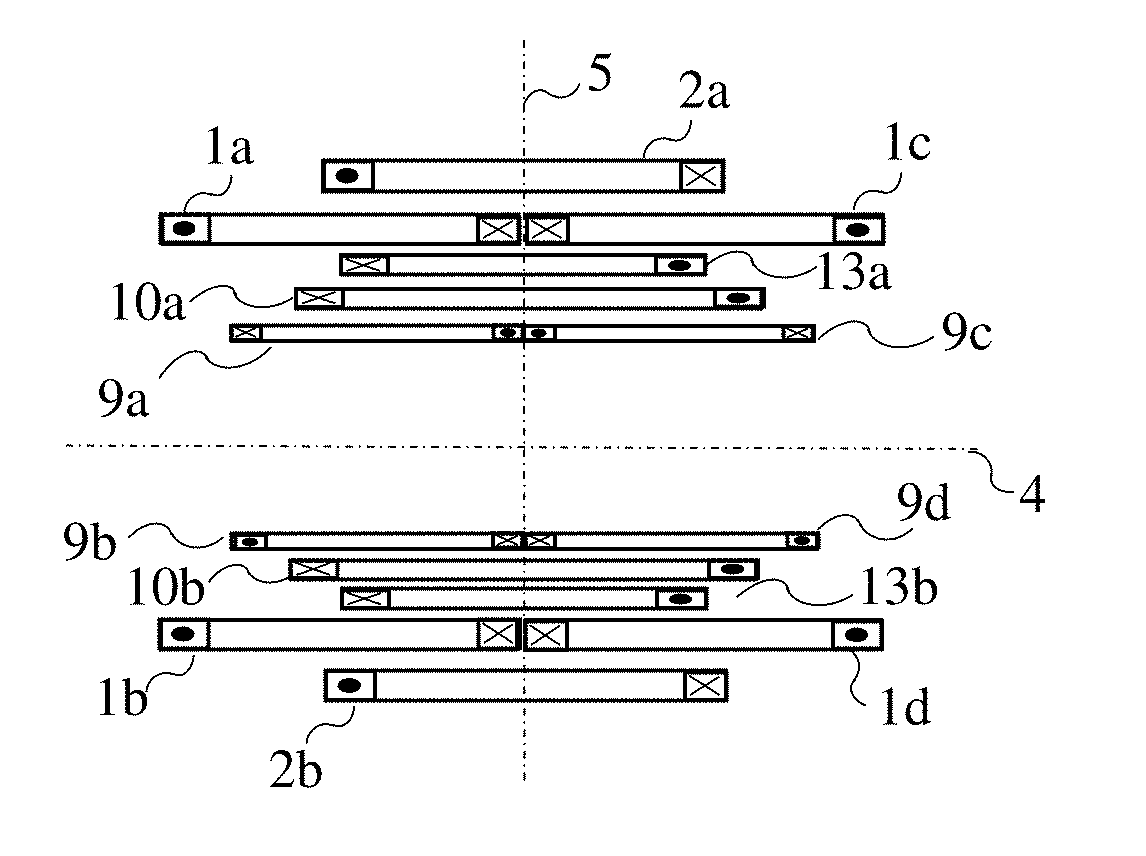
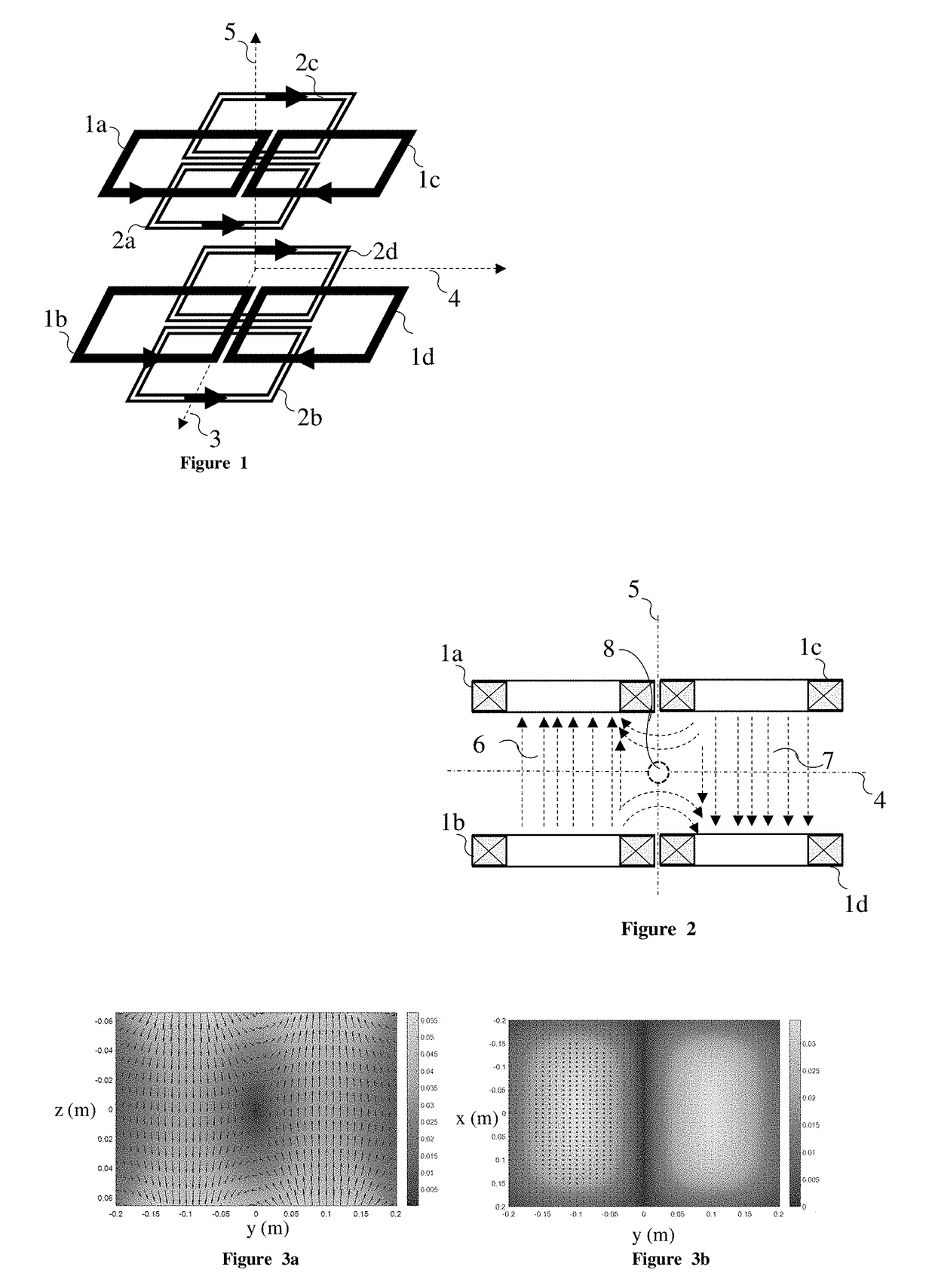
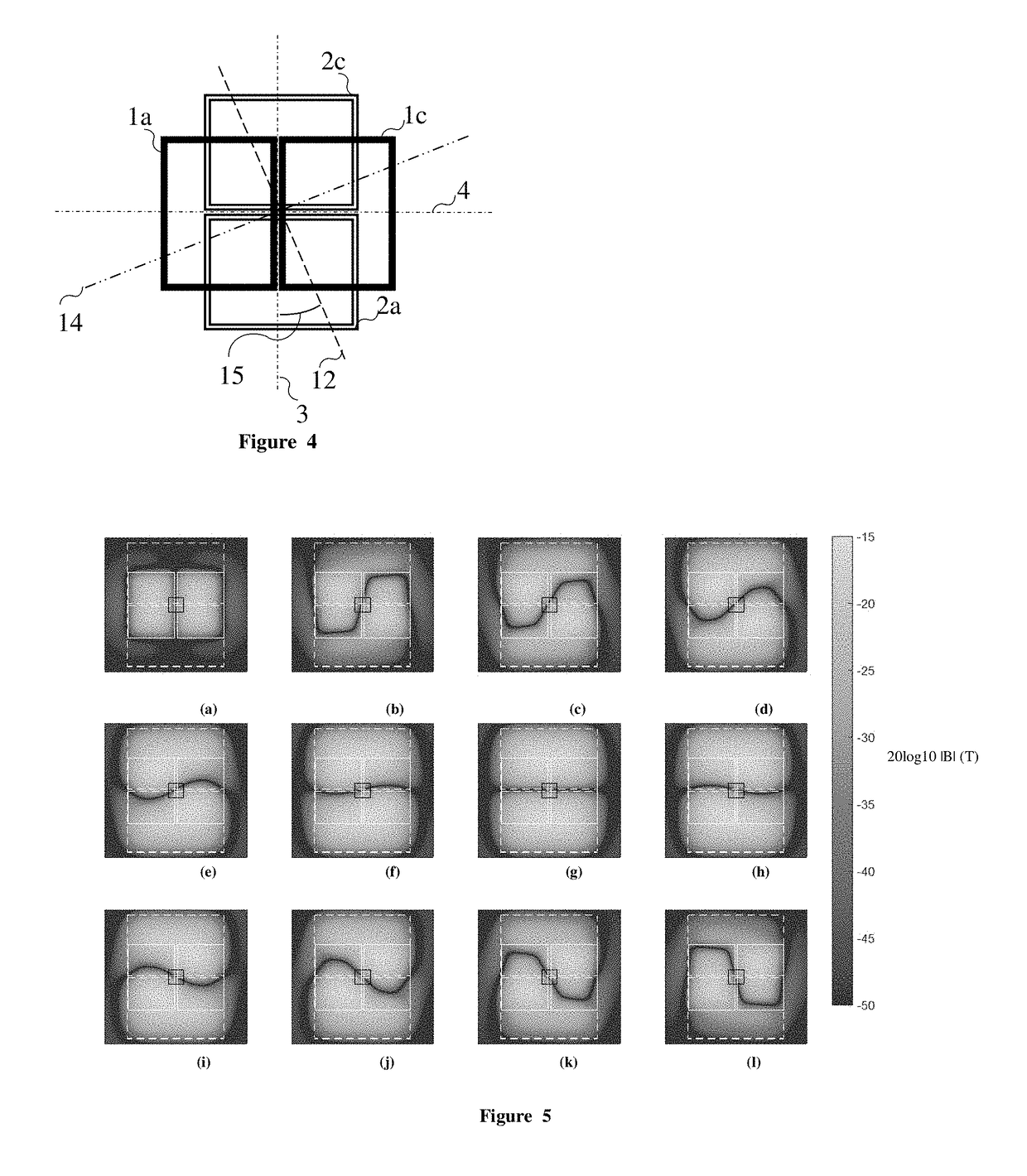
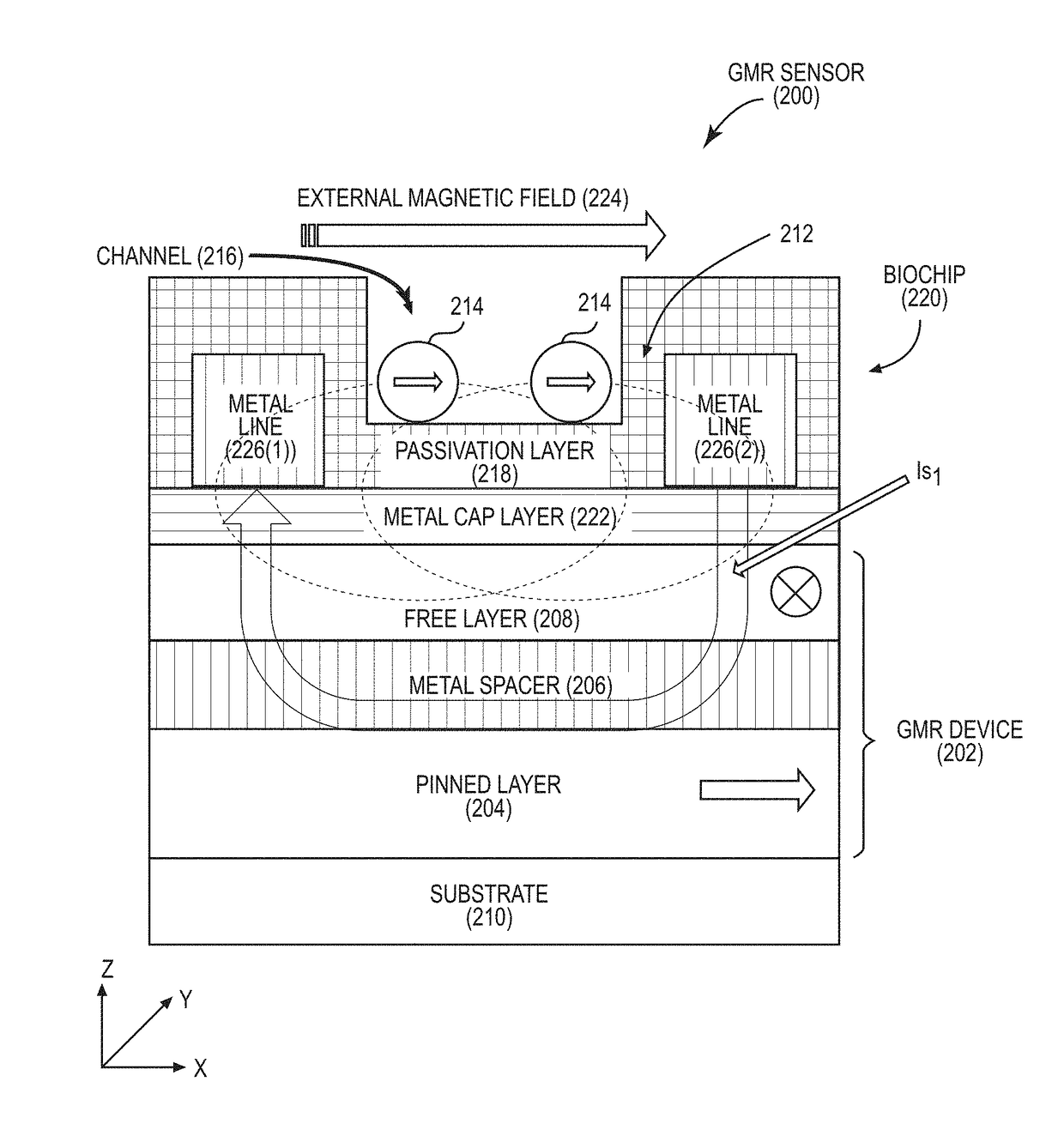
Patents
Literature
129results about "Measurements of magnetic particles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
InactiveUS20070166730A1Easy to detectQuality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismResonance measurementAnalyte
Owner:MENON INT
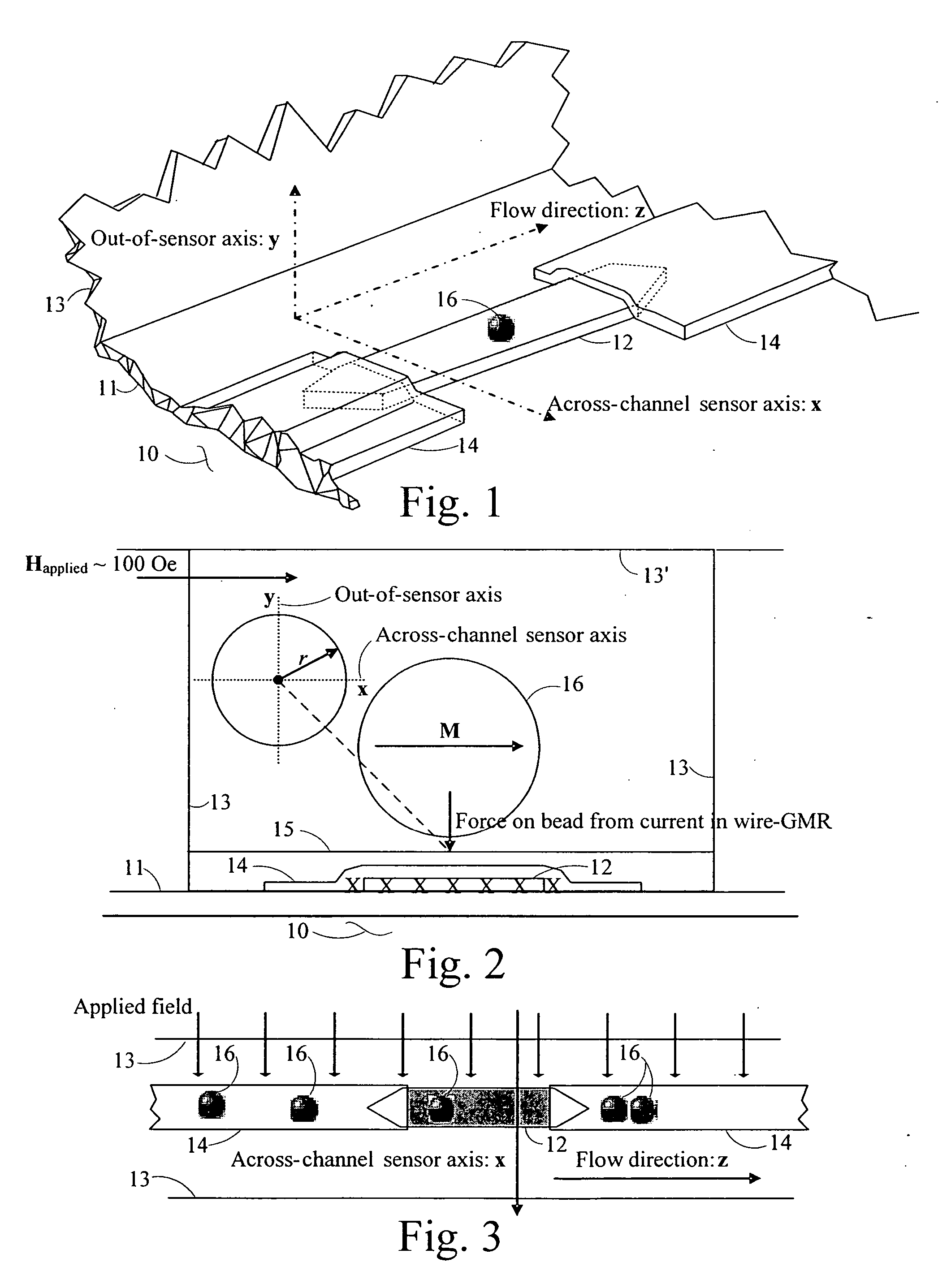
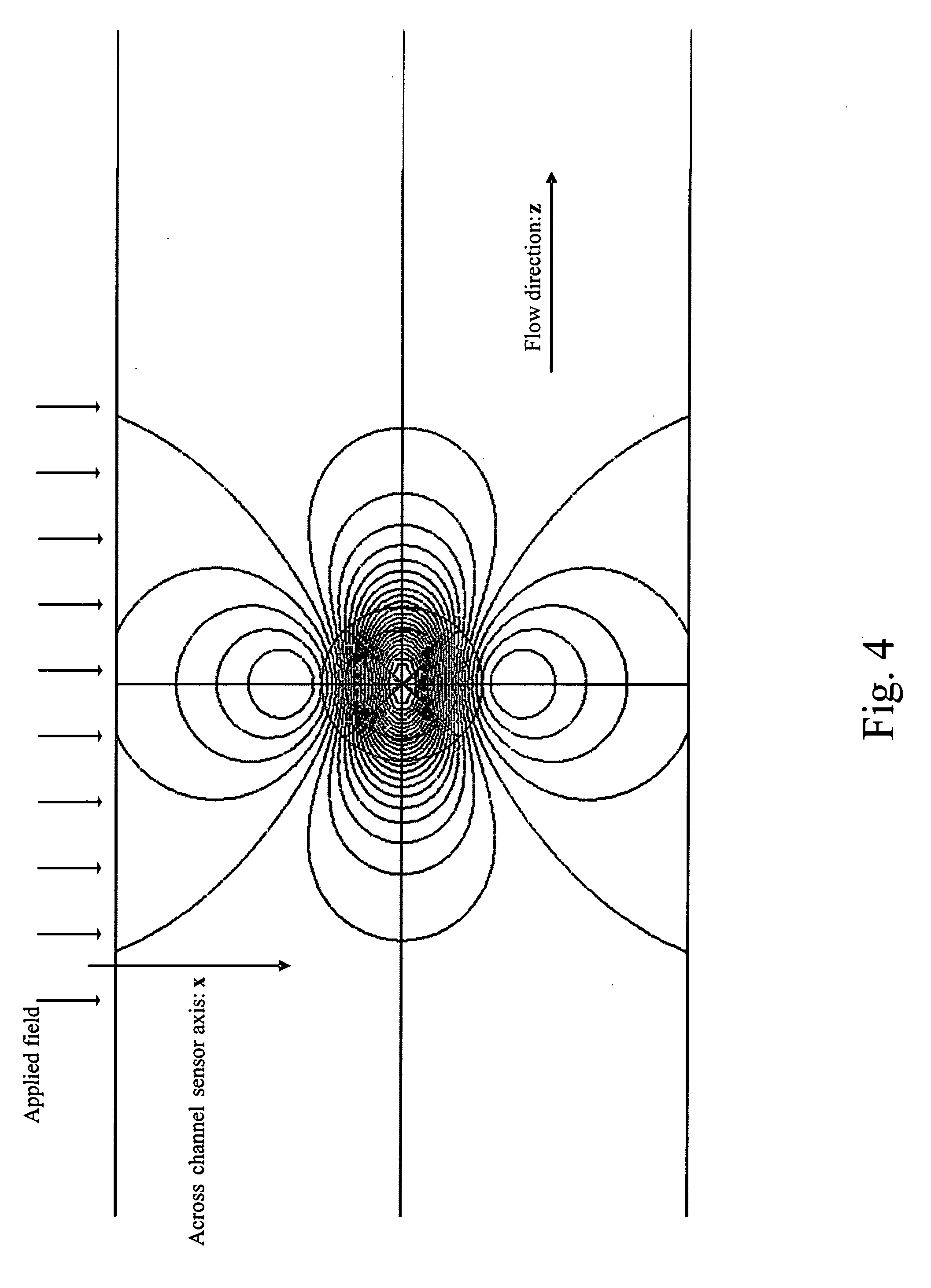
Magnetic particle flow detector
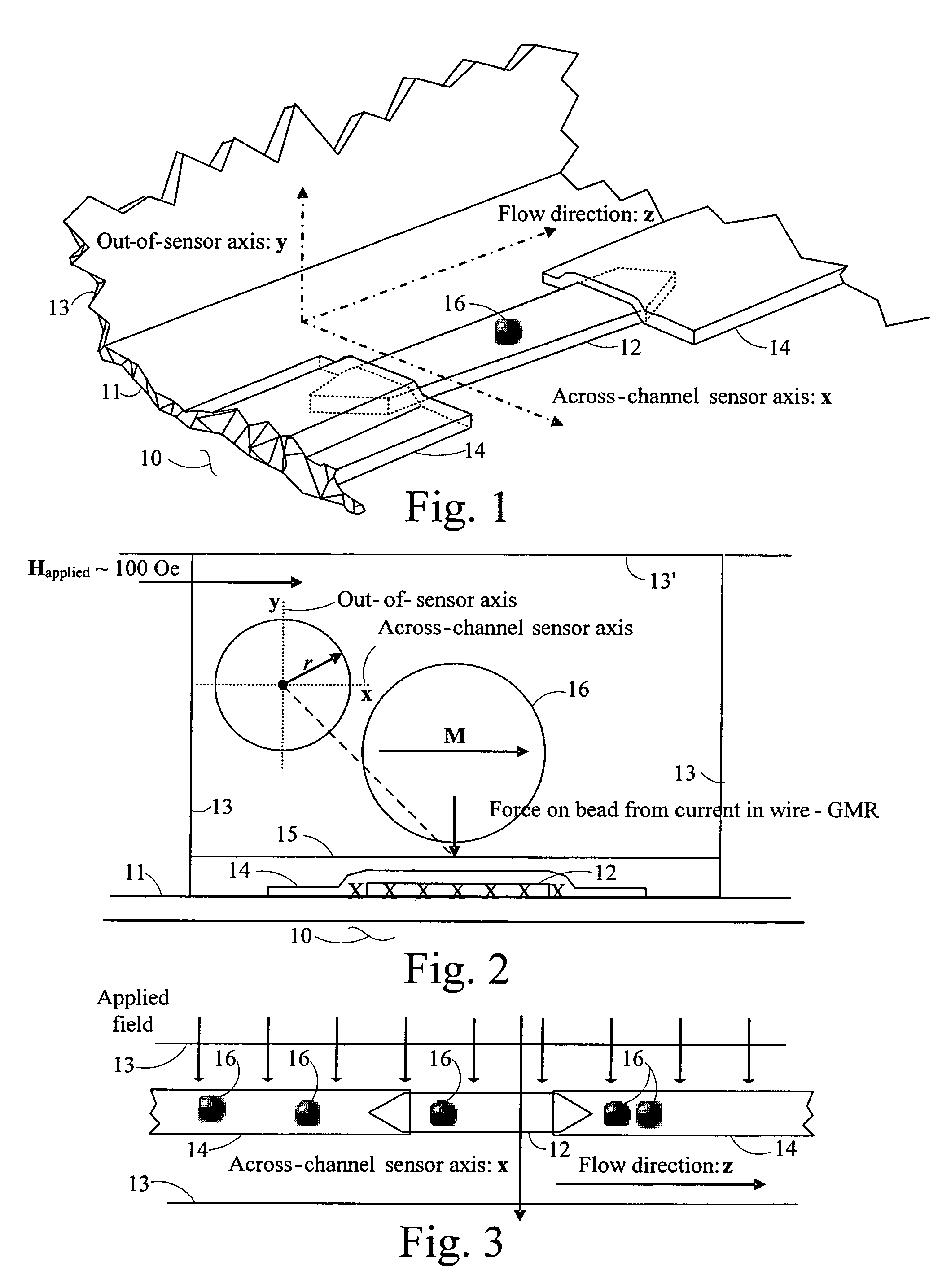
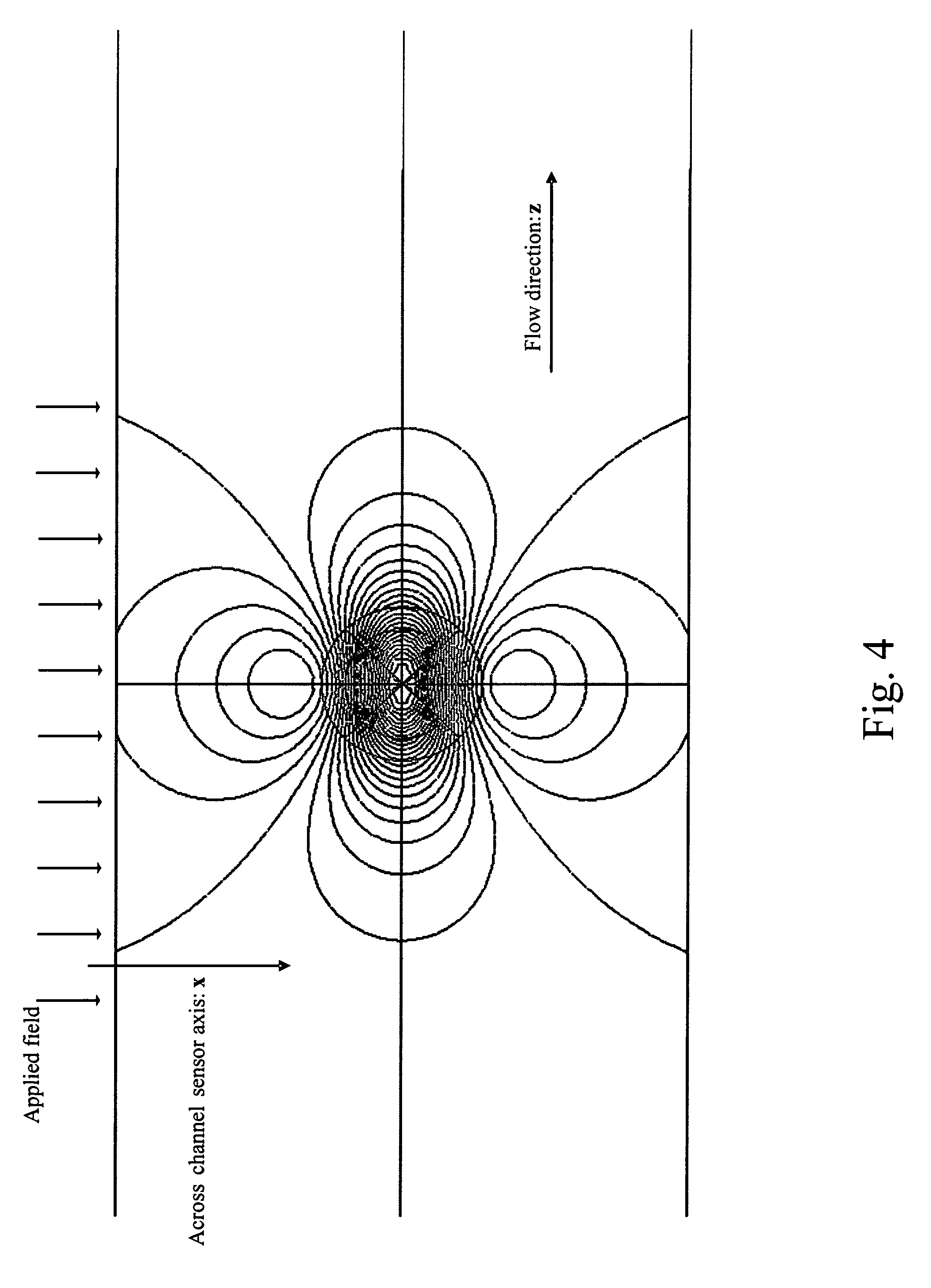
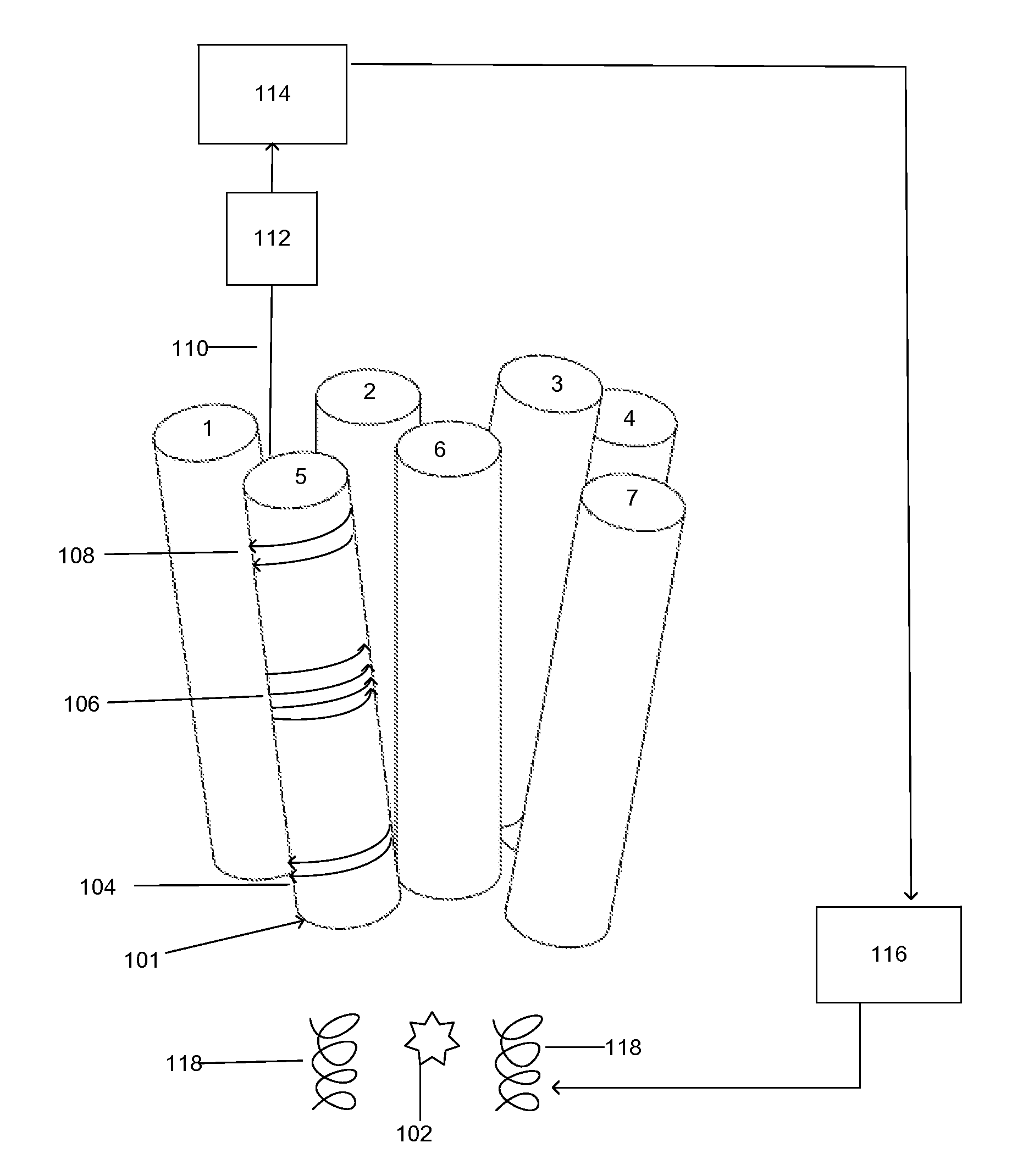
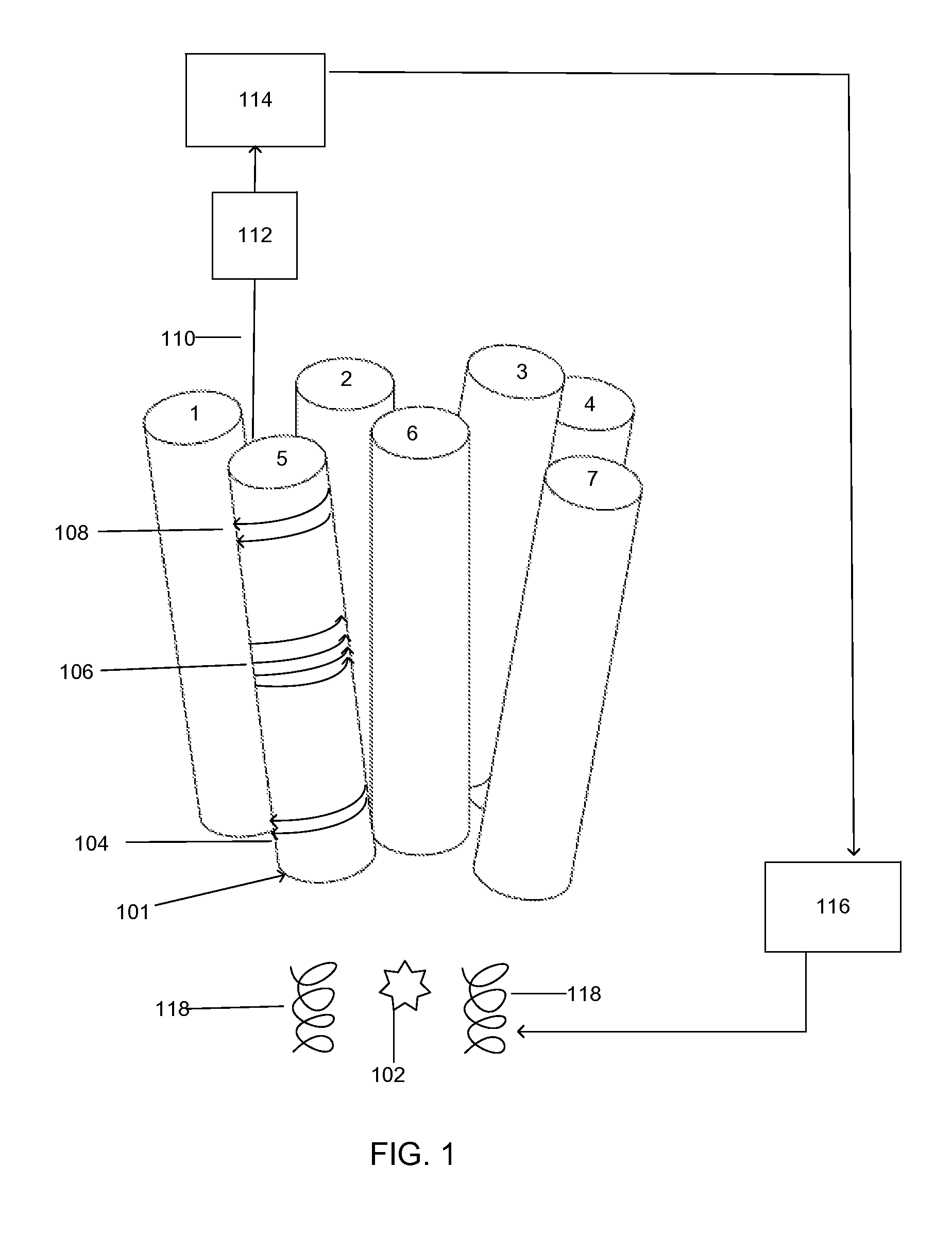
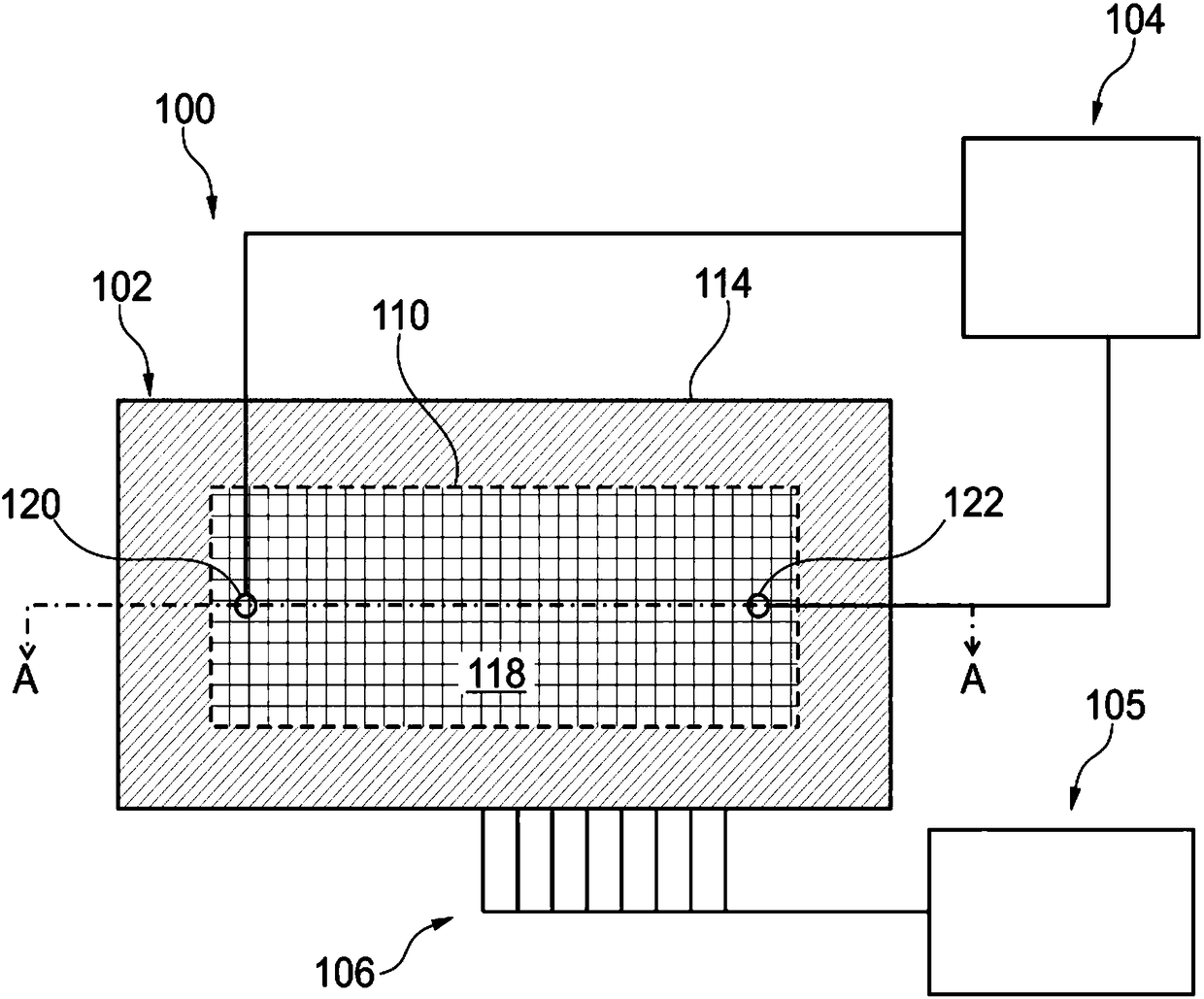
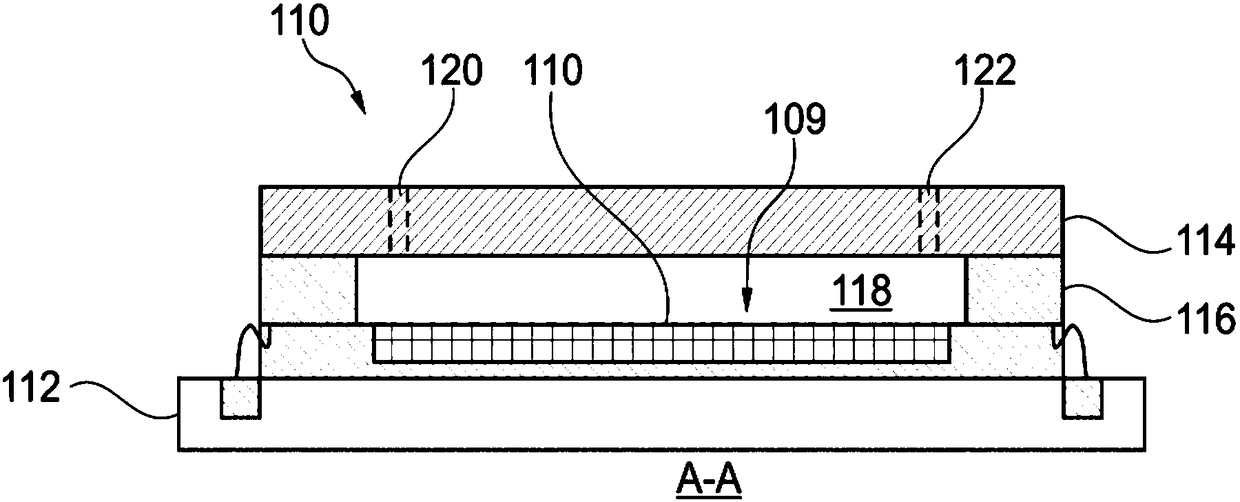
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field detection system having a substrate supporting a magnetic field sensor in a channel with a first electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap and in direct contact with at least some surface of the magnetic field sensor ands a second electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap in a region thereof adjacent to, but separated from, the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:NVE CORP
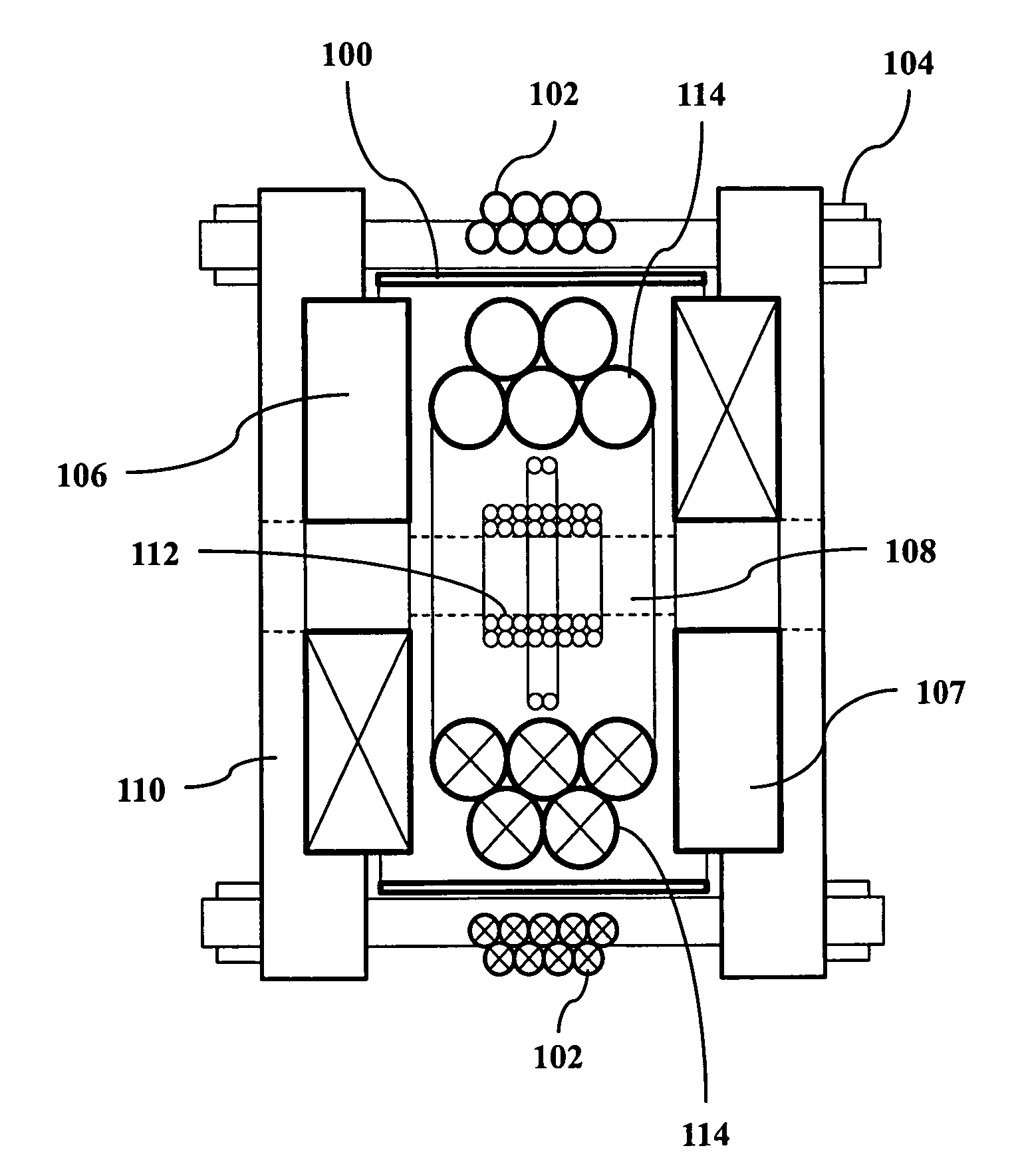
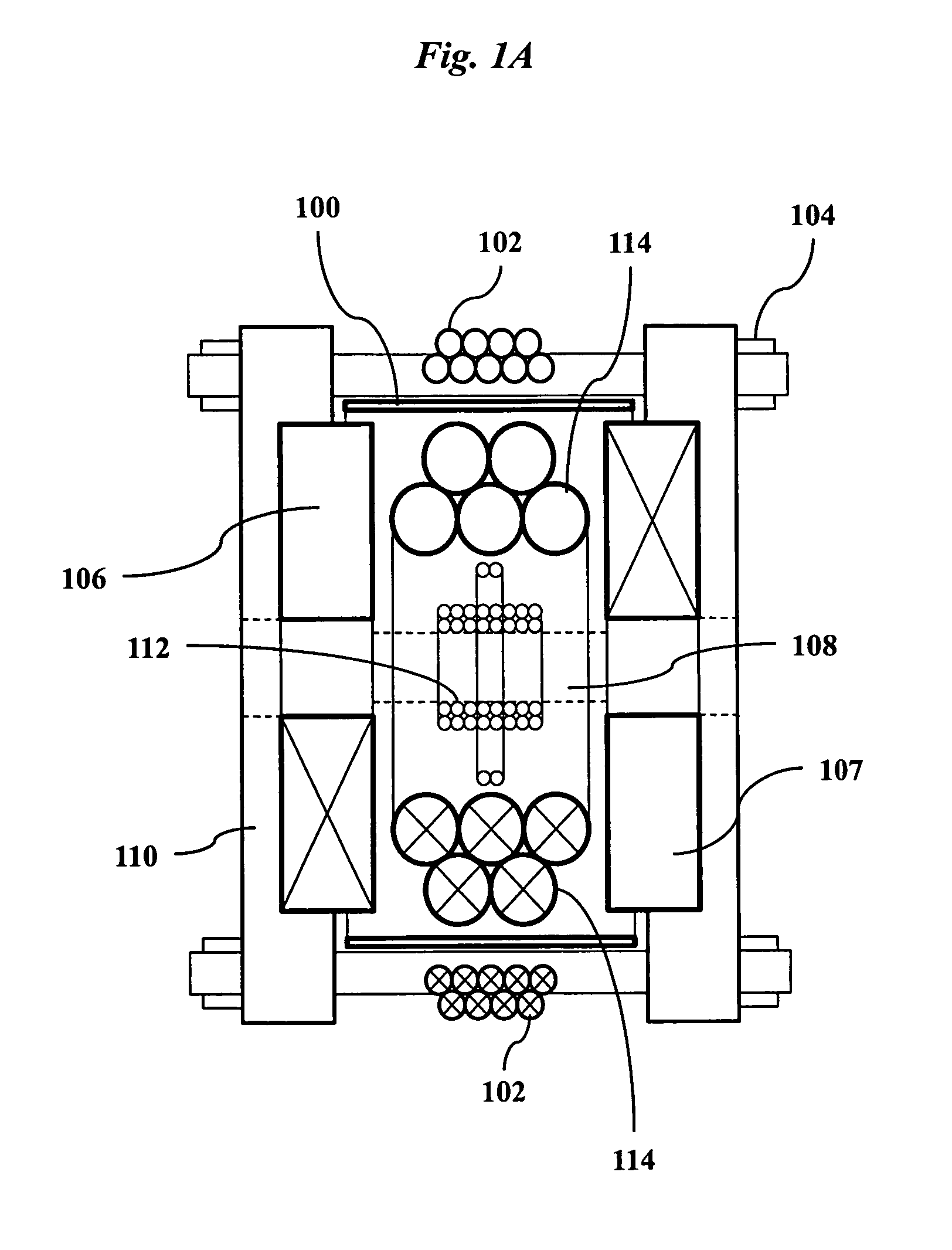
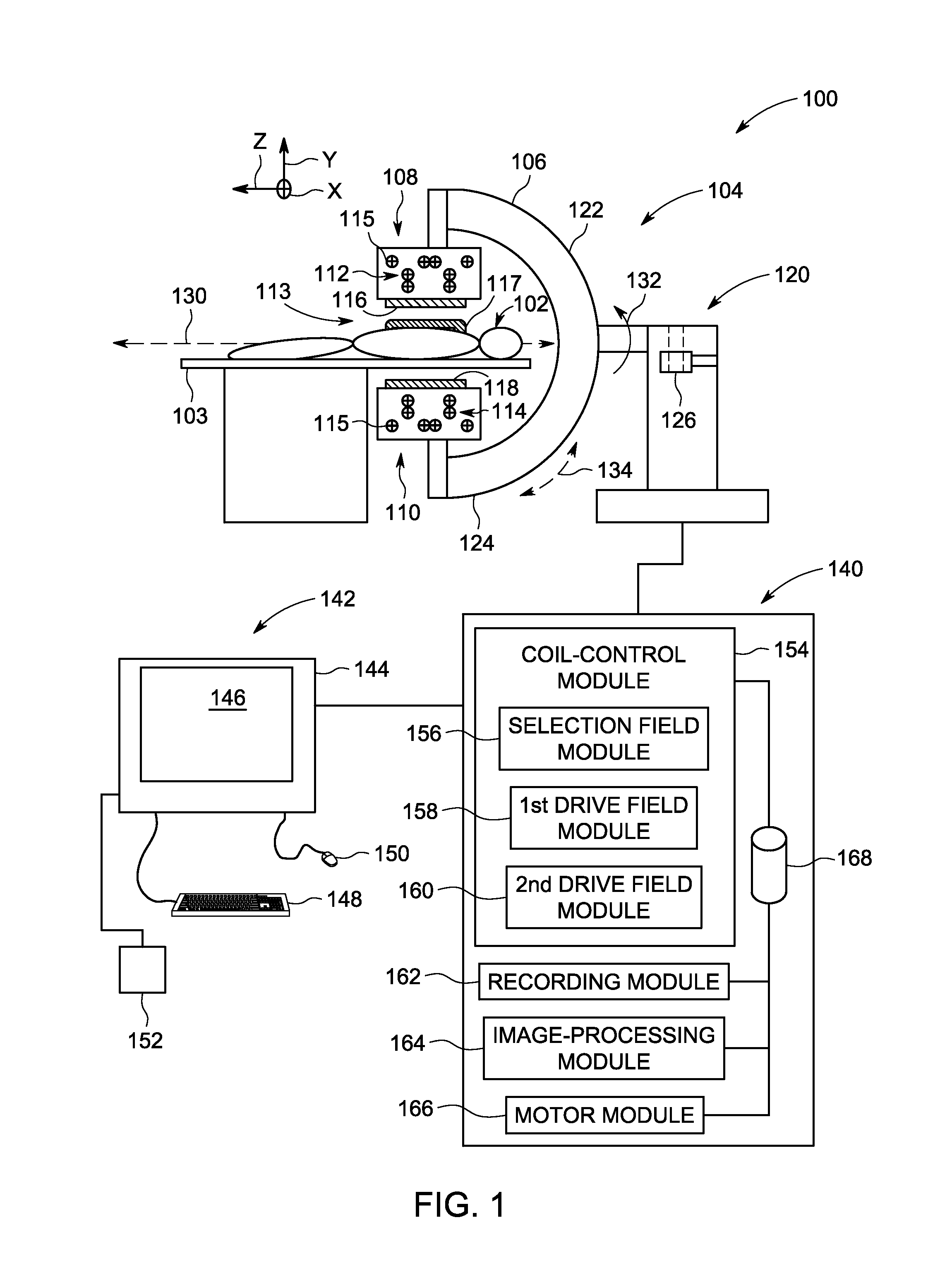
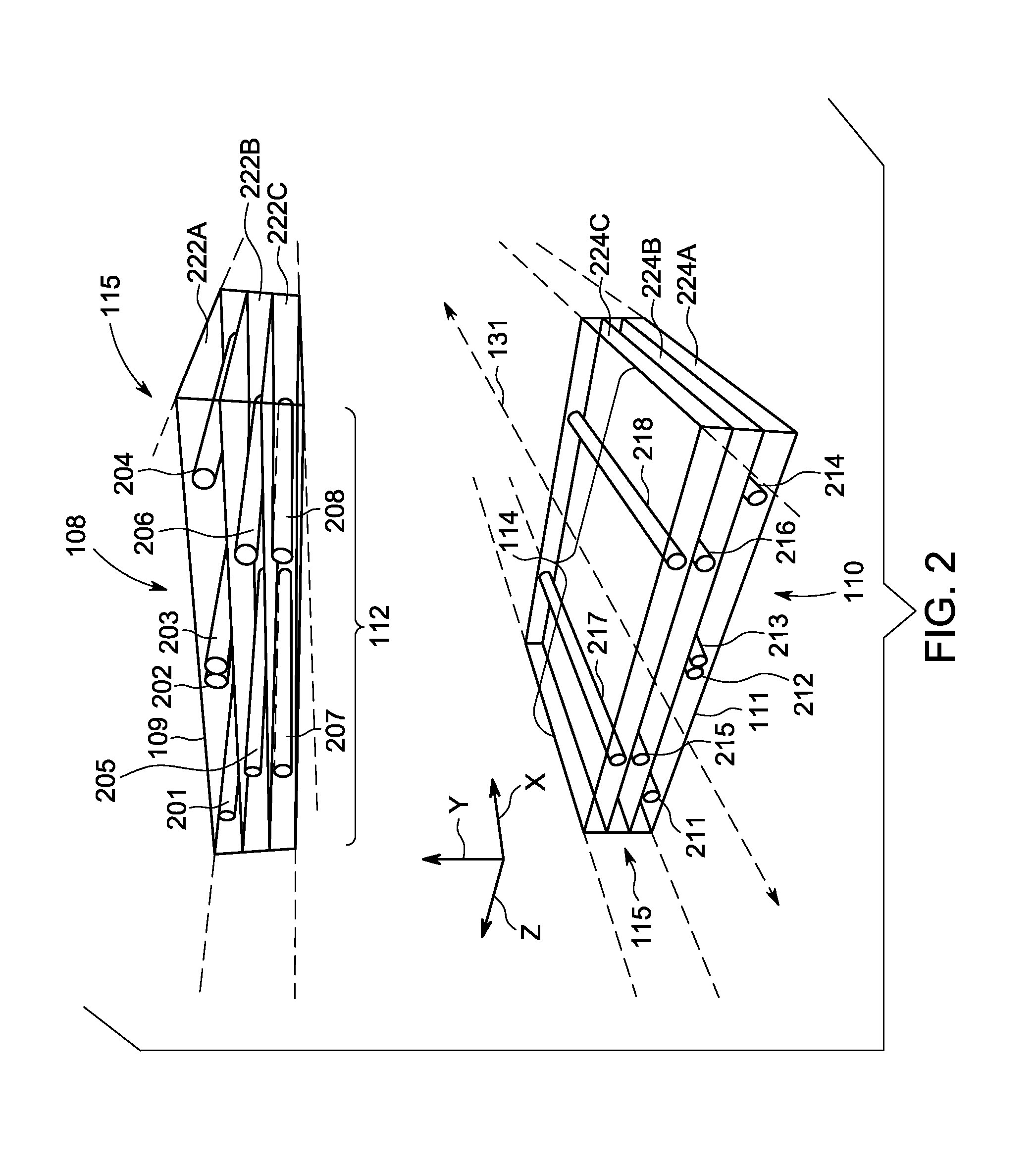
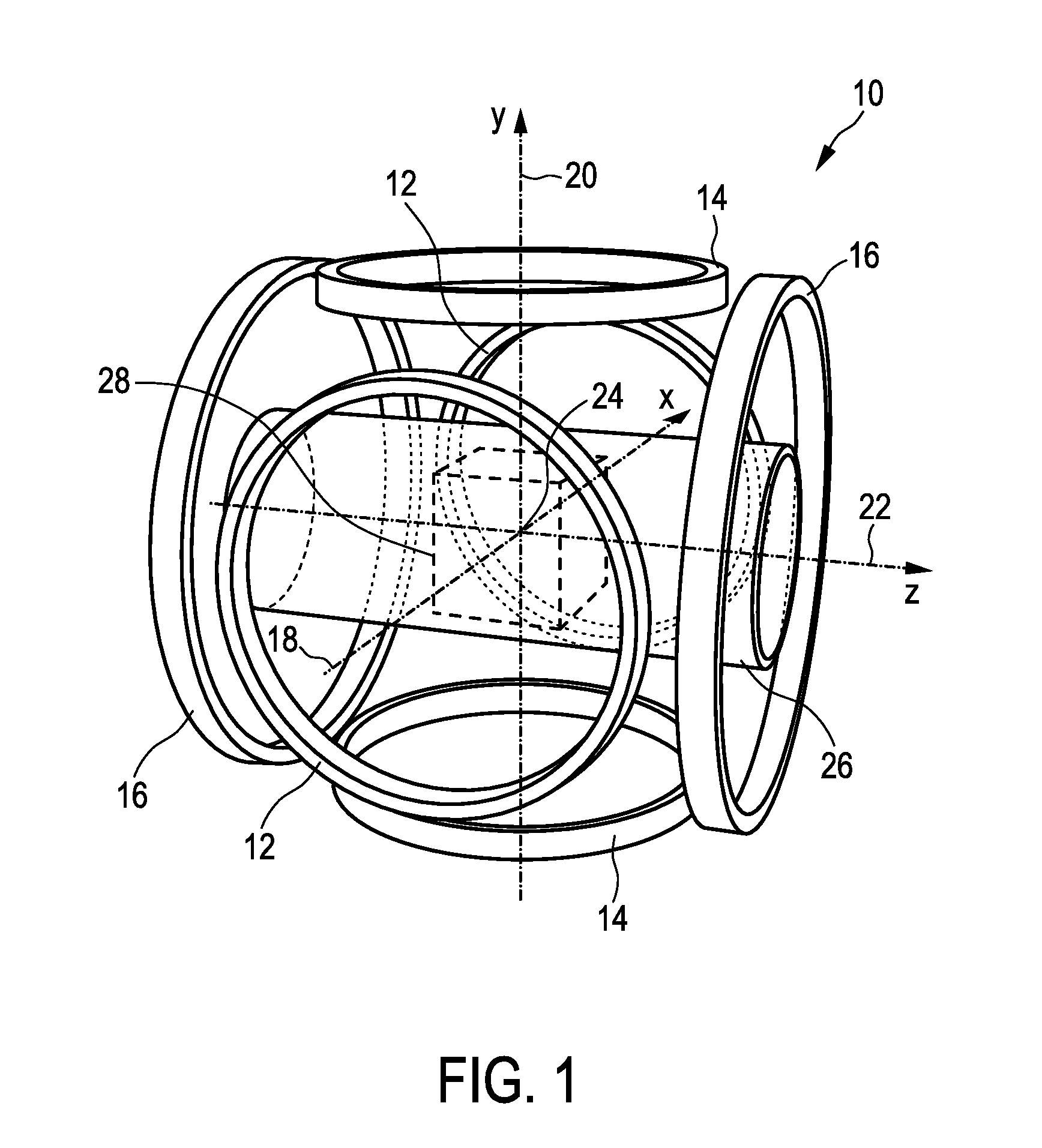
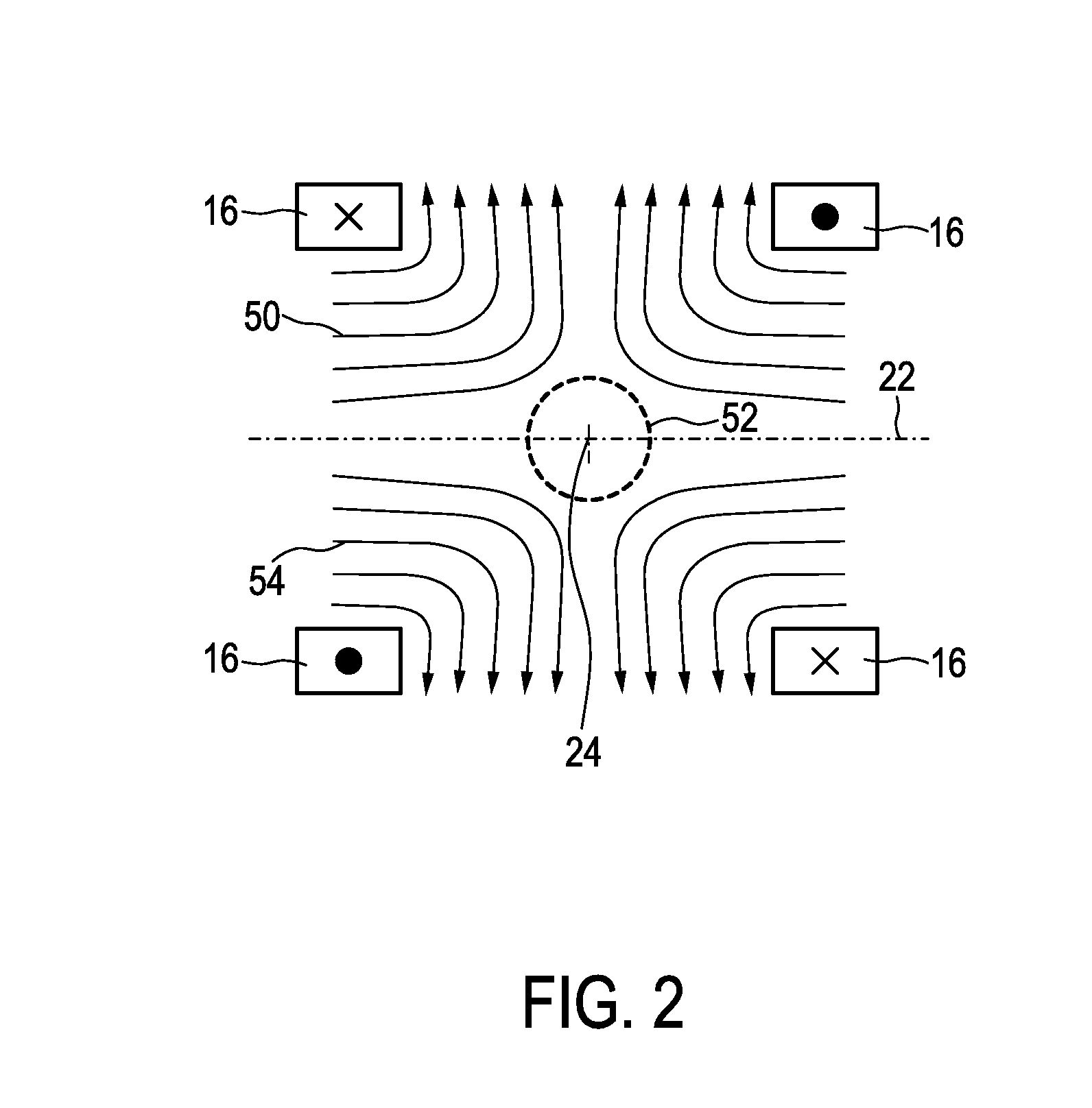
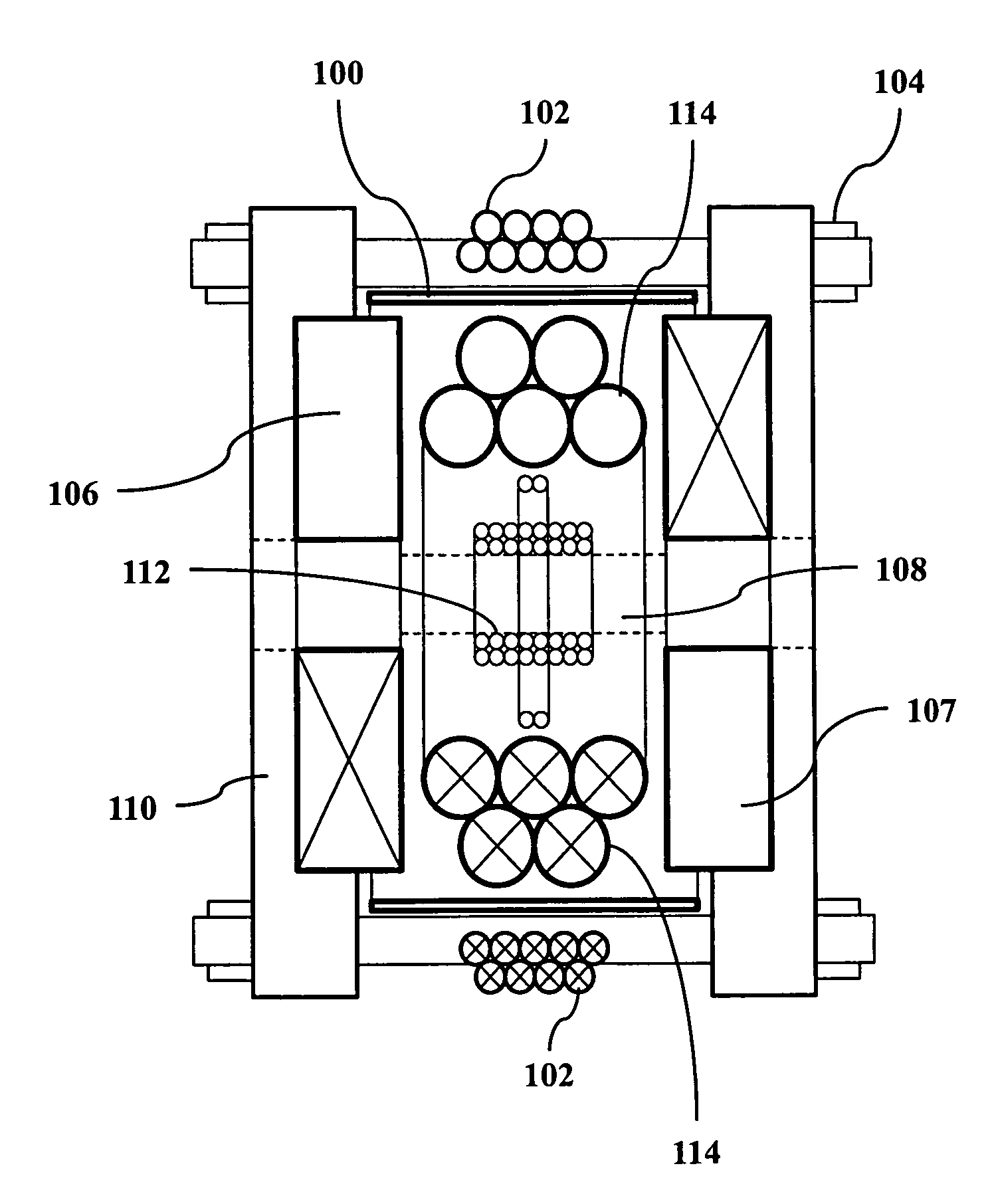
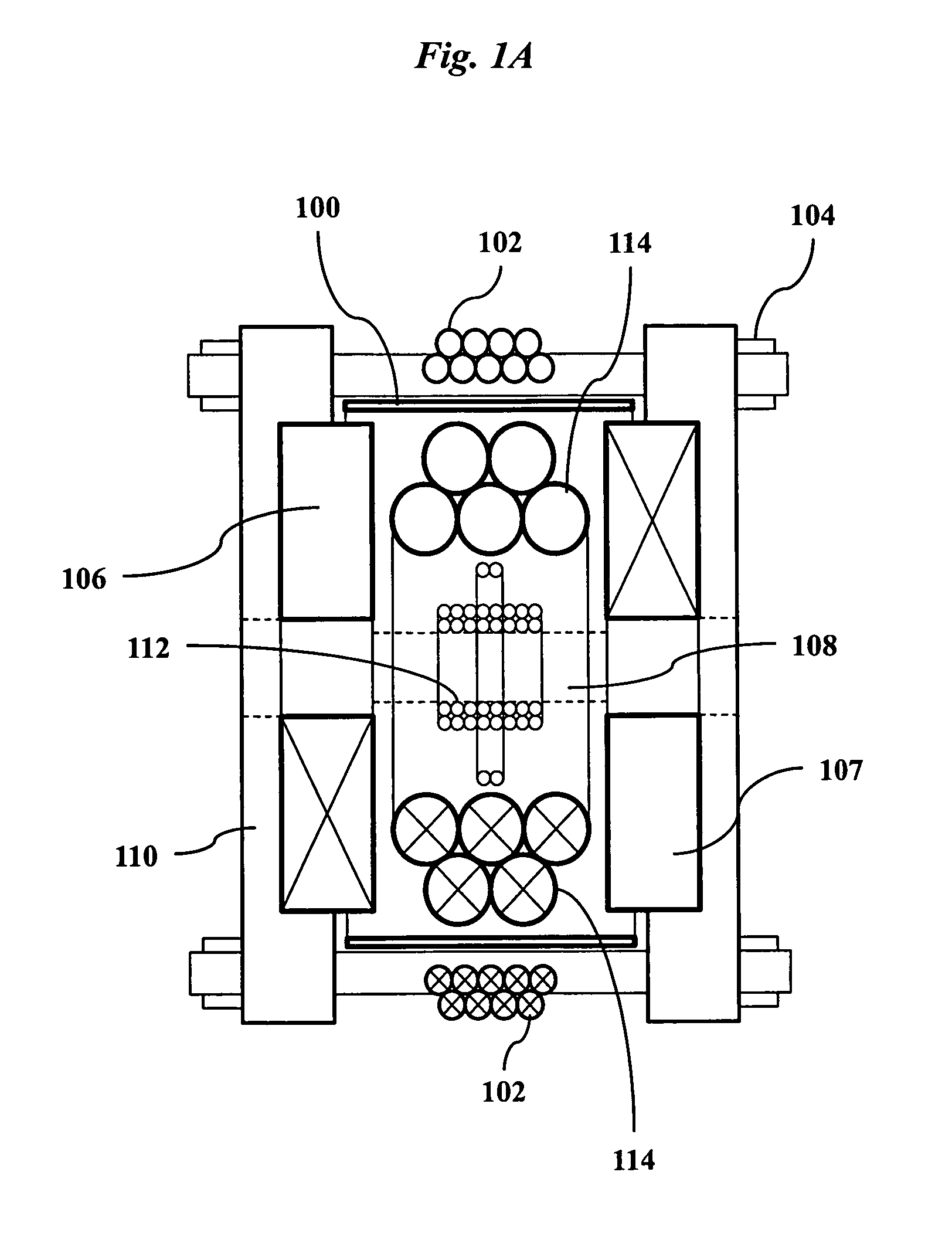
Improved techniques for magnetic particle imaging
ActiveUS20110089942A1Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
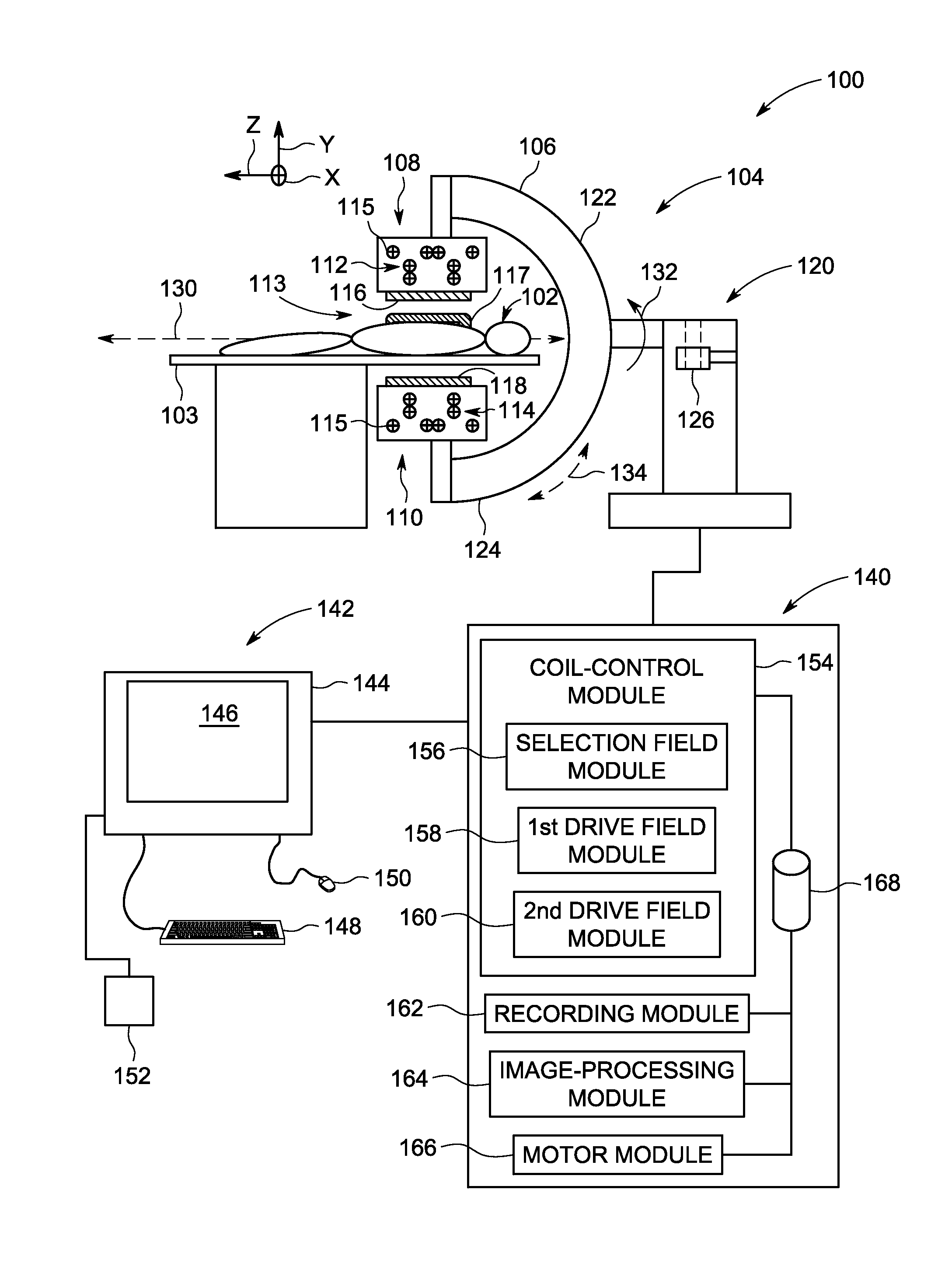
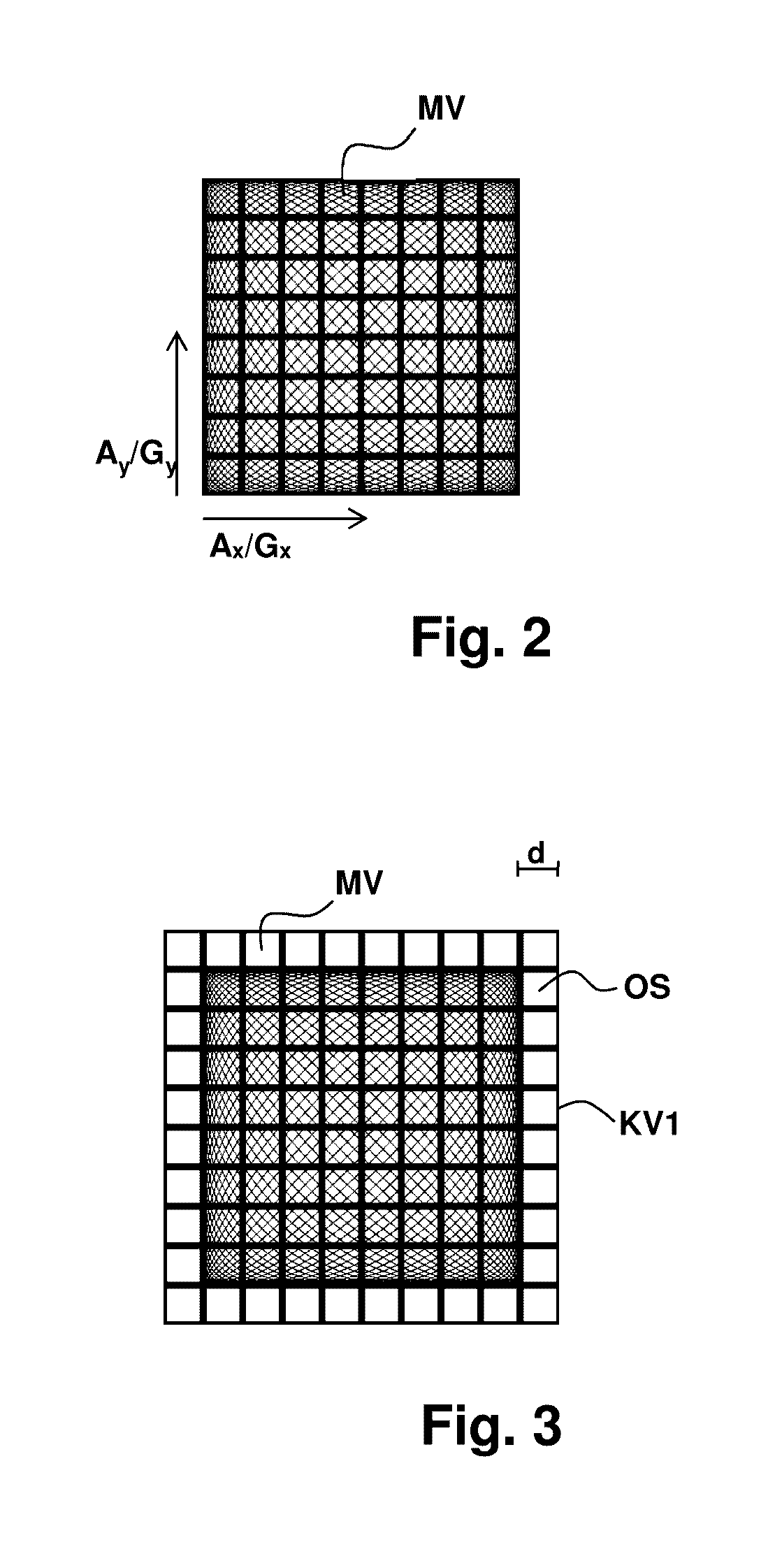
A magnetic particle imaging apparatus includes magnets [106,107] that produce a gradient magnetic field having a field free region (FFR), excitation field electromagnets [102,114] that produce a radiofrequency magnetic field within the field free region, high-Q receiving coils [112] that detect a response of magnetic particles in the field free region to the excitation field. Field translation electromagnets create a homogeneous magnetic field displacing the field-free region through the field of view (FOV) allowing the imaging region to be scanned to optimize scan time, scanning power, amplifier heating, SAR, dB / dt, and / or slew rate. Efficient multi-resolution scanning techniques are also provided. Intermodulated low and radio-frequency excitation signals are processed to produce an image of a distribution of the magnetic nanoparticles within the imaging region. A single composite image is computed using deconvolution of multiple signals at different harmonics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Detection device and method
ActiveUS20090085557A1High magnetizationDecrease of magnetisationElectrical measurementsSusceptibility measurementsCarrier fluidMagnetic response
The present invention relates to method and device for detecting changes of a magnetic response of at least one magnetic particle in a carrier fluid. The method comprises: using a measuring procedure comprising measuring the characteristic rotation time of said magnetic particle, said measuring procedure further involving measuring Brownian relaxation in said carrier fluid under influence of an external pulsed excitation magnetic field, and based on said influence of said external pulsed excitation magnetic field measuring a hydrodynamic volume of a particle or a change in a hydrodynamic volume of the particle change upon modification of an effective volume of the particle or its interaction with said carrier fluid by detecting change of magnetization of the particle with time by monitoring change of an output signal in detection coil.
Owner:ACREO SWEDISH ICT
Superparamagnetic particle imaging and its applications in quantitative multiplex stationary phase diagnostic assays
ActiveUS20190317167A1Improve responseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresStationary phasePoint of care
Superparamagnetic nanoparticle-based analytical method comprising providing a sample having analytes in a sample matrix, providing a point of care chip having analytical regions, each of which is a stationary phase having at least one or more sections, labeling each of the analytes with a superparamagnetic nanoparticle and immobilizing the labeled analytes in the stationary phase, providing an analytical device having a means for exciting the superparamagnetic nanoparticles in vitro and a means for sensing, receiving, and transmitting response of the excited superparamagnetic nanoparticles, placing the chip in the analytical device and exciting the superparamagnetic nanoparticles in vitro, sensing, receiving, and transmitting the response of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles, and analyzing the response and determining characteristic of the analytes, wherein the response of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles comprises harmonics. The present invention also provides the hybrid point of care chip and analyzer to be used in the analytical method.
Owner:MARS SCI LTD
Magnetic particle flow detector
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field detection system having a substrate supporting a magnetic field sensor in a channel with a first electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap and in direct contact with at least some surface of the magnetic field sensor ands a second electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap in a region thereof adjacent to, but separated from, the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:NVE CORP
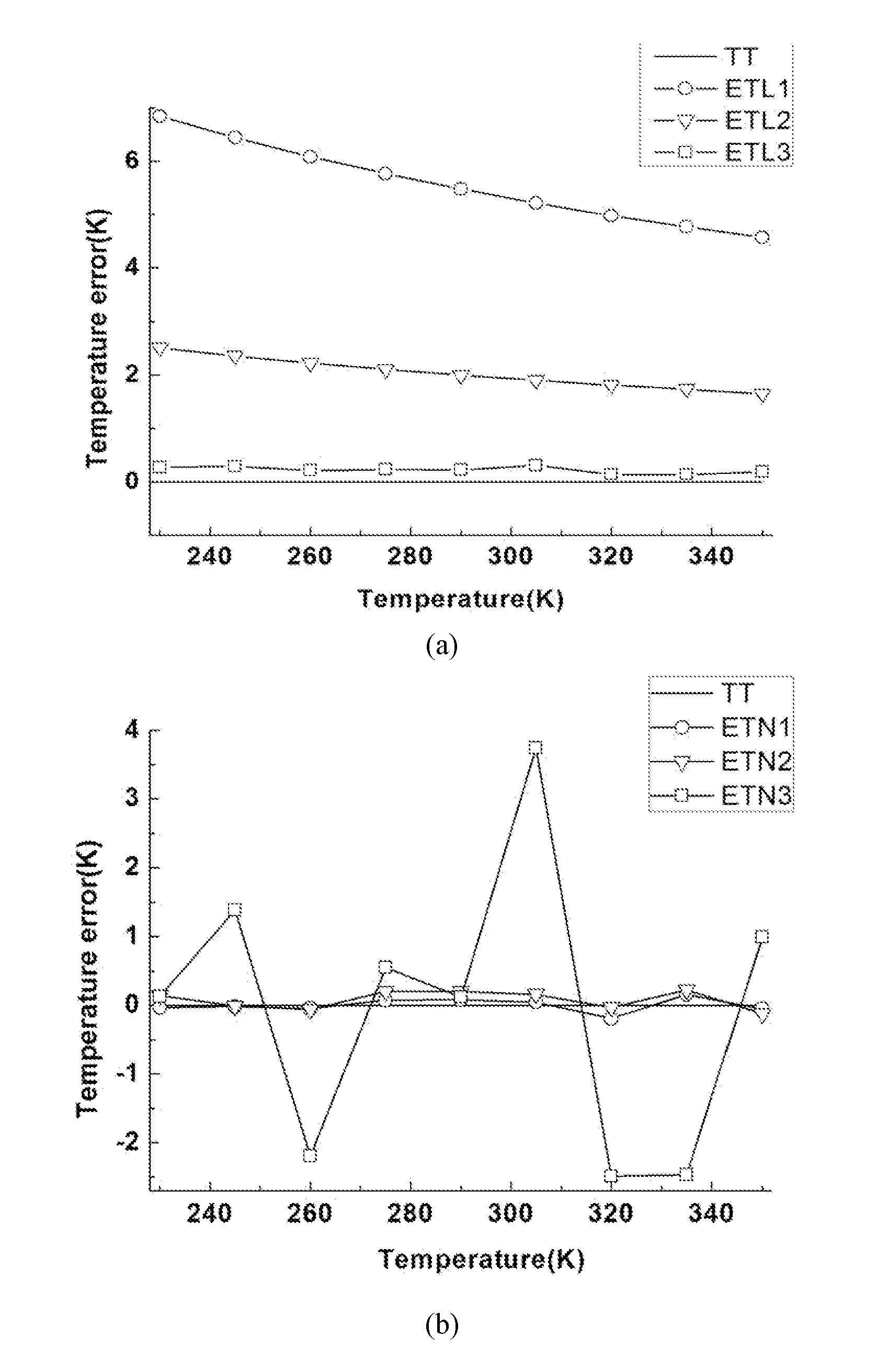
Magnetic nano temperature imaging method and magnetic nano temperature imaging system
ActiveCN103892809ASolving for temperature has no effectAccurately obtainedThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansHarmonicMagnetite Nanoparticles
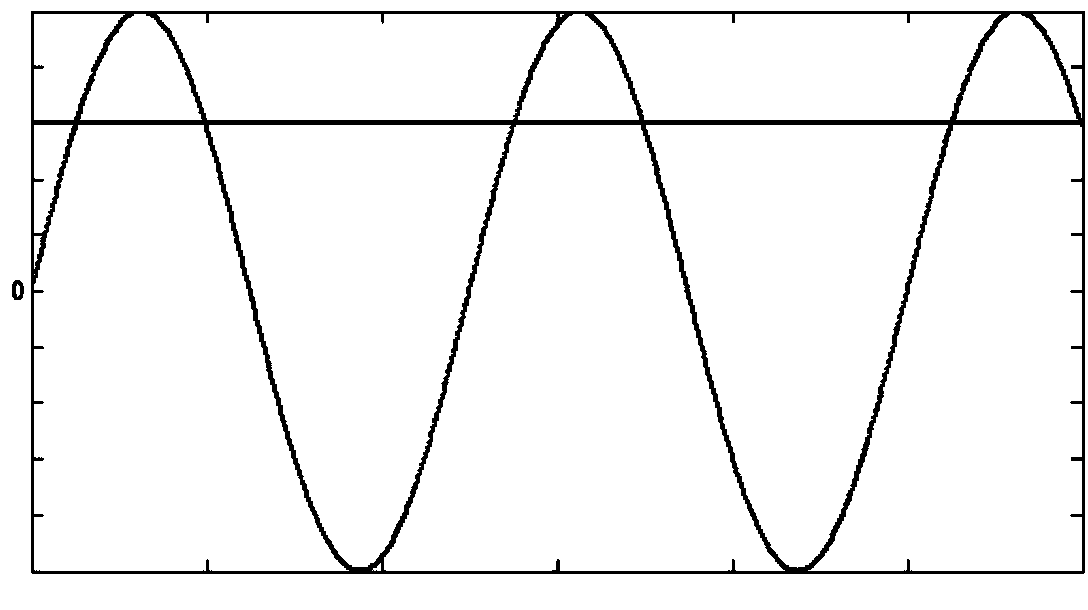
The invention discloses a magnetic nano temperature imaging method. The method includes applying a constant direct-current magnetic field and a constant alternating-current magnetic field to an area where magnetic nanoparticle samples are positioned at the same time, collecting alternating-current magnetized strength signals of magnetic nanoparticles, and detecting out each odd harmonic amplitude value; replacing a constant direct-current gradient field by a combined direct-current magnetic field containing a gradient magnetic field, collecting alternating-current magnetized strength signals of the magnetic nanoparticles, and detecting out each odd harmonic amplitude value; calculating difference of the harmonic amplitude values of the two times; utilizing Taylor series of a Langevin function to unfold and establish a relation formula of the odd harmonic amplitude values and temperature, and solving the relation formula to acquire in-vivo temperature; changing the direct-current gradient field to a next position until temperature measuring of the whole one-dimensional space is completed. Different exciting magnetic fields are applied to the magnetic nanoparticles, so that temperature imaging of the one-dimensional space is converted into solving of point temperature of each minizone, and a temperature field of the one-dimensional space can be precisely and quickly acquired without knowing concentration of the magnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Systems and methods using magnetically-responsive sensors for determining a genetic characteristic
ActiveUS20180237850A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical resistance and conductanceBiology
Sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS) method is provided that includes providing a detection apparatus that includes an array of magnetically-responsive sensors. Each of the magnetically-responsive sensors is located proximate to a respective designated space to detect a magnetic property therefrom. The detection apparatus also includes a plurality of nucleic acid template strands located within corresponding designated spaces. The method also includes conducting a plurality of SBS events to grow a complementary strand by incorporating nucleotides along each template strand. At least some of the nucleotides are attached to corresponding magnetic particles having respective magnetic properties. Each of the plurality of SBS events includes detecting changes in electrical resistance at the magnetically-responsive sensors caused by the respective magnetic properties of the magnetic particles. The method also includes determining genetic characteristics of the complementary strands based on the detected changes in electrical resistance.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Physical unclonable functions having magnetic and non-magnetic particles
ActiveUS9553582B1Reliability increasing modificationsCoding/ciphering apparatusPhysical unclonable functionImage View
A physical unclonable function (PUF) having magnetic and non-magnetic particles is disclosed. Measuring both magnetic field and image view makes the PUF difficult to counterfeit. PUF may be incorporated into a user-replaceable supply item for an imaging device. A PUF reader may be incorporated into an imaging device to read the PUF. Other systems are disclosed.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Systems and methods for magnetic material imaging
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
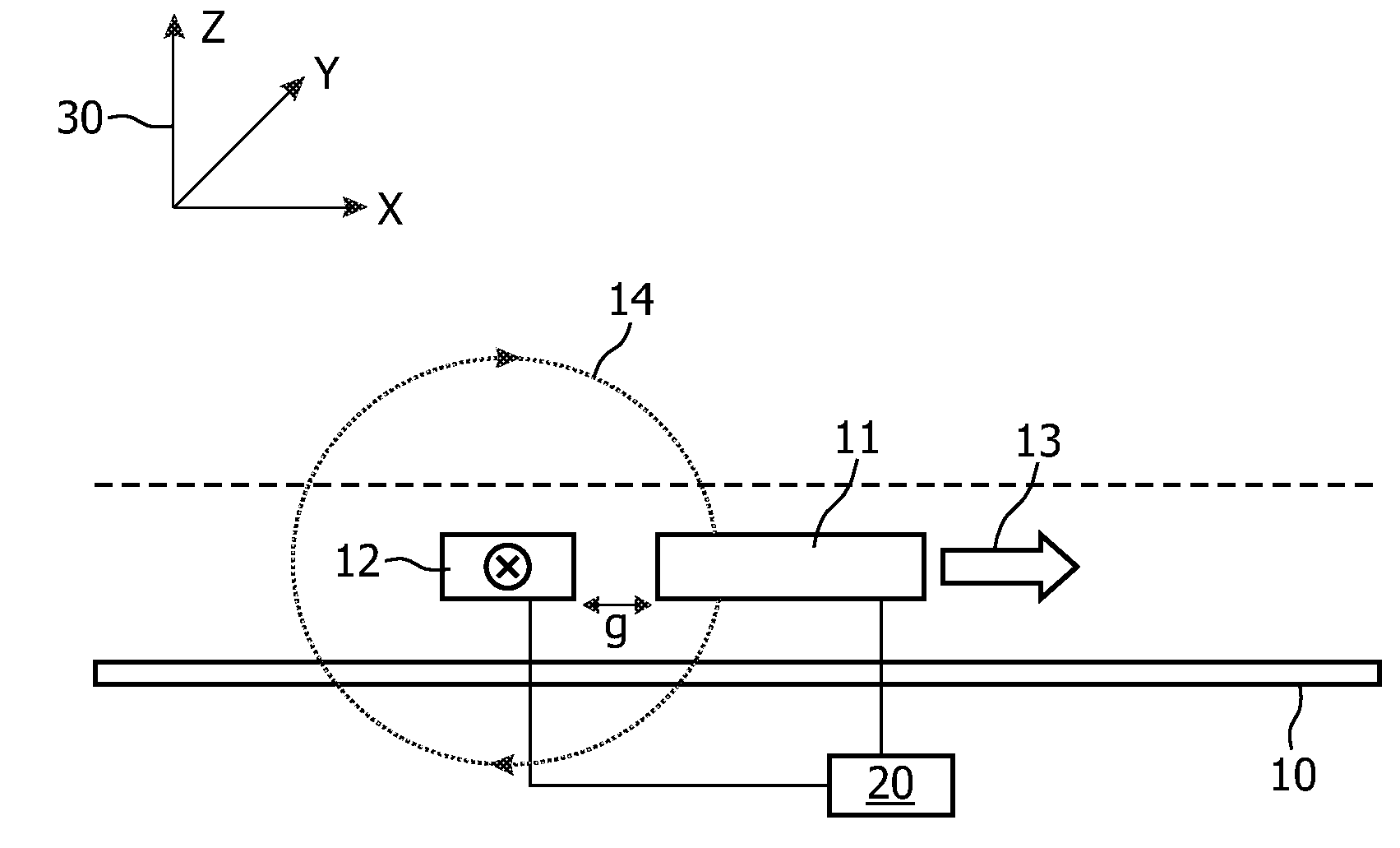
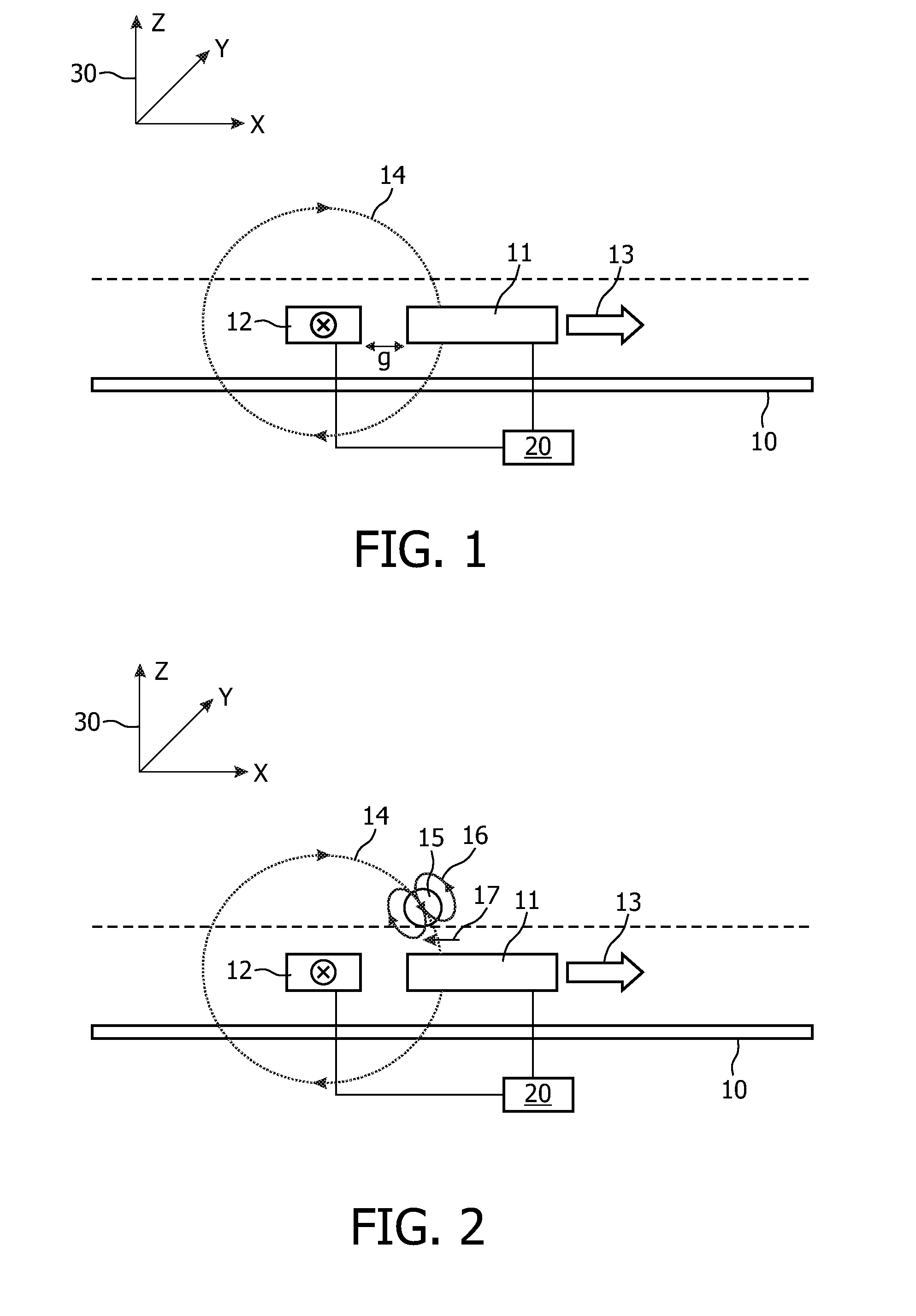
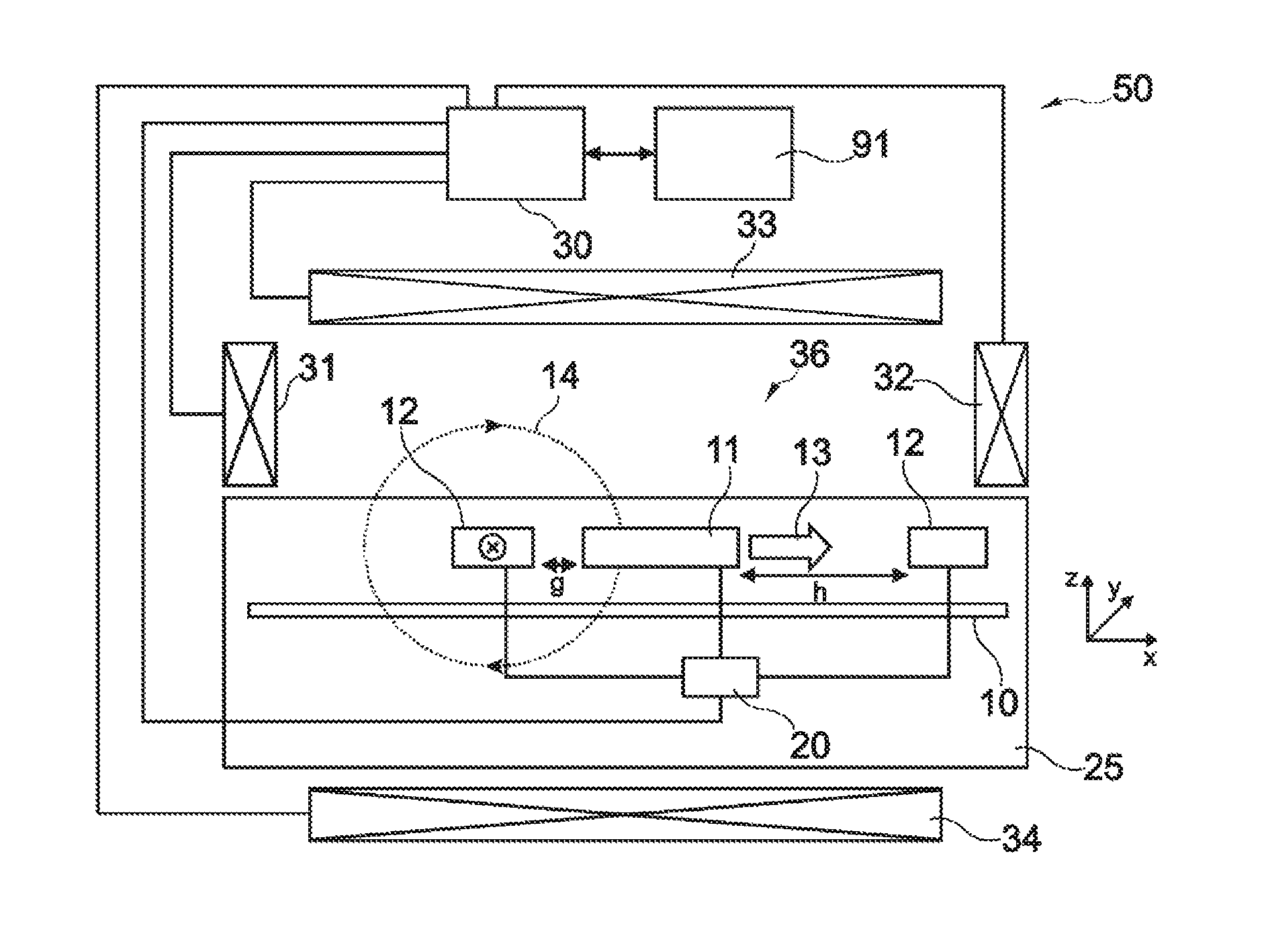
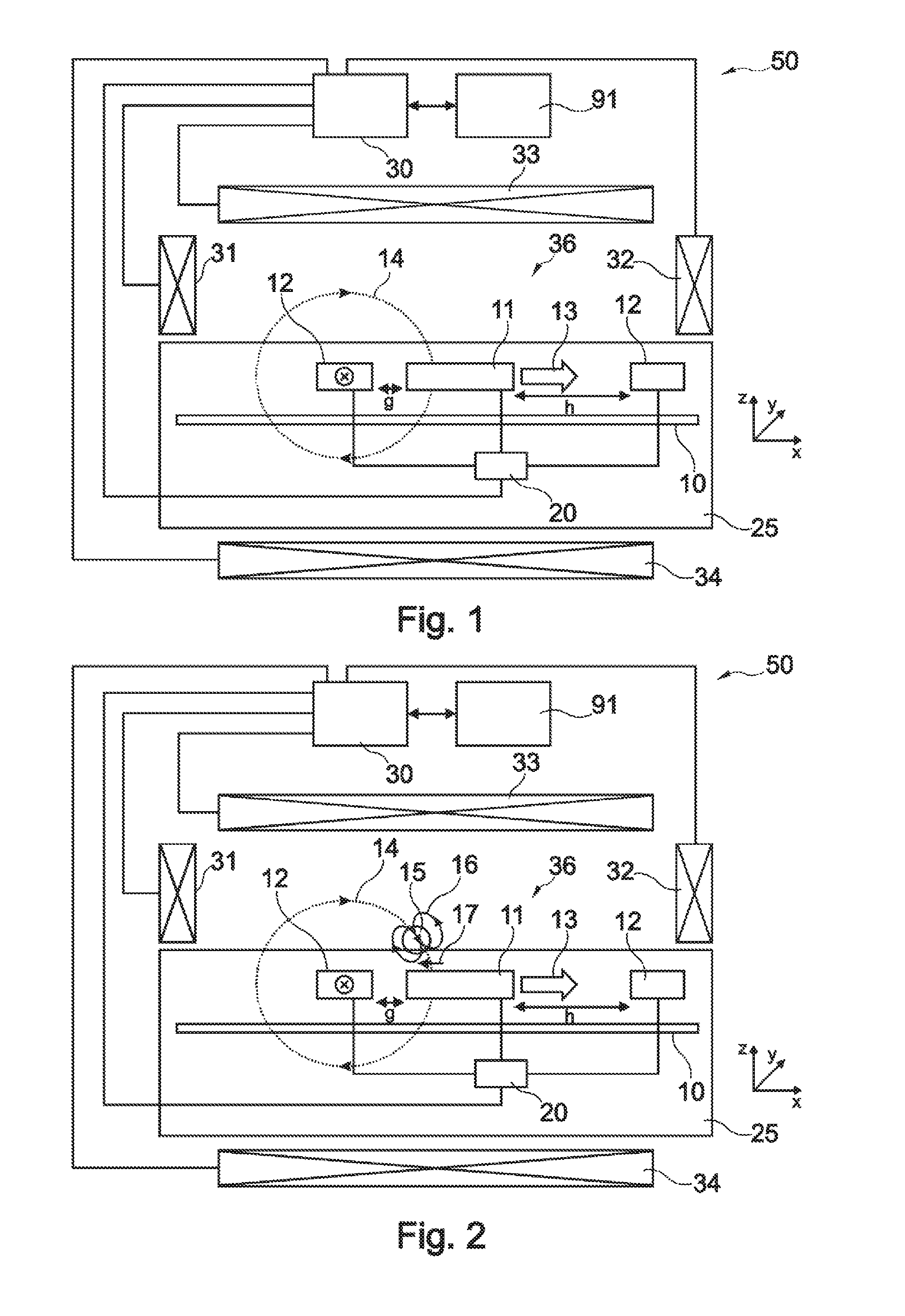
Magnetic sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20090237844A1Improve sensor performanceReduce resistanceBiological particle analysisRecord information storageExcitation signalSignal source
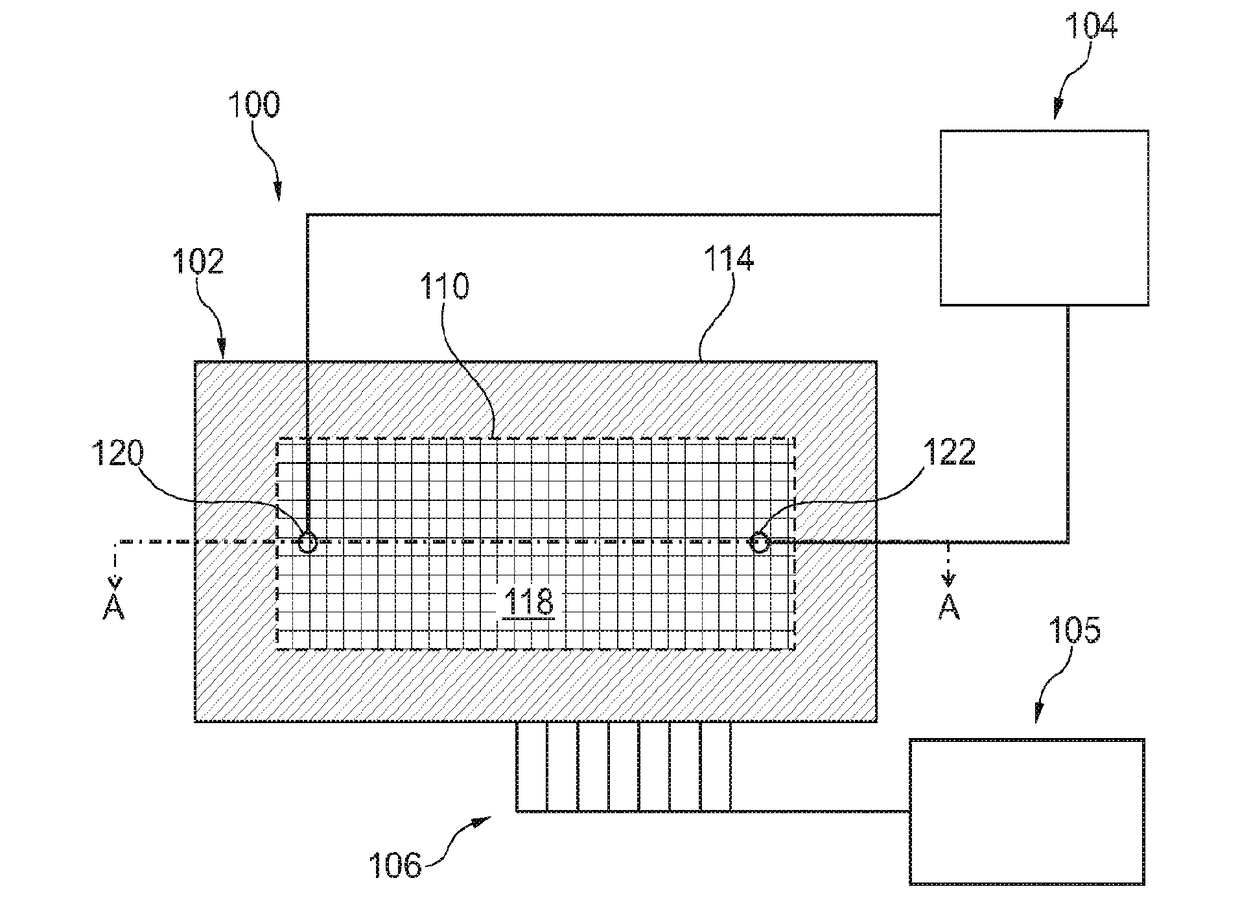
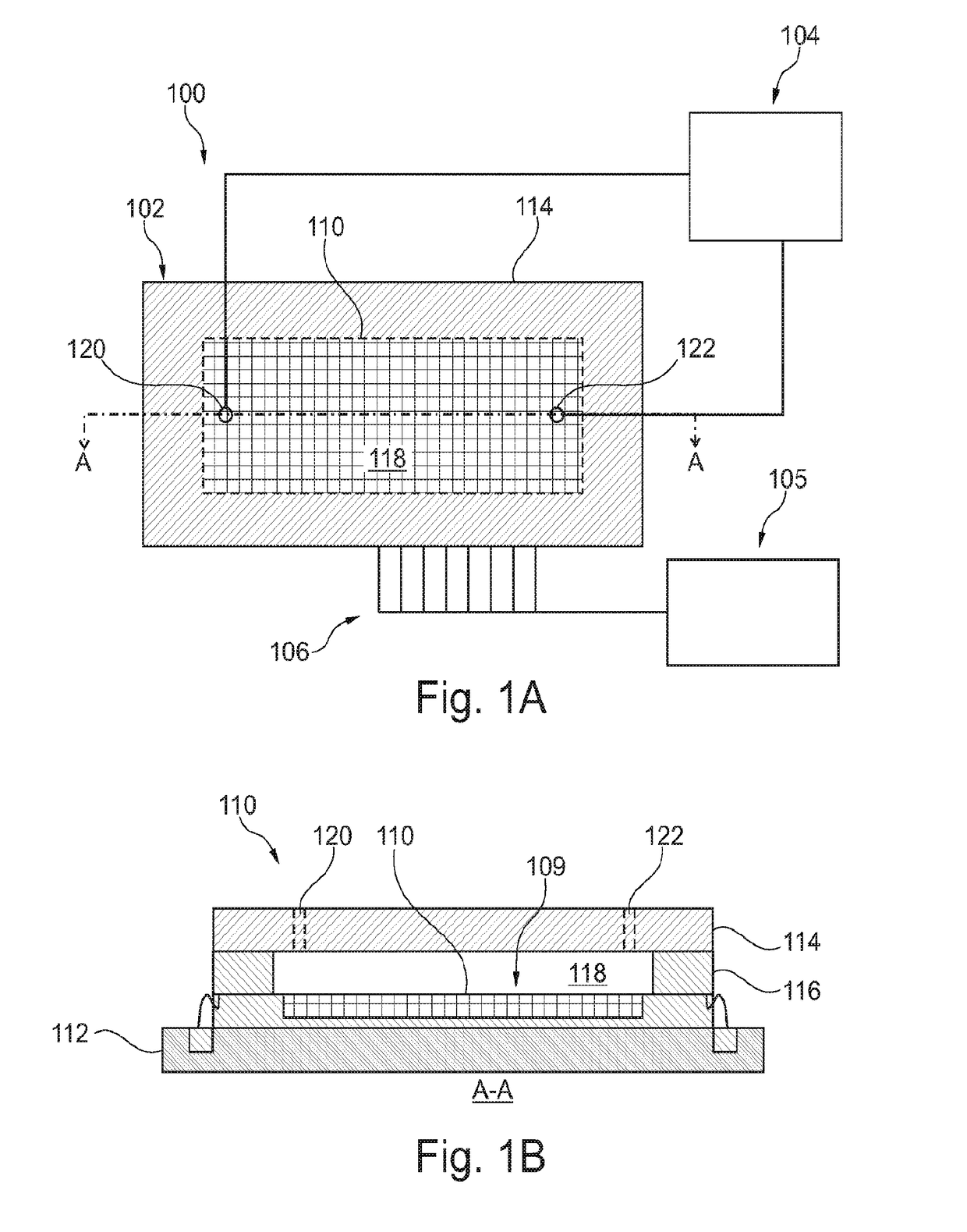
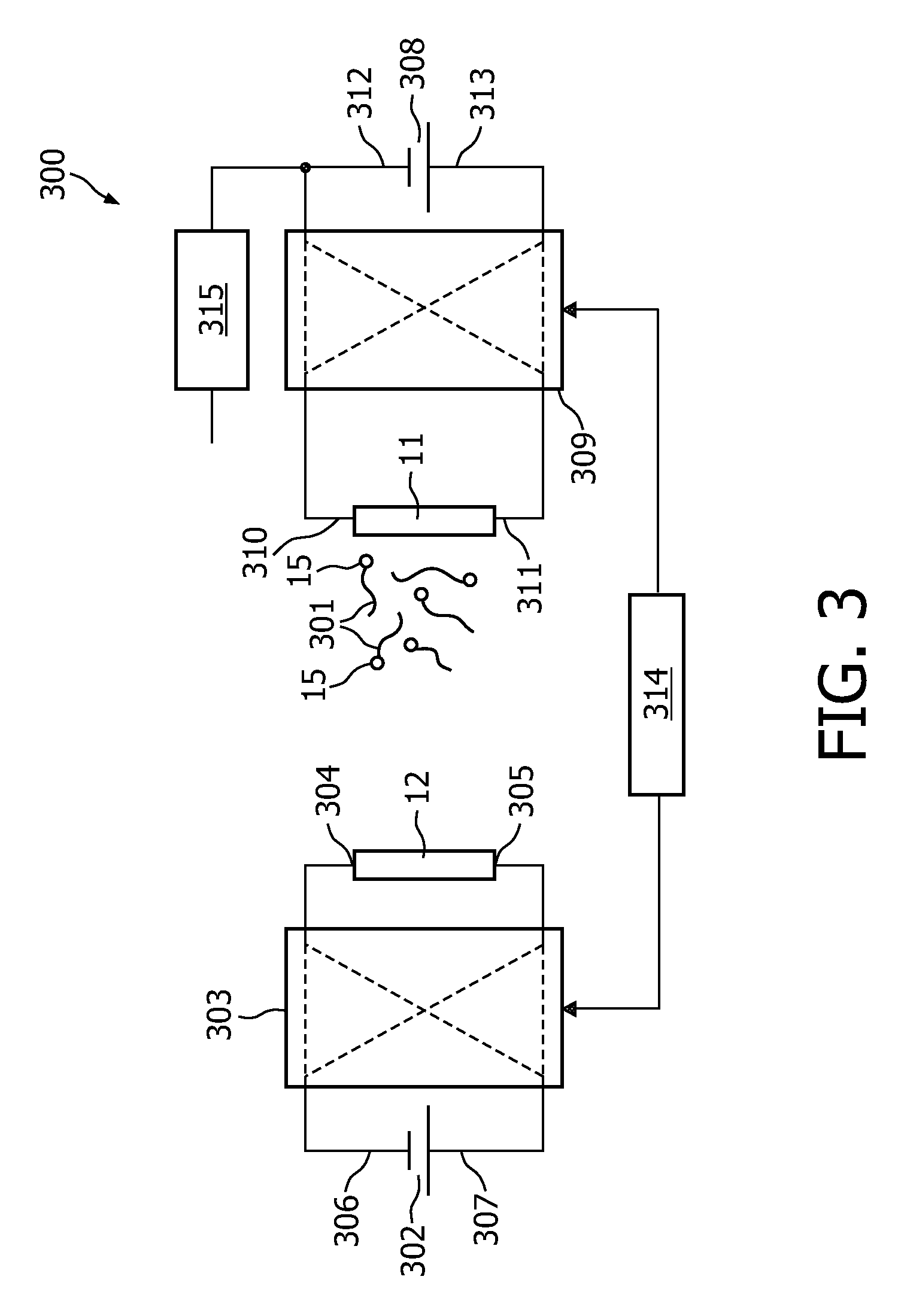
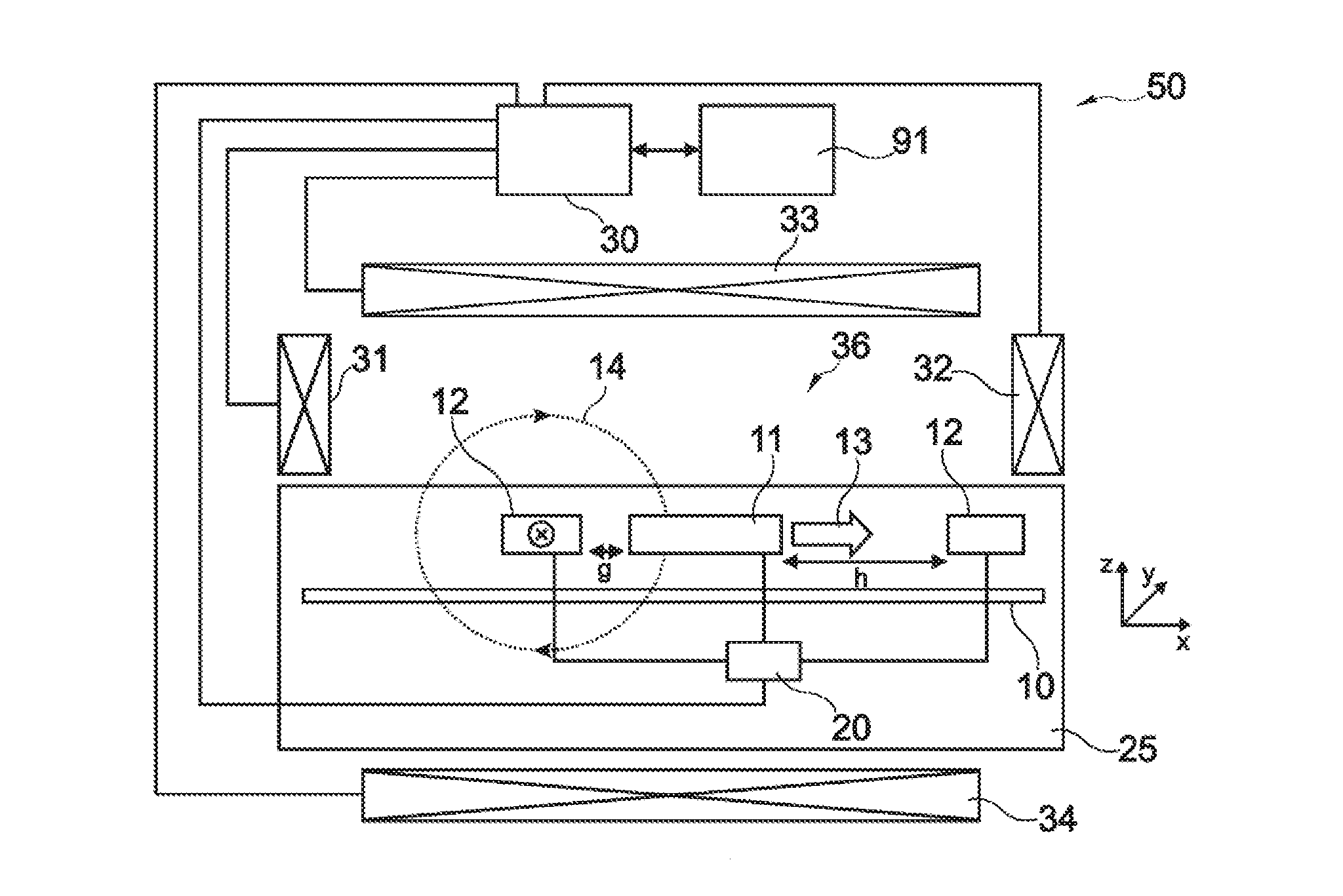
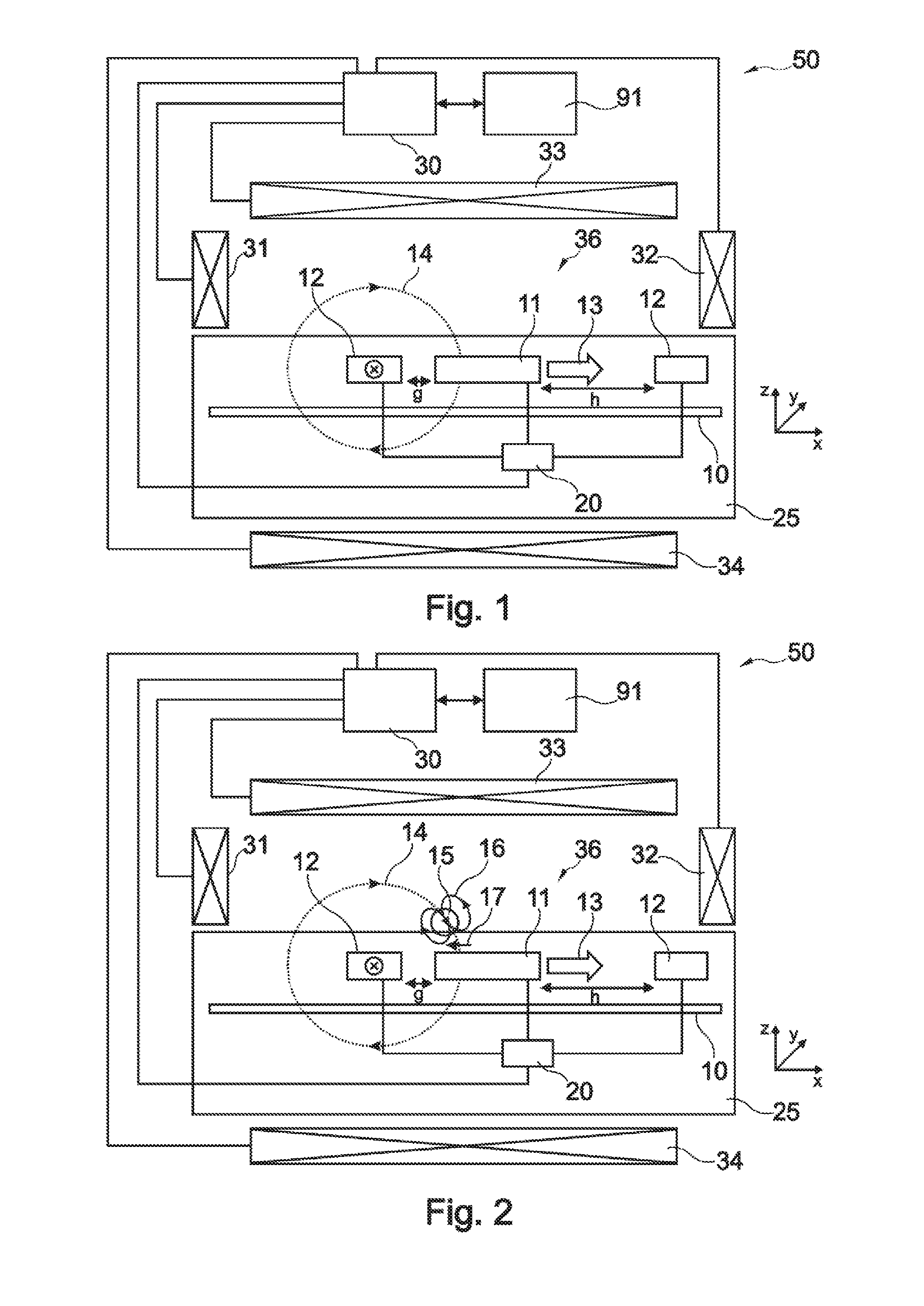
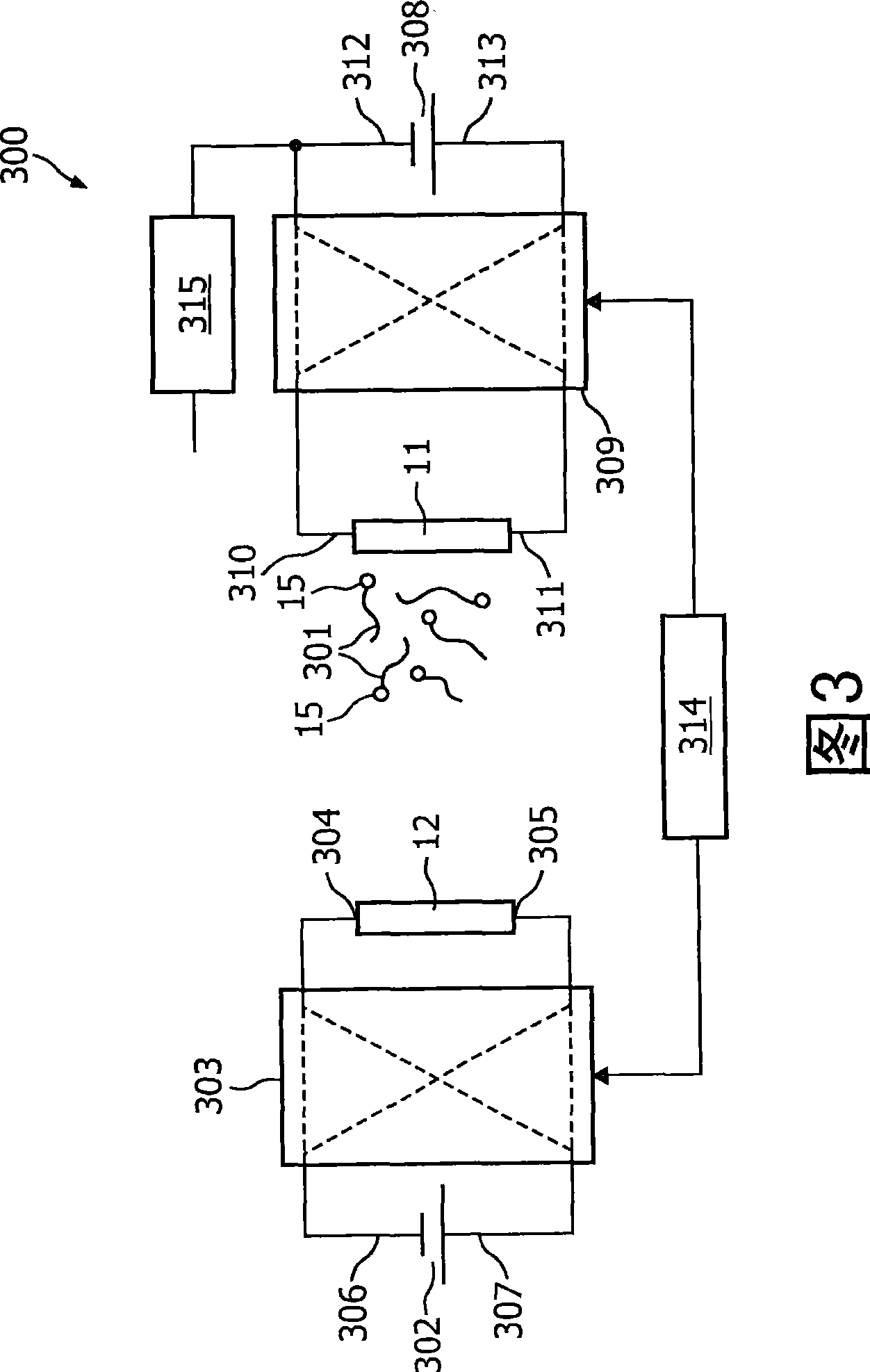
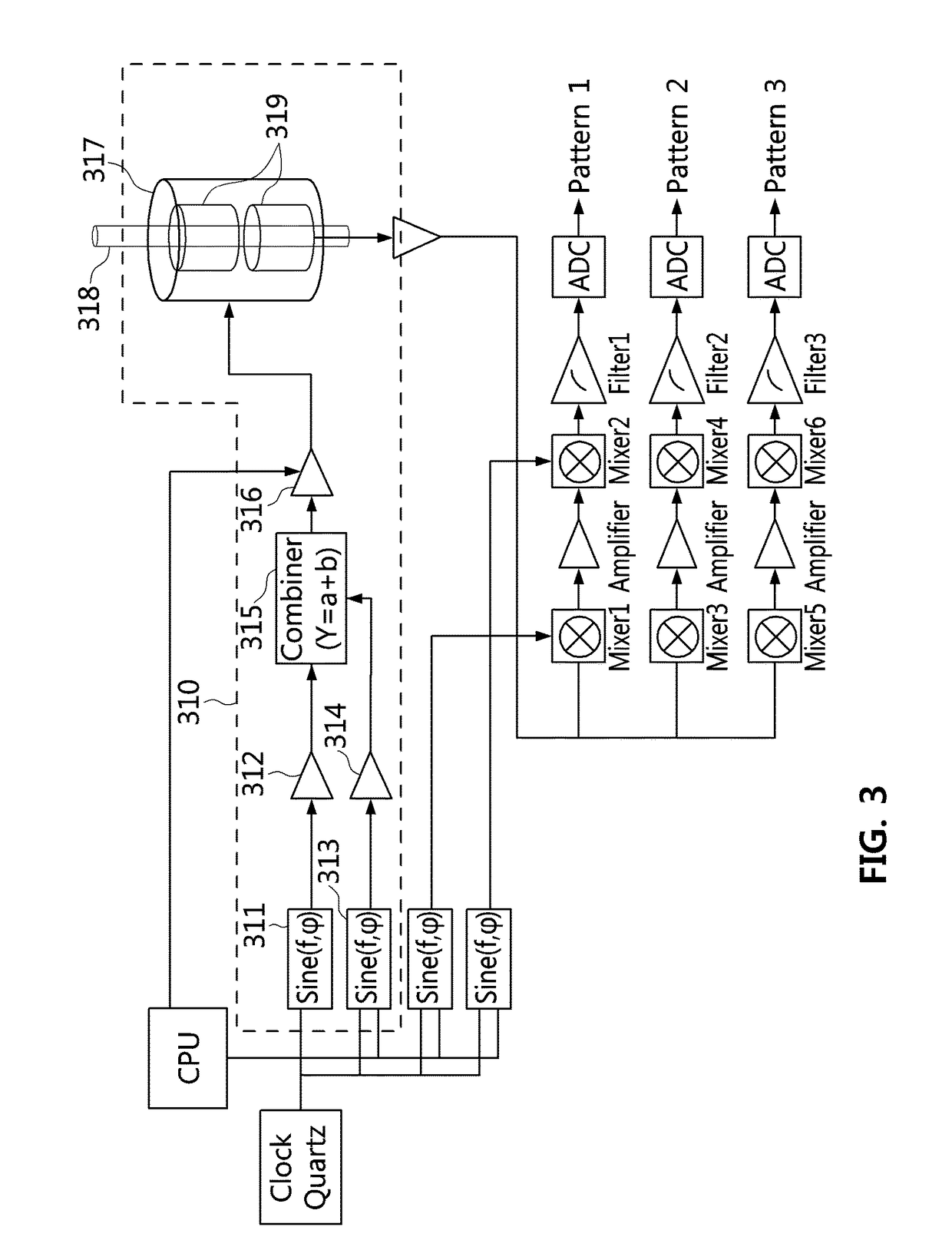
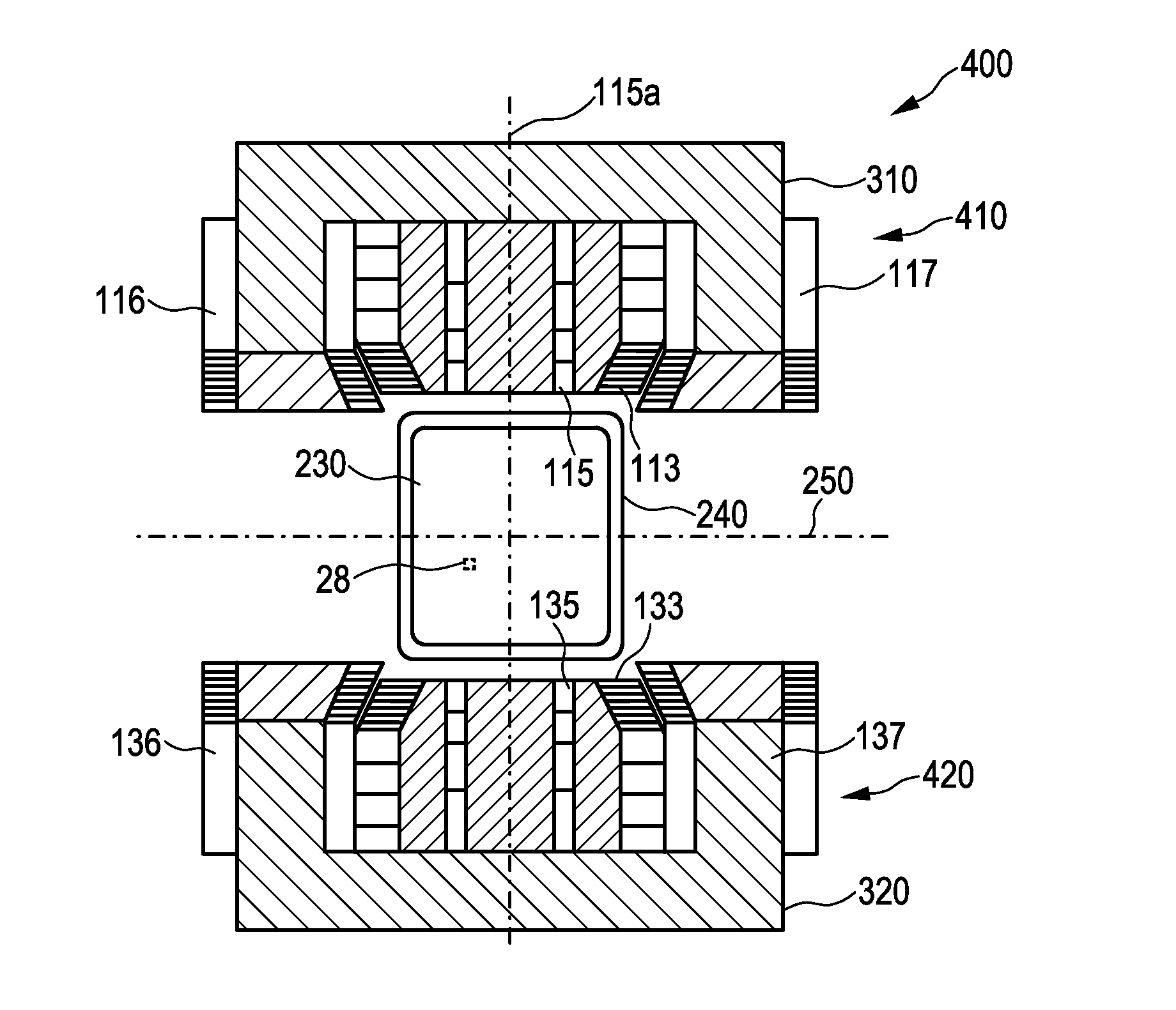
A magnetic sensor device (300) for sensing magnetic particles (15), the magnetic sensor device (300) comprising a magnetic field generator unit (12) adapted for generating a magnetic field, an excitation signal source (302) adapted for supplying the magnetic field generator unit (12) with a static electric excitation signal, an excitation switch unit (303) adapted for switching between different modes of electrically coupling the excitation signal source (302) to the magnetic field generator unit (12), and a sensing unit (11) adapted for sensing a signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles (15) in the generated magnetic field.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
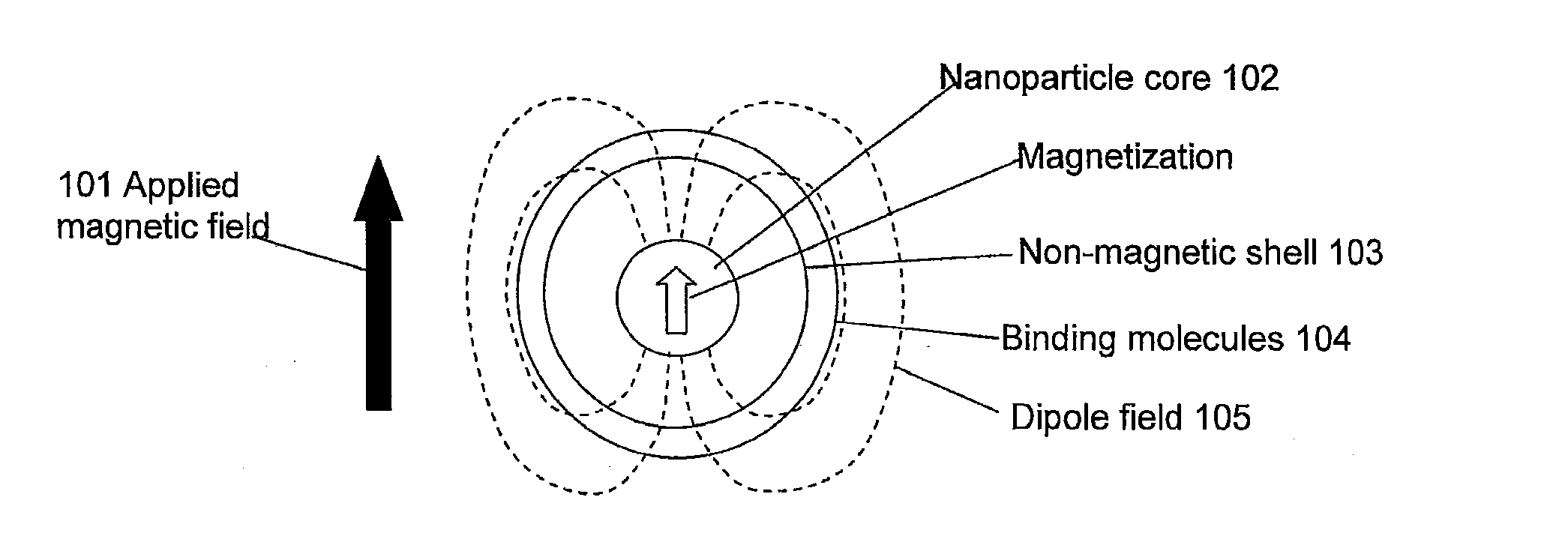
Detection, measurement, and imaging of cells such as cancer and other biologic substances using targeted nanoparticles and magnetic properties thereof
ActiveUS20120035458A1Useful propertyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSubstance useParamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention can provide a method of determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of a biological substance, comprising: (a) exposing a sample to a plurality of targeted nanoparticles, where each targeted nanoparticle comprises a paramagnetic nanoparticle conjugated with one or more targeting agents that preferentially bind with the biological substance, under conditions that facilitate binding of the targeting agent to at least one of the one or more biological substances; (b) subjecting the sample to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of the nanoparticles; (c) measuring a magnetic field of the sample after decreasing the magnetic field applied in step b below a threshold; (d) determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of the one or more biologic substances from the magnetic field measured in step (c).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
ActiveUS20100324828A1Dissipate more thermal energyHigh currentNanomagnetismMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansControl unitMagnetic field
A sensor device (50) for sensing magnetic particles (15), the sensor device (50) comprising a substrate (25) and a sensing unit (11, 20) provided on and / or in and / or near the substrate (25) and being adapted for sensing a detection signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles (15), and a magnetic field control unit (30 to 34) provided off the substrate (25) and being adapted for generating a time-dependent magnetic field for interaction with the magnetic particles (15).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS NEDERLAND BV
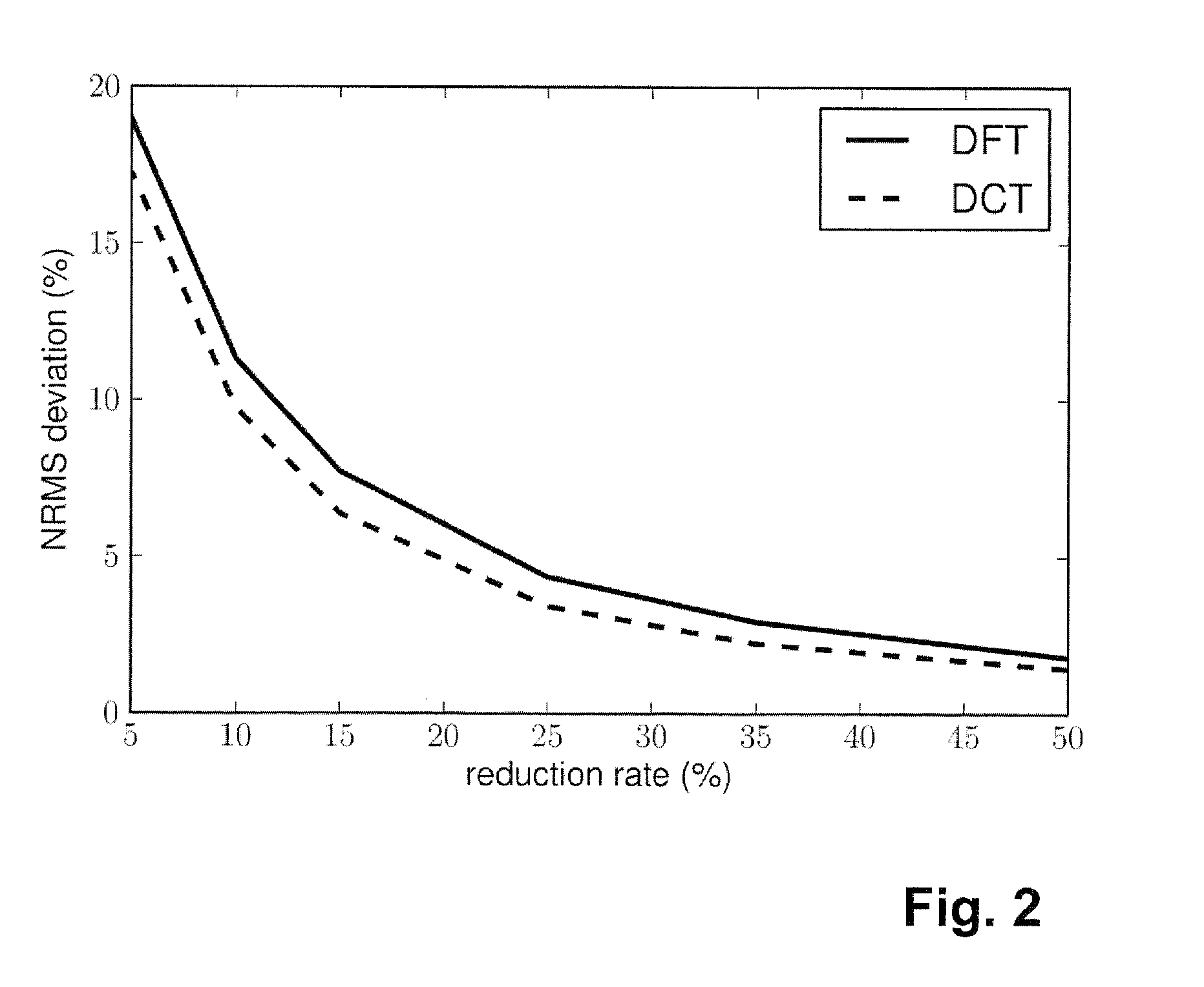
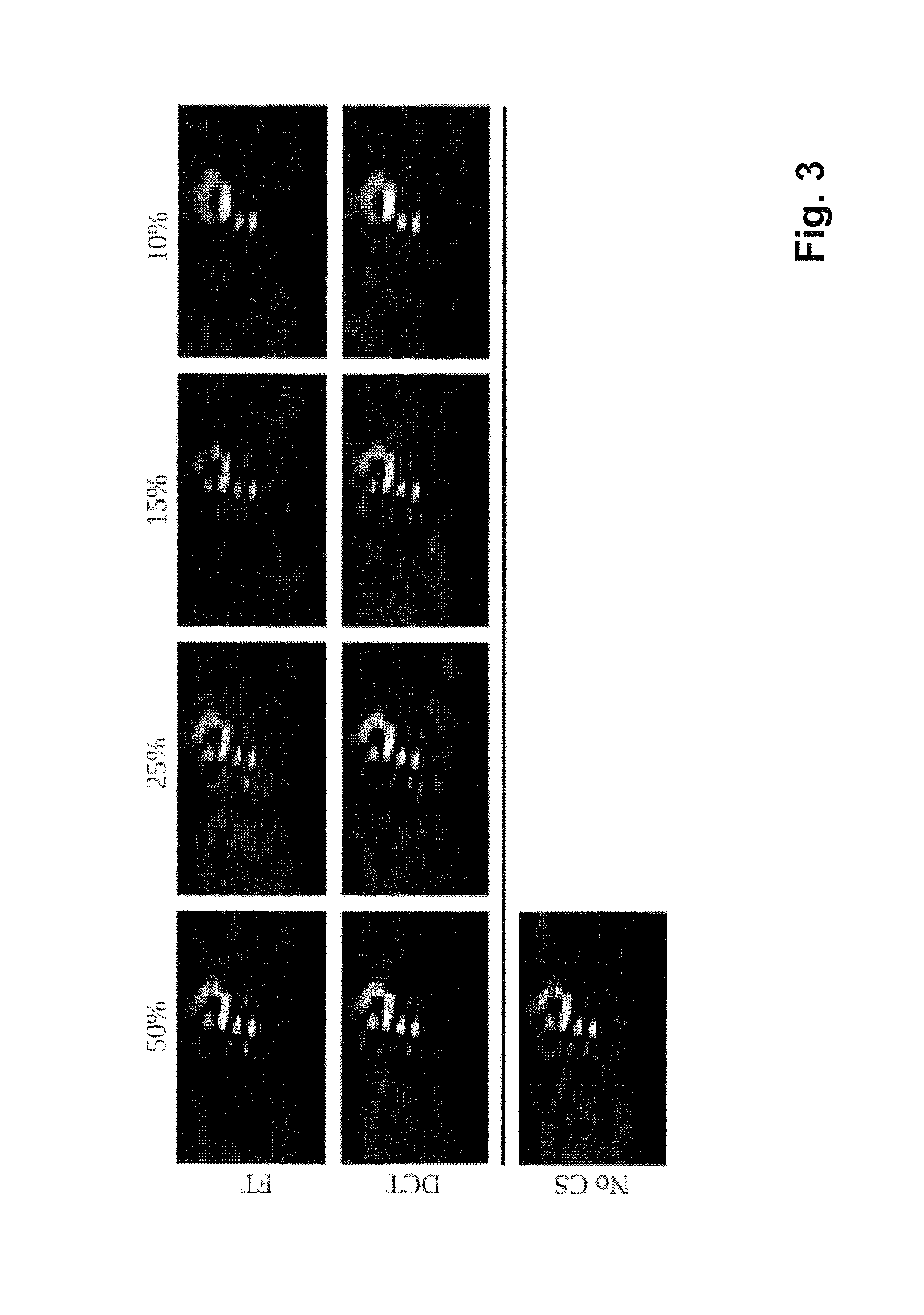
Calibration method for an MPI(=Magnetic particle imaging) apparatus
ActiveUS20150221103A1Reduce rebuild timeImprove approximationReconstruction from projectionCode conversionMagnetic particle imagingVoxel
A calibration method for an MPI (=magnetic particle imaging) apparatus for conducting an MPI experiment, wherein the calibration method comprises m calibration MPI measurements with a calibration test piece and uses these measurements to create an image reconstruction matrix with which the signal contributions of N voxels within an investigation volume of the MPI apparatus are determined, wherein compressed sensing steps are applied in the calibration method with a transformation matrix that sparsifies the image construction matrix, and wherein only a number M<N of calibration MPI measurements for M voxels are carried out, from which the image reconstruction matrix is created and stored. This specifies an efficient method for determination of the system matrix for the MPI imaging method, which does not require much time to determine an MPI system function and nevertheless achieves a high degree of precision.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
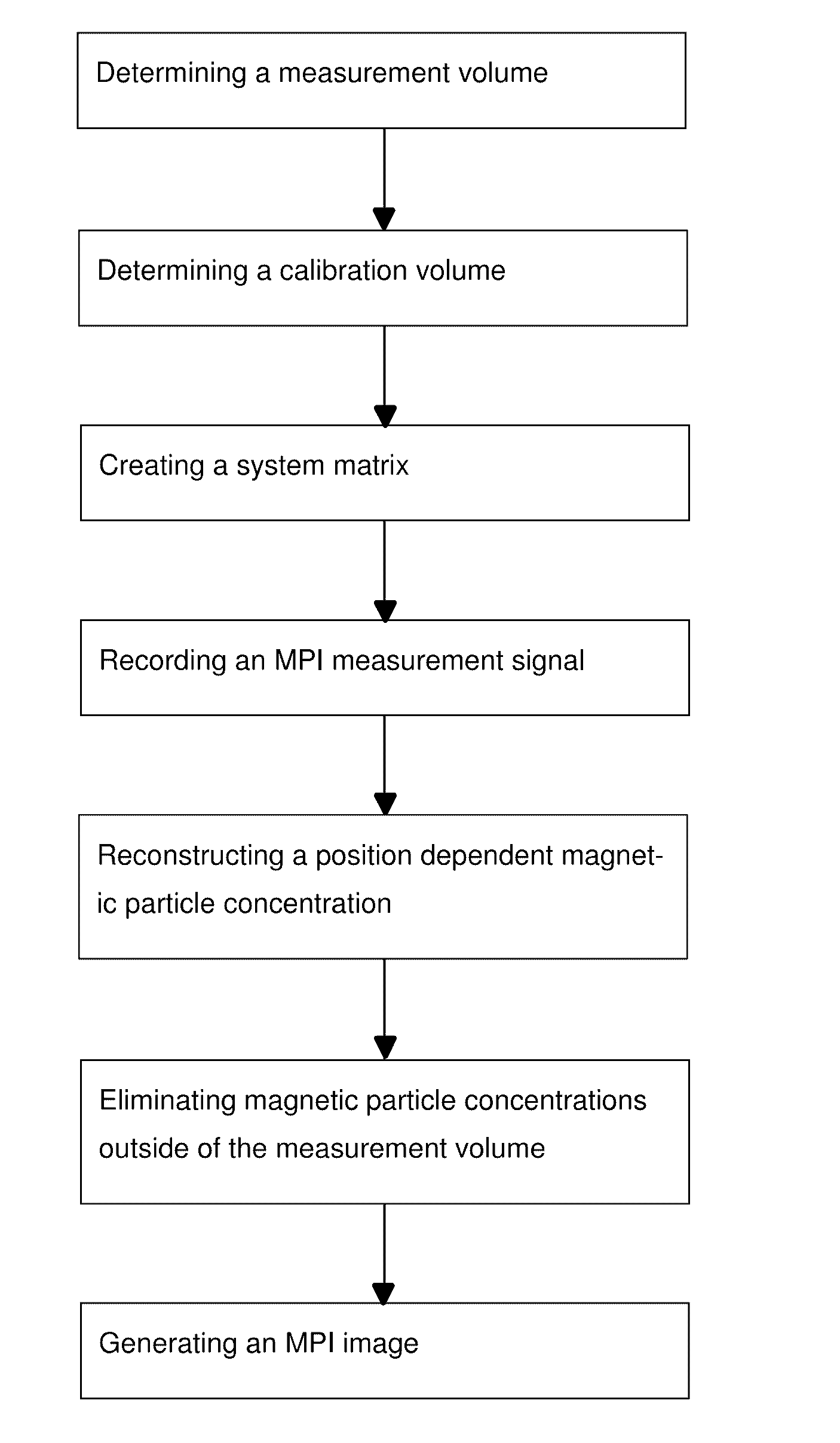
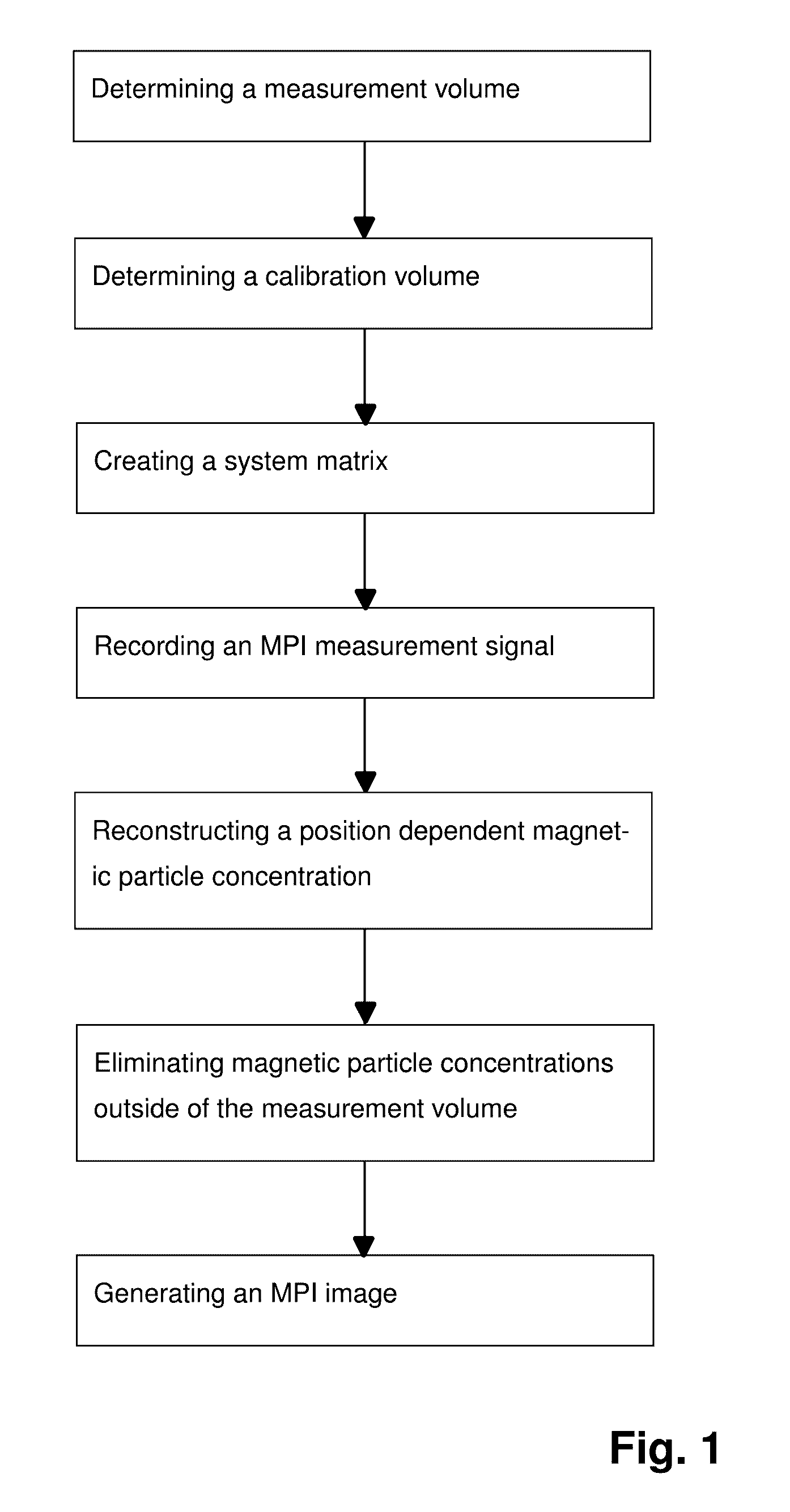
MPI method
An MPI method determines calibration and measurement volumes, wherein the calibration volume is larger than the measurement volume and the overall measurement volume is arranged within the calibration volume. Calibration signals are detected and a system matrix S is created. An MPI measuring signal u is recorded, a location-dependent magnetic particle concentration c with magnetic particle concentration values ci within the calibration volume is reconstructed and the magnetic particle concentration values ci are associated with voxels in the calibration volume. Magnetic particle concentration values ci which were associated with voxels outside of the measurement volume are discarded and an MPI image is generated which exclusively contains magnetic particle concentration values ci which were associated with the voxels within the measurement volume. MPI image data are thereby generated with little artefacts within a short time even in case of high magnetic particle densities outside of the measurement volume.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Biomagnetic detection and treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
ActiveUS8060179B1Reducing effect of drugKeep for a long timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRemanenceMedicine
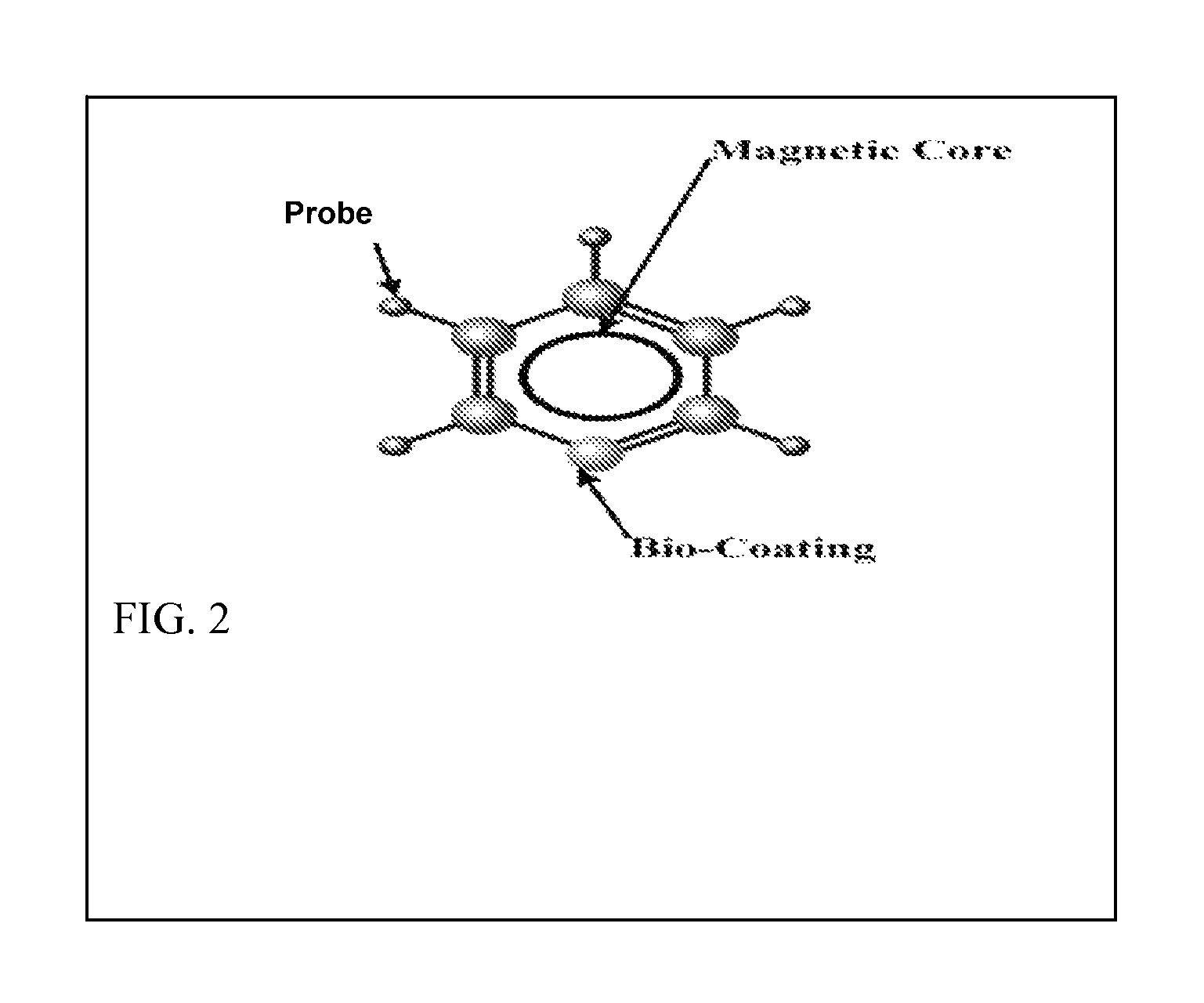
SQUID imaging of a subject's head after the subject having been administered superparamagnetic nanoparticles comprising: an iron-containing core, a coating covering the core and a probe molecule conjugated to the coating wherein the probe molecule locates the superparamagnetic nanoparticle to a target in the brain that is characteristic of the neurodegenerative disease; magnetizing the superparamagnetic nanoparticles using external magnetic coils; and measuring the decaying remanence magnetic fields of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles attached to the target and not from unattached superparamagnetic nanoparticles to obtain magnetic field measurements.
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Open bore field free line magnetic particle imaging system
ActiveUS20180231629A1High sensitivityFast imagingSensorsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNon symmetricMagnetic particle imaging
An open bore coil system enabling electronic steering and rotation of a Field Free Line (FFL) inside a large volume. An FFL is generated by placing two parallel coil pairs (fed with alternating current directions) side by side. Using two of these coil groups, the FFL can be rotated in the plane perpendicular to the coil axes. The FFL can be translated in the rotation plane of the FFL using a coil pair placed on the same axis with the other coils. It can also be translated in the perpendicular plane by asymmetrical coil excitation. As all the coils in the system are parallel, the imaged object can be reached from the sides during imaging.
Owner:ASELSAN ELEKTRONIK SANAYI & TICARET ANONIM SIRKETI
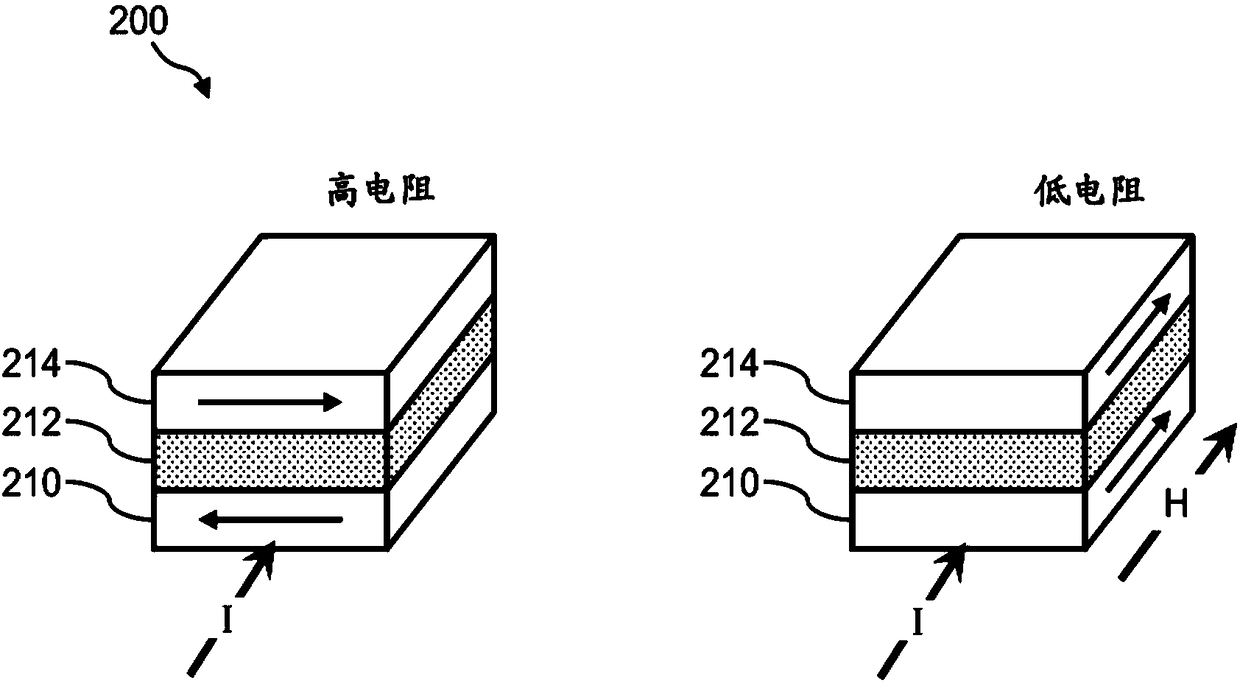
Tunnel magneto-resistive (TMR) sensors employing tmr devices with different magnetic field sensitivities for increased detection sensitivity
ActiveUS20180284200A1Easy to changeReduce magnetization angleMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic anisotropy
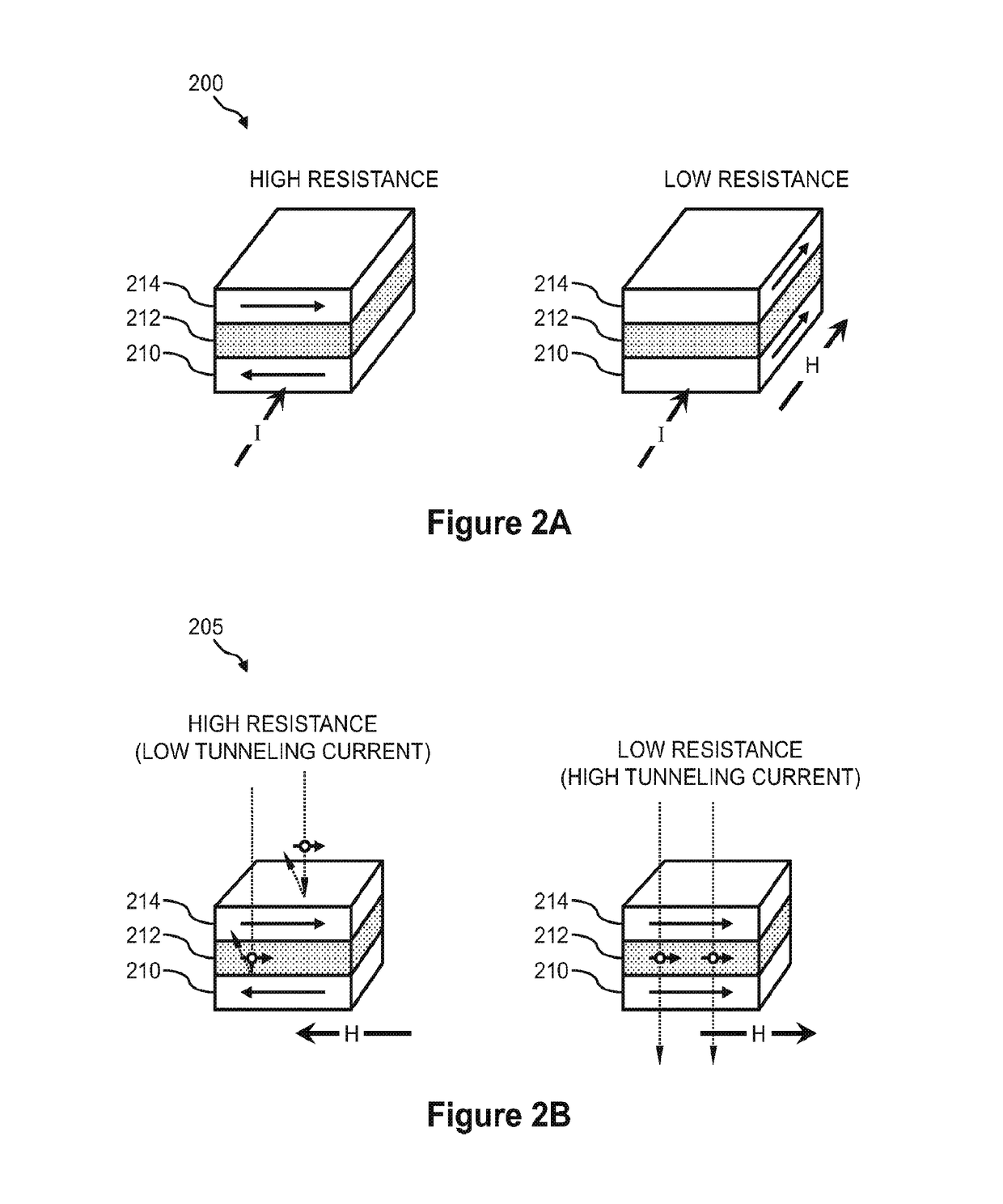
Tunnel magneto-resistive (TMR) sensors employing TMR devices with different magnetic field sensitivities for increased detection sensitivity are disclosed. For example, a TMR sensor may be used as a biosensor to detect the presence of biological materials. In aspects disclosed herein, free layers of at least two TMR devices in a TMR sensor are fabricated to exhibit different magnetic properties from each other (e.g., MR ratio, magnetic anisotropy, coercivity) so that each TMR device will exhibit a different change in resistance to a given magnetic stray field for increased magnetic field detection sensitivity. For example, the TMR devices may be fabricated to exhibit different magnetic properties such that one TMR device exhibits a greater change in resistance in the presence of a smaller magnetic stray field, and another TMR device exhibits a greater change in resistance in the presence of a larger magnetic stray field.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
A magnetic sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
InactiveCN101438179ABiological particle analysisMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesElectricityExcitation signal
A magnetic sensor device (300) for sensing magnetic particles (15), the magnetic sensor device (300) comprising a magnetic field generator unit (12) adapted for generating a magnetic field, an excitation signal source (302) adapted for supplying the magnetic field generator unit (12) with a static electric excitation signal, an excitation switch unit (303) adapted for switching between different modes of electrically coupling the excitation signal source (302) to the magnetic field generator unit (12), and a sensing unit (11) adapted for sensing a signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles (15) in the generated magnetic field.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus and method for detecting nonlinear magnetic particle based on single excitation coil
InactiveUS20170067971A1Reduce expensesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFundamental frequencyParticle physics
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Systems and methods using magnetically-responsive sensors for determining a genetic characteristic
ActiveCN108138229AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayElectrical resistance and conductance
Sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS) method is provided that includes providing a detection apparatus that includes an array of magnetically-responsive sensors. Each of the magnetically-responsive sensors islocated proximate to a respective designated space to detect a magnetic property therefrom. The detection apparatus also includes a plurality of nucleic acid template strands located within corresponding designated spaces. The method also includes conducting a plurality of SBS events to grow a complementary strand by incorporating nucleotides along each template strand. At least some of the nucleotides are attached to corresponding magnetic particles having respective magnetic properties. Each of the plurality of SBS events includes detecting changes in electrical resistance at the magnetically-responsive sensors caused by the respective magnetic properties of the magnetic particles. The method also includes determining genetic characteristics of the complementary strands based on the detected changes in electrical resistance.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
ActiveUS20130059293A1Improve bindingReduce activity timeNanomagnetismMicrobiological testing/measurementResonance measurementAnalyte
A system and method are provided to detect target analytes based on magnetic resonance measurements. Magnetic structures produce distinct magnetic field regions having a size comparable to the analyte. When the analyte is bound in those regions, magnetic resonance signals from the sample are changed, leading to detection of the analyte.
Owner:MENON BIOSENSORS
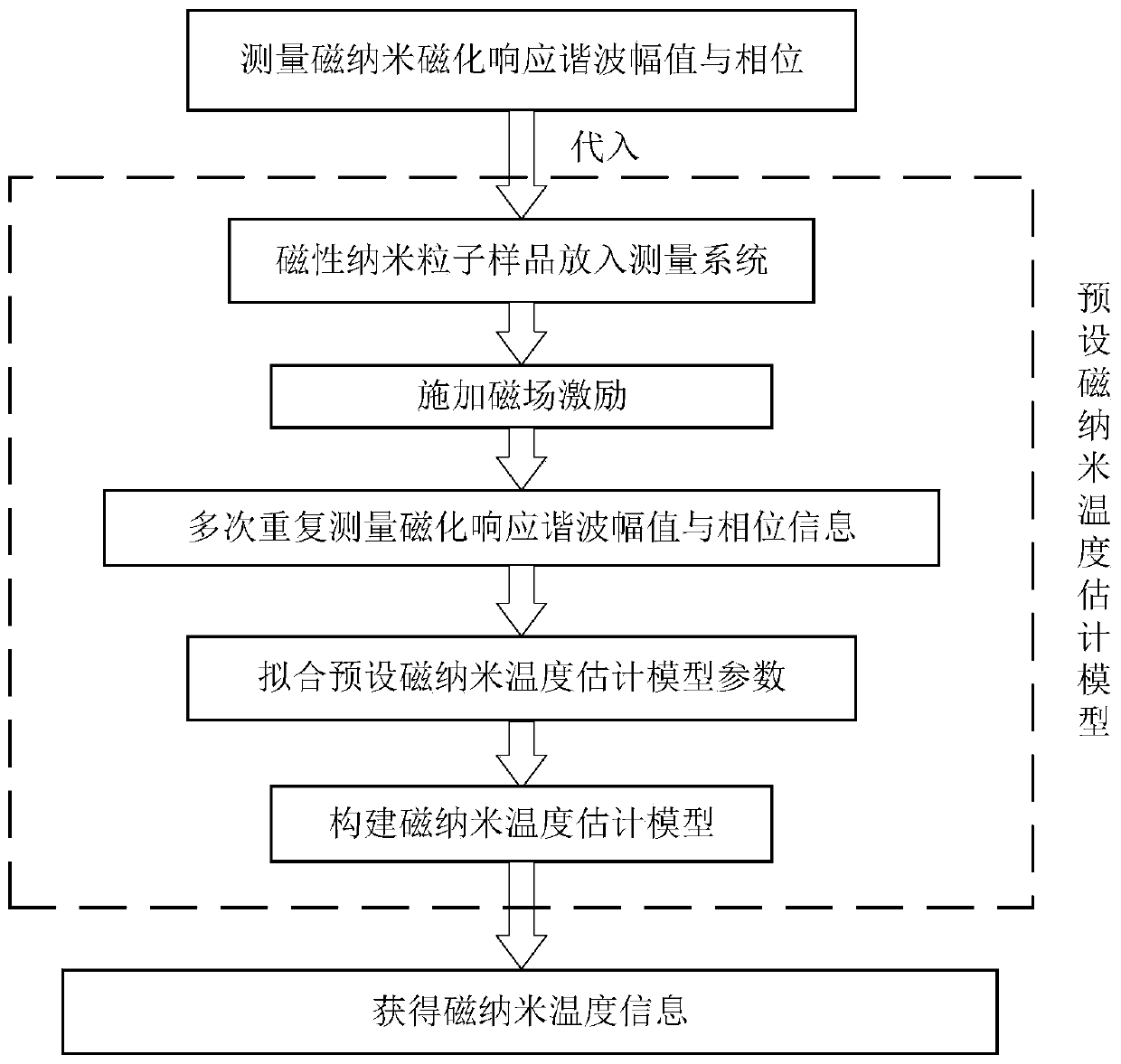
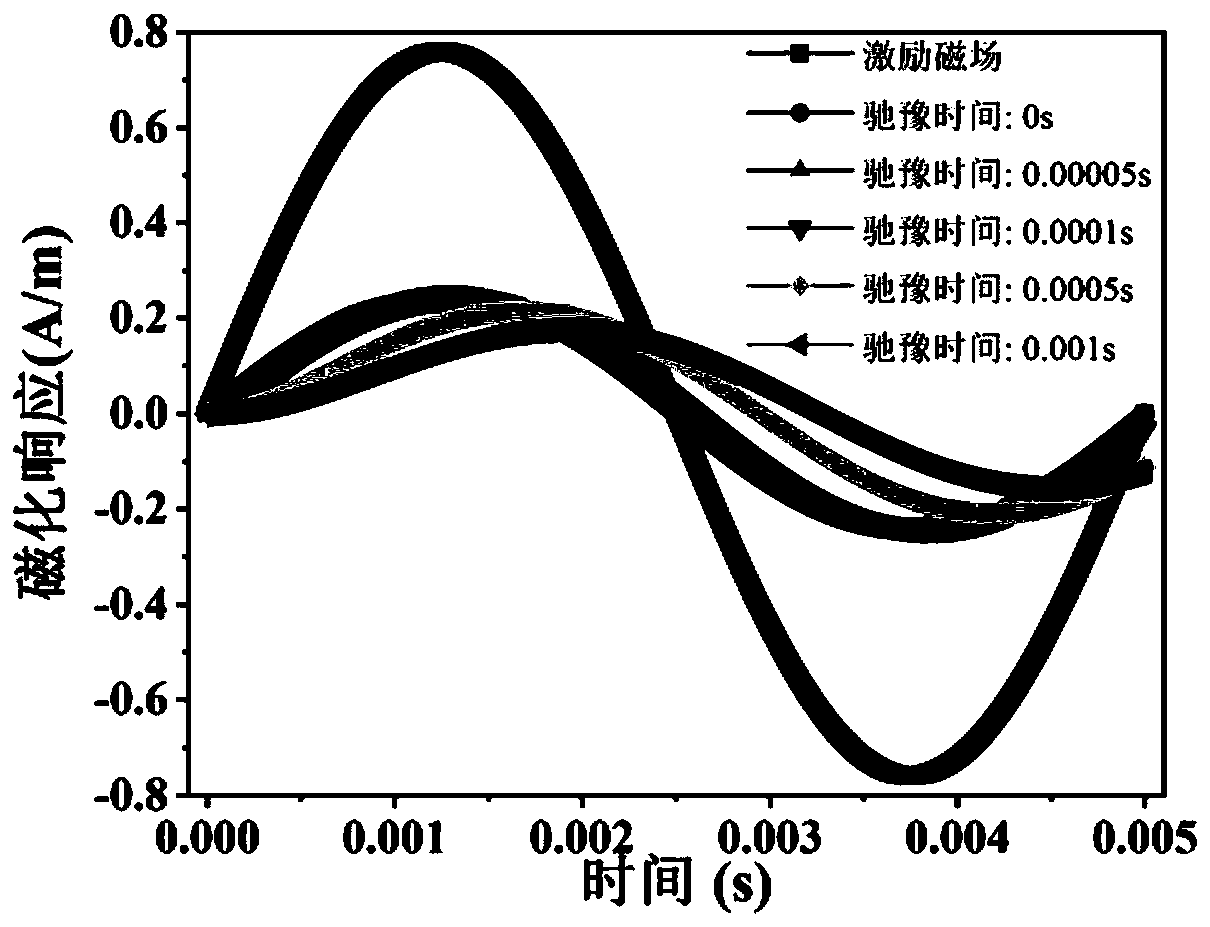
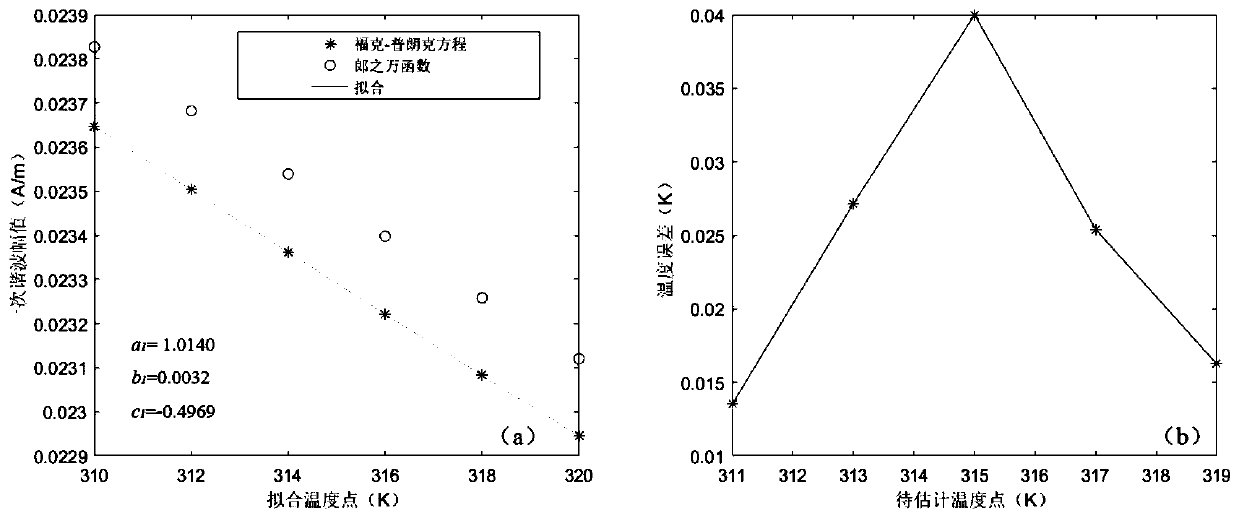
High-precision magnetic nano temperature estimation method and system based on Fokker-Planck
ActiveCN110705072ASolve the problem of low temperature measurement accuracyHigh precisionMagnetisation measurementsDesign optimisation/simulationParticle imagingImage resolution
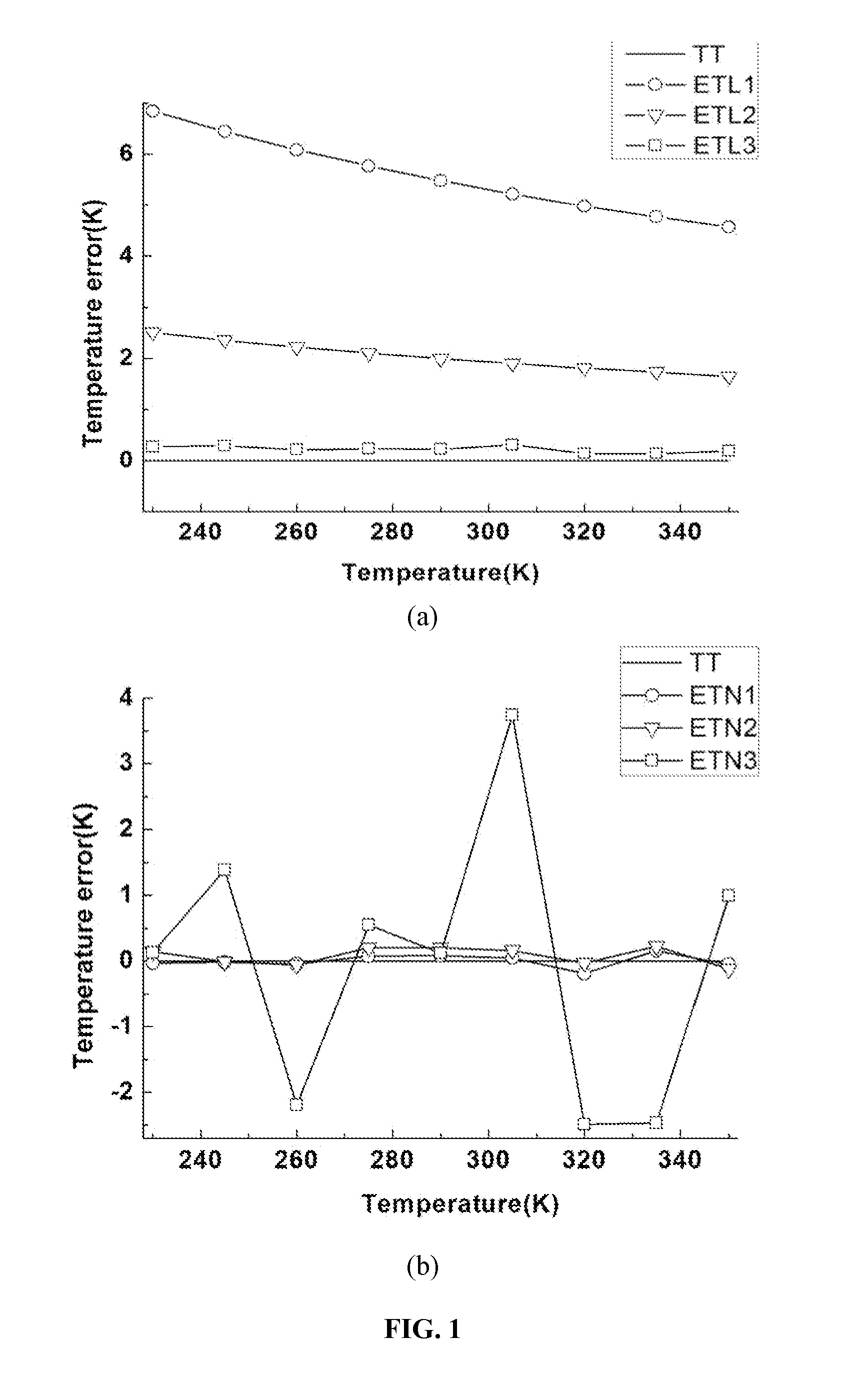
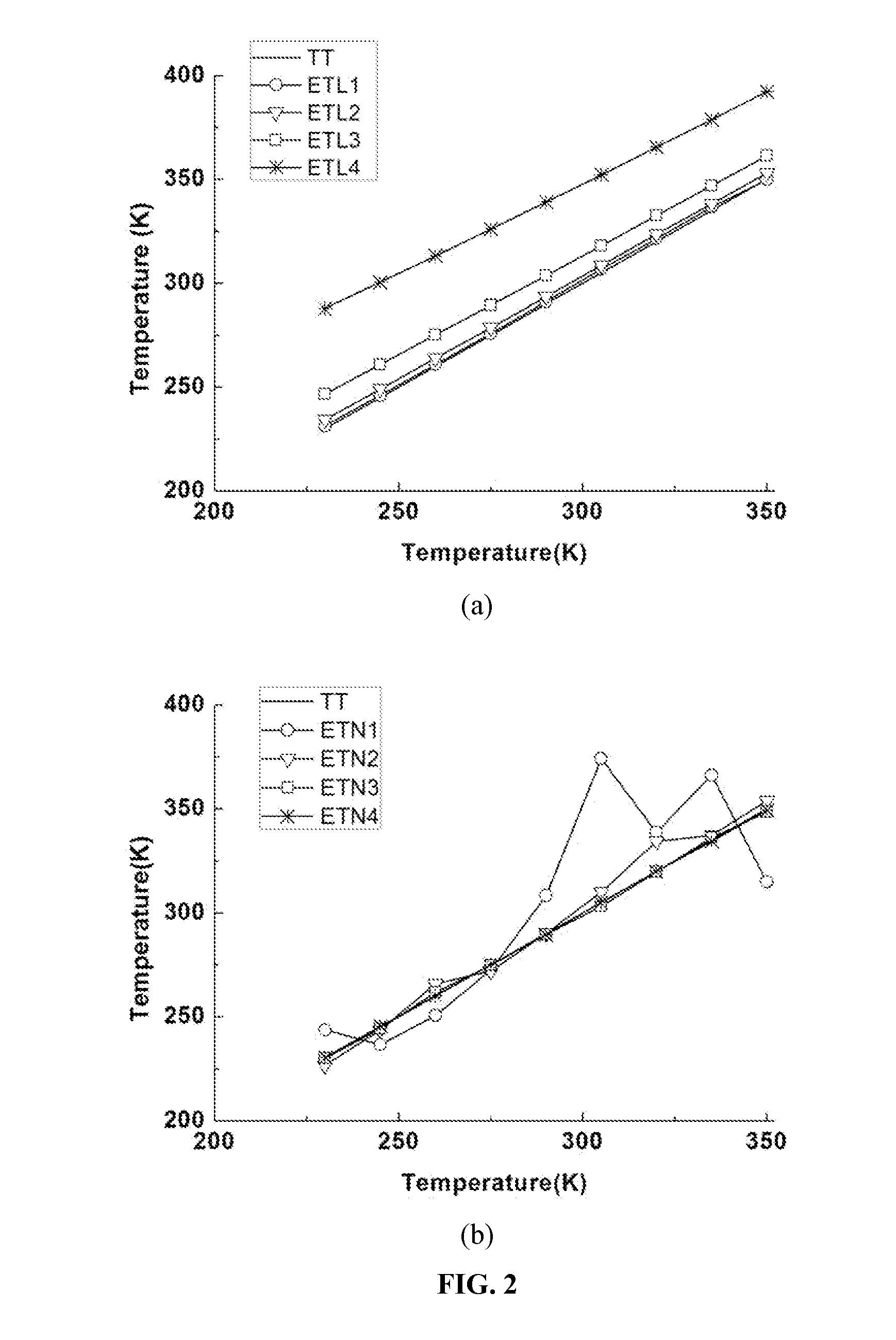
The invention provides a high-precision magnetic nano temperature estimation method and system based on Fokker-Planck. The method comprises: constructing a magnetic nanoparticle temperature estimationmodel through a Fokker-Planck formula, measuring the magnetization response harmonic amplitude and phase information of the magnetic nanoparticles multiple times through a magnetic field informationdetection device, and fitting model parameters in the magnetic nanoparticle temperature estimation model; placing a sample to be detected in the magnetic field information detection device, measuringand substituting the harmonic amplitude and phase information of the sample under the excitation of an external magnetic field into the preset magnetic nanoparticle temperature estimation model, and solving the magnetic nanoparticle temperature information. According to the invention, the temperature information of the magnetic nanoparticles under the excitation of a medium-high frequency magneticfield can be accurately obtained. The problem that the conventional Langevin Function is not suitable on occasions of medium-high frequency excitation is solved, the application fields of magnetic nano temperature measurement and magnetic nano particle imaging technologies are expanded, and the measurement precision and the time-space resolution are improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Sensor device for and a method of sensing magnetic particles
ActiveUS8190372B2Undesired interactionImprove accuracyNanomagnetismMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticle interactionAtomic physics
A sensor device for sensing magnetic particles, the sensor device including a substrate and a sensing unit provided on and / or in and / or near the substrate. The sensing unit is configured to sense a detection signal indicative of the presence of the magnetic particles. The sensor device further includes a magnetic field control unit which may be provided off the substrate and is configured to generate a time-dependent magnetic field for interaction with the magnetic particles.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS NEDERLAND BV
Detection, measurement, and imaging of cells such as cancer and other biologic substances using targeted nanoparticles and magnetic properties thereof
The present invention can provide a method of determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of a biological substance, comprising: (a) exposing a sample to a plurality of targeted nanoparticles, where each targeted nanoparticle comprises a paramagnetic nanoparticle conjugated with one or more targeting agents that preferentially bind with the biological substance, under conditions that facilitate binding of the targeting agent to at least one of the one or more biological substances; (b) subjecting the sample to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of the nanoparticles; (c) measuring a magnetic field of the sample after decreasing the magnetic field applied in step b below a threshold; (d) determining the presence, location, quantity, or a combination thereof, of the one or more biologic substances from the magnetic field measured in step (c).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Removal of background in mpi
The present invention relates to an apparatus (100) for detecting magnetic particles in a field of view (28), which apparatus comprises selection means, drive means, receiving means for acquiring detection signals, and reconstruction means (152) for reconstructing an image of the field of view (28) from detection signals, said detection signals including a plurality of frequency components, wherein one or more frequency components are selected and / or weighted by use of a frequency component specific signal quality factor obtained from background signal measurements and wherein only selected and / or weighted frequency components are used for reconstruction of the image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Techniques for magnetic particle imaging
ActiveUS8847592B2Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Device for measuring magnetic particles and corresponding method
ActiveUS8026716B2Accurate measurementLess sensitiveElectrostatic separationBiological material analysisMagnetic markerAnalyte
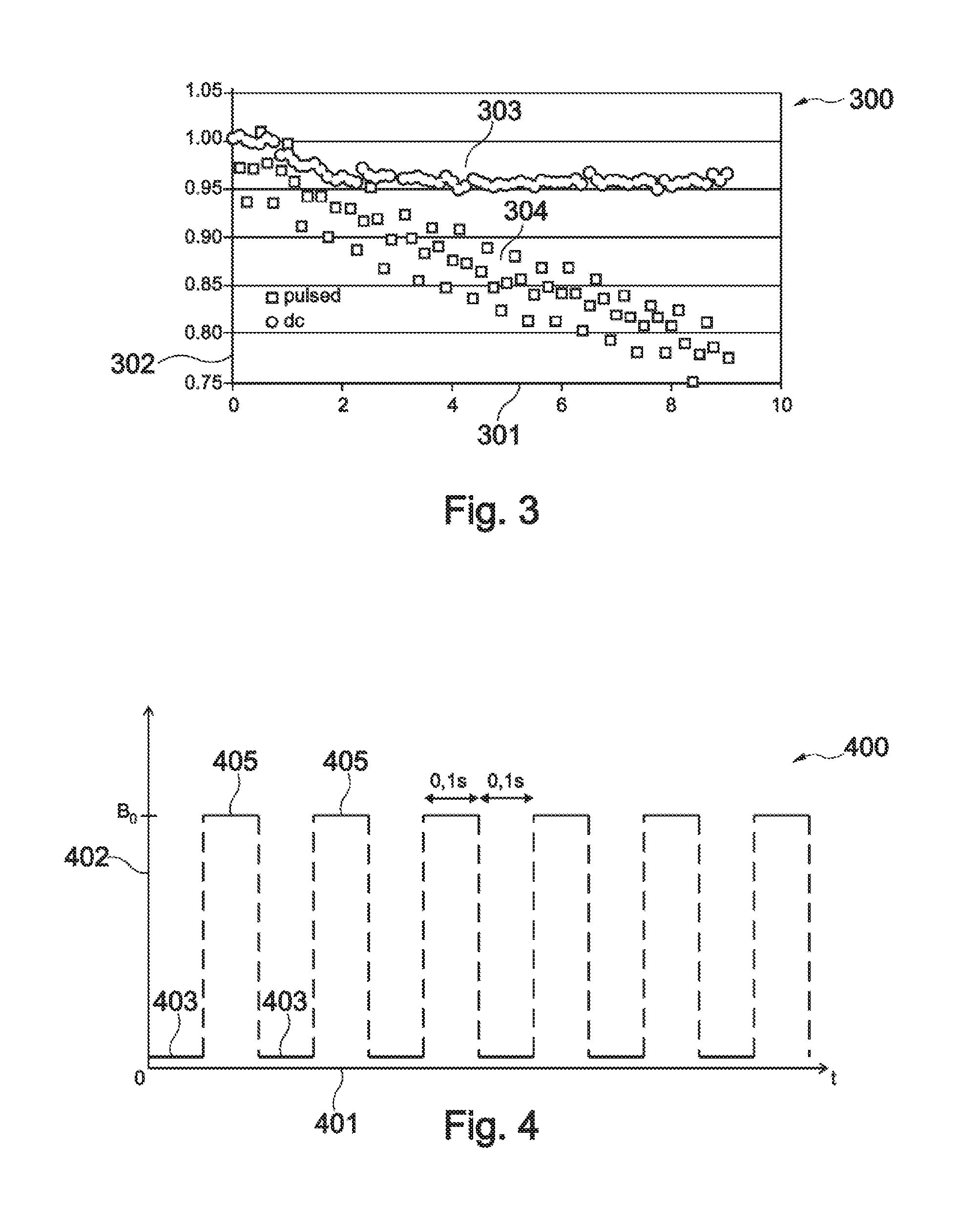
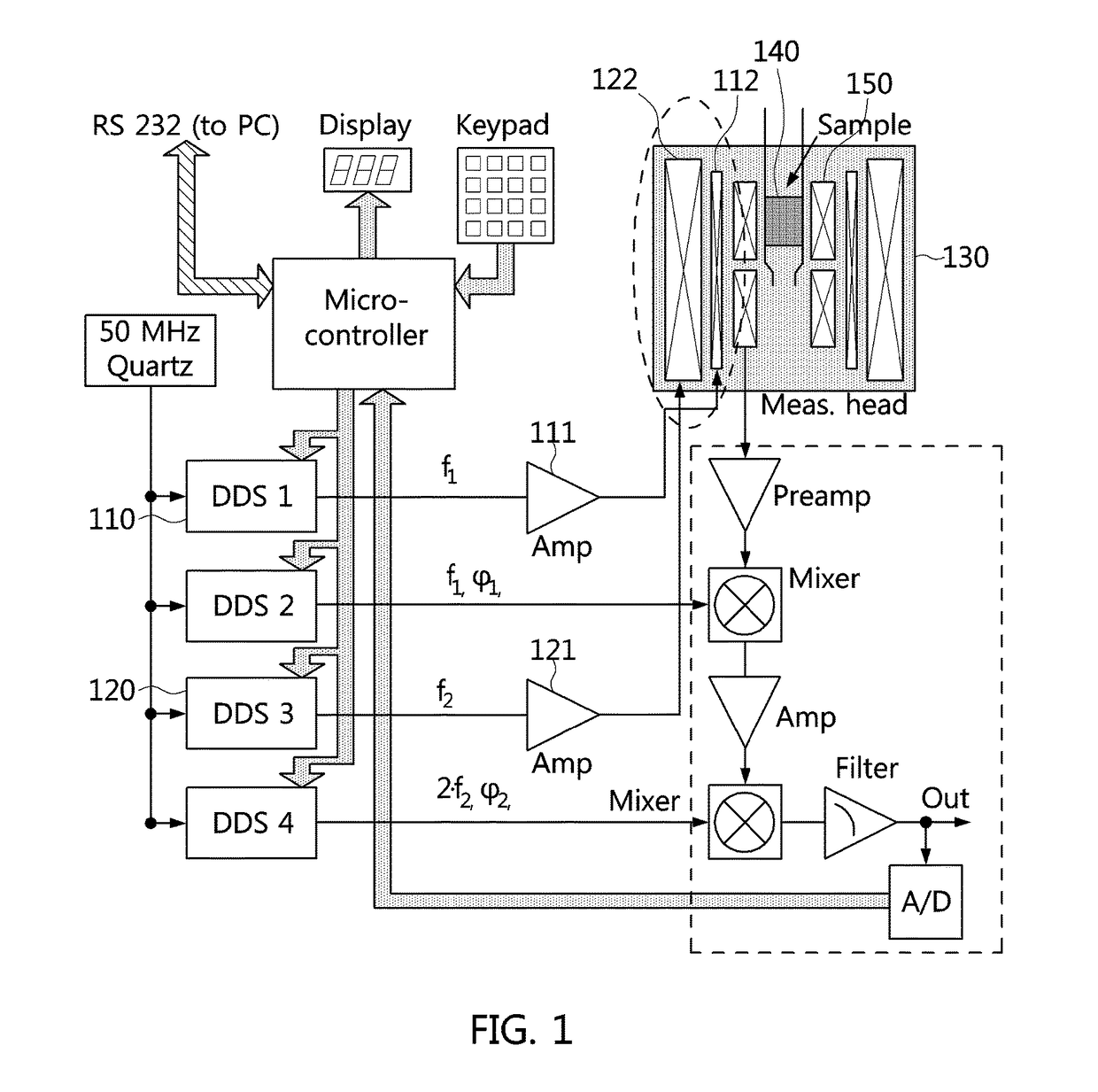
The invention concerns a device for the qualitative or quantitative measurement of a magnetically labelled analyte. The device includes a coil arrangement for measuring the analyte from a sample absorbed in a test base. The coil arrangement includes at least one measuring coil and a reference coil arranged in connection with it. From the signal of the coil arrangement a change in inductance correlating to the content of the magnetically labelled analyte is arranged to be detected. The change in inductance is arranged to be detected from a change (ΔA, Δφ) in amplitude and / or phase appearing in the output signal of the coil arrangement, which is arranged to be measured at the frequency of the input signal. In addition, the invention also relates to a corresponding method.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST +1
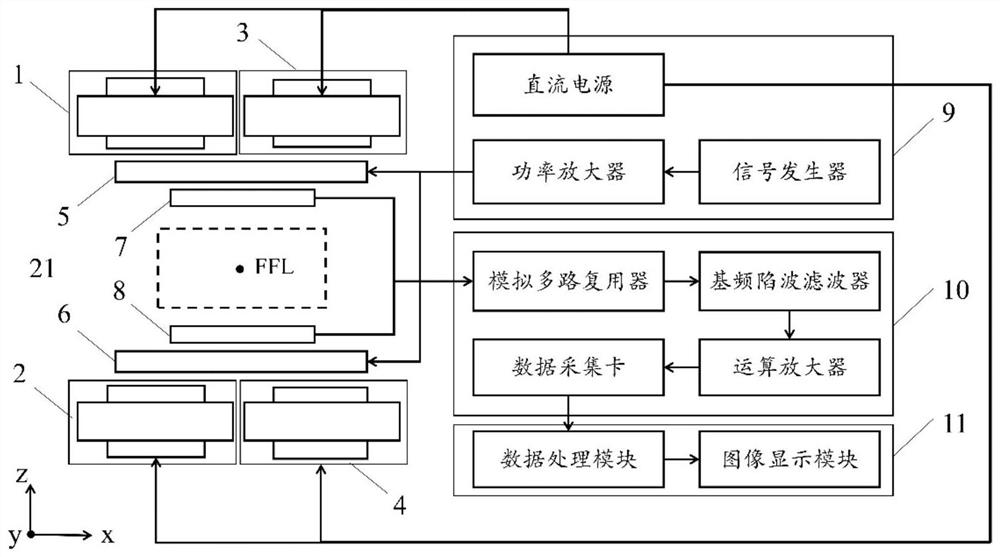
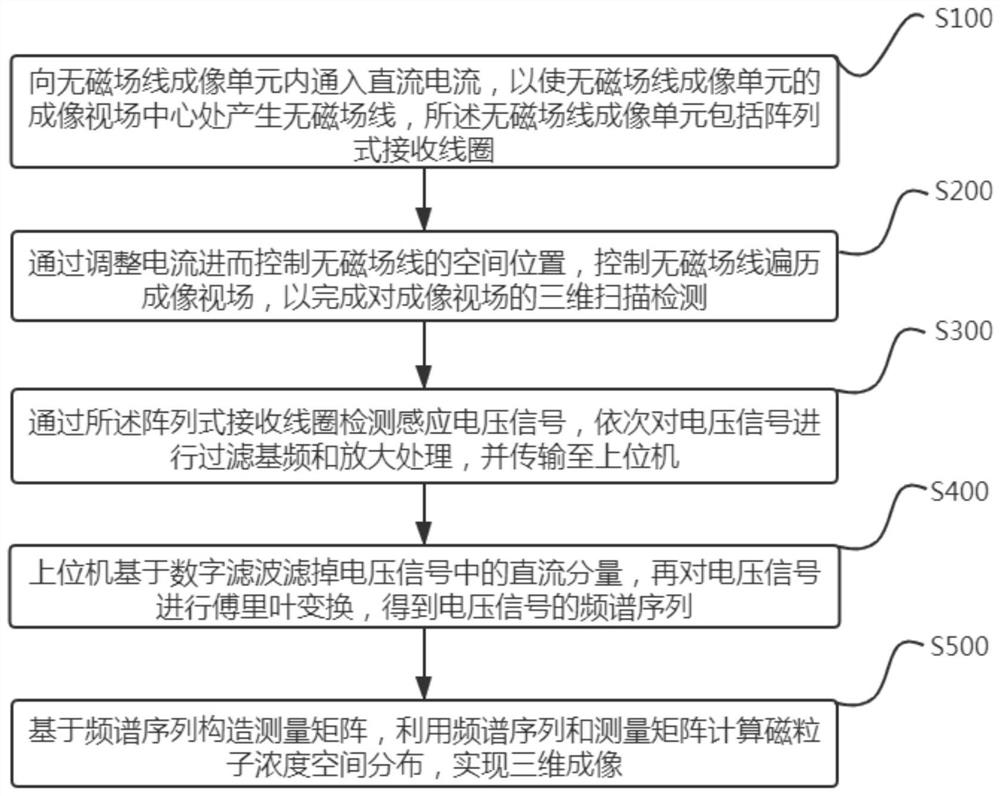
Open type magnetic particle three-dimensional imaging system and method based on array type receiving coil
ActiveCN113433495AGuaranteed SensitivityGuaranteed uniformityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRapid imagingFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to the field of biomedical imaging and particularly relates to an open type magnetic particle three-dimensional imaging system and method based on array type receiving coils, and aims to solve a problem of contradiction between imaging precision and imaging speed in the prior art. The system comprises a non-magnetic field line generation module, a non-magnetic field line driving module, a signal detection module, a current excitation module, a signal conditioning module and an image reconstruction module. The imaging method comprises the following steps that a non-magnetic field line is constructed; the spatial position of the non-magnetic field line is adjusted by adjusting the current; an array type receiving coil of the signal detection module is used for detecting an induced voltage signal, then the induced voltage signal is processed by the signal conditioning module to obtain a signal without a fundamental frequency component, a direct current component in the voltage signal is filtered out by a digital filtering technology, and then Fourier transform is carried out on the voltage signal to obtain a frequency spectrum sequence of the voltage signal; and a measurement matrix of the array type receiving coil is constructed, and magnetic particle concentration space distribution is calculated by using the frequency spectrum sequence and the measurement matrix to realize three-dimensional high-precision rapid imaging.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Paramagnetism-based remote temperature measurement method for magnetic nanoparticle
InactiveUS20120239341A1Increase speedImprove real-time performanceThermometer detailsNanotechMagnetic susceptibilityObservational error
The invention discloses a paramagnetism-based remote temperature measurement method for magnetic nanoparticles, and the method comprises: applying multiple times of excited magnetic fields on the area of a magnetic nano sample, constructing an equation group between the different excited magnetic fields and corresponding magnetic susceptibilities according to the Langevin's paramagnetic theorem, and obtaining the information of temperature and sample concentration via the equation group. The invention is capable of more precisely and more quickly detecting the temperature of an object, and especially applicable for the detection of thermal motion at bio-molecular level. Experiments indicate the measurement error is less than 0.56K.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Biological substance pretreatments Biochemistry cleaning apparatus Biomass after-treatment Enzymology/microbiology apparatus Tissue/virus culture apparatus Measurements of magnetic particles Material analysis by using resonance Specific use bioreactors/fermenters Measurements of magnetic beads labelled molecules Immunoassays
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com