Patents
Literature
110 results about "Wearable robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
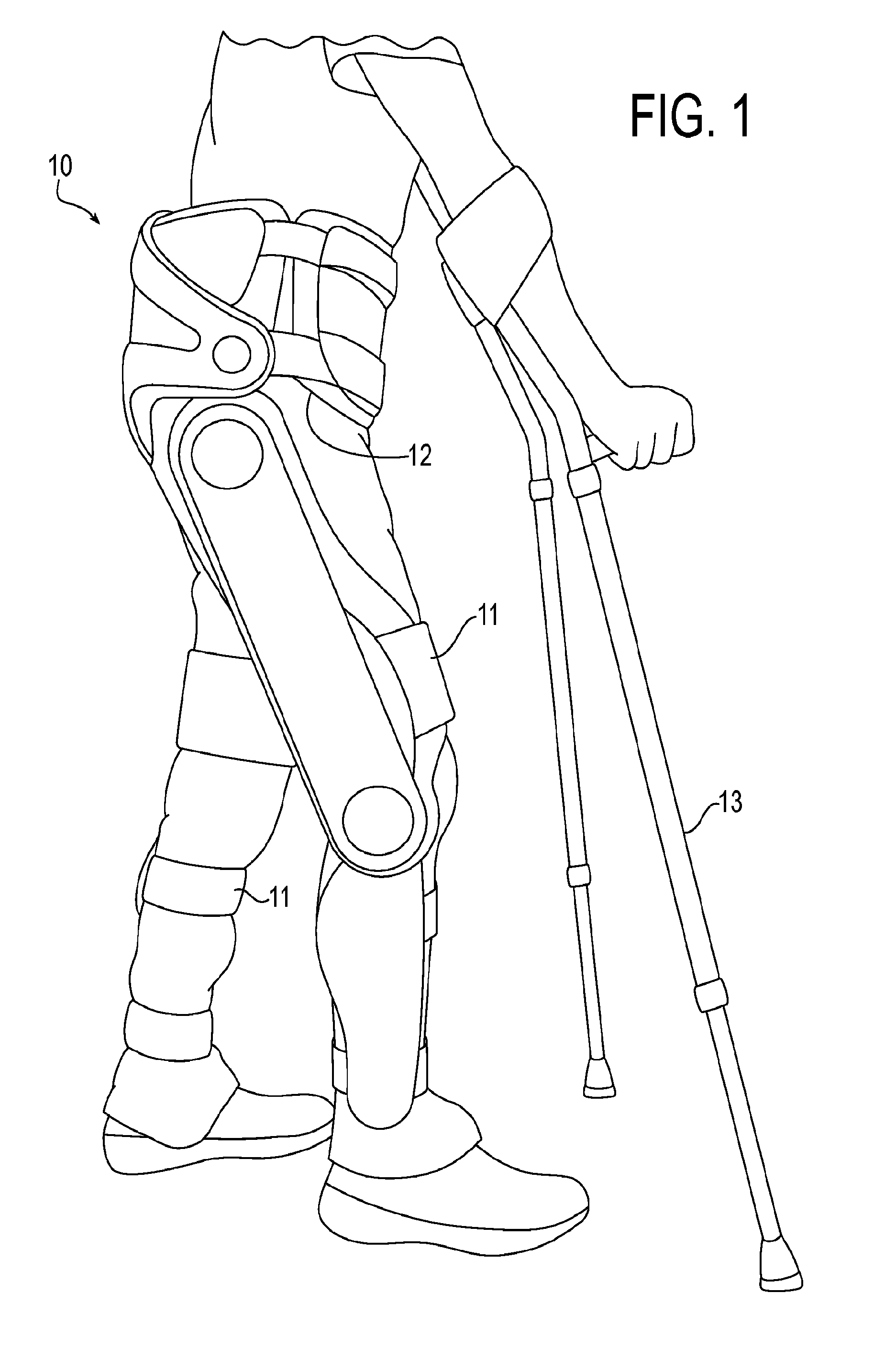
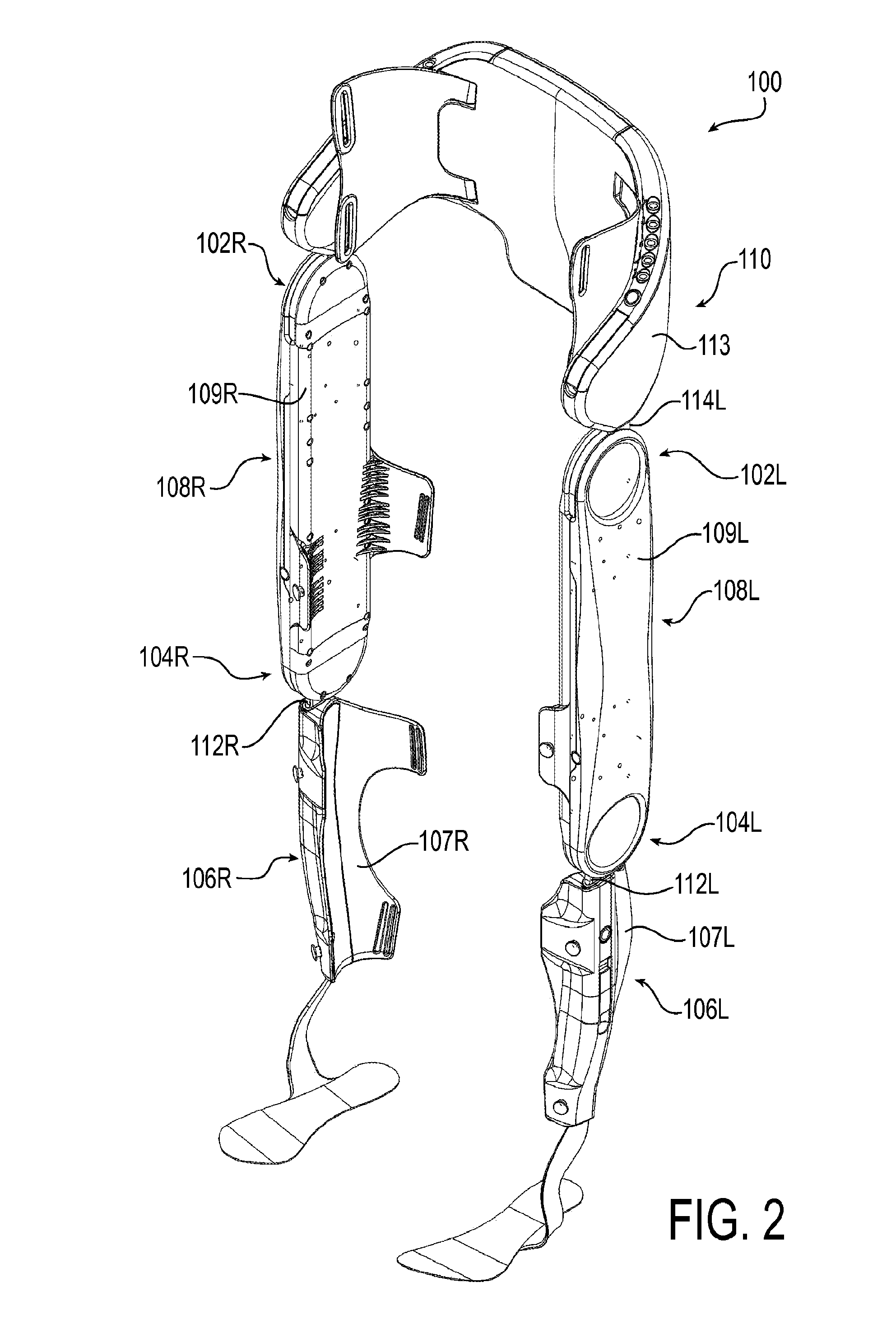
A wearable robot is a specific type of wearable device that is used to enhance a person's motion and/or physical abilities. Wearable robots are also known as bionic robots or exoskeletons.
Robotic System for Simulating a Wearable Device and Method of Use
ActiveUS20130158444A1Reduce weightAccurately and rapidly modelProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsRobotic systemsControl system
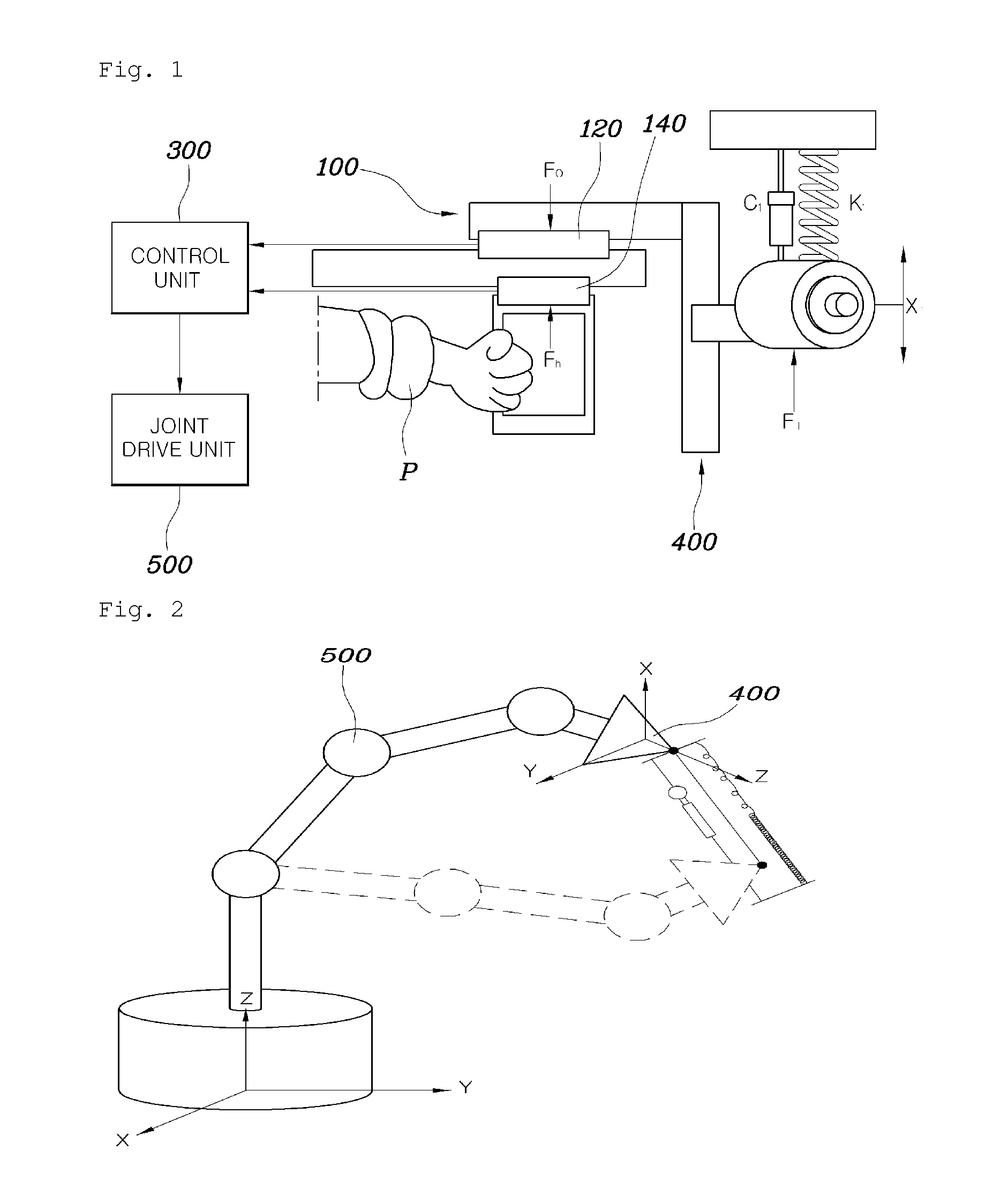
A robotic system for simulating a wearable device actuation delivery mechanism and the source removed from the actuation delivery mechanism that is linked to the actuation delivery mechanism by at least one cable. A sensing system detects a physiological feature of the subject and, based on feedback from the sensing system, a control system linked to both the sensing system and the actuation source modulates the actuation source, and thereby modulating actuation of the joint of a subject in response to the physiological future sensed by the sensing system. A method for simulating a wearable robotic system employs the robotic system of the invention to thereby provide a model on which to base design of an ambulatory prosthetic for a subject.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
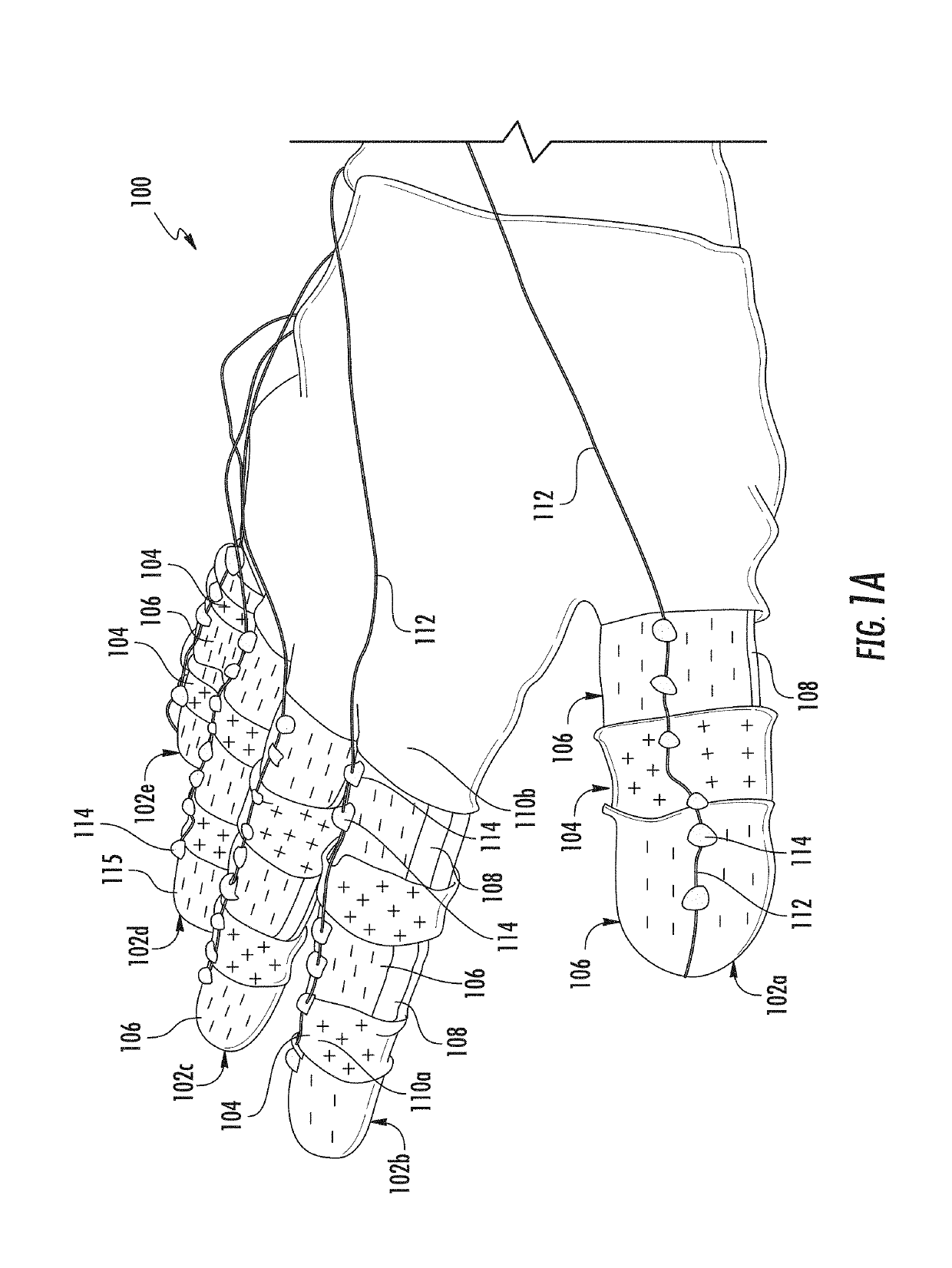
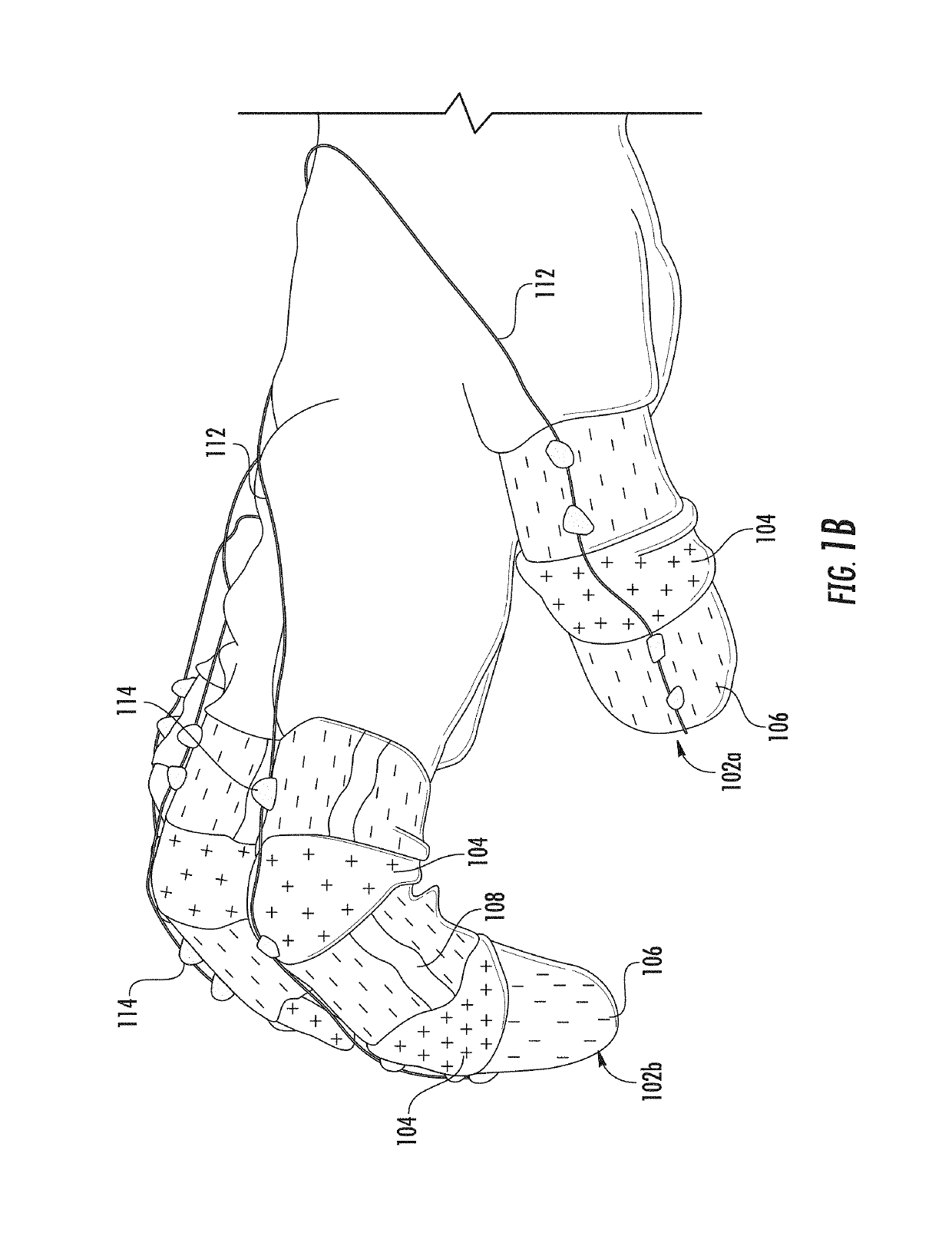
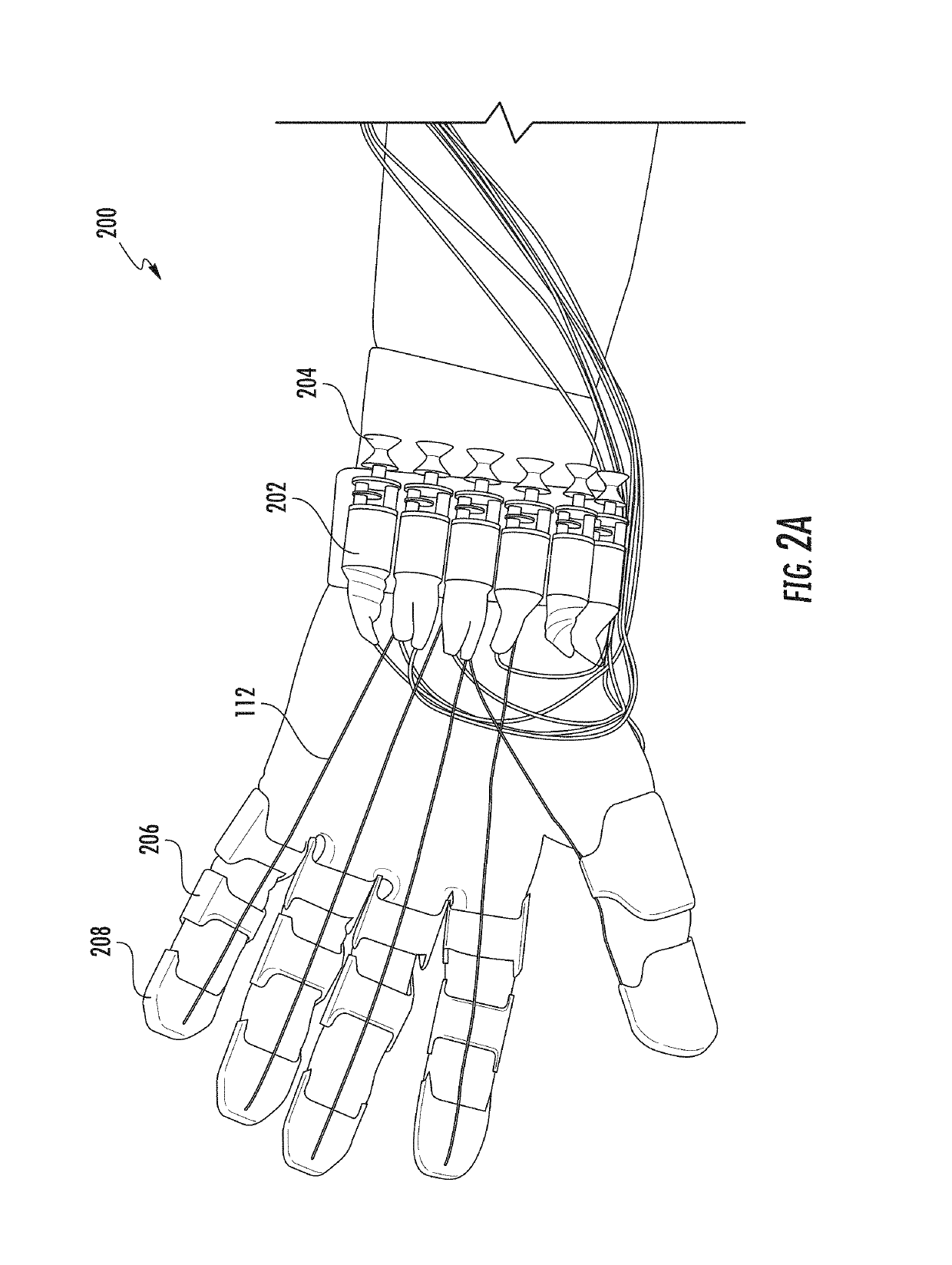
Wearable Devices, Wearable Robotic Devices, Gloves, and Systems, Methods, and Computer Program Products Interacting with the Same
ActiveUS20170168565A1Input/output for user-computer interactionChiropractic devicesEngineeringActuator
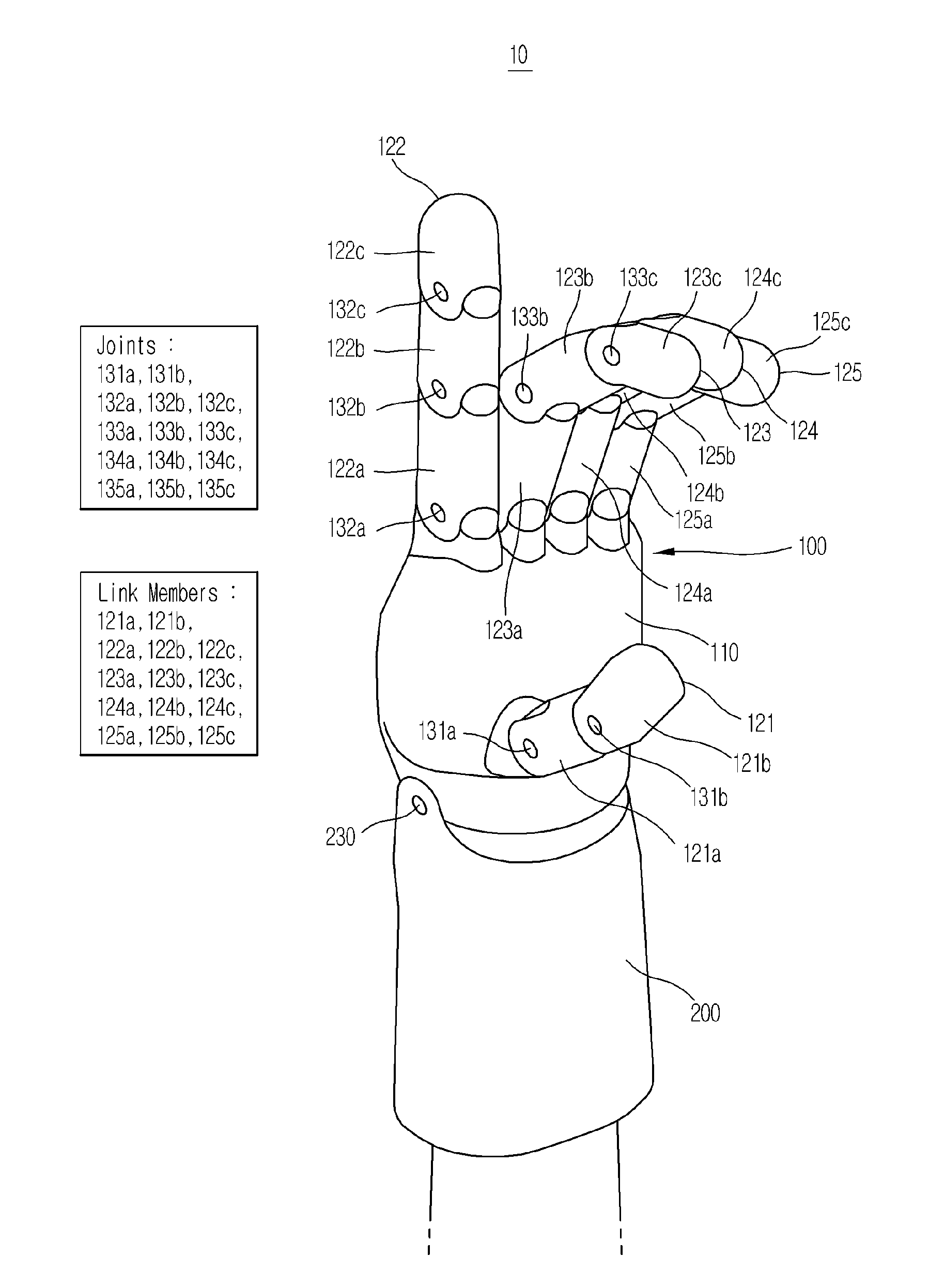
One aspect of the invention provides a wearable device including: at least one compliant region adapted and configured to be placed over a joint of a subject and at least two flexible but less compliant regions coupled to opposite ends of the compliant region. Another aspect of the invention provides a wearable robotic device including a wearable device as described herein and at least one actuator adapted and configured to move the flexible but less compliant regions relative to each other.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Multiple-freedom degree wearing type rehabilitation training robot for function of hand and control system thereof
InactiveCN101433491AFeel comfortableAdjustable sizeChiropractic devicesManipulatorLittle fingerRobotic arm
The invention discloses a multi-freedom wearable robot for hand function recovery. The robot comprises mechanical arms and mechanical fingers; the mechanical fingers consist of a mechanical thumb, a forefinger, a middle finger, a ring finger and a little finger, wherein the forefinger, the middle finger, the ring finger and the little finger have the same structure as that of the thumb; the mechanical forefinger mainly comprises air muscle, a finger end bracket, a first middle connecting piece, a finger front end bracket and a second middle connecting piece which are connected in turn through a connecting rod; the air muscle drives the second middle connecting piece to move through a rigid string so that the finger of a patient makes lituate and adduction exercises; the inside of each connecting piece is provided with a pressure spring; and inside walls of the two connecting pieces are distributed with rolling beads to reduce friction between the connecting rod and the connecting pieces. The invention also provides a control system and an integrated electricity stimulation system of the robot to assist a patient to rebuild muscle function. The robot provides an assisted exercise mechanism for the fingers, has multiple freedom degrees and dimension adjustable movement mechanism, and can effectively assist the patient to finish repeated training of composite exercise for fingers and complicated finger dividing exercise.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wearable robotic system for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs
ActiveUS20110251533A1Simple structureLower the volumeDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesRobotic systemsEngineering
The present invention relates to a wearable robot system for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs that has an improved structure to reproduce in detail motion of a human body by selecting a wearing type structure such that robot links move correspondingly to the motion of the upper limbs while decreasing the volume of a rehabilitation and assistance device based on a robot for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs. According the present invention, it is possible to decrease the volume and increase the available space, in addition to creating smooth motion without interfering with the human body by creating a plurality of robot motion paths and selecting the best path from them, because an operation of four degrees of freedom can be achieved by an operation procedure using redundant.
Owner:HANSUNG UNIV IND UNIV COOPERATION FOUND +1
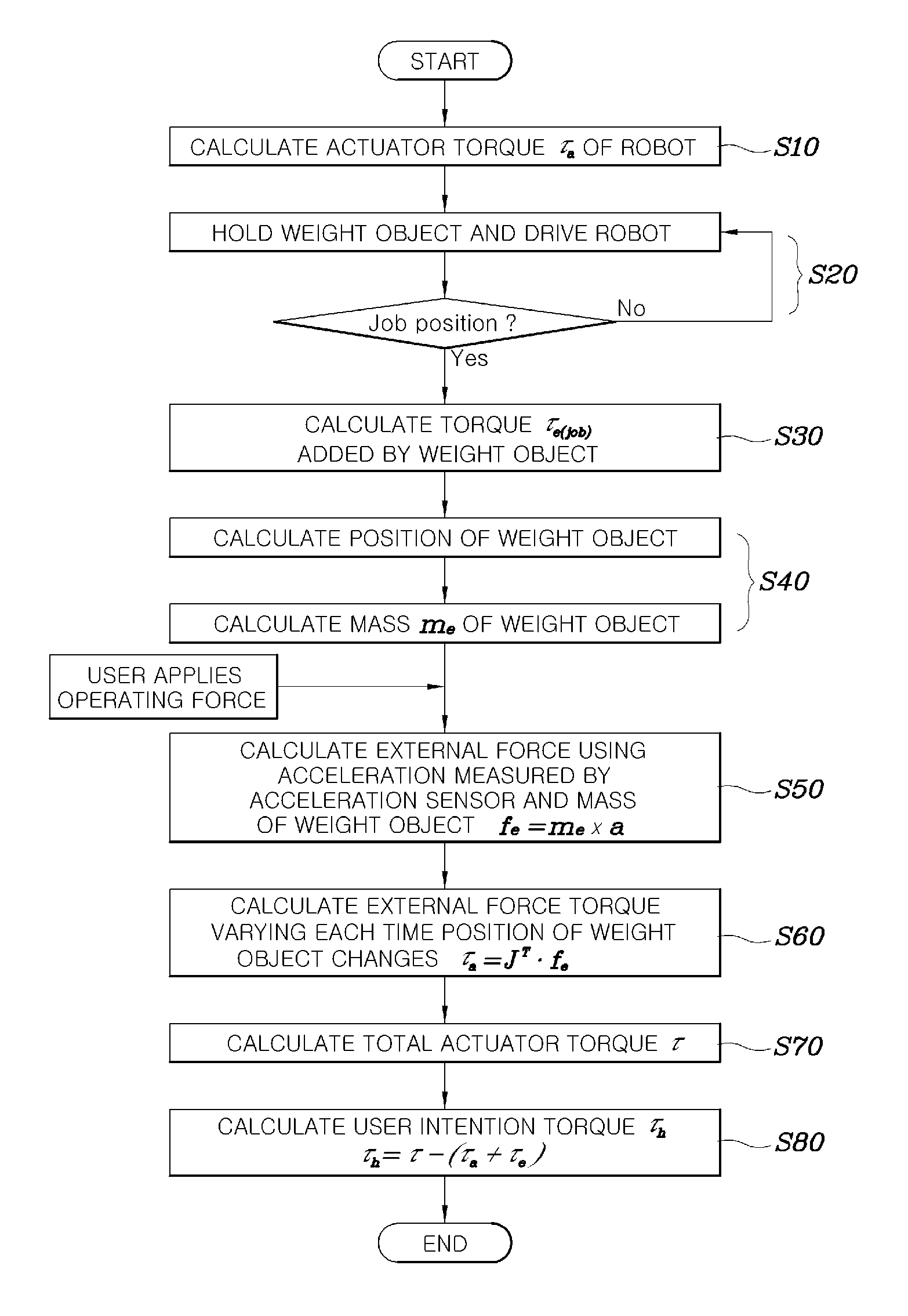
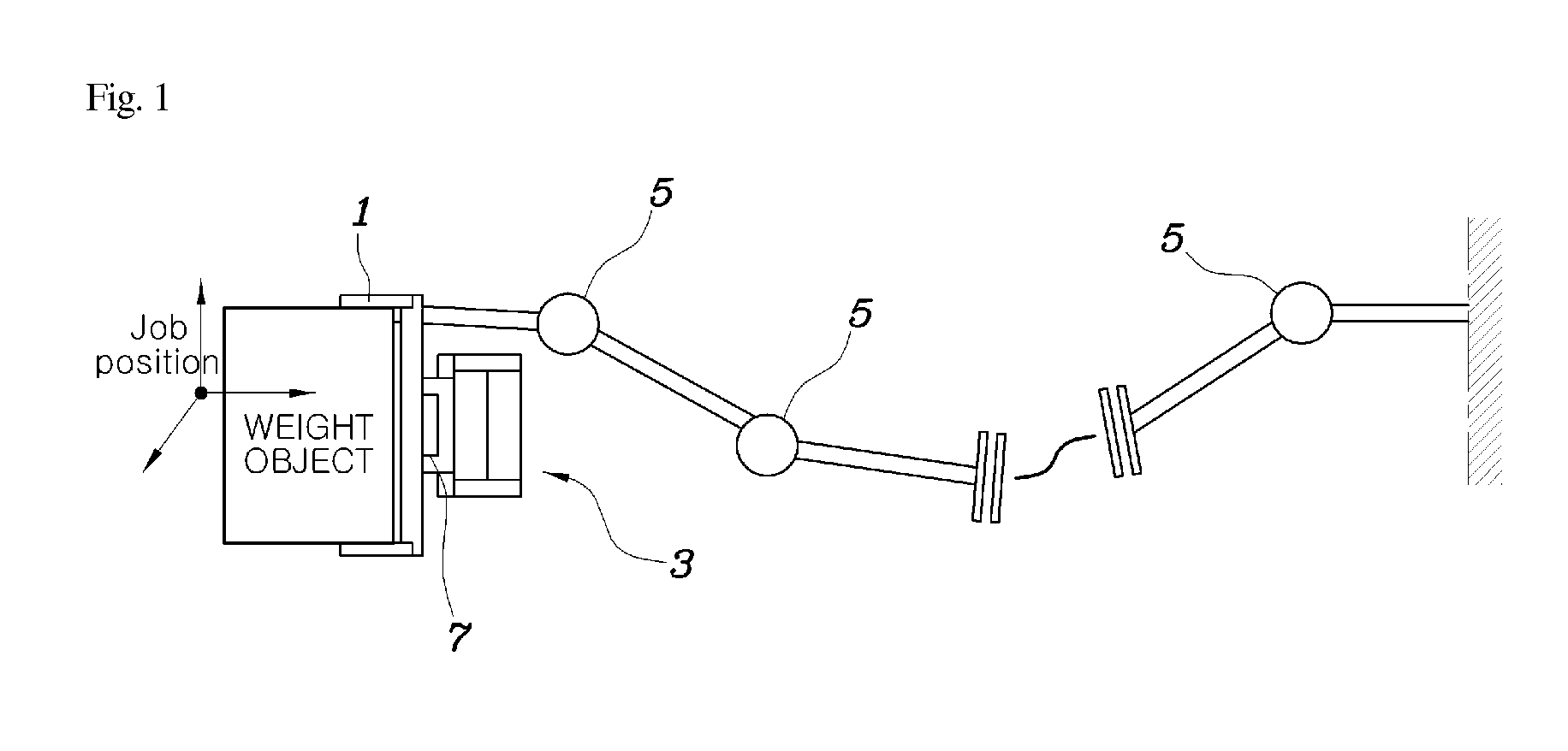
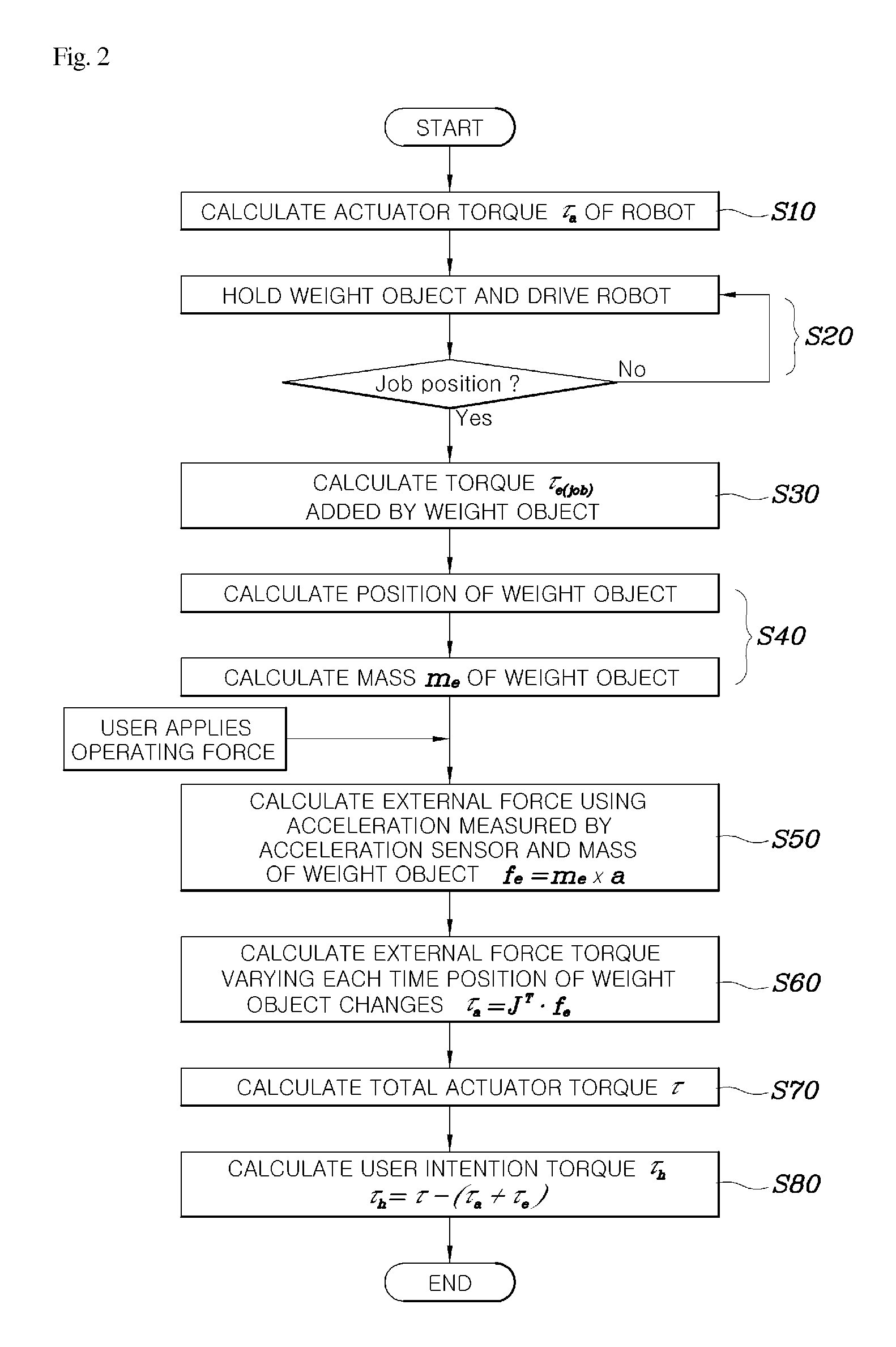
Method of operating a wearable robot
ActiveUS20130173060A1Simply and rapidly extractLow costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl theoryElectrical current
Disclosed herein is a method of obtaining the intended manipulation torque of a user for a wearable robot. The method allows the wearable robot, the motion of each joint of which is operated by a motor and which is capable of measuring a variation in current in the motor of each joint and calculating a torque at each joint, to simply and rapidly extract the intended manipulation torque of the user using both an acceleration value (e.g., measured by an acceleration sensor installed on a gripper), and the current variation of the motor, in a state in which the wearable robot does not know the weight of a weight object to be lifted with the gripper. Accordingly, the wearable robot may be suitably controlled at a comparatively lower cost.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Wearable robotic device
ActiveUS20170049659A1Improve usabilityExpanded size rangeProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesSystems designUsability
A self-aligning, self-drawing coupler for coupling body assemblies together improves usability of a wearable robotic device. A self-contained removable actuator cassette improves the ease of manufacture and of replacing parts in the field. A tensioning retention system designed for one handed operation makes donning and doffing a wearable robotic device easier. A two-stage attachment system increases the range of sizes a wearable robotic device will fit. A removable, integrated ankle-foot orthotic system makes donning and doffing a wearable robotic device easier. An infinitely adjustable, integrated ankle-foot orthotic system increases the range of sizes a wearable robotic device will fit. A manually-removable hip-wing attachment system makes field changes easier, and protecting such a system from inadvertent disengagement during operation increases safety.
Owner:EKSO BIONICS HLDG INC
Wearable robot for detecting and suppressing tremor of human arms and method for suppressing tremor thereof
InactiveCN101612043AHigh degree of anthropomorphismSimple structureNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringFilter algorithmClosed loop
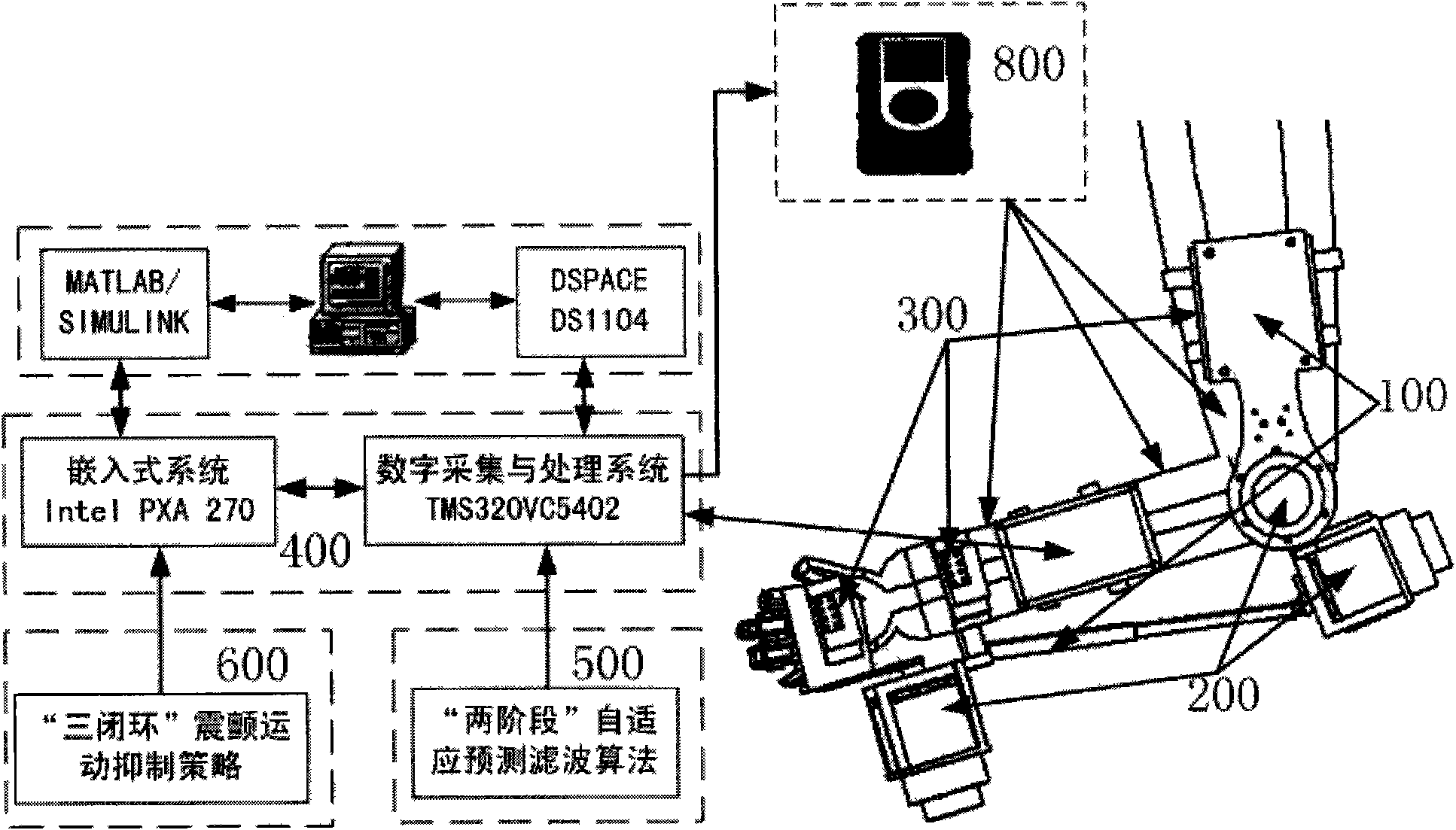
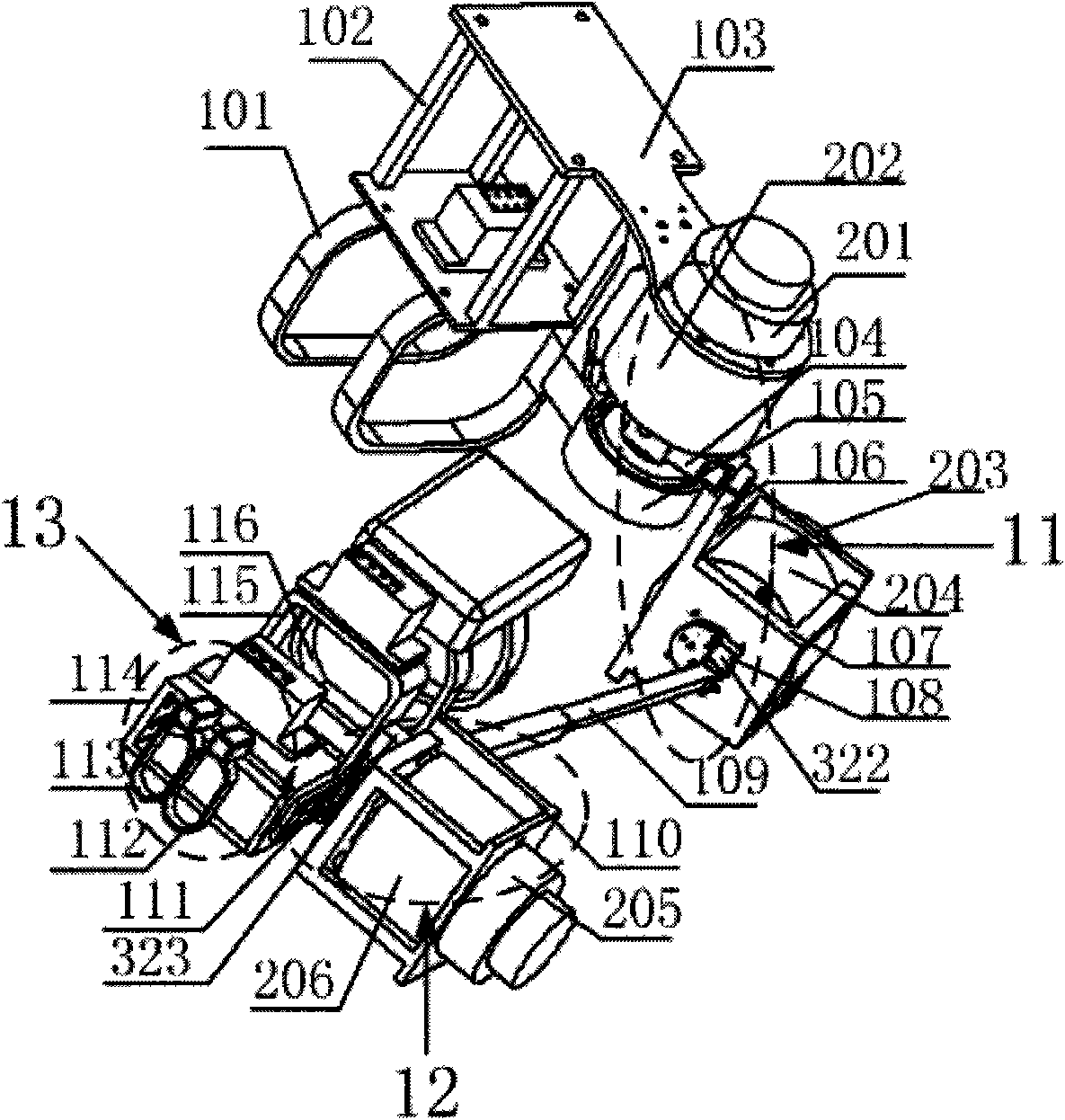
The invention discloses a wearable robot for detecting and suppressing tremor of human arms and a method for suppressing the tremor thereof. The robot comprises a wearable exoskeleton system, a tremor excitation system, a tremor movement detection system and a signal processing and control system. The invention provides a comprehensively utilized 'three closed loop' mixed tremor suppression strategy based on the biological force loading technology and the functional neuromuscular stimulation technology. When the tremor patients carry out daily activities such as writing, raising arms and the like, the tremor movement detection system senses the movement information of the arms and isolates tremor movement signals from normal movement signals through the 'two-stage' adaptive prediction filtering algorithm; the 'three closed loop' tremor movement suppression control strategy is adopted to respectively control a functional neuromuscular stimulation device and a DC motor system to generate tremor movement with the same amplitude and 'opposite' phase positions so as to achieve the aim of suppressing arm tremor of the patients and improve the quality of lives of the tremor patients.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system
PendingCN109568089ASolve the problem that it is difficult to maintain the balance of usersAvoid secondary damageWalking aidsExoskeleton robotEngineering
The invention discloses a slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system which is divided into a lower limb wearable exoskeleton robot and a slave robot. The slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system comprises two translational degrees of freedom, two vertical weight loss degrees of freedom of the slave robot and six rotational degrees of freedom of two legs,hip and knee of the wearable robot. The lower limb wearable exoskeleton robot is fixed on lower limbs and waist of a patient and provides walking assistance according to the gait of the patient and helps the patient to complete the walking action; and the slave robot is connected with the lower limb wearable exoskeleton robot to play a role in supporting the patient and reducing the weight, so that the corresponding following movement can be realized according to the walking of the patient. The slave-type lower limb gait training rehabilitation robot system is mainly used for solving variouslower limb movement dysfunctions caused by the central nerve injury, provides the safe, long-acting and large-range gait training for the patient and can improve the lower limb rehabilitation trainingefficiency of the patient.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wearable robot for assisting muscular strength of lower extremity
ActiveUS20110264016A1Reduce weightUse minimizedChiropractic devicesWalking aidsMuscle strengthMuscles of the hip
A wearable robot for assisting muscular strength of the lower extremity of a user: The wearable robot can be worn on user's legs and includes a central securing part, a hip joint part hingably coupled to either side of a lower end of the central securing part, a femur part fastened to the hip joint part and having rigidity, a knee part including an outer frame and a knee assistant, and a drive unit fastened to one of the hip joint part and the knee joint part to allow operation of the joint part. The outer frame includes an upper side outer frame fastened to a lower end of the femur part and a lower side outer frame fastened to the upper side outer frame by a rotatable knee joint part Both the upper side outer frame and the lower side outer frame are fastened to the knee assistant worn by the user.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
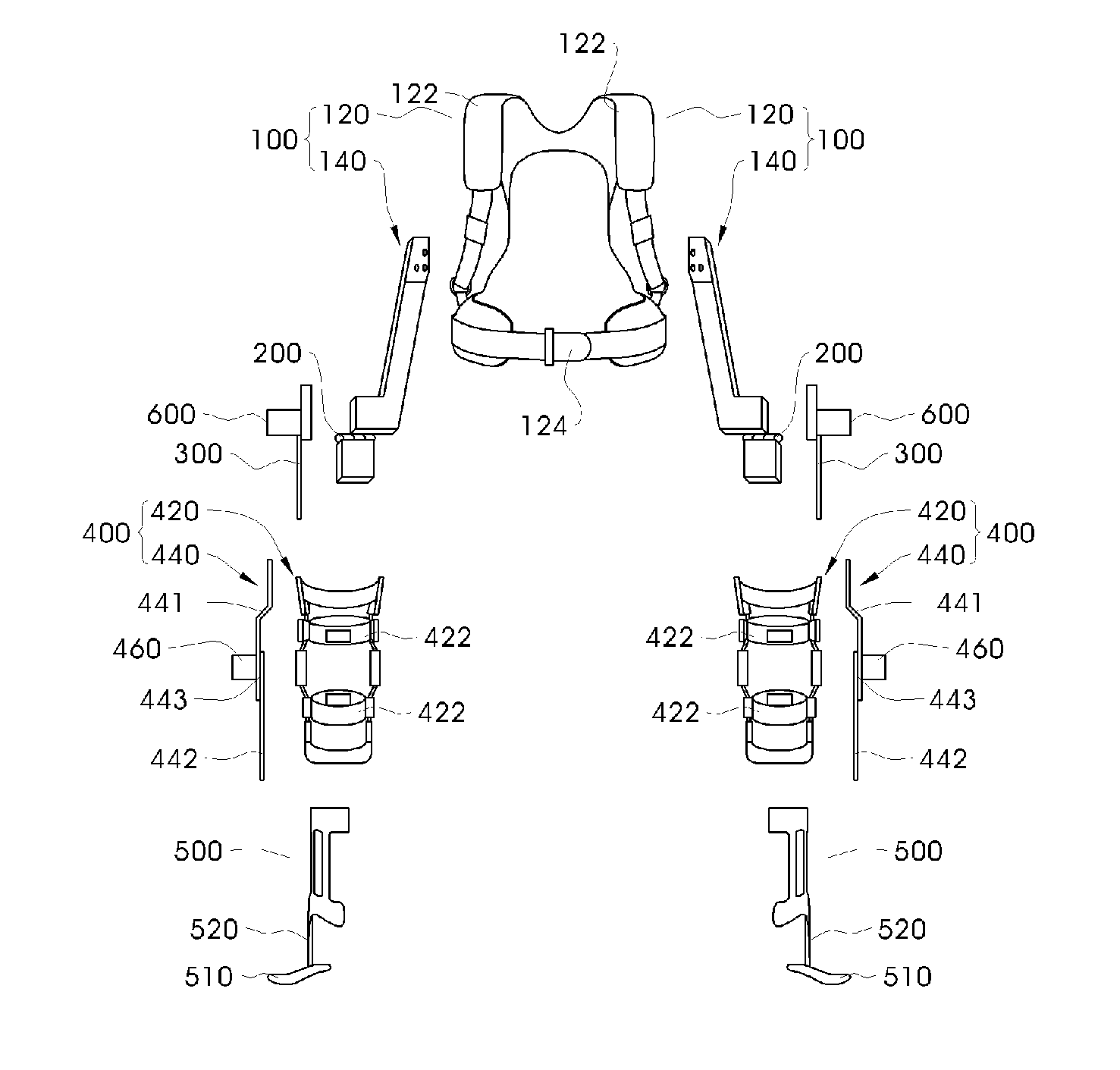
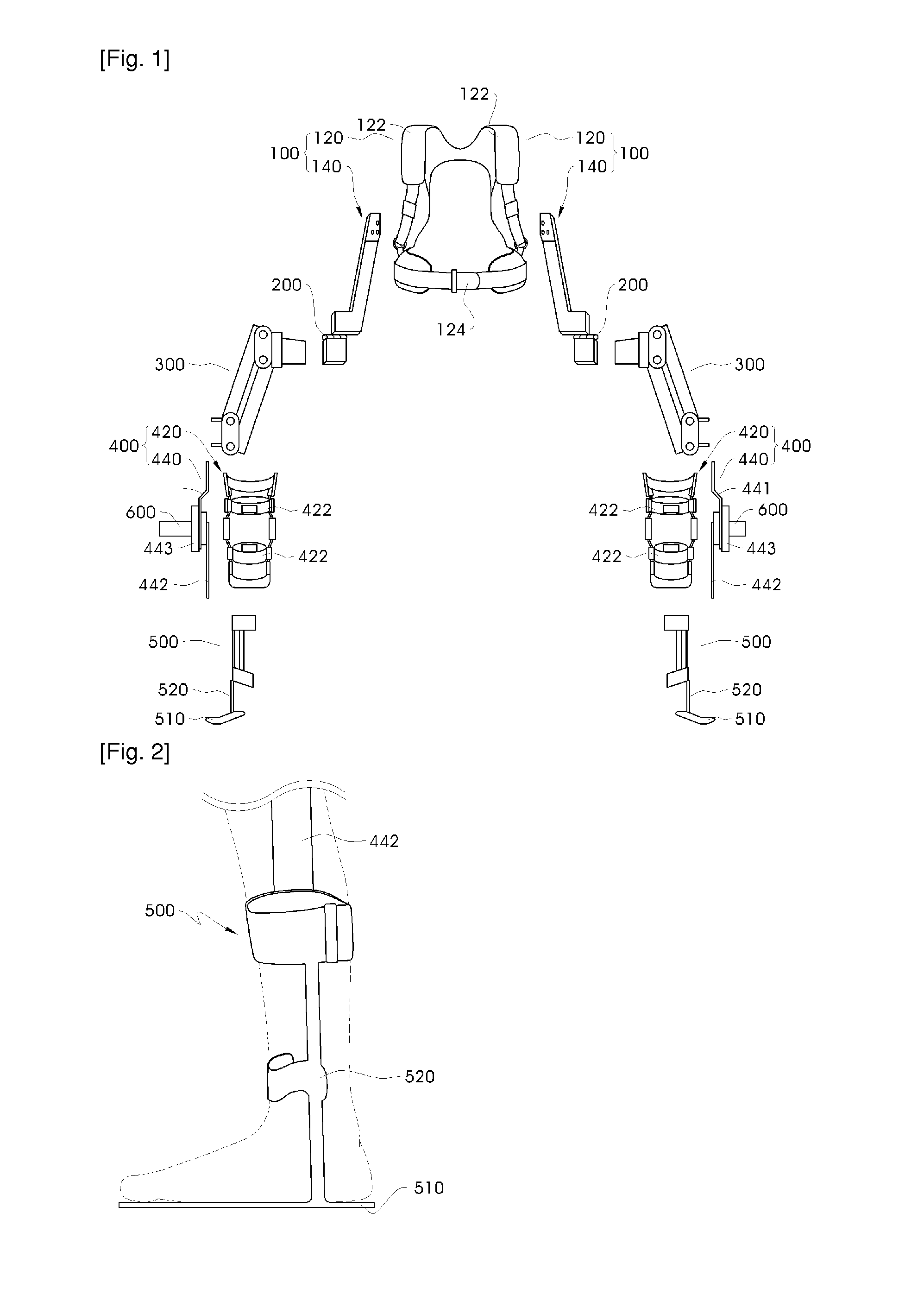
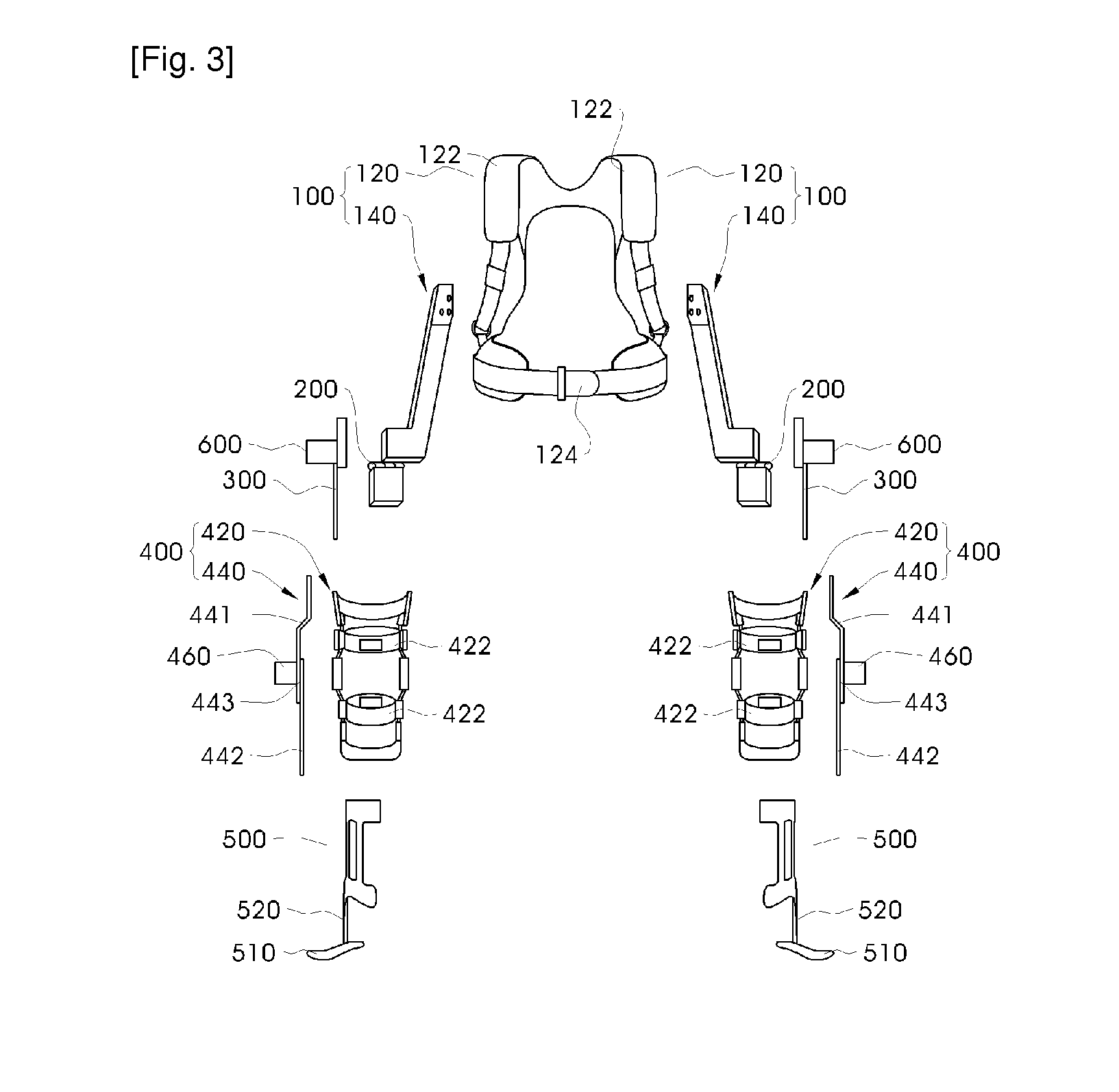
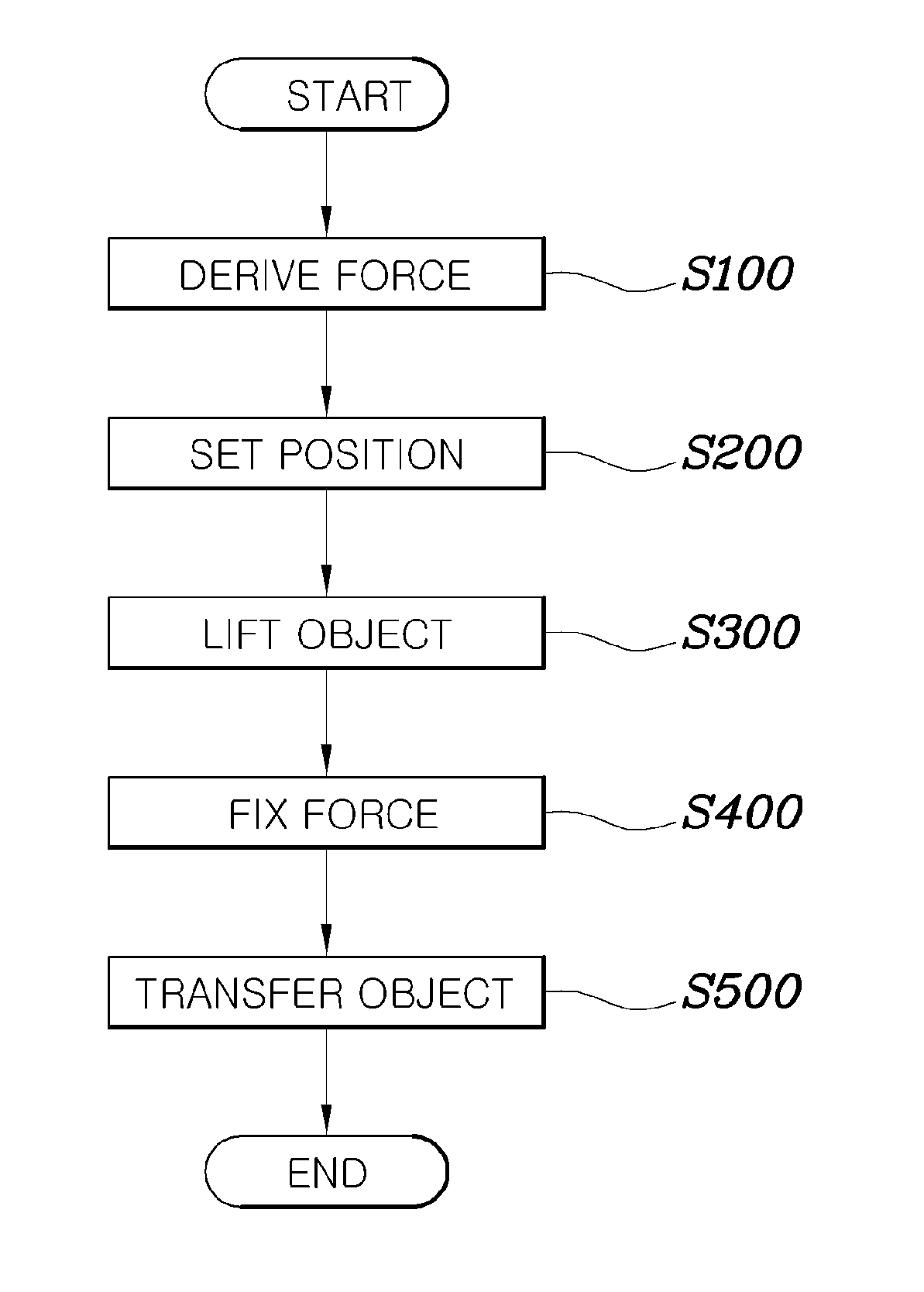
Method and system for controlling lifting operation of wearable robot
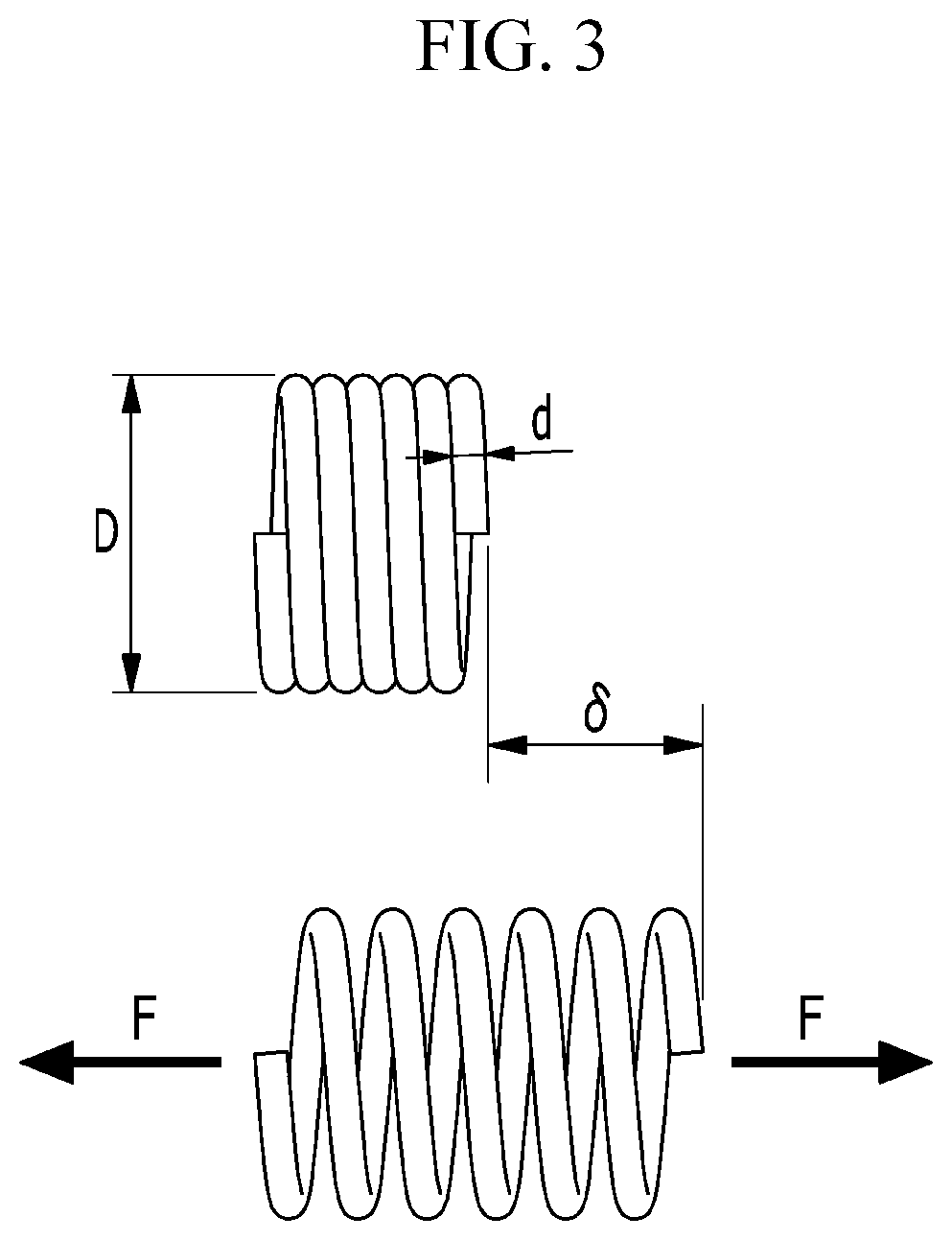
ActiveUS20130173058A1Constant forceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationWearable robot
Disclosed herein is a method and system for controlling the lifting operation of a wearable robot. A final force that must be applied by the robot to an object upon conducting a lifting operation is derived based on a difference between a weight force applied by the object to the robot and an apply force applied by a wearing user to the robot. A target position to which the robot lifts the object is set. A spring-damper virtual force model is applied to an end of the robot and to joints of the robot, the final force is converted into final torques required by the joints of the robot by being incorporated into the virtual force model, and then the joints of the robot are operated based on the final torques. The final force is fixed once the robot has lifted the object to the target position.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Wearable robot and teaching method of motion using the same
InactiveUS20130204435A1Programme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorHuman–computer interactionHuman language
A wearable robot may be worn by a user to record or teach a motion, including a motion such as sign language. The wearable robot includes a mode to record sign language data in a system by a sign language expert wearing the wearable robot and a mode to teach the sign language data recorded in the system to a sign language learner wearing the wearable robot. A user who wishes to learn sign language may easily learn sign language. In particular, a disabled person, who has poor eyesight and is unable to watch a video that teaches sign language, may learn sign language very intuitively using the wearable robot. Further, a user who has normal eyesight may also learn sign language more easily than from using a video which teaches sign language or from a sign language expert.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wearable robot for assisting muscular strength of lower extremity
ActiveUS8702632B2Reduce weightUse minimizedChiropractic devicesWalking aidsMuscles of the hipEngineering
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Wearable devices, wearable robotic devices, gloves, and systems, methods, and computer program products interacting with the same
One aspect of the invention provides a wearable device including: at least one compliant region adapted and configured to be placed over a joint of a subject and at least two flexible but less compliant regions coupled to opposite ends of the compliant region. Another aspect of the invention provides a wearable robotic device including a wearable device as described herein and at least one actuator adapted and configured to move the flexible but less compliant regions relative to each other.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
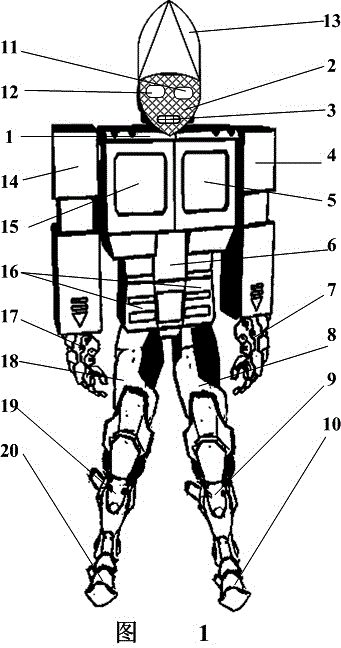
Special wearable robot armor for teenager national defense scientific literacy education and training
The invention relates to a special wearable robot armor for teenager national defense scientific literacy education and training. The special wearable robot armor comprises a robot armor main body chest armor, a face mask, a face mask breathing opening, a left upper arm armor, a left chest light-emitting armor, an abdominal armor, a left hand armor protecting sleeve, a left leg hip bone armor protecting sleeve, a left leg armor protecting sleeve, a left foot armor protecting sleeve, a face mask left eye light-emitting visual chip, a face mask right eye light-emitting visual chip, a helmet armor, a right upper arm armor, a right chest light-emitting armor, a left and right waist protecting light-emitting armor, a right hand armor protecting sleeve, a right leg hip bone armor protecting sleeve, a right leg armor protecting sleeve and a right foot armor protecting sleeve. The special wearable robot armor has the advantages that the face mask left eye and right eye armors, the left chest and right chest armors and the left and right protecting waist light-emitting armor of the wearable robot armor are provided with wireless charging LED (light emitting diode) chips; by utilizing function displaying, the interest of a teenager on the research of military wearable robot devices is enlightened, and the patriotic enthusiasm of the teenager devoting to the science and research carrier of China military warfare robots and medical rescue robots is encouraged.
Owner:FOSHAN SANSHUI DISTRICT XIWANG HUOJU EDUCATIONAL TECH CO LTD
Exoskeleton-Based Exercise and Training Device
A wearable robotic device configured to provide exercise for a human user. A primary use of the device is to address muscle and bone density loss for astronauts spending extended periods in microgravity. In one configuration the device applies a compressive force between a users feet and torso. This force acts very generally like gravity—forcing the user to exert a reactive force. The compressive force is precisely controlled using a processor running software so that a virtually endless variety of force applications are possible. For example, the wearable device can be configured to apply a gravity-simulating force throughout the device's range of motion. The robotic device may also be configurable for non-wearable uses. In these cases the robotic device may act as an exercise machine. The programmable nature of the force application allows the device to simulate weight-training devices and other useful exercise devices. The device's functions may be implemented in a microgravity environment or a normal terrestrial environment.
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION
Wearable robotic system for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs
ActiveUS8968220B2Simple structureLower the volumeDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesRobotic systemsEngineering
The present invention relates to a wearable robot system for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs that has an improved structure to reproduce in detail motion of a human body by selecting a wearing type structure such that robot links move correspondingly to the motion of the upper limbs while decreasing the volume of a rehabilitation and assistance device based on a robot for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs. According the present invention, it is possible to decrease the volume and increase the available space, in addition to creating smooth motion without interfering with the human body by creating a plurality of robot motion paths and selecting the best path from them, because an operation of four degrees of freedom can be achieved by an operation procedure using redundant.
Owner:HANSUNG UNIV IND UNIV COOPERATION FOUND +1
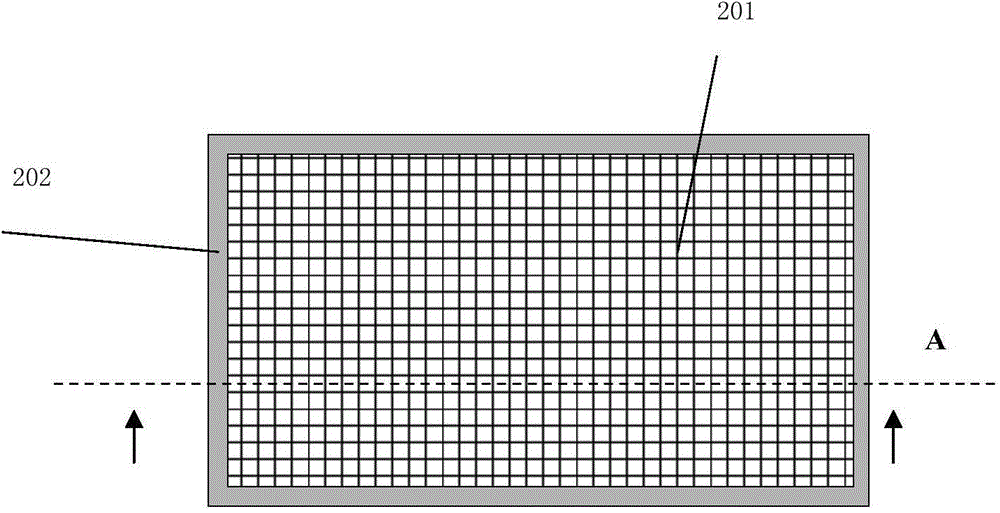
Wearable robot skin based on multiple layers of air bags
The invention discloses wearable robot skin based on multiple layers of air bags. The wearable robot skin comprises an epidermal layer, an installation layer used for clinging to a robot body, and a plurality of layers of air bags arranged between and wrapped with the epidermal layer and the installation layer; each of the installation layer and the epidermal layer is made of a flexible material; each of the air bags is equipped with a one-way valve used for inflating; a flexible support frame is arranged in each of the air bags and used for installing and fixing a pressure sensor and a temperature sensor; a connecting wire is placed in each of the flexible support frames and used for connecting the pressure sensor and the temperature sensor in each of the air bags with data acquisition equipment outside the robot skin; the I / O channels of the data acquisition equipment are in one-to-one correspondence to the air bags. The wearable robot skin based on the multiple layers of air bags is simple in structure, economic and reliable, endows a robot with tactile sensation, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and system for controlling wearable robot
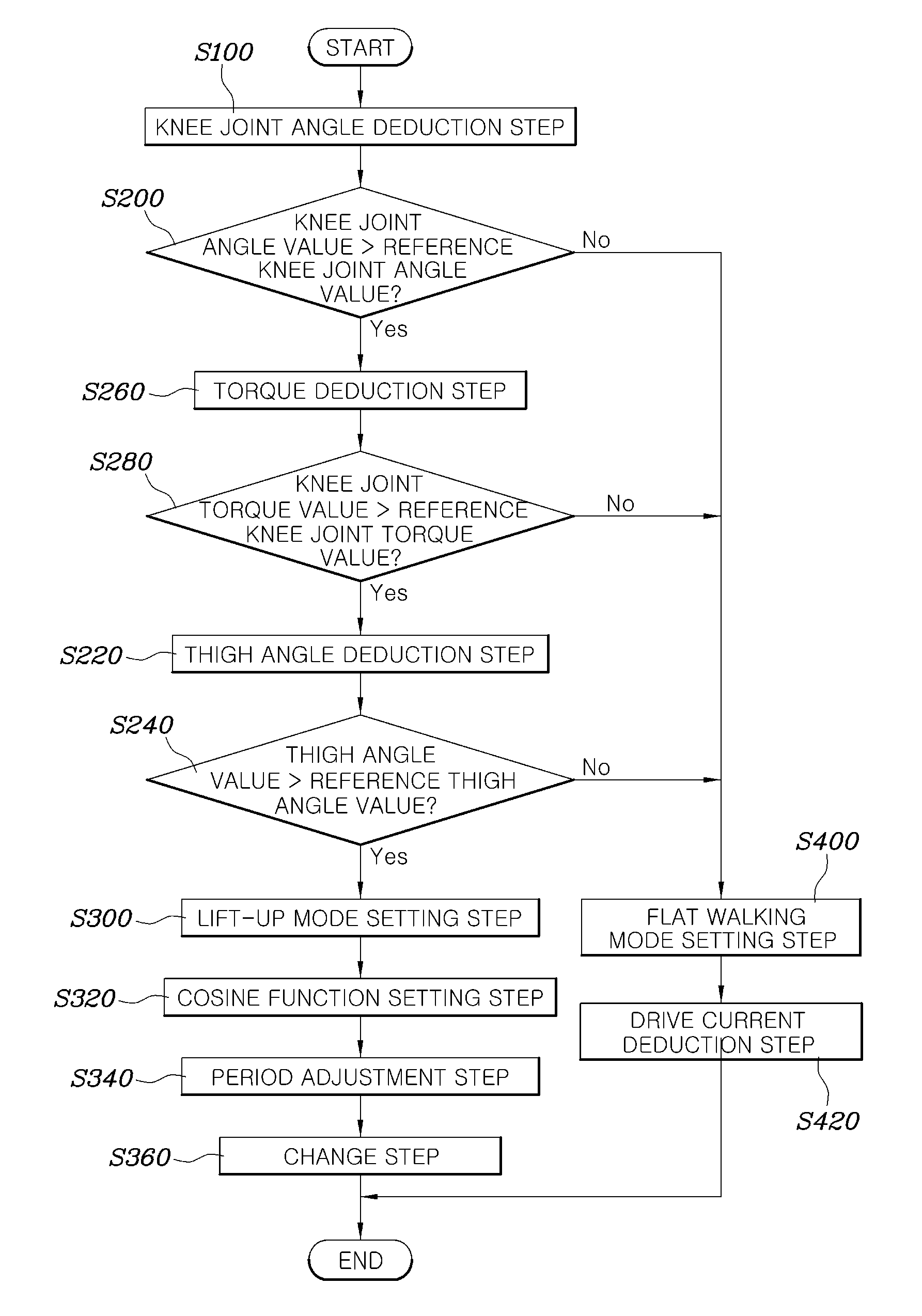
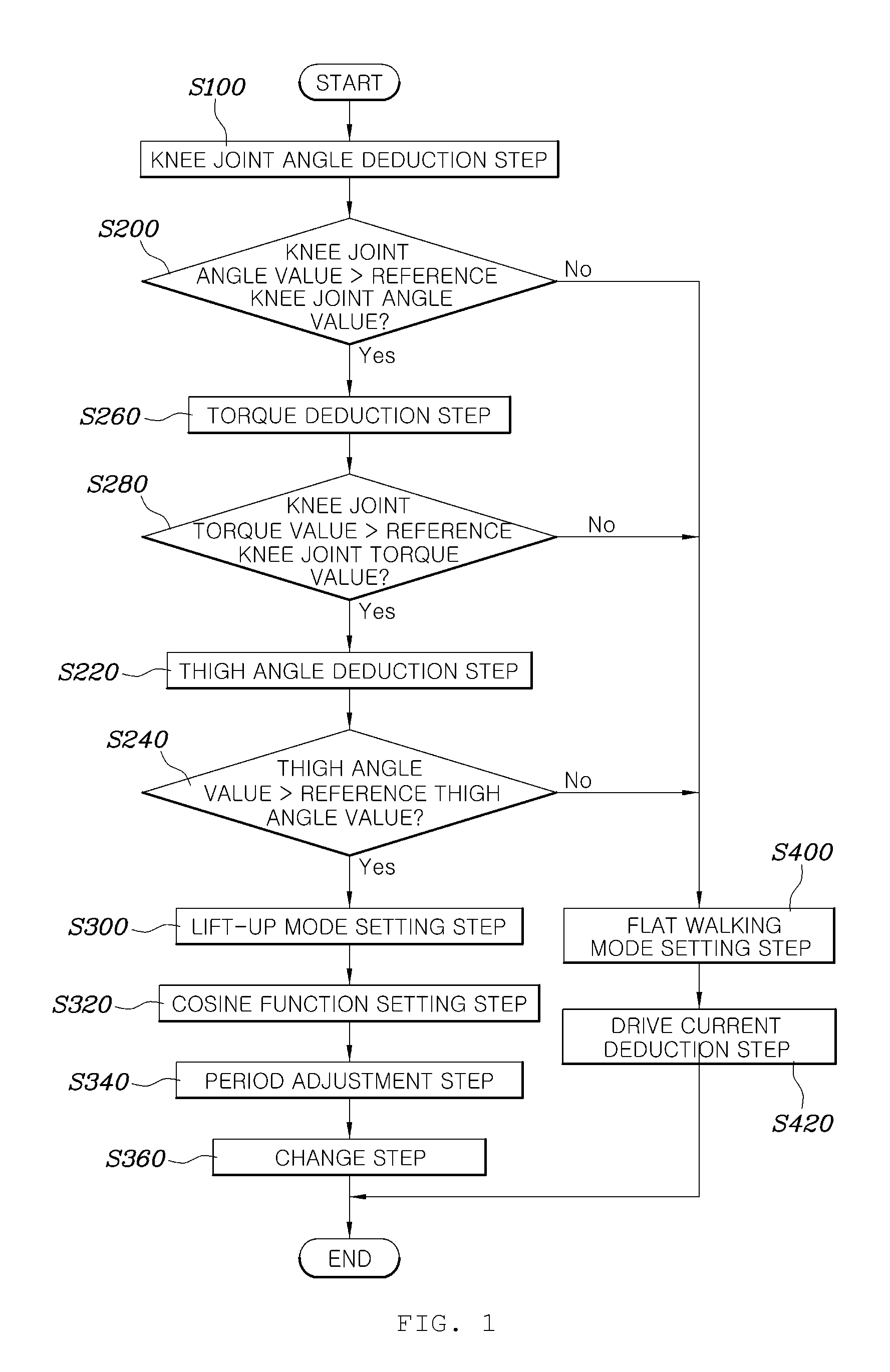
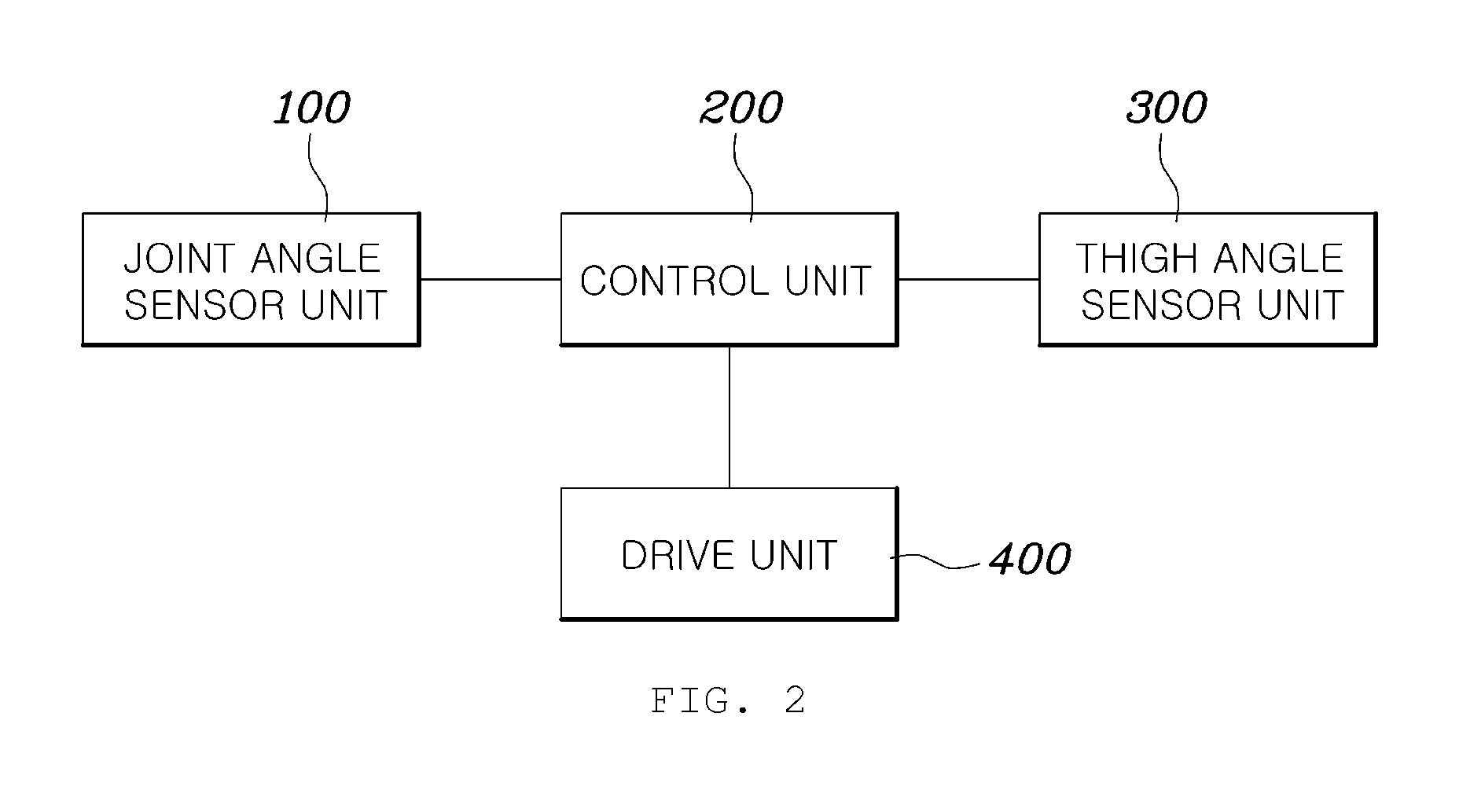
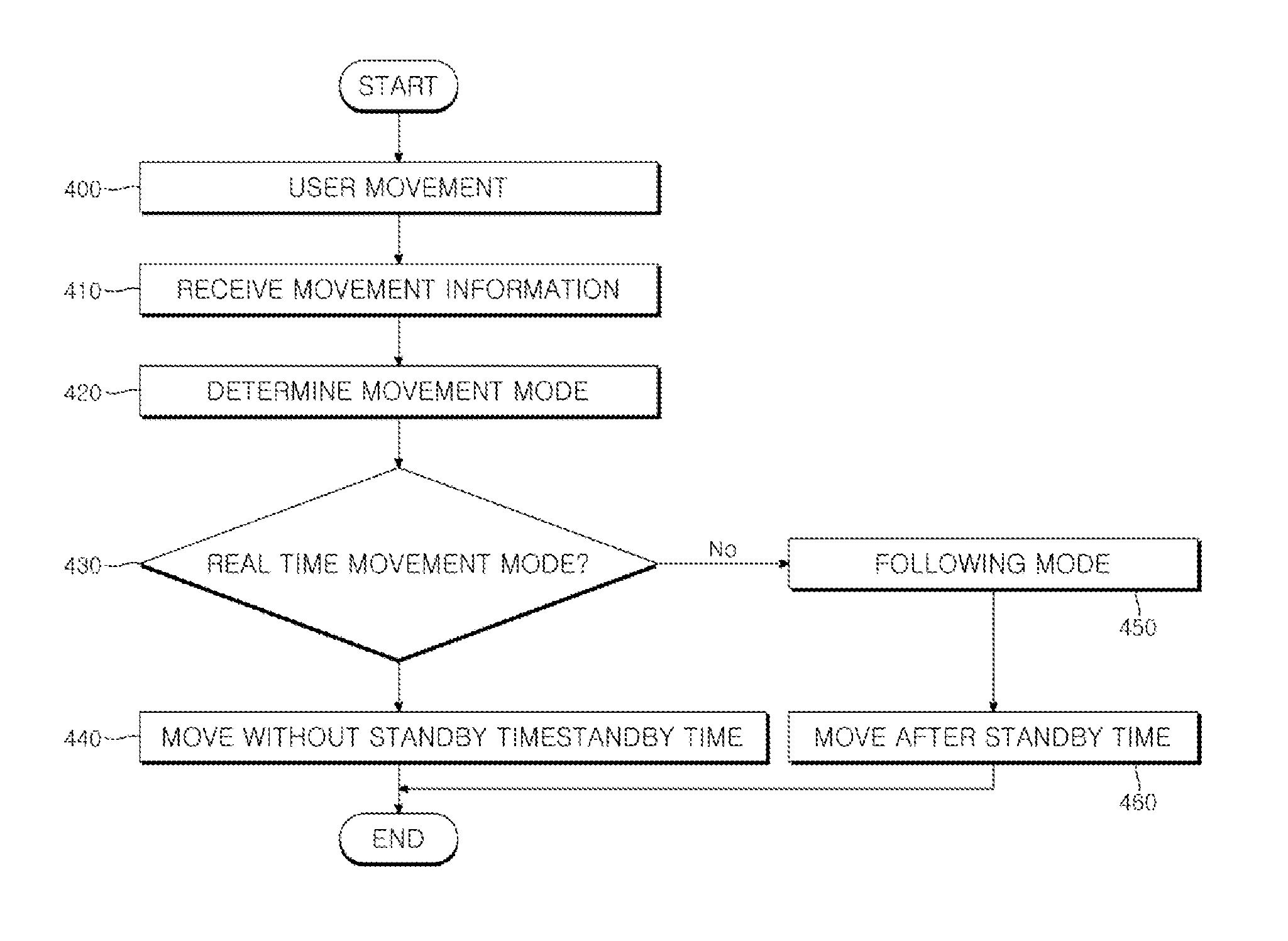
A method for controlling a wearable robot includes deducing a knee joint angle value of a robot using a joint angle sensor in a control unit, comparing the deduced knee joint angle value with a reference knee joint angle value previously stored in the control unit, deducing a thigh angle value using a thigh angle sensor in the control unit when the deduced knee joint angle value exceeds the reference knee joint angle value, comparing the deduced thigh angle value with a reference thigh angle value previously stored in the control unit, and setting an operation mode of the robot to a lift-up mode in the control unit when the thigh angle value exceeds the reference thigh angle value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Wearable robot and control method thereof
ActiveUS20140188275A1Easy to operateImprove mobilityPillowsProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
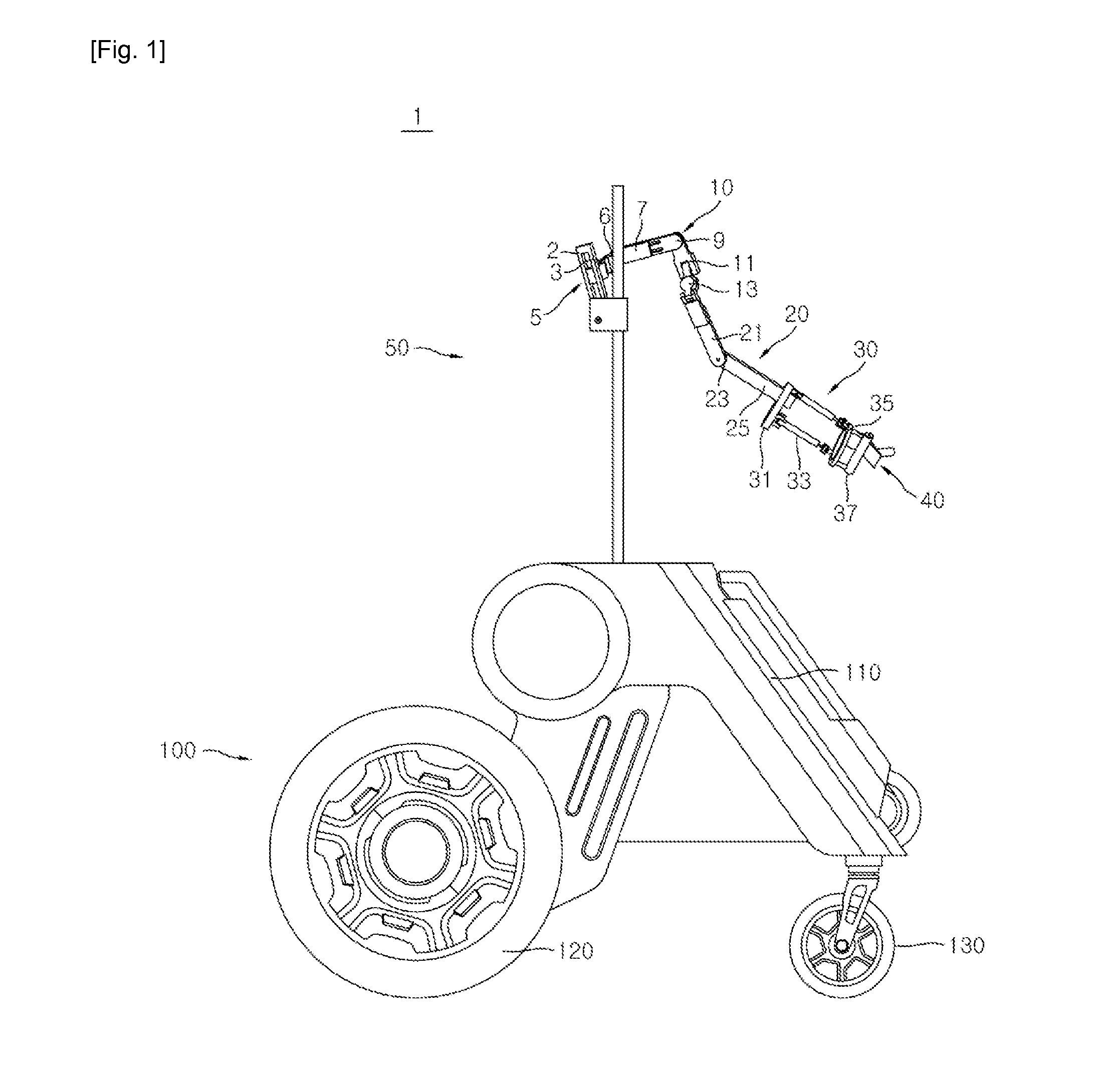
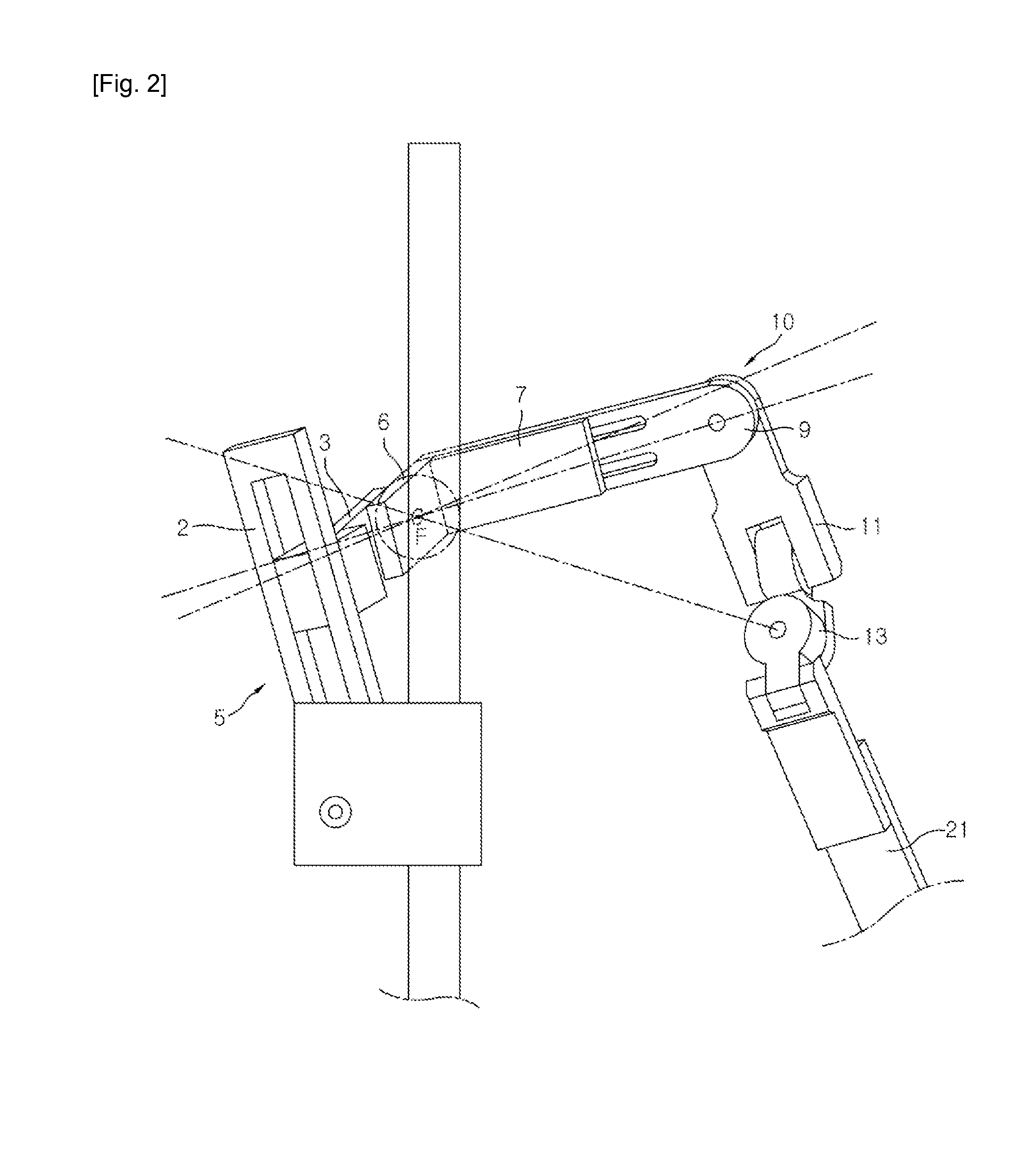
Disclosed herein is a wearable robot with improved operability and mobility through improvement of the upper limb structure thereof. The wearable robot includes an upper limb muscular power assist device to perform an articulation motion with a predetermined degree of freedom, the upper limb muscular power assist device being wearable by a user, and a mobile platform connected to the upper limb muscular power assist device to move according to information regarding movement speed and movement direction of the user in a rolling fashion. Consequently, mobility of the wearable robot and operation efficiency of the user are improved.
Owner:FOUND OF SOONGSIL UNIV IND COOP
Upper limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot
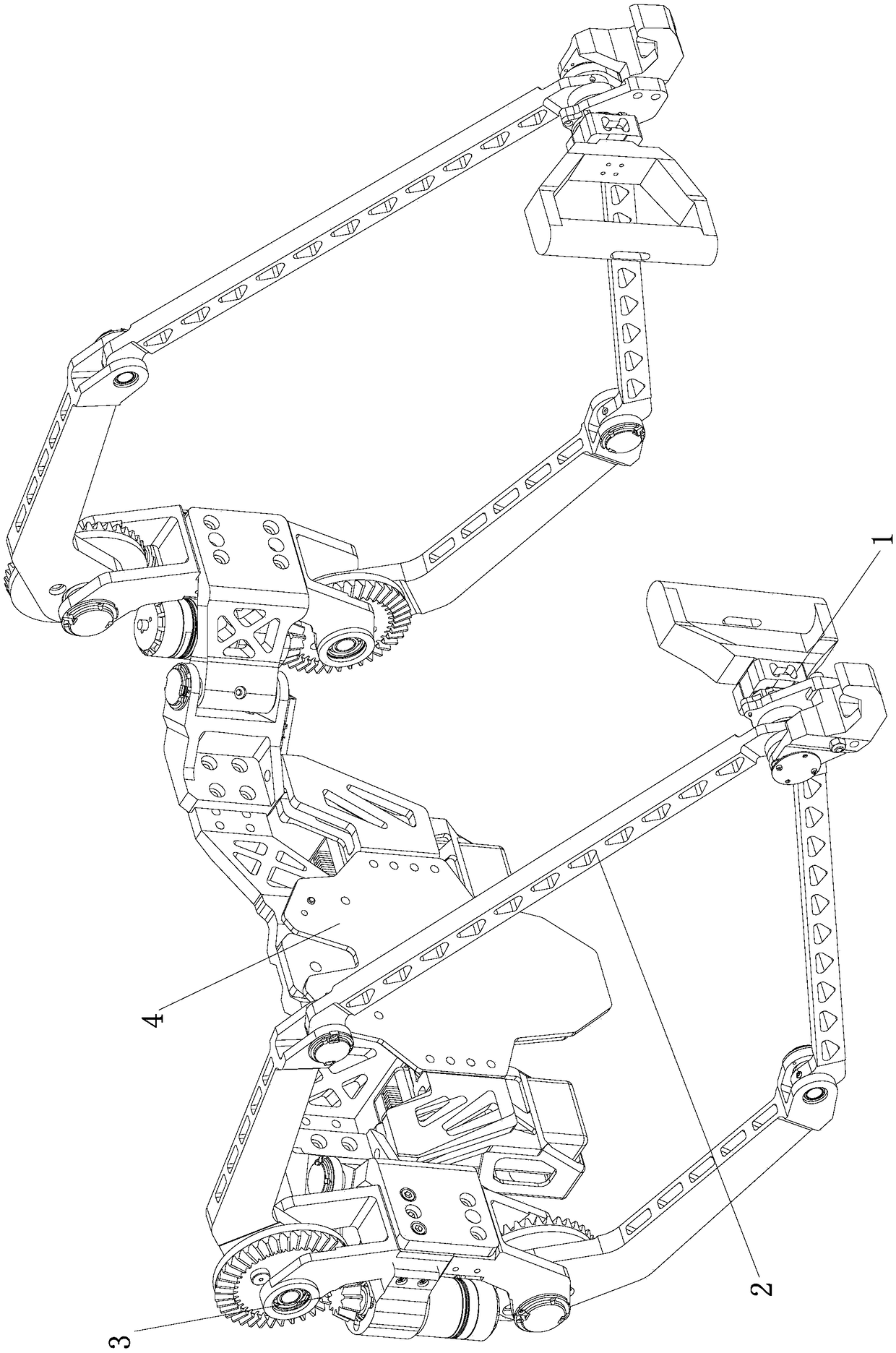
ActiveCN108839000AIncrease stiffnessImprove driving abilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsConnection typeExoskeleton robot
The invention discloses an upper limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot, and relates to a wearable robot. The upper limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot comprises hands, arms, a back, driving mechanisms and a control module; and the two sides of the back are connected with the driving mechanisms correspondingly, the control module is installed on the back, the hands are connected with the arms, each arm is of a parallel type joint structure, the arms are driven by the driving mechanisms, and the driving mechanisms are controlled by the control module. Compared with a traditional serial-connection type upper limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot, the upper limb power-assisted exoskeleton robot has the advantages that the rigidity is large, the load capacity is also improved, and the controleffect is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Esoskeleton equipped with electro-or-magneto-rheological fluid type semi-active joints
InactiveUS20200009719A1Relieve pressureReduced constructive complexityProgramme-controlled manipulatorLiquid resistance brakesUpper limbMagneto rheological
The present invention relates to the field of wearable robotic devices that physically interact with humans, and in particular refers to a wearable exoskeleton, in particular for the upper limb. The invention refers to an electro- or magneto-rheological fluid type semi-active joint purposely conceived to be used to make the exoskeleton. It comprises a first body and a second body, slidably coupled to each other, with a “flow mode” rotating configuration, which allows to have a fluid flow moved by a pressure gradient induced by the circular movement of a piston in a chamber, with constructive simplicity and decrease of wear.
Owner:SIGNO MOTUS SRL
Lower limb exoskeleton system with actively adjustable leg rod length and control method of lower limb exoskeleton system with actively adjustable leg rod length
ActiveCN111805511ARhythm change gait adaptabilityGait prediction is accurateProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsThighLower extremity joint
The invention relates to a lower limb exoskeleton system with actively adjustable leg rod length and a control method of the lower limb exoskeleton system with the actively adjustable leg rod length,and belongs to the technical field of wearable robots. The control method comprises the steps that according to parameter detection data representing that the lower limb exoskeleton system is in an action state, a thigh rod unit and a shank rod unit are controlled to adjust the leg rod lengths of the thigh rod unit and the shank rod unit until the position deviation between the joint rotation center position of the lower limb exoskeleton system and the lower limb joint rotation center position of a wearer is compensated. According to the control method of the lower limb exoskeleton system withthe actively adjustable leg rod length, the use safety is improved while the wearing comfort can be effectively improved, and the control method of the lower limb exoskeleton system with the activelyadjustable leg rod length can be widely applied to rehabilitation training of patients with lower limb weakness or hemiplegia or walking assistance of old people.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Control system of wearable robot for helping disabled
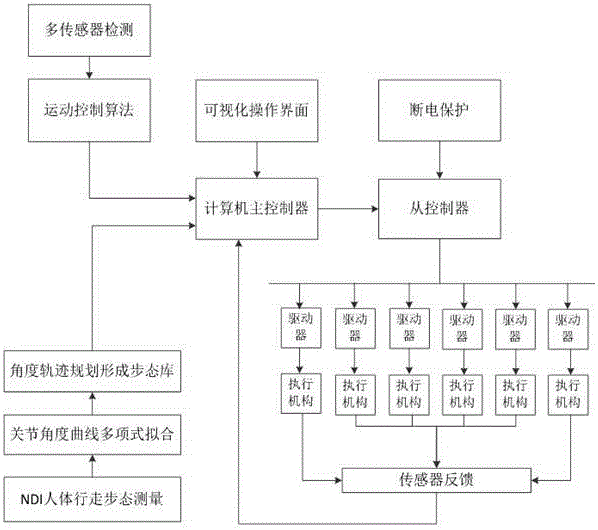
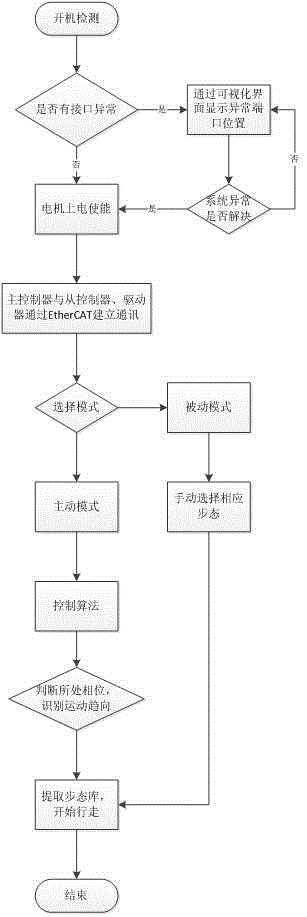
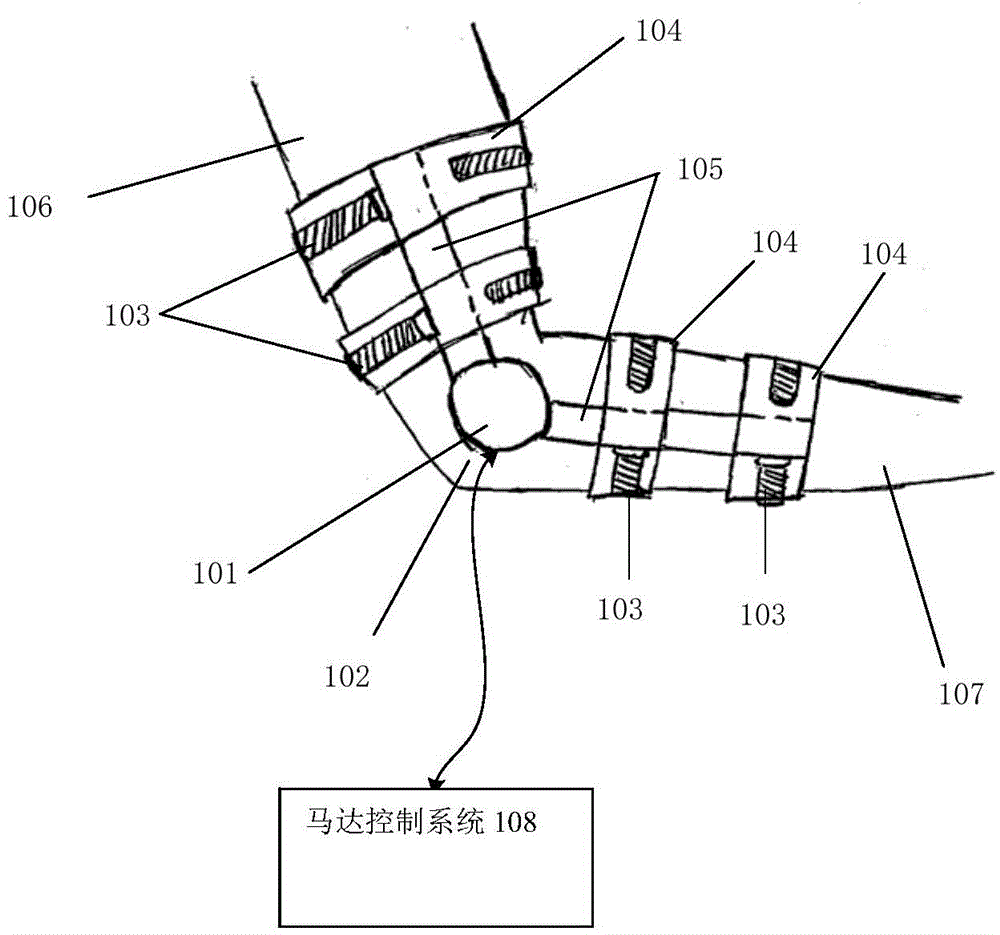
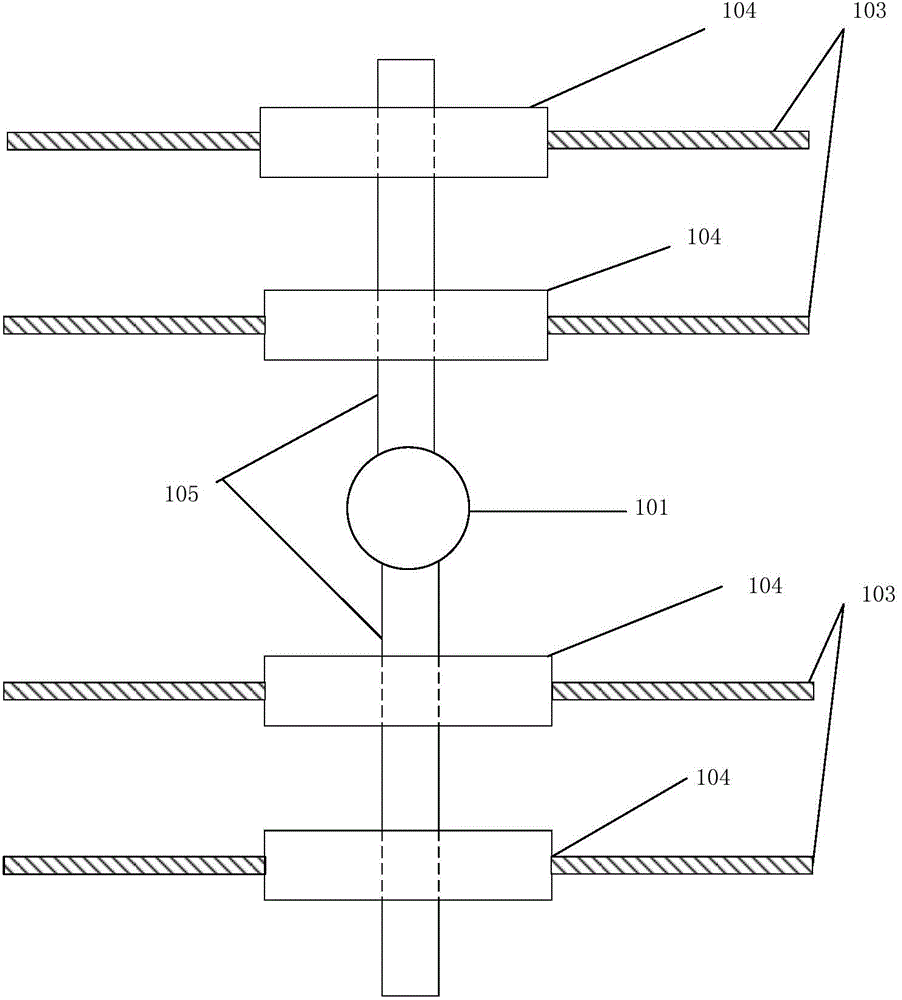
InactiveCN105014672ALarge capacityRealize walking motionManipulatorClosed loop feedbackComputer module
The invention discloses a control system of a wearable robot for helping the disabled. The control system comprises a master controller, a slave controller, a driver, an executing mechanism, a power source, a visual operation interface, an alarm module and a power-off protection module. A fieldbus communication manner, a control algorithm and personification gait design are adopted. The master controller is used for operating the algorithm, calling gaits, planning tracks, reading, feeding back and controlling the work of all the modules. The slave controller is a controller of a subnet. An EtherCAT bus is adopted in the fieldbus communication manner, and communication between the slave controller and the driver is formed. The control algorithm controls and adjusts movement of the executing mechanism in real time based on PID closed loop feedback. An NID optical locating and tracking system is adopted in the personification gait design for acquiring the movement curves of all the joints in the walking process of a human body. The robot can walk. The robot is formed in a fitting manner completely based on the actual walking gaits of the human body, the walking human simulation degree of the robot is high, and the robot acts smoothly and is high in degree of attachment to the human body.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MFG TECH
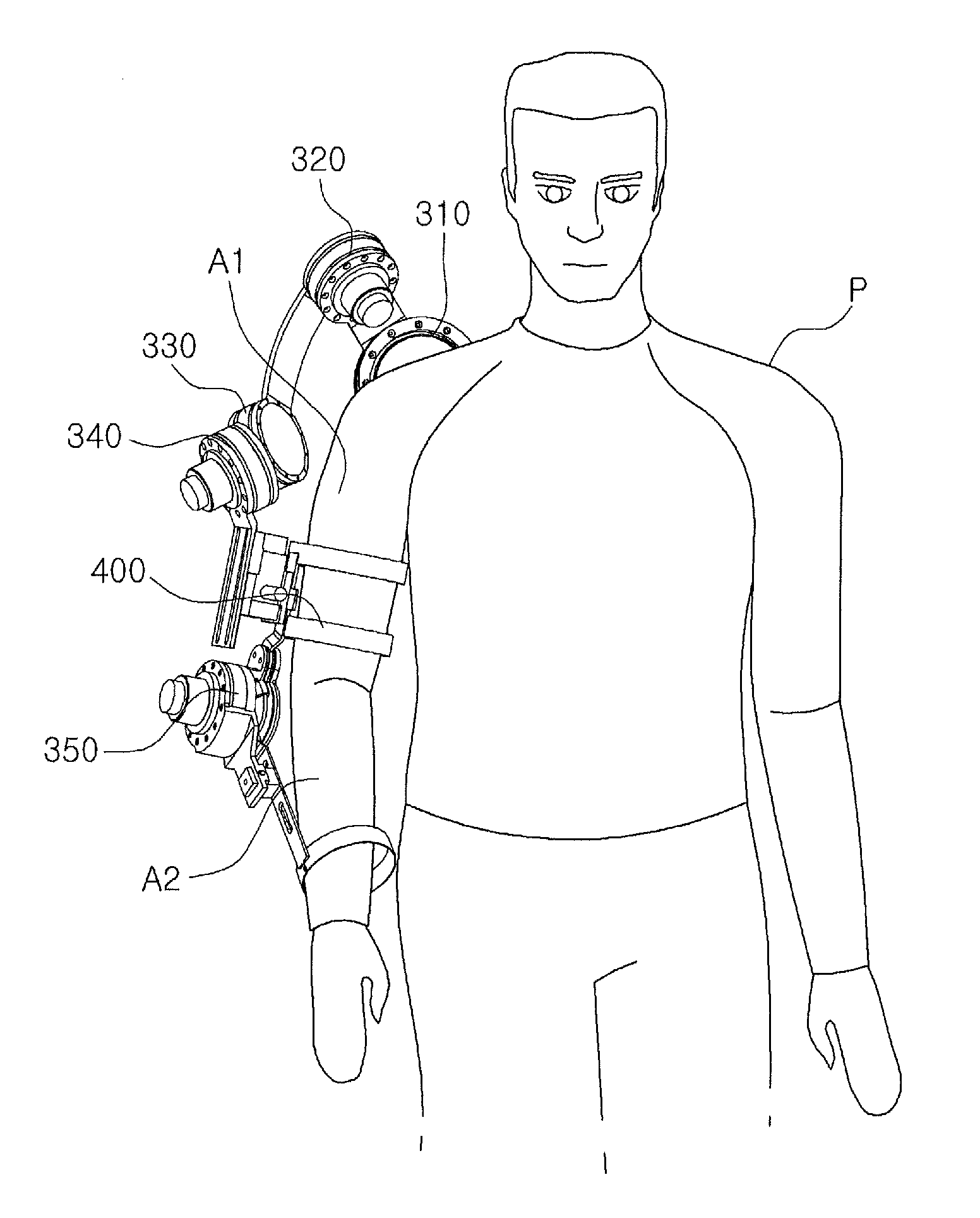
Mechanism for alleviating the effects of joint misalignment between users and wearable robots
ActiveUS20190160653A1Programme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesEngineeringParallel manipulator
Implementations described and claimed herein involve a shoulder exoskeleton having a spherical parallel manipulator with a plurality of parallel linear actuators connected to a base coupled to a user's arm. A passive slip mechanism is operatively coupled to the spherical parallel manipulator as well as being coupled to the user's arm. The slip mechanism increases system mobility and prevents joint misalignment caused by the translational motion of the user's glenohumeral joint from introducing mechanical interference.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Robot control method and system and robot
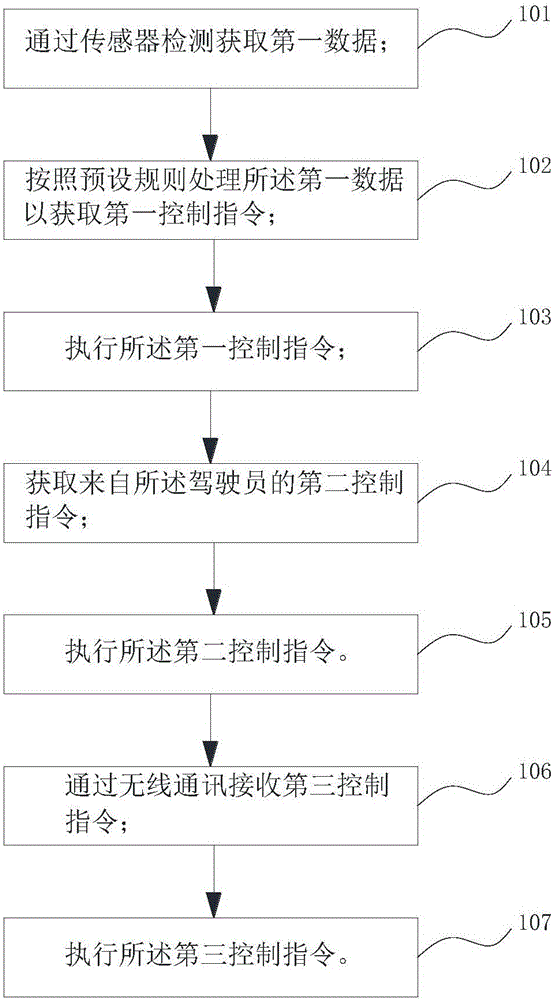
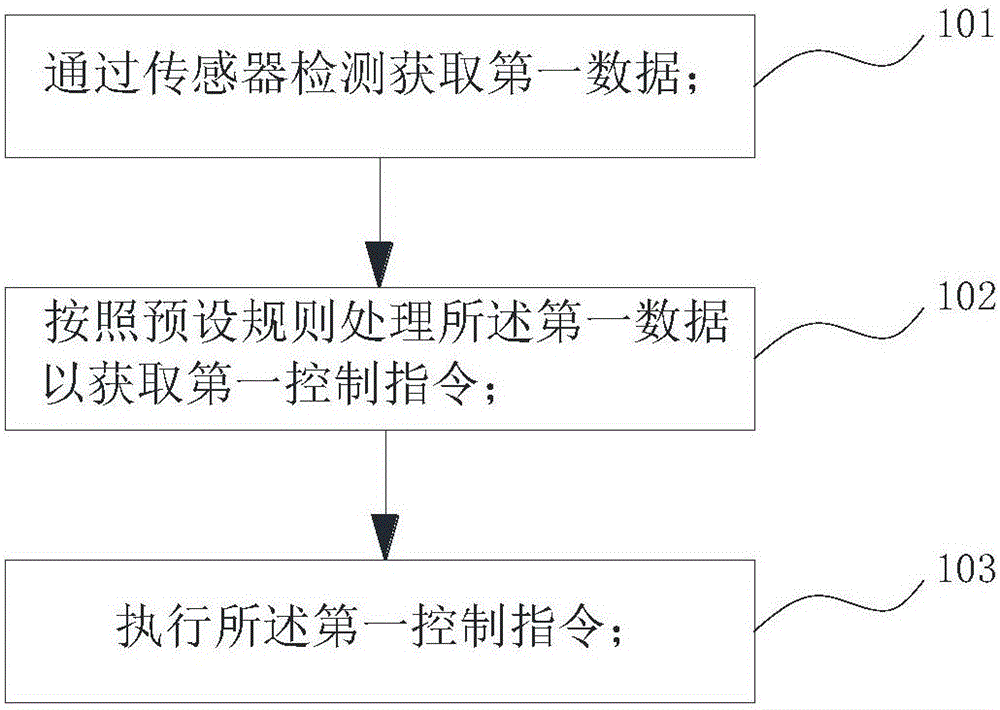
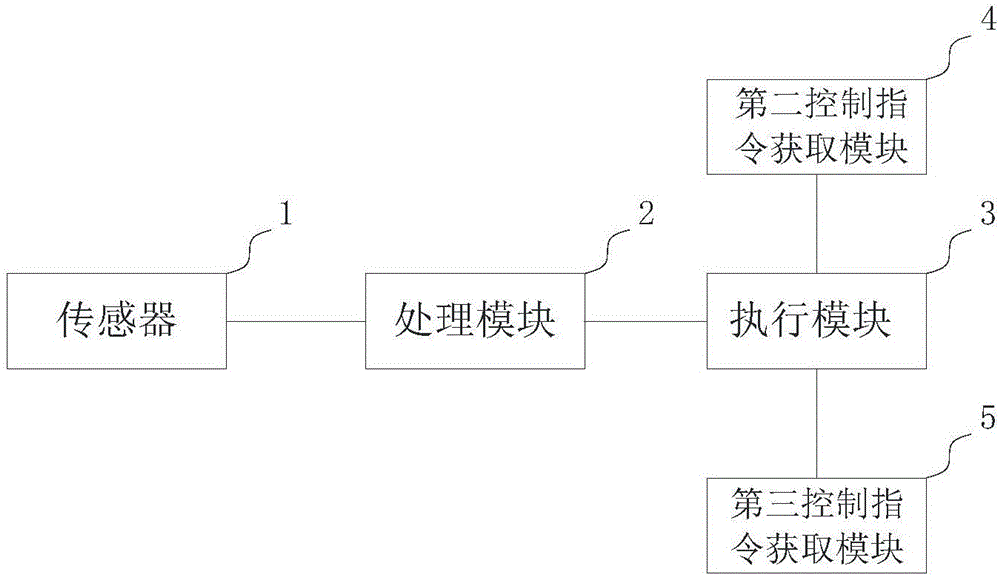
ActiveCN105965475ARealize automatic operationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDriver/operatorControl system
The invention discloses a robot control method and system and a robot. The robot is internally provided with a cavity used for accommodating a driver, and the head of the driver is located at the chest of the robot. The control method comprises the steps that first data are obtained by detection of a sensor; the first data are treated according to a preset rule to obtain a first control instruction; and the first control instruction is executed. According to the steps, the first data comprise motion parameters of the driver and / or environmental information of the environment. According to the robot control method provided by the invention, the control instruction is obtained on the basis of the motion parameters of the driver and / or the environmental information of the environment detected through the sensor, corresponding executive operation is conducted, and thus, the wearable robot achieves automatic operation of partial functions.
Owner:ZHIZAOWEILAI BEIJING ROBOT SYST TECH CO LTD
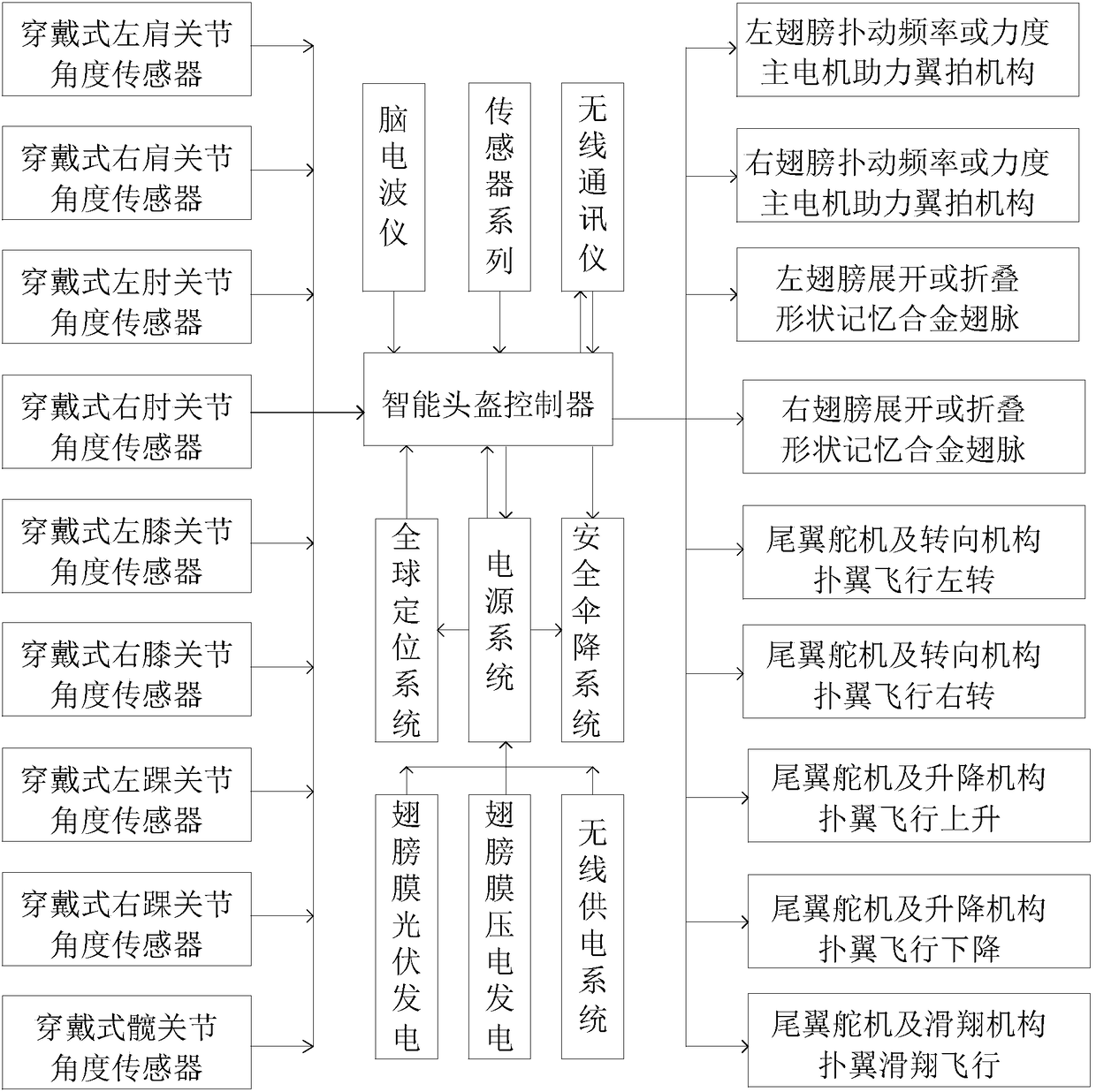
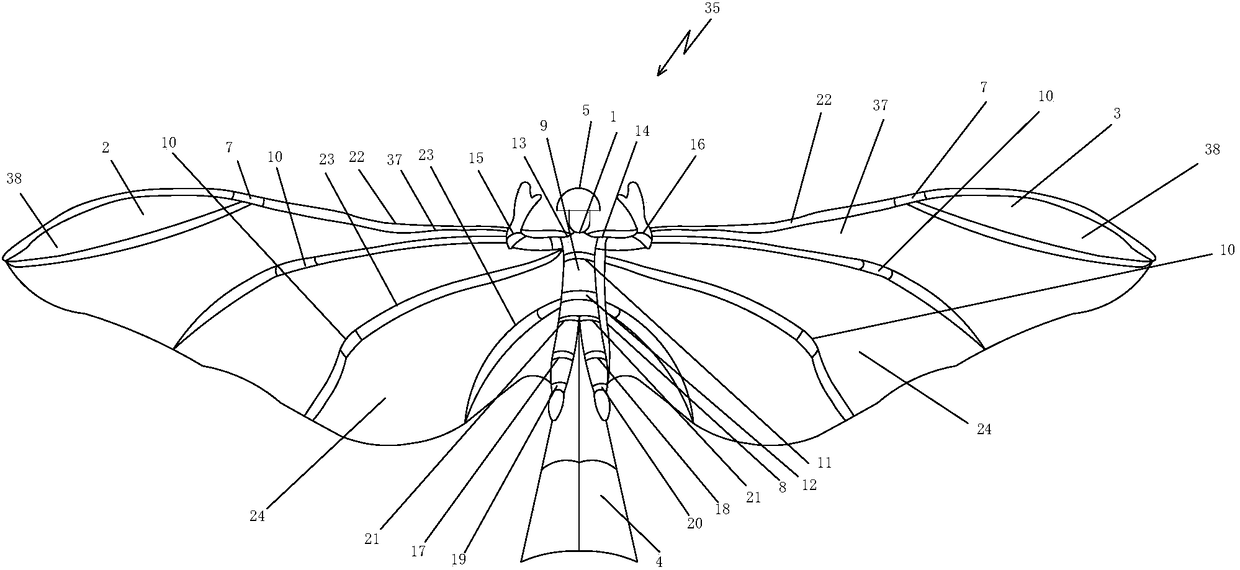
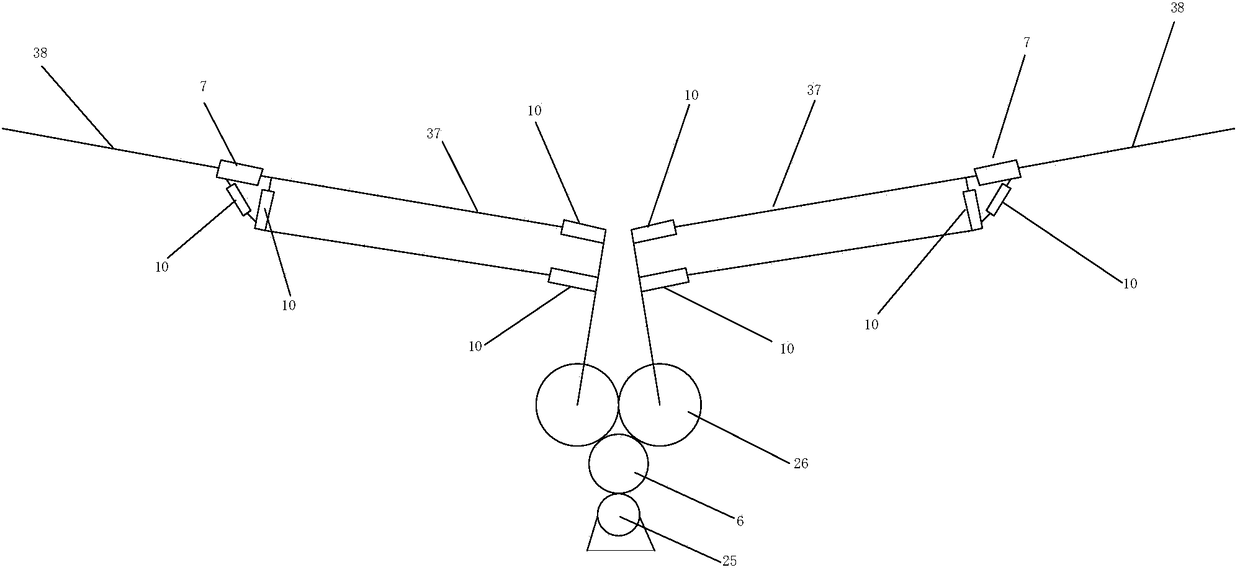
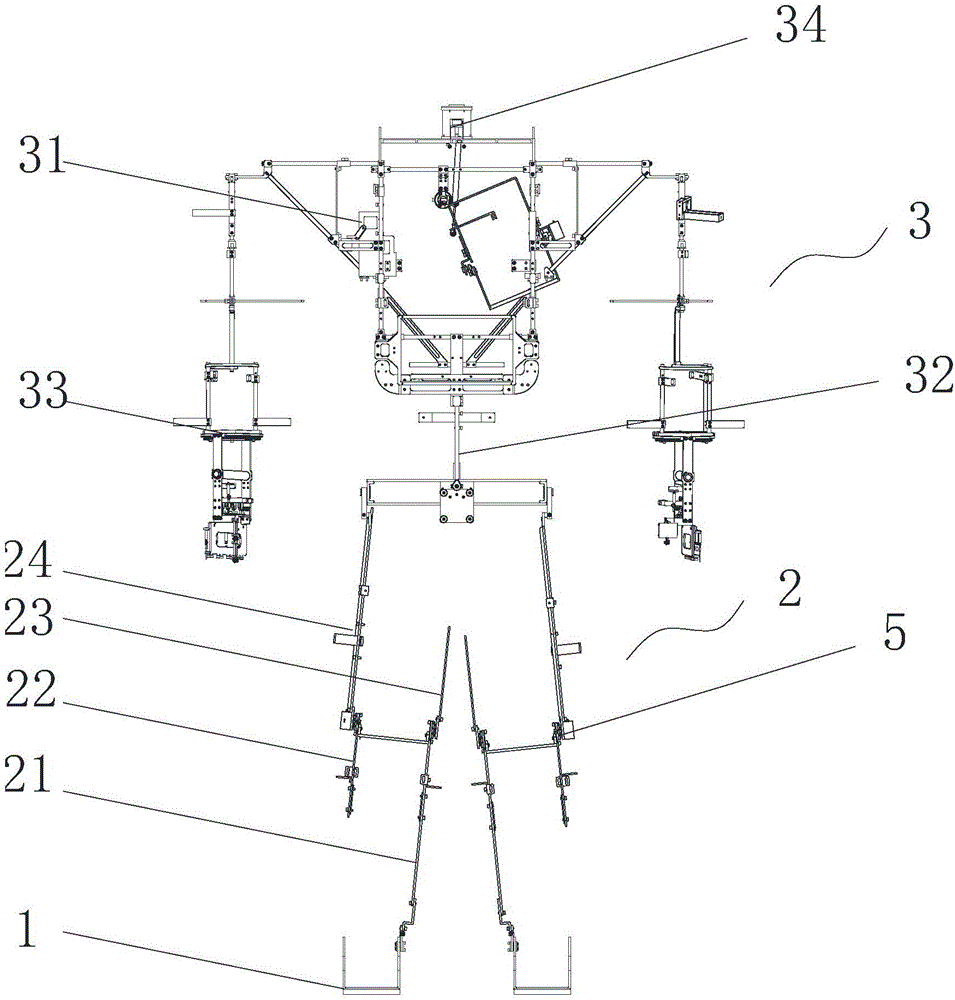
Wearable robot powering human flapping wing aircraft
The invention discloses a wearable robot powdering human flapping wing aircraft which comprises a wearable powering human flapping wing flight robot, a left wing, a right wing, a tail steering gear and transmission mechanism, a power system and a powering take-off gear. The wearable powering human flapping wing flight robot comprises a wearer's helmet, a wearer's joint angle sensor, a main motor powering wing flap mechanism, a shape memory alloy wing vein powering folding deformation mechanism, a wearer's flapping wing flight prone plate, an intelligent helmet controller, sensor series, a global positioning system, an electroencephalography, a radio communicator, a foldable and expandable vibration foot wheel and a safety parachute device. Through combination of the main motor powering wing flap mechanism, the shape memory alloy wing vein powering folding deformation mechanism, the tail steering gear and transmission mechanism and the intelligent helmet controller, the fun of human powering adaptive flapping wing flight is achieved, and safety, comfort, lightness and convenience in flapping wing flight experienced by human body are achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Skeleton device used for wearable robot and wearable robot
The invention discloses a skeleton device used for a wearable robot and the wearable robot. The skeleton device comprises foot skeletons, leg skeletons and an upper body skeleton; the foot skeletons are used for being erected on bearing bases; the leg skeletons are borne on the foot skeletons; the upper body skeleton is borne on the leg skeletons; joints of the foot skeletons, the leg skeletons and the upper body skeleton are connected through rotating connection mechanisms; the inner sides of the foot skeletons, the leg skeletons and the upper body skeleton are provided with a cavity used for containing a driver; and the head of the driver is located on the chest portion of the upper body skeleton. The skeleton device used for the wearable robot stands on the bearing bases through the foot skeletons, other parts of the skeleton device are sequentially borne on the foot skeletons, most of the weight of the skeleton device is borne by the skeleton device itself, and therefore at least most of the weight of the wearable robot is borne by the wearable robot itself, and the weight of the wearable robot does not need to be borne by the driver.
Owner:ZHIZAOWEILAI BEIJING ROBOT SYST TECH CO LTD
Wearable robot for assisting upper limb movement by using artificial muscle
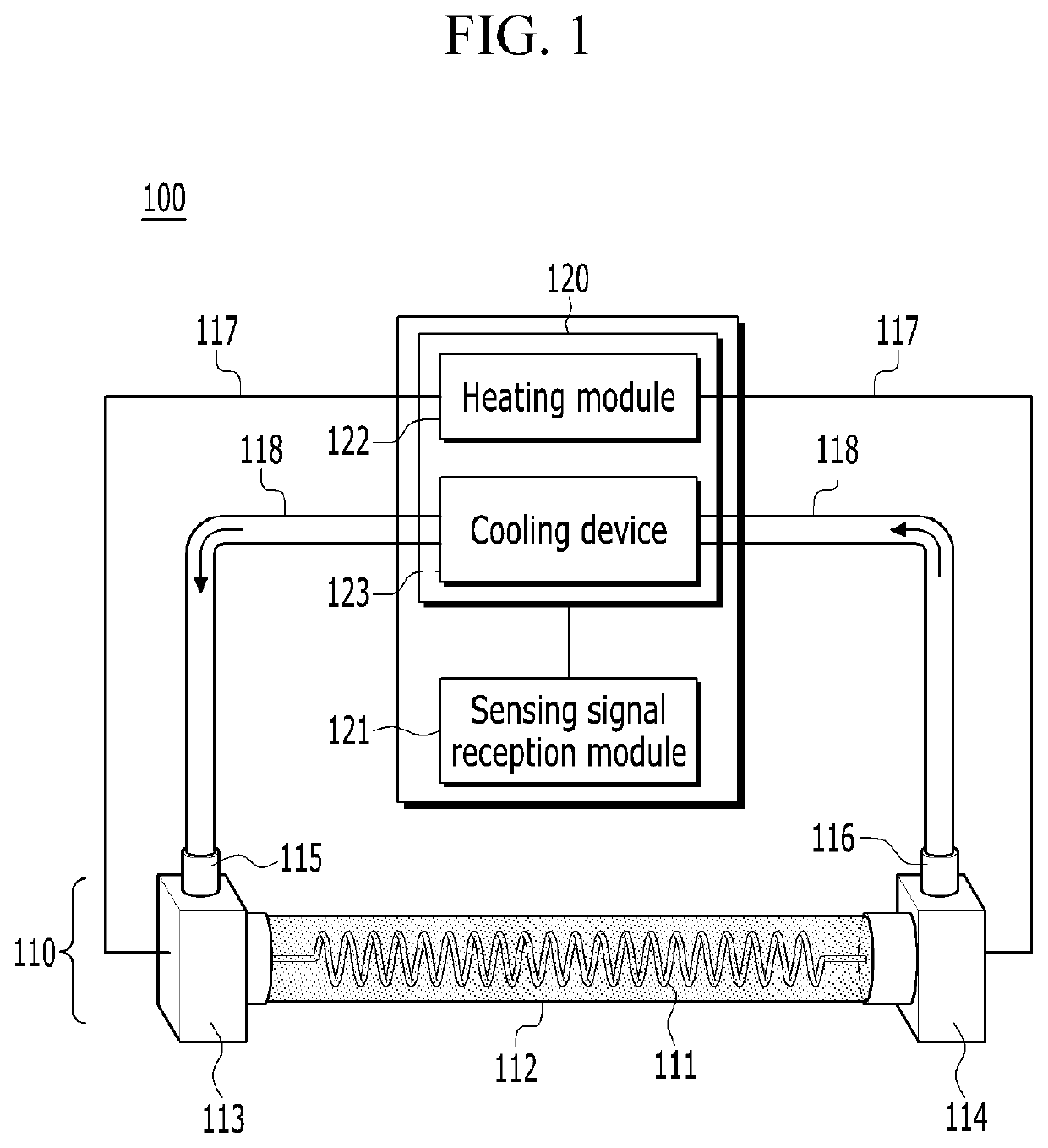
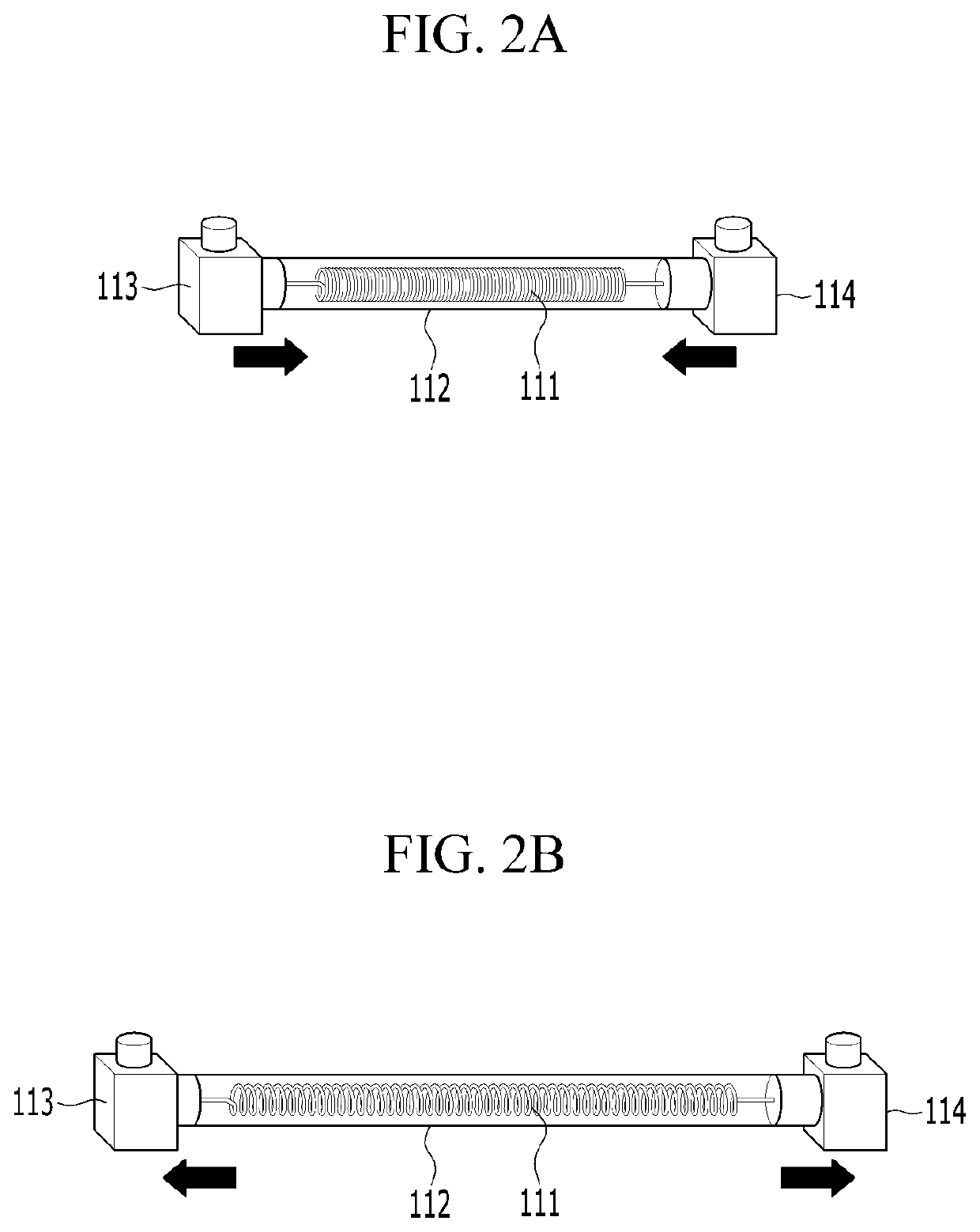
PendingUS20210196555A1Efficient implementationEffectively imitatingDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesControl cellEngineering
Disclosed is a wearable robot for assisting a wrist, including: a plurality of flexible actuators; and a control unit configured to control any one of the plurality of flexible actuators to be contracted or relaxed according to a wrist movement of a wearer. Each of the plurality of flexible actuators includes: a driving part which is contractively deformed by a current or transfer heat applied from the control unit or is relaxed when the heat is lost, and a refrigerant circulating part which is implemented to surround the driving part and circulates a refrigerant so that the contractively deformed driving part is cooled under control of the control unit.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Wearable Robotic Device With Bracing System
A wearable robotic device for the rehabilitation training of a limb with moisture and pressure management functions. Such wearable robotic device comprises a motor rotation system and a bracing system, wherein the motor rotation system comprises a motor and a motor control system; and the bracing system comprises a framework of structural members that is attachable to and detachable from the limb, one or more textile bracing cushions and one or more fastening belts attached to each of the textile bracing cushions such that the fastening belts and the textile bracing cushions in combination are capable of attaching the wearable robotic device onto the limb.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Walking intension detection device and system of walk and method thereof
A walking intention detection device and a system and a method thereof are provided. The walking intention detection device includes a lower wearing part into which a walker's foot is inserted and an upper wearing part disposed over the lower wearing part to cover a top of a foot and a heel of a walker. A tension sensor is disposed between the lower wearing part and the upper wearing part and is configured to measure a force delivered to the lower wearing part and the upper wearing part in response to a walking motion. In addition, a walking intention is detected when the wearable robot is used to provide the stability of the walking operation, thereby improving the marketability and convenience and the walking performance of the wearable robot is increased by the simplified mechanism, thereby creating the higher efficiency at the low costs.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com