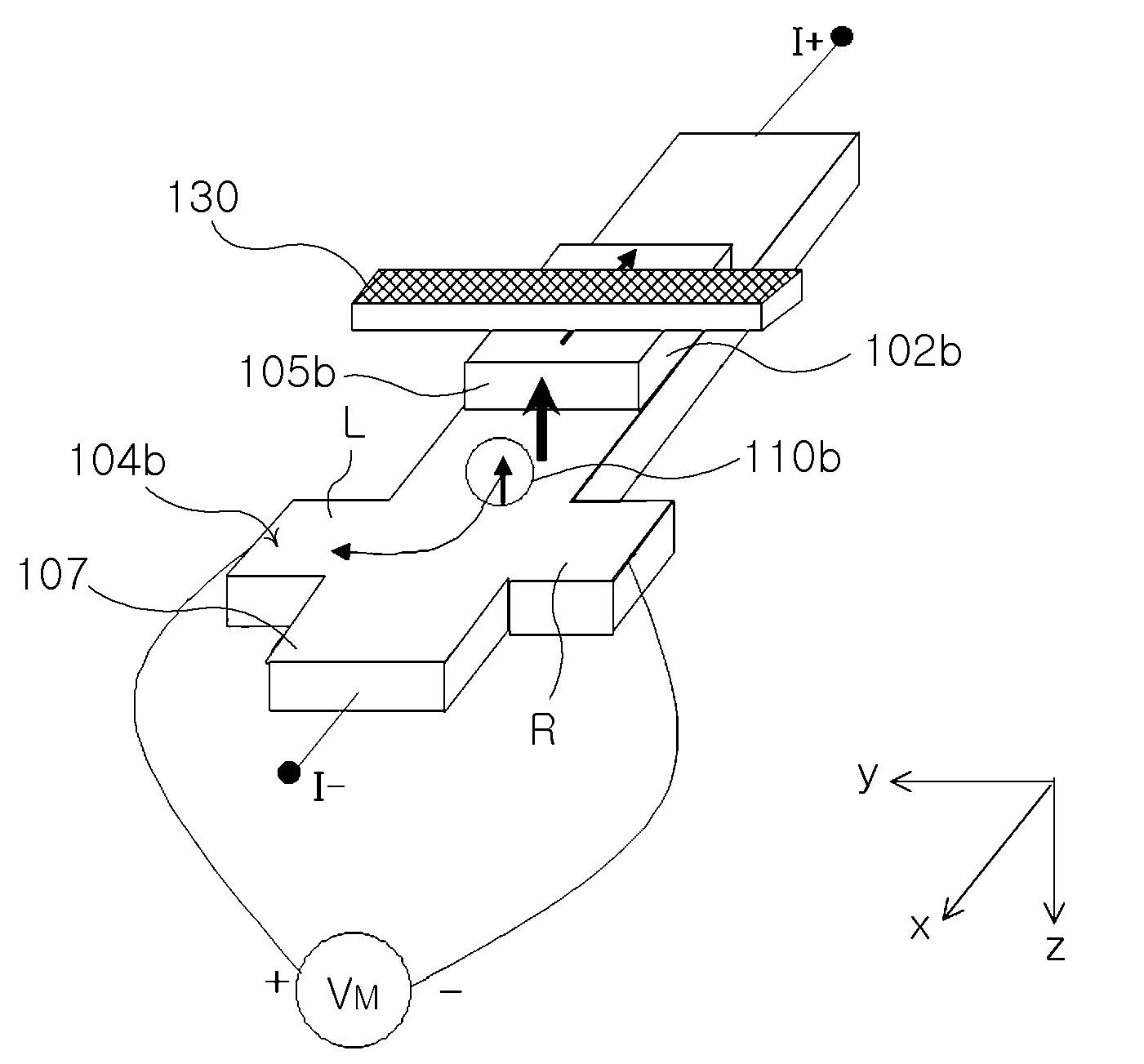
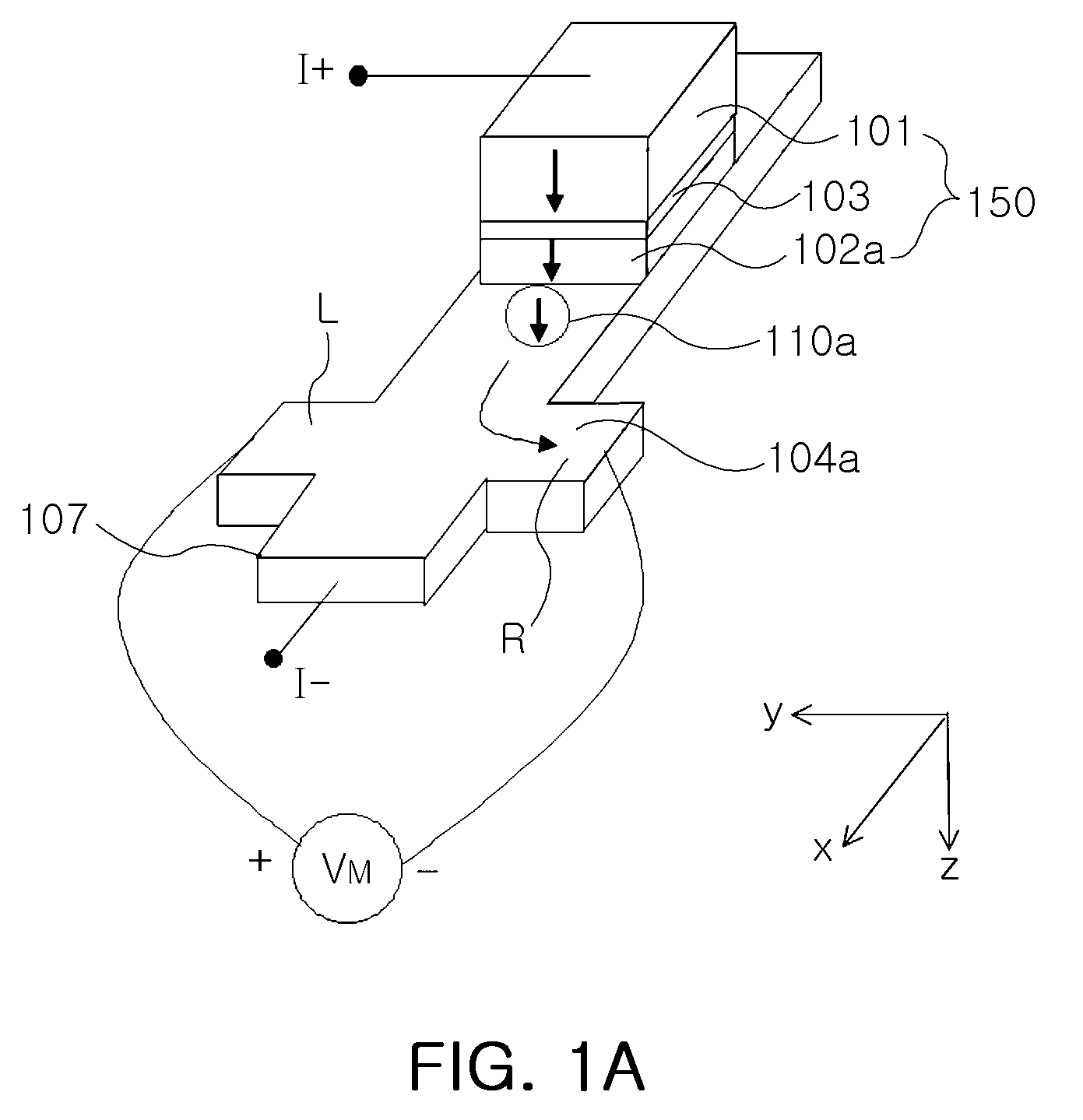
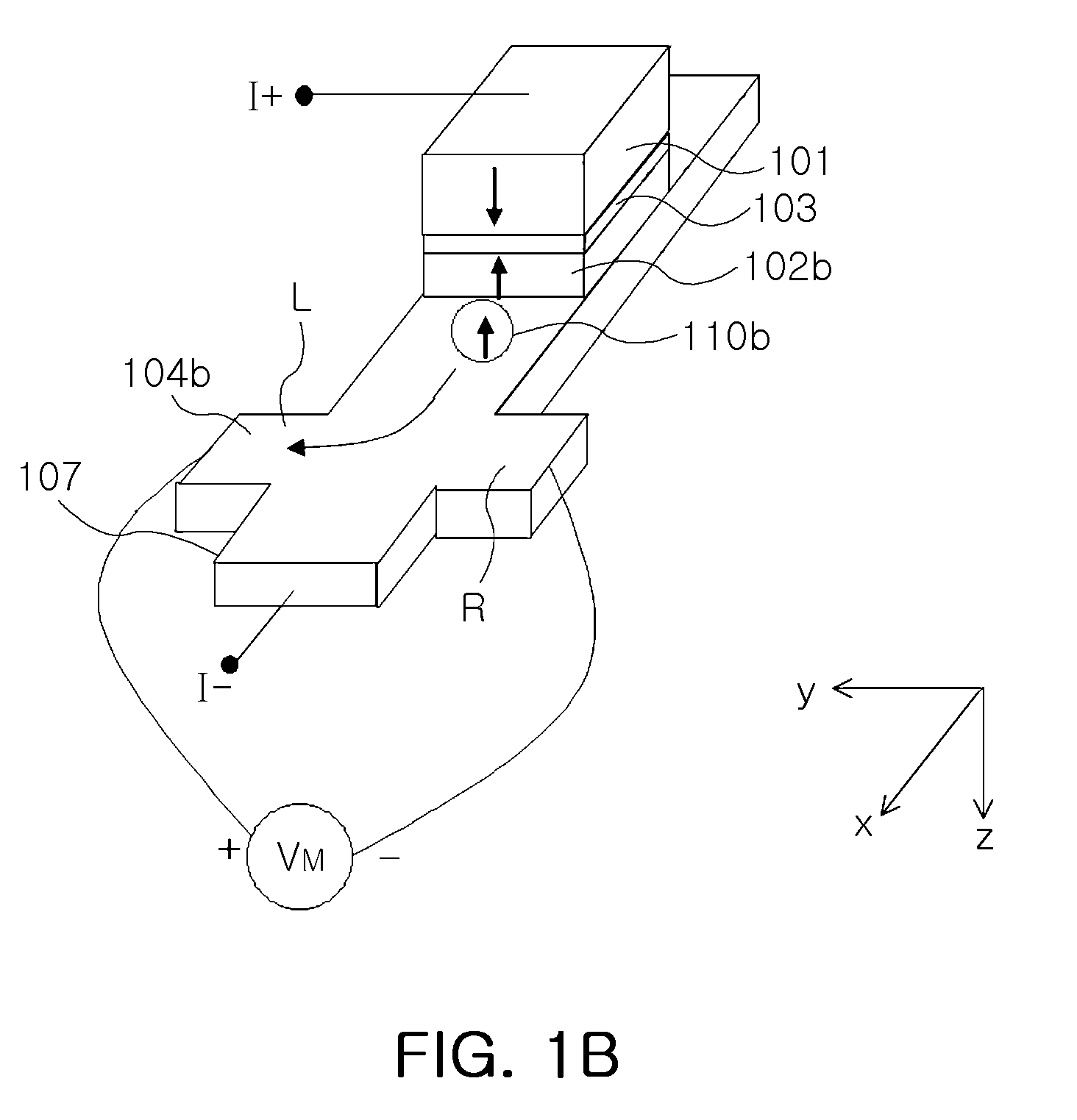
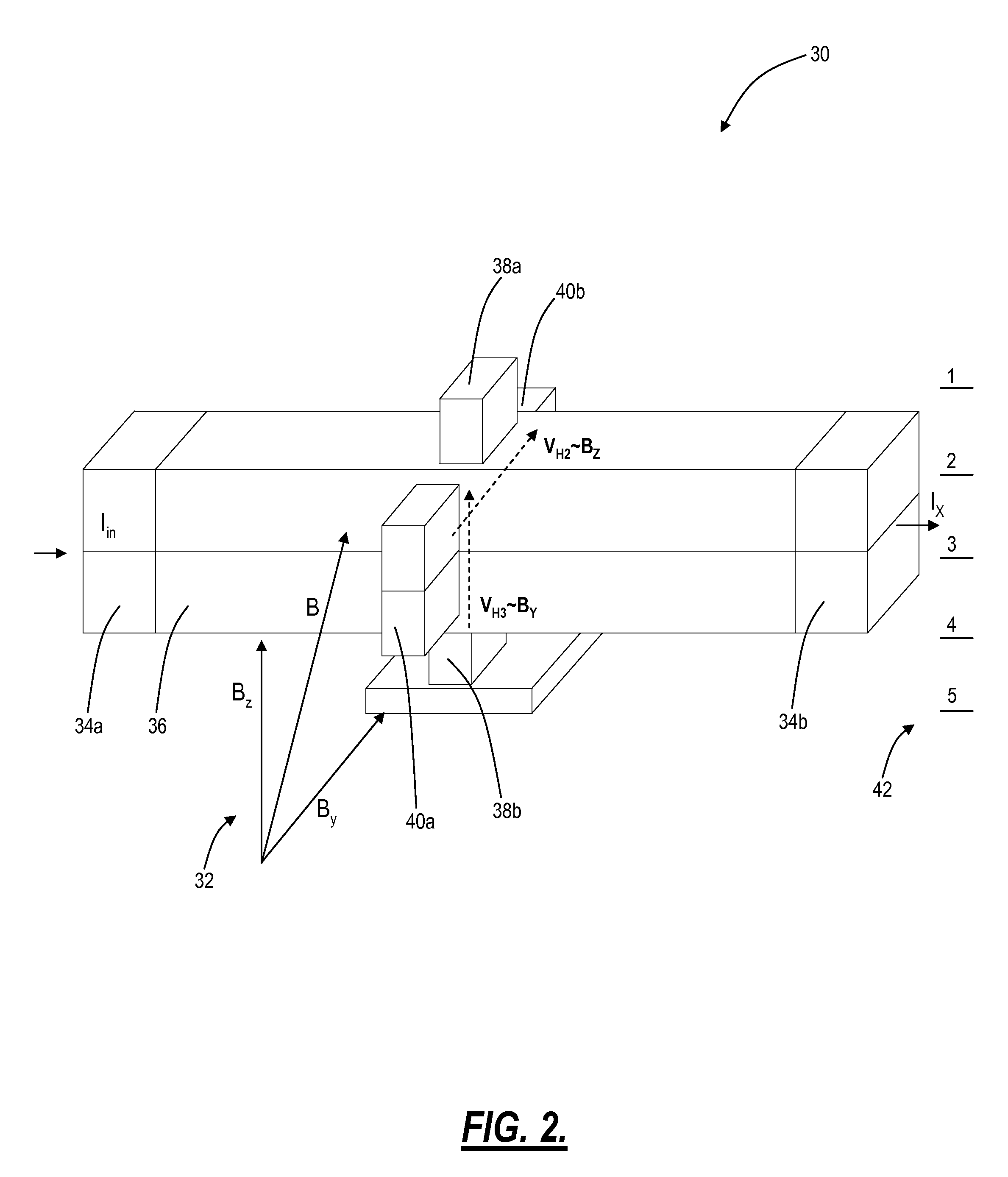Patents
Literature
200results about "Galvano-magnetic devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
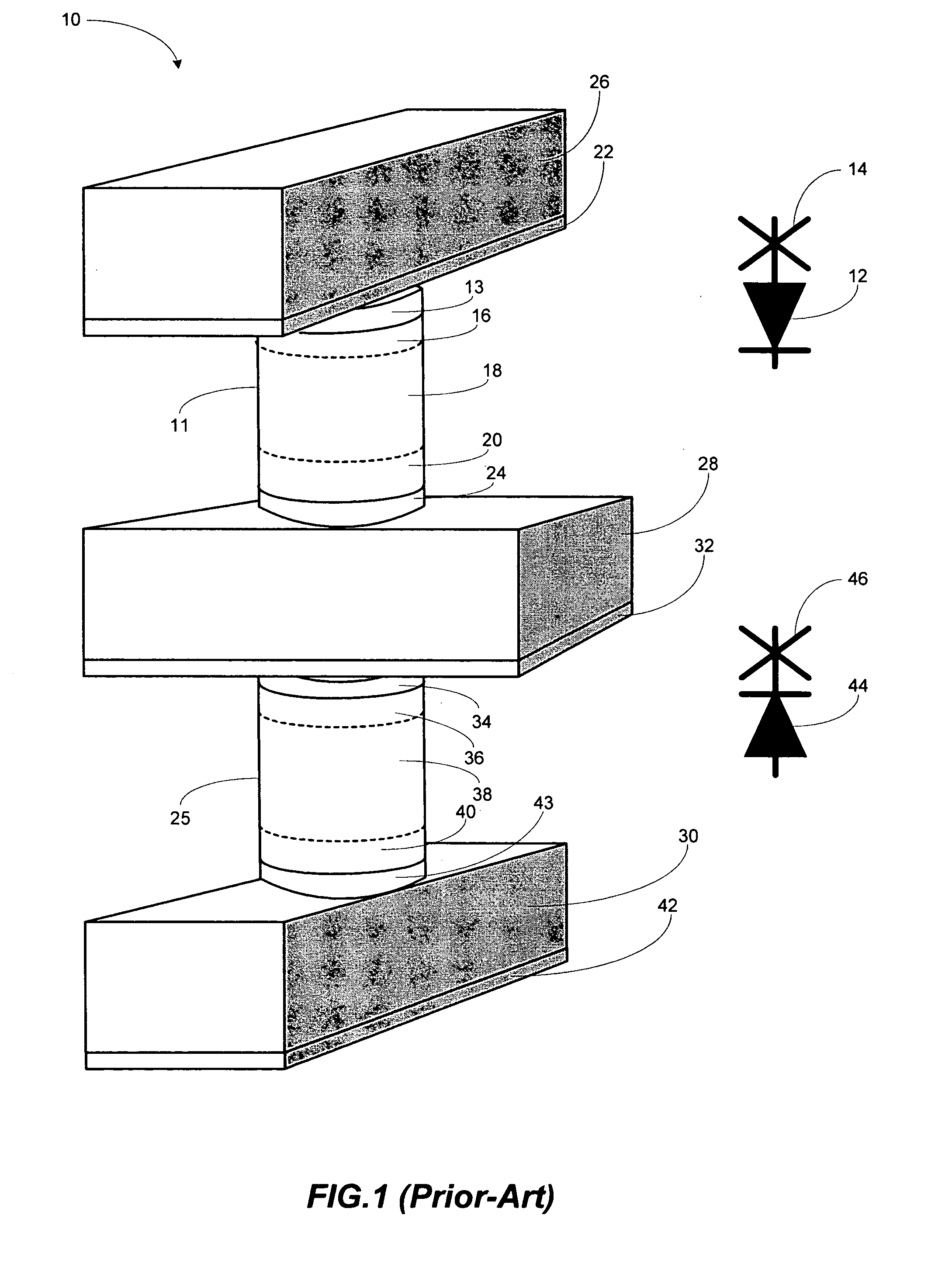
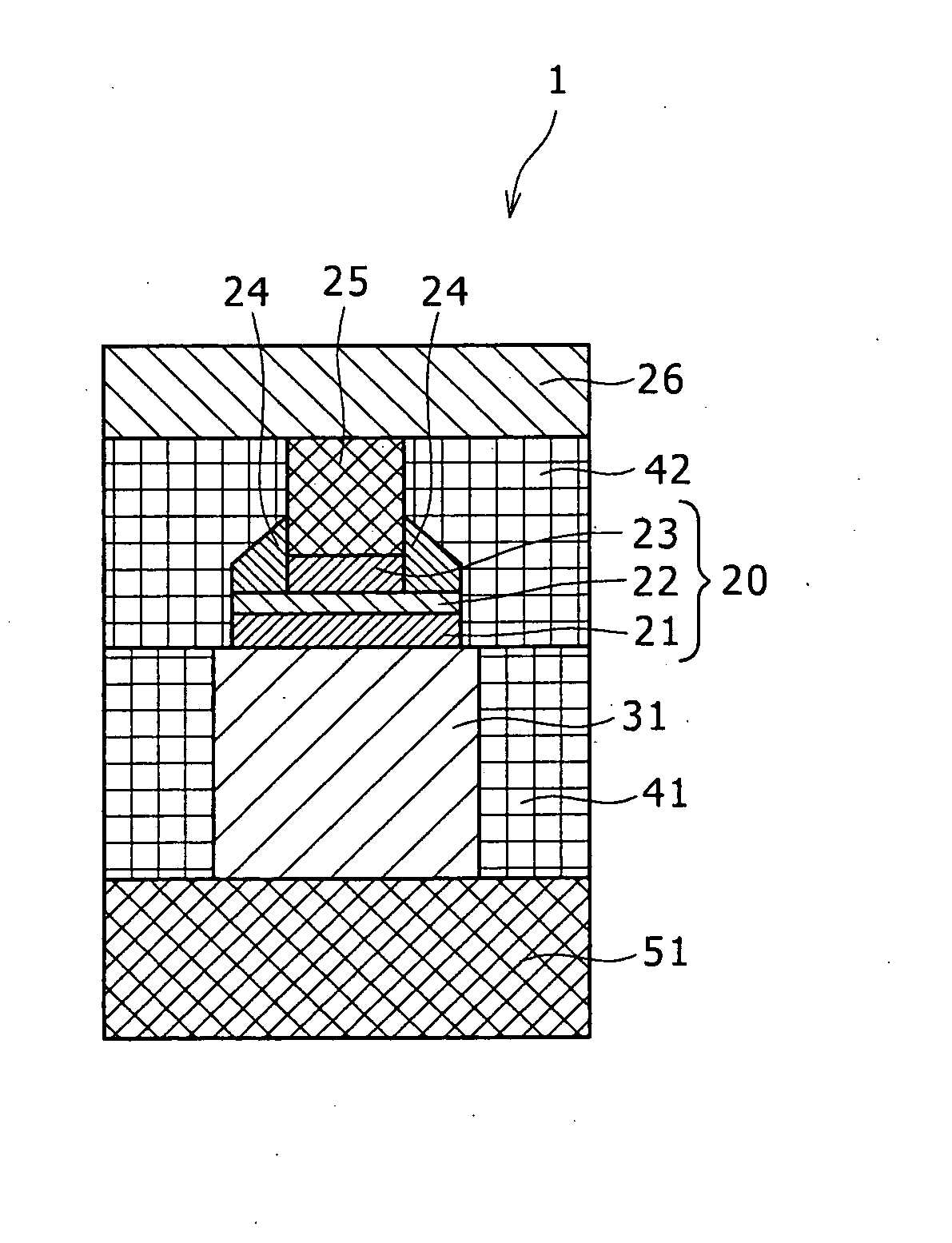
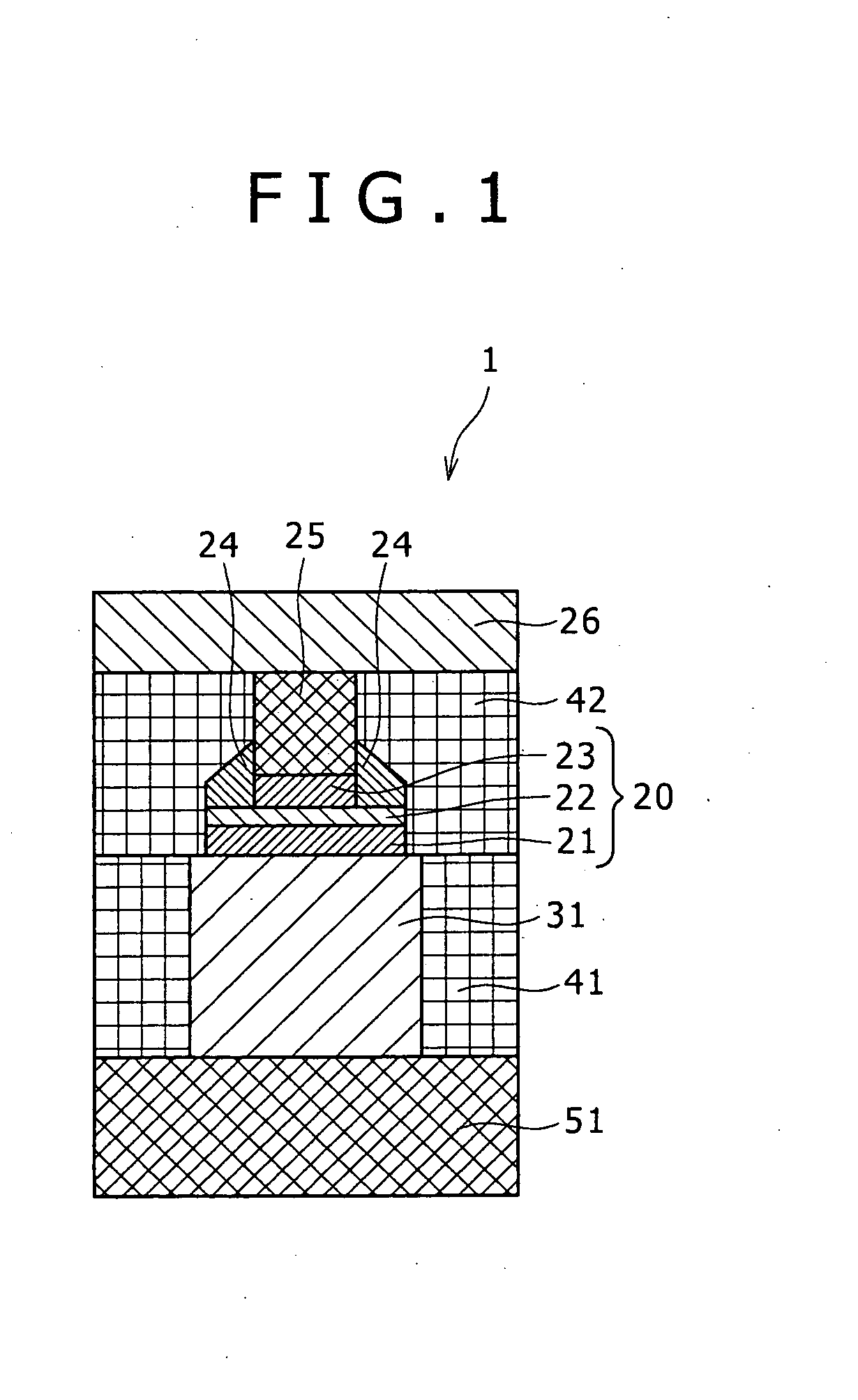
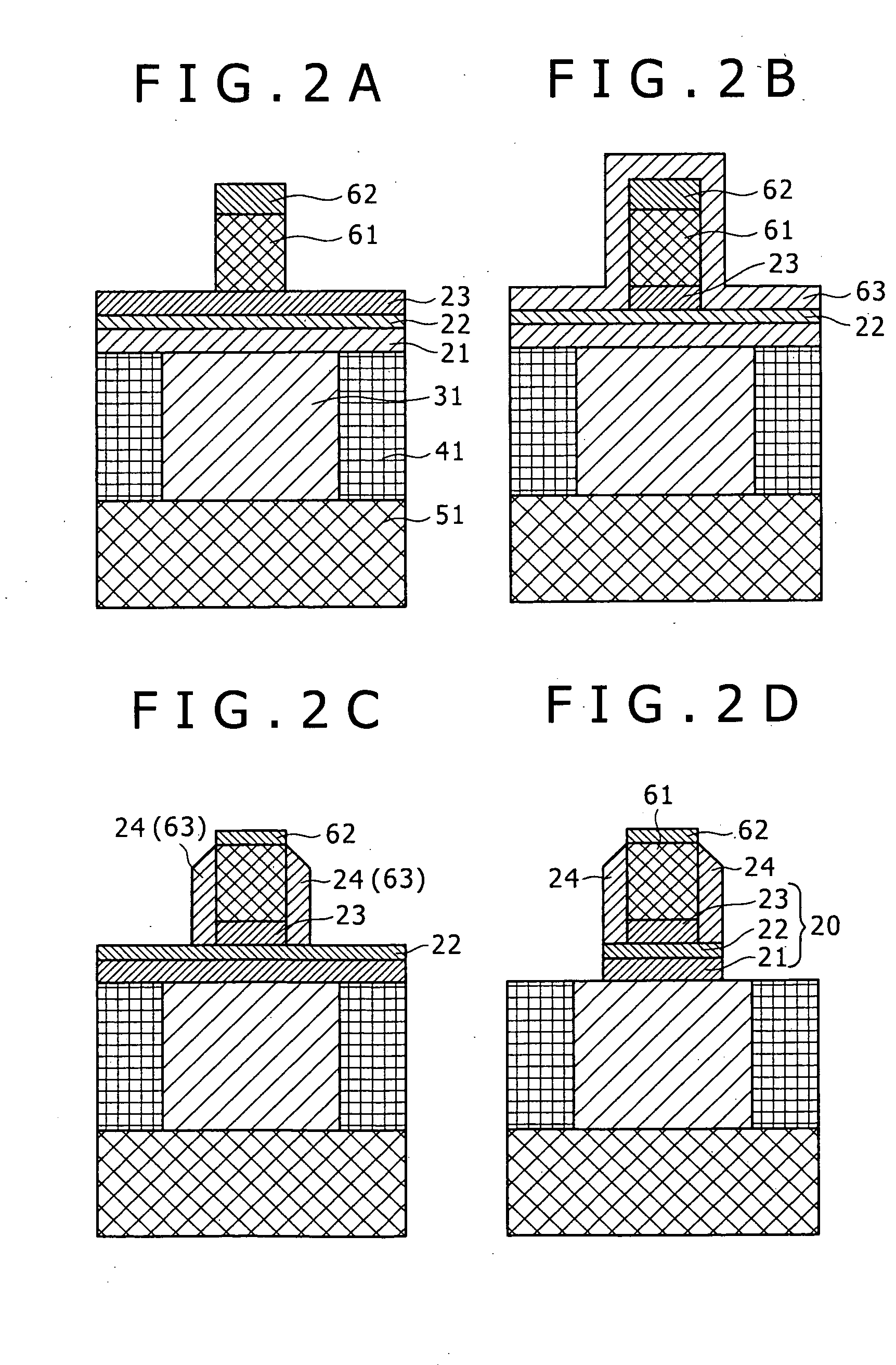
Unipolar resistance random access memory (RRAM) device and vertically stacked architecture
InactiveUS20070132049A1Improve performanceGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesRandom access memoryEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention includes a low-cost unipolar rewritable variable-resistance memory device, made of cross-point arrays of memory cells, vertically stacked on top of one another and compatible with a polycrystalline silicon diode.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
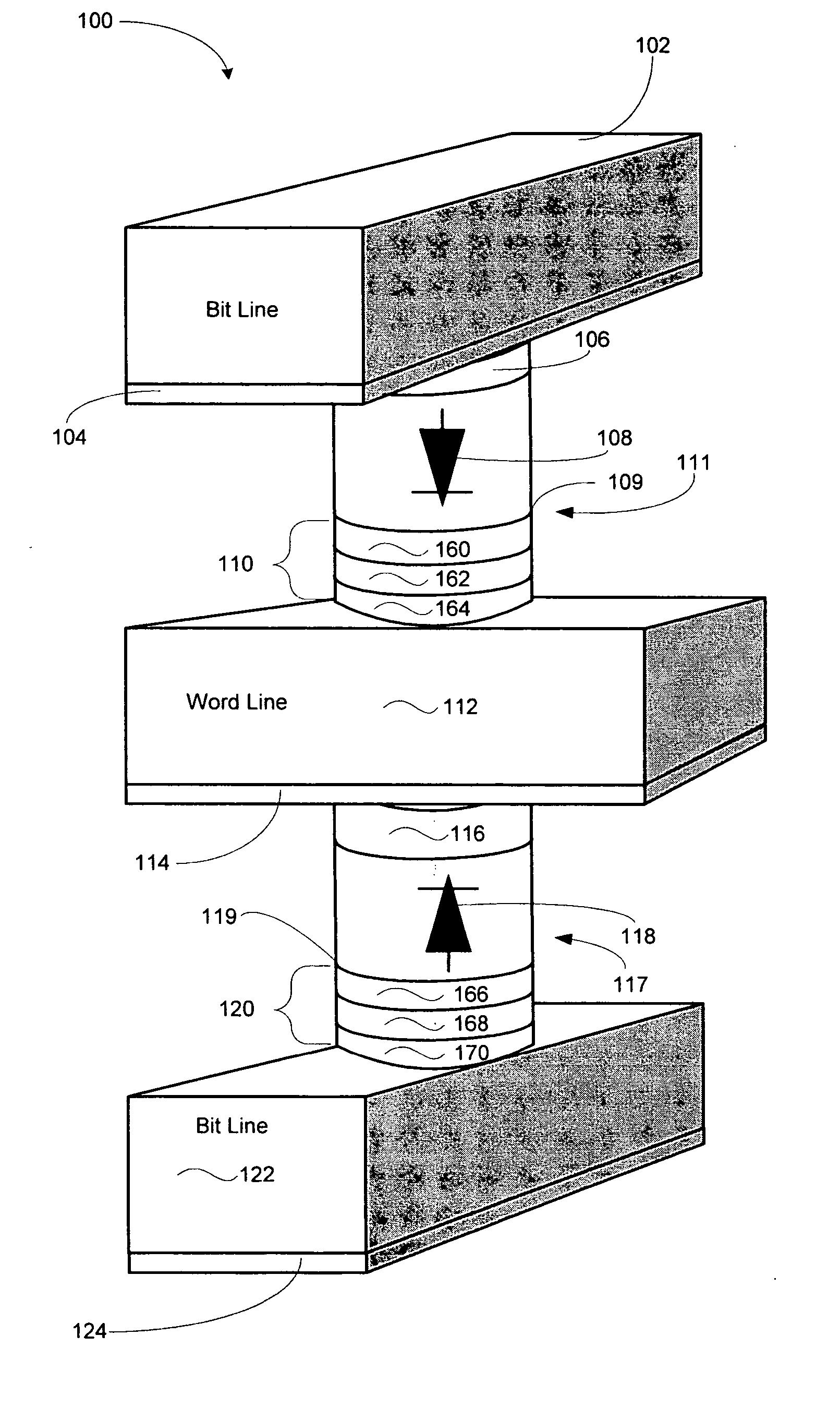
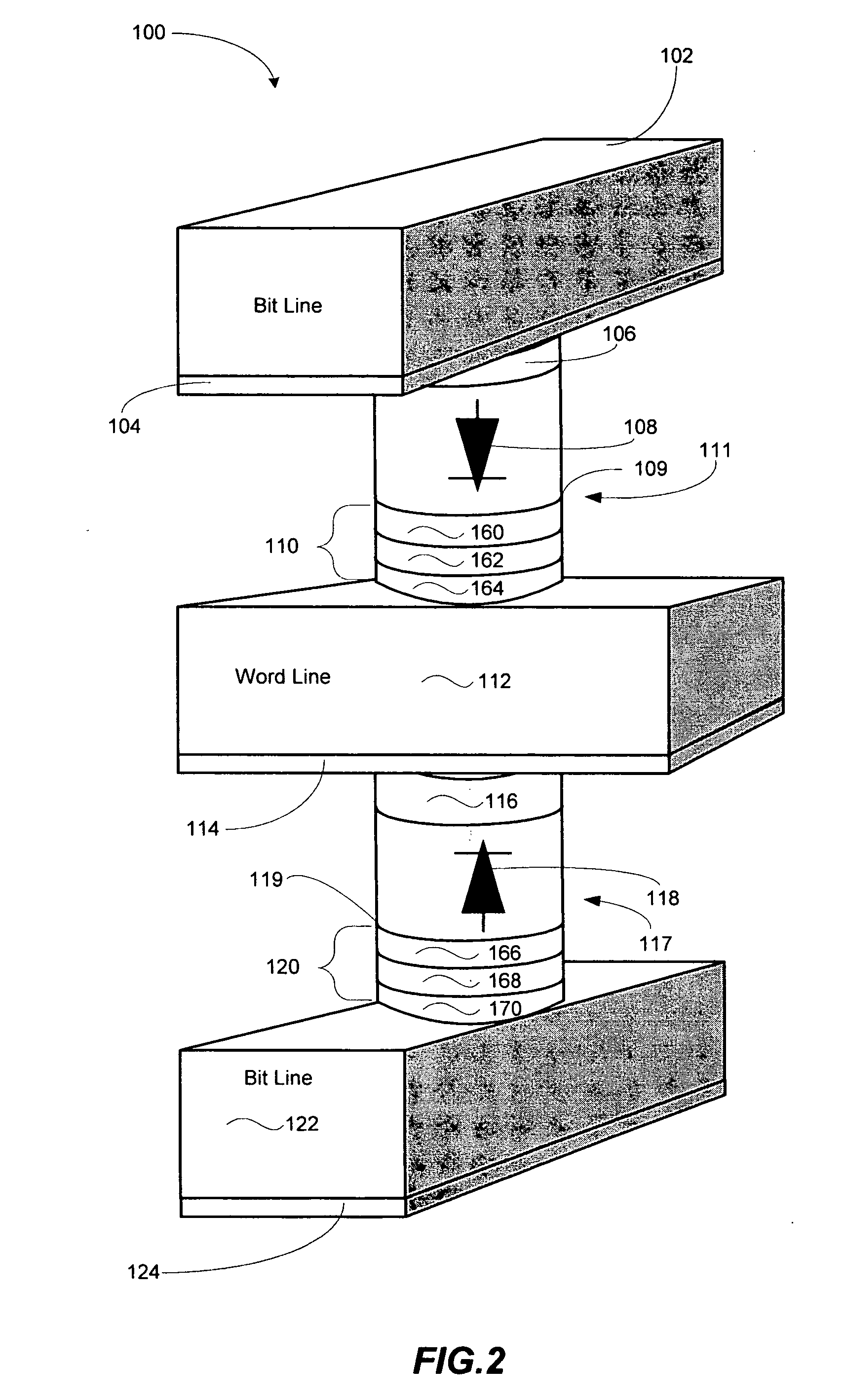
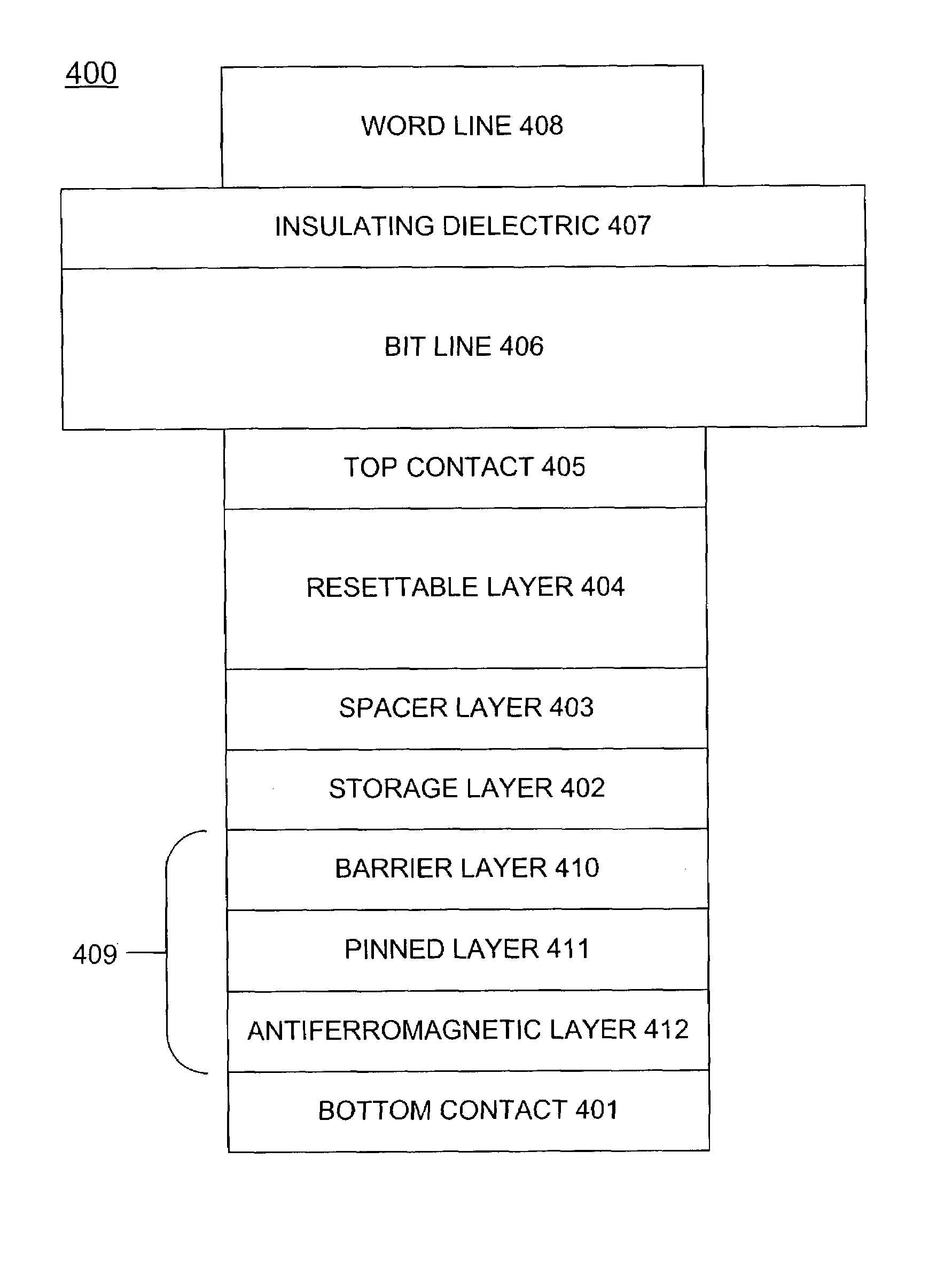
Spin-transfer multilayer stack containing magnetic layers with resettable magnetization
InactiveUS7190611B2Minimizing densityReduce process complexityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesHigh densitySpin transfer
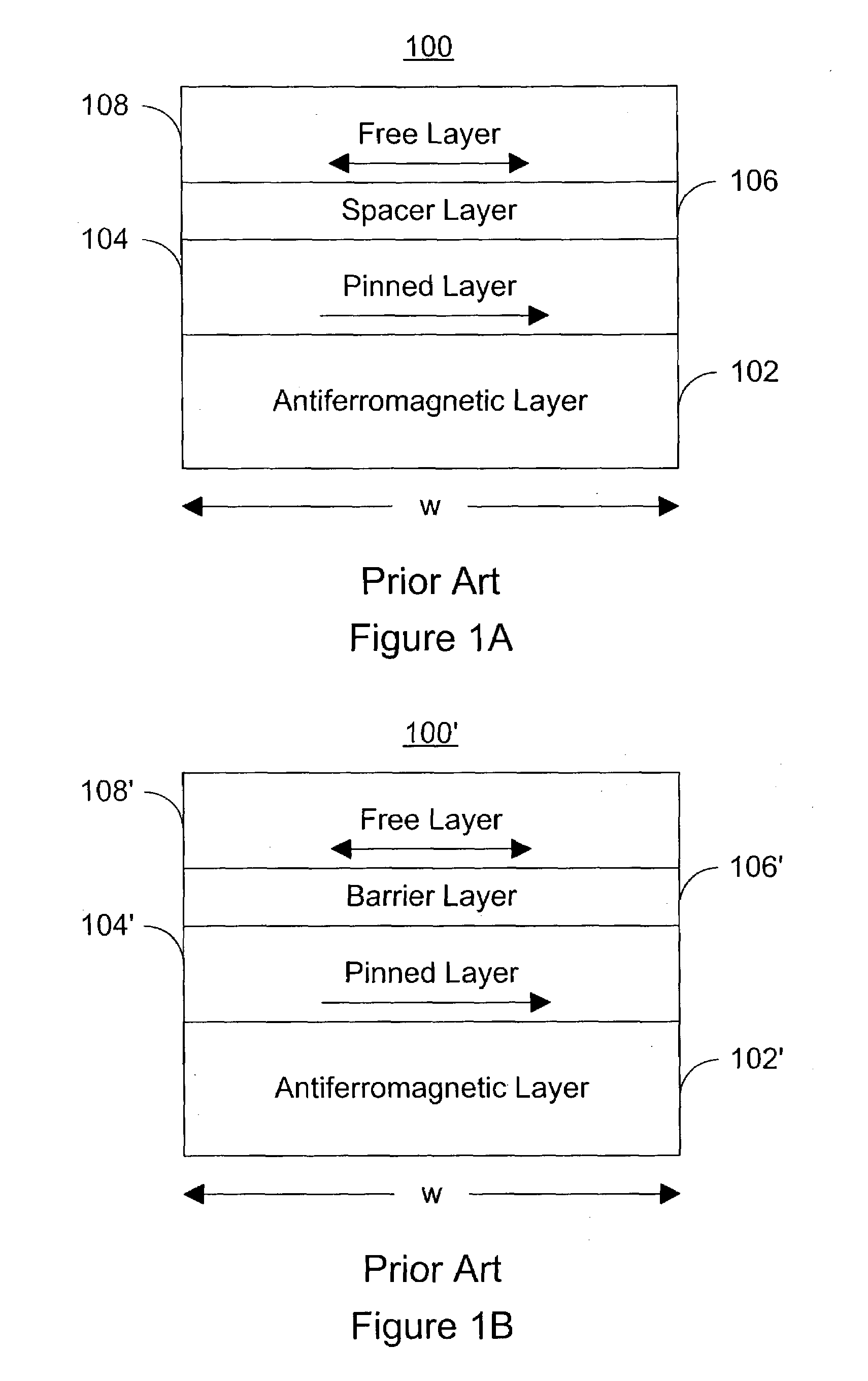
A magnetic element for a high-density memory array includes a resettable layer and a storage layer. The resettable layer has a magnetization that is set in a selected direction by at least one externally generated magnetic field. The storage layer has at least one magnetic easy axis and a magnetization that changes direction based on the spin-transfer effect when a write current passes through the magnetic element. An alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure formed from a tunneling barrier layer, a pinned magnetic layer and an antiferromagnetic layer that pins the magnetization of the pinned layer in a predetermined direction. Another alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure that is formed from a tunneling barrier layer and a second resettable layer having a magnetic moment that is different from the magnetic moment of the resettable layer of the basic embodiment.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Dual axis magnetic sensor
A two-axis magnetic field sensor includes a substrate, a first sensor having at least one magnetoresistive element formed of GMR material on the substrate has a free layer having an easy axis of effective anisotropy field in a first direction. The first sensor is sensitive to magnetic field components perpendicular to the first direction. A current is caused to flow through the first sensor and variations in the resistivity of the first sensor due to the first magnetic field components are sensed. A second sensor having at least one magnetoresistive element formed of GMR material on the substrate has a free layer having an easy axis of effective anisotropy field in a direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction. The second sensor is sensitive to second magnetic field components perpendicular to its easy axis of effective anisotropy. A current is caused to flow through the second sensor and variations in the resistivity of the second sensor due to second magnetic field components are sensed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Magnetic sensor and method for detecting magnetic field
InactiveUS20070290682A1Lower Offset VoltageGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesDriving currentElectricity
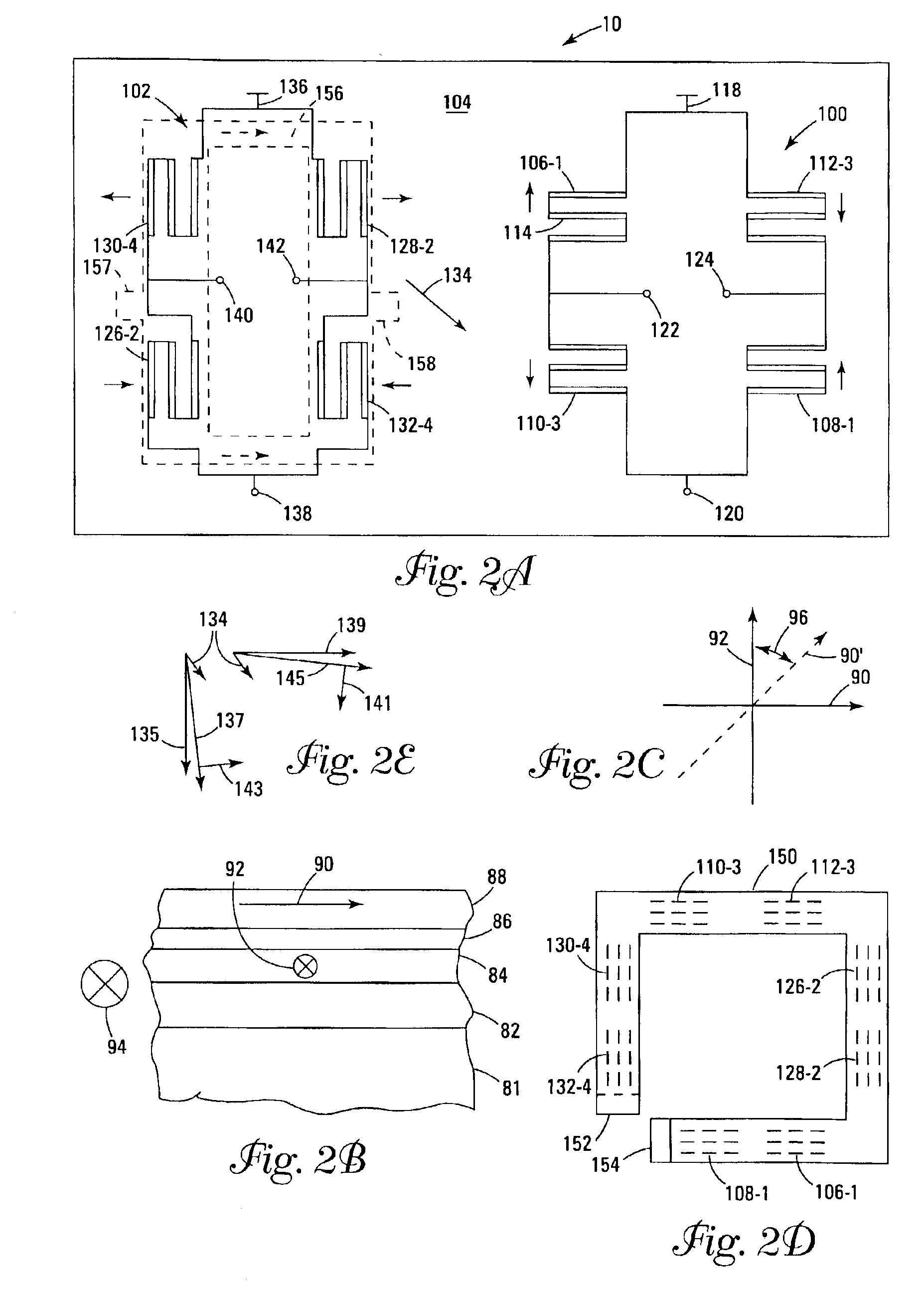
A magnetic sensor includes: a substrate; a semiconductor region; a magnetic field detection portion; a pair of first electrodes; and two pairs of second electrodes. One pair of second electrodes includes first and second terminals, and the other pair includes third and fourth terminals. The first and third terminals are disposed on one side, and the second and fourth terminals are disposed on the other side. The first and fourth terminals are electrically coupled, and the second and third terminals are electrically coupled. The magnetic field detection portion and the first and second electrodes provide a vertical Hall element. One of the first and second electrodes supplies a driving current, and the other one detects the Hall voltage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Integrated sensor having a magnetic flux concentrator
ActiveUS7476953B2High sensitivityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesCurrent sensorMagnetic flux
An integrated sensor has a magnetic field sensing element and first and second relatively high magnetically permeable members forming a gap, wherein the magnetic field element is disposed within the gap. The magnetically permeable members provide an increase in the flux experienced by the magnetic field sensing element in response to a magnetic field. The integrated sensor can be used as a current sensor, a proximity detector, or a magnetic field sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Current sensor
ActiveUS20070096716A1Lower resistanceImprove cooling effectGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCurrent sensor
A current sensor includes a conductor line, and a magnetic sensor in which resistance value changes according to a current magnetic field produced by a current to be detected flowing through the conductor line. The conductor line includes: a pair of parallel portions each having a same and uniform cross-sectional area, while extending in parallel with each other separated at a first distance therebetween; a connecting portion connecting one end of one of the parallel portions and one end of the other of the parallel portions; and a pair of terminal portions each connected to the other end of each of the parallel portions, while extending to face with each other separated at a second distance therebetween, the second distance being wider than the first distance, the terminal portions each having a larger cross-sectional area than that of each of the parallel portions.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic particle flow detector
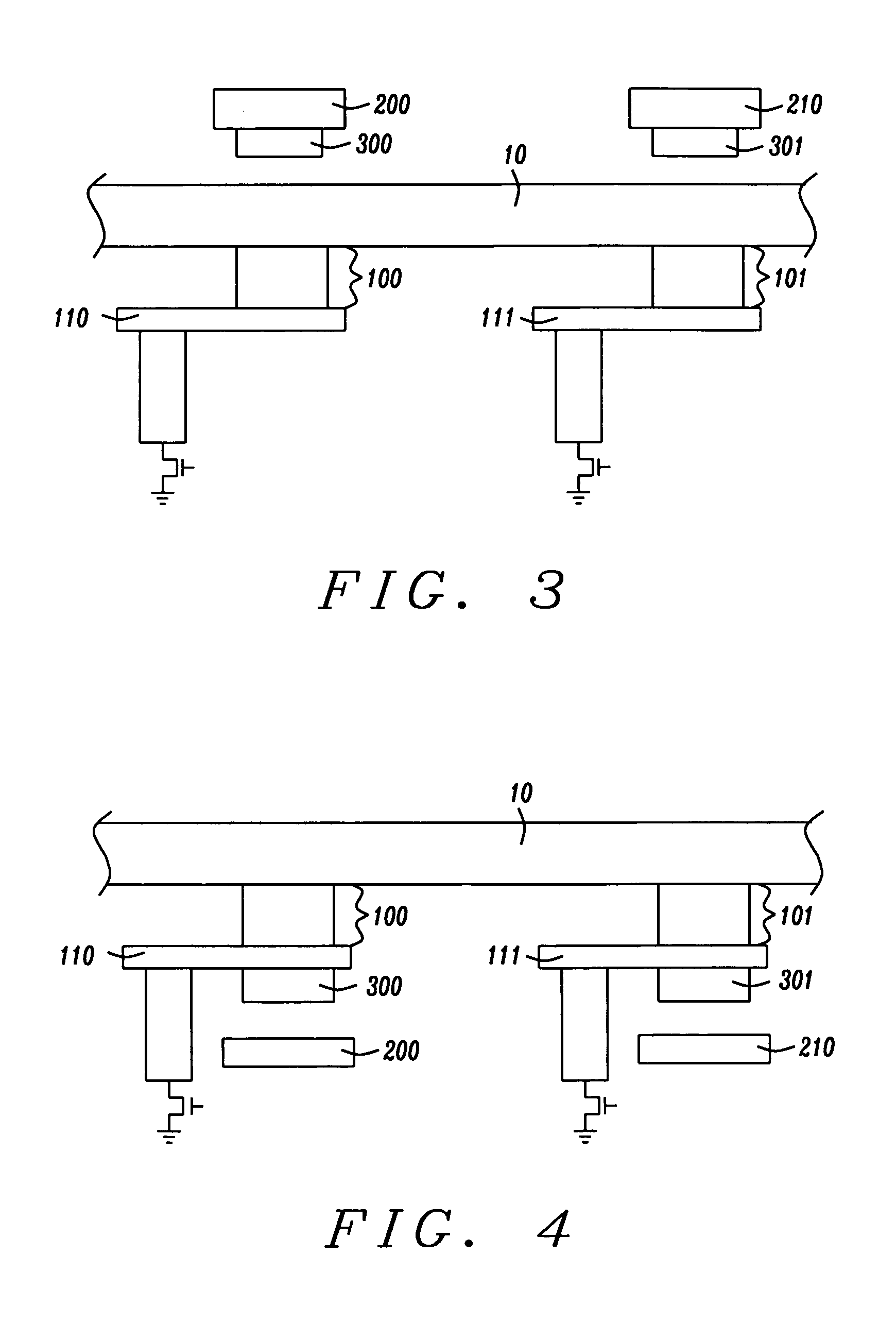
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field detection system having a substrate supporting a magnetic field sensor in a channel with a first electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap and in direct contact with at least some surface of the magnetic field sensor ands a second electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap in a region thereof adjacent to, but separated from, the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:NVE CORP
High density and high programming efficiency MRAM design
InactiveUS6864551B2Improved reliability against electromigrationEasy to manufactureGalvano-magnetic devicesNanoinformaticsHigh densityMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic memory includes a magnetic element. The magnetic element is written using a first write line and a second write line and resides at an intersection between the first and second write lines. The second write line is oriented at an angle to the first write line. The second write line has a top and at least one side. At least a portion of the second write line is covered by an insulating layer. A magnetic layer covers a portion of the insulating layer. The portion of the insulating layer resides between the magnetic layer and the second write line. The magnetic layer includes a soft magnetic material.
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
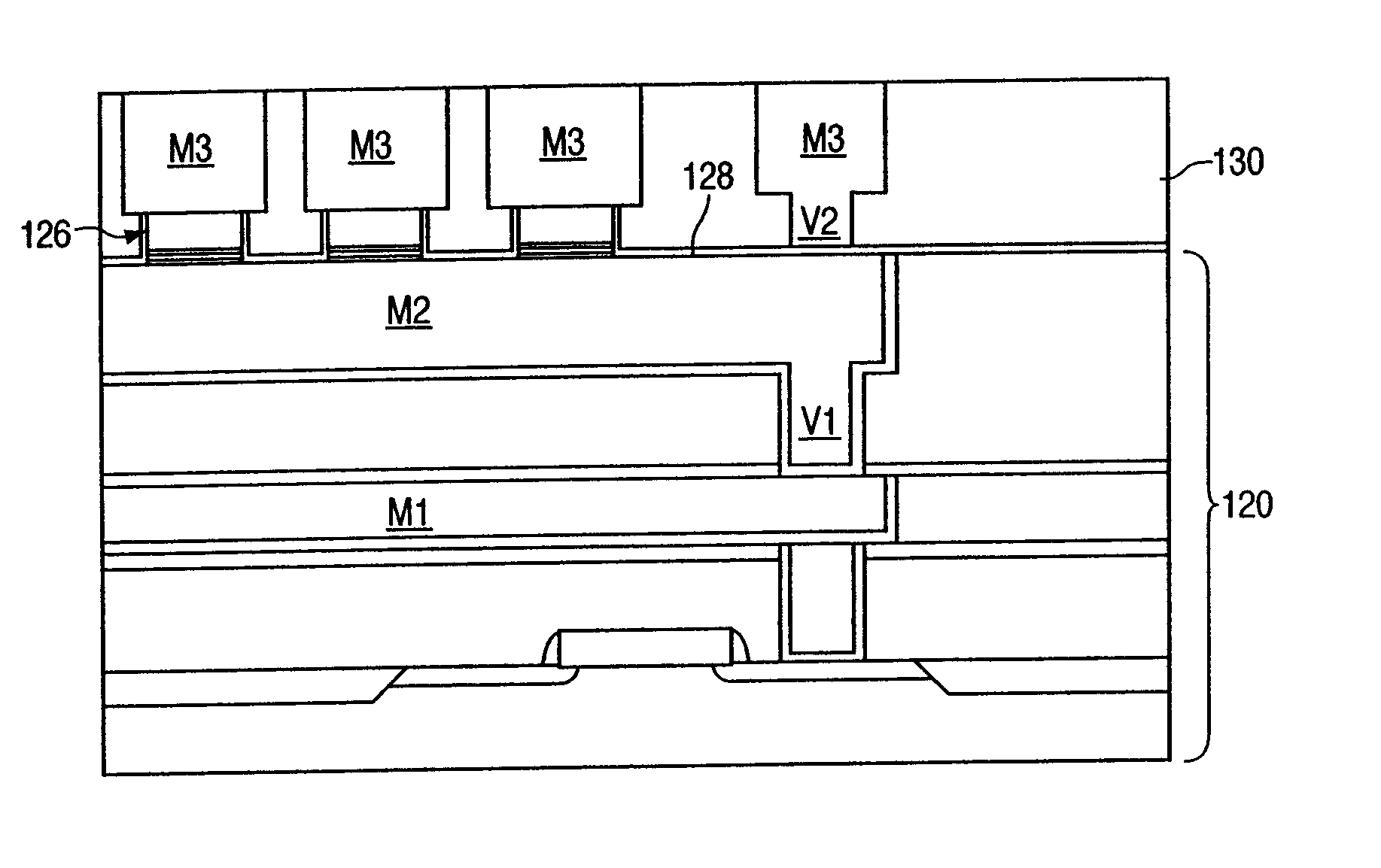
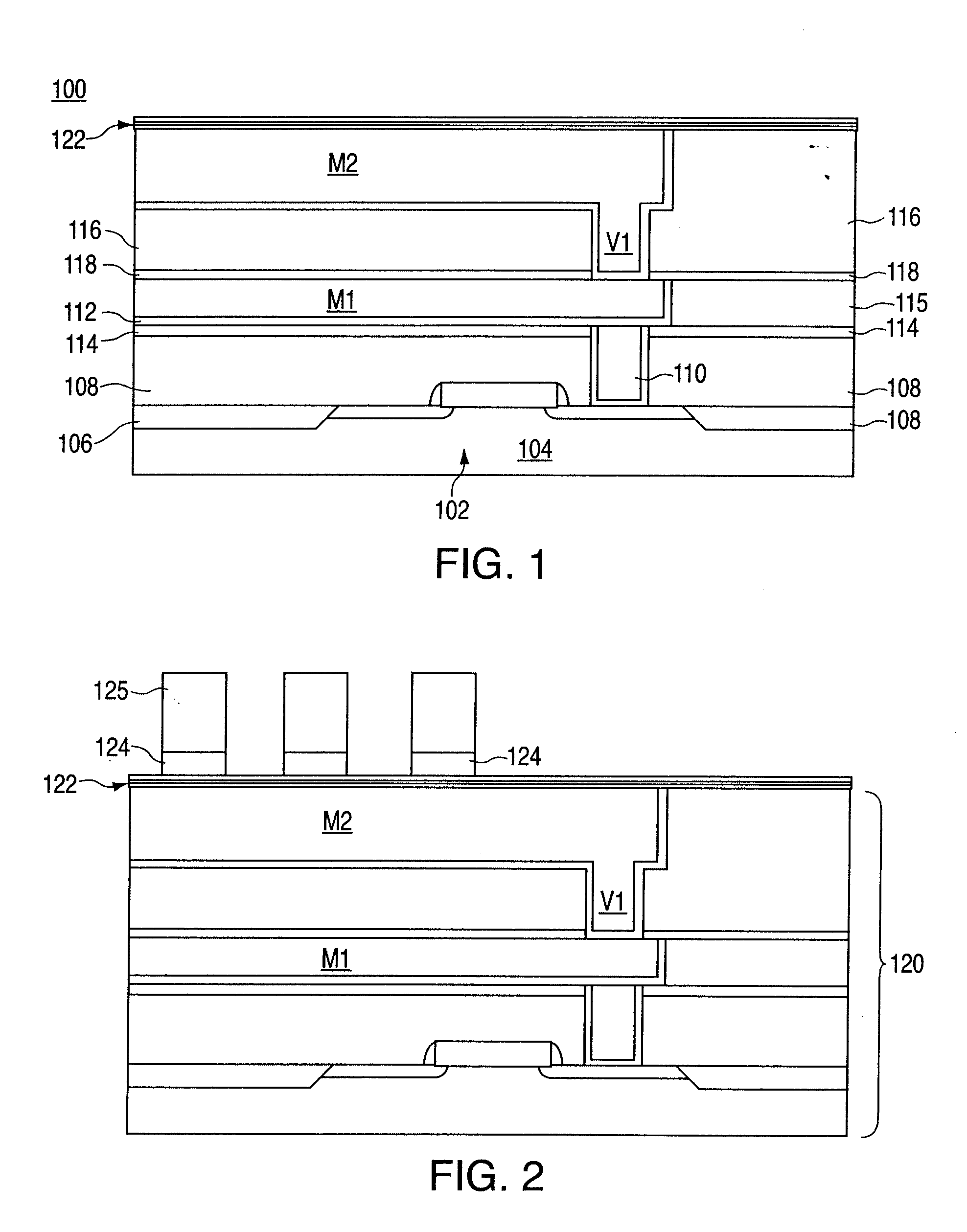
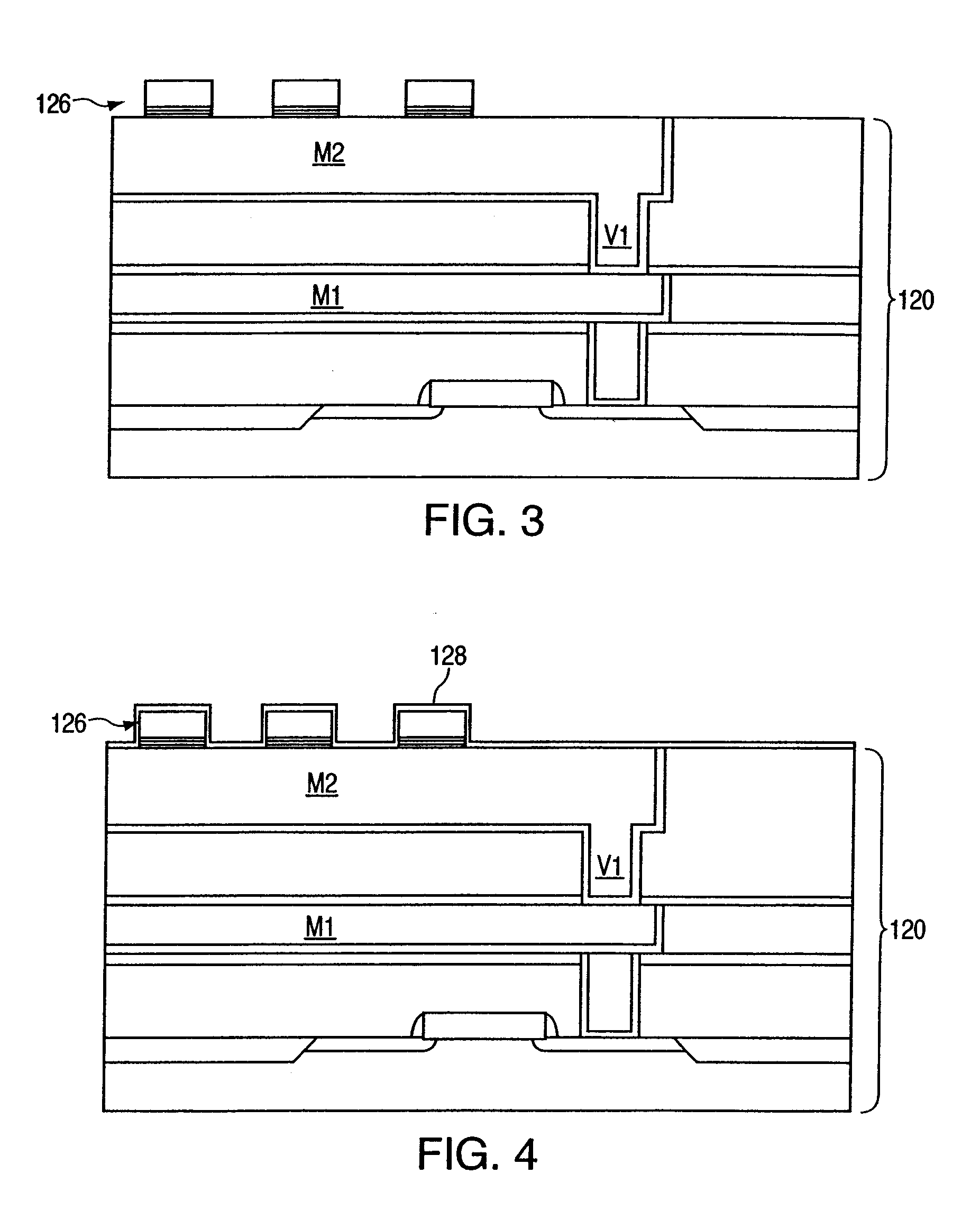
Magnetic random access memory and method of fabricating thereof
ActiveUS20050023581A1Galvano-magnetic devicesNanoinformaticsRandom access memoryCondensed matter physics
A device structure and method for forming an interconnect structure in a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) device. In an exemplary embodiment, the method includes defining a magnetic stack layer on a lower metallization level, the magnetic stack layer including a non-ferromagnetic layer disposed between a pair of ferromagnetic layers. A conductive hardmask is defined over the magnetic stack layer, and selected portions of the hardmask and the magnetic stack layer, are then removed, thereby creating an array of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) stacks. The MTJ stacks include remaining portions of the magnetic stack layer and the hardmask, wherein the hardmask forms a self aligning contact between the magnetic stack layer and an upper metallization level subsequently formed above the MTJ stacks.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Resistor having a predetermined temperature coefficient
ActiveUS7777607B2Galvano-magnetic devicesNanomagnetismElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic reluctance
A material stack has an electrical resistance generally the same in the presence of a magnetic field and in the presence of no magnetic field. The electrical resistance of the material stack has a temperature coefficient generally the same as a magnetoresistance element.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
MRAM with split read-write cell structures
InactiveUS20070164380A1Efficient storageLow switching thresholdGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesAspect ratioMagnetic orientation
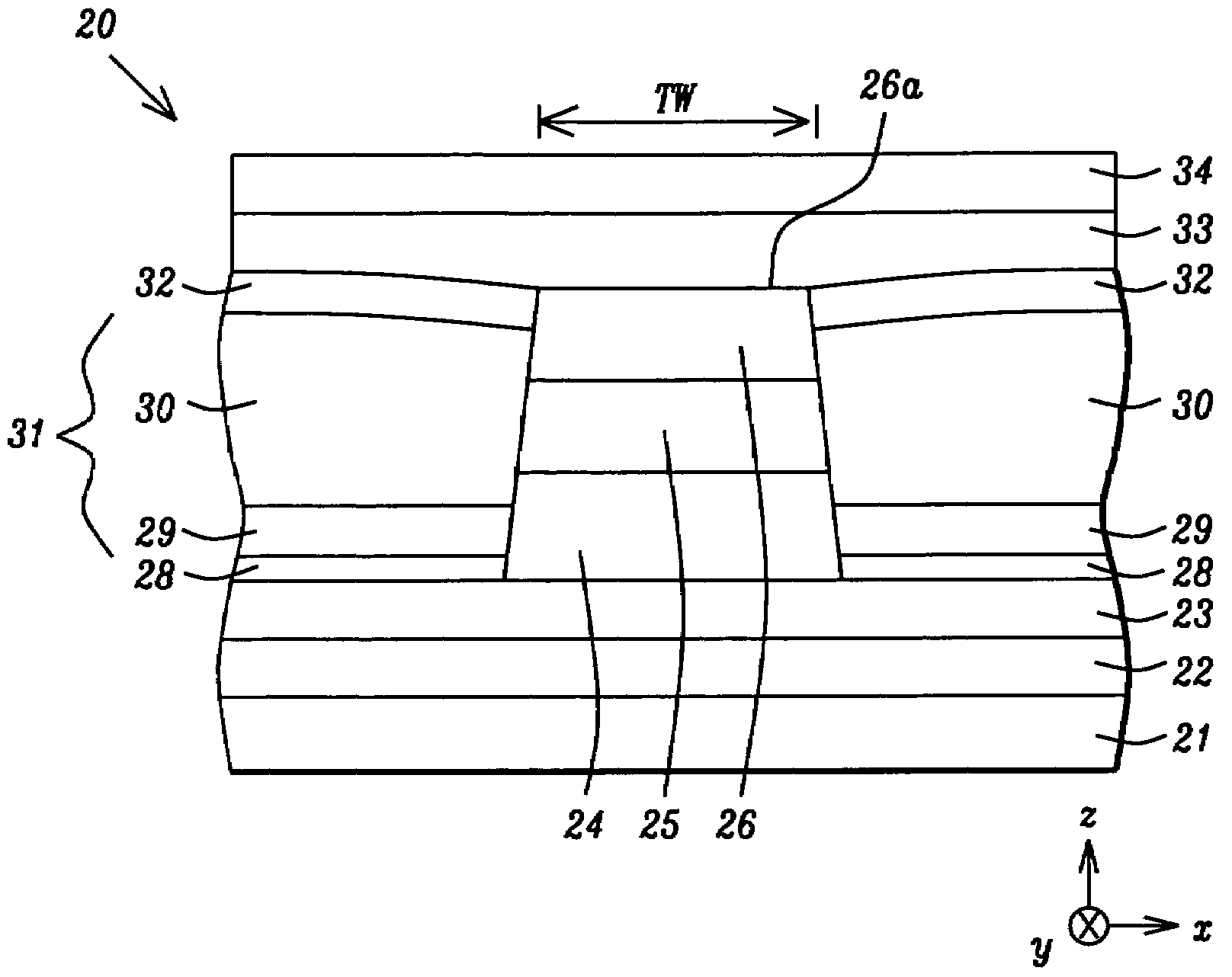
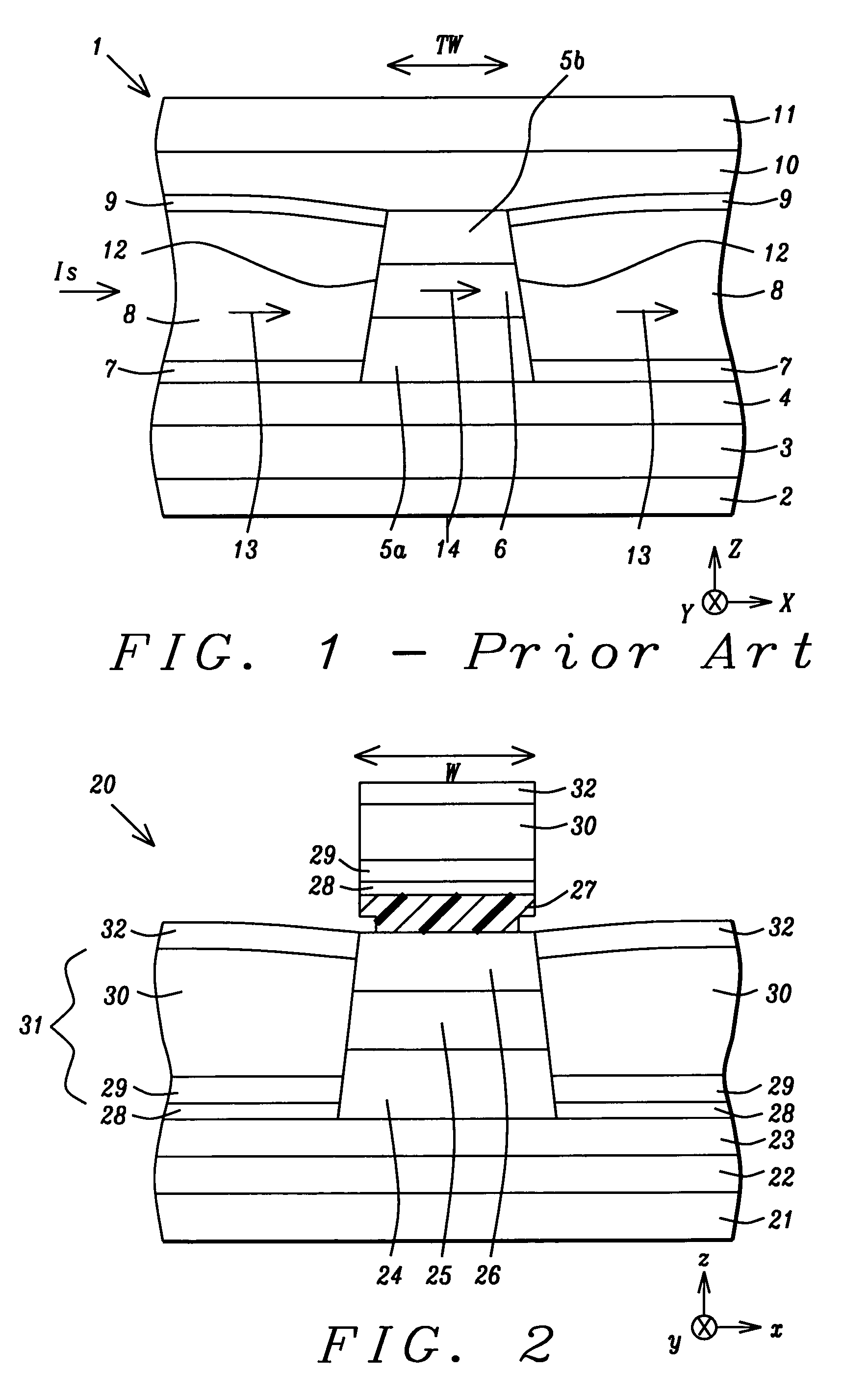
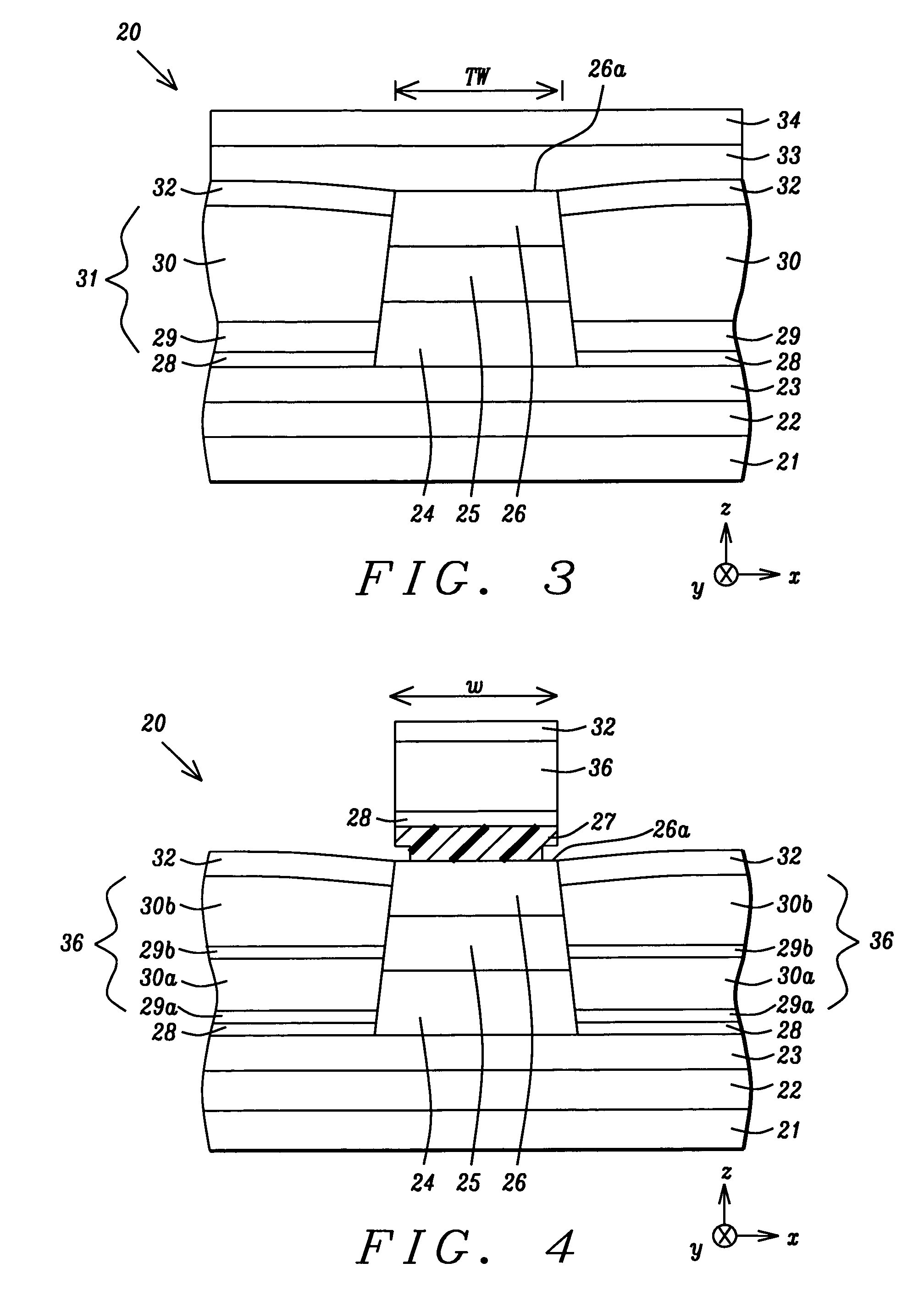
An MRAM cell is formed in two separate portions. A first portion, that includes a pinned layer, a tunneling barrier layer and first free layer part, is used to read the value of a stored bit of information. A second portion includes a second free layer part on which information is written and stored. The second free layer part is formed with a high aspect ratio cross-section that renders it strongly magnetically anisotropic and enables it to couple to the relatively isotropic first free layer through a magnetostatic interaction. This interaction aligns the magnetization of the first free layer part in an opposite direction to the magnetization of the second free layer part. The magnetic orientation of the first free layer part relative to that of its adjacent pinned layer determines the resistance state of the first cell portion and this resistance state can be read by passing a current through the first cell portion. Thus, in effect, the first cell portion becomes a remote sensing device for the magnetization orientation of the second free layer part
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
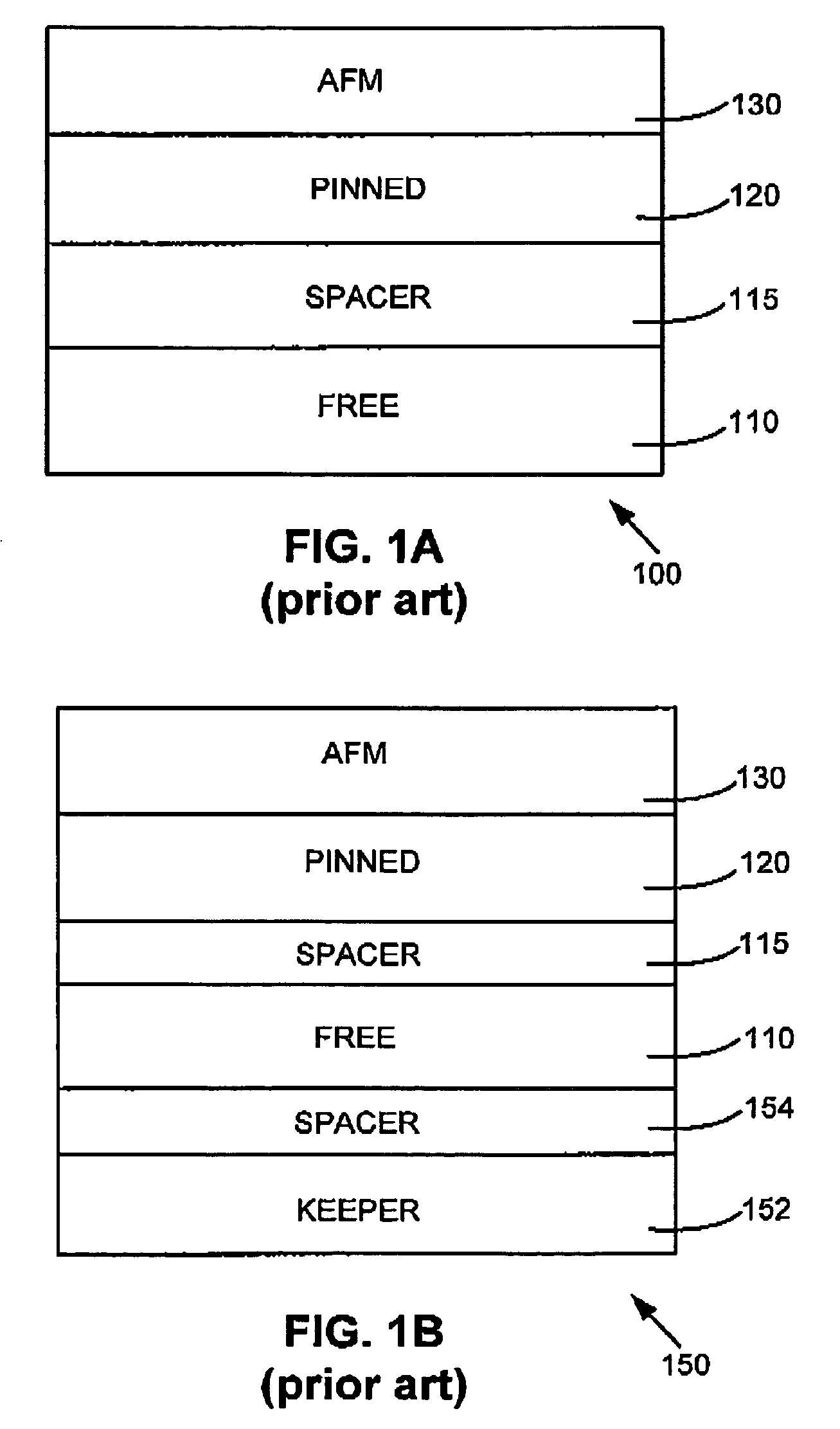
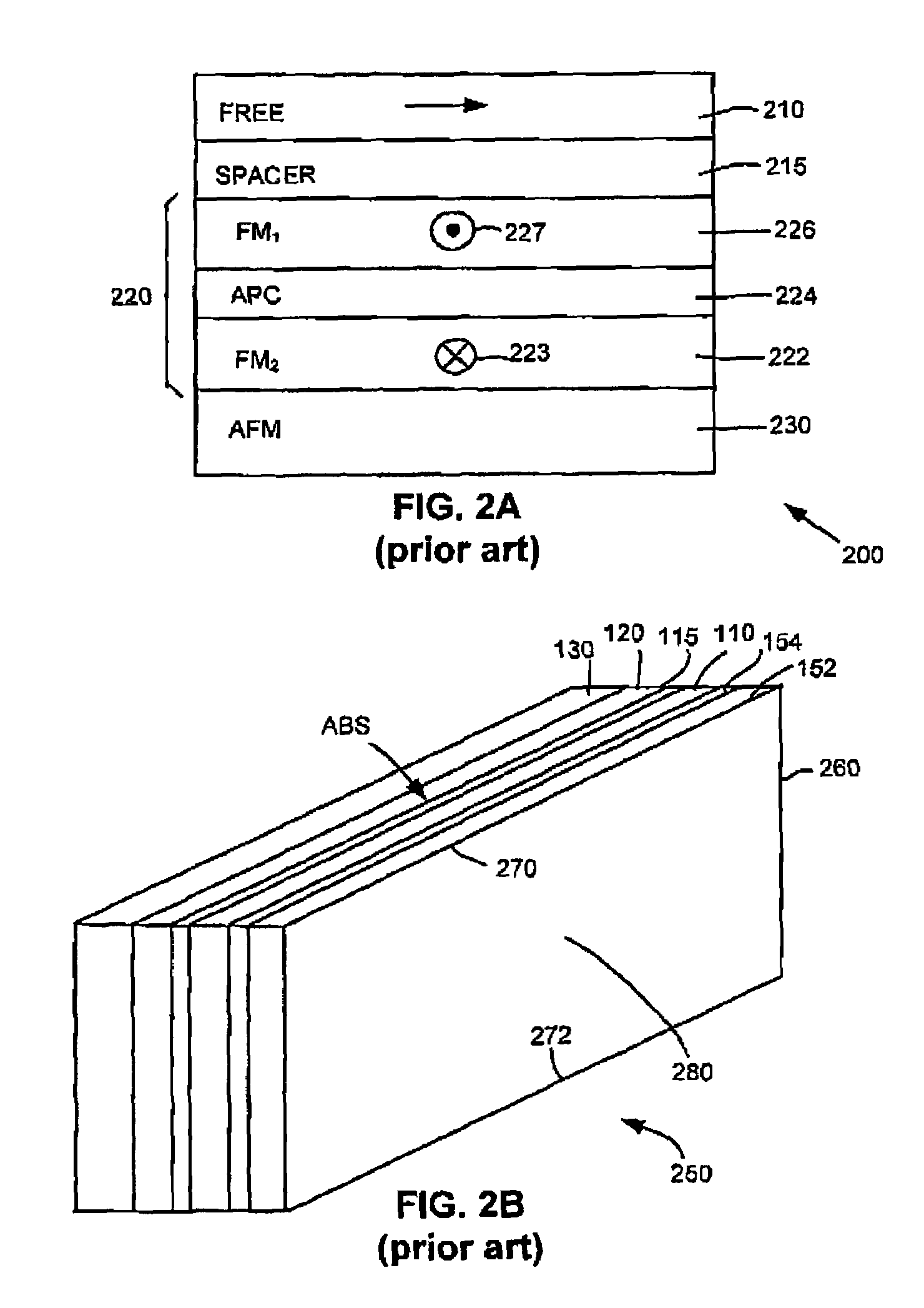
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head, magnetic head assembly, magnetic storage system
InactiveUS20050167770A1Increase contactEffectively applying the bias magnetic fieldNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic storage
Disclosed are a high-sensitivity and high-reliability magnetoresistance effect device (MR device) in which bias point designing is easy, and also a magnetic head, a magnetic head assembly and a magnetic recording / reproducing system incorporating the MR device. In the MR device incorporating a spin valve film, the magnetization direction of the free layer is at a certain angle to the magnetization direction of a second ferromagnetic layer therein when the applied magnetic field is zero. In this, the pinned magnetic layer comprises a pair of ferromagnetic films as antiferromagnetically coupled to each other via a coupling film existing therebetween. The device is provided with a means of keeping the magnetization direction of either one of the pair of ferromagnetic films constituting the pinned magnetic layer, and with a nonmagnetic high-conductivity layer as disposed adjacent to a first ferromagnetic layer on the side opposite to the side on which the first ferromagnetic layer is contacted with a nonmagnetic spacer layer. With that constitution, the device has extremely high sensitivity, and the bias point in the device is well controlled.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
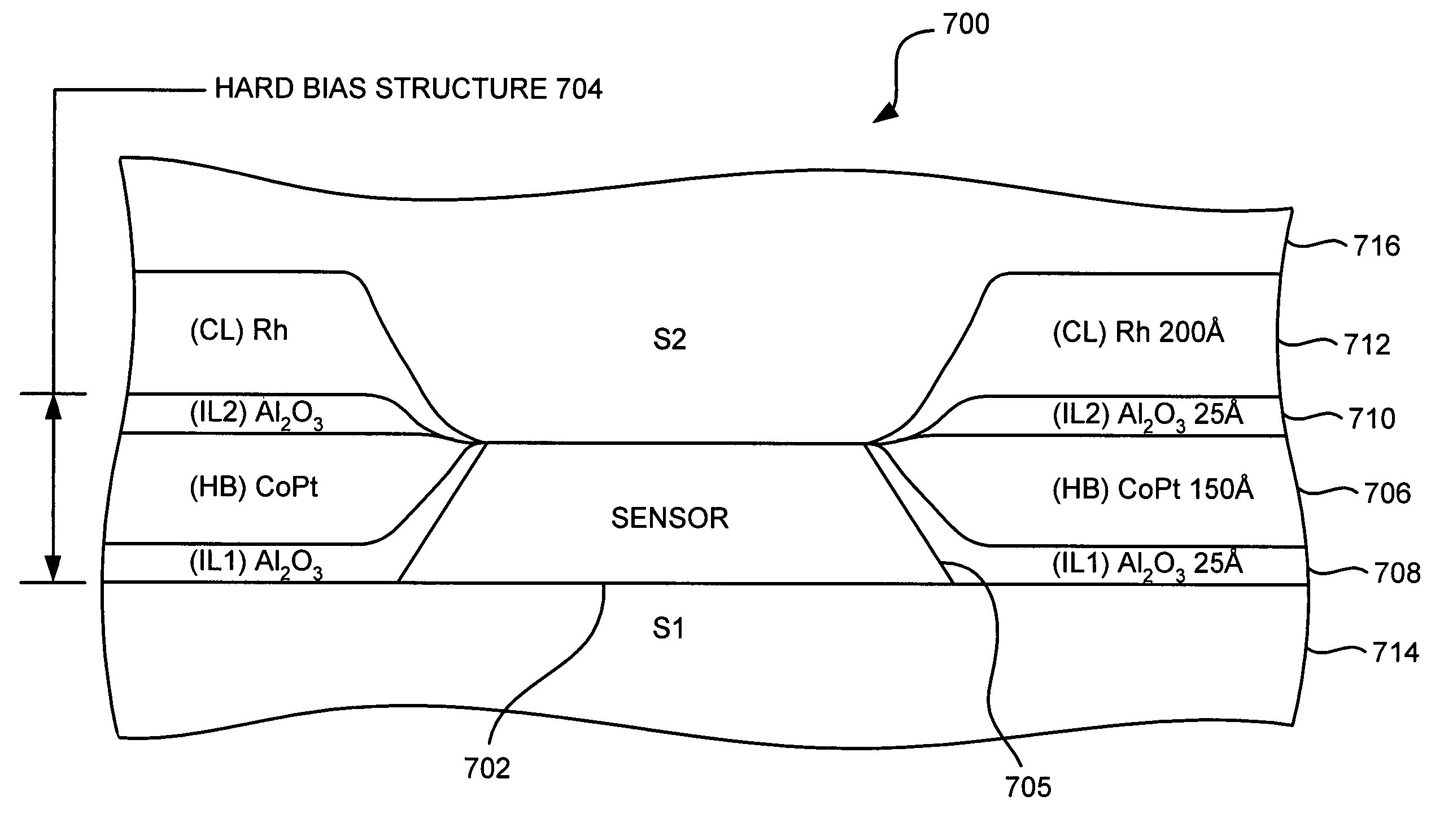
Composite hard bias design with a soft magnetic underlayer for sensor applications
ActiveUS7446987B2Improve noiseEnhanced signalGalvano-magnetic devicesNanomagnetismSpinsProcess window
A hard bias structure for biasing a free layer in a MR element within a magnetic read head is comprised of a soft magnetic underlayer such as NiFe and a hard bias layer comprised of Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 or Co65Cr15Pt20 that are rigidly exchange coupled to ensure a well aligned longitudinal biasing direction with minimal dispersions. The hard bias structure is formed on a BCC seed layer such as CrTi to improve lattice matching. The hard bias structure may be laminated in which each of the underlayers and hard bias layers has a thickness that is adjusted to optimize the total Hc, Mrt, and S values. The present invention encompasses CIP and CPP spin values, MTJ devices, and multi-layer sensors. A larger process window for fabricating the hard bias structure is realized and lower asymmetry output and NBLW (normalized base line wandering) reject rates during a read operation are achieved.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory
InactiveCN101064114AThermally stableGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryRecording layer
It is possible to provide a magnetoresistive effect element and a magnetic storage which has thermal stability even if it is made fine and in which the magnetization in the magnetic recording layer can be inverted at a low current density. A magnetoresistive effect element includes: a magnetization pinned layer having a magnetization pinned in a direction; a magnetization free layer of which magnetization direction is changeable; a tunnel barrier layer provided between the magnetization pinned layer and the magnetization free layer; a first antiferromagnetic layer provided on the opposite side of the magnetization pinned layer from the tunnel barrier layer; and a second antiferromagnetic layer which is provided on the opposite side of the magnetization free layer from the tunnel barrier layer and which is thinner in thickness than the first antiferromagnetic layer, wherein the direction of the magnetization of the free magnetization layer can be converted by pouring an electron whose polarity is changed in spin polarization into the free magnetization layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Apparatus for current measurement
InactiveUS7336064B2Simple designHigh effectMeasurement using dc-ac conversionGalvano-magnetic devicesElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
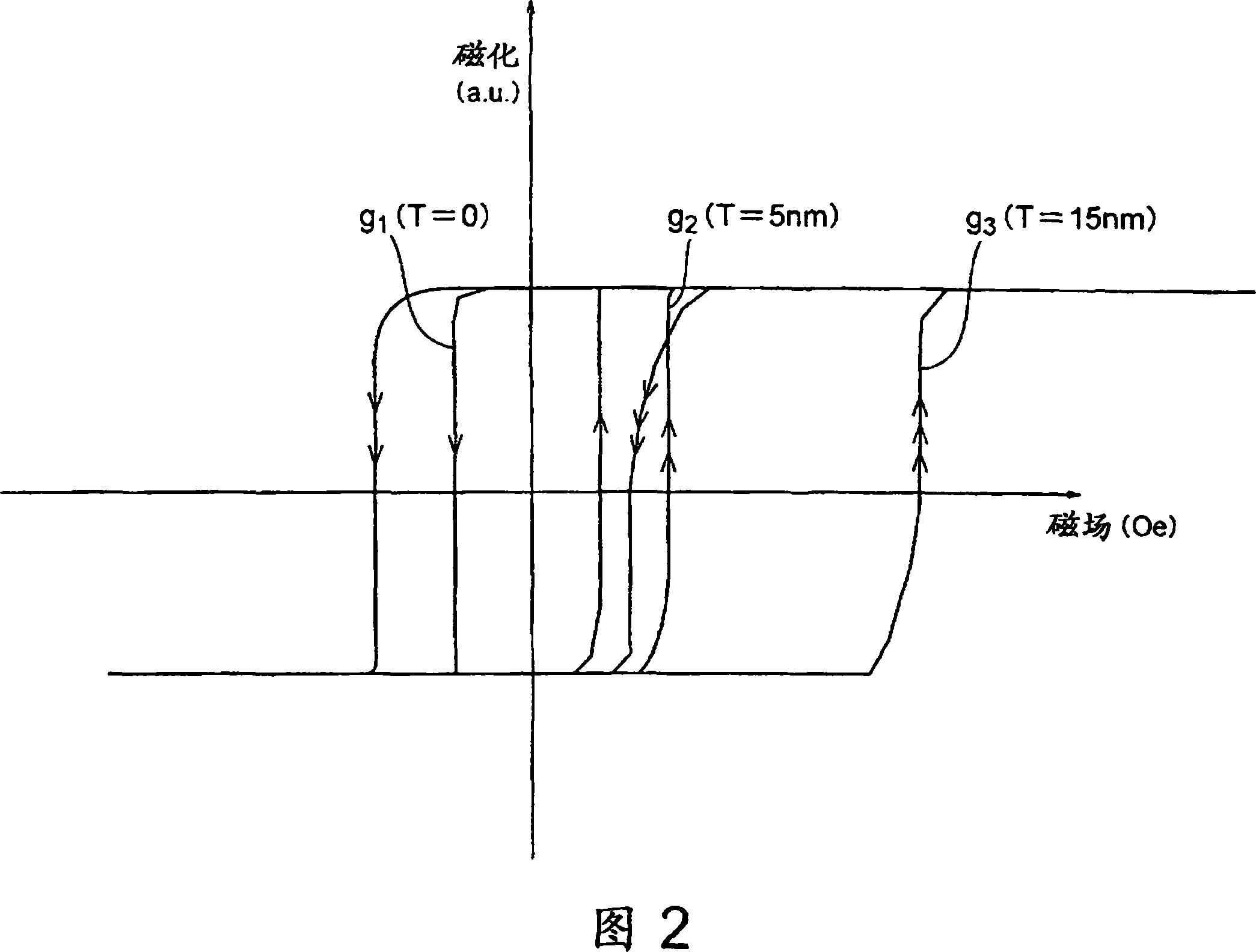
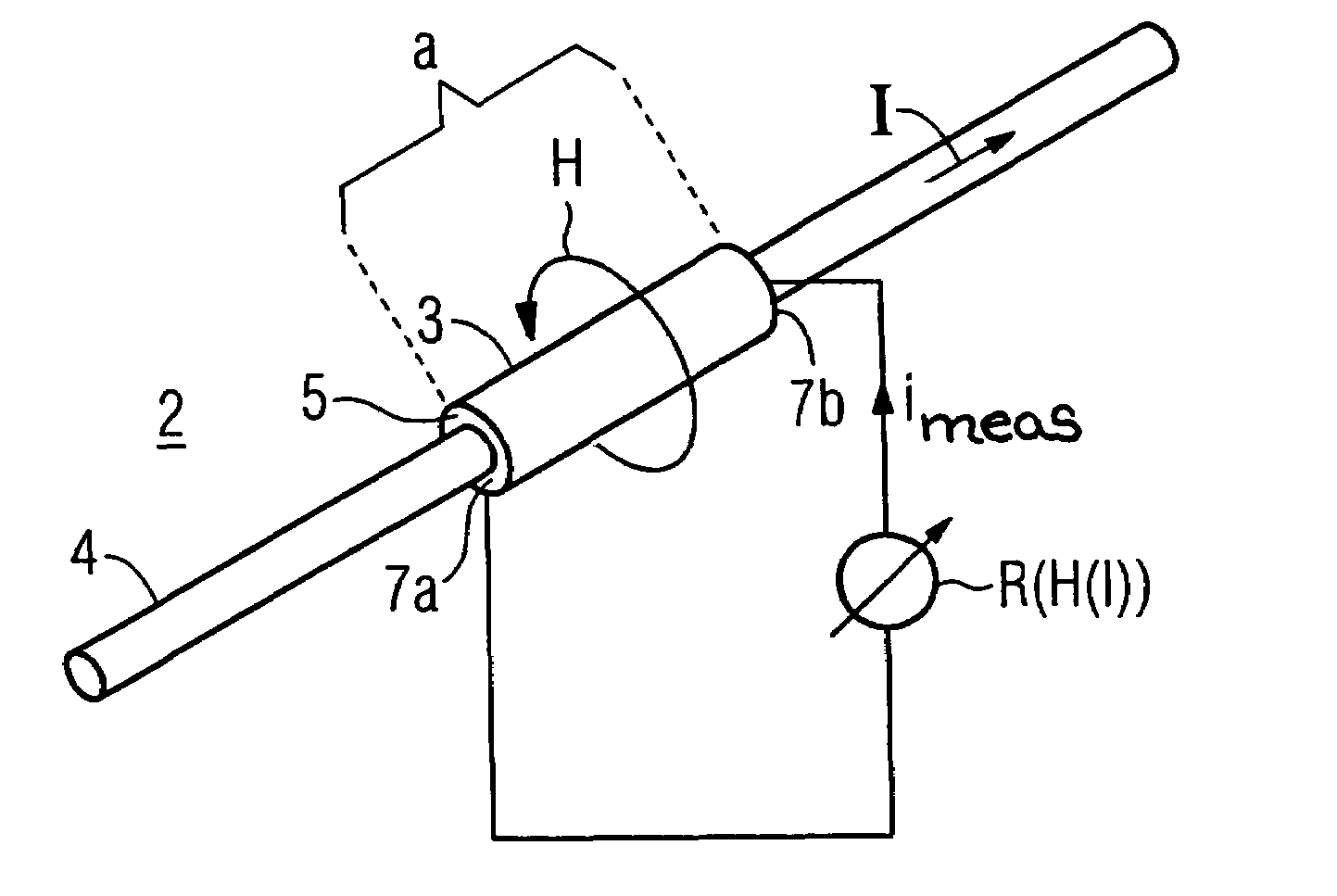
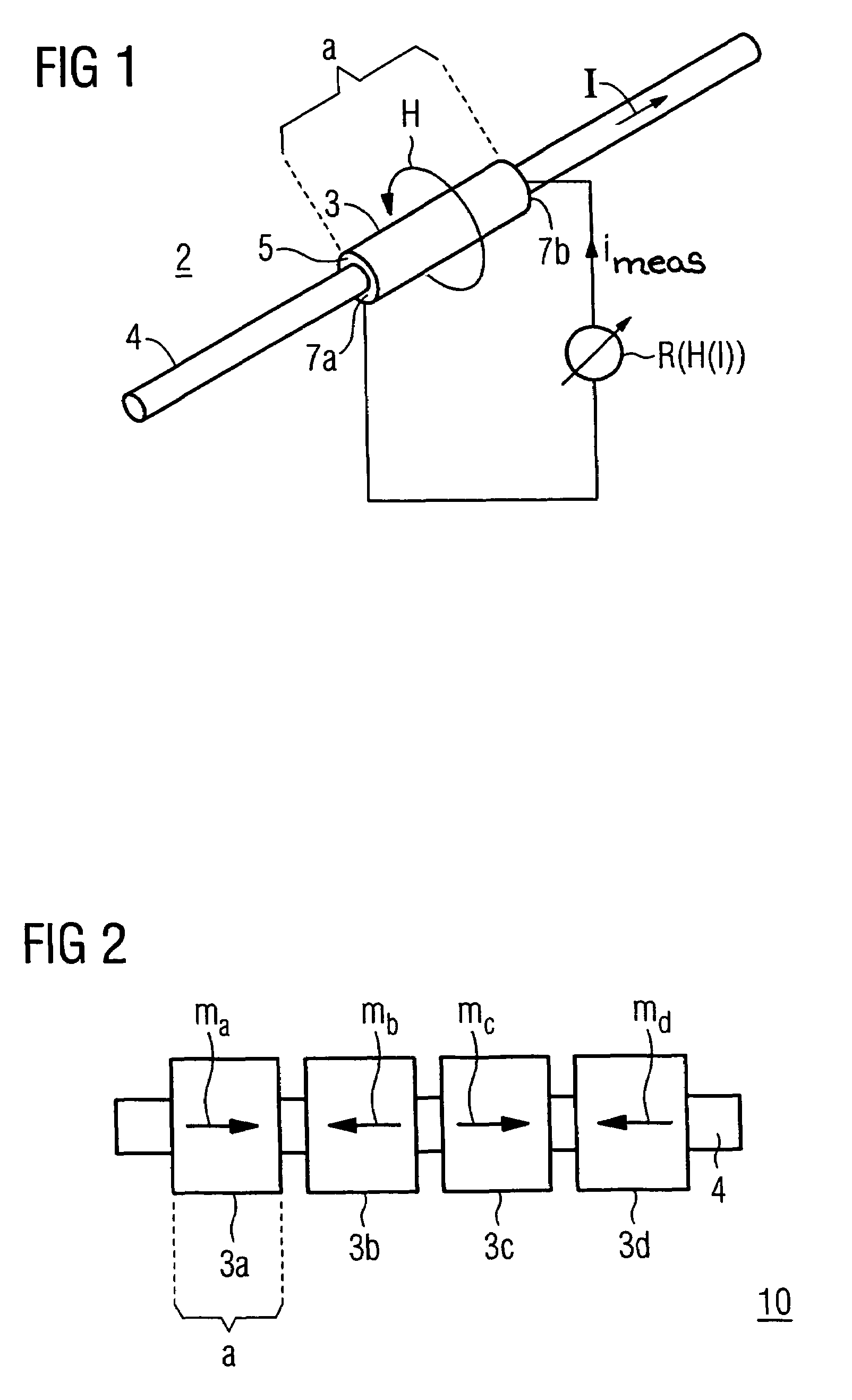
The apparatus for measurement of a current which is flowing in an axially elongated electrical conductor at a first electrical potential. The apparatus contains at least one associated sensor element associated with the conductor that is electrically isolated from it at a second electrical potential different from the first electrical potential of the electrical conductor, and having magnetoresistive characteristics. The sensor element is intended to form a loop which is magnetically closed around the conductor in the circumferential direction, with the resistance value being tapped off at axially opposite ends. Its magnetoresistive part is preferably composed of a non-metallic powder composite material with a high magnetoresistive effect.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
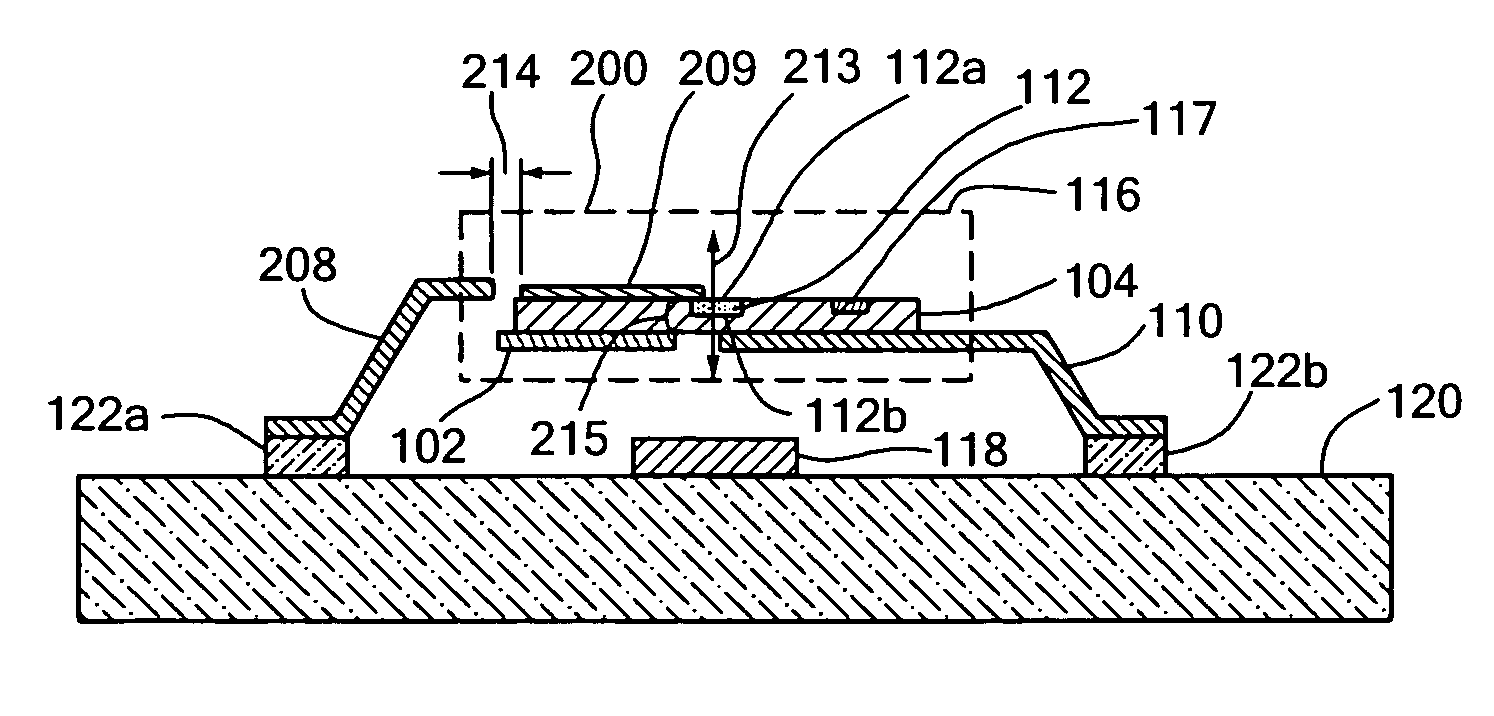
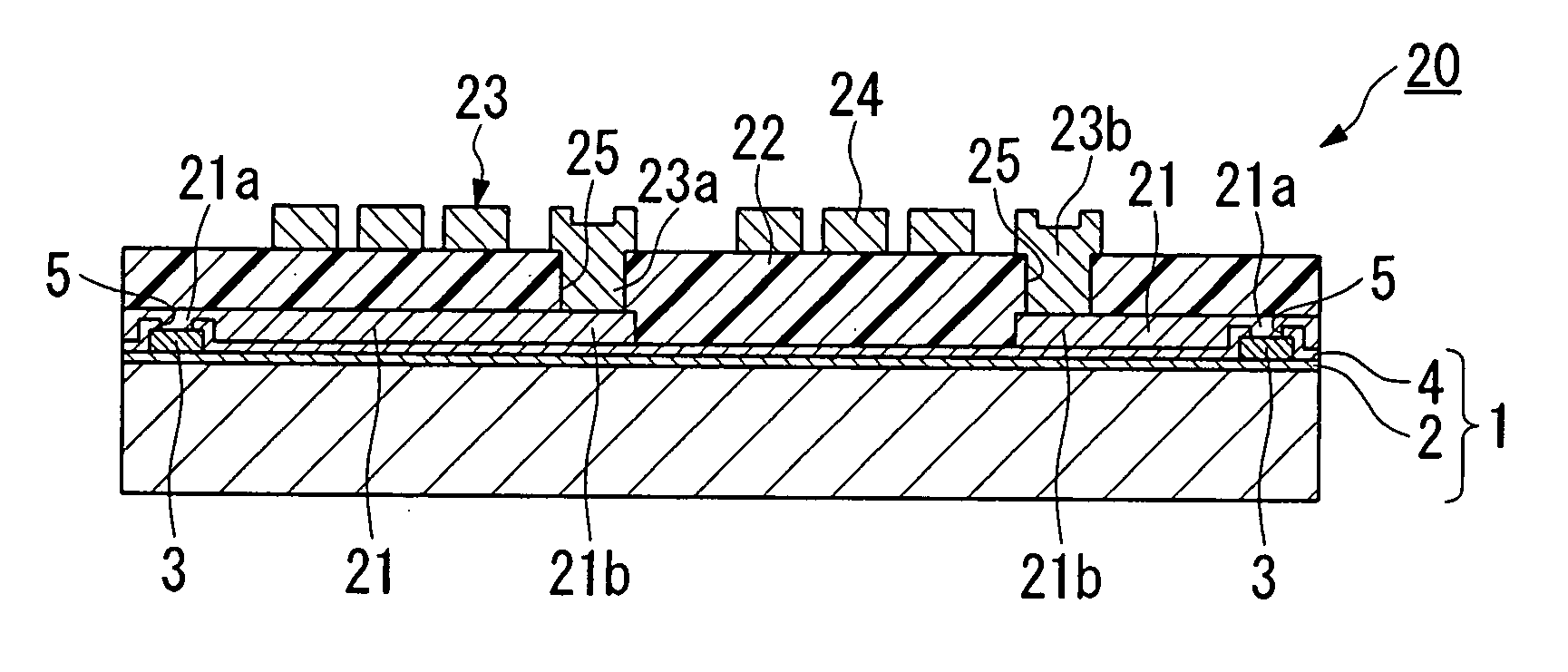
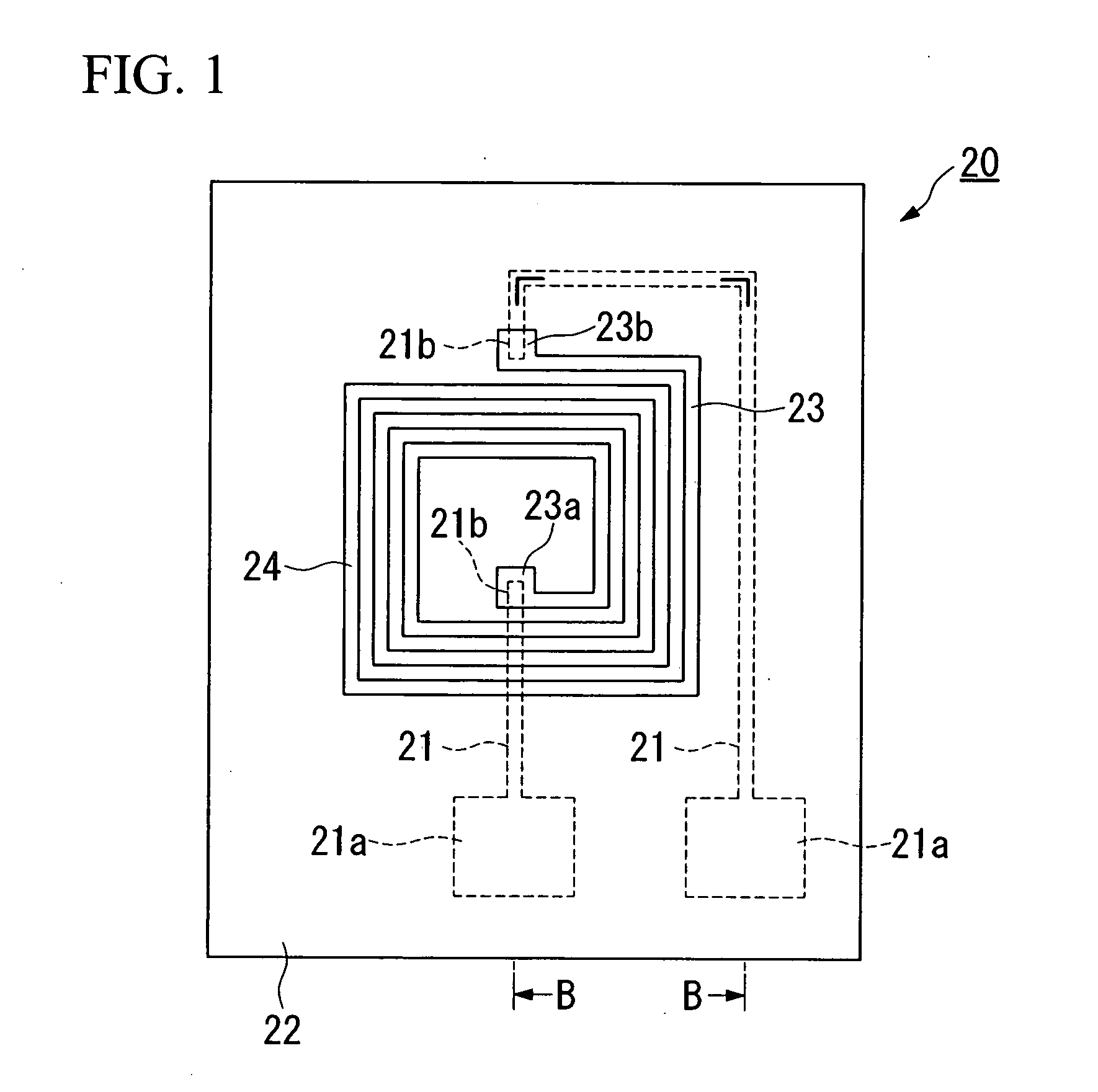
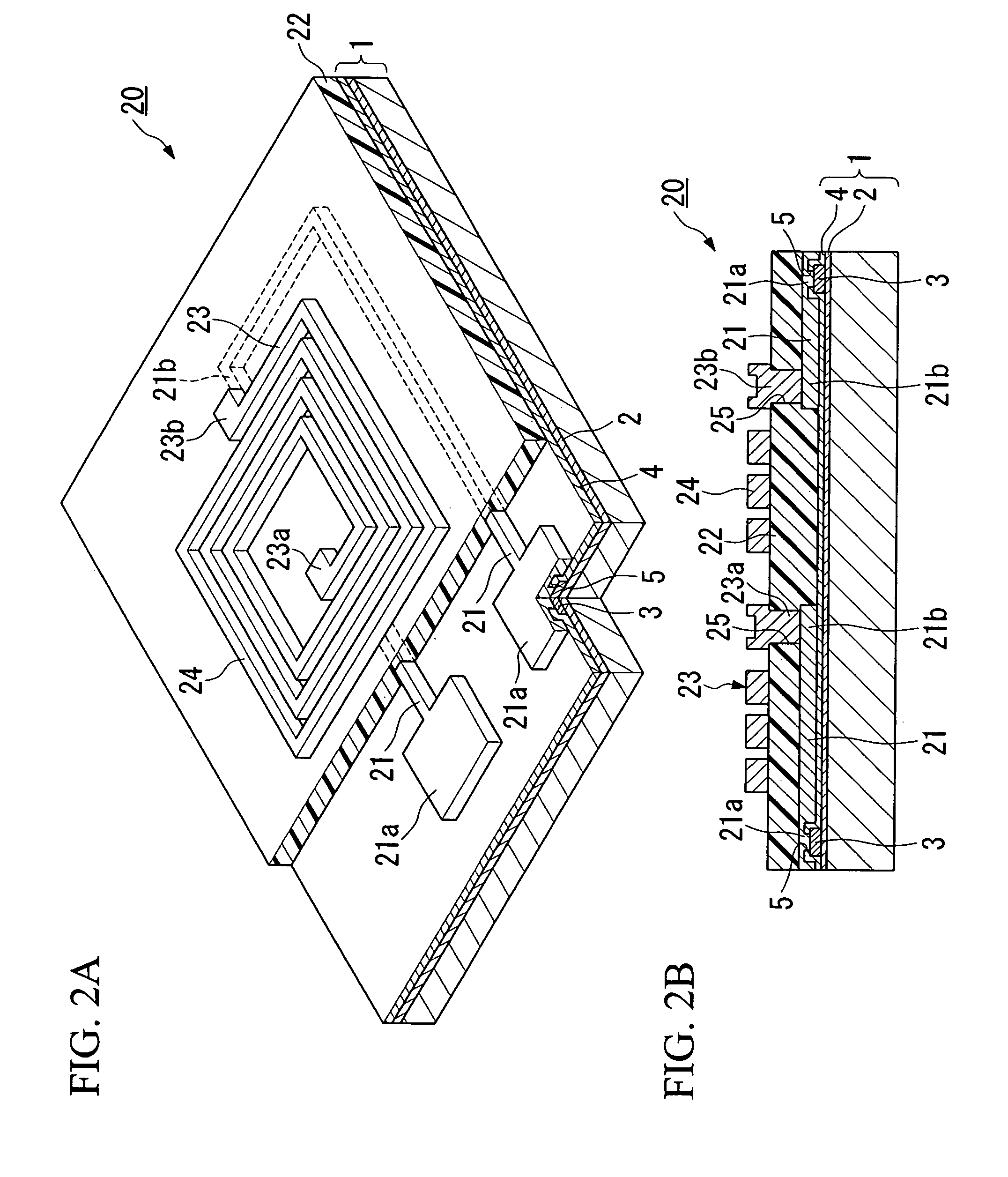
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
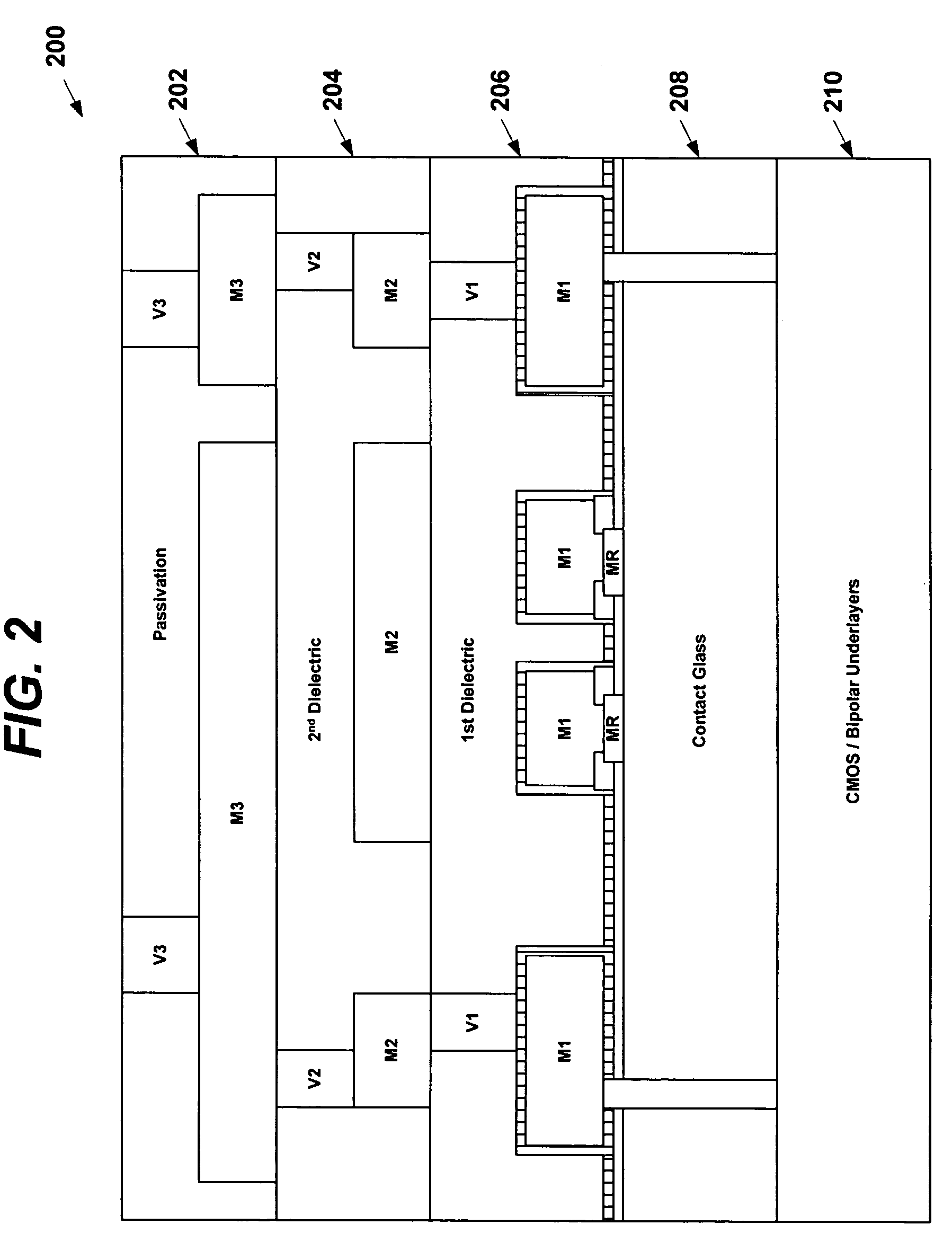
InactiveUS20060022287A1Reduce energy lossImprove performanceLine/current collector detailsGalvano-magnetic devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
Owner:FLIPCHIP INT
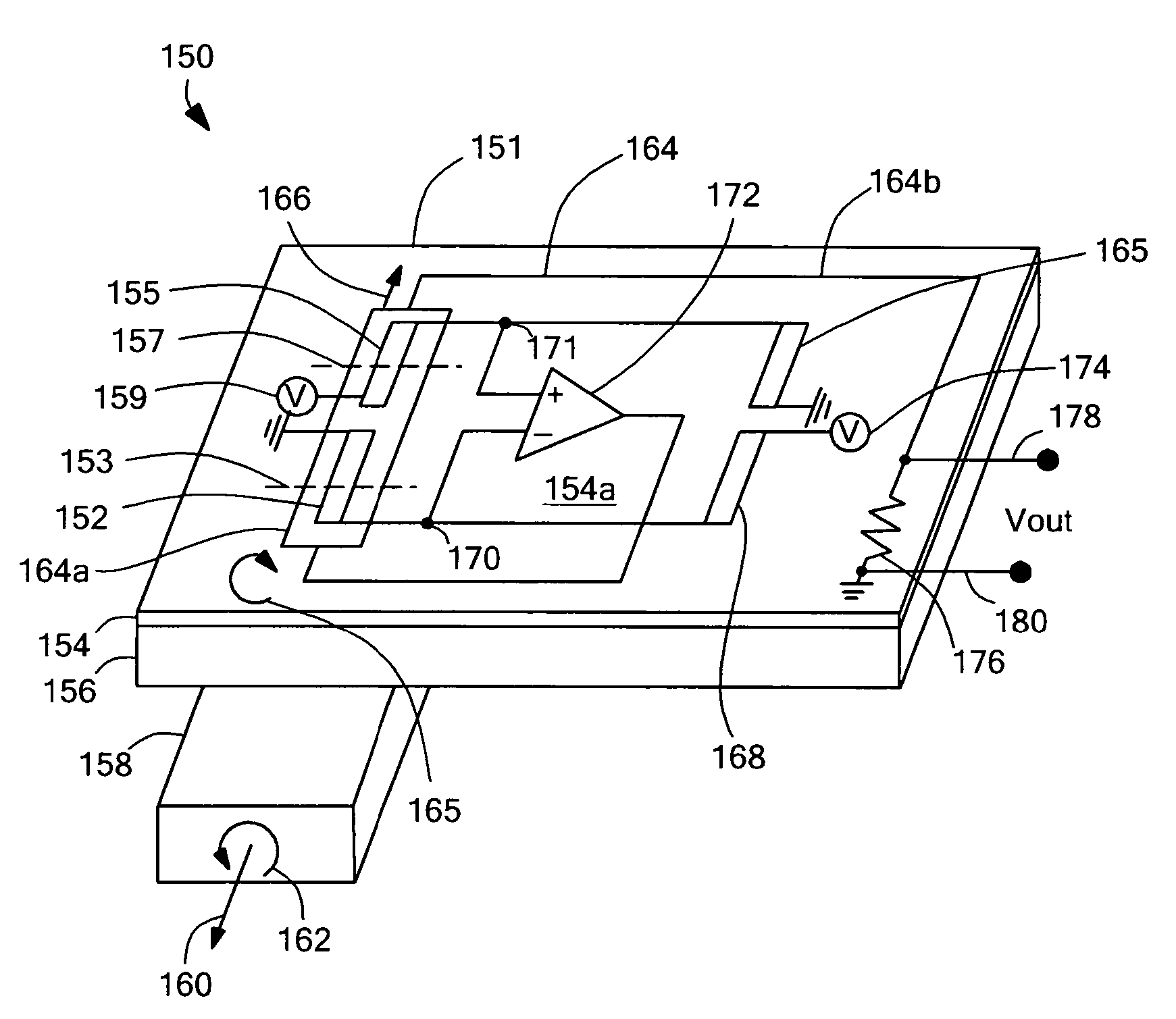
MEMS 2d and 3D magnetic field sensors and associated manufacturing method
ActiveUS20100097059A1Galvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesMicroelectromechanical systemsAbsolute measurement
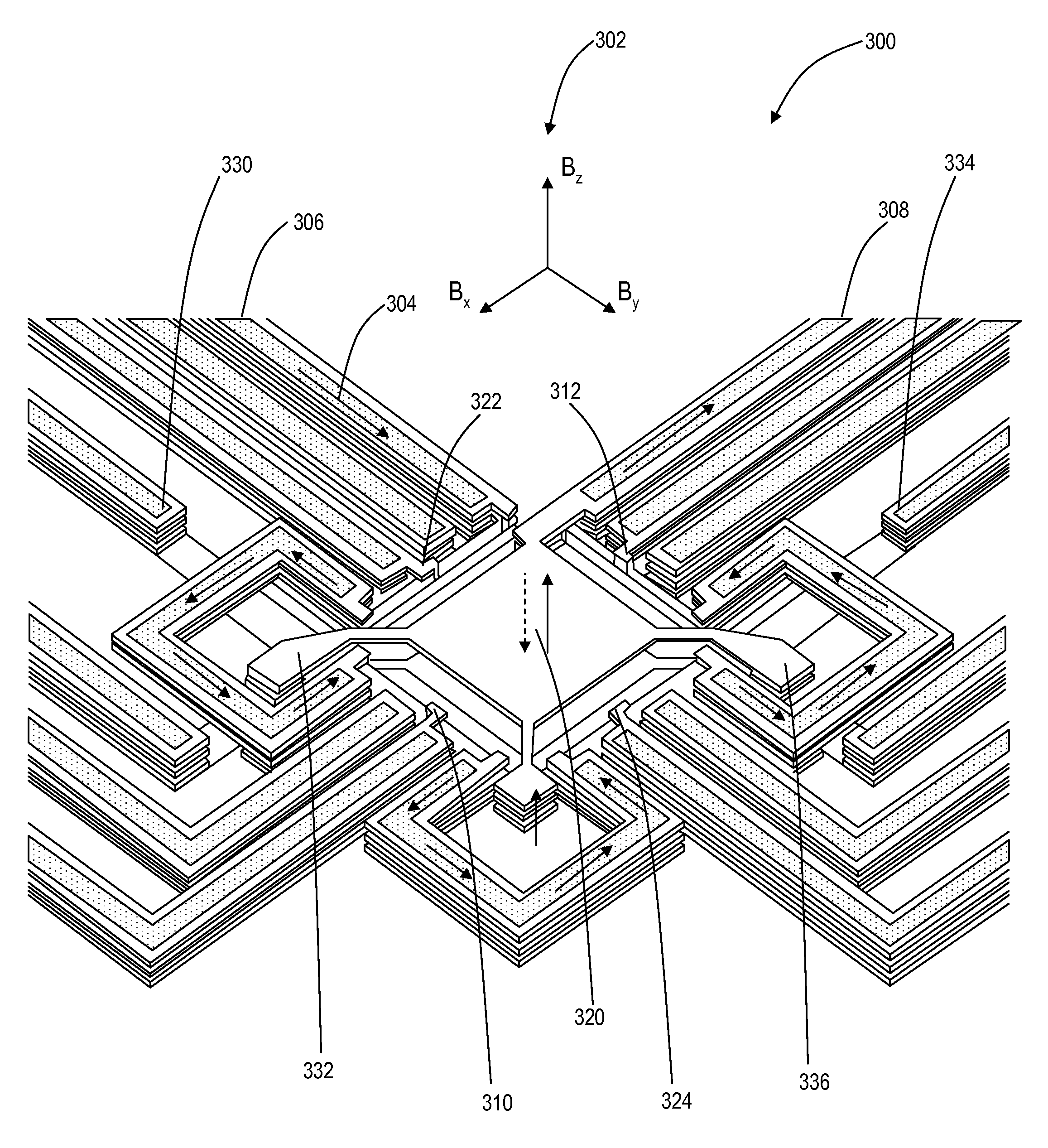
The disclosure provides Hall effect device configurations capable of measuring magnetic fields in two dimensions (2D) and three dimensions (3D) along with associated microelectromechanical system (MEMS) manufacturing methods. The present invention includes various geometric layout configurations for 2D and 3D Hall effect devices with multidimensional magnetic field sensing elements. Advantageously, the present invention can provide, simultaneously and independently, absolute measurement of each of the components (i.e., x-, y-, and z-components) of a magnetic field. Additionally, the geometric layout configurations enable the Hall effect devices to be constructed with MEMS fabrication techniques.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
Magnetic memory device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070278603A1Small space requirementWell formedGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryRecording layer
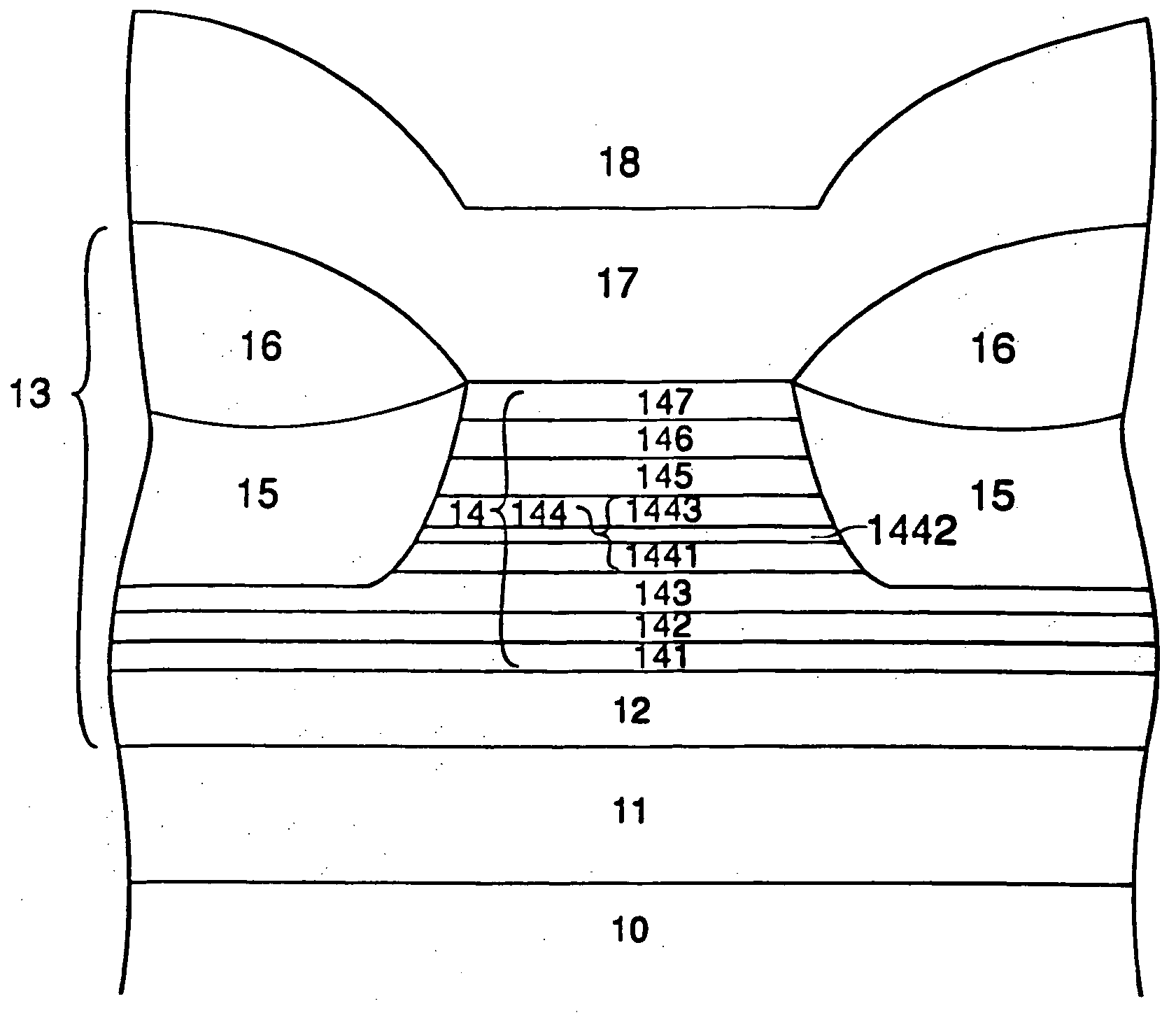
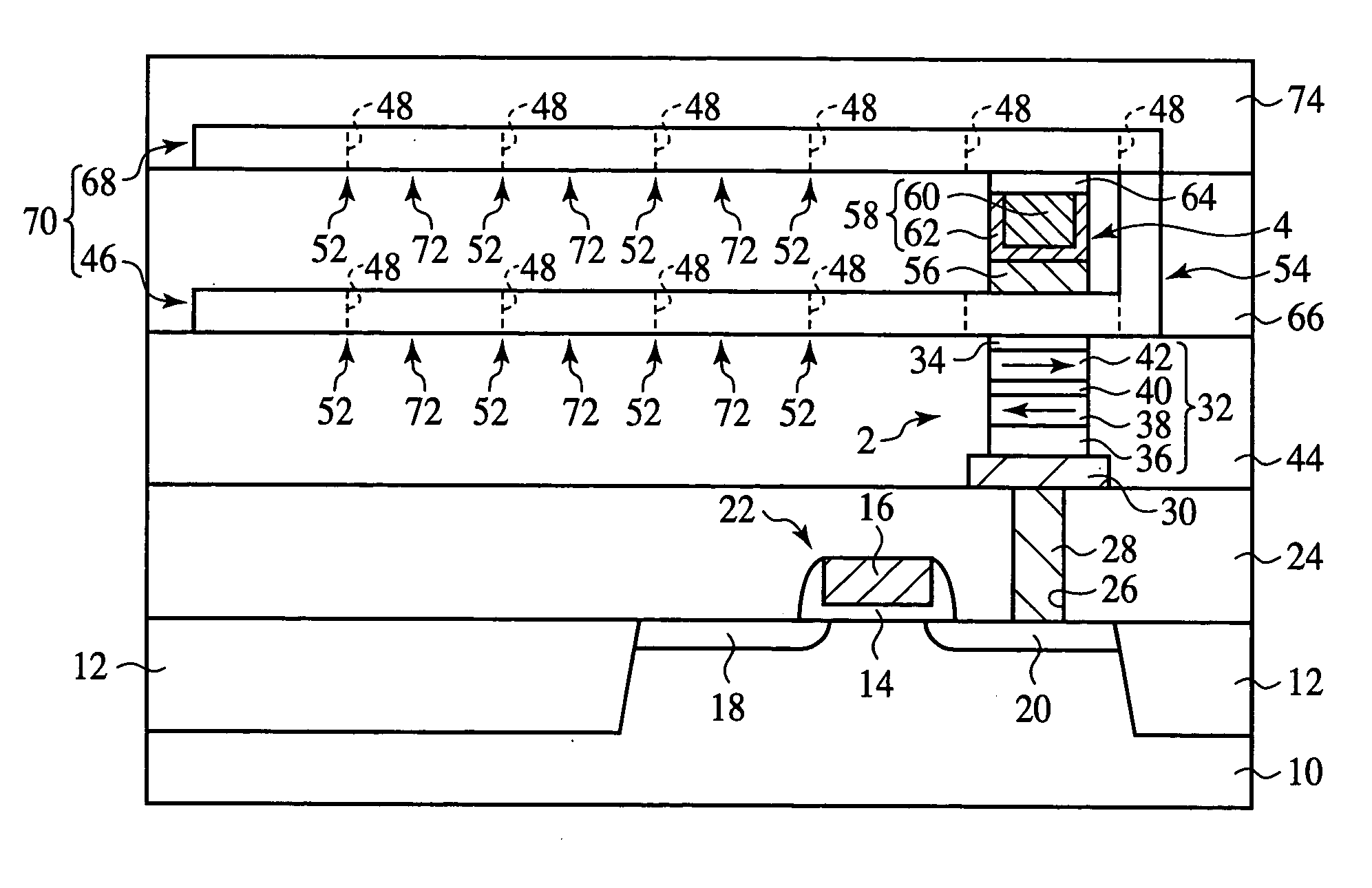
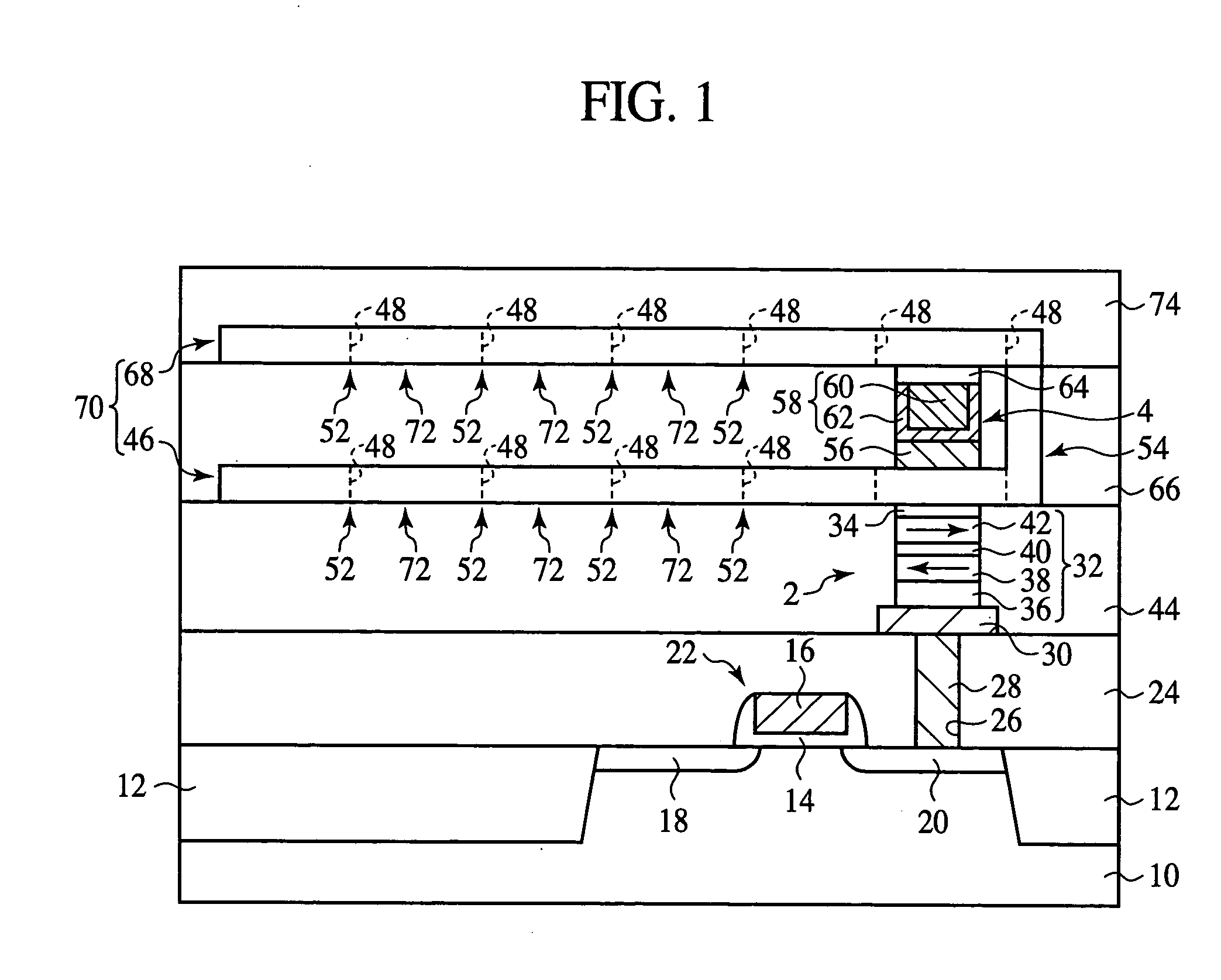
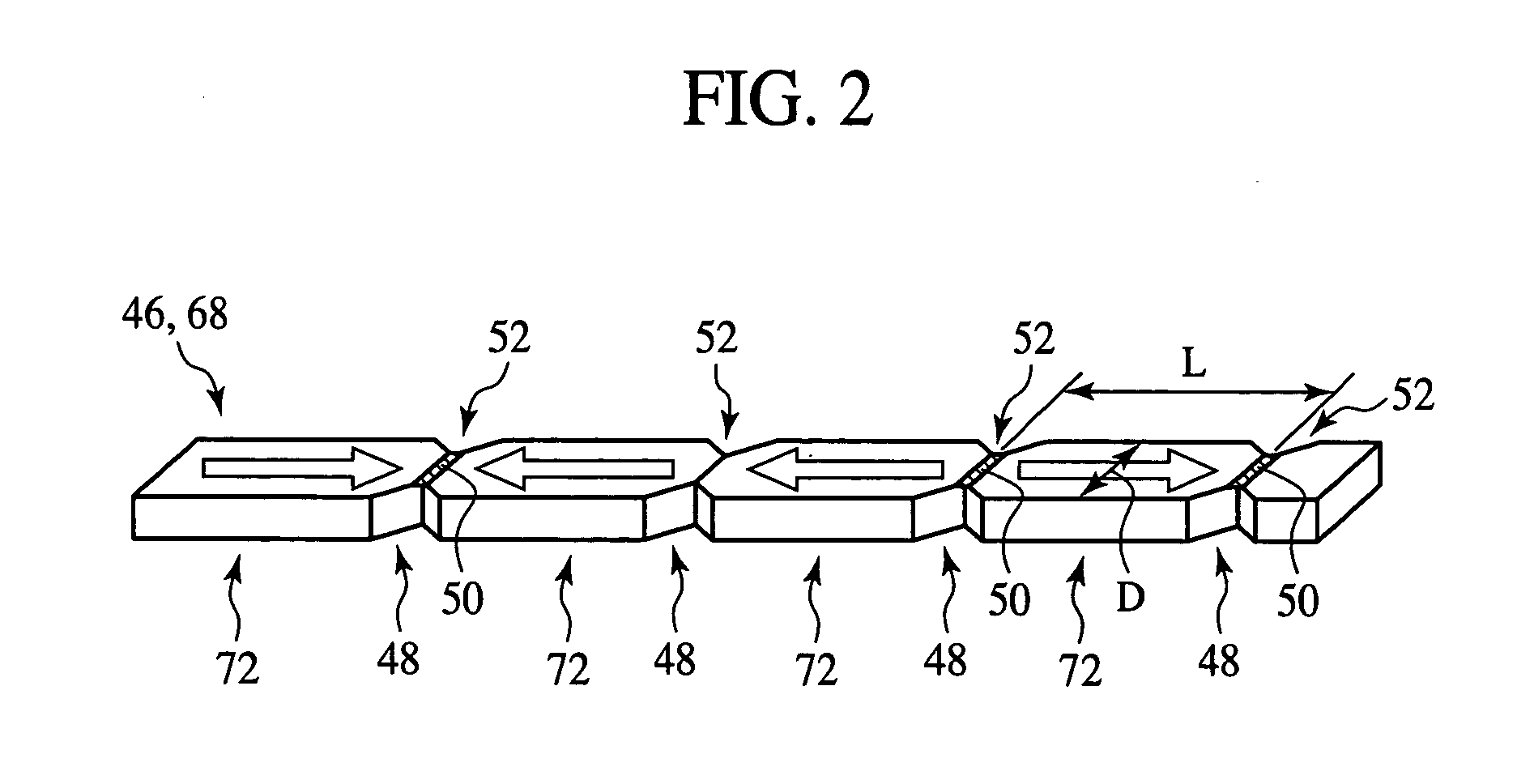
The magnetic memory device comprises a recording layer 70 formed linearly over a substrate 10 and having a plurality of pinning sites 52 for restricting the motion of domain walls 50 formed at a prescribed pitch and having the regions between the plural pinning sites 52 as recording bits 72. The recording layer 70 includes a first recording layer portion 46 and a second recording layer portion 68, and the second recording layer portion 68 is positioned above the first recording layer portion 46 and has one end connected to one end of the first recording layer portion 46. The second recording layer portion 68 is formed above the first recording layer portion 46, and the end of the second recording layer portion 68 is connected to one end of the first recording layer portion 46, whereby the space required to form the recording layer 70 can be small.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
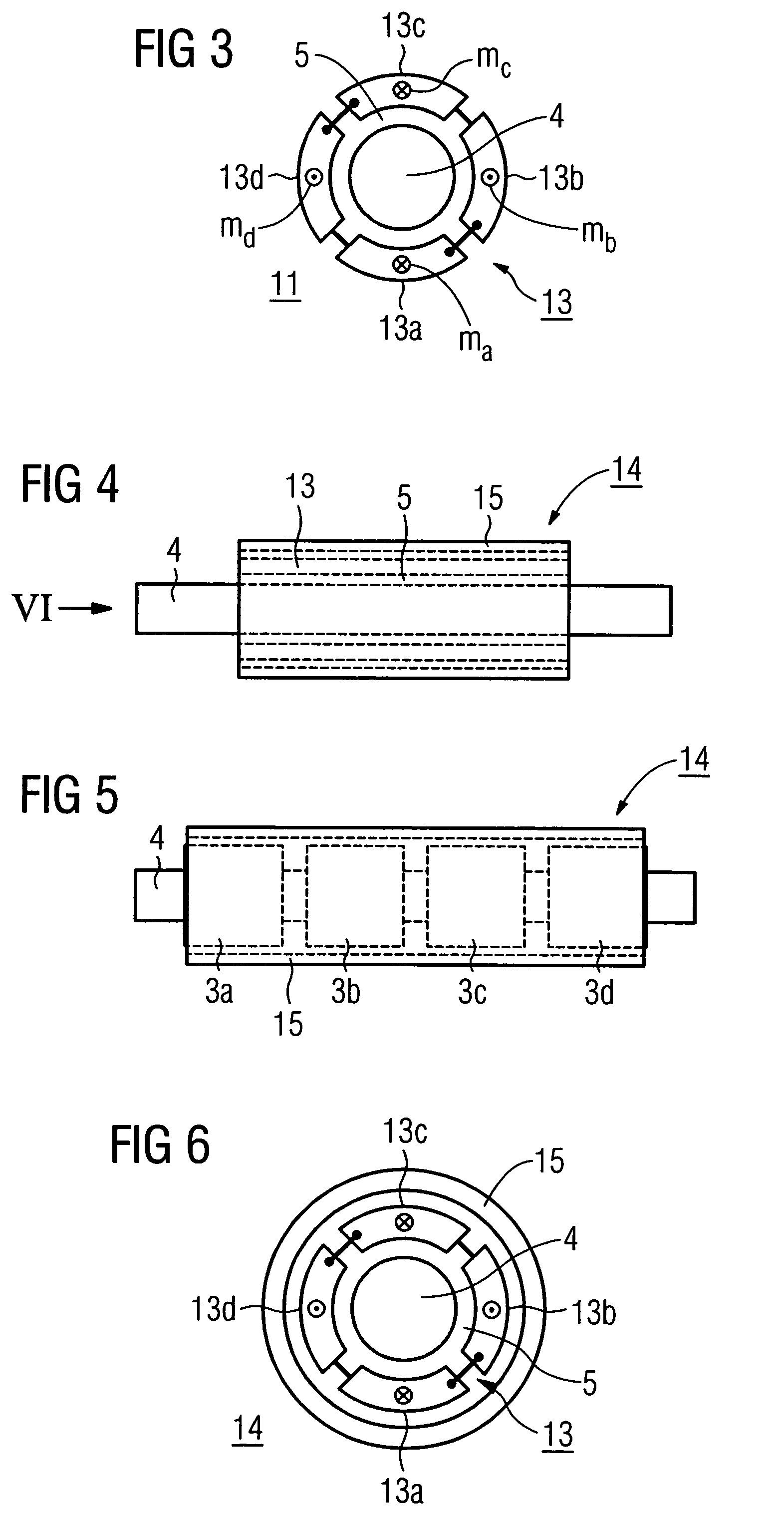
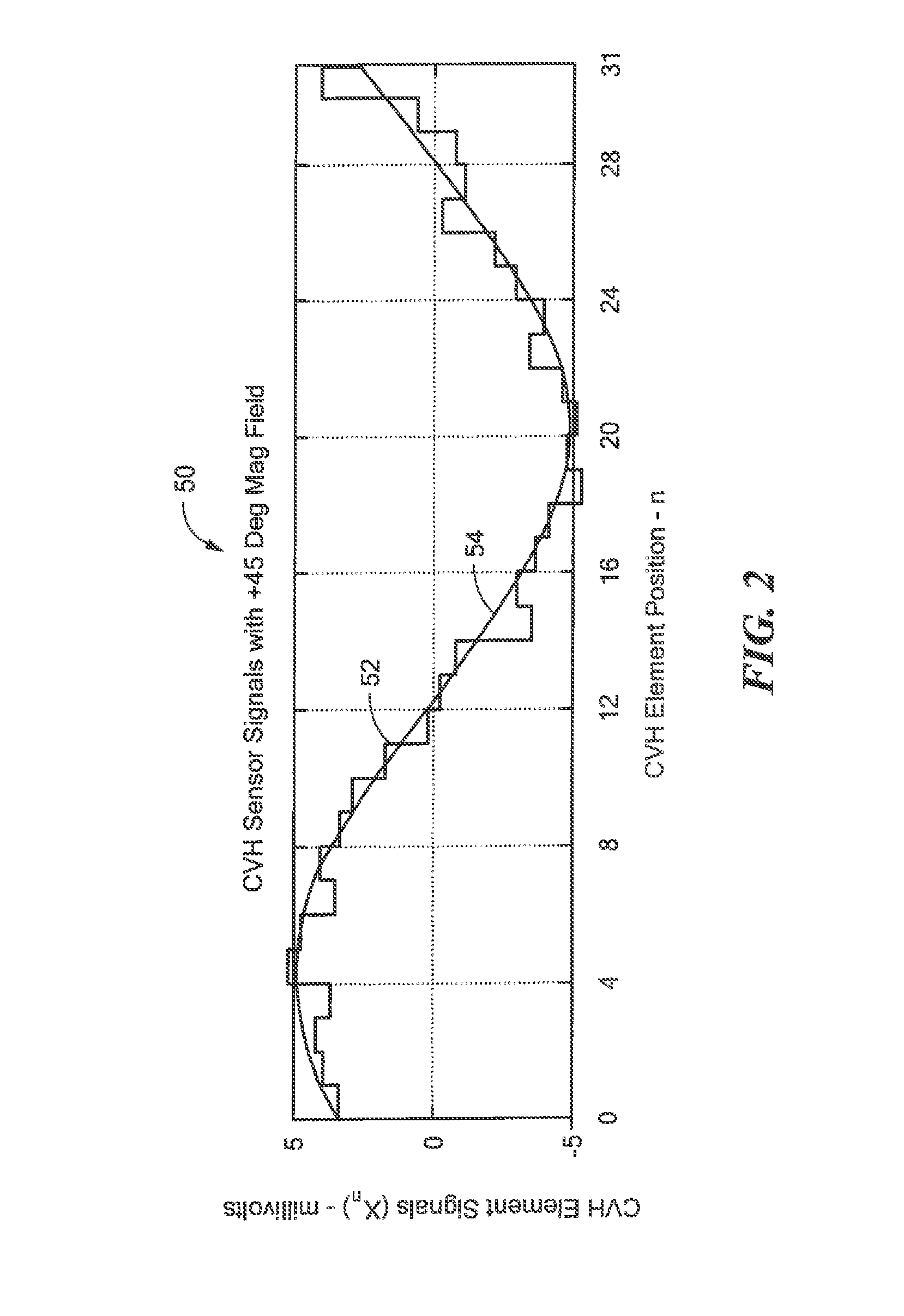
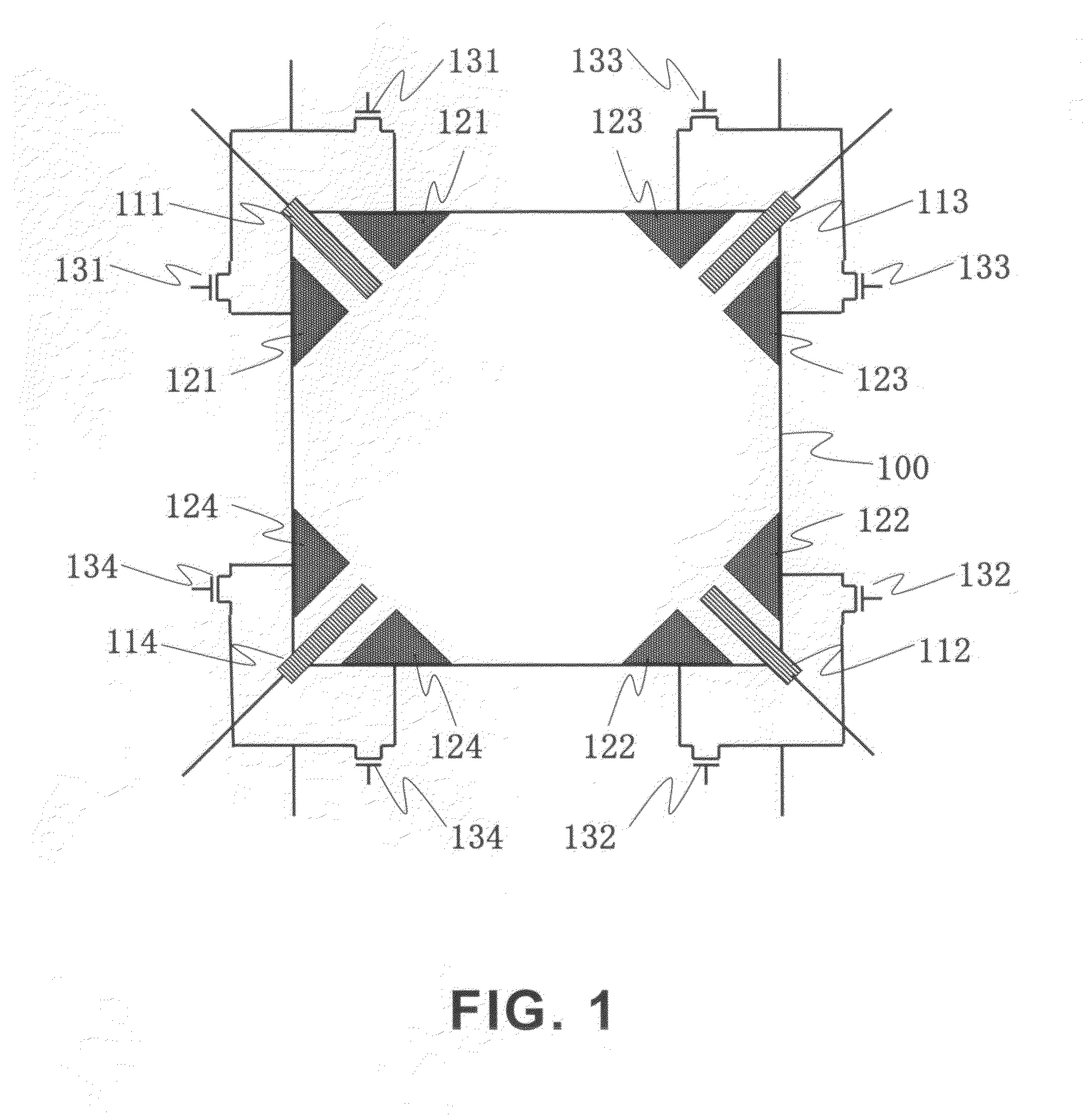
Magnetic field sensor and method of fabricating a magnetic field sensor having a plurality of vertical hall elements arranged in at least a portion of a polygonal shape
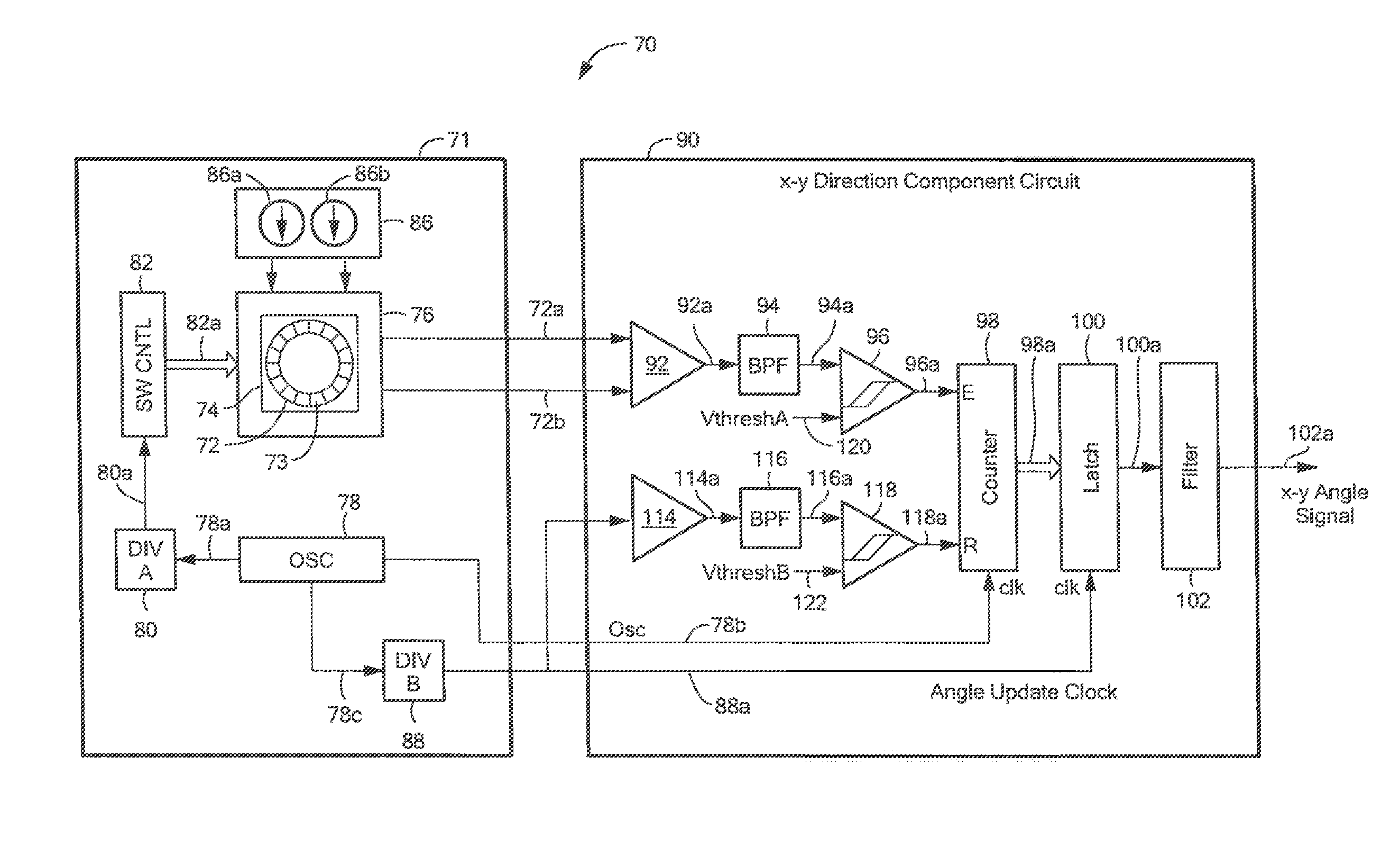
ActiveUS20140175584A1Galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic measurementsHall elementCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field sensor has a plurality of vertical Hall elements arranged in at least a portion of a polygonal shape. The magnetic field sensor includes an electronic circuit to process signals generated by the plurality of vertical Hall elements to identify a direction of a magnetic field. A corresponding method of fabricating the magnetic field sensor is also described.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Hall sensor
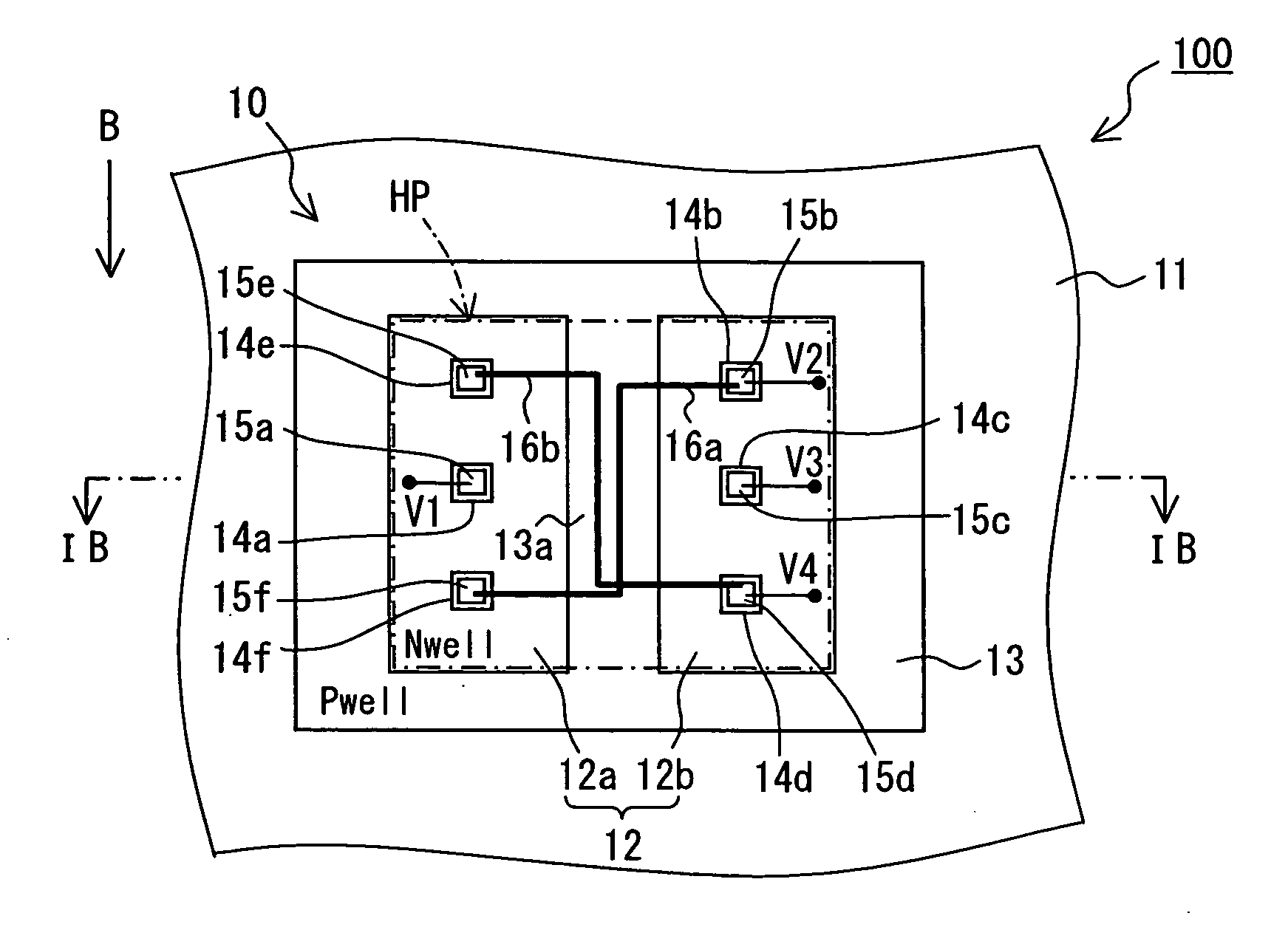
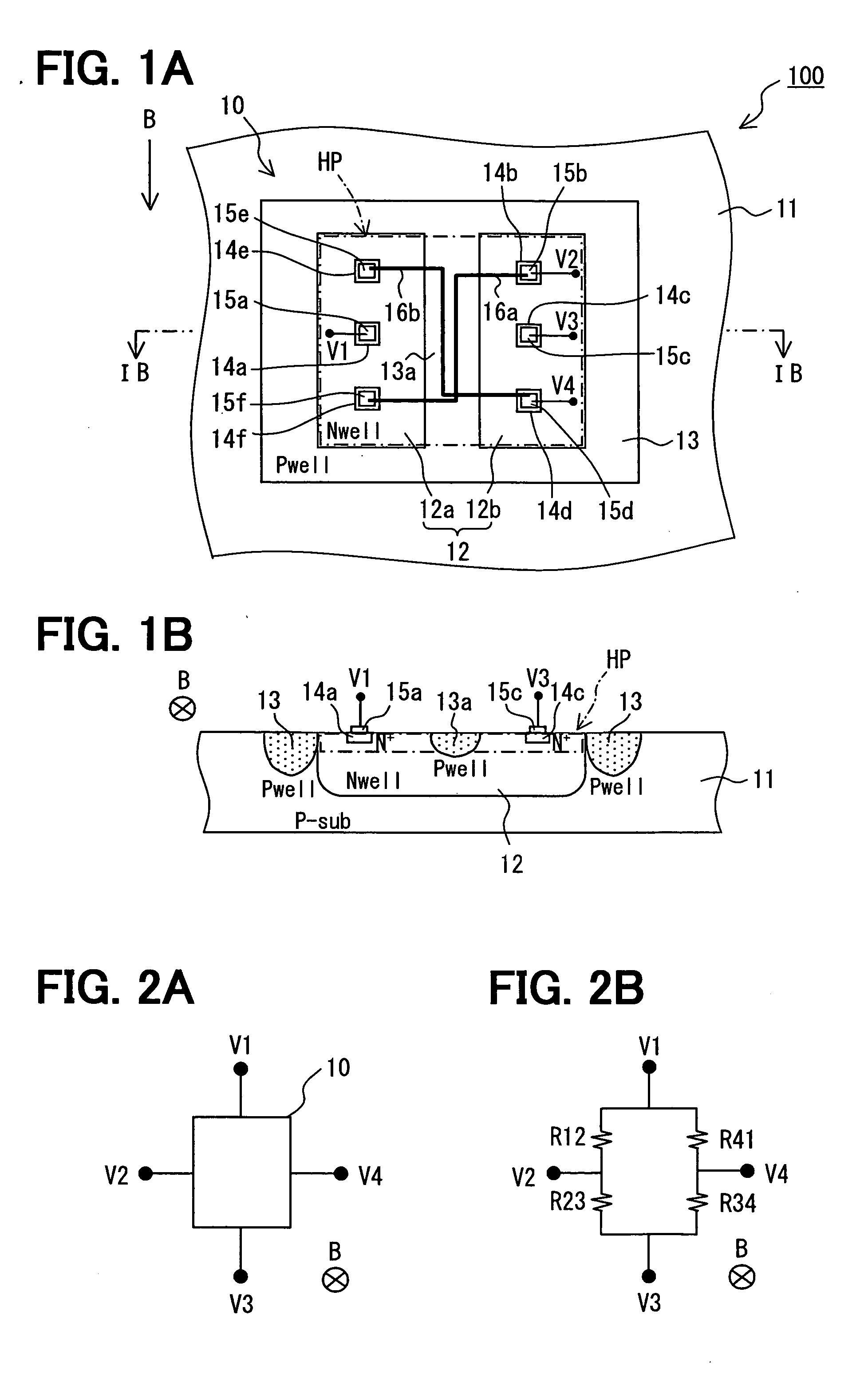
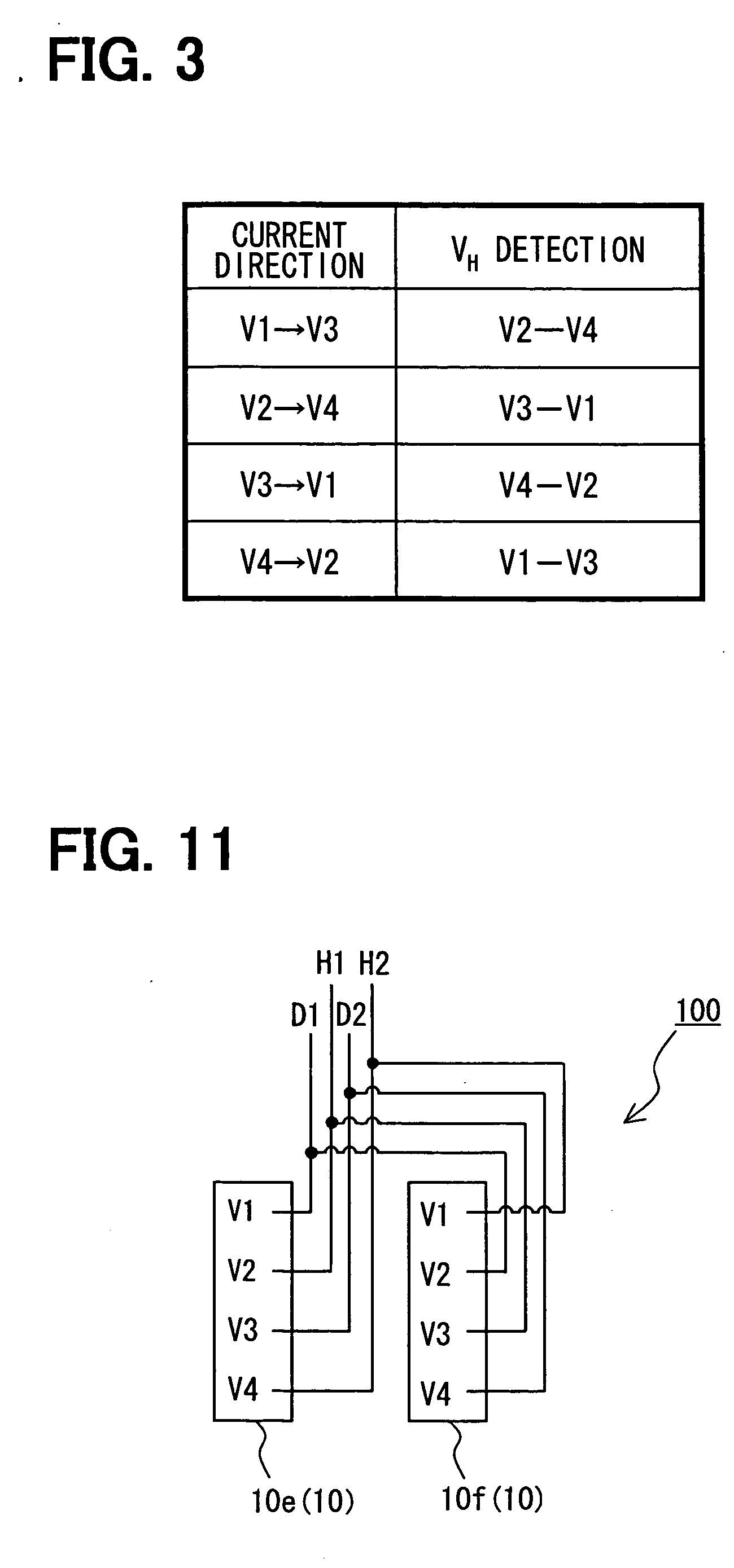
InactiveUS20120001279A1Eliminate Offset VoltageHigh sensitivityGalvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic measurementsElectricityPower flow
Provided is a highly-sensitive Hall element capable of eliminating an offset voltage without increasing the chip size. At the four vertices of a square Hall sensing portion, Hall voltage output terminals and control current input terminals are respectively arranged independently from each other. The Hall voltage output terminals all have the same shape. The control current input terminals are arranged on both sides of the Hall voltage output terminals, respectively, to be spaced apart from the Hall voltage output terminals so as to prevent electrical connection to the Hall voltage output terminals, and have the same shape at the four vertices.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Magnetic memory device and method for reading magnetic memory cell using spin hall effect
InactiveUS20100027330A1Easily read stored dataGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesSpin Hall effectMagnetic memory
A magnetic memory device includes a substrate for reading and a magnetic memory cell. The substrate has a channel layer. The magnetic memory cell is formed on the substrate and has a magnetized magnetic material that transfers spin data to electrons passing the channel layer. Data stored in the magnetic memory cell are read by a voltage across both side ends of the channel layer that is generated when the electrons passing the channel layer deviate in the widthwise direction of the channel layer by a spin Hall effect.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Structure providing enhanced self-pinning for CPP GMR and tunnel valve heads
InactiveUS7330339B2Easy to fixAvoid conducting electricityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesCouplingMagnetic moment
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
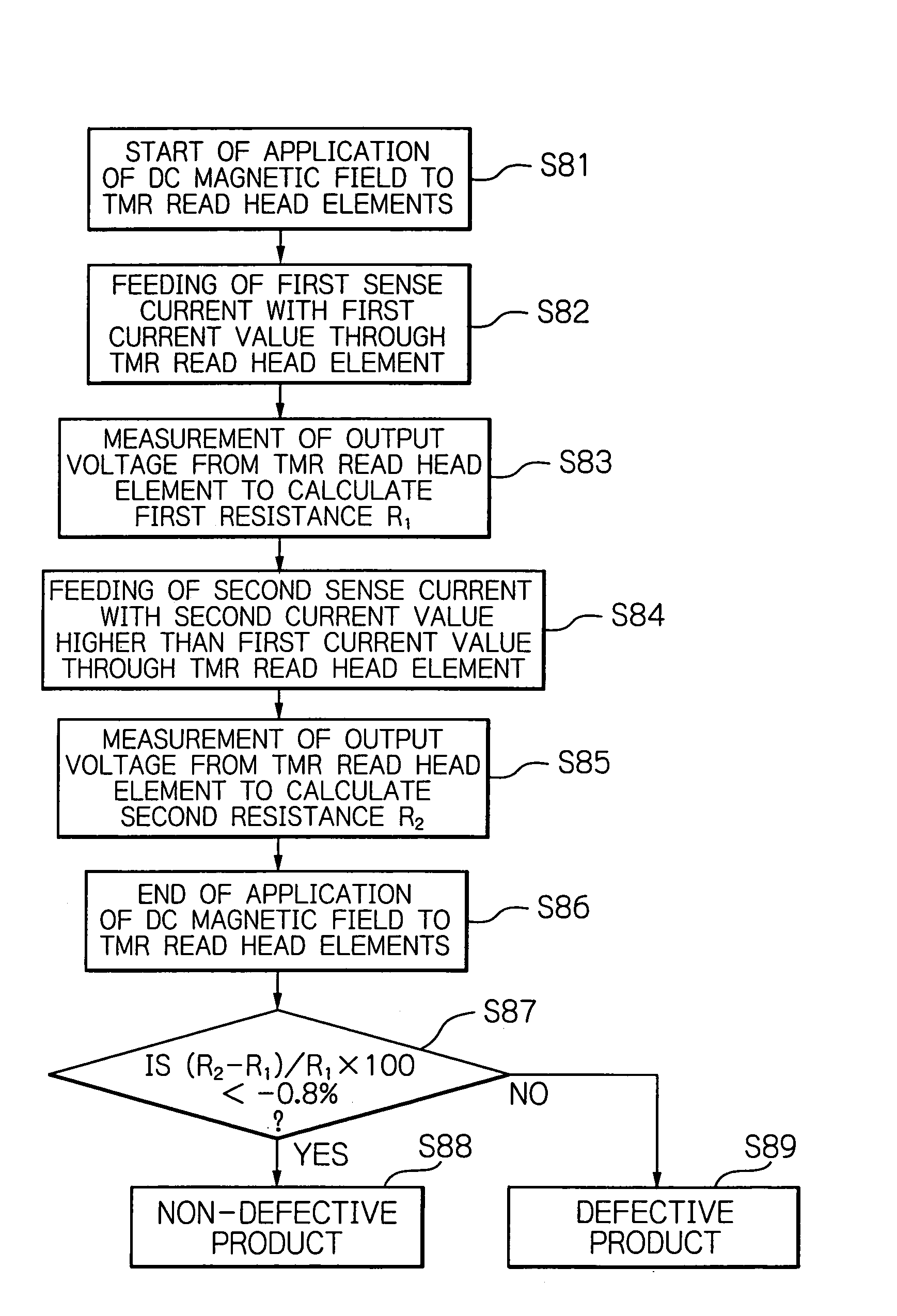
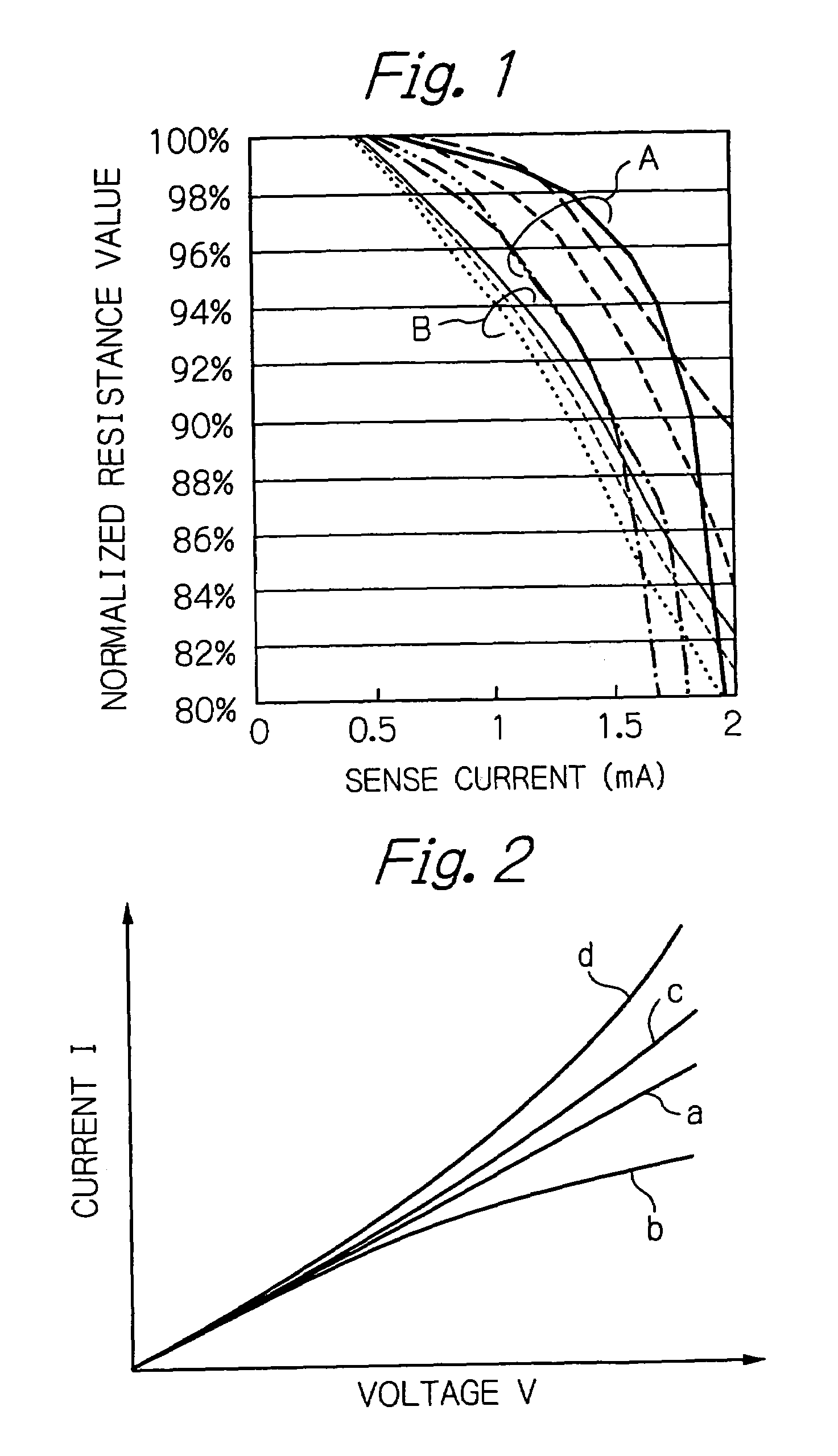
Method and apparatus for testing tunnel magnetoresistive effect element, manufacturing method of tunnel magnetoresistive effect element and tunnel magnetoresistive effect element
ActiveUS7417442B2Reliability can be quickly and easilyThe process is convenient and fastNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Magnetoelectric random storage unit and storage with same
ActiveCN101834271AReduce distractionsReduce distanceGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesCouplingMagnetization
The invention discloses a magnetoelectric random storage unit which comprises a ferroelectric oxide layer, a ferromagnetic free layer, a tunnel barrier layer, a ferromagnetic fixed layer, a first electrode and a second electrode, wherein the ferromagnetic free layer is formed on the ferroelectric oxide layer; the tunnel barrier layer is formed on the ferromagnetic free layer; the ferromagnetic fixed layer is formed on the tunnel barrier layer; the first electrode and the second electrode are formed on two sides of the ferroelectric oxide layer; and under the actions of the electric field applied to the ferroelectric oxide layer by the first electrode and the second electrode, the magnetization direction in the ferromagnetic free layer is controlled through the magnetoelectric coupling action. The invention also provides a storage with the magnetoelectric random storage unit. The embodiment of the invention can write in information data with the electric field, and has the advantages of nonvolatility, low write-in power consumption, high storage density and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Sensor module with mold encapsulation for applying a bias magnetic field
The invention relates to a sensor module with mold encapsulation for applying a bias magnetic field, and also relates to a method of manufacturing the same, which includes providing a substrate comprising a magnetically sensitive sensor element. The sensor element and the substrate are encapsulated with at least one mold material that is configured to apply a bias magnetic field to the sensor element.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Semiconductor device and magneto-resistive sensor integration
A magnetic-sensing apparatus and method of making and using thereof is provided. The sensing apparatus may be fabricated from semiconductor circuitry and a magneto-resistive sensor. A dielectric may be disposed between the semiconductor circuitry and the magneto-resistive sensor. In one embodiment, the semiconductor circuitry and magneto-resistive sensor are formed into a single package or, alternatively, monolithically formed into a single chip. In another embodiment, some of the semiconductor circuitry may be monolithically formed on a first chip with the magneto-resistive sensor, while other portions of the semiconductor circuitry may be formed on a second chip. As such, the first and second chips may be placed in close proximity and electrically connected together or alternatively have no intentional electrical interaction, Exemplary semiconductor devices that might be implemented include, without limitation, capacitors, inductors, operational amplifiers, set / reset circuitry for the magneto-resistive sensors, accelerometers, pressure sensors, position sensing circuitry, compassing circuitry, etc.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Sensor structure and magnetic field sensor
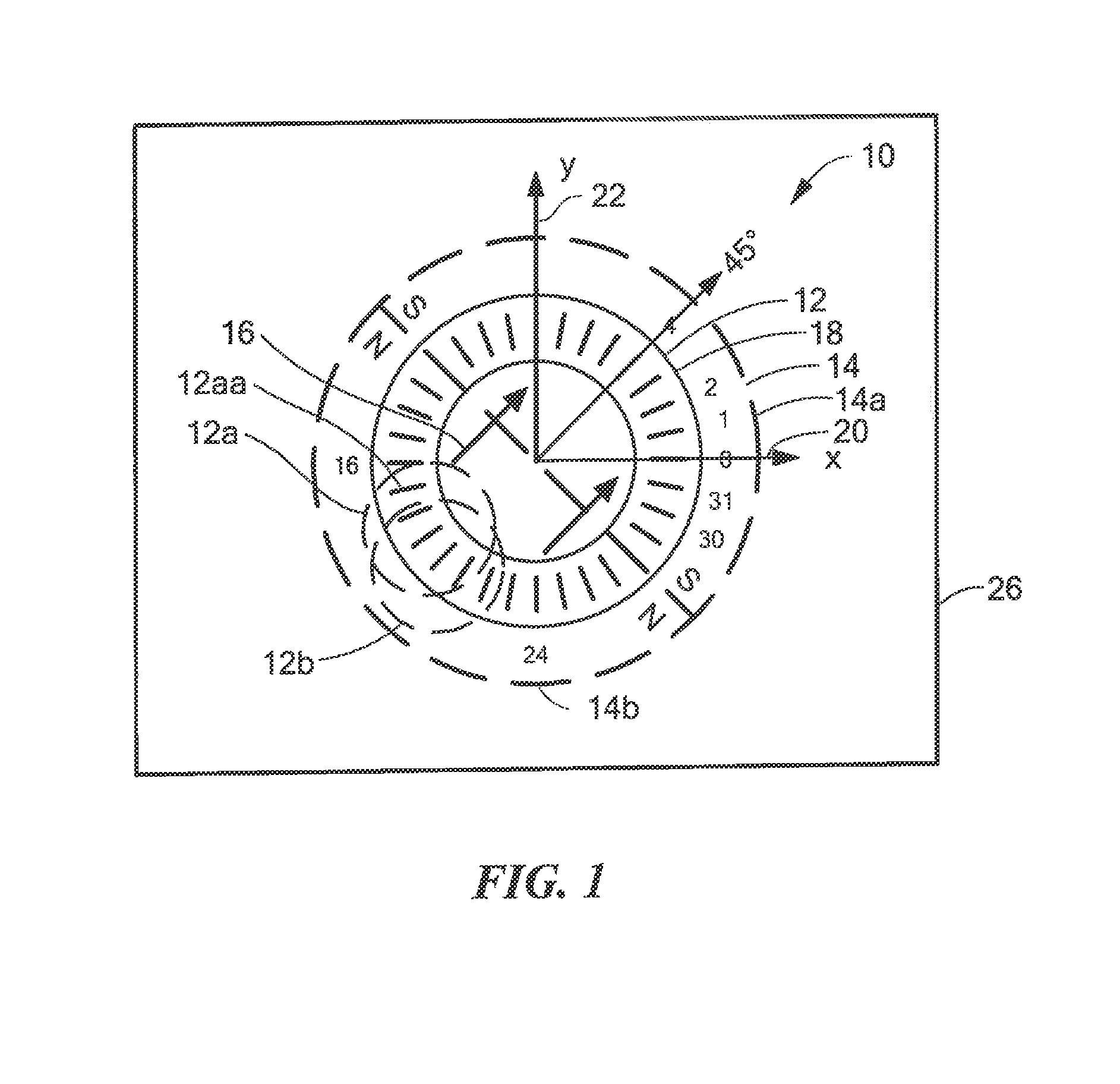
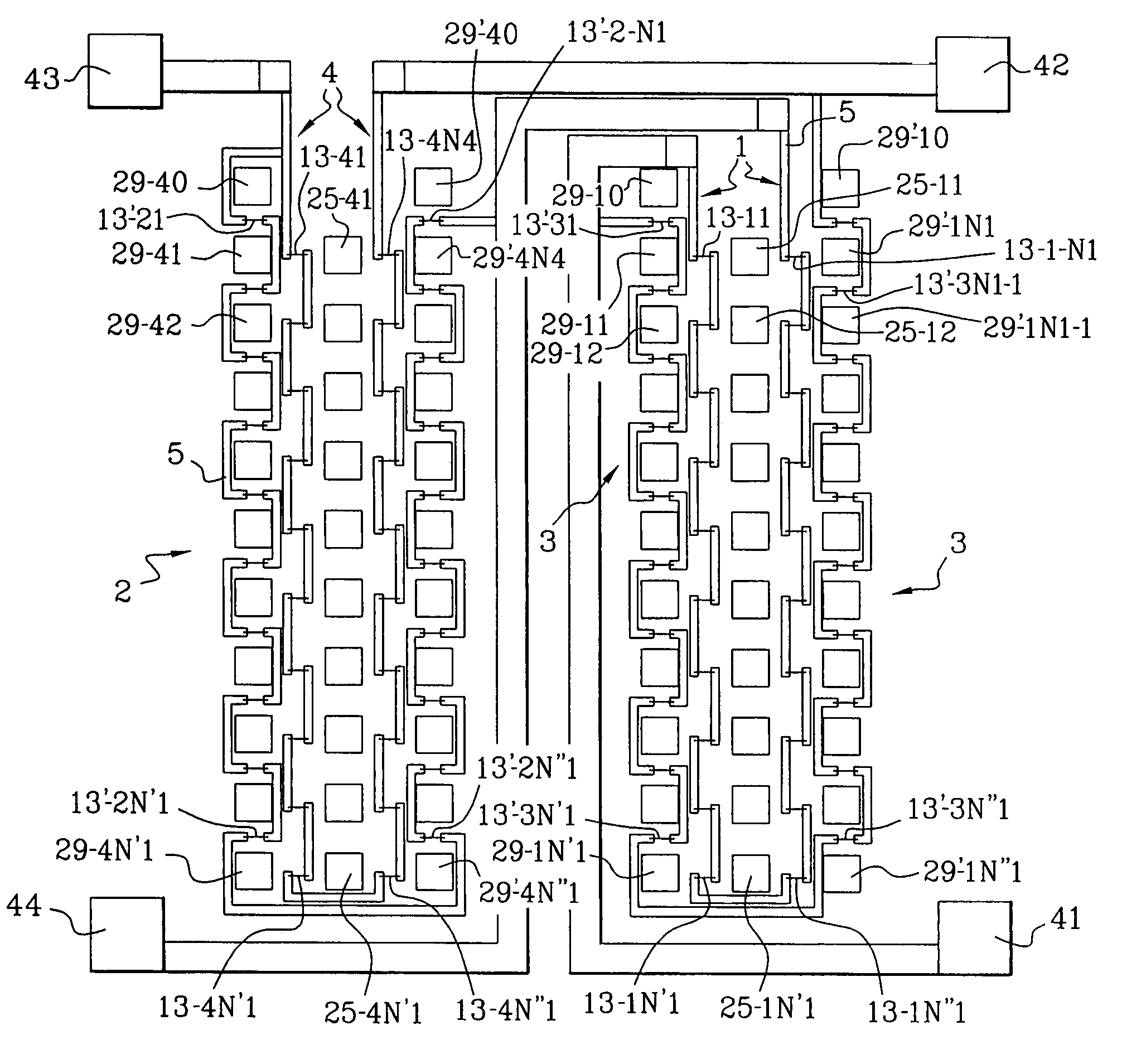
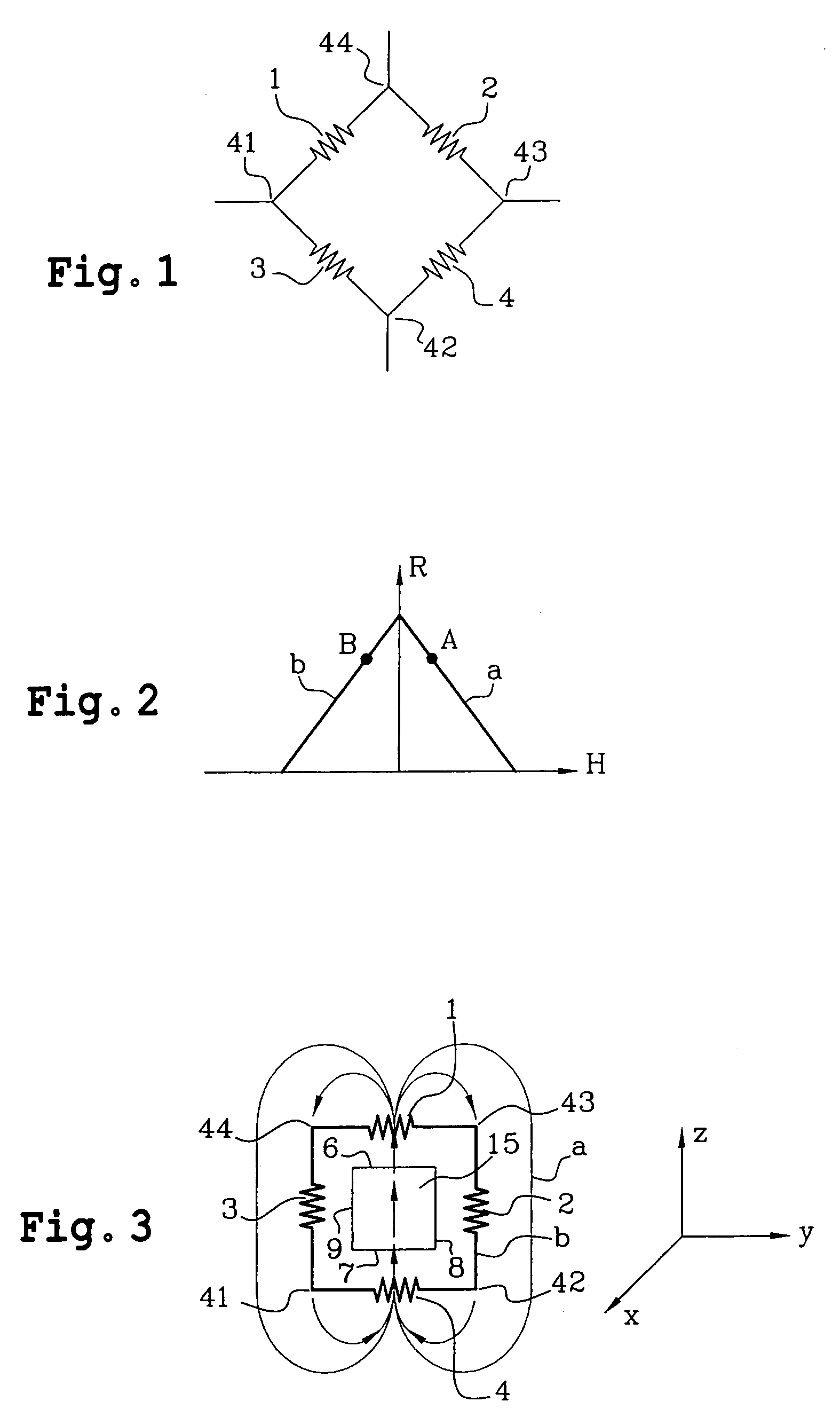
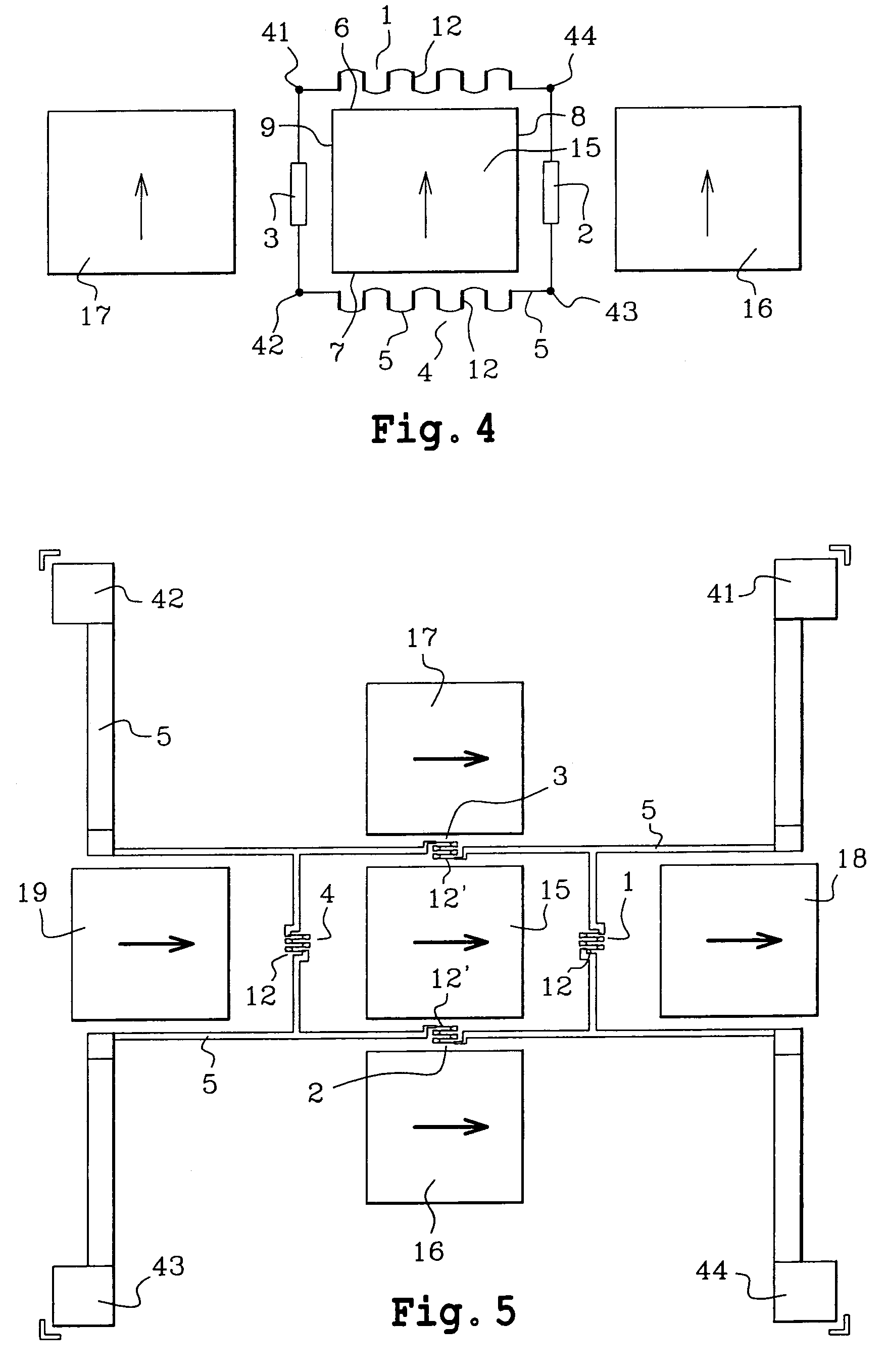
InactiveUS7176679B2Good reproducibilityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesMagnetic leakageAxial field
A method and an apparatus of a magnetic field sensor structure are disclosed. The magnetic field sensor structure is formed by a bridge of four magnetoresistors (1–4), wherein each magnetoresistor has a longitudinal direction, and each magnetoresistor (1–4) is polarised by magnets (15–19). Also, each magnet has a main magnetisation field along an axial magnetisation direction, and a magnetic leakage field. The polarisation magnets (15–19) and the magnetoresistors (1–4) are arranged in the form of layers on the same substrate. In one embodiment, the polarisation magnets (15–19) are at the same level as the magnetoresistors (1–4) wherein the polarisation magnets (15–19) have the same main magnetisation direction, which is contained in the plane of the layers. The magnetoresistors have their longitudinal direction parallel with that of the axial direction of the magnets. In one embodiment, two magnetoresistors are arranged in the axial field of magnets and two others are in the magnet leakage field.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Magnetic memory, a method of manufacturing the same, and semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus
InactiveUS20070181964A1Improve reliabilityLarge capacity promotionGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryEngineering
A magnetic memory includes a magnetic tunneling junction element having a reference layer, a tunnel barrier layer and a recording layer laminated in order, information being written to the recording layer in accordance with spin injection magnetization reversal caused by a current, information written to the recording layer being read out using a current. The magnetic tunneling junction element is disposed on a plug connected to a selection transistor, and a sidewall insulating film covering a side portion of the recording layer of the magnetic tunneling junction element is formed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Planar extraordinary magnetoresistance sensor
An extraordinary magnetoresistance (EMR) sensor has a planar shunt and planar leads formed on top of the sensor and extending downward into the semiconductor active region, resulting. Electrically conductive material, such as Au or AuGe, is first deposited into lithographically defined windows on top of the sensor. After liftoff of the photoresist a rapid thermal annealing process causes the conductive material to diffuse downward into the semiconductor material and make electrical contact with the active region. The outline of the sensor is defined by reactive etching or other suitable etching techniques. Insulating backfilling material such as Al-oxide is deposited to protect the EMR sensor and the edges of the active region. Chemical mechanical polishing of the structure results in a planar sensor that does not have exposed active region edges.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thin film 3 axis fluxgate and the implementation method thereof
InactiveCN101427394AAccurate detectionGalvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleDual axisMagnetic thin film
There is provided a thin film tri-gate fluxgate for detecting a component of a magnetic field in directions of three axes, the thin film tri-gate fluxgate comprising: two first thin film fluxgates of a bar-type disposed on a plane for detecting horizontal components of the magnetic field in direction of dual axis; and a plurality of second thin film fluxgates for detecting a vertical component of the magnetic field, wherein each of the first thin film fluxgates and the plurality of the second thin film fluxgates comprises a drive coil for applying a power, a pickup coil for detecting a voltage and, a magnetic thin film, and wherein the plurality of the second thin film fluxgates are substantially perpendicular to each of the first thin film fluxgates wherein a length of the magnetic thin film of each of the plurality of the second thin film fluxgates is shorter than that of each of the two first thin film fluxgates, and wherein two end portions of each of the plurality of the second thin film fluxgates is wider than a center portion thereof.
Owner:MICROGATE
Popular searches
Digital storage Semiconductor devices Negative temperature coefficient thermistors Magnitude/direction of magnetic fields Magnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devices Voltage/current isolation Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Record information storage Magnetic recording Measurements of magnetic particles
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com