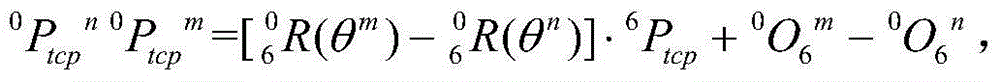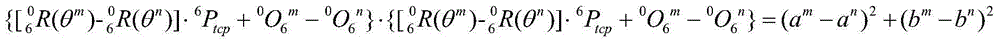Patents
Literature
444 results about "Joint rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Rotating Joint, also known as a rotary union or rotary joint, is an intersection between a stationary part and a rotating part. This joint allows the rotation of the united parts and provides a seal between the stationary part and the rotating part to allow the flow of fluid between...
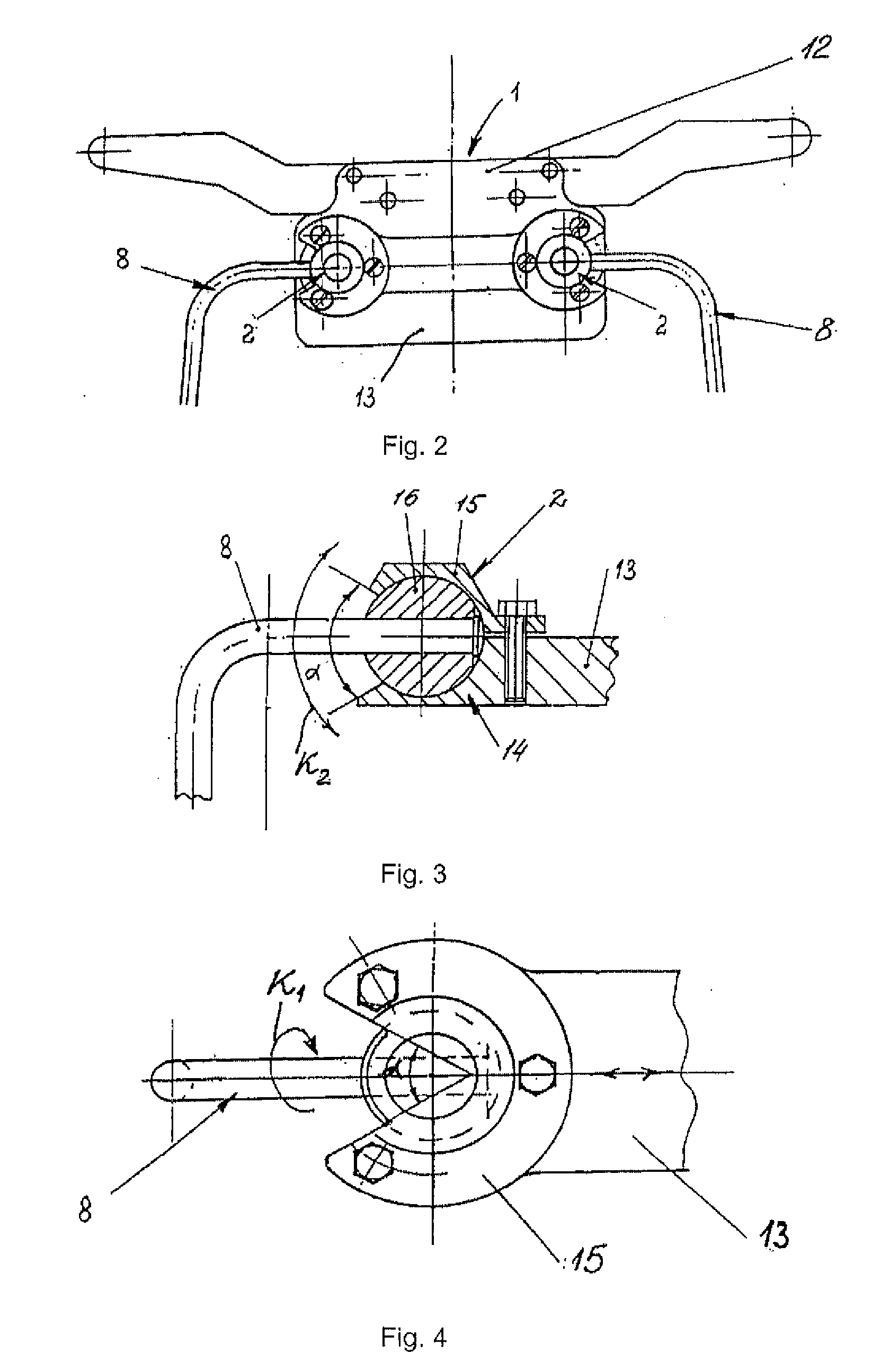
Wrist with decoupled motion transmission
InactiveUS6969385B2Reduce inertiaImprove device performanceMechanical apparatusJointsEngineeringActuator
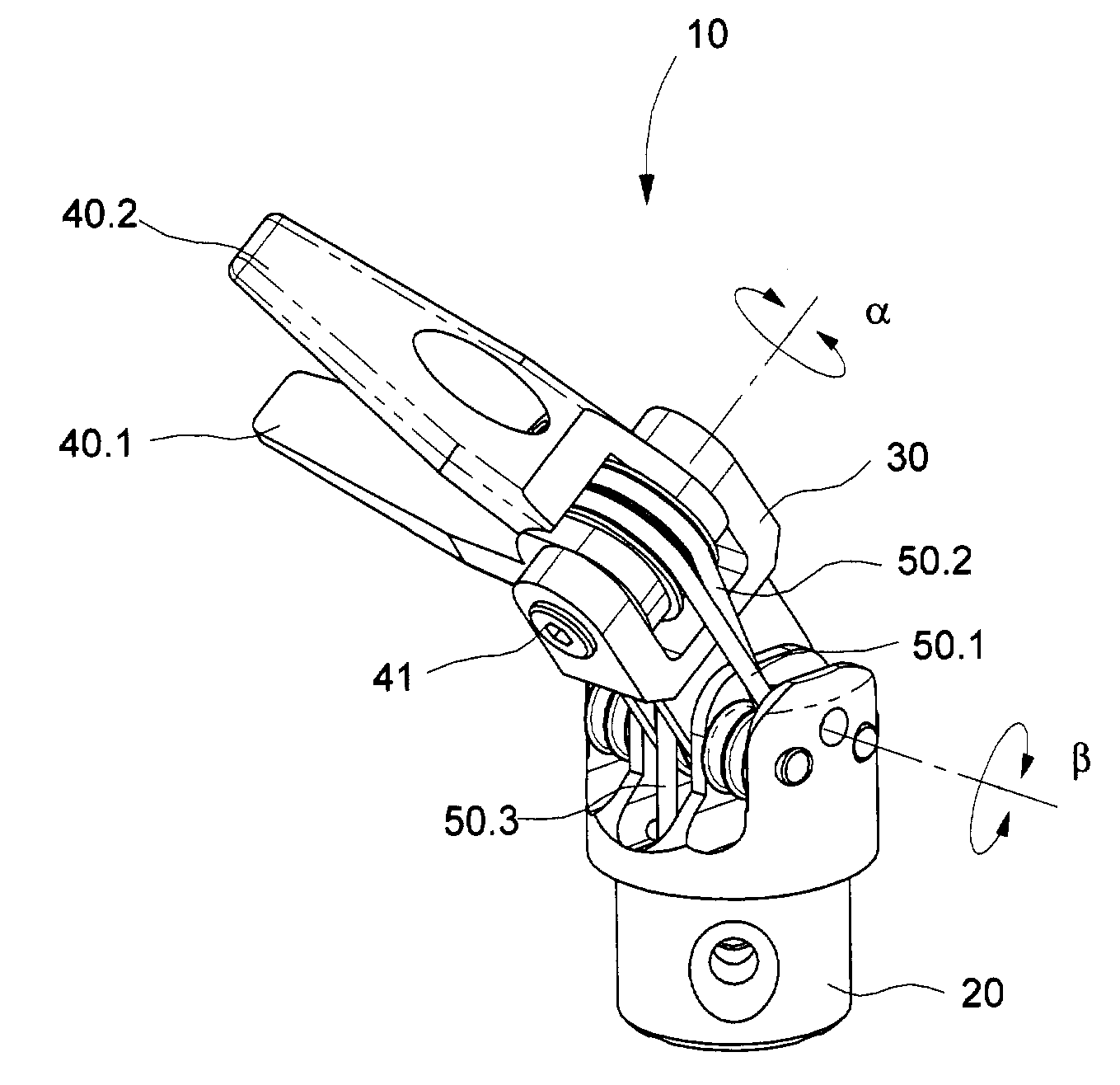
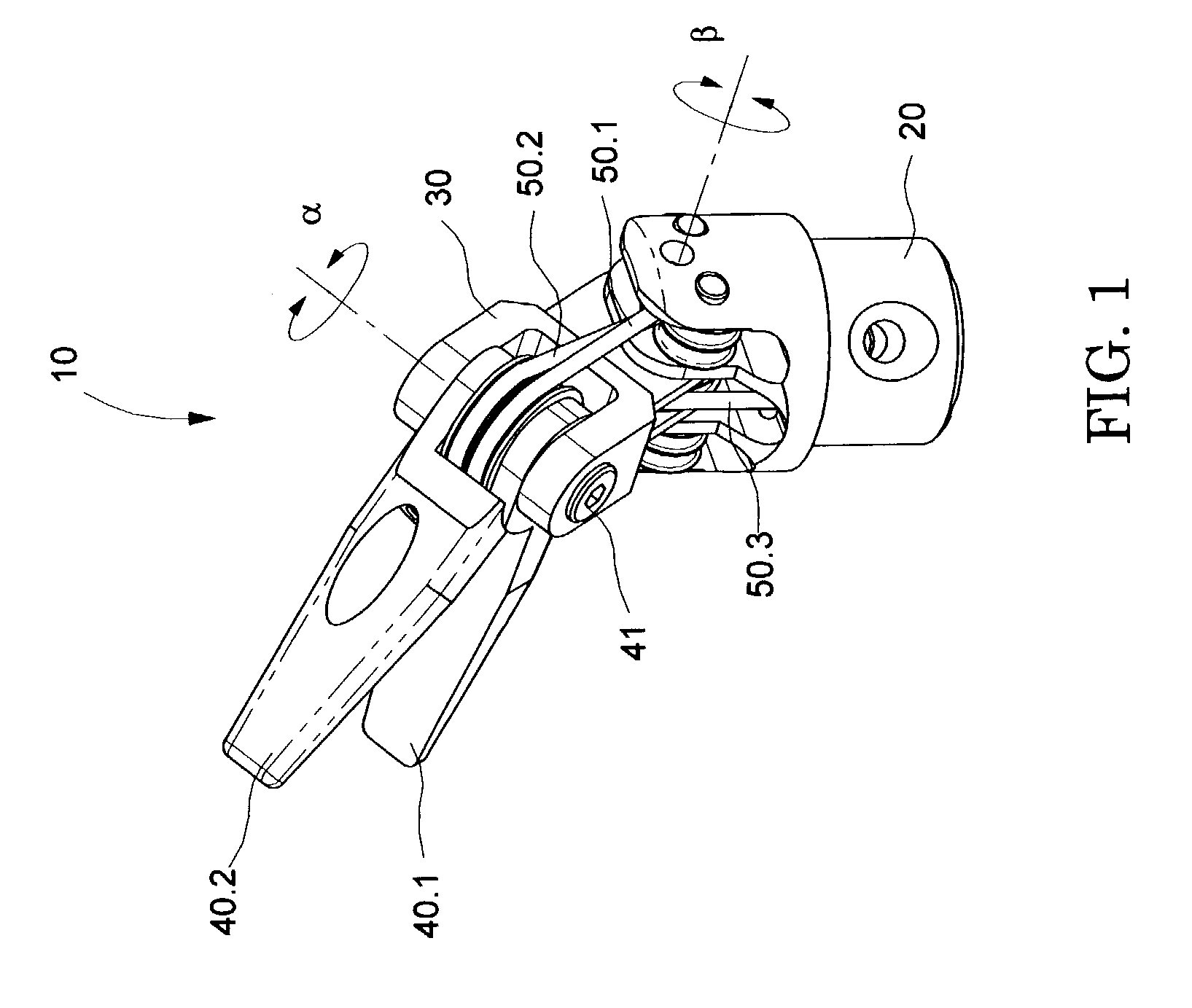
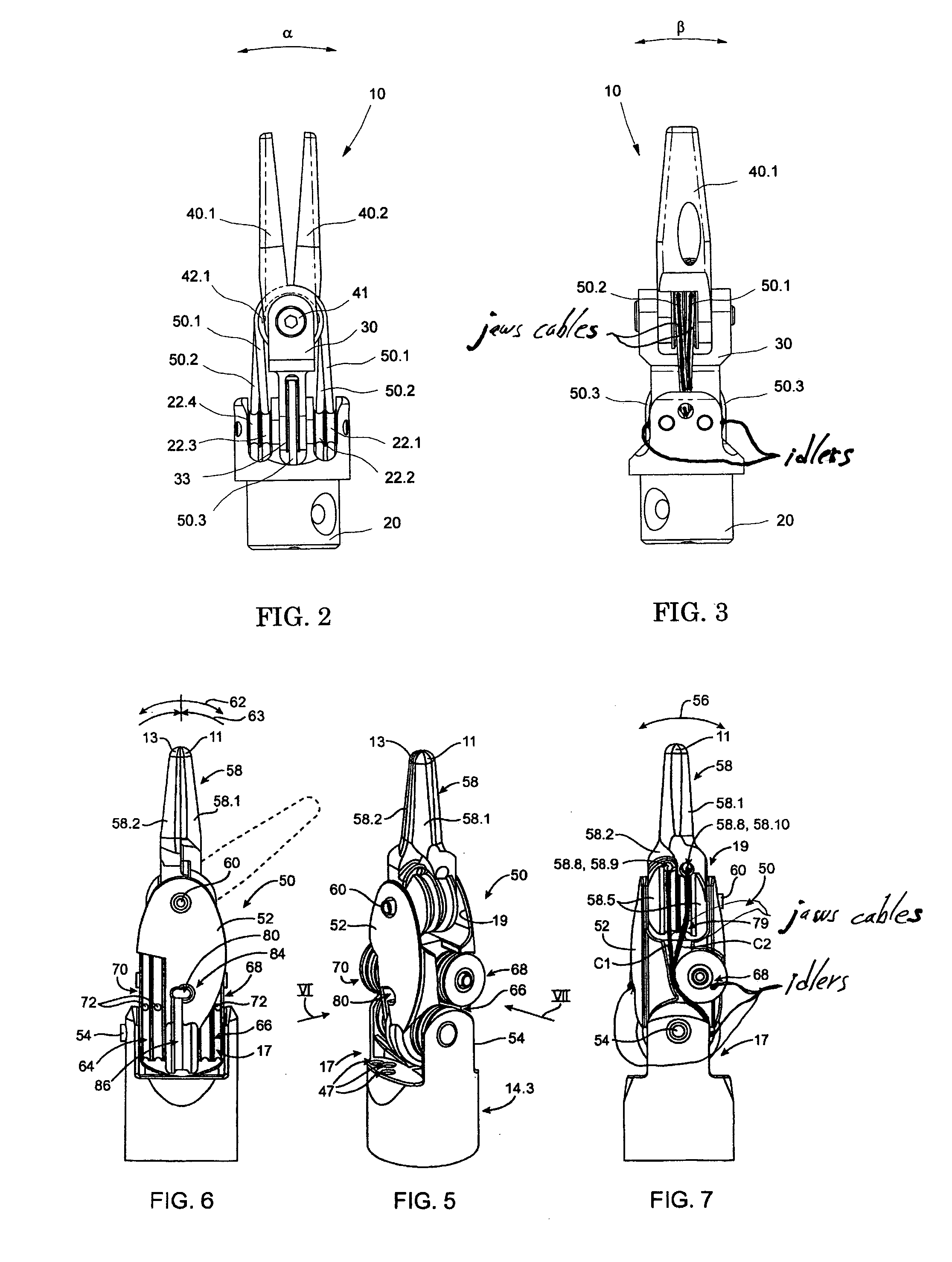
The present invention is a wrist mechanism and a method for making robotic devices in which the transmission of motion, force and / or torque around a revolute joint can be accomplished without coupling. This construction allows mounting the actuators on the base or lower elements of a mechanism, so that only linkage elements move the end-effector. Thus reducing inertia of the moving elements and increasing performance of the device. The decoupled motion of the end-effector or links is achieved by routing their transmission cables around idler pulleys placed parallel to the joint rotation axis on an optimal position such any stretch on the transmission cable is minimized. In particular, this construction can be use for robotic surgical tools that have two independently driven jaws, decoupled and orthogonal from its articulating wrist. This device may be used in grasping, cutting, suturing or alike operations.
Owner:MOREYRA MANUEL RICARDO
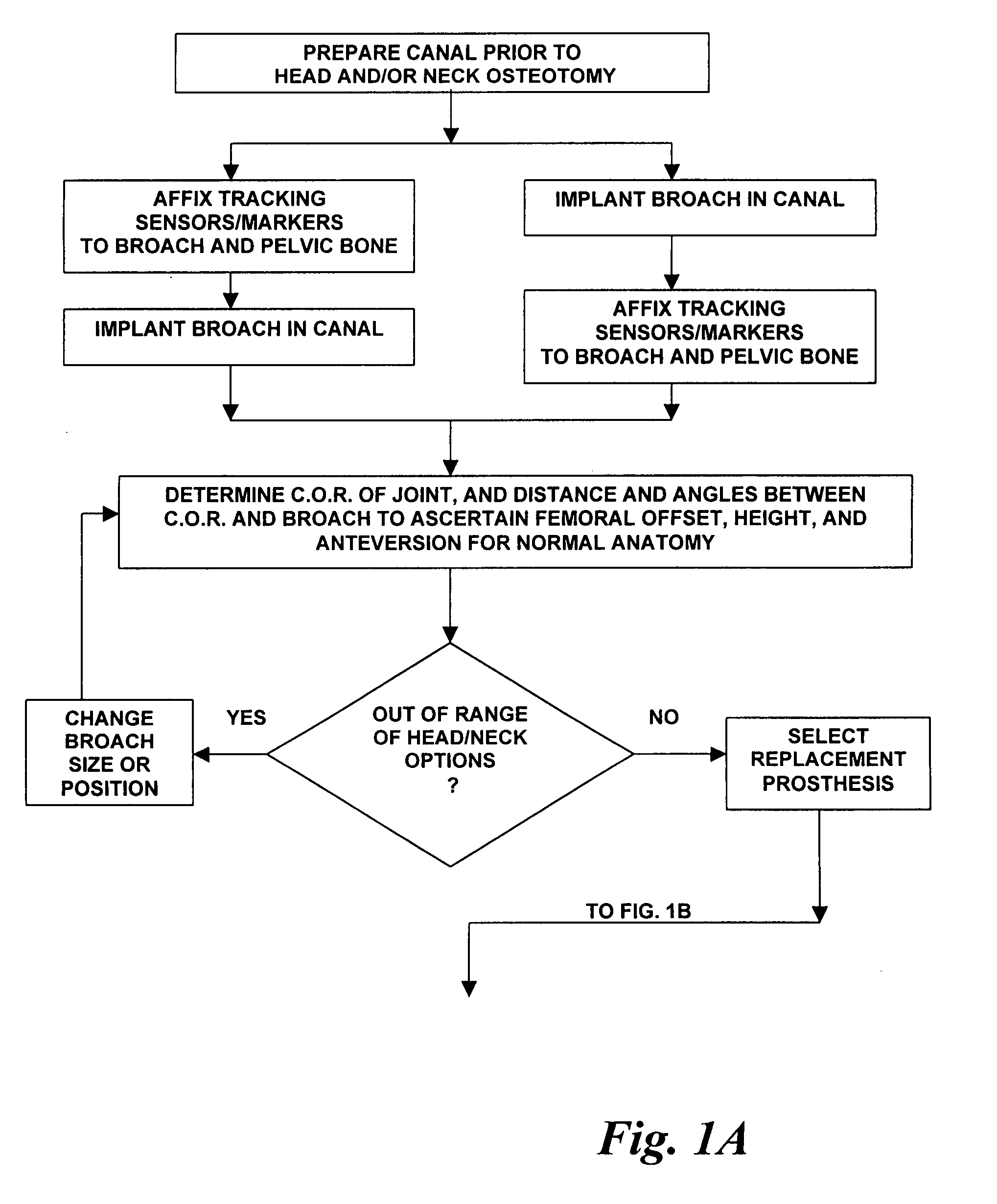
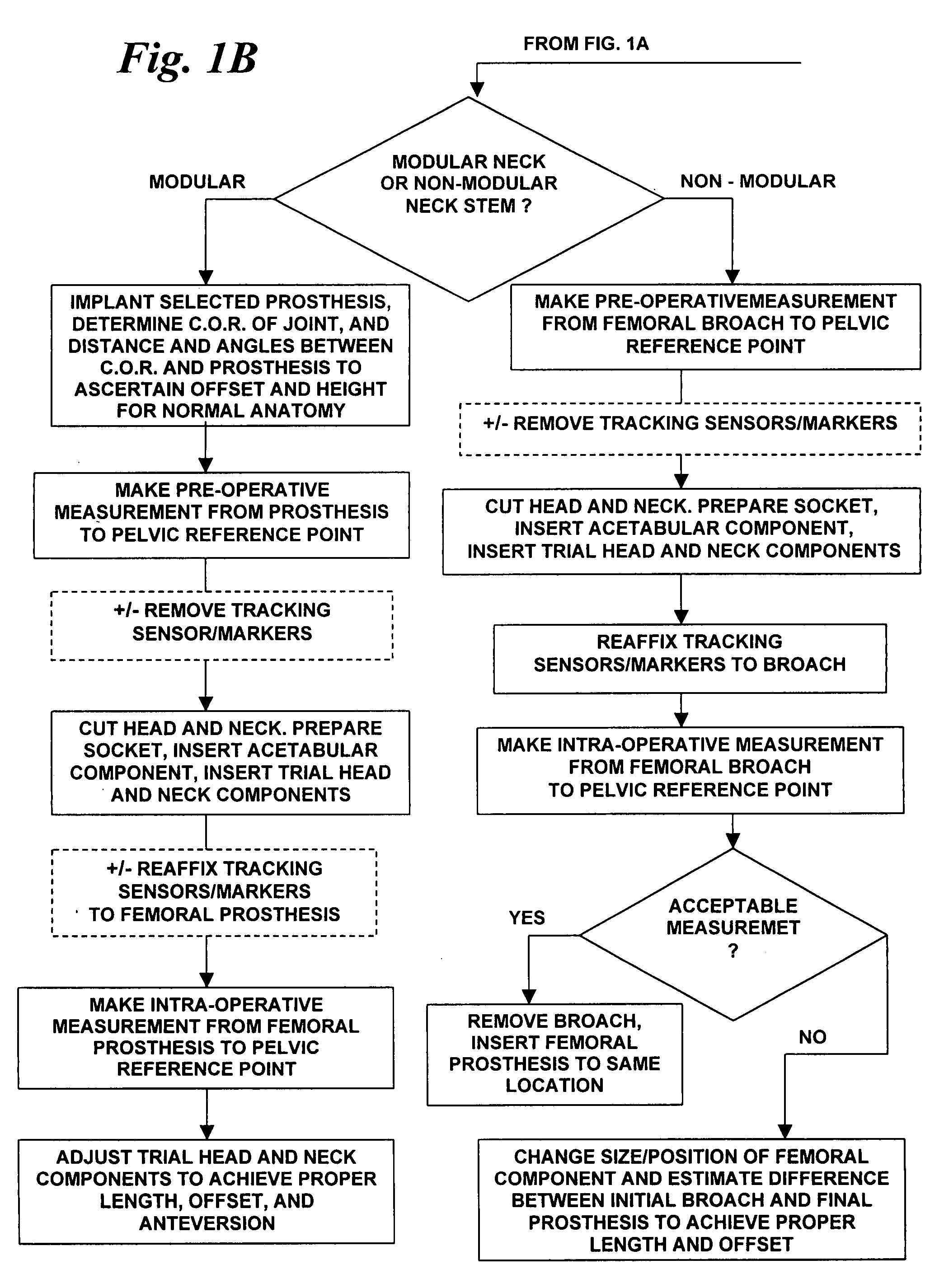
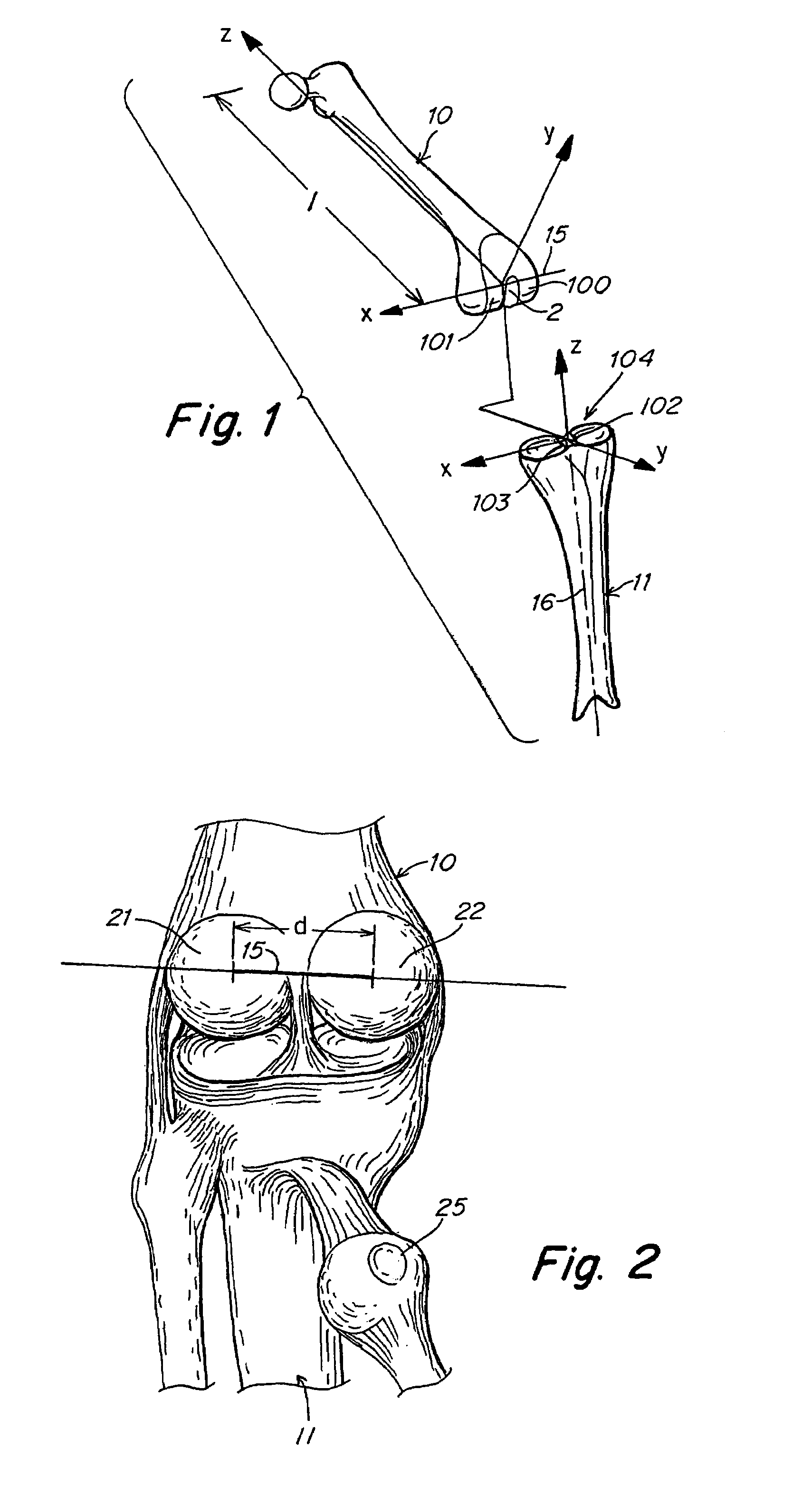
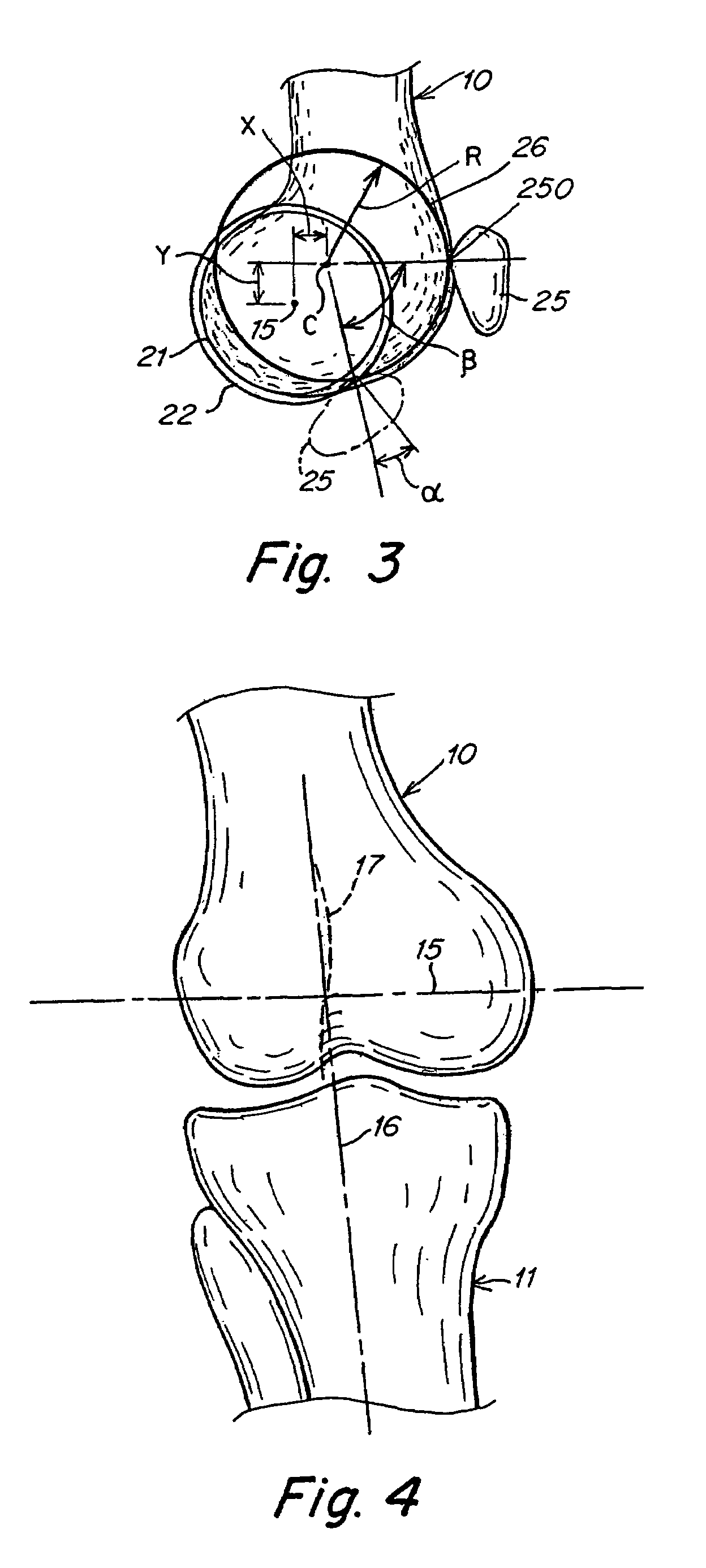
Total joint replacement component positioning as predetermined distance from center of rotation of the joint using pinless navigation
InactiveUS20080146969A1Precise positioningAccurate measurementSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationArticular surfacesArticular surface
A system and method used in total joint arthroplasty of a ball and socket joint such as hip and shoulder replacements for accurate positioning of a prosthesis through pinless surgical navigation during replacement surgery according to a predetermined distance from the center of rotation of the replaced joint and / or articular surface to obtain the proper length, offset, and biomechanics of the replaced joint.
Owner:KURTZ WILLIAM B
Wrist with decoupled motion transmission
InactiveUS20030208186A1Reduce inertiaImprove device performanceMechanical apparatusDiagnosticsEngineeringActuator
The present invention is a wrist mechanism and a method for making robotic devices in which the transmission of motion, force and / or torque around a revolute joint can be accomplished without coupling. This construction allows mounting the actuators on the base or lower elements of a mechanism, so that only linkage elements move the end-effector. Thus reducing inertia of the moving elements and increasing performance of the device. The decoupled motion of the end-effector or links is achieved by routing their transmission cables around idler pulleys placed parallel to the joint rotation axis on an optimal position such any stretch on the transmission cable is minimized. In particular, this construction can be use for robotic surgical tools that have two independently driven jaws, decoupled and orthogonal from its articulating wrist.
Owner:MOREYRA MANUEL RICARDO
Arrangement for ascertaining function-determining geometric parameters of a joint of a vertebrate
InactiveUS20050182320A1Easy to operateReduce riskSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceStereo cameraMeasurement point
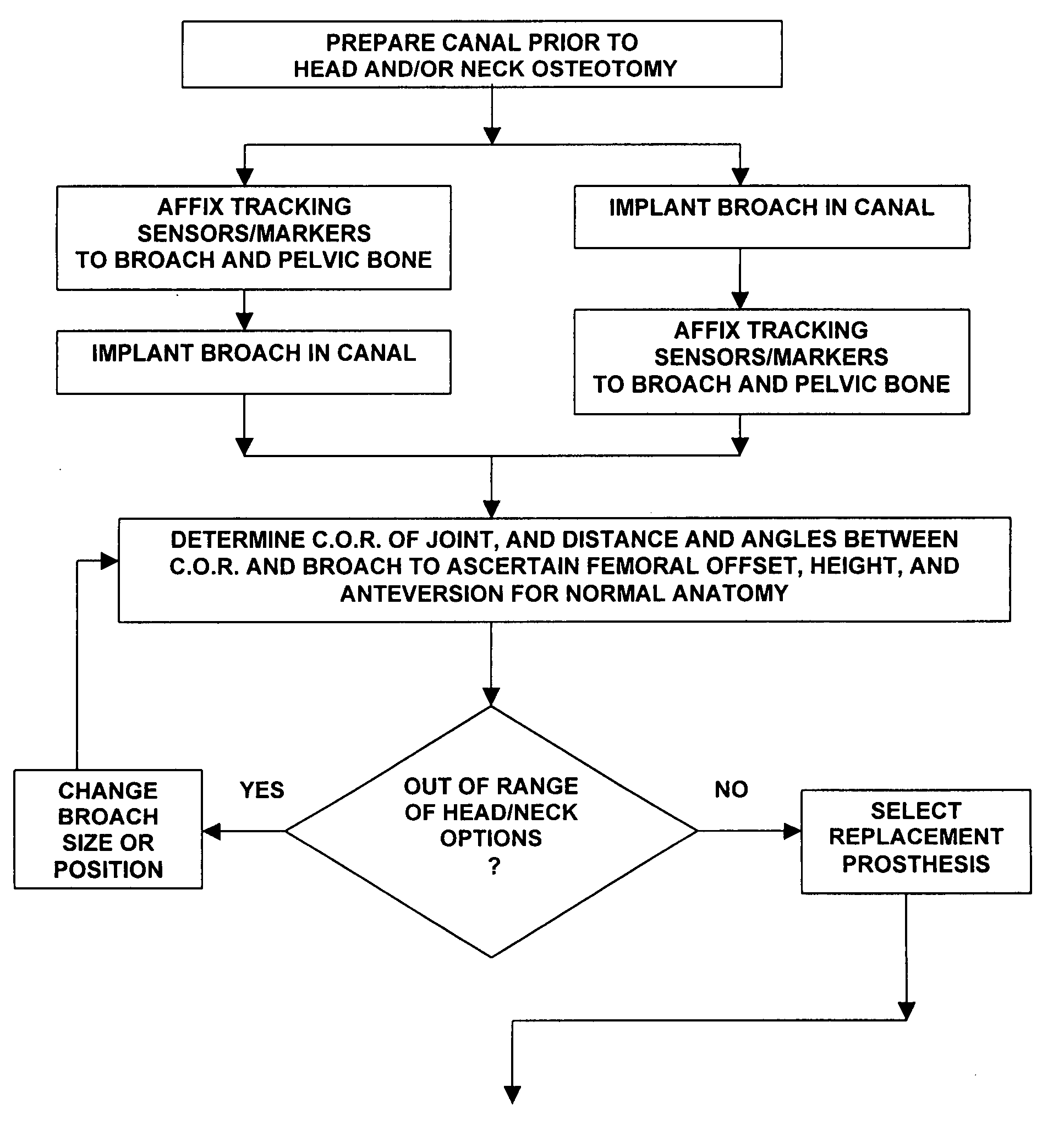
Arrangement for ascertaining function-determining geometric parameters of a joint of a vertebrate, especially a hip or shoulder joint of a human being, in preparation for the installation of a joint replacement implant, especially a hip or shoulder socket or an associated stem implant, by means of an optical coordinate-measuring procedure, having a stereocamera or stereocamera arrangement for the spatial recording of optical transducer signals, a mobile multipoint transducer which is in the form of a movable sensor for sensing bony references in the joint region in order to determine the coordinates thereof, at least one bone-fixed multipoint transducer which is configured for rigid attachment, especially screwed or clamped attachment, (in a region sufficiently distant from the joint) to an extremity originating from the joint, especially close to the proximal end of a femur or a humerus, an interactive sequence controller for controlling the sequential registration and storage of a set of measurement point coordinates supplied by the mobile multipoint transducer and sets of measurement point coordinates recorded in a first plurality of positions of the bone-fixed multipoint transducer in a plurality of rotated positions of the extremity and their subsequent processing in accordance with a previously stored processing sequence, an evaluation unit for evaluating the sets of measurement point coordinates supplied by the multipoint transducers and recorded by the camera arrangement for the purpose of determining the geometric parameters, which comprises means for determining the transversal, vertical and sagittal body axes as well as means for carrying out an iterative procedure, especially an adjustment calculation in accordance with the least squares method, to determine the coordinates of the center of rotation of the joint, and an output unit, which is connected to the sequence controller and to the evaluation unit, for issuing manipulation proposals to an operating surgeon in accordance with the predetermined process sequence and in dependence upon the results of the determination of the geometric parameters, and for displaying the results of the evaluation.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Adjustable tension prosthetic ankle rotatory device for lower limb apparatus
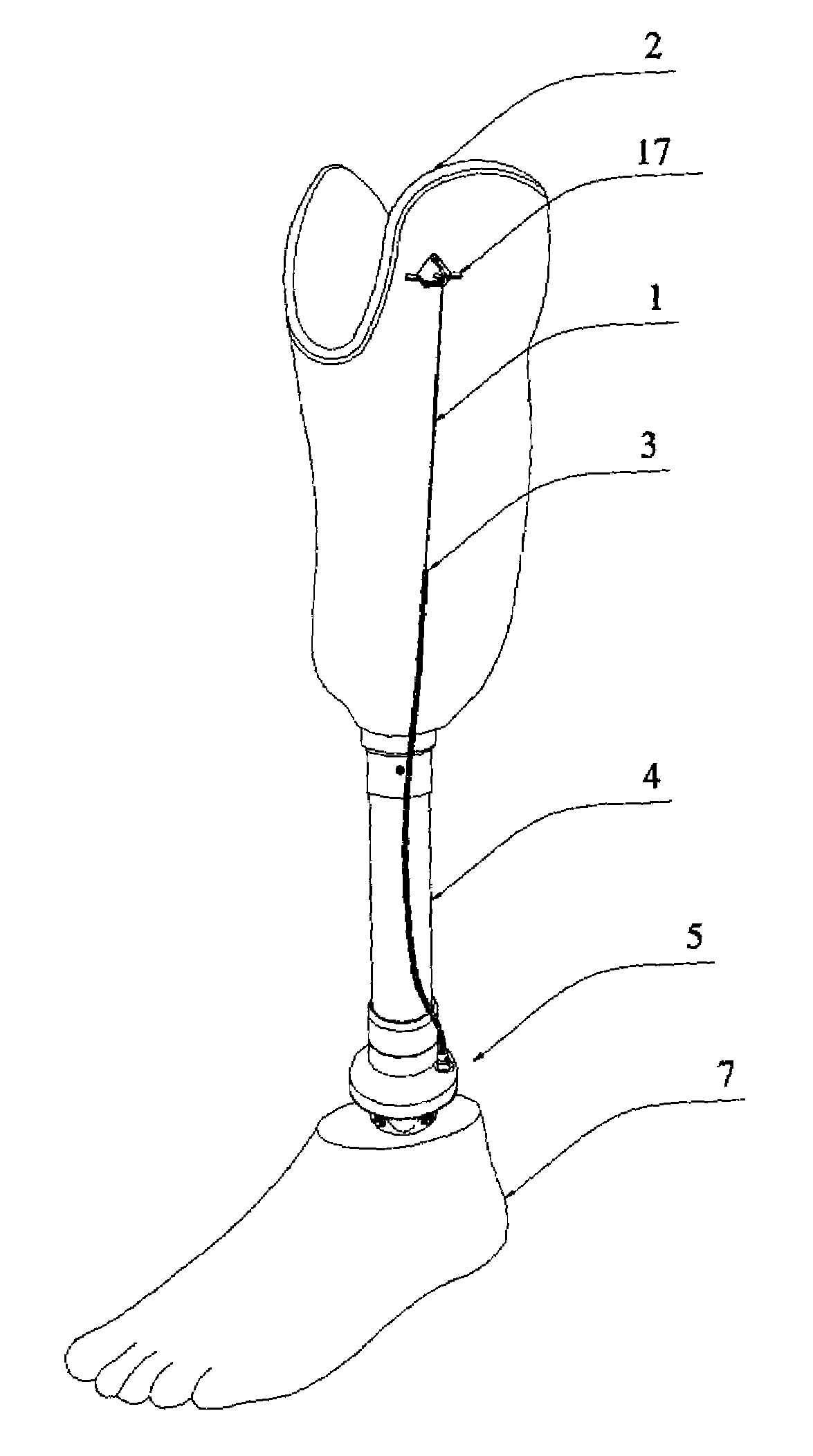
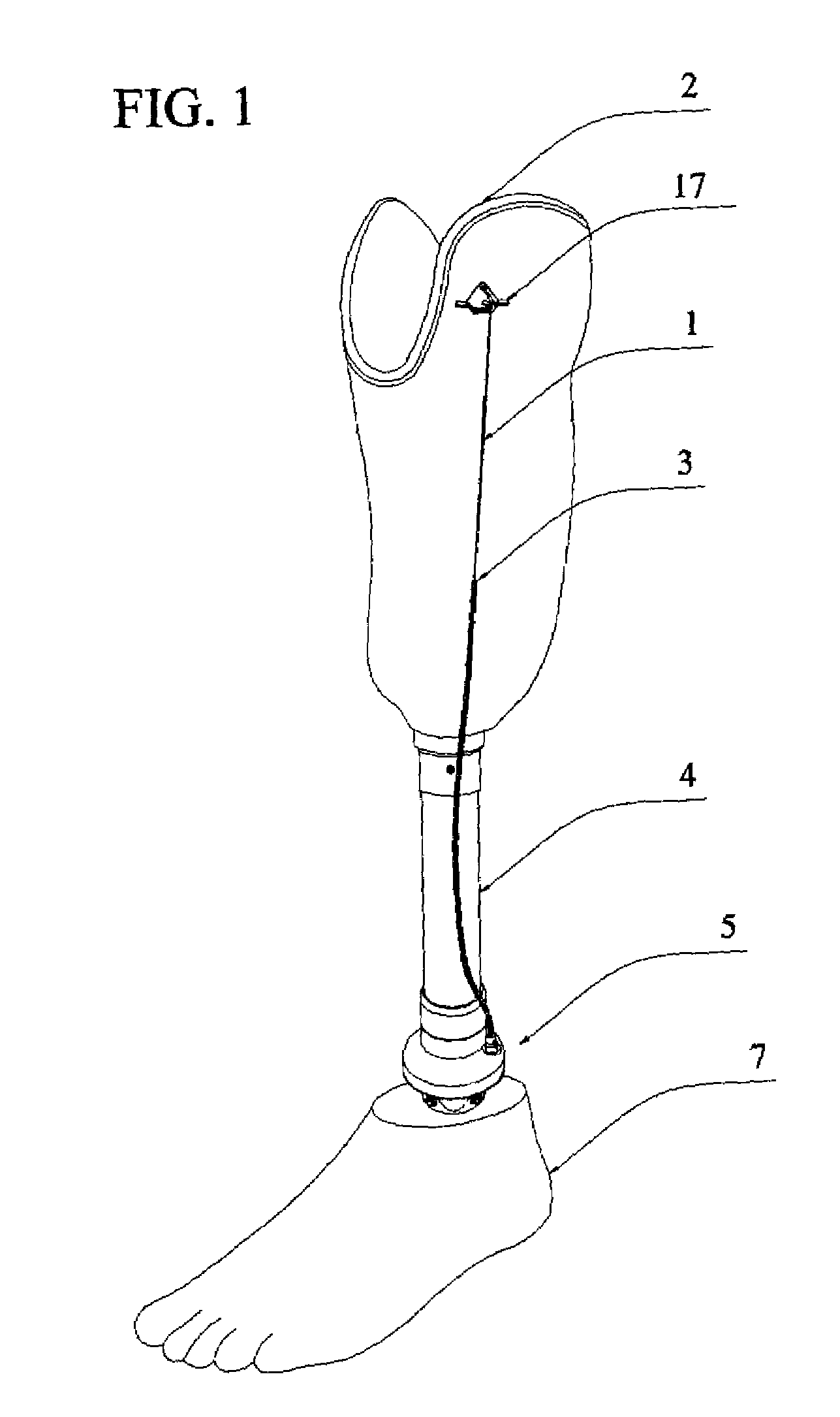
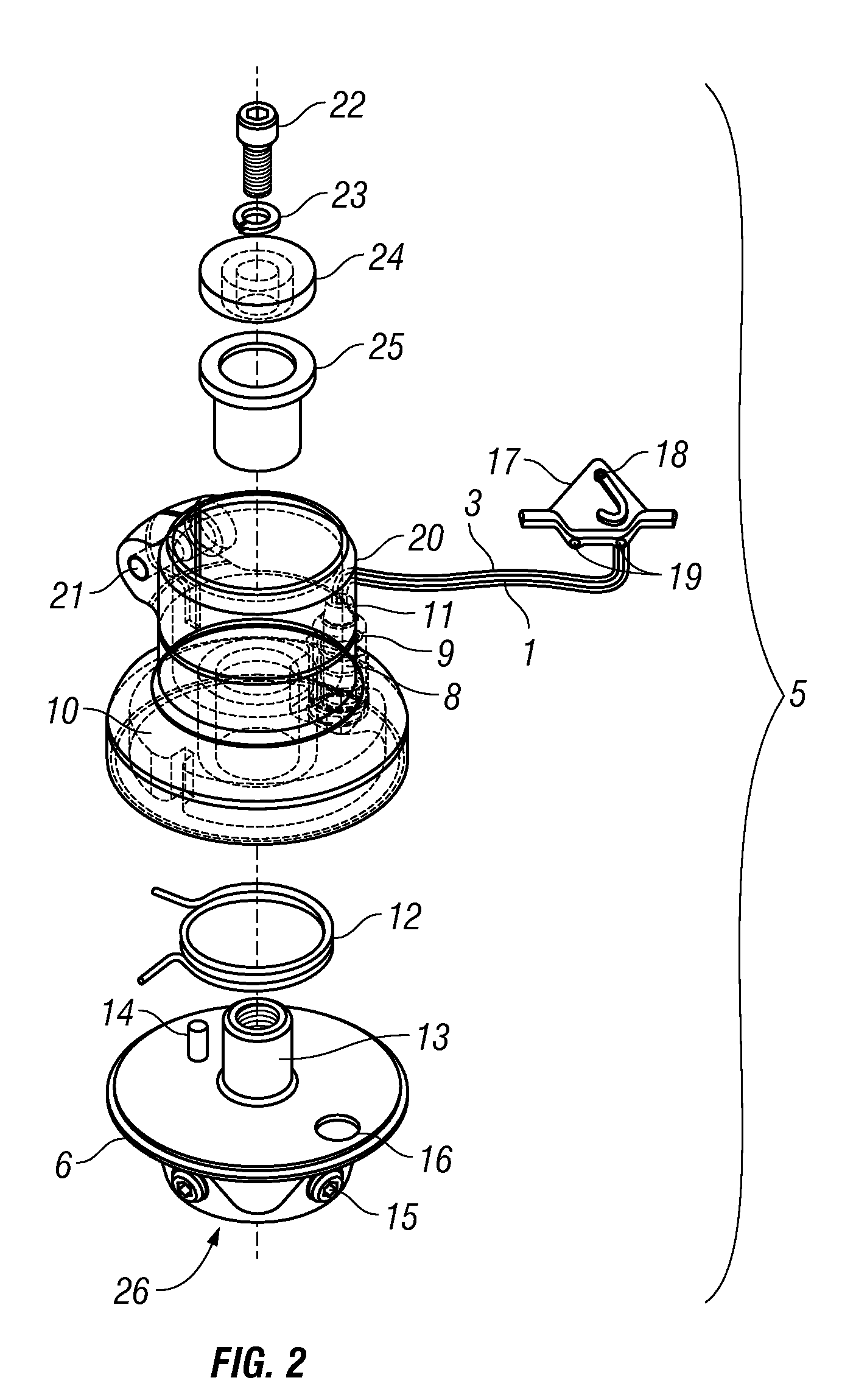
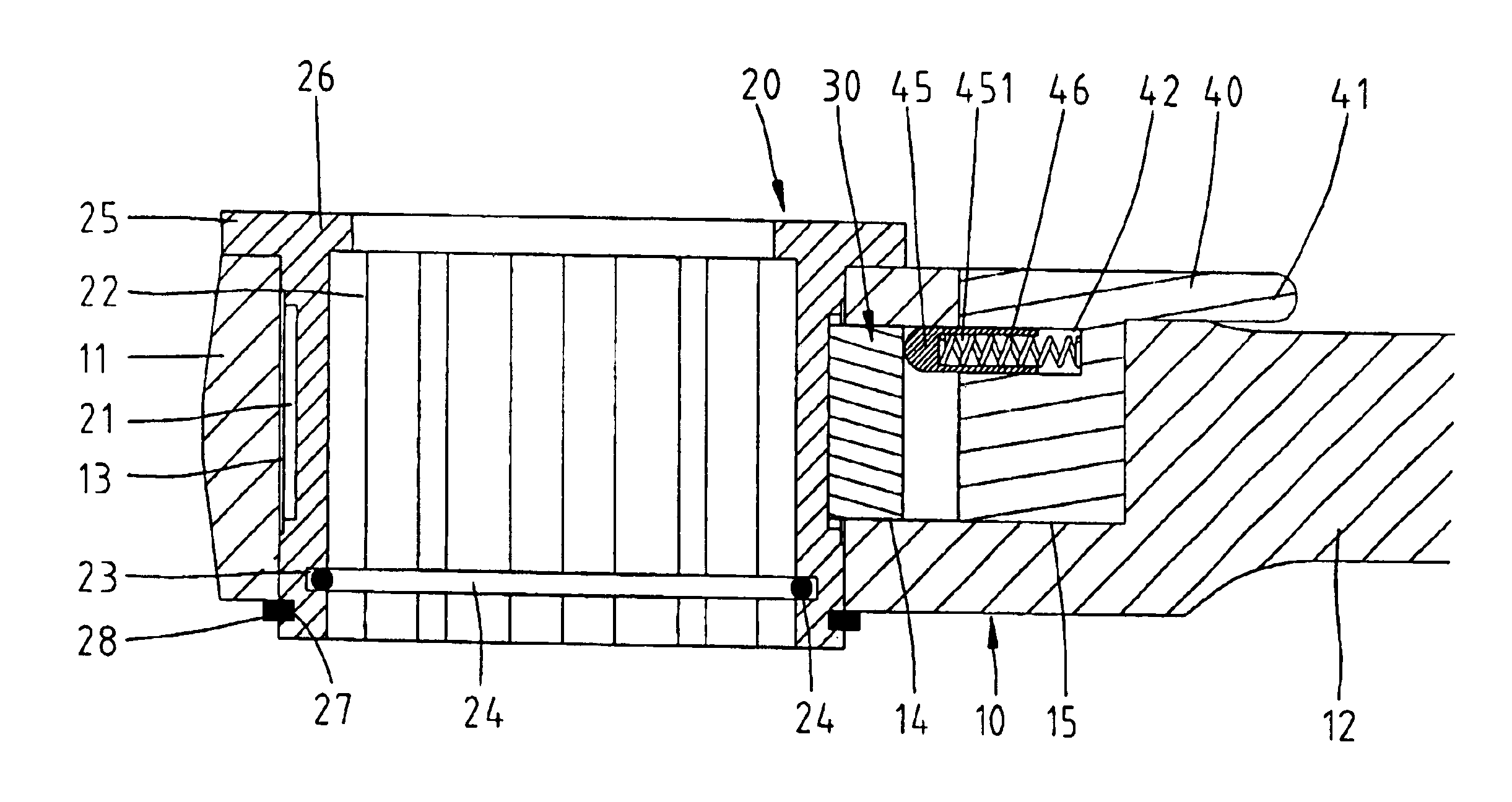
A transtibial patellar tendon bearing (PTB) prosthesis for below the knee amputees is disclosed. The prosthesis includes a socket, and a foot prosthesis attached to a modular shank component using a foot rotator device. Using the rotator device, the foot component of the prosthesis may be smoothly and axially rotated internally or externally ±150° with respect to the shank component about the axis of the shank component. The wide range of axial rotation enables a more even load distribution on the whole lower limb of an amputee and enables an amputee to comfortably assume a wide range of biomechanical positions, such as sitting or kneeling. A recoil spring, having a selectable tension, is positioned within the rotatable component and selectively limits and retains the relative rotation of the upper portion and the lower portions. A locking mechanism selectively prevents rotation when the foot component is engaged.
Owner:AL TURAIKL MOHMMED H S
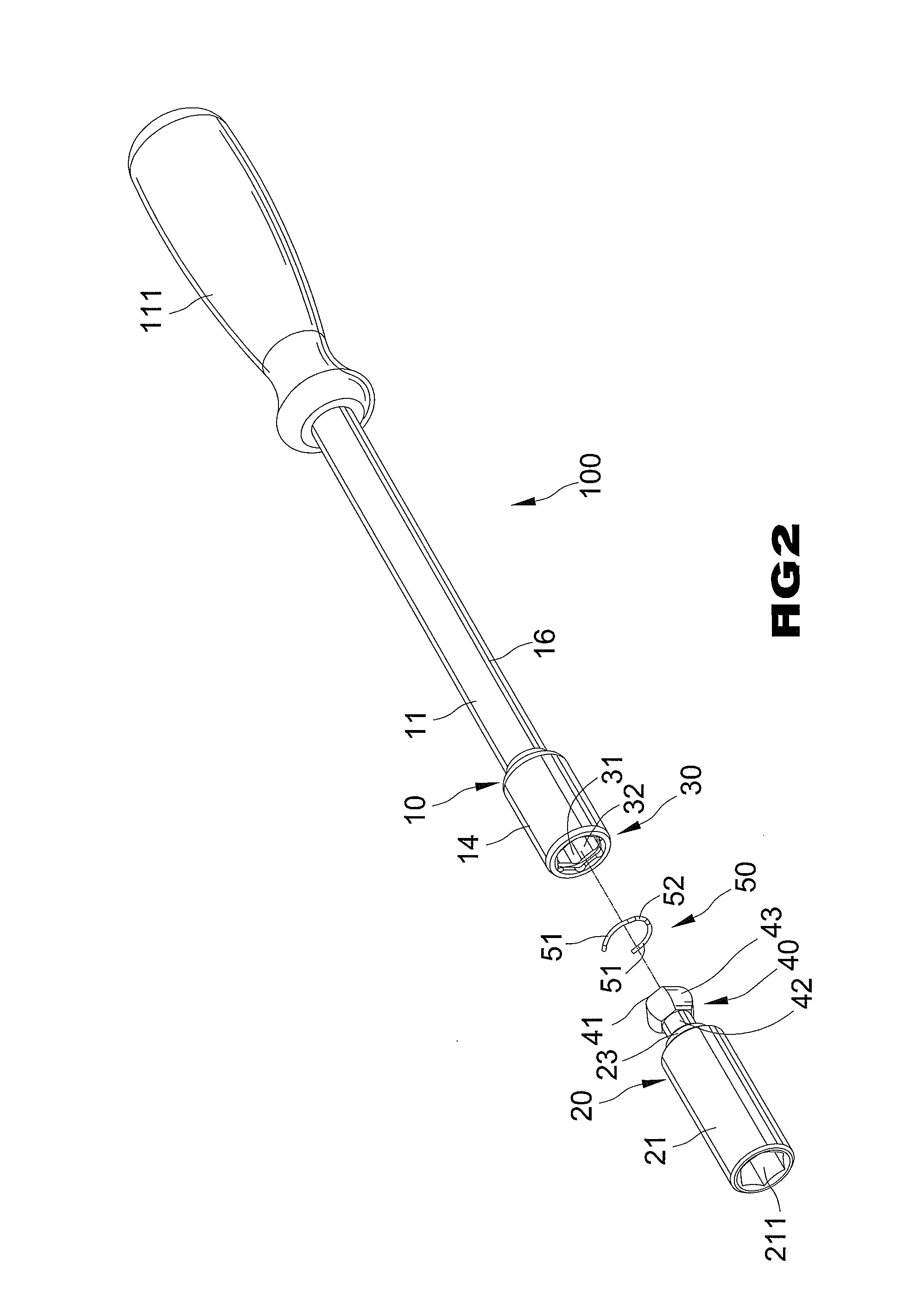
Ratcheting wrench with quick tightening/loosening functions and fine adjusting functions
A ratcheting wrench includes a handle, a head extending from an end of the handle and having a hole communicated with a compartment in the end of the handle, a drive member rotatably mounted in the hole of the head, and a ratcheting mechanism. The drive member includes an inner periphery for securely holding a fastener-driving member, allowing joint rotation when the drive member is turned. The drive member further includes a flange formed on an end of an outer periphery thereof and located outside the head for manual rotation of the drive member. The ratcheting mechanism is mounted in the compartment of the handle and engaged with the teeth of the drive member, allowing the handle to selectively move in a ratcheting direction for tightening / loosening a fastener and in a free turning direction reverse to the ratcheting direction in which the fastener is not turned.
Owner:HU BOBBY
Method for uniquely solving inverse kinematics numerical value of joint type mechanical arm
ActiveCN109895101AOvercoming the requirement of full rankSimple modeling methodProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoints typesEngineering
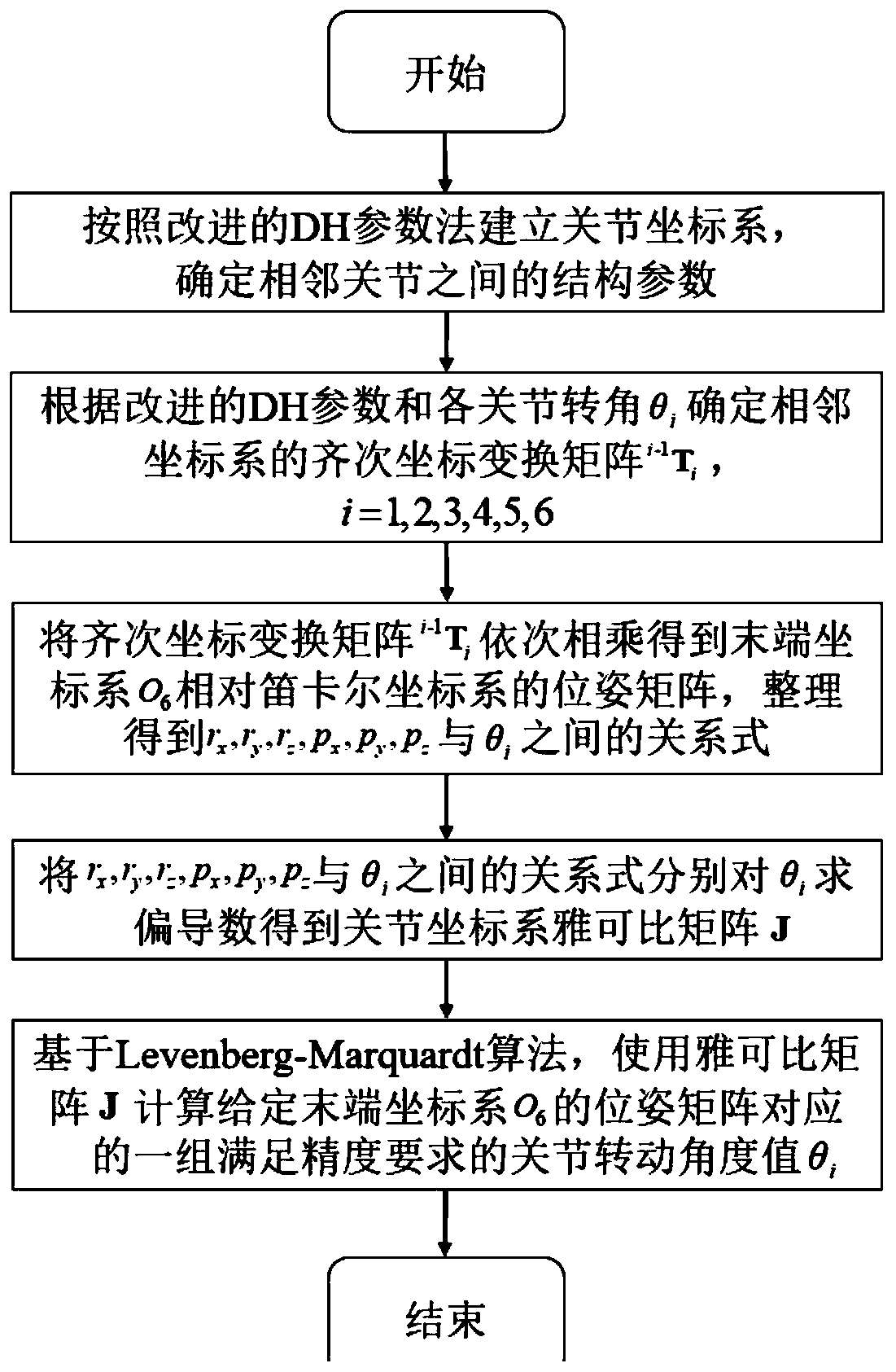
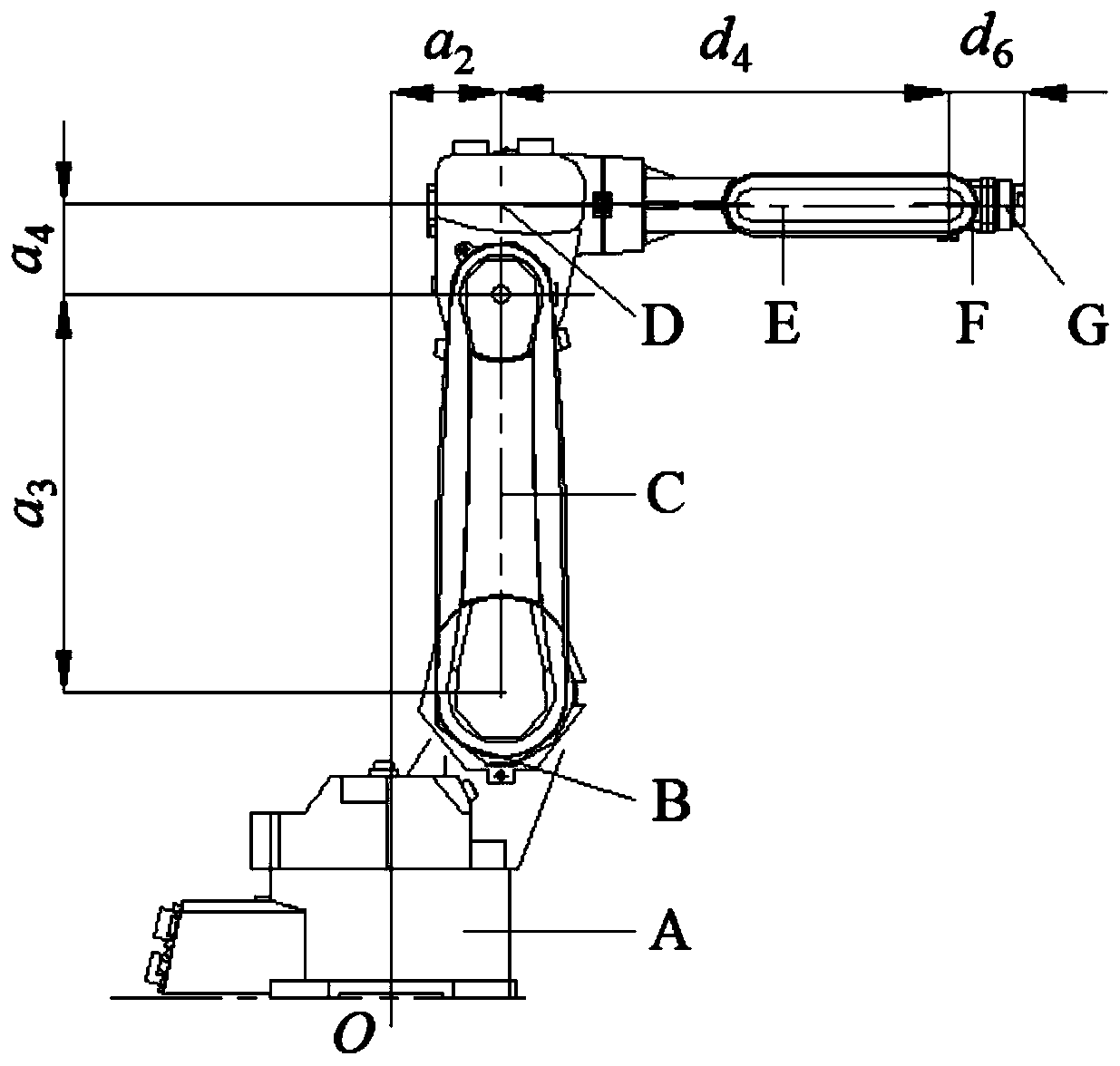
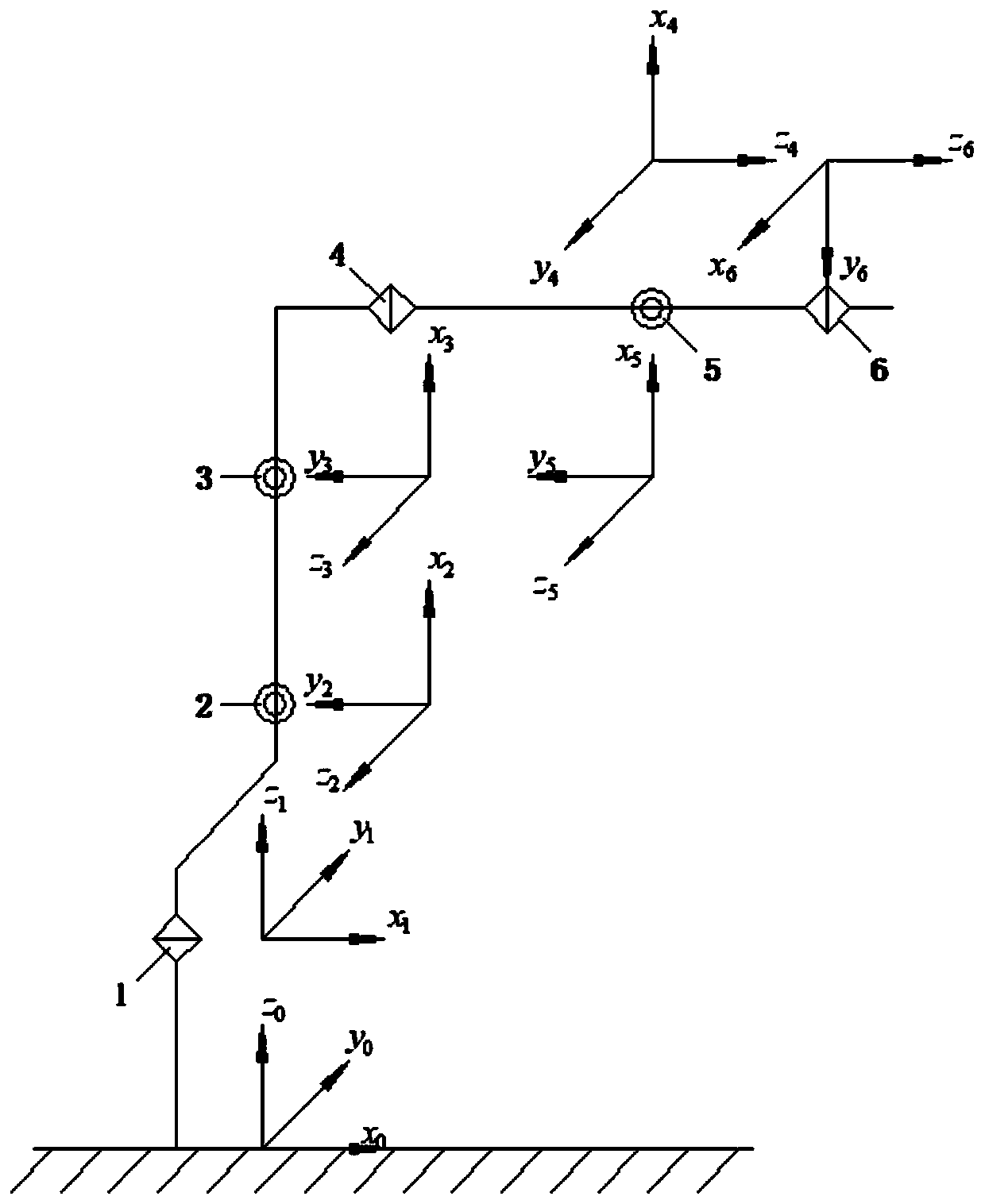
The invention discloses a method for uniquely solving the inverse kinematics numerical value of the joint type mechanical arm, belongs to the technical field of modern intelligent manufacturing, relates to the technical field of industrial robots, relates to a method for uniquely solving the inverse kinematics numerical value of a joint type six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm with shoulder joints facing forward. According to the method, a mechanical arm joint coordinate system is built according to an improved DH parameter method, four structural geometrical parameters between adjacent joints of the mechanical arm are determined, a homogeneous coordinate transformation matrix of two adjacent coordinate systems is calculated. For a given pose matrix of a tail end coordinate system O6, animproved newton iteration method, namely a Levenberg marquardt iterative algorithm is adopted, the inverse kinematics solution of the joint coordinate system is calculated by using a jacobian matrix J, and the six joint rotation angle values theta i which correspond to the pose matrix and meet the precision requirement are obtained. The method overcomes the requirement that a traditional newton iteration method needs to fully rank the jacobian matrix j, the modeling method is simple, clear and effective, the method has the characteristics of being high in solving precision, high in solving speed and simple and feasible in solving process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Ratcheting wrench with quick tightening/loosening functions and fine adjusting functions
Owner:HU BOBBY
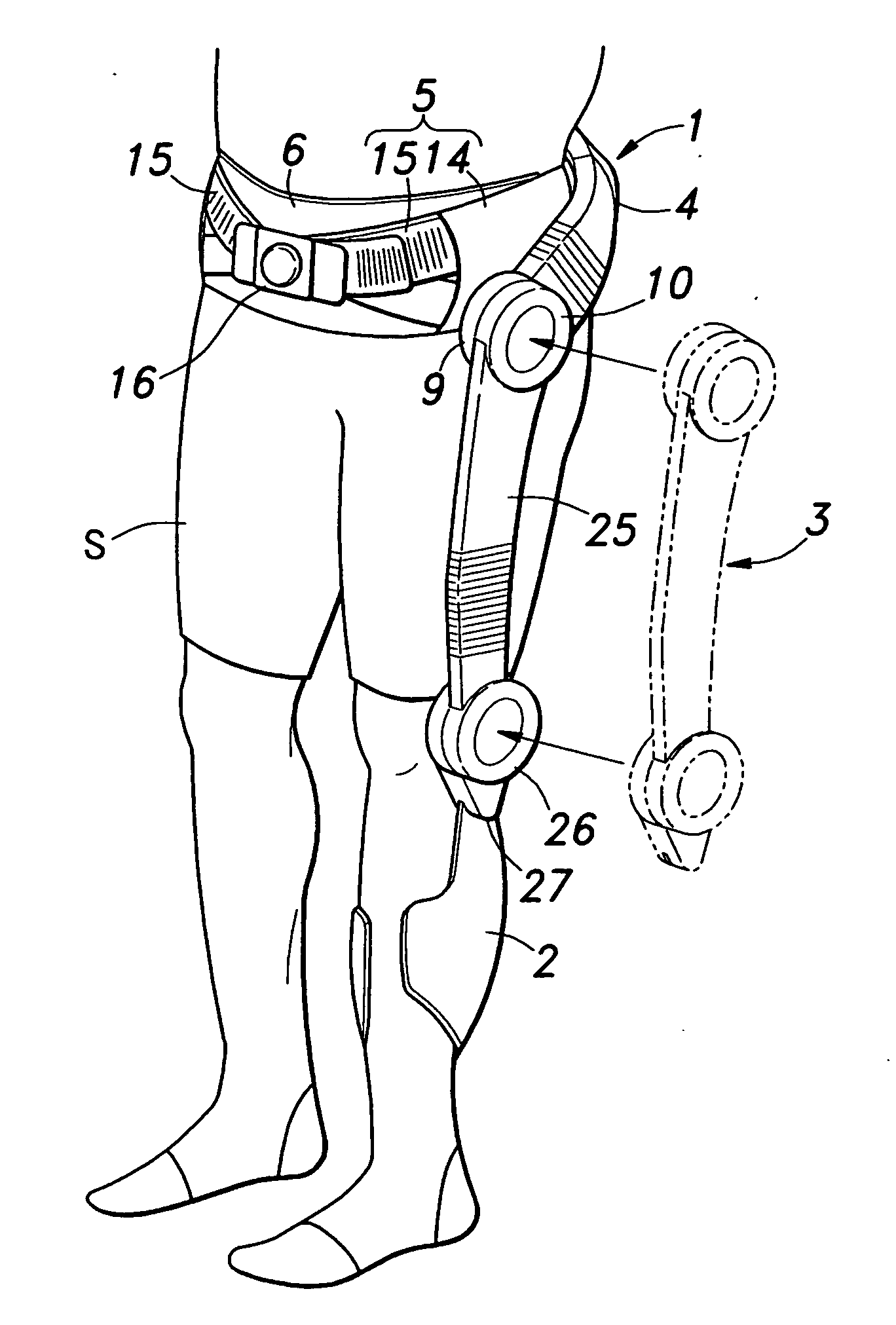
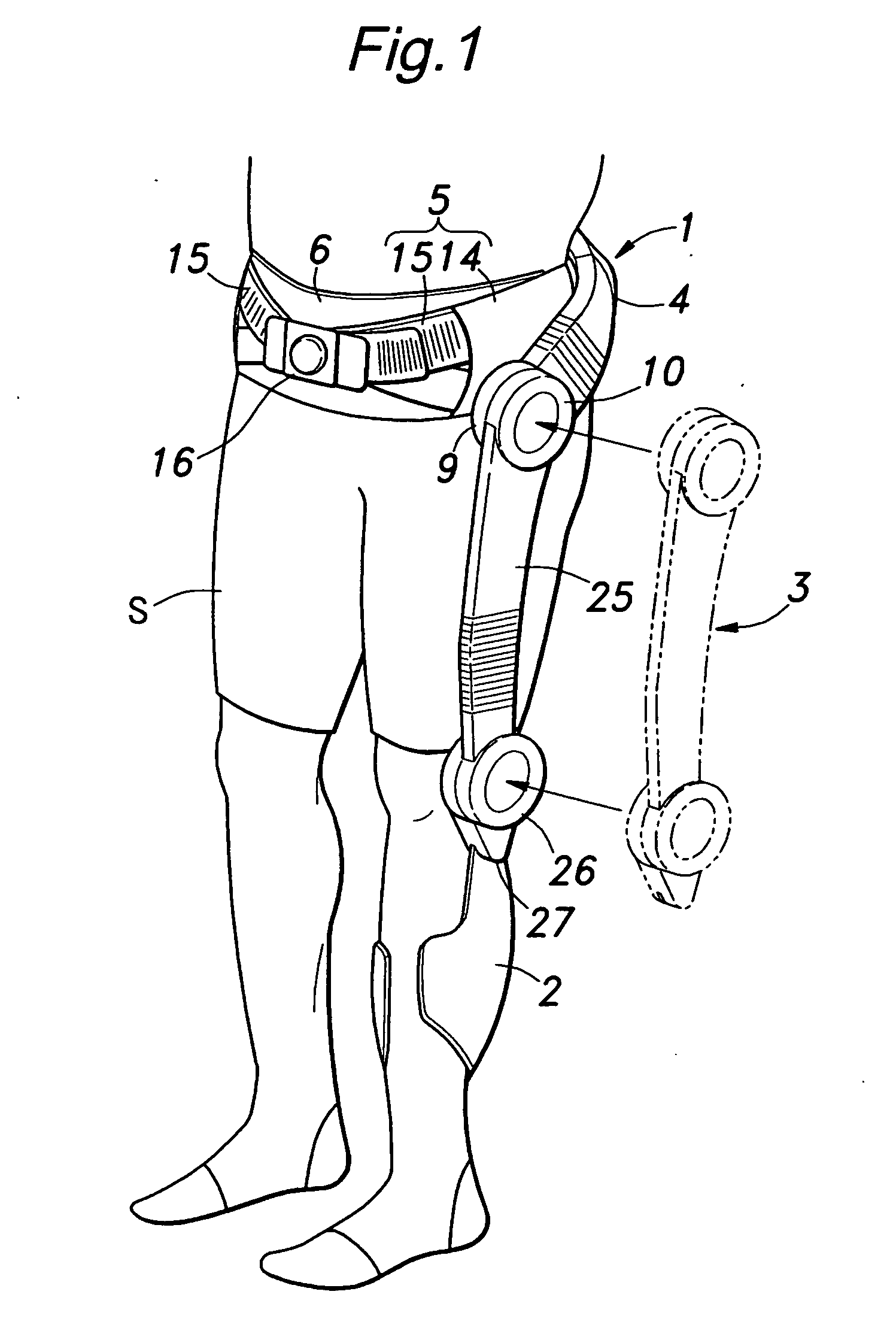
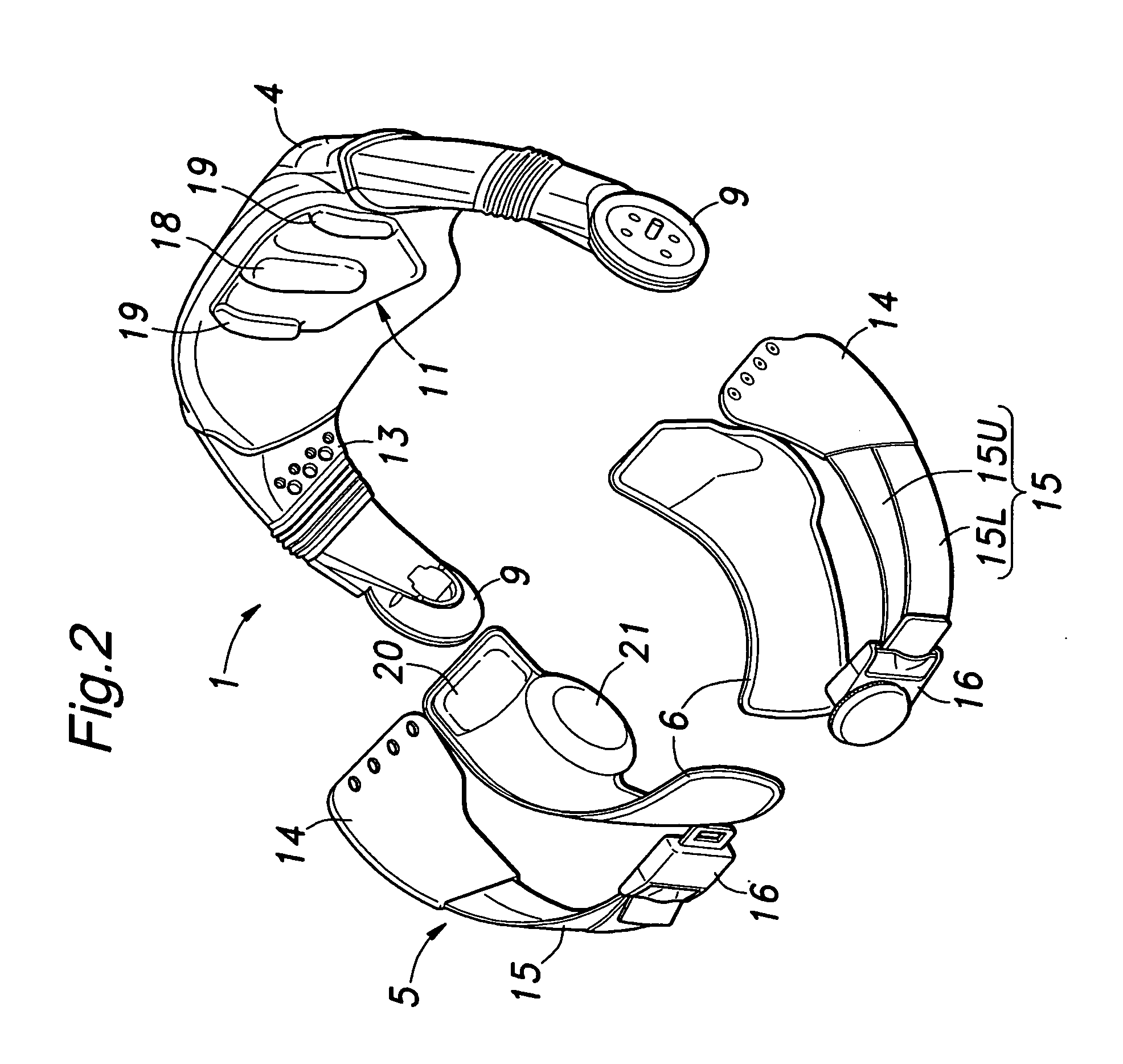
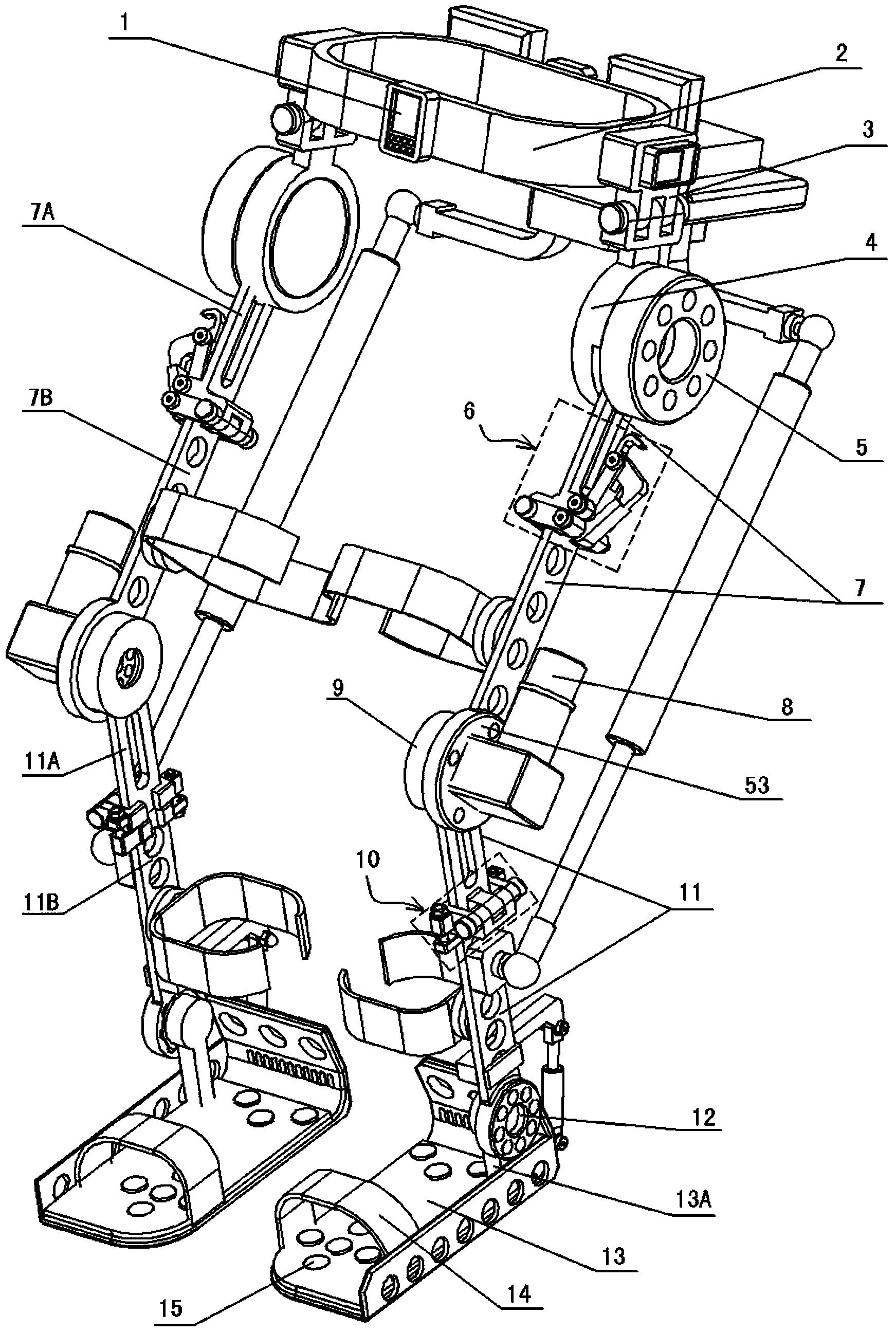
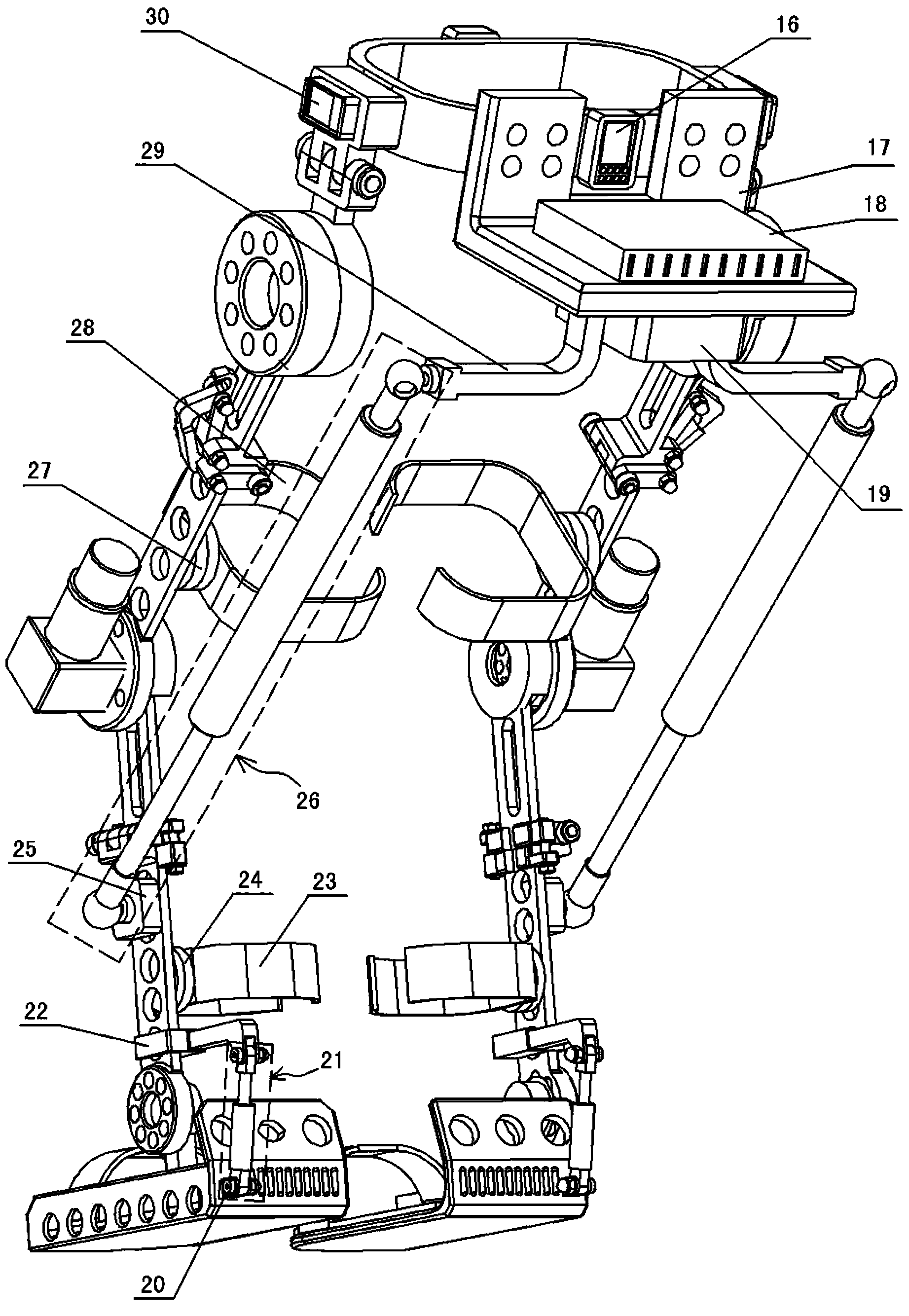
Walking assistance device
InactiveUS20070106190A1Minimize biasLittle strengthChiropractic devicesWalking aidsHip rotationCoxal joint
In order to achieve a walking assistance device that can be securely fitted to the user's body while allowing a certain degree of freedom, a walking assistance device is provided comprising a hip joint rotational force generator (hip joint actuator 10) mounted on a side of a hip joint and a knee joint rotational force generator (knee joint actuator 26) mounted on a side of a knee joint to provide an assisting force to a movement of a lower limb, wherein the hip joint rotational force generator is fitted to the body via a first linkage means (link plate 30) having at least two degrees of freedom, and wherein the hip joint rotational force generator and the knee joint rotational force generator are connected to each other via a second linkage means (link bar 25) having an expandable and contractable means. In this way, deformation in lateral and torsional directions of the first linkage means and expansion / contraction of the second linkage means can absorb a deviation in position between the joints of the user's body and the assisting force generators.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
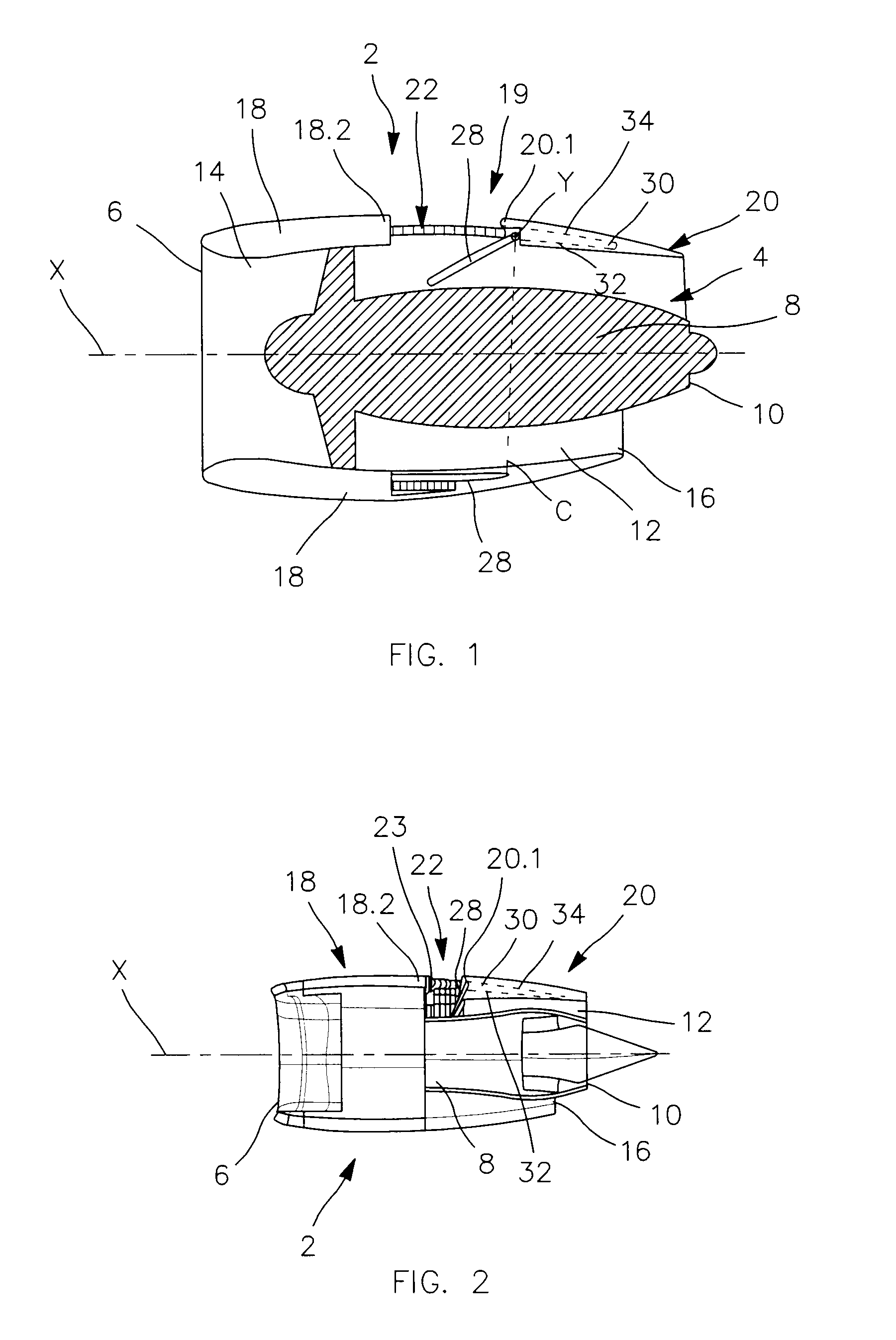
Nacelle for aircraft comprising means of reversing thrust and aircraft comprising at least one such nacelle
ActiveUS20090321561A1Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantityEngine fuctionsSpraying apparatusNacelleRest position
Aircraft nacelle comprising a cowling and an engine, the cowling comprising a fixed portion and a mobile portion able to slide in order to define a radial opening with the mobile portion, a thrust reverser system comprising a plurality of flaps intended to be deployed in order to seal at least partially an annular channel surrounding the engine, the mobile portion of the cowling comprising an annular housing extending longitudinally in order to receive the flaps in rest position. Each flap is linked to the fixed portion by a pivot joint and is linked to the mobile portion by a sliding-pivot joint, in such a way that a sliding of the mobile portion in separating from the fixed portion provokes a rotation of each flap around the axis of rotation of the joint with the fixed portion.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Knee joint prosthesis with a femoral component which links the tibiofemoral axis of rotation with the patellofemoral axis of rotation
A femoral component is provided for use in a knee joint prosthesis. The femoral component may be configured to provide one or more desirable kinematic relationships with a tibial component and / or patella so as to mimic the flexion and extension motion of a natural knee joint. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a substantially circular pathway during knee flexion and extension. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a curved patellar path during flexion and extension, and the curved patellar path has an origin located anterior and proximal to the geometrical center axis of the knee. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a curved patellar path that lies in a plane which is parallel to and offset from a plane that extends through the center of the femoral head of a femur and is perpendicular to the geometric center axis of the knee. The femoral component may be configured so that at least a portion of the patella substantially follows a patellar path in a plane perpendicular to the geometrical center axis of a knee throughout knee flexion.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
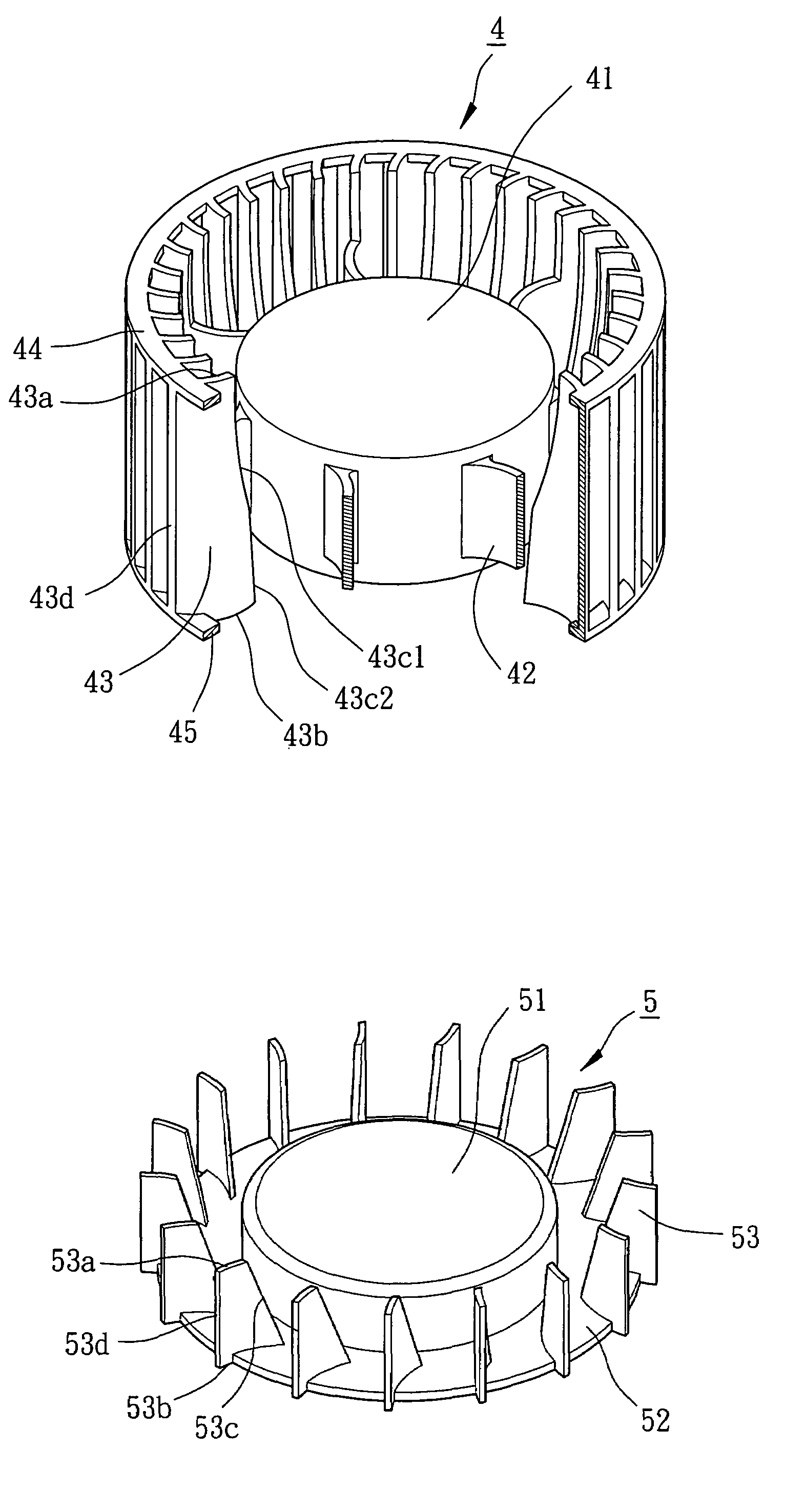
Impeller for radial-flow heat dissipating fan
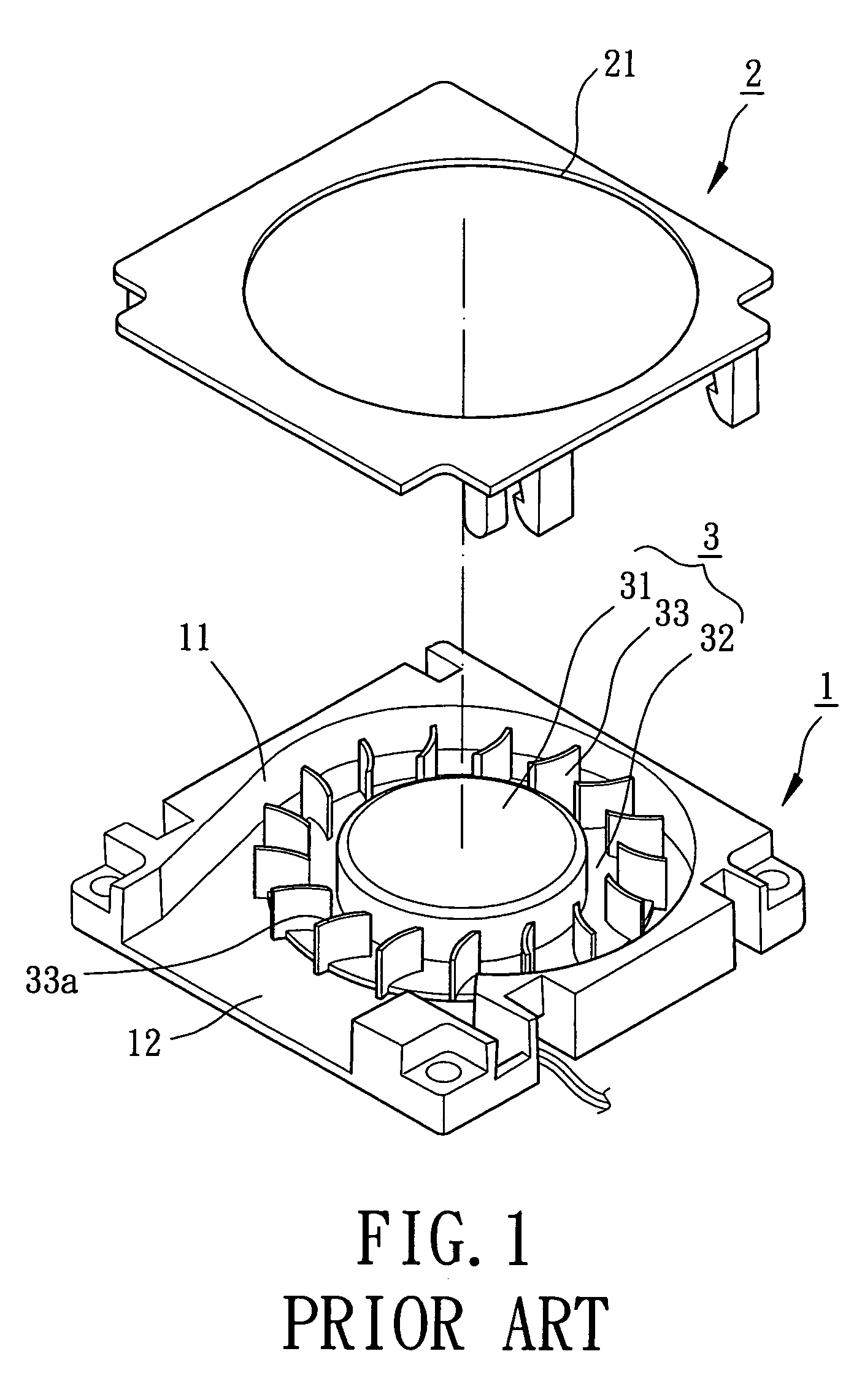
An impeller for a radial-flow heat dissipating fan includes a hub and a plurality of blades surrounding the hub. The blades are connected to a circumference of the hub to allow joint rotation of the hub and the blades. More than one blade include an air inlet side edge and an air outlet side edge. The air inlet side edge of each of the more than one blade has a radial length smaller than that of the air out side edge, thereby increasing an air inlet amount and smoothly changing incoming axial airflow into centrifugal airflow.
Owner:SUNONWEALTH ELECTRIC MACHINE IND
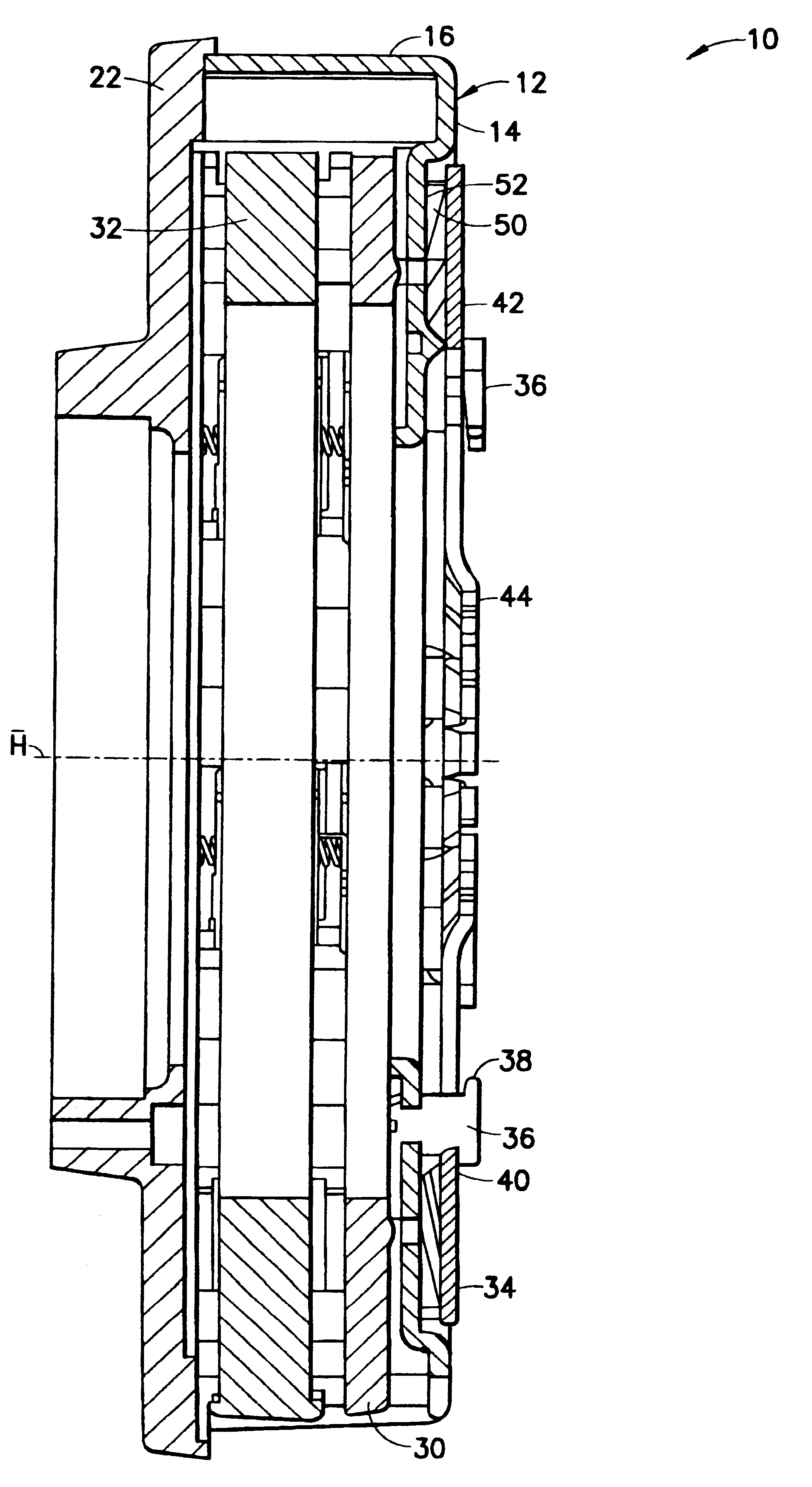
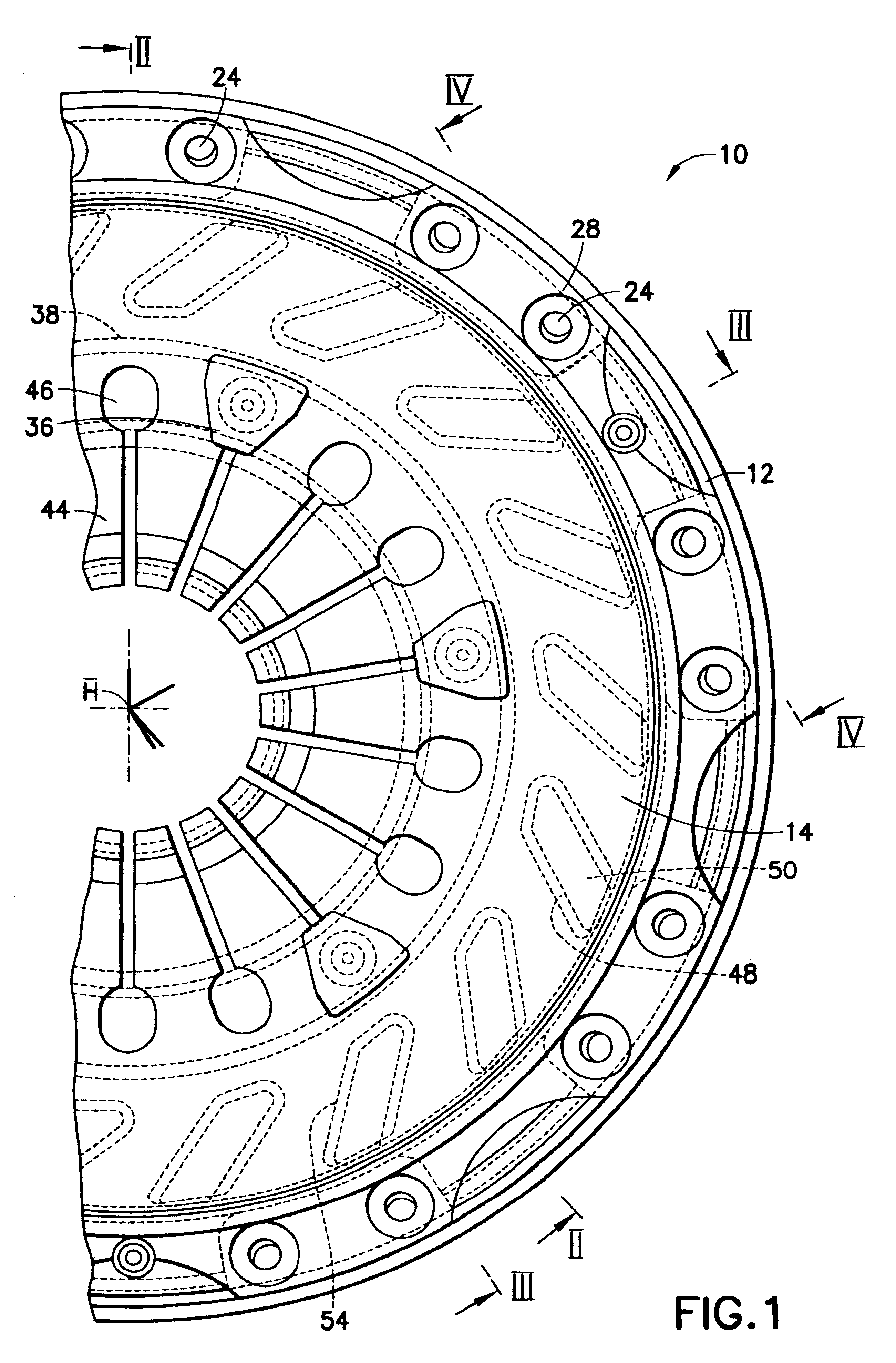
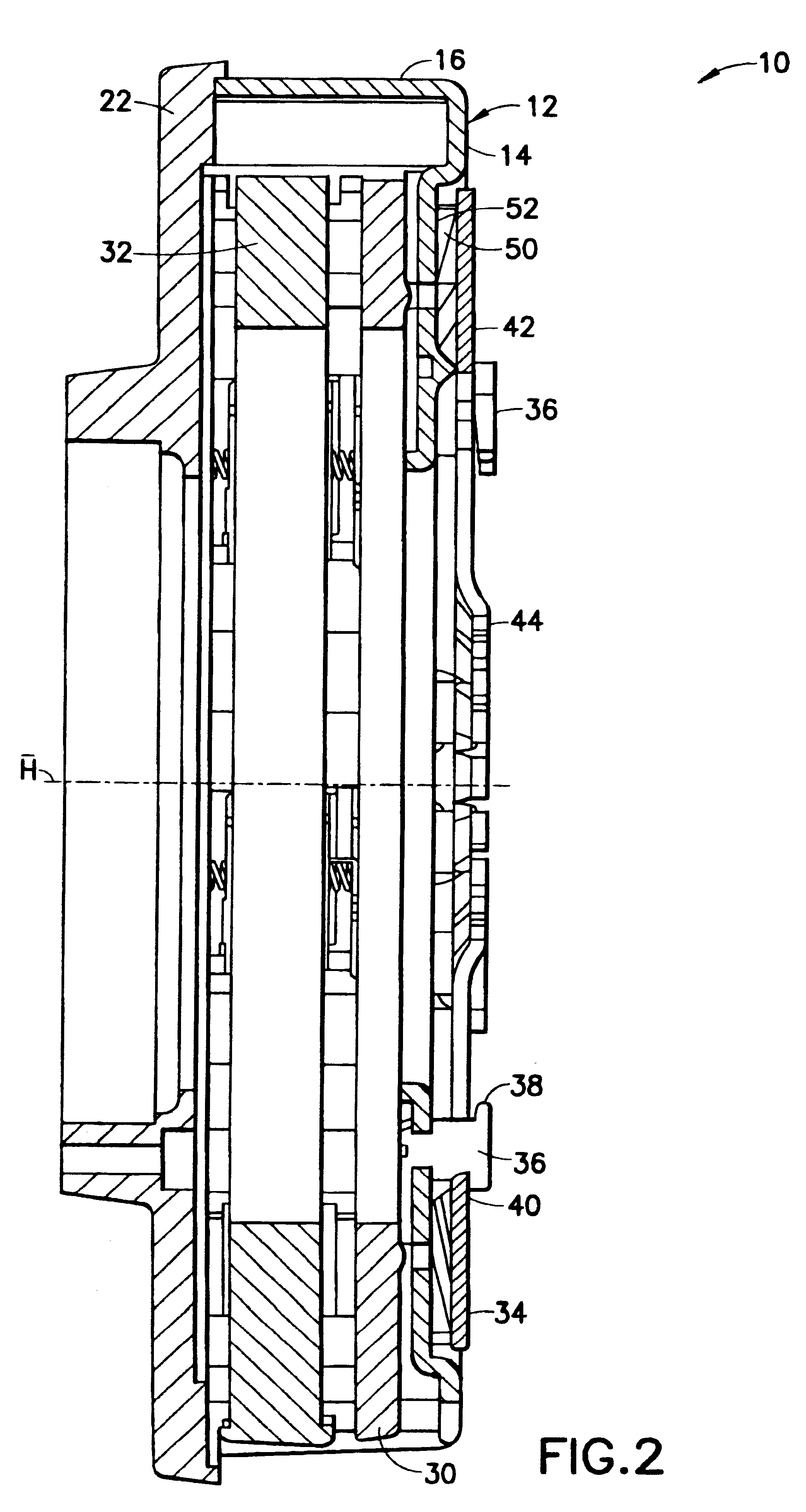
Pressure plate subassembly
A pressure plate subassembly for a friction clutch includes a housing connectable to an abutment arrangement for joint rotation about an axis of rotation, a pressure plate arranged in the housing so that the pressure plate is rotatable together with the housing about the axis of rotation (A) and so that the pressure plate is displaceable relative to the housing in the direction of the axis of rotation, and a force accumulator for generating a pressure force, the force accumulator being supported on the housing and on the pressure plate. The force accumulator is arranged outside the housing.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Tendon rope parallel skillful under-driven bionic robot finger device
InactiveCN101804633AGood Ready Grab StanceImprove grasping anthropomorphismGripping headsGearingLittle fingerEngineering
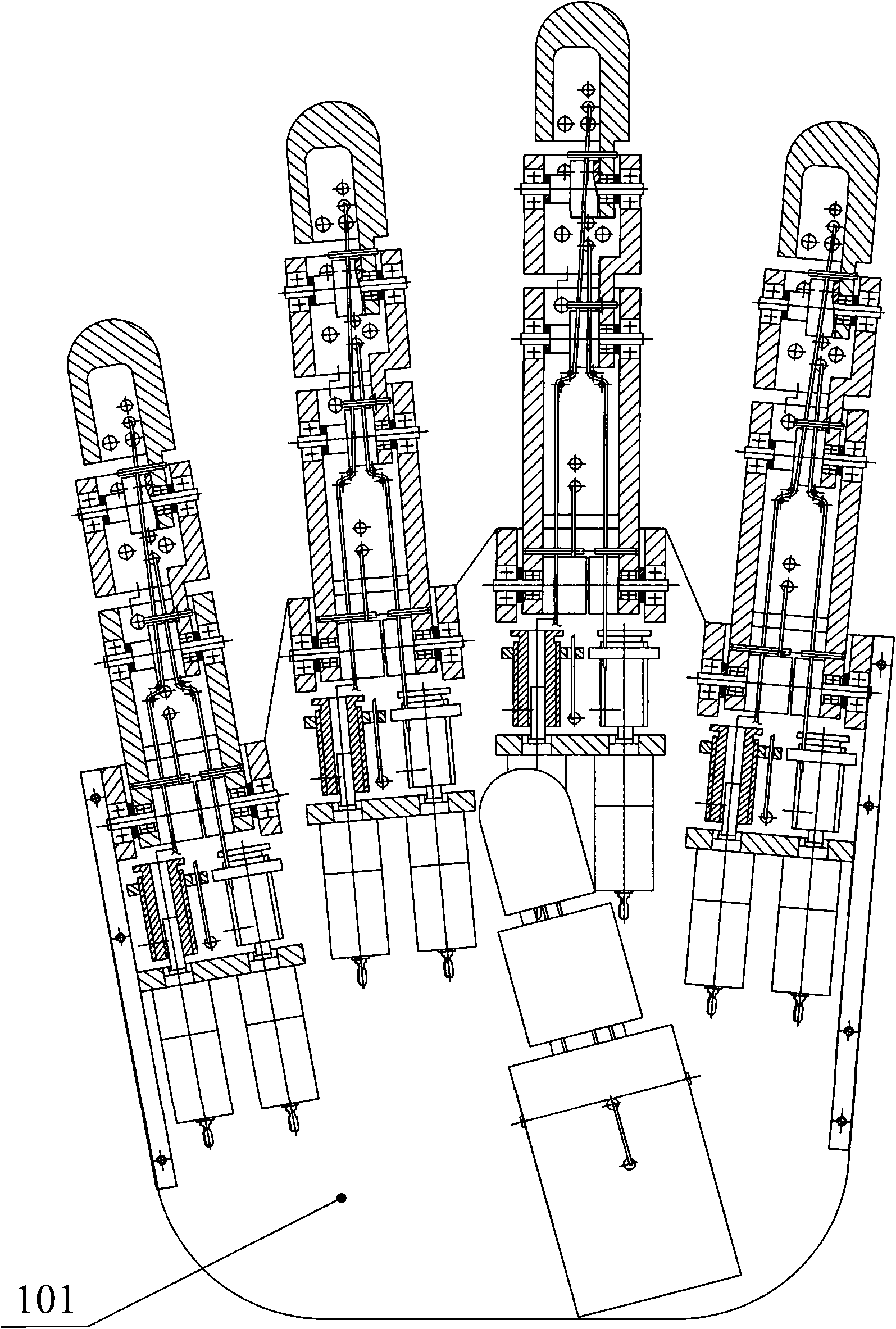
The invention discloses a tendon rope parallel skillful under-driven bionic robot finger device, which belongs to the technical field of anthropomorphic robots. The device is provided with 5 independently-controlled fingers and 14 joint freedom degrees and driven by 10 motors, wherein the middle finger, the ring finger, the little finger and the index finger have the same structures and are in double-motor driven three-joint rotations; and the thumb is fixedly connected in a palm and is in double-motor driven two-joint rotation. The fingers have similar structures, and comprehensively achieve the special effect of combining variable primary configuration and adaptive grab of the fingers by using motors, tendon ropes and reset spring pieces. The device can flexibly bend the middle joint of the finger before grabbing to reach a stable anthropomorphic pre-bending posture and grab an object in an adaptive under-driven mode during grabbing. The device has the advantages of compact structure, high integration degree and appearance, size, form and action close to human hands, can stably grab and automatically adapt to the objects with different shapes and sizes, also can perform simple operation, and is suitable to be used as an output terminal of the anthropomorphic robot.
Owner:WUXI RES INST OF APPLIED TECH TSINGHUA UNIV +1
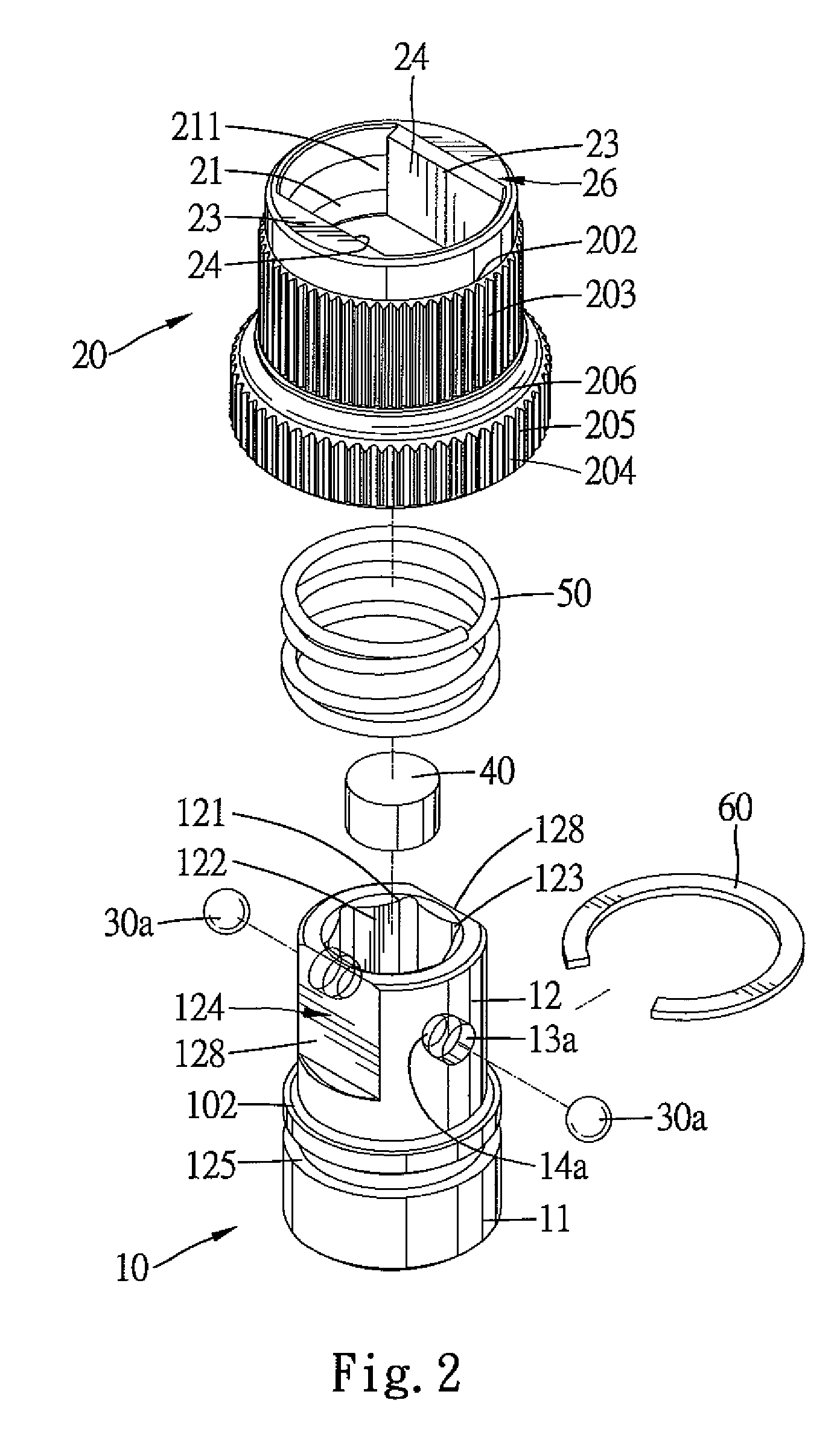
Chuck for bit
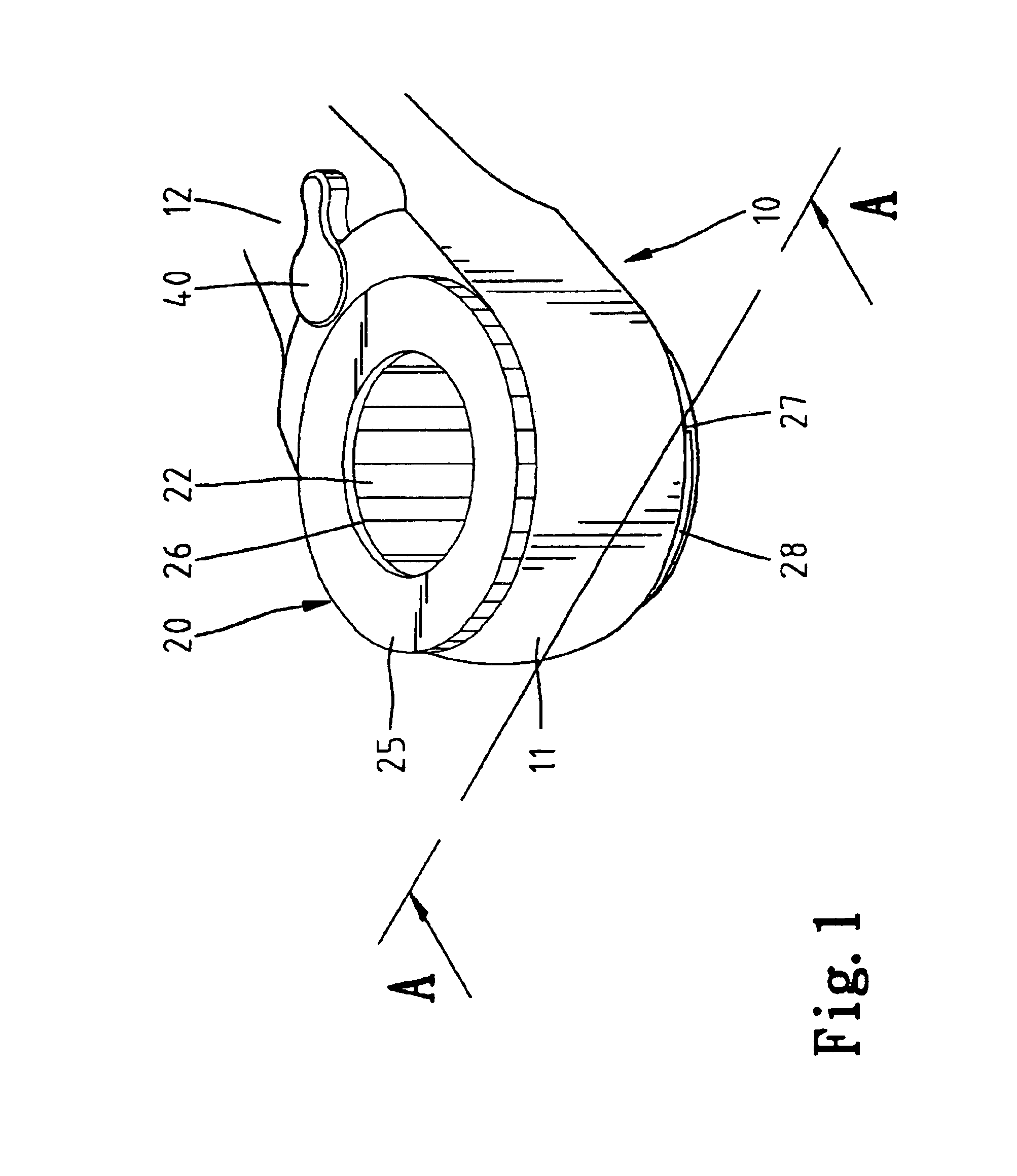
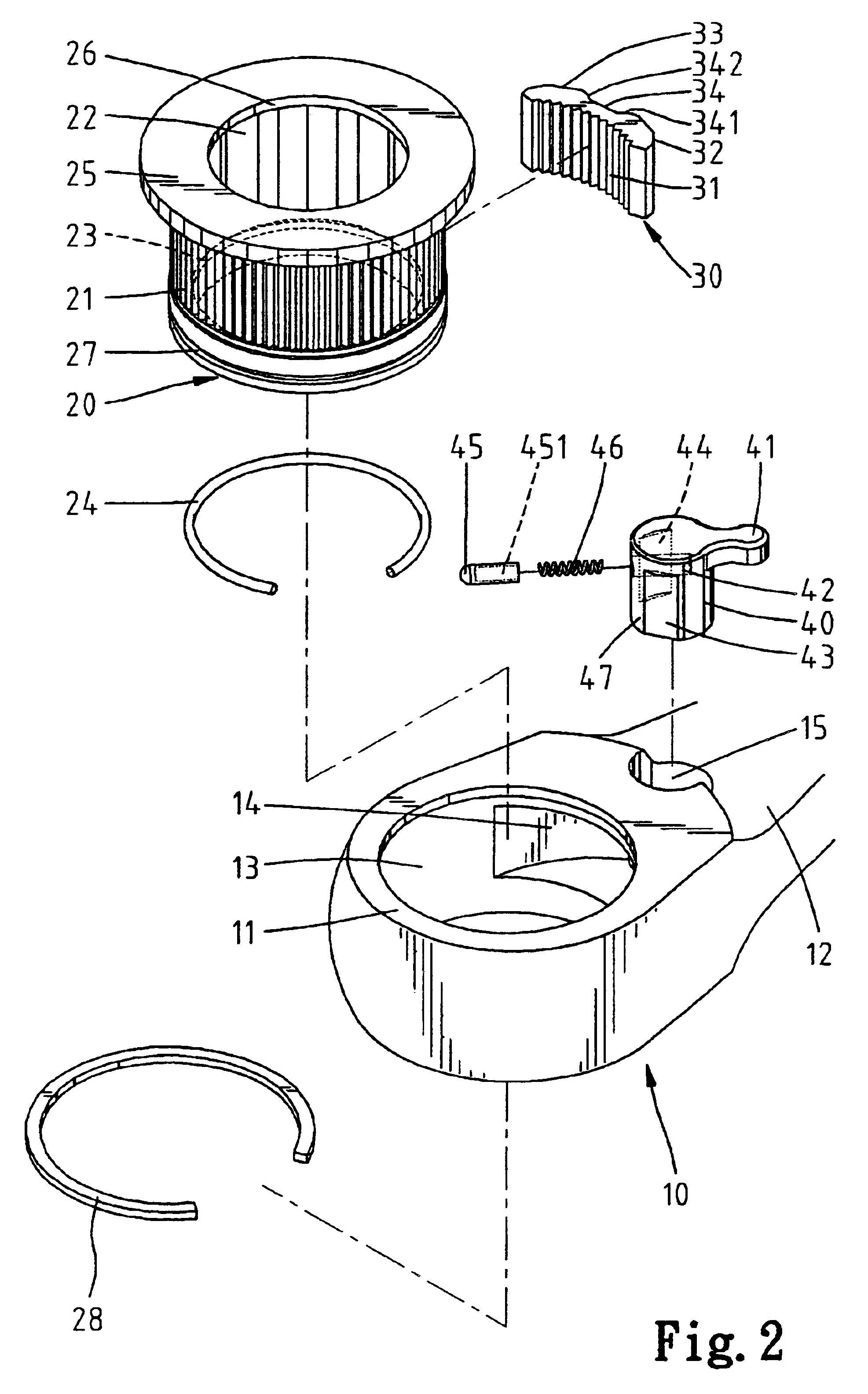
A chuck includes a body having an engaging groove for releasably receiving a bit. A sleeve is mounted around and movable relative to the body along a longitudinal axis of the body between a coupling position in which the bit is retained in the engaging groove and a releasing position allowing removal or insertion of the bit. The sleeve further includes an engaging section that slideably abuts a coupling section of the body. The engaging section is engaged with the coupling section to allow joint rotation of the body and the sleeve about the longitudinal axis. The sleeve further includes a flange with a frictional outer periphery to provide friction when the sleeve is manually rotated about the longitudinal axis by rotating the frictional outer periphery. Furthermore, the flange can be gripped by a user to move the sleeve to the releasing position.
Owner:HU BOBBY
Suspension type self-adaptive weight reducing device for rehabilitation training and rehabilitation training robot
ActiveCN107693301ARoughly constant weight lossImprove the effect of rehabilitation treatmentDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesBlock and tackleGravity center
The invention discloses a suspension type self-adaptive weight reducing device for rehabilitation training and a rehabilitation training robot. The device comprises a foldable mobile training frame, alower limb training assistive device carrying device, a weight reducing vest, a pulley rope system and a self-adaptive weight reducing box, the box is internally provided with a rope winding device and a self-adaptive gravity following device, the rope winding device is connected with a rope roller through a coupling by means of a servo motor cooperating with a speed reducer, and the reduced gravity is provided for a patient by winding or releasing the rope; the rope is led out by the rope roller and winds around a pulley on the side face of a mounting plate to be connected with the weight reducing vest through a pulley block on the self-adaptive gravity following device, the gravity position is calculated by collecting the joint rotation angle of the patient, a motor of the self-adaptivegravity following device is controlled to drive a lead screw to rotate through the coupling, and a shifting board connected with a lead screw nut drives a movable pulley to do liner motion. In this way, the length of the suspension rope in the training process of the patient is adjusted, gravity following is achieved, and the roughly constant reduce gravity is maintained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Upper arm of robot
ActiveCN103895032ACompact structureEasy to assembleProgramme-controlled manipulatorArmsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationGear wheel
The invention discloses an upper arm of a robot. The upper arm comprises a wrist joint power input device and a wrist joint. The wrist joint power input device comprises a fourth joint servo motor, a fifth joint servo motor, a sixth joint servo motor, and a motor protection cover. The wrist joint comprises a fourth joint reducer, a fifth joint reducer, a sixth joint reducer, a fourth joint power shaft, a fifth joint power shaft, a sixth joint power shaft, a fourth joint rotation arm, a fifth joint rotation arm and a tail-end mechanical flange. The fifth joint power shaft is arranged in the sixth joint power shaft, and the sixth joint power shaft is arranged in the fourth joint power shaft. The upper arm of the robot is compact in structure, easy to assemble, high in transmission efficiency, adjustable in gear clearance, small in overall volume of wrists of the industrial robot, flexible and portable; the fifth and sixth joints are same in modulus optimization, part specifications can be reduced, butch production can be facilitated, and the problems about dispersion of power distribution and routing of servo motor cables in an original structure can be solved.
Owner:成都三译智能技术有限公司
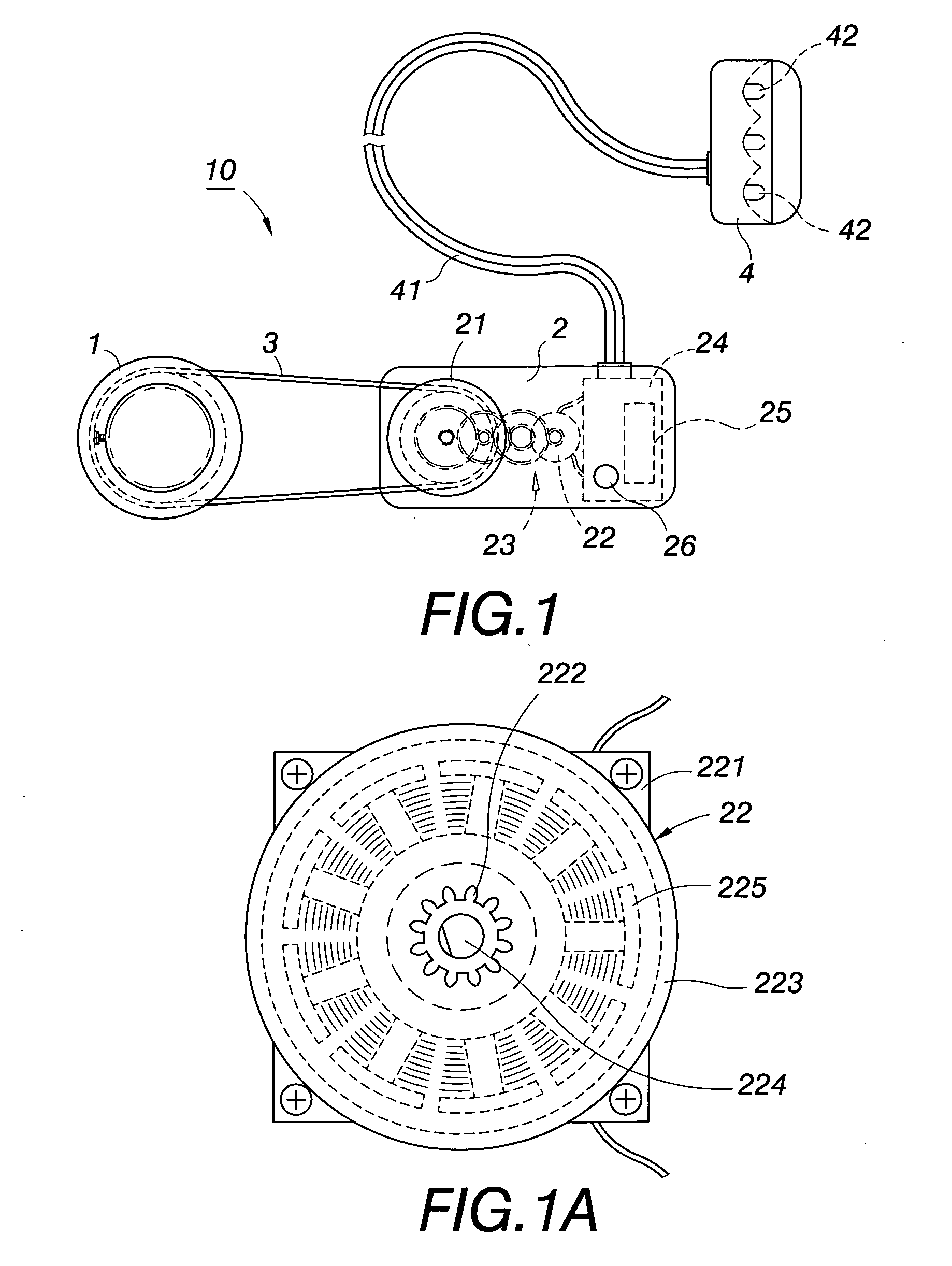
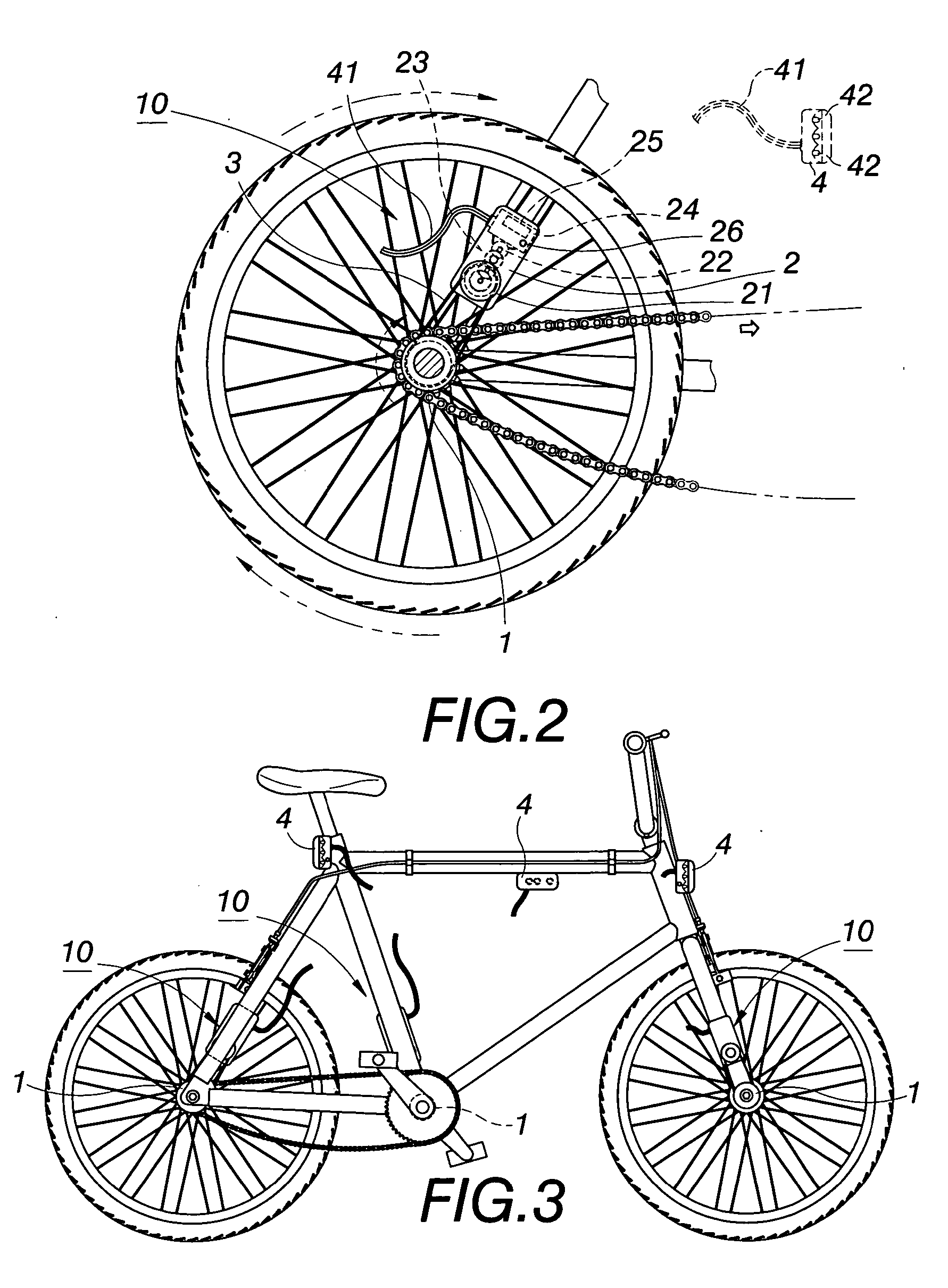
Emitting light device for bicycles
An emitting light device of the present invention is realized on the bicycle to generate and conserve electric power, to light the emitting light device. In practice a driven wheel combined with rotating portion (i.e. rear wheel) of the bicycle to form a center-pivot type of axis-joint rotating structure. A bicycle dynamo includes 1. an actuated wheel and a dynamo with a set of differential gears between them, 2. a PCB, and 3. a battery accumulator. A transmission belt is rotated around the driven and actuated wheels; an emitting light base has conducting cords connected to PCB of the dynamo. As the driven wheel rotates, the actuated wheel is driven to rotate by the transmission belt. The speed ratio of transmission is changed by a set of differential gears to run the dynamo generate DC electricity and conserve electricity for battery. DC electricity can be applied to light LED.
Owner:WANG TSENG FAN +1
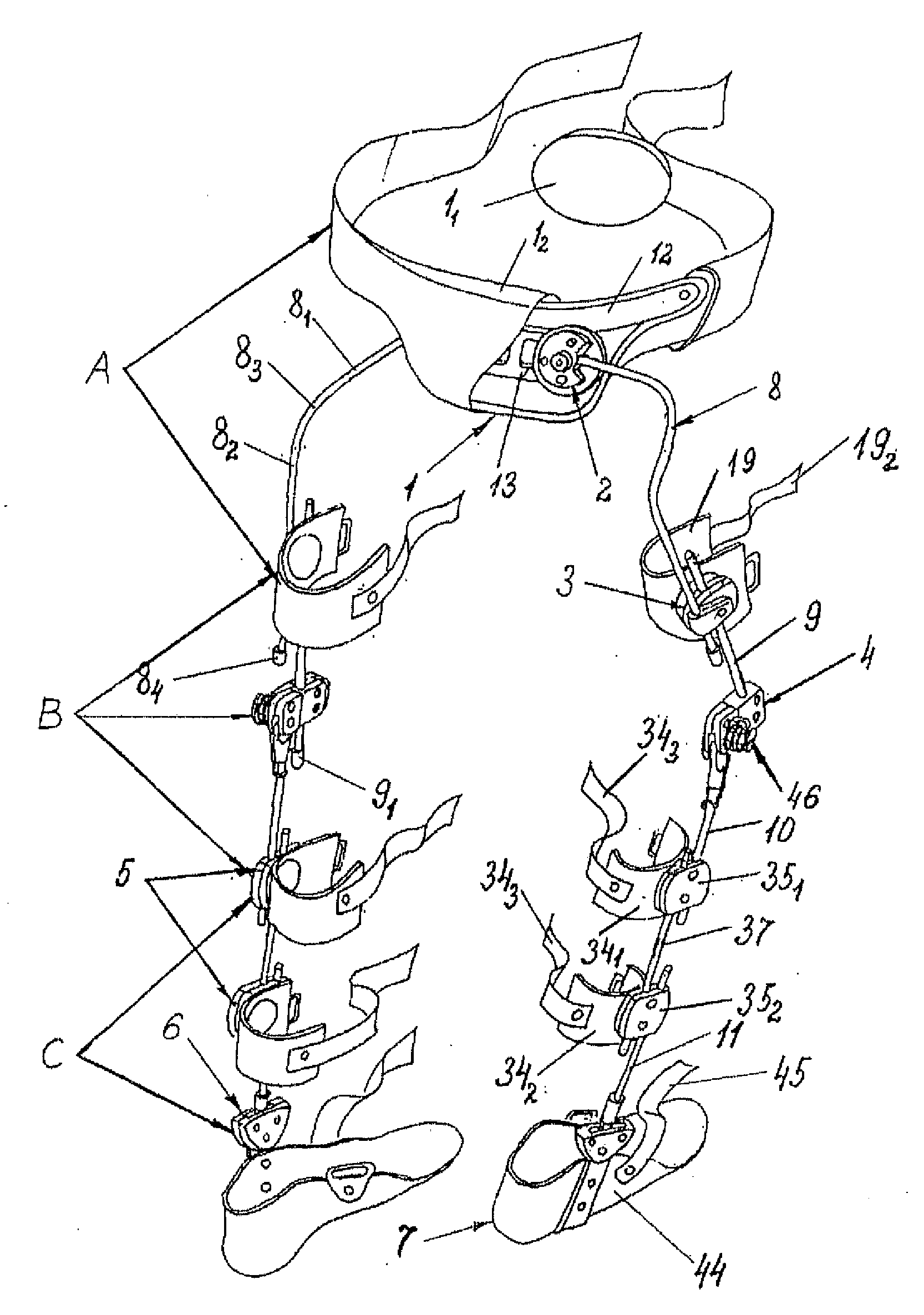
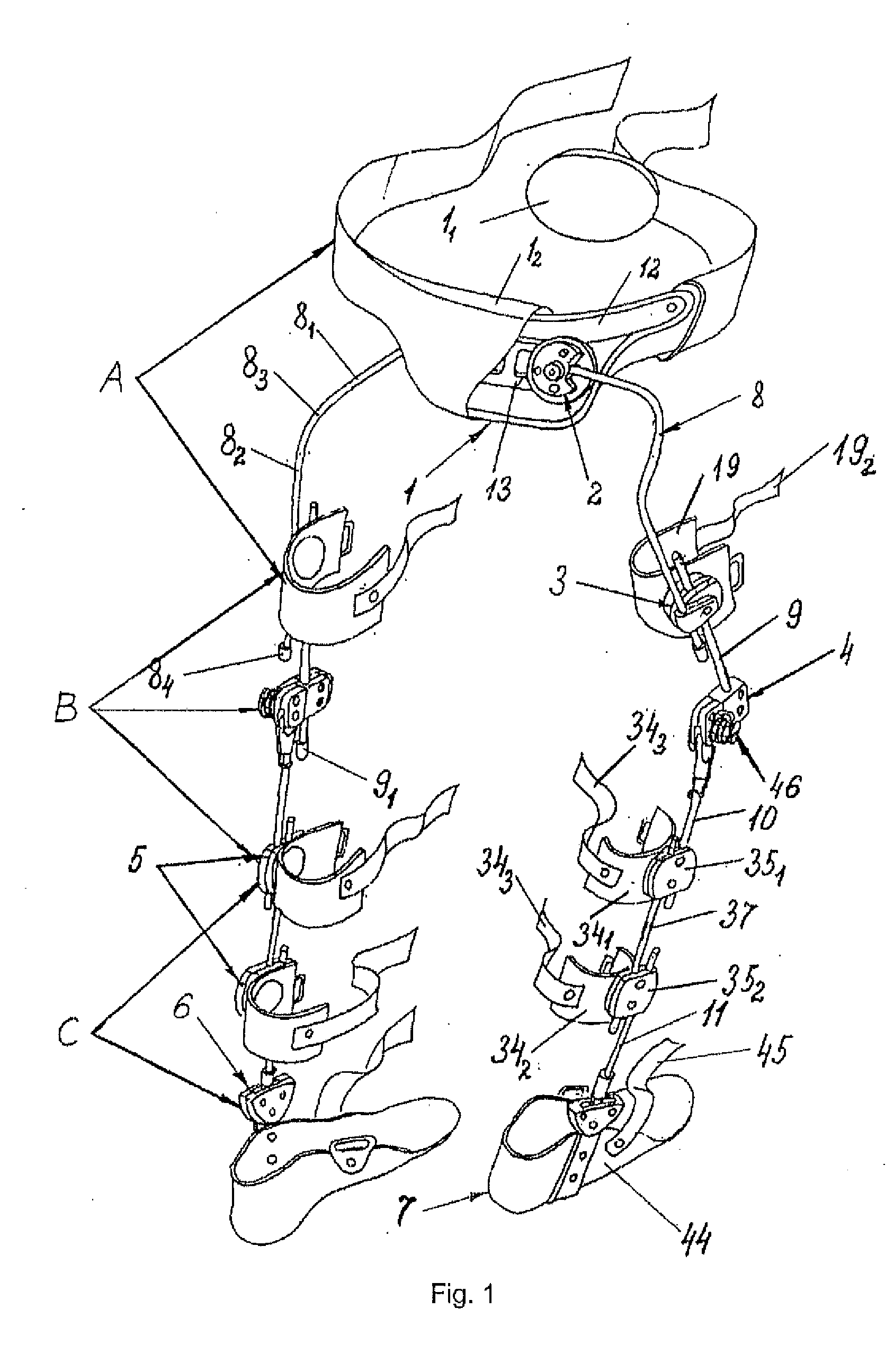
Method for correcting pathological configurations of segments of the lower extremities and device for realizing same
InactiveUS20120259259A1Raise the possibilityFreedom of movementFractureOrthopedic corsetsTibiaRange of motion
The invention relates to a method for the step-by-step correction of the position of the longitudinal axes of segments of the lower extremities in the horizontal and / or frontal and / or sagittal planes, that comprises the simultaneous dosed correction of the imbalance of forces in the muscles supporting the corresponding joints, the reduction of the pathological configurations of the segments, and the fixation of corrected segments using at least one module of a modular exoskeleton capable of individual adjustment for bringing, during each step, the position of the longitudinal axis of each segment closer to the physiologically correct position, and for permitting movements about the corrected rotation axes of the joints within a predetermined range defined by the modular exoskeleton. The proposed device for correcting pathological configurations of segments of the lower extremities comprises a modular exoskeleton, the modules of which can be used independently or in various combinations. The modular exoskeleton comprises at least one adjustable pelvis belt (1, 47), at least one means (3, 51) for holding the thigh in a given position, at least one means (4, 89) for rotating the tibia, at least one means (5, 121) for holding the tibia in a given position, at least one means (6, 130) for correcting the position of the foot and the movement range thereof at the foot-tibia joint, at least one means (7, 146) for accommodating the foot, and a set of fixation members each in the form of a cylindrical rod (8, 9, 10, 11, 37, 52, 83, 90, 124, 141, 142) capable of linear positioning movement and / or rotation and / or free linear movement.
Owner:ZAKRYTOE AKTSIONERNOE OBSCHESTVO NAUCHNO PROIZVODSTVENNY TSENTR OGONEK
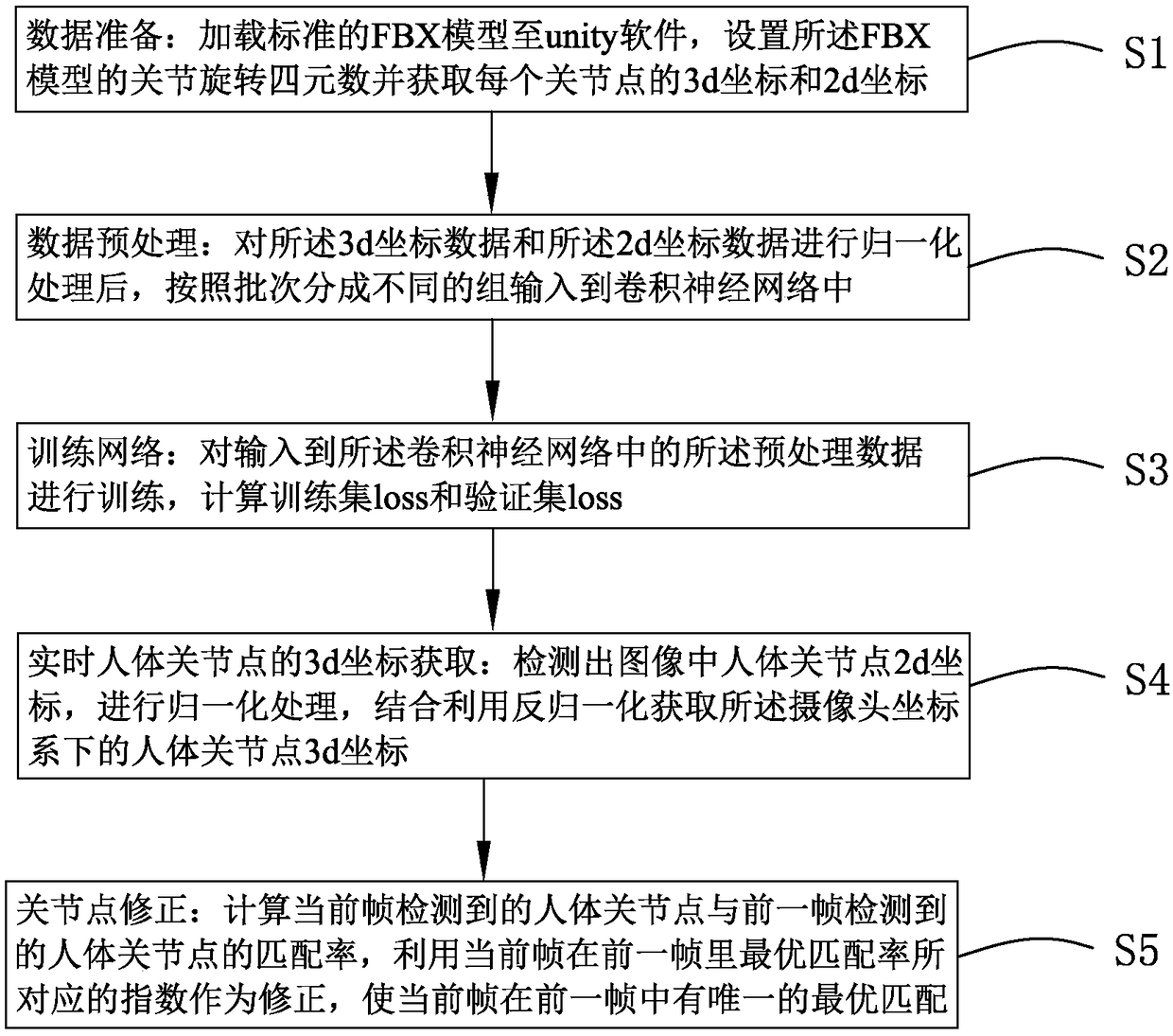
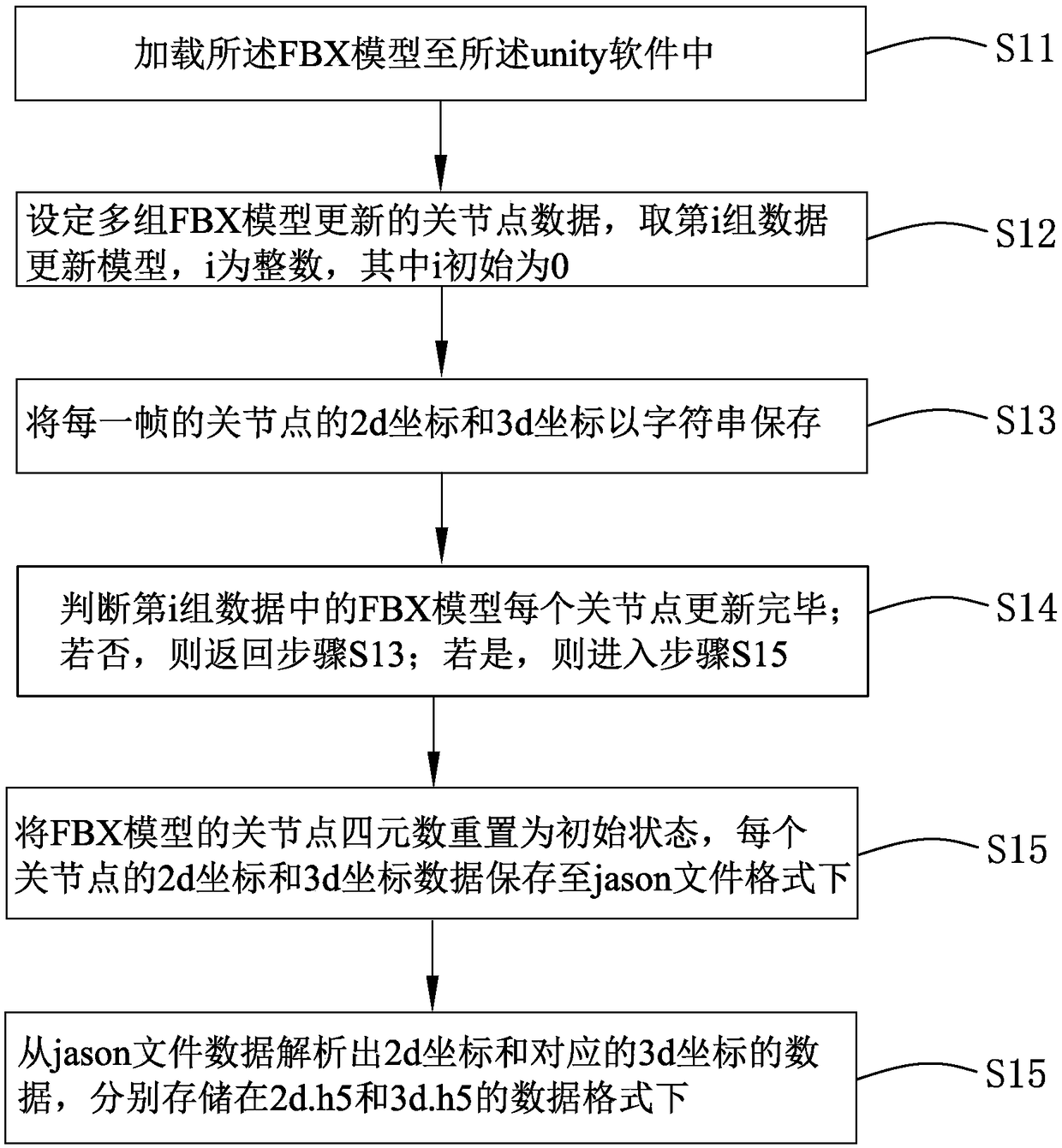
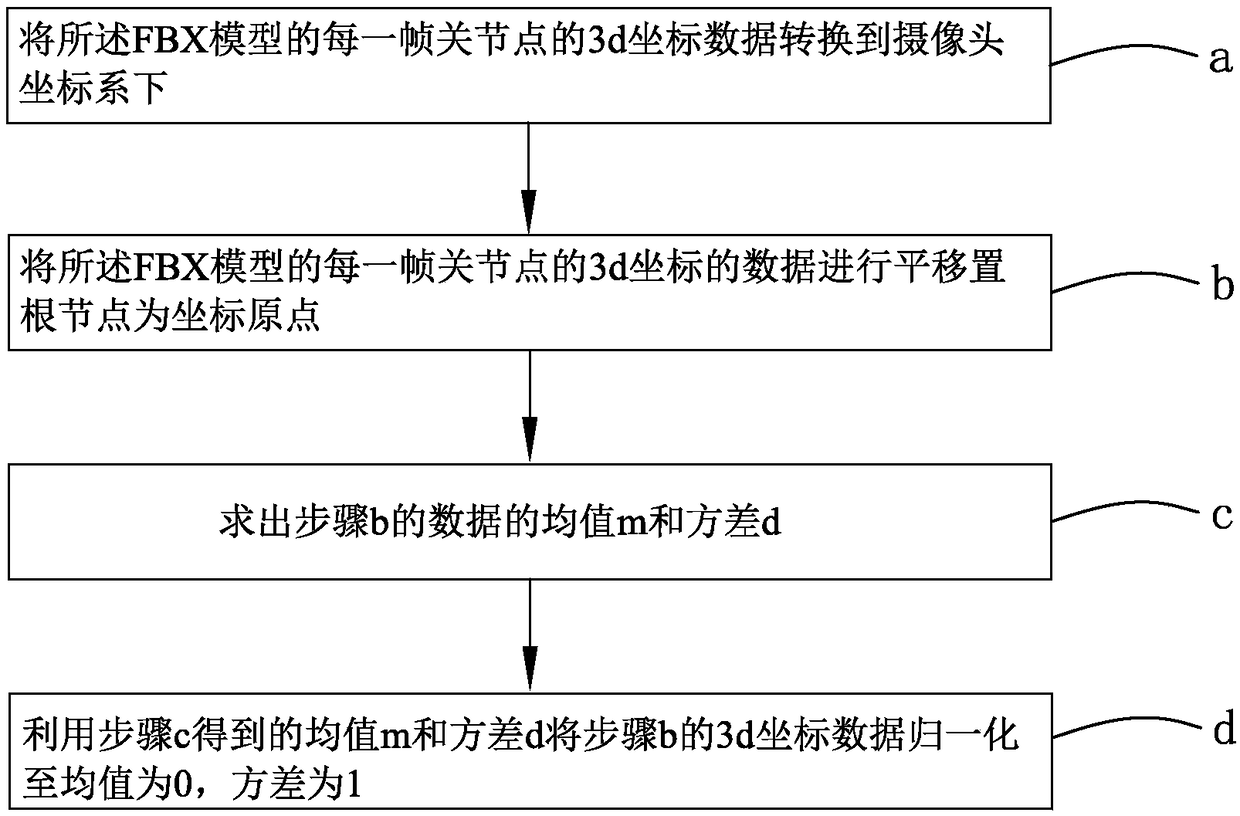
Method for acquiring 3d (three-dimensional) coordinates of human skeleton joint points on basis of deep learning
ActiveCN108829232ALow costReduce computationInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementApplicability domainHuman skeleton
The invention provides a method for acquiring 3d (three-dimensional) coordinates of human skeleton joint points on the basis of deep learning. The method comprises the following steps of: data preparation, i.e., loading a standard FBX model to unity software, setting a joint rotation quaternion of the FBX model and acquiring 3d coordinates and 2d coordinates of each joint point; data preprocessing, i.e., carrying out normalization processing on 3d coordinate data and 2d coordinate data and inputting into a convolutional neural network; network training, i.e., calculating a training set loss and a verification set loss; and real-time acquisition of the 3d coordinates of the human joint points, i.e., after detecting out the 2d coordinates of the human joint points in an image and carrying out normalization processing, inputting to the convolutional neural network, and combining and utilizing anti-normalization to acquire the 3d coordinates of the human joint points under a camera coordinate system. Compared to the related art, the method for acquiring the 3d coordinates of the human skeleton joint points on the basis of deep learning, which is provided by the invention, is low in hardware cost, high in accuracy and wide in application range.
Owner:深圳市同维通信技术有限公司
Method for folding wearable lower limb assisting robots
The invention discloses a method for folding wearable lower limb assisting robots. The method is characterized by comprising detaching leg following support elastic components from assisting mechanical legs, and sequentially outwardly turning hinge centers of the upper end edges of hip joint rotation limiting discs and the lower portions of bosses by 90-degree angles by the aid of thigh folding components and shank folding components; outwardly and oppositely folding the assisting mechanical legs at the shank folding components; inwardly and oppositely folding the assisting mechanical legs at the thigh folding components; obtaining portable bodies of the wearable lower limb assisting robots. The wearable lower limb assisting robots are in initial states when central connecting lines of thigh connecting rods and shank connecting rods are at mutual coincidence positions. The method has the advantages that the wearable lower limb assisting robots can be turned into the portable bodies with compact structures and can be used with loading and transporting trolley cases, so that users can conveniently carry and store the wearable lower limb assisting robots in various modes, and daily activity and nursing requirements such as walking and stair ascending and descending of the users can be effectively met.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Robot tool central point calibration method using two-dimensional measurement functional tablet
ActiveCN104457645AAchieve coincidenceAvoid overlappingMeasurement devicesJoint coordinatesSimulation
The invention discloses a robot tool central point calibration method using a two-dimensional measurement functional tablet. A robot is controlled to enable a TCP to make contact with a measurement area of a calibration tool more than three times in different postures in the calibration process, joint coordinate information of the robot is recorded in the contact process, and the two-dimensional coordinates of the contact points in a measurement plane are output through the two-dimensional position measurement function of the calibration tool; the coordinates of the TCP in a robot tail end tool coordinate system are calculated according to measured joint rotation angle information of the robot and the coordinate data of the contact points on the tablet and in combination with the structural parameters of the robot, and the calibration accuracy is evaluated. According to the calibration method, the TCP of the robot does not need to coincide with the same fixed point multiple times, the point-point coincidence requirement is weakened to point-surface coincidence, and operation is easy. When the TCP of the robot has small deviation, autonomous calibration can be realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flexible mechanical arm synchronous measurement method, system and device
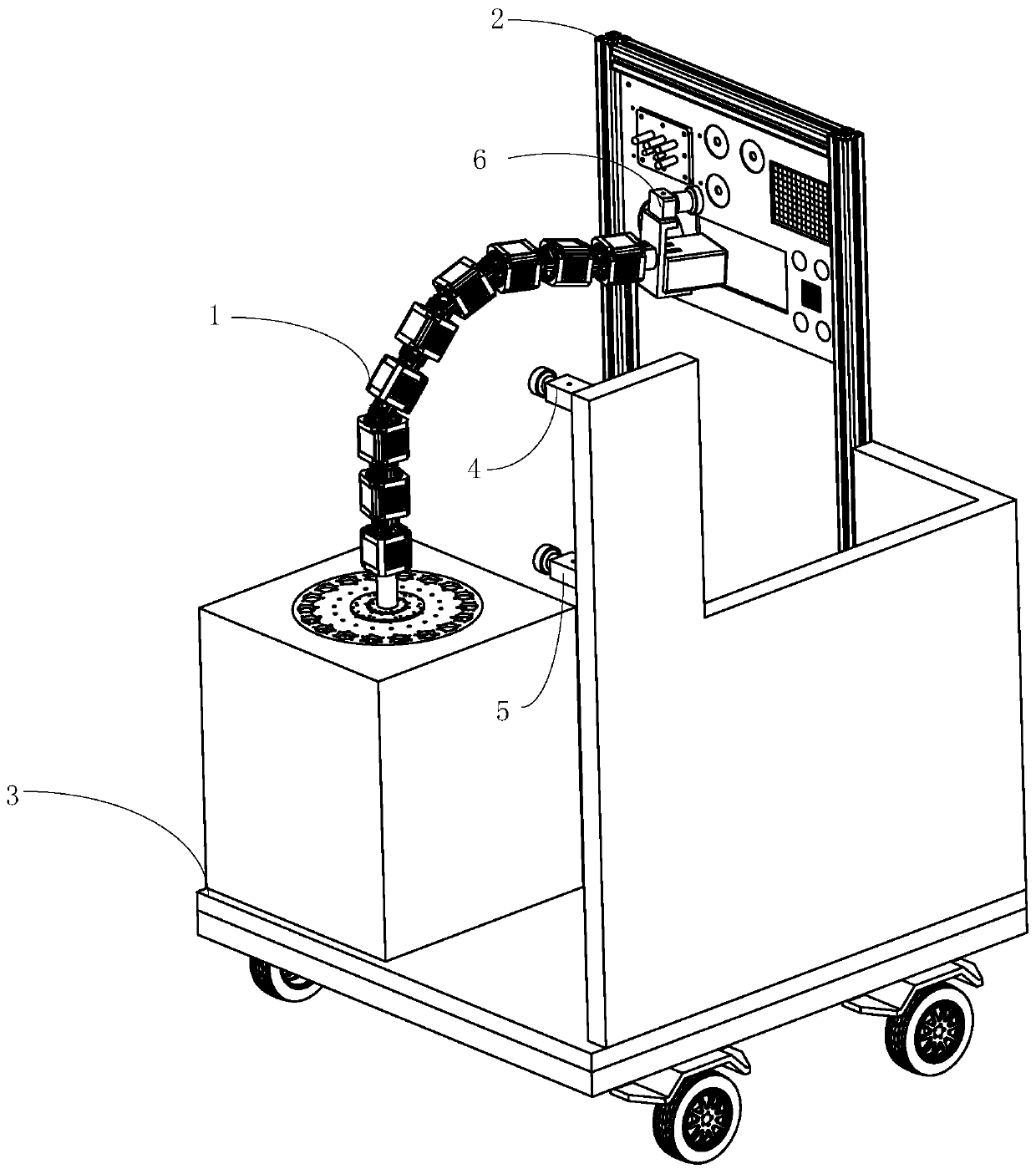
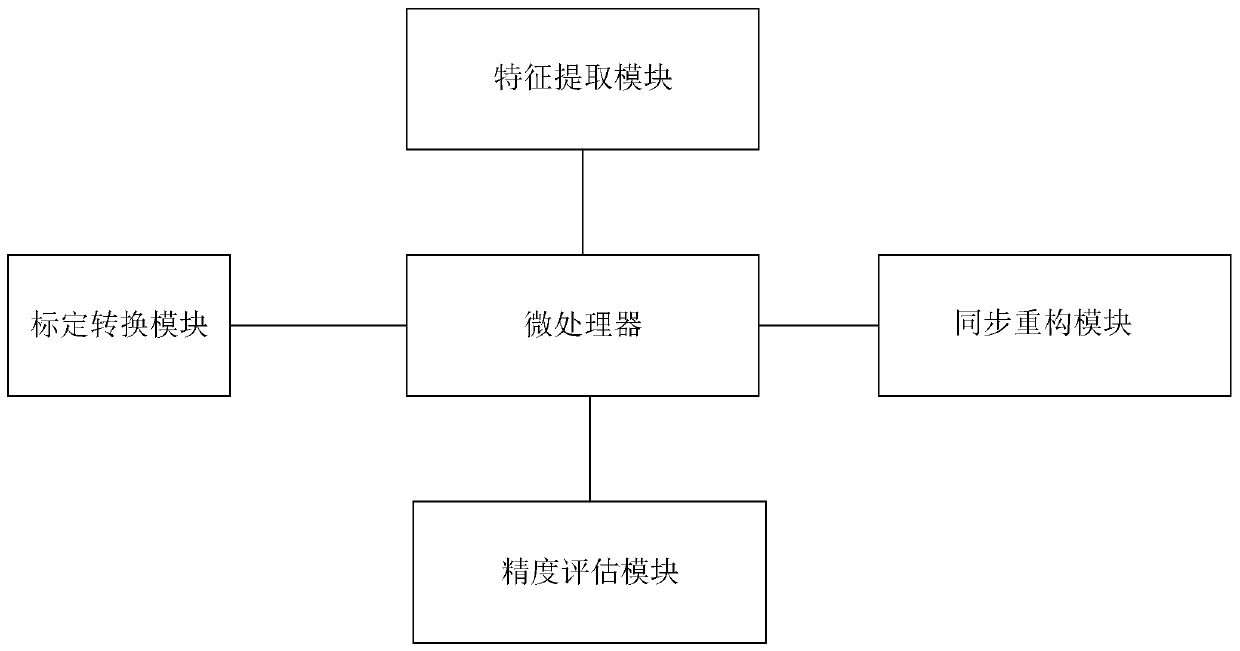
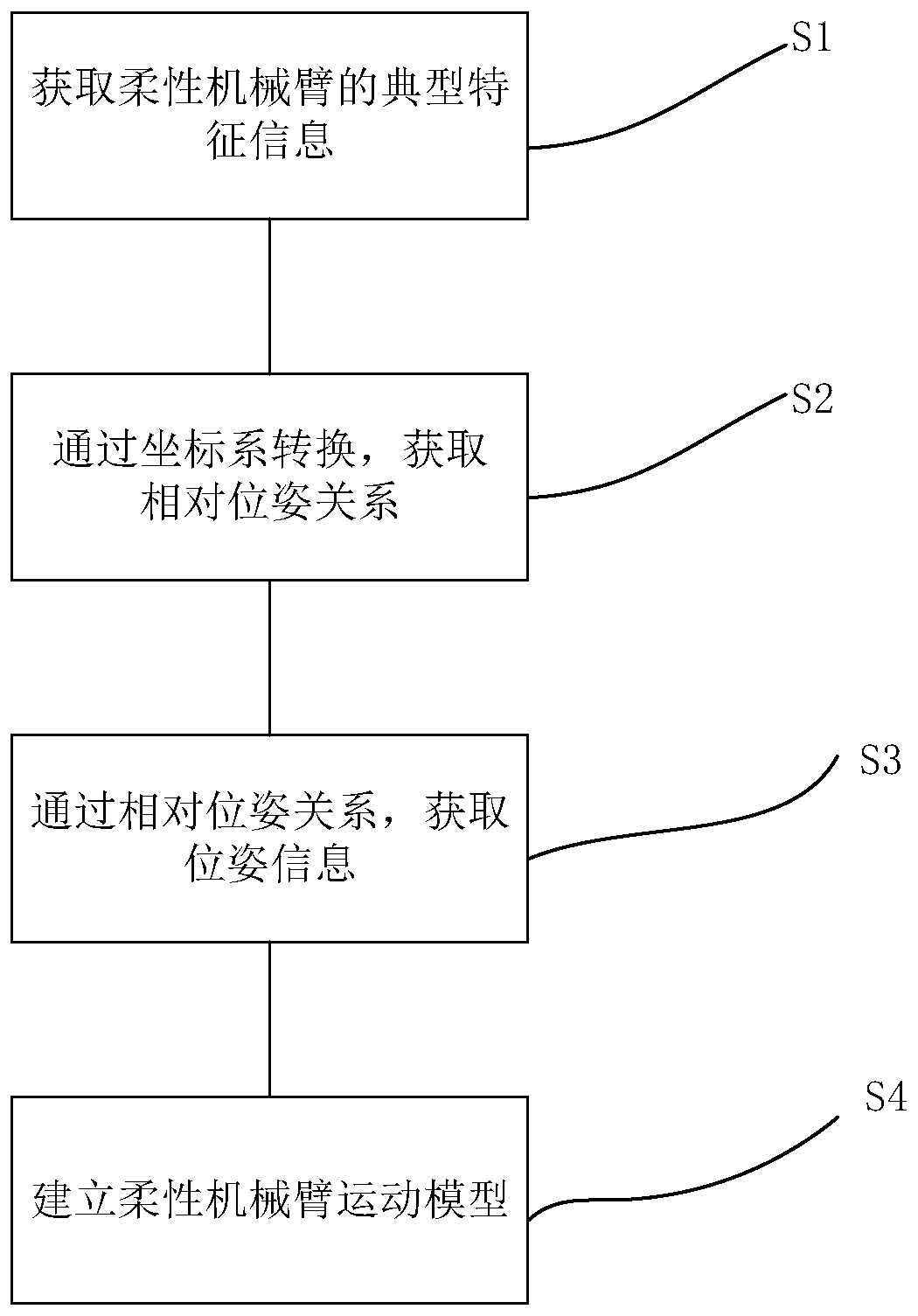
ActiveCN110695993AQuickly obtain typical characteristic informationAccurate acquisition of revolving jointsProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a flexible mechanical arm synchronous measurement method and a flexible mechanical arm synchronous measurement system with the synchronous measurement method. The flexible mechanical arm synchronous measurement method includes the following steps that typical characteristic information of a flexible mechanical arm is acquired; coordinate system conversion is carried out, sothat the relative posture relationship of a base, all joint rotation centers and the tail end of the flexible mechanical arm is acquired; posture information of all rotation joints and the tail end of the flexible mechanical arm and a hand-eye camera relative to the movable base is acquired through the relative posture relationship; and a flexible mechanical arm motion model is established according to the posture information, the typical characteristic information of the flexible mechanical arm is rapidly acquired, coordinate conversion is carried out, then the posture information of all therotation joints and the tail end of the flexible mechanical arm is precisely acquired, and the flexible mechanical arm motion model is precisely established. According to the flexible mechanical armsynchronous measurement method, system and device, the flexible mechanical arm motion model can be precisely established, and precision measurement is carried out.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Assembly system for synchronizing devices in a gearbox
InactiveCN1604997AImprove utilizationRoughly constant spoke thicknessMechanical actuated clutchesCouplings for rigid shaftsCouplingEngineering
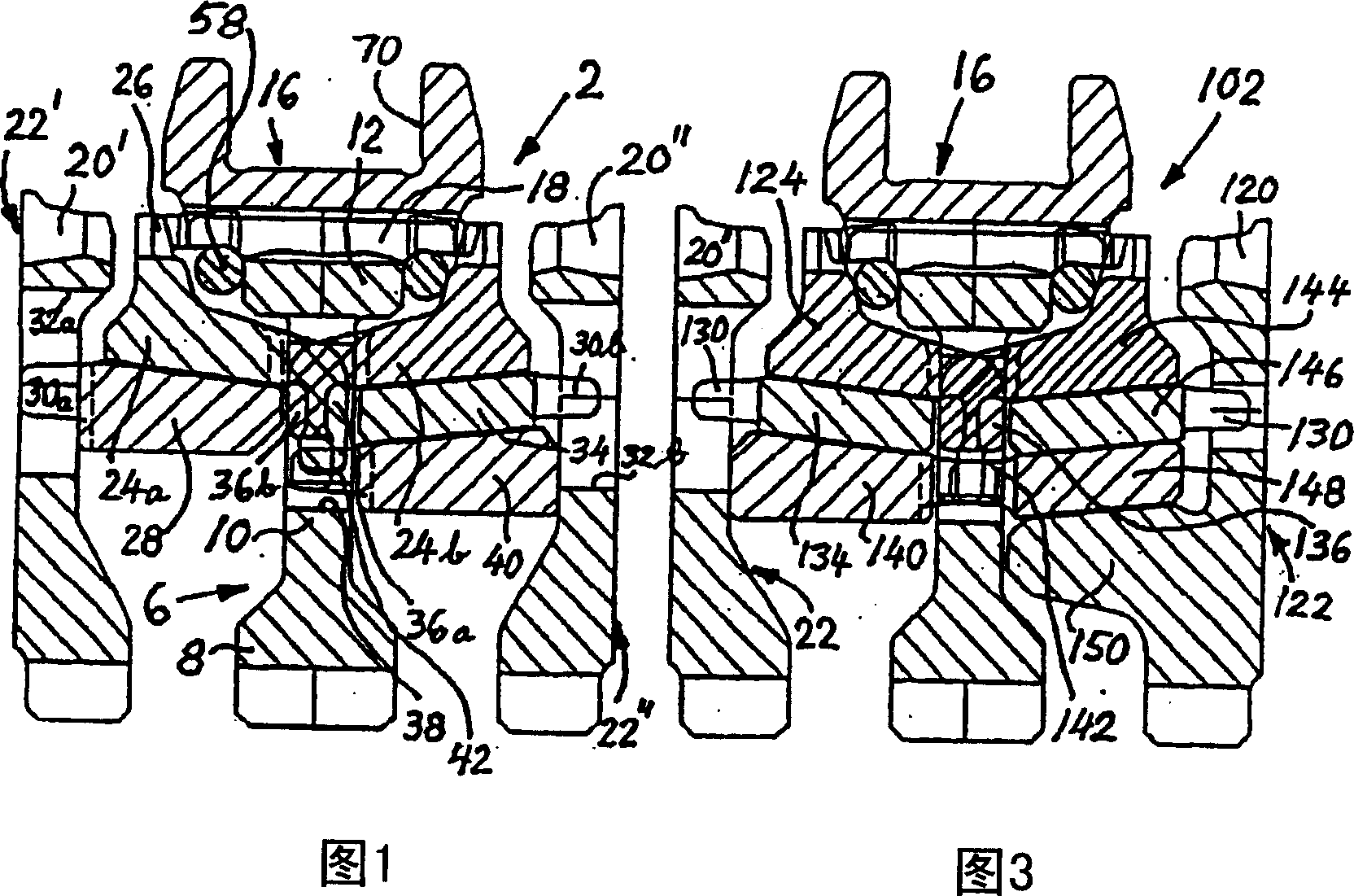
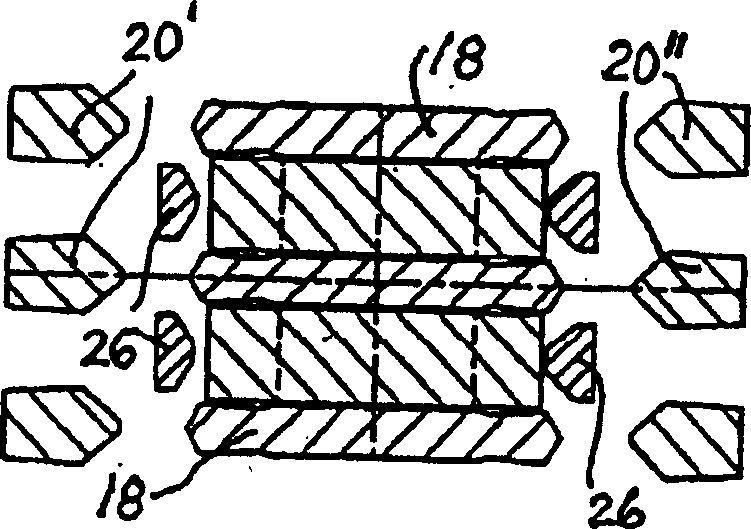
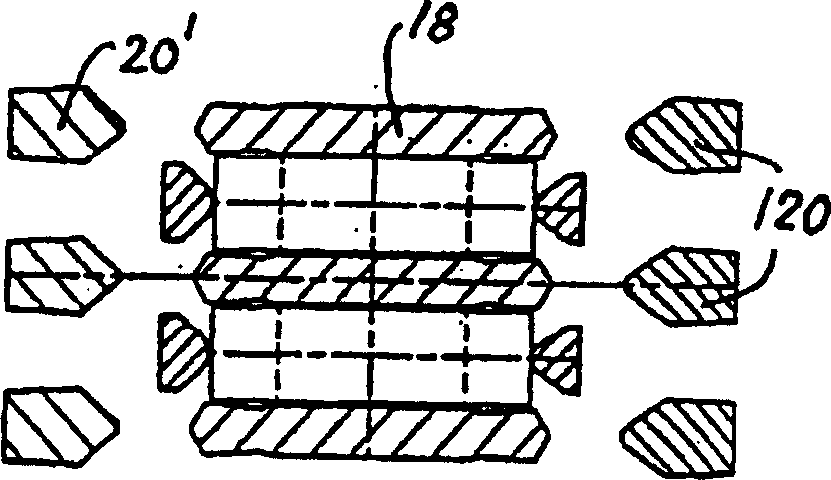
Structuring system for synchronising devices for a gearbox, whereby the synchronising device comprises: a carrier (6) which is mounted on, and for joint rotation with, a gearbox shaft (4) and which has not only a hub portion (8) connected to the shaft but also a web portion (10), which carrier supports for joint rotation with it but axial mobility relative to it a surrounding shift sleeve (16) whereby the carrier can be coupled to a coupling element (22',22'') fastened firmly to a gearwheel mounted rotatably on the shaft; at least one inner synchronising ring (28, 40) with conical outer friction surface; an outer synchronising ring (24a, 24b) with conical inner friction surface and external locking teeth (26); an intermediate synchronising ring (34) fitted between the inner and outer synchronising rings. The structuring system is usable for single, double or triple synchronisation versions, and the outer synchronising ring (24a, 24b) has driving protrusions (36a, 36b) which engage at least halfway in the web portion of the carrier. Each driving protrusion is situated in an engagement aperture (38). The synchronising ring (28, 34) immediately within the outer synchronising ring provided with locking teeth (26) has on its side facing away from the web portion of the carrier axial driving protrusions (30a, 30b) which each engage in respective adjacent coupling elements (22', 22'').
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Dogging device for latch assembly
A dogging device includes a base mounted in a housing of a latch assembly. The base includes a hole through which a shaft rotatably extends. A limiting keyway extends from the hole and receives and limits rotation of a shaft key on the shaft. A dogging member includes a through-hole receiving the shaft. A keyway extends from the through-hole and receives the shaft key of the shaft, allowing joint rotation of the shaft and the dogging member. By engaging a tool with a driving groove in an end of the shaft or by utilizing a lock core key to turn a lock core that directly pivots the dogging member, the dogging member is pivotable between a first position engaged with a latching / unlatching control rod of the latch assembly to lock a latch bolt in a retracted state and a second position disengaged from the latching / unlatching control rod.
Owner:I TEK METAL MFG
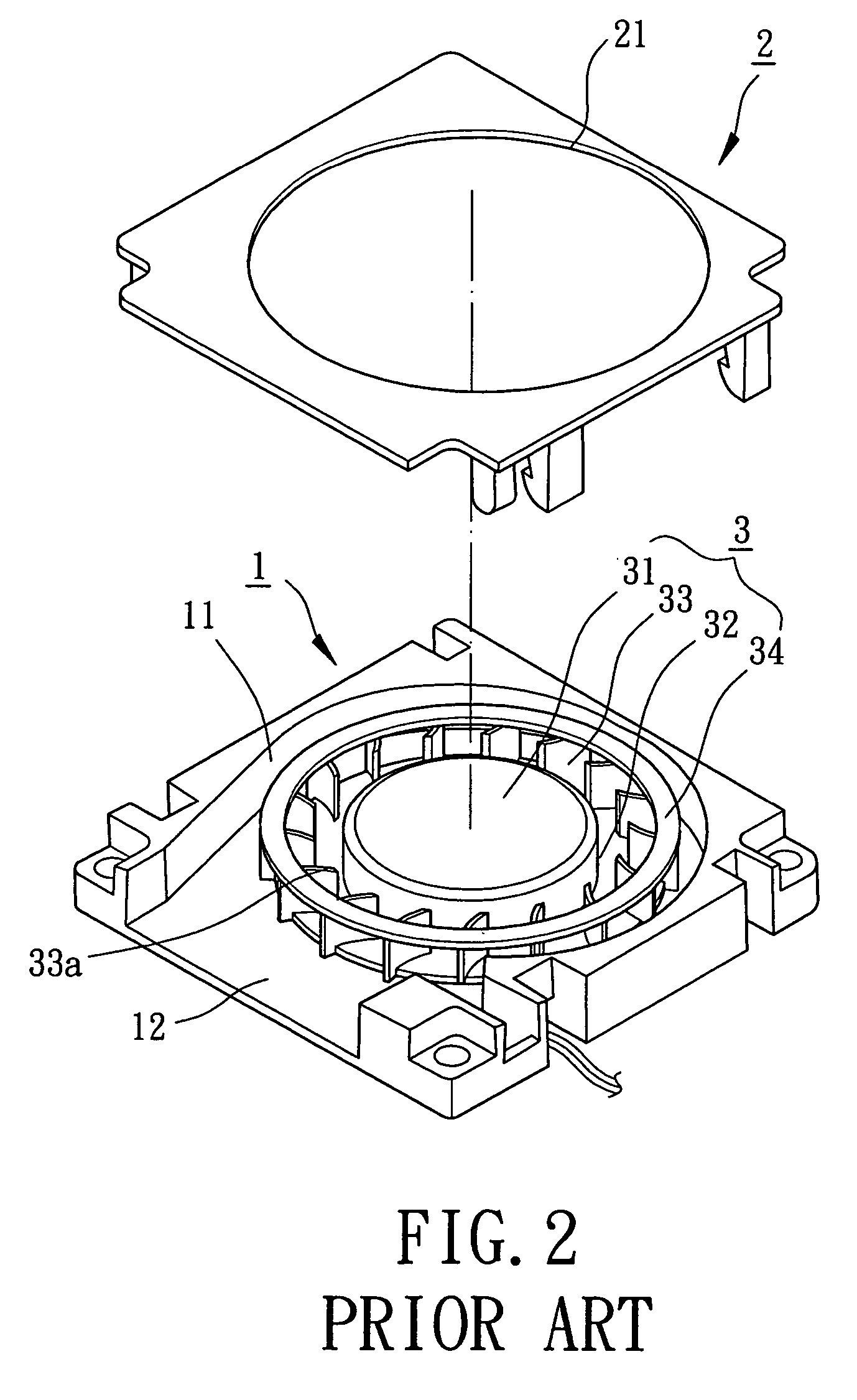
Impeller for radial-flow heat dissipating fan
An impeller for a radial-flow heat dissipating fan includes a hub and a plurality of blades surrounding the hub. The blades are connected to a circumference of the hub to allow joint rotation of the hub and the blades. The impeller includes an air inlet side and a bottom side. Distribution of the blades at the air inlet side of the impeller is sparser than that at the bottom side of the impeller, thereby increasing an air inlet amount.
Owner:CHINOOK SCIENCES +1
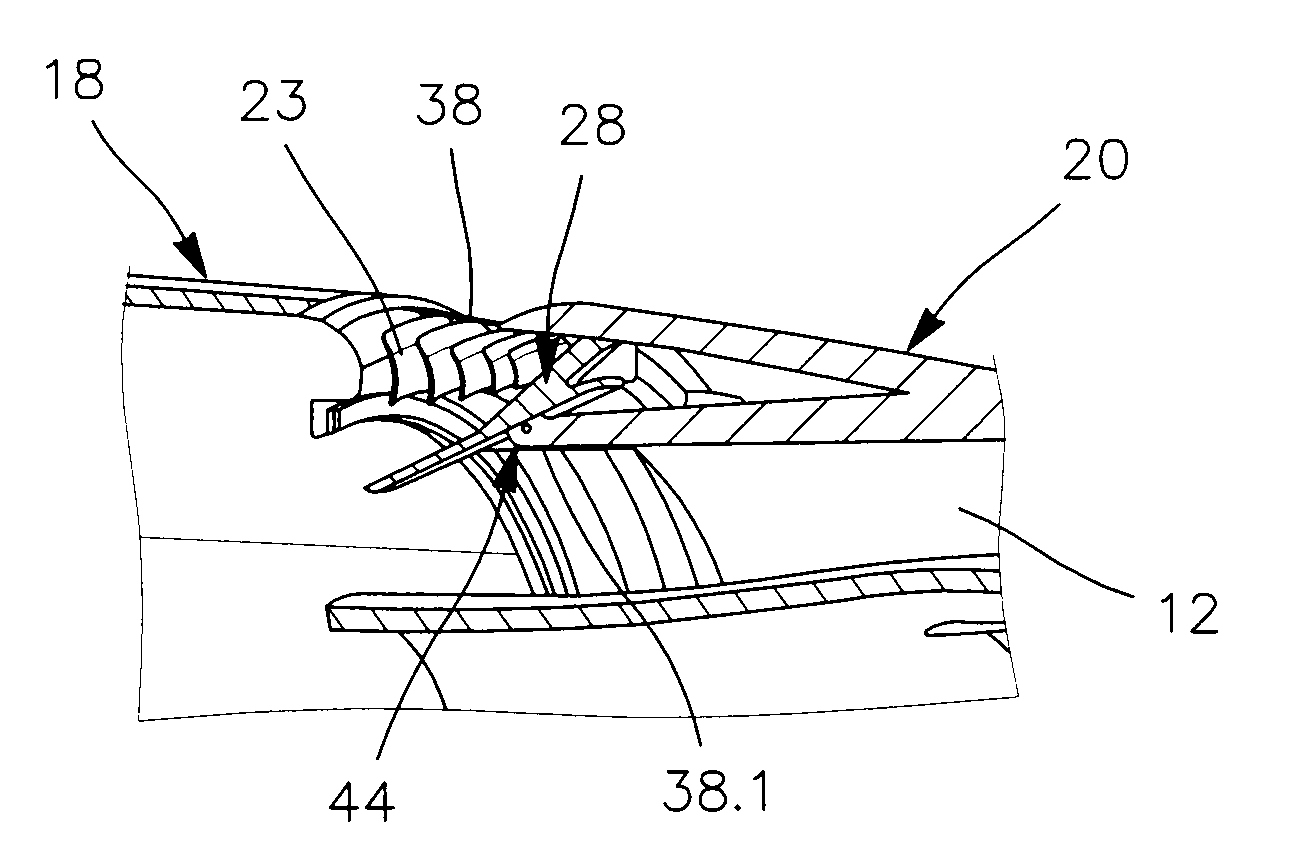
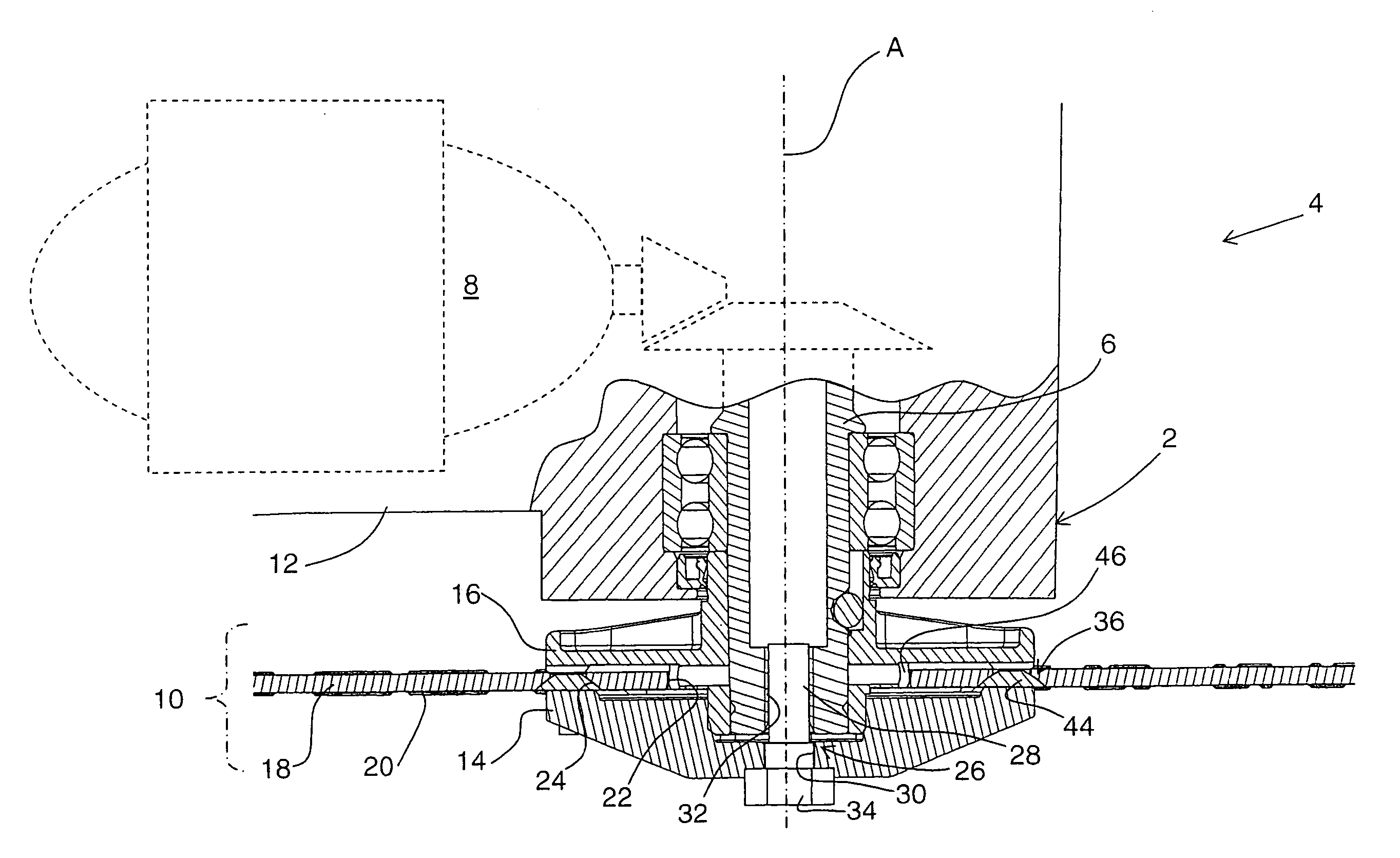
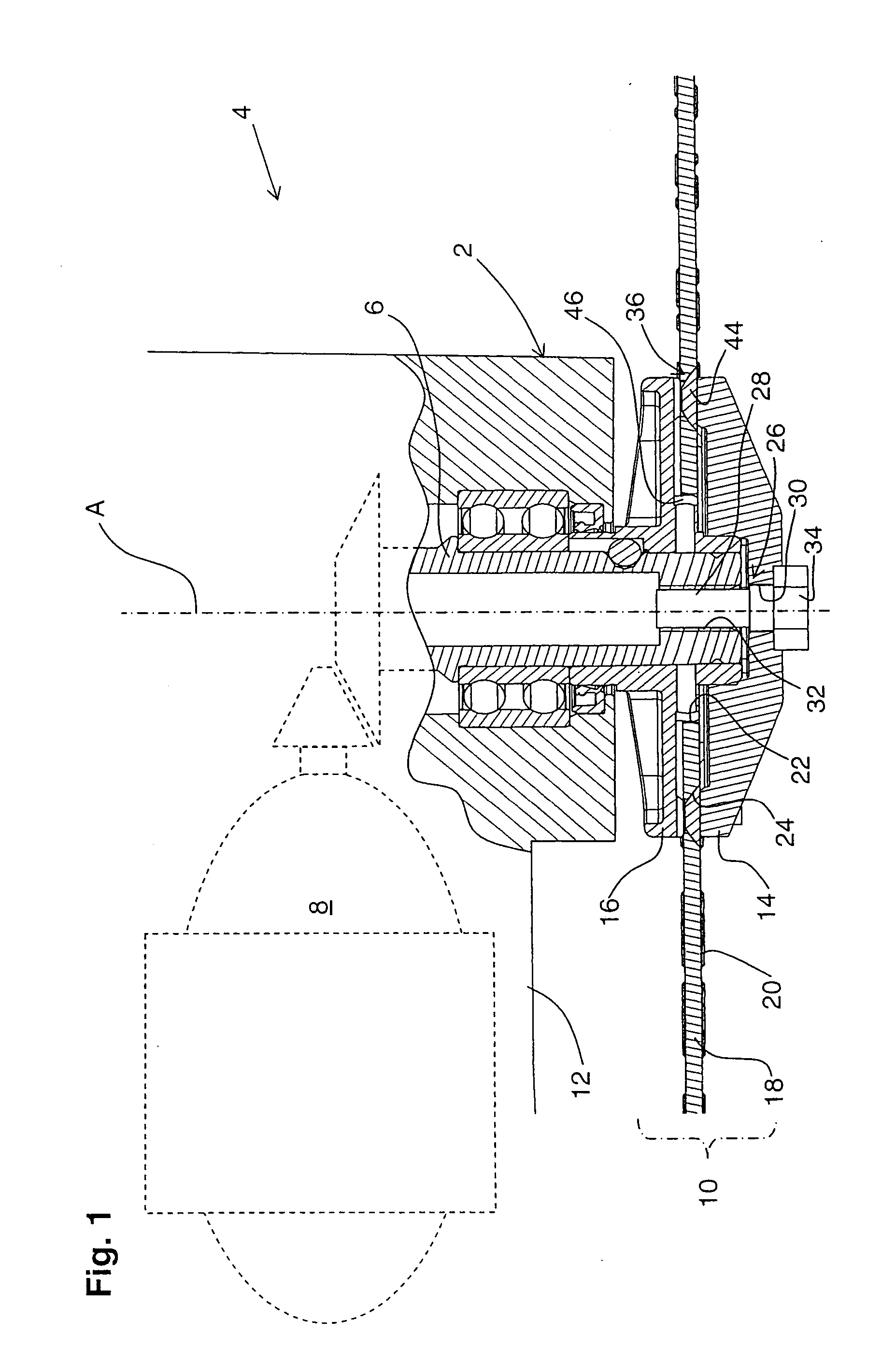
Hand-held power tool with ratchet percussion mechanism
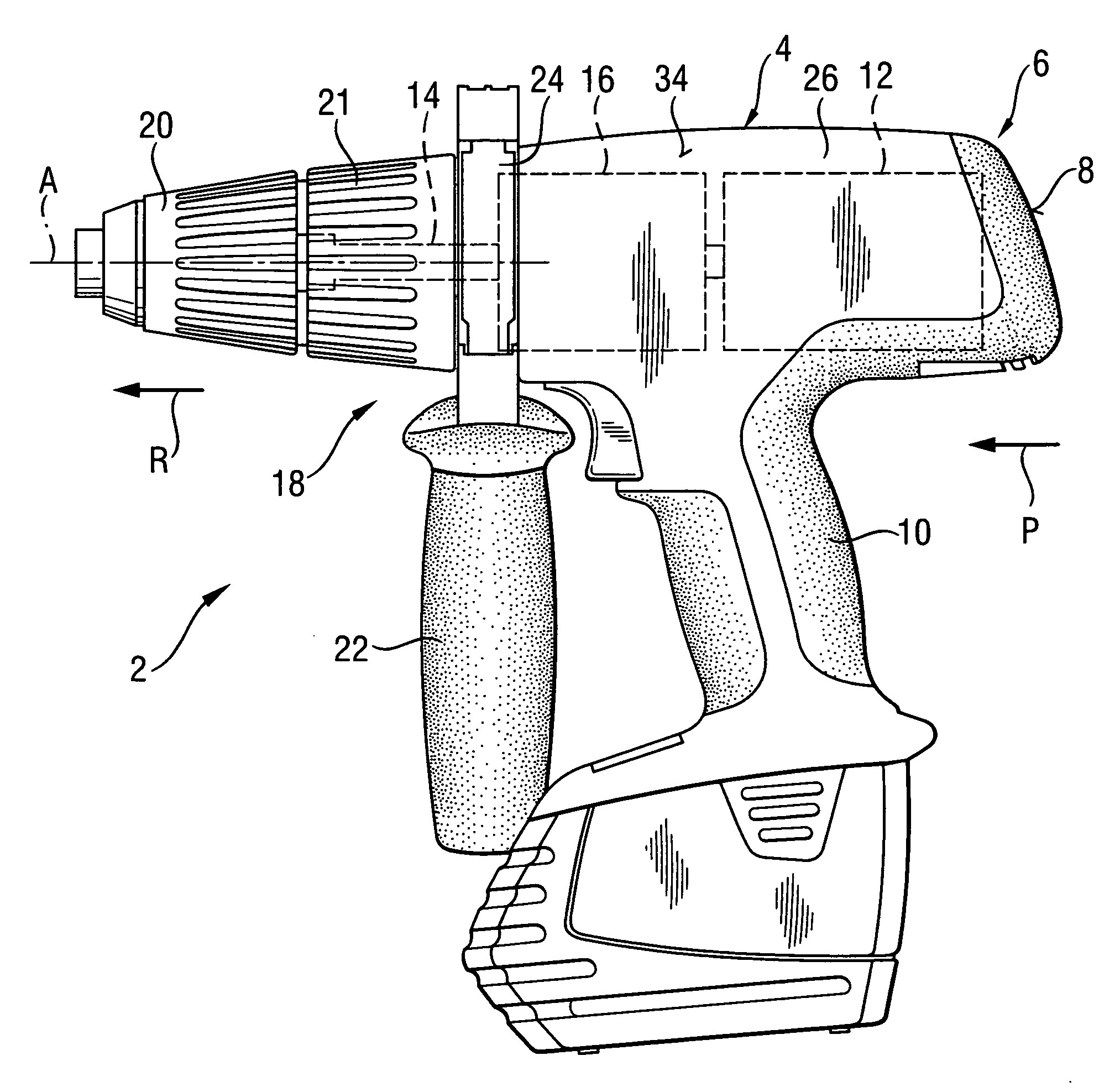
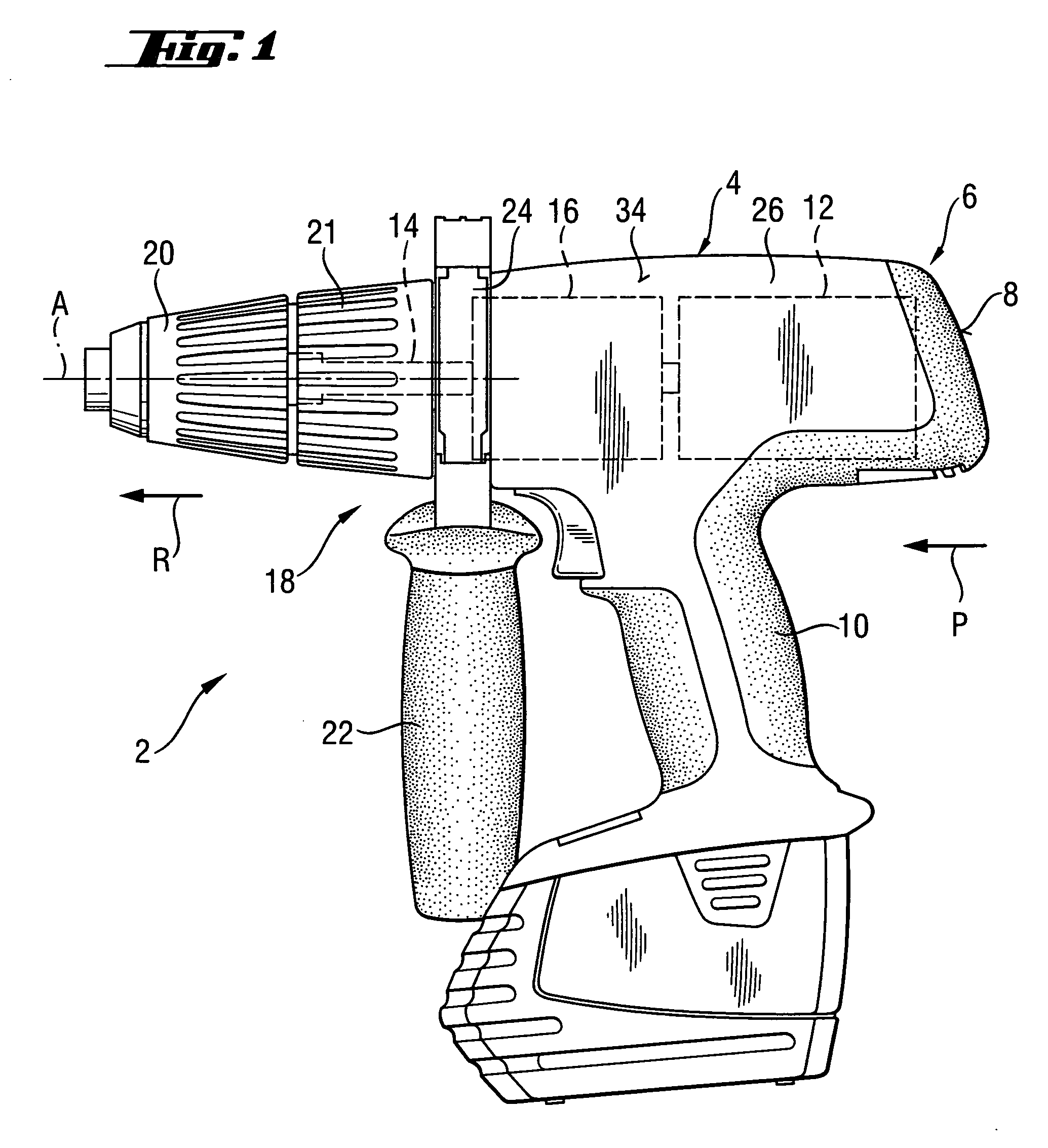
InactiveUS20070137875A1Improve efficiencyImprove stabilityDrilling rodsConstructionsHand heldPower tool
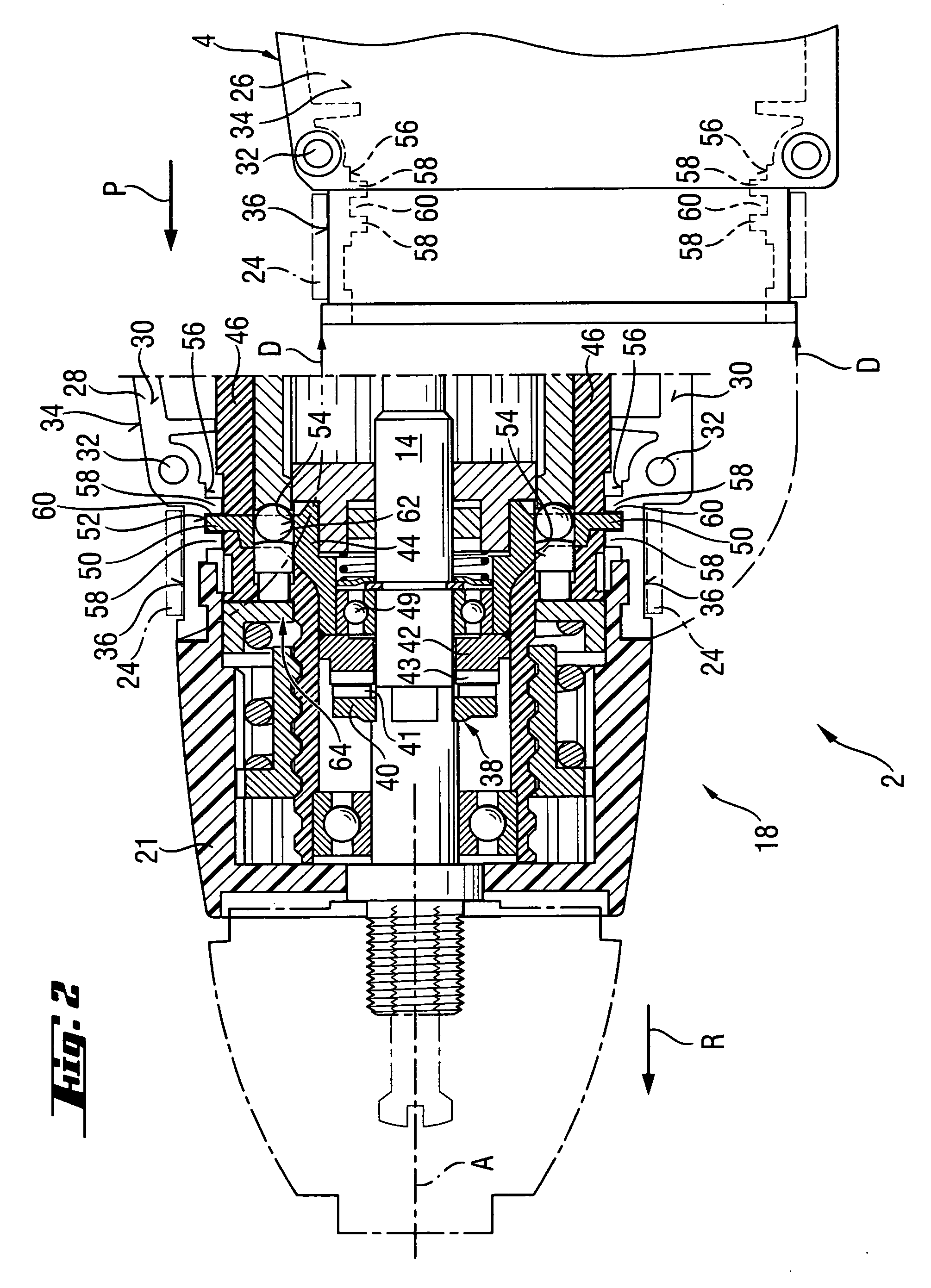
An electric hand-held power tool (2) has a main housing (4) of a shell-type construction a tool spindle (14) projecting from the main housing (4) at a working tool-side end (18) of the housing and which can be rotated around a operational axis (A) by a motor (12) and a gear unit (16) which are accommodated in the main housing (4), with an axial percussion movements being applied to the tool spindle (14) by a ratchet percussion mechanism (38) having a toothed rim (43), which is fixed with respect to the housing and which is connected to a supporting body (44) that is supported in the main housing (4), the toothed rim (43) cooperating with a toothed rim (41) which is movable so as to be coupled with the tool spindle (14) for joint rotation therewith, and the supporting body (44) being supported by a supporting element (58) in a direction remote from the working tool-side end (18) of the housing, with the supporting element (58) being formed in a circumferentially extending manner at an inner surface (56) of an outer shell (34) of the main housing (4), and the supporting body (44) directly contacting the supporting element (58).
Owner:HILTI AG
Rotary spraying robot for automobile hub mold
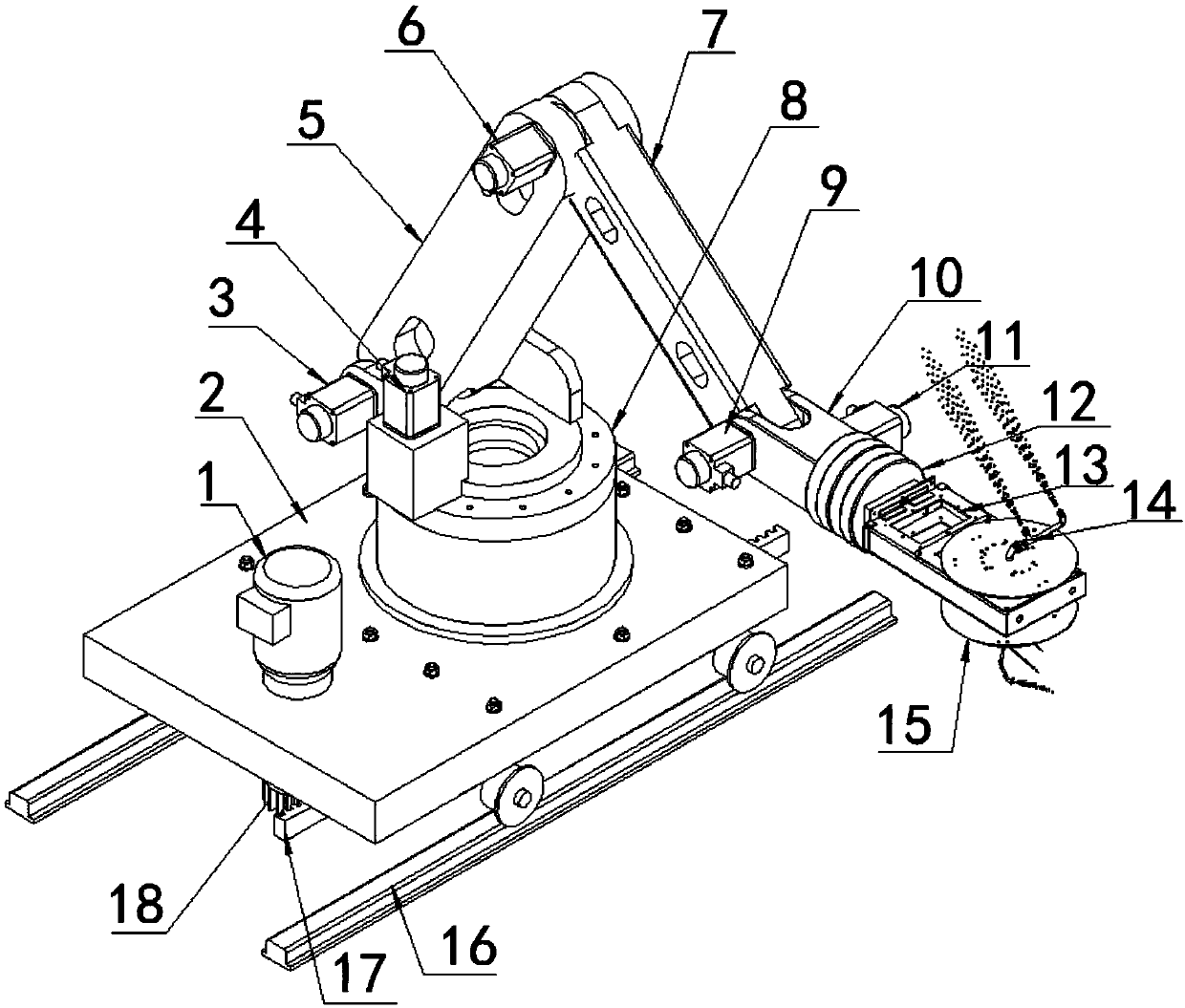
PendingCN107650130ASimple structureEasy to manufactureProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpraying apparatusEngineeringSprayer
The invention relates to a rotary spraying robot for an automobile hub mold. The rotary spraying robot for the automobile hub mold comprises a traveling trolley, a rotary base, a plurality of joints,a rotary arm and a rotary spraying machine, wherein the rotary base is installed on the traveling trolley, the multiple joints are installed on the rotary base, the rotary arm is installed at the tailsection of joint, and the rotary spraying machine is installed on the rotary arm. The multiple joints, the rotary base, the traveling trolley and the rotary arm move cooperatively, the posture of a nozzle in the space range is adjusted, and thus the rotary spraying robot is suitable for spraying of different curved face hubs.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHAOYANG TECH CO LTD
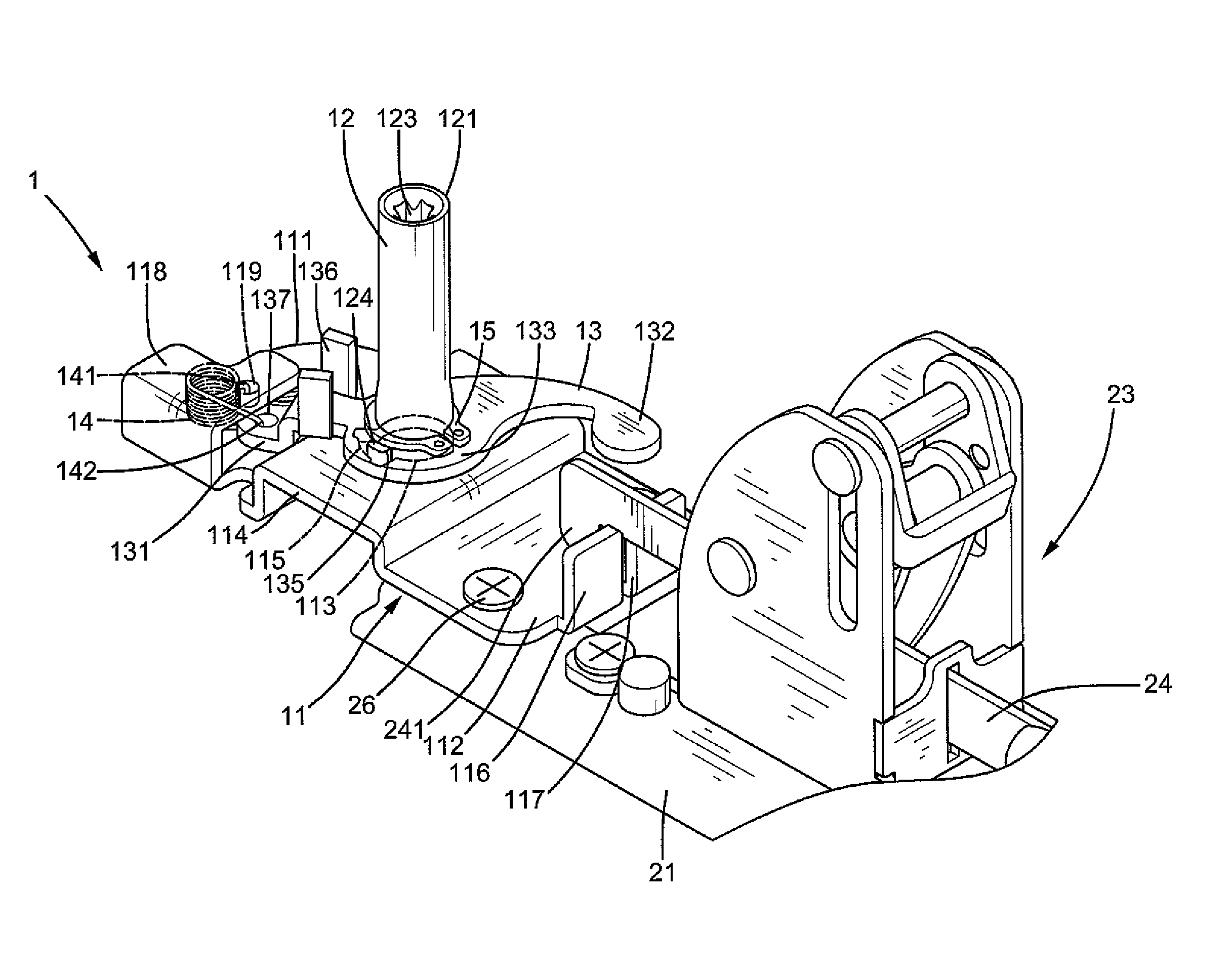
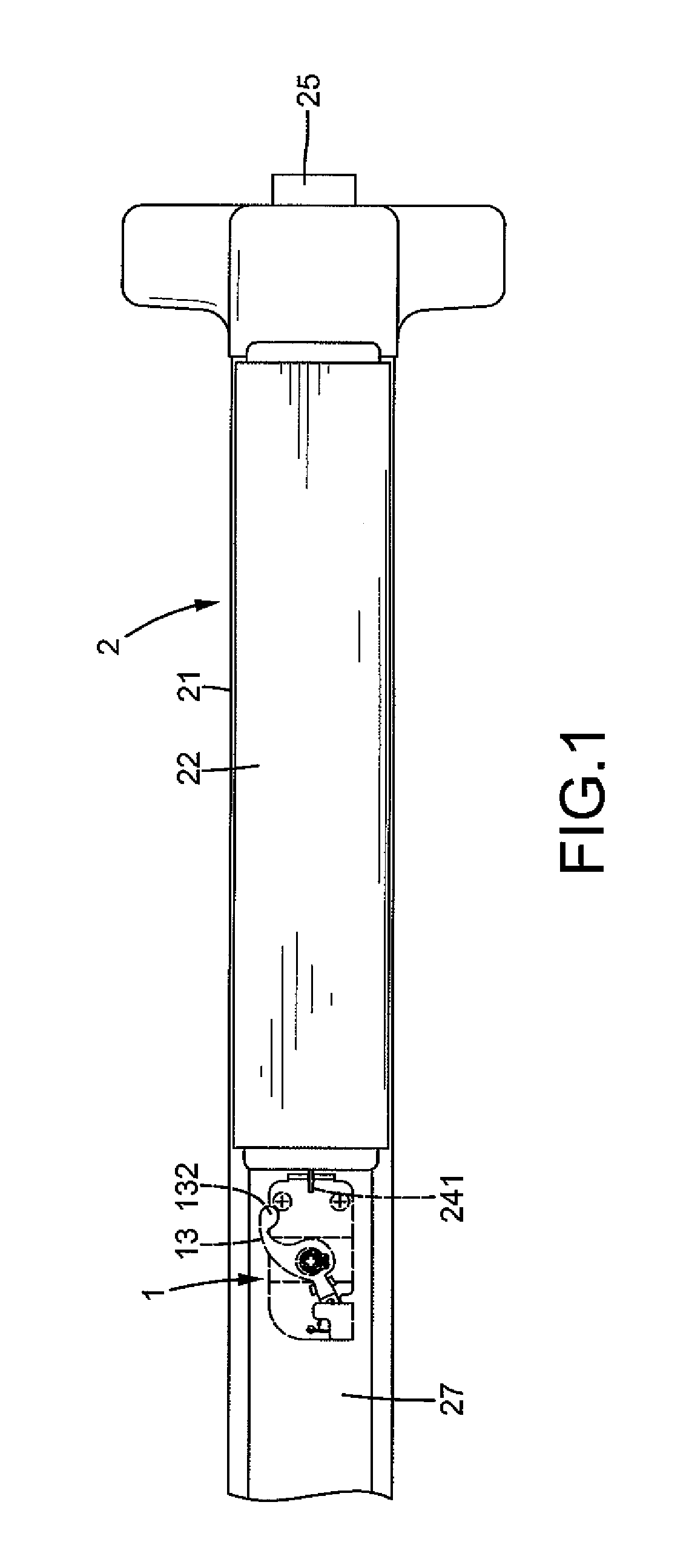
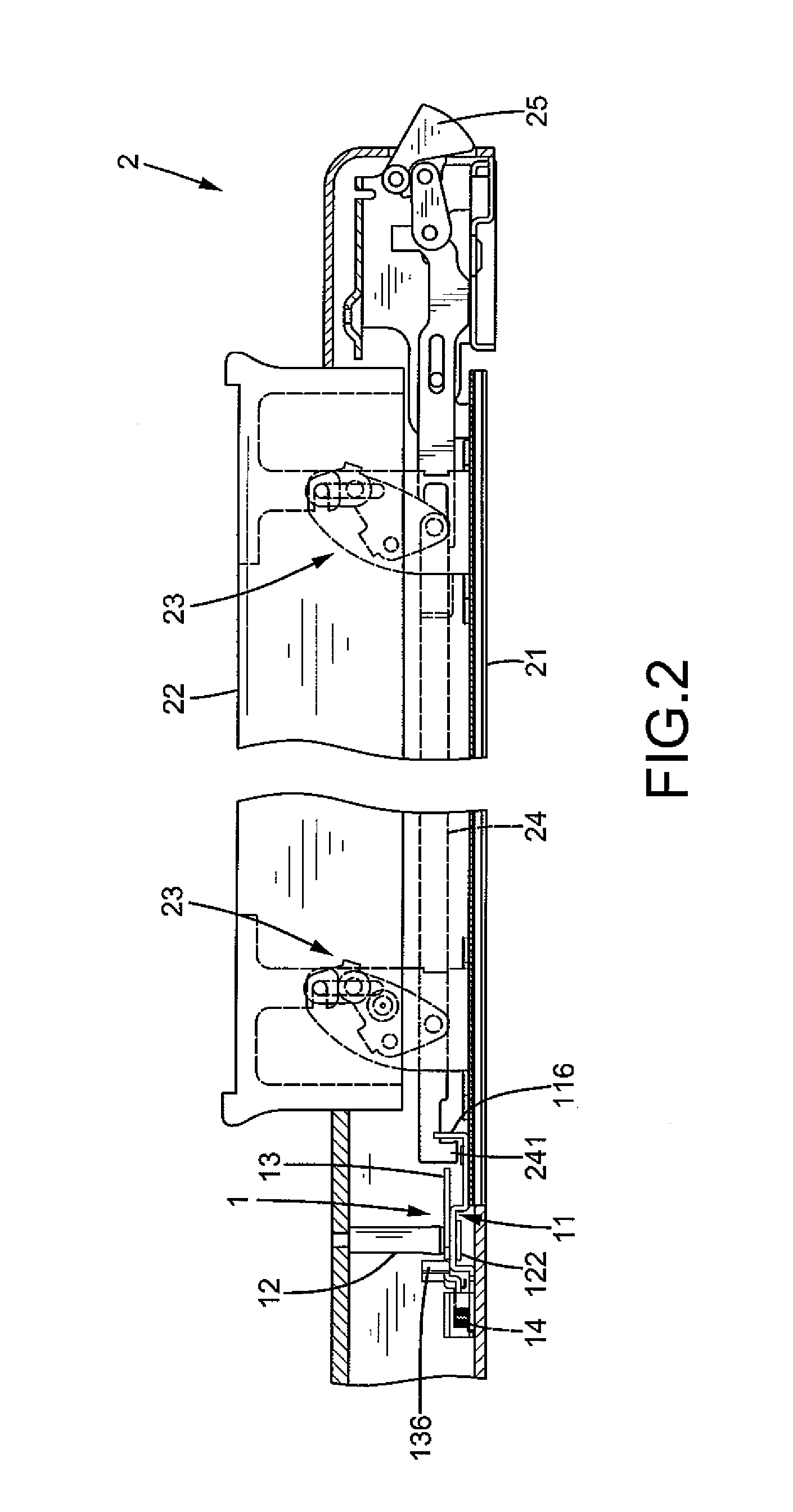
Tool Assembly with Coaxial/Universal Coupling
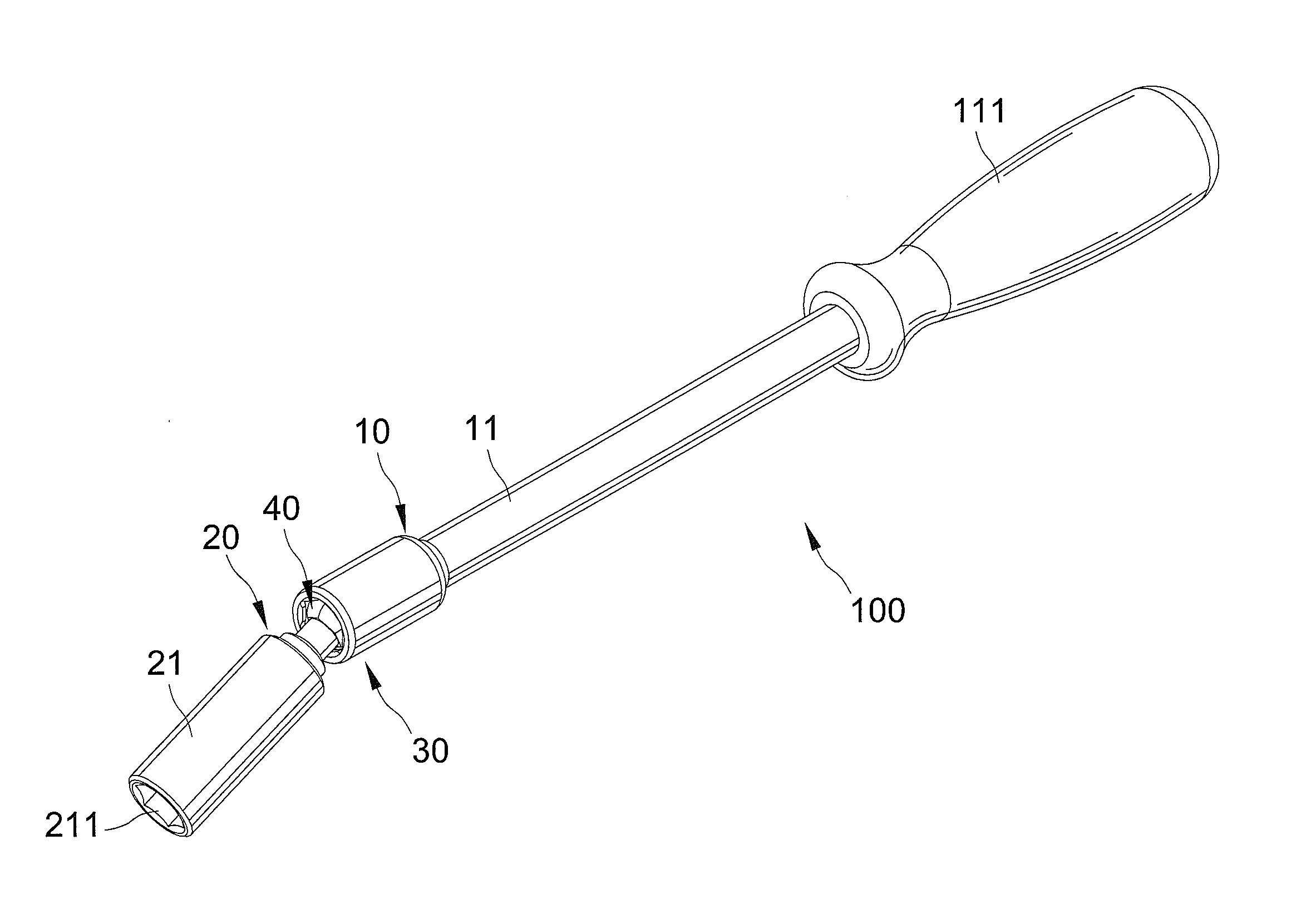
A tool assembly includes a body having a receptacle. An adapter includes a shoulder, a head, and a neck interconnecting the head and the shoulder. The head engages with an inner periphery of the receptacle, allowing joint rotation of the adapter and the body. The head is slideably received in the receptacle between first and second positions. A C-clip is received in a retaining groove in the inner periphery of the receptacle. When the head is in the first position, the shoulder is received in the receptacle, the C-clip distends and clamps the shoulder to keep the adapter to be coaxial to the body. When the head is in the second position, the shoulder is outside of the receptacle, the C-clip abuts an outer periphery of the head, and the head is rotatable to a position such that the adapter is at an angle to the body.
Owner:HU BOBBY
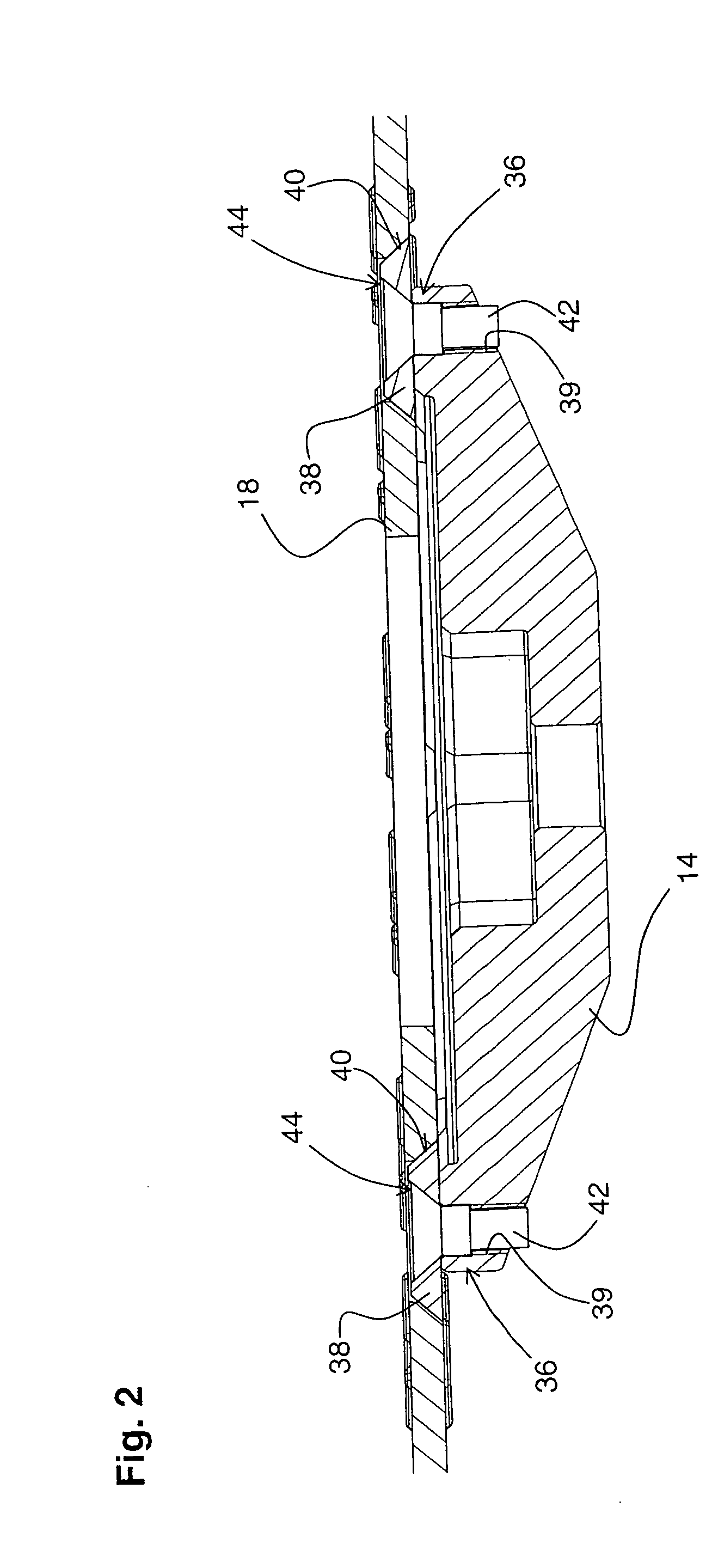
Tool holder for a disc-shaped working tool
ActiveUS20080017007A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to manufactureGrinding wheel securing apparatusPortable grinding machinesCouplingEngineering
A tool holder or a disc-shaped working tool (18) has a working tool holding member (14) and a working tool holding counter-member (16) rotatable, together with the working tool holding member, (14) about an operational axis (A) and cooperating with the working tool holding member (14) for receiving therebetween the working tool (18) for joint rotation therewith; central securing element (26) for securing the working tool (18) between the working tool holding member (14) and the working tool holding counter-member (16); and at least one coupling element (44) associated with the working tool holding member (14), radially spaceable from the central securing element (26) and having a rotary stop for forming a releaseable plug-in connection with at least one through-bore (24) formed in the working tool (18).
Owner:HILTI AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com