Patents
Literature
1217results about "Liquid resistance brakes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
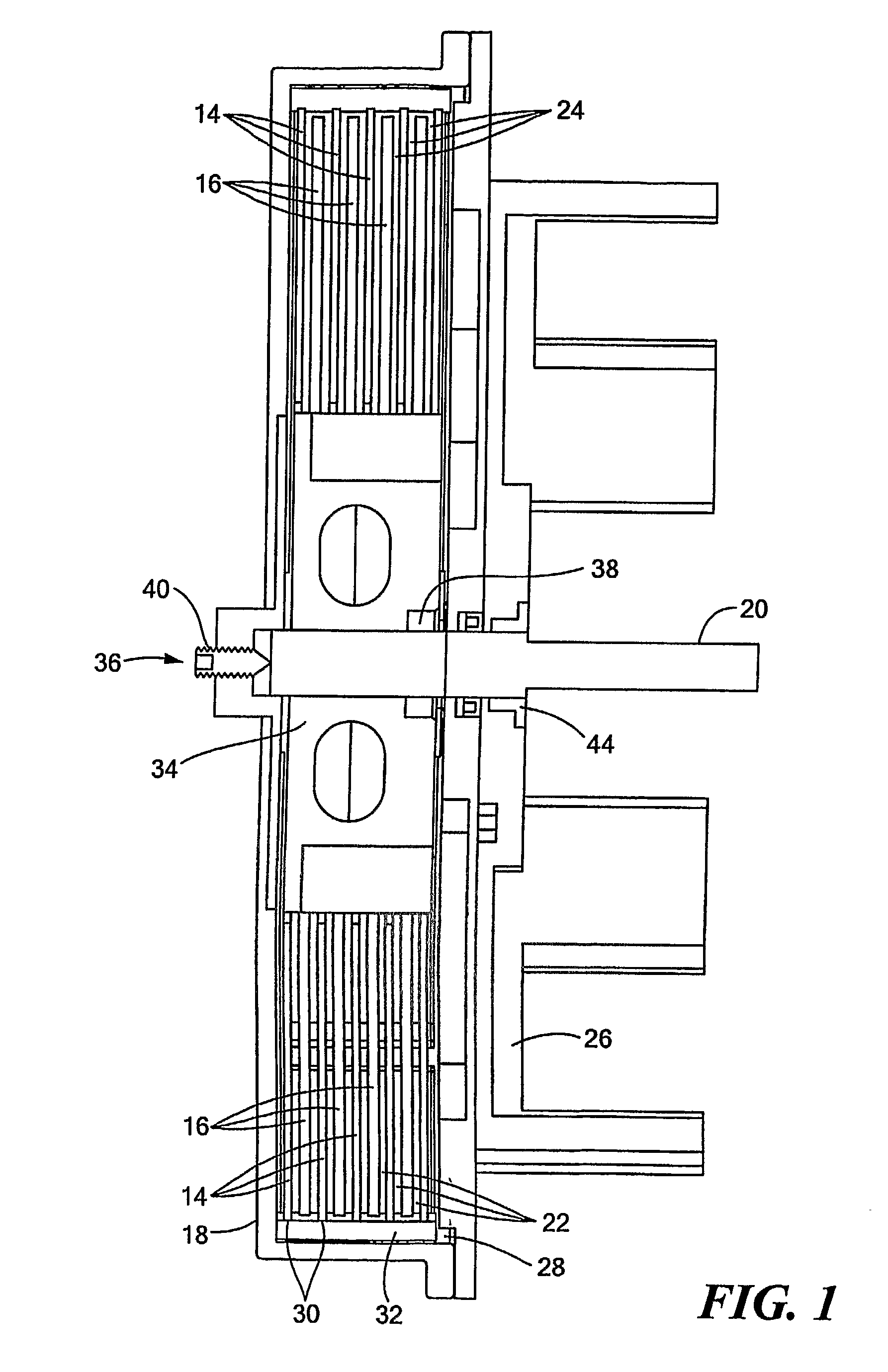
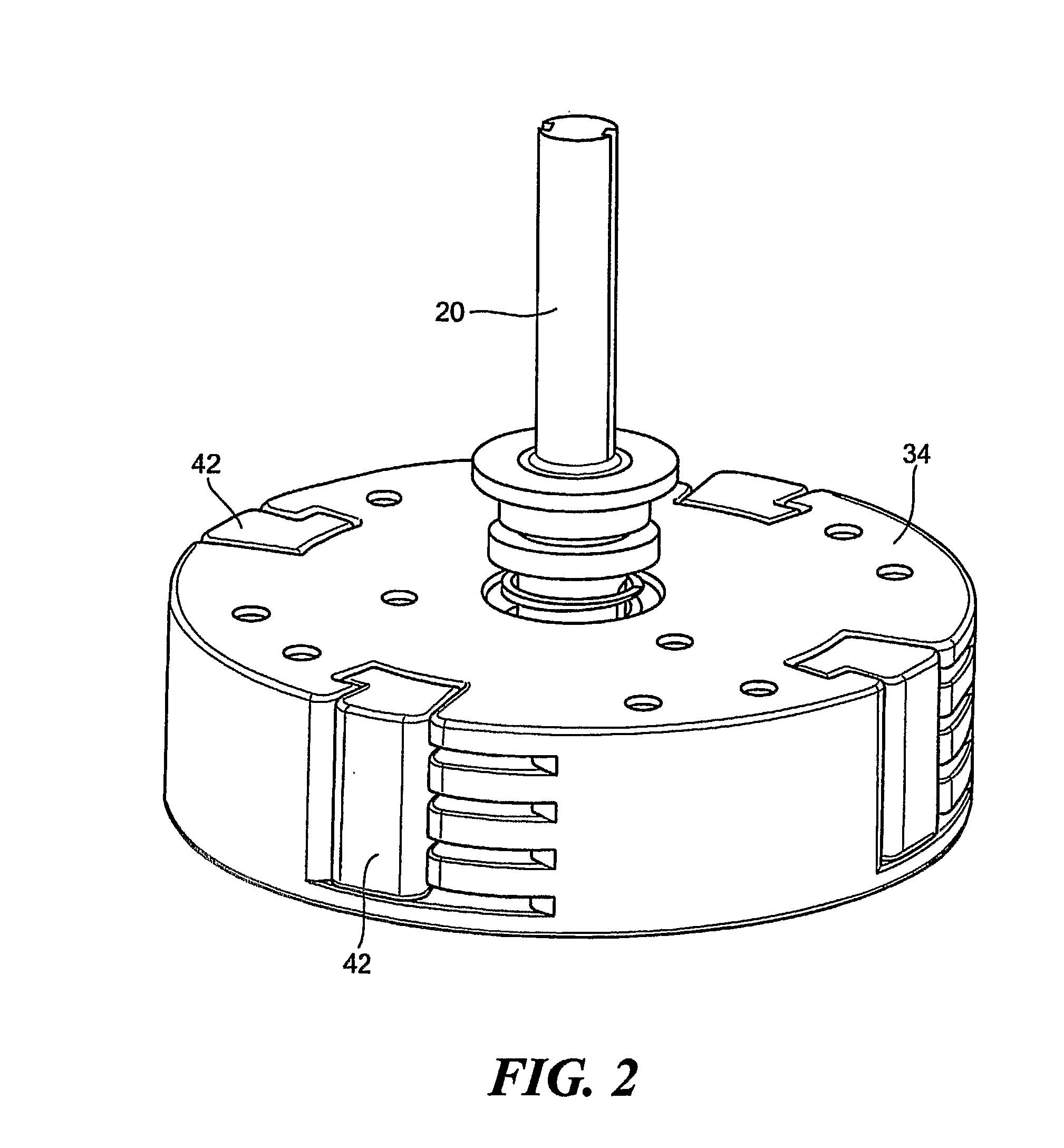
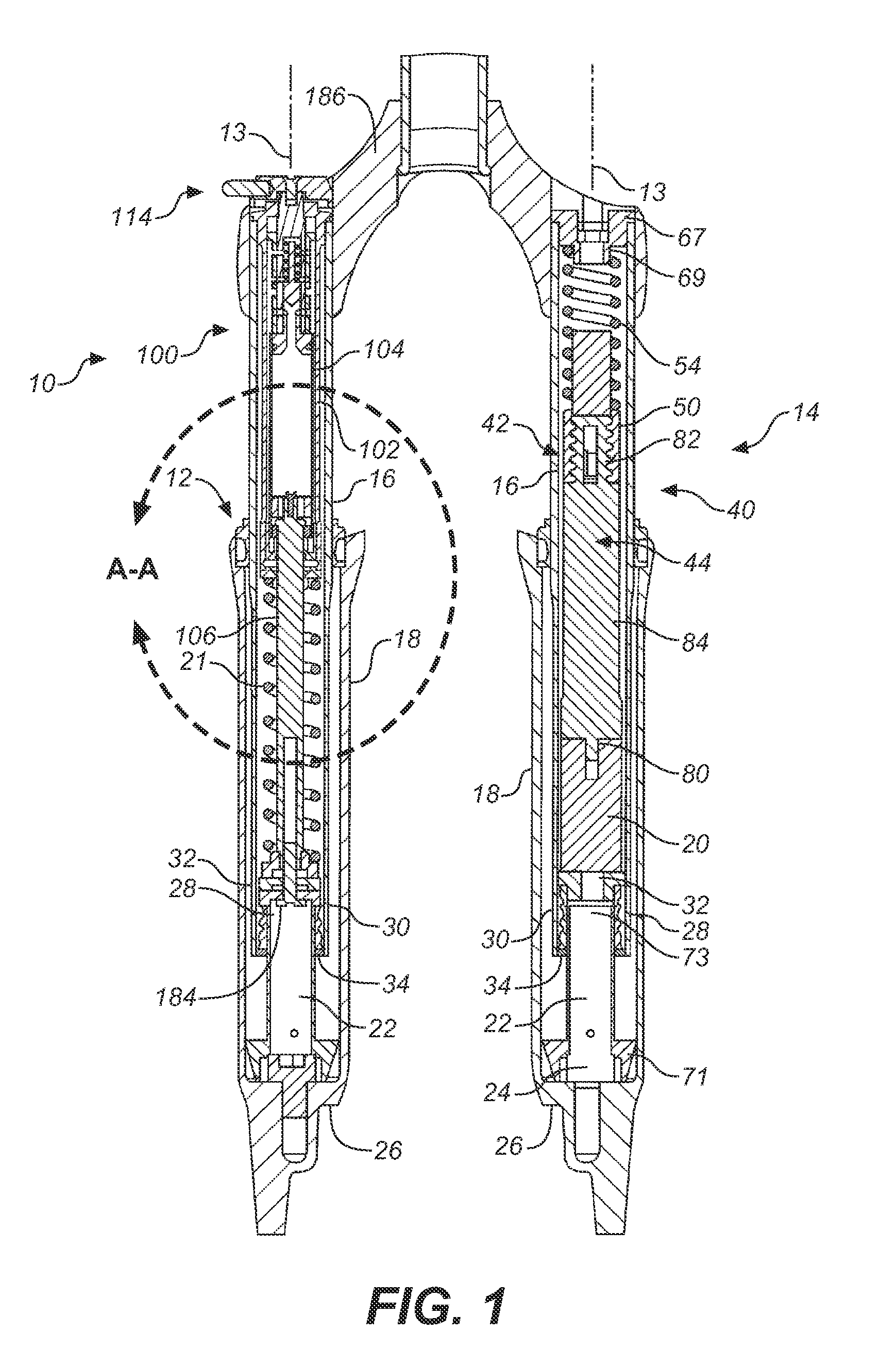
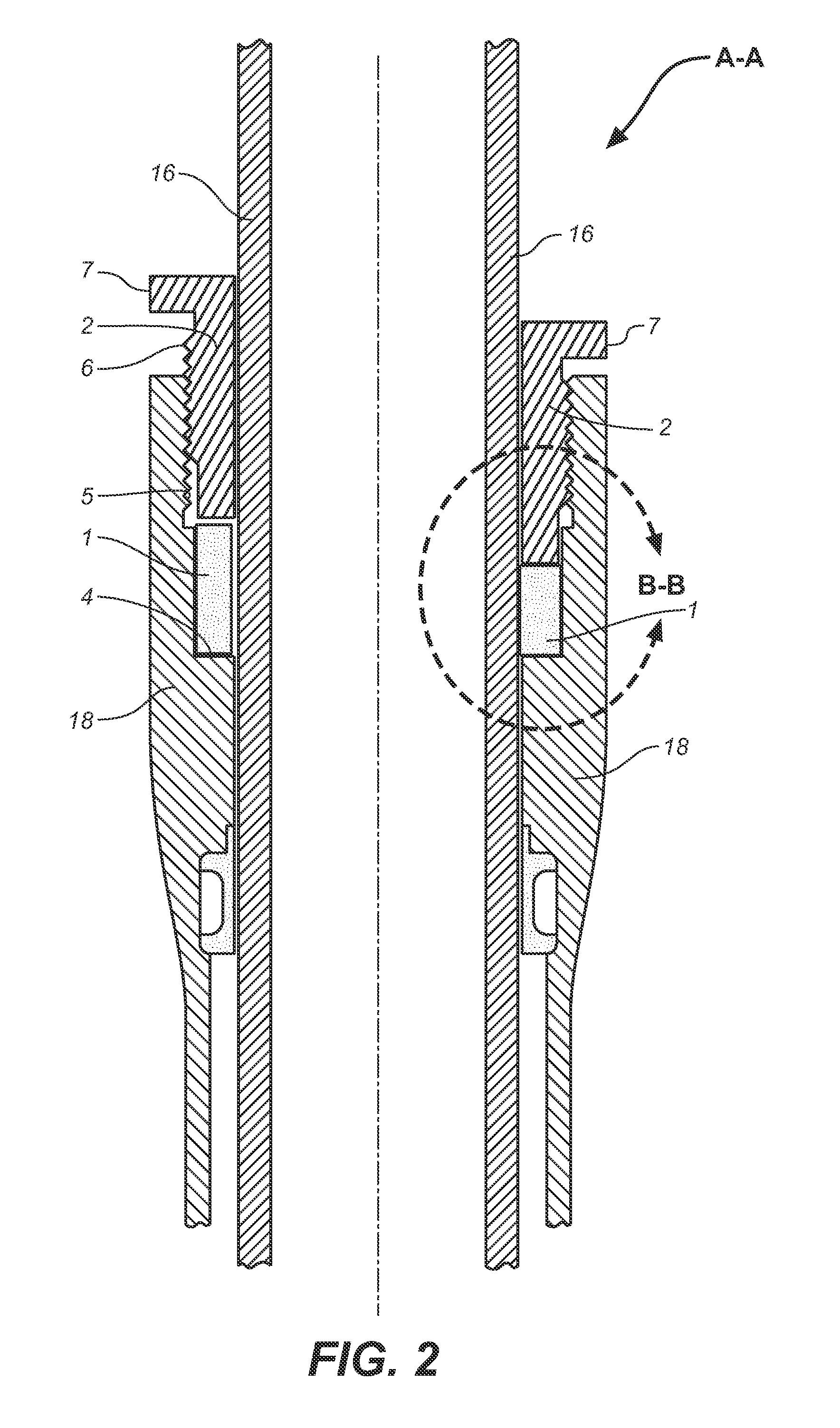
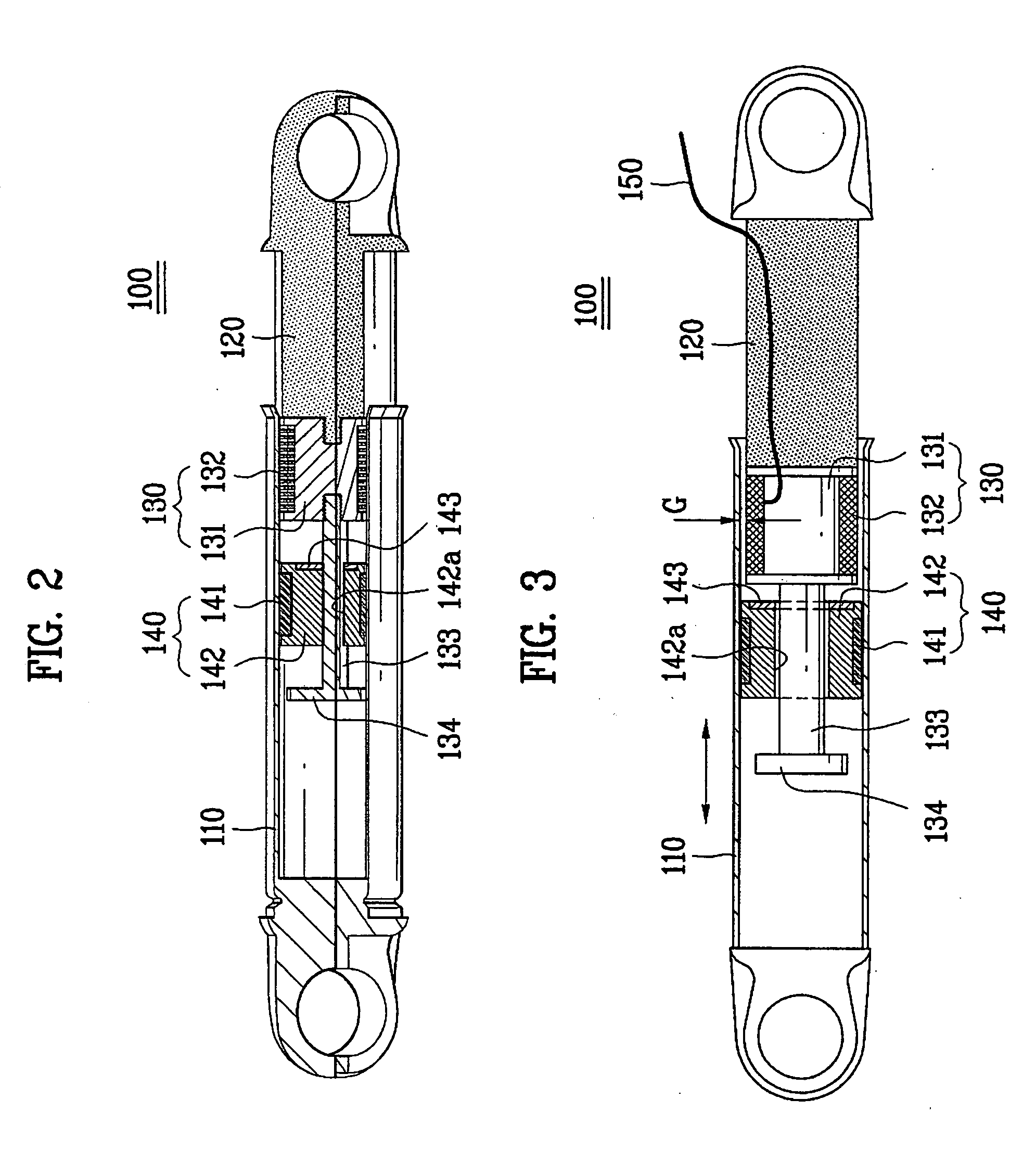
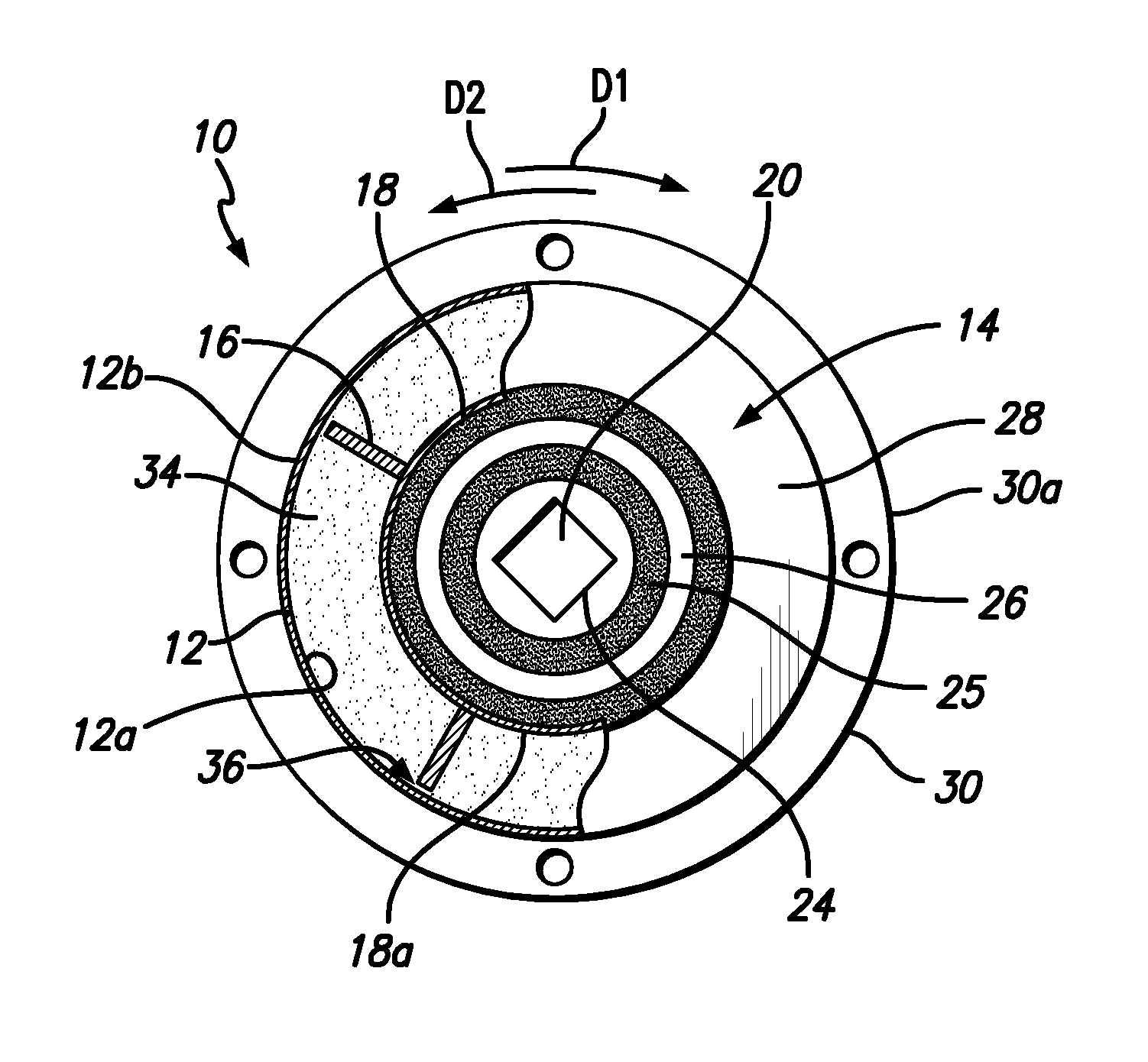
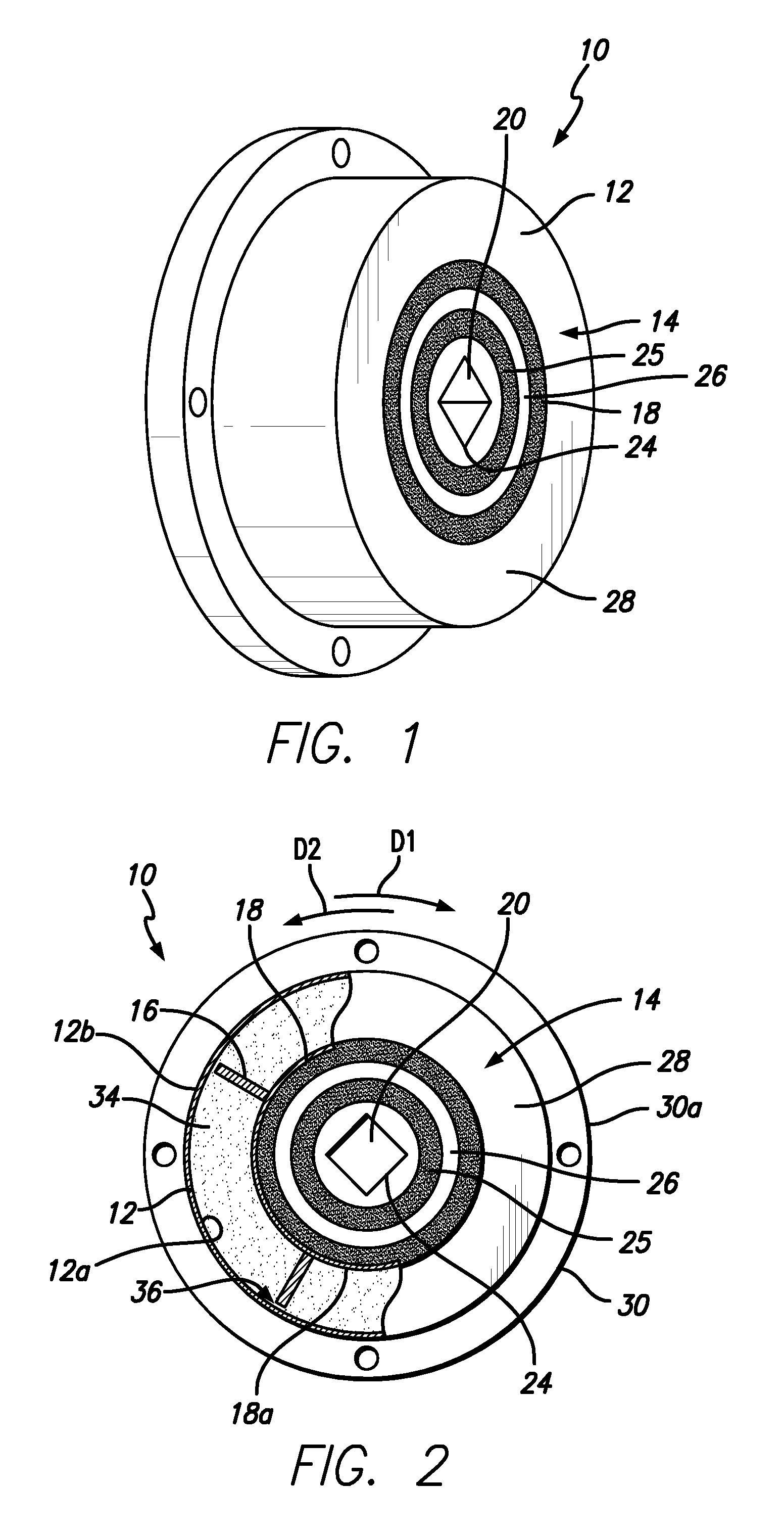
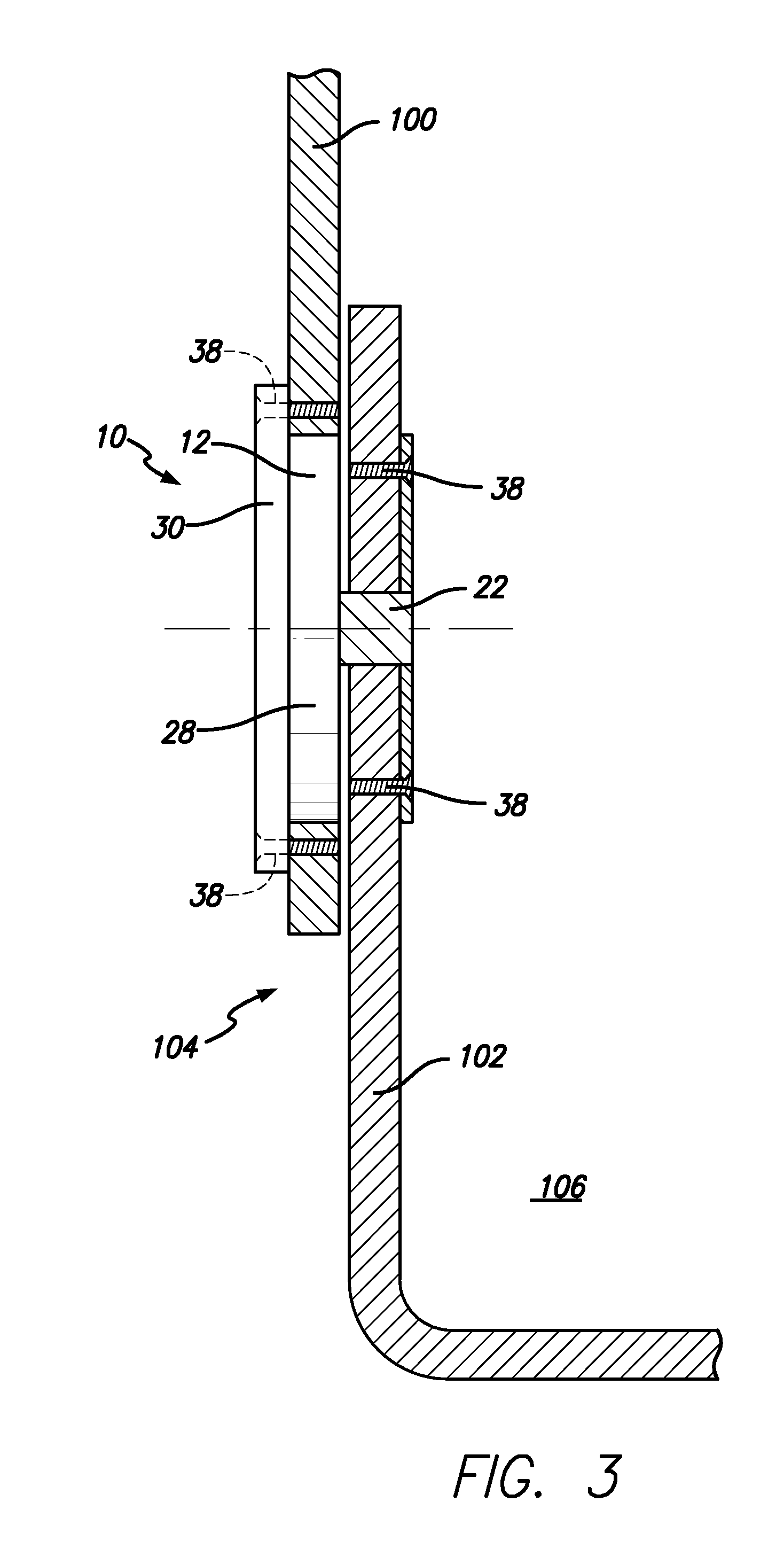
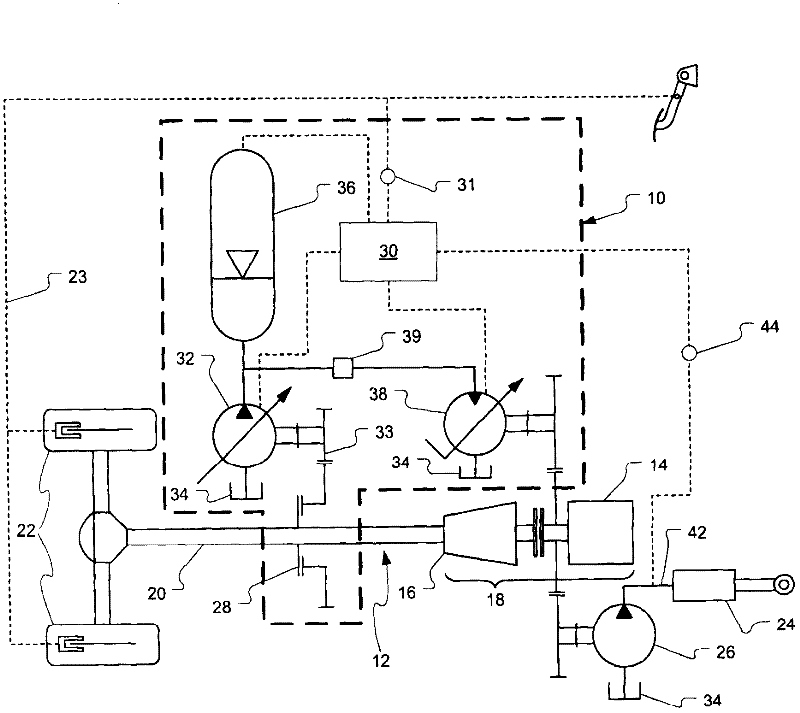
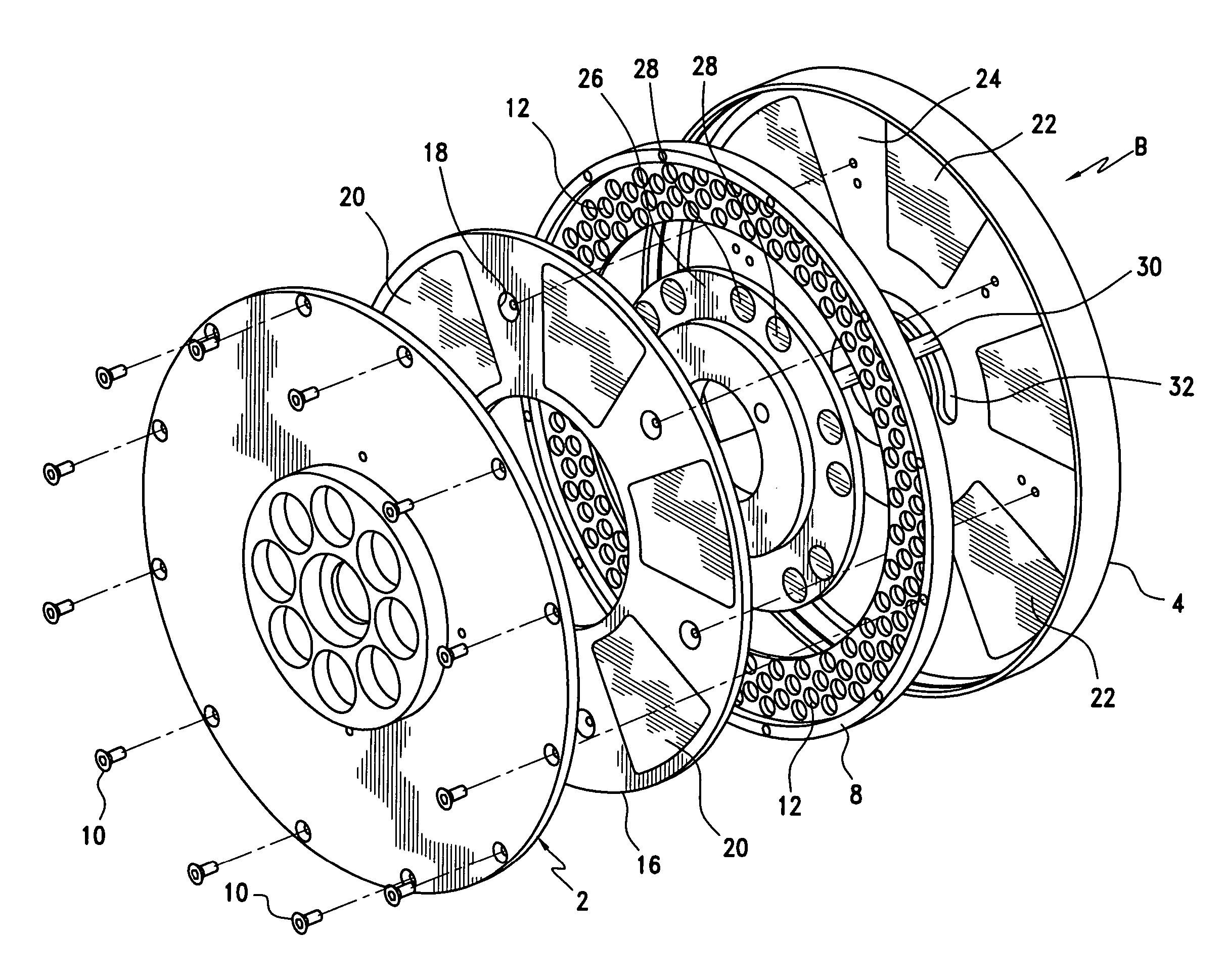
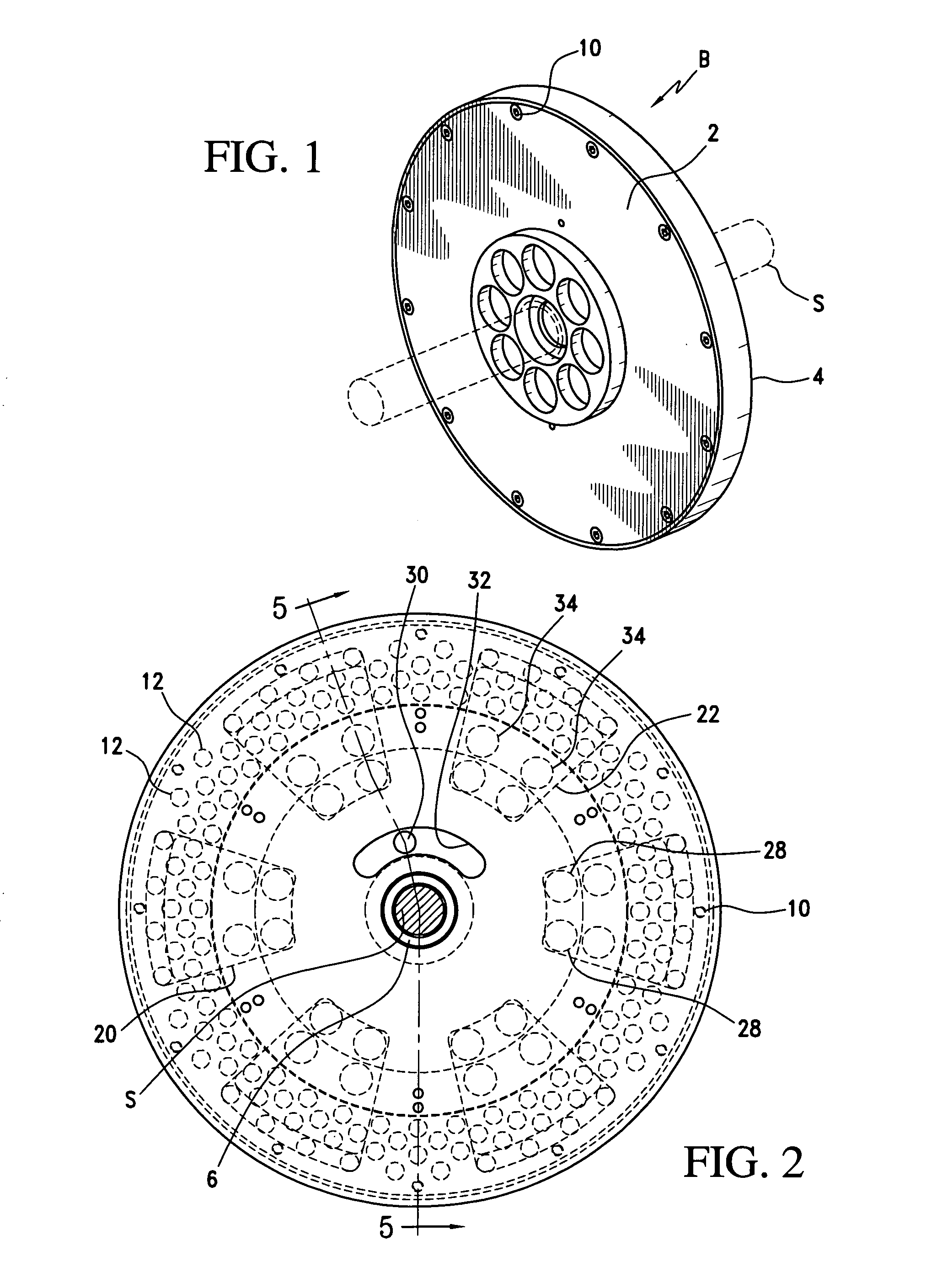
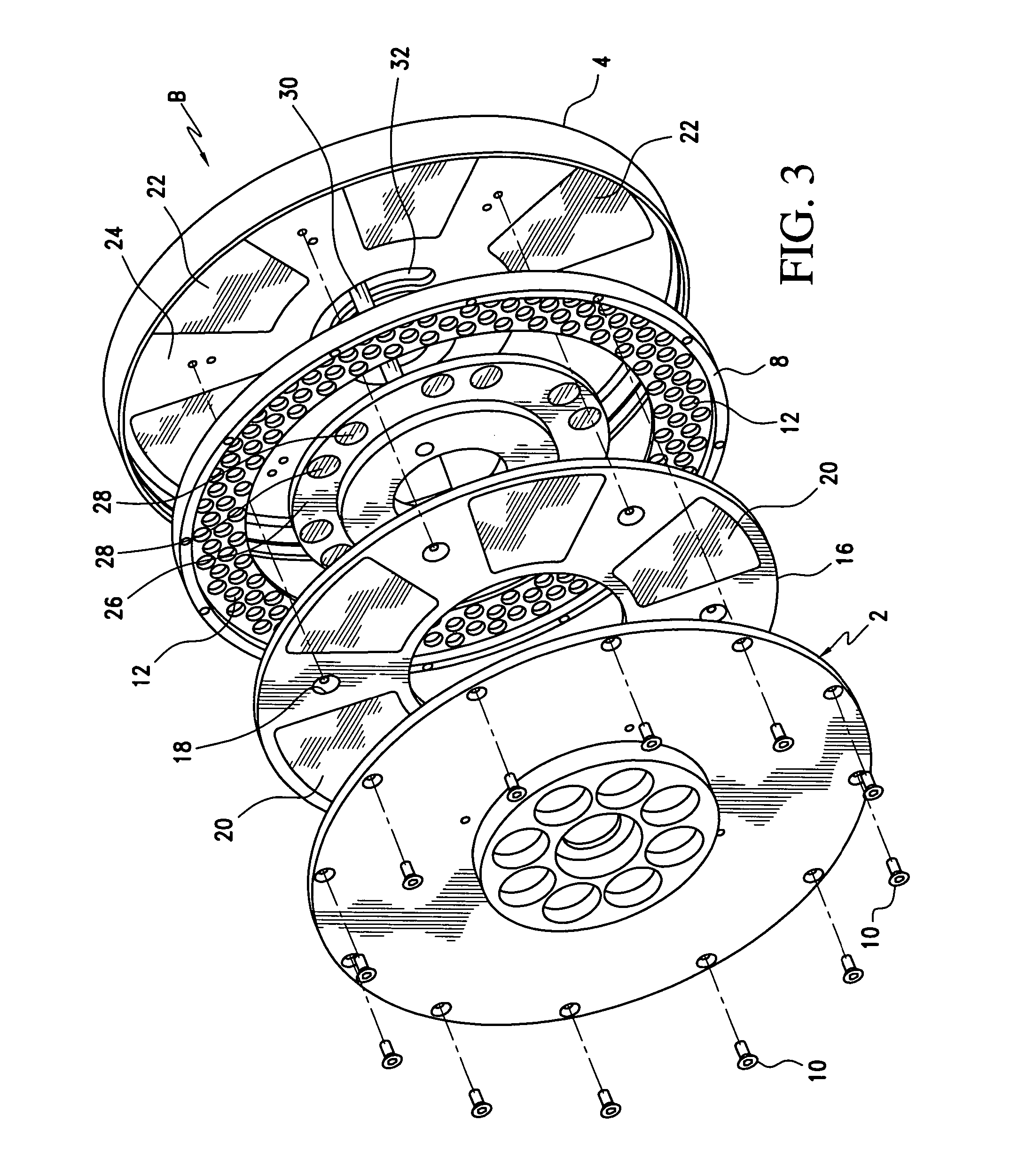
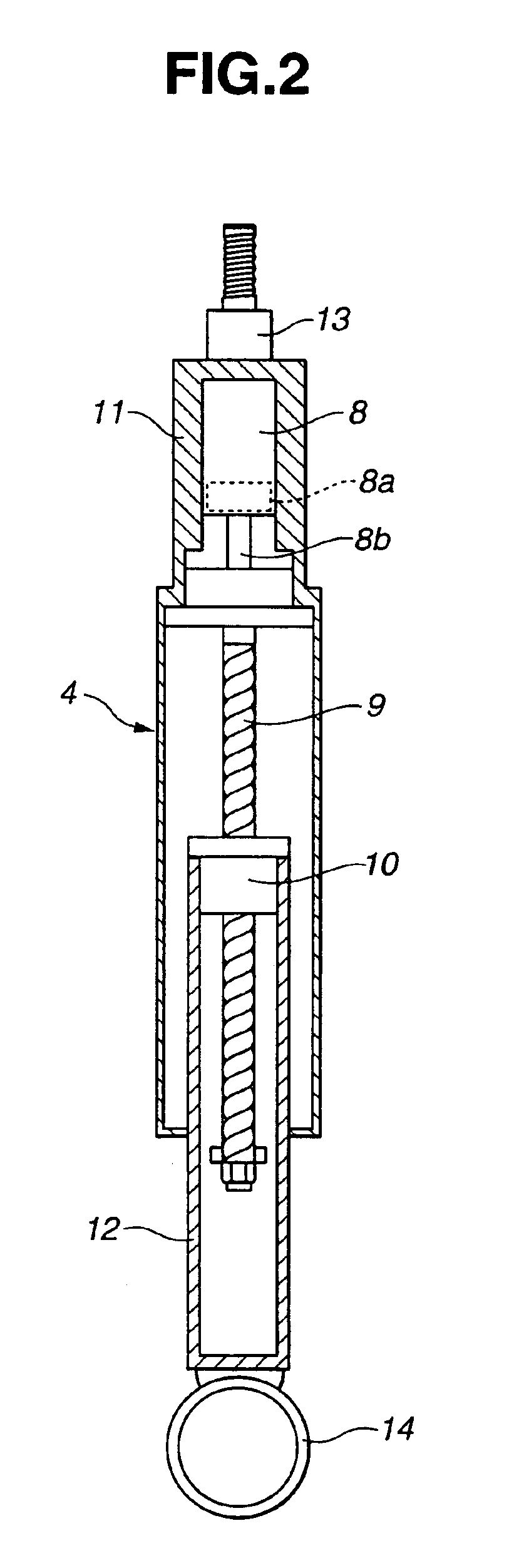
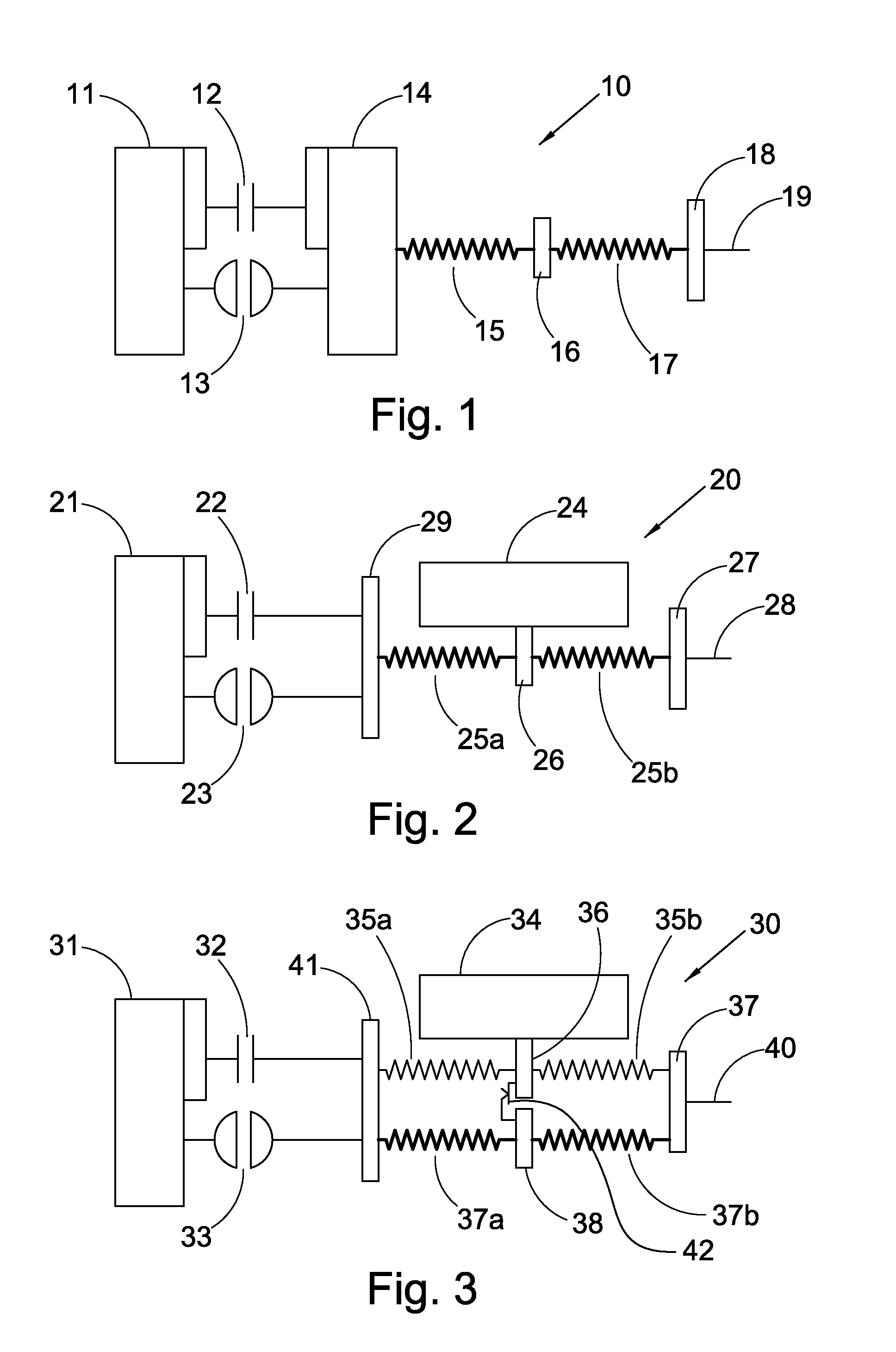
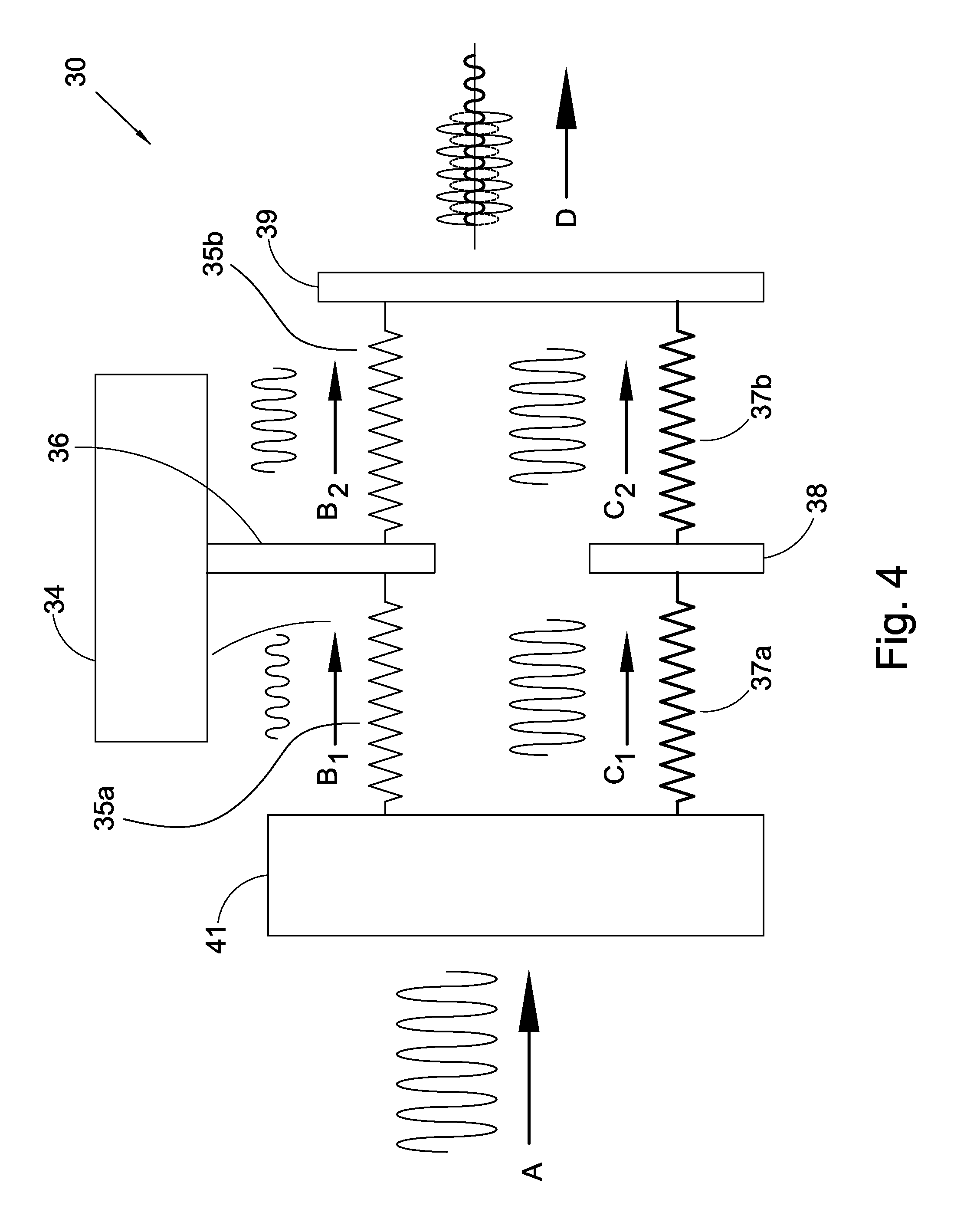
Pump drivetrain damper system and control systems and methods for same
ActiveUS10316832B2Reduce vibrationLiquid resistance brakesPositive displacement pump componentsControl signalDrivetrain
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
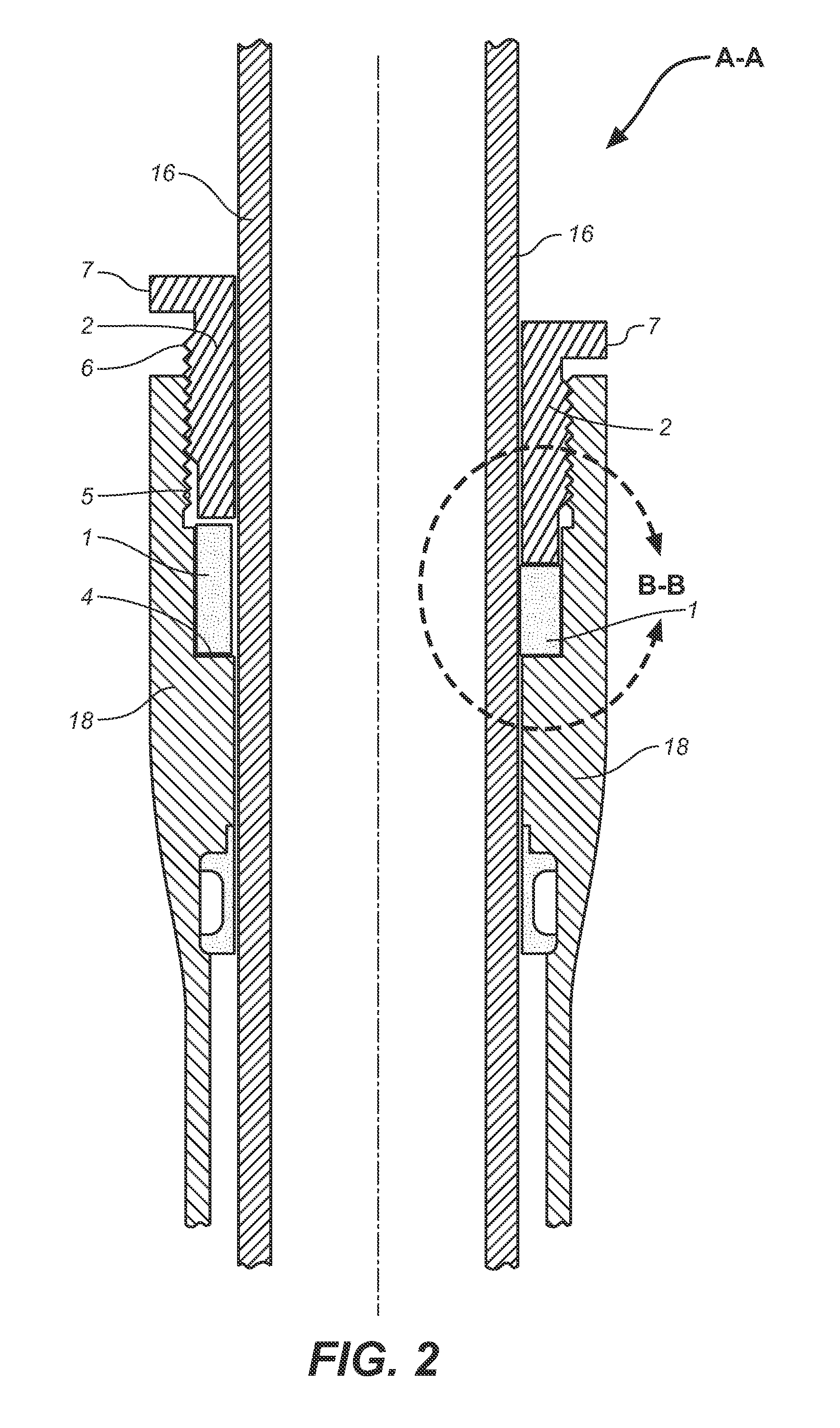
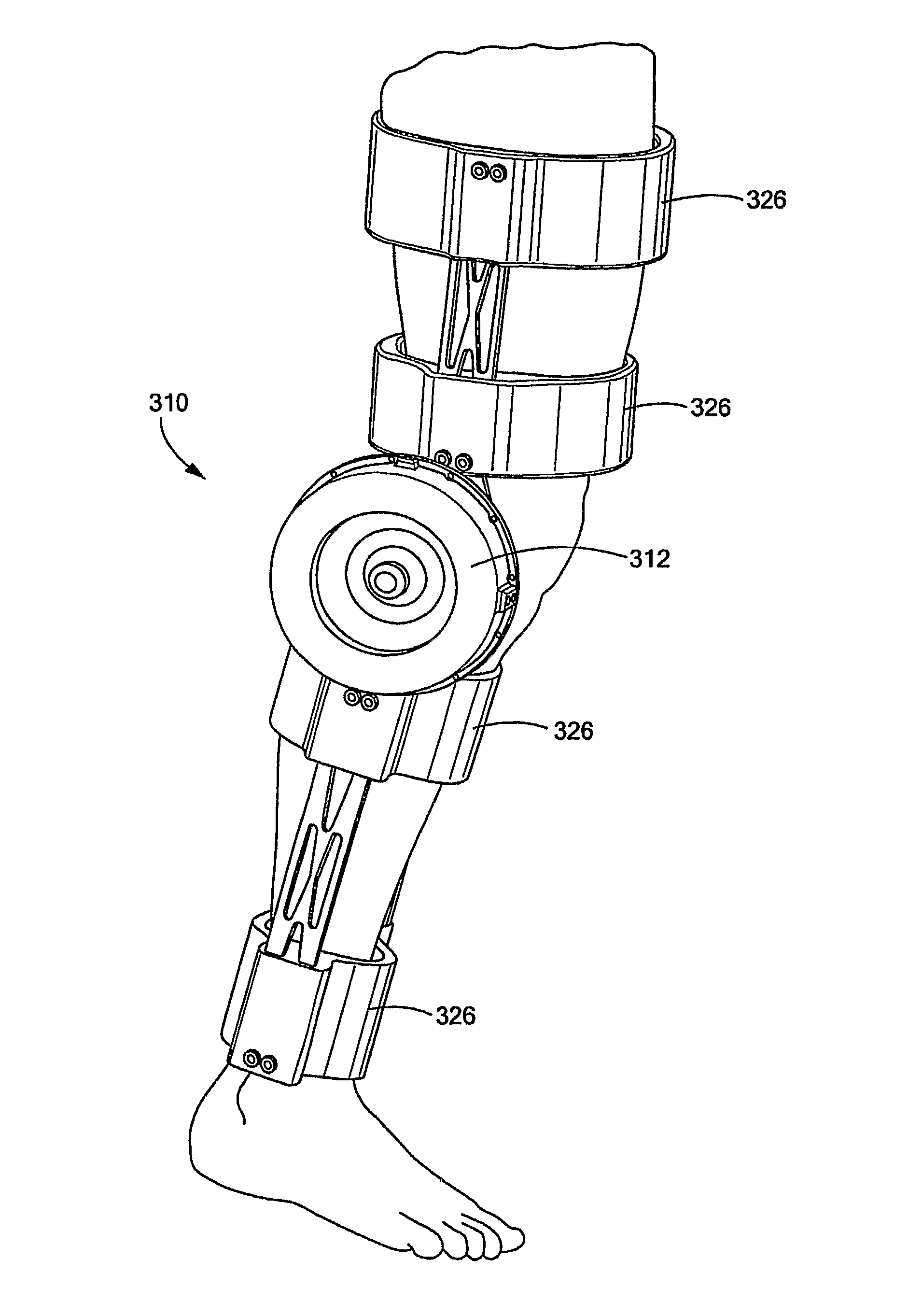
Electro-Rheological Fluid Brake and Actuator Devices and Orthotic Devices Using the Same
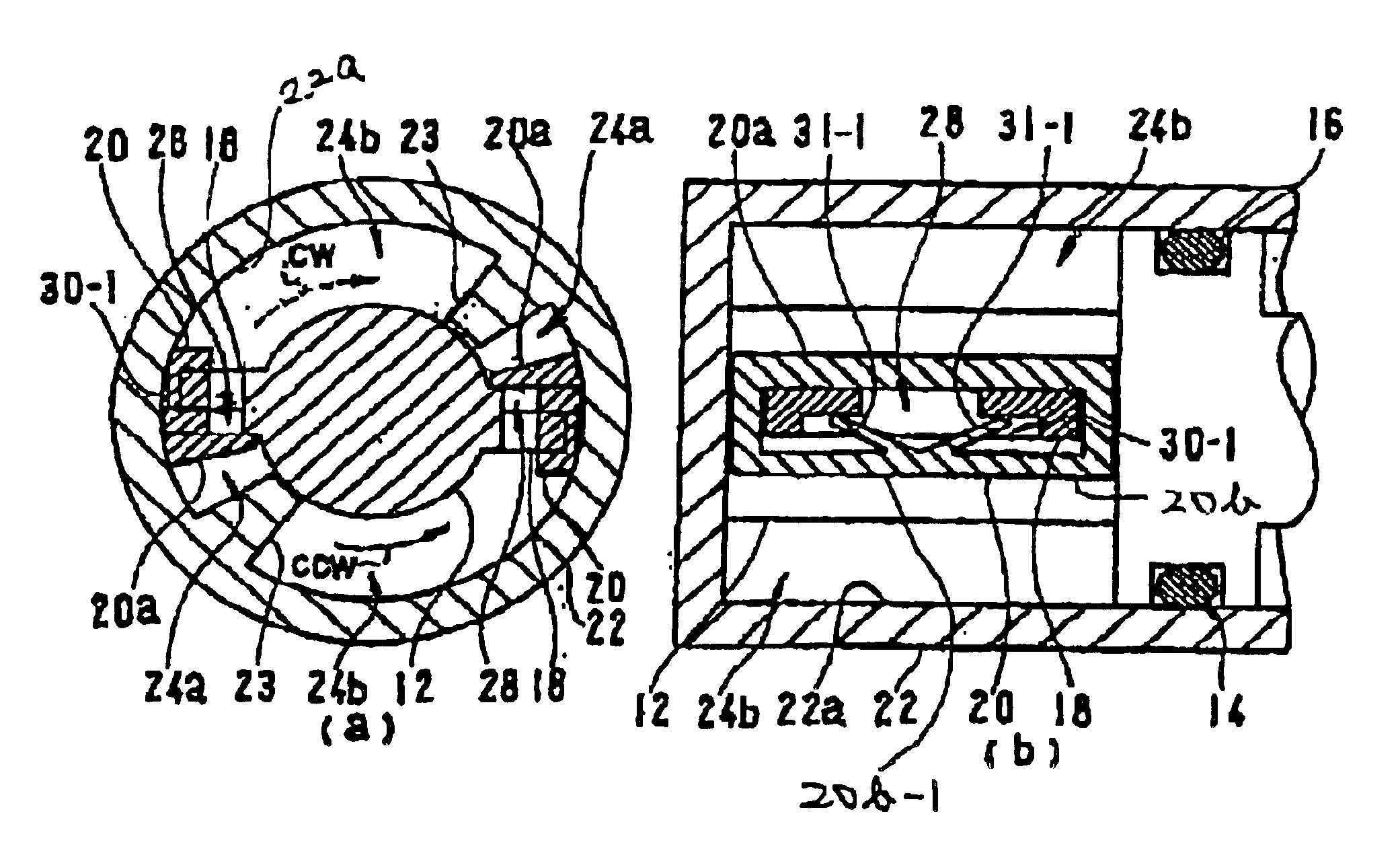
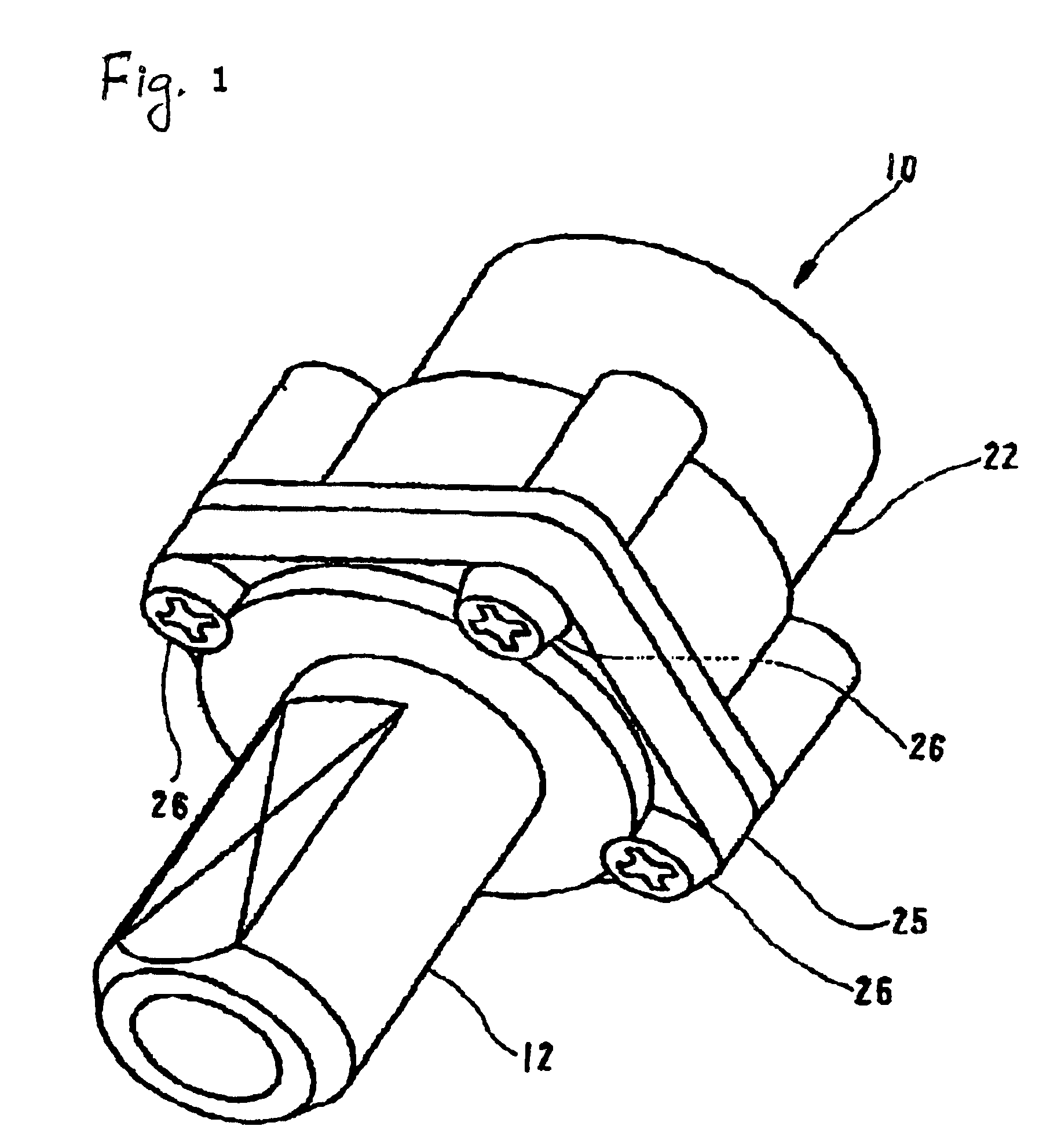
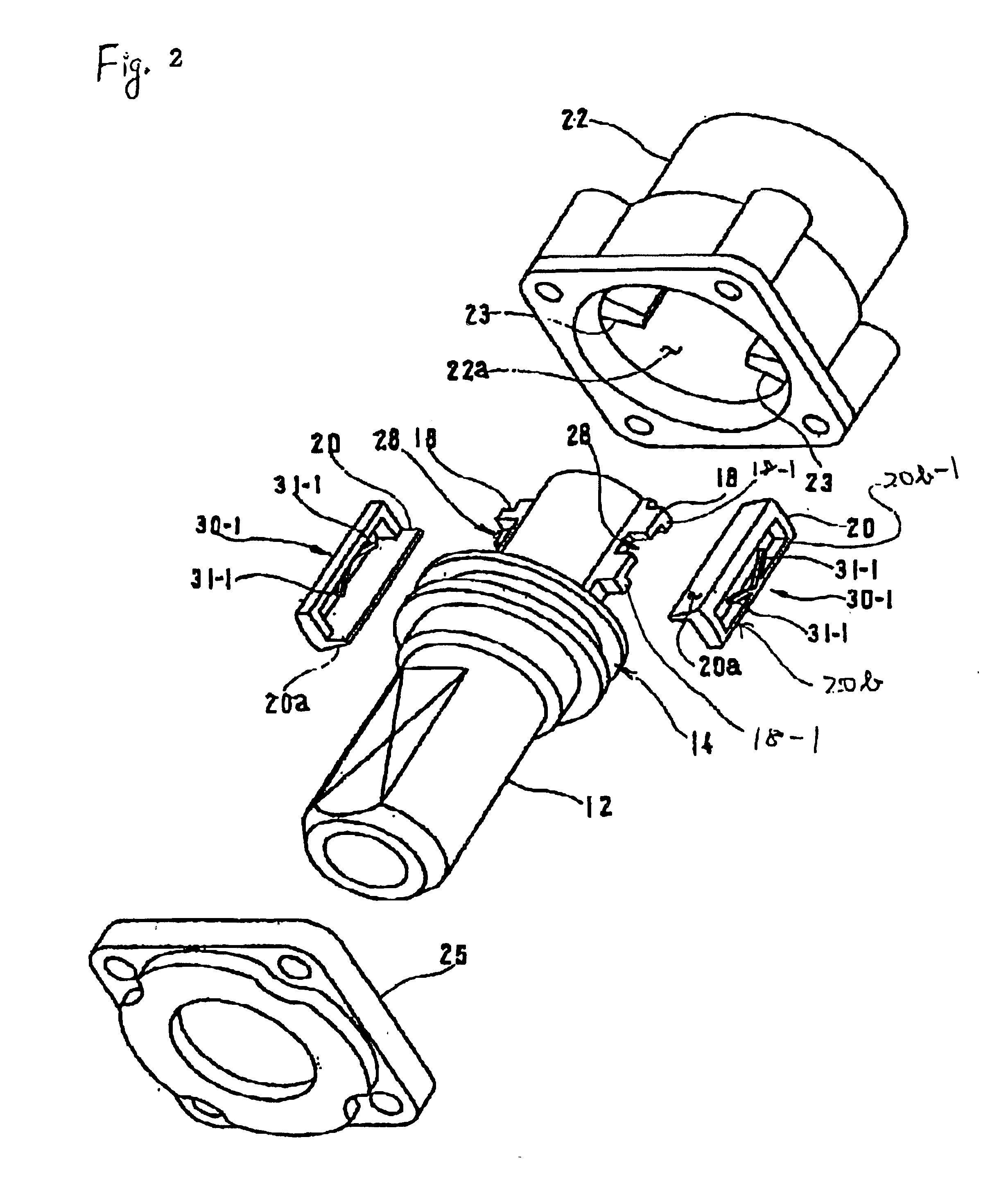
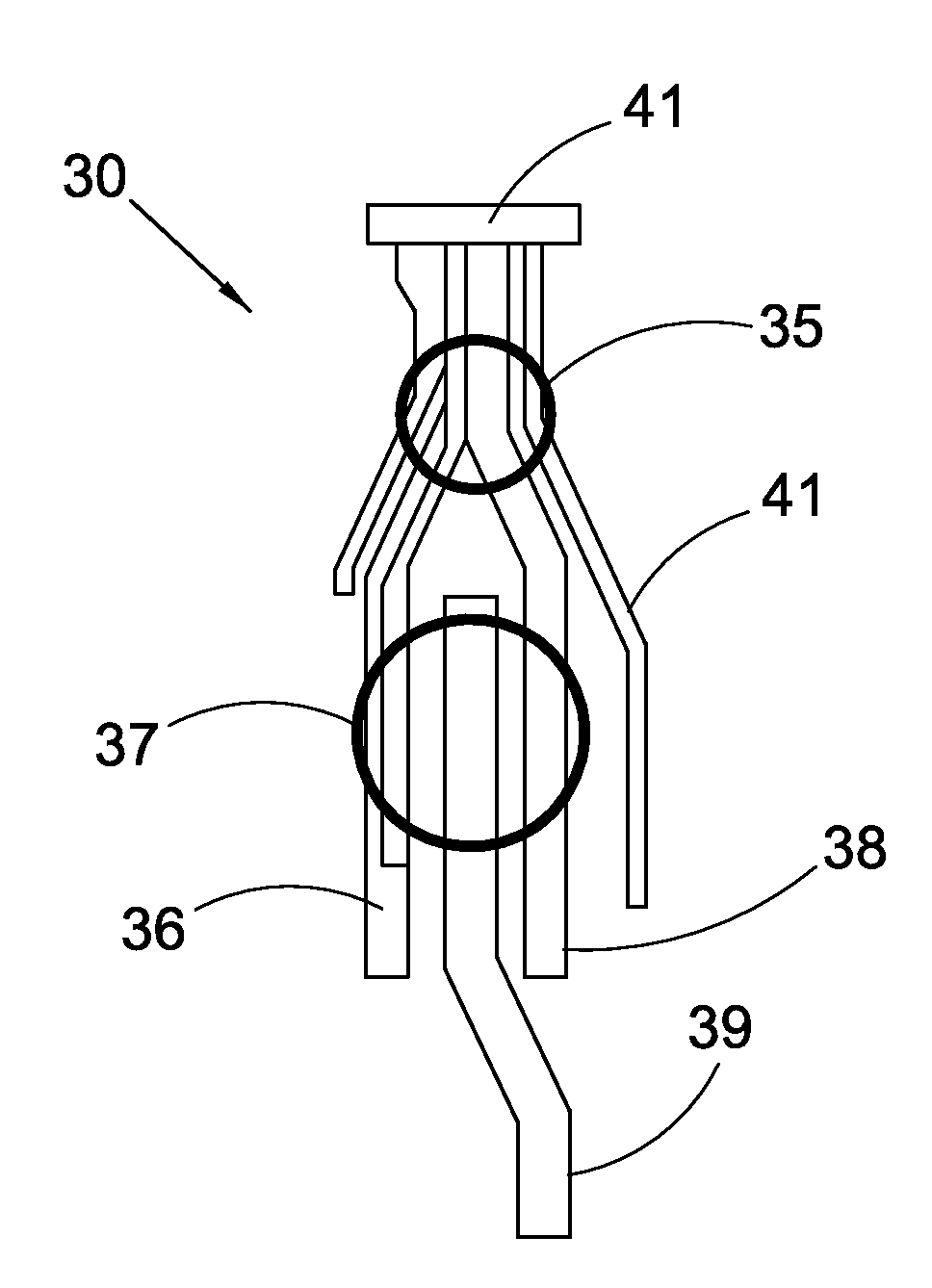
InactiveUS20080097269A1Strong and highly tunable torque capabilityLiquid resistance brakesSpringsActuatorOrthotic device
Electro-rheological fluid brake or actuator devices provide controllable resistance with or without inclusion of active torque output in either direction of rotation under manual or computer control. The brake and actuator devices are suitable for use in an orthotic device for a joint, such as the knee or elbow.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for suspension lock out and signal generation
Methods and apparatus for regulating the function of a suspension system are disclosed herein. Suspension characteristics often contribute to the efficiency of a suspended system. Depending on the desired operating parameters of the suspended system, it may be desirable to alter the functional characteristics of the suspension from time to time in order to maintain or increase efficiency. The suspension hereof may be selectively locked into a substantially rigid configuration, and the damping fluid may be phase separated and / or cooled to increase damping rate during use (or offset rate degradation). The suspension hereof may generate power usable to achieve any or all of the foregoing or to be stored for use elsewhere in the suspended system or beyond.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Electro-rheological fluid brake and actuator devices and orthotic devices using the same
InactiveUS8142370B2Strong and highly tunable torque capabilityLiquid resistance brakesSpringsElectrical resistance and conductanceActuator
Electro-rheological fluid brake or actuator devices provide controllable resistance with or without inclusion of active torque output in either direction of rotation under manual or computer control. The brake and actuator devices are suitable for use in an orthotic device for a joint, such as the knee or elbow.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
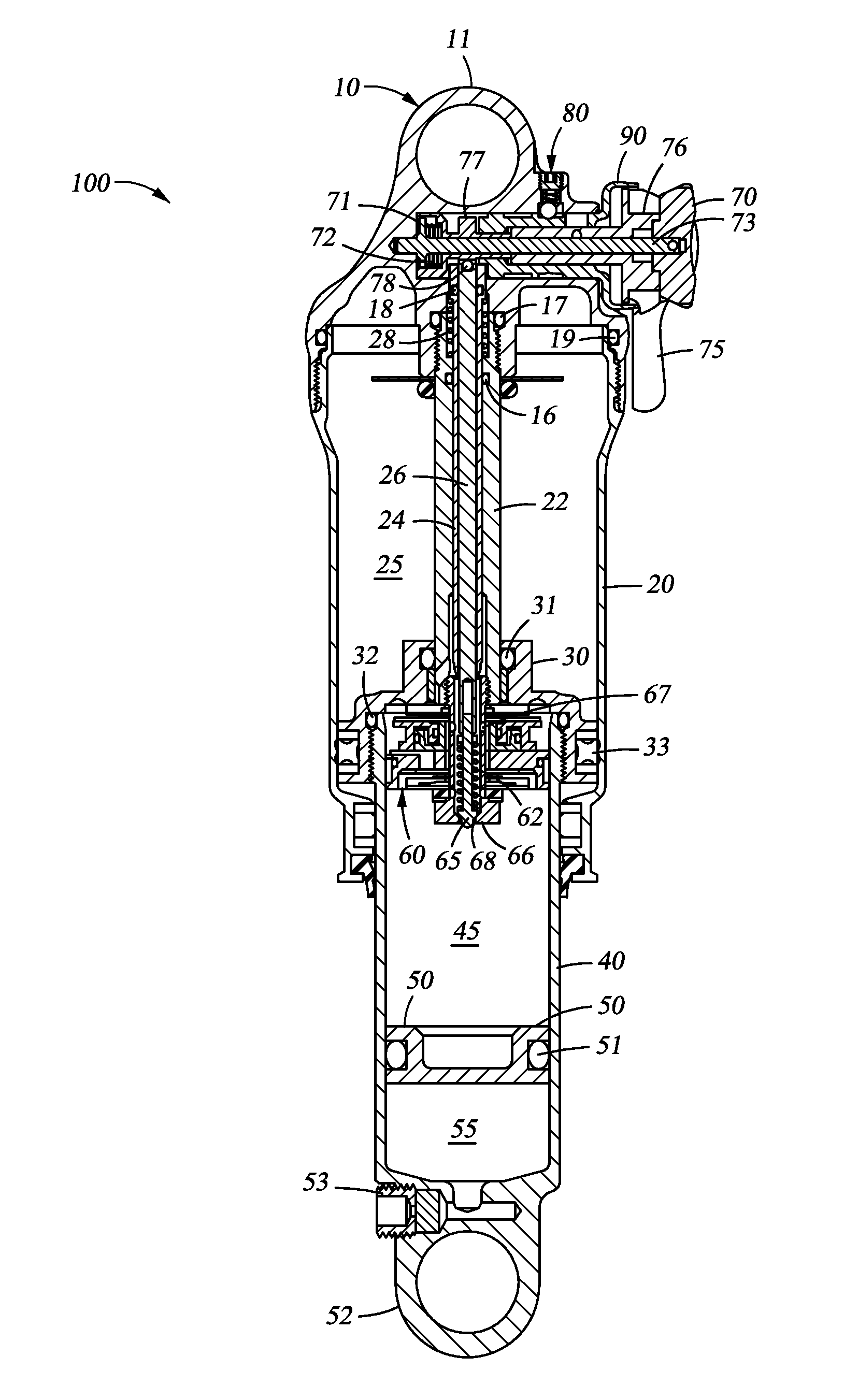
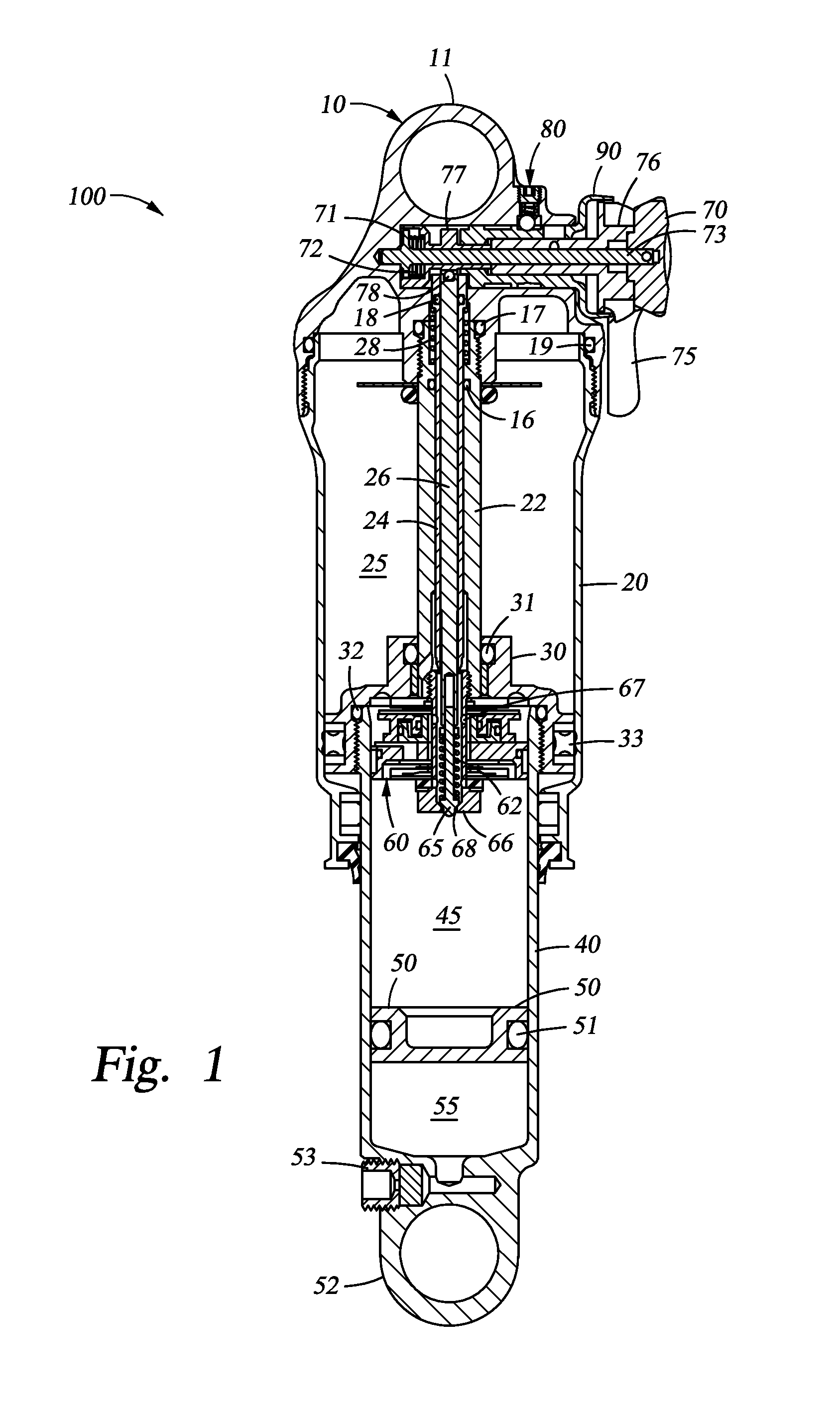
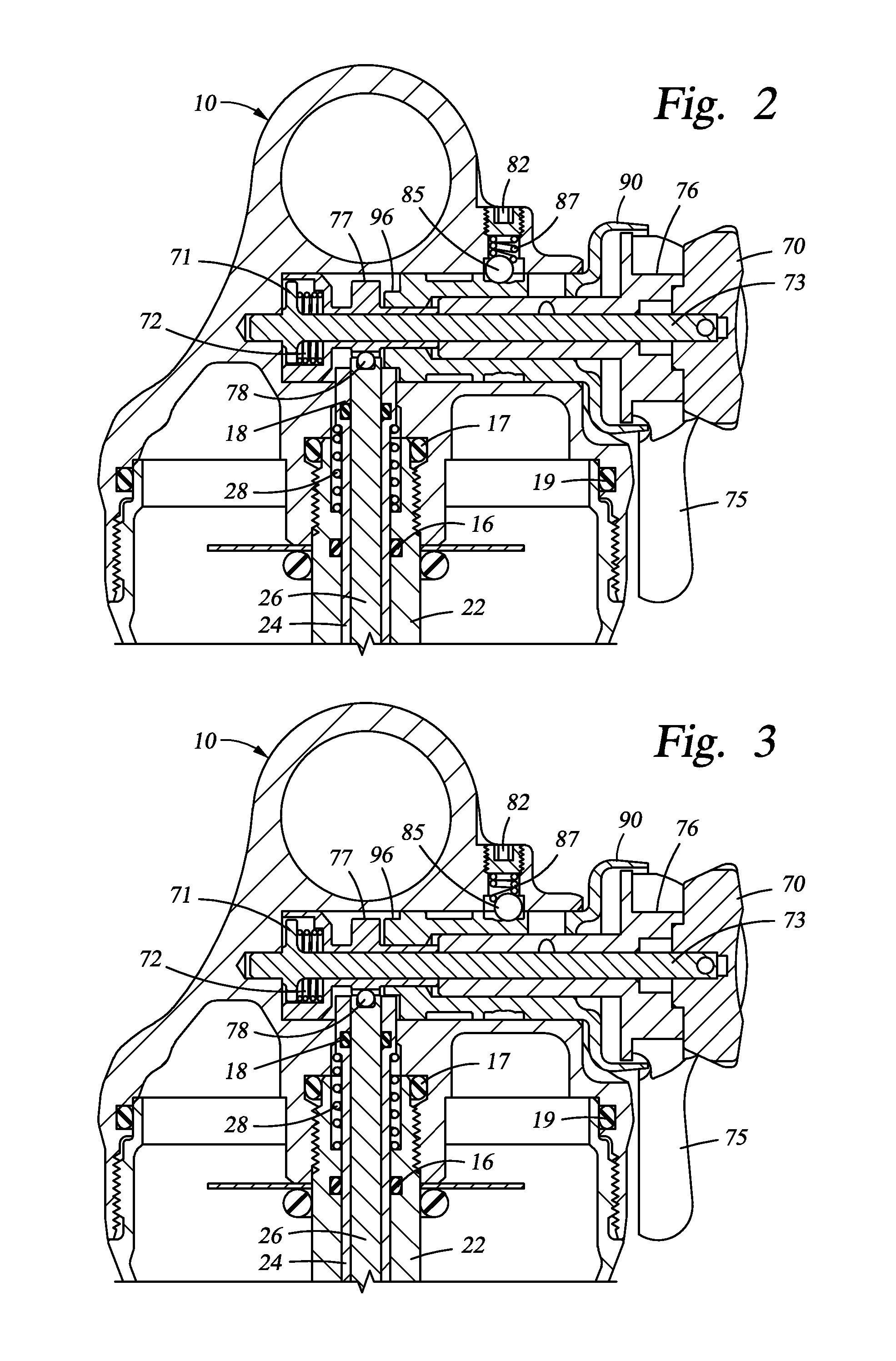
Controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber
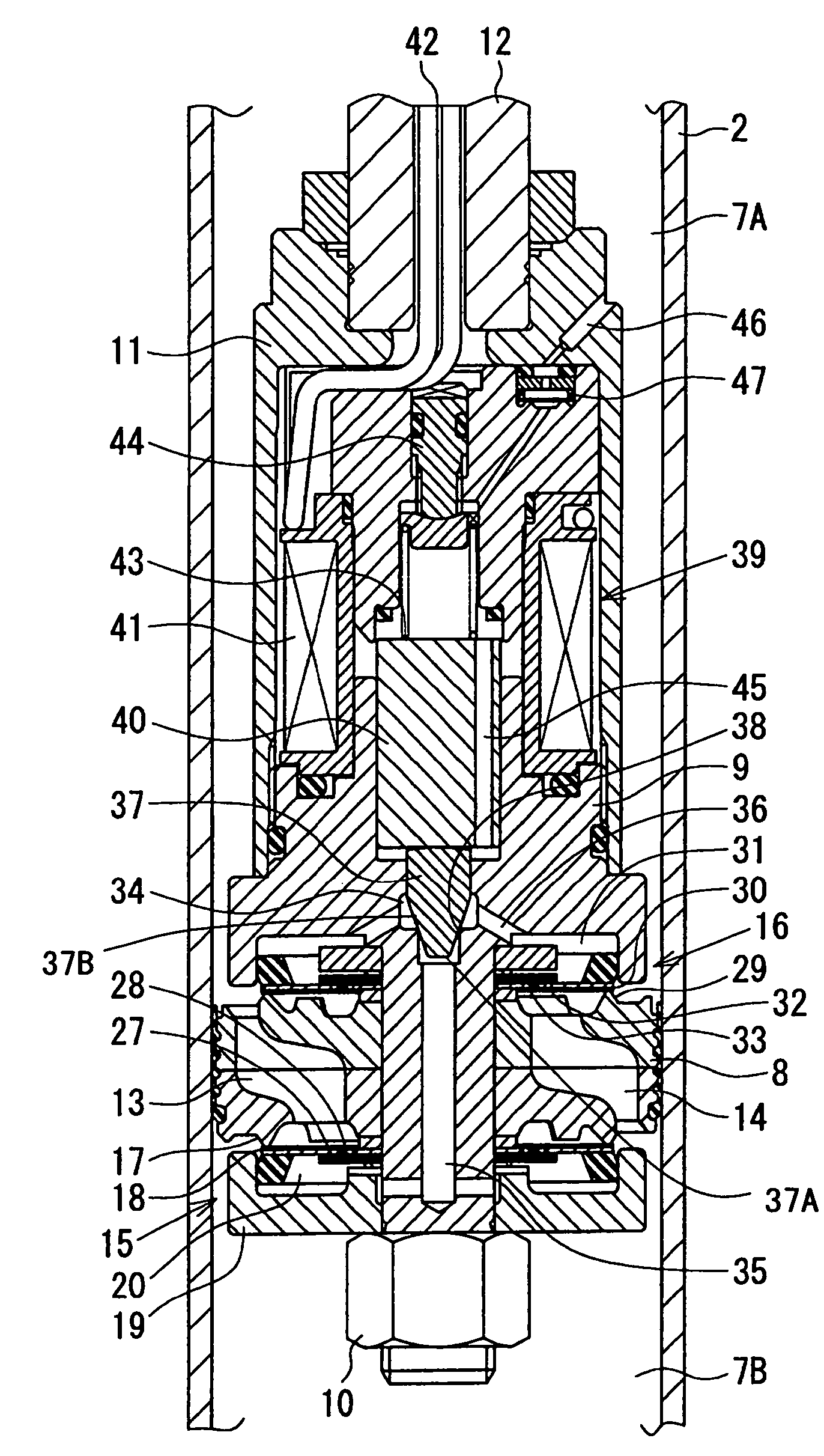
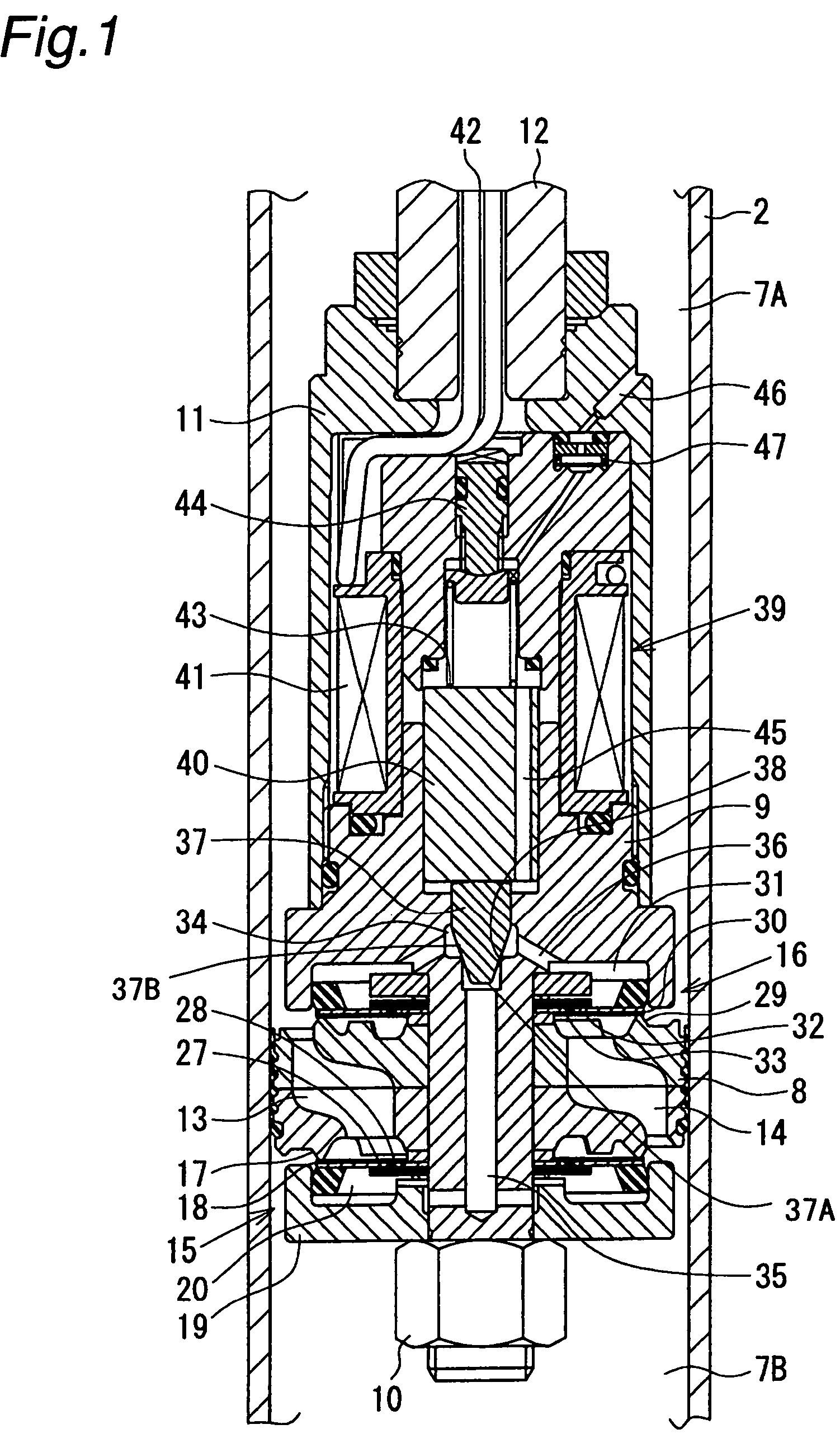
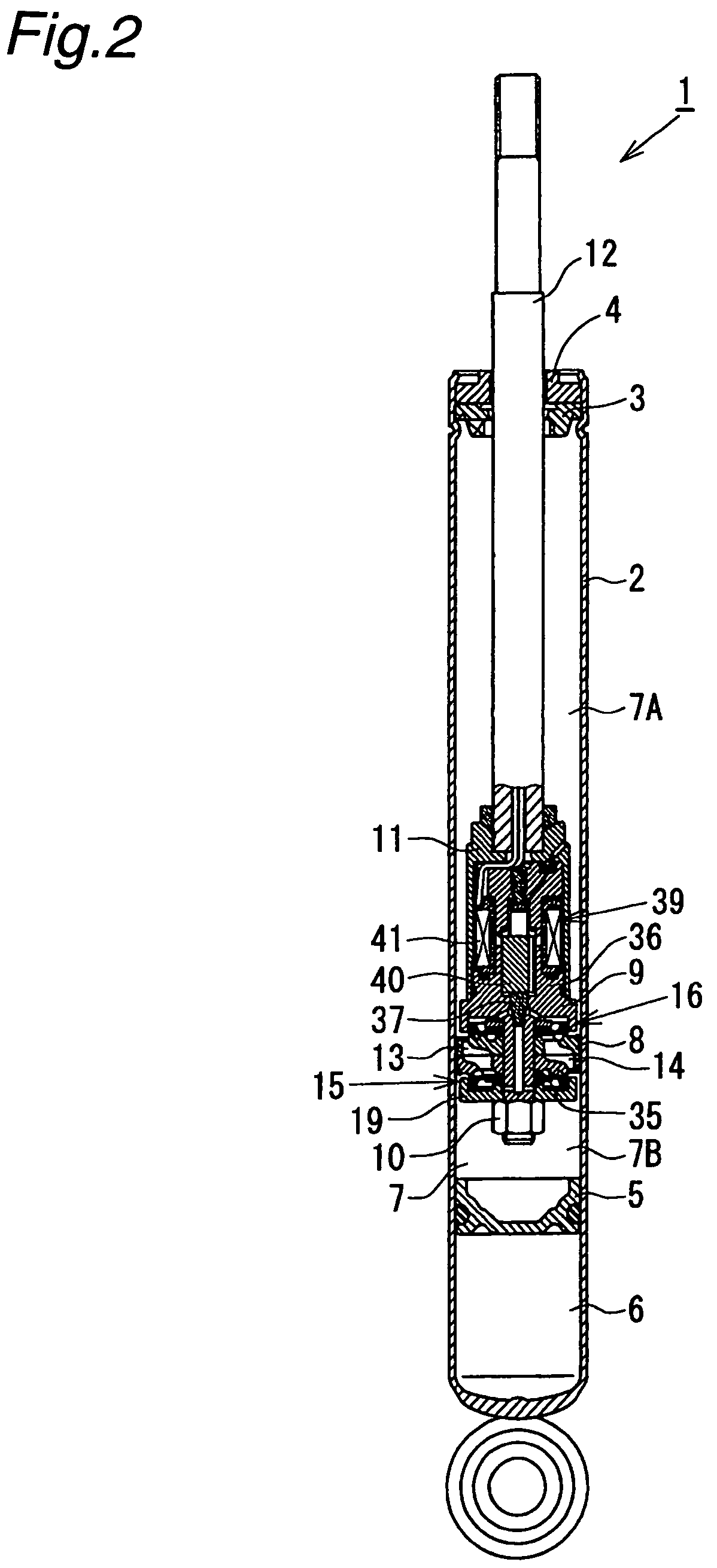
A controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber including a pilot type damping valve having a back-pressure chamber for each of an extension stroke and a compression stroke. A piston connected to a piston rod is fitted into a sealed cylinder in which a hydraulic fluid is contained. During an extension stroke of the piston rod, the hydraulic fluid in an upper cylinder chamber flows to a lower cylinder chamber through an extension-side hydraulic fluid passage, an extension-side orifice hydraulic fluid passage, an extension-side back-pressure chamber, an axial hydraulic fluid passage, a radial hydraulic fluid passage, a compression-side back-pressure chamber, an extension-side check valve and a compression-side hydraulic fluid passage. During a compression stroke, the hydraulic fluid in the lower cylinder chamber flows to the upper cylinder chamber through the compression-side hydraulic fluid passage, the compression-side orifice passage, the compression-side back-pressure chamber, the radial hydraulic fluid passage, the axial hydraulic fluid passage, the extension-side back-pressure chamber, the compression-side check valve and the extension-side hydraulic passage. The hydraulic fluid passage for an extension stroke and the hydraulic fluid passage for a compression stroke have some elements in common, thus simplifying the structure of the controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Methods and apparatus for suspension lock out and signal generation
Methods and apparatus for regulating the function of a suspension system are disclosed herein. Suspension characteristics often contribute to the efficiency of a suspended system. Depending on the desired operating parameters of the suspended system, it may be desirable to alter the functional characteristics of the suspension from time to time in order to maintain or increase efficiency. The suspension hereof may be selectively locked into a substantially rigid configuration, and the damping fluid may be phase separated and / or cooled to increase damping rate during use (or offset rate degradation). The suspension hereof may generate power usable to achieve any or all of the foregoing or to be stored for use elsewhere in the suspended system or beyond.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
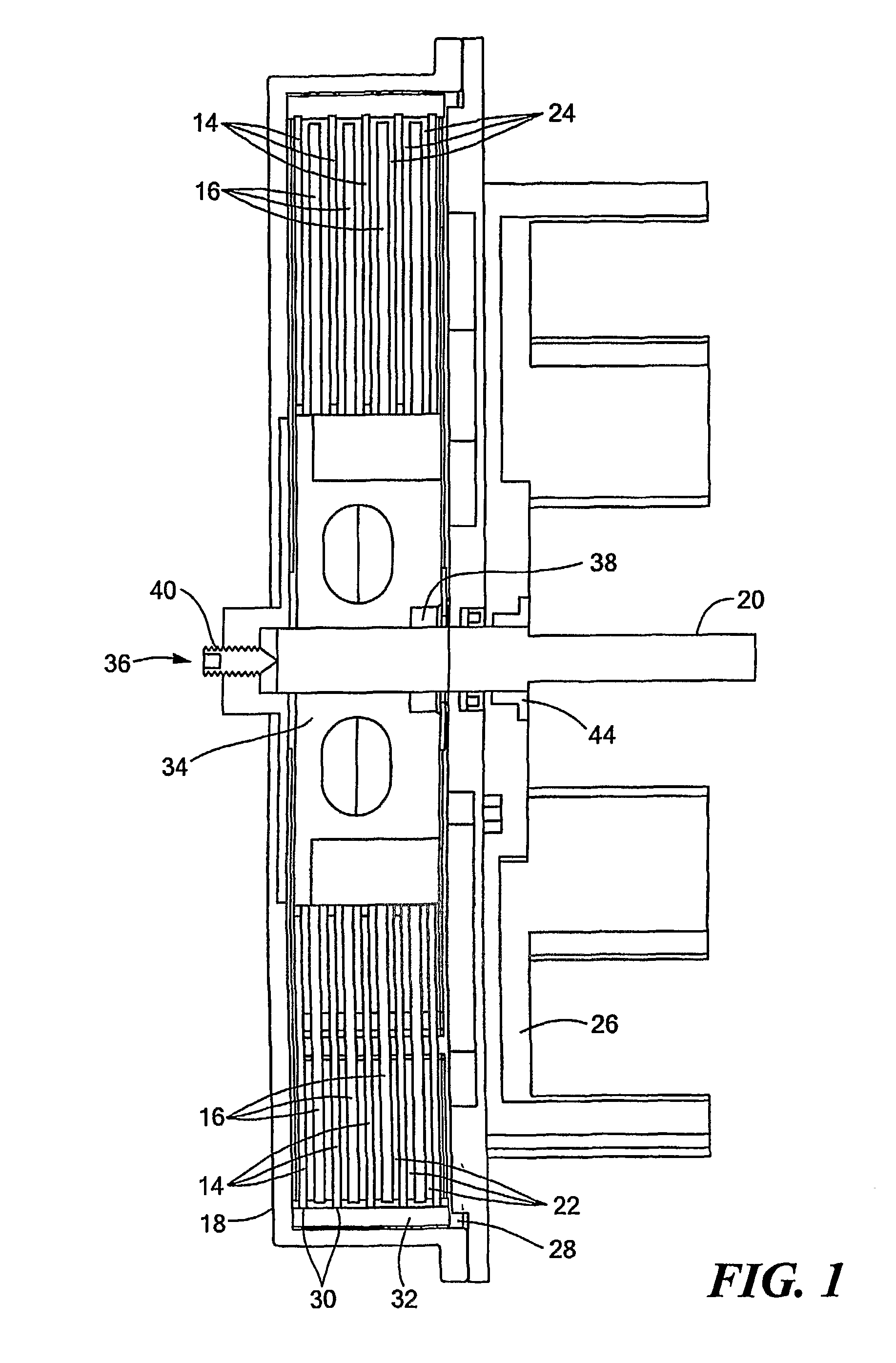
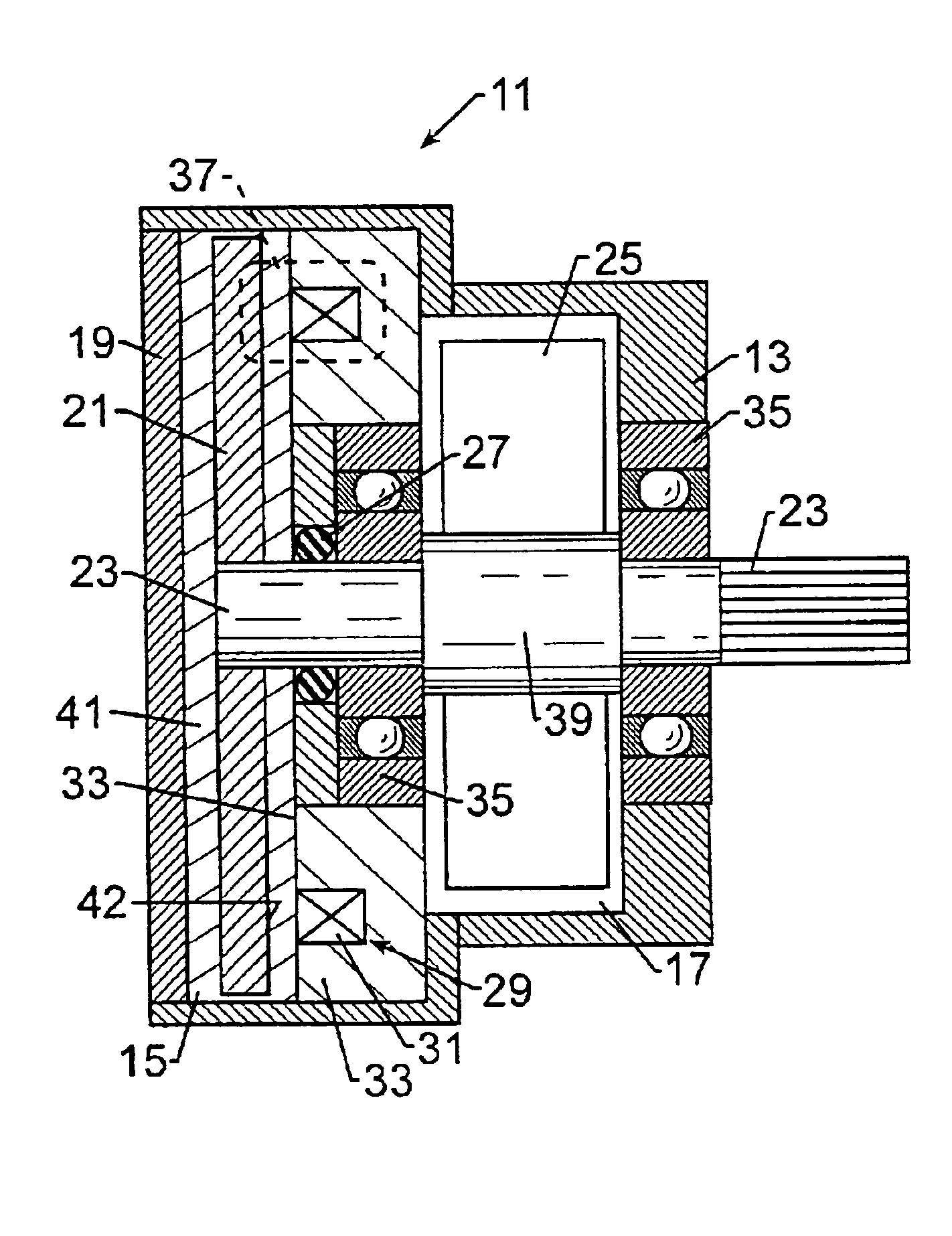
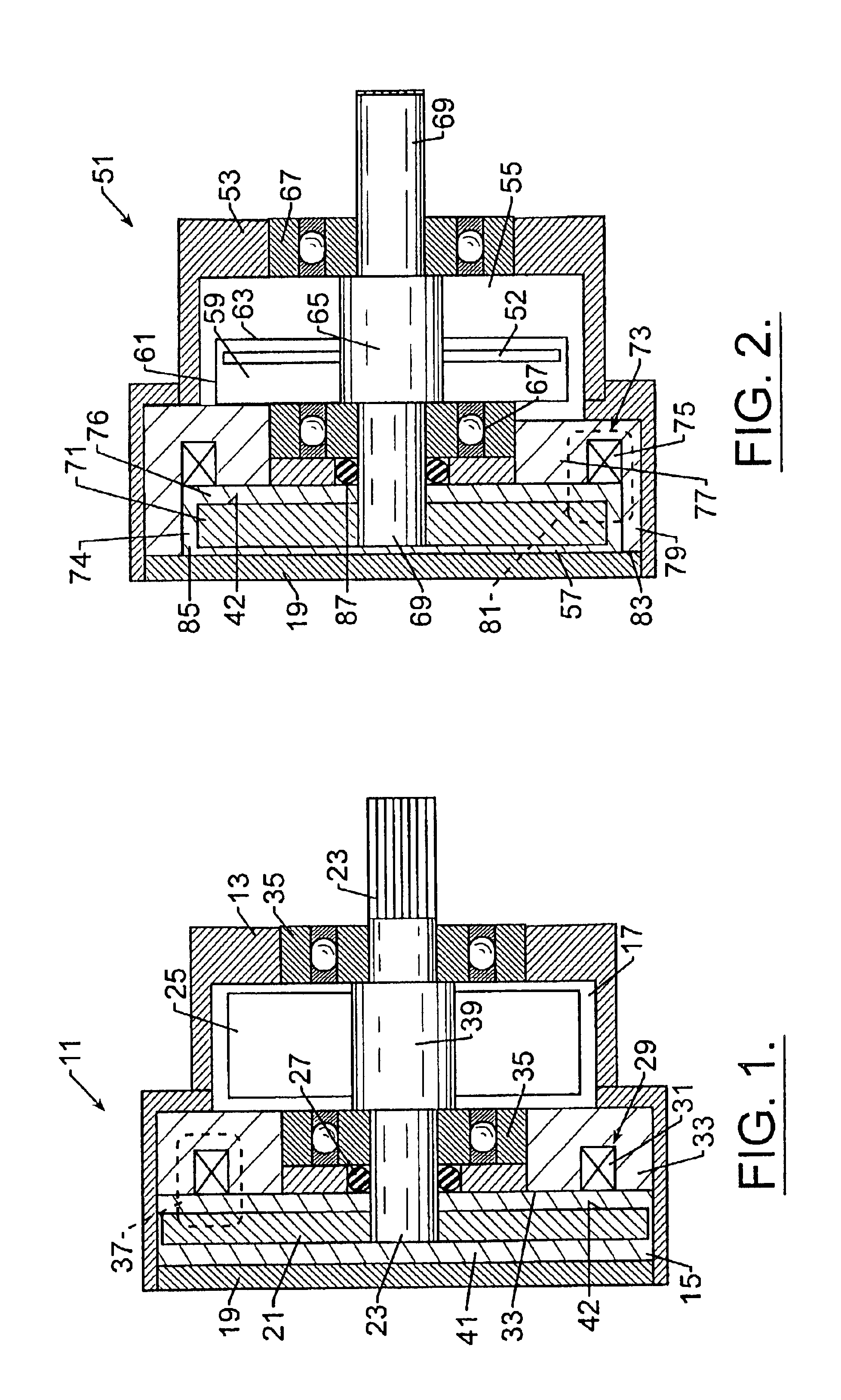
Brake with field responsive material
InactiveUS6854573B2Prevent rotationSome backlashLiquid resistance brakesSpringsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A controllable brake includes a rotor supported on one shaft end. The rotor is housed within a chamber containing a field controllable material which is acted upon by a magnetic field generator to change the rheology of the material and thereby impede movement of the rotor. The shaft is supported by two bearings which, in combination with the housing define a second housing chamber adapted to enclose means for monitoring and / or controlling the brake and in this way, an integrated, compact controllable brake is provided.
Owner:LORD CORP
Magnetorheological fluid-controlled vehicle suspension damper
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Construction variable rotary magnetic current flowing deforming brake
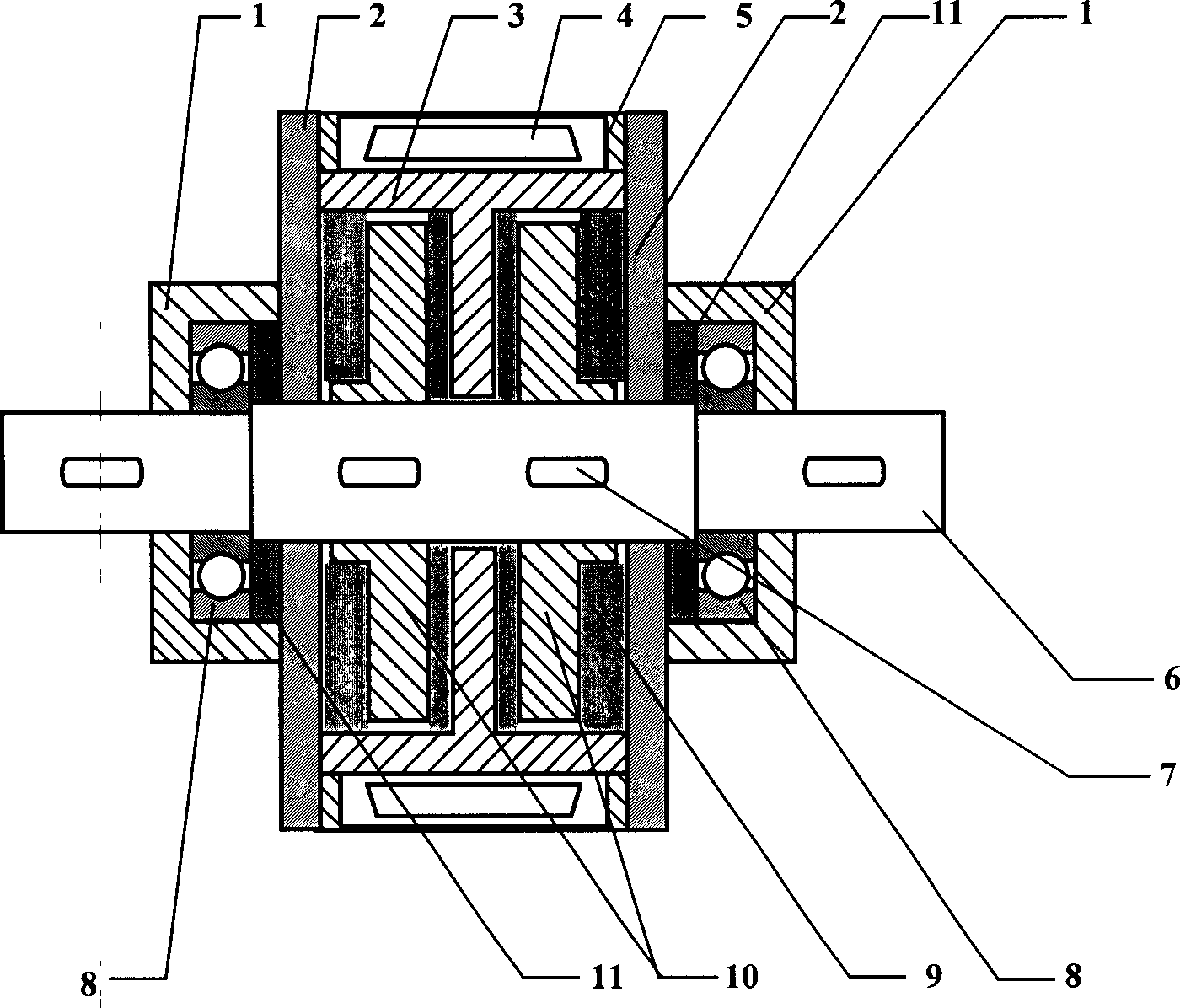
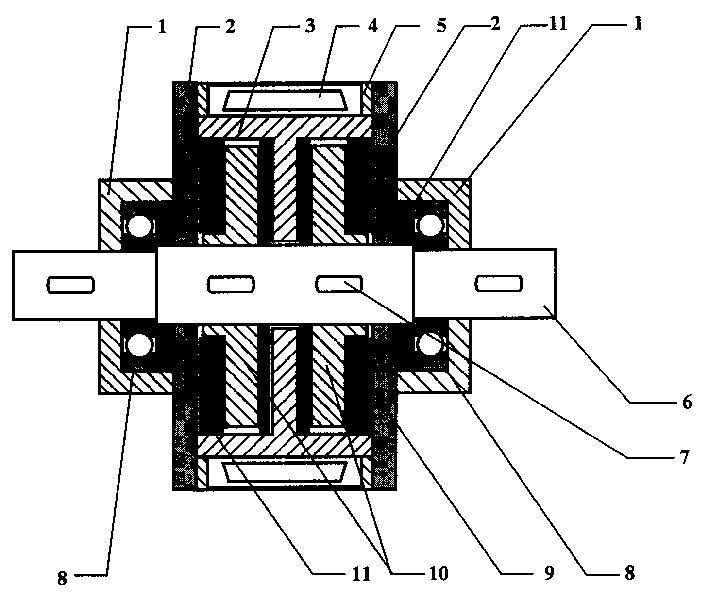
InactiveCN1482376ALarge damping torqueImproving magnetorheological efficiencyLiquid resistance brakesMagnetic currentRotating disc
Construction variable rotary magnetic current flowing deforming brake, mainly comprises a bearing end cap, sealing cap, magnetic conduction inside tube and outside tube, magnet coil, rotation shaft, positioning key, bearing, magnetic current variation liquid, rotating disc and sealing material, wherein the magnetic conduction inside tube and outside tube are both cylinders made of magnetic conduction material, and a separating arrangement is arranged on the magnetic conduction inner tube, the rotation shaft crosses the the magnetic conduction inner tube and connects with the rotating disc, the magnet coil is adhered into the magnetic conduction outer tube, and encloses the magnetic conduction inner tube, the magnetic current flowing deformation liquid is injected into the magnetic conduction inner tube, the separating arrangement is arranged on the magnetic conduction inner tube divides the brake into two chambers, which can determine to mount one or two rotating discs. The brake according to the invention can increase the magnetic current flowing deformation efficiency, and guarantees a large damping moment for the brake.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Washer, damper thereof, and control method thereof
The present invention provides a washer, damper thereof, and control method thereof, by which noise is reduced by adjusting a damping force of the damper in a manner of turning on / off power of the damper according to an oscillation frequency of a vibrating body such as a washer. The control method reduces noise by supplying power to a damper in an excessive vibration state of a vibrating body such as a washer or by cutting off the power supplied to the damper in a normal vibration state of the vibrating body.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Methods and apparatus for variable damping adjuster
Methods and apparatus for a damper adjustment assembly that comprises an adjuster having a first detent at a first axial location, and a second detent at a second axial location. The assembly may further comprise a housing having a keeper for engaging the first and second detents. The method may comprise rotating the adjuster within the housing, and engaging the keeper with the first detent at the first axial location. The method may further comprise further rotating the damping adjuster within the housing and engaging the keeper with the second detent at the second axial location on the adjuster.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Prosthetic knee and rotary hydraulic chamber
An improved prosthetic knee joint utilizes a rotary hydraulic chamber with internal flow control and positioned with hydraulic chamber opposite the upper joint section. A polycentric knee joint is provided with a forward flexion bumper and a cable extension assist for improved gait performance.
Owner:HOSMERDORRANCE CORP
Protective athletic equipment
ActiveUS20150101899A1More commercial practicalityAvoid less flexibilityLiquid resistance brakesBufferCompressed fluidCustom fitting
Custom fitting protective athletic equipment composed of larger compressive chambers to generally surround a body part as well a plurality of smaller compressive chambers, which can be shaped to absorb rotational impact forces, outside the larger compressive chambers. A hard or yielding shell positioned either outside the chambers or between them can provide additional impact dampening and protection. Both the larger and smaller compressible chambers preferably contain compressible fluid, such as air, another gas, gel or liquid. Valves are preferably provided in the chambers so that the fluid can be controlled when an impact is received. A method is also disclosed to use three-dimensional scanning techniques and three-dimensional 3D printer manufacturing techniques to produce the protective athletic equipment of the present invention.
Owner:ROUSSEAU RES INC
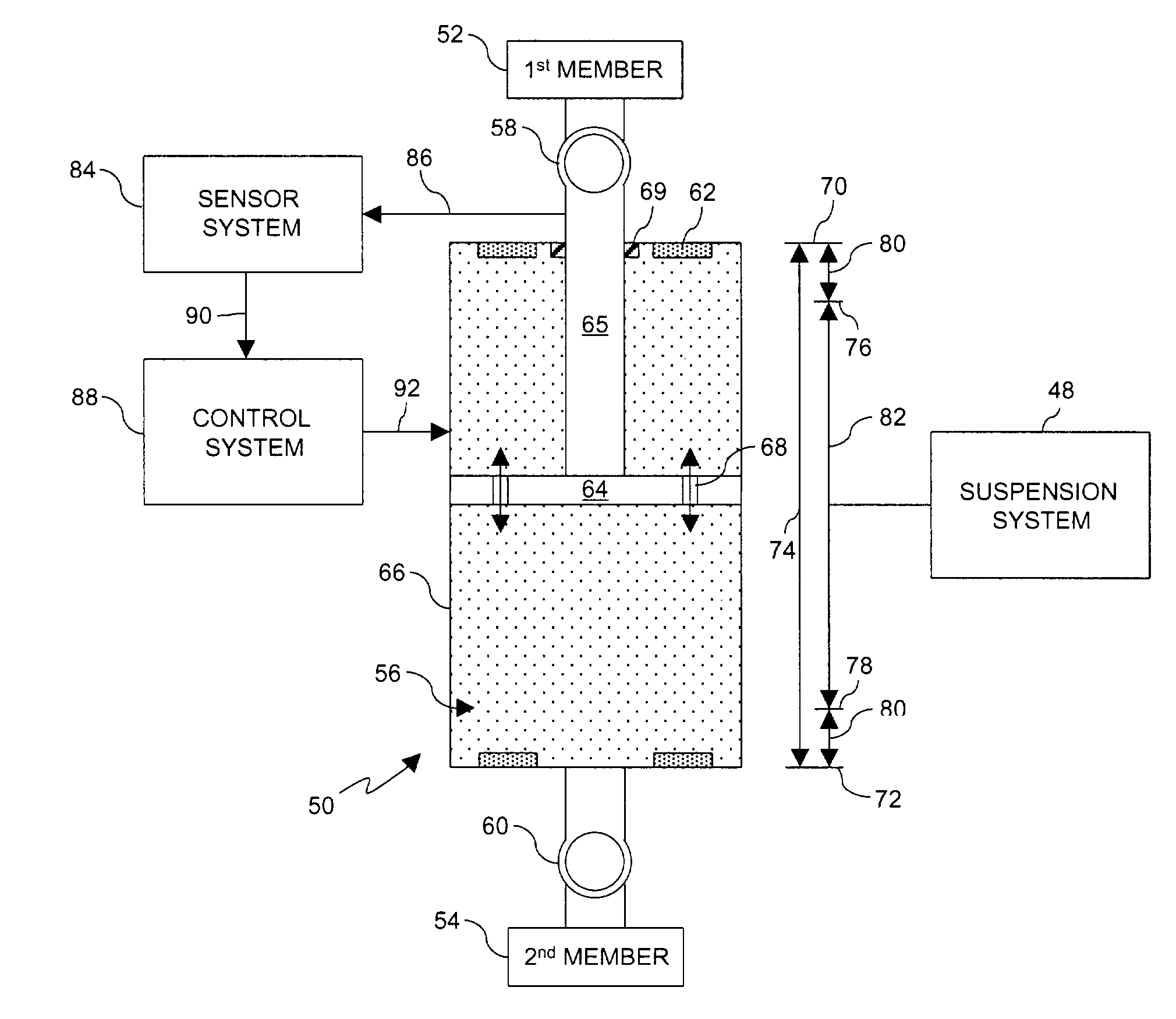
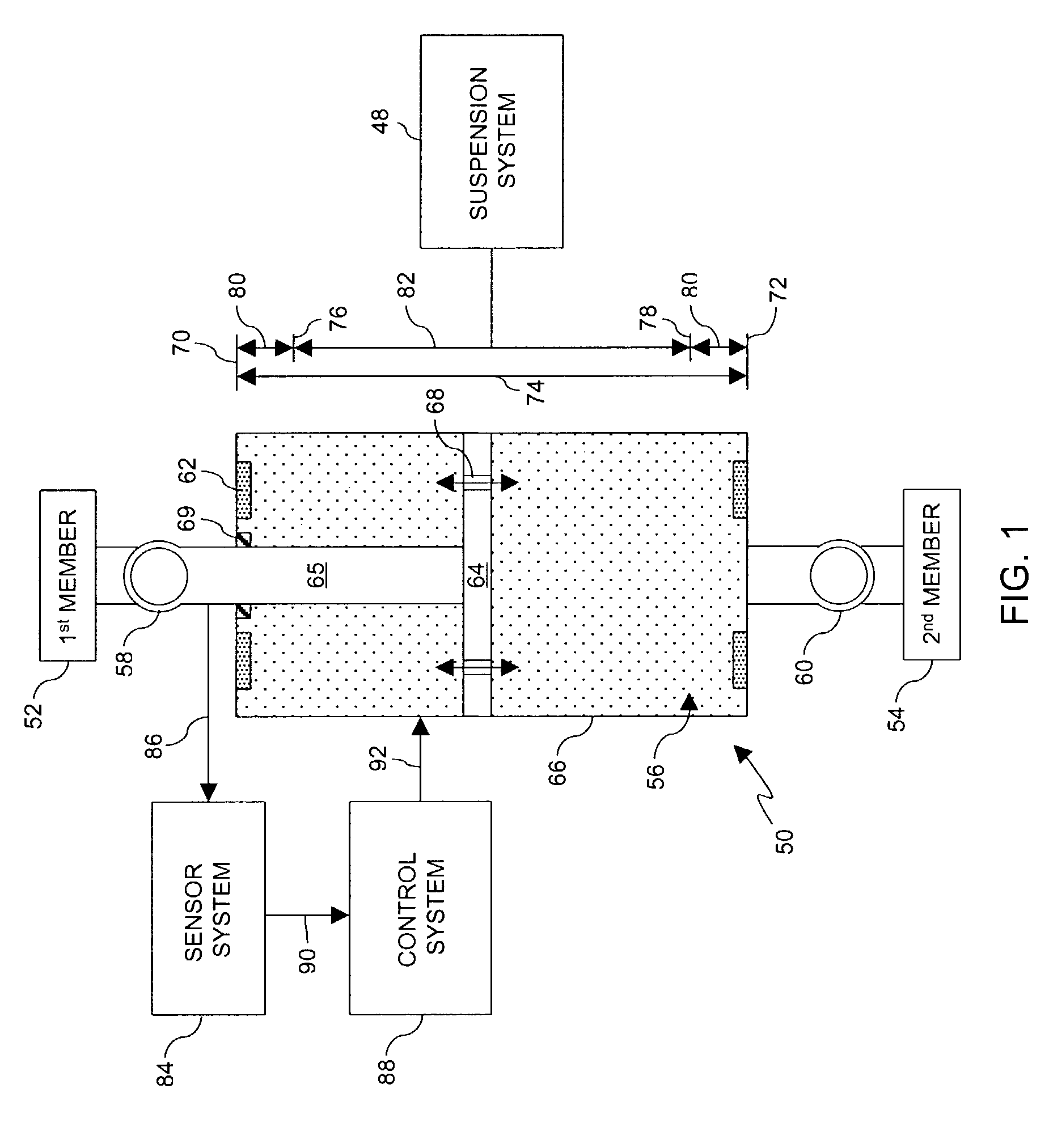
Adjustable damping control with end stop
A damper device comprising a first mode having a first level of damping, a second mode having a second level of damping corresponding to a predetermined function, a sensor system having a first output corresponding to a normal position and a second output corresponding to an end stop approaching position, and a control system operable for receiving the first output and the second output and executing the first mode and the second mode. The damper device is operable in the first mode when the control system receives the first output and is operable in the second mode when the control system receives the second output. A controllable suspension system comprising a damper device, a magnetic probe, a sensor system comprising at least one position sensor operable for sensing the position of the magnetic probe, and a control system electronically connected to the sensor system and the damper device, wherein the control system is operable for receiving an output from the sensor system and executing a predetermined function to control the damper device. Electric signals are supplied to the damper device from the control system during system operation to provide damping sufficient to prevent end stop collisions.
Owner:LORD CORP
Slide damper with spring assist
InactiveUS6910557B2Prevent rotationFacilitates reengagingLiquid resistance brakesSpringsEngineeringControl theory
A slide damper for use with an associated sliding object that is movable between a first position and a second position provides an assisted, dampened return. The slide damper includes a housing having a track, a gear on the housing and a cover configured for movement along the housing. The cover further includes a track engaging pin for engaging the housing track as the cover moves along the housing. A biasing element operably connects the cover and the housing to bias the cover to the second position. A damper assembly is disposed within the cover and includes a damper housing having a geared outer periphery, a damping material disposed in the damper housing and a rotor disposed at least in part within the damper housing for cooperating with the damping material. The rotor has a shaft and is rotatable relative to the damper housing. The rotor shaft extends through the cover and a damper gear operably connects the shaft and the housing gear. The damper assembly is selectively engaged in which the rotor rotates relative to the damper housing when the cover is moved toward the second position and movement of the damper gear along the housing gear is dampened, and disengaged in which the rotor is stationary relative to the damper housing when the cover is moved toward the first position and movement of the damper gear along the housing gear is unimpeded.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Freewheeling rotary damping mechanism
ActiveUS20130207529A1Great and less dampingLiquid resistance brakesSpringsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A damping mechanism that includes a housing with an inner circumferential surface defined by an assembly outer race, an axle shaft that is rotatable with respect to the housing, and a transmission assembly operatively associated with the axle shaft and disposed within the housing. The transmission assembly includes an assembly intermediate race. A fluid space that includes fluid therein is defined between the assembly intermediate race and the inner circumferential surface of the assembly outer race. A vane is disposed between the assembly intermediate race and the inner circumferential surface of the assembly outer race. The vane includes a restriction space defined therein. When the axle shaft rotates in the first direction, the transmission assembly transmits rotation from the axle shaft to the vane, and when the axle shaft rotates in the second direction, the transmission assembly transmits less rotation to the first vane than when the axle shaft rotates in the first direction.
Owner:SAFRAN CABIN INC
Impact absorber
An impact absorber for decelerating a vehicle during a collision with an obstacle by hydraulic damping forces and pneumatic spring forces includes two tubes that are telescopically displaceable one inside the other. An internal tube of the two tubes is closed off to the outside by a base. A gas space subjected to high pressure is disposed adjacent said base and interacts with a first liquid space via a separating piston which is axially guided in the internal tube in a sealed manner. The first liquid space is hydraulically connected to a second liquid space via a throttle opening through an intermediate wall attached inside the internal tube. A working piston attached to a piston rod is guided in the internal tube in a sealing manner and interacts via the piston rod with a third liquid space in an external one of the two tubes. A control which can be connected to two chambers is provided to extend the impact absorber or to return it to a normal position.
Owner:MANNESMANN BOGE
Damper
InactiveUS6913125B2Increase torqueImprove shear resistanceLiquid resistance brakesSpringsEngineeringShock absorber
A damper includes a housing having a cylindrical shape and filled with a viscous fluid, a first rotor rotatably received in the housing and having a first connecting portion formed at an end portion thereof, and a second rotor rotatably housed in the housing coaxially with the first rotor and having a second connecting portion formed at an end portion thereof. The first and second connecting portions engage to allow the first and second rotors together, and forms a space therebetween to allow the viscous fluid to pass therethrough. An elastic member urges the first connecting portion and the second connecting portion to connect together, and accumulates an elastic force in a state that the connection between the first and second connecting portions is released.
Owner:NIFCO INC
Braking energy recovery system for vehicles and vehicles equipped with the system
ActiveCN102300754AOvercome or alleviate shortcomingsAuxillary drivesHydrostatic brakesHydraulic motorDrive shaft
A braking energy recovery system adapted for use on a vehicle and a vehicle having such a system installed. The vehicle has an engine-transmission assembly, a driveshaft, a braking system and an auxiliary system. The energy recovery system comprises a first pump, a hydraulic accumulator and a hydraulic motor. The first pump is a variable displacement hydraulic pump. The hydraulic accumulator is connected to the first pump and is operative to store hydraulic fluid under pressure. The hydraulic motor is hydraulically connected to the accumulator to receive hydraulic fluid. The motor is adapted to drive a second hydraulic pump, which is hydraulically connected to the auxiliary system, using hydraulic energy stored in the accumulator.
Owner:14156048 CANADIAN CO
Heart cam and damper unit and opening/closing controlling device using the same
InactiveUS7032985B1Improve work performanceImproves efficiency in assembly operationLiquid resistance brakesVehicle arrangementsEngineeringCam
A heart cam and damper unit includes a base member having fixed cylindrical portions and a stopper portion, a rotating member having a movable cylindrical portion which is rotatably assembled to the fixed cylindrical portion with a viscous fluid interposed between the movable cylindrical portion and the fixed cylindrical portions, and a pinion gear rotating integrally with the movable cylindrical portion, a heart cam member rotatable fitted around an outer periphery of an outwardly located one of the fixed cylindrical portion and the movable cylindrical portion, and a device interposed between the base member and the heart cam member and adapted to rotatably urge the heart cam member toward the stopper portion. The heart cam and damper unit is interposed between a main body portion and a movable portion which undergoes opening and closing action with respect to the main body portion and is constantly urged in an opening direction.
Owner:PIOLAX CO LTD
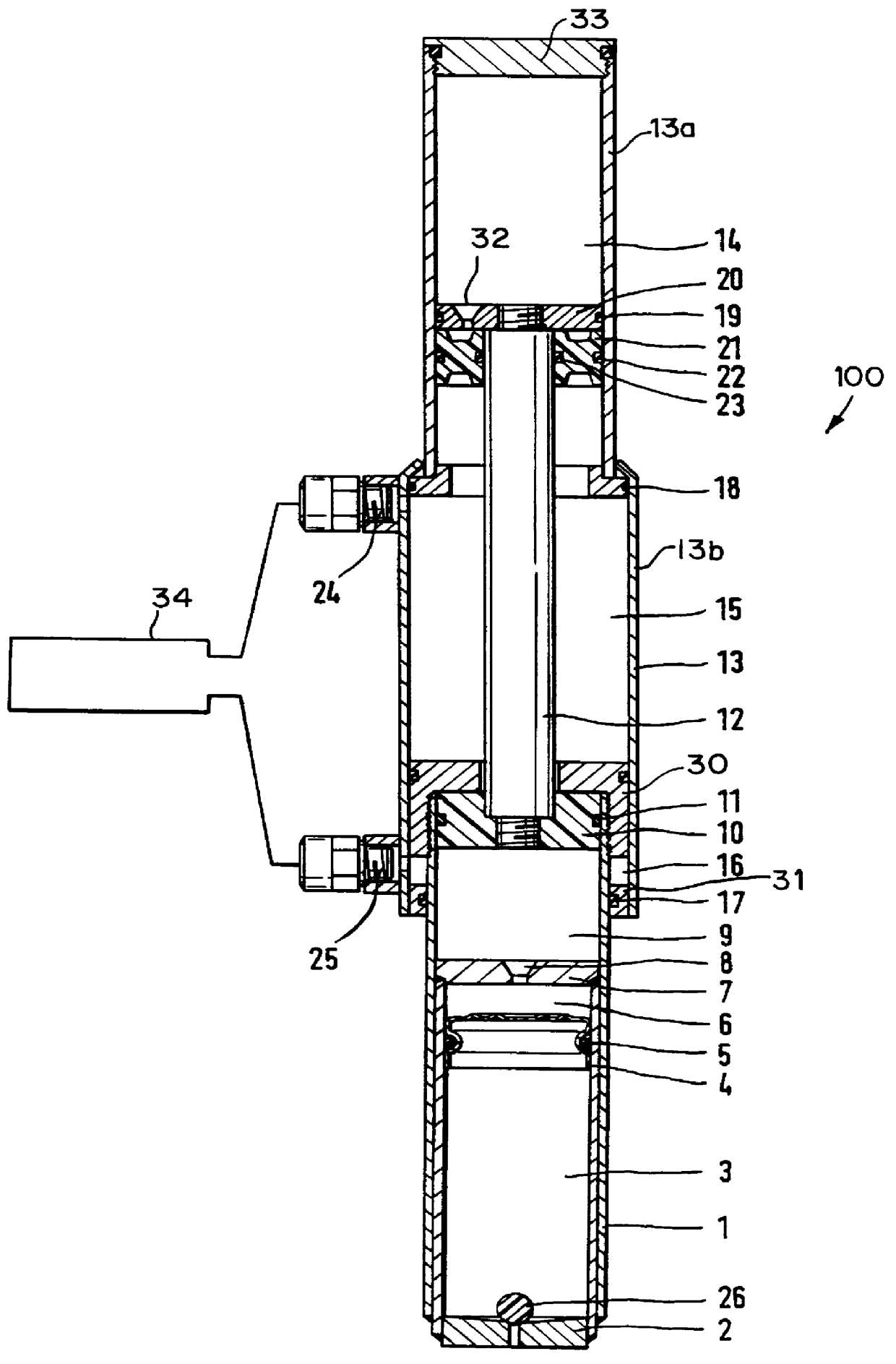
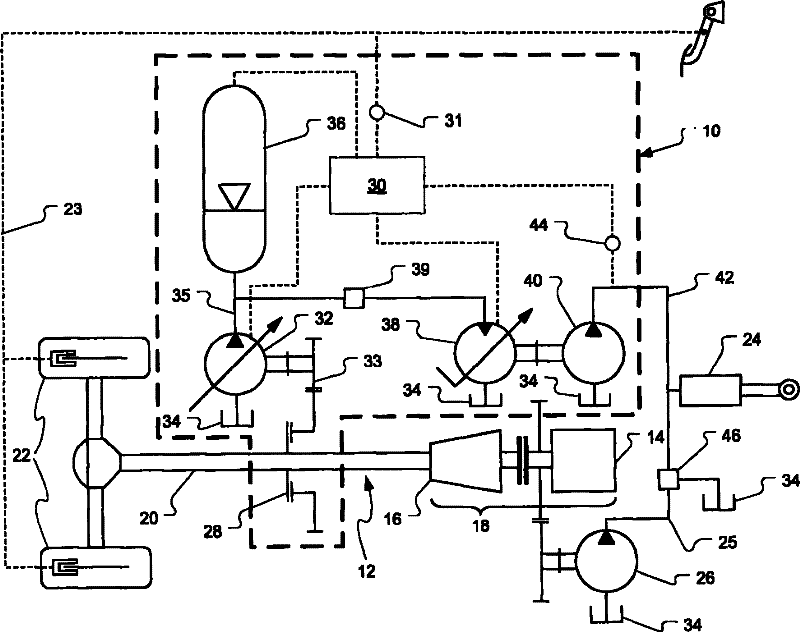
Pump drivetrain damper system and control systems and methods for same
ActiveUS20150377318A1Reduce vibrationRotating vibration suppressionLiquid resistance brakesControl signalDrivetrain
In one aspect, there is provided a damper control system for a reciprocating pump assembly according to which control signals are sent to electromagnets. In another aspect, there is provided a method of dampening vibrations in a pump drivetrain according to which a beginning of torque variation is detected and at least a portion of the torque variation is negated. In another aspect, signals or data associated with pump characteristics are received from sensors, torque characteristics and damper response voltages per degree of crank angle are calculated, and control signals are sent to electromagnets. In another aspect, a damper system includes a fluid chamber configured to receive a magnetorheological fluid; a flywheel disposed at least partially within the fluid chamber and adapted to be operably coupled to a fluid pump crankshaft; and a magnetic device proximate the flywheel. The magnetic device applies a variable drag force to the flywheel.
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
Multiple-disc type magnetorheological brake
InactiveCN102146968AGood heat dissipationImprove cooling effectLiquid resistance brakesMagnetic currentBrake torque
The invention relates to a multiple-disc type magnetorheological brake which mainly comprises a transmission shaft, a wheel hub, a drive friction plate group, a driven friction plate group, inner and outer magnetic isolation rings, an exciting coil with a U-shaped iron core, magnetic-conducting side plates and a magnetic isolation casing. A sealing ring is used for sealing magnetorheological fluid between the drive friction plate group and the driven friction plate group; the drive friction plate group and the driven friction plate group are respectively sleeved on the magnetic isolation rings and the wheel hub through splines; the drive friction plate group is separated from the driven friction plate group by the inner magnetic isolation ring and the outer magnetic isolation ring; the exciting coil with the U-shaped iron core is directly spliced in iron core jacks of the magnetic conducting side plates; and the braking torque can be changed through changing the current intensity of the coil. When the braking torque is not enough, the quantity of friction plates can be increased or the quantity of the exciting coil with the U-shaped iron core can be increased to adapt to the big torque braking. The multiple-disc type magnetorheological brake has the advantages that the structure is compact, the braking torque is big, the assembly and the disassembly are convenient, the coil is easily used for radiating the heat, and the number of turns wounded by the coil is more.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Suspension device
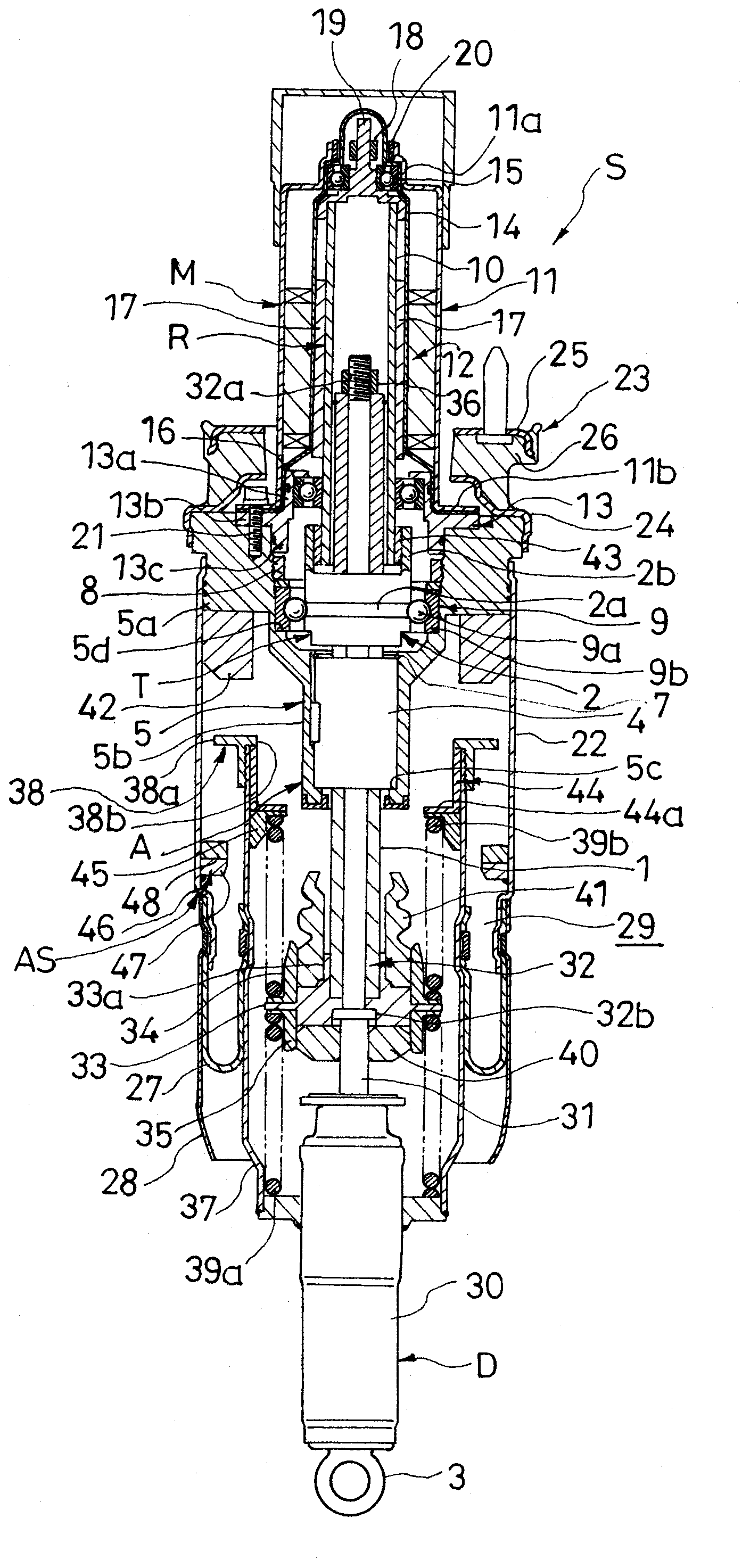
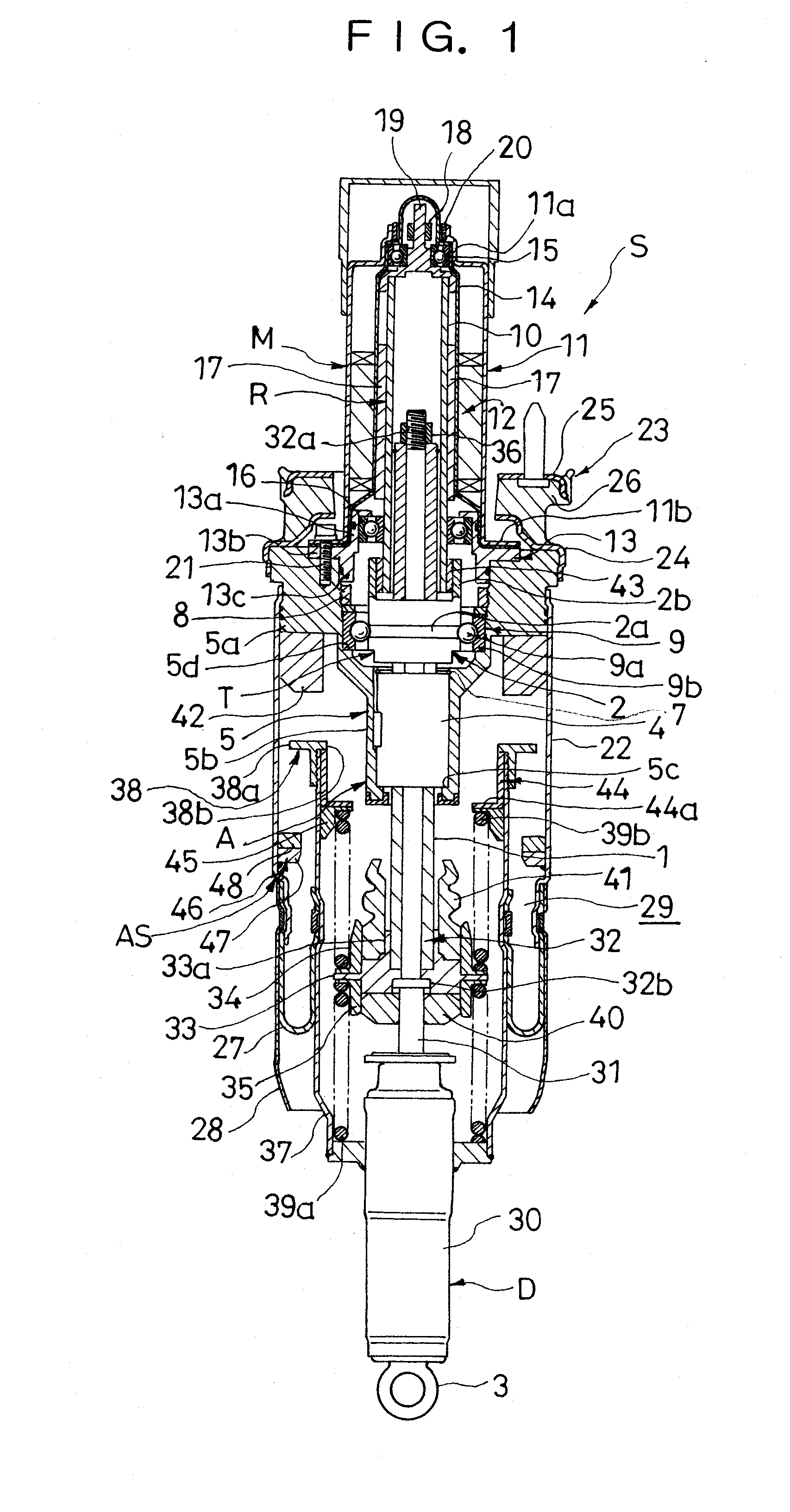
ActiveUS20090321201A1Weight moreReduce overall outer diameterLiquid resistance brakesSpringsLinear motionAir spring
According to problem solving means of the present invention, in a suspension device (S) comprising a motion transforming mechanism (T) for transforming a linear motion of a linear motion member (1) into a rotational motion of a rotating member (2) and a motor (M) connected to the rotating member (2) in the motion transforming mechanism (T), an air spring (AS) is provided, the air spring (AS) including a tubular air chamber (22) connected to the motor (M), an air piston (37) connected to the linear motion member (1) and being tubular and smaller in diameter than the air chamber (22), and a diaphragm (27) interposed between the air chamber (22) and the air piston (37), a stopper (38a) is provided on an outer periphery of the air piston (37), and a stopper seat (46) is provided on an inner periphery of the air chamber (22) so as to be put in abutment against the stopper (38a) upon maximum extension of the suspension device involving relative separation of the air chamber (22) and the air piston (37) with respect to each other.
Owner:KYB CORP
Sleeved bracing useful in the construction of earthquake resistant structures
InactiveUS7188452B2Improve securityPrevent bucklingLiquid resistance brakesLiquid based dampersBuckling-restrained braceEarthquake resistant structures
A buckling restrained brace includes an elongate, hollow sleeve, an elongate yielding core extending substantially through the length of the sleeve, and a buckling constraining element between the yielding core and the inner surface of the hollow sleeve and spaced apart from at least one surface of the yielding core, leaving a gap therebetween. The buckling constraining element may be spaced apart from and, thus, the gap may exist between two or more surfaces of the yielding core. Additionally, an inner sleeve, or liner, may be positioned between the buckling constraining element and the yielding core, with the liner being spaced apart from at least one surface of the yielding core. The buckling restrained brace is useful in absorbing loads, such as seismically induced loads, that are exerted upon a steel frame.
Owner:COREBRACE LLC
Rotary motion control device
This invention is a rotary motion control device comprising a housing, a rotor for connection to a rotary member to be braked, a magnetorheological material contacting the rotor, a first set of magnets having alternating magnetic orientation and a second set of magnets having alternating magnetic orientation, the first and second sets of magnets are adapted for selective alignment with respect to each other so that the magnetic orientation of one of the magnet sets may be repositioned relative to the other of the magnet sets to modulate the overall field strength of the magnets and change the viscosity of the magnetorheological material so that the shearing force on the rotor is increased or decreased. The invention further includes a fishing reel with a brake and a method for controlling the speed of a rotating member.
Owner:MAP HLDG
Vibration damping apparatus
InactiveUS20110017561A1Suppression problemReduce vibrationLiquid resistance brakesSpringsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A vibration damping apparatus has a first looped rope member and a second looped rope member each having a loop portion formed of a rope member in a loop shape, the rope member being formed by twining a plurality of linear members. Further, the vibration damping apparatus has a first base member and a second base member disposed in an up-and-down of the first looped rope member. The first looped rope member is fixed to the first base member and the second base member with the loop portion standing up. The second looped rope member is fixed to an intersecting portion, in one of the first base member and the second base member, intersecting a fixing portion of the first looped rope member with the loop portion standing up.
Owner:TANAKA SEISHIN KOZO LAB
Electromagnetic suspension system for vehicle
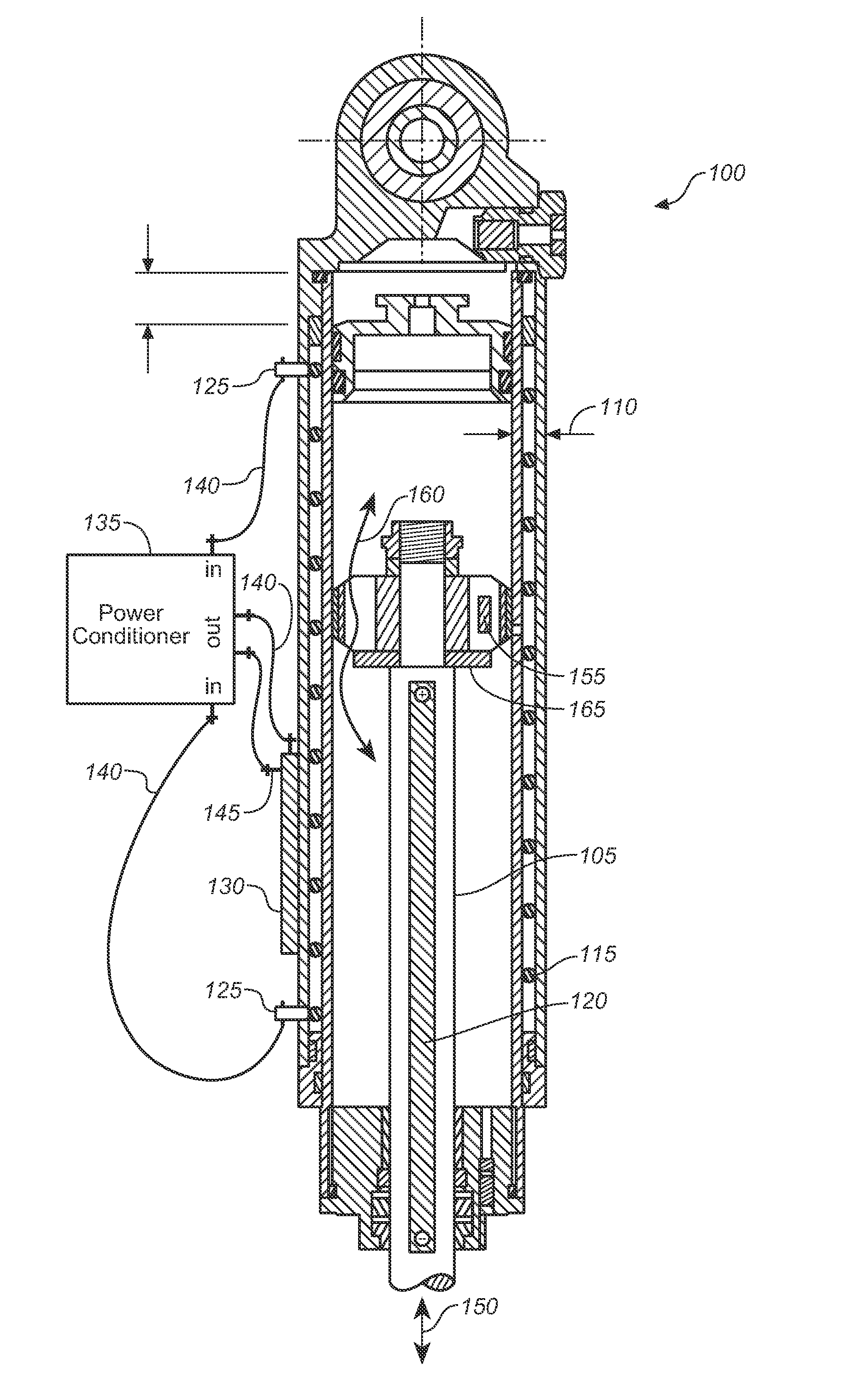
ActiveUS7005816B2Effectively overcome drawbacksEasy to controlAuxillary drivesLiquid resistance brakesElectricityMotor control
An electromagnetic suspension system for a vehicle, comprises an electromagnetic actuator interposed between a sprung mass and an unsprung mass and disposed substantially in parallel with an spring element. An electric motor is provided for driving the electromagnetic actuator. A motor controller is configured to calculate a displacement input applied to the electromagnetic actuator and to control the electric motor in a manner that the electromagnetic actuator generates an optimum damping force corresponding to the displacement input. A motor control circuit is provided for the electric motor, through which the electric motor is connected to the motor controller. Additionally, an electrical damping element is electrically connected to the motor control circuit and in parallel with the electric motor to generate a damping force in a passive manner under a dynamic braking of the electric motor in response to the displacement input to the electromagnetic actuator from the unsprung mass.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Damping unit and refrigerator having the same
InactiveUS20090261701A1Accurate speedSimple structureLiquid resistance brakesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rotary damper device
InactiveUS6840355B2Quickly operating brakingQuickly damper functionLiquid resistance brakesSpringsRotational axisEngineering
A rotary damper device includes a case in which a viscous fluid is filled and sealed, a rotation shaft relatively rotatably supported by the case, a rotation vane formed protruded from the rotation shaft, and a check valve mounted on a tip part of the rotation vane. A passage where the viscous fluid passes through is formed in the rotation vane. The check valve is provided with an opposing face part facing the passage and a frame body interposing the rotation vane. An elastic member for energizing the opposing face part of the check valve for closing the passage of the rotation vane is formed in either the rotation vane or the opposite side of the frame body of the opposing face part.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Double path torsional damper
The present invention is a double path torsion isolator for use in conjunction with a torque converter. Each of the two vibration paths includes a flange with a spring connection to each of the torque converter cover and an output connection attached to the transmission shaft. The torque converter turbine is connected to one of the flanges to provide a different frequency to the associated vibration path. When the lockup clutch is engaged, the engine vibration is divided along the two vibration paths toward the common output connection. The vibration frequency of the paths are adjusted so that the frequencies of the two paths are 180° out of phase at the output connection providing a vibration cancellation effect to the output connection.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com