Patents
Literature
99results about "Hydrostatic brakes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
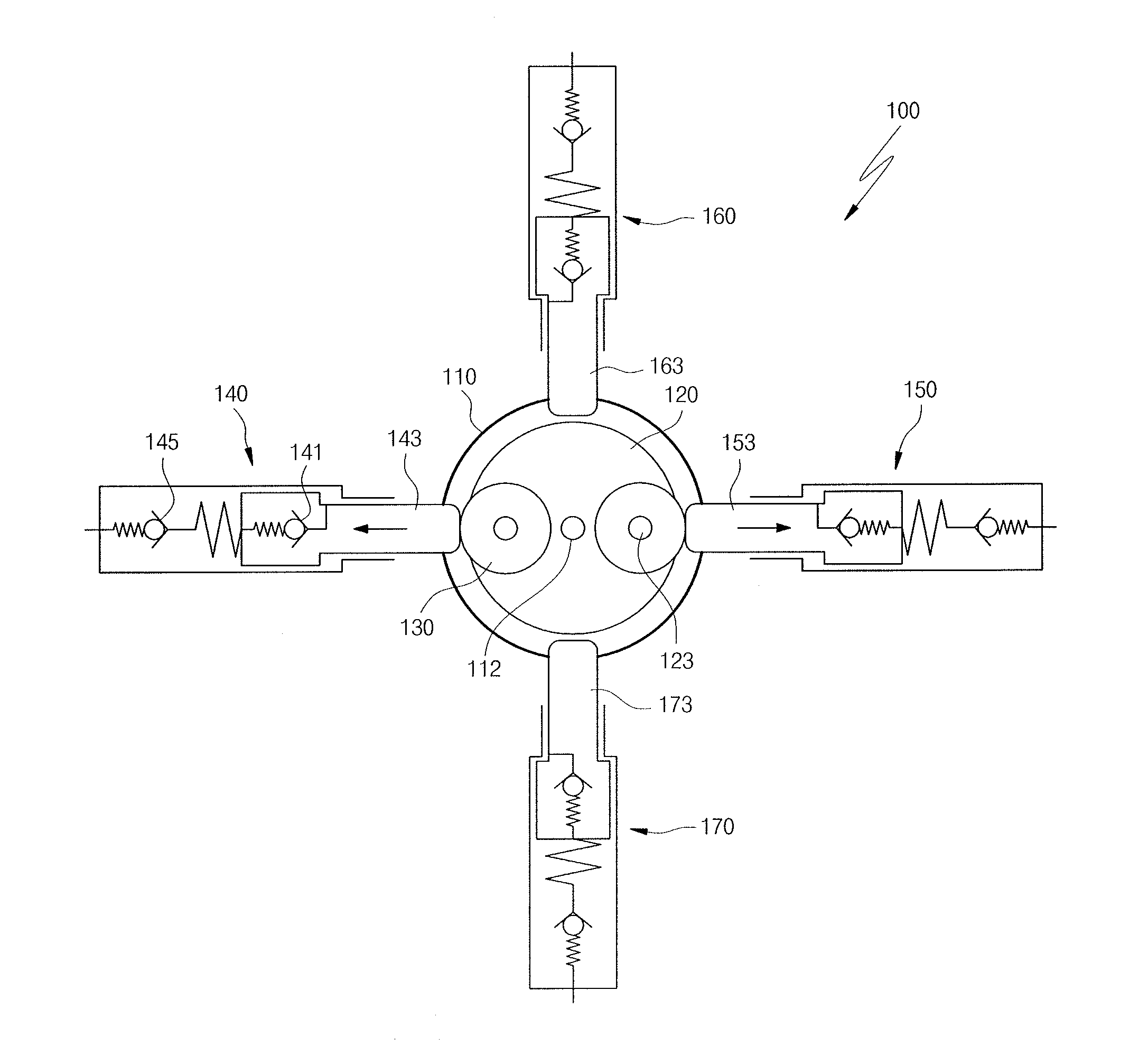
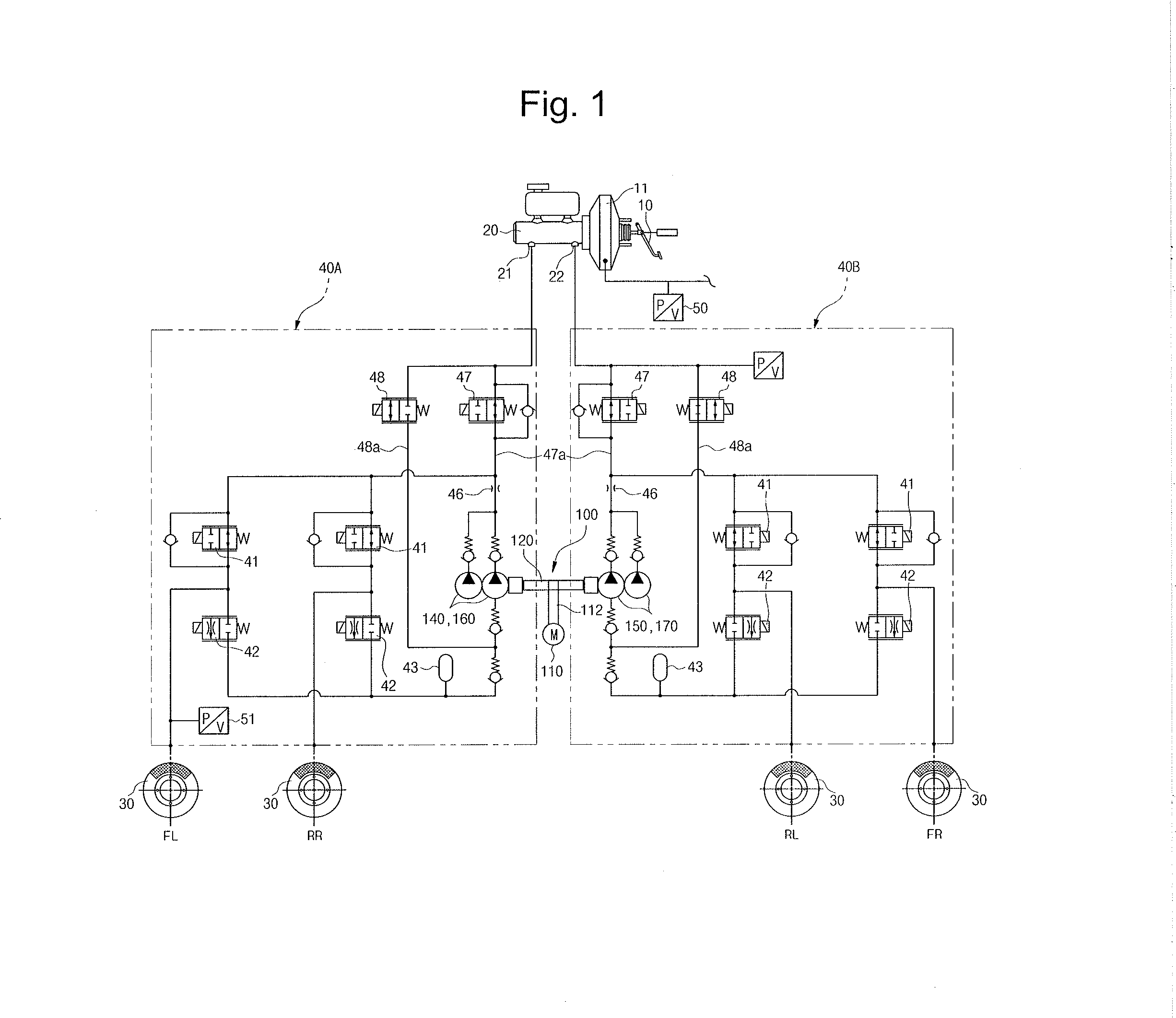
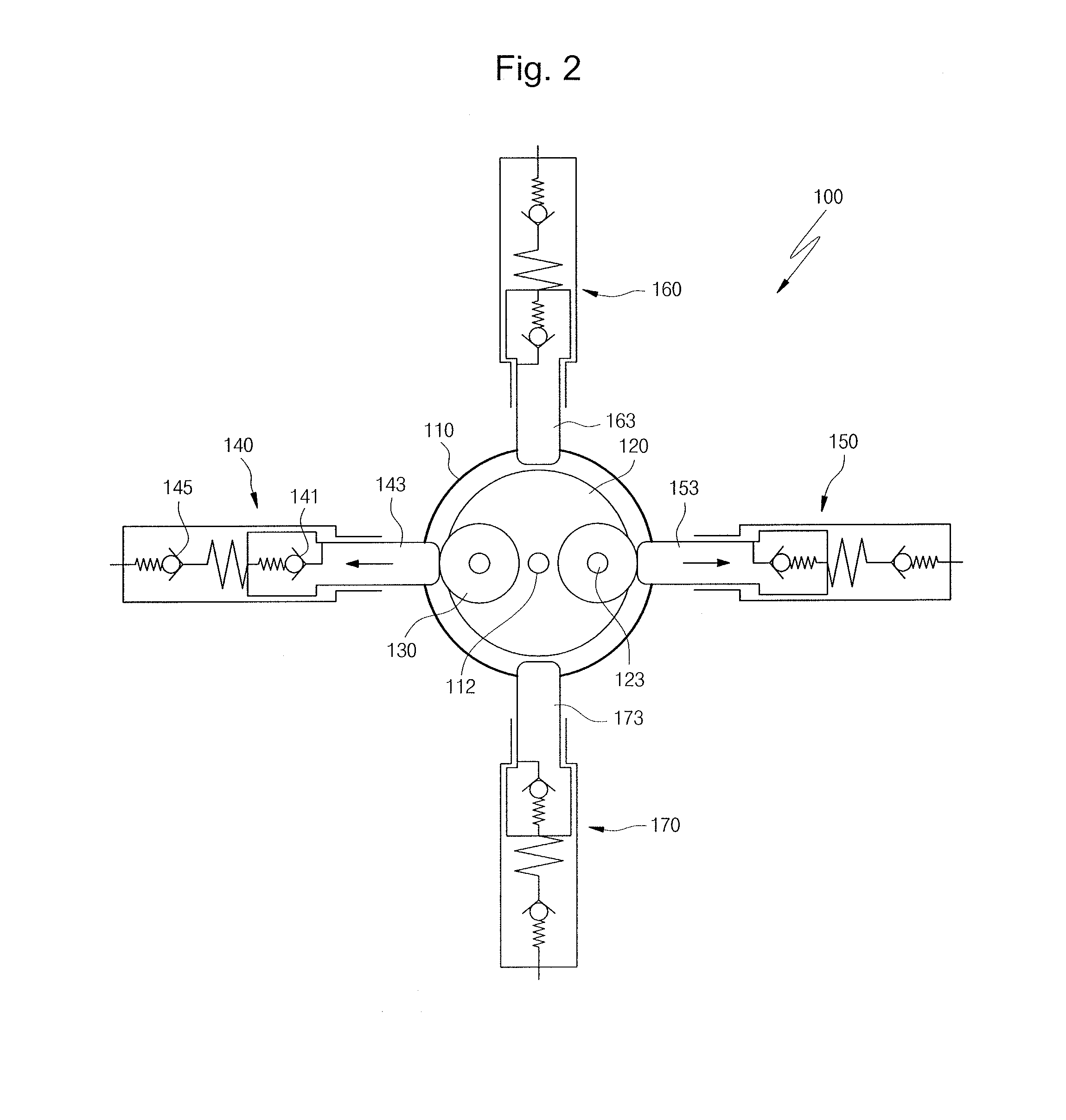
Pump unit of electronic control brake system
InactiveUS20150030483A1Reduce vibrationReduce noiseHydrostatic brakesBraking action transmissionRotational axisReciprocating motion
Disclosed is a pump unit of an electronic control brake system installed in a bore formed in a modulator block, the pump unit including a motor having a rotating shaft, a carrier having a center portion thereof installed on the rotating shaft, and provided with connecting shafts that are spaced apart from the center portion to both sides by a predetermined interval to be disposed in line with each other, a pressing member installed on each of the connecting shafts, and a first piston pump and a second piston pump each provided with a piston configured to be reciprocated by making contact with an outer circumferential surface of the pressing member according to rotation of the carrier, the first piston pump and the second piston pump disposed in line with each other.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Braking energy recovery system for vehicles and vehicles equipped with the system
ActiveCN102300754AOvercome or alleviate shortcomingsAuxillary drivesHydrostatic brakesHydraulic motorDrive shaft
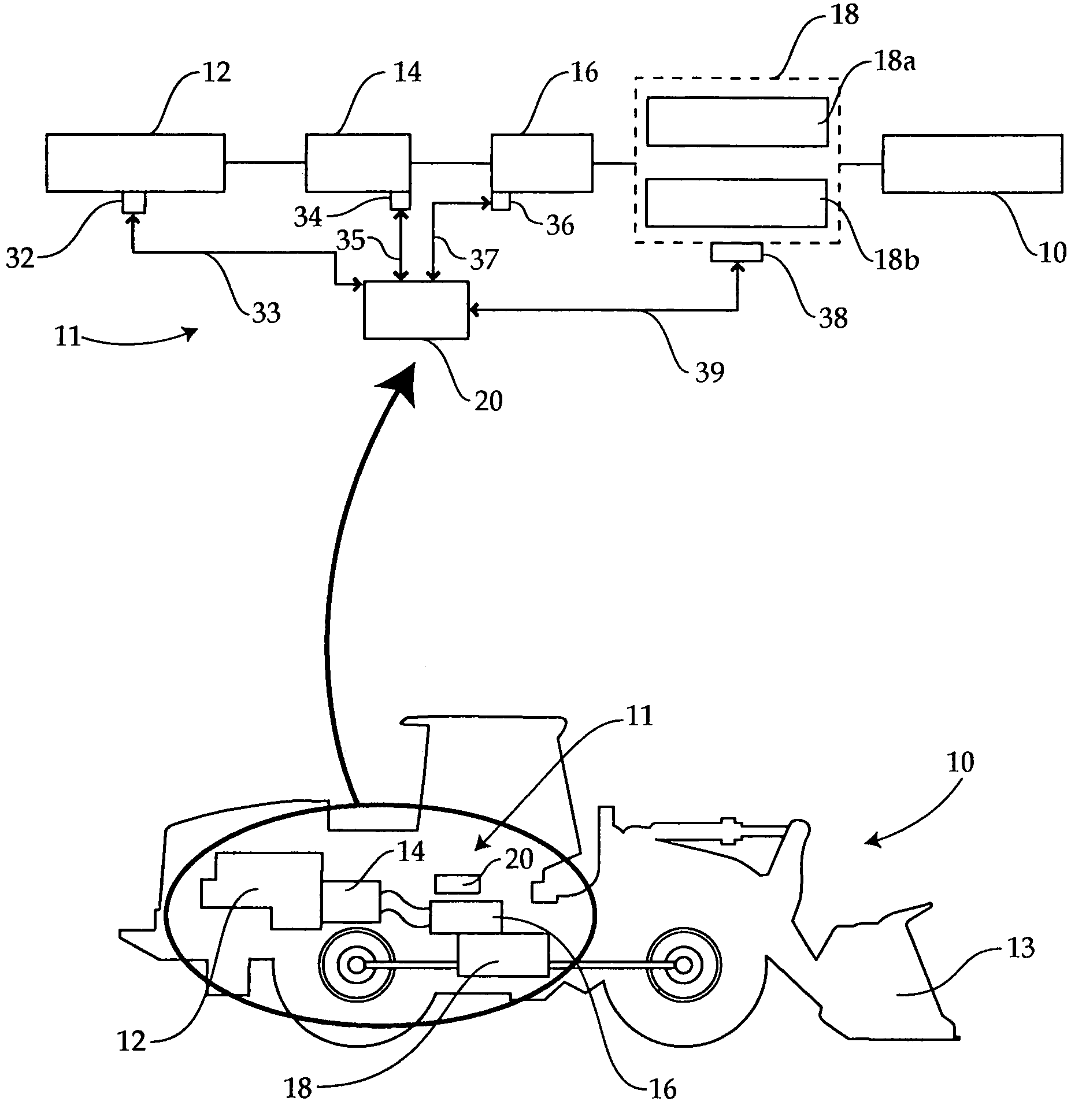
A braking energy recovery system adapted for use on a vehicle and a vehicle having such a system installed. The vehicle has an engine-transmission assembly, a driveshaft, a braking system and an auxiliary system. The energy recovery system comprises a first pump, a hydraulic accumulator and a hydraulic motor. The first pump is a variable displacement hydraulic pump. The hydraulic accumulator is connected to the first pump and is operative to store hydraulic fluid under pressure. The hydraulic motor is hydraulically connected to the accumulator to receive hydraulic fluid. The motor is adapted to drive a second hydraulic pump, which is hydraulically connected to the auxiliary system, using hydraulic energy stored in the accumulator.
Owner:14156048 CANADIAN CO
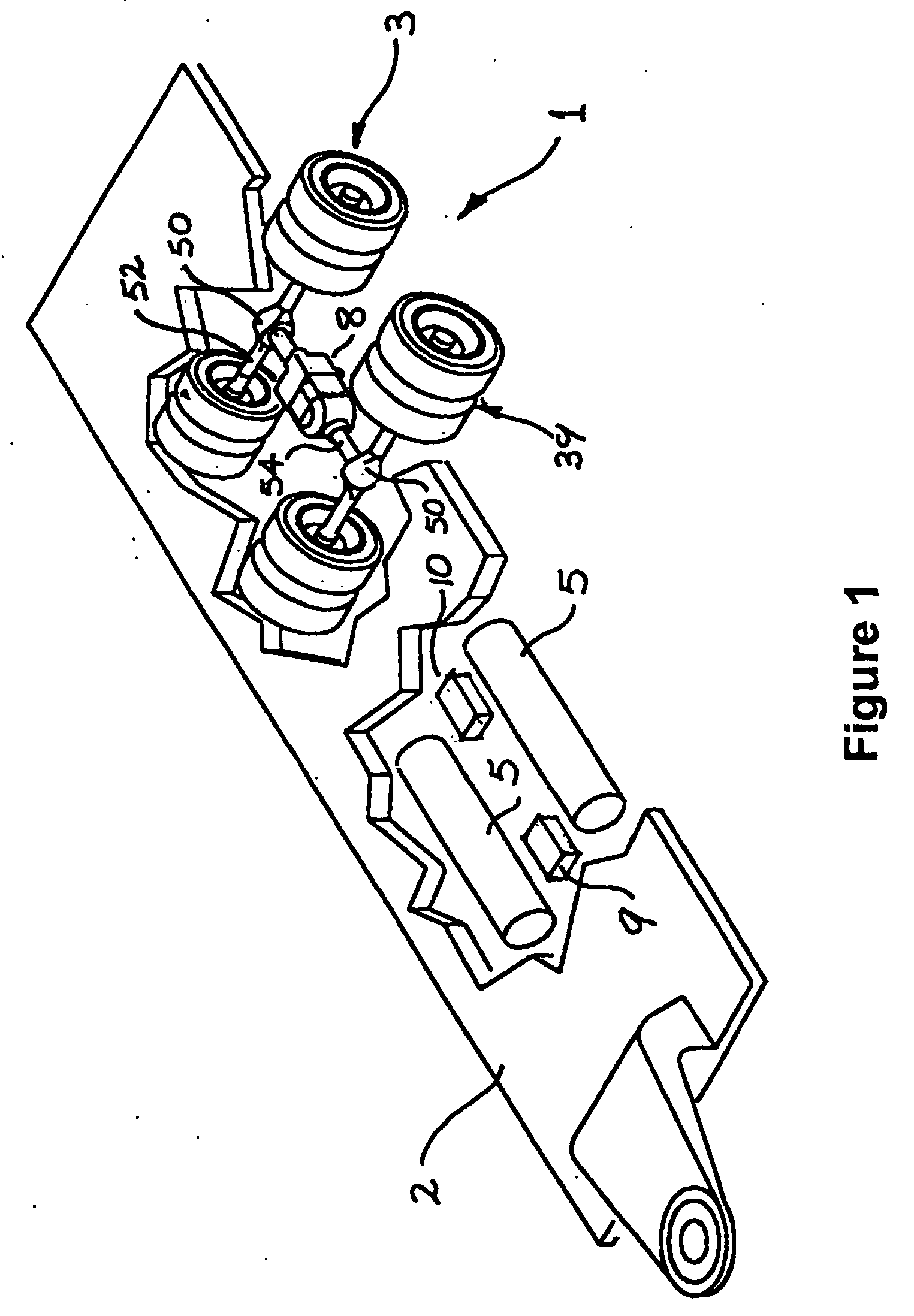
Regenerative drive system for trailers
A regenerative energy management system (1) adapted for use with a compound vehicle including a prime mover, drive train and a trailer (2) including independent wheels (3) isolated from the prime mover drive train. The system (1) includes energy accumulation means (5) operable selectively to store and release energy through controlled receipt and release of pressurised hydraulic fluid; a positive displacement hydraulic pump / motor assembly (8) in fluid communication with the energy accumulation means (5); and a low-pressure hydraulic reservoir (9) in fluid communication with pump / motor assembly. The pump / motor assembly (8) has a drive shaft for connection to at least one of the wheels (3). In a braking mode, the assembly (8) retards the associated wheel (3) by pumping hydraulic fluid into the accumulation means (5) while in a driving mode, it supplies supplementary power using hydraulic fluid from the accumulation means (5) and in a neutral mode, it exerts no substantial driving or retarding influence on the wheel (3).
Owner:PERMO DRIVE RES & DEV
Hydraulic regenerative braking for a vehicle
ActiveUS20070126284A1Improve compactnessMinimize frontal weightHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeKinetic energy
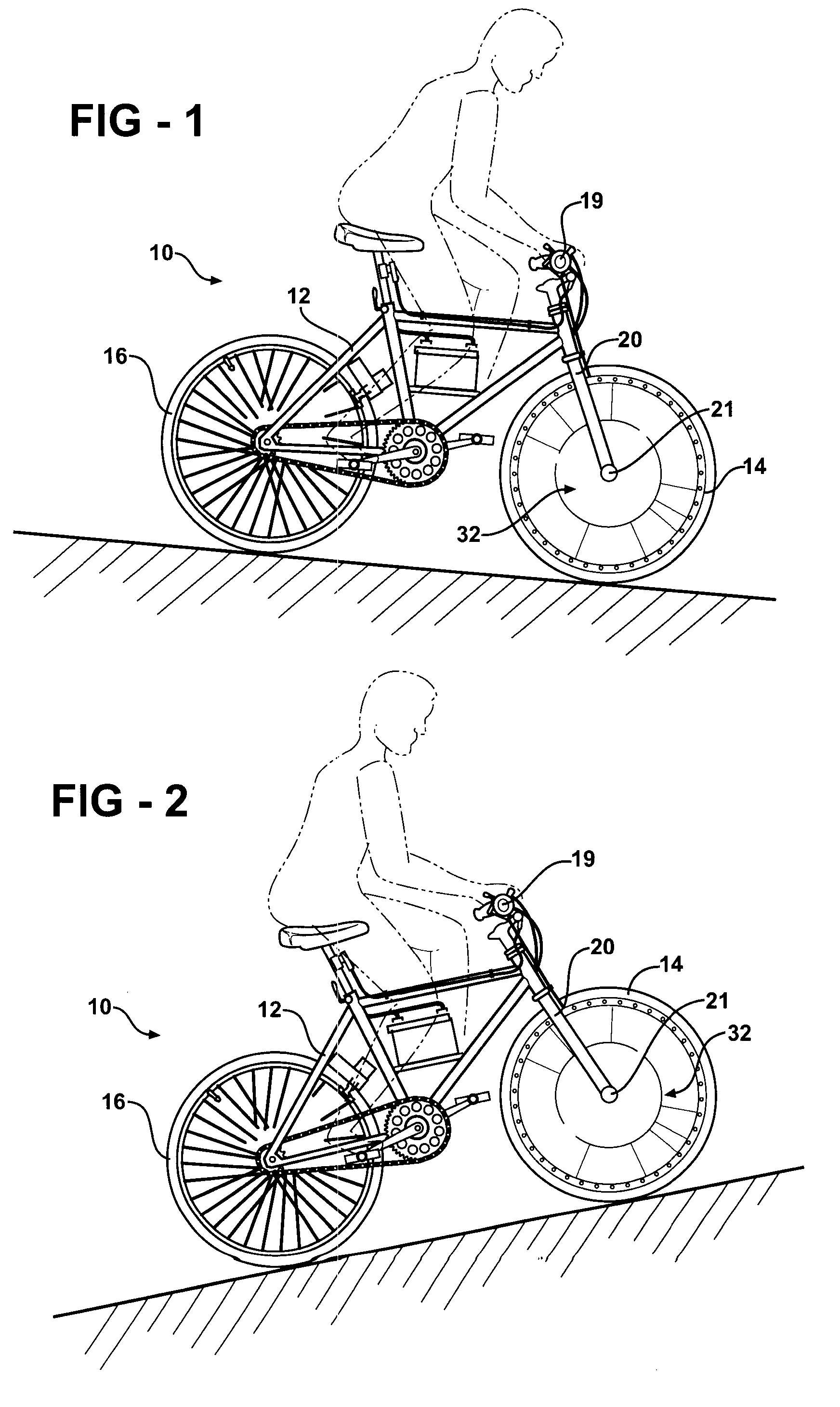
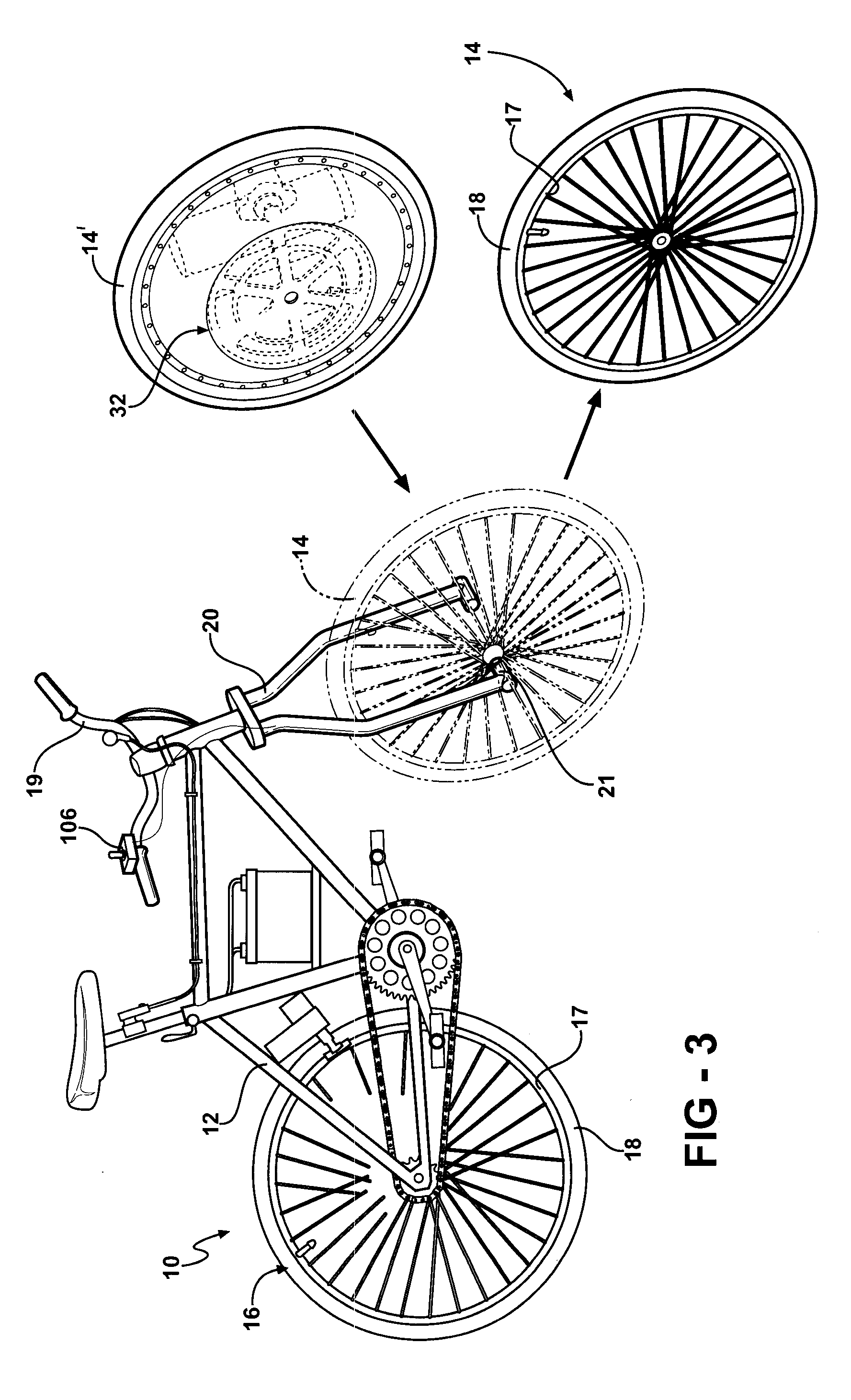
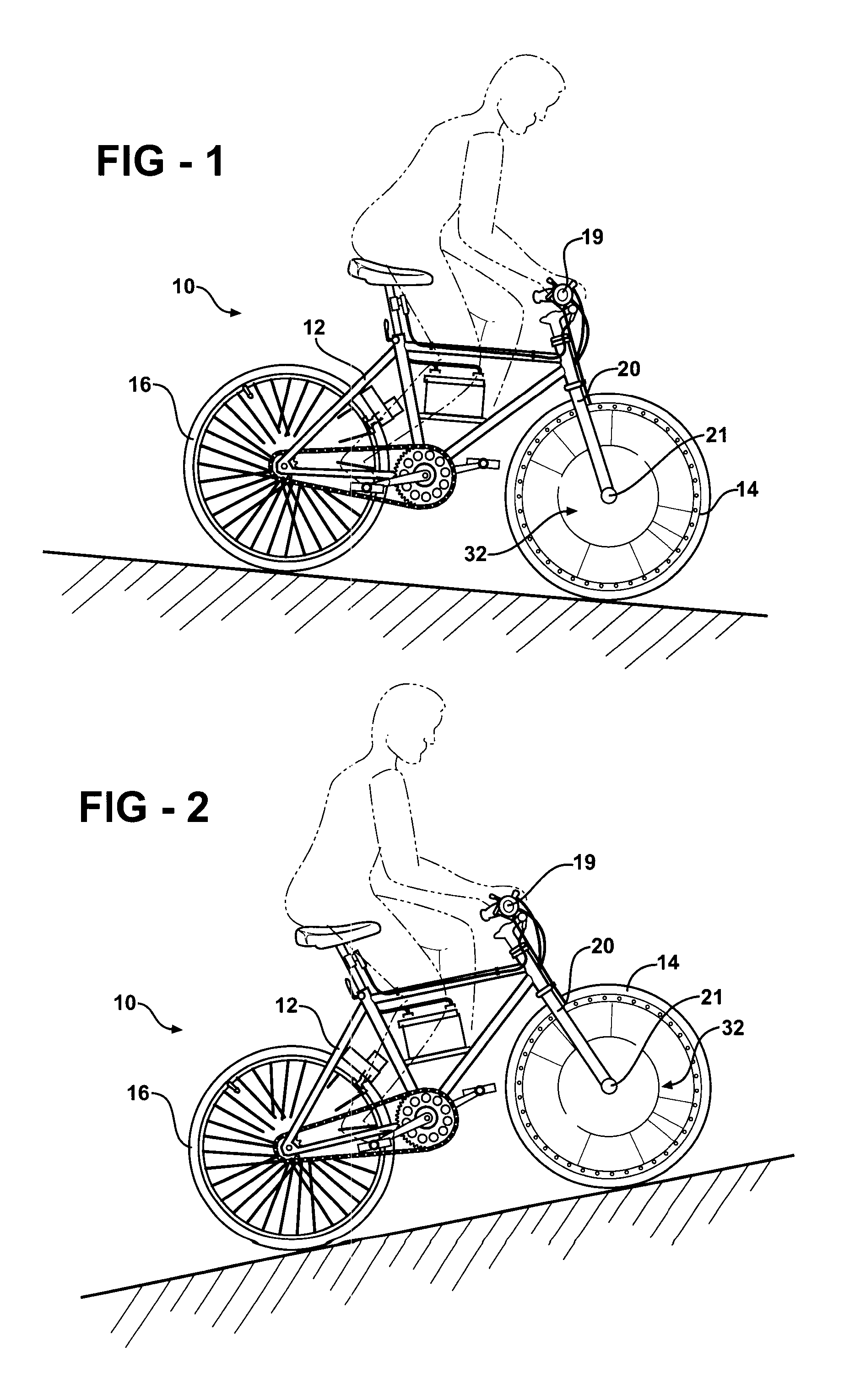
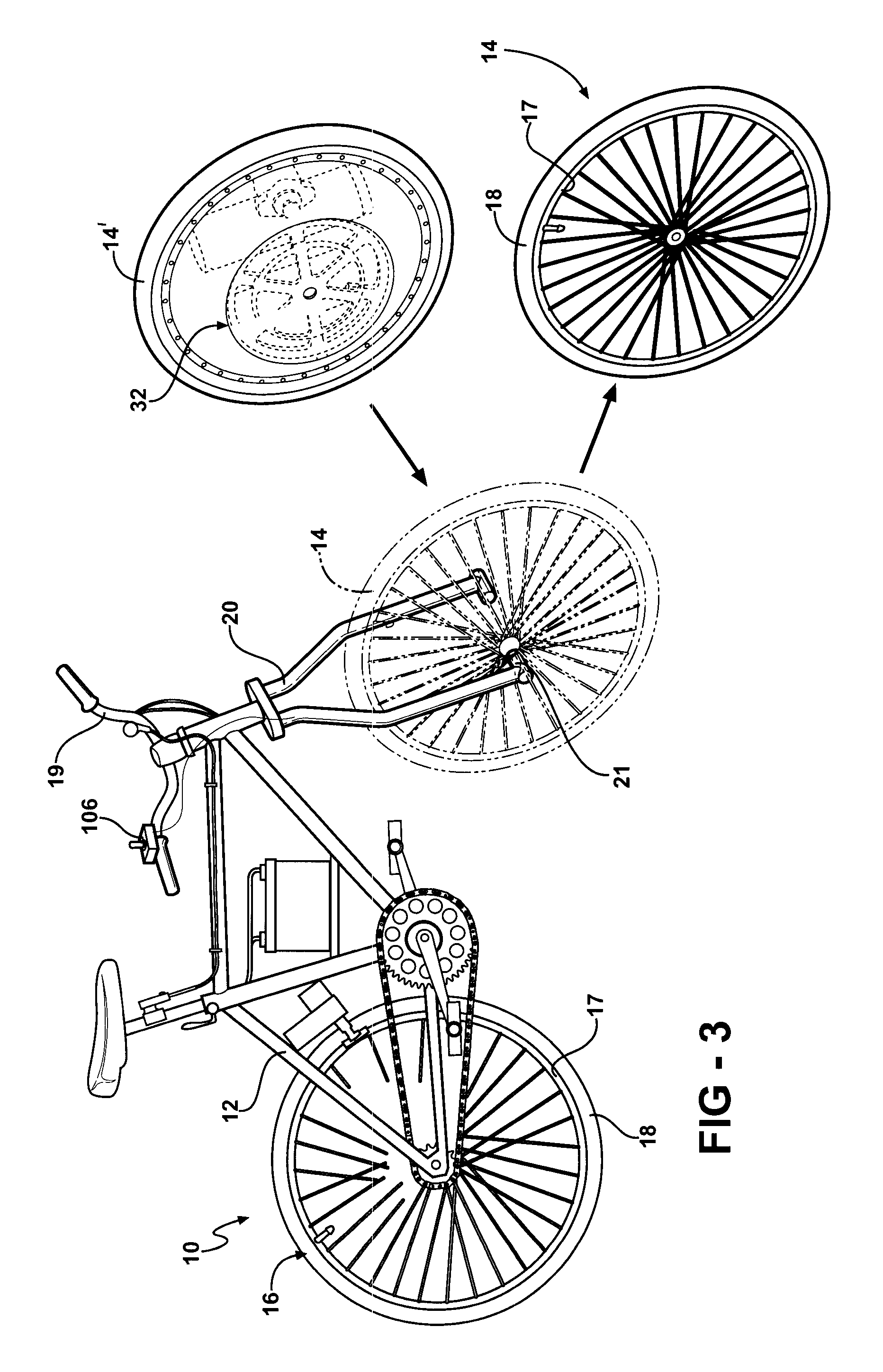
A regenerative brake of the present invention presents a hydraulic device disposed in a front hub of a bicycle wheel. The device allows the bicycle to recapture part of the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost when braking and make use of that power either by storing it for future use or feeding it back into a power system to be used. The hydraulic device may also be stored in a rear hub of the bicycle wheel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
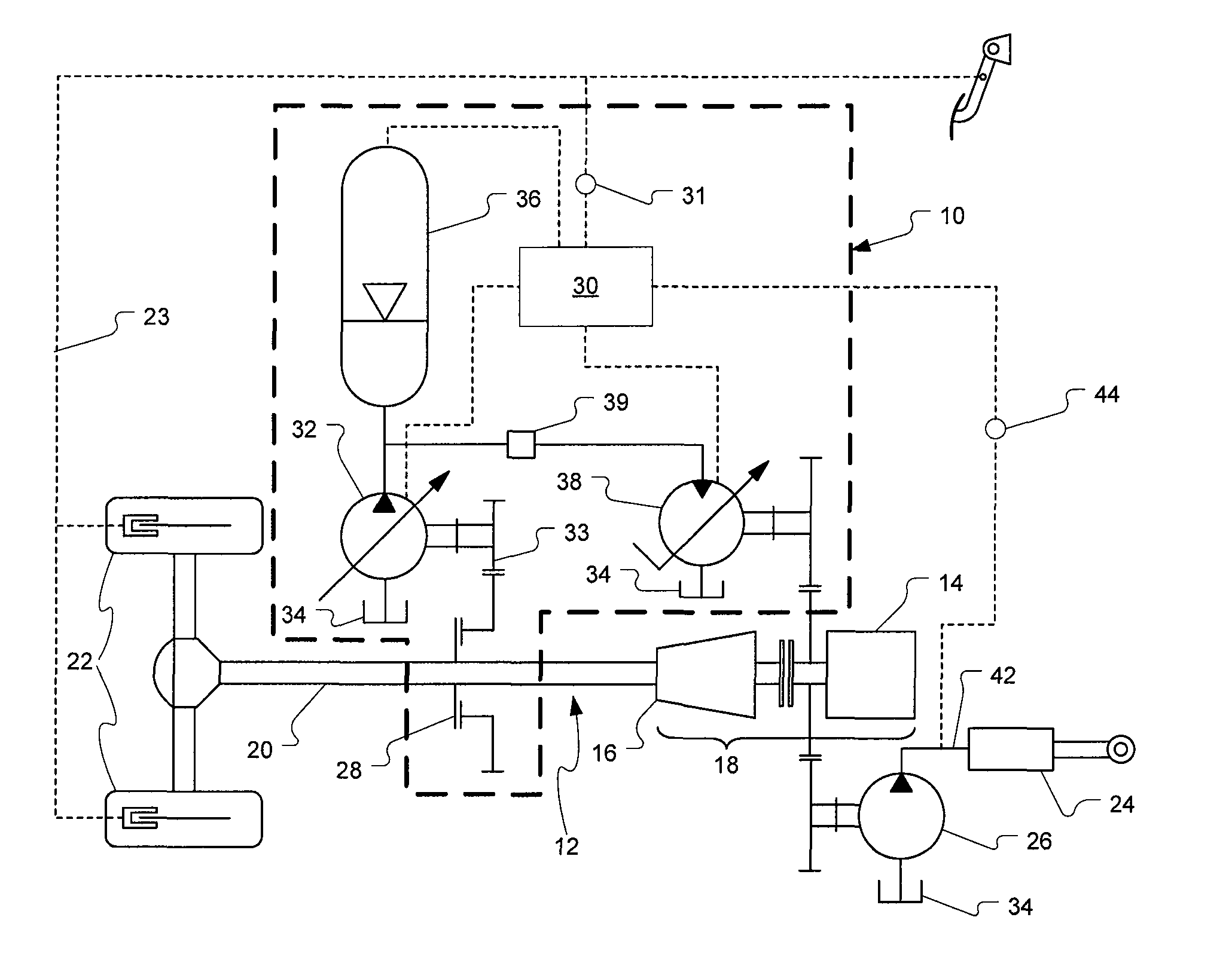
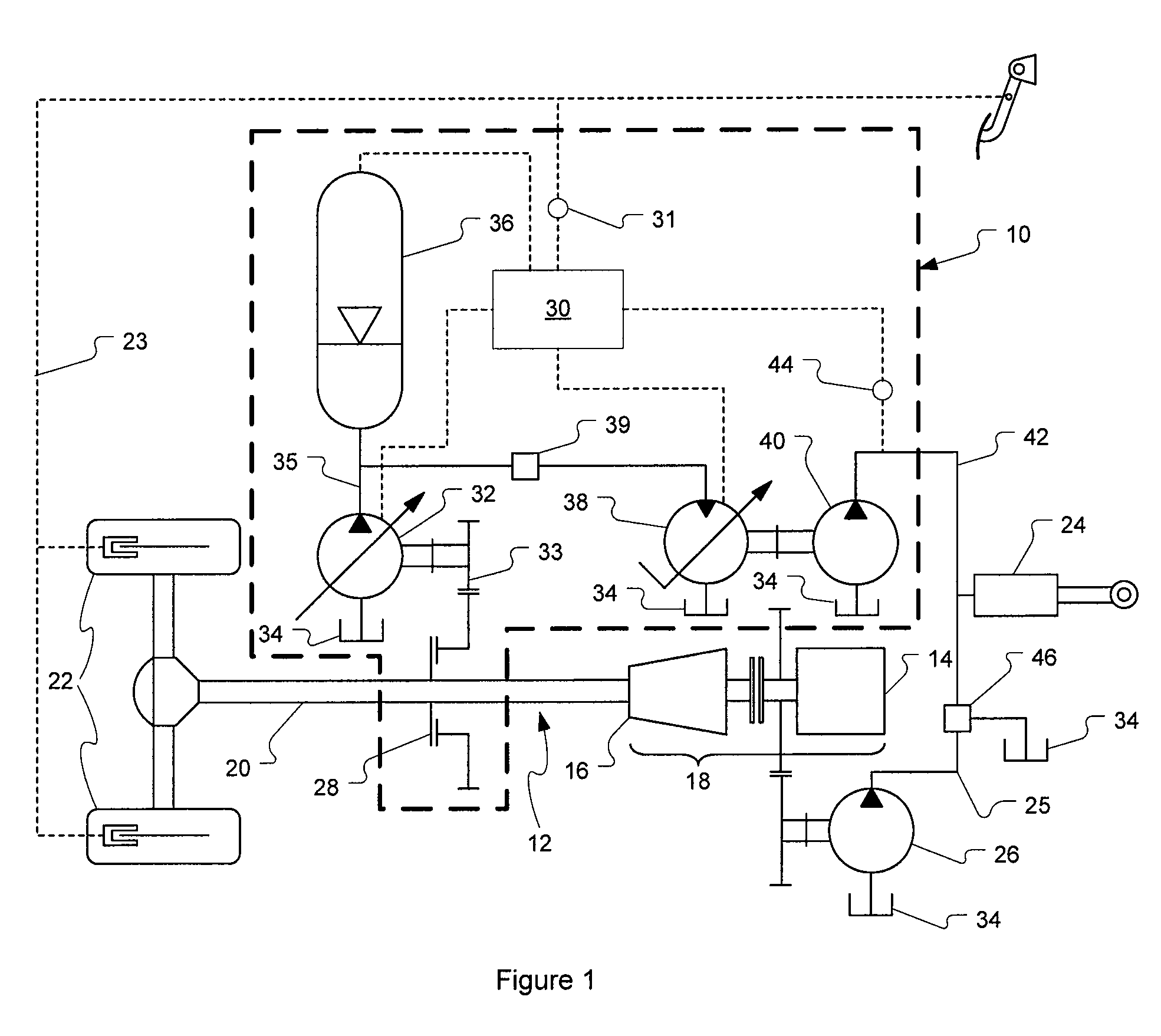
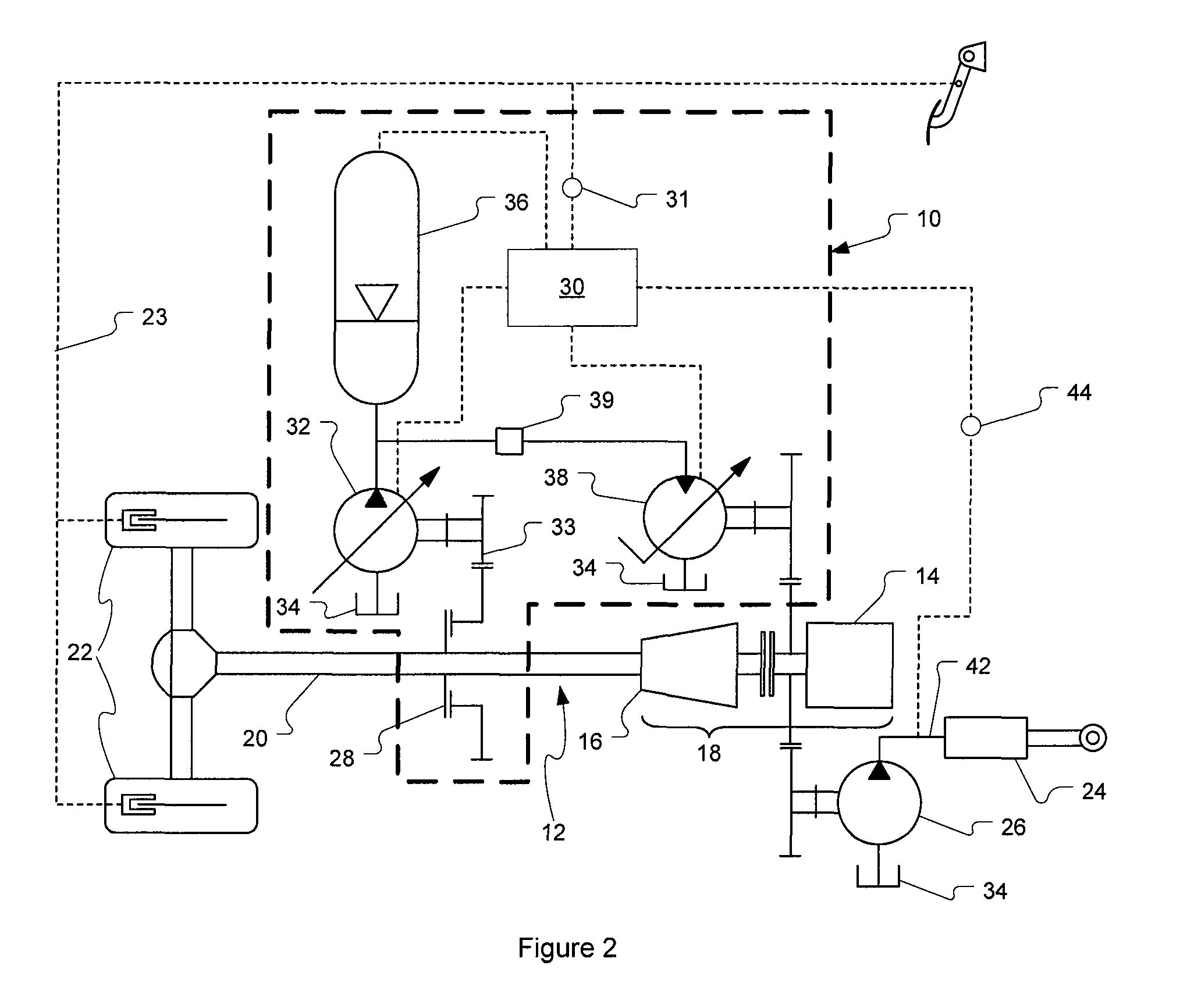
Control system and method for braking a hydrostatic drive machine
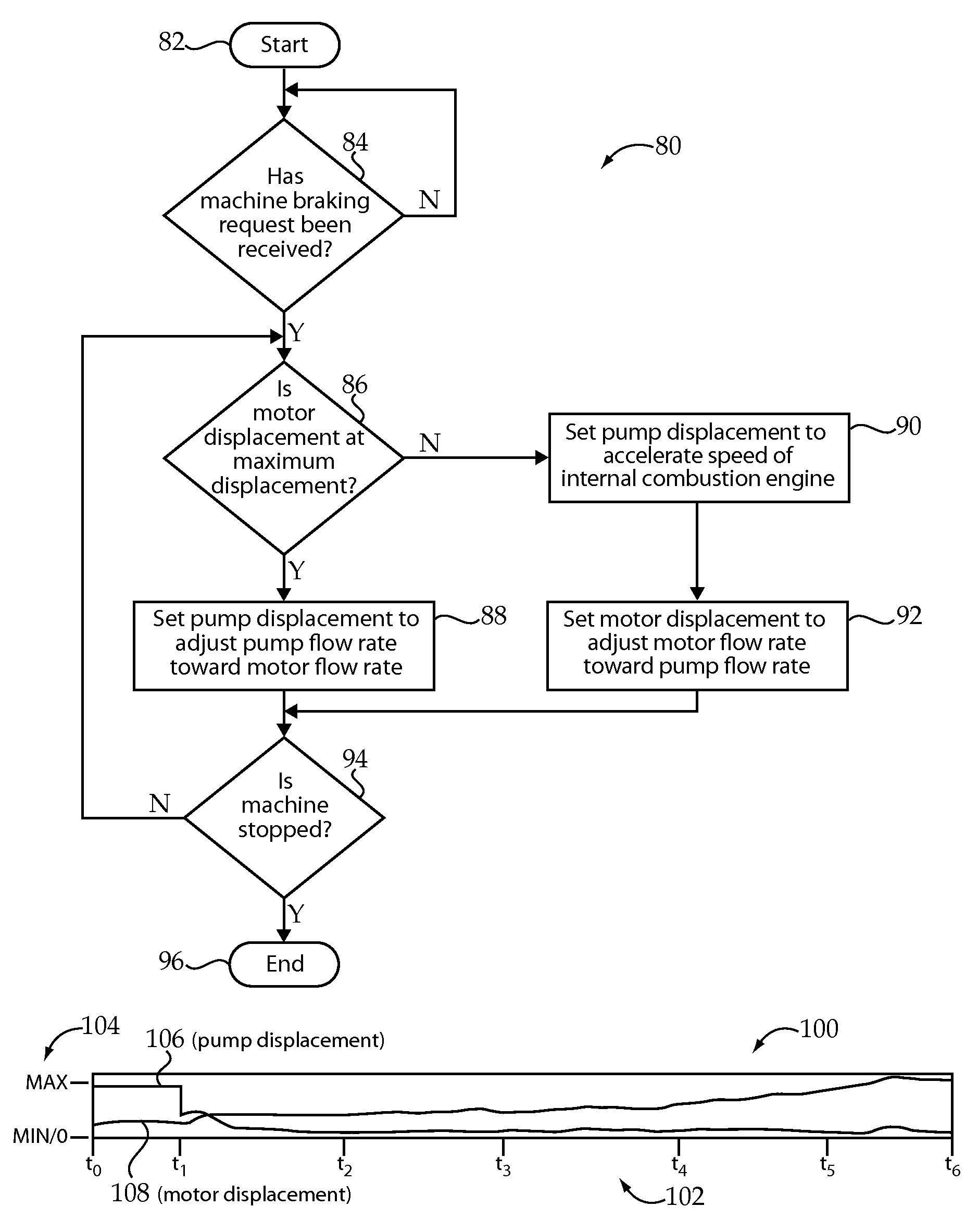
ActiveUS20100050620A1Reduce displacementIncrease displacementHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsControl systemMaximum displacement
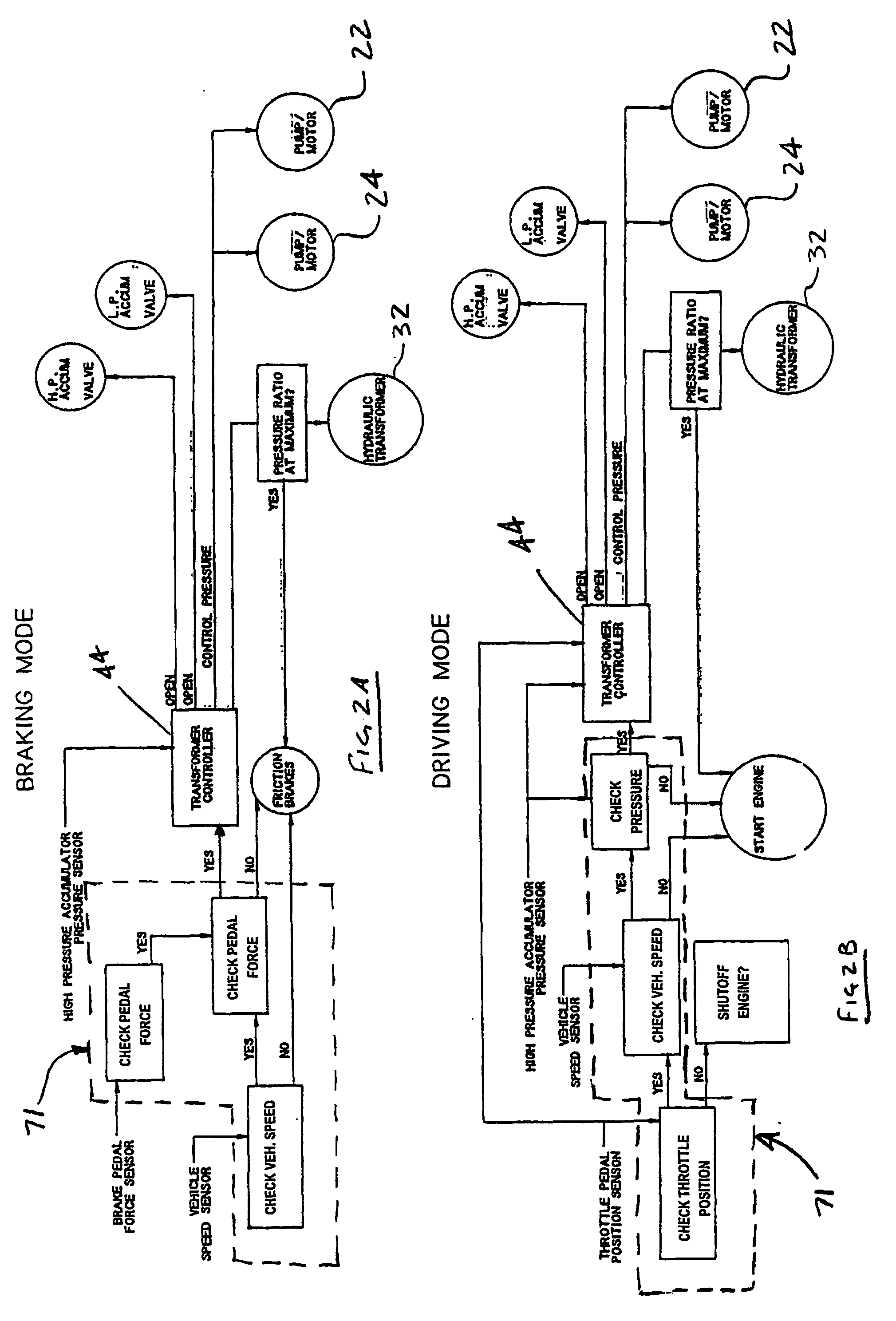
A method of braking a hydrostatic drive machine includes steps of reducing a displacement of a pump of a hydrostatic drive system to a non-zero displacement, and increasing a displacement of a motor of the hydrostatic drive system to a displacement that is less than a maximum displacement. The method also includes a step of accelerating an engine of the hydrostatic drive system toward a desired engine speed range.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Brake system for vehicle including continuously variable belt transmission
A brake system is provided for a vehicle equipped with a continuously variable belt transmission (hereafter a “CVT”) having a CVT input shaft and a CVT output shaft. The CVT functions as a clutch-disengagement action for isolating rotation of the CVT output shaft from the CVT input shaft when a rotary speed of the CVT input shaft is reduced to a certain level. The vehicle is equipped with a prime mover driving the CVT input shaft so that an output rotary speed of the prime mover defines the rotary speed of the CVT input shaft. The vehicle includes an accelerator manipulator for controlling the output rotary speed of the prime mover. The brake system can cause a resistance against the rotation of the CVT output shaft using the accelerator manipulator to reduce the output rotary speed of the prime mover to make the CVT function as the clutch-disengagement action.
Owner:KANZAKI KOKYUKOKI MFG
Hydraulic regenerative braking system for a vehicle
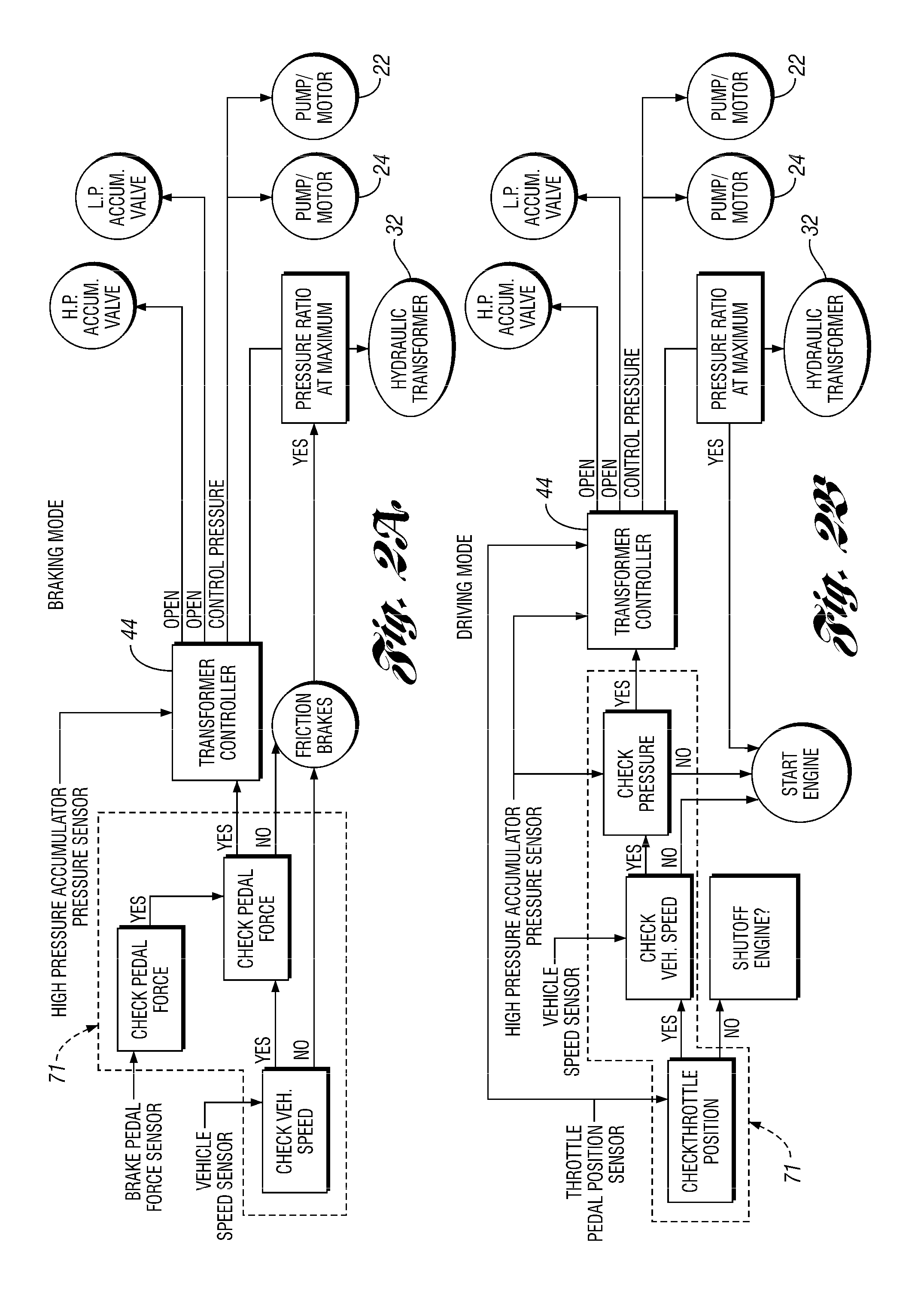
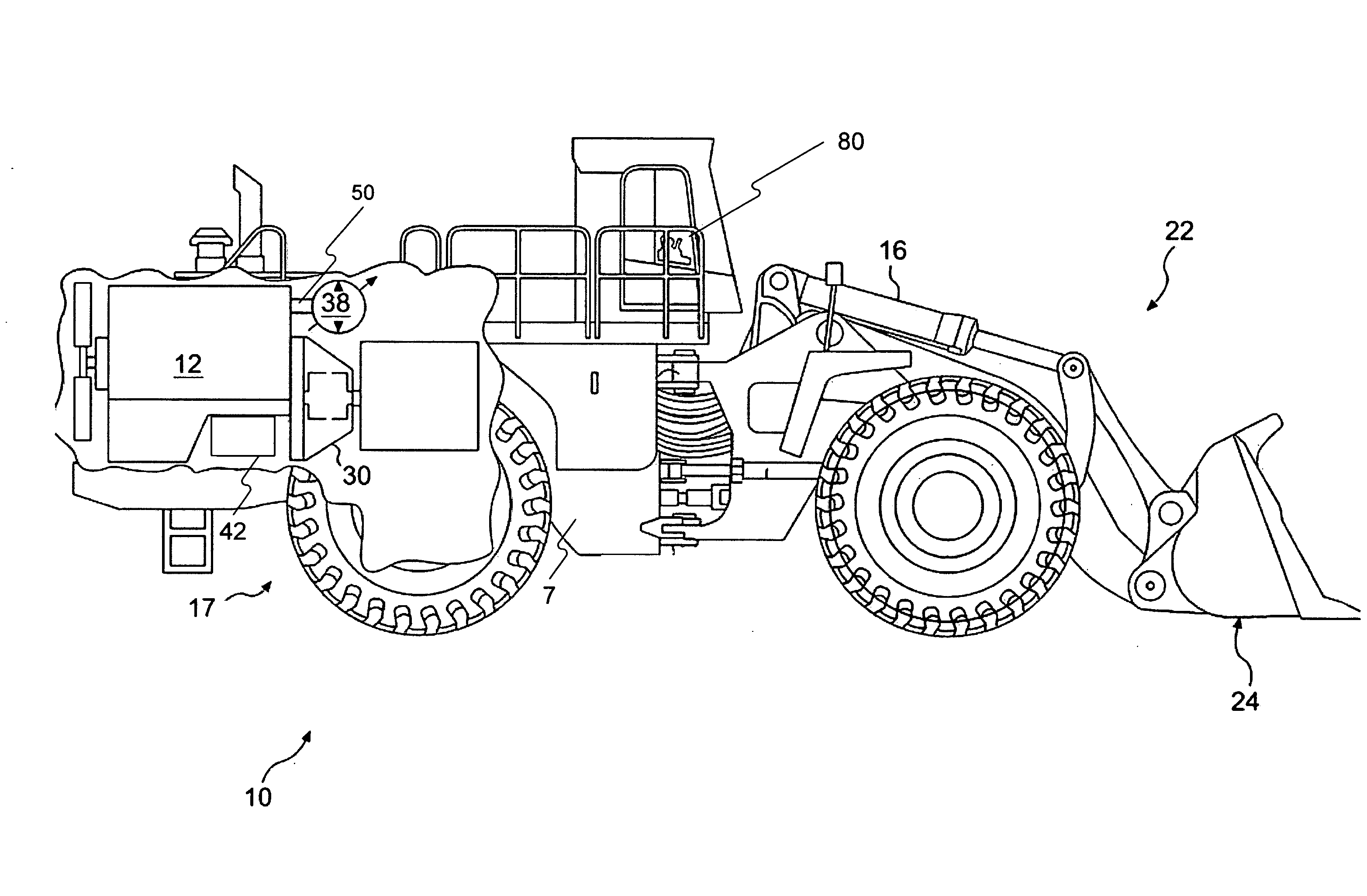
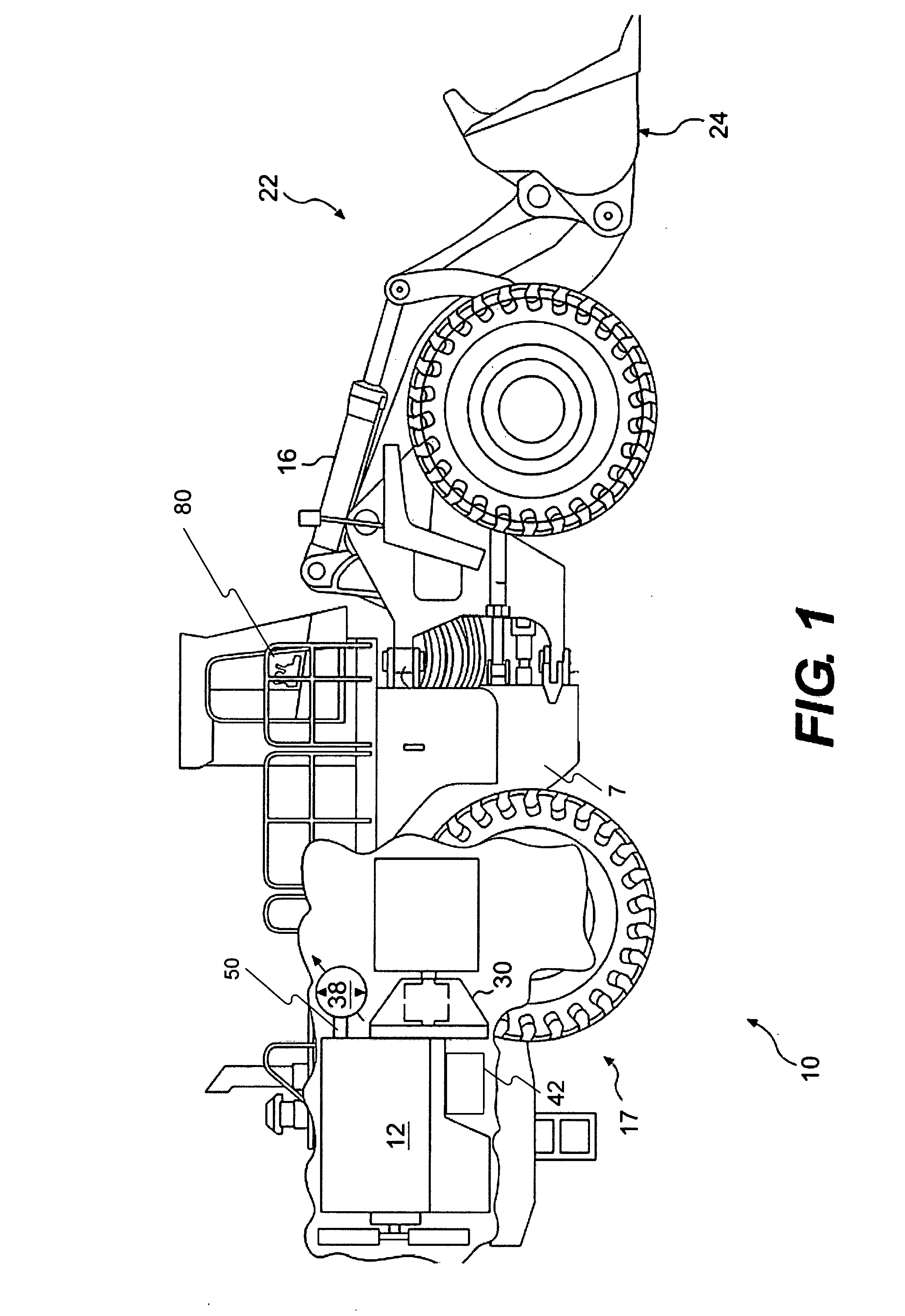
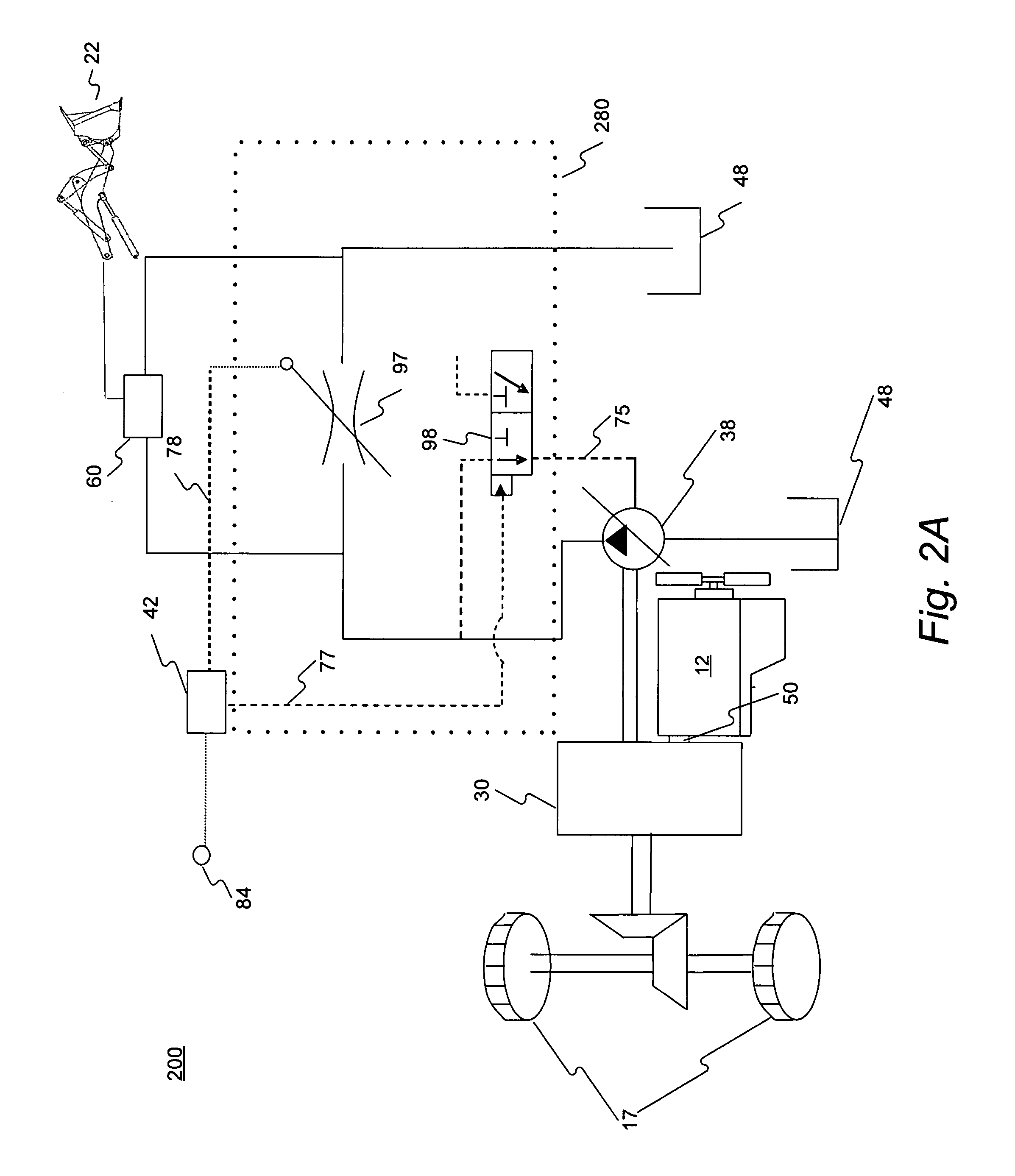
InactiveUS7562944B2Save spaceEliminate needHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeTransformer
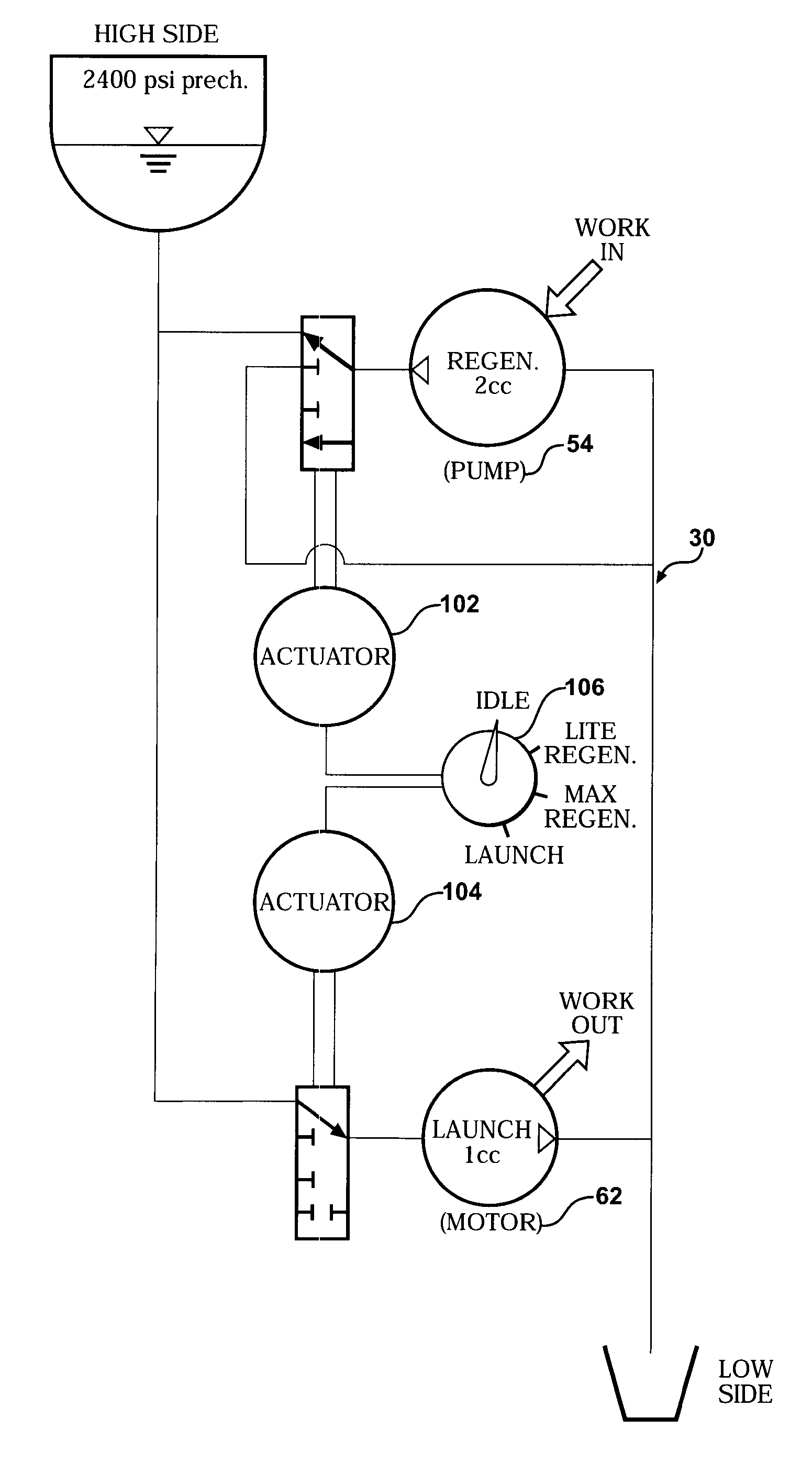
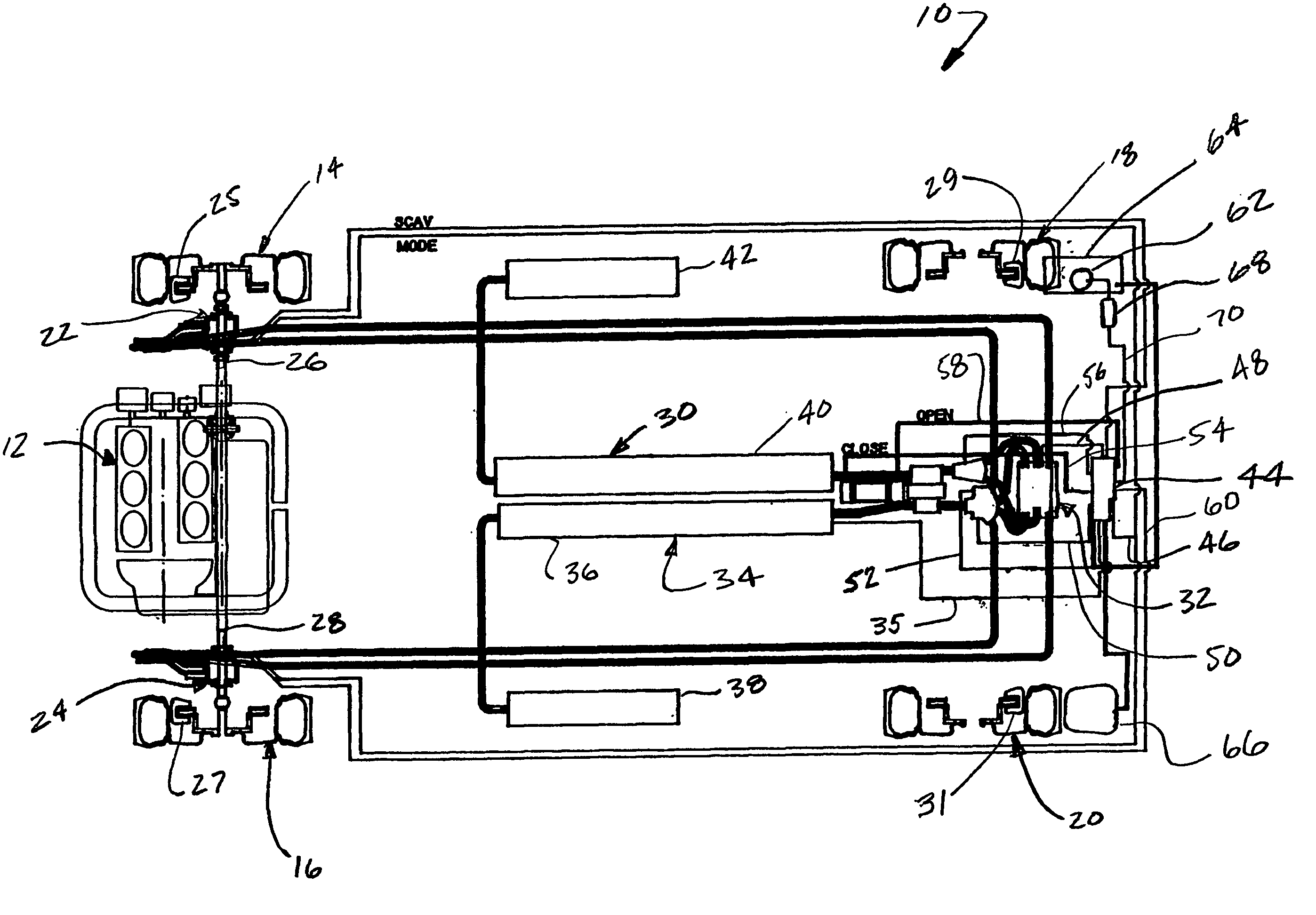
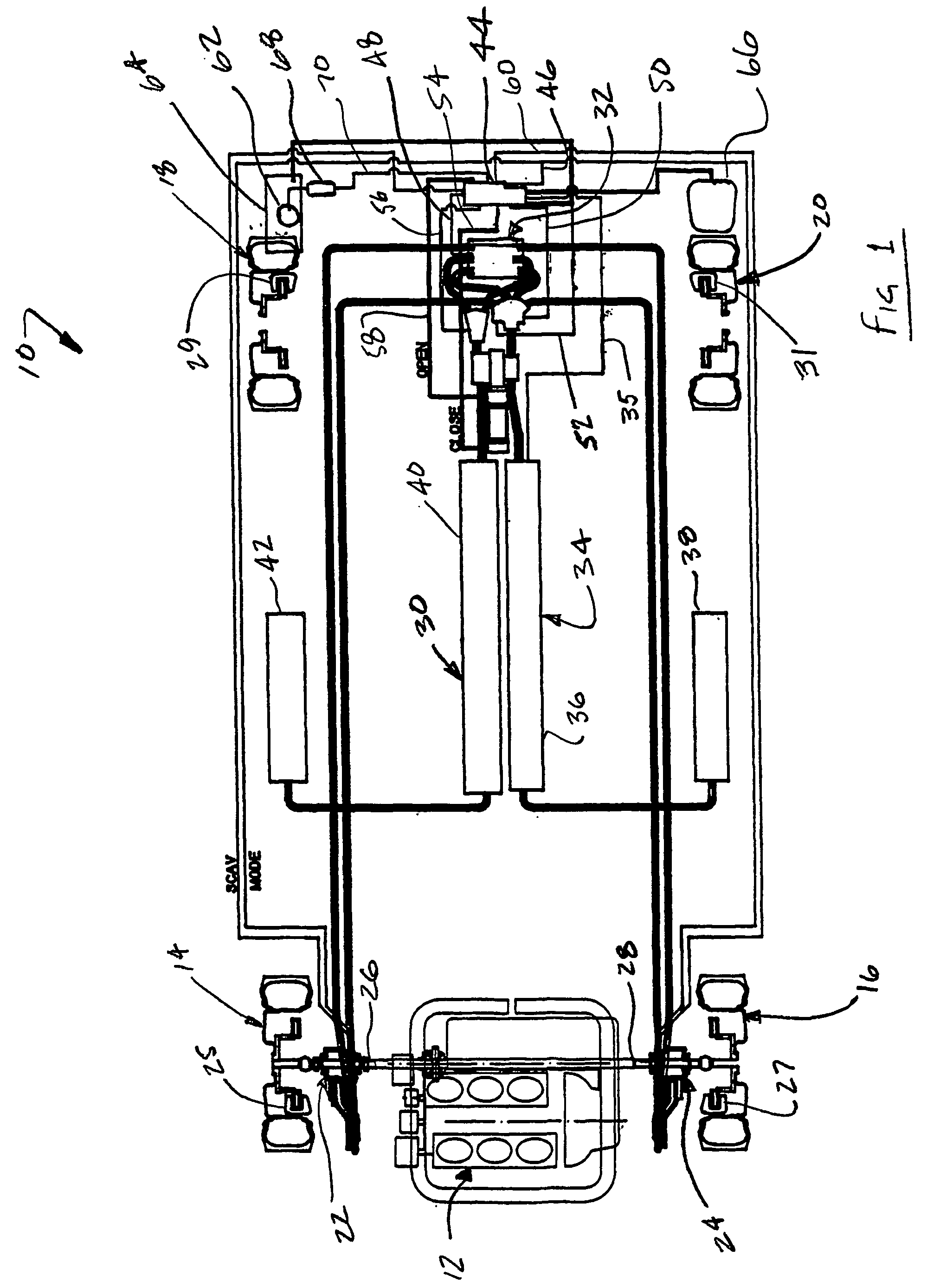
A hydraulic regenerative braking system for a vehicle is provided. The system includes two hydraulic machines, each of which is disposed proximate a corresponding vehicle wheel. A transformer is in communication with each of the hydraulic machines, and with a pair of accumulators. Each of the hydraulic machines is operable as a pump, pumping fluid to at least one of the accumulators when the vehicle is braking. Each of the hydraulic machines is also operable as a motor, receiving pressurized fluid and transferring torque to the vehicle wheels. The transformer is operable to vary the pressure of the fluid received by the hydraulic machines.
Owner:WALKER FRANK H
Machine retarder
A system is provided for controllably absorbing energy associated with a machine. The system may include a power source configured to provide power to a hydraulic pump, wherein the hydraulic pump is configured to provide a flow of fluid to a hydraulic dissipation circuit and to one or more implement system hydraulic cylinders, and wherein the hydraulic dissipation circuit is configured to generate a load associated with the hydraulic pump. The system may also include at least one valve configured to provide the flow of fluid to the hydraulic dissipation circuit in response to one or more control signals and a controller configured to receive an input signal from an operator actuated device, and generate the one or more control signals based on the input signal.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
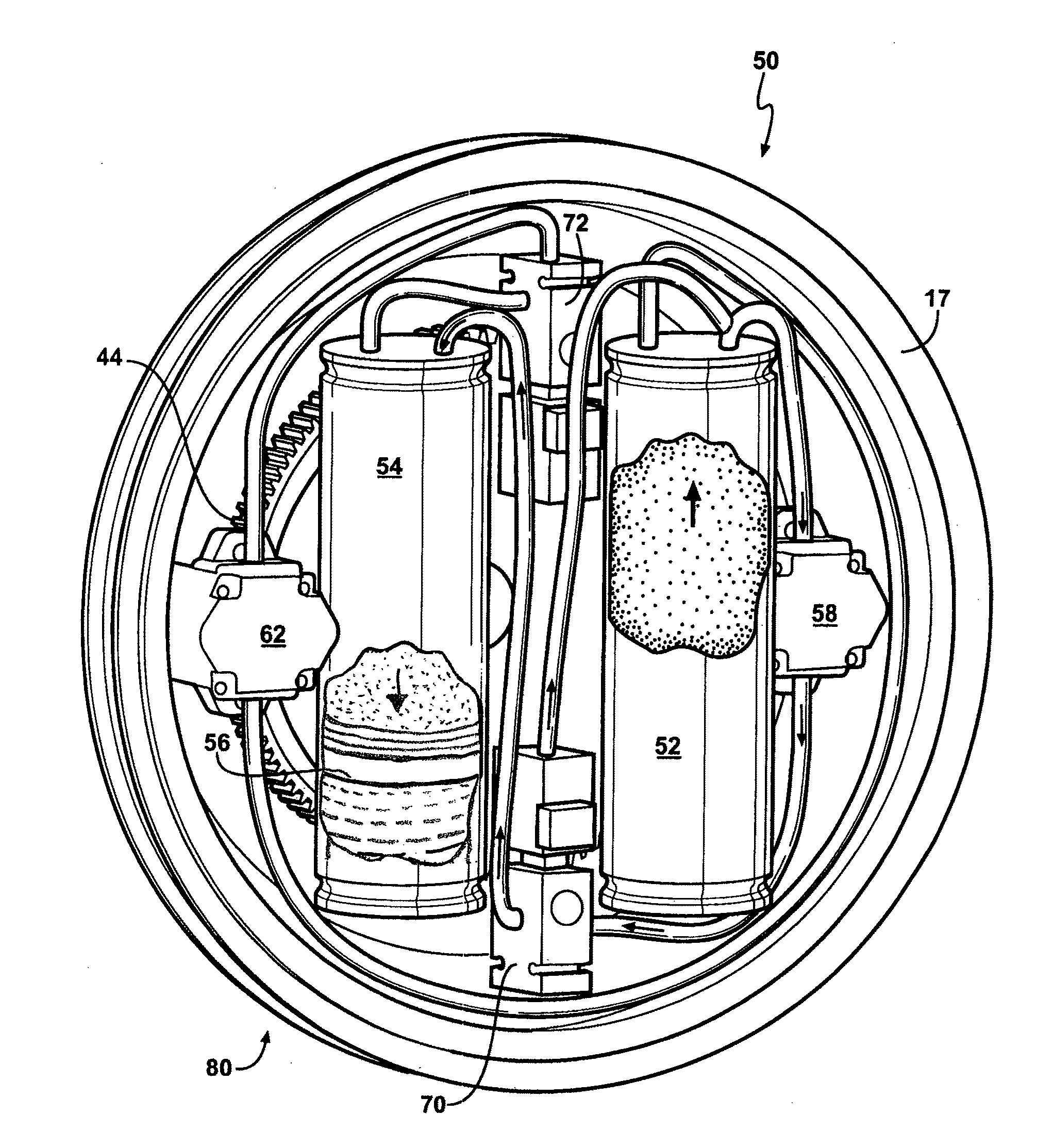
Hydraulic regenerative braking system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20060055238A1Save spaceEliminate needHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeTransformer
A hydraulic regenerative braking system for a vehicle is provided. The system includes two hydraulic machines, each of which is disposed proximate a corresponding vehicle wheel. A transformer is in communication with each of the hydraulic machines, and with a pair of accumulators. Each of the hydraulic machines is operable as a pump, pumping fluid to at least one of the accumulators when the vehicle is braking. Each of the hydraulic machines is also operable as a motor, receiving pressurized fluid and transferring torque to the vehicle wheels. The transformer is operable to vary the pressure of the fluid received by the hydraulic machines.
Owner:WALKER FRANK H
Downshift in hydrostatic drive work machine
The present disclosure provides a hydrostatic drive work machine, and a method and control module having a control algorithm for performing a downshifting event in the work machine. The method includes the step of inducing a retarded mode in the work machine, if upon commanding a downshift the work machine is not in a retarded mode. The method further includes the steps of adjusting a displacement of each of a variable displacement pump and a variable displacement motor in a hydrostatic drive of the work machine, and increasing pressure on a low clutch of the work machine. The control algorithm includes means for inducing a retarded mode in the work machine, if the work machine is not in a retarded mode upon commanding a downshift, with at least one of a variable displacement motor and a variable displacement pump in a hydrostatic drive of the work machine.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
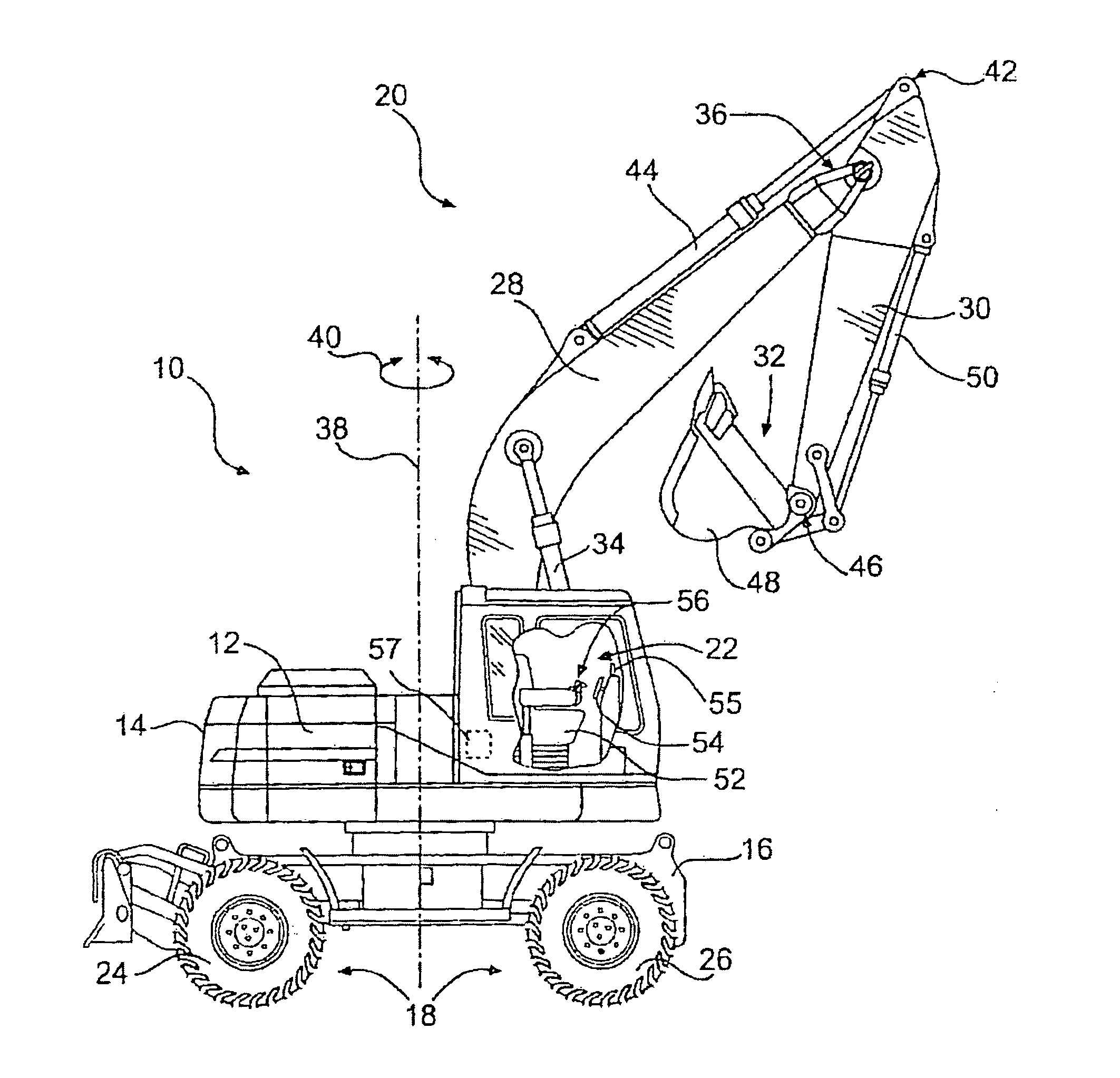
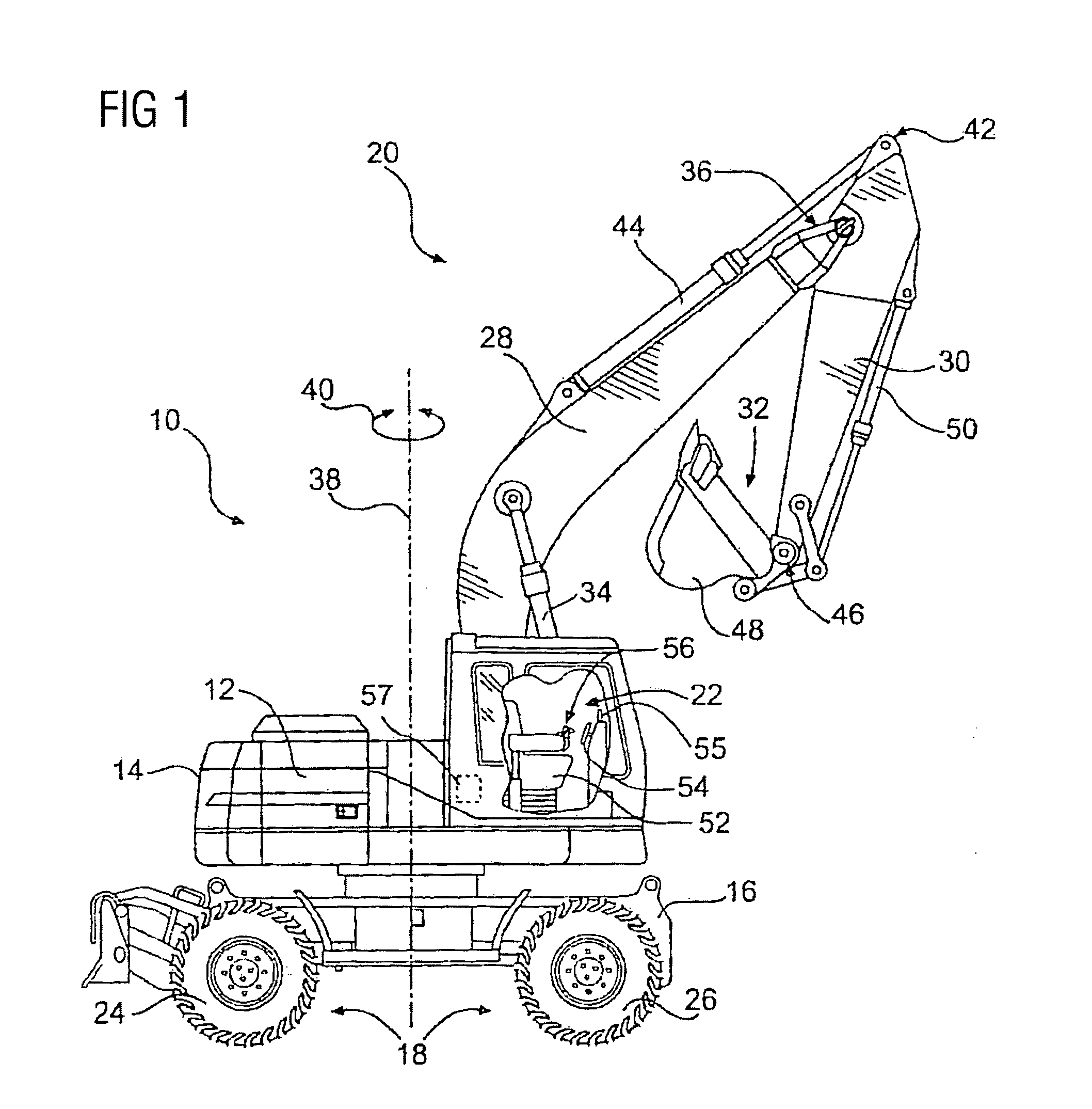
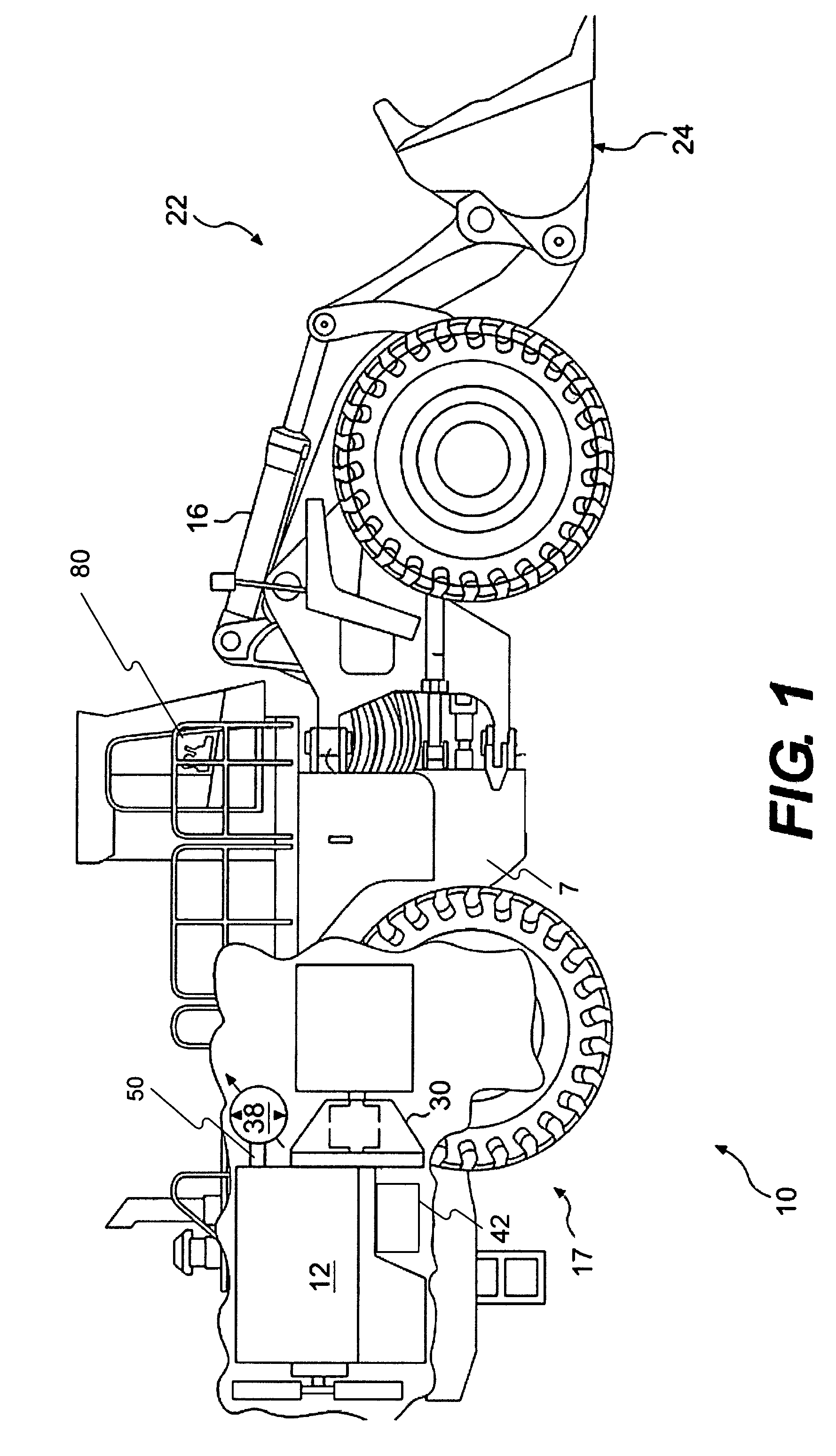
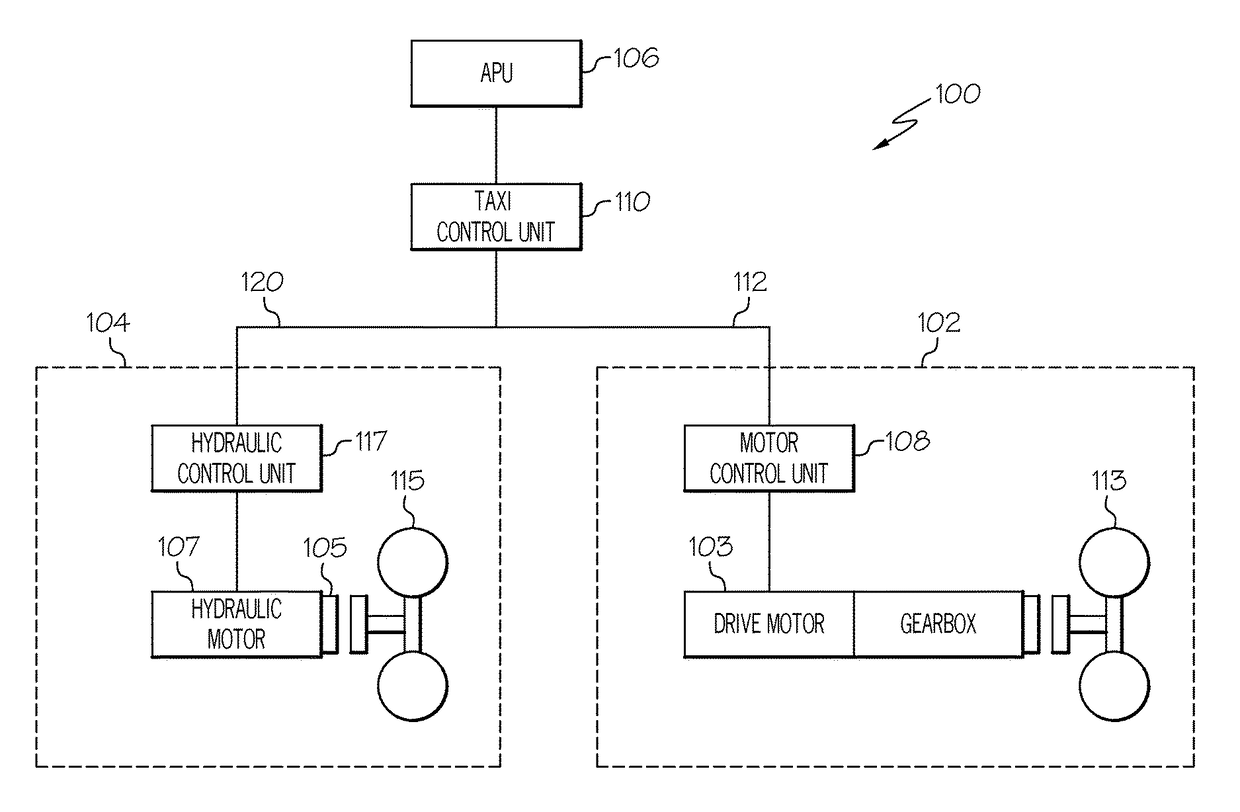
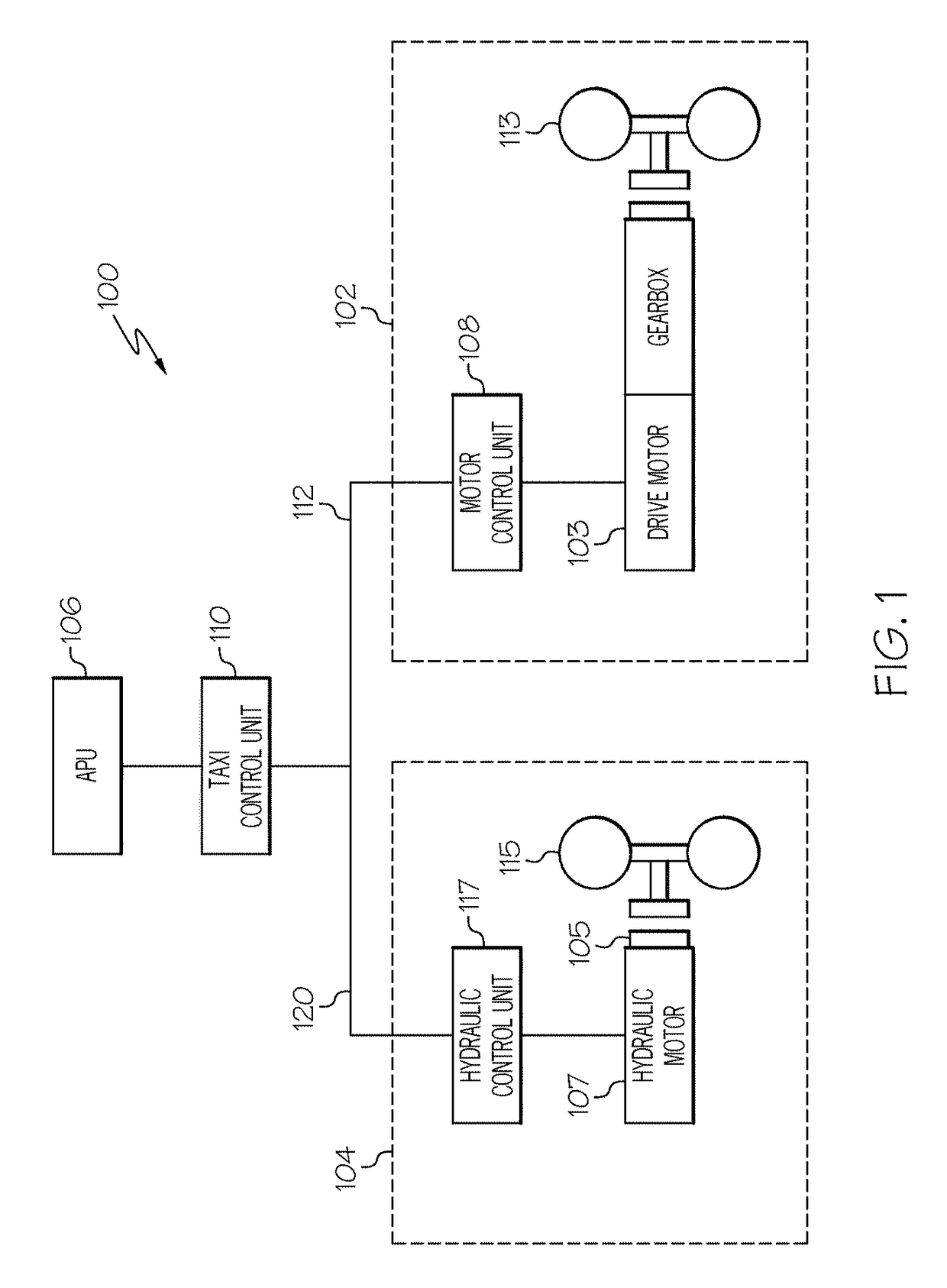
Aircraft landing gear wheel-drive system
An aircraft landing gear wheel-drive system includes a first wheel drive unit for driving a first landing gear wheel of the aircraft and a second wheel drive unit for driving a second landing gear wheel of the aircraft. The first wheel drive unit has a first range of torque to speed (T / S) ratios. The second wheel drive unit has a second range of T / S ratios. The first range of T / S ratios is greater than the second range of T / S ratios.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
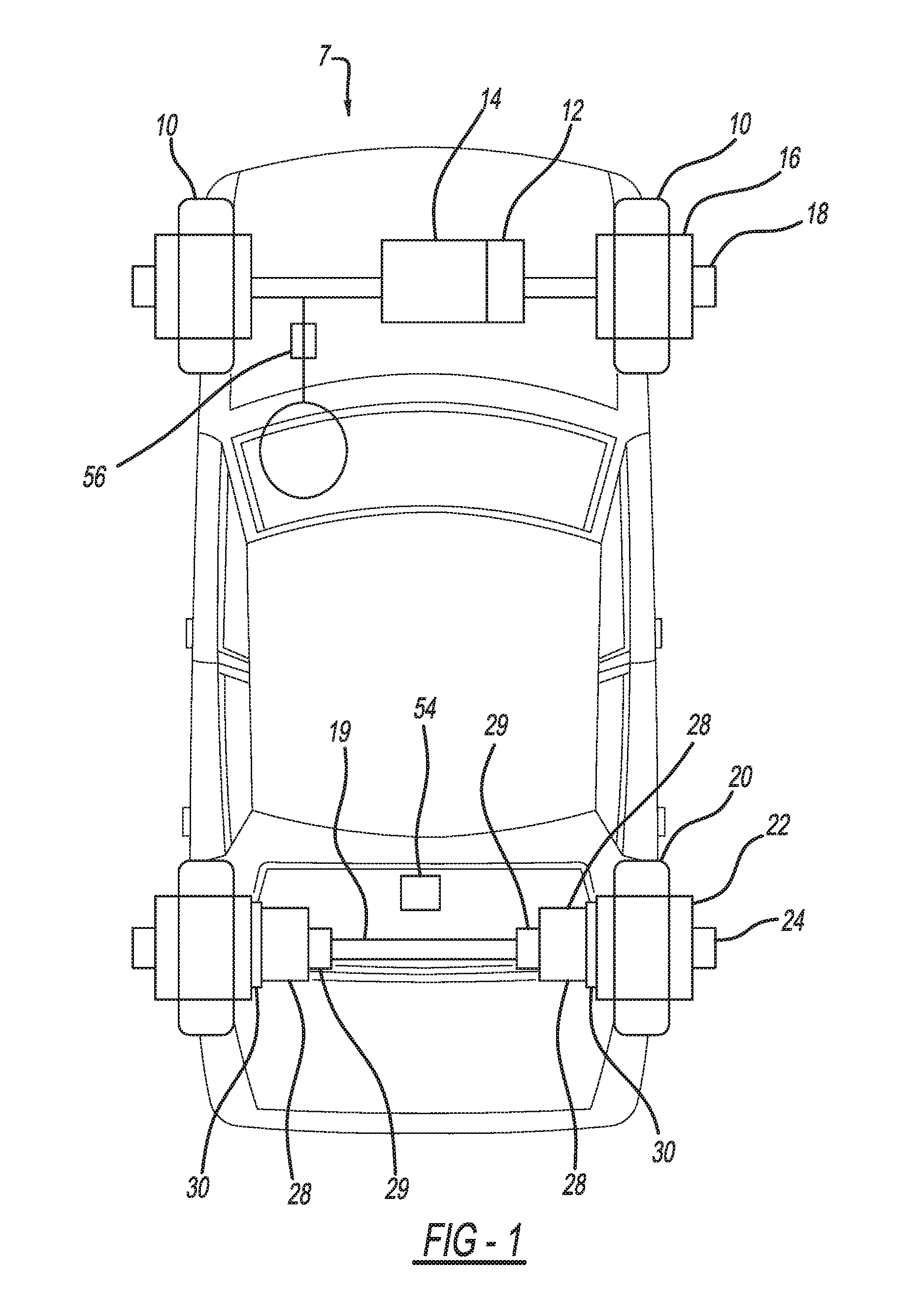
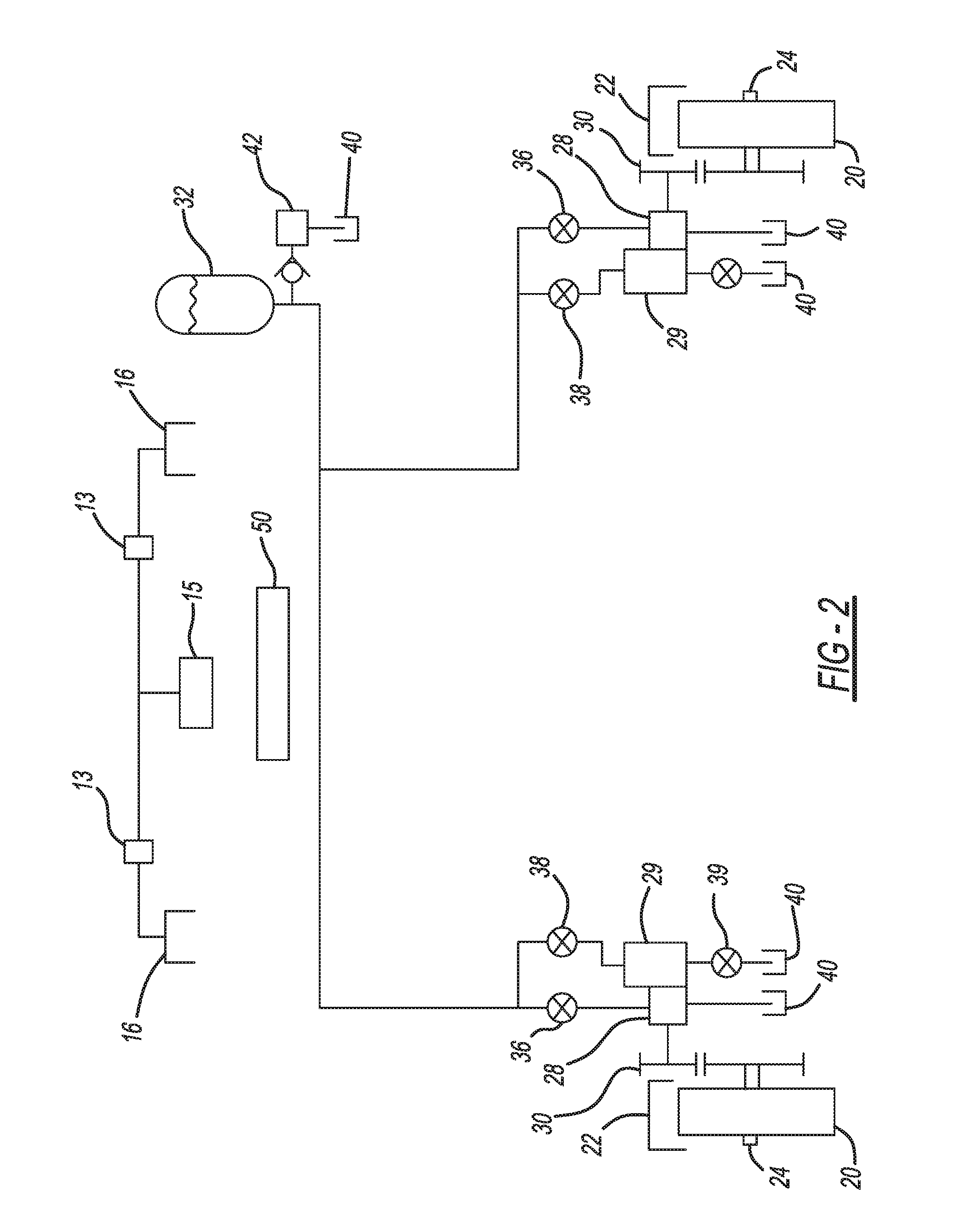
Braking energy recovery system for a vehicle and vehicle equipped with the same
ActiveUS8087733B2Overcomes or mitigates one or more disadvantagesEasy to modifyHydrostatic brakesAuxillary drivesHydraulic motorHydraulic pump
Owner:DEV EFFENCO INC +1
Paving collision avoidance system
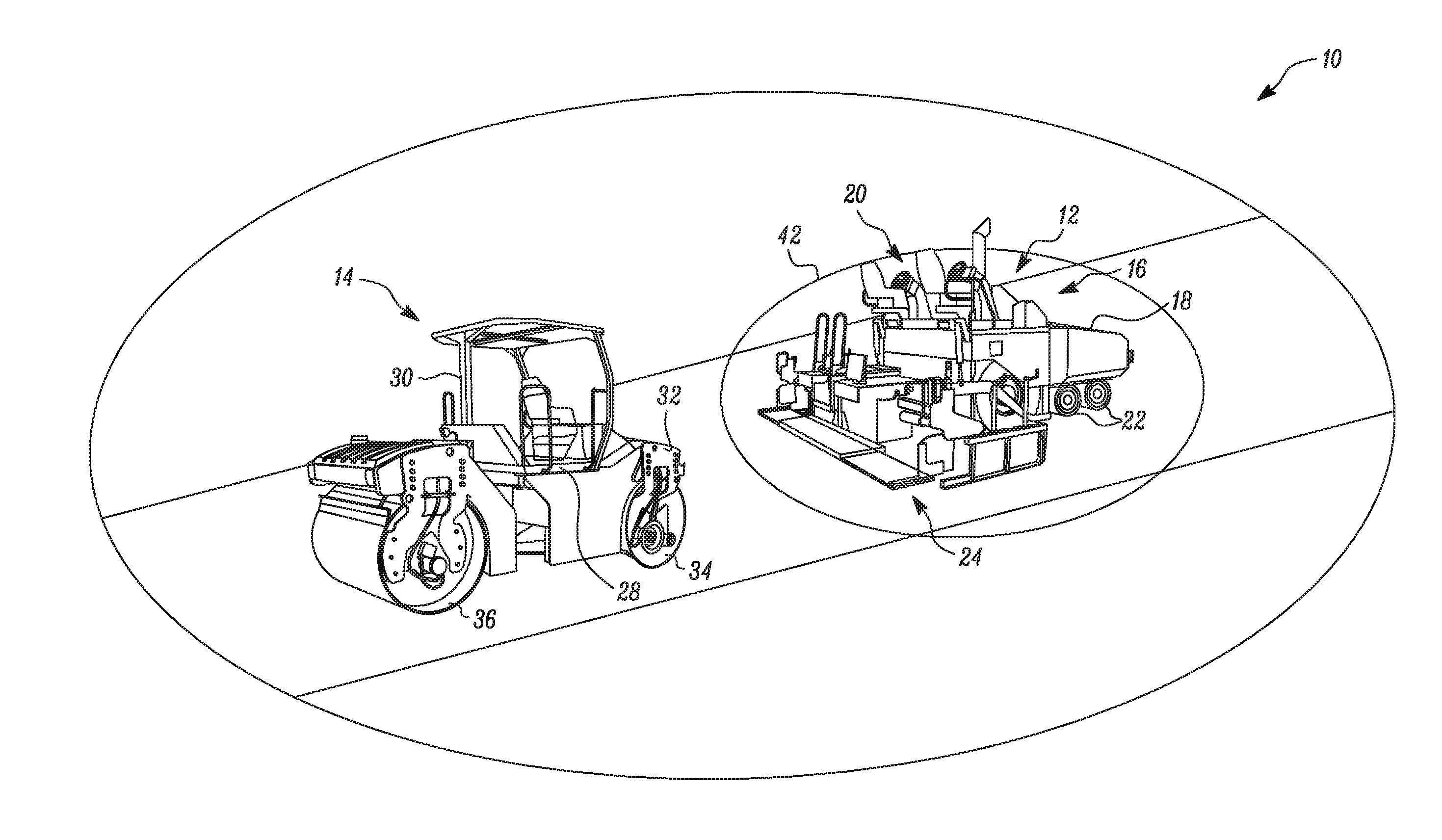
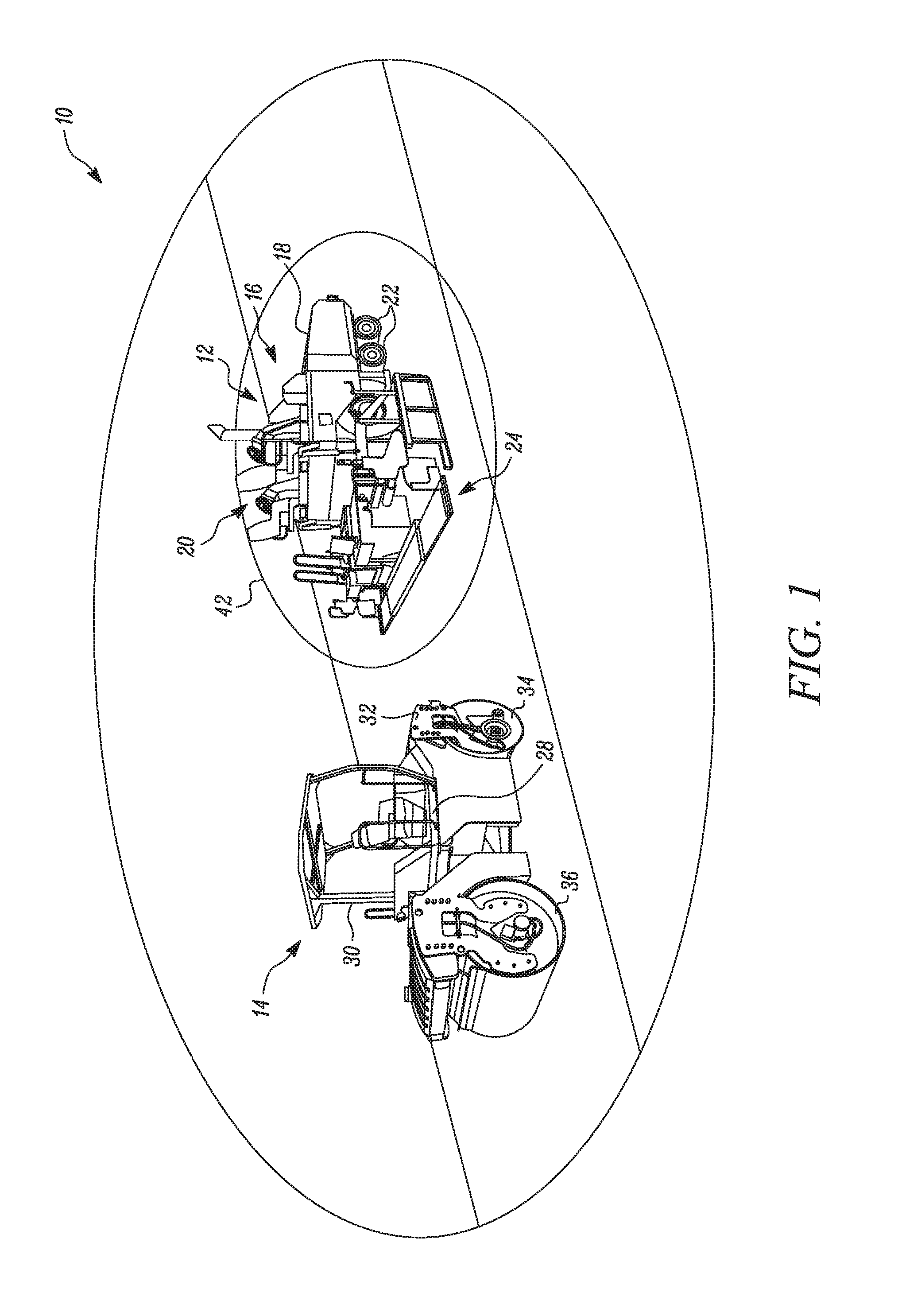
InactiveUS20170010621A1Hydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsEngineeringCollision avoidance system
A paving collision avoidance system includes a paving machine, a compactor, and a controller. The compactor has a hydrostatic braking capability. The controller is configured to stop the compactor when it enters a predetermined boundary determined by the momentum of the compactor and the relative positions of the paving machine and the compactor.
Owner:CATERPILLAR PAVING PROD INC
Traveling working machine
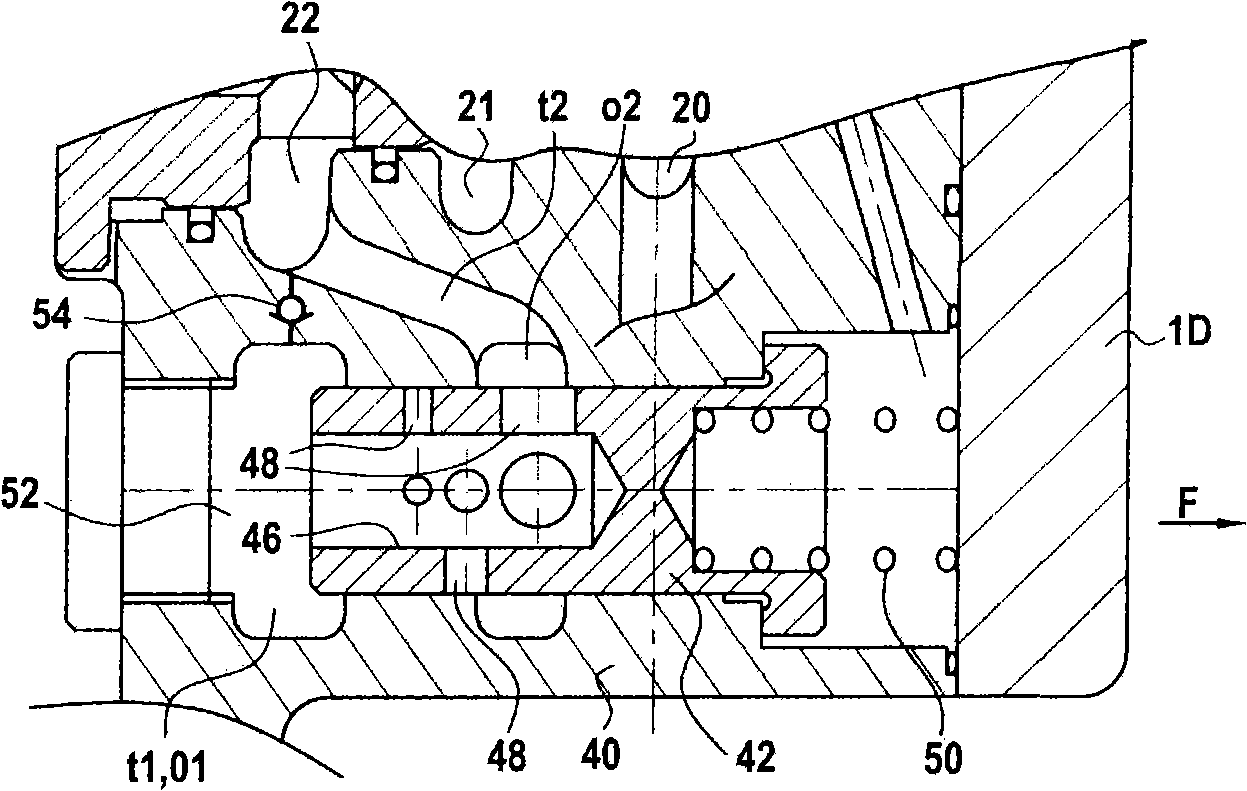
ActiveUS20090309412A1Double safetyEasy constructionHydrostatic brakesBraking action transmissionBrake pressureEngineering
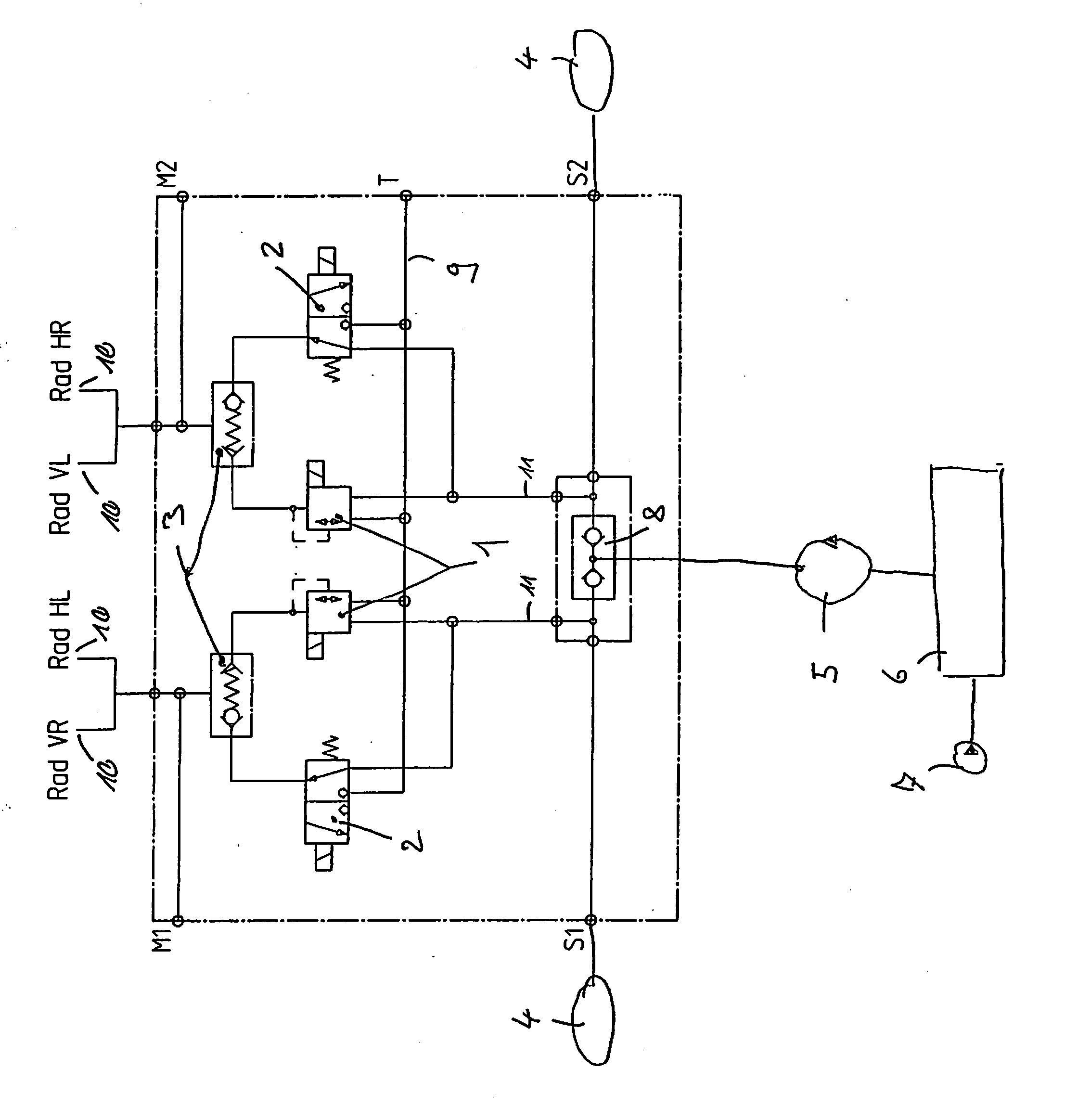
The present invention relates to a traveling working machine, in particular a hydraulic excavator, with a traveling gear and with a hydraulic service brake system for the traveling gear, which is supplied with brake pressure via at least one brake valve. In accordance with the invention, the brake valve can be actuated electrically, wherein it is connected with a control element via an electric control line, by means of which an operator can brake the traveling working machine.
Owner:LEIBHERR HYDRAULIKBAGGER GMBH
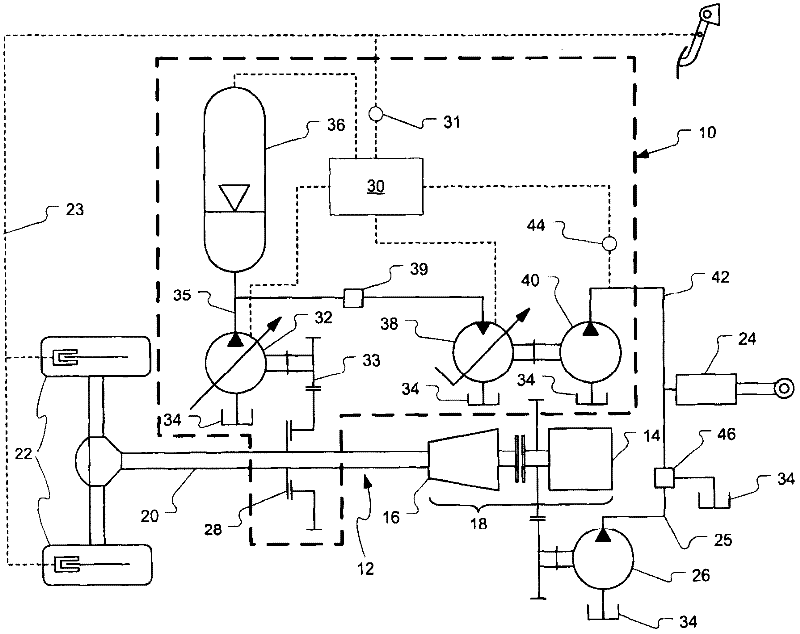
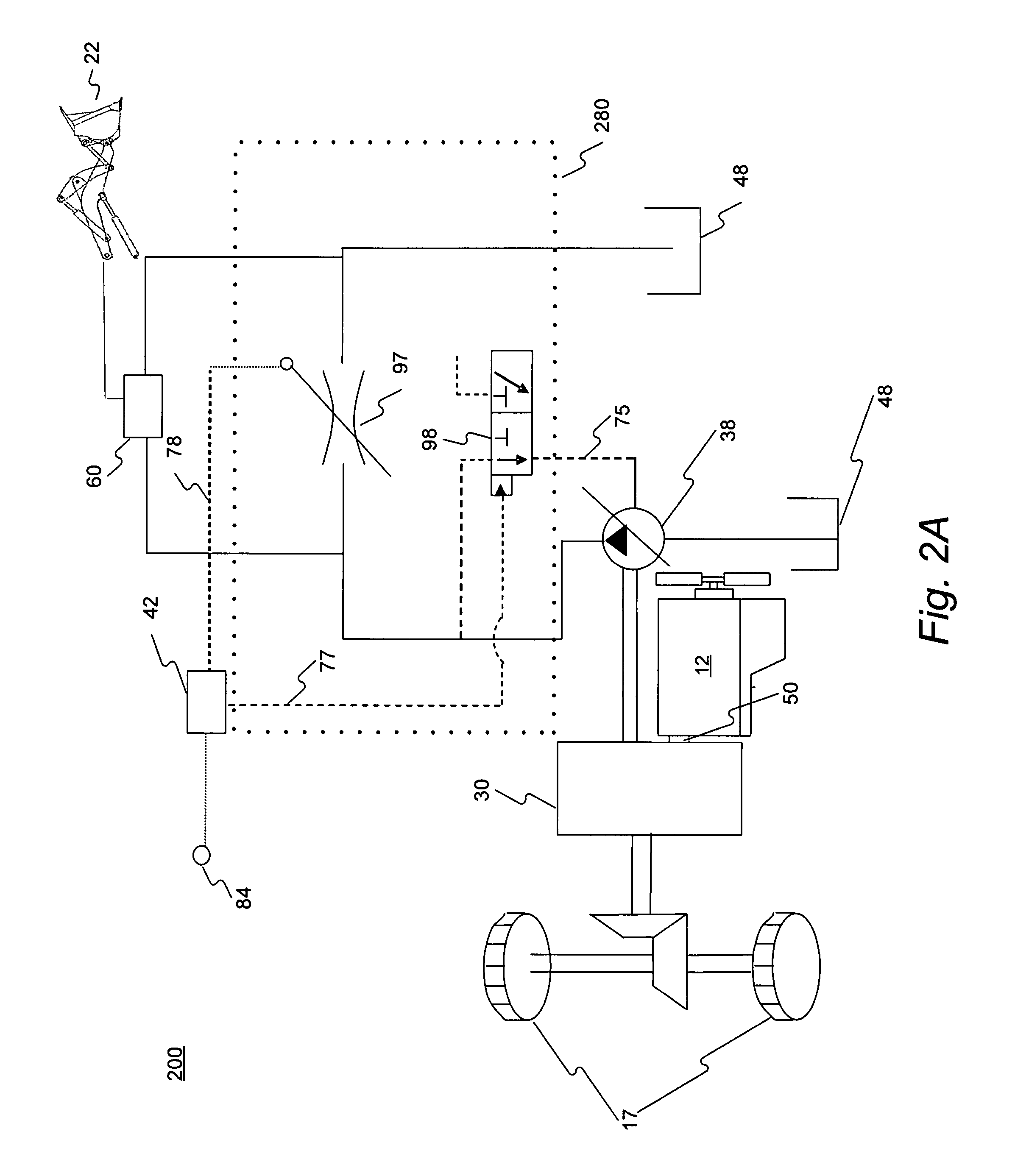
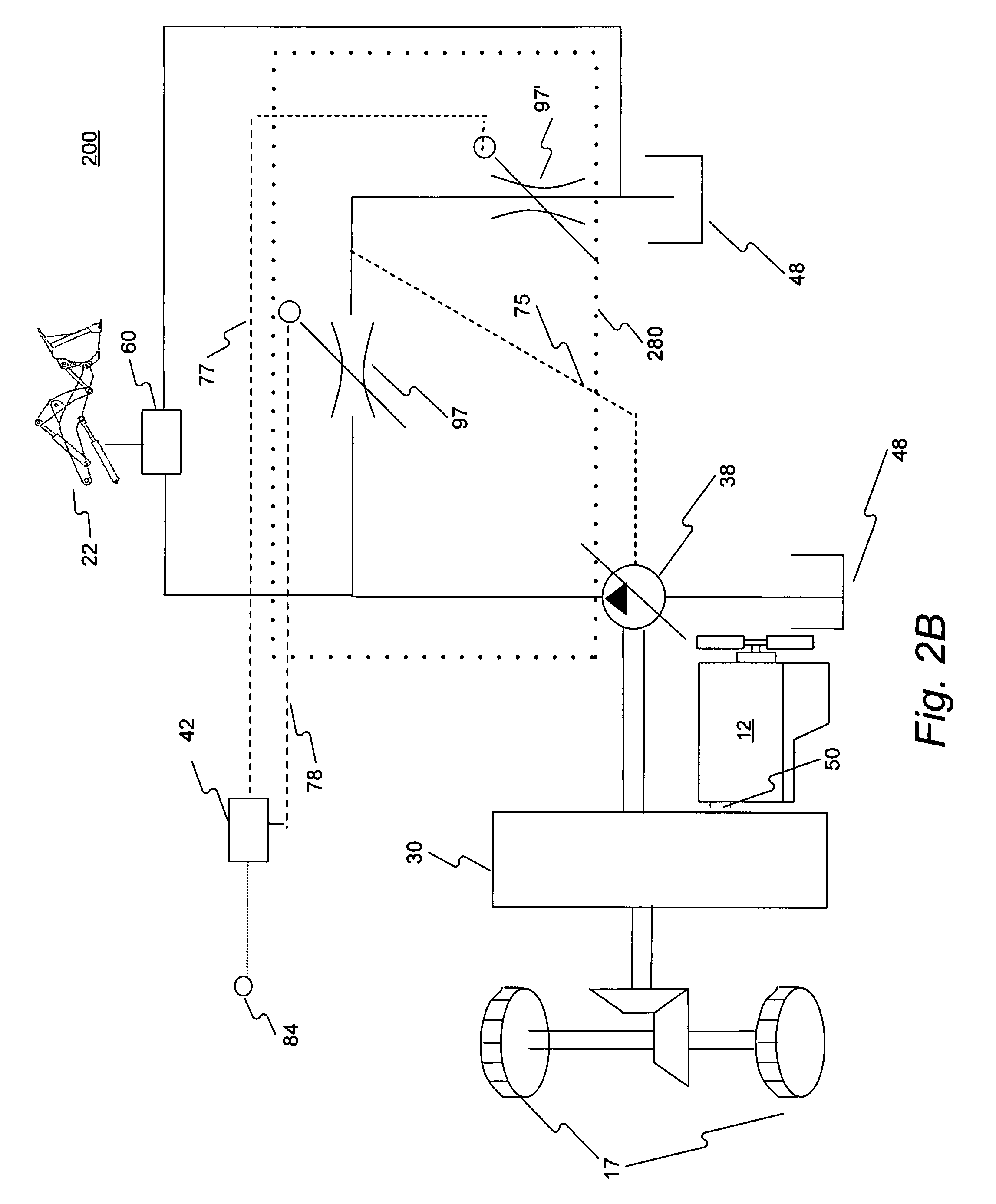
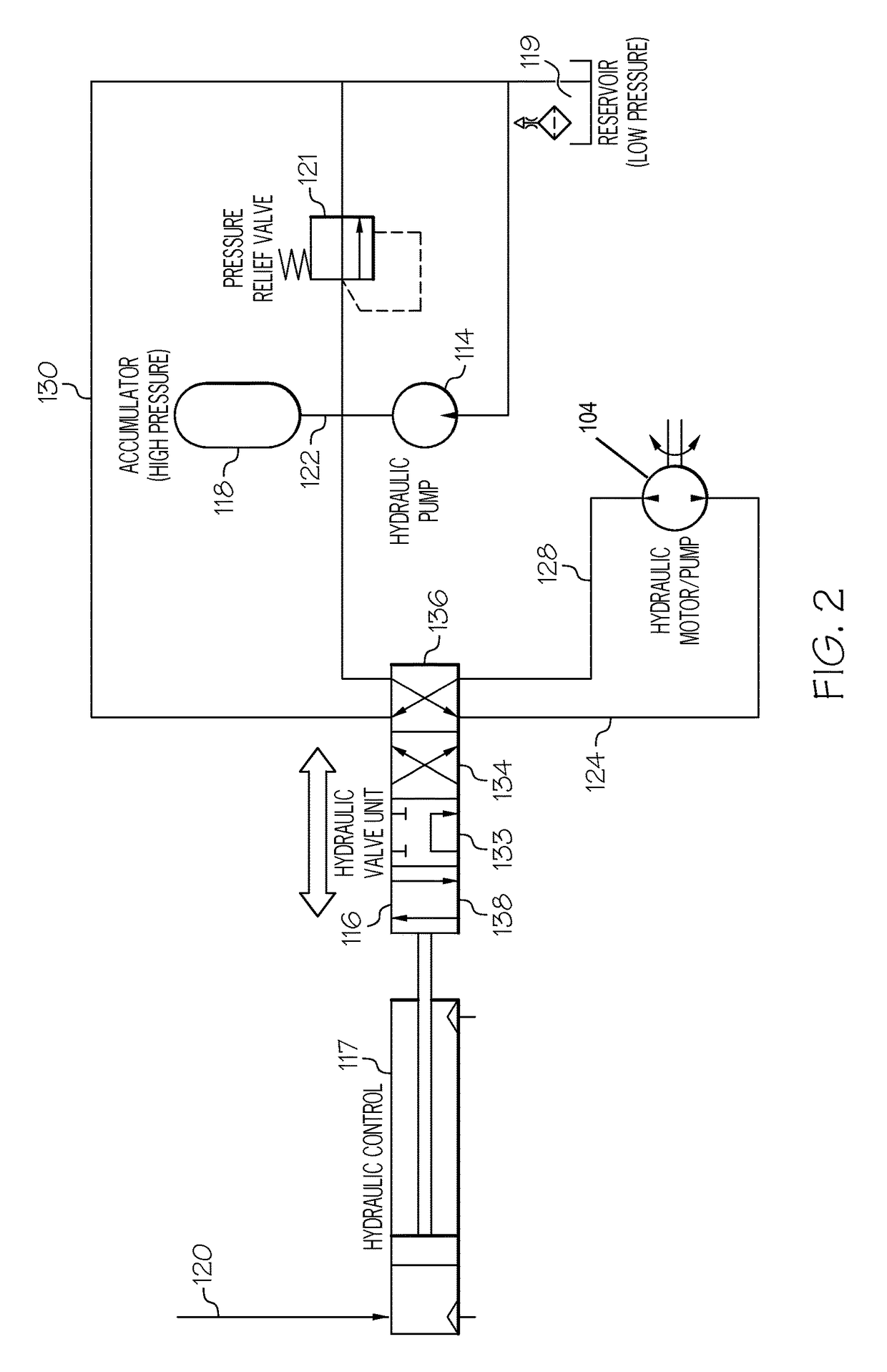
Closed loop drive circuit with external brake assist
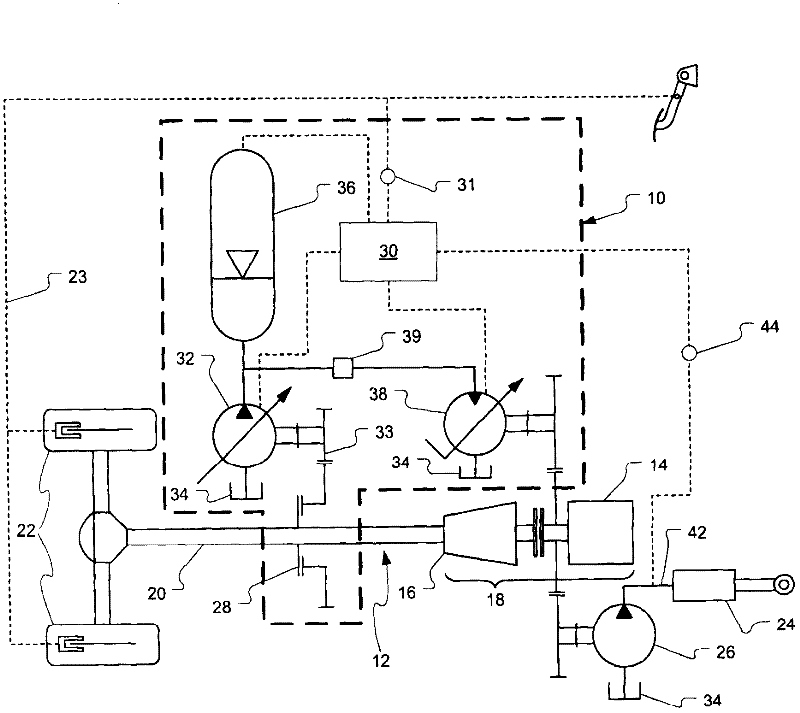
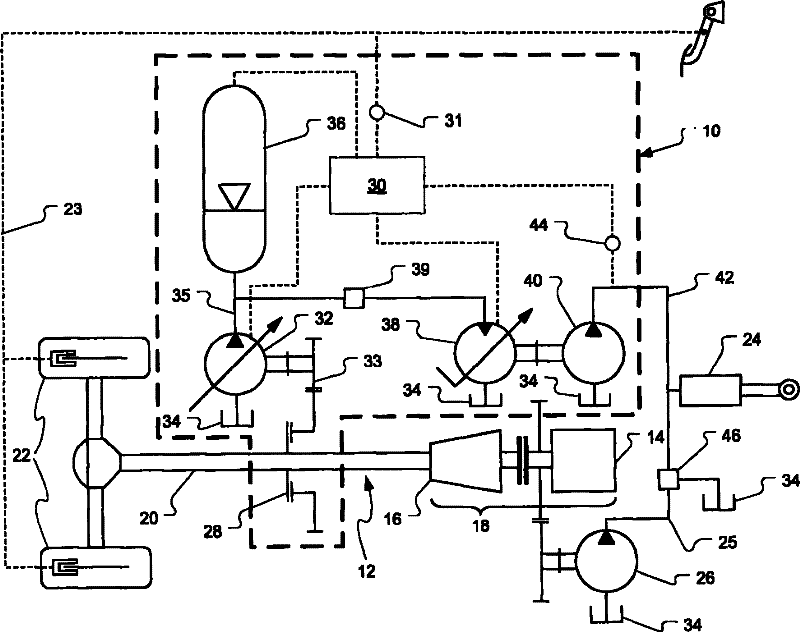
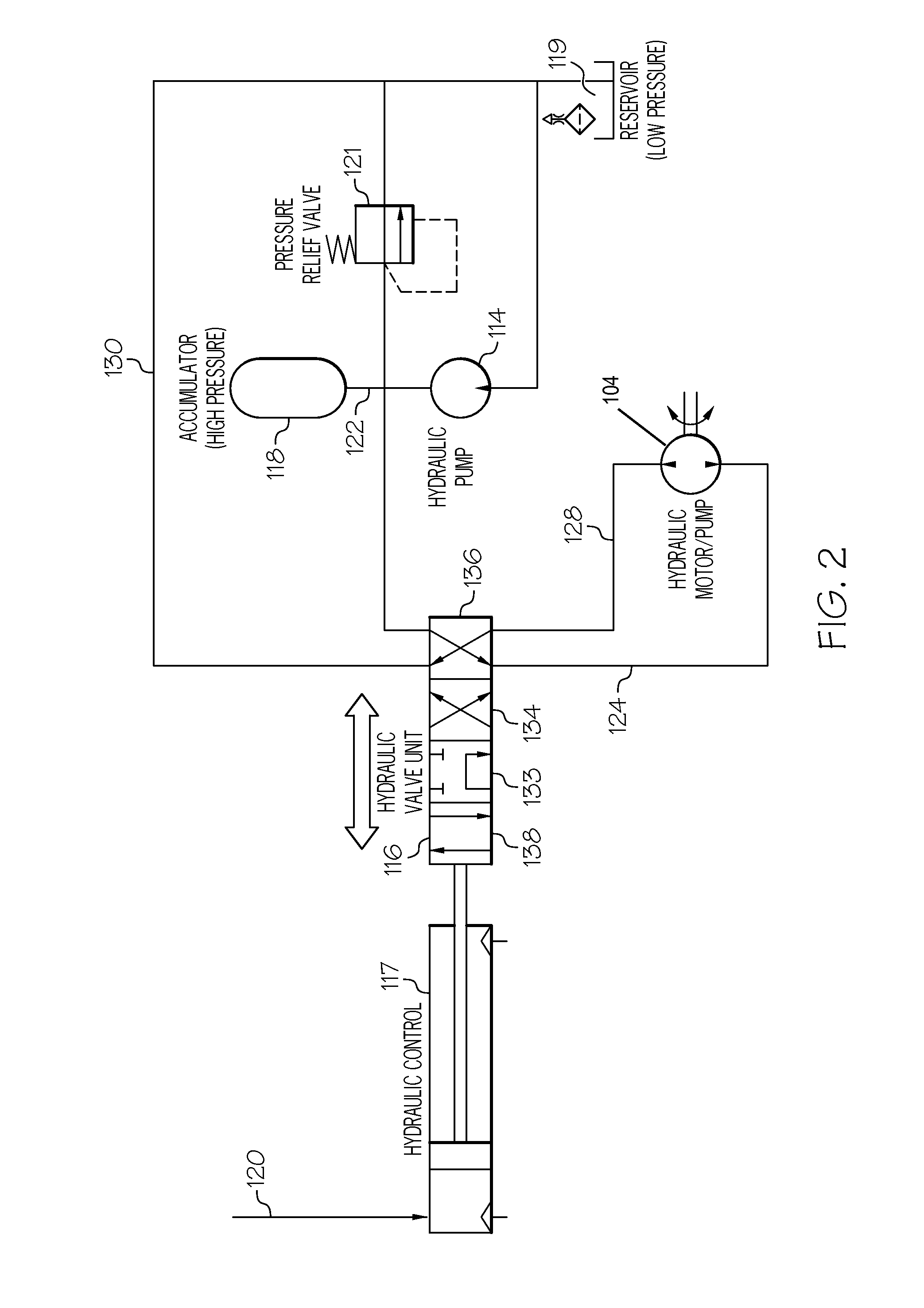
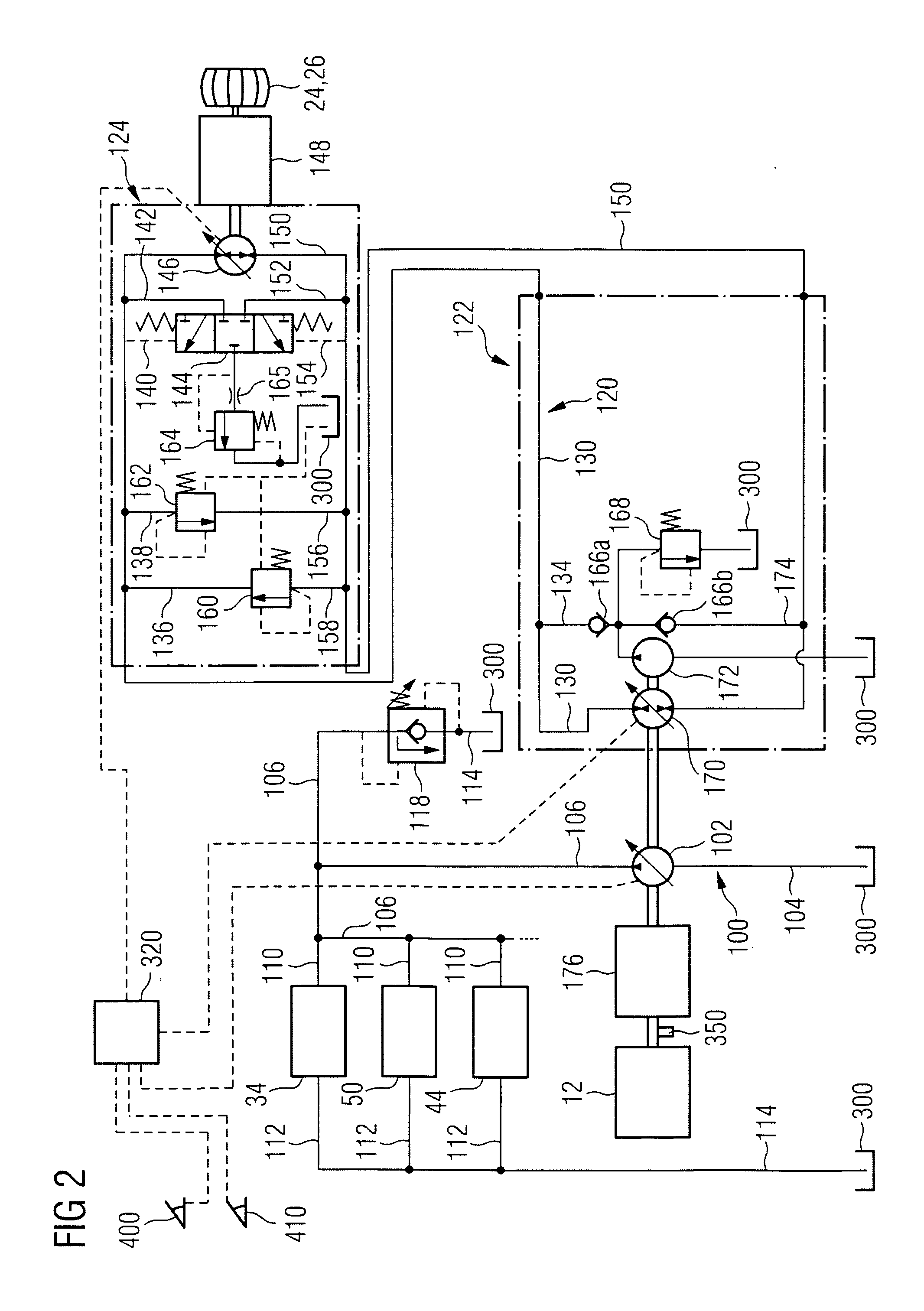
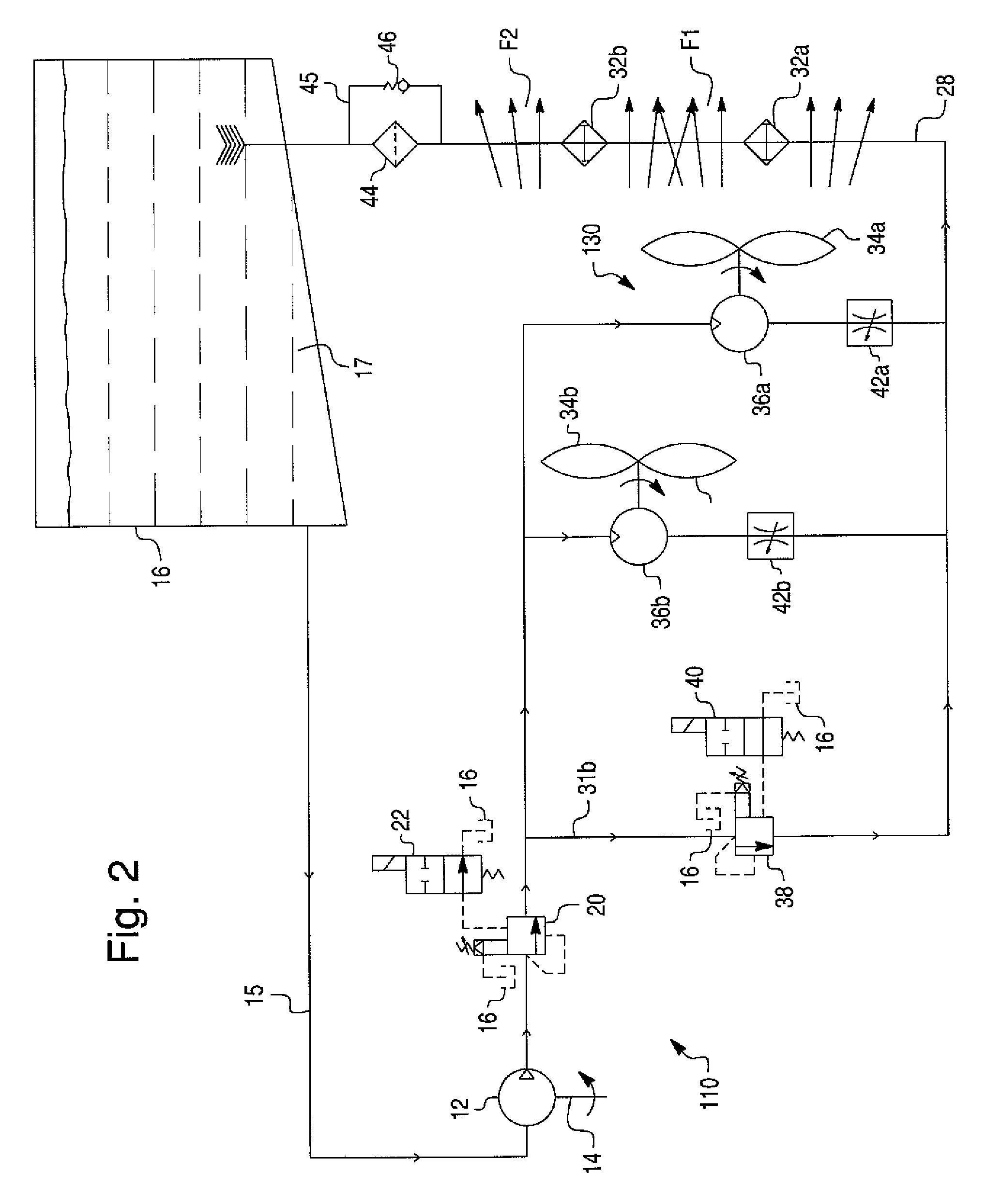
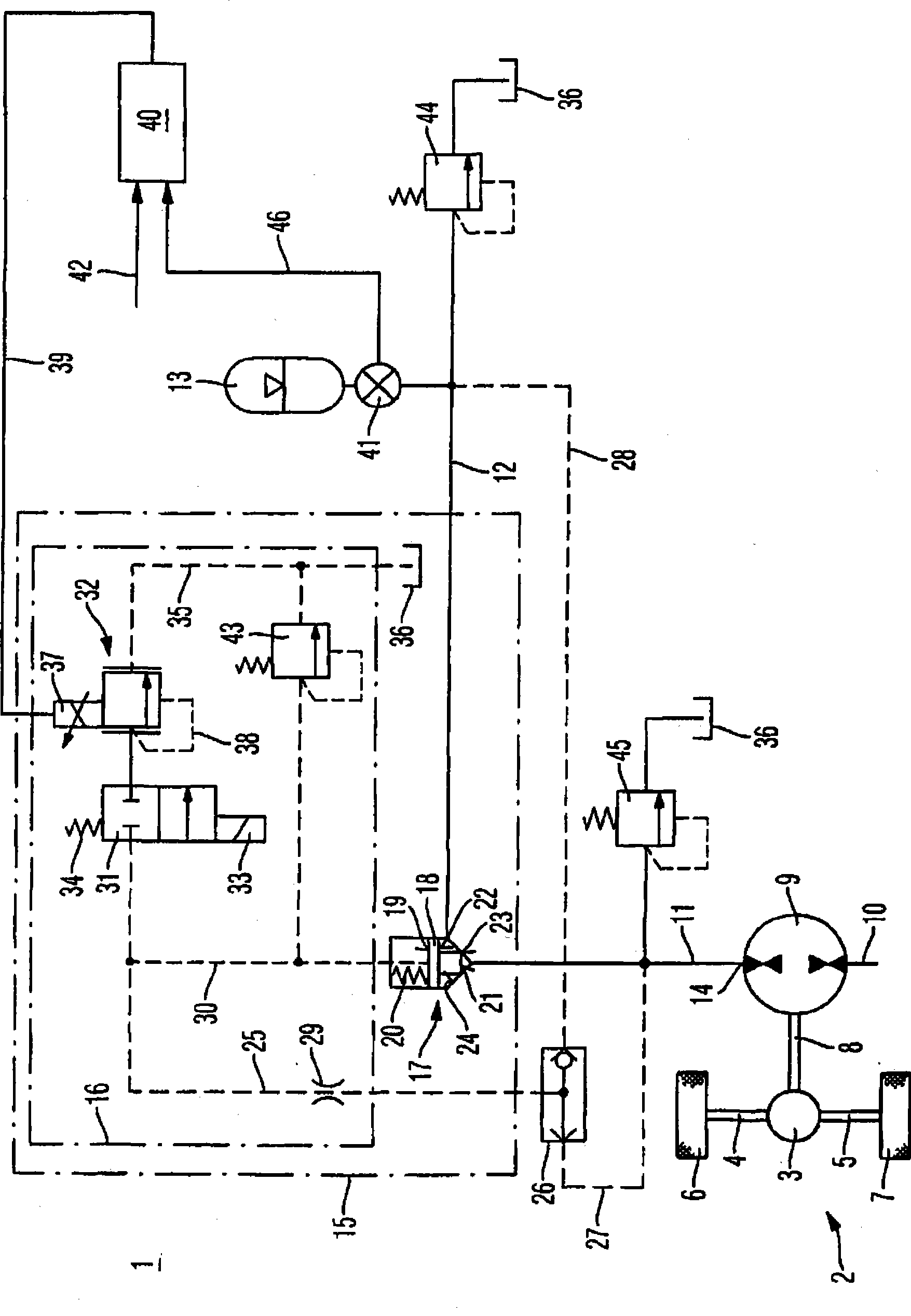
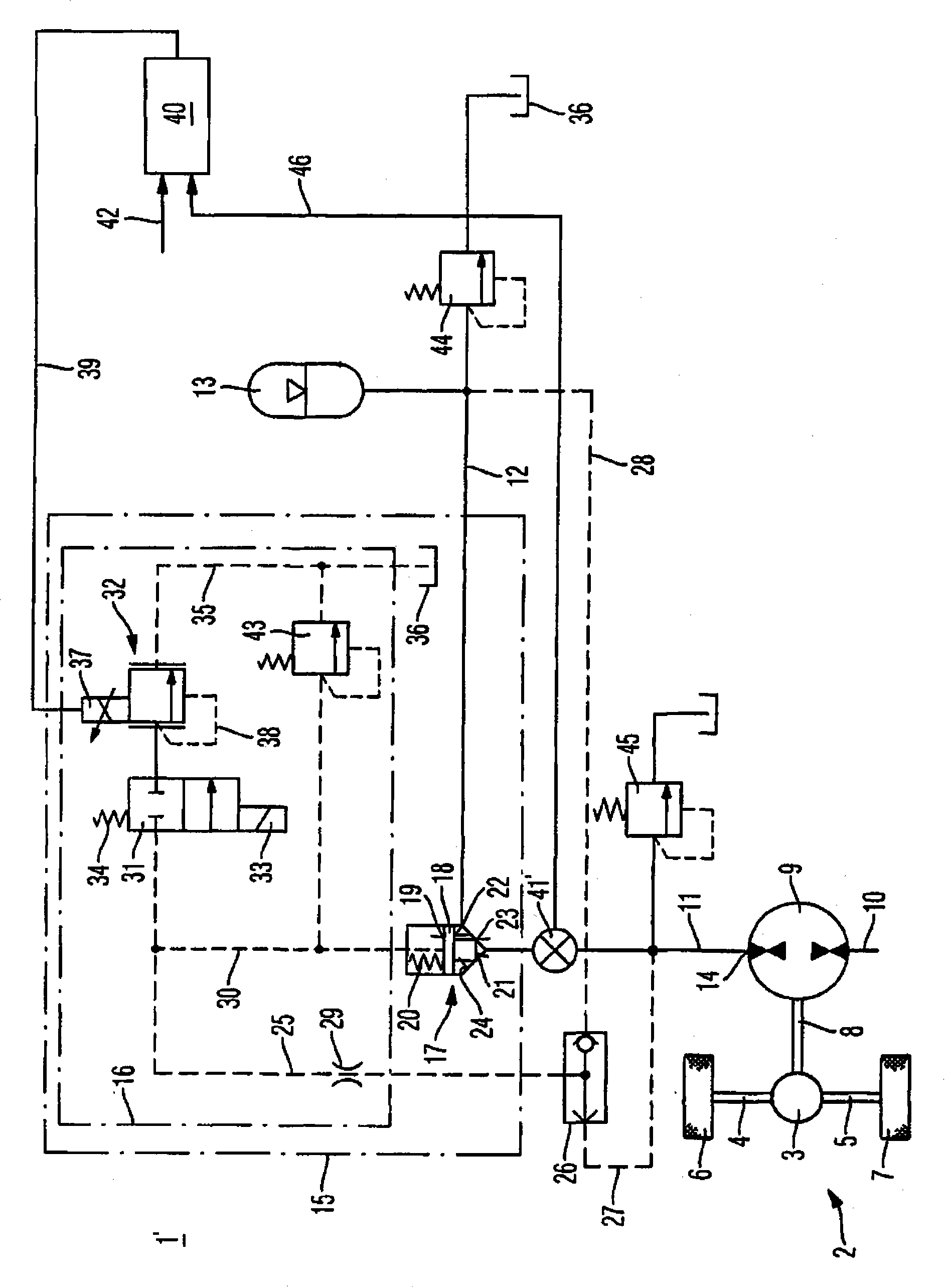
A hydrostatic drive system for a vehicle (10) comprises an open circuit (100), a closed travel circuit (120), an electronic controller (320), and a main variable displacement hydraulic pump (102) driven by an internal combustion engine (12) equipped with a speed sensor (350). The main variable displacement hydraulic pump may be configured to supply hydraulic fluid to a hydraulic consumer (34, 44, 50) via a hydraulic supply line (106). A pressure relief valve (118) may be connected to a reservoir (300) and may be permanently connected to the hydraulic supply line of the open circuit. The electronic controller may be configured to run a strong braking mode in which the electronic controller at least partially increases the displacement of the main variable displacement hydraulic pump such that hydraulic fluid is discharged via the permanently connected pressure relief valve into the reservoir if the sensed engine speed is higher than a predetermined maximum engine speed.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Downshift in hydrostatic drive work machine
The present disclosure provides a hydrostatic drive work machine, and a method and control module having a control algorithm for performing a downshifting event in the work machine. The method includes the step of inducing a retarded mode in the work machine, if upon commanding a downshift the work machine is not in a retarded mode. The method further includes the steps of adjusting a displacement of each of a variable displacement pump and a variable displacement motor in a hydrostatic drive of the work machine, and increasing pressure on a low clutch of the work machine. The control algorithm includes means for inducing a retarded mode in the work machine, if the work machine is not in a retarded mode upon commanding a downshift, with at least one of a variable displacement motor and a variable displacement pump in a hydrostatic drive of the work machine.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
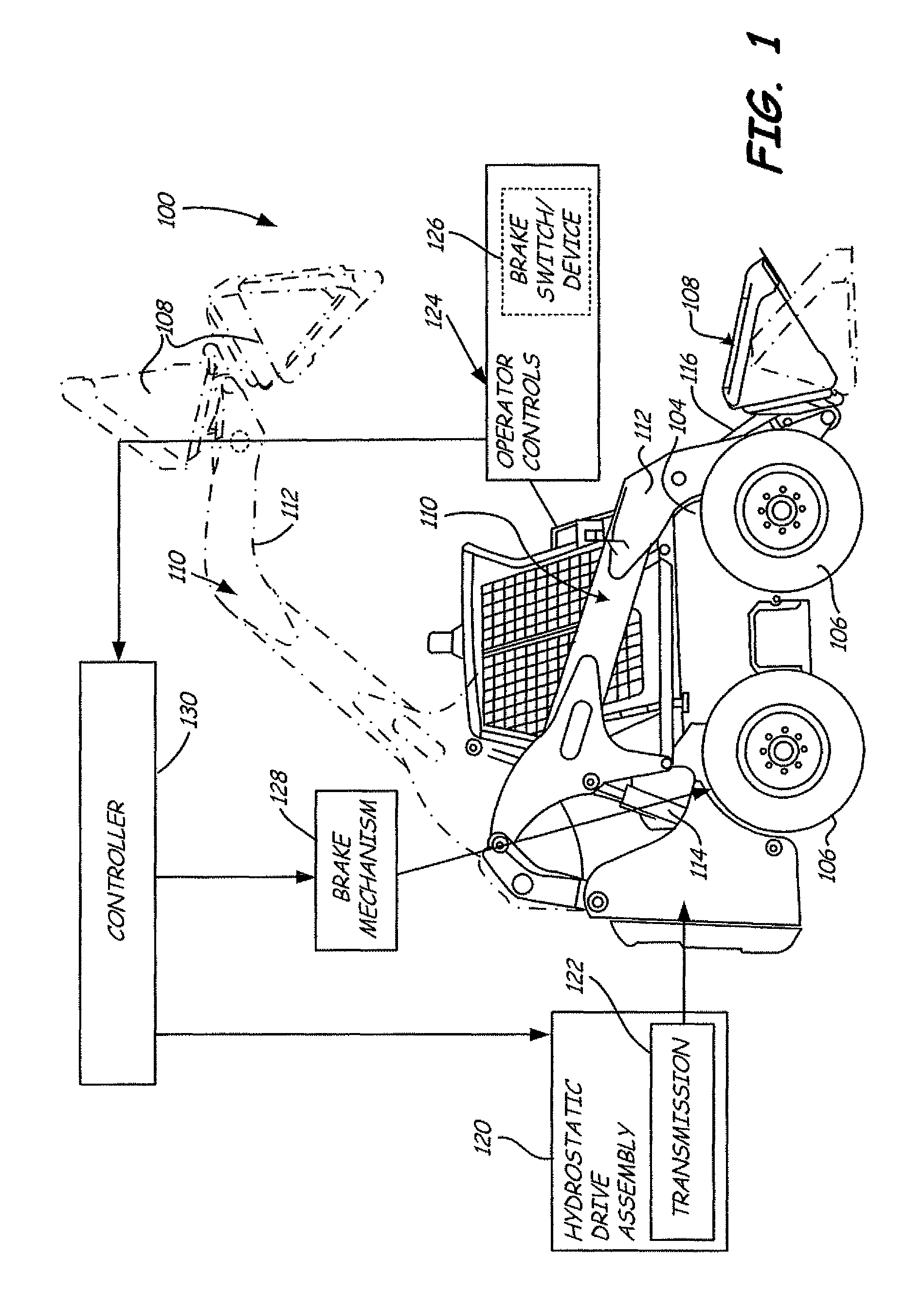
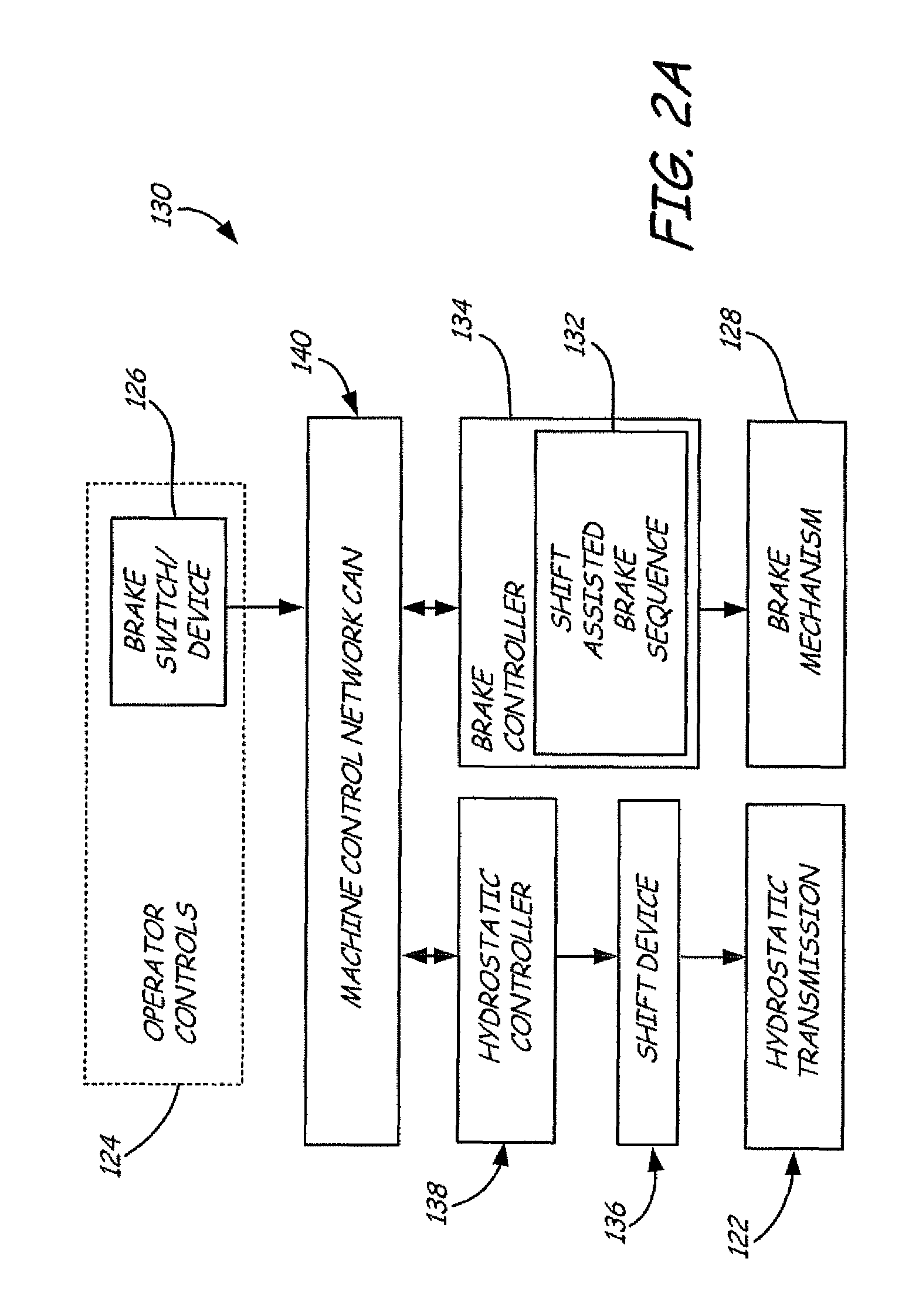
Shift assisted braking for a power machine or vehicle
ActiveUS7762923B2Reduces impact and wearReduce torqueHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsLow speedControl system
Owner:DOOSAN BOBCAT NORTH AMERICA INC
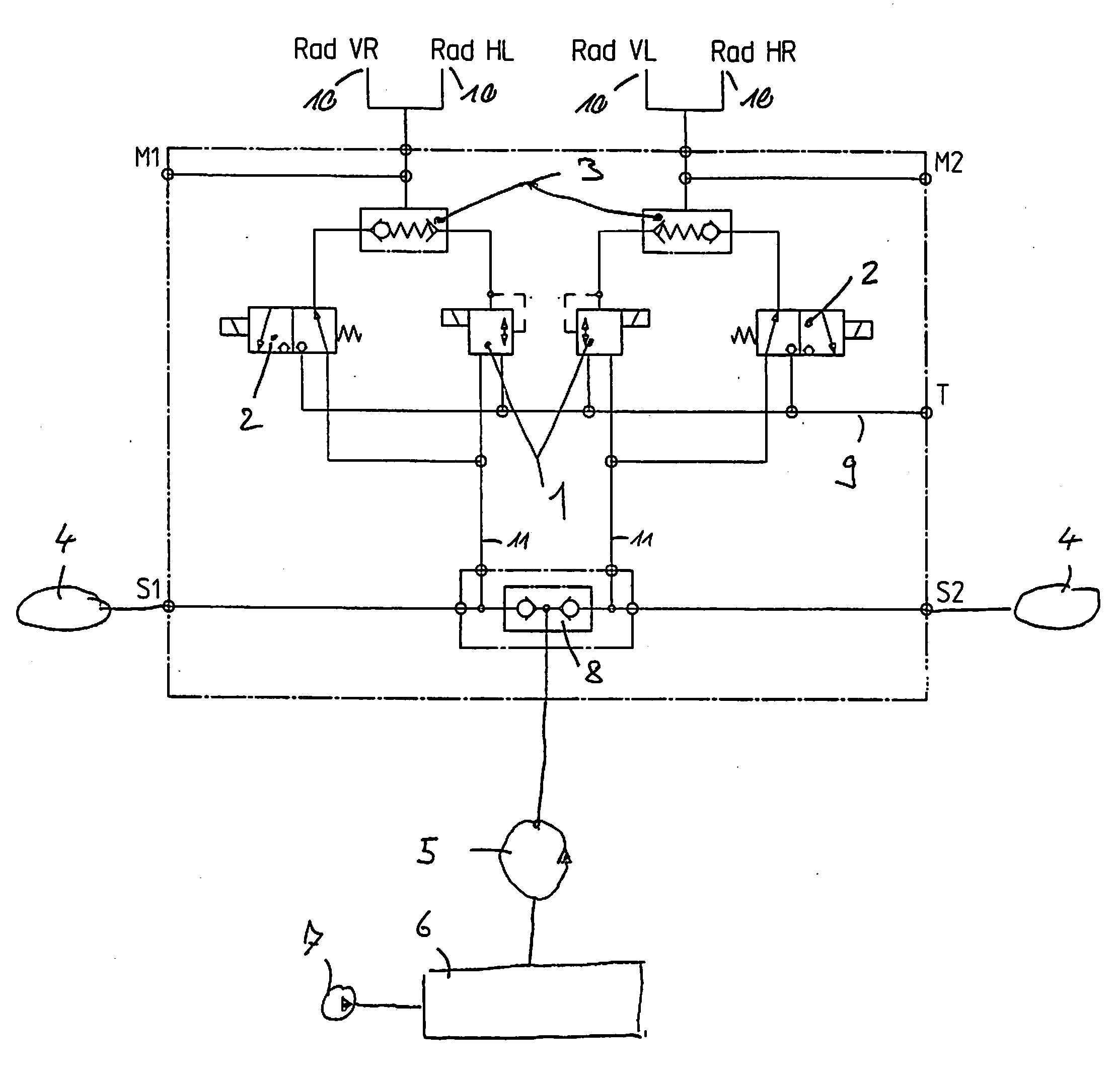
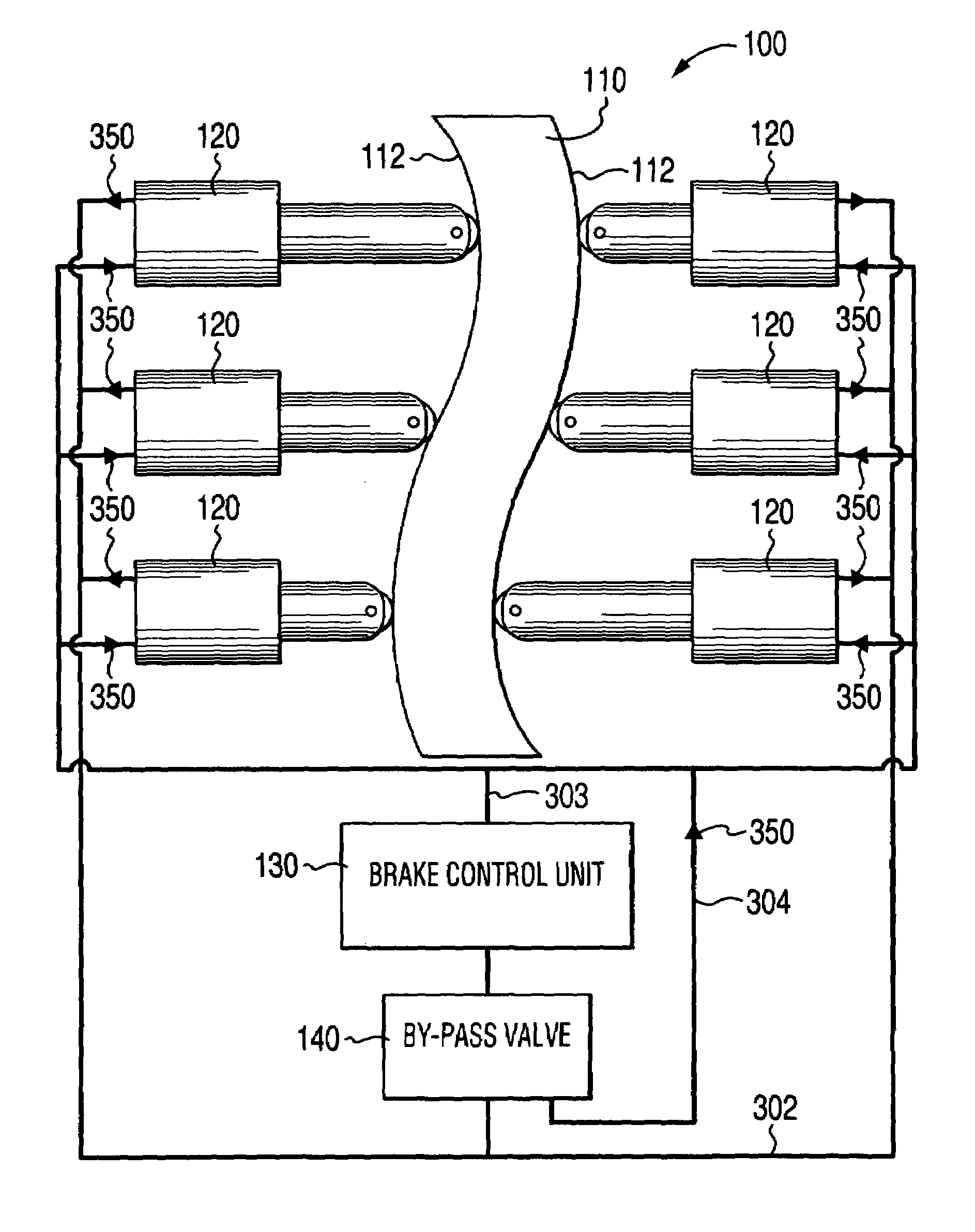
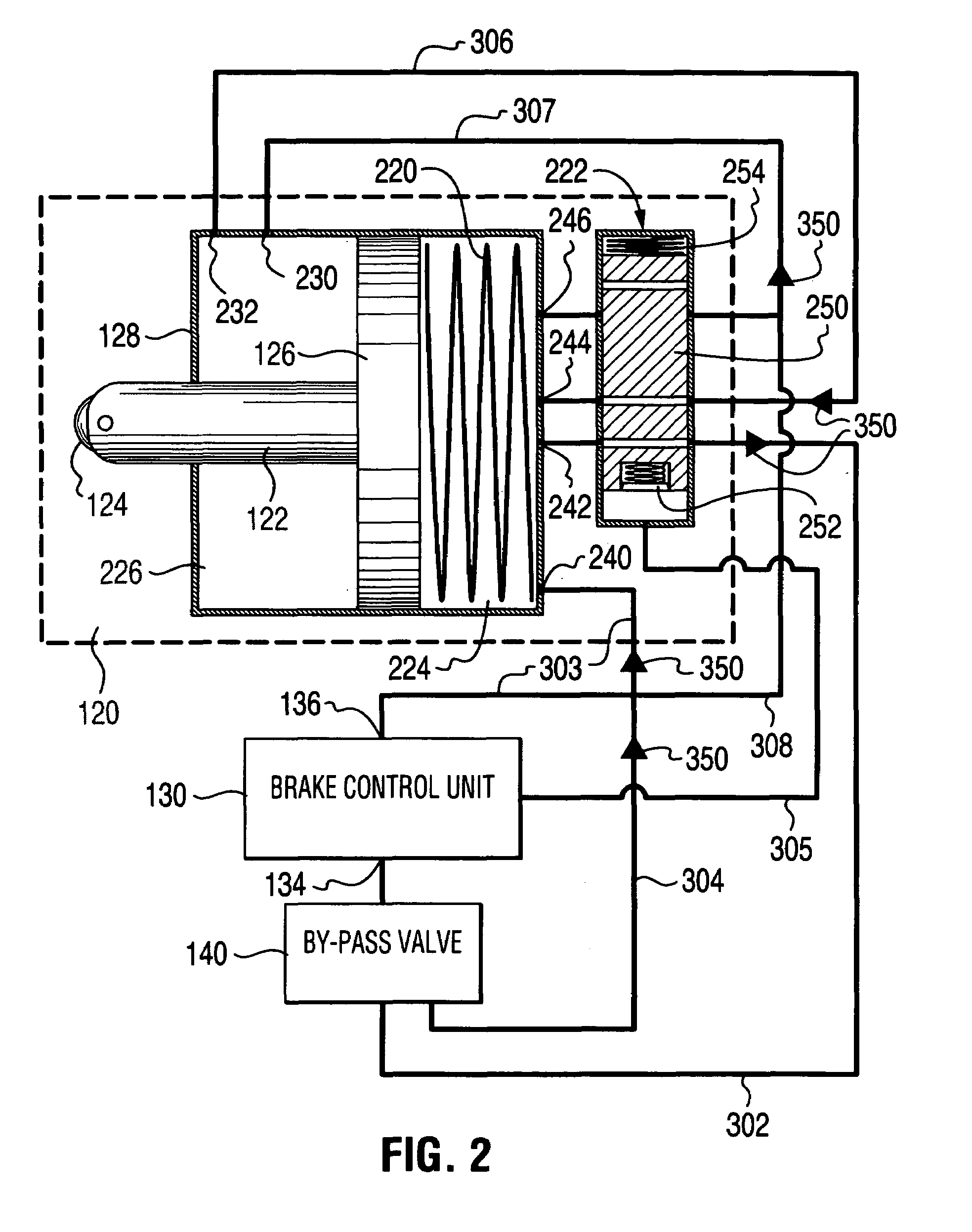
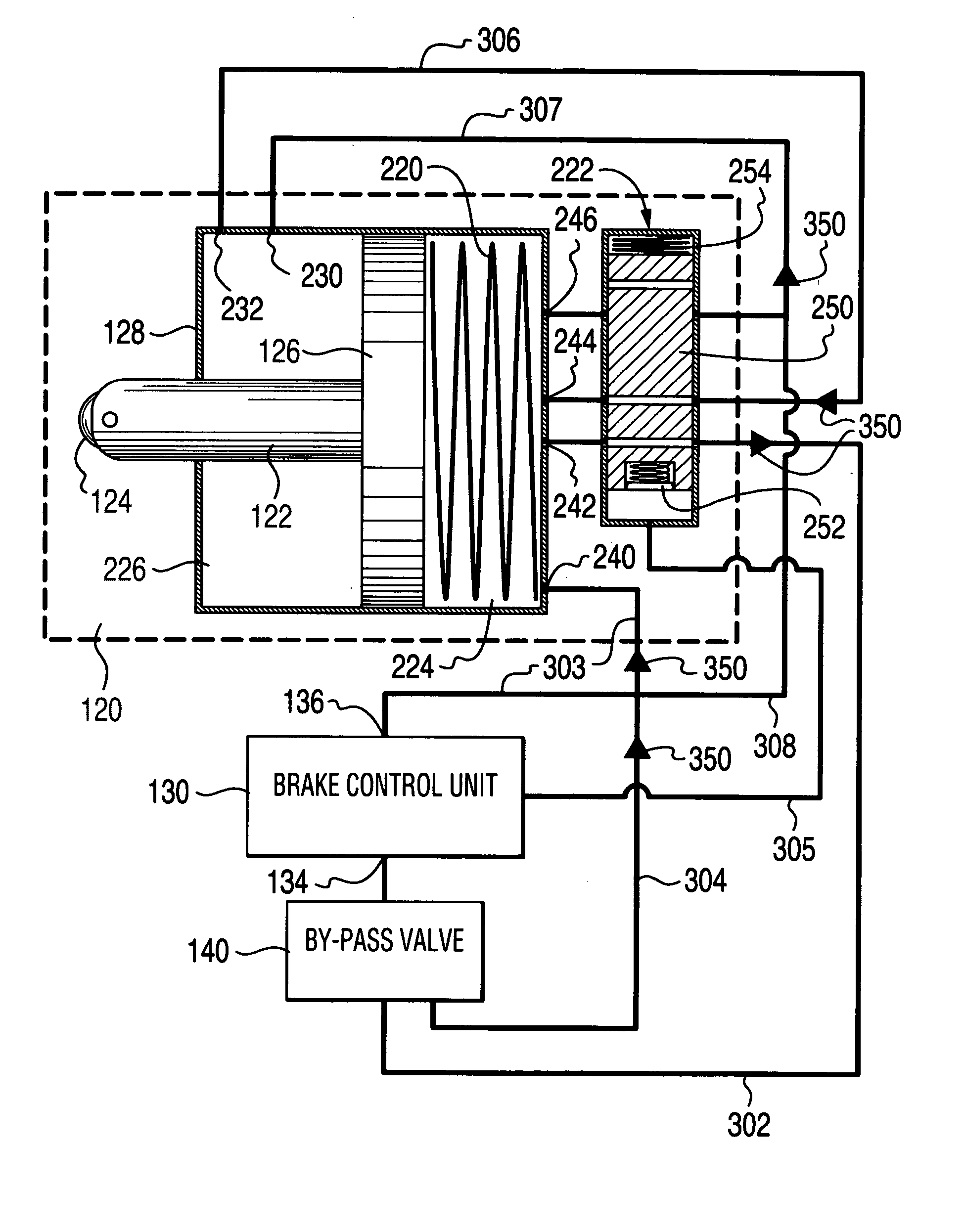
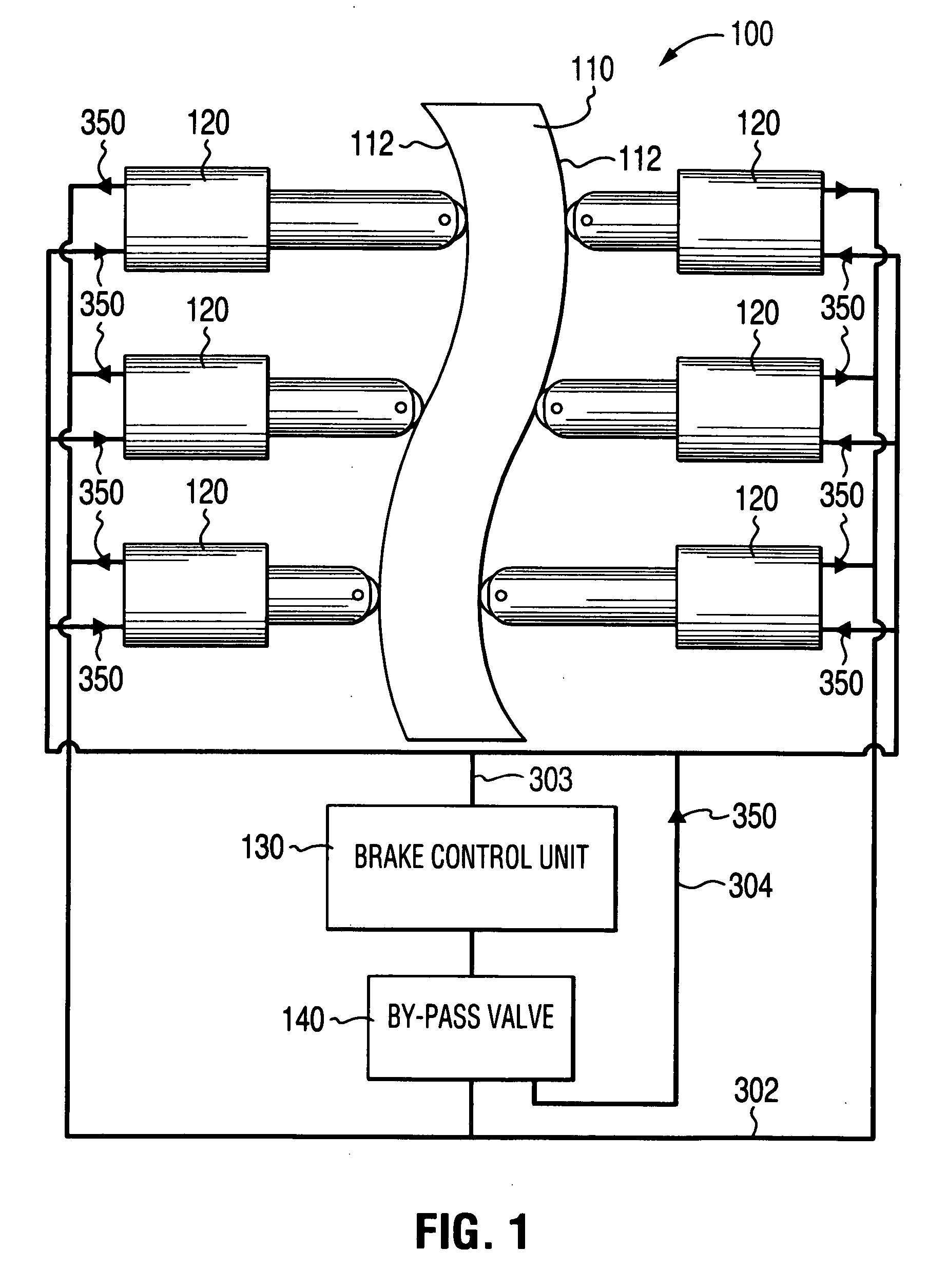
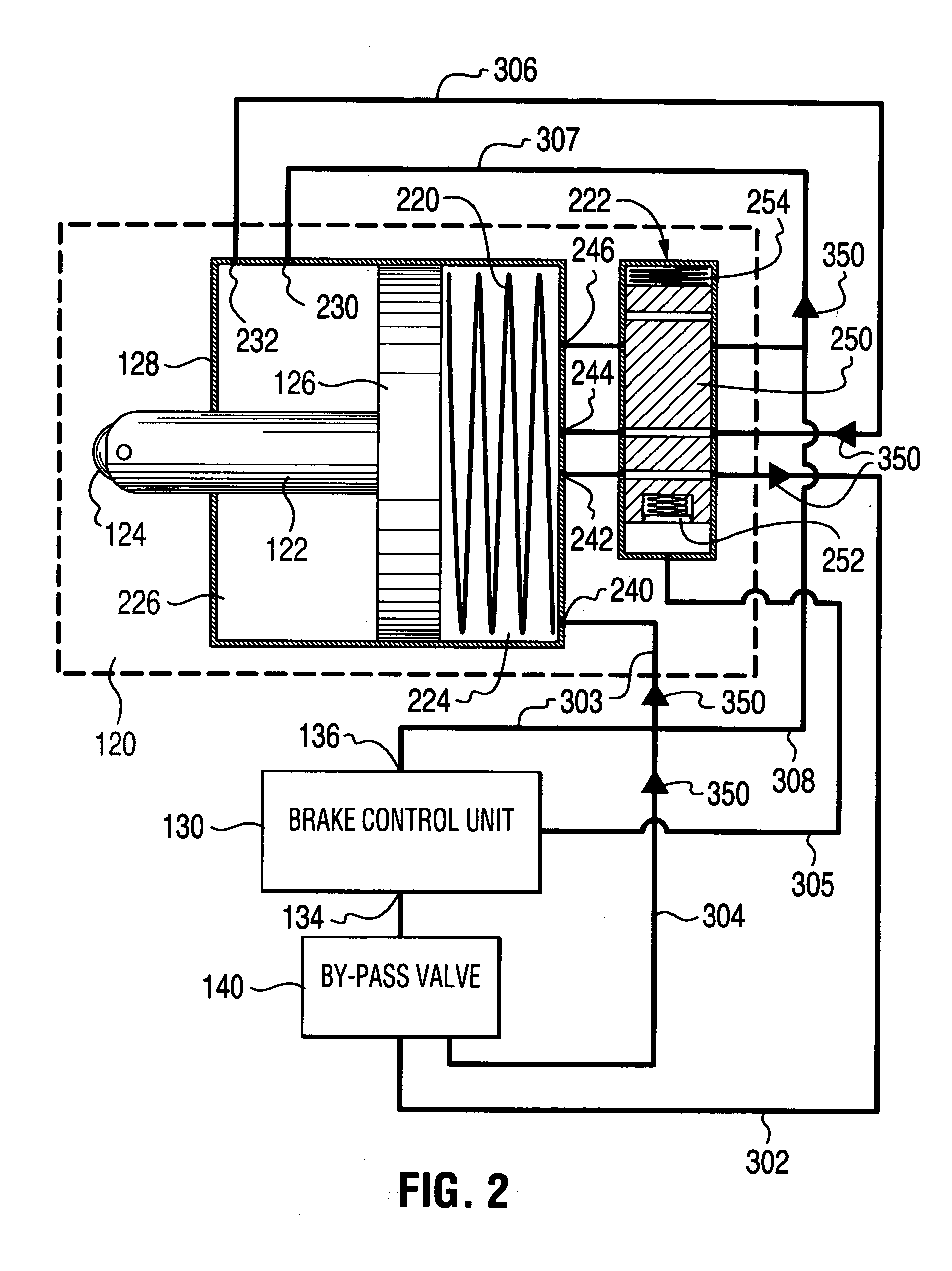
Self-energizing brake system
A braking system comprised of a rotor, a plurality of actuators, a brake control unit and a by-pass valve. When in a brake-on mode of operation, the brake control unit effects braking by restricting the flow of a working fluid that is pumped in and out by each of the plurality of actuators as they engage the rotating rotor. The degree of restriction to the flow of the working fluid can be varied to adjust the amount of braking force applied. The brake system is self-energizing in that it is not reliant on a substantial external source to create the operating pressure necessary to effect braking. Operating the by-pass valve into a by-pass on position effectively negates the generation of braking forces normally resulting from operation into the brake-on mode of operation while still allowing the actuators to engage the rotor and working fluid to be circulated.
Owner:TONAND BRAKES
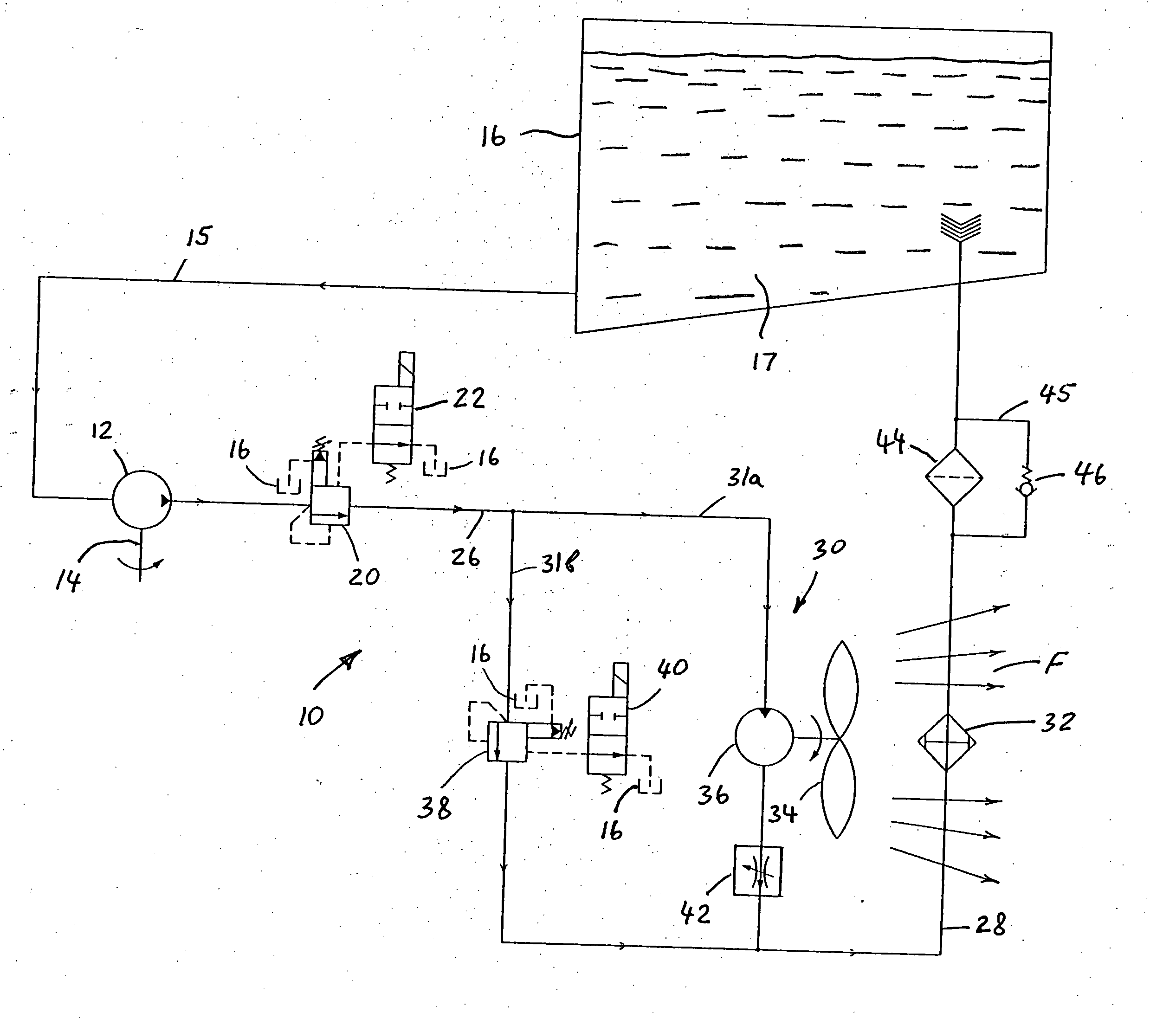
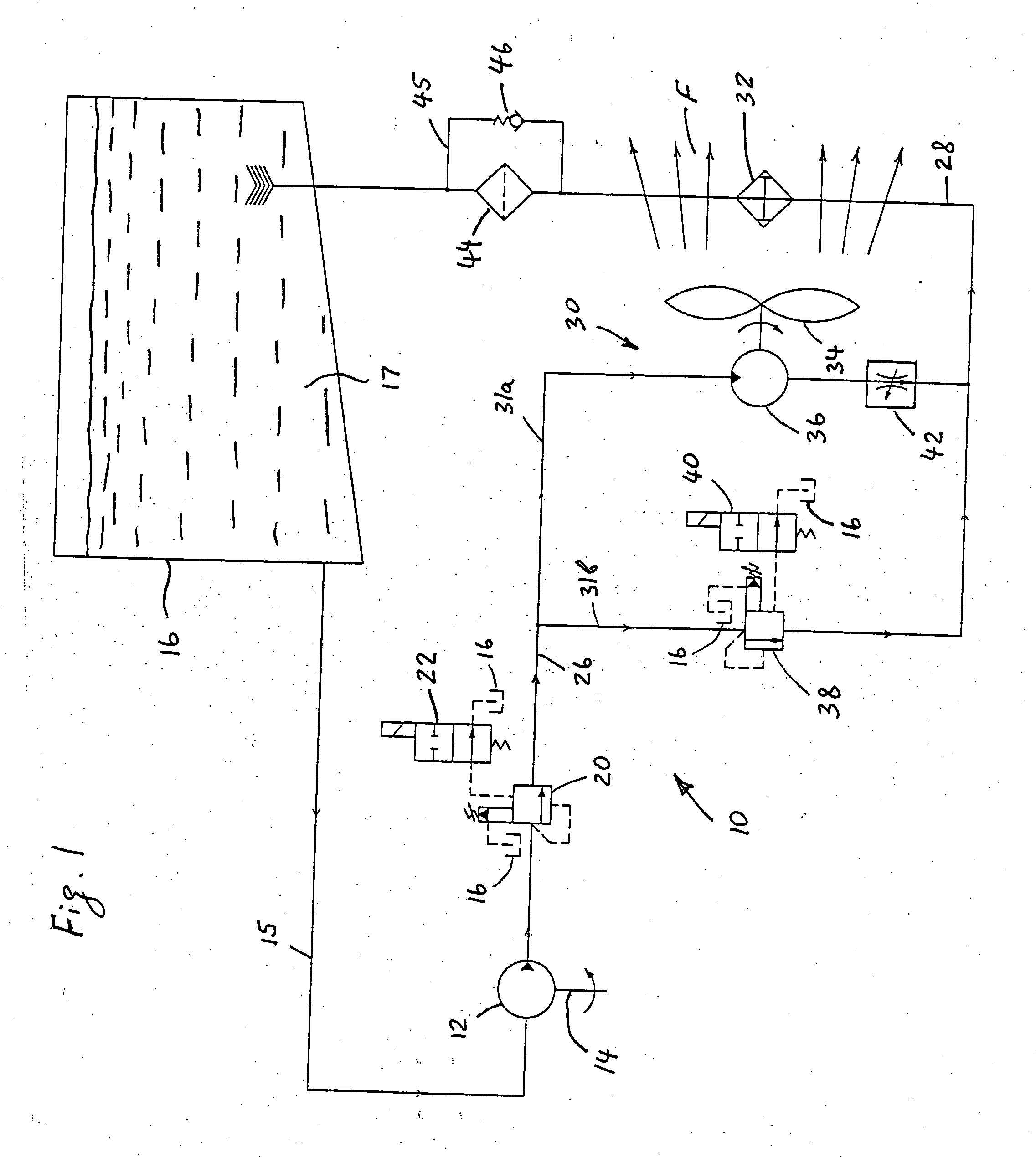
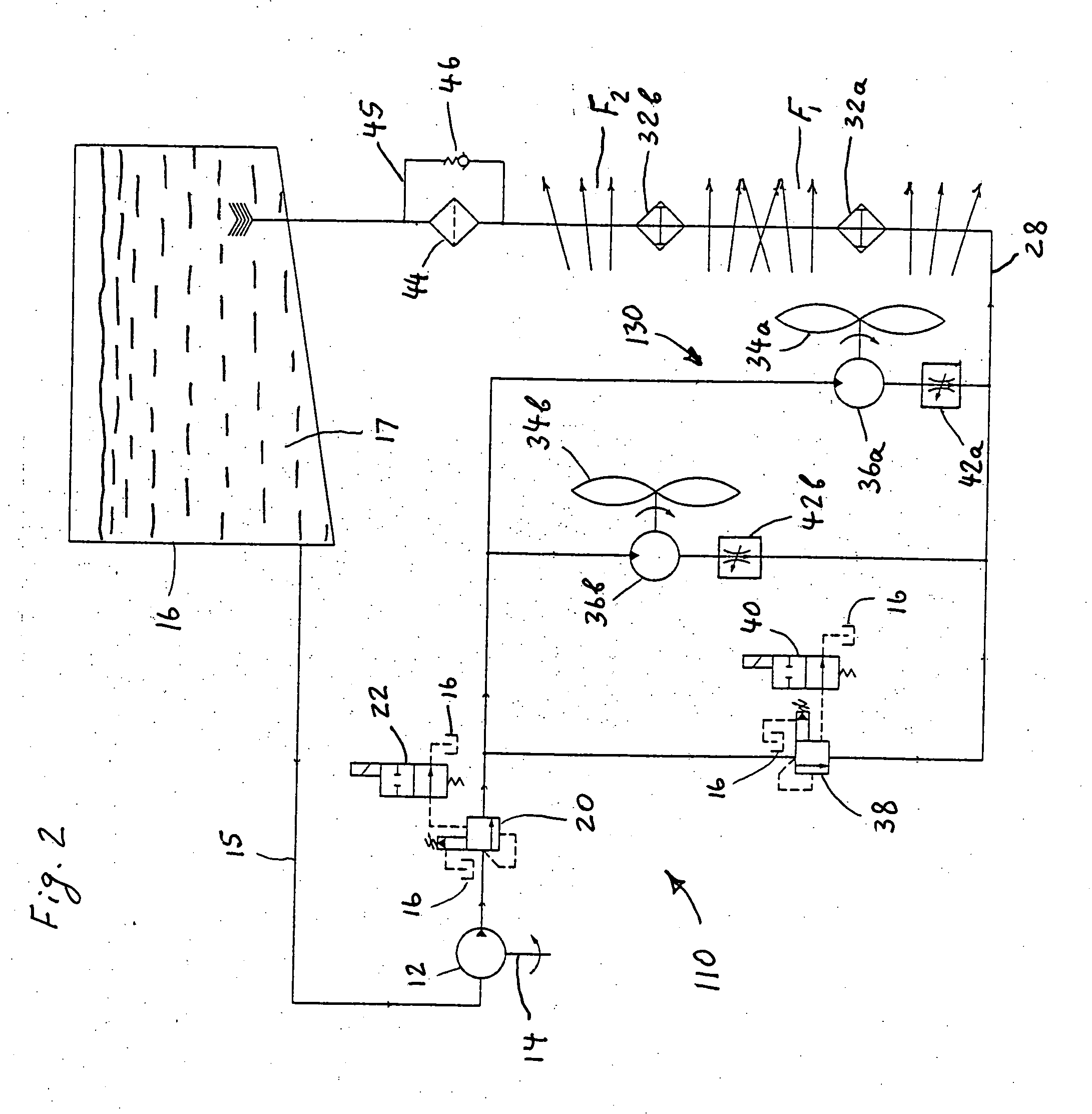
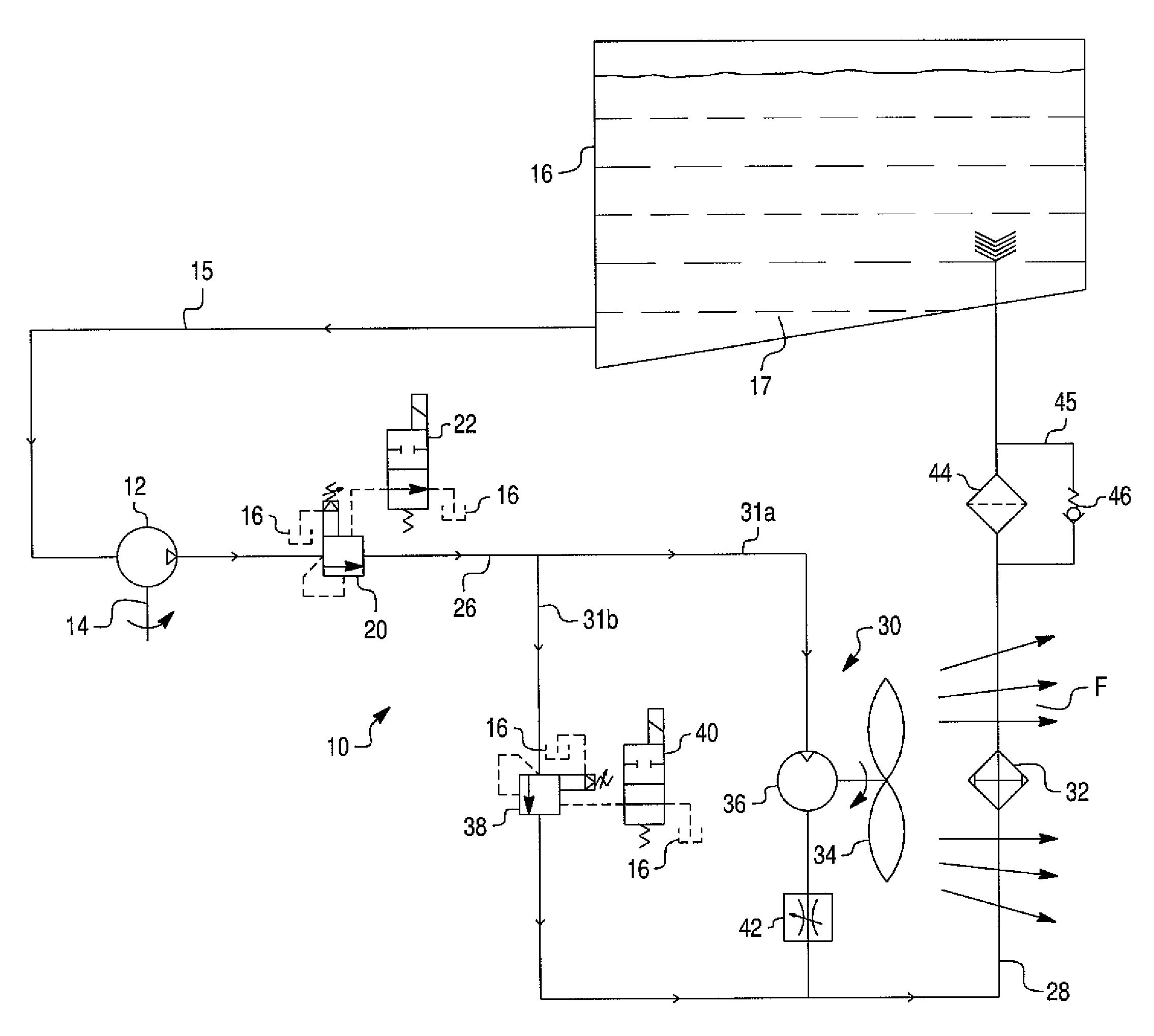
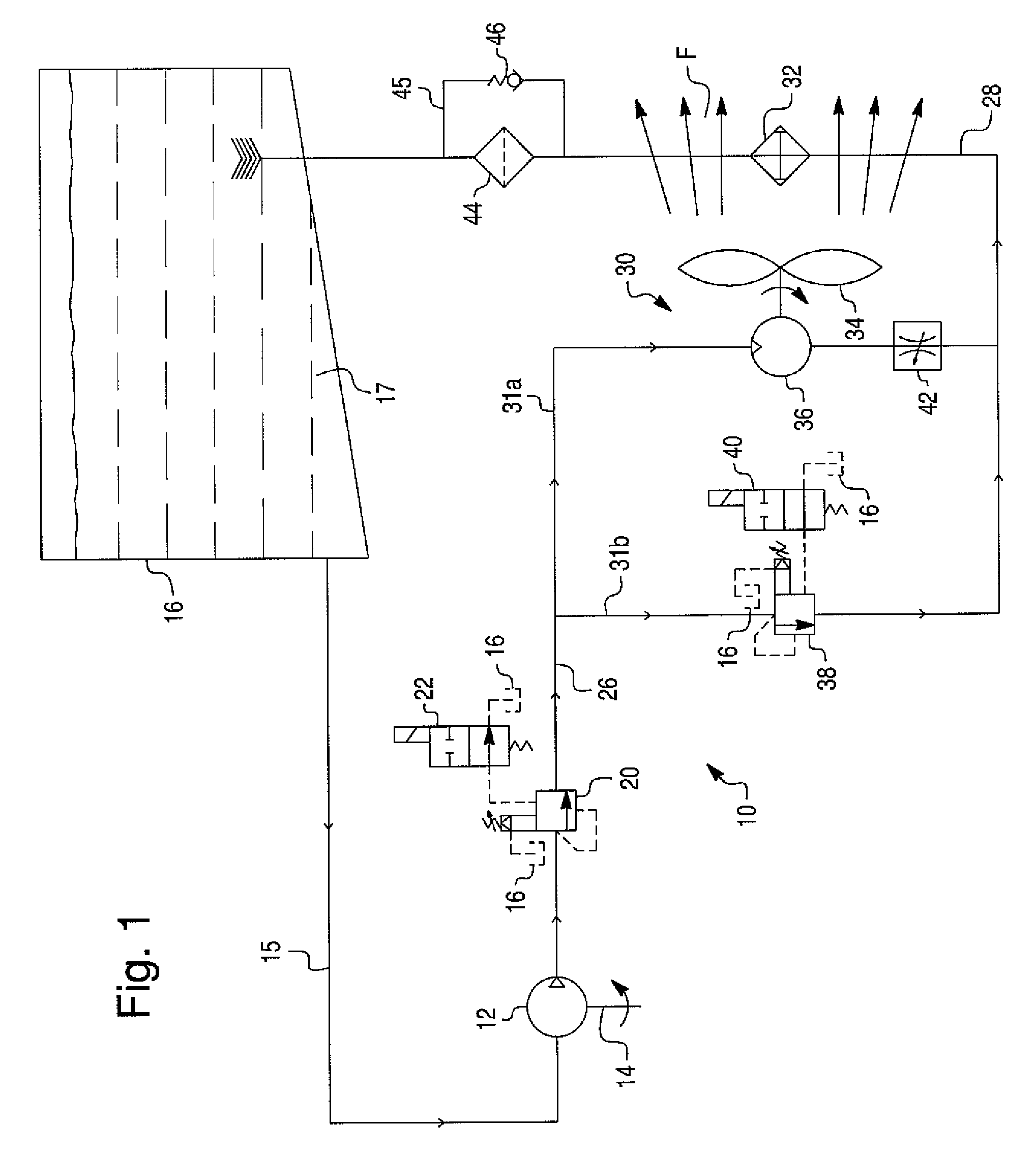
Energy conversion and dissipation system
A hydraulic energy conversion and dissipation system comprises a hydraulic retarder pump driven by a source of a mechanical energy needed to be dissipated for converting the mechanical energy into a waste hydraulic energy, a hydraulic flow retarder provided for converting the waste hydraulic energy into a thermal energy, at least one heat exchanger for dissipating the thermal energy generated by the hydraulic flow retarder and at least one cooling fan provided for producing a forced air flow through the heat exchanger. The cooling fan is driven by a corresponding hydraulic motor powered by the waste hydraulic energy of the pressurized hydraulic fluid flow generated by the hydraulic retarder pump for further dissipating the waste hydraulic energy. The system further includes a hydraulic fluid reservoir in fluid communication with an inlet of the hydraulic retarder pump.
Owner:BOSCH REXROTH AG
Machine retarder
A system is provided for controllably absorbing energy associated with a machine. The system may include a power source configured to provide power to a hydraulic pump, wherein the hydraulic pump is configured to provide a flow of fluid to a hydraulic dissipation circuit and to one or more implement system hydraulic cylinders, and wherein the hydraulic dissipation circuit is configured to generate a load associated with the hydraulic pump. The system may also include at least one valve configured to provide the flow of fluid to the hydraulic dissipation circuit in response to one or more control signals and a controller configured to receive an input signal from an operator actuated device, and generate the one or more control signals based on the input signal.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Aircraft landing gear wheel-drive system
An aircraft landing gear wheel-drive system includes a first wheel drive unit for driving a first landing gear wheel of the aircraft and a second wheel drive unit for driving a second landing gear wheel of the aircraft. The first wheel drive unit has a first range of torque to speed (T / S) ratios. The second wheel drive unit has a second range of T / S ratios. The first range of T / S ratios is greater than the second range of T / S ratios.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Energy conversion and dissipation system
A hydraulic energy conversion and dissipation system comprises a hydraulic retarder pump driven by a source of a mechanical energy needed to be dissipated for converting the mechanical energy into a waste hydraulic energy, a hydraulic flow retarder provided for converting the waste hydraulic energy into a thermal energy, at least one heat exchanger for dissipating the thermal energy generated by the hydraulic flow retarder and at least one cooling fan provided for producing a forced air flow through the heat exchanger. The cooling fan is driven by a corresponding hydraulic motor powered by the waste hydraulic energy of the pressurized hydraulic fluid flow generated by the hydraulic retarder pump for further dissipating the waste hydraulic energy. The system further includes a hydraulic fluid reservoir in fluid communication with an inlet of the hydraulic retarder pump.
Owner:BOSCH REXROTH AG
Hydraulic regenerative braking for a vehicle
ActiveUS7992948B2Improve compactnessReduce weightHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeKinetic energy
A regenerative brake of the present invention presents a hydraulic device disposed in a front hub of a bicycle wheel. The device allows the bicycle to recapture part of the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost when braking and make use of that power either by storing it for future use or feeding it back into a power system to be used. The hydraulic device may also be stored in a rear hub of the bicycle wheel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
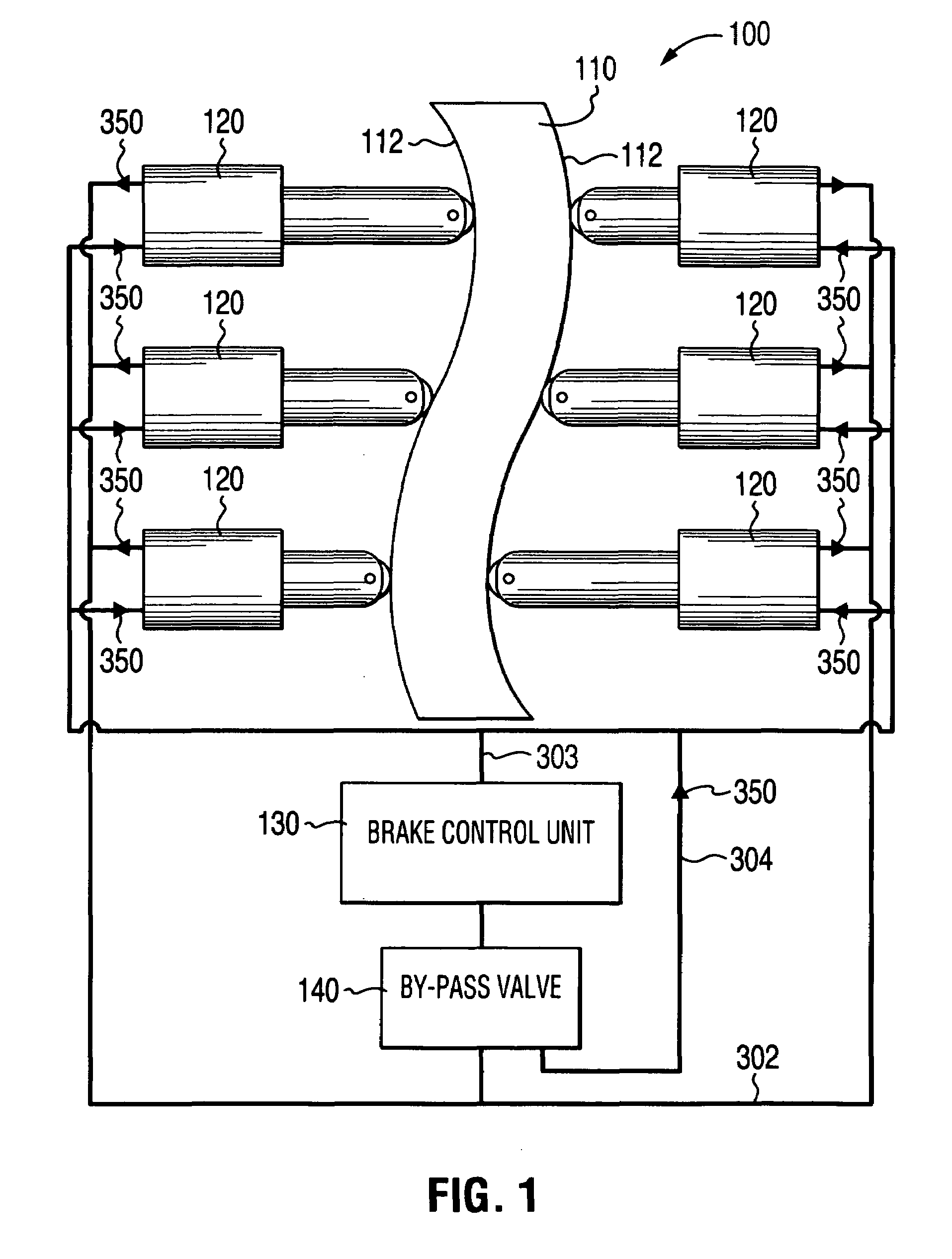
Self-energizing brake system
A braking system comprised of a rotor, a plurality of actuators, a brake control unit and a by-pass valve. When in a brake-on mode of operation, the brake control unit effects braking by restricting the flow of a working fluid that is pumped in and out by each of the plurality of actuators as they engage the rotating rotor. The degree of restriction to the flow of the working fluid can be varied to adjust the amount of braking force applied. The brake system is self-energizing in that it is not reliant on a substantial external source to create the operating pressure necessary to effect braking. Operating the by-pass valve into a by-pass on position effectively negates the generation of braking forces normally resulting from operation into the brake-on mode of operation while still allowing the actuators to engage the rotor and working fluid to be circulated.
Owner:TONAND BRAKES
Electro-hydraulic traction support
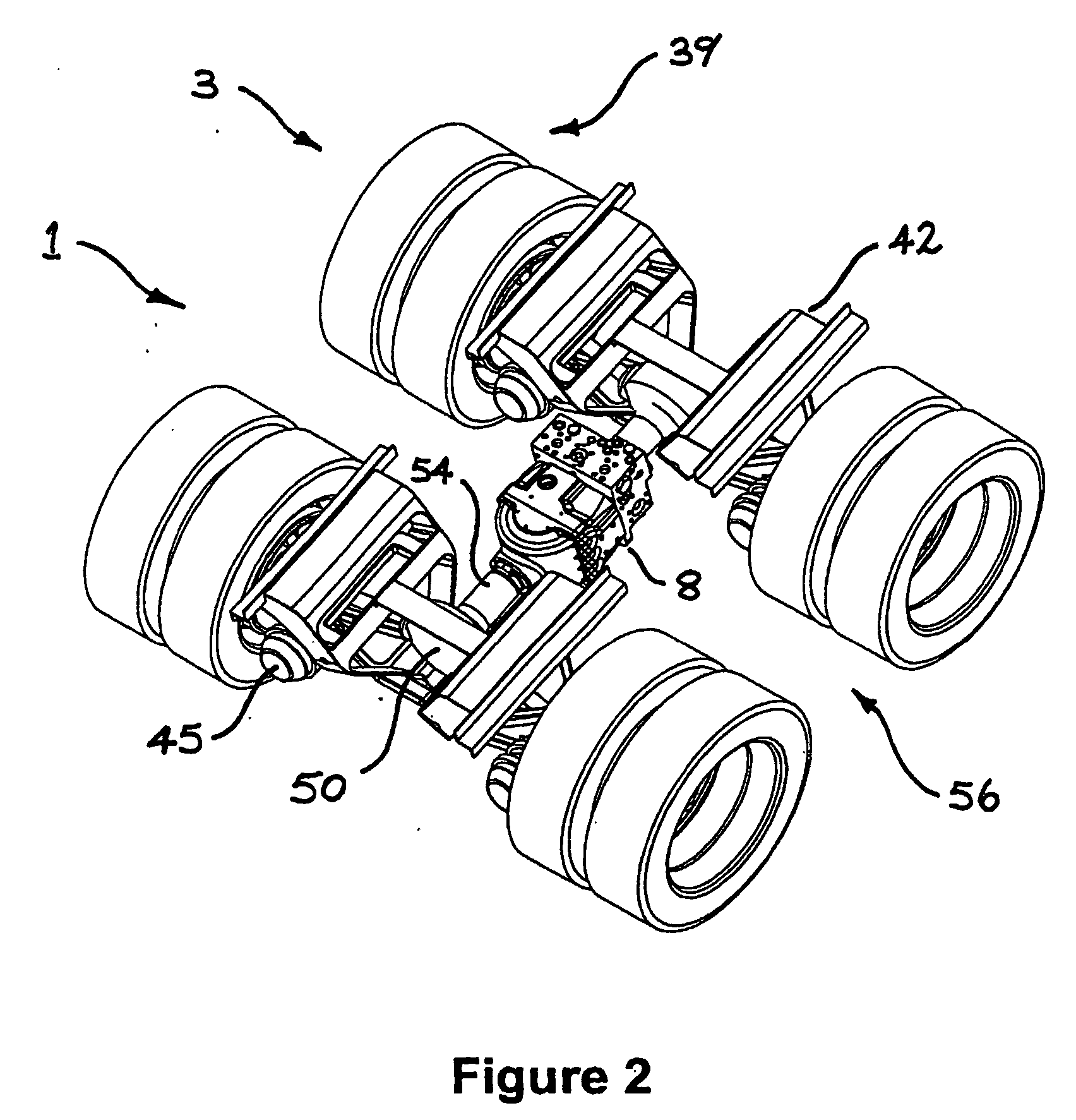
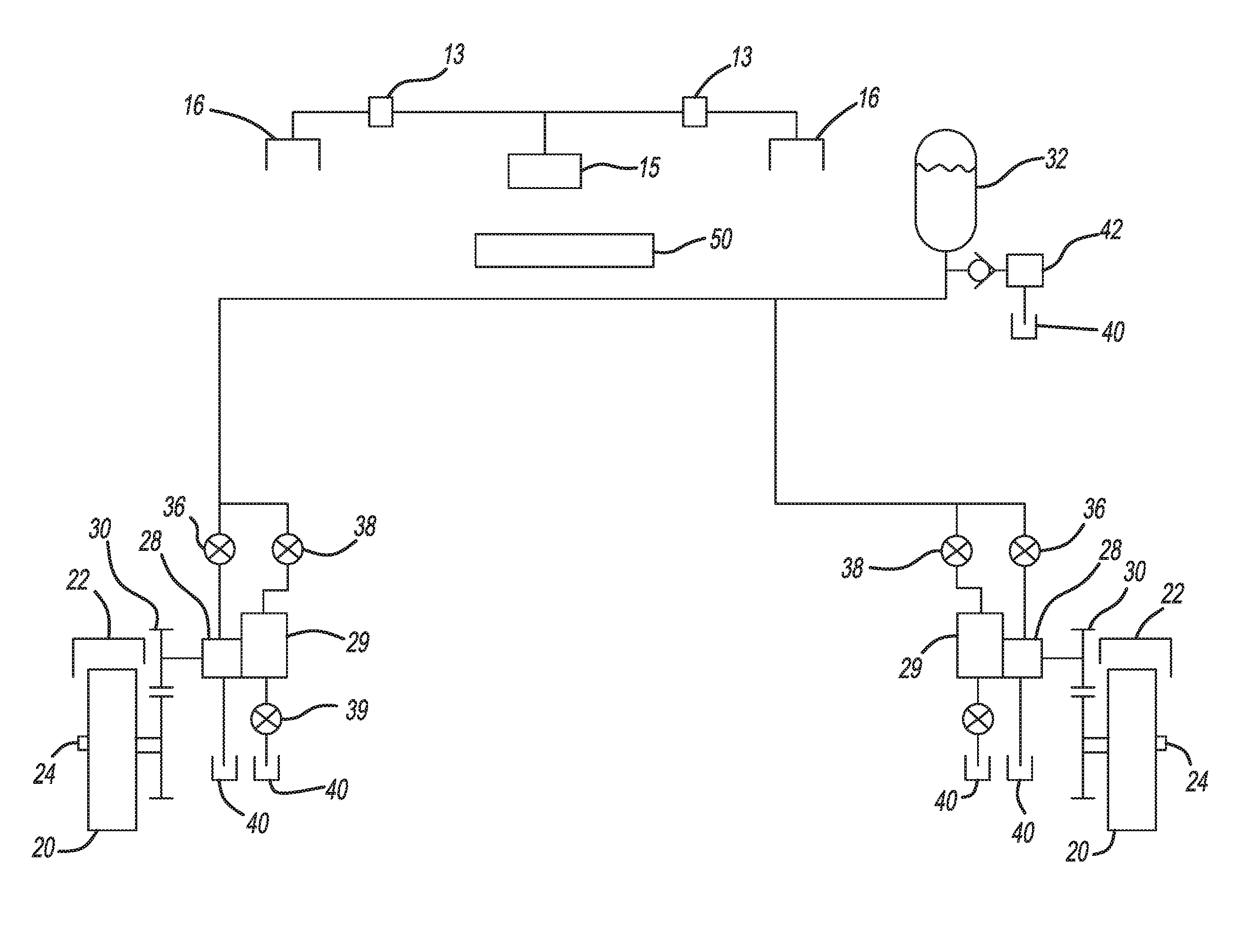
A traction control system is provided for a vehicle having wheels driven on a primary axle via an engine, and wheels on a secondary axle torsionally isolated from the engine. Wheel speed sensors and brakes are provided for each wheel. A motor / hydraulic pump is operatively associated with each secondary axle wheel for selectively powering the secondary axle wheel or being regenerativly powered by the secondary axle wheel for regenerative braking. A clutch is provided to connect each secondary axle wheel with the secondary axle wheel's motor / hydraulic pump. An accumulator is provided to hydraulically power the secondary axle wheels and to accept regenerative pressure from the secondary axle wheel's motor / hydraulic pump. A wheel valve is provided for each respective secondary axle wheel for selectively connecting the secondary axle wheel's motor / hydraulic pump with the accumulator. A controller is provided to control the primary axle and secondary axle wheels. The controller commands braking and powering of the primary and secondary axle wheels during low traction events.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
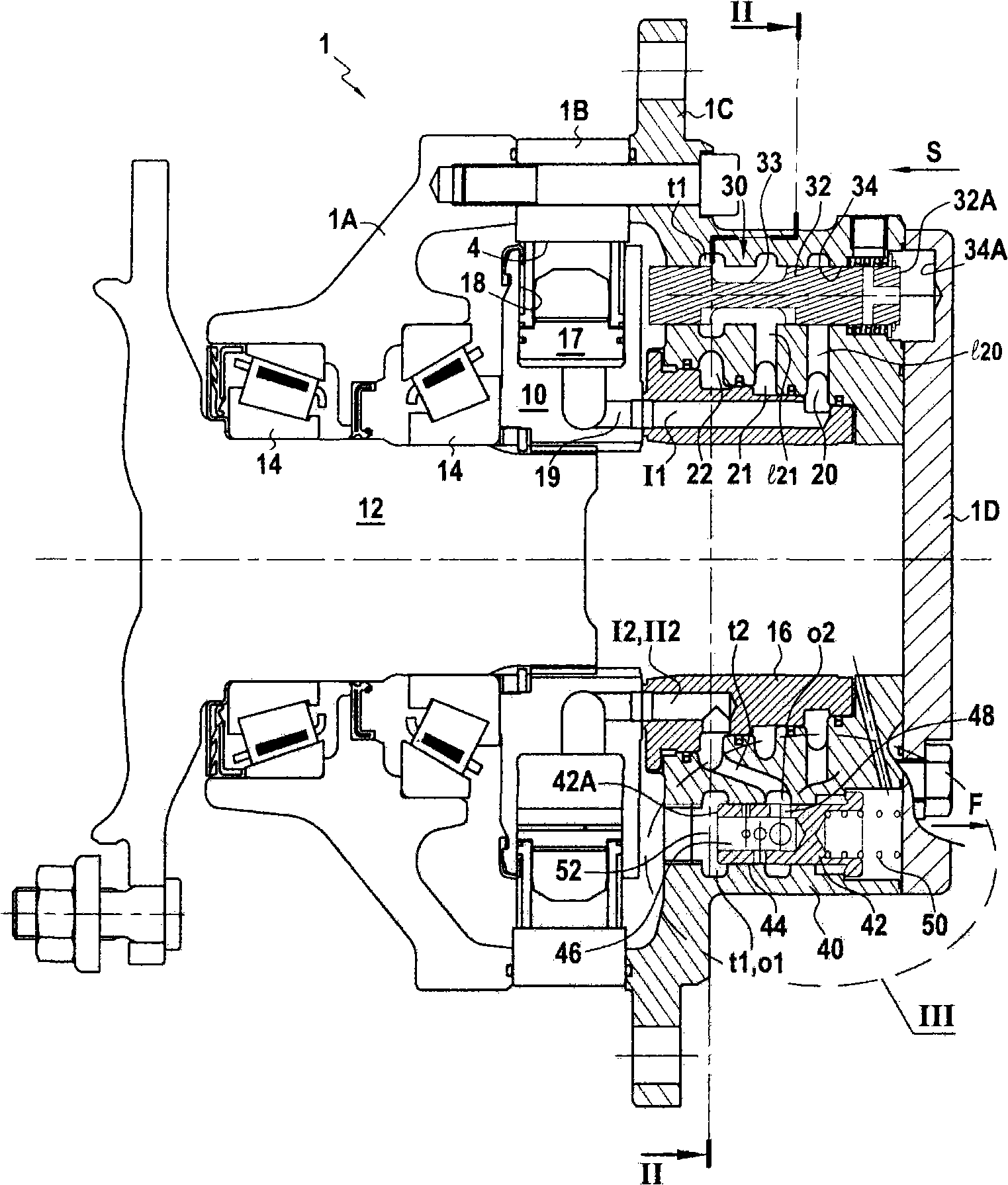
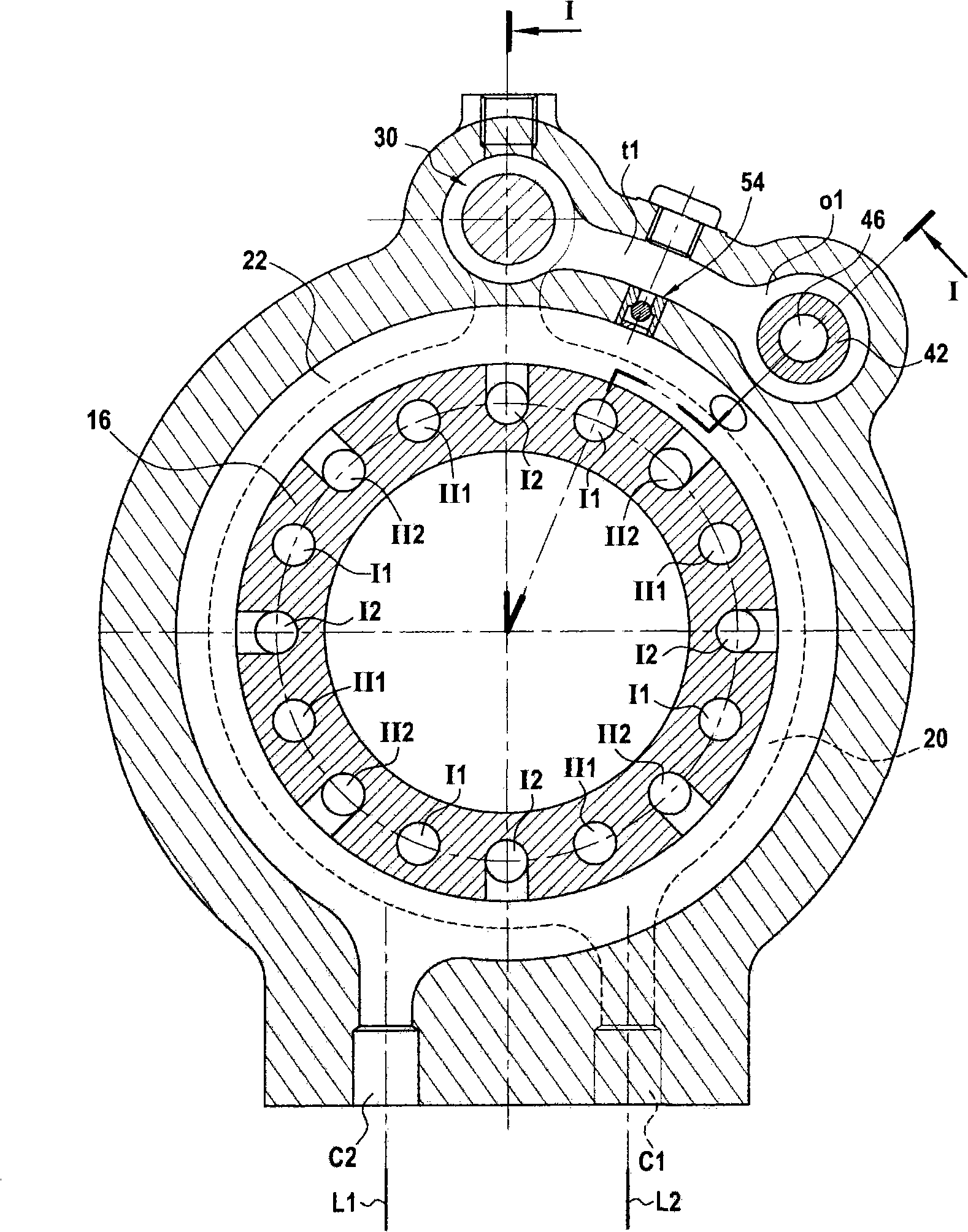
Device for managing the displacement of a hydraulic motor or a group of hydraulic motors
A motor having two series of distribution ducts each having two groups of ducts. The displacement selector (30) is able to occupy a large displacement position (i) in which the first groups of distribution ducts (I1 and II2) of the first series are connected to a main duct (L1) while the second groups (I2 and II2) are connected to the other main duct (L2), and a small displacement configuration (ii) in which the first group of distribution ducts (I1) of the first series is connected to a main duct, the second group of distribution ducts (I2) of the first series is connected to the other main duct and a bypass connection exists between the first and the second group of distribution ducts (II1 and II2) of the second series. The device has a restriction (42 and 48) in order, in the small displacement configuration, to restrict this bypass connection.
Owner:POCLAIN HYDRAULICS IND
Drive with an energy recovery function having a brake pressure control valve
InactiveCN101472775AAllows for variable throttlingLow level of complexityHydrostatic brakesBraking element arrangementsEnergy recoveryEngineering
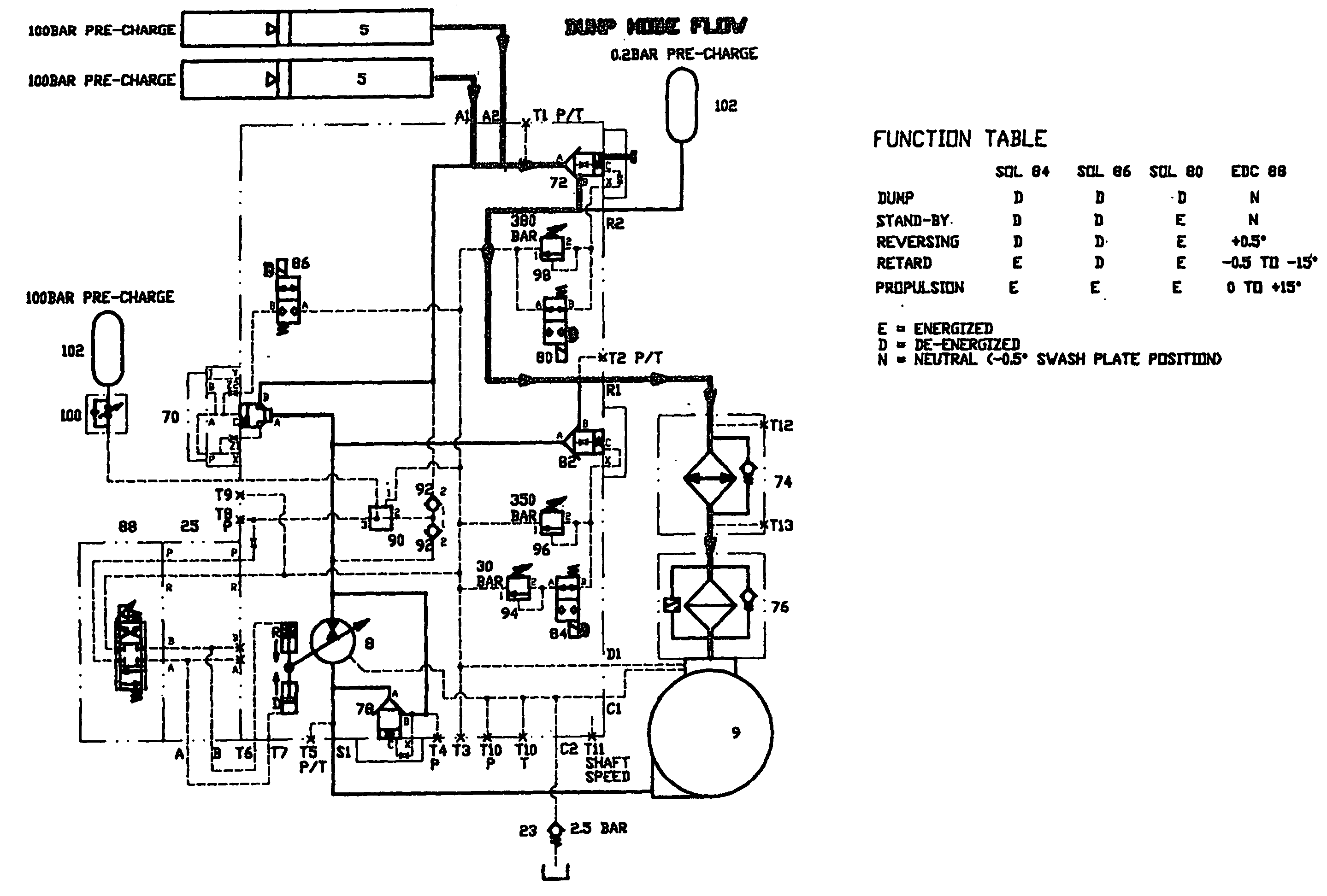
The invention relates to a drive (1) having an energy recovery function. The drive having an energy recovery function comprises a hydrostatic piston machine (9) and at least one storage element (13) which is connected to said hydrostatic piston machine. Said hydrostatic piston machine (9) and the at least one storage element (13) are connected together by means of a storage line. Said storage line is divided into a first storage line section (11) and into a second storage line section (12) by a throttle value unit (15). Said throttle valve unit (15) comprises a control pressure valve unit (16) and a built-in valve (17). The control pressure valve unit (16) produces a control pressure which acts upon the built-in valve (17).
Owner:HYDROMATIK GMBH
Hydraulic oil pump no-abrasion braking system
InactiveCN103129541AGuaranteed normal operationRailway hydrostatic brakesHydrostatic brakesMachine partsDrive shaft
The invention provides a hydraulic oil pump no-abrasion braking system. Currently, a conventional hydraulic oil pump is used for offering kinetic energy to other parts. The system enables the hydraulic oil pump to be not used as a kinetic energy source, but to be used for consuming the kinetic energy brought by inertia of vehicles; the hydraulic oil pump no-abrasion braking system is designed especially for solving the defects which exist on large, medium and small vehicles in the prior braking technology. Installing the no-abrasion braking system on an automobile can guarantee the safety of the automobile at the uttermost, for the vehicles which need frequently braking, braking failure caused by flushing and heating of a brake drum or a tray is avoided. When a valve of the oil pump is thoroughly closed, oil resistance inside the oil pump is converted into mechanical energy. Tyres are prevented from rotating through a gearbox, a transmission shaft, a rear axle and a haft shaft so that the vehicles can quickly stop, and meantime, abrasion of the braking drum and other machine parts is reduced at a large extent.
Owner:陈惠贤
Control system and method for braking a hydrostatic drive machine
ActiveUS8261544B2Reduce displacementIncrease displacementHydrostatic brakesRotary clutchesControl systemMaximum displacement
A method of braking a hydrostatic drive machine includes steps of reducing a displacement of a pump of a hydrostatic drive system to a non-zero displacement, and increasing a displacement of a motor of the hydrostatic drive system to a displacement that is less than a maximum displacement. The method also includes a step of accelerating an engine of the hydrostatic drive system toward a desired engine speed range.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Hydrostatic pump destroke braking mechanism
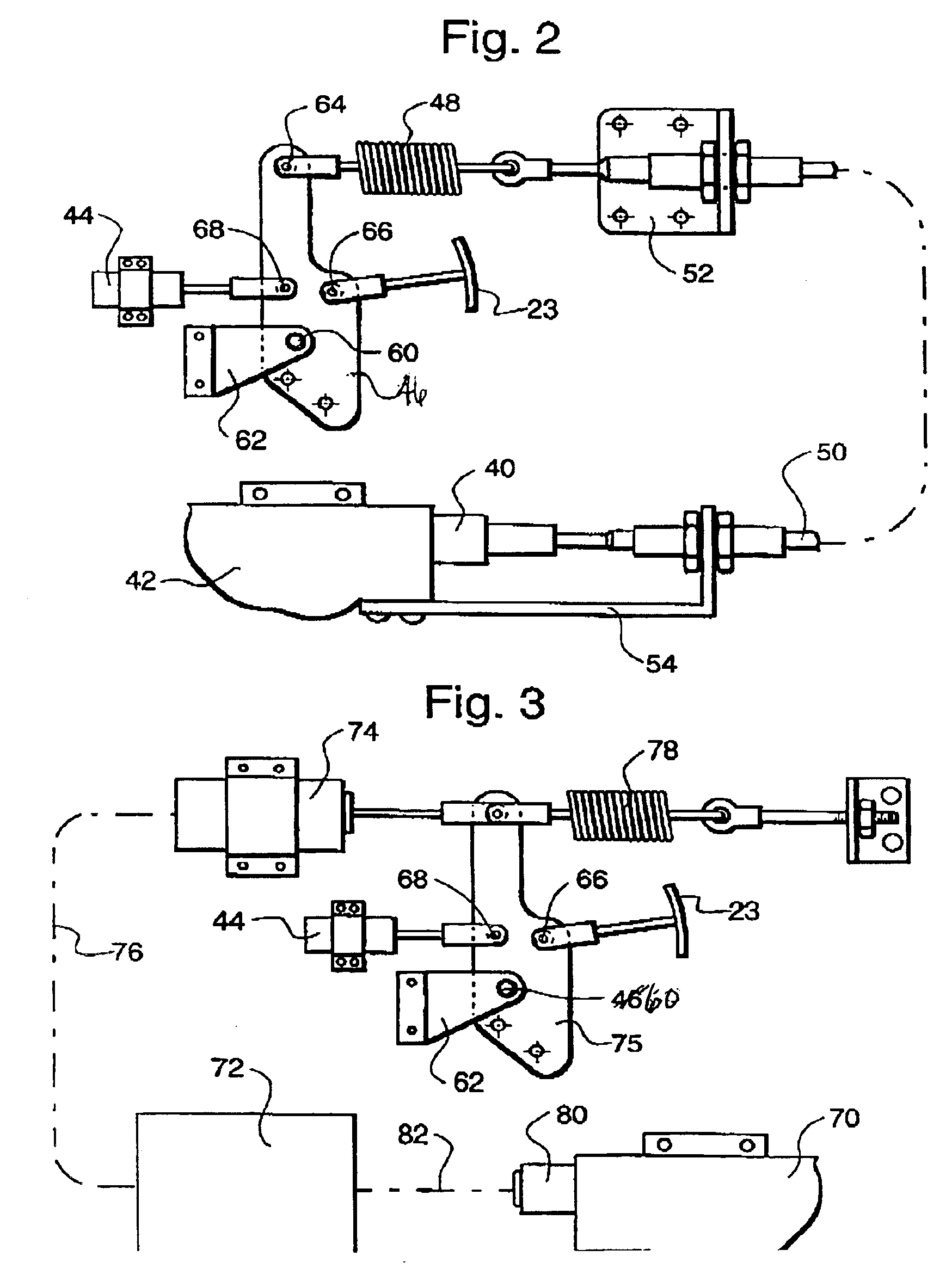
InactiveUS7077221B2Effectively slowEffectively stopAuxillary drivesHydrostatic brakesEngineeringServomechanism
A mechanism that interconnects the service brakes of a hydrostatically driven tractor with the hydrostatic pump to more effectively slow or stop the tractor, for example when towing a trailer. The service brakes are connected to a control servo on the hydrostatic pump such that actuation of the service brakes will destroke the pump, eliminating or reducing the torque of the pump as a factor to be overcome in slowing or stopping movement of the tractor. Both mechanical and electronic versions of the mechanism are effective in slowing and stopping the tractor.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com