Patents
Literature
60 results about "Stereoscopic visualization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
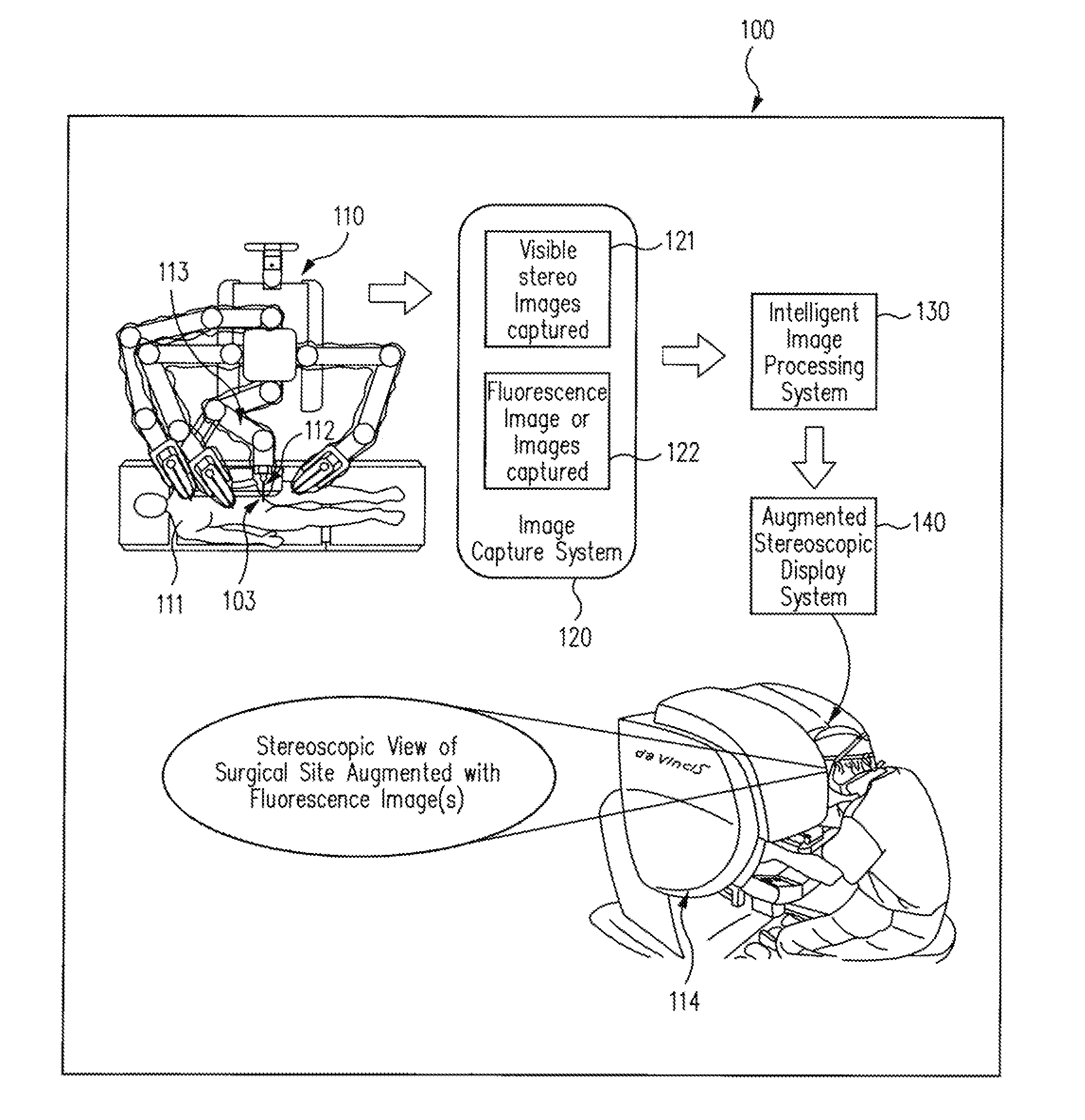
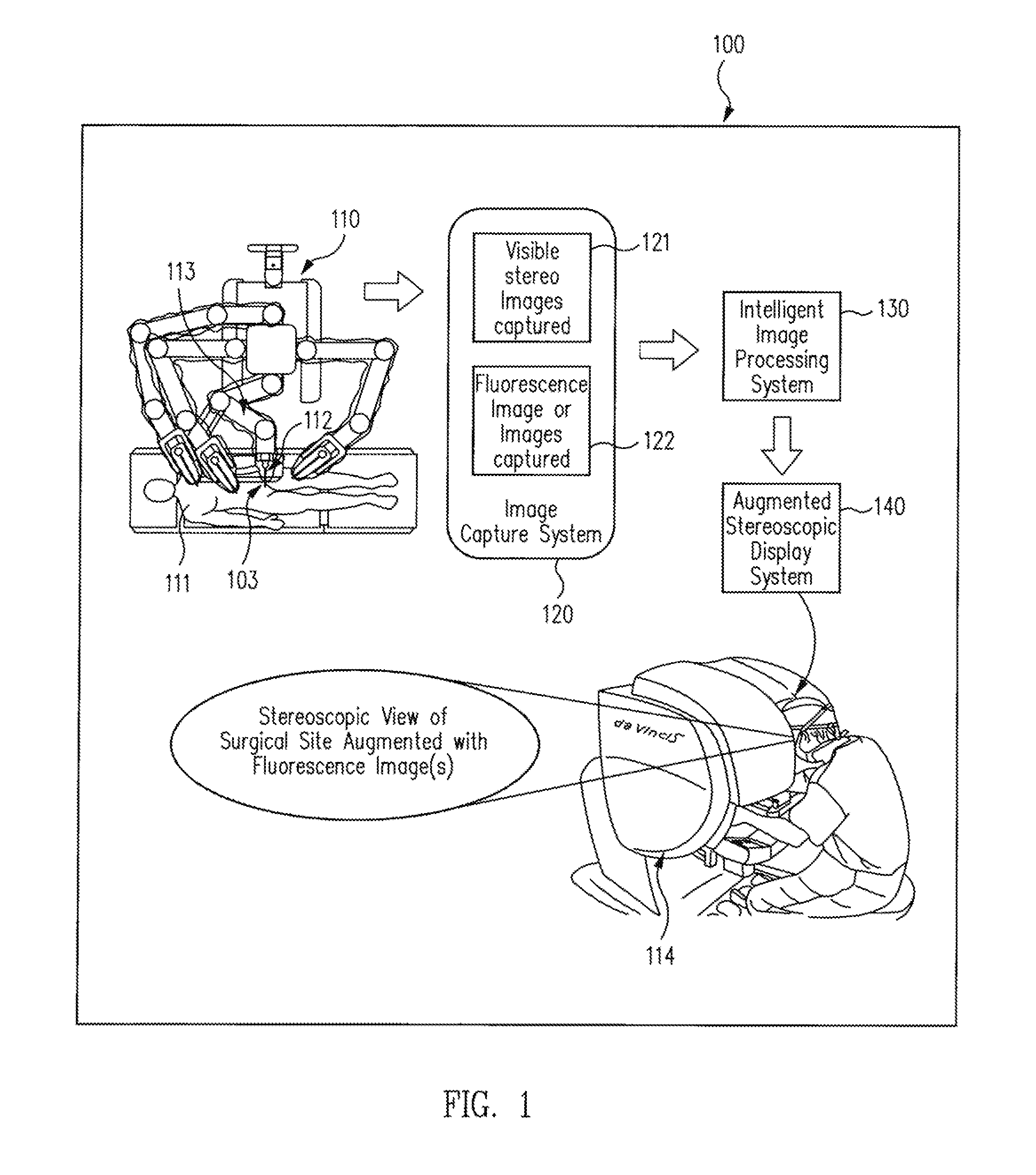
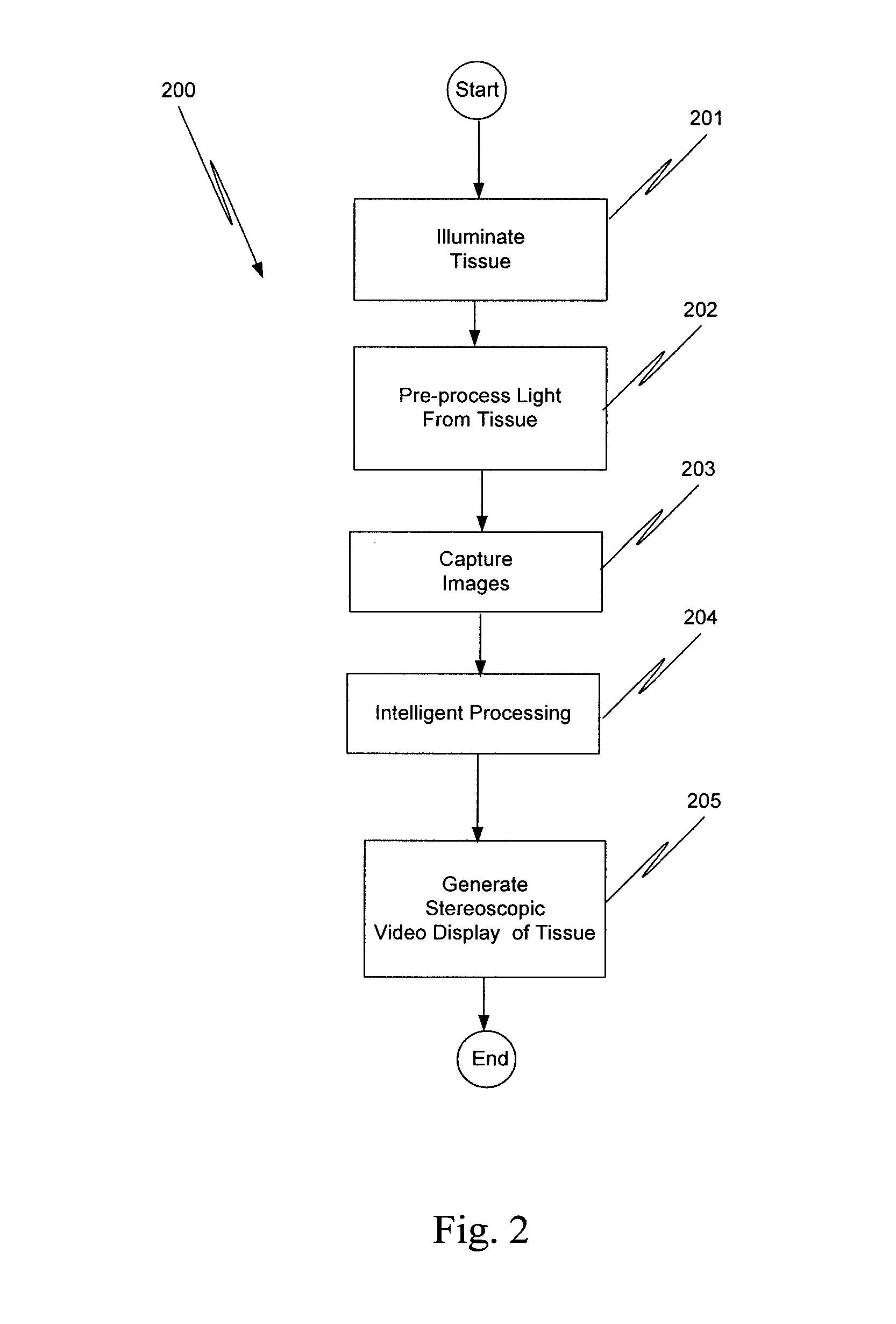
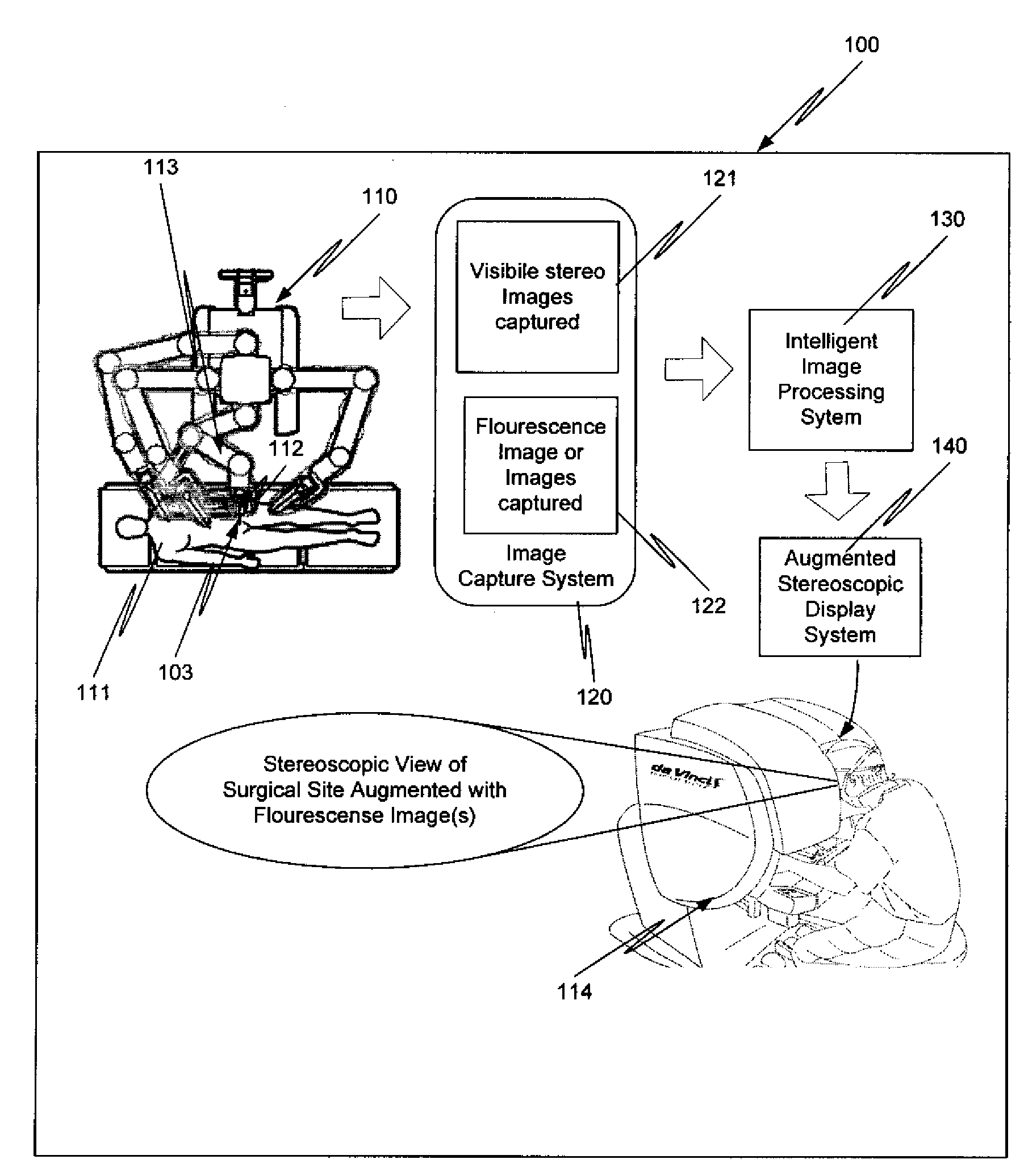
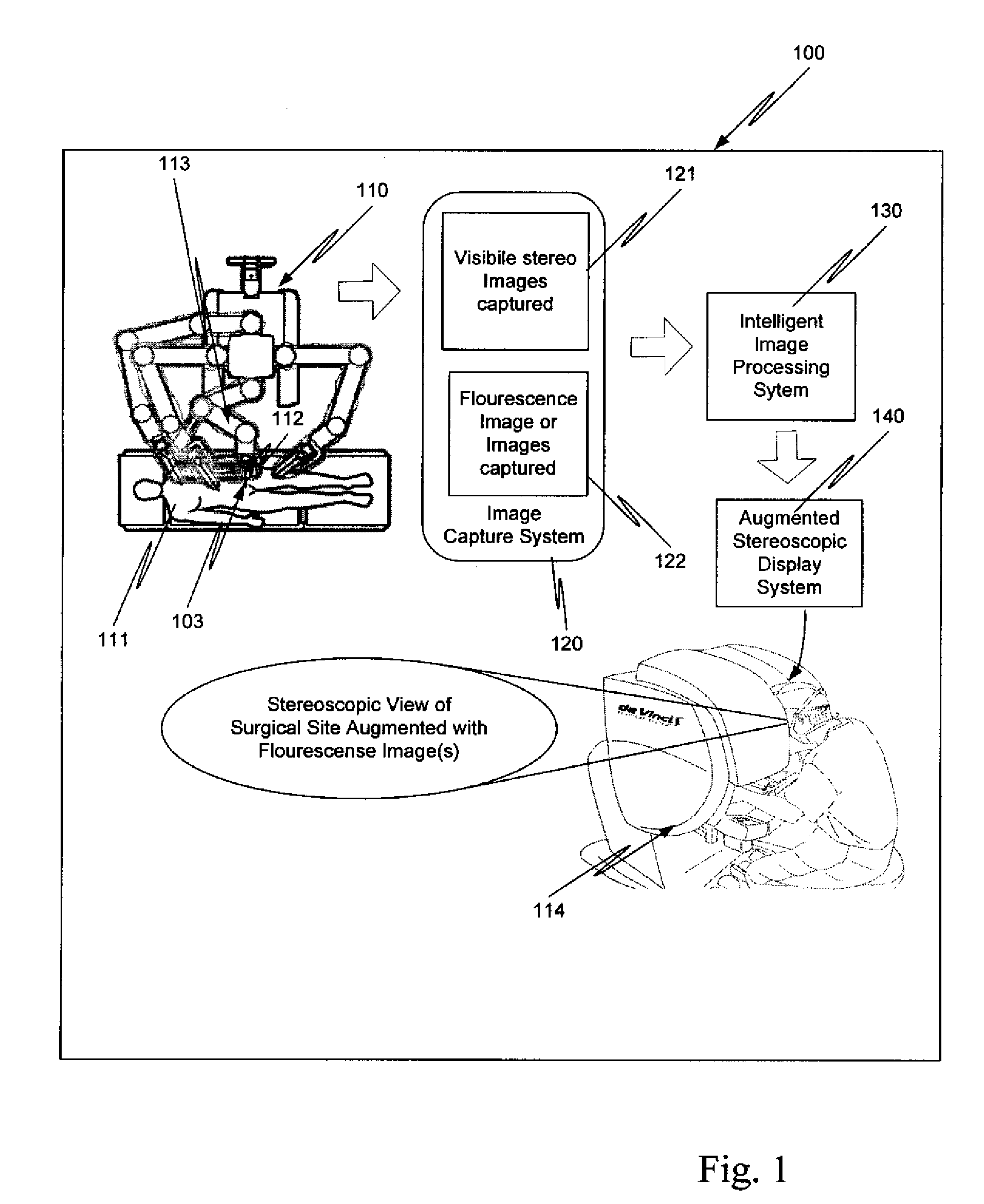
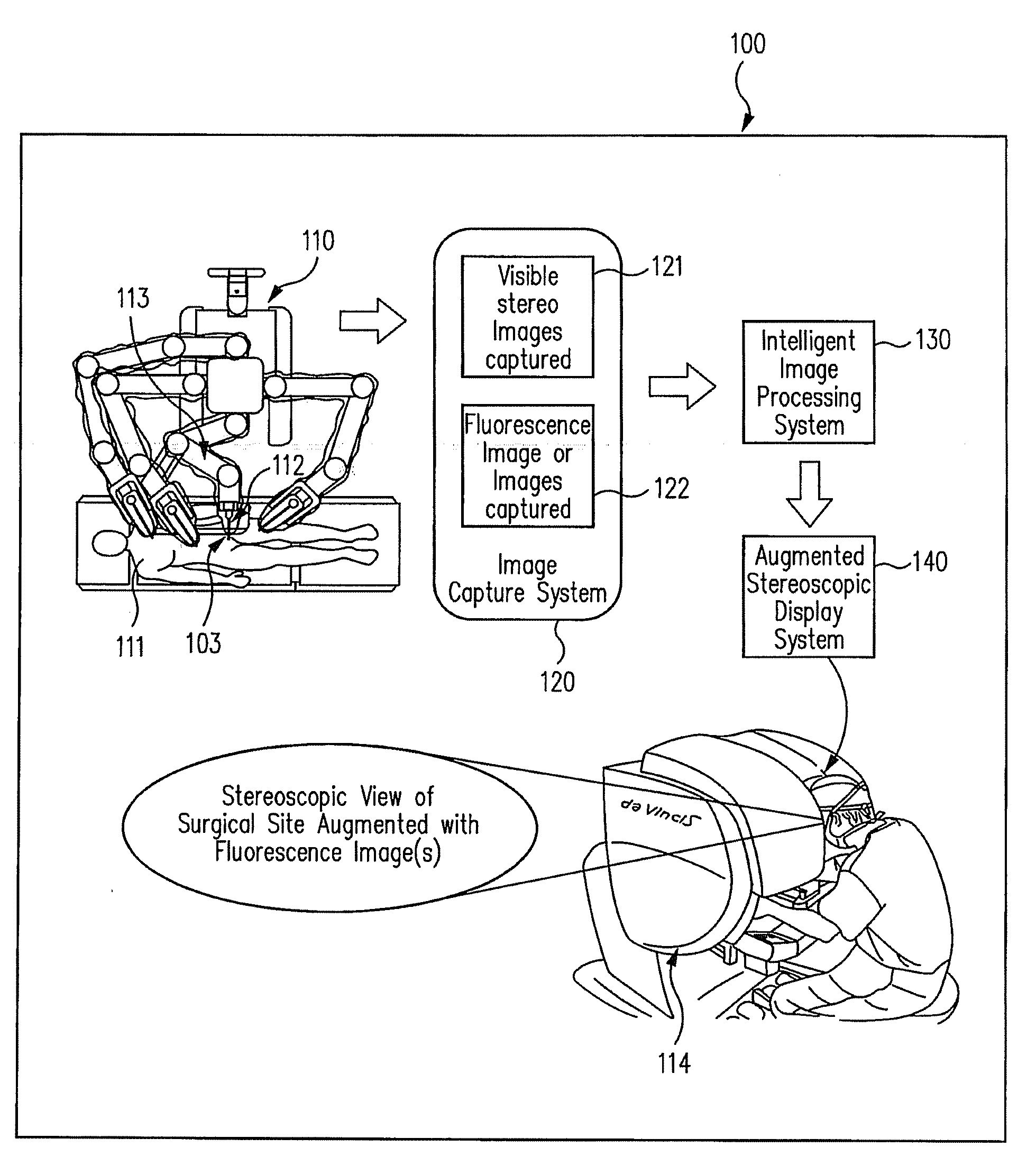
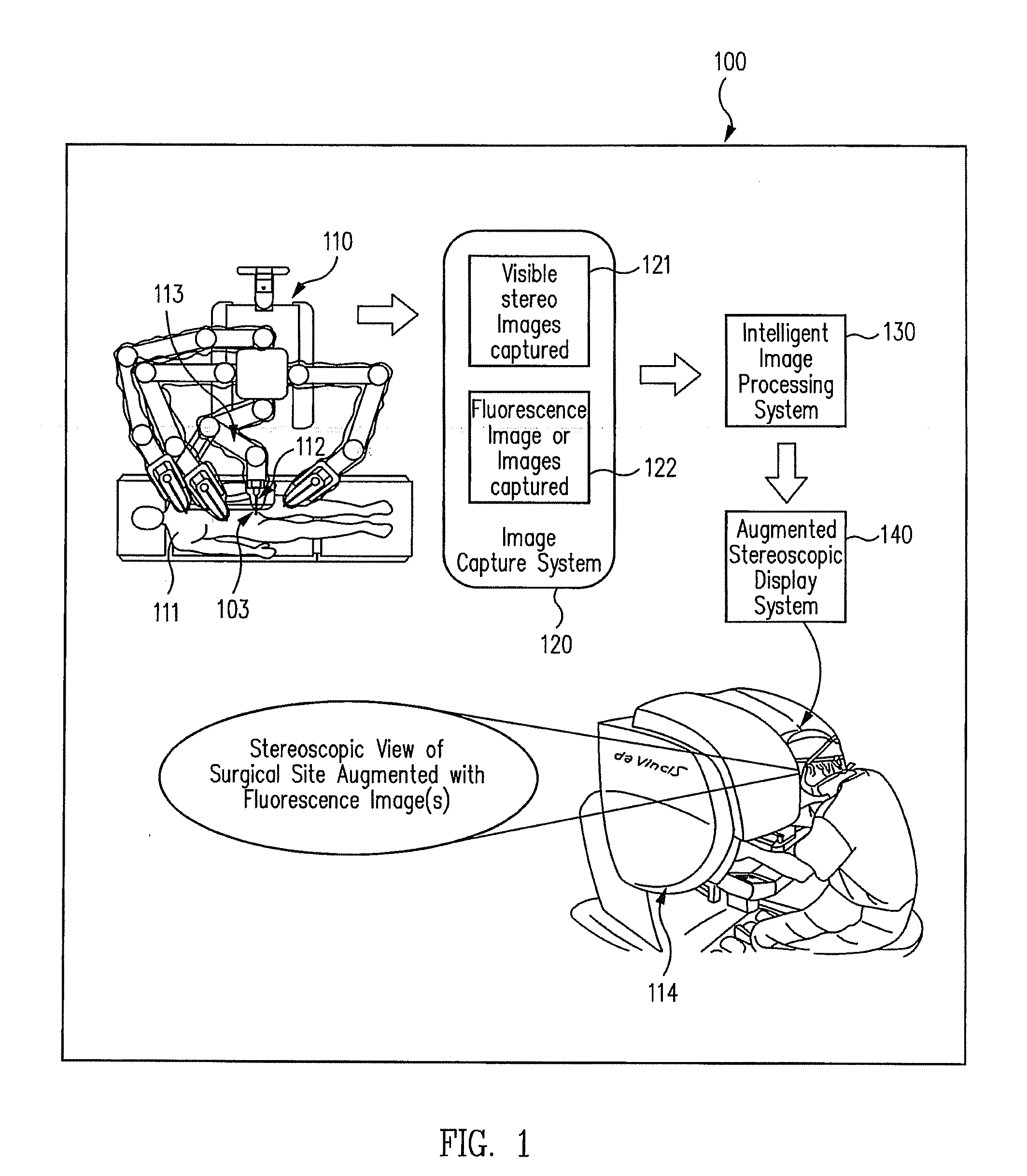
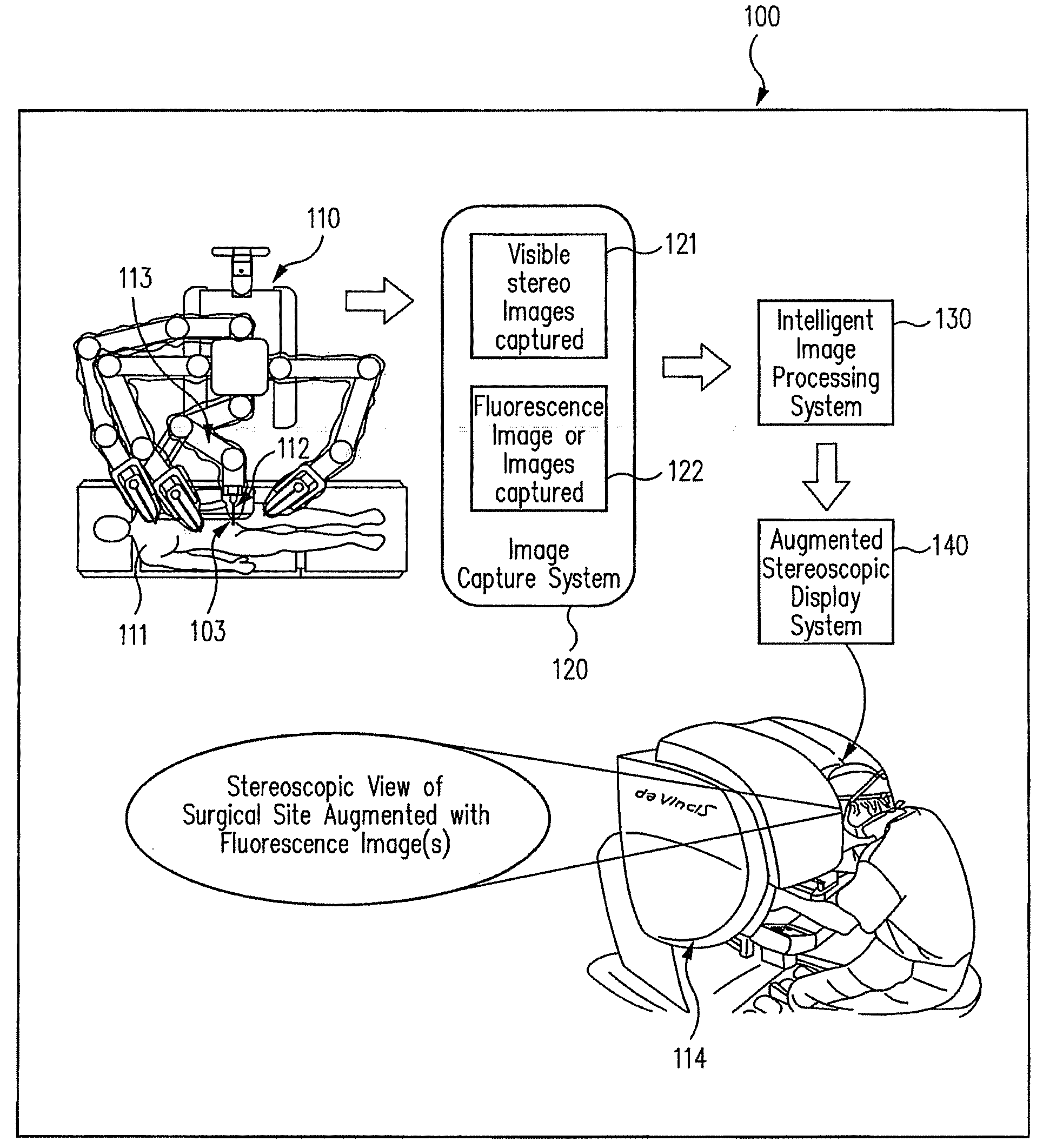
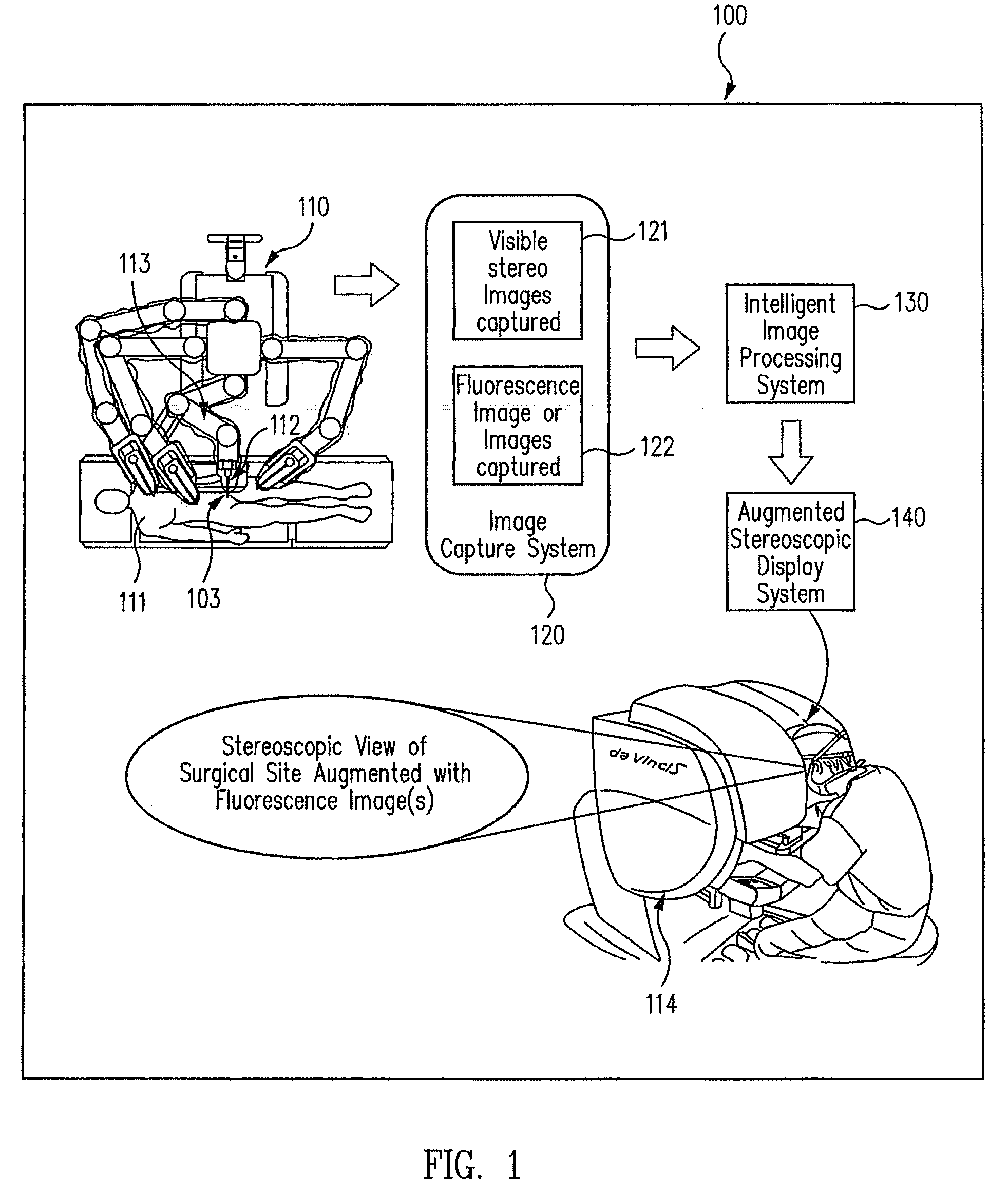
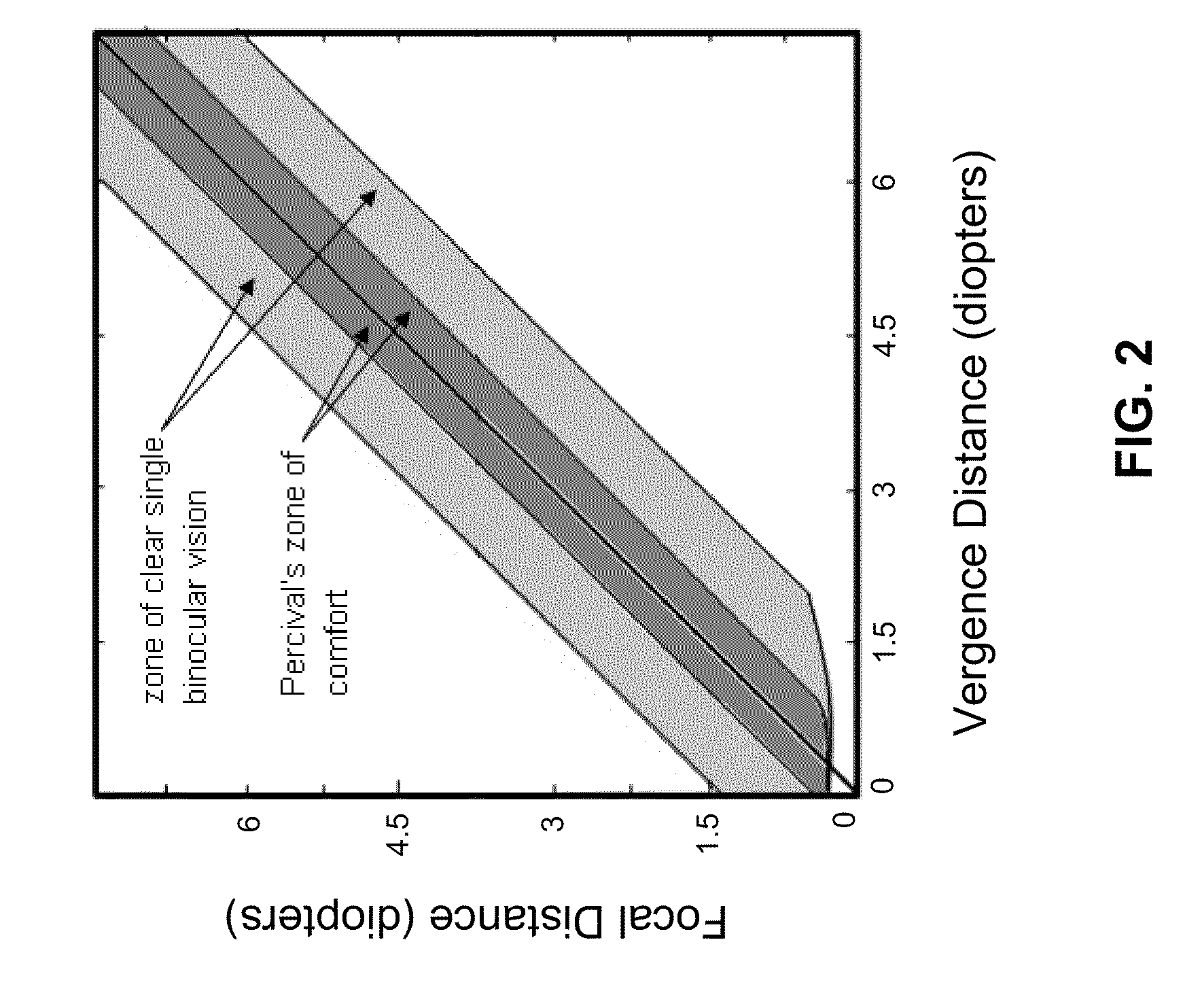
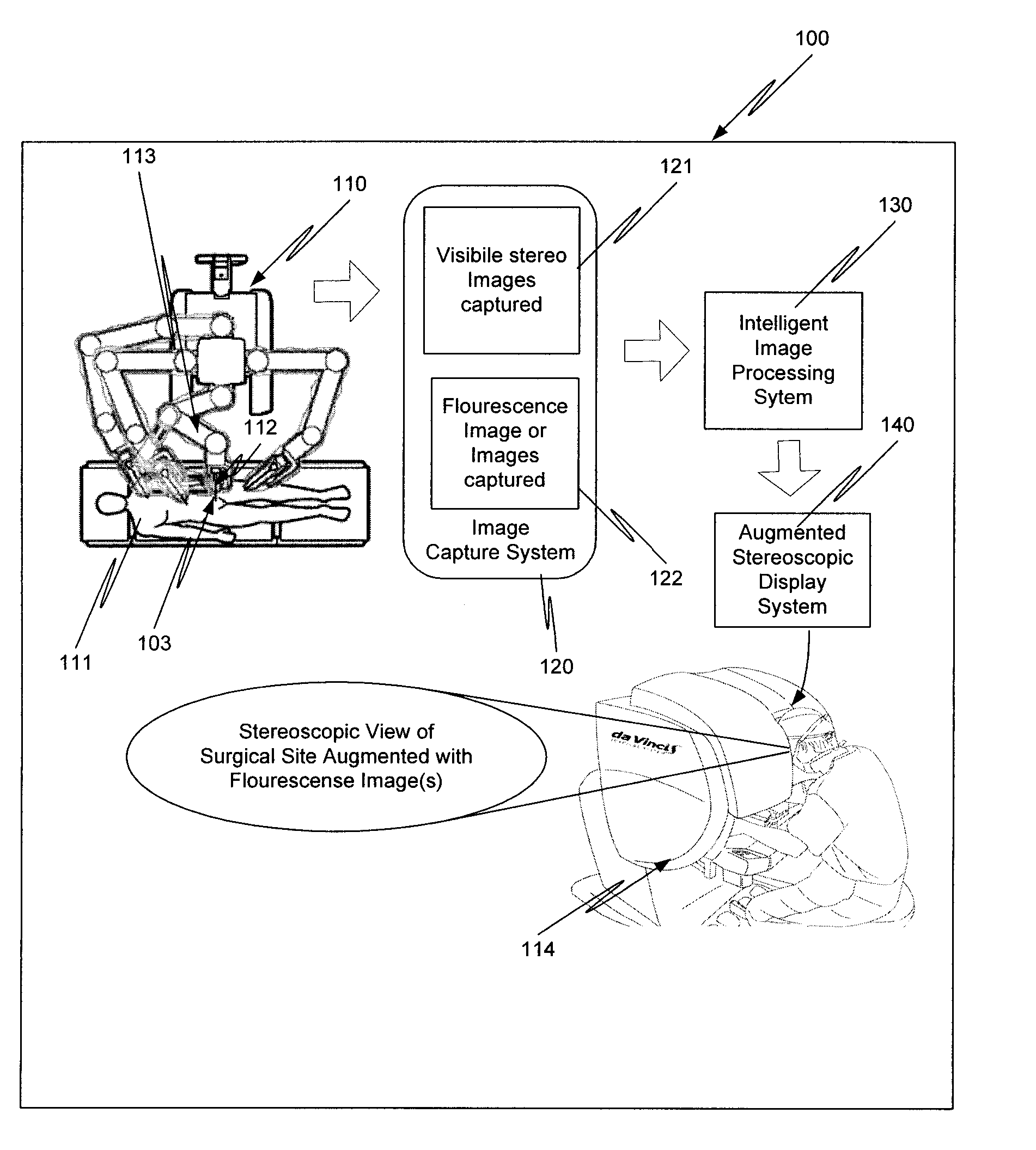
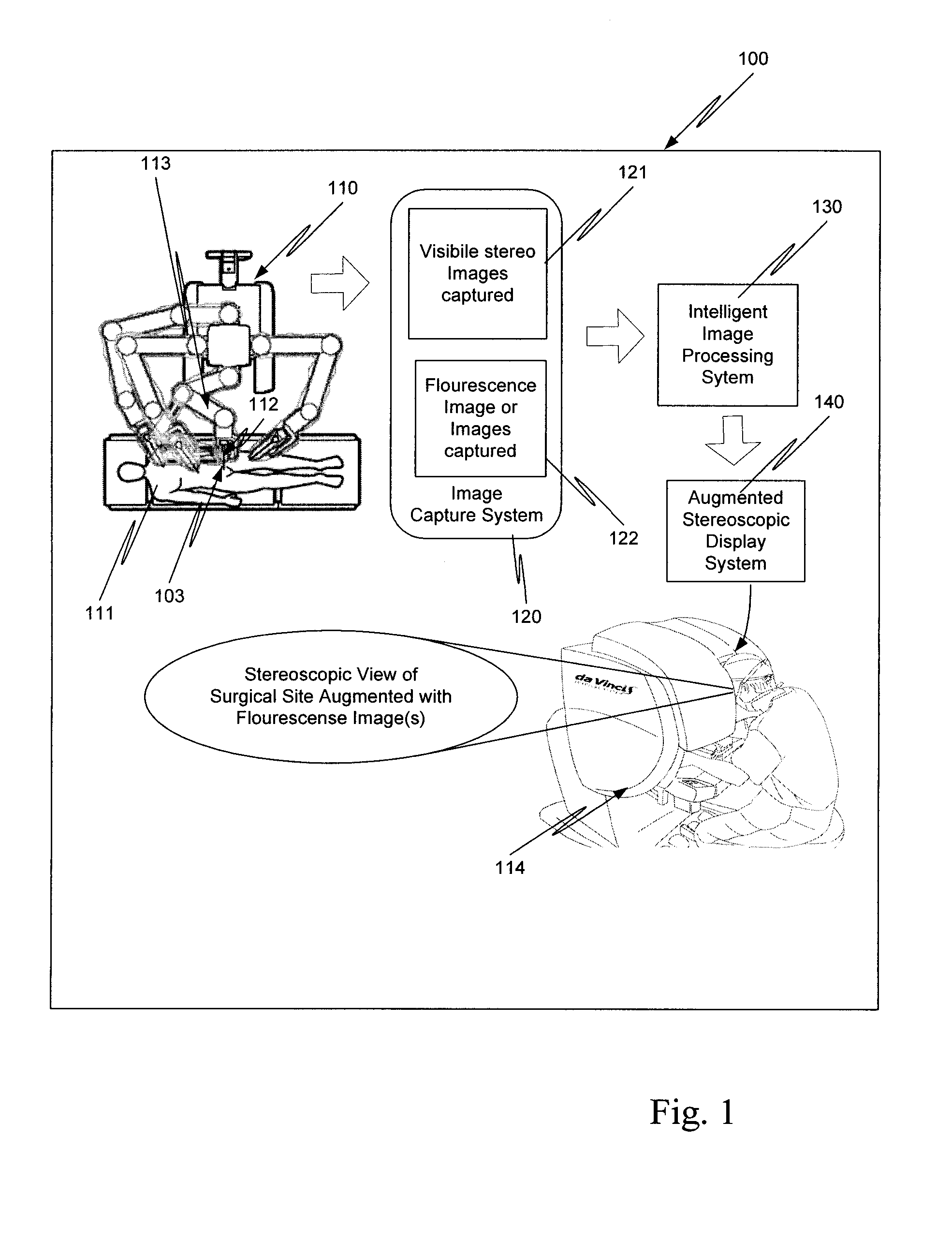
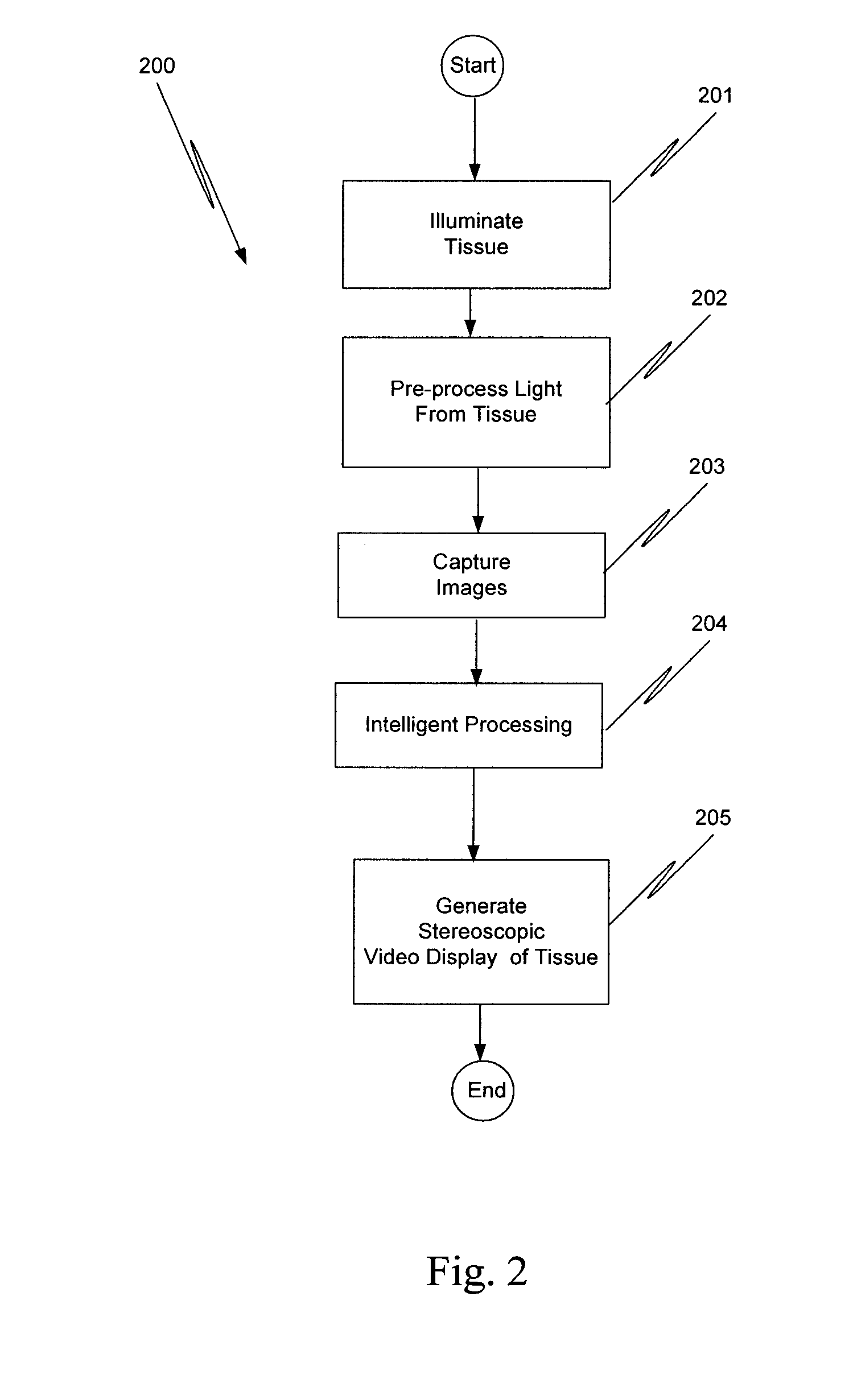
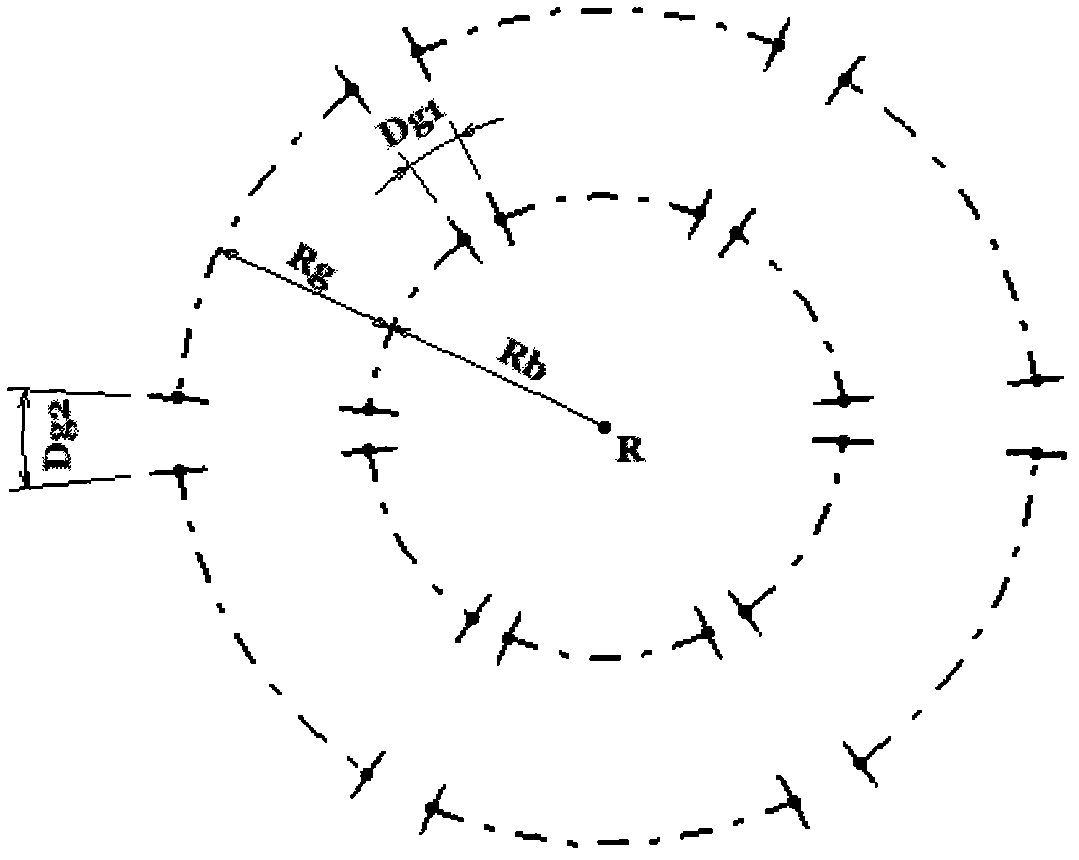
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot using a captured fluorescence image and captured stereoscopic visible images
ActiveUS20090268010A1Avoid attenuationMaterial analysis by optical meansEndoscopesStereoscopic visualizationSurgical robot
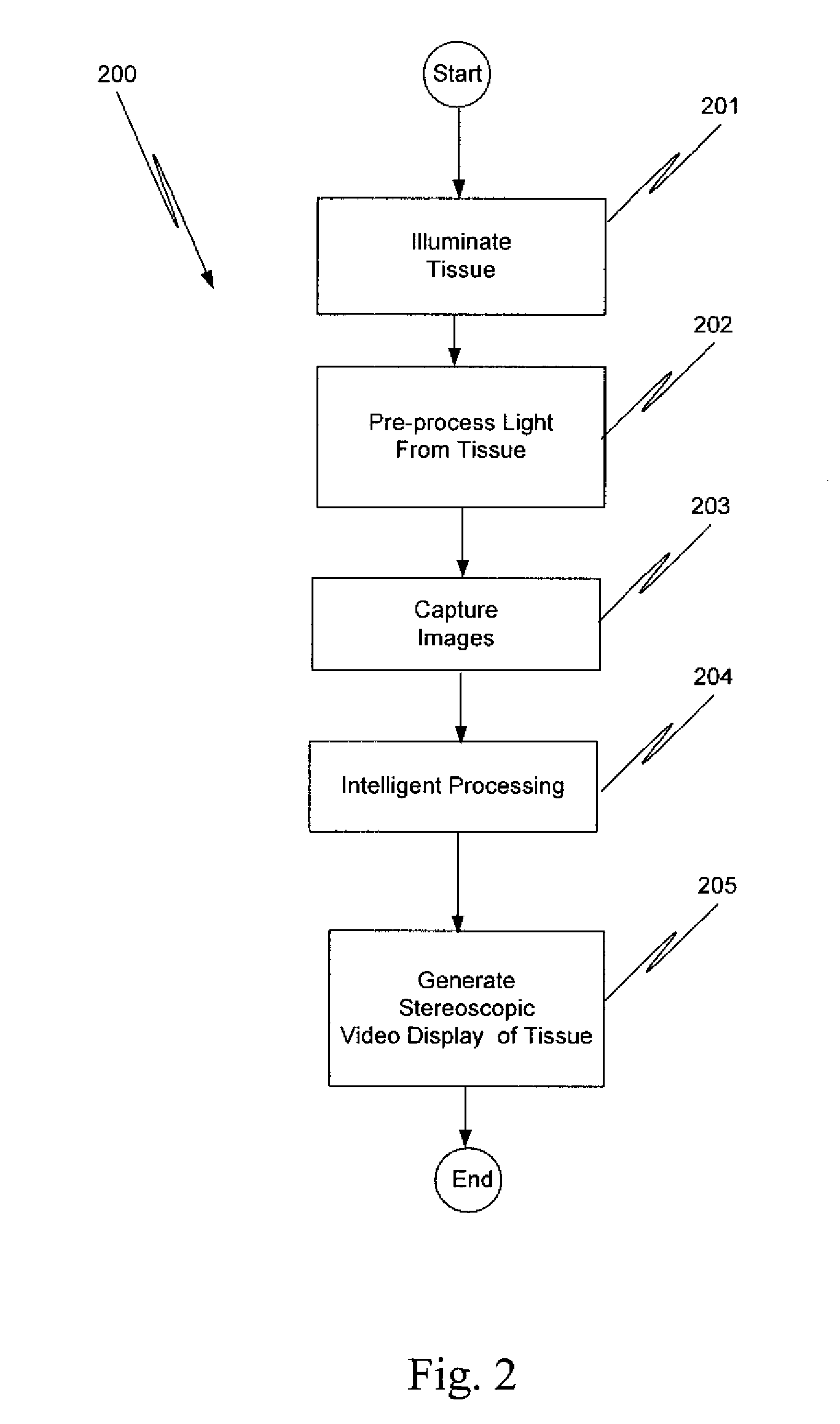
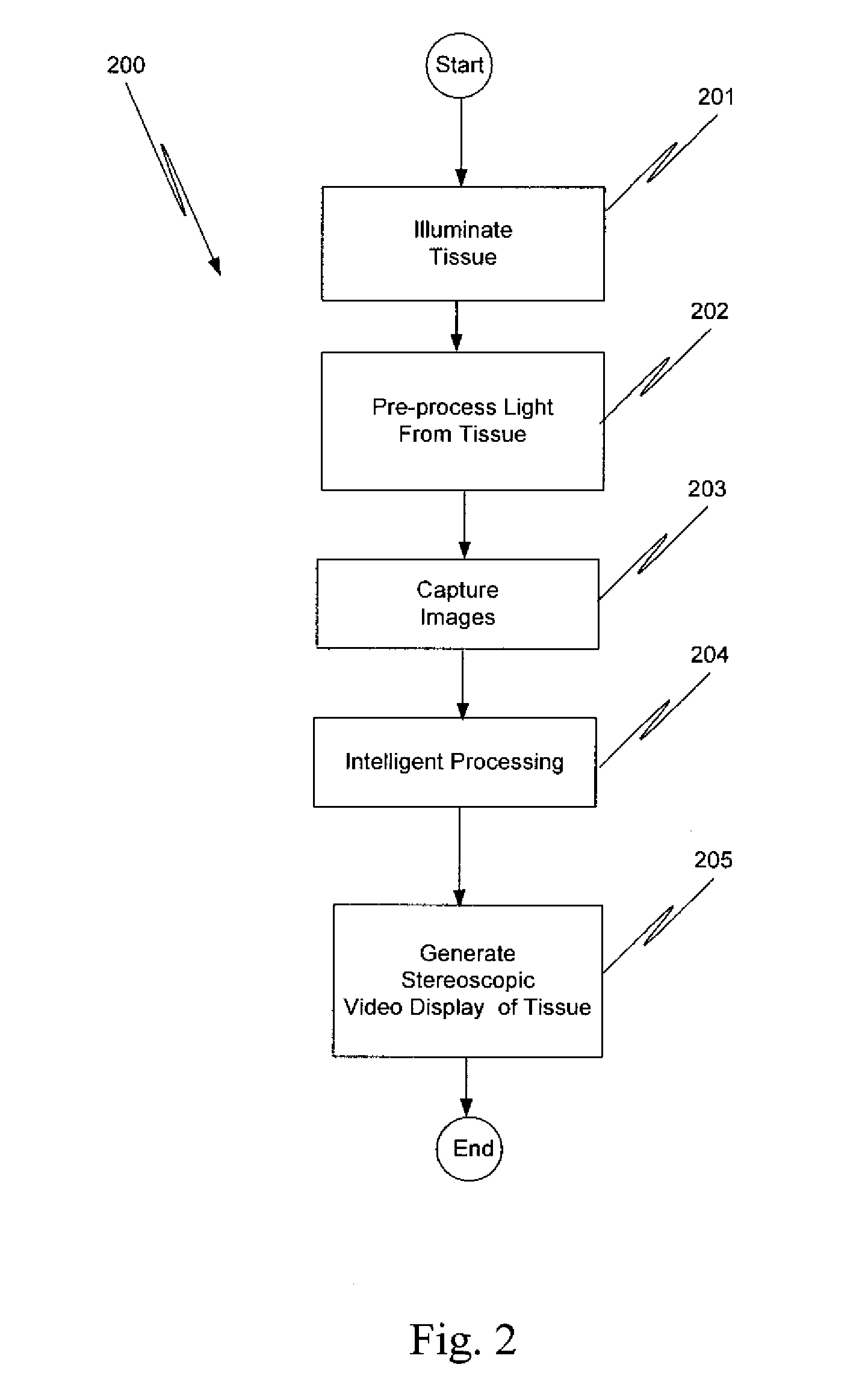
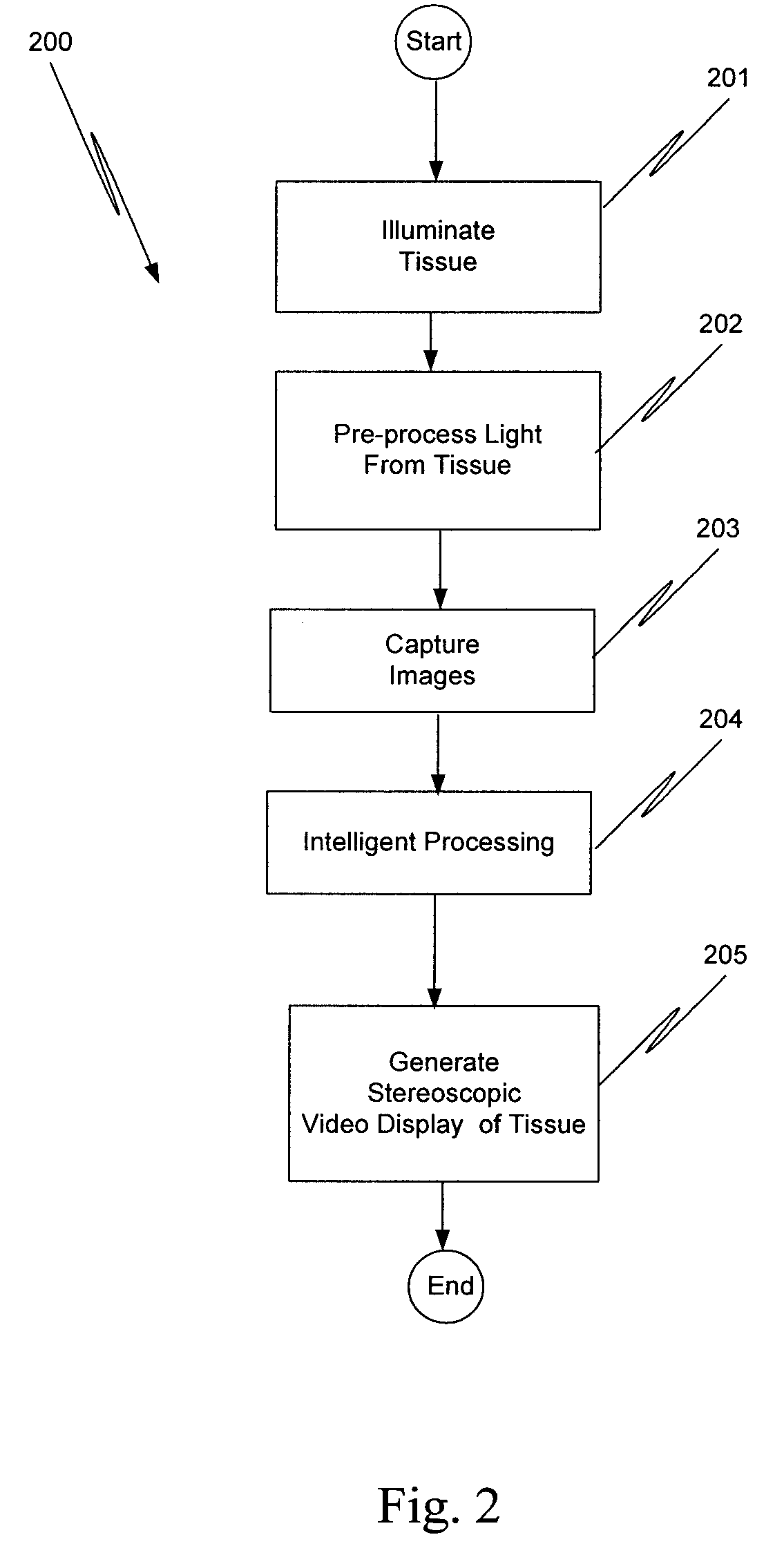
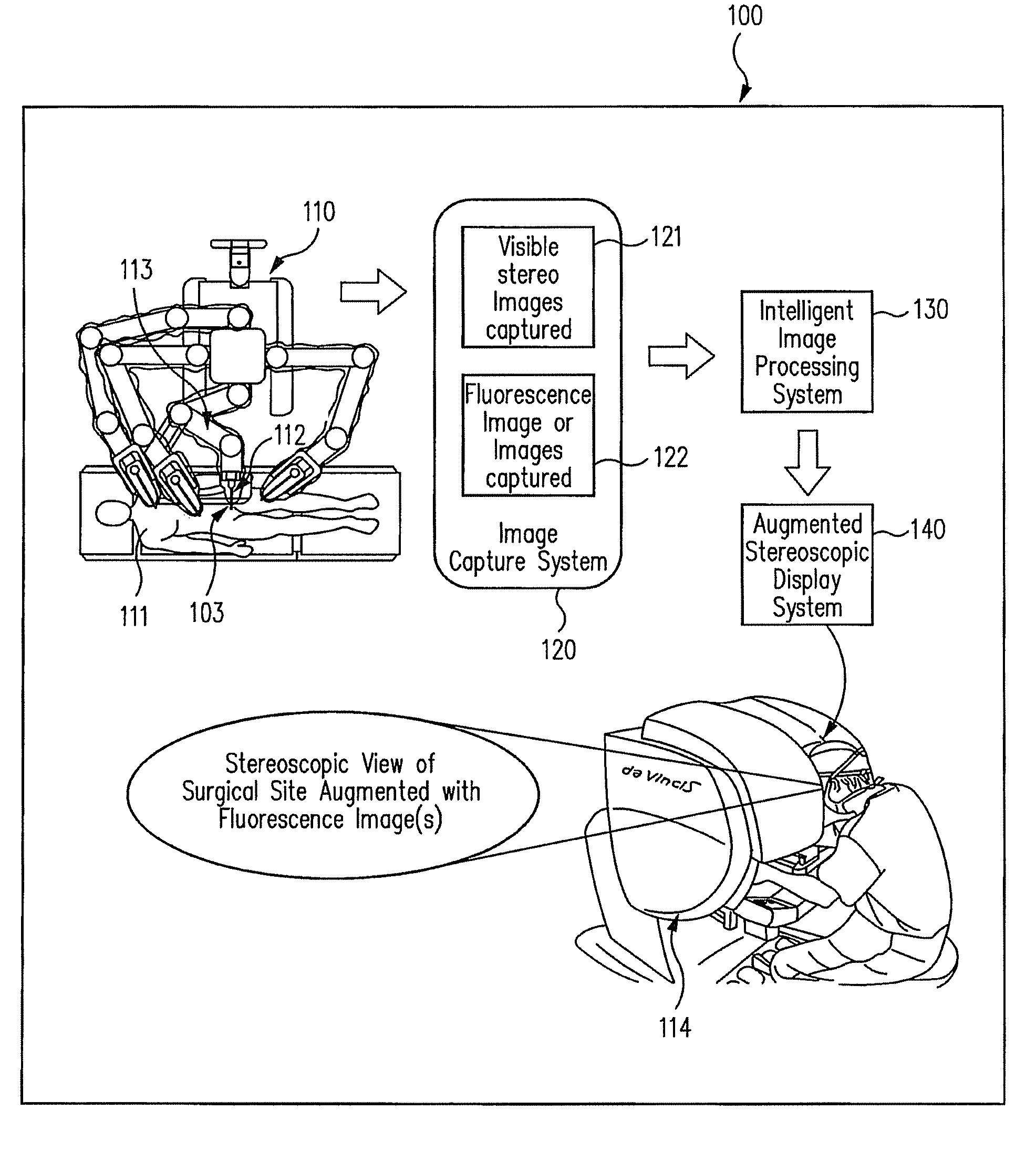
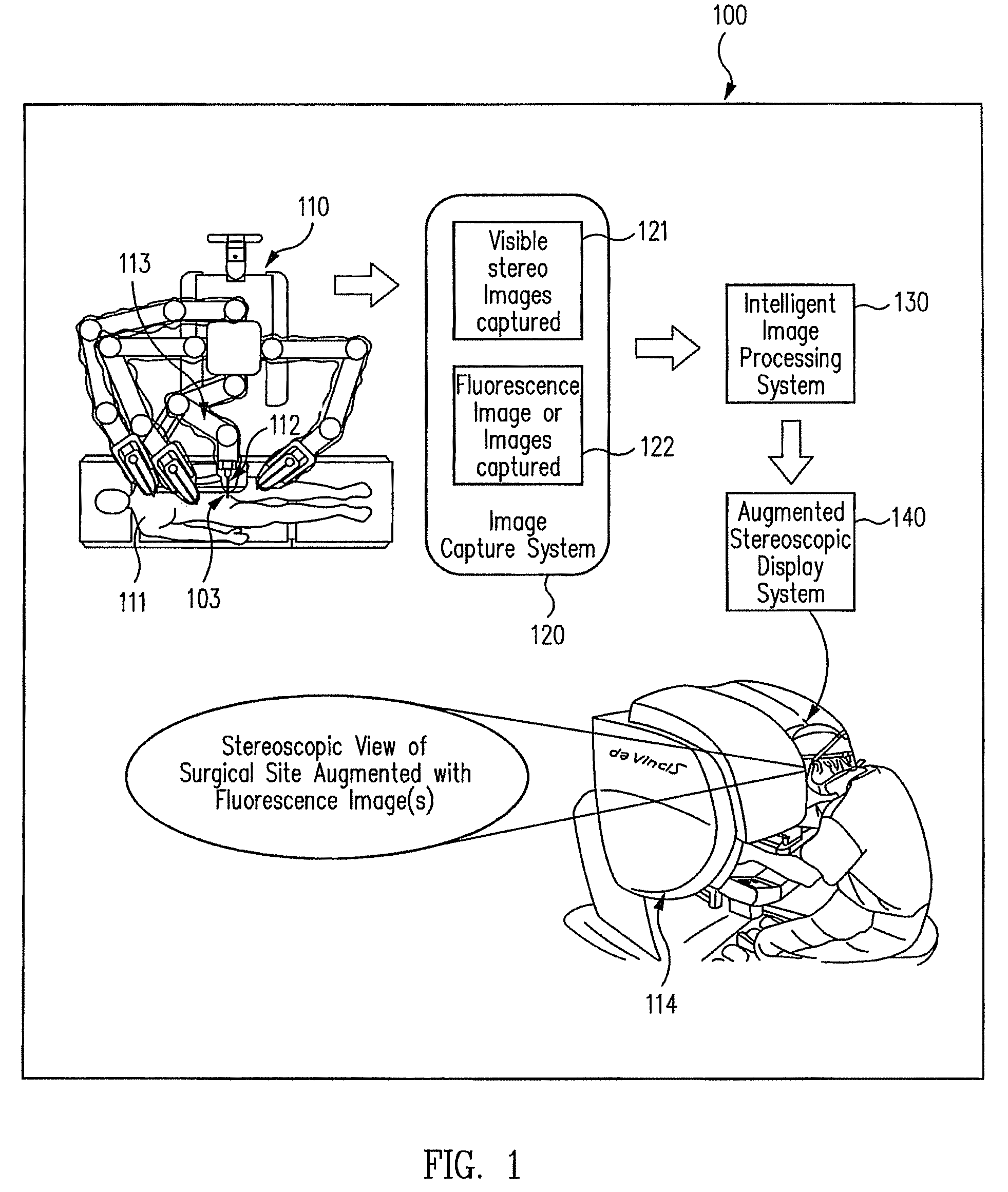
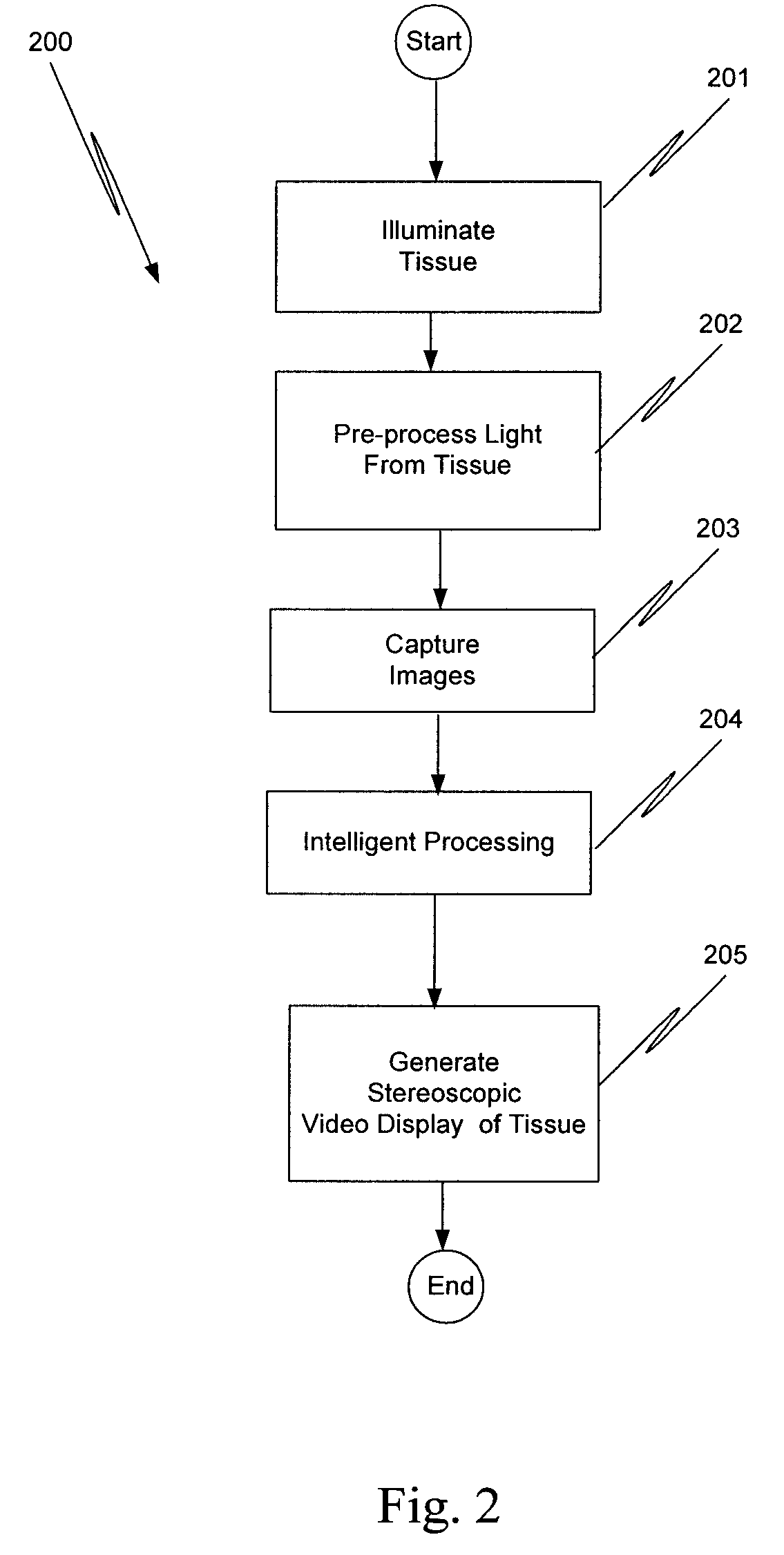
An illumination channel, a stereoscopic optical channel and another optical channel are held and positioned by a robotic surgical system. A first capture unit captures a stereoscopic visible image from the first light from the stereoscopic optical channel while a second capture unit captures a fluorescence image from the second light from the other optical channel. An intelligent image processing system receives the captured stereoscopic visible image and the captured fluorescence image and generates a stereoscopic pair of fluorescence images. An augmented stereoscopic display system outputs a real-time stereoscopic image comprising a three-dimensional presentation of a blend of the stereoscopic visible image and the stereoscopic pair of fluorescence images.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
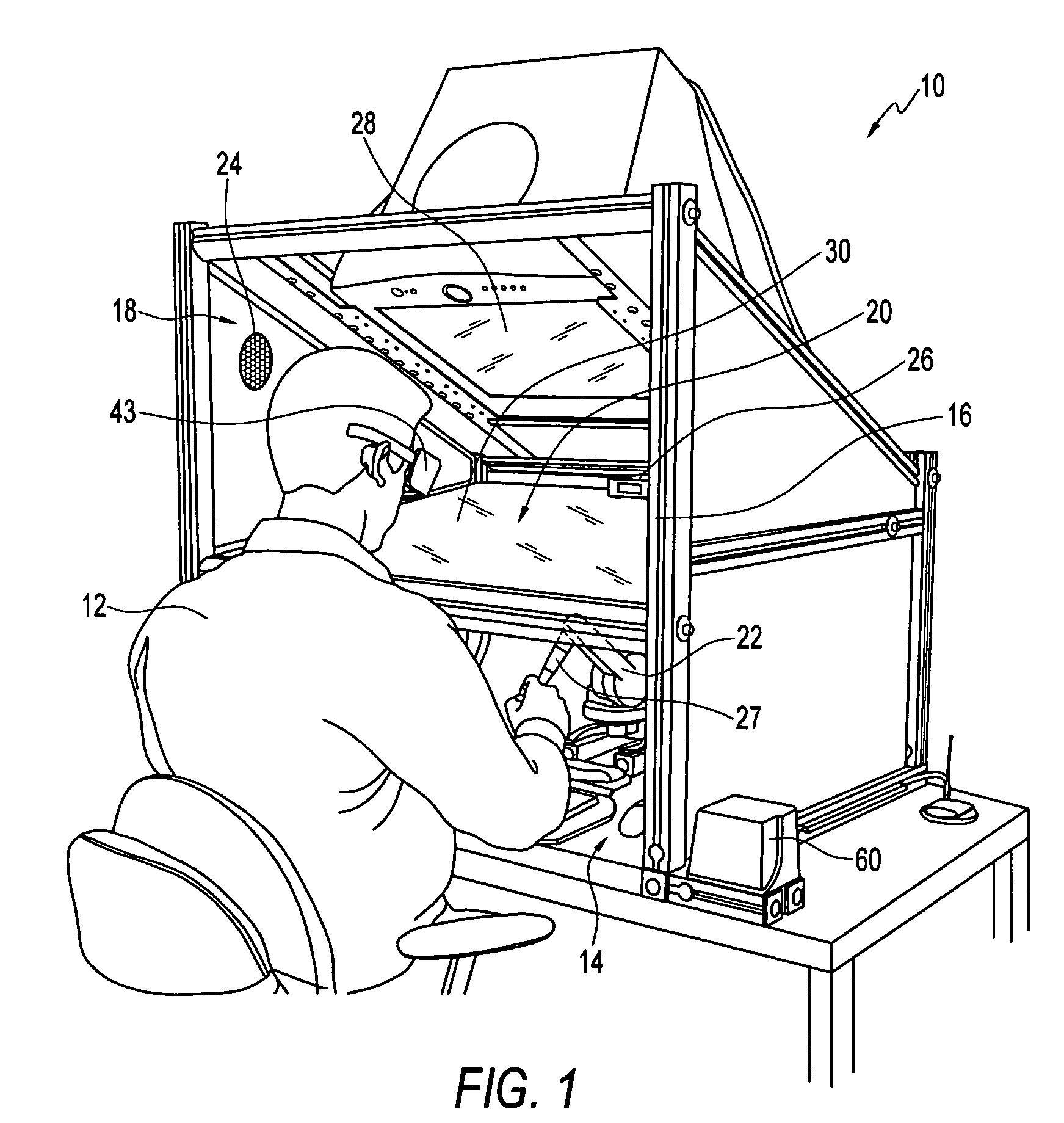
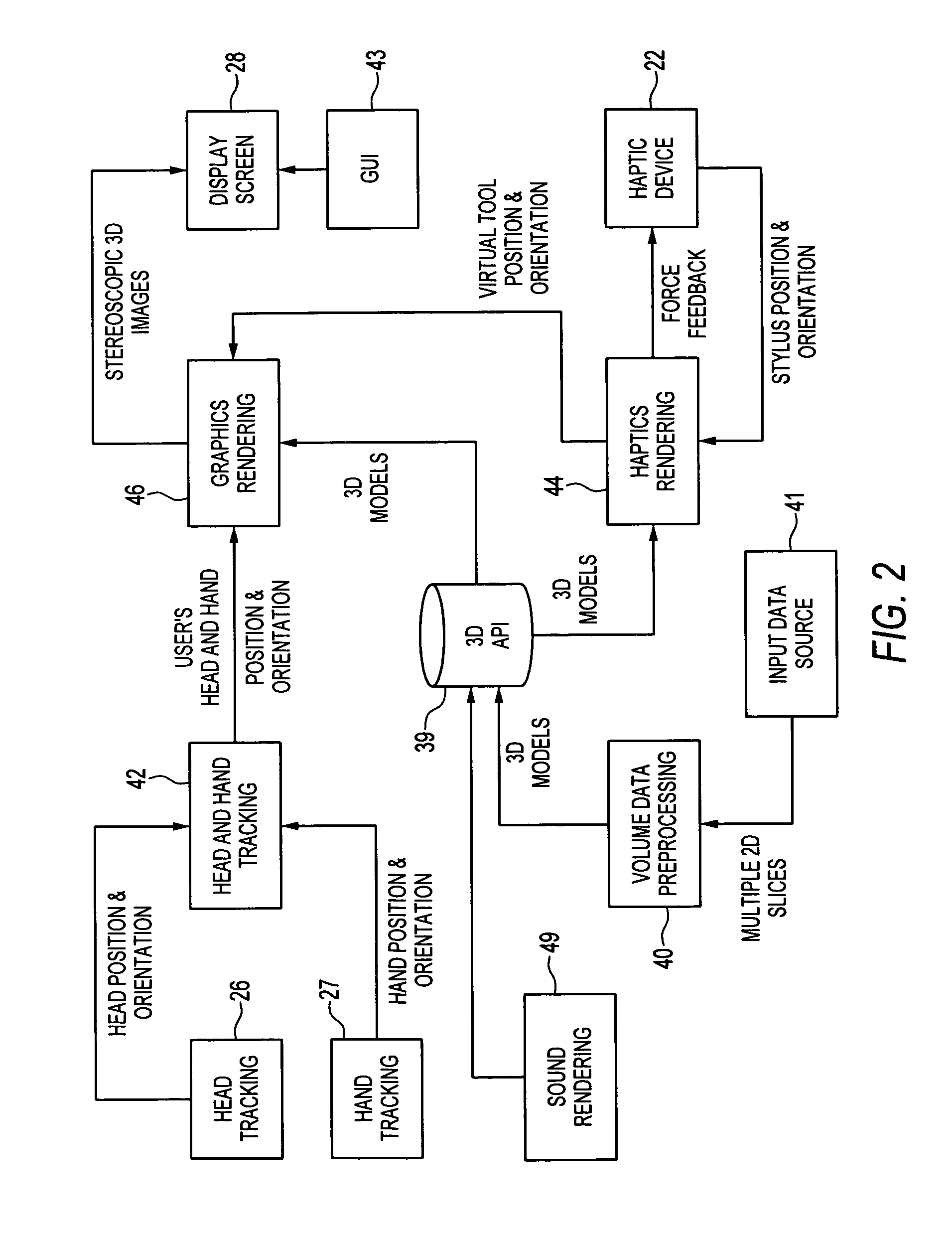
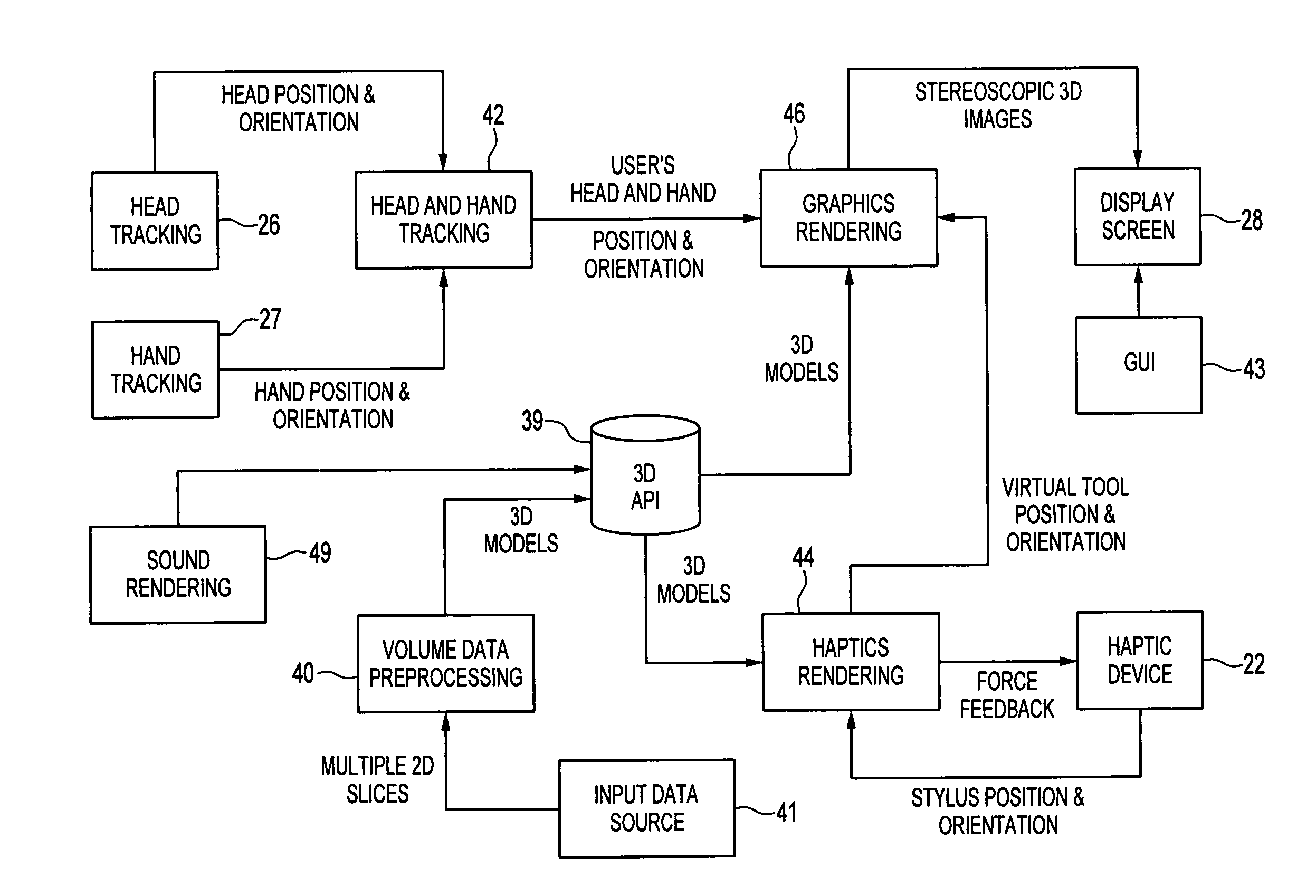
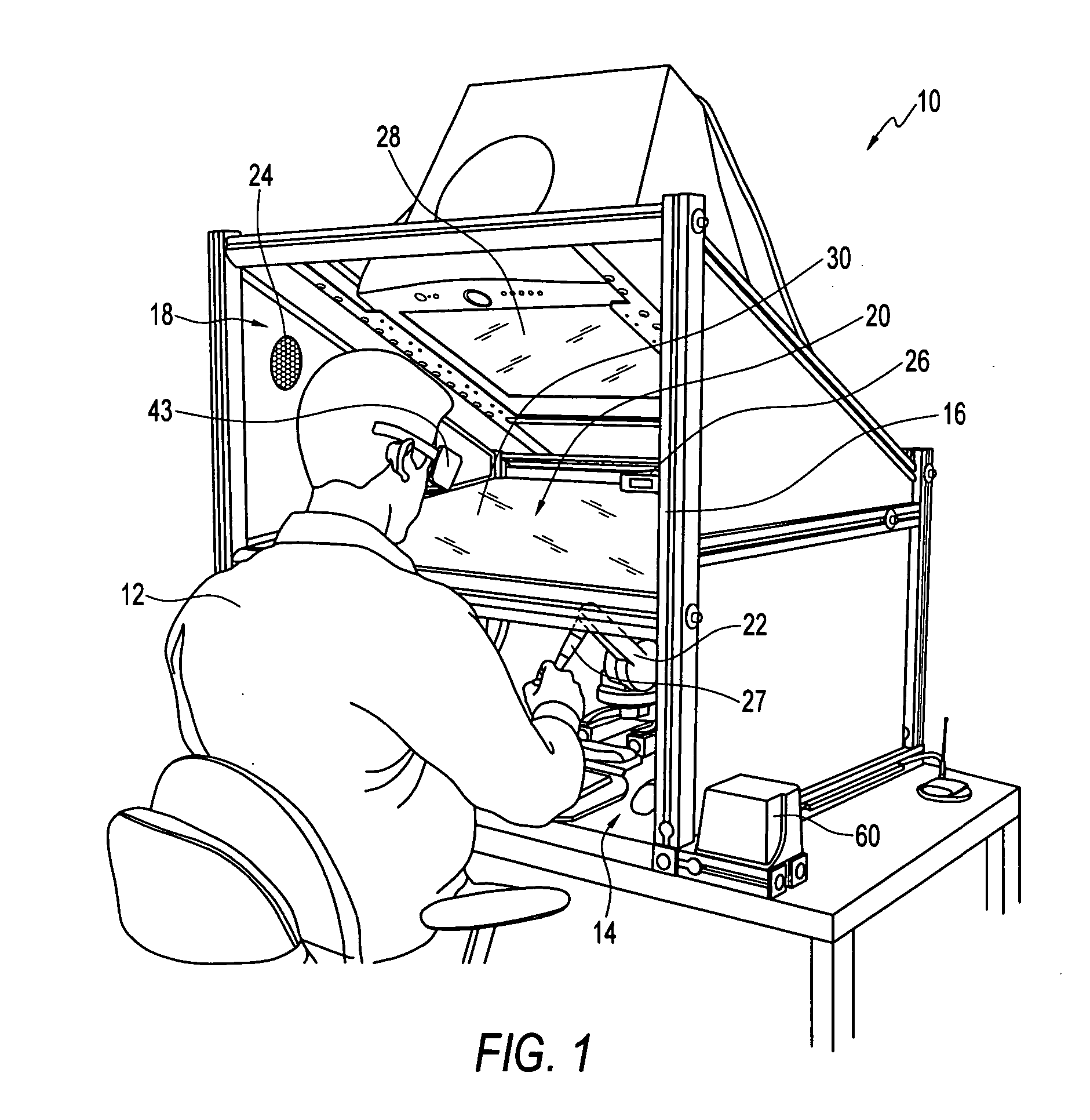
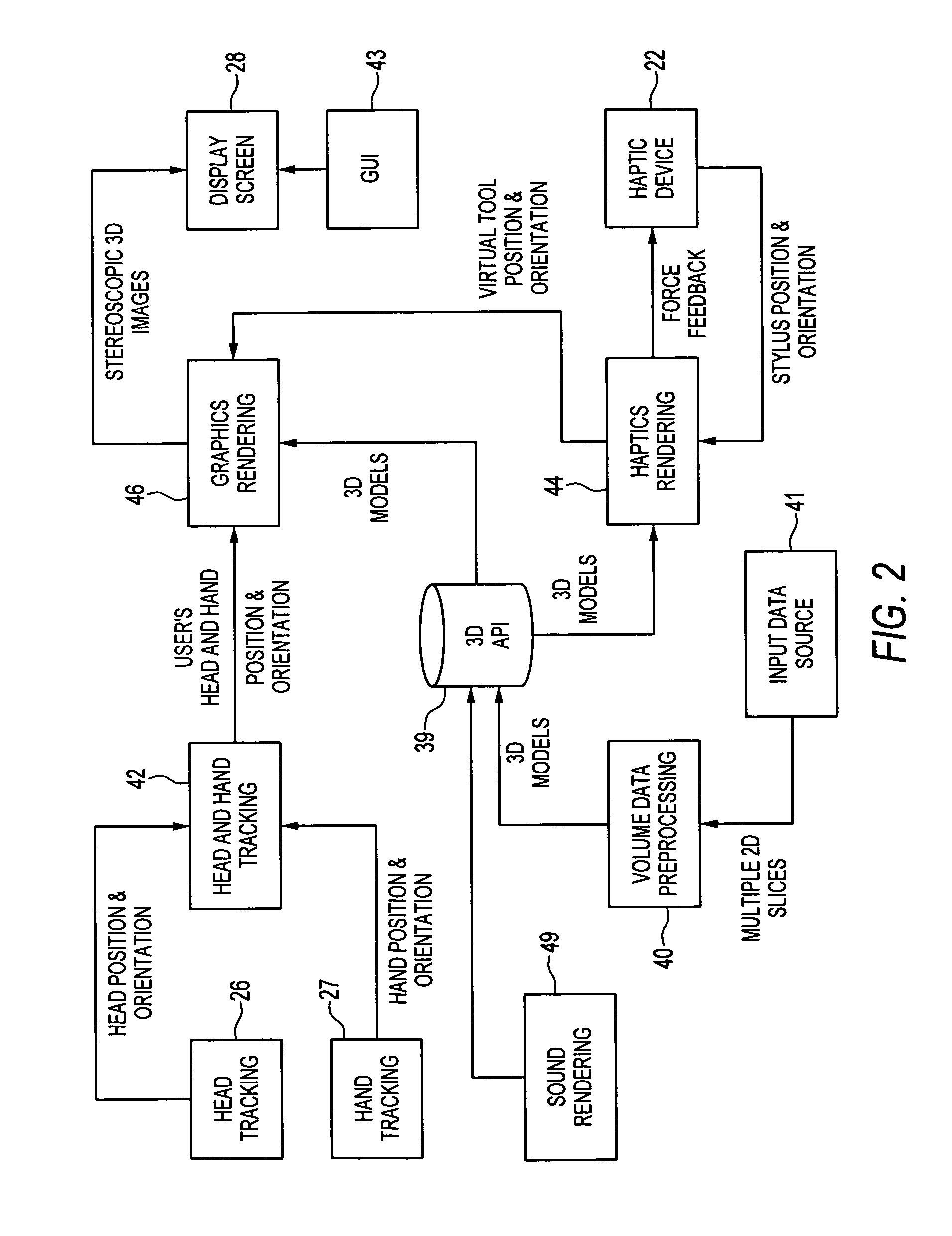
Compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system
InactiveUS7812815B2High resolutionIncrease pixel densityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingStereoscopic visualizationGraphics
The invention provides compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system that produces an augmented reality environment. The system is equipped with software and devices that provide users with stereoscopic visualization and force feedback simultaneously in real time. High resolution, high pixel density, head and hand tracking ability are provided. Well-matched haptics and graphics volumes are realized. Systems of the invention are compact, making use of a standard personal display device, e.g., a computer monitor, as the display driver. Systems of the invention may therefore be inexpensive compared to many conventional virtual reality systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system
InactiveUS20070035511A1High resolutionIncrease pixel densityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsStereoscopic visualization
The invention provides compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system that produces an augmented reality environment. The system is equipped with software and devices that provide users with stereoscopic visualization and force feedback simultaneously in real time. High resolution, high pixel density, head and hand tracking ability are provided. Well-matched haptics and graphics volumes are realized. Systems of the invention are compact, making use of a standard personal display device, e.g., a computer monitor, as the display driver. Systems of the invention may therefore be inexpensive compared to many conventional virtual reality systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
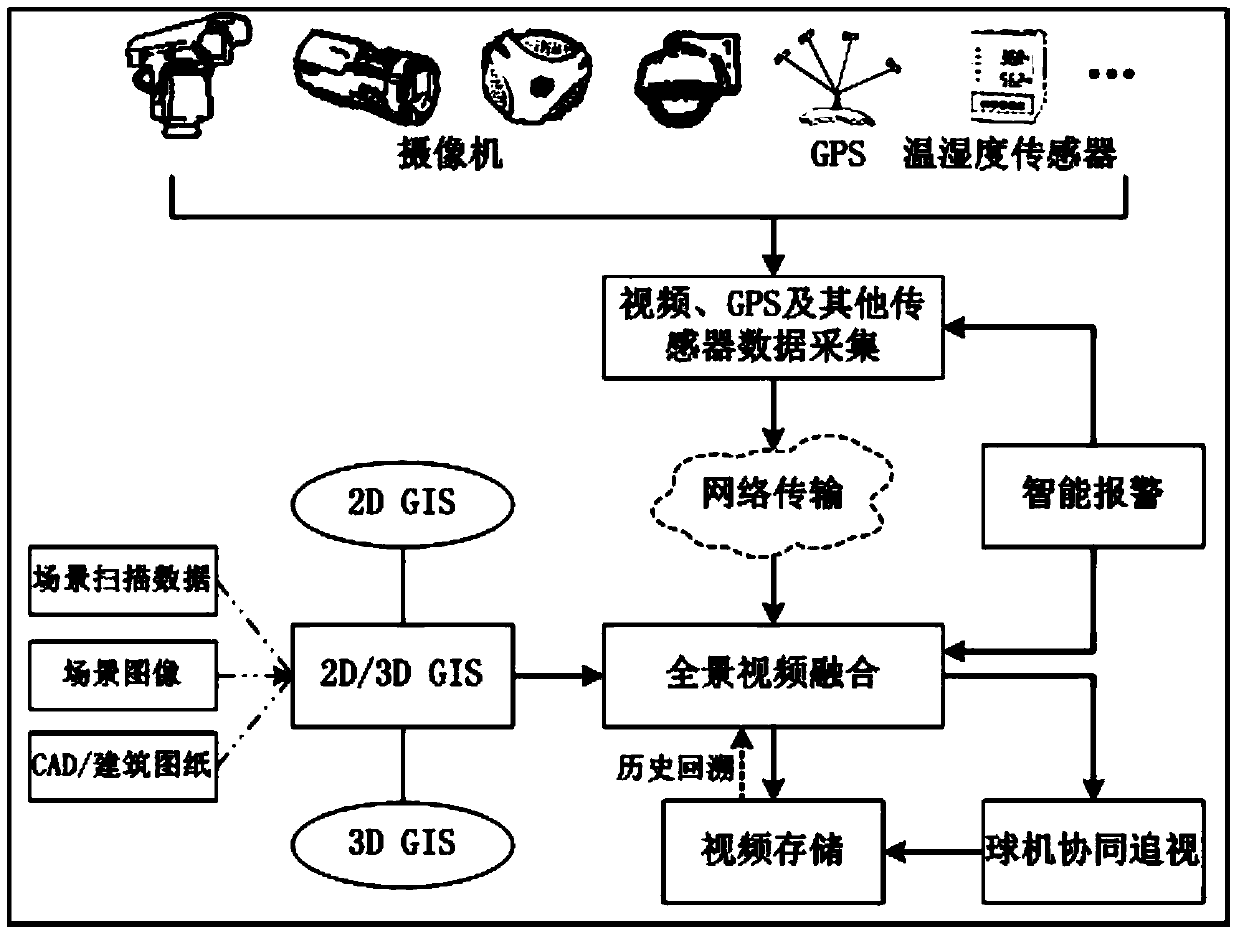
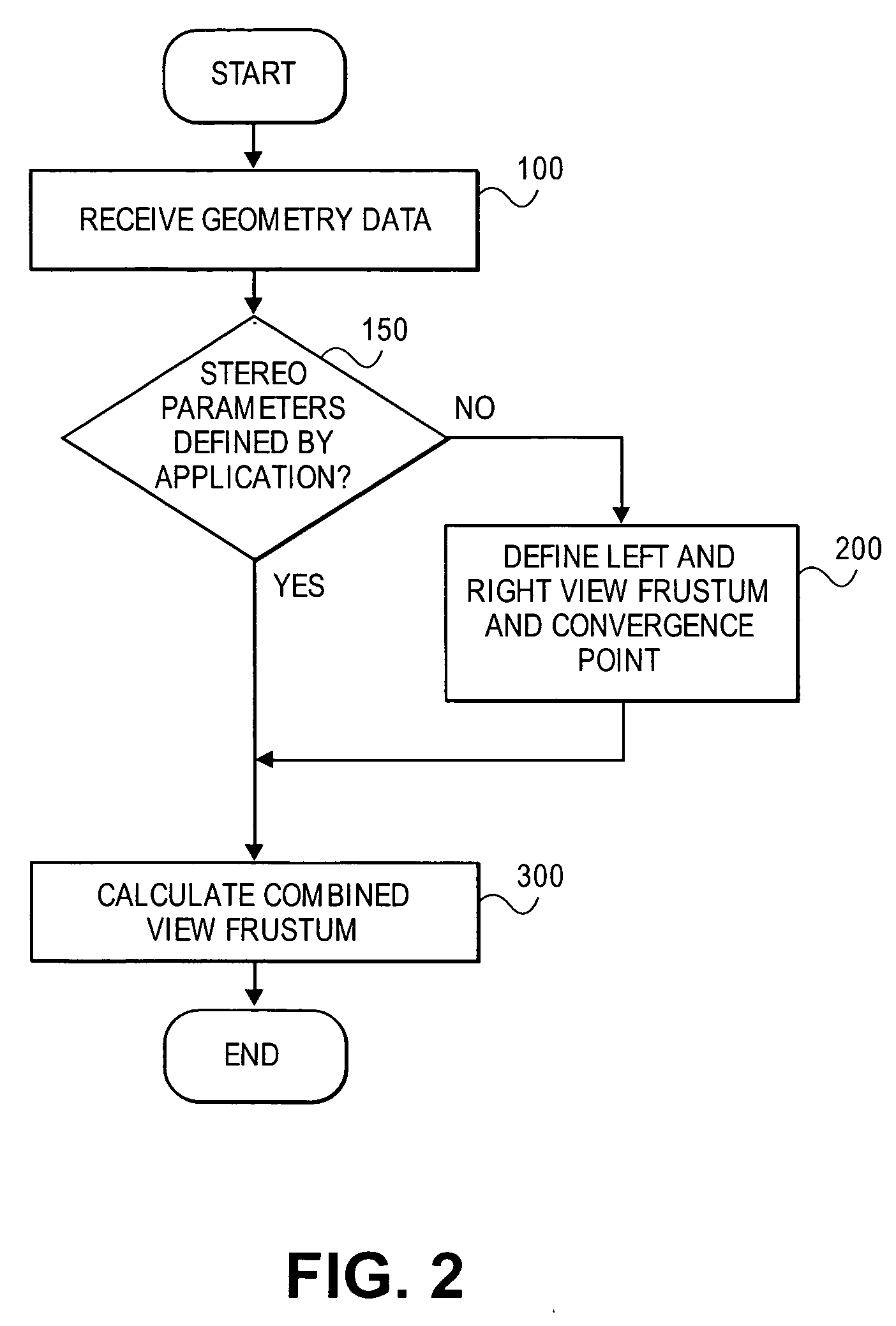
Full space-time three-dimensional visualization method
ActiveCN103795976AWide applicabilityClosed circuit television systemsSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic visualizationMultidimensional data
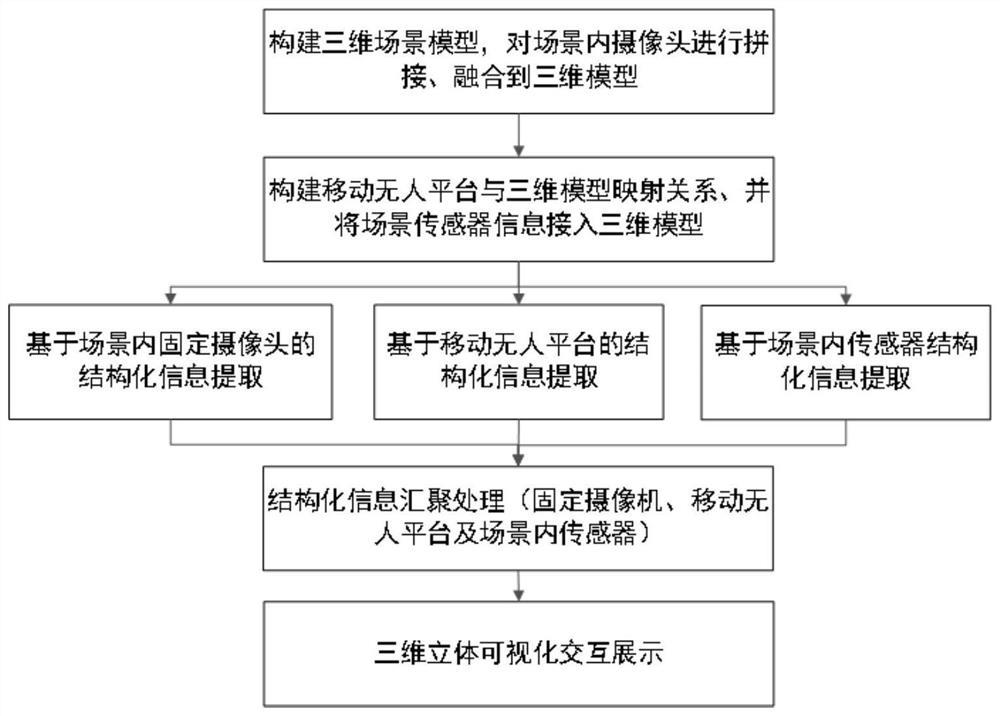
The invention provides a full space-time three-dimensional visualization method. The method includes the following steps: real-time video data collected by a camera are packaged and converted in terms of a format; real-time fixed angle video data are spliced and fused in 3D GIS spatial data, so as to form a panoramic three-dimensional video; an event target of the panoramic three-dimensional video serves as a driving force to realize a camera cooperative pursuit; according to a result by the packet and format conversion, the real-time video data are stored in a storage device to form history video data; and the fixed angle video data are spliced and fused in the 3D GIS spatial data, so as to realize the full space-time three-dimensional visualization display of the history video. In addition, in order to realize video intelligent analysis and realize multidimensional data fusion and three-dimensional visualization display in a full scene, the invention also provides a full scene video intelligent analysis method and a multi-type data full space-time three-dimensional visualization method. The full space-time three-dimensional visualization method provides an effective means for the macro command monitoring, overall correlation, and comprehensive scheduling, and is high in applicability.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENGAN RONGHAN TECH
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot using a camera unit with a modified prism
ActiveUS20090268011A1Avoid attenuationMaterial analysis by optical meansEndoscopesStereoscopic visualizationSurgical robot
An endoscope with a stereoscopic optical channel is held and positioned by a robotic surgical system. A first capture unit captures: a visible first color component of a visible left image combined with a fluorescence left image from first light from one channel in the endoscope; a visible second color component of the visible left image from the first light; and a visible third color component of the visible left image from the first light. A second capture unit captures: a visible first color component of a visible right image combined with a fluorescence right image from second light from the other channel in the endoscope; a visible second color component of the visible right image from the second light; and a visible third color component of the visible right image from the second light. An augmented stereoscopic outputs a real-time stereoscopic image including a three-dimensional presentation including the visible left and right images and the fluorescence left and right images.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
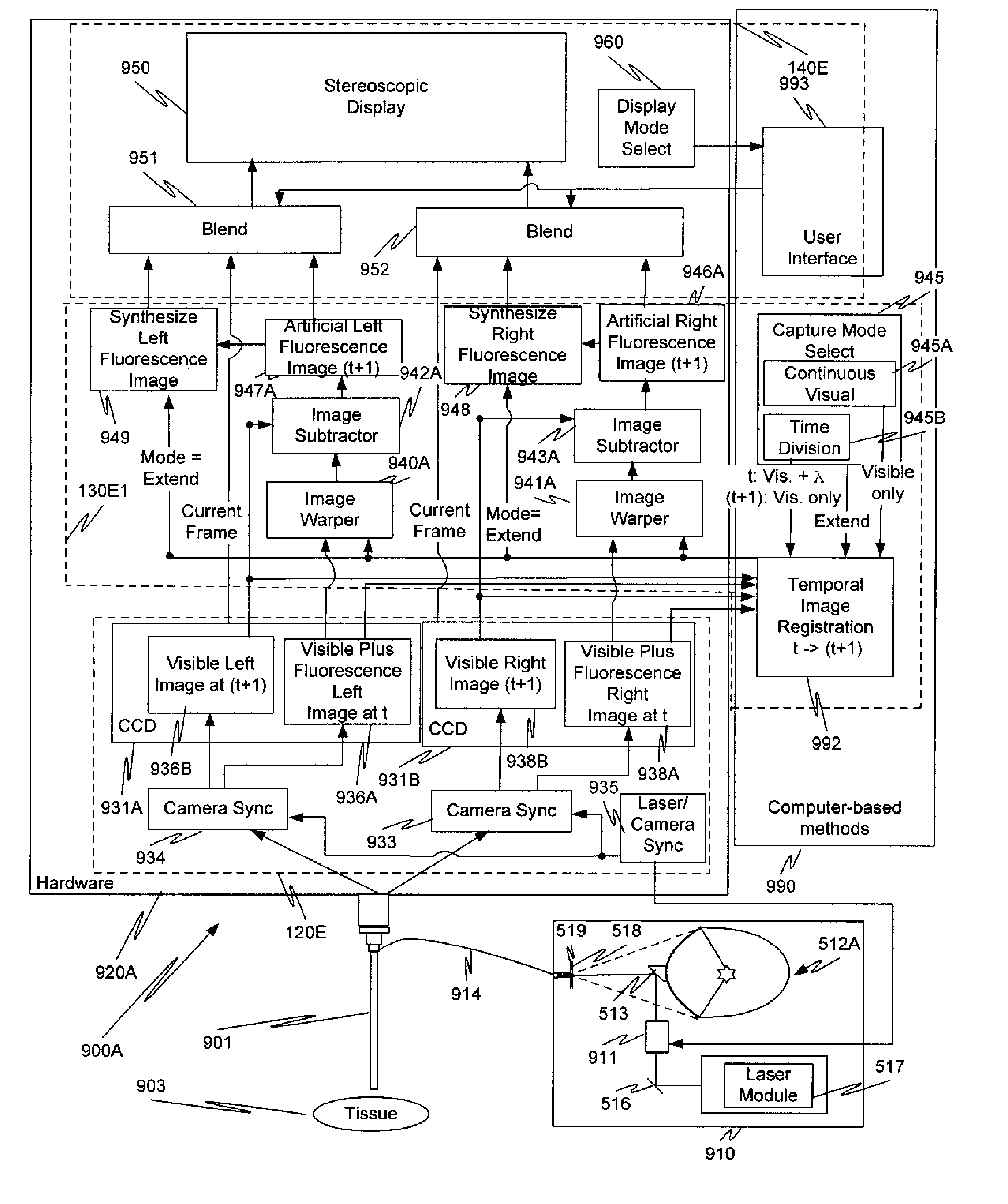
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot using time duplexing
ActiveUS20090270678A1Avoid attenuationEndoscopesMaterial analysis by optical meansStereoscopic visualizationSurgical robot
An endoscope with a stereoscopic optical channel is again held and positioned by a robotic surgical system. A capture unit captures (1) at a first time, a first image from light from the channel; and (2) at a second time different from the first time, a second image from the light. Only one of the first image and the second image includes a combination of a fluorescence image and a visible image. The other of the first image and the second image is a visible image. An intelligent image processing system generates an artificial fluorescence image using the captured fluorescence image. An augmented stereoscopic display system outputs an augmented stereoscopic image of at least a portion of the tissue comprising the artificial fluorescence image.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
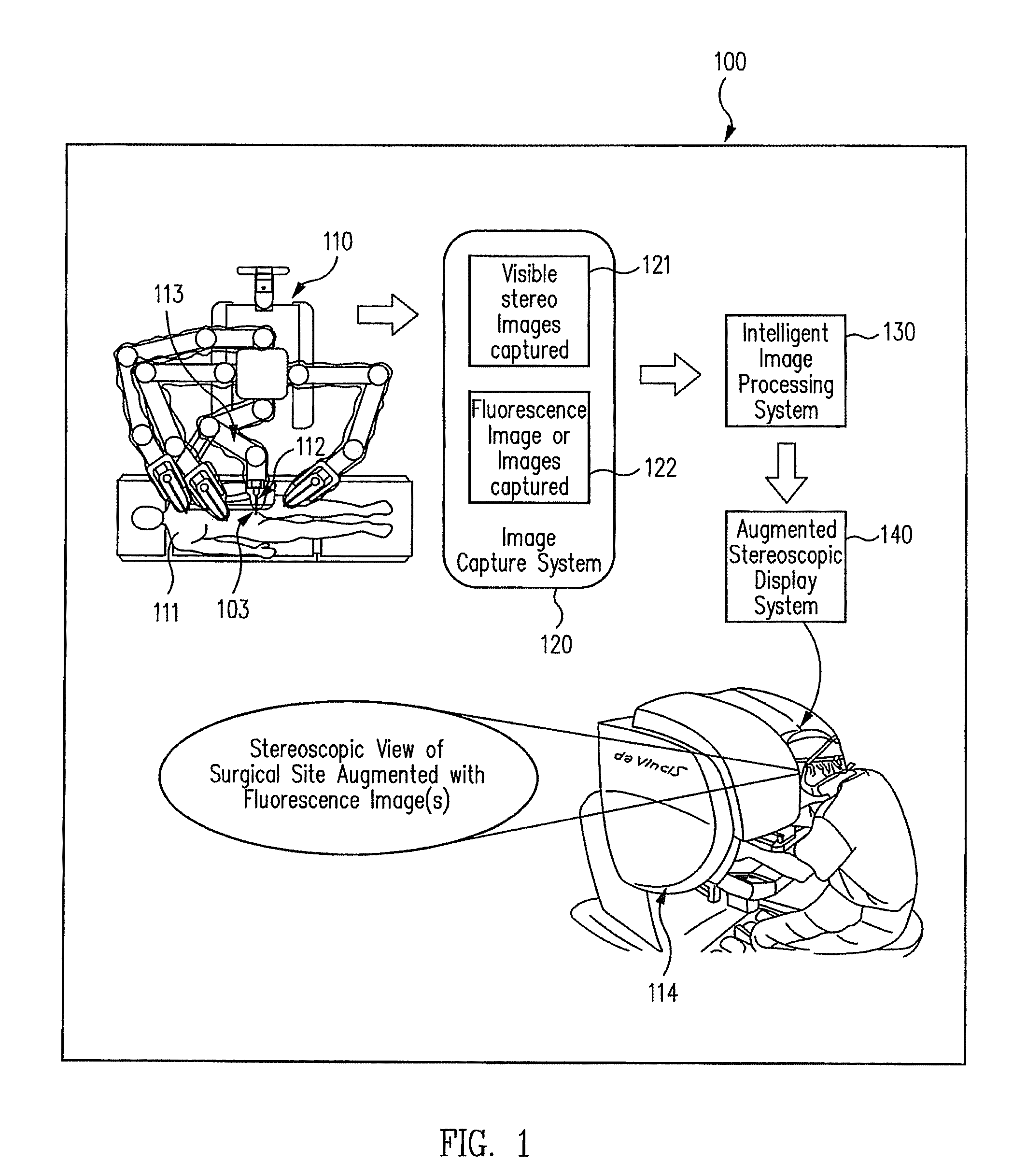
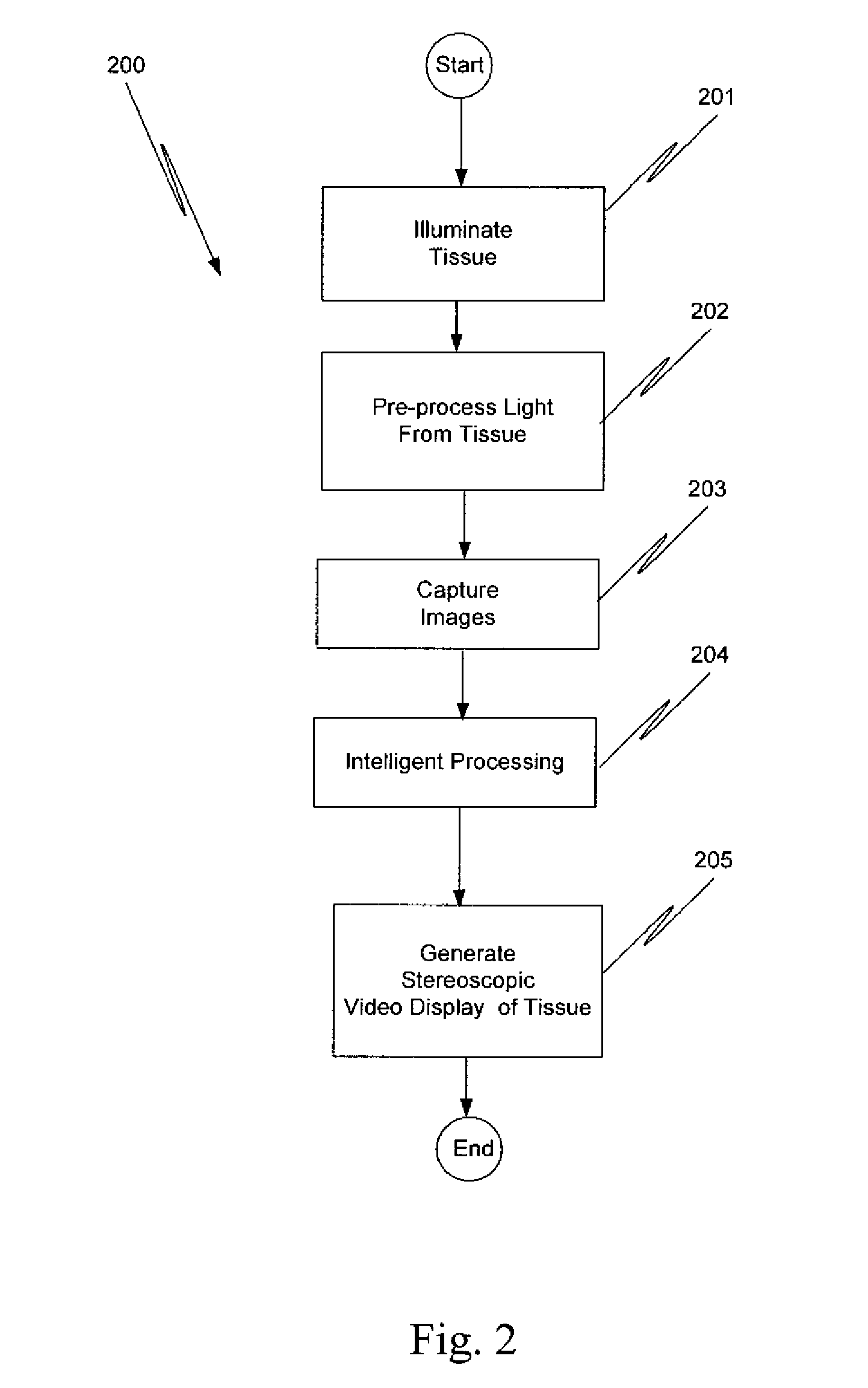
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot
ActiveUS20090268015A1Avoid attenuationEndoscopesMaterial analysis by optical meansStereoscopic visualizationStereoscopic video
A robotic surgical system positions and holds an endoscope. A visible imaging system is coupled to the endoscope. The visible imaging system captures a visible image of tissue. An alternate imaging system is also coupled to the endoscope. The alternate imaging system captures a fluorescence image of at least a portion of the tissue. A stereoscopic video display system is coupled to the visible imaging system and to the alternate imaging system. The stereoscopic video display system outputs a real-time stereoscopic image comprising a three-dimensional presentation of a blend of a fluorescence image associated with the captured fluorescence image, and the visible image.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot
ActiveUS8169468B2Avoid attenuationMaterial analysis by optical meansEndoscopesStereoscopic visualizationStereoscopic video
A robotic surgical system positions and holds an endoscope. A visible imaging system is coupled to the endoscope. The visible imaging system captures a visible image of tissue. An alternate imaging system is also coupled to the endoscope. The alternate imaging system captures a fluorescence image of at least a portion of the tissue. A stereoscopic video display system is coupled to the visible imaging system and to the alternate imaging system. The stereoscopic video display system outputs a real-time stereoscopic image comprising a three-dimensional presentation of a blend of a fluorescence image associated with the captured fluorescence image, and the visible image.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
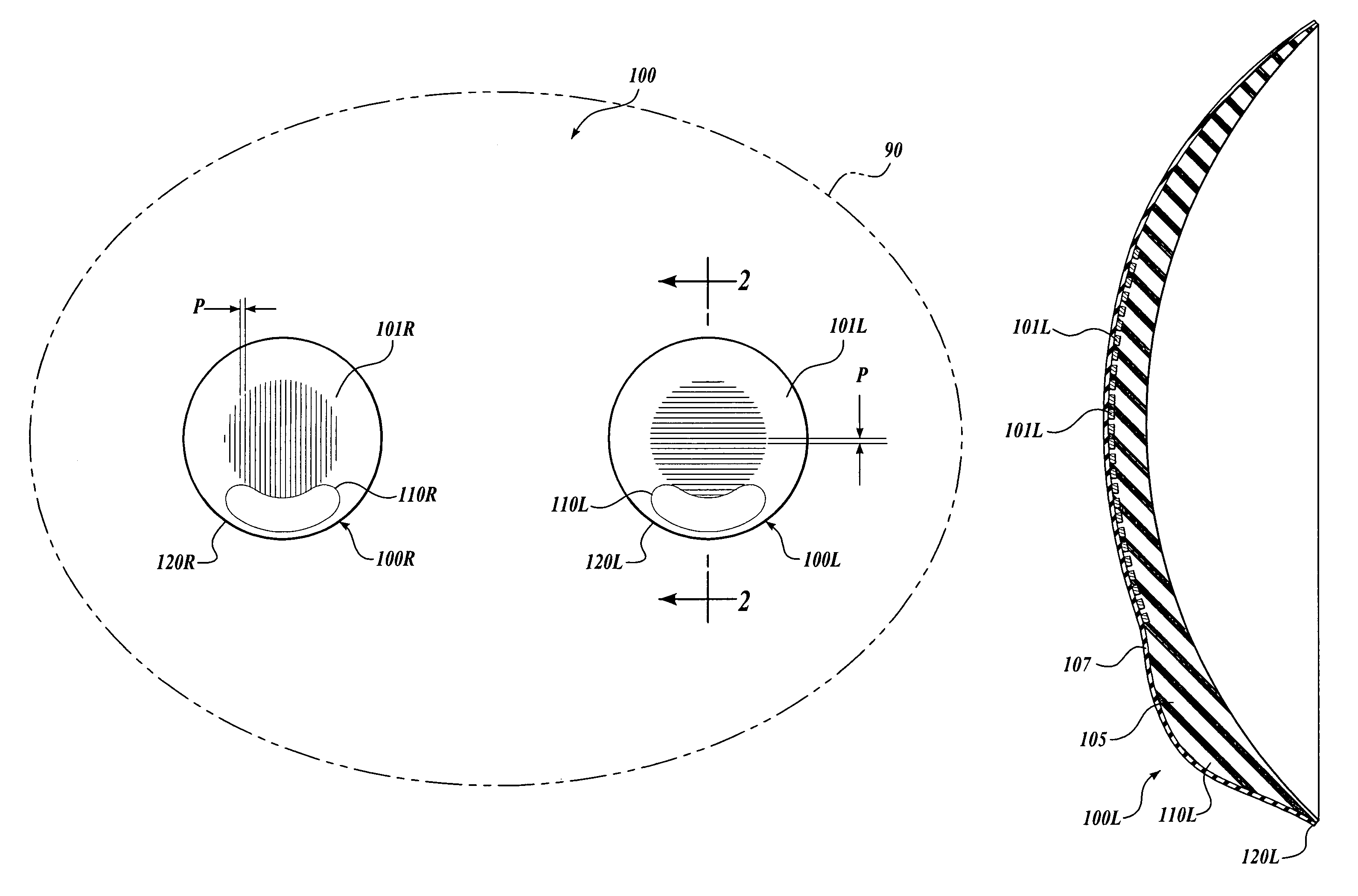
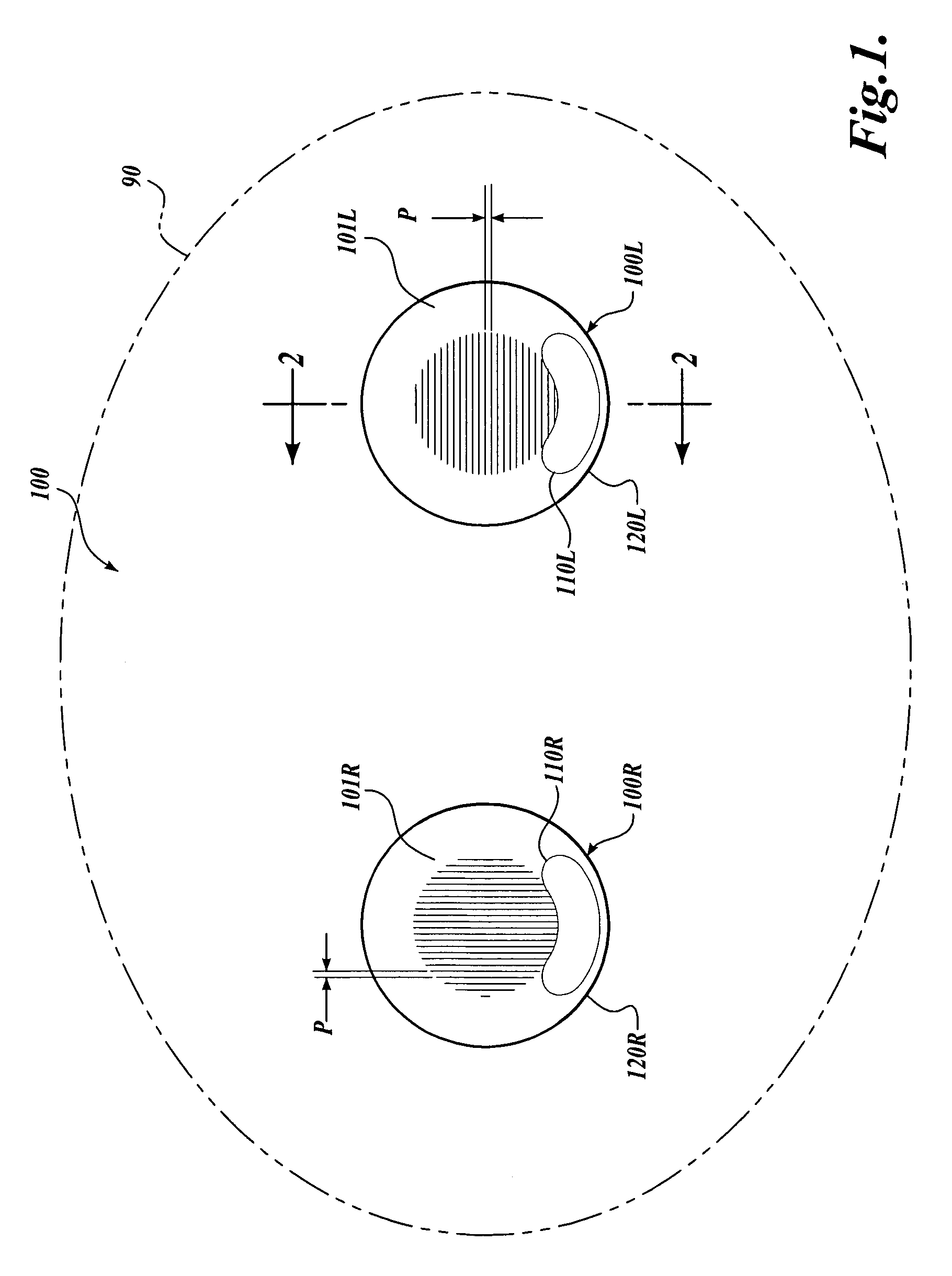
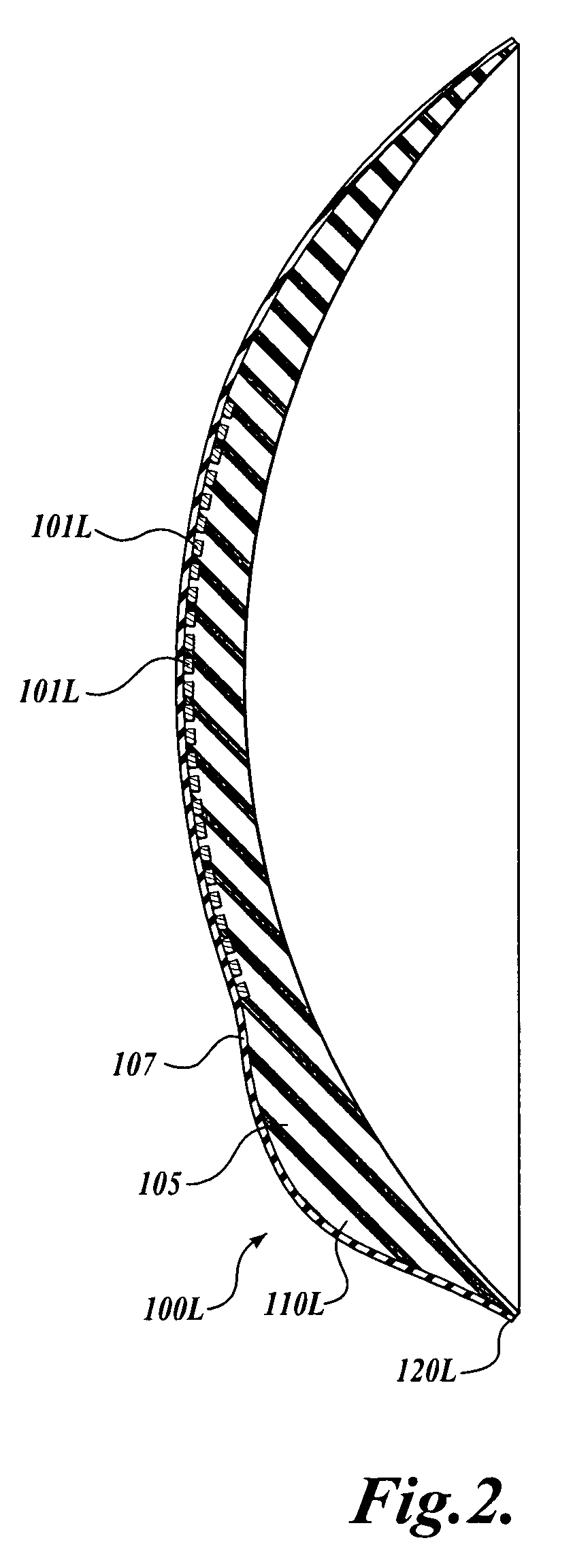
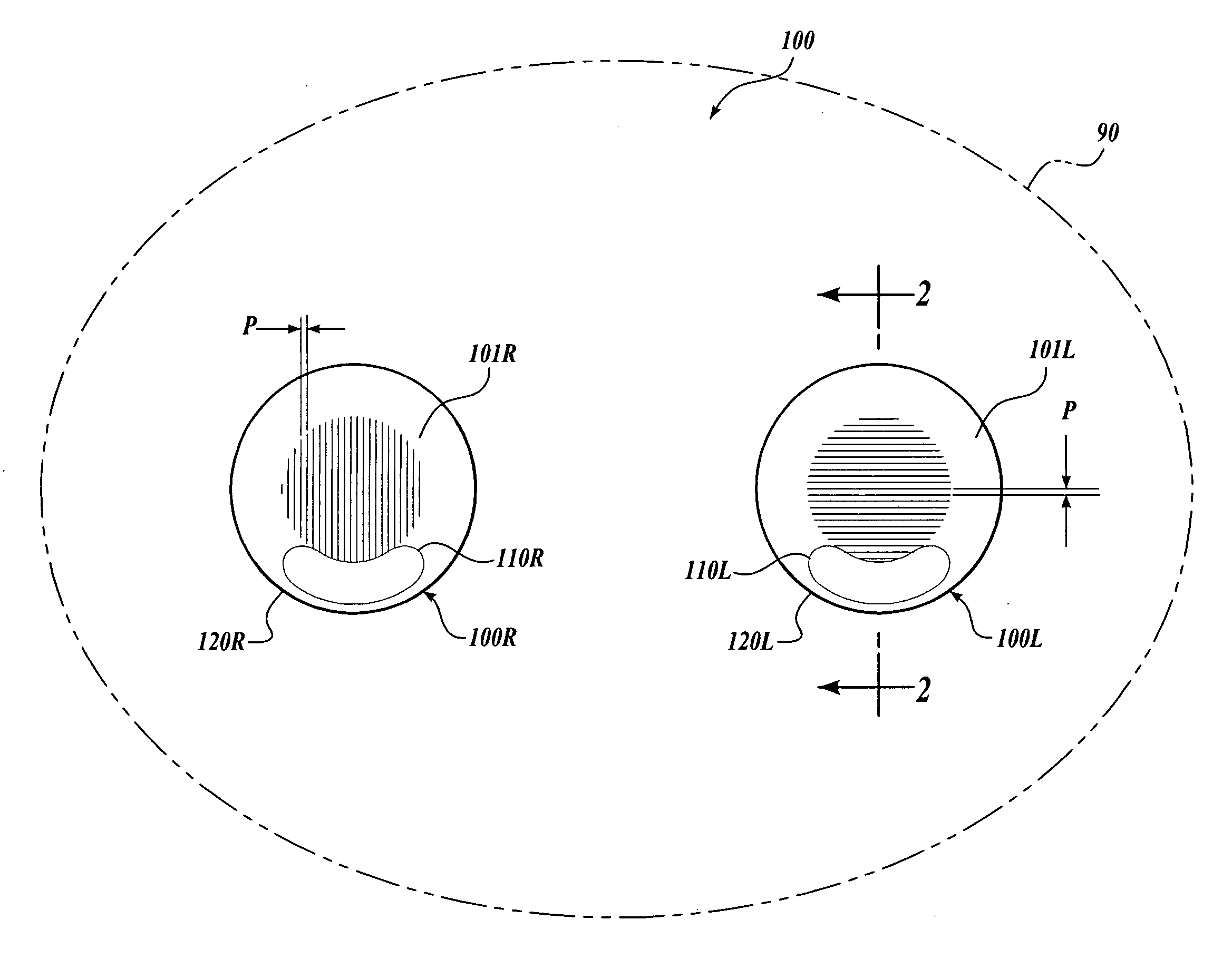
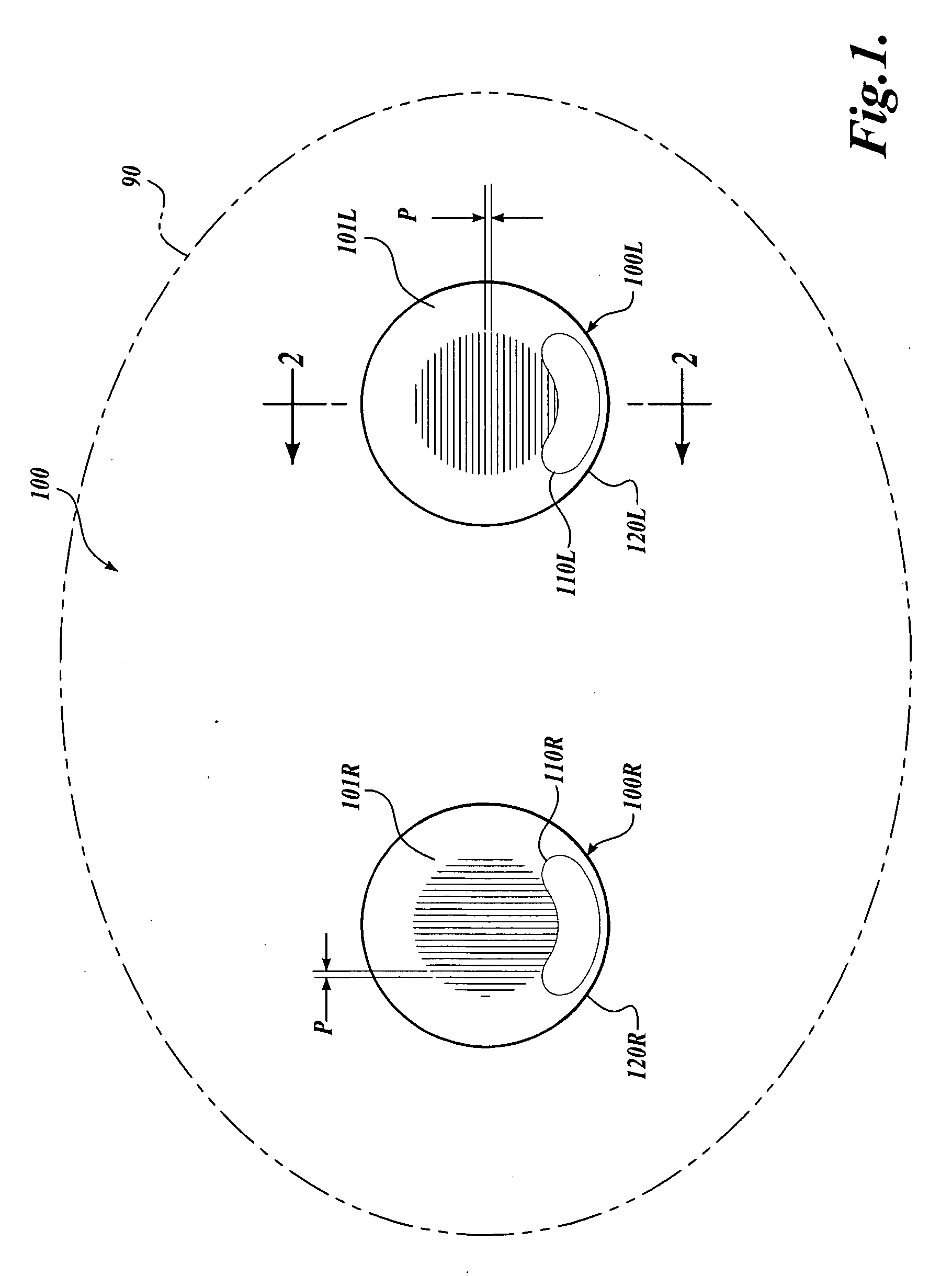
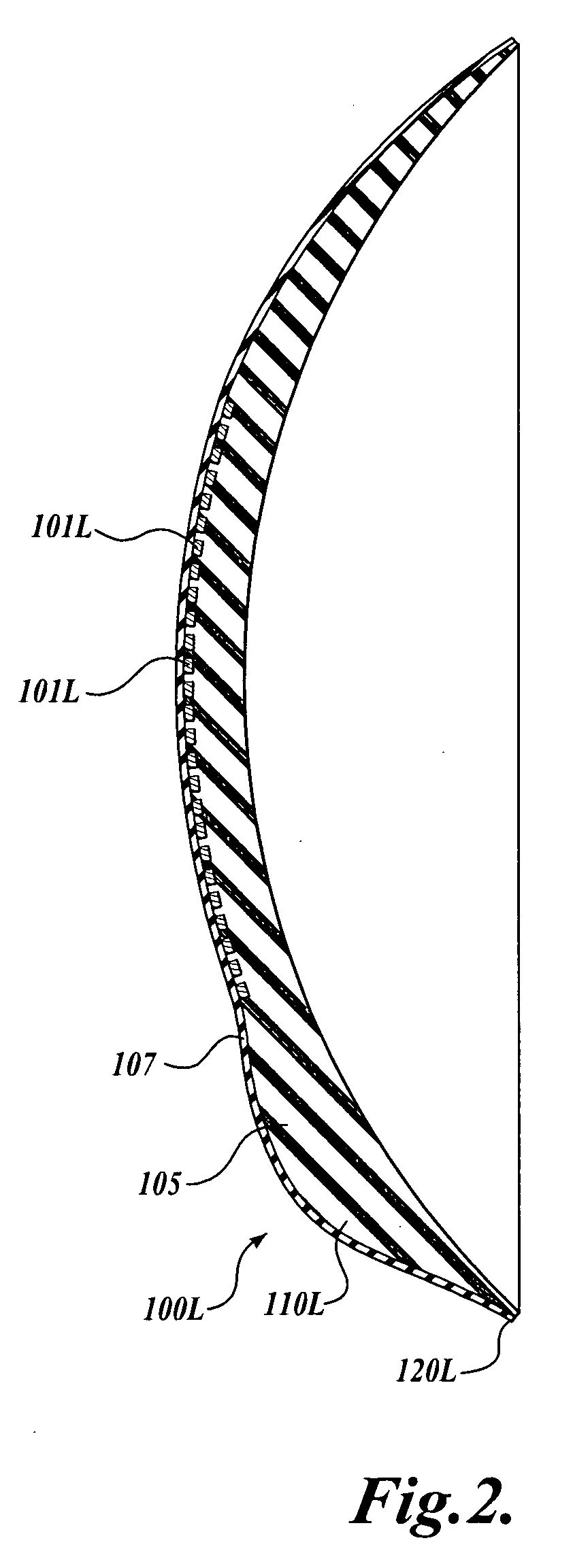
Contact lens for three dimensional visualization
A contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens comprising a first lens substrate incorporating a first polarizer, and a right contact lens comprising a lens substrate incorporating a second polarizer. The first polarizer comprises a first plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a first direction. The second polarizer comprises a second plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a second direction. The left contact lens and the right contact lens each comprises a rotational stabilization means, such that, during use, the first direction is adapted to orient in an approximately orthogonal direction to the second direction. In another embodiment, a contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens and a right contact lens, each coded with different colors.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Contact lens for three dimensional visualization
A contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens comprising a first lens substrate incorporating a first polarizer, and a right contact lens comprising a lens substrate incorporating a second polarizer. The first polarizer comprises a first plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a first direction. The second polarizer comprises a second plurality of parallel lines having sub-wavelength pitch and oriented in a second direction. The left contact lens and the right contact lens each comprises a rotational stabilization means, such that, during use, the first direction is adapted to orient in an approximately orthogonal direction to the second direction. In another embodiment, a contact lens set for stereoscopic visualization includes a left contact lens and a right contact lens, each coded with different colors.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
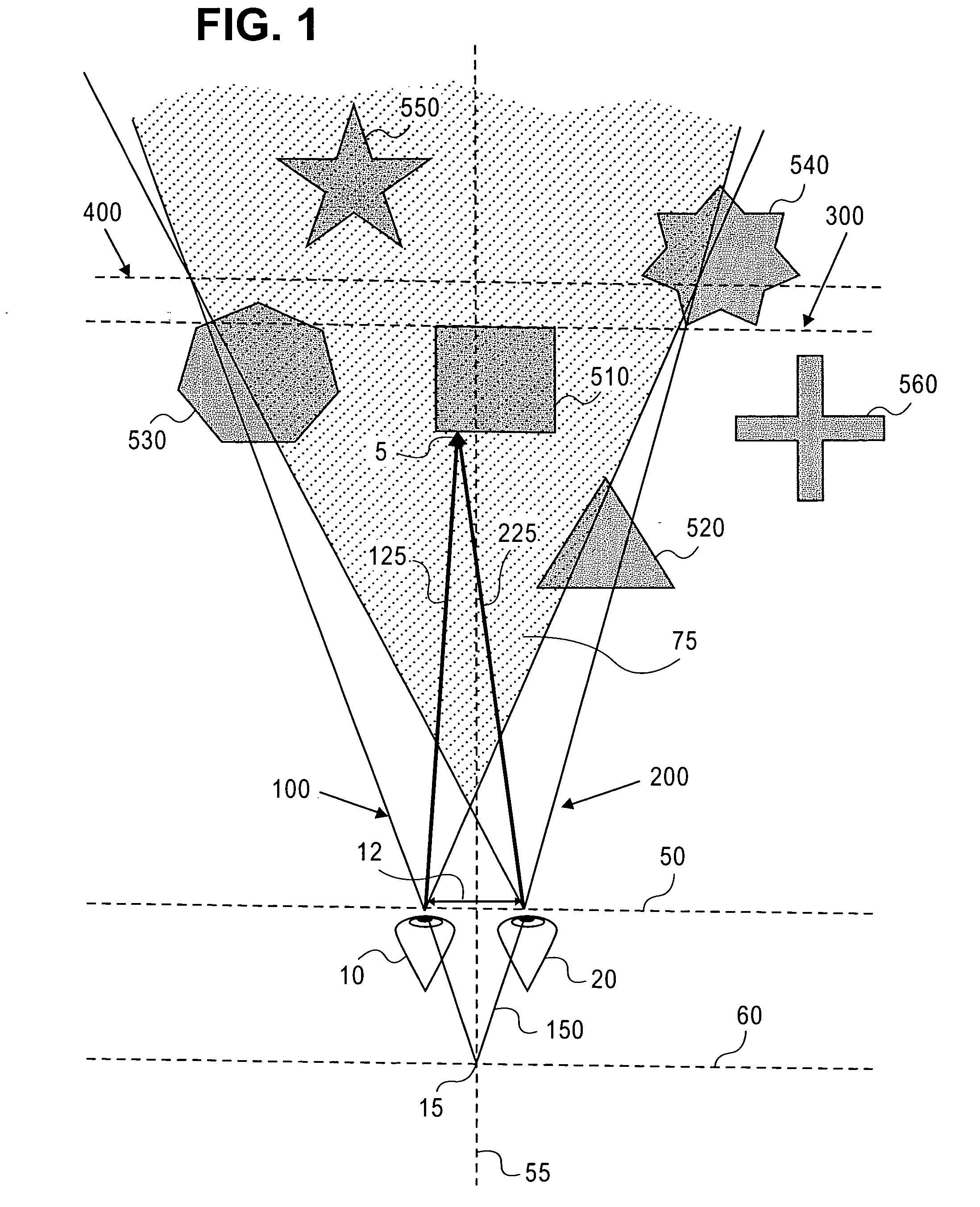
Stereoscopic visualization system
Apparatus for presenting a stereoscopic image to a viewer, the apparatus comprising:a stereoscopic video system comprising:first and second image sensors for acquiring, respectively, first and second images of a scene;a display system for displaying the first image to the first eye of the viewer and the second image to the second eye of the viewer; andparallax adjusting means for adjusting the parallax between the first and second images.A method for presenting a stereoscopic image to a viewer, the method comprising:providing a stereoscopic video system comprising:first and second image sensors for acquiring, respectively, first and second images of a scene;a display system for displaying the first image to the first eye of the viewer and the second image to the second eye of the viewer; andparallax adjusting means for adjusting the parallax between the first and second images; andoperating the stereoscopic video system so as to provide a stereoscopic image to the user wherein parallax has been adjusted.
Owner:VIKING SYST
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot using a captured visible image combined with a fluorescence image and a captured visible image
ActiveUS20090268012A1Avoid attenuationMaterial analysis by optical meansEndoscopesStereoscopic visualizationImaging processing
An endoscope with a stereoscopic optical channel is held and positioned by a robotic surgical system. A capture unit captures (1) a visible first image and (2) a visible second image combined with a fluorescence second image from the light. An intelligent image processing system receives (1) the visible first image and (2) the visible second image combined with the fluorescence second image and generates at least one fluorescence image of a stereoscopic pair of fluorescence images and a visible second image. An augmented stereoscopic display system outputs a real-time stereoscopic image including a three-dimensional presentation including in one eye, a blend of the at least one fluorescence image of a stereoscopic pair of fluorescence images and one of the visible first and second images; and in the other eye, the other of the visible first and second images.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
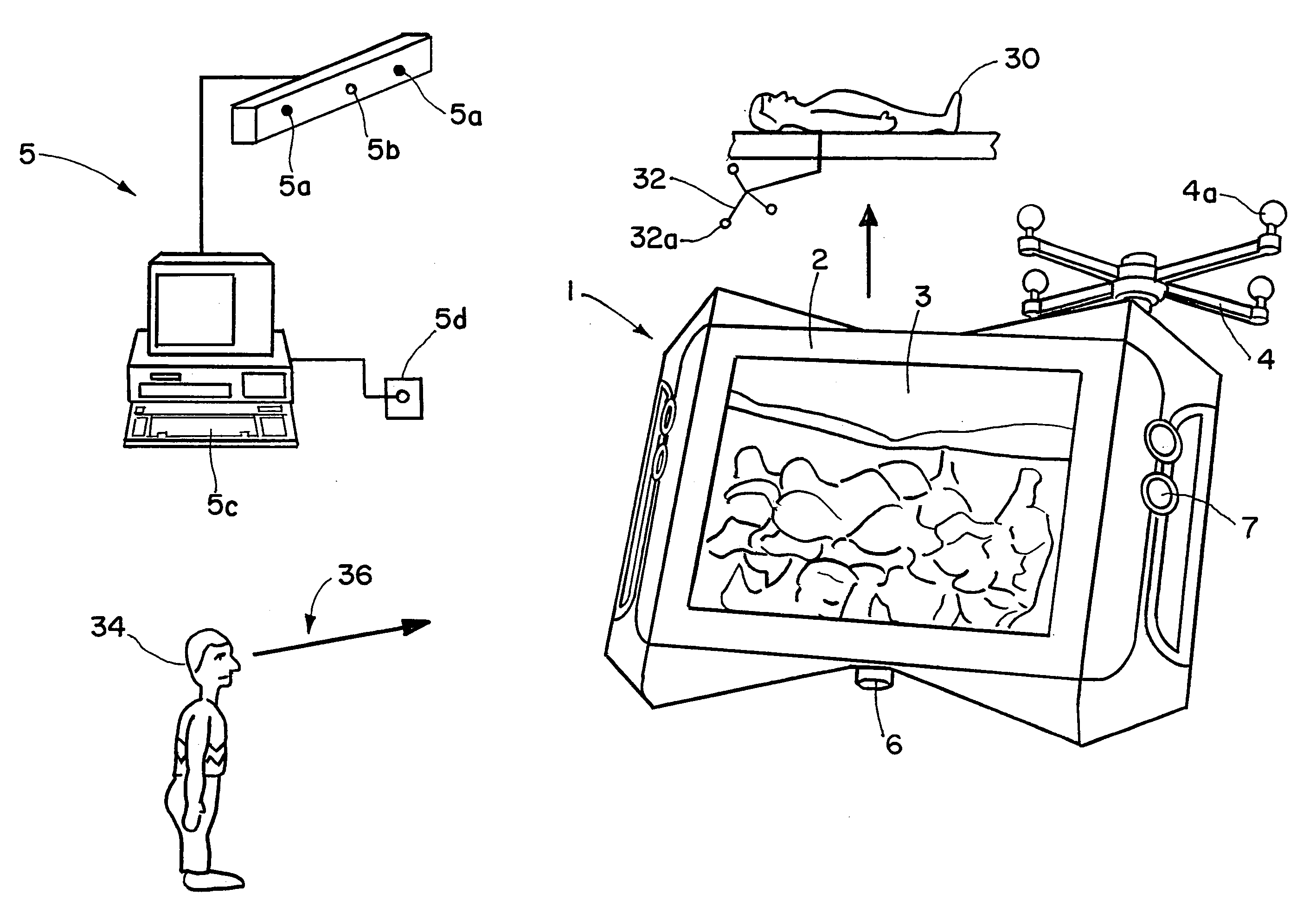
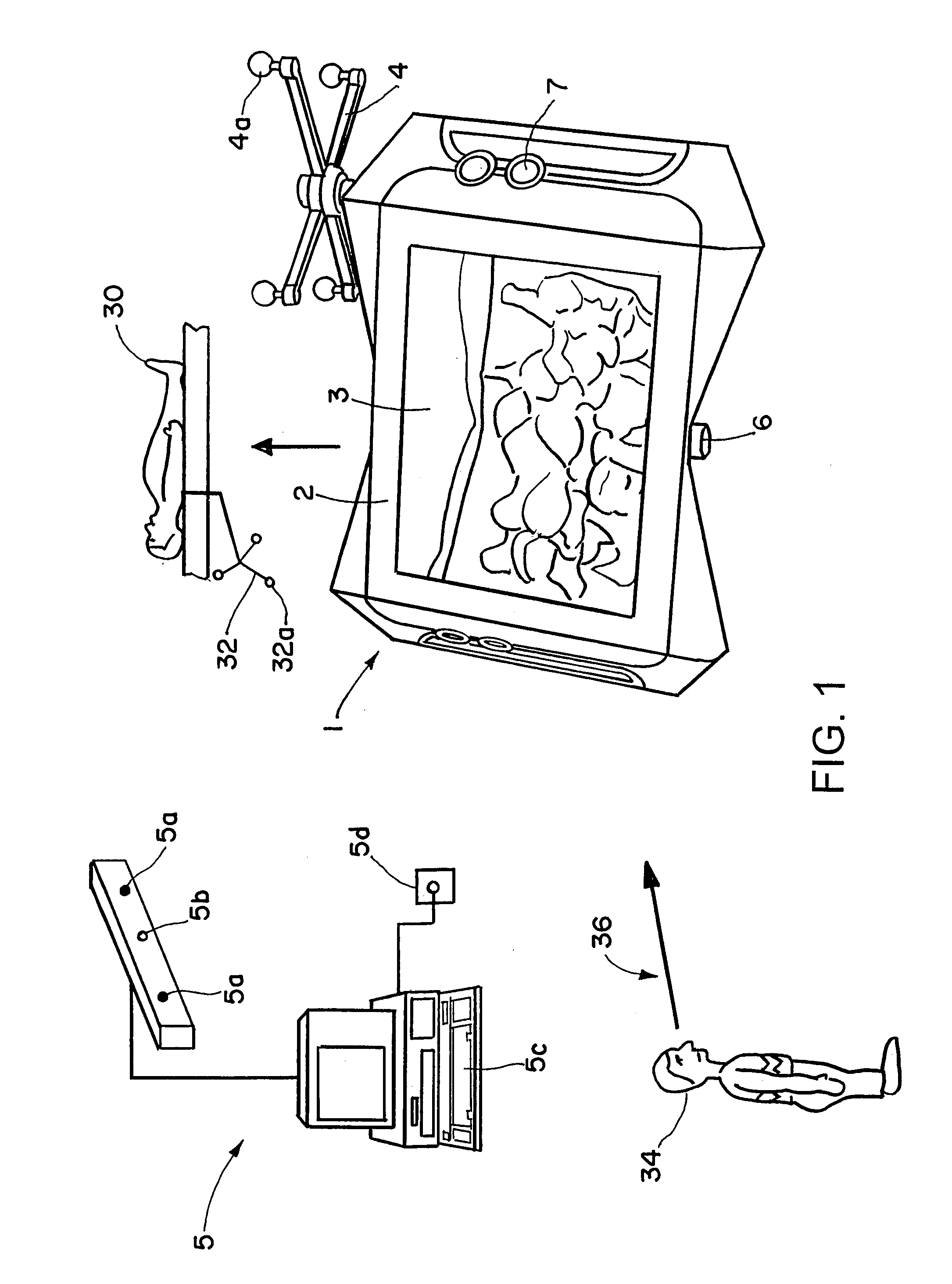
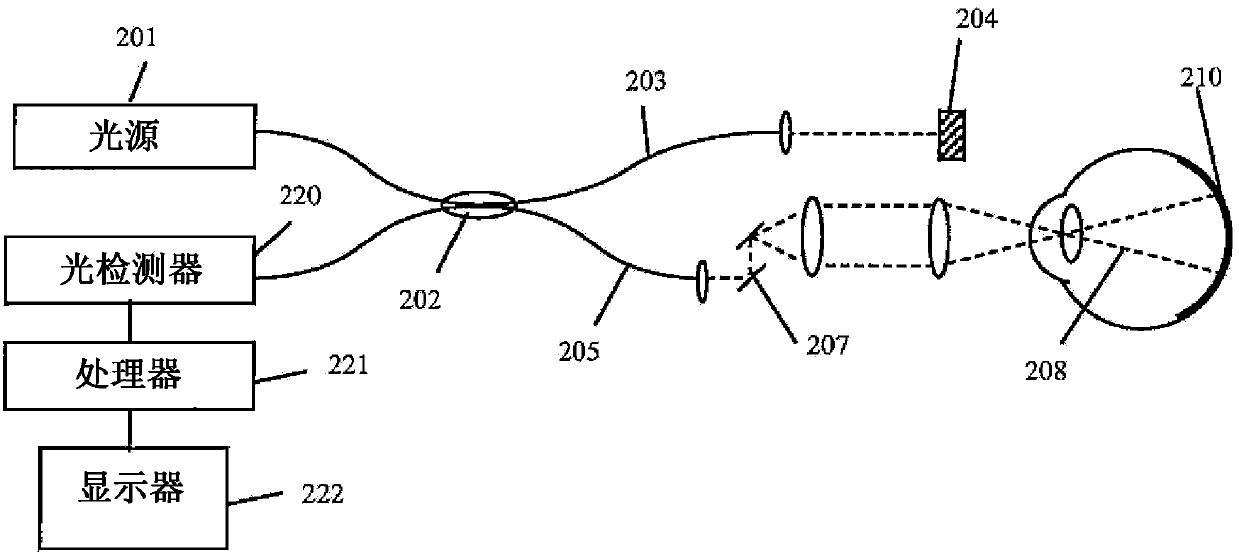
Stereoscopic visualization device for patient image data and video images
ActiveUS7463823B2High resolutionIncrease flexibilityPrintersProjectorsStereoscopic visualizationDisplay device
A system for visually combining patient image data from transillumination and / or tomographic imaging methods and / or object image data with video images includes an image display device having an auto-stereoscopic monitor, at least one camera and a computer-assisted navigation system. The navigation system is operable to detect spatial positions of a part of the patient's body via a first tracking device attached to the body, and spatial positions of said image display device and / or said at least one camera via a second tracking device attached to the image display device or the camera, wherein the image display device and the at least one camera are assigned to each other and are formed as a portable unit.
Owner:BRAINLAB
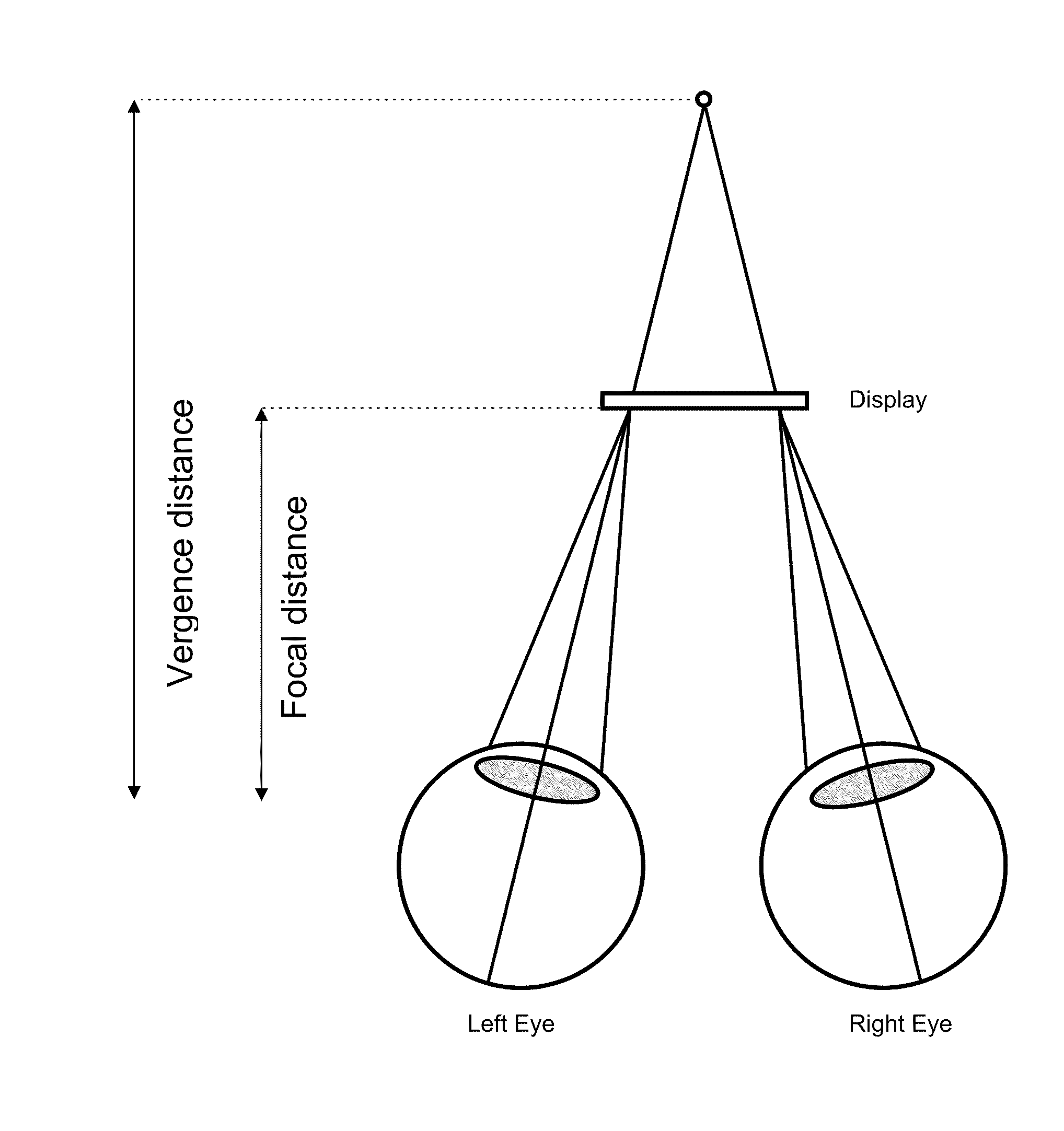
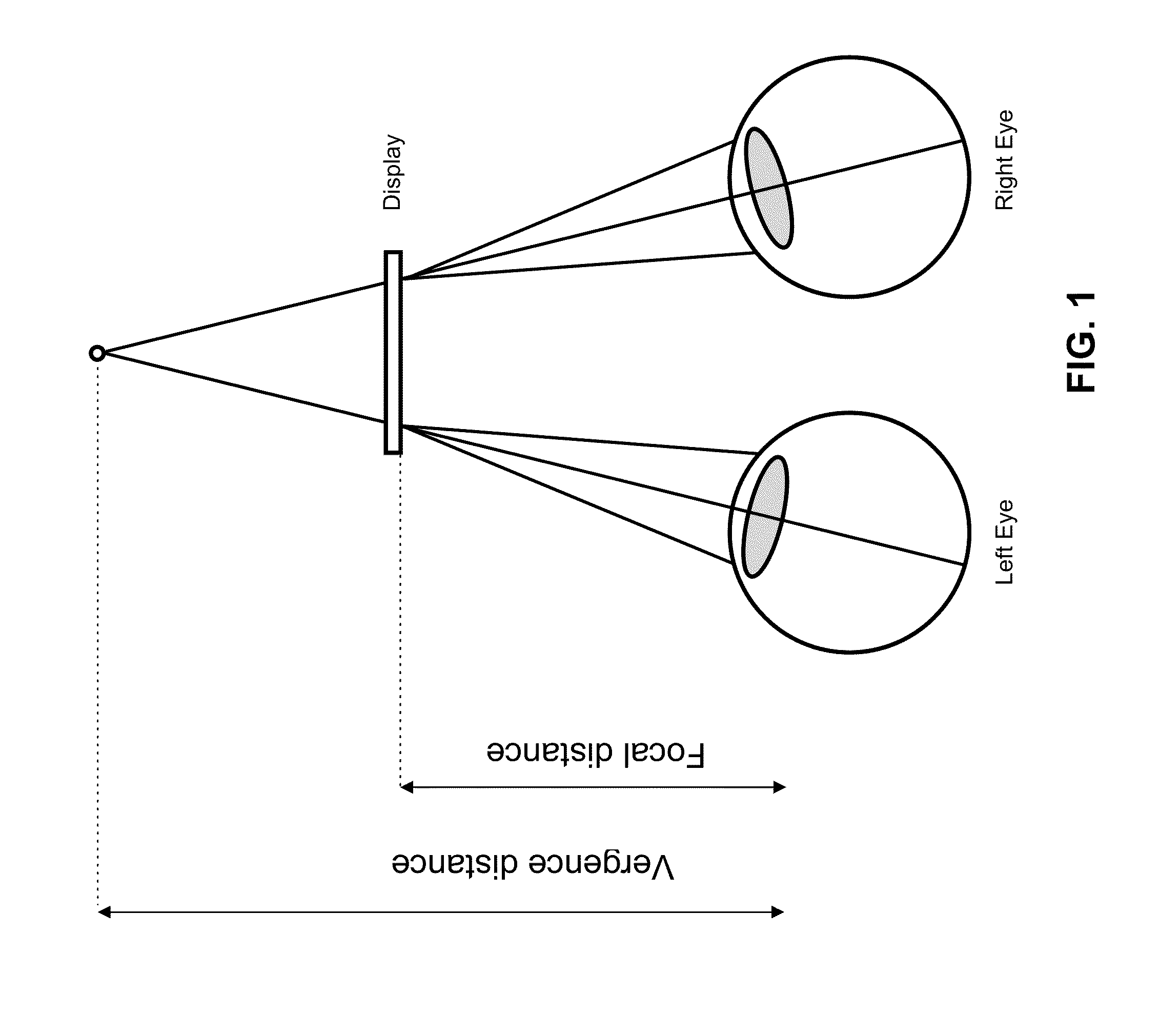
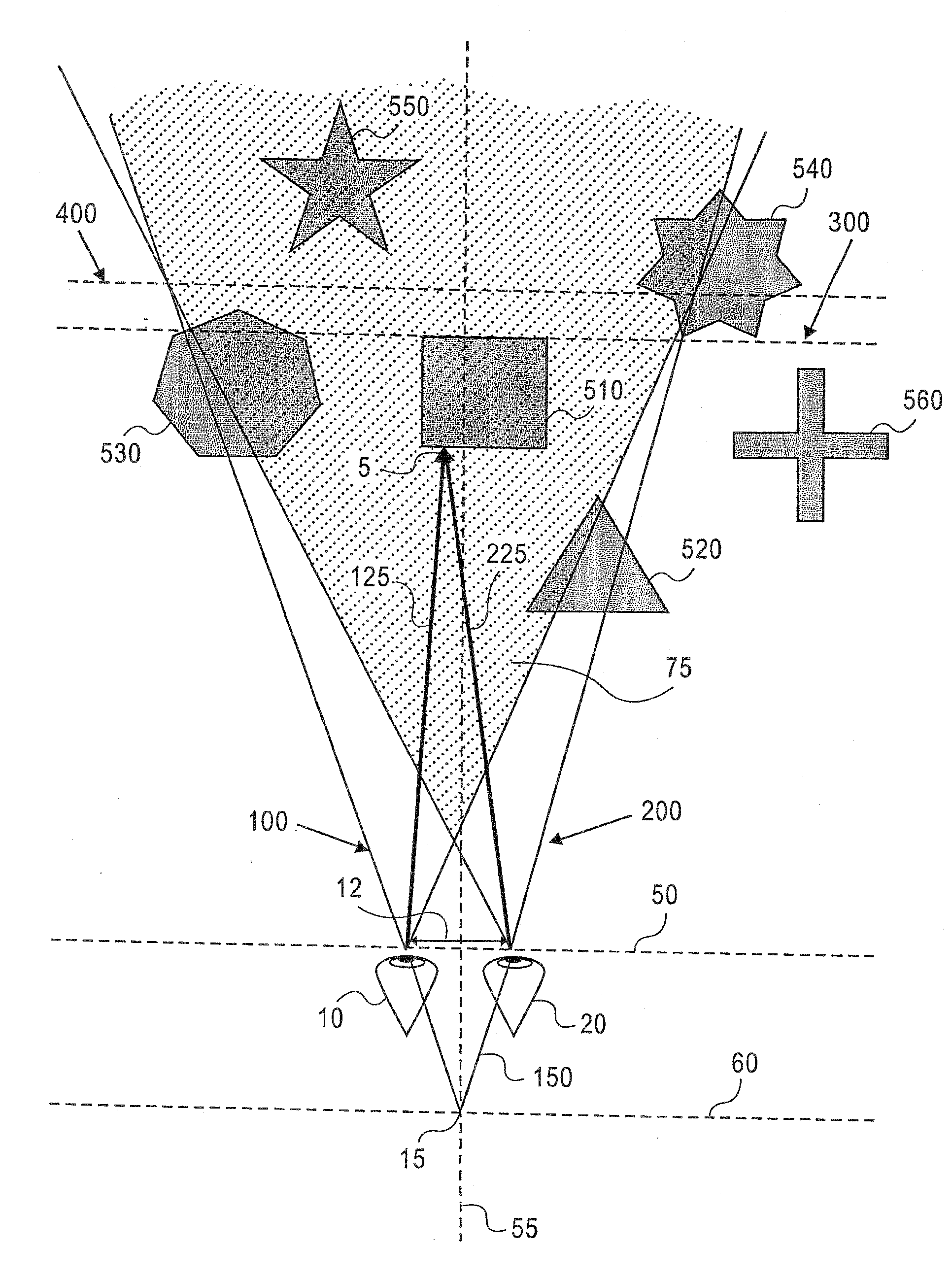
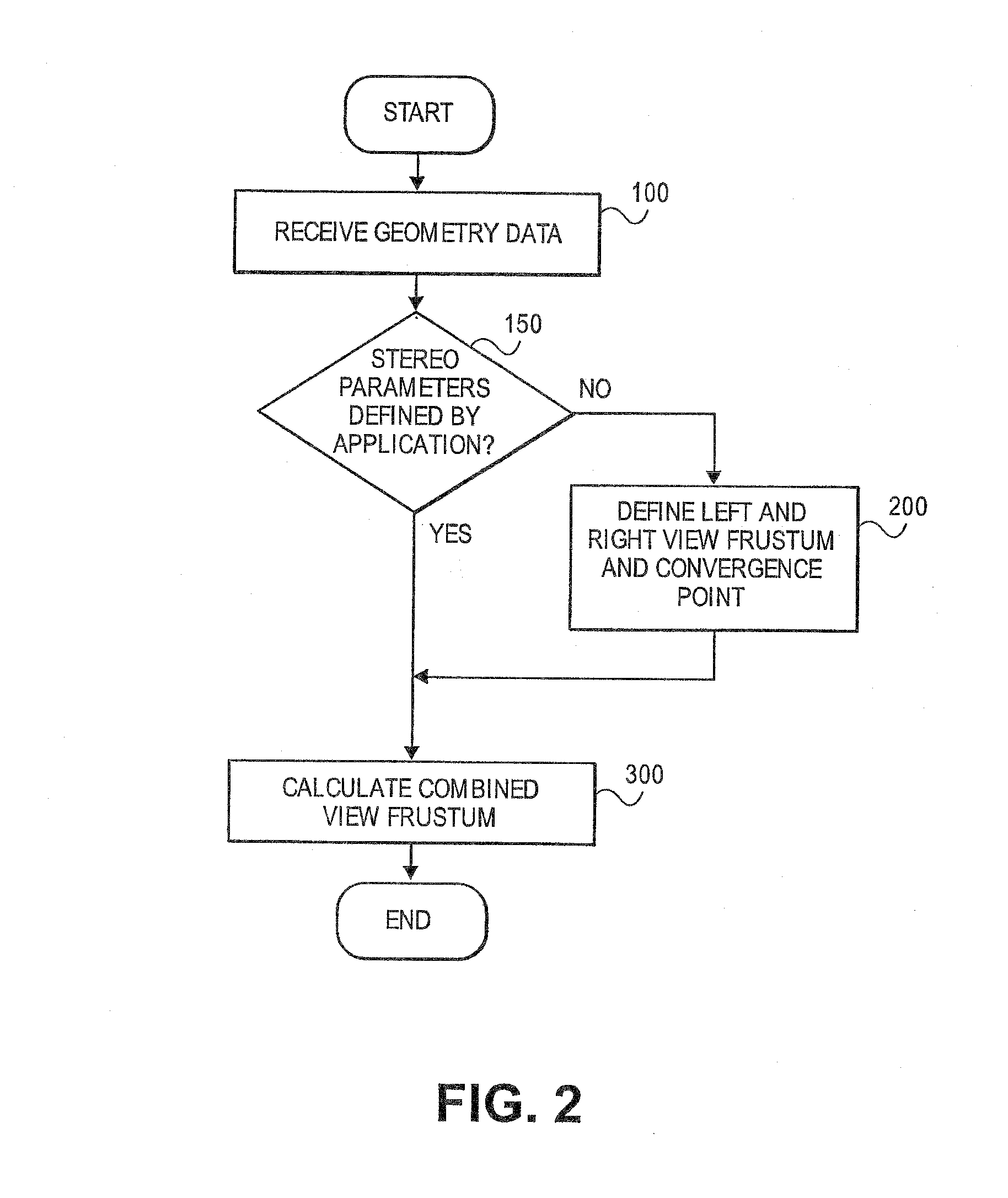
Optimized stereoscopic visualization
InactiveUS20100328428A1Steroscopic systems3D-image renderingStereoscopic visualizationComputer science
The present invention discloses a method comprising: calculating an X separation distance between a left eye and a right eye, said X separation distance corresponding to an interpupilary distance in a horizontal direction; and transforming geometry and texture only once for said left eye and said right eye.
Owner:INTEL CORP
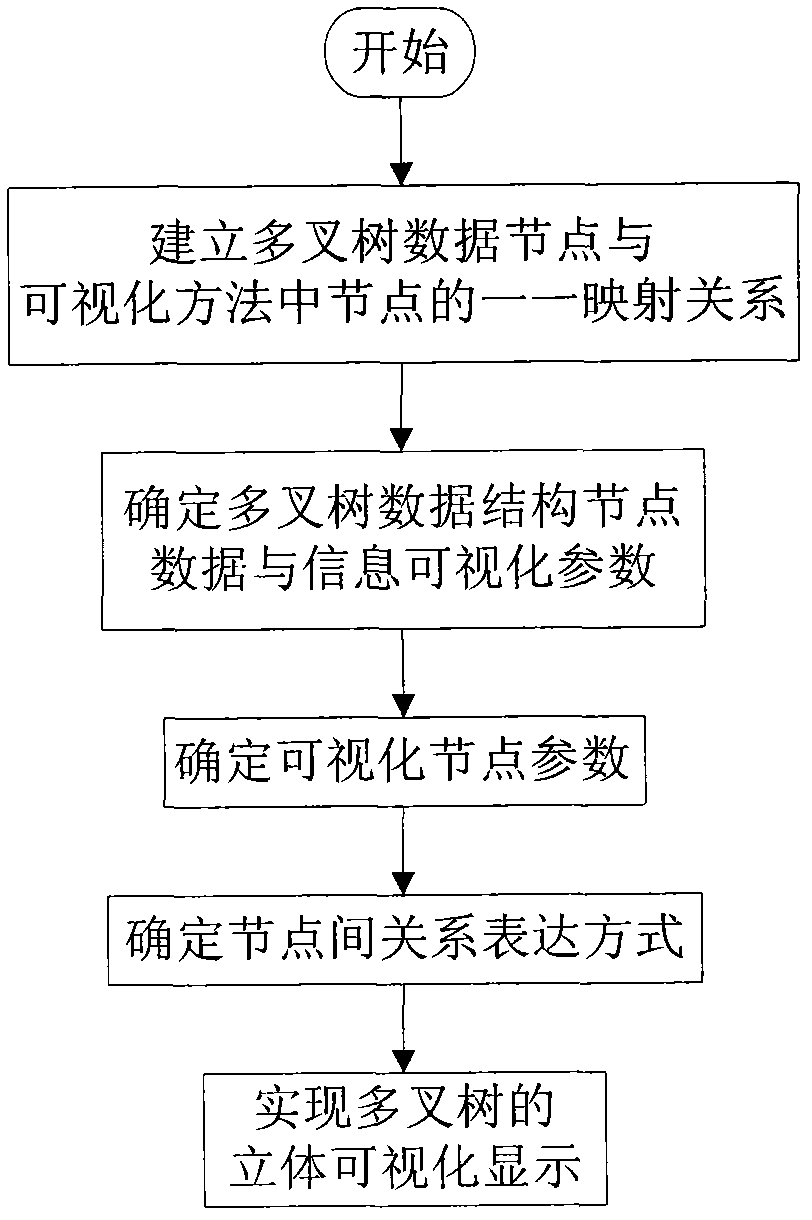
Three-dimensional ring visualization method of multi-branch tree data structure
ActiveCN101989178AIncrease profitClear expression2D-image generationSpecial data processing applicationsStereoscopic visualizationNODAL
The invention relates to a three-dimensional ring visualization method of a multi-branch tree data structure. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing the mapping relationship between the multi-branch tree data nodes and the nodes in the visualization methods to realize that the node information expressed by the visual nodes in each visualization method correspond to that of the corresponding multi-branch tree data nodes; 2) determining the node data of the multi-branch tree data structure and the information visual parameter; 3) determining the parameters of the visual nodes; 4) determining the expression way of the relationships of nodes (the relationship of brother nodes and the relationship of father and son nodes), modifying or adding the related parameters of the visual nodes with the expression demand; and 5) according to the parameters set by the step 2), 3) and 4), combining the information visualization of the multi-branch tree data nodes with the visual curved nodes to realize the three-dimensional visualization display of the multi-branch tree; and ensuring that the overall visual shape of the combined nodes still corresponds the characteristics of thearc body, and maintaining the characteristics of layers, clusters and other structures. The method is simple and has good application effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Augmented stereoscopic visualization for a surgical robot using time duplexing
ActiveUS8167793B2Avoid attenuationEndoscopesMaterial analysis by optical meansStereoscopic visualizationImaging processing
An endoscope with a stereoscopic optical channel is again held and positioned by a robotic surgical system. A capture unit captures (1) at a first time, a first image from light from the channel; and (2) at a second time different from the first time, a second image from the light. Only one of the first image and the second image includes a combination of a fluorescence image and a visible image. The other of the first image and the second image is a visible image. An intelligent image processing system generates an artificial fluorescence image using the captured fluorescence image. An augmented stereoscopic display system outputs an augmented stereoscopic image of at least a portion of the tissue comprising the artificial fluorescence image.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
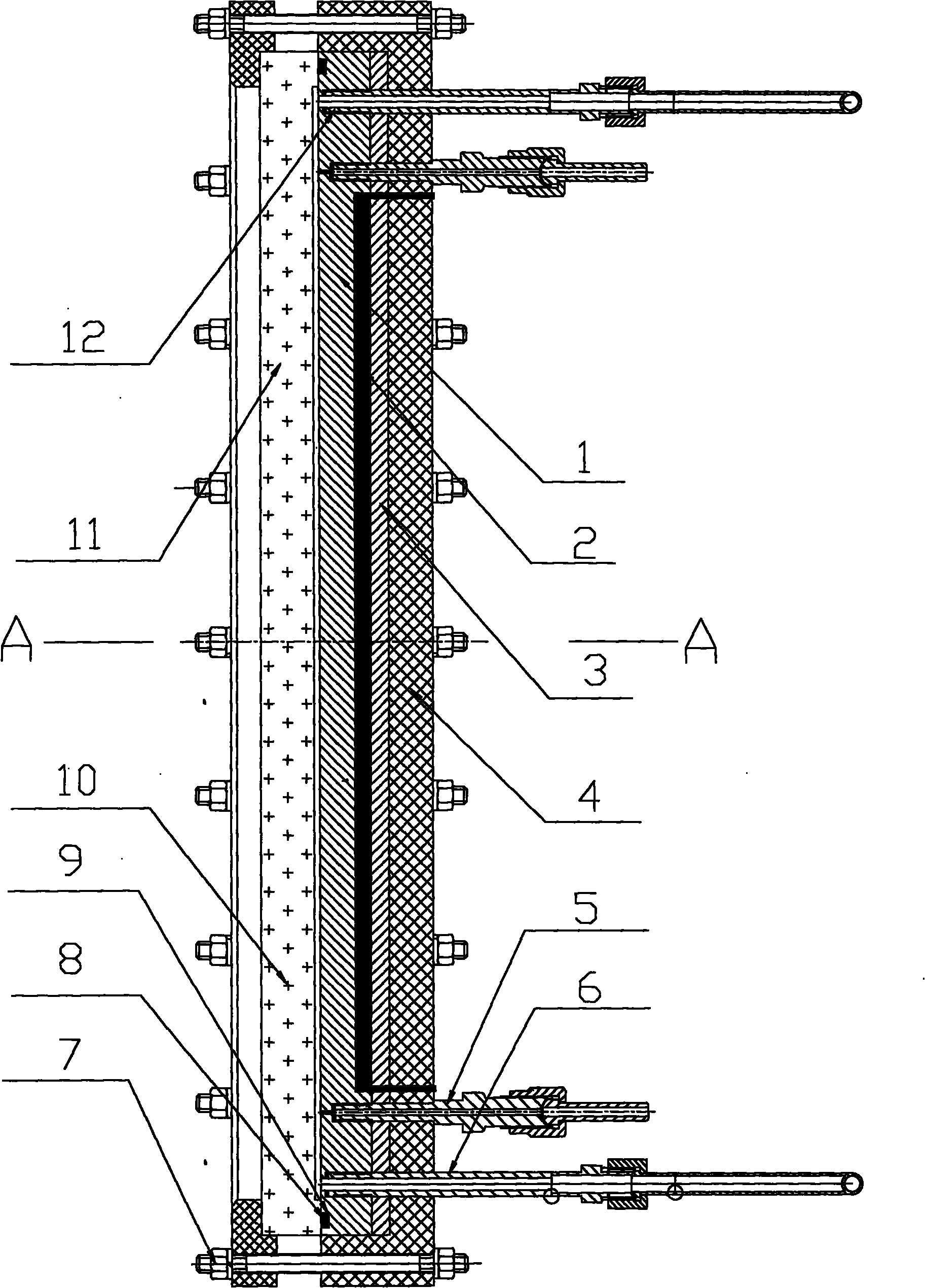
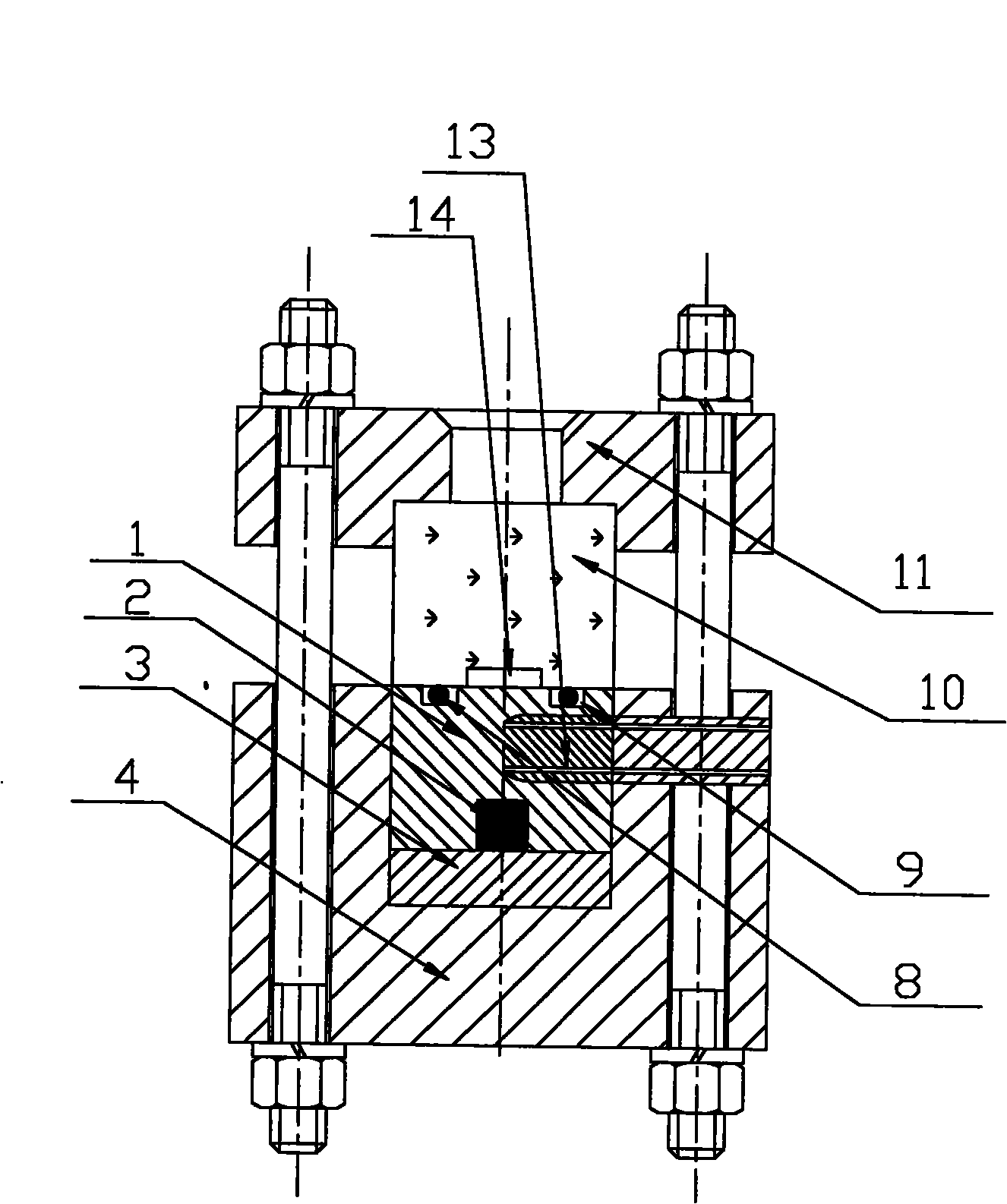
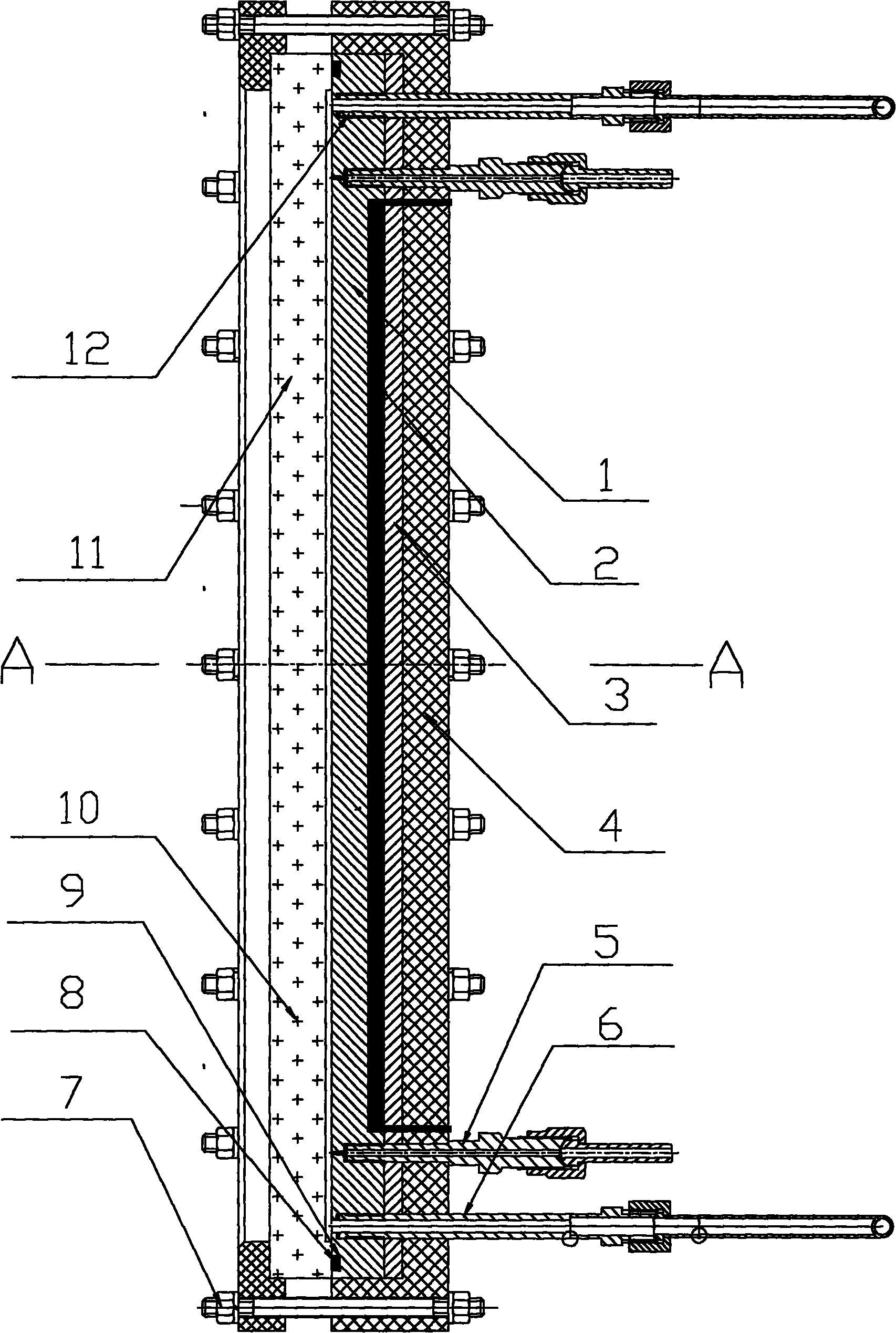
Experimental device of rectangular narrow seam for single-phase and two-phase three-dimensional visualization
InactiveCN102313641AGuaranteed sealing performanceEvenly distributedFlow propertiesHydrodynamic testingStereoscopic visualizationBottom pressure
The invention belongs to a simulation device for research of a single-phase and two-phase bubble behavior and a flow pattern, which comprises a thermal conduction copper plate, a visual window, an electric heating component, a bottom pressure-bearing body, a pressure measuring component and other components. The thermal conduction copper plate and a concave flow channel of a rectangular narrow seam of the visual window for a closed channel of the rectangular narrow seam, and thus an experimental device of the rectangular narrow seam for research on single-phase and two-phase three-dimensional visualization is formed. The single-phase flow state, the three-dimensional bubble state, the flow pattern conversion and other evolution laws in the rectangular narrow seam channel can be observed based on wide-surface and narrow-surface three-dimensional visualization, and conditions can be provided for in-depth revealing of flow and heat transfer mechanism in the narrow channel.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
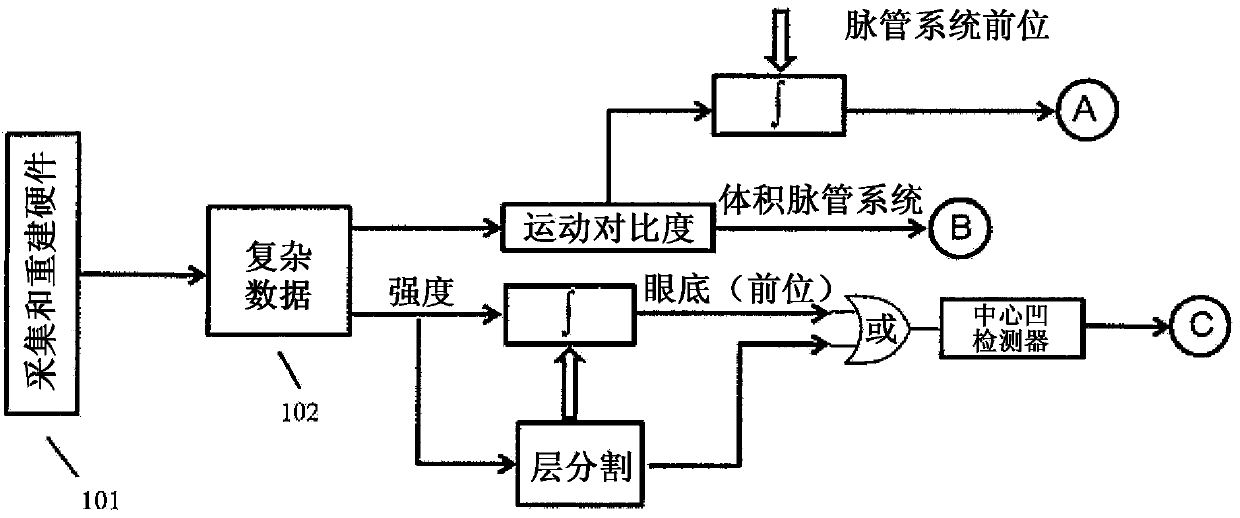
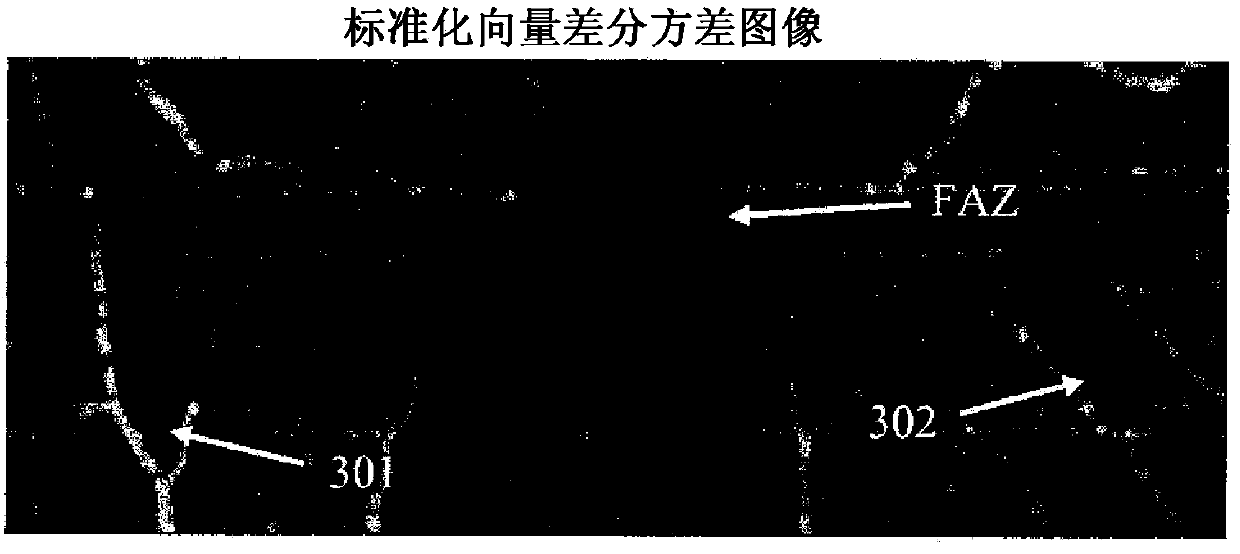
Analysis and visualization of OCT angiography data
ActiveCN104271031AImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionStereoscopic visualizationOct angiography
Methods for analyzing and visualizing OCT angiography data are presented. In one embodiment, an automated method for identifying the foveal avascular zone in a two dimensional en face image generated from motion contrast data is presented. Several 3D visualization techniques are presented including one in which a particular vessel is selected in a motion contrast image and all connected vessels are highlighted. A further embodiment includes a stereoscopic visualization method. In addition, a variety of metrics for characterizing OCT angiography image data are described.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Method for simulating optical components for the stereoscopic production of spatial impressions
InactiveUS20050233788A1Easy to implementAvoid distortionVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsStereoscopic visualizationPerformed Observation
The invention relates to a simulation method, especially to a method for simulating spatial impressions which are produced by means of an image generator and one or several filter arrays. The method according to the invention essentially comprises the following steps: a) Specification of the geometry of the image generator, b) specification of the geometry of the filter array, c) specification of a spatial arrangement geometry in relation to the image generator and the filter array in a three-dimensional coordinate system (X,Y,Z), d) specification of two monocular positions of observation in front of the said arrangement geometry, e) specification of a combined image containing bits of partial information from several views Ak (k=1 . . . n) of a scene, f) determination of a first and a second secondary image containing image elements of the specified combined image which are visible to the eye of an observer in the specified first and second monocular position of observation on the basis of the specified filter array geometry in conjunction with the specified image generator geometry and the spatial arrangement geometry, and g) stereoscopic visualization of the first and second secondary images as a left and right stereoscopic image, respectively.
Owner:PHOENIX 3D +1
Stereoscopic visualization system
Apparatus for presenting a stereoscopic image to a viewer, the apparatus including an endoscope; and a stereoscopic video camera optically connected to the endoscope, wherein the stereoscopic video camera includes first and second optical channels for acquiring, respectively, first and second images of a scene from the endoscope; first and second image sensors for acquiring, respectively, the first and second images from the first and second optical channels, the first and second image sensors being positioned along an axis; and parallax adjusting means for adjusting the parallax of a stereoscopic image acquired by the first and second image sensors and presented on a display.
Owner:VIKING SYST
Stereoscopic visualization system
Apparatus for presenting a stereoscopic image to a viewer, the apparatus comprising:a stereoscopic video system comprising:first and second image sensors for acquiring, respectively, first and second images of a scene;a display system for displaying the first image to the first eye of the viewer and the second image to the second eye of the viewer; andparallax adjusting means for adjusting the parallax between the first and second images.A method for presenting a stereoscopic image to a viewer, the method comprising:providing a stereoscopic video system comprising:first and second image sensors for acquiring, respectively, first and second images of a scene;a display system for displaying the first image to the first eye of the viewer and the second image to the second eye of the viewer; andparallax adjusting means for adjusting the parallax between the first and second images; andoperating the stereoscopic video system so as to provide a stereoscopic image to the user wherein parallax has been adjusted.
Owner:VIKING SYST
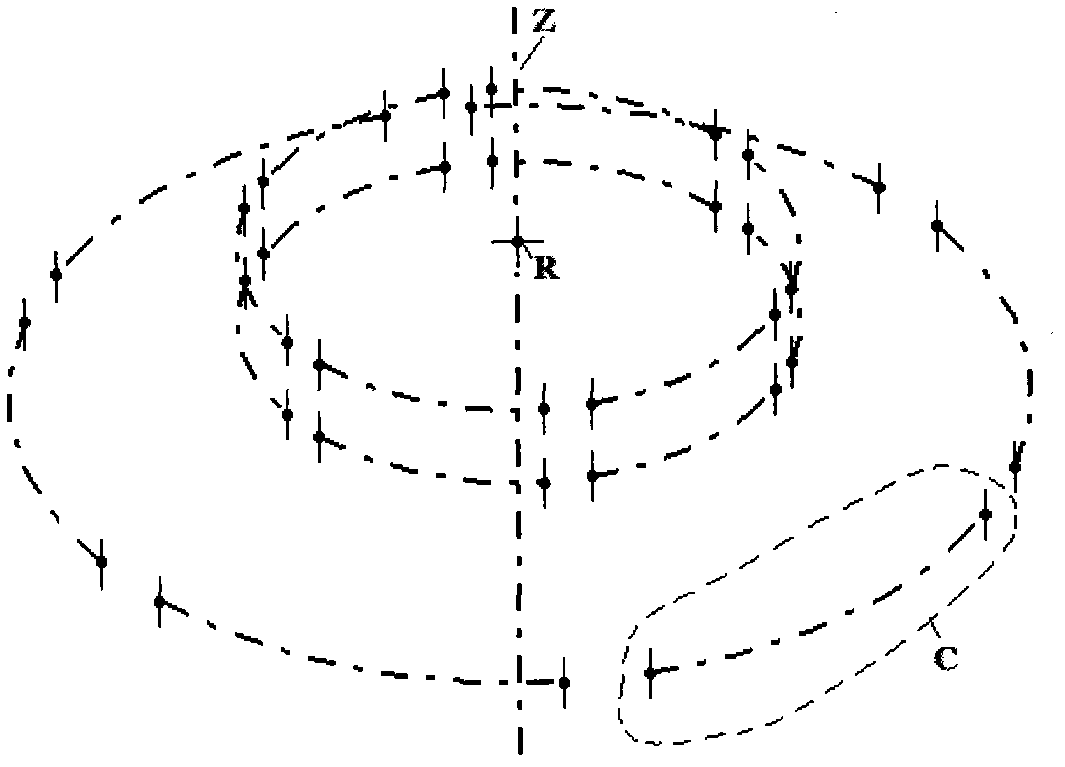
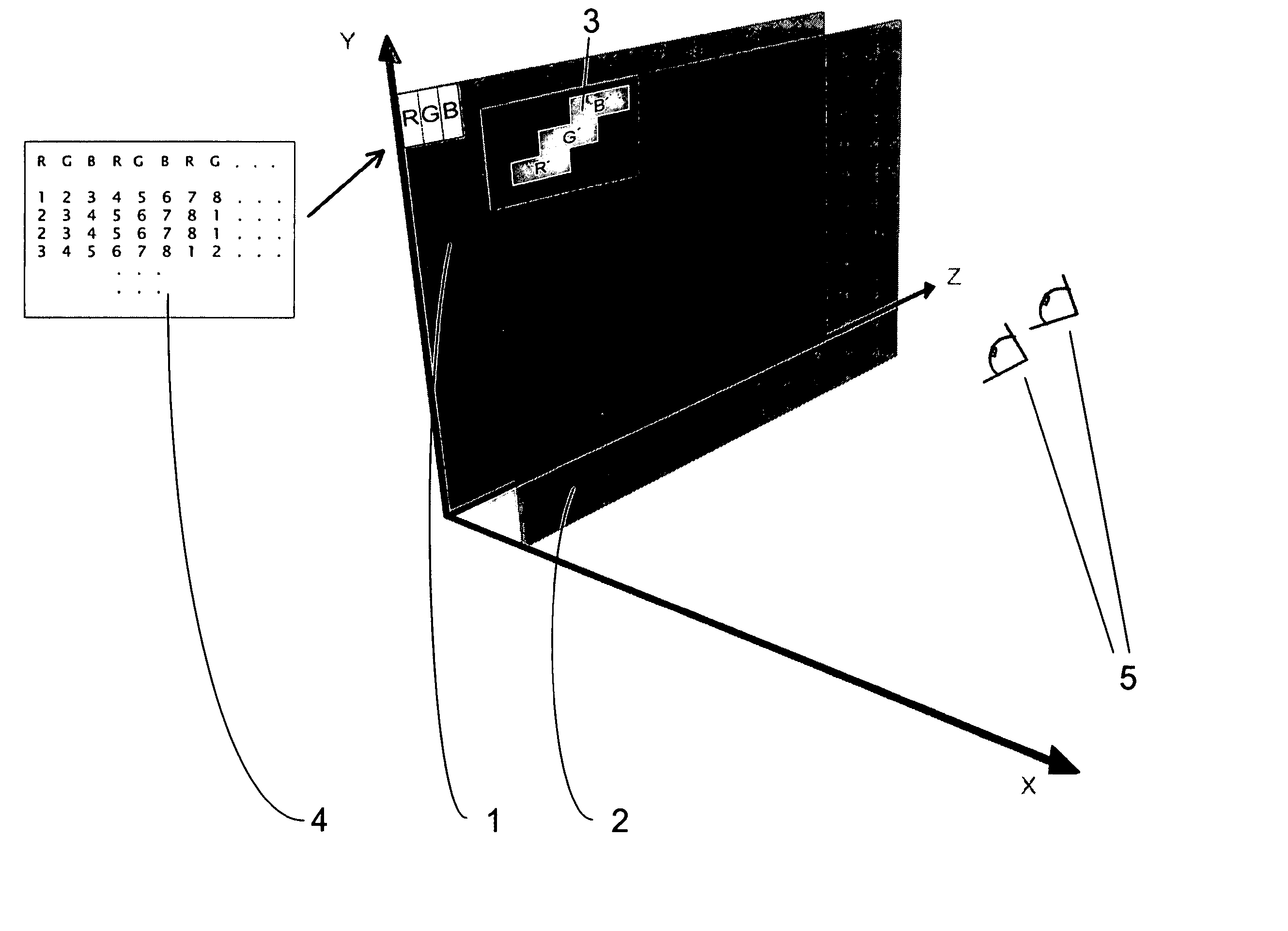
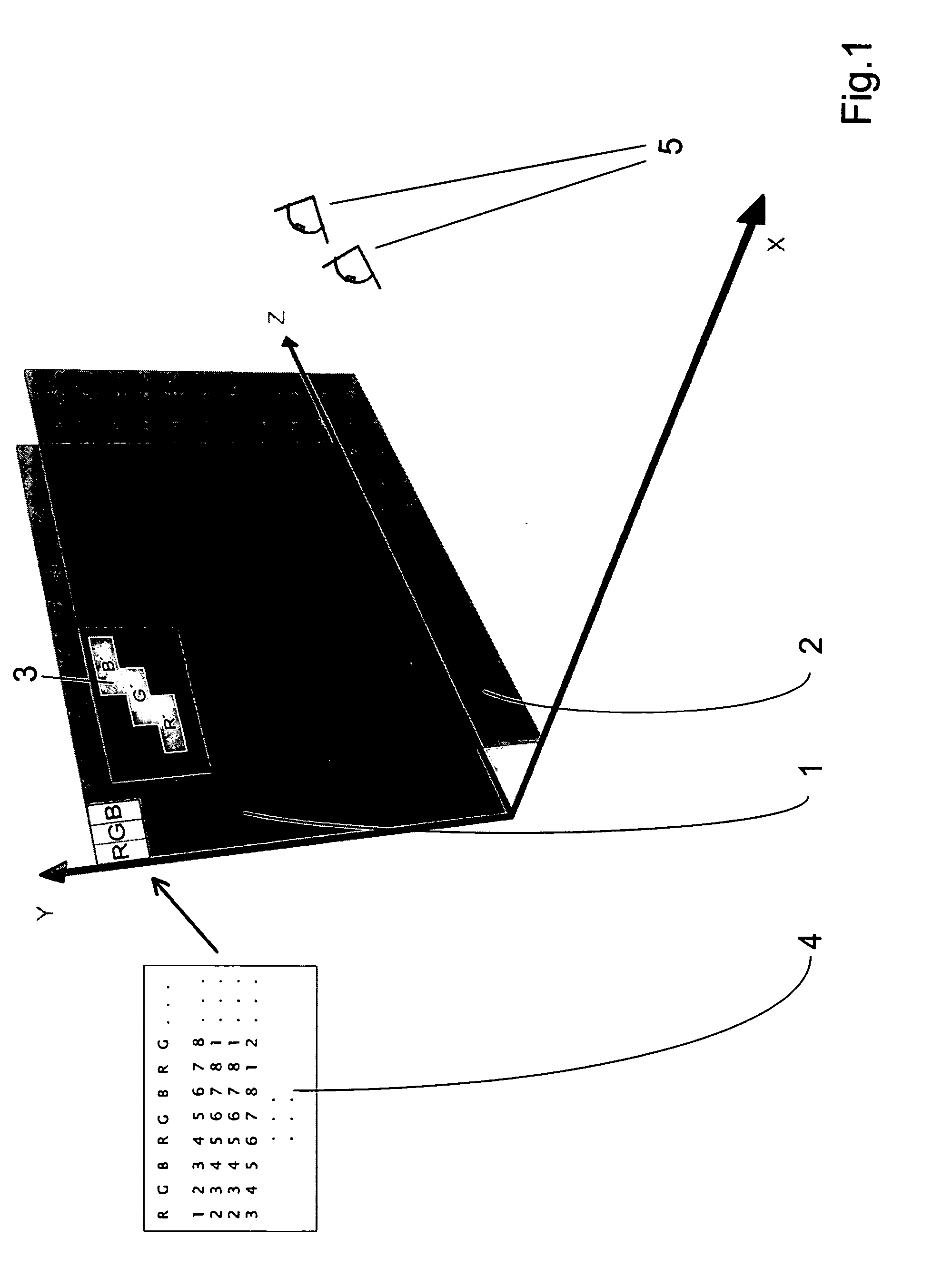
Method and Arrangement for Spatial Display
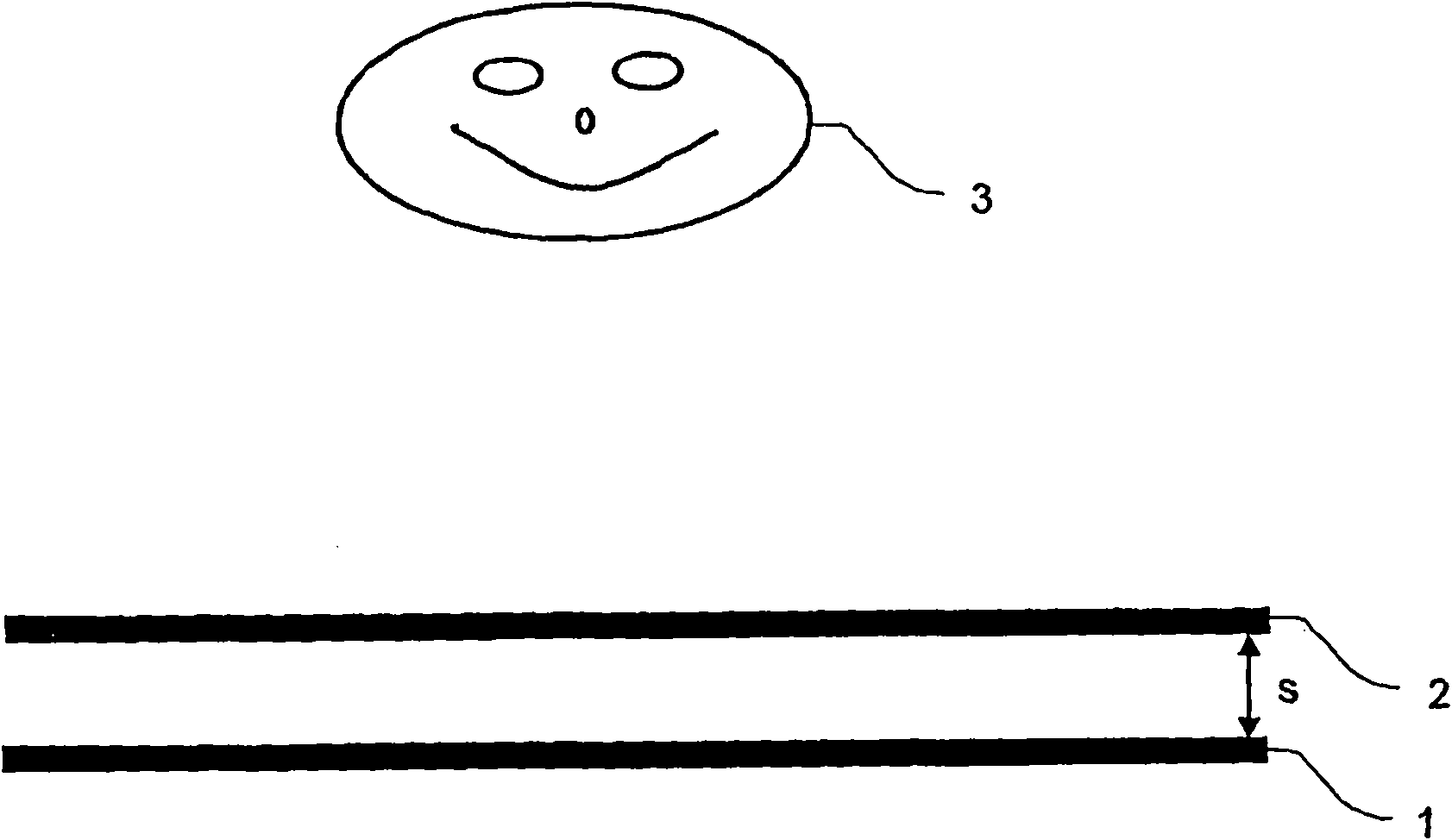
InactiveUS20110249331A1Improve perceptionIncrease brightnessSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsStereoscopic visualizationVisual perception
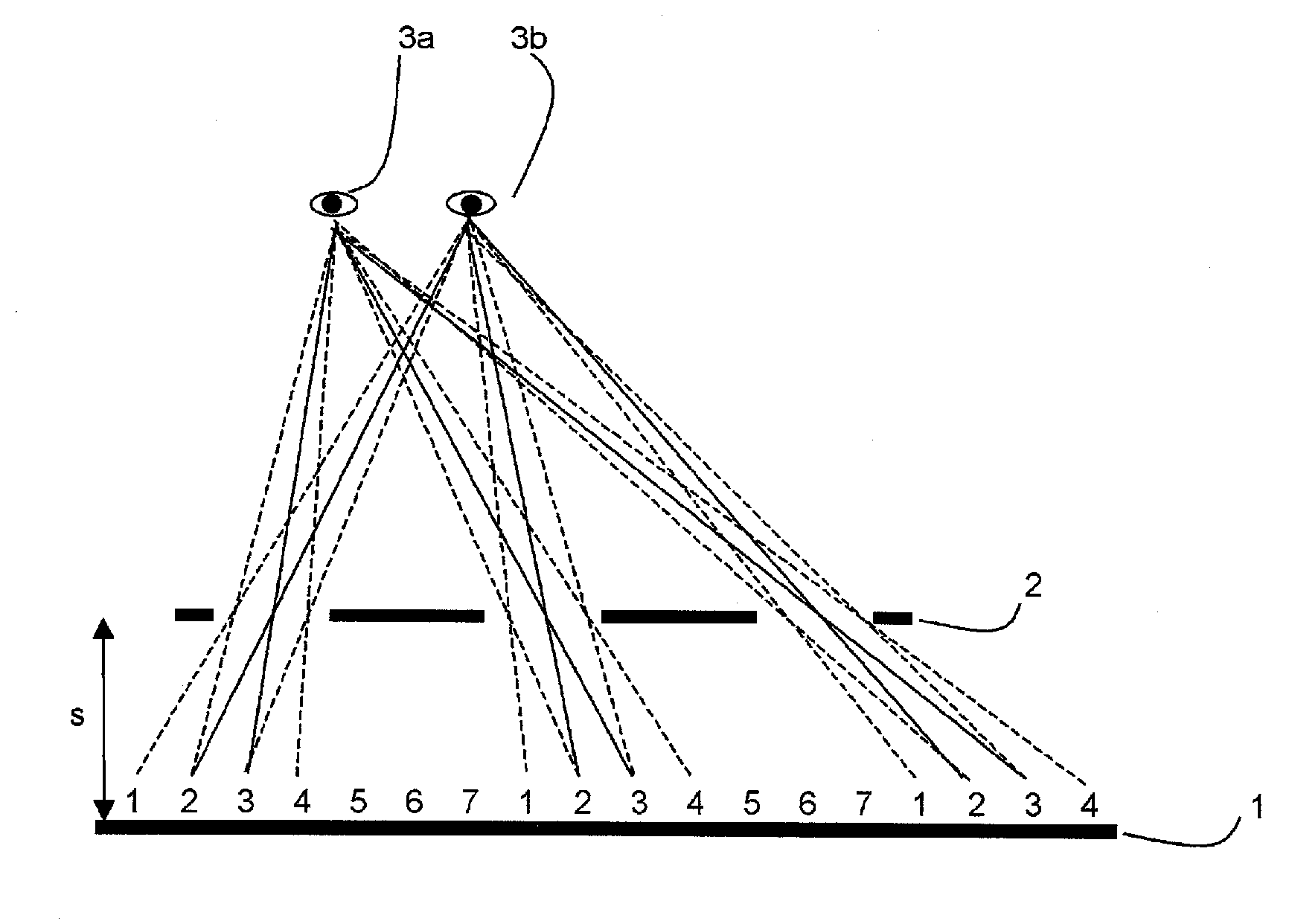
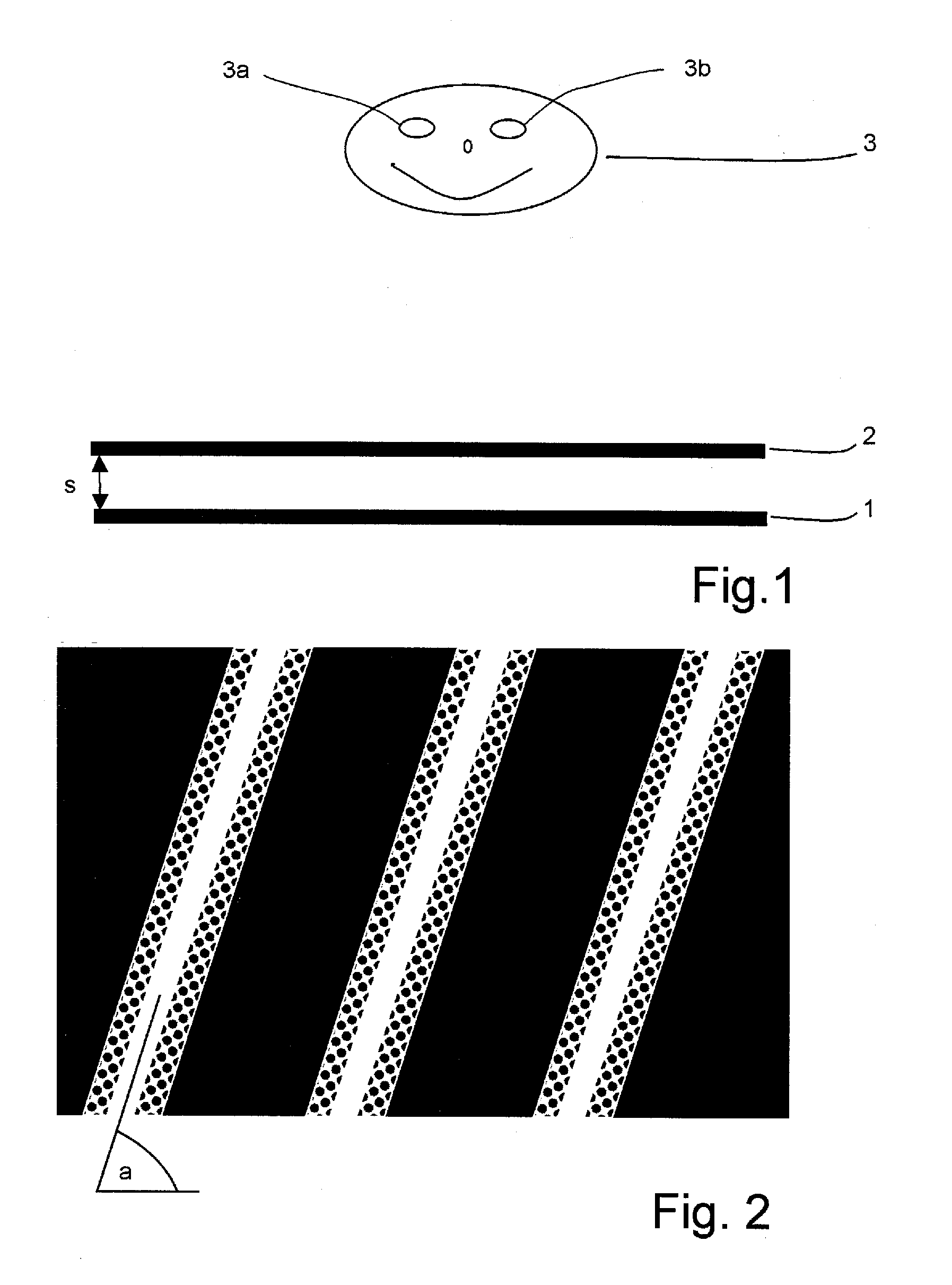
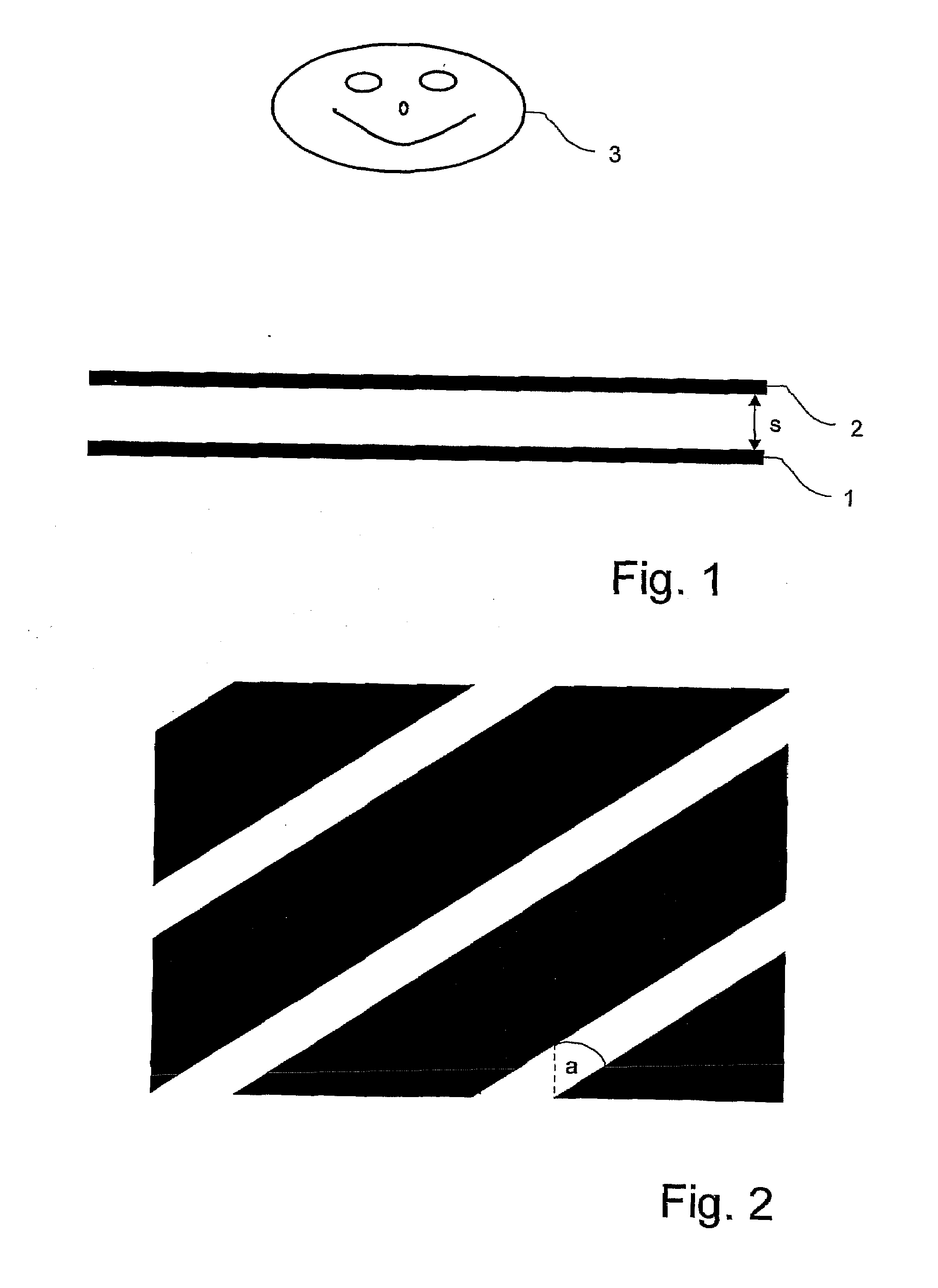
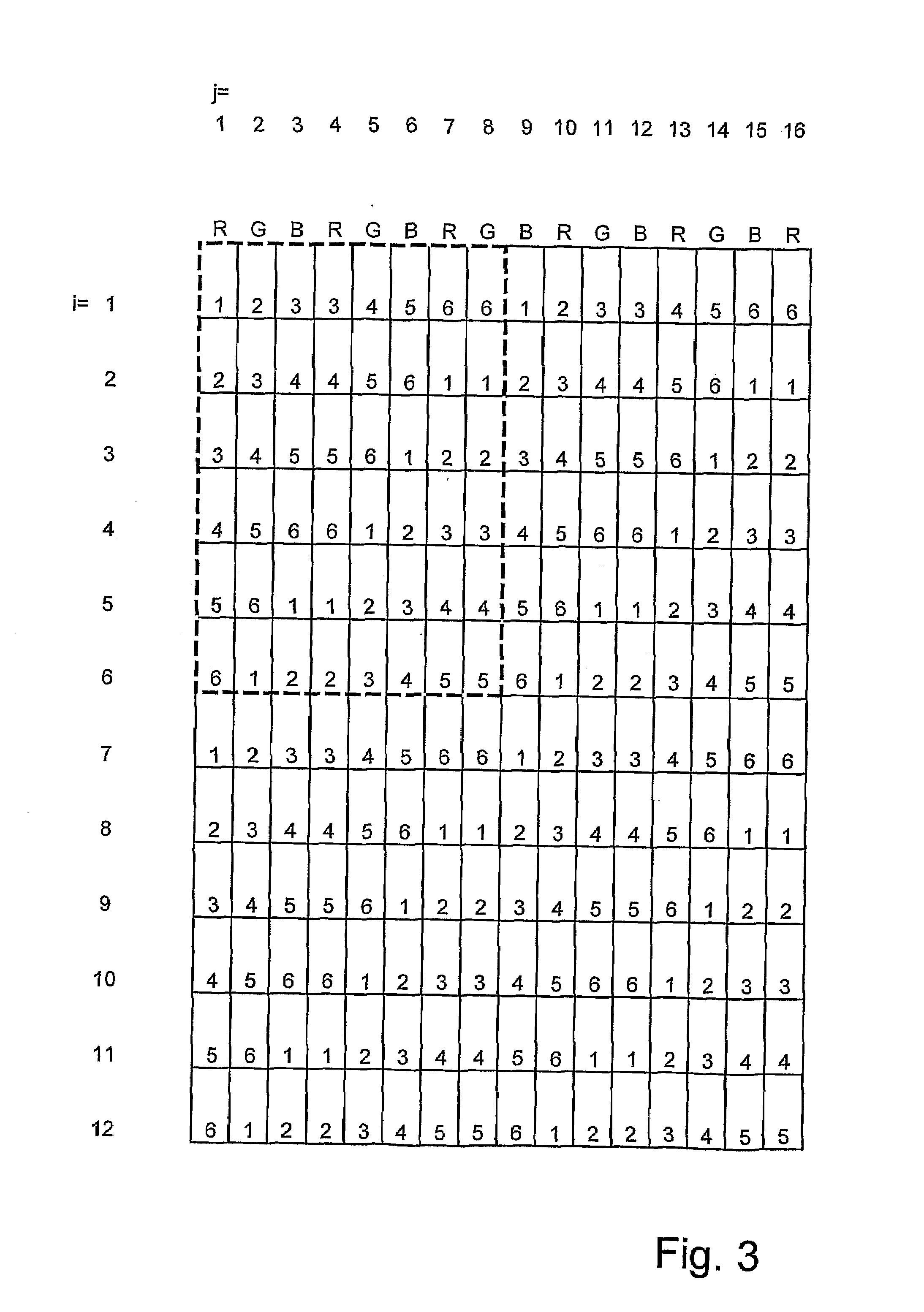
The invention relates to a method and an arrangement for spatial display, in particular to a display that can be perceived in three dimensions simultaneously by several viewers without viewing aids, also known as autostereoscopic visualization. With the invented method, bits of partial information from different views A(k) with k=1, . . . , n and n>1 are made visible on a grid (1) of pixels x(i,j) with rows (i) and columns (j), and at least one parallax barrier screen (2) is arranged in front of or behind the grid (1) of pixels x(i,j) at a distance s, which contains at least semitransparent segments, the segments corresponding essentially to stripes delimited by straight-line edges, which run uninterruptedly from one margin of the parallax barrier screen (2) to an opposite or adjoining margin, so that one or several viewers (3), because of the viewing restriction effected by the at least one parallax barrier screen (2), will see at least partially different pixels x(i,j) and / or parts thereof with each of their two eyes (3a, 3b), so that each of the two eyes (3a, 3b) perceives at least partially different views A(k) and, thus, a spatial visual impression results.
Owner:VISUMOTION
Method and arrangement for three-dimensional representation
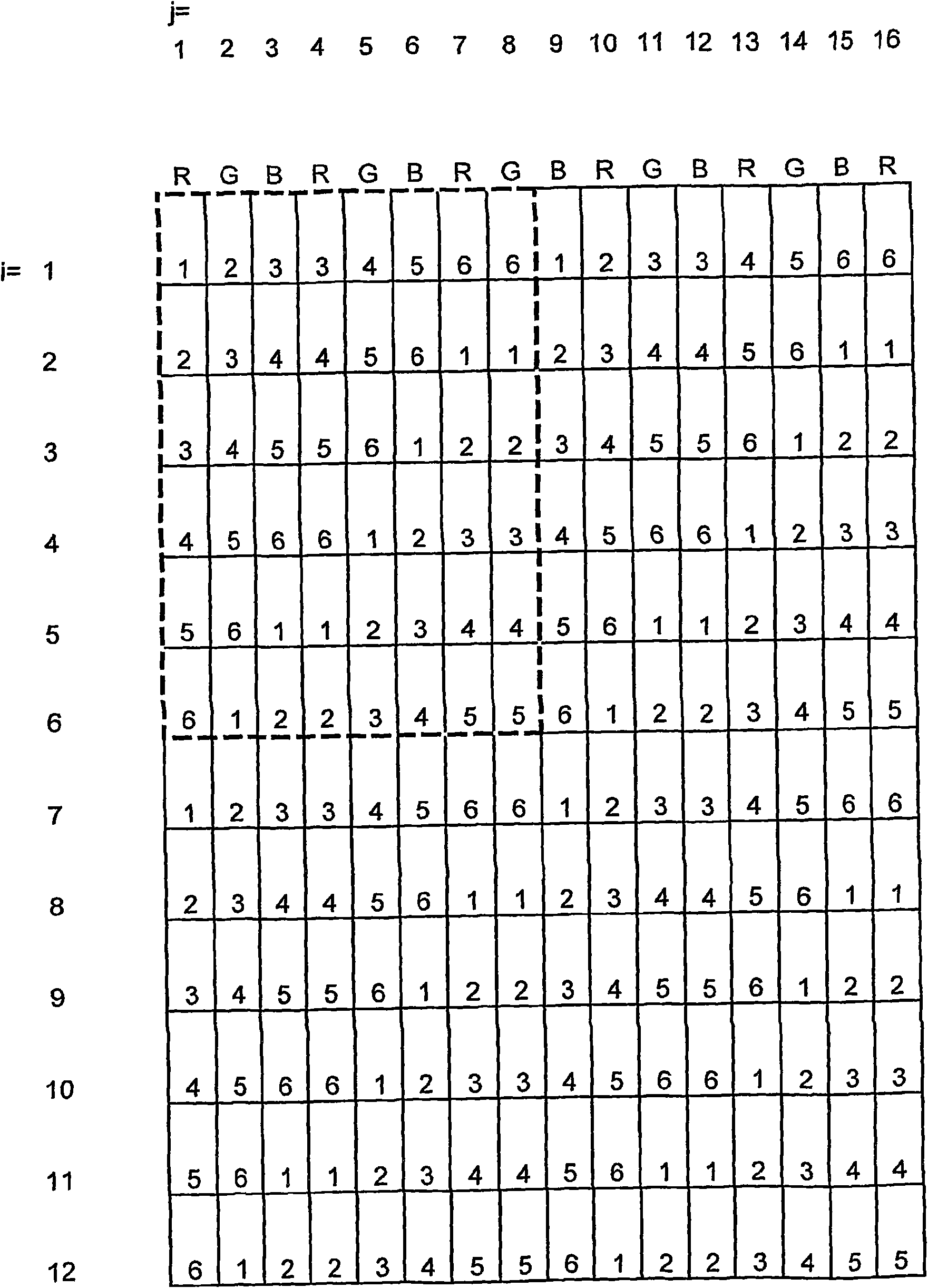
InactiveUS20100046069A1Improve perceptionIncrease impressionSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsStereoscopic visualizationViewpoints
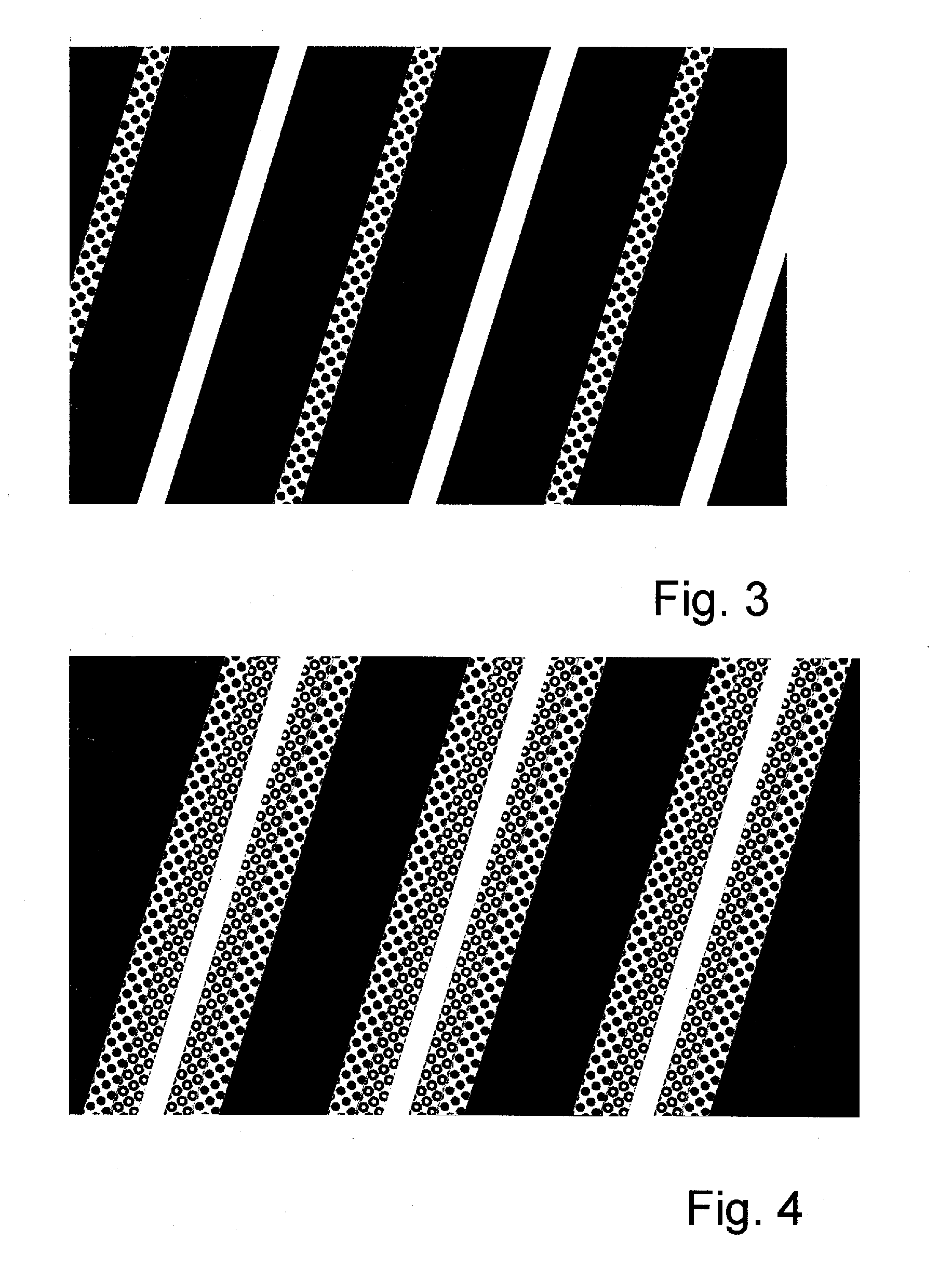
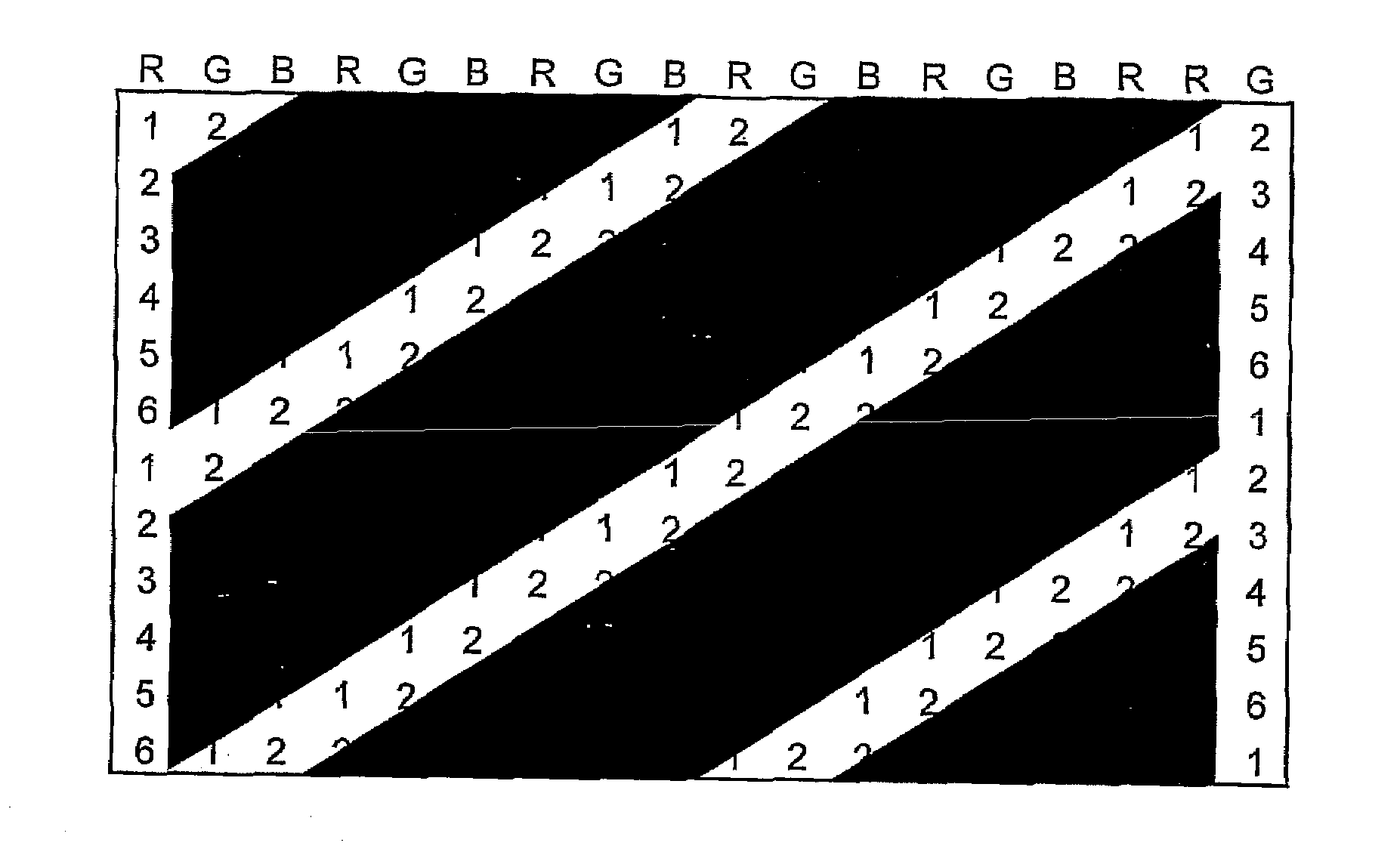
The invention relates to the field of spatial representation, particularly to images which are spatially perceivable for simultaneous multiple viewers without auxiliary devices so-called autostereoscopic visualization. The invention addresses the problem of creating a form of autostereoscopic representation based on barrier technology in order to achieve an improved perceptibility for multiple simultaneous viewers. This problem is solved by a method for spatial representation wherein image section data of different viewpoints A(k), where k=1, . . . , n and n=6 or n=7, are made visible on a grid of image elements x(i,j), and at least one parallax barrier screen containing alternating opaque and transparent sections is placed at a distance before or behind the grid of image elements x(i,j). The transparent sections substantially correspond to straight bordered lines which, during the parallel projection of parallax barrier screens onto the grid of image elements x(i,j), are inclined to at least 21 degrees with respect to the vertical direction of the grid of image elements x(i,j) and, furthermore, each have the width of at least 1.9 image elements x(i,j) in the horizontal direction of the grid of image elements x(i,j).
Owner:WISE VISION HLDG
Power grid current hierarchical partitioned three-dimensional visualized display method
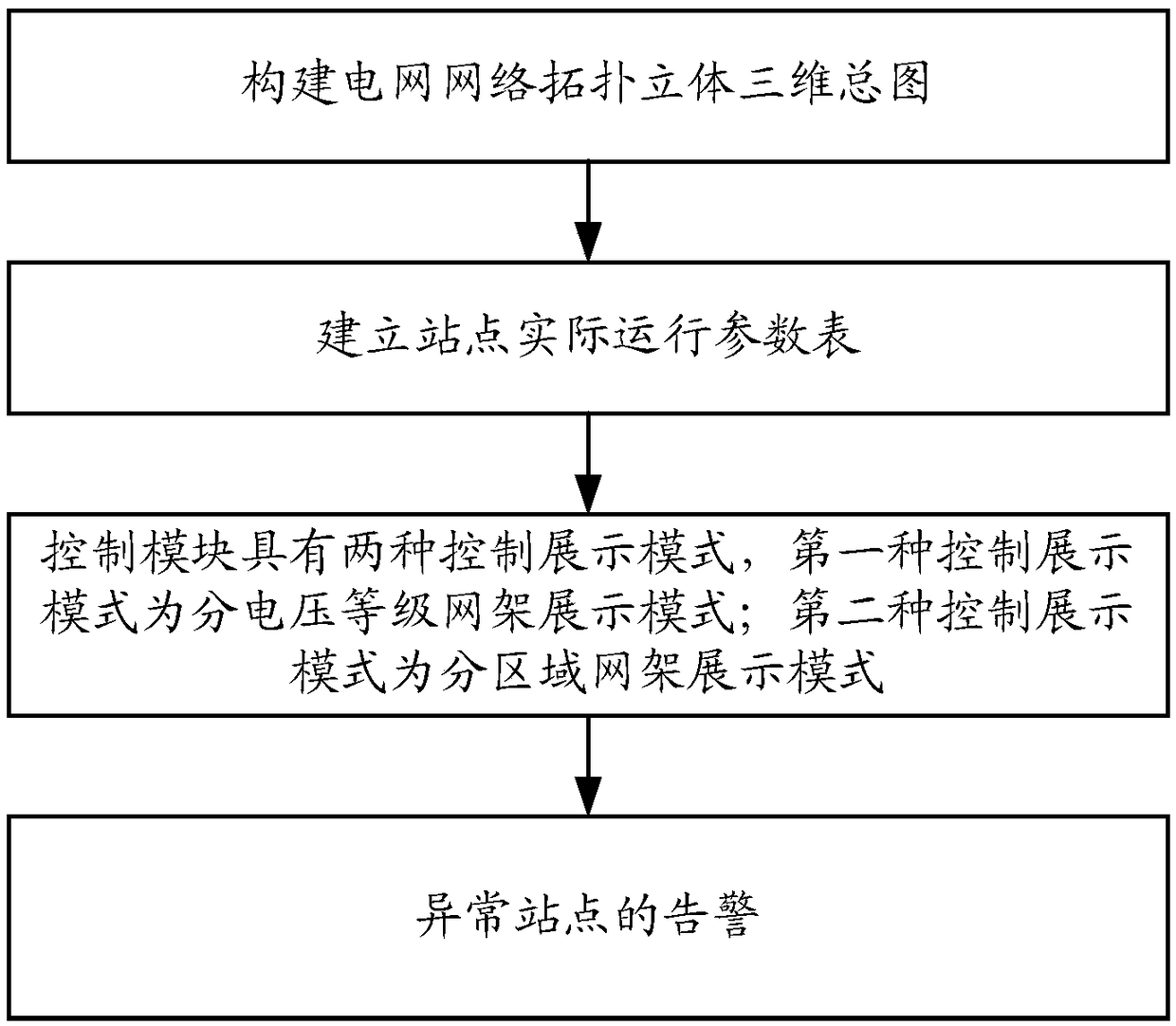
ActiveCN108763669AImprove user experienceFlexible switchingSpecial data processing applicationsStereoscopic visualizationElectricity
The invention provides a power grid current hierarchical partitioned three-dimensional visualized display method. The method comprises the steps that a power grid network topological three-dimensionalgeneral drawing is constructed; a site actual operation parameter list is established; and a control module has two control display modes, wherein the first control display mode is a voltage-level rack display mode, and the second control display mode is a partitioned rack display mode. The method has the advantages that (1) switching between a hierarchical display mode and a partitioned displaymode can be performed flexibly, and since association linkage operation is performed through n-level tree storage structures, system configuration complexity can be lowered, hierarchical display and partitioned display speed can be increased, and user usage experience can be improved; and (2) the method has the two display effects of hierarchical display and partitioned display, pertinent displayof connecting lines is realized effectively according to a user demand, the complexity of the connecting lines is lowered, a dispatcher can observe the power distribution relation among all station sites quickly, clearly and visually, and it is convenient for the dispatcher to make a dispatching decision efficiently.
Owner:CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID COMPANY +1
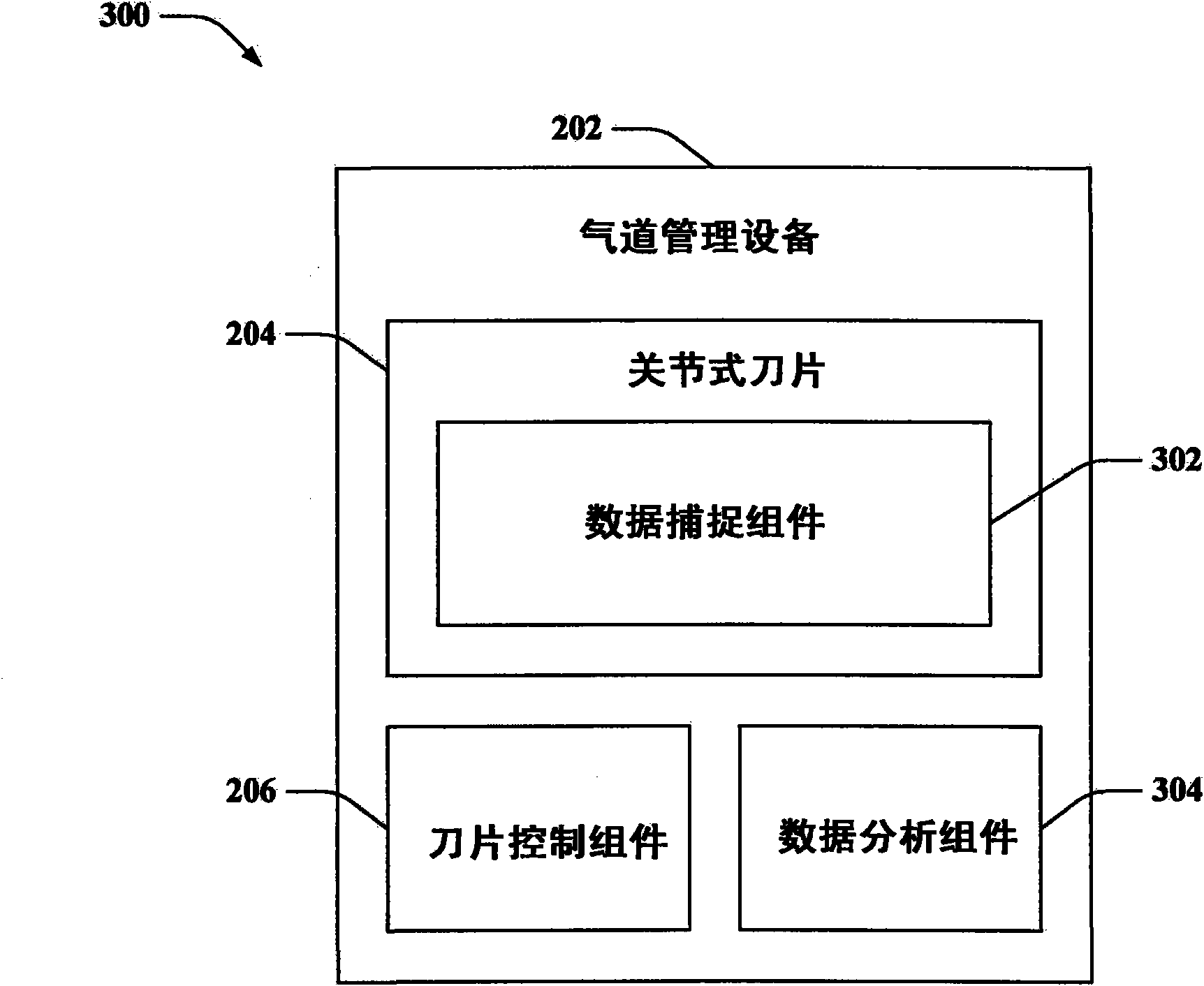
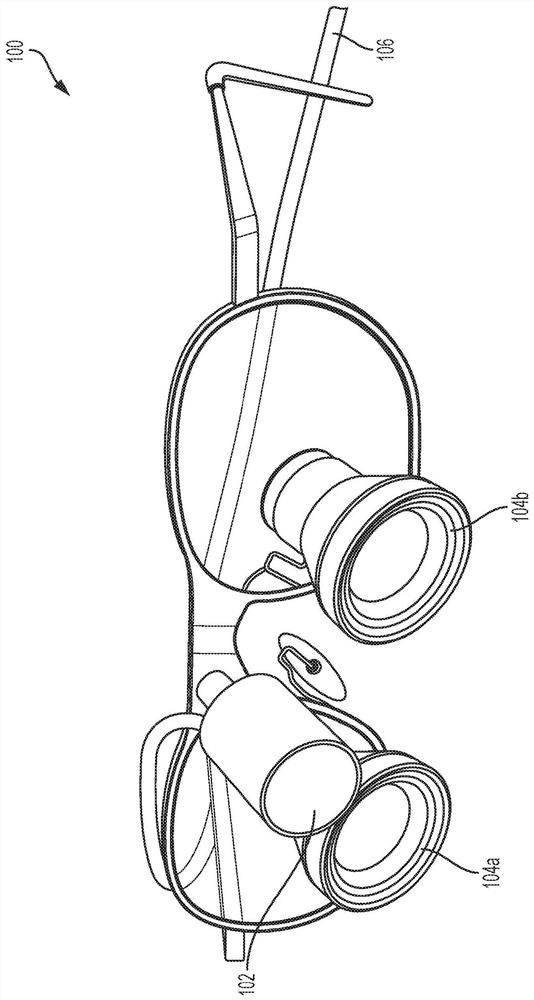
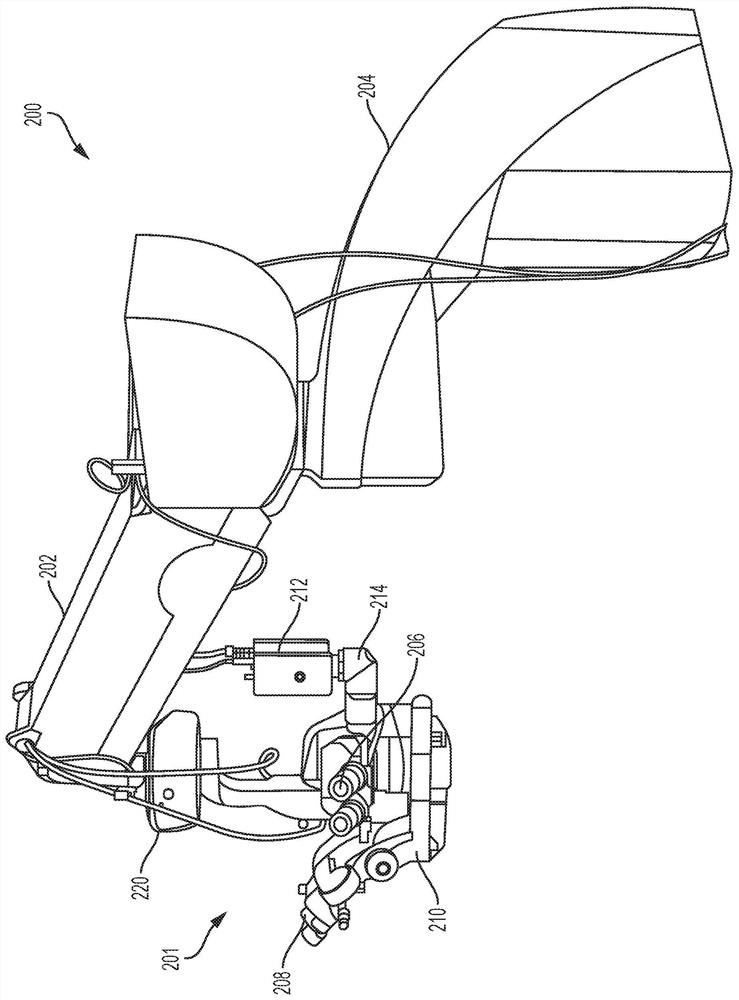
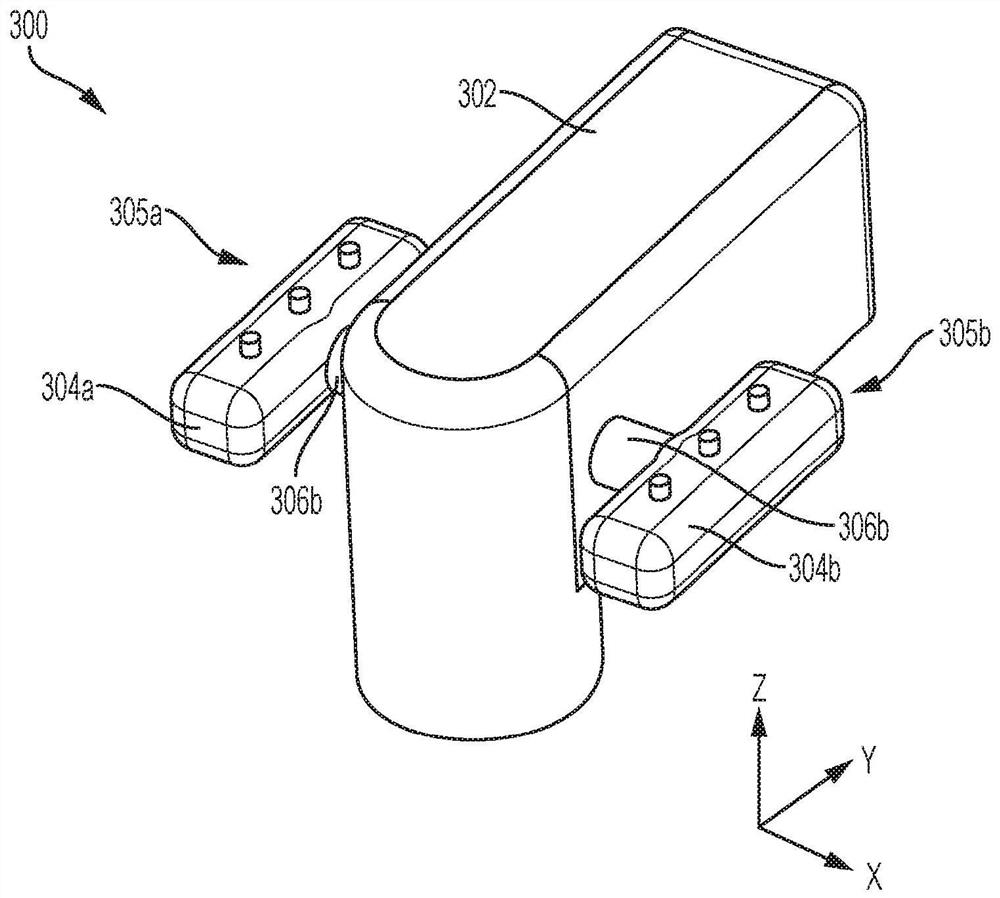
Airway management
The claimed subject matter provides systems and / or methods that facilitate improving visualization associated with intubation. A dynamically articulating laryngoscope blade can be controlled to configure to normal anatomic variants and pathologic abnormalities to facilitate placing of an endotracheal tube into a patient's trachea. Further, cameras can be integrated into and / or mounted upon the dynamically articulating laryngoscope blade. The cameras can enable stereoscopic visualization of the laryngeal aperture allowing for depth perception. Moreover, the cameras can be moved independently of the blade allowing for optimal viewing of the laryngeal opening.
Owner:AVN MEDICAL TECH
Stereoscopic visualization camera and integrated robotics platform
PendingCN112074248AProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsPattern recognitionStereoscopic visualization
A robotic imaging apparatus is disclosed. A robotic imaging apparatus includes a robotic arm, a stereoscopic camera, and a sensor positioned between the robotic arm and the stereoscopic camera. The sensor transmits output data that is indicative of translational and rotational force imparted on the stereoscopic camera by an operator. The robotic imaging apparatus also includes a processor that isconfigured to determine a movement sequence for the robotic arm based on a current position of the robotic arm and the output data from the sensor and to cause at least one of the joints of the robotic arm to rotate based on the determined movement sequence via one or more motor control signals provided to the at least one joint. The rotation of the at least one joint provides power-assisted movement of the robotic arm based on the detected translational and rotational forces imparted by the operator.
Owner:ALCON INC
Optimized Stereoscopic Visualization
InactiveUS20130093767A1Steroscopic systems3D-image renderingStereoscopic visualizationComputer science
The present invention discloses a method comprising: calculating an X separation distance between a left eye and a right eye, said X separation distance corresponding to an interpupilary distance in a horizontal direction; and transforming geometry and texture only once for said left eye and said right eye.
Owner:BOOTH JR LAWRENCE A +1
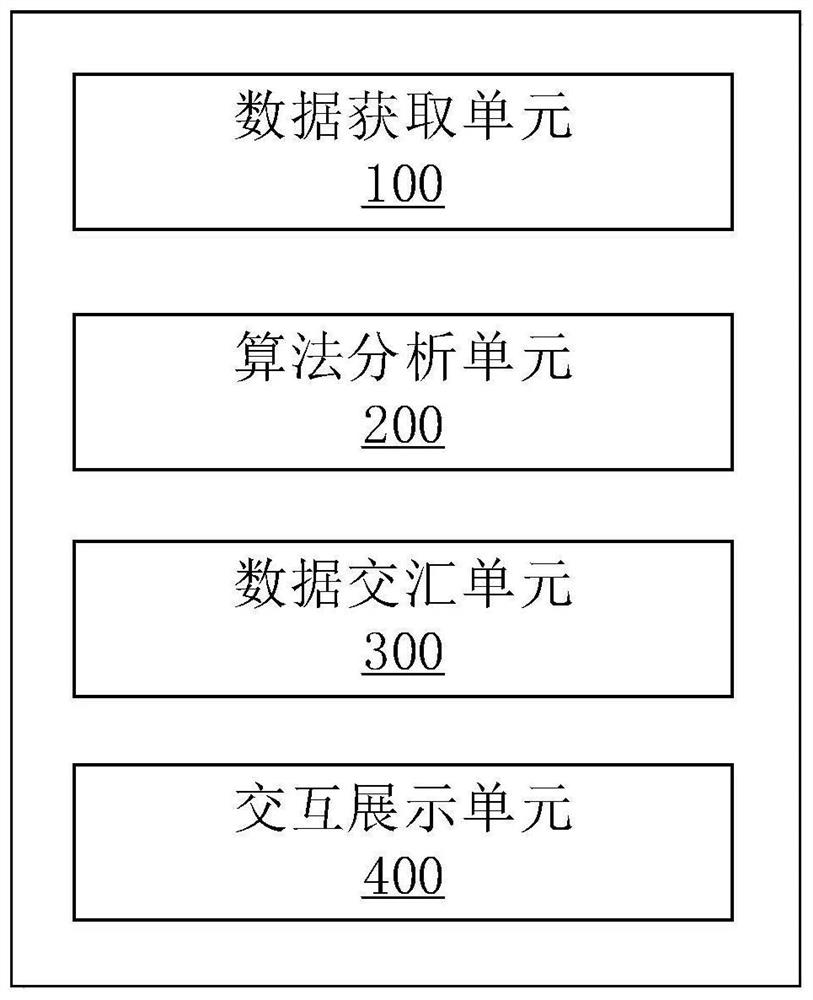
Interactive display system, method and equipment based on three-dimensional visualization
PendingCN114399606AImprove judgment effectSolve the problem of visual blind spotsGeometric CADImage enhancementVideo monitoringStereoscopic visualization
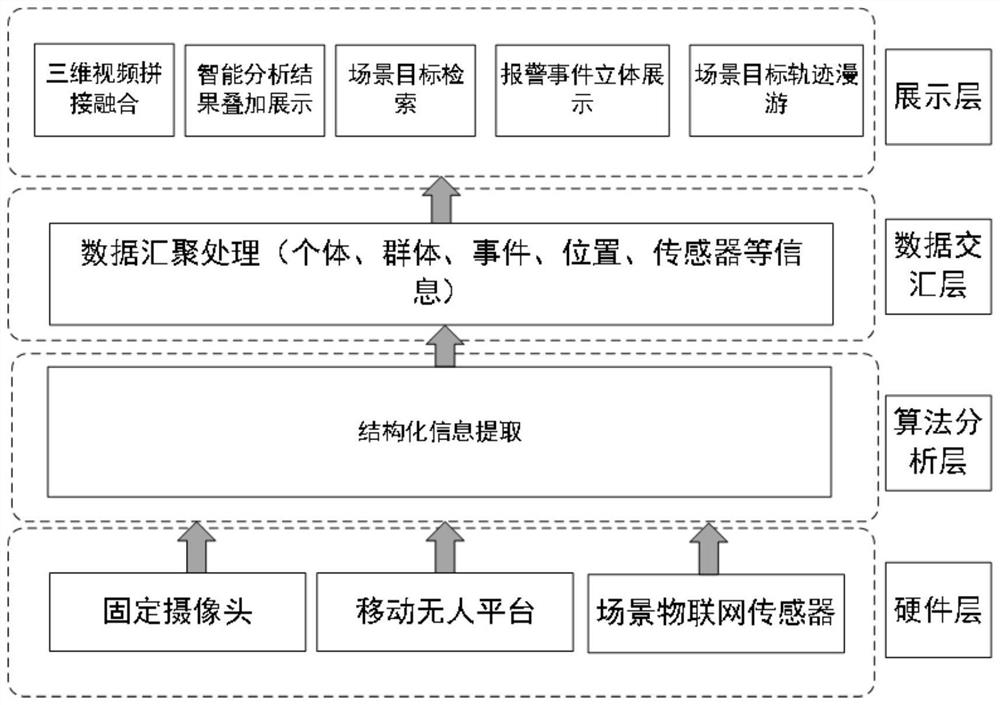
The invention belongs to the technical field of video monitoring, and particularly relates to an interactive display system, method and equipment based on stereoscopic visualization. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem that a three-dimensional panoramic monitoring system causes a visual blind area due to the limitation of the visual angle of a fixed monitoring device, and is poor in target recognition and retrieval effect due to the absence of information of an Internet of Things sensor capable of performing auxiliary judgment in a scene. The system comprises a data acquisition unit configured to acquire data acquired by a fixed monitoring device, a mobile monitoring device and each Internet of Things sensor in a target scene; an algorithm analysis unit configured to extract the structured information; the data convergence unit is configured to perform data convergence; and the interactive display unit is configured to carry out multi-dimensional three-dimensional visual interactive display. According to the method, the visual blind area caused by the limited visual angle of fixed monitoring equipment is solved, the target recognition and retrieval effect is improved, and meanwhile the problem that the analysis result lags behind and is displayed in an overlapped mode is solved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
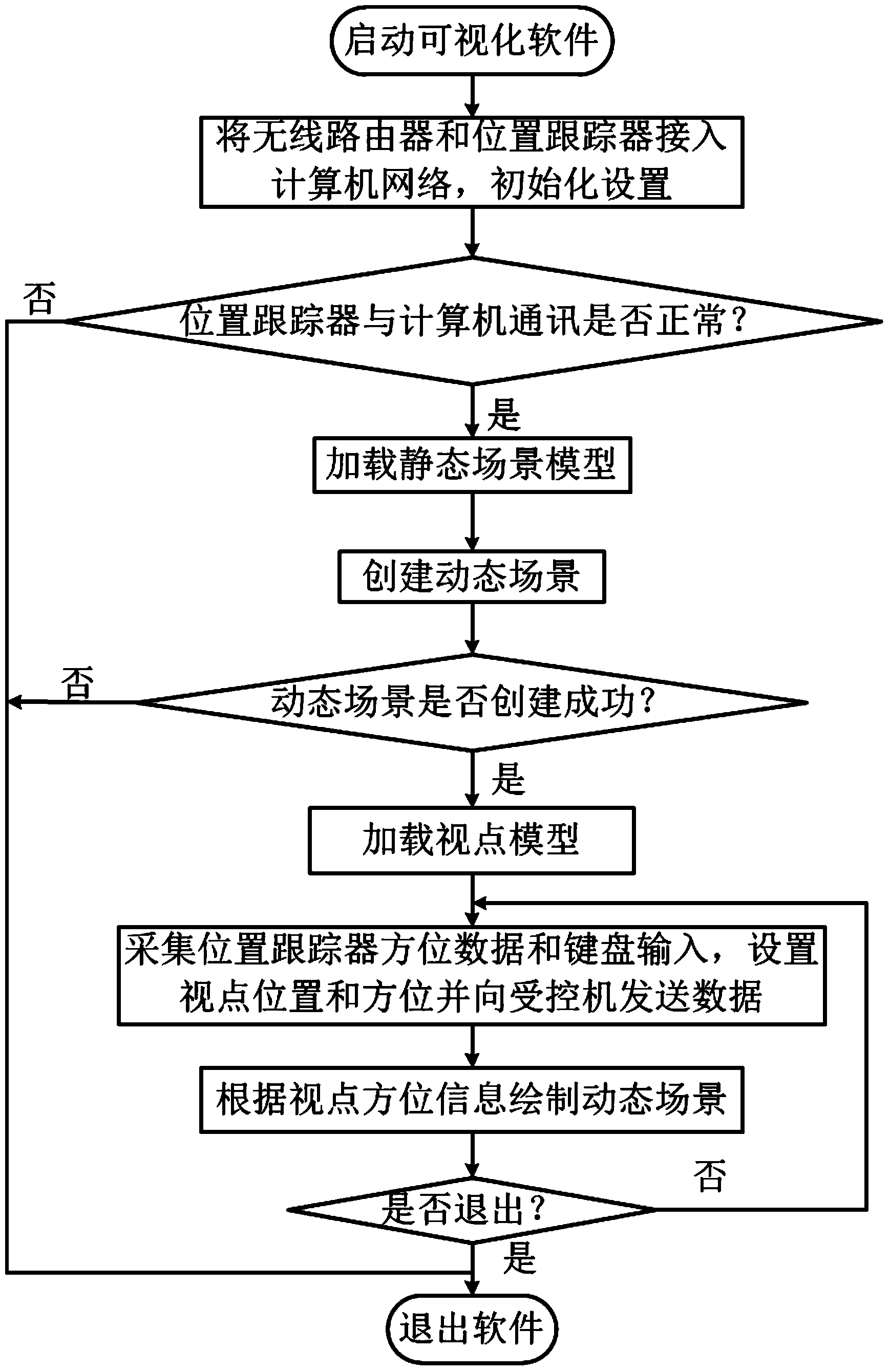
Dynamic aircraft assembly scene real-time and three-dimensional visualization method based on head-mounted displayer
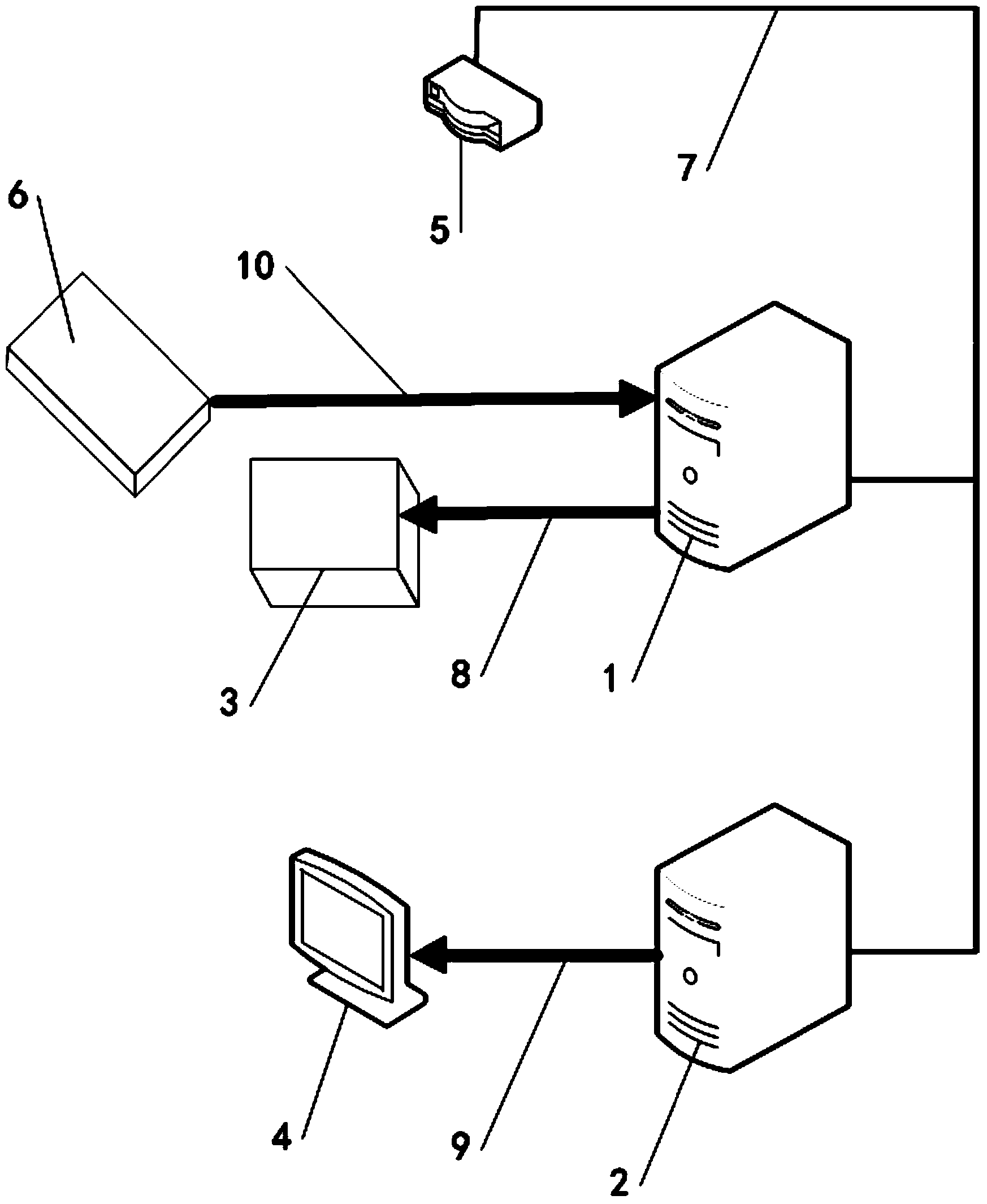
InactiveCN103942384AAction modification is simple and convenientImprove experienceSpecial data processing applicationsViewpointsDisplay device
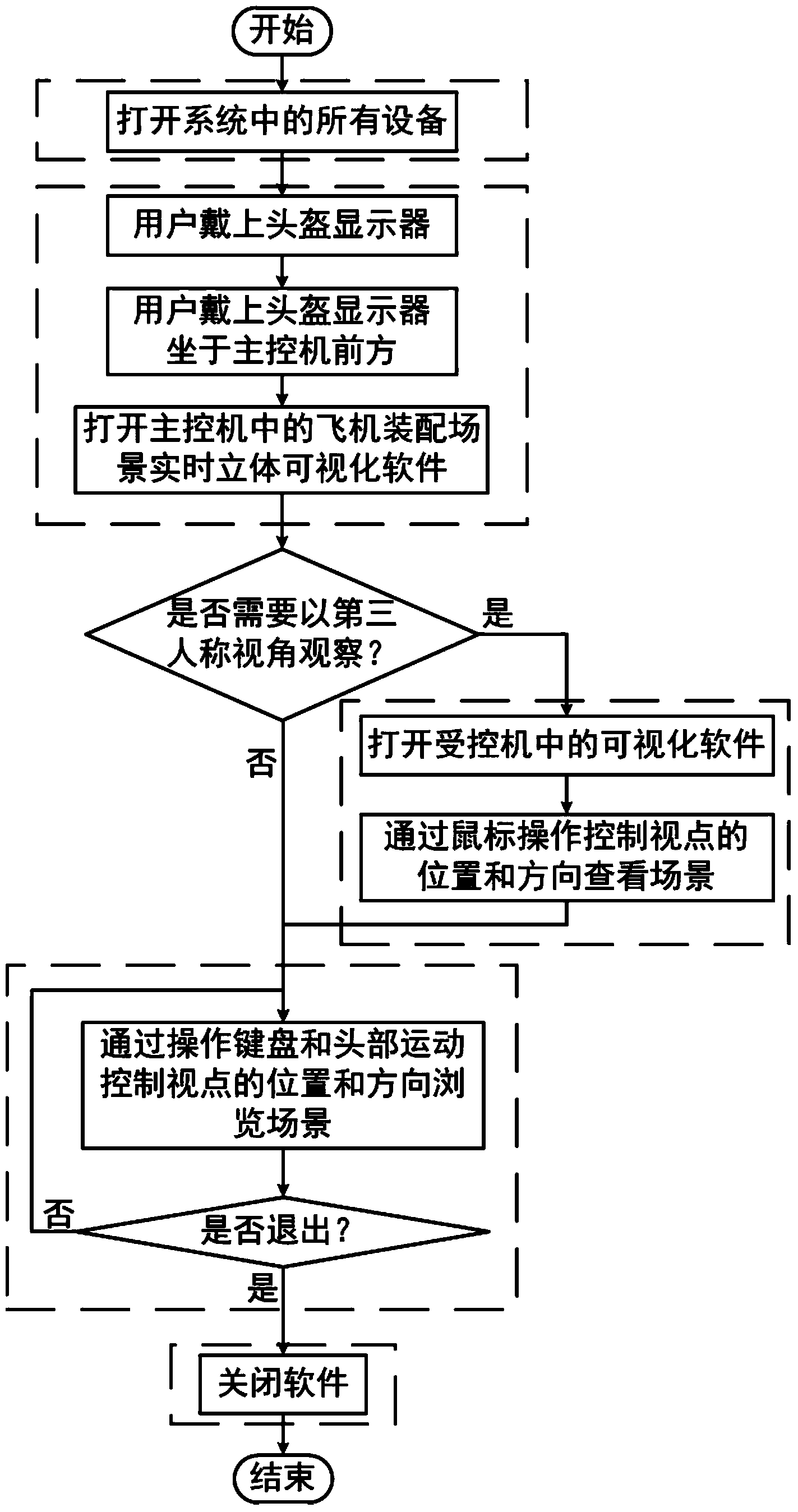
Provided is a dynamic aircraft assembly scene real-time and three-dimensional visualization method based on a head-mounted displayer. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a position tracker, a controlling computer and a controlled computer both in a computer network cluster, a wireless router and the head-mounted displayer are started; secondly, a user puts on the head-mounted displayer, sits in front of the controlling computer and runs aircraft assembly scene real-time and three-dimensional visual software in the controlling computer, wherein data of the position tracker can be acquired in real time and sent to the controlled computer in the software running process; thirdly, the user controls the position of a viewpoint through a keyboard and controls the visual angle direction by rotating the head to view a dynamic assembly simulation scene; fourthly, in the running process of a program of the controlling computer, the user runs a visual program in the controlled computer, the program receives viewpoint data sent by the controlling computer to drive a viewpoint model, and the user can view the aircraft assembly scene in real time at a third-person visual angle through mouse operation; fifthly, the simulation process is ended, and the visual program in the controlling computer and the visual program in the controlled computer are quit respectively.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and arrangement for three-dimensional representation
InactiveCN101803393AImprove image brightnessImprove perceptibilitySteroscopic systemsStereoscopic visualizationViewpoints
The invention relates to the field of spatial representation, particularly to images which are spatially perceivable for simultaneous multiple viewers without auxiliary devices so-called autostereoscopic visualization. The invention addresses the problem of creating a form of autostereoscopic representation based on barrier technology in order to achieve an improved perceptibility for multiple simultaneous viewers. This problem is solved by a method for spatial representation wherein image section data of different viewpoints A(k), where k=1,...,n and n=6 or n=7, are made visible on a grid of image elements x(i,,j), and at least one parallax barrier screen containing alternating opaque and transparent sections is placed at a distance before or behind the grid of image elements x(i,,j). The transparent sections substantially correspond to straight bordered lines which, during the parallel projection of parallax barrier screens onto the grid of image elements x(i,,j), are inclined to at least 21 degrees with respect to the vertical direction of the grid of image elements x(i,,j) and, furthermore, each have the width of at least 1.9 image elements x(i,,j) in the horizontal direction of the grid of image elements x(i,,j).
Owner:智信集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com