Lower limb exoskeleton system with actively adjustable leg rod length and control method of lower limb exoskeleton system with actively adjustable leg rod length
A control method and exoskeleton technology, which can be applied to program-controlled manipulators, appliances that help people move, and manufacturing tools, etc., which can solve the problems of lack of prediction function, cost reduction, and weak limb sensory ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
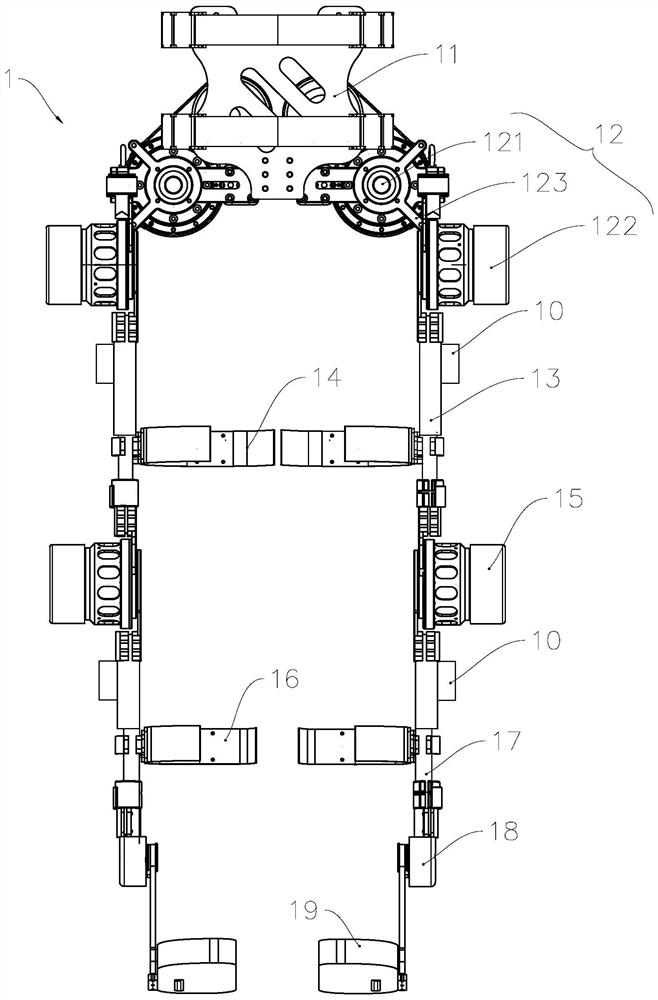
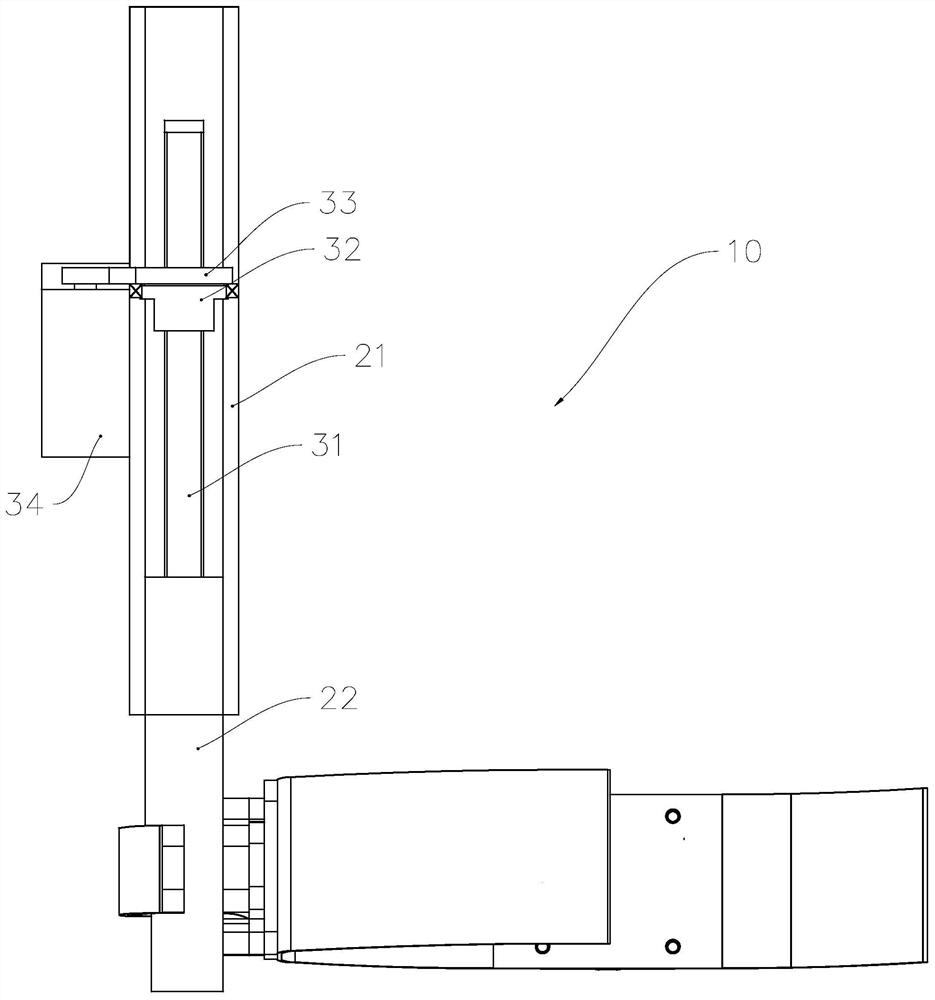
[0046] see Figure 1 to Figure 4 , The lower extremity exoskeleton system of the present invention includes a control unit, a detection unit and an exoskeleton 1 . The control unit includes a processor and a memory, and the detection unit outputs a detection signal to the control unit. In this embodiment, the detection unit includes an angle sensor for detecting the angle of each joint and a tension sensor placed on the strap for detecting the tension of the strap ; The control unit outputs control signals to the driving mechanisms of the exoskeleton to drive the exoskeleton to walk according to a predetermined trajectory.
[0047] The exoskeleton 1 includes a waist wearing unit 11 , a hip joint unit 12 , a thigh bar 13 , a thigh strap 14 , a knee joint unit 15 , a calf strap 16 , a calf bar 17 , an ankle unit 18 and a flexible sole unit 19 . The waist wearing unit 11 is used for fixing the exoskeleton system and the waist of the human body; the thigh bar 13 is used to drive ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] As a description of Embodiment 2 of the present invention, only the differences from Embodiment 1 above will be described below.
[0061] In this embodiment, the control method includes an acquisition step S21, a calculation step S22, and an adjustment step S23, and the specific process is as follows:
[0062] Obtaining step S21, acquiring joint angle data of the skeletal system of the lower limbs.
[0063] In the calculation step S22, according to a preset calculation model, the target leg lengths of the thigh bar unit and the calf bar unit are calculated based on the joint angle data.
[0064] In this step, based on the relationship between the existing leg length and joint angle, the calculation model is a cubic spline fitting calculation model represented by the following formula:
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] Among them, H hip (α) and H knee (β) are the target leg lengths of the exoskeleton thigh rod and calf rod, respectively, α and β are the hip joint and k...
Embodiment 3
[0070] As an explanation of Embodiment 3 of the present invention, only the differences from Embodiment 1 above will be described below.
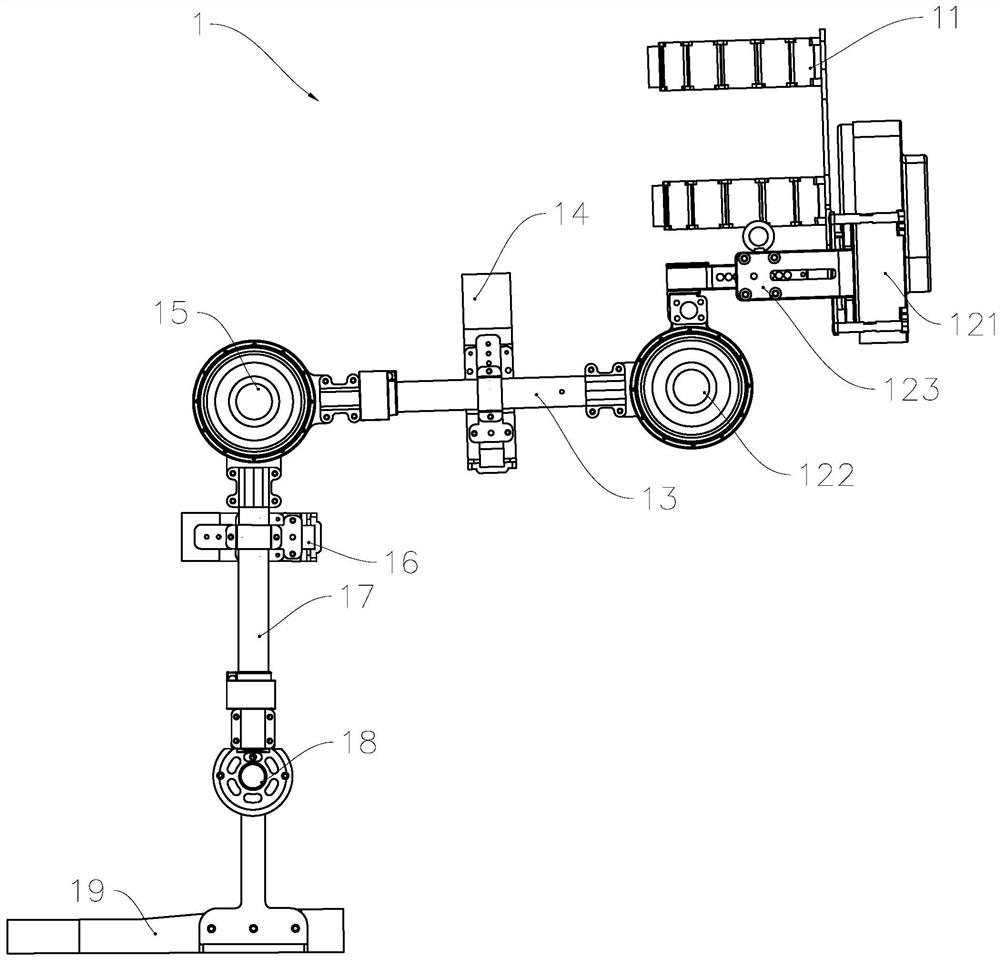
[0071] In the control methods of the two above-mentioned embodiments, the thigh rod unit and the calf rod unit are controlled to adjust the parameters based on the parameter detection data that characterizes the lower extremity exoskeleton system being in motion, such as strap tension detection data and joint angle data. The length of the leg bar is to compensate for the position deviation between the joint rotation center position of the lower limb exoskeleton system and the wearer's lower limb joint rotation center position; and in this embodiment, during the use of the lower limb exoskeleton system, not only its legs The length of the rod is properly adjusted, and during the movement, based on the deformation of the walking rhythm, the swing state of the leg rod of the hip joint unit controller is controlled.
[0072] like Figure 5 As ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com