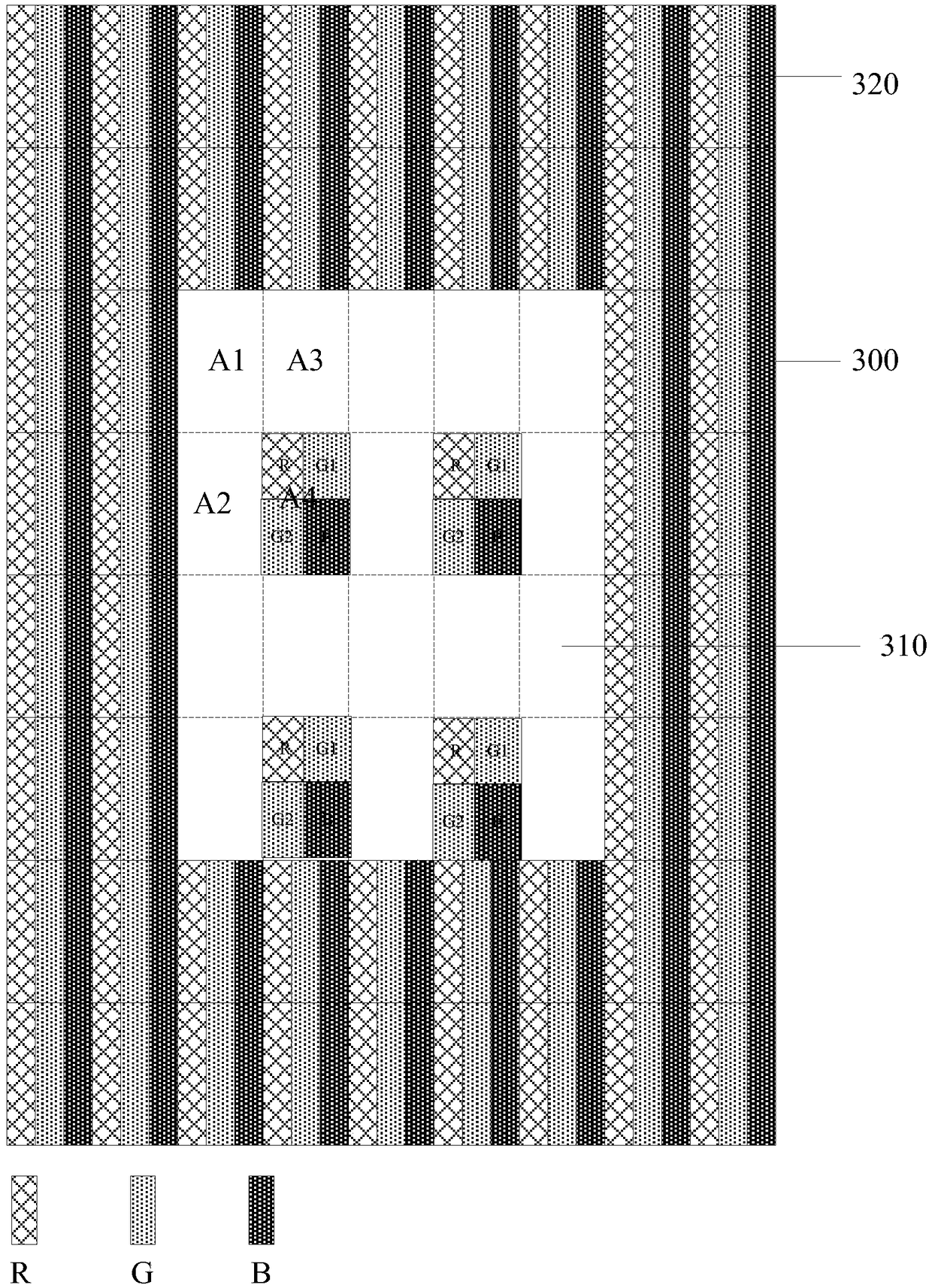
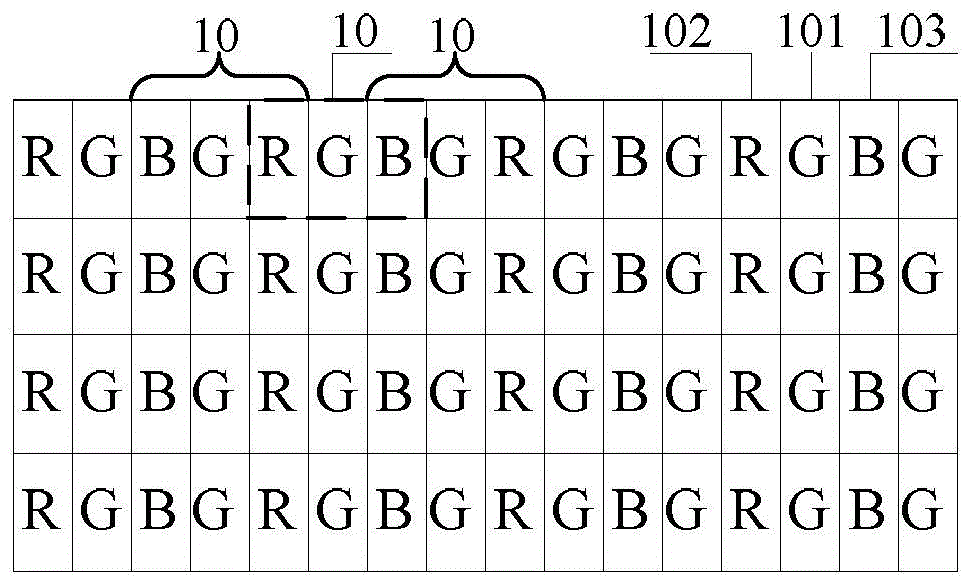Patents
Literature
947 results about "Pixel density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
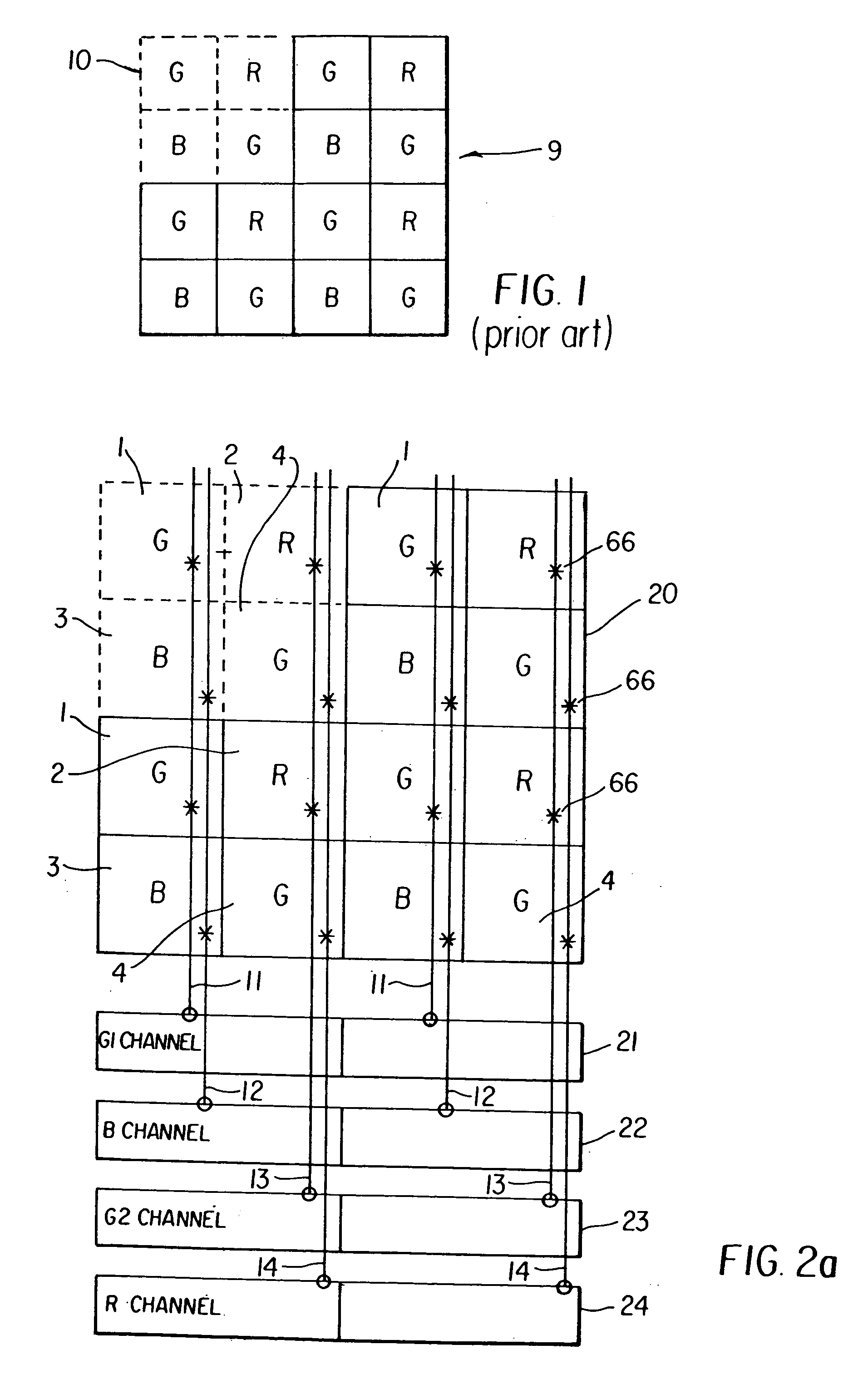
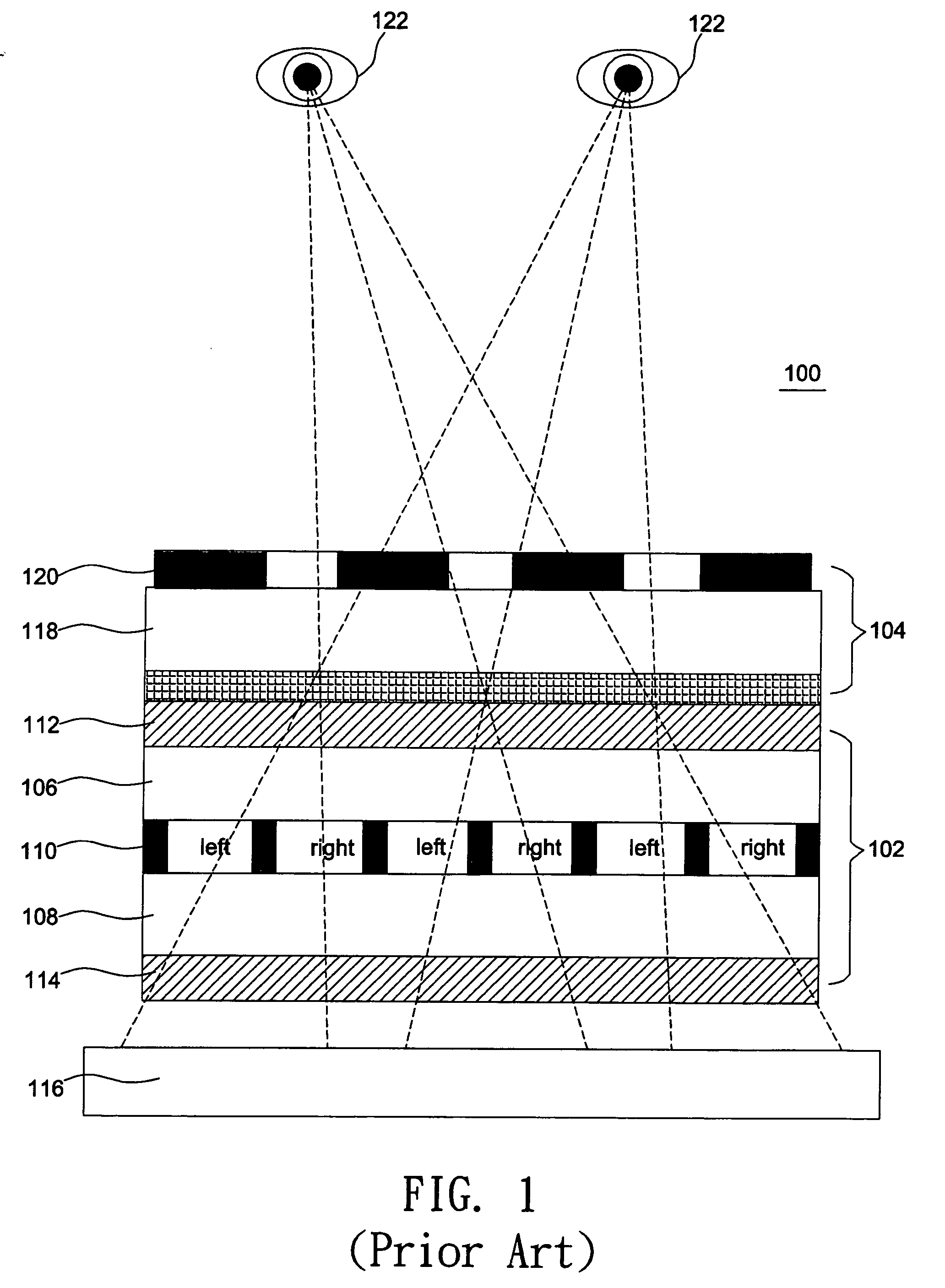
Pixels per inch (ppi) and pixels per centimetre (ppcm or pixels/cm) are measurements of the pixel density (resolution) of an electronic image device, such as a computer monitor or television display, or image digitizing device such as a camera or image scanner. Horizontal and vertical density are usually the same, as most devices have square pixels, but differ on devices that have non-square pixels.
System and method for a portable multimedia client
InactiveUS20050012723A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersPixel densityDisplay device
Owner:MOVE MOBILE SYST
Multimedia client interface devices and methods
InactiveUS20090259969A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersPixel densityDisplay device
Owner:PALLAKOFF MATT
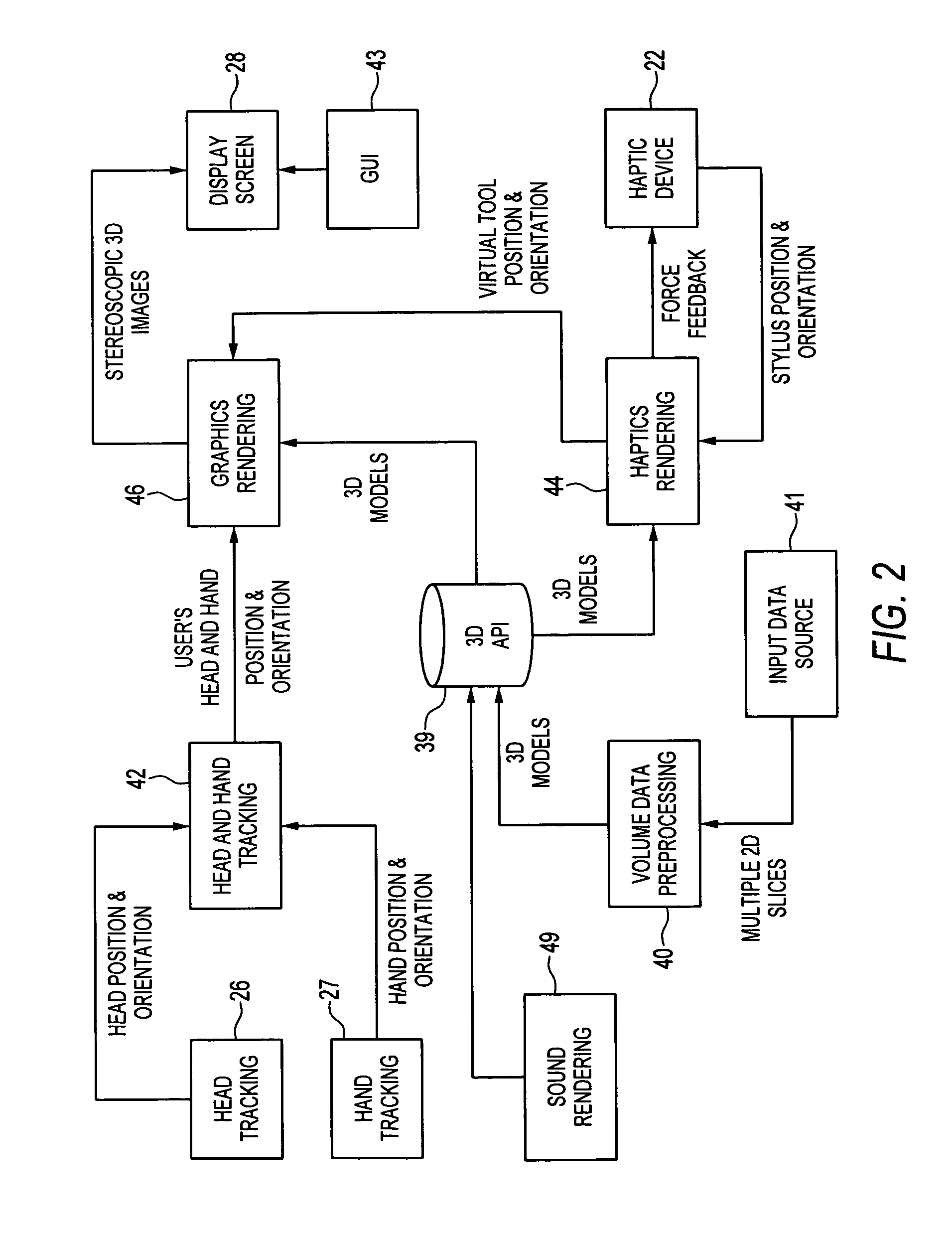
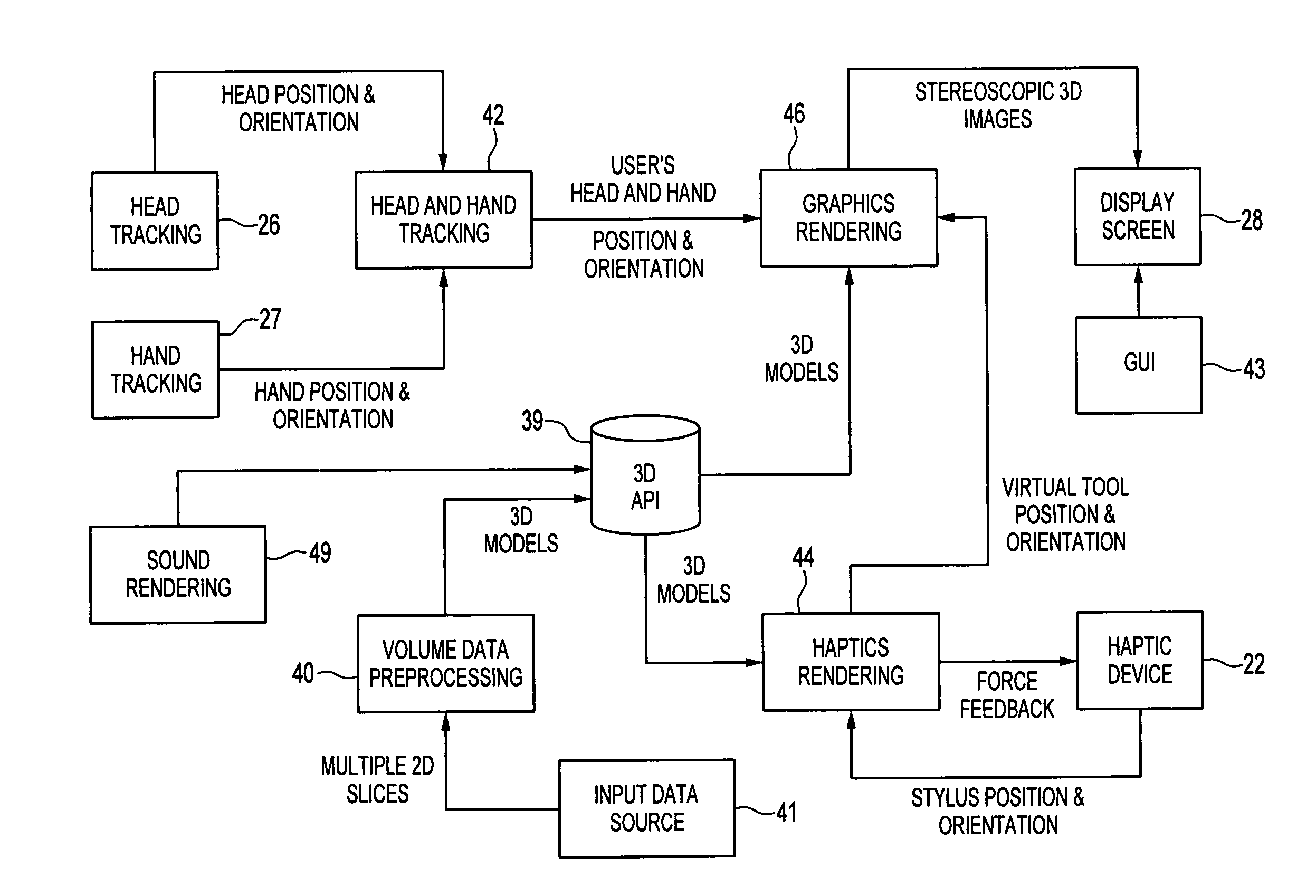
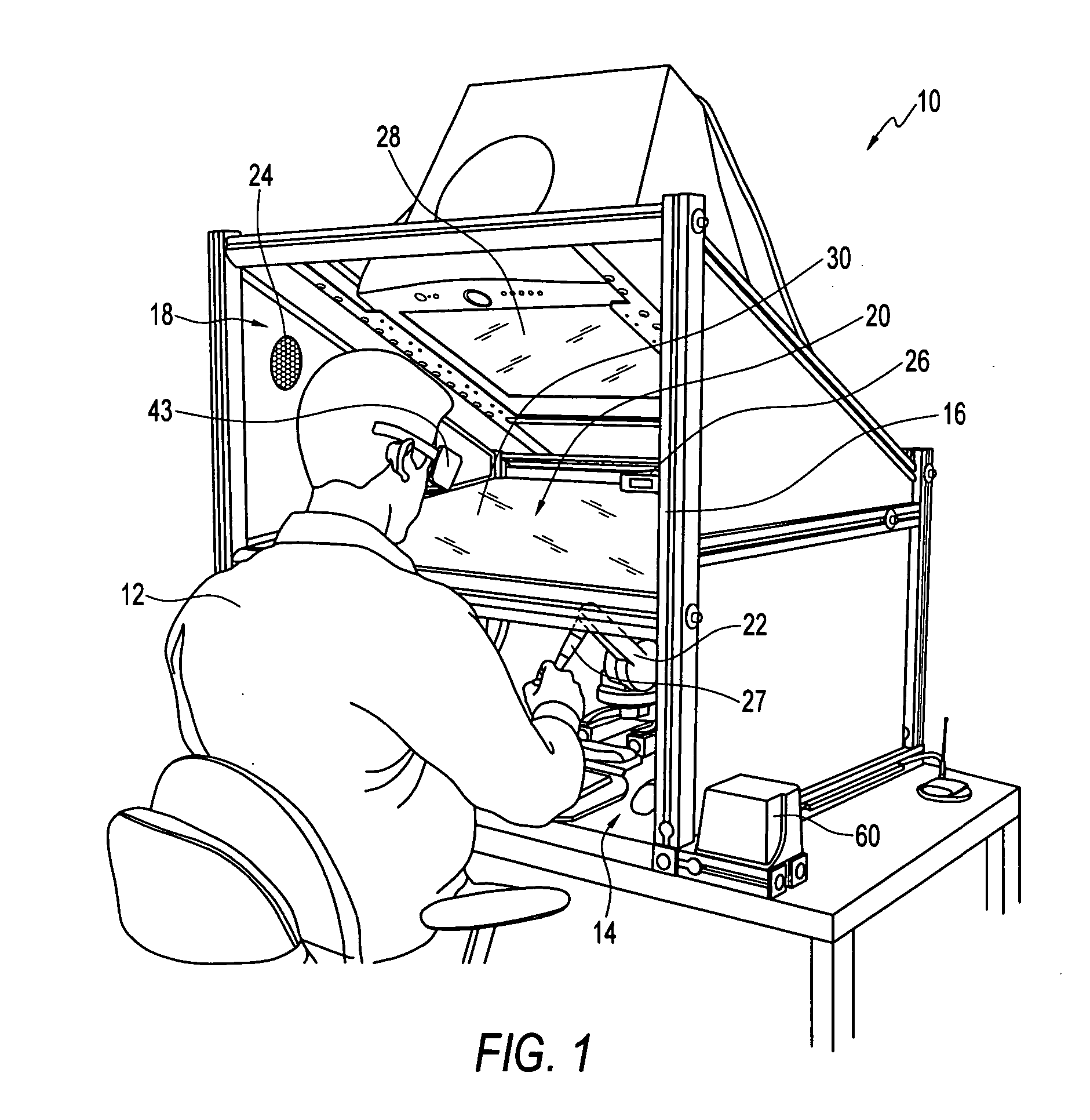
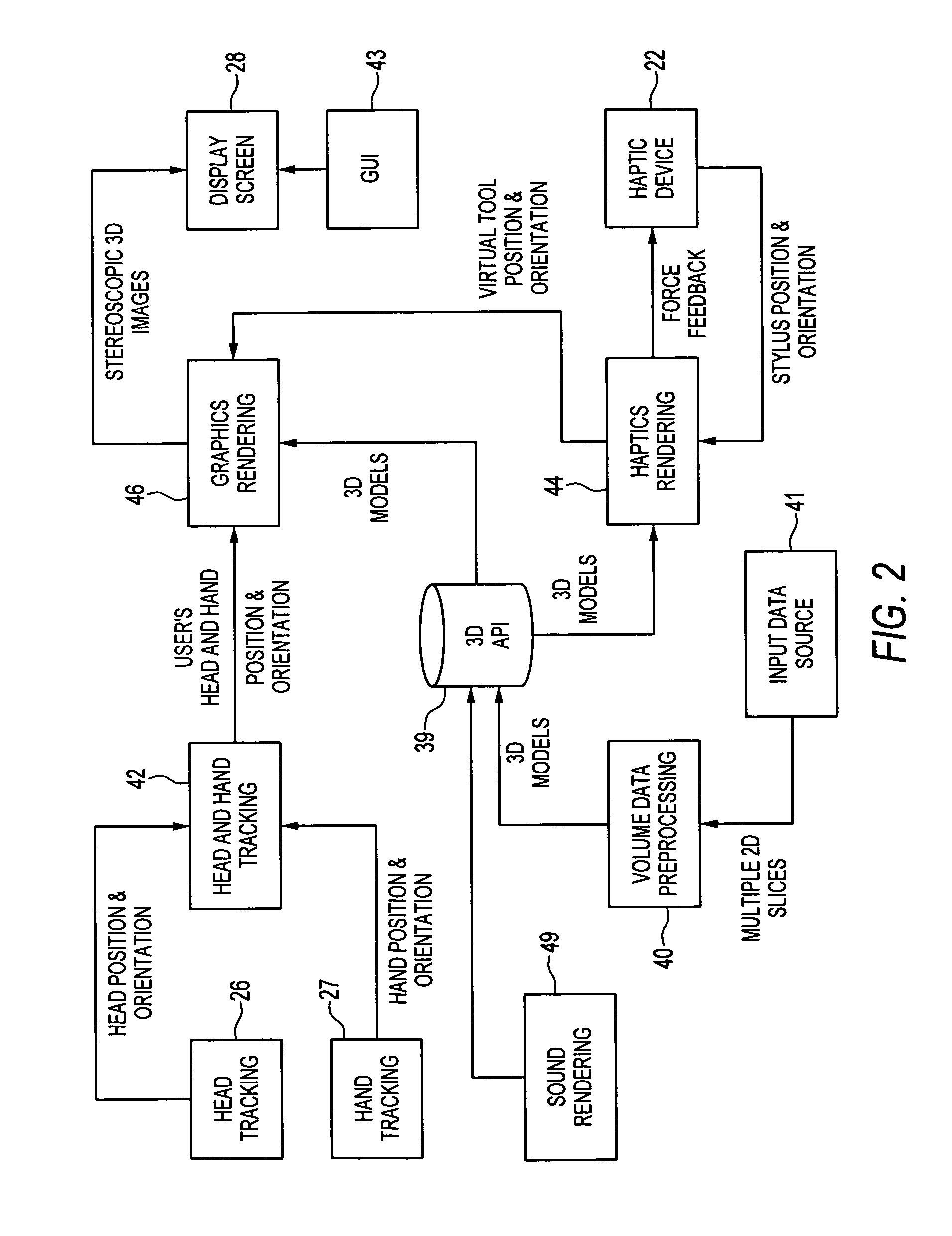
Compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system
InactiveUS7812815B2High resolutionIncrease pixel densityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingStereoscopic visualizationGraphics
The invention provides compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system that produces an augmented reality environment. The system is equipped with software and devices that provide users with stereoscopic visualization and force feedback simultaneously in real time. High resolution, high pixel density, head and hand tracking ability are provided. Well-matched haptics and graphics volumes are realized. Systems of the invention are compact, making use of a standard personal display device, e.g., a computer monitor, as the display driver. Systems of the invention may therefore be inexpensive compared to many conventional virtual reality systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system
InactiveUS20070035511A1High resolutionIncrease pixel densityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsStereoscopic visualization
The invention provides compact haptic and augmented virtual reality system that produces an augmented reality environment. The system is equipped with software and devices that provide users with stereoscopic visualization and force feedback simultaneously in real time. High resolution, high pixel density, head and hand tracking ability are provided. Well-matched haptics and graphics volumes are realized. Systems of the invention are compact, making use of a standard personal display device, e.g., a computer monitor, as the display driver. Systems of the invention may therefore be inexpensive compared to many conventional virtual reality systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
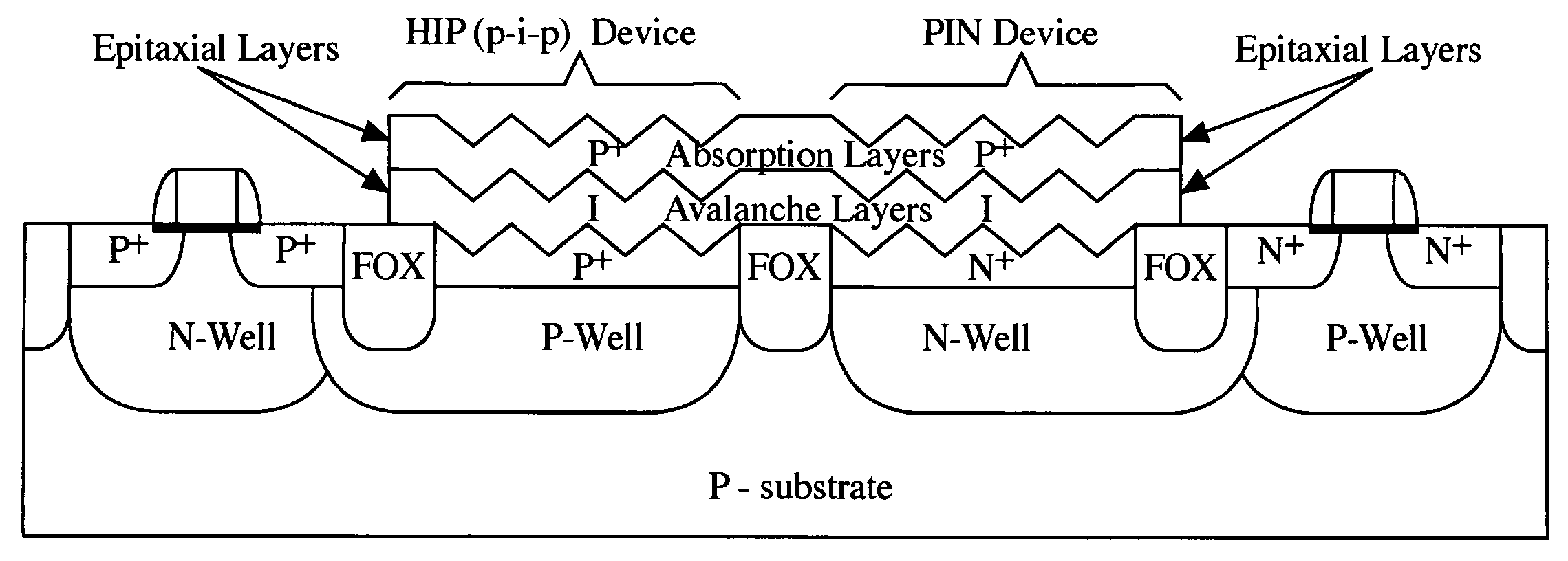
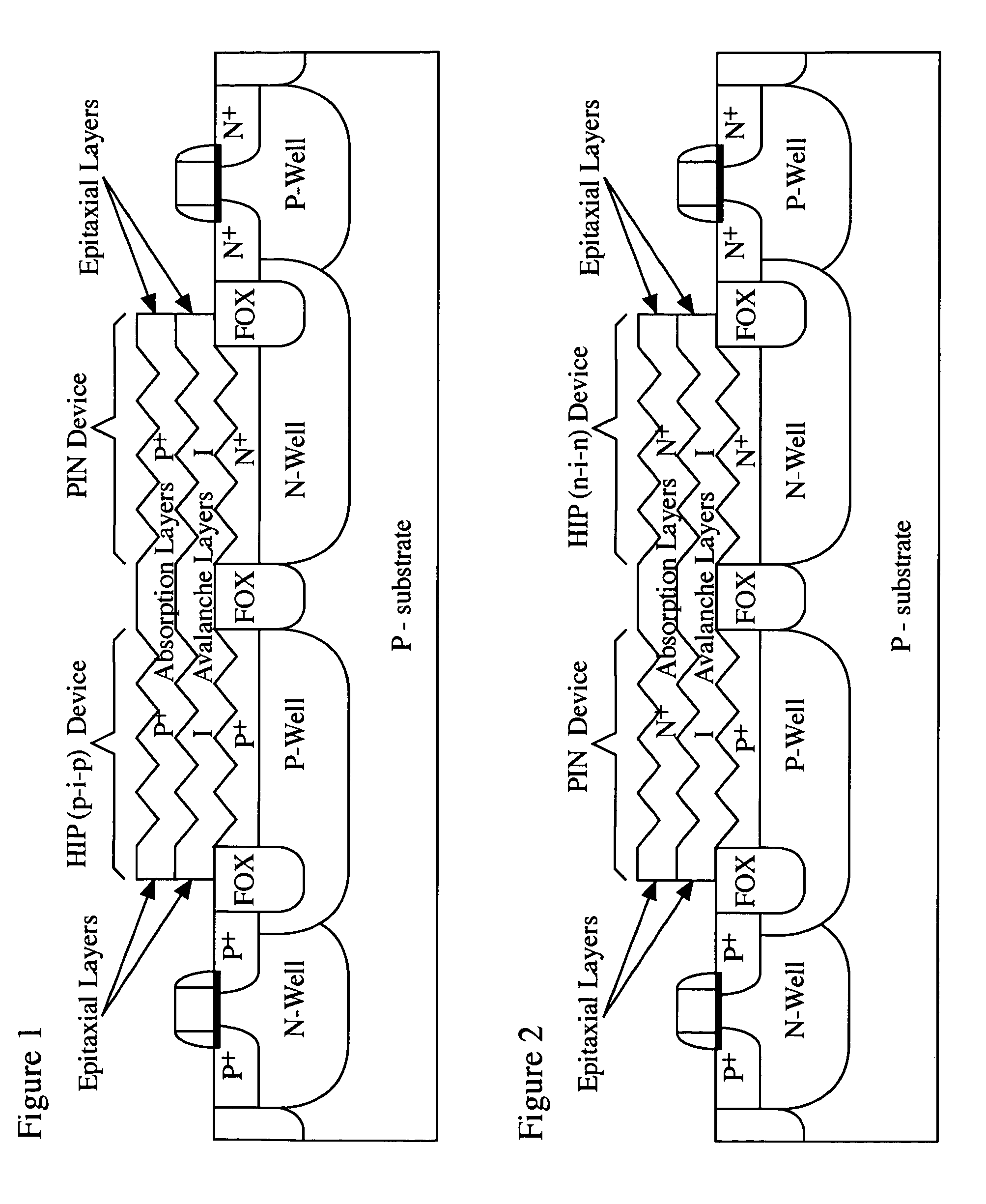
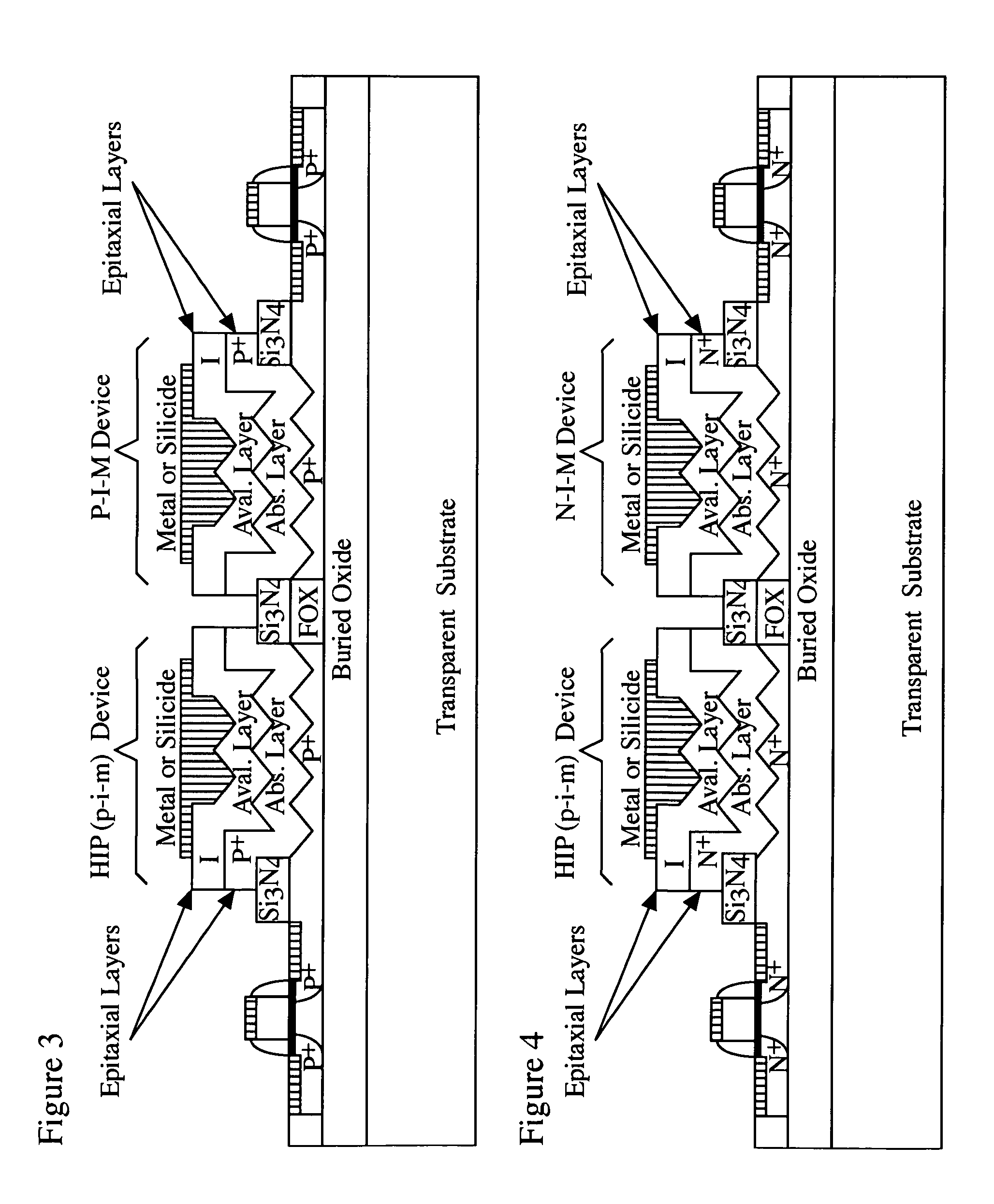
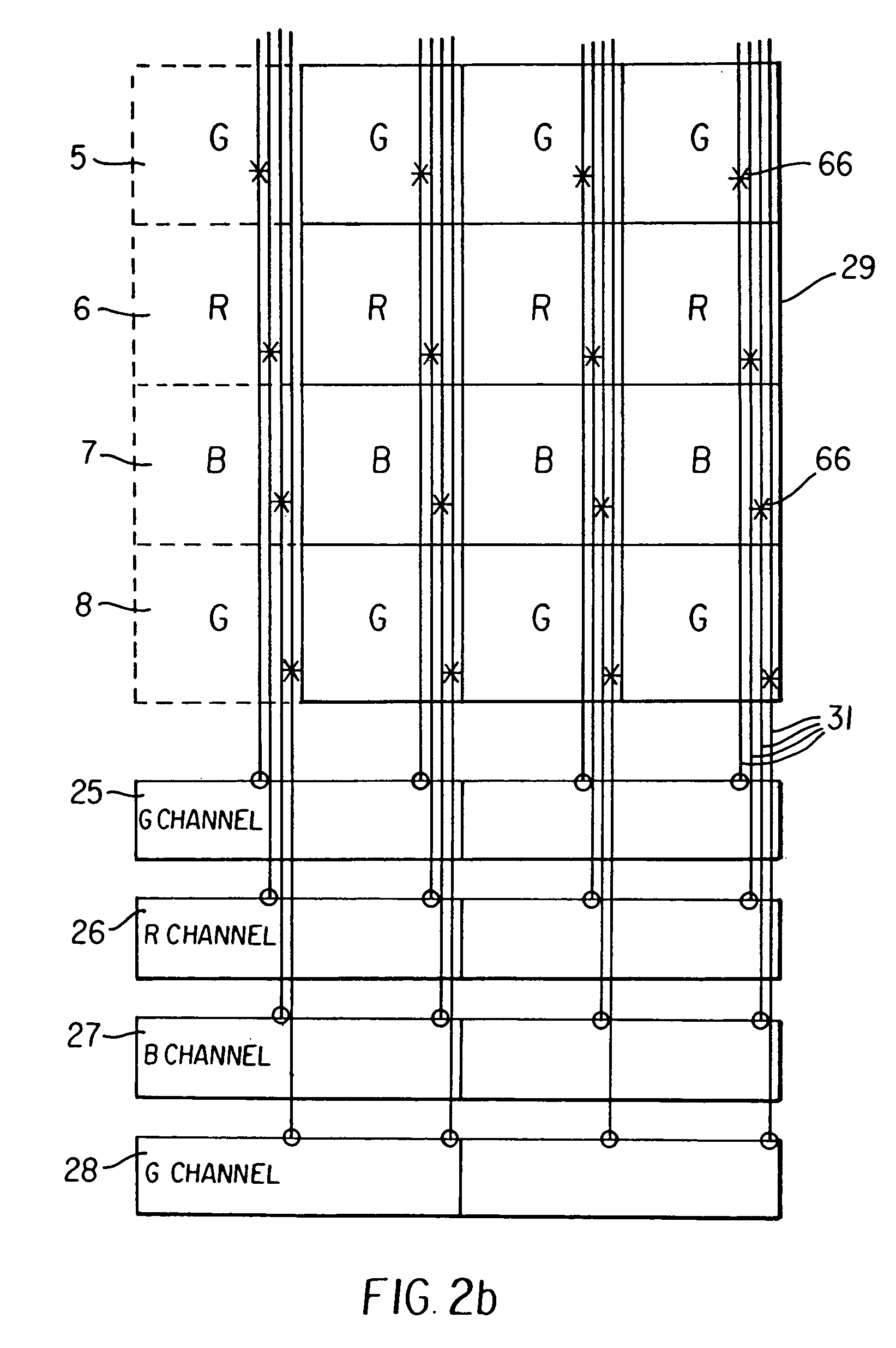
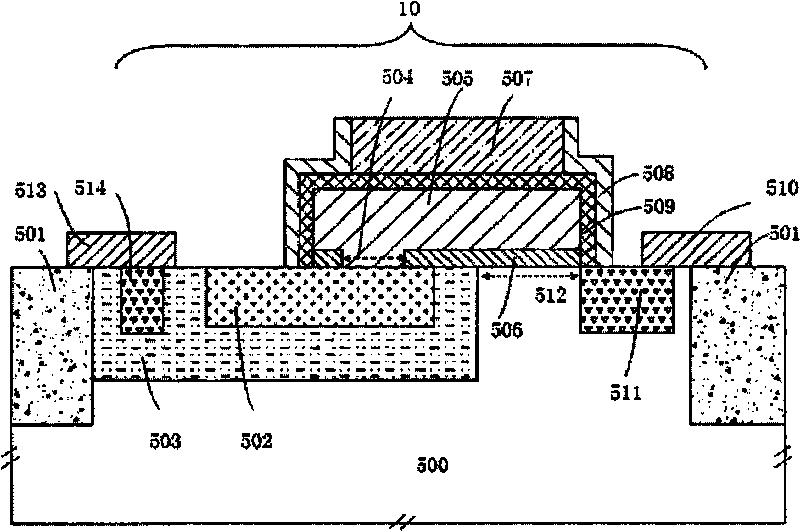
Light-sensing device
ActiveUS7521737B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionPixel density
A method of fabricating light-sensing devices including photodiodes monolithically integrated with CMOS devices. Several types of photodiode devices (PIN, HIP) are expitaxially grown in one single step on active areas implanted in a common semiconductor substrate, the active areas having defined polarities. The expitaxially grown layers for the photodiode devices may be either undoped or in-situ doped with profiles suitable for their respective operation. With appropriate choice of substrate materials, device layers and heterojunction engineering and process architecture, it is possible to fabricate silicon-based and germanium-based multi-spectral sensors that can deliver pixel density and cost of fabrication comparable to the state of the art CCDs and CMOS image sensors. The method can be implemented with epitaxially deposited films on the following substrates: Silicon Bulk, Thick-Film and Thin-Film Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI), Germanium Bulk, Thick-Film and Thin-Film Geranium-On-Insulator (GeOI).
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Display screen and display device
ActiveCN108269840AMeet the requirements of normal displayHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPixel densityTransmittance
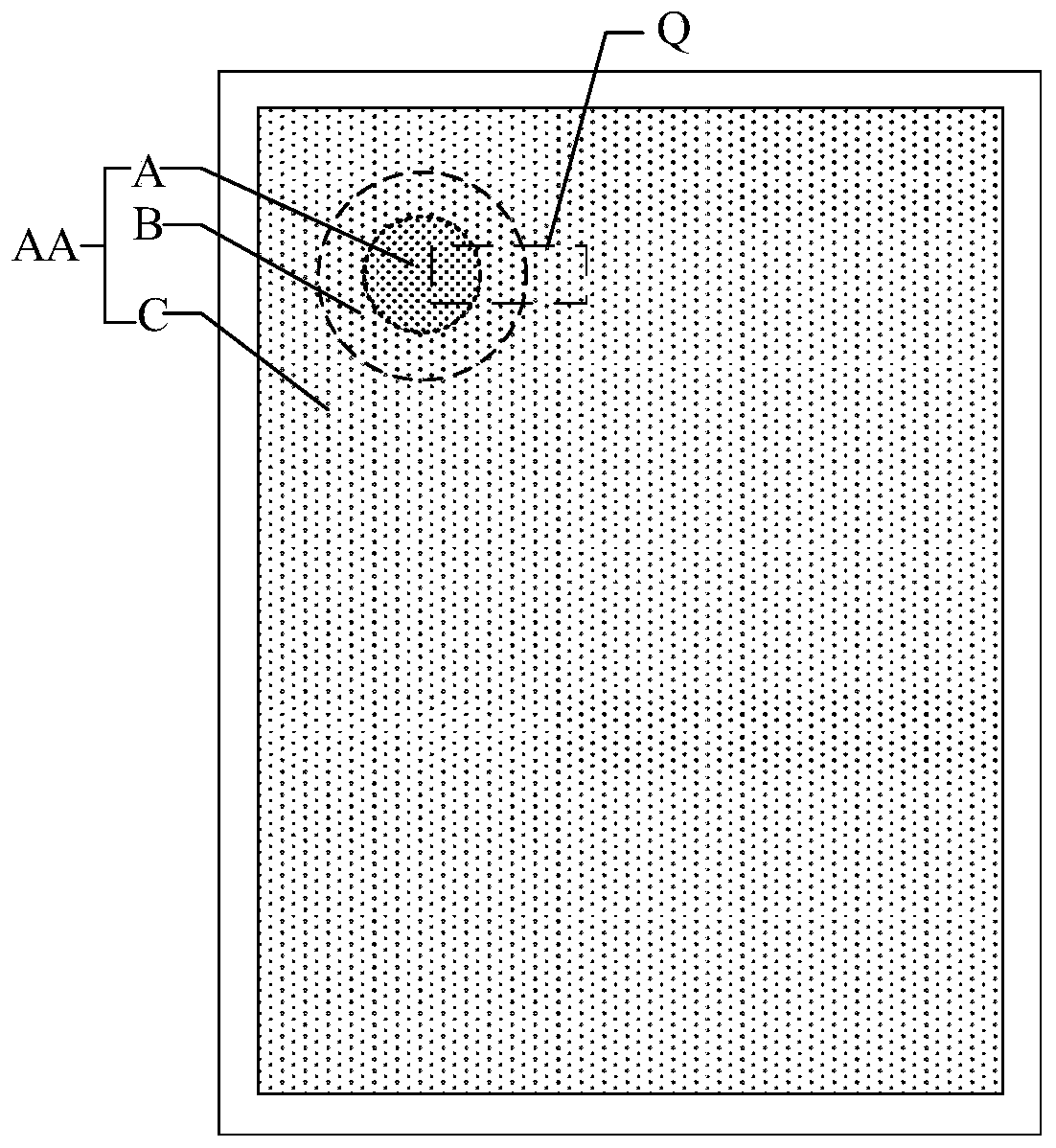
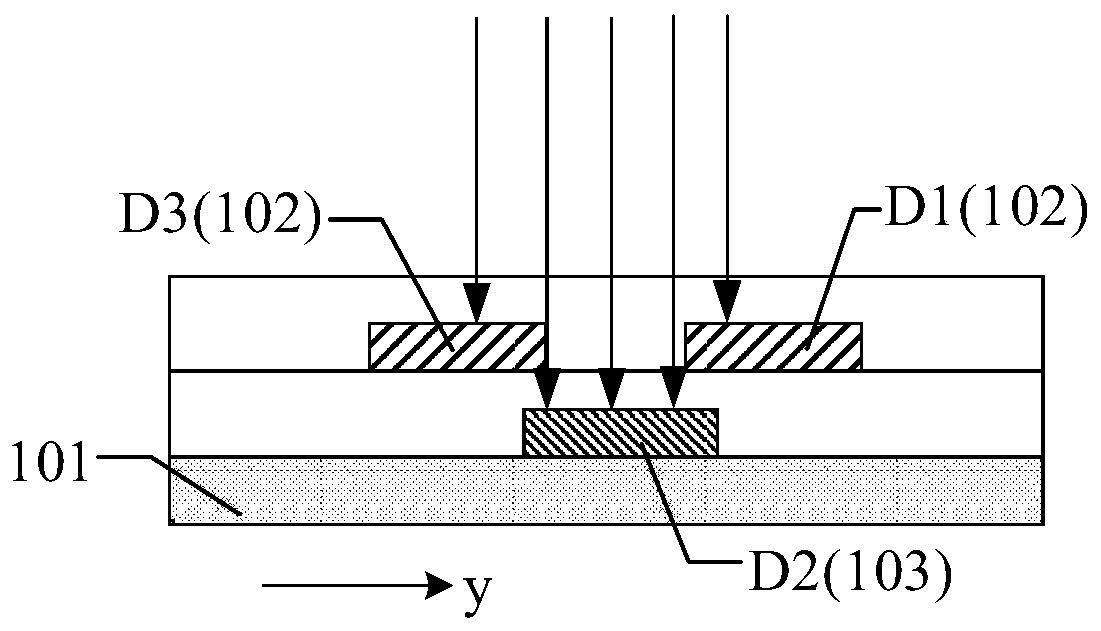
The present invention discloses a display screen and a display device. The display screen comprises a first display area, a second display area being adjacent to the first display area, and a third display area being adjacent to the second display area and being located at one side opposite to one side, adjacent to the first display area, of the second display area; the sub pixel density of the first display area is smaller than the sub pixel density of the second display area; and the sub pixel density of the second display area is smaller than the sub pixel density of the third display area.The sub pixel density at a camera of a display screen is regulated to meet a requirement of normal display of the camera and considers the requirement that high light transmittance needs to be maintained at the camera, a front camera does not need to reserve a position, a non-display area above a valid display area can be omitted to enlarge the screen-to-body ratio and optimize the use experienceso as to solve the technical problem that the user's experience is not good caused by the existence of the non-display area.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
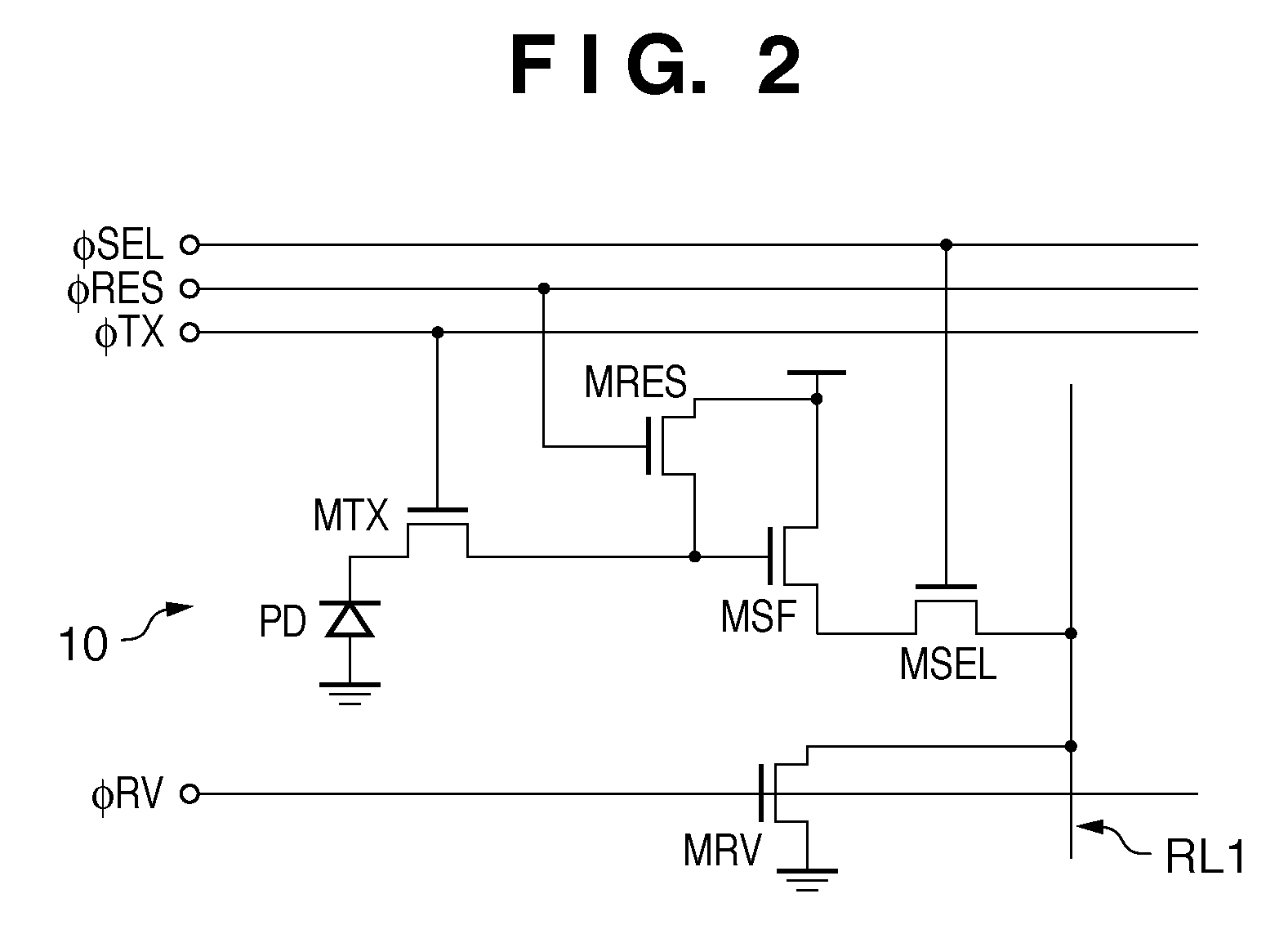
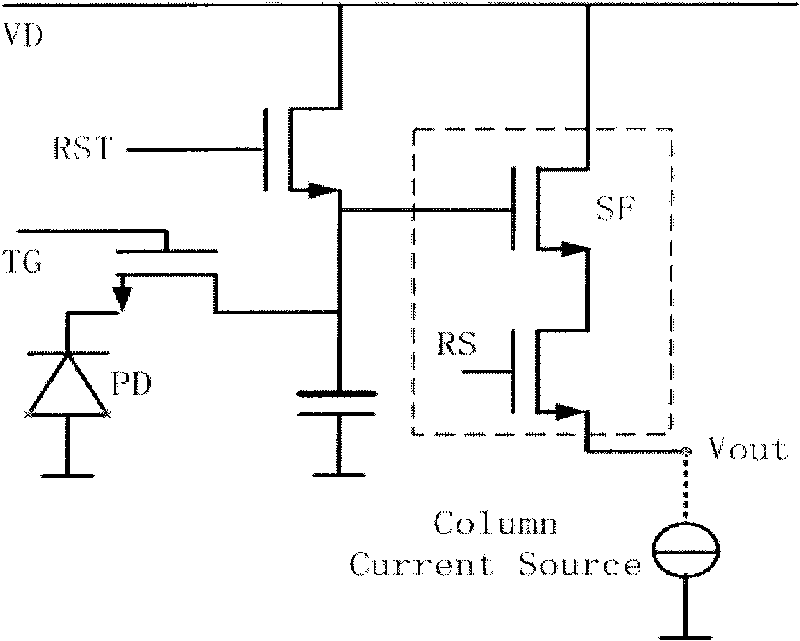
Image sensor pixel for global electronic shuttering
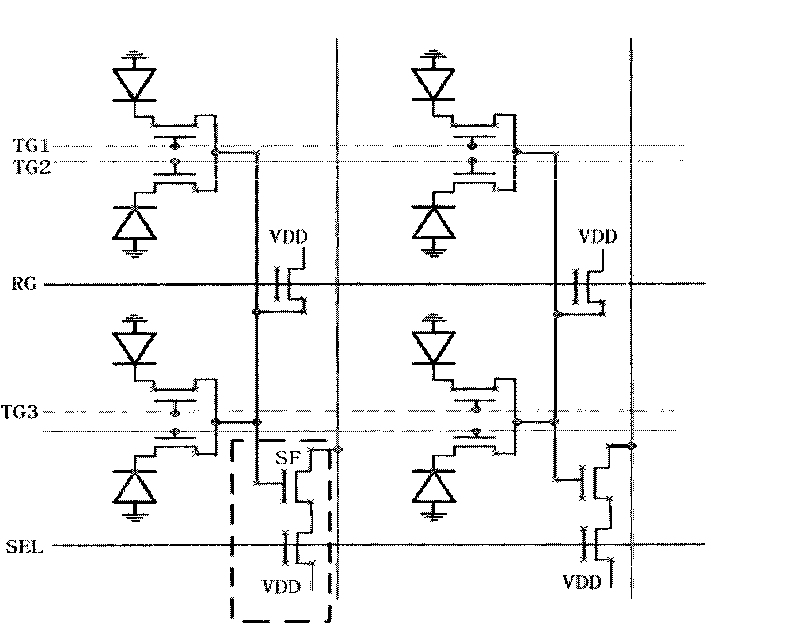
InactiveUS7129979B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorPixel density
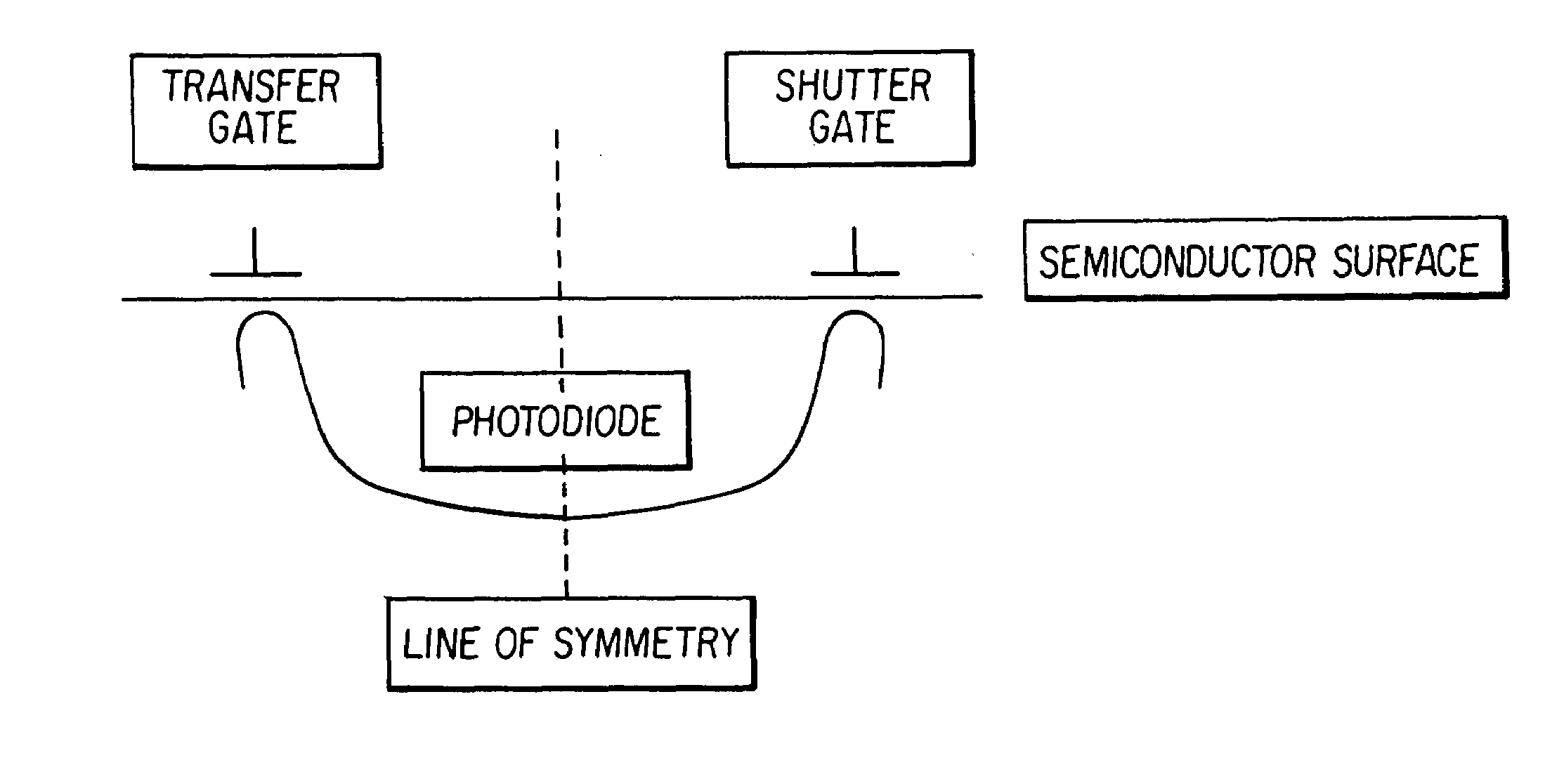
A pixel design for CMOS image sensors that has a high frame rate potential and, therefore, provides motion capture capabilities. The pixel is designed for global electronic shuttering so every pixel is exposed simultaneously to images incident upon the pixel array plane. The present invention has the advantages of: (1) Allowing the accommodation of changes in the pixel output groupings for different monochrome output format or CFA patterns with only changes in metal routing layers; (2) allowing true electronic shuttering to image moving scene with all the pixels having the same capture time windows; and (3) providing a symmetric global shutter gate and transfer gate to minimize pixel related fixed pattern noise. The pixel architecture provides for a CMOS based, active pixel image sensor comprising an array of pixels formed in rows and columns, with each of the pixels containing at least one active circuit element. There are a plurality of output channels formed such that each of the output channels are operatively connected to a subset of pixels wherein each of the pixel have an attribute that is the same. The pixel architecture also provides an output gate region and a shutter gate region that are symmetric about the center of the pixel. By arranging the shutter and transfer gates, a symmetric manner about the center of the pixel, a more efficient transfer of electrons to these gates is provided. A Pixel Output Bus structure allows configurable connections to column-wise signal busses that provide parallel output channels.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Image sensing apparatus and image capturing system
ActiveUS20090021621A1Increase frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPixel densityComputer science
An image sensing apparatus comprises: a pixel array; a selection unit which selects a readout region in the pixel array; and a readout unit which reads out a signal from the readout region, wherein in thinning-out readout, the readout unit reads out signals from a first readout region corresponding to the whole pixel array at a first pixel density in a first frame period and reads out signals from a second readout region corresponding to a part of the pixel array at a second pixel density in a second frame period, the second pixel density being higher than the first pixel density, and in thinning-out readout, the selection unit causes pixels in the first readout region to perform a charge accumulation operation for a first accumulation period and causes pixels in the second readout region to perform the charge accumulation operation for a second accumulation period.
Owner:CANON KK
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN110504289AGood optical performanceIncrease the areaStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectricityOptical Module
The invention provides a display panel and a display device. The display panel comprises a display area including an optical module setting area, a transition area and a conventional area, wherein thetransition area at least half surrounds the optical module setting area, and the conventional area at least half surrounds the transition area; pixels comprise a first pixel, a transition pixel and aconventional pixel, wherein the first pixel is located in the optical module setting area, the transition pixel is located in the transition area, the conventional pixel is located in the conventional area, the pixel density of the optical module setting area is a first density, the pixel density of the transition area is a second density, the pixel density of the conventional area is a third density, the first density is less than the third density, and the second density is less than the third density; a first pixel circuit is electrically connected to the first pixel, and at least part ofthe first pixel circuit is located in the transition area. The invention can improve the light transmittance of the optical module setting area.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
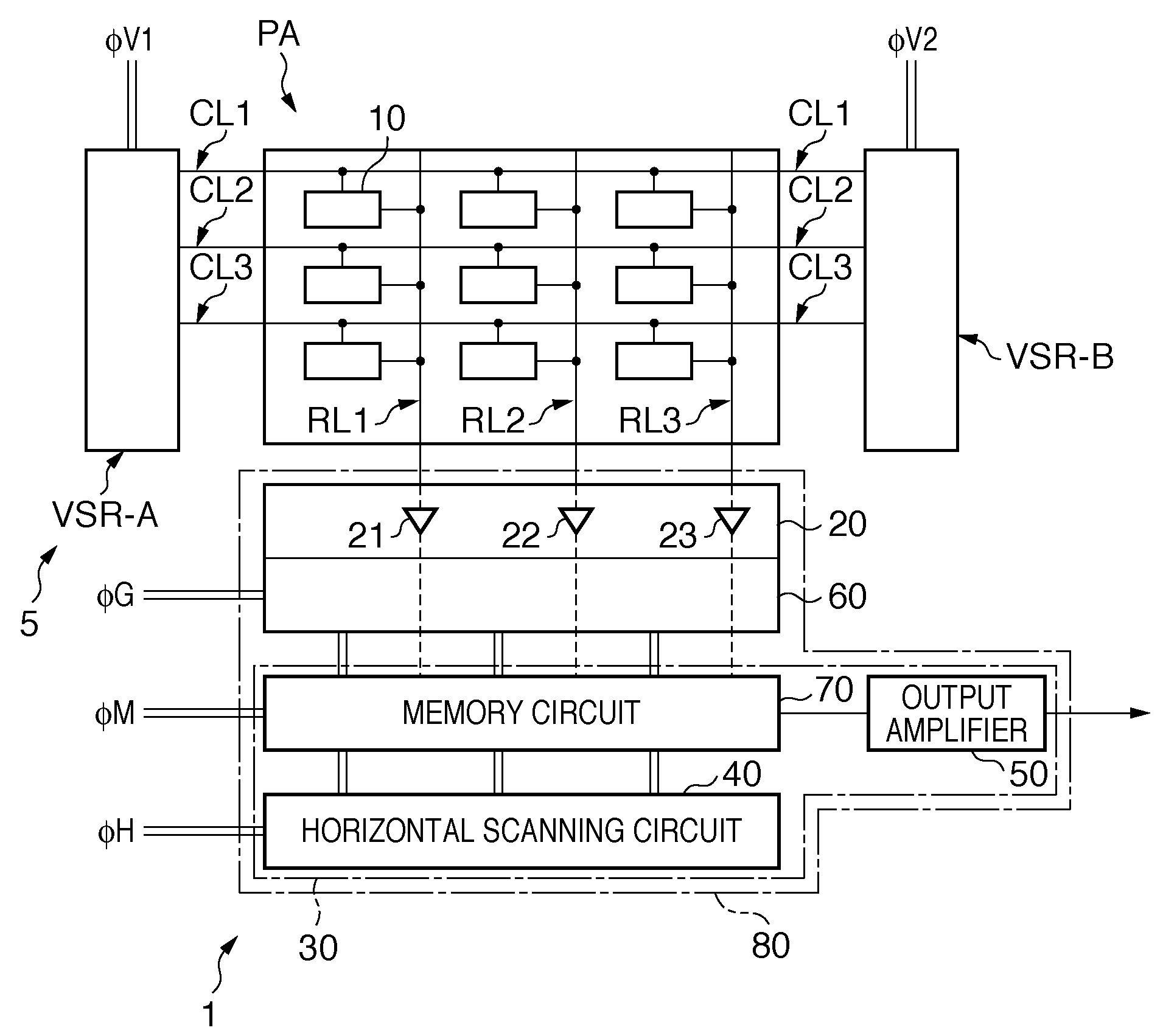
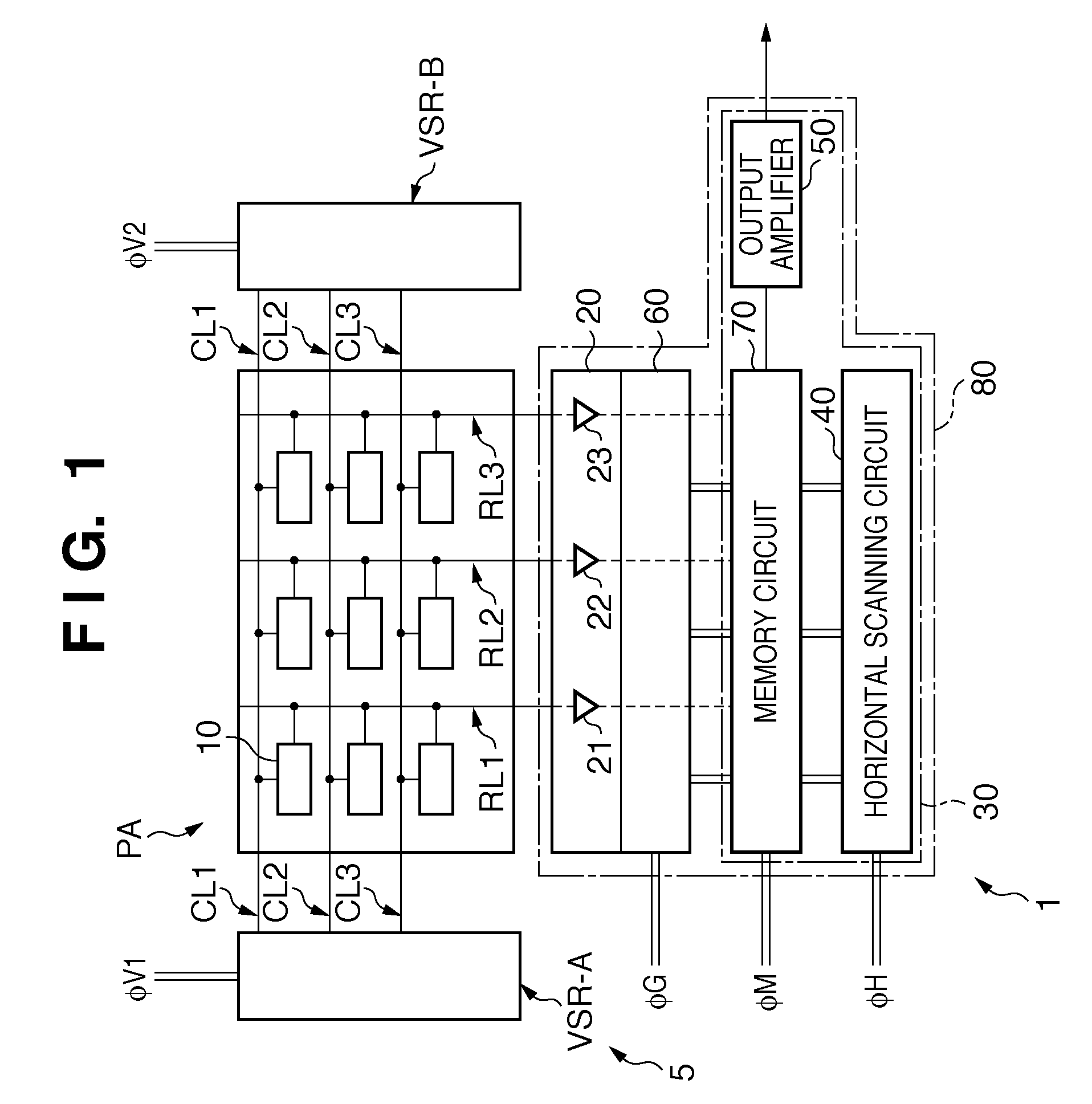
Column-row addressable electric microswitch arrays and sensor matrices employing them
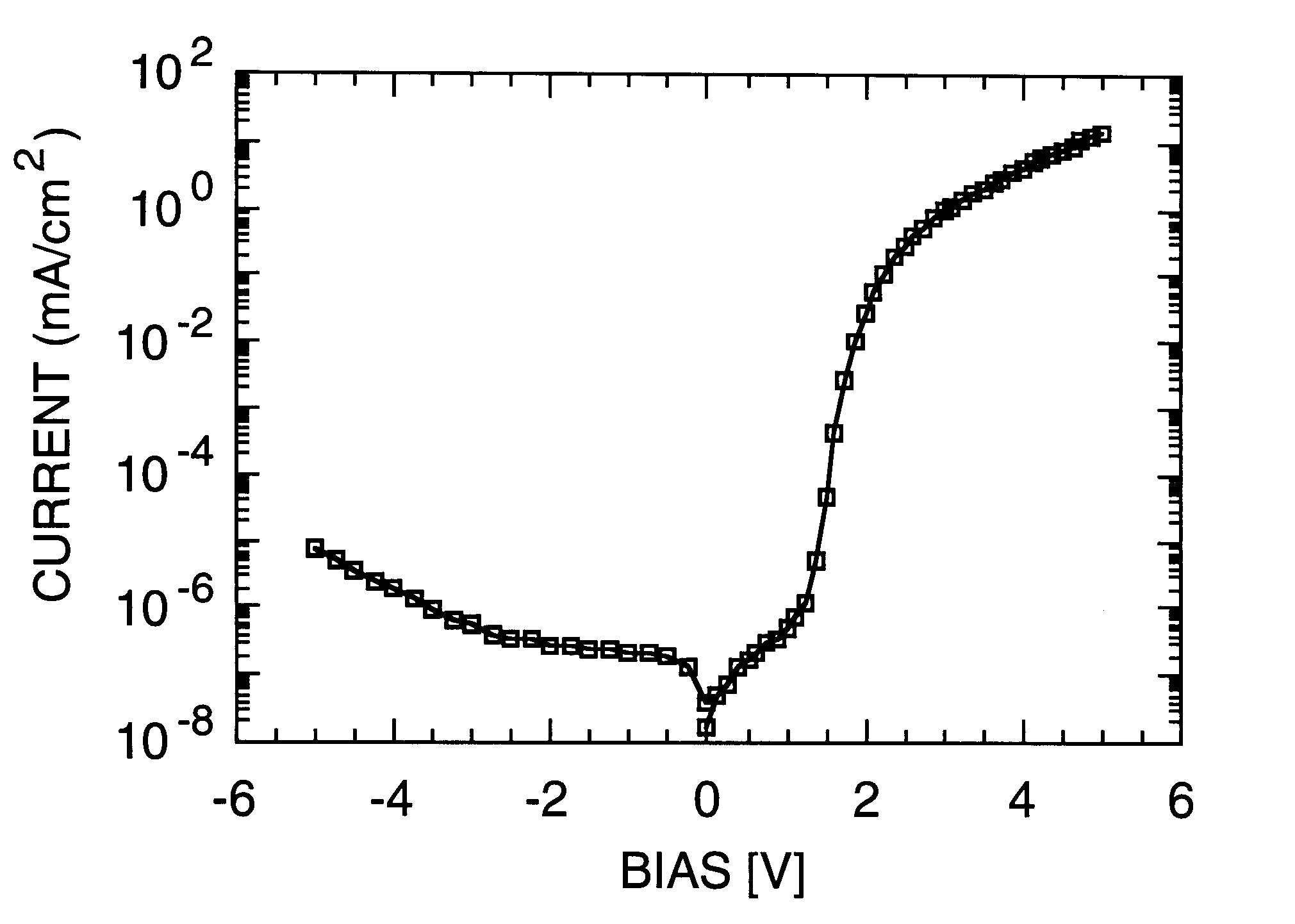
The present invention relates generally to fabricating two-terminal electric microswitches comprising thin semiconductor films and using these microswitches to construct column-row (x-y) addressable microswitch matrices. These microswitches are two terminal devices through which electric current and electric potential (or their derivatives or integrals) can be switched on and off by the magnitude or the polarity of the external bias. The microswitches are made from semiconducting thin films in a electrode / semiconductor / electrode, thin film configuration. Column-row addressable electric microswitch matrices can be made in large areas, with high pixel density. Such matrices can be integrated with a sensor layer with electronic properties which vary in response to external physical conditions (such as photon radiation, temperature, pressure, magnetic field and so on), thereby forming a variety of detector matrices.
Owner:DUPONT DISPLAY +1
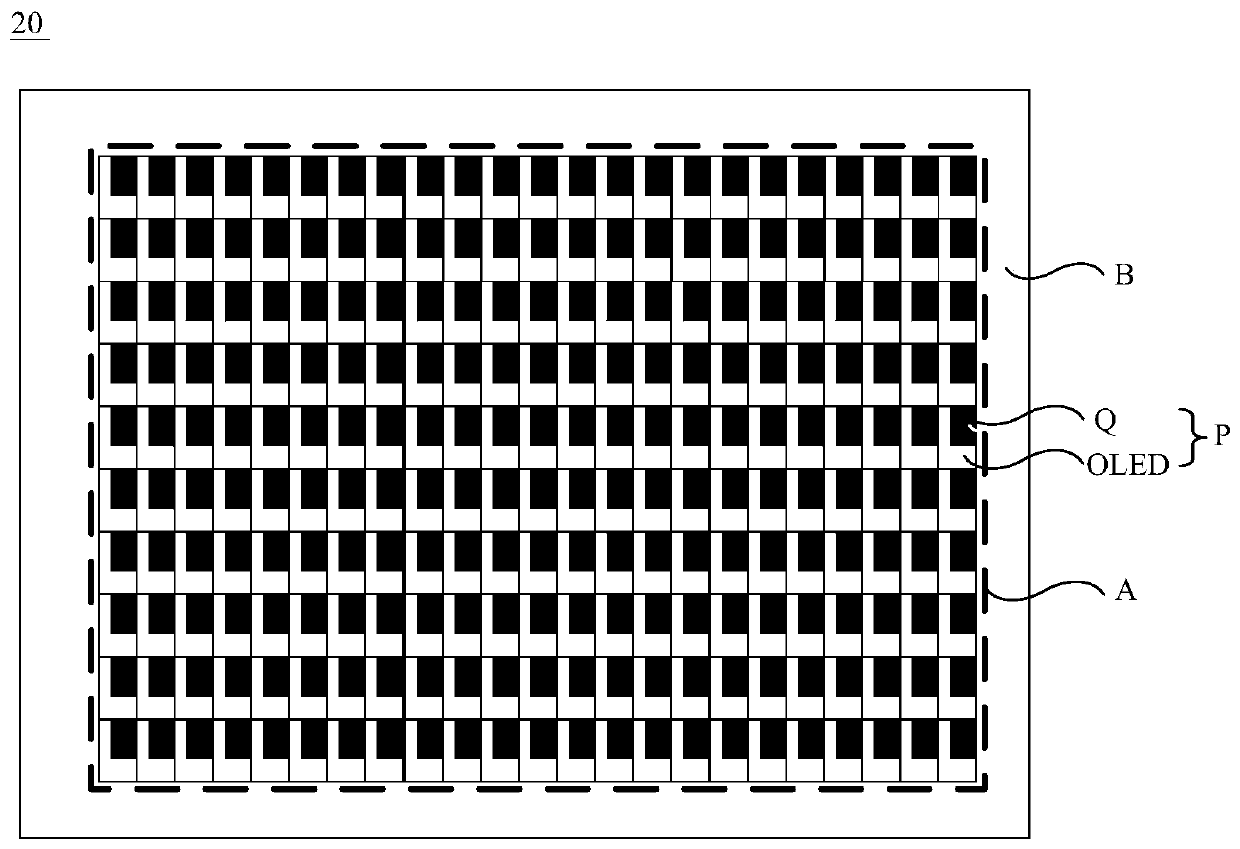
Display screen and terminal
The invention provides a display screen and a terminal, and relates to the technical field of display. The invention is used for solving the problem of how to improve the transmittance of an OLED display screen. The display screen comprises a substrate, at least one high-density pixel group and at least one low-density pixel group. The high-density pixel group comprises a plurality of first pixelsarranged in an array, and the low-density pixel group comprises a plurality of second pixels arranged in an array. The first pixel comprises at least three first sub-pixels used for displaying threeprimary colors respectively, and each first sub-pixel at least comprises a first driving circuit and a first light-emitting device electrically connected with the first driving circuit. The second pixel comprises at least three second sub-pixels used for displaying three primary colors respectively. Each second sub-pixel at least comprises a second driving circuit and a second light-emitting device electrically connected with the second driving circuit. The pixel density of the first display area where the first pixels arranged in the array mode are located is larger than the pixel density ofthe second display area where the second pixels arranged in the array mode are located.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
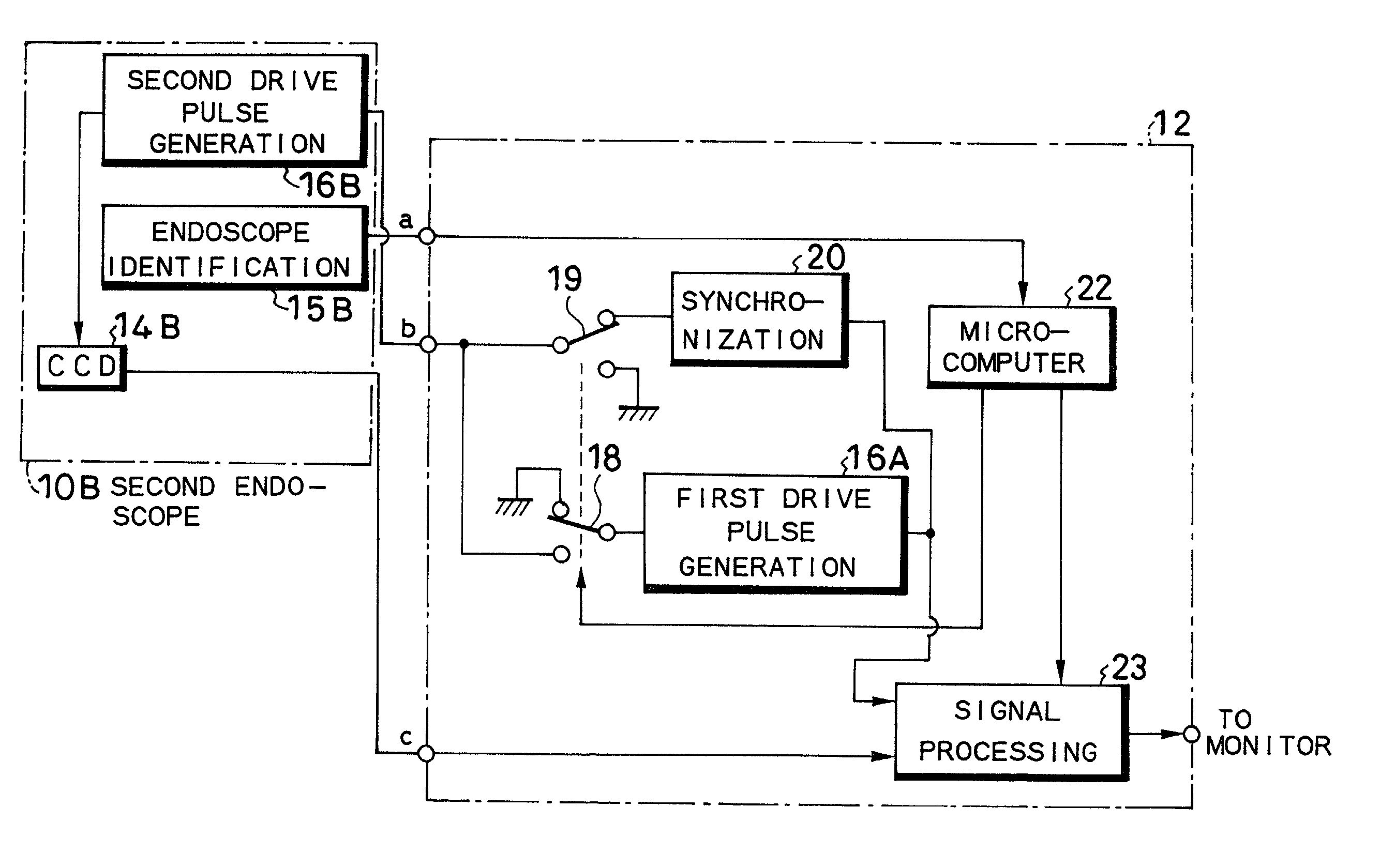
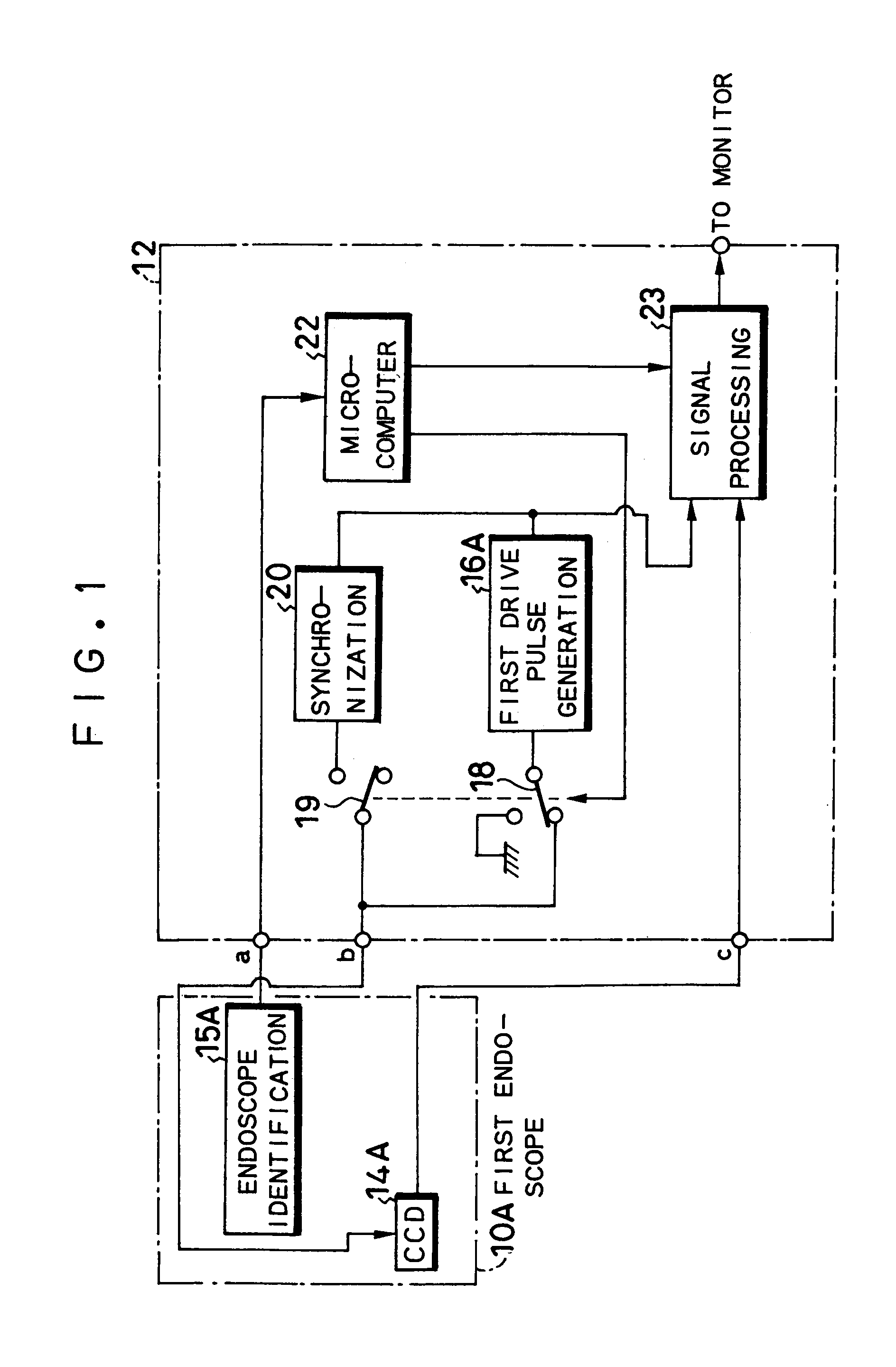
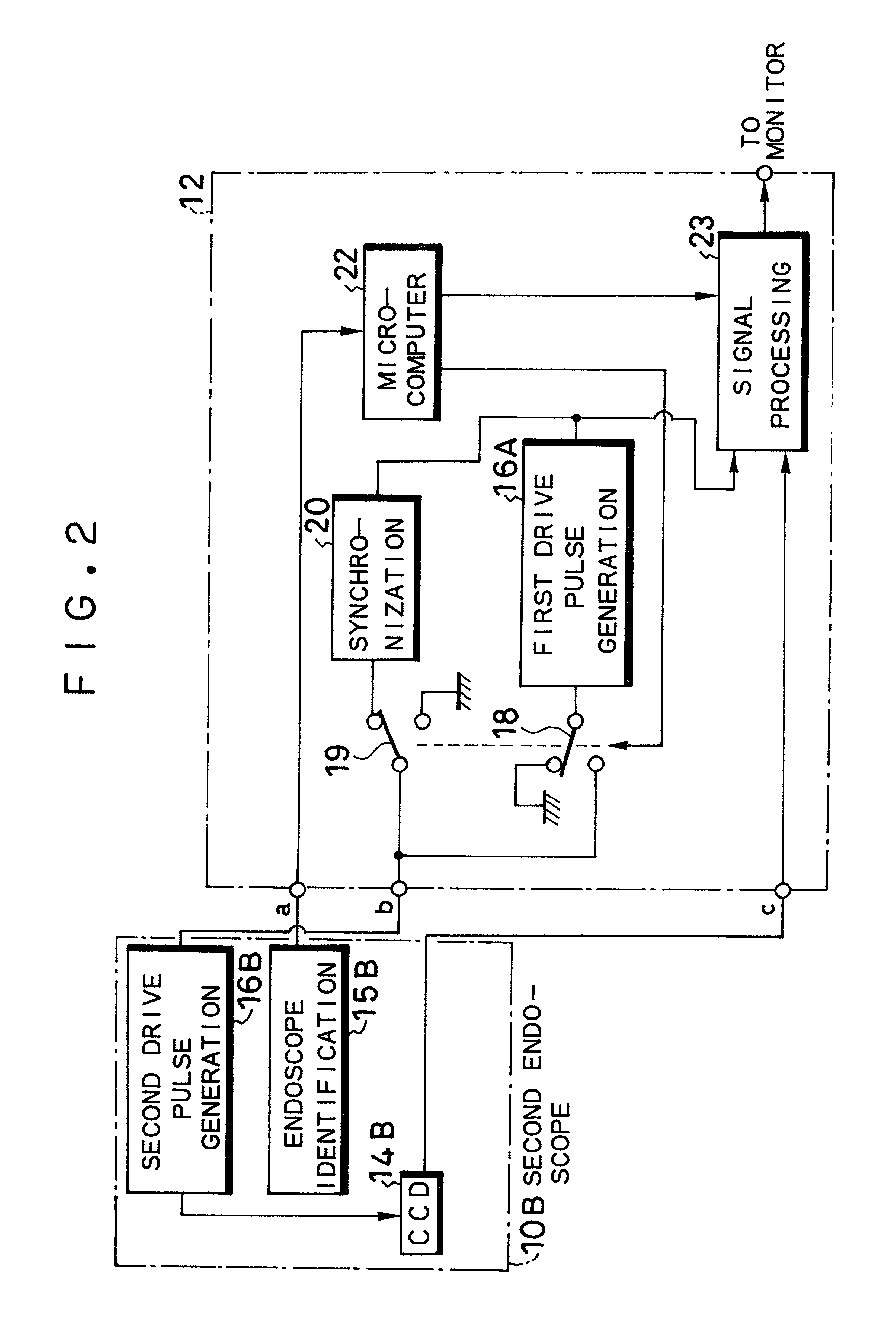
Electronic endoscope apparatus adaptable to endoscopes equipped with imaging device with different pixel density
InactiveUS6992694B2Low costAvoid wastingTelevision system detailsSurgeryPixel densitySignal processing circuits
An electronic endoscope apparatus including: a first endoscope having a first imaging device; and a second endoscope having a second imaging device with a different pixel density and a second drive pulse generation circuit, wherein a processor unit, which connects the two endoscopes, comprises: a first drive pulse generation circuit for driving the first imaging device, a synchronization circuit for generating a synchronizing signal synchronous with the signal of the second drive pulse generation circuit, a switching circuit for activating the synchronization circuit when the second endoscope is connected, and a signal processing circuit for processing the signals obtained by the first imaging device and for processing the signals obtained by the second imaging device based on the synchronizing signal. By this configuration, a single processor unit will suffice even when employing an imaging device with a different pixel density.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Visual display with increased field of view
ActiveUS7495638B2Reduce loadAttenuation bandwidthTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesPixel densityDisplay device
This invention provides a continuous display with non-uniform pixel density, forming a foveated display. A single, continuous display has a higher pixel density at the center of the display than at the periphery of the display. Where two continuous displays are used in accordance with the present invention, the central forward gaze of the viewer's image will be displayed in high resolution while the leftmost portion of the left eye display will be in low resolution and the rightmost portion of the right eye display will be in low resolution. The pixel resolution of the visual display may correspond to the visual acuity of the human eye. A foveated image display system using a continuous display with non-uniform pixel density increases the field of view while reducing the image bandwidth. A foveated image display system may be hardware-based by employing anamorphic lenses or sensors rather than relying upon image interpolation to modify the resolution of the resultant image data communicated to the continuous display with non-uniform pixel density.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
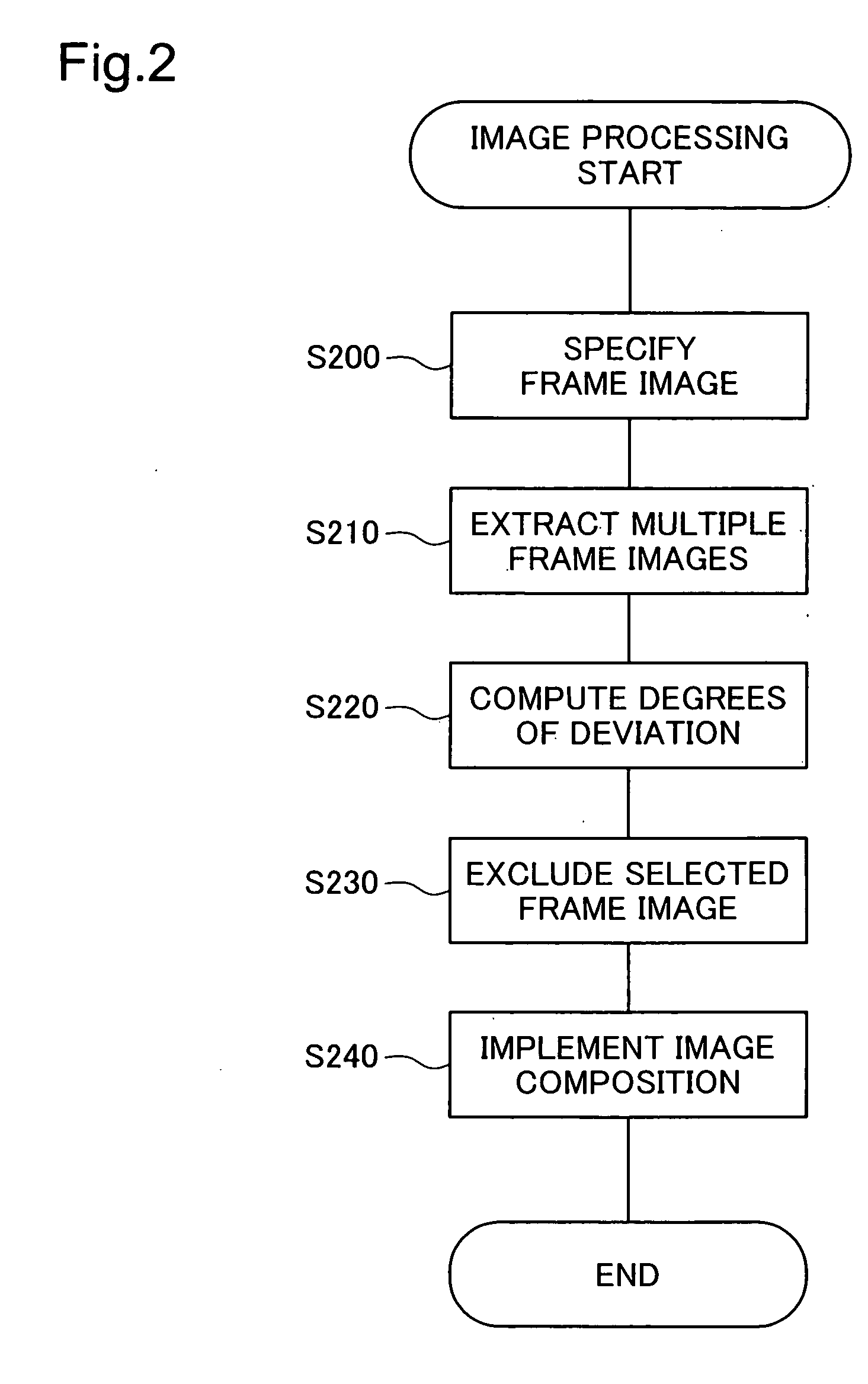
Image processing device, image processing method, program thereof, and recording medium
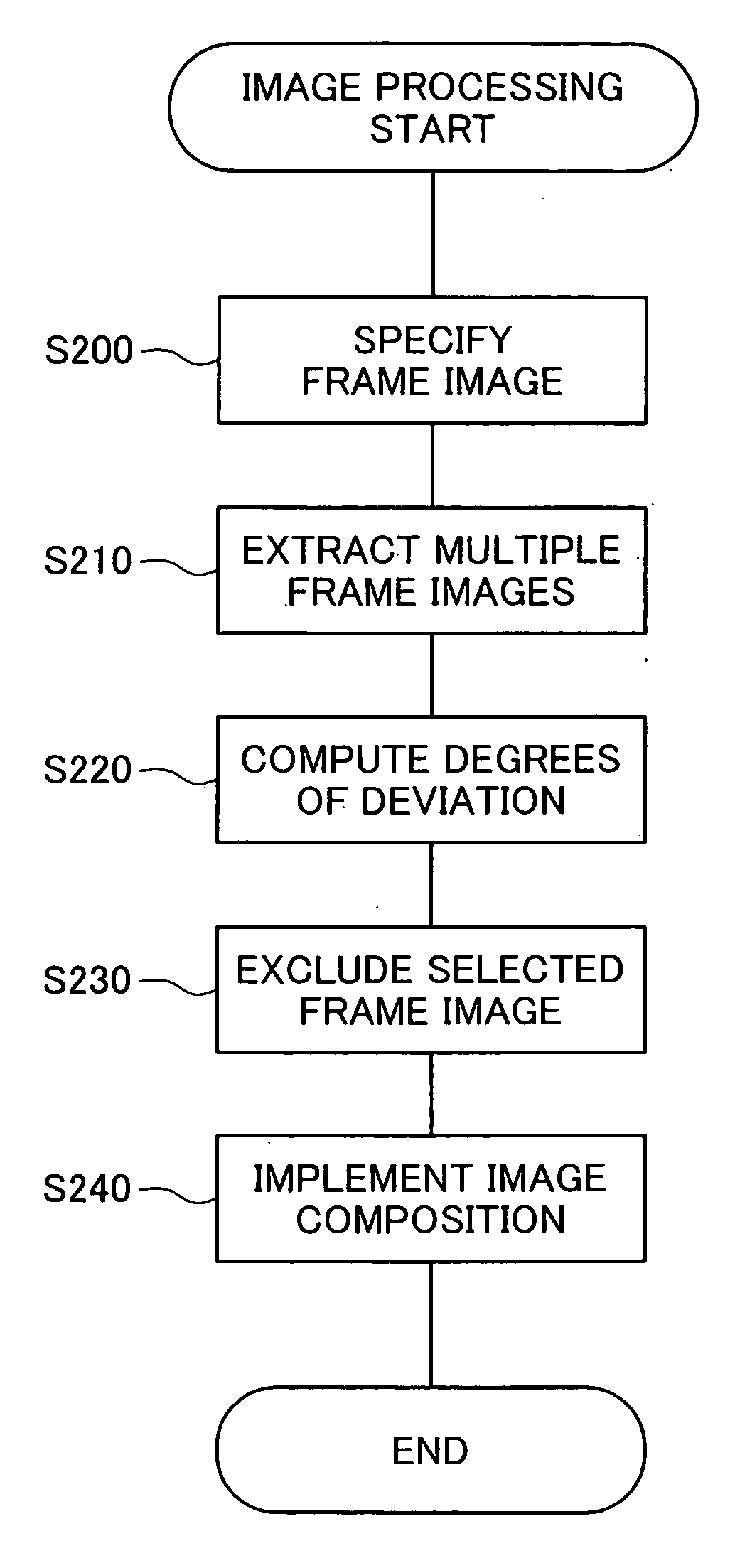
InactiveUS20070133901A1Increase pixel densityEasy to operateImage analysisGeometric image transformationImage extractionPixel density
An image processing apparatus of the invention generates one still image having a high pixel density from multiple images. The image processing apparatus includes: an image extraction module that extracts the multiple images used for generation of the one still image; a deviation computation module that computes a degree of deviation between each combination of the extracted multiple images; an exclusion module that excludes any image having the computed degree of deviation out of a preset threshold range from the extracted multiple images; and an image composition module that combines remaining images other than the excluded image to generate the one still image. This arrangement of the invention ensures efficient image processing to generate one high-resolution still image from multiple images.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical system for head mounted display
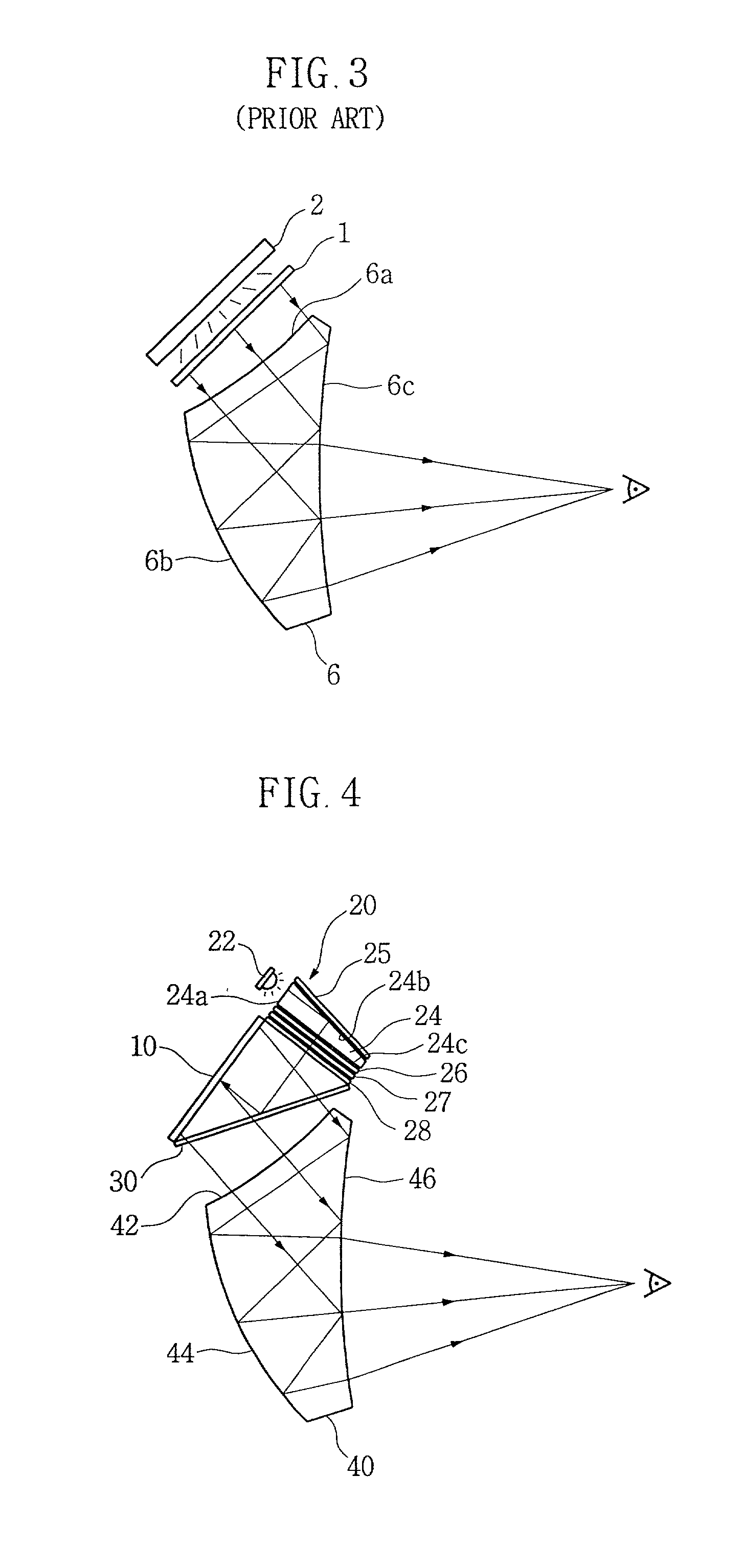
InactiveUS20020015233A1Television system detailsPolarising elementsPixel densityLiquid-crystal display
The present invention relates to a head mounted display that is constructed such that stereoscopic images can be seen on a liquid crystal display screen disposed adjacent to two human eyes. The present invention provides an optical system for a head mounted display, comprising a light source; a light guide panel which has a side portion, a top portion and a bottom portion, which receives light rays emitted from the light source through the side portion, reflects the light rays substantially perpendicular to a direction of the light rays, and emits the light rays toward the top portion, and which emits most of the light rays incident on the top portion through the bottom portion; a frontlight liquid crystal display screen which is disposed to face the top portion of the light guide panel and on which images are displayed by reflecting the light rays emitted from the top portion of the light guide panel and causing the light rays to be incident on the top portion of the light guide panel; and a free-form-surface prism disposed in front of the bottom portion of the light guide panel for magnifying the images on the liquid crystal display screen by reflecting and focusing the light rays which are reflected from the frontlight liquid crystal display screen and emitted toward the bottom portion of the light guide panel. According to the an optical system for a head mounted display of the present invention, there is an advantage in that its production costs can be reduced, since the optical system for the head mounted display of the present invention employs the frontlight liquid crystal display screen which is inexpensive and has a high pixel density. Further, there is another advantage in that the use efficiency of the light source can be enhanced, since the optical system of the present invention includes the inexpensive light emitting diode and the light guide panel for reflecting the light rays emitted from the light emitting diode and focusing the light rays within a range of the predetermined angles.
Owner:DAEYANG ENG
Endoscope image pickup optical system
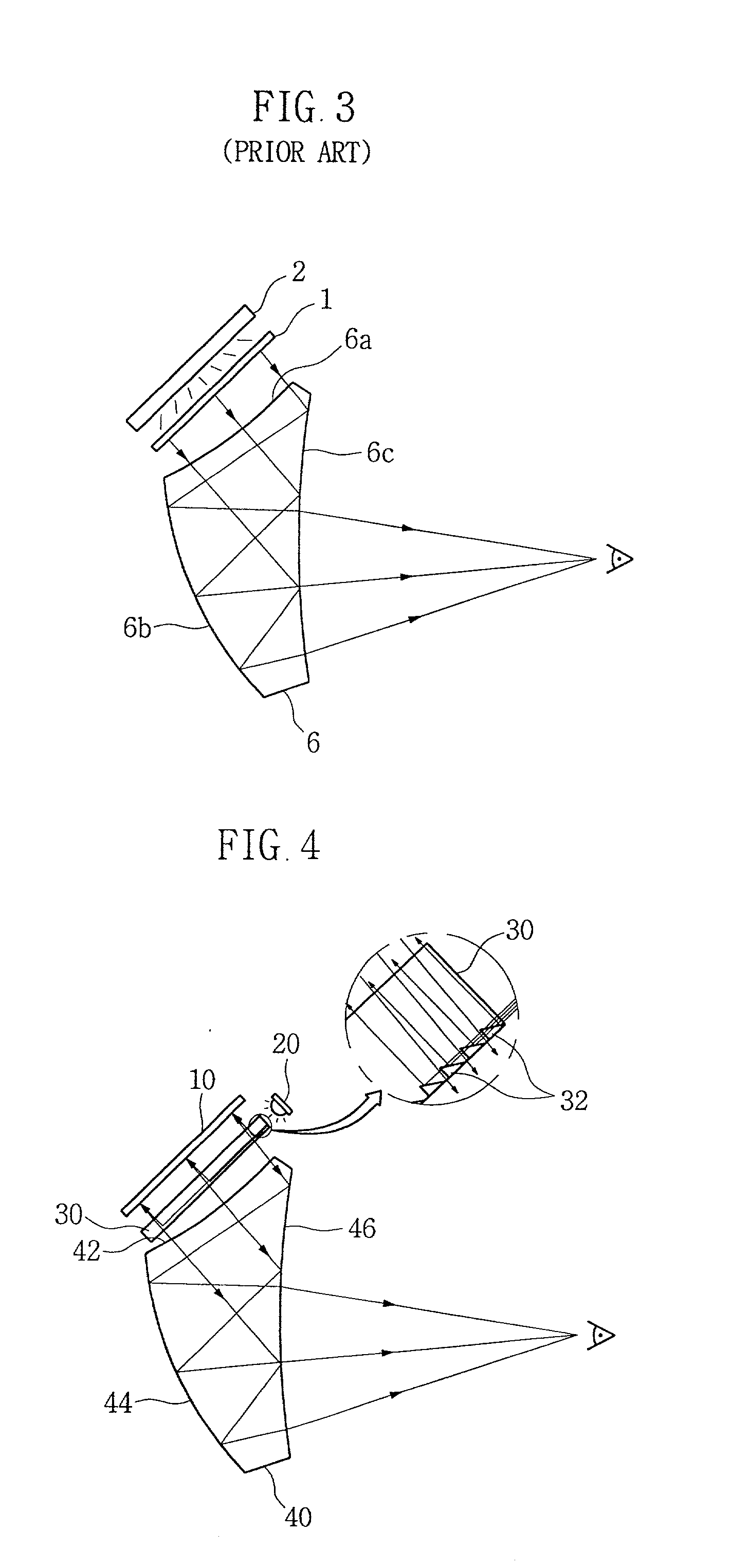
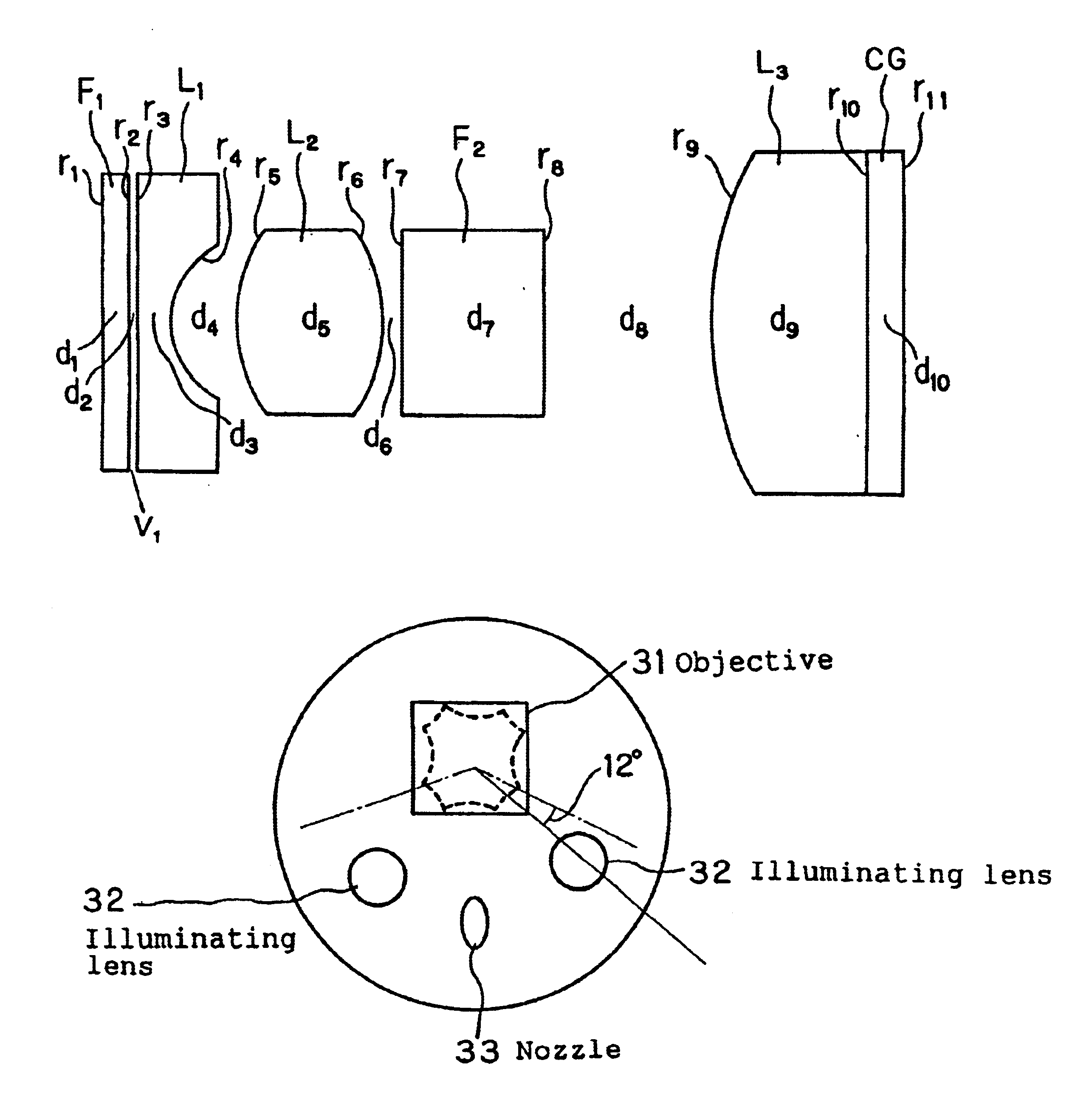
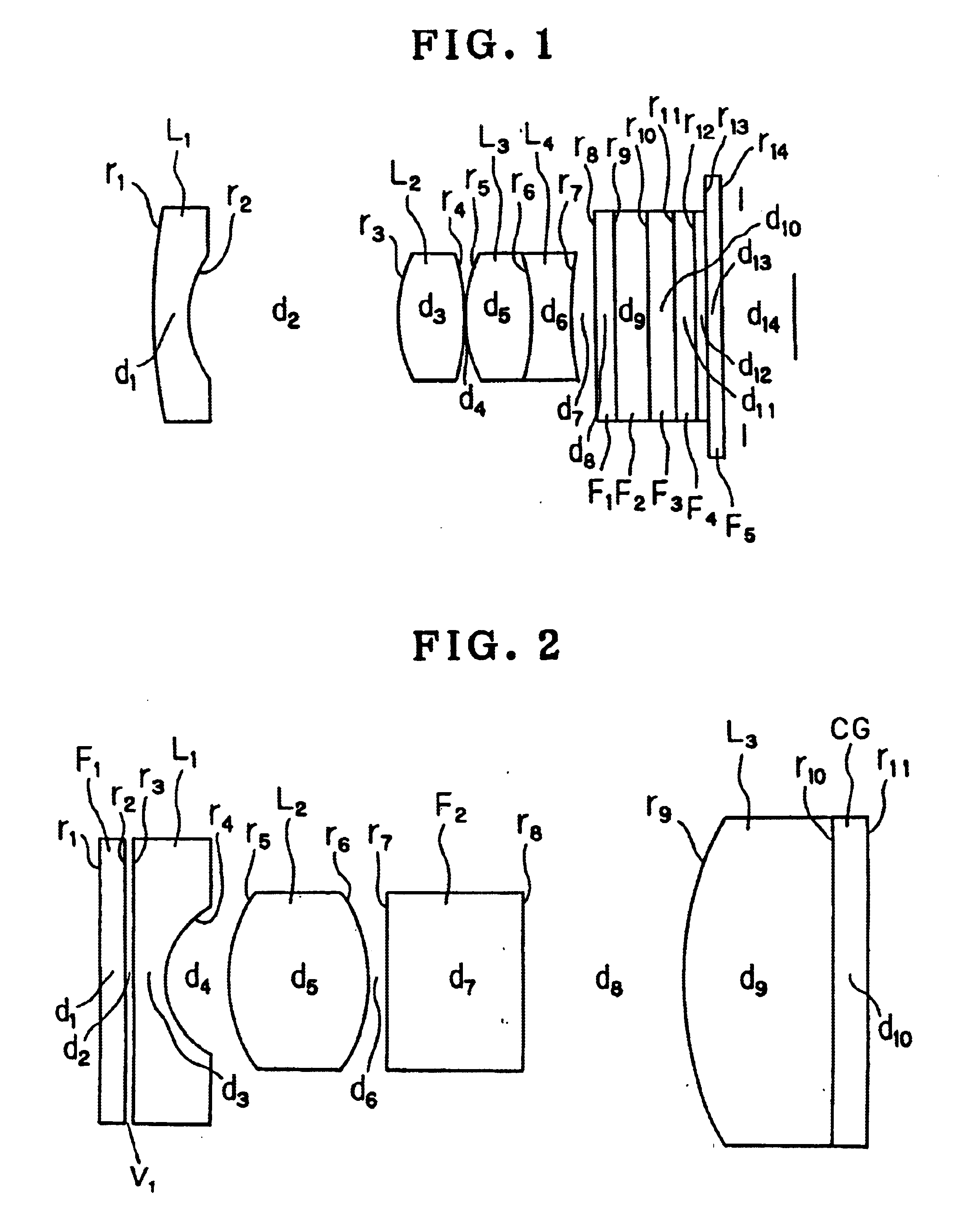
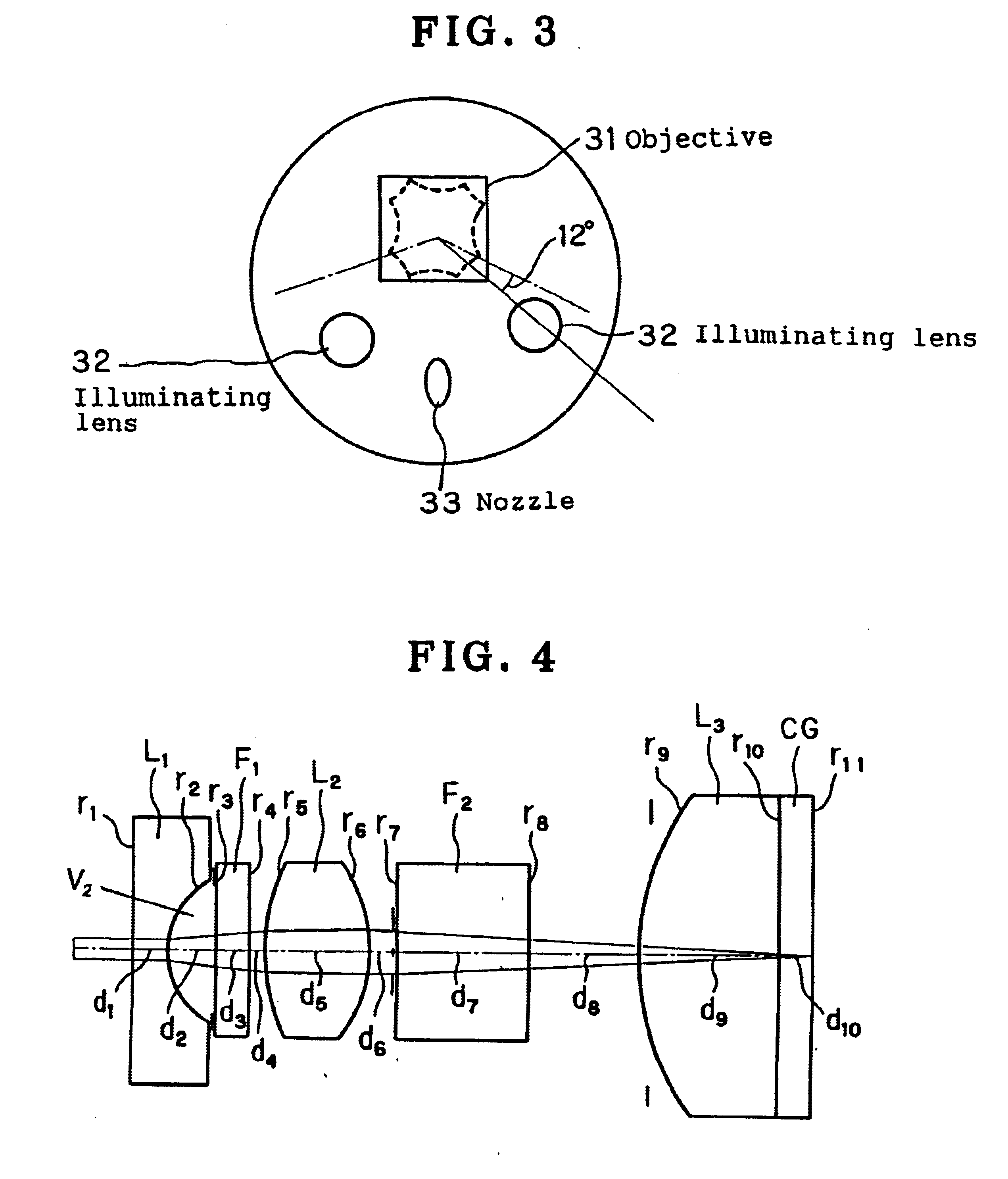
InactiveUS6905462B1Increase the diameterReduce overall outer diameterTelevision system detailsSurgeryPixel densityParallel plate
An endoscope optical system is capable of obtaining favorable endoscopic images at all times by overcoming the conventional disadvantages that diagnosis is hindered by image quality disturbance due to the increase in pixel density resulting from the reduction in pixel pitch of solid-state image pickup devices and also due to the conventional arrangement of an objective front optical element in an optical system having a short focal length or in an optical system having a large F-number. In an image pickup apparatus using a monochromatic high-density solid-state image pickup device in which the average pixel pitch (H+V) / 2 of the pixel pitch H in the horizontal direction and the pixel pitch V in the vertical direction with respect to the monitor scanning line is not more than 4.65 μm, or using an interline type color high-density solid-state image pickup device in which the average pixel pitch (H+V) / 2 is not more than 3.1 μm, the volume V1 of an air layer between a plane-parallel plate (F1) closest to the object side in the image pickup optical system and a piano-concave negative lens (L1) satisfies the following condition:V1<4 mm3 (1)
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN110379836ASolve uneven brightnessImprove the display effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPixel densityDark spot
The invention relates to a display panel, which is characterized in that the opening area of any sub-pixel arranged in a first transition display area is larger than that of a same-color sub-pixel arranged in a first display area, and the opening area of any sub-pixel arranged in the first transition display area is less than that of a same-color sub-pixel arranged in a second display area; the minimum distance between any two most adjacent same-color sub-pixels arranged in the first display area is x, the minimum distance between any two most adjacent same-color sub-pixels respectively arranged in the first transition display area and the second display area is y, and the minimum distance between any two most adjacent same-color sub-pixels arranged in the second display area is z, y is greater than or equal to x and less than or equal to z, and the opening area of the sub-pixel is a light emitting area of the sub-pixel. The display panel can effectively reduce the difference in visionof users due to the different sub-pixel per inch (PPI) between the first display area and the second display area, avoid the occurrence of dark spots or dark lines and improve the display effect. Theinvention further provides a display device.
Owner:YUNGU GUAN TECH CO LTD
Display screen and display apparatus
ActiveCN108364967AMeet the requirements of normal displayIncrease the proportionStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPixel densityComputer graphics (images)
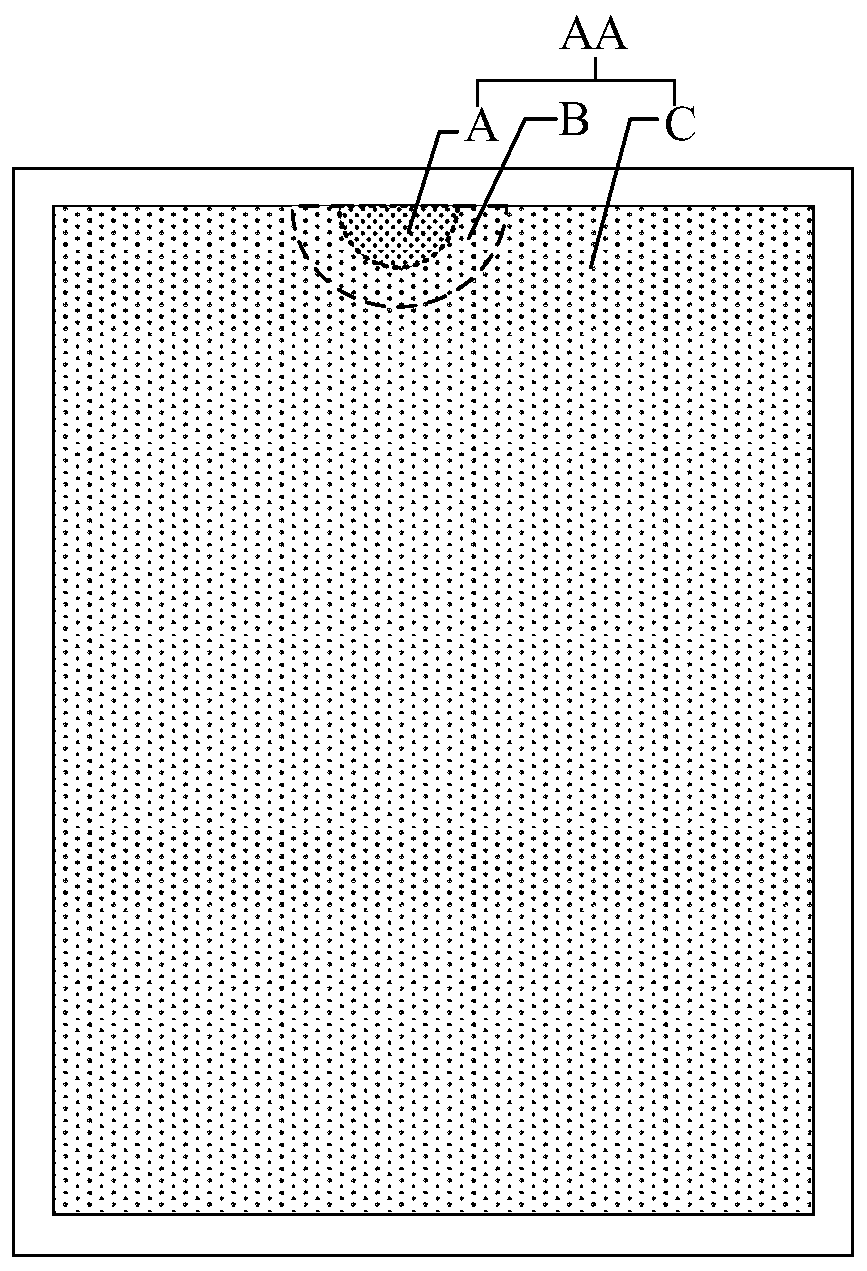
The invention relates to a display screen. The display screen comprises a first region and a second region; the sub pixel density in the first region is lower than that in the second region. By adjusting the sub pixel density in a camera position, the requirement of normal display of the camera can be satisfied while the requirement of relatively high transmittance of the camera is also met; and position reservation for a preposition camera is not needed, so that a non-display region above a display region can be omitted, the screen-to-body ratio is increased and user experience is optimized,thereby solving the technical problem of poor user experience caused by existence of the non-display region.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical system for head mounted display
The present invention relates to a head mounted display that is constructed such that stereoscopic images can be seen on a liquid crystal display screen disposed adjacent to eyes. The present invention provides an optical system for a head mounted display, comprising a light source; an illuminating prism for controlling an optical path of light rays from the light source by reflecting and refracting the light rays; a polarizer for polarizing the light rays emitted from the illuminating prism; a polarization beam splitter for reflecting the polarized light rays emitted from the polarizer; a frontlight liquid crystal display screen on which images are displayed by means of the light rays reflected by the polarization beam splitter; and a free-form-surface prism disposed in front of the polarization beam splitter for magnifying the images on the liquid crystal display screen by reflecting and converging the light rays emitted from the liquid crystal display screen. According to the present invention, since the optical system for the head mounted display employs the frontlight liquid crystal display screen which is inexpensive and has a high pixel density, there is an advantage in that its production costs can be reduced. Further, the optical system includes the inexpensive light emitting diode, and the illuminating prism and the plurality of sheets for diffusing and focusing the light rays emitted from the light emitting diode, so that the use efficiency of the light source can be enhanced.
Owner:DAEYANG ENG
Methods and apparatuses for controlling display devices
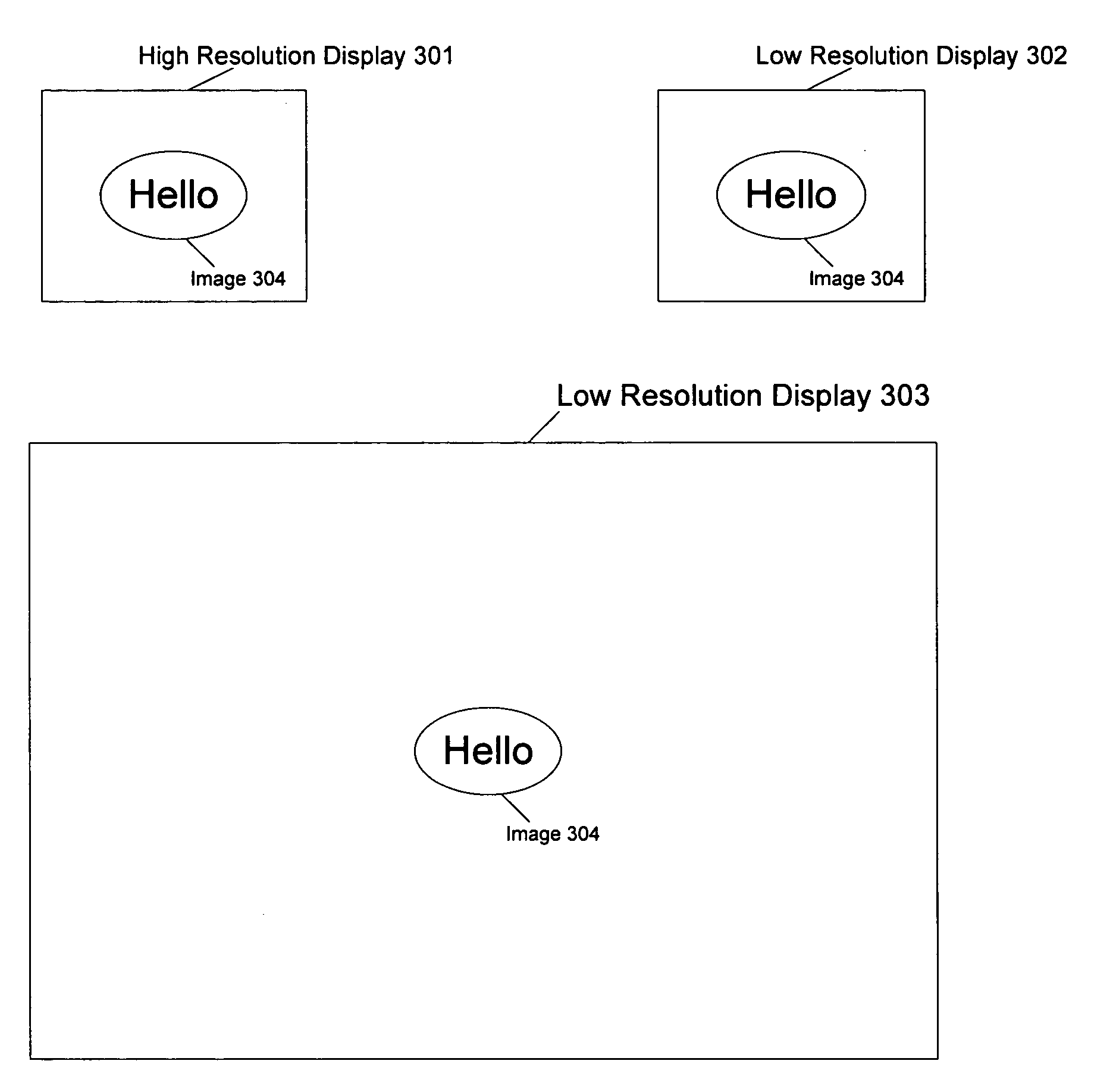
ActiveUS20080030425A1Image memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsPixel densityImage resolution
Methods and apparatuses for per display scale factors within a multiple display system are described.In one aspect of the invention, a machine implemented method includes setting a scale factor for each window buffer equal to an extreme scale factor among a plurality of displays. The method further includes transferring data from each window buffer into a corresponding frame buffer for one of the plurality of displays by setting a scale factor of each frame buffer equal to the scale factor of the corresponding display.In one example according to this aspect, the method further includes displaying on a high resolution display and a low resolution display an image, stored in the corresponding frame buffers, with substantially the same physical size even though the displays have different scale factors and pixel densities. Also, the extreme scale factor is one of the largest scale factor or the smallest scale factor.
Owner:APPLE INC
Image display device and optical element for forming stereoscopic image used in the same
InactiveUS20070086090A1Improve image qualitySteroscopic systemsOptical elementsParallaxPixel density
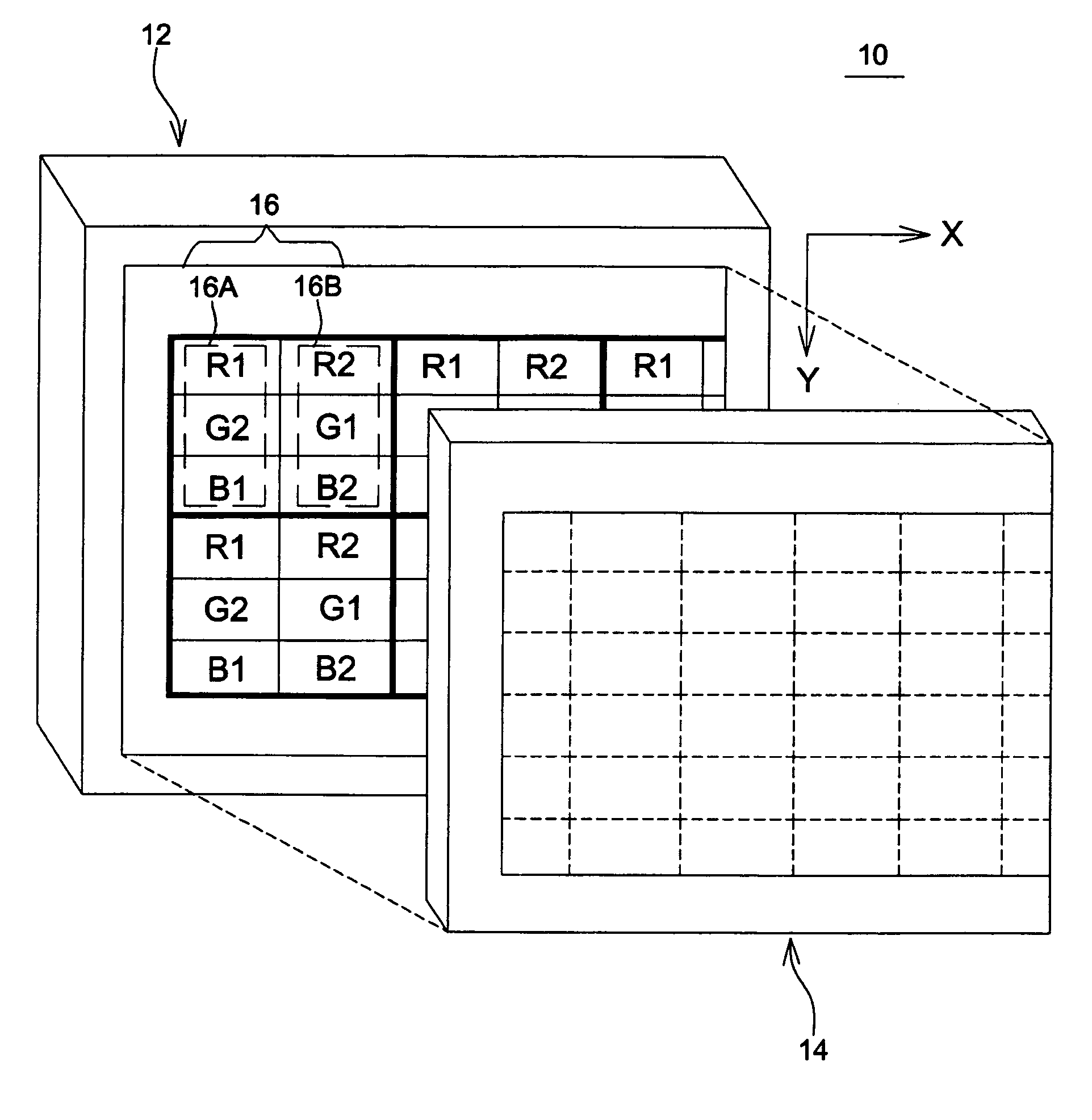
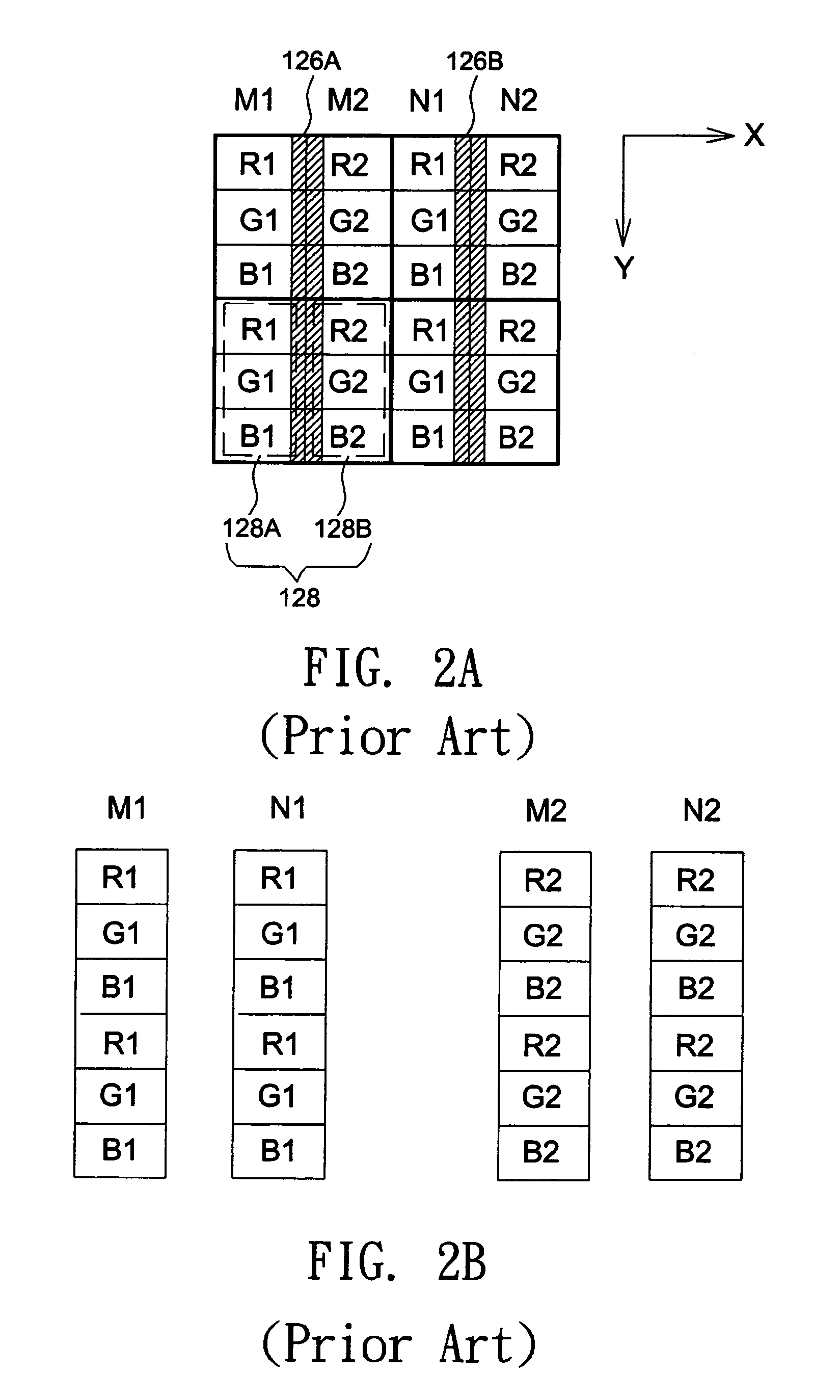
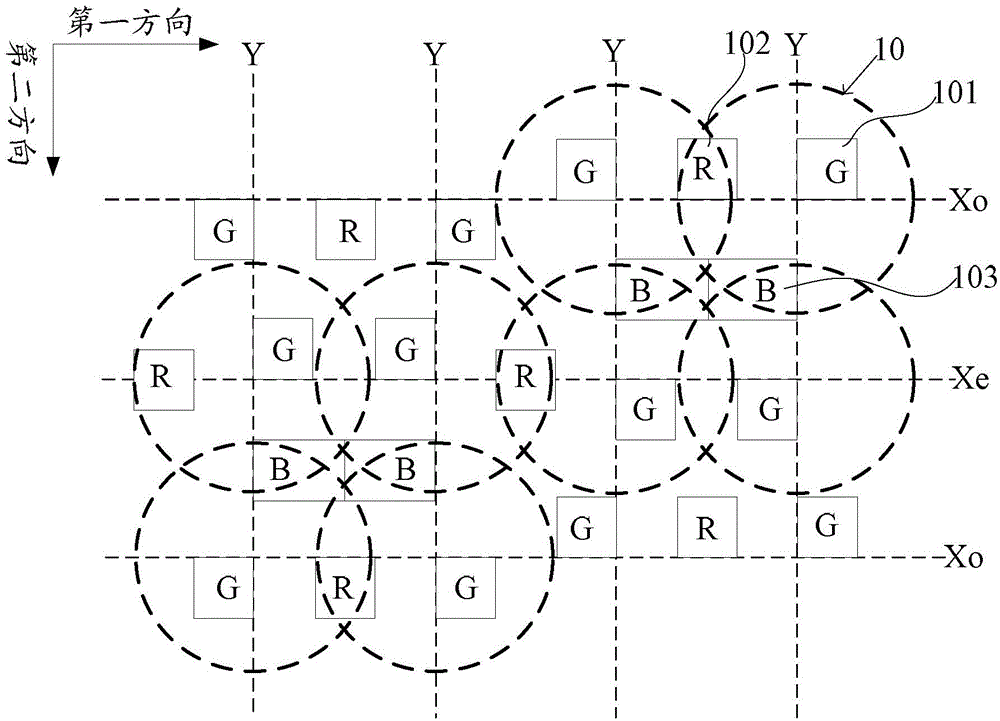
An image display device includes a display panel and a parallax optic. The display panel is provided with a stripe sub-pixel arrangement in which sub-pixels arranged in a first direction have identical colors, and sub-pixels arranged in a second direction have distinct colors. The pixel density in the first direction is twice the pixel density in the second direction of the stripe sub-pixel arrangement. The parallax optic has view-separation elements arranged in the first direction into multiple rows. Each view-separation element is positioned corresponding to two adjacent sub-pixels, and the view-separation elements in one row are staggered relative to the view-separation elements in immediately adjacent rows.
Owner:WINTEK CORP
Semiconductor photosensitization device, production method and application thereof
ActiveCN101707202AReduce manufacturing costHigh image resolutionTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionPixel density
The invention discloses a semiconductor photosensitization device which comprises a source electrode, a drain electrode, a control grid, a floating grate region, a substrate, and a p-n node diode for connecting a floating gate region and a drain electrode. The floating grate region of the semiconductor photosensitization device is used for storing charges, and the floating grate potential of the semiconductor photosensitization device is related to light exposure intensity and time, thus, the invention can be used as a semiconductor photosensitization device. The invention also discloses production methods of the semiconductor photosensitization device and an image sensor, as well as an image sensor formed by arrays formed by the semiconductor photosensitization device. The semiconductor photosensitization device can simplify the design of a single pixel unit in a traditional image sensor and reduce the area occupied by the single pixel unit, thereby improving the pixel density of the image sensor, increasing the resolution of the image sensor and reducing the production cost of the image sensor.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
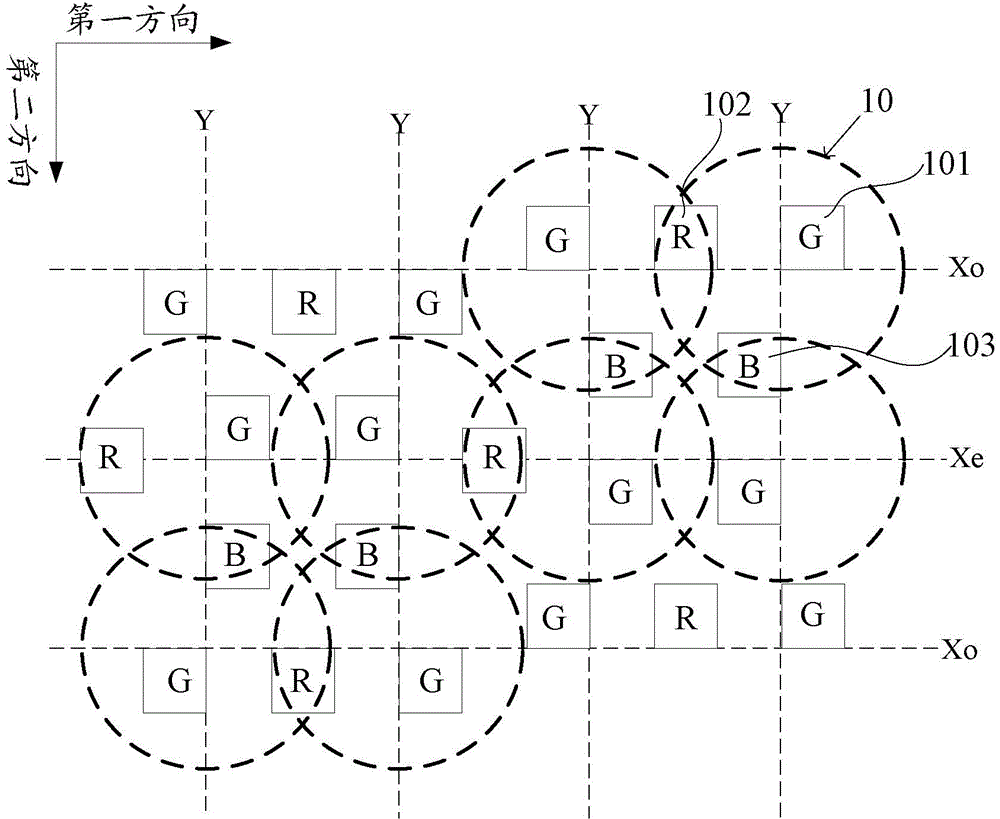
Pixel arraying structure, display panel and display device
ActiveCN104597655AReduce processing difficultyAvoid excessSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsPixel densityDisplay device
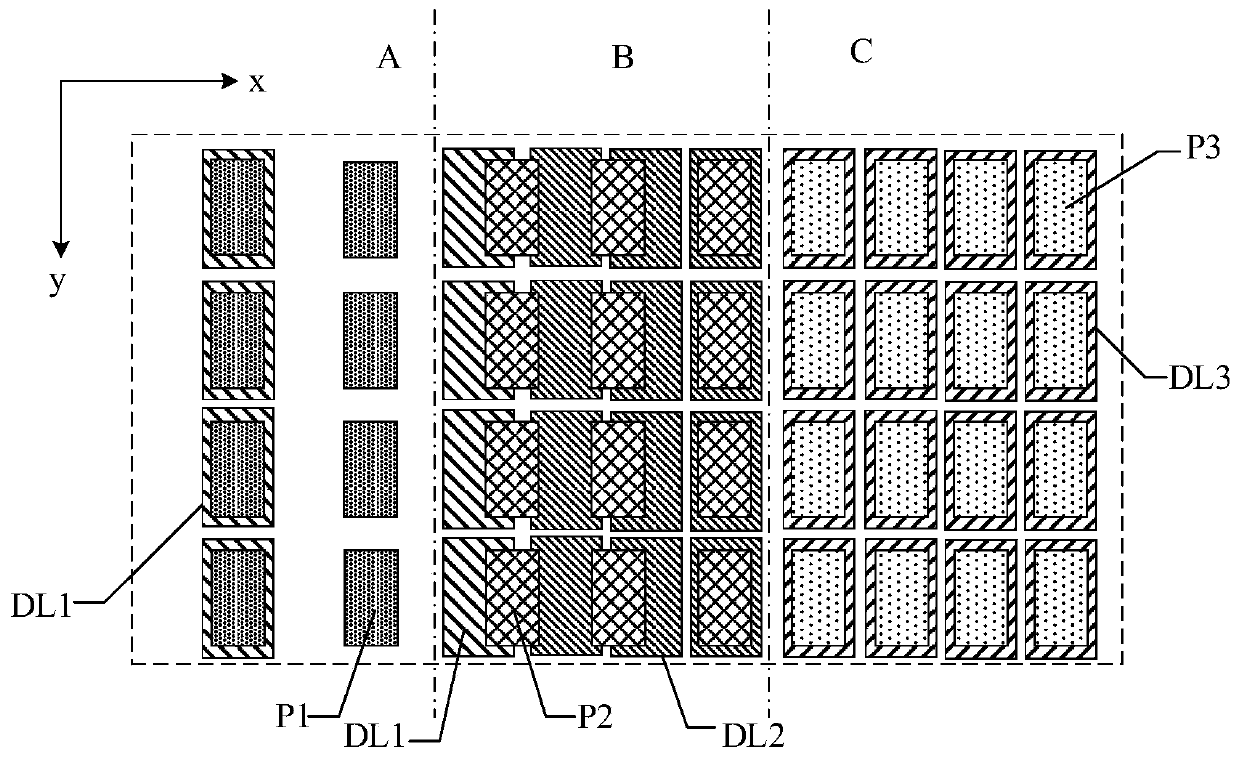
The embodiment of the invention provides a pixel arraying structure, a display panel and a display device, and relates to the field of display technologies. Compared with the prior art, the technology difficulty in preparing the display device is reduced; the pixel arraying structure comprises a plurality of first sub-pixels, a plurality of second sub-pixels and a plurality of third sub-pixels; each pixel comprises a first sub-pixel; each second sub-pixel and each third sub-pixel are shared by at least two adjacent pixels respectively; the density of the sub-pixels is 1.5 times of that of the density of the pixels in the first direction of the pixel array; the density of the sub-pixels is 1.5 times of that of the density of the pixels in the second direction of the pixel array; the first direction and the second direction are different directions. The pixel arraying structure is used for high-resolution display devices.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Electronic imaging system
InactiveUS6882366B1High rate outputHigh outputTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh frame ratePixel density
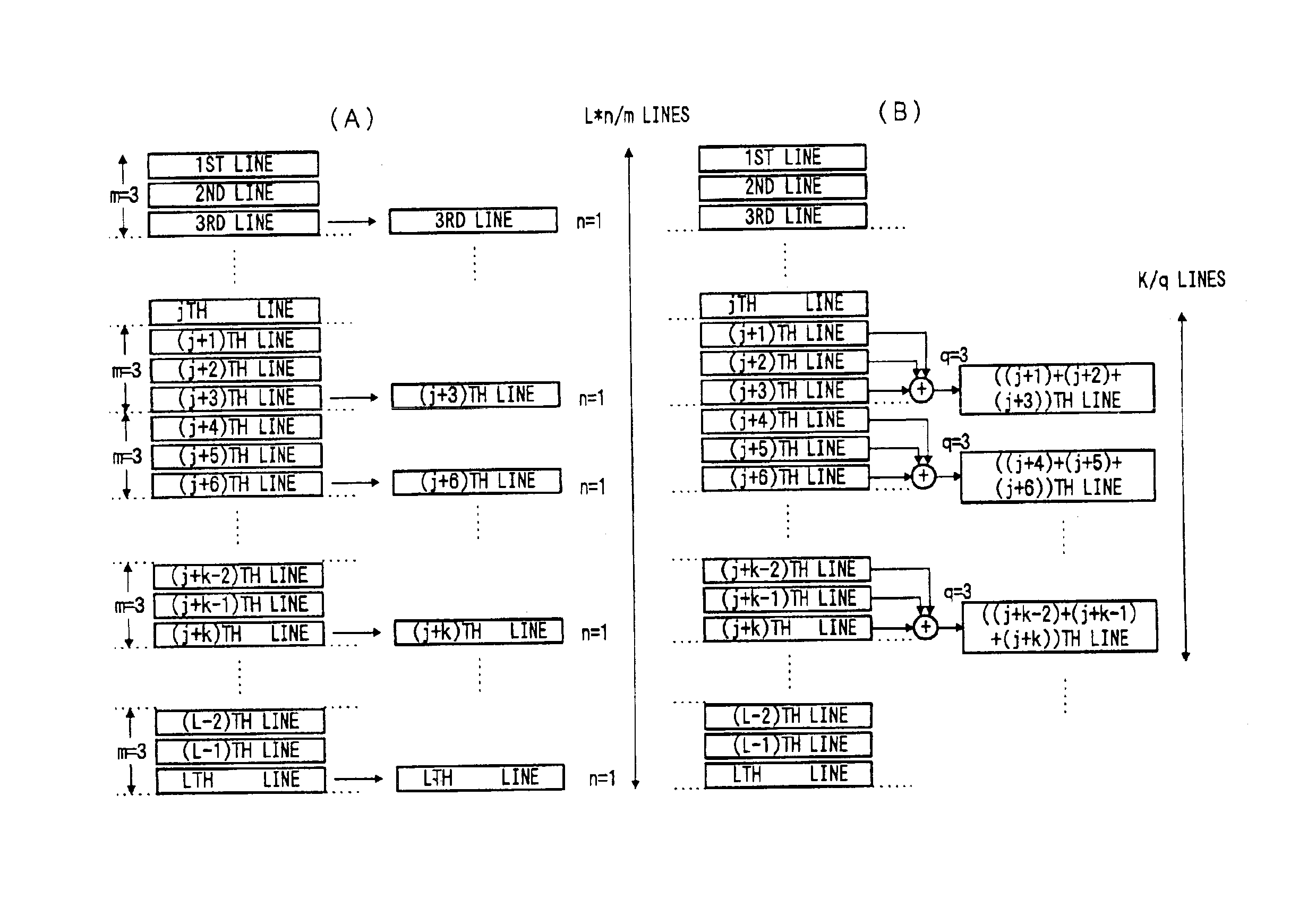
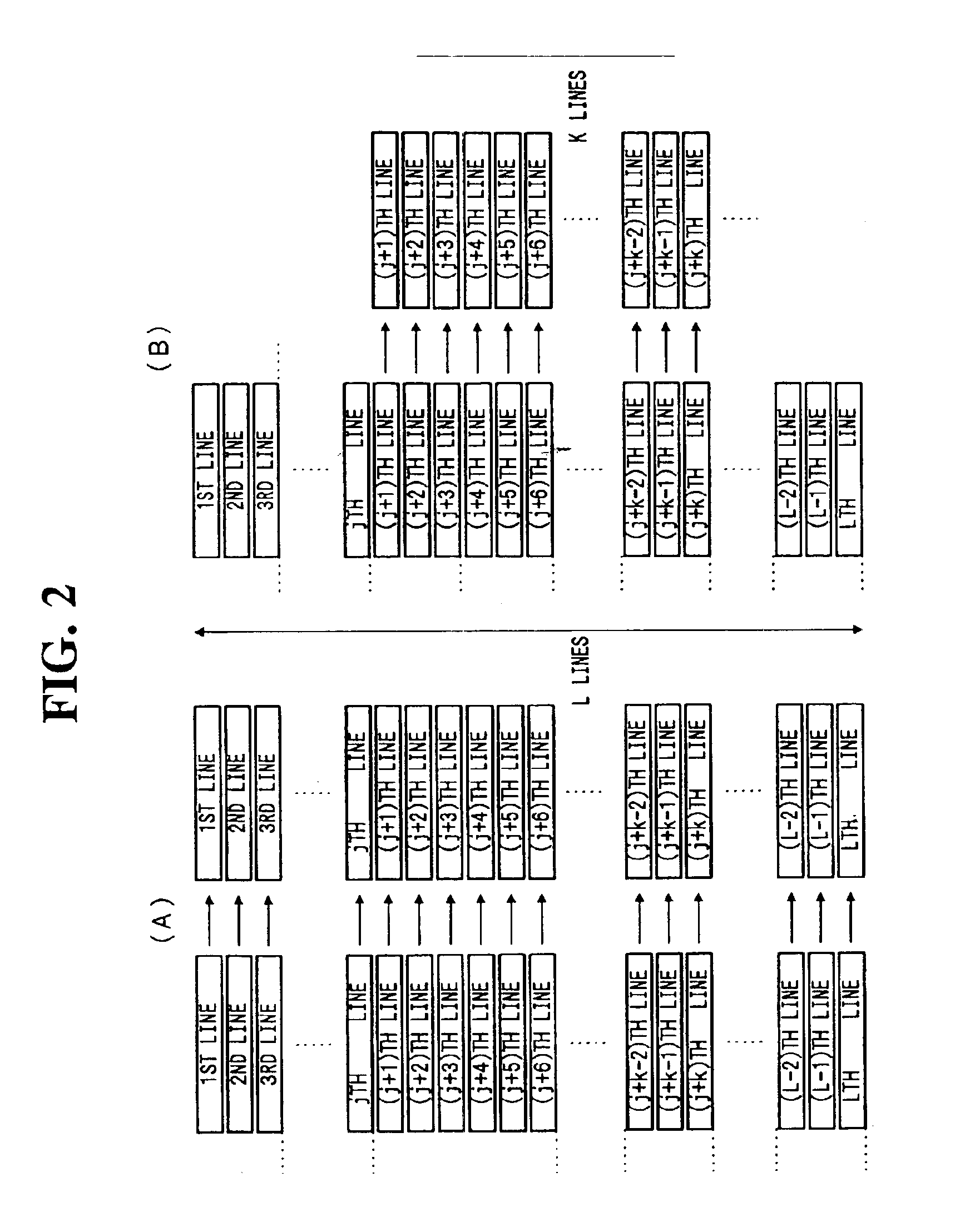
An electronic imaging system includes a CCD image sensor arrangement having a two dimensional array of pixels. The pixel array converts light incident thereon to an electric signal. The pixels are arranged in a plurality of horizontal rows or lines, the lines being arranged vertically. A control arrangement selectively controls operational modes of the system. One mode provides for sequential scan reading out of pixel signals for entire lines of the CCD for still picture recording. Another mode provides for reading out pixel signals concerning k (k is a positive integer) vertically continuous lines of the CCD for still picture recording or dynamic image processing. Thus it is possible to provide a high pixel density solid-state image sensor output at a high frame rate without use of any high drive frequency.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Algorithmic technique for increasing the spatial acuity of a focal plane array electro-optic imaging system
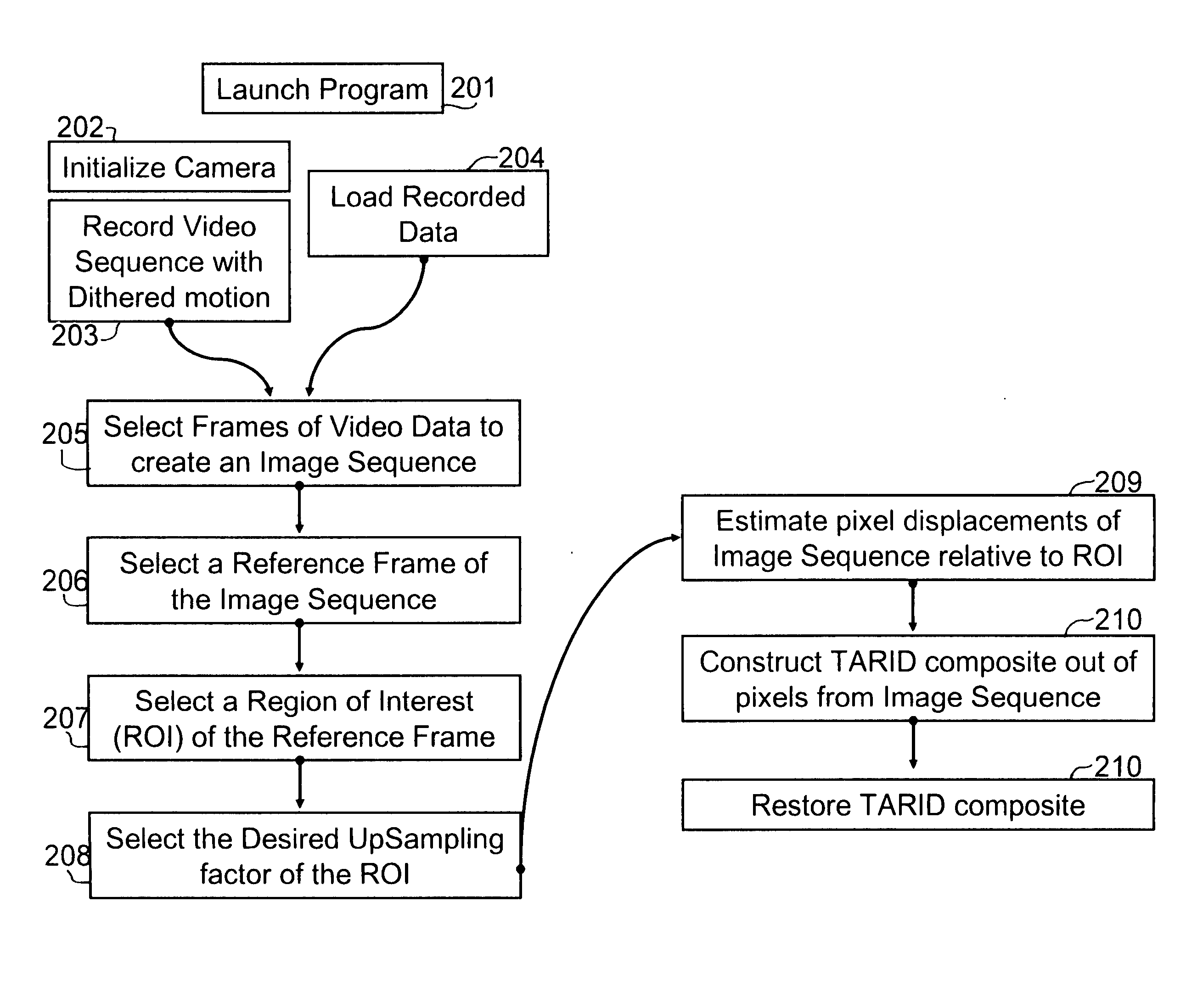
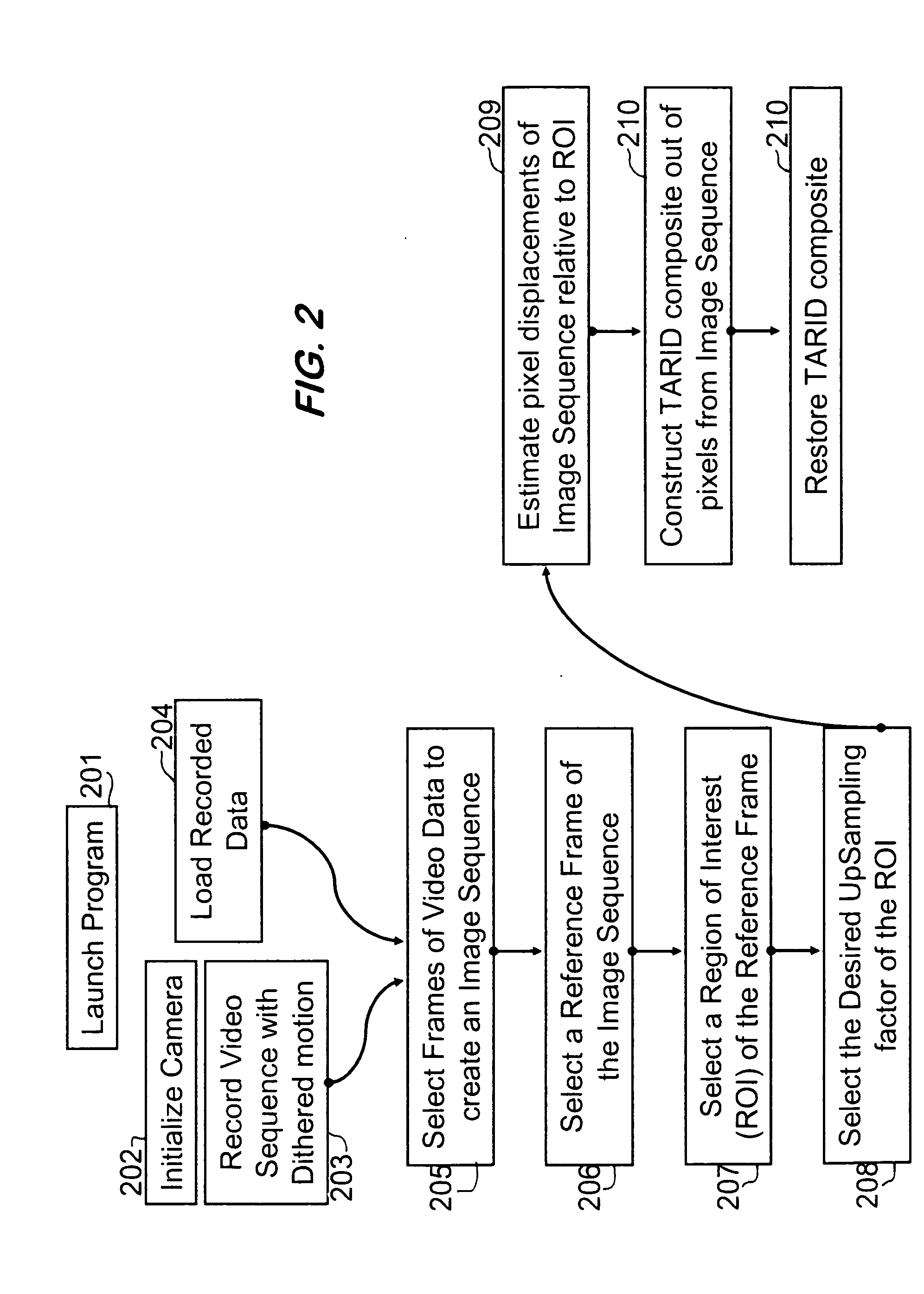
InactiveUS20050201637A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease the physically achievable resolution of an imaging systemTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationPixel densityVideo sequence
A system for enhancing images from an electro-optic imaging sensor and for reducing the necessary focal length of a sensor while preserving system acuity. This system uniquely reduces the necessary focal length and enhances images by collecting a video sequence, estimating motion associate with this sequence, assembling video frames into composite images, and applying image restoration to restore the composite image from pixel, lens blur, and alias distortion. The invention synthetically increases the pixel density of the focal plane array. Thus it reduces the necessary size of the projected blur circle or equivalently it reduces the minimum focal length requirements.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Optimized distribution of light extraction from an edge lit light source
InactiveUS7762704B2Reliable methodUniform lightPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesEffective densityPixel density
An edge-lit panel features extractor patterns that produce uniform illumination. The effective density of extractor pattern pixels is adjusted to achieve uniform illumination. A method of adjusting the effective pixel density of extractor pattern pixels to achieve uniform illumination entails adjusting areas of darkness of a grayscale image, then producing a binary image by dithering the grayscale image, and applying an extractor pattern corresponding to the binary image to a surface of the panel. The extractor pixels correspond to pixels of the binary image derived from a dithered grayscale image, with the darkness of the grayscale image increasing with distance from the light source. Effective pixel density is increased to compensate for attenuated output in dim areas. By adjusting gray shading darkness of a grayscale image, pixel density can be adjusted to achieve uniform light emission. The extractor pixels may be applied using a radiation curable ink, which can be used in high speed inkjet printers that can achieve production speeds. The resulting print is waterproof, embossed and vibrant.
Owner:BRYTER TECH
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN110874990APromote lowerMitigating the impact of optical performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPixel densityDisplay device
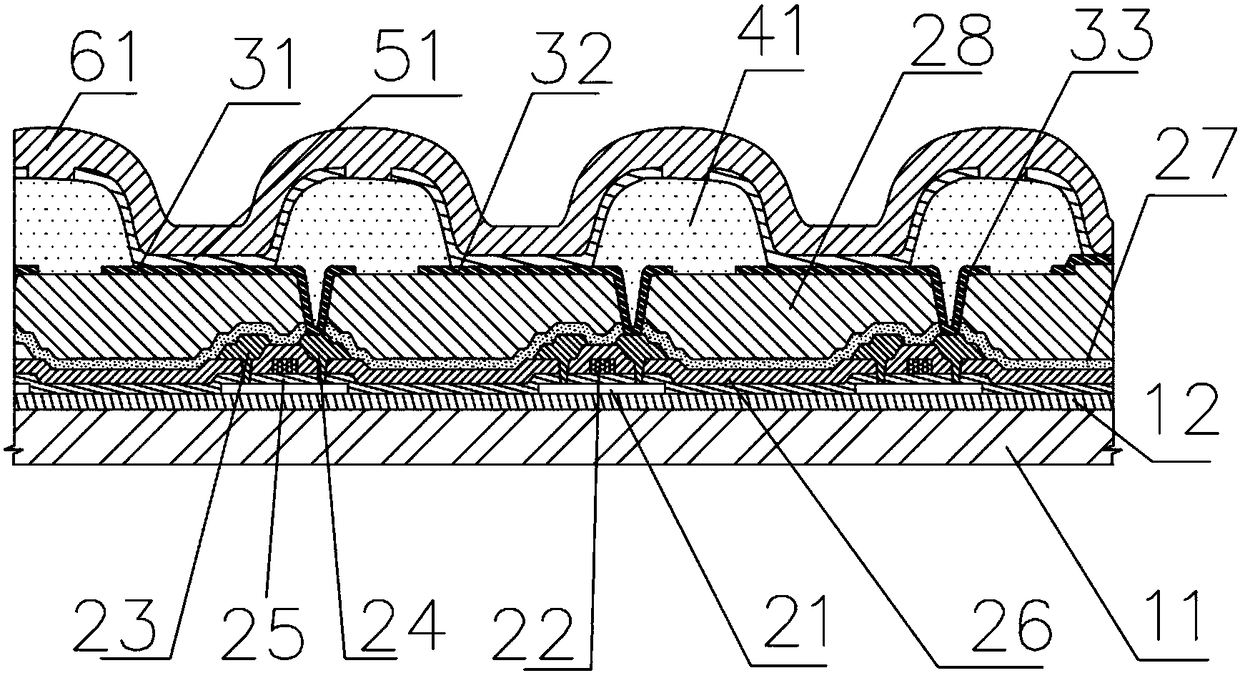
The embodiment of the invention provides a display panel and a display device. The display panel comprises a display area, wherein the display area comprises a first display area, a transition area and a second display area, wherein the sub-pixel density of the first display area, the transition area and the second display area is gradually increased. The first display area comprises a plurality of first sub-pixels, and a first pixel circuit for driving the first sub-pixels is located in the transition area, so that the light transmission area of the first display area is increased. The firstsub-pixels are electrically connected with the first pixel circuit through a connecting line. Each of a first line segment, a second line segment and a third line segment belongs to a different connecting line, and the first line segment, the second line segment and the third line segment all extend in a first direction and are sequentially arranged in a second direction. There is no gap between the first line segment and the second line segment arranged in sequence, and there is no gap between the second line segment and the third line segment arranged in sequence, so that the light transmittance of the first display area can be improved, the diffraction phenomenon when the light ray penetrates through the first display area is improved, and the optical performance of an under-screen optical device is improved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optimized distribution of light extraction from an edge lit light source
InactiveUS20100124074A1Reliable methodUniform lightPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesPixel densityEffective density
An edge-lit panel features extractor patterns that produce uniform illumination. The effective density of extractor pattern pixels is adjusted to achieve uniform illumination. A method of adjusting the effective pixel density of extractor pattern pixels to achieve uniform illumination entails adjusting areas of darkness of a grayscale image, then producing a binary image by dithering the grayscale image, and applying an extractor pattern corresponding to the binary image to a surface of the panel. The extractor pixels correspond to pixels of the binary image derived from a dithered grayscale image, with the darkness of the grayscale image increasing with distance from the light source. Effective pixel density is increased to compensate for attenuated output in dim areas. By adjusting gray shading darkness of a grayscale image, pixel density can be adjusted to achieve uniform light emission. The extractor pixels may be applied using a radiation curable ink, which can be used in high speed inkjet printers that can achieve production speeds. The resulting print is waterproof, embossed and vibrant.
Owner:BRYTER TECH
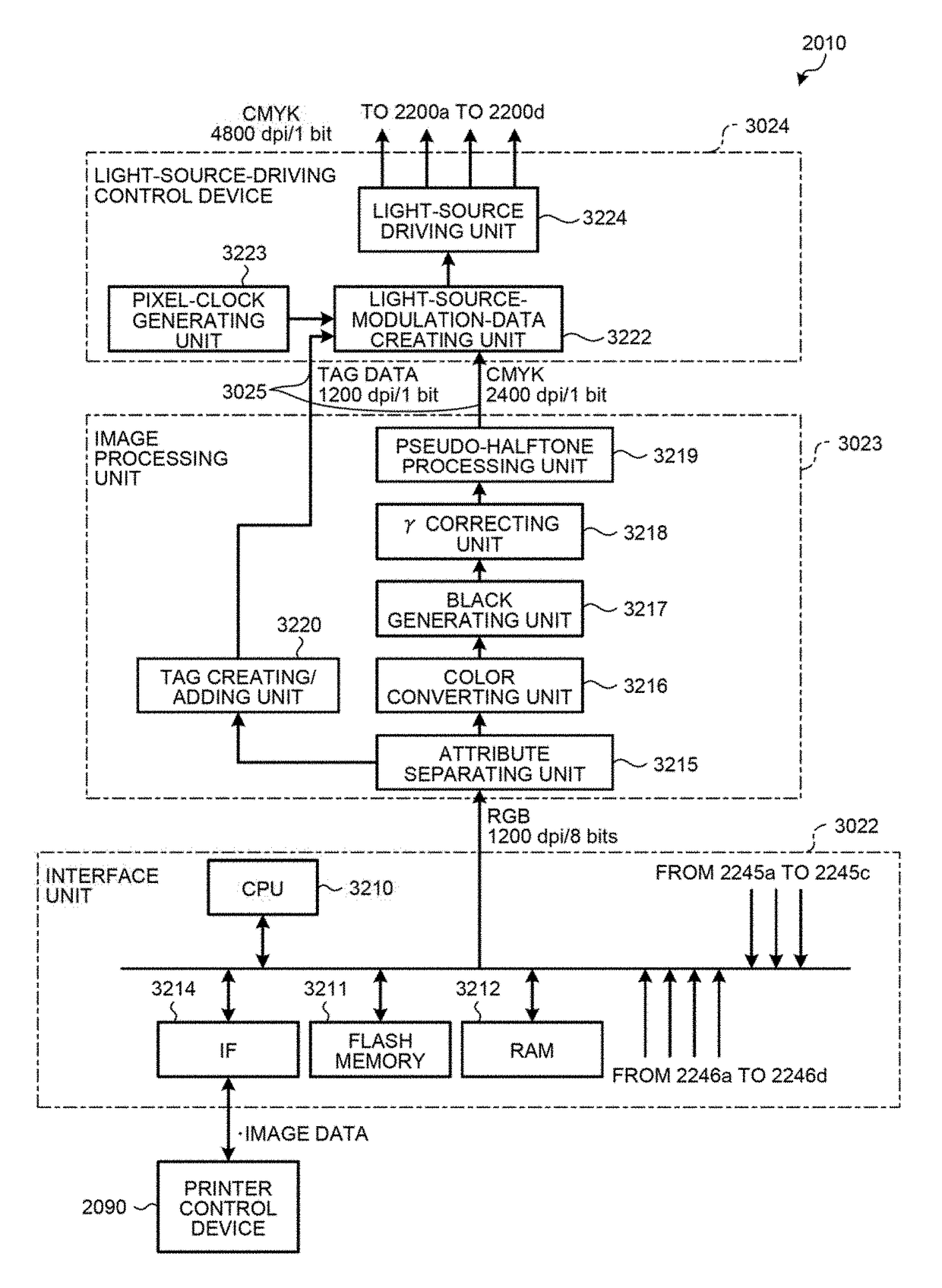
Light-source-driving control device, image forming apparatus, and light-source driving method
ActiveUS9779334B2Visual representatino by photographic printingElectrographic process apparatusPixel densityPower modulation
A light-source-driving control device thins a pixel at an edge portion of image data by a first pixel width; sets a second pixel width at the edge portion such that a ratio between the first and second pixel widths is constant; creates light amount information including a first light amount with which a pixel not included in the set second pixel width is exposed, and a second light amount with which a pixel included in the second pixel width is exposed; selects the first or second light amount based on a power-modulation control signal; drives light sources according to the selected light amount and a light-source-modulation pulse signal; and counts an addition value of pixel density considering a pixel width and a light amount, based on a data-width setting signal based on the second pixel width, and on a light-amount setting signal based on the light amount information.
Owner:RICOH KK
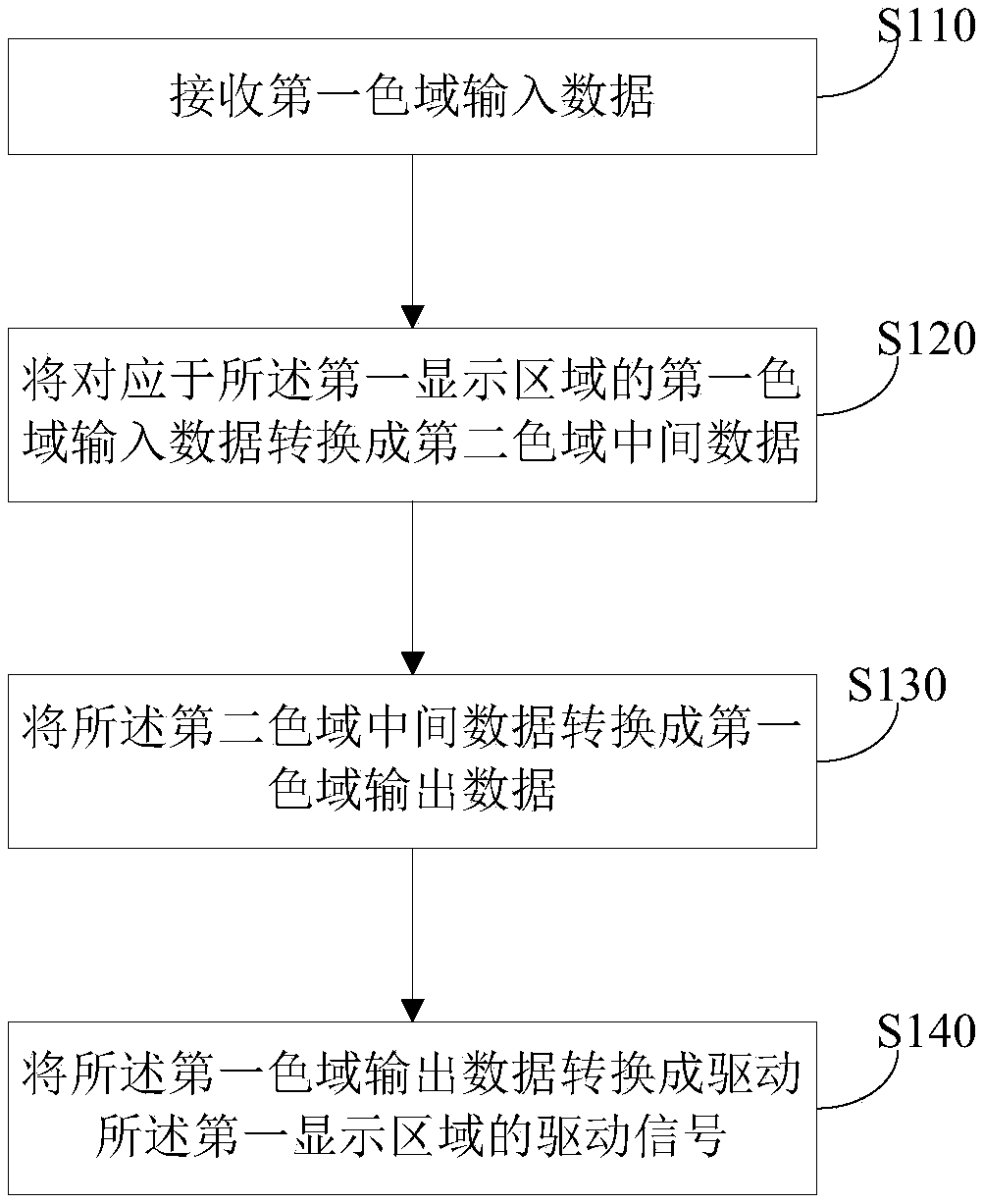
Driving method and device of display panel and display device
An embodiment of the invention discloses a driving method and device of a display panel and a display device. The display panel comprises a first display area with the first pixel density and a seconddisplay area in the second pixel density greater than the first pixel intensity. The driving method of the display panel comprises that input data of a first color gamut is received; the first gamutinput data corresponding to the first display area is converted into second color-gamut intermediate data; the second color-gamut intermediate data is converted into first color-gamut output data; andthe first color-gamut output data is converted into a driving signal driving the first display area.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com