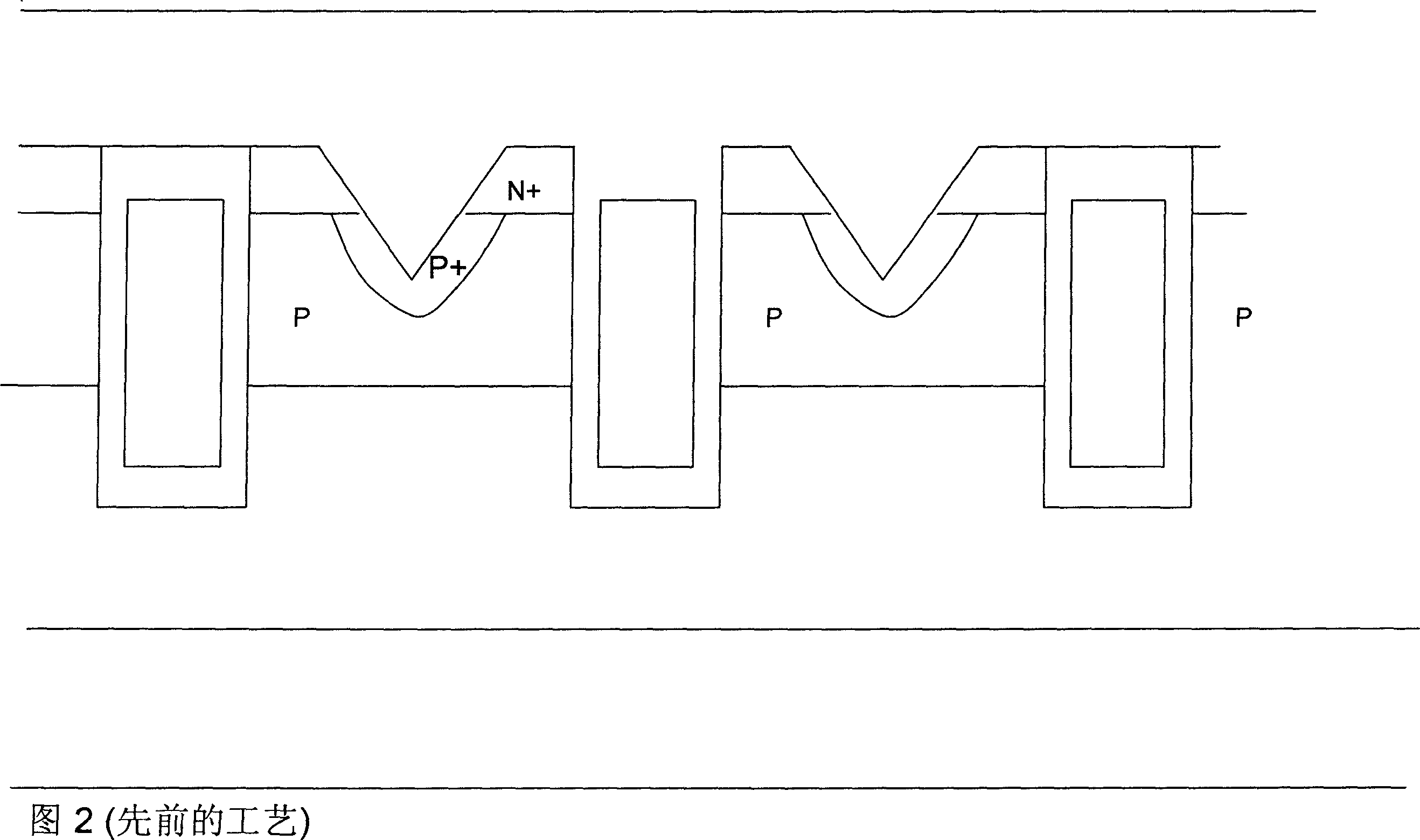Patents
Literature
349 results about "Ultra high density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
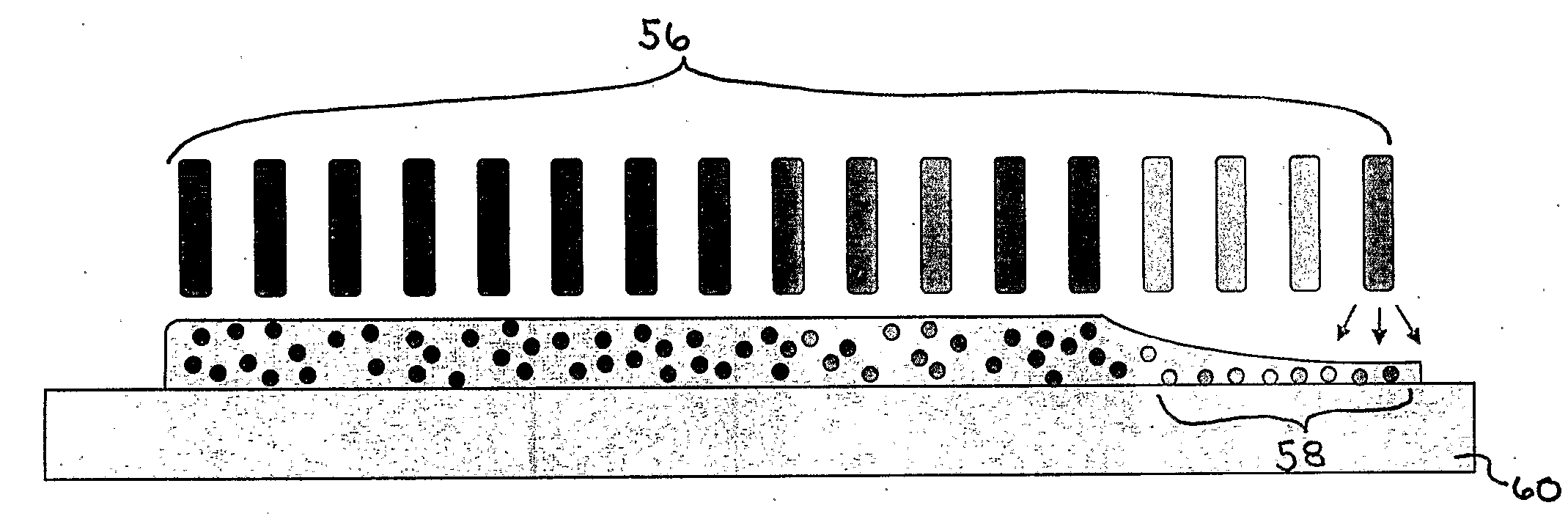
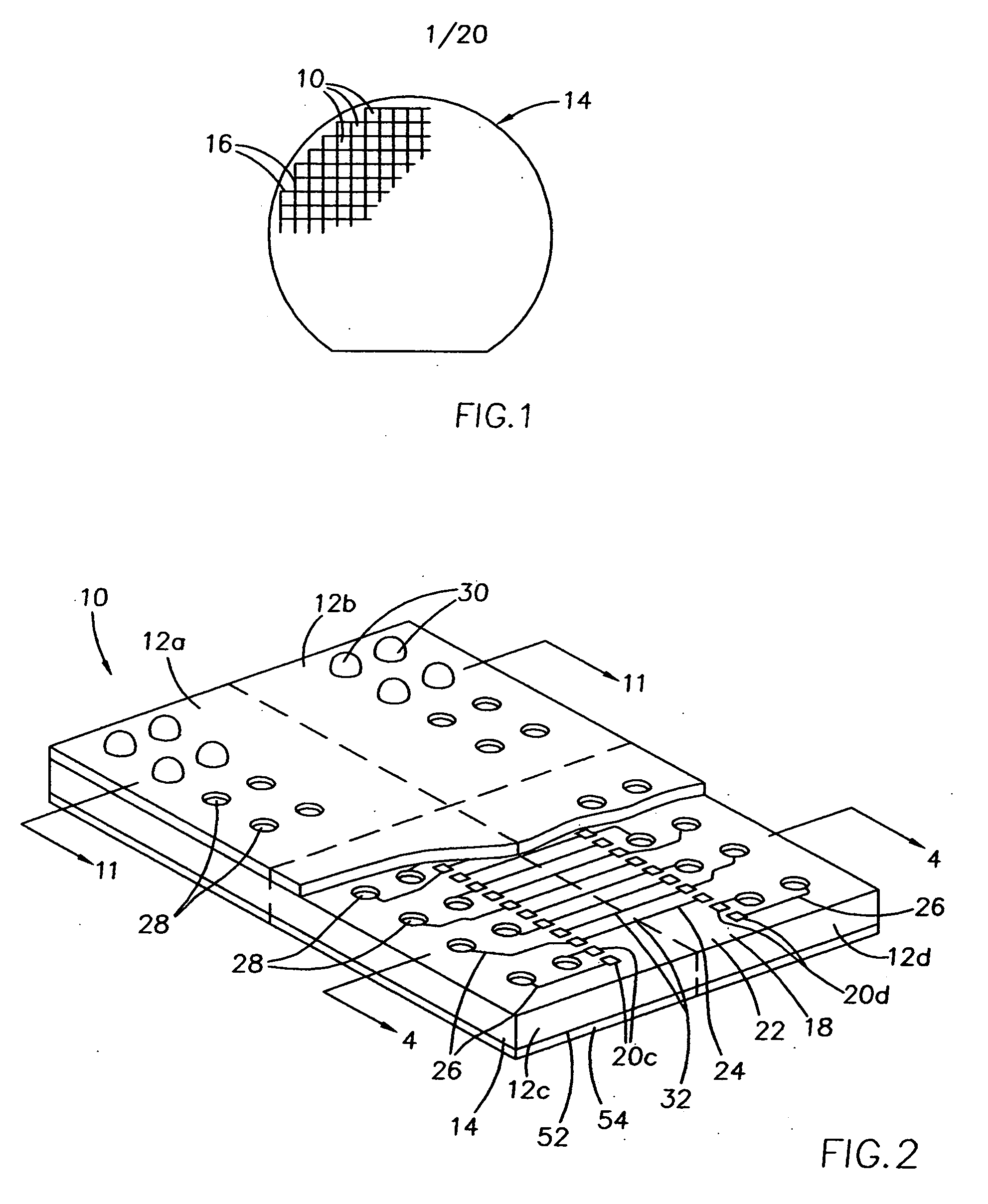
Ultra High Density Modules provides an interface between MPO Trunks and LC interface of active equipment. Pre-assembled MPO modules improve the speed of installation. Modules with external MPO ports can be easily connected to trunks or fanouts.
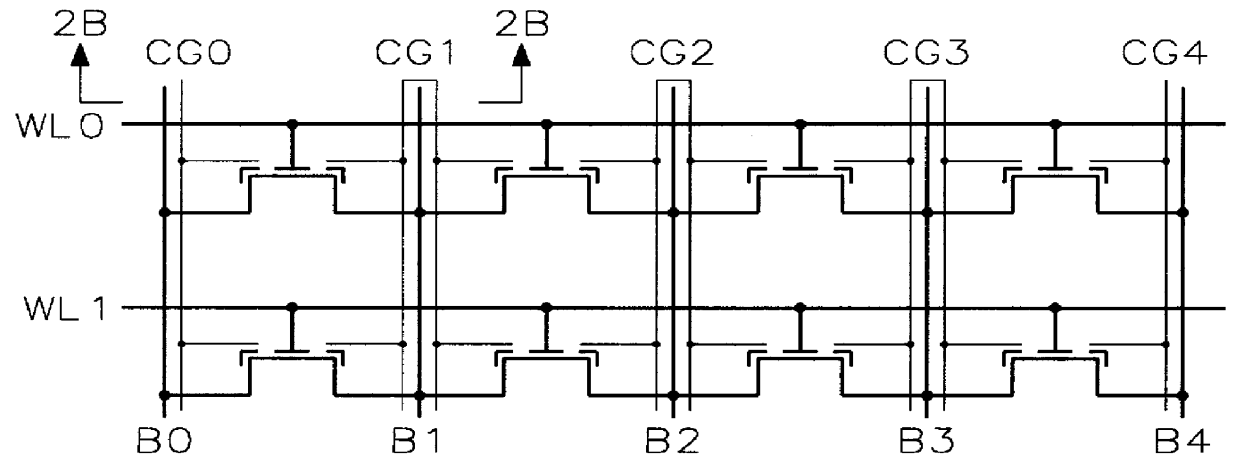
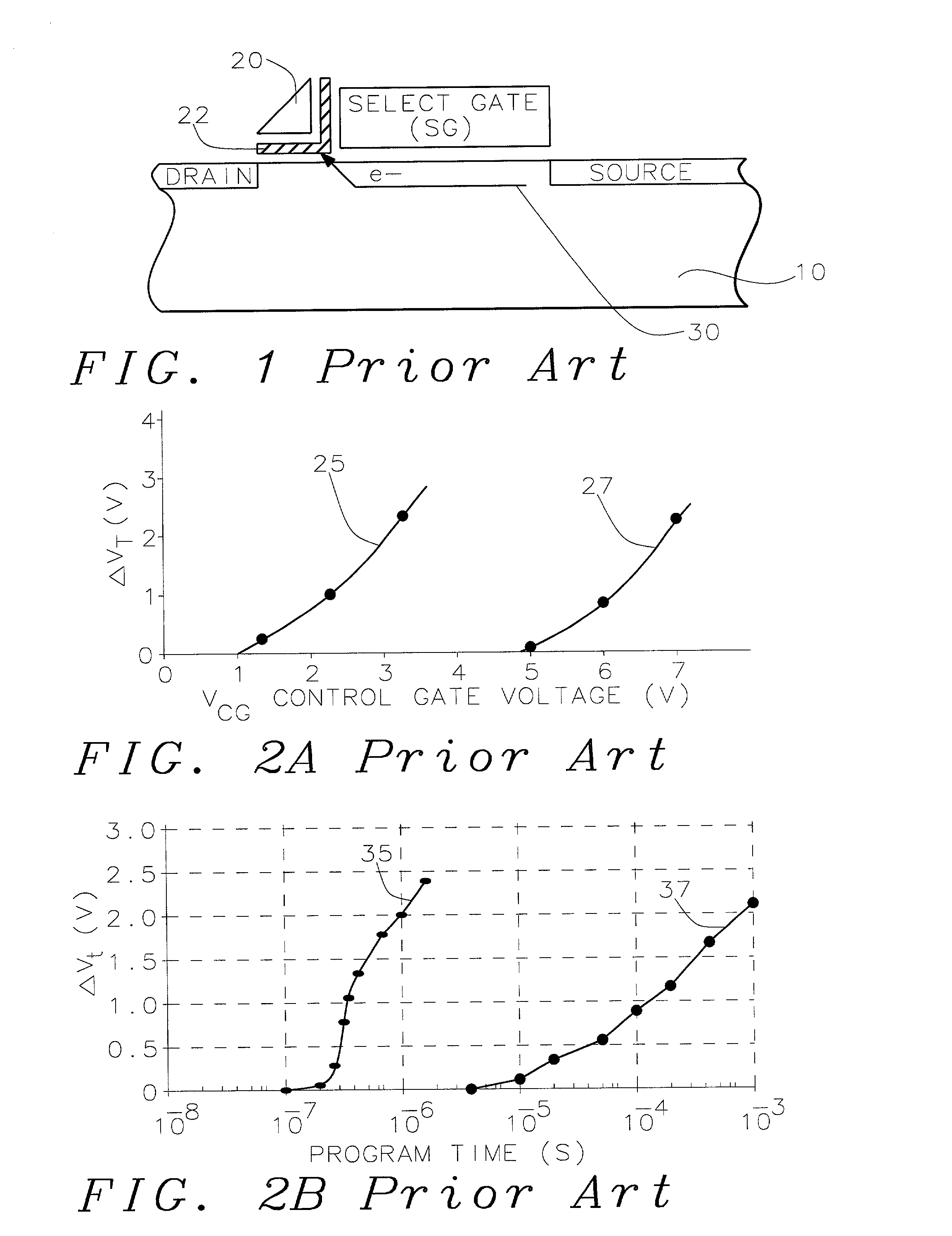
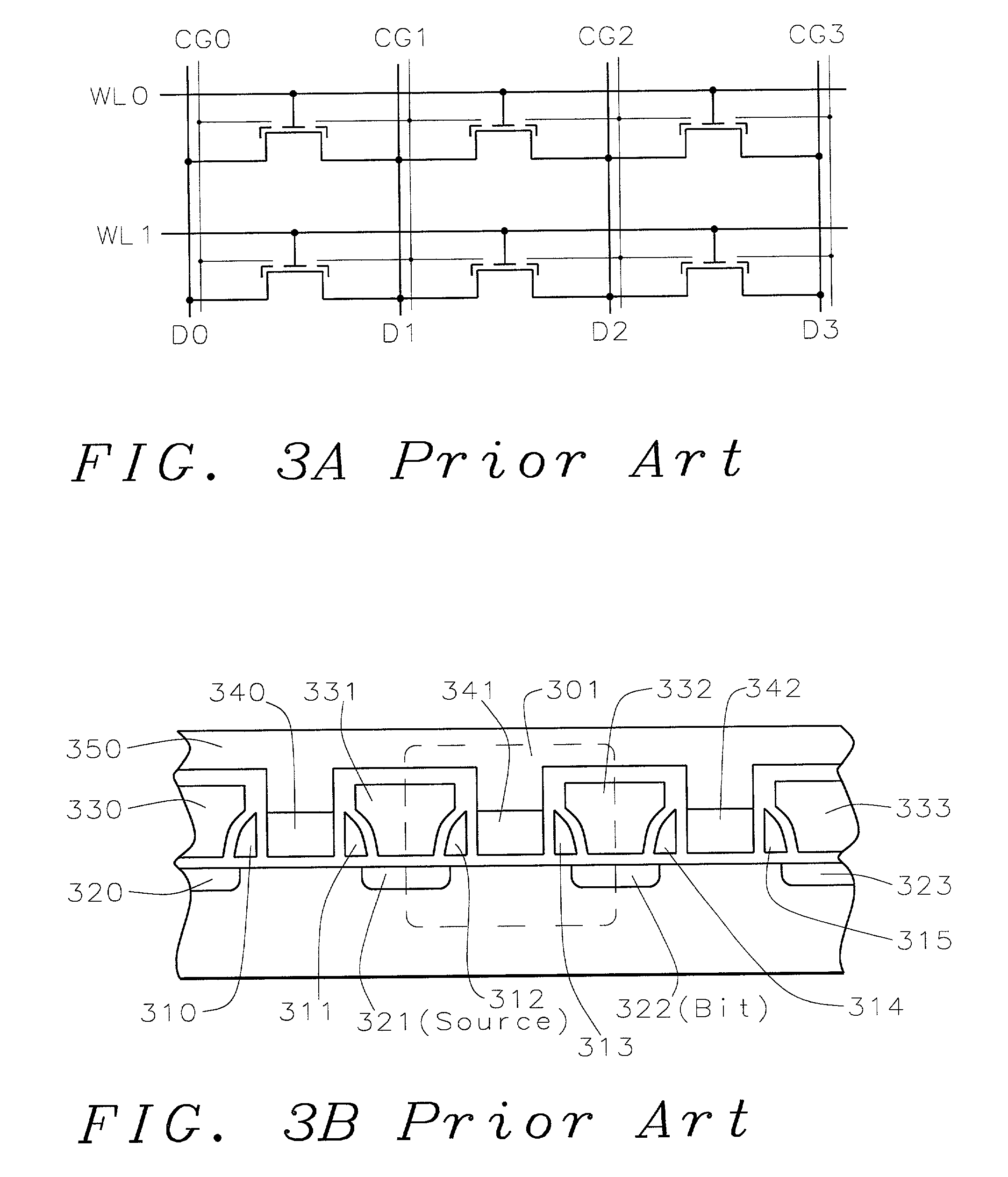
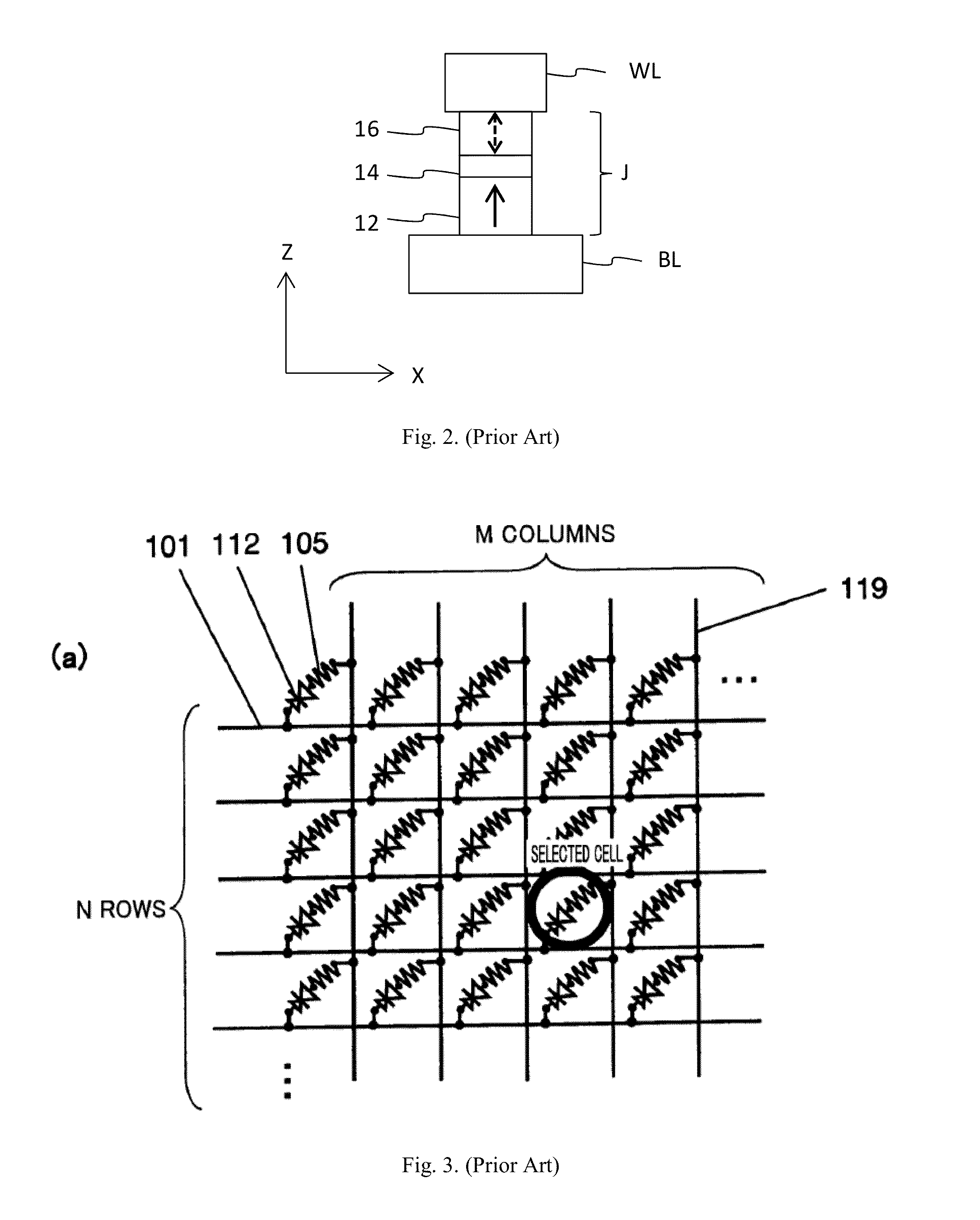
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic MONOS memory
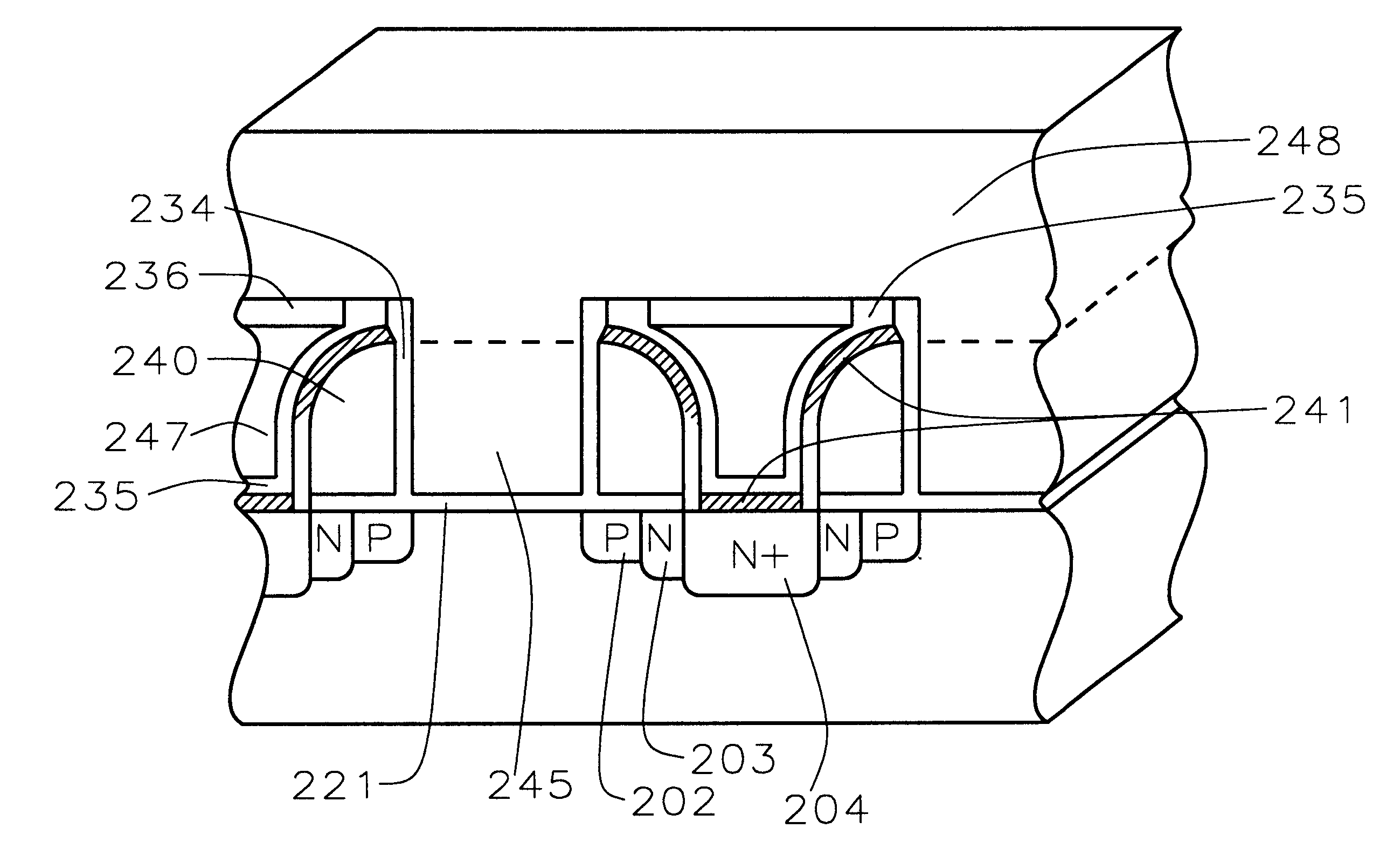
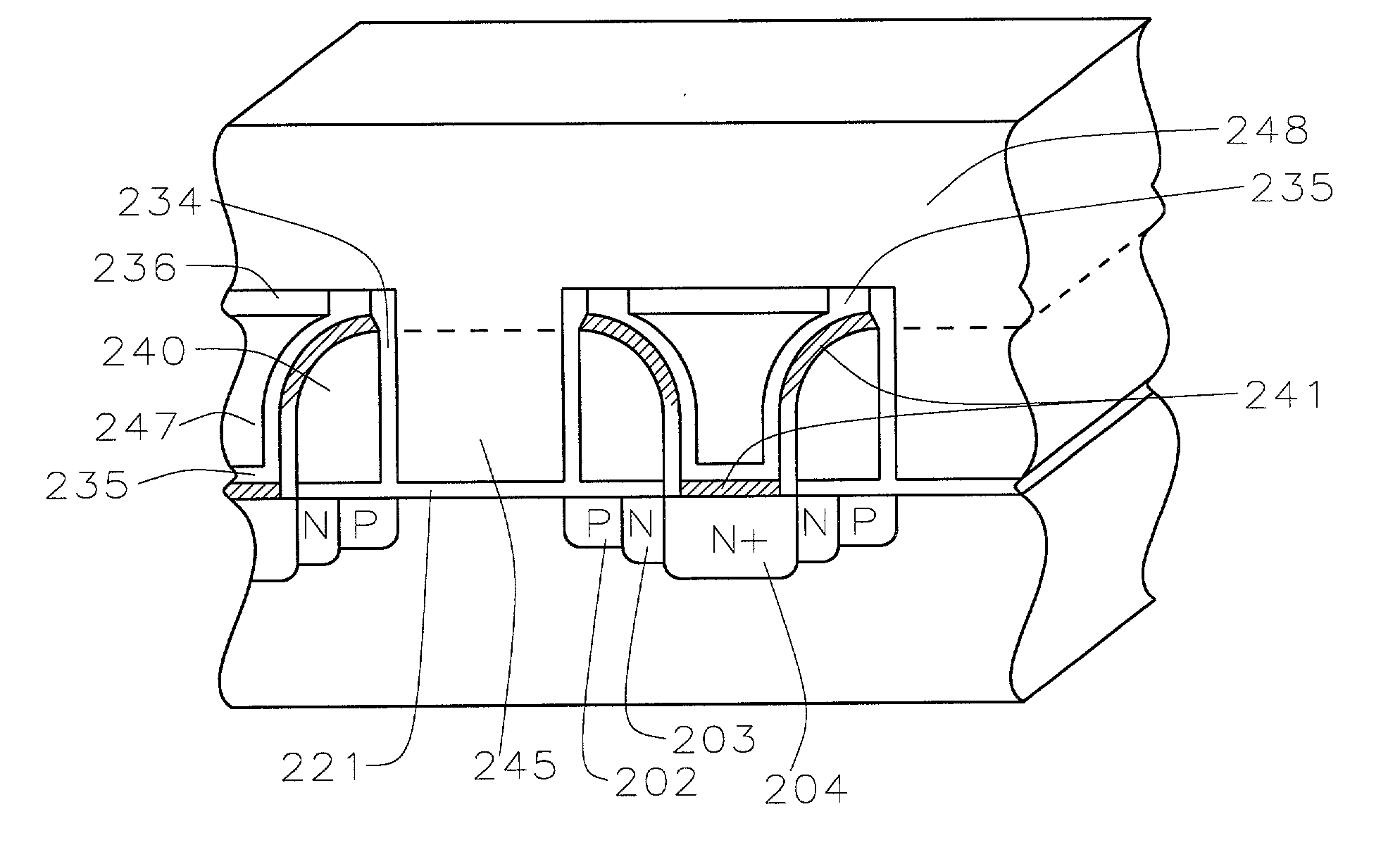
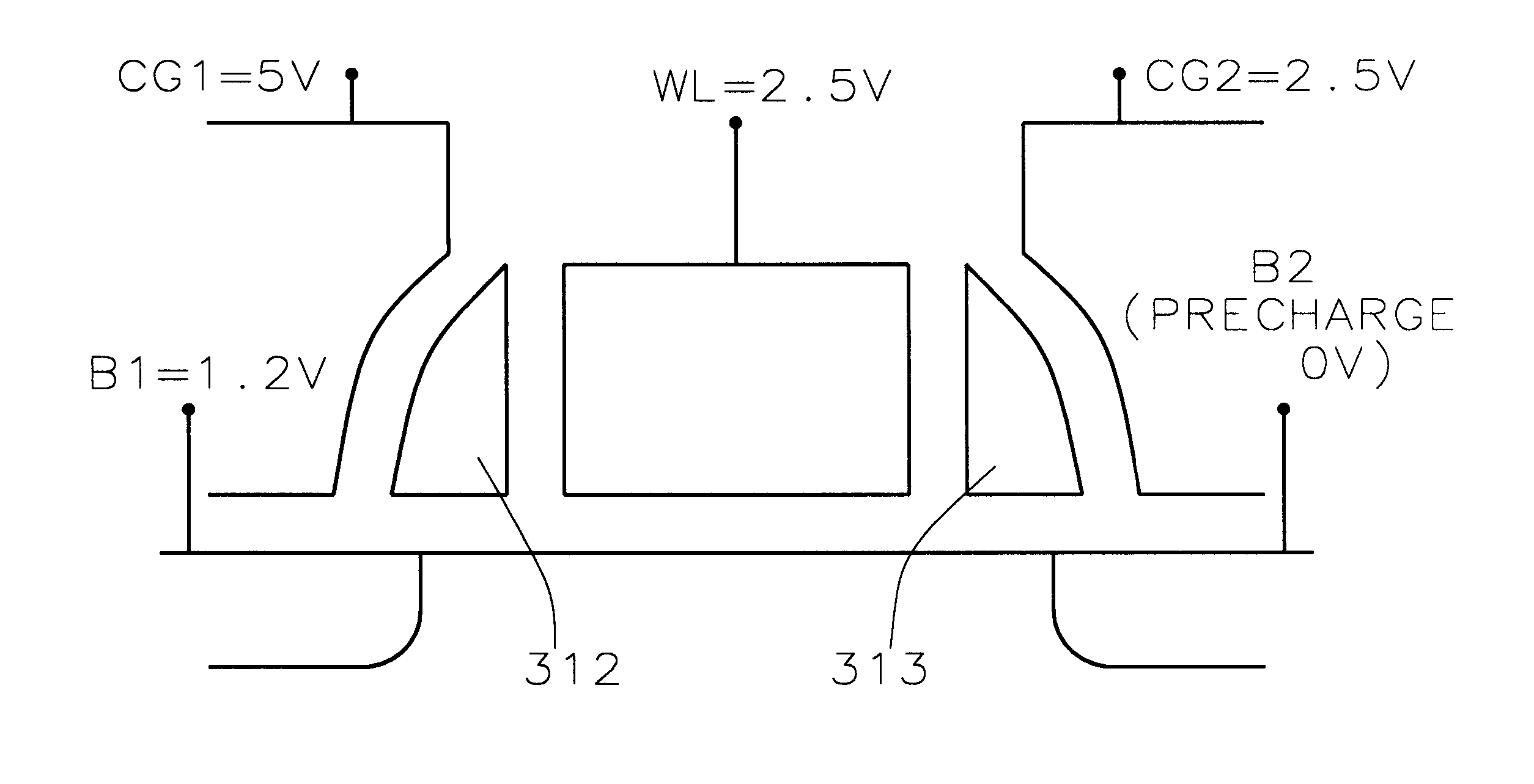
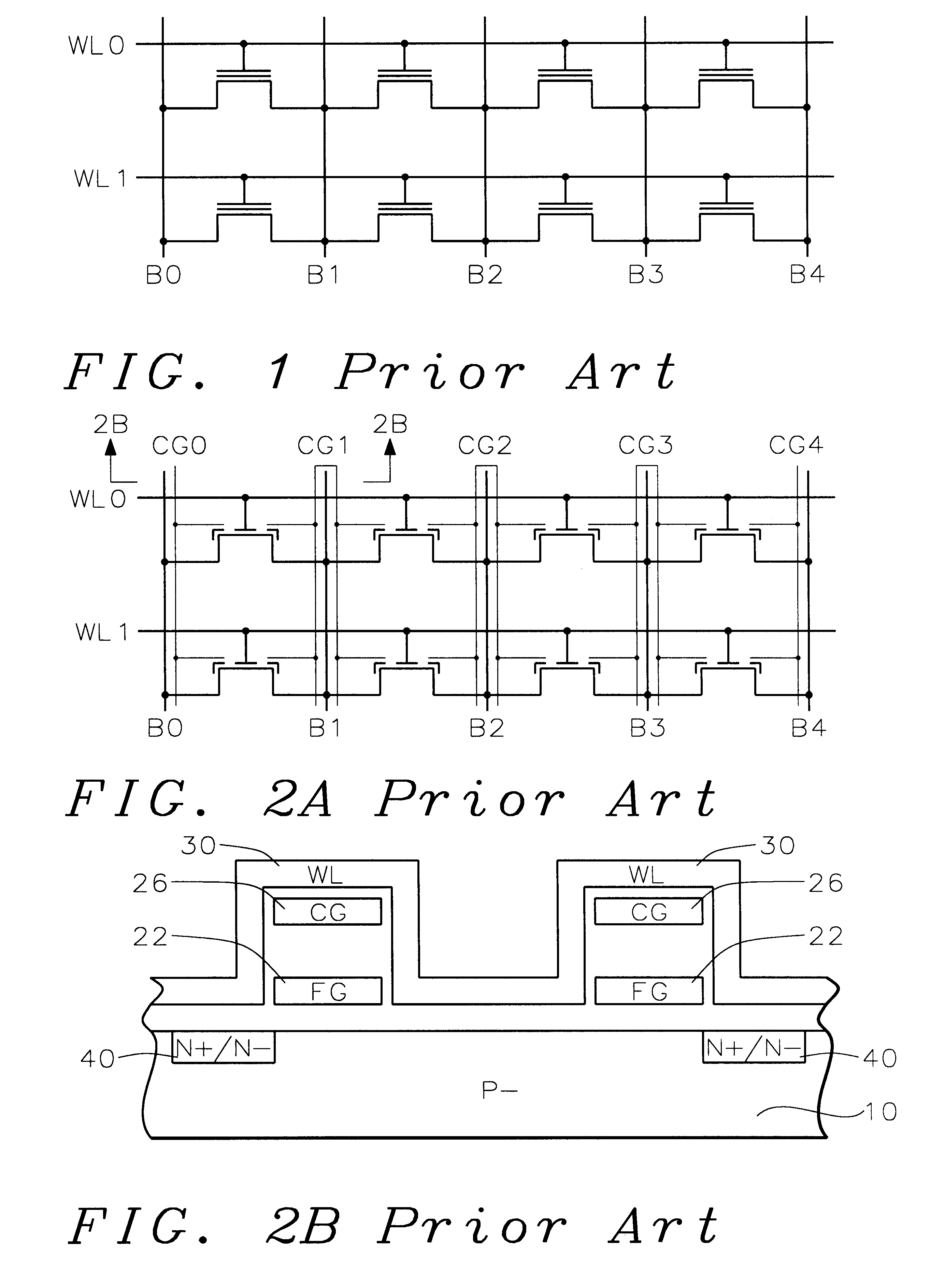
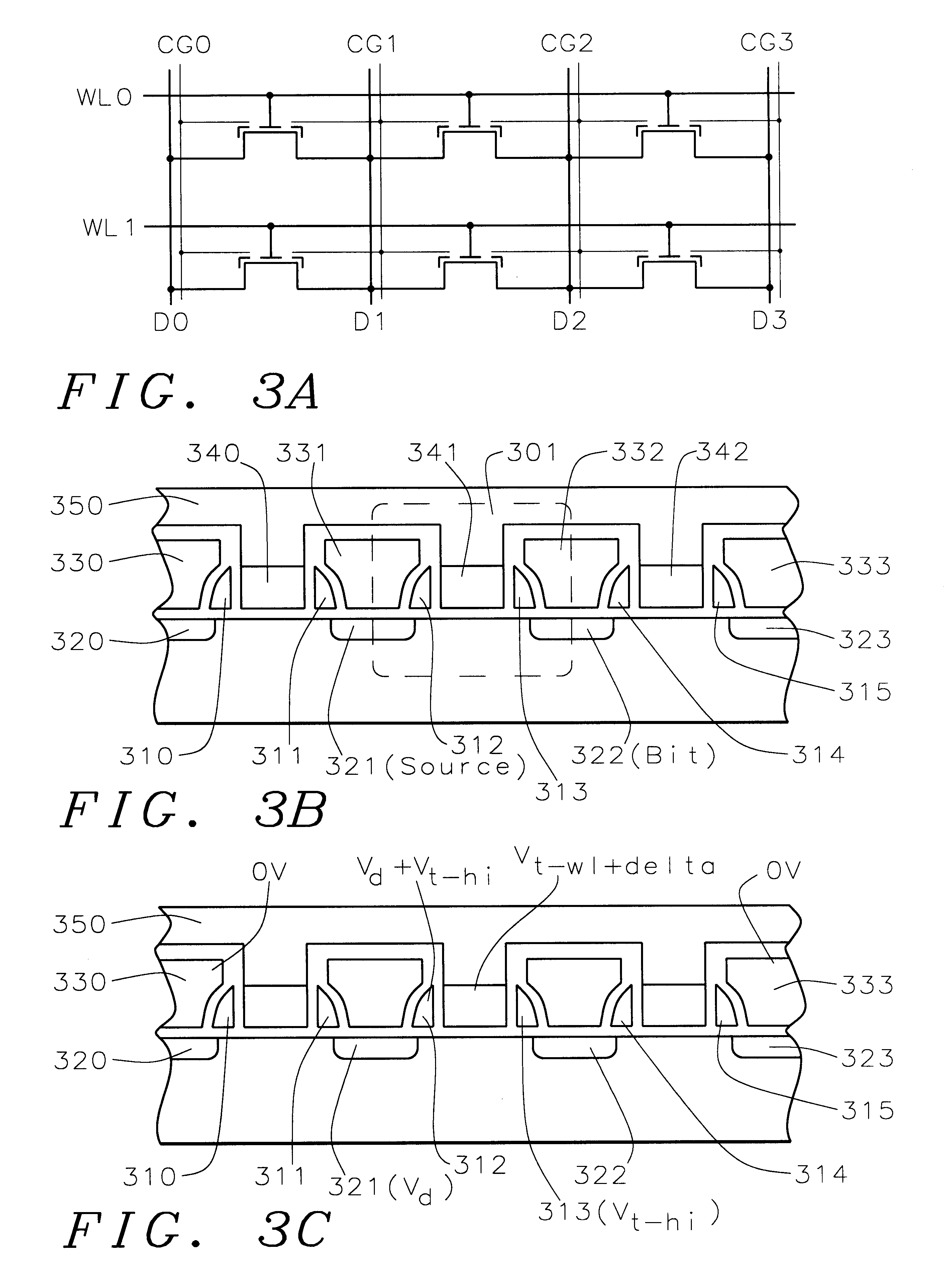
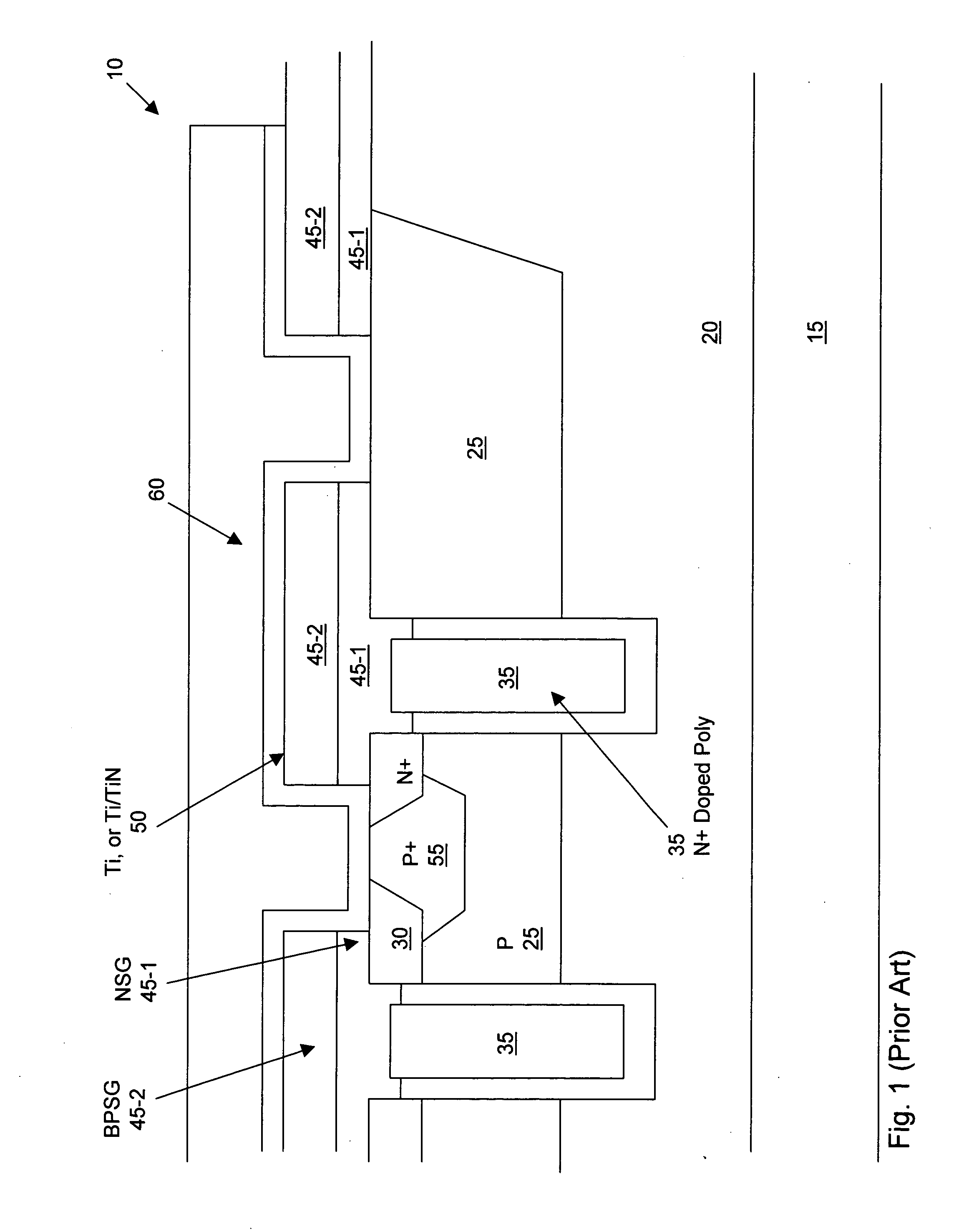
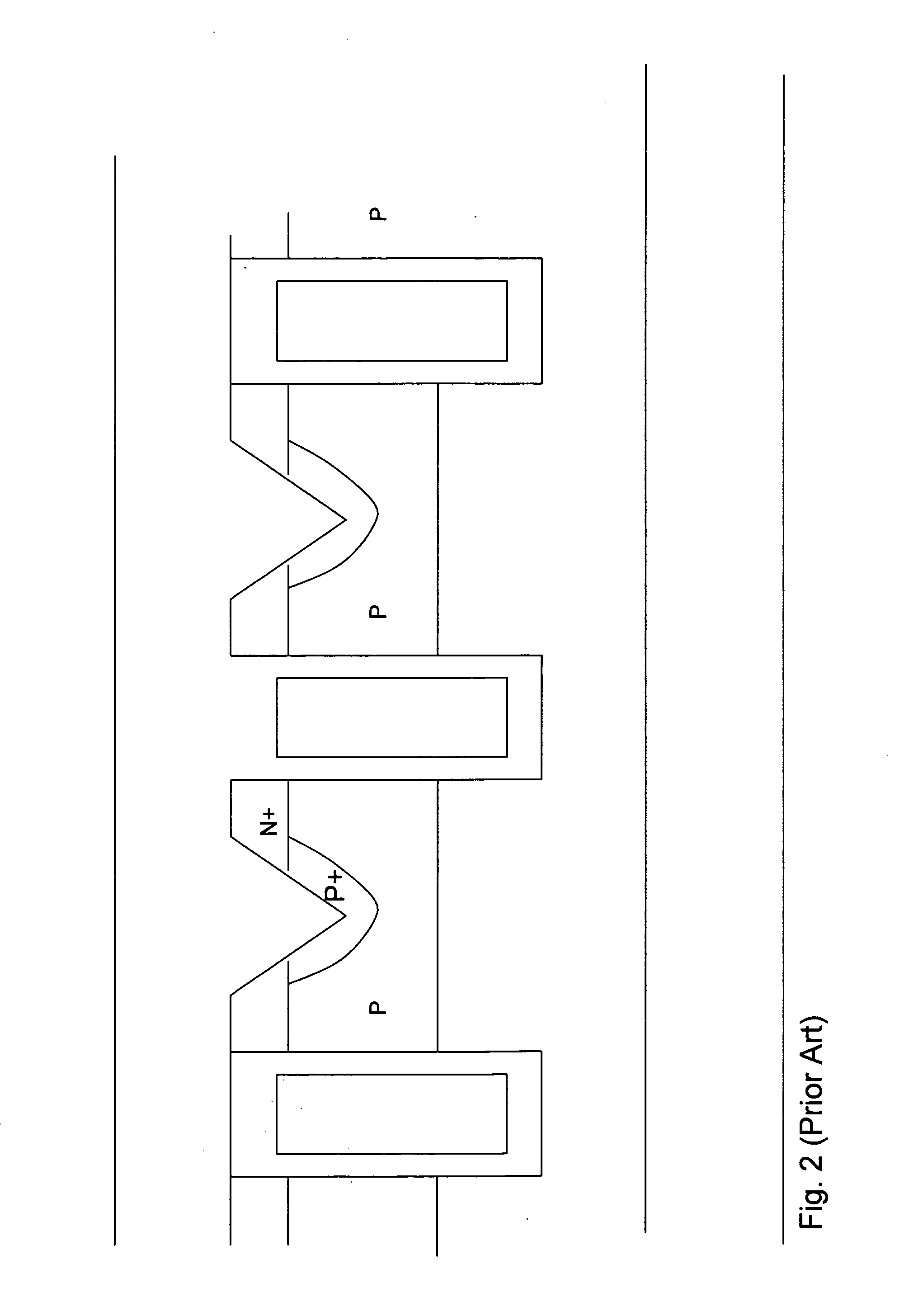
A fast low voltage ballistic program, ultra-short channel, ultra-high density, dual-bit multi-level flash memory is described with a two or three polysilicon split gate side wall process. The structure and operation of this invention is enabled by a twin MONOS cell structure having an ultra-short control gate channel of less than 40nm, with ballistic injection which provides high electron injection efficiency and very fast program at low program voltages of 3~5V. The cell structure is realized by (i) placing side wall control gates over a composite of Oxide-Nitride-Oxide (ONO) on both sides of the word gate, and (ii) forming the control gates and bit diffusion by self-alignment and sharing the control gates and bit diffusions between memory cells for high density. Key elements used in this process are: 1) Disposable side wall process to fabricate the ultra short channel and the side wall control gate with or without a step structure, and 2) Self-aligned definition of the control gate over the storage nitride and the bit line diffusion, which also runs in the same direction as the control gate. The features of fast program, low voltage, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level MONOS NVRAM of the present invention include: 1) Electron memory storage in nitride regions within an ONO layer underlying the control gates, 2) high density dual-bit cell in which there are two nitride memory storage elements per cell, 3) high density dual-bit cell can store multi-levels in each of the nitride regions, 4) low current program controlled by the word gate and control gate, 5) fast, low voltage program by ballistic injection utilizing the controllable ultra-short channel MONOS, and 6) side wall control poly gates to program and read multi-levels while masking out memory storage state effects of the unselected adjacent nitride regions and memory cells. The ballistic MONOS memory cell is arranged in the following array: each memory cell contains two nitride regions for one word gate, and ½ a source diffusion and ½ a bit diffusion. Control gates can be defined separately or shared together over the same diffusion. Diffusions are shared between cells and run in parallel to the side wall control gates, and perpendicular to the word line.
Owner:HALO LSI INC
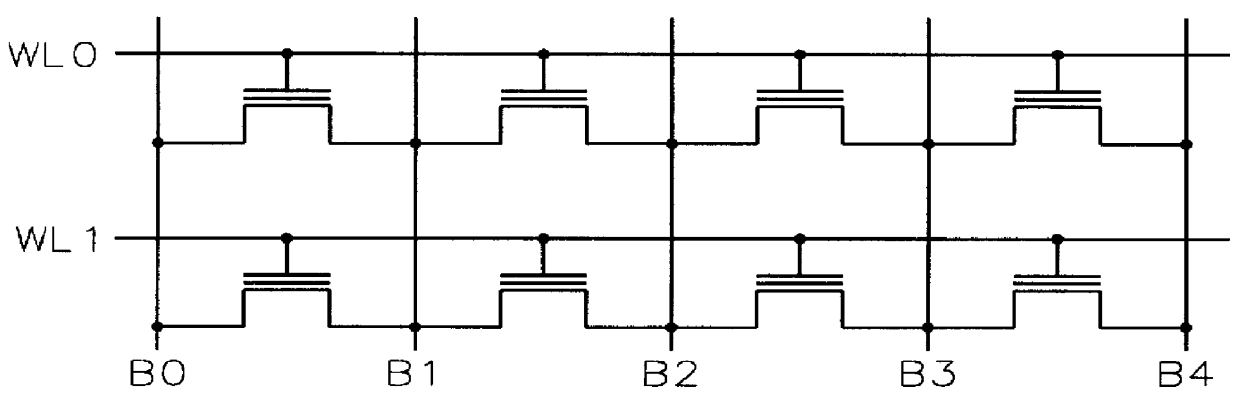
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic flash memory
An fast program, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level flash memory process, which can be applied to a ballistic step split gate side wall transistor, or to a ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor, which enables program operation by low voltage requirement on the floating gate during program is described. Two side wall floating gates are paired with a single word line select gate, and word lines are arranged to be perpendicular both the bit lines and control gate lines. Two adjacent memory cells on the same word line do not require an isolation region. Also, the isolation region between adjacent memory cells sharing the same bitline is defined by the minimum lithography feature, utilizing a self align fill technique. Adjacent memory cells on the same word line share bitline diffusion as well as a third poly control gate. Control gates allow program and read access to the individual floating gate. In addition to the dual-bit nature of the cell, density can be even further improved by multi-level storage. In one embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic step split gate side wall transistor. In a second embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor. Both types of ballistic transistors provide fast, low voltage programming. The control gates are used to override or suppress the various threshold voltages on associated floating gates, in order to program to and read from individual floating gates. The targets for this non-volatile memory array are to provide the capabilities of high speed, low voltage programming (band width) and high density storage.
Owner:HALO LSI DESIGN & DEVICE TECH
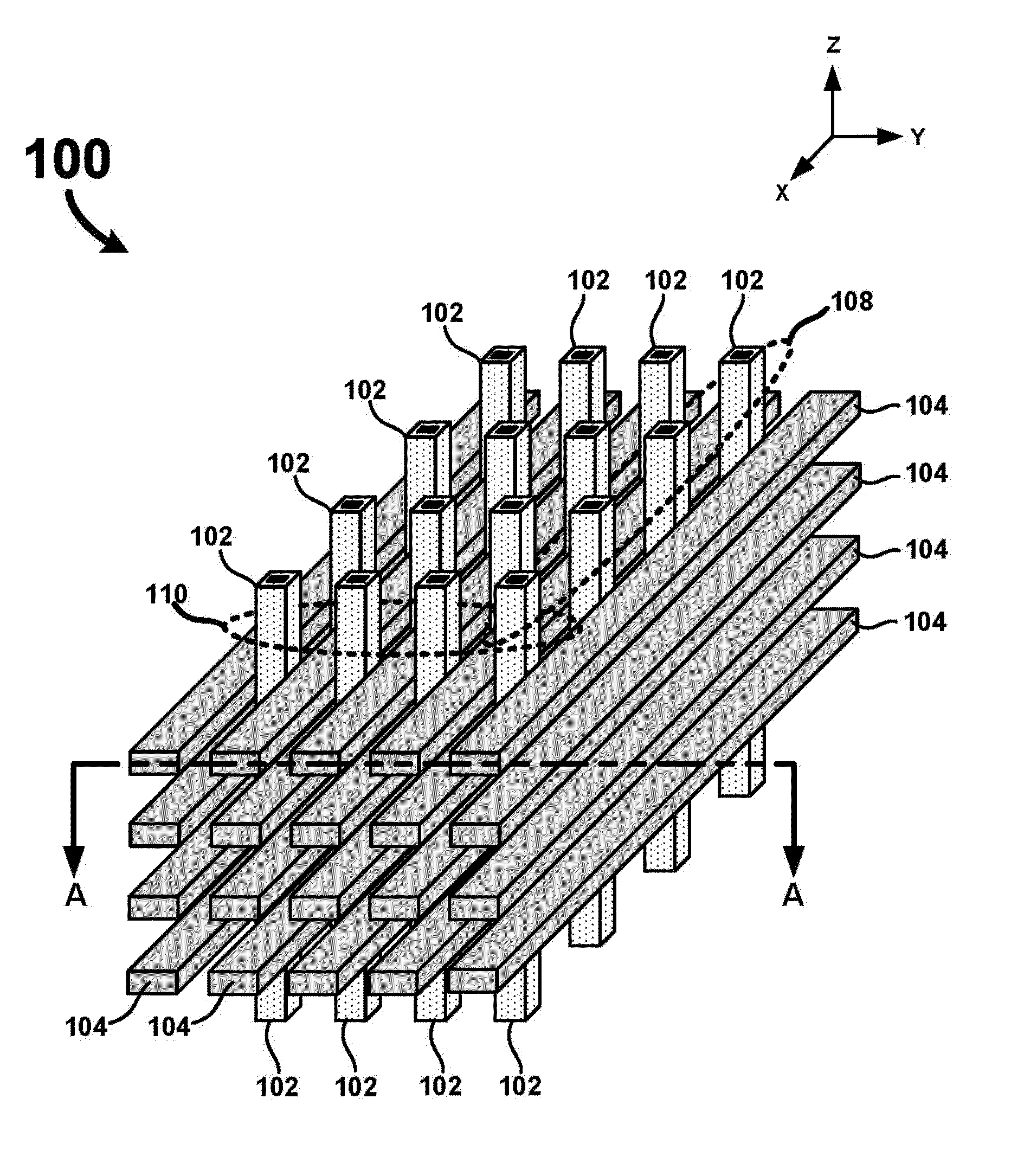
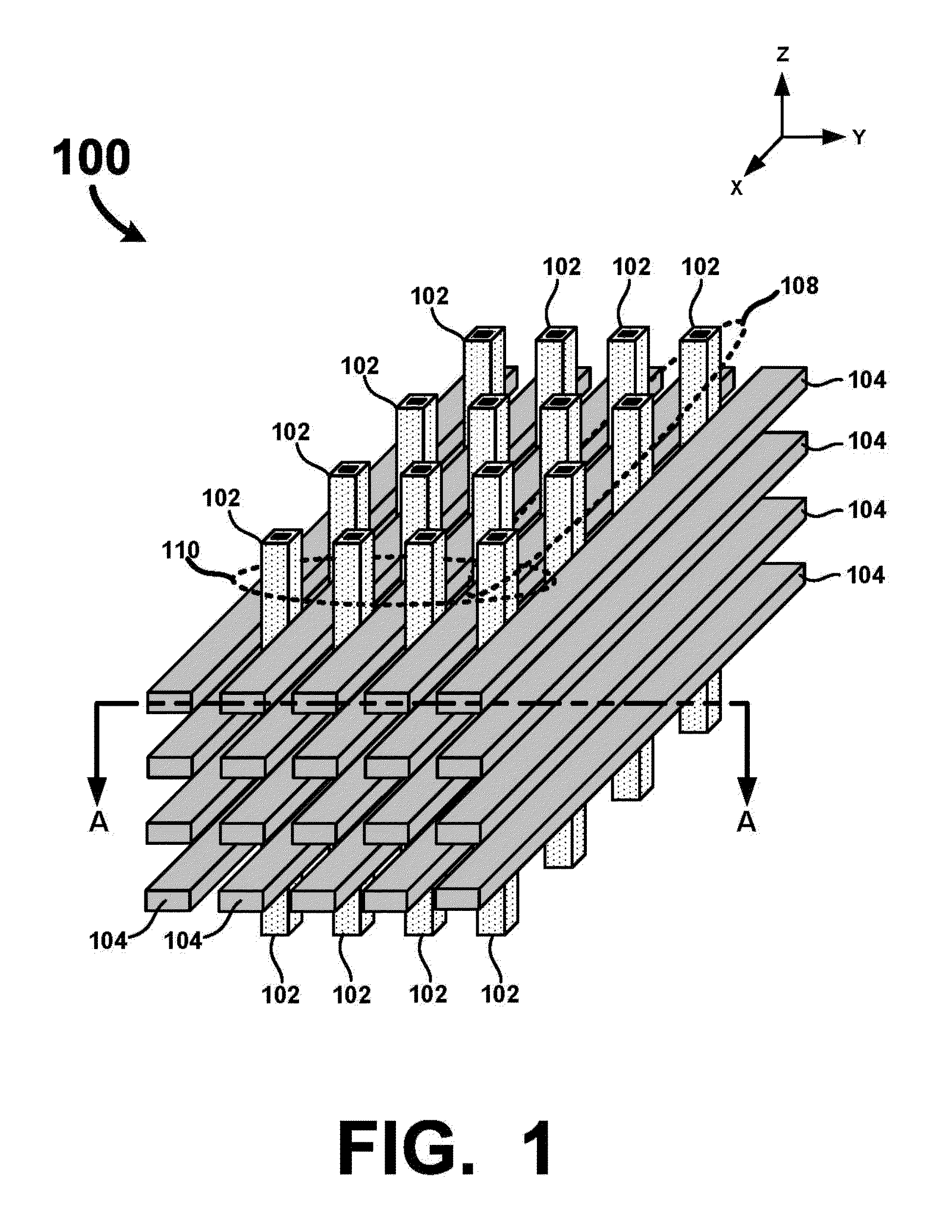
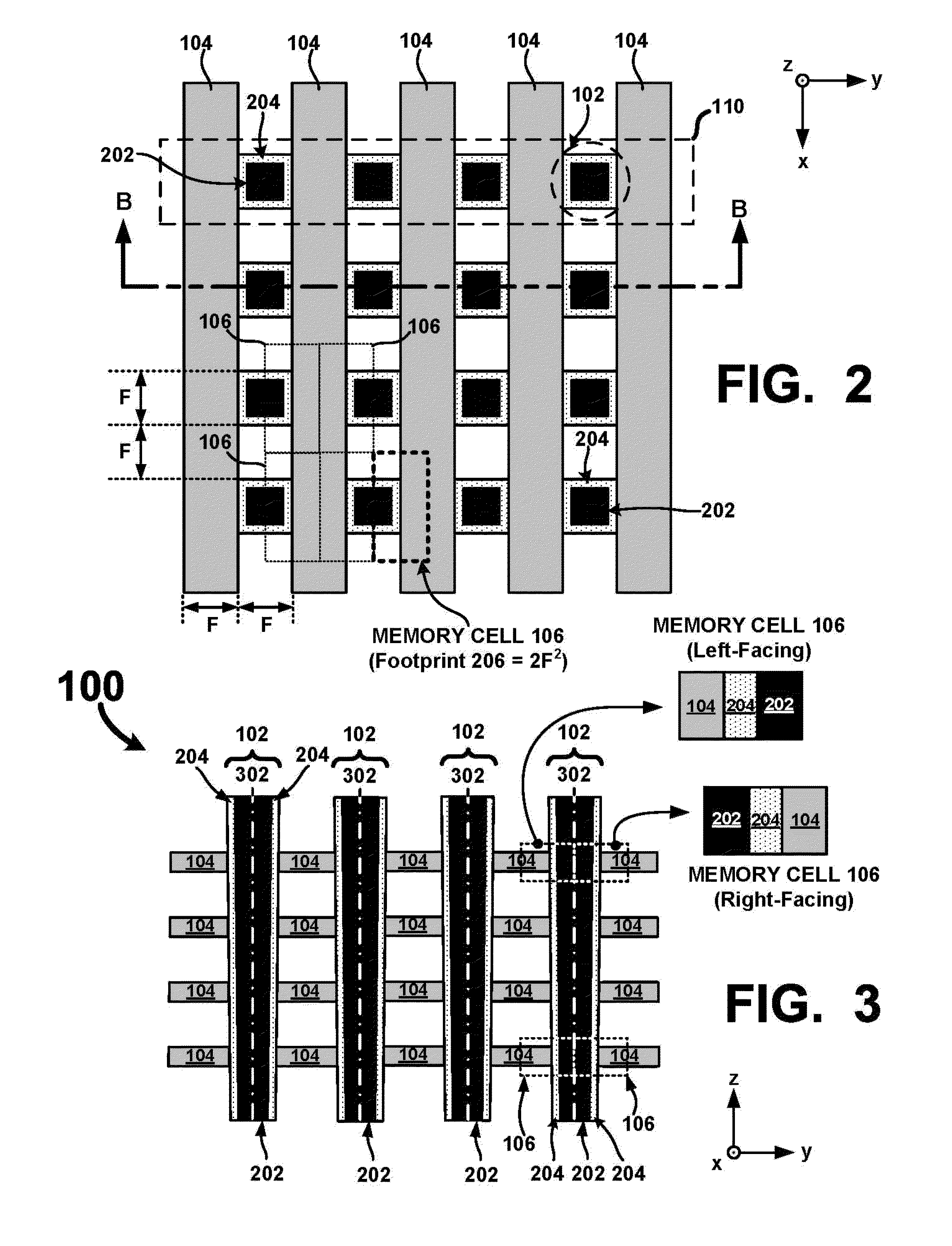
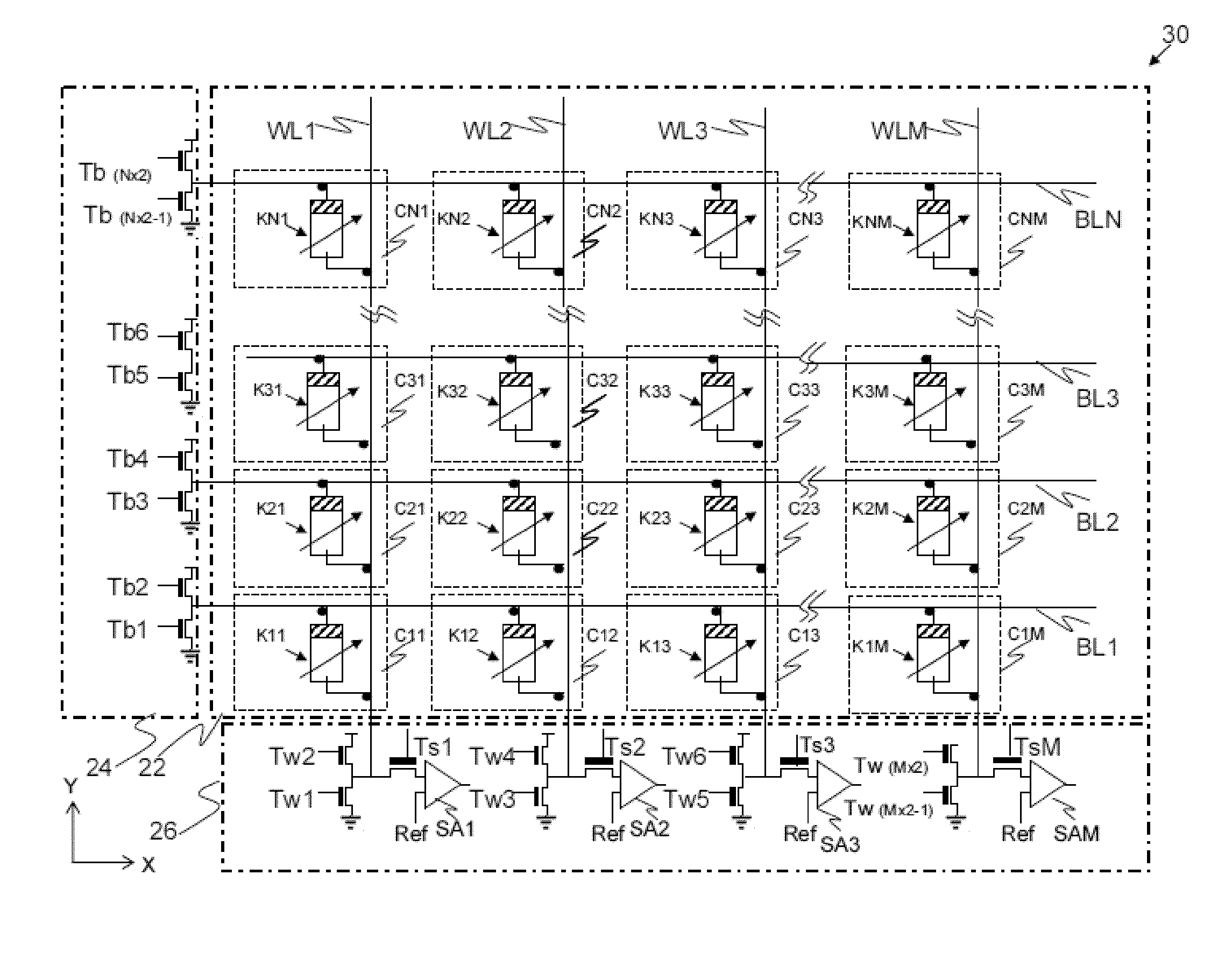
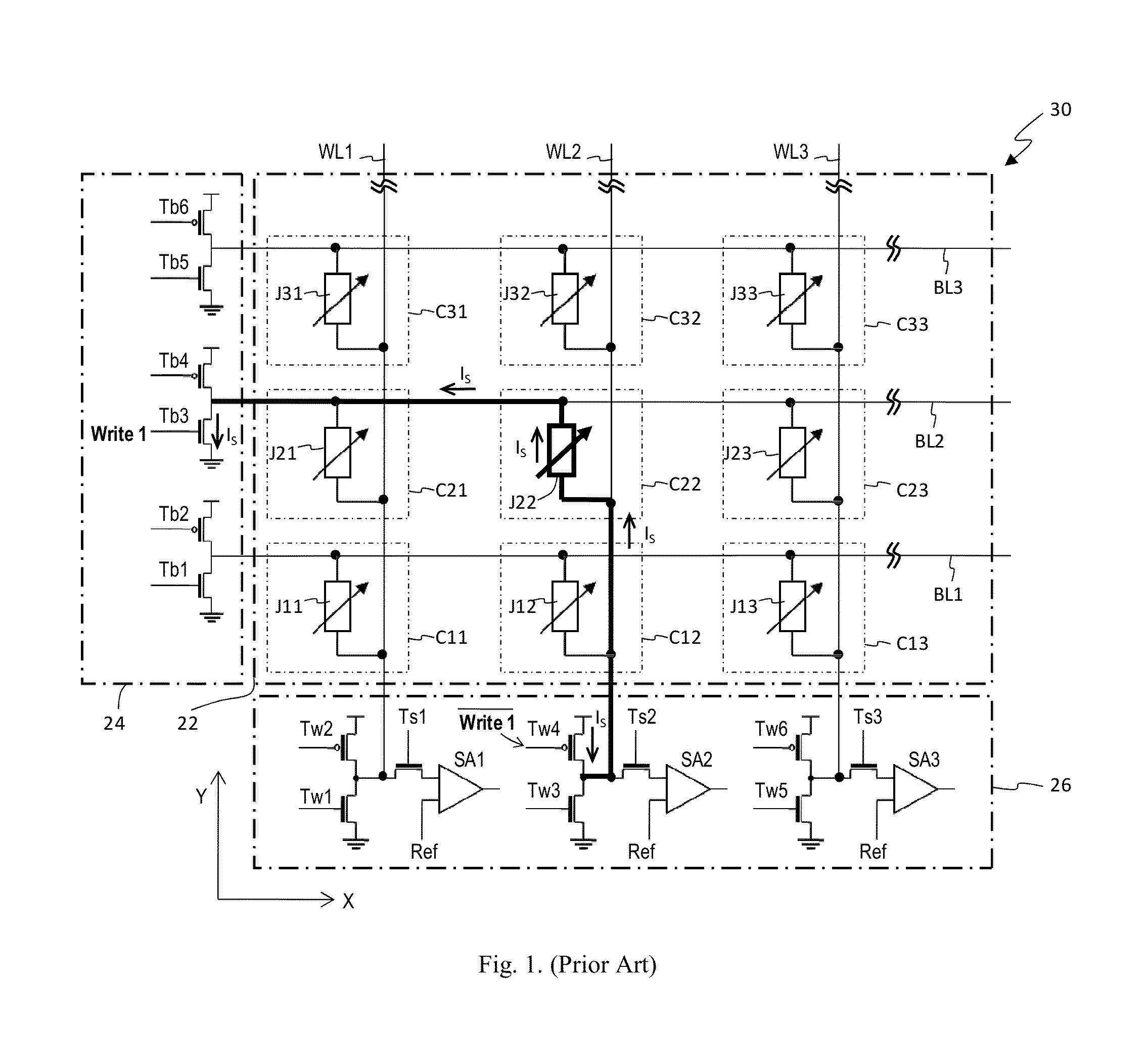
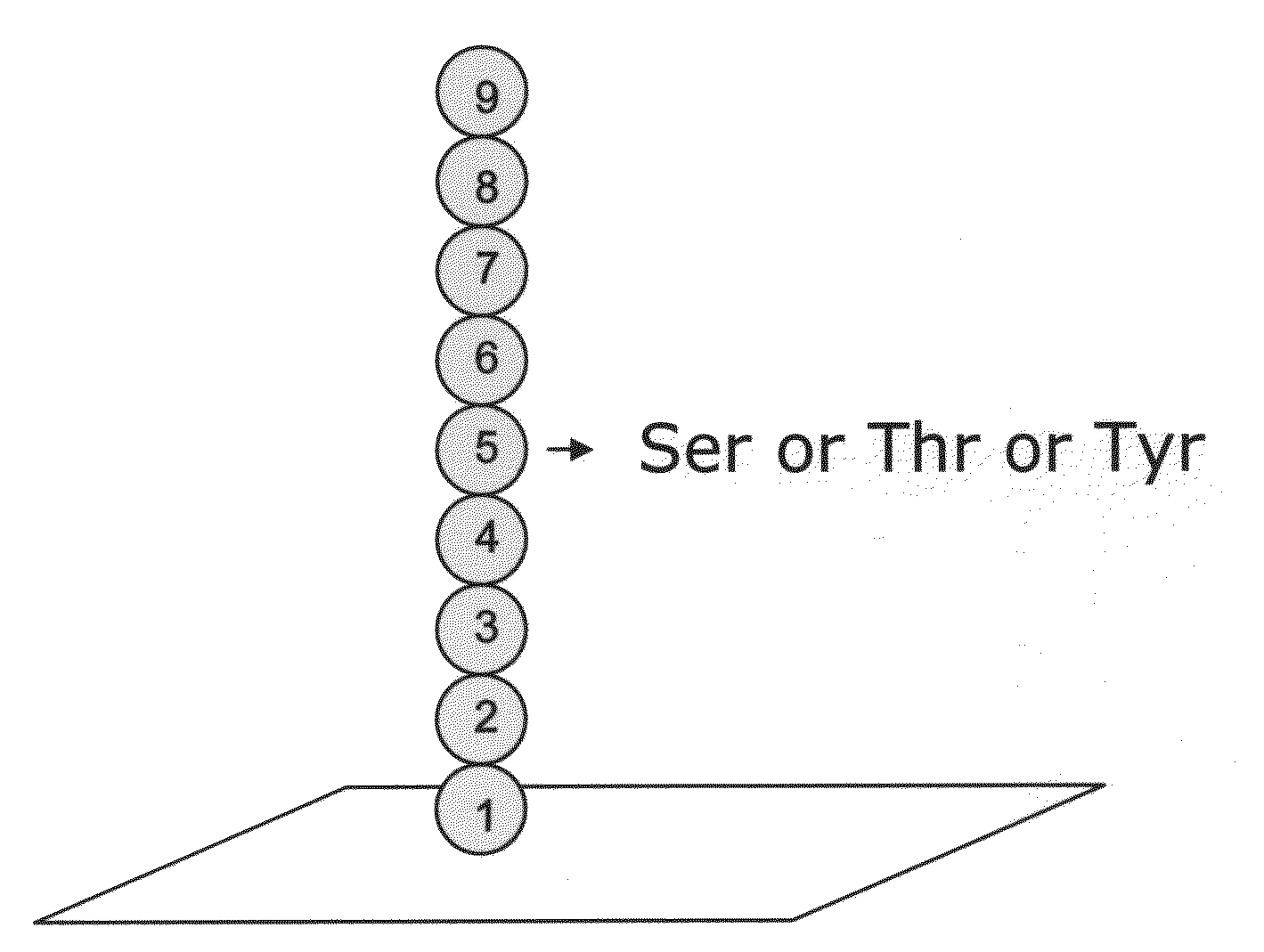
Vertical Cross Point Arrays For Ultra High Density Memory Applications
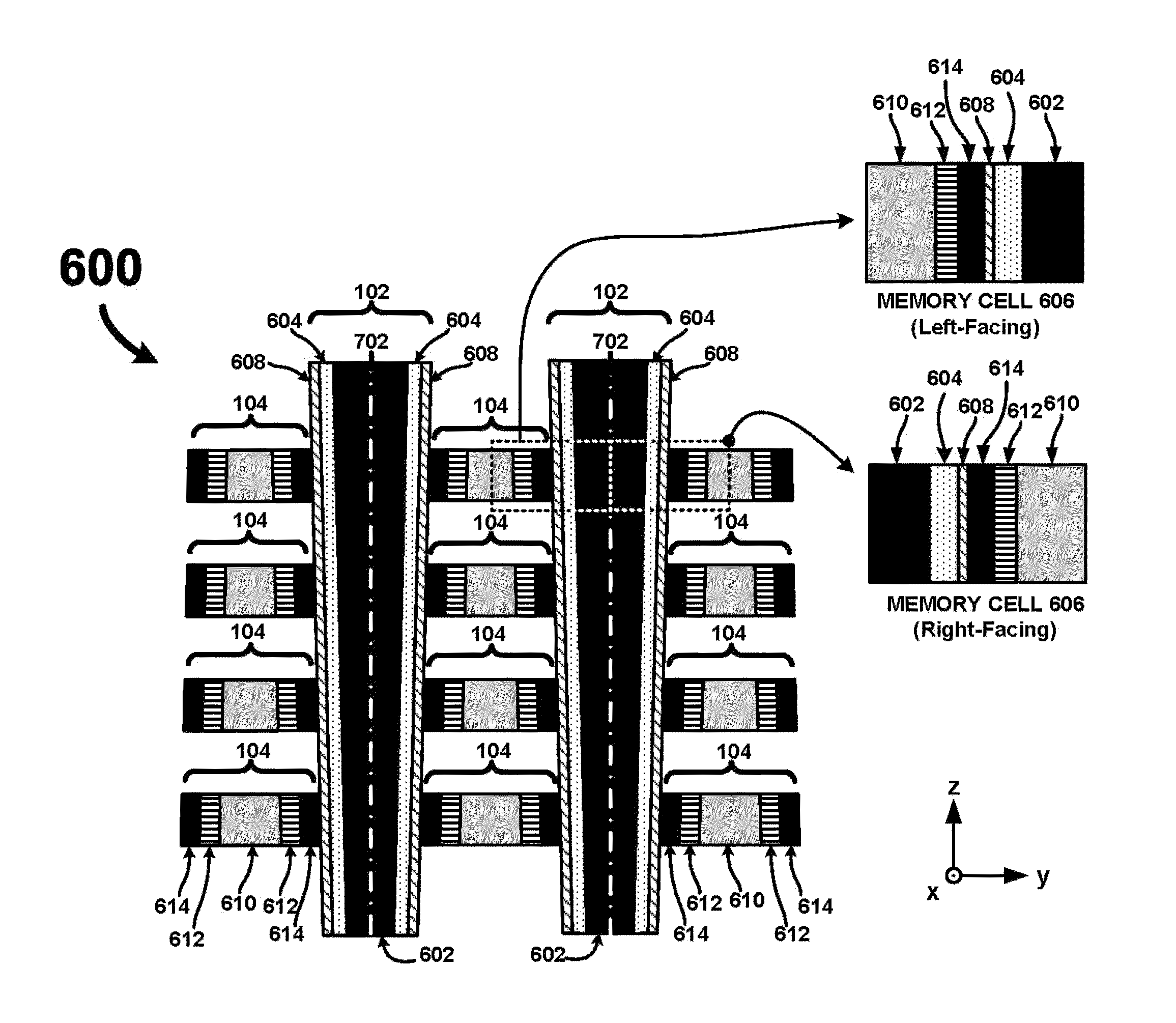
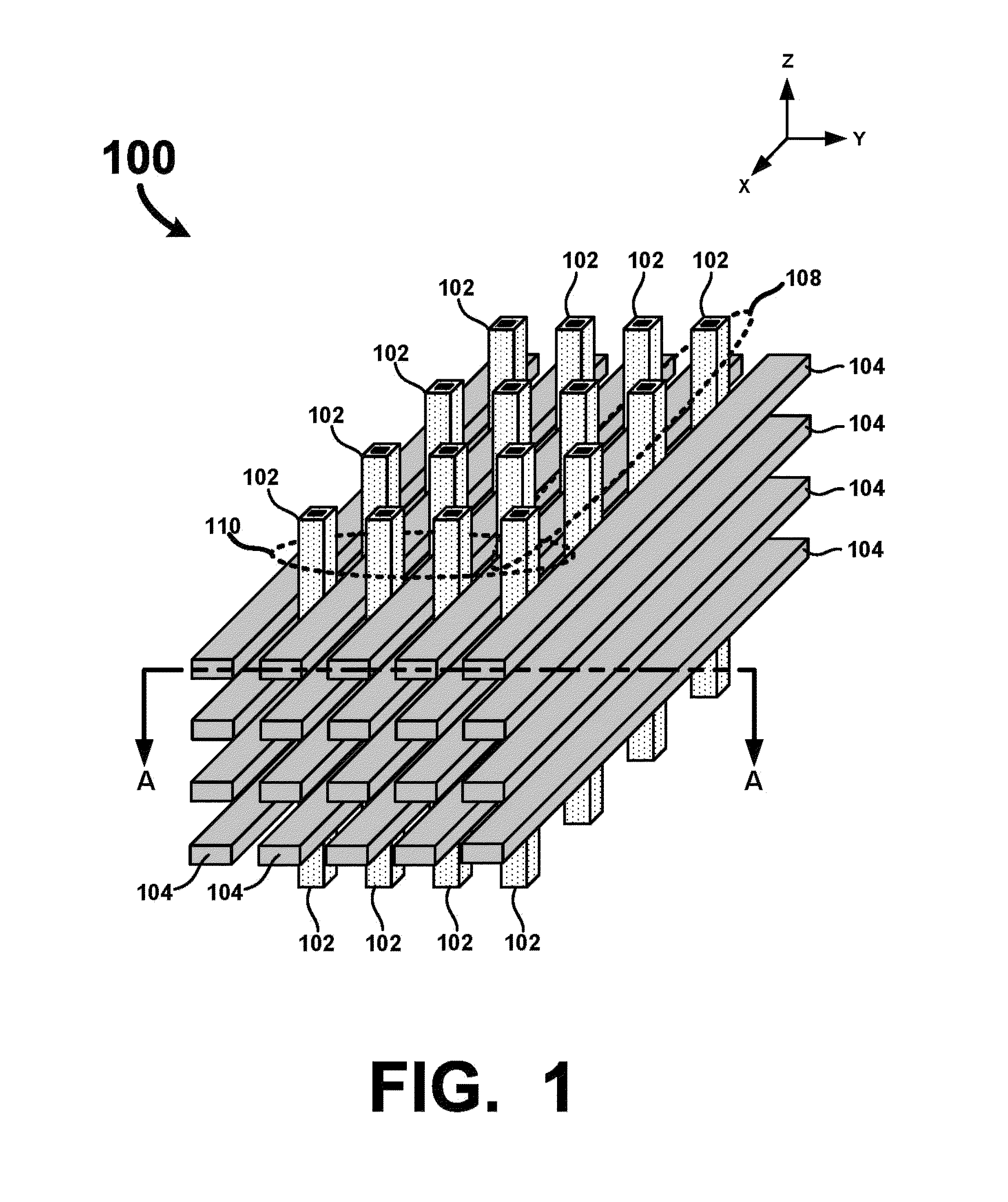
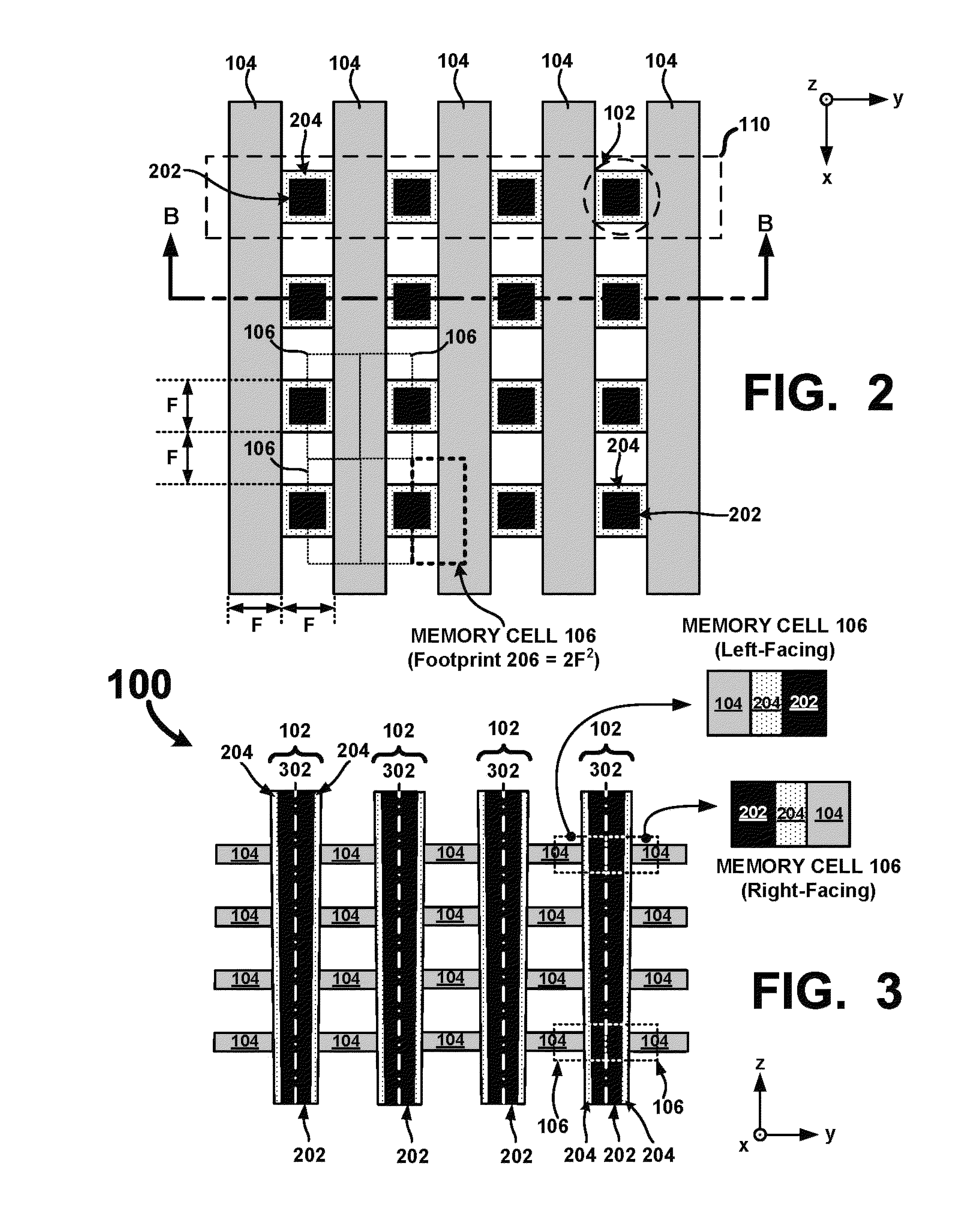
An ultra-high-density vertical cross-point array comprises a plurality of horizontal line layers having horizontal lines interleaved with a plurality of vertical lines arranged in rows and columns. The vertical lines are interleaved with the horizontal lines such that a row of vertical lines is positioned between each consecutive pair of horizontal lines in each horizontal line layer. Each vertical line comprises a center conductor surrounded by a single or multi-layered memory film. Accordingly, when interleaved with the horizontal lines, two-terminal memory cells are integrally formed between the center conductor of each vertical line and each crossing horizontal line. By configuring the vertical and horizontal lines so that a row of vertical lines is positioned between each consecutive pair of horizontal lines, a unit memory cell footprint of just 2F2 may be realized.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
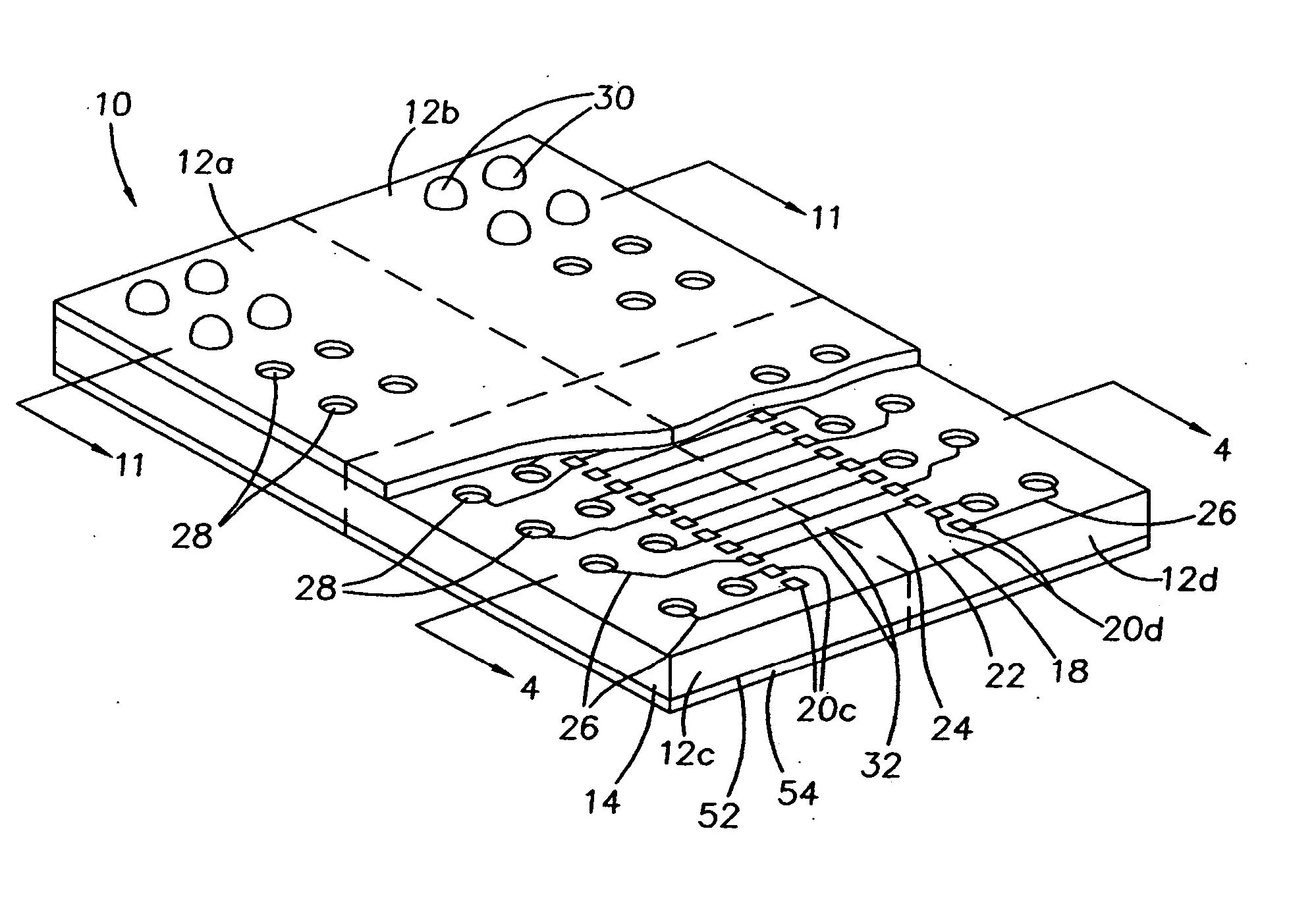
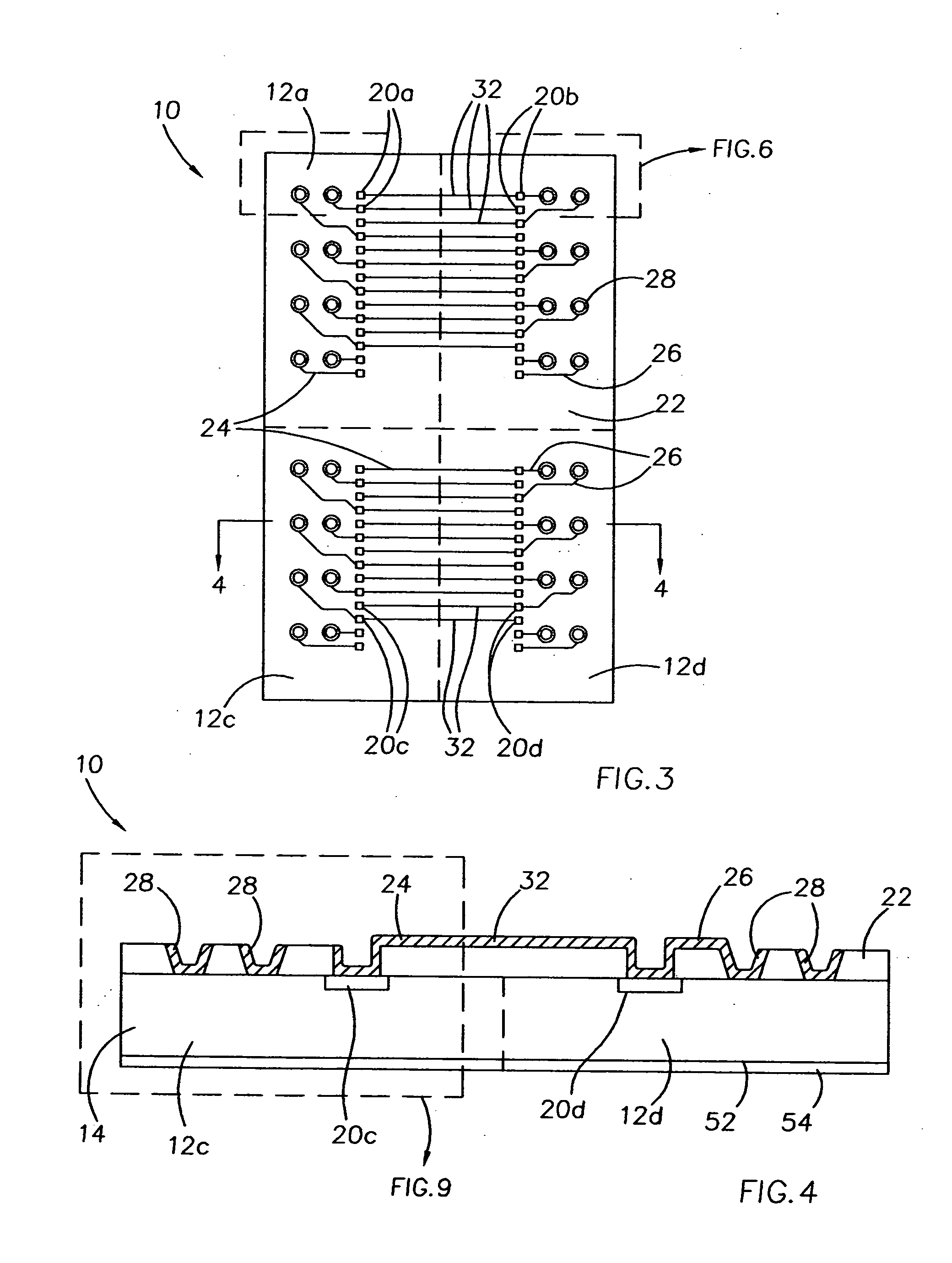
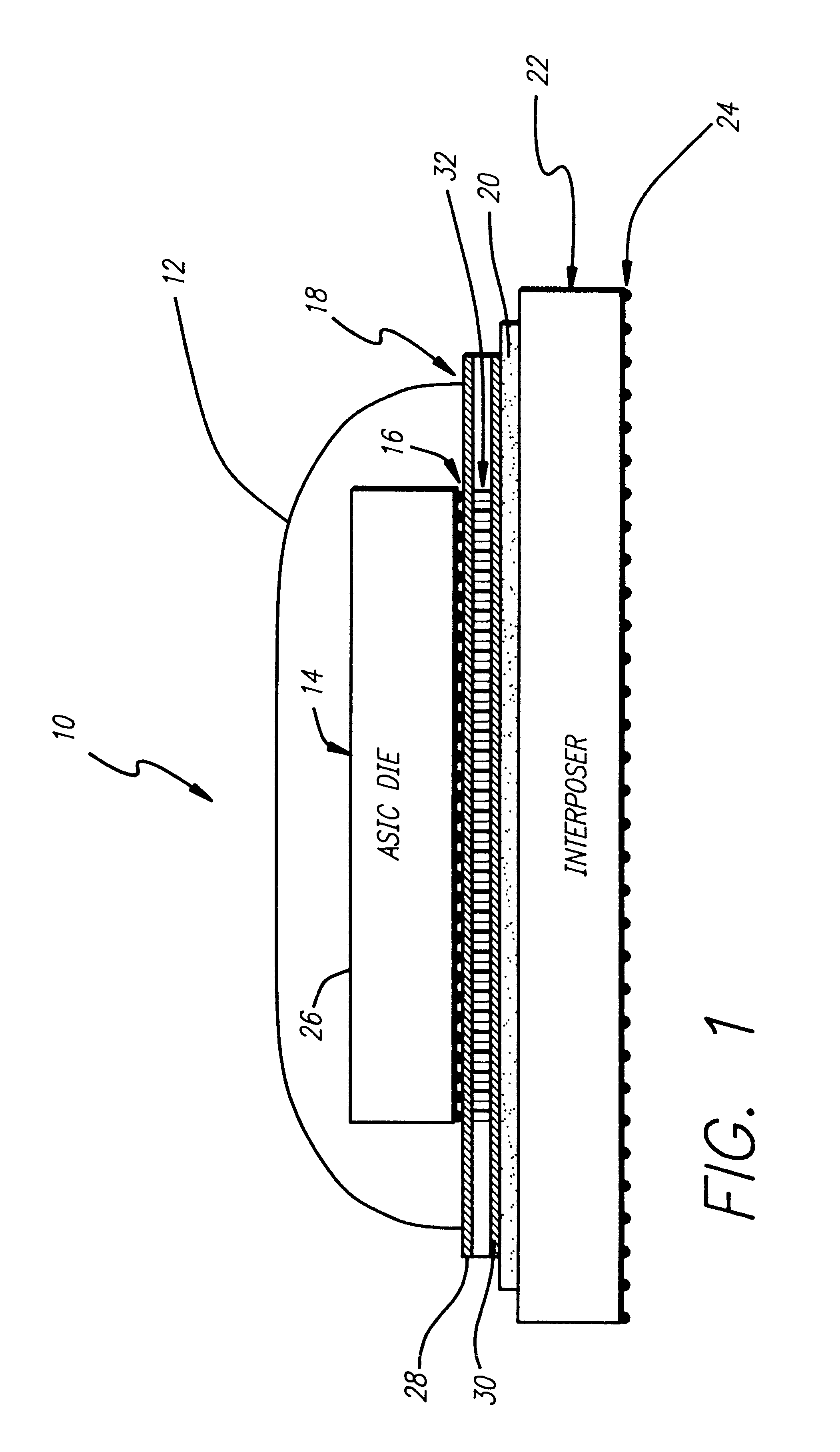
Ultra-thin interposer assemblies with through vias
ActiveUS20120106117A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsGraphicsElectricity
A 3D interconnect structure comprising an ultra-thin interposer having a plurality of ultra-high density of through-via interconnections defined therein. The 3D interposer electrically connects first and second electronic devices in vertical dimension and has the same or similar through-via density as the first or second electronic devices it connects. The various embodiments of the interconnect structure allows 3D ICs to be stacked with or without TSVs and increases bandwidth between the two electronic devices as compared to other interconnect structures of the prior art. Further, the interconnect structure of the present invention is scalable, testable, thermal manageable, and can be manufactured at relatively low costs. Such a 3D structure can be used for a wide variety of applications that require a variety of heterogeneous ICs, such as logic, memory, graphics, power, wireless and sensors that cannot be integrated into single ICs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for Fabricating a Long-Range Ordered Periodic Array of Nano-Features, and Articles Comprising Same
A long range, periodically ordered array of discrete nano-features (10), such as nano-islands, nano-particles, nano-wires, non-tubes, nano-pores, nano-composition-variations, and nano-device-components, are fabricated by propagation of a self-assembling array or nucleation and growth of periodically aligned nano-features. The propagation may be induced by a laterally or circularly moving heat source, a stationary heat source arranged at an edge of the material to be patterned (12), or a series of sequentially activated heaters or electrodes. Advantageously, the long-range periodic array of nano-features (10) may be utilized as a nano-mask or nano-implant master pattern for nano-fabrication of other nano-structures. In addition, the inventive long-range, periodically ordered arrays of nano-features are useful in a variety of nanoscale applications such as addressable memories or logic devices, ultra-high-density magnetic recording media, magnetic sensors, photonic devices, quantum computing devices, quantum luminescent devices, and efficient catalytic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
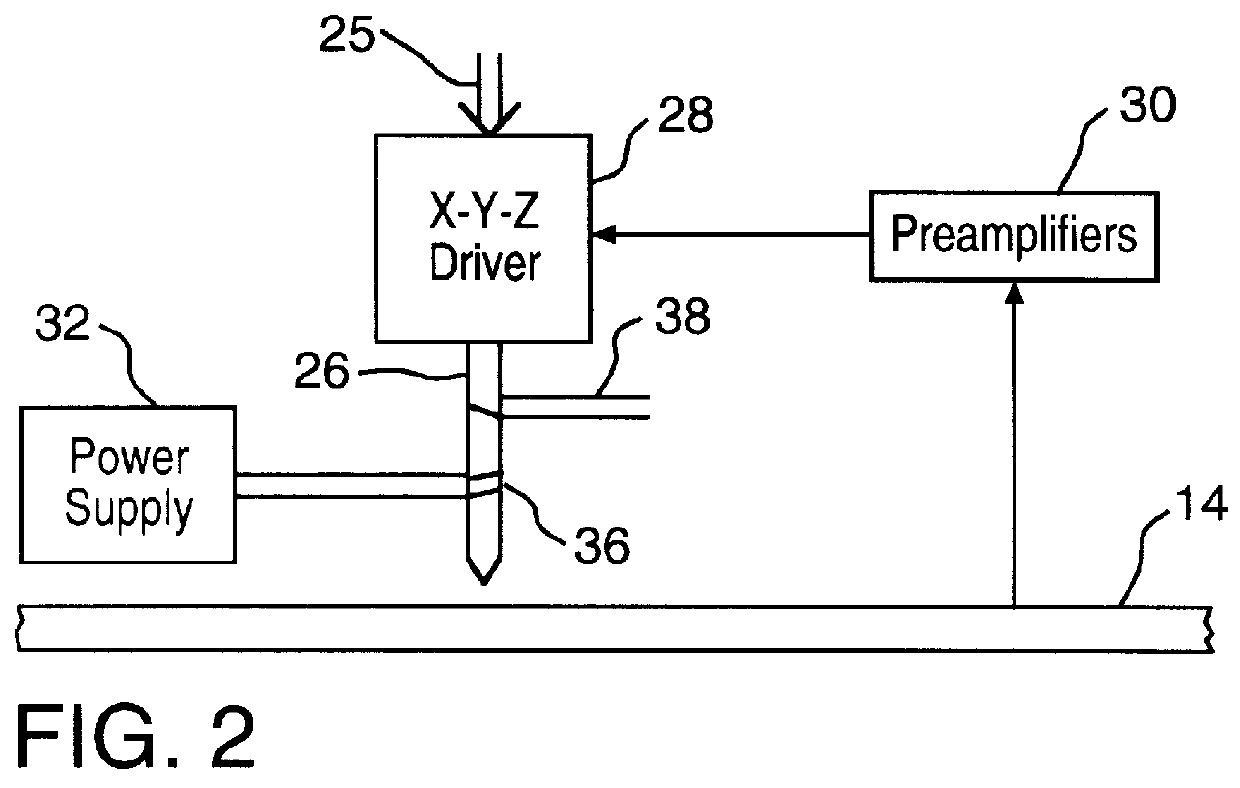
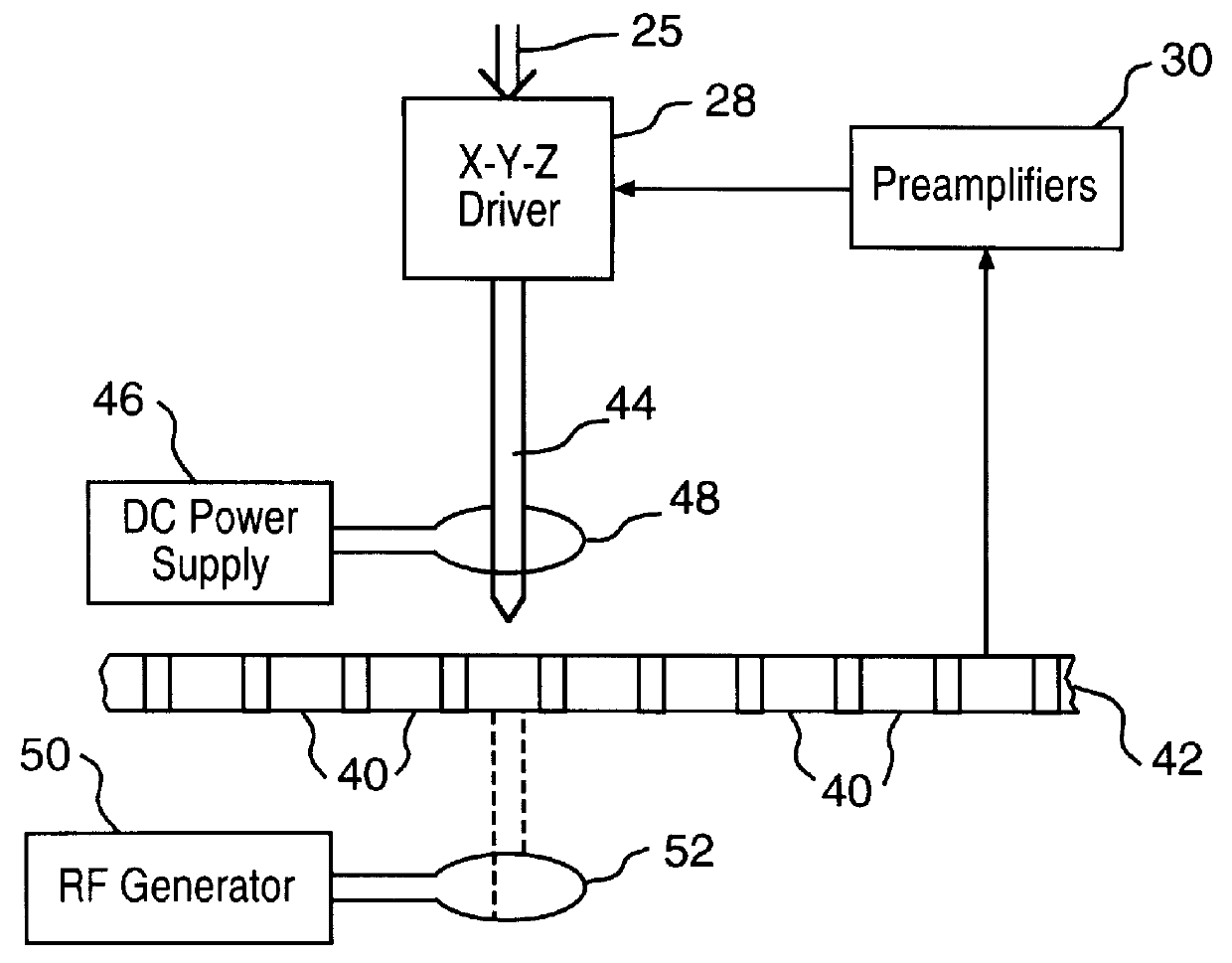
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing with a probe on erasable magnetic media
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing on an erasable magnetic medium include using a micromachined mechanism having two probes for writing to the medium. Use of the two probe embodiment eliminates the need to change the magnetic orientation of the probe. In another embodiment, a single probe is provided which is heated to the vicinity of its Curie temperature to enable the magnetic orientation of the probe to be switched. The probe may be heated to its Curie temperature through the use of a heating element or a focused laser. In another embodiment of the present invention, either the magnetic orientation of the probe or the magnetic orientation of the medium may be switched through the combination of a static magnetic field, a radio frequency magnetic field and, under certain circumstances, the magnetic field of the probe. In all cases, the writing techniques enable information to be written to a magnetic medium in a manner which enables the information to be erased and the medium rewritten.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Integration substrate with a ultra-high-density capacitor and a through-substrate via
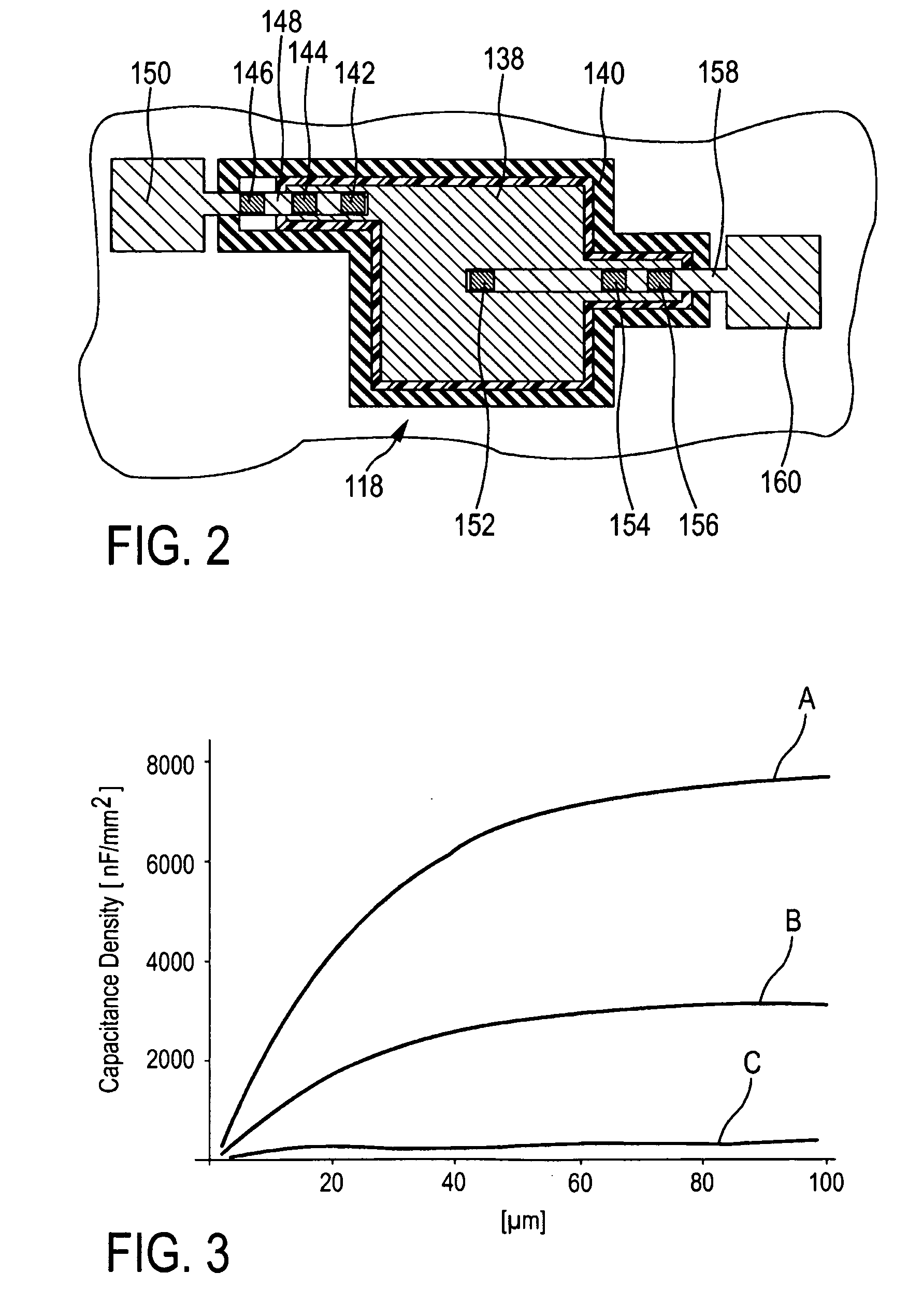
ActiveUS20100244189A1Simple to introduce into existing production lineIncrease capacitance densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicrometerEngineering
An integration substrate for a system in package comprises a through-substrate via and a trench capacitor wherein with a trench filling that includes at least four electrically conductive capacitor-electrode layers in an alternating arrangement with dielectric layers. —The capacitor-electrode layers are alternatingly connected to a respective one of two capacitor terminals provided on the first or second substrate side. The trench capacitor and the through-substrate via are formed in respective trench openings and via openings in the semiconductor substrate, which have an equal lateral extension exceeding 10 micrometer. This structure allows, among other advantages, a particularly cost-effective fabrication of the integration substrate because the via openings and the trench openings in the substrate can be fabricated simultaneously.
Owner:MURATA INTEGRATED PASSIVE SOLUTIONS
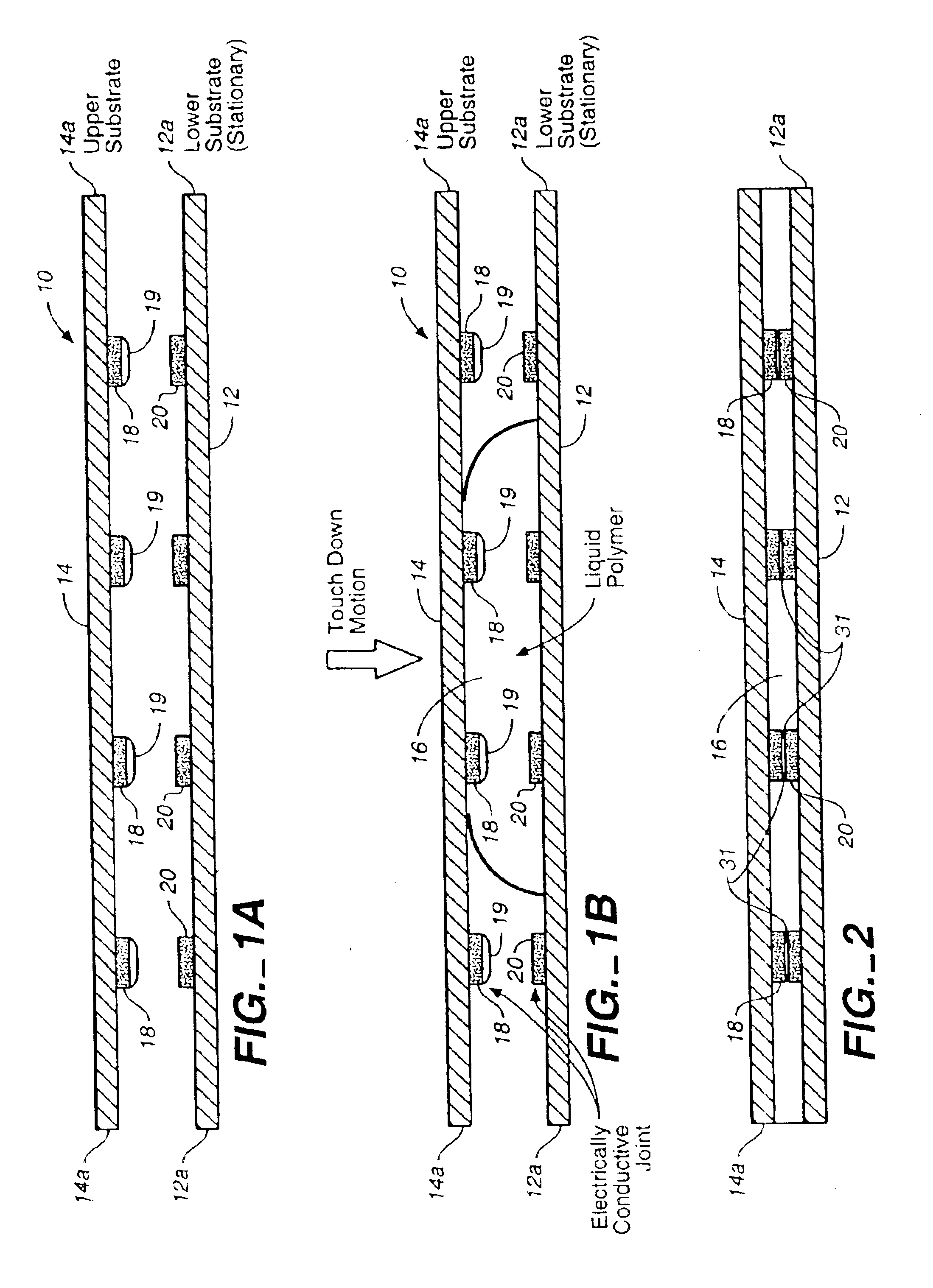
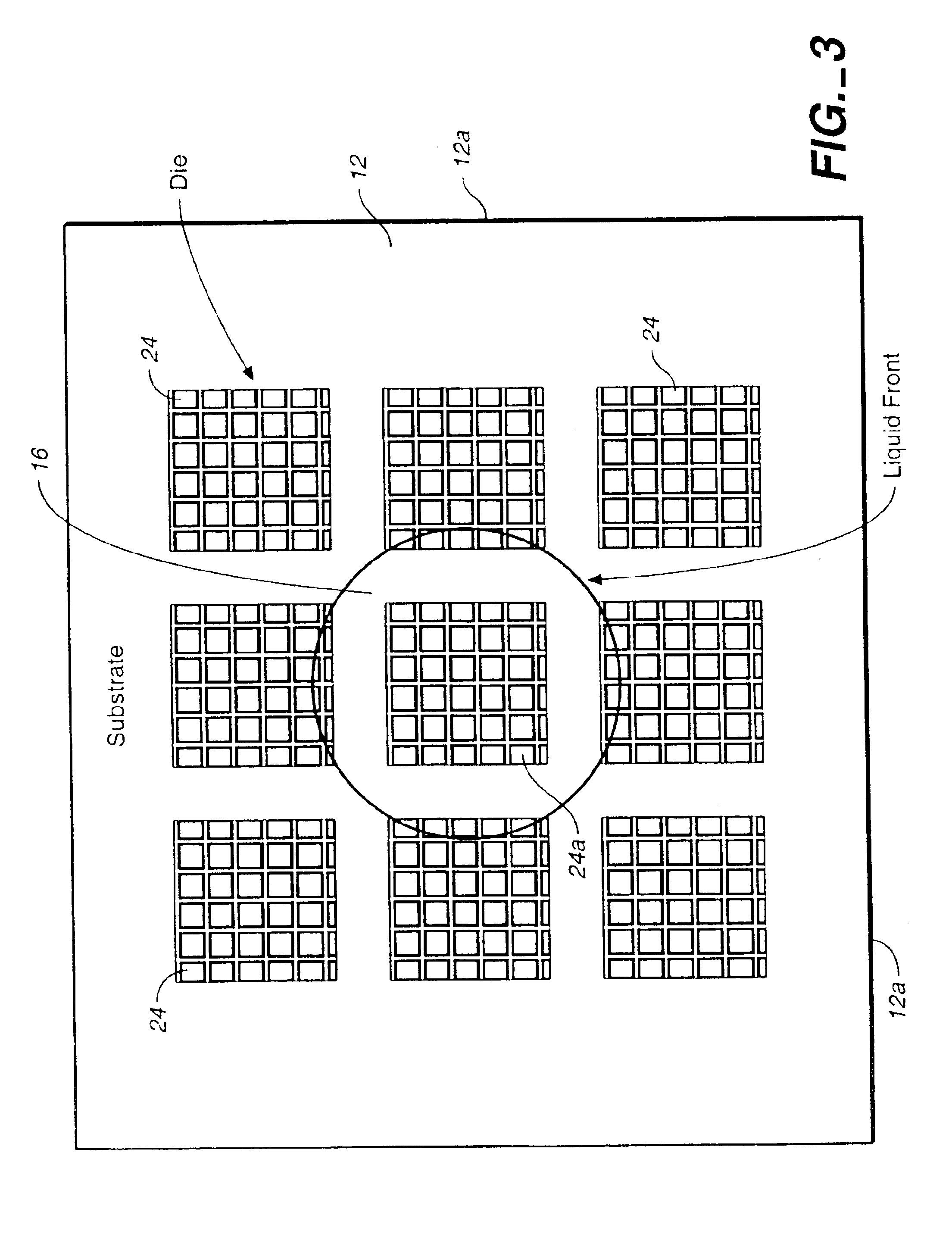
Method for joining and an ultra-high density interconnect
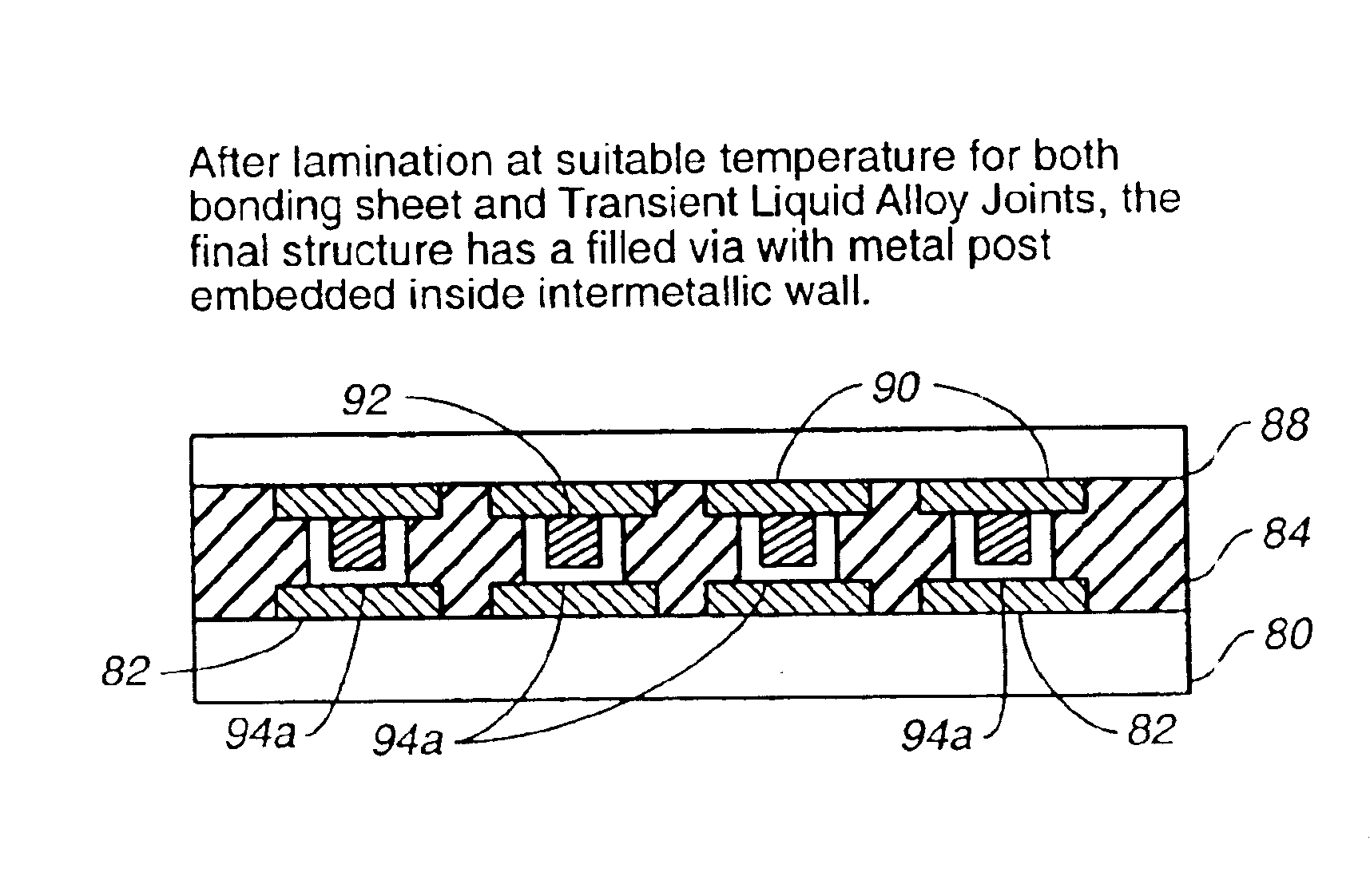
Embodiments of the invention are directed to a method comprising depositing a dielectric layer on a circuitized layer having a conductive region. The dielectric layer is preferably a bonding sheet. An aperture is formed in the dielectric layer over the conductive region. A conductive body, disposed on another circuitized substrate, is inserted into the aperture. The conductive body comprises a main region (e.g., a conductive post) and a depletion region (e.g., a thin layer of metal or transient liquid alloy bonding material). The depletion region contacts the conductive region on the circuitized layer, and the circuitized layers are laminated together. Heat and pressure can be applied to the combination in order to form an intermetallic region from the depletion region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Vertical cross point arrays for ultra high density memory applications
ActiveUS8937292B2Large capacitySolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
An ultra-high-density vertical cross-point array comprises a plurality of horizontal line layers having horizontal lines interleaved with a plurality of vertical lines arranged in rows and columns. The vertical lines are interleaved with the horizontal lines such that a row of vertical lines is positioned between each consecutive pair of horizontal lines in each horizontal line layer. Each vertical line comprises a center conductor surrounded by a single or multi-layered memory film. Accordingly, when interleaved with the horizontal lines, two-terminal memory cells are integrally formed between the center conductor of each vertical line and each crossing horizontal line. By configuring the vertical and horizontal lines so that a row of vertical lines is positioned between each consecutive pair of horizontal lines, a unit memory cell footprint of just 2F2 may be realized.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
Method and system for joining and an ultra-high density interconnect
Techniques are given for determining the data transmission or sending rates in a router or switch of two or more input queues in one or more input ports sharing an output port, which may optionally include an output queue. The output port receives desired or requested data from each input queue sharing the output port. The output port analyzes this data and sends feedback to each input port so that, if needed, the input port can adjust its transmission or sending rate.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
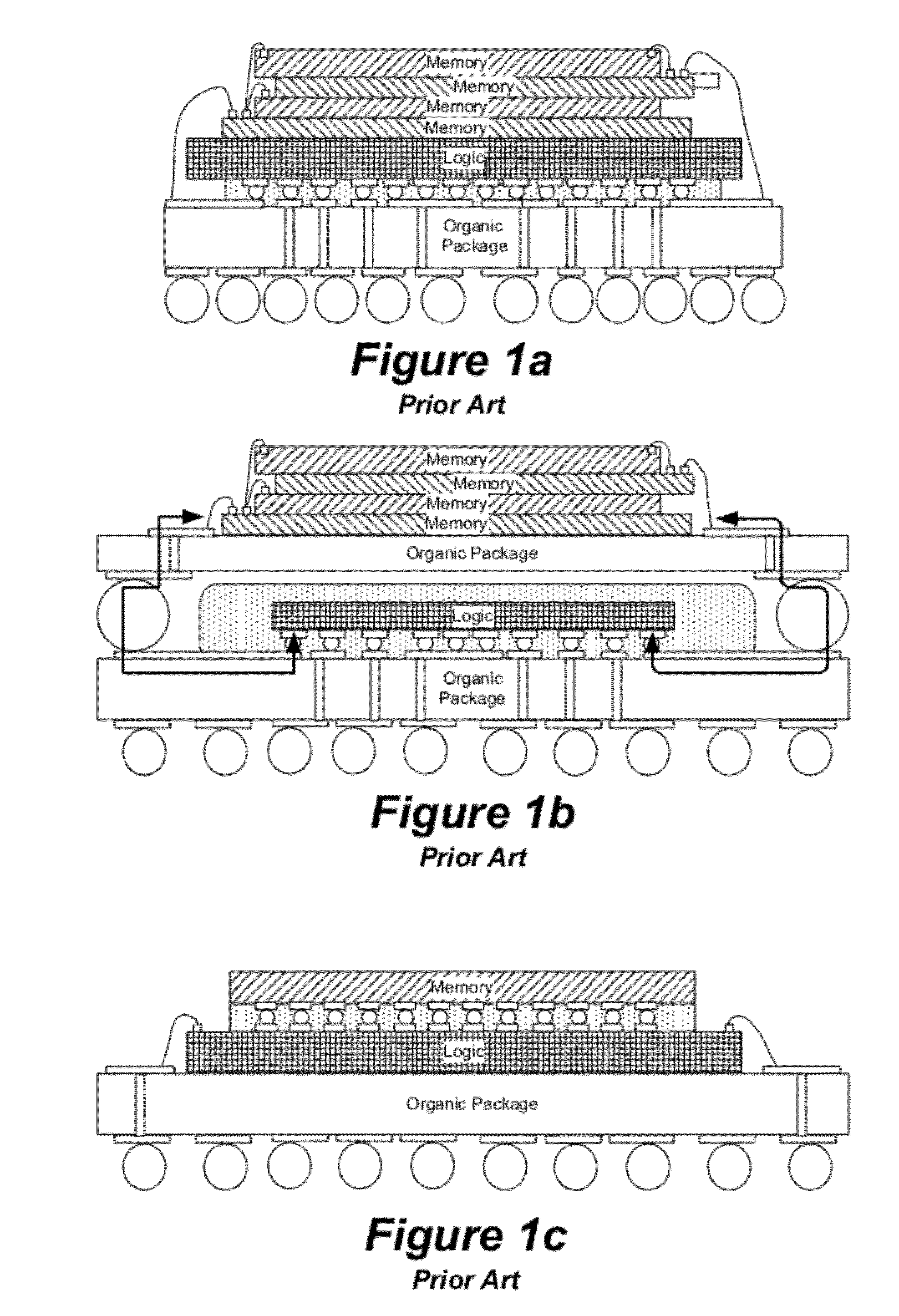
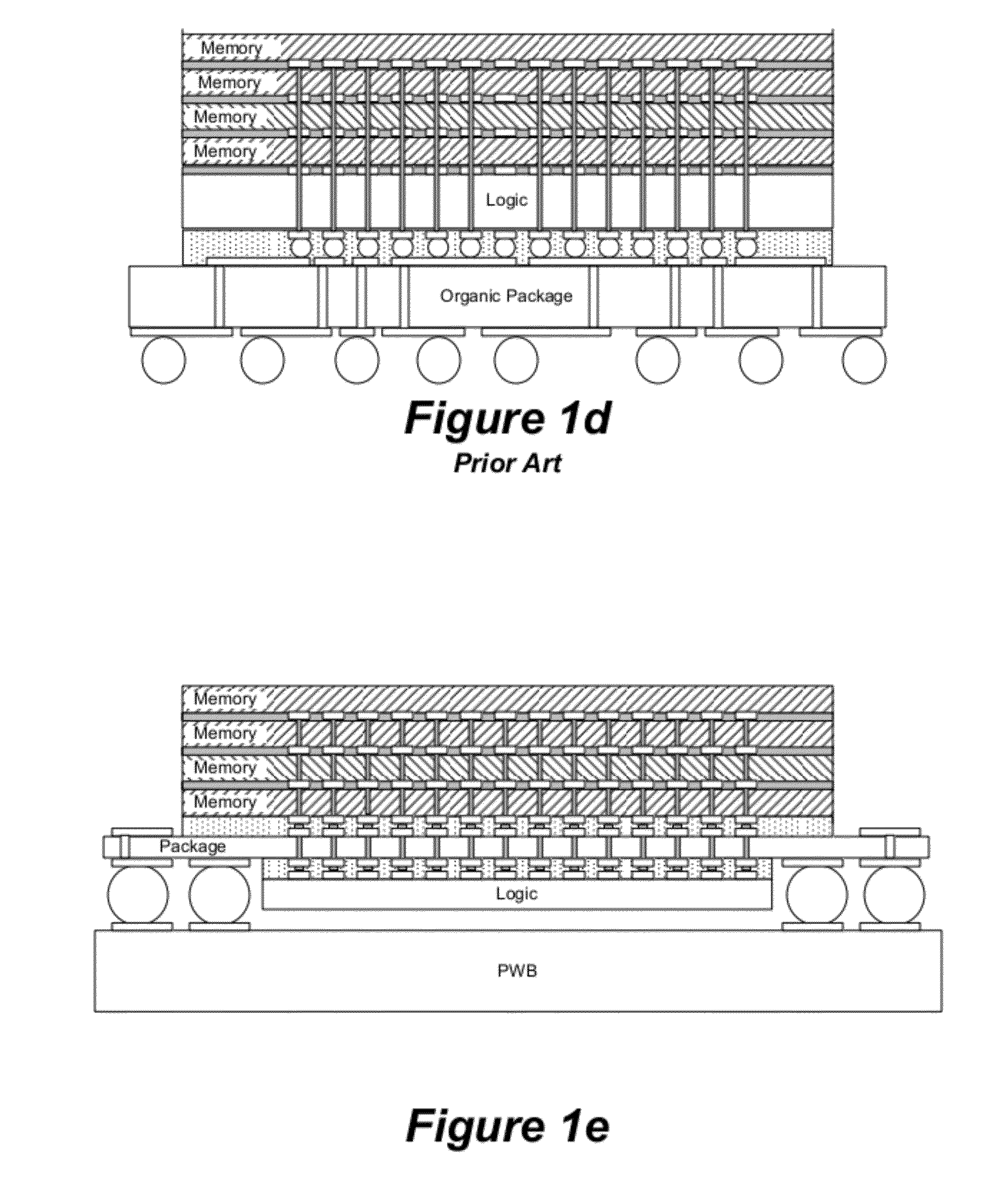
4d device process and structure
InactiveUS20110170266A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringUltra high density
a 4D device comprises a 2D multi-core logic and a 3D memory stack connected through the memory stack sidewall using a fine pitch T&J connection. The 3D memory in the stack is thinned from the original wafer thickness to no remaining Si. A tounge and groove device at the memory wafer top and bottom surfaces allows an accurate stack alignment. The memory stack also has micro-channels on the backside to allow fluid cooling. The memory stack is further diced at the fixed clock-cycle distance and is flipped on its side and re-assembled on to a template into a pseudo-wafer format. The top side wall of the assembly is polished and built with BEOL to fan-out and use the T&J fine pitch connection to join to the 2D logic wafer. The other side of the memory stack is polished, fanned-out, and bumped with C4 solder. The invention also comprises a process for manufacturing the device. In another aspect, the invention comprises a 4D process and device for over 50× greter than 2D memory density per die and an ultra high density memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
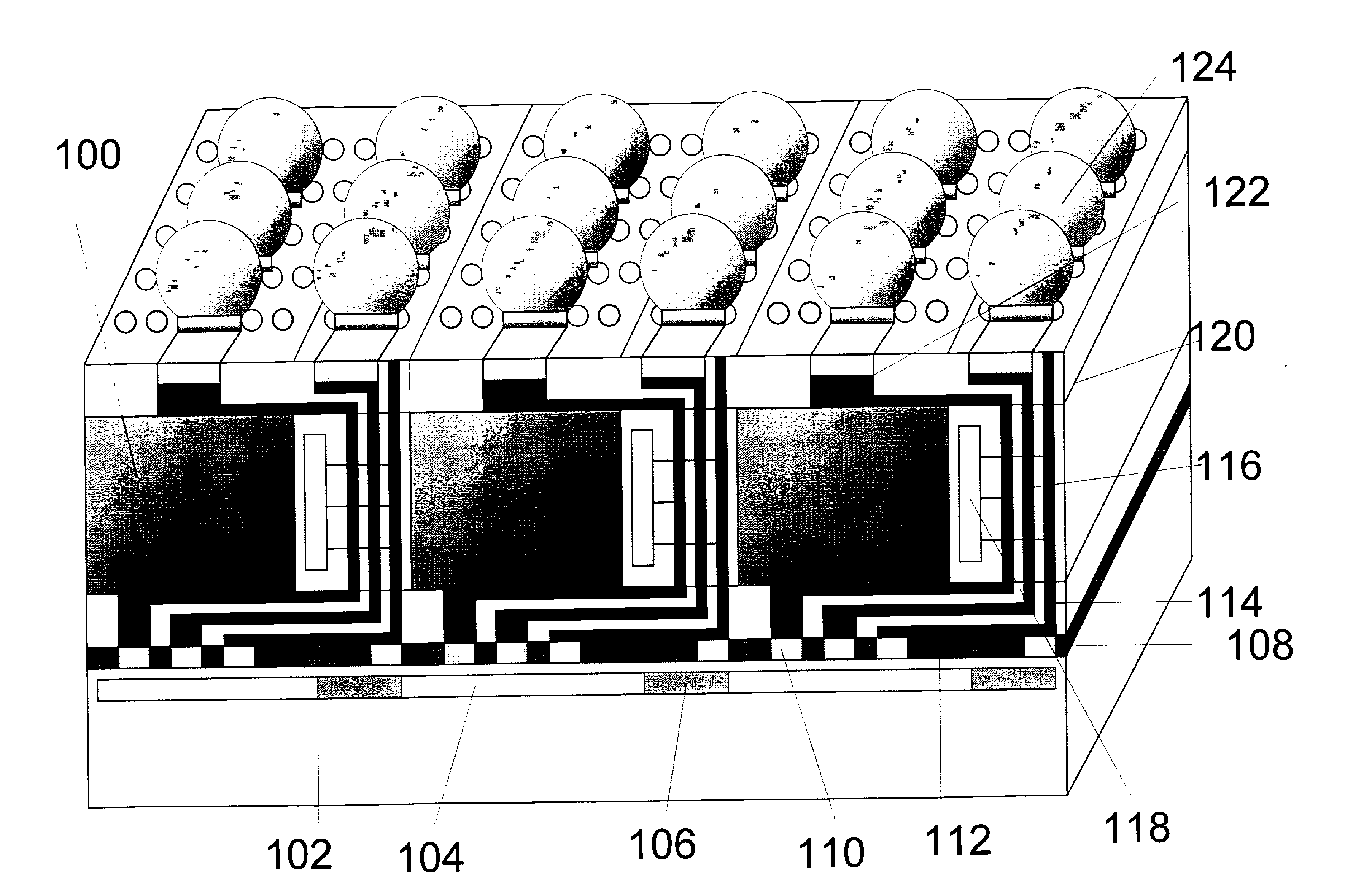
Super high density module with integrated wafer level packages
InactiveUS20050048695A1Increase memory capacityLow profileSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerStatic random-access memory
A wafer level package, and a semiconductor wafer, electronic system, and a memory module that include one or more of the wafer level packages, and methods of fabricating the die packages on a wafer level, and integrated circuit modules that include one or more packages are provided. In one embodiment, the die package comprises a redistribution layer interconnecting two or more dies disposed on a substrate, typically a semiconductor wafer, the redistribution layer including a first trace connecting a bond pad of each of two dies, and a second trace connecting one of the bond pads of the two dies to a ball pad. The die package of the invention can comprise memory devices such as static random access memories (SRAMs), and can be incorporated into a variety of electronic systems as part of a memory package such as single in line memory modules (SIMMs) or dual in line memory modules.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
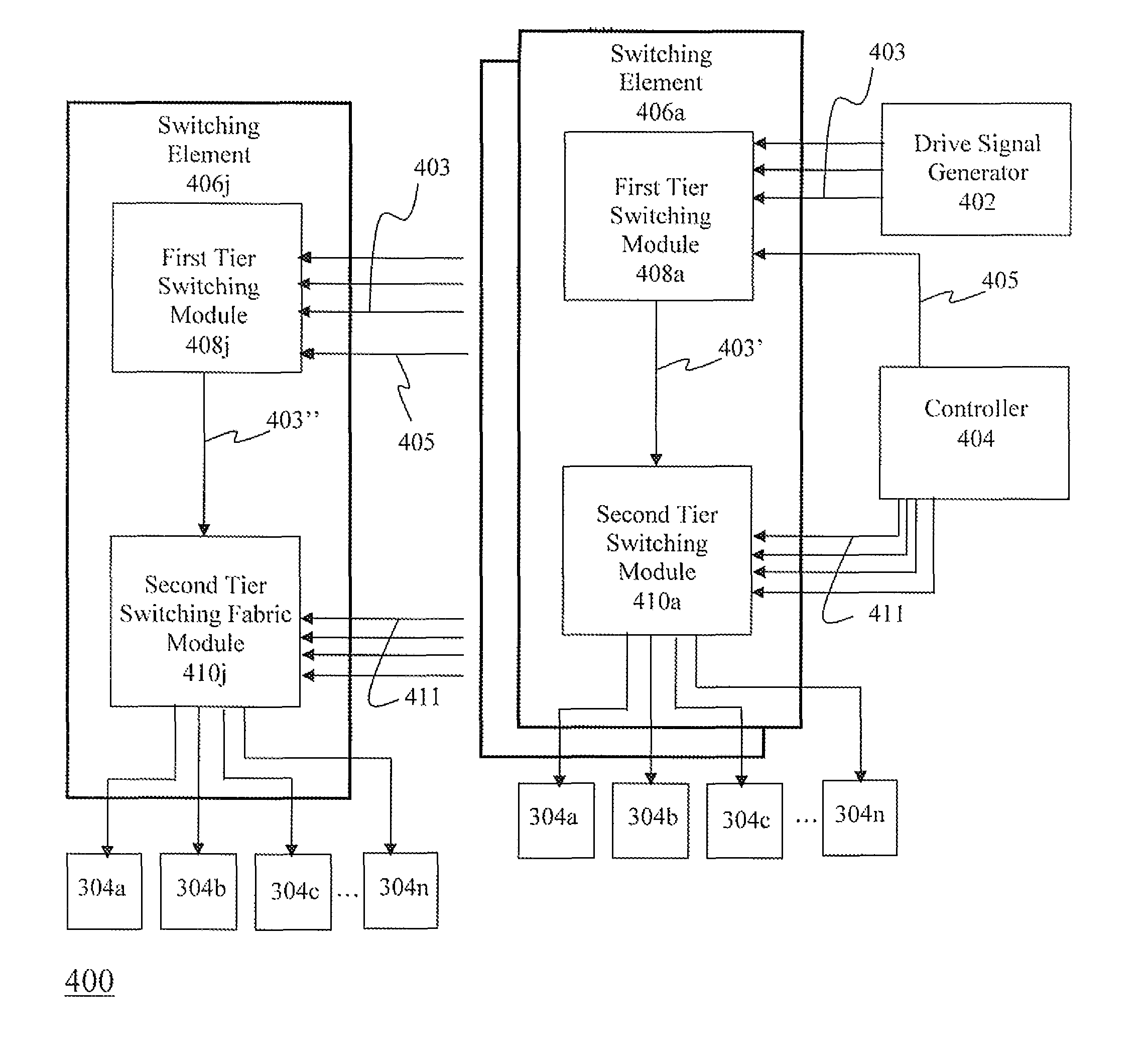
Hierarchical Switching in Ultra-High Density Ultrasound Array
ActiveUS20070167781A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesDriver circuitPhase difference
A focused ultrasound system comprises a transducer having a multiplicity of transducer elements, drive circuitry that generates and outputs a plurality of drive signals, each offset by a respective phase difference, and a controller for selectively coupling the drive signals to respective transducer elements, the controller including a plurality of first tier switching modules and second tier switching modules. Each first tier module receives as an input the plurality of drive signals and outputs one of the drive signals in response to a drive signal selection signal. Each second tier module is coupled to a respective grouping of transducer elements and selectively couples a respective selected drive signal output from a first tier switching module to one or more of the transducer elements in response to a transducer element selection signal.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
Photochromic and electrochromic compounds and methods of synthesizing and using same
ActiveUS7777055B2Efficiently neutralizedMinimize diffusionLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryFiberCyclopentene
This invention relates to novel photochromic and electrochromic monomers and polymers based on 1,2-dithienylcyclopentene derivatives and method of using and synthesizing same. The compounds are reversibly interconvertible between different isomeric forms under suitable photochromic or electrochromic conditions. The electrochromic conversion may be catalytic. The application also relates to ultra-high density homopolymers prepared using ring-opening methathesis polymerization (ROMP) where the central ring of the 1,2-bis(3-thienyl)-cyclopentene is incorporated directly into the polymer backbone. The monomer units may be readily functionalized to enable the synthesis of polymers with diverse structural and electronic properties. The compounds have many potential applications including high-density optical information storage systems, photoregulated molecular switches, reversible holographic systems, ophthalmic lenses, actinometry and molecular sensors, photochromic inks, paints and fibers and optoelectronic systems such as optical waveguides, Bragg reflectors and dielectric mirrors.
Owner:SOLUTIA CANADA INC
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic MONOS memory
A fast low voltage ballistic program, ultra-short channel, ultra-high density, dual-bit multi-level flash memory is described. The structure and operation of this invention is enabled by a twin MONOS cell structure having an ultra-short control gate channel of less than 40 nm, with ballistic injection which provides high electron injection efficiency and very fast program at low program voltages of 3~5V. The ballistic MONOS memory cell is arranged in the following array: each memory cell contains two nitride regions for one word gate, and ½ a source diffusion and ½ a bit diffusion. Control gates can be defined separately or shared together over the same diffusion. Diffusions are shared between cells and run in parallel to the side wall control gates, and perpendicular to the word line. The features of fast program, low voltage, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level MONOS NVRAM of the present invention include: 1) Electron memory storage in nitride regions within an ONO layer underlying the control gates, 2) high density dual-bit cell in which there are two nitride memory storage elements per cell, 3) high density dual-bit cell can store multi-levels in each of the nitride regions, 4) low current program controlled by the word gate and control gate, 5) fast, low voltage program by ballistic injection utilizing the controllable ultra-short channel MONOS, and 6) side wall control poly gates to program and read multi-levels while masking out memory storage state effects of the unselected adjacent nitride regions and memory cells.
Owner:HALO LSI INC
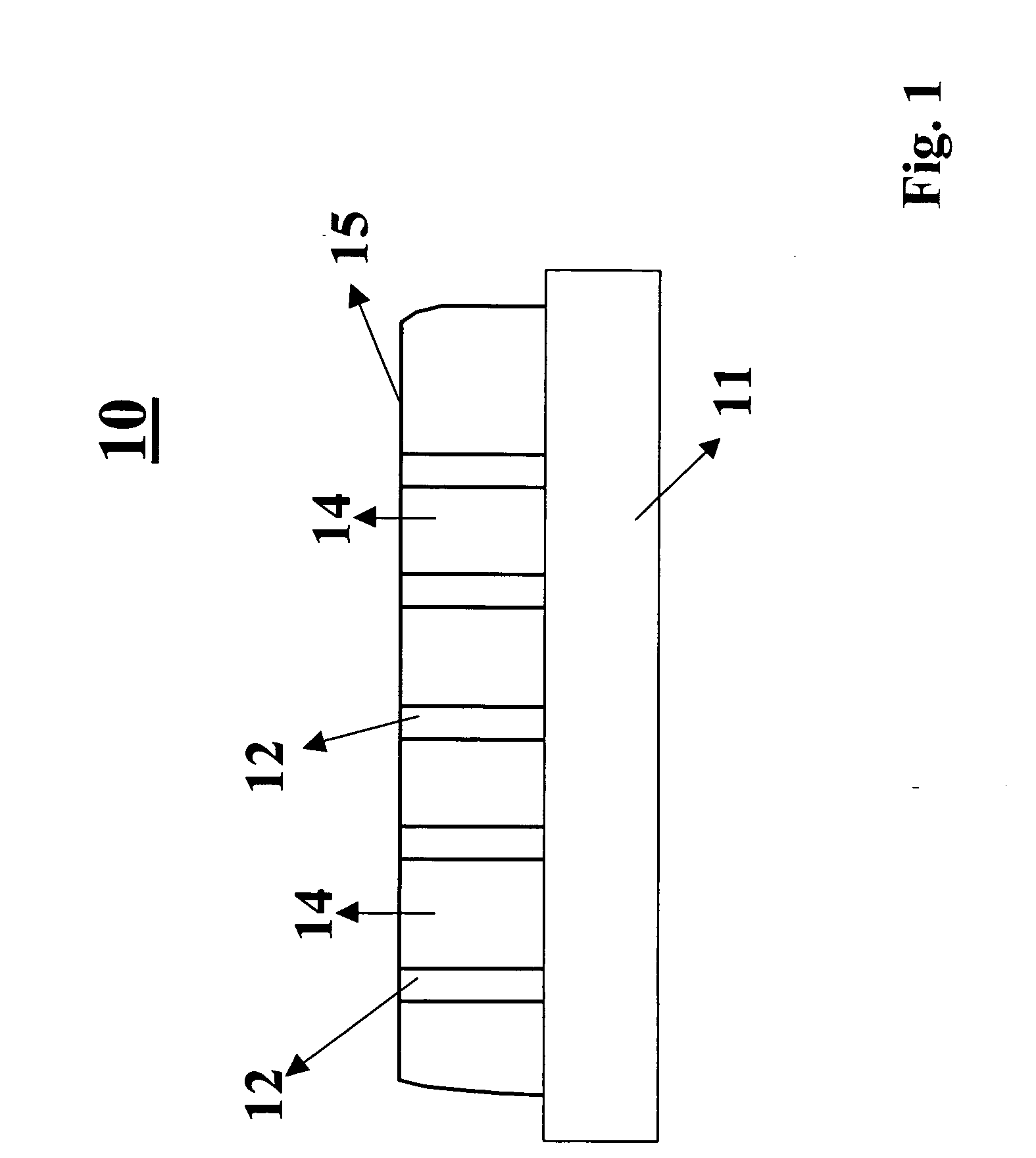
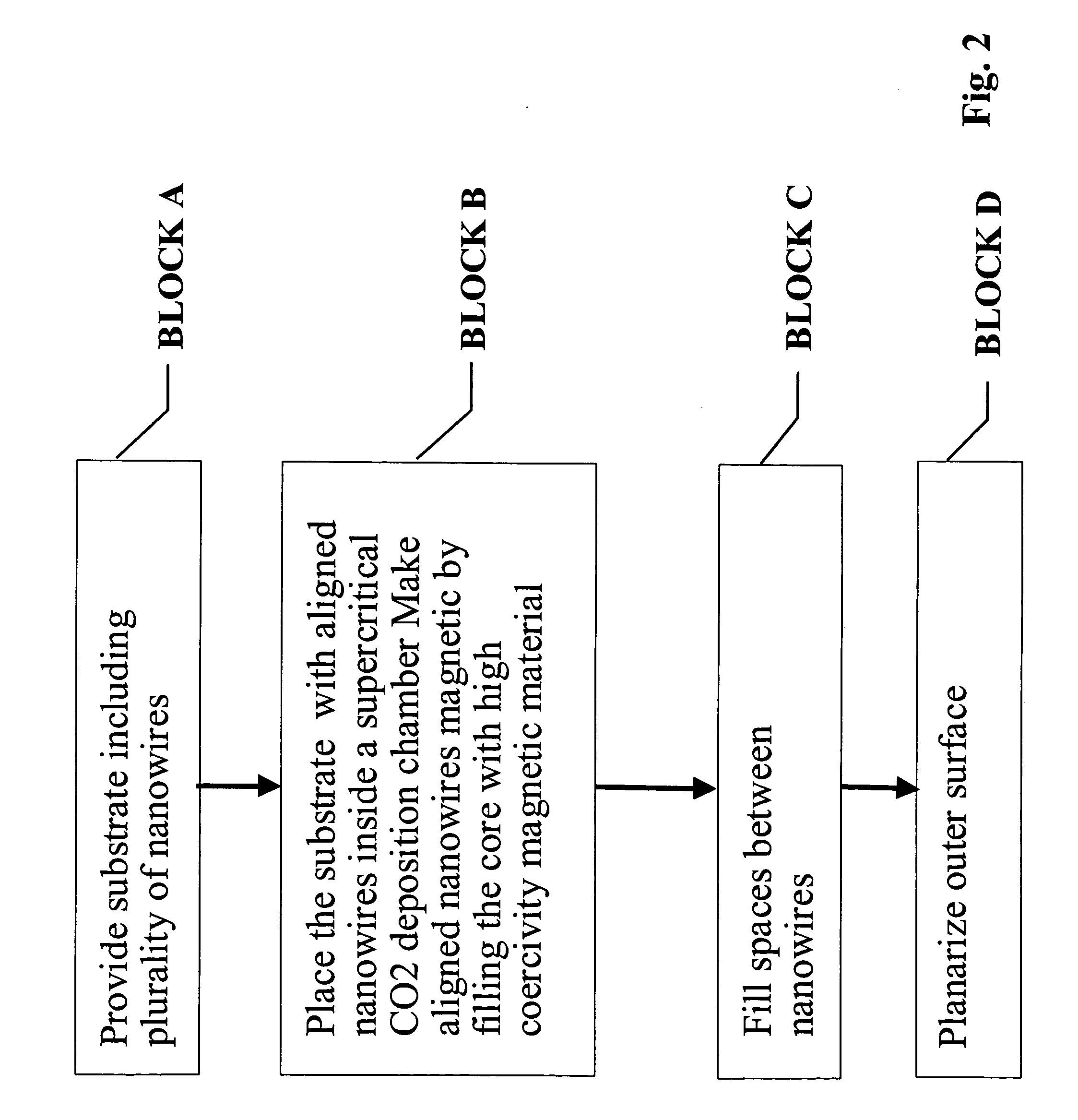
Ultra-high-density magnetic recording media and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20050079282A1High density recordingImprove coercive forceNanoinformaticsRecord information storageNanowireHigh density
In accordance with the invention, a high density recording medium is fabricated by novel methods. The medium comprises an array of nanomagnets disposed within a matrix or on the surface of substrate material. The nanomagnets are advantageously substantially perpendicular to a planar surface. The nanomagnets are preferably nanowires of high coercivity magnetic material inside a porous matrix or an array of vertically aligned nanotubes, or on the surface of flat substrate. Such media can provide ultra-high density recording with bit size less than 50 nm and even less than 20 nm. A variety of techniques are described for making such media.
Owner:JIN SUNGHO
Low Cost High Density Nonvolatile Memory Array Device Employing Thin Film Transistors and Back to Back Schottky Diodes
InactiveUS20140103471A1Low costEliminate needSolid-state devicesDigital storageHigh densityEngineering
An improved crosspoint memory array device comprising a plurality of memory cells, each memory cell being disposed at an intersection region of bit and word conductive lines, electrically coupled to one of the first conductive lines at a first terminal and to one of the second conductive lines at a second terminal, and comprising a controllable electrical resistance, wherein a back to back Schottky diode is located between each memory cell and one of the said conductive lines, and wherein each conductive line is electrically coupled to at least two thin film transistors (TFTs). The device is substantially produced in BEOL facilities without need of front end semiconductor production facilities, yet can be made with ultra high density and low cost.
Owner:TACHO HLDG LLC
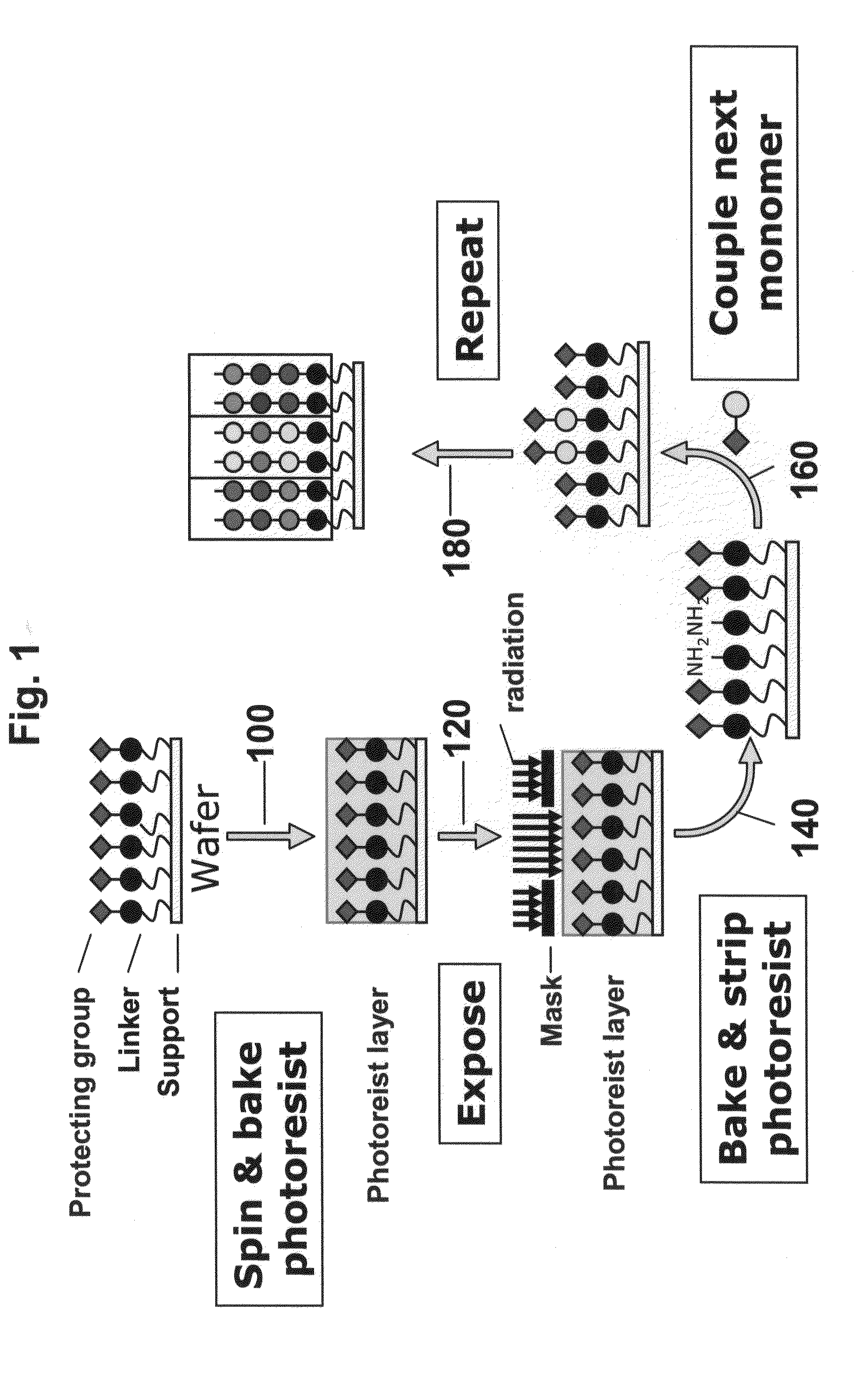
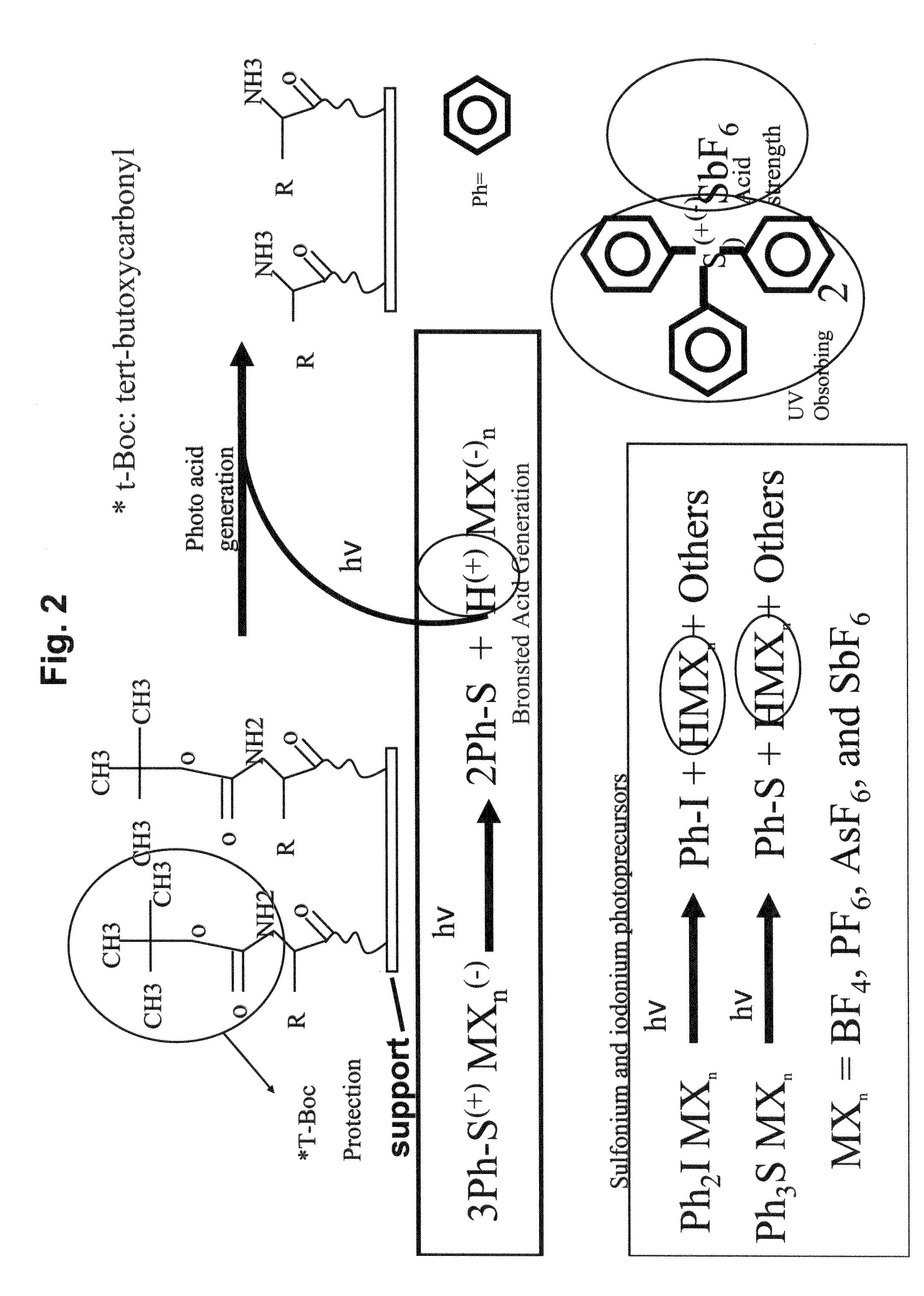
High density peptide arrays containing kinase or phosphatase substrates
Peptide arrays and uses thereof for diagnostics, therapeutics and research. Ultra high density peptide arrays are generated using photolithography, such as using photoresist techniques.
Owner:DIGITAB
Hierarchical switching in ultra-high density ultrasound array
ActiveUS8608672B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesDriver circuitPhase difference
A focused ultrasound system comprises a transducer having a multiplicity of transducer elements, drive circuitry that generates and outputs a plurality of drive signals, each offset by a respective phase difference, and a controller for selectively coupling the drive signals to respective transducer elements, the controller including a plurality of first tier switching modules and second tier switching modules. Each first tier module receives as an input the plurality of drive signals and outputs one of the drive signals in response to a drive signal selection signal. Each second tier module is coupled to a respective grouping of transducer elements and selectively couples a respective selected drive signal output from a first tier switching module to one or more of the transducer elements in response to a transducer element selection signal.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
High density interconnect module
InactiveUS6396710B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityEngineering
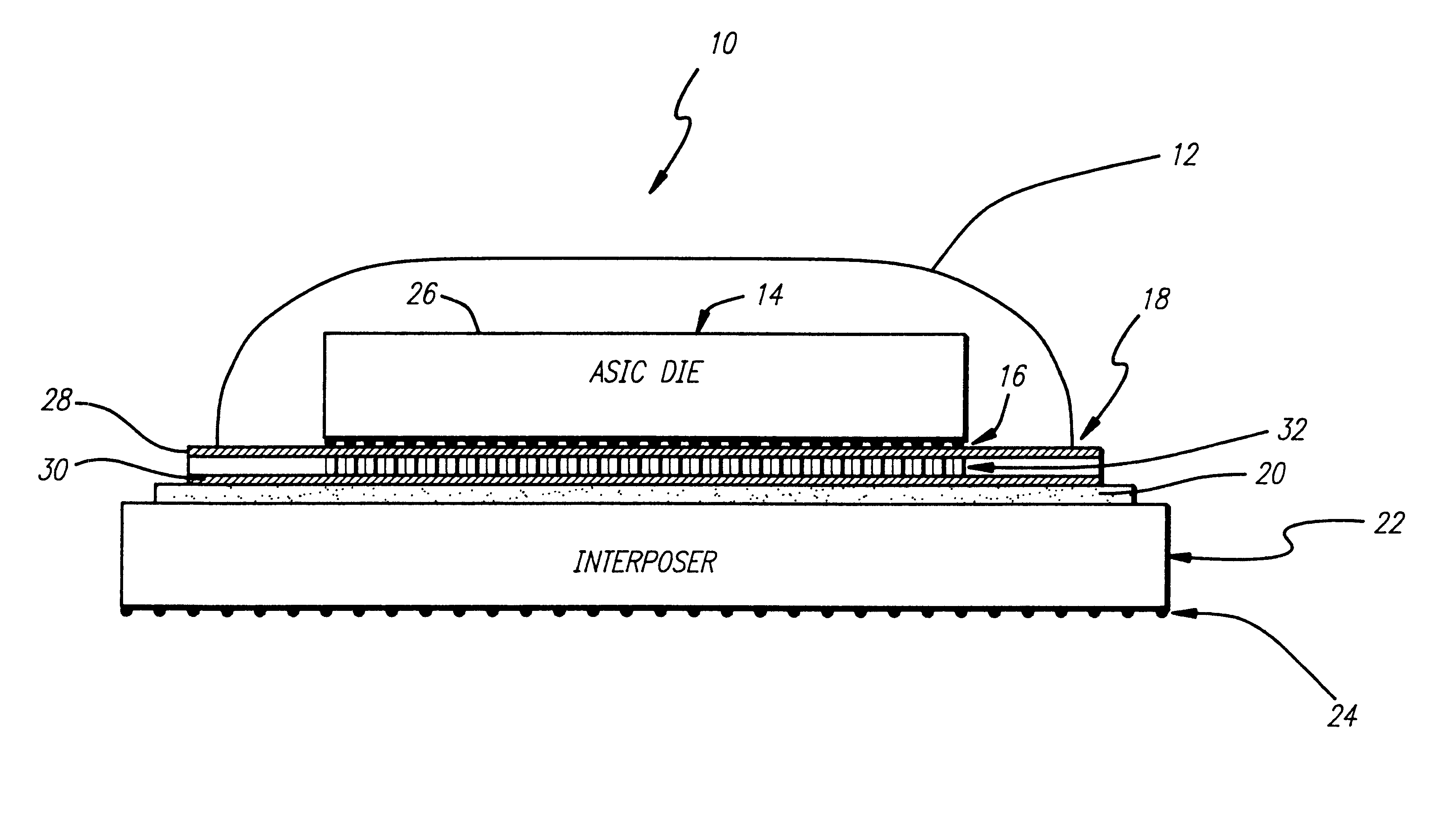
A cost-effective packaging system (10) for ultra high density input / output (integrated circuits (14). The packaging system includes a first circuit chip (14) that has a first pattern of contacts (16) distributed across a surface area of the chip (14). The first pattern of contacts (16) represents input / output connections (16). A three-dimensional circuit (18) is disposed spatially parallel with respect to the first circuit chip (14) and organizes the input / output connections (16) into a second pattern of contacts (24, 30) suitable for connection to a second circuit (22). In a specific embodiment, the three-dimensional circuit (18) is a double sided DECAL (18). The double-sided DECAL (18) includes a substrate (18) having a first circuit pattern (28) spatially parallel with a second circuit pattern (30) on or in the substrate (18). The first and second circuit patterns (28 and 30) are interconnected. The first circuit pattern (28) has a third pattern of contacts (16) coincident with the first pattern of contacts (16) on the first circuit chip (14). The first circuit pattern (28) and / or the second circuit pattern (30) are ball grid arrays or coaxial connector arrays. The second circuit (22) is disposed spatially parallel with respect to the three-dimensional circuit (18). The second circuit (22) is a ceramic or laminate interposer that facilitates further organization of the input / output connections (16, 24). The interposer (18) includes a ball grid array (24) or a coaxial connector grid array (18) to facilitate the organization. A z-axis adhesive (20) is disposed between the interposer (22) and the three-dimensional circuit (18). A non-hermetic sealer (12) disposed over the first circuit chip (14).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
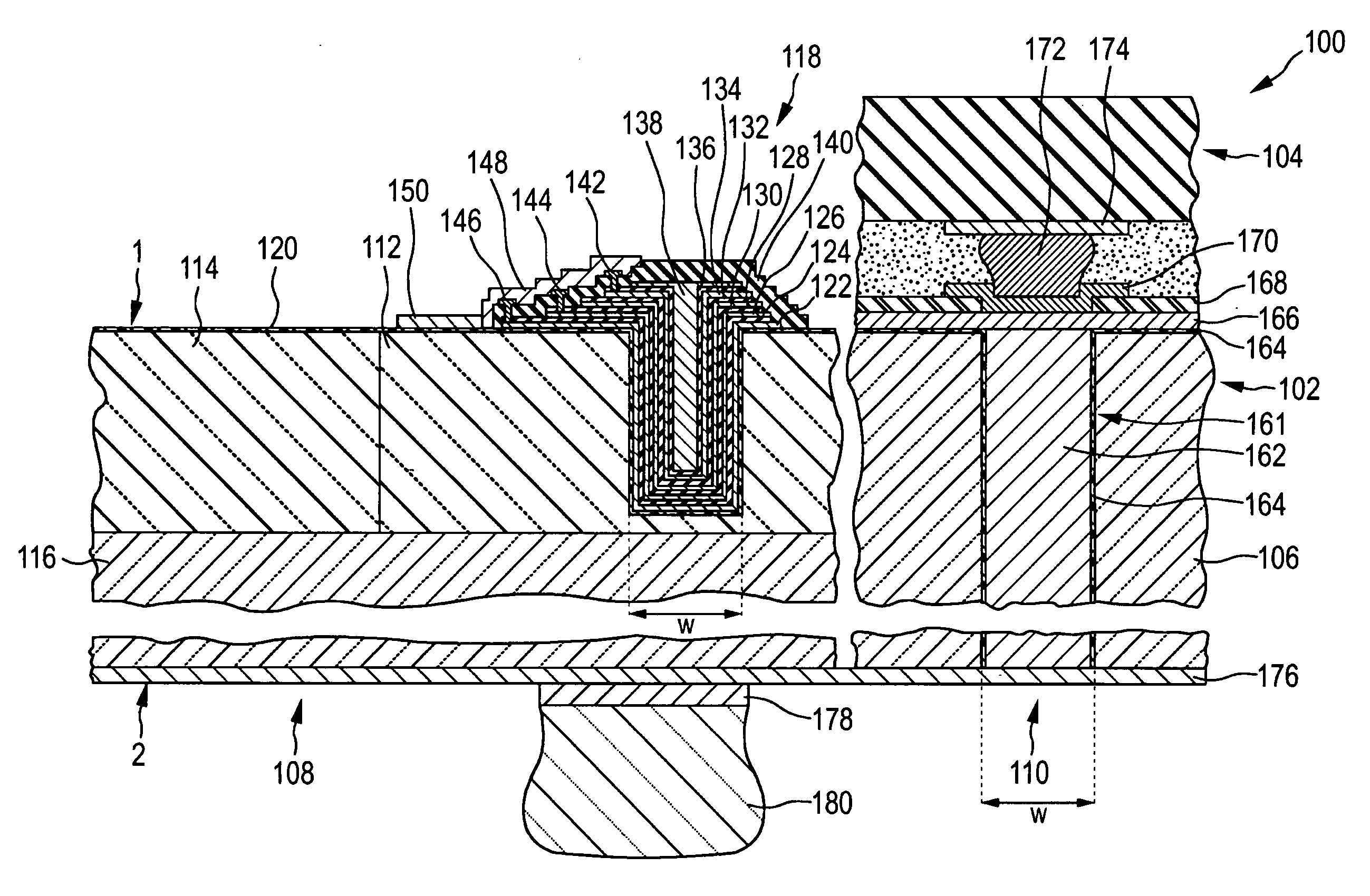
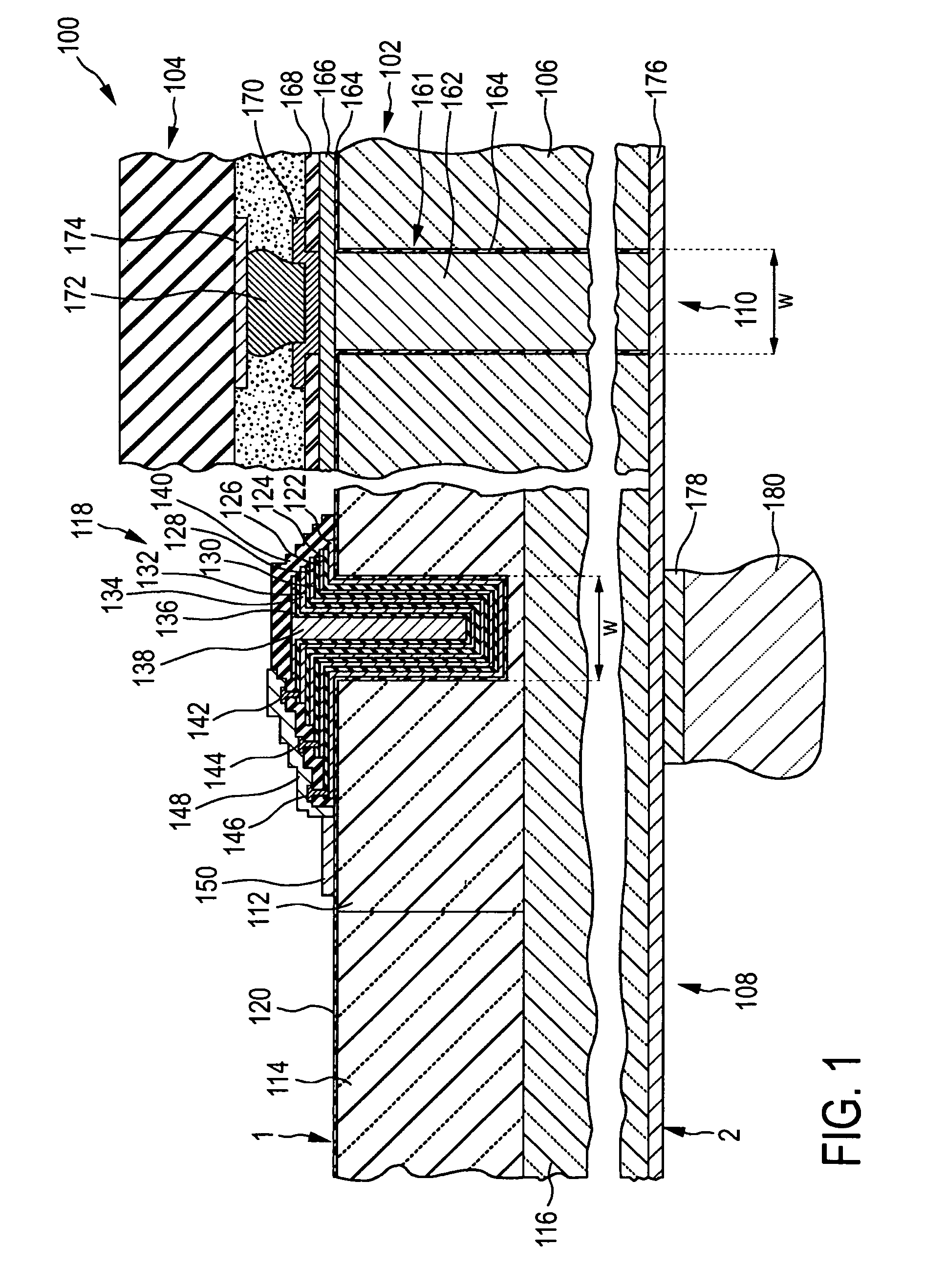
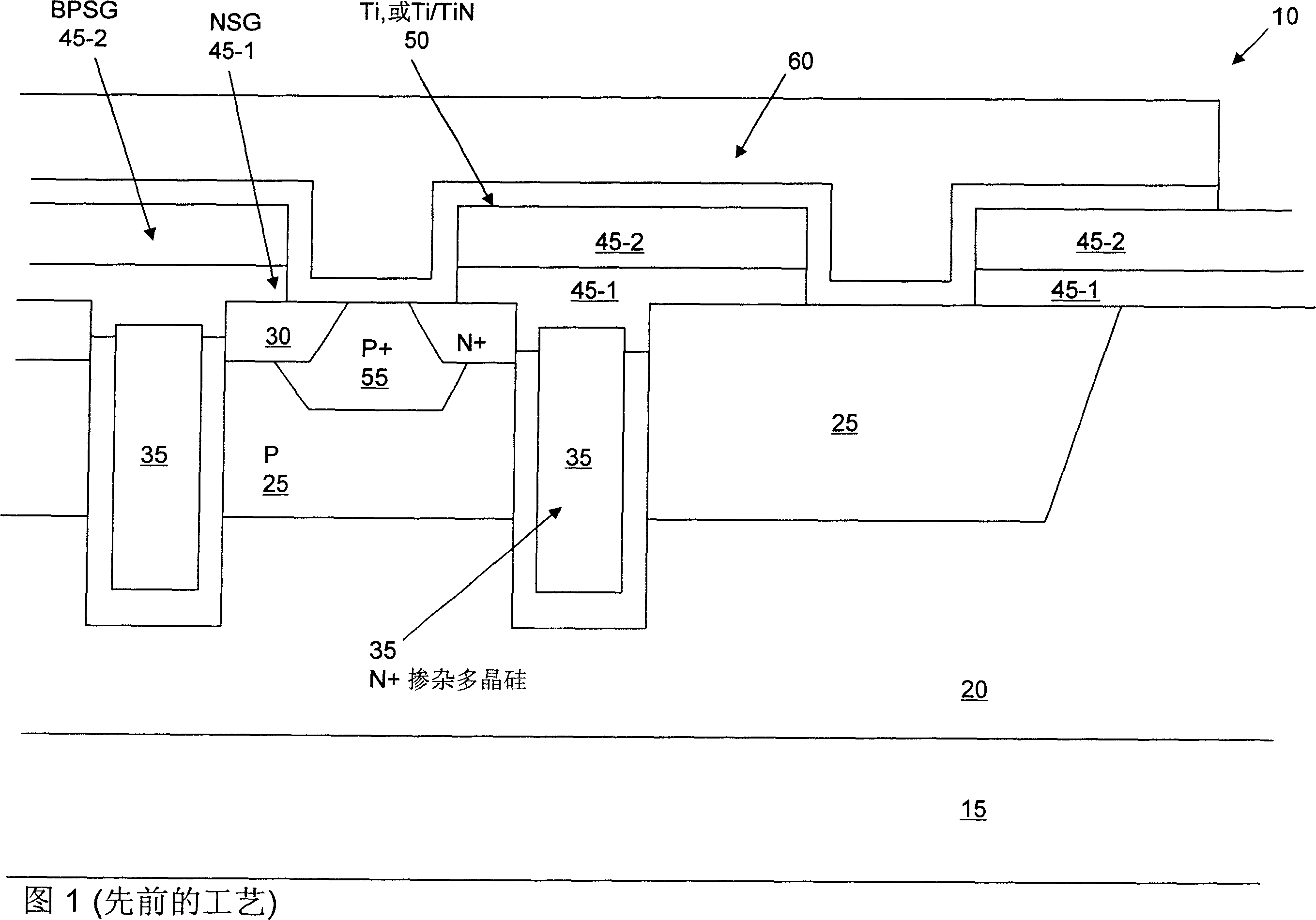
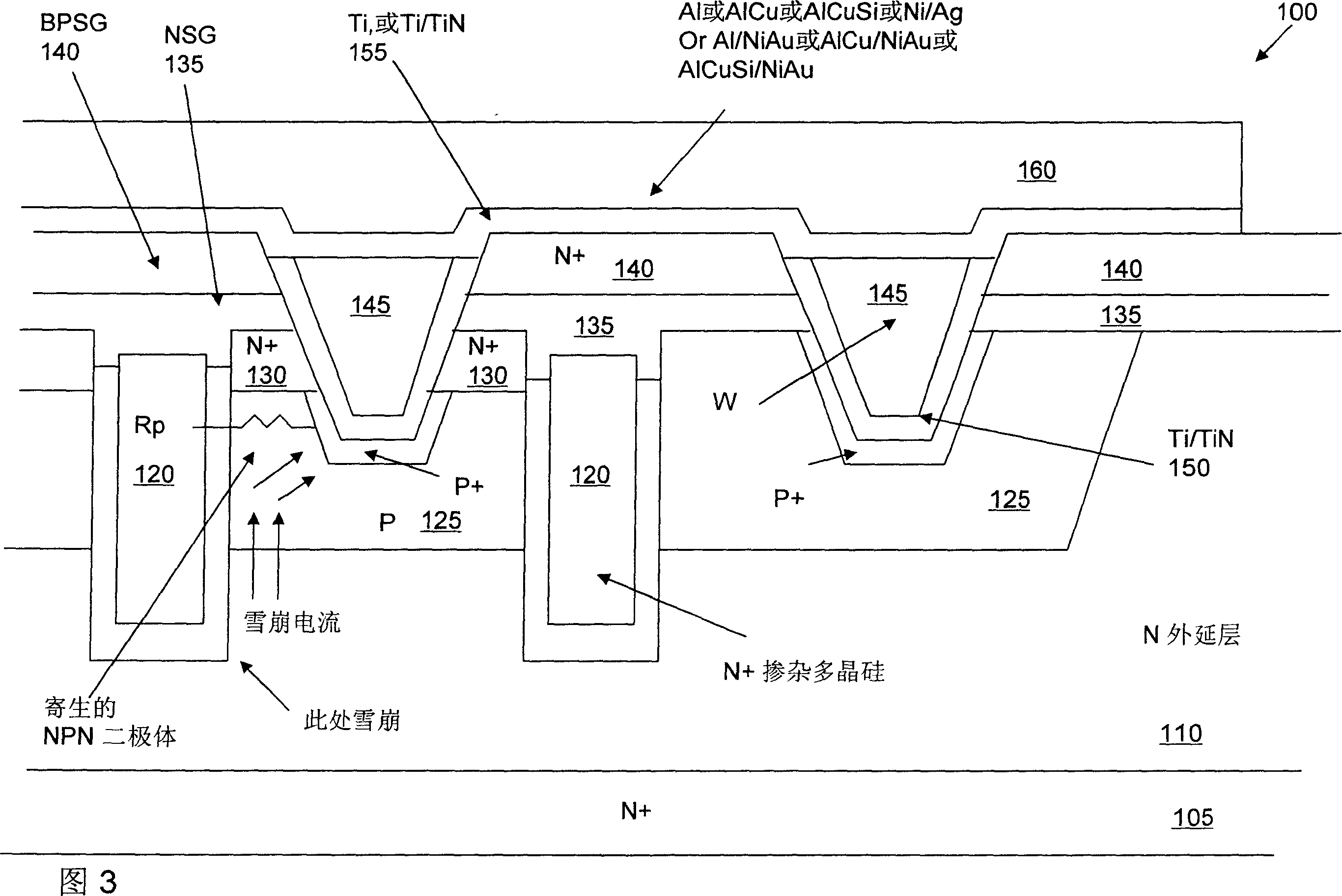
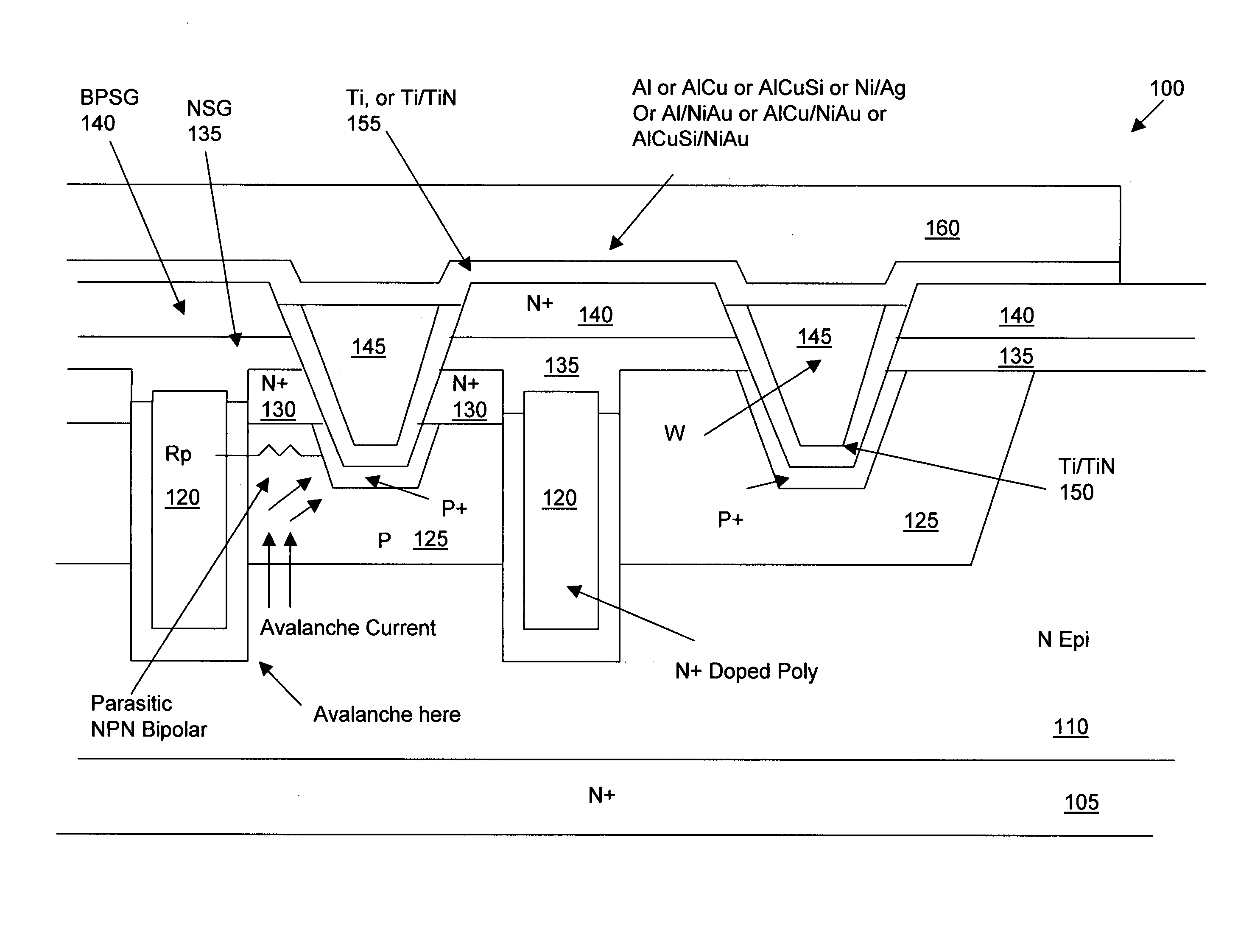
Structure for avalanche improvement of ultra high density trench mosfet
A trench metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) cell having a trenched gate surrounded by a source region between a body region disposed above a drain on the bottom surface of a substrate Inside. The MOSFET cell also has a source-body contact trench opened such that its sidewalls extend substantially perpendicular to the upper surface into the source and body region and are filled with contact metal plugs. forming a body-resistance reducing region doped with a body impurity to surround the source-body contact trench to reduce the body-region resistance between the source-body contact metal and the trench gate to improve avalanche ability.
Owner:谢福渊
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic flash memory
An fast program, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level flash memory process, which can be applied to a ballistic step split gate side wall transistor, or to a ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor, which enables program operation by low voltage requirement on the floating gate during program is described. Two side wall floating gates are paired with a single word line select gate, and word lines are arranged to be perpendicular both the bit lines and control gate lines. Two adjacent memory cells on the same word line do not require an isolation region. Also, the isolation region between adjacent memory cells sharing the same bitline is defined by the minimum lithography feature, utilizing a self align fill technique. Adjacent memory cells on the same word line share bitline diffusion as well as a third poly control gate. Control gates allow program and read access to the individual floating gate. In addition to the dual-bit nature of the cell, density can be even further improved by multi-level storage. In one embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic step split gate side wall transistor. In a second embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor. Both types of ballistic transistors provide fast, low voltage programming. The control gates are used to override or suppress the various threshold voltages on associated floating gates, in order to program to and read from individual floating gates. The targets for this non-volatile memory array are to provide the capabilities of high speed, low voltage programming (band width) and high density storage.
Owner:HALO LSI DESIGN & DEVICE TECH
Structure for avalanche improvement of ultra high density trench MOSFET
InactiveUS20060273384A1Increase cell densityLower body resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetBody contact
A trenched metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) cell that includes a trenched gate surrounded by a source region encompassed in a body region above a drain region disposed on a bottom surface of a substrate. The MOSFET cell further includes a source-body contact trench opened with sidewalls substantially extend vertically relative to a top surface into the source and body regions and filled with contact metal plug. A body-resistance reduction region doped with body-doped is formed to surround the source-body contact trench to reduce a body-region resistance between the source-body contact metal and the trenched gate to improve an avalanche capability.
Owner:M MOS SEMICON
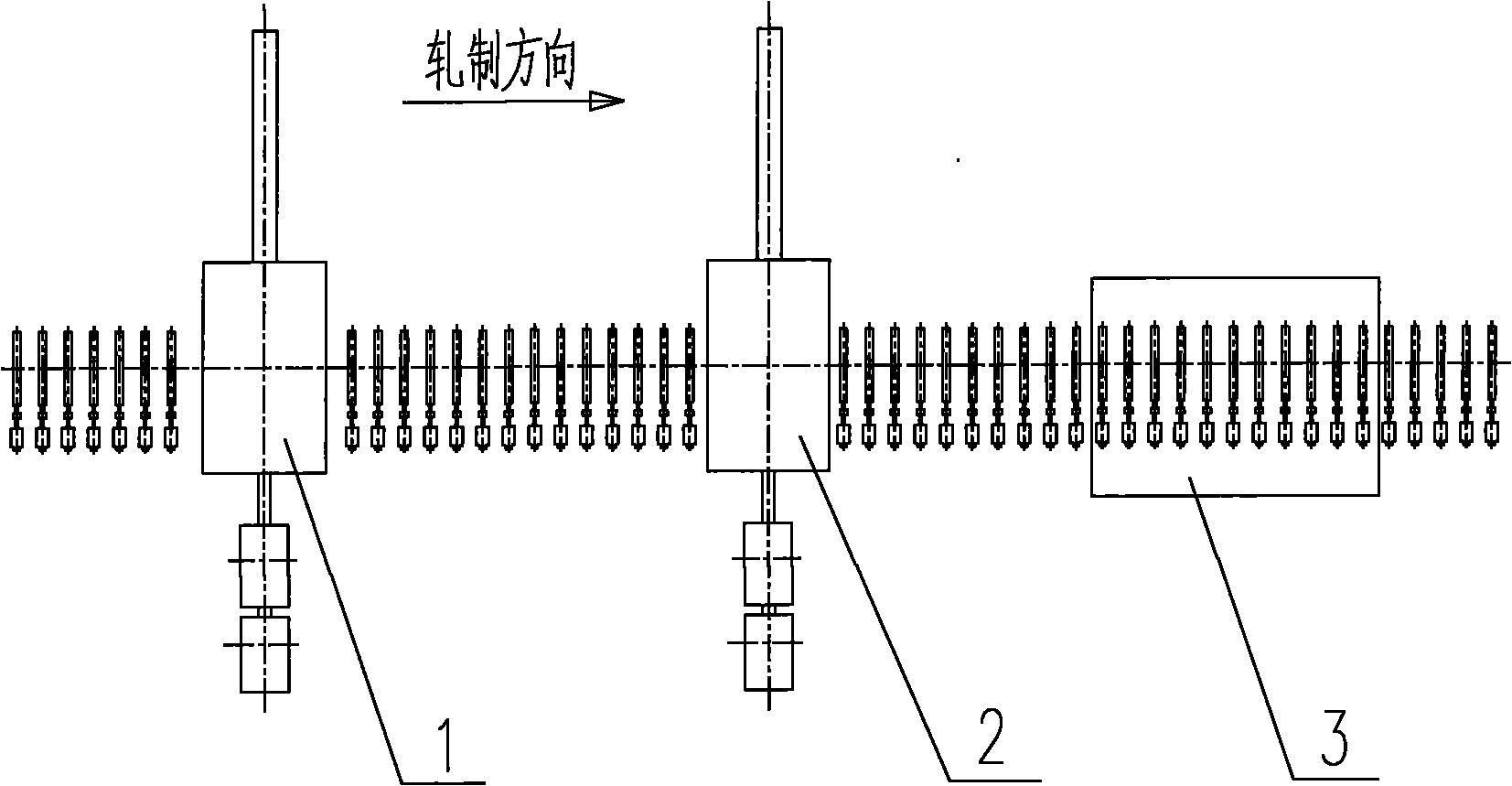
Cooling method of heavy and medium plate controlled rolling intermediate blank
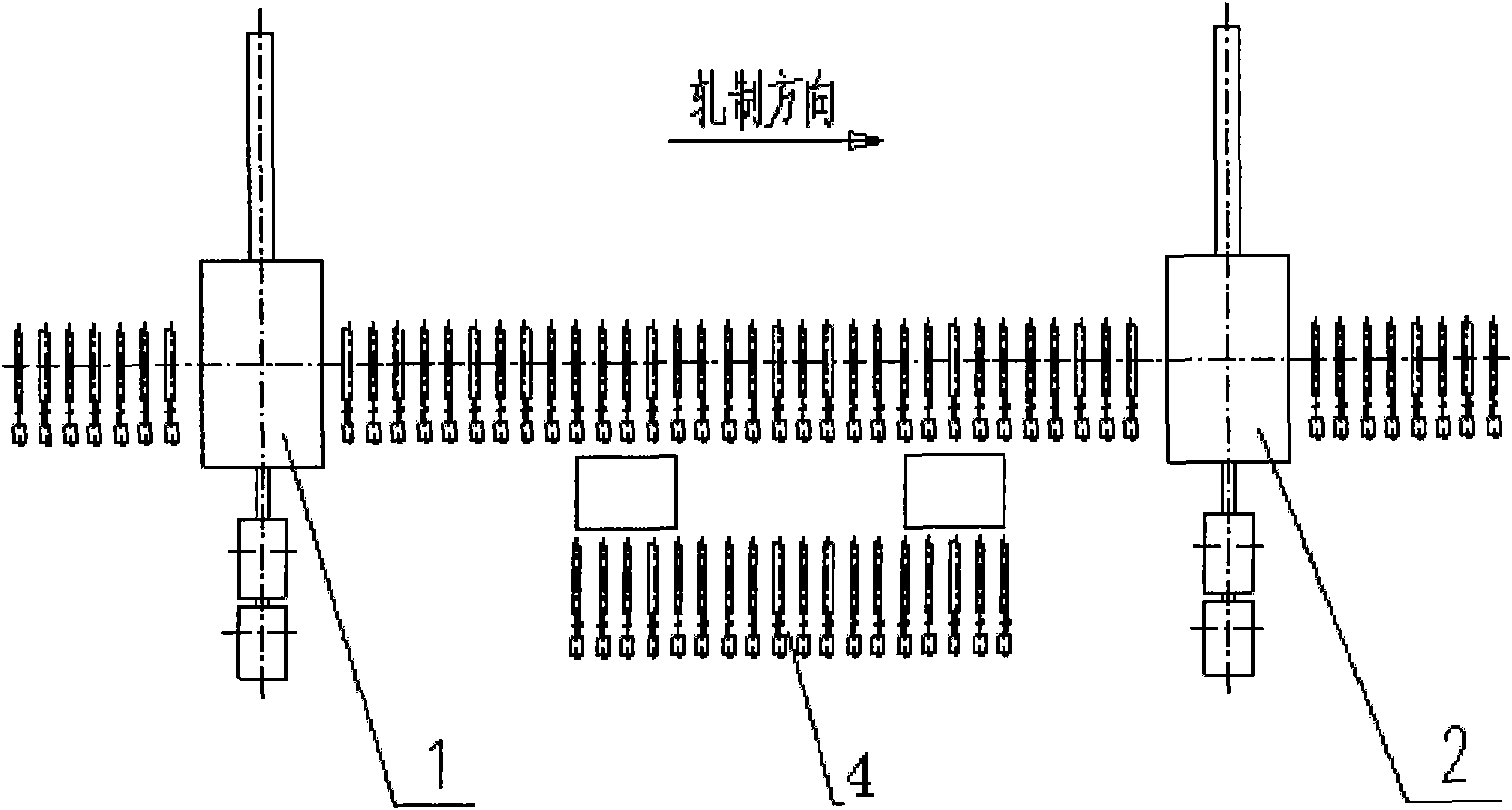
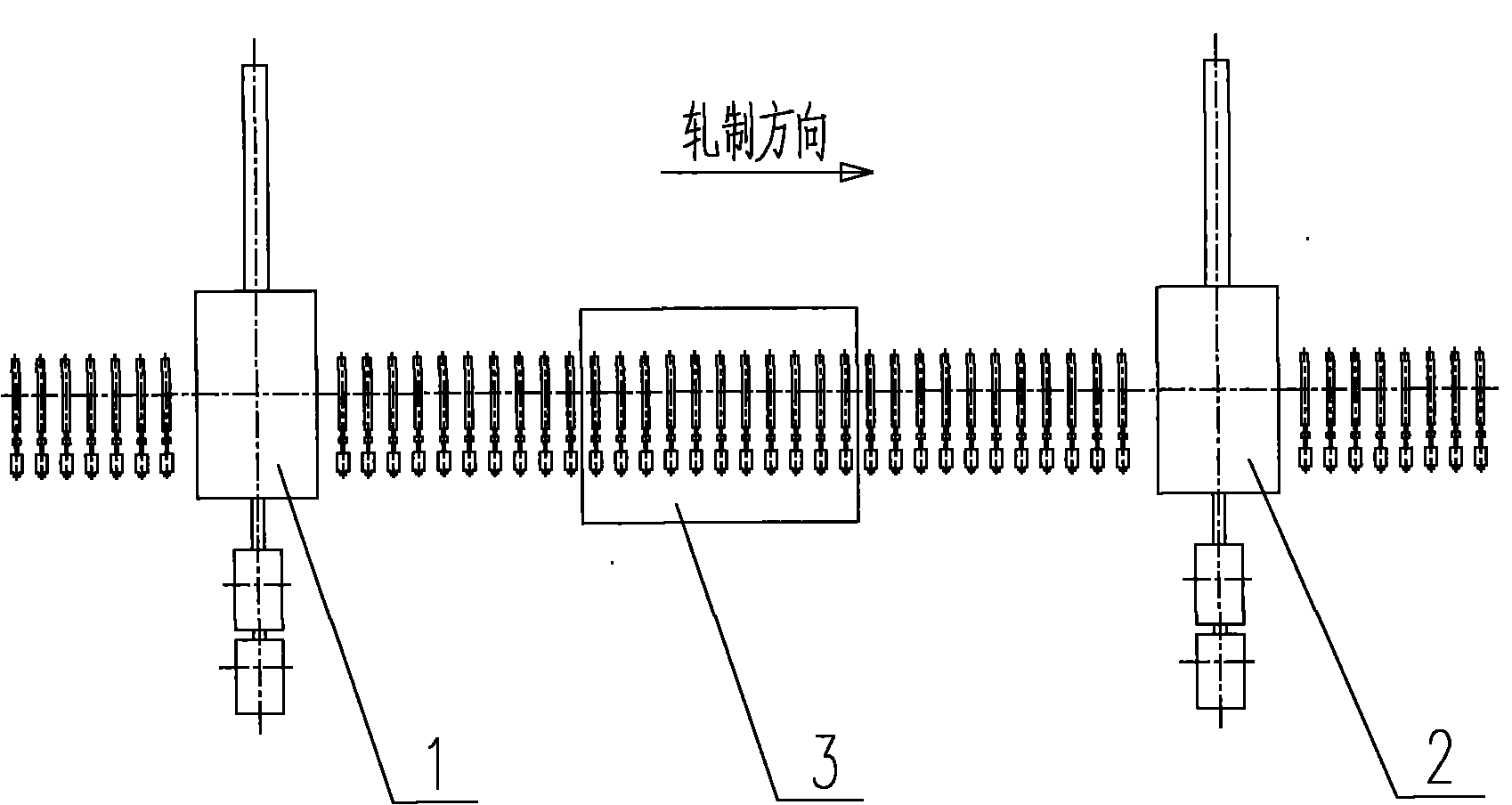
InactiveCN101829688ALess investmentImprove applicabilityTemperature control deviceWater qualityWater cycling
The invention belongs to a producing and cooling technique of rolled steel, relating to a cooling method of a heavy and medium plate controlled rolling intermediate blank, which can be realized by both a single-stand heavy and medium plate roll and a double-stand heavy and medium plate roll. The cooling method comprises the following steps of: transmitting a roughly rolled intermediate blank with the thickness range of 30-110 mm in an austenite recrystallization zone into an intermediate controlled cooling zone from a transmission roller way for rapidly cooling to 800-950 DEG C, and then transmitting the intermediate blank into the roll for rolling in a non- recrystallization zone after short-time air cooling and temperature evening. In the intermediate cooling process, an upper collecting pipe and a lower collecting pipe with high density or ultra-high density are adopted to impact, jet and cool the intermediate blank, and specific technological parameters are accurately controlled by a computer. Water is cooling water for the roll with the pressure of 0.3-1.0 MPa in a common water circulating system for workshops. The intermediate cooling holding time is 30-70% shorter than that of the conventional process so that the production efficiency is improved, and due to austenite grain refinement after intermediate controlled cooling, the mechanical properties of a steel plate can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
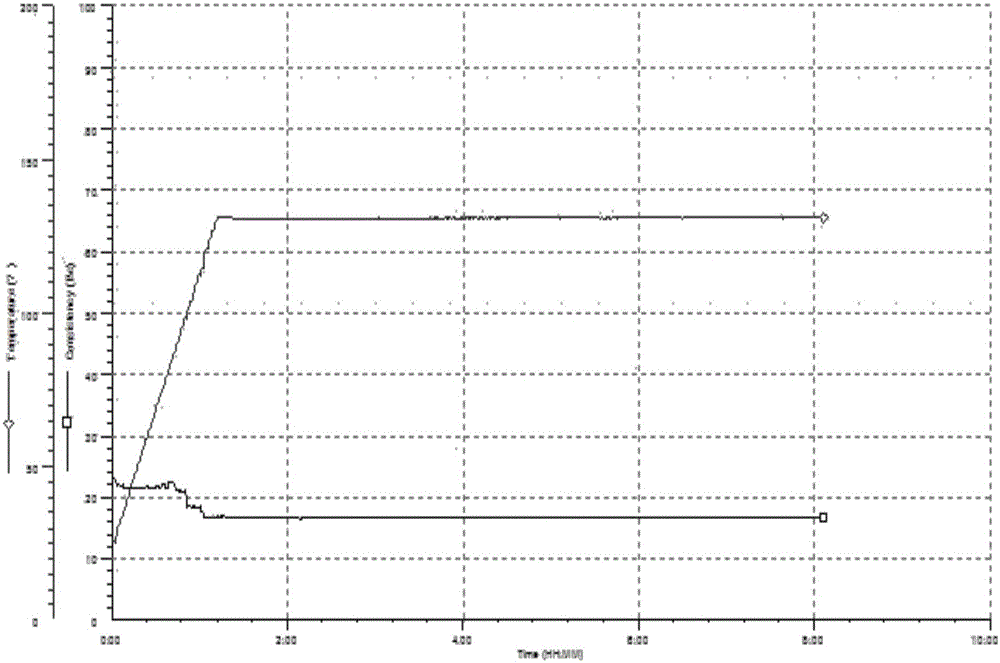
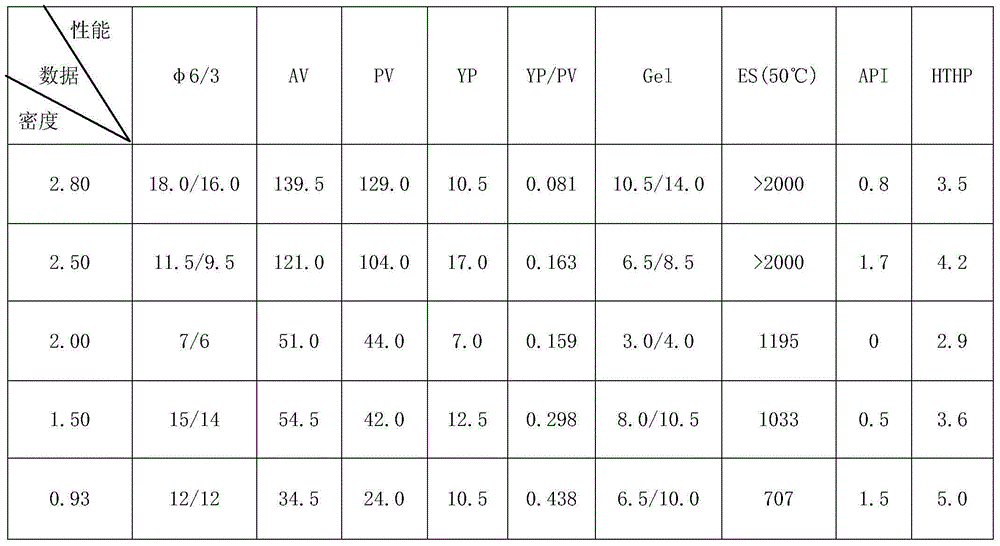
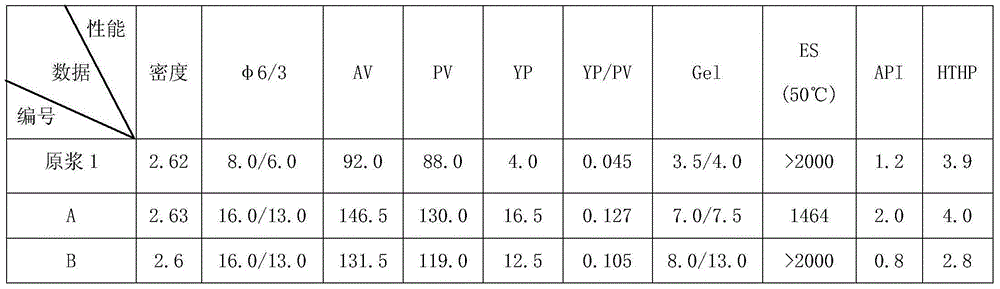
Ultra-high density oil-based drilling fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105623628AHigh breaking voltageExcellent emulsification stabilityDrilling compositionWater basedUltra high pressure
The present invention discloses an ultra-high density oil-based drilling fluid and a preparation method thereof. Oil-based drilling fluids in the prior art have the problems of poor emulsion stability and rheology, and easily lead to well wall chipping and collapsing, and blocking, long drilling cycle and other complex situations can be caused. The ultra-high density oil-based drilling fluid has a density of 0.93g / cm<3> to 2.80g / cm<3>, and comprises base oil, an emulsifier, a wetting agent, a tackifier, a filtrate loss reducer, a shear strength improving agent, an alkalinity adjusting agent, an aqueous solution of calcium chloride, a blocking agent, a weighting agent and the like, a formula and the preparation method of the ultra-high density oil-based drilling fluid are improved. The ultra-high density oil-based drilling fluid has good emulsifying stability and rheology, as well as mud shale strong inhibition, has the characteristics of small dosages of a variety of treatment agents, low preparation cost, high emulsion-breaking voltage, good rheology, low fluid loss, resistance to water, soil and salt and water-based drilling fluid and strong cement paste pollution performance and the like, and can be used in special drilling work in ultra-high pressure oil and gas wells, shale gas wells and strong water sensitive formation extended reach wells, horizontal wells and the like.
Owner:成都西油华巍科技有限公司 +1
Resin film
ActiveUS20190180781A1High-density recordingAdjustmentDisposition/mounting of recording headsBase layers for recording layersYoung's modulusEngineering
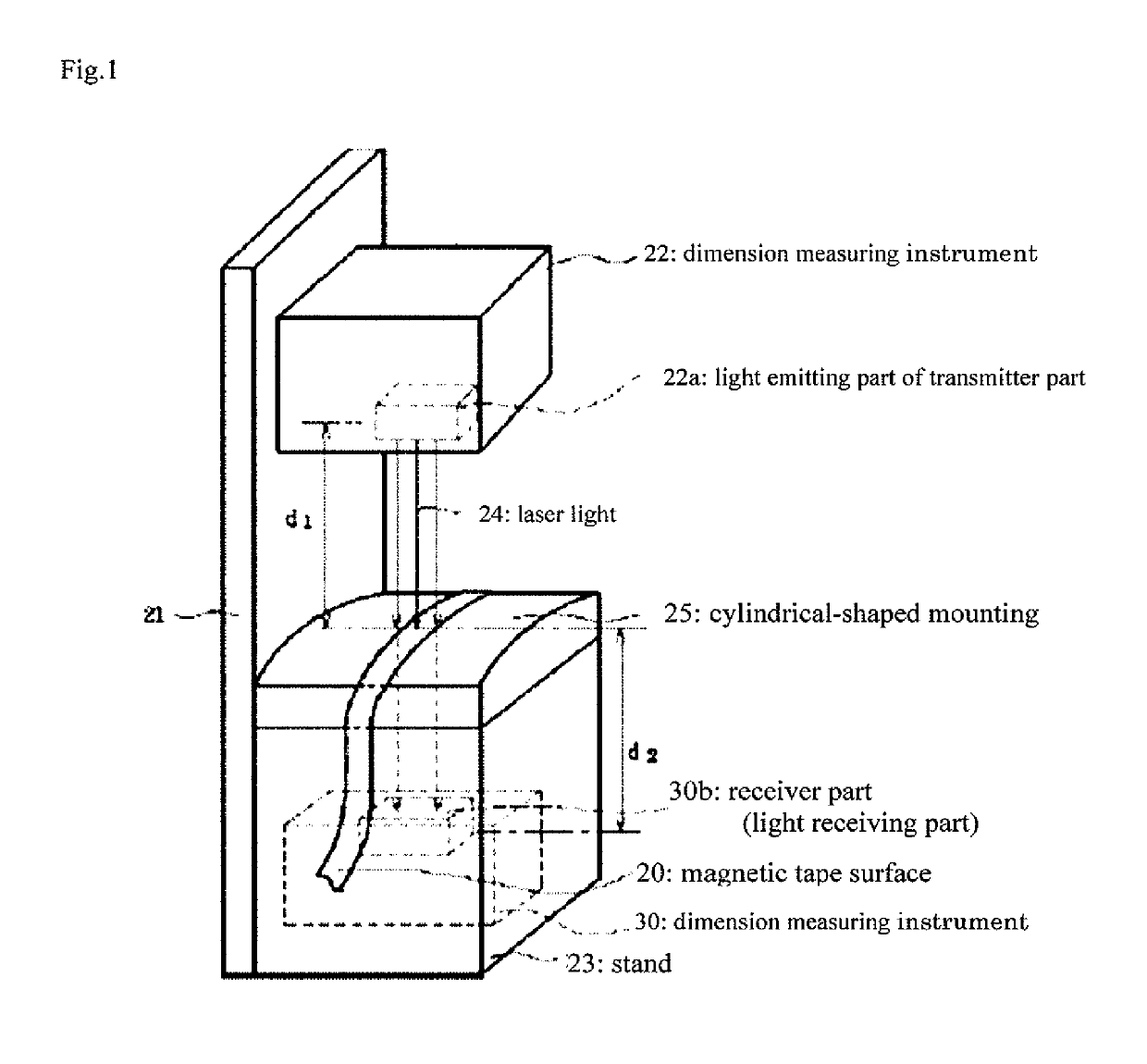
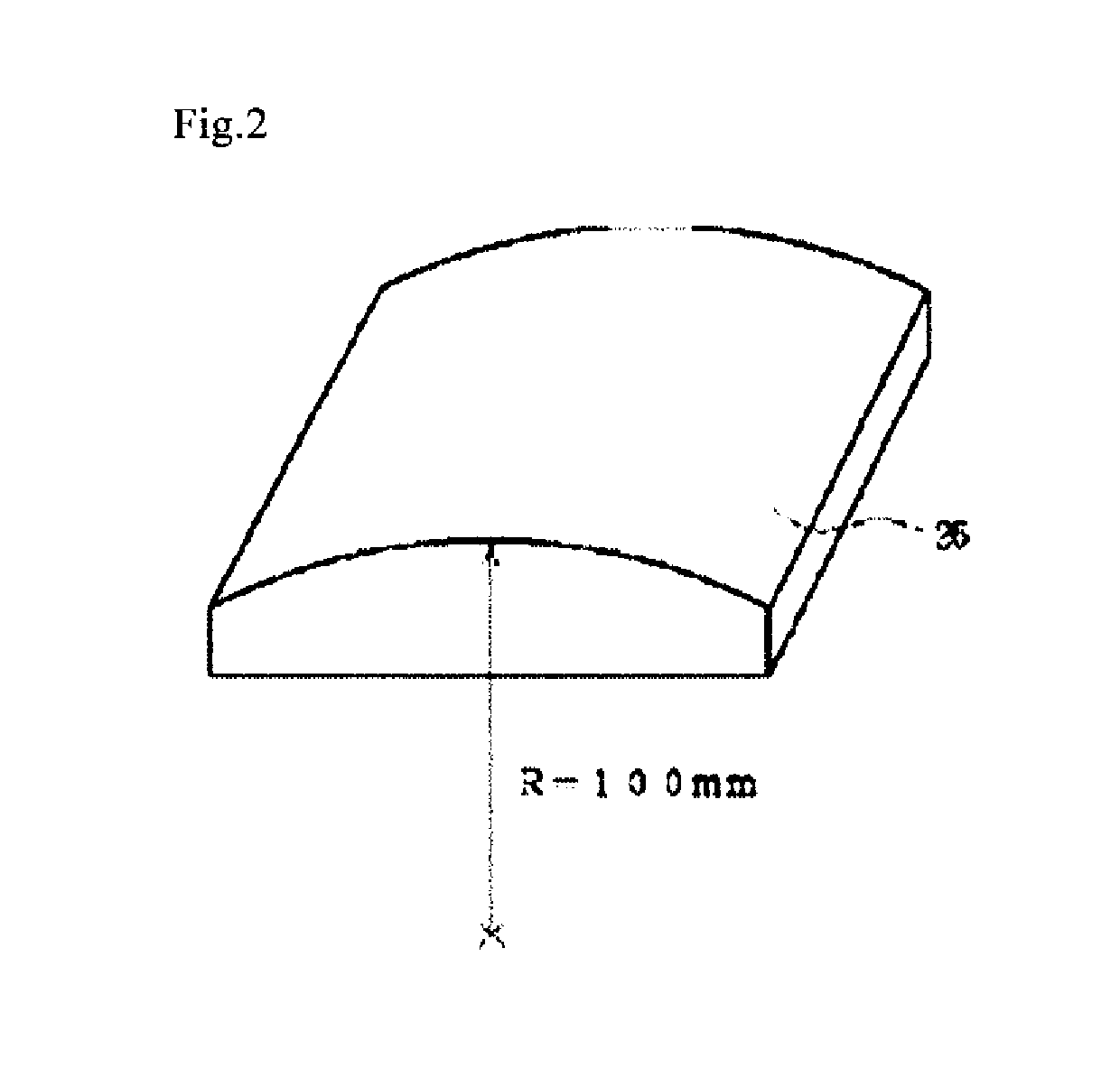
To provide a resin film, of which dimensional stability required of an ultra-high density recording medium can be controlled easily by drive tension, and which has processability at high temperature in a processing step of the resin film into a magnetic recording medium. A resin film having a Young's modulus in the film longitudinal direction of 1 GPa or more and a film thickness of 1 μm or more, wherein the product of the Young's modulus in the longitudinal direction and the thickness is 5 GPa·μm or more and 20 GPa·μm or less and wherein a dimensional change in the film longitudinal direction is −2% or more and +2% or less when the film is heated at a rate of 5° C. / min under a load of 2 kg / mm2 applied in the longitudinal direction and the temperature has reached 110° C., the resin film satisfying at least either of the following (1) or (2): (1) the Young's modulus in the film longitudinal direction is 6 GPa or less and the film thickness is 4.5 μm or less; and (2) the Young's modulus in the film longitudinal direction is 4 GPa or less and the film thickness is 6 μm or less.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
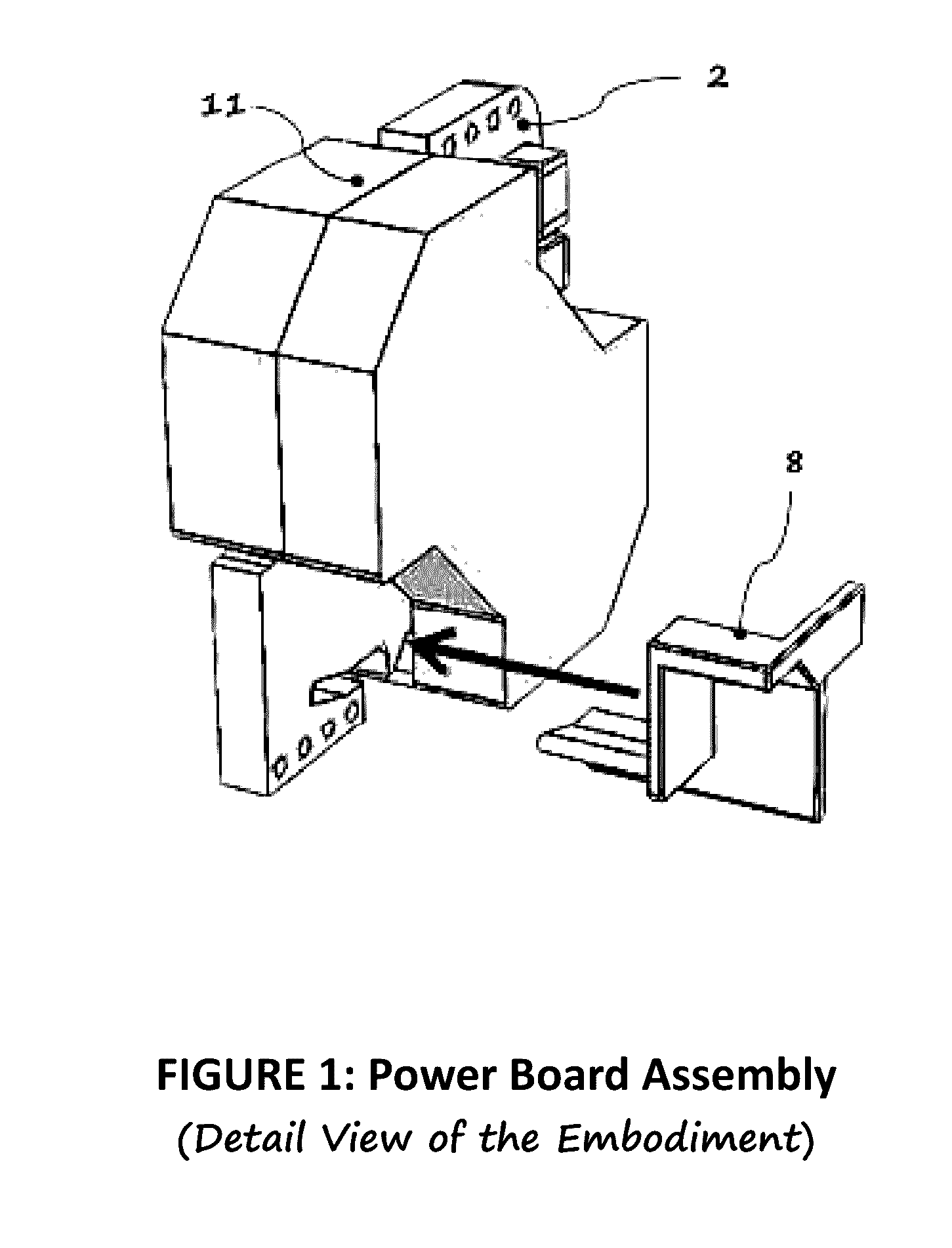
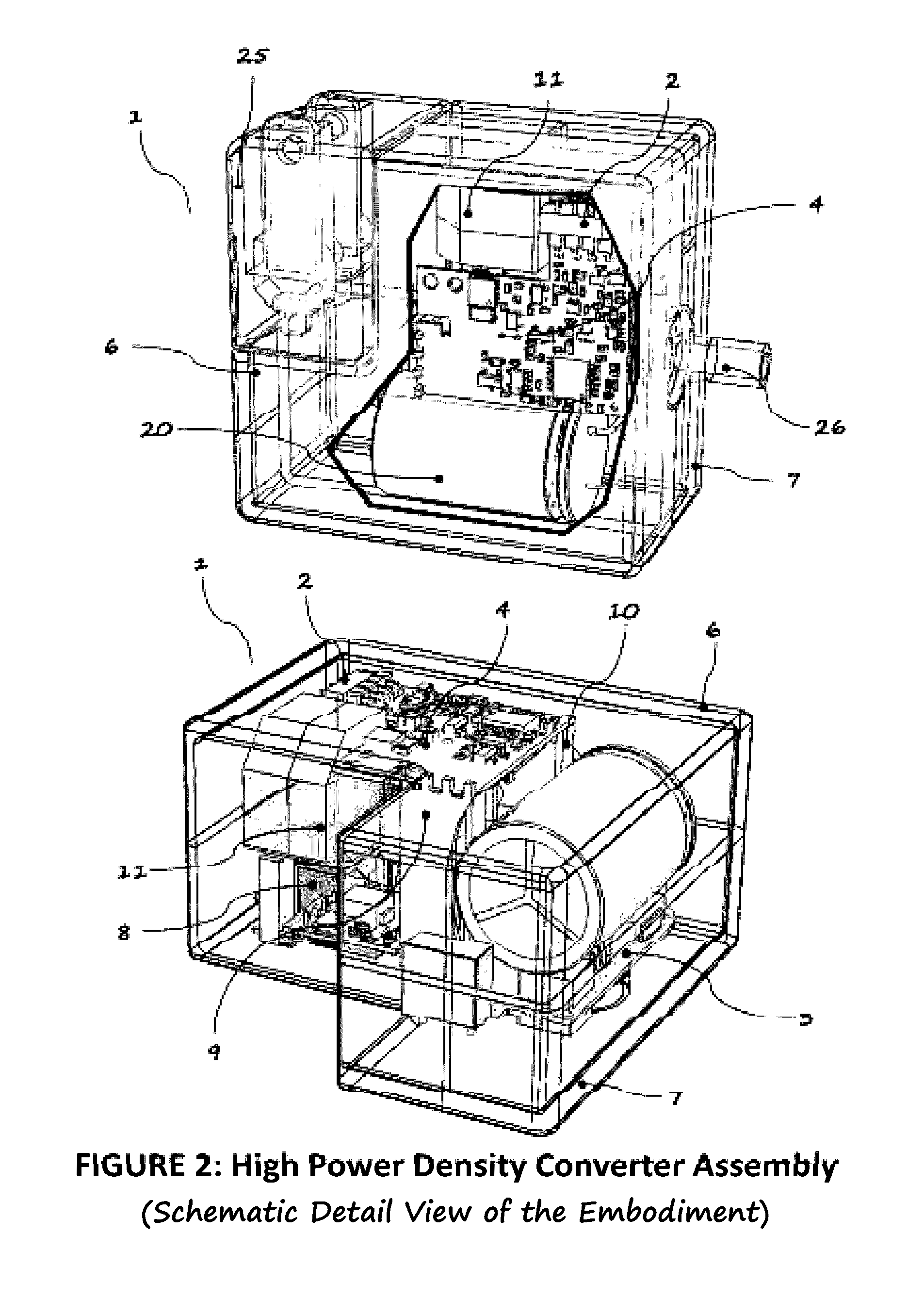
Packaging method for very high density converters
InactiveUS20160359426A1Improve power densitySmall and efficientAc-dc conversion without reversalActive shieldingAC adapterHigh density
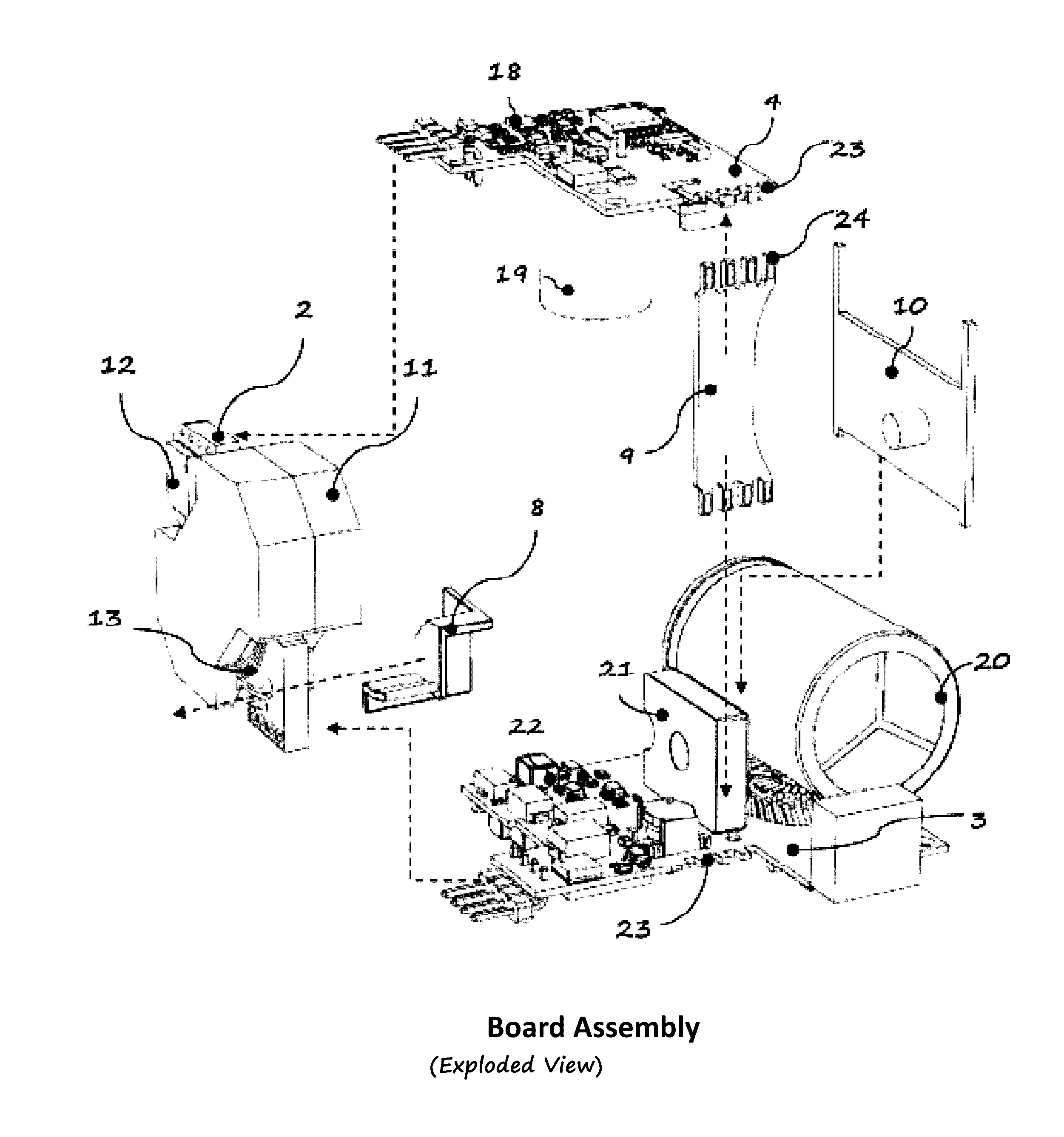
Meeting todays requirement in power supply technology demands significant technological advancement in optimizing circuit topology, components and materials, thermal and packaging designs. These requirements are being pushed mainly by continuously increasing power density and efficiency requirements. Ultimately, these trends will come to a point whereby limitations from the above mentioned technological advancements is dependent on one of the above, which is the packaging design. To realize this dependence, we need to look at the growing power systems for modern equipment out there. Let us enumerate some of the available AC adapters in terms of power densities of a 45 W adapter. Firstly, square type architecture introduced by Apple is about 7 W / in3, considering the packaging has a profile limitation whereby its AC plug is removable thus occupying relatively bigger chunk of the volume. The next one is by Asus of similar profile to Apple incorporating the AC Plug eliminating the socket assembly in the packaging; which packs about 9 W / in3. Lastly, the typical rectangular profile by Eos which is about 7 W / in3. As for this particular embodiment it is about 40% smaller in profile, in contrast to the 45 W Apple packaging, with increase power density of about 12 W / in3. Packaging design method plays a great role in achieving the above requirements for a very high density converters.
Owner:ROMPOWER ENERGY SYST
Information recording media and information recording drive
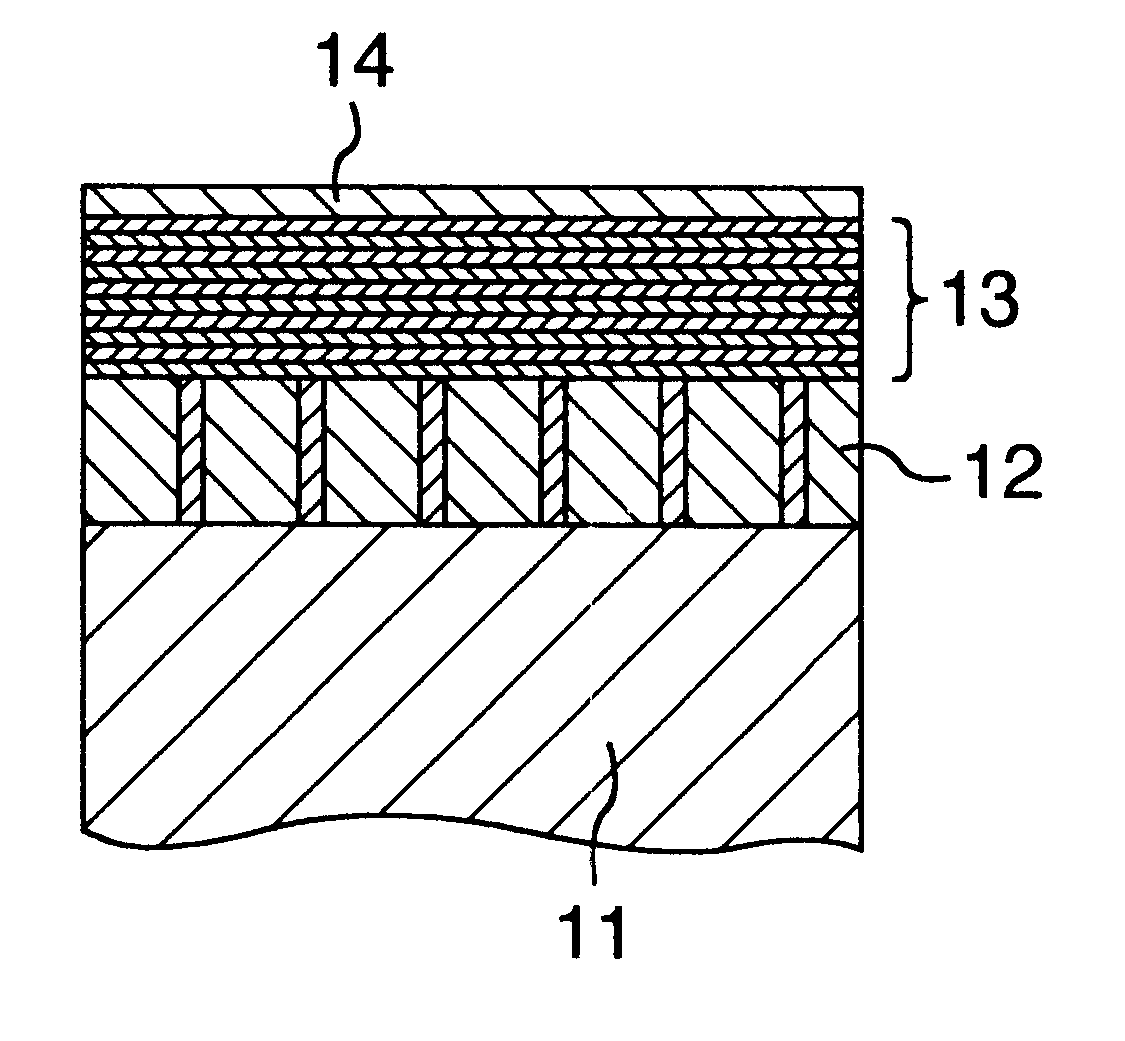
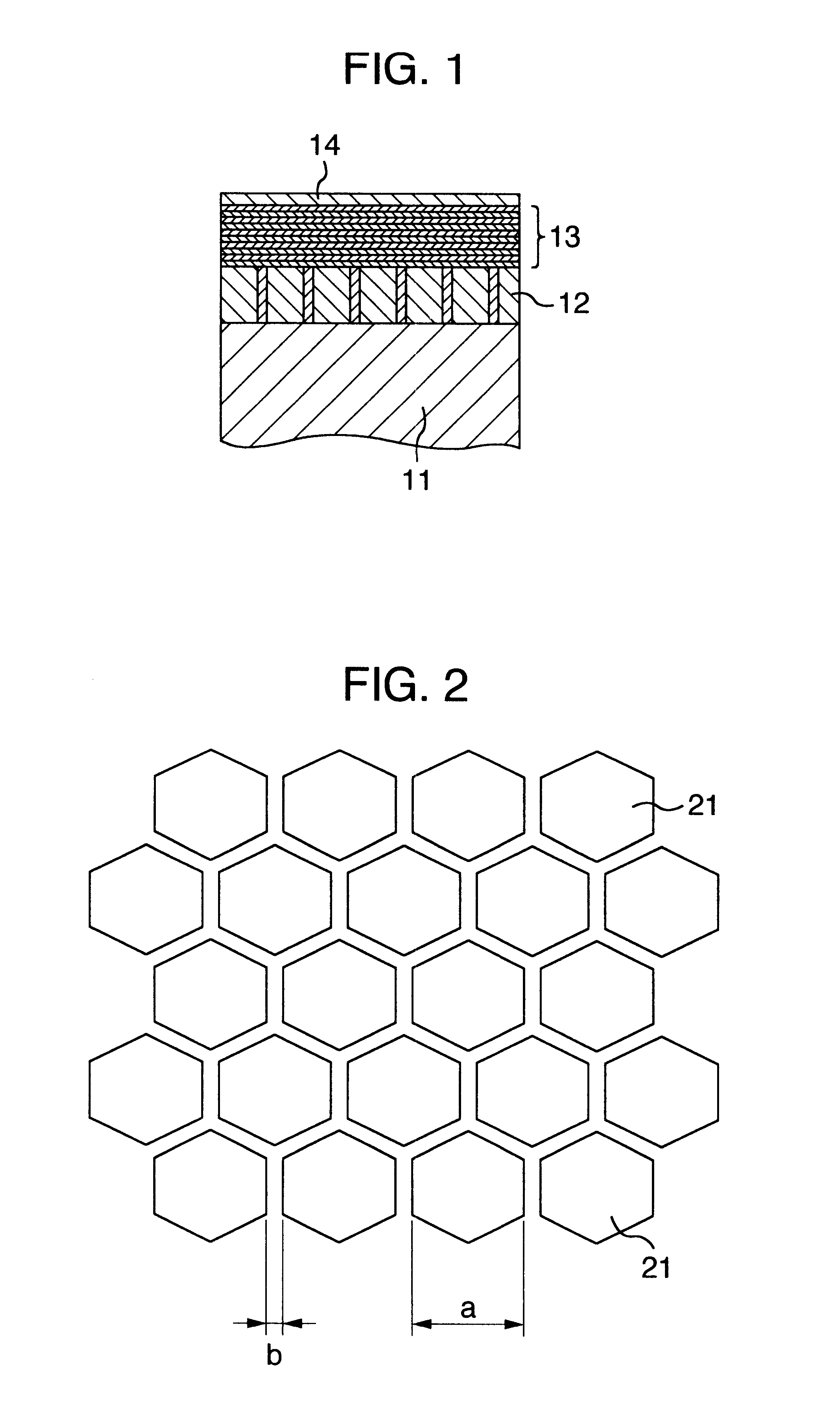
InactiveUS6534206B1Limited in their speed of movementPrecise positioningBase layers for recording layersLayered productsSilicon oxideAlloy
A magneto-optical storage apparatus including an ultra-high density information recording media having an inorganic compound layer 12 on a substrate 11, and in the inorganic compound layer 12, an oxide of at least one kind selected from silicon oxide, aluminum oxide, titanium oxide, tantalum oxide, and zinc oxide exists in an amorphous state at a grain boundary of crystal grain of an oxide of at least one kind selected from cobalt oxide, iron oxide, and nickel oxide. The media has a magnetic layer 13 made of an artificial lattice multilayer obtained by alternately laminating a Co layer or an alloy layer consisting of Co as a main phase and a metal element layer of at least one kind selected from Pt and Pd onto the layer 12. Thus, a distribution of magnetic properties serving as a pinning site of the movement of a magnetic wall in case of recording information to the magnetic layer 13 is formed in the magnetic layer 13.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD +1
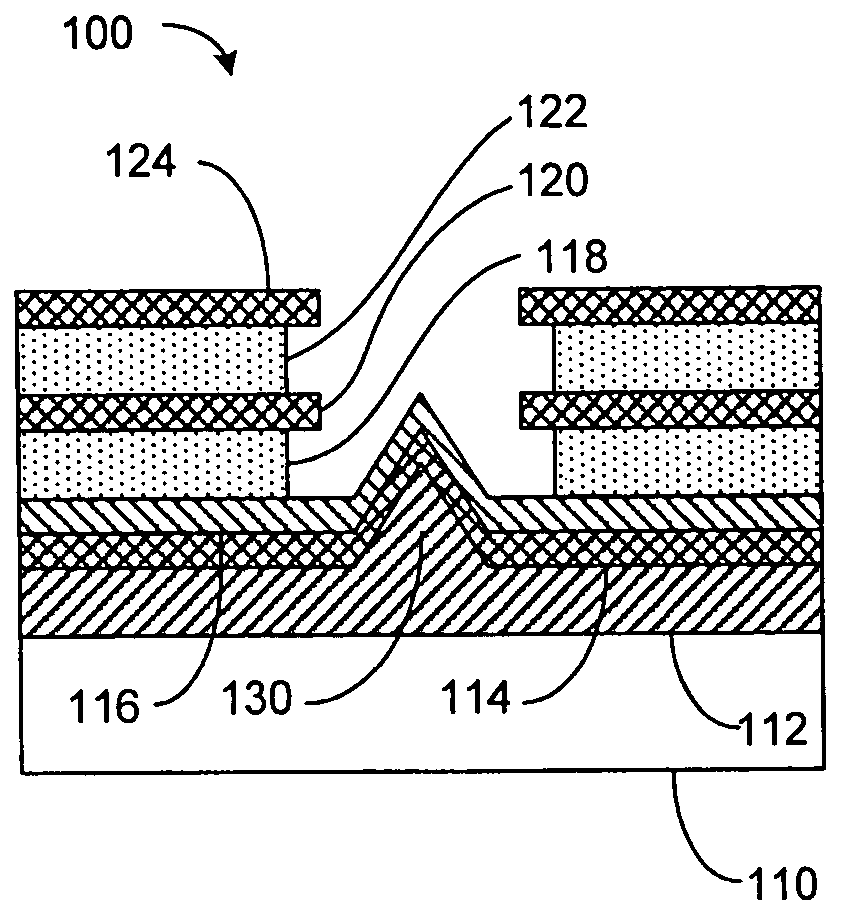
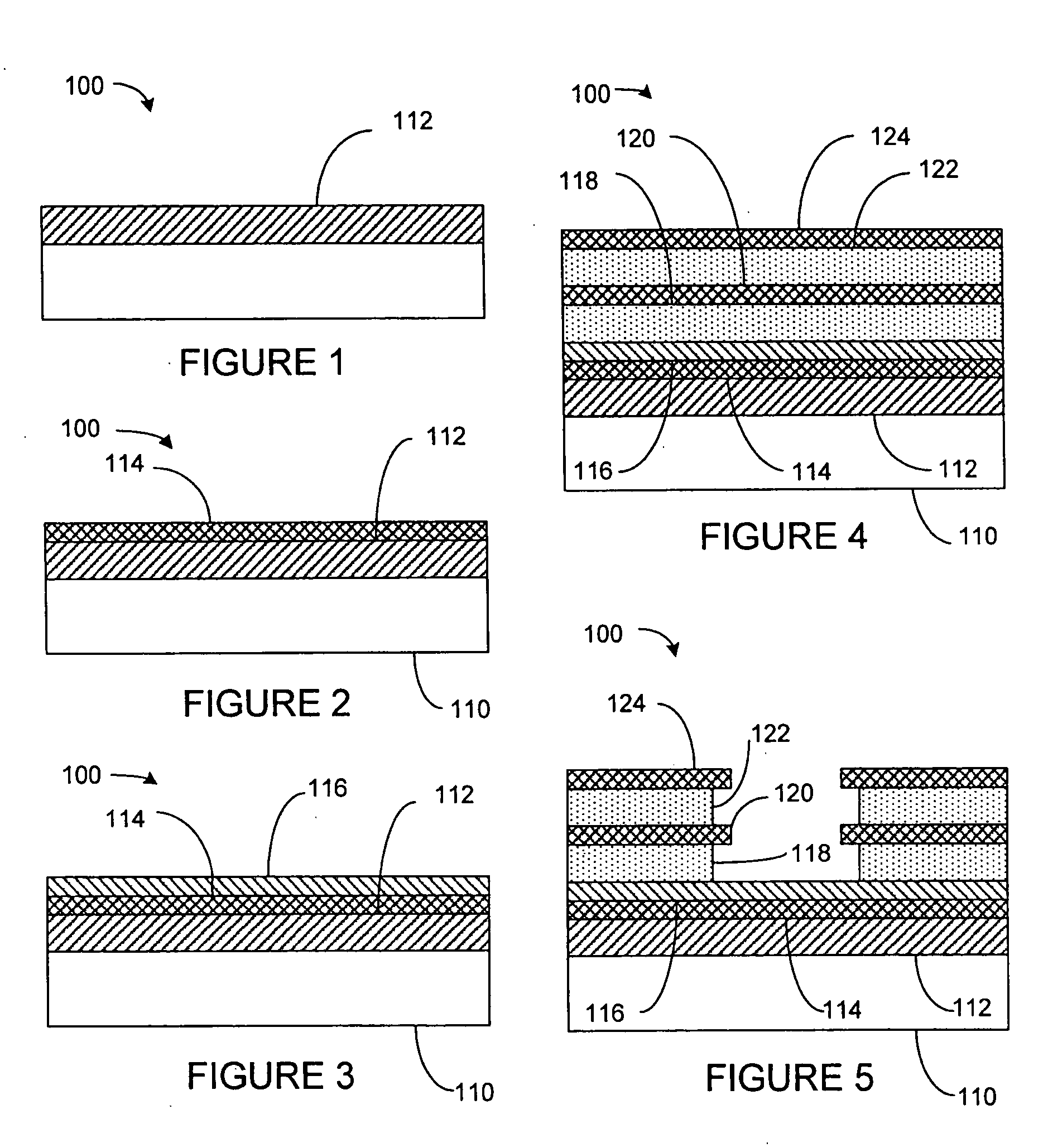
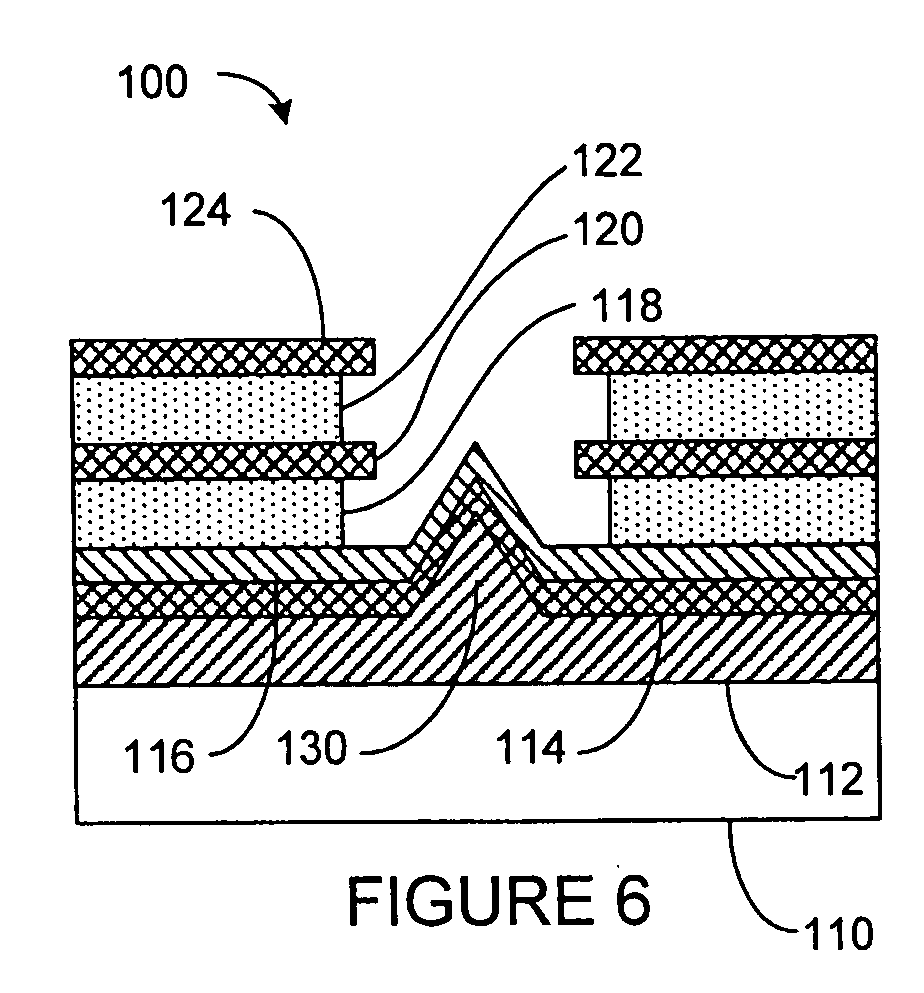
Electron emitter device for data storage applications and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050029920A1Improve abilitiesLamp incadescent bodiesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceTitanium nitride
A field emission device, which among other things may be used within an ultra-high density storage system, is disclosed. The emitter device includes an emitter electrode, an extractor electrode, and a solid-state field controlled emitter that utilizes a Schottky metal-semiconductor junction or barrier. The Schottky metal-semiconductor barrier is formed on the emitter electrode and electrically couples with the extractor electrode such that when an electric potential is placed between the emitter electrode and the extractor electrode, a field emission of electrons is generated from an exposed surface of the semiconductor layer. Further, the Schottky metal may be selected from typical conducting layers such as platinum, gold, silver, or a conductive semiconductor layer that is able to provide a high electron pool at the barrier. The semiconductor layer placed on the Schottky metal is typically very weakly conductive of n-type and has a wide band gap in order to create conditions conducive to creating induced negative electron affinity at applied fields necessary to provide electron emission. One type of wide band-gap material can be selected from titanium dioxide or titanium nitride or other comparable materials.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Ultra-high Density Diffraction Grating
InactiveUS20100053611A1High resolutionUltra-high density diffractionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSoft x rayVolumetric Mass Density
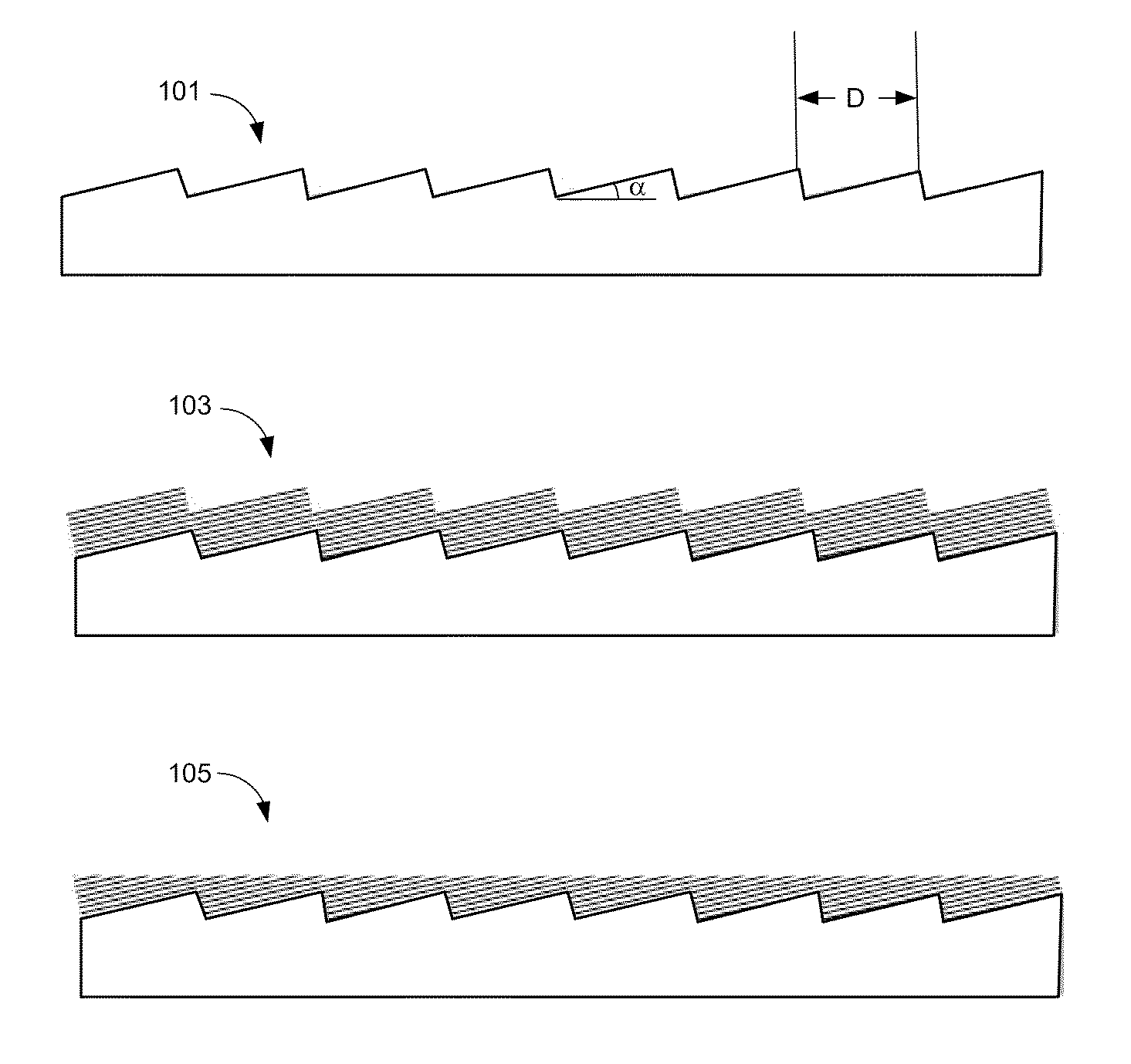
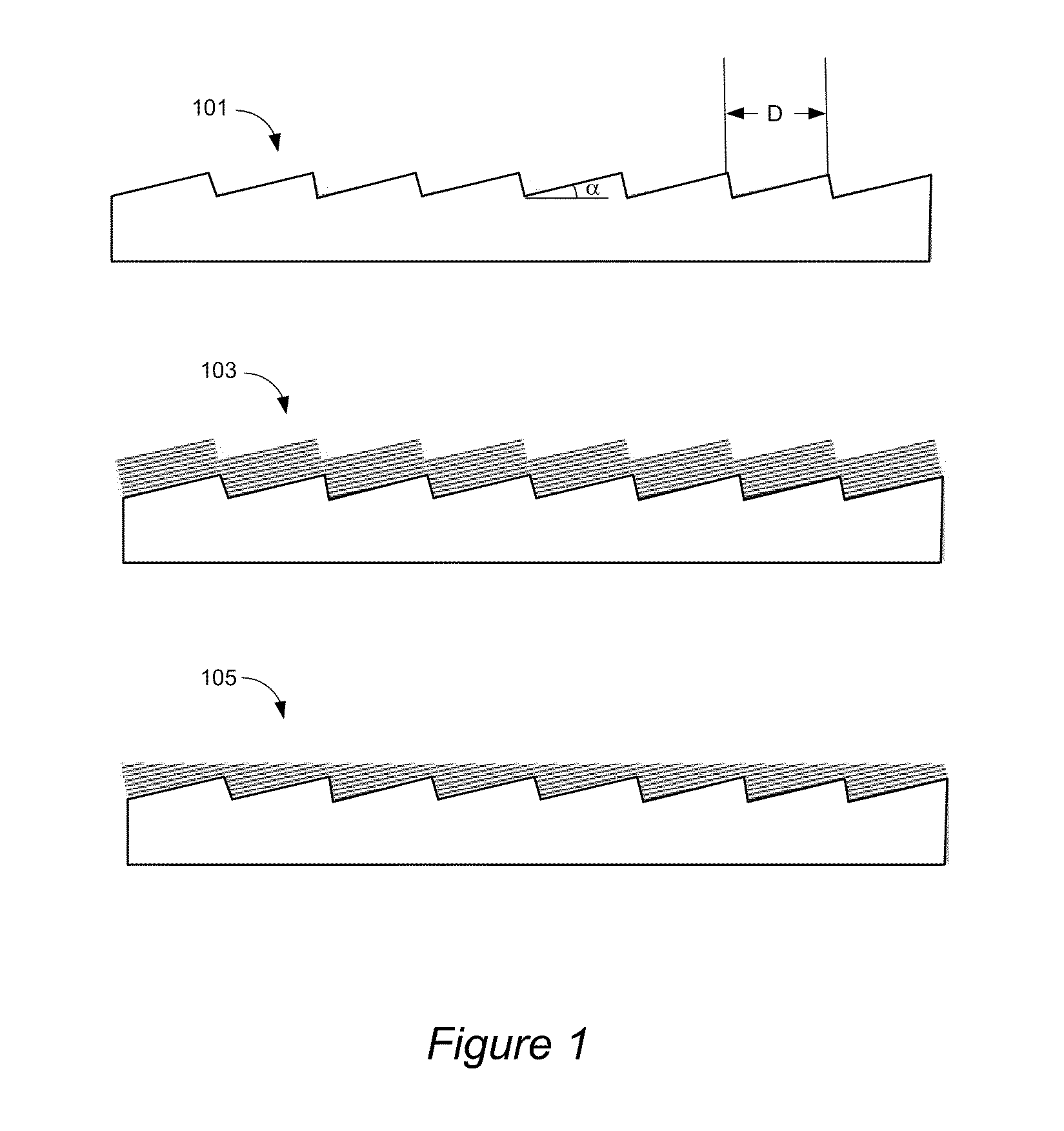
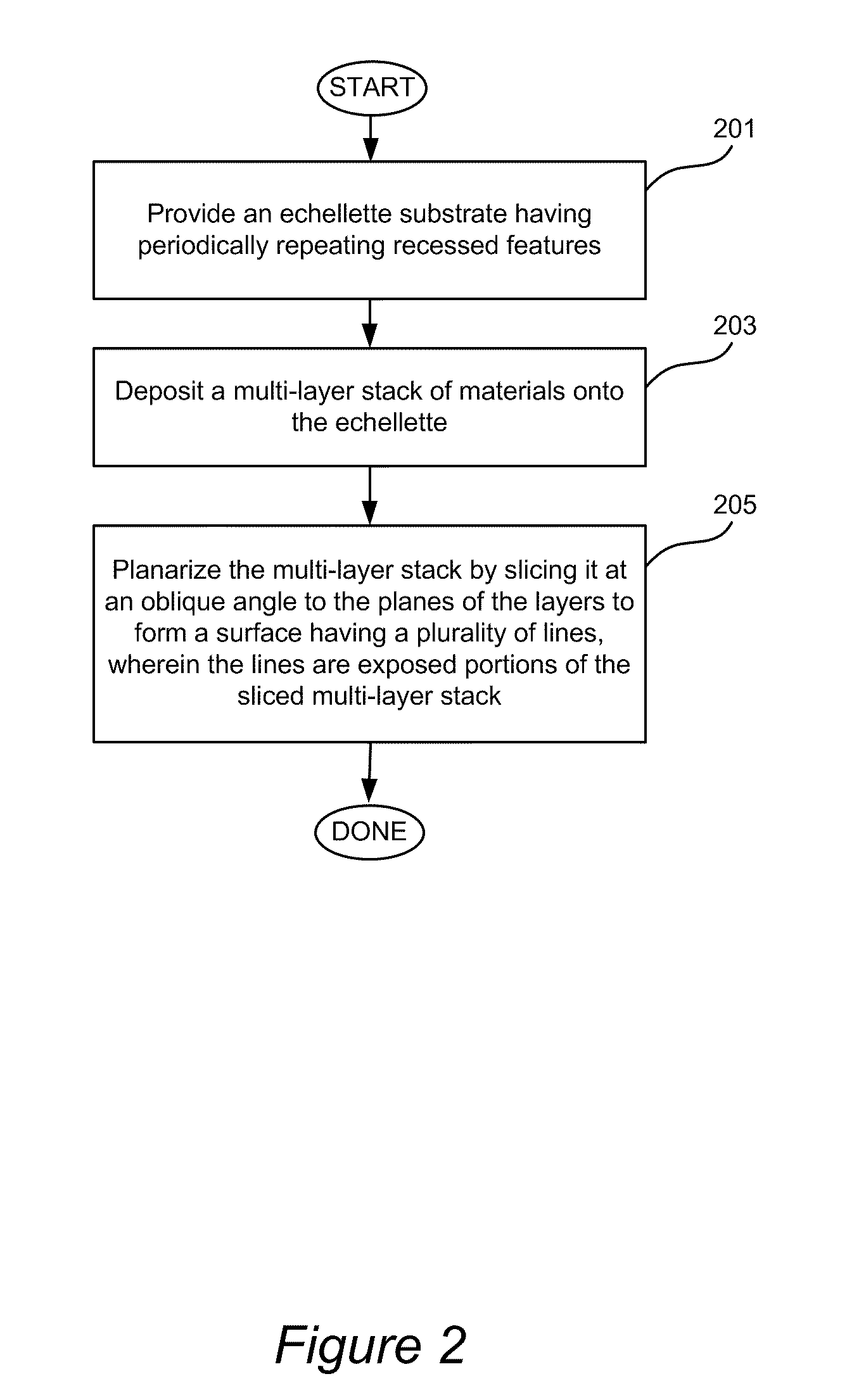
A diffraction grating structure having ultra-high density of grooves comprises an echellette substrate having periodically repeating recessed features, and a multi-layer stack of materials disposed on the echellette substrate. The surface of the diffraction grating is planarized, such that layers of the multi-layer stack form a plurality of lines disposed on the planarized surface of the structure in a periodical fashion, wherein lines having a first property alternate with lines having a dissimilar property on the surface of the substrate. For example, in one embodiment, lines comprising high-Z and low-Z materials alternate on the planarized surface providing a structure that is suitable as a diffraction grating for EUV and soft X-rays. In some embodiments, line density of between about 10,000 lines / mm to about 100,000 lines / mm is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com