Patents
Literature
1111 results about "Magnetic orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
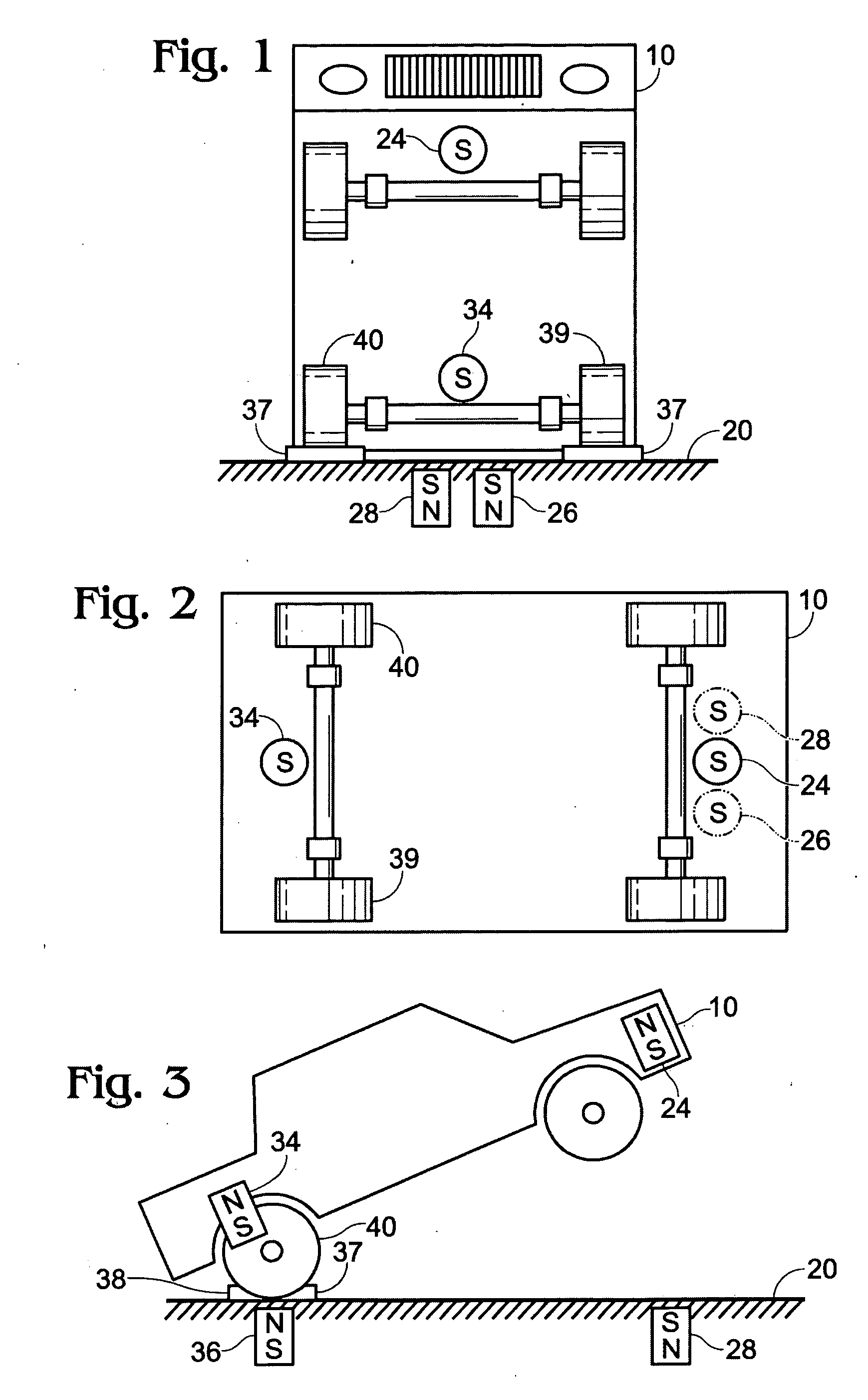
A magnetic orientation the same as that of Earth's current magnetic field. Magnetic orientations in rock that are opposite to the current orientation of Earth's magnetic field. A change in Earth's magnetic field in which the north magnetic pole becomes the south magnetic pole and vice versa.
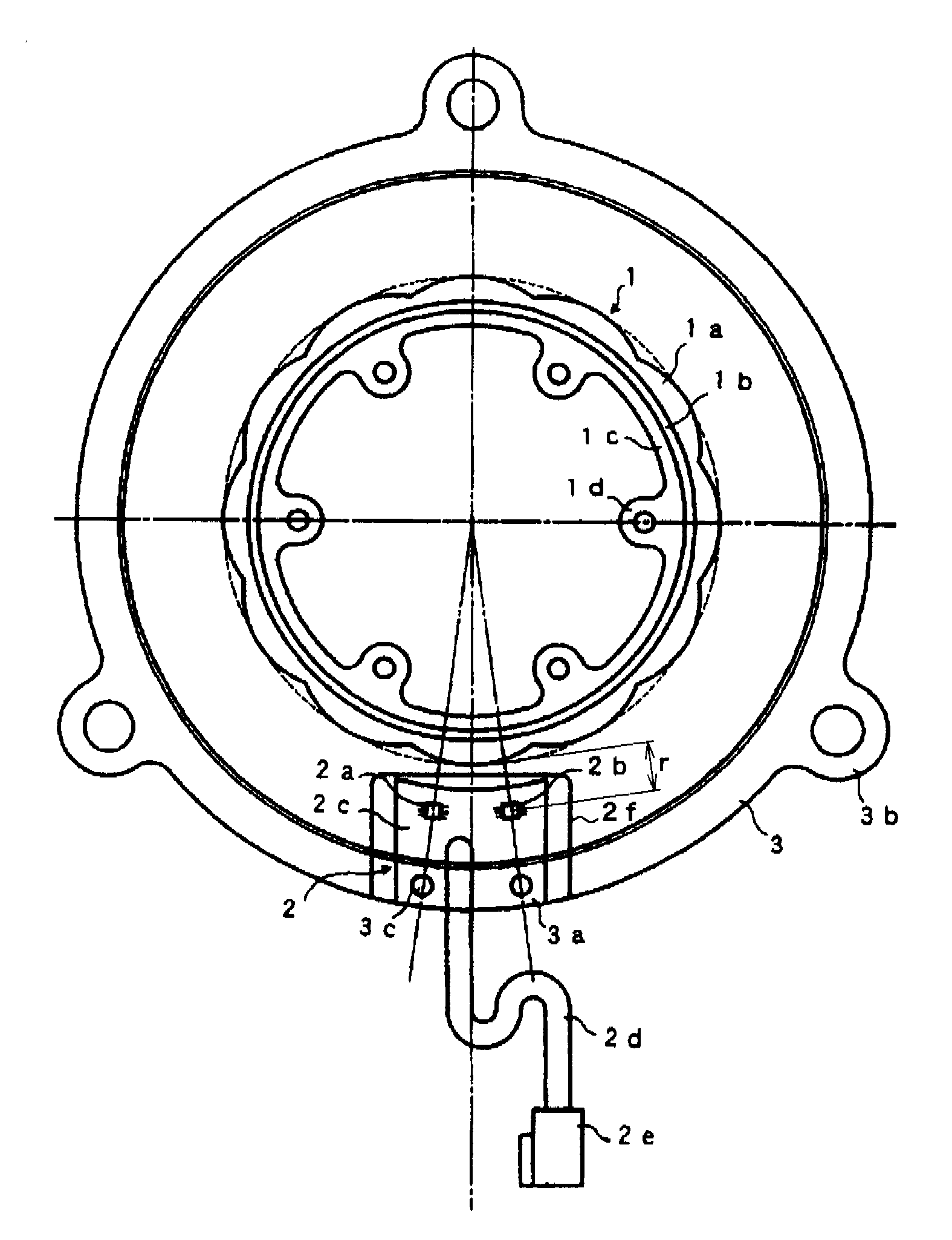
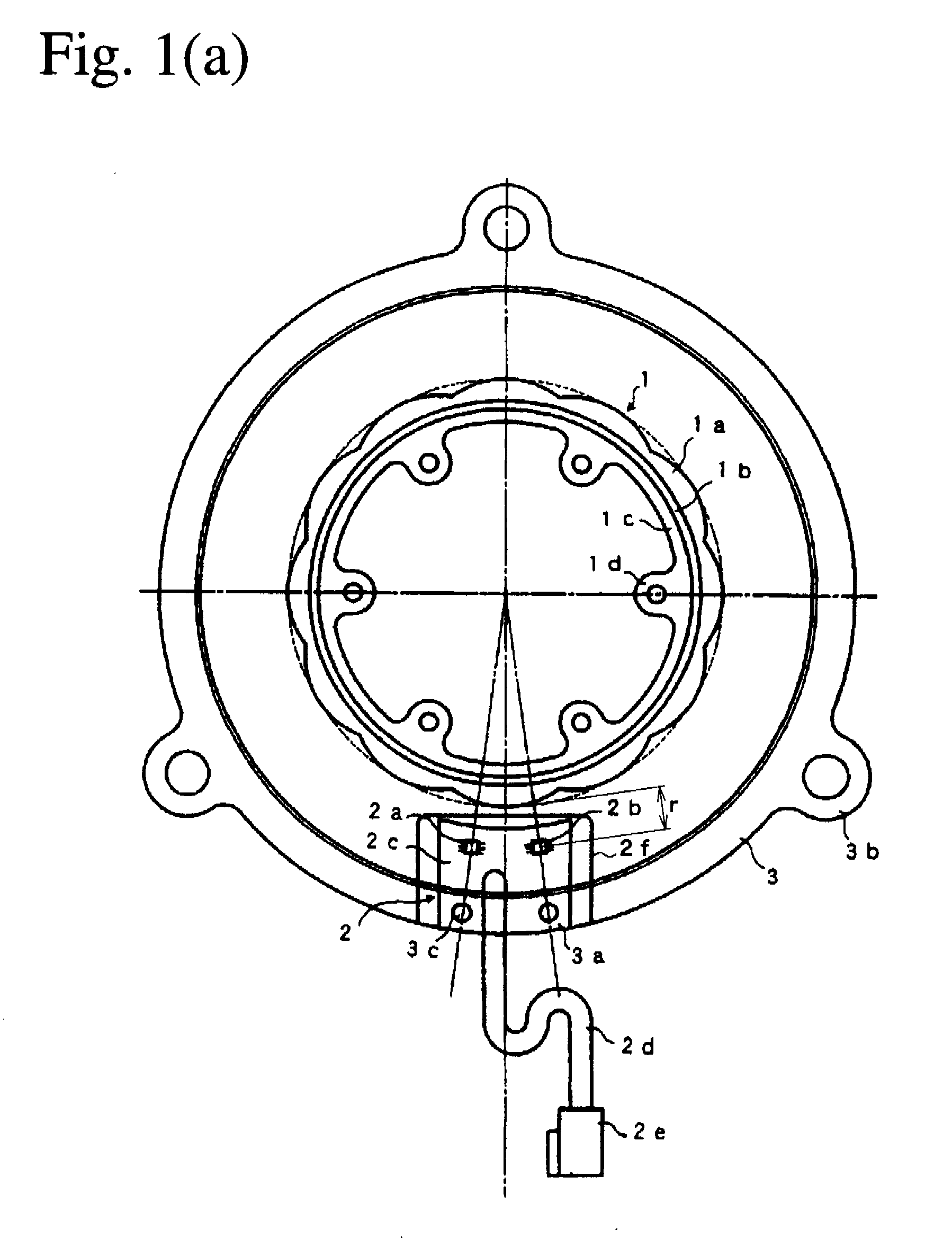
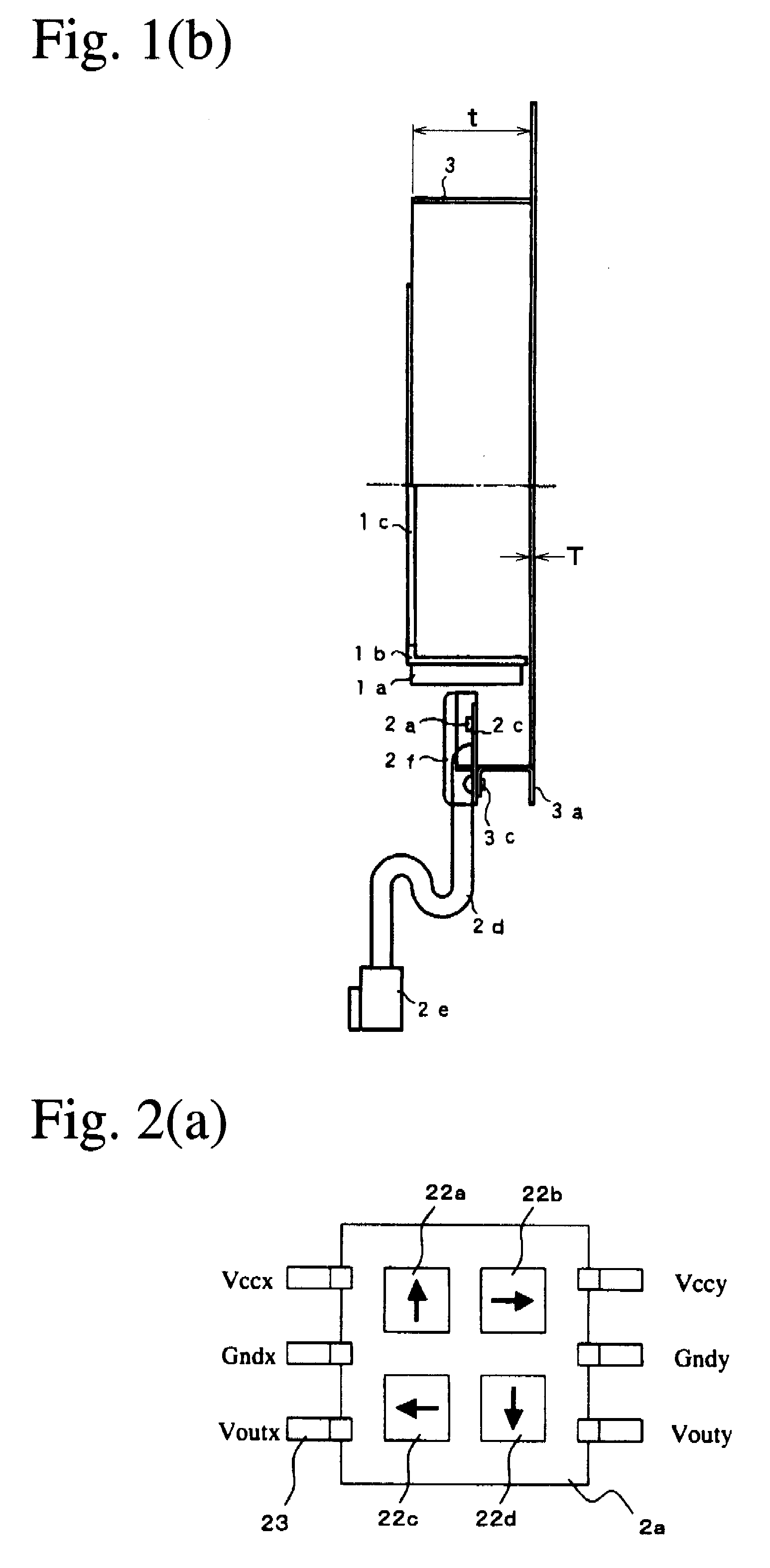
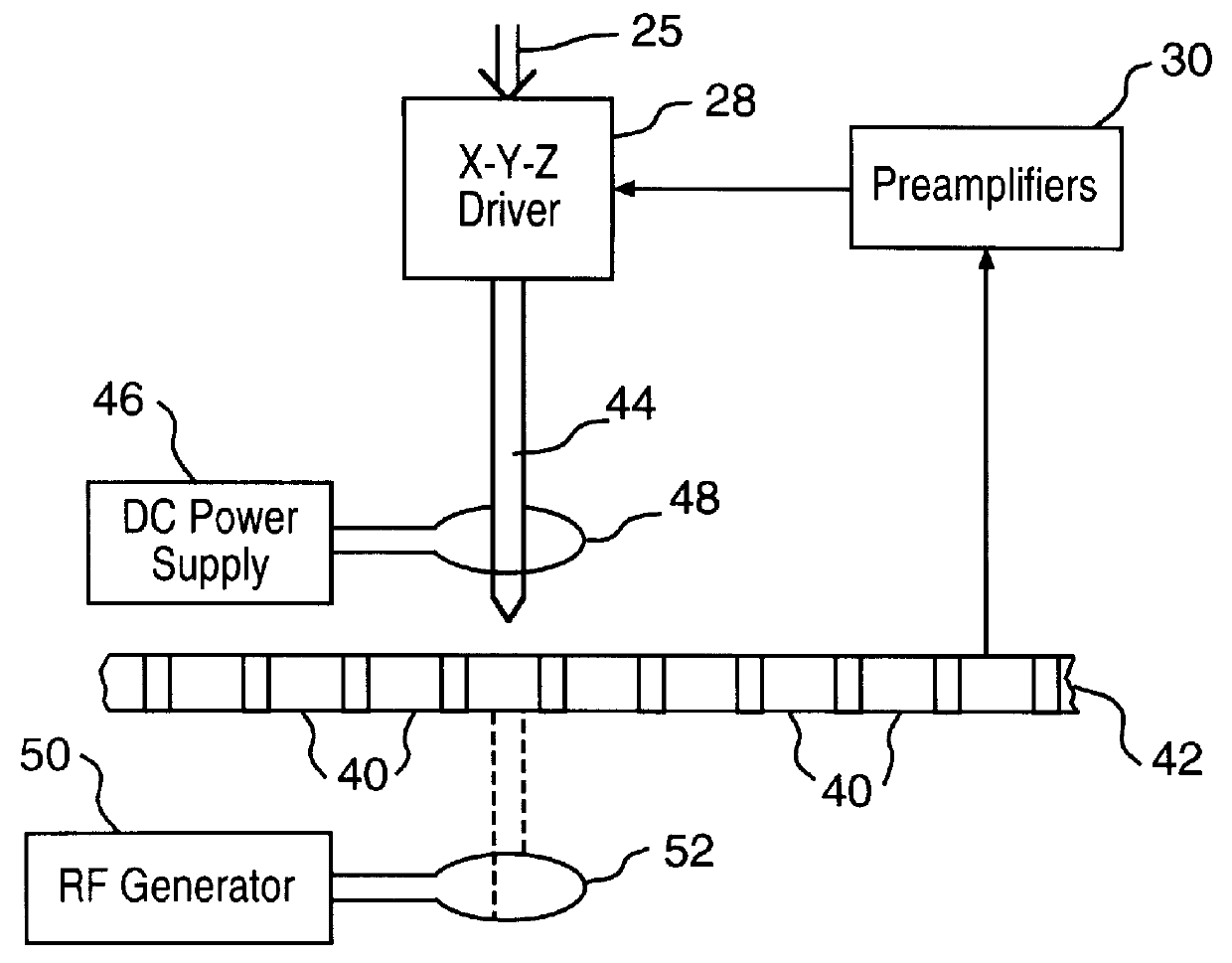
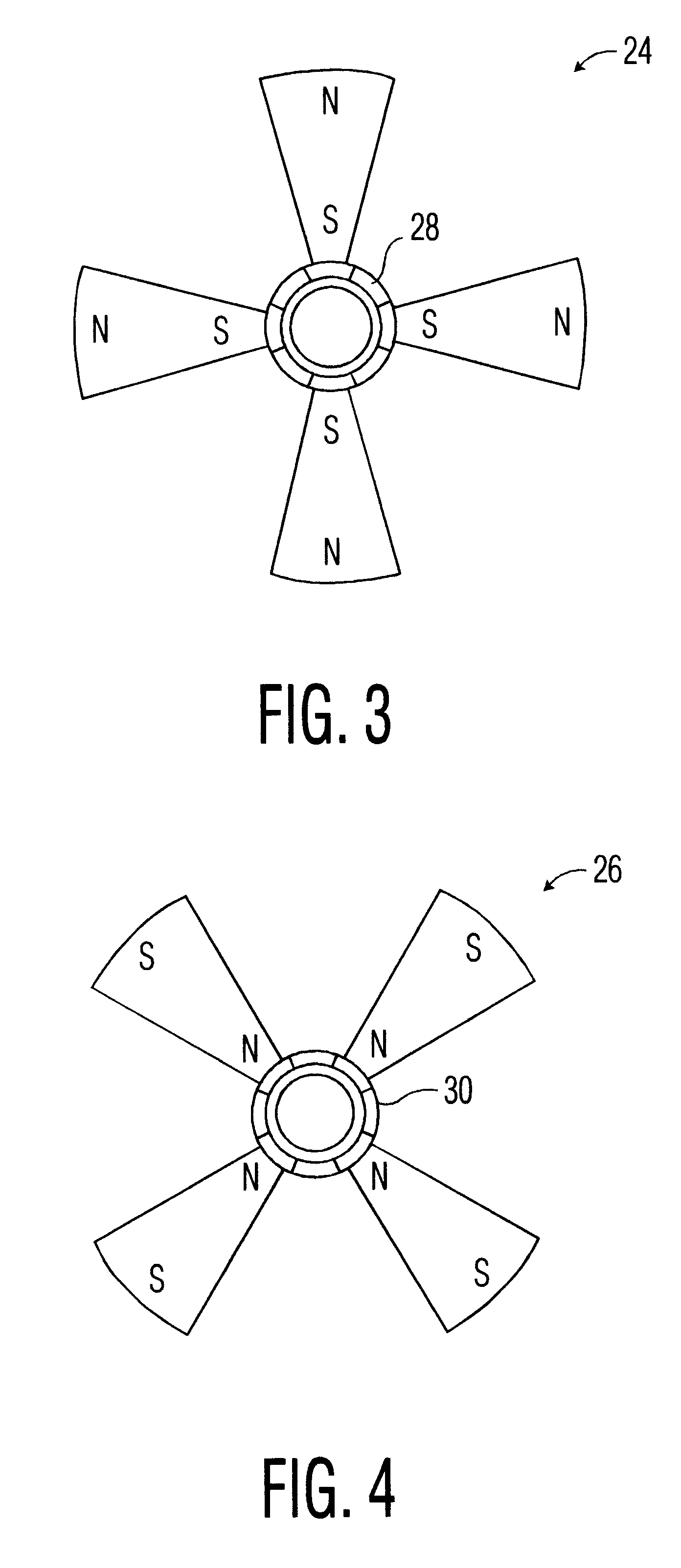
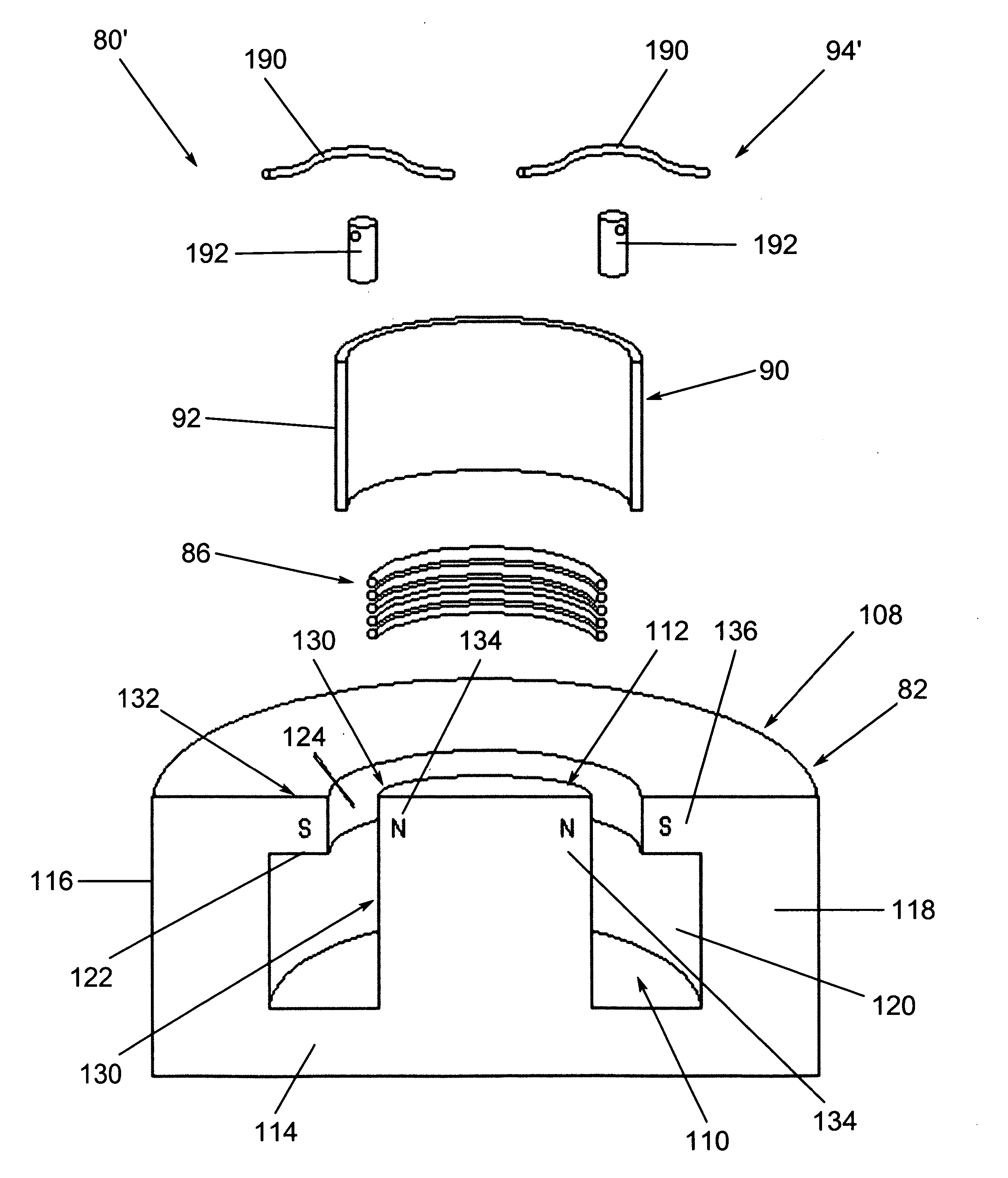
Rotation-angle-detecting apparatus, rotating machine, and rotation-angle-detecting method
ActiveUS20090206827A1High resolutionAccurate measurementUsing electrical meansConverting sensor outputMagnetic polesSpin valve
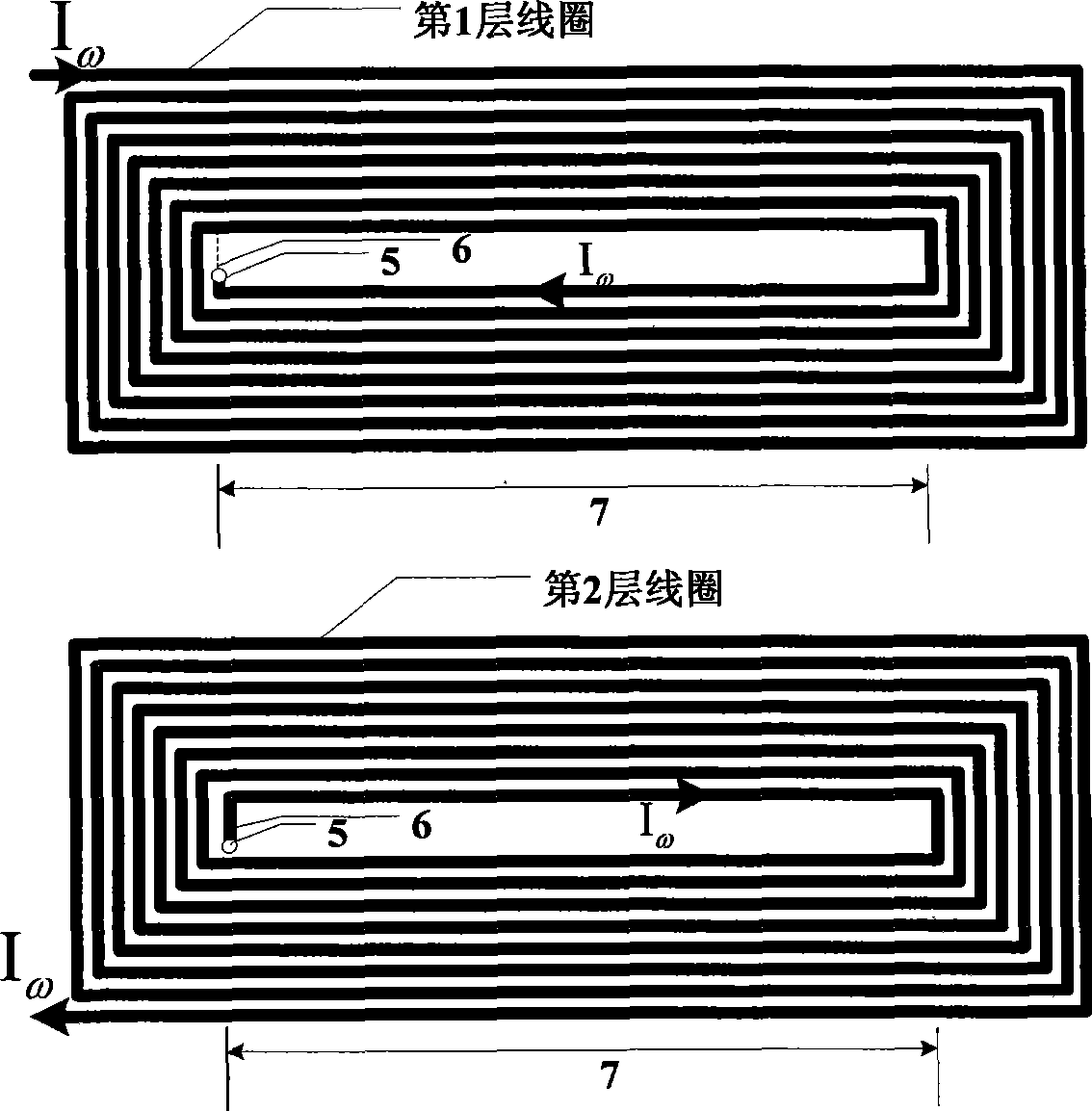
A rotation-angle-detecting apparatus comprising a magnet rotor having 4 or more magnetic poles on the surface, and sensor device for detecting magnetic flux from the magnet rotor, and an electronic circuit for outputting a signal representing the rotation angle of the magnet rotor using pluralities of signals obtained from the sensor device, the sensor device having pluralities of spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive devices for outputting two or more different phase signals from a rotating magnetic field near the rotating magnet, each spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device having a pinned layer and a free layer, the magnetization direction of the pinned layer being fixed, and the magnetization direction of the free layer rotating depending on a magnetic field direction, pluralities of the spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive devices comprising a first spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device having a reference magnetic-field-sensing direction, and a second spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device having a magnetic-field-sensing direction different from that of the first spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive device.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
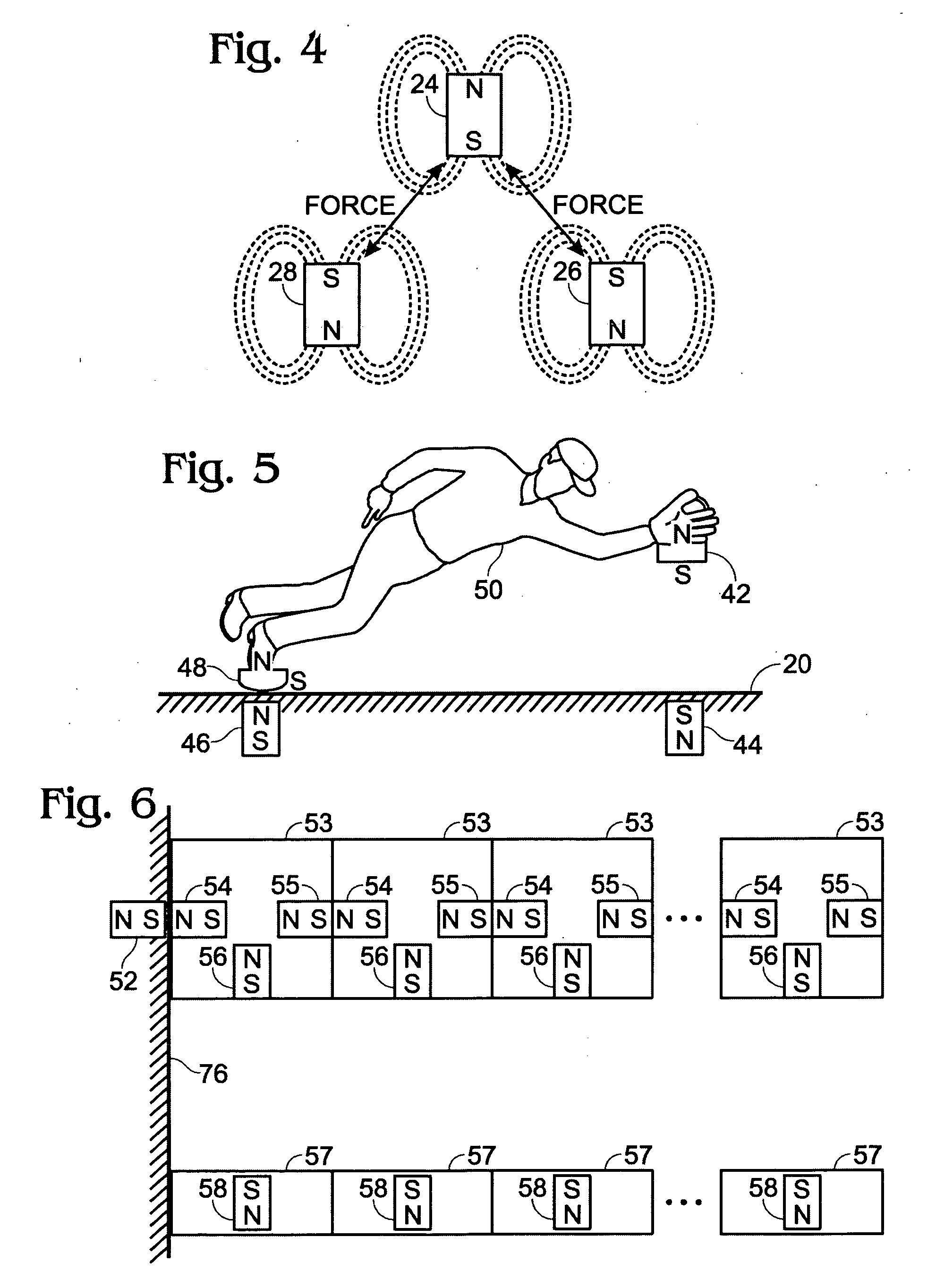
Levitation of objects using magnetic force
InactiveUS20060214756A1Enhancing its appealImprove stabilityPermanent magnetsMagnetic materialsMagnetic tension forceLevitation
The invention disclosed is a method of levitating one or both ends of an object permanently or temporarily, or altering the distance between two objects or the momentum of an object by manipulating the direction of the magnetic field of a permanent or electromagnet.
Owner:ELLIHAY CORP
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing with a probe on erasable magnetic media
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing on an erasable magnetic medium include using a micromachined mechanism having two probes for writing to the medium. Use of the two probe embodiment eliminates the need to change the magnetic orientation of the probe. In another embodiment, a single probe is provided which is heated to the vicinity of its Curie temperature to enable the magnetic orientation of the probe to be switched. The probe may be heated to its Curie temperature through the use of a heating element or a focused laser. In another embodiment of the present invention, either the magnetic orientation of the probe or the magnetic orientation of the medium may be switched through the combination of a static magnetic field, a radio frequency magnetic field and, under certain circumstances, the magnetic field of the probe. In all cases, the writing techniques enable information to be written to a magnetic medium in a manner which enables the information to be erased and the medium rewritten.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
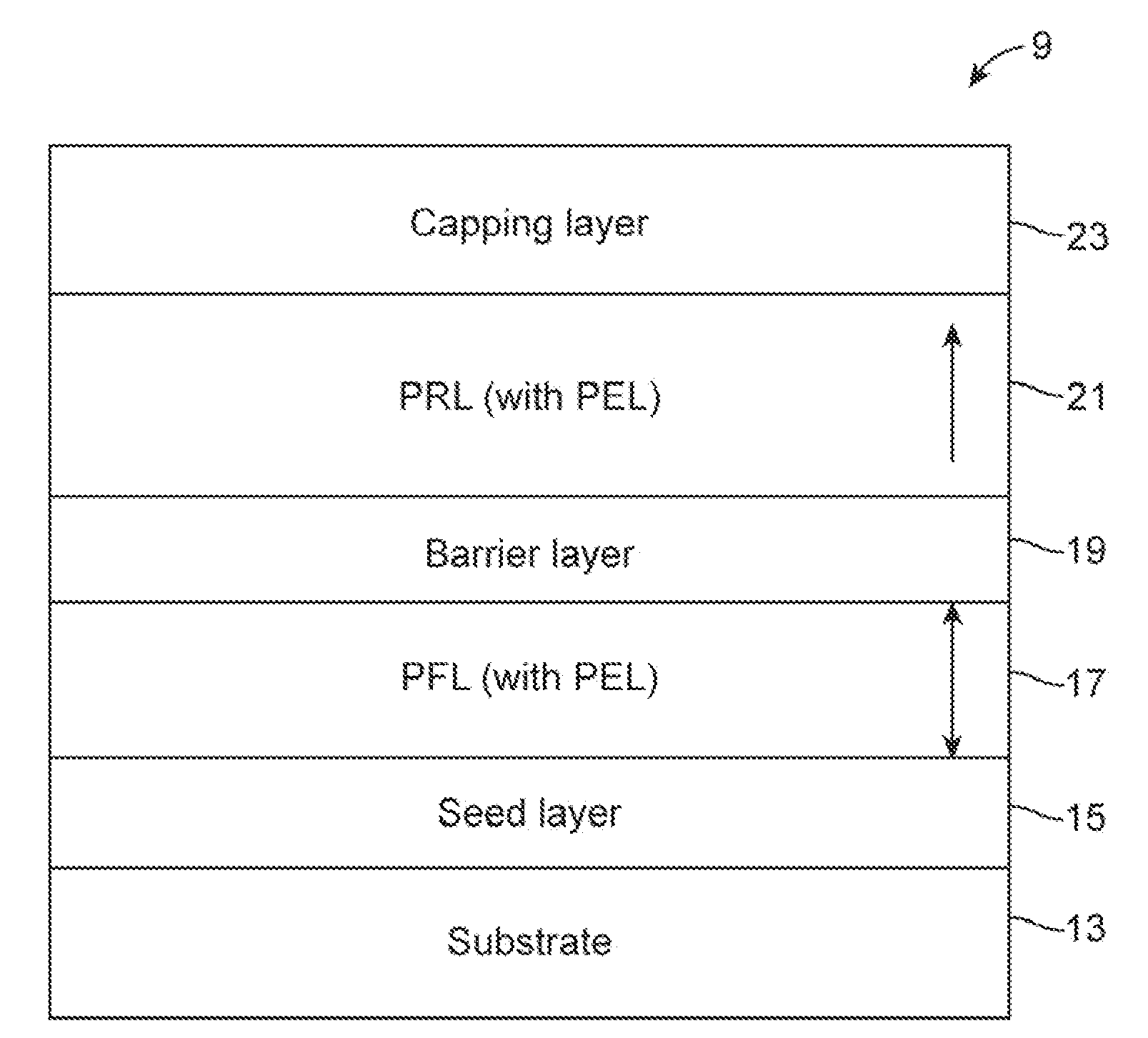
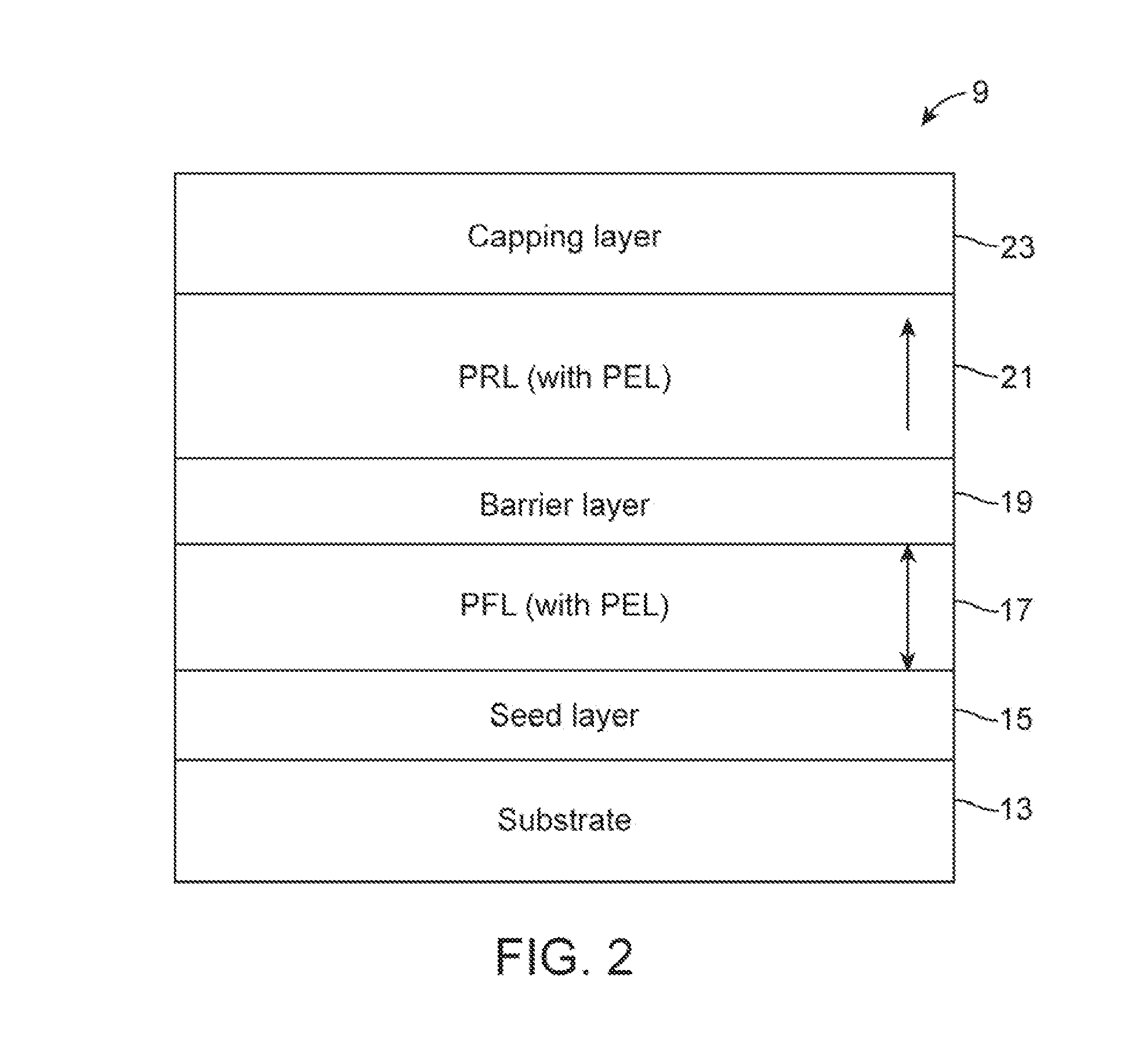
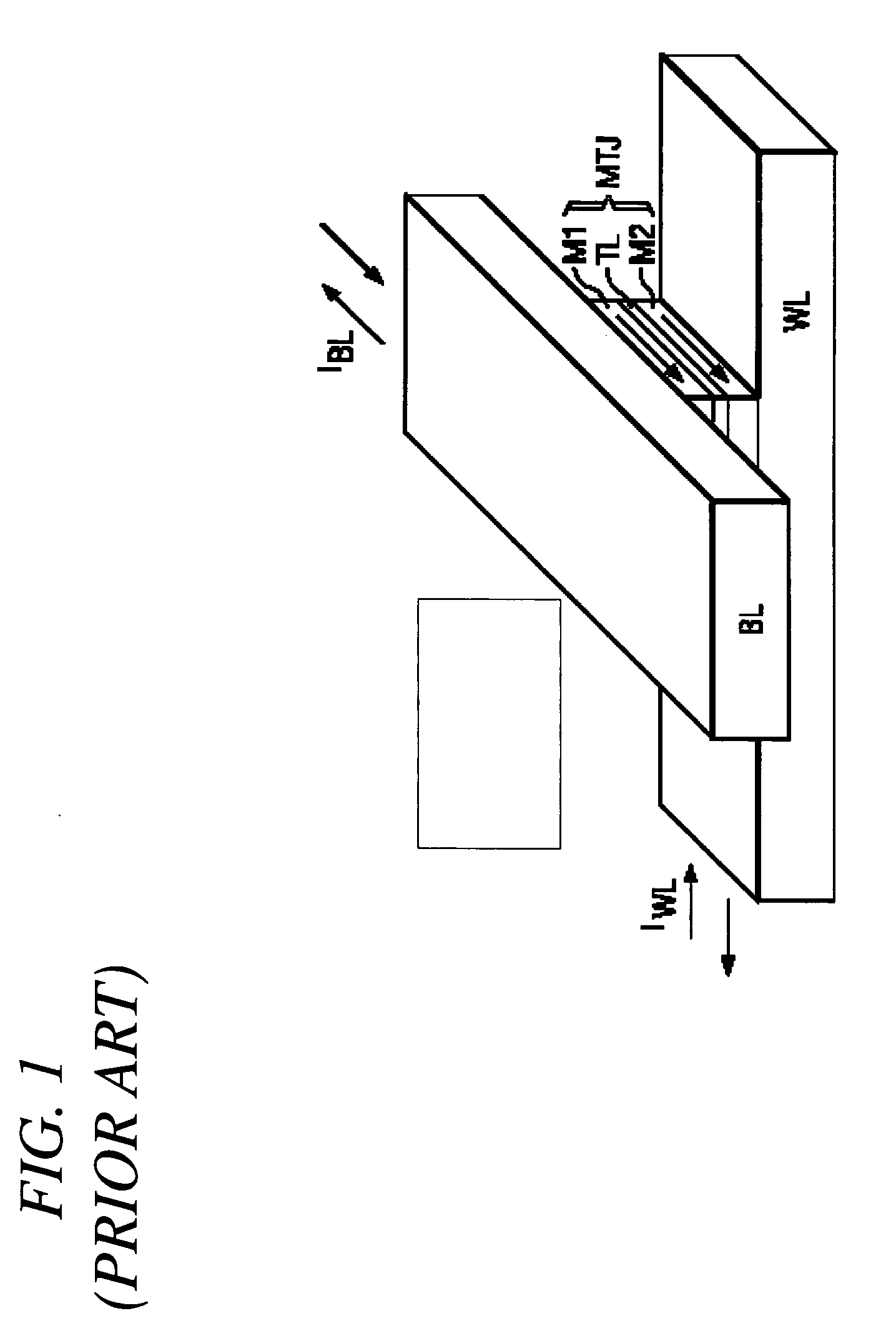
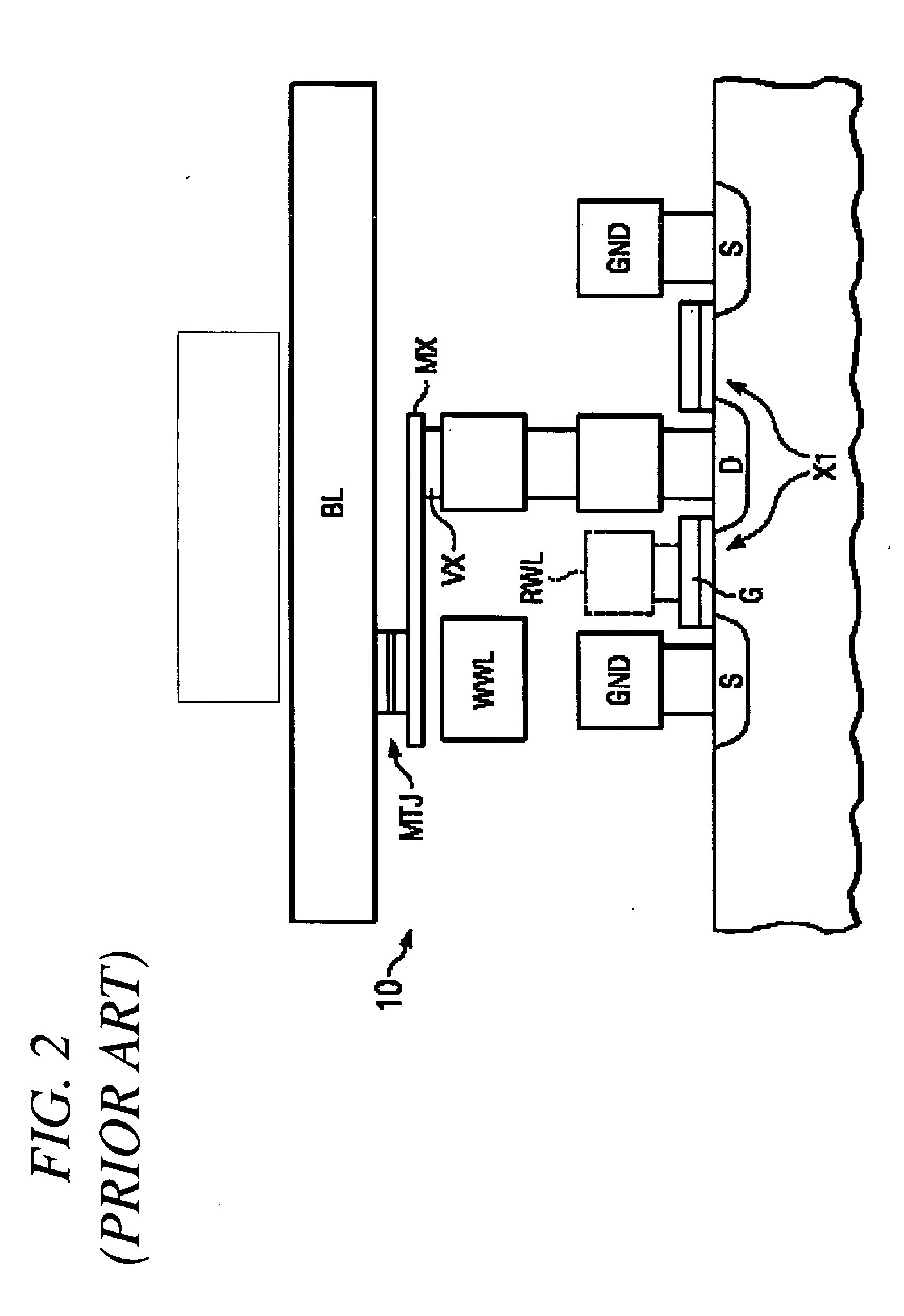
Memory system having thermally stable perpendicular magneto tunnel junction (MTJ) and a method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20120146167A1Increase stiffnessReduced dampingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsRandom access memoryMagneto
A spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory (STTMRAM) element employed to store a state based on the magnetic orientation of a free layer, the STTMRAM element is made of a first perpendicular free layer (PFL) including a first perpendicular enhancement layer (PEL). The first PFL is formed on top of a seed layer. The STTMRAM element further includes a barrier layer formed on top of the first PFL and a second perpendicular reference layer (PRL) that has a second PEL, the second PRL is formed on top of the barrier layer. The STTMRAM element further includes a capping layer that is formed on top of the second PRL.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Sensor for detecting the direction of a magnetic field in a plane
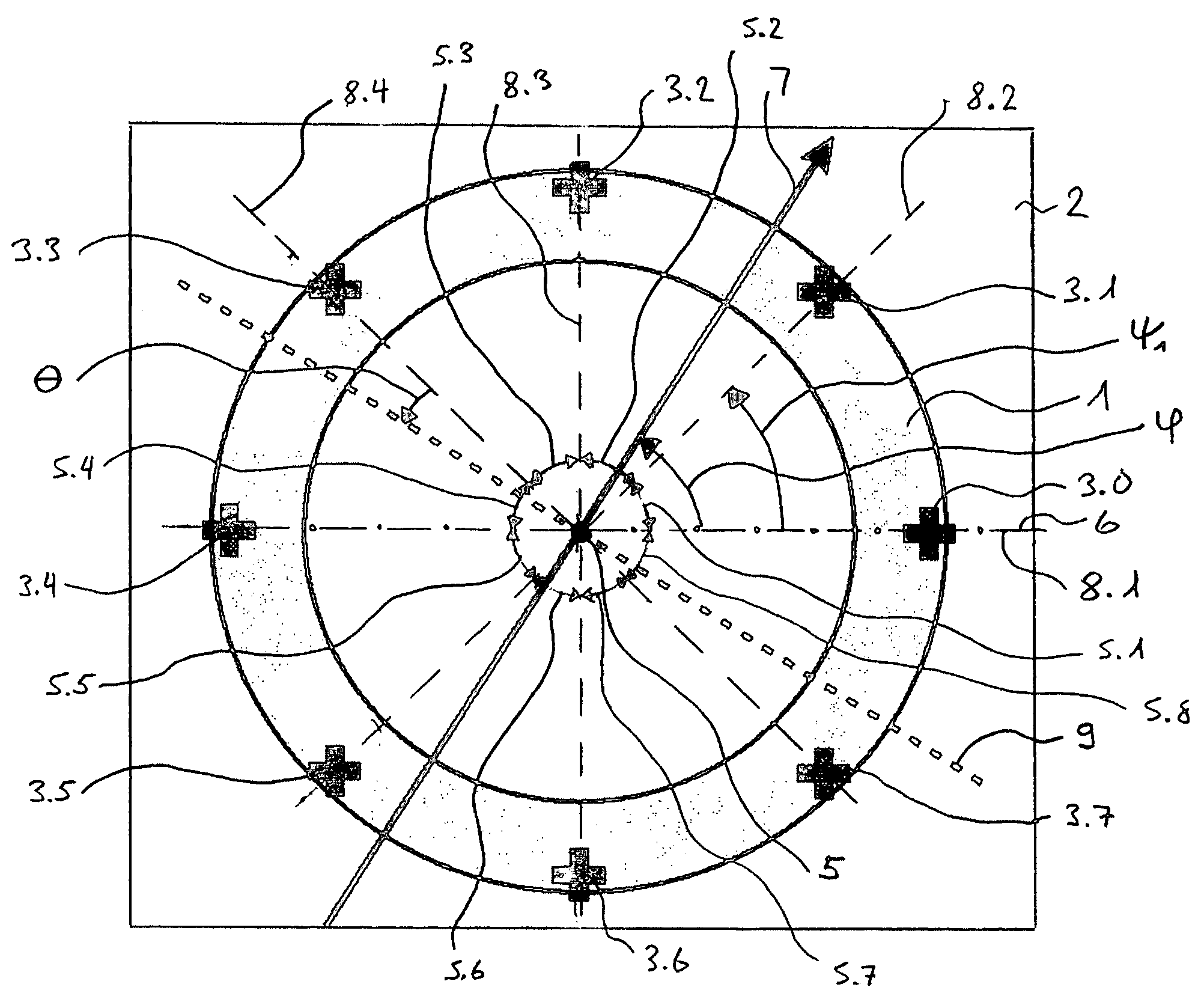
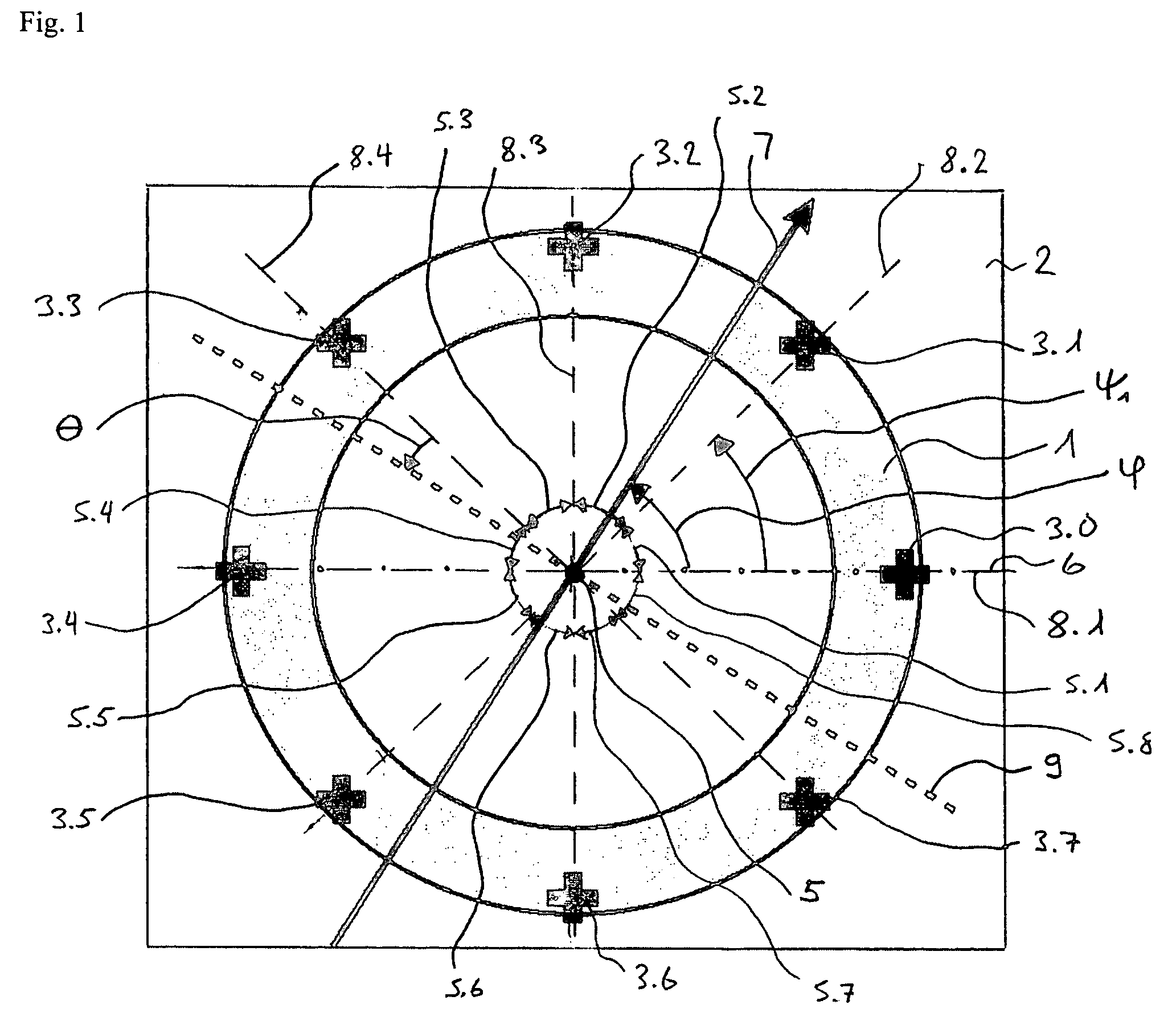
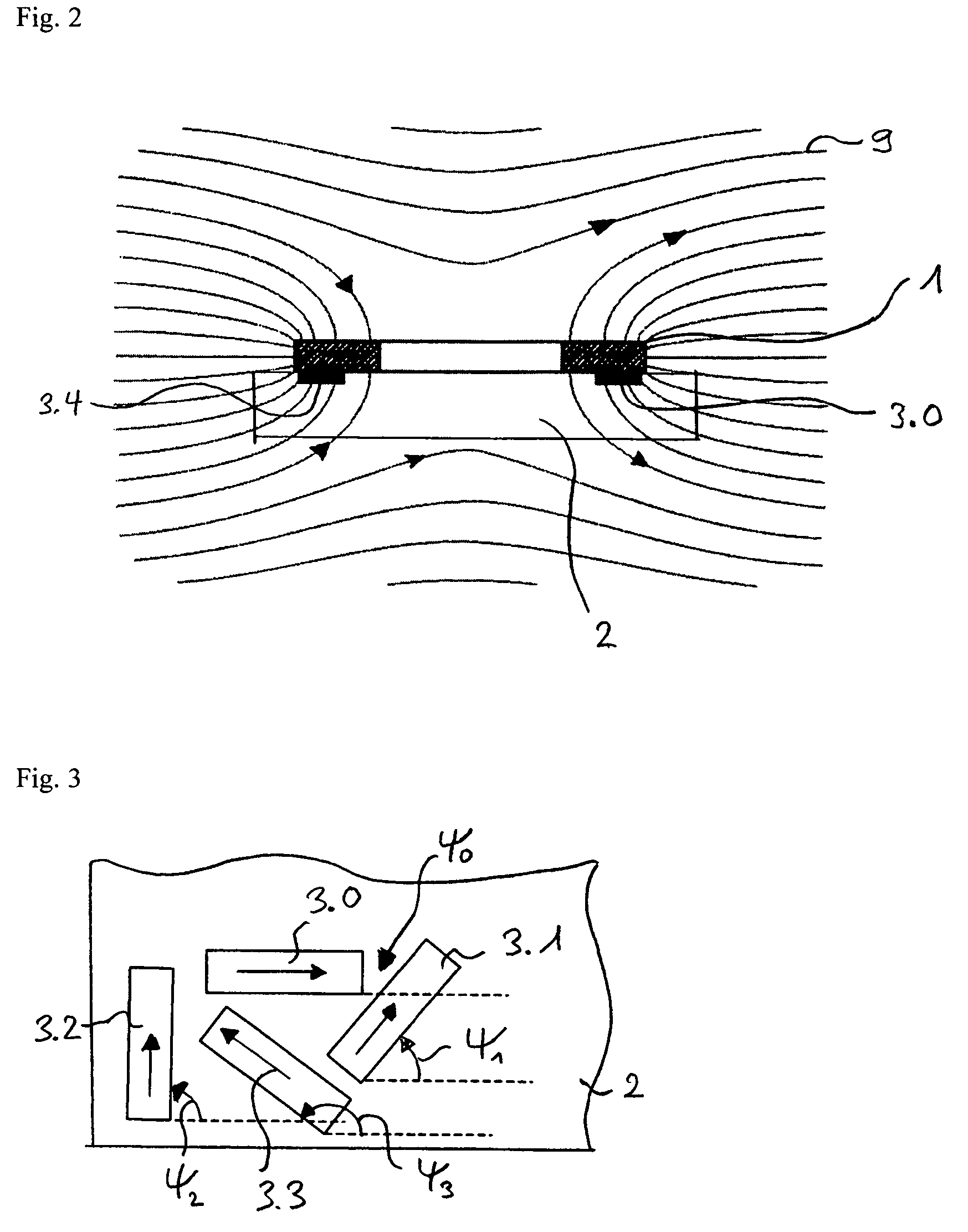
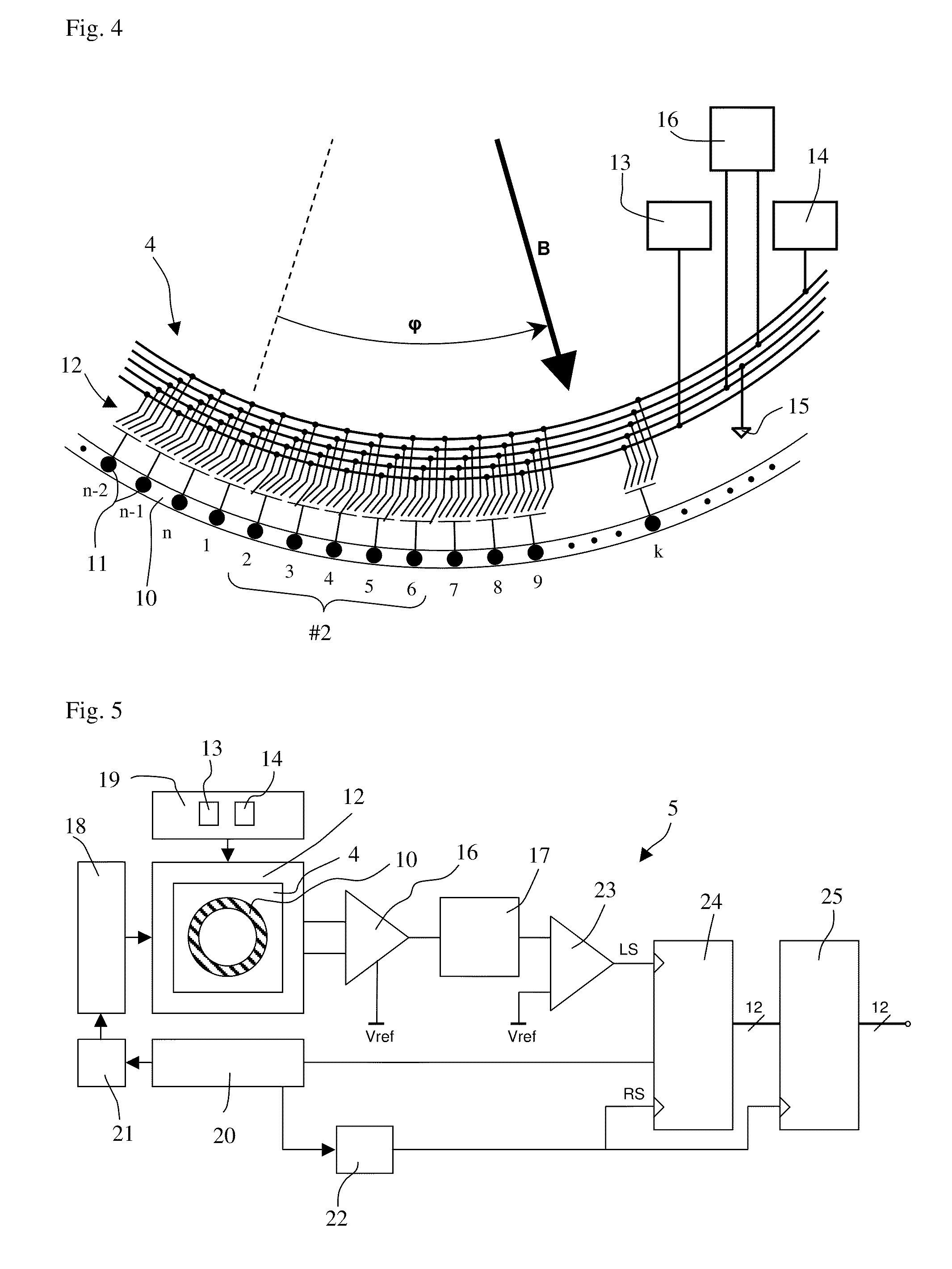
ActiveUS7235968B2High angular accuracyImprove accuracyMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCommon pointPhysics
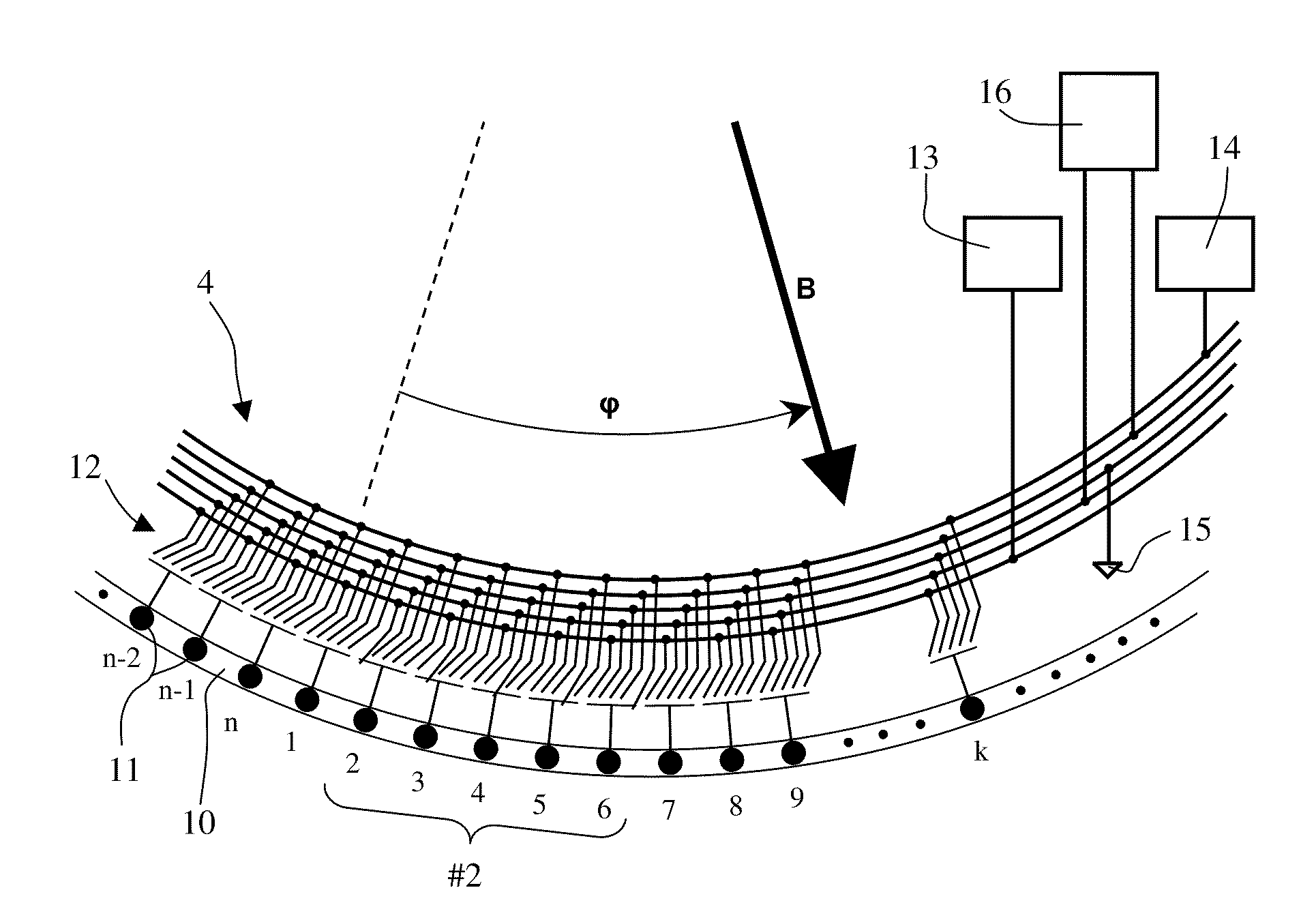
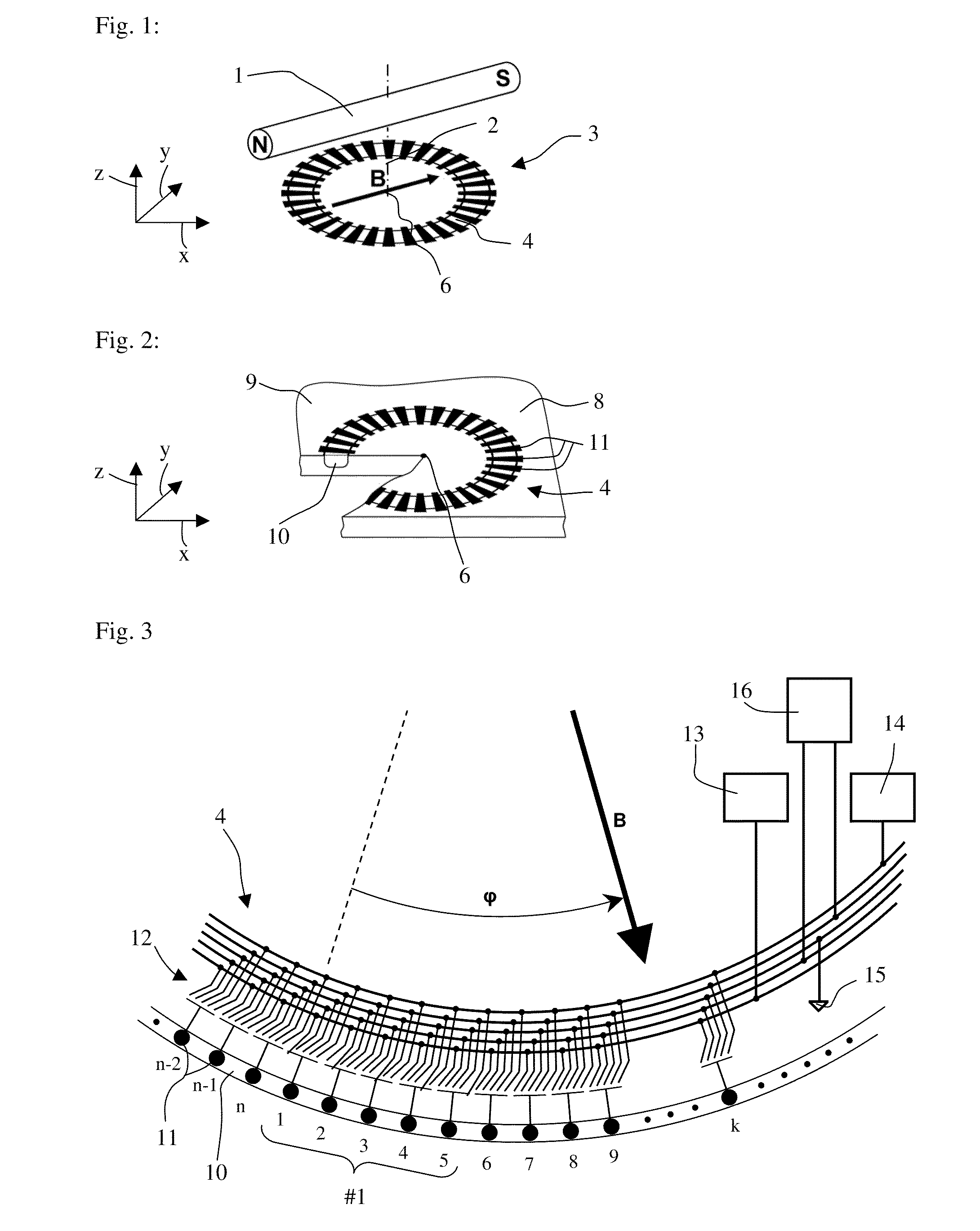
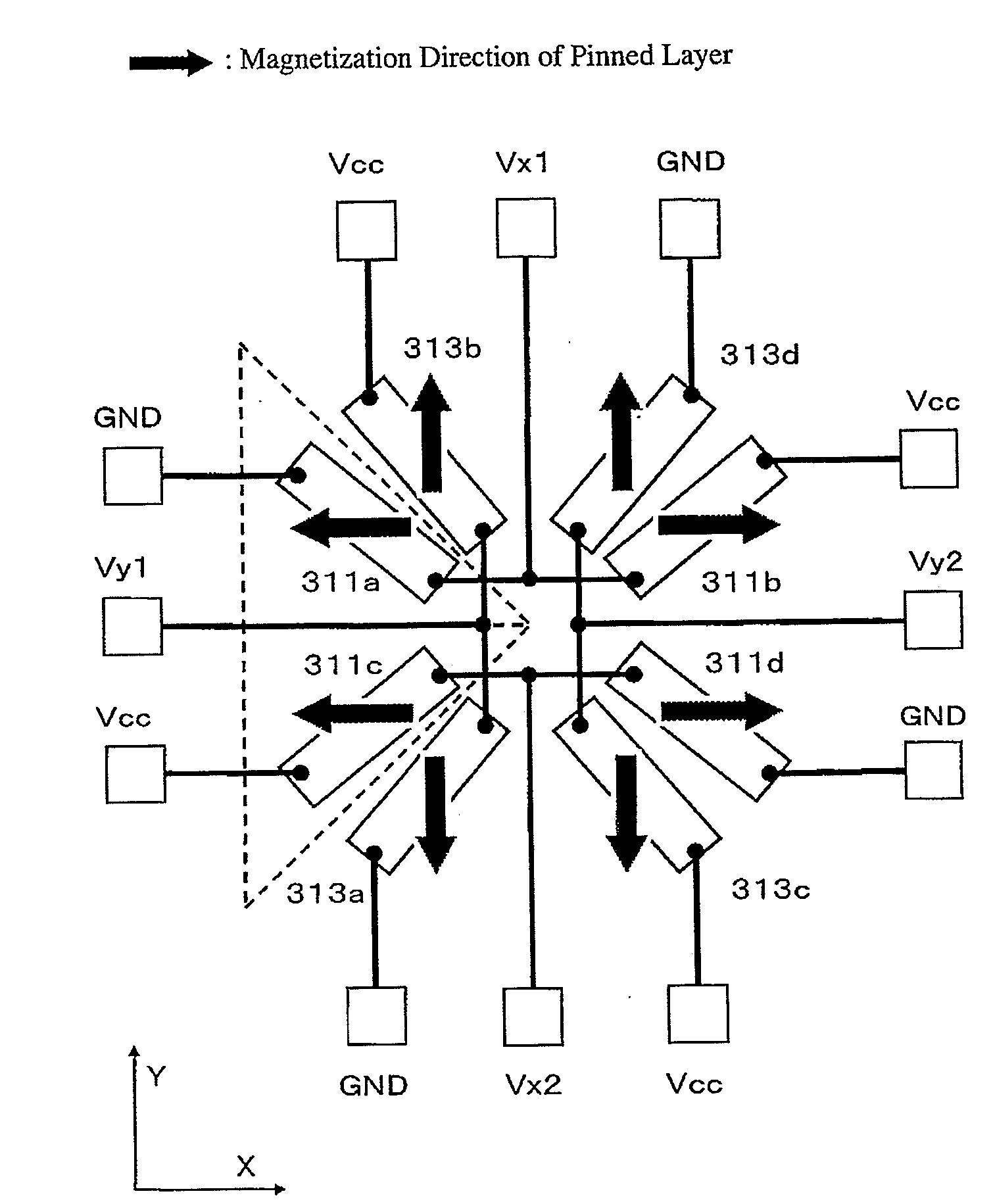
The invention relates to a sensor for detecting the direction of a magnetic field in a plane whose direction can be defined by the indication of a polar angle ?. Said sensor comprises a number of n magnetic field sensors (3.0 to 3.7). A measurement axis (8.1 to 8.4) is assigned to each magnetic field sensor in such a manner that the absolute value of the output signal of the magnetic field sensor is largest when the magnetic field runs parallel to the measuring axis. All measuring axes intersect at a common point (5). The number k of measuring axes is equal to at least three. An operating mode is provided during which two magnetic field sensors are selected for calculating the angle ?. These two magnetic field sensors belong to different measuring axes, and the values of the output signals thereof are less than those of the output signals of the magnetic field sensors belonging to the other measuring axes.
Owner:MELEXIS TECH NV
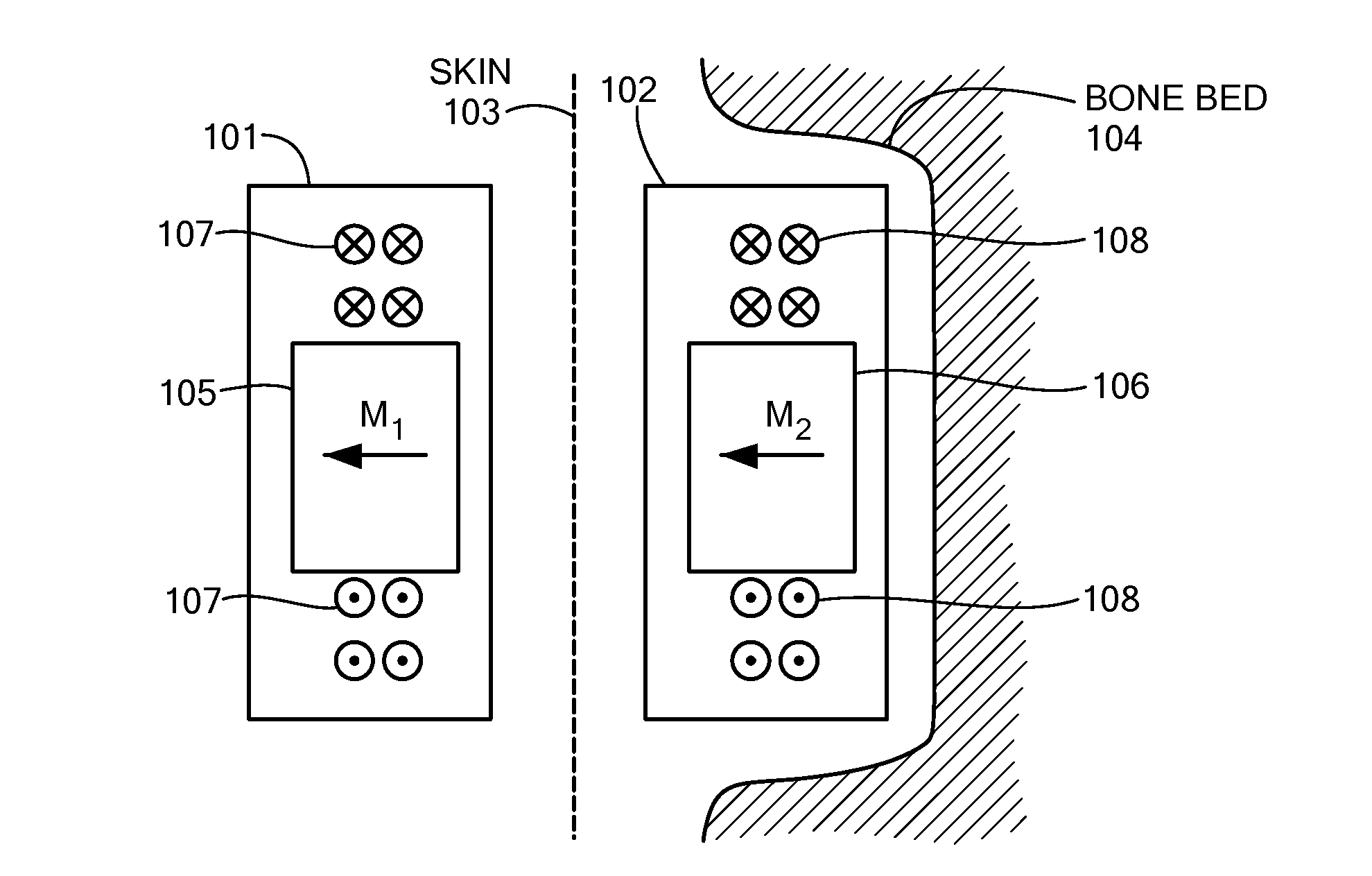
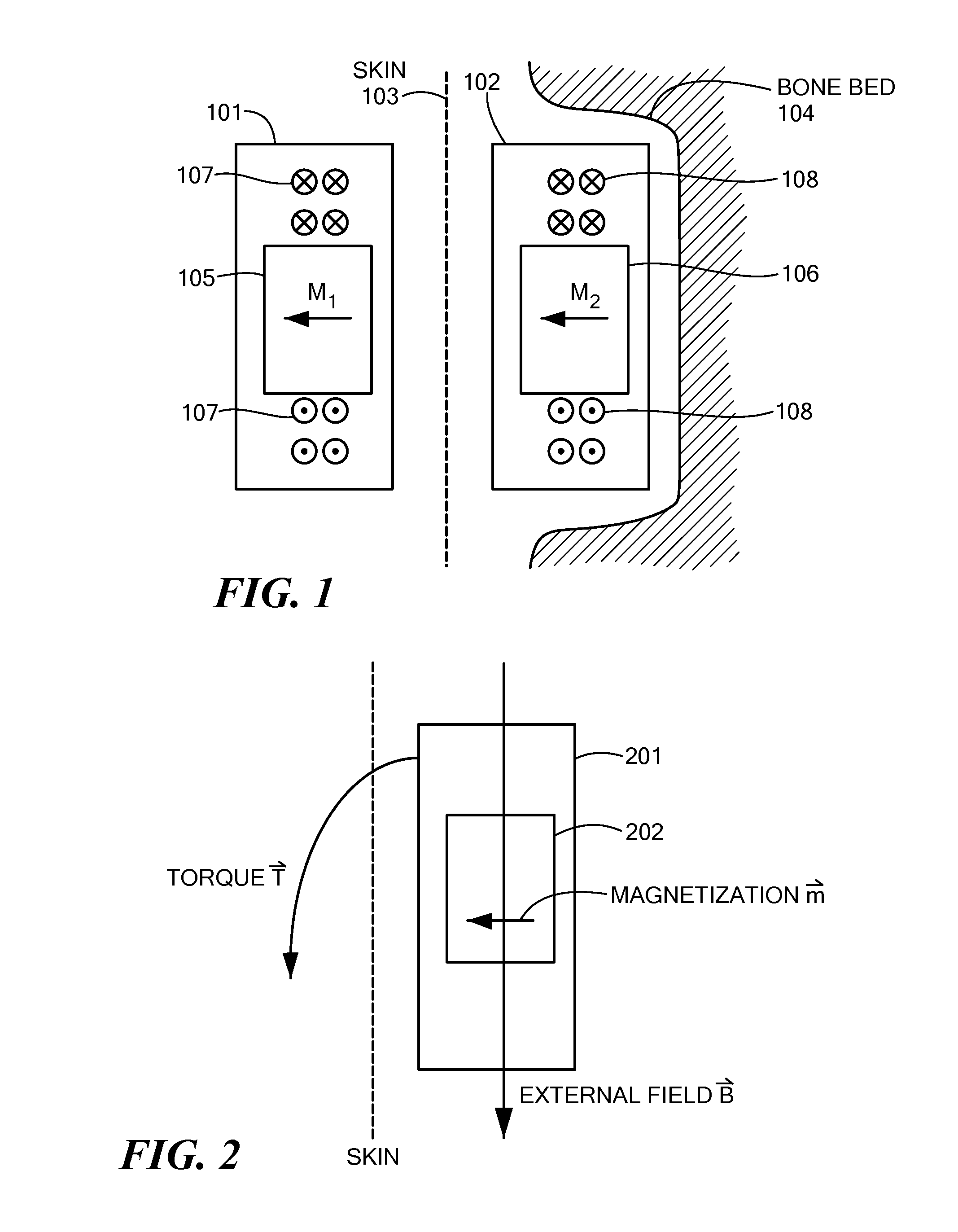
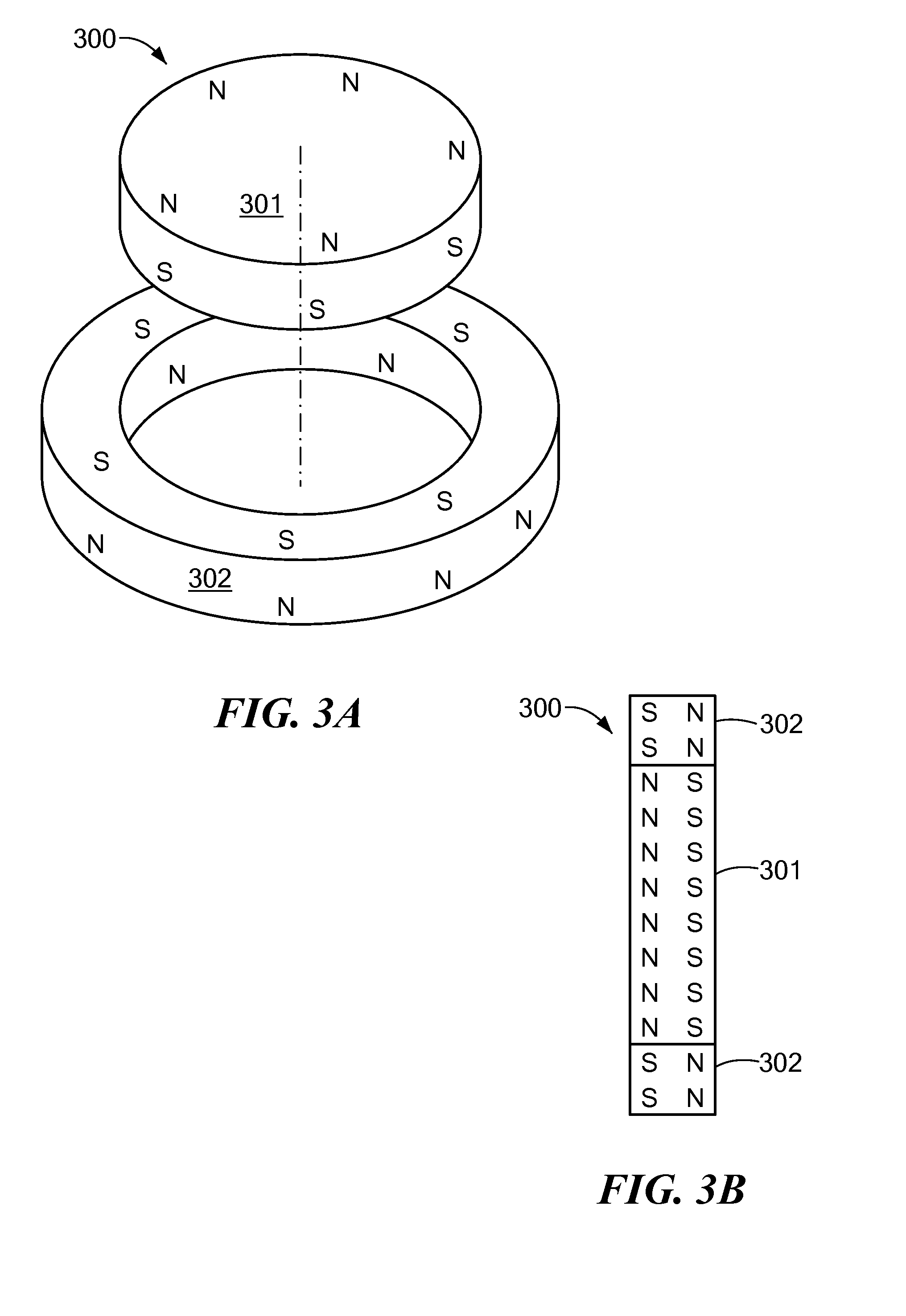
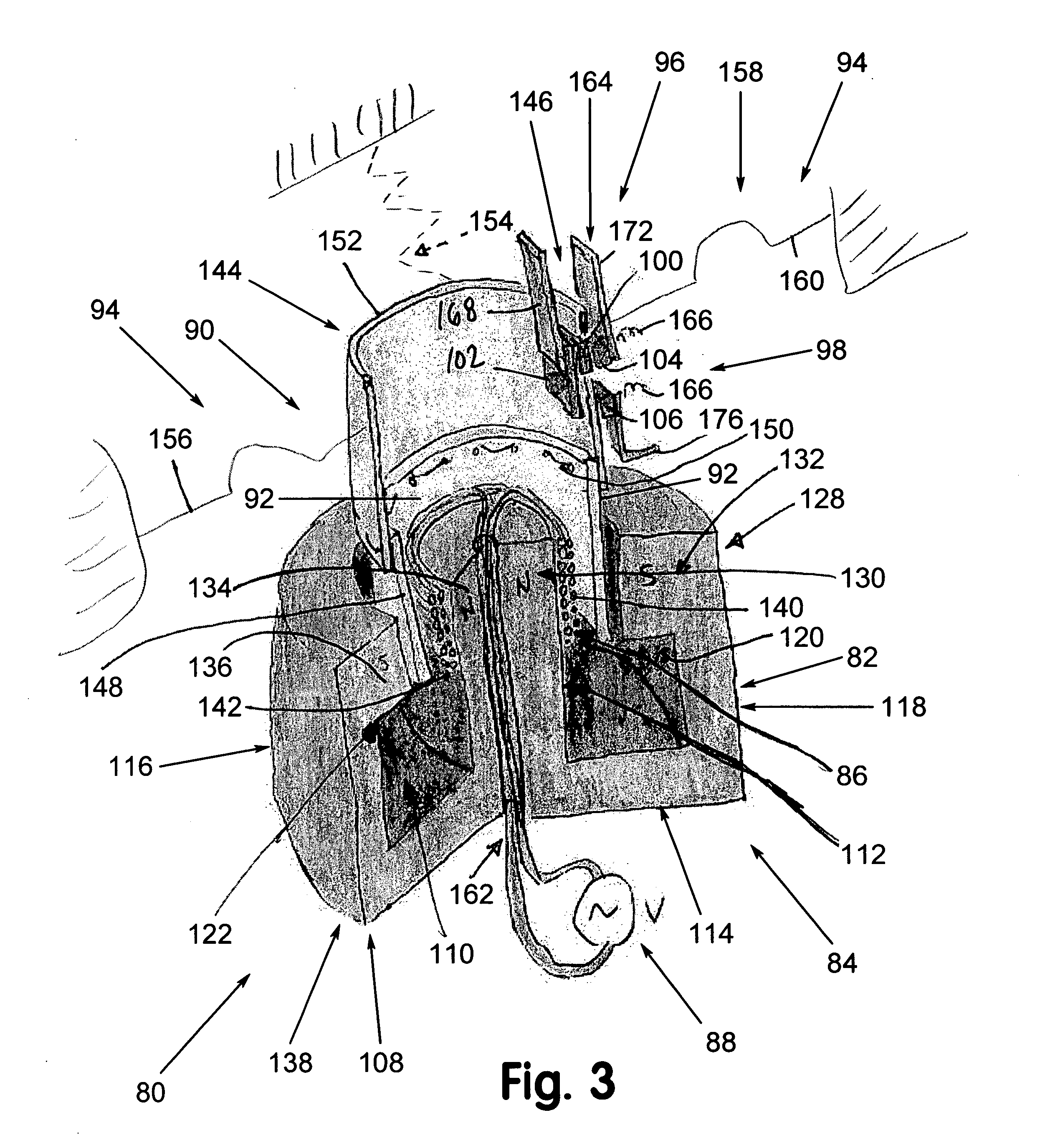
Magnetic Attachment Arrangement for Implantable Device
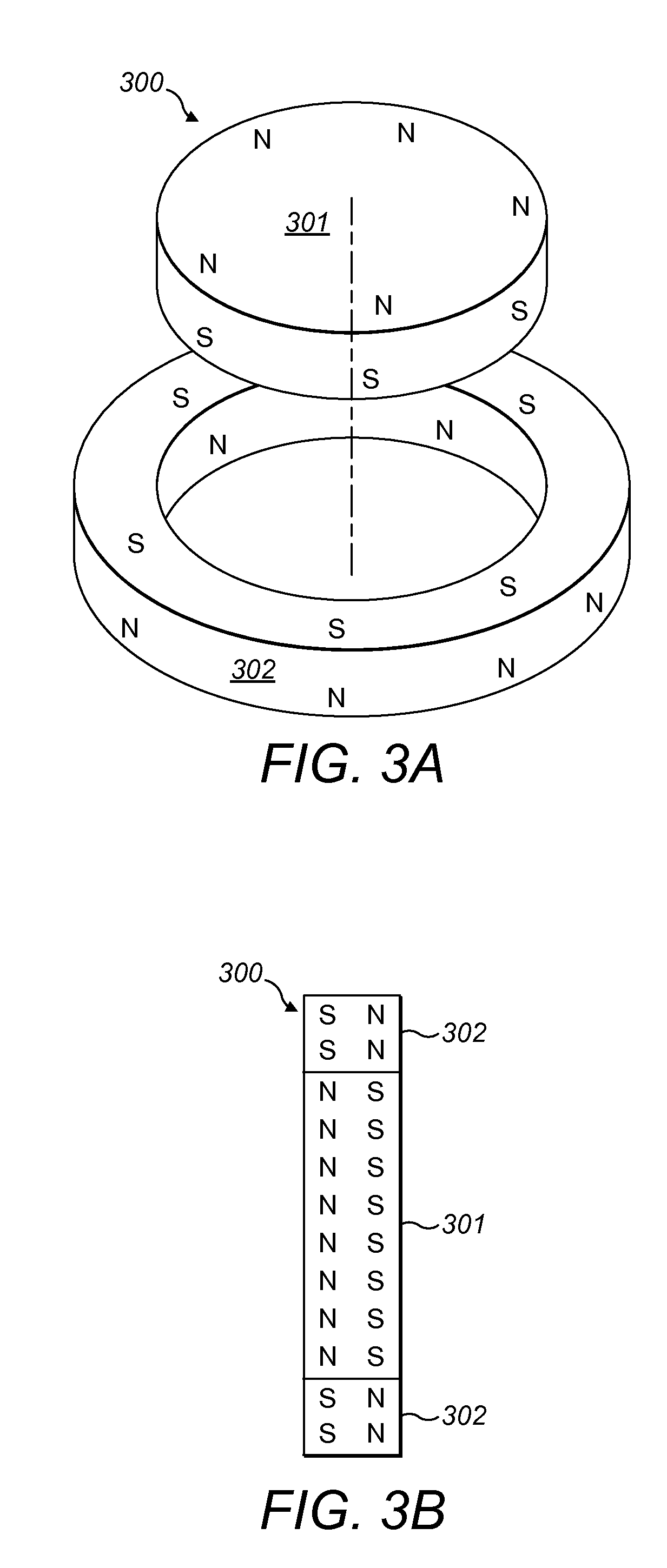
A magnet arrangement is described for use in implantable devices. An implantable housing contains a portion of an implantable electronic system. A cylindrical implant magnet arrangement within the housing includes multiple adjacent magnetic sections wherein at least two of the magnetic sections have opposing magnetic orientations in opposite magnetic directions. There may also be a similar external housing having a corresponding magnet arrangement.
Owner:VIBRANT MED EL HEARING TECH
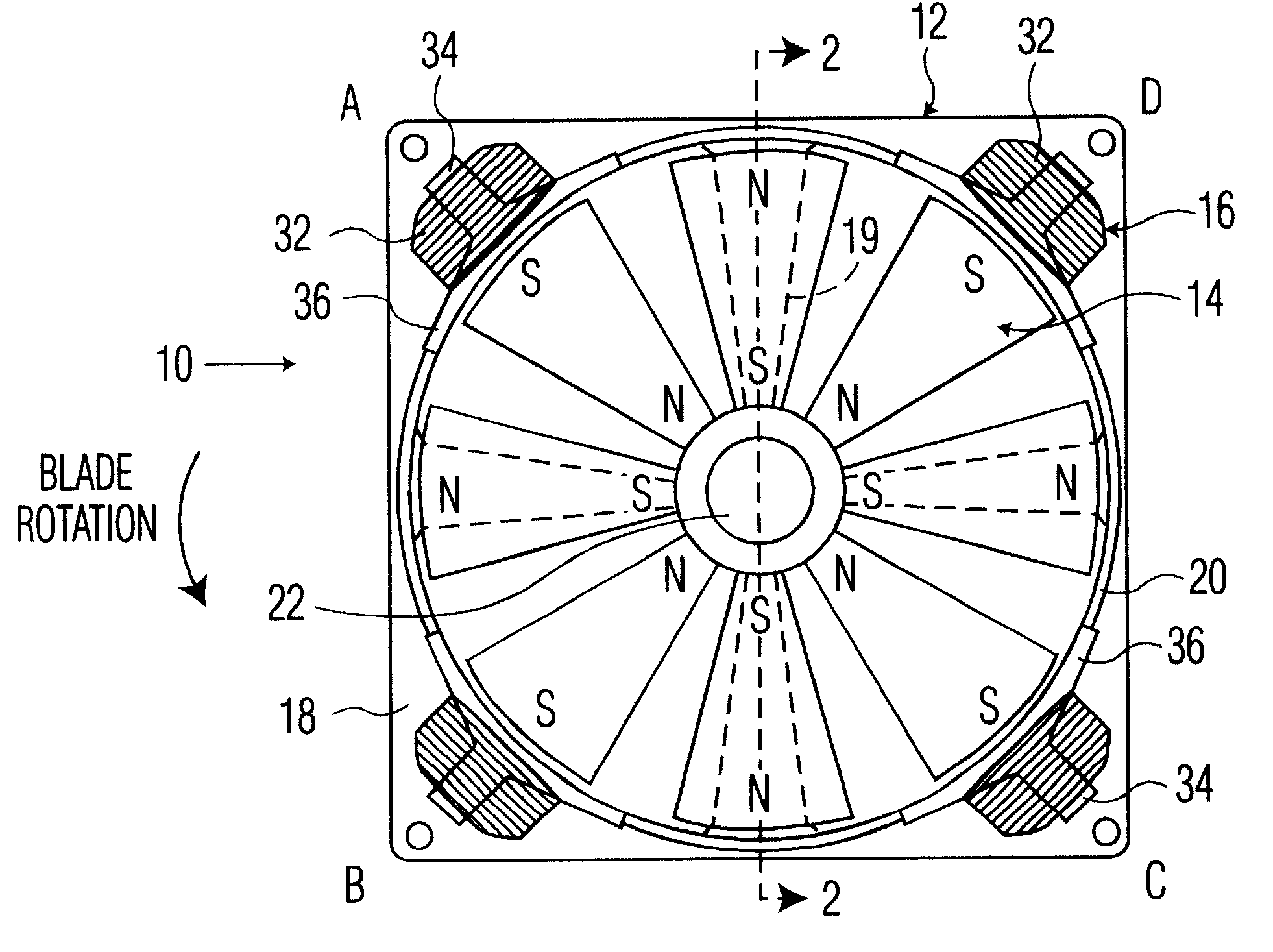
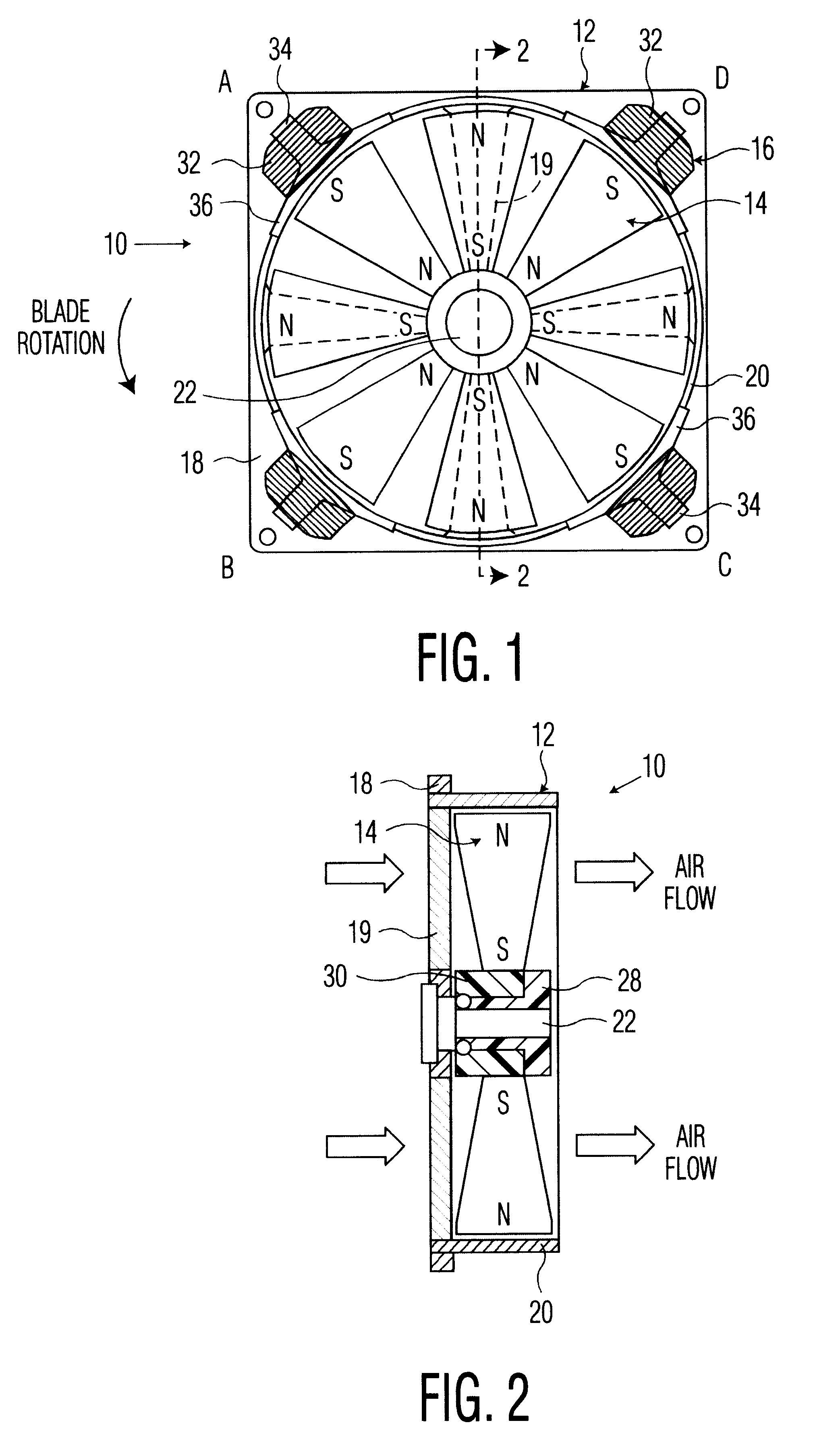
Fan with magnetic blades
InactiveUS6194798B1MiniaturizationReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsPump componentsStator coilEngineering
A DC driven fan with blades made of magnetized material and permanently magnetized in the radial direction and cooperating with a plurality of electromagnetic stator coils mounted external to the outer fan edges. Adjacent blades have alternate N-S, S-N radial magnetic orientations. In one embodiment, the blades are mounted in a non-ferrous hub and in an alternate embodiment they are mounted in a ferrous hub so that adjacent blades function like a U or V-shaped magnet. Blades can be made of magnetized ferrous, ferromagnetic, or magnetized plastic depending upon the application and blade strength specifications.
Owner:AIR CONCEPTS
Magnetic orientation device, manufacture device and manufacture method of magnetic pigment printed product
ActiveCN102529326AImprove the three-dimensional effectPattern printingPretreated surfacesEngineeringSubstrate surface
The invention provides a magnetic orientation device, a manufacture device and a manufacture method of a magnetic pigment printed product. The magnetic orientation device comprises a drive device and a magnet, wherein the drive device is used for driving the magnet to rotate around a rotation shaft; and the rotating magnet produces a magnetic field to realize magnetic orientation of magnetic pigment flakes in magnetic ink printed on the substrate surface of the printed product, thereby forming a magnetically oriented pattern with three-dimensional effect in the magnetic ink. According to the invention, the magnetic orientation device, the manufacture device and the manufacture method of the magnetic pigment printed product provided by the invention can improve the three-dimensional effect of the magnetically orientated pattern by using the magnetic field produced by the rotating magnet to realize magnetic orientation of the magnetic pigment flakes in the magnetic ink.
Owner:HUIZHOU FORYOU OPTICAL TECH
Plane plate vibration device and switch employing the same
ActiveUS6937124B1Input/output for user-computer interactionRepeater circuitsClassical mechanicsPhysics
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
Magnetic Field Sensor For Measuring A Direction Of A Magnetic Field In A Plane
ActiveUS20100164491A1Solid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesControl signalElectronic switch
A magnetic field sensor for measuring a direction of a magnetic field in a plane comprises a sensing structure comprising a ring-shaped well, a plurality of contacts of equal size placed at equal distance from each other along the ring-shaped well, and an electronic circuit comprising a plurality of electronic switches associated with the contacts of the sensing structure, a logic block for controlling the electronic switches, at least one current source, a means for measuring a difference between a first voltage and a second voltage, a timing circuit providing a control signal for controlling the logic block and providing a reference signal, wherein the logic block is adapted to close and open the electronic switches under the control of the control signal according to a predetermined scheme such that a predetermined number of contacts of the plurality of contacts form a vertical Hall element that is supplied with current from the at least one current source and that has two contacts connected to the means for measuring, and such that the vertical Hall element is moved in steps along the ring-shaped well, and a means for measuring a phase shift between the reference signal and an output signal of the voltage measuring means.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
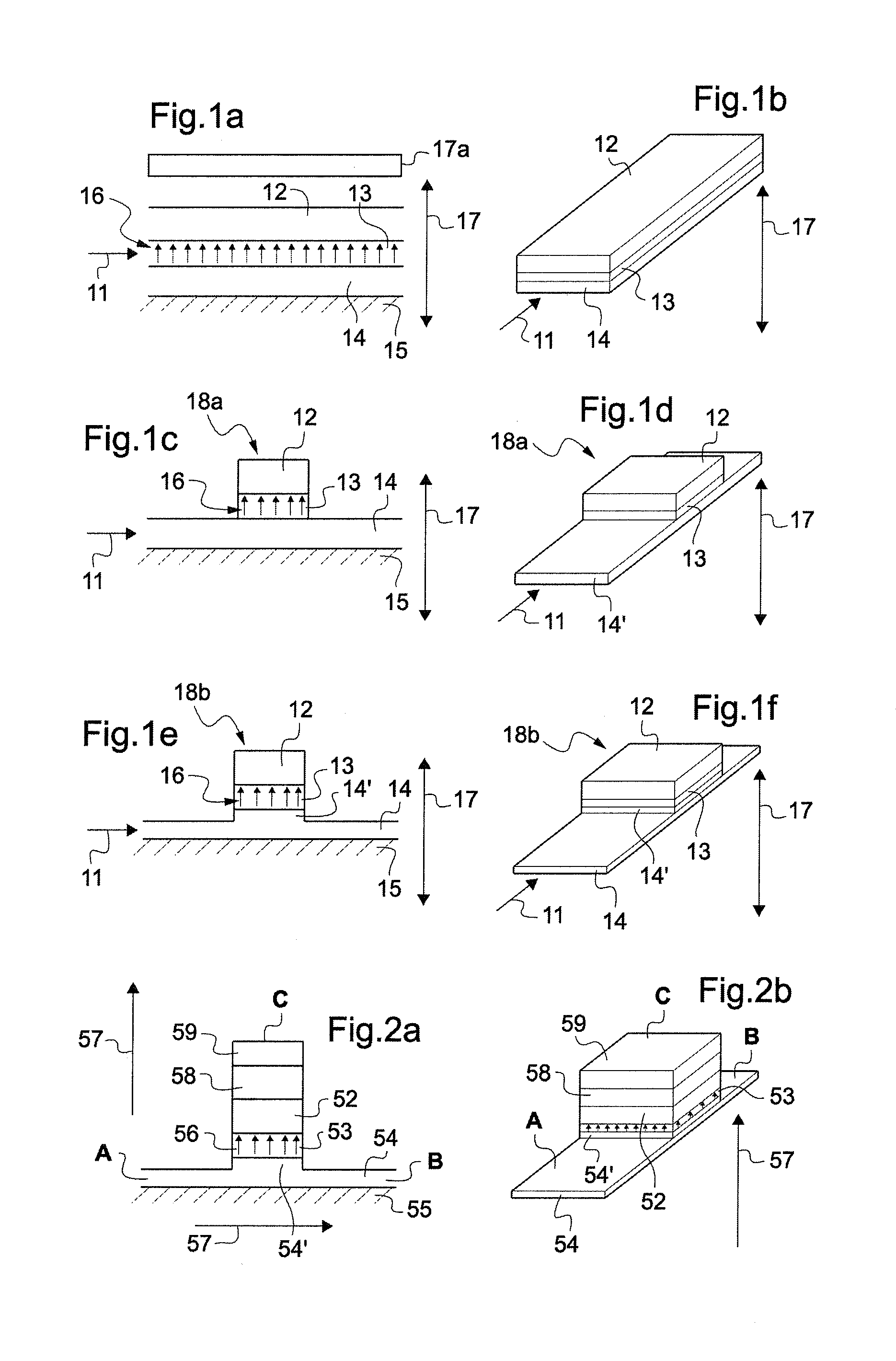
Writable magnetic element
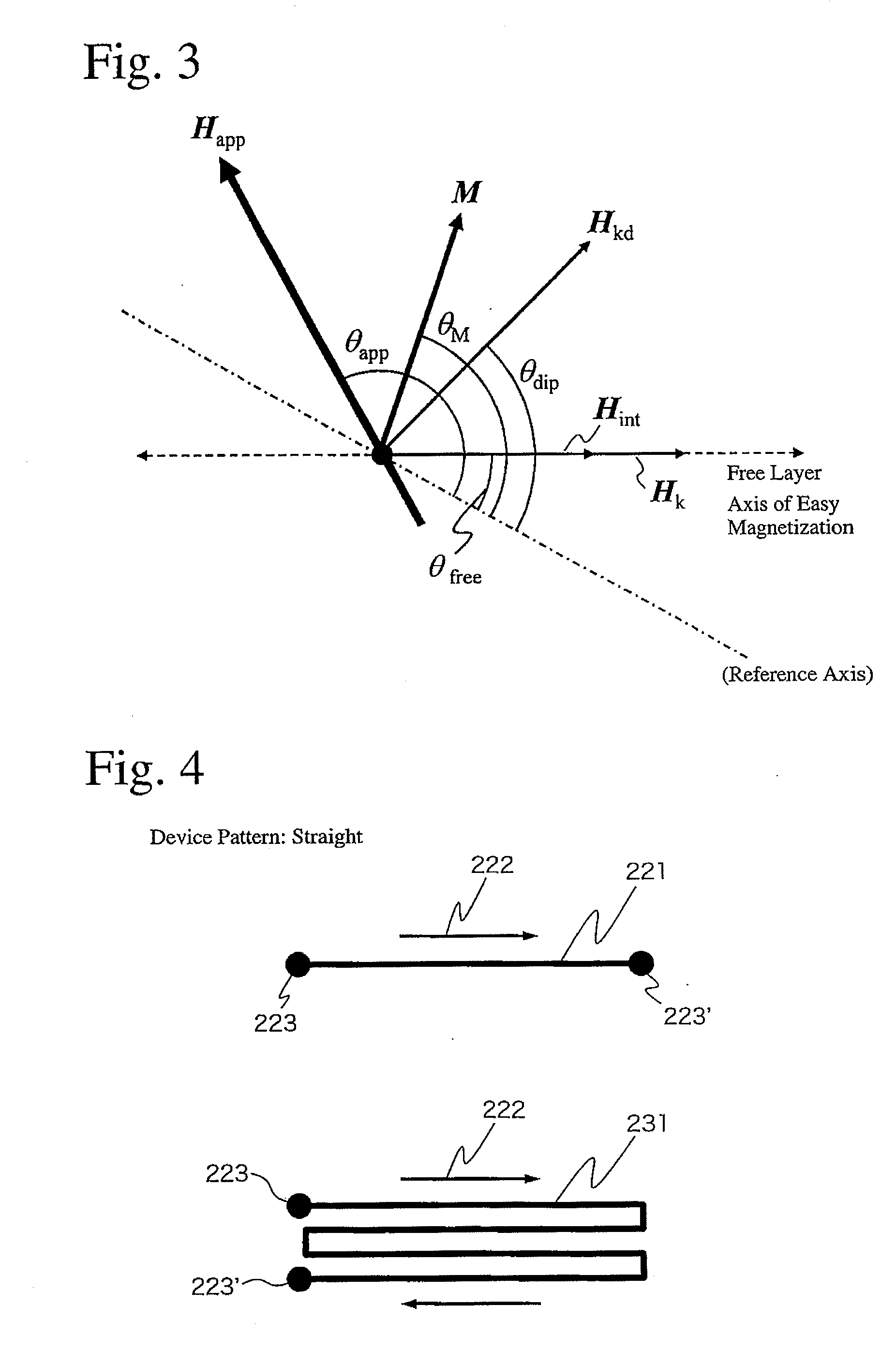
ActiveUS8350347B2PresenceLower energy barrierNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetizationCentral layer
The invention relates to a writable magnetic element comprising a stack of layers presenting a write magnetic layer, wherein the stack has a central layer of at least one magnetic material presenting a direction of magnetization that is perpendicular to the plane of the central layer, said central layer being sandwiched between first and second outer layers of non-magnetic materials, the first outer layer comprising a first non-magnetic material and the second outer layer comprising a second non-magnetic material that is different from the first non-magnetic material, at least the second non-magnetic material being electrically conductive, and wherein it includes a device for causing current to flow through the second outer layer in a current flow direction parallel to the plane of the central layer, and a device for applying a magnetic field along a magnetic field direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the central layer.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +4
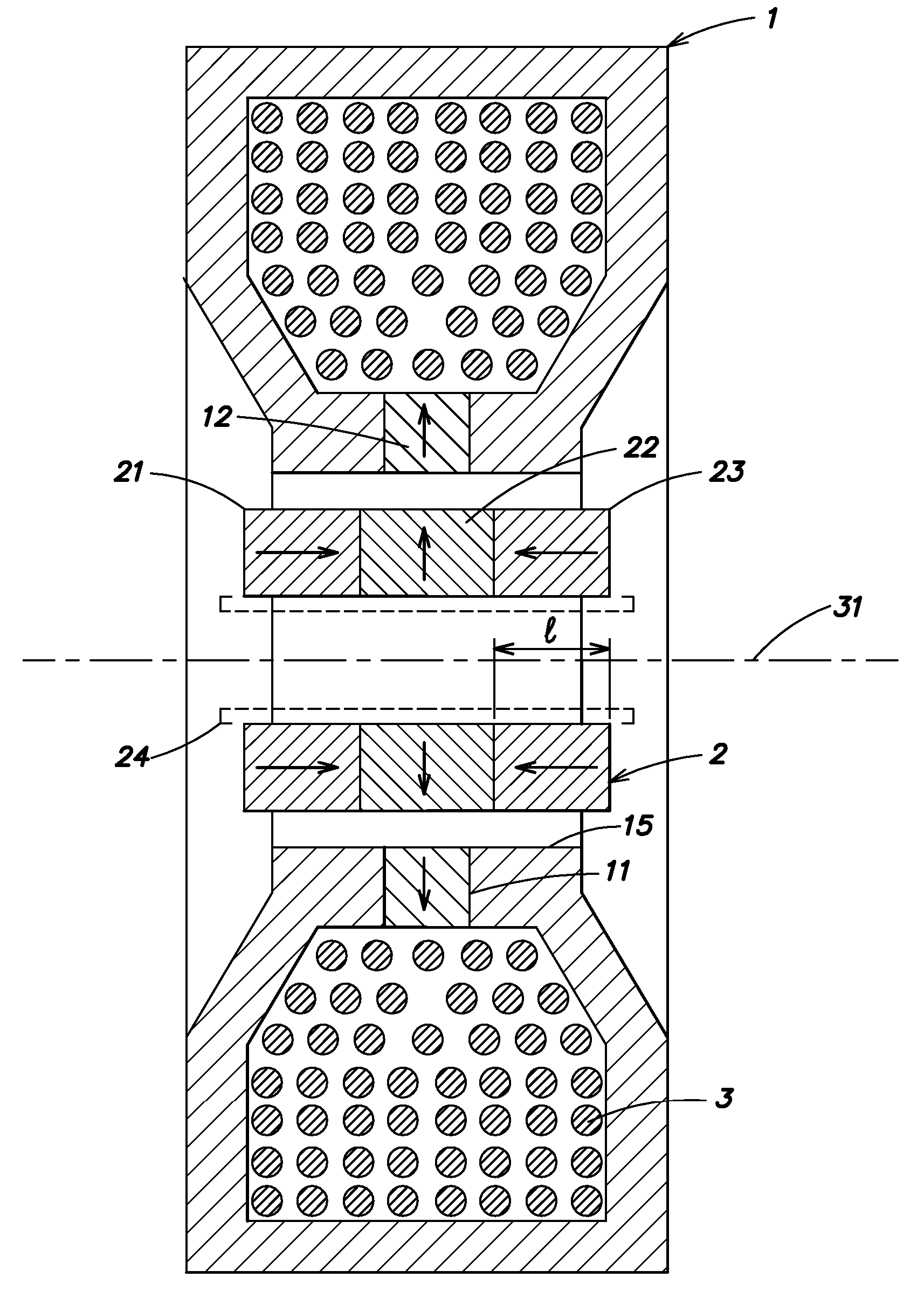
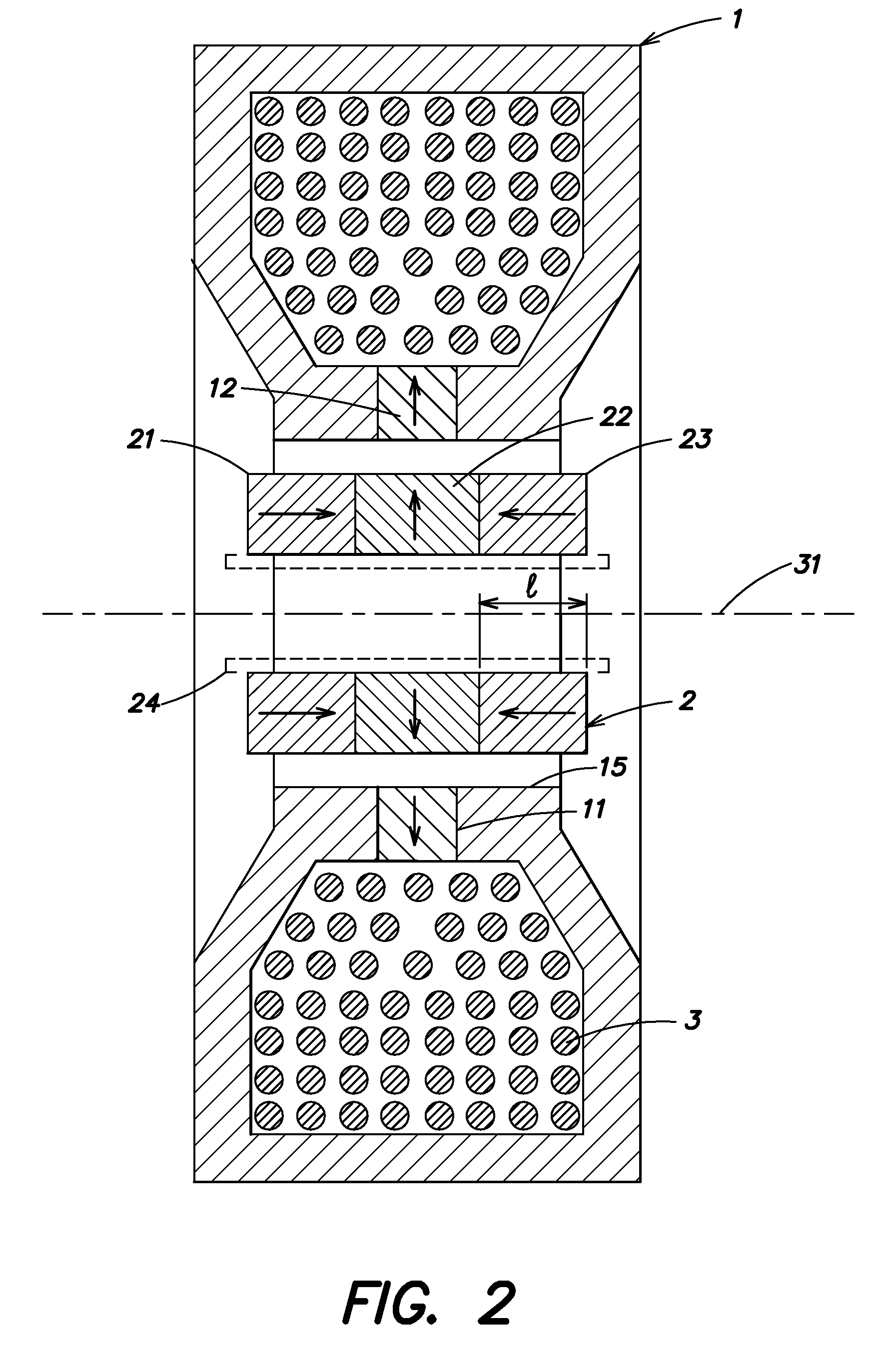
Variable field magnet apparatus
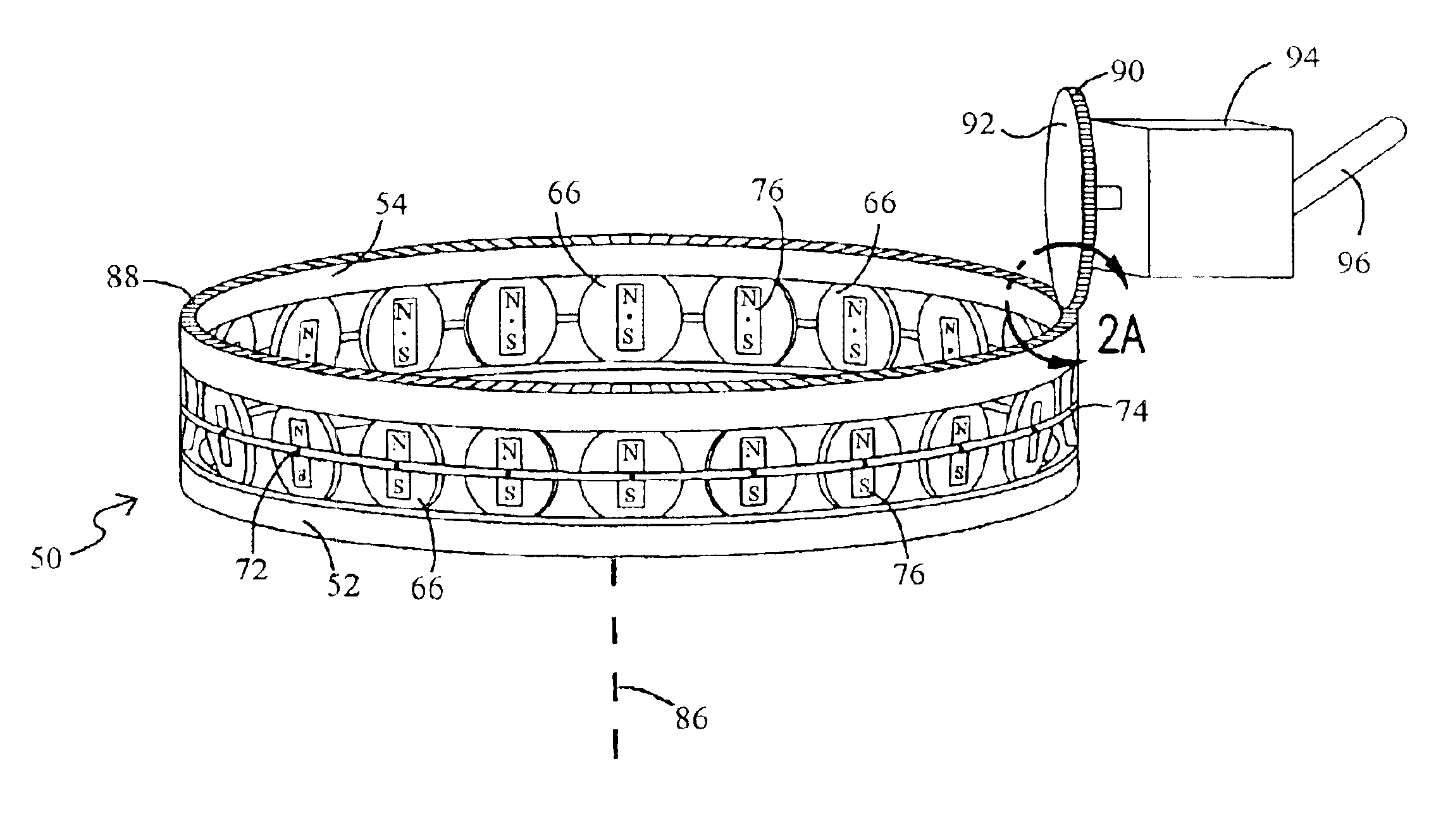
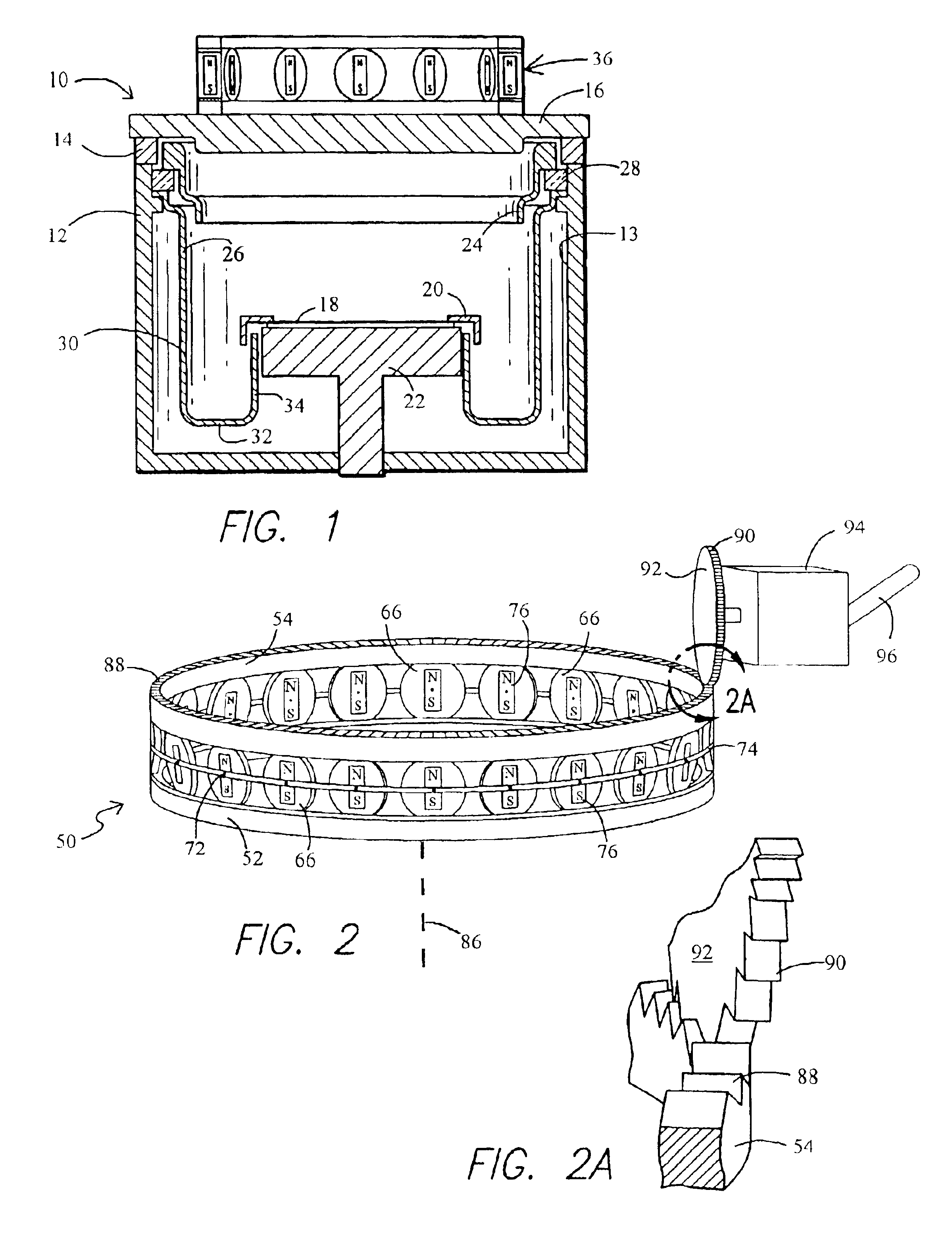
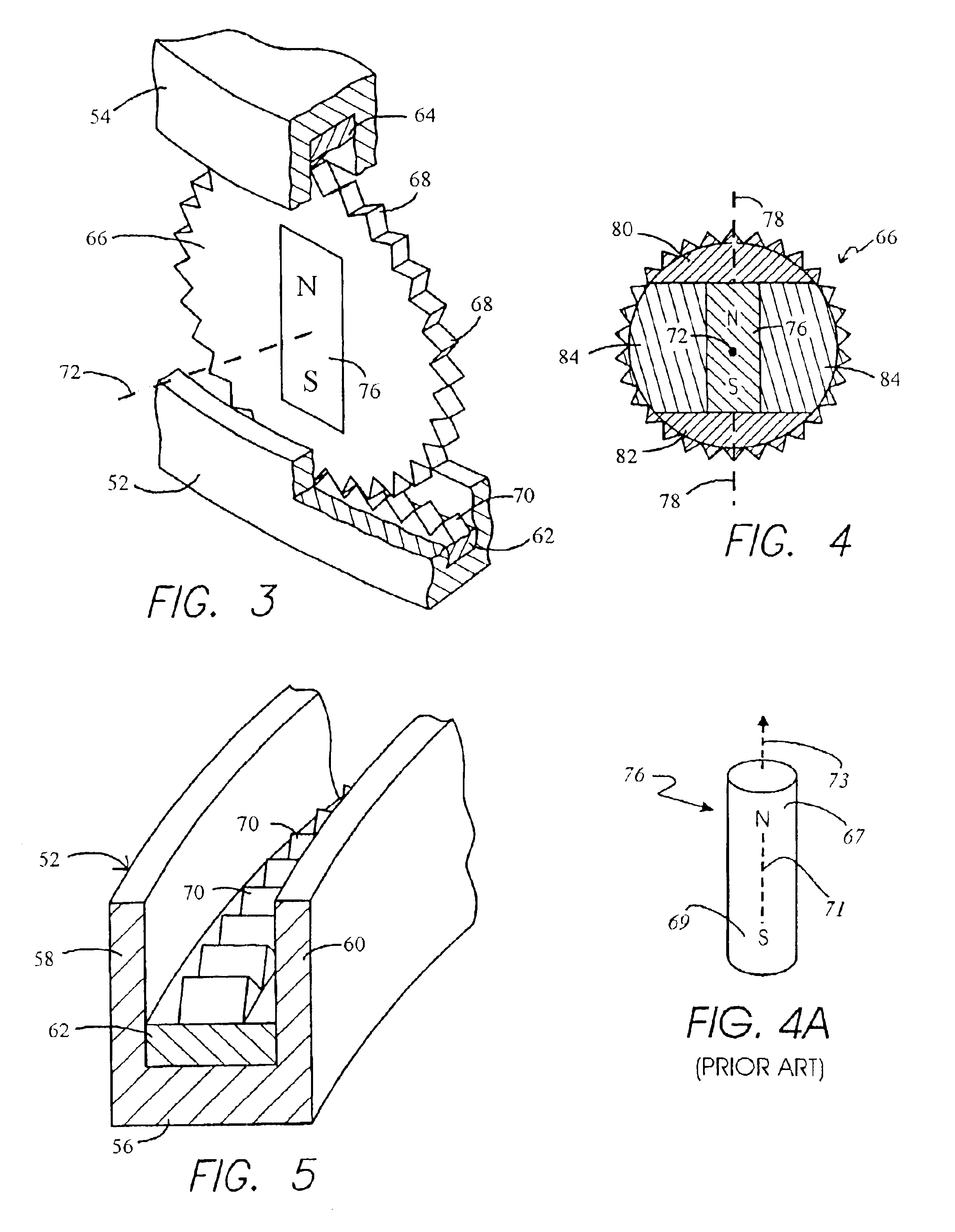
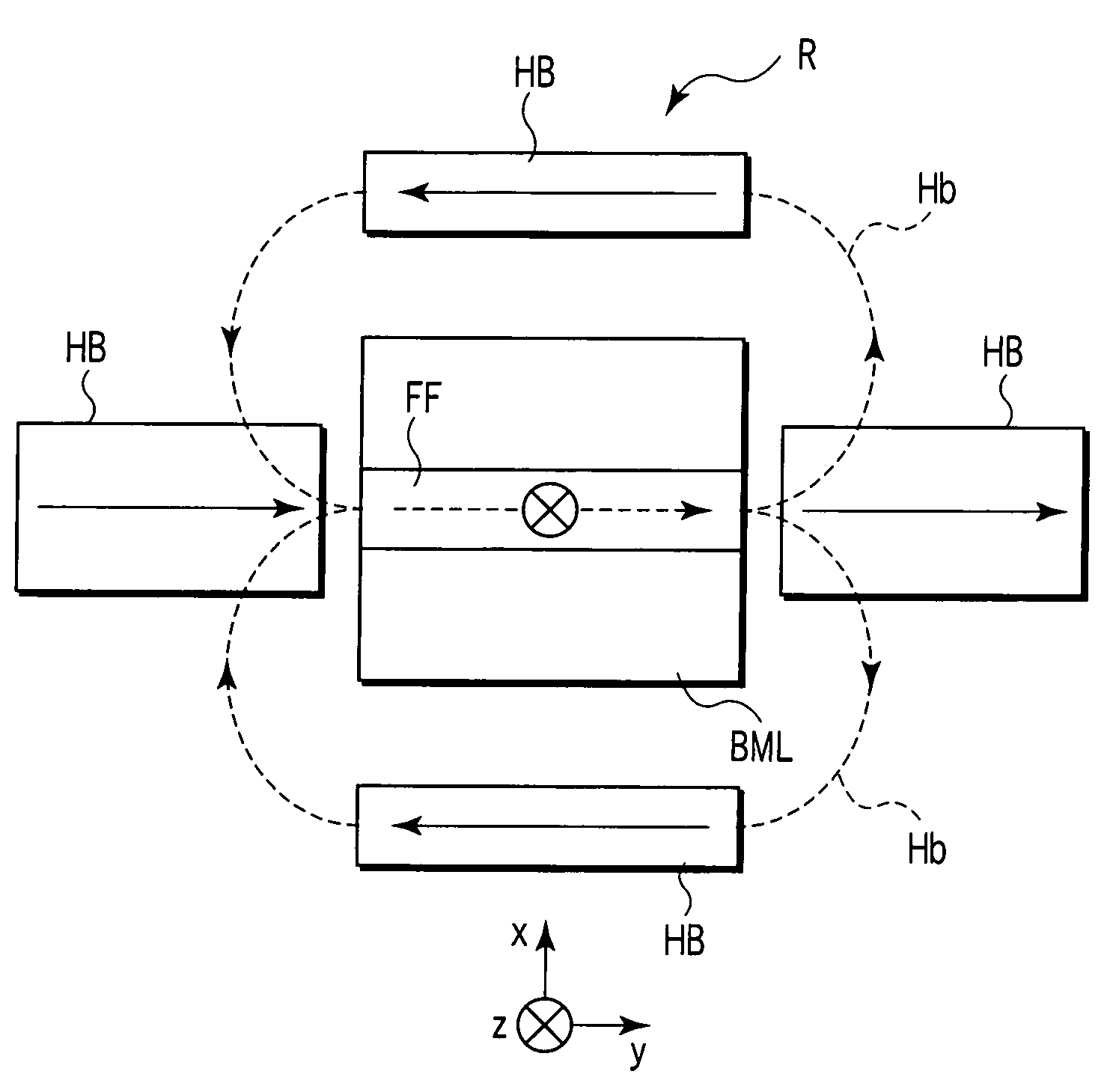
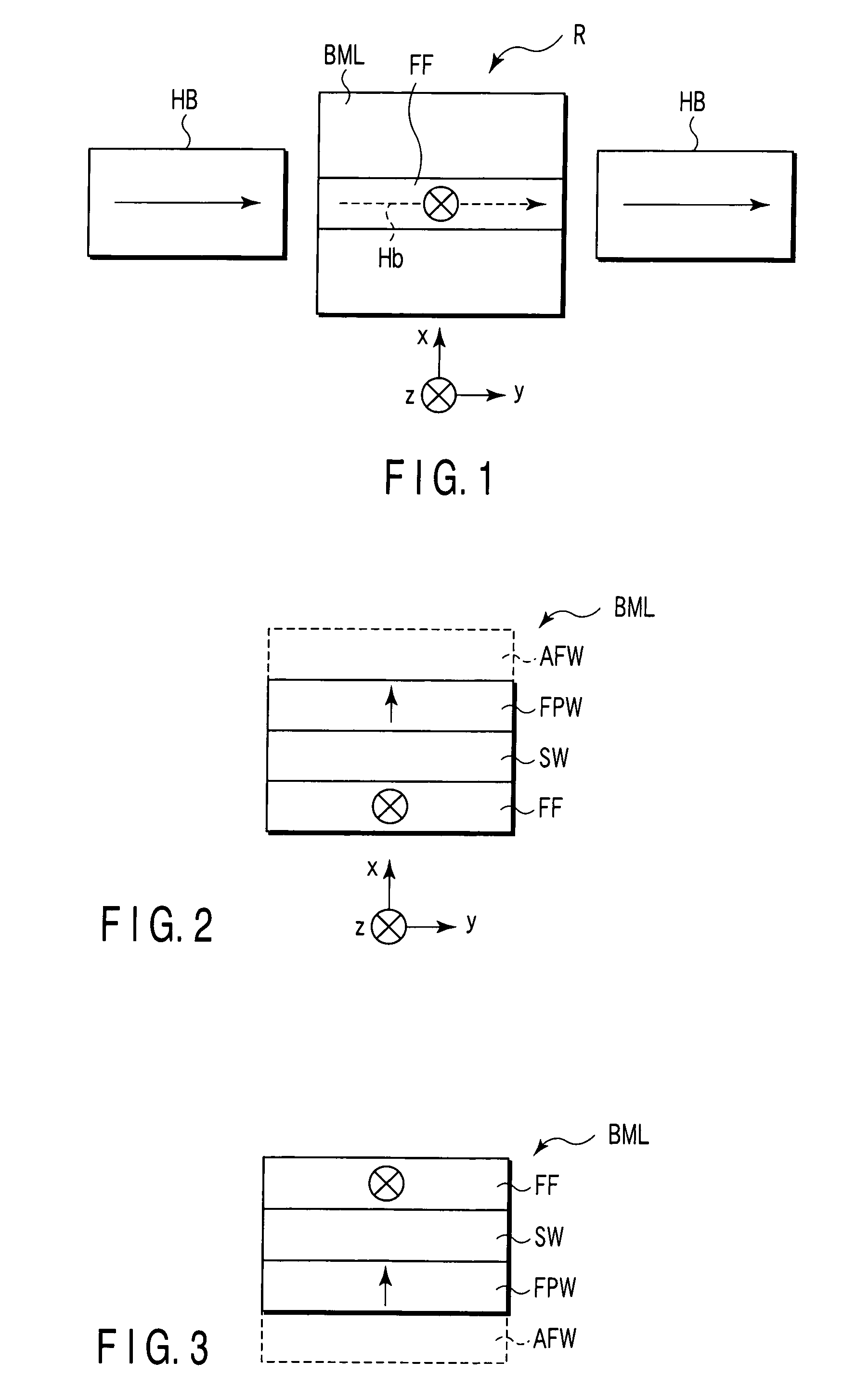
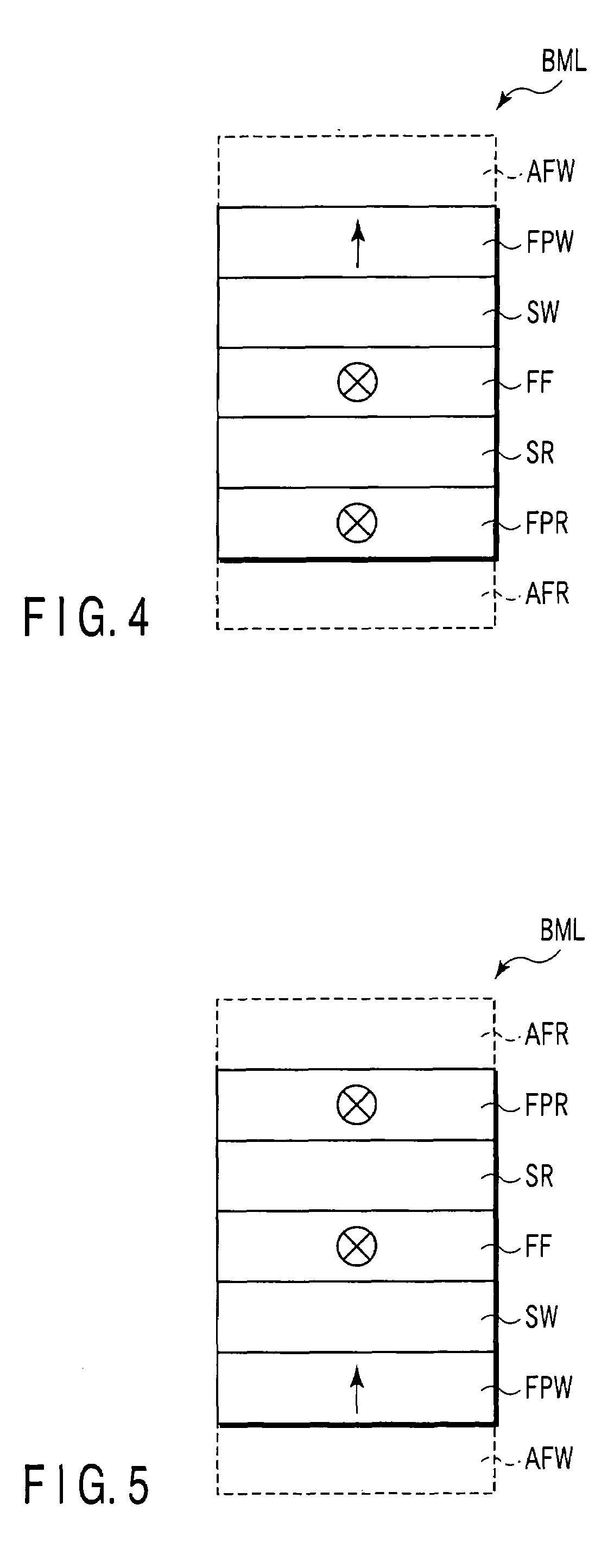
A magnet assembly for producing a varying magnetic field is provided wherein a plurality of permanent magnets are interposed between two members which are constructed of a ferromagnetic material. Each of the magnets is rotatable and has a north and south magnetic pole. Each of the magnets is disposed so that the north magnetic poles of the plurality of permanent magnets have a common magnetic orientation with respect to the first member. An orienter, such as, for example, a ring gear and pinion arrangement, is coupled to the magnets to change their common magnetic orientation with respect to the first member. The magnetic field projected by the assembly varies as a function of the orientation of the magnets.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
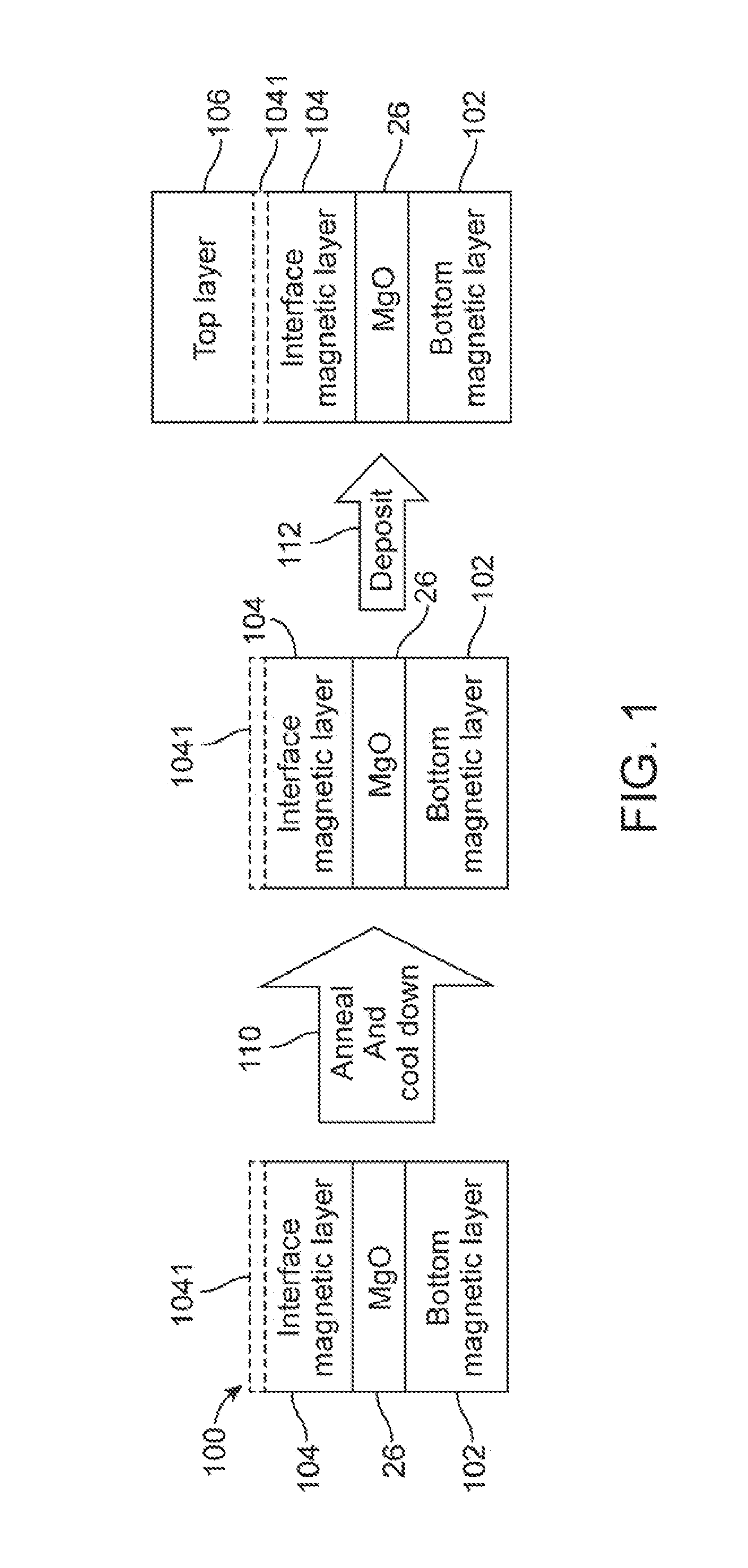
Magnetic tunnel junction device and its method of fabrication
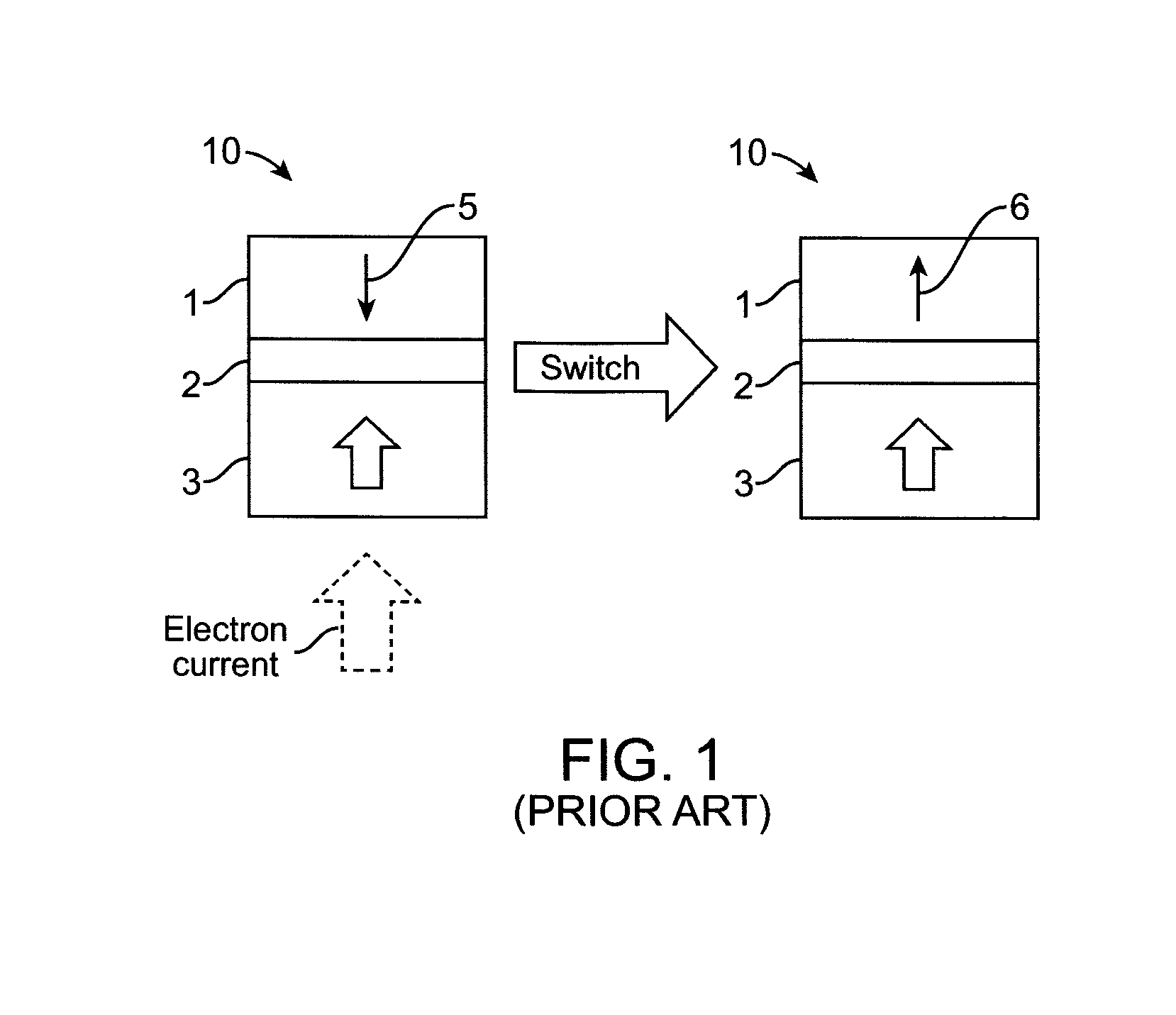
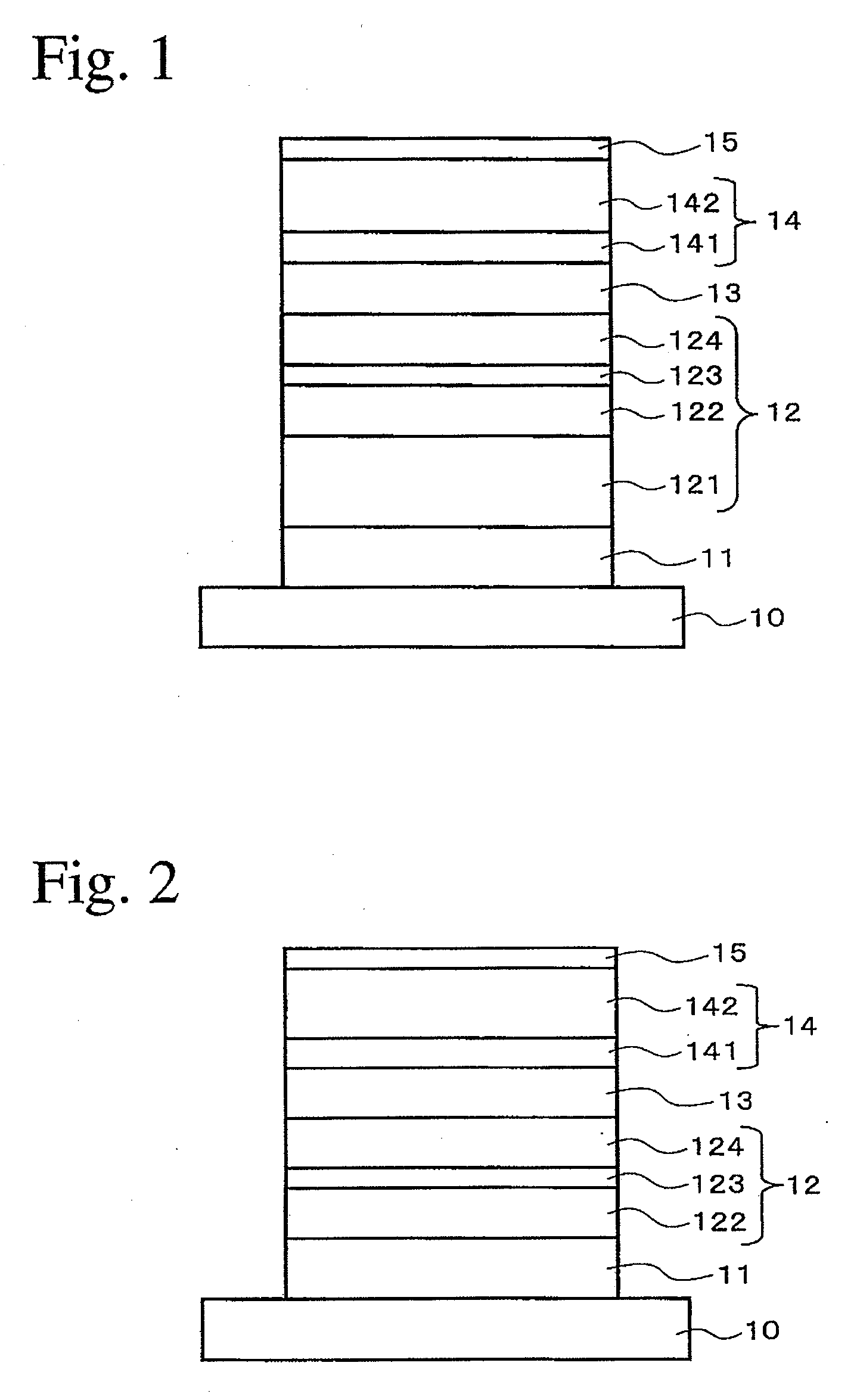
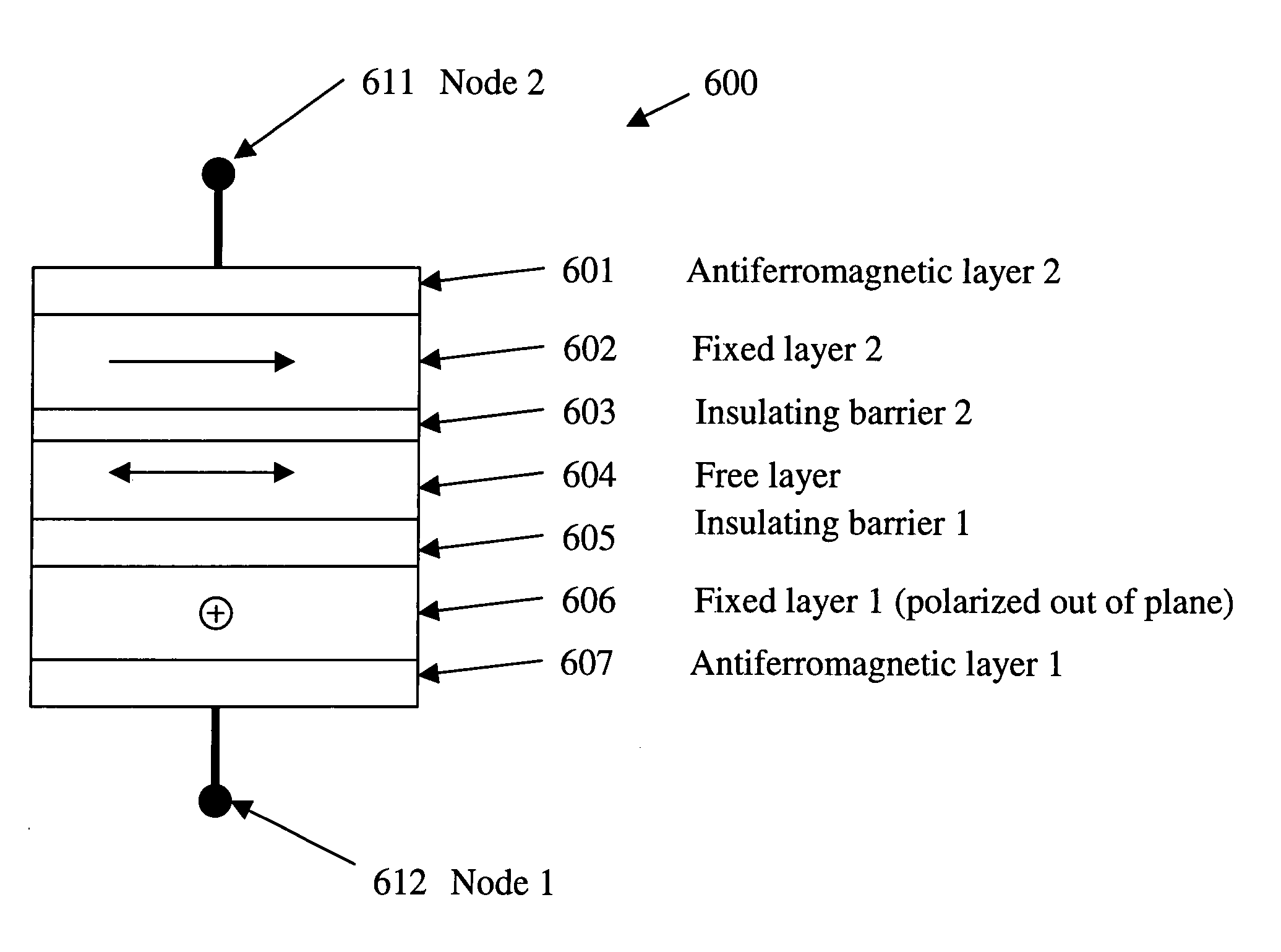
The present invention provides a magnetic tunnel junction memory element comprising two pinned ferromagnetic layers having magnetic orientations pointing in opposite directions and a sense layer arranged between the two pinned ferromagnetic layers and separated from each by a nonmagnetic tunnel barrier layer. The invention also provides methods of fabricating magnetic tunnel junction memory elements as well as magnetoresistive memory devices and processor systems comprising such memory elements.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Measurement device of critical current properties of high-temperature superconducting tape
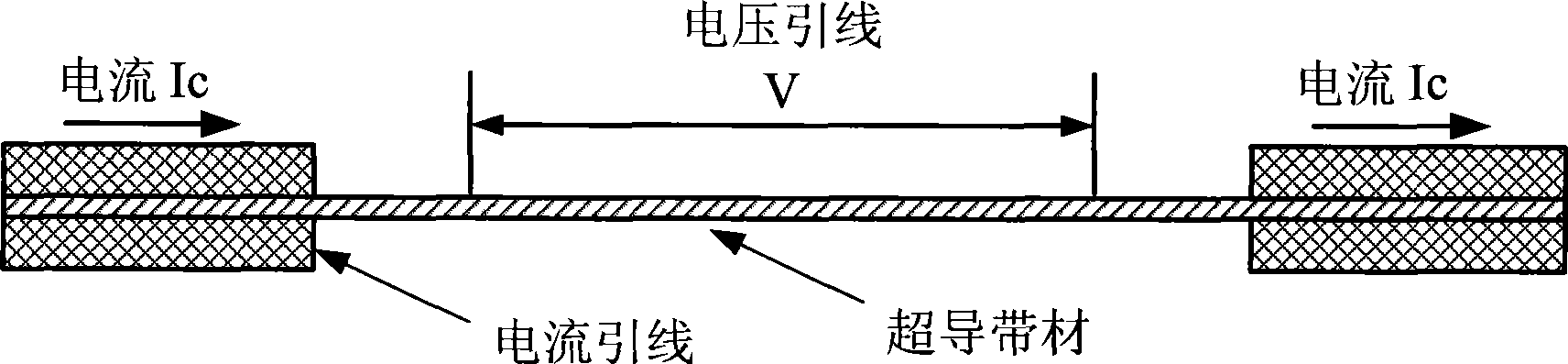
ActiveCN101446609AMeasuring critical current characteristicsRealize critical current characteristic measurementElectrical testingMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsYttrium barium copper oxideMeasurement device
The invention provides a measurement device of critical current properties of a high-temperature superconducting tape, and the device comprises a superconducting tape sample rack 1, a Hall magnetic field probe 2, a temperature probe 3, a background magnetic field magnet 4, a rotary rod 5, a rotary handle 6, a superconducting tape current lead wire 7, a background magnetic field magnet current lead wire 8, a low-temperature dewar 9, a cooling medium storage container 10, a low-temperature cooling medium 11, an extraction valve 12, a carburetor 13, a vacuum unit 14, a GM refrigerator 15, a background magnetic field magnet DC power supply 16, a superconducting DC power supply 17 and a system control, data acquisition and processing system 18. The device can simply and rapidly calculate the temperature, the background magnetic field and the impact factors on the change of the direction of the magnetic field thereof, thereby being applicable to the measurement of the critical current properties of yttrium barium copper oxide YBCO high-temperature superconducting tape.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
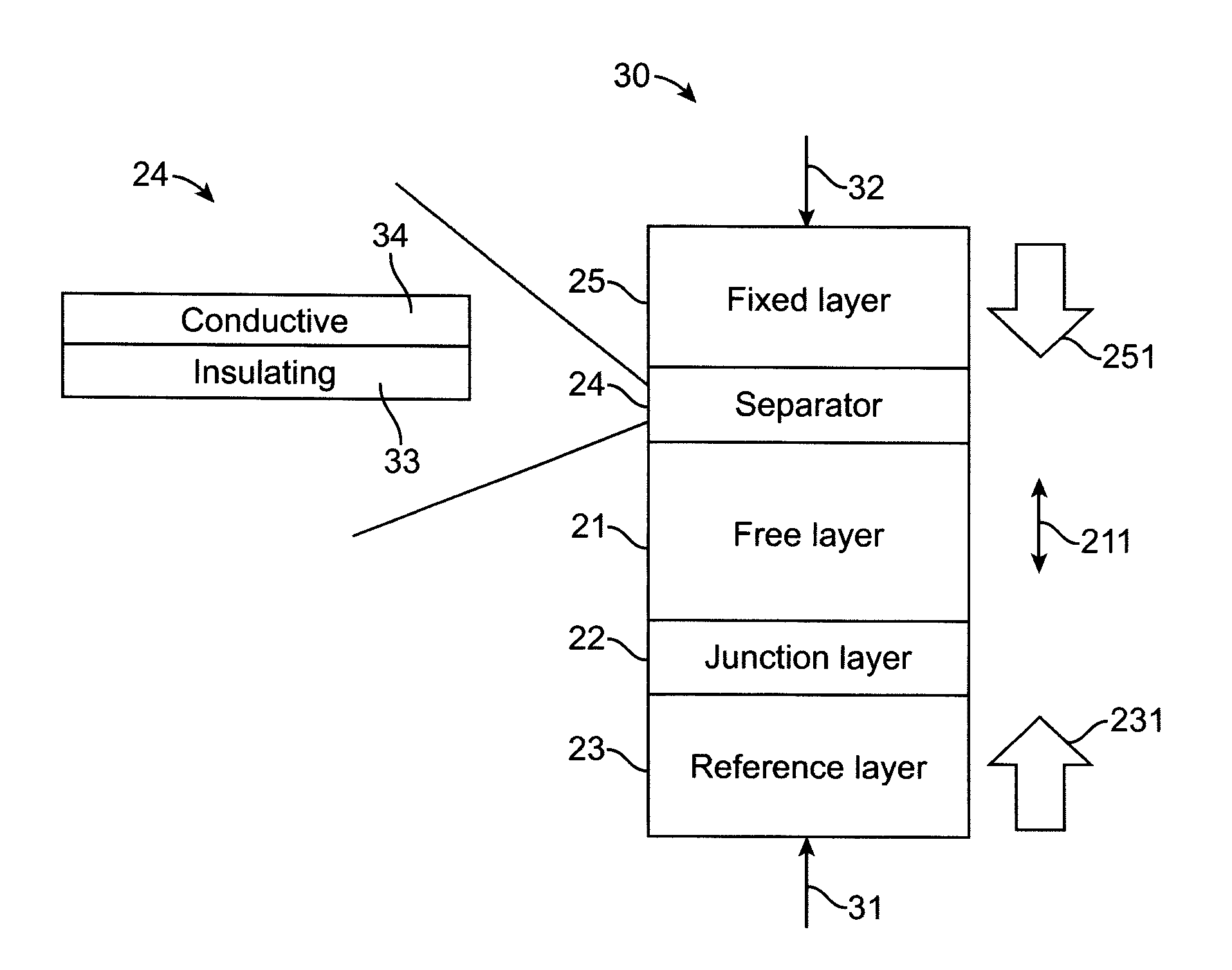
Perpendicular sttmram device with balanced reference layer
A spin toque transfer magnetic random access memory (STTMRAM) element comprises a reference layer, which can be a single layer structure or a synthetic multi-layer structure, formed on a substrate, with a fixed perpendicular magnetic component. A junction layer is formed on top of the reference layer and a free layer is formed on top of the junction layer with a perpendicular magnetic orientation, at substantially its center of the free layer and switchable. A tuning layer is formed on top of the free layer and a fixed layer is formed on top of the tuning layer, the fixed layer has a fixed perpendicular magnetic component opposite to that of the reference layer. The magnetic orientation of the free layer switches relative to that of the fixed layer. The perpendicular magnetic components of the fixed layer and the reference layer substantially cancel each other and the free layer has an in-plane edge magnetization field.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
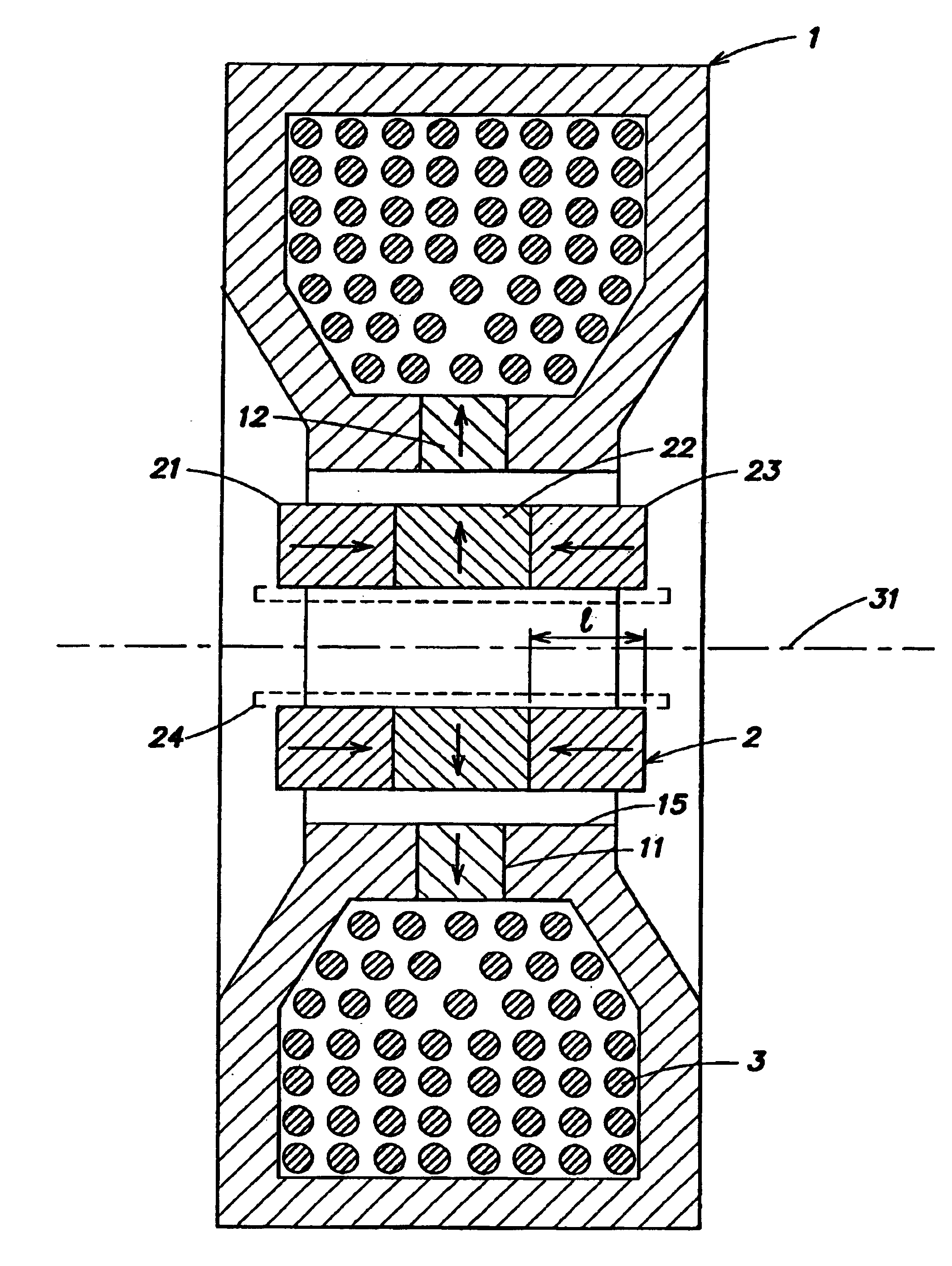
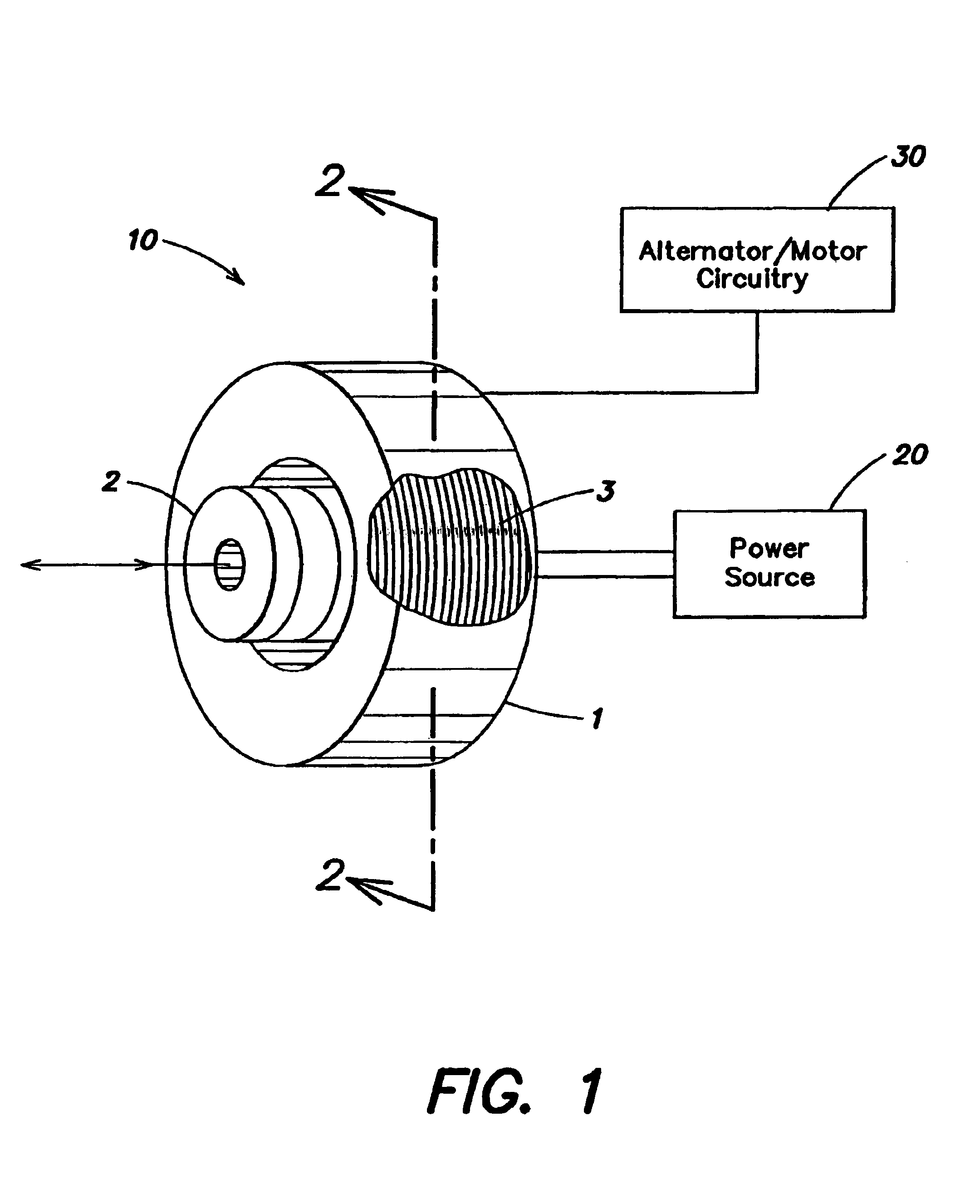
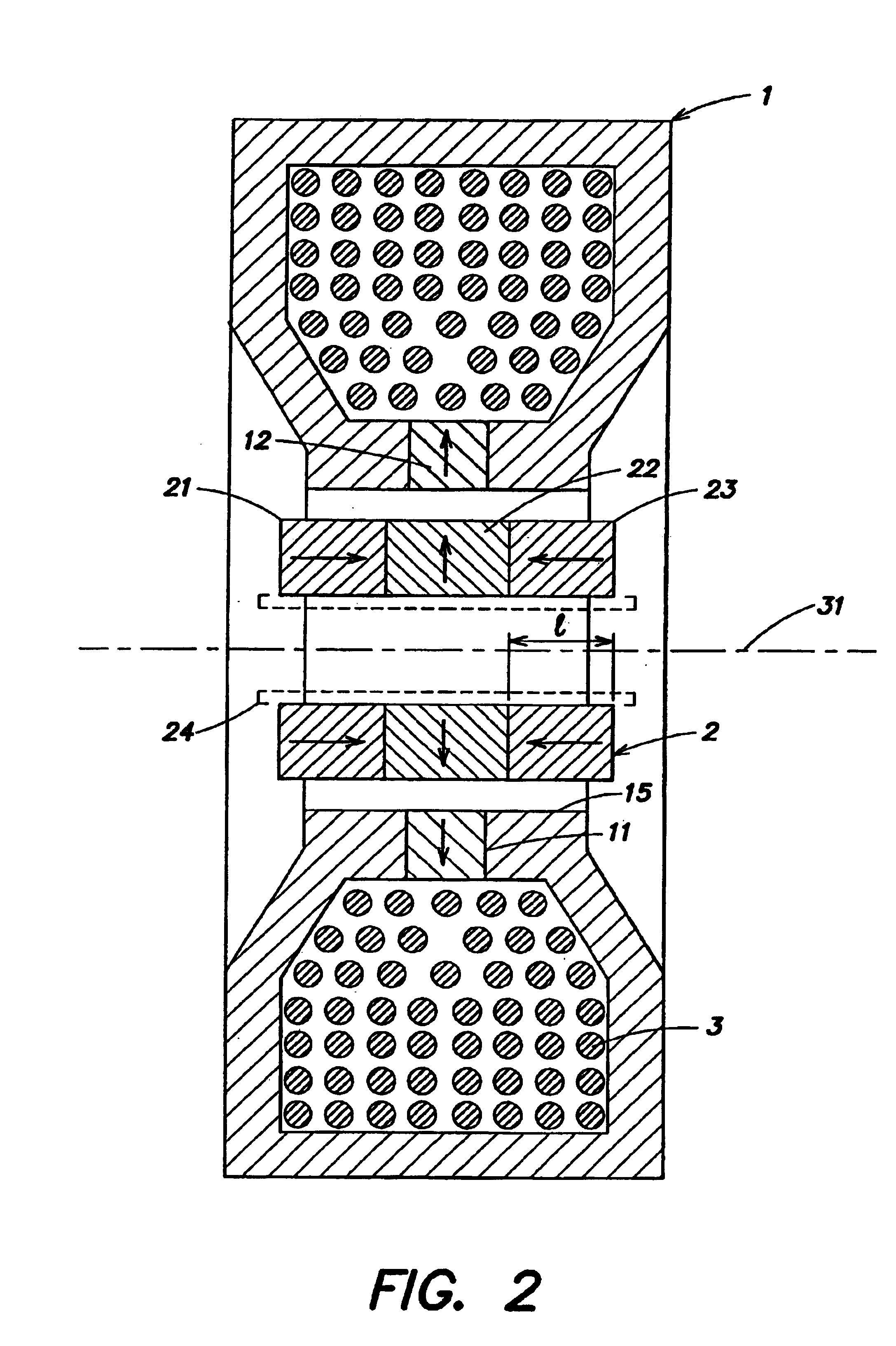
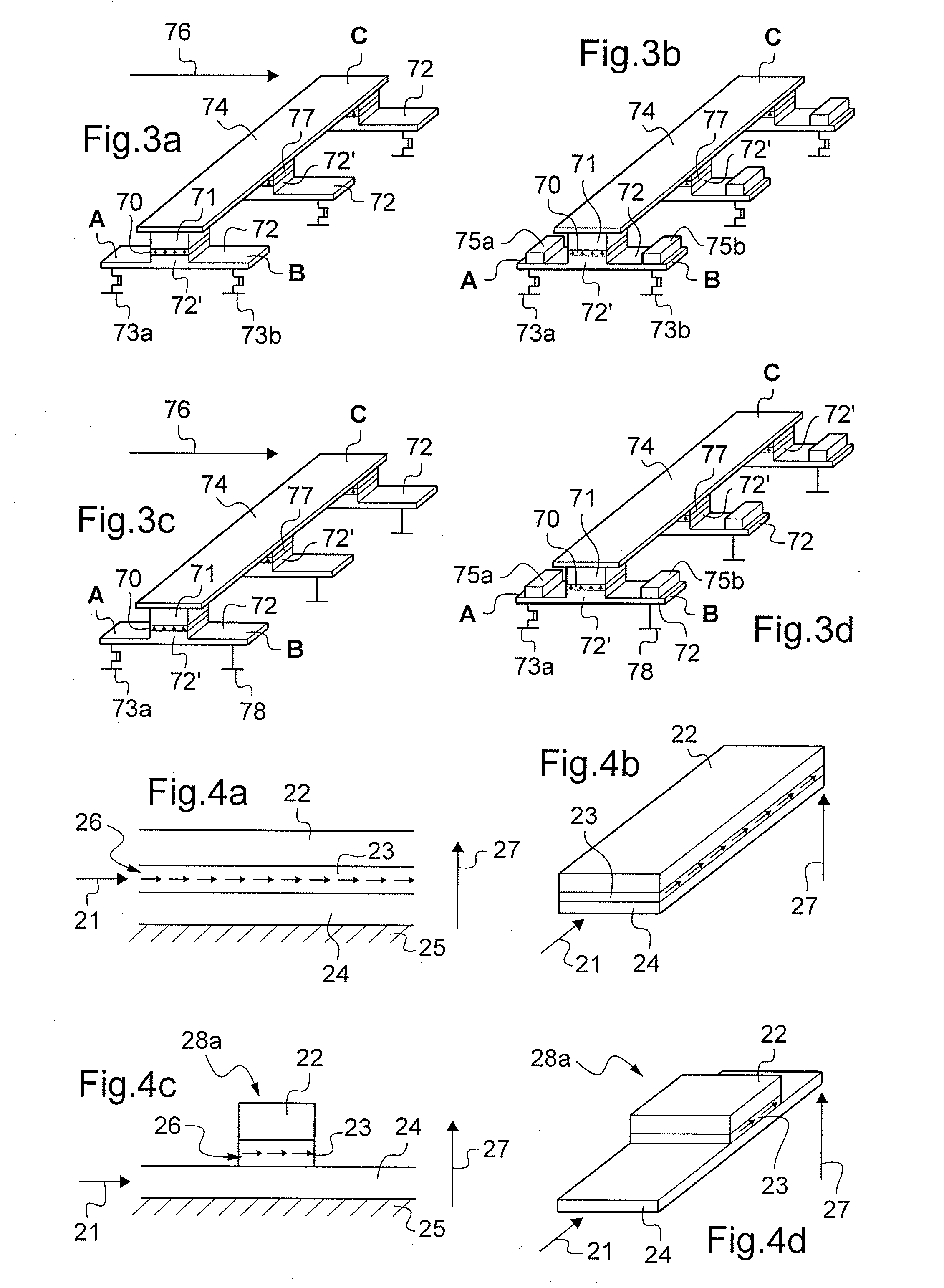
Linear electrical machine for electric power generation or motive drive
InactiveUS6914351B2Propulsion systemsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsAlternatorElectric power
A linear electrical machine may function as an alternator or a motor. Three annular magnets may be provided that move relative to a core. The magnets may all have a different magnetic orientation. Two magnets may have a north pole oriented in a direction parallel to an axis along which the magnets move relative to the core. Another magnet may have a north pole oriented in a direction perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:TIAX LLC
Magnetic Attachment Arrangement for Implantable Device
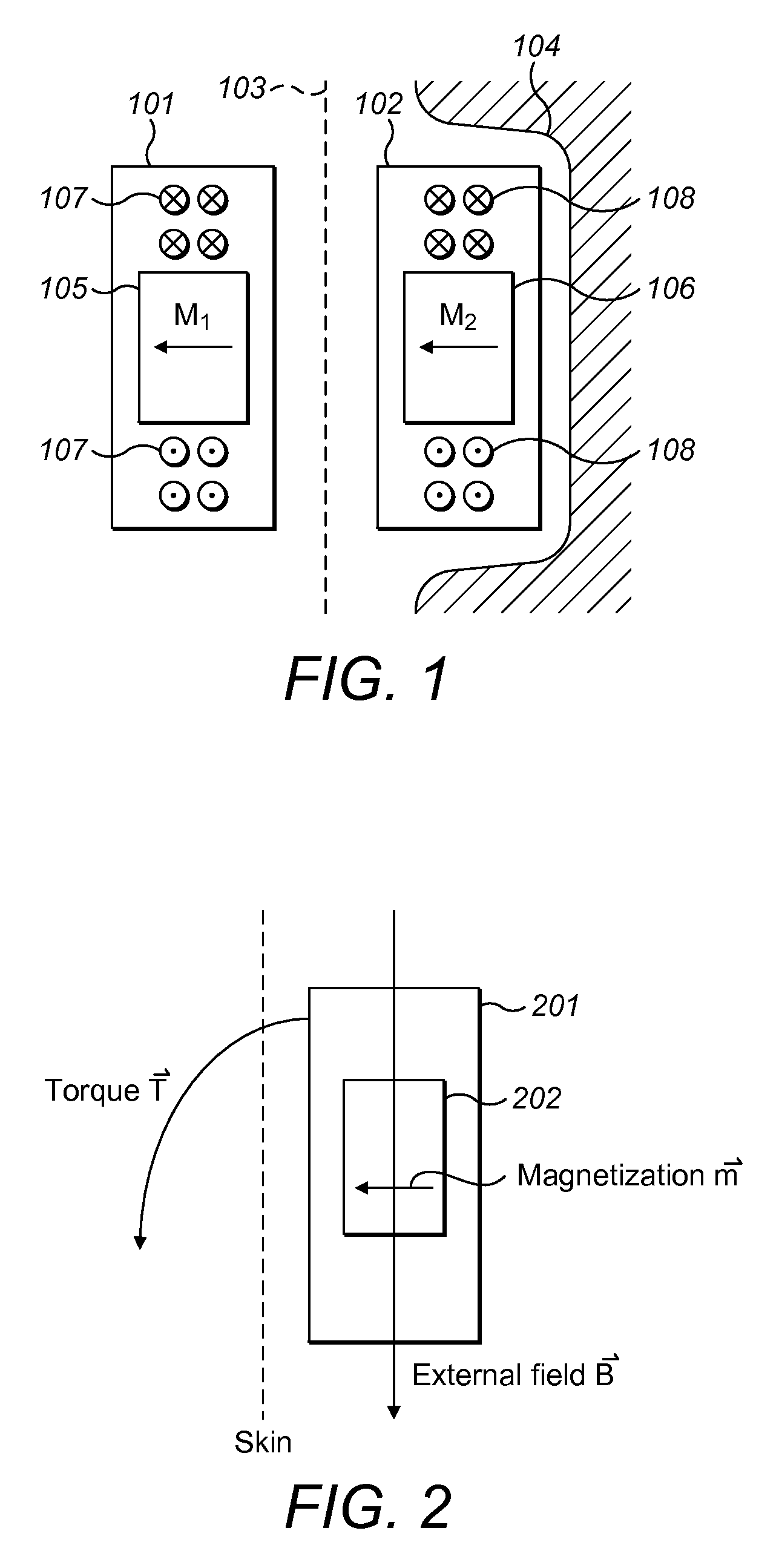
An arrangement is described for an implantable medical system. An implant housing contains a portion of an implantable electronic system and has a planar outer surface adapted to lie parallel to overlying skin in an implanted patient. An implant magnet arrangement is located within the housing and adapted to magnetically interact with a corresponding external magnet in an external device on the skin of the implanted patient over the implant housing. The implant magnet arrangement includes an inner center disc having a magnetic dipole parallel to the planar outer surface of the implant housing with an inner magnetic orientation in an inner magnetic direction, and an outer radial ring having a magnetic dipole parallel to the planar outer surface of the implant housing with an outer magnetic orientation in an outer magnetic direction opposite to the inner magnetic direction.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Electromagnetical ultrasonic thickness-measuring method
InactiveCN101398298AWith non-contactUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUltrasonic sensorReflected waves
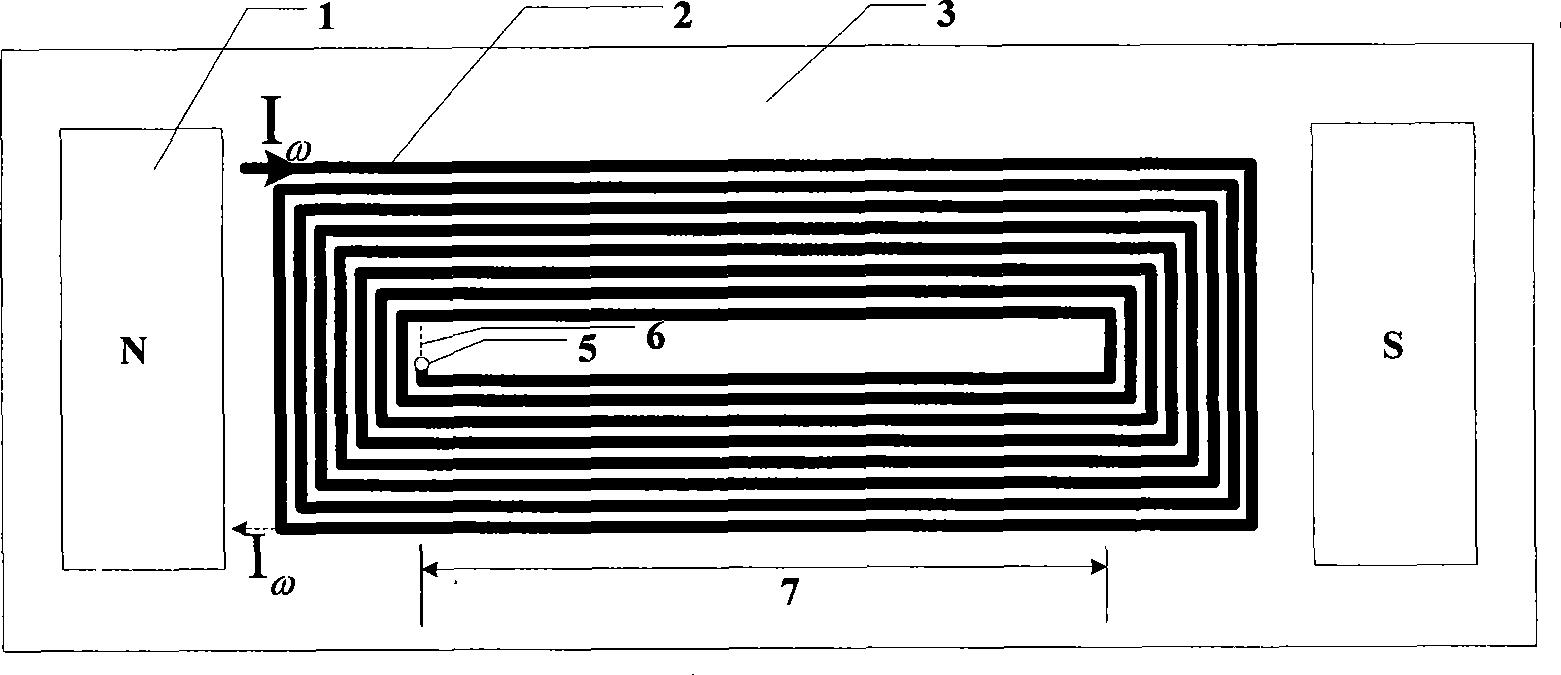
The invention discloses a method for detecting ferrous magnetic material thickness by utilizing electromagnetic ultrasound, and is characterized in that a magnet inside an electromagnetic ultrasound transducer takes a U-shaped permanent magnet, a coil takes a PCB double-layer coil that takes the shape of a Chinese character, 'Hui' and is positioned at an opening of the permanent magnet, and an effective lead part of the coil is parallel to the direction of a bias magnetic field. In thickness measurement, the electromagnetic ultrasound transducer is positioned on a detected object, high-frequency electric sinusoidal pulse current passes through the coil, according to the magnetostrictive effect, the detected object generates partial stretching deformation and oscillation, and consequently excites ultrasonic transverse wave and leads the ultrasonic transverse wave to spread downwards in a direction vertical to surfaces of the detected object. The ultrasonic wave is reflected by a lower surface of the detected object, and then the reflected wave is received by the coil. A received ultrasonic signal is collected and input into a computer after being amplified. If the ultrasonic wave spreading velocity in the detected object is v, and the spreading time is t, then the thickness of the detected object d is equal to a half of v multiplied by t. The method for detecting ferrous magnetic material thickness by realizing the thickness detection of ferrous magnetic materials, has the non-contact and couplant-free advantages, and can be used in high-temperature environment and for detecting materials with rough surfaces.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
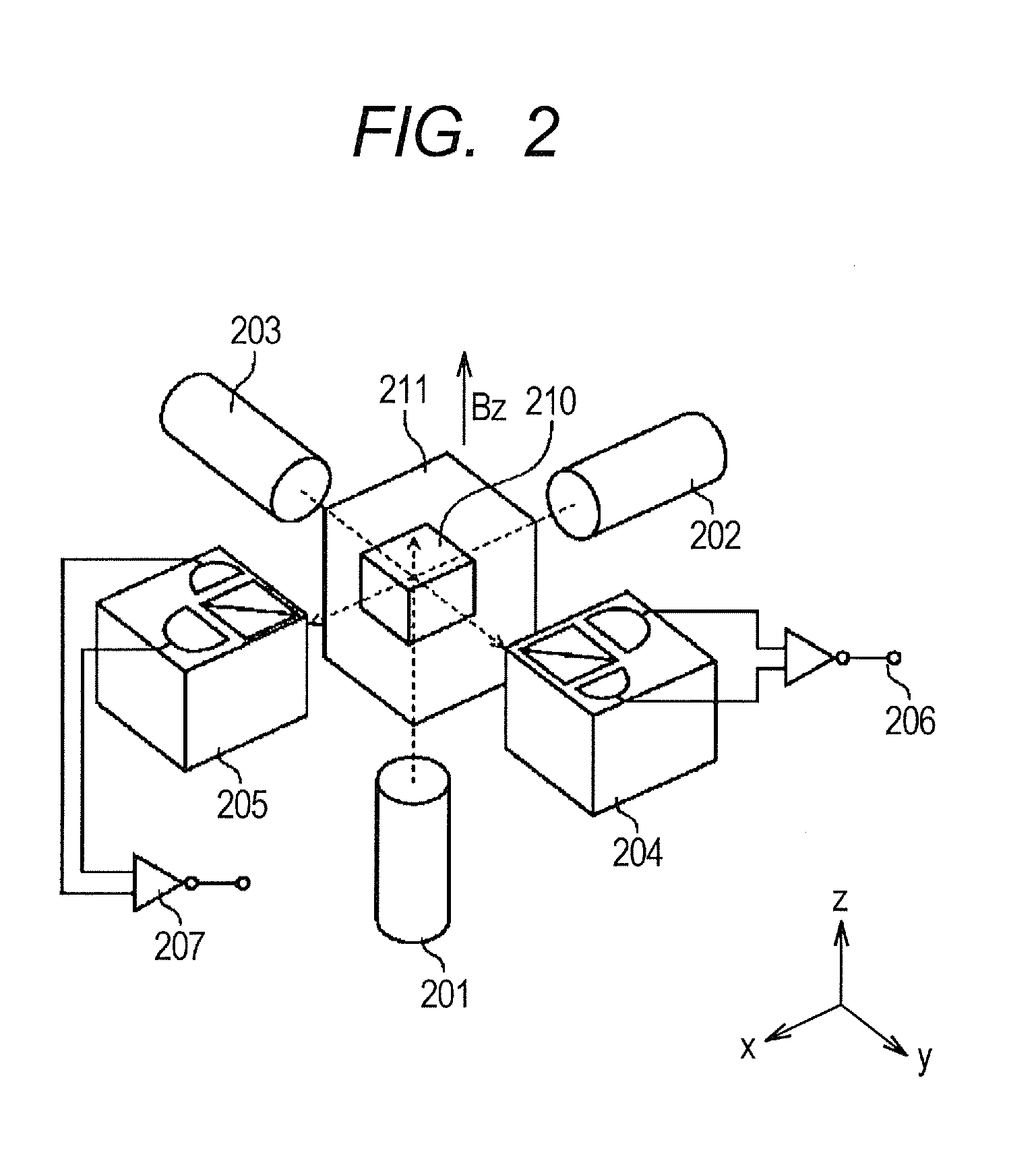
Magnetic sensor and rotation-angle-detecting apparatus
ActiveUS20090189601A1Reduce angle errorSuppressed influenceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic anisotropyInter layer
A magnetic sensor comprising a bridge circuit in which four magnetoresistive devices are connected, the magnetoresistive device comprising a spin-valve, giant-magnetoresistive film comprising a pinned layer having unidirectional magnetic anisotropy, a free layer whose magnetization direction is rotated in alignment with an external magnetic field direction, and an intermediate layer sandwiched by the pinned layer and the free layer, and at least one of the magnetoresistive devices meeting the condition of 36°≦θ<45°, wherein θ is an acute angle between its longitudinal direction and the magnetization direction of the pinned layer.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Read out scheme for several bits in a single MRAM soft layer
InactiveUS20060013039A1Increase memory densityReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageSoft layerElectrical resistance and conductance
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device is configured to store at least two bits of data in a single cell utilizing the variable resistance characteristic of a MTJ. The MTJ includes a soft and two fixed magnetic layers with fixed field directions oriented in perpendicular directions. The soft magnetic layer is separated from the fixed layers by insulating layers preferably with different thicknesses, or with different material compositions. The resulting junction resistance can exhibit at least four distinct resistance values dependent on the magnetic orientation of the free magnetic layer. The cell is configured using a pattern with four lobes to store two bits, and eight lobes to store three bits. The resulting cell can be used to provide a fast, non-volatile magnetic random access memory (MRAM) with high density and no need to rewrite stored data after they are read, or as a fast galvanic isolator.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
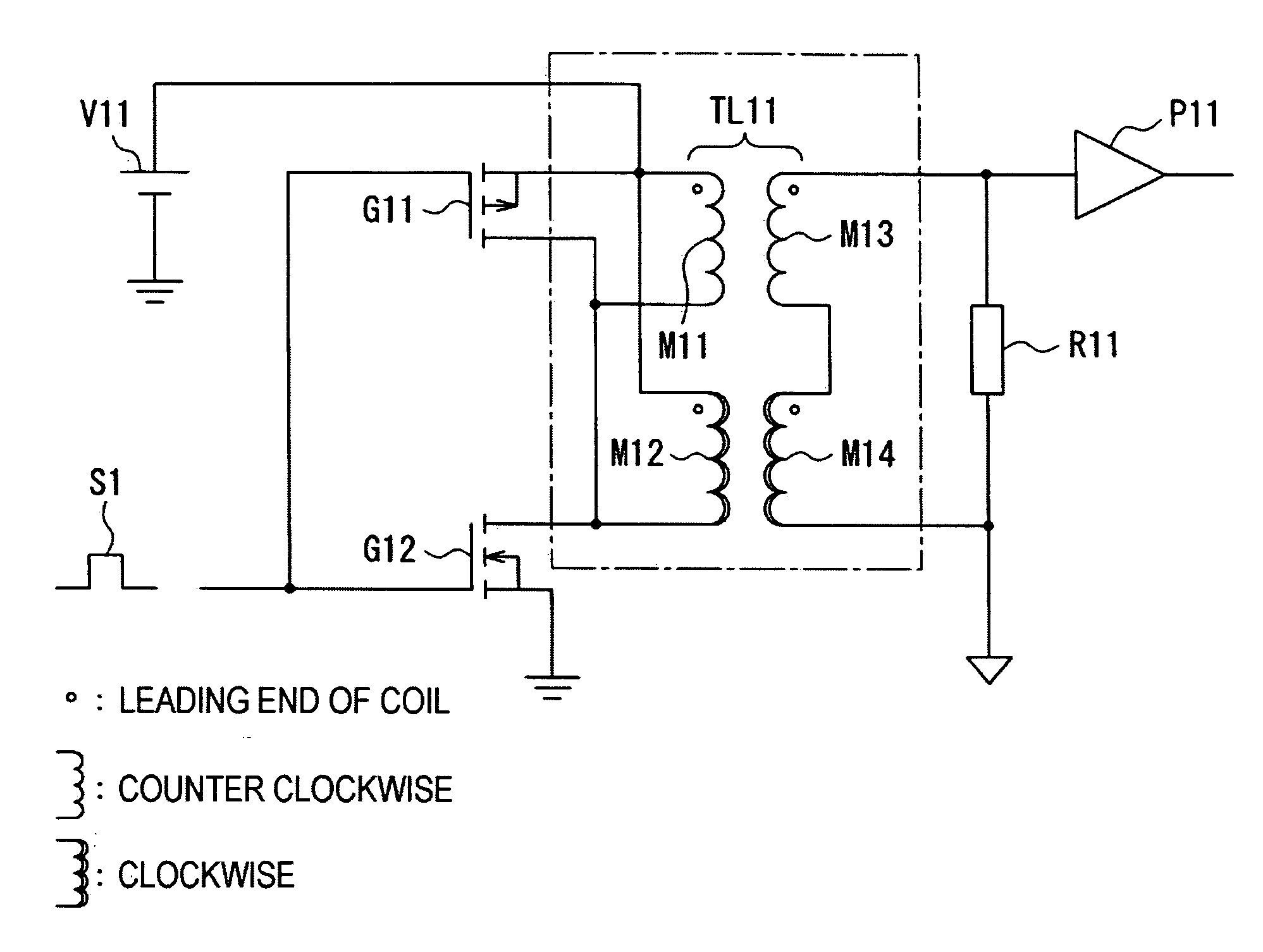
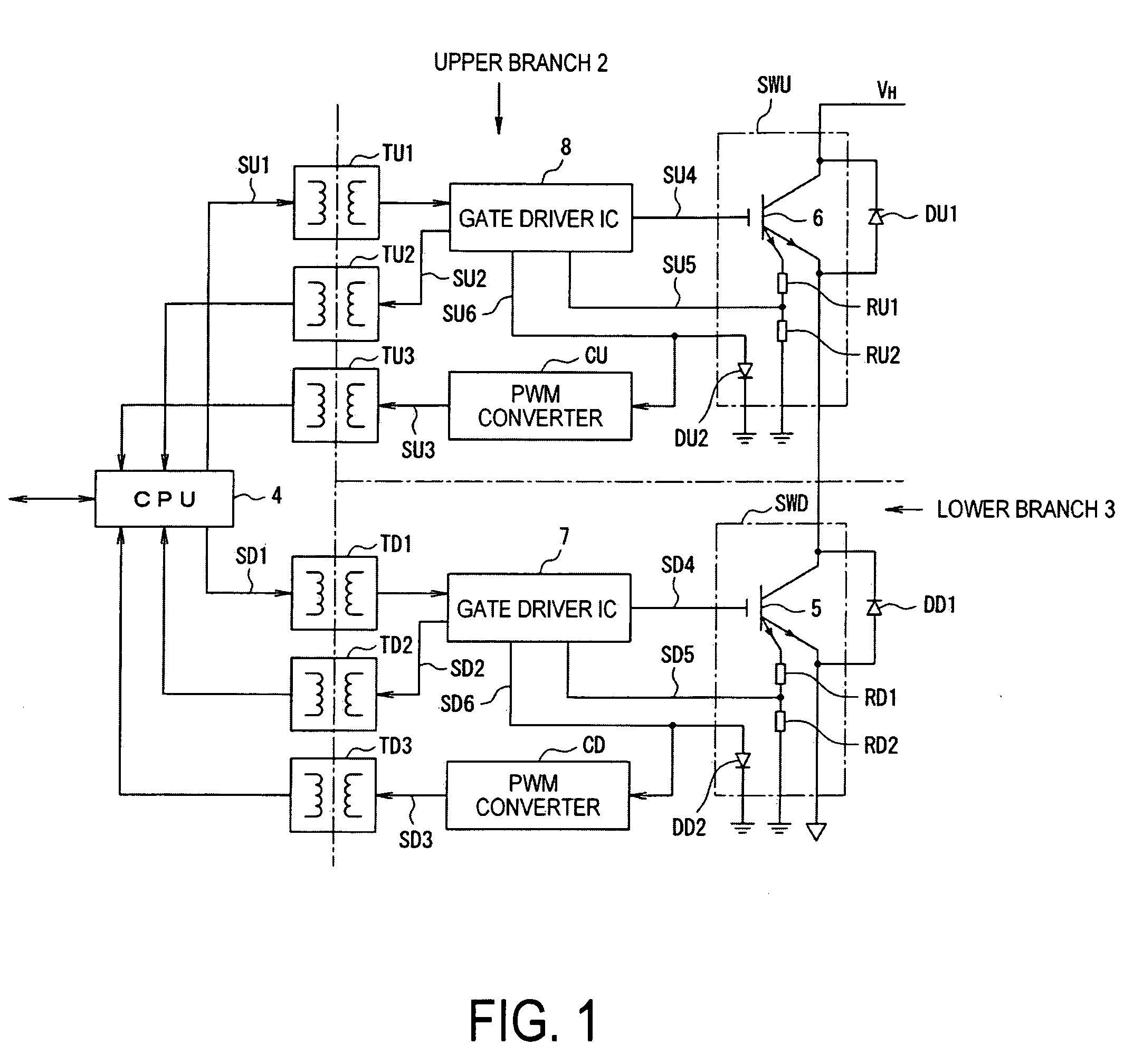
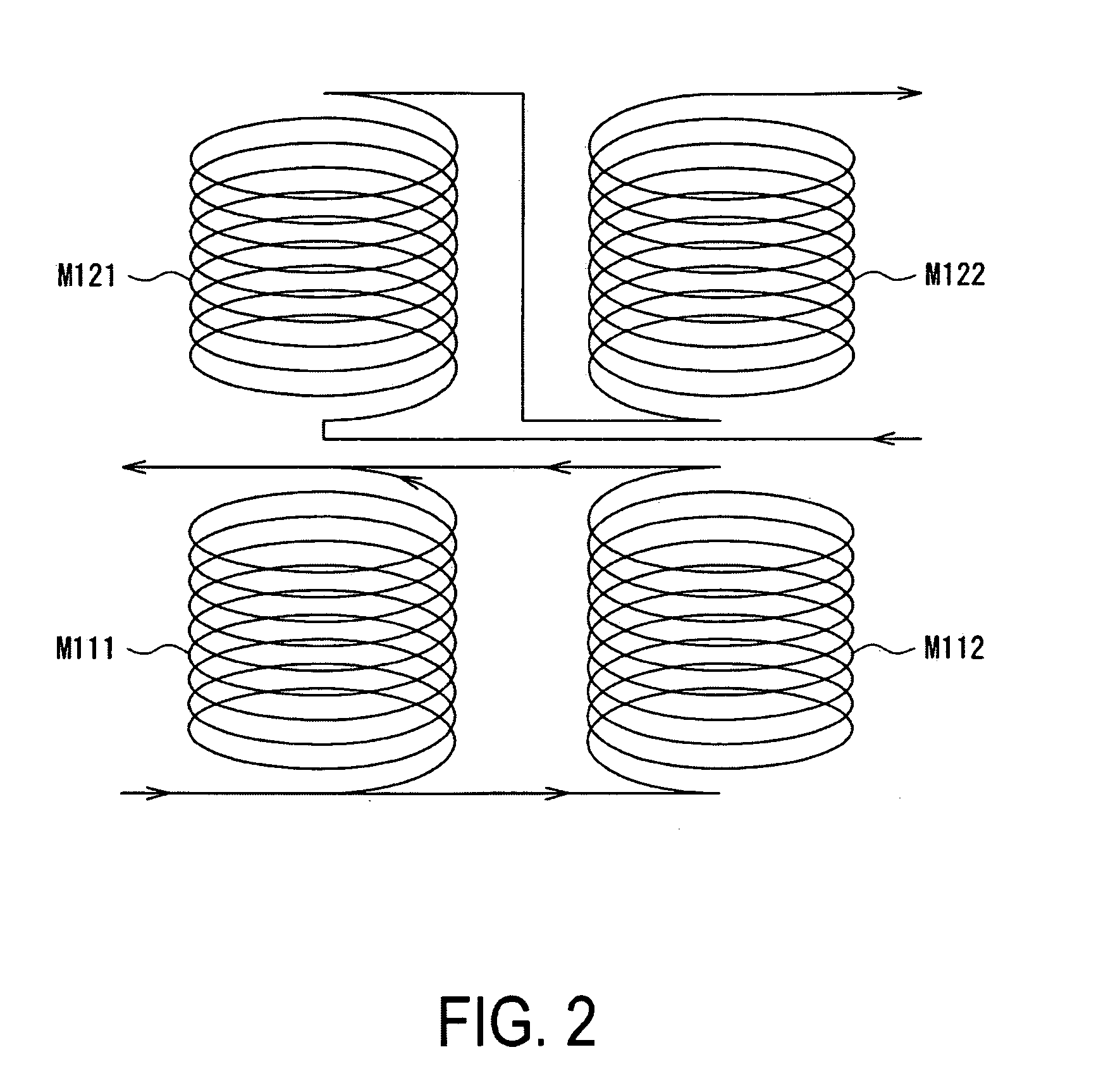
Transformer unit, and power converting device
InactiveUS20080266042A1Reduce overlayLow costDc-dc conversionSolid-state devicesLow voltageTransformer
A transformer unit and a power converting device, which lessen the influence of noise caused by an external magnetic flux, while reducing the temperature dependency of a coupling coefficient, and which transfer signals while insulating a low-voltage and a high-voltage side electrically. Air-core type insulated transformers have a first and second winding of a primary winding as a sending side and a first and second winding of a secondary winding as a receiving side. The windings of the primary winding are connected in parallel and are wound so that the directions of magnetic fields generated by an exciting current oppose each other. The windings of the secondary winding are wound so that electromotive forces to be generated by an external magnetic flux cancel each other, and are connected in series so as to raise the electromotive forces by a signal magnetic flux generated by the primary winding.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
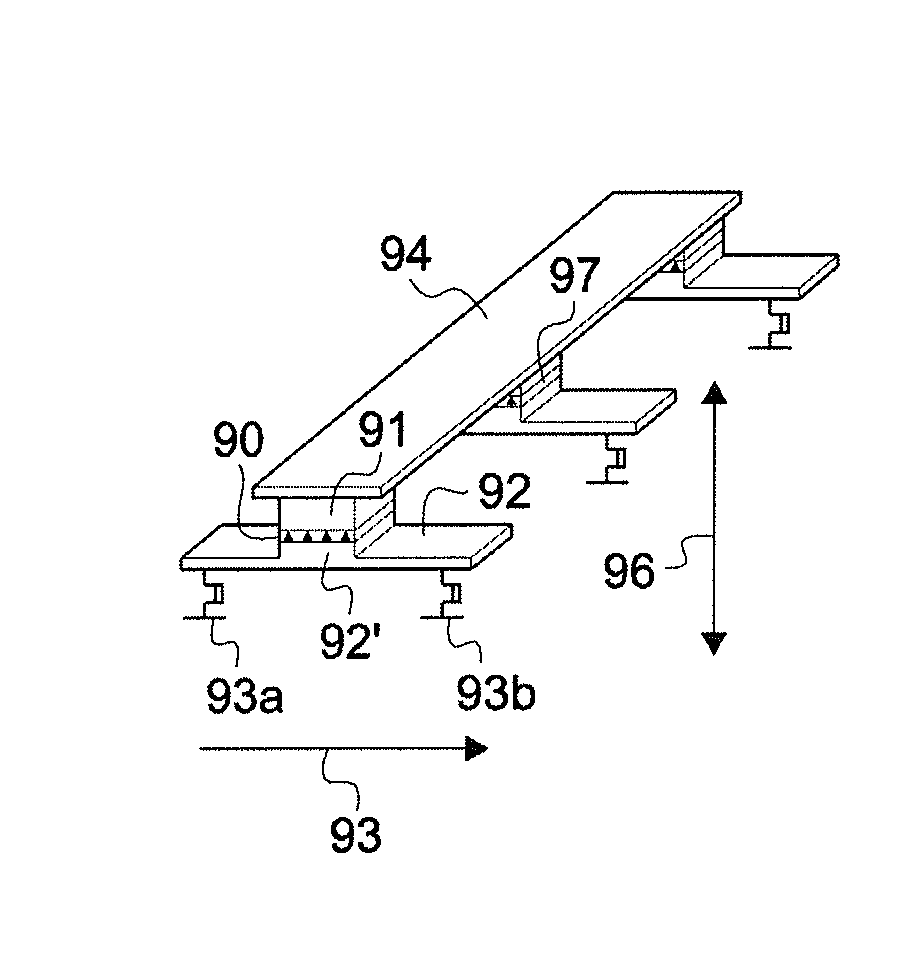
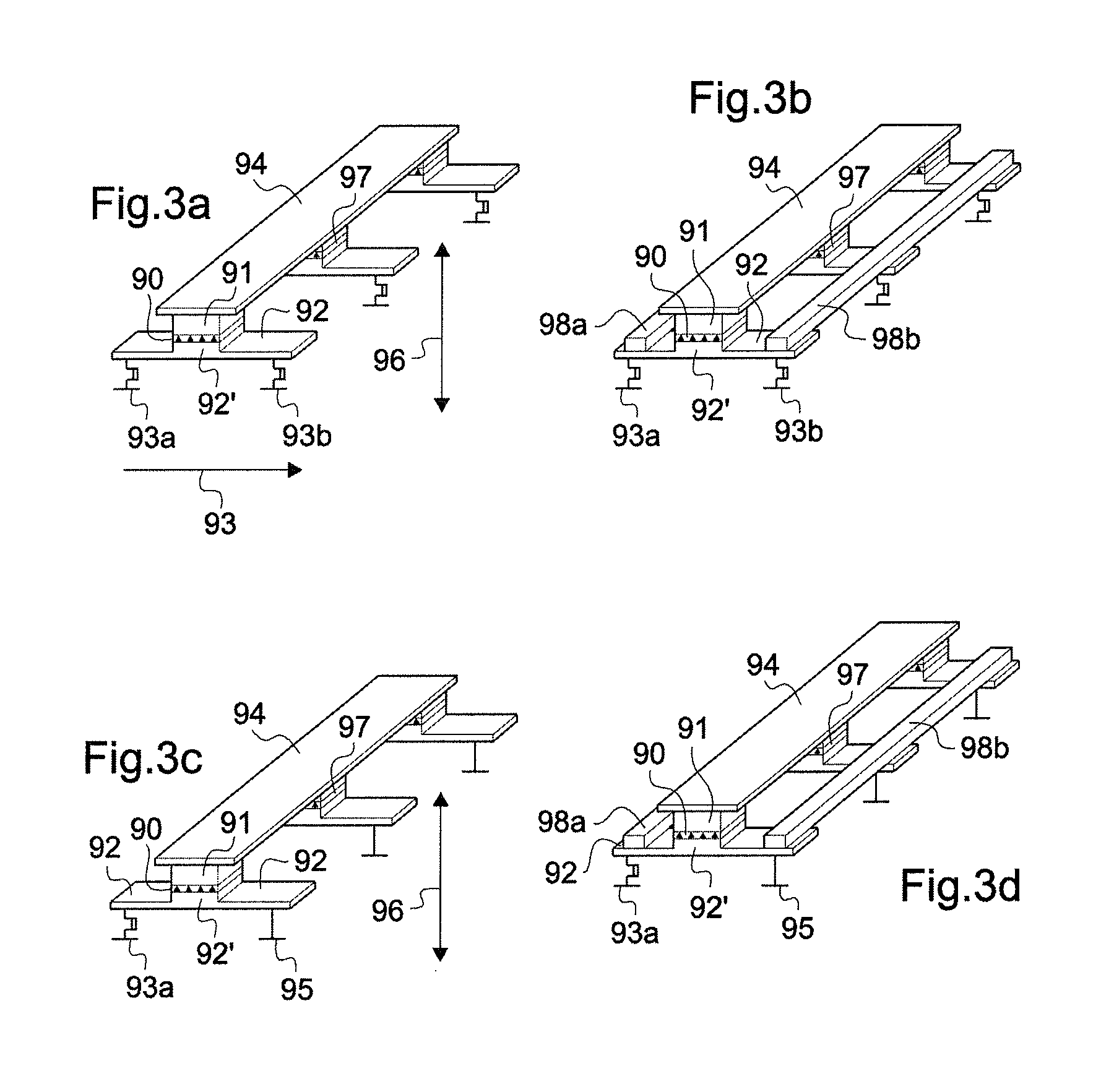
Writable Magnetic Memory Element
The invention relates to a writable magnetic element comprising a stack of layers presenting a write magnetic layer, wherein the stack has a central layer of at least one magnetic material presenting a direction of magnetization that is parallel or perpendicular to the plane of the central layer, said central layer being sandwiched between first and second outer layers of non-magnetic materials, the first outer layer comprising a first non-magnetic material and the second outer layer comprising a second non-magnetic material that is different from the first non-magnetic material, at least the second non-magnetic material being electrically conductive, wherein it includes a device for causing current to flow through the second outer layer and the central layer in a current flow direction parallel to the plane of the central layer, and a device for applying a magnetic field having a component along a magnetic field direction that is either parallel or perpendicular to the plane of the central layer and the current flow direction, and wherein the magnetization direction and the magnetic field direction are mutually perpendicular.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +4
Linear electrical machine for electric power generation or motive drive
InactiveUS20070108850A1Increase magnet flux linkageImprove permeabilityMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsAlternatorReciprocating motion
A linear electrical machine may function as an alternator or a motor. Three annular magnets may be provided that move relative to a core. The magnets may all have a different magnetic orientation. Two magnets may have a north pole oriented in a direction parallel to an axis along which the magnets move relative to the core. Another magnet may have a north pole oriented in a direction perpendicular to the axis. The core may include a plurality of ferromagnetic core elements; and a support structure composed of a composite material defining plural spaces, each for receiving one of the plurality of core elements. The core may further include a core shield disposed on the support structure substantially following a perimeter of the support structure defining an opening through which a reciprocating element can pass. Furthermore, the magnets may be supported in a reciprocating element having a low reluctance ferromagnetic frame there being a clearance gap between the machine core and the reciprocating element, the frame having a thicker section adjacent the gap, so as to desirably increase magnet flux linkage with an armature coil.
Owner:TIAX LLC
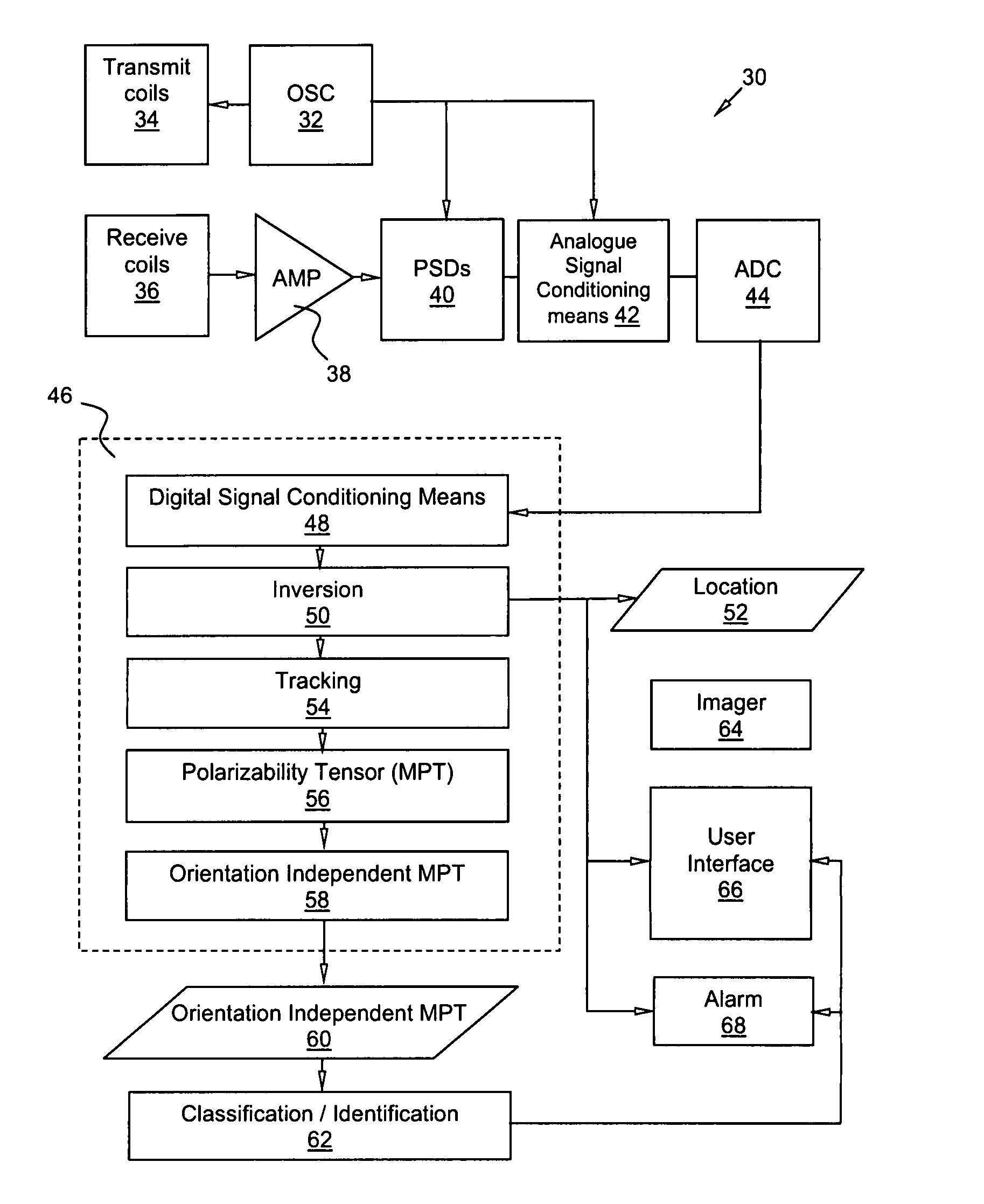
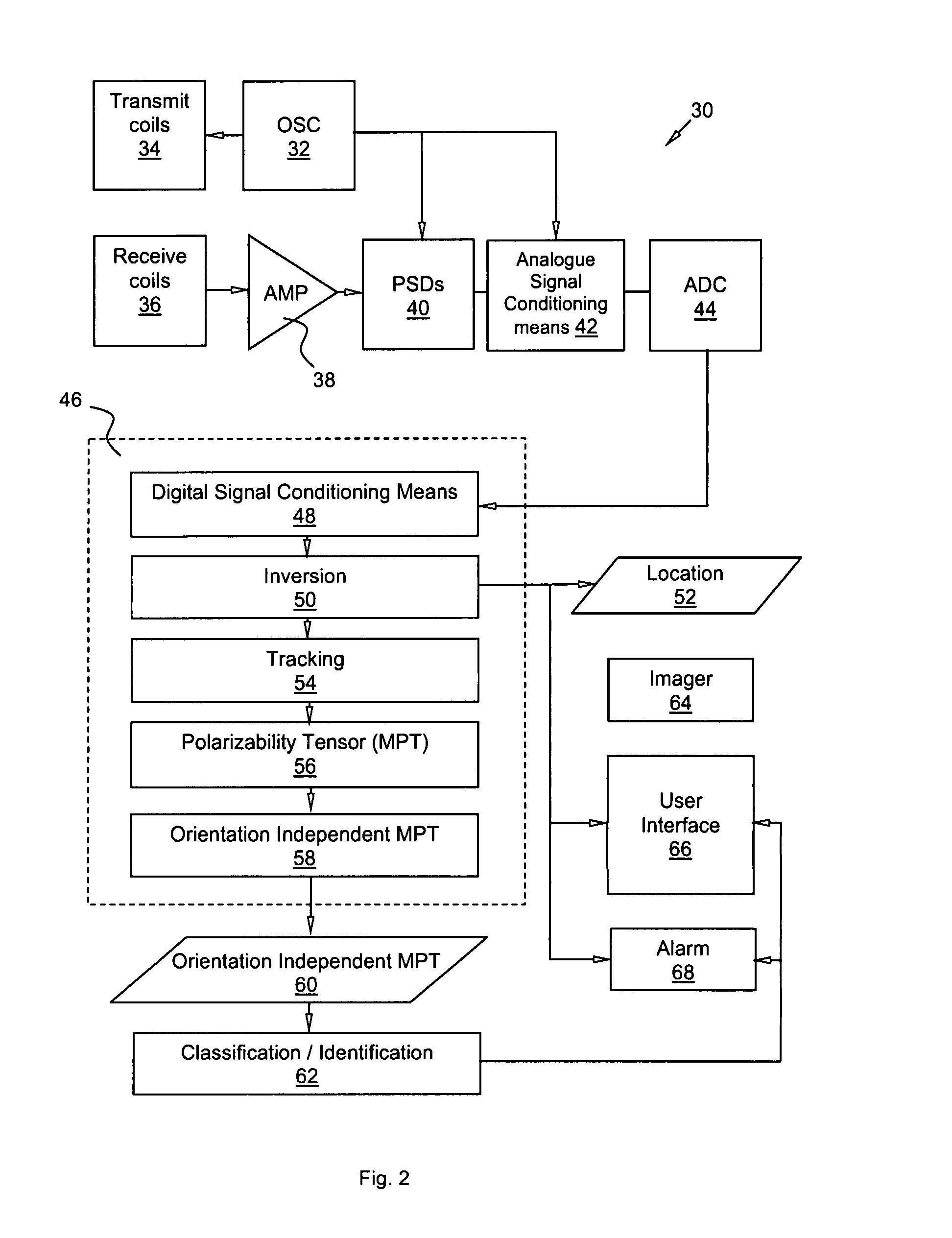
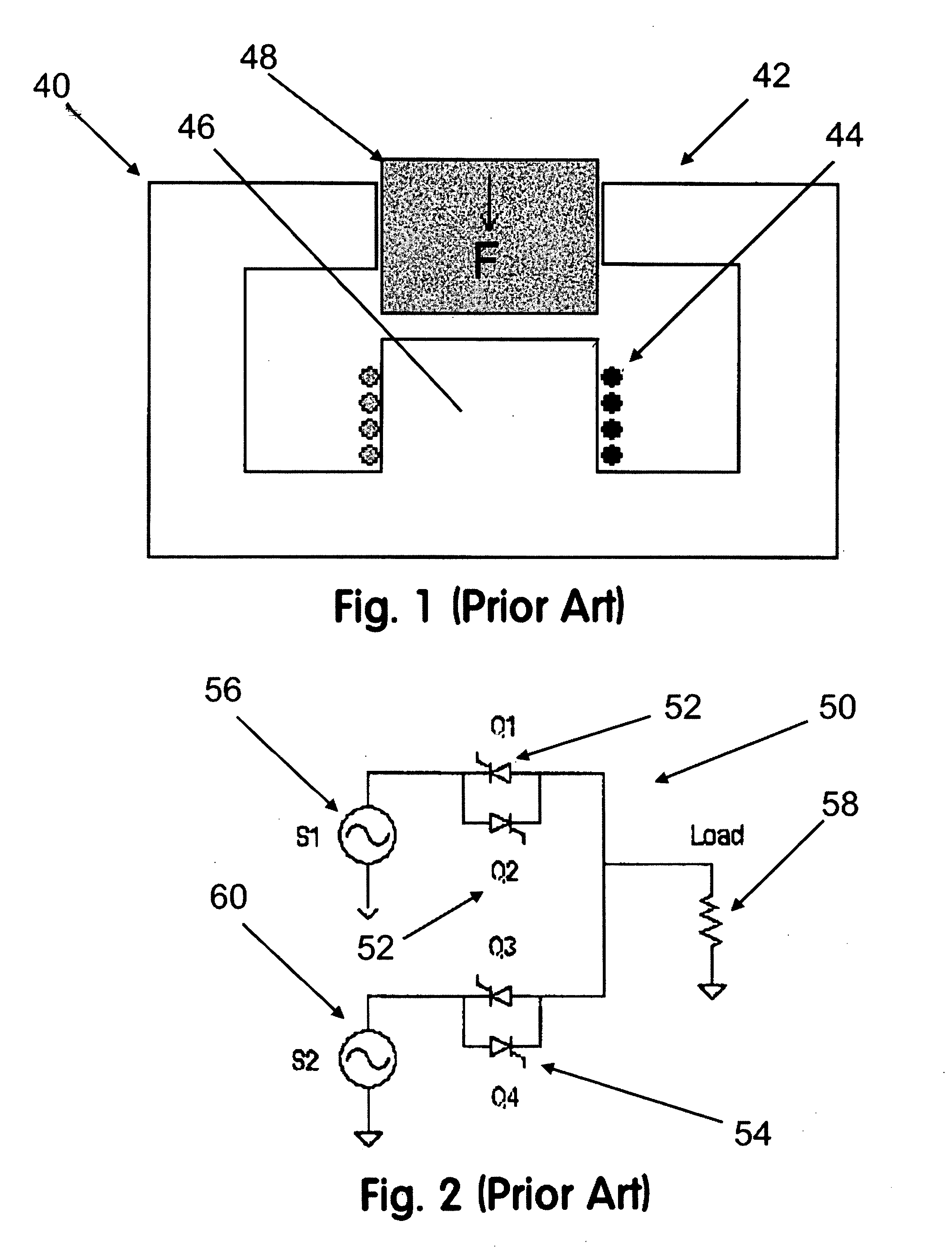
Metal object detecting apparatus
ActiveUS7545140B2Magnetic property measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurement pointMetallic Object
A metal object detecting apparatus comprising, a transmitter for generating a primary magnetic field having a resultant magnetic field direction which varies along any substantially linear path through a surveillance volume such that at three locations along said path the resultant magnetic field points in three mutually substantially orthogonal directions; a detector for measuring a secondary magnetic field at a plurality of positions as a function of time due to the presence of a metal object within the surveillance volume as it passes a plurality of measurement points there-through; and a processor for determining from the measured secondary magnetic fields a track through the surveillance volume comprising a plurality of locations of the metal object and a magnetic moment thereof at each location, the processor being adapted in use to derive there-from a magnetic signature that is characteristic of the metal object and independent of the orientation and track of the metal object.
Owner:METRASENS
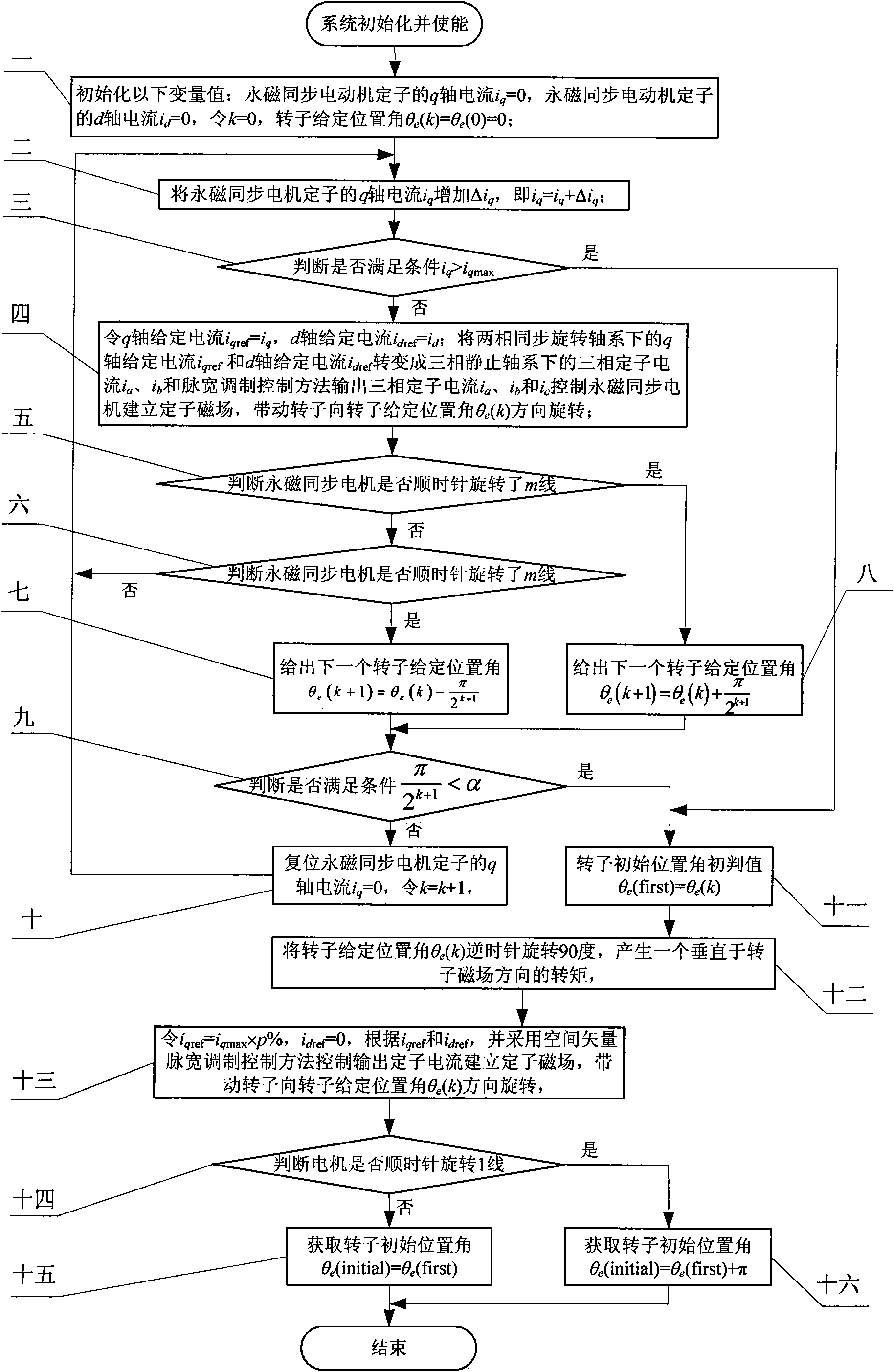
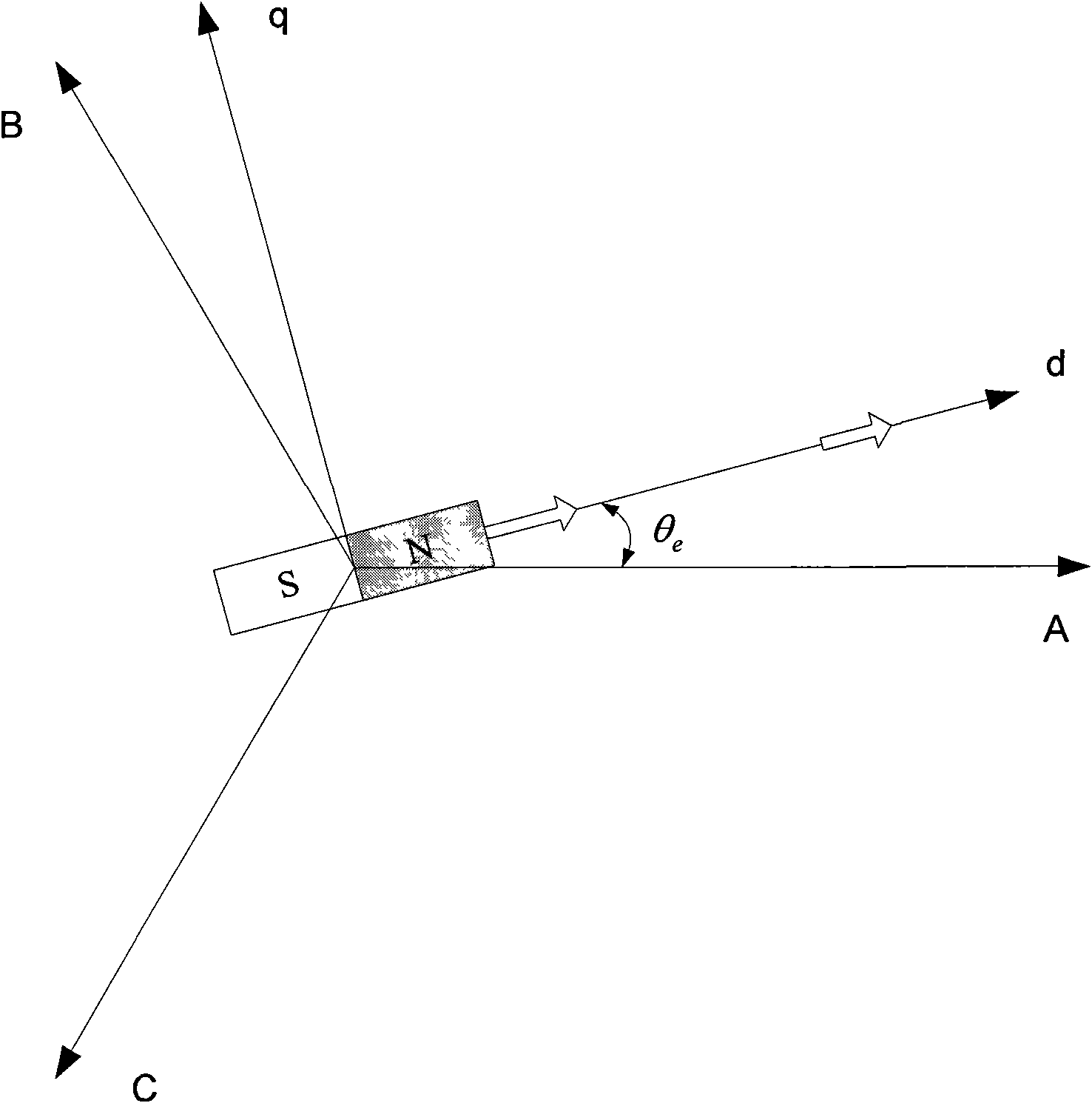
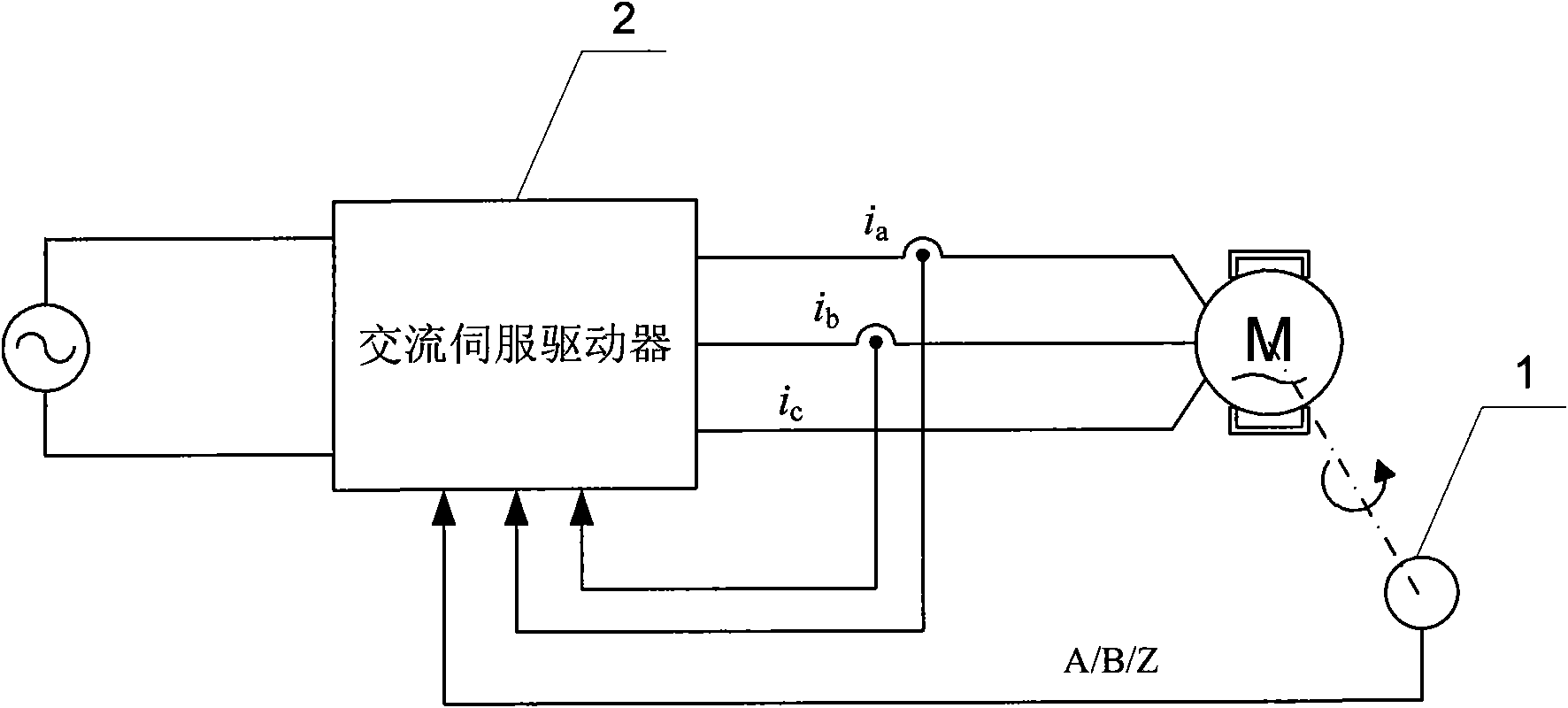
Method for determining initial position angle of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN101594114AClear logicImprove reliabilityVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlPosition anglePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to a method for determining an initial position angle of a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, which belongs to the field of motor control. The invention aims to solve the problems that a rotor detection method provided by a patent of a method and a device for detecting an initial position of a motor rotor in an alternating current servo system has complex logical decision and easy failure of detection. The method for determining the initial position angle of the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor comprises the following steps: controlling the amplitude and the phase of the current of a d shaft and a q shaft under a two-phase synchronous rotating shaft system to further control the amplitude and the phase of the current of a three-phase stator under a three-phase stationary shaft system; controlling the rotation of the motor rotor under a given stator magnetic field; and according to a pulse signal fed back by an incremental encoder, making the direction of the given magnetic field gradually and circularly approach the actual position angle of the rotor until the direction of the given stator magnetic field corresponding to the current of the d shaft and the q shaft is coincident with the direction of a rotor magnetic field. The direction of a given stator current magnetic field is changed by 90 degrees, so that a torque vertical to the direction of the rotor magnetic field is generated on the rotor, and according to the rotating direction of the rotor, the initial position angle of the actual rotor is determined.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
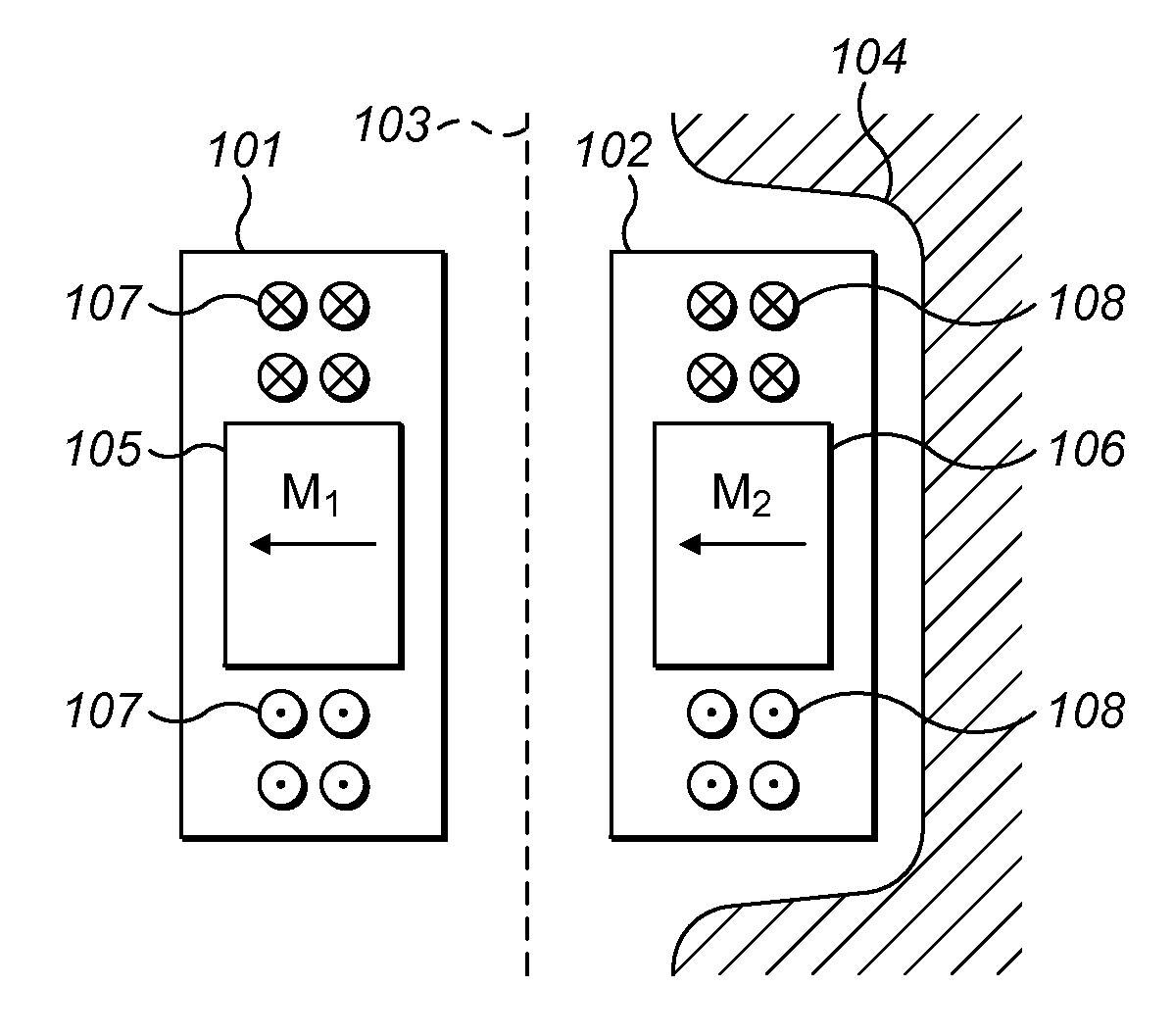
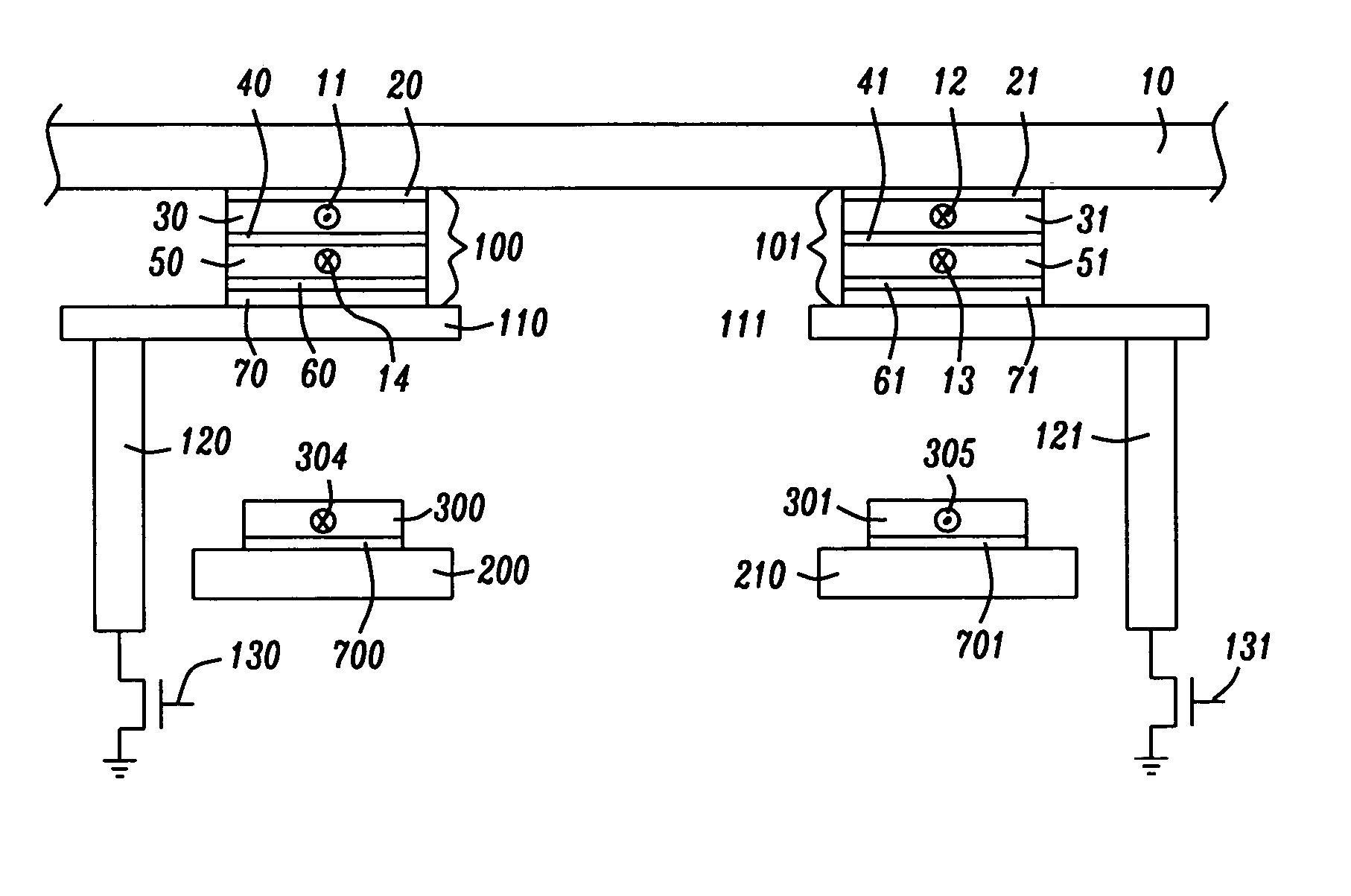
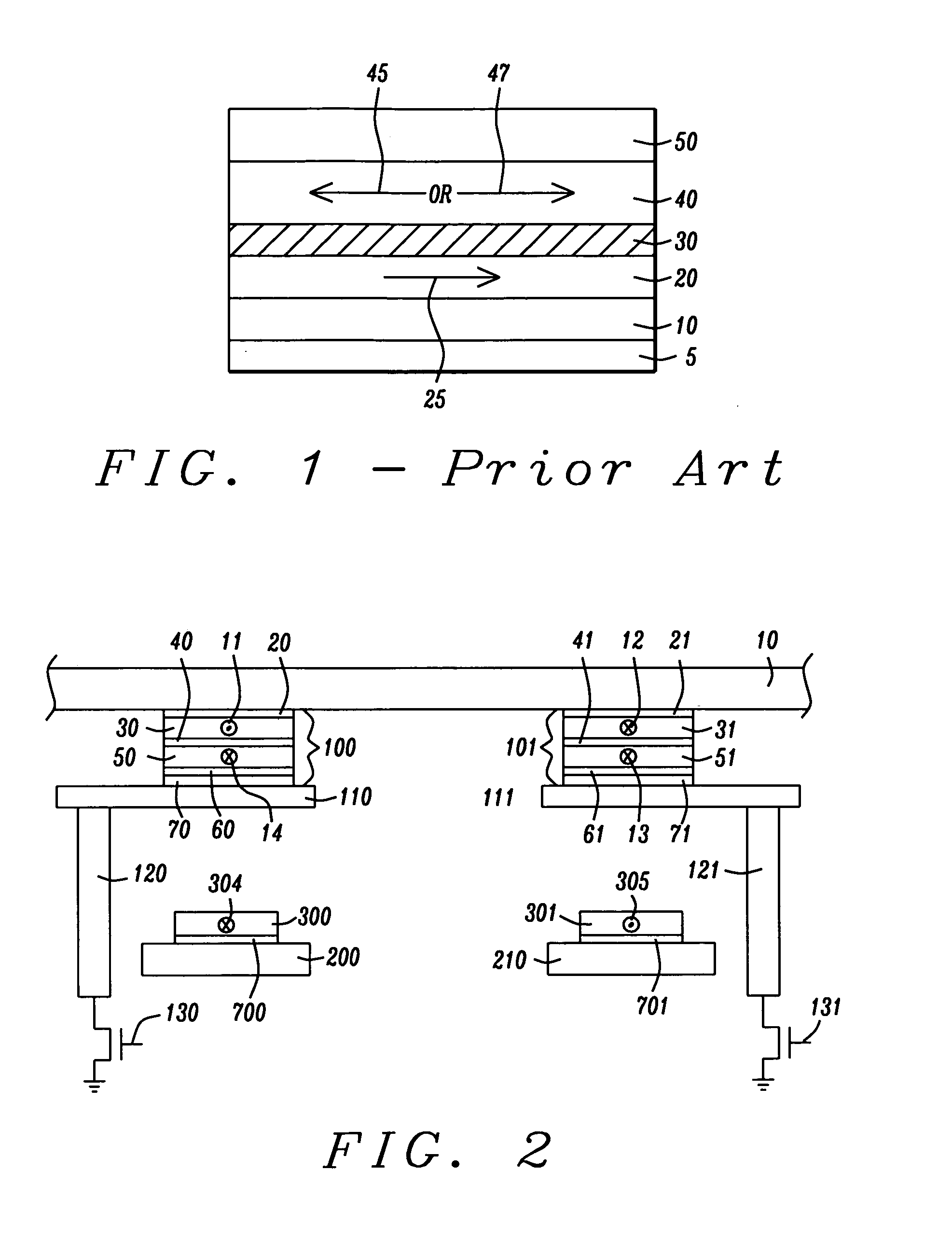
MRAM with split read-write cell structures
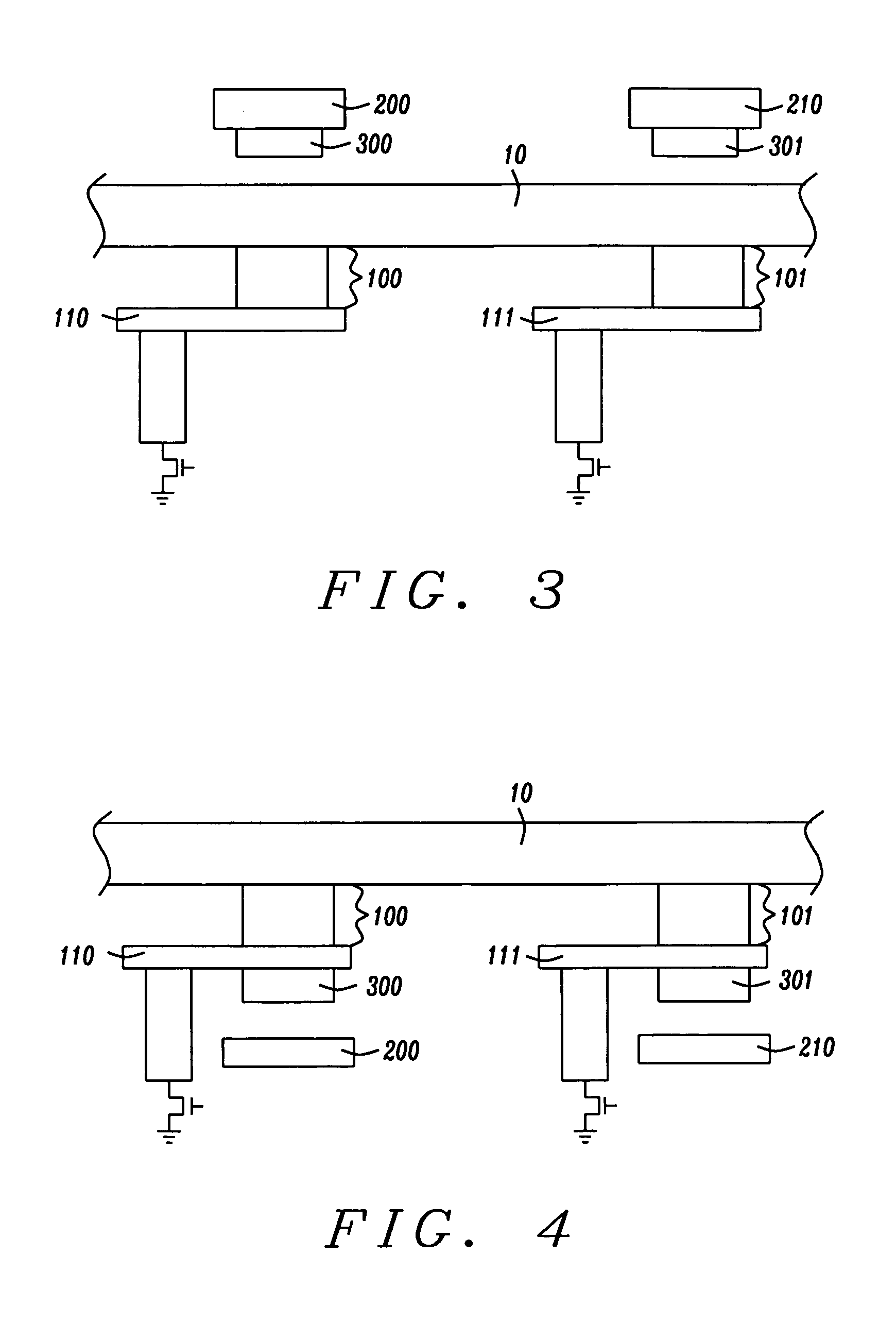
InactiveUS20070164380A1Efficient storageLow switching thresholdGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesAspect ratioMagnetic orientation
An MRAM cell is formed in two separate portions. A first portion, that includes a pinned layer, a tunneling barrier layer and first free layer part, is used to read the value of a stored bit of information. A second portion includes a second free layer part on which information is written and stored. The second free layer part is formed with a high aspect ratio cross-section that renders it strongly magnetically anisotropic and enables it to couple to the relatively isotropic first free layer through a magnetostatic interaction. This interaction aligns the magnetization of the first free layer part in an opposite direction to the magnetization of the second free layer part. The magnetic orientation of the first free layer part relative to that of its adjacent pinned layer determines the resistance state of the first cell portion and this resistance state can be read by passing a current through the first cell portion. Thus, in effect, the first cell portion becomes a remote sensing device for the magnetization orientation of the second free layer part
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetic recording element, magnetic recording apparatus and recording method of information
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
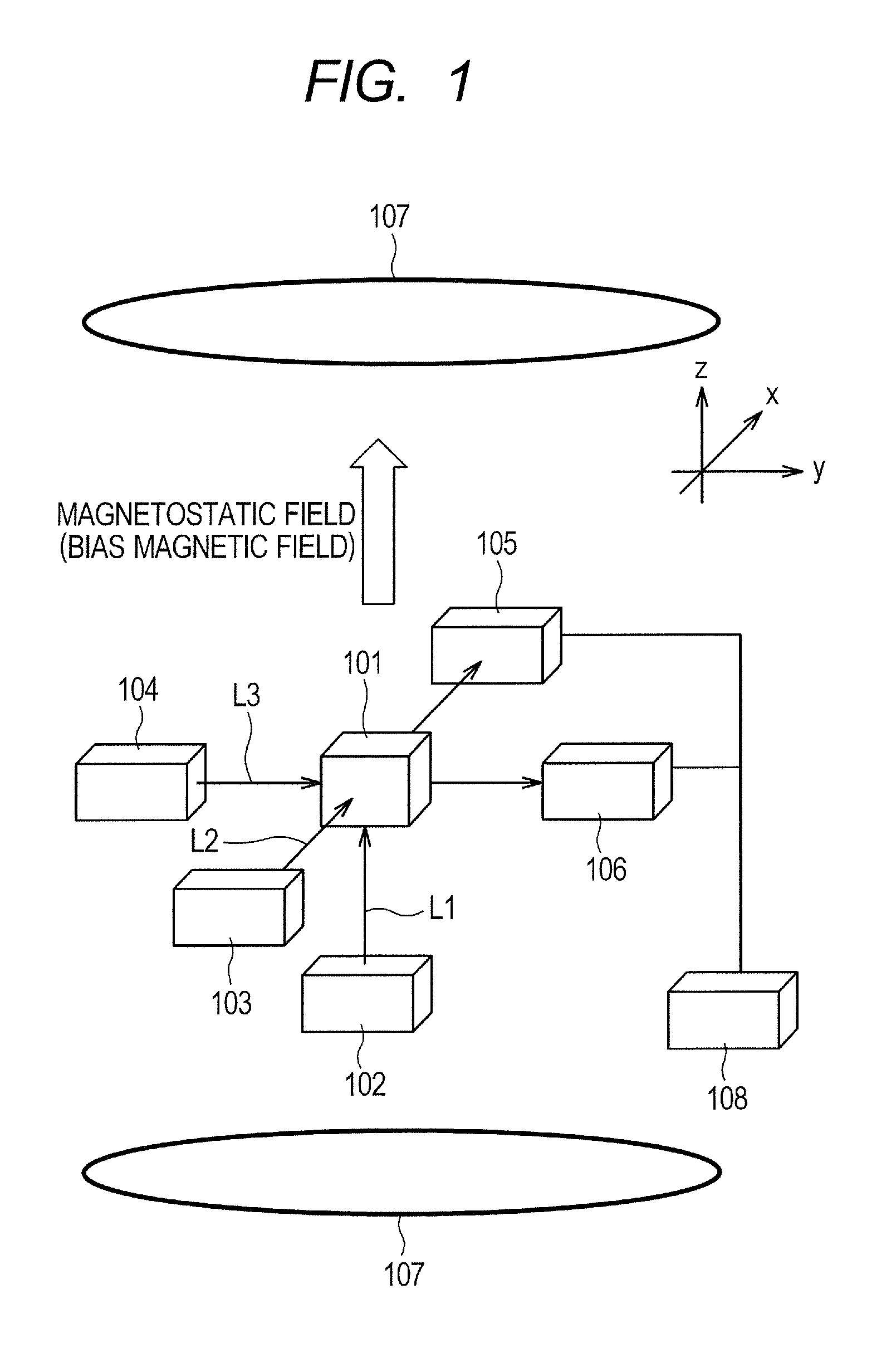
Magnetic Field Sensor for Sensing Rotation of an Object
ActiveUS20130238278A1Accurate signalSolid-state devicesLinear/angular speed measurementAcousticsAngle of rotation
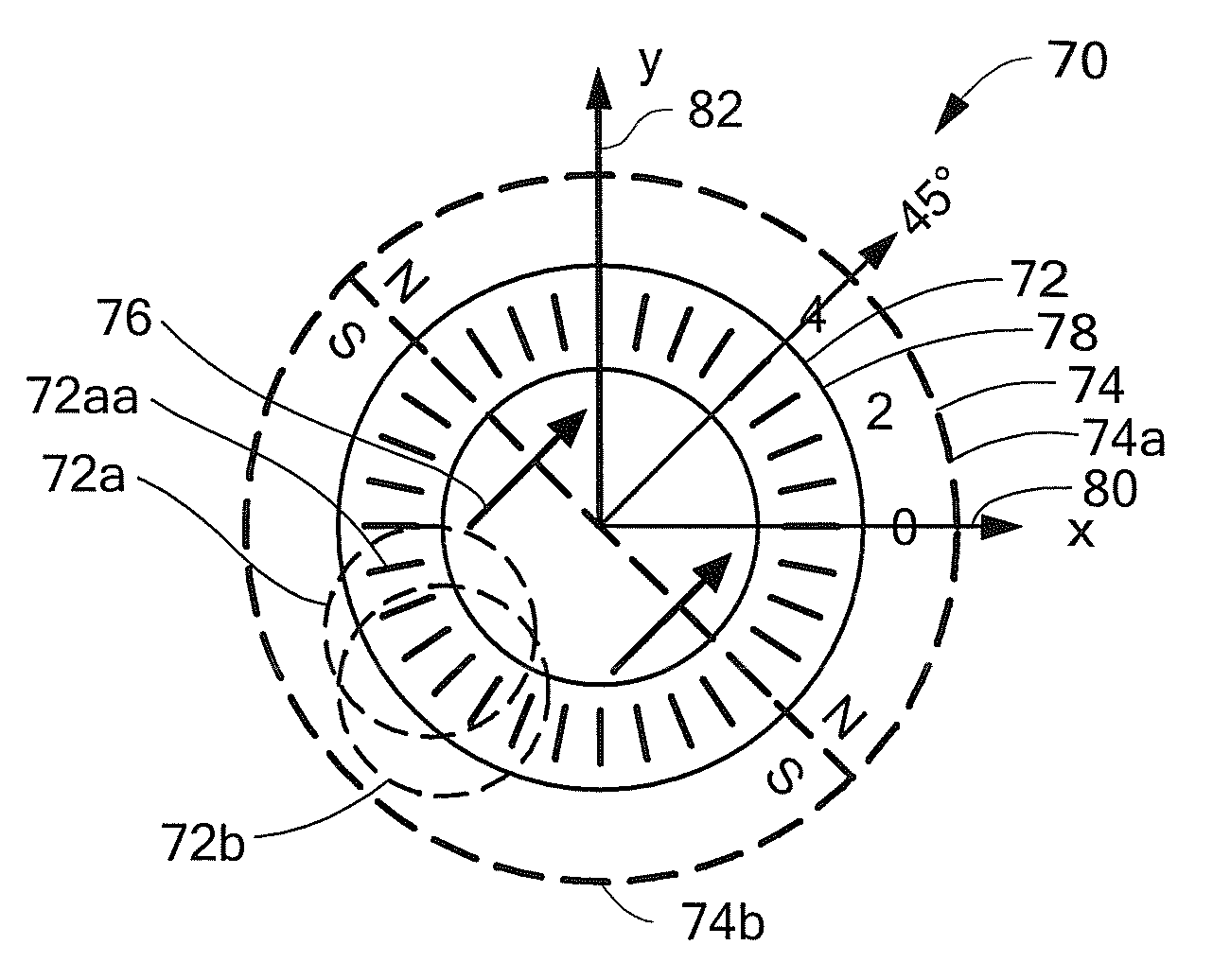
A magnetic field sensor uses an angle sensor to measure and angle of rotation of a target object to which a magnet is attached. The angle sensor in combination with electronics can generate an angle sensor output signal related to a direction of a magnetic field of the magnet. The angle sensor output signal can be compared to thresholds to generate a magnetic field sensor output signal the same as a known true power on state (TPOS) sensor output signal. A corresponding method is also described.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Optically pumped magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS8941377B2Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesOptical polarizationAlkali metal
An optically pumped magnetometer and a magnetic sensing method acquire information as to strengths of magnetic fields in two different directions. A pump light having a circularly polarized component, first probe light having a liner polarized component and second probe light having a linearly polarized component are emitted to a cell containing a group of alkali metal atoms so as to form a crossing region A magnetic field applying unit applies a static magnetic field in a direction of the pump light incident on the crossing region during the emission of the pump light, the first probe light and the second probe light. And, information as to strengths of magnetic fields in two different directions perpendicular to the direction of the static magnetic field in the cell from the rotation angles of a polarization planes of the first and second probe lights during passage through the cell is calculated.
Owner:CANON KK
Eddy current inductive drive electromechanical linear actuator and switching arrangement
ActiveUS20060061442A1Reliable and reliableSimple designContact mechanismsElectromagnetic relaysTransfer switchEngineering
The present invention is directed to an inductively driven electromagnetic linear actuator arrangement employing eddy currents induced by a fixed drive coil to drive its armature. Eddy current focusing fields are employed to direct the eddy currents using Lorentz forces to maximize armature speed. The armature includes a shorted driven coil in a DC magnetic field. This can be supplied by a permanent magnet. When current is applied, a force is felt by the coil in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. Such an actuator is well suited for electrical switching applications including transfer switching applications, circuit breaker applications, and ground fault interrupter applications.
Owner:POWERPATH TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com