterfeiting effectLight effect designsDiffraction gratingsRefractive indexEngineering
The invention provides an optical anti-counterfeiting element capable of overcoming the defect of few color types of the current optical anti-counterfeiting element. The optical anti-counterfeiting element comprises a substrate (2), a sub-wavelength embossment structure (5) and a coating (6) with a multi-layer structure, wherein the substrate (2) comprises a first surface (3) and a second surface (4); the sub-wavelength embossment (5) is formed on all or a part of the first surface (3); and the coating (6)with the multi-layer structure is formed on all or a part of the sub-wavelength embossment structure (5) and comprise a dielectric layer formed by dielectric material with refractive index less than 1.8.
Owner:ZHONGCHAO SPECIAL SECURITY TECH +1
Phononic metamaterials for vibration isolation and focusing of elastic waves
ActiveUS8833510B2Non-rotating vibration suppressionSound producing devicesWaveform shapingAcoustic wave
A methodology for designing structured metamaterials that can reflect, absorb and focus the propagation of both scalar acoustic and vector elastic waves is described. Three exemplary representative inventions based on the disclosed invention are described, illustrating i) compact ultra-wide broadband isolation, ii) sub-wavelength gaps and negative index propagation utilizing a single material platform, and iii) a fundamentally new method of producing multiple high frequency spectral gaps. Such metamaterial designs possess a wide range of potential applications, ranging from but not limited to, isolating an entity from external mechanical or acoustical vibrations, compact focusing lenses as well as cascaded high frequency filters for wave shaping and nonlinear wave propagation control.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
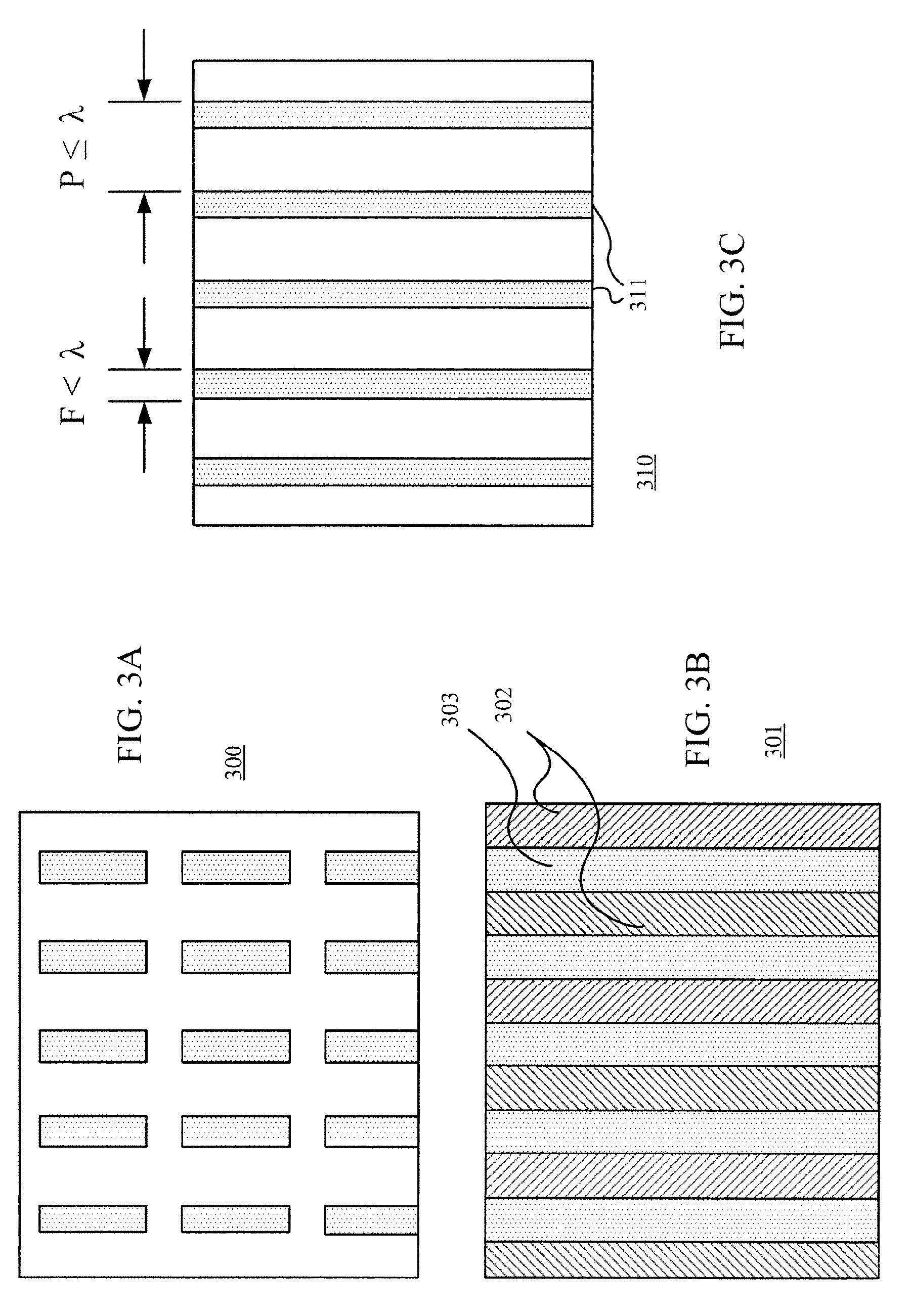
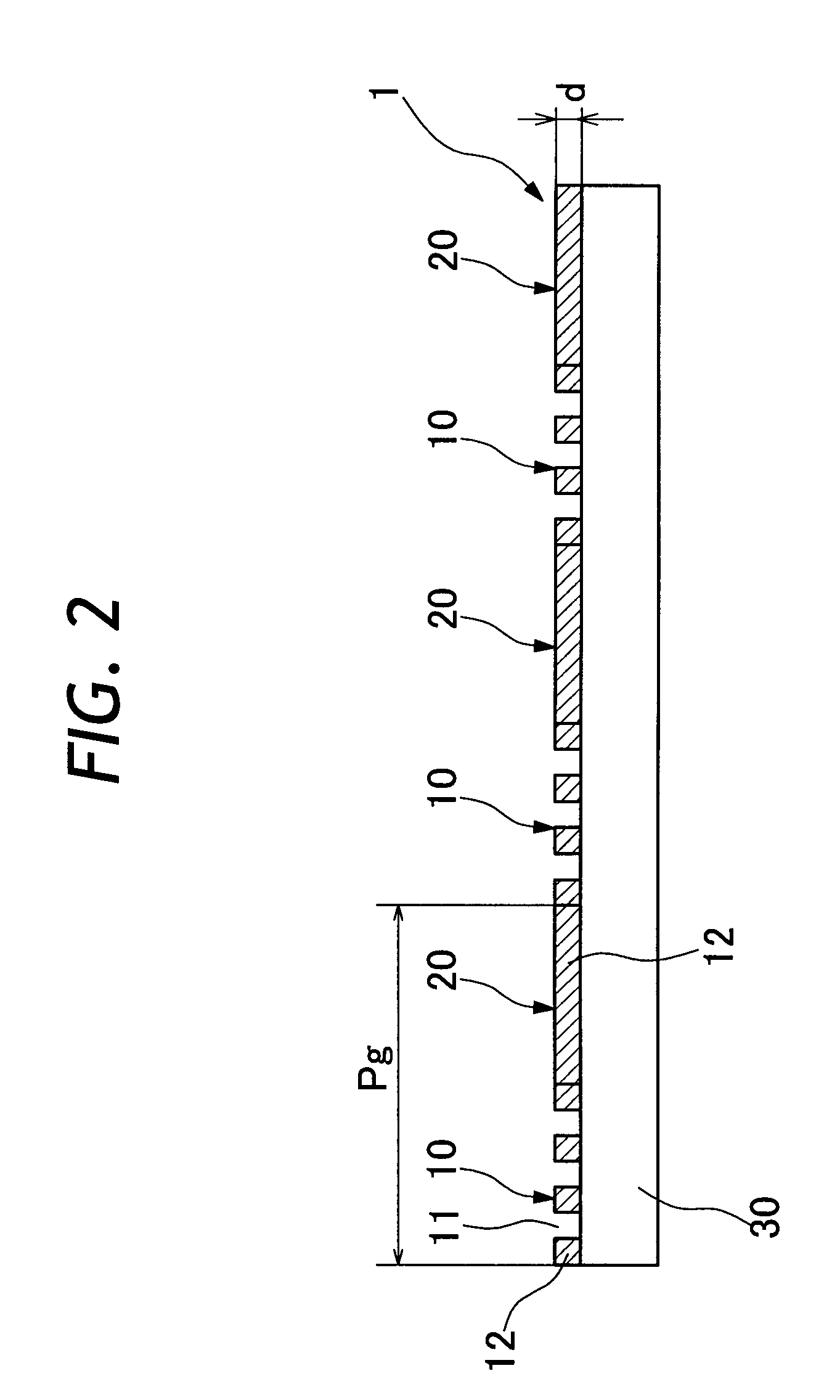
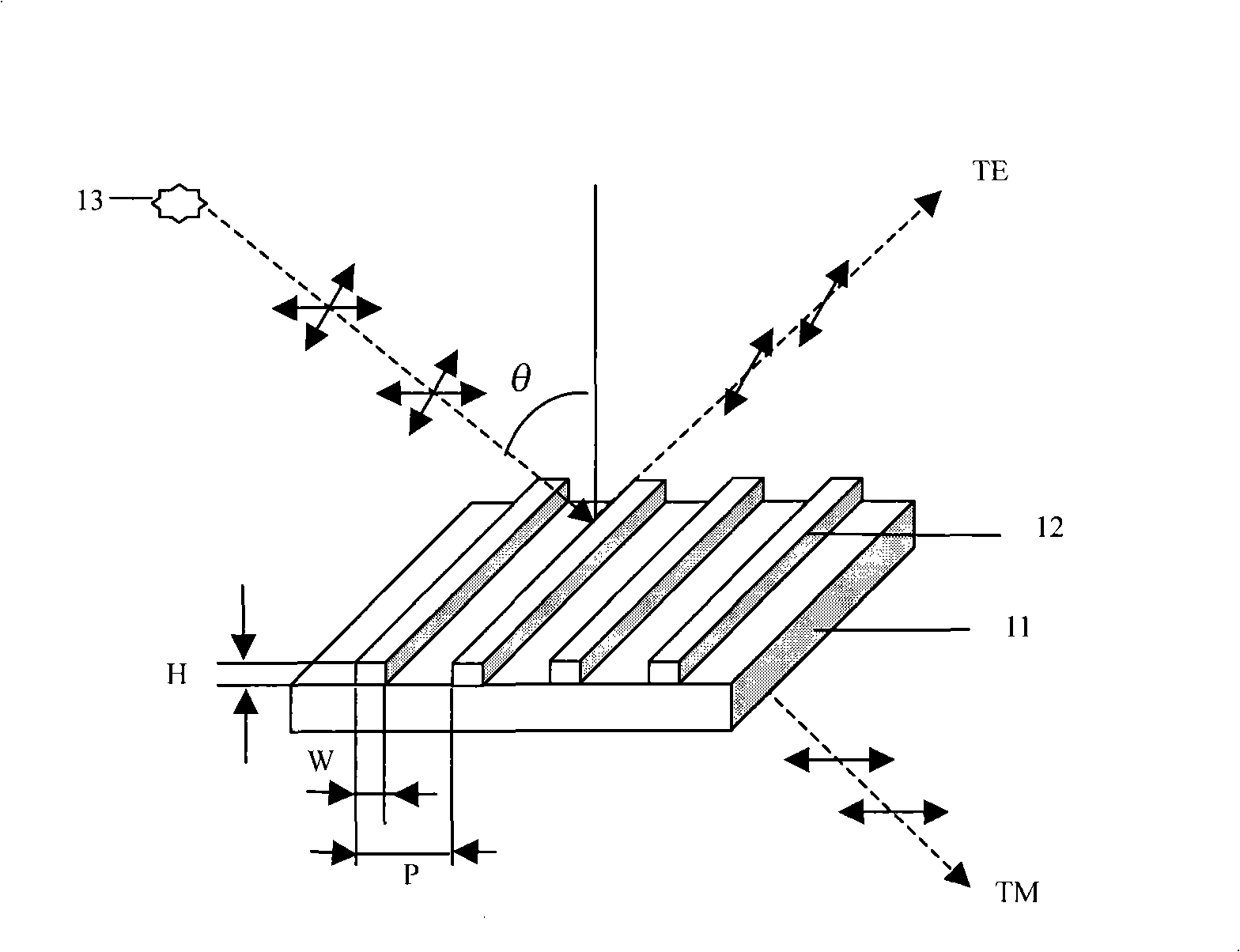
High transmittance sub-wavelength structure polarization module
InactiveUS7046441B2Spread the wordHigh light transmittancePolarising elementsDiffraction gratingsLength waveSub wavelength
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for integrated circuit layout optimization
InactiveUS20070101303A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designResolution enhancement technologiesLithographic artist
A method and apparatus for integrated circuit layout optimization are provided. In the conventional art, the major challenges in building integrated circuits (IC) at sub-wavelength geometries include i) to ensure the design intent is faithfully transferred onto silicon; ii) to ensure the design is manufacturable, or with acceptable yield subject to process variations. The present invention provides the method to process a layout database to optimize or correct or fix layout violations or enhancements. The layout violations are identified through various means such as design rules, recommended rules, timing / signal integrity / power constraints, lithography rules, Resolution Enhancement Technologies (RET) requirements and preferences, and process and manufacturing constraints. Particularly, the method, techniques and procedures of creating software tools of the present invention used to perform the layout violations or enhancements are disclosed.
Owner:LIZOTECH
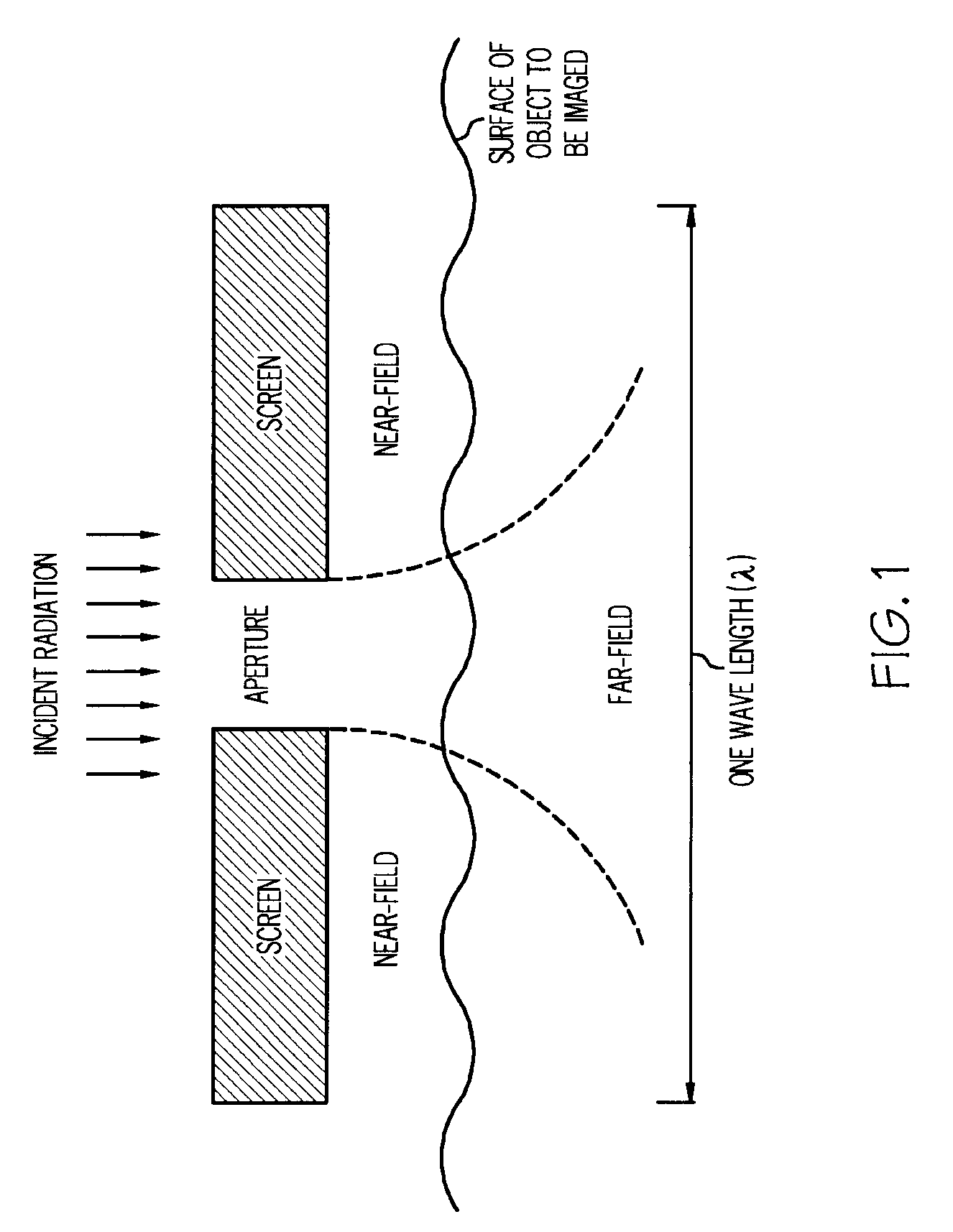
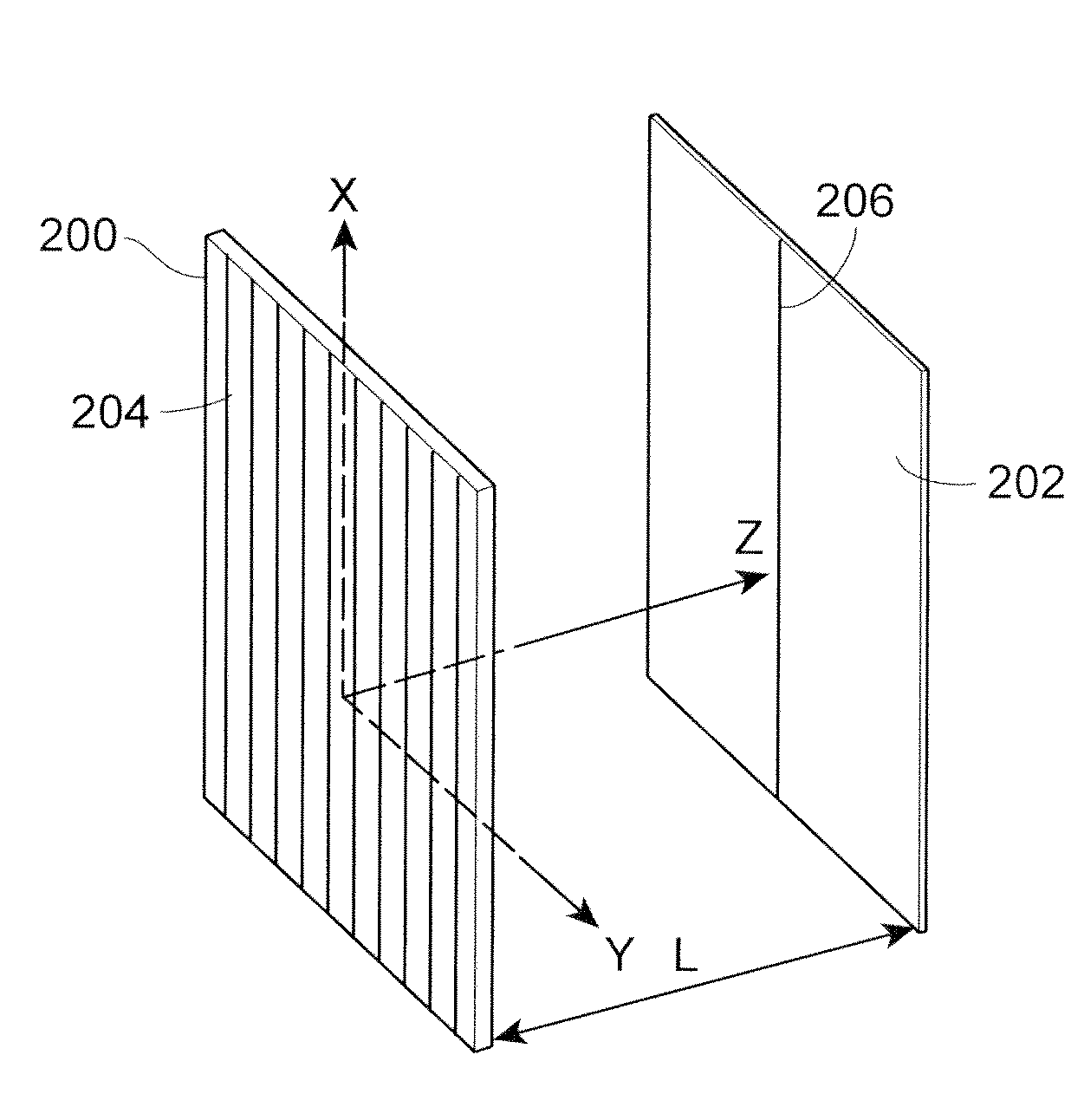
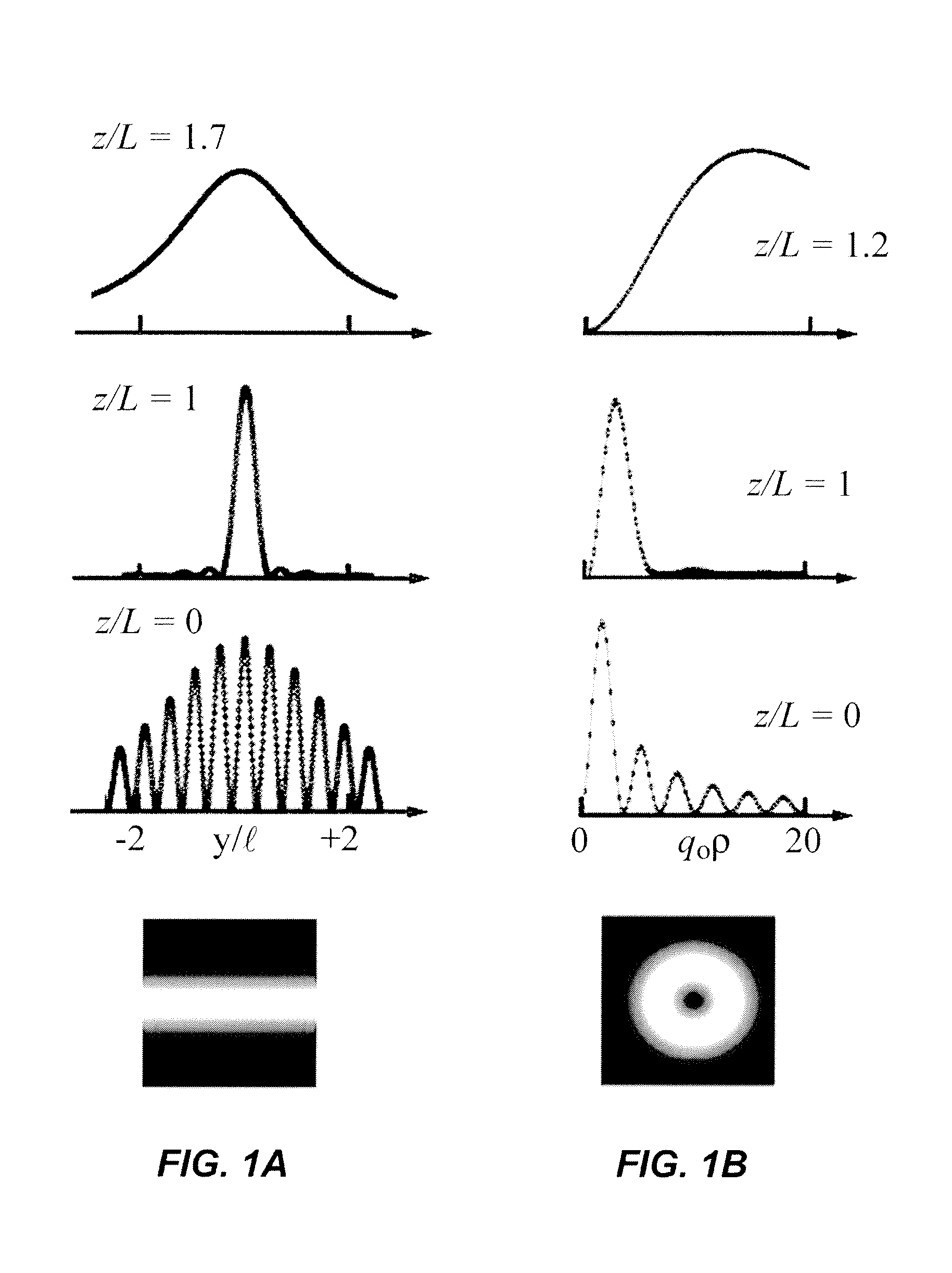
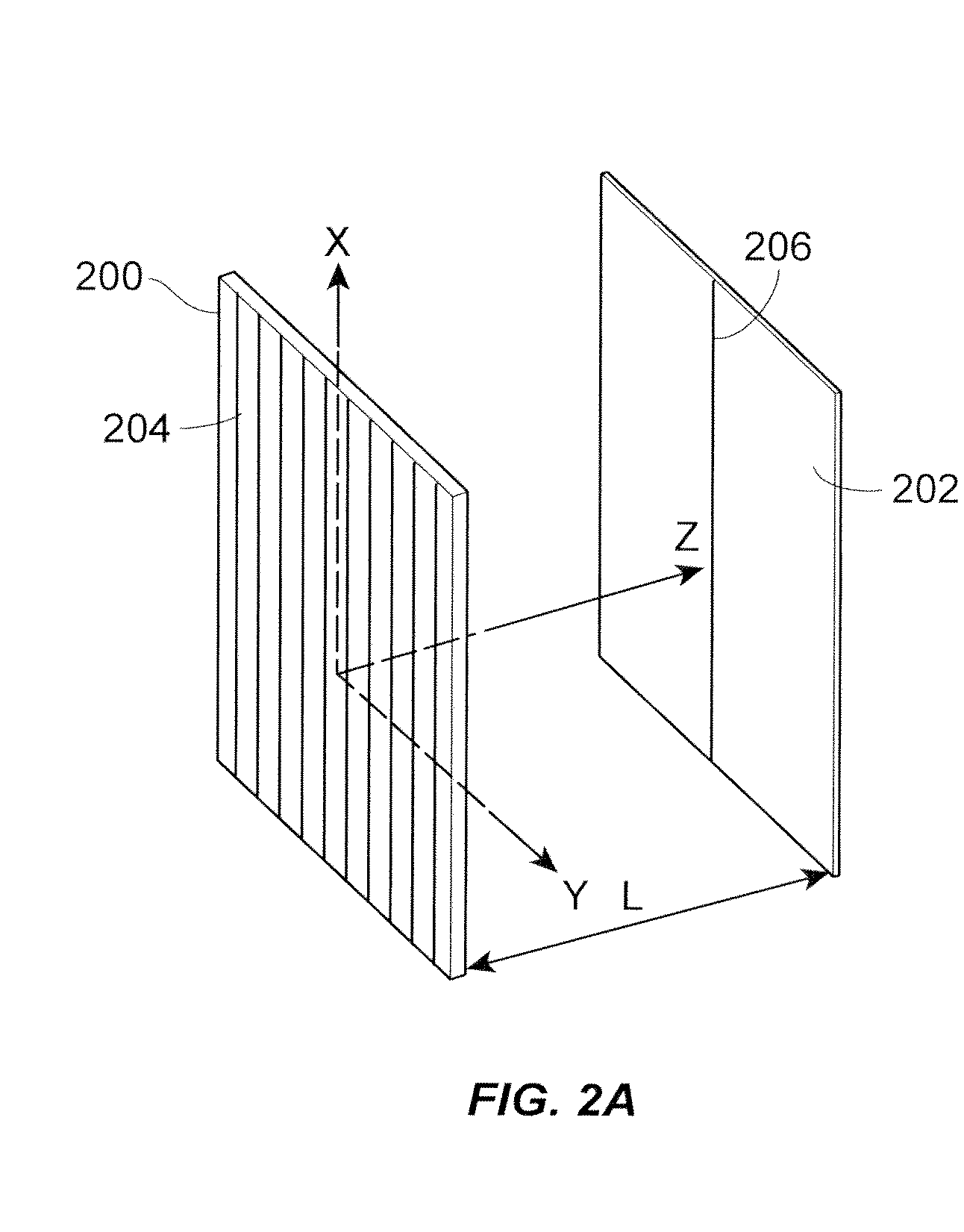
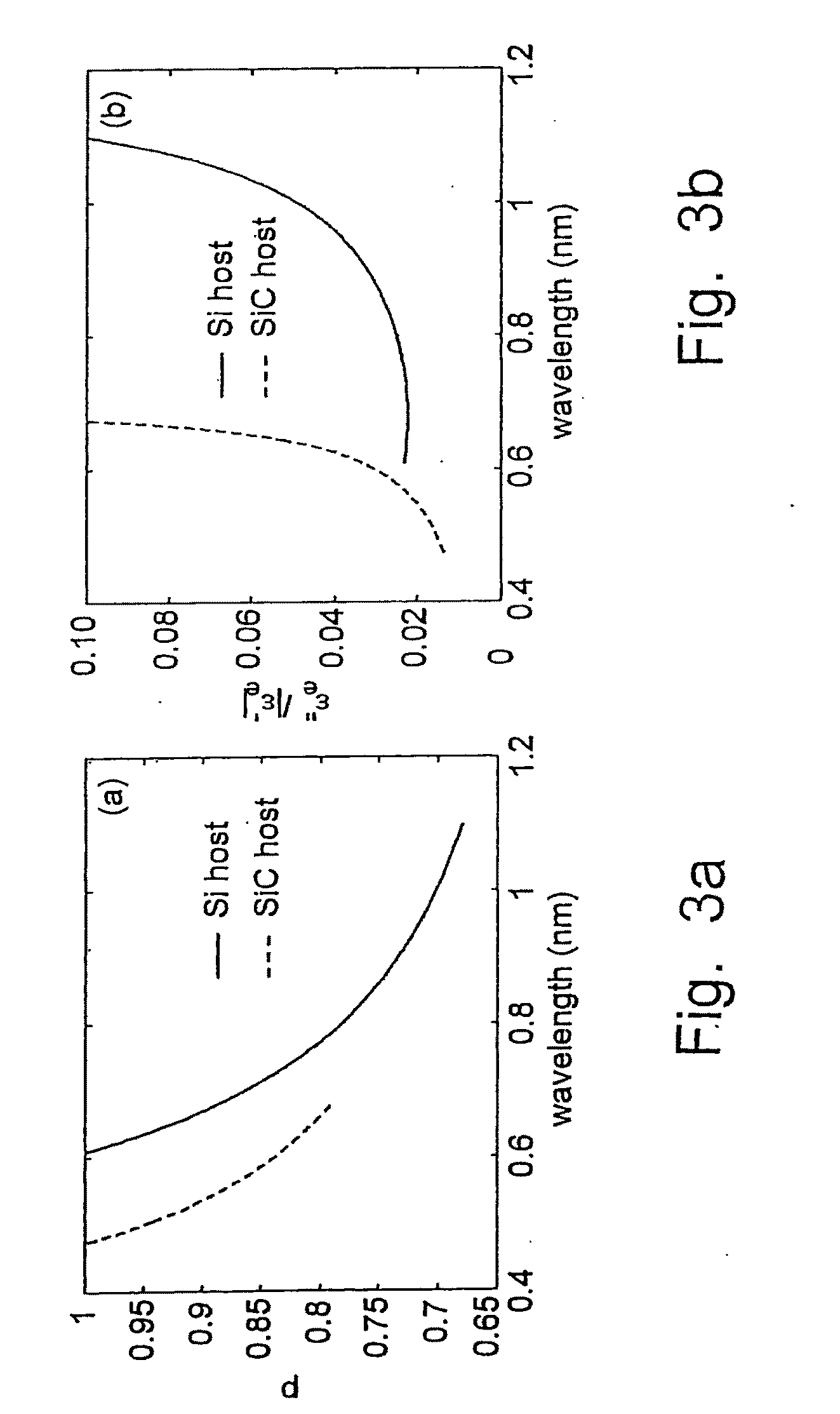
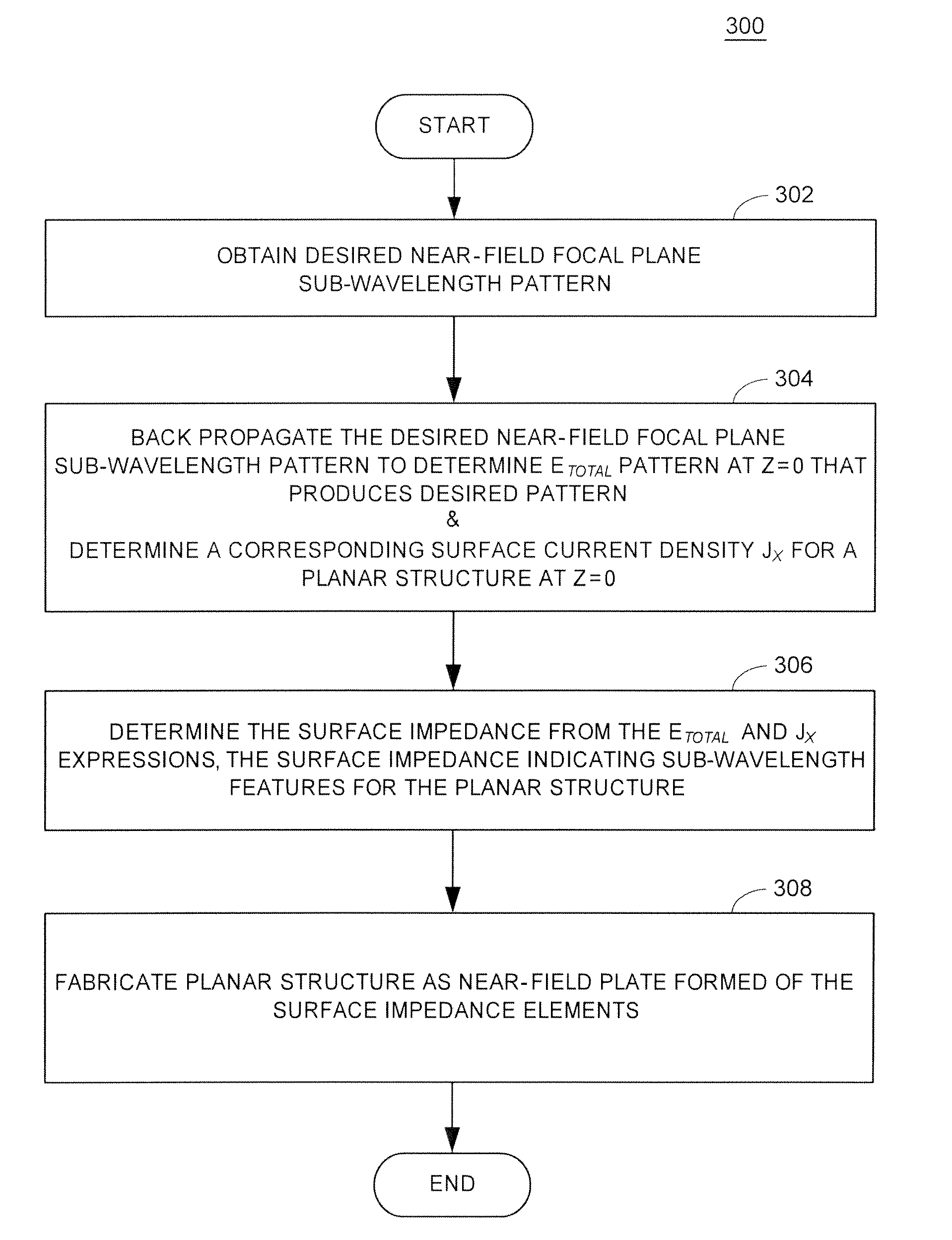
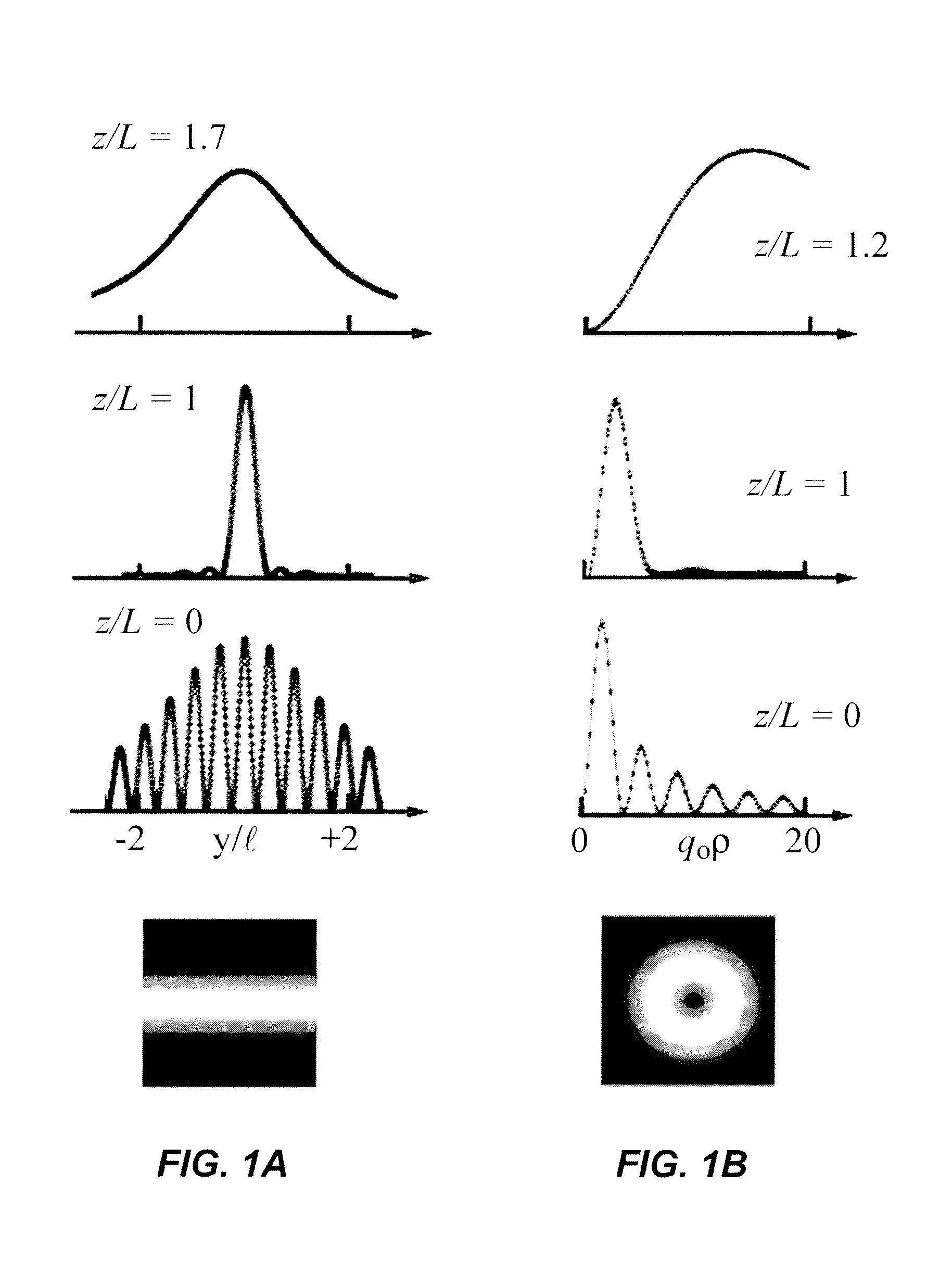
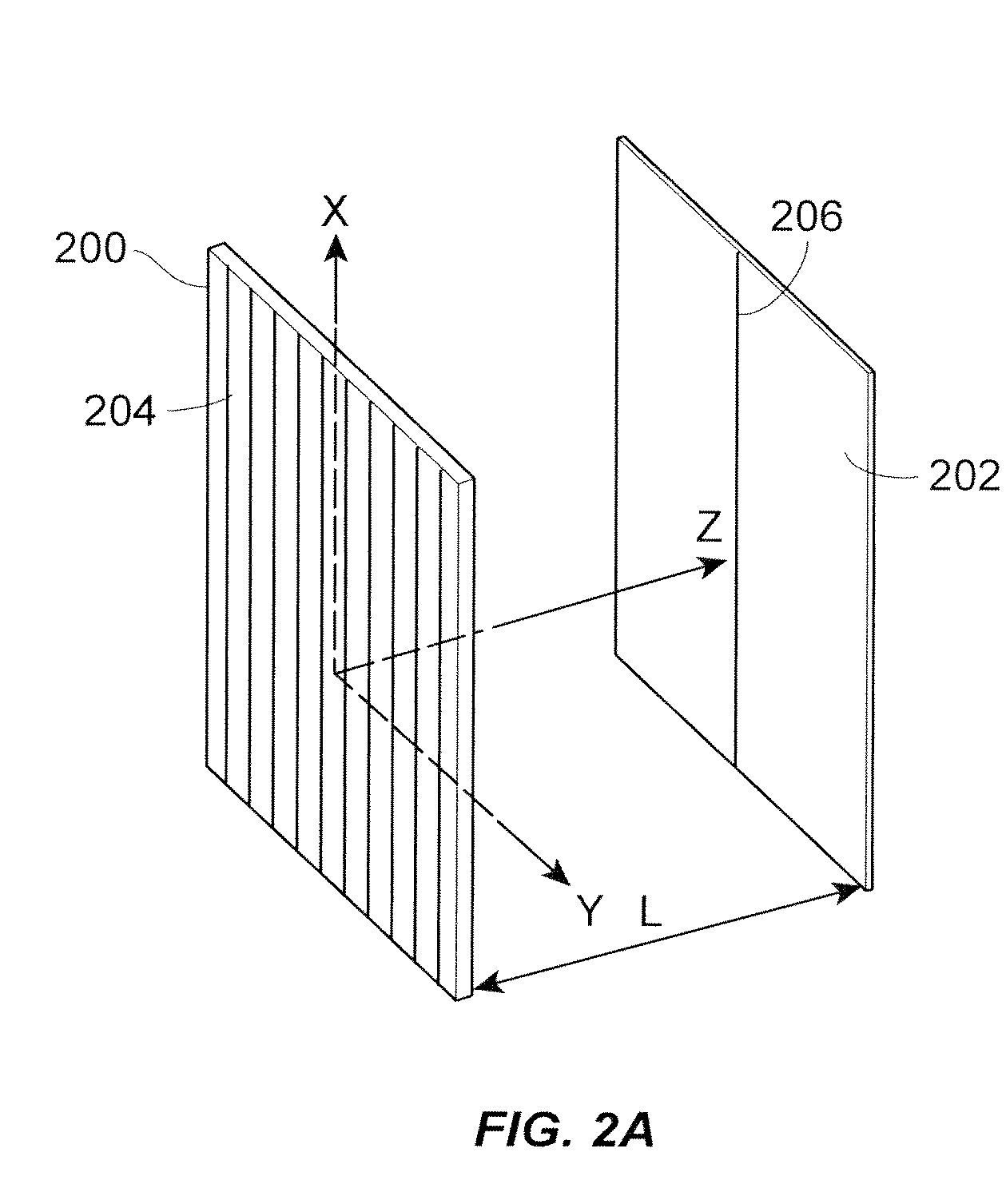
Apparatus for Sub-Wavelength Near-Field Focusing of Electromagnetic Waves
ActiveUS20090303154A1Radiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsGratingElectromagnetic radiation
Planar sub-wavelength structures provide superlensing, i.e., electromagnetic focusing beyond the diffraction limit. The planar structures use diffraction to force the input field to converge to a spot on the focal plane. The sub-wavelength patterned structures manipulate the output wave in such a manner as to form a sub-wavelength focus in the near field. In some examples, the sub-wavelength structures may be linear grating-like structures that can focus electromagnetic radiation to lines of arbitrarily small sub-wavelength dimension, or two dimensional grating-like structures and Bessel (azimuthally symmetric) structures that can focus to spots of arbitrarily small sub-wavelength dimensions. The particular pattern for the sub-wavelength structures may be derived from the desired focus. Some examples describe sub-wavelength structures that have been implemented to focus microwave radiation to sub-wavelength dimensions in the near field.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
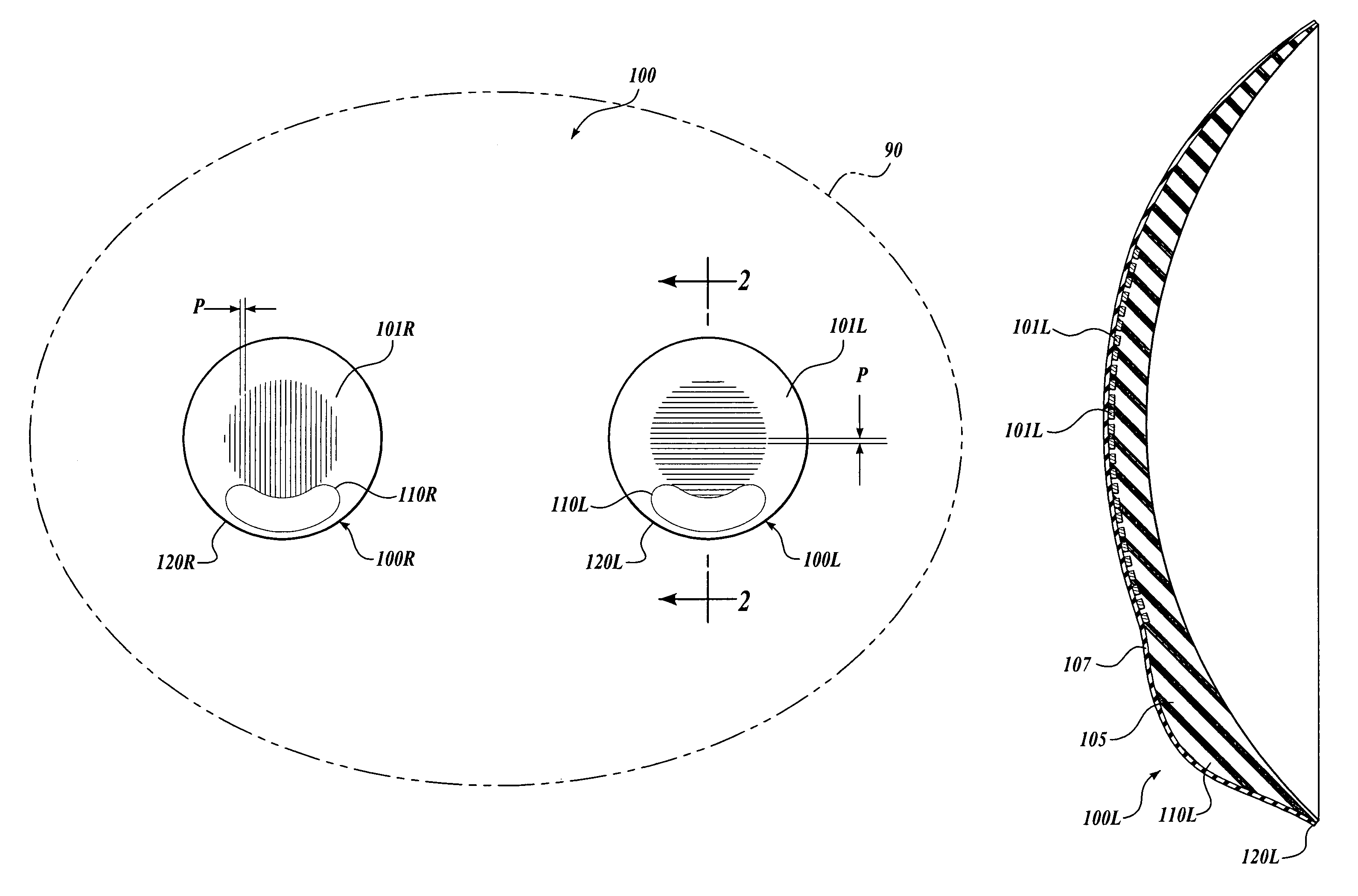
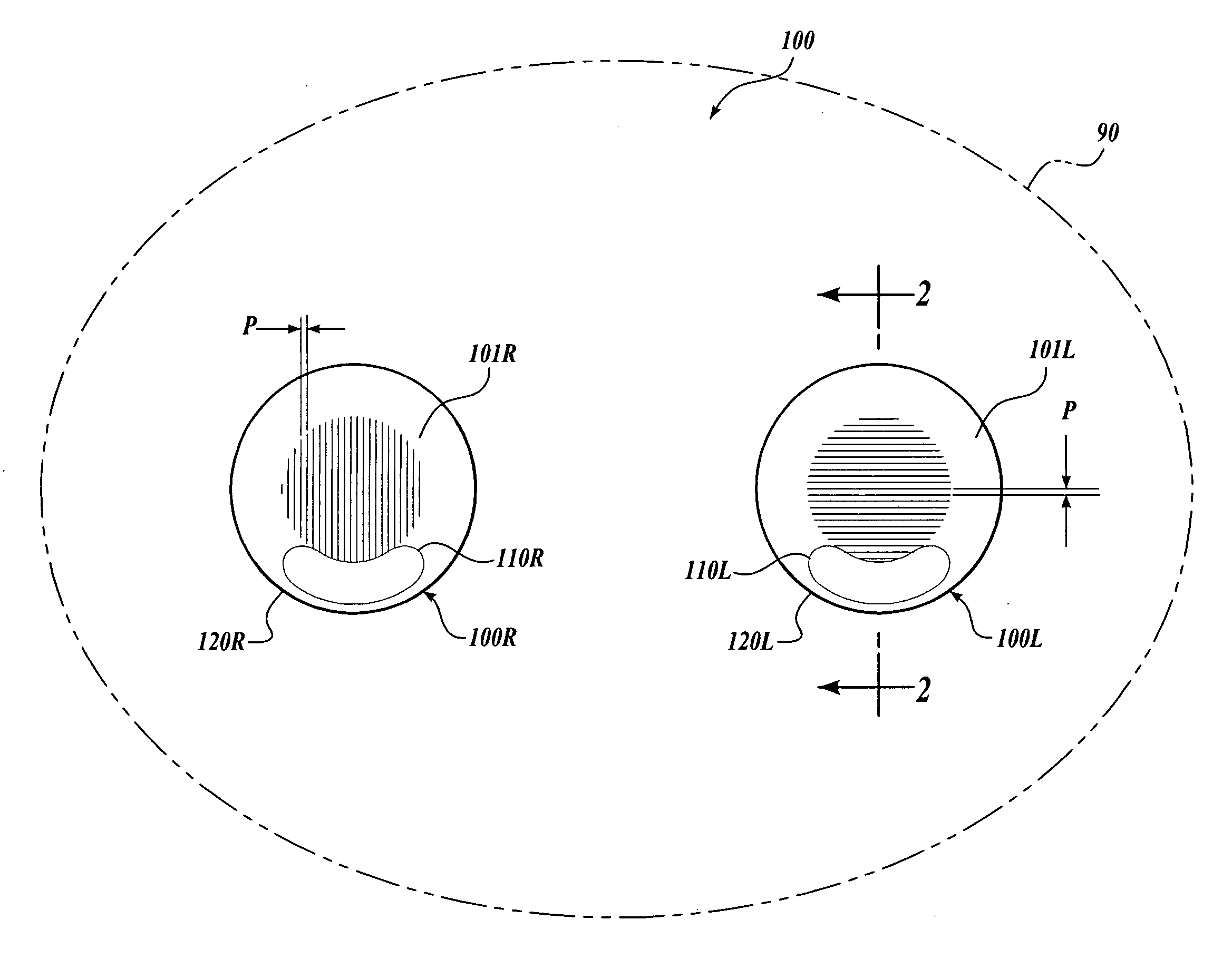
Contact lens for three dimensional visualization
A contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens comprising a first lens substrate incorporating a first polarizer, and a right contact lens comprising a lens substrate incorporating a second polarizer. The first polarizer comprises a first plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a first direction. The second polarizer comprises a second plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a second direction. The left contact lens and the right contact lens each comprises a rotational stabilization means, such that, during use, the first direction is adapted to orient in an approximately orthogonal direction to the second direction. In another embodiment, a contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens and a right contact lens, each coded with different colors.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Diffraction device
InactiveUS20070229955A1Satisfactory diffraction efficiencyDiffraction gratingsPeriodic alternatingPhase shifted
A diffraction device having, on a transparent substrate plate, a diffraction pattern composed of periodically alternating array of first and second phase control zones. Each one of the first and second phase control zones is provided with an infinitesimal ruled structure in a pitch of the order of sub-wavelength, i.e., in a pitch smaller than the shortest wavelength of incident light, thereby to control phase shifts to the same angle in a plural number of wave ranges. The infinitesimal ruled structure in the first and second phase control zones are disposed in perpendicularly intersecting relation with each other. Thus, the diffraction device can diffract incident light with a diffraction efficiency free from dependency on wavelength and give a performance not dependent on the direction of polarization of incident light.
Owner:FUJINON SANO
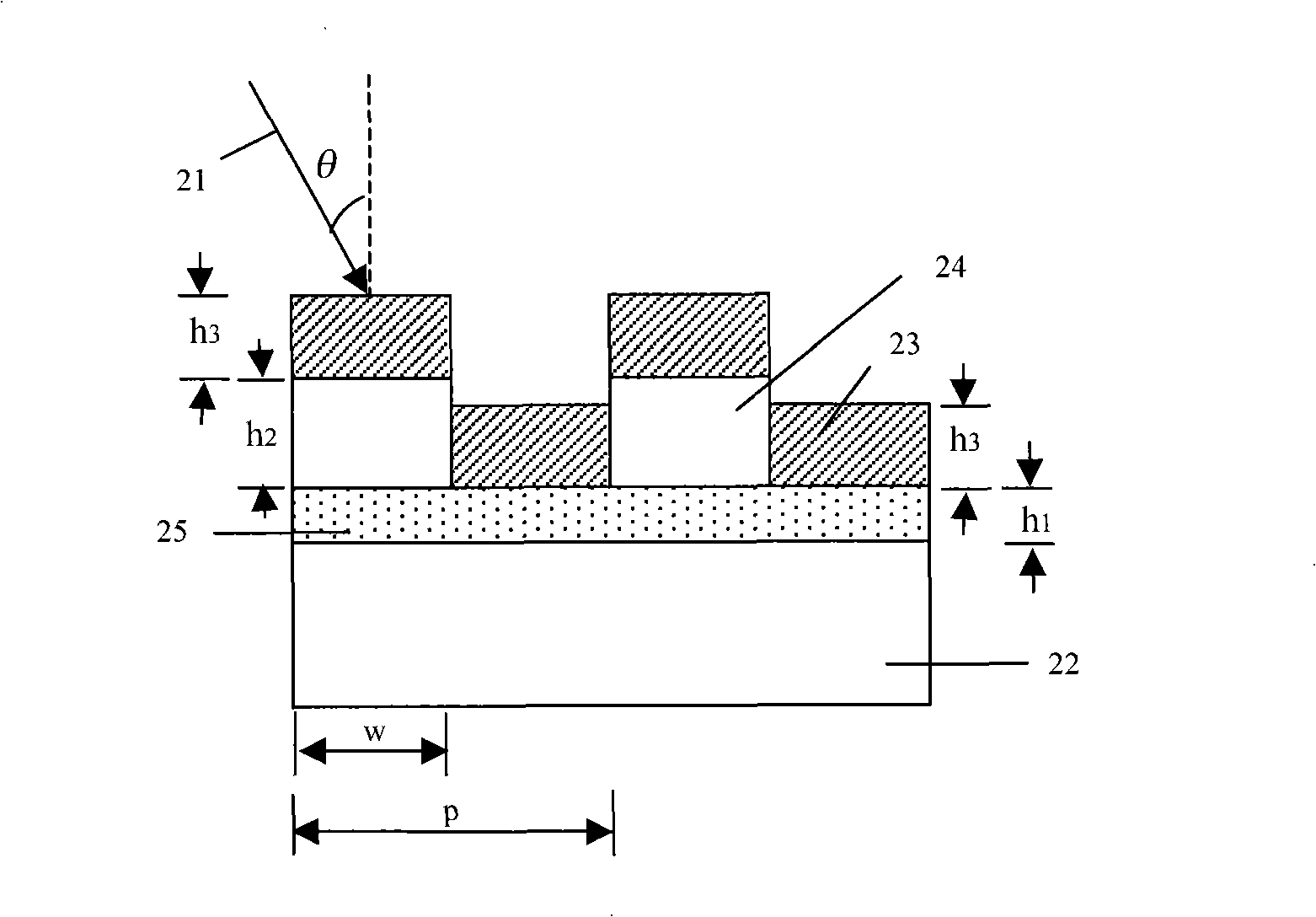
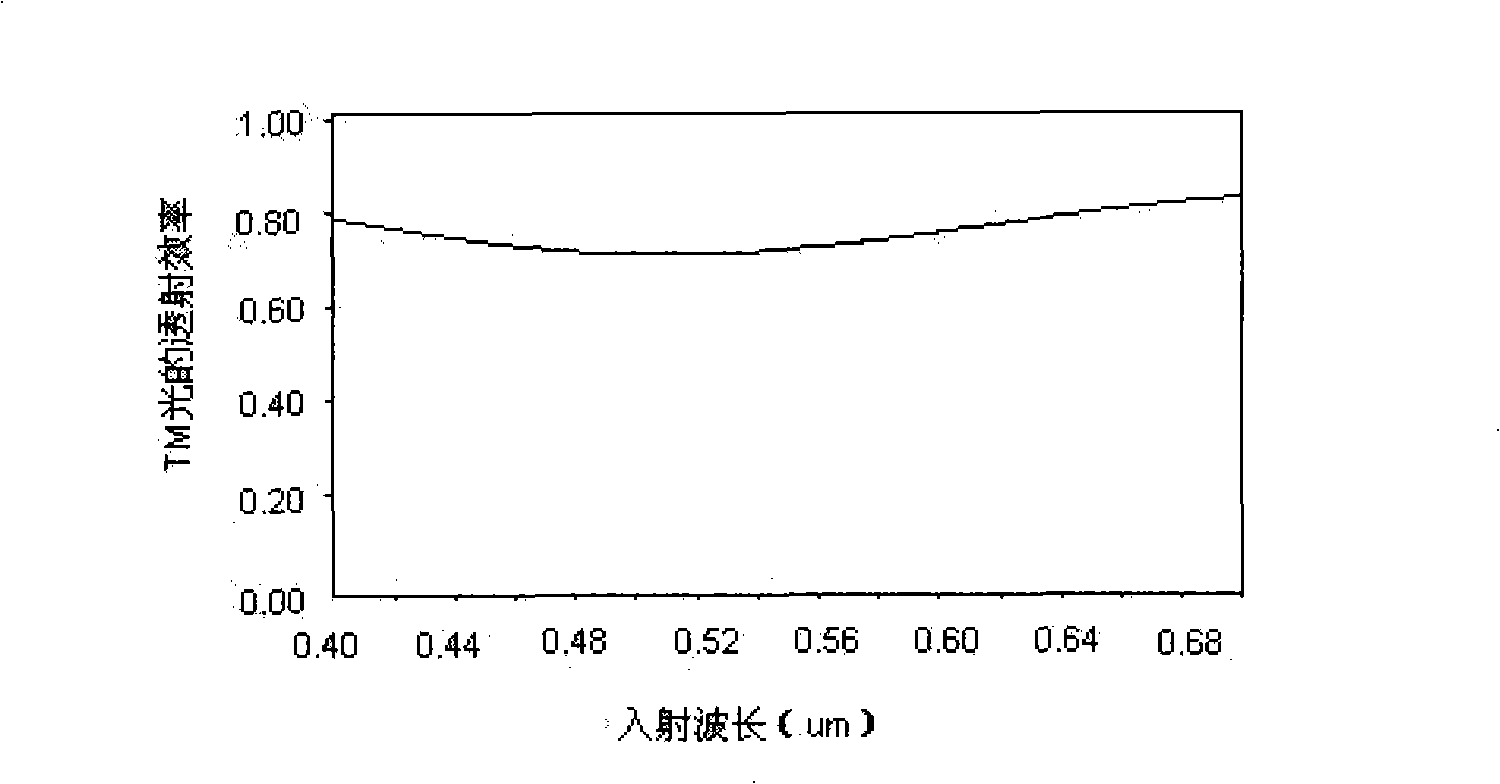
Sub-wavelength grate structure polarizing film and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101290371ASpectral heightHigh polarization conversion effectPhotomechanical apparatusPolarising elementsGratingRefractive index
The invention discloses a polaroid sheet with a subwavelength grating structure, which comprises a transparent substrate, a dielectric grating, a first metal layer and a second metal layer. The dielectric grating is provided with ridges and grooves which are periodically arranged at intervals, the first metal layer is covered on the ridges of the dielectric grating, the second metal layer is covered in the grooves of the dielectric grating, and the period of the dielectric grating is less than the wavelength of incident light. The invention is characterized in that: a high refractive index dielectric layer is arranged between the transparent substrate and the dielectric grating, and the refractive index of the high refractive index dielectric layer is between 1.6 and 2.4. The transmission efficiency and the extinction ratio of TM light of the polaroid sheet are improved by adding the high refractive index dielectric layer between the transparent substrate and the dielectric grating. In the whole visible light waveband, the polaroid sheet has high transmission efficiency, high extinction ratio, and wide incident angle range. In the process, a nano-imprint technique is adopted to process and produce, the production process is simple and convenient and is easy to operate, an etching process is not needed, and the processing cost is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Resolution radar using metamaterials
ActiveUS20090135086A1High resolutionWeapons typesWaveguide type devicesRadar systemsImage resolution
A radar system includes at least one transmit array comprising a plurality of metamaterial elements. The radar system further includes at least one near-field stimulator for inputting electromagnetic signal to the transmit array so that a sub-wavelength target is illuminated with an electromagnetic wave.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
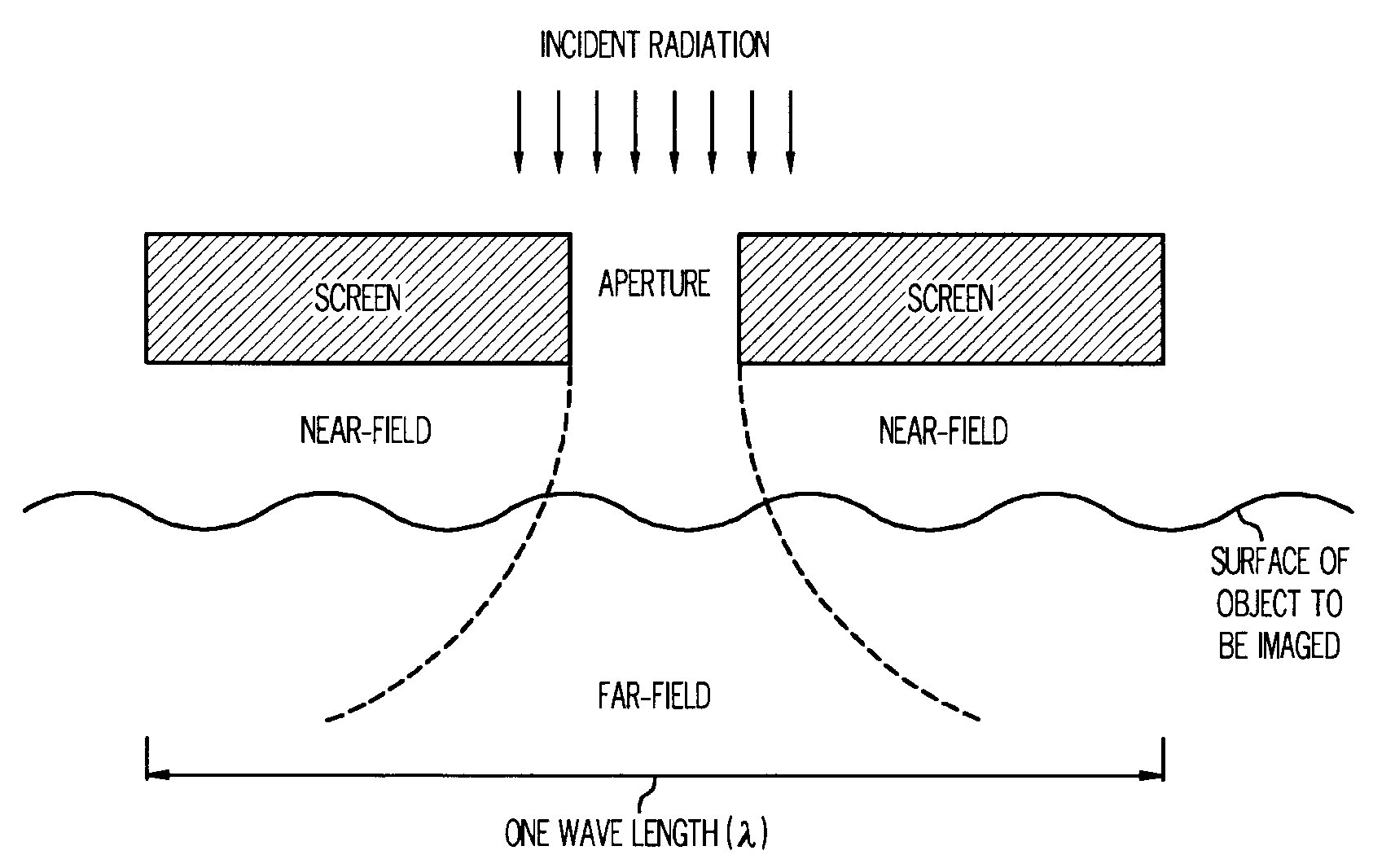
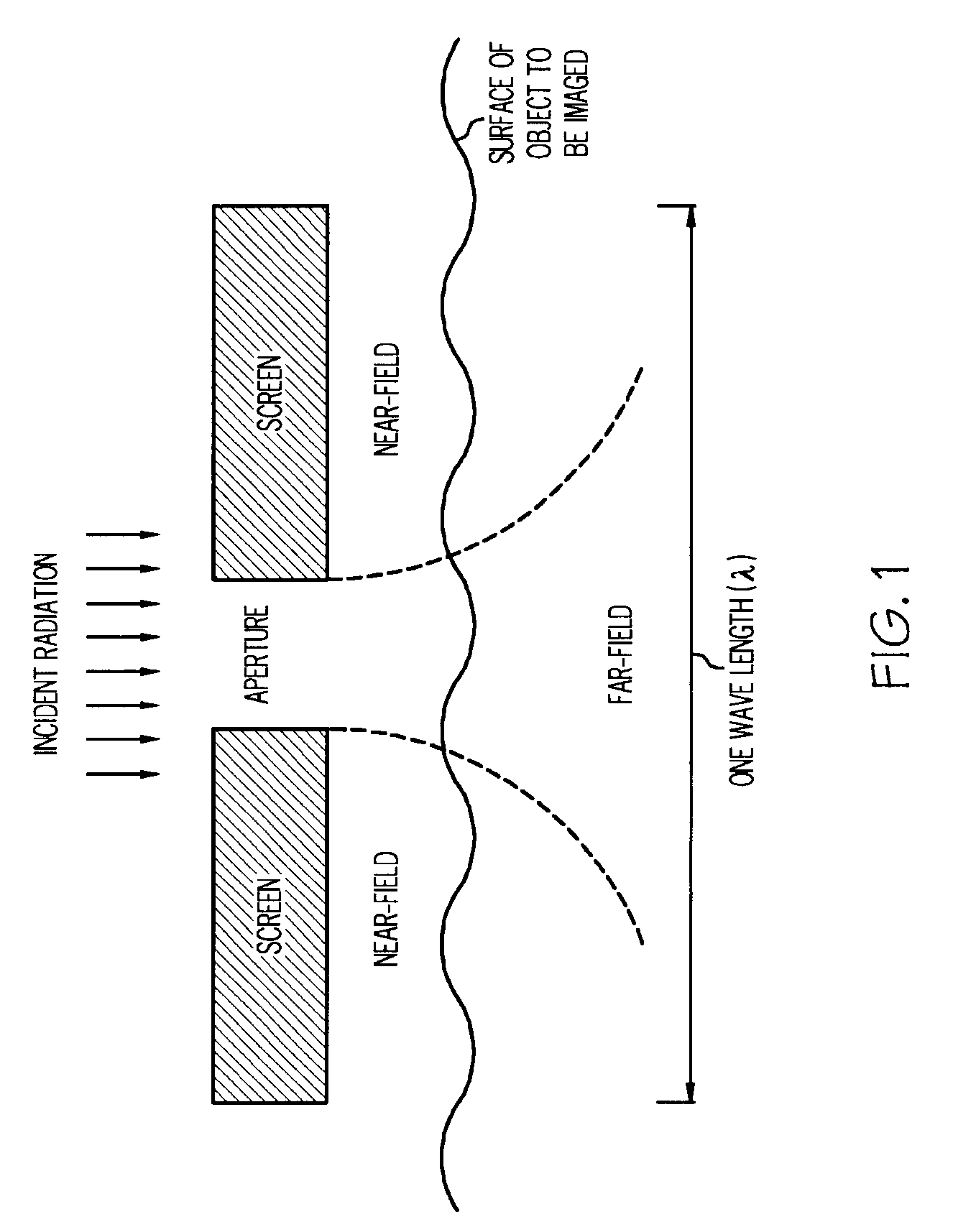
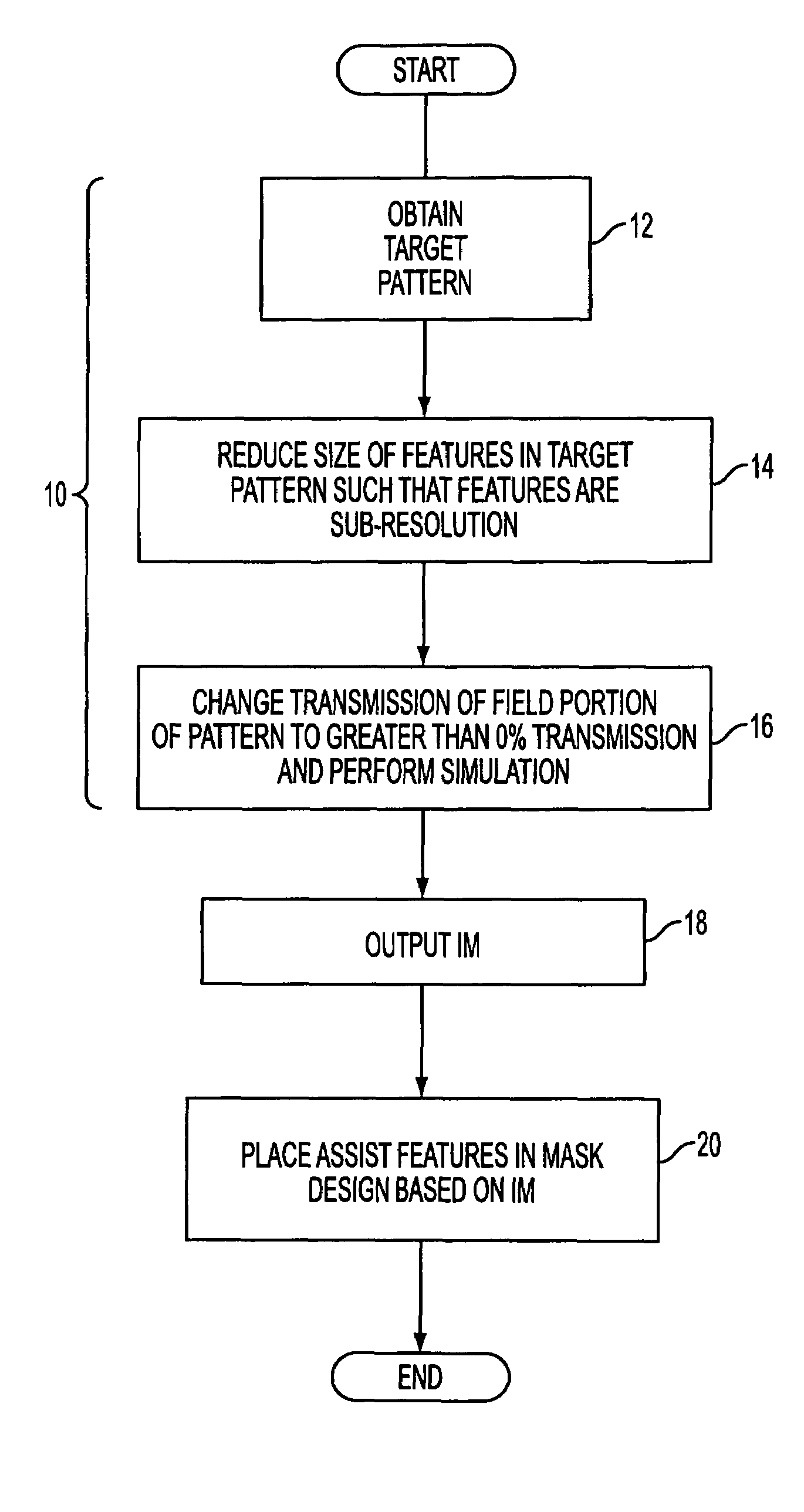
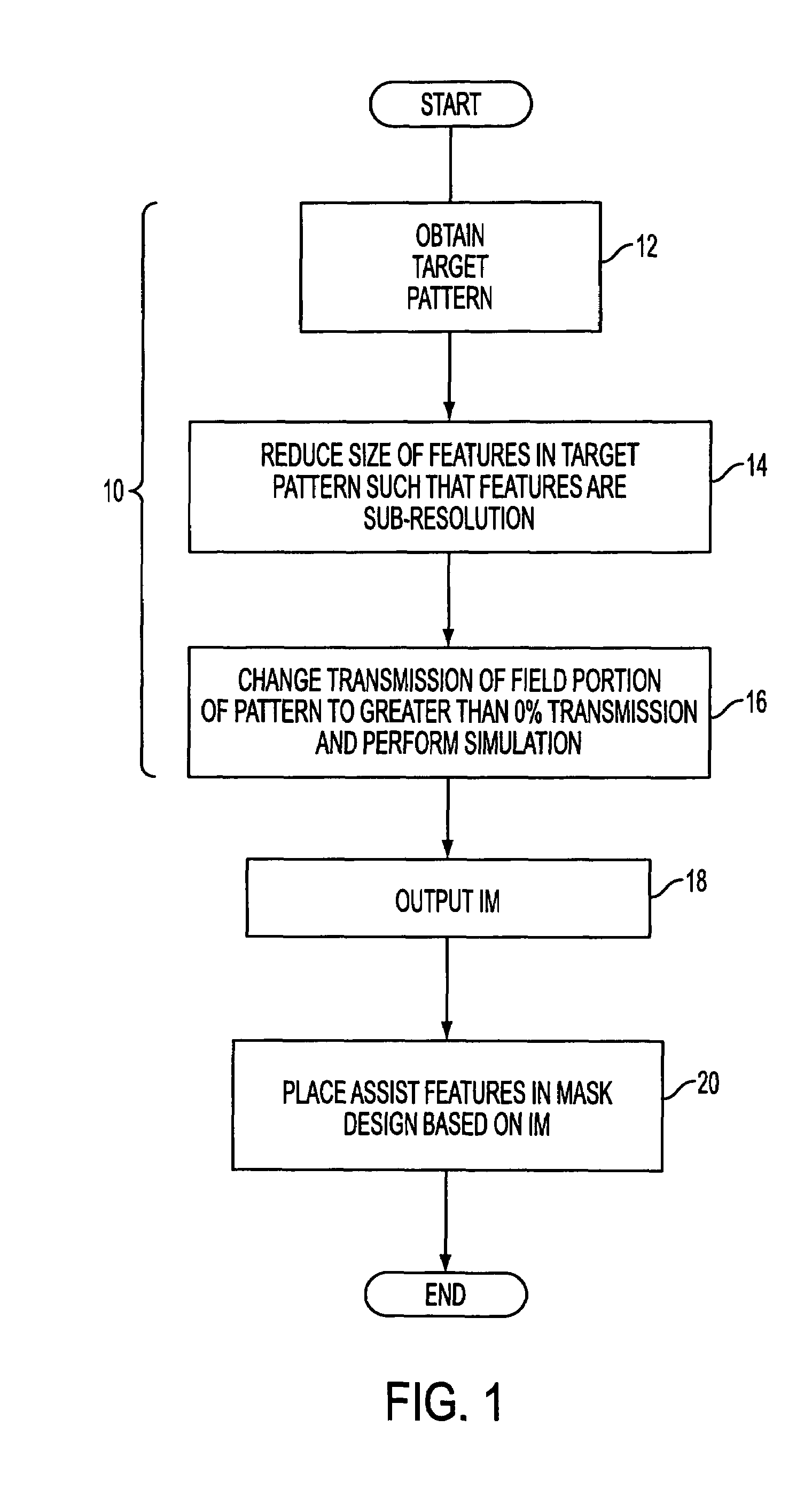
Method and apparatus for providing optical proximity features to a reticle pattern for deep sub-wavelength optical lithography
ActiveUS7247574B2Improve printing effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringWavelength
A method of generating a mask design having optical proximity correction features disposed therein. The methods includes the steps of obtaining a desired target pattern having features to be imaged on a substrate; determining an interference map based on the target pattern, the interference map defining areas of constructive interference and areas of destructive interference between at least one of the features to be imaged and a field area adjacent the at least one feature; and placing assist features in the mask design based on the areas of constructive interference and the areas of destructive interference.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Optical polymer blend with bimodal particle sizes
ActiveUS6979704B1Reduce CTEReduce light scatterMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresAdhesiveOptical polymers
An optical polymer blend includes sub-wavelength particles to modify the refractive index of a polymer to match the refractive index of micro-particles added to adjust the bulk coefficient of thermal expansion of the blend. A relatively large amount of material may be added to the resin to adjust the bulk coefficient of thermal expansion without unduly increasing the viscosity of the blend before setting. In some applications blends are used for molded or extruded optical elements, in other applications, blends are used for optical adhesives with low coefficients of thermal expansion.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
3D Polarized Eyewear
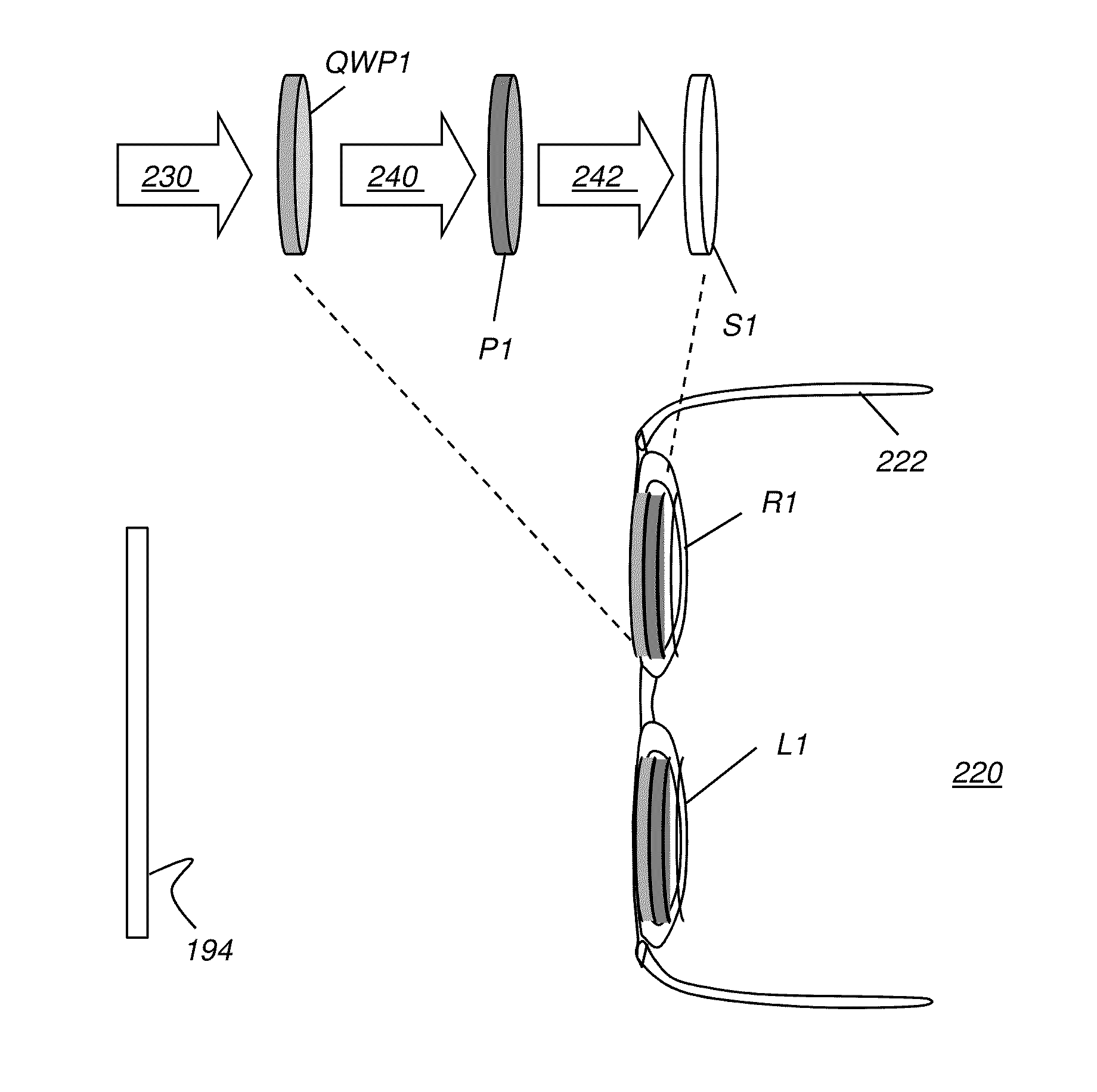
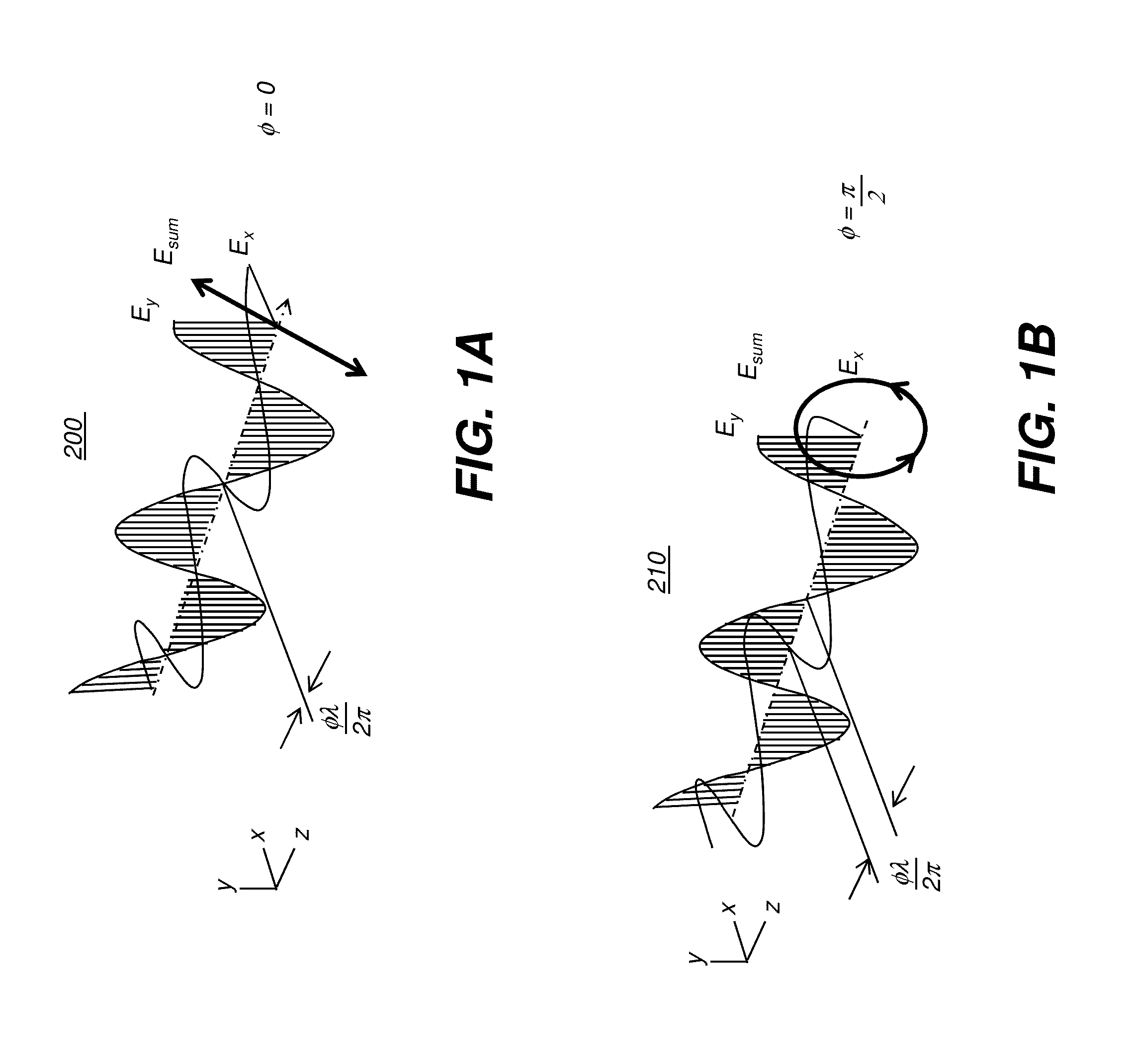
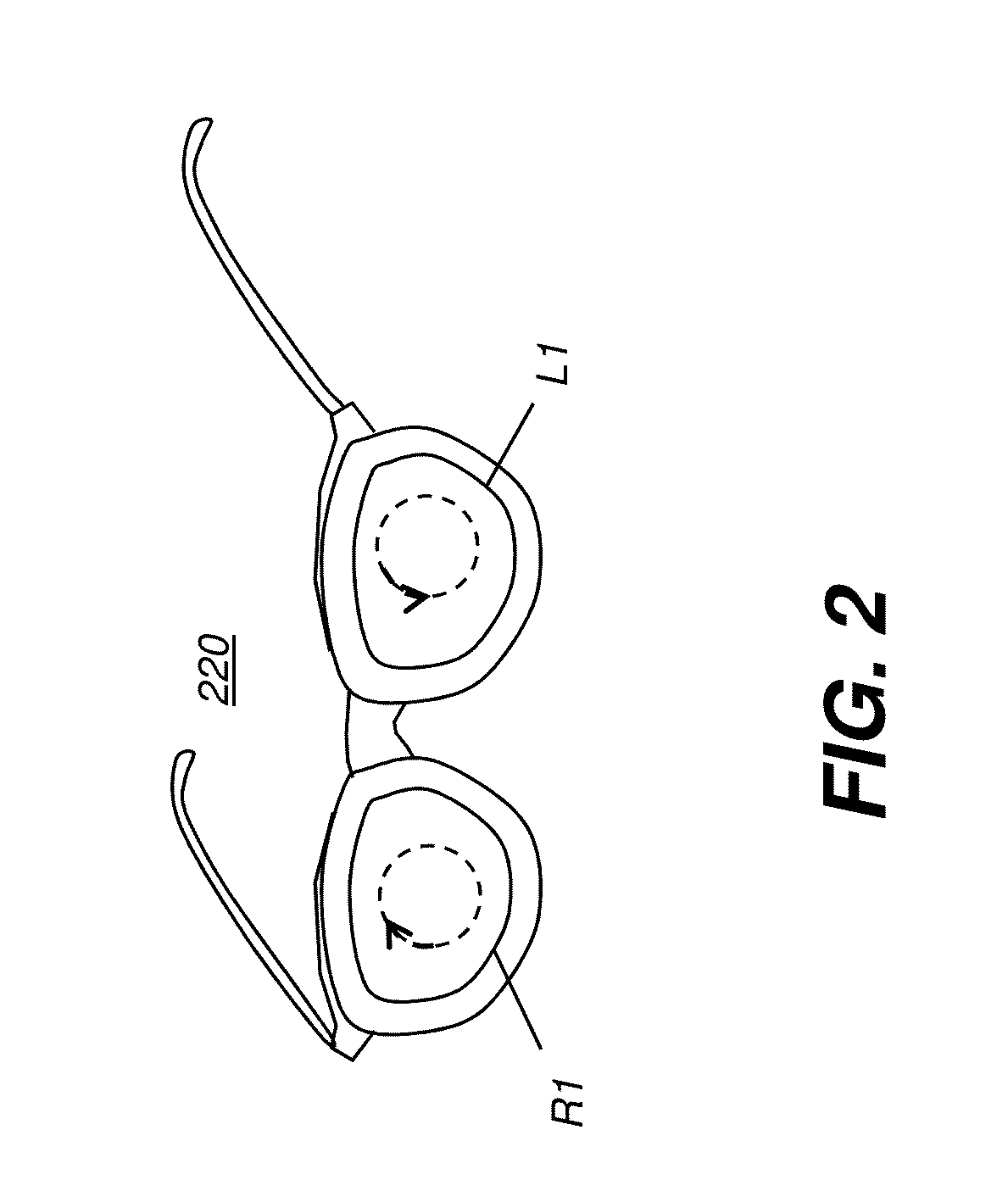
An article of eyewear for viewing a 3D display has at least one lens, wherein the at least one lens has a substrate lens material that is transparent to visible light and has a curved surface. A circular polarizer is formed on the substrate lens material and has a linear polarizer with a polarization axis and a quarter wave plate with a retardation axis that is inclined at substantially 45 degrees from the polarization axis along the curved surface. Either or both of the linear polarizer and the quarter wave plate are formed as sub-wavelength elongated structure devices.
Owner:SOL GRID
Contact lens for three dimensional visualization
A contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens comprising a first lens substrate incorporating a first polarizer, and a right contact lens comprising a lens substrate incorporating a second polarizer. The first polarizer comprises a first plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a first direction. The second polarizer comprises a second plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a second direction. The left contact lens and the right contact lens each comprises a rotational stabilization means, such that, during use, the first direction is adapted to orient in an approximately orthogonal direction to the second direction. In another embodiment, a contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens and a right contact lens, each coded with different colors.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Near field super lens employing tunable negative index materials
ActiveUS20100134898A1High resolutionFast and accurate calculationNanoopticsMicroscopesCamera lensBio molecules
A tunable super-lens (TSL) for nanoscale optical sensing and imaging of bio-molecules and nano-manufacturing utilizes negative-index materials (NIMs) that operate in the visible or near infrared light. The NIMs can create a lens that will perform sub-wavelength imaging, enhanced resolution imaging, or flat lens imaging. This new TSL covers two different operation scales. For short distances between the object and its image, a near-field super-lens (NFSL) can create or enhance images of objects located at distances much less than the wavelength of light. For the far-zone, negative values are necessary for both the permittivity ε a permeability μ. While well-structured periodic meta-materials, which require delicate design and precise fabrication, can be used, metal-dielectric composites are also candidates for NIMs in the optical range. The negative-refraction in the composite films can be made by using frequency-selective photomodification.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Apparatus for sub-wavelength near-field focusing of electromagnetic waves
ActiveUS8003965B2Radiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsGratingWavelength
Planar sub-wavelength structures provide superlensing, i.e., electromagnetic focusing beyond the diffraction limit. The planar structures use diffraction to force the input field to converge to a spot on the focal plane. The sub-wavelength patterned structures manipulate the output wave in such a manner as to form a sub-wavelength focus in the near field. In some examples, the sub-wavelength structures may be linear grating-like structures that can focus electromagnetic radiation to lines of arbitrarily small sub-wavelength dimension, or two dimensional grating-like structures and Bessel (azimuthally symmetric) structures that can focus to spots of arbitrarily small sub-wavelength dimensions. The particular pattern for the sub-wavelength structures may be derived from the desired focus. Some examples describe sub-wavelength structures that have been implemented to focus microwave radiation to sub-wavelength dimensions in the near field.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Light-induced directed self-assembly of periodic sub-wavelength nanostructures
ActiveUS20090214885A1Small feature sizeExcellent long-range orderCasting plantsNanoinformaticsWavelengthNanostructure
In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention provides a system for the light-induced directed self-assembly (LIDSA) of periodic sub-wavelength nanostructures, including: a light source for delivering a beam of photons; a reaction chamber disposed adjacent to the light source; a gas including one or more precursor materials disposed within the reaction chamber; and a substrate disposed within the reaction chamber, wherein the substrate is positioned and configured to receive the beam of photons; wherein the beam of photons causes a periodic sub-wavelength nanostructure of one or more constituents of the one or more precursor materials to form on a surface of the substrate. In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention also provides an associated method.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
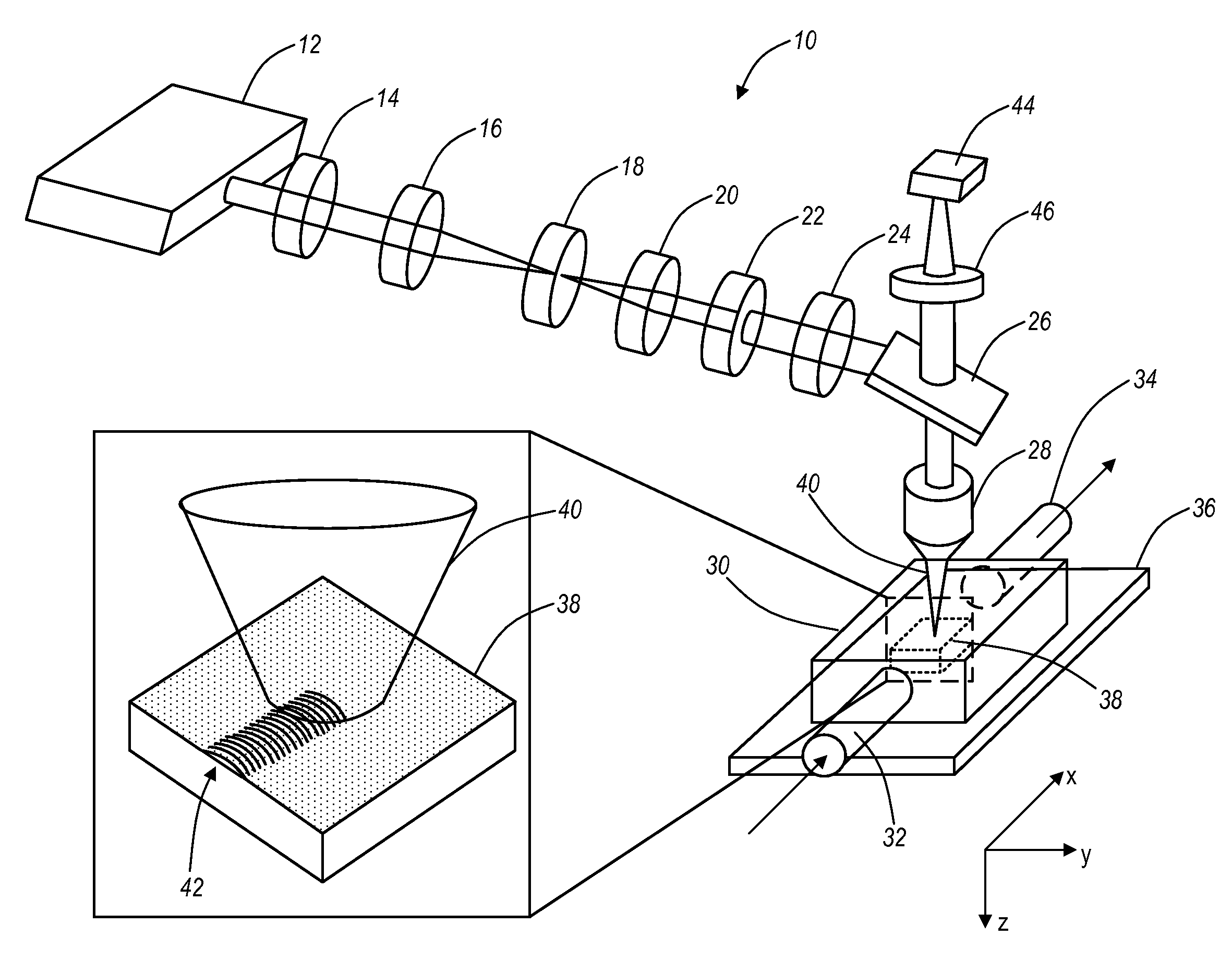
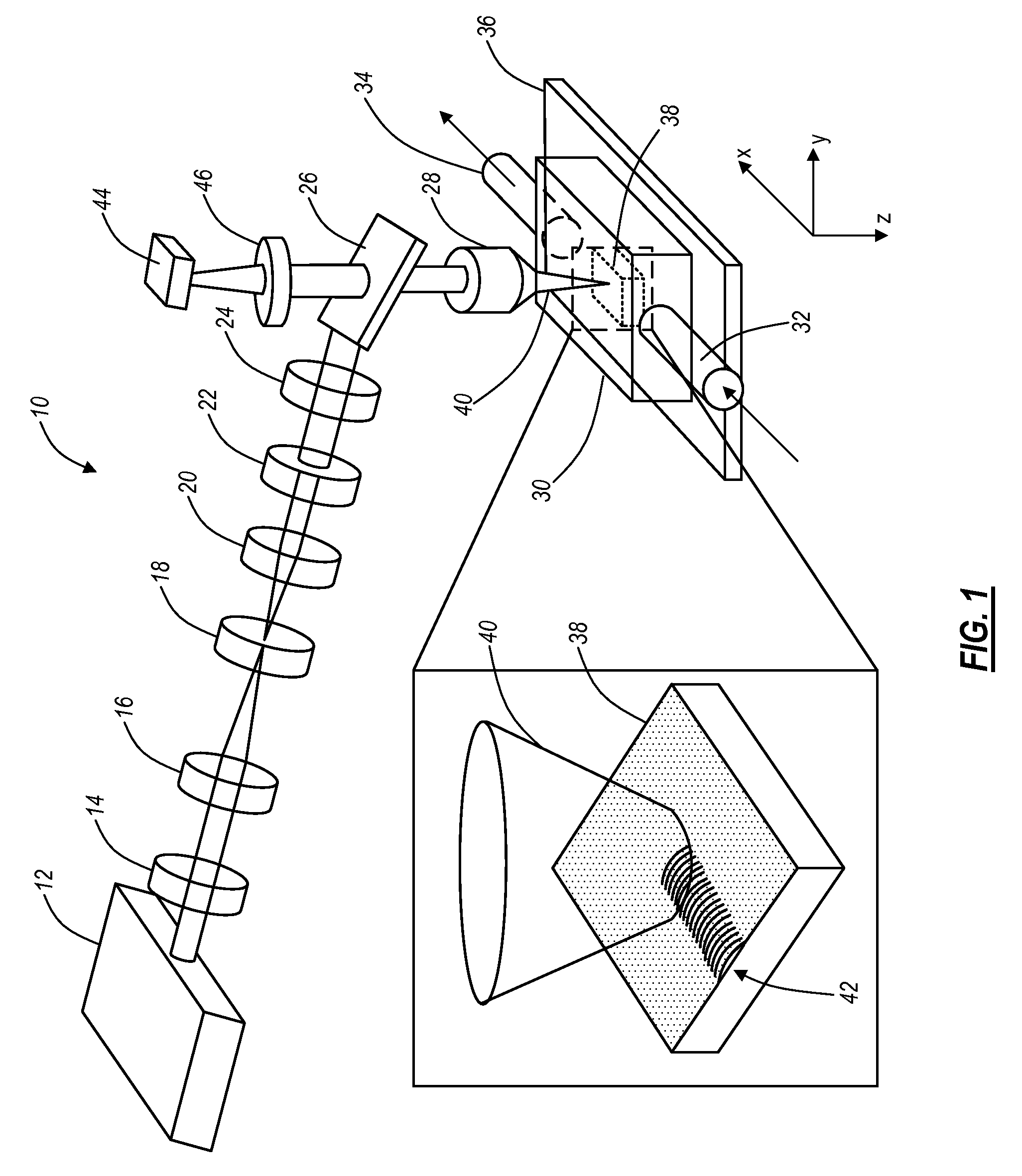
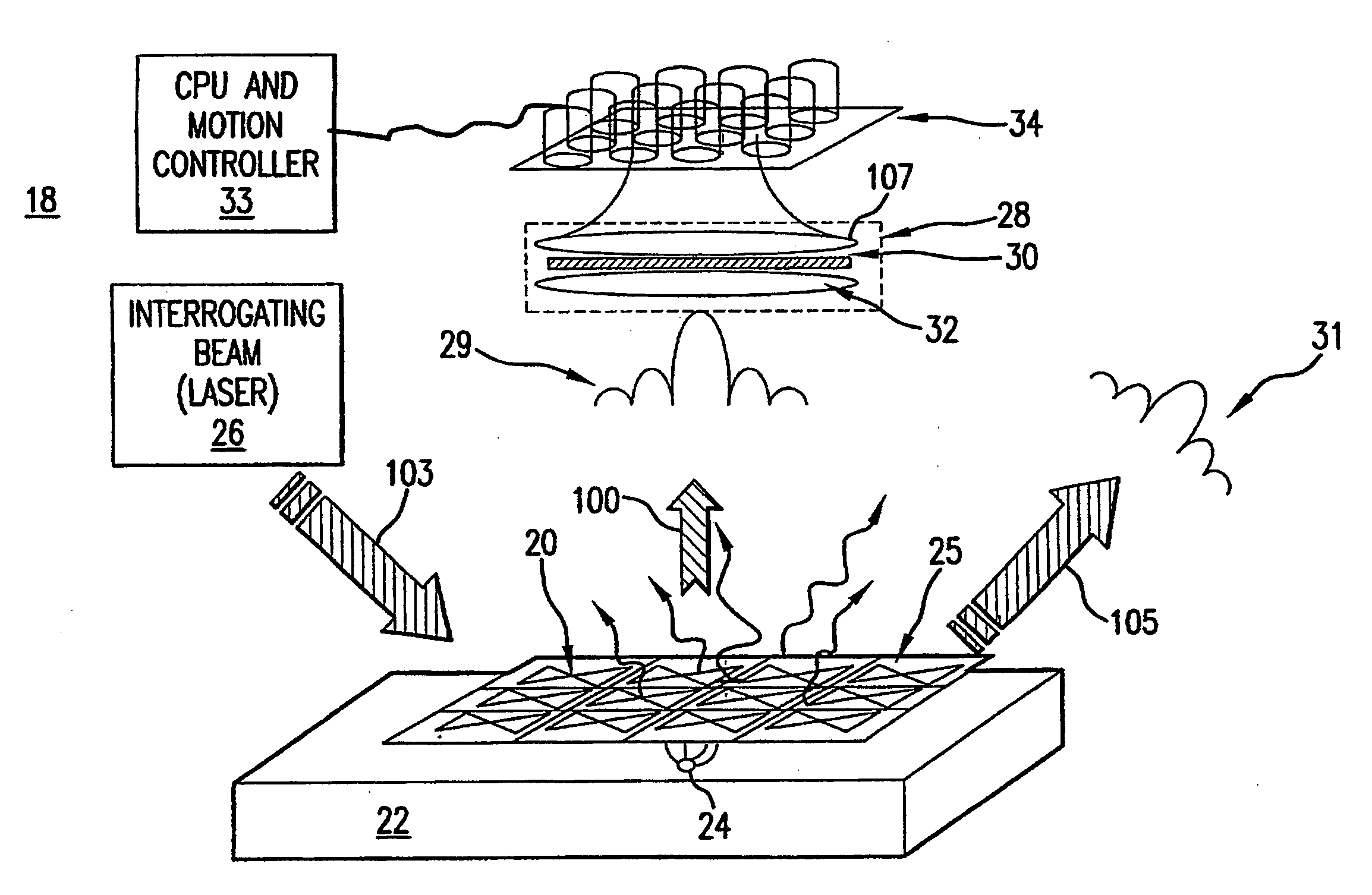
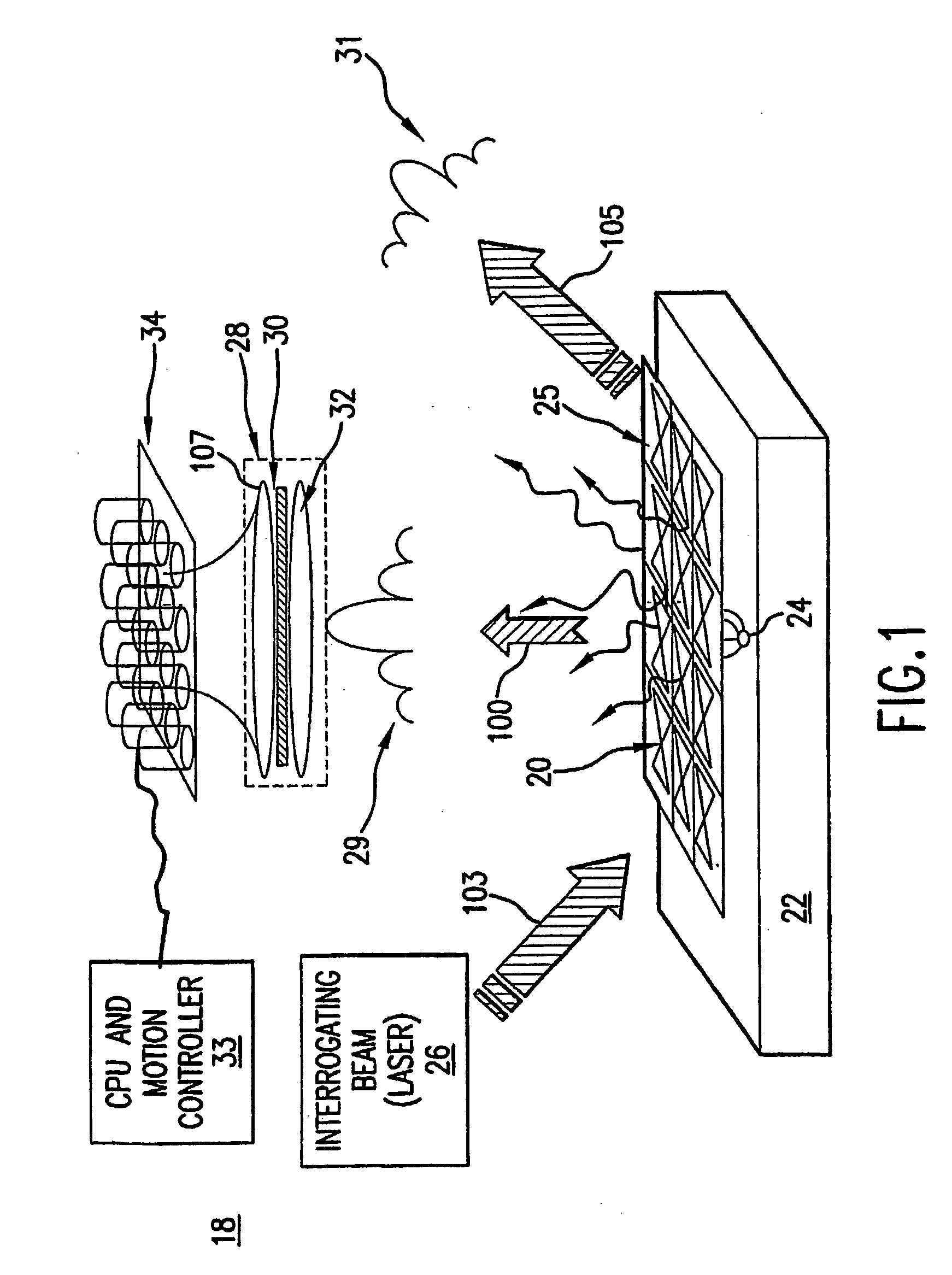
Wave interrogated near field arrays system and method for detection of subwavelength scale anomalies
InactiveUS20060065856A1Retaining convenienceRetaining speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsImaging processingOptical frequencies
An array of antenna elements (20) can be used to detect subwavelength sized anomalies on a surface below the array. An array (20) is illuminated at optical frequencies by a coherent optical energy source (26). The change in reactance and radiated power of the antenna elements that results from the proximity of the anomaly to the near field of the antenna element's open-circuited is detected and holographically filtered to eliminate the radiation caused by the antenna array itself. Image processing is performed on the detected scattered radiation (100) to determine whether an anomaly is present and to locate the anomaly and its characteristics.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Optical device, method of producing the same, optical pickup, and optical information processing device
InactiveUS20050195485A1Improve compatibilitySmall sizeIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical articlesInformation processingOptical pickup
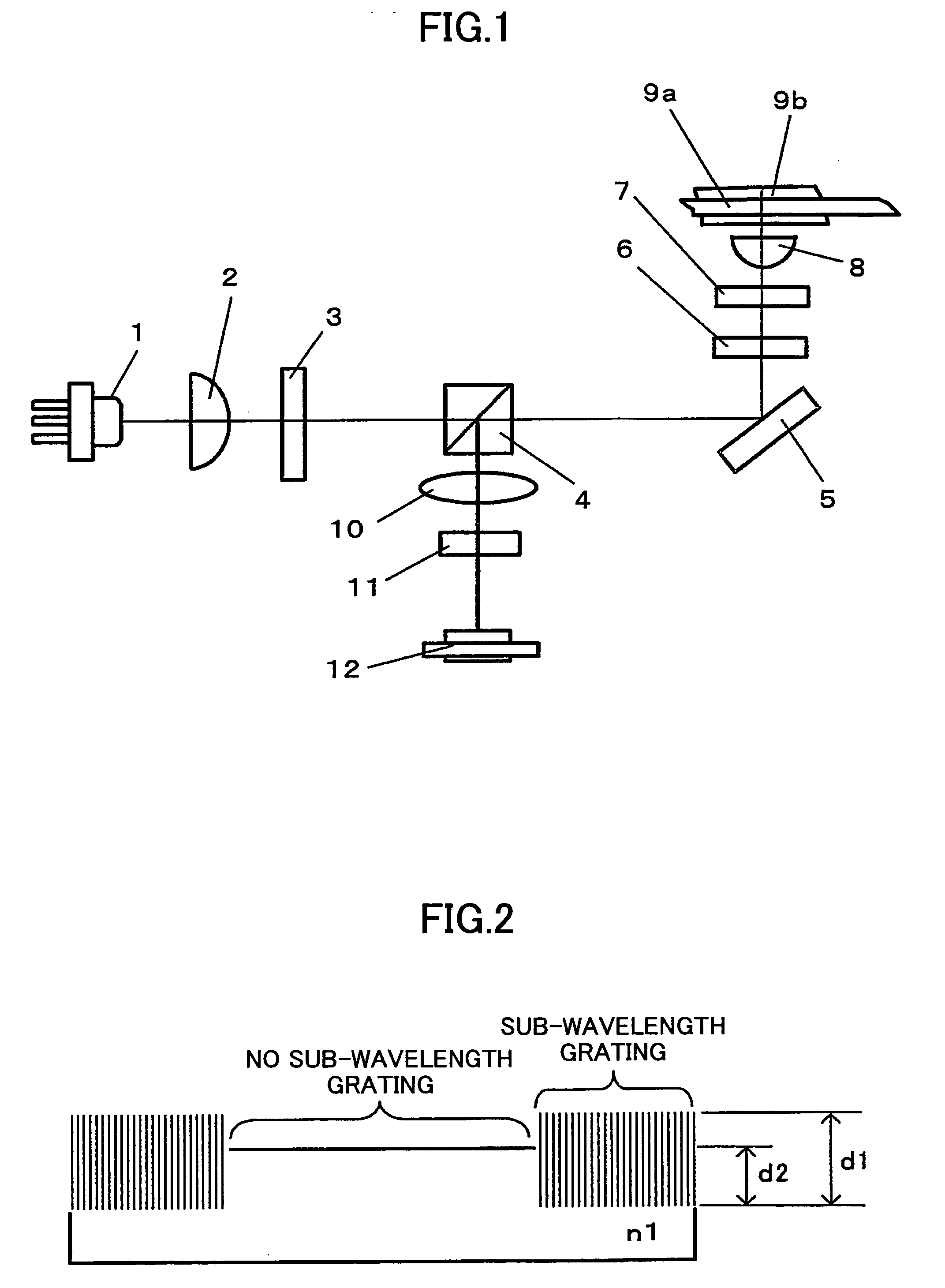
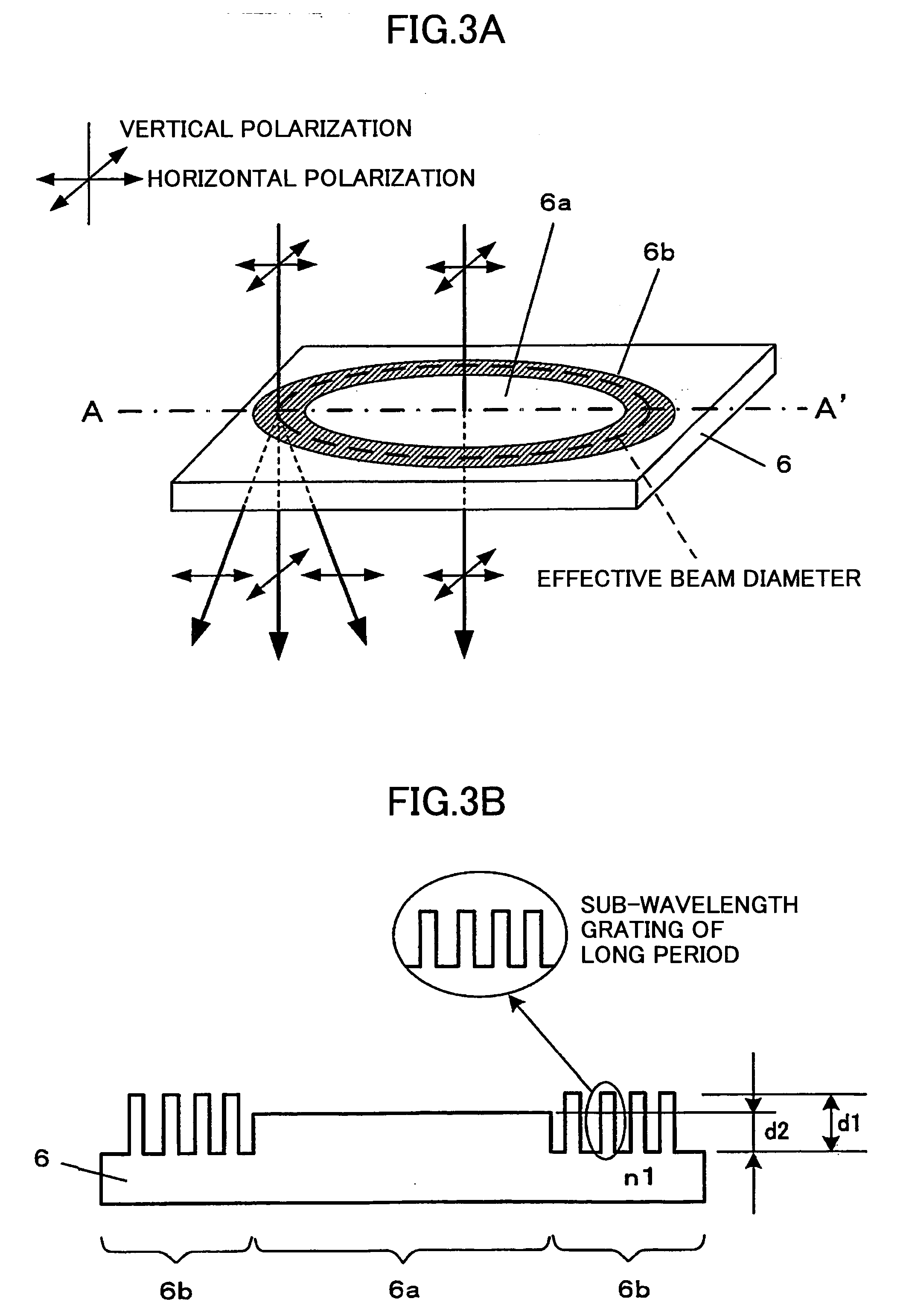
An optical device having a sub-wavelength grating formed in a specified region is disclosed that is able to prevent wave front degradation accompanying a phase difference of a polarized light beam passing through the optical device. The optical device includes a circular-belt-like region where the sub-wavelength diffraction grating is formed, and a center portion where the sub-wavelength diffraction grating is not formed. A vertically polarized light beam used for operations on a blue-light optical recording medium A has a phase difference in the sub-wavelength diffraction grating to be an integral multiple of 2π and hence is transmitted through the sub-wavelength diffraction grating. A horizontally polarized light beam used for operations on a blue-light optical recording medium is diffracted by the sub-wavelength diffraction grating. The light path length L1 of the light beam passing through the circular-belt-like region is the same as that of the light beam passing through the center portion without the sub-wavelength grating.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com