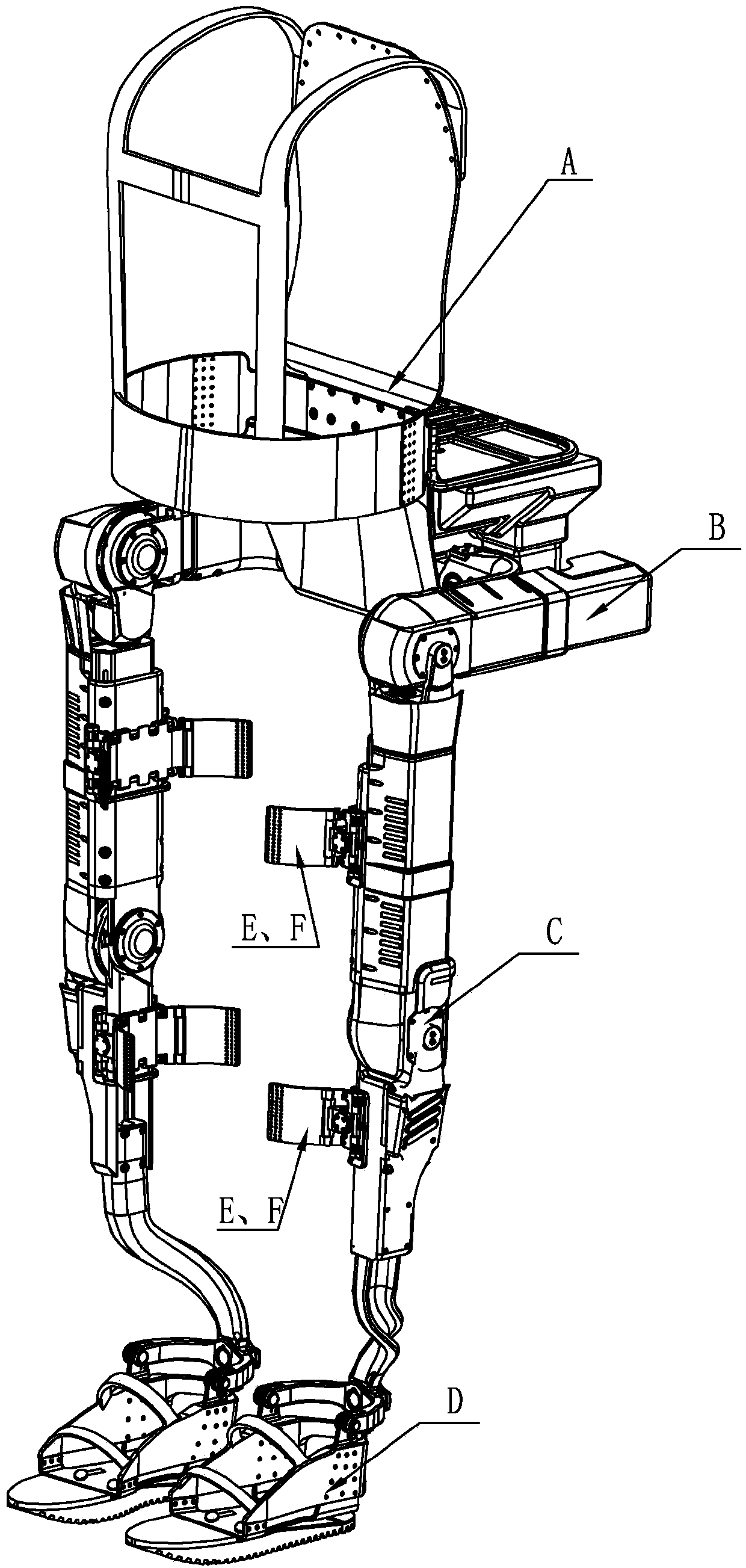
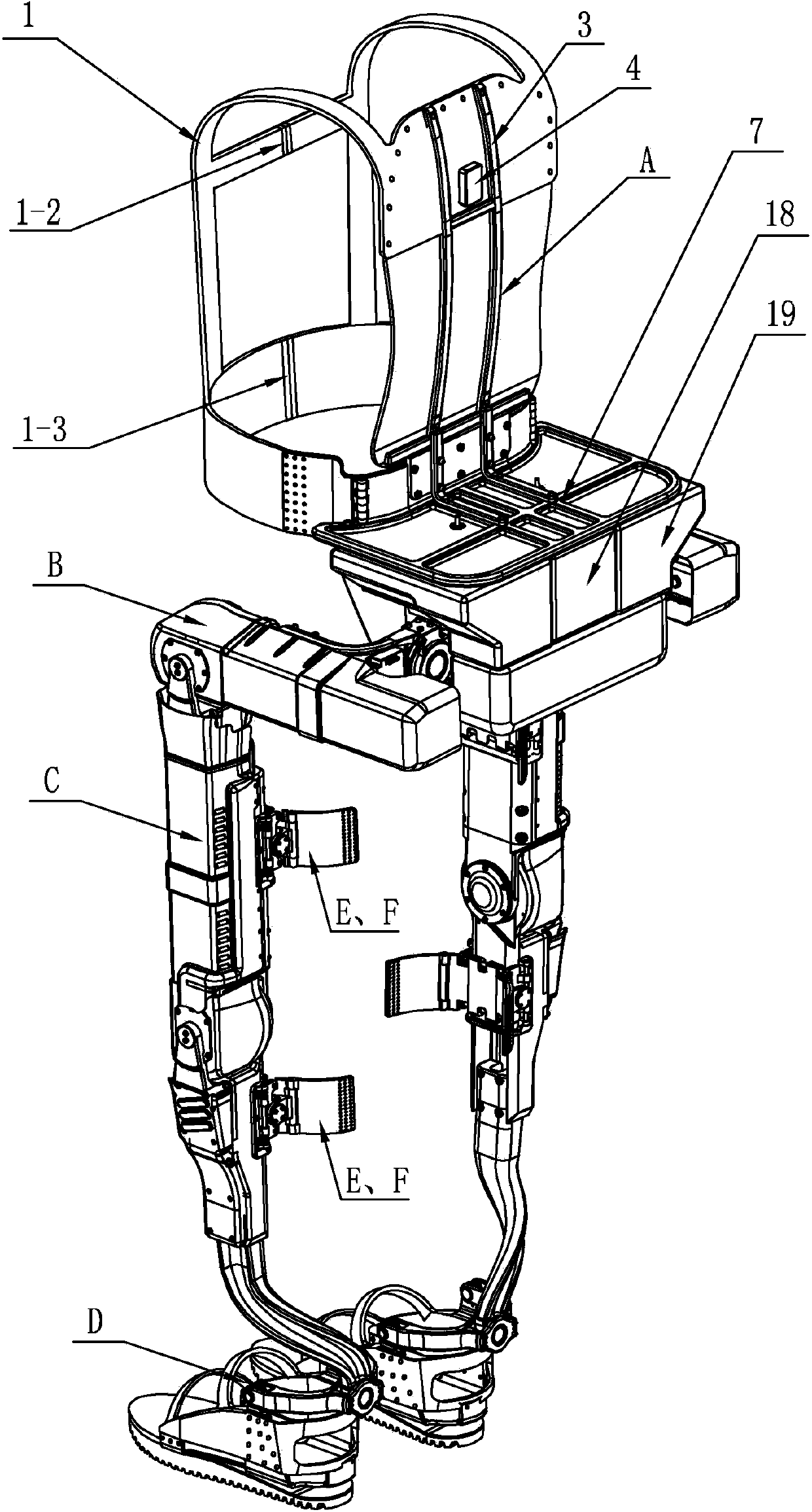
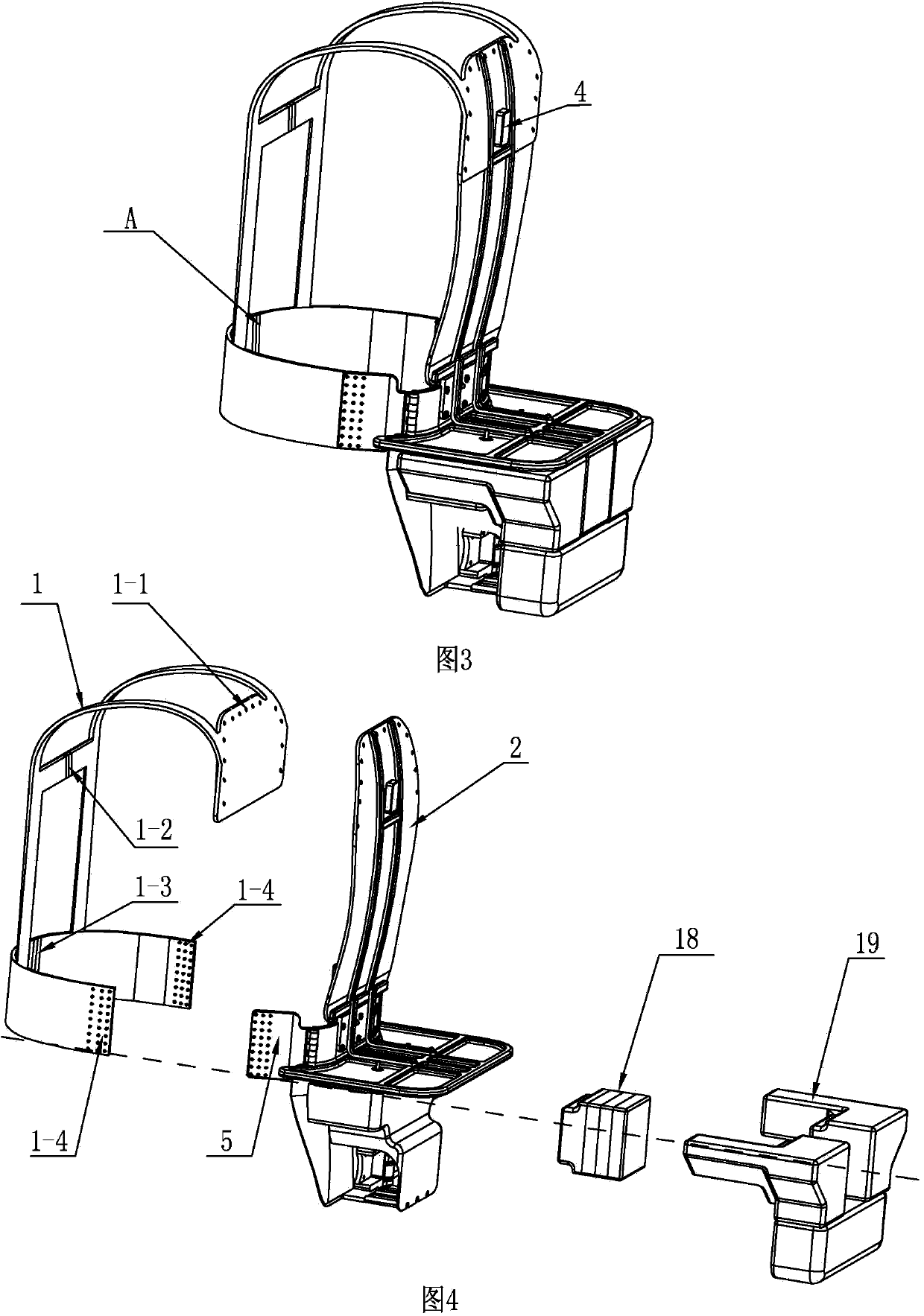
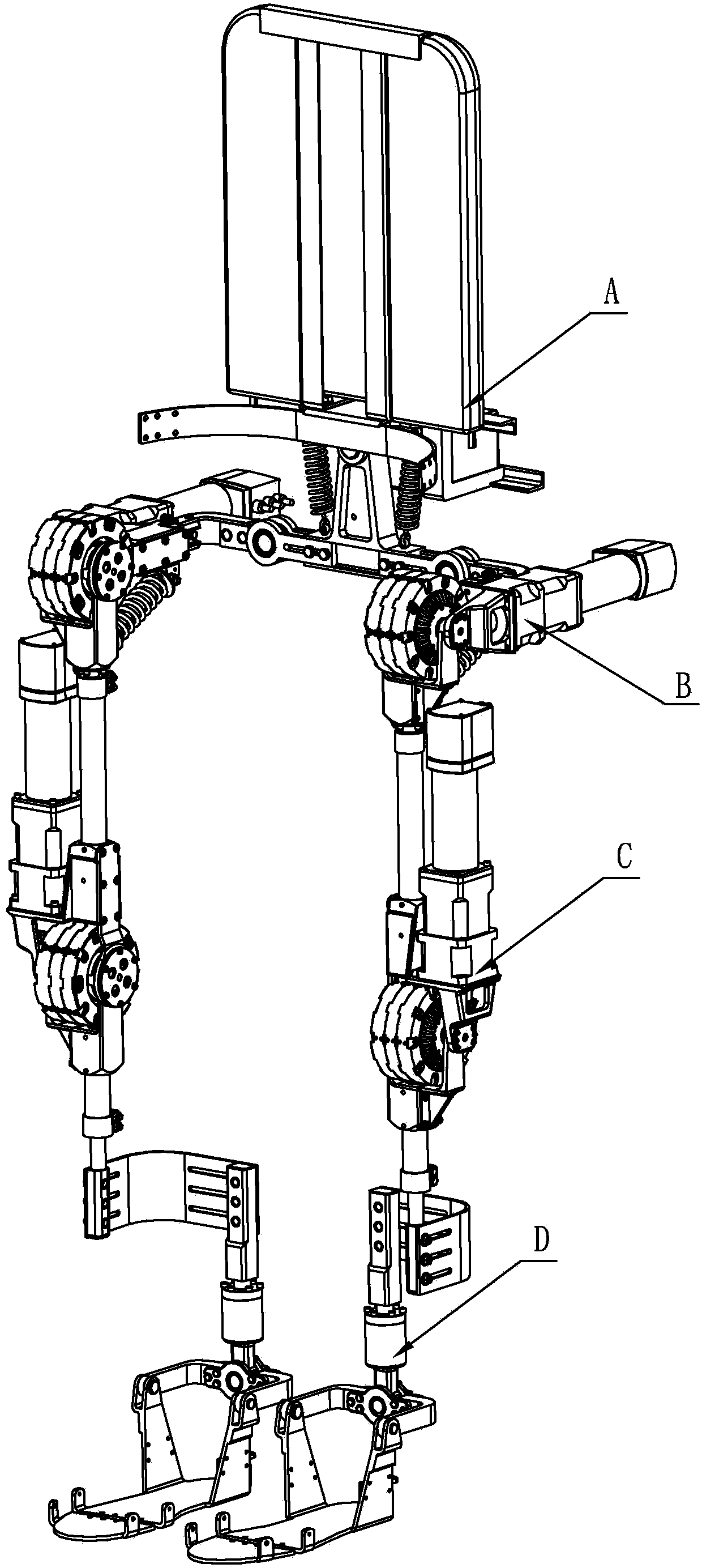
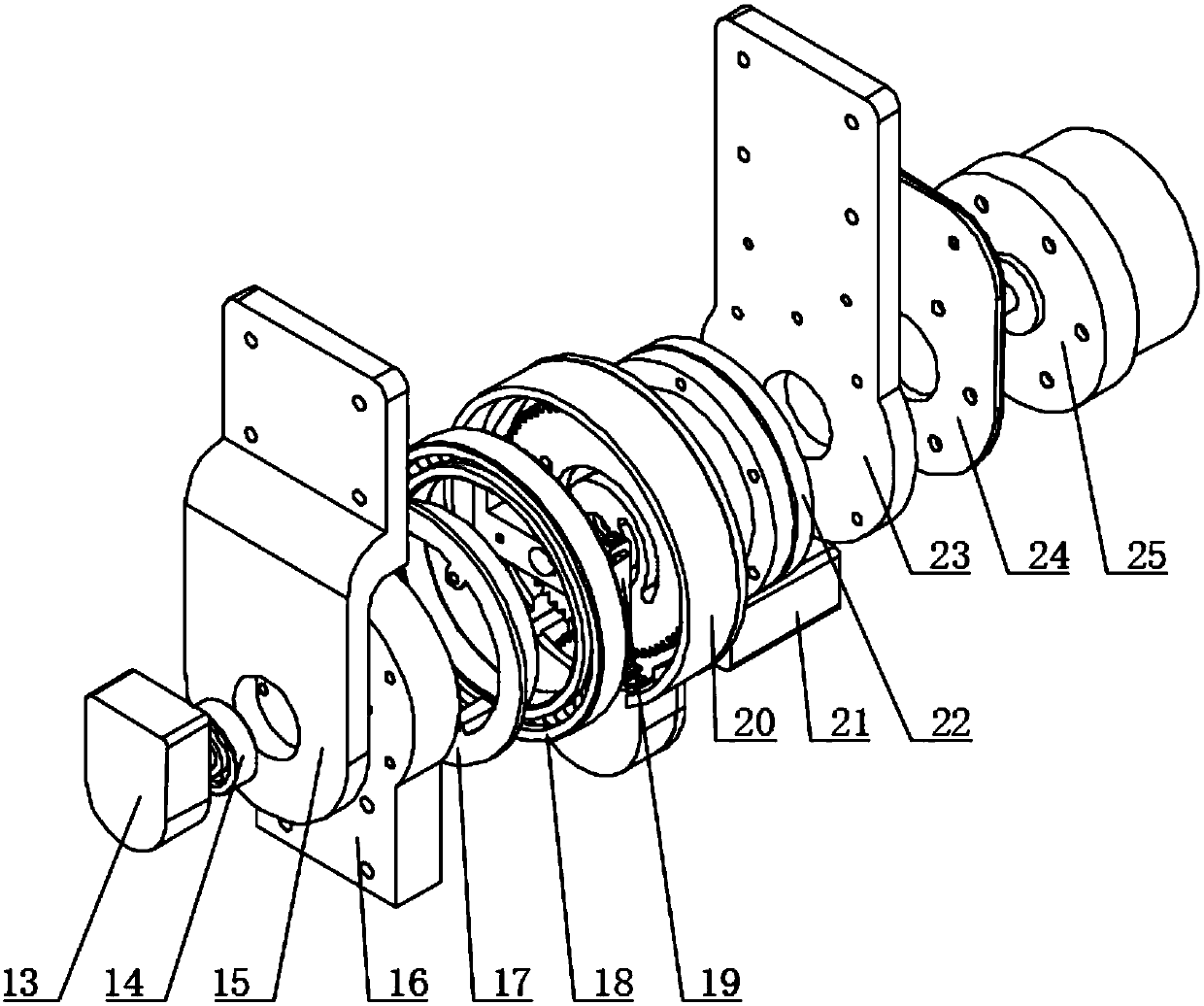
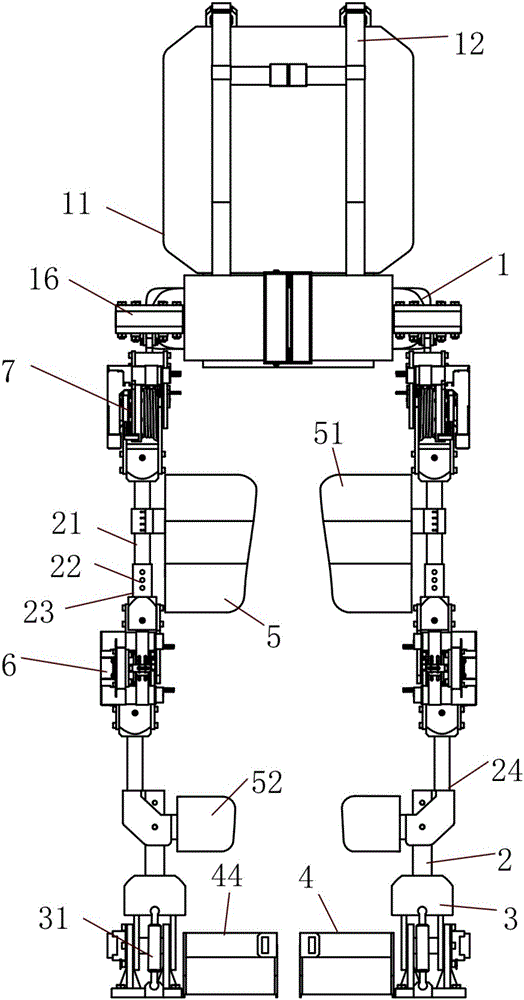
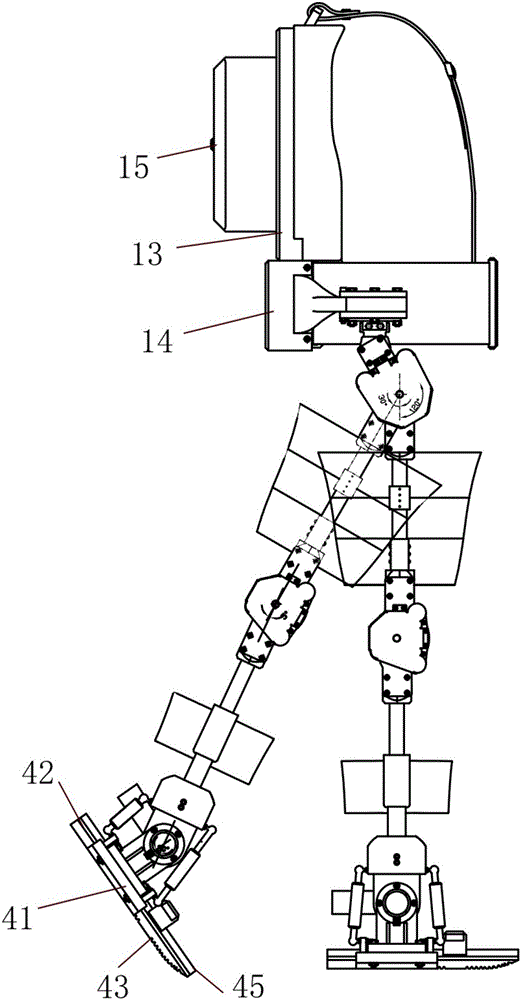
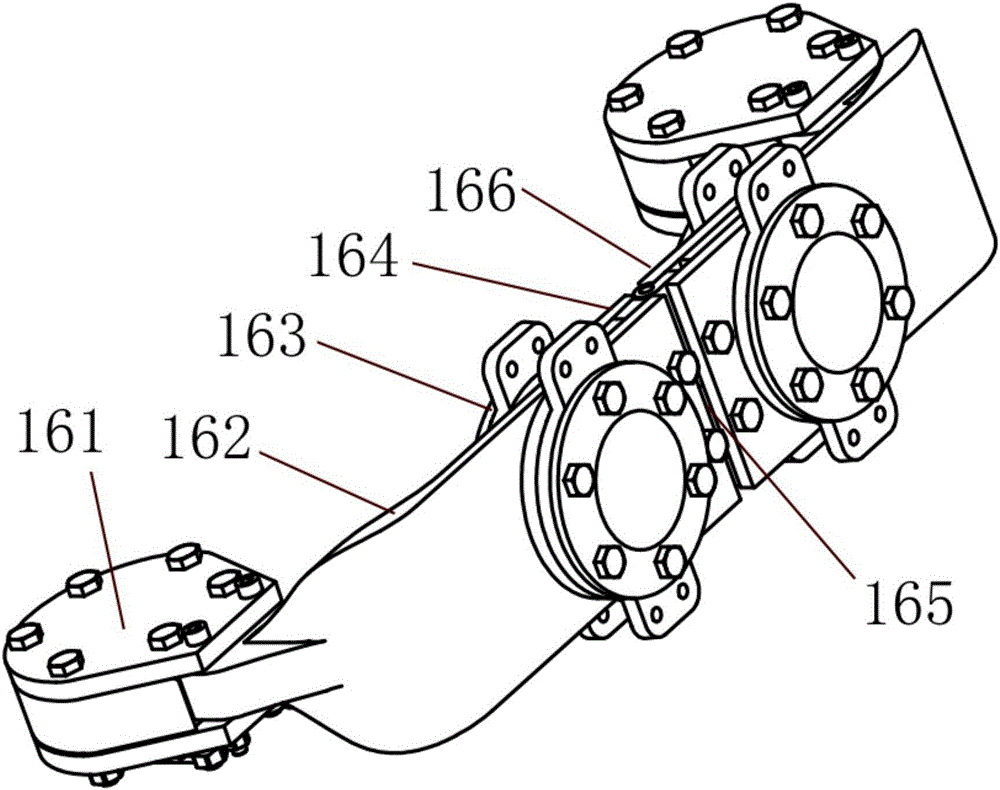
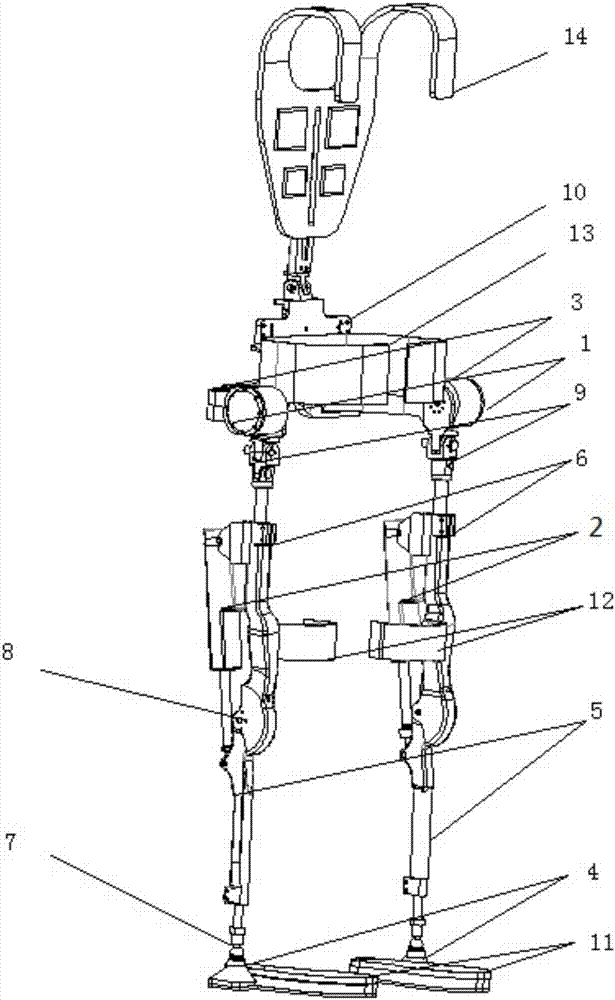
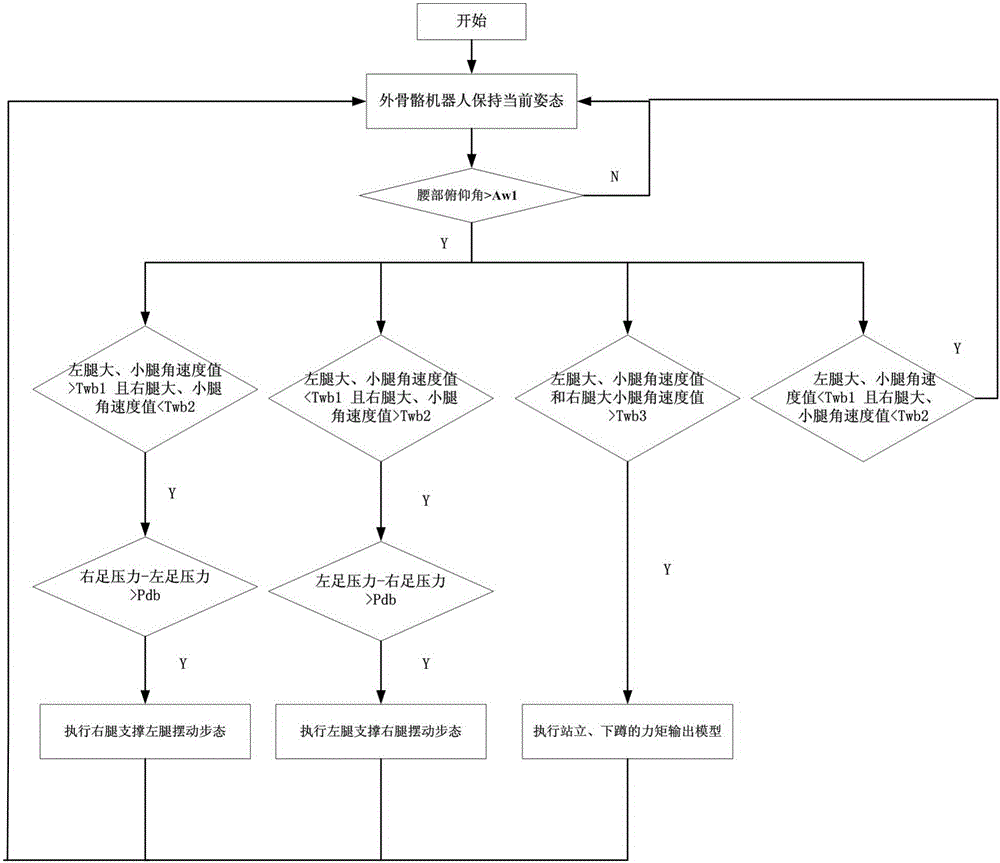
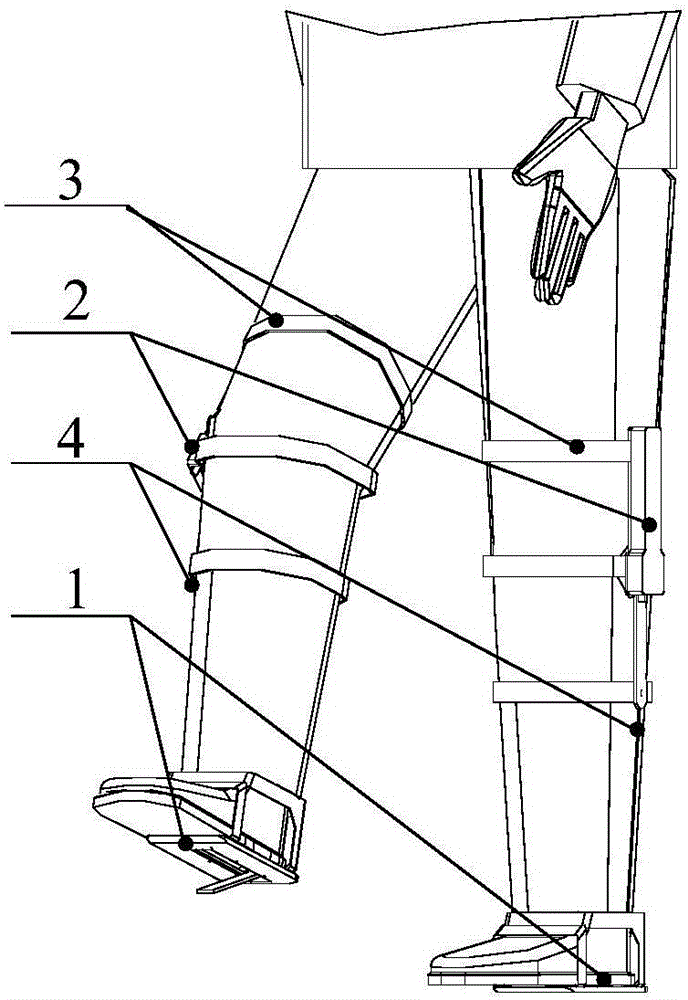
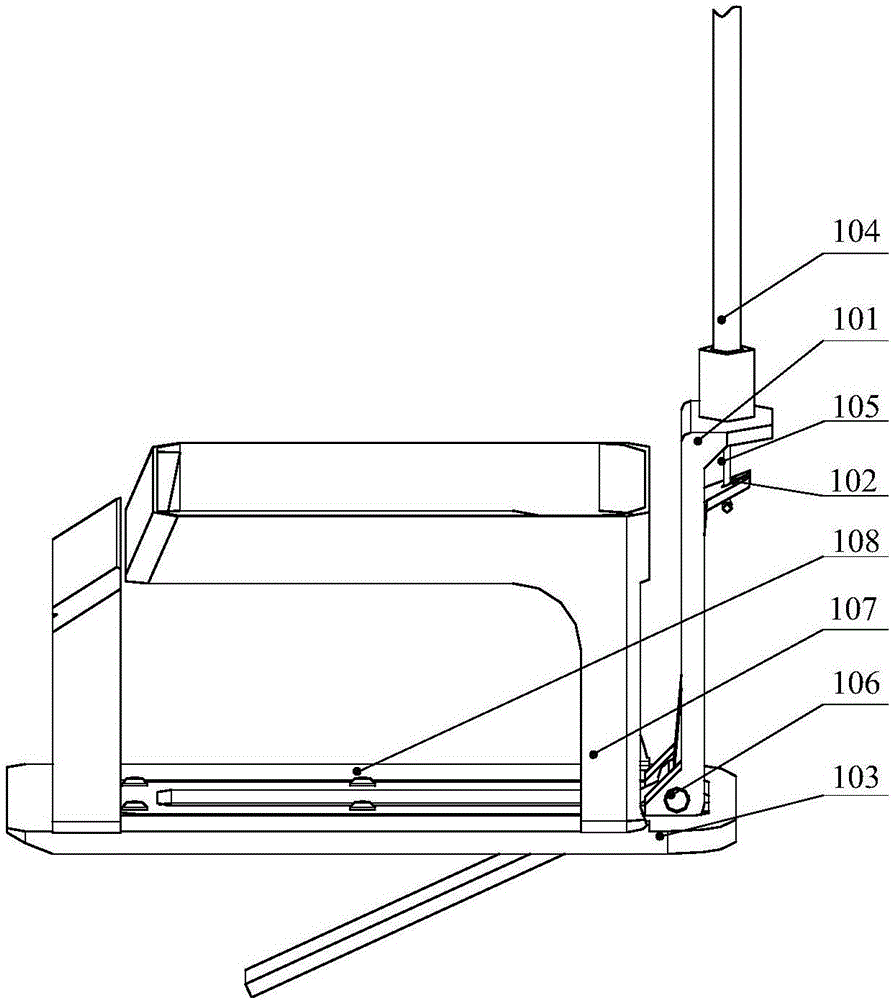
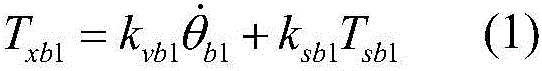Patents
Literature
816 results about "Exoskeleton robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting lower limbs
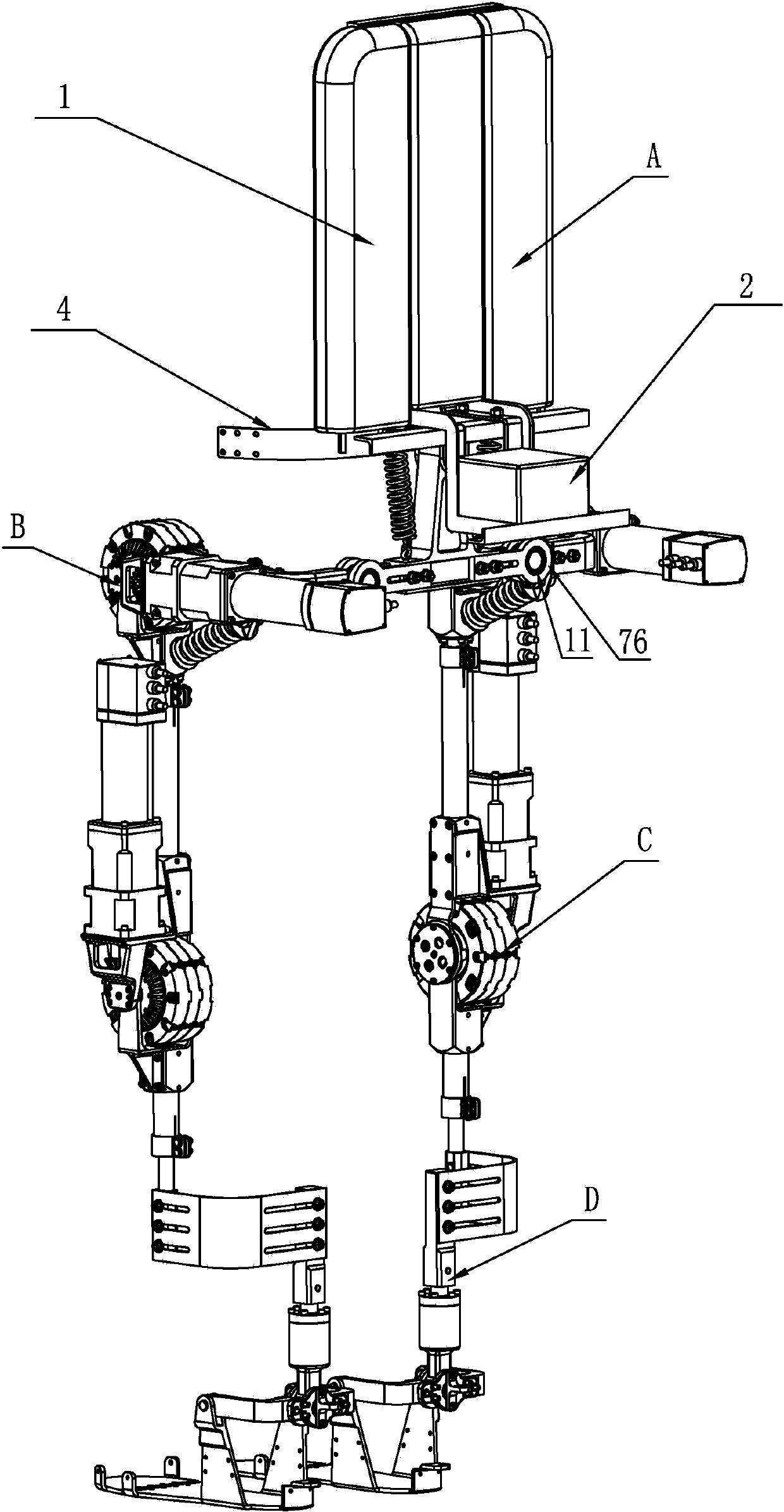
ActiveCN103610568ARealize the safety requirements of mechanical limitConvenient and accurate adjustment of telescopic lengthChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighExoskeleton robot
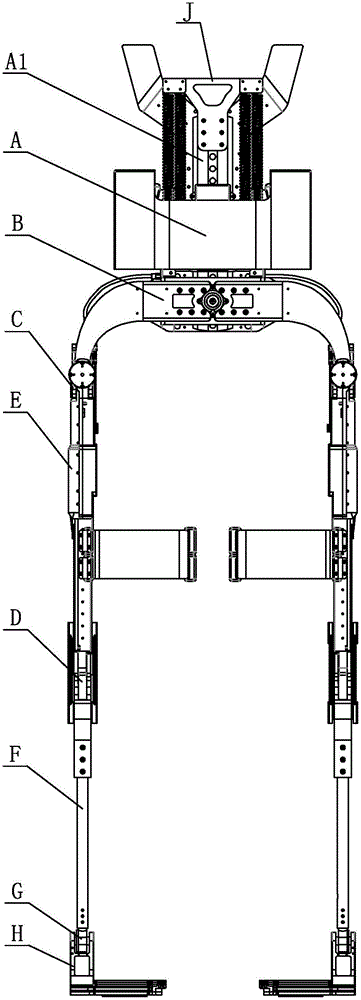
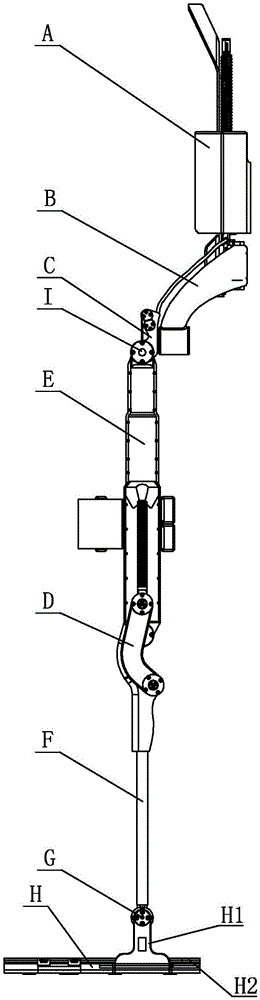
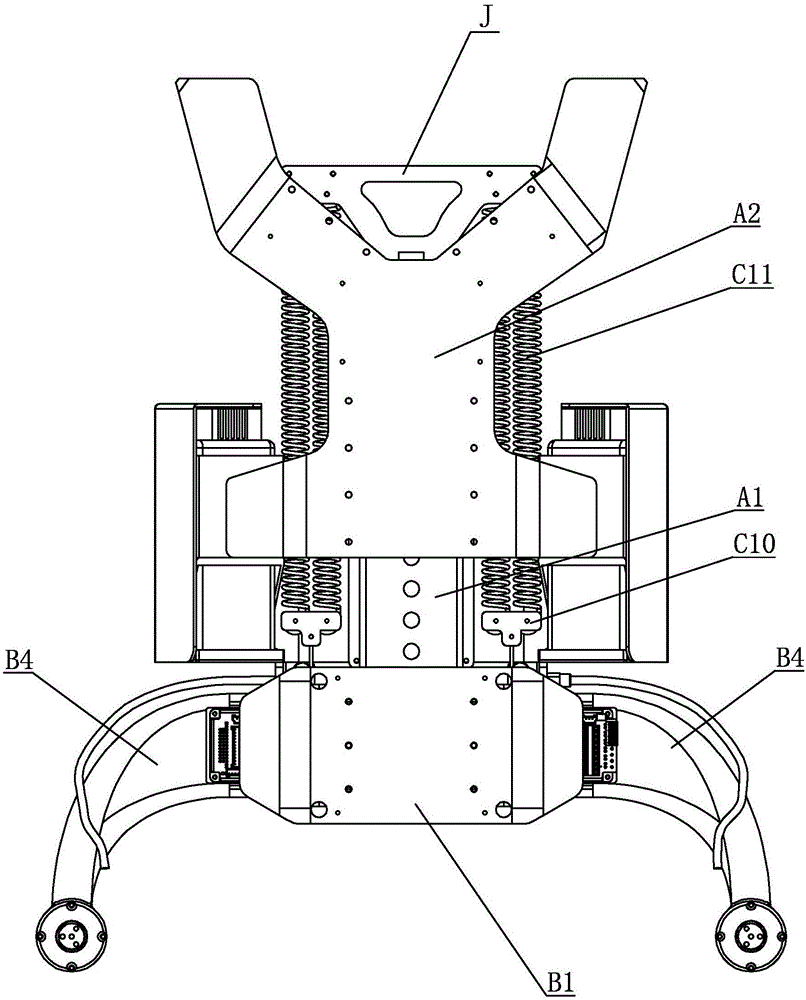
The invention relates to an external skeleton robot, in particular to a human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs aims to solve the problems that an existing external skeleton robot is low in coupling degree of motion space and poor in wearing comfort, reliability and adaptation, and power needed by a motor is large. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs comprises an upper body back part, a left leg and a right leg. The left leg and the right leg respectively comprise a hip drive system, a knee drive system and a foot wearing system. A rear side connection board of the waist is in rotating connection with a load installation board. Each hip joint supporting board is provided with a first motor and a first reducer, wherein the first motor is provided with an encoder, and the output end of the first motor provided with the encoder is connected with the input end of the first reducer. Each hip joint connecting board can rotate in the vertical plane. Each thigh stretching board is in detachable connection with the corresponding hip joint connecting board. The output end of a main drive mechanism is connected with each crus connecting board. The lower surfaces of elastic boards are bonded with the upper surfaces of the rubber soles of the feet. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs can assist in walking.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Portable energy-storage type external skeleton assisting robot
ActiveCN103610524AIntrusion Length AdjustmentEasy to disassemble and assembleArtificial legsThighExoskeleton robot
The invention relates to an external skeleton assisting robot, in particular to a portable energy-storage type external skeleton assisting robot. The problems that an existing lower limb external skeleton assisting robot worn on the human body is poor in assisting effect so that the loading capacity of the human body can be reduced, the wearing comfort for the human body is poor, the universality is poor, and the field environmental suitability is poor are solved. The portable energy-storage type external skeleton assisting robot comprises the upper body back, the left leg and the right leg, and the left leg and the right leg respectively comprise a hip driving system, a thigh driving system and a shank wearing system. A hip joint energy-storage mechanism comprises a connecting base, a stretching rod, a second spring and a stopping sheet, and a first bevel gear is meshed with a second bevel gear. Each hip driving system comprises a second motor with a coder, a second reducer, a third bevel gear, a fourth bevel gear, a thigh connecting rod, a knee joint support, a knee joint connecting plate, an angle sensor, a series connection elastic combination body, a knee joint gearbox body, a knee joint shaft and an end cover. The portable energy-storage type external skeleton assisting robot is suitable for being worn outdoors for walking assisting.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Human lower extremity exoskeleton walking aid rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN104490568AImprove comfortImprove reliabilityChiropractic devicesWalking aidsExoskeleton robotCoxal joint
A human lower extremity exoskeleton walking aid rehabilitation robot belongs to the technical field of medical rehabilitation equipment, and comprises a lower back movement module, a hip joint movement module, a knee joint movement module and an ankle joint movement module, wherein a back servo motor drives a hip joint to move through a crank and rocker mechanism and a space four-links mechanism; an electric knee push rod drives a knee joint to move; an electric ankle push rod drives an ankle joint to move. The human lower extremity exoskeleton walking aid rehabilitation robot helps a patient with lower limb paralysis to stand and walk, and the flexion and extension movement of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint is controlled by acquiring pressure signals of soles of feet, so that the patient is helped to stride; the construction and model design of the ankle joint inversion and eversion passive driving degree of freedom can help to reduce impact from the ground, is conductive to reducing the burden of a user keeping balance of the self and the exoskeleton robot in a frontal plane, is beneficial for the patient to walk comfortably, and improves the rehabilitation training efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Walk-aiding exoskeleton robot system and control method
InactiveCN101791255ACompact designMeet the actual sports requirementsWalking aidsArtificial legsHuman bodyExoskeleton robot
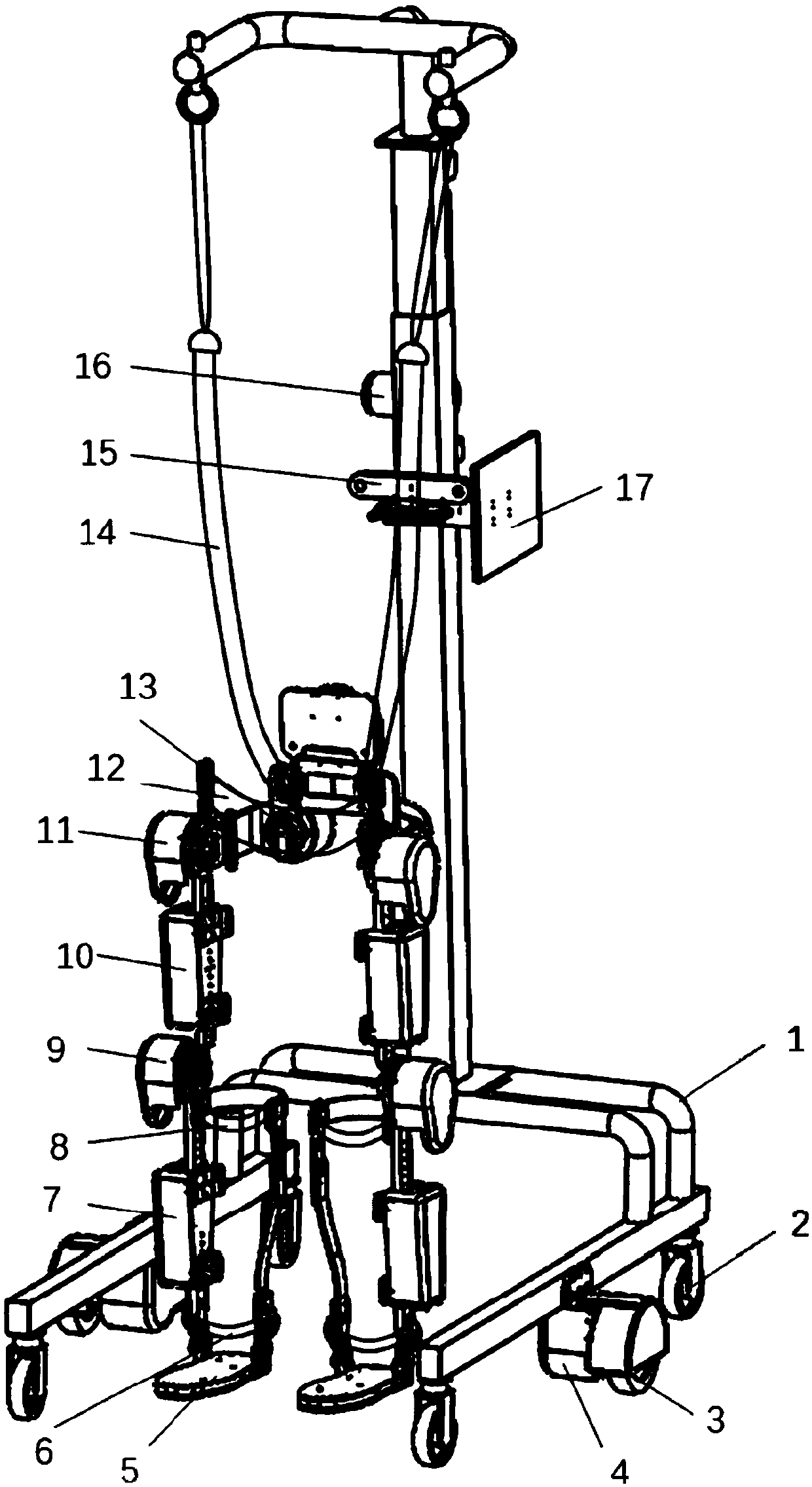
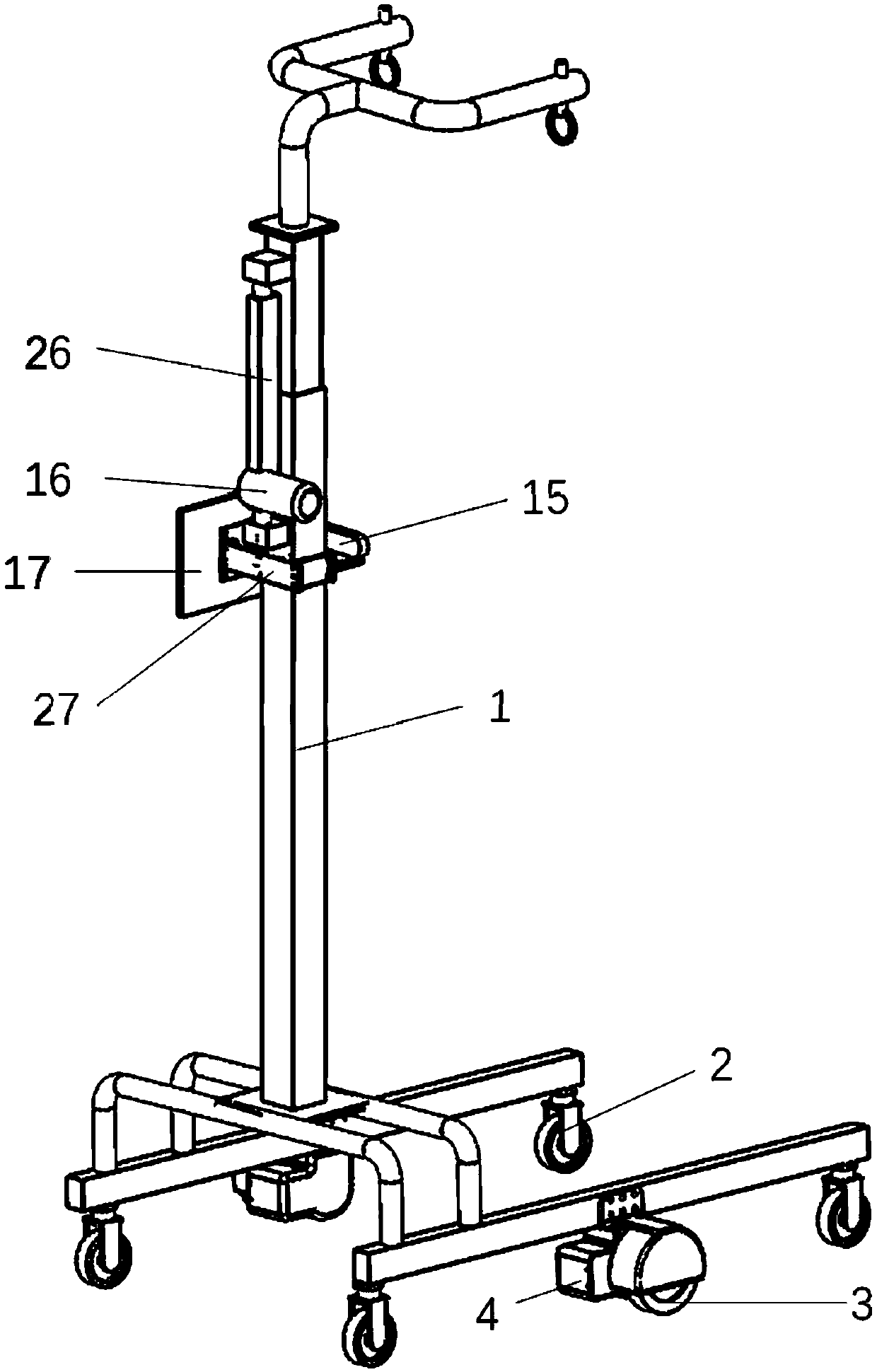
The invention relates to a walk-aiding exoskeleton robot system and a control method, which belong to the technical field of rehabilitation engineering. The system comprises a hanging support, a moving platform, joints, protecting sleeves, a sensor module, a signal acquisition module, a central processing module and a motion control module, wherein the hanging support is fixed on the moving platform, the joints are connected with the hanging support to form an exoskeleton robot, the sensor module, the signal acquisition module, the central processing module and the motion control module are sequentially connected, the sensor module is used for acquiring joint angles, the interacting force of the exoskeleton robot and the human being and the myoelectric signals of the muscles of the human body, the signal acquisition module carries out signal conditioning and digital-to-analog conversion, the central processing module carries out action generation and the reverse solution of motion, and transmits an action command to the motion control module, and the motion control module is connected with the exoskeleton robot and generates a pulse signal to control the coordinated motion of the exoskeleton robot. The invention realizes the synchronous motion of the exoskeleton robot and the human body and real-time active control.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Exoskeleton robot system with human motion detecting function and control method of robot system
ActiveCN104188675AMeet the needs of correctly judging human motion intentionGuaranteed comfortWalking aidsArtificial legsHuman bodyThigh
The invention relates to an exoskeleton robot system with a human motion detecting function and a control method of the robot system and aims to solve the problems that an existing exoskeleton assistance robot often aims at the typical gait of walking on the flat ground, is poor in universality and cannot correctly judge human motion intensions, motion coordination between the exoskeleton robot and a human body cannot be kept, and good assistance effect on complex road surfaces cannot be achieved. The exoskeleton robot system comprises an upper body back, a left leg and a right leg. Each of the left leg and the right leg comprises a hip drive system, a thigh drive system and a shank wearing system. The upper body back comprises a back support and shoulder straps. Each thigh drive system comprises a thigh binding strap. Each shank wearing system comprises a leg binding strap, an upper rubber pad, a lower rubber pad and a heel plate. The exoskeleton robot system further comprises a sensing detecting control system. The exoskeleton robot system is applicable to assistance walking and human motion posture detecting and control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot gait pattern identification method and system
InactiveCN103876756AEasy to wearGet rid of the bondageWalking aidsMuscle exercising devicesHuman bodyExoskeleton robot
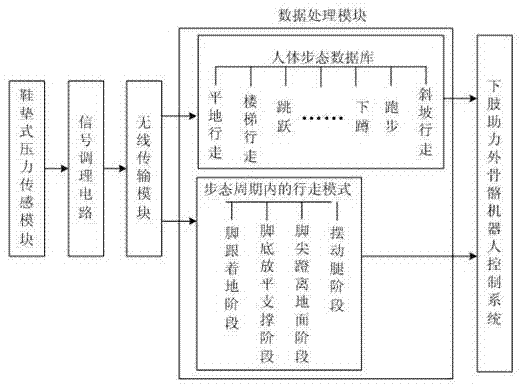
The invention provides a lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot gait pattern identification method and system. The method comprises the steps that a pressure sensing device embedded into a shoe sole of a lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot is used for detecting shoe sole pressure information of a wearer, the obtained shoe sole pressure information is compared and matched with walking modes in a human body gait database, a walking mode is obtained through judgment, movement phases in a gait period are identified, and a movement phase is obtained through judgment; data are processed and analyzed, results obtained after identification and matching are transmitted to a lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot control system to be used as a control basis. The walking mode and the detailed movement phase in each gait period of the lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton wearer provide the abundant decision basis for control over the lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton. The lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot gait pattern identification method and system not only can provide movement information of the wearer for the lower limb power-assisted exoskeleton, but also can be widely applied to human body gait identification.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Variable stiffness lower limb external skeleton robot
ActiveCN107773384ASmooth movementAdaptableProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesVariable stiffnessThigh
The invention discloses a variable stiffness lower limb external skeleton robot which comprised a back plate, a flexible waist adjusting mechanism, hip joint mechanisms, thighs, knee joint mechanisms,shanks, ankle joint mechanisms, two driving degrees of freedom and three driven degrees of freedom. A driving control system is arranged on the back plate, the flexible waist adjusting mechanism is fixed with the back plate and connected with the thighs through the hip joint mechanisms, and the thighs are connected with the shanks and the ankle joint mechanisms through the knee joint mechanisms.According to the variable stiffness lower limb external skeleton robot, driving is performed by the aid of a variable stiffness driver, so that the robot is smooth in movement and high in safety, physical structures of lower limbs of human bodies can be effectively fitted by the aid of the two driving degrees of freedom and the three driven degrees of freedom, length adjusting mechanisms are arranged at the waists, the thighs and the shanks, so that the robot can adapt to physical sizes of different users, and the robot is wearable and has flexibility in the movement by the aid of the flexiblewaist adjusting mechanism. The robot can be applied and popularized in aspects of rehabilitation training, boosting and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Lower-limb-boosting exoskeleton robot
ActiveCN105965483AReduce harmReduce equipment burdenProgramme-controlled manipulatorExoskeleton robotEngineering
The invention discloses a lower-limb-boosting exoskeleton robot comprising an upper body structure, leg structures, knee joints and hip joints. Each leg structure comprises a thigh structure and a shank structure. Each hip joint is connected with the upper body structure and the corresponding thigh structure. Each knee joint is connected with the corresponding thigh structure and the corresponding shank structure. The upper body structure comprises a waist assembly, and the size of the waist assembly can be adjusted. The waist assembly comprises hip connecting blocks connected with the hip joints. Each knee joint comprises a first thigh connecting seat, a second shank connecting seat and two first motors, wherein the first thigh connecting seat is connected to the corresponding thigh structure, the second shank connecting seat is connected to the thigh connecting seat in a rotary manner, and the two first motors are connected to the first thigh connecting seat and drive the second shank connecting seat to rotate relative to the first thigh connecting seat.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot based on rope-pulley mechanism
ActiveCN107137207AReduce consumptionReduce the numberProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesExoskeleton robotCoxal joint
The invention provides an underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot based on a rope-pulley mechanism, and relates to an underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot. The robot aims to solve the problems that a prior active joint-driving exoskeleton has large self-mass, large drive energy consumption, and a passive joint exoskeleton cannot provide effective assistance. The robot comprises a harness device, a drive control power system, two thigh bar devices, two leg bar devices, two ankle devices, two drive devices and two strings; wherein each drive device includes a motor shell bracket, a first motor shell, a waist frame, a planetary reducer, a second motor shell, a servo motor, a third motor shell, a hip joint spline shaft, a drive pulley, an elastic actuator, a first shaft sleeve, a small bevel gear, a large bevel gear, a second shaft sleeve, a fourth motor shell, a fifth motor shell, a sixth motor shell, a fixing plate and two first bearing end covers with bearings. The underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot based on the rope-pulley mechanism is used for the field of assistance exoskeleton robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
External skeleton robot for exercising lower limbs and exercise control method thereof
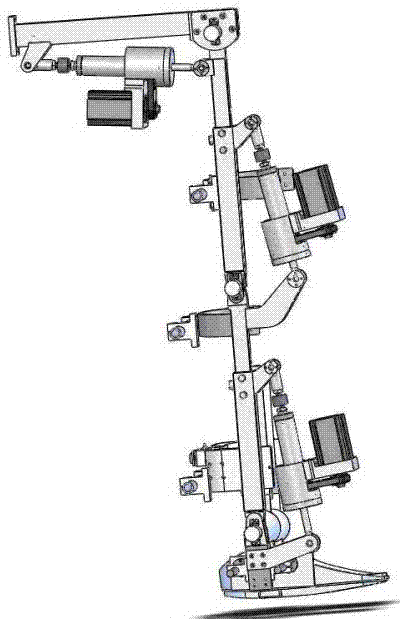
InactiveCN103040586AIncrease active participationRealize lower limb assist walking movementGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesHuman bodyExoskeleton robot
The invention relates to an external skeleton robot for exercising lower limbs and an exercise control method thereof. The robot comprises the following four parts of a support balance frame, external skeleton mechanical legs, a running machine and a control system. The exercise control method has two modes, namely a passive walking exercise mode and an active walking exercise mode. In the passive walking exercise mode, the robot is controlled to drive an operator to complete specific exercise or exercise by a correct physiological gait trajectory; in the active walking exercise mode, the robot inhibits the limited abnormal exercise of the operator, directly corrects the limited abnormal exercise or generates gait exercise trajectories expected by the operator through a self-adaptive controller and indirectly fulfills the aim that the robot supplies walking exercise auxiliary force and resistance. The external skeleton robot can improve the exercise ability of limbs of human bodies, can assist persons walking and can reduce the exercise intensity under the condition that the persons bear load or walk for a long time.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Interactive Exoskeleton Robotic Knee System
An interactive exoskeleton robotic knee system for assist walking and gait training. The system comprises of an exoskeleton framework to be attached to the thigh and shank of the user's leg; electric motor; mechanical lock; motion sensor assembled on the lower limb unit, and a control box. The system provides extension and flexion movement in the knee joint.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Bionic lower limb exoskeleton robot based on rope drive
ActiveCN106956243AImprove fitReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesThighExoskeleton robot
The invention relates to a bionic lower limb exoskeleton robot based on rope drive. The bionic lower limb exoskeleton robot comprises a backpack, a waist mechanism, thigh fixing devices, knee joint mechanisms, shank fixing devices and ankle joint mechanisms. A drive control system is placed in the backpack, the backpack is mounted on a waist support of the waist mechanism, a hip joint box is connected to the lower end of the waist support, the upper ends of the thigh fixing devices are connected with thigh connecting parts stretching out of the hip joint box, the lower ends of the thigh fixing devices are connected with the inner side of a knee joint box, the lower end of a swing plate stretching out of the lower end of the knee joint box is connected with the upper ends of the shank fixing devices, the lower ends of the shank fixing devices are connected with an ankle joint connecting plate on an ankle joint box, and ankle joint shafts stretching out of the inner side of the ankle joint box are connected with shoes. The motion error of the exoskeleton robot and the human body can be greatly reduced, the exoskeleton robot can be batter attached to the thighs, the bionic property is high, the size is small, the thickness is small, the mass is small, wearing is comfortable, operation is easy and convenient, and walking is stable.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Robot for multiple posture exoskeleton lower limb rehabilitation training
InactiveCN1973806ATargeted rehabilitation trainingThe effect of optimal rehabilitation exerciseProgramme-controlled manipulatorGymnastic exercisingExoskeleton robotPhysical Therapy Modality
The present invention discloses one exoskeleton robot for multiple posture lower limb rehabilitation. The robot includes one support, one guard rail and suspending system, one exoskeleton training system and one computerized control system. The robot is developed through combining international Brunnstrom training method with the physical therapy and operating therapy for apoplexy patient with paralyzed lower limbs. Different training modes, including active pace mode, passively controlled pace mode, passive damp-adjustable pace mode, etc may be realized for different apoplexy patients in different treating stages. The robot is suitable for the lower limb rehabilitating training of patient in sitting, standing or lying state.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
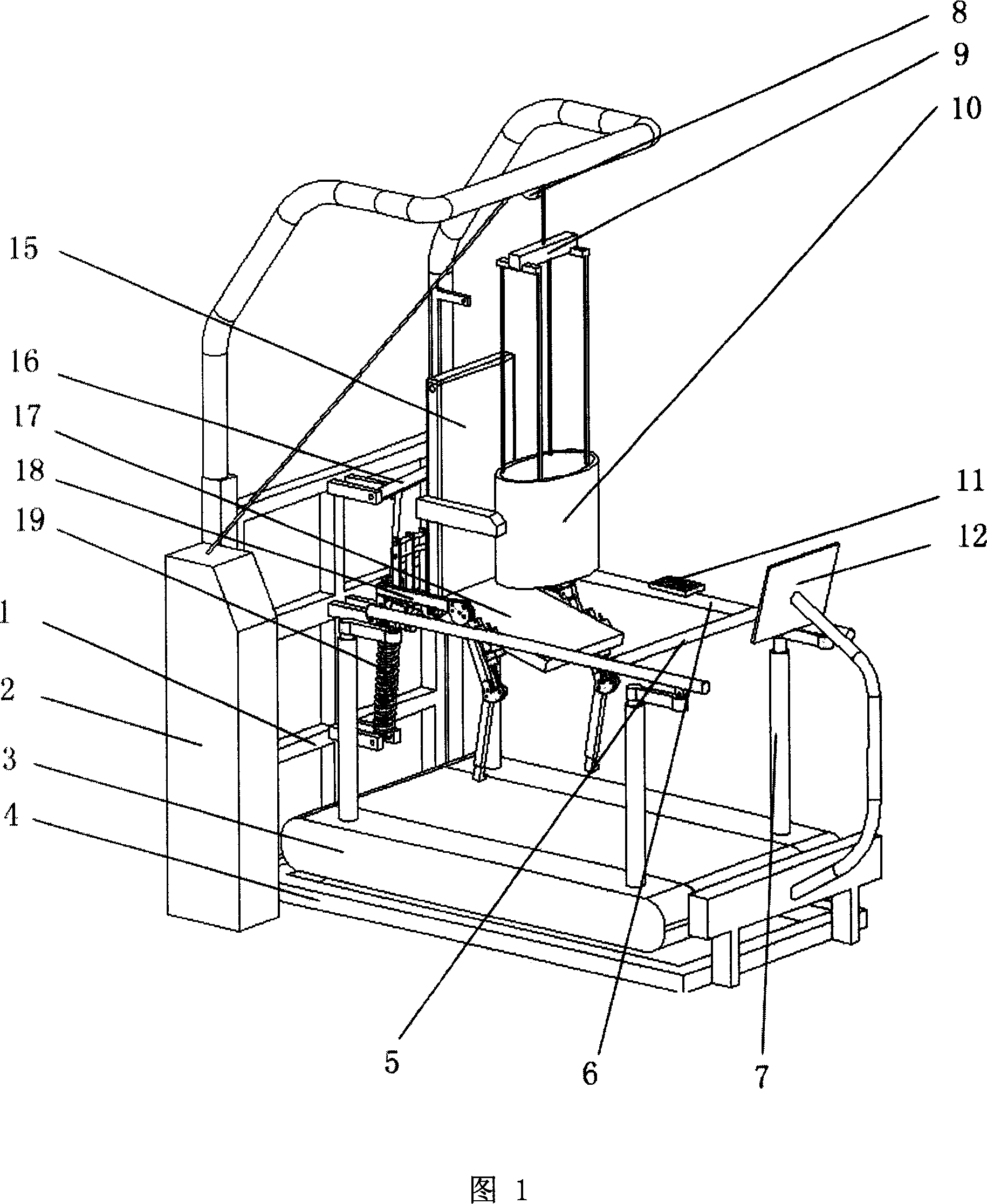
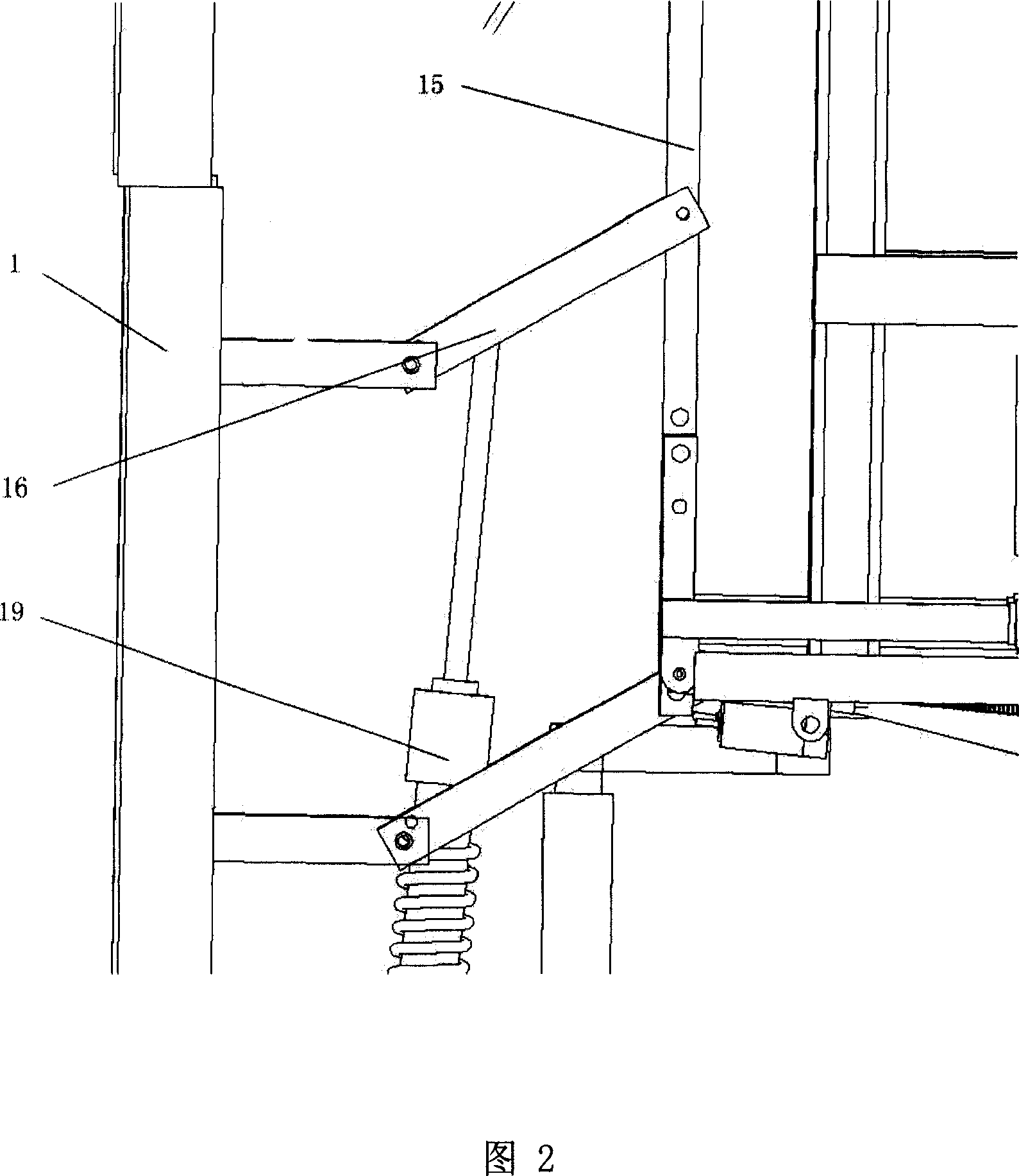
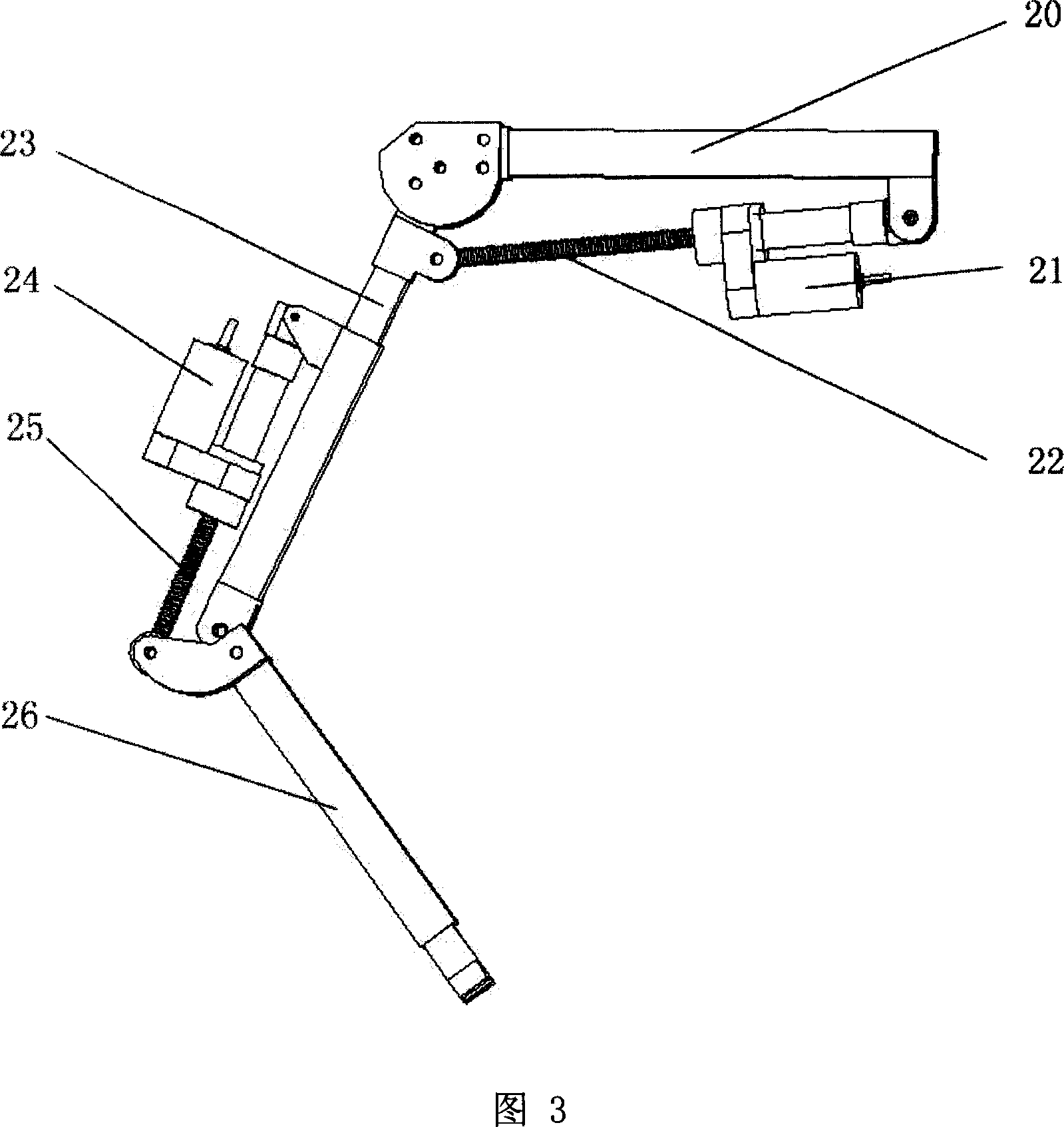
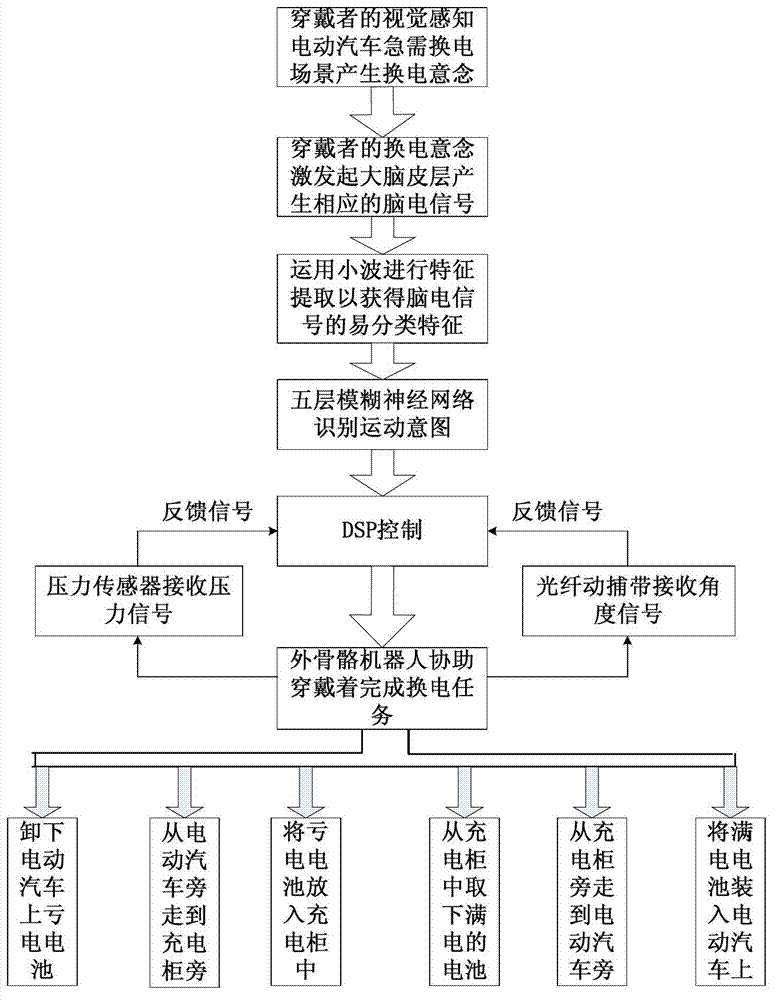
Exoskeleton robot system for reloading batteries of electric vehicle
InactiveCN102922508AShorten energy recharge timeImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectric propulsion mountingExoskeleton robotAutomotive battery
The invention discloses an exoskeleton robot system for reloading batteries of an electric vehicle. The exoskeleton robot system comprises a wearer motion information acquisition module, a wearer motion signal analysis processing module, an exoskeleton robot control module and an exoskeleton robot mechanical structure module, wherein the wearer motion information acquisition module transmits an acquired wearer EEG (electroencephalogram) signal to the wearer motion signal analysis processing module; the wearer motion signal analysis processing module carries out analysis processing on the wearer EEG signal so as to recognize a motion intention of a wearer, converts the EEG signal into a motion signal and transmits the motion signal to the exoskeleton robot control module; and the exoskeleton robot control module receives the motion signal and can control the exoskeleton robot mechanical structure module to move according to the motion signal. The system provided by the invention is a man-machine integrated mechanical power system closely linked with people, can provide protection, additional power and capability for people, can strengthen human performance, and can enable manipulators to easily finish a challenge task.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Exoskeleton robot system and kinematics extremity detection-based control method
The invention discloses an exoskeleton robot system and a kinematics extremity detection-based control method, and relates to an exoskeleton robot system and a control method to solve the problems that an accurate control effect cannot be achieved by the traditional electromyographic signal detection method for assisting in improving the walk of a human body, and man-machine interaction performance is low and an effective control method is lacked in the aspect of resisting self weight in the process of assisting in doing walk of the human body. The exoskeleton robot system comprises an upper body back, a left leg and a right leg; the left leg and the right leg respectively comprise a hip driving system, a knee driving system, a foot wearing system and a binding device; the exoskeleton robot system also comprises insole plates, a back detection shell, a nine-axis flight attitude measurement module, an industrial control computer, two thin film pressure sensors, two first angle sensors, two second angle sensors, two three-axis inclination sensors and three sets of three-dimensional contact force detection device. The exoskeleton robot system and the method are used for assisting in walking and performing detection and control of a moving posture of the human body.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Lasso drive based upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot
ActiveCN104873360AReduce quality problemsReduce inertiaChiropractic devicesMedial rotationExoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a lasso drive based upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot comprising a wrist outward swaying / inward retraction joint, a wrist forward flexion / backward extension joint, a wrist medial rotation / lateral rotation joint, an elbow forward flexion / backward extension joint, a shoulder forward flexion / backward extension joint, a shoulder forward flexion / backward extension joint, a shoulder medial rotation / lateral rotation joint and a lasso drive device. The shoulder, elbow and wrist medial rotation / lateral rotation joints are connected with motors fixed on a support through lassos, and driving moment is transmitted to all the joints through the lassos; the wrist outward swaying / inward retraction joint and the wrist forward flexion / backward extension joint are directly driven by motors; encoders are arranged in the motors and used for measuring internal posture of the exoskeleton; a six-dimensional force sensor is mounted to the wrist and used for measuring man-machine interaction force; balance springs are mounted to the shoulder and the elbow, and gravity balance of the whole mechanism can be realized. The problem of overlarge joint weight and inertia is solved, lightweight design is realized, power consumption is reduced effectively, system safety performance is improved, and multi-mode rehabilitation training can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Light active and passive combined lower-limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a light active and passive combined lower-limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot. A back and a waist are arranged up and down; a waist bundling connecting piece on the waist is connected with a back supporting piece on the back; hip joint rotary shafts on hip joints are hinged to waist hip connecting pieces on the waist; a spring upper pressing plates on the hip joints are connected with a spring adjusting plate; the spring adjusting plate is positioned at the upper end of the back supporting piece and is connected with the back supporting piece; leading pulley seats are fixedly connected with a waist fixing plate on the waist; the upper ends of thighs are hinged to connecting plates on the hip joints through leg hip connecting shafts; steel wire fixed parts on the hip joints are fixedly mounted on outer walls of thighs; the lower ends of the thighs are hinged to the upper ends of knee joint supporting shells through knee joint connecting shafts; a motor encoder, a motor, a speed reducer, a coupler and a lead screw are sequentially arranged in a knee joint from top to bottom; the upper end of shanks are connected with the knee joint supporting shells; and the lower ends of the shanks are hinged to feet through foot joint shafts. The light active and passive combined lower-limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot is used for military loadbearing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
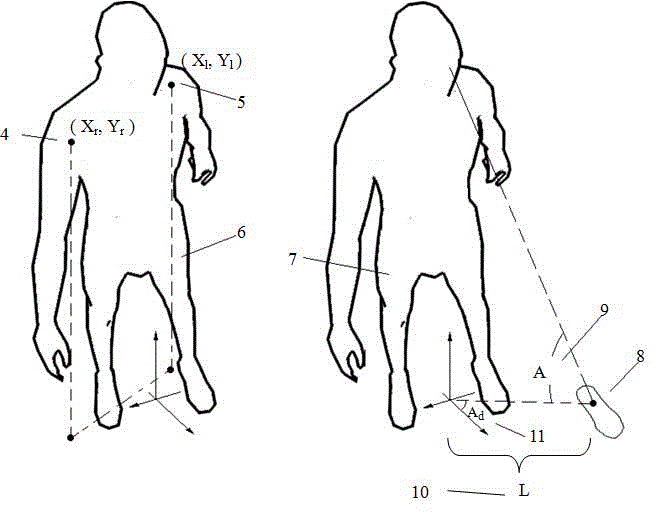
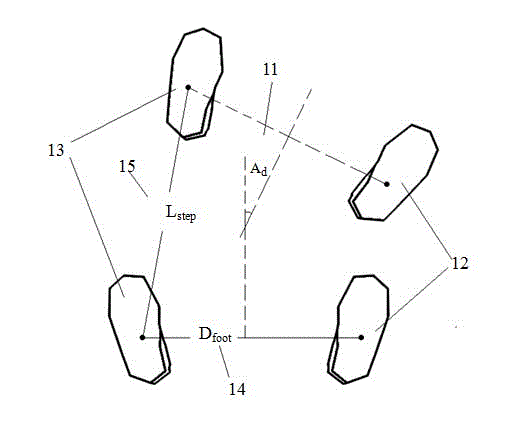
Method for judging lower-limb movement intentions of exoskeleton walking aid robot wearer
The invention provides a method for judging the lower-limb movement intentions of an exoskeleton walking aid robot wearer. Aiming at the deficiency of a human movement following control mode or a hand operation mode adopted by the conventional exoskeleton robot, the method judges the lower-body movement intentions of the wearer according to the unconscious shoulder movements and the habitual action of looking of the wearer. The method can be used for controlling an exoskeleton robot with a self-balancing function to help the wearer accomplish common lower-lime movements such as taking steps, turning, getting over obstacles, standing up and sitting down. The method frees the wearer from doing actual low-limb movements before the robot, thus avoiding extra physical exertion caused by man-robot interaction. The method also frees the wearer from learning special exoskeleton robot operating skills, is suitable for old persons with week strength and reduces the burden in learning exoskeleton robot using skills.
Owner:陶宇虹
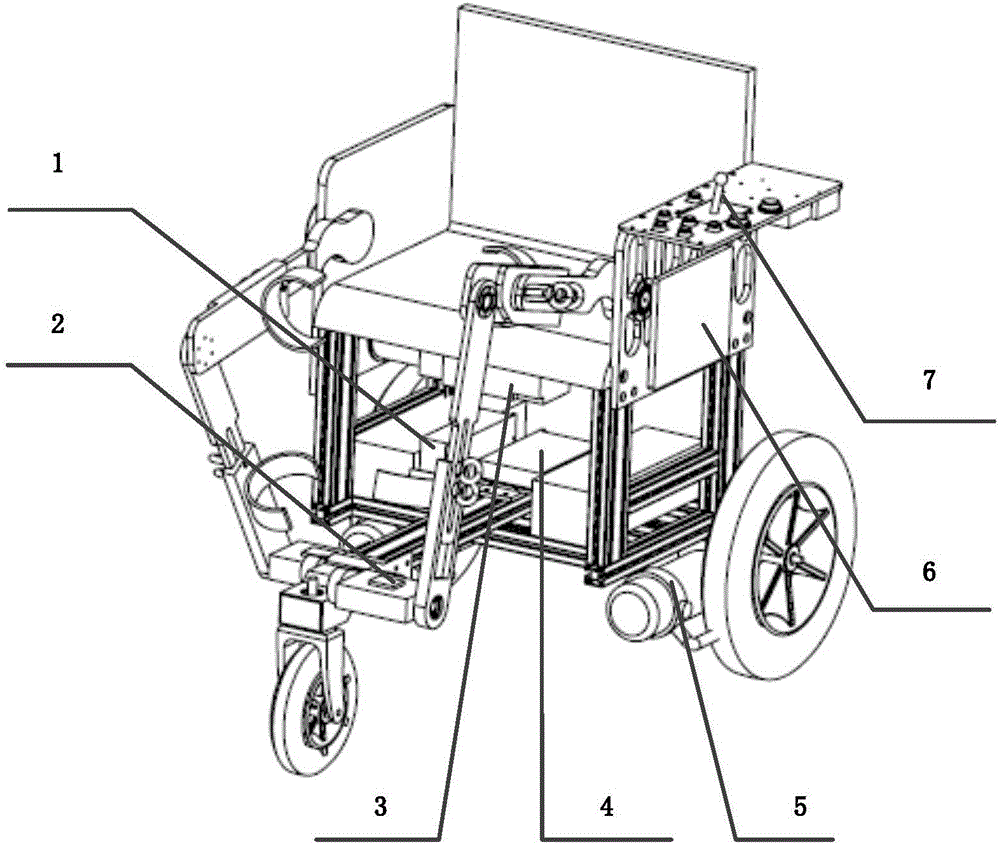
Rehabilitation and walking exoskeleton robot based on master-slave control
ActiveCN106510985AEliminate fearAchieve rehabilitative exerciseGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesExoskeleton robotWheelchair
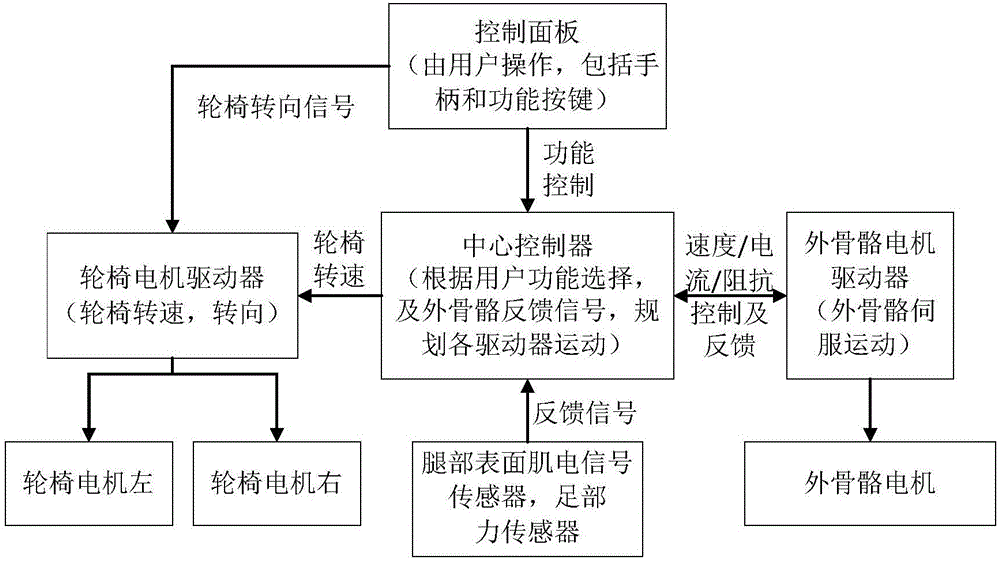
The invention discloses a rehabilitation and walking exoskeleton robot based on master-slave control. The rehabilitation and walking exoskeleton robot based on master-slave control comprises a wheelchair, an exoskeleton, a central controller and a battery pack, wherein the wheelchair comprises a wheelchair frame, an operation panel, a wheelchair motor driver and a wheelchair motor; the exoskeleton comprises an exoskeleton framework, an exoskeleton motor driver, an exoskeleton motor and a sensor system; and the central controller is capable of receiving a function control signal from the operation panel and a feedback signal from the sensor system, setting a movement working mode and a rehabilitation working mode of the robot, and outputting control signals to the wheelchair and the exoskeleton, thus the motion of the exoskeleton and the movement of the wheelchair can be cooperatively controlled. The rehabilitation and walking exoskeleton robot based on master-slave control, which is disclosed by the invention, adequately considers the subjective motion intention of a user, and is high in functionality, simple to control, safe and reliable, and remarkable in rehabilitation effect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Exoskeleton robot and controller system thereof
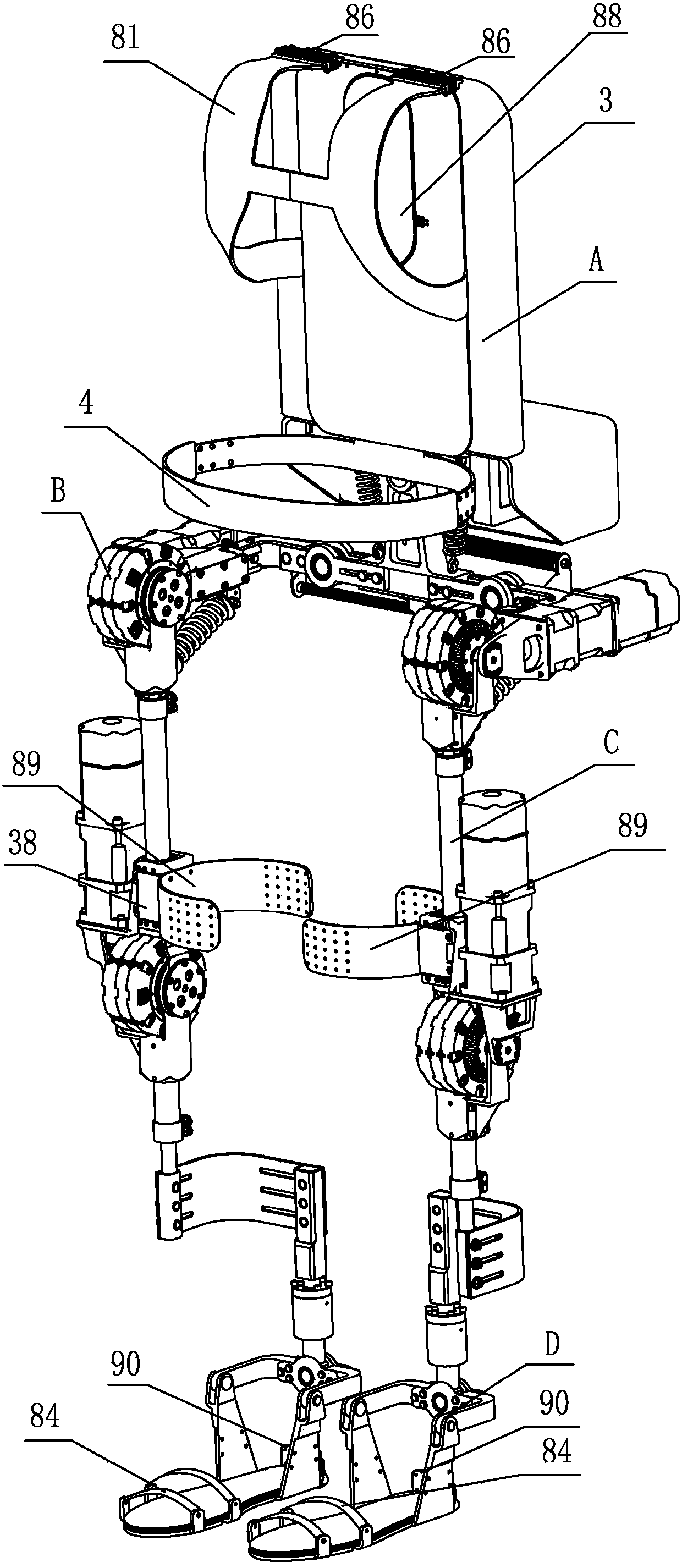
ActiveCN110695959AEasy to add/removeEasy to put on and take offProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHuman bodyExoskeleton robot
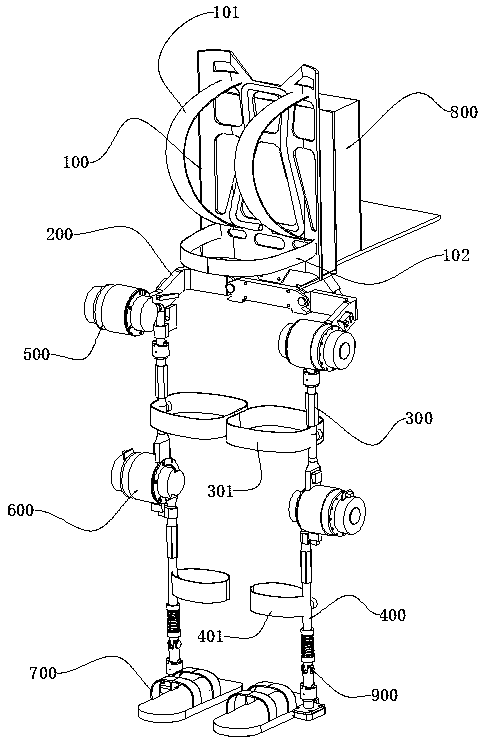
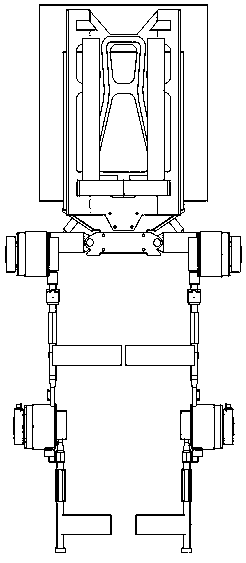
The invention relates to an exoskeleton robot and a controller system thereof. The exoskeleton robot comprises a back pad, a waist ring, a left thigh assembly, a right thigh assembly, a left calf assembly, a right calf assembly, a left shoe part and a right shoe part. The back pad is connected with the waist ring and located above the waist ring; the left thigh assembly and the right thigh assembly are connected with the left side and the right side of the waist ring through corresponding hip joint assemblies; the left thigh assembly and the right thigh assembly are connected with the left calf assembly and the right calf assembly through knee assemblies; and the left shoe part and the right shoe part are connected with the left calf assembly and the right calf assembly through ankle jointassemblies. The exoskeleton robot is mainly used for human body load supporting, the load capacity of a human body can be greatly improved, and the exoskeleton robot is easy to wear, fits human bodymechanics and greatly improves the fit degree with a user.
Owner:展视网(北京)科技有限公司
Bionic rigidity-changeable flexible knee joint of exoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a bionic rigidity-changeable flexible knee joint of an exoskeleton robot. The bionic rigidity-changeable flexible knee joint includes an elastic sheet arranged on a knee jointbody, a brushless direct current motor arranged on a crus inner board and for providing power, and a knee joint rotation shaft, wherein one end of an inner side of the knee joint rotation shaft is fixed with a thigh connection rod; the elastic sheet includes an outer ring and an inner ring, and an S-shaped elastic member is connected between the outer ring and the inner ring; the outer ring is fixedly connected to the thigh connection rod; one end of the brushless direction current motor has a small spiral bevel gear; the small spiral bevel gear is engaged with a big spiral bevel gear sleevingthe knee joint rotation shaft; the big spiral bevel gear is clamped with the inner ring; a pawl module is arranged on the crus inner board; a cam rotation plate is fixed on an outer end of the knee joint rotation shaft; one end of a tension spring is fixed on the cam rotation plate through a steel wire rope, and the other end of the tension spring is fixed on a ratchet wheel rotation plate of thepawl module. The bionic rigidity-changeable flexible knee joint adopts flexible drive, can relieve an instant ground impact force while a foot contacts a ground, can protect a human knee joint from being damaged, and can make walking more comfortable.
Owner:布法罗机器人科技(成都)有限公司
Assistance exoskeleton robot
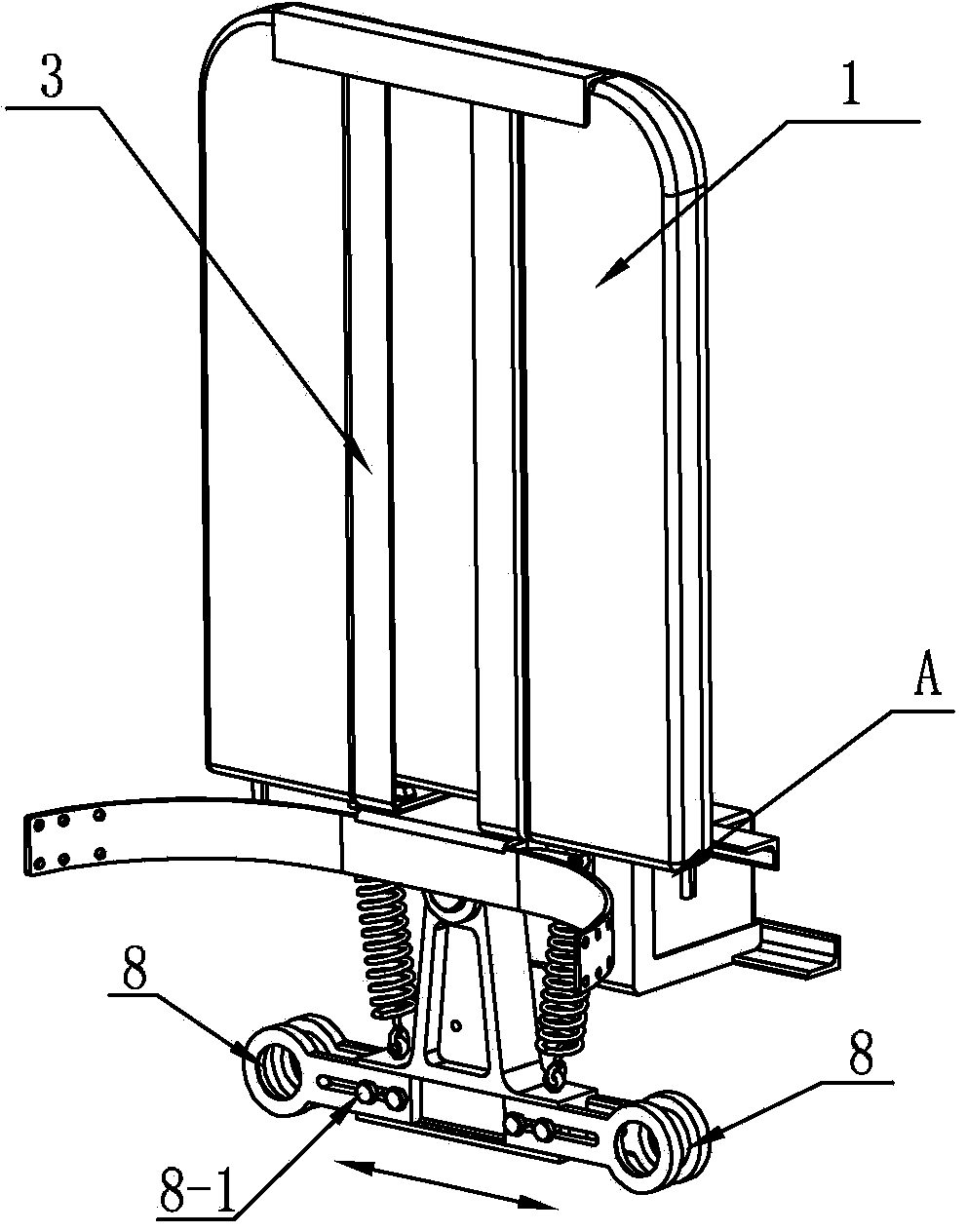
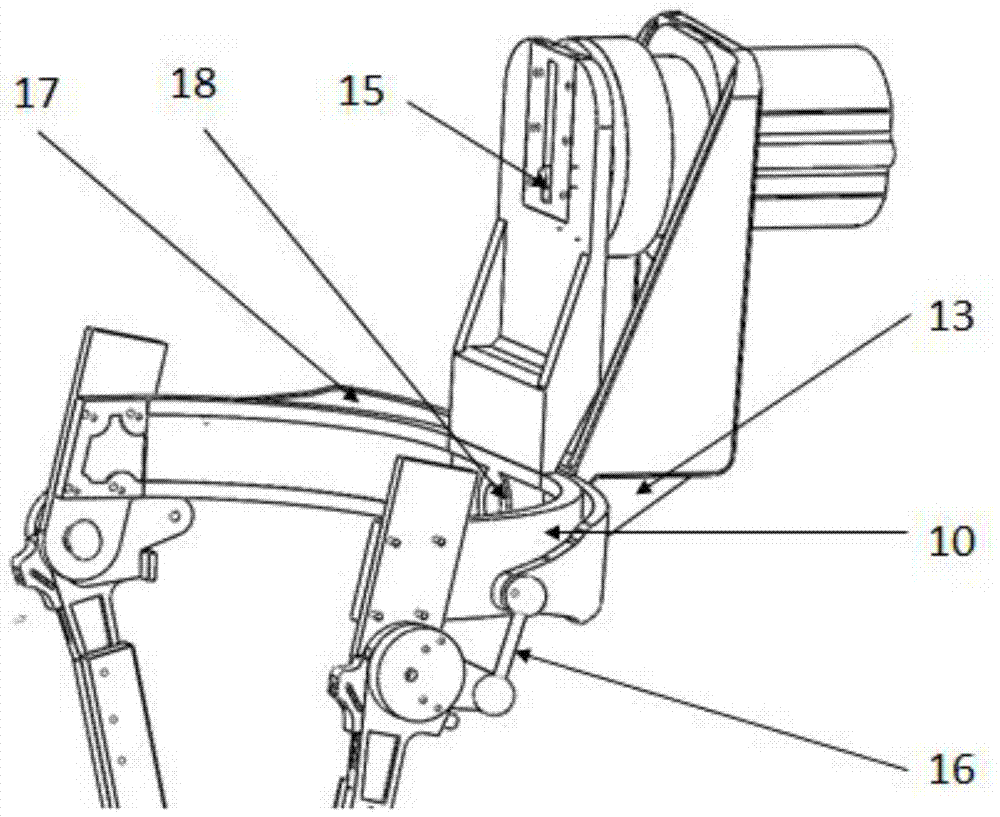
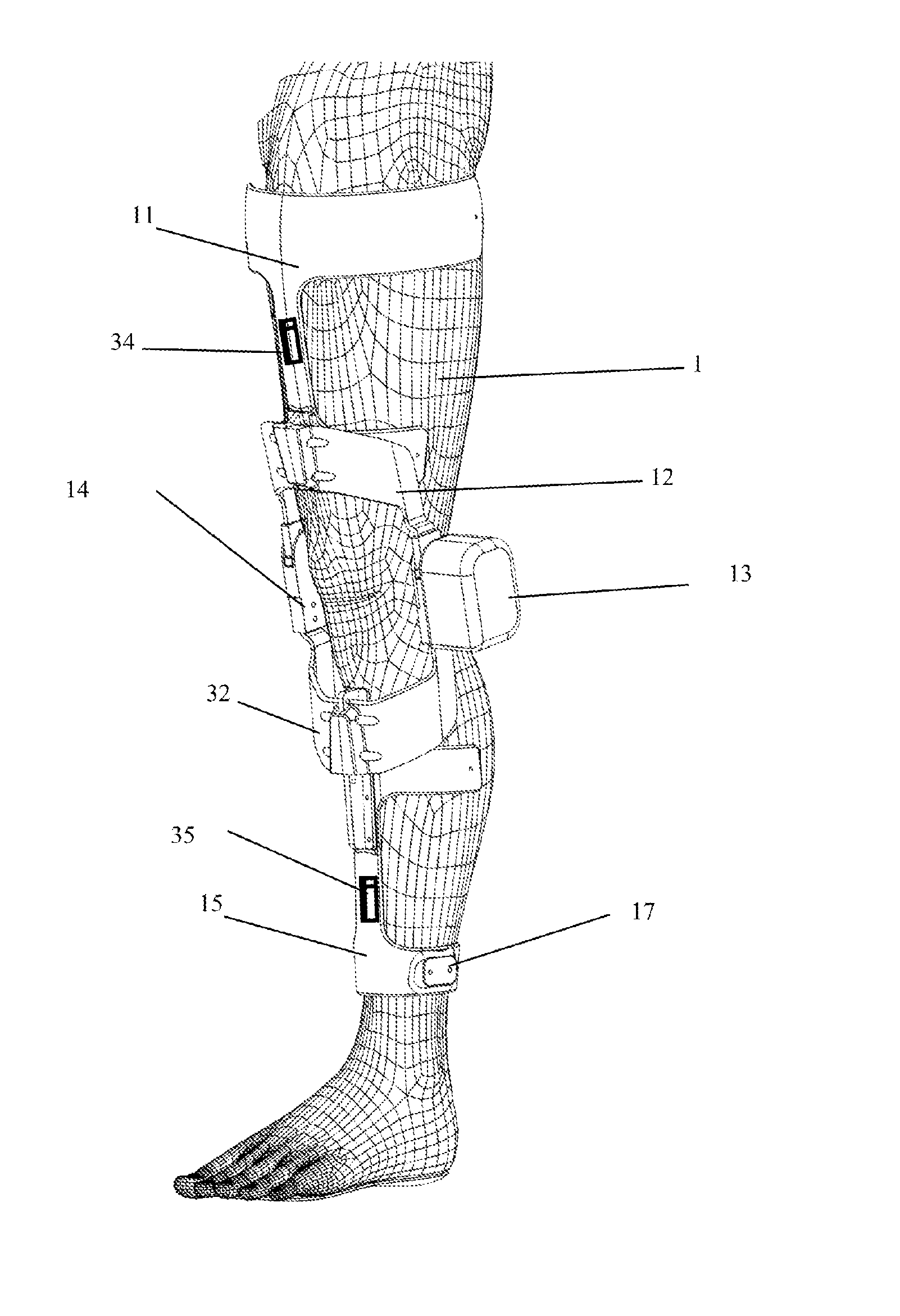
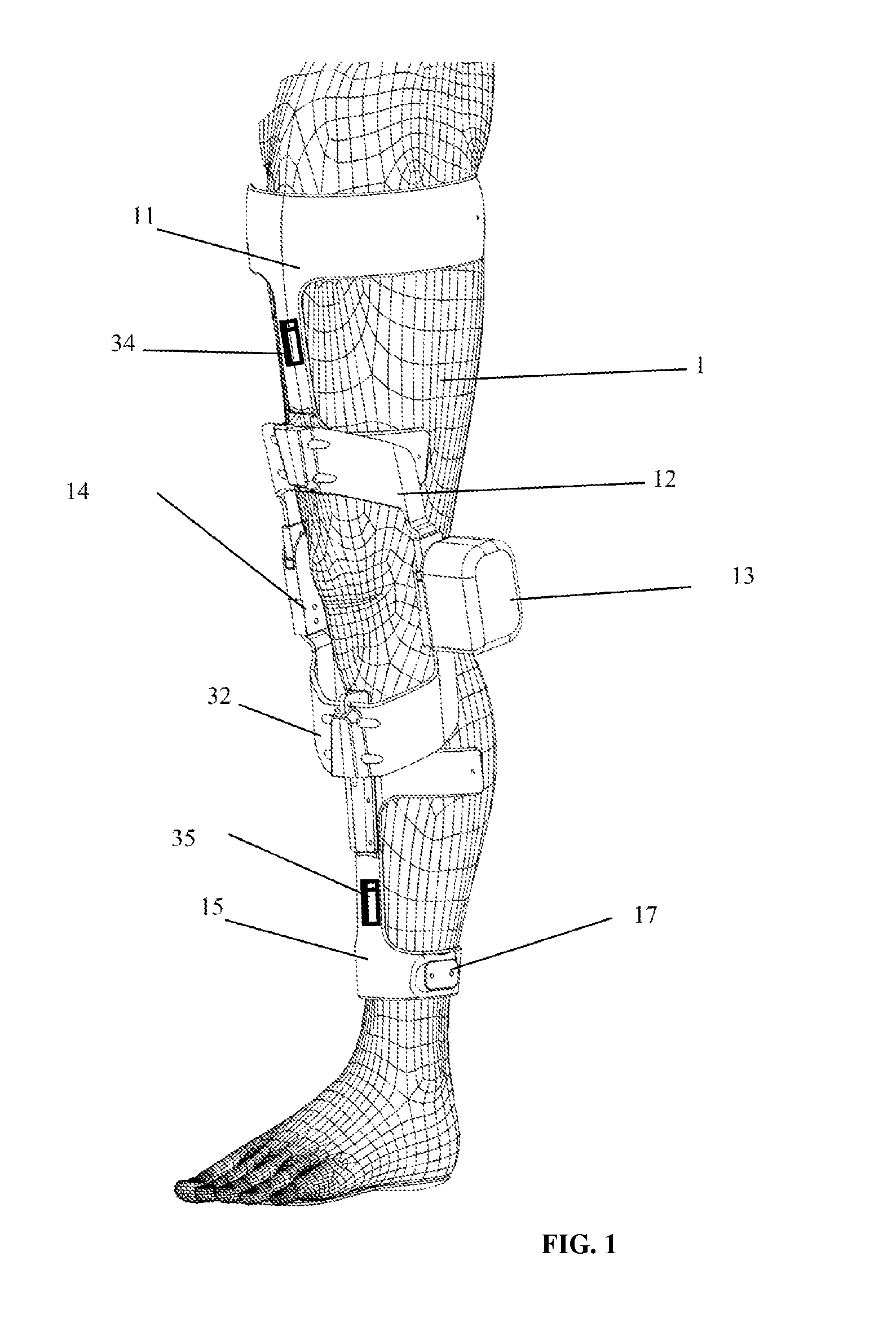
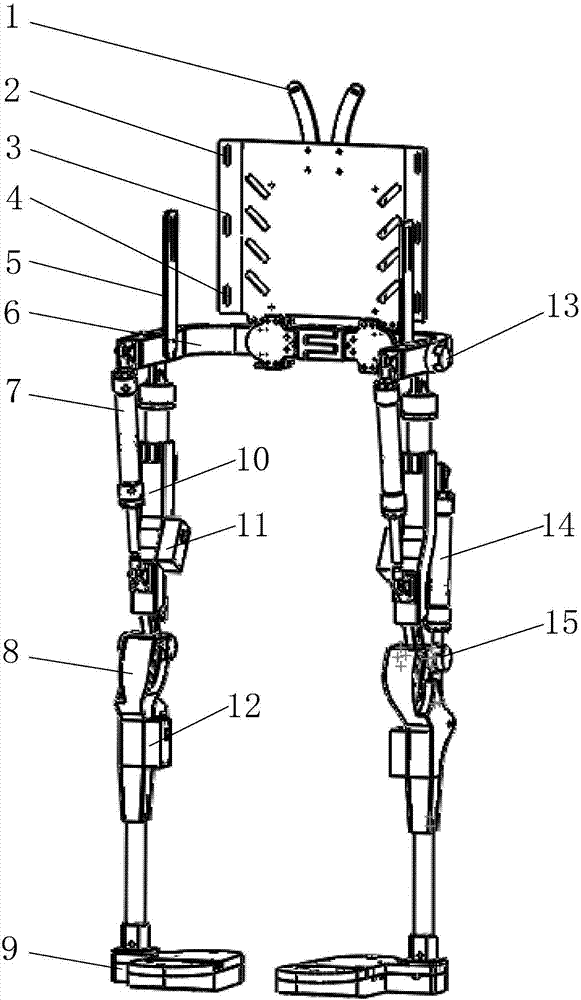
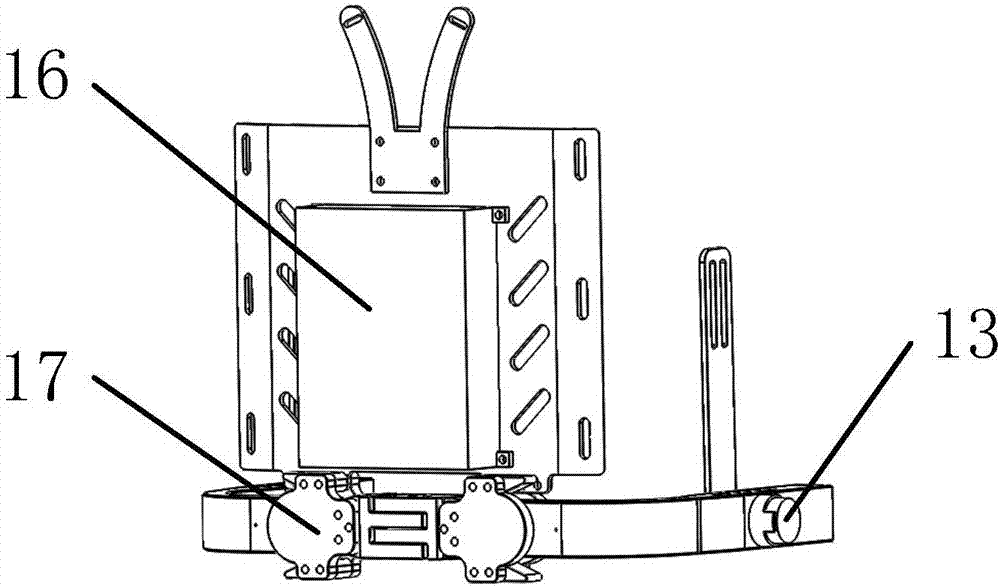
ActiveCN104758142ASimple mechanical structureLow machining accuracy requirementsChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighExoskeleton robot
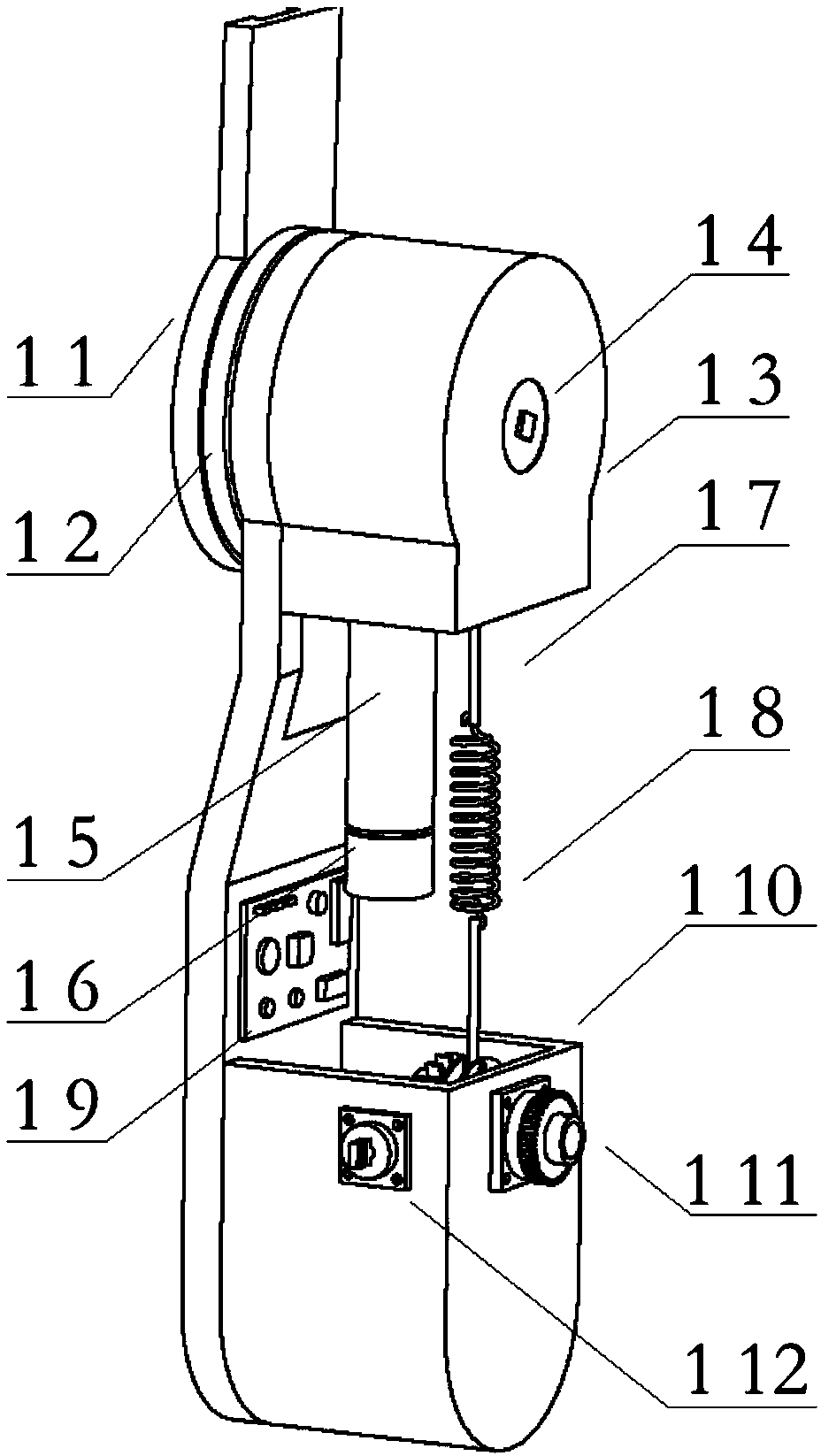
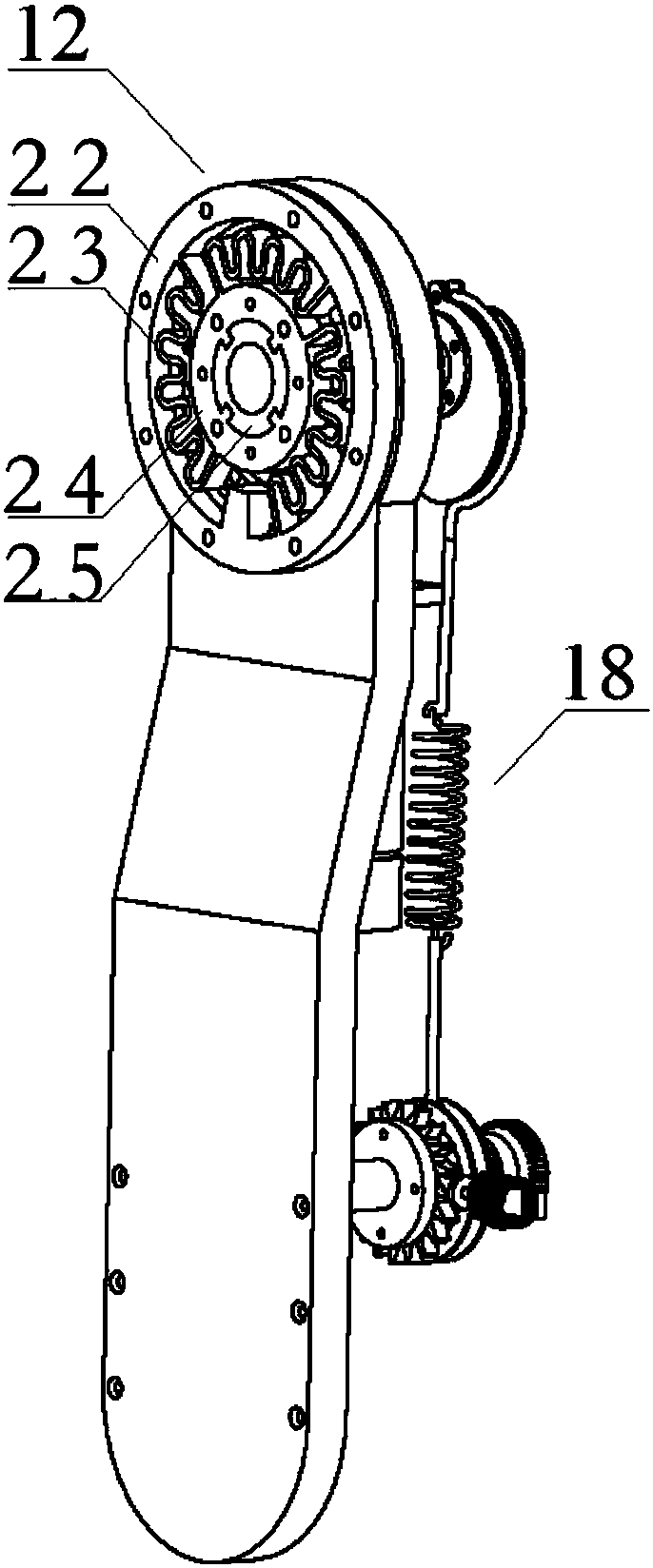
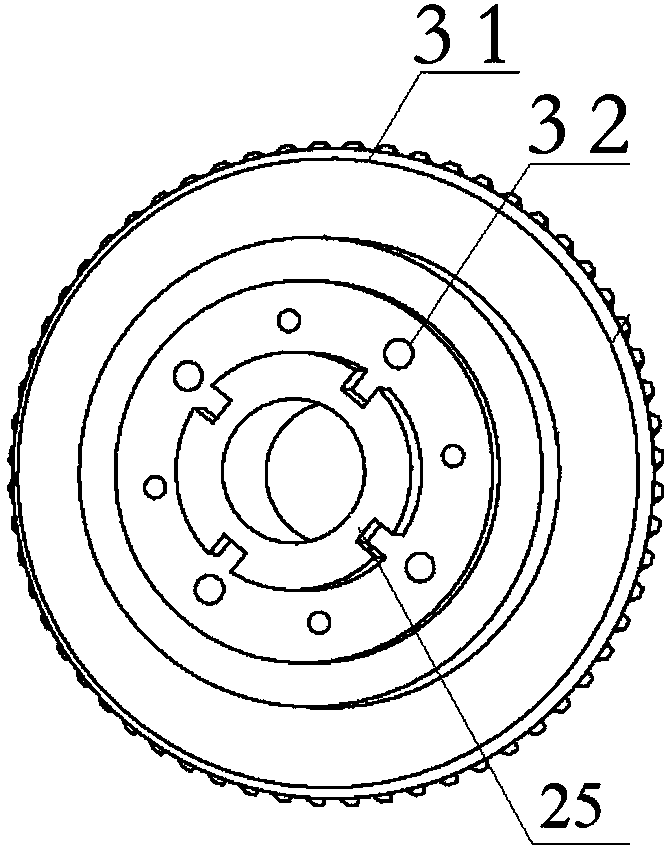
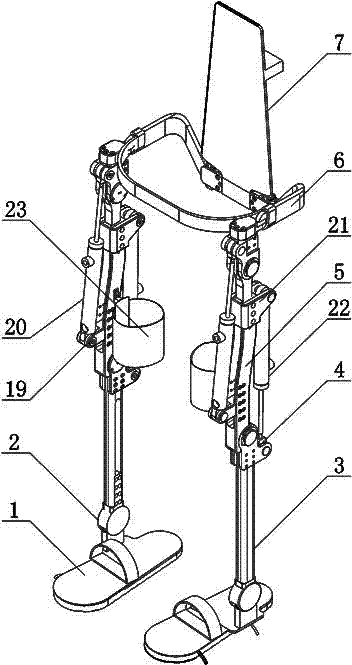
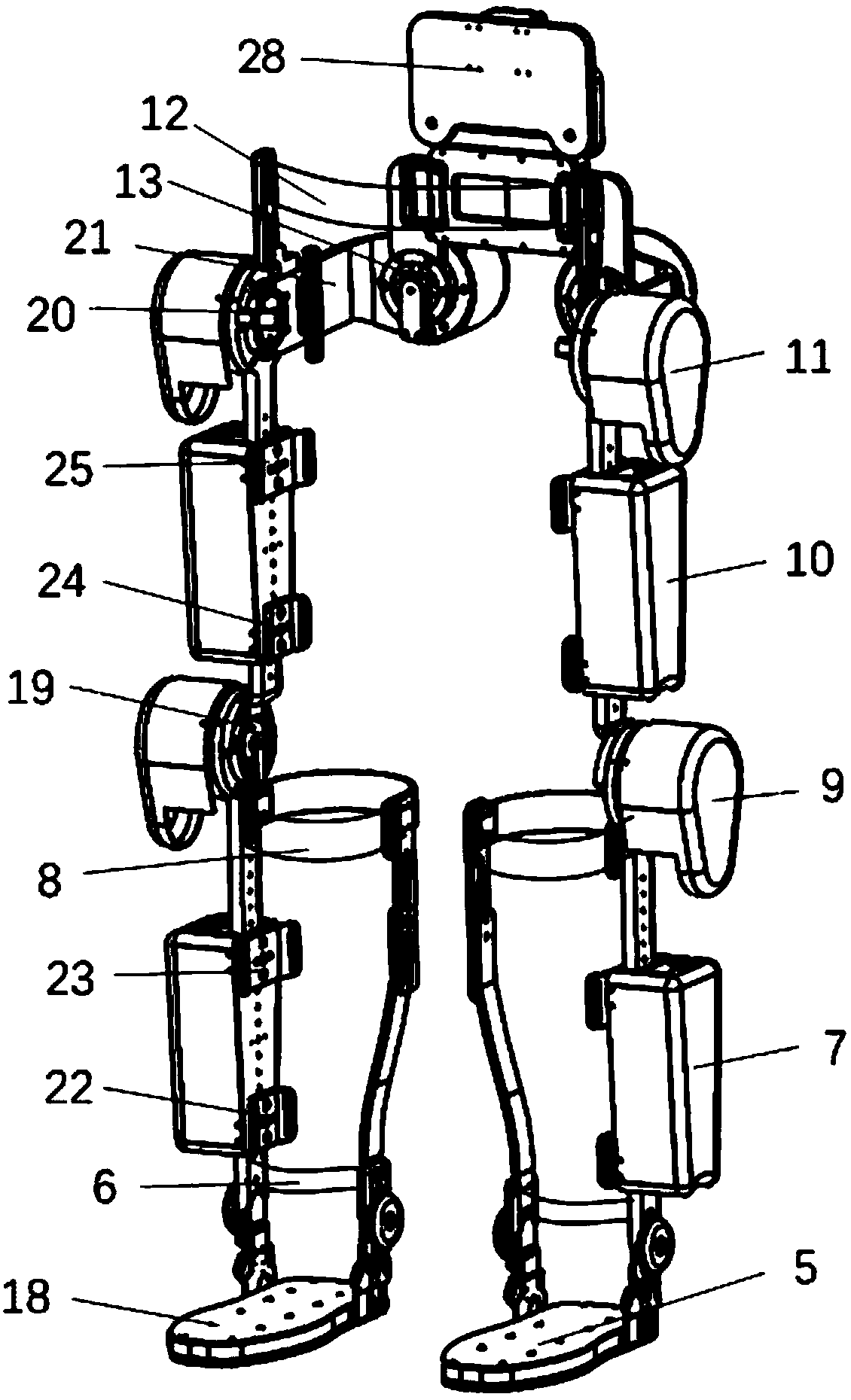
The invention relates to an assistance exoskeleton robot. The assistance exoskeleton robot comprises shoe body assemblies (1), ankle assemblies (2), shanks (3), knees (4), thigh assemblies (5), a hip joint assembly (6) and a back support (7), wherein each shoe body assembly (1) comprises a rubber insole (8), a front sole (9) and a back sole (10); the ankle assembly (2) comprises a connection block (12), a hinge board (13), a rotation pair (14) and a connection rod (15); the keens (4) are in an L-shaped structure; the upper end of each shank (3) is hinged with the corner of the L-shaped structure of the corresponding knee (4); the thigh assembly (5) comprises a thing main body, an oil cylinder A (20) and an oil cylinder B (22); the hip joint assembly (6) comprises a hip joint main body (24) and a hip joint band (25). The assistance exoskeleton robot has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and high comfort level; the ankles have multiple degrees of freedom.
Owner:布法罗机器人科技(成都)有限公司
Control system and method for external skeleton robot
InactiveCN108283569AImprove real-time performanceImprove accuracyElectrotherapyDiagnosticsThree dimensional simulationExoskeleton robot
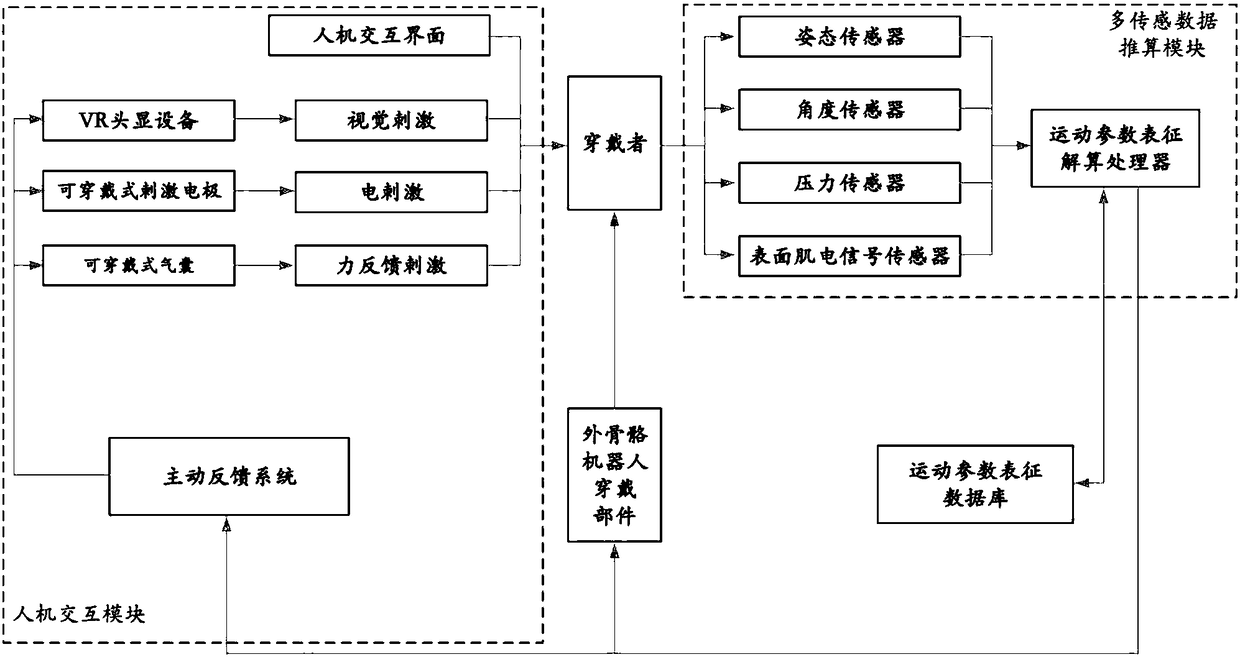
The invention relates to a control system and method for an external skeleton robot. The system and method are used for solving the problems that an existing rehabilitation external skeleton robot islow in universality, the motion intention of the human body cannot be correctly judged, and the function effect of man-machine cooperation cannot be achieved. The control system for the external skeleton robot comprises an attitude sensor, an angle sensor, a pressure sensor, a surface electromyographic signal sensor, a processor, an external skeleton robot wearing part and a man-machine interaction module. According to the control system and method, a motion representation database is established, the motion intention of the lower limbs of a wearer can be accurately judged through a large number of samples, assisting is conducted accordingly, and the assisting real-time performance and accuracy are improved; three-dimensional simulation display and scene simulation display are conducted through VR head display equipment, the visual simulation is provided for the wearer, the initiative participation degree of the wearer is increased, and the control system is beneficial to the nerve andmuscle recovery of the affected part.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS
Auxiliary light-weight integrated multi-freedom-degree lower limb exoskeleton
ActiveCN106965156AIncrease tilt DOFImprove matchProgramme-controlled manipulatorThighExoskeleton robot
The invention discloses an auxiliary light-weight integrated multi-freedom-degree lower limb exoskeleton and relates to the field of bionic wearable exoskeleton robots. The auxiliary light-weight integrated multi-freedom-degree lower limb exoskeleton comprises a back mounting board, a waist connection part, a hip bionic structure, a hip joint, a thigh bionic structure, a knee joint, a crus bionic structure, an ankle joint and a foot bionic structure; the ankle joint is arranged at the edge of the upper surface of the foot bionic structure; the crus bionic structure is fixedly connected with the foot bionic structure; the thigh bionic structure is installed on the knee joint at the top of the crus bionic structure; the hip joint is fixedly installed at the upper end of the thigh bionic structure; the hip bionic structure is fixedly installed at the upper end of the hip joint; the waist connection part is fixedly connected with the hip bionic structure; and the back mounting board is vertically and fixedly connected with the waist connection part. Through integration of freedom of degrees of all joints, an active joint drive structure is added, the light-weight structure form enhances the man-machine safety and wearing comfort under the condition of meeting the load requirements, and the auxiliary effect of the exoskeleton is improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS
Multi-phase gait switching control system and control method for power-assisted exoskeleton robot
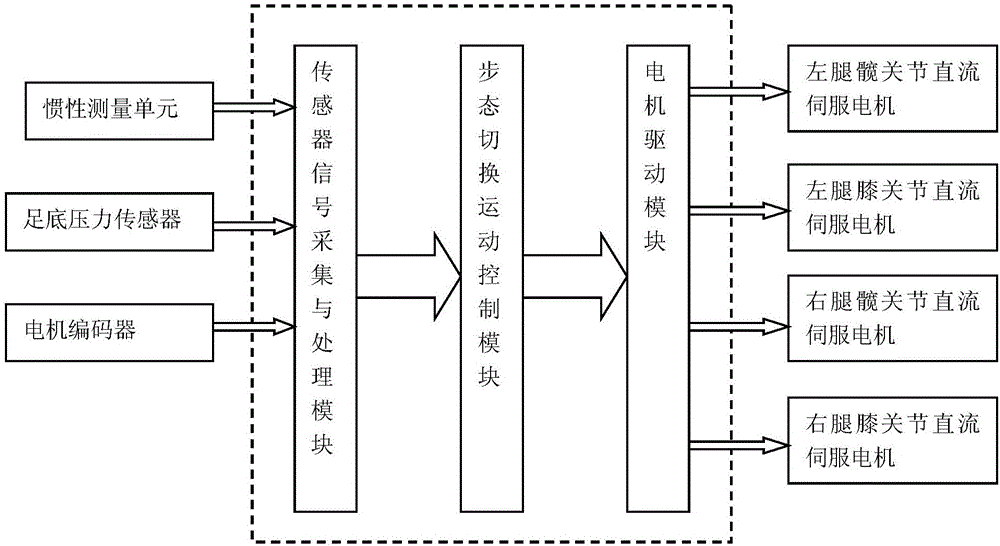
ActiveCN106325273AProtect personal safetyImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPosition/course control in two dimensionsExoskeleton robotMotor power
The invention discloses a multi-phase gait switching control system and control method for a power-assisted exoskeleton robot. The multi-phase gait switching control system is characterized in that the multi-phase gait switching control system includes a sensor module, a signal acquisition and processing module, a gait switching motion control module and a motor driving module; and sensors comprise inertial measurement units, plantar pressure sensors and motor encoders. With the multi-phase gait switching control system and control method for the power-assisted exoskeleton robot of the invention adopted, the output of lower hip joint and knee-joint motor power-assisted torque under various of phase gaits and smooth switching between the phase gaits can be planned under a condition that the exoskeleton robot bears a heavy object, and the coordination and flexibility of the movement of the limbs of the weight-bearing exoskeleton equipment can be realized.
Owner:江苏中科伟思智能机器人科技有限公司
Unpowered wearable auxiliary walking assisting mechanism
The invention discloses an unpowered wearable auxiliary walking assisting mechanism. The unpowered wearable auxiliary walking assisting mechanism comprises driving force formation assemblies and knee joint assisting executing assemblies. Based on a lever principle and a crank slide block structure mechanism, the walking assisting mechanism disclosed by the invention adopts a working manner of same-side parallel driving input of left and right feet; a self-gravity effect of a human body is utilized and Bowden cables are used as a medium for transmitting a pulling force between the driving force formation assemblies and the knee joint assisting executing assemblies; the driving force formation assembly of the left foot provides a driving force for a left leg knee joint auxiliary torque executing assembly; the driving force formation assembly of the right foot provides a driving force for a right leg knee joint auxiliary torque executing assembly, so that torques for assisting left and right leg knee joints to bend and extend are generated in a walking process, and the aim of assisting walking is realized. The unpowered wearable auxiliary walking assisting mechanism disclosed by the invention has small inertia; the defects that the inertia of rigid mechanisms including a common leg assisting mechanism or an external skeleton robot and the like is great, damages to knee joints of people are easy to cause, the comfort is poor and the like are overcome, and the safety and comfort of the mechanism are remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Double-lasso driving flexible joint used for exoskeleton robot
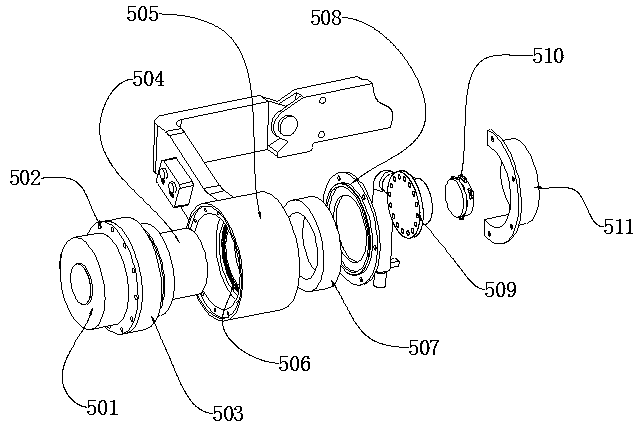
ActiveCN104068985AReduce quality problemsReduce inertiaJointsChiropractic devicesFlexible MechanismsExoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a double-lasso driving flexible joint used for an exoskeleton robot, which comprises a drive mechanism, a pre-tightening mechanism, a lasso transmission mechanism, a flexible mechanism and an exoskeleton joint. A motor drives a drilling roller to rotate; the two ends of a rope are respectively fixedly connected with the driving roller and a load roller; a driving torque is delivered to the load roller through the lasso transmission mechanism; the load roller is fixedly connected with the exoskeleton joint to drive the joint to move; a positioning hole and a positioning groove both capable of limiting the motion range of the joint are formed in the load roller; the pre-tightening mechanism adjusts a pre-tightening force of a rope by changing the screwing depth of a pre-tightening bolt so as to avoid looseness of a drive system; the flexible mechanism enables the joint to achieve flexibility and can measure an output torque based on a displacement offset of the motor and the joint. The double-lasso driving flexible joint used for the exoskeleton robot can realize separation of the motor and the exoskeleton robot, overcomes the problems of the quality of each joint of the exoskeleton and too great inertia, and can perform precise position control and force control on the drive joint.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system
PendingCN109568089ASolve the problem that it is difficult to maintain the balance of usersAvoid secondary damageWalking aidsExoskeleton robotEngineering
The invention discloses a slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system which is divided into a lower limb wearable exoskeleton robot and a slave robot. The slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system comprises two translational degrees of freedom, two vertical weight loss degrees of freedom of the slave robot and six rotational degrees of freedom of two legs,hip and knee of the wearable robot. The lower limb wearable exoskeleton robot is fixed on lower limbs and waist of a patient and provides walking assistance according to the gait of the patient and helps the patient to complete the walking action; and the slave robot is connected with the lower limb wearable exoskeleton robot to play a role in supporting the patient and reducing the weight, so that the corresponding following movement can be realized according to the walking of the patient. The slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system is mainly used for solving variouslower limb movement dysfunctions caused by the central nerve injury, provides the safe, long-acting and large-range gait training for the patient and can improve the lower limb rehabilitation trainingefficiency of the patient.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
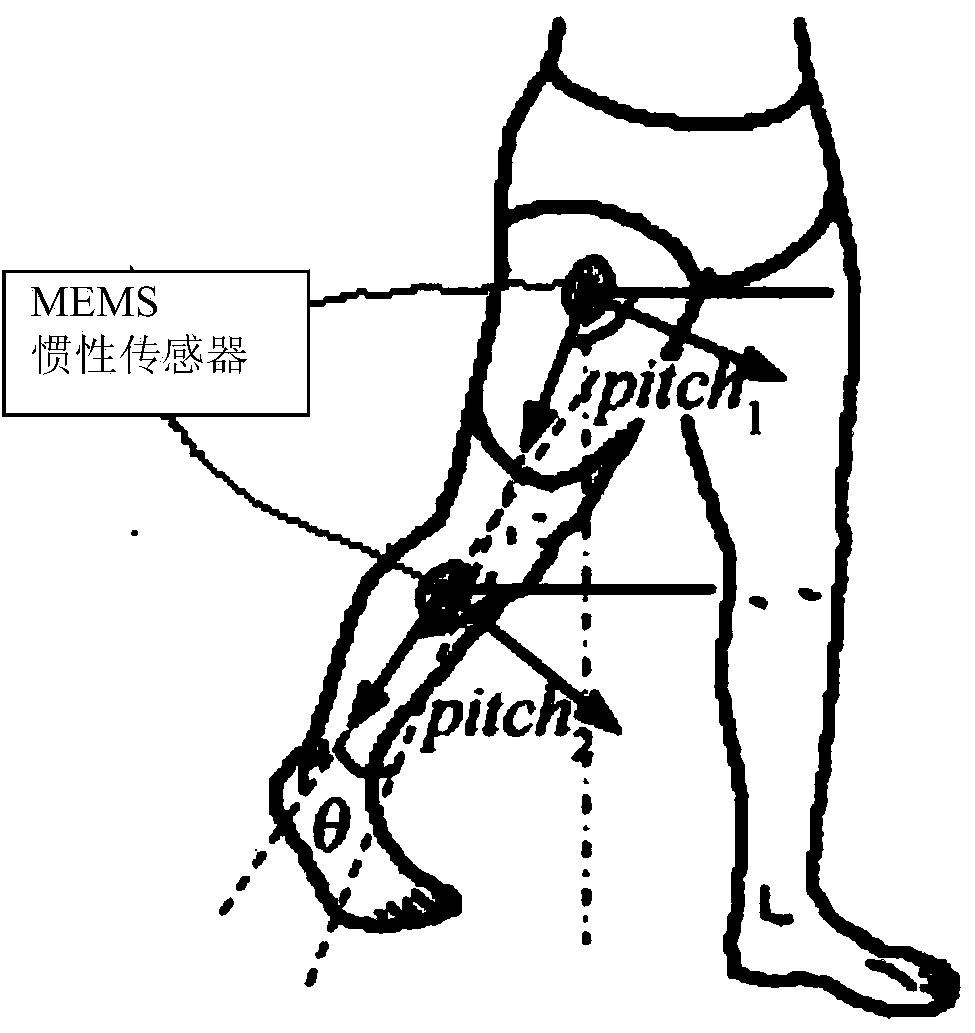
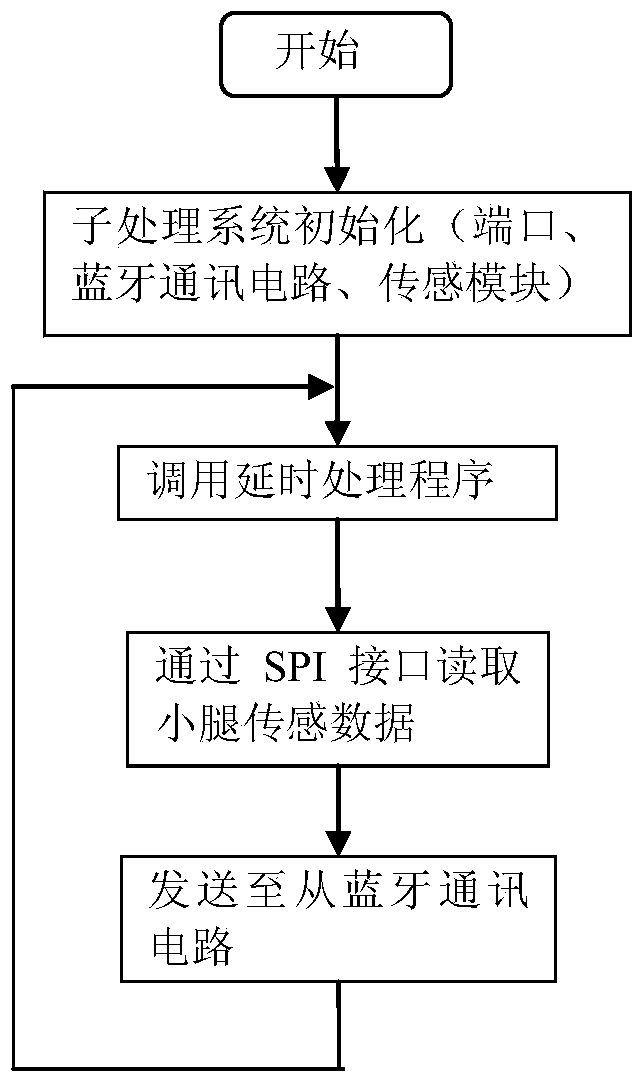
Human knee joint angle wireless detection system and method based on MEMS inertial sensors
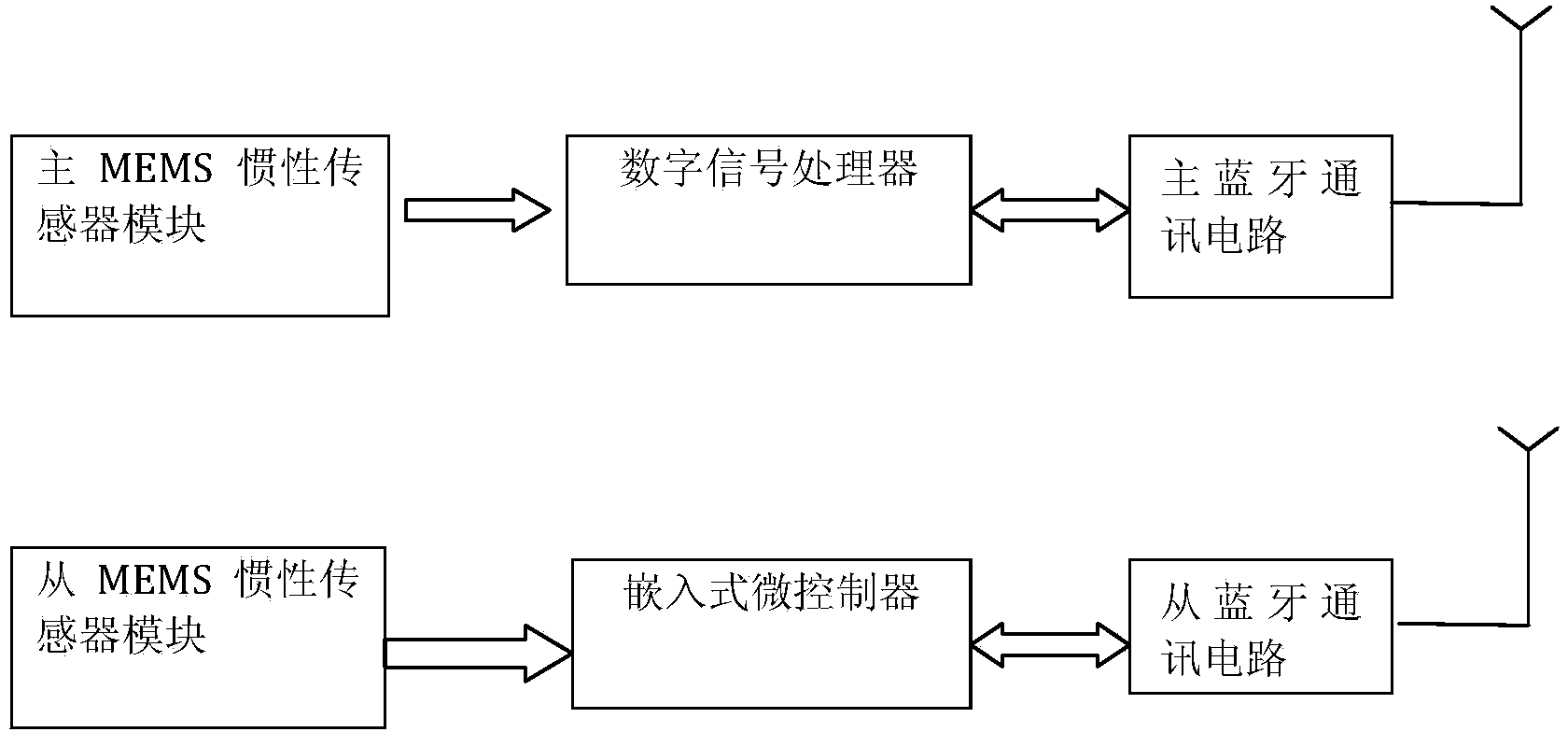
The invention provides a human knee joint angle wireless detection system and method based on MEMS inertial sensors, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The human knee joint angle wireless detection system comprises a main processing system and a node processing subsystem which are respectively arranged in positions of the thigh and shank of a human lower limb. The method includes allowing the main processing system to combine thigh acceleration and angular velocity information and shank acceleration and angular velocity information which are respectively sent by a main MEMS inertial sensor module and an auxiliary MEMS inertial sensor module so as to calculate the tilts of the thigh and shank of the human lower limb, acquiring knee joint angle information during walking, and outputting knee joint angle information to an exoskeleton robot control system through a Bluetooth manner. According to the system and method, data from a gyroscope and an accelerometer are combined, angle information of the human knee joint can be respectively detected in real time, and discomfort of a wearer can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Leg device with interaction force parameter measurement for lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a leg device with interaction force parameter measurement for a lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot, and particularly relates to a lower limb exoskeleton robot for dependent ambulation. The interaction force parameter measurement is completed by means of an interaction force sensors, including a thigh interaction force sensor and a shank interaction force sensor. By taking thigh for instance, one side of the sensor is fixed on the inner side of the thigh, and a flexible bandage is fixed on the measurement region of the other side of the sensor and is used for fixing the thigh of a patient with lower limb injury, and the interaction force between a human body and exoskeleton can be measured when the exoskeleton drives the patient to move. Interaction force information, joint angle information and sole pressure information are intensively processed as exoskeleton control data, the exoskeleton is adjusted for different patients and different conditions, the patient feels comfortable when wearing the dependent ambulation exoskeleton, the body situation of the patient can be understood conveniently, and convenience is provided to rehabilitation training.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com