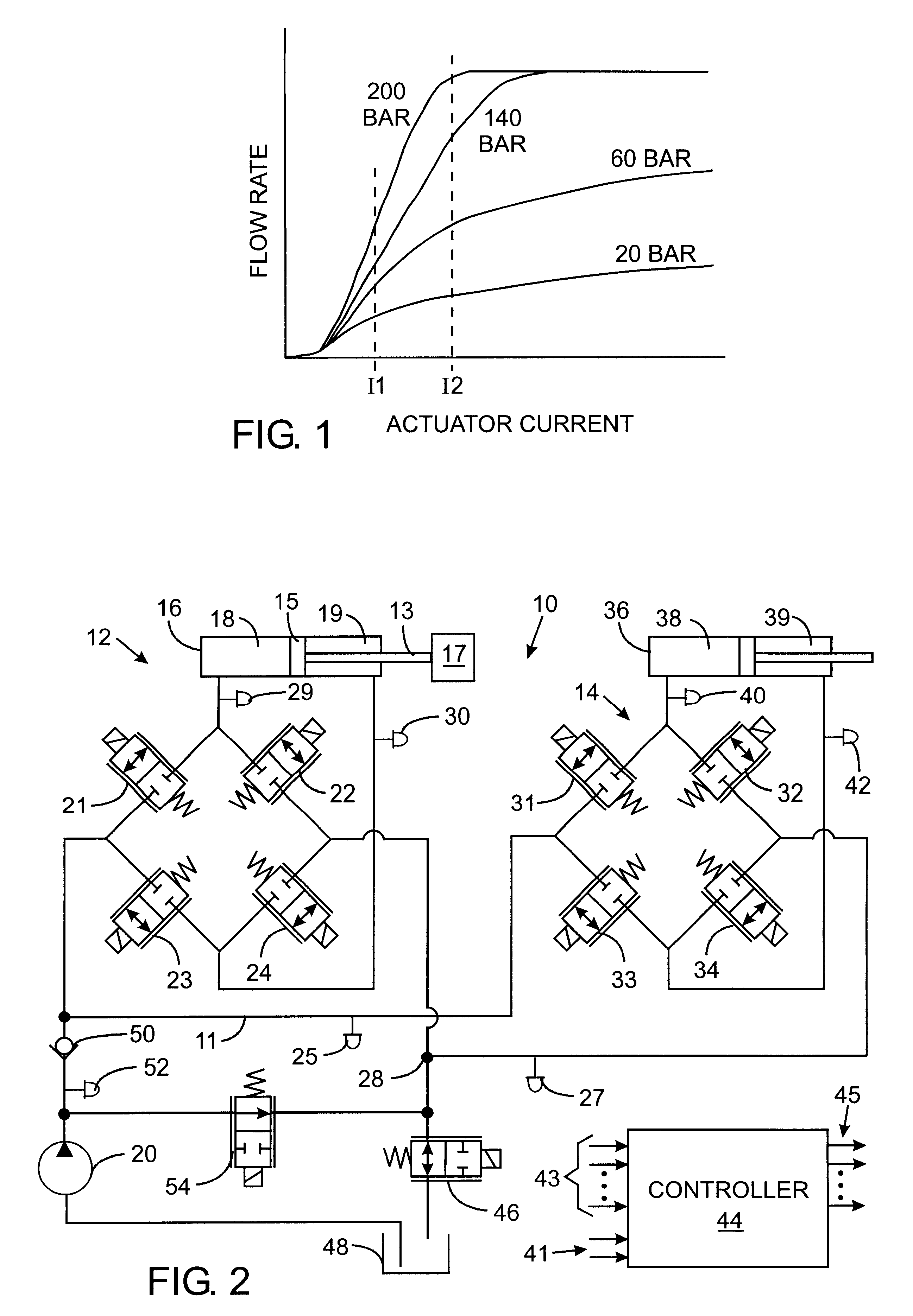
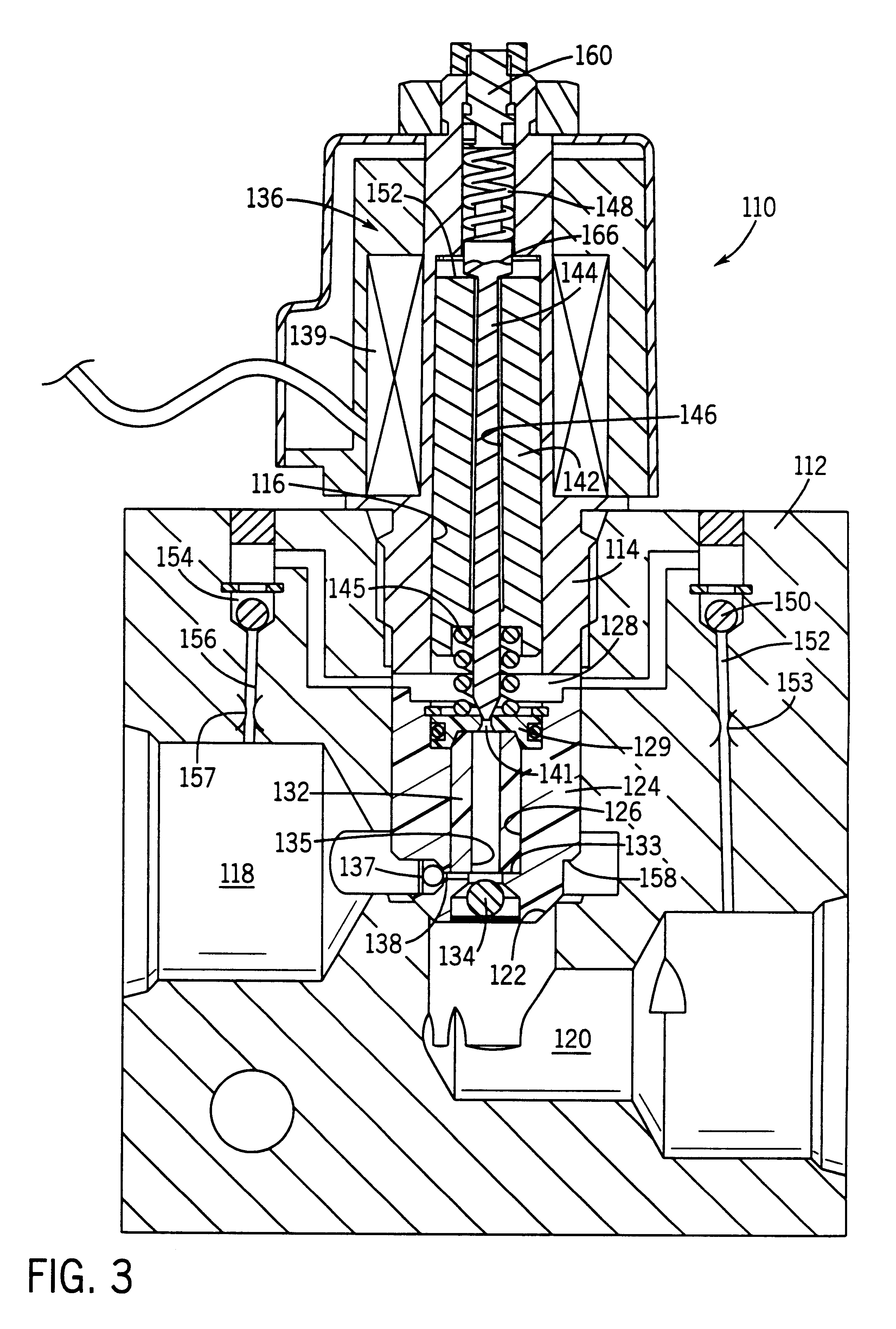
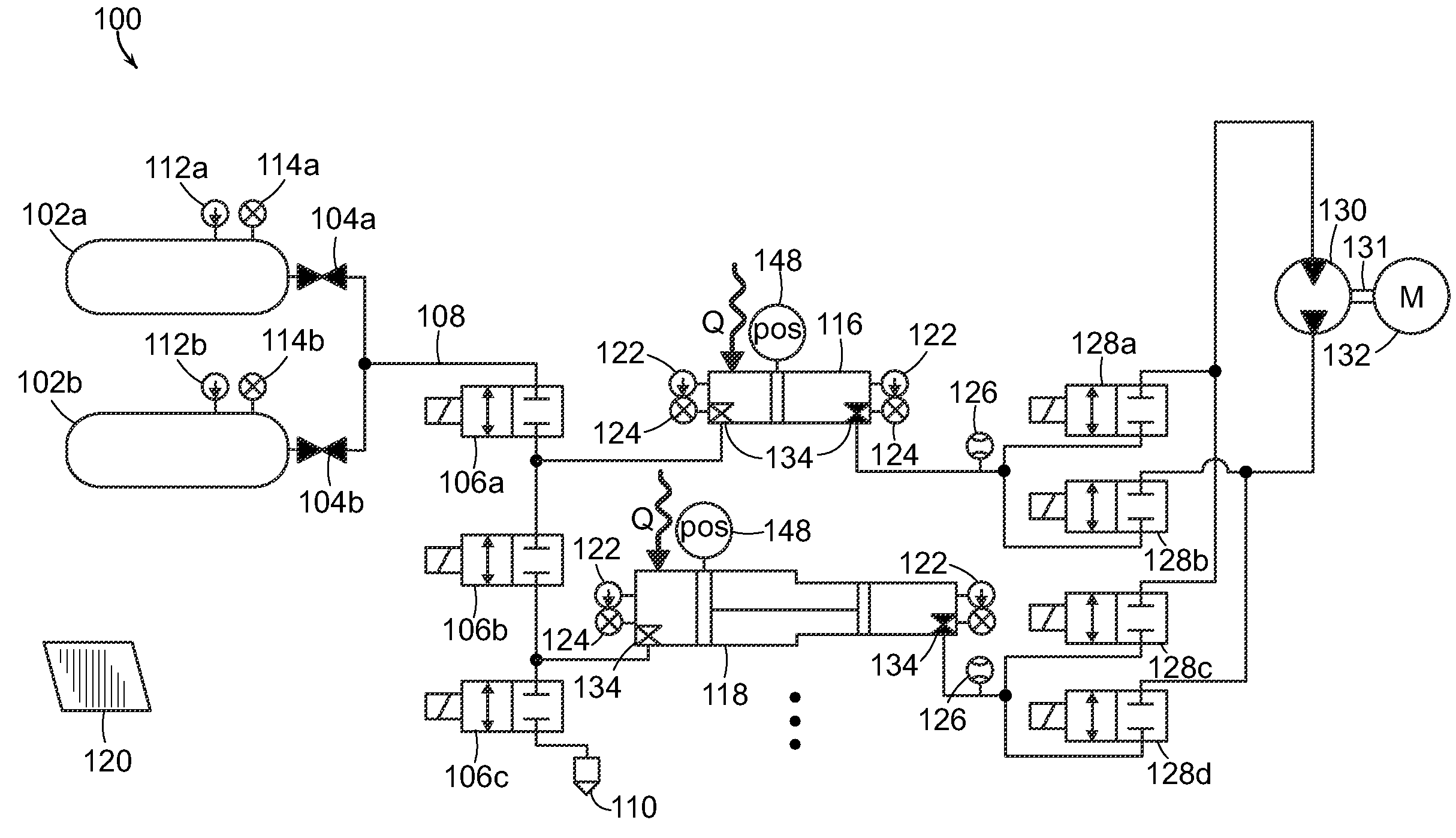
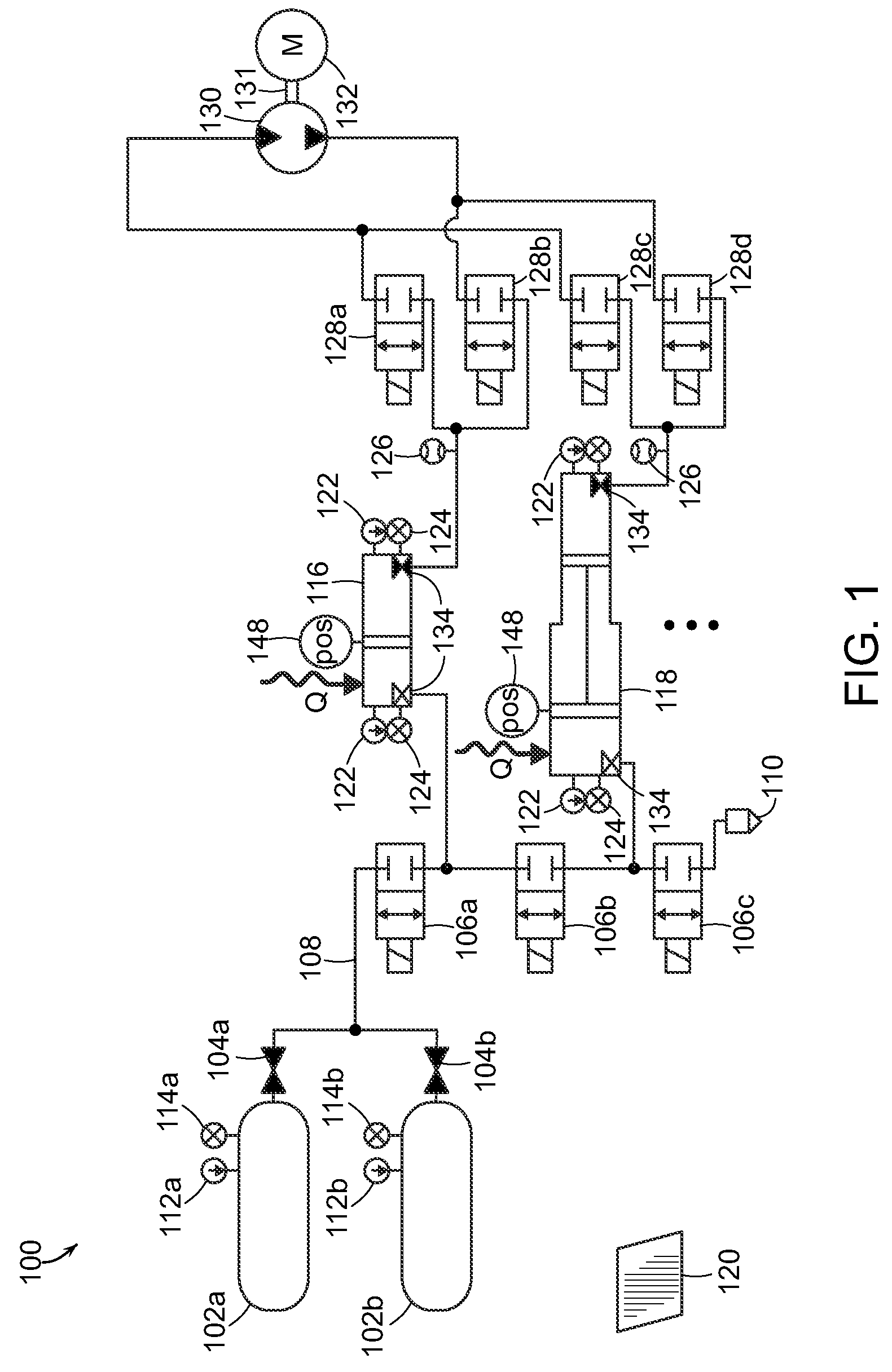
Patents
Literature
8223results about "Servometer circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
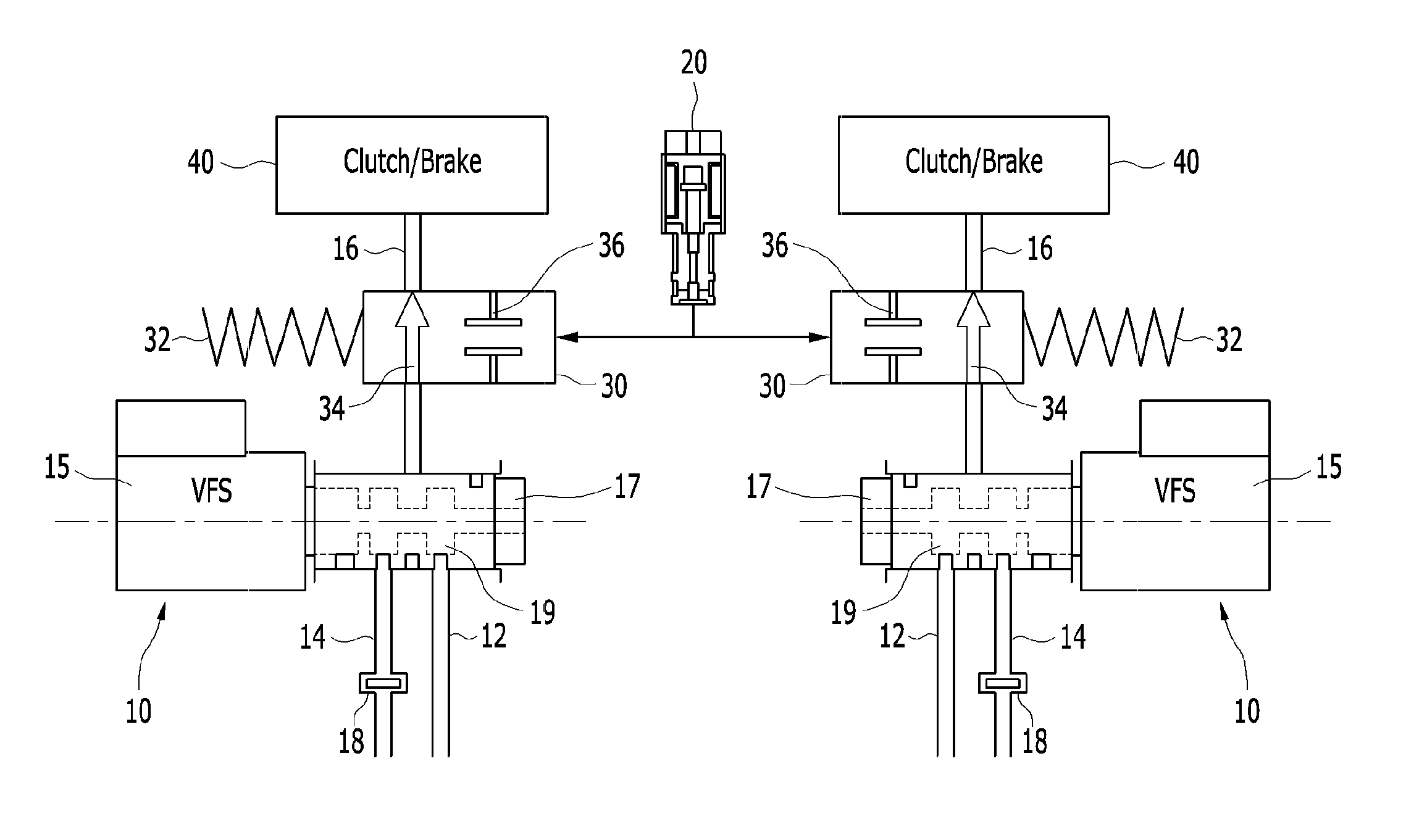
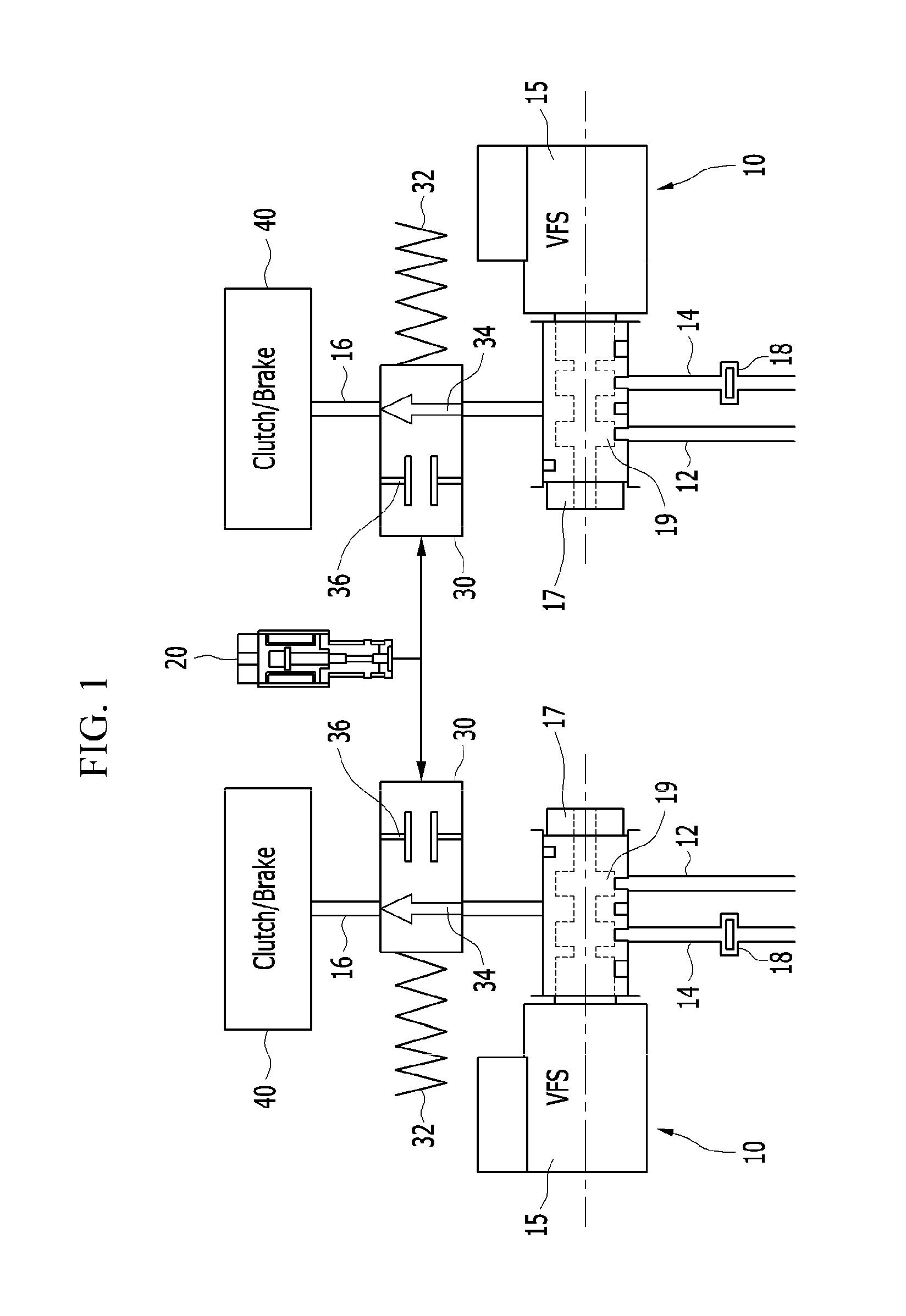
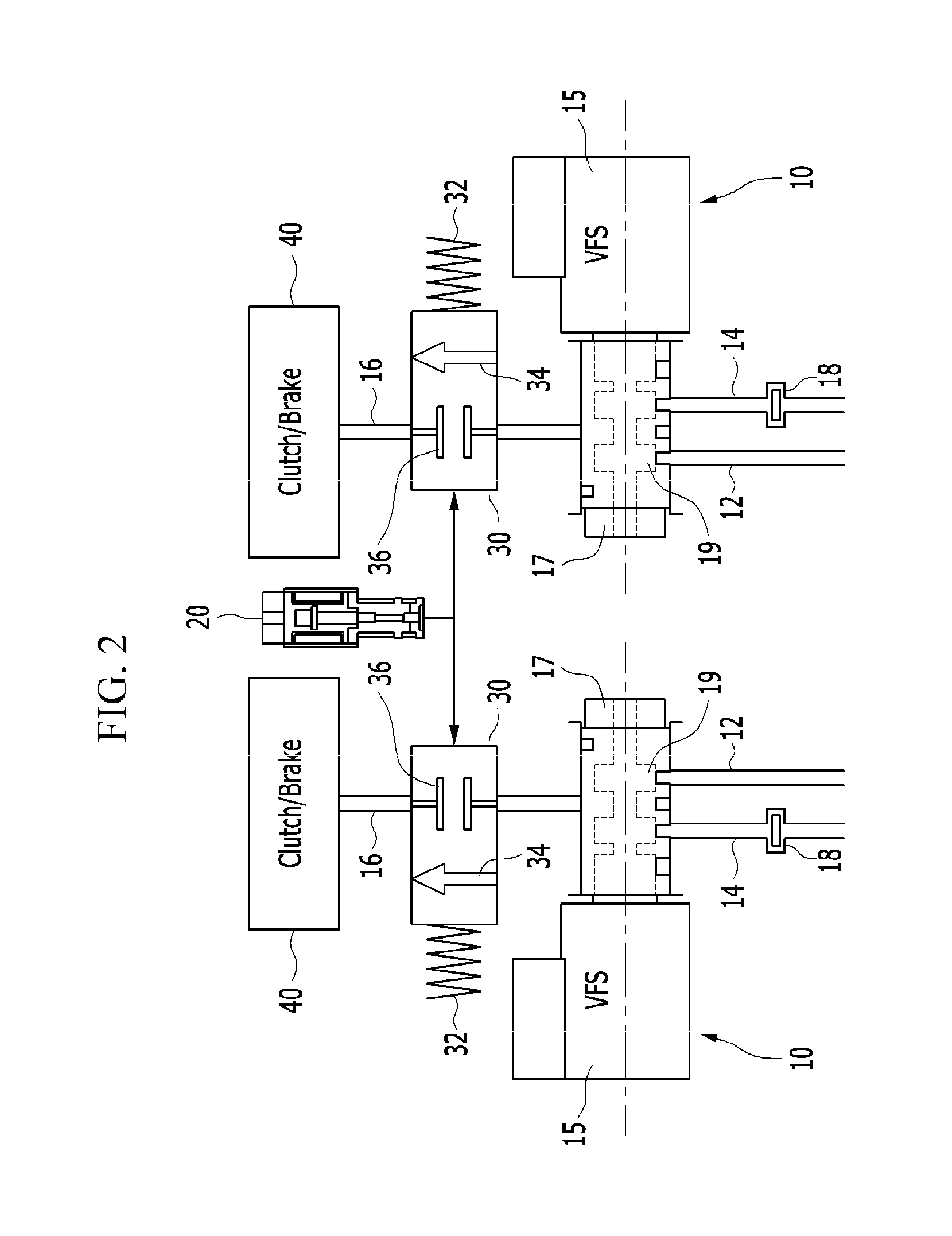
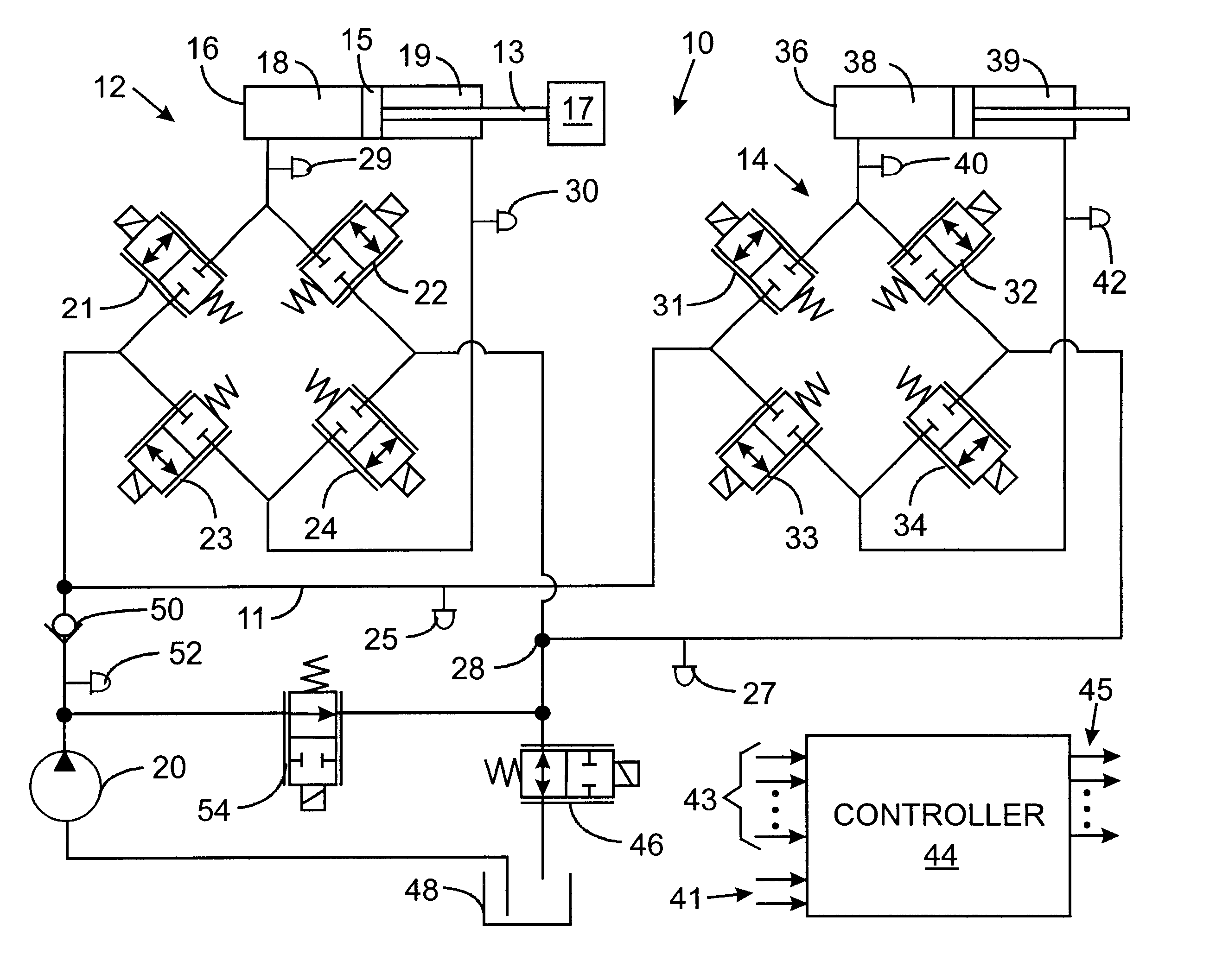
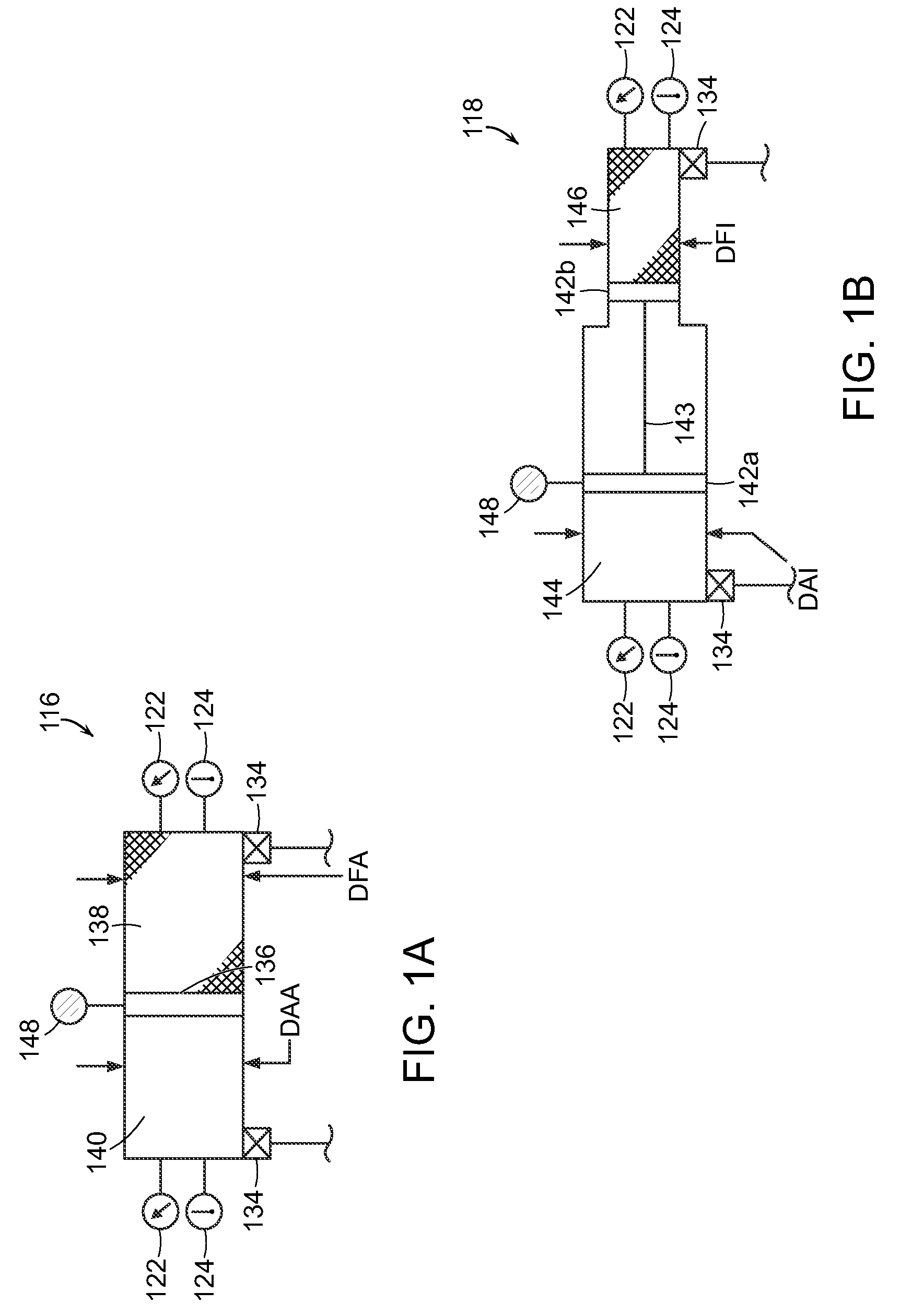
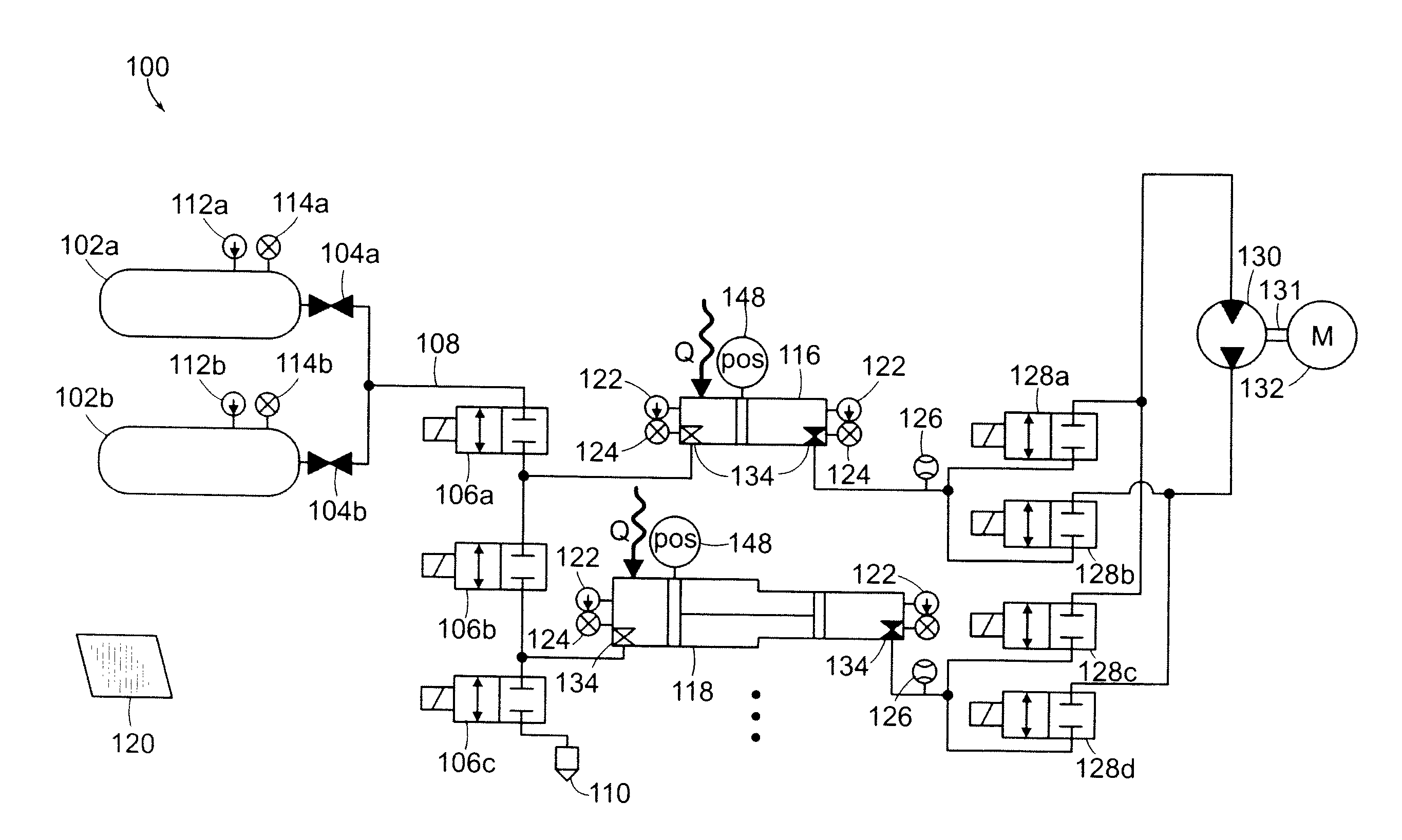
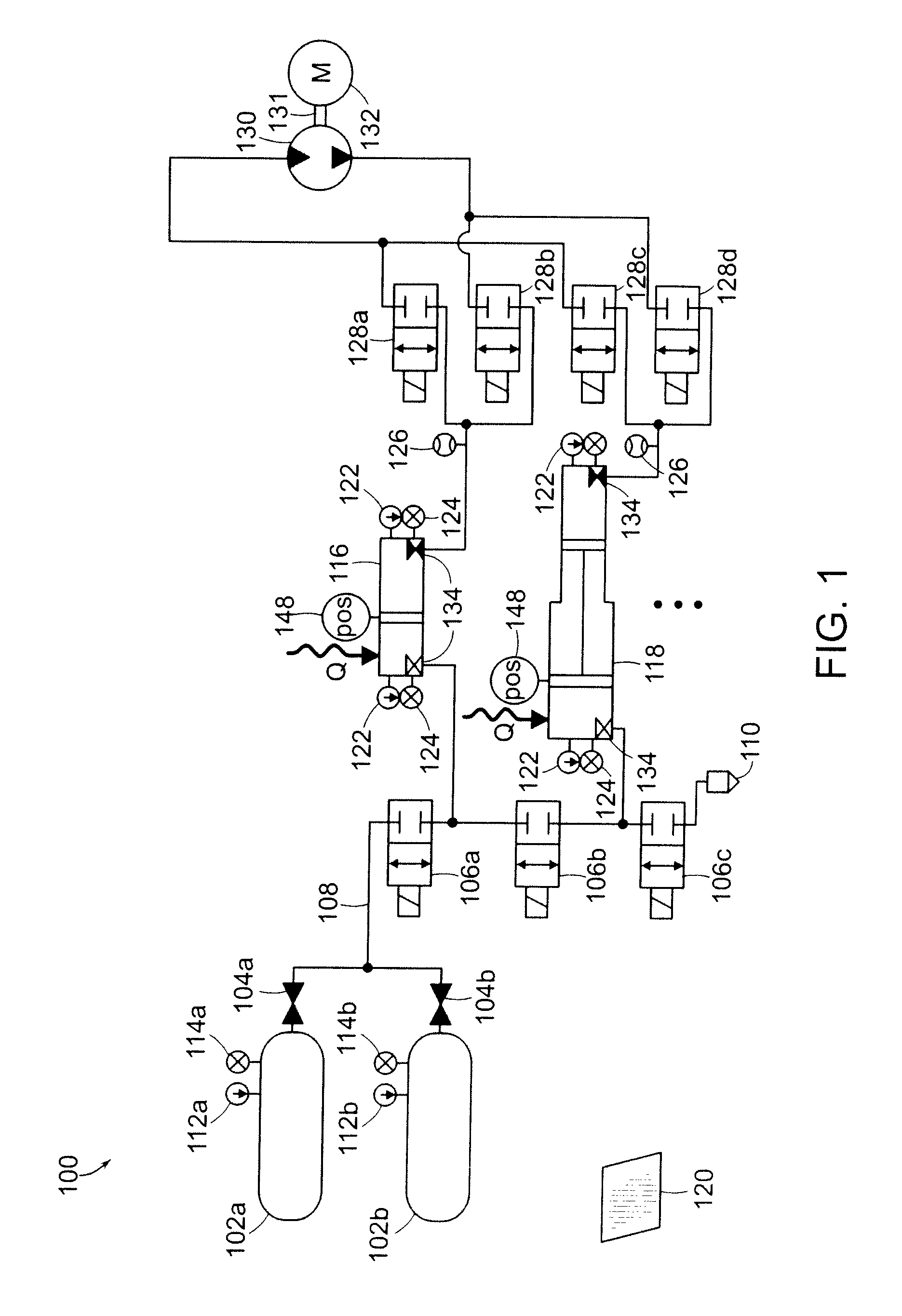
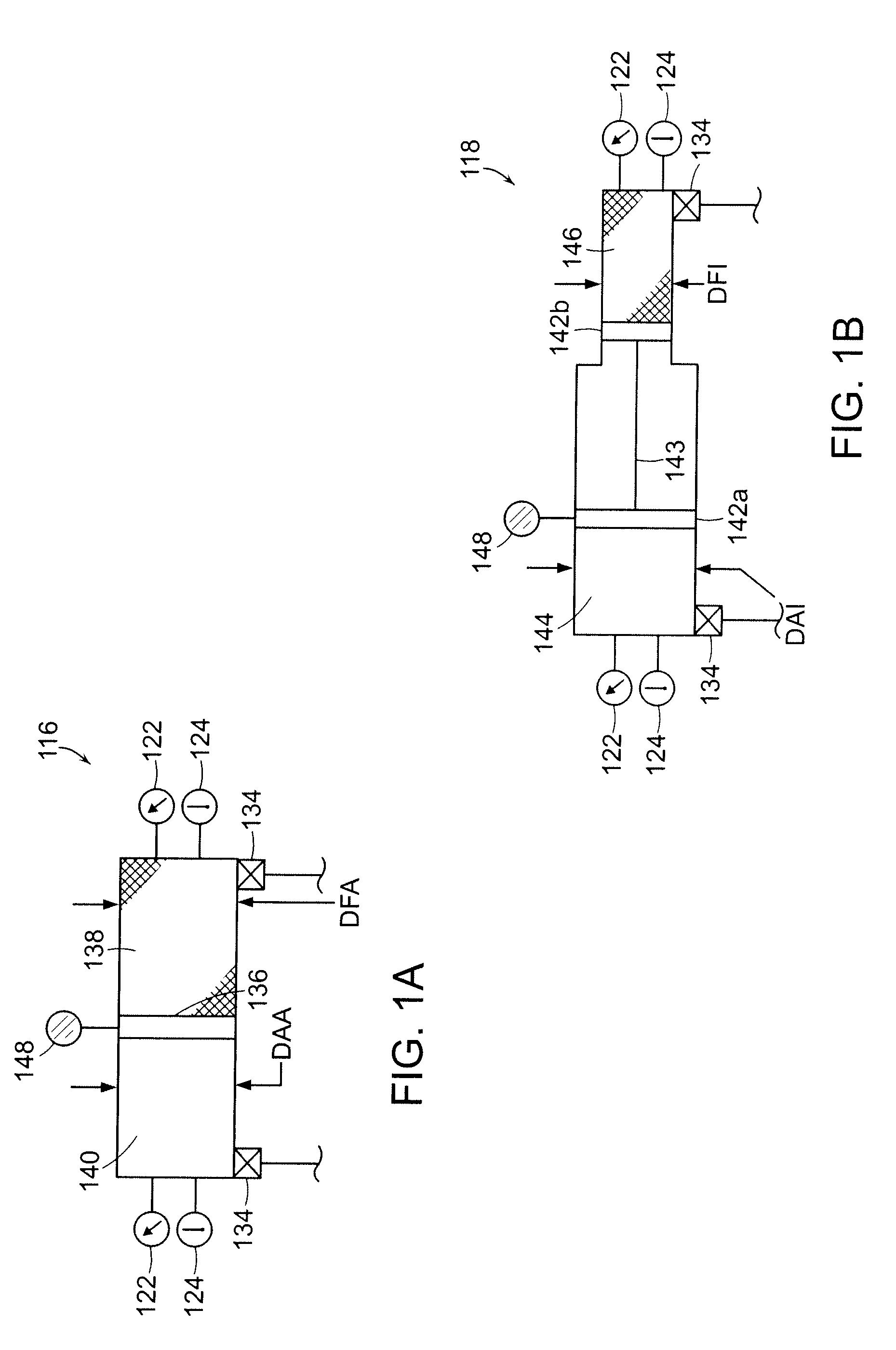
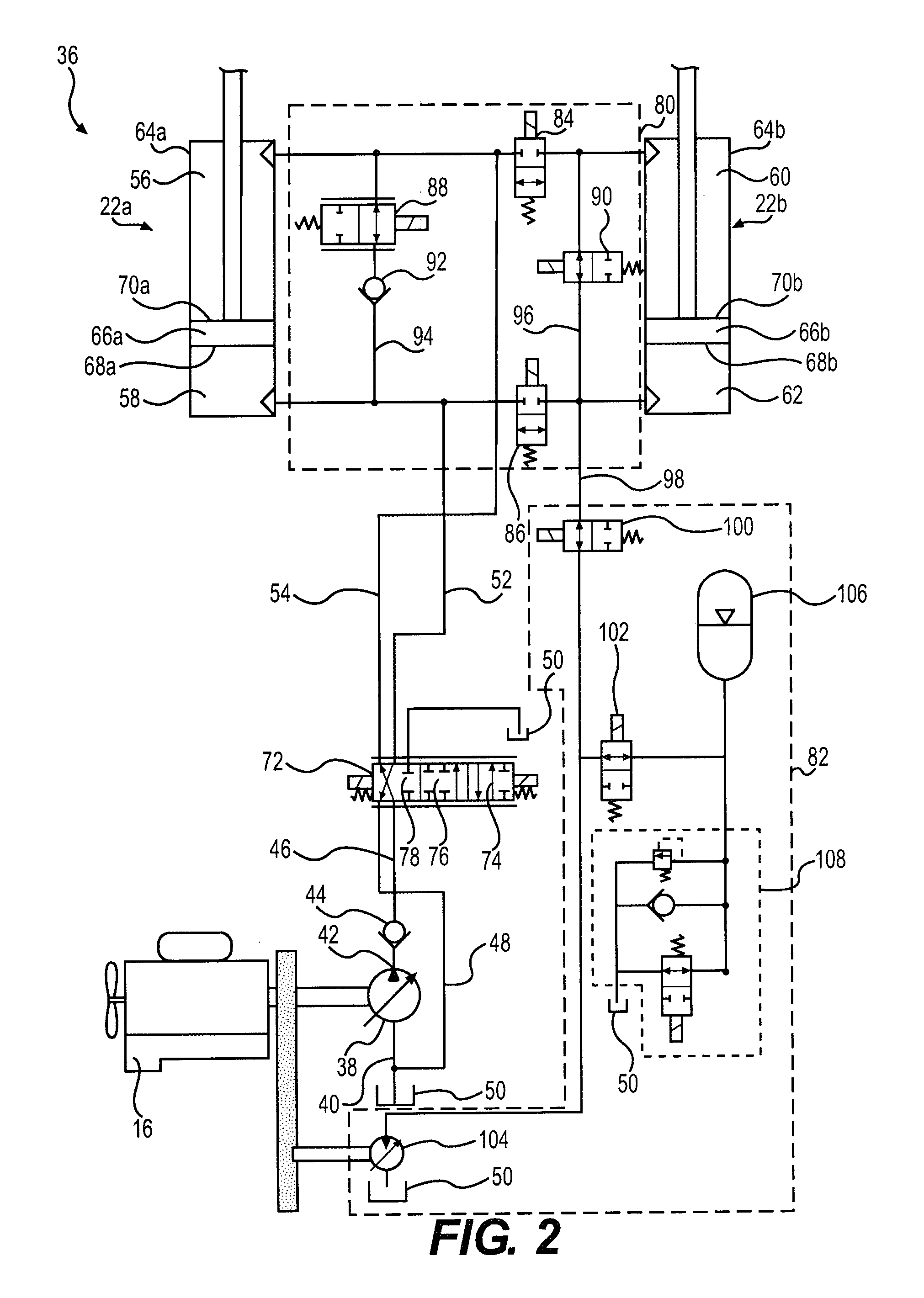
Hydraulic circuit for automatic transmission
ActiveUS9488197B2Rapidly and effectively removing foreign materialFluid-pressure actuator safetyClutchesProportional controlAutomatic transmission
A hydraulic circuit may include a proportional control solenoid valve controlling hydraulic pressure such that an operating hydraulic pressure required by the friction member is supplied to the friction member; a supply hydraulic path connecting the proportional control solenoid valve with the friction member, and adapted to supply hydraulic pressure controlled by the proportional control solenoid valve to the friction member; and a switch valve disposed in the supply hydraulic path so as to selectively open / close the supply hydraulic path.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
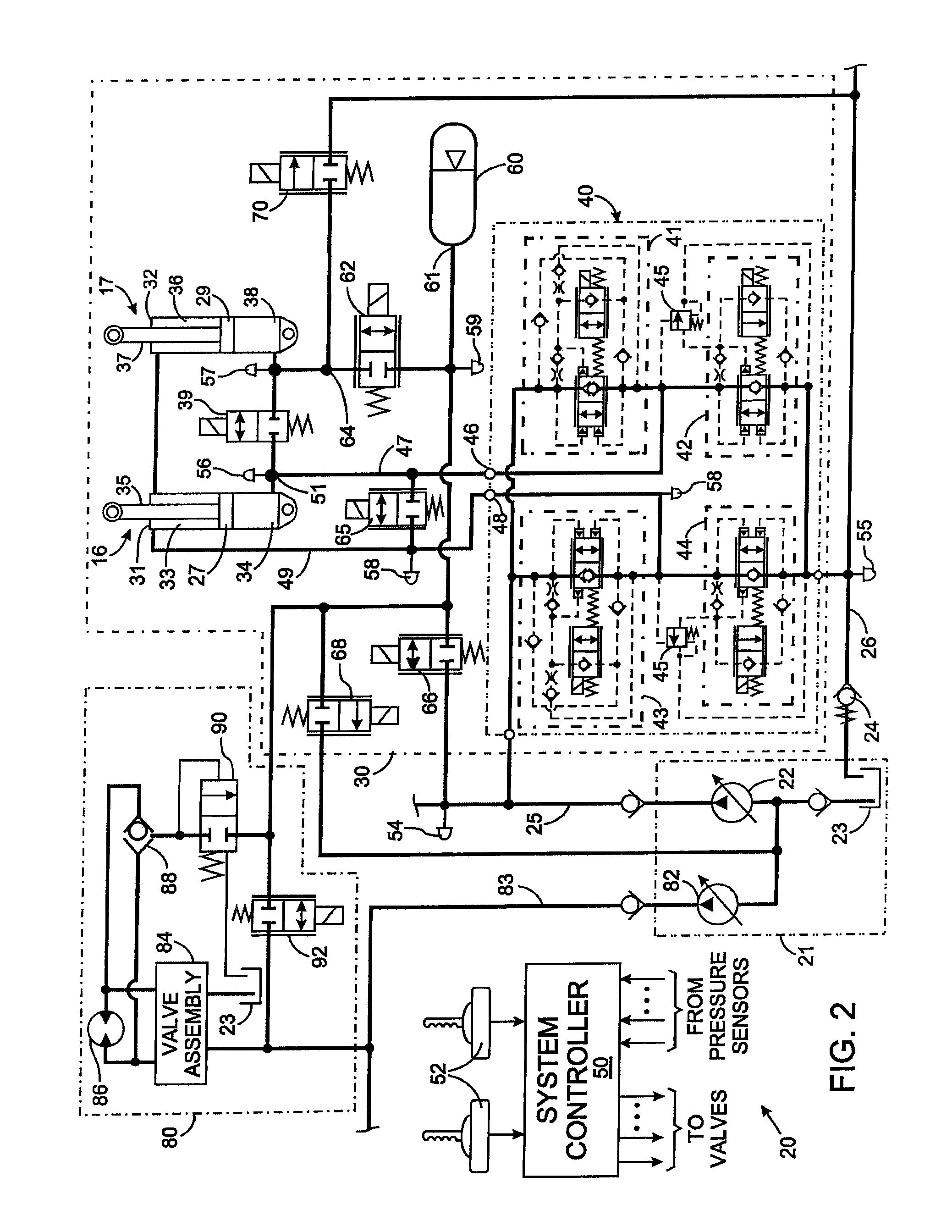
Hydraulic circuit with a return line metering valve and method of operation
A hydraulic system controls the flow of fluid to and from several functions on a machine. Each function has a valve assembly through which fluid is supplied under pressure from a source to an actuator and through which fluid returns from the actuator to a shared return line connected by a return line metering valve to the system tank. There are several regeneration modes of operation in which fluid exhausted from one port is supplied into the other port of the same actuator, which eliminates or reduces the amount of hydraulic fluid that must be supplied from the source. In some regeneration modes, input fluid for an actuator is obtained from another hydraulic function via the shared return line. In these regeneration modes an electronic controller operates the return line metering valve to restrict fluid from flowing into the tank from the shared return line, so that the fluid will be available to be supplied into an actuator port.
Owner:HUSCO INT INC
Systems and methods for energy storage and recovery using compressed gas
InactiveUS7832207B2Increase energy densityExpand/compress the gas more evenlyFluid couplingsAccumulator installationsEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention relates to methods and systems for the storage and recovery of energy using open-air hydraulic-pneumatic accumulator and intensifier arrangements that combine at least one accumulator and at least one intensifier in communication with a high-pressure gas storage reservoir on a gas-side of the circuits and a combination fluid motor / pump, coupled to a combination electric generator / motor on the fluid side of the circuits.
Owner:SUSTAINX
Systems and Methods for Energy Storage and Recovery Using Rapid Isothermal Gas Expansion and Compression
InactiveUS20100089063A1Increase energy densityHigh outputElectrical storage systemInternal combustion piston enginesProduct gasEngineering
The invention relates to systems and methods for rapidly and isothermally expanding and compressing gas in energy storage and recovery systems that use open-air hydraulic-pneumatic cylinder assemblies, such as an accumulator and an intensifier in communication with a high-pressure gas storage reservoir on a gas-side of the circuits and a combination fluid motor / pump, coupled to a combination electric generator / motor on the fluid side of the circuits. The systems use heat transfer subsystems in communication with at least one of the cylinder assemblies or reservoir to thermally condition the gas being expanded or compressed.
Owner:SUSTAINX
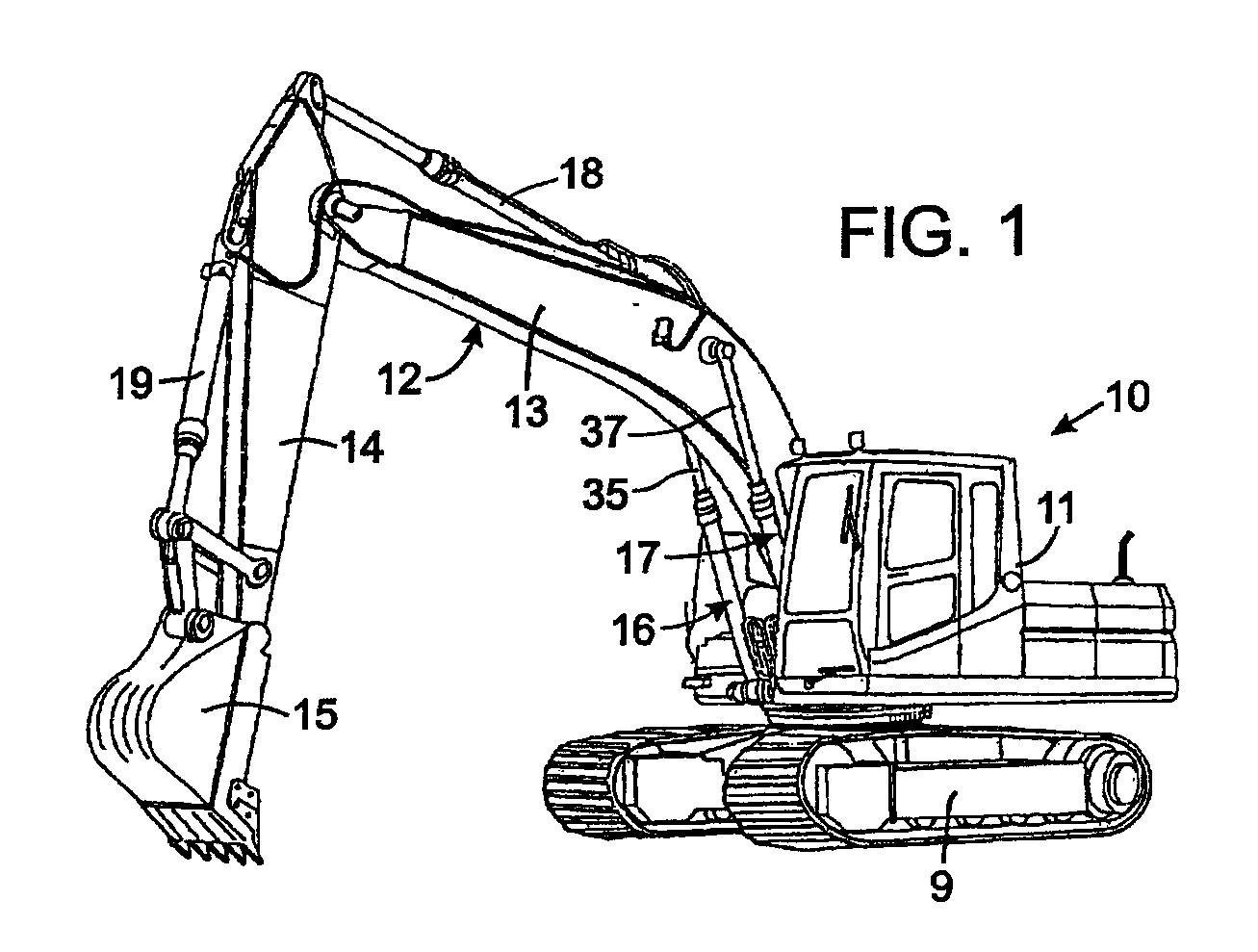
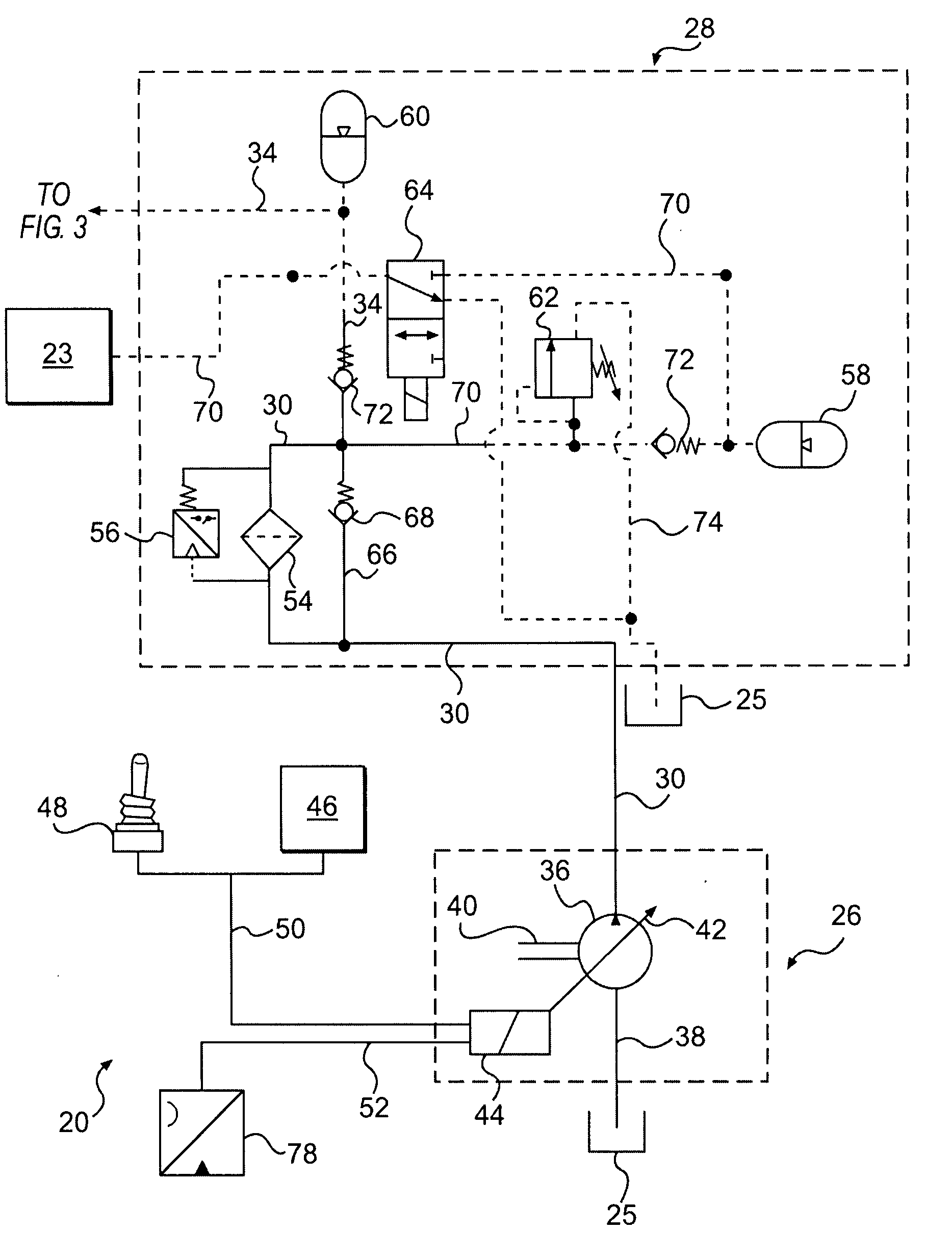
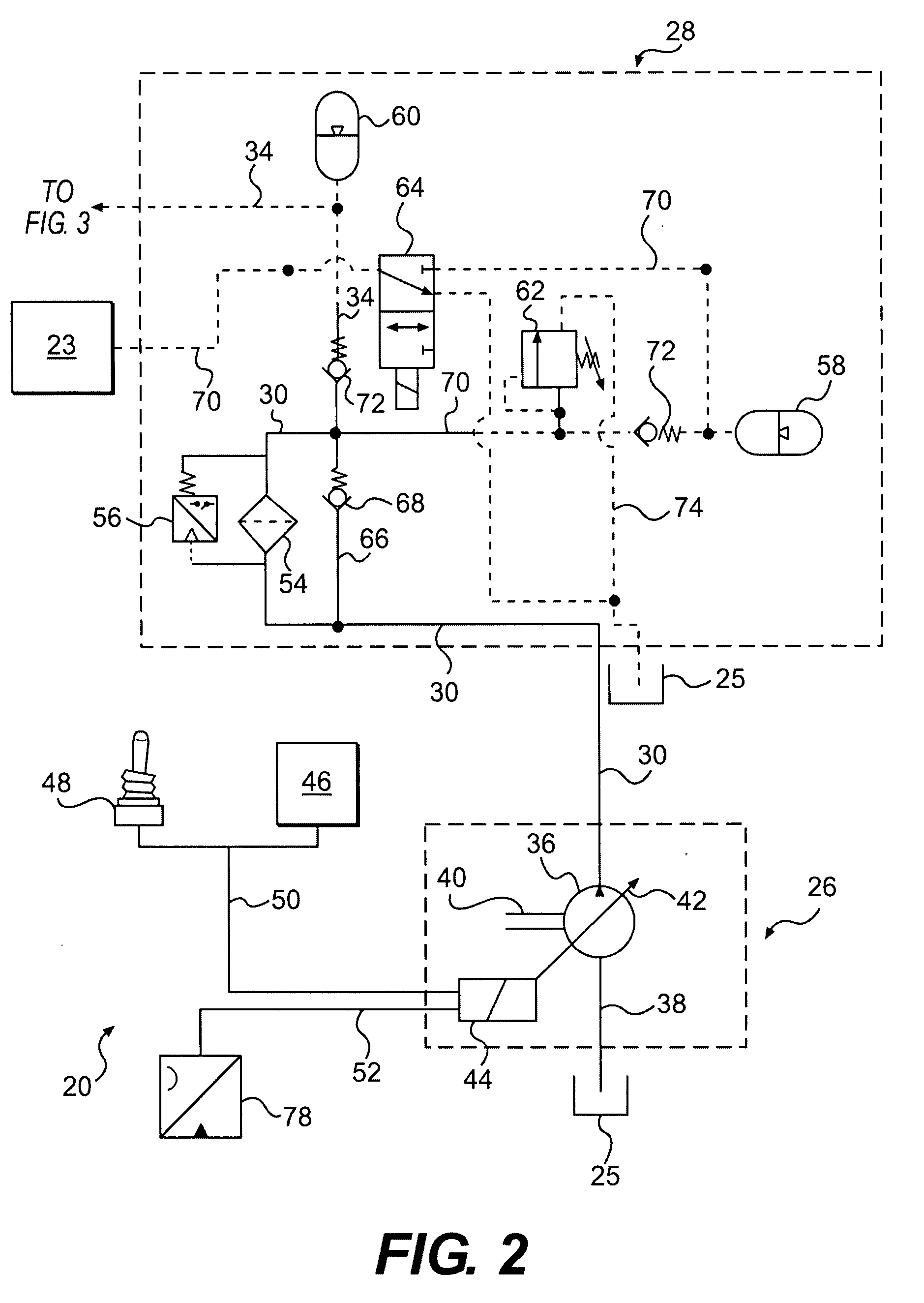
Flow management system for hydraulic work machine
A flow management system capable of providing adjustable hydraulic fluid flow or pressure at a common line to supply bidirectional pumps in electro-hydrostatic actuation systems and conditioning re-circulated hydraulic fluid. The system enables flow sharing between multiple actuation systems and minimization of energy consumption by a power-on-demand approach and / or electrical energy regeneration while eliminating the need for an accumulator. The system has particular application to electro-hydrostatic actuation systems that typically include bi-directional electric motor driven pumps and unbalanced hydraulic actuators connected within closed circuits to provide work output against external loads and reversely recover energy from externally applied loads.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
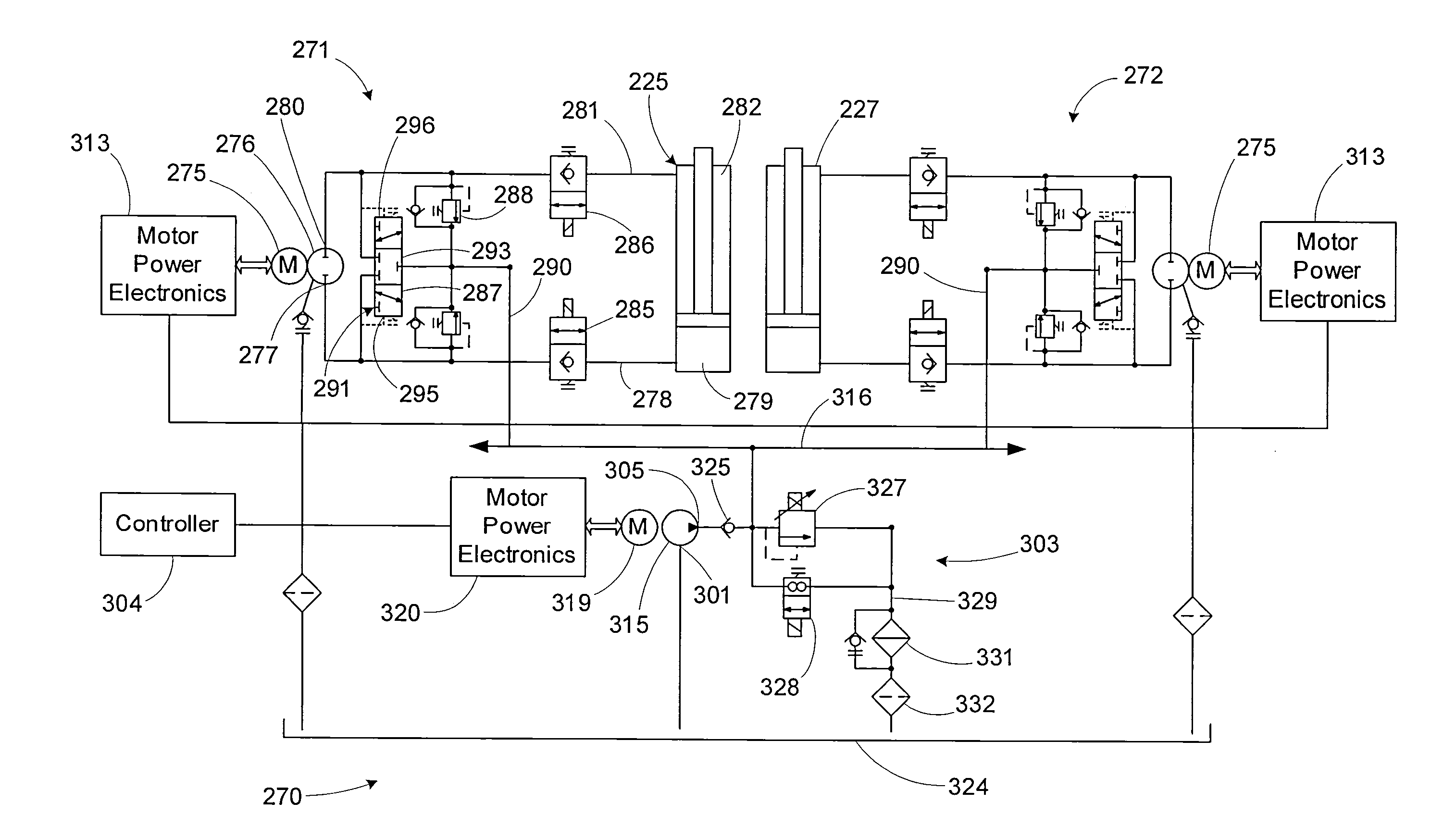
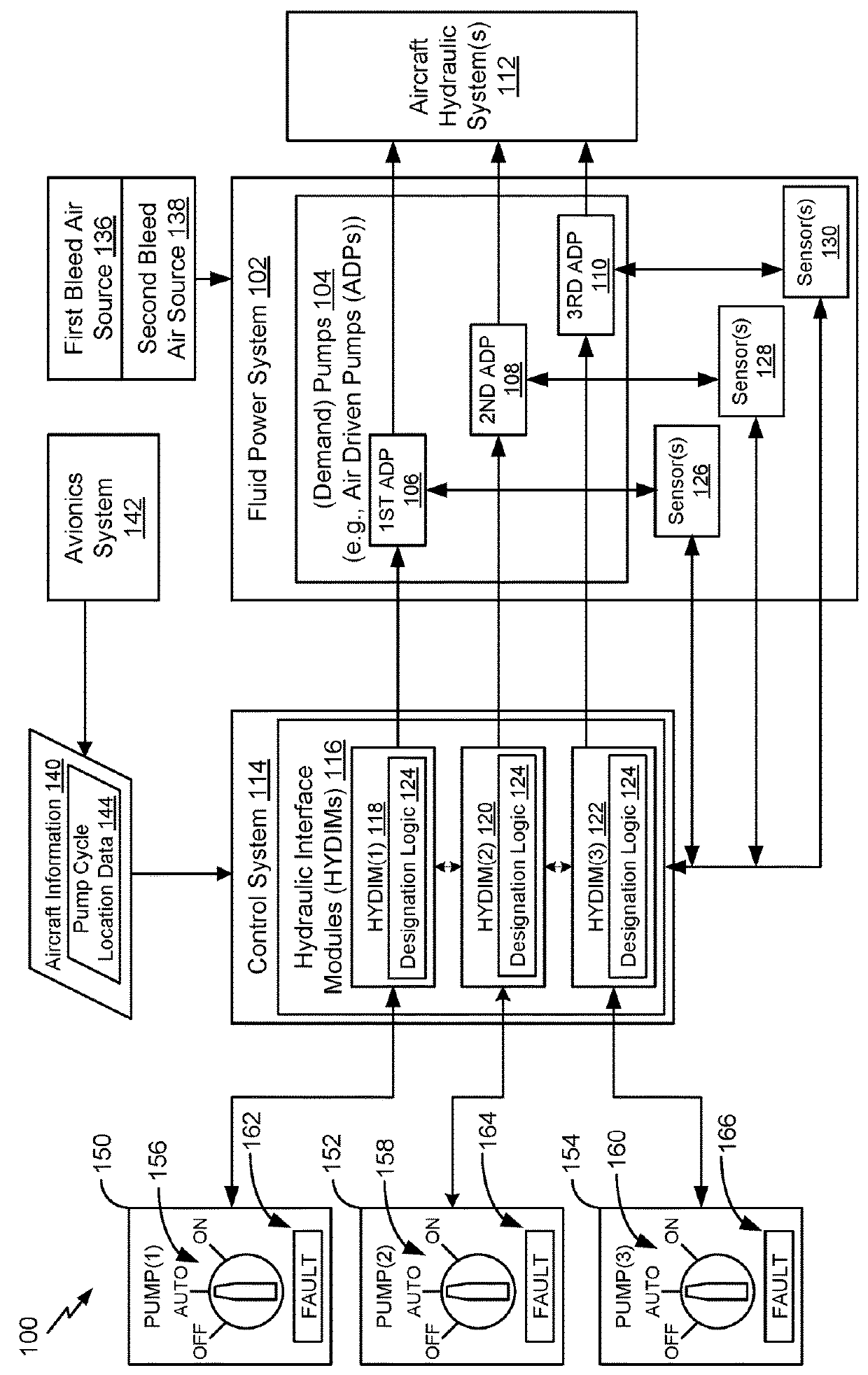
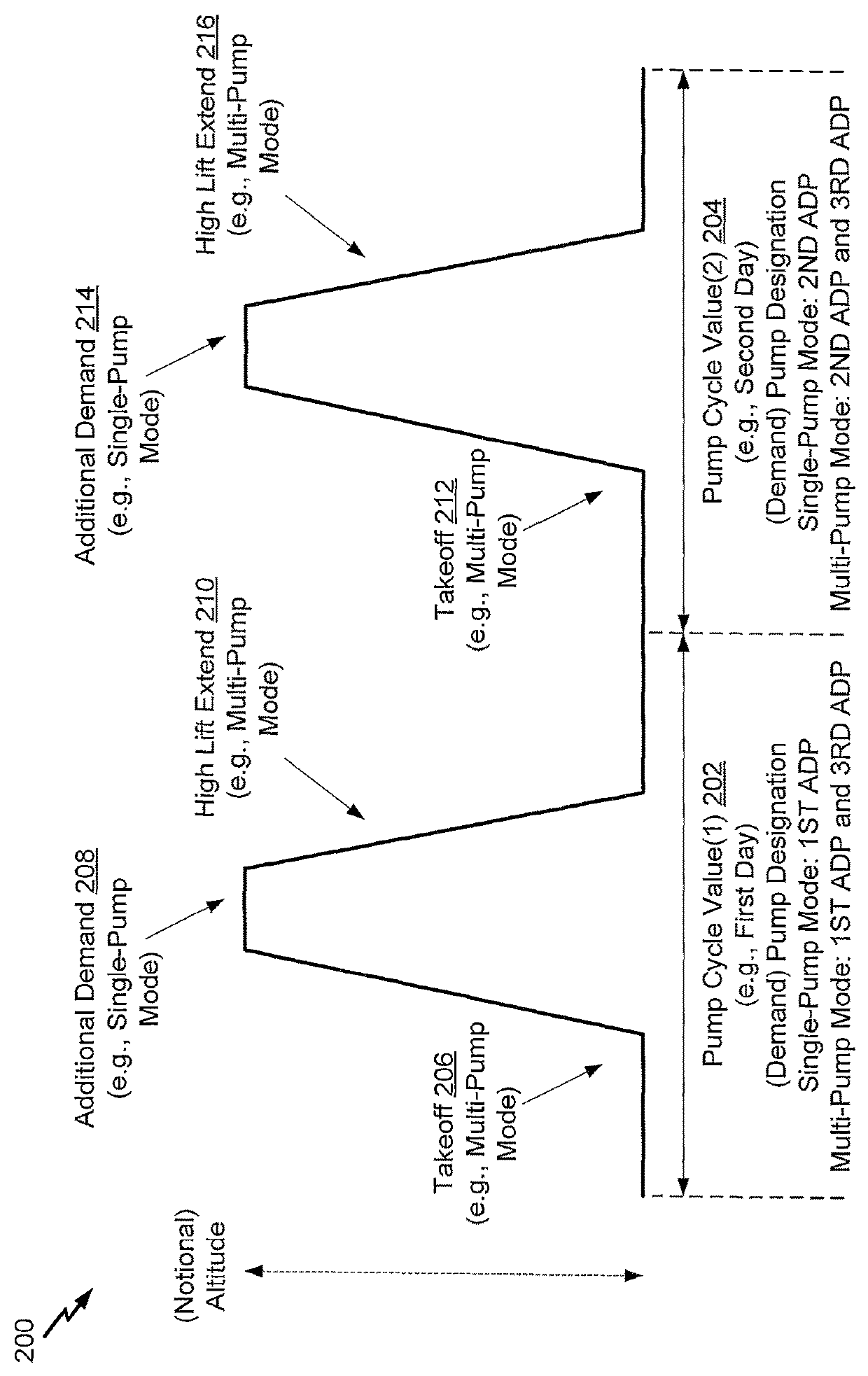
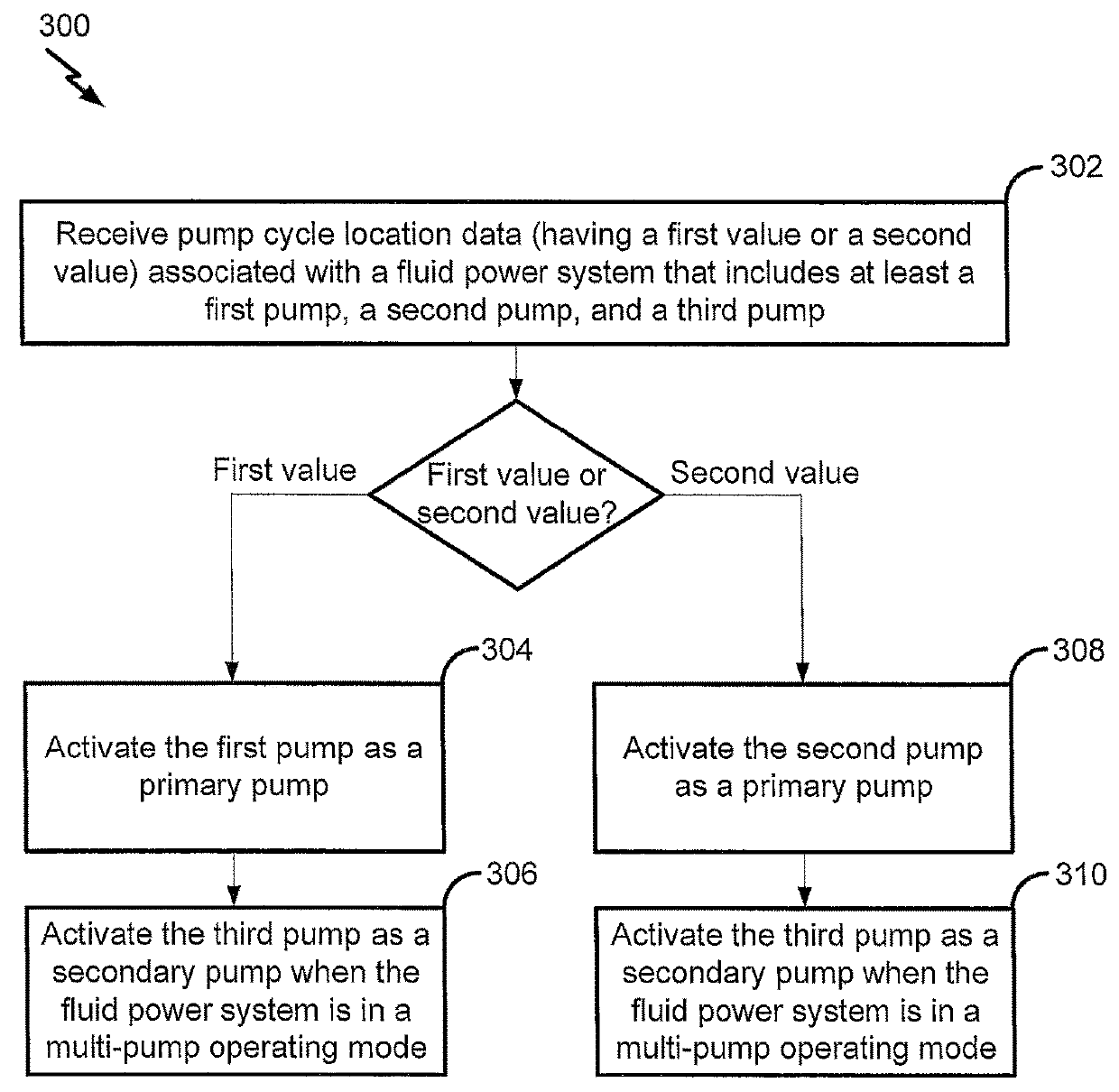
Dynamic activation of pumps of a fluid power system
A method includes receiving pump cycle location data associated with a fluid power system. The fluid power system includes a plurality of pumps (including at least a first pump, a second pump, and a third pump). Based on the pump cycle location data having a first value, the method includes activating the first pump as a primary pump. Based on the pump cycle having a second value, the method includes activating the second pump as the primary pump. The method also includes activating the third pump as a secondary pump when the fluid power system is in a multiple-pump operating mode.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
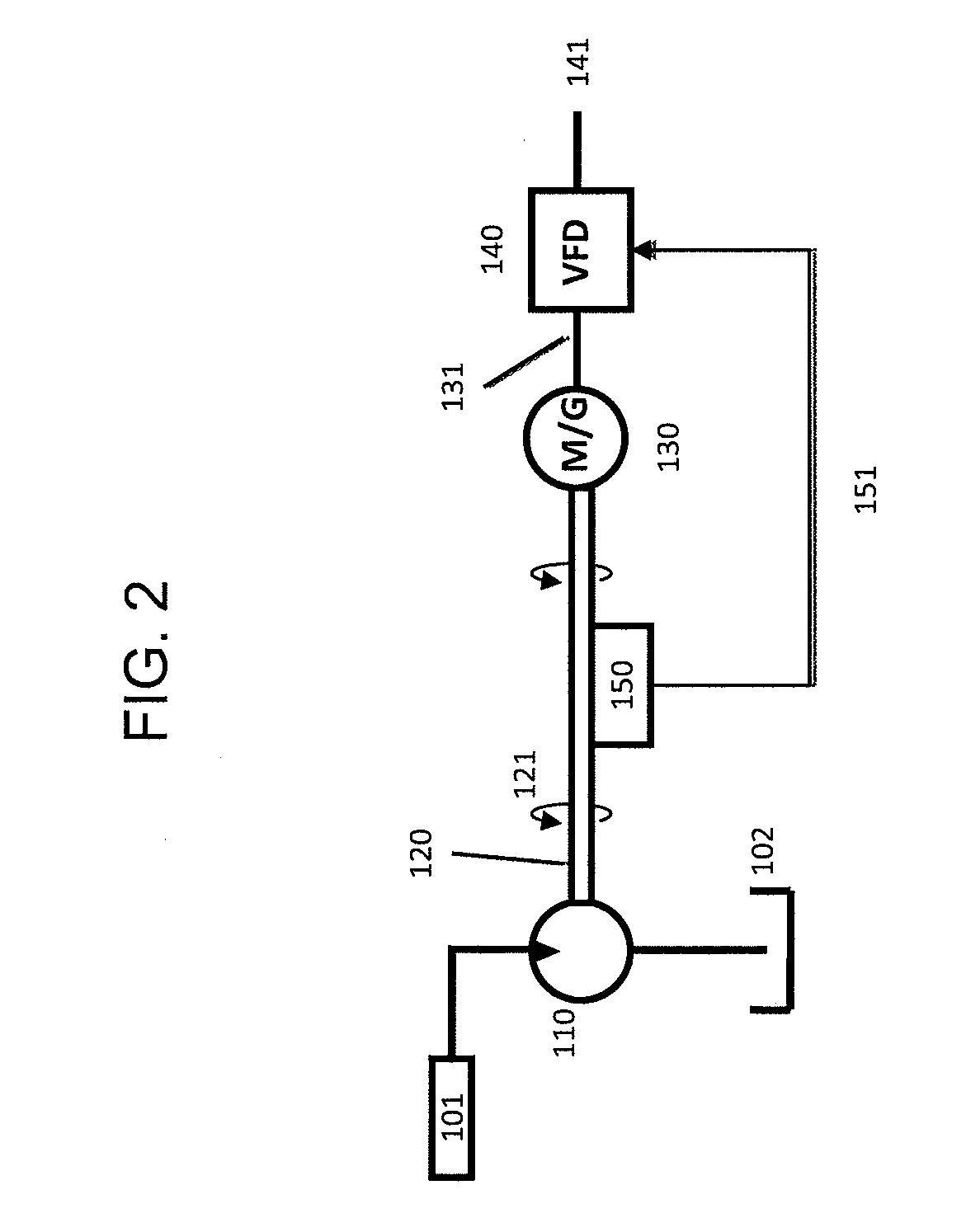
Energy recovery system
An energy recovery system for a machine is disclosed. The energy recovery system may have a pump configured to provide a flow of pressurized fluid. The energy recovery system may also have a first fluid actuator with a first chamber and a second chamber and being configured to receive the pressurized fluid, a second fluid actuator with a third chamber and a fourth chamber and being configured to receive the pressurized fluid, and a first valve fluidly connected between the pump and the first and second actuators. The energy recovery system may additionally include an isolation unit with a first selectively restrictable passageway fluidly connecting the first chamber, the third chamber, and a first outlet of the first valve, and a second selectively restrictable passageway fluidly connecting the second chamber, the fourth chamber, and a second outlet of the first valve, as well as an energy recovery unit in fluid communication with the isolation unit. The isolation unit may be configured to direct a flow of pressurized fluid from the second actuator to the energy recovery unit. The energy recovery unit may be configured to convert the flow of pressurized fluid to a first mechanical power output.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Systems and Methods for Energy Storage and Recovery Using Compressed Gas
InactiveUS20090282822A1Increase energy densityExpand/compress the gas more evenlyFluid couplingsAccumulator installationsThermodynamicsGas cylinder
The invention relates to methods and systems for the storage and recovery of energy using open-air hydraulic-pneumatic accumulator and intensifier arrangements that combine at least one accumulator and at least one intensifier in communication with a high-pressure gas storage reservoir on a gas-side of the circuits and a combination fluid motor / pump, coupled to a combination electric generator / motor on the fluid side of the circuits.
Owner:SUSTAINX
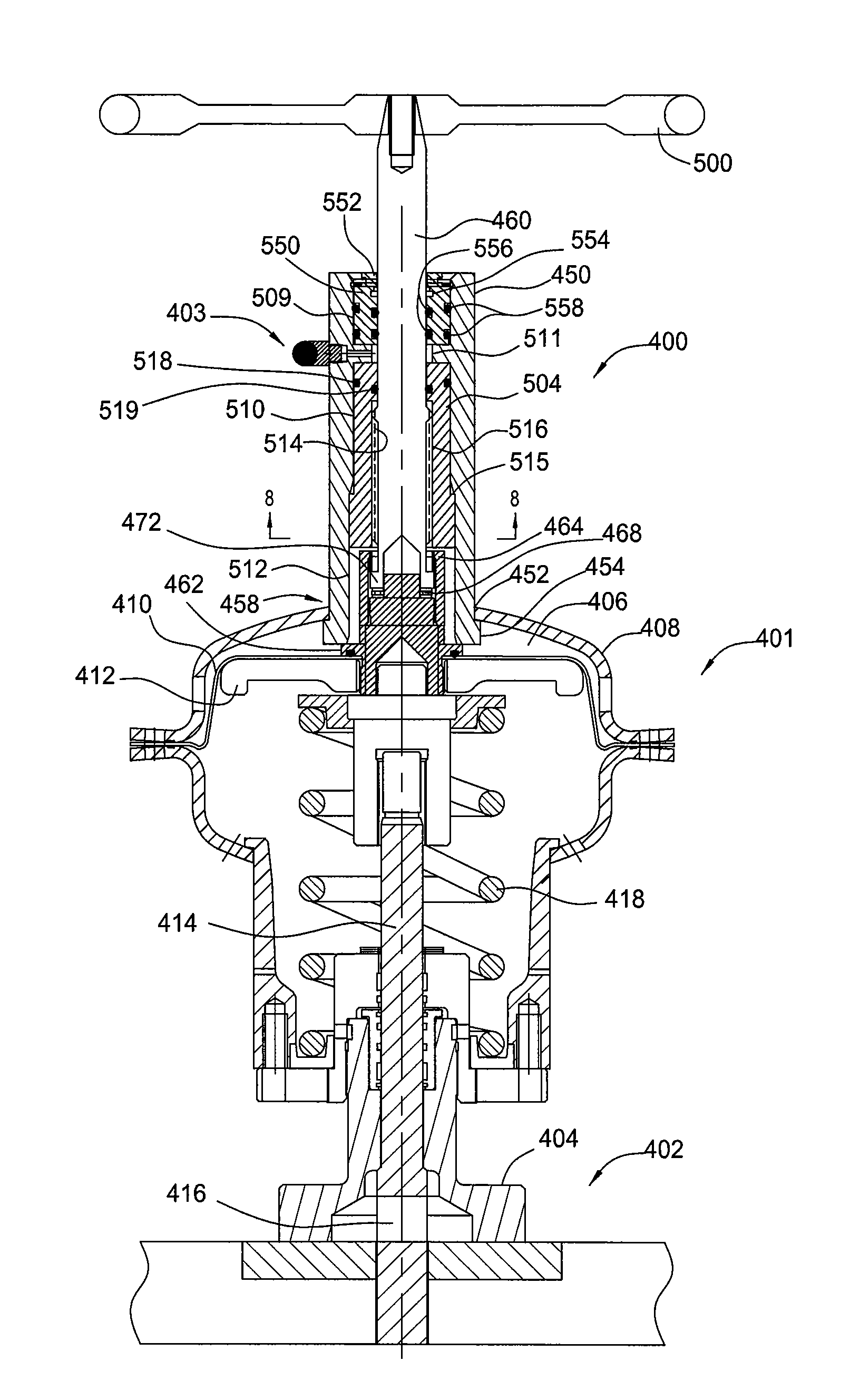
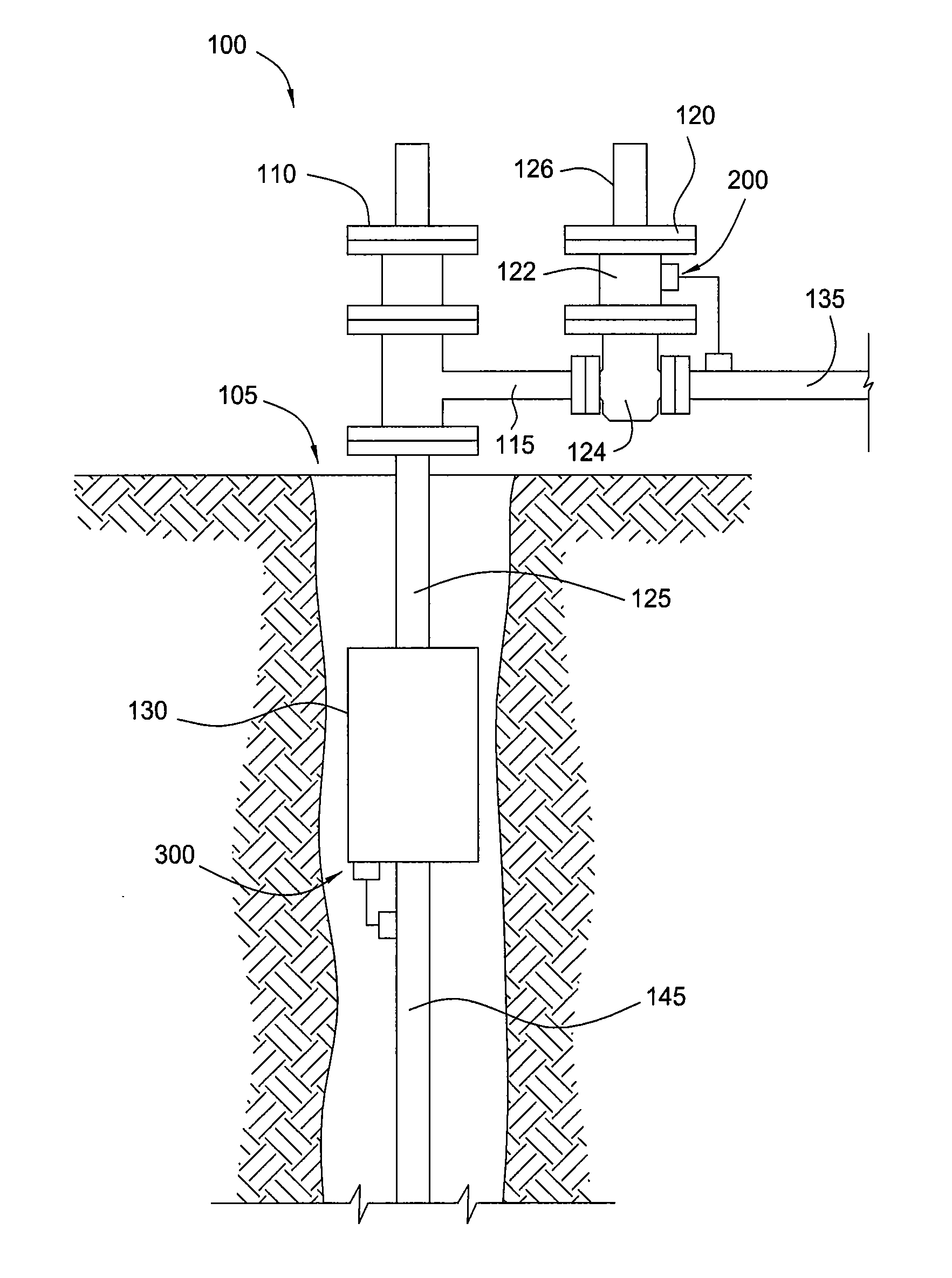
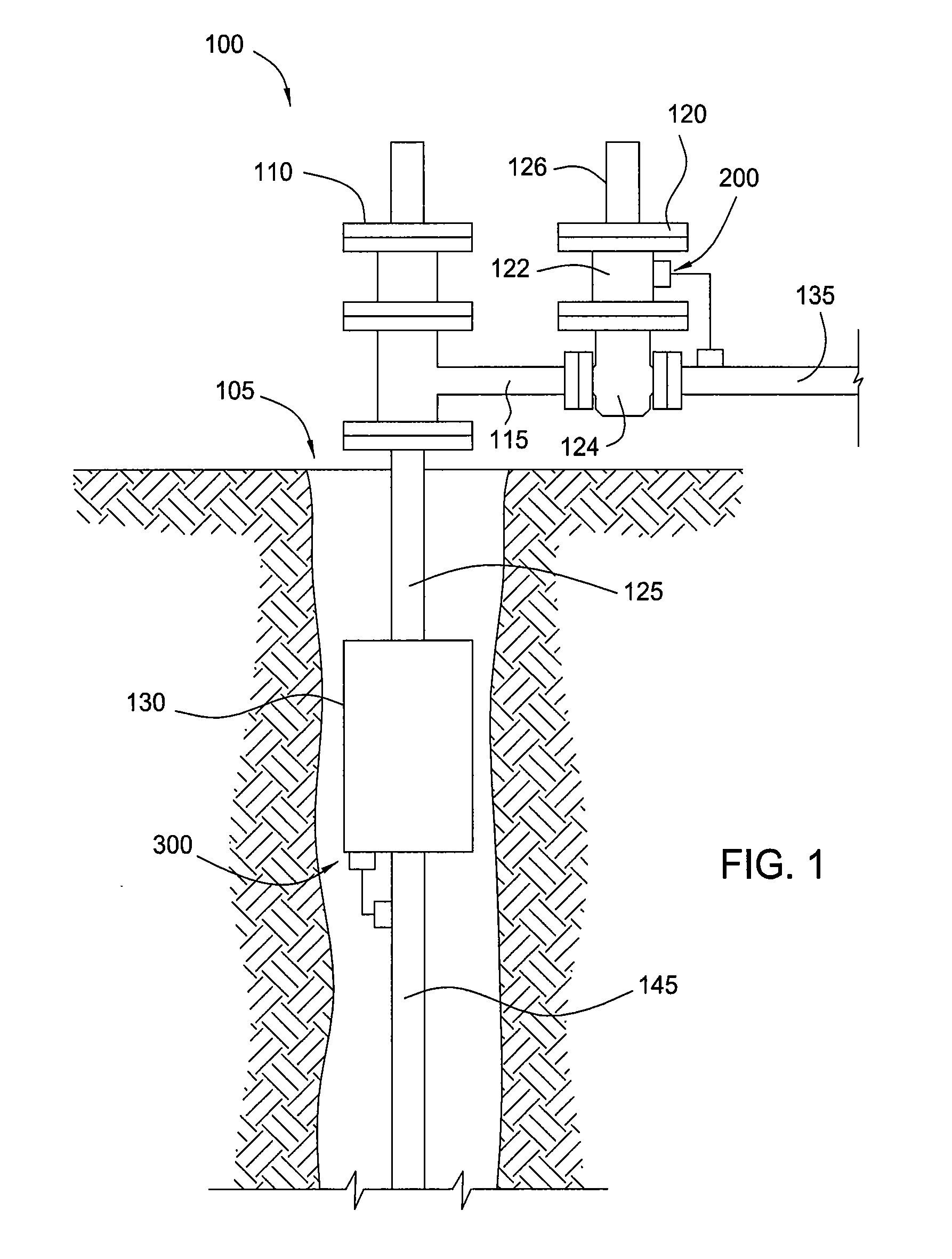
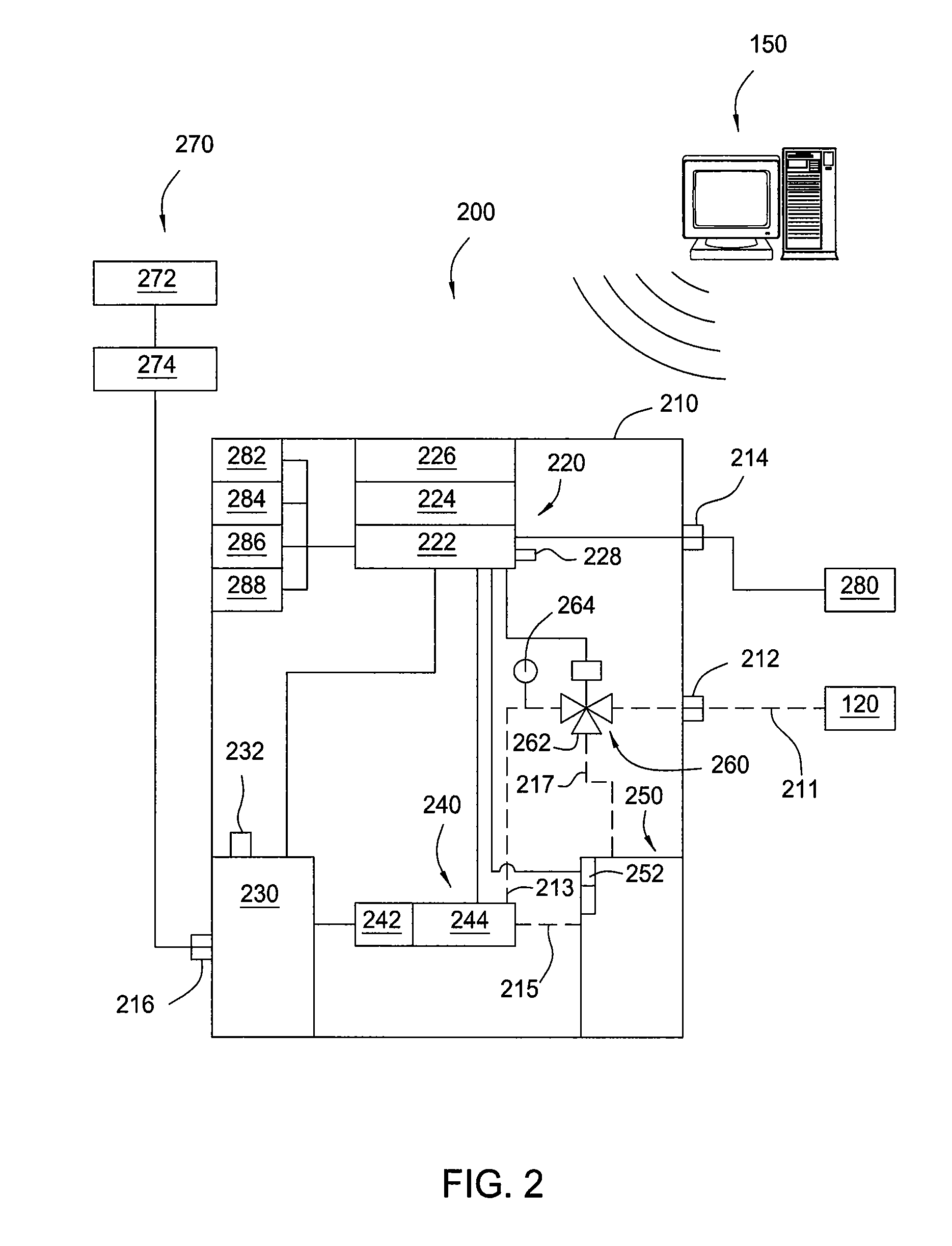
Safety valve control system and method of use
ActiveUS20120227983A1Reduce fluid pressureFluid-pressure actuator safetyEqualizing valvesControl systemTransducer
A safety valve control system may include a remotely operable control assembly, a first transducer, a valve assembly, and a compressor assembly in communication with the control assembly. The control assembly is operable to actuate the pump and valve assemblies to supply fluid to actuate the safety valve into open and closed positions, in response to one or more signals received from the first transducer. A method of operation may include maintaining the safety valve in an open or closed position while sensing a physical property with the control system; communicating a signal corresponding to the sensed physical property to the control system; and automatically closing or opening the safety valve in response to a comparison of the sensed physical property to a pre-set condition.
Owner:SAFOCO
Energy recovery and reuse techniques for a hydraulic system
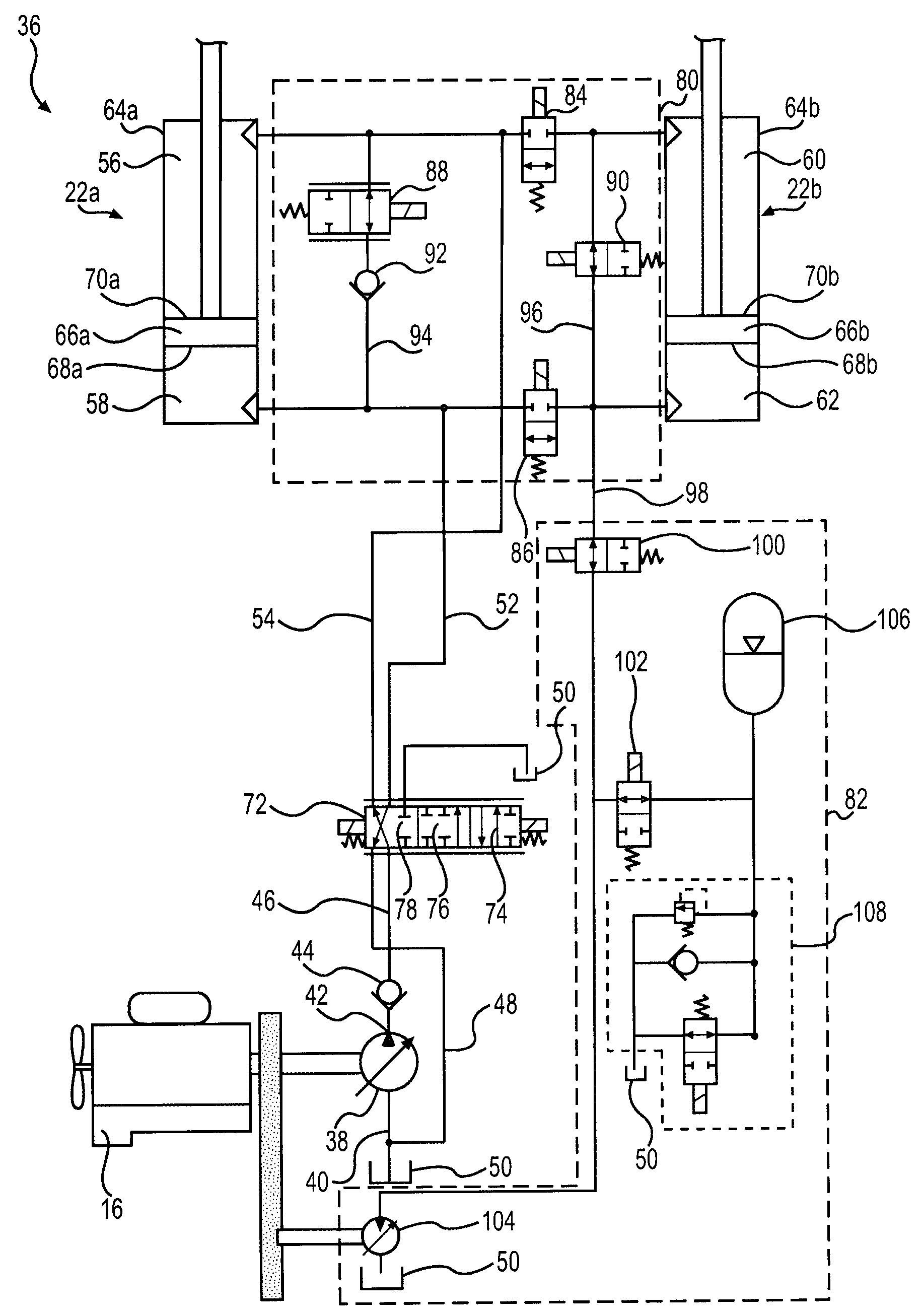
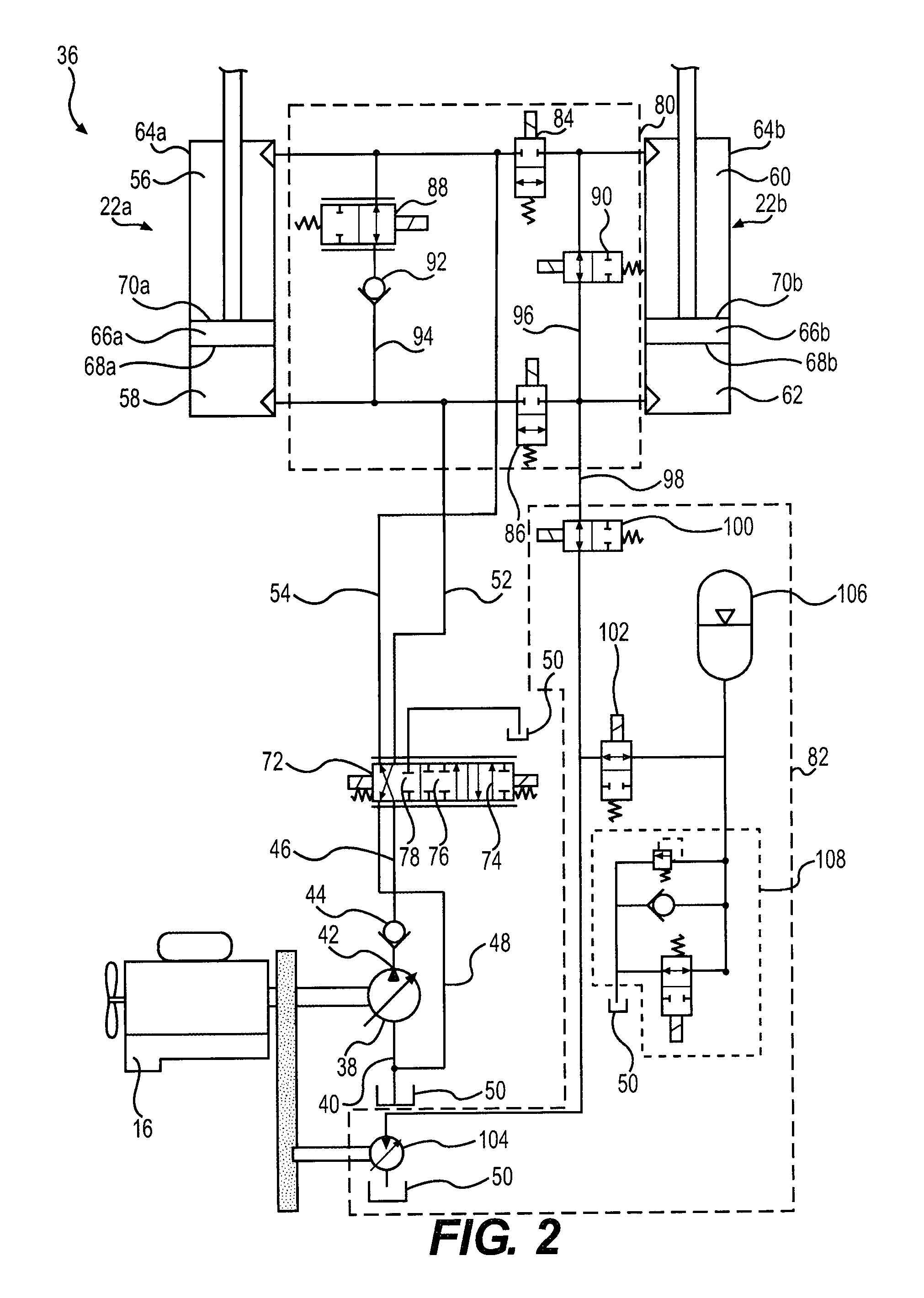
A hydraulic system has a valve assembly with two workports coupled to chambers of first and second cylinders which are connected mechanically in parallel to a machine component. A separation control valve is connected between first chambers of both cylinders, and a shunt control valve is connected between the workports. A recovery control valve couples an accumulator to the first chamber of the second cylinder. Opening and closing the valves in different combinations routes fluid from one or both cylinders into the accumulator where the fluid is stored under pressure, and thereafter enables stored fluid to be used to power one or both cylinders. The shunt control valve is used to route fluid exhausting from one chamber of each cylinder to the other chambers of those cylinders. Thus the hydraulic system recovers and reuses energy in various manners.
Owner:HUSCO INT INC
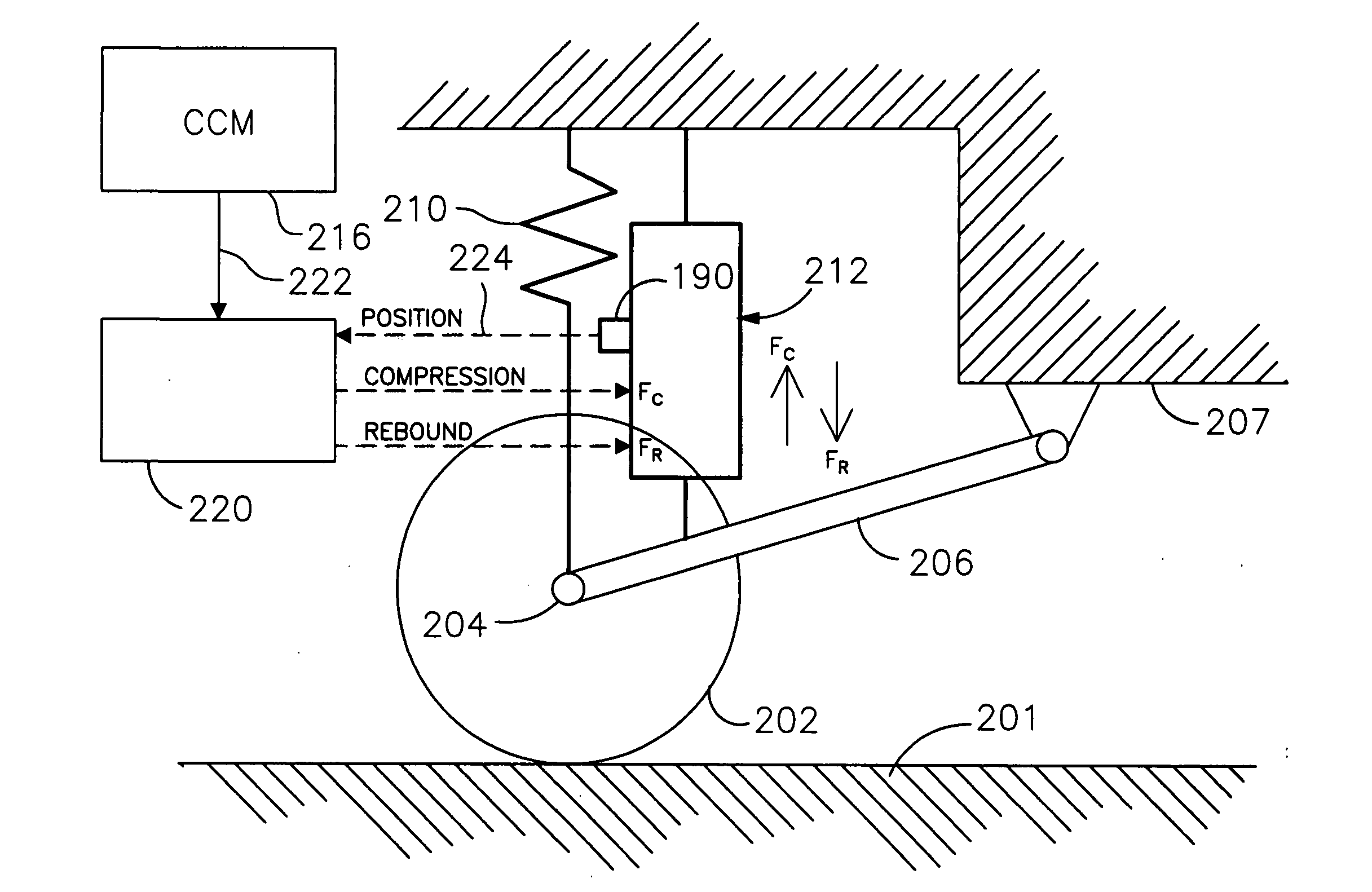
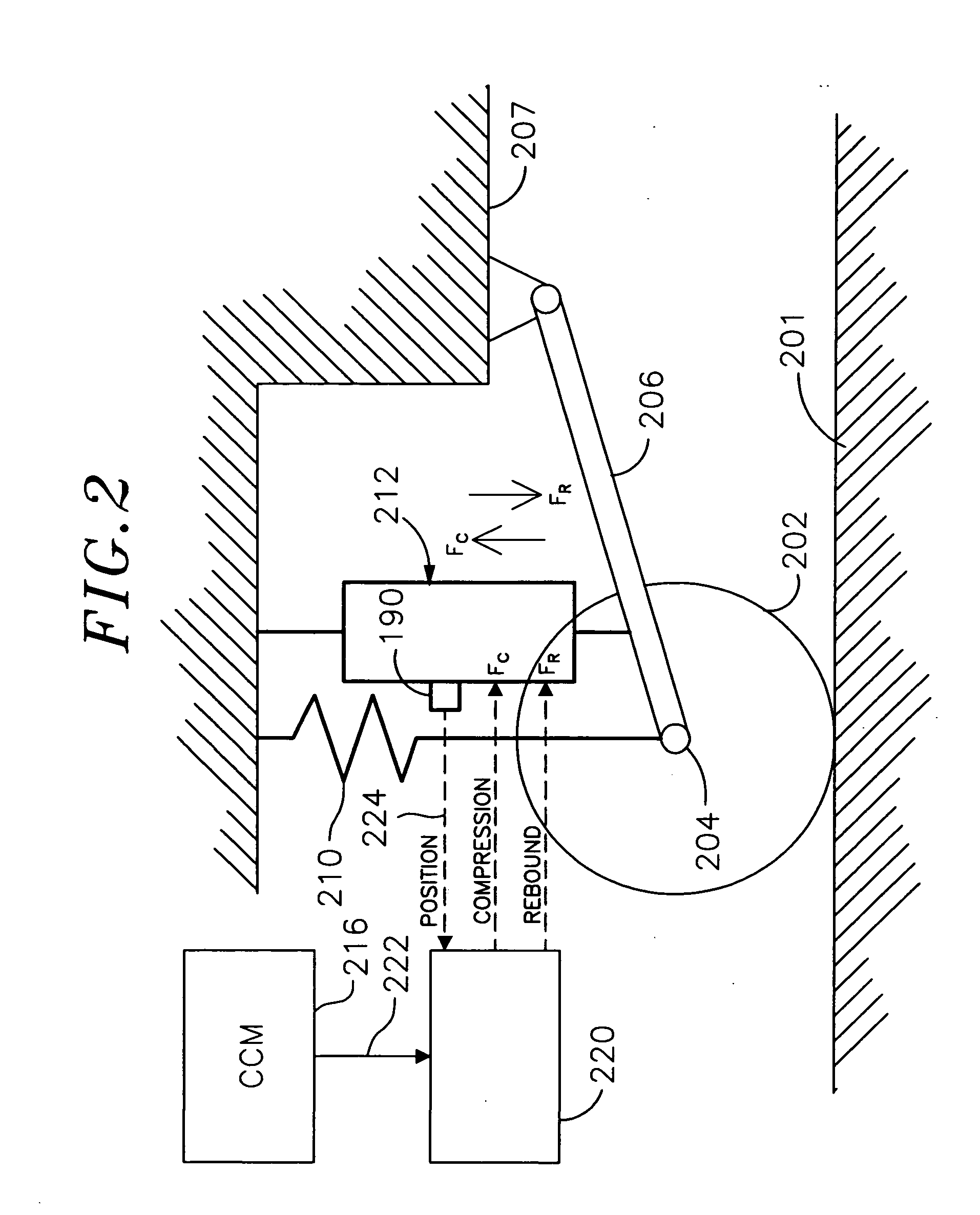
Enhanced computer optimized adaptive suspension system and method
InactiveUS20050098401A1Minimizing body motionIncrease fluid pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpringsComputer optimizationControl signal
A system and method for controlling a damping system. The system has at least two dampers for damping between sprung and unsprung masses in the compression and rebound directions. Sensors generate signals based on position and other parameters of motion representative of the displacement between the sprung and unsprung masses. The process determines the appropriate compression and rebound forces to be applied at the wheels. A regulator responds to at least one of the independent compression and rebound control signals for adjusting, respectively, at least one of compression and rebound resisting forces of the dampers between the masses. Compliance for the dampers is emulated with software to produce the desired compliance forces. The distributed controller includes a processor that is responsive to signals representative of the position signals for forming the compression and rebound control signals for the regulator as a function of motion between the masses or a motion of a vehicle in which the dampers are located. The system has the capability of locking the suspension when parked.
Owner:GREAT NORTHERN TECH
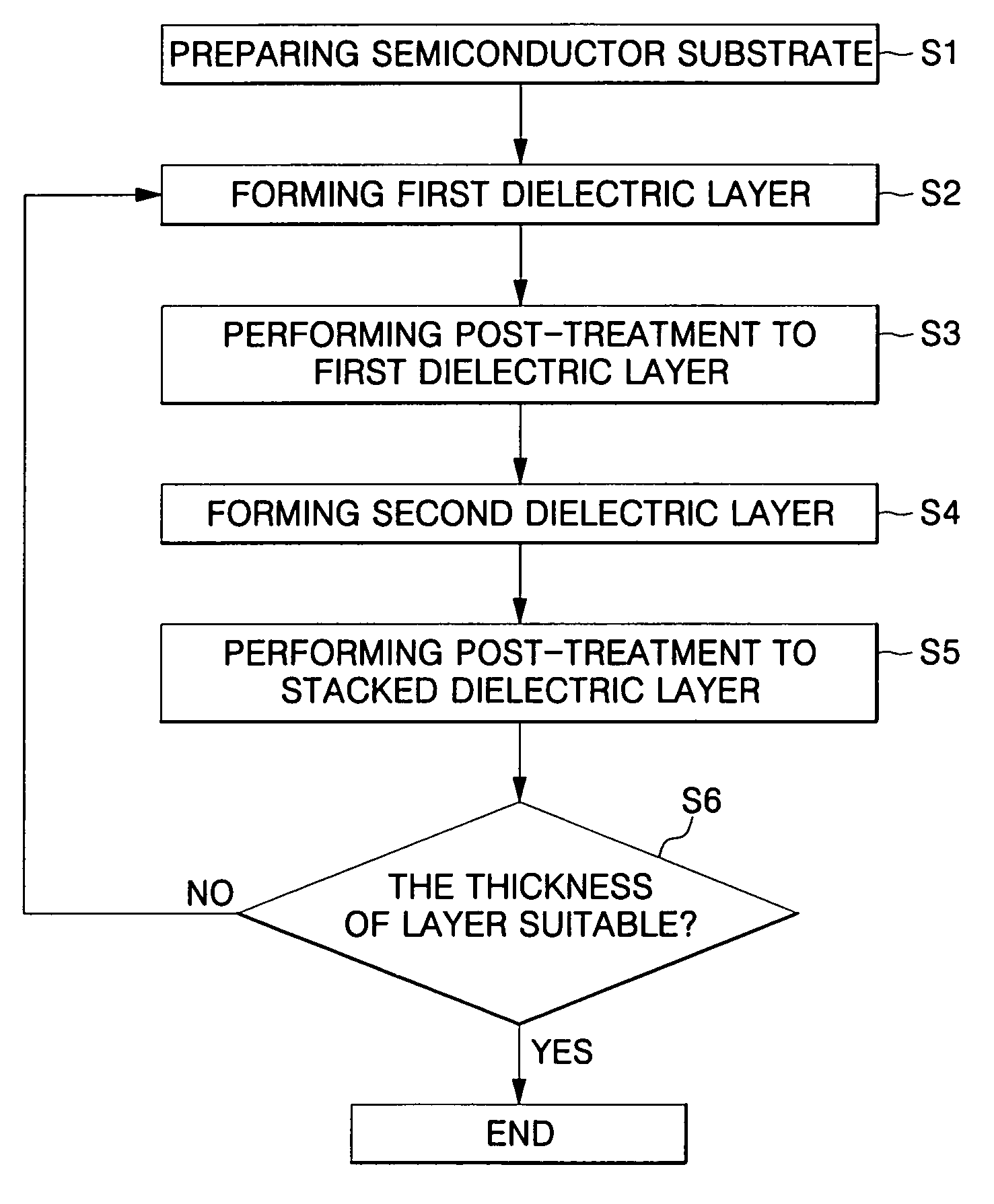
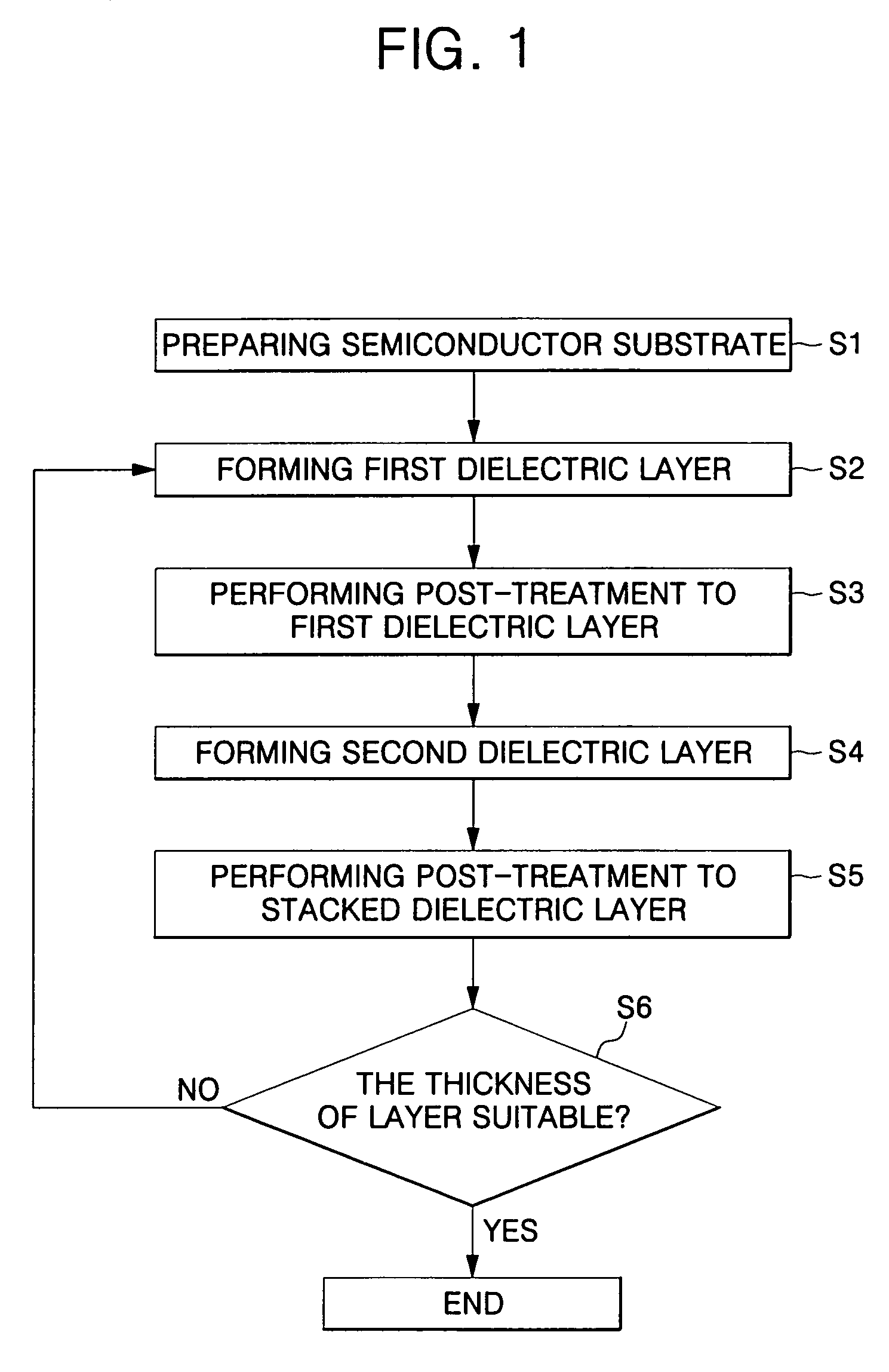
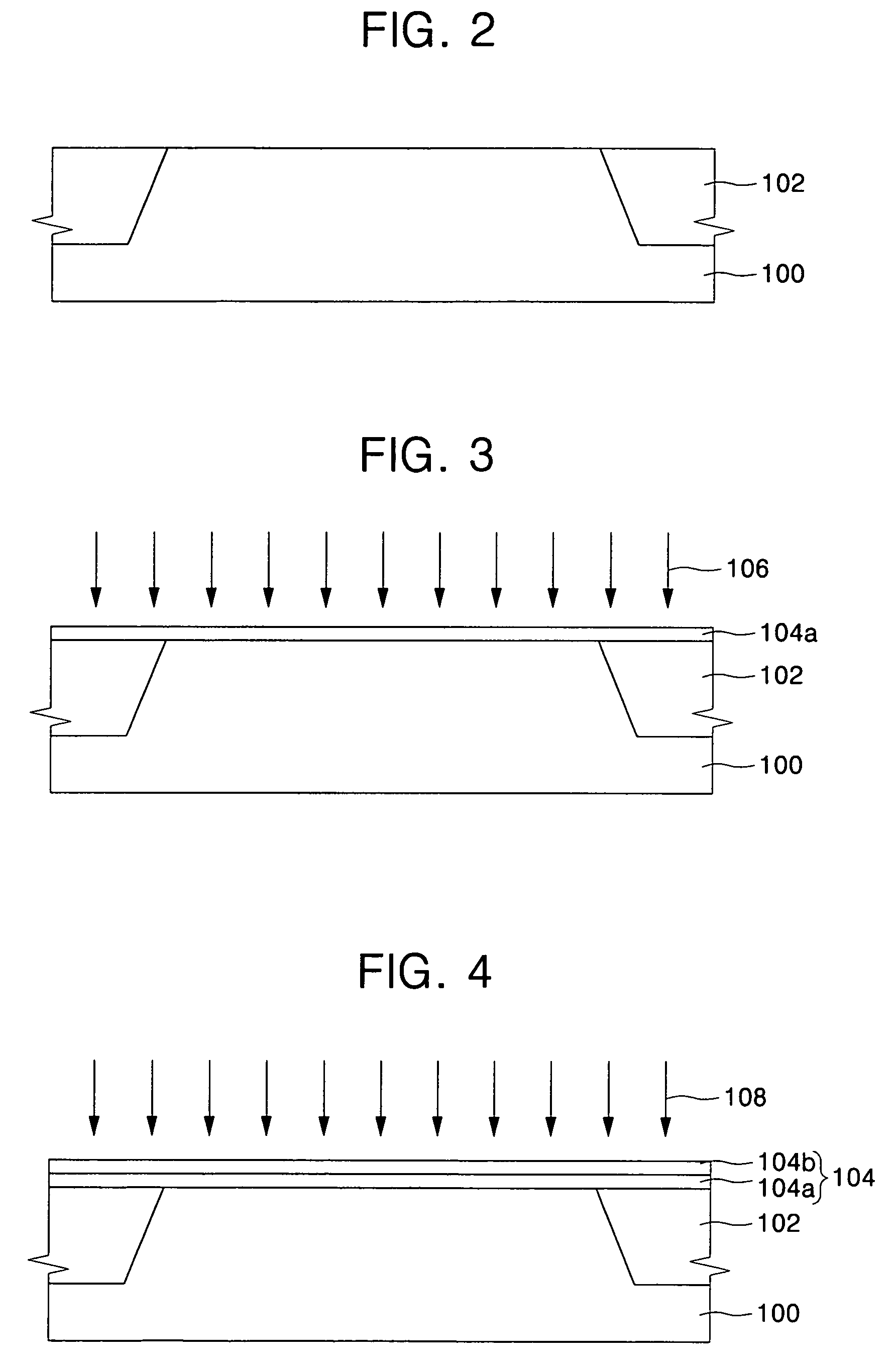
Method of fabricating high-k dielectric layer having reduced impurity
ActiveUS20050233598A1Impurity content is minimizedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhysical chemistryEngineering
Methods of fabricating high-k dielectric layers having reduced impurities for use in semiconductor applications are disclosed. The methods include the steps of: forming a stacked dielectric layer having a first dielectric layer and a second dielectric layer formed on a semiconductor substrate using an ALD method, in combination with a post-treatment step performed to the stacked dielectric layer. The steps of forming the stacked dielectric layer and performing the post-treatment are repeated at least once, thereby fabricating the high-k dielectric layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Working machine driving unit
InactiveUS20050246082A1ShortfallEfficient sharingAnalogue computers for trafficServomotorsWork unitActuator
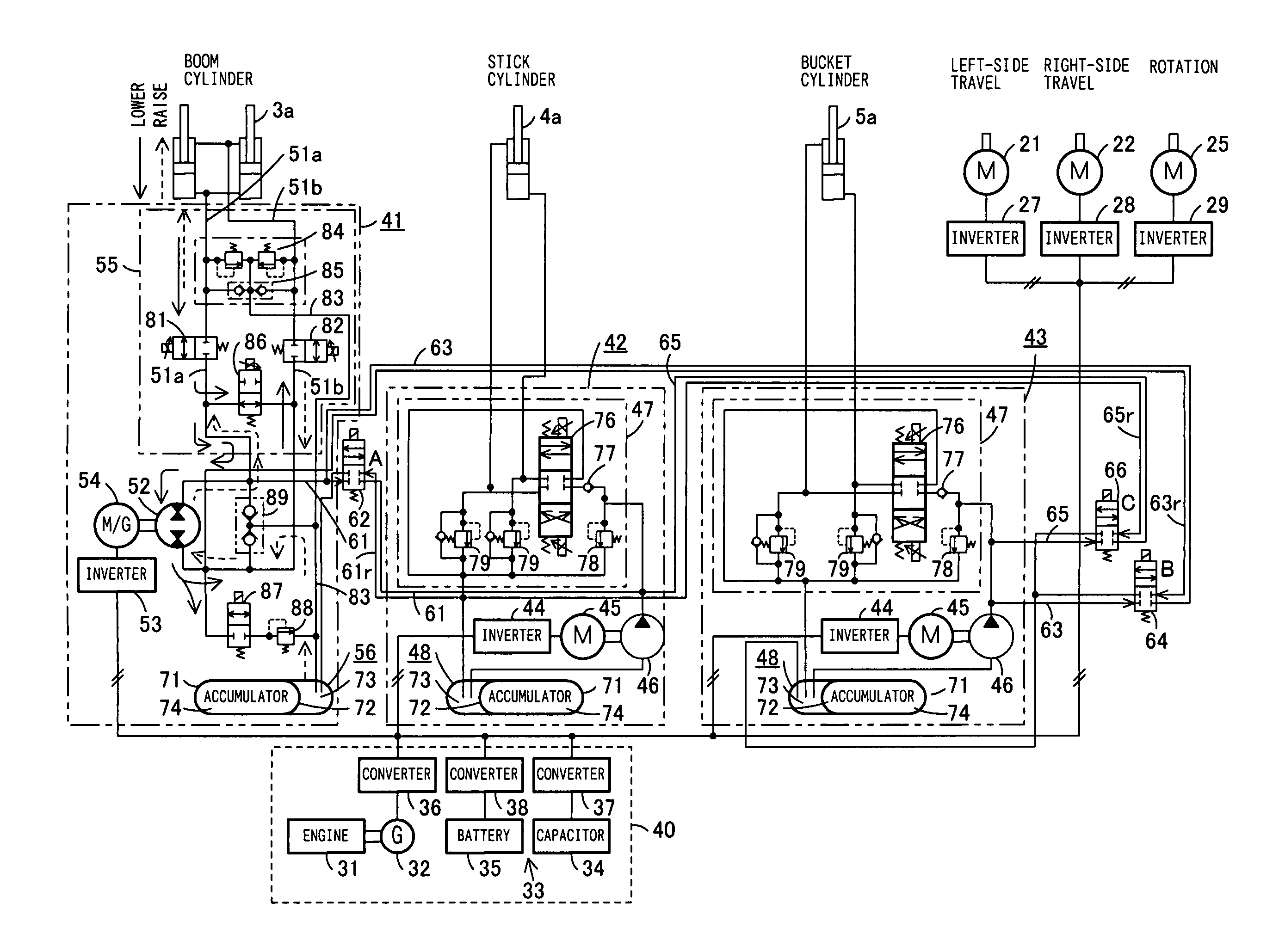
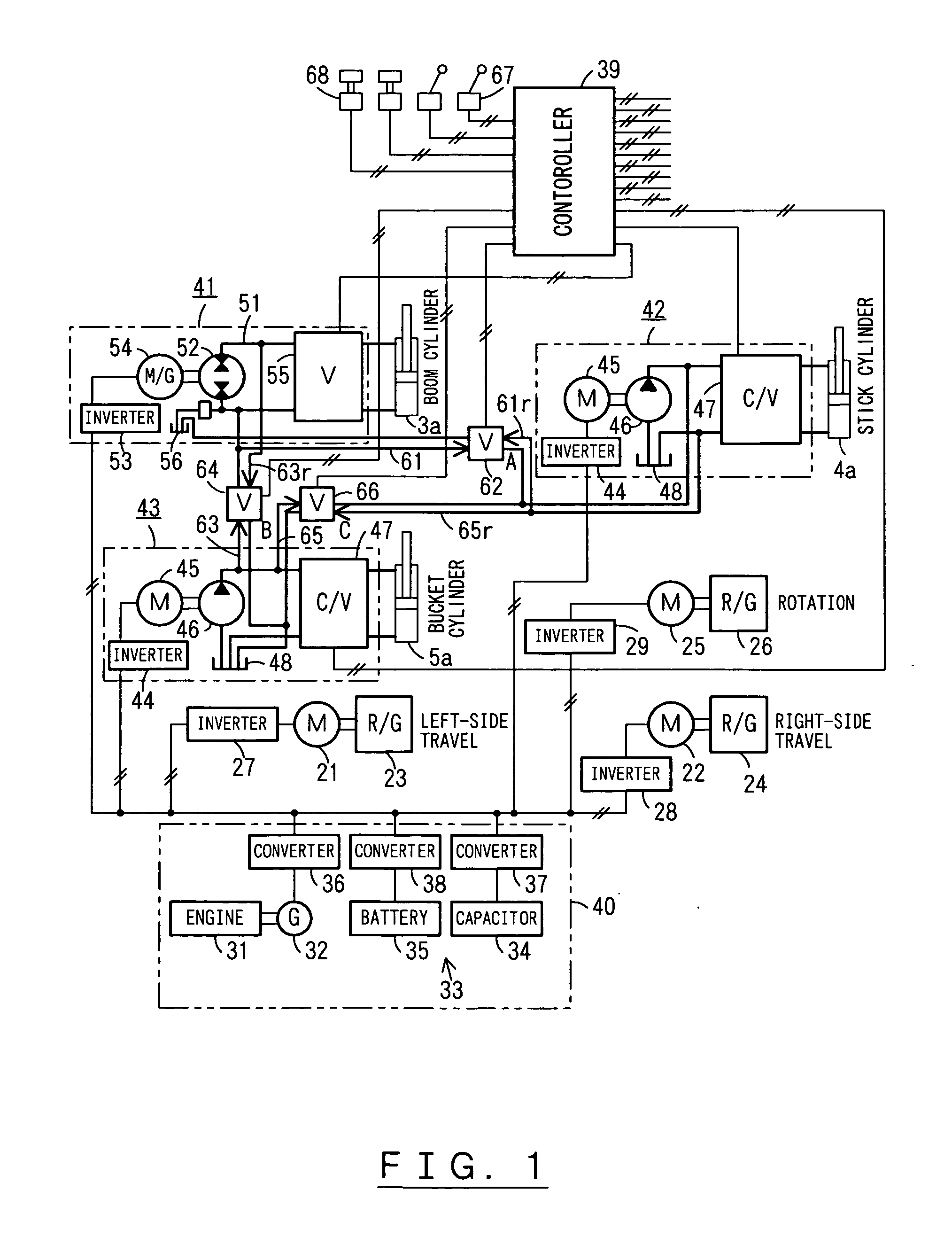
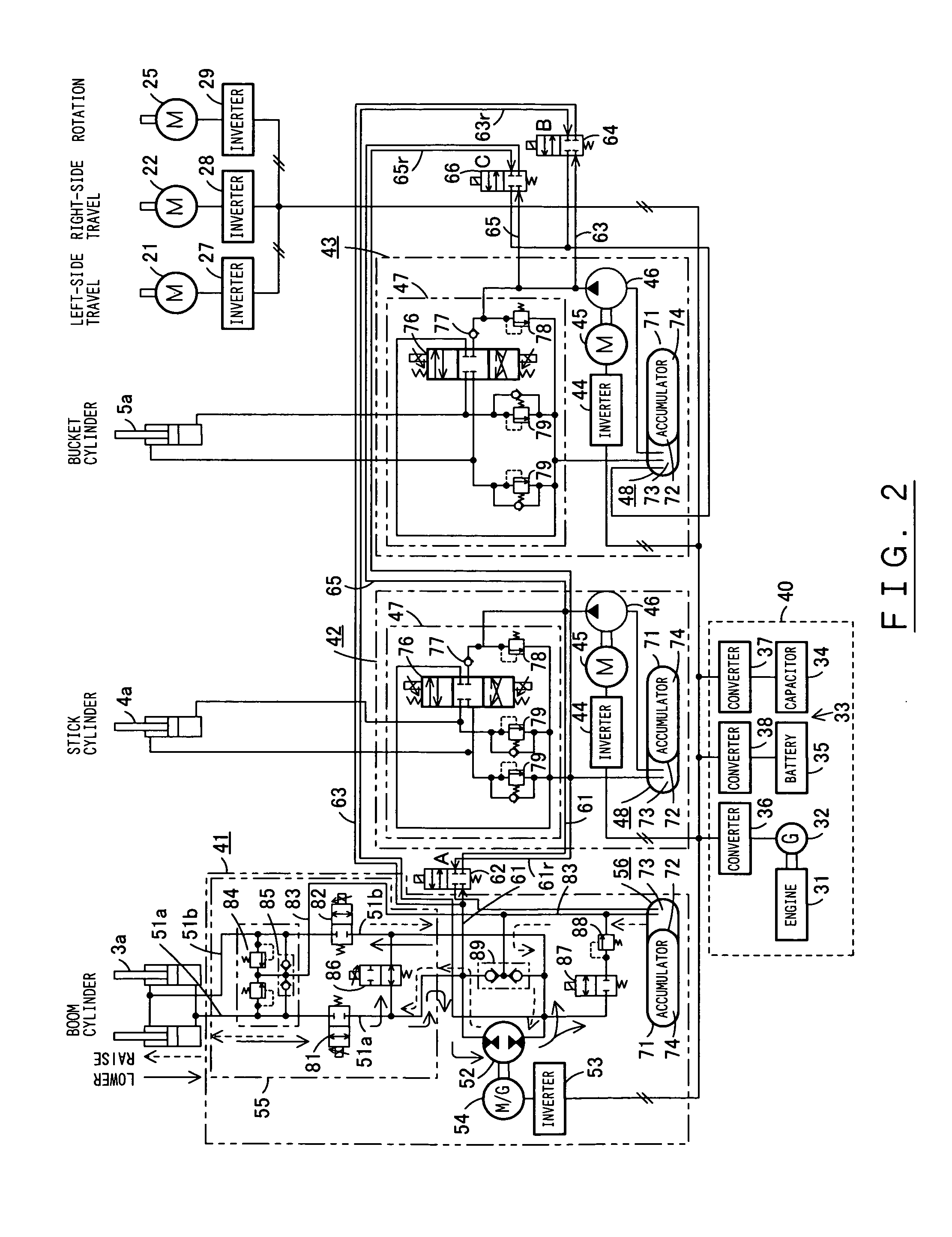
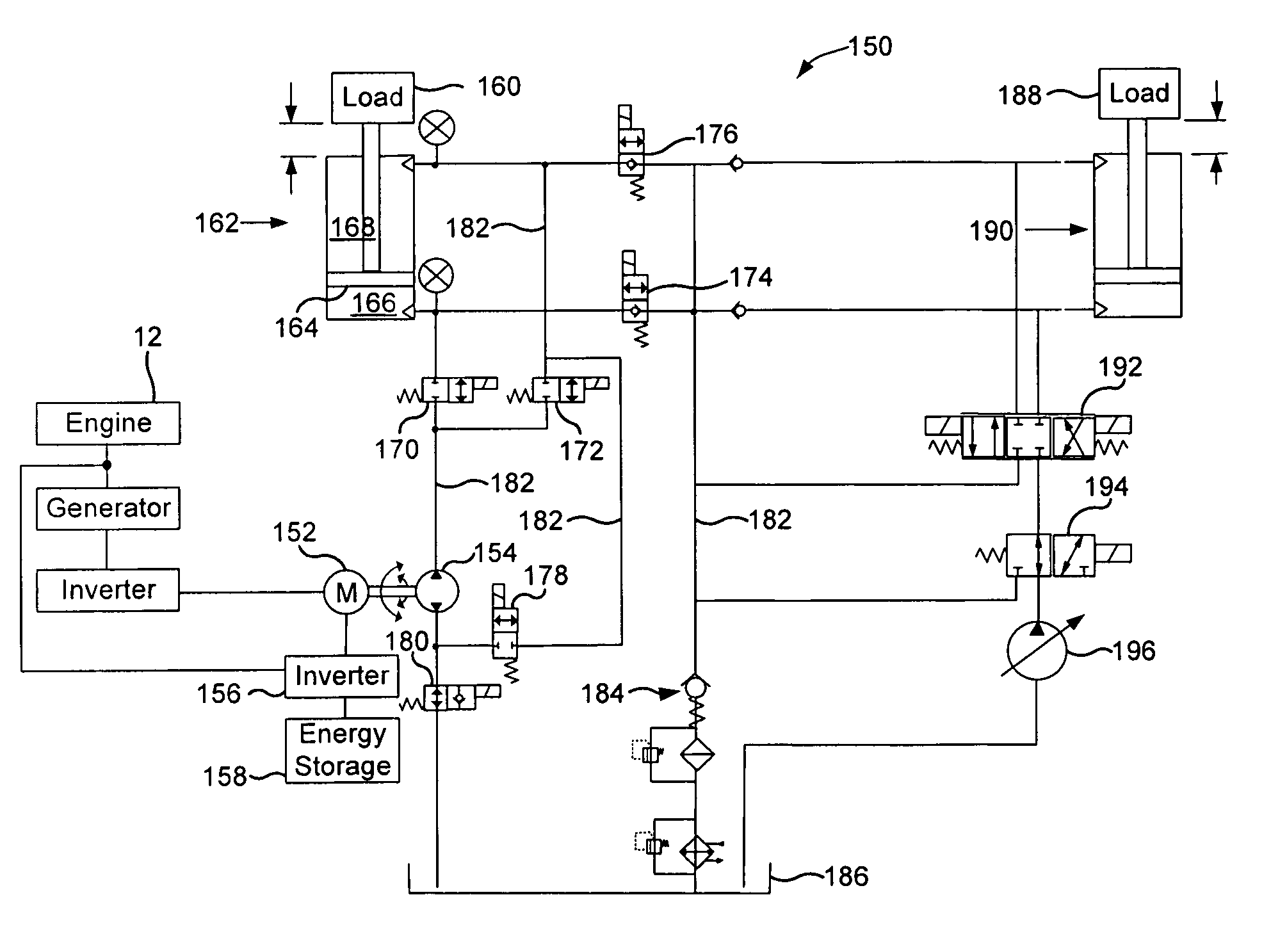
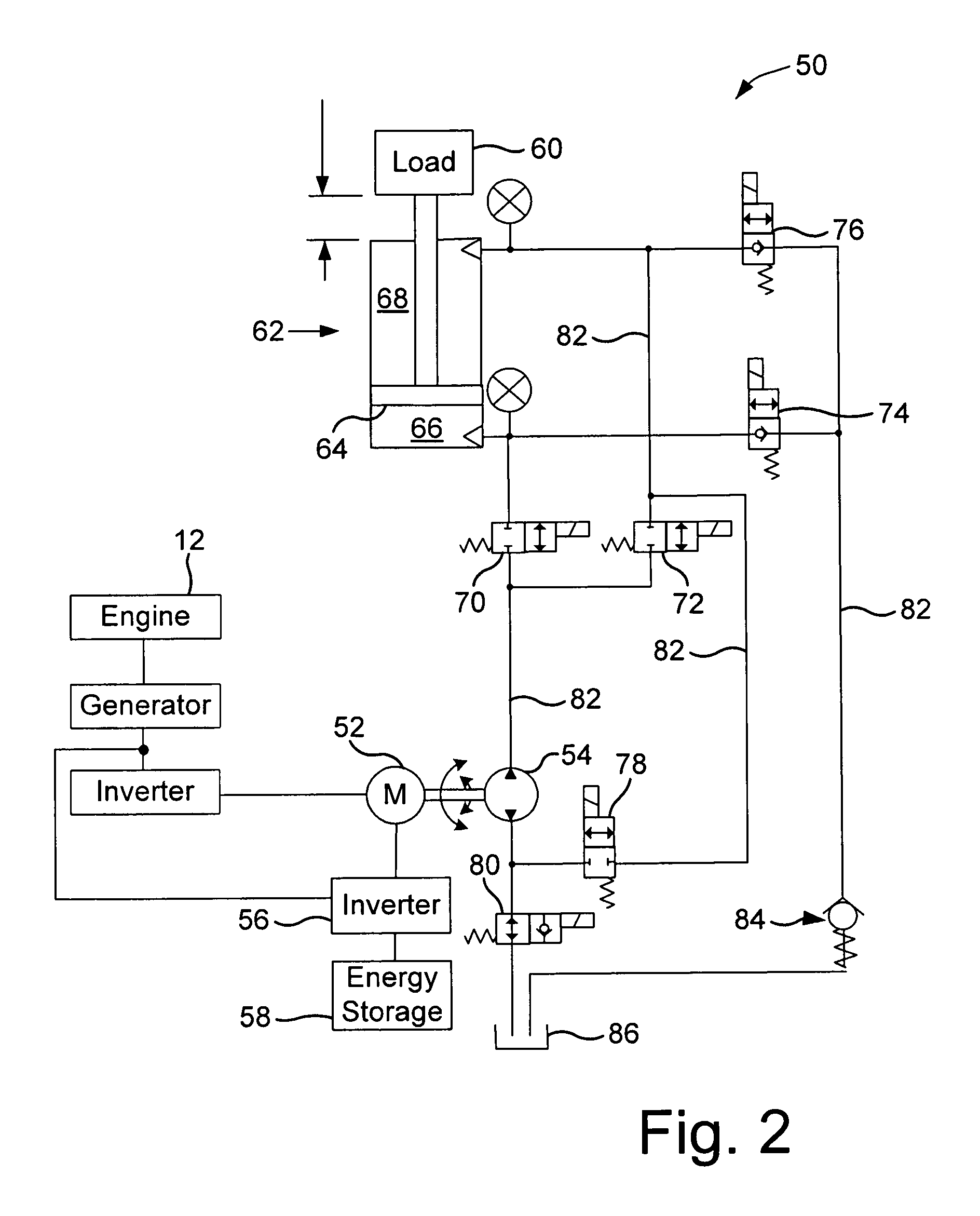
A driving device of a work machine includes a power generator adapted to be driven by an engine, and a power storage device for storing the electric power generated by the power generator. Electric motors and a motor generator, both adapted to be operated by electric power supplied from either one or both of the power generator and the power storage device respectively drive pumps and a pump motor. Supporting circuits for feeding supporting hydraulic oil are provided between a plurality of driving circuits that drive a plurality of hydraulic actuators of a working unit by oil hydraulics generated by the pumps and the pump motor. By enabling the plurality of driving circuits to effectively share excess energy, the invention makes possible a compact construction of a driving device of a work machine.
Owner:SHIN CATERPILLAR MITSUBISHI LTD CORP
Hybrid machine with hydraulic drive device
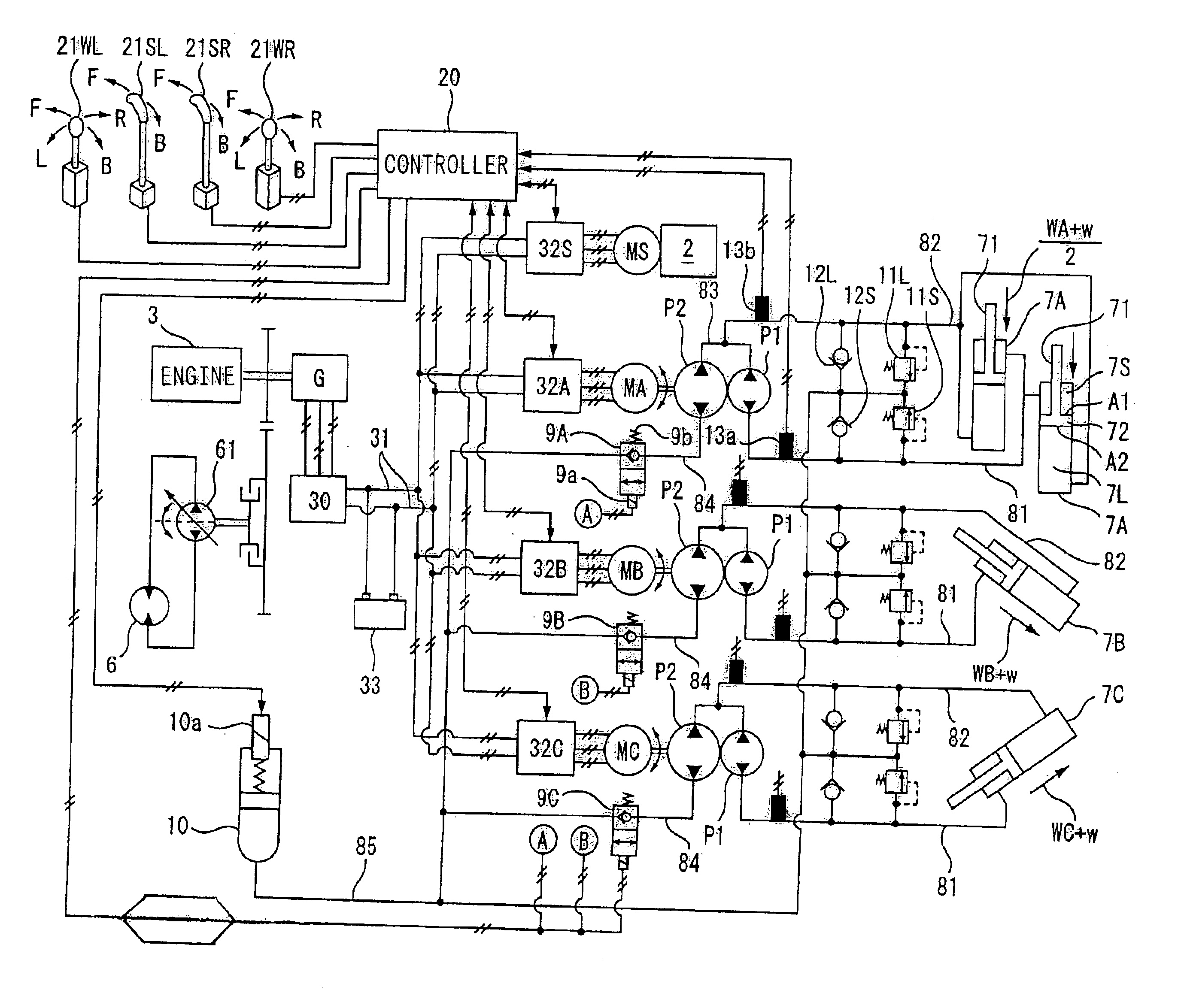
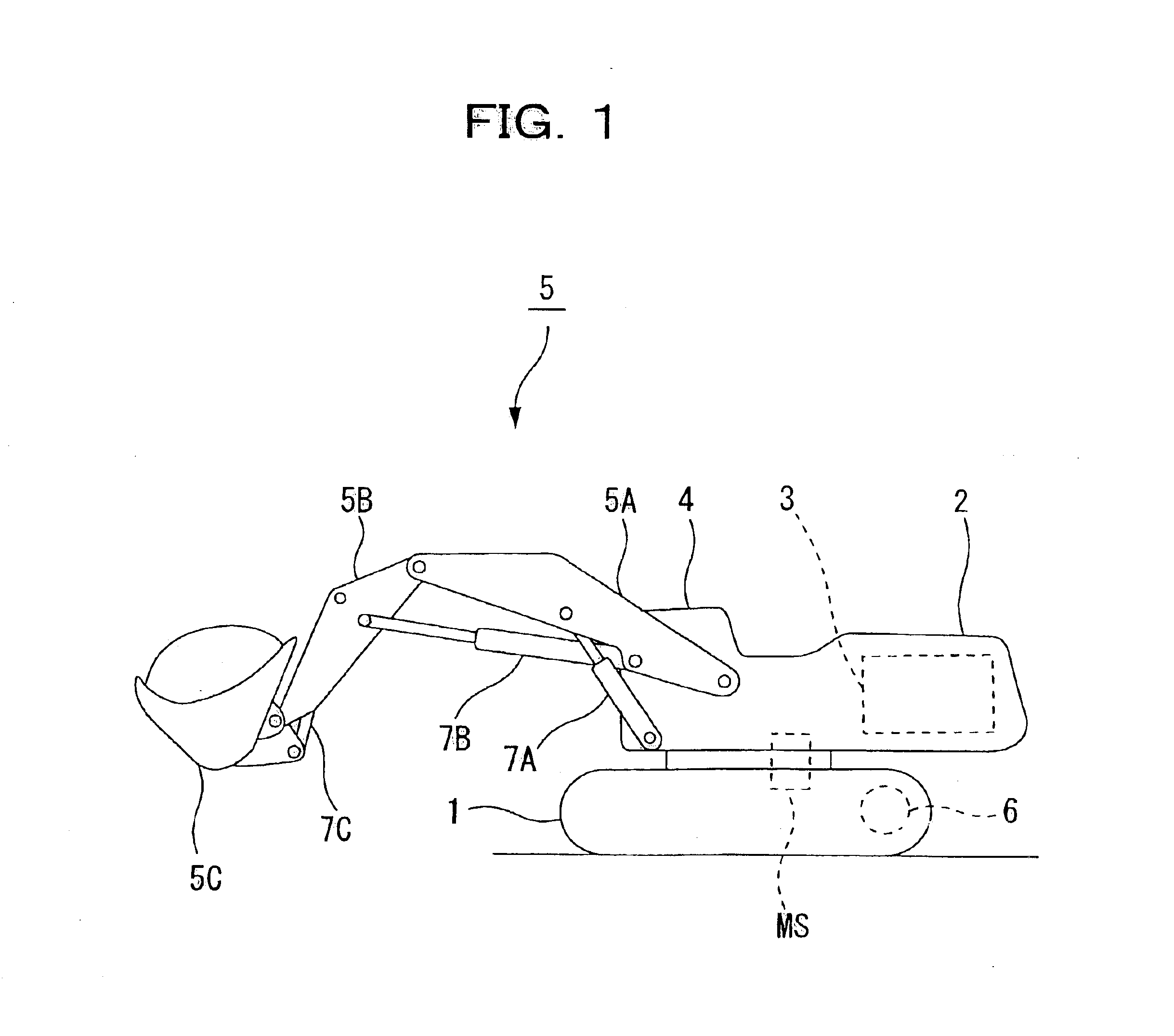
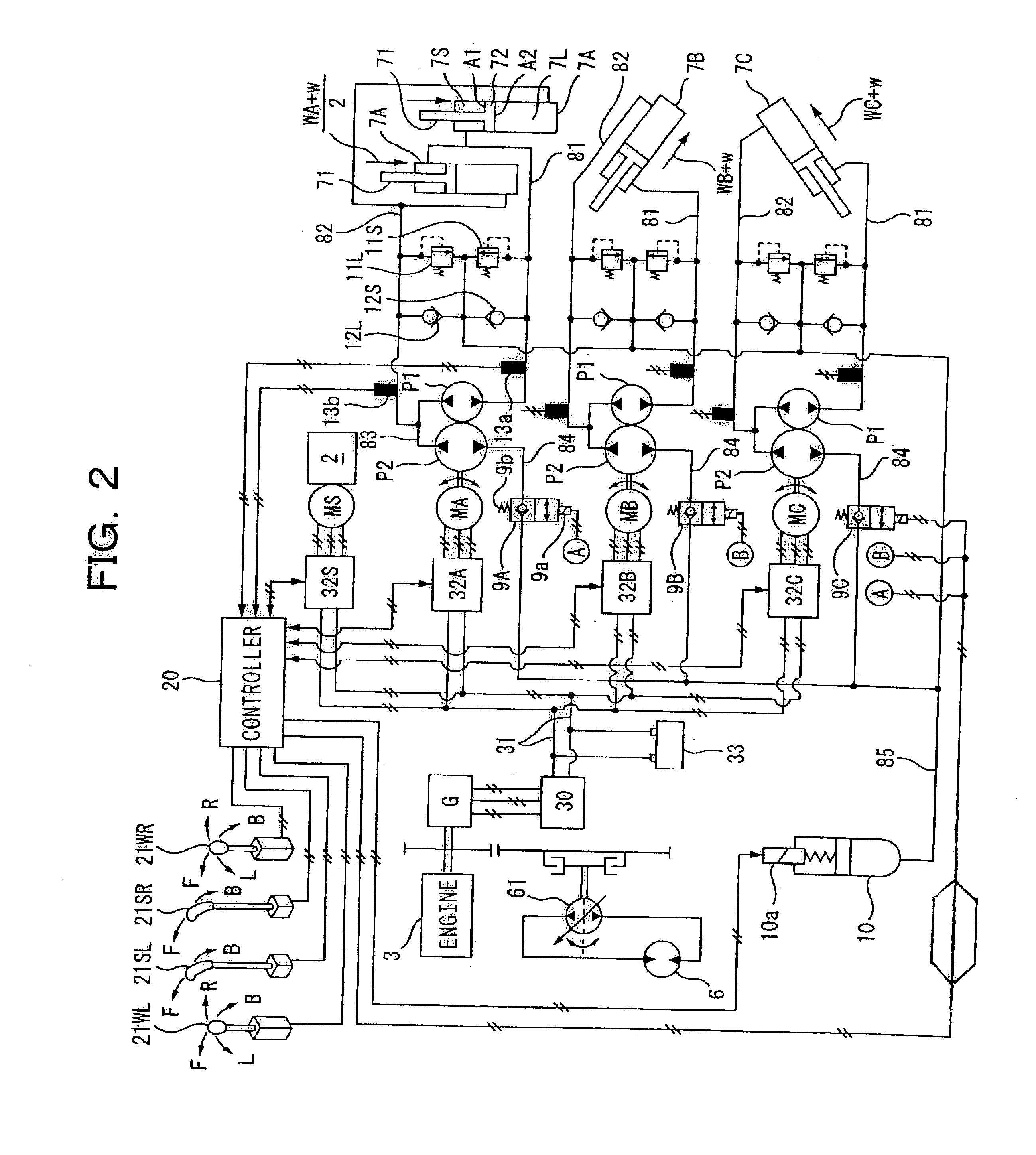
A hybrid machine with a hydraulic drive device having hydraulic actuators allowed to operate against and by external loads is provided. To this end, the hybrid machine comprises hydraulic cylinders (7), first hydraulic pumps (P1) connected, with closed circuits, to head side pressure receiving chambers (7S) and bottom side pressure receiving chambers (7L) of the hydraulic cylinders (7), and second hydraulic pumps (P2) connected, with open circuits, to the bottom side pressure receiving chambers (7L) and an external oil chamber (10), wherein the first and second hydraulic pumps (P1, P2) are connected to electric motors (M) so as to be driven.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Compact hydraulic accumulator
InactiveUS20080308168A1Light weightEasy maintenanceFluid couplingsCheck valvesWorking fluidGas cylinder
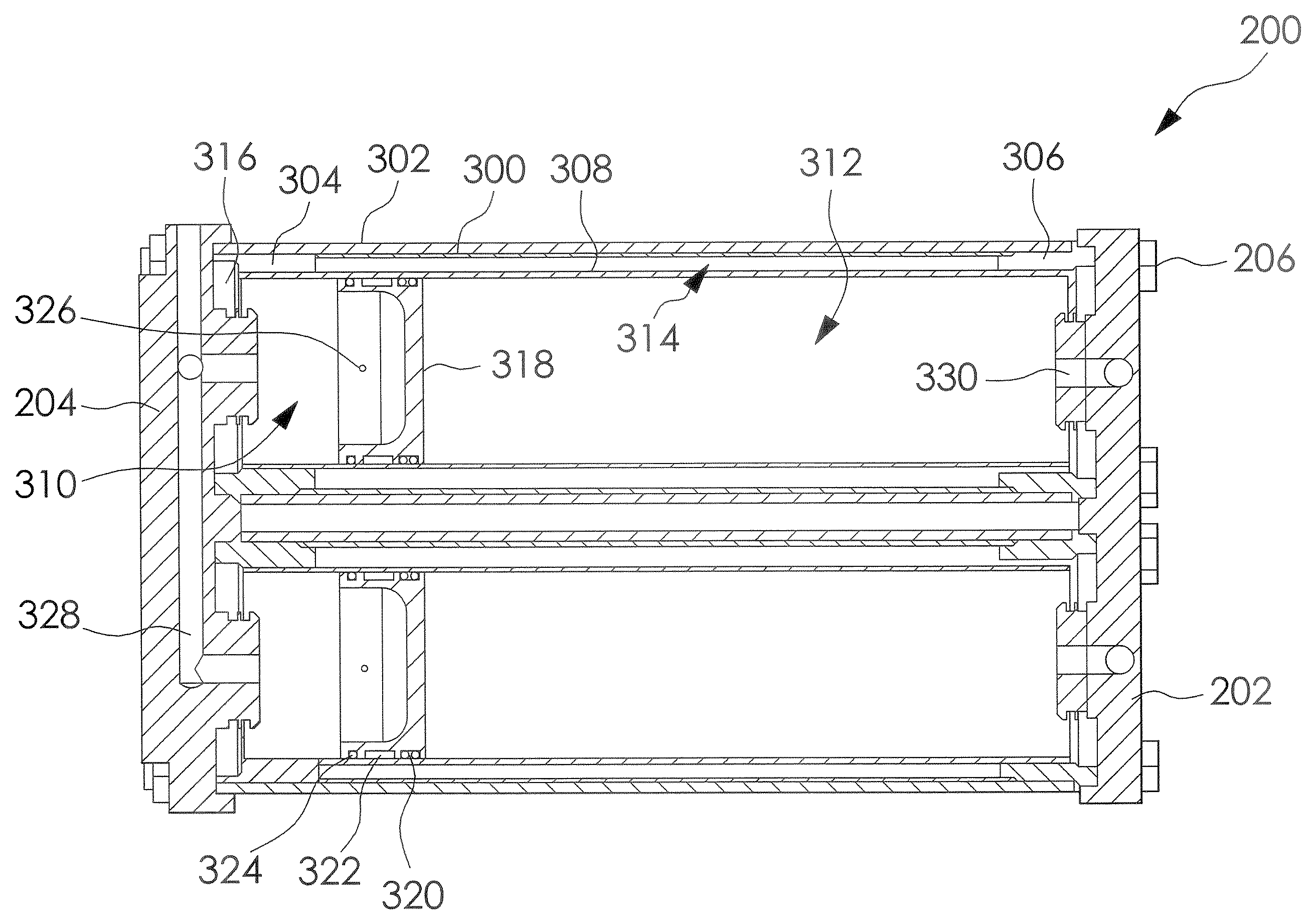
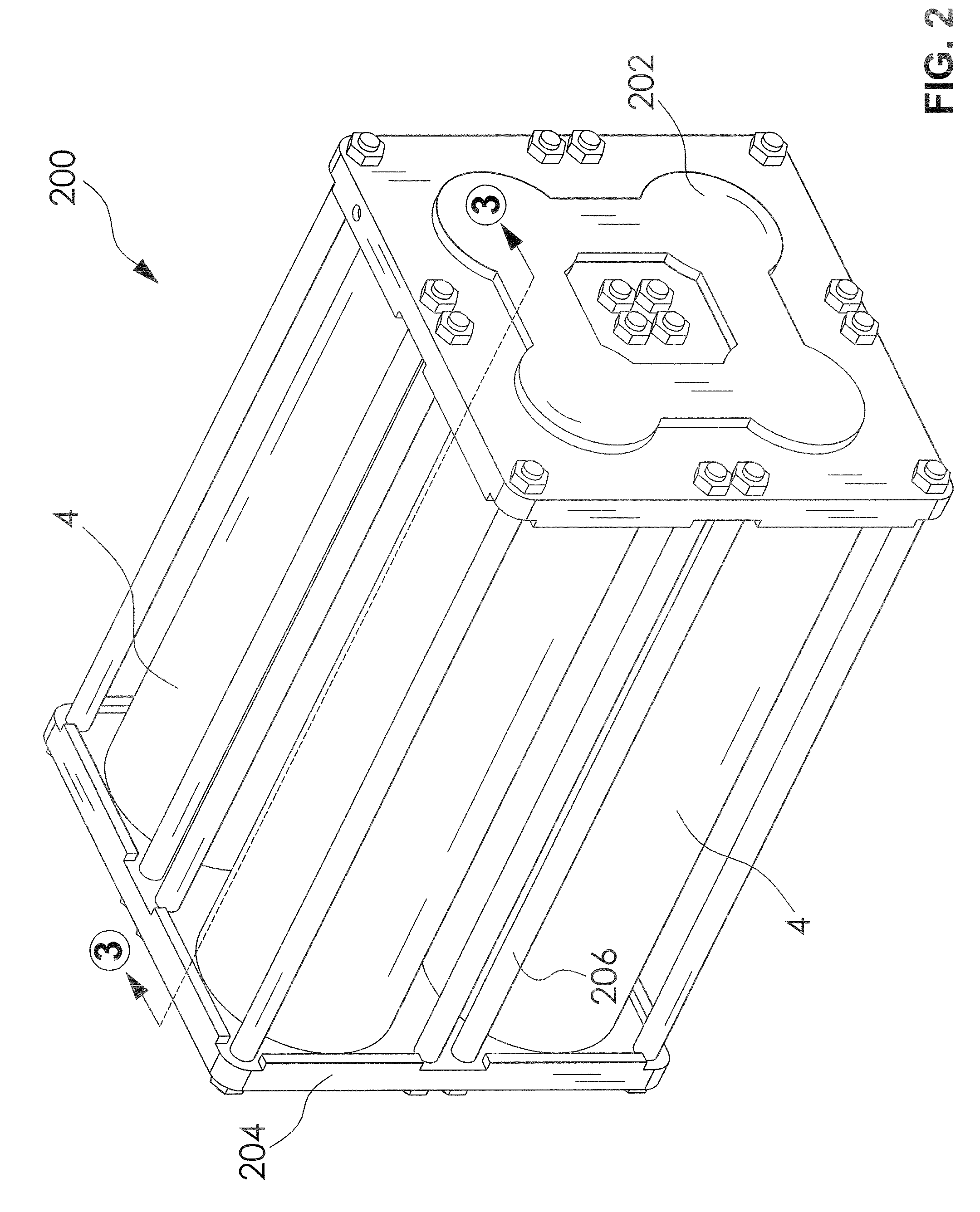
A lightweight, optimally efficient, easily serviced, piston-in-sleeve high pressure accumulator is provided. The accumulator includes one or more cylindrical composite pressure vessel separate end cap manifolds. A piston slidably disposed in a thin impermeable internal sleeve in the accumulator separates two chambers, one adapted for containing a working fluid and the other adapted for containing gas under pressure. Gas is provided in a volume between the impermeable internal sleeve and the composite pressure vessel wall. Additional gas is optionally provided in gas cylinders. Further components are provided for withstanding harmful effects of radial flexing of the composite vessel wall under high pressures, and from stresses present in use in mobile applications such as with a hydraulic power system for a hydraulic hybrid motor vehicle.
Owner:NRG ENTERPRISES
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326062A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
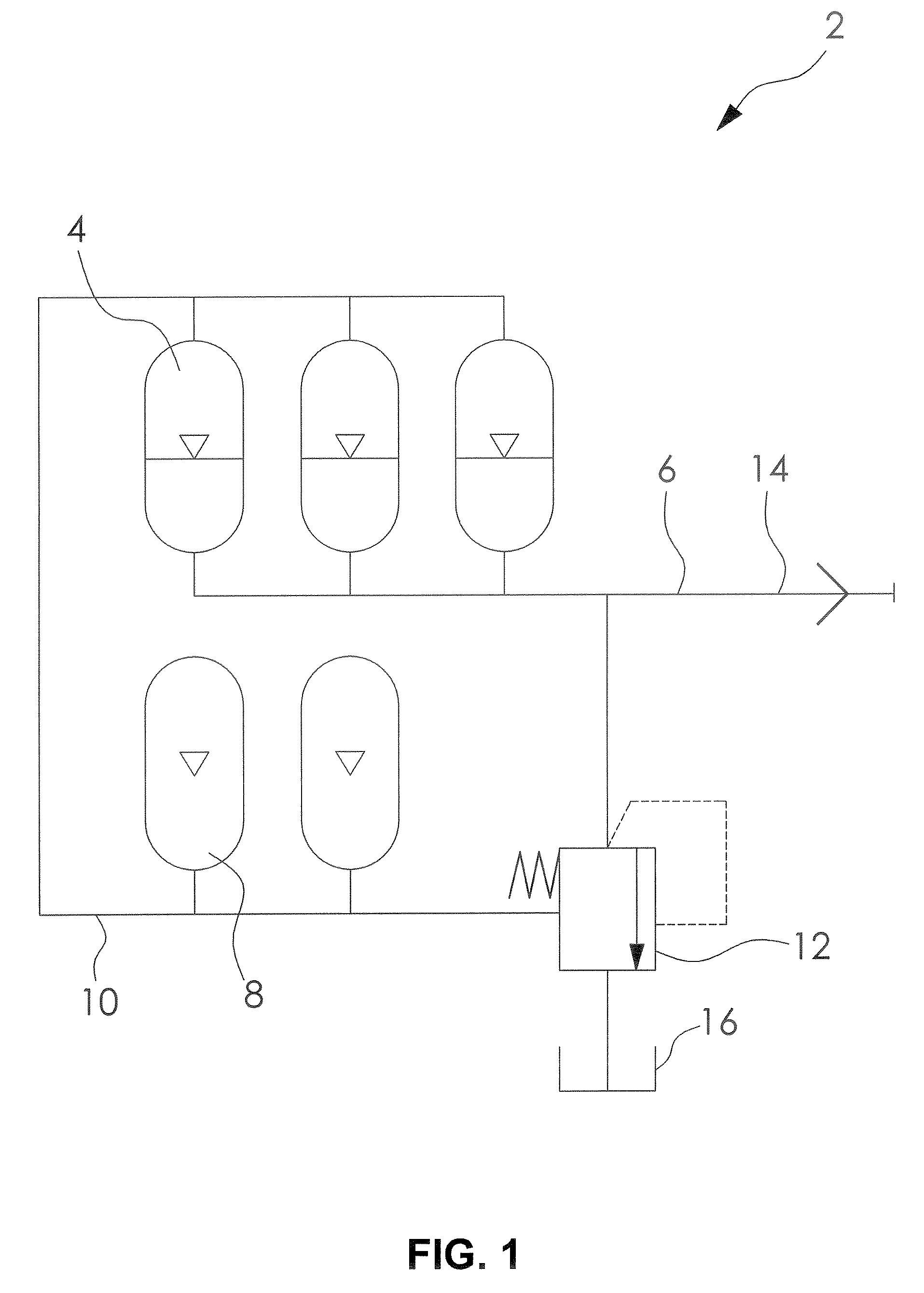
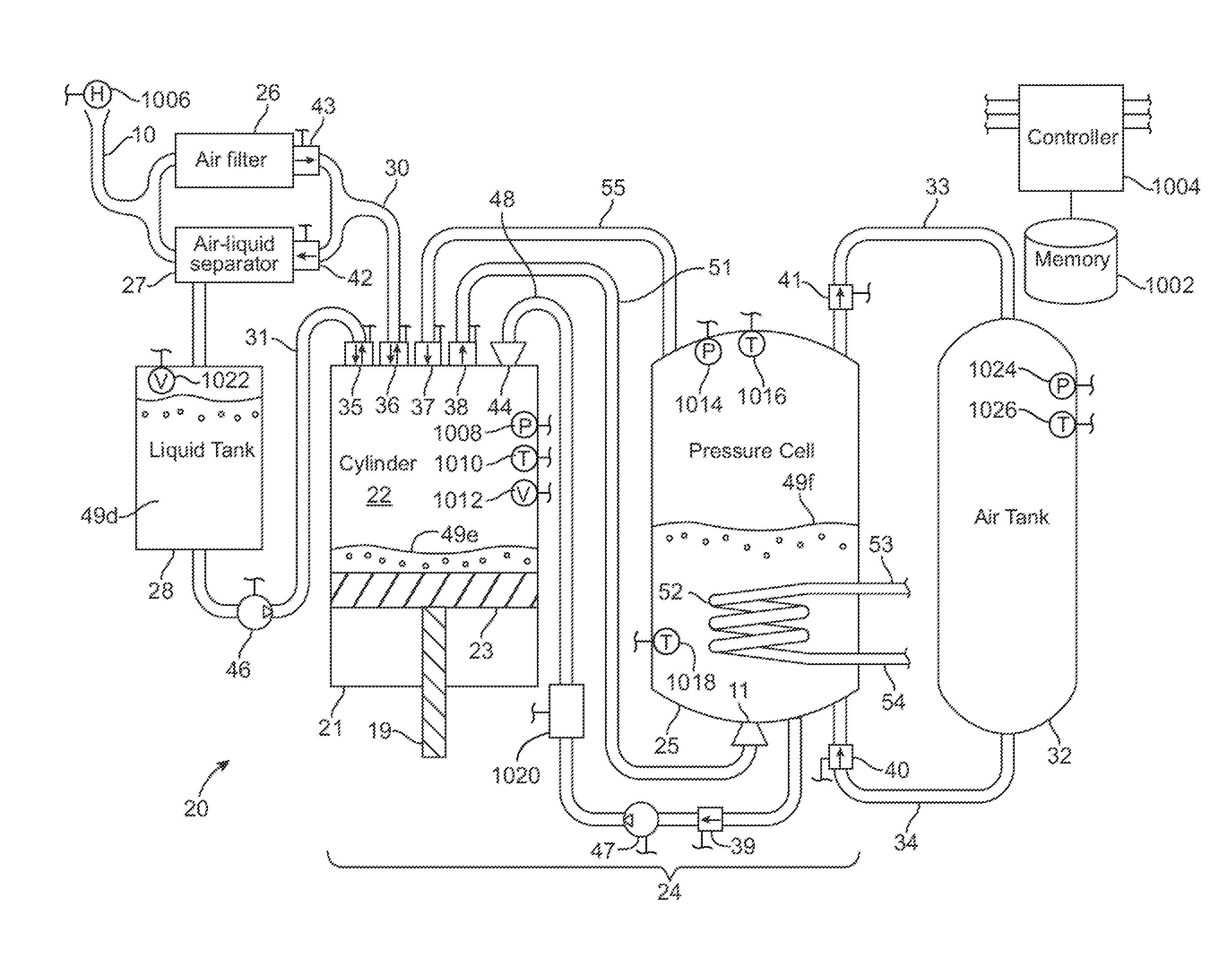
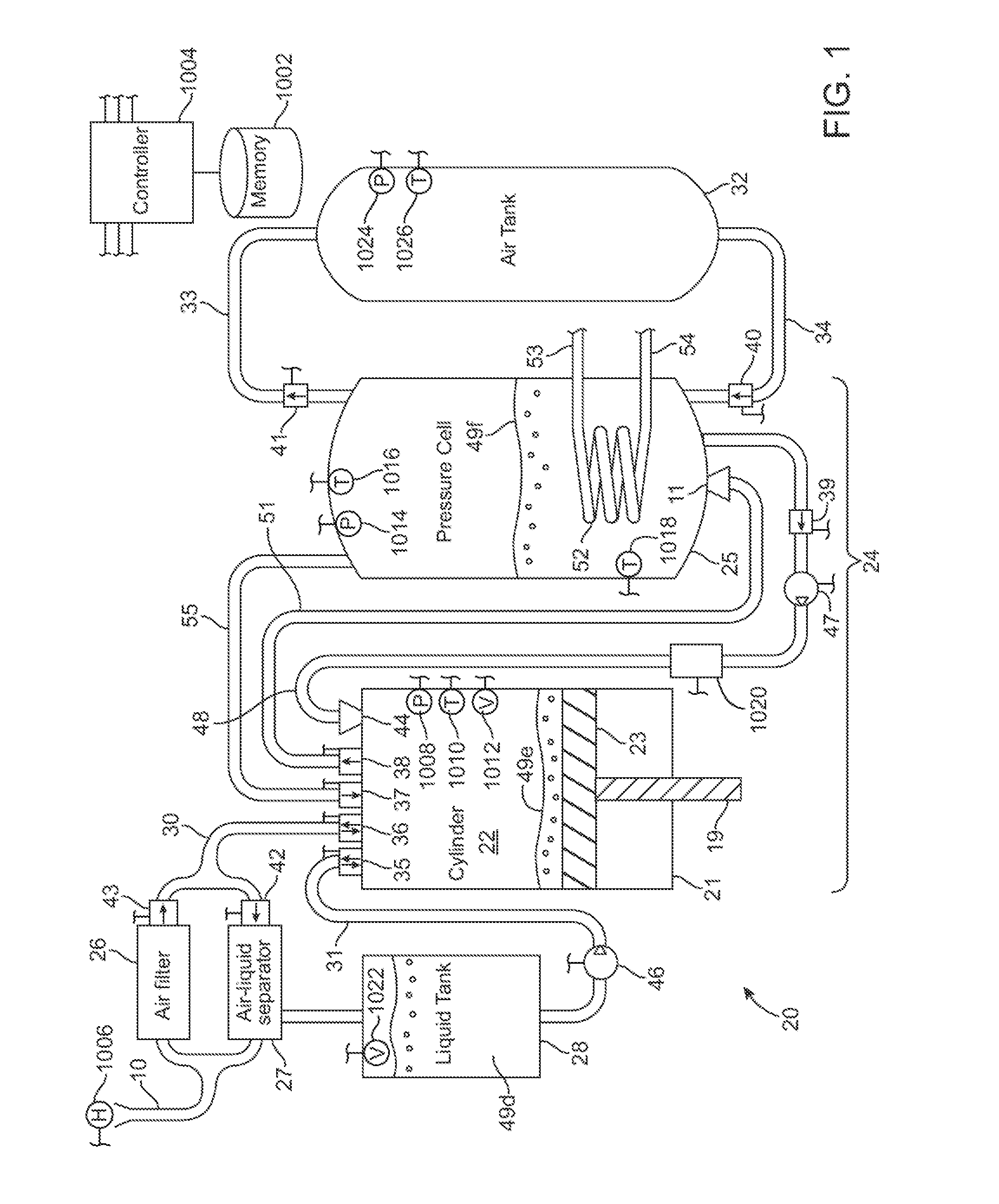
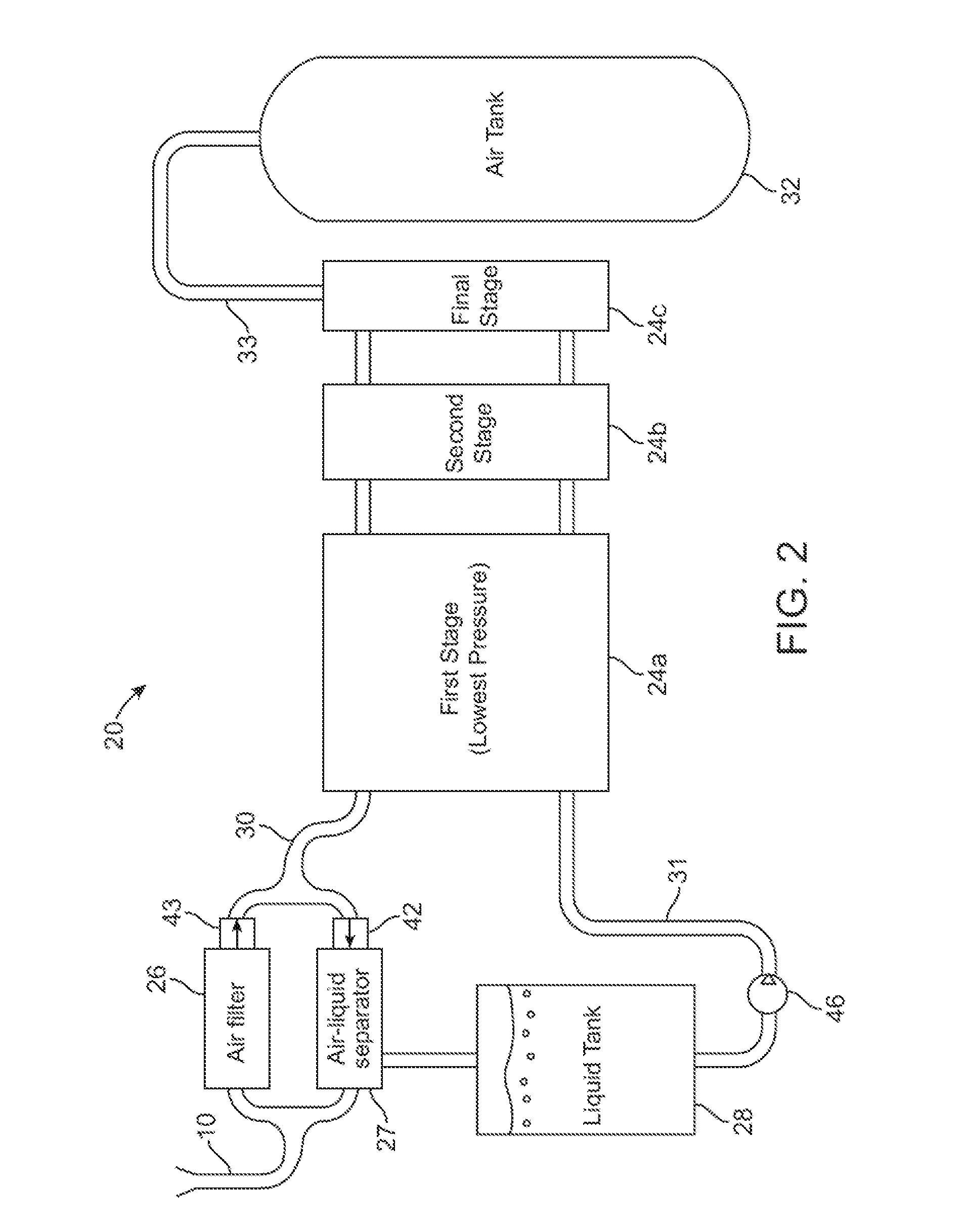
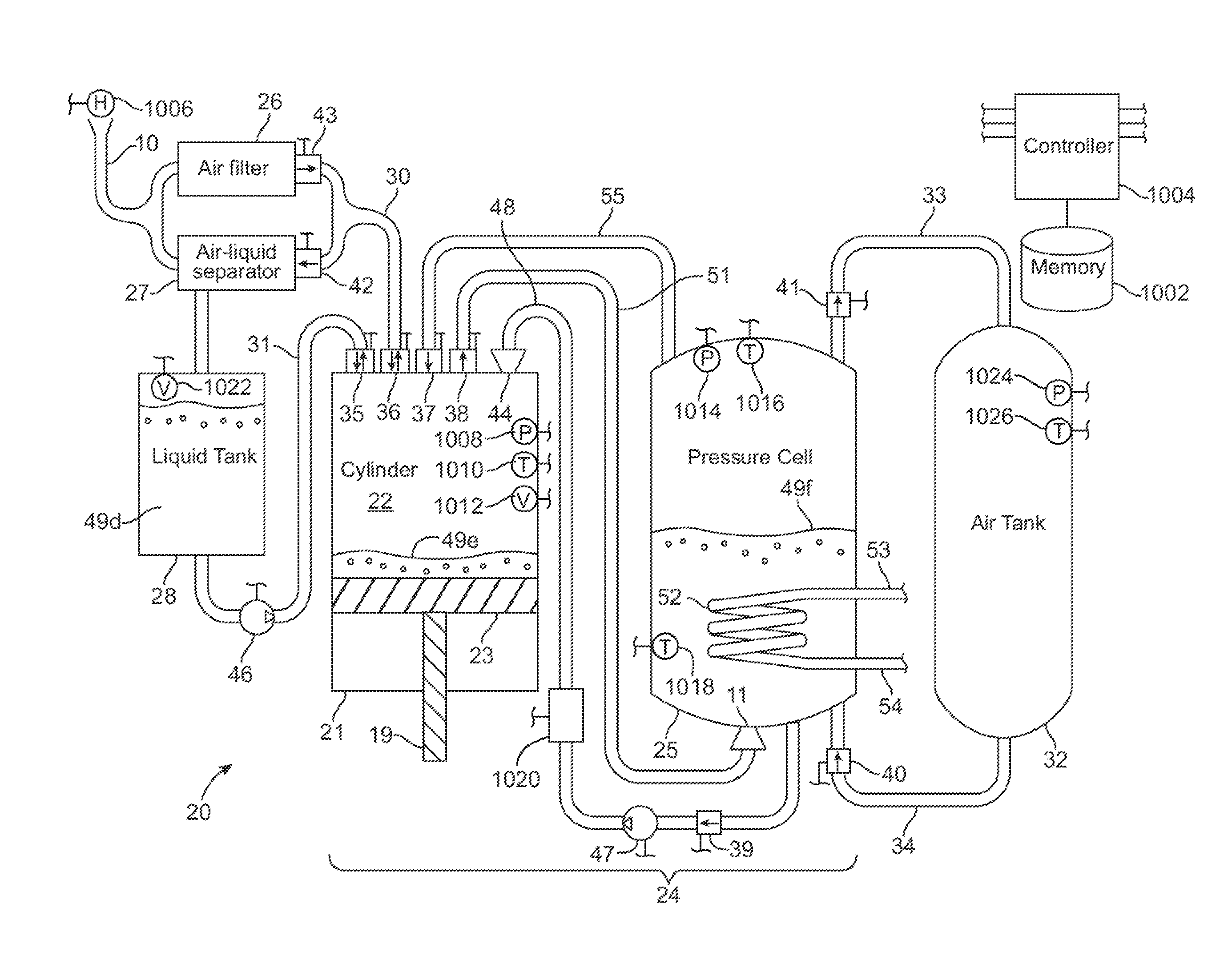
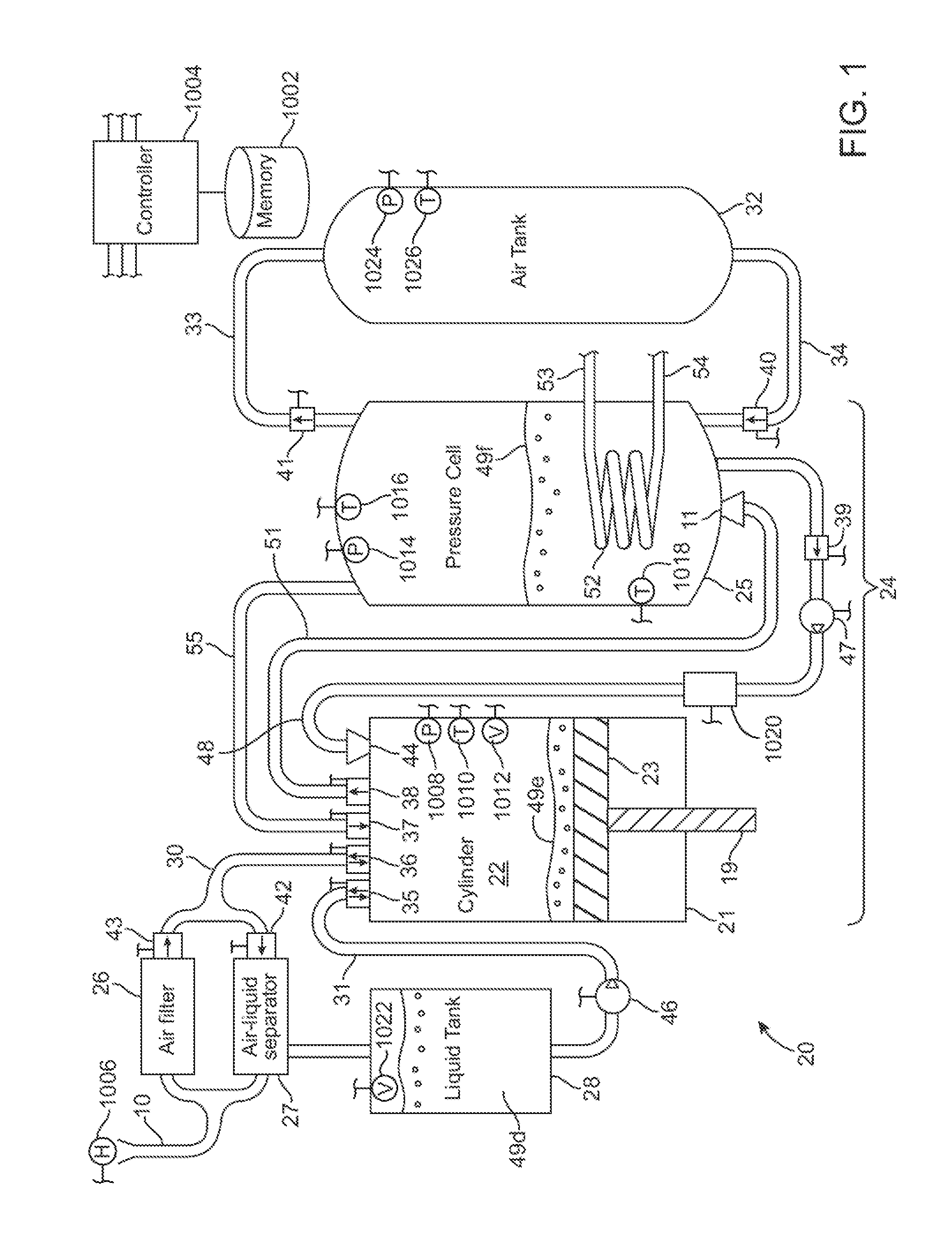
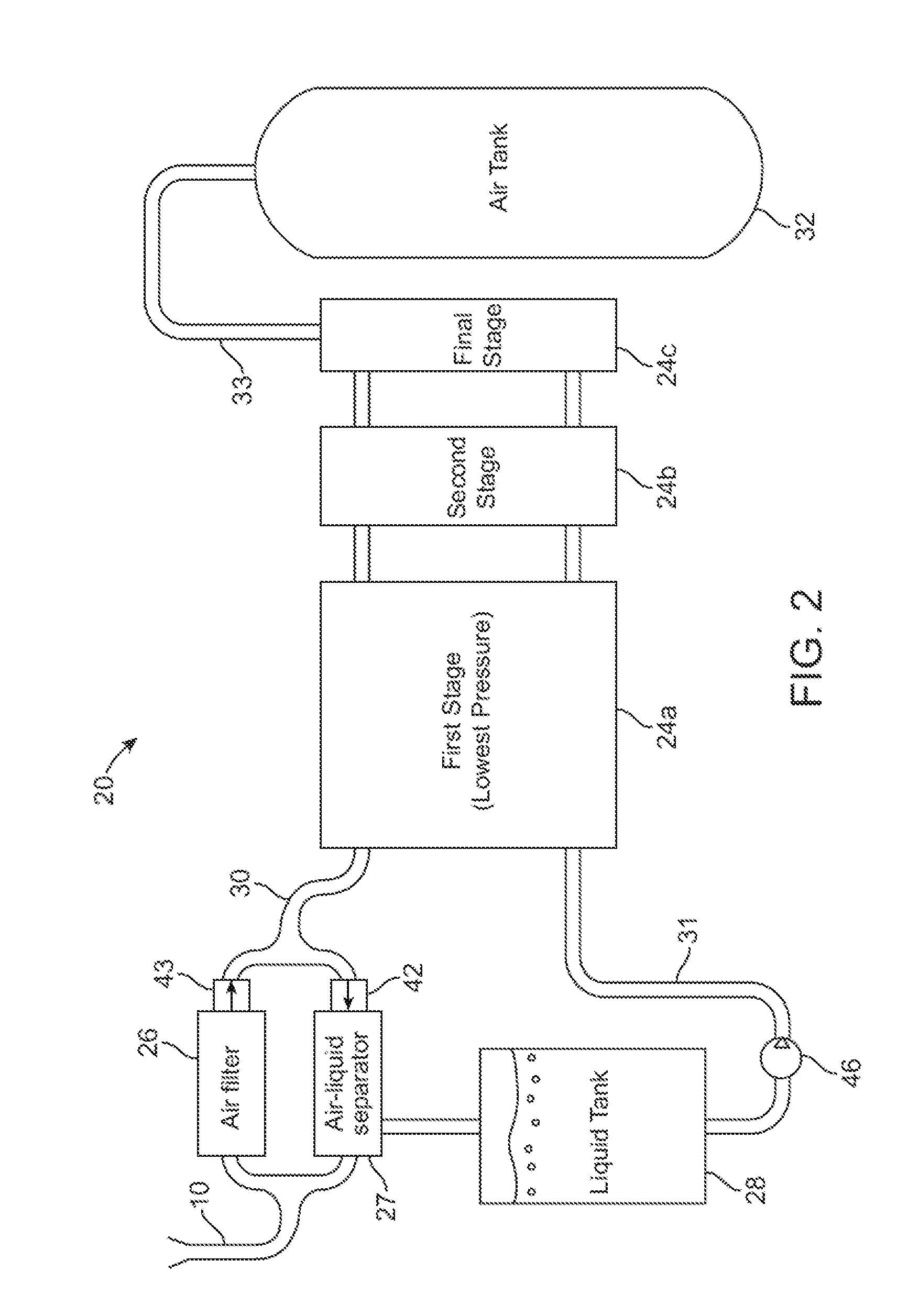
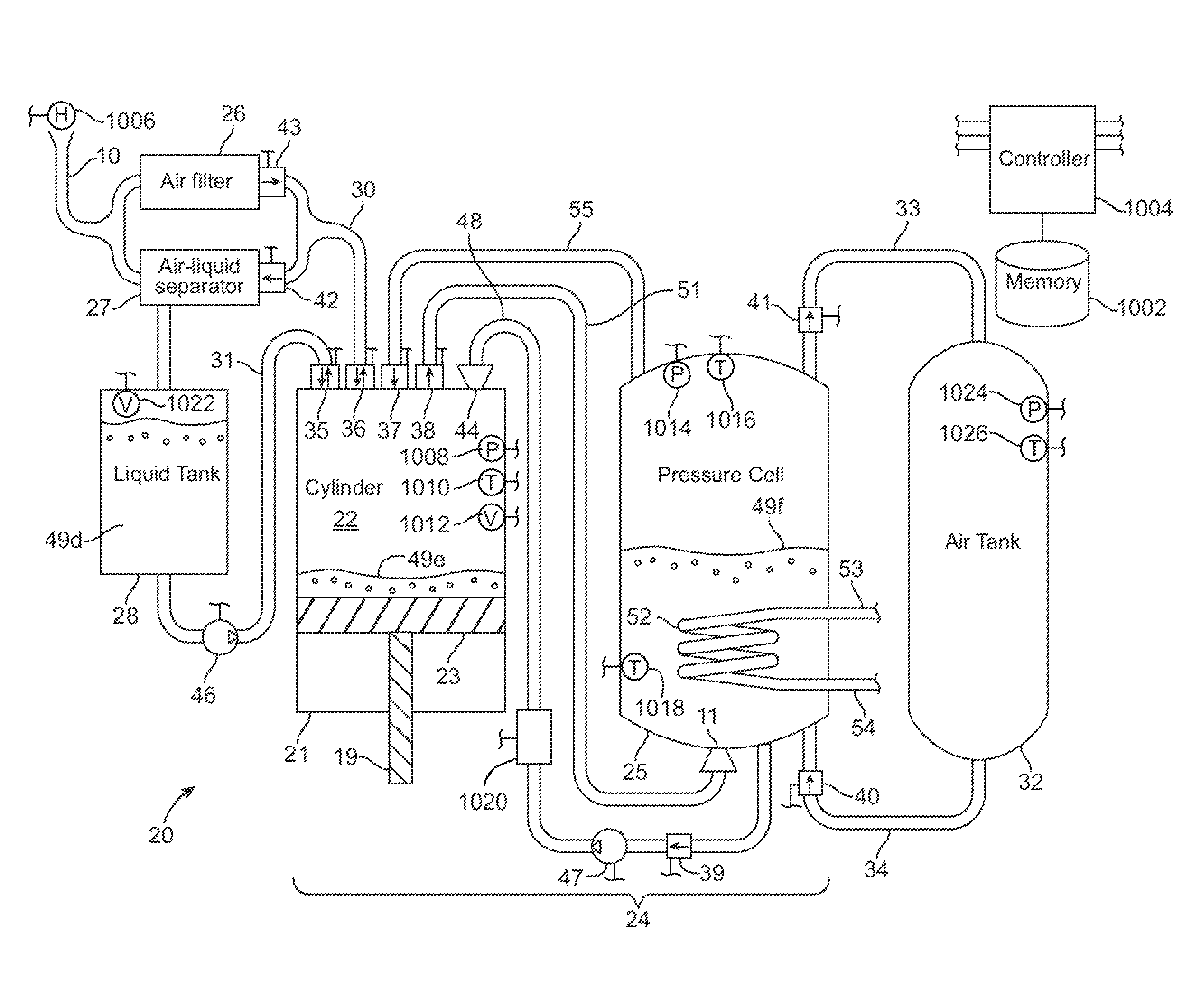
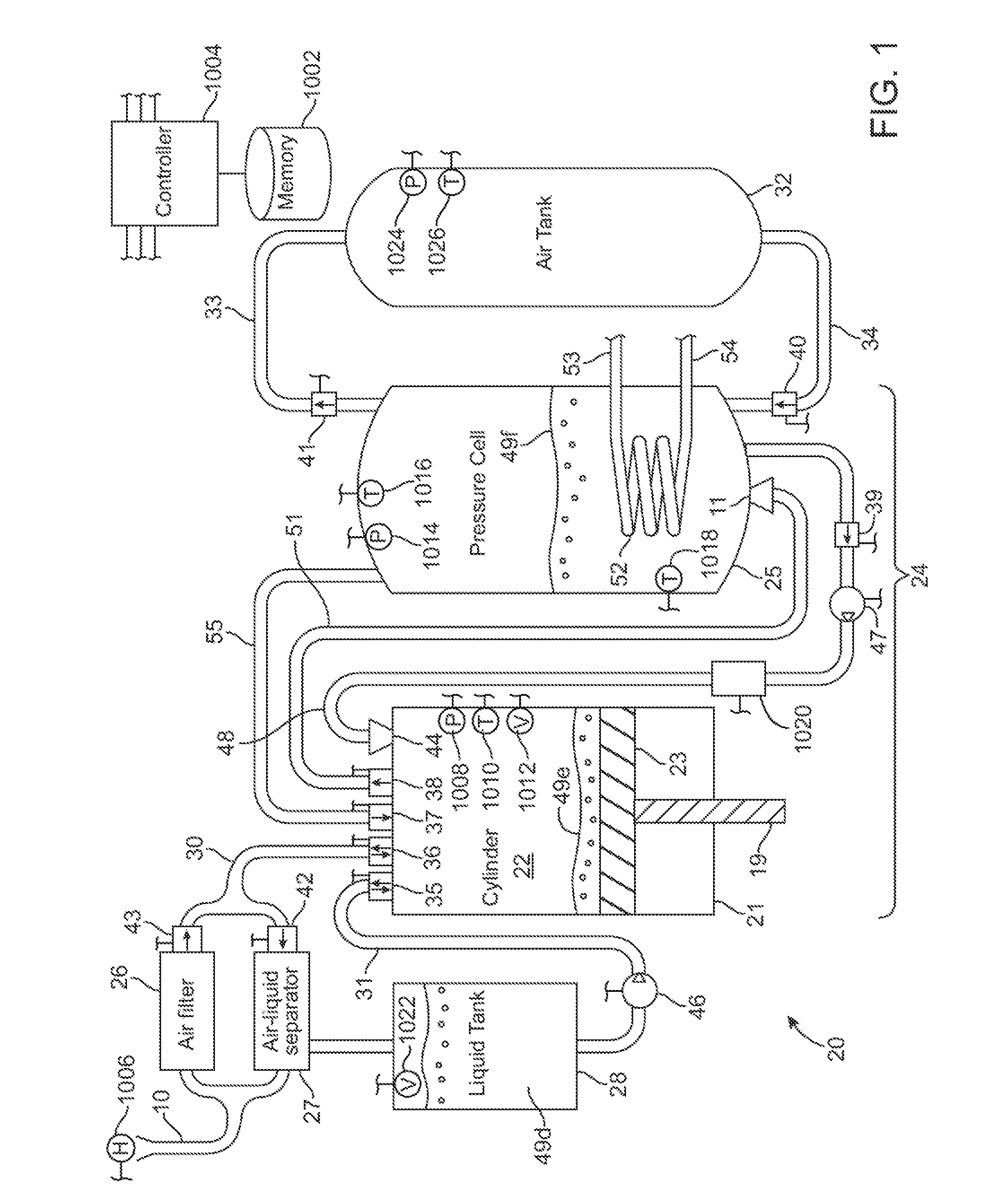
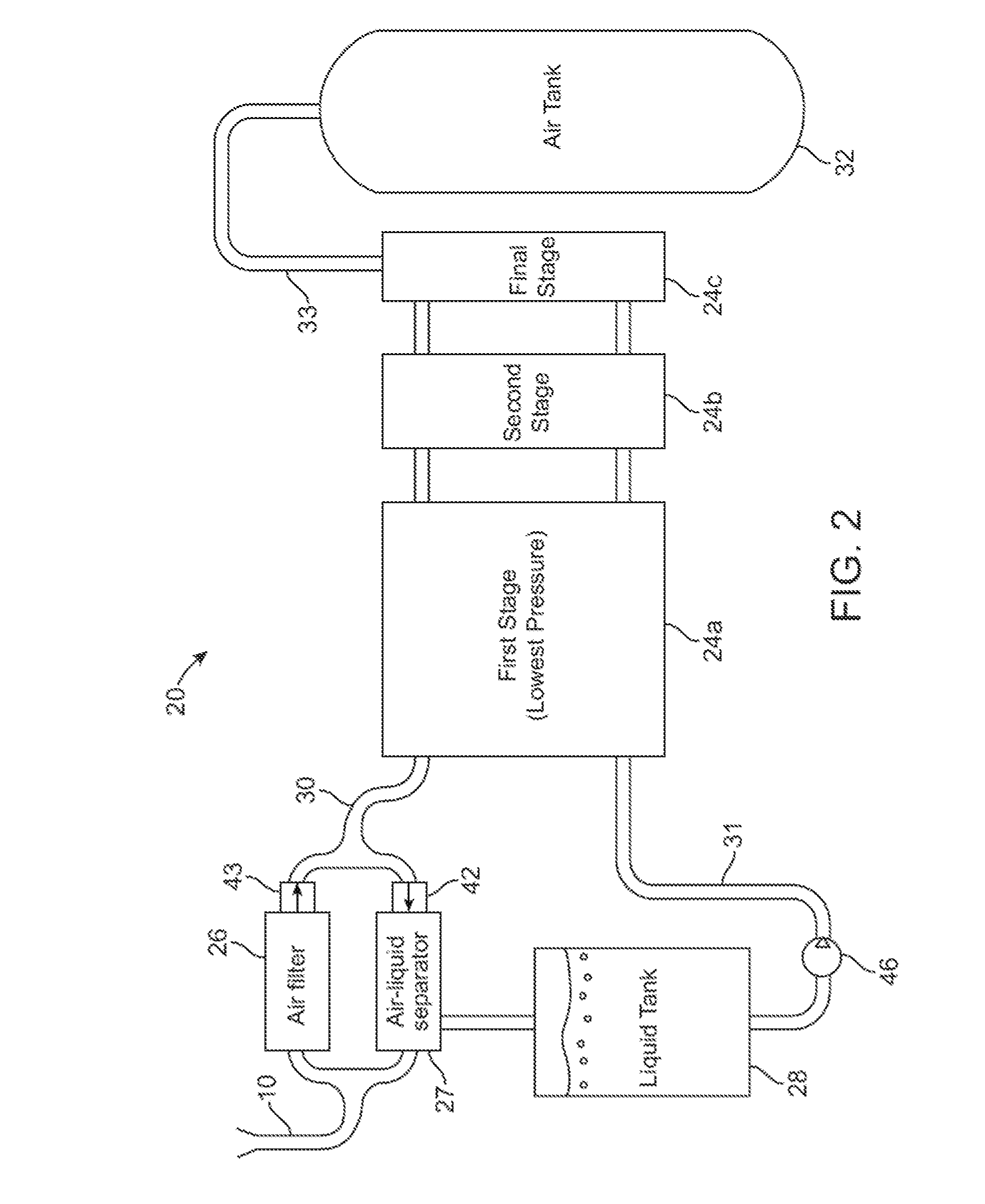
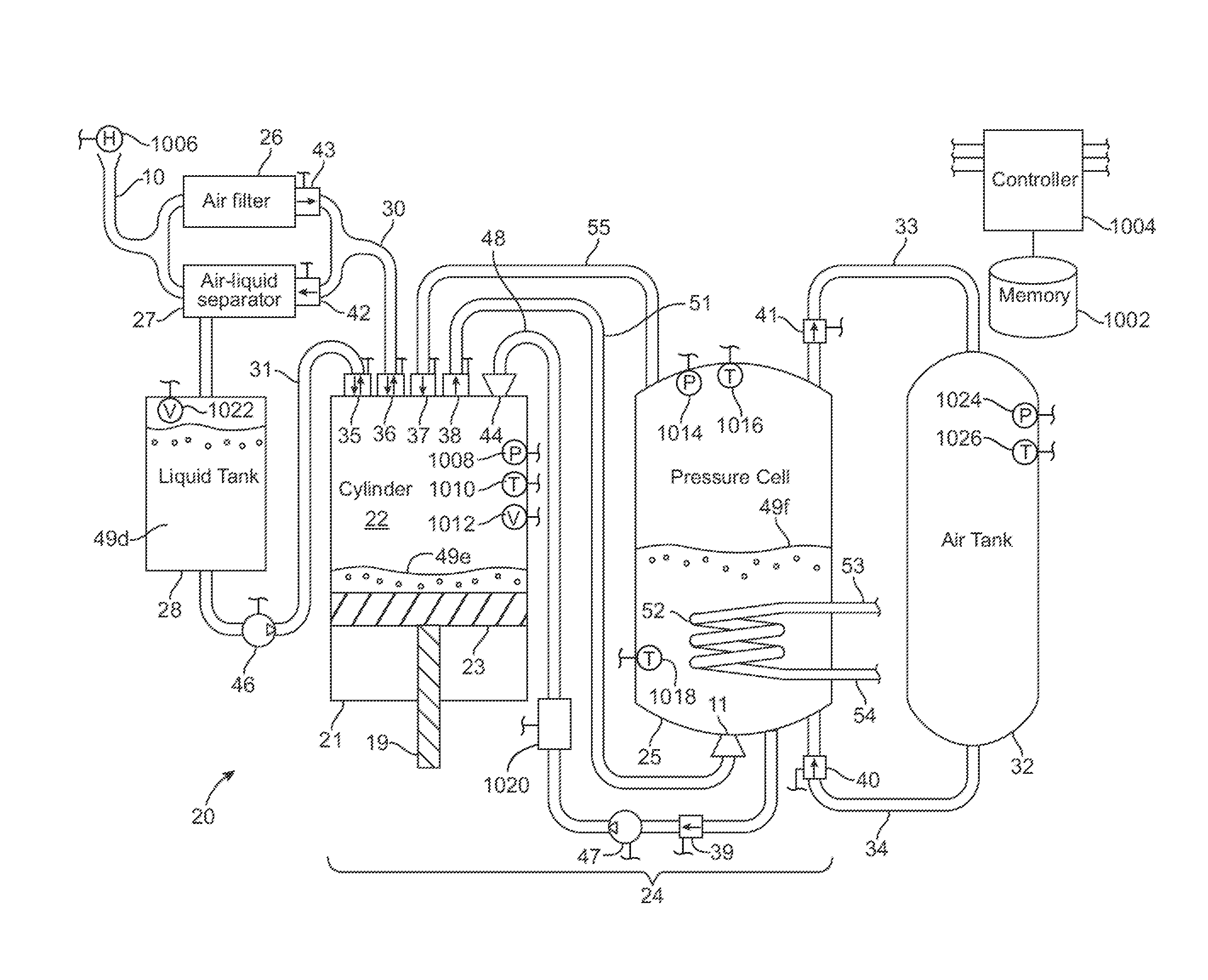
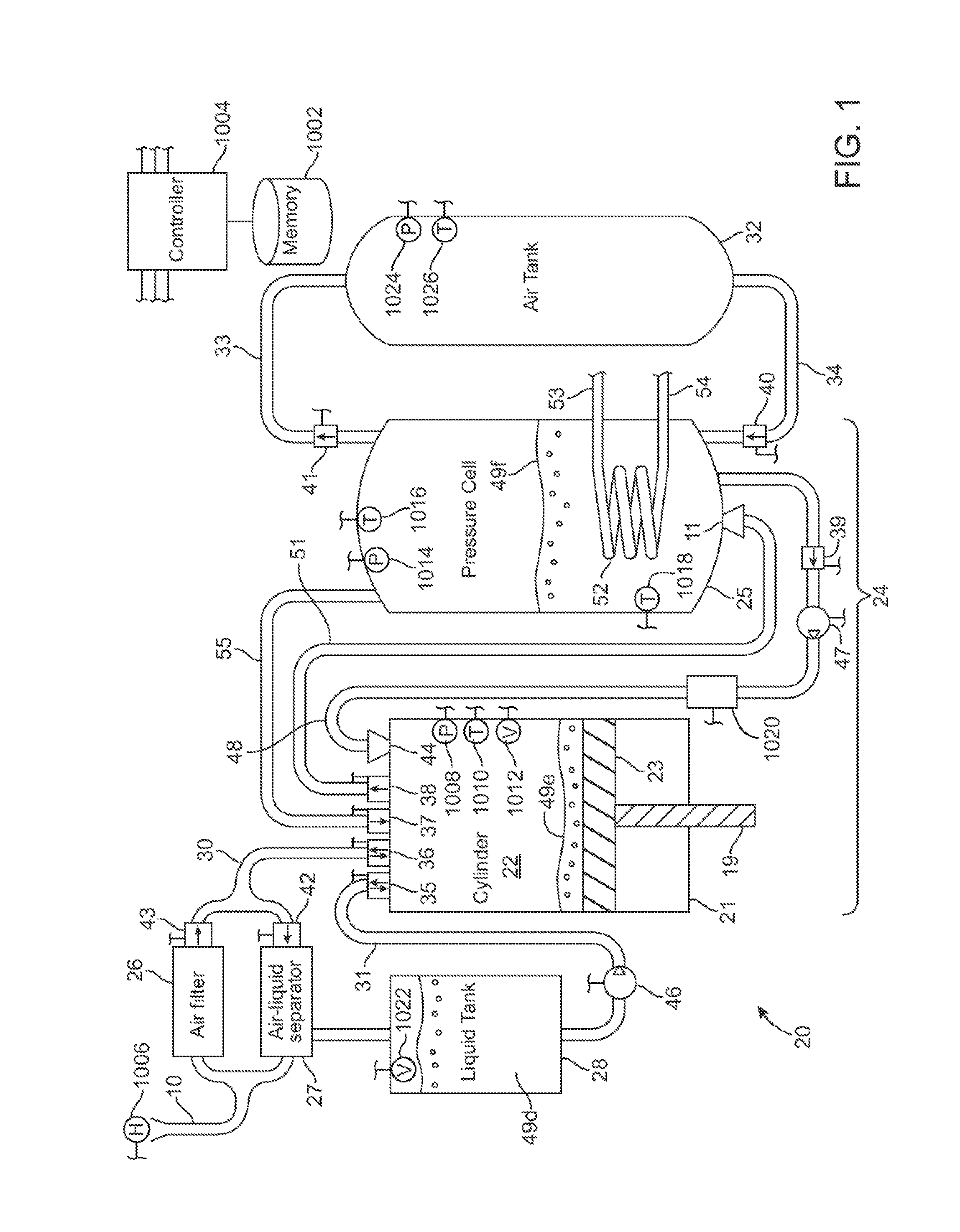
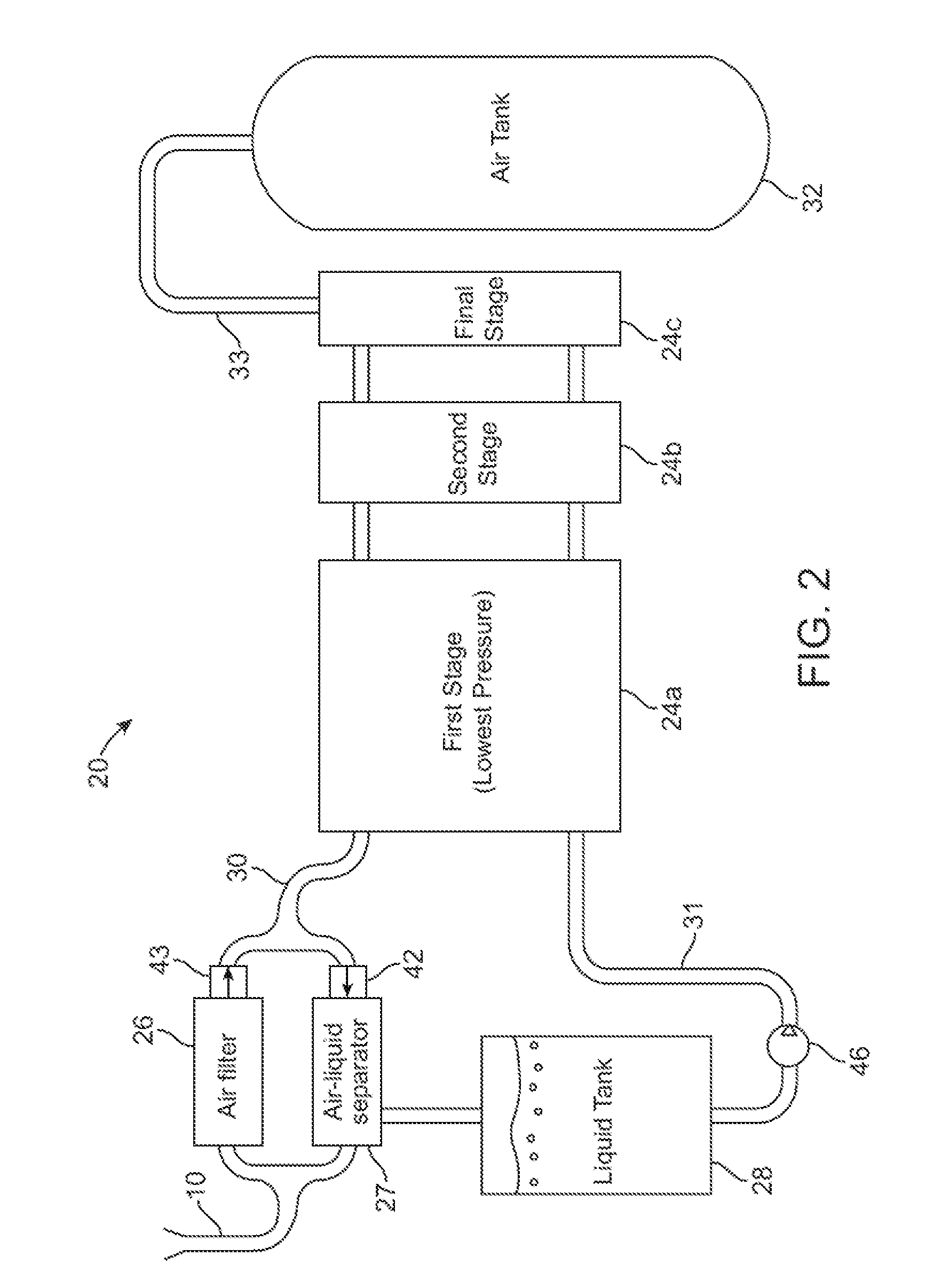
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Method and device for attenuating the motion of hydraulic cylinders of mobile work machinery
InactiveUS7318292B2Good conditionServomotorsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersHydraulic cylinderEngineering
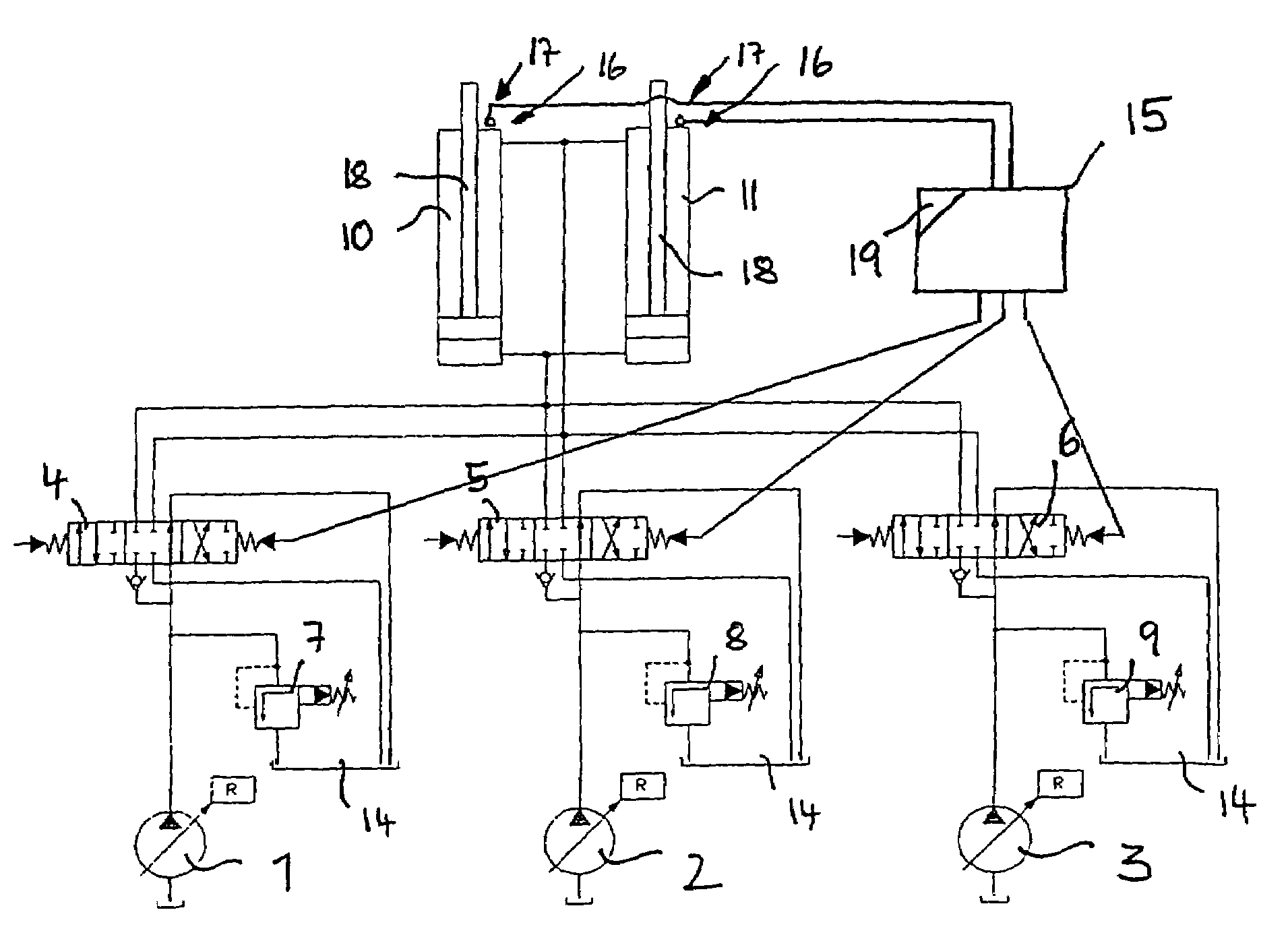
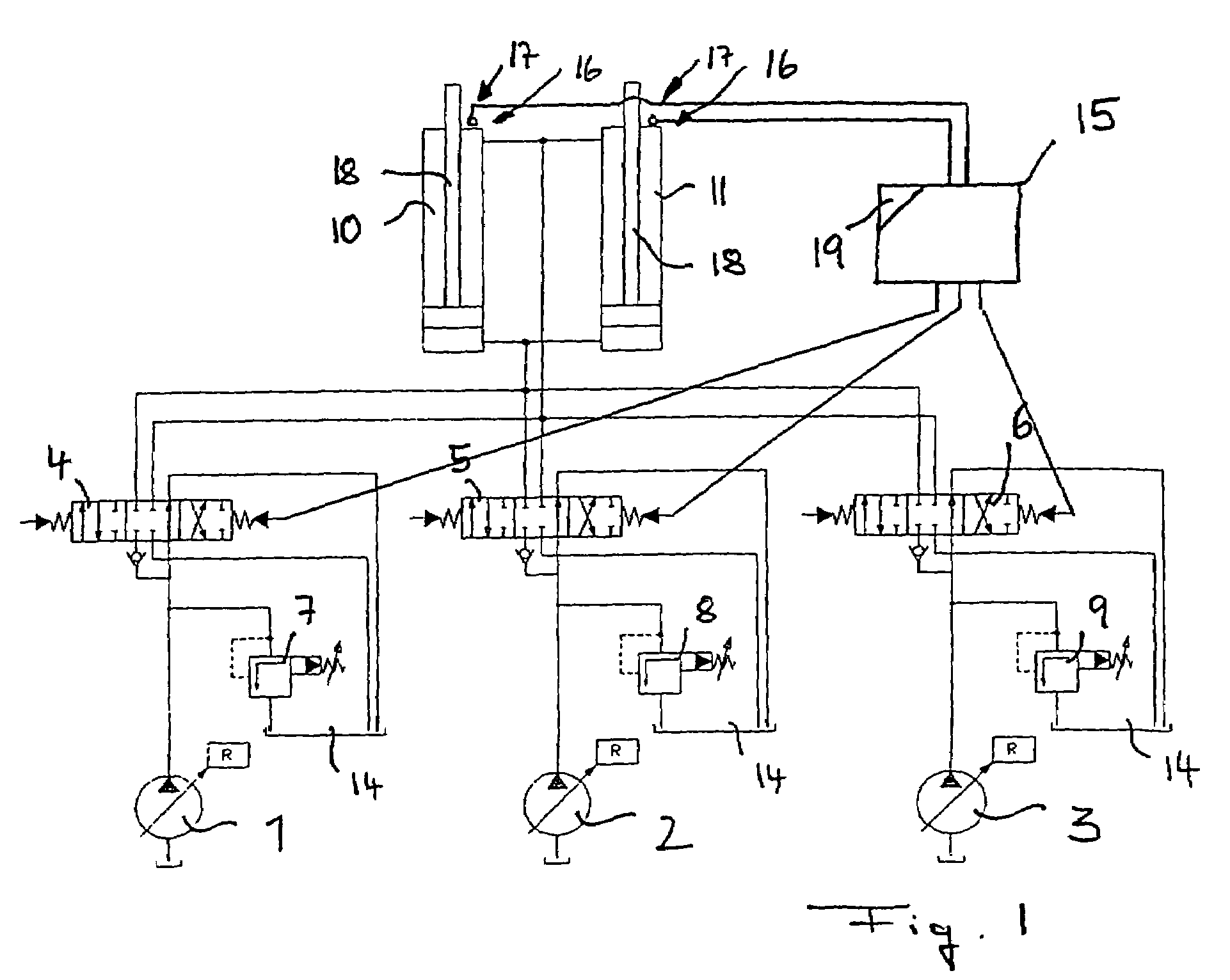
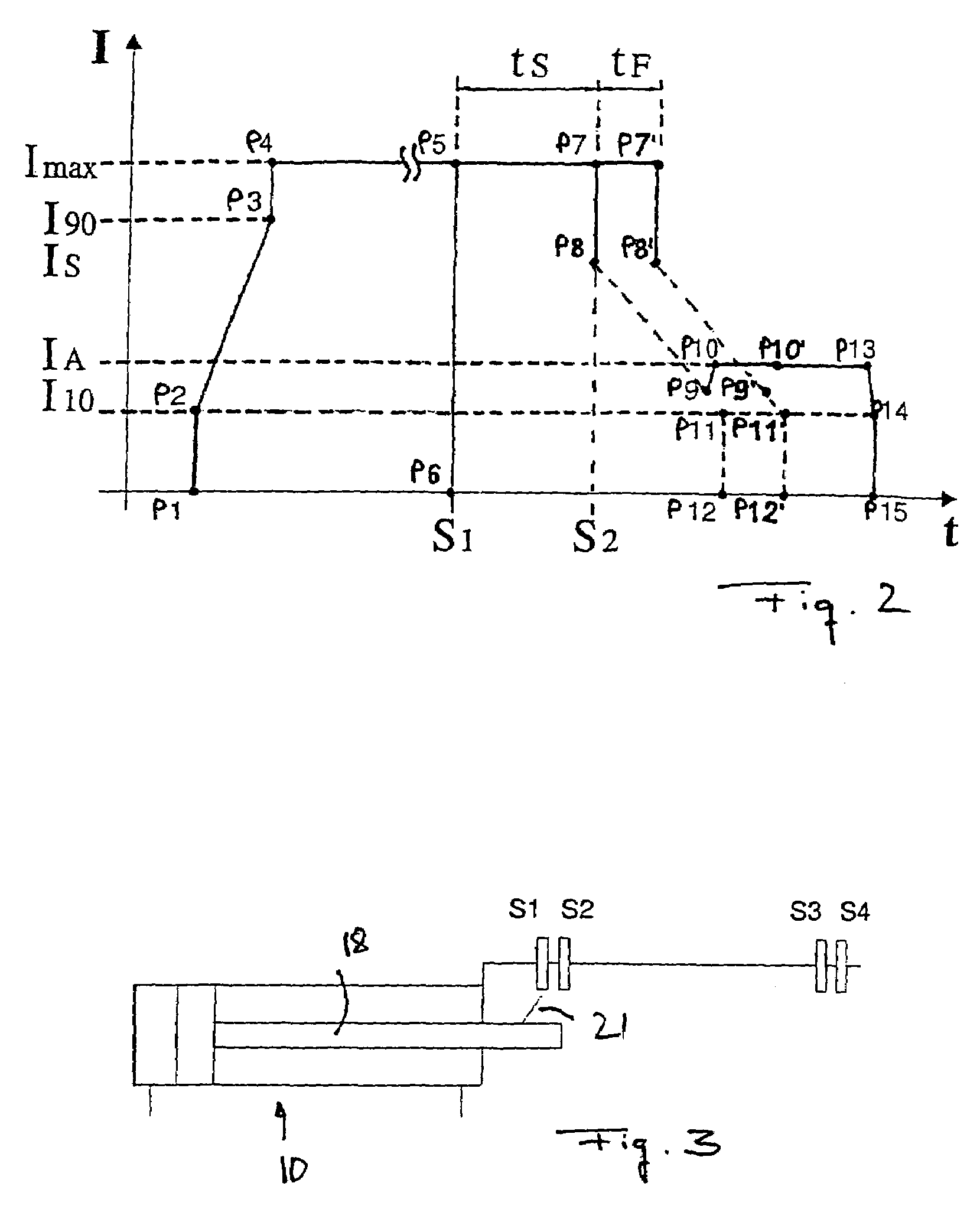
The present invention relates to a method for attenuating the motion of hydraulic cylinders of mobile work machinery, in particular of hydraulic excavators, in which prior to the hydraulic cylinder reaching one of the limits of travel, its motion speed is reduced, and the hydraulic cylinder is moved to the respective limit of travel at reduced speed; wherein for the purpose of reducing the speed, the inflow to, and / or the outflow from, the hydraulic cylinder are / is throttled by a flow control device. According to the invention, the method is characterized by, prior to the respective limit of travel being reached, the motion speed of the hydraulic cylinder is registered, and the point in time when throttling commences is changed depending on the registered motion speed. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a device for attenuating the motion of hydraulic cylinders of mobile work machinery, in particular of hydraulic excavators, a position registering device for registering a preliminary limit position of the hydraulic cylinder, a control device for throttling the inflow and / or outflow of the hydraulic cylinder, and a control device for controlling the flow control device when the preliminary limit position is reached. According the invention, the device has a speed registering device for registering the motion speed of the hydraulic cylinder when the preliminary limit position is reached, and the control device has a delay device for delaying driving the flow control device, depending on the recorded motion speed.
Owner:LIEBHERR FRANCE
Hydraulic accumulator health monitor
A system and method to diagnose the operational health of a hydraulic accumulator are provided. The system can include a hydraulic accumulator selectively coupled to a hydraulic actuator, such as a swing motor. The accumulator can be charged by movement of the actuator. A pressure sensor can be associated with the accumulator to determine an accumulator pressure. A controller can be connected to the pressure sensor. The controller can determine a charge curve based on a relationship between an actuator operational parameter associated with the actuator movement and the accumulator pressure. The controller can compare the charge curve to a previously defined charge curve or range to determine an error between the charge curve and the previously defined charge curve or range. The degree of the error can be associated with the operational health of the accumulator, and if too large, the operator may be notified of the status.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Method for surveying the condition of a control valve, and a valve apparatus
InactiveUS6131609AImprove securityLow costFluid-pressure actuator testingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControl signalEngineering
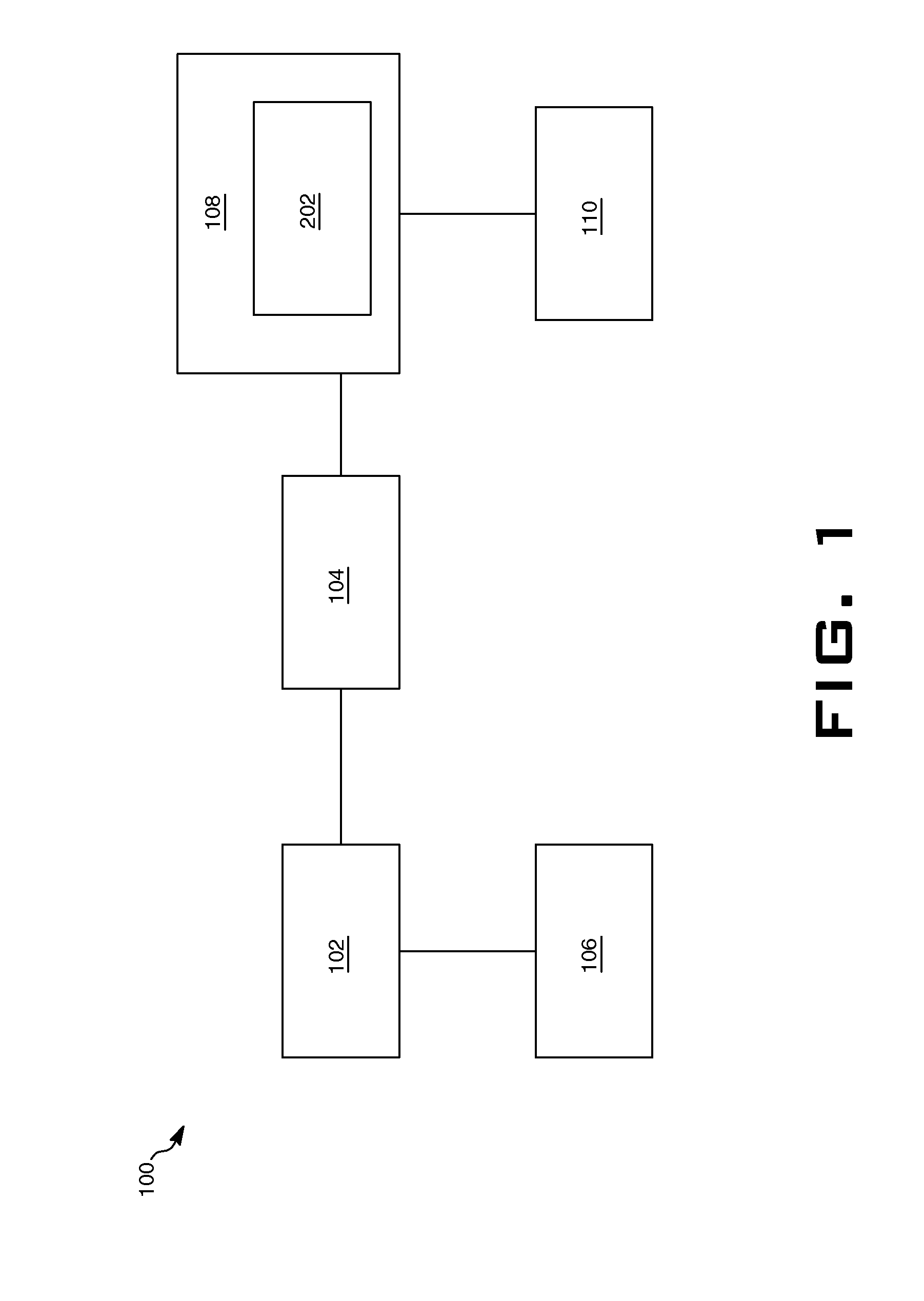
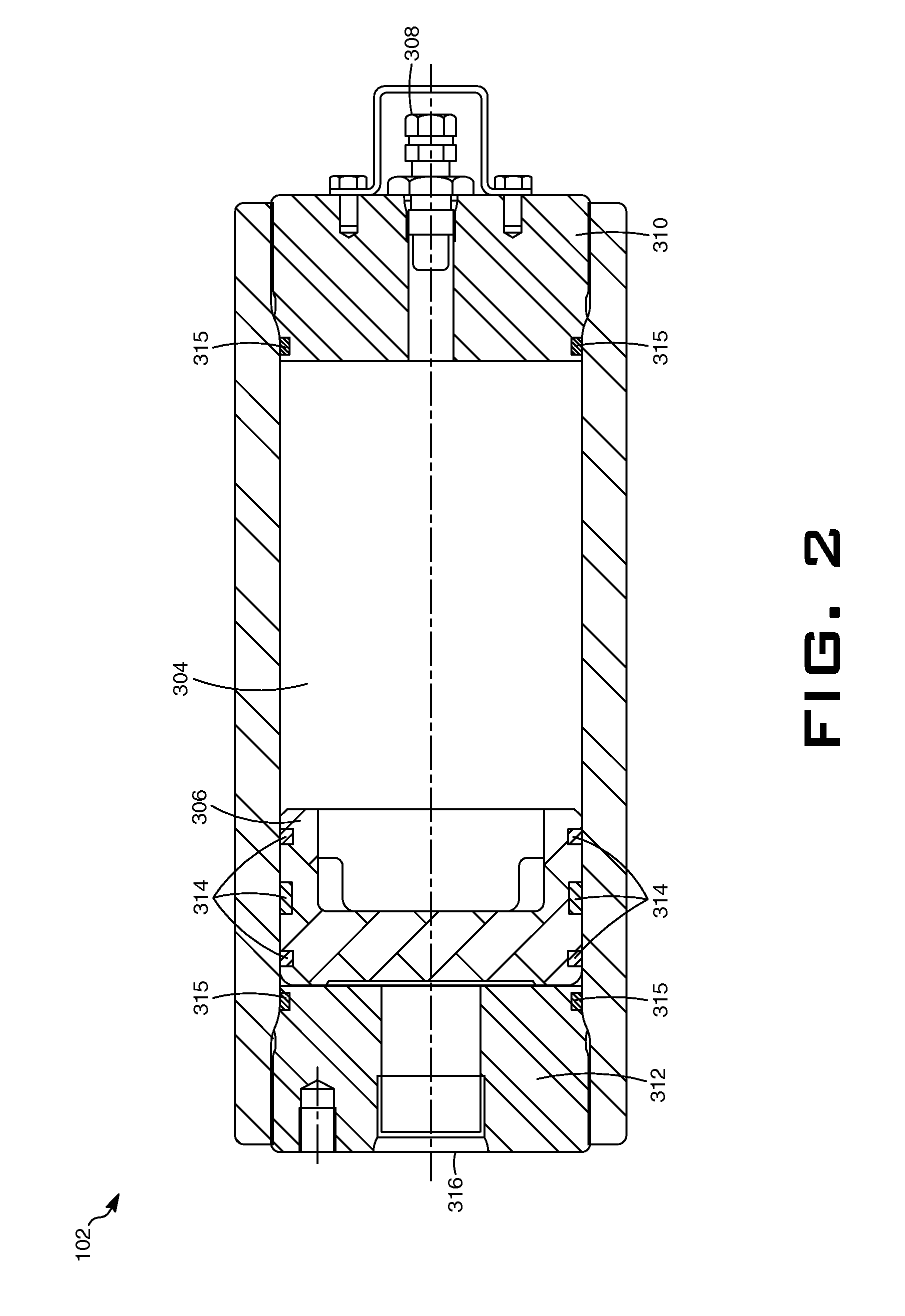
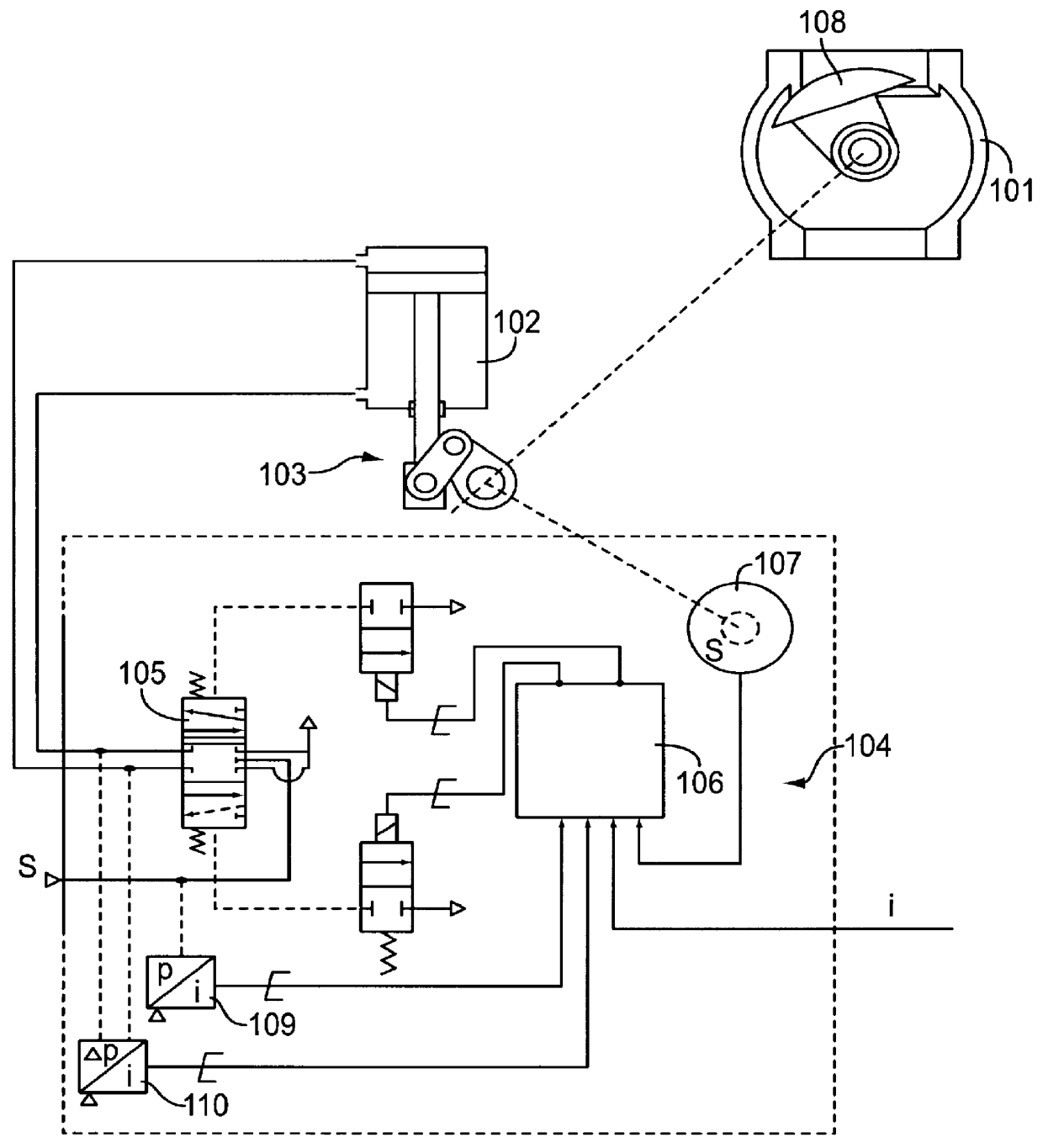
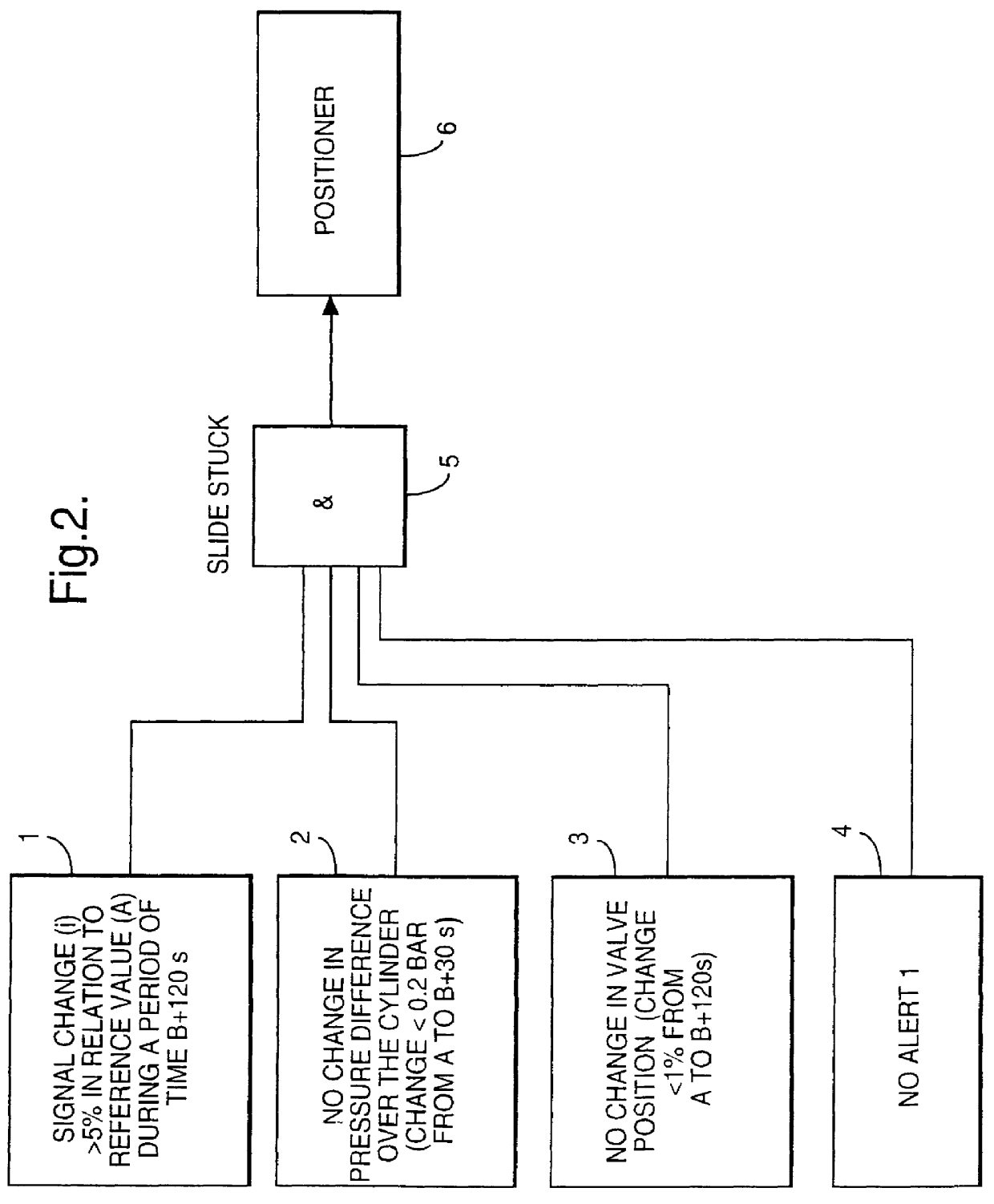
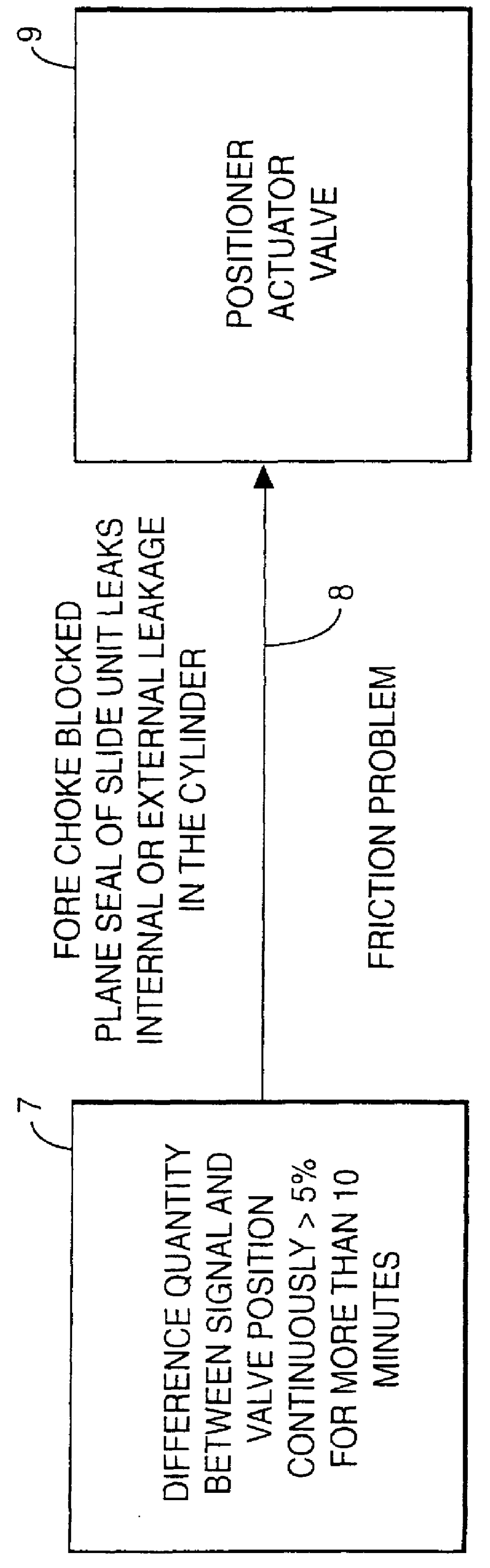
PCT No. PCT / FI97 / 00359 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 4, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 4, 1999 PCT Filed Jun. 9, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 48026 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 18, 1997A method and a valve apparatus for surveying the condition of a control valve. The position of the valve (101) is adjusted by means of an actuator (103) controlled by an electropneumatic positioner (104) and operated by means of pressure medium. The operation of the valve is monitored by sensors (109, 110, 107) that read the readings from the control signal, the input pressure of the positioner, the difference between the input and output pressure of the actuator, and the position of the valve. A fault causing a deviating reading will be located by using the readings given by the sensors and deduction rules stored in the microprocessor of the actuator. In an initial situation, when the valve is in balance state, the readings given by the sensors are stored at least from the control signal, valve position and the difference between the input and output pressure of the actuator. When the operation is continued, the readings given by the sensors are compared with the readings of the initial situation. If the deviations exceed certain limit values and remain there continuously for a certain period of time, a fault message will be given that indicates the location of the fault.
Owner:NELES CONTROLS
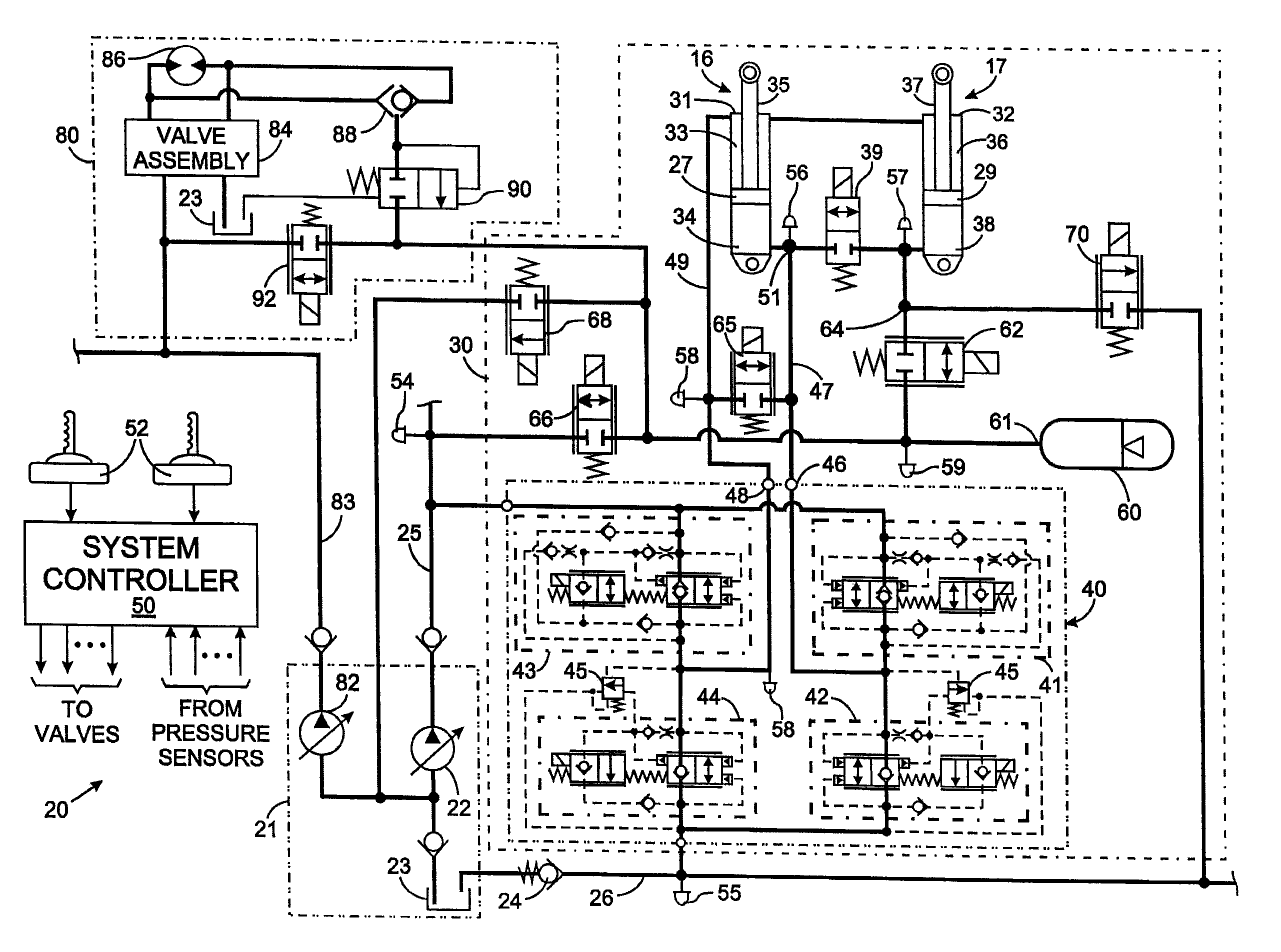
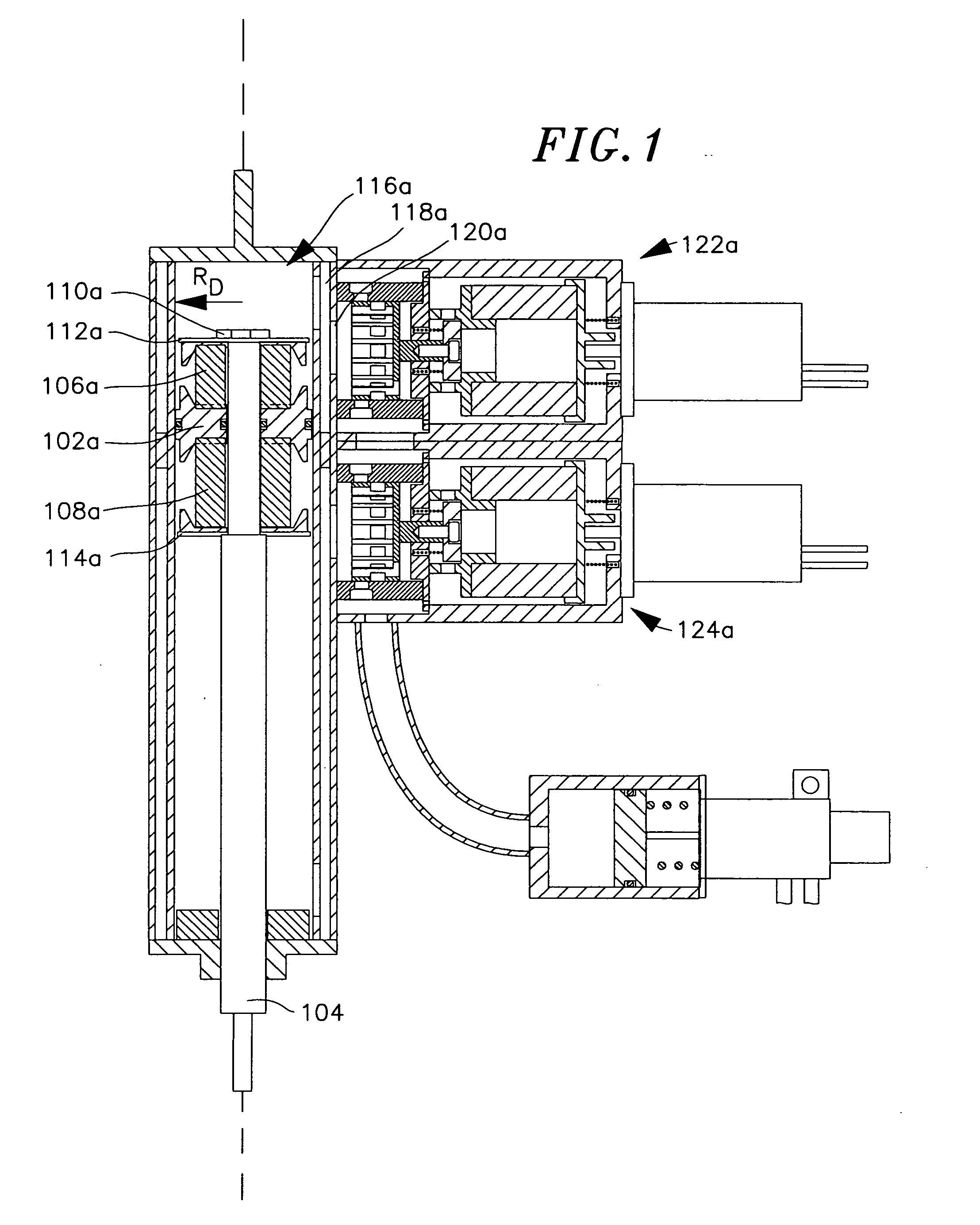
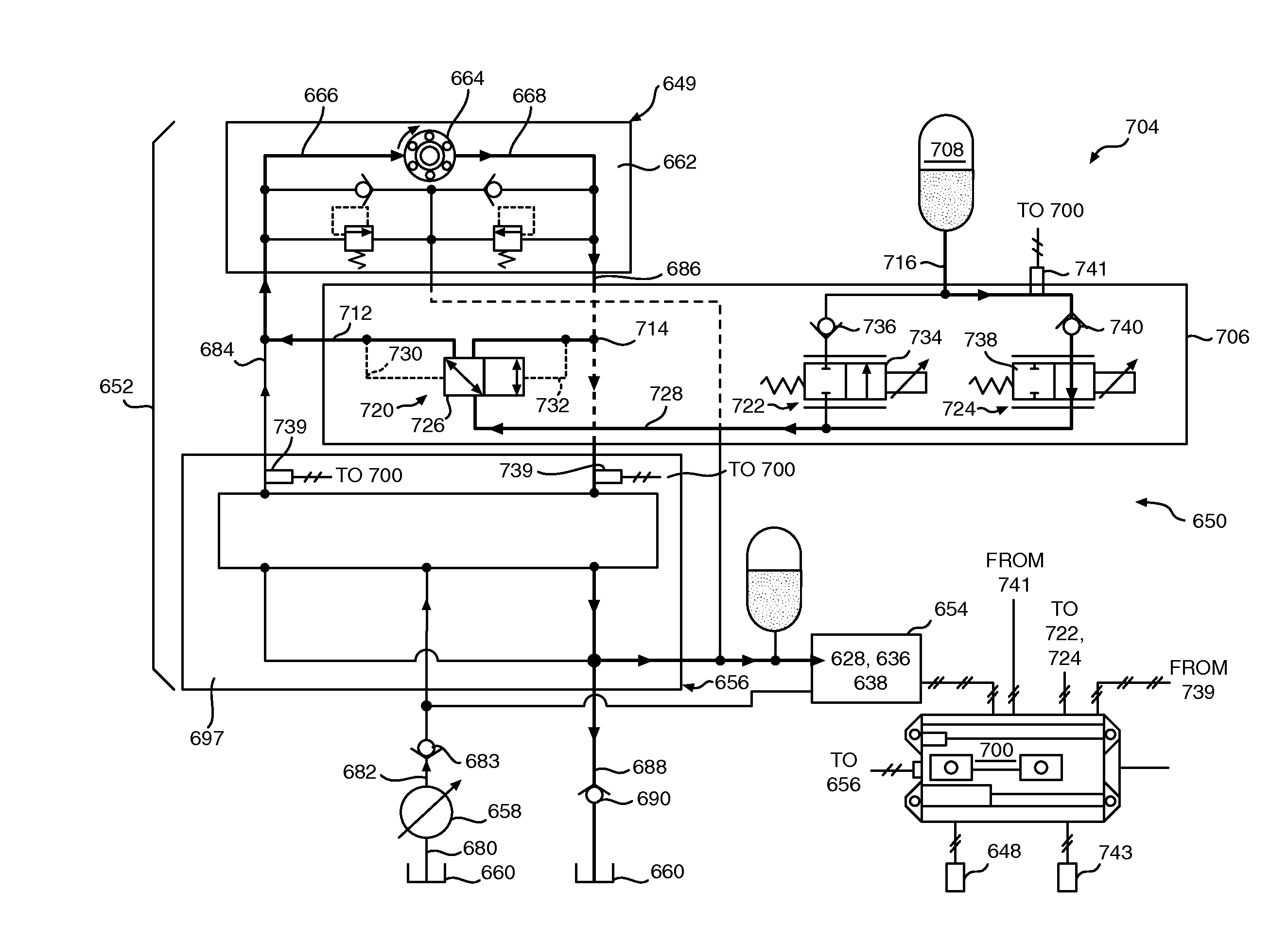
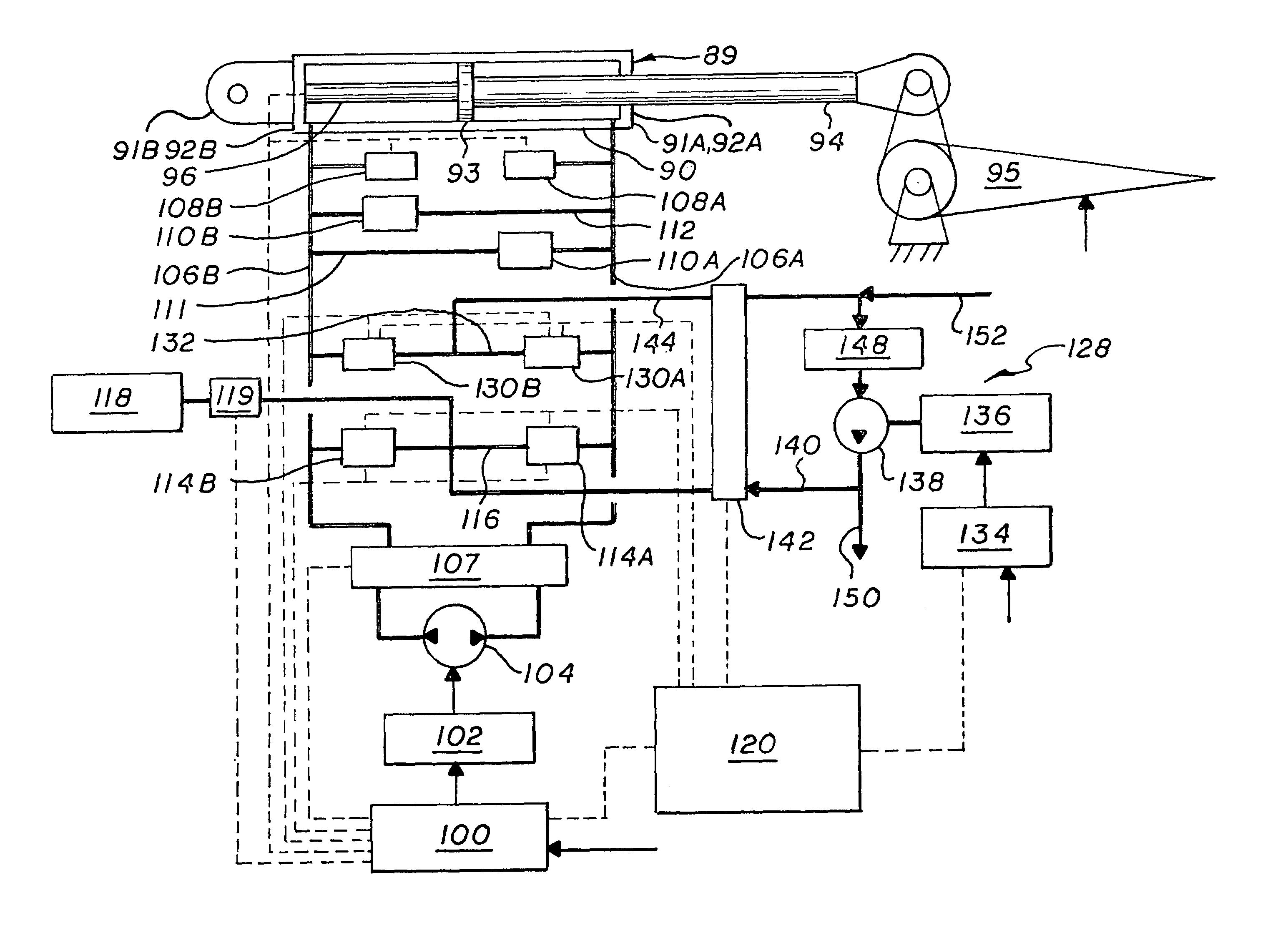
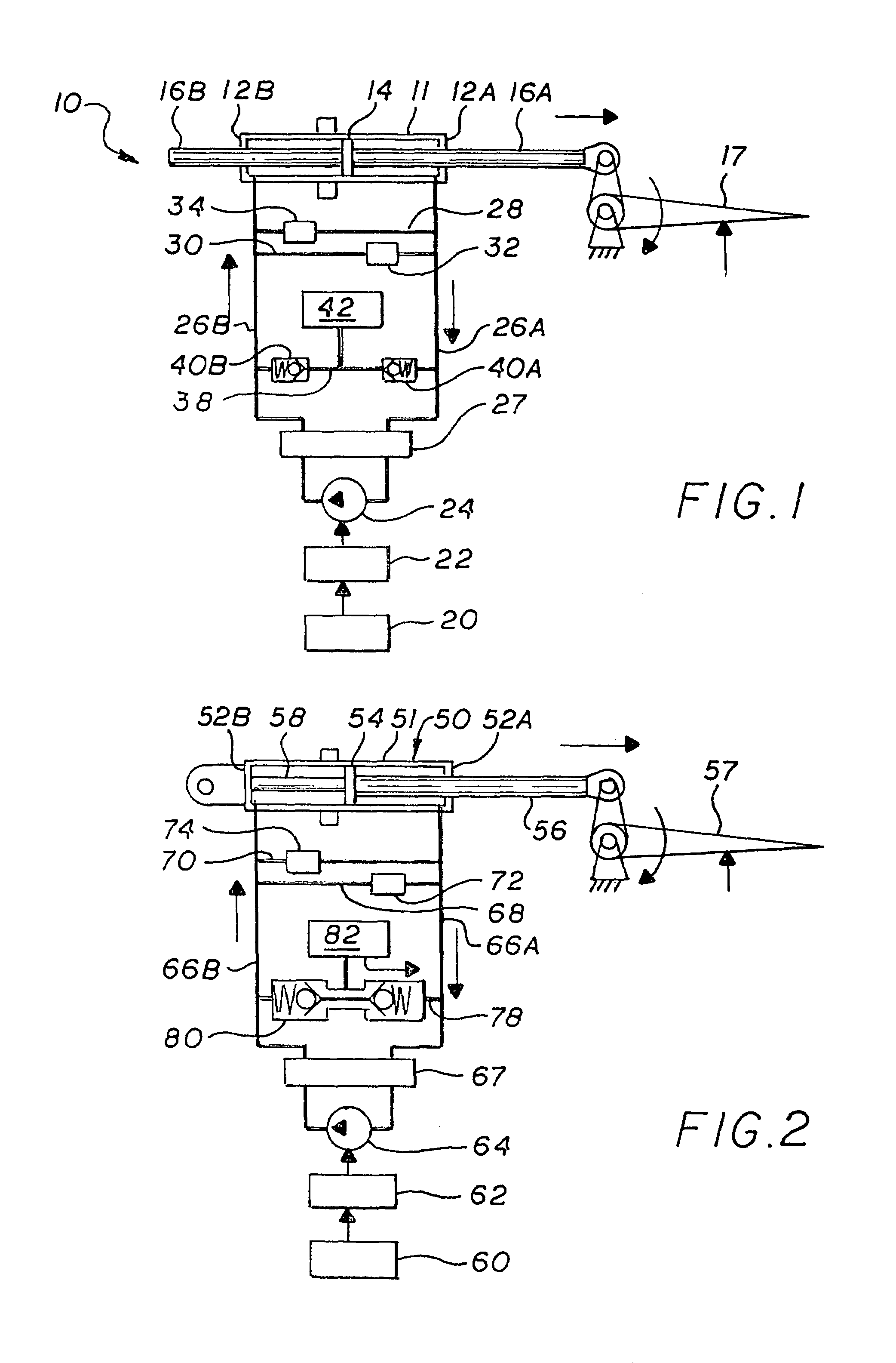
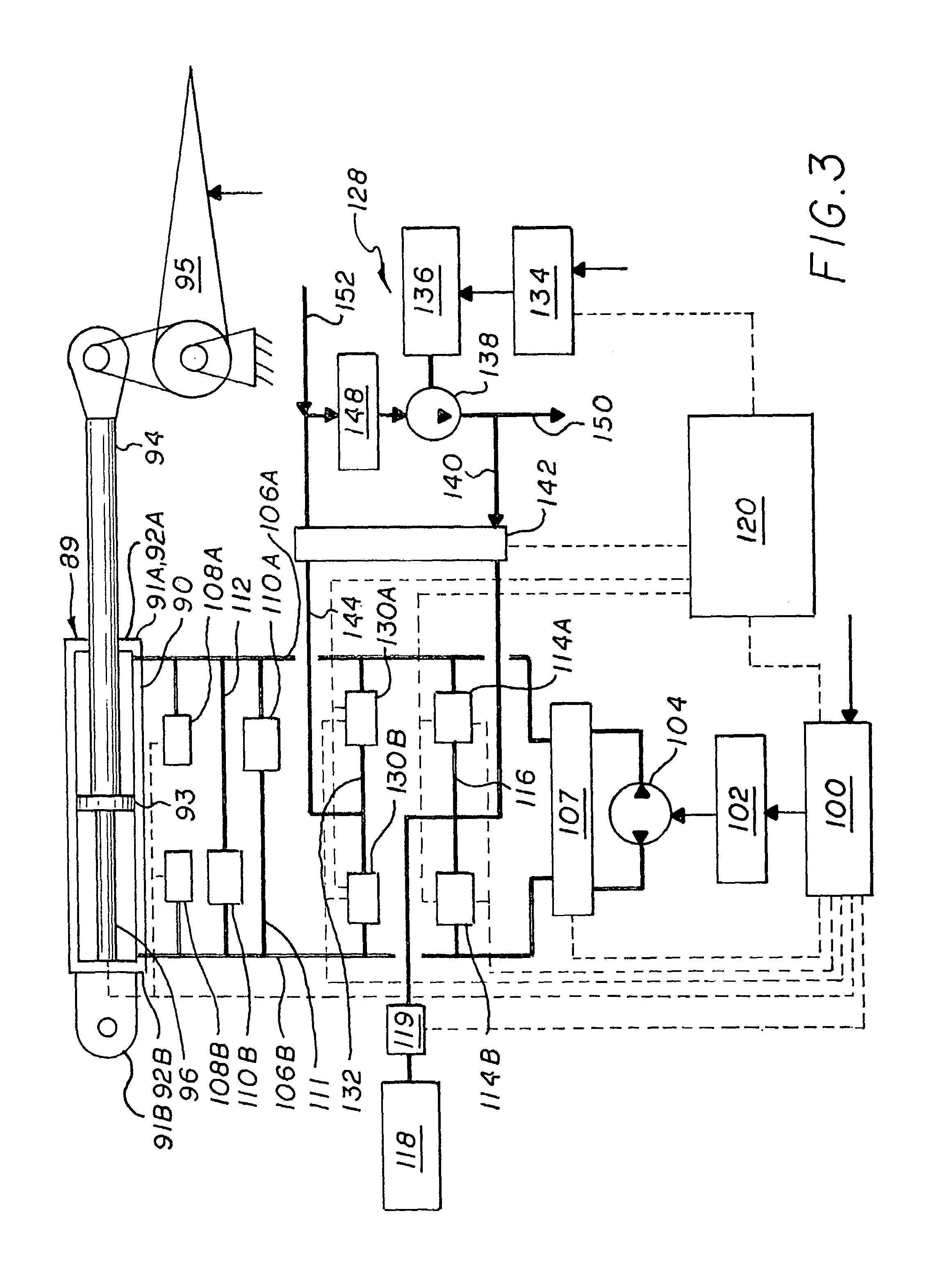
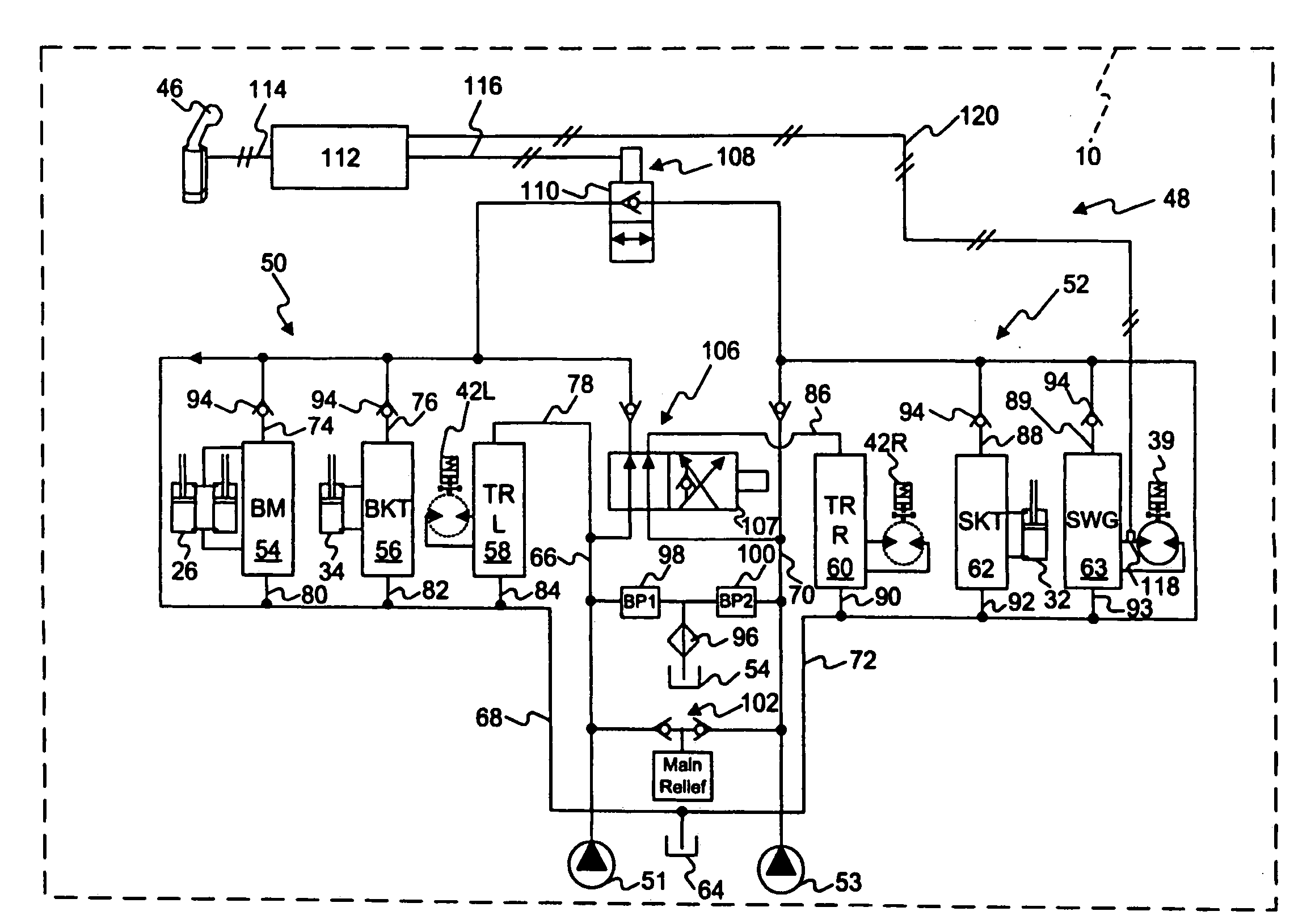
Electro-hydraulic actuator system
The system includes a hydraulic powered actuator. A pump system having first and second hydraulic lines is coupled to the first and second ports, respectively and is capable of providing hydraulic fluid to either the first and second lines. First and second pressure sensors are coupled to the first and second lines, respectively. A third line is coupled between the first and second lines and includes first and second valves mounted in series therein. Preferably, the first and second valves are capable of latching in the open position. A reservoir is coupled to the third line between the first and second valves. A shut off valve is included for cutting off the flow from the reservoir.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Hydrostatic drive system with variable charge pump
A hydraulic system is provided having a reservoir configured to hold a supply of fluid. The hydraulic system also has a variable displacement pump configured to supply charge fluid and pilot control fluid to the hydraulic system. In addition, the hydraulic system has a closed-loop portion configured to receive charge fluid from the variable displacement pump and drive a mechanism. The hydraulic system further has a pilot fluid supply portion configured to direct pilot control fluid from the variable displacement pump to closed-loop portion.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Hydraulic system
A ground engaging vehicle including a movable member, a hydraulically driven actuator, a hydraulic pump, a plurality of valves and at least one hydraulic conduit. The hydraulically driven actuator is coupled to the movable member and the actuator has a first chamber and a second chamber. The plurality of non-proportional valves include a first valve, a second valve, a third valve and a fourth valve. The at least one hydraulic conduit couples the pump with the first valve and the second valve. The first valve is in direct fluid communication with the first chamber. The second valve is in direct fluid communication with the second chamber. The third valve is in direct fluid communication with the first chamber and the fourth valve is in direct fluid communication with the second chamber. The first valve and the second valve each include an open position and a closed position.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Systems and Methods for Improving Drivetrain Efficiency for Compressed Gas Energy Storage
InactiveUS20100229544A1Improve efficiencyIncreasing electric motorElectrical storage systemFluid couplingsHydraulic motorConstant power
Generally, the invention relates to power generation and energy storage. In particular, to systems and methods for providing constant power from hydraulic inputs having widely-varying pressures. More particularly, the invention relates to hydraulic-pneumatic energy storage and recovery systems that include either a fixed or variable displacement hydraulic motor and control systems that allow a user to maintain constant power from the fixed or variable displacement hydraulic motor.
Owner:SUSTAINX
Energy recovery system
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326069A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
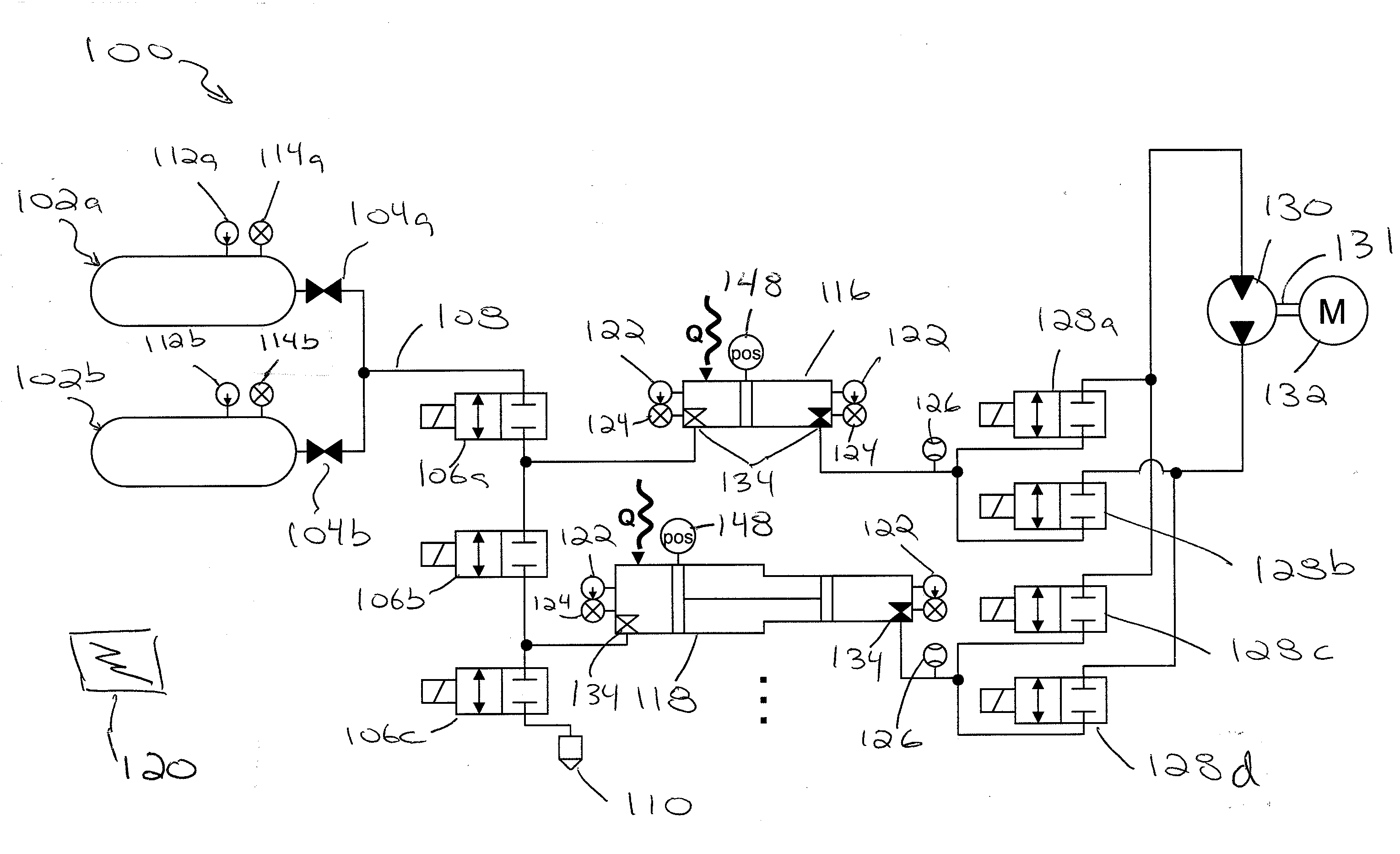
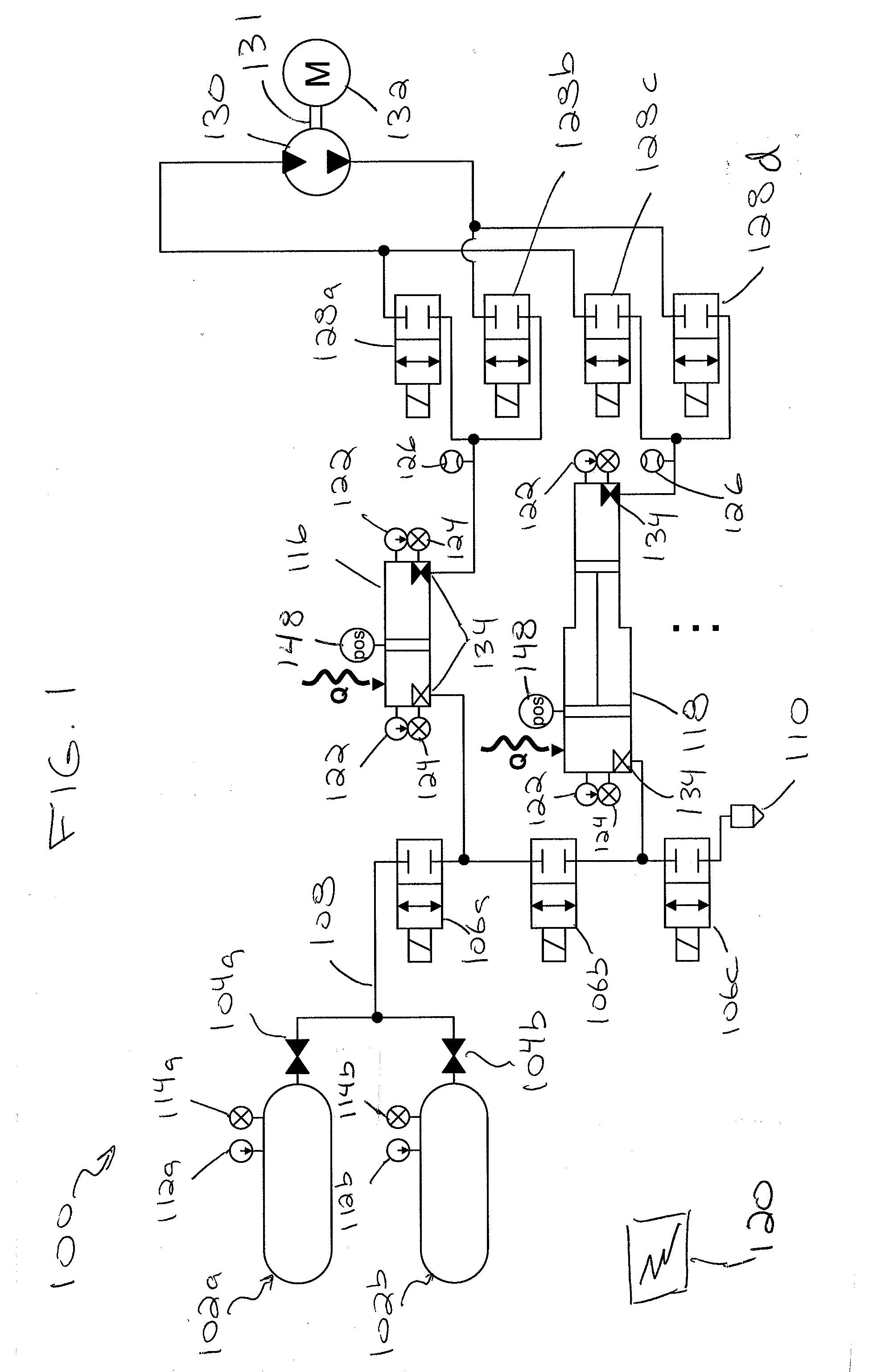
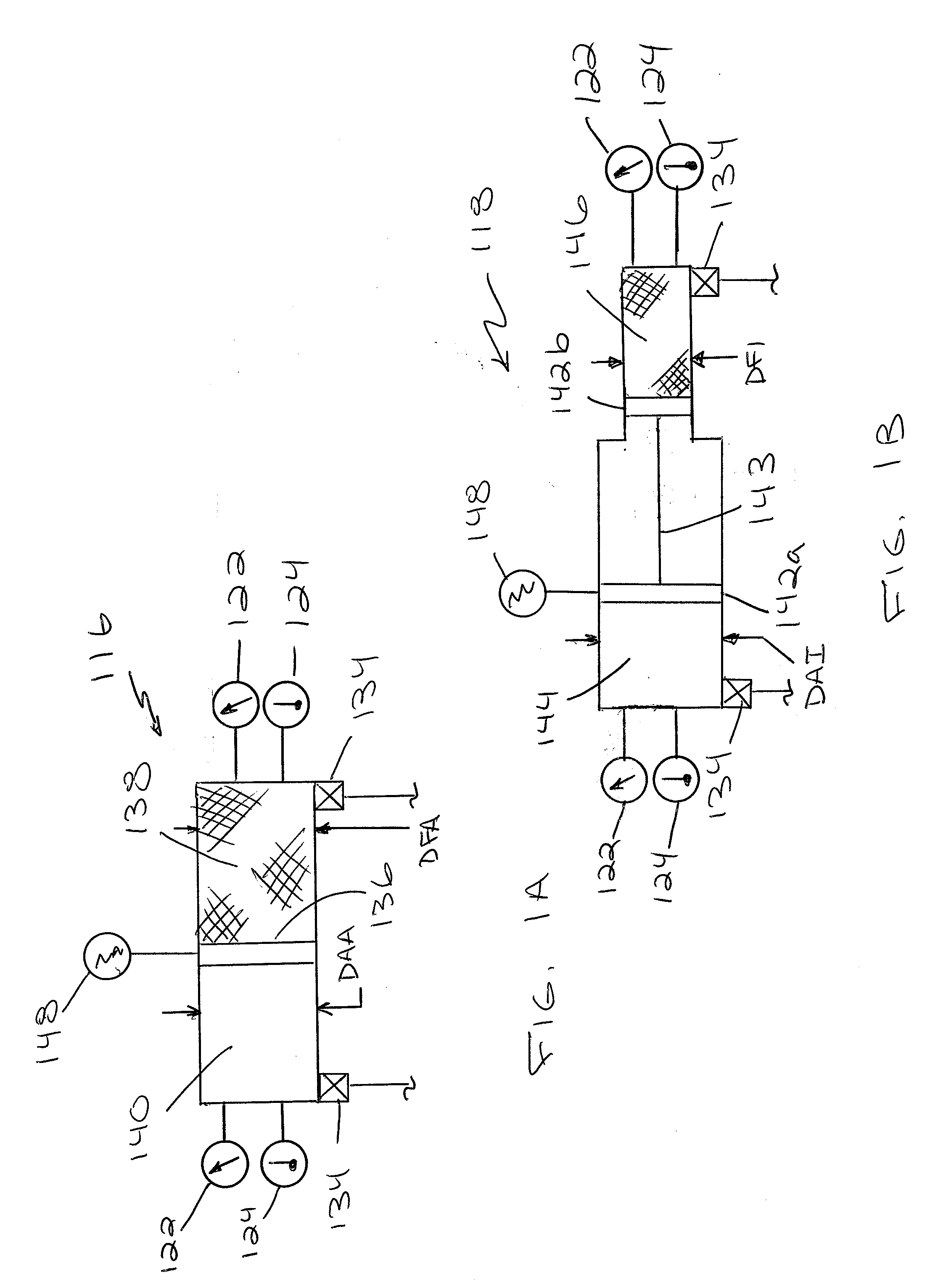
Multi-actuator pressure-based flow control system
A hydraulic control system for a work machine is disclosed. The hydraulic control system has a fluid actuator, a supply of pressurized fluid, and a control valve movable to selectively pass pressurized fluid to the fluid actuator. The hydraulic control system also has a sensor configured to sense the pressure of the pressurized fluid passed to the fluid actuator and a controller in communication with the control valve and the sensor. The controller is configured to receive an input indicative of a desired velocity of the fluid actuator and to determine a fluid flow rate corresponding to the desired velocity. The controller is also configured to determine a ratio of the sensed pressure to a stall pressure of the supply and to scale down the determined flow rate an amount based on the determined ratio. The controller is further configured to move the control valve an amount corresponding to the scaled down flow rate.
Owner:CATEPILLAR SARL +2
Hydraulic circuit, energy recovery device, and hydraulic circuit for work machine
InactiveUS20090288408A1Increase speedImprove work efficiencyFluid couplingsServomotor componentsSolenoid valveHydraulic circuit
A hydraulic circuit that enables smooth absorption of the energy of a return fluid from a hydraulic actuator by means of an energy recovery motor. A return fluid passage to which the fluid discharged from a boom cylinder is branched is provided at the tank passage side of a solenoid valve of a boom control circuit. The return fluid passage comprises two return passages, which are provided with a flow rate ratio control valve for controlling a ratio of fluid that branches off into the return passages. The flow rate ratio control valve is comprised of a solenoid valve disposed in the return passage, which is provided with an energy recovery motor, and a solenoid valve disposed in the return passage, which branches off the upstream side of the solenoid valve.
Owner:CATEPILLAR SARL
Safety valve control system and method of use
A safety valve control system may include a remotely operable control assembly; a first transducer, a valve assembly, and a pump assembly in communication with the control assembly; and a fluid reservoir in communication with the valve and pump assemblies and a safety valve. The control assembly is operable to actuate the pump and valve assemblies to supply and return fluid from the fluid reservoir to actuate the safety valve into open and closed positions, in response to one or more signals received from the first transducer. A method of operation may include maintaining the safety valve in an open position while sensing a physical property with the control system; communicating a signal corresponding to the sensed physical property to the control system; and automatically closing the safety valve in response to a comparison of the sensed physical property to a pre-set condition.
Owner:SAFOCO
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326068A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326064A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com