Patents
Literature
1721 results about "Electrical switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for switching on-off a group or all lights or appliances of premises
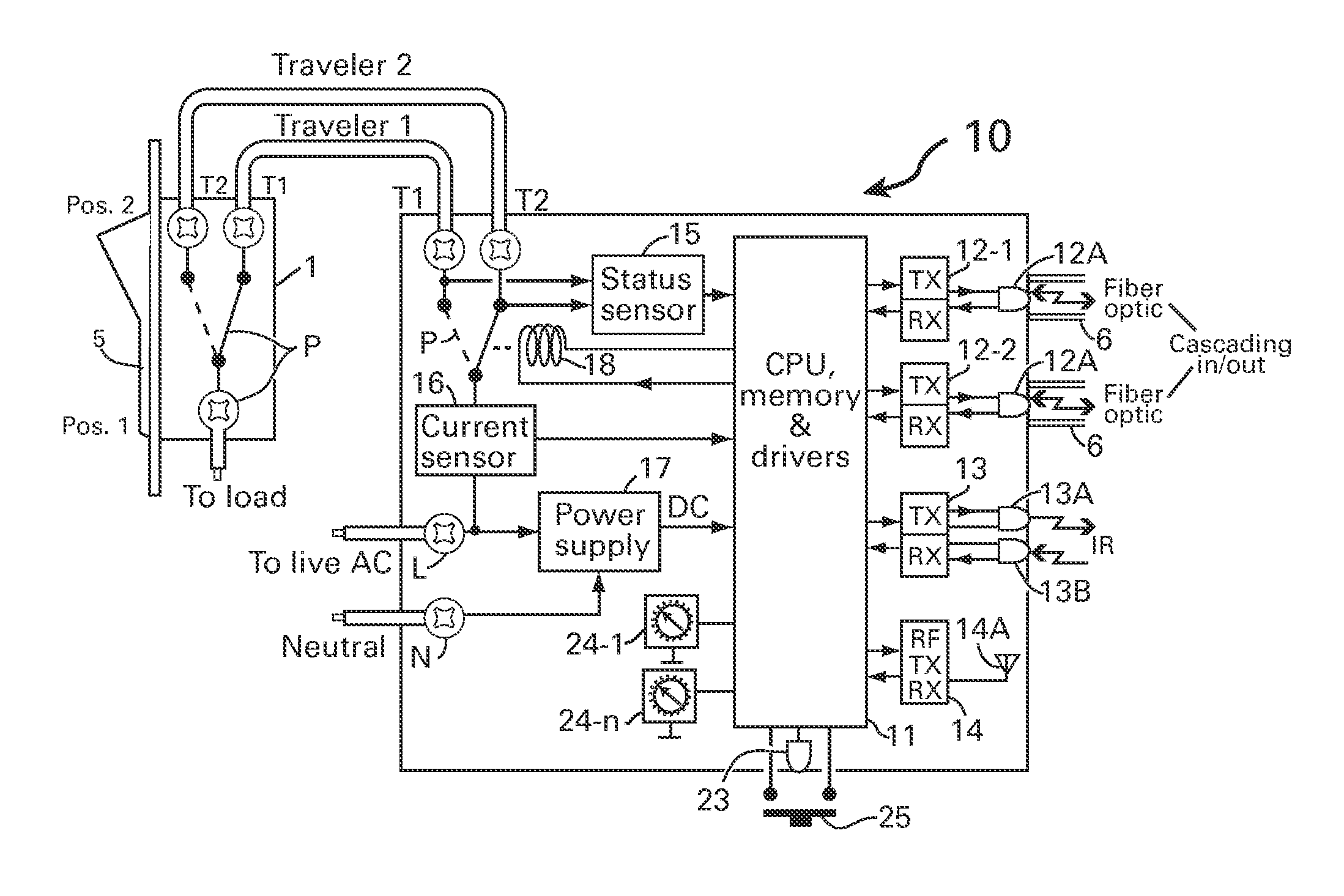
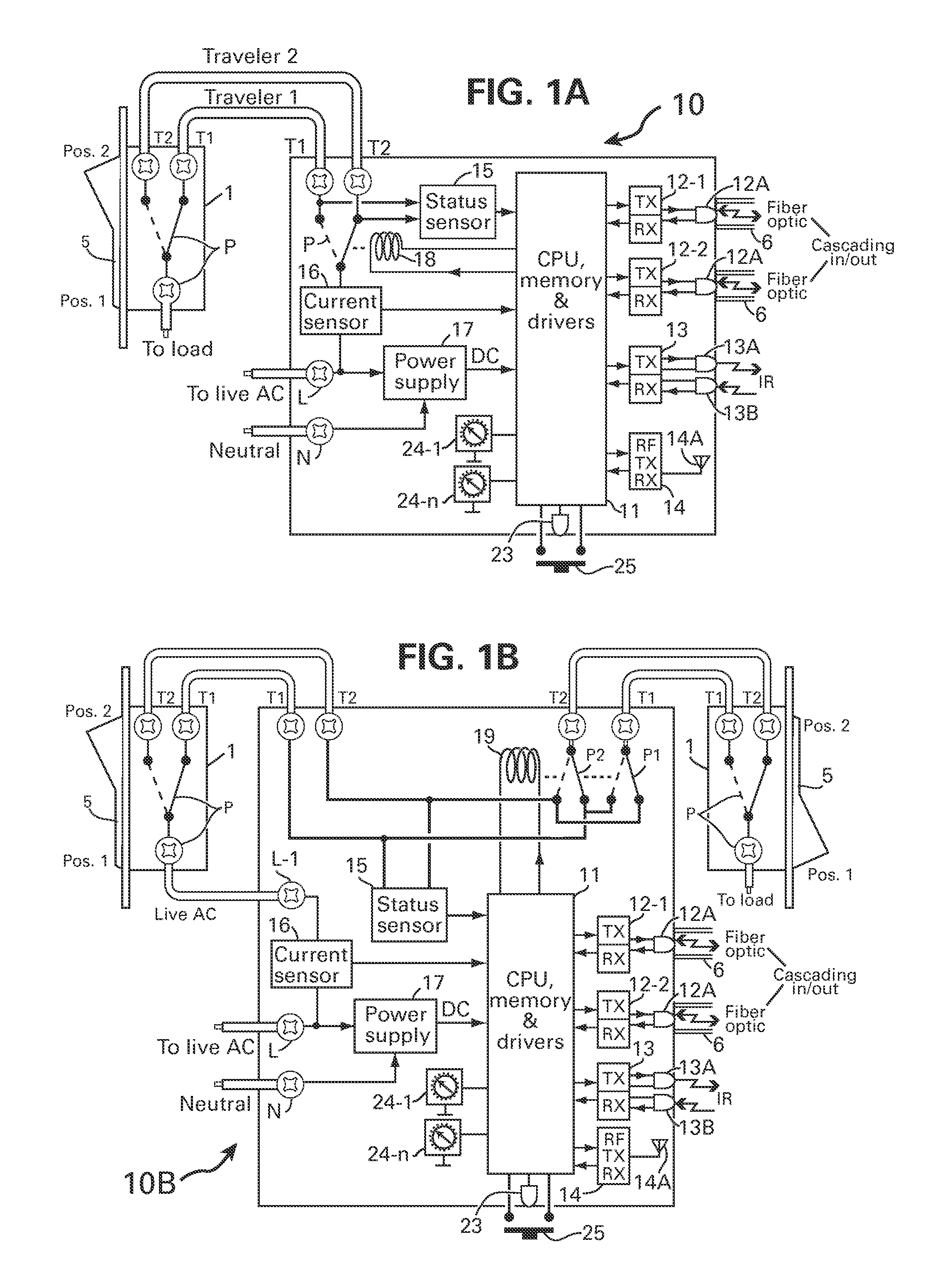
ActiveUS8269376B1Provide convenienceProvide efficiencyBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsCircuit arrangementsResidenceCurrent sensor
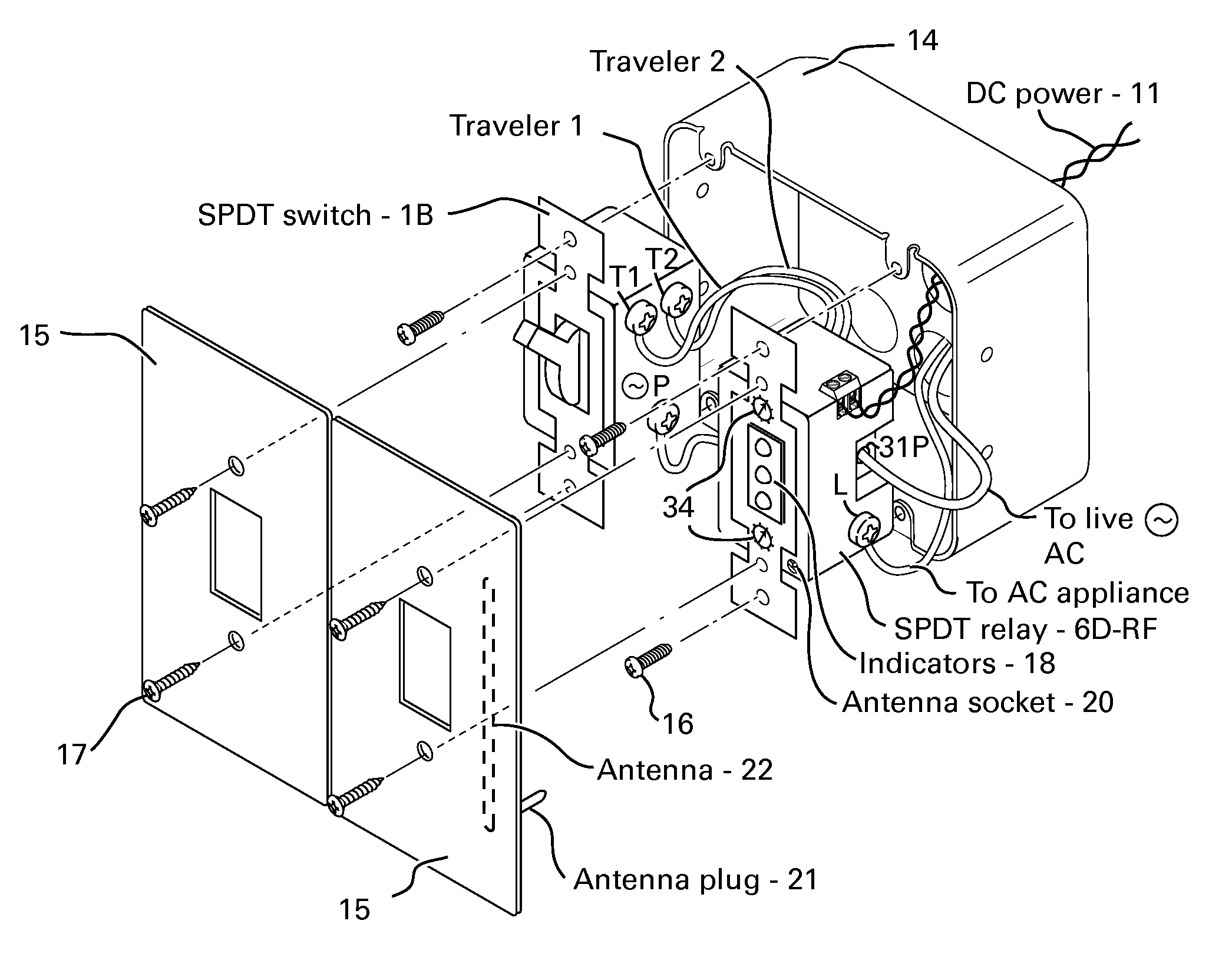
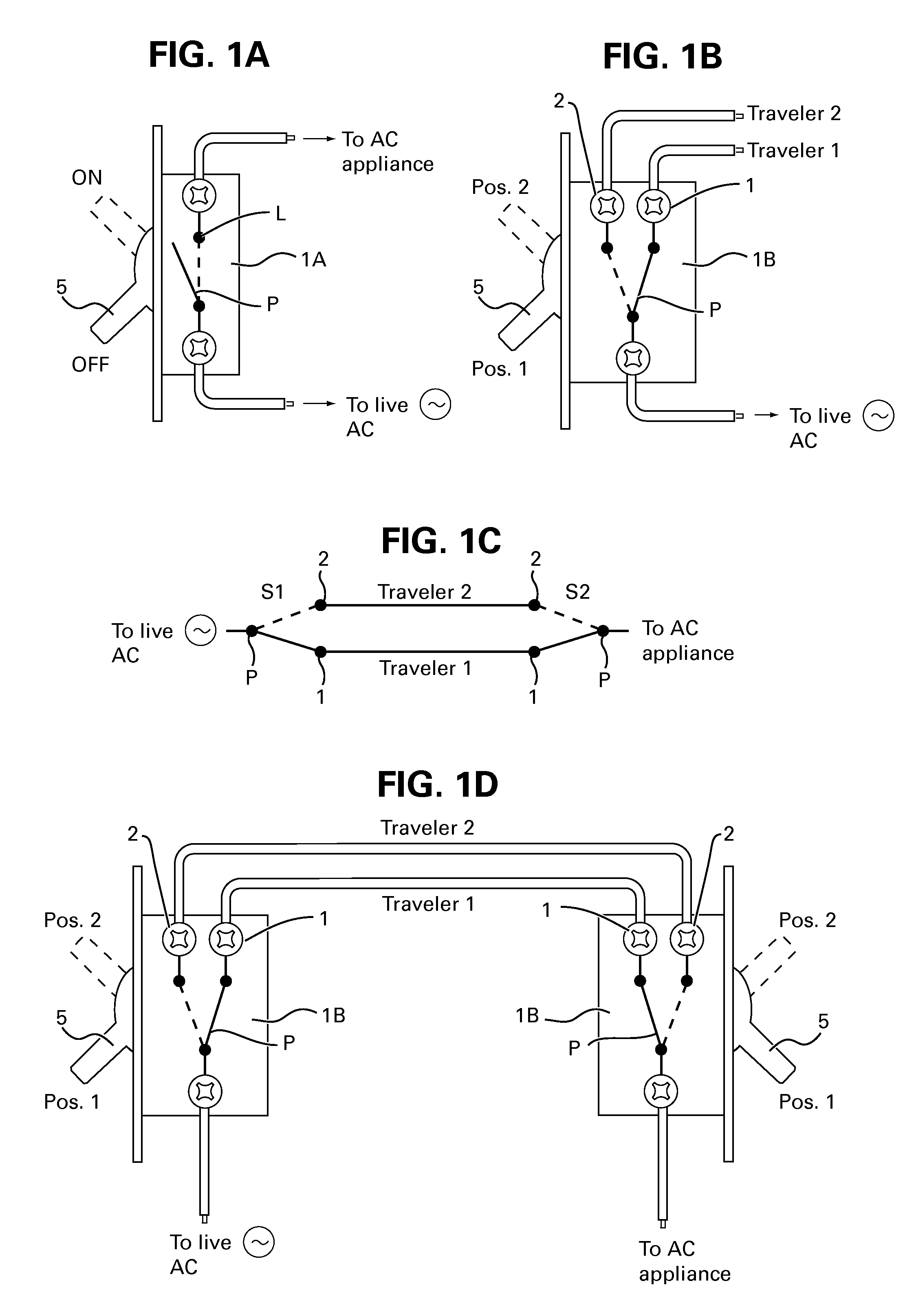
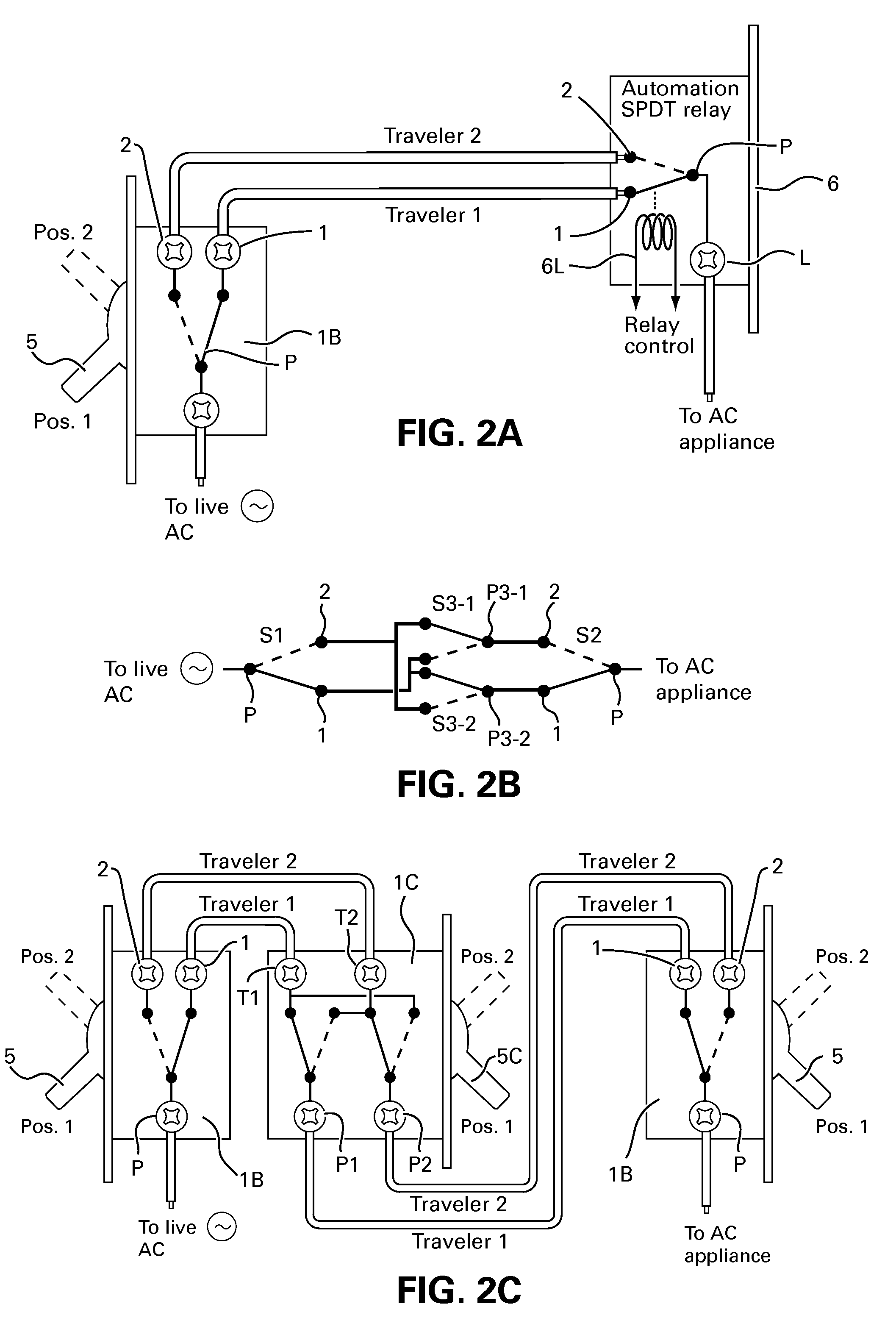
A method and apparatus for switching AC appliances and lights of residences and other automation systems through SPDT or DPDT relays connected in electrical circuit with SPDT or DPDT switch including a current sensor and / or a status sensor. The operating key of the relay and the key lever of the electric switch can each be used for operating a dedicated appliance or light, a group of appliance and lights and all appliance and / or lights including scenarios setup via the many well known two way, three way or four way light switches, by operating the switch lever or key in multi steps. The SPDT or DPDT relays are operated via RF, IR and fiber optic communicating two way signal for operating the lights and reporting statuses.
Owner:ELBEX VIDEO LTD
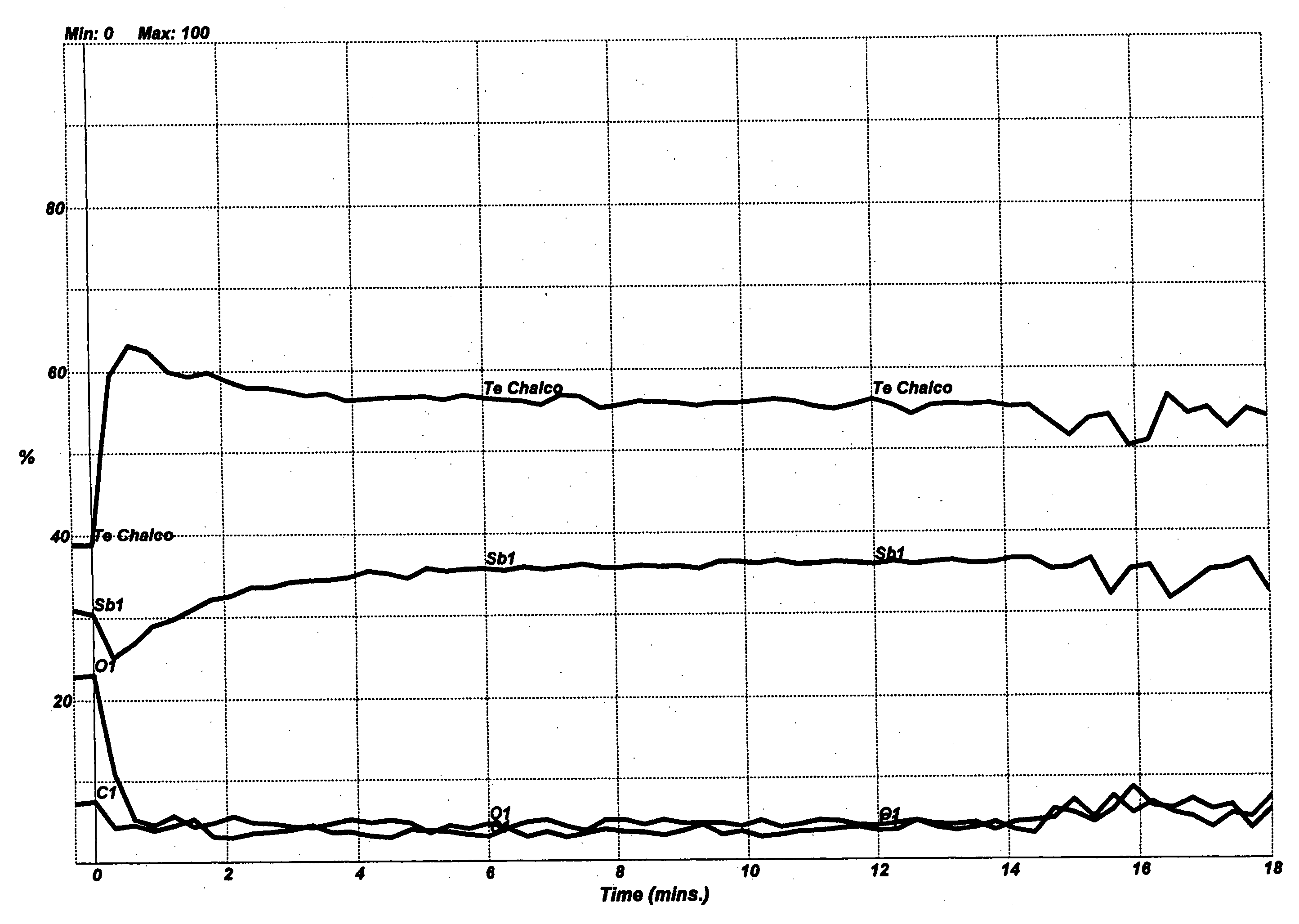
Chemical vapor deposition of chalcogenide materials
A chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process for preparing electrical and optical chalcogenide materials. In a preferred embodiment, the instant CVD-deposited materials exhibit one or more of the following properties: electrical switching, accumulation, setting, reversible multistate behavior, resetting, cognitive functionality, and reversible amorphous-crystalline transformations. In one embodiment, a multilayer structure, including at least one layer containing a chalcogen element, is deposited by CVD and subjected to post-deposition application of energy to produce a chalcogenide material having properties in accordance with the instant invention. In another embodiment, a single layer chalcogenide material having properties in accordance with the instant invention is formed from a CVD deposition process including three or more deposition precursors, at least one of which is a chalcogen element precursor. Preferred materials are those that include the chalcogen Te along with Ge and / or Sb.
Owner:OVONYX
Transistor with workfunction-induced charge layer
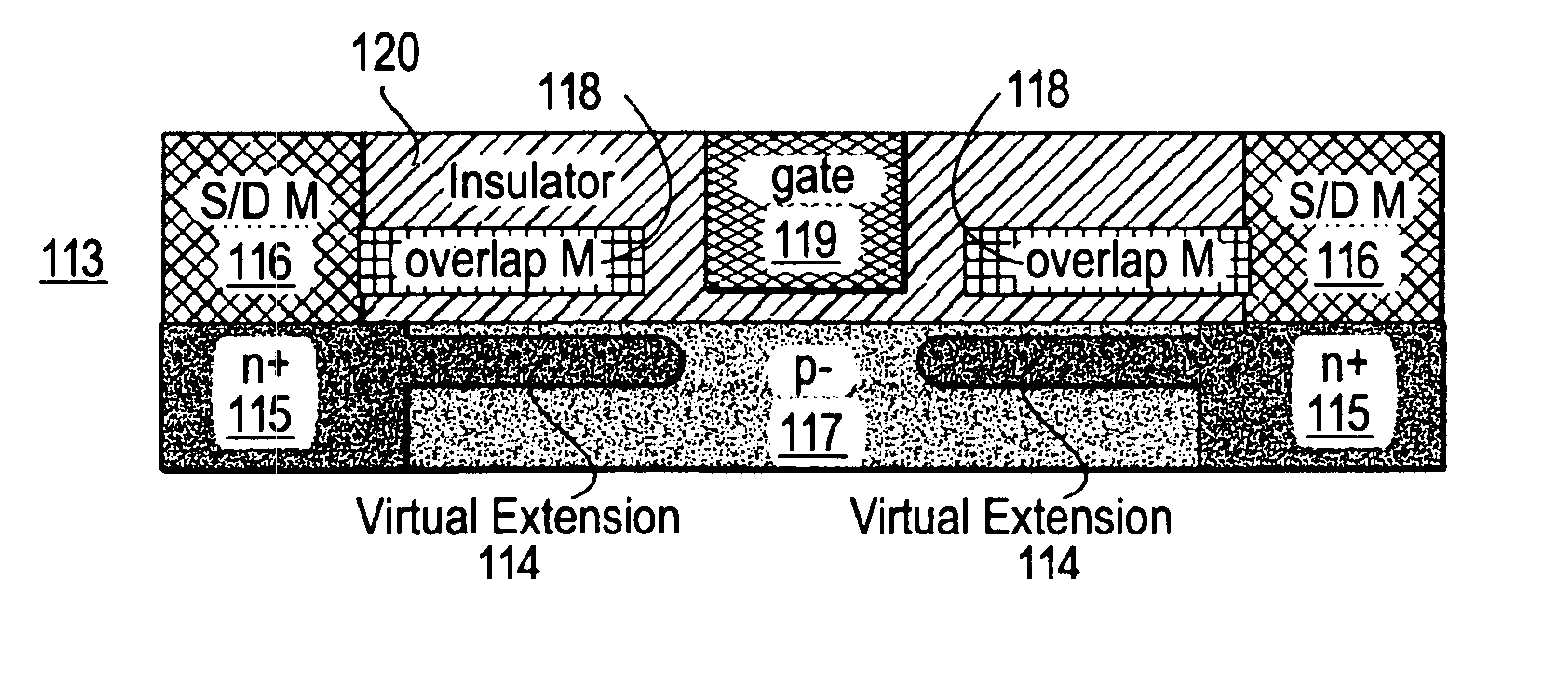
ActiveUS6891234B1ConductivityImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorCharge layer
An electrical switching device includes a semiconductor having a channel therein which is proximate to at least on channel tap in an extension region and also to a gate. A conductor (e.g., a metal) is disposed proximate to the extension region but is electrically isolated from both the extension region and the gate (e.g., through the use of one or more insulators). The conductor has a workfunction outside of the bandgap of a semiconductor in the extension region and therefore includes a layer of charge in the extension region. The magnitude and polarity of this layer of charge is controlled through selection of the metal, the semiconductor, and the insulator.
Owner:ACORN SEMI LLC
Manually operated switch for enabling and disabling an RFID card
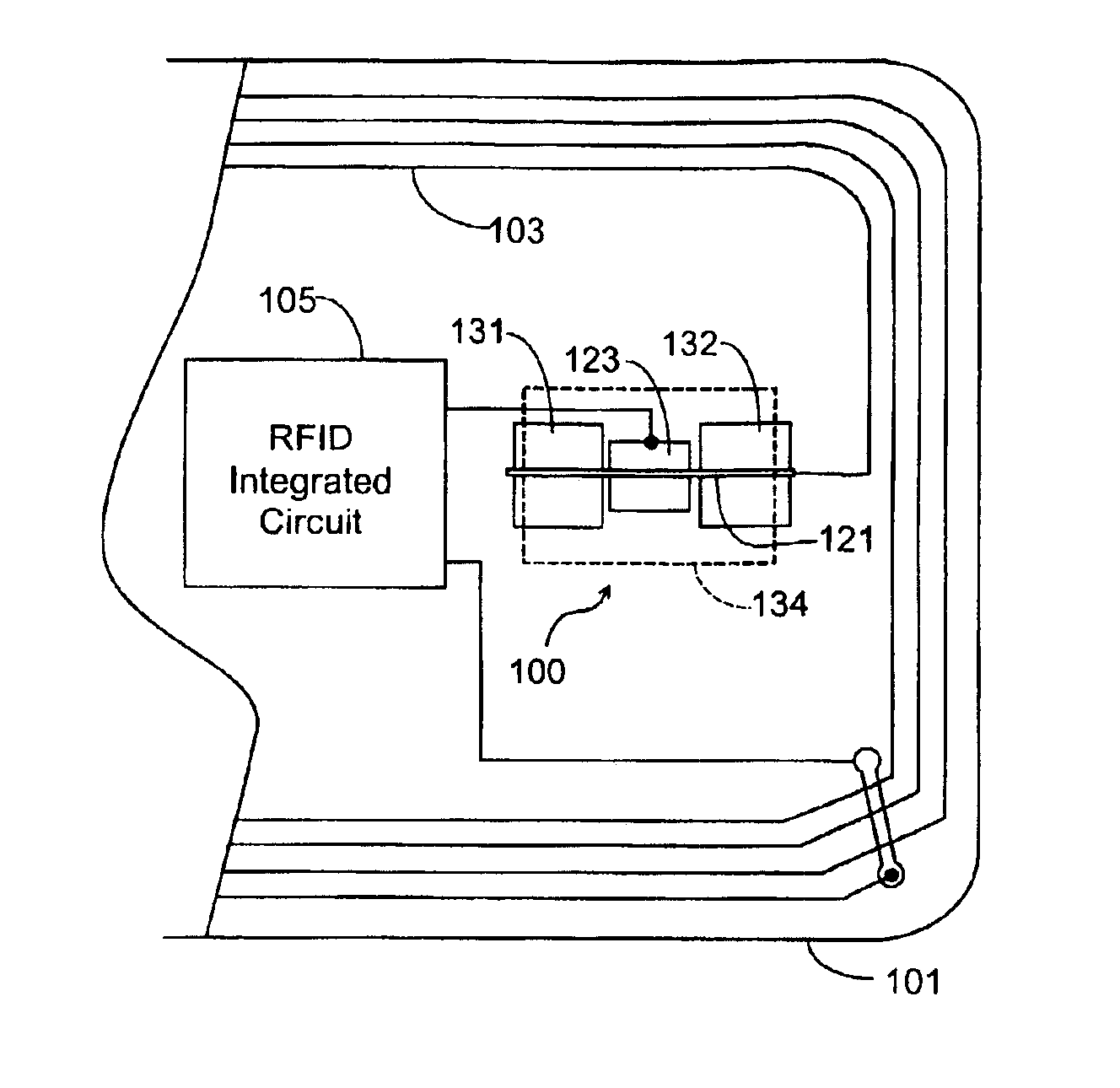
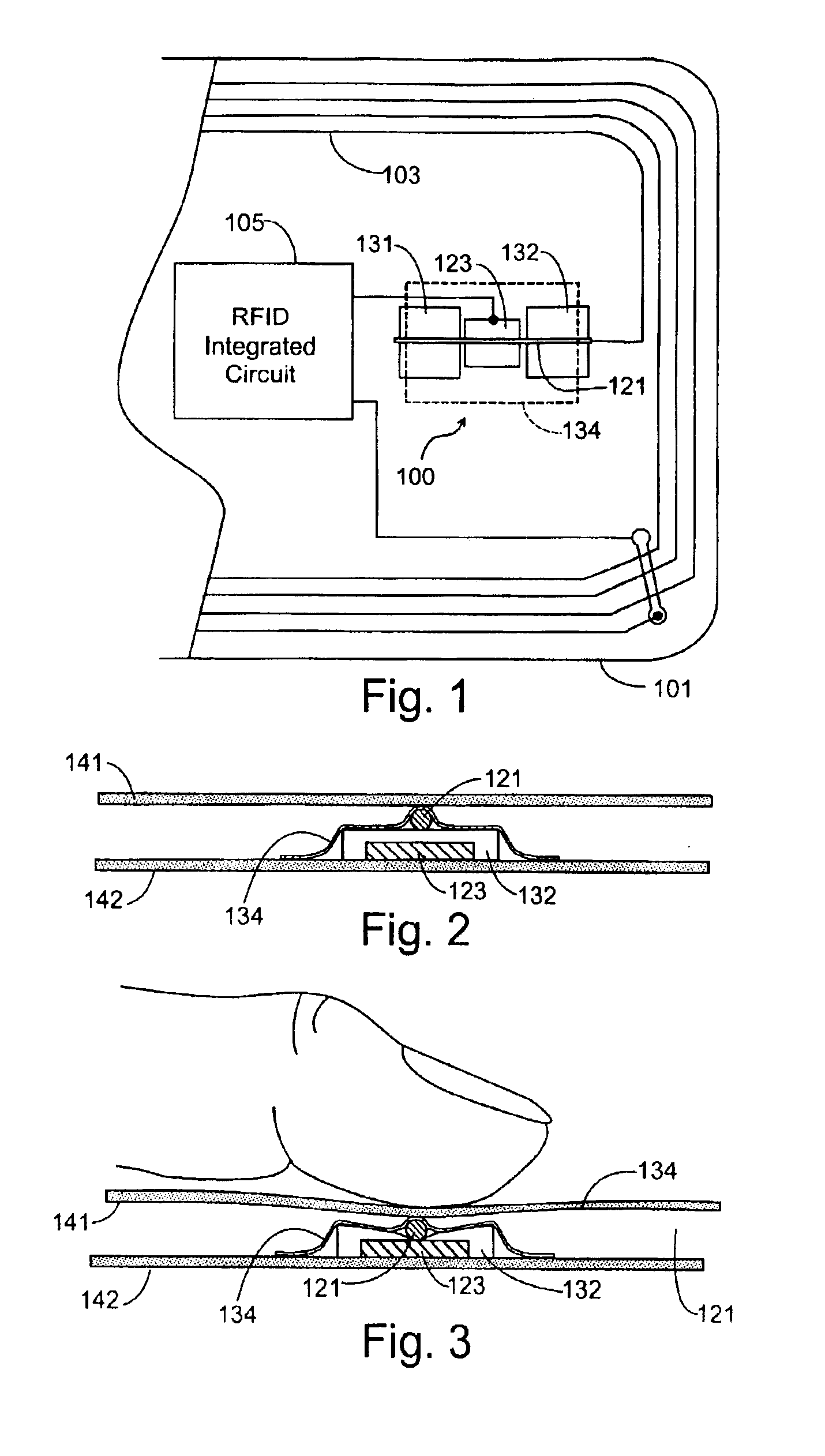
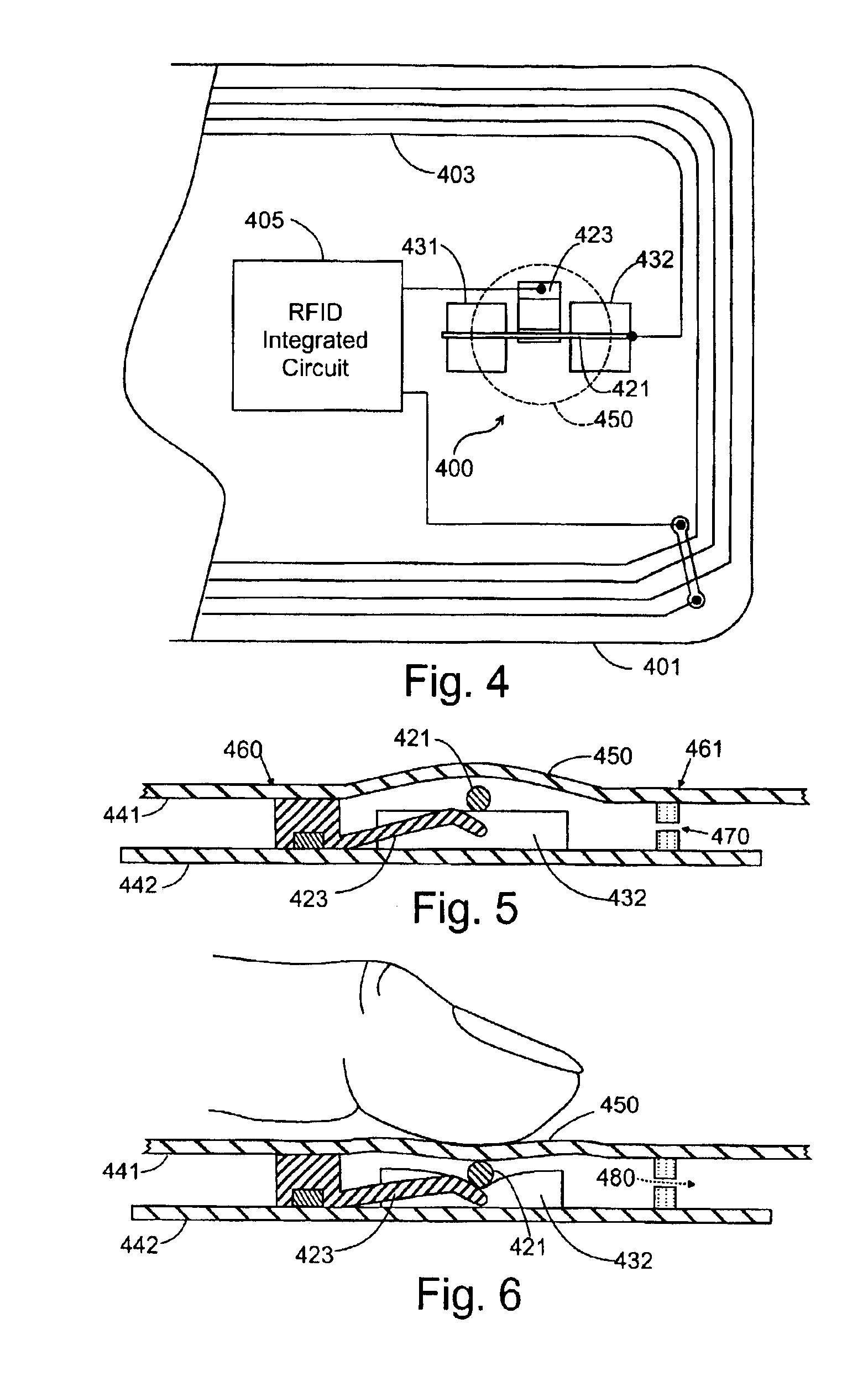
InactiveUS6863220B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransceiverEngineering
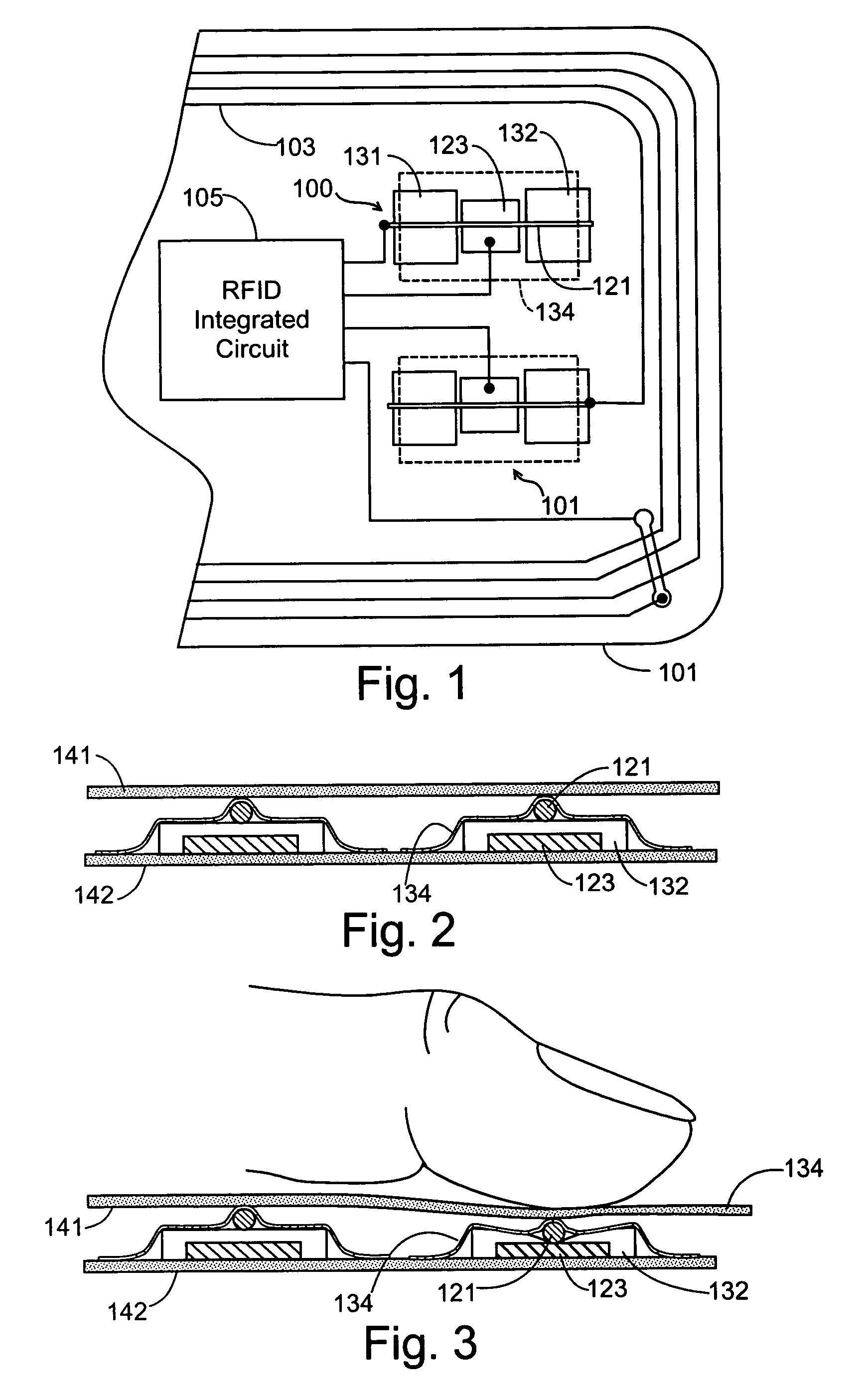
A radio operated data card whose outer jacket forms a sealed protected housing for internal electrical components, including an RFID integrated circuit which incorporates data storage and a radio frequency transceiver, an on card antenna, and manually operated, normally open electrical switch contacts connected between the on-card electronic circuitry and the antenna. The open switch contacts normally disable the card, protecting the data on the card from being surreptitiously read until the switch contacts are intentionally closed by the cardholder to enable data transfer to occur. The cardholder may activate the card by applying external pressure to the surface of the card at a predetermined position, closing the switch contacts which open again automatically when pressure is removed. A tactile indicia on the surface of the card allows the cardholder to determine by touch where the card should be pressed to enable data transfers to occur. In an alternate embodiment, a mating key in the possession of the cardholder may be brought into proximity with the card to close the normally open switch to permit information to be read from the card.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Latch position indicator system and method
Latch position indicator systems remotely determine whether a latch assembly is latched or unlatched. The latch assembly may be a single latch assembly or a dual latch assembly. An oilfield device may be positioned with the latch assembly. Non-contact (position), contact (on / off and / or position) and hydraulic (flowmeter), both direct and indirect, embodiments include fluid measurement systems, an electrical switch system, a mechanical valve system, and proximity sensor systems.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
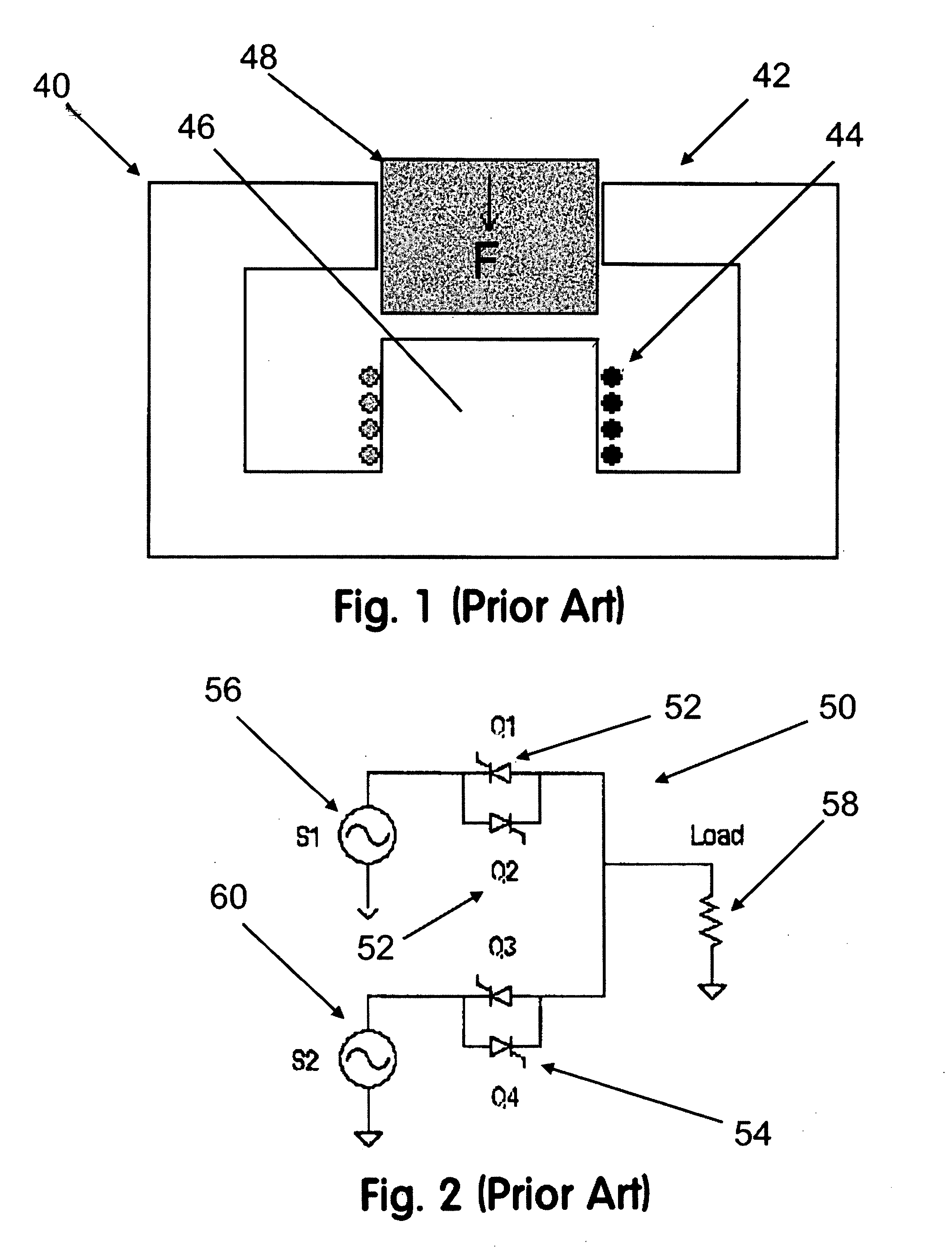
Method and area electric power system detecting islanding by employing controlled reactive power injection by a number of inverters
ActiveUS20110115301A1Easy to detectLevel controlConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower inverterElectricity
An area electric power system includes a number of direct current power sources, and a number of inverters operatively associated with the number of direct current power sources. Each of the number of inverters is structured to provide real power and controlled reactive power injection to detect islanding. An output is powered by the number of inverters. A number of electrical switching apparatus are structured to electrically connect the number of inverters to and electrically disconnect the number of inverters from a utility grid. A number of devices are structured to detect islanding with respect to the utility grid responsive to a number of changes of alternating current frequency or voltage of the output.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
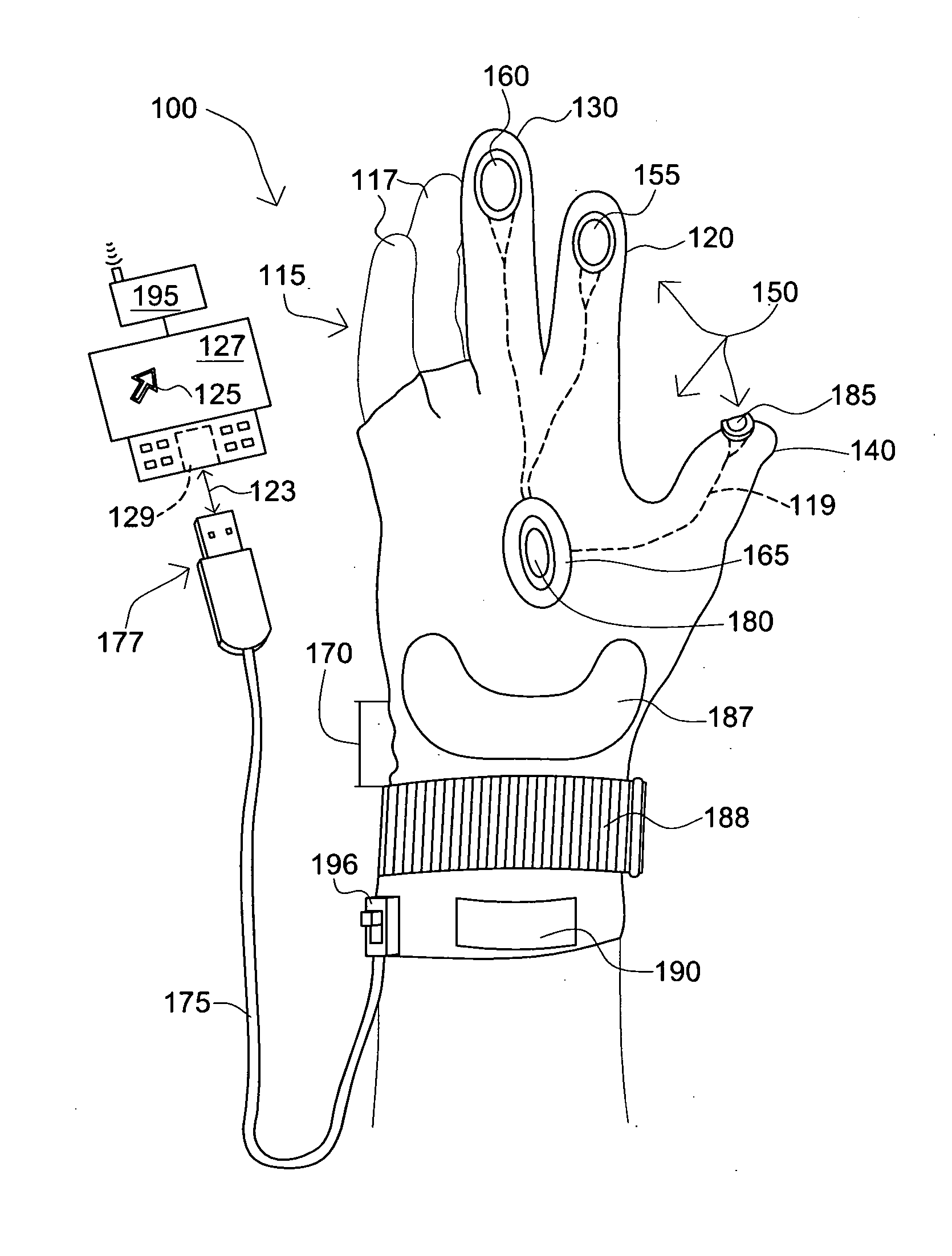
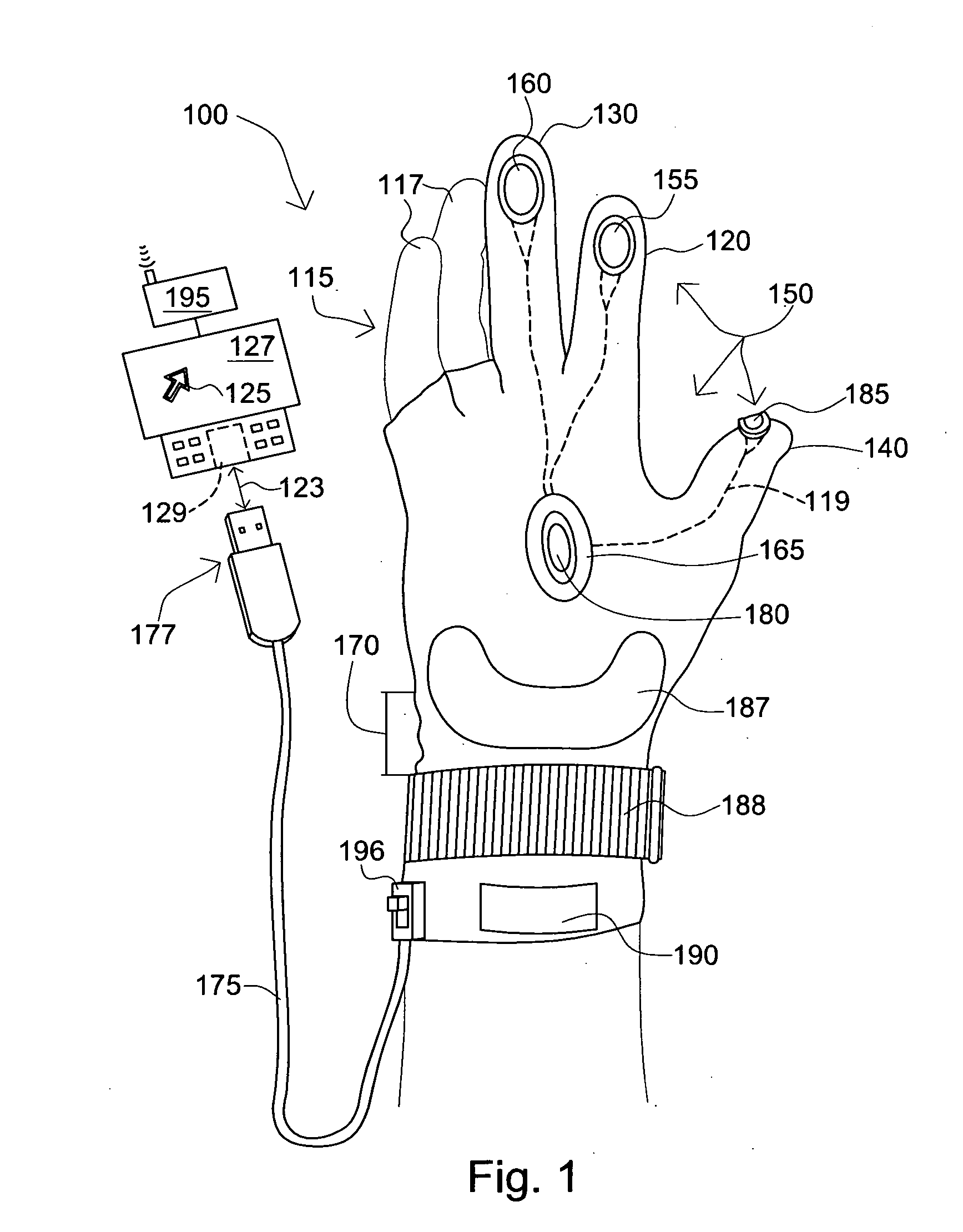
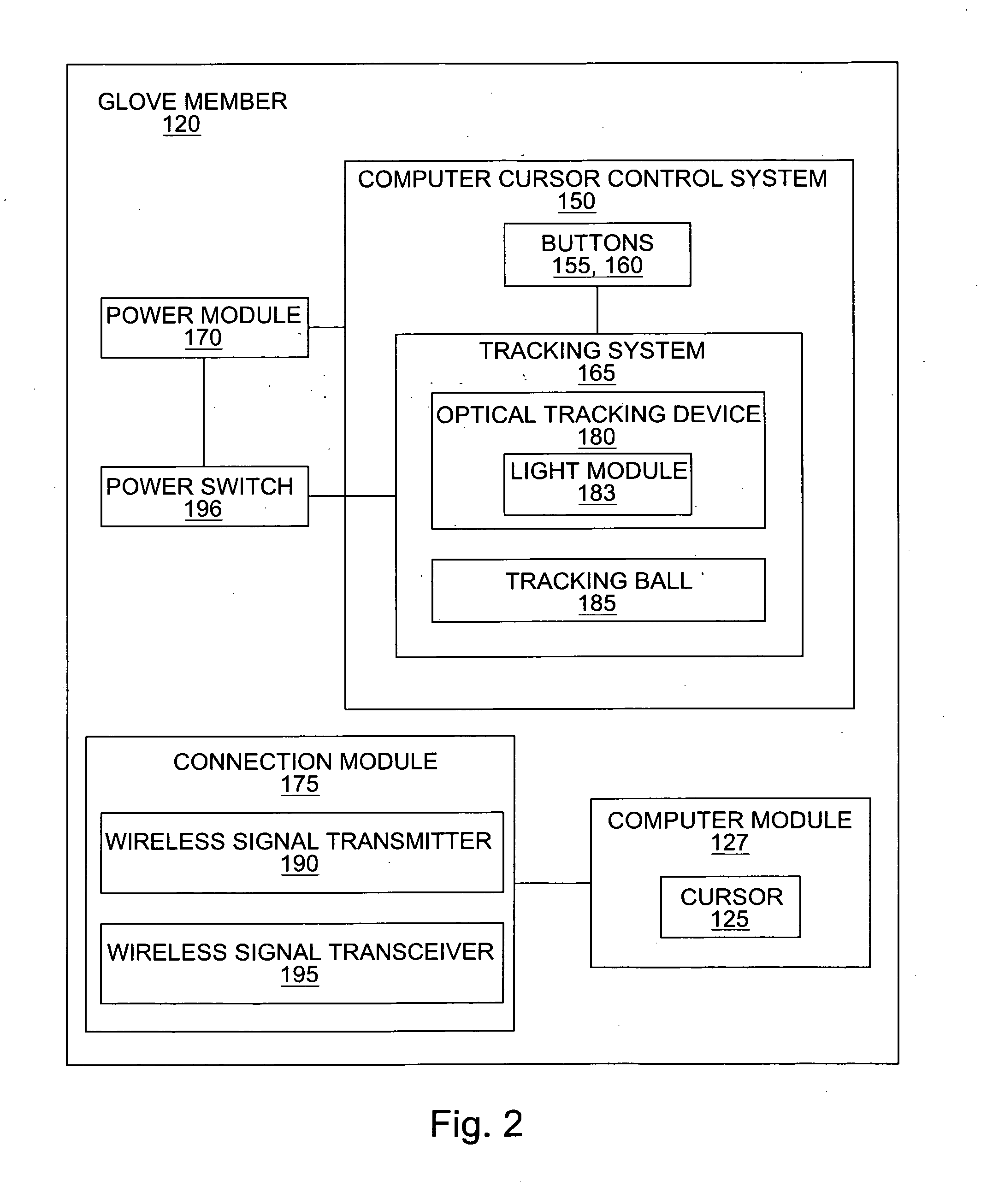
Computer mouse glove
InactiveUS20090153477A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer usersControl system
Owner:SAENZ VALENTIN L
Variable temperature vaporizer
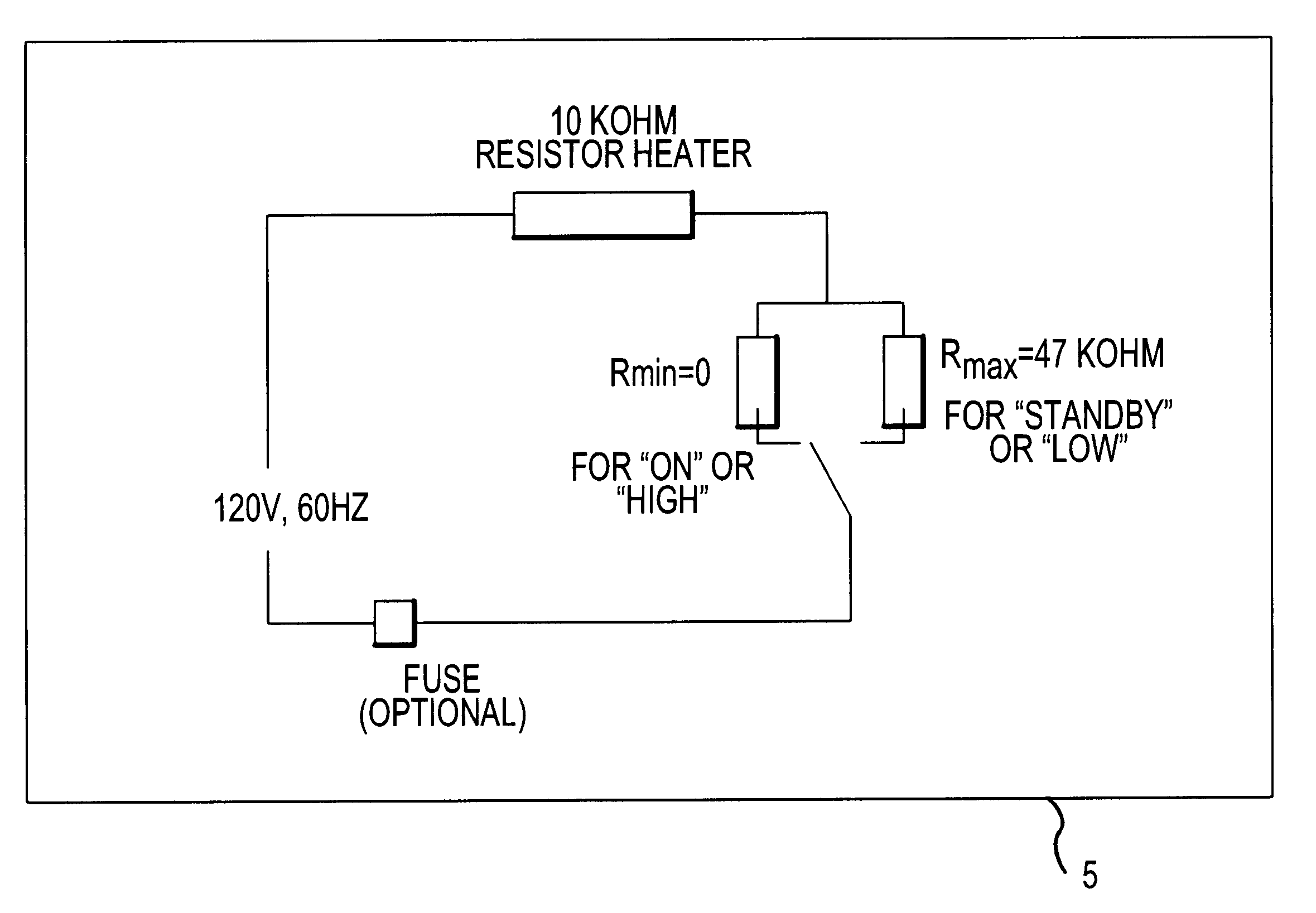
The present invention suitably provides a method and apparatus for controlling the temperature of a liquid vaporizer heating element, and thereby the rate of evaporation and level of fragrance delivery from the same. In accordance with one exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the device may include a switch that suitably allows the temperature of various types of heating elements to be controlled for different levels of fragrance output. For example, an exemplary embodiment may include a two-pronged plug adaptable to typical outlets that might be found in residential homes or businesses. In accordance with another exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the electrical switch generally provides varying resistance values to the electric circuitry of the vaporizer such that, by changing the switch setting, the operating temperature of the wick is controlled and thus the rate of fragrance evaporation from the vaporizer.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Methods and apparatus for wireless RFID cardholder signature and data entry
InactiveUS7100835B2Preferential responseHigh precisionSensing record carriersRecord carriers used with machinesTransceiverData signal
A radio operated data card whose outer jacket forms a sealed protected housing for internal electrical components, including an RFID integrated circuit which incorporates data storage and a radio frequency transceiver, and one or more on-card antenna structures. Manually operated electrical switching elements, or antenna structures which are responsive to the positioning of conductive members, such as the human hand, at particular locations on or near the surface of the card, are connected to the on-card electronic circuitry. The switching elements or antenna elements are selectively operated by the cardholder who manipulates the card in predetermined ways to generate data signals that may be used to activate the card, store data in the card, or transmit data to the reader.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Wireless system for one or more electrical switching apparatus
ActiveUS20060119344A1Power network operation systems integrationBase element modificationsSwitchgearElectrical switching
A system displays information from and controls electrical switching apparatus, such as circuit breakers. The system includes a plurality of circuit breakers having separable contacts and a plurality of conditions, such as bus temperature and contact wear. A plurality of sensors are structured to sense the conditions of the circuit breakers and to communicate the sensed conditions over corresponding wireless signals. A display and control unit is operatively associated with the circuit breakers and is structured to receive the corresponding wireless signals and display information corresponding to the sensed conditions or to control the circuit breakers based upon one or more of the sensed conditions.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
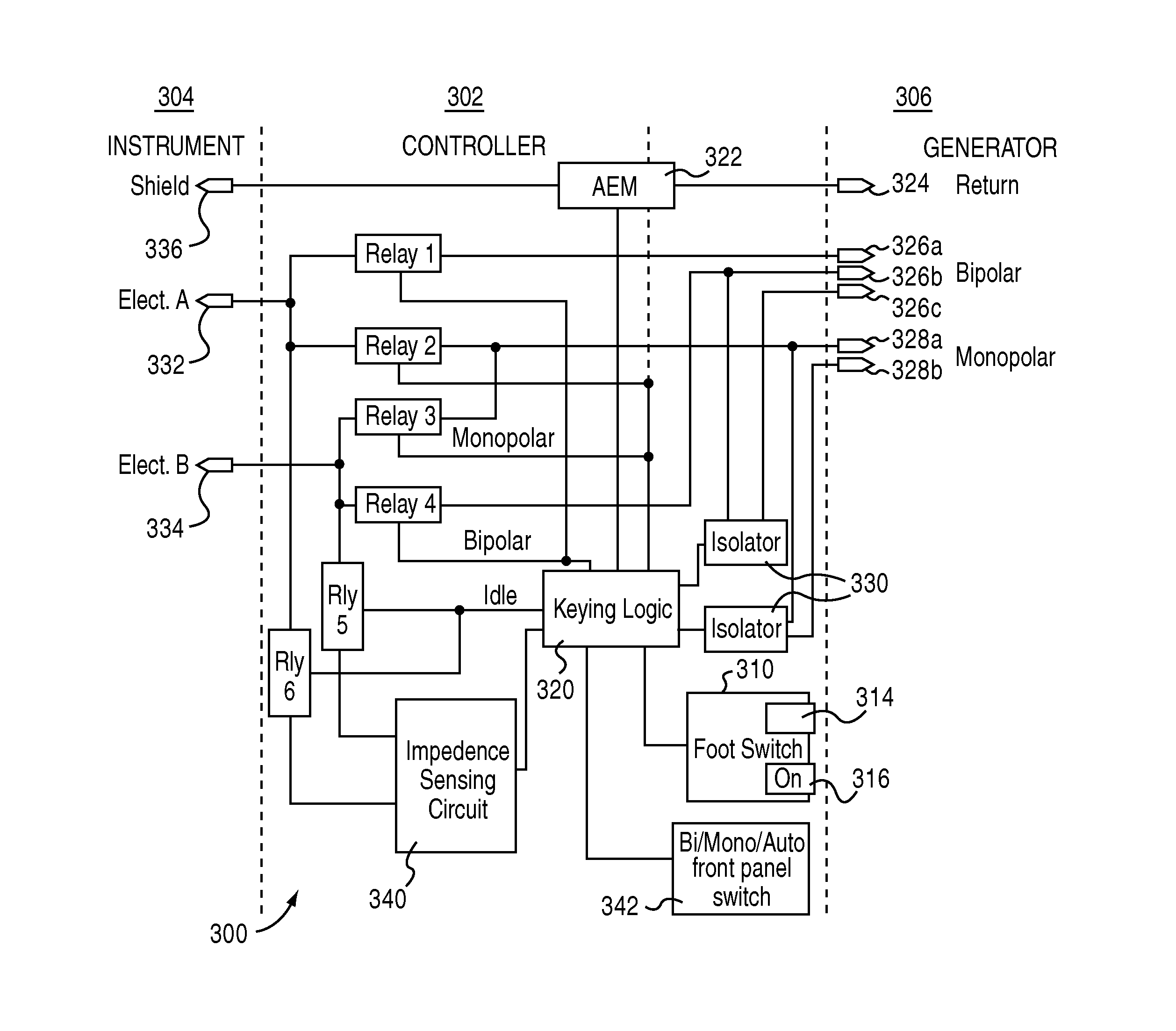
Combined bipolar and monopolar electrosurgical instrument and method
An electrical switching system for use in various types of electrosurgical instruments and related tools comprises a system adapted to automatically determine which of at least two electrical current modes to deliver through an electrosurgical instrument based on a condition sensed by the electrosurgical instrument. In another embodiment, the electrical switching system comprises a generator, the generator including a first electrical distribution systems for delivering monopolar electrical energy, and a second electrical distribution system for delivering bipolar electrical energy, a controller coupled to the generator for selecting based on an input which of the first and second electrical distribution systems to activate.
Owner:ENCISION INC
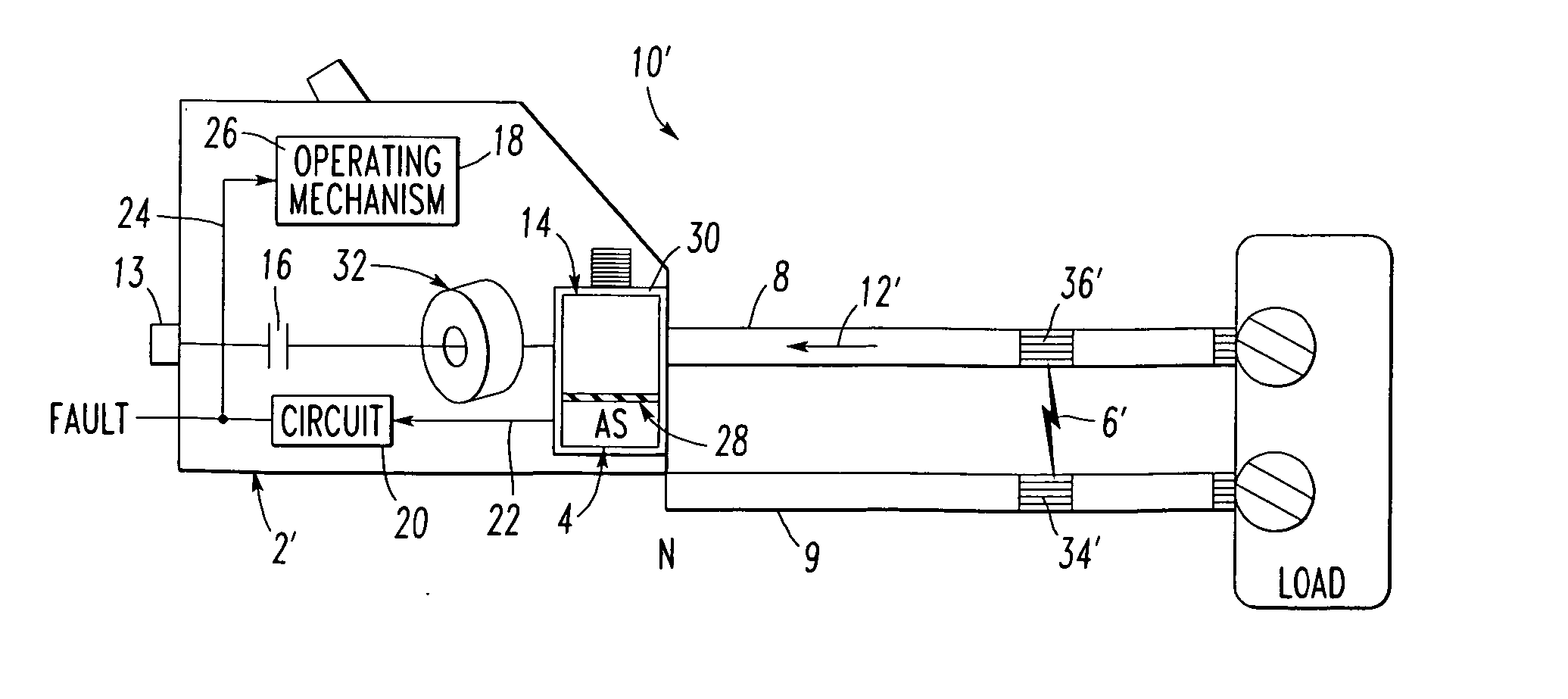
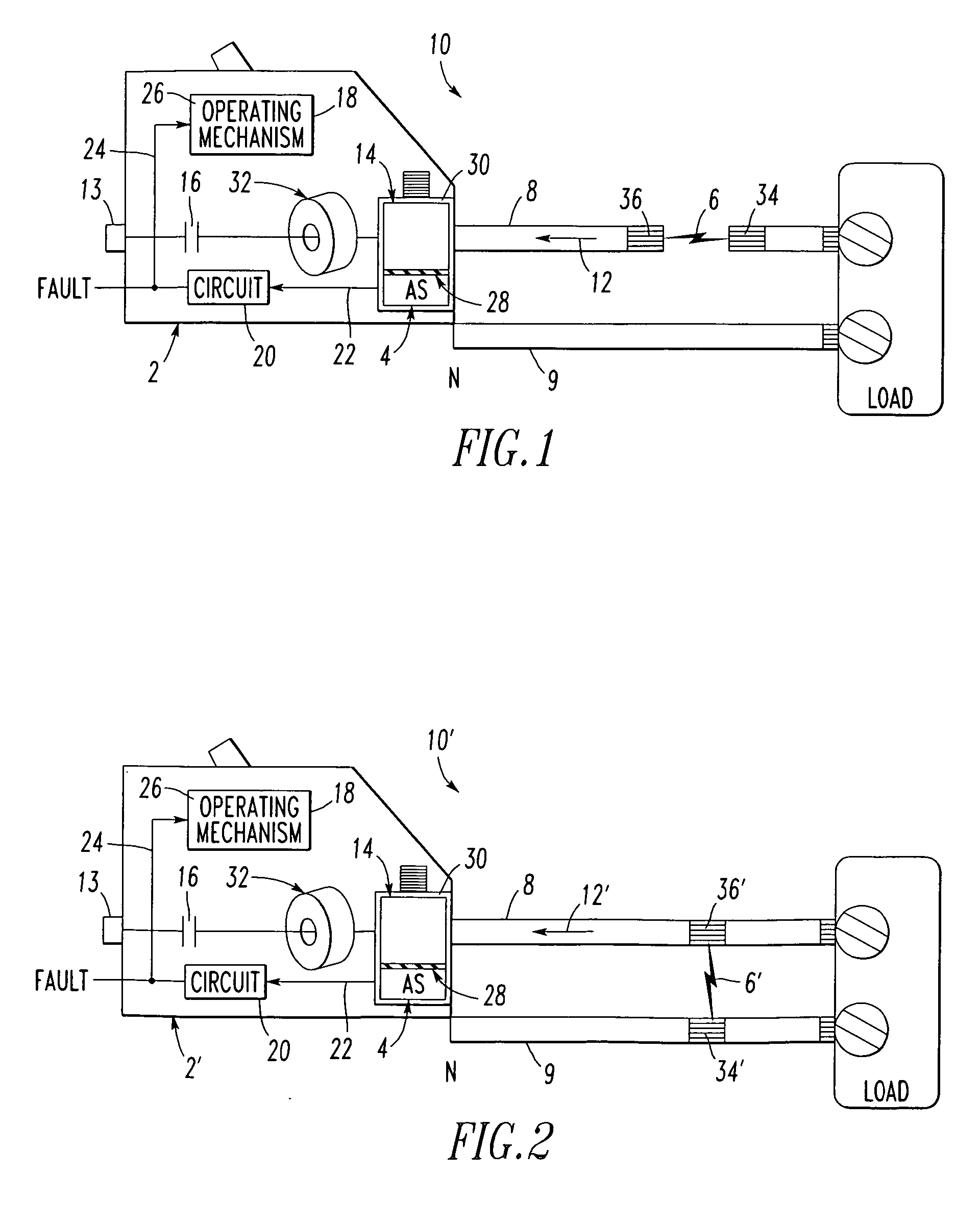
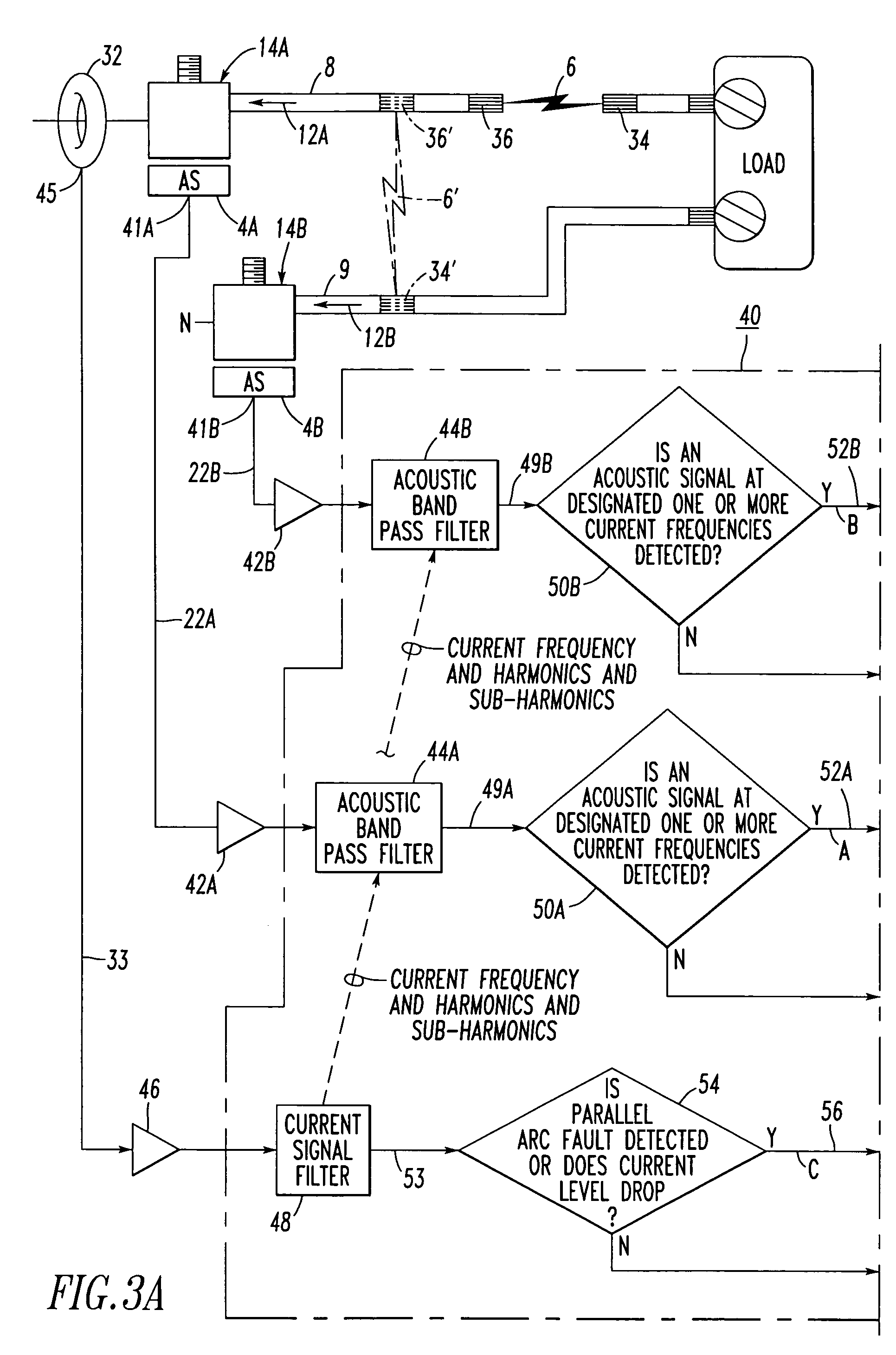
Electrical switching apparatus and method including fault detection employing acoustic signature
ActiveUS20060164097A1Electronic circuit testingEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectricityEngineering
A circuit breaker detects a fault, such as an arc fault or glowing contact, of a power circuit. The circuit breaker includes a first lug and a second acoustic lug adapted to be electrically connected to the power circuit. Separable contacts are electrically connected in series between the first lug and the second acoustic lug. An operating mechanism is adapted to open and close the separable contacts. An acoustic sensor is coupled to the second acoustic lug. The acoustic sensor is adapted to sense an acoustic signal from the second acoustic lug. The acoustic signal is operatively associated with the fault of the power circuit. A circuit inputs the sensed acoustic signal and is adapted to detect the fault therefrom.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
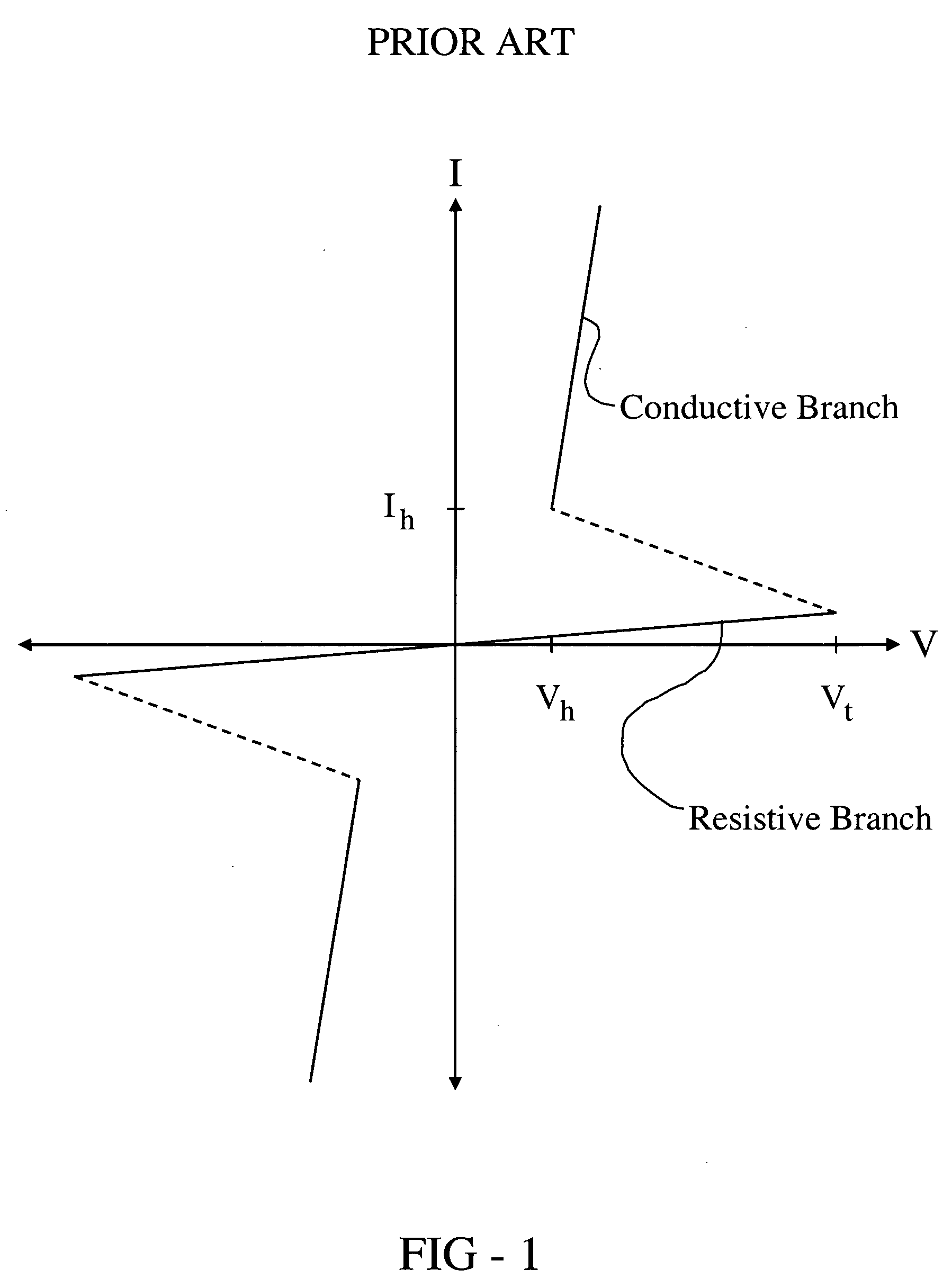
Method for manufacturing resistively switching memory devices
InactiveUS20050250281A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The present invention relates to a reproducible conditioning during the manufacturing of a resistively switching CBRAM memory cell comprising a first electrode and a second electrode with an active material positioned therebetween. The active material is adapted to be placed in a more or less electroconductive state by means of electrochemical switching processes. A CBRAM memory cell manufactured pursuant to the method according to the invention has, due to the improved conditioning, more reliable and more distinctly evaluable electrical switching properties. Moreover, no more forming step is necessary with the method according to the present invention.
Owner:ADESTO TECH
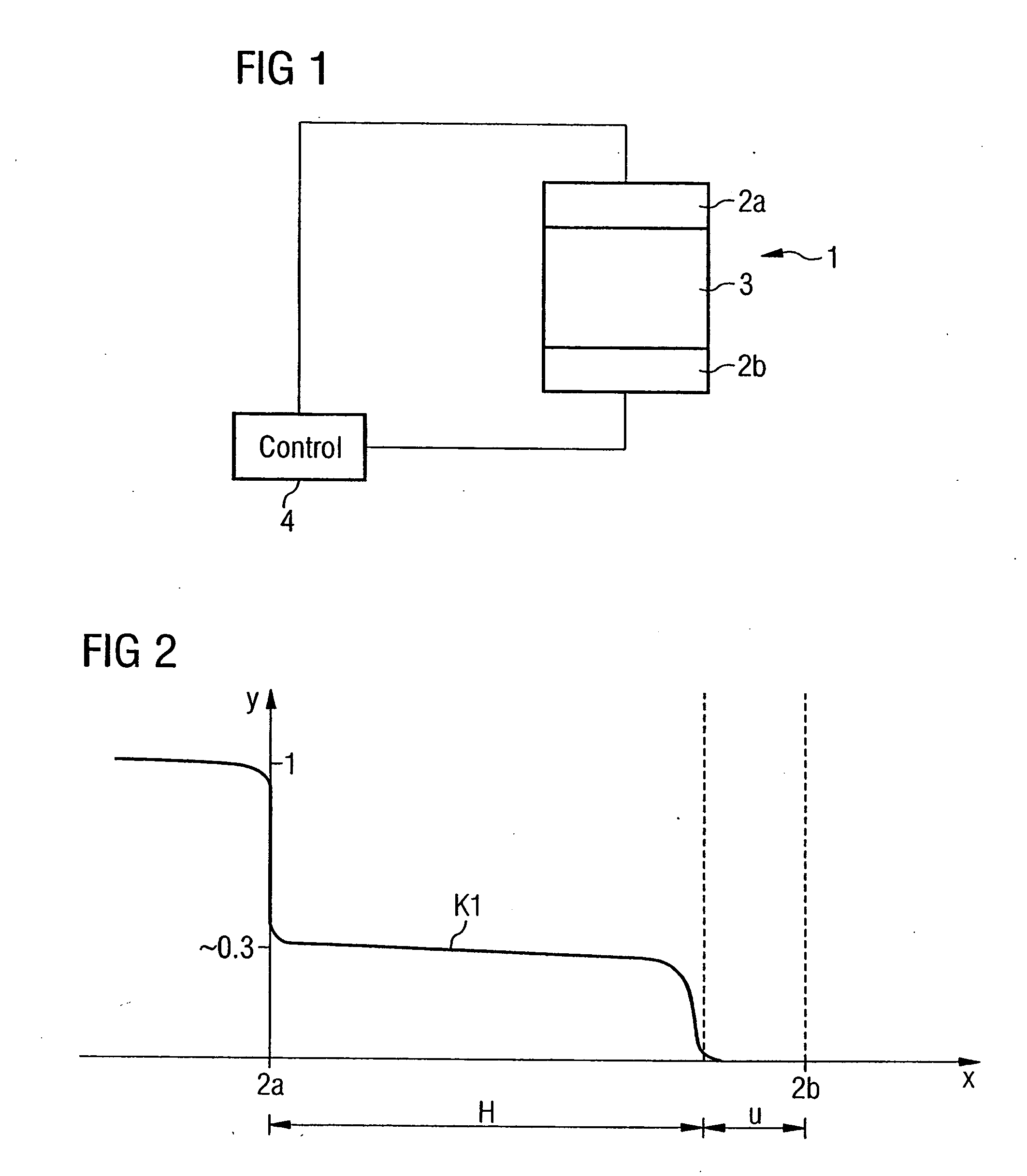
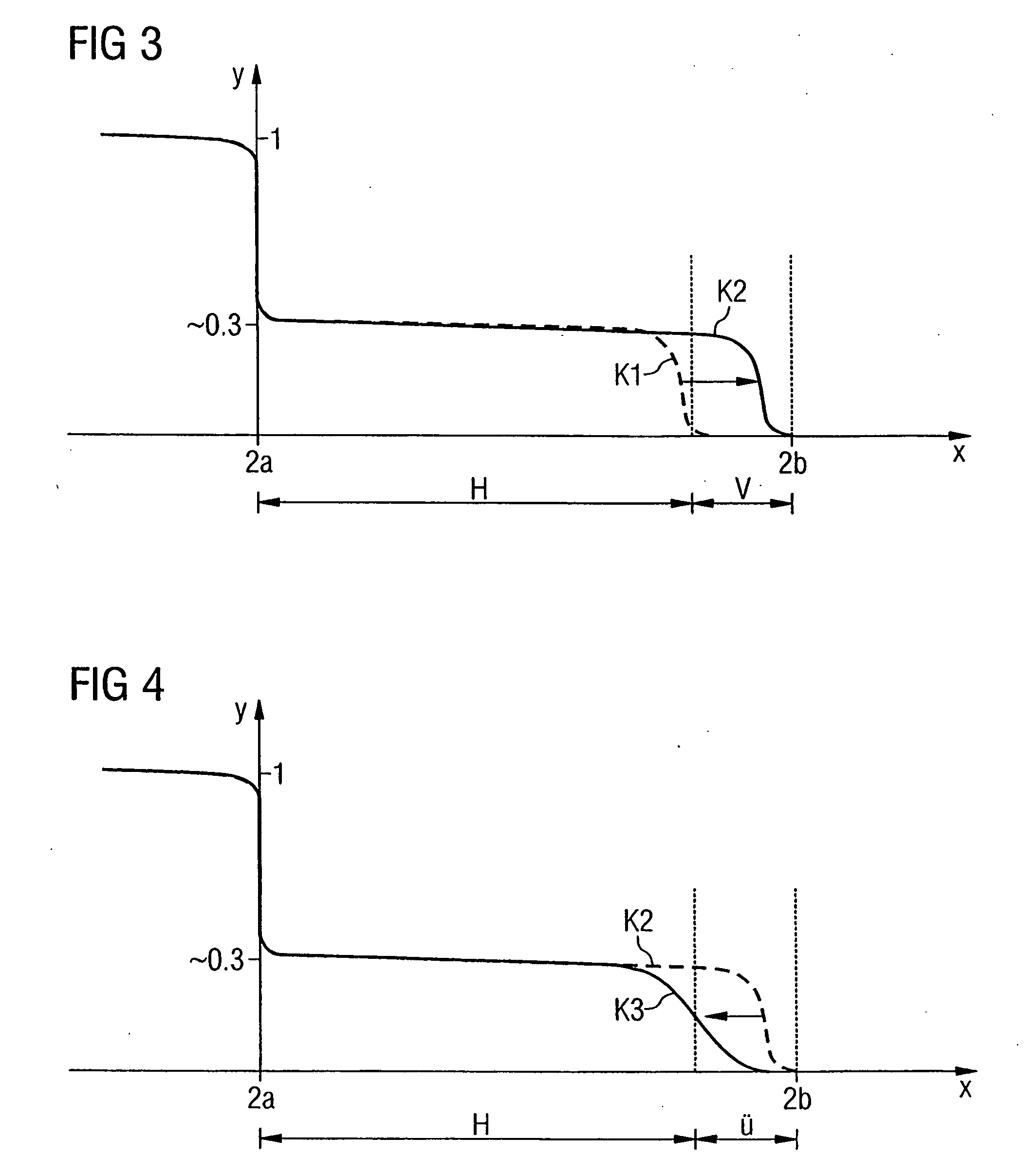
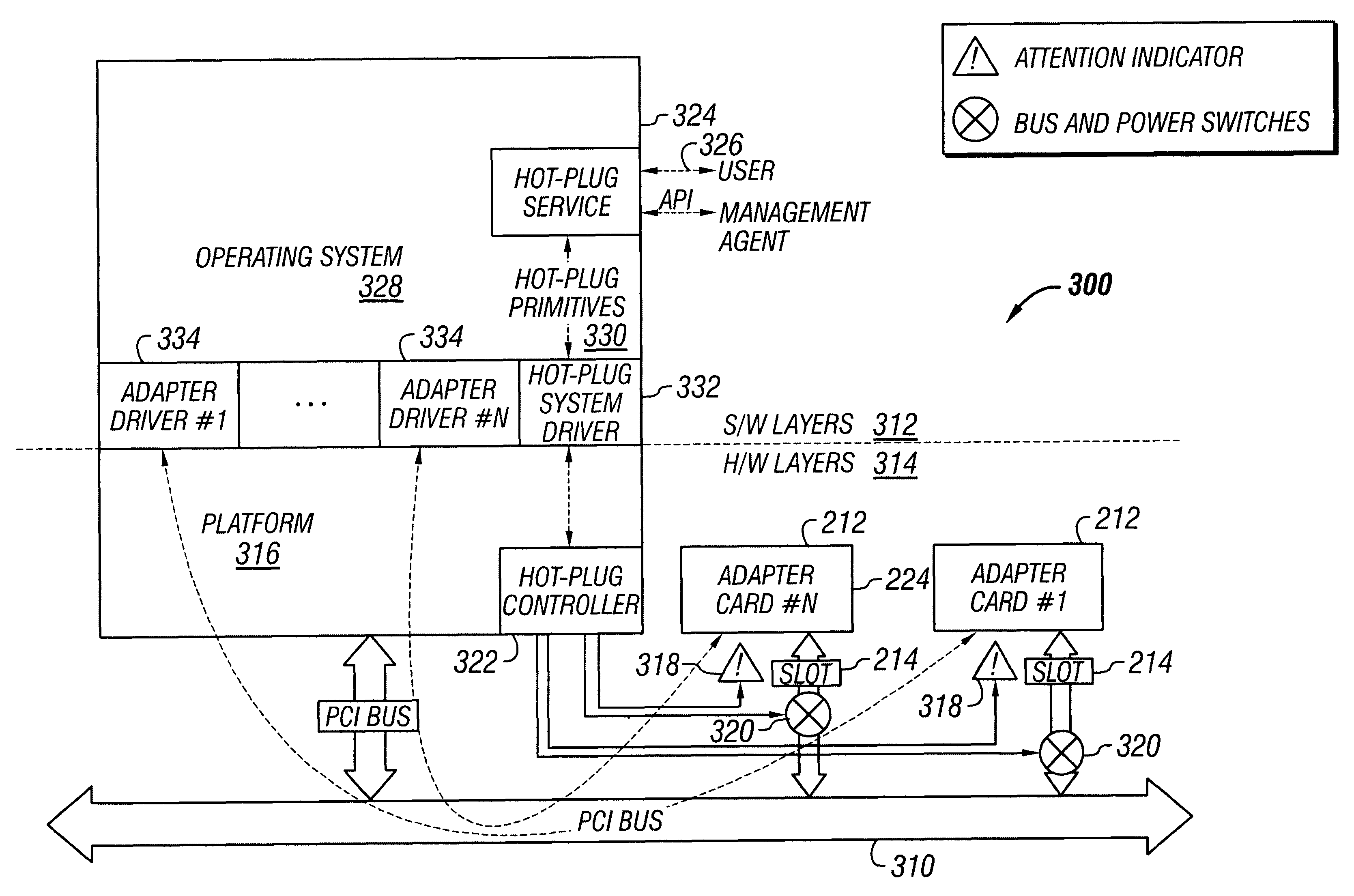
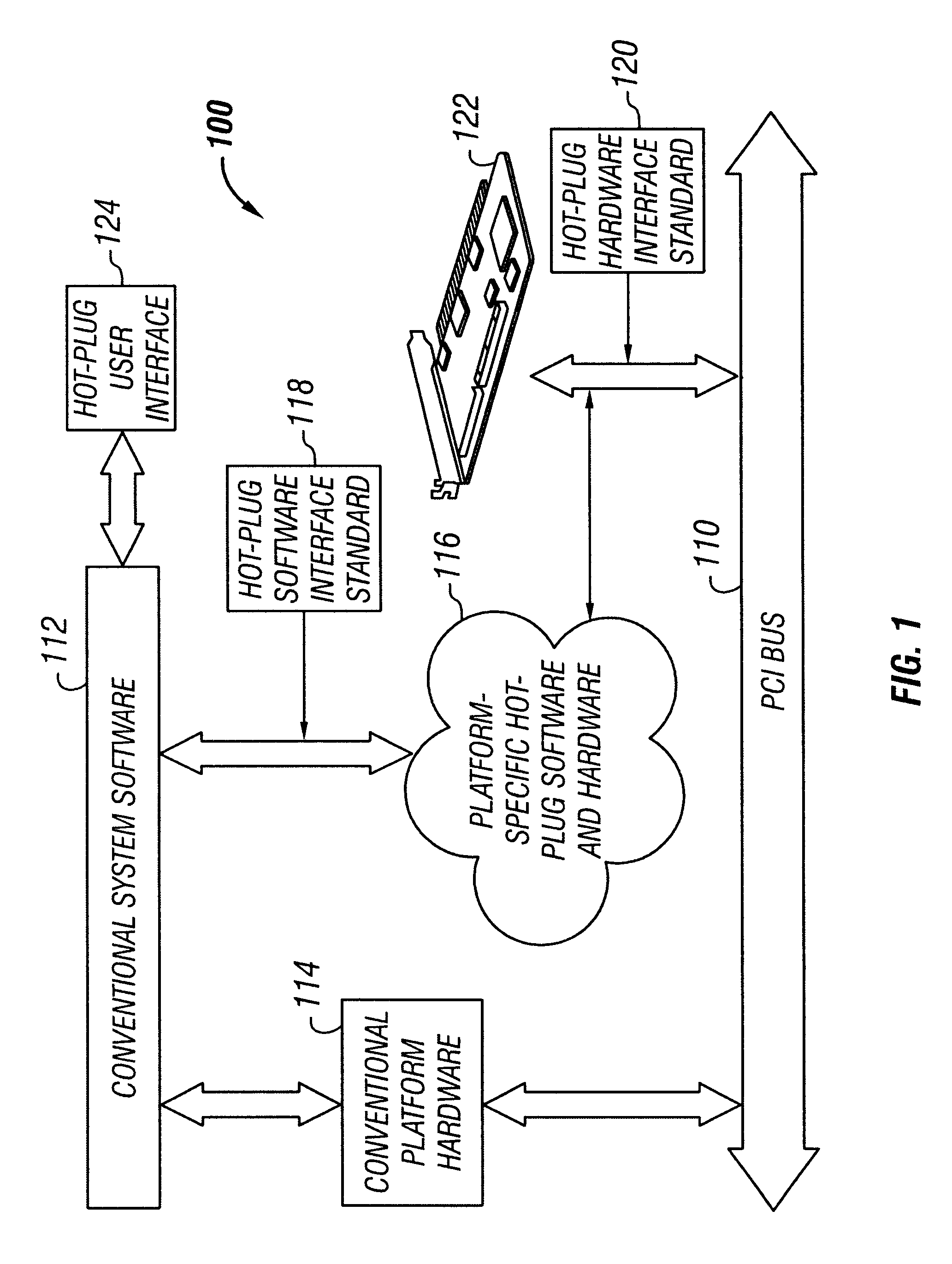
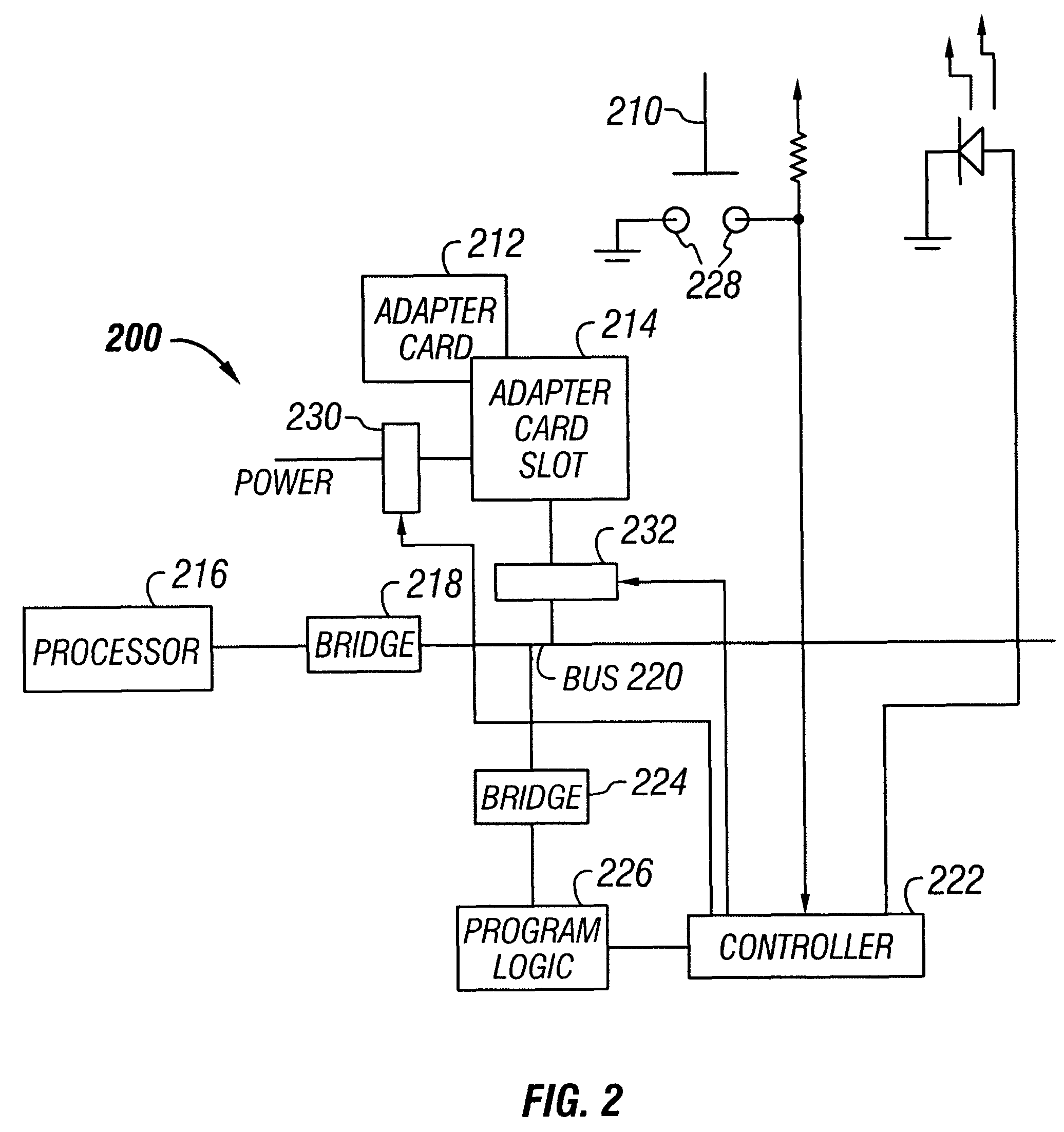
Hot-plug interface for detecting adapter card insertion and removal
InactiveUS6286066B1Component plug-in assemblagesRecord carriers used with machinesElectrical conductorComputerized system
Adapter cards generally have a metal bracket at one end. The adapter card attaches to an adapter card slot of a computer system by fastening the bracket to a connector on the computer system. Conventionally, the bracket is fastened to the connector using a screw. It has been discovered that an electrically-conductive flip-down retainer advantageously functions as an improved fastener to secure the adapter card to the connector. The electrically-conductive flip-down retainer is a single structure that performs the combined functions of an electrical switch and a mechanical fastener. The electrically-conductive flip-down retainer includes electrical contacts that form a closed circuit when the bracket is fastened to the connector and an open circuit when the bracket is not fastened. The electrical contacts are connected to conductors extending to a controller. The controller monitors the status of the electrical switch of the electrically-conductive flip-down retainer and controls application of power to the adapter card slot, typically under control of an operating system. The controller terminates power to the adapter card slot when the electrically-conductive flip-down retainer is unfastened, indicating that the adapter card is disengaged from the adapter card slot. The controller restores power to the adapter card slot when the electrically-conductive flip-down retainer is fastened, indicating the adapter card is engaged with the adapter card slot.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
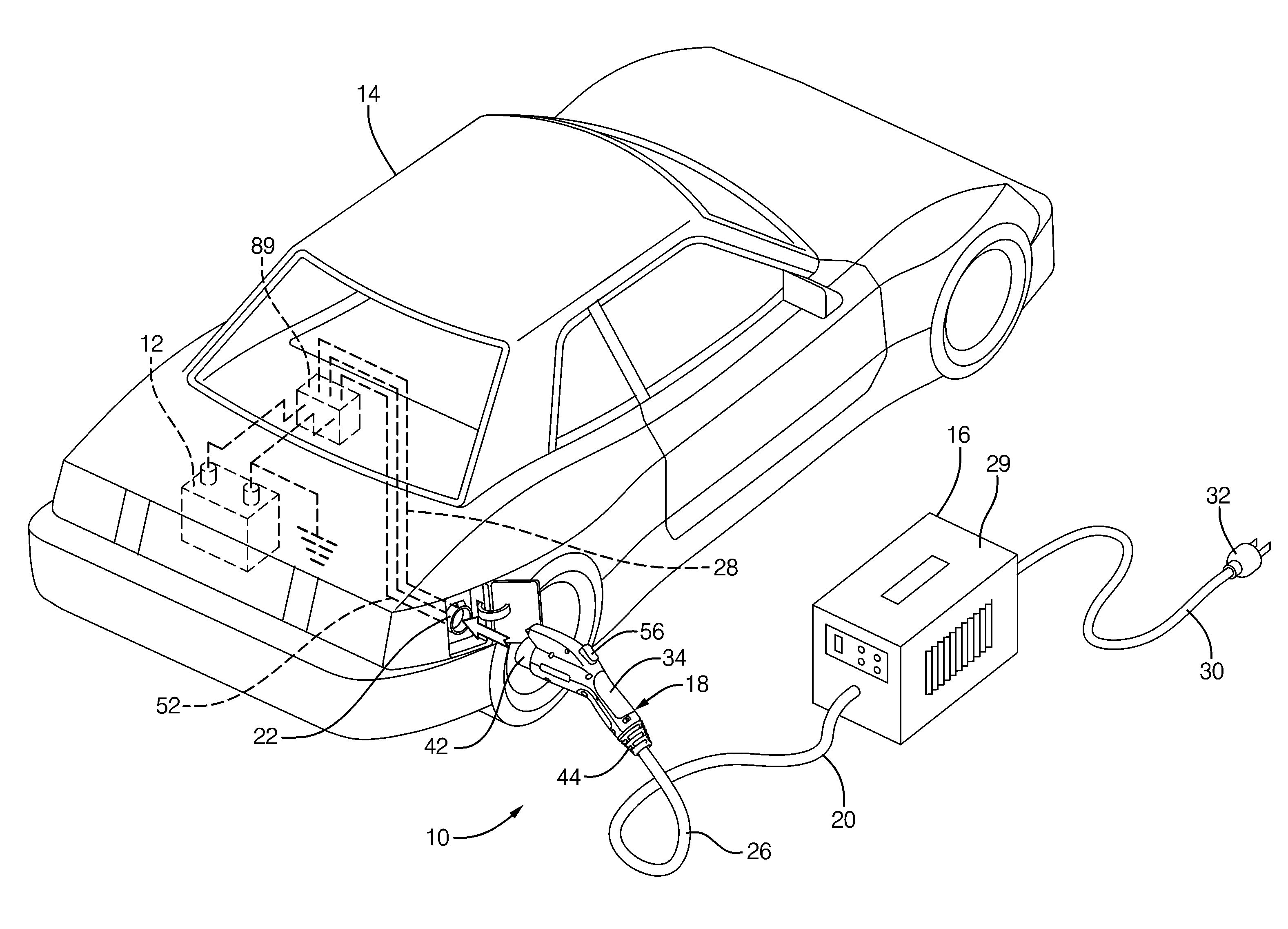
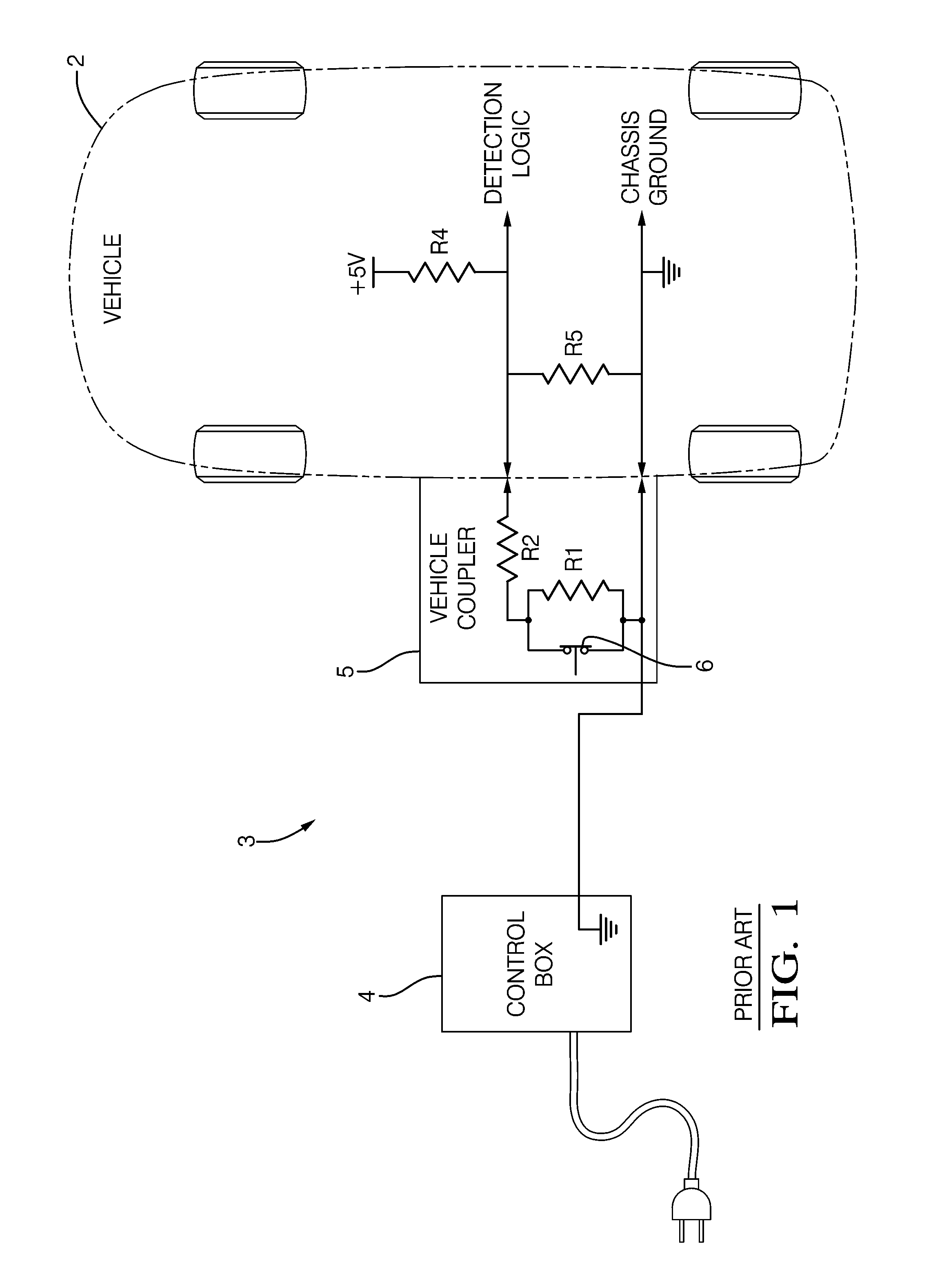
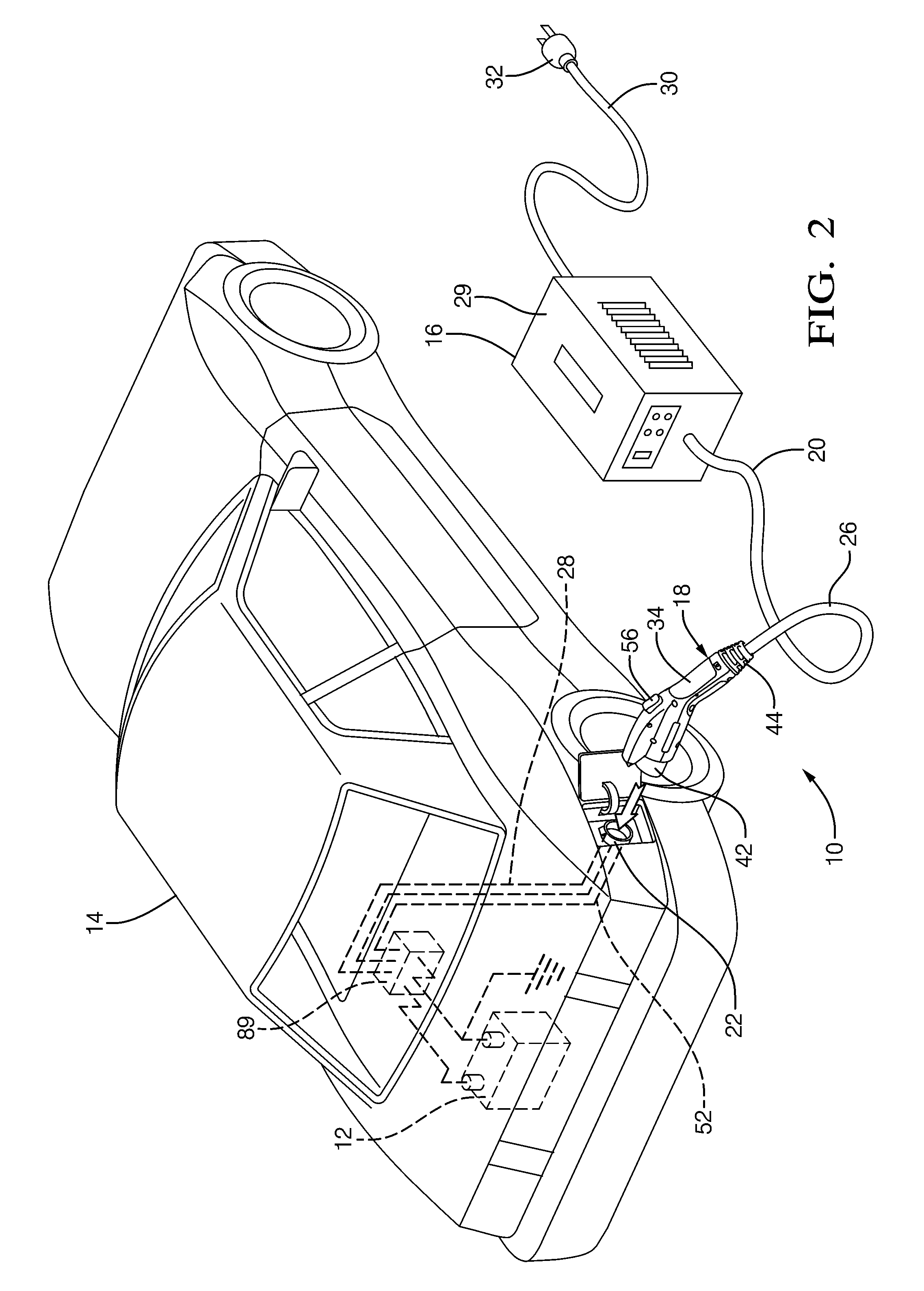
Battery charger having non-contact electrical switch
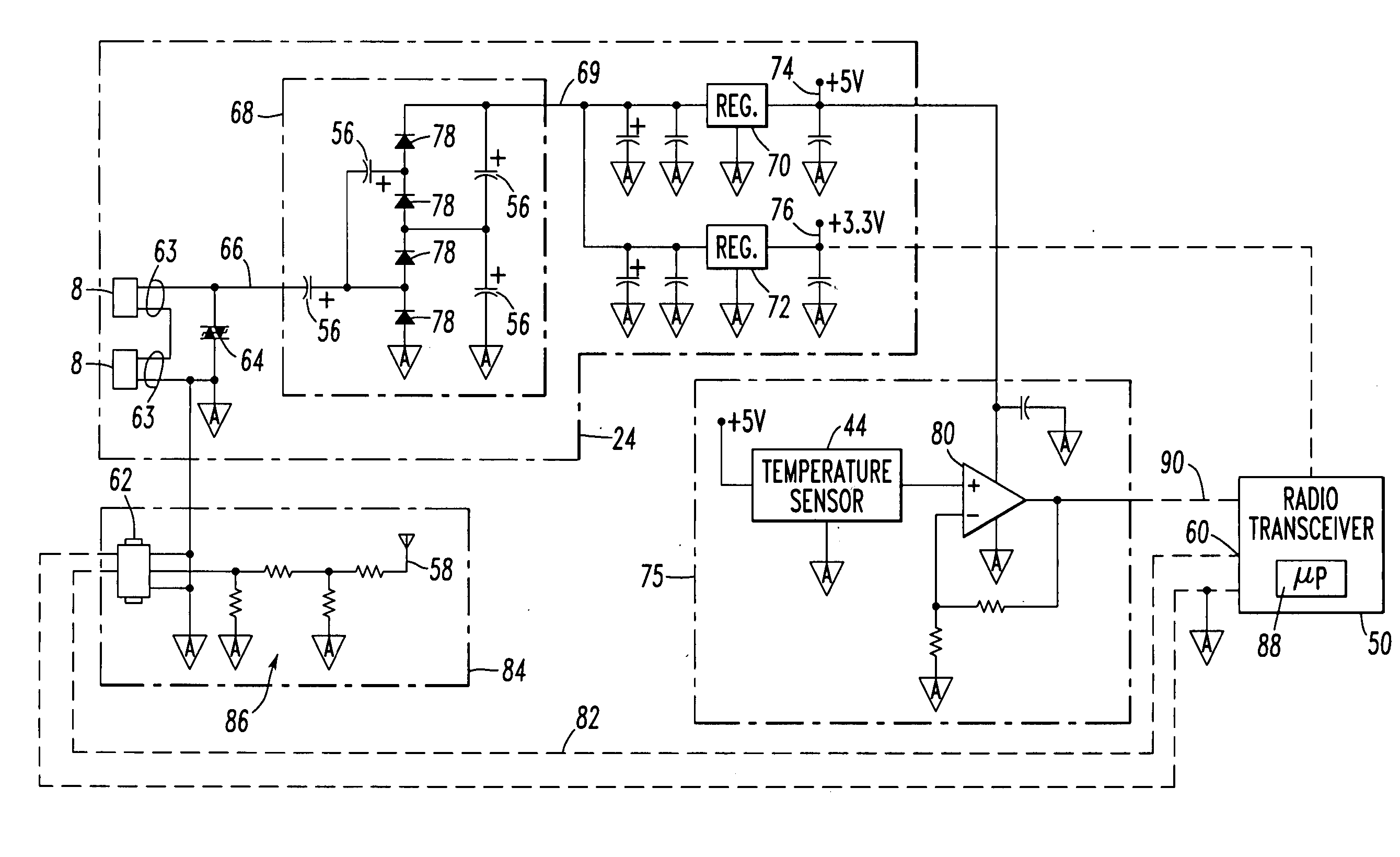
The handle of a charge coupler includes a mechanical latch that securely mechanically locks the handle to the vehicle passively when the handle is manually attached to the vehicle by a human operator to create an electrical connection between the vehicle and the charger. The handle also has an actuator movable by the operator from a deactivated state to a first and a second position activated state. The mechanical latch operates independently of the state of the actuator when the handle is being manually attached but being mechanically released by the actuator when it is moved to its second activated state. A non-contact electrical switch means associated with the actuator breaks the electrical connection when the actuator is moved to the first position activated state before releasing the mechanical latch at said second activated position.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
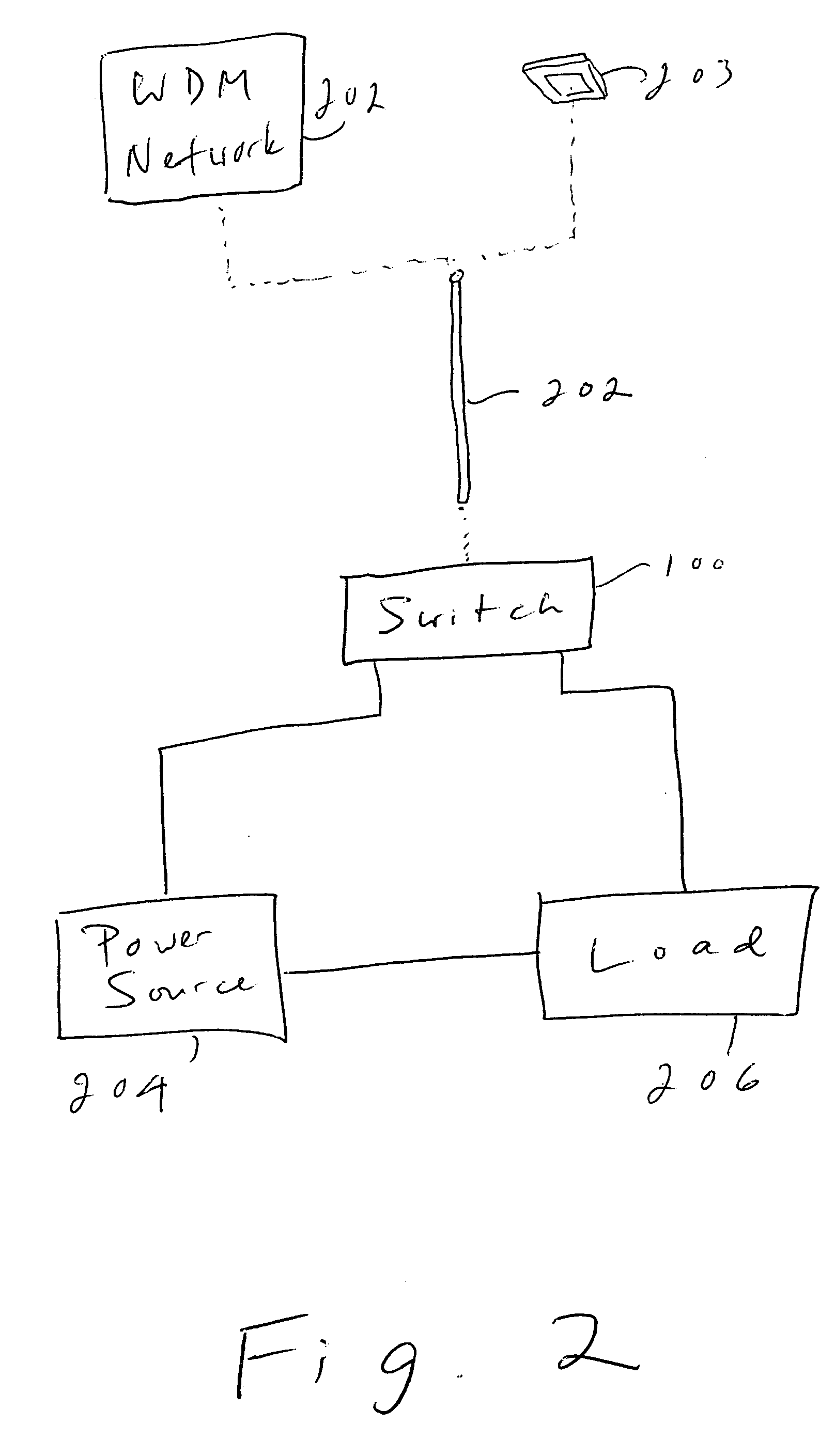
Method and Apparatus for Remotely Operating AC Powered Appliances from Video Interphones or Shopping Terminals
ActiveUS20090103228A1Low costMinimal exposureEnergy efficient ICTPower network operation systems integrationEngineeringAC power
A method for adding and connecting a remotely operated SPDT relay to an electric power circuit of an AC appliance connected to a manually actuated electrical SPDT switch for integrating said AC appliance into an home automation network, each said relay and said SPDT switch includes a pole terminal and dual traveler terminals and said relay is similar to a shape and a size of an AC switch fit for installation into a standard electrical box.
Owner:ELBEX VIDEO LTD
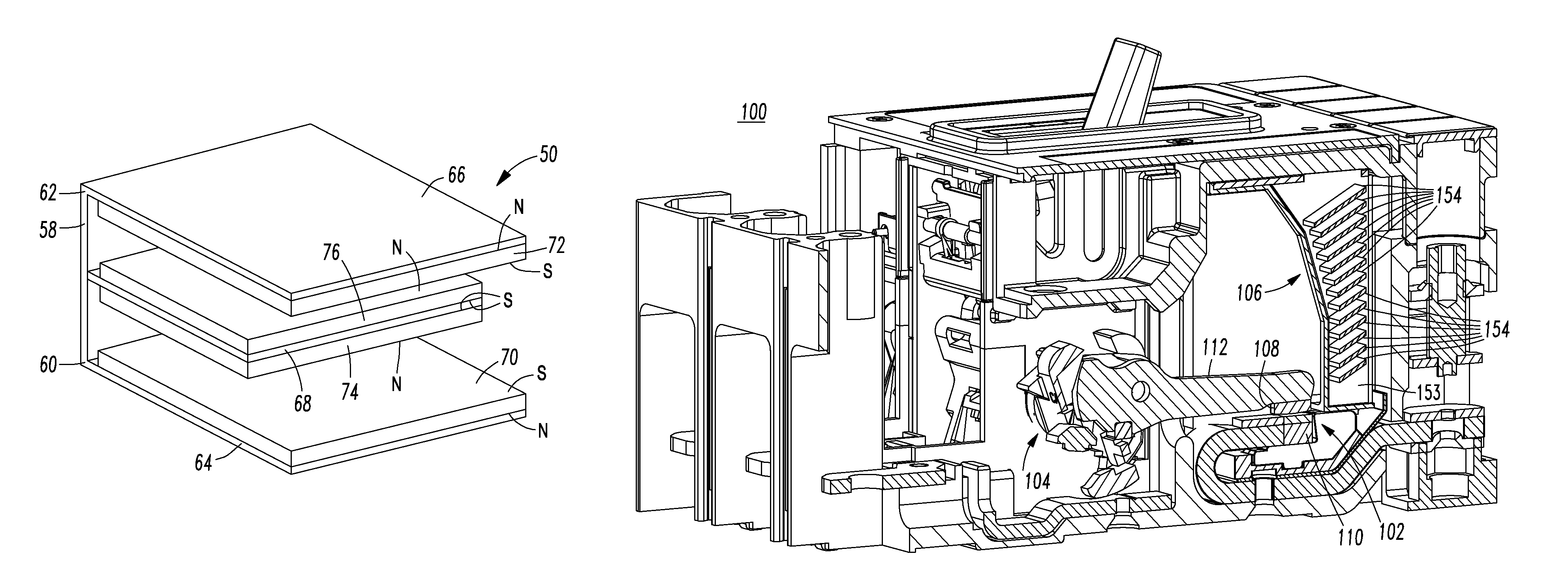
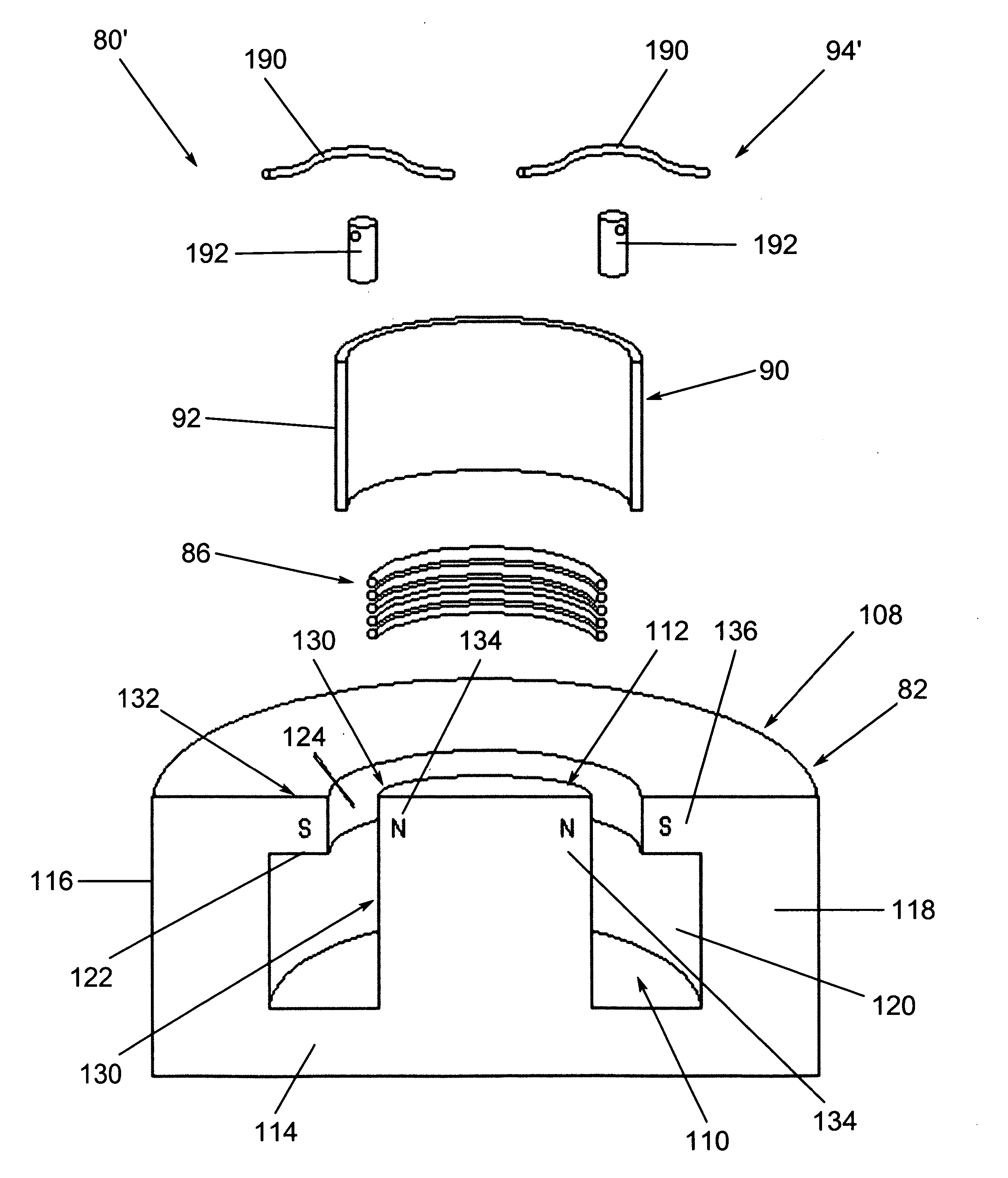
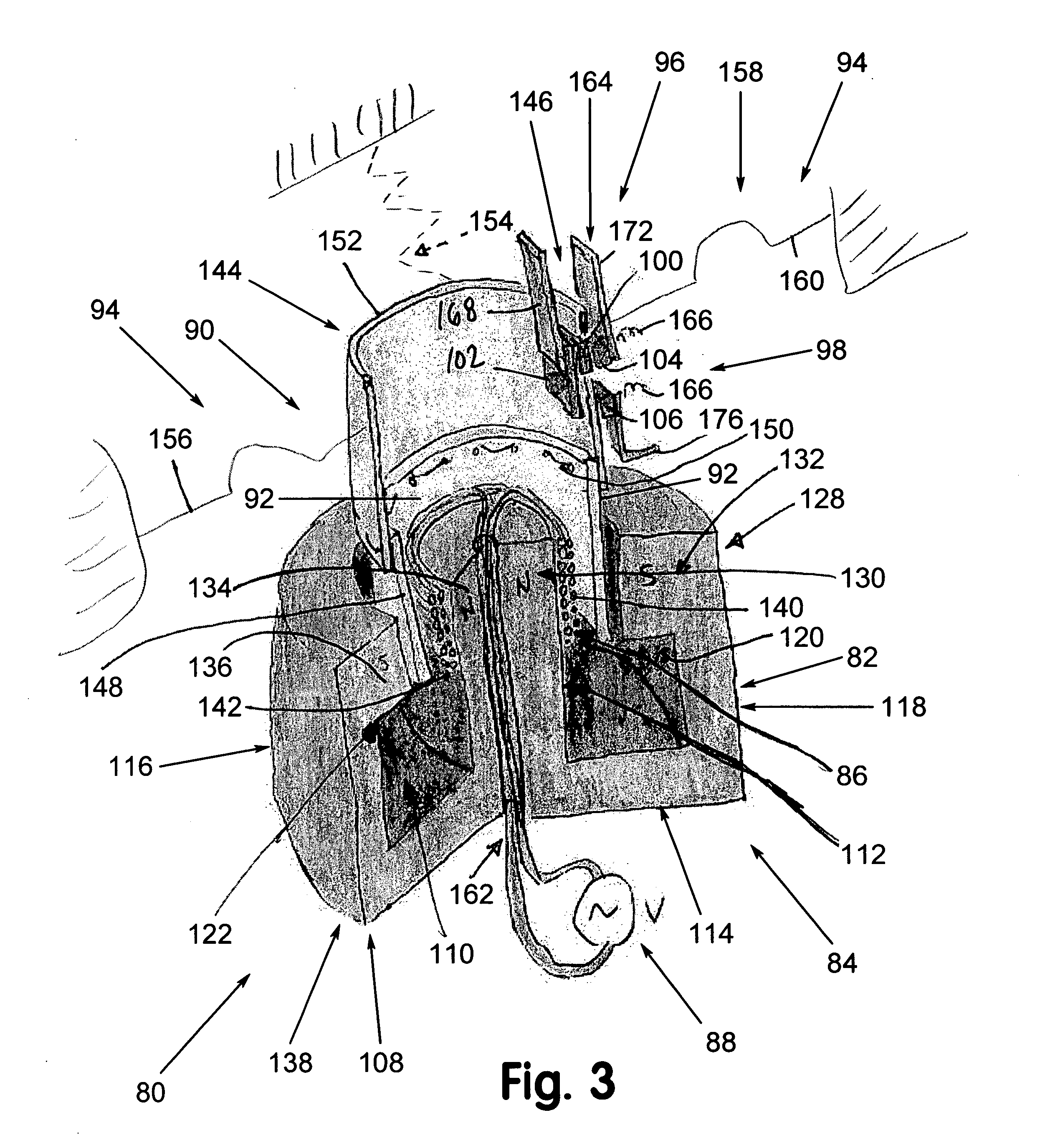
Single direct current arc chamber, and bi-directional direct current electrical switching apparatus employing the same
A single direct current arc chamber includes a ferromagnetic base having first and opposite second ends, a first ferromagnetic side member disposed from the first end, a second ferromagnetic side member disposed from the opposite second end, a third ferromagnetic member disposed from the ferromagnetic base intermediate the ferromagnetic side members, a first permanent magnet having a first magnetic polarity disposed on the first ferromagnetic side member and facing the third ferromagnetic member, and a second permanent magnet having the first magnetic polarity disposed on the second ferromagnetic side member and facing the third ferromagnetic member.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Assemblies including extendable, reactive charge-containing actuator devices
InactiveUS7063019B2Maximal work performanceAvoid breakingIncandescent ignitionPyrotechnical actuatorsElectricityActuator
An assembly including a support housing and an actuator device. The actuator device includes an extendable initiator cup including at least one non-random fold and at least in part defining a storage chamber containing a reactive charge reactable to produce reaction products. The extendable initiator cup longitudinally extends from a first length to a second, greater length upon reaction initiation of the reactive charge. The extendable initiator cup is at least partially disposed within a longitudinally extending bore of the support housing. The support housing is effective to limit lateral expansion of the extendable initiator cup upon reaction initiation of the reactive charge. The assembly can include an electrical conductive member or an electrical switch. The extendable initiator cup can extend to sever the electrical conductive member or disengage the electrical switch, thereby interrupting the conduction of electricity through an electrical system. Alternatively, the extendable initiator cup can extend to engage the electrical switch thereby allowing the conduction of electricity through an electrical system.
Owner:AUTOLIV ASP INC
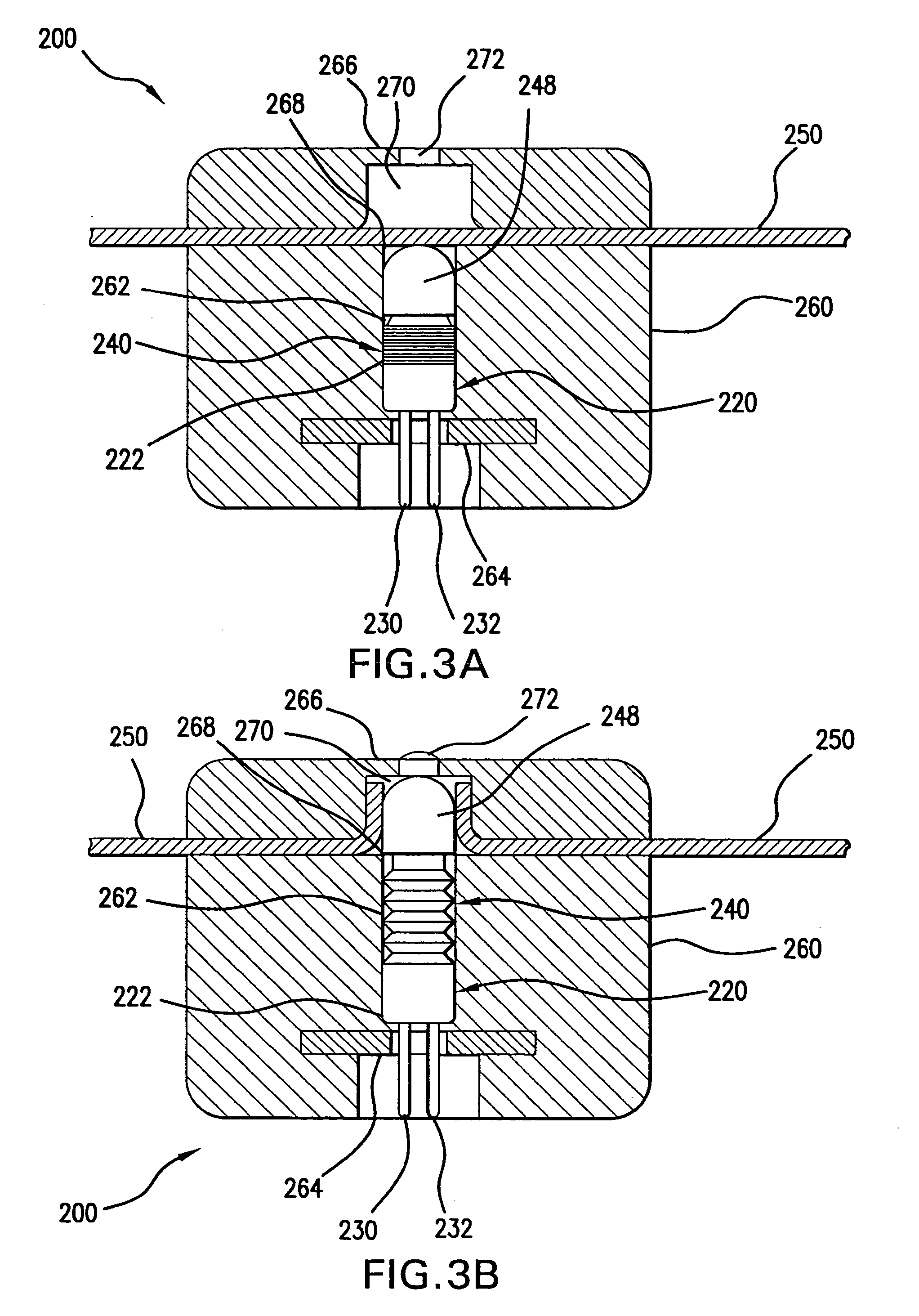
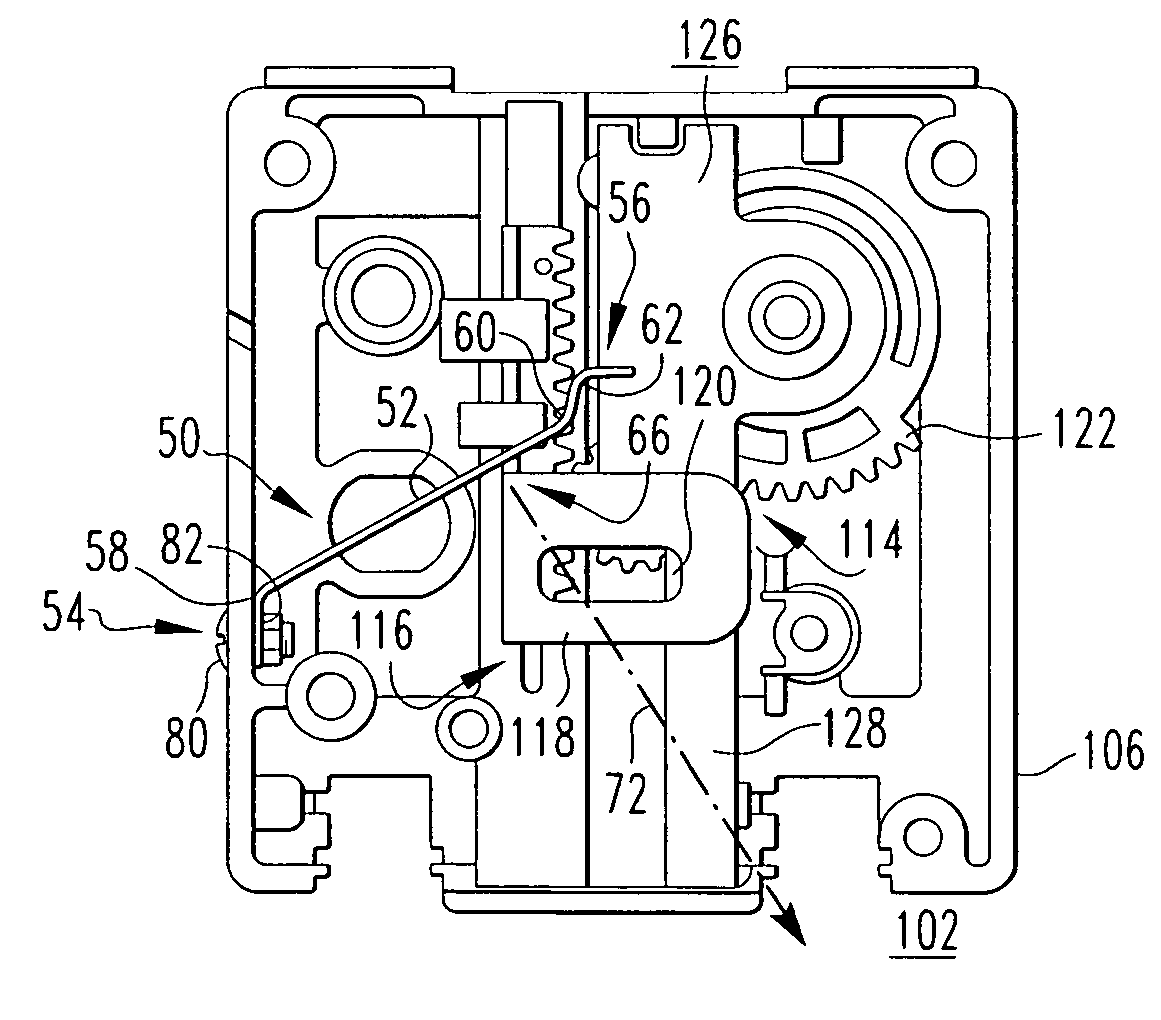
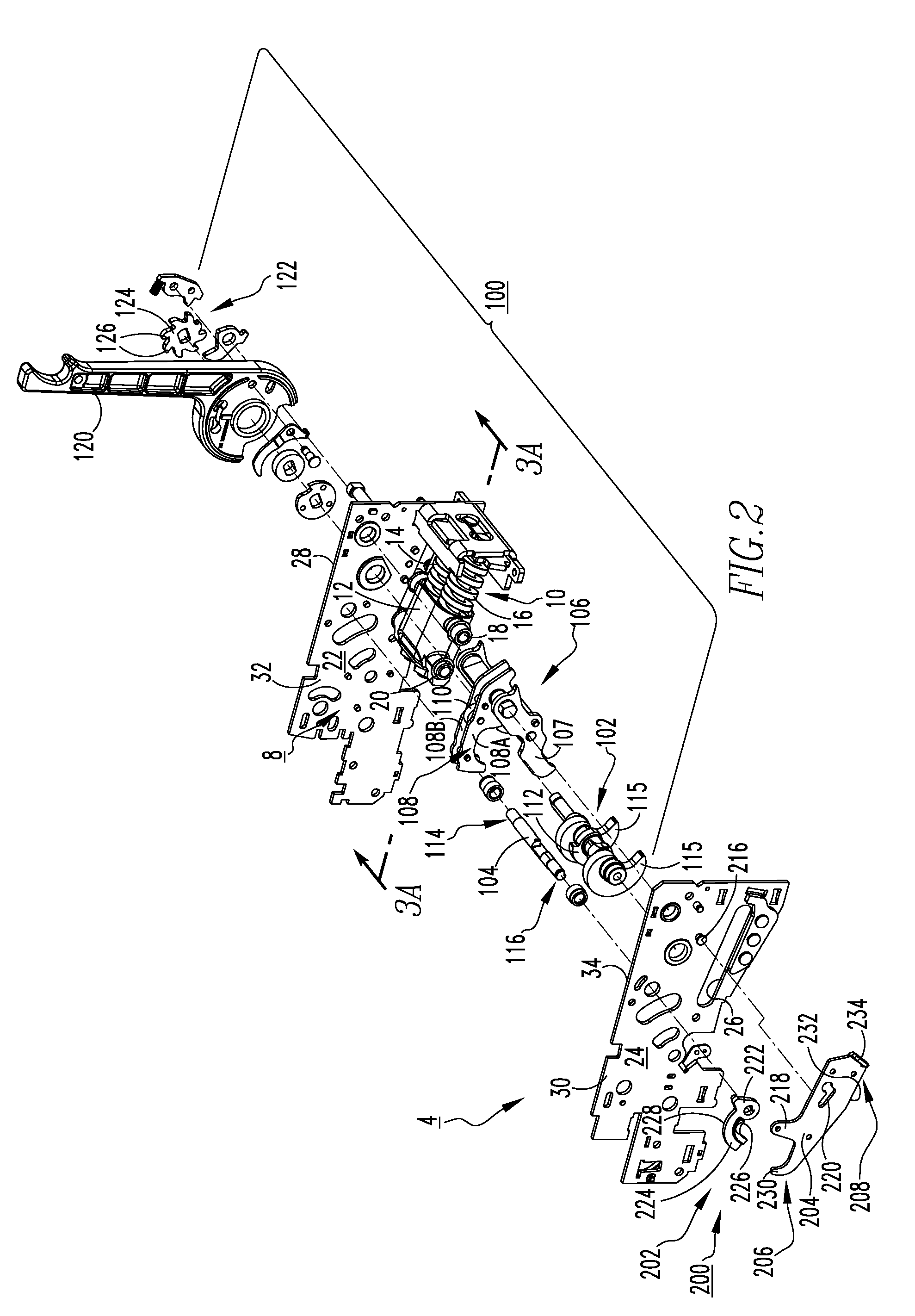
Handle attachment, assist mechanism therefor, and electrical switching apparatus employing the same
ActiveUS7186933B2Promote sportsSufficient energyControlling membersSwitchgear with withdrawable carriageWave shapeEngineering
An assist mechanism is for a handle attachment of a circuit breaker having a housing with an operating member operable among a plurality of positions. The handle attachment includes a casing coupled to the circuit breaker housing and enclosing an actuating assembly which interconnects the circuit breaker operating member with a handle that is operable from the exterior of the casing. The assist mechanism is a wave spring having a first end coupled to the casing, and a second end having a wave bend that divides the second end into three sections having three corresponding tangential vector forces. The tangential vector forces provide a bias to the actuating assembly of the handle attachment that differs depending on the position of the circuit breaker operating member. In this manner, the assist mechanism augments energy generated by movement of the operating member and translates it into a corresponding handle attachment movement.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Intelligent electrical switching device
InactiveUS6952084B2Simple and cheap to manufactureMore reliableElectric circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical batteryBiological activation
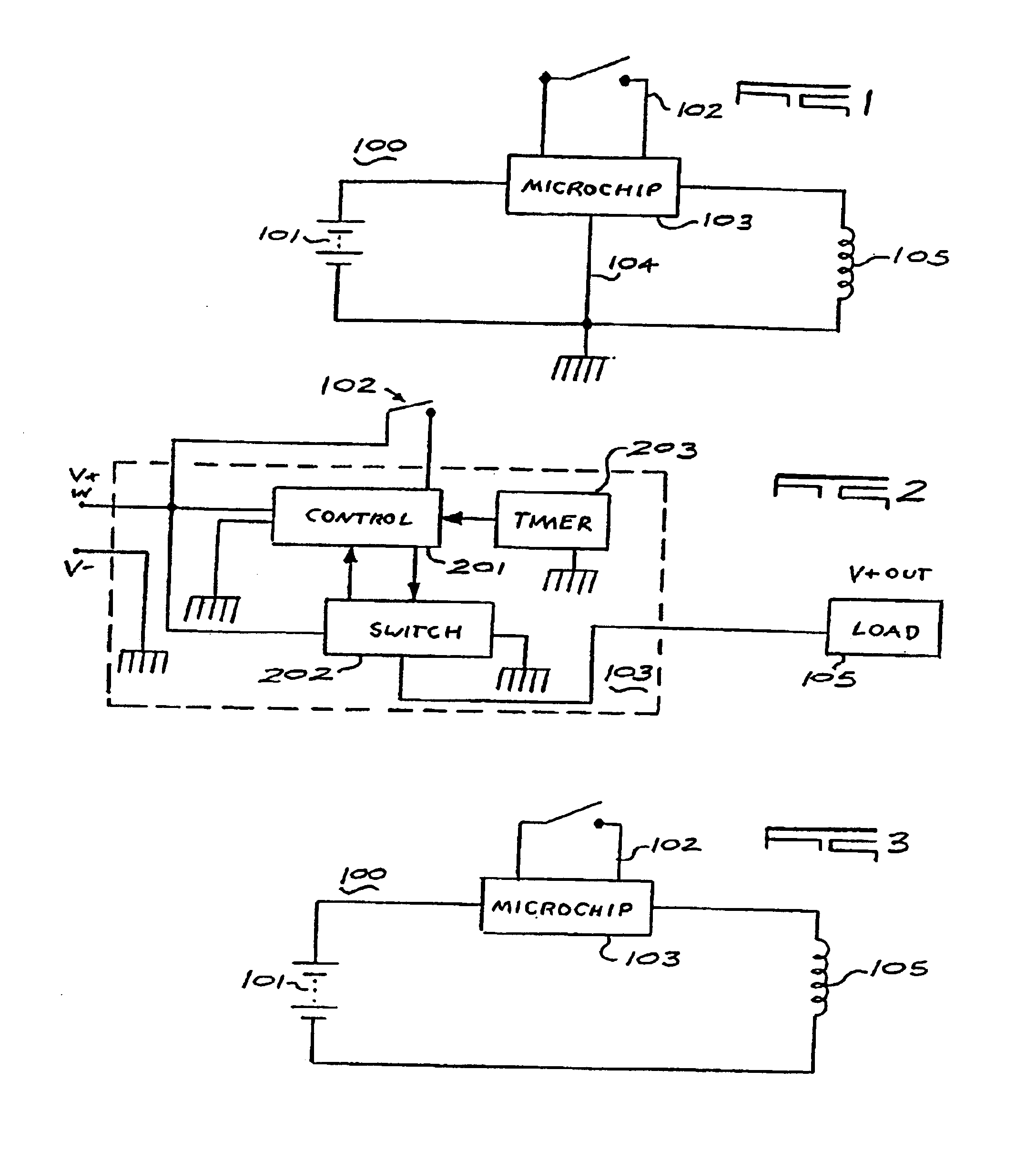
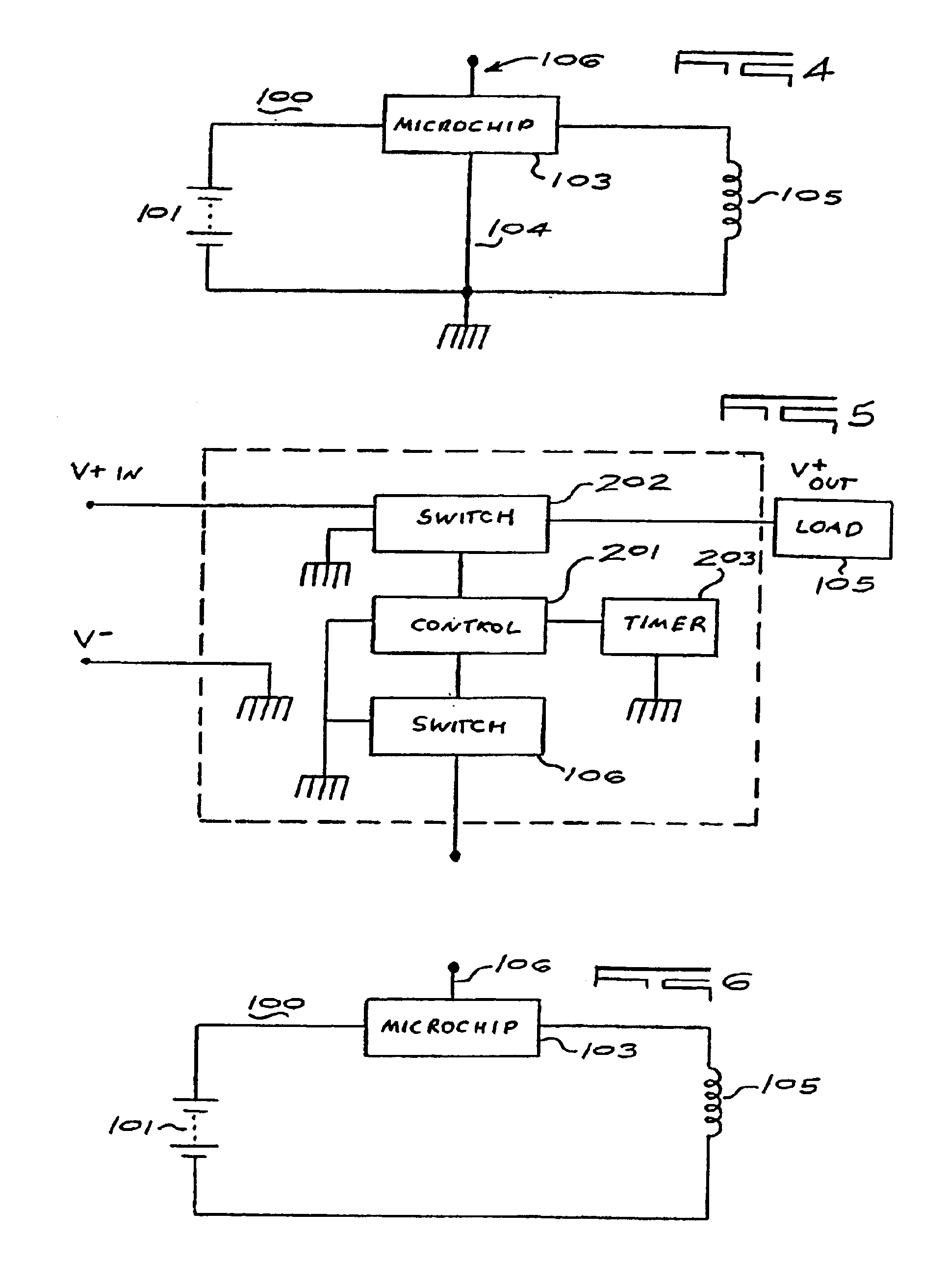
The present invention, according to a preferred embodiment, is directed to portable electronic devices which operate on exhaustible power sources, for example, batteries. The electronic devices of the present invention comprise at least one signal switch and a microchip in communication with the switch wherein the switch is only capable of transmitting a signal to the microchip that the switch has been activated or deactivated. The microchip is in communication with the exhaustible power source of the electronic device and controls (i) the power on / off function of the device, (ii) at least one other function of the device in response to activation and deactivation signals from the switch, and (iii) an automatic shut off function in response to the receipt of an activation signal from the switch.
Owner:AZOTEQ PTY LTD +1
Self-contained illumination device for medicine containers
A self-contained illumination device for illuminating medicine container labels in low-light level conditions is provided. The illumination means includes a light source component for illumination, an electrical switch component to control the light source, supporting circuitry components to energize the light source, and a housing structure for supporting and enclosing the components, directing the illumination to the label, and coupling the illumination device to a medicine container receptacle or a conventional medicine container cap.
Owner:LABEL-LITE LLC
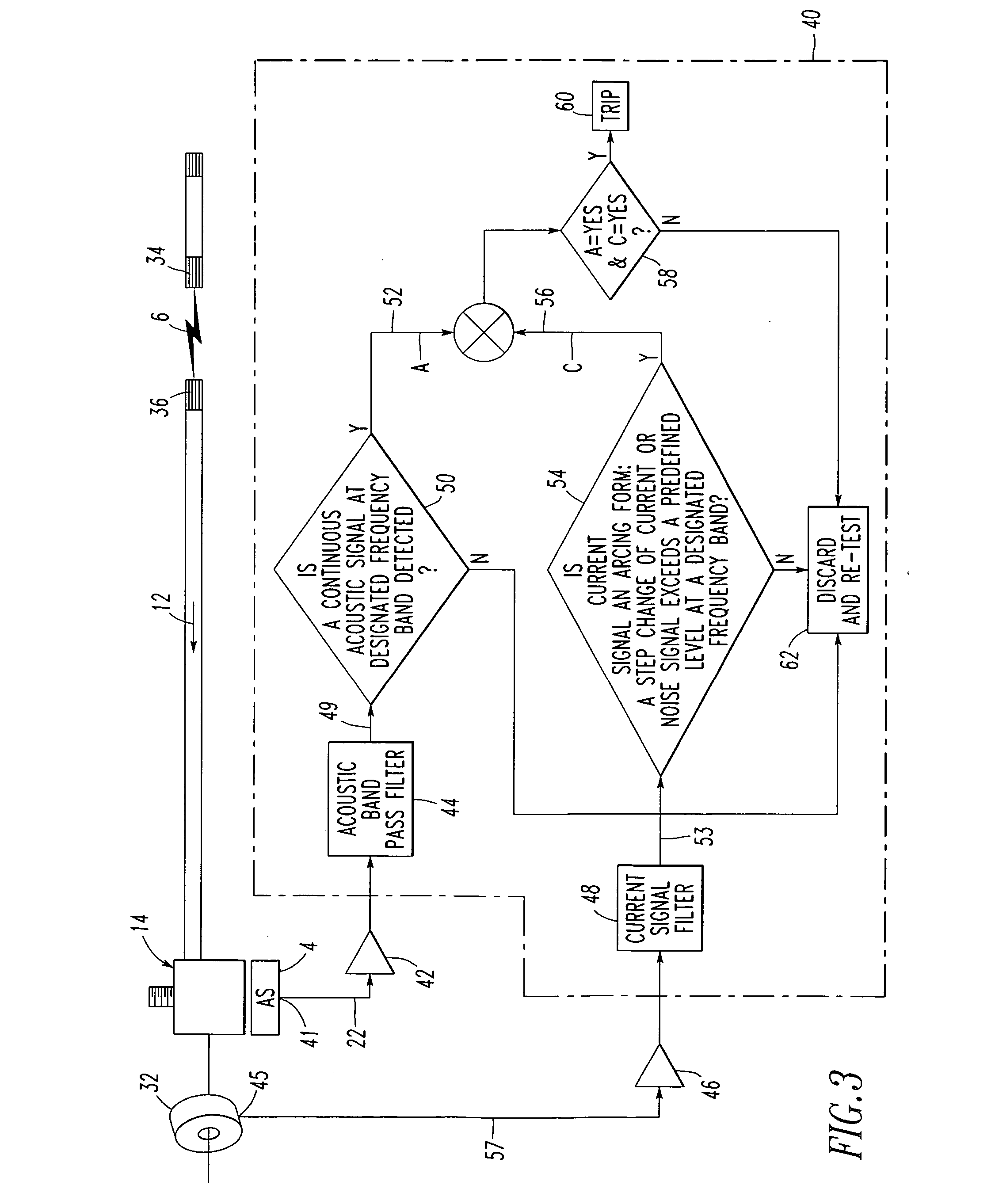
Electrical switching apparatus and method employing acoustic and current signals to distinguish between parallel and series arc faults
ActiveUS7403129B2Electronic circuit testingEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectricityHemt circuits
A circuit breaker includes a first lug and second and third acoustic lugs electrically connected to a power circuit. Separable contacts are electrically connected in series between the first lug and the second acoustic lug. An operating mechanism opens and closes the separable contacts. A first acoustic sensor is coupled to the second acoustic lug and senses a first acoustic signal from the second acoustic lug. A second acoustic sensor is coupled to the third acoustic lug and senses a second acoustic signal from the third acoustic lug. The first and second acoustic signals are operatively associated with a power circuit fault. A current sensor senses a current flowing between the first and second lugs. A circuit inputs the sensed acoustic signals and the sensed current and detects and distinguishes a parallel arc fault or a series arc fault from the sensed acoustic signals and the sensed current.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
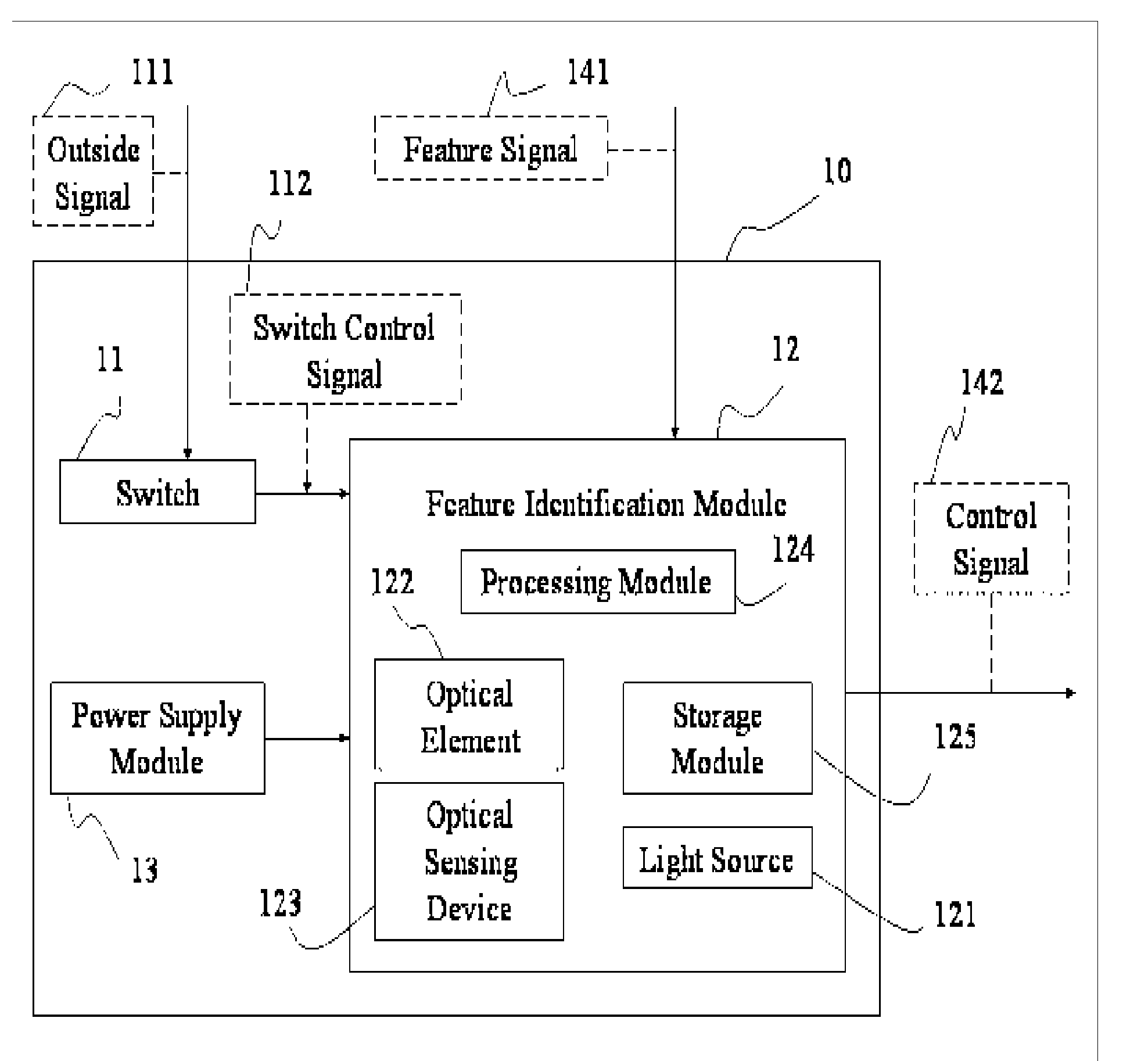
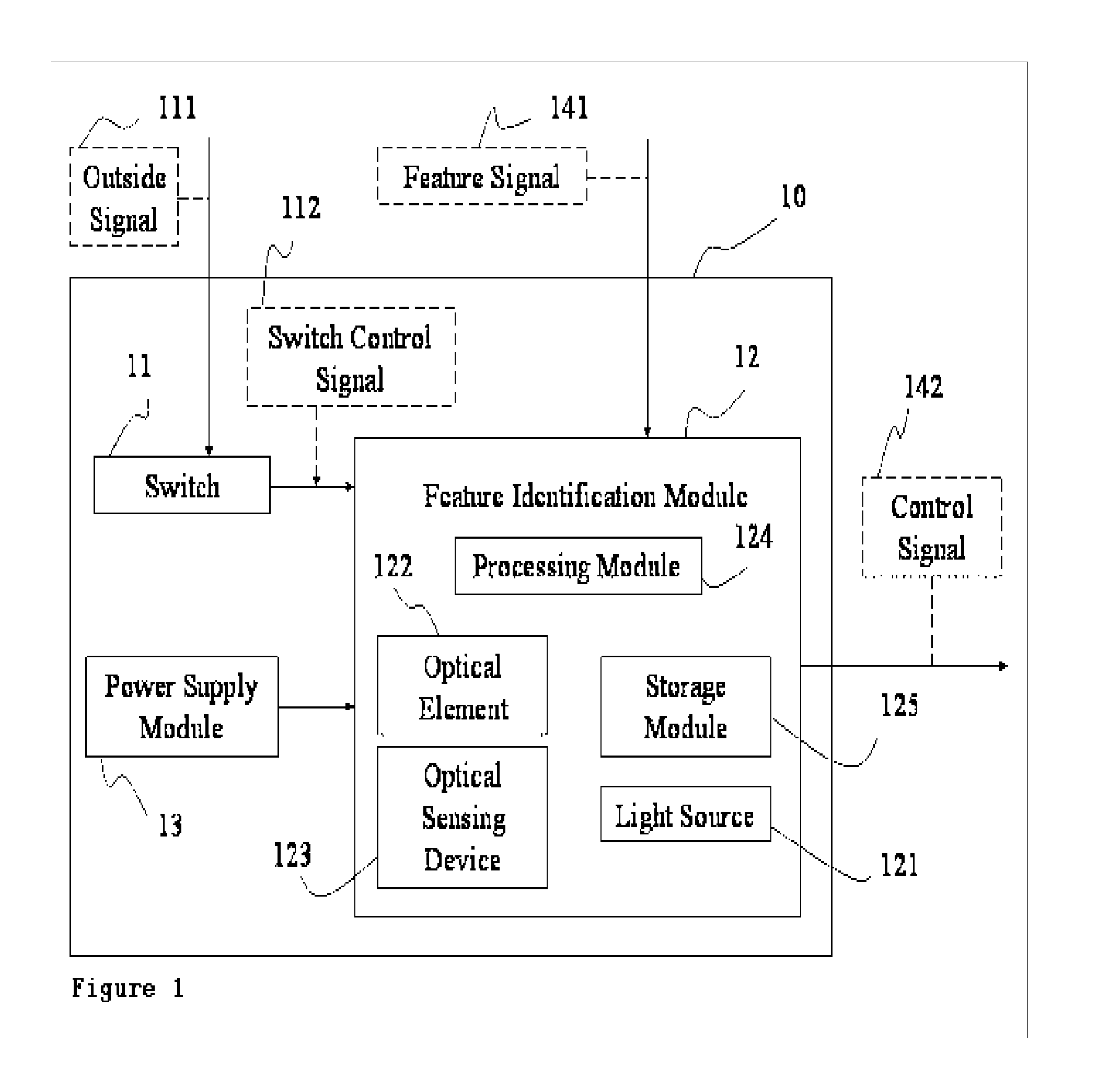
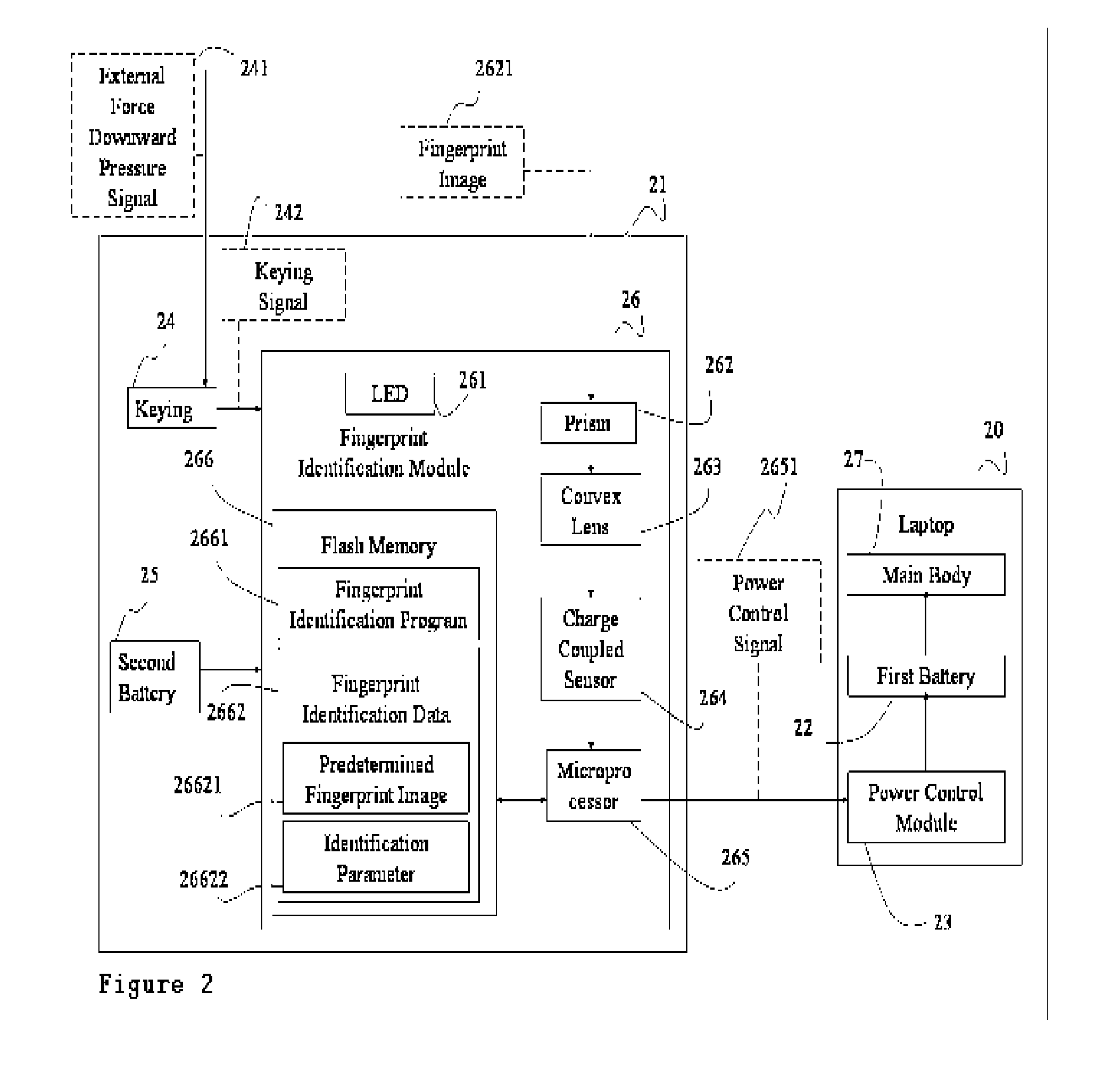
Electrical Switch Device with Feature Identification and Method
InactiveUS20070160269A1Improve securityImprove convenienceElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisElectricityControl signal
An electrical switch device with feature identification and a method are applied for an electronic apparatus having a first power supply module. The electrical switch device comprises a switch, a feature identification module and a second power supply module. The second power supply module supplies power to the feature identification module. The switch generates a switch control signal based on an outside signal. The feature identification module is used to receive a feature signal and implements an identification action, then determines whether the first power supply module is activated based on the switch control signal and the identification result.
Owner:NANOGATE OPTOELECTRONICS ROBOT
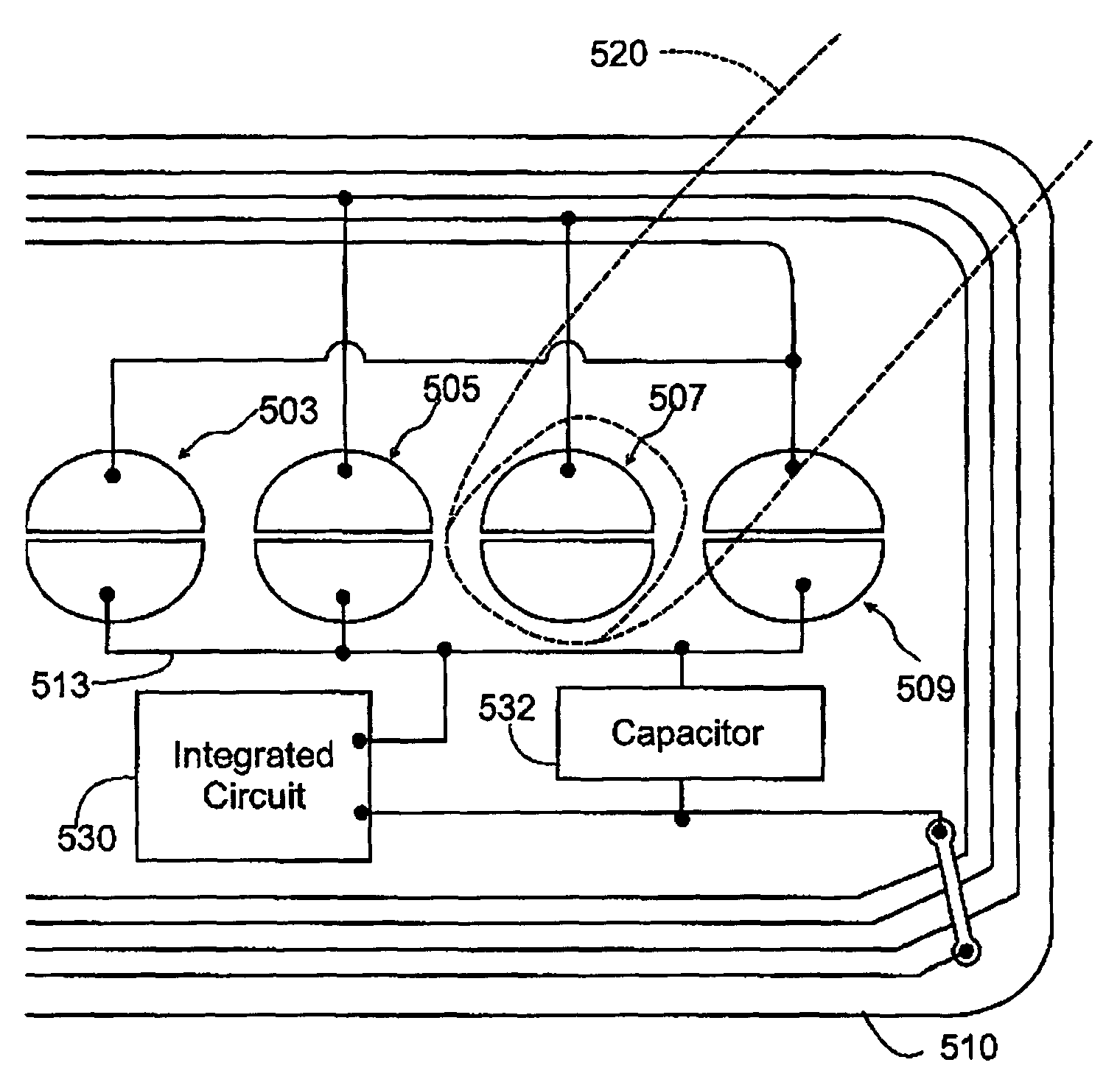
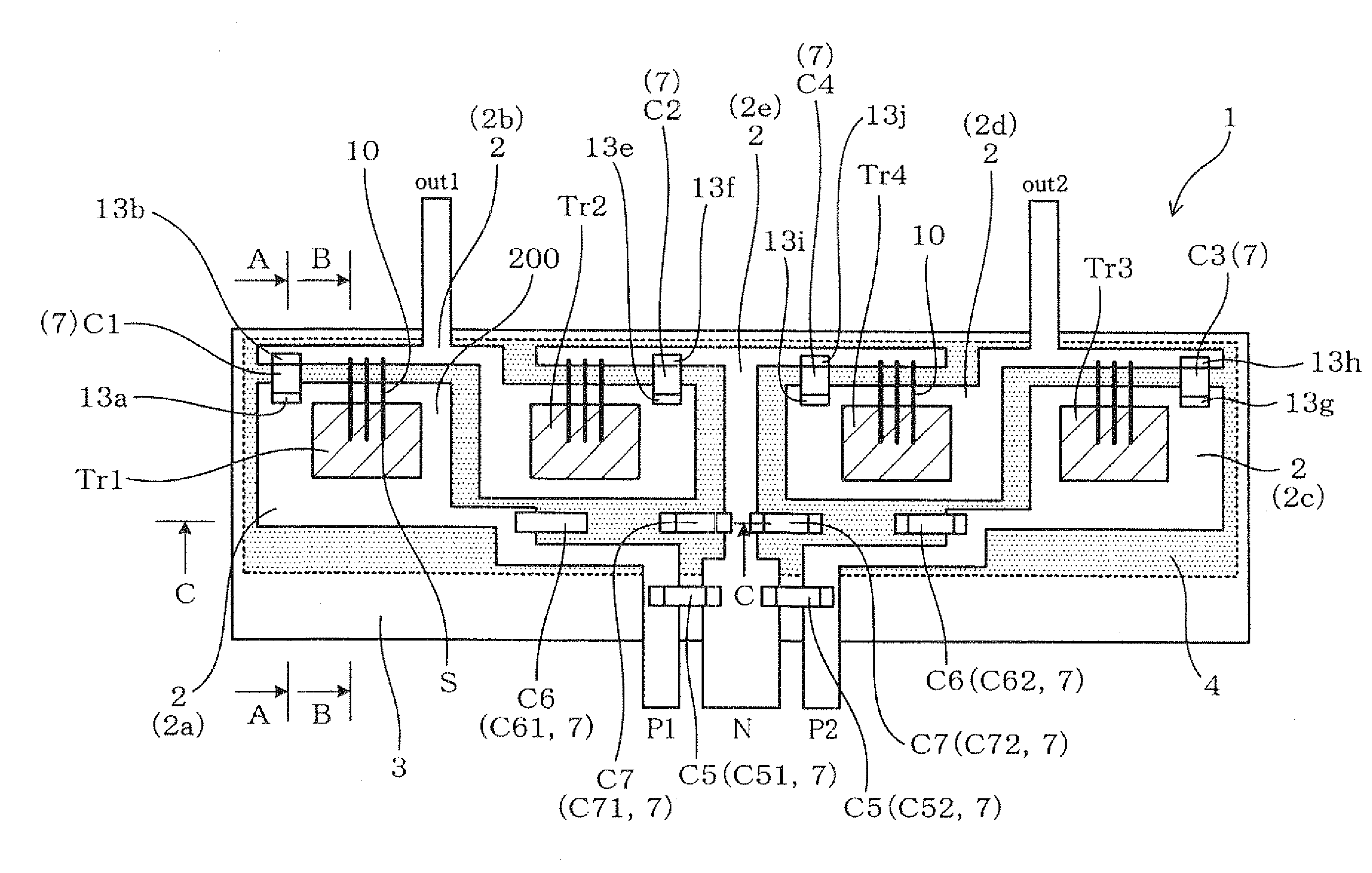
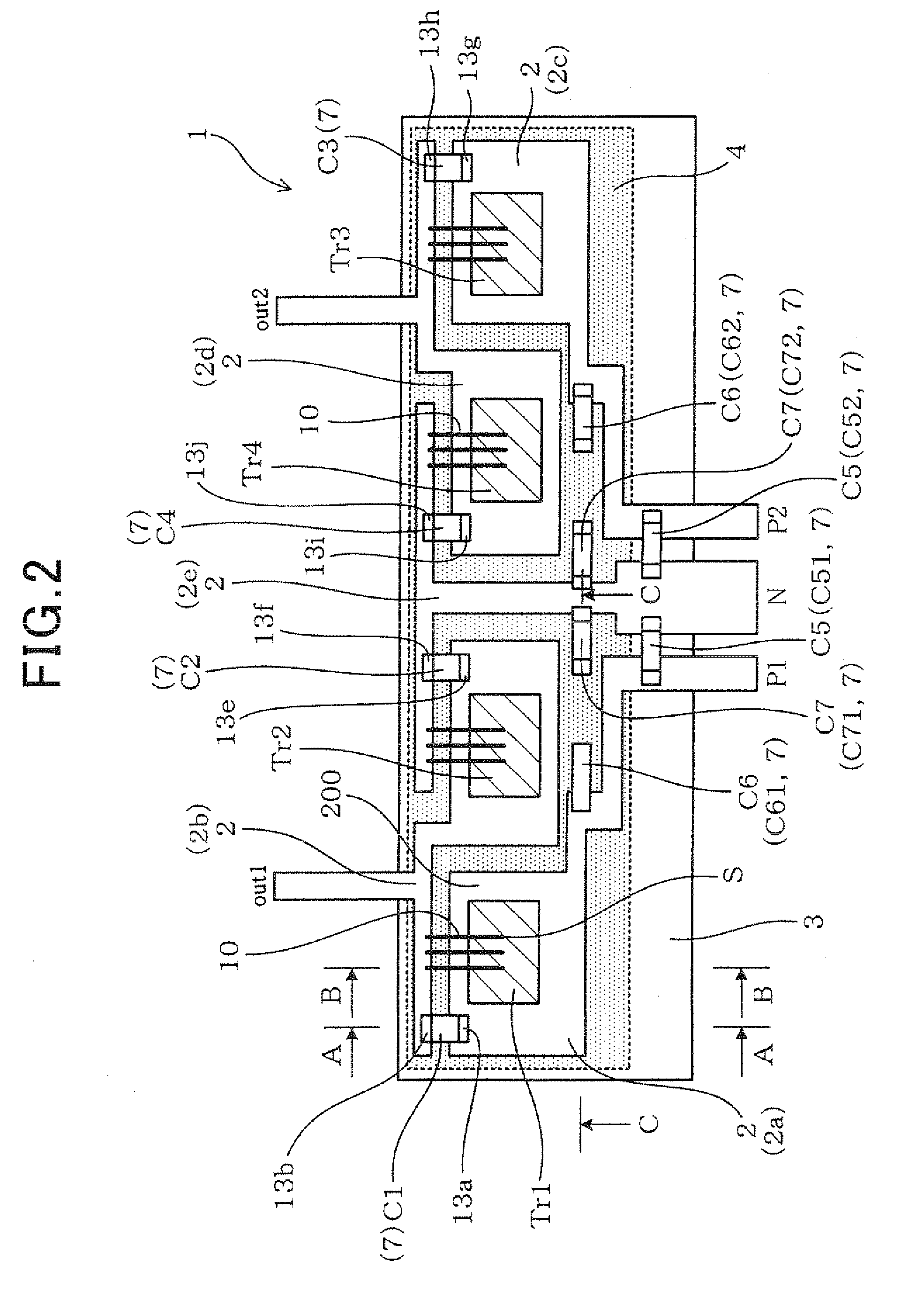
Semiconductor module with electrical switching elements
ActiveUS20110291236A1Inductance causedMoreSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityComputer module
A semiconductor module is provided which is capable of lowering surges caused when switching elements are switched on and off. The module has a plurality of lead frames, switching elements, electronic components, and a sealing member. The switching elements are electrically connected to the lead fames respectively. Part of the lead frames, the switching elements, and the electronic components are sealed by the sealing member. The electronic components are mounted on primary surfaces of the lead frames respectively.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for detecting insufficient contact pressure in a switching unit, device for implementing such a method, and switching unit including such a device
ActiveUS11211218B2Machine gearing/transmission testingSwitch power arrangementsContact pressureKinematic chain
A method for detecting insufficient contact pressure between two contacts of an electrical switching unit, including a device for resetting a mechanism for controlling the switching unit following a closure maneuver of the mechanism, the resetting device including a motor configured to complete the closure maneuver of the control mechanism. The method involves detecting whether the motor completes the closure and whether a resetting torque corresponds to a normal resetting torque, by analyzing an envelope curve of current consumed by the motor over time, and, if the motor completes the closure, deducing that a wear is a result of wear in the mechanism or a kinematic chain, and if the motor completes the closure and the resetting torque corresponds to an abnormal rescuing torque, deducing that the wear corresponds to wear in the motor or parts involved in compressing the closure spring.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Optically controlled electrical switching device based on wide bandgap semiconductors
InactiveUS20060054922A1Improve Power Control EfficiencyHigh-temperature operationMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsPower switchingEngineering
A power switching device includes an optically controlled component using a semiconducting carbon nanotube. An optical signal transmitted over an optical fiber controls the conductivity of the nanotube. The nanotube transmits a signal controlled by the optical signal to a wide-bandgap semiconductor power switch, which switches the power.
Owner:PETTIT JOHN W
Eddy current inductive drive electromechanical linear actuator and switching arrangement
ActiveUS20060061442A1Reliable and reliableSimple designContact mechanismsElectromagnetic relaysTransfer switchEngineering
The present invention is directed to an inductively driven electromagnetic linear actuator arrangement employing eddy currents induced by a fixed drive coil to drive its armature. Eddy current focusing fields are employed to direct the eddy currents using Lorentz forces to maximize armature speed. The armature includes a shorted driven coil in a DC magnetic field. This can be supplied by a permanent magnet. When current is applied, a force is felt by the coil in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. Such an actuator is well suited for electrical switching applications including transfer switching applications, circuit breaker applications, and ground fault interrupter applications.
Owner:POWERPATH TECH INC
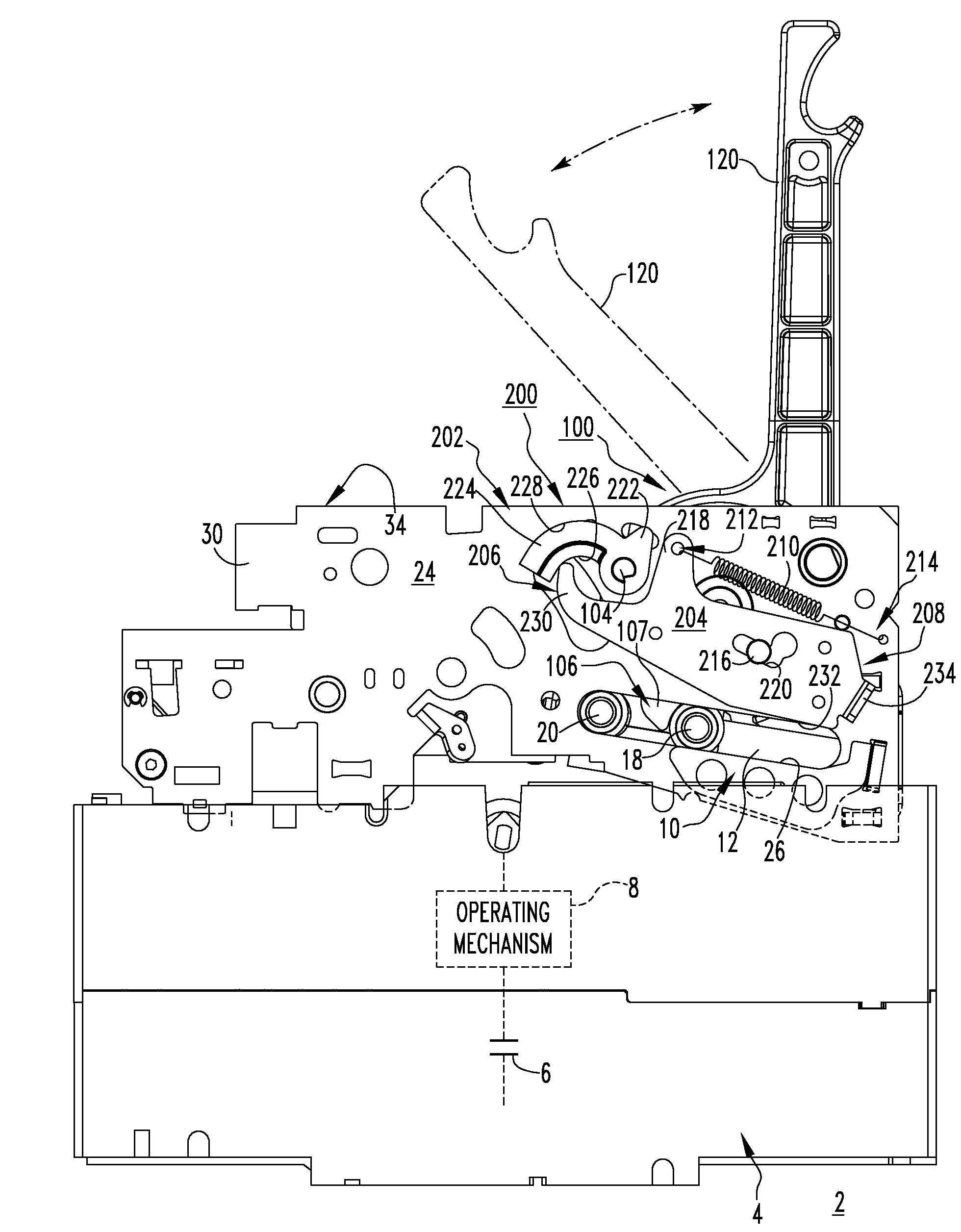
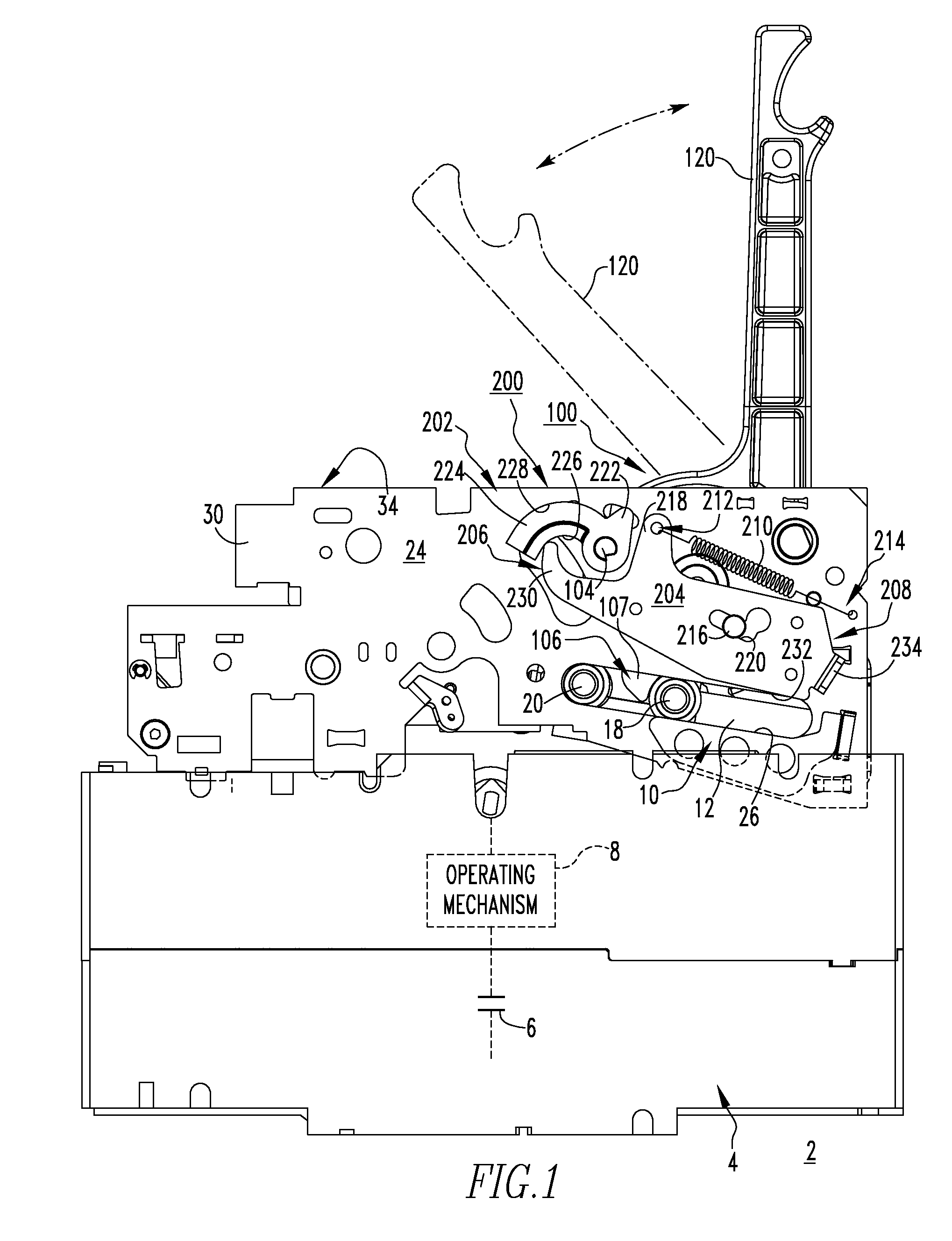
Electrical switching apparatus, and charging assembly and interlock assembly therefor
An interlock assembly is provided for a circuit breaker charging assembly. The charging assembly includes a cam shaft, a latch mechanism, such as a D-shaft, a latch assembly, and a charging handle. The charging handle pivots the cam shaft. The D-shaft is pivotable between first and second positions corresponding to the D-shaft latching and unlatching the latch assembly, respectively. The interlock assembly includes a lever coupled to and pivotable with the D-shaft, and a latch interlock pivotably coupled to the circuit breaker housing. The latch interlock moves between locked and unlocked positions corresponding respectively to the first end of the latch interlock moving the lever to position the D-shaft in the second position and the first position. Unless and until the stored energy mechanism is substantially fully charged, the latch interlock is disposed in the locked position and the latch assembly is movable with respect to the D-shaft.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
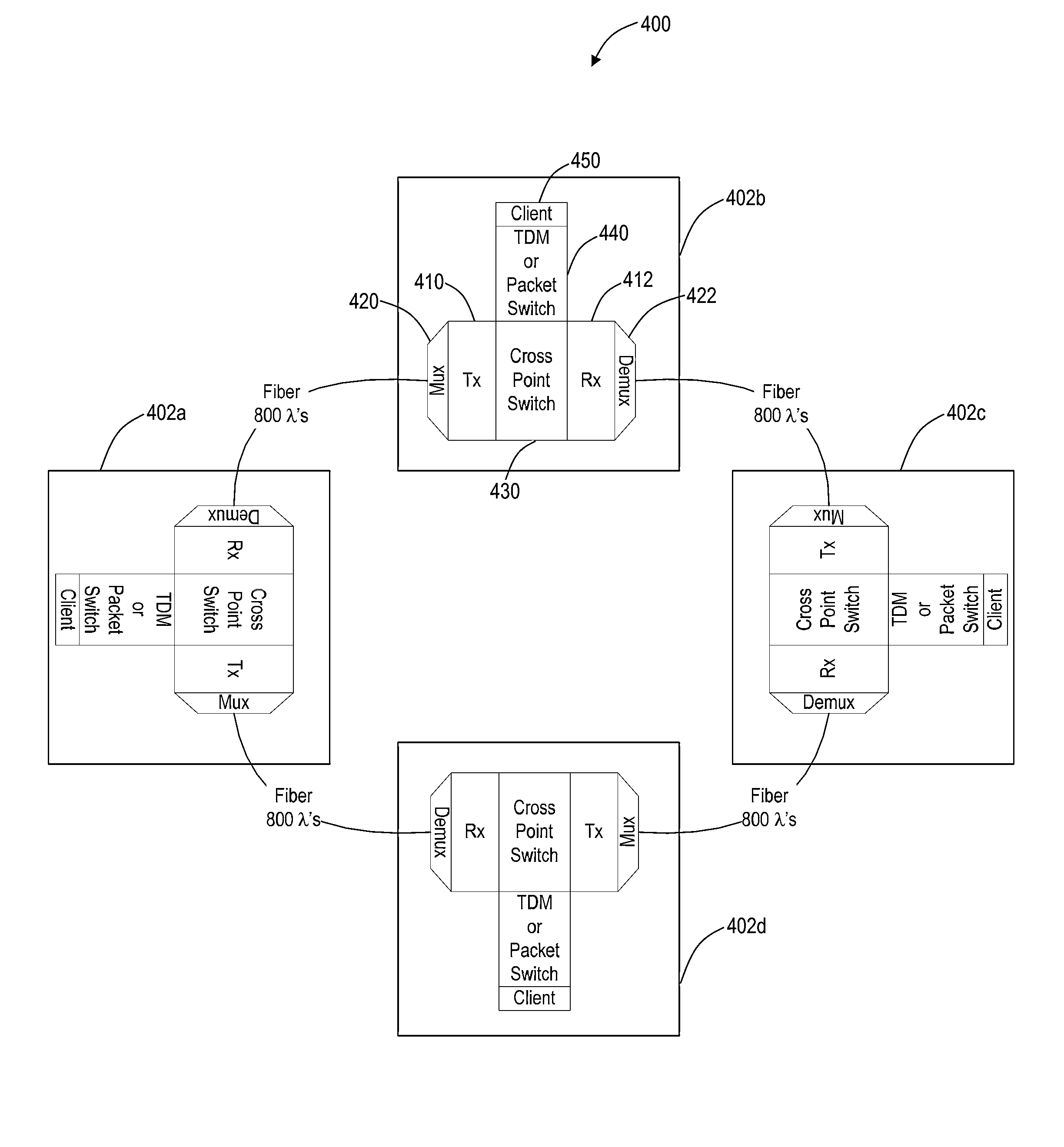
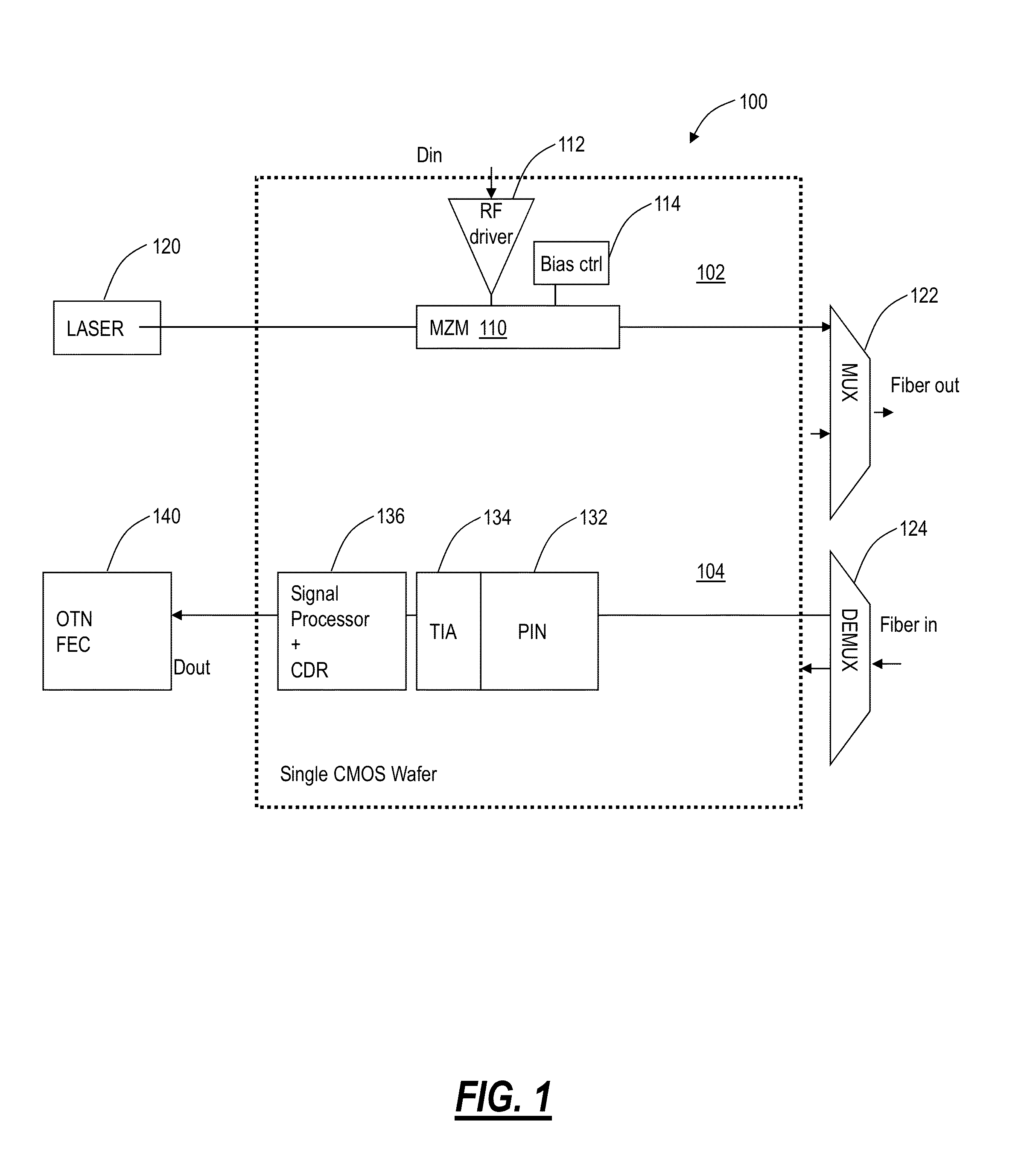
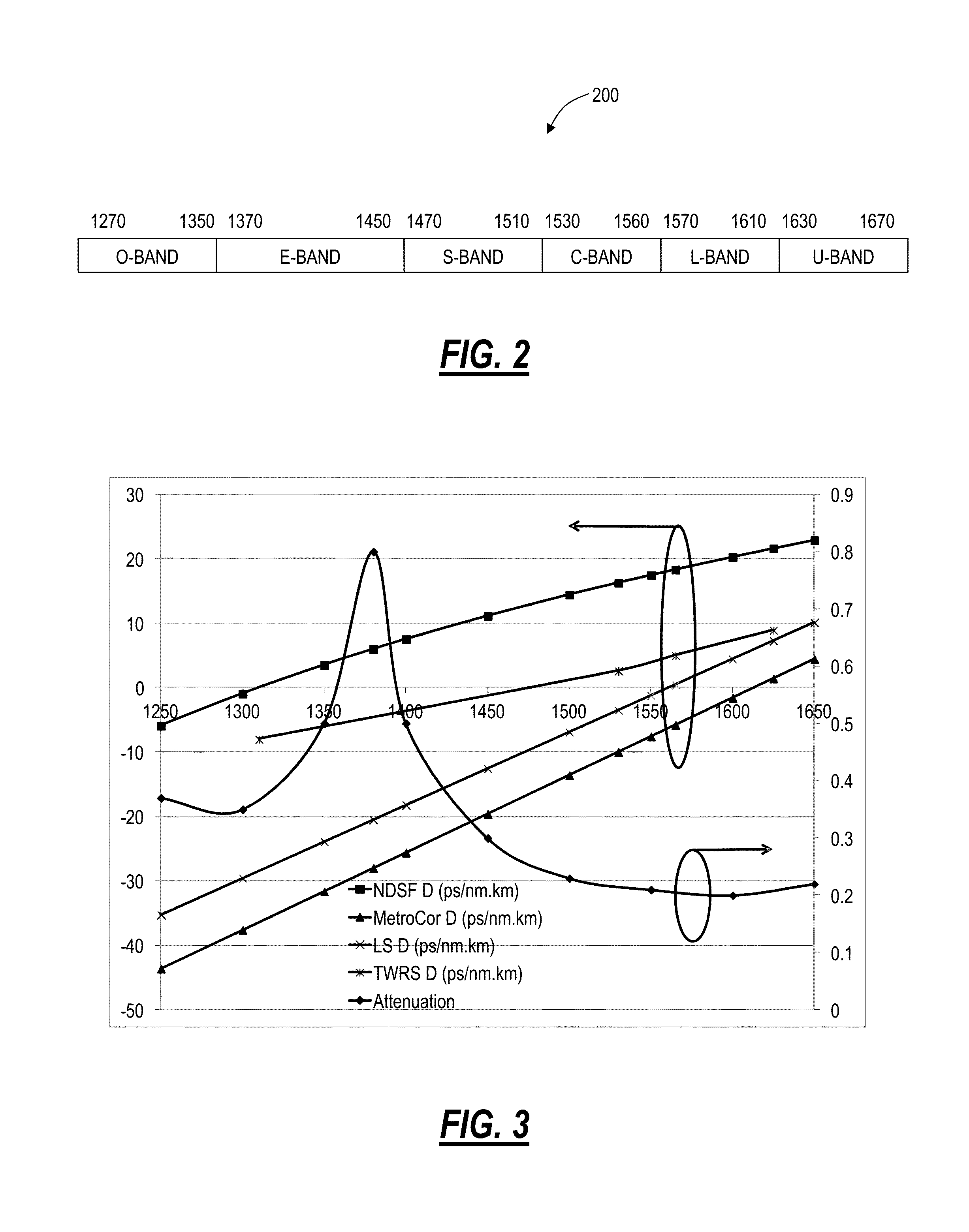
High capacity fiber-optic integrated transmission and switching systems
A reconfigurable electrical add / drop multiplexing node, a network, and optoelectronic integrated circuit form a novel high capacity fiber-optic integrated transmission and switching system with a baseline target capacity in excess of 1 Tbps. The node, network, and circuit can leverage optoelectronic integration of transmission and switching components along with using the full “transparency” window of modern optical fibers from about 1270 nm to about 1670 nm for a large number of relatively low-rate wavelengths. The electrical switching fabric can be part of a Reconfigurable Electrical Add / Drop Multiplexer (READM) with similar functionality as a Reconfigurable Optical Add / Drop Multiplexer (ROADM) except in a highly integrated fashion with the transmission components. The electrical switching fabric can implement flow switching on a composite signal to provide comparable functionality to optical components in electrical circuitry such as in Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductors.
Owner:CIENA
ARC baffle, and ARC chute assembly and electrical switching apparatus employing the same
An arc baffle for an arc chute assembly of a circuit breaker includes a first baffle member disposed at or about the second end of the arc chute assembly and including a plurality of first venting holes, a second baffle member including a plurality of second venting holes and being coupled to and disposed opposite from the first baffle member, and a filter assembly disposed at or about the second baffle member and including a number of filter elements. The first and second venting holes of the first and second baffle members are offset to induce turbulent flow of ionized gases being discharged from the arc chute assembly. The filter elements of the filter assembly filter the turbulent flow. An arc chute assembly and an electrical switching apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com