Patents
Literature
450results about How to "High peak power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and devices for charge management for three-dimensional sensing
InactiveUS6906793B2Minimal overheadEffective coloringTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSHigh frequency modulation
Structures and methods for three-dimensional image sensing using high frequency modulation includes CMOS-implementable sensor structures using differential charge transfer, including such sensors enabling rapid horizontal and slower vertical dimension local charge collection. Wavelength response of such sensors can be altered dynamically by varying gate potentials. Methods for producing such sensor structures on conventional CMOS fabrication facilities include use of “rich” instructions to command the fabrication process to optimize image sensor rather than digital or analog ICs. One detector structure has closely spaced-apart, elongated finger-like structures that rapidly collect charge in the spaced-apart direction and then move collected charge less rapidly in the elongated direction. Detector response is substantially independent of the collection rate in the elongated direction.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
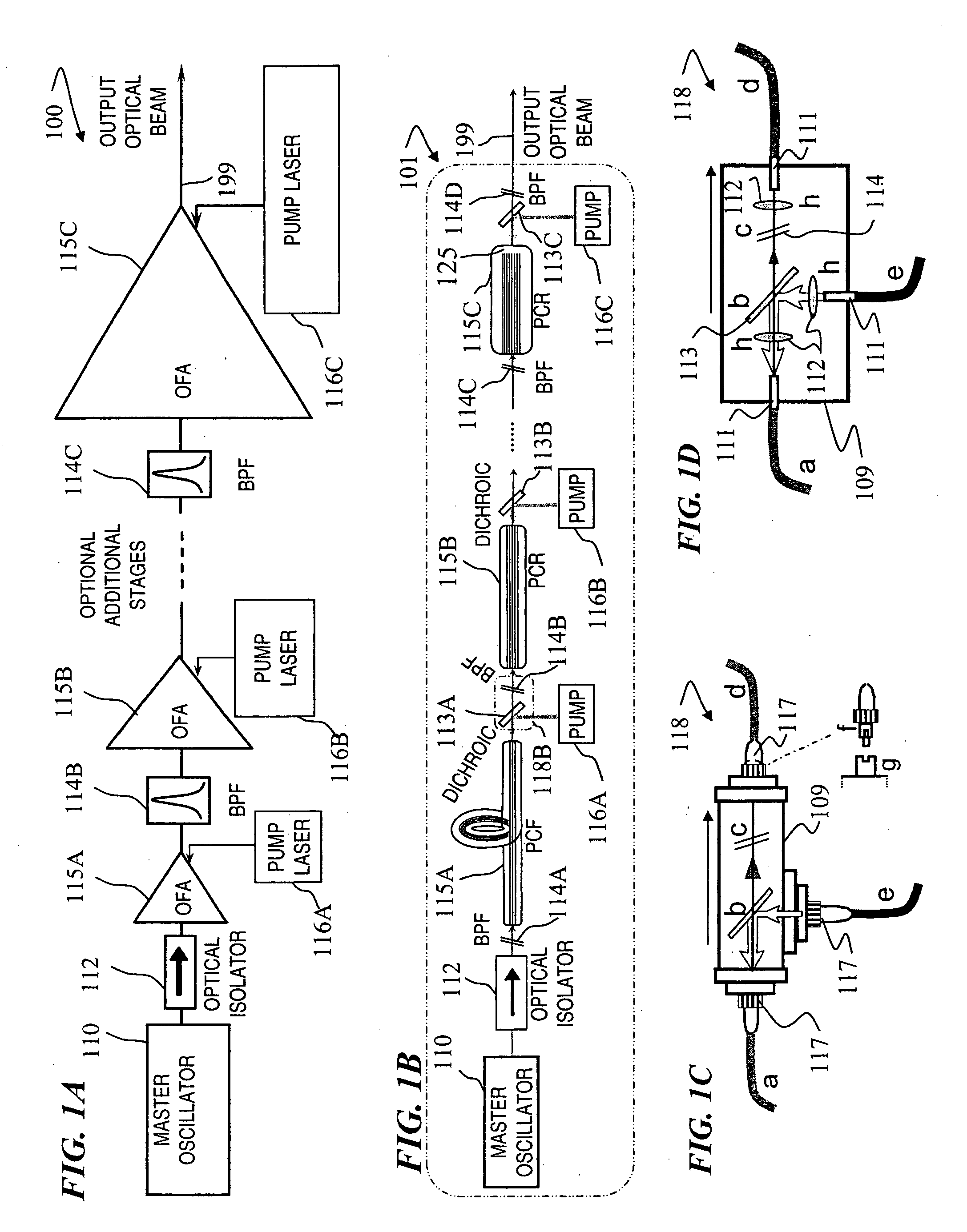
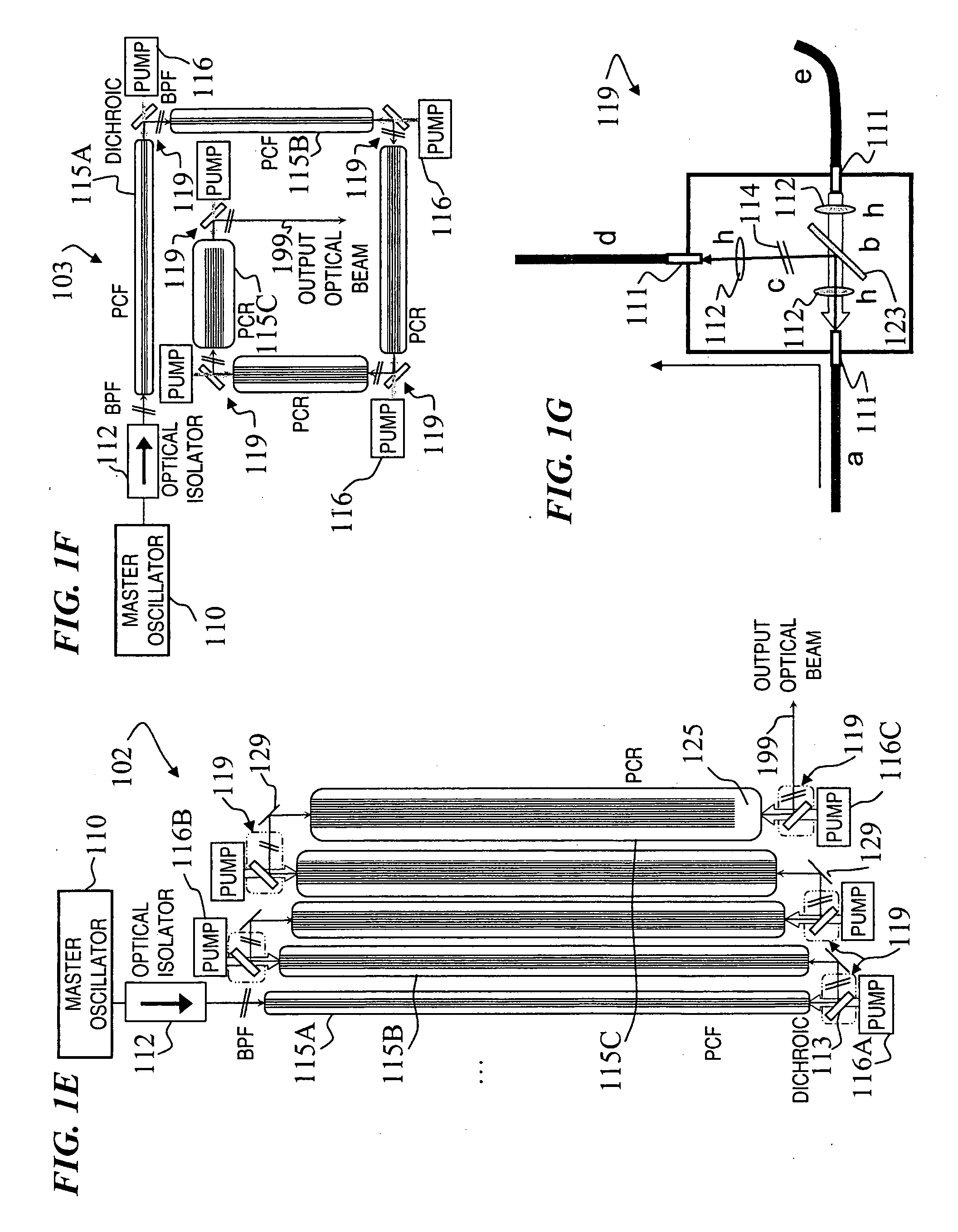
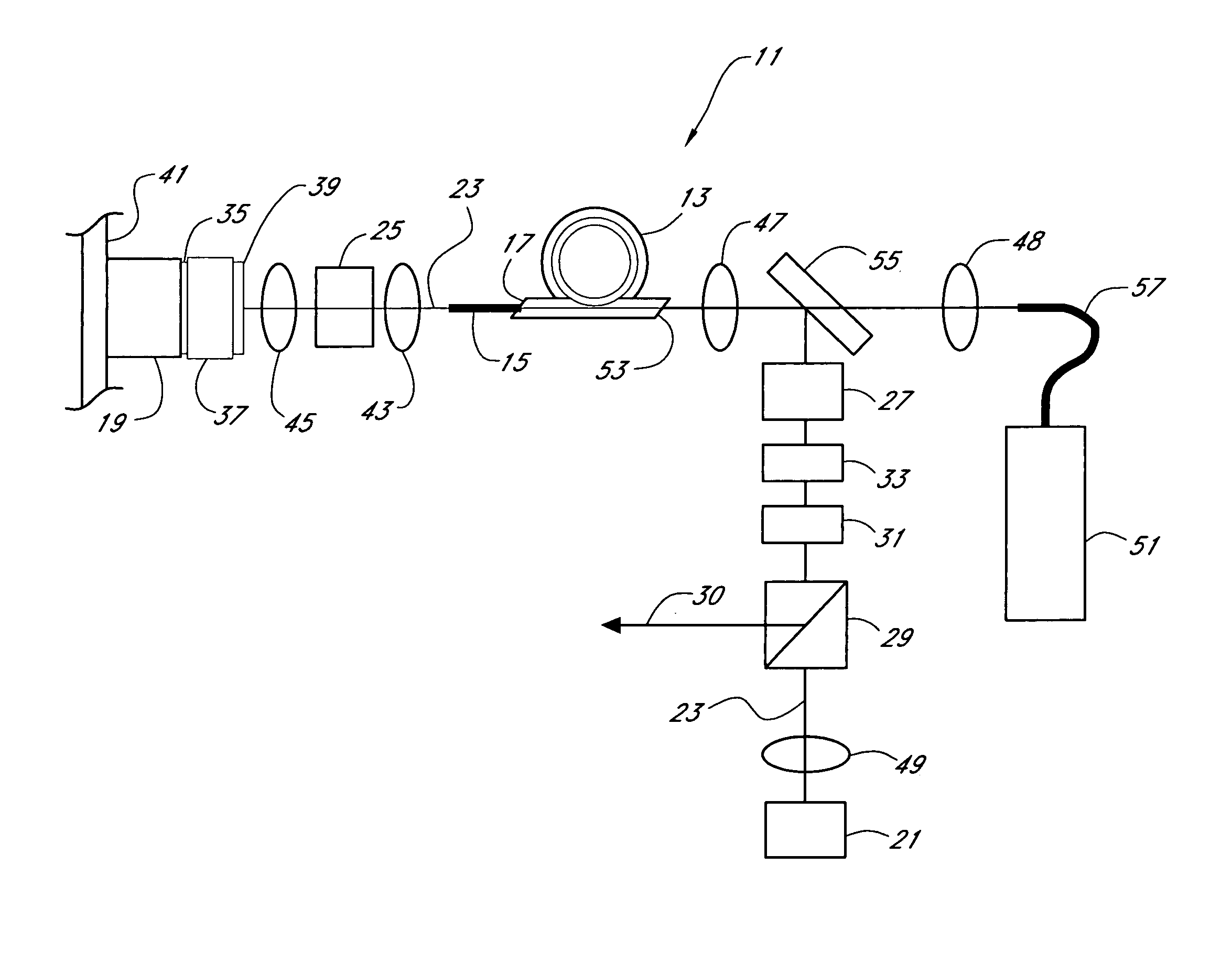
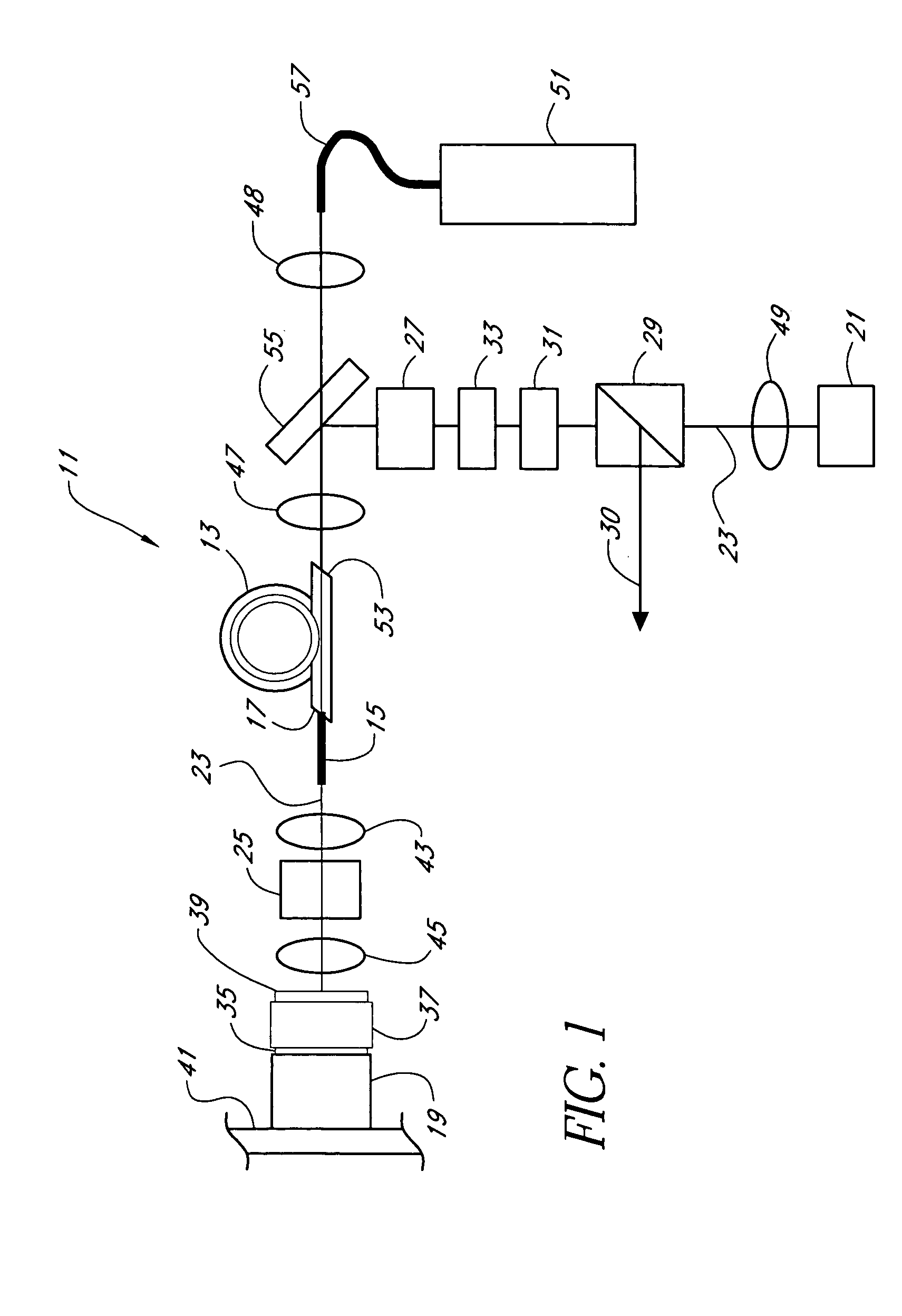
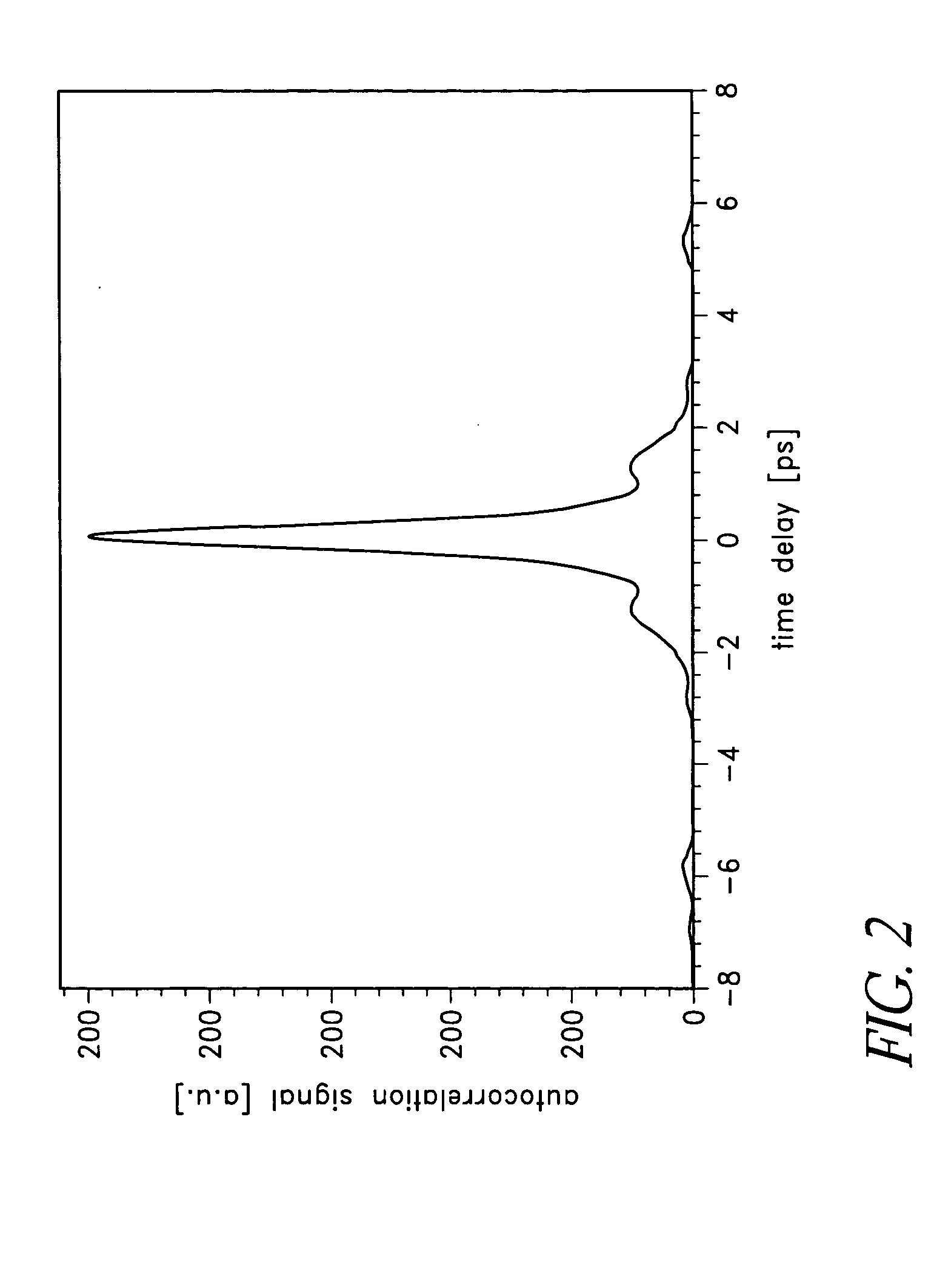
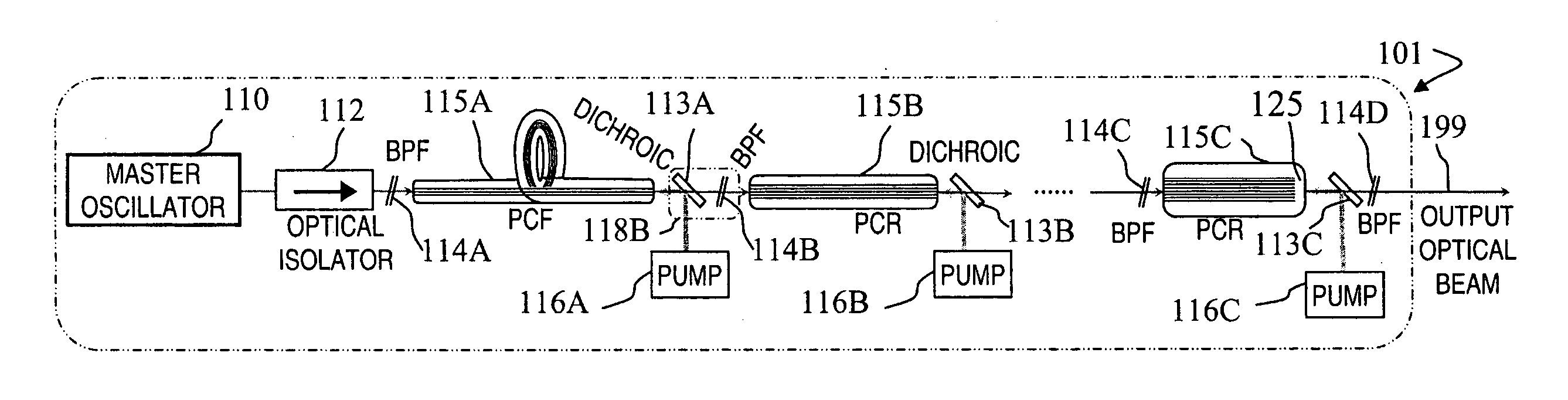
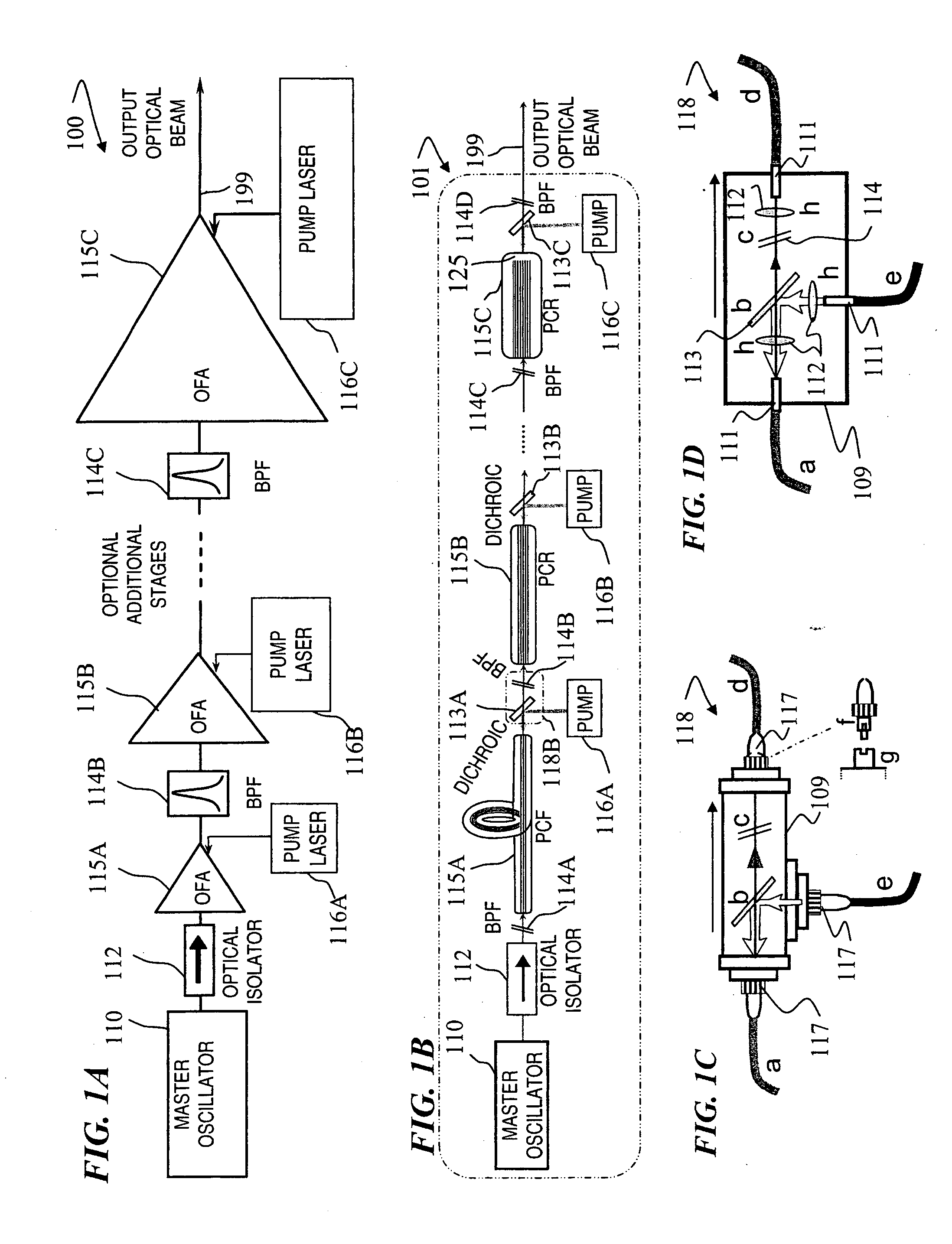
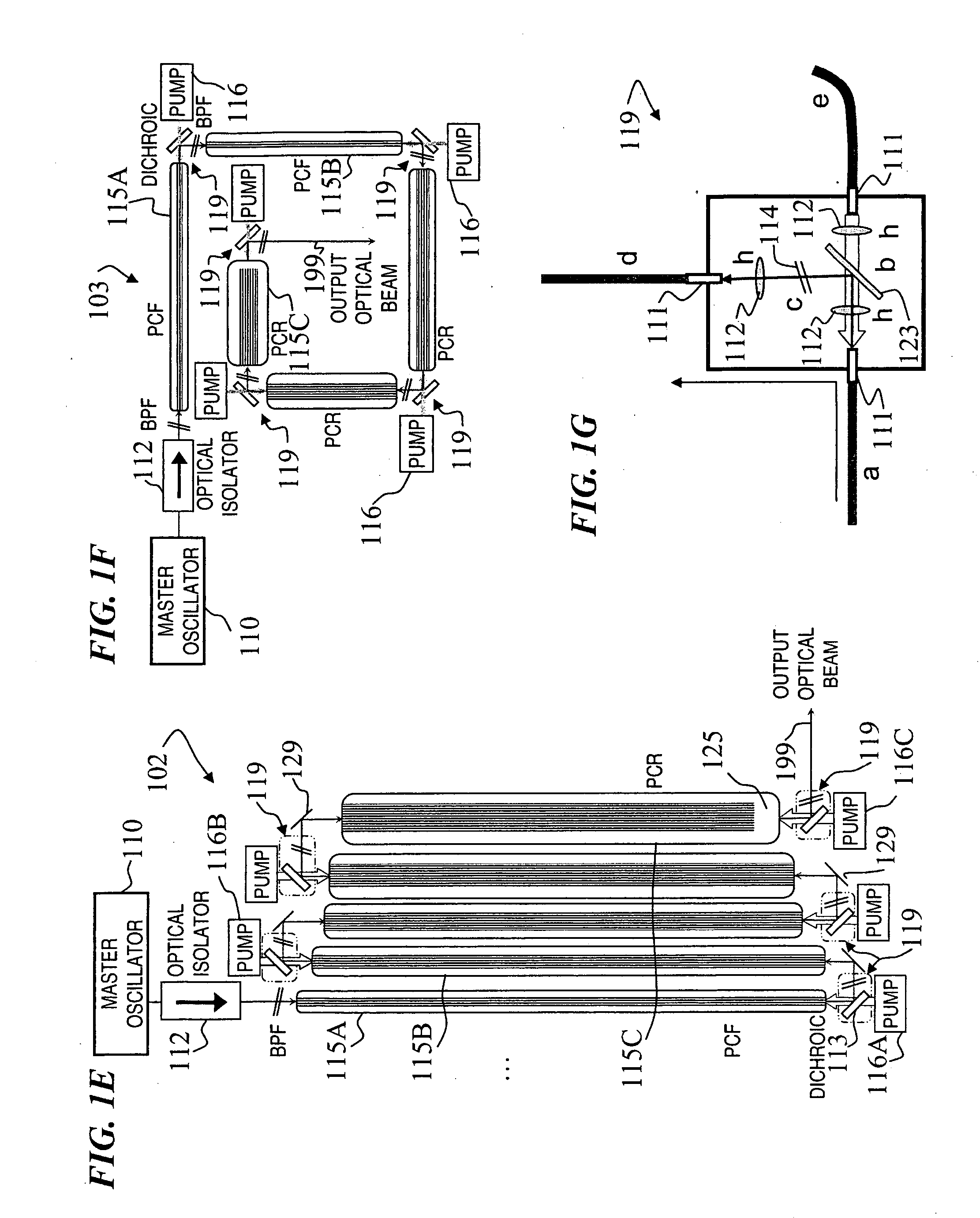
Fiber- or rod-based optical source featuring a large-core, rare-earth-doped photonic-crystal device for generation of high-power pulsed radiation and method
ActiveUS20070041083A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRare earthEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
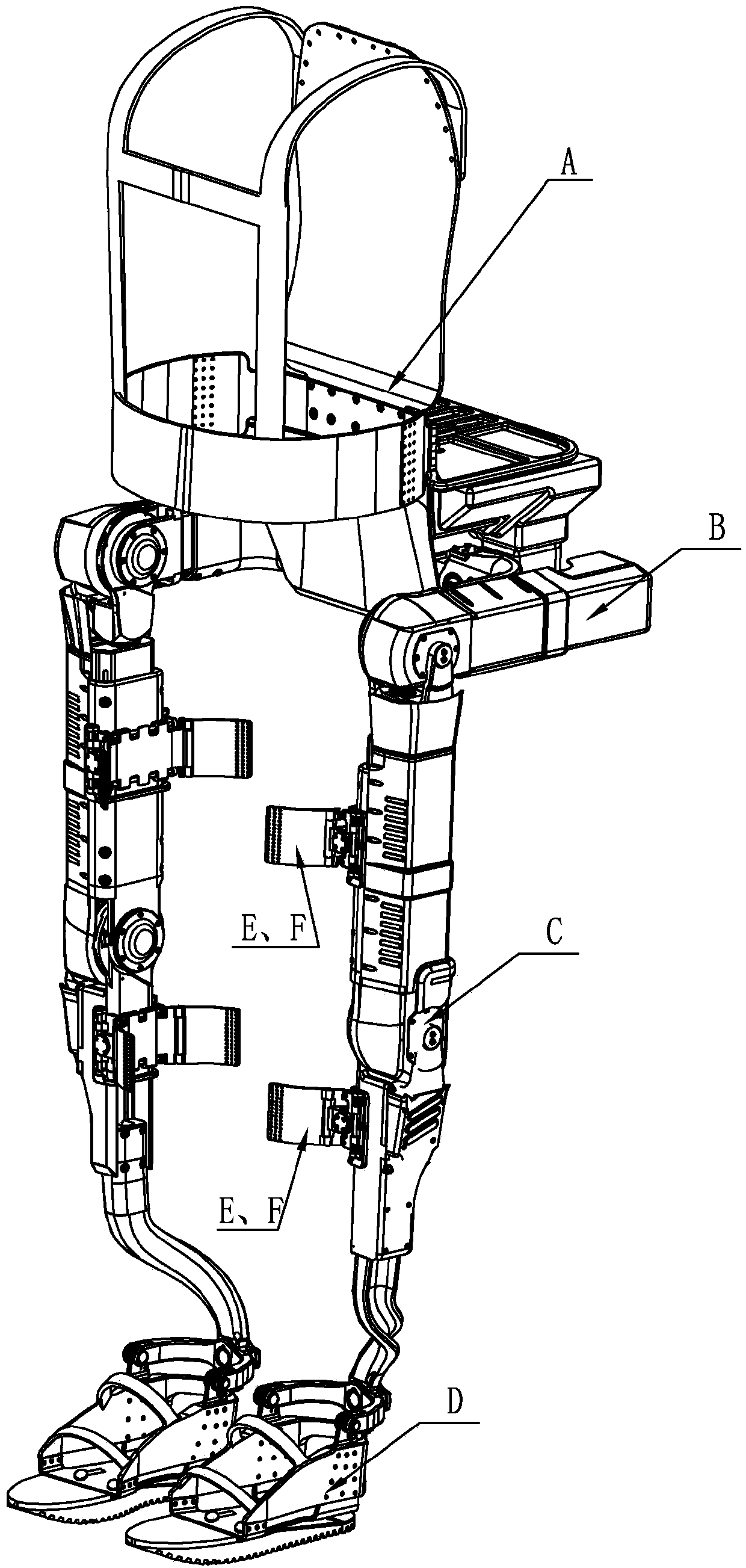
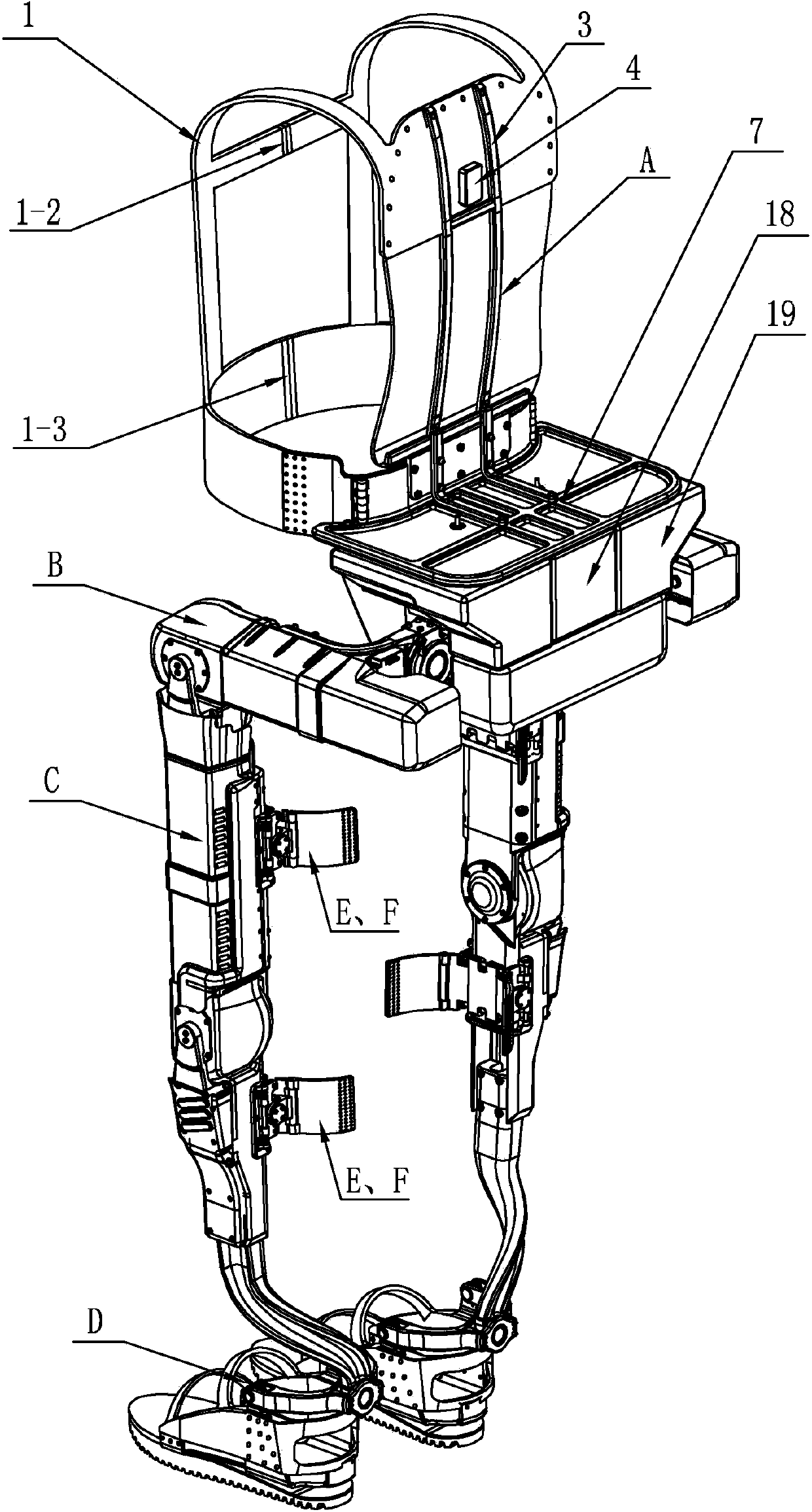
Human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting lower limbs
ActiveCN103610568ARealize the safety requirements of mechanical limitConvenient and accurate adjustment of telescopic lengthChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighExoskeleton robot
The invention relates to an external skeleton robot, in particular to a human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs aims to solve the problems that an existing external skeleton robot is low in coupling degree of motion space and poor in wearing comfort, reliability and adaptation, and power needed by a motor is large. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs comprises an upper body back part, a left leg and a right leg. The left leg and the right leg respectively comprise a hip drive system, a knee drive system and a foot wearing system. A rear side connection board of the waist is in rotating connection with a load installation board. Each hip joint supporting board is provided with a first motor and a first reducer, wherein the first motor is provided with an encoder, and the output end of the first motor provided with the encoder is connected with the input end of the first reducer. Each hip joint connecting board can rotate in the vertical plane. Each thigh stretching board is in detachable connection with the corresponding hip joint connecting board. The output end of a main drive mechanism is connected with each crus connecting board. The lower surfaces of elastic boards are bonded with the upper surfaces of the rubber soles of the feet. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs can assist in walking.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Nonlinear optical device
ActiveUS6856737B1Enhances bandwidth accessibleEfficient nonlinear interactionLaser detailsFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierLength wave
There is provided a non-linear optical device for enhancing the bandwidth accessible in the nonlinear generation of an optical signal. The device comprises a planar optical waveguide, the planar optical waveguide being operative to generate an optical output from an optical input having an input bandwidth by means of a non-linear optical process, the optical output having a wavelength within an accessible bandwidth, wherein the planar optical waveguide is operative to enhance the accessible bandwidth such that the ratio of the accessible bandwidth to the input bandwidth is at least 4. The device is particularly applicable to broad optical continuum generation, but may also be used in a parametric oscillator or amplifier arrangement with broad tuning range.
Owner:QUANTUM NIL LTD +1
Power supply and method for controlling it
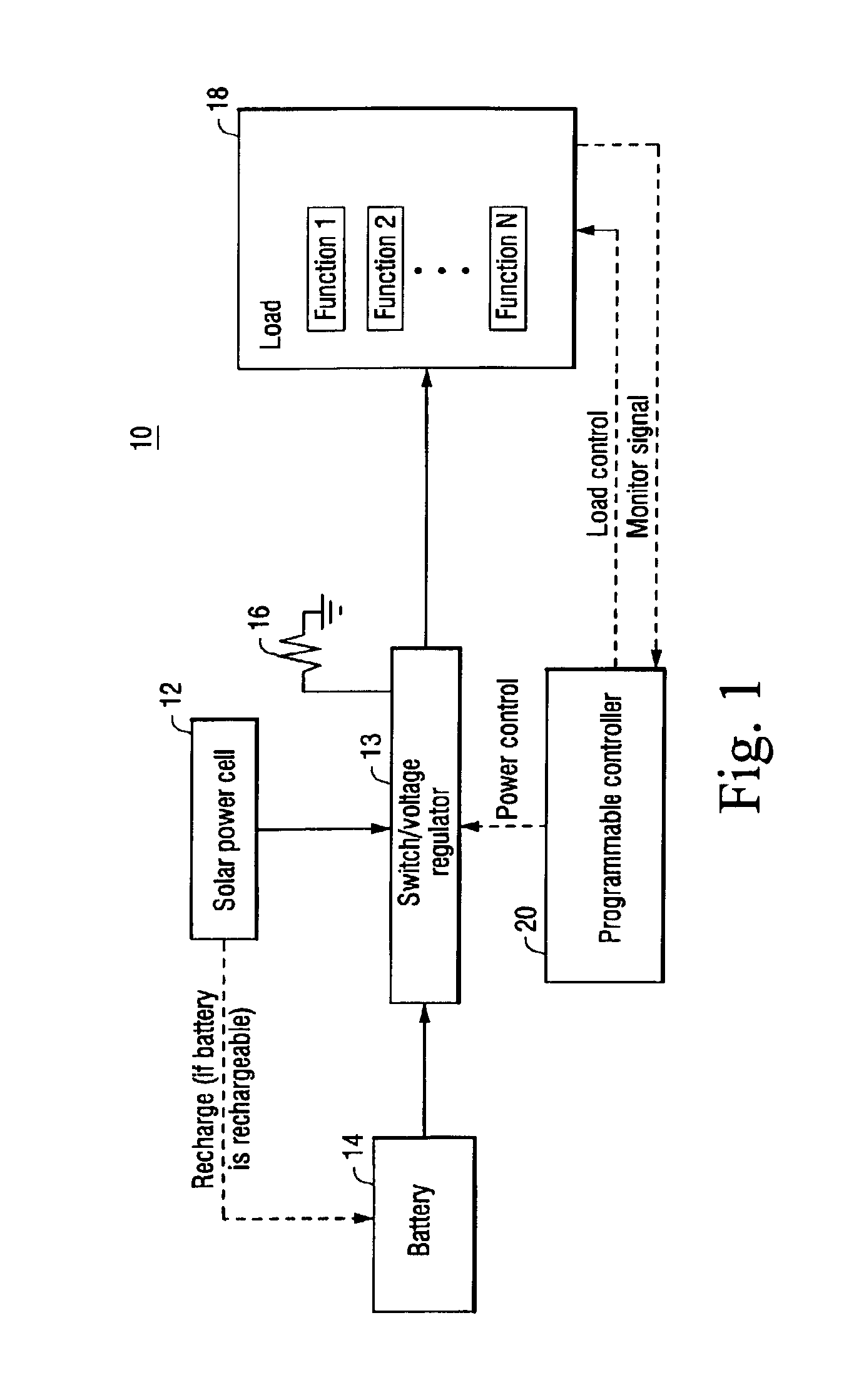
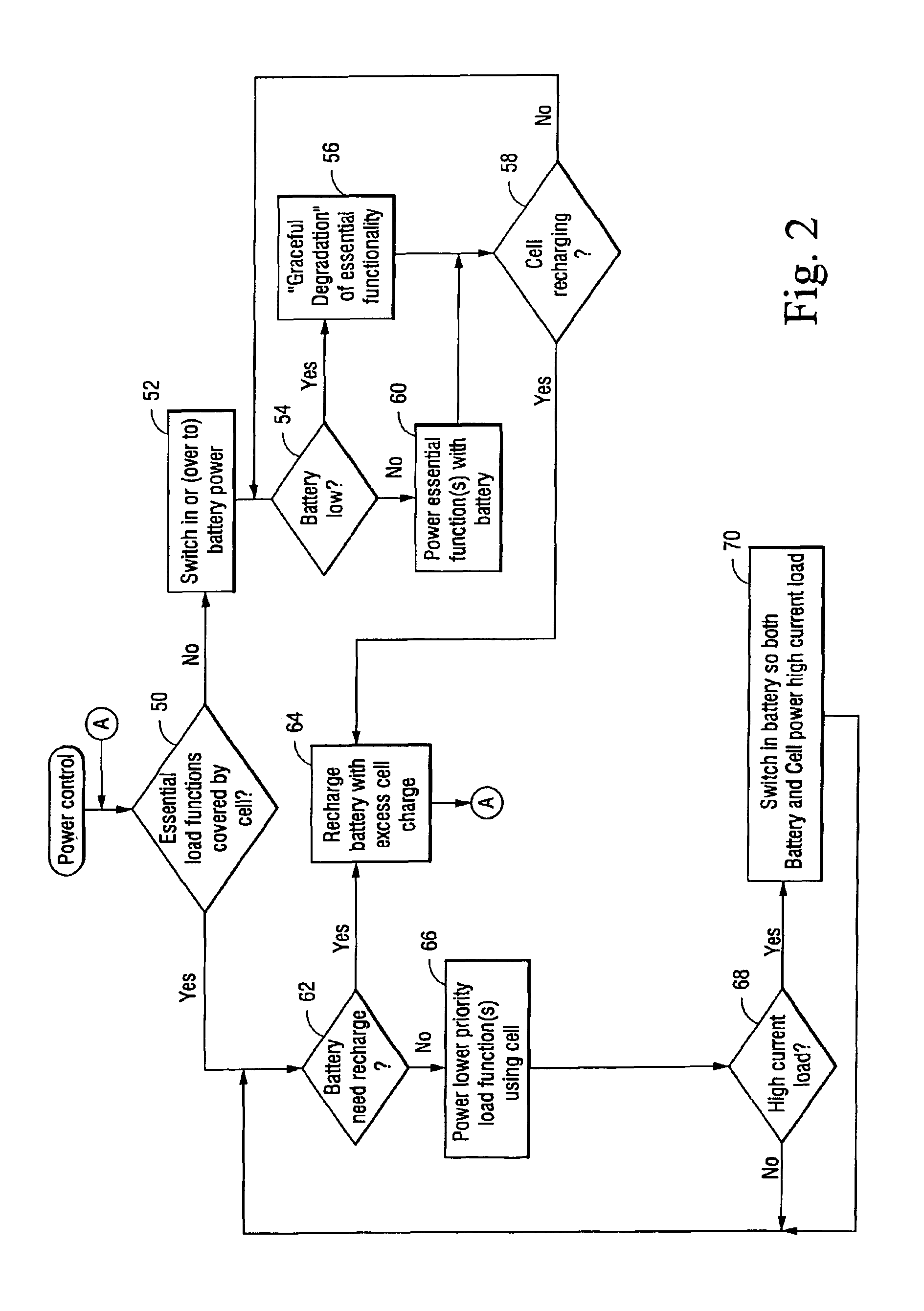
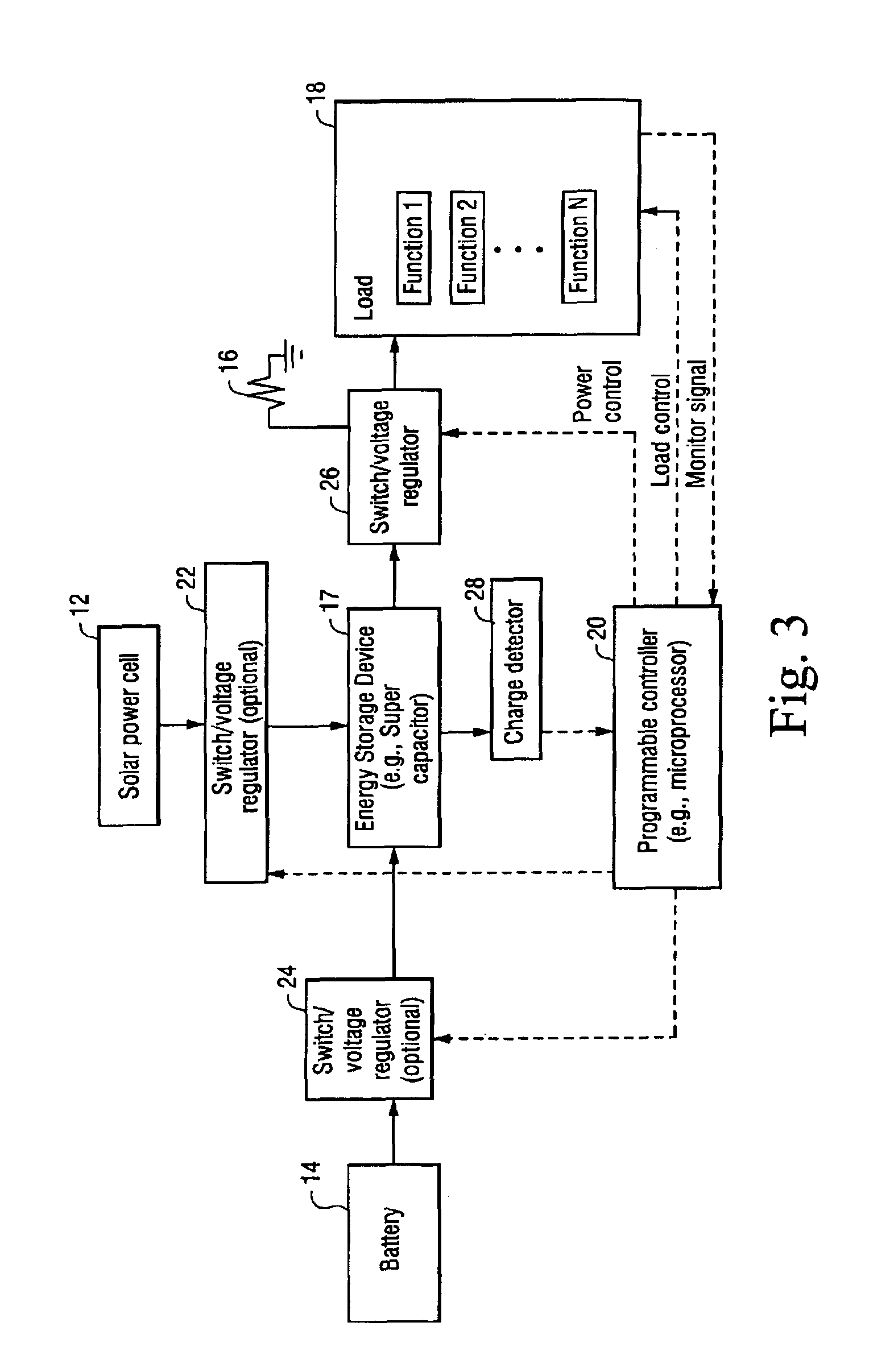
InactiveUS6914411B2High peak powerHigh power loadBatteries circuit arrangementsLoad balancing in dc networkSupply energySolar power
A self-powered apparatus includes a solar power cell, a battery, and a load. The load may include one or more load functions performed using power provided by one or both of the solar power cell and the battery. The inclusion of a battery permits the solar power cell to be sized much smaller than if the solar power cell was the only supply of power. A programmable controller selectively regulates power provided to one or more load functions and also selectively regulates whether one or both of the power cell and battery supplies the power. Switching circuitry, controlled by the programmable controller, selectively couples one or both of the battery and the solar cell to supply energy for powering the load. In a preferred example embodiment, the controller couples the battery and / or solar cell to charge a super capacitor, which then is selectively controlled to power the load. The programmable controller determines and prioritizes load function power requirements, and based thereon, determines which load functions will be powered based the priority of the load function requirements and the amount of power that can be supplied by the solar power cell as supplemented by the battery.
Owner:PCS FERGUSON
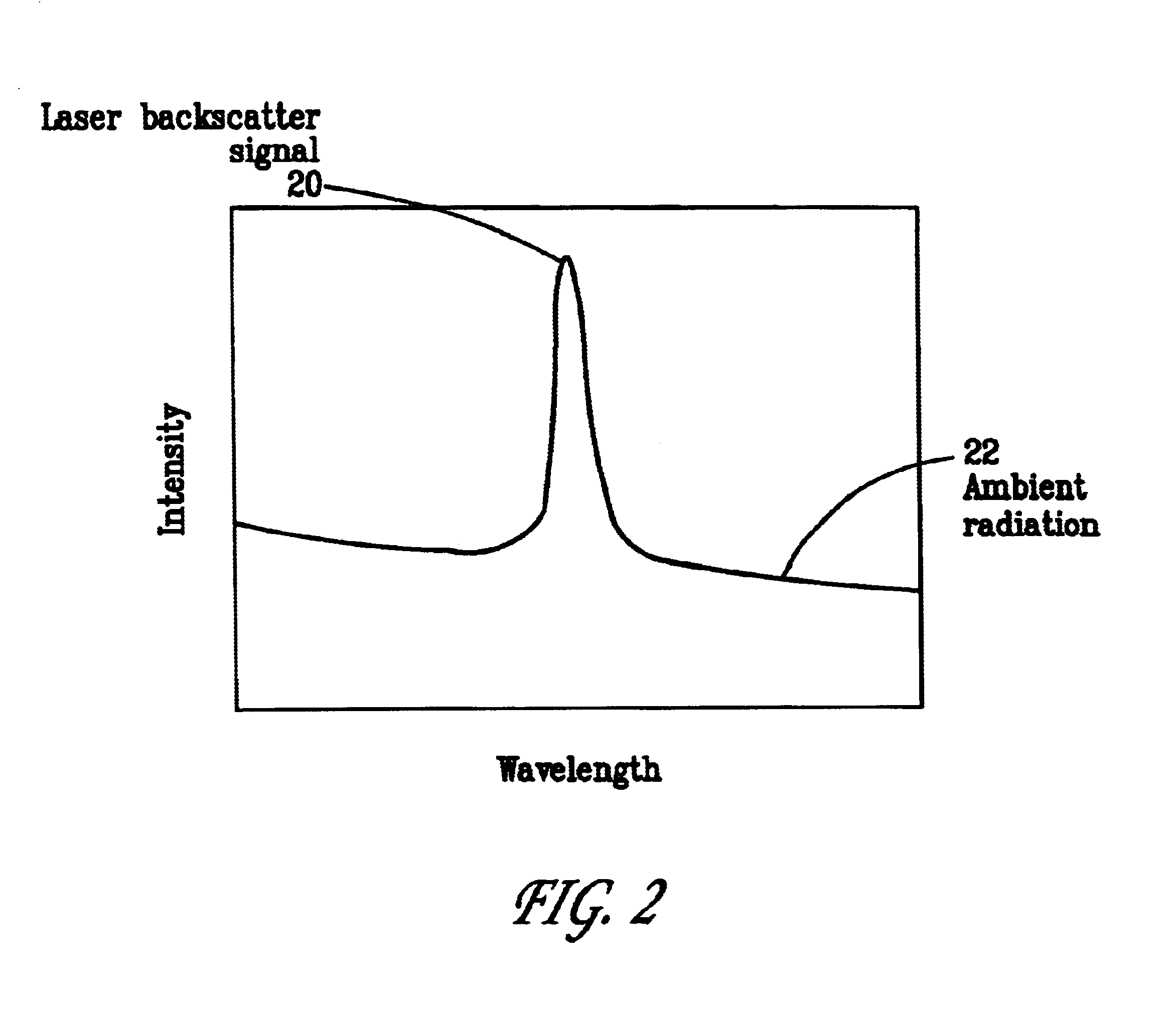
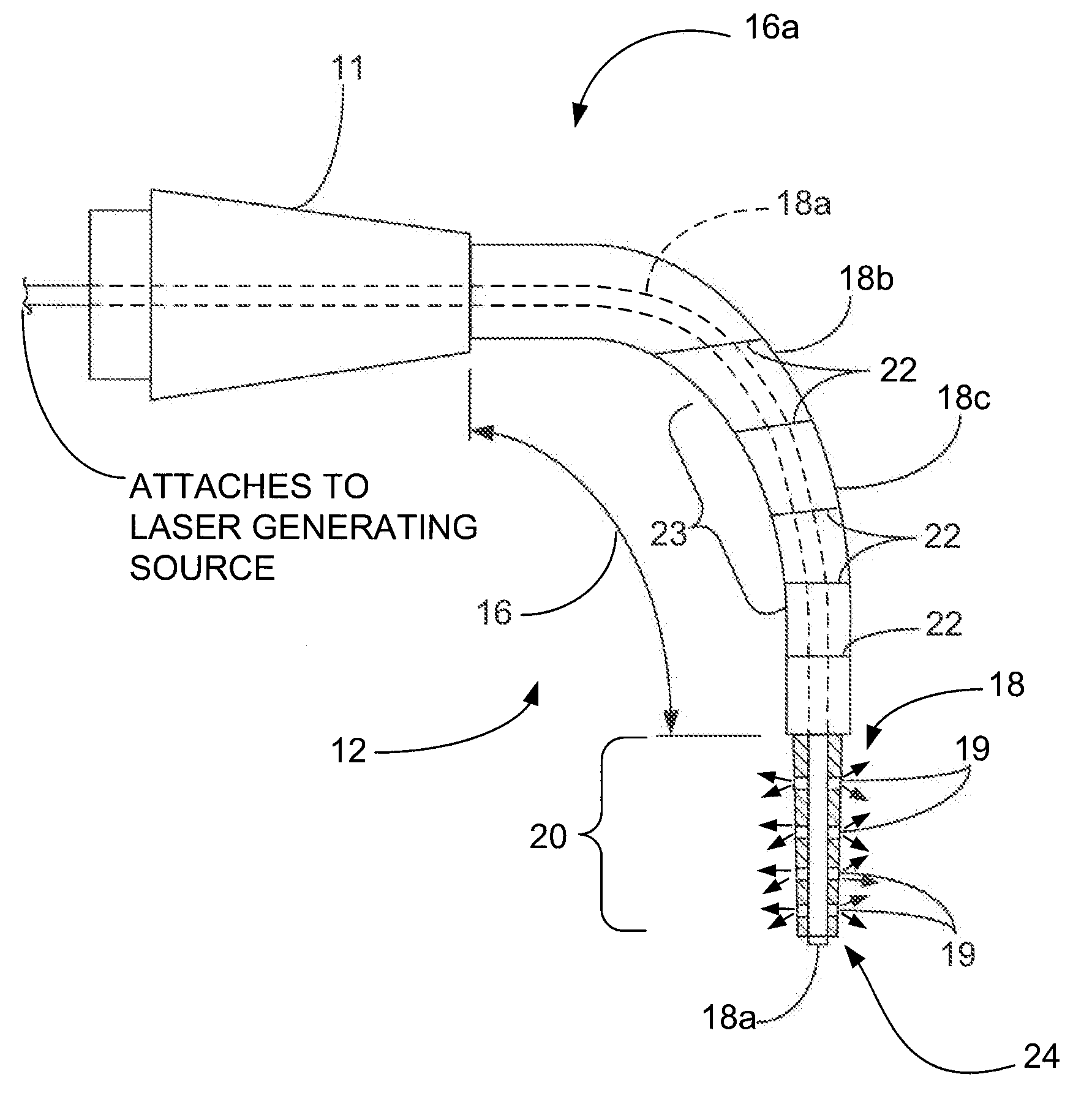
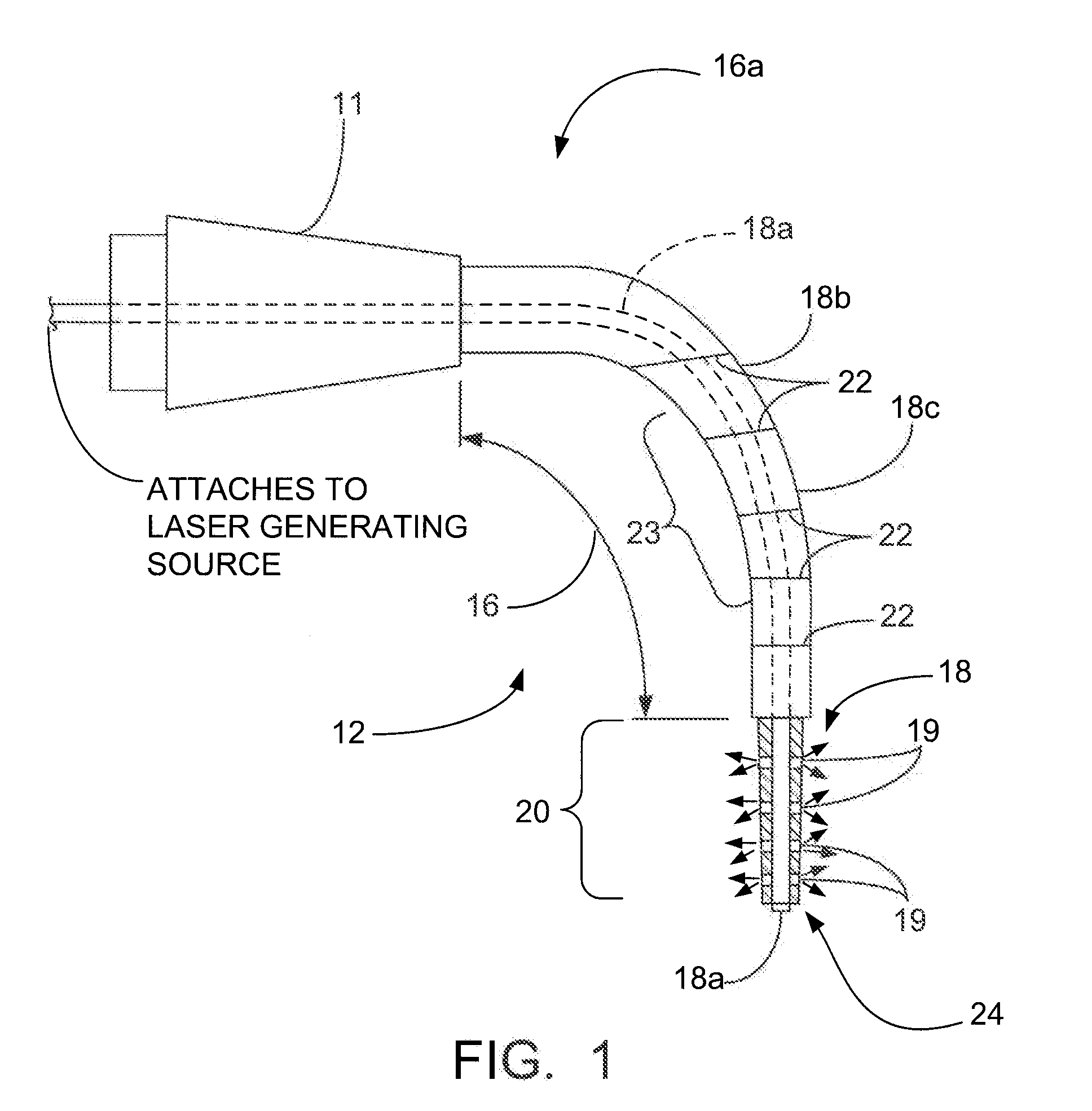
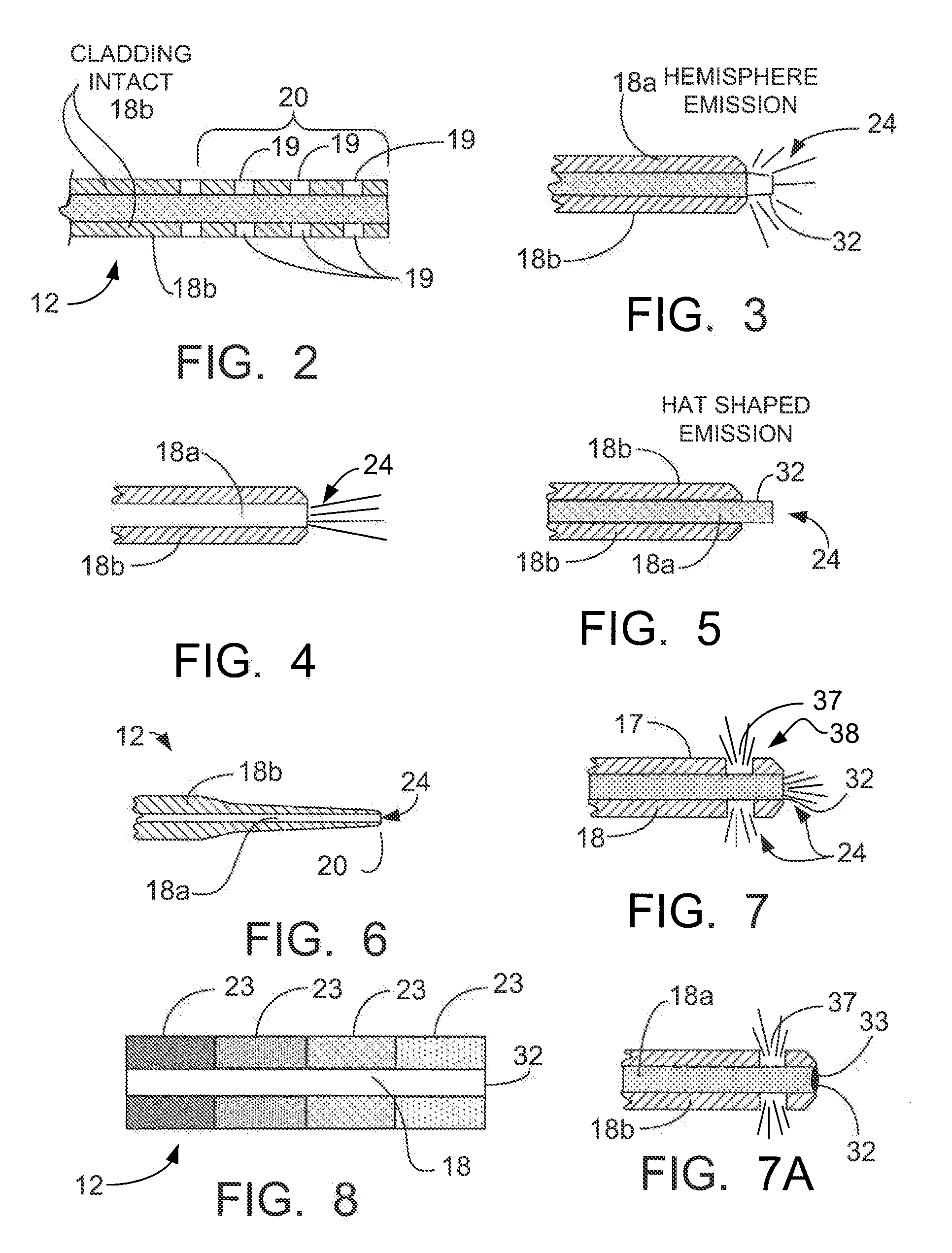
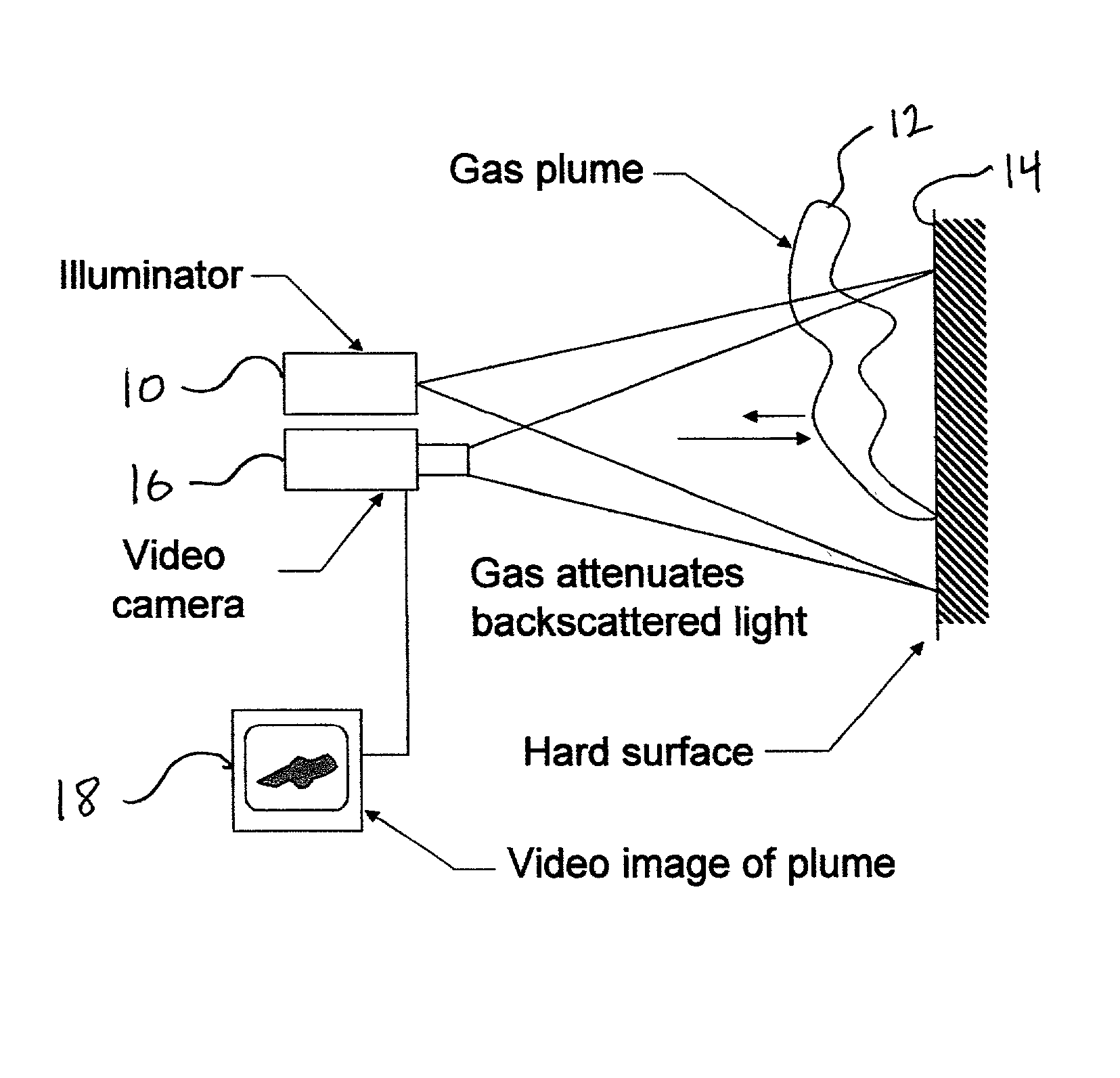
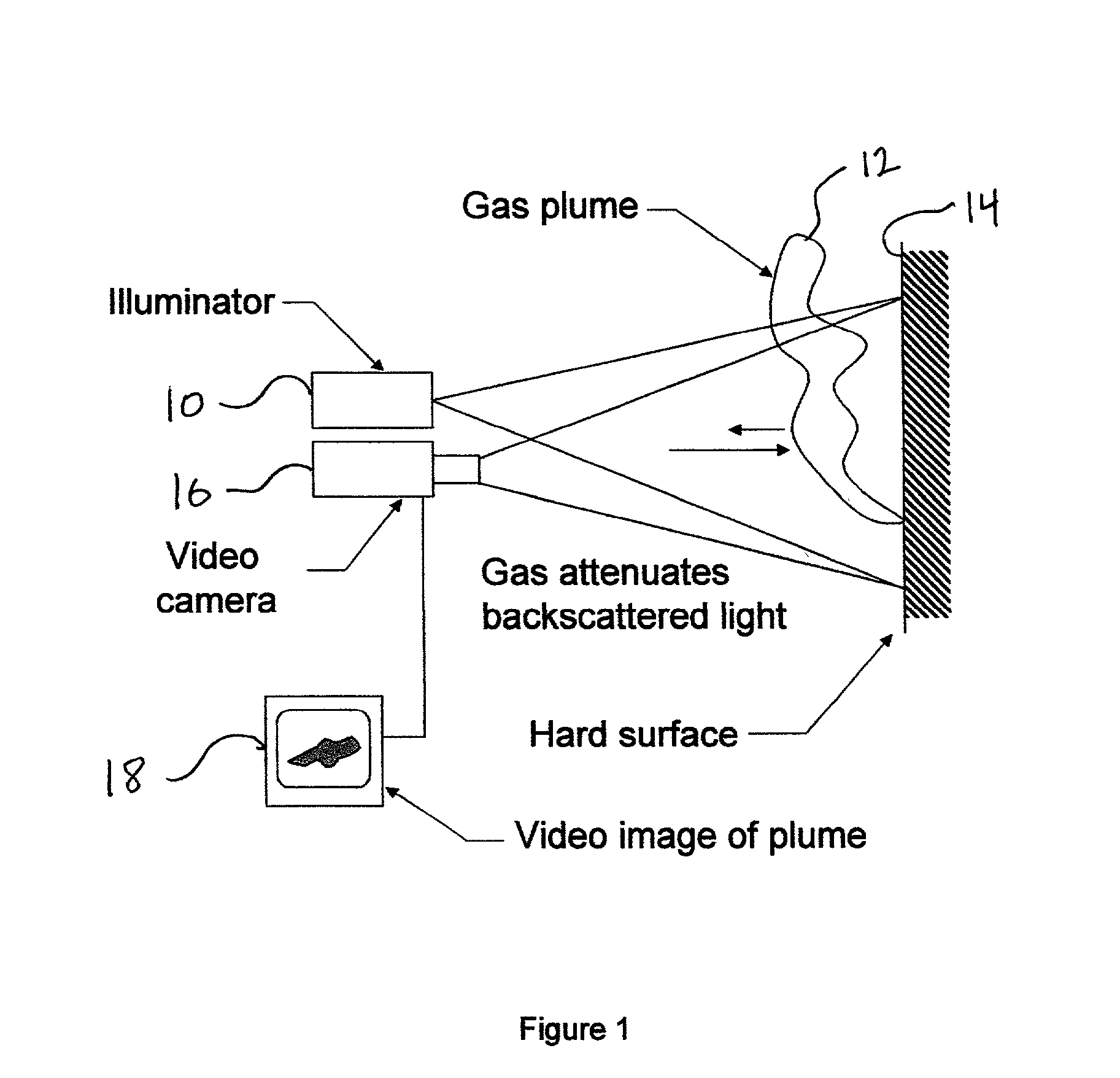
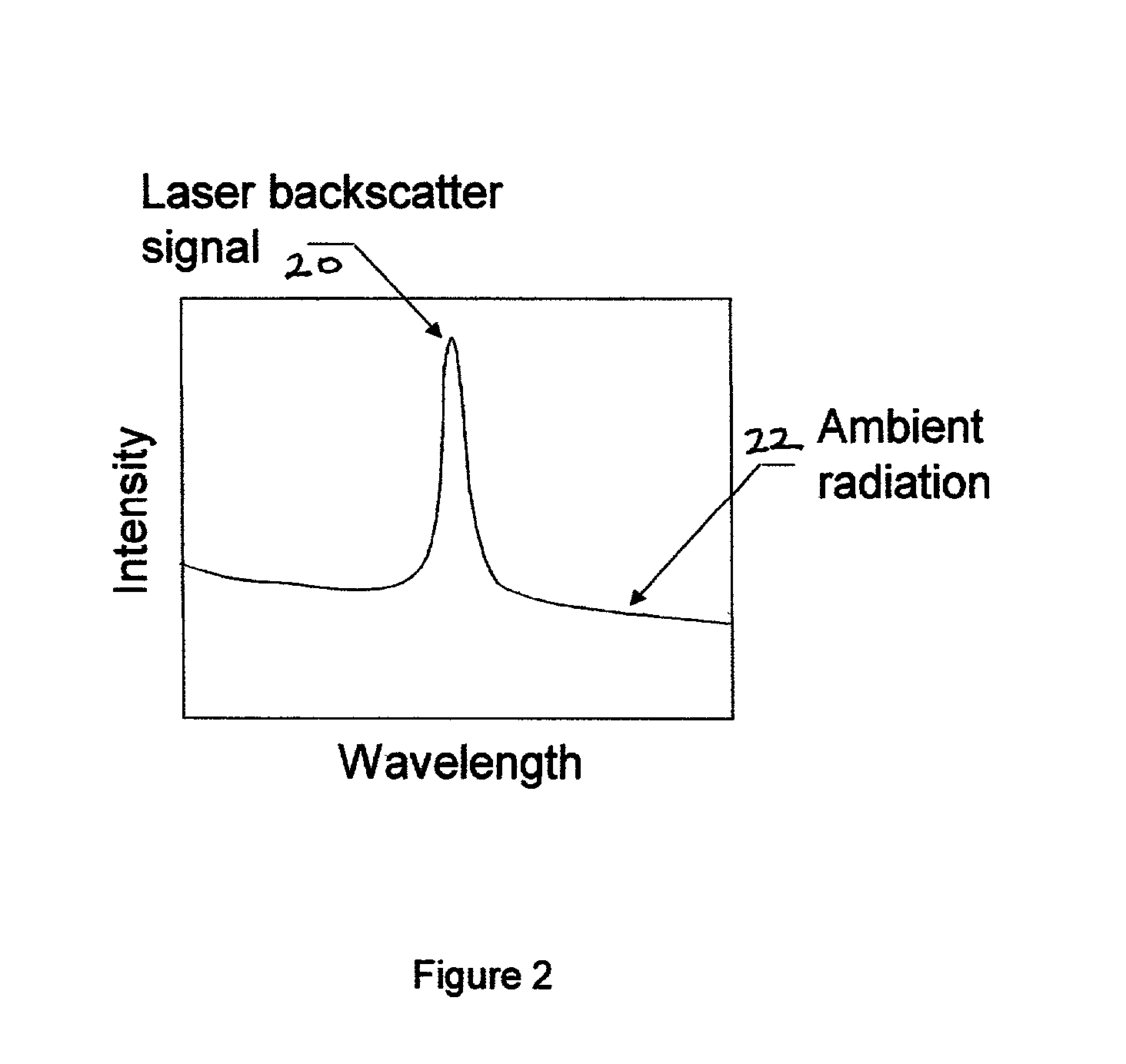
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
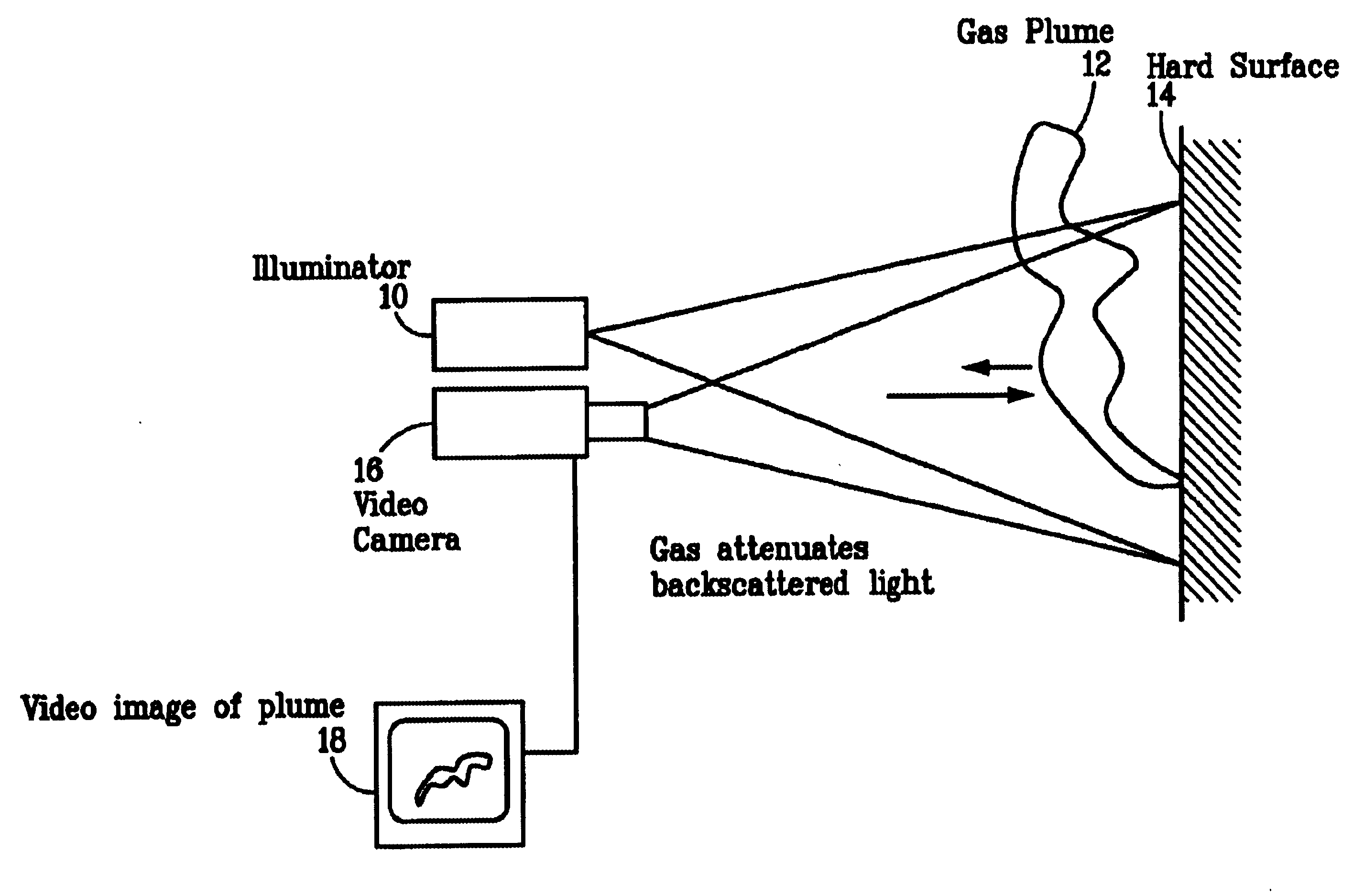
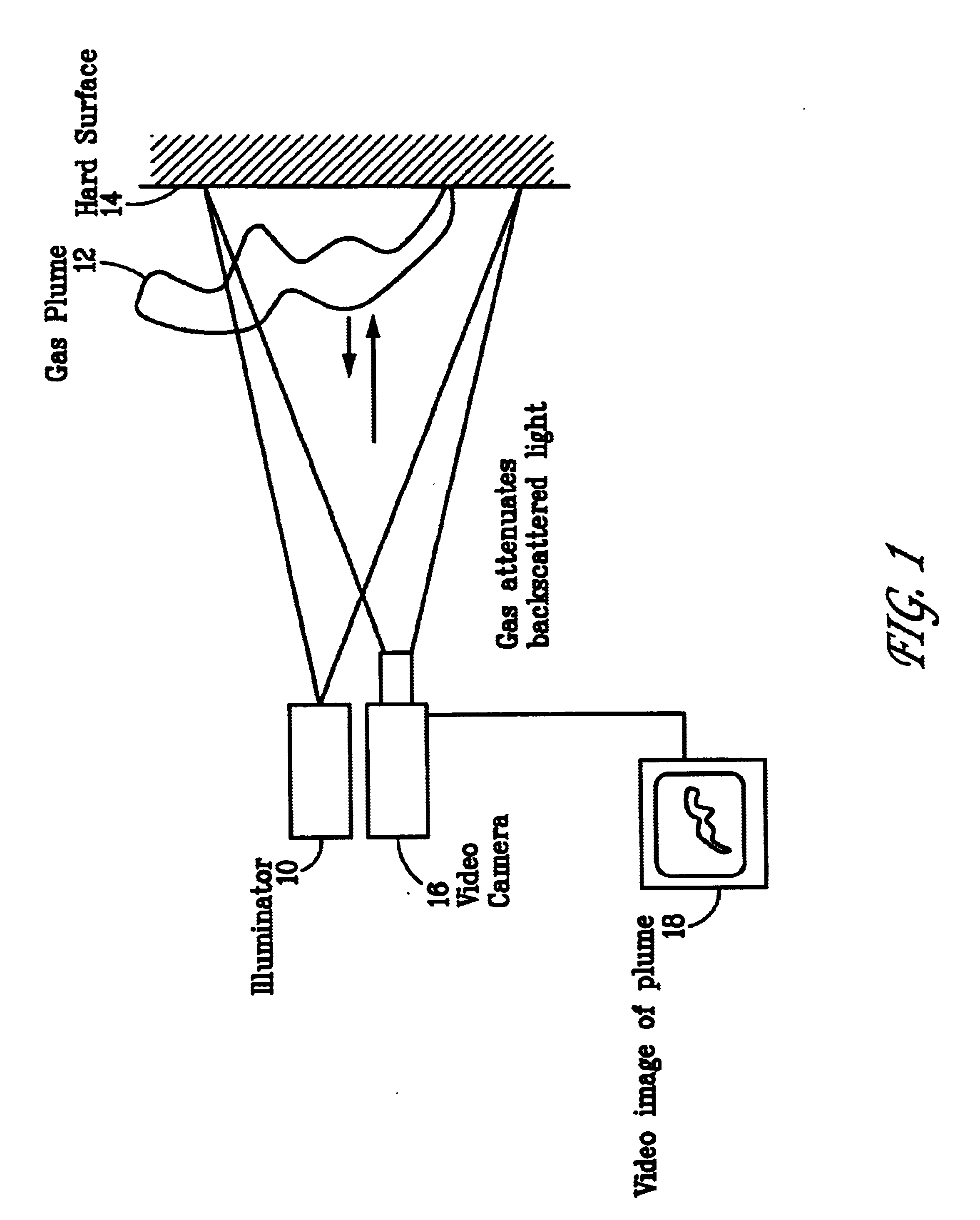
InactiveUS6690472B2Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMobile vehicleFluence
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Method and Apparatus for Disinfecting or Sterilizing a Root Canal System Using Lasers Targeting Water
InactiveUS20090130622A1Sufficient deliveryEnhanced light absorptionSurgical instrument detailsDental toolsDiseaseEnergy absorption
Method and apparatus for disinfecting and / or sterilizing a root canal system by targeting the water content of disease and debris in the canals. The laser technique of employs a frequency of the wavelength emissions between about 930 to about 1065 nanometers with an optimum of 980 nm. This range of wavelengths targets the water content of tissue cells and pathogens as well as any residual organic debris in water within the root canal system after its preparation while being poorly absorbed by the surrounding dentin. The selection of the optimum wavelength produces significant effects generating and advancing treatment to the targeted aqueous environments. This is due to the rapid energy absorption by the water and the subsequent creation of gas bubbles, liberation of heat and subsequent propulsion of waves of heat and gas that impact along the canal walls and ramifications resulting in an enhanced bacterial kill and cleaning of the canal walls and ramifications. No dyes or other additives are necessary to enhance the effectiveness of the laser kill of bacteria, etc.
Owner:BOLLINGER JAMES EDWIN +2
Mode-locked multi-mode fiber laser pulse source
InactiveUS20050008044A1High energy storageIncrease the sectionCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersPeak value
A laser utilizes a cavity design which allows the stable generation of high peak power pulses from mode-locked multi-mode fiber lasers, greatly extending the peak power limits of conventional mode-locked single-mode fiber lasers. Mode-locking may be induced by insertion of a saturable absorber into the cavity and by inserting one or more mode-filters to ensure the oscillation of the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fiber. The probability of damage of the absorber may be minimized by the insertion of an additional semiconductor optical power limiter into the cavity. To amplify and compress optical pulses in a multi-mode (MM) optical fiber, a single-mode is launched into the MM fiber by matching the modal profile of the fundamental mode of the MM fiber with a diffraction-limited optical mode at the launch end, The fundamental mode is preserved in the MM fiber by minimizing mode-coupling by using relatively short lengths of step-index MM fibers with a few hundred modes and by minimizing fiber perturbations. Doping is confined to the center of the fiber core to preferentially amplify the fundamental mode, to reduce amplified spontaneous emission and to allow gain-guiding of the fundamental mode. Gain-guiding allows for the design of systems with length-dependent and power-dependent diameters of the fundamental mode. To allow pumping with high-power laser diodes, a double-clad amplifier structure is employed. For applications in nonlinear pulse-compression, self phase modulation and dispersion in the optical fibers can be exploited. High-power optical pulses may be linearly compressed using bulk optics dispersive delay lines or by chirped fiber Bragg gratings written directly into the SM or MM optical fiber. High-power cw lasers operating in a single near-diffraction-limited mode may be constructed from MM fibers by incorporating effective mode-filters into the laser cavity. Regenerative fiber amplifiers may be constructed from MM fibers by careful control of the recirculating mode. Higher-power Q-switched fiber lasers may be constructed by exploiting the large energy stored in MM fiber amplifiers.
Owner:FERMANN MARTIN E +1
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides for amplification of high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS20070104431A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical radiationPromiscuous behaviour
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
InactiveUS20020071122A1Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsFluenceRadiation
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Nonlinear optical device
InactiveUS20050047739A1Enhanced optical confinementHigh peak powerLaser detailsFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierLength wave
There is provided a non-linear optical device for enhancing the bandwidth accessible in the nonlinear generation of an optical signal. The device comprises a planar optical waveguide, the planar optical waveguide being operative to generate an optical output from an optical input having an input bandwidth by means of a non-linear optical process, the optical output having a wavelength within an accessible bandwidth, wherein the planar optical waveguide is operative to enhance the accessible bandwidth such that the ratio of the accessible bandwidth to the input bandwidth is at least 4. The device is particularly applicable to broad optical continuum generation, but may also be used in a parametric oscillator or amplifier arrangement with broad tuning range.
Owner:QUANTUM NIL LTD +1
Systems for CMOS-compatible three-dimensional image sensing using quantum efficiency modulation
InactiveUS20030076484A1Improve resolution accuracyEffective duty cycle is greaterOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationCapacitancePhotodetector
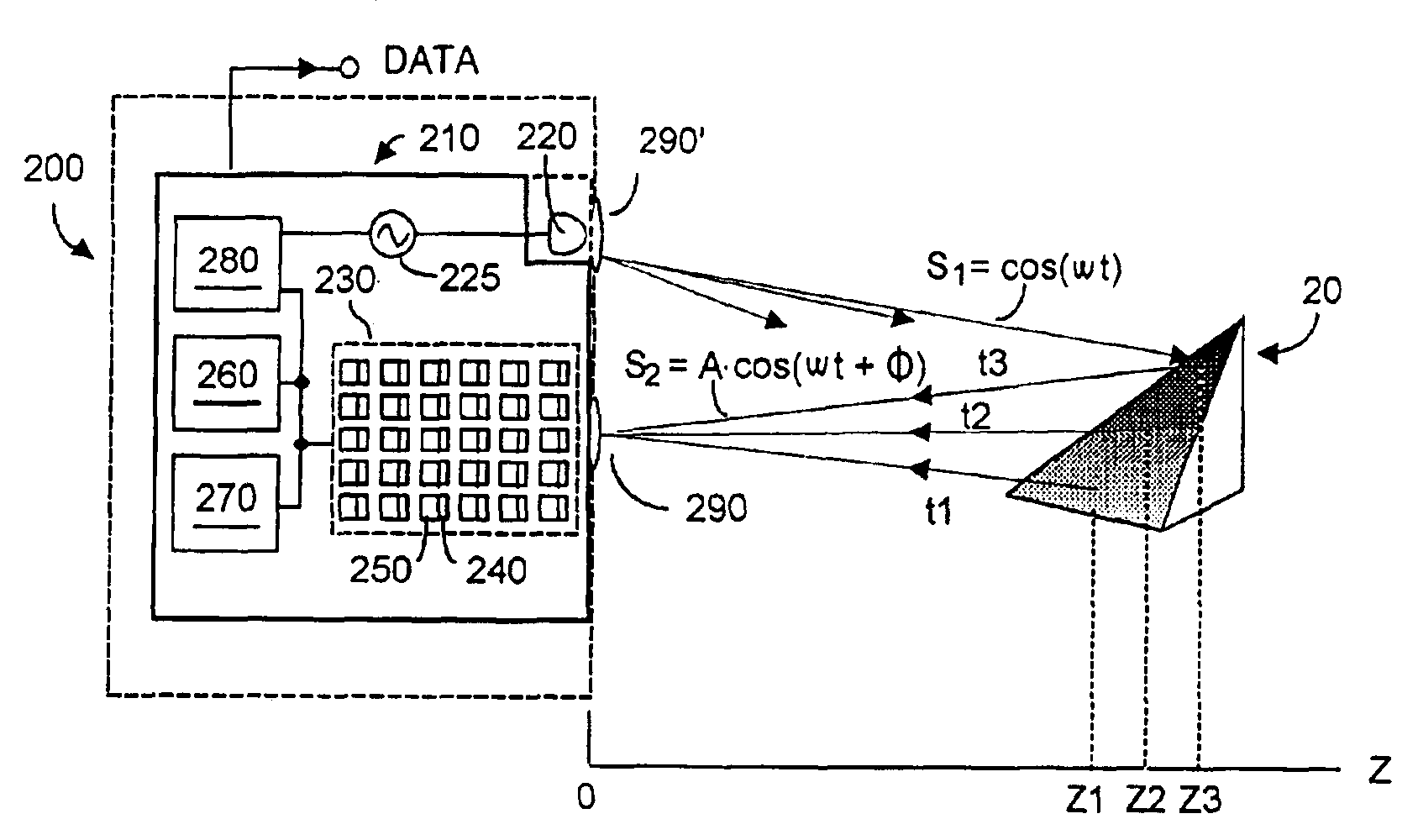
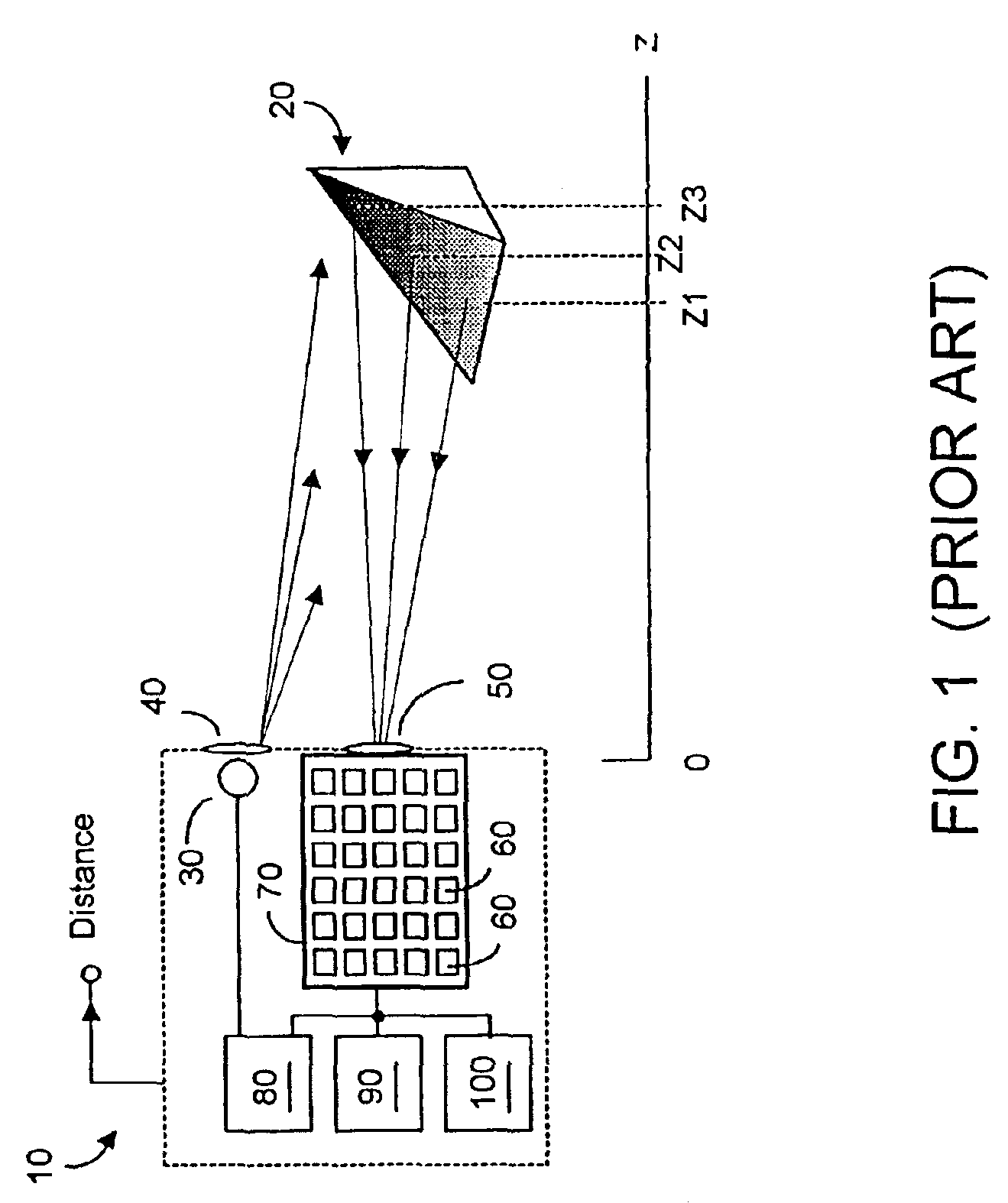
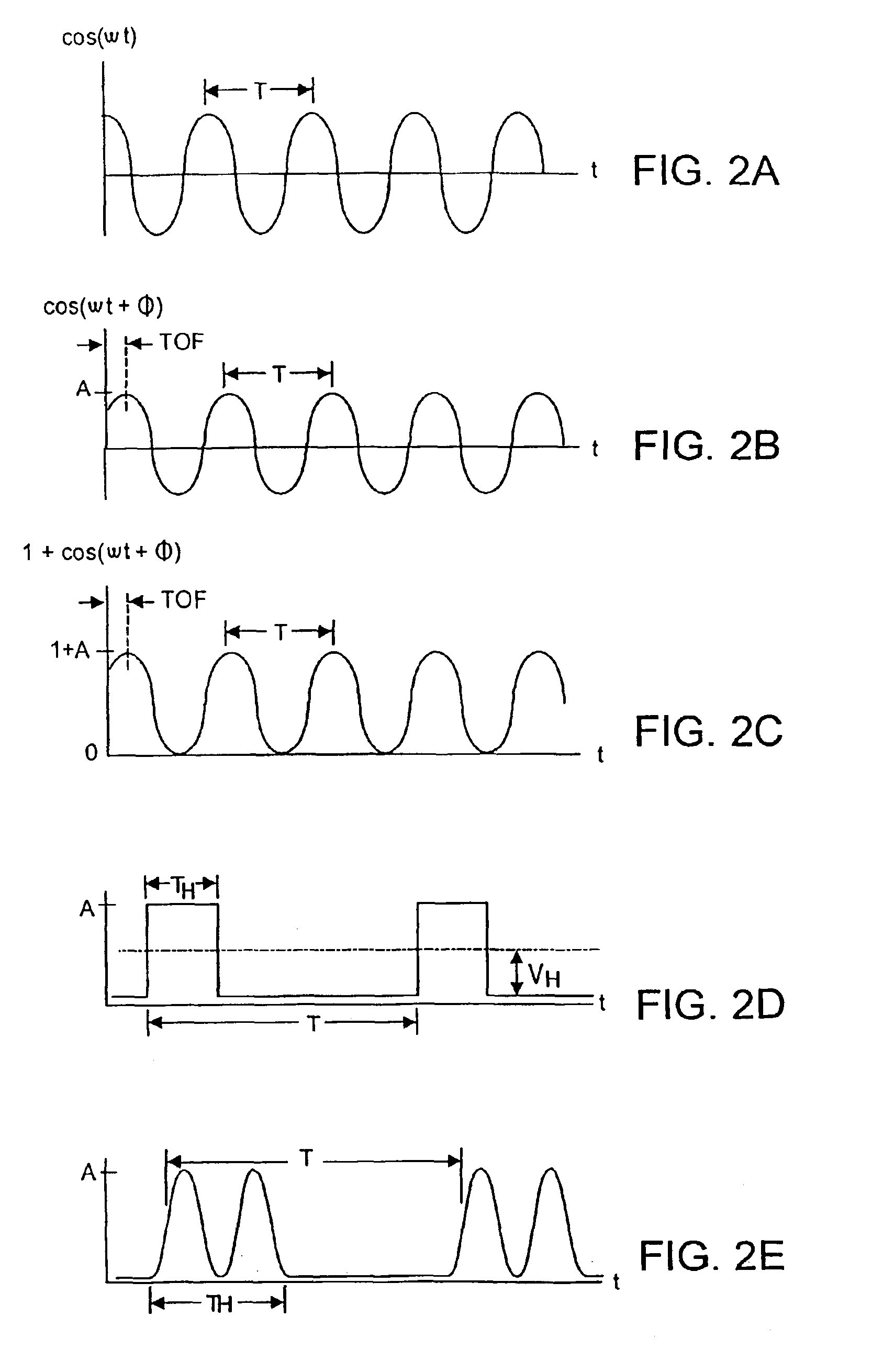
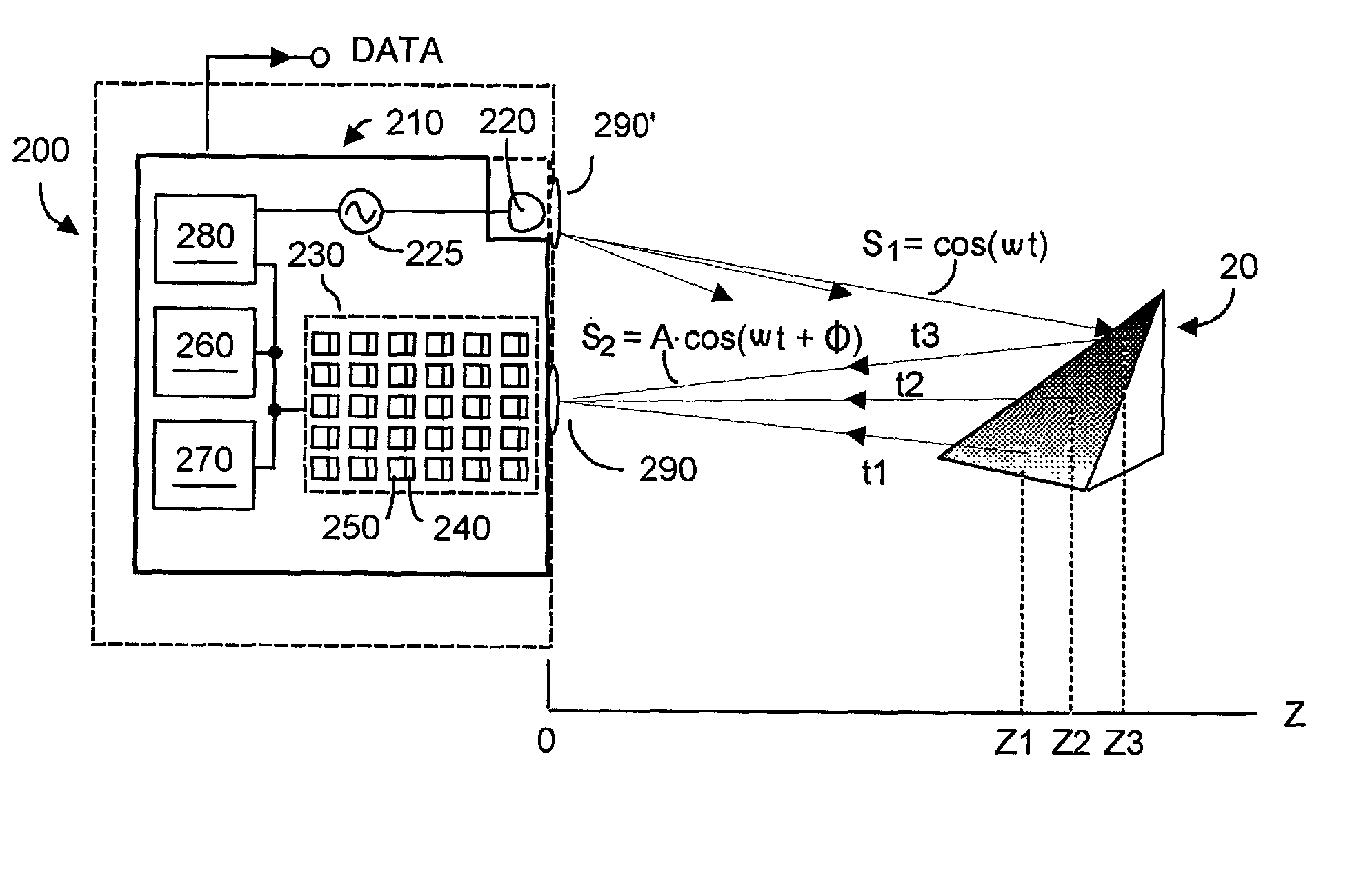
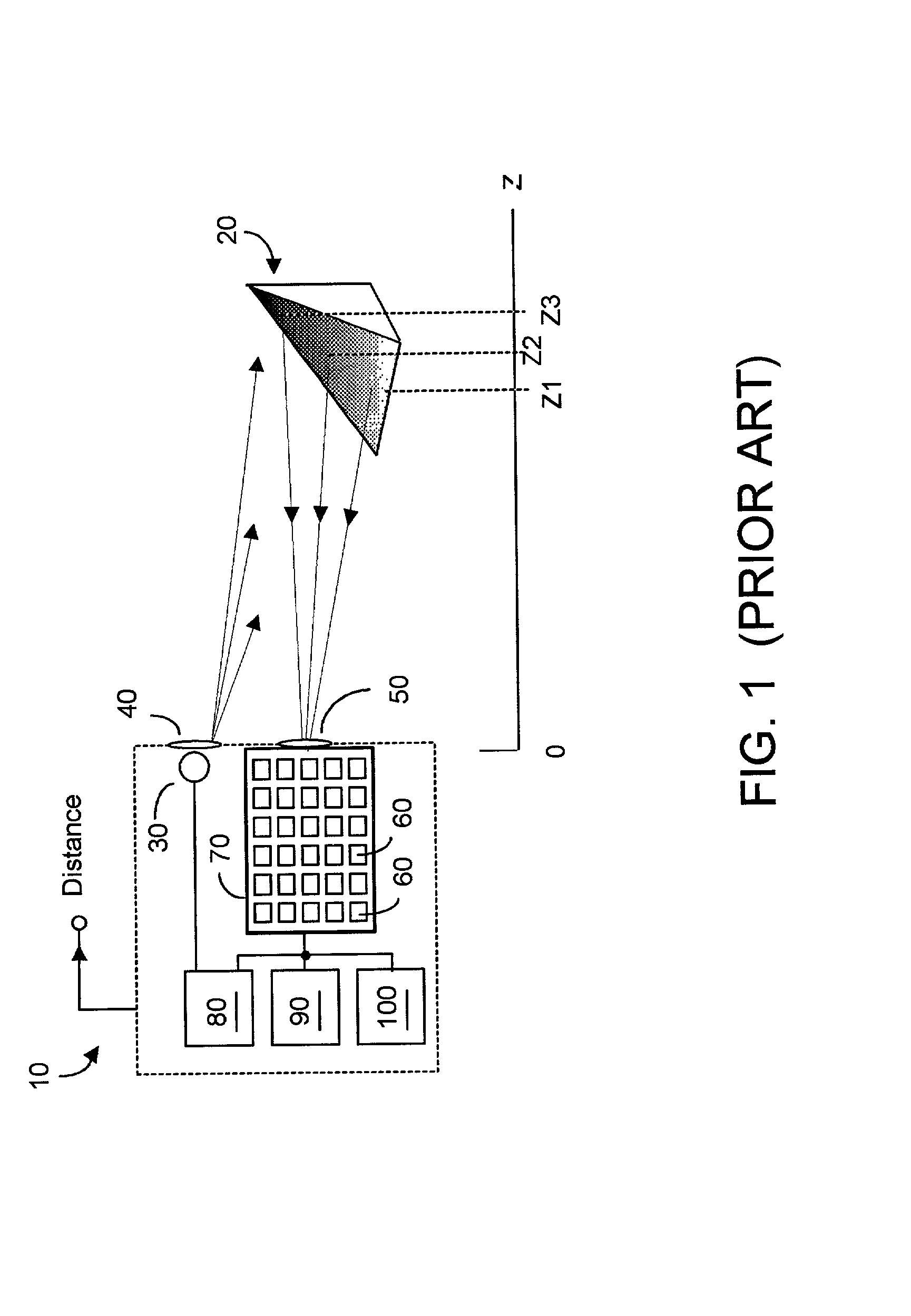
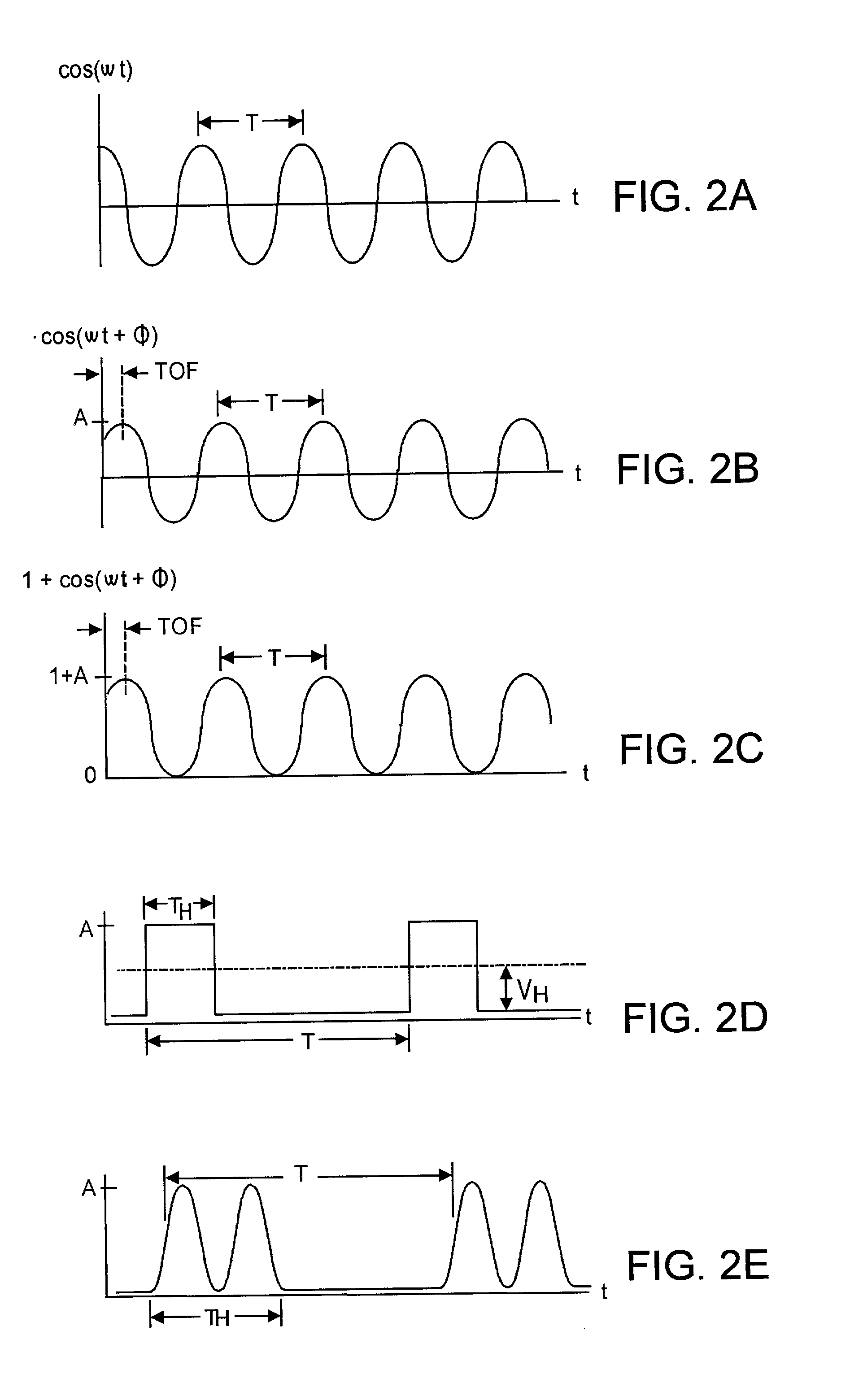
A preferably CMOS-implementable system measures distance and / or brightness by illuminating a target with emitted optical energy having a modulated periodic waveform whose high frequency component may be idealized as S.sub.1=cos(.omega..multidot.t). A fraction of the emitted optical energy is reflected by a target and detected with at least one in a plurality of semiconductor photodetectors. Photodetector quantum efficiency is modulated to process detected signals to yield data proportional to the distance z separating the target and photodetector. Detection includes measuring phase change between the emitted optical energy and the reflected fraction thereof. Quantum efficiency can be modulated with fixed or variable phase methods and may be enhanced using enhanced photocharge collection, differential modulation, and spatial and temporal multiplexing. System power requirements may be reduced with inductors that resonate with photodetector capacitance at the operating frequency. The system includes on-chip photodetectors, associated electronics, and processing.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet solid-state laser sources based on nonlinear frequency conversion in periodically poled materials
InactiveUS7570676B2Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsNonlinear crystalsLight source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
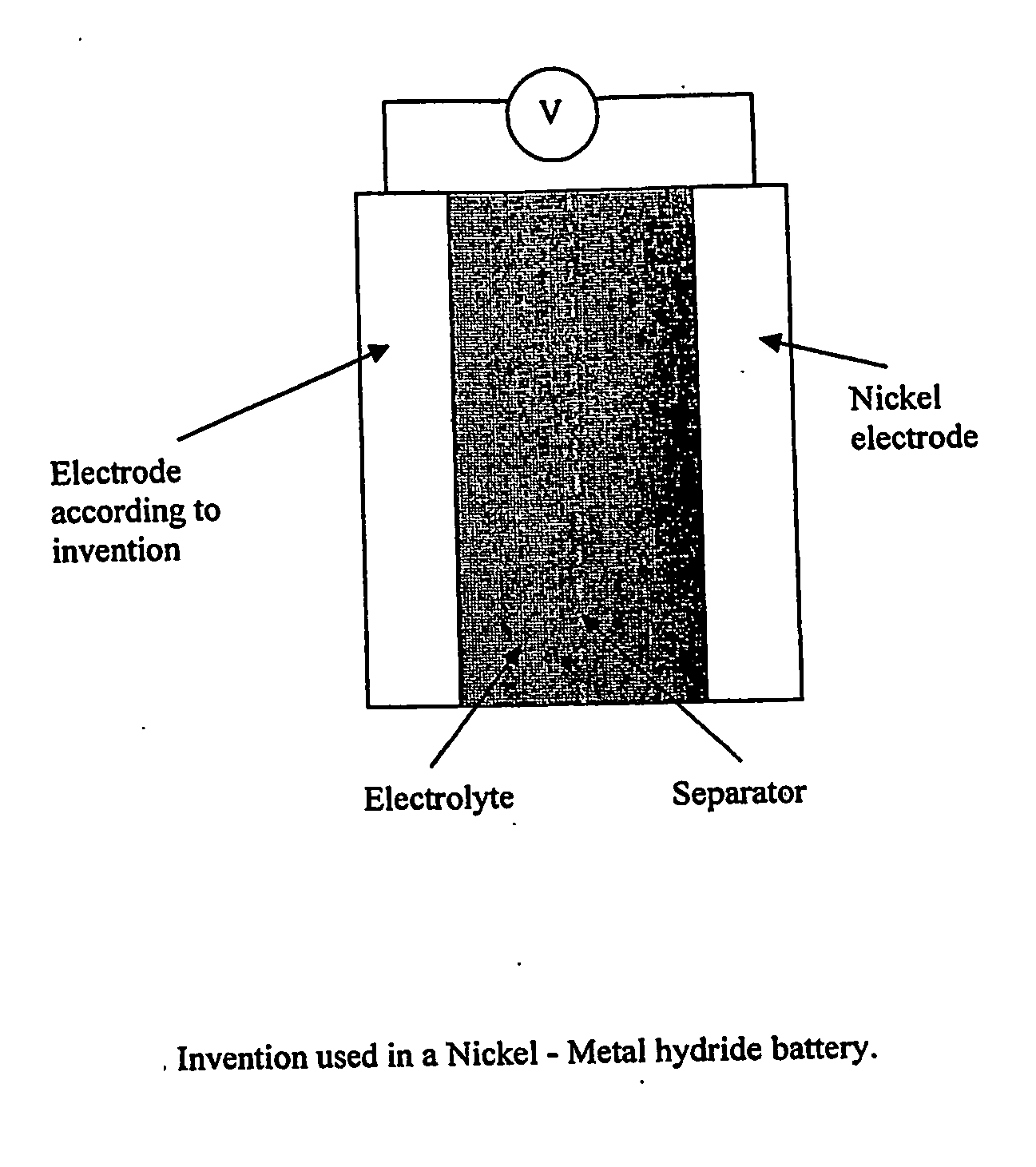
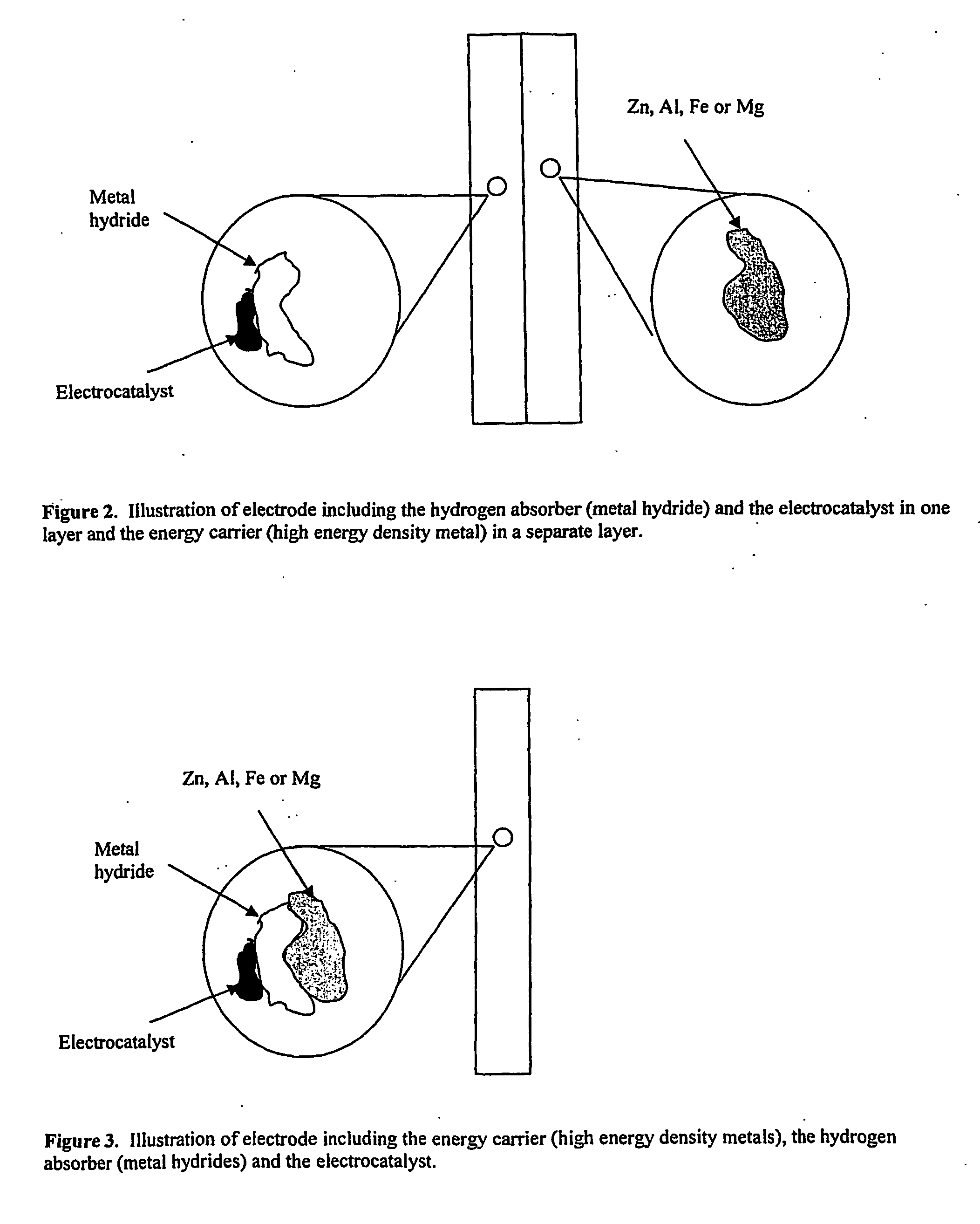
Electrode, method of its production, metal-air fuel cell and metal hydride cell
InactiveUS20070077491A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh energy capacityElectrode rolling/calenderingHydrogenFuel cellsReaction rate
The invention described concerns an anode electrode comprising a hydrogen storage material / alloy and a high energy density metal. In addition a hydrogen electrocatalyst may be added to increase the hydrogen reaction rate. The high energy density metal is selected from a group consisting of Al, Zn, Mg and Fe, or from a combination of these metals. A method of production of an electrode comprising a hydrogen storage alloy and a high energy density metal is also described. The method comprises sintering or binding a high energy density metal powder and / or hydrogen storage alloy into at least one thin street, and calendaring or pressing said sheet forming the electrode. The anode electrode may be used in metal hydride batteries and metal air fuel cells.
Owner:REVOLT TECH LTD
Q-switched microlaser apparatus and method for use
ActiveUS20080247425A1Improve cooling effectGuaranteed uptimeLaser cooling arrangementsResonatorLaser
A monolithic passively Q switched microlaser includes an optically transparent heat conductive element bonded to a gain medium, which is in turn bonded to a saturable absorber, which may also be bonded to a second optically transparent heat conductive element. Only the gain medium and saturable absorber are disposed within the laser resonator.
Owner:KK TOPCON +1
Injection seeding of frequency-converted Q-switched laser
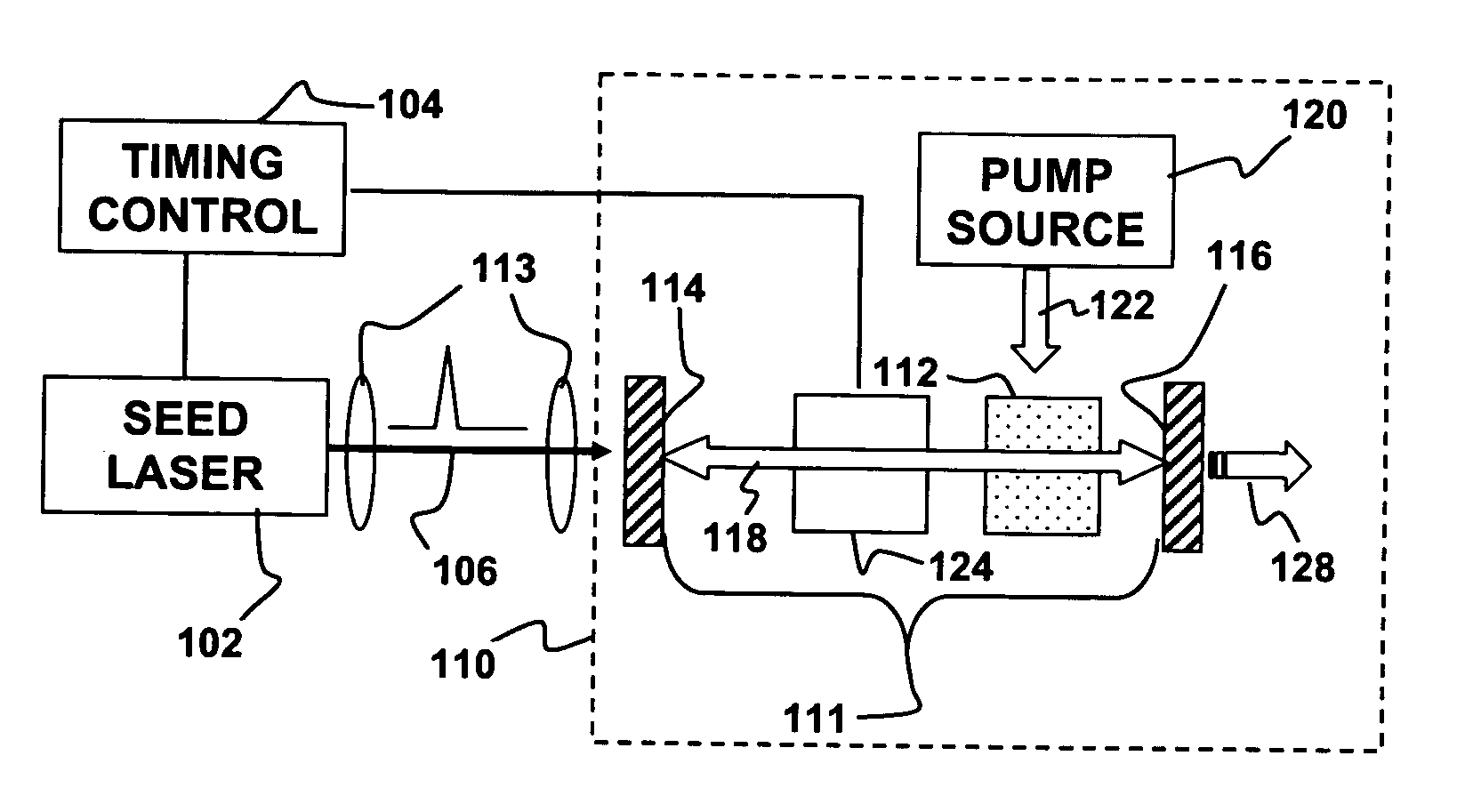
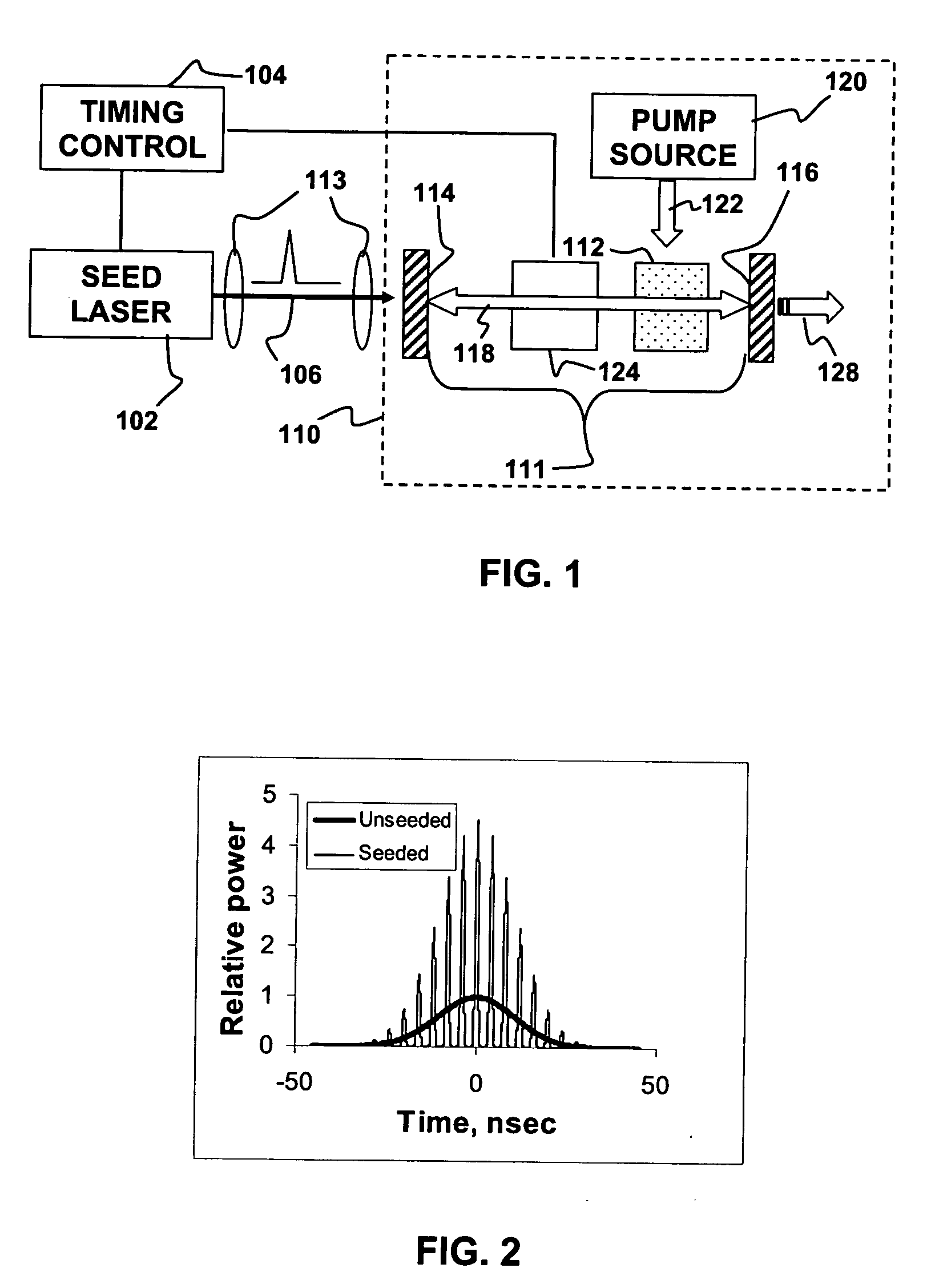
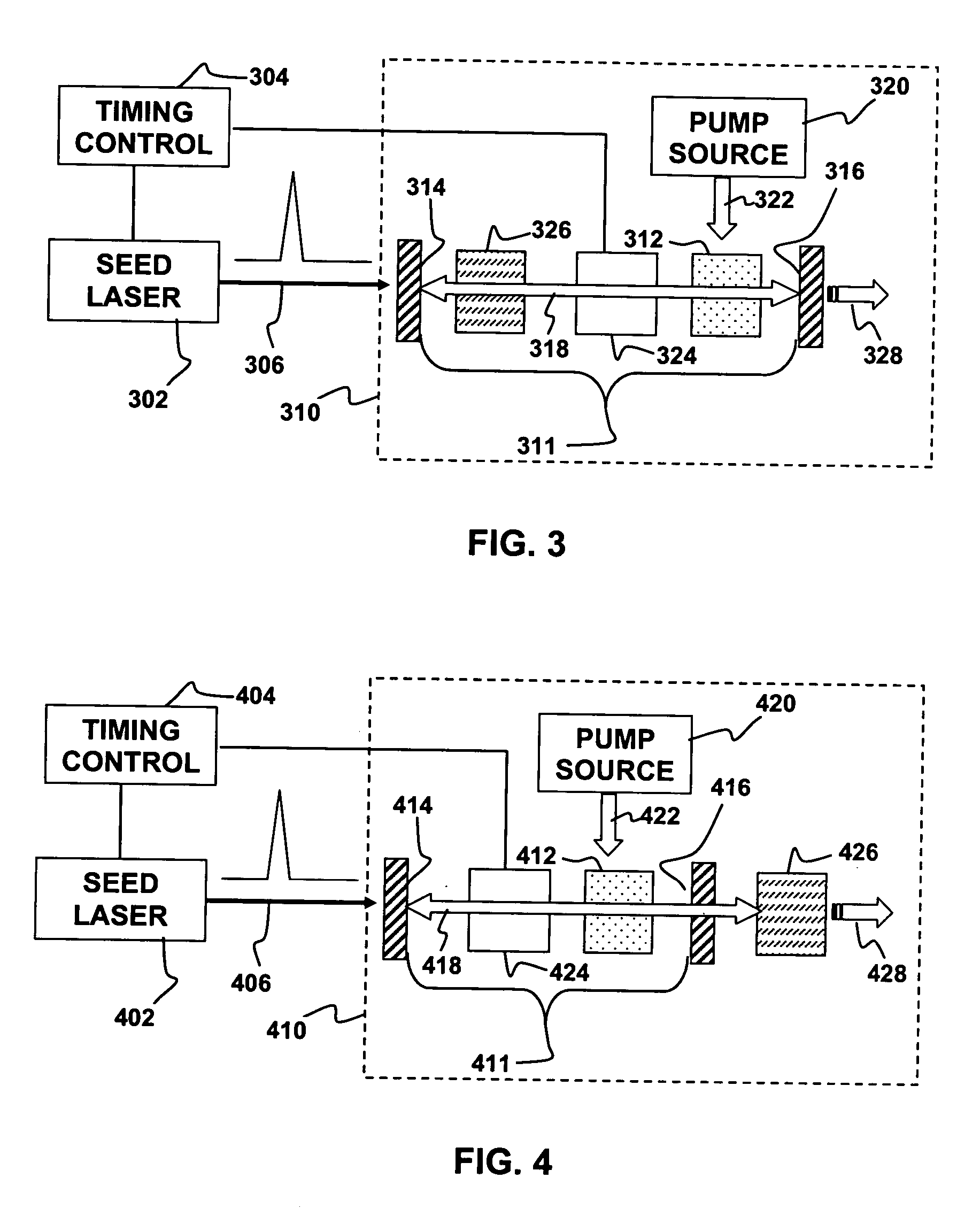
ActiveUS20060268950A1Efficient non-linear frequency conversionHigh peak powerLaser detailsPhysicsLinear process
A non-linearly frequency-converted Q-switched laser is “injection seeded” with short pulses from another laser, called a seed laser. Radiation produced by the Q-switched laser is frequency converted in a non-linear process. The injection seeding can enhance peak power and frequency conversion efficiency while reducing damage to a non-linear medium used to frequency convert radiation generated by the Q-switched laser.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
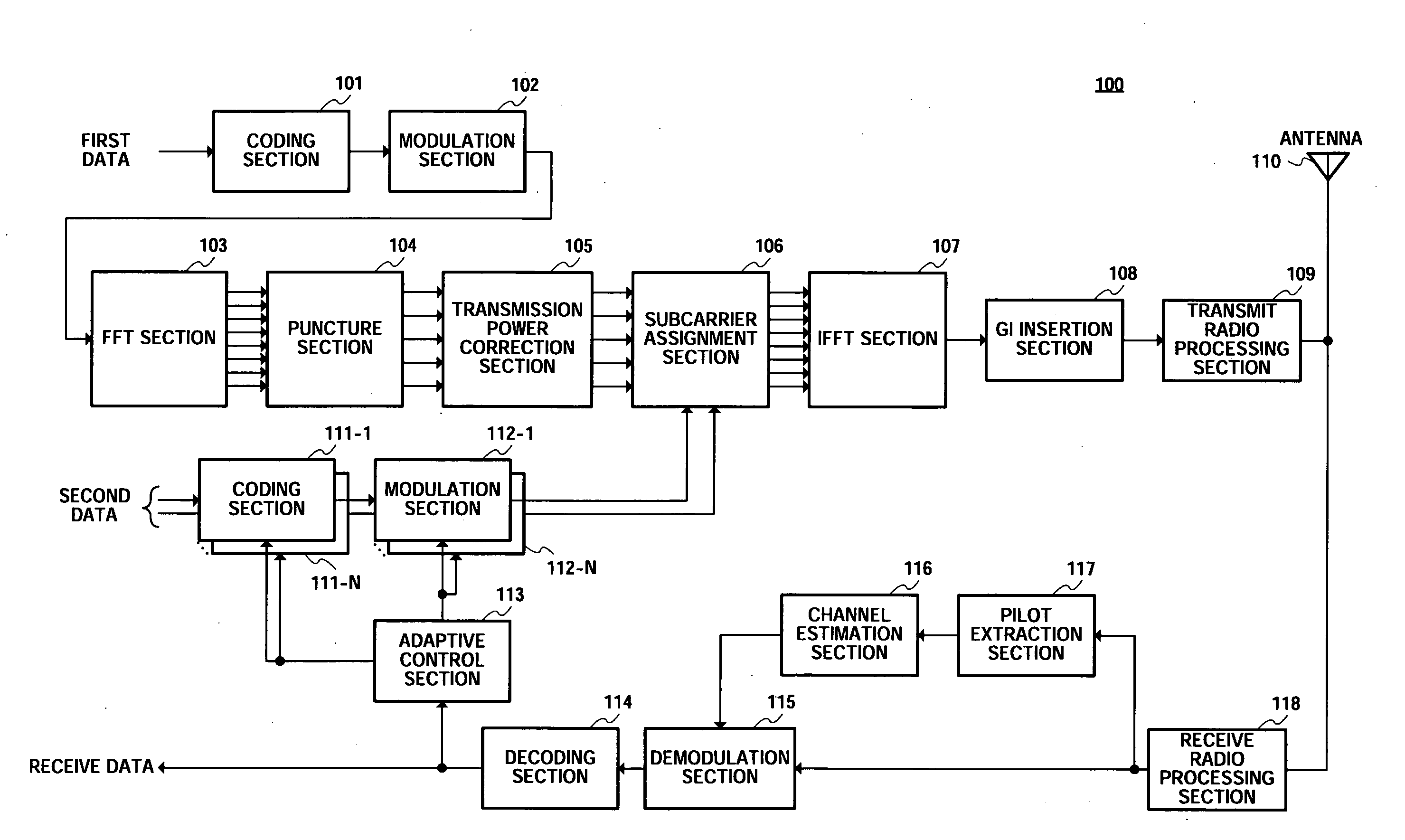
Radio Transmission Device and Radio Reception Device
ActiveUS20080304584A1Improve throughputHigh peak powerPower managementMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCarrier signalTelecommunications
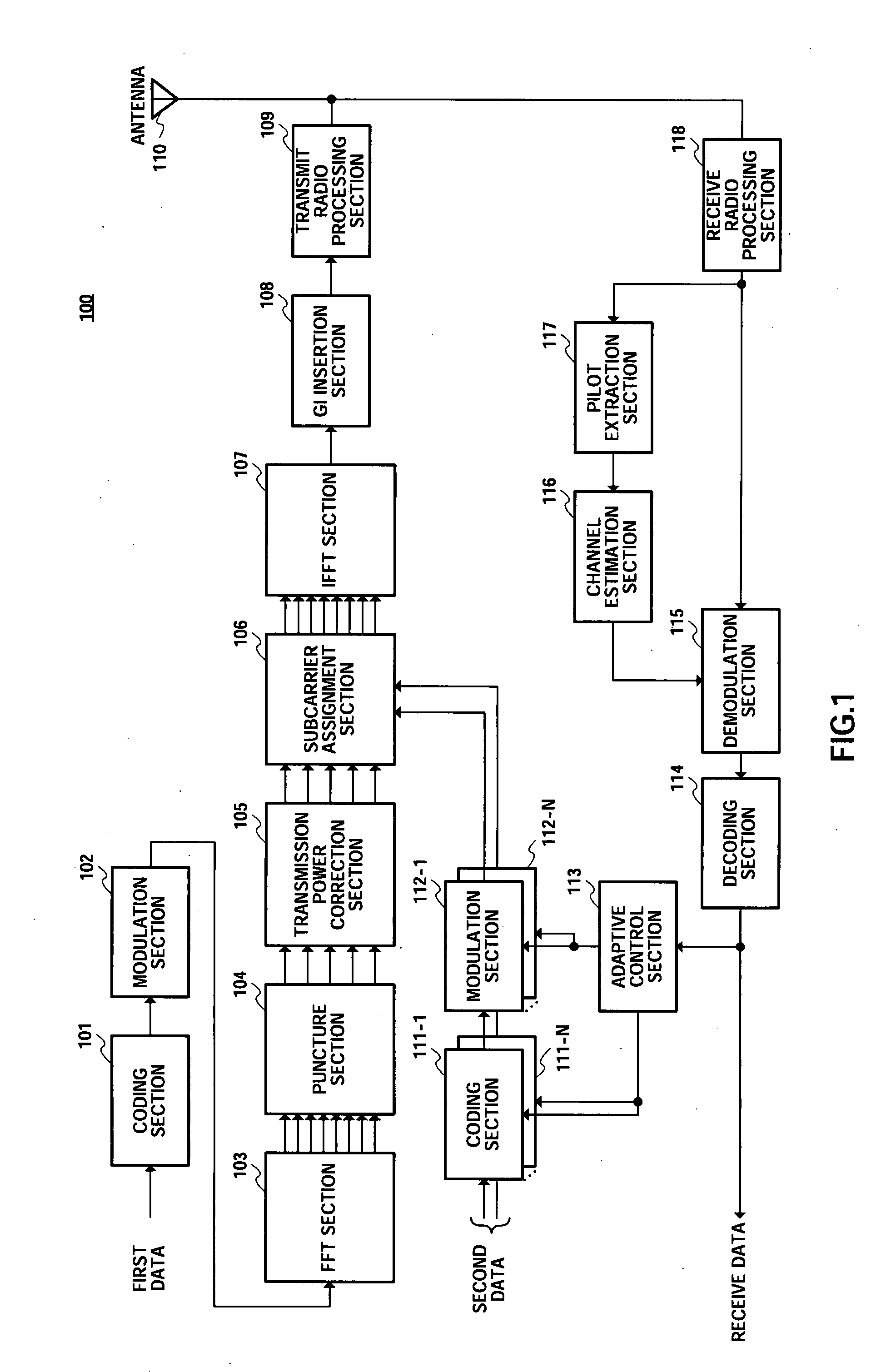
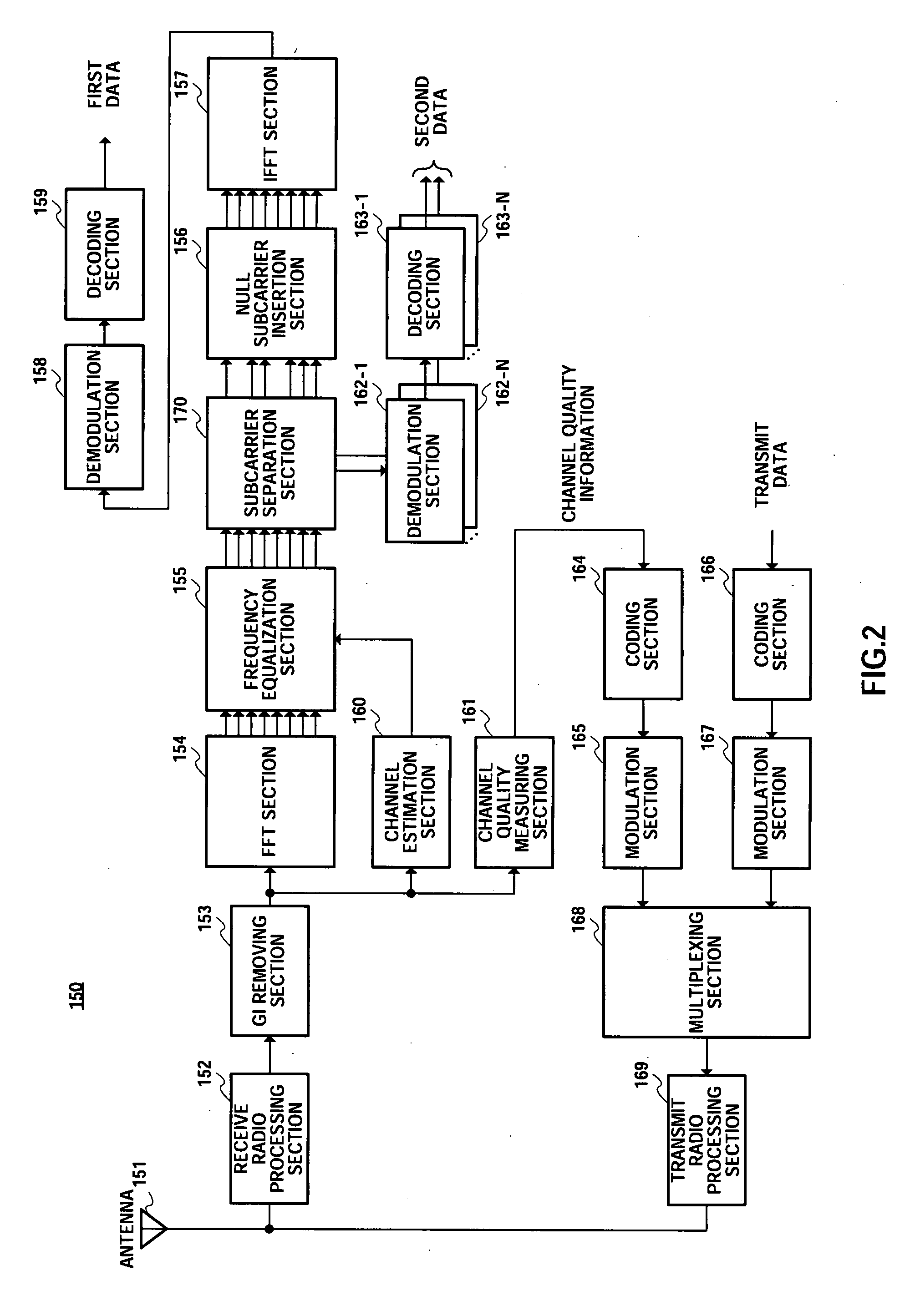
There is disclosed a radio transmission device capable of improving the throughput. The radio transmission device (100) transmits a first signal and a second signal which are different from each other. In the radio transmission device (100), an FFT unit (103) subjects first data to an FFT process. A sub-carrier allocation unit (106) maps the first data which has been subjected to the FFT process and the second data into different frequencies. An IFFT unit (107) subjects the mapped signal to the IFFT transform. A transmission radio processing unit (109) transmits the signal which has been subjected to the IFFT processing, with a single carrier.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Nonlinear optical device
InactiveUS20050047702A1Enhanced optical confinementEasy to integrateOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsAudio power amplifierMichelson interferometer
There is provided a non-linear optical device for enhancing the bandwidth accessible in the nonlinear generation of an optical signal. The device comprises a planar optical waveguide, the planar optical waveguide being operative to generate an optical output from an optical input having an input bandwidth by means of a non-linear optical process, the optical output having a wavelength within an accessible bandwidth, wherein the planar optical waveguide is operative to enhance the accessible bandwidth such that the ratio of the accessible bandwidth to the input bandwidth is at least 4. The device is particularly applicable to broad optical continuum generation, but may also be used in a parametric oscillator or amplifier arrangement with broad tuning range. The planar waveguide geometry permits easy integration in more complex photonic integrated circuits such as a Michelson interferometer for low coherence interferometry based optical coherence tomography.
Owner:MESOPHOTONICS LTD
Fluorescence observing apparatus
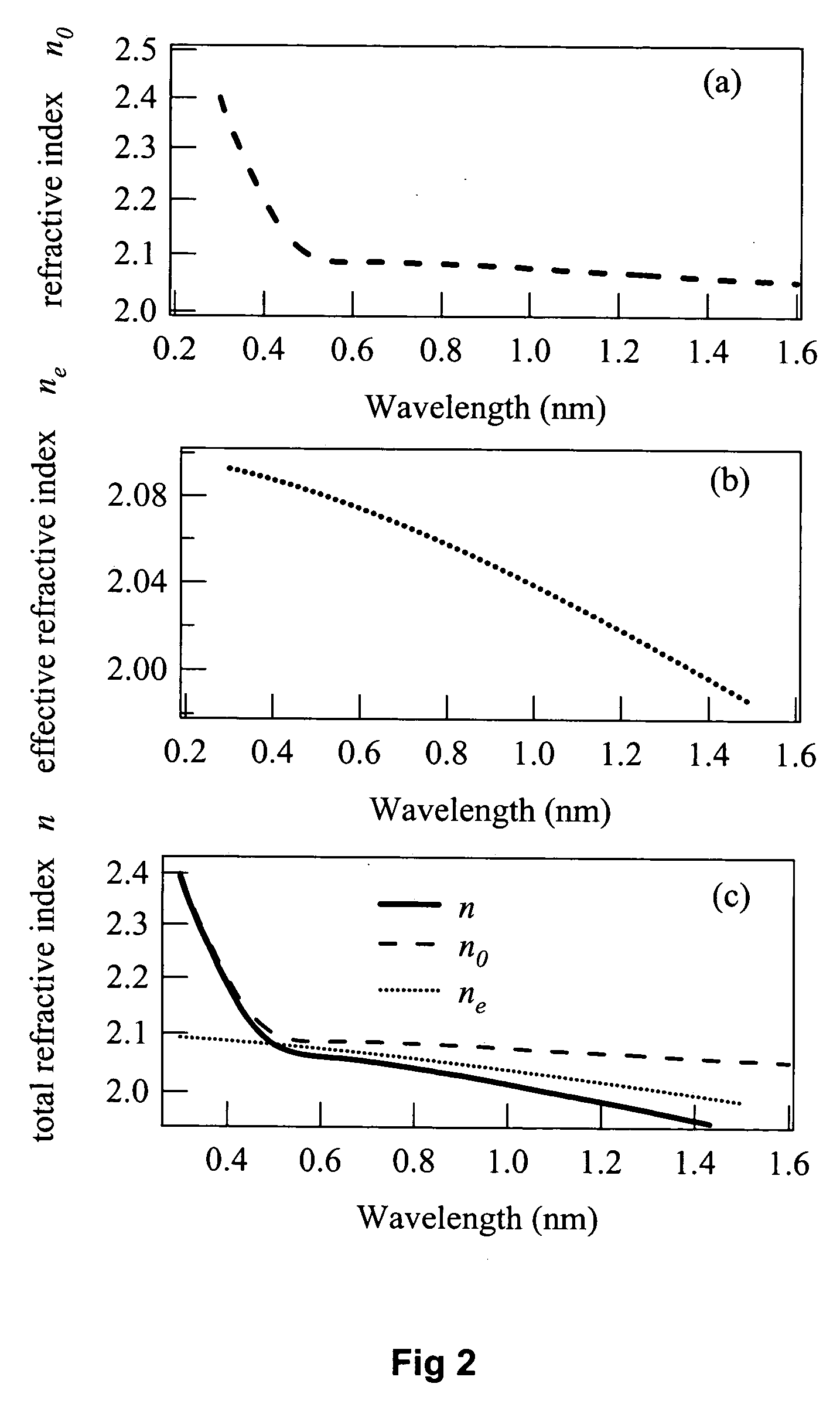
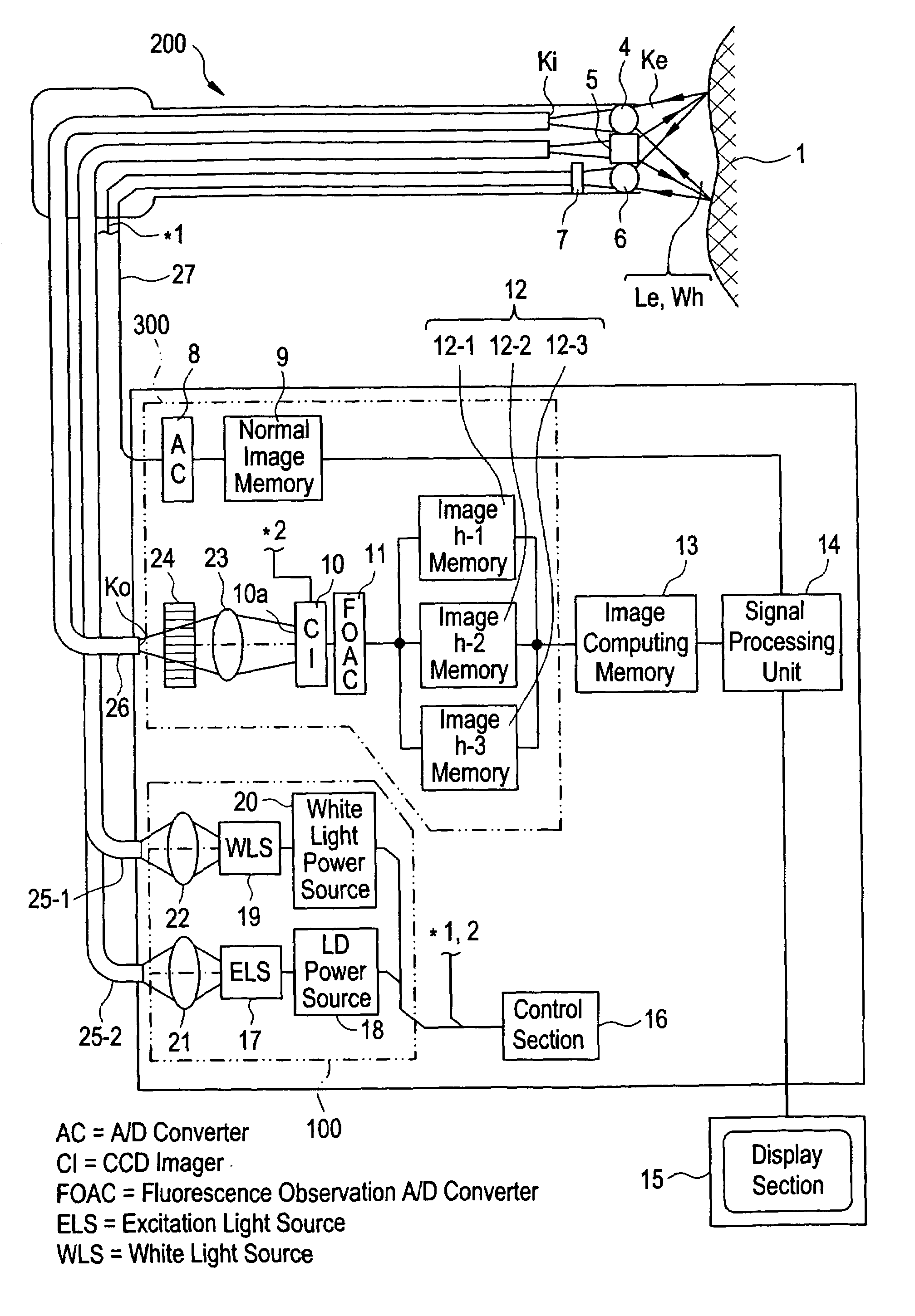
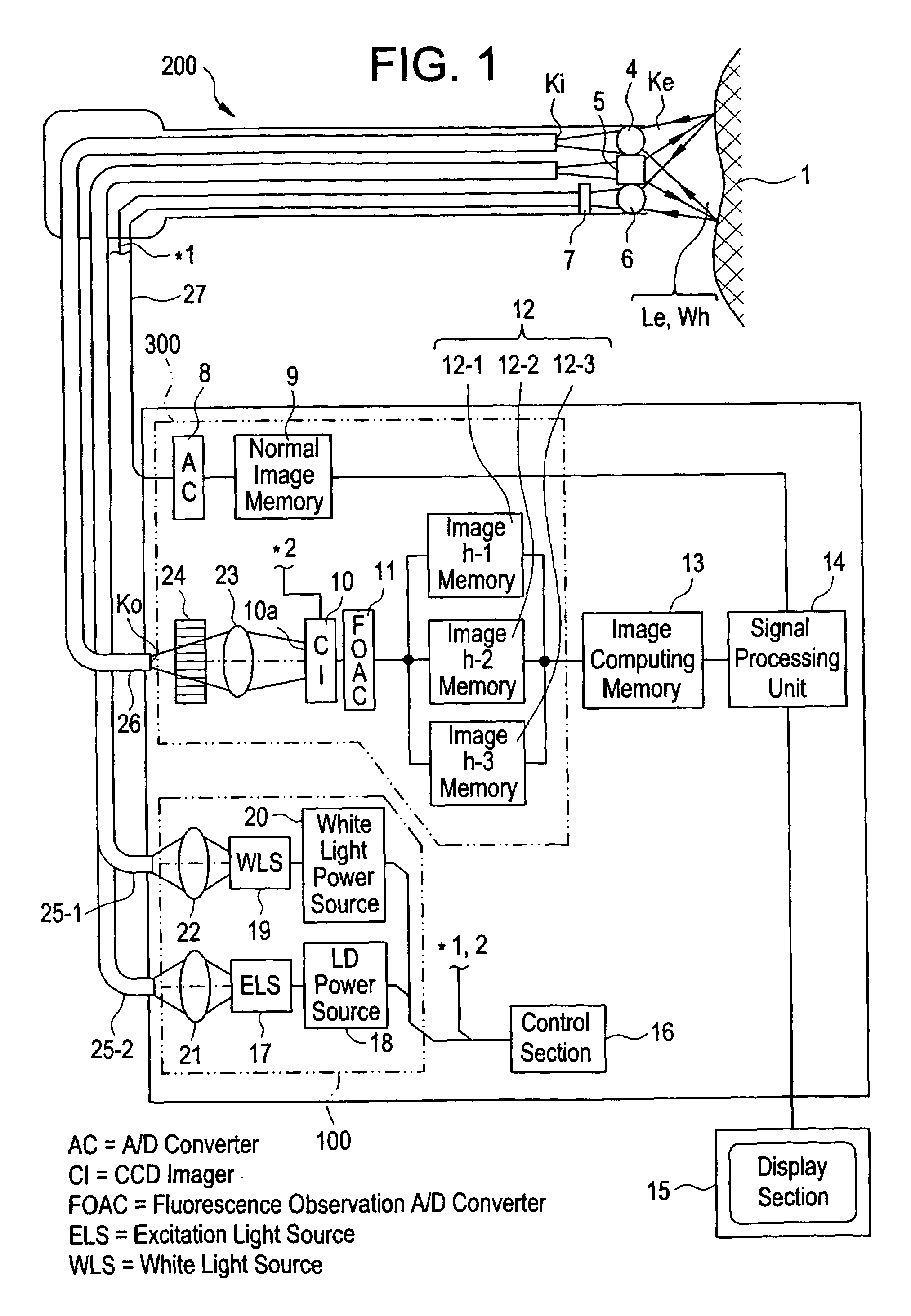
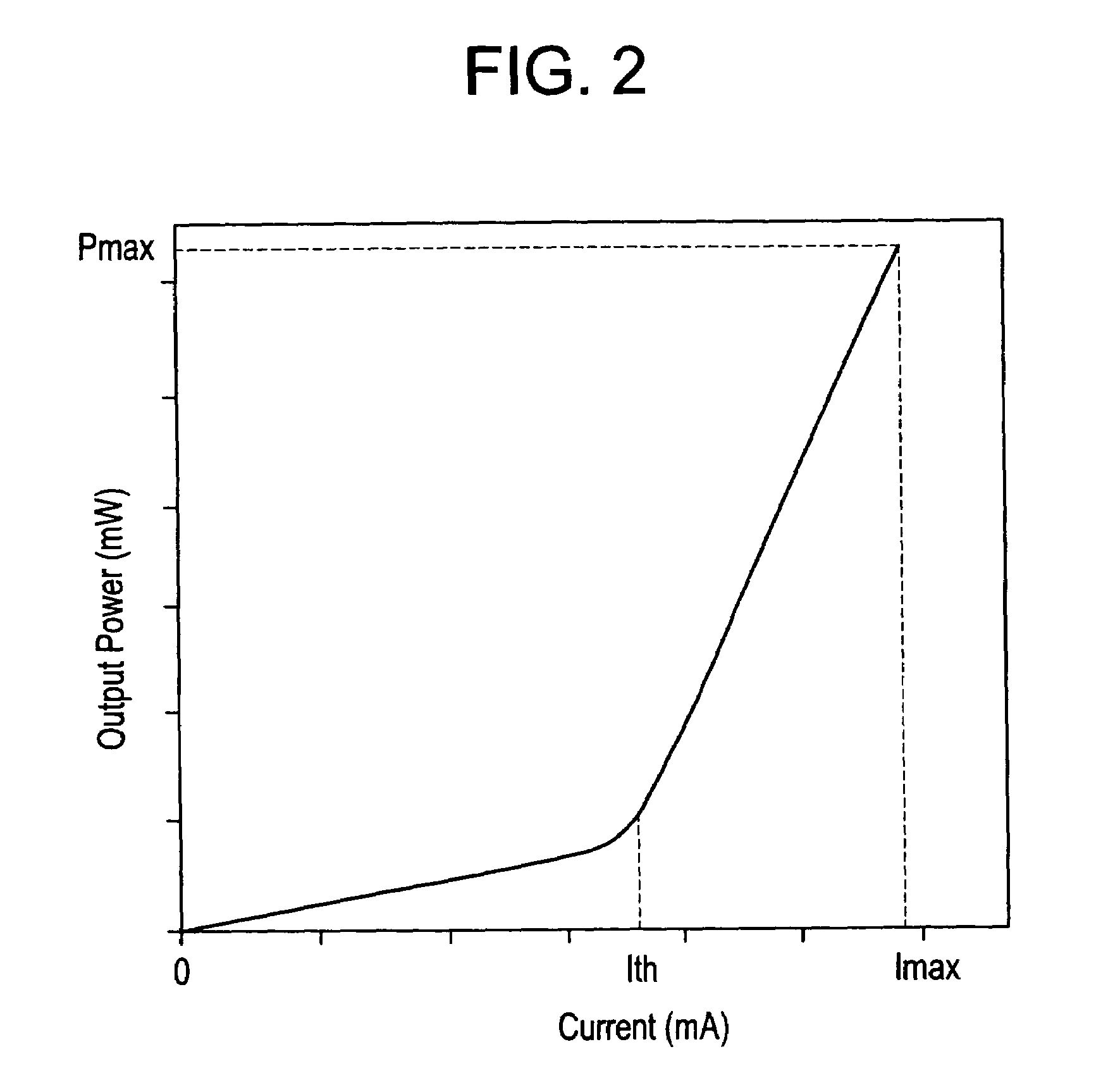
InactiveUS7062311B1High output powerHigh peak powerOptical radiation measurementRadiation measurementLight irradiationFluorescence
A fluorescence observing apparatus including a light source for emitting excitation light, an excitation light irradiation section for irradiating the excitation light to a sample, and a fluorescence measurement section for measuring fluorescence emitted from the sample by the irradiation of the excitation light. In the fluorescence observing apparatus, a GaN semiconductor laser is employed as the light source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet
InactiveUS20070263693A1Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsUltravioletLaser source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Micro-nano structure preparation method on metallic material surface using femtosecond laser
InactiveCN101380693AHeat conduction effects are reduced and eliminatedHigh peak powerLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention discloses a method for preparing a micron / nano structure on the surface of a metal material by using femtosecond laser. The preparation steps thereof are as follows: after mechanical grinding and polishing are carried out on the surface of the metal material, then the surface is ultrasonically washed by ionized water; a femtosecond laser technique is adopted: in the air environment, a 10*micro objective is used for vertically focusing an incident femtosecond laser pulse on the surface of the material; the radius of a laser beam at the focus position is 5 microns; besides, the surface of the material is adjusted to the position which has 10 to 250 microns to the focus plane of the objective along the reverse direction of the beam, thus being capable of generating the micron / nano structure on the surface of the metal material by inducing. The method has the advantages of simple technique, being convenient and practical, no pollution and being capable of improving and enhancing the thermal radiation efficiency of the material in a broad spectrum range.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Stable solid state raman laser and method of operating same
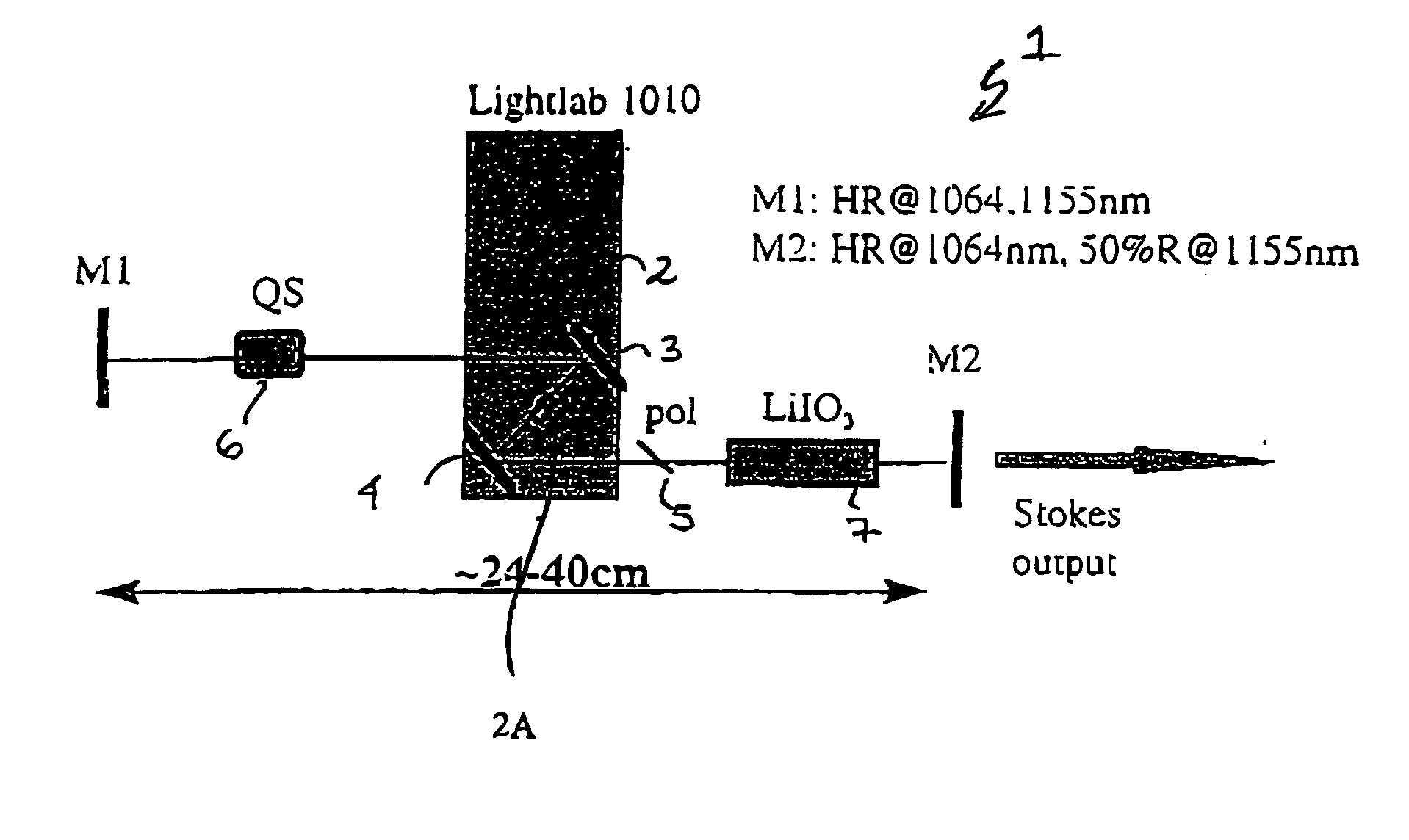
InactiveUS20040028090A1Effective approachLimited scalabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSolid massInstability
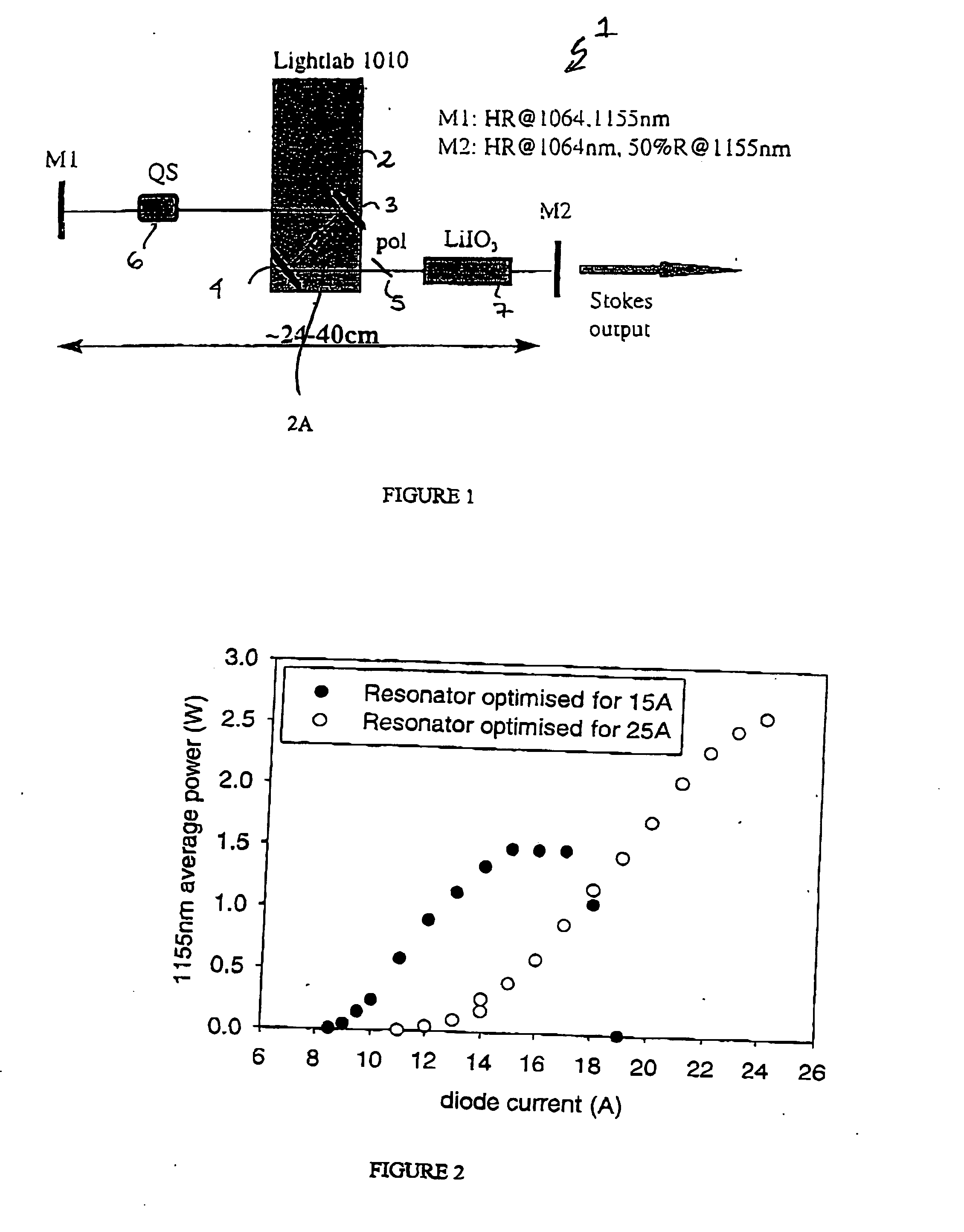
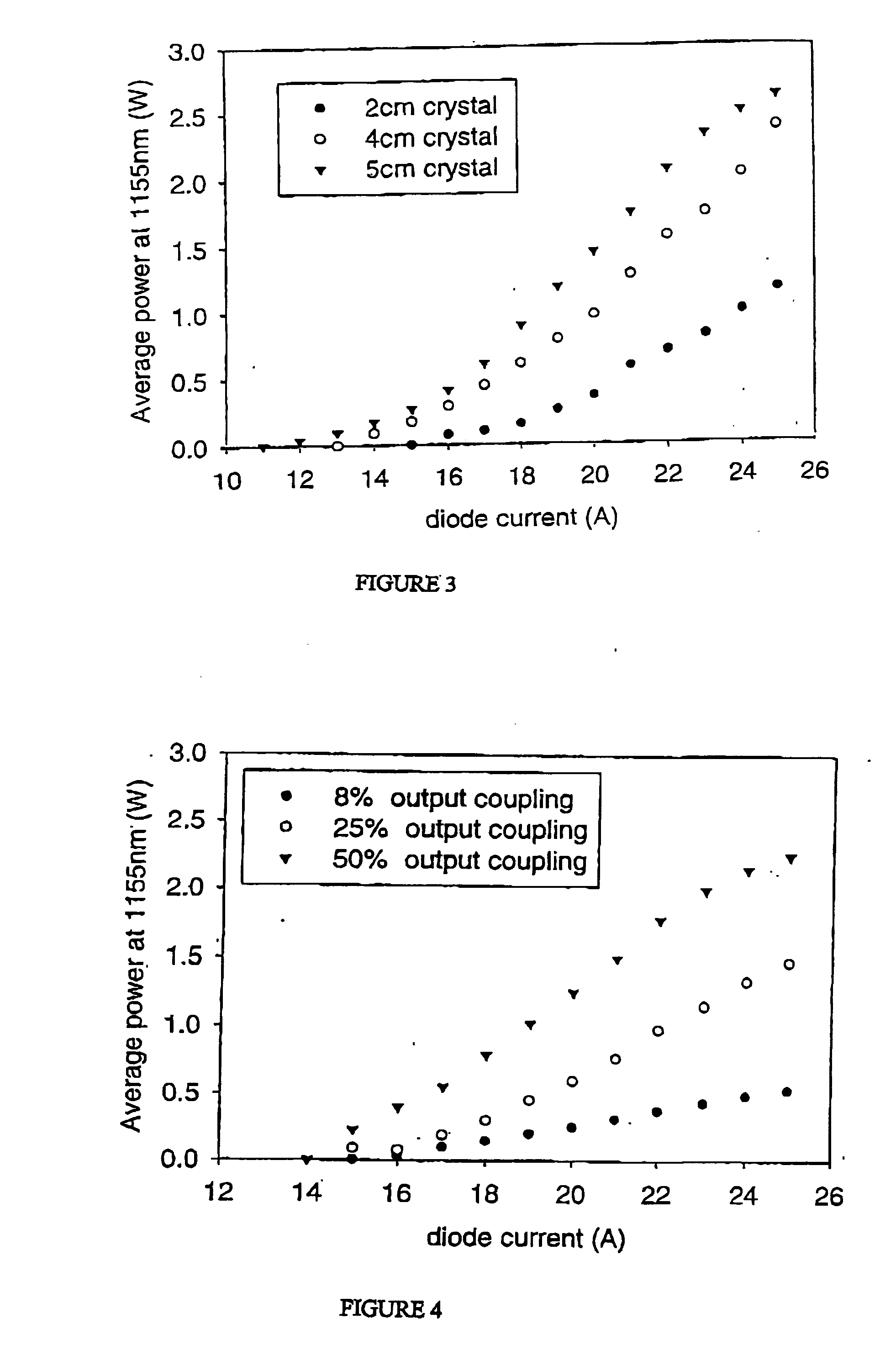
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser (1), the solid-state Raman laser including: (a) a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors (M1 and M2), (b) a laser material (2A) located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, (c) a solid Raman medium (7) located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and (d) an output coupler (M2) for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of (i) the position of the laser material (2A) relative to the position of the Raman medium (7) in the cavity, (ii) the length of the cavity and (iii) the curvature of at least one of the reflectors (M1 or M2), is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) as a result of thermal effects in the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Quantum cascade laser suitable for portable applications
ActiveUS20080304524A1Sufficient brightnessHigh efficiencySpectrum investigationSighting devicesOptoelectronicsPassive cooling
A highly portable, high-powered infrared laser source is produced by intermittent operation of a quantum cascade laser power regulated to a predetermined operating range that permits passive cooling. The regulation process may boost battery voltage allowing the use of more compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Double-optical frequency comb optical imaging method based on continuous frequency stabilized laser
The invention discloses a double-optical frequency comb optical imaging method based on a continuous frequency stabilized laser. According to the optical imaging method, two optical frequency comb seed resources are locked onto a stable outside atomic clock through a repetition frequency control module, meanwhile, an electric signal which has optical comb frequency instability is extracted through interaction between the continuous frequency stabilized laser and the laser output by the two optical frequency comb seed resources, radio-frequency signal power distribution and processing are conducted on the electric signal, a part of the electric signal is directly used for feedback control of the laser resonator character of the two optical frequency comb seed resources so as to stabilize the output carrier envelope phase frequency of a semiconductor laser unit, the other part of the electric signal is used for being mixed with a periodical interference spectrum signal generated by a double-optical comb imaging system so as to further counteract the frequency variations of the optical comb system, and therefore the measurement precision of the whole double-optical comb imaging system is controlled from two aspects and quick and super-high-resolution optical comb coherent imaging is achieved.
Owner:华东师范大学重庆研究院
Q-switched, cavity dumped laser systems for material processing
InactiveUS7058093B2High strengthLow powerActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsEngravingPeak value
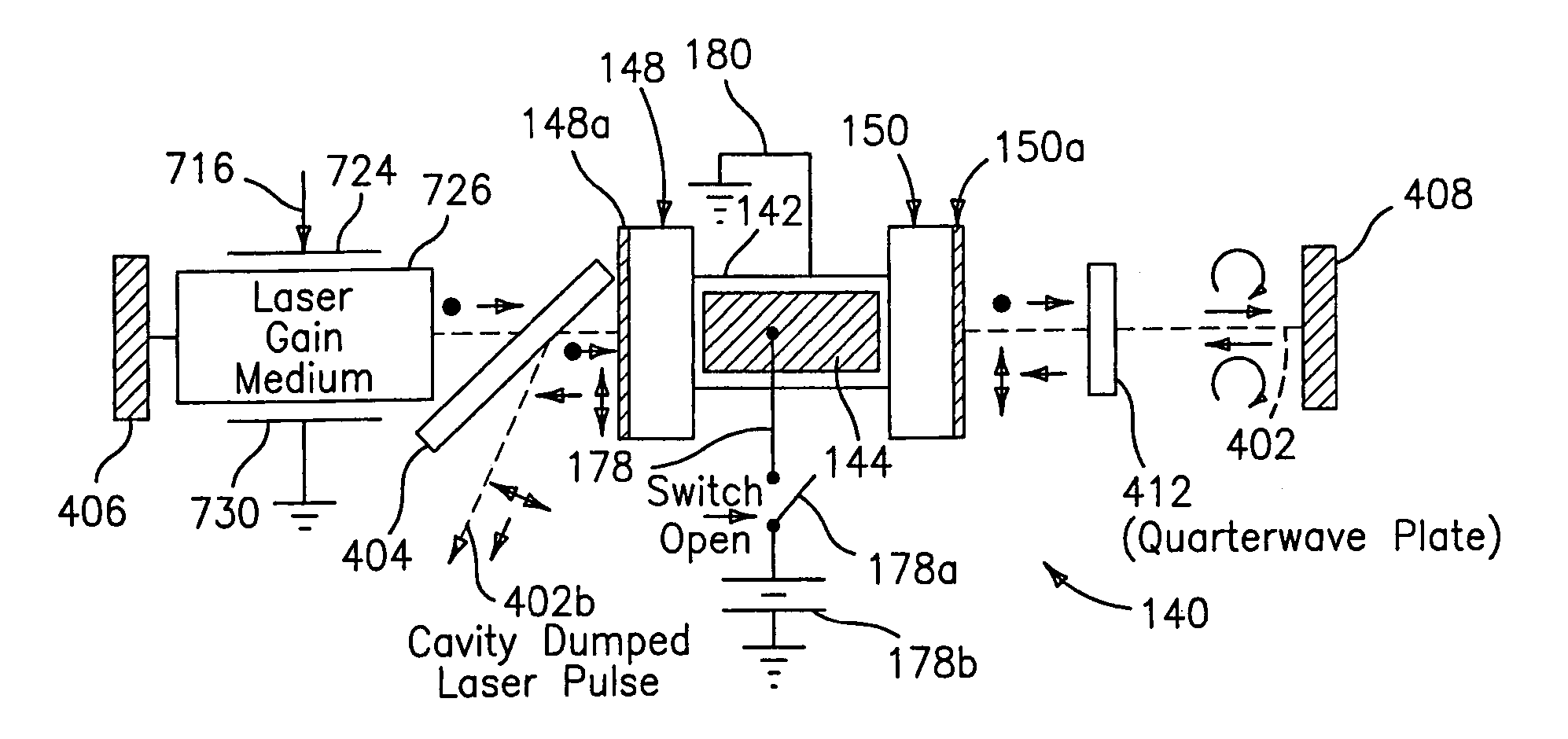
This disclosure discusses techniques for obtaining wavelength selected simultaneously super pulsed Q-switched and cavity dumped laser pulses utilizing high optical damage threshold electro-optic modulators, maintaining a zero DC voltage bias on the CdTe electro-optic modulator (EOM) so as to minimize polarization variations depending on the location of the laser beam propagating through the CdSe EOM crystal, as well as the addition of one or more laser amplifiers in a compact package and the use of simultaneous gain switched, Q-switched and cavity dumped operation of CO2 lasers for generating shorter pulses and higher peak power for the hole drilling, engraving and perforation applications.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Ac-dc converter
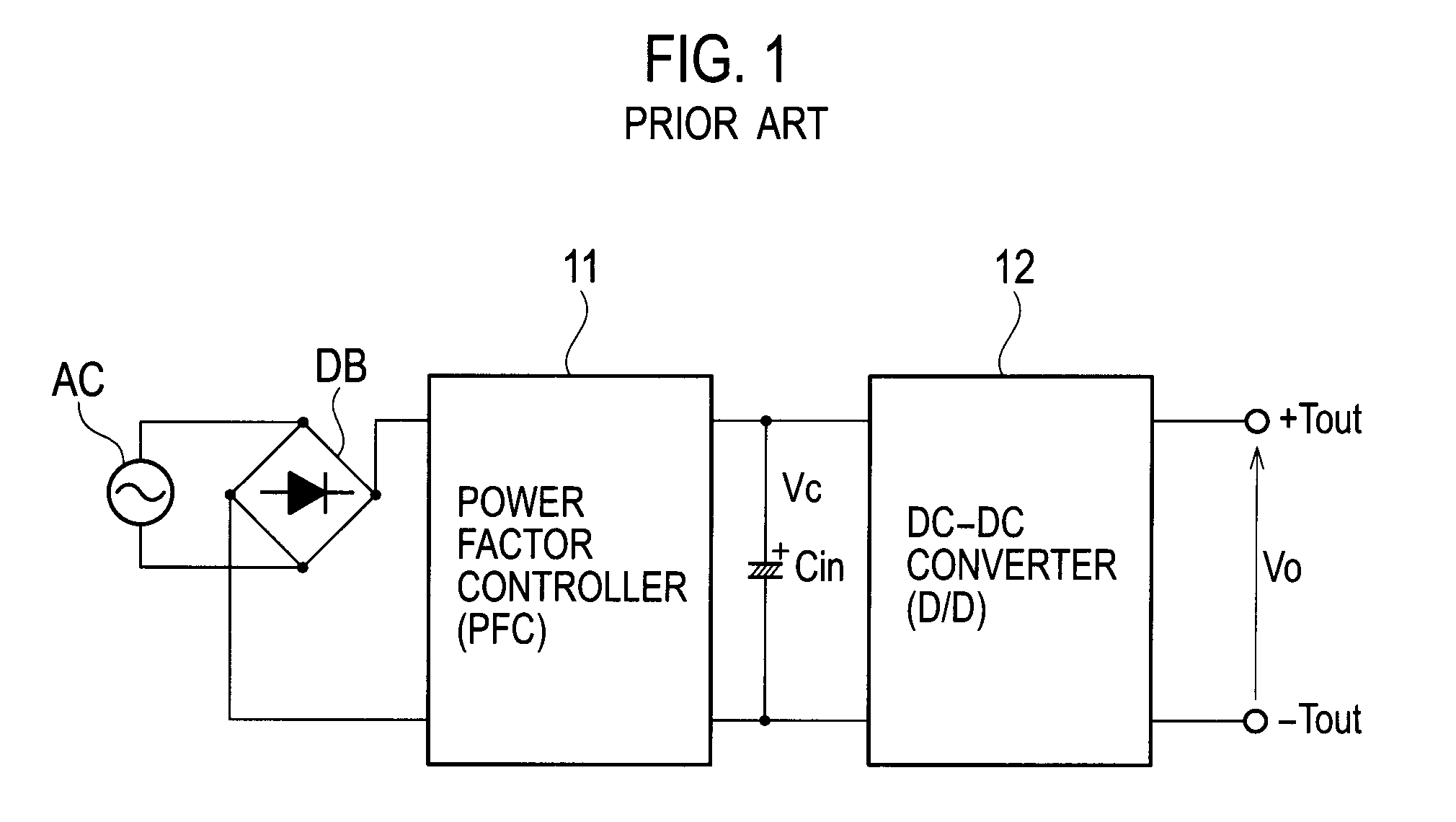
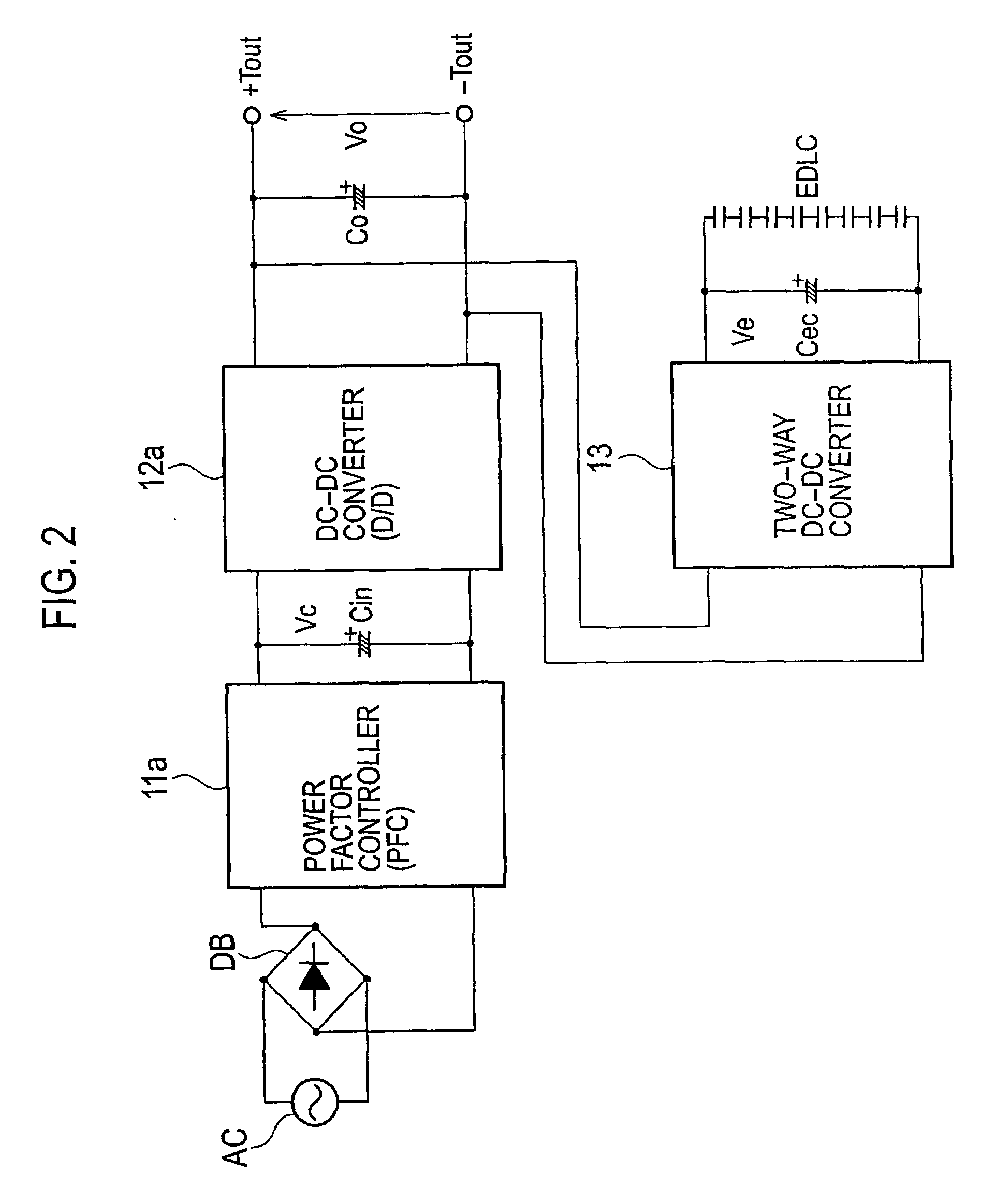
InactiveUS20090027930A1High peak powerAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterPower factor control
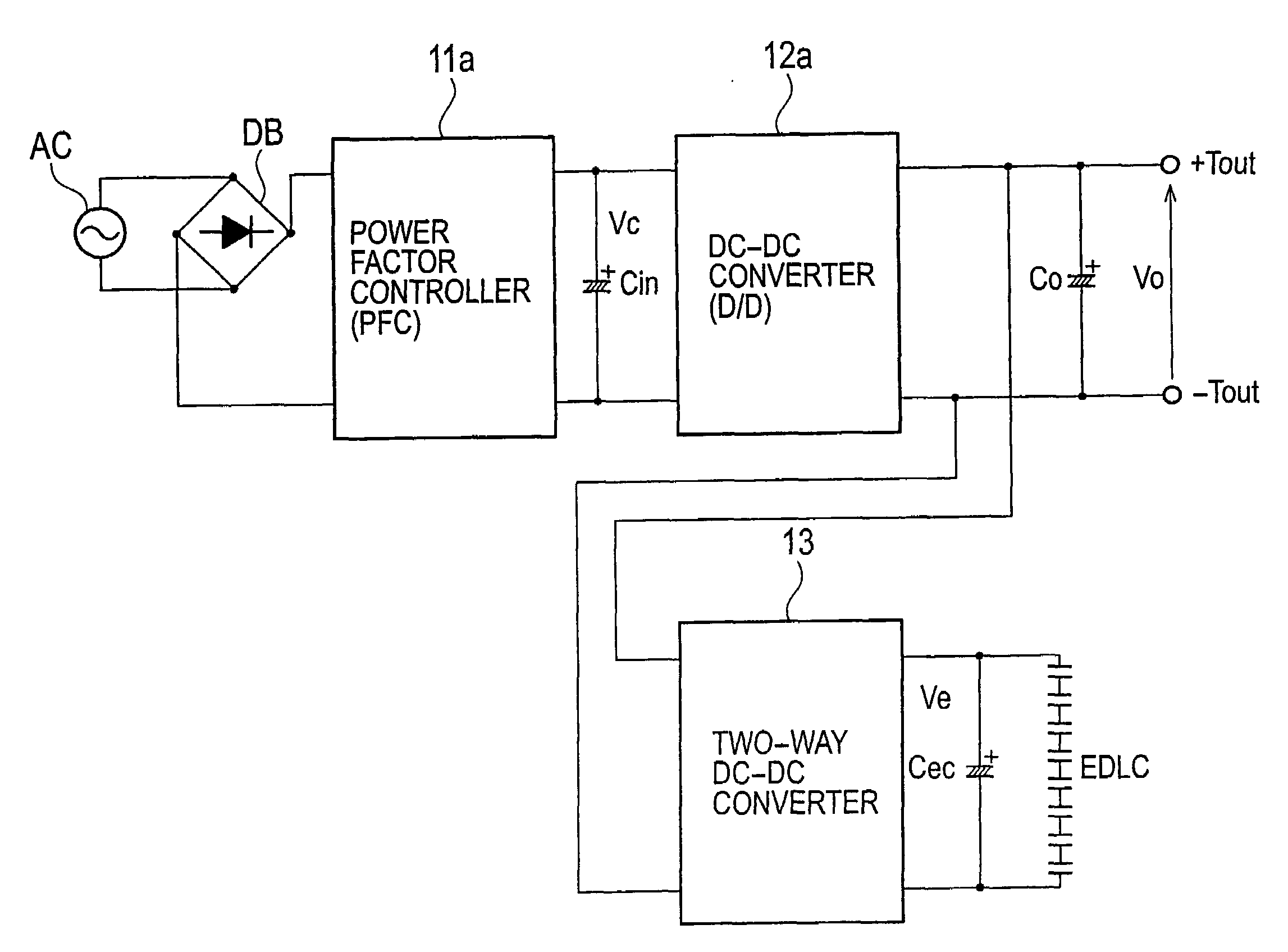
An AC-DC converter includes a rectifier DB for rectifying an alternating current supplied from an alternating power source AC, a power factor controller 11 connected to an output side of the rectifier DB to improve a power factor, a DC-DC converter 12 that converts a voltage outputted from the power factor controller 11 to another voltage and also outputs either a power or a current limited to a predetermined value, a capacitor for storing an energy and a two-way converter 13 having one input / output terminals connected to output terminals of the DC-DC converter 12 and the other input / output terminals connected to the capacitor to carry out a two-way power conversion.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
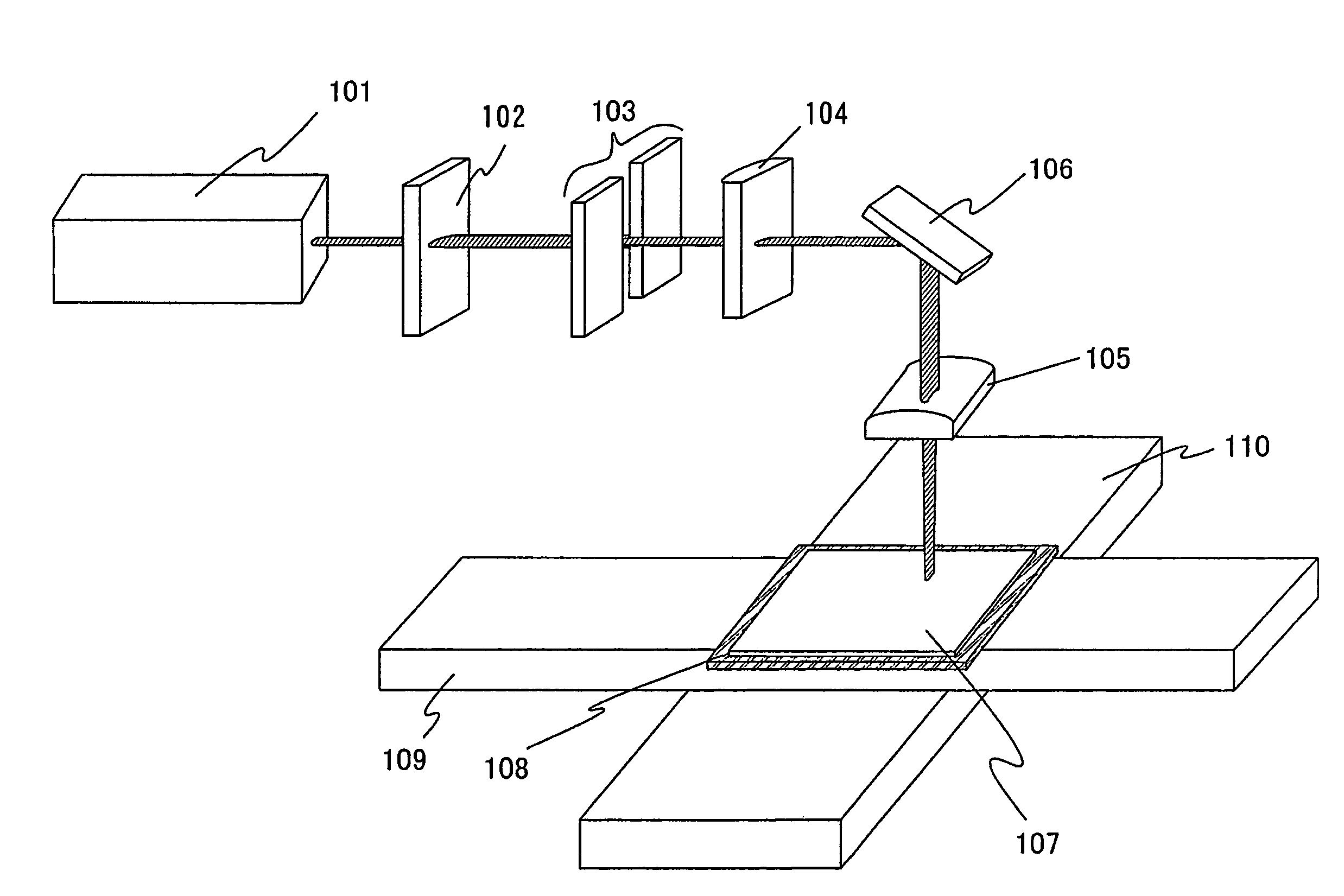
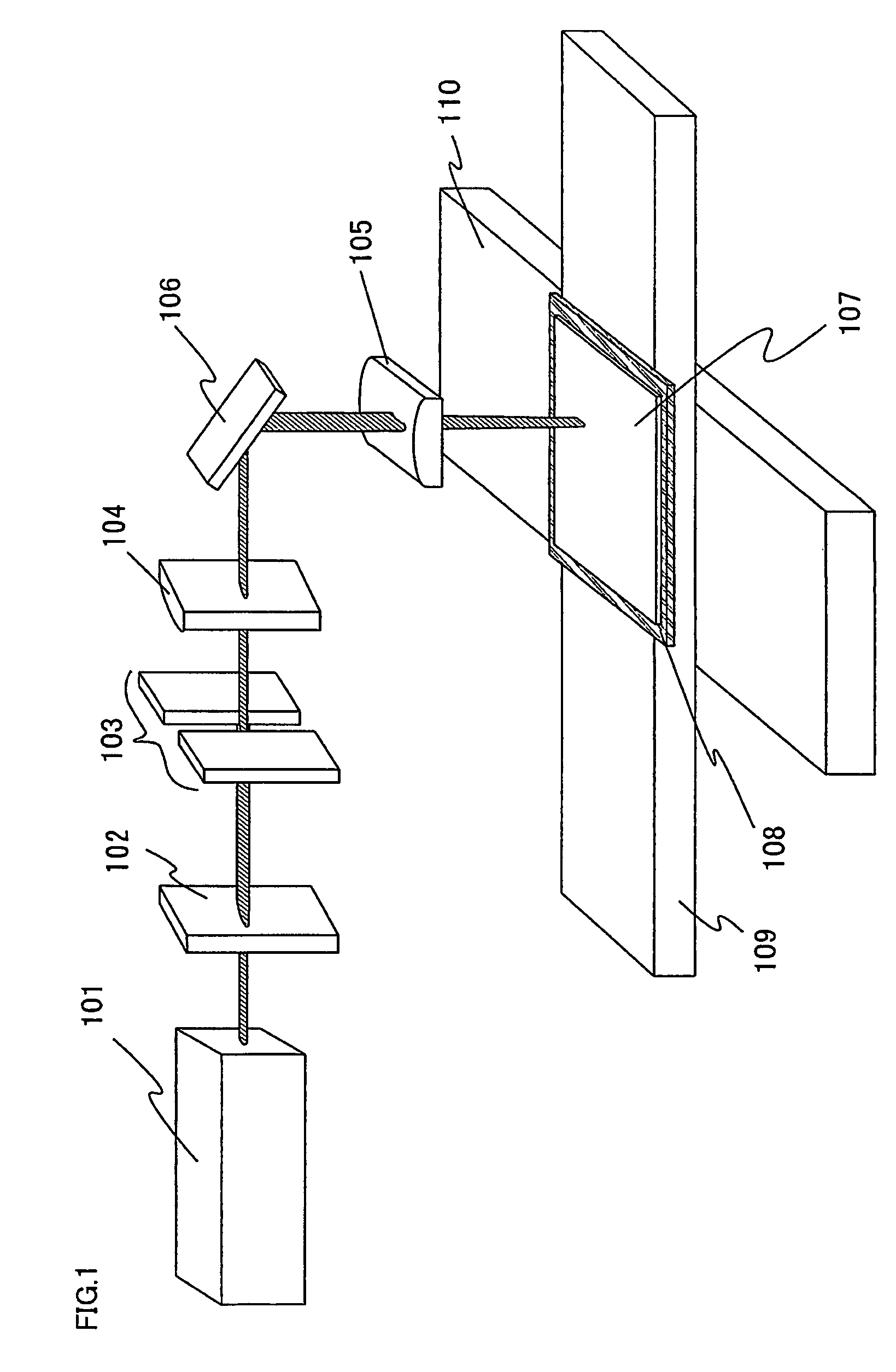
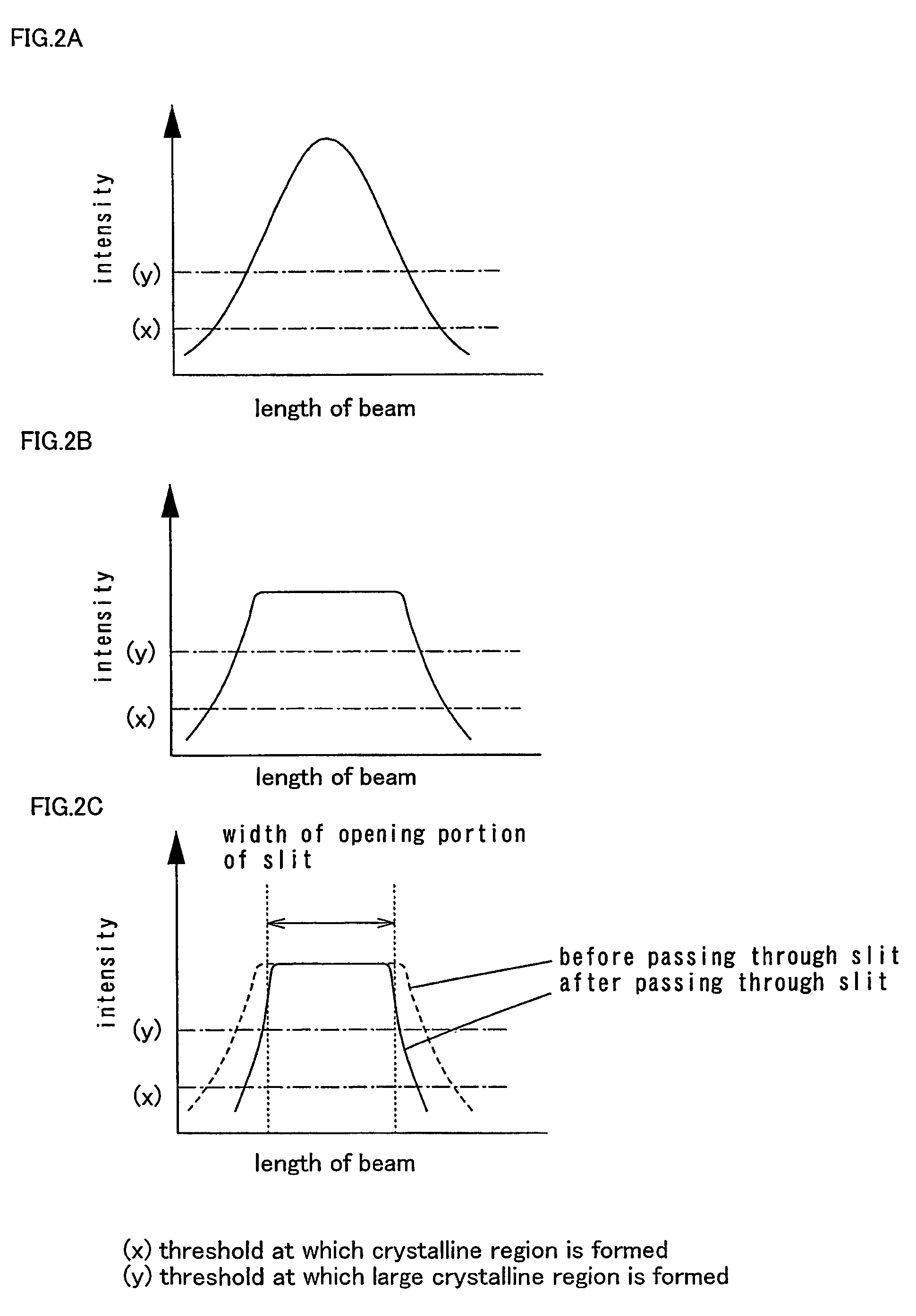
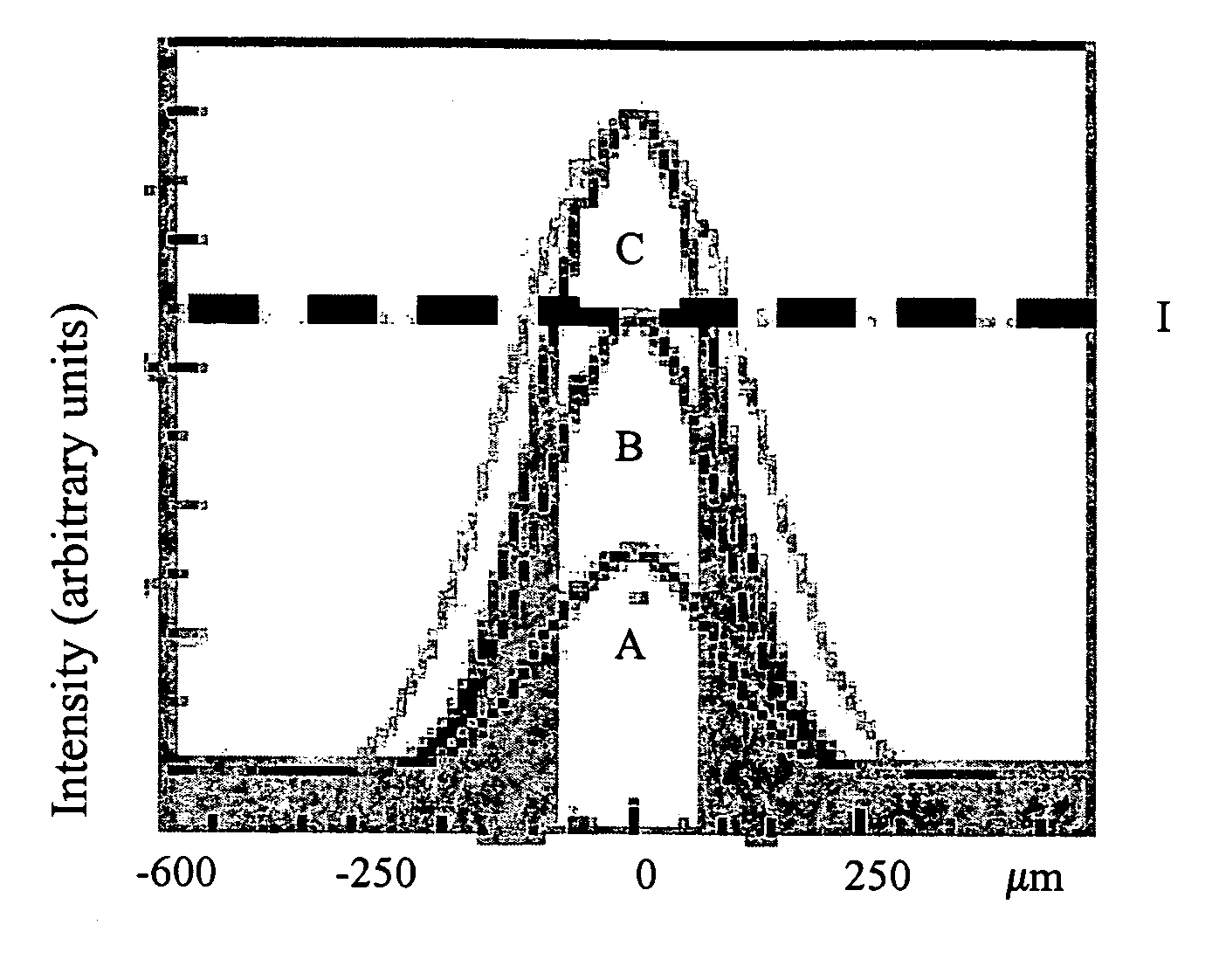
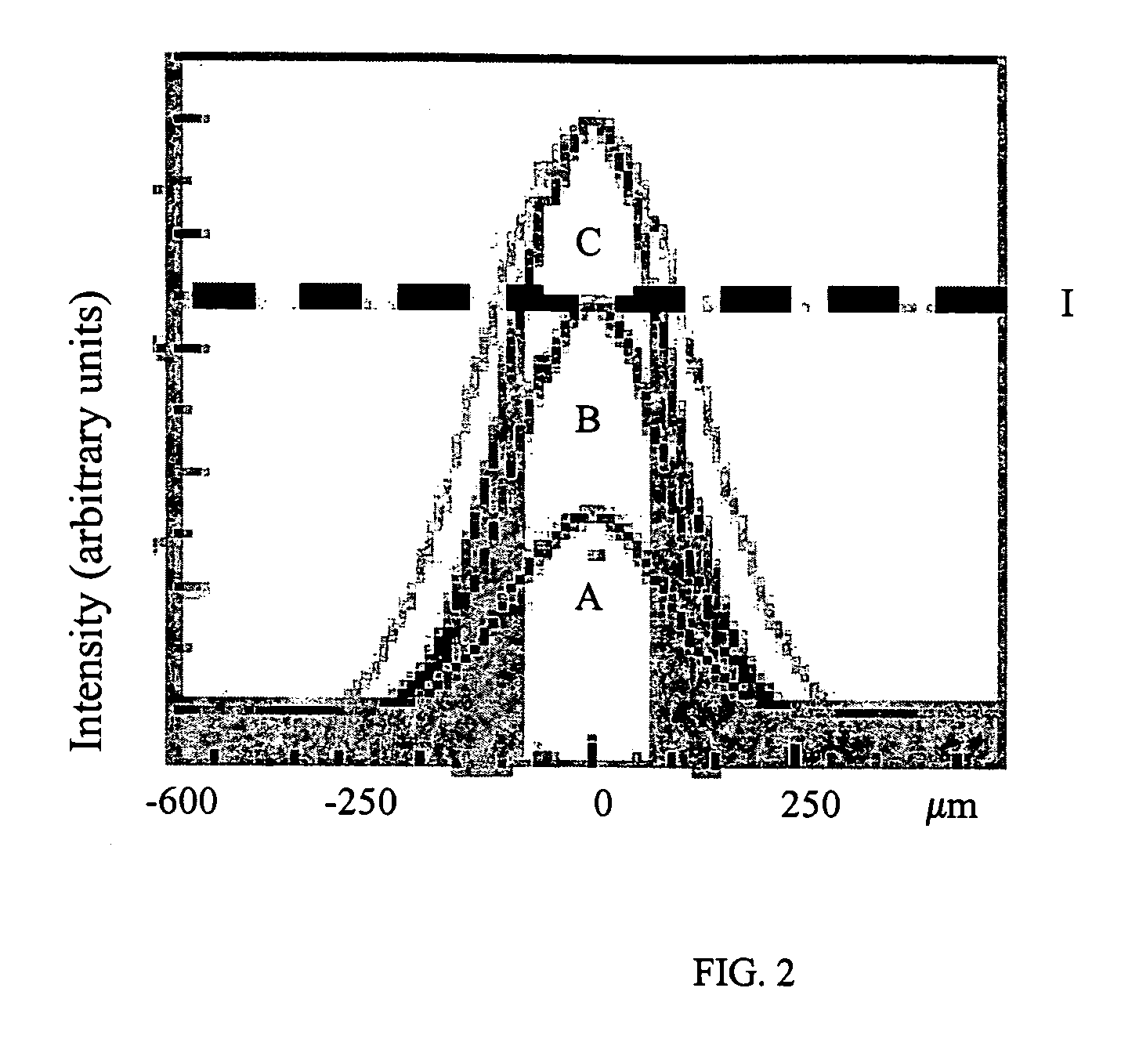
Laser irradiation apparatus and laser irradiation method
ActiveUS8395084B2Reduced areaHigh repetition rateElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesLight beamOptoelectronics
A laser beam having homogeneous intensity distribution is delivered without causing interference stripes of a laser to appear on an irradiation surface. A laser beam emitted from a laser oscillator passes through a diffractive optical element so that the intensity distribution thereof is homogenized. The beam emitted from the diffractive optical element then passes through a slit so that low-intensity end portions in a major-axis direction of the beam are blocked. Subsequently, the beam passes through a projecting lens and a condensing lens, so that an image of the slit is projected onto the irradiation surface. The projecting lens is provided so that the slit and the irradiation surface are conjugated. Thus, the irradiation surface can be irradiated with the laser having homogeneous intensity while preventing the diffraction by the slit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
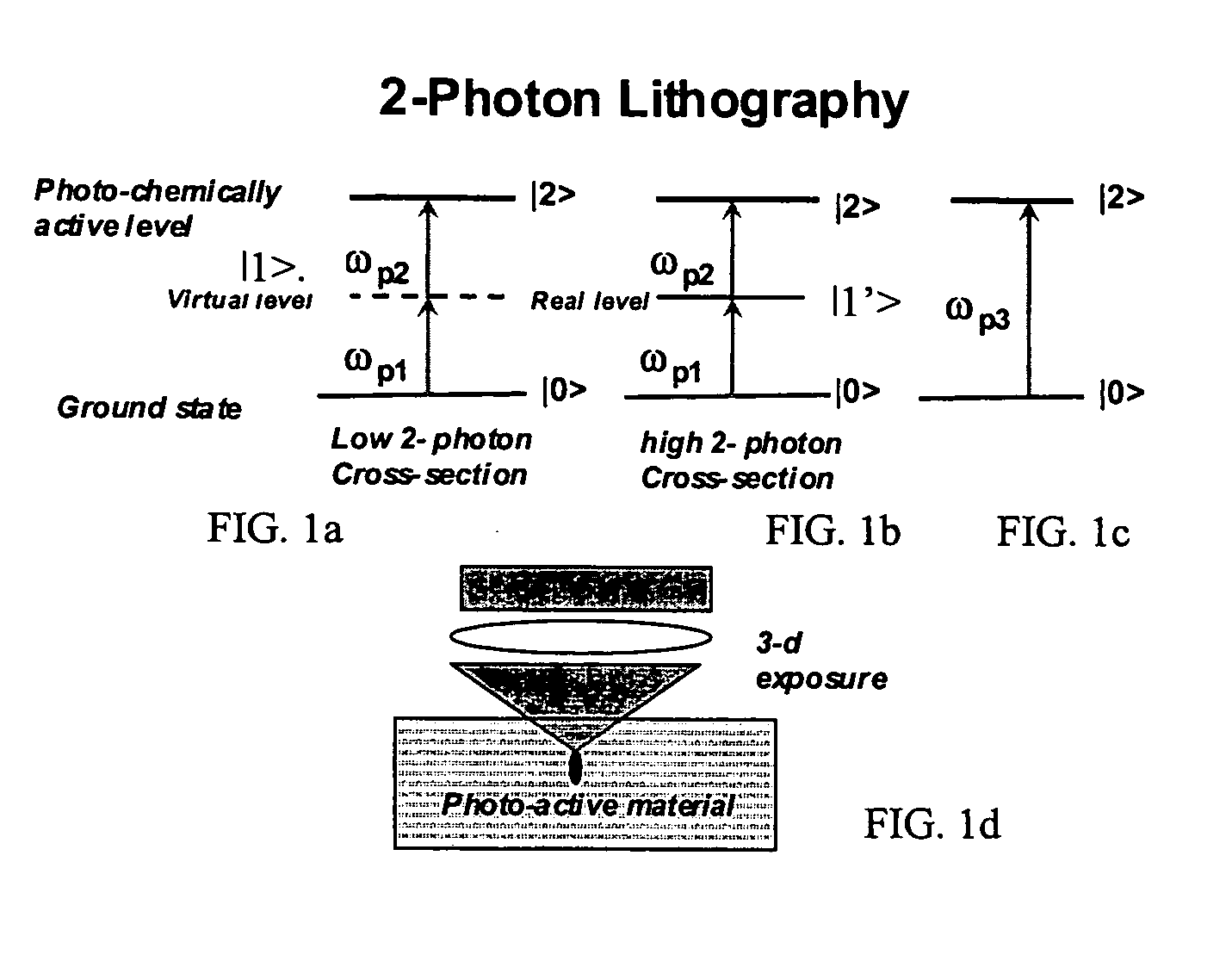
Multi-photon lithography
InactiveUS20050254035A1Improve imaging resolutionShort wavelengthElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusTime domainHigh peak
A system and method for patterned exposure of a photoactive medium is described wherein a pulsed optical beam with a high peak-power is stretched in the time domain to reduce the peak power while maintaining the average power. The stretched pulse illuminated a pattern, such as a transparent or reflective photolithography mask. The pattern is then imaged onto the photoactive medium after recompressing the beam. This arrangement prevents damage to the mask by the high peak power of the pulsed optical beam.
Owner:CHROMAPLEX
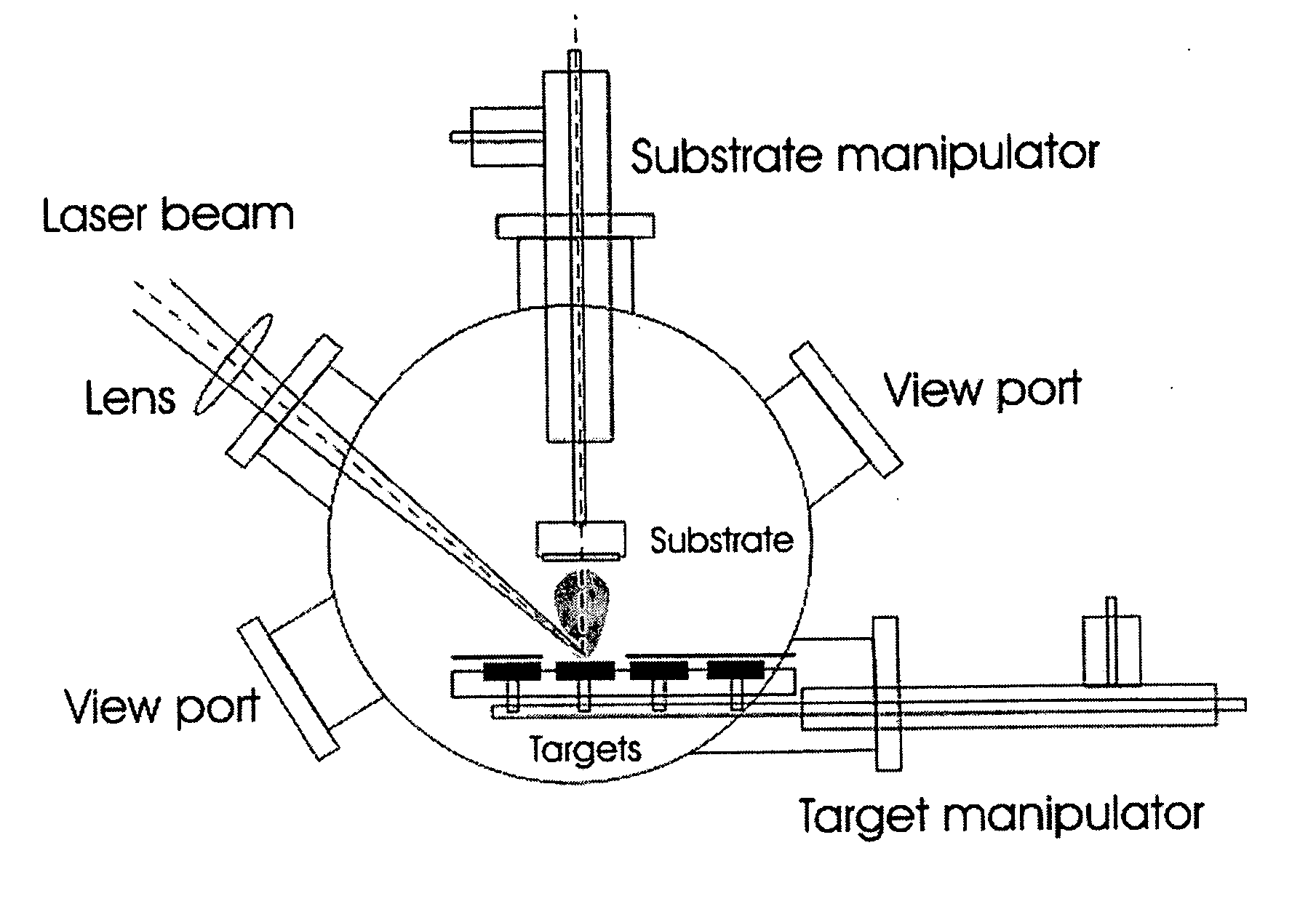
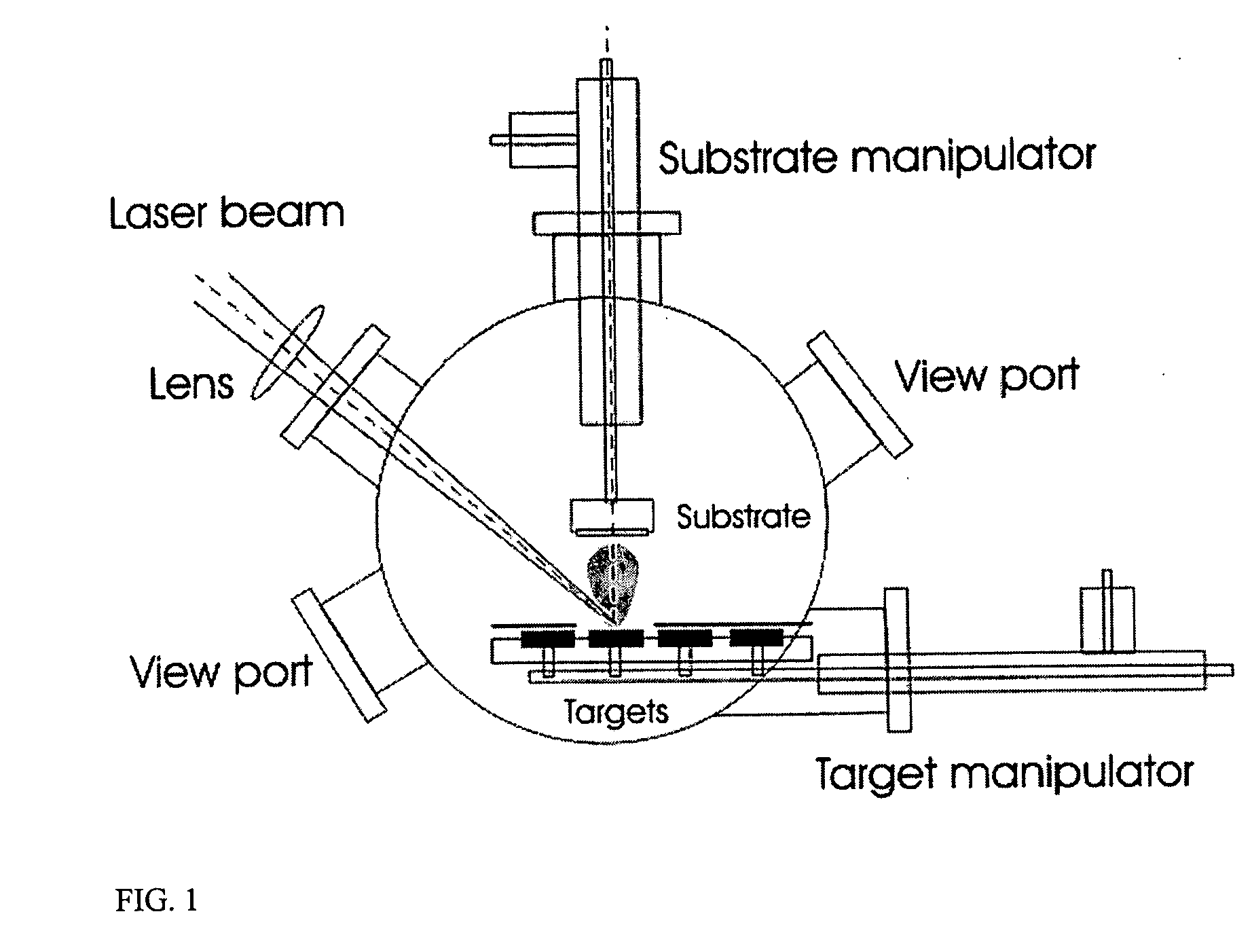
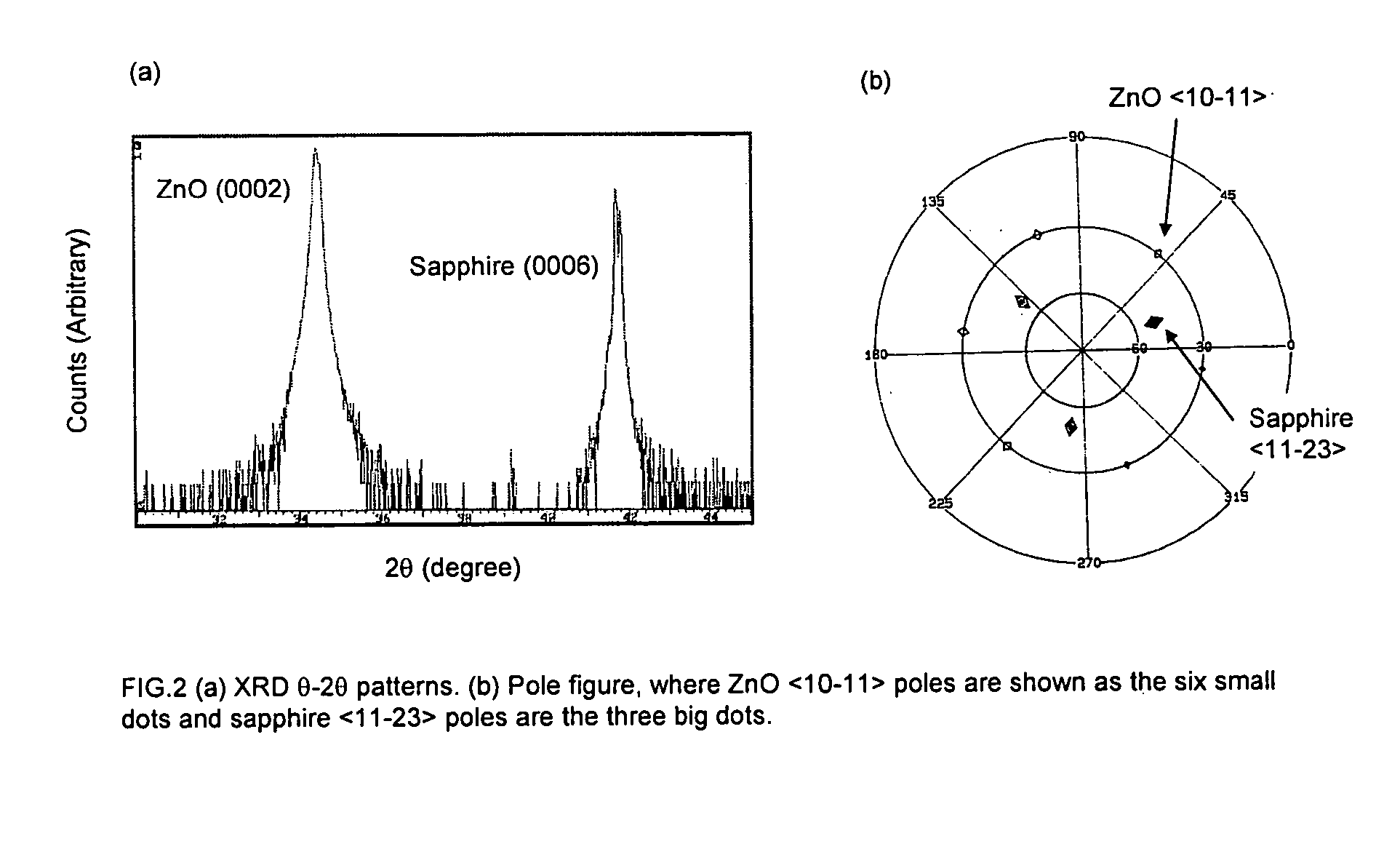
P-type semiconductor zinc oxide films process for preparation thereof, and pulsed laser deposition method using transparent substrates
InactiveUS20070243328A1High concentrationImprove conductivityElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingPulsed laser depositionLaser source
A p-type semiconductor zinc oxide (ZnO) film and a process for preparing the film are disclosed. The film is co-doped with phosphorous (P) and lithium (Li). A pulsed laser deposition scheme is described for use in growing the film. Further described is a process of pulsed laser deposition using transparent substrates which includes a pulsed laser source, a substrate that is transparent at the wavelength of the pulsed laser, and a multi-target system. The optical path of the pulsed laser is arranged in such a way that the pulsed laser is incident from the back of the substrate, passes through the substrate, and then focuses on the target. By translating the substrate towards the target, this geometric arrangement enables deposition of small features utilizing the root of the ablation plume, which can exist in a one-dimensional transition stage along the target surface normal, before the angular width of the plume is broadened by three-dimensional adiabatic expansion. This can provide small deposition feature sizes, which can be similar in size to the laser focal spot, and provides a novel method for direct deposition of patterned materials.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com