Patents
Literature
104 results about "Magnetic particle imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
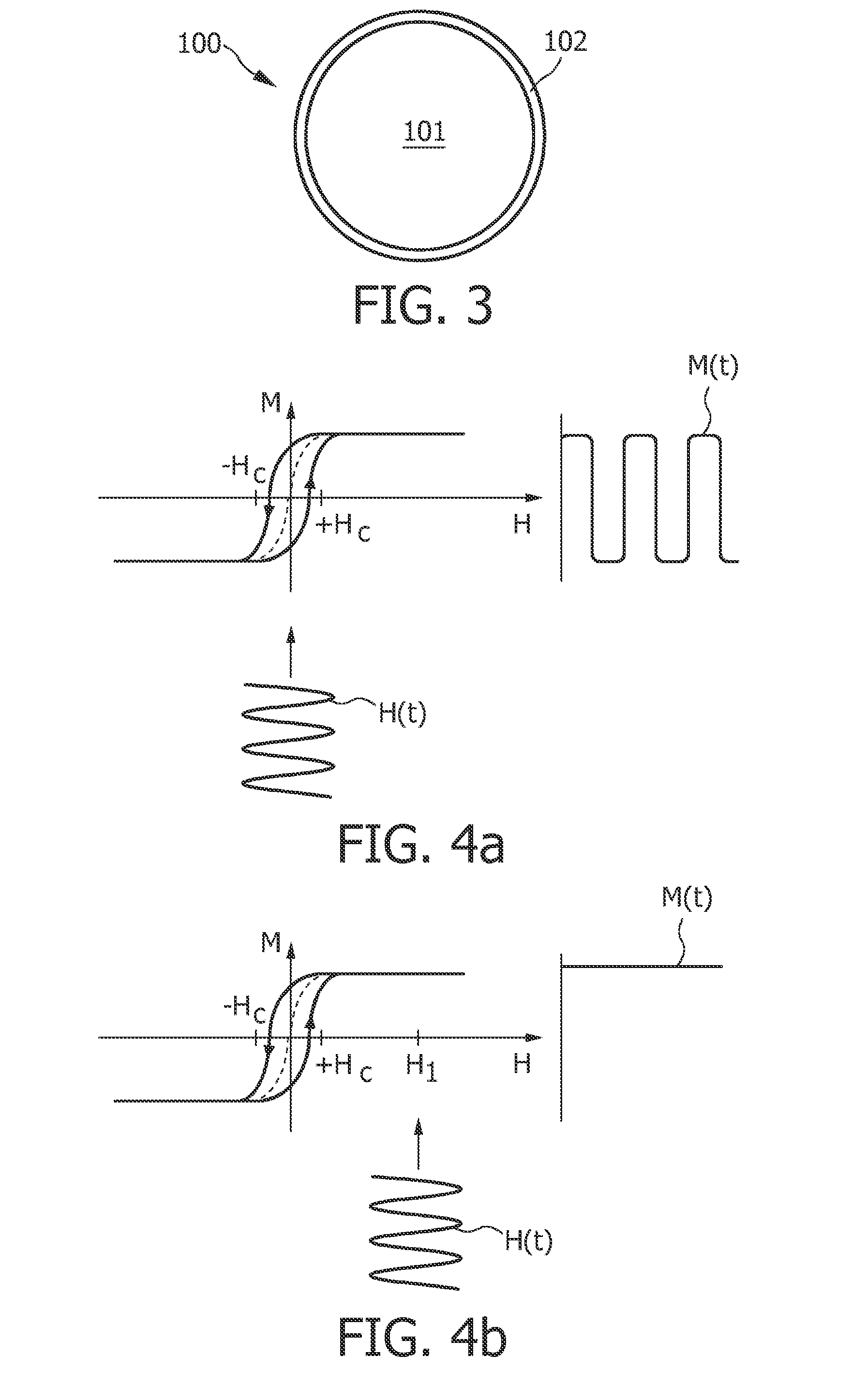
Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) is an emerging non-invasive tomographic technique that directly detects superparamagnetic nanoparticle tracers. The technology has potential applications in diagnostic imaging and material science. Currently, it is used in medical research to measure the 3-D location and concentration of nanoparticles. Imaging does not use ionizing radiation and can produce a signal at any depth within the body. MPI was first conceived in 2001 by scientists working at the Royal Philips Research lab in Hamburg. The first system was established and reported in 2005. Since then, the technology has been advanced by academic researchers at several universities around the world. The first commercial MPI scanners have recently become available from Magnetic Insight and Bruker Biospin.
Improved techniques for magnetic particle imaging
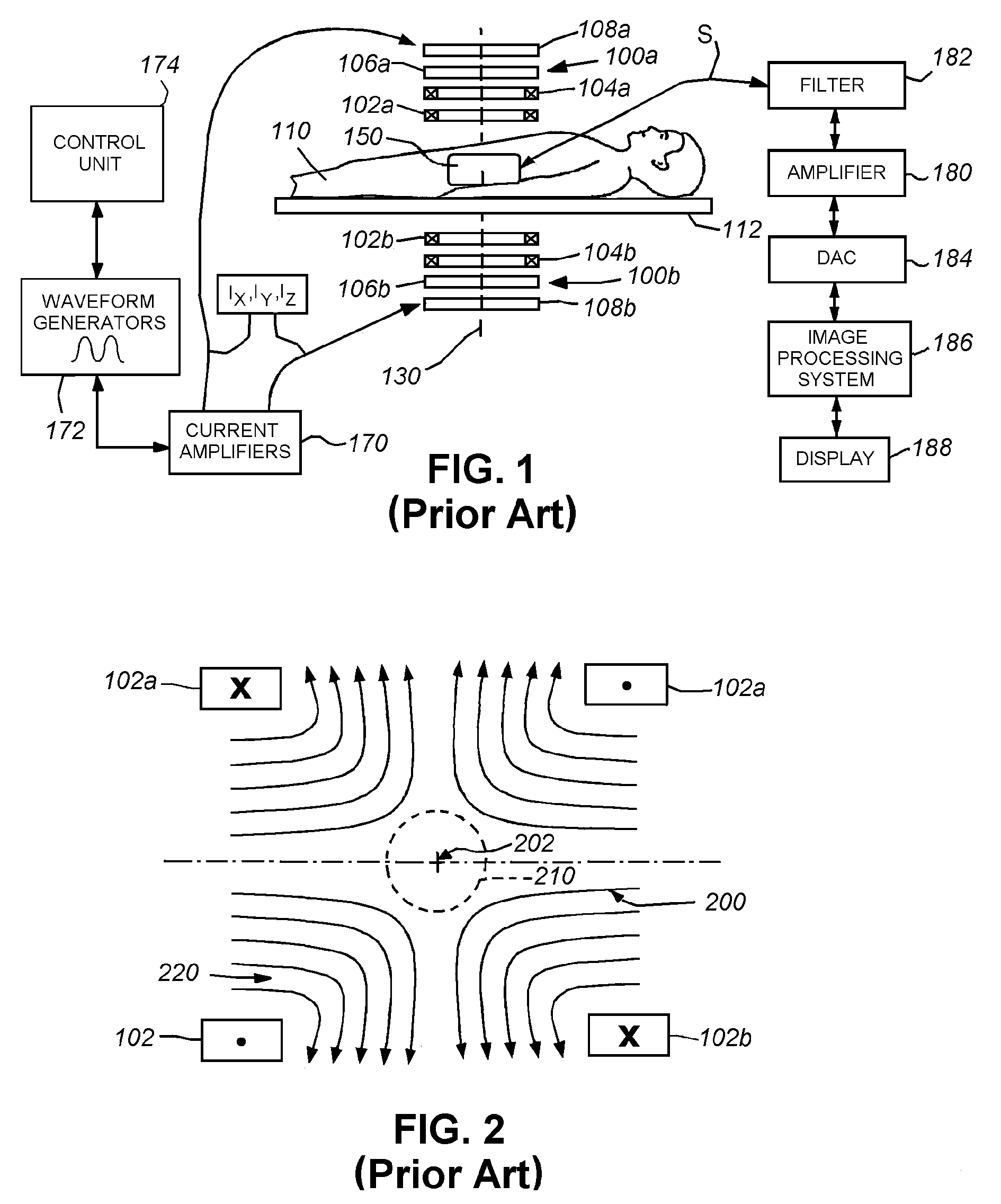
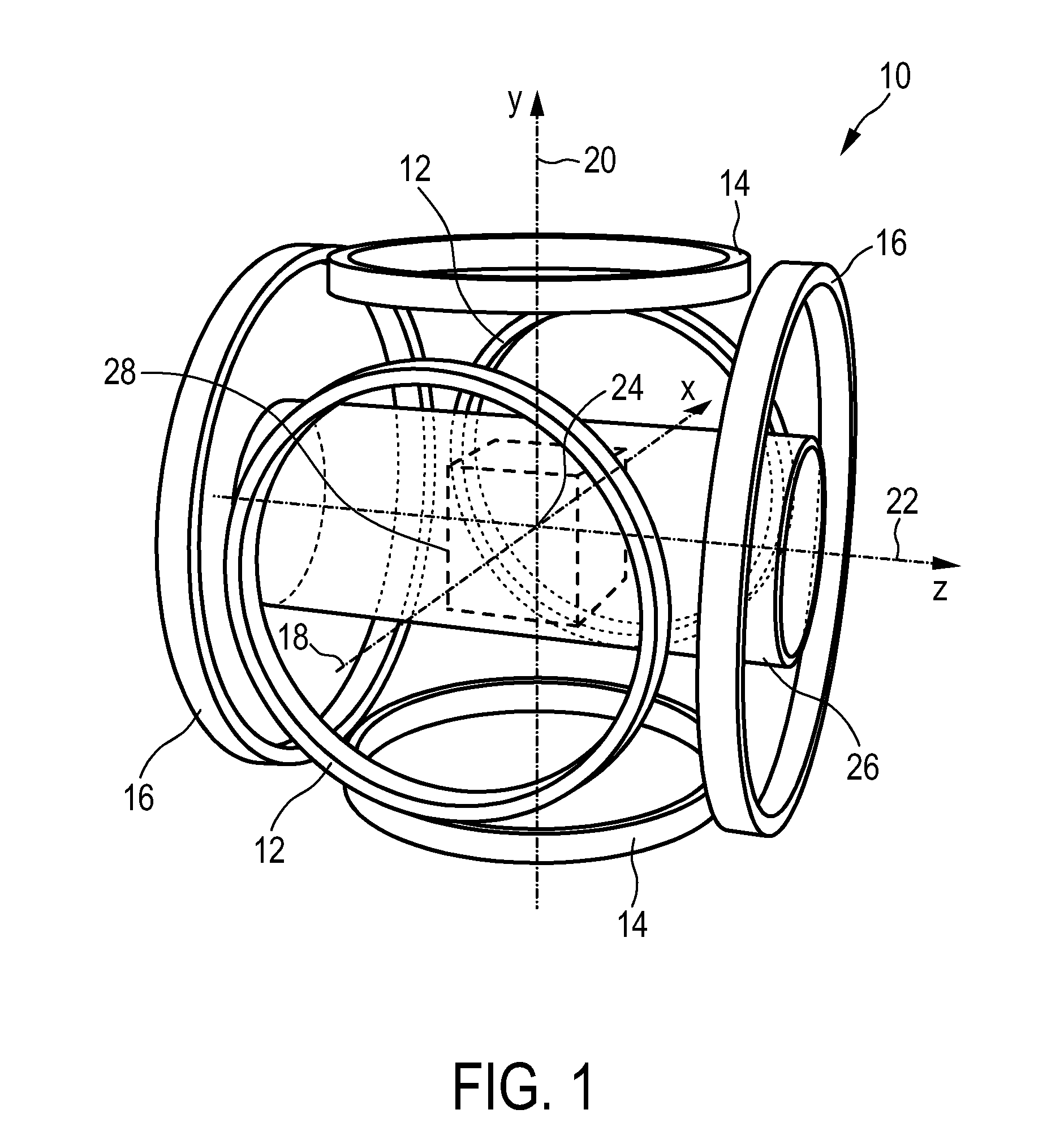
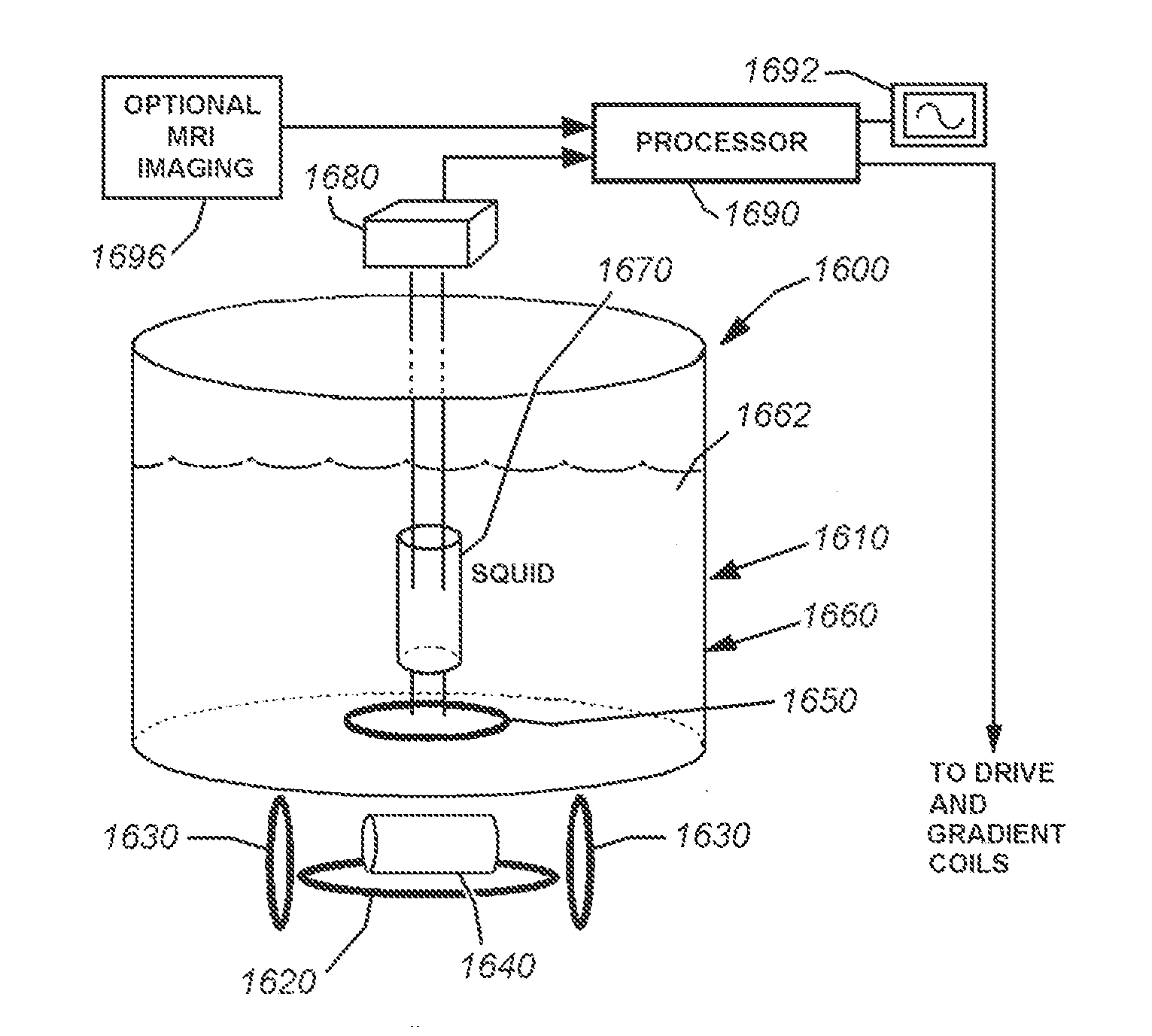
ActiveUS20110089942A1Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
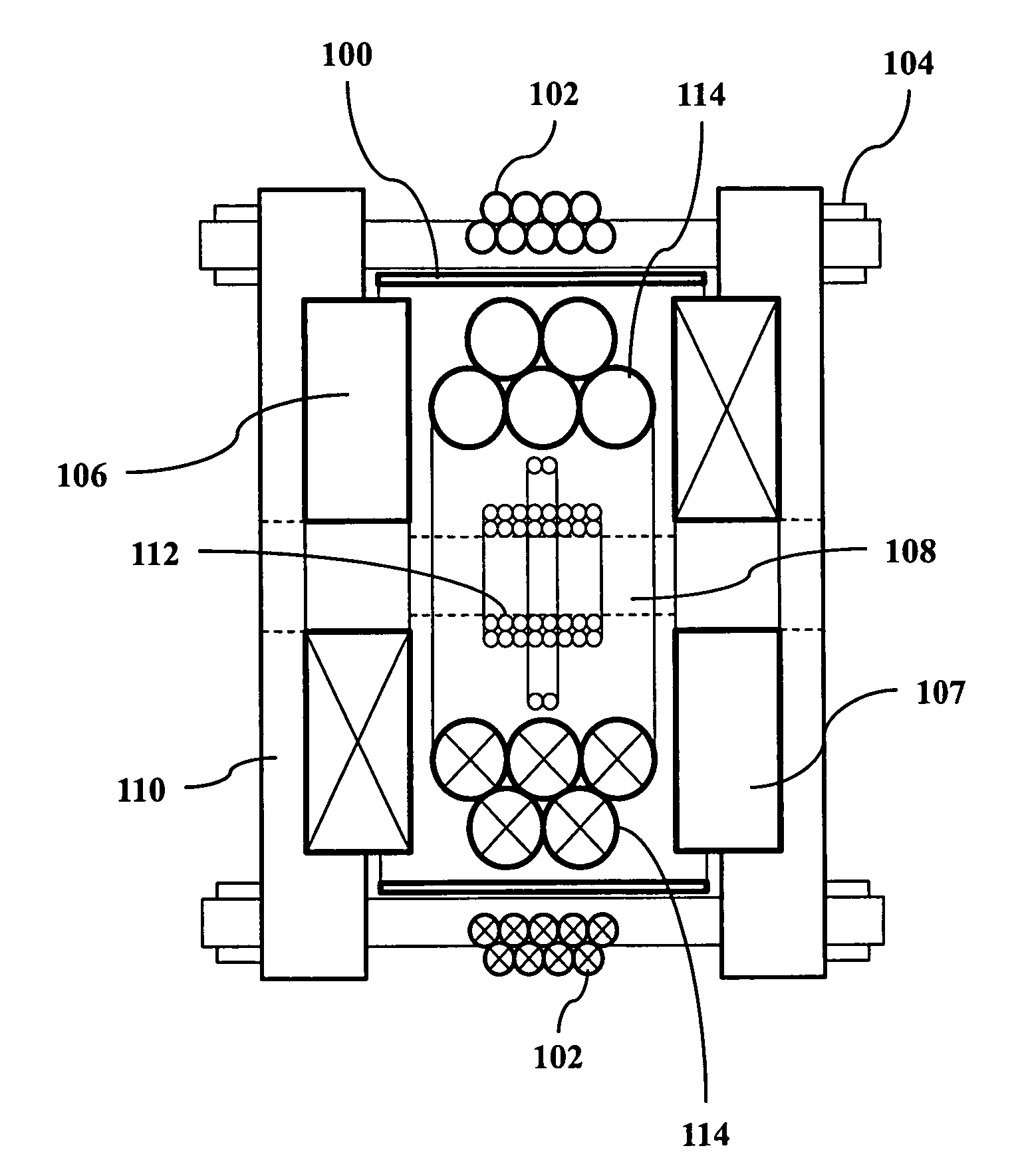
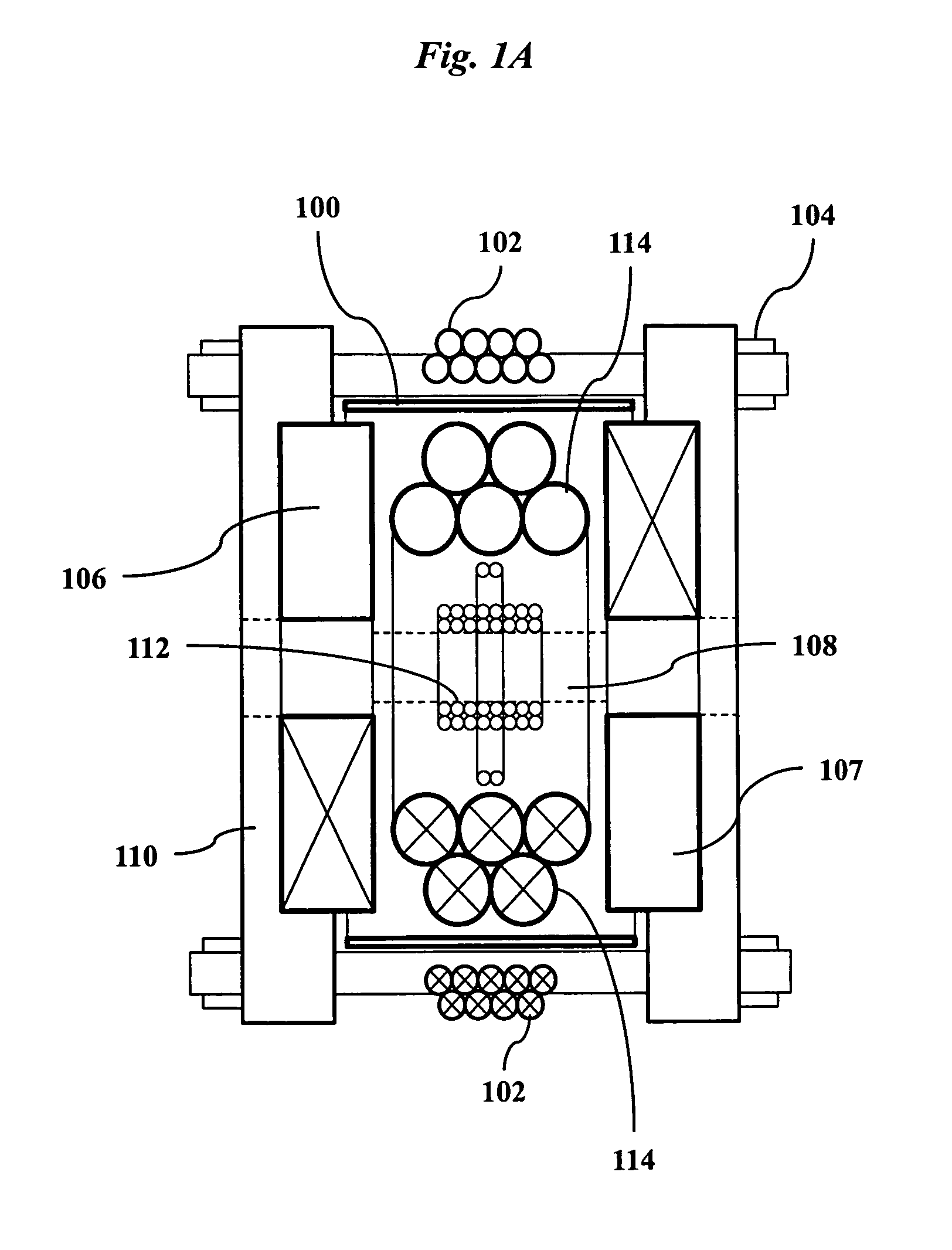
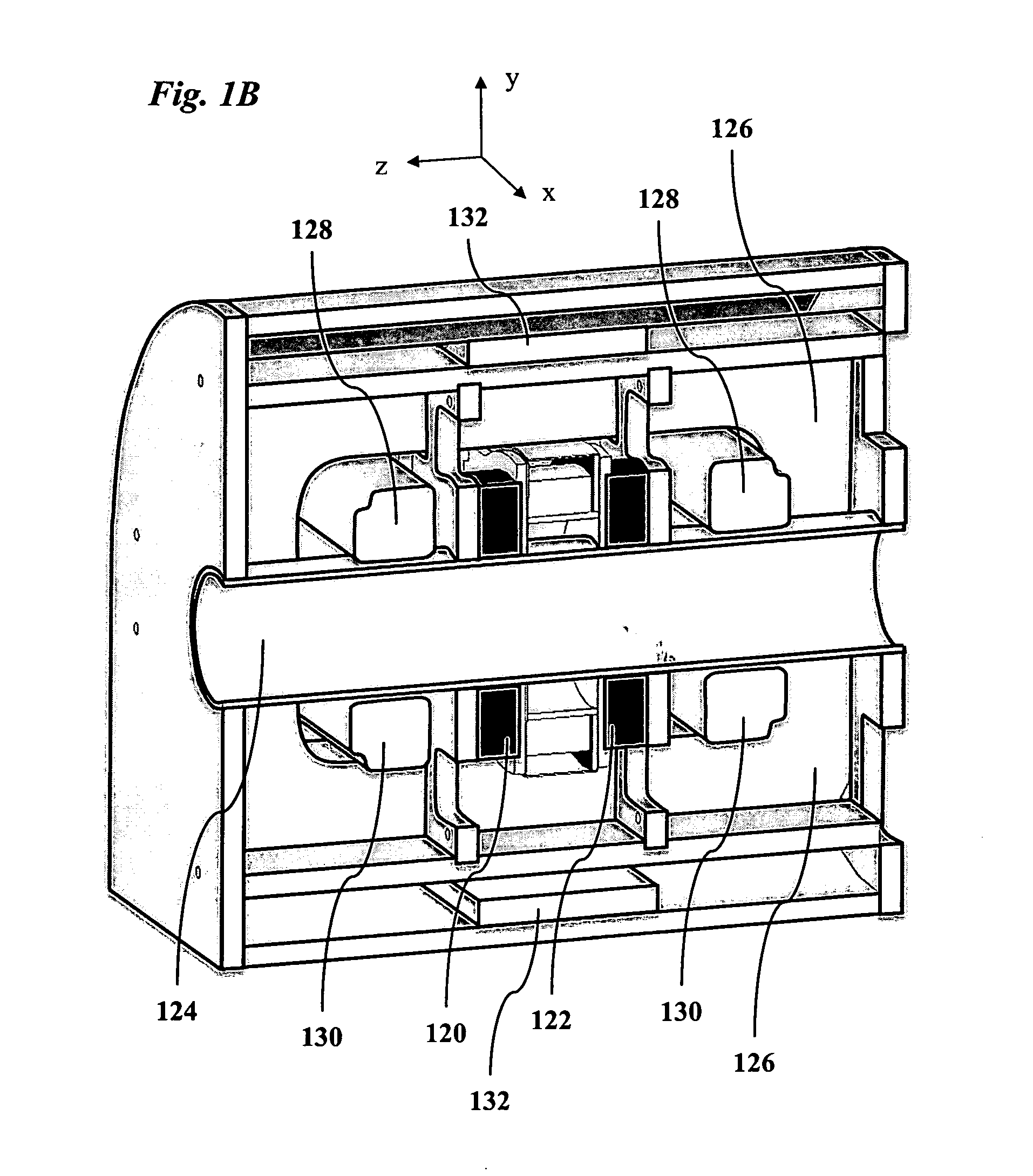
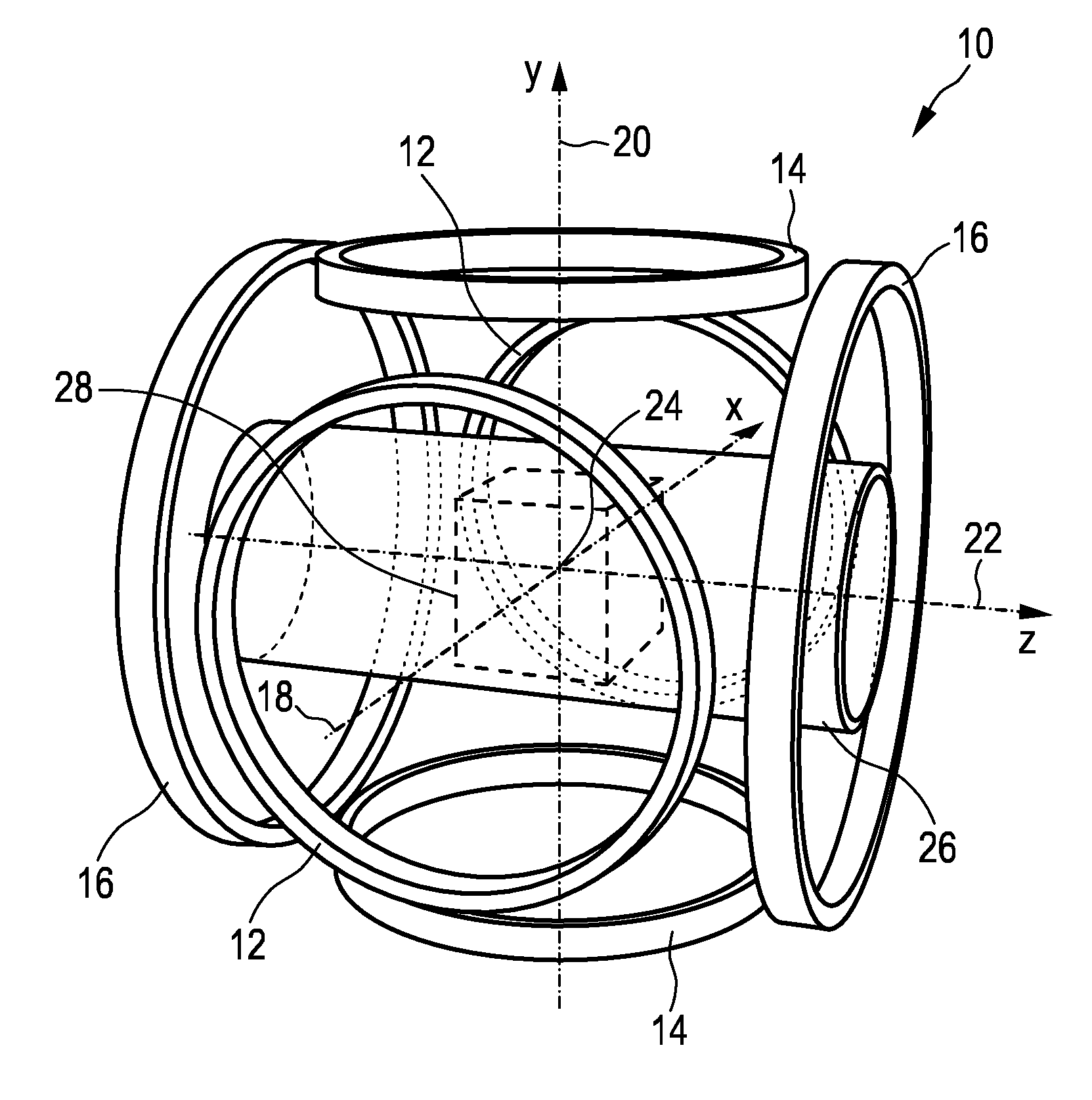
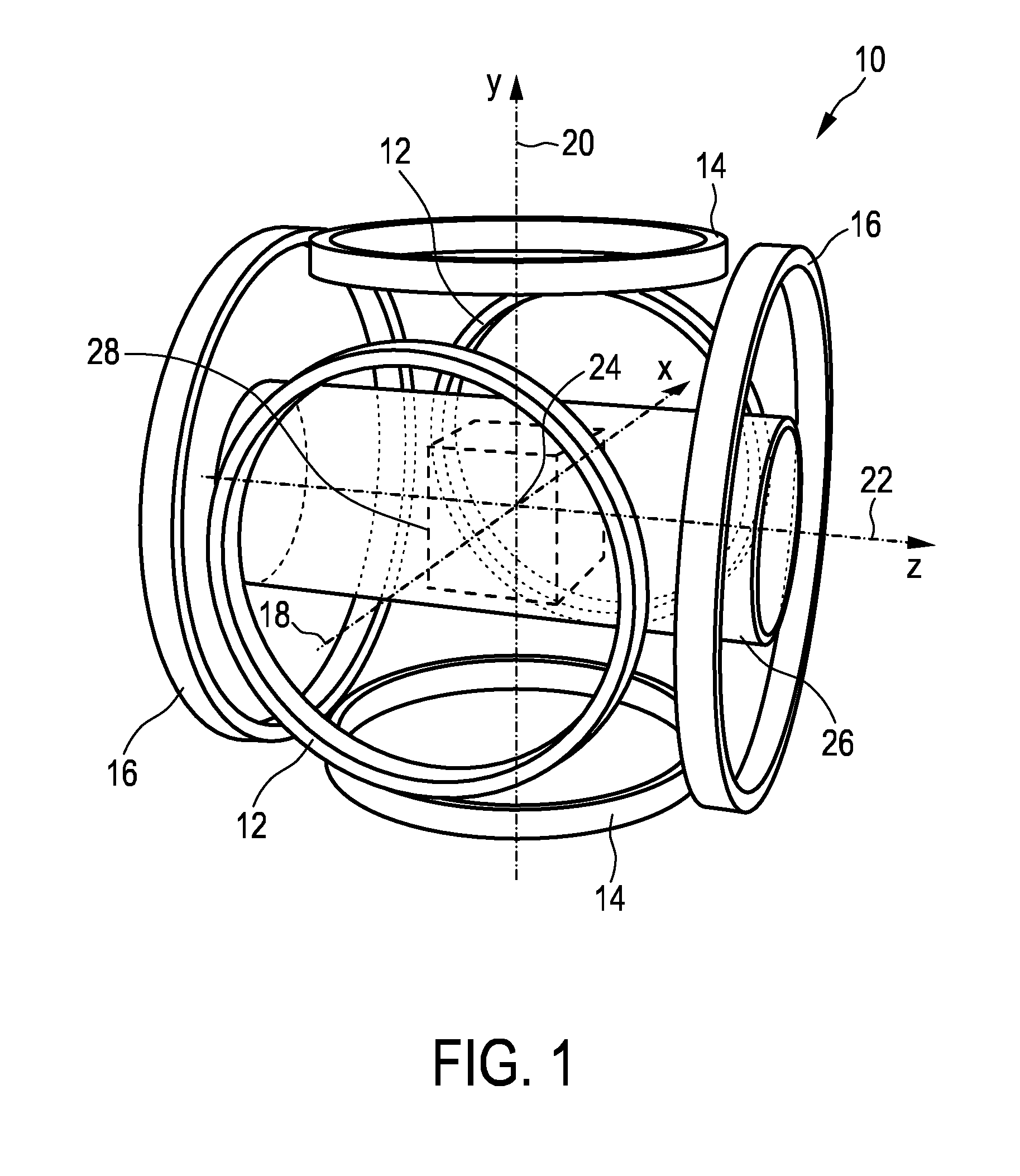
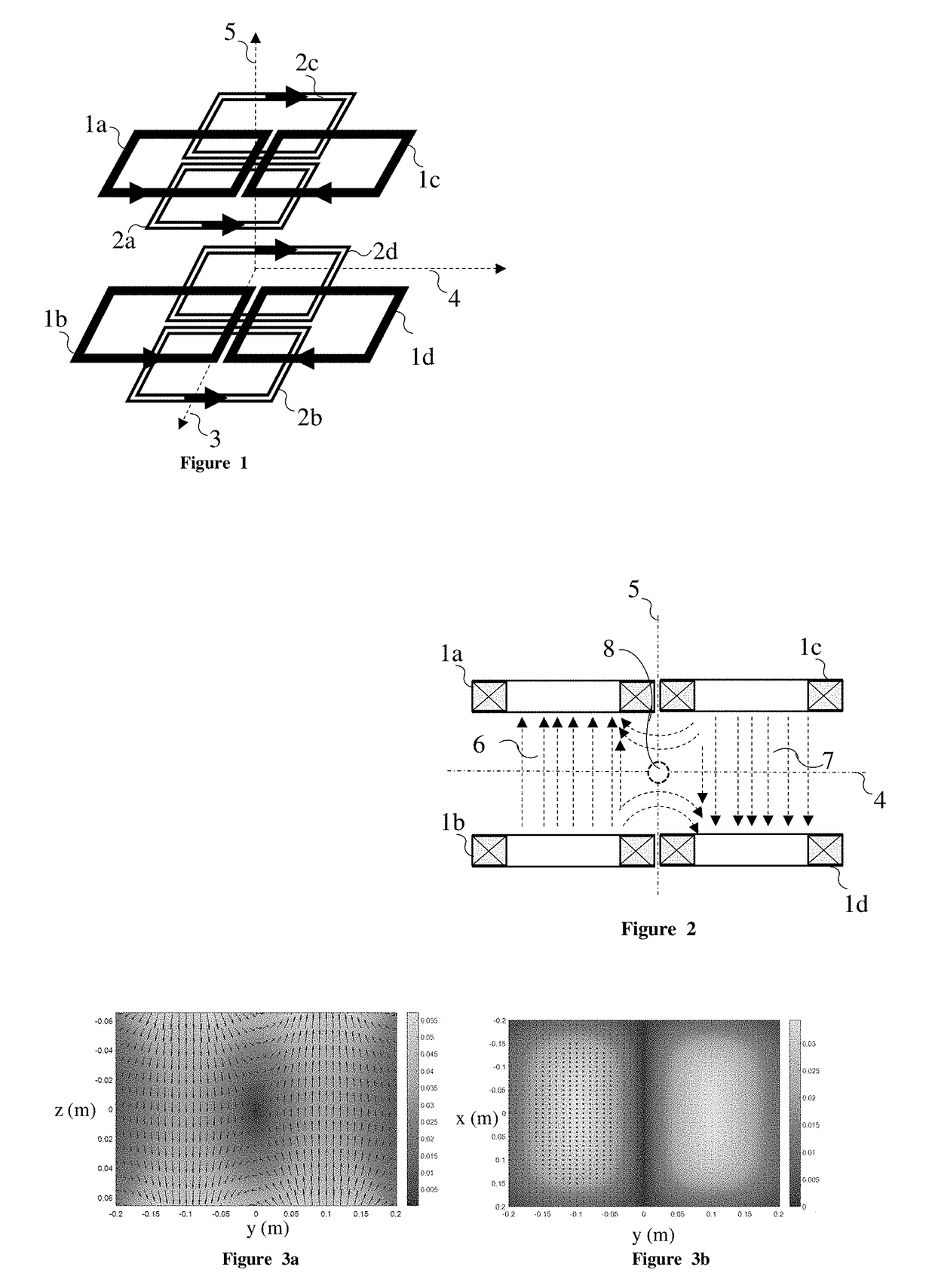
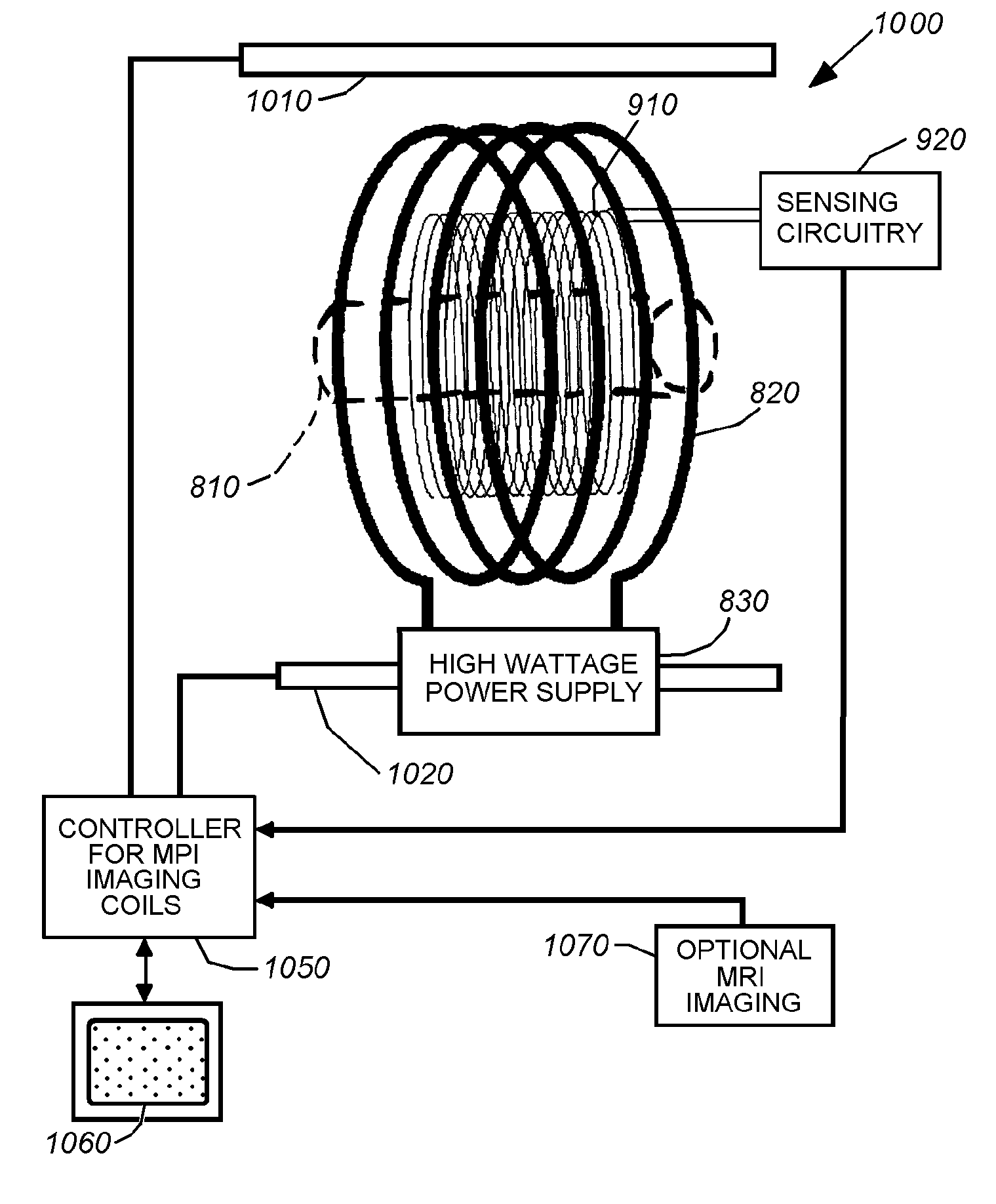
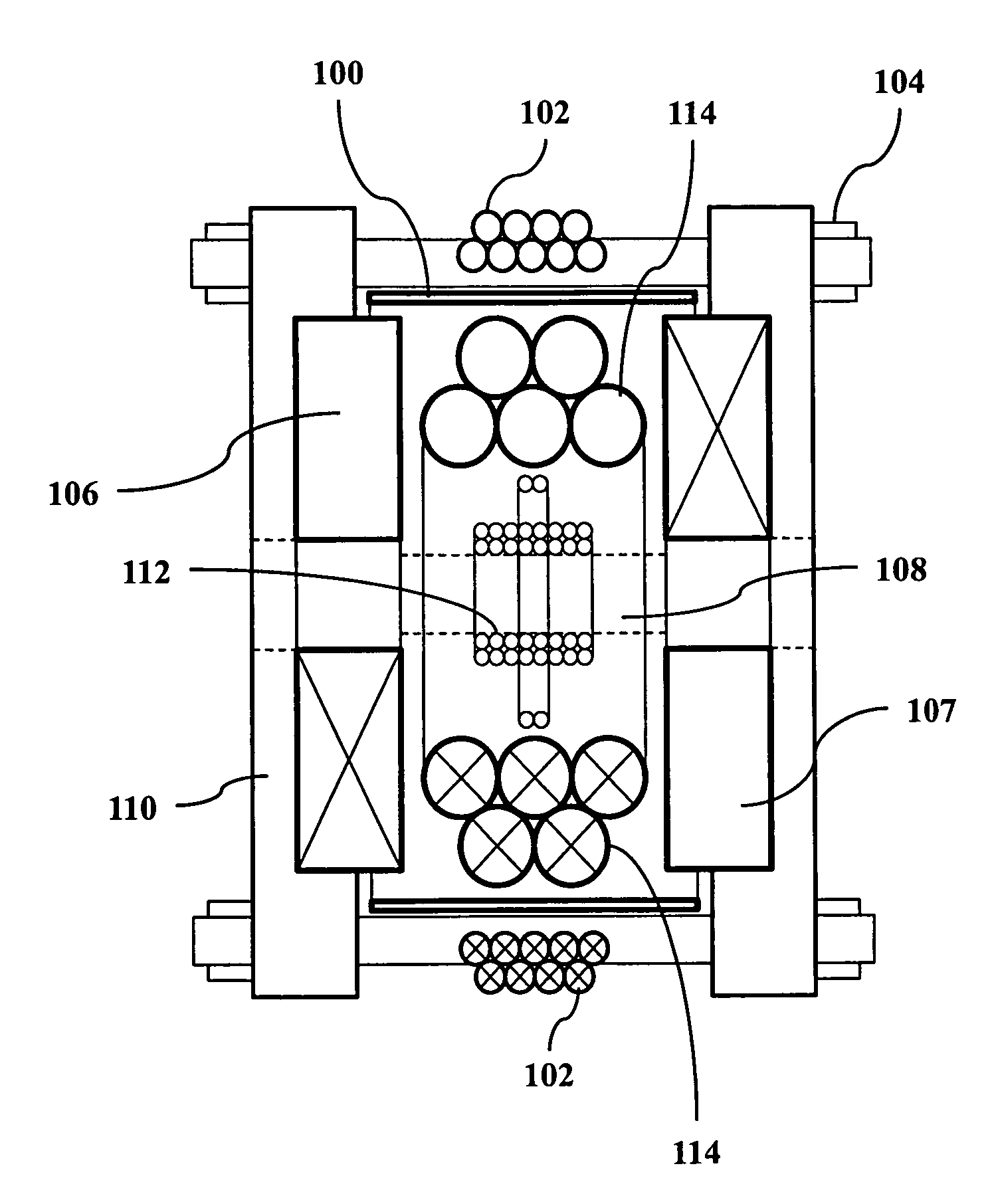
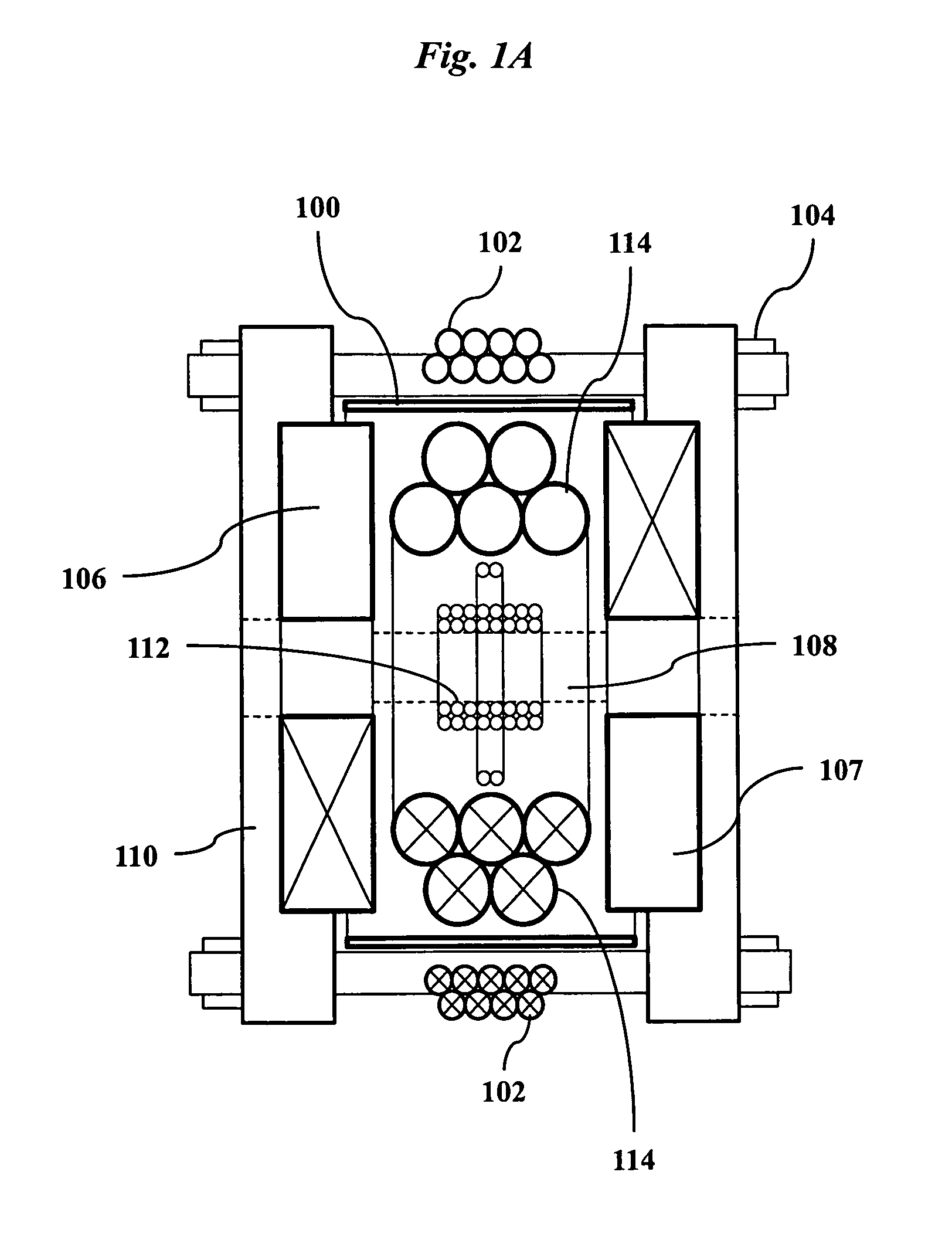
A magnetic particle imaging apparatus includes magnets [106,107] that produce a gradient magnetic field having a field free region (FFR), excitation field electromagnets [102,114] that produce a radiofrequency magnetic field within the field free region, high-Q receiving coils [112] that detect a response of magnetic particles in the field free region to the excitation field. Field translation electromagnets create a homogeneous magnetic field displacing the field-free region through the field of view (FOV) allowing the imaging region to be scanned to optimize scan time, scanning power, amplifier heating, SAR, dB / dt, and / or slew rate. Efficient multi-resolution scanning techniques are also provided. Intermodulated low and radio-frequency excitation signals are processed to produce an image of a distribution of the magnetic nanoparticles within the imaging region. A single composite image is computed using deconvolution of multiple signals at different harmonics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for use of nanoparticles in imaging and temperature measurement
ActiveUS20090115415A1Improve rendering capabilitiesHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismMagnetic property measurementsBinding energyMagnetic particle imaging
This invention provides a system and method that improves the sensitivity and localization capabilities of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) by using combinations of time-varying and static magnetic fields. Combinations of magnetic fields can be used to distribute the signals coming from the magnetic particles among the harmonics and other frequencies in specific ways to improve sensitivity and to provide localization information to speed up or improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of imaging and / or eliminate the need for saturation fields currently used in MPI. In various embodiments, coils can be provided to extend the sub-saturation region in which nanoparticles reside; to provide a static field offset to bring nanoparticles nearer to saturation; to introduce even and odd harmonics that can be observed; and / or to introduce combinations of frequencies for more-defined observation of signals from nanoparticles. Further embodiments provide for reading of the signal produced by cyclically saturated magnetic nanoparticles in a sample so as to provide a measurement of the temperature of those nanoparticles. The spectral distribution of the signal generated provides estimates of the temperature of the nanoparticles. Related factors may also be estimated—binding energies of the nanoparticles, phase changes, bound fraction of the particles or stiffness of the materials in which the nanoparticles are imbedded.
Owner:DARTMOUTH HITCHCOCK CLINIC
Arrangement and method for influencing and/or detecting magnetic particles
InactiveUS20120065491A1Improve accuracyReadily availableElectrotherapySensorsCoil arrayMagnetic particle imaging
The present invention relates to an arrangement and a method for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles in a region of action, in particular for monitoring of intra-cerebral or intra-cranial bleeding using Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI). A common coupling unit per coil of a coil array is provided for coupling all signals for generating the magnetic fields to the set of common coils. Further, the same coils are used for acquiring detection signals. In this way a small scanner can be built that can be left permanently or can be provided periodically to the patient, in particular for bleeding monitoring.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Calibration method for an MPI(=Magnetic particle imaging) apparatus
ActiveUS20150221103A1Reduce rebuild timeImprove approximationReconstruction from projectionCode conversionMagnetic particle imagingVoxel
A calibration method for an MPI (=magnetic particle imaging) apparatus for conducting an MPI experiment, wherein the calibration method comprises m calibration MPI measurements with a calibration test piece and uses these measurements to create an image reconstruction matrix with which the signal contributions of N voxels within an investigation volume of the MPI apparatus are determined, wherein compressed sensing steps are applied in the calibration method with a transformation matrix that sparsifies the image construction matrix, and wherein only a number M<N of calibration MPI measurements for M voxels are carried out, from which the image reconstruction matrix is created and stored. This specifies an efficient method for determination of the system matrix for the MPI imaging method, which does not require much time to determine an MPI system function and nevertheless achieves a high degree of precision.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Coil arrangement for mpi
ActiveUS20140320132A1Reduce the maximum voltageSignificant differenceElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic measurementsMagnetic particle imagingField element
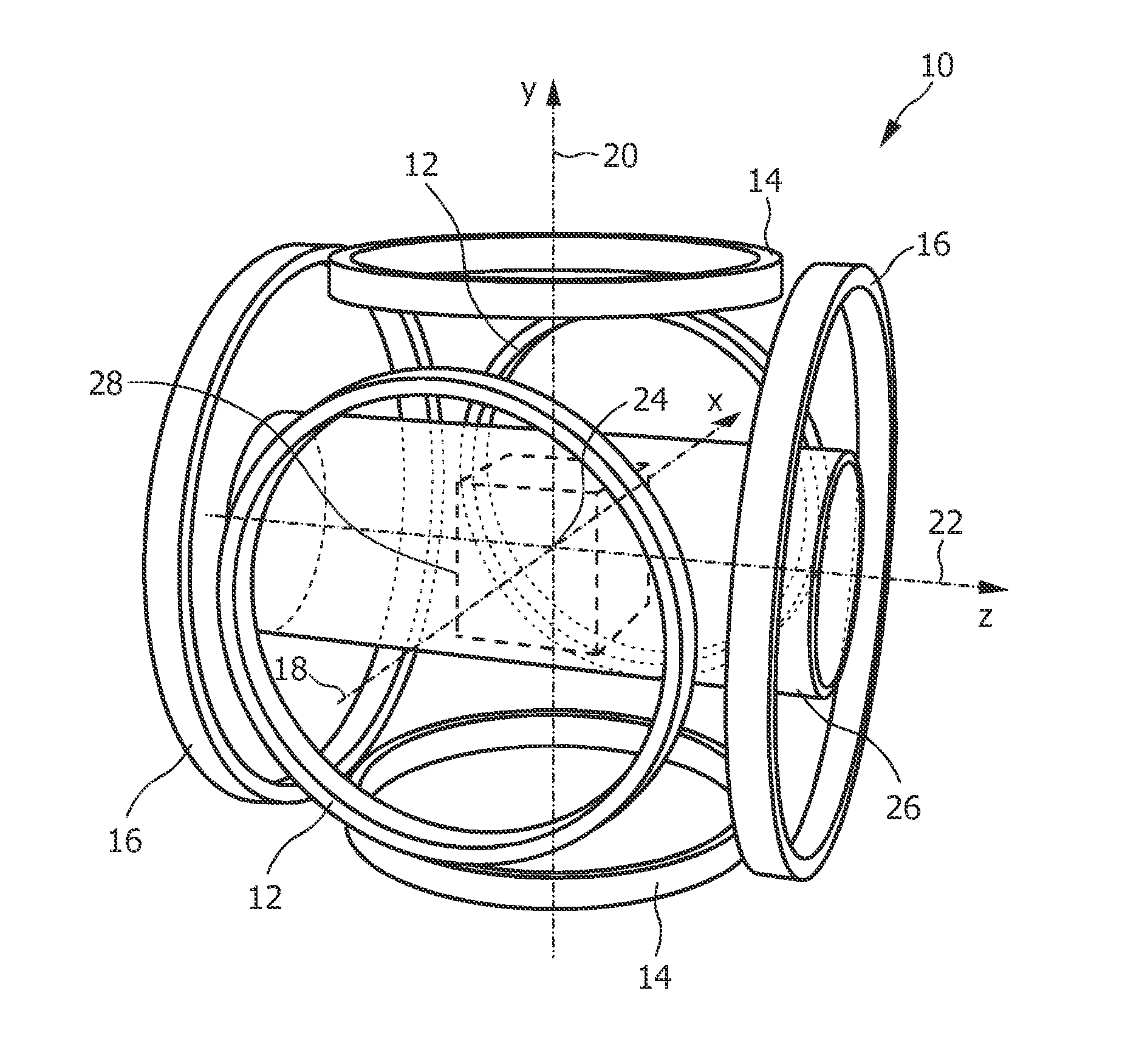
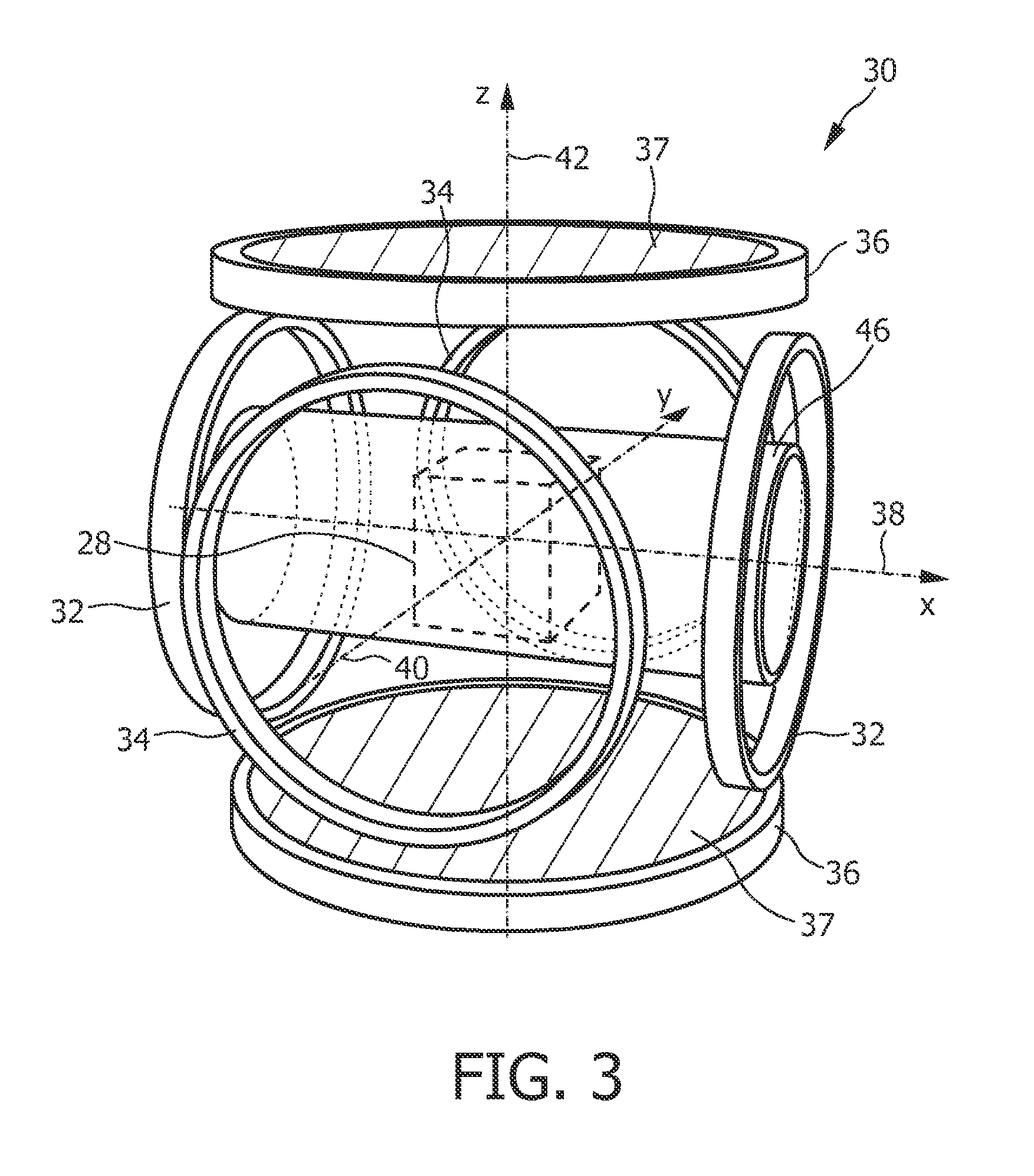
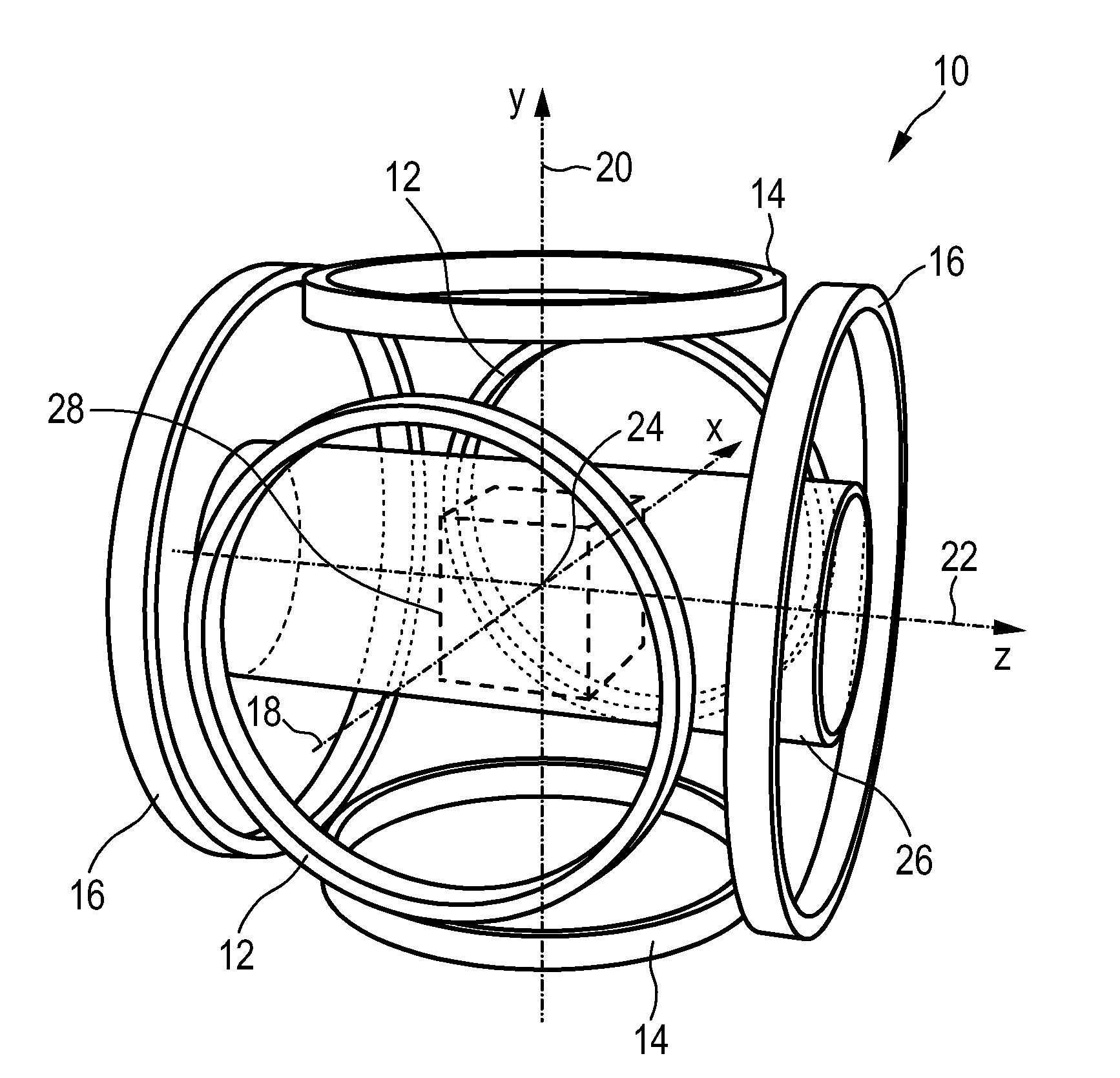
The present invention relates to a coil arrangement, in particular for use in a magnetic particle imaging apparatus (100), comprising a coil split into at least two coil segments, wherein the winding direction is inverted between at least one coil segment to another coil segment, and a capacitor coupled between at least two adjacent coil segments. Further, the present invention relates to such a magnetic particle imaging apparatus, in particular an apparatus (100) for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles in a field of view (28), which apparatus comprises selection means and drive means (120) wherein at least one drive field coil and / or at least one selection field coil representing a selection field element is implemented by a coil arrangement as proposed according to the present invention.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Open bore field free line magnetic particle imaging system
ActiveUS20180231629A1High sensitivityFast imagingSensorsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNon symmetricMagnetic particle imaging
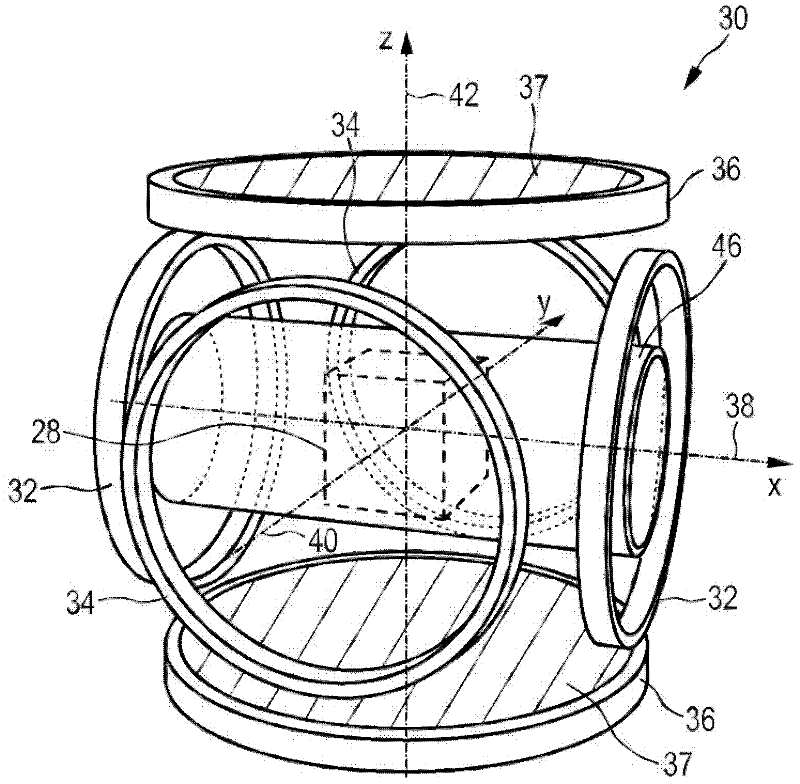
An open bore coil system enabling electronic steering and rotation of a Field Free Line (FFL) inside a large volume. An FFL is generated by placing two parallel coil pairs (fed with alternating current directions) side by side. Using two of these coil groups, the FFL can be rotated in the plane perpendicular to the coil axes. The FFL can be translated in the rotation plane of the FFL using a coil pair placed on the same axis with the other coils. It can also be translated in the perpendicular plane by asymmetrical coil excitation. As all the coils in the system are parallel, the imaged object can be reached from the sides during imaging.
Owner:ASELSAN ELEKTRONIK SANAYI & TICARET ANONIM SIRKETI
Apparatus and method for influencing and/or detecting magnetic particles
InactiveUS20120153949A1Less tuningEasy to controlMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic particle imagingHigh density
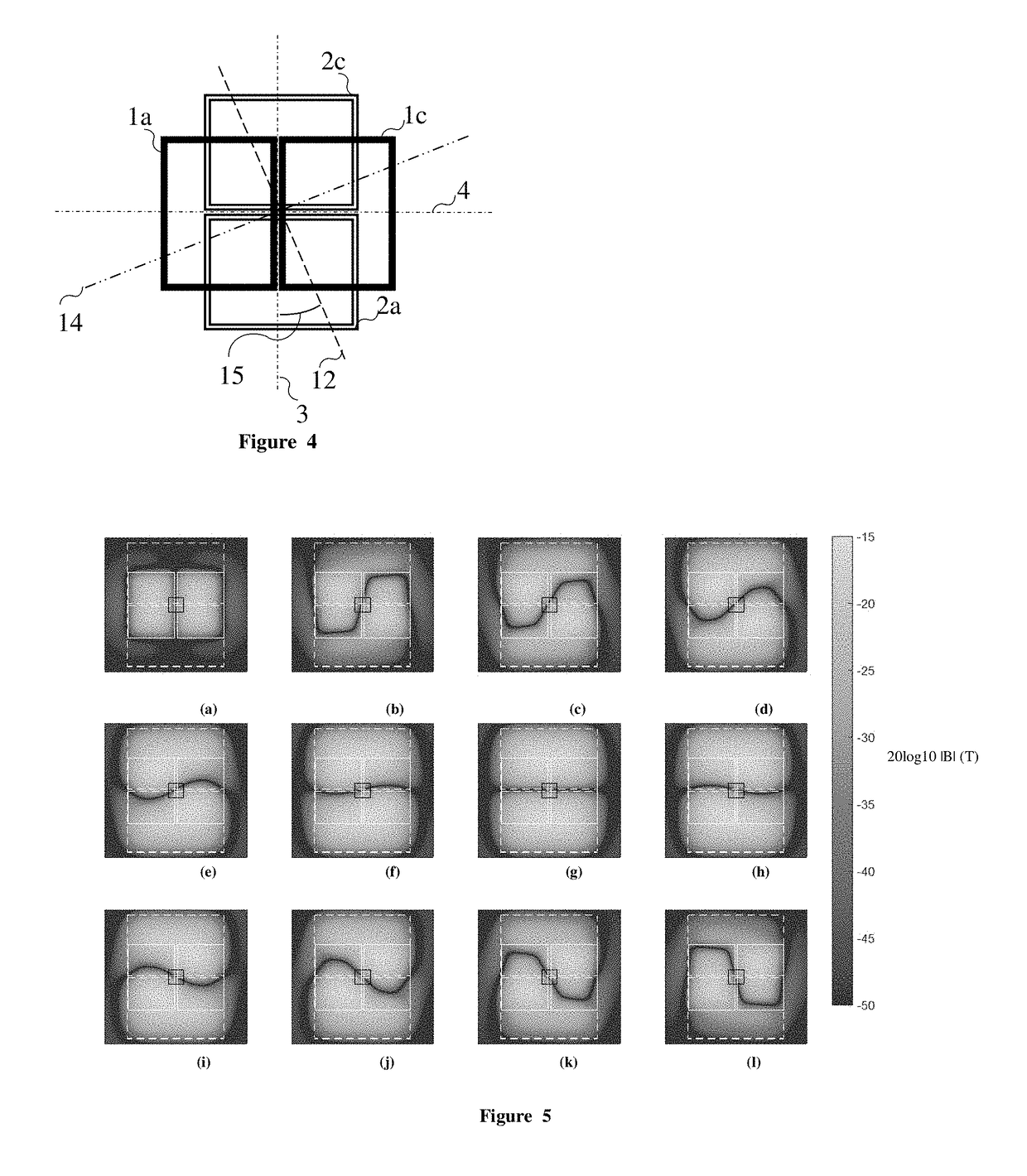
The present invention relates to an MPI (Magnetic Particle Imaging) apparatus and a method for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles in a field of view. Rather than moving the FFP (field free point) along a single, time-consuming high density trajectory it is proposed to use a number of low density trajectories with travelling phase, wherein each of said low density trajectories has the form of a closed curve differently located within the field of view.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
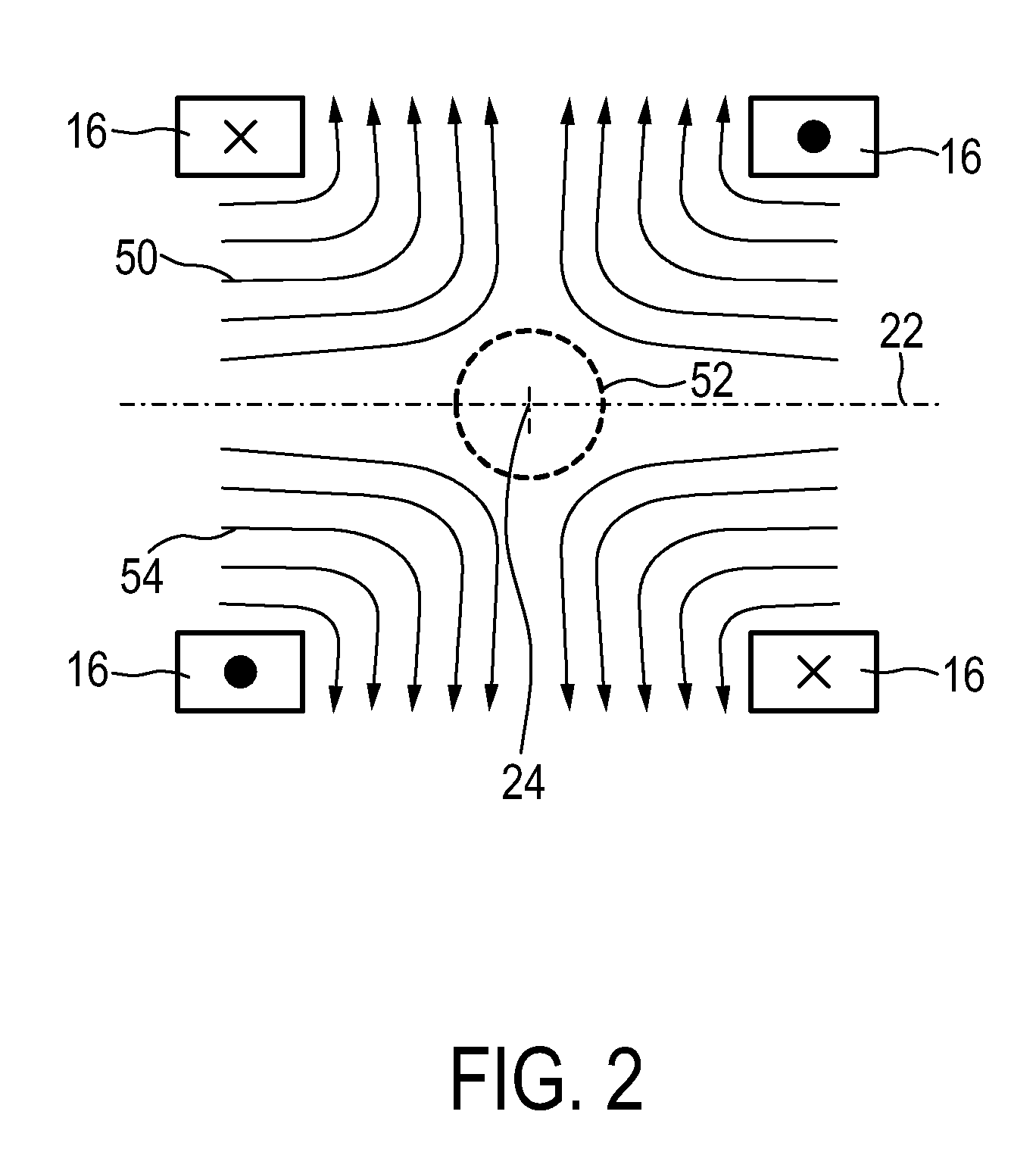
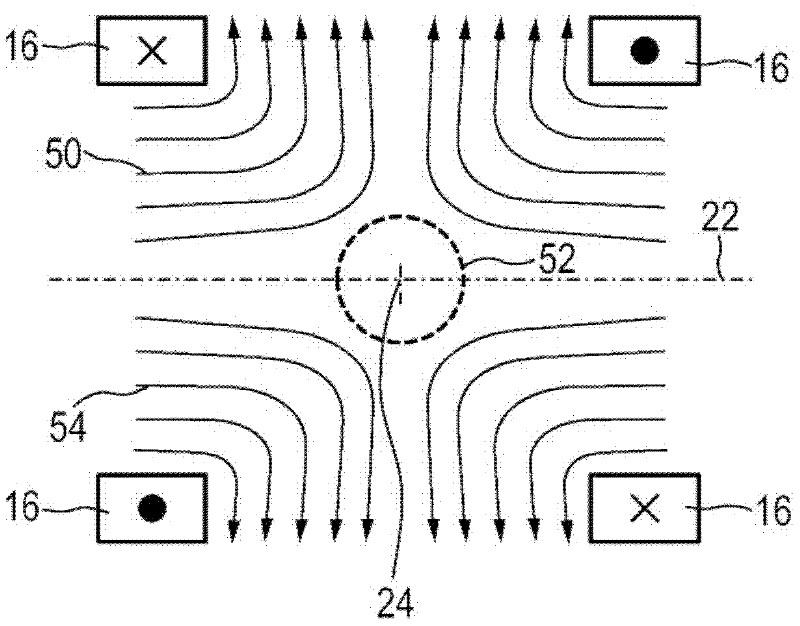
Apparatus and method for influencing and/or detecting magnetic particles in a field of view
ActiveUS20120153948A1Quick and easy encodingQuick and easy and reconstructionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingControl signal
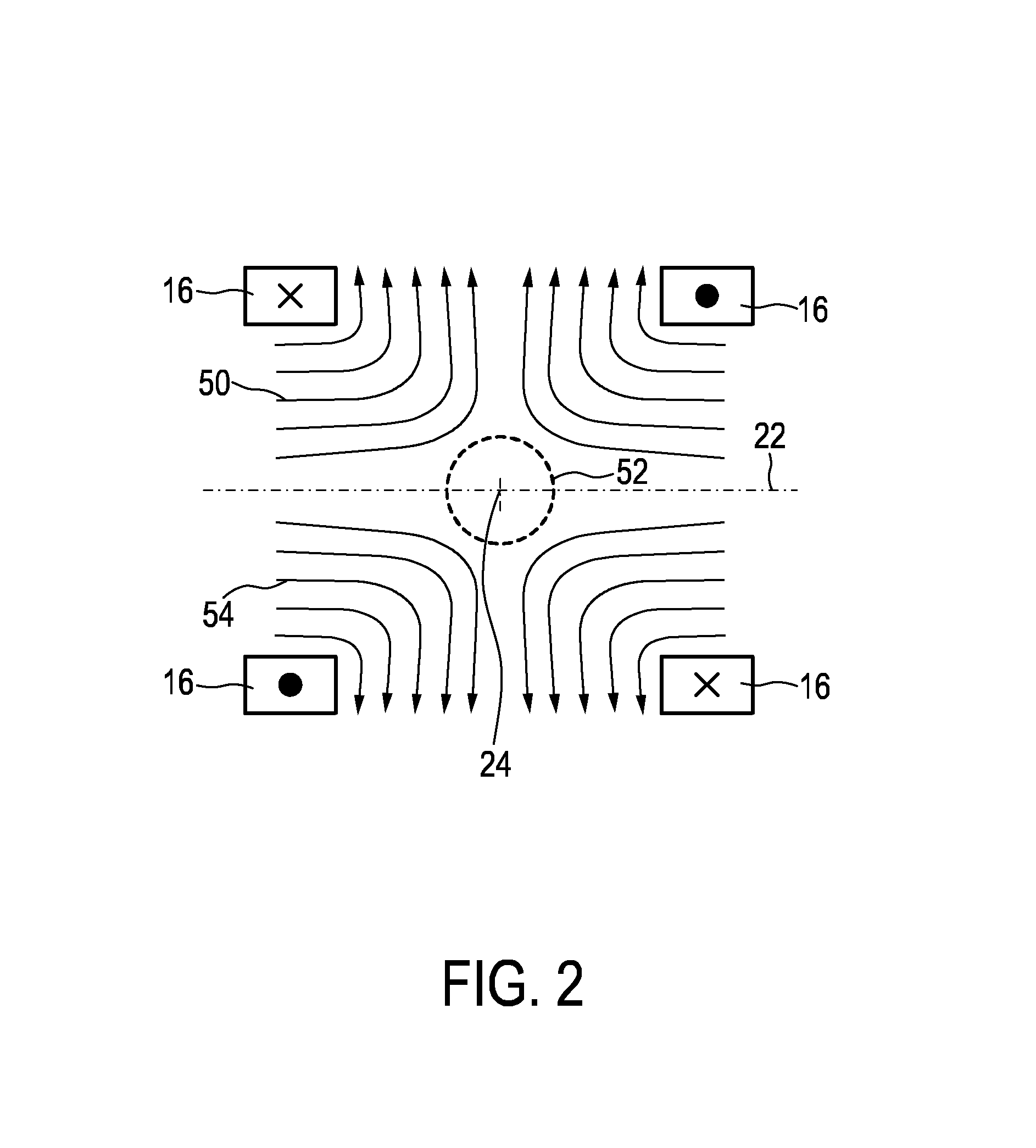
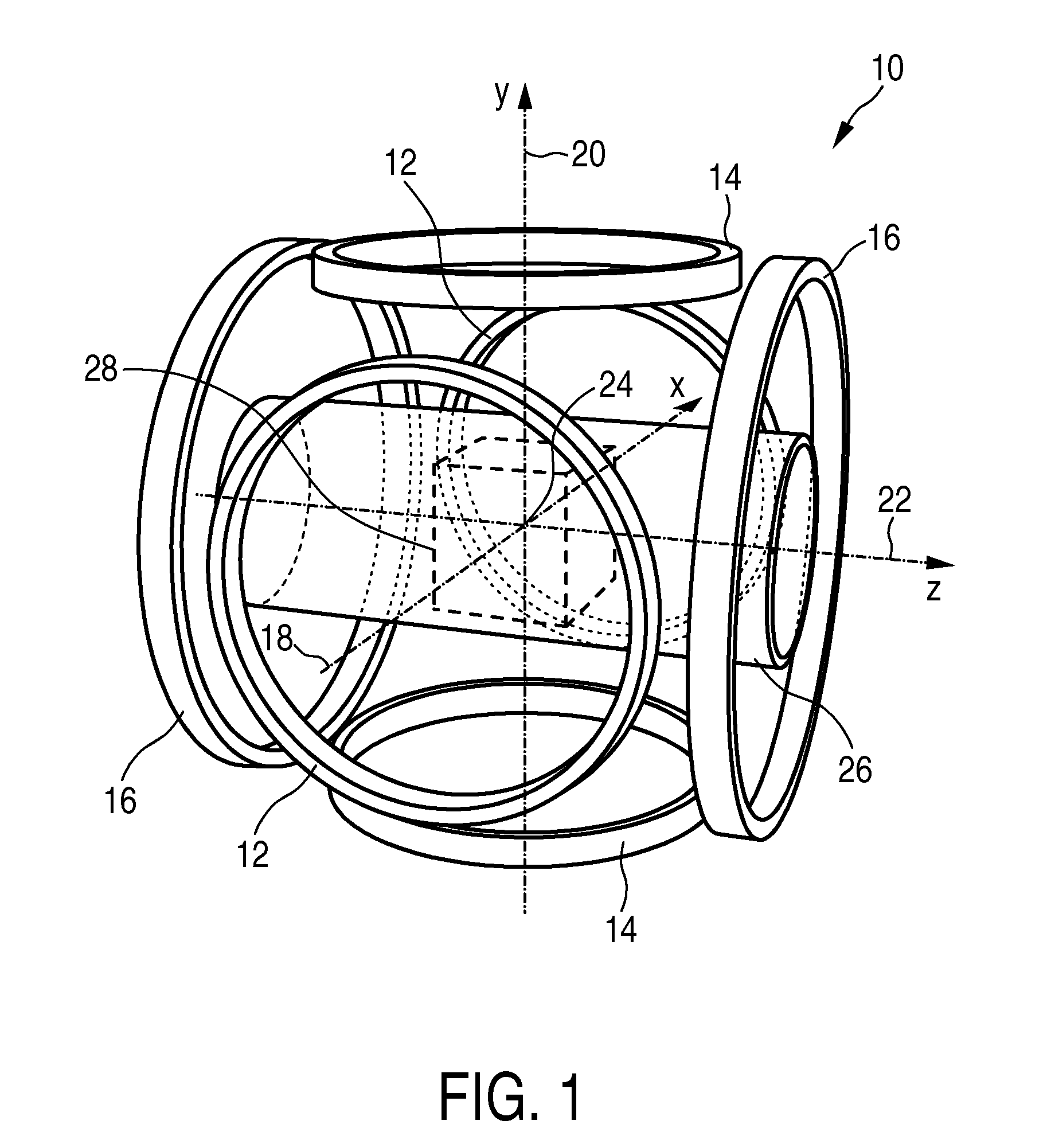
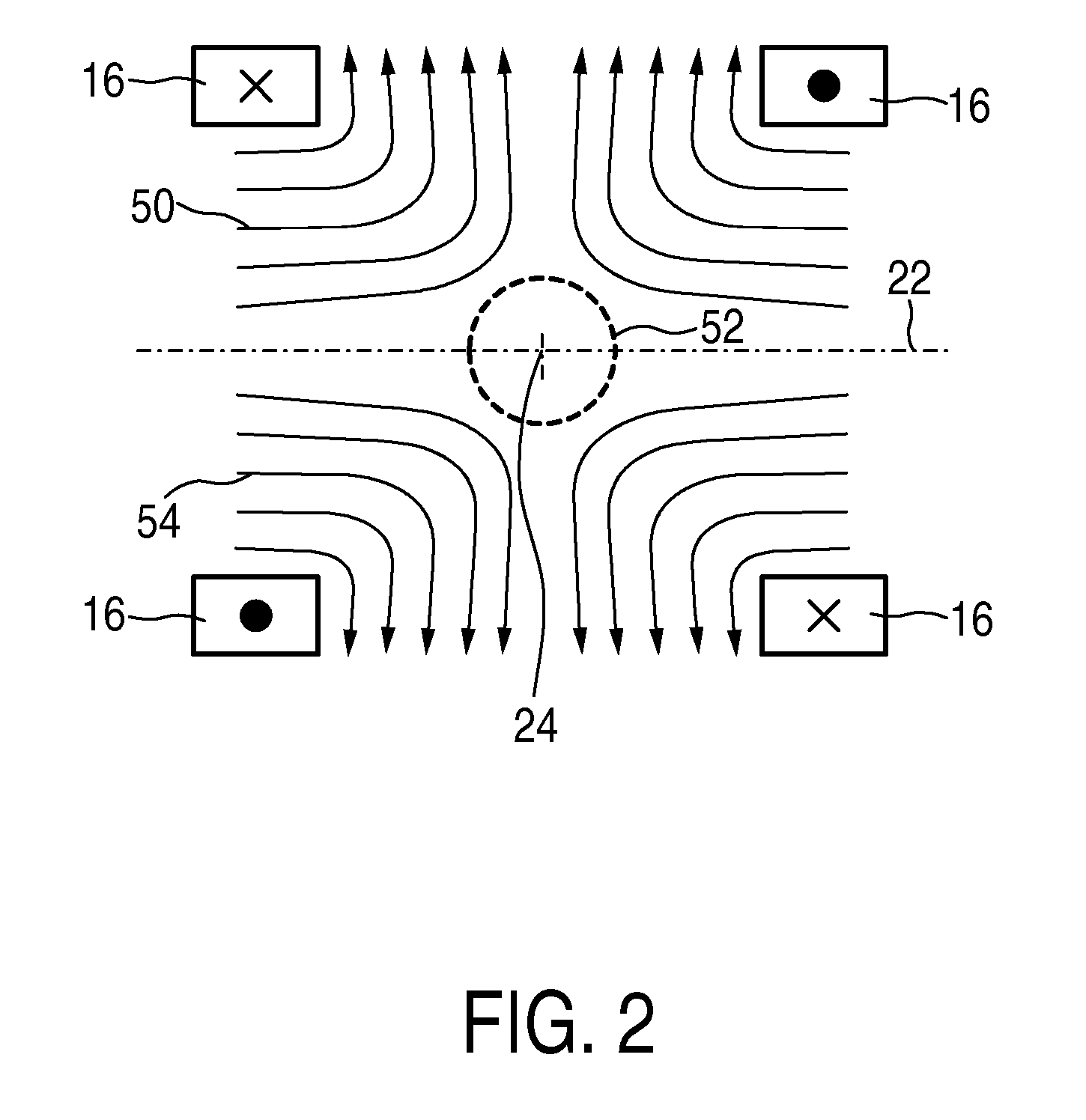
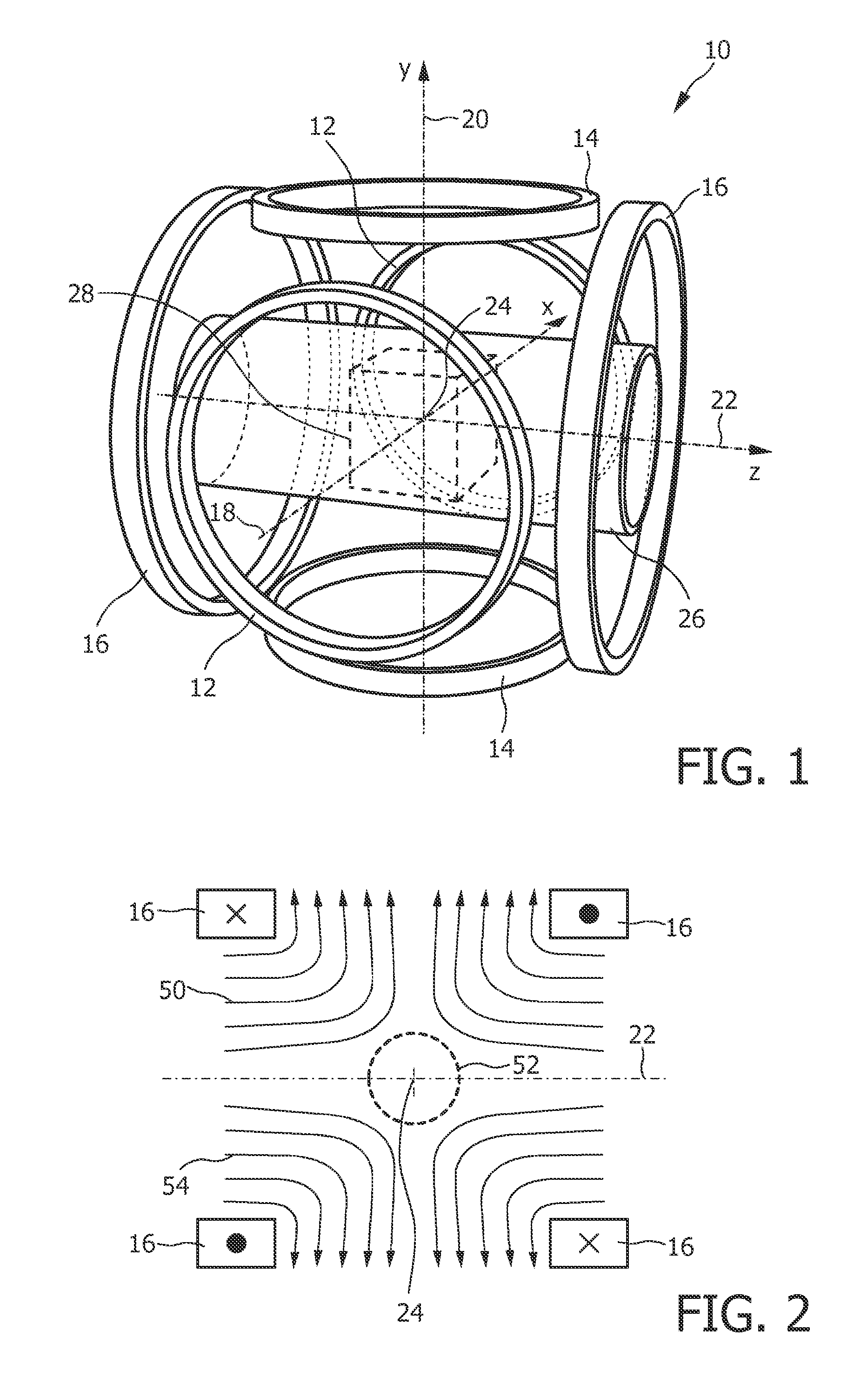
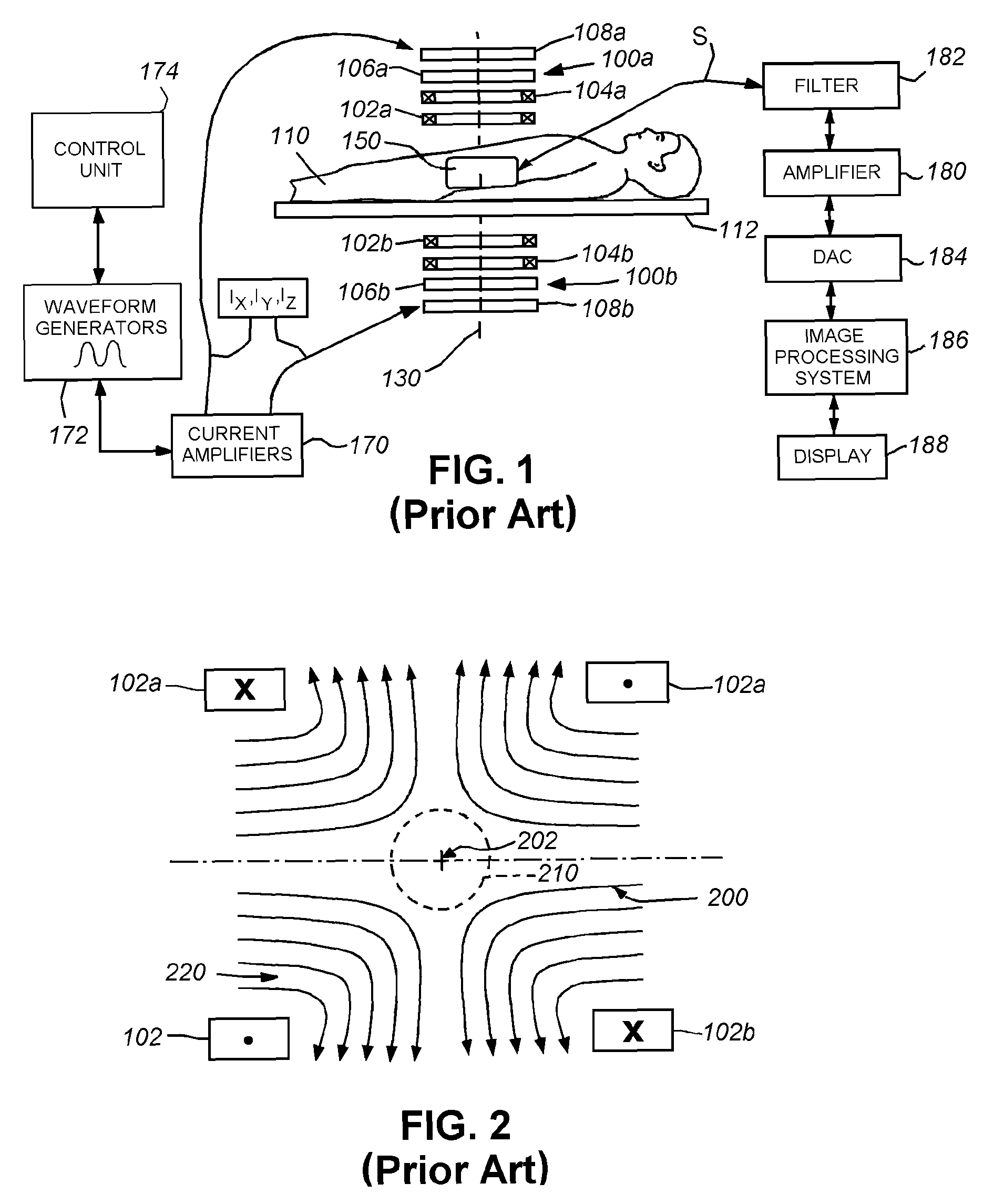
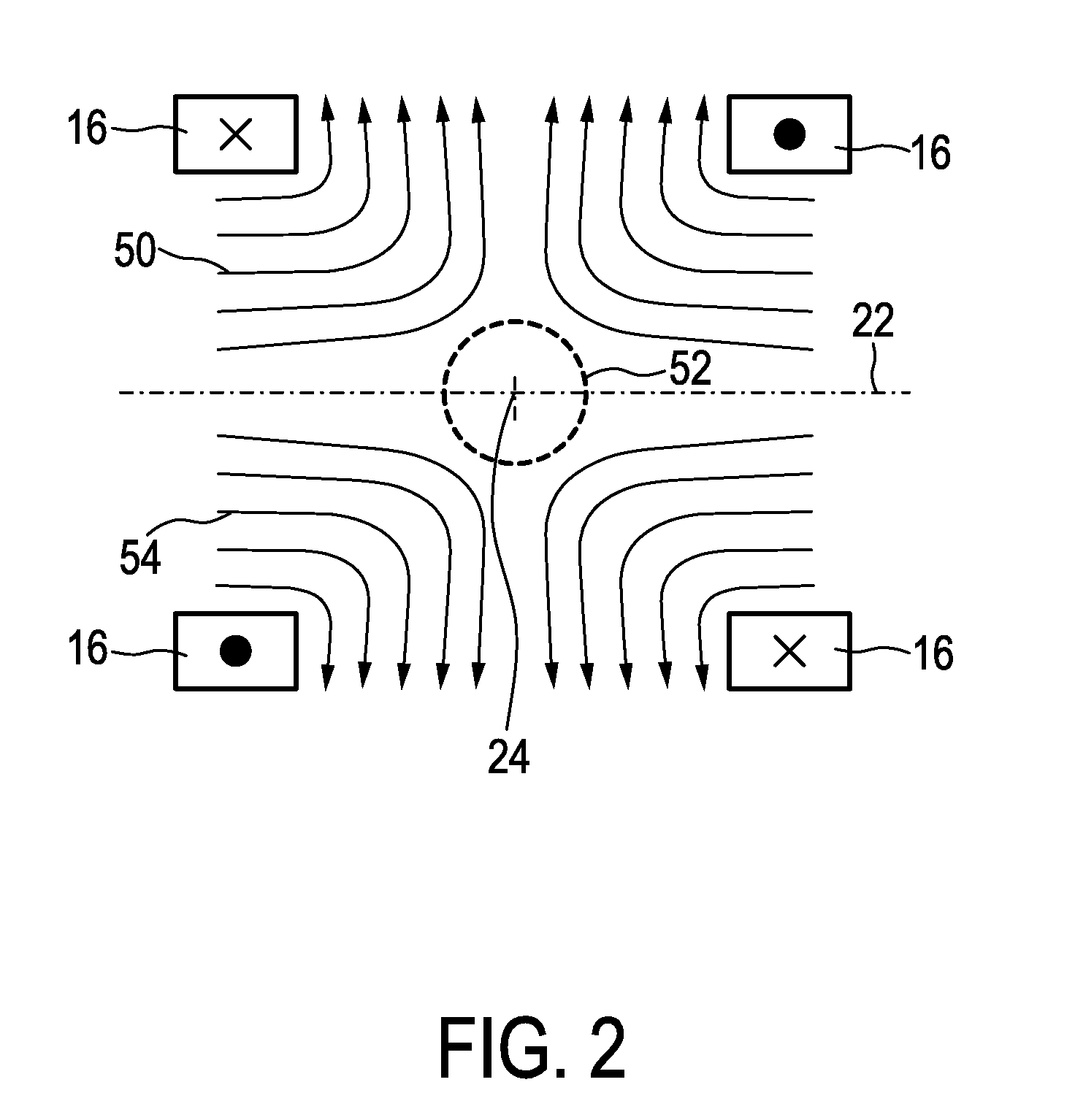
The present invention relates to an apparatus (100) for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles in a field of view (28), wherein the field of view (28) comprises at least one sub field of interest covering at least a portion of an object of interest containing magnetic particles. The apparatus (100) applying the known principle of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) comprises selection means for generating a magnetic selection field (50) having the known field pattern showing a field free point (FFP), drive means for changing the position in space of the FFP by means of a magnetic drive field, receiving means for acquiring detection signals depending on the magnetization of the magnetic particles within the field of view (28), a control unit (150) for controlling a signal receiving unit (140) comprised in the receiving means for acquiring a set of high resolution detection signals and a set of low resolution detection signals, wherein the set of high resolution detection signals depends on the magnetization of at least one subfield of interest and the set of low resolution detection signals depends on the magnetization of at least one adjacent subfield being arranged adjacent to the at least one subfield of interest, and a reconstruction unit (152) for reconstructing a particle distribution quantity depending on the set of high resolution detection signals and the set of low resolution detection signals. The present invention further relates to a corresponding method as well as to a computer program.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for use of nanoparticles in imaging and temperature measurement
ActiveUS7994786B2Improve rendering capabilitiesHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsBinding energyMagnetic particle imaging
This invention provides a system and method that improves the sensitivity and localization capabilities of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) by using combinations of time-varying and static magnetic fields. Combinations of magnetic fields can be used to distribute the signals coming from the magnetic particles among the harmonics and other frequencies in specific ways to improve sensitivity and to provide localization information to speed up or improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of imaging and / or eliminate the need for saturation fields currently used in MPI. In various embodiments, coils can be provided to extend the sub-saturation region in which nanoparticles reside; to provide a static field offset to bring nanoparticles nearer to saturation; to introduce even and odd harmonics that can be observed; and / or to introduce combinations of frequencies for more-defined observation of signals from nanoparticles. Further embodiments provide for reading of the signal produced by cyclically saturated magnetic nanoparticles in a sample so as to provide a measurement of the temperature of those nanoparticles. The spectral distribution of the signal generated provides estimates of the temperature of the nanoparticles. Related factors may also be estimated—binding energies of the nanoparticles, phase changes, bound fraction of the particles or stiffness of the materials in which the nanoparticles are imbedded.
Owner:DARTMOUTH HITCHCOCK CLINIC
Apparatus and method for determining at least one electromagnetic quantity
InactiveUS20120126800A1Easy and not very time-consumingAccurate measurementMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringParticle imagingMagnetic particle imaging
The present invention relates to an apparatus (100) for determining at least one electromagnetic quantity characterizing an electromagnetic property of an object, in particular a human body, wherein said object contains magnetic particles. The apparatus (100) applying the known principle of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) comprises selection means for generating a magnetic selection field (50) having the known field pattern showing a field free point (FFP), drive means for changing the position in space of the FFP by means of a magnetic drive field, receiving means for acquiring detection signals depending on the magnetization of the magnetic particles within a field of view (28) and a reconstruction unit (152) for reconstructing a particle distribution quantity depending on the detection signals. The apparatus (100) further comprises a control unit (150) for controlling the receiving means for acquiring a first set of detection signals corresponding to a first drive field frequency and a second set of detection signals corresponding to a second drive field frequency, with both drive field frequencies differing from each other. The control unit (15) further controls the reconstruction unit (152) for reconstructing a first particle distribution quantity depending on the first set of detection signals and a second particle distribution quantity depending on the second set of detection signals. The apparatus (100) further comprises a determination unit (160) for determining the electromagnetic quantity depending on the first and second particle distribution quantity. The present invention further relates to a corresponding method as well as to a computer program.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
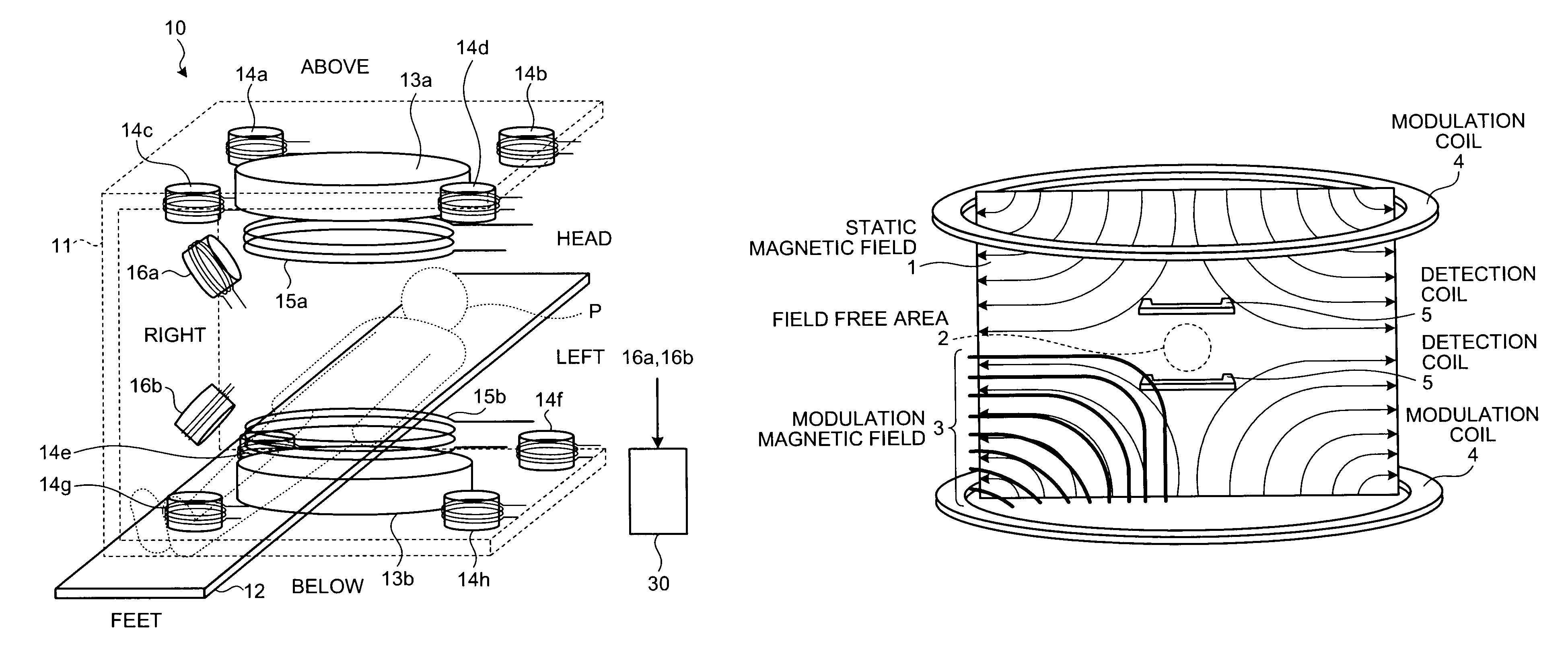
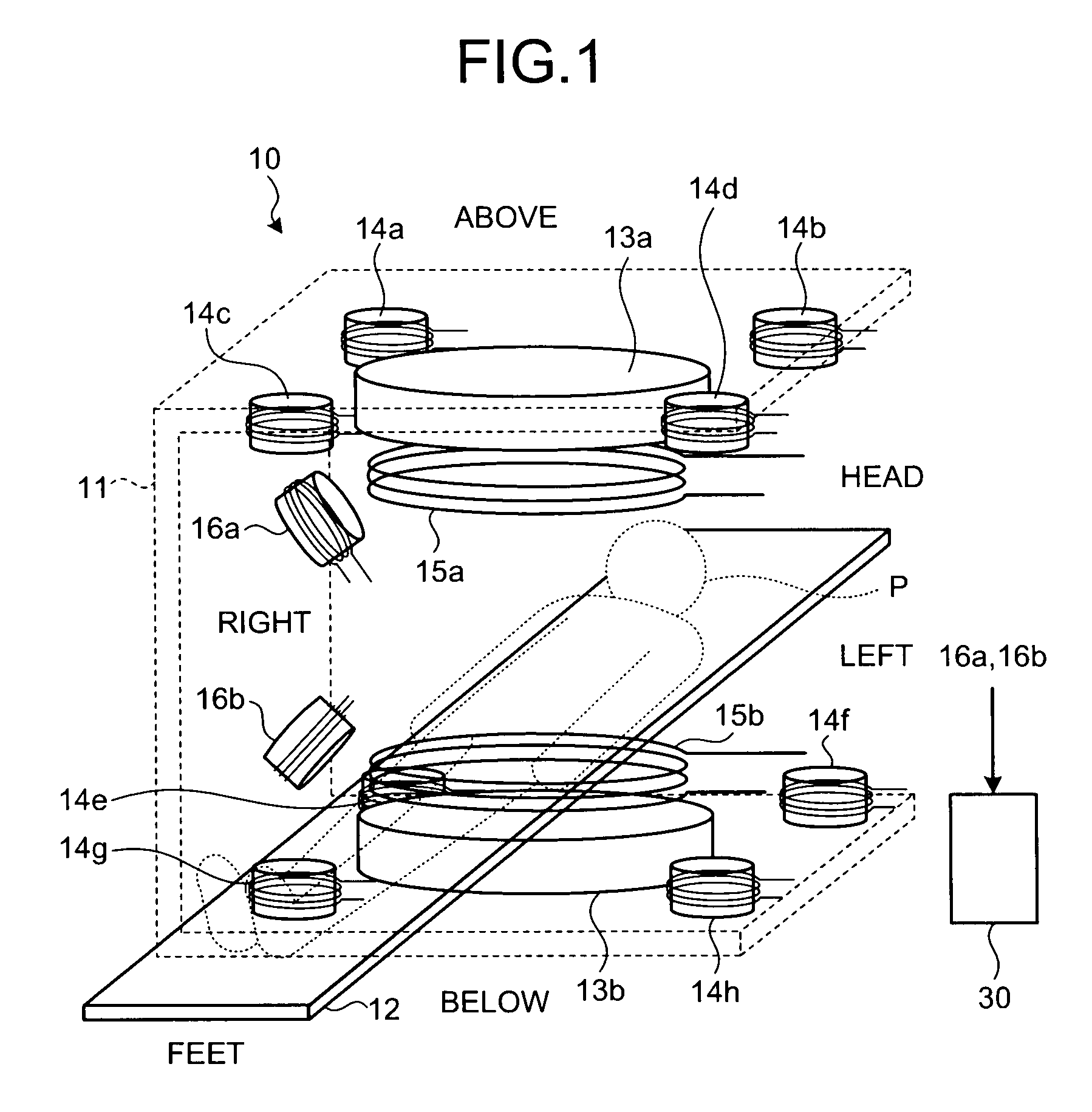
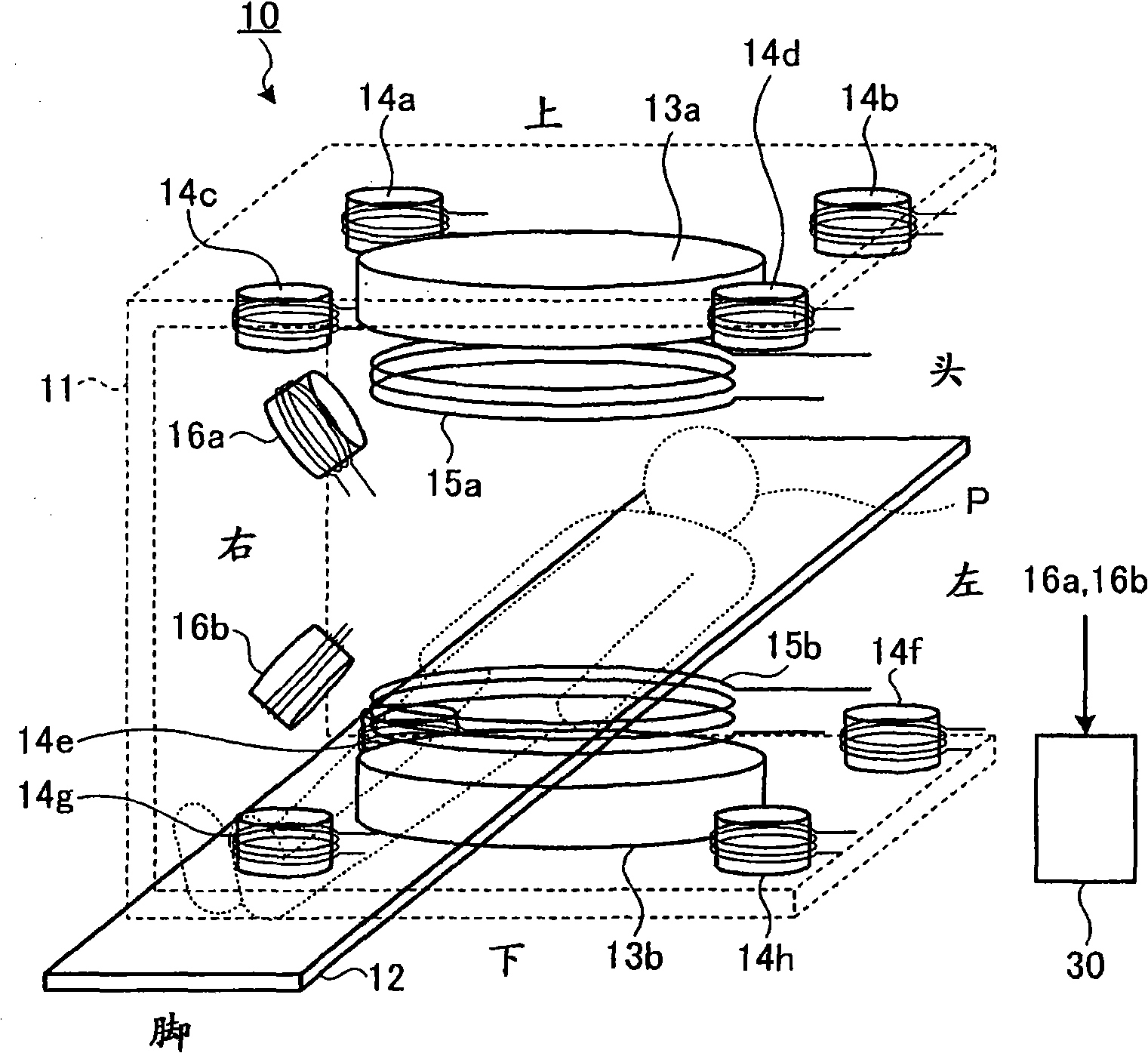
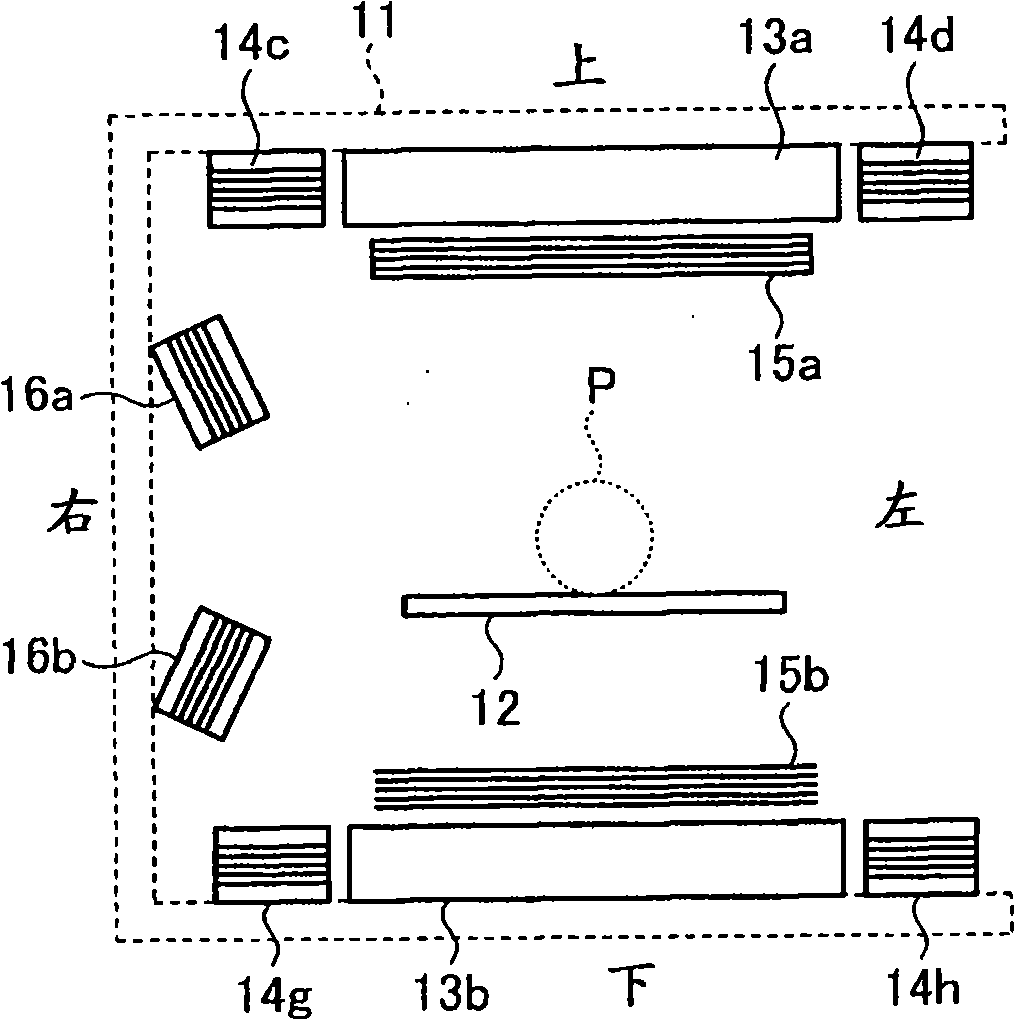
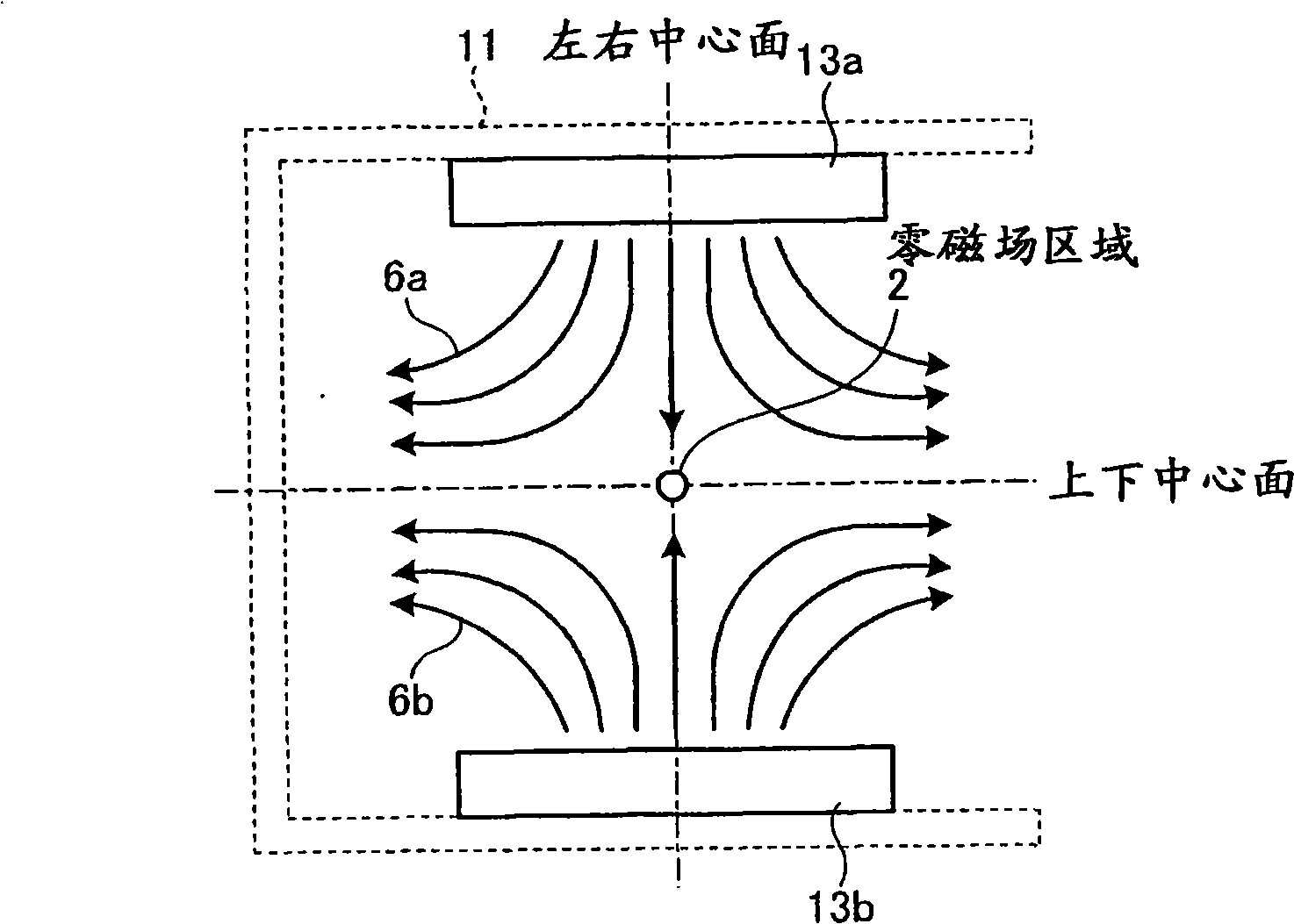
Magnetic particle imaging apparatus, method of disposing detection coil for magnetic particle imaging apparatus, and magnetic flux detecting apparatus
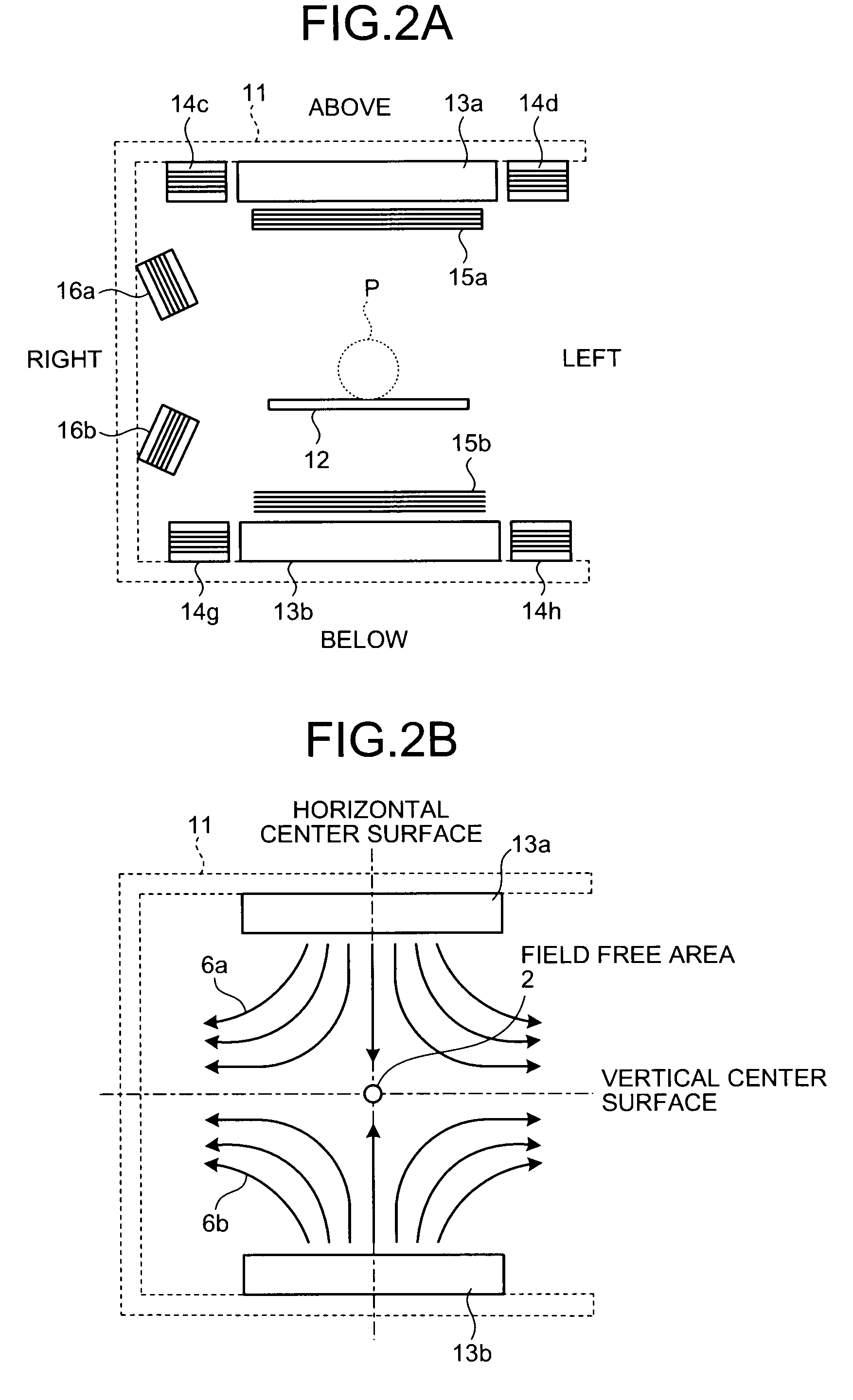
In a magnetic particle imaging apparatus that forms an image of a distribution of magnetic particles based on changes in a magnetic flux generated by magnetization of the magnetic particles, modulation coils that magnetize magnetic particles present in a field free area by applying a modulation magnetic field to the field free area, and detection coils are disposed such as to suppress an influence caused by a magnetic flux of the modulation magnetic field applied by the modulation coils and included in a detected magnetic flux.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Compositions containing magnetic iron oxide particles, and use of said compositions in imaging methods
InactiveUS20070036729A1Suitability of the compositionsHigh proportionNanomedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringLymphatic SpreadMagnetic particle imaging
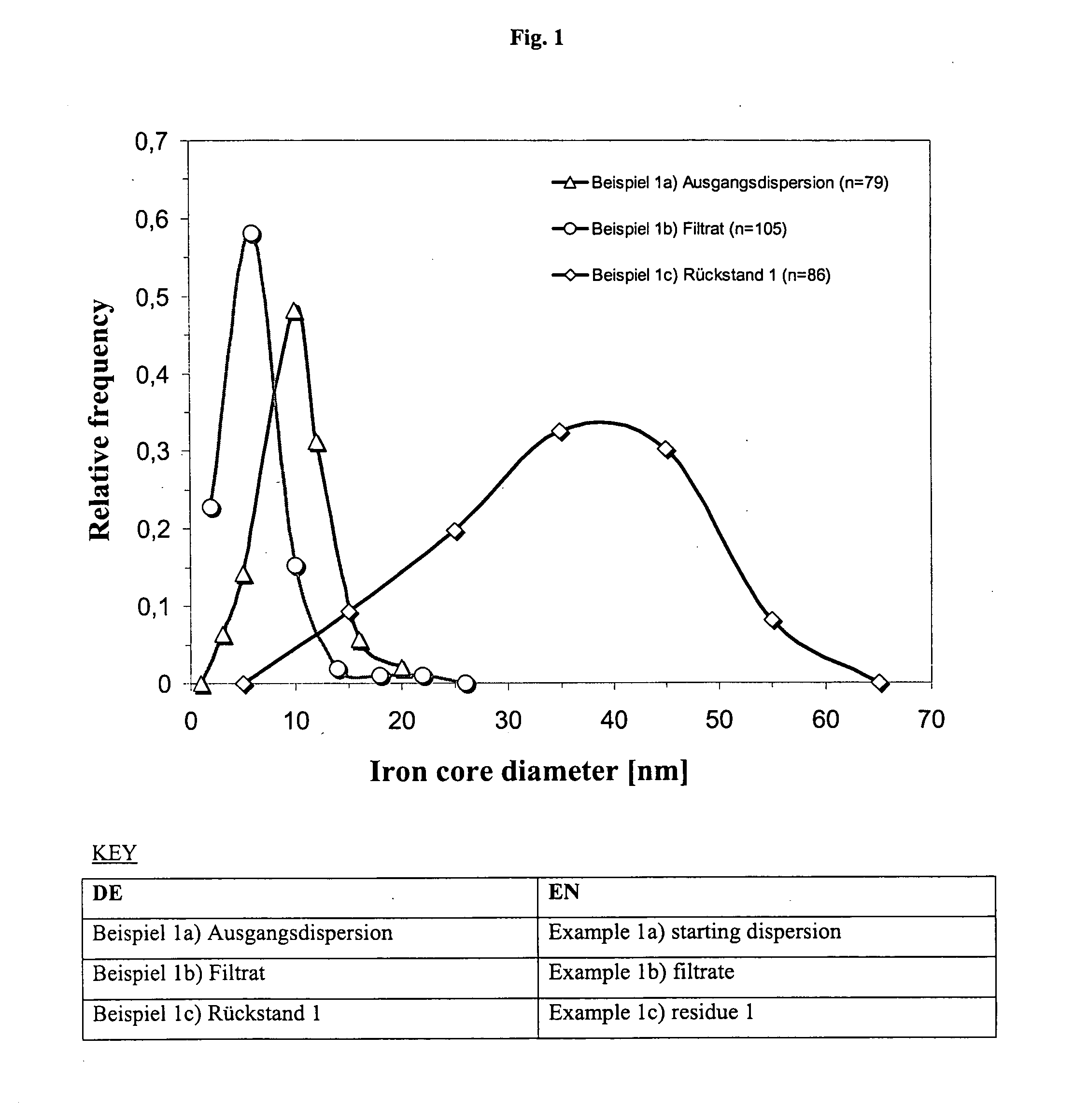
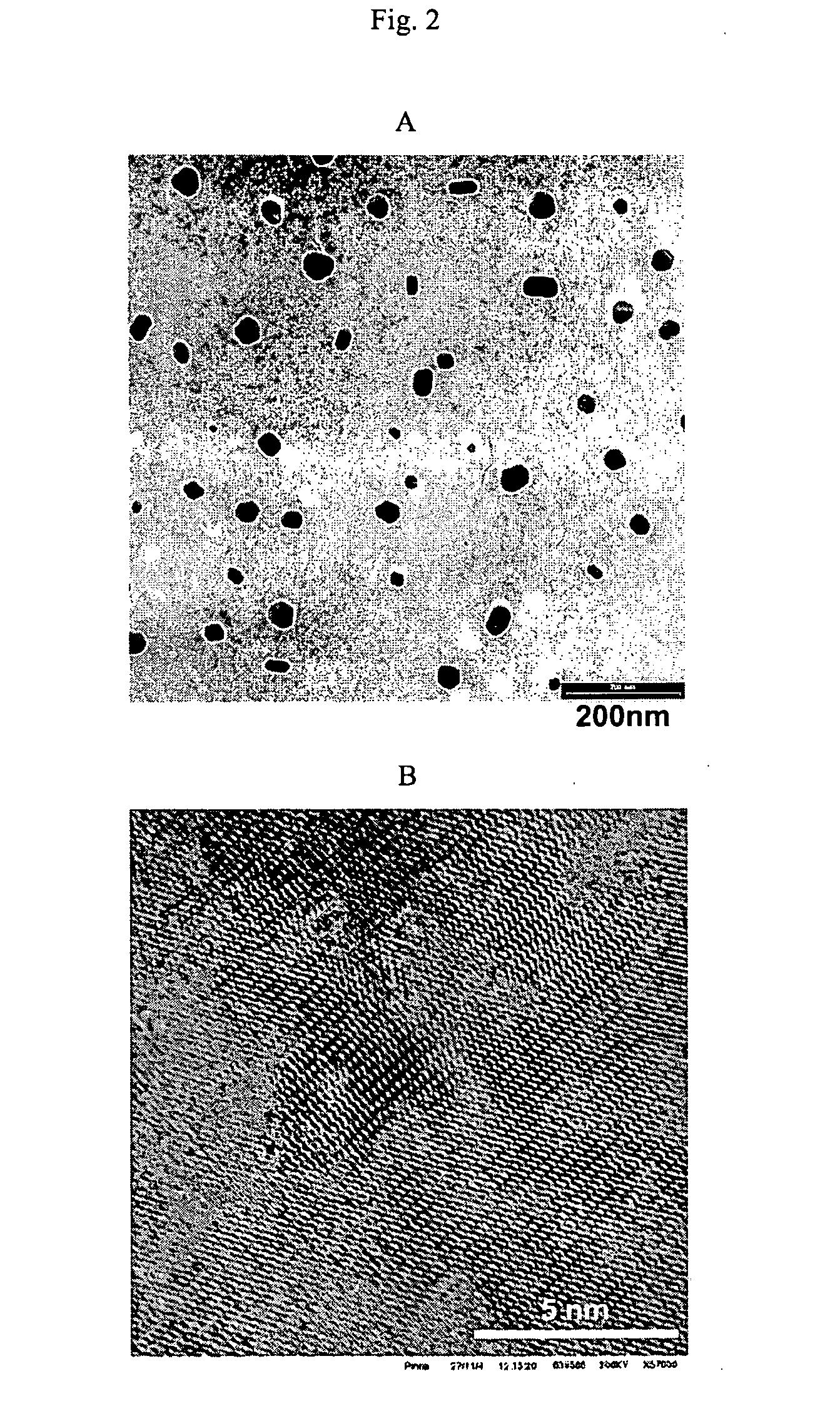
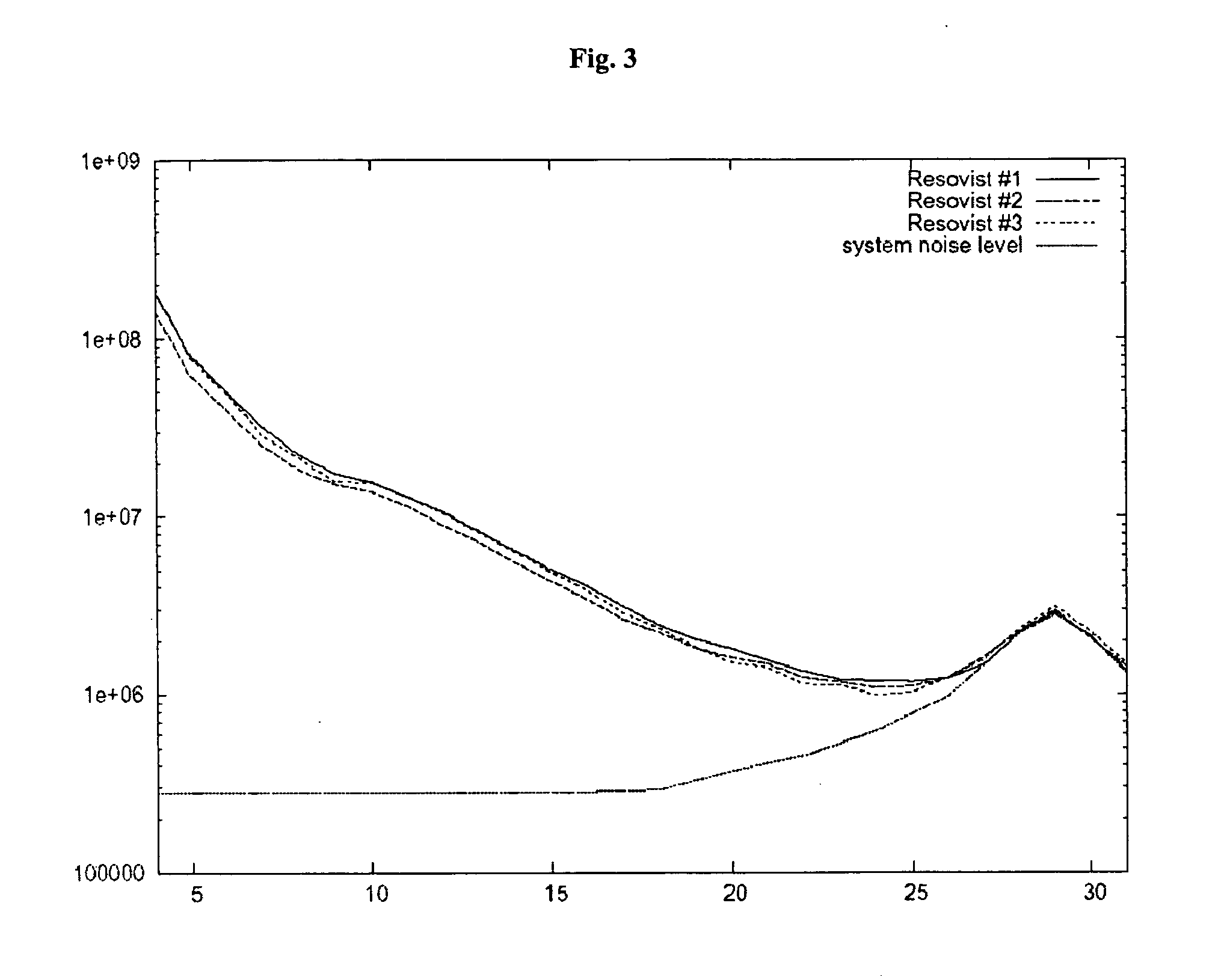
The present invention relates to complexes which contain magnetic iron oxide particles in a pharmaceutically acceptable shell, said particles having a diameter of 20 nm to 1 μm with an overall particle diameter / core diameter ratio of less than 6, and to the use of these complexes in magnetic particle imaging (MPI). Particular preference is given to the use of these compositions in examining the gastrointestinal tract, the vascular system of the heart and cranial components, in the diagnosis of arteriosclerosis, infarctions, and tumors and metastases, for example of the lymphatic system.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for use of nanoparticles in imaging and temperature measurement
ActiveUS20110273176A1Improve rendering capabilitiesHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic particle imagingHarmonic
This invention provides a system and method that improves the sensitivity and localization capabilities of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) by using combinations of time-varying and static magnetic fields. Combinations of magnetic fields can be used to distribute the signals coming from the magnetic particles among the harmonics and other frequencies in specific ways to improve sensitivity and to provide localization information to speed up or improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of imaging and / or eliminate the need for saturation fields currently used in MPI. In various embodiments, coils can be provided to extend the sub-saturation region in which nanoparticles reside; to provide a static field offset to bring nanoparticles nearer to saturation; to introduce even and odd harmonics that can be observed; and / or to introduce combinations of frequencies for more-defined observation of signals from nanoparticles. Further embodiments provide for reading of the signal produced by cyclically saturated magnetic nanoparticles in a sample so as to provide a measurement of the temperature of those nanoparticles.
Owner:DARTMOUTH HITCHCOCK CLINIC
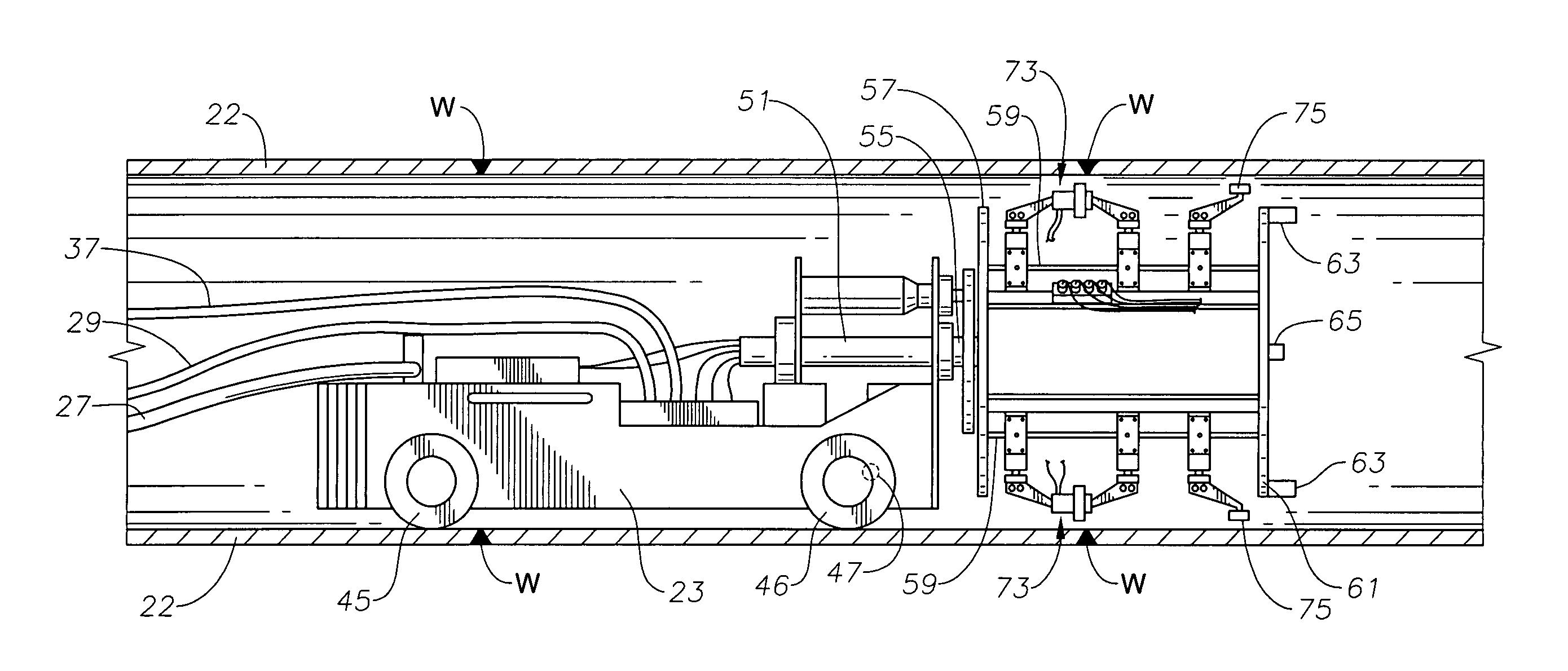
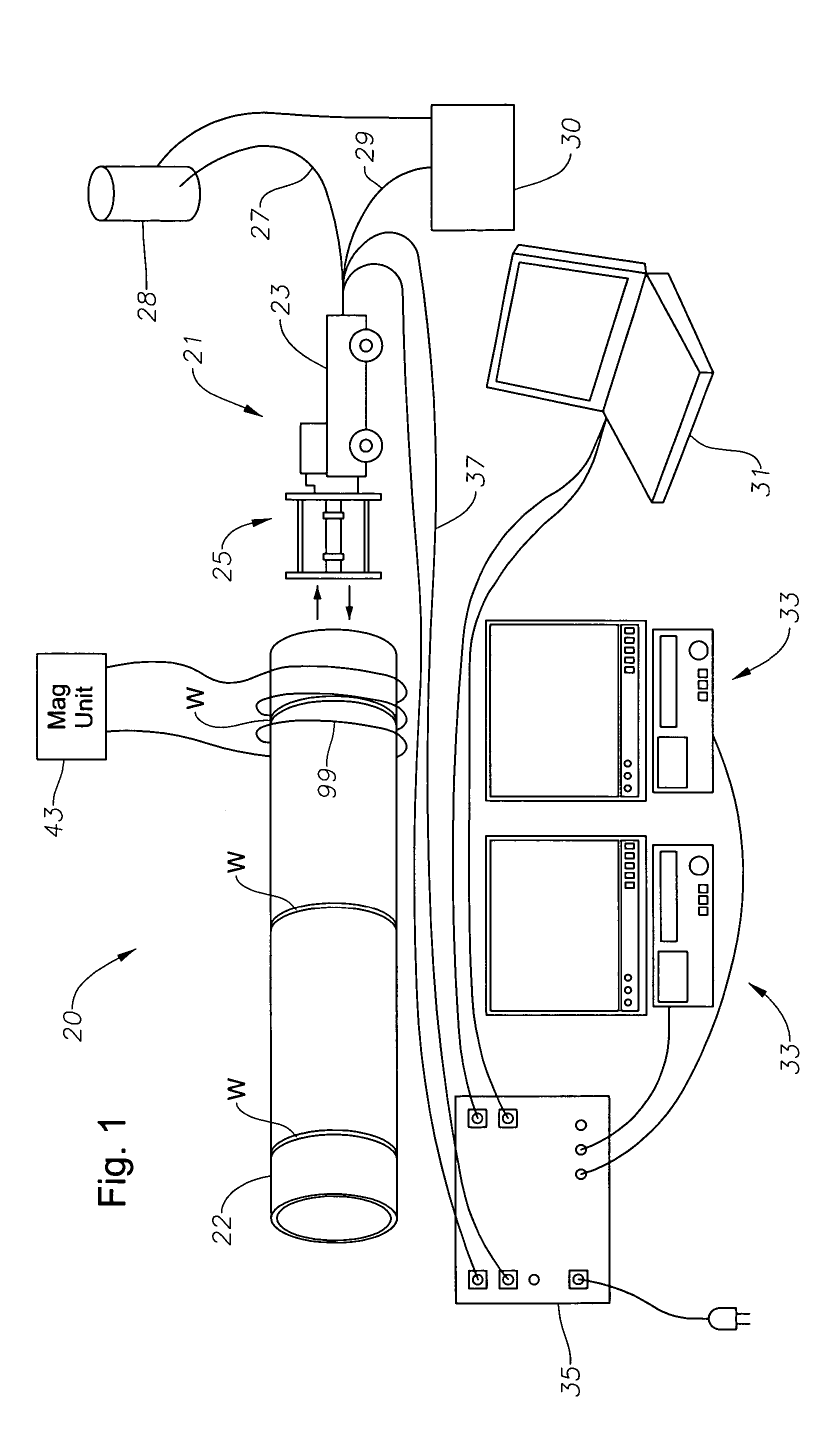
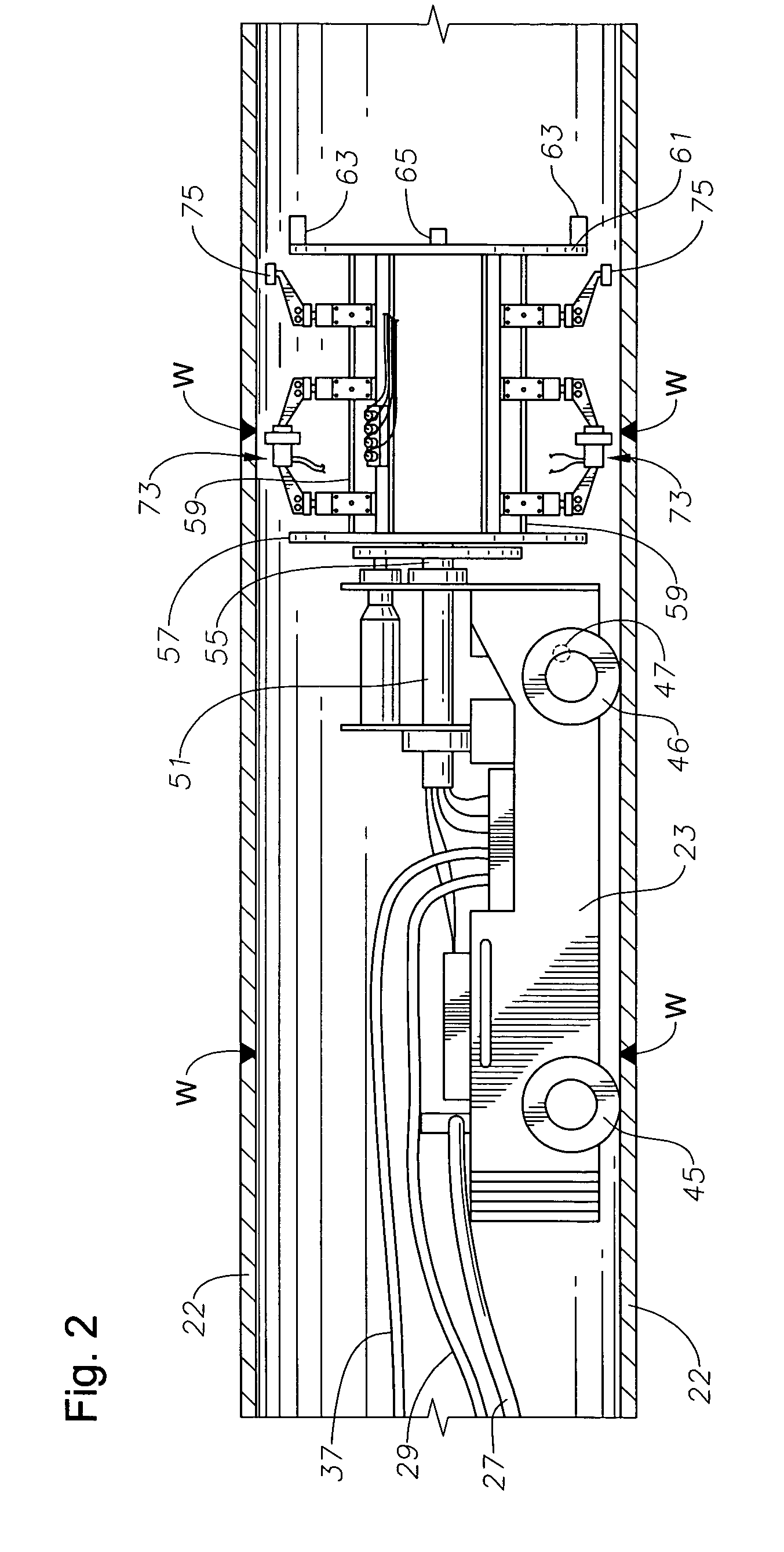
Internal riser inspection system, apparatus and methods of using same
InactiveUS7107863B2Prevent accidental contactImprove acquisitionSurveyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDrive wheelMagnetic particle imaging
A system for inspecting a pipe weld from within a pipe through use of magnetic particle imaging “MPI” includes an apparatus having a head unit that carries a wire wheel brush for cleaning an inspection area along an inner diameter of a pipe weld, and an MPI medium dispenser for spraying an MPI medium upon the inspection area, both controlled by an operator. The head unit also includes a video inspection device controlled by the operator and used for viewing at least portions of the inspection area after being sprayed with the MPI medium and when under the influence of a magnetic field to determine if the weld has any defects. The head unit is connected to a drive unit. The drive unit includes a frame having a longitudinal axis and mounted on a set of drive wheels, and a set of support wheels spaced axially from the drive wheels. A linear drive motor mounted to the frame and coupled to the drive wheels moves the head unit linearly along an interior of the pipe between weld inspection areas to allow the operator to locate and inspect the welds from within the pipe.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Apparatus and method for determining at least one electromagnetic quantity
InactiveCN102469952ADiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field sensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetization
The present invention relates to an apparatus (100) for determining at least one electromagnetic quantity characterizing an electromagnetic property of an object, in particular a human body, wherein said object contains magnetic particles. The apparatus (100) applying the known principle of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) comprises selection means for generating a magnetic selection field (50) having the known field pattern showing a field free point (FFP), drive means for changing the position in space of the FFP by means of a magnetic drive field, receiving means for acquiring detection signals depending on the magnetization of the magnetic particles within a field of view (28) and a reconstruction unit (152) for reconstructing a particle distribution quantity depending on the detection signals. The apparatus (100) further comprises a control unit (150) for controlling the receiving means for acquiring a first set of detection signals corresponding to a first drive field frequency and a second set of detection signals corresponding to a second drive field frequency, with both drive field frequencies differing from each other. The control unit (15) further controls the reconstruction unit (152) for reconstructing a first particle distribution quantity depending on the first set of detection signals and a second particle distribution quantity depending on the second set of detection signals. The apparatus (100) further comprises a determination unit (160) for determining the electromagnetic quantity depending on the first and second particle distribution quantity. The present invention further relates to a corresponding method as well as to a computer program.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic particle imaging apparatus, method of disposing detection coil for magnetic particle imaging apparatus, and magnetic flux detecting apparatus
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Arrangement and method for detecting and/or locating a magnetic material in a region of action
InactiveUS20110246103A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce in quantityDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical measurementsMagnetic particle imagingImage resolution
In Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) the reconstruction requires the knowledge of a so called system function. This function describes the relation between spatial position and frequency response and is currently measured once for a scanner set-up and a tracer material. For reasonable resolutions and fields of view the system function becomes quite large, resulting in large acquisition times to obtain reasonable signal-to-noise. However, the system function has a number of properties which can be used to improve signal-to-noise. According to the present invention use is made of the spatial symmetry and / or identical responses at different frequencies for this purpose.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
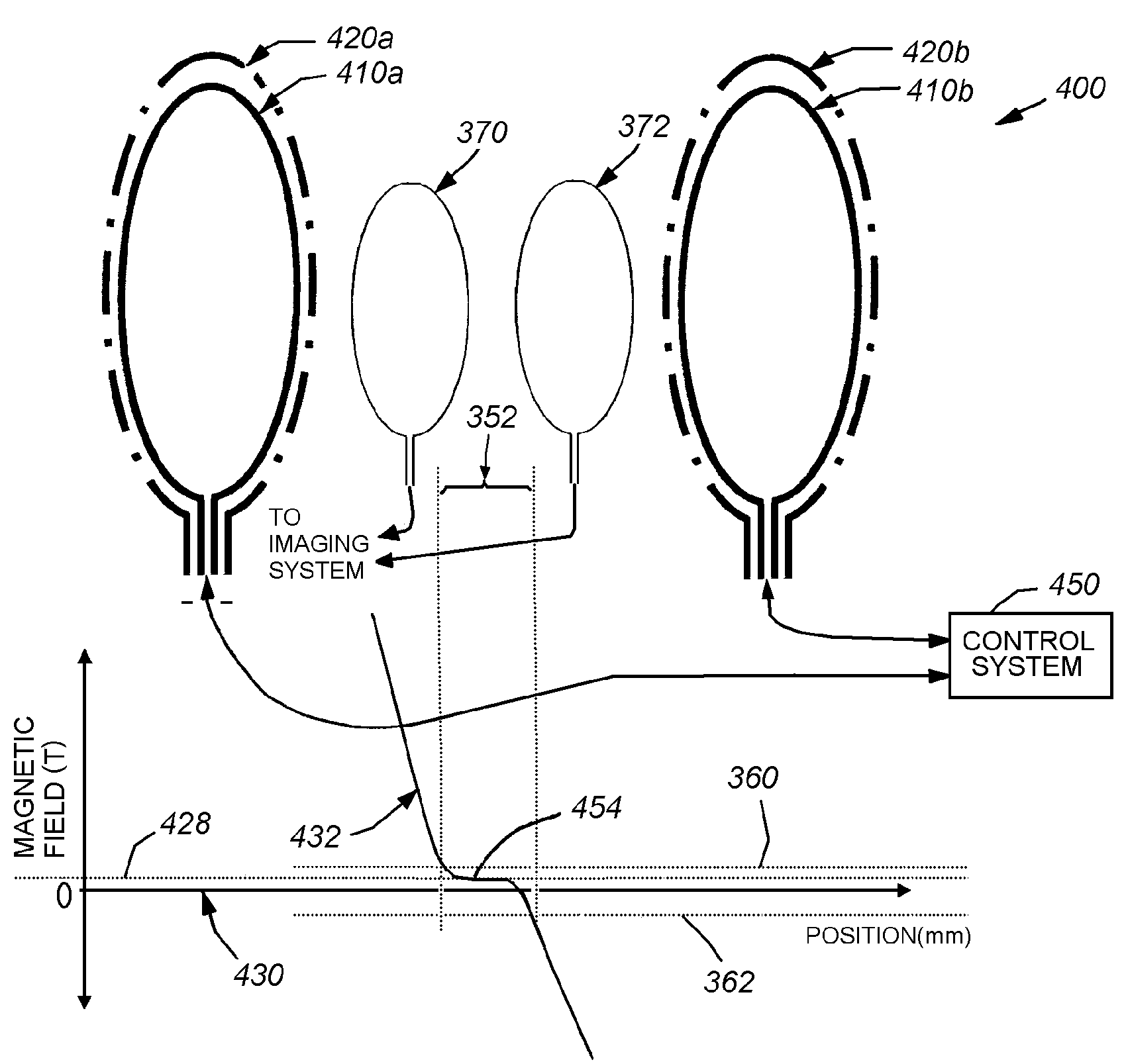
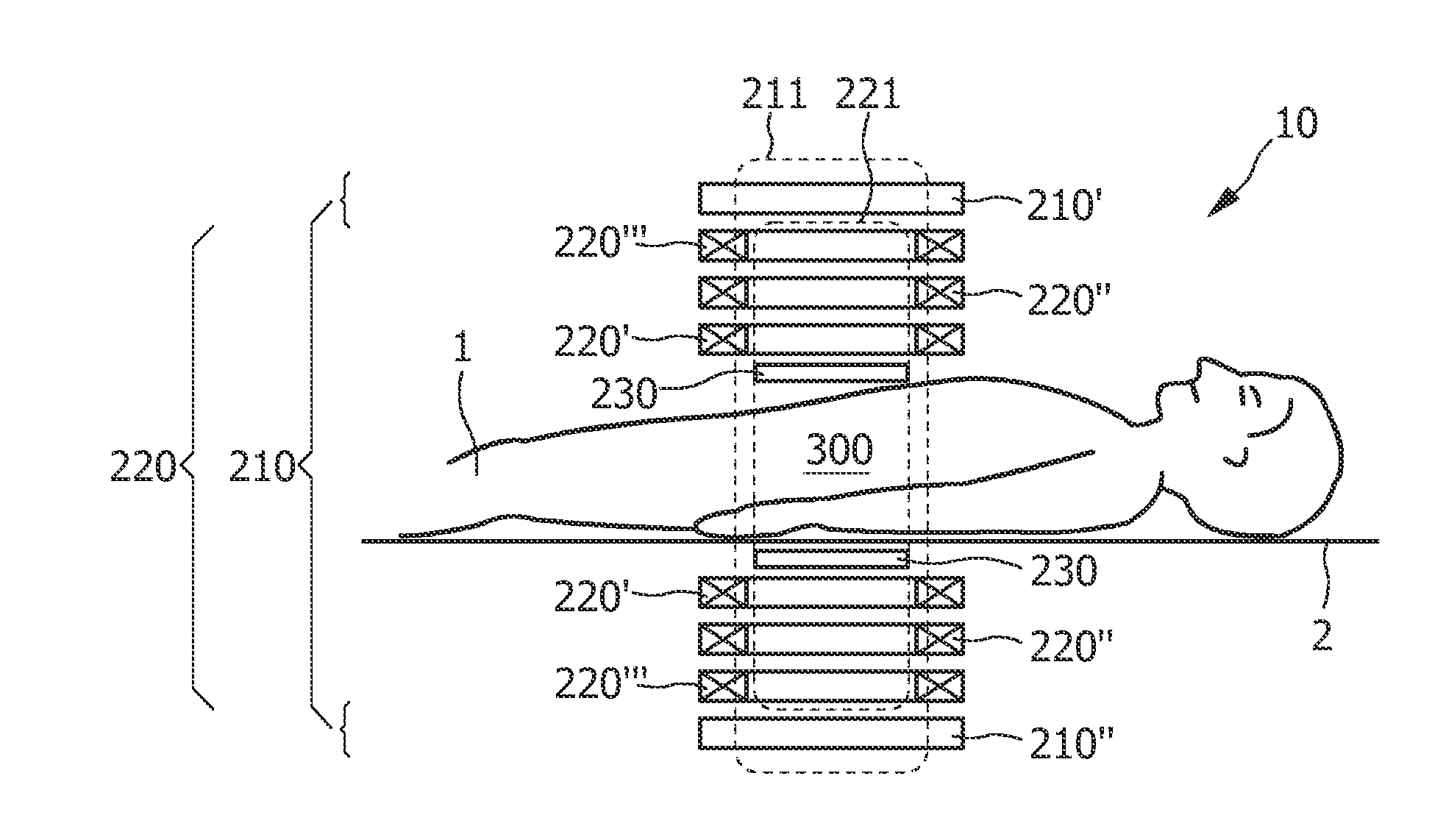
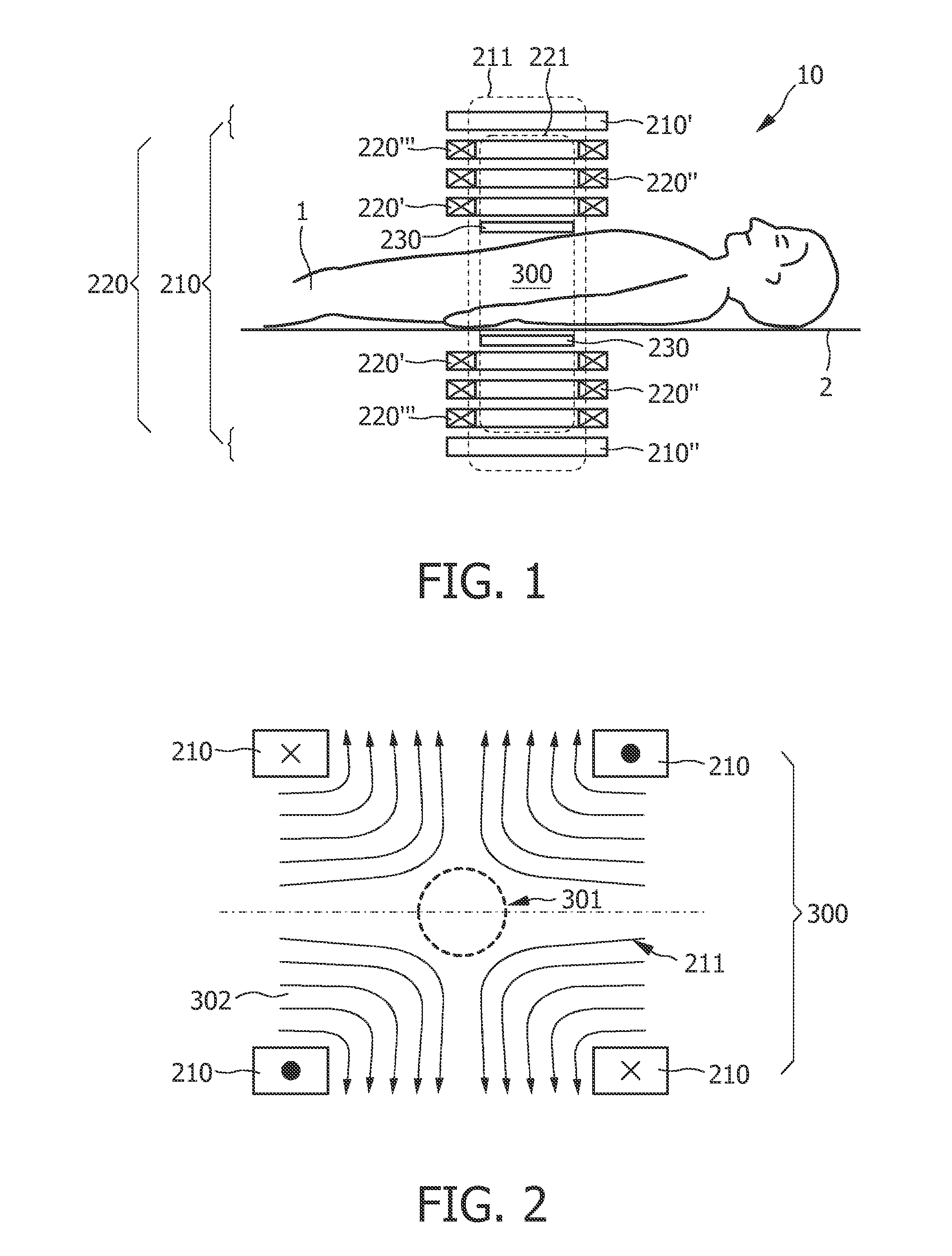
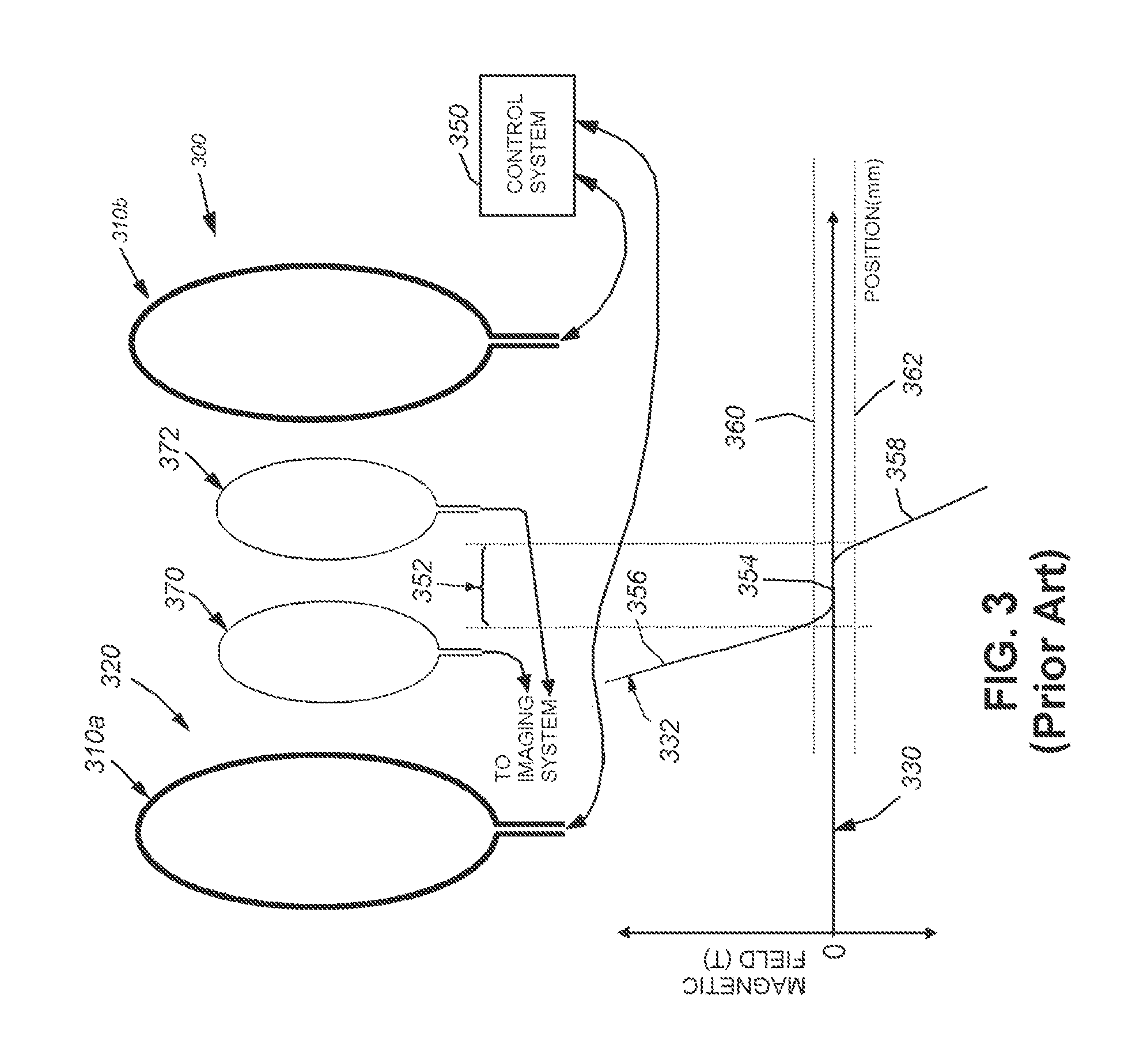
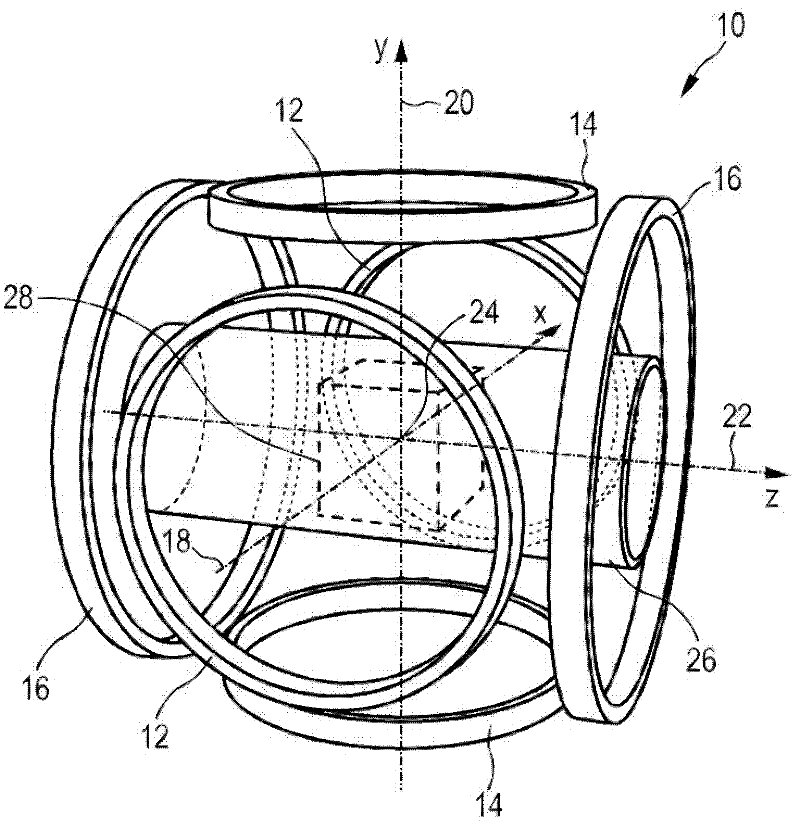
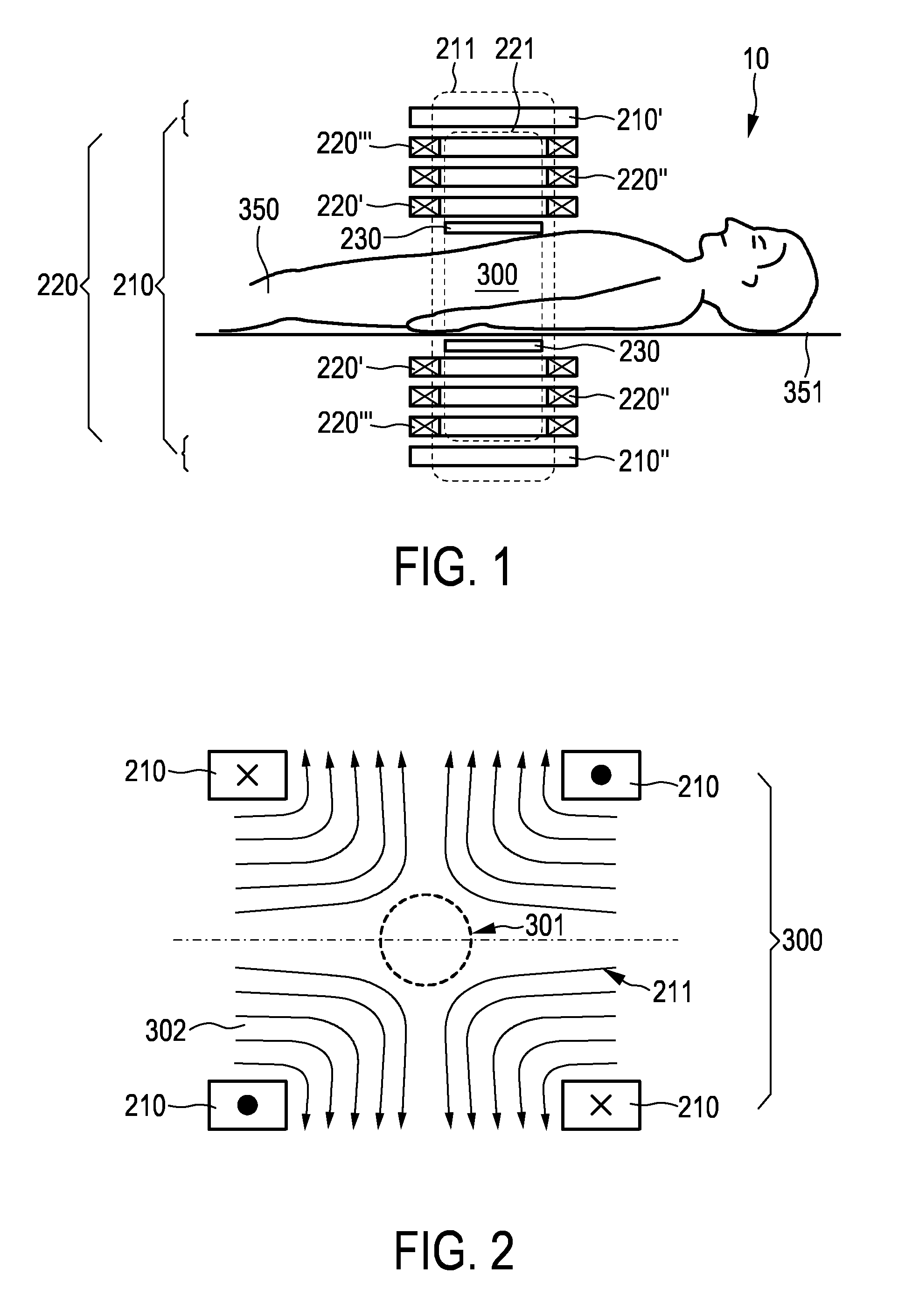
Arrangement with variable selection field orientation for magnetic particle imaging
ActiveUS20110234217A1Improve imaging resolutionSpatial selectivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic gradient
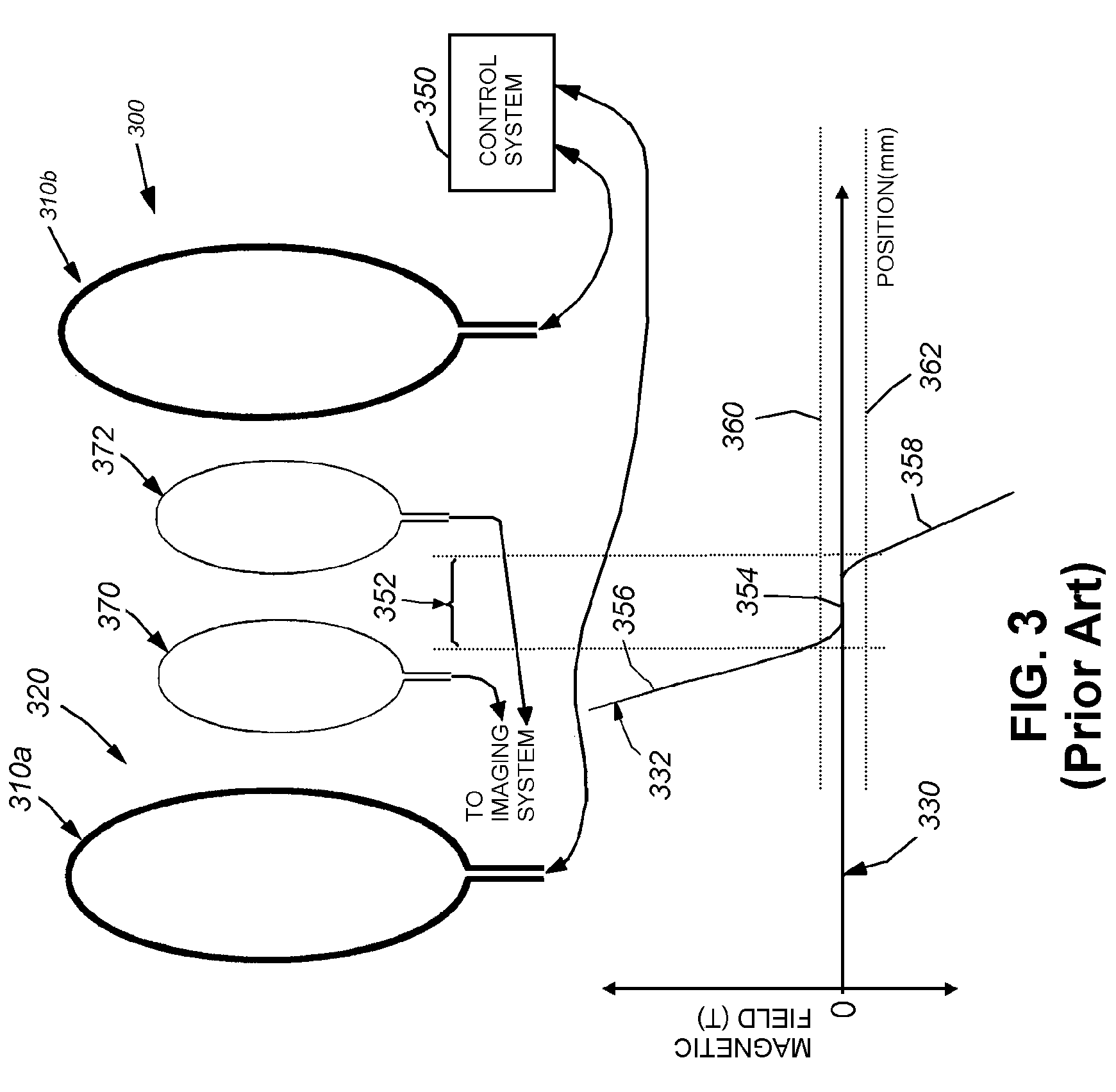
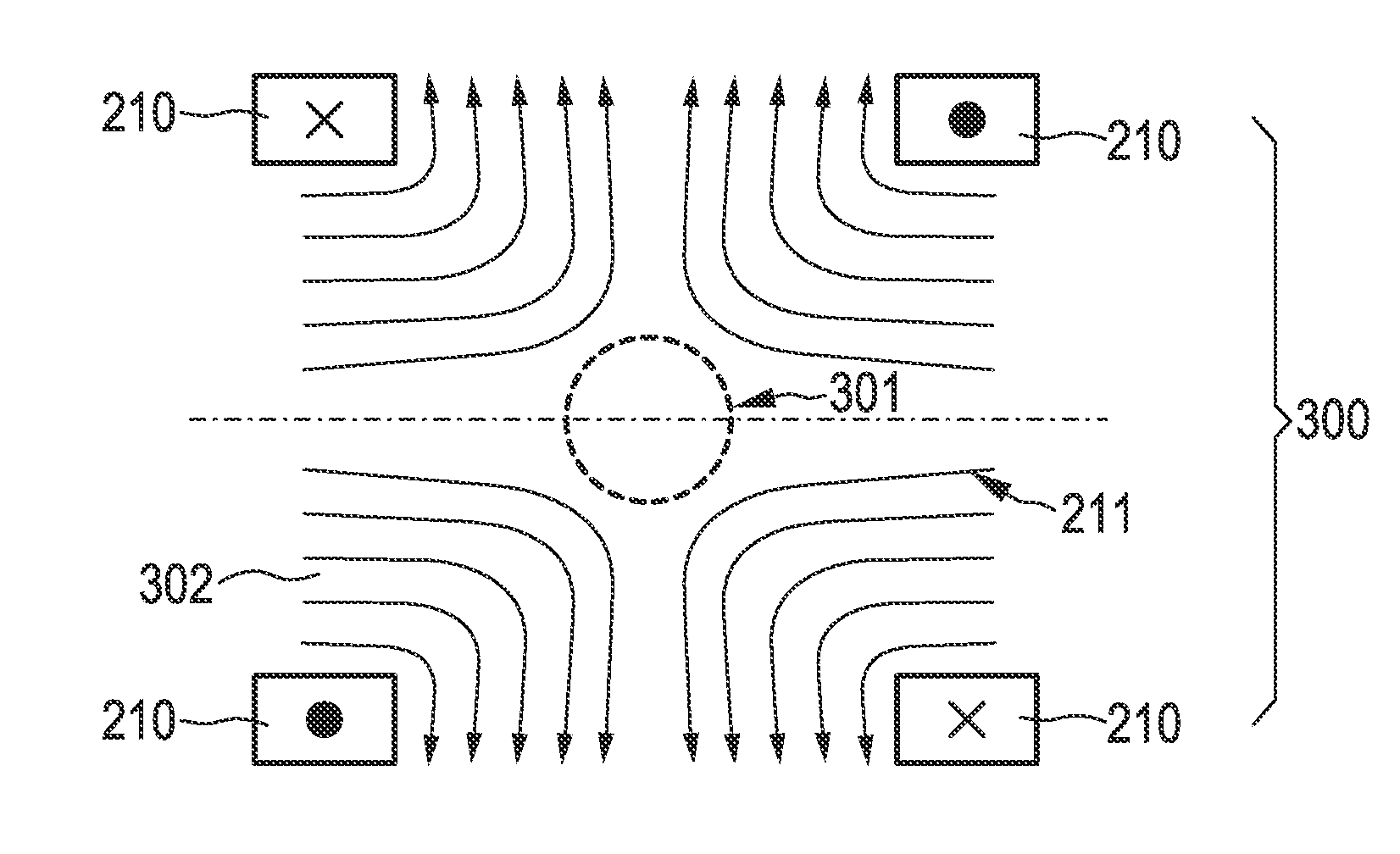
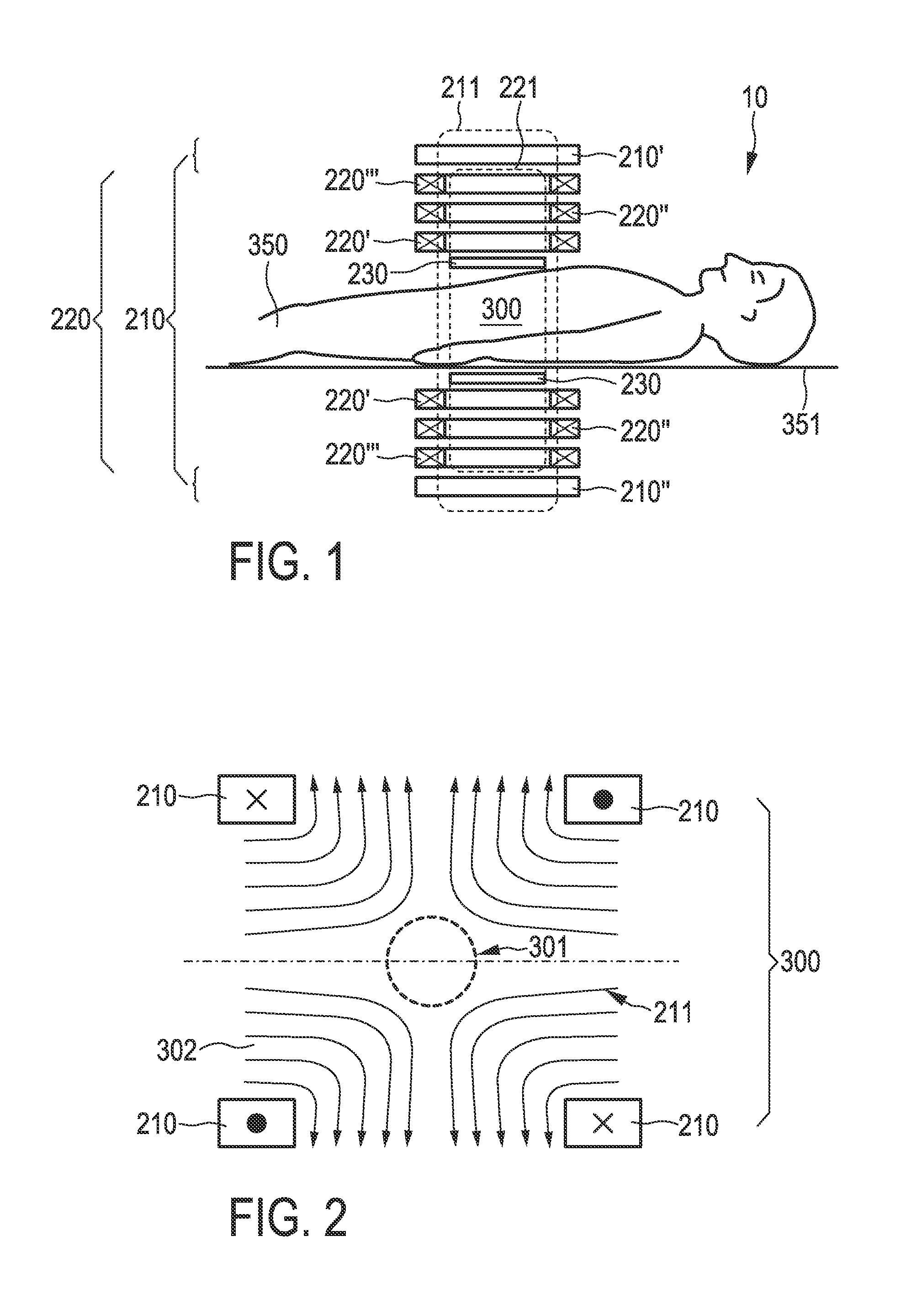
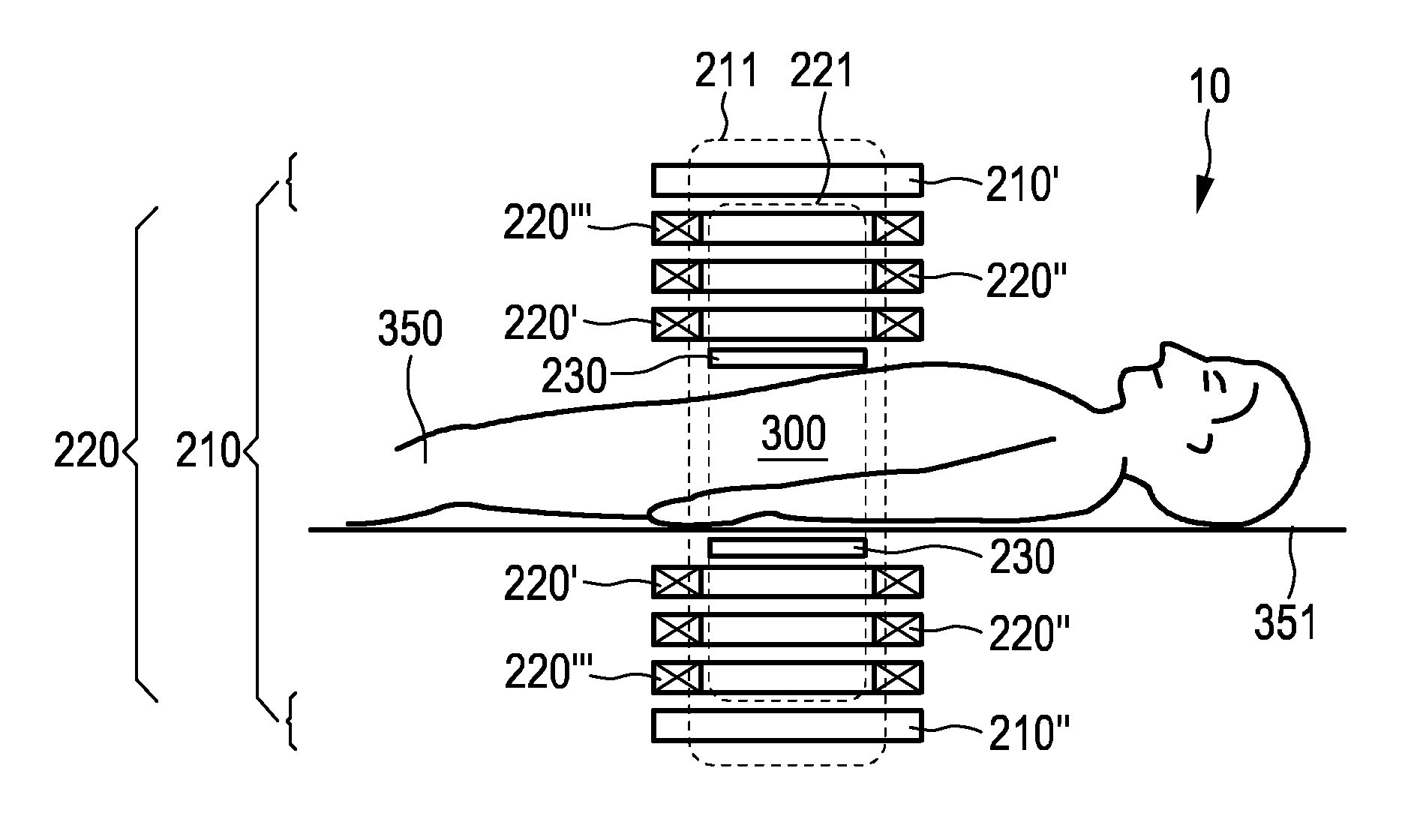
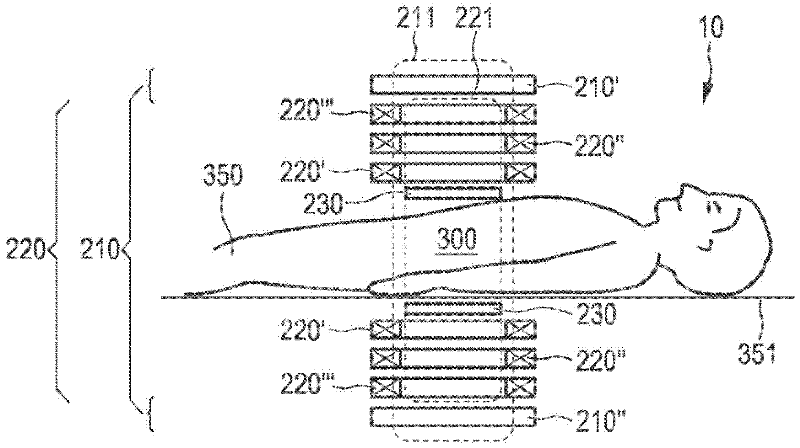
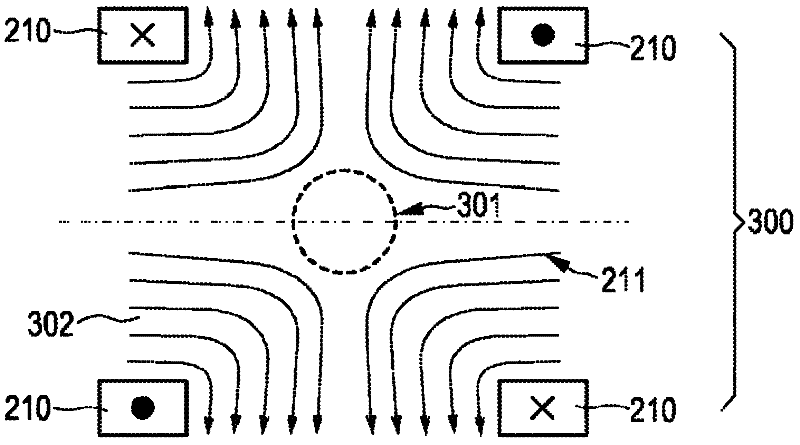
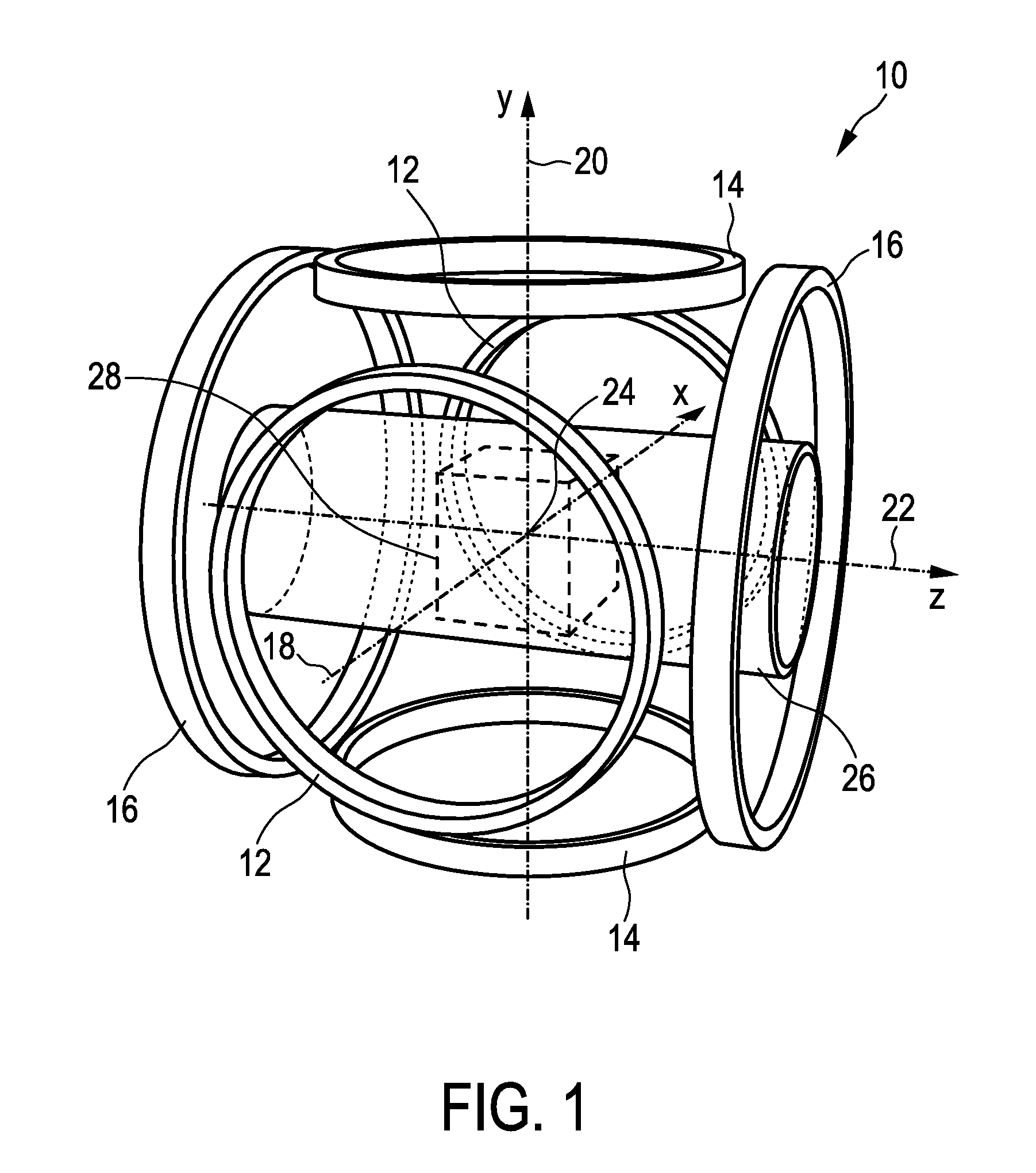
The present invention relates to an arrangement (10) for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles (100) in a region of action (300), which comprises selection means (210) for generating a magnetic selection field (211) having a pattern in space of its magnetic field strength such that a first sub-zone (301) having a low magnetic field strength and a second sub-zone (302) having a higher magnetic field strength are formed in the region of action (300). The arrangement further comprises drive means (220) for changing the position in space of the two sub-zones (301, 302) in the region of action (300) by means of a magnetic drive field (221) so that the magnetization of the magnetic material changes locally. The arrangement further comprises receiving means (230) for acquiring detection signals, which detection signals depend on the magnetization in the region of action (300), which magnetization is influenced by the change in the position in space of the first and second sub-zone (301, 302). Control means (76) are further introduced for controlling the selection means (210) to individually set the gradient strength of at least one of the static magnetic gradient fields (211) in a desired direction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic particle imaging system based on magnetic field-free line scanning
ActiveCN110367983APrecise positioningHigh precisionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingPower flow
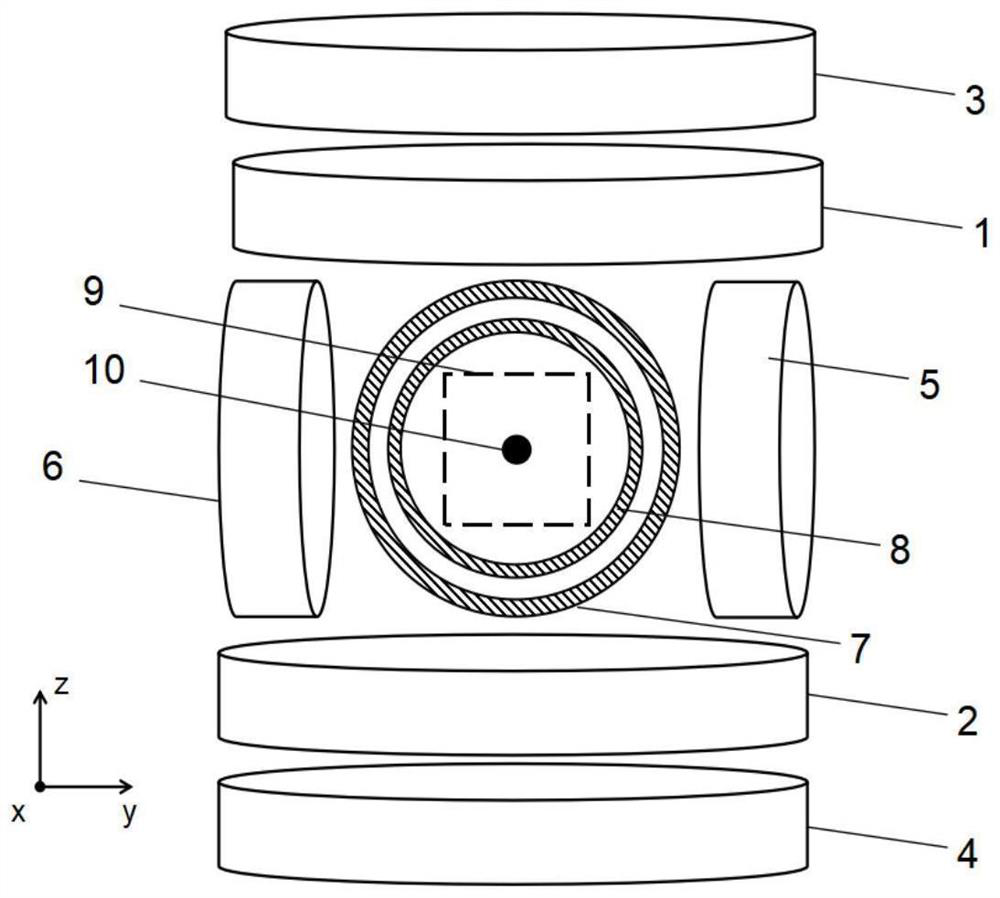
The invention belongs to the field of magnetic particle imaging, particularly relates to a magnetic particle imaging system based on magnetic field-free line scanning and is intended to solve the problem that a magnetic particle imaging system has unsatisfactory sensitivity and resolution. The magnetic particle imaging system based on magnetic field-free line scanning comprises a magnet unit, an induction coil, an imaging table, and a control and imaging device; the magnet unit comprises two pairs of circular magnets in axial orthogonal arrangement and a tubular magnet; two circular magnets ineach pair of circular magnets are coaxial; the tubular magnet is arranged in an enclosure space of the two pairs of circular magnets, and the axis of the tubular magnet crosses through an orthogonalpoint of the axes of the two pairs of circular magnets and is perpendicular to a plane formed by the axes of the two pairs of circular magnets; the control and imaging device is used to control changes in magnetic fields of the magnets in the magnet unit according to set control instructions so that magnetic field-free line rotation and / or shift is achieved; magnetic particle imaging is performedon current signals generated in the induction coil according to an induction magnetic field. The magnetic particle imaging system has the advantages that magnetic particle positioning precision is improved and resolution is increased.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
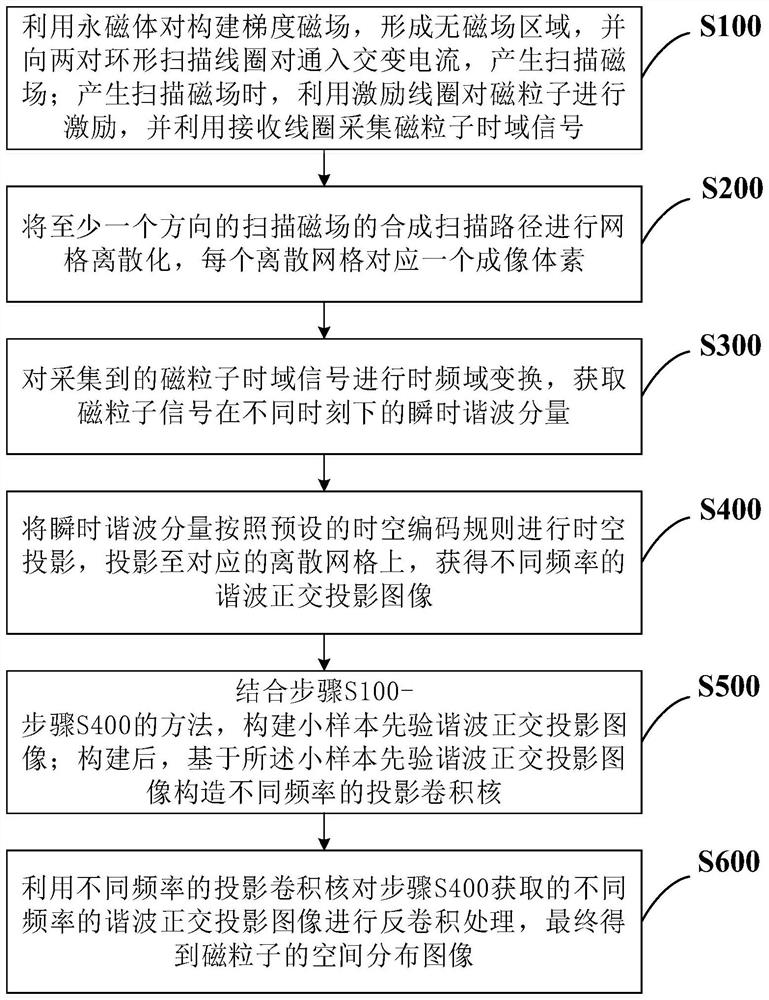
Magnetic particle imaging method, system and equipment based on harmonic orthogonal projection
PendingCN114246574AImprove spatial resolutionHigh-resolutionReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic particle imagingHigh resolution imaging
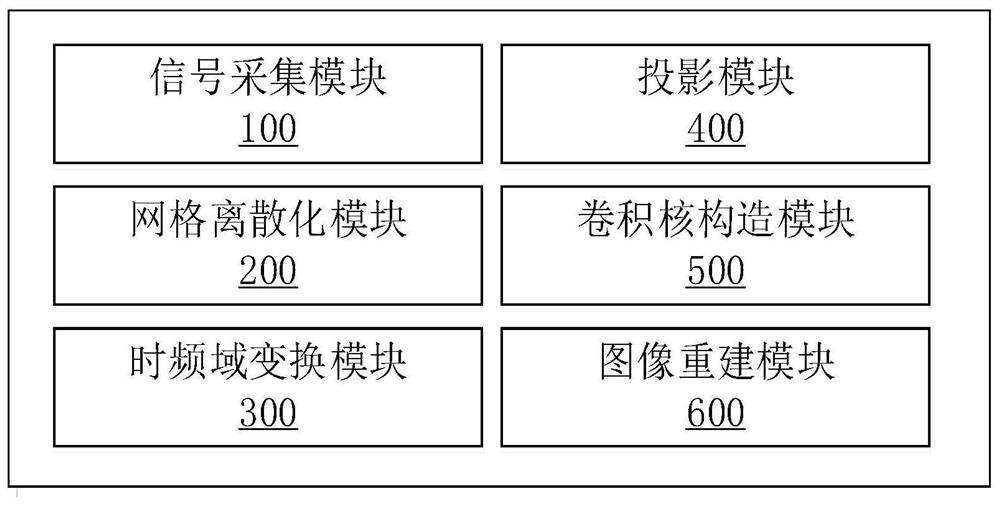
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical imaging, particularly relates to a magnetic particle imaging method, system and equipment based on harmonic orthogonal projection, and aims to solve the problem that an existing magnetic particle imaging method cannot realize rapid high-resolution imaging under the conditions of a high driving magnetic field and a low gradient magnetic field. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a magnetic particle time domain signal; performing grid discretization on a composite scanning path of the scanning magnetic field; performing time-frequency domain transformation on the acquired magnetic particle time domain signal; projecting the instantaneous harmonic components to the corresponding discrete grids to obtain harmonic orthogonal projection images with different frequencies; constructing a small sample prior harmonic orthogonal projection image, and further constructing projection convolution kernels of different frequencies; and performing deconvolution on the harmonic orthogonal projection image by using the projection convolution kernel to obtain a spatial distribution image of the magnetic particles. According to the invention, the spatial resolution of magnetic particle imaging is improved, and spatial distribution rapid high-resolution imaging of magnetic particles under the condition of a strong excitation magnetic field is realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Arrangement and method for detecting and/or locating a magnetic material in a region of action
In Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) the reconstruction requires the knowledge of a so called system function. This function describes the relation between spatial position and frequency response. For reasonable resolutions and field of views the system function becomes quite large, resulting in large acquisition times for the system function and high memory demand during reconstruction. The present invention proposes to reduce the size of the system function matrix by making use of structural properties of the matrix. Such properties are, for instance, spatial symmetries reducing the number ofcolumns and identical responses at different frequencies reducing the number of rows. In other embodiments the matrix can be transformed to a sparse representation using appropriate base functions.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
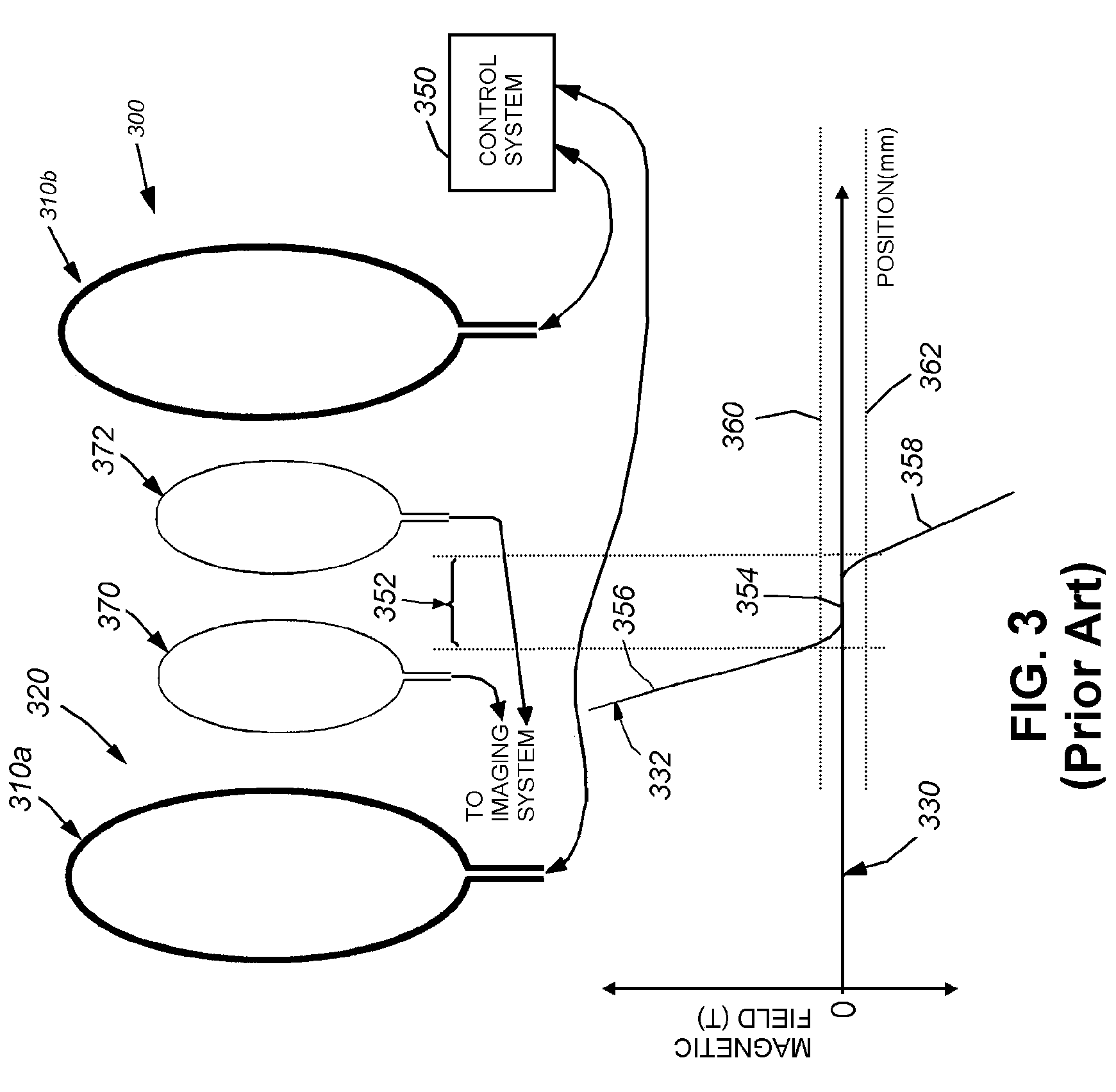
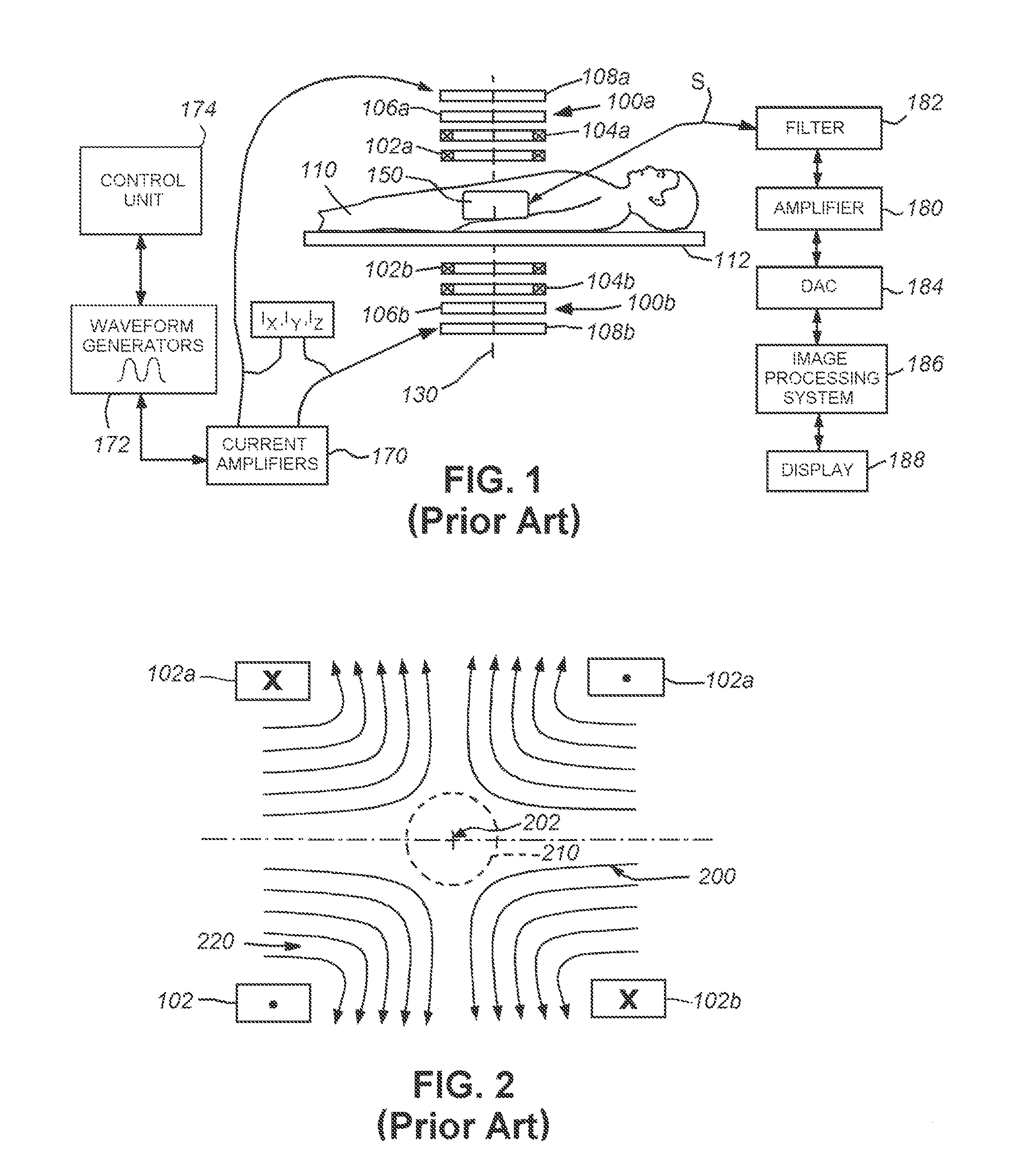
Techniques for magnetic particle imaging
ActiveUS8847592B2Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
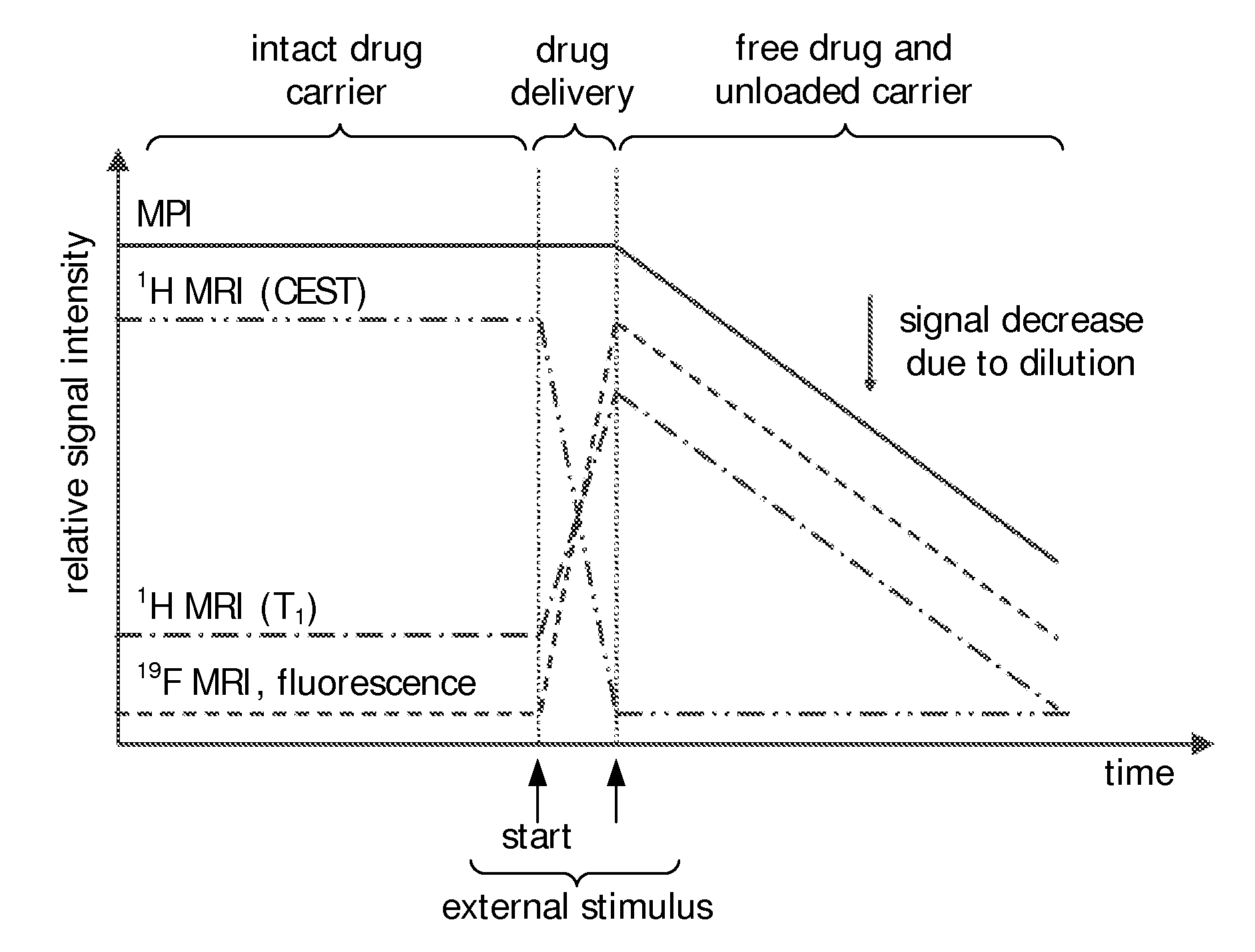
Stimuli-responsive carriers for mpi-guided drug delivery
InactiveUS20120100079A1High sensitivityHigh resolutionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsMagnetic particle imagingStimuli responsive
The present invention relates to a composition comprising a shell structure forming a cavity, wherein said shell structure comprises a drug and wherein said composition is associated with at least one contrast agent; wherein said shell structure is capable of releasing its contents into the exterior upon the application of an external stimulus and wherein said contrast agent comprises magnetic particles which are capable of being detected by Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI), wherein at least more than 5% (w / w) of the magnetic particles comprised in said contrast agent have a magnetic moment of at least −18 m 2 A, 10 wherein said magnetic particles are preferably composed of Fe, Co, Ni, Zn or Mn or alloys thereof or oxides of any of these. The present invention further relates to the use of such a composition or a composition comprising a shell structure forming a cavity, wherein said shell structure comprises a drug and wherein said composition is associated with at least one contrast agent, wherein said contrast agent is capable of being detected by MPI and wherein said shell structure is capable of releasing its contents into the exterior upon the application of an external stimulus as a carrier for a controlled delivery of a drug, as well as to a method of data acquisition for the control of a drug delivery process comprising the detection or localization via MPI of such compositions. In a further aspect the present invention relates to such compositions for treating a pathological condition, wherein the treatment comprises the release of the drug by the application of a stimulus.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
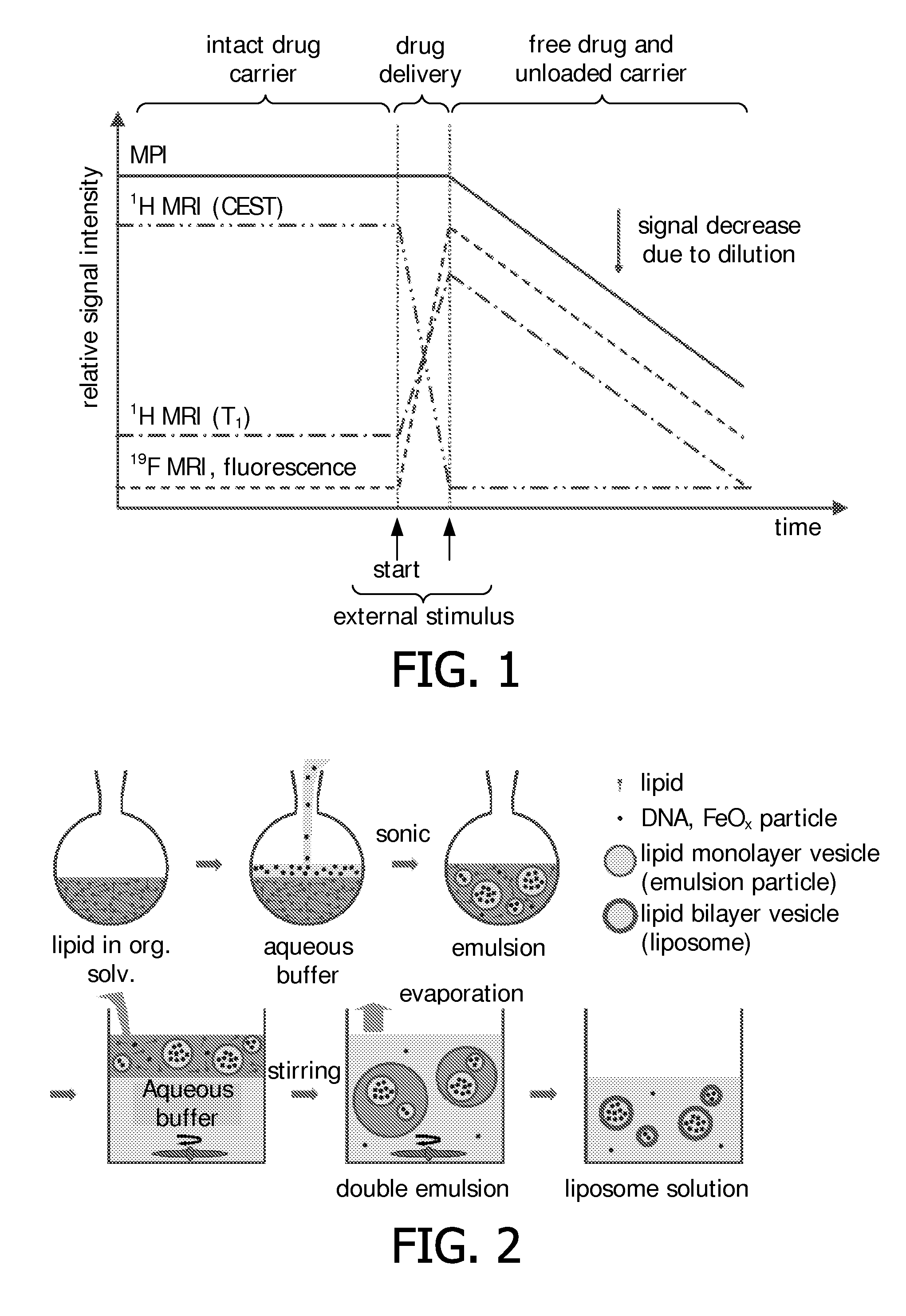
Clustered magnetic particles as tracers for magnetic particle imaging
InactiveUS20110182821A1Improve magnetic propertiesGood monodispersityDispersion deliveryNanomedicinePhysicsMagnetic particle imaging
The invention provides a magnetic tracer material for use in magnetic particle imaging and a manufacturing method thereof. The magnetic tracer material comprises clusters of a plurality of magnetic particles that are clustered in a controlled way to form individual entities, for example, stabilized oil droplets, solid emulsion particles, liposomes, polymersomes or vesicles, or naturally occurring biological entities such as cells or viruses.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic particle imaging detection system and method and electronic equipment
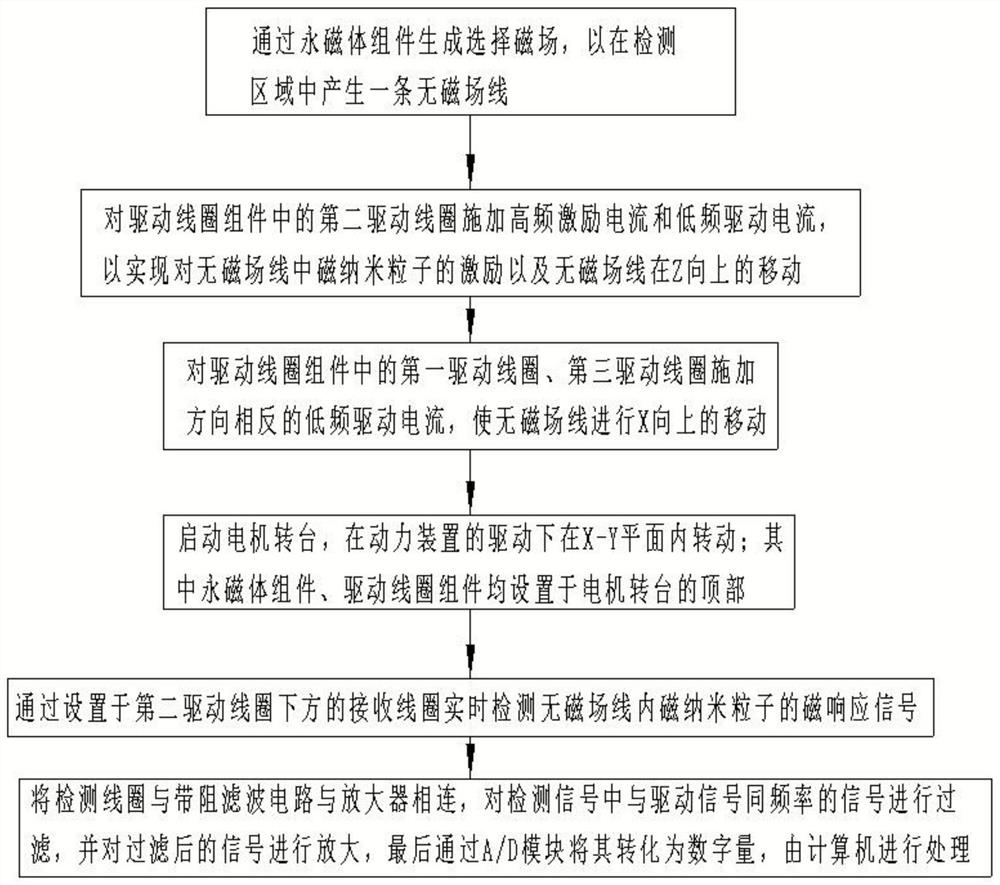
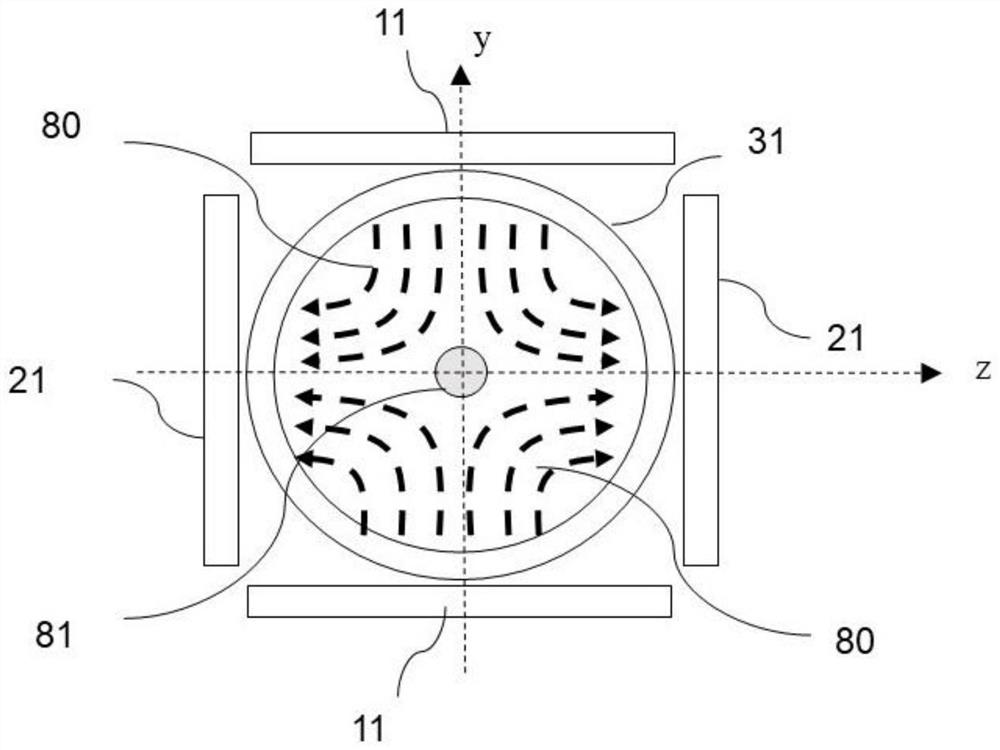
ActiveCN113288106ACompact structureReduce volumeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLow noiseMagnetic particle imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical imaging detection, particularly relates to a three-dimensional magnetic particle imaging detection system and method and electronic equipment, and aims to solve the problems that a magnetic particle imaging detection device is closed in structure, large in size and poor in flexibility. The system comprises a permanent magnet assembly, a driving coil assembly, a receiving coil, a motor turntable and a processing circuit; the permanent magnet assembly is used for generating non-magnetic field lines in a detection space; the driving coil assembly is used for generating an oscillating magnetic field perpendicular to the non-magnetic-field lines. the receiving coil is used for receiving a magnetic response signal generated by the magnetic nanoparticles in the detection space; the motor turntable can rotate under the driving of the power device; the processing circuit comprises a band elimination filter circuit, an amplifier and an A / D module; the band elimination filter circuit is used for attenuating a fundamental frequency signal in the detection signal; the amplifier is used for carrying out low-noise amplification on the detection signal; and the A / D module is used for sampling the signal and converting the signal into a digital quantity. According to the magnetic particle imaging detection system structure is compact, the size is small, and open type detection can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Whole-body-oriented three-dimensional magnetic particle imaging method, system and equipment
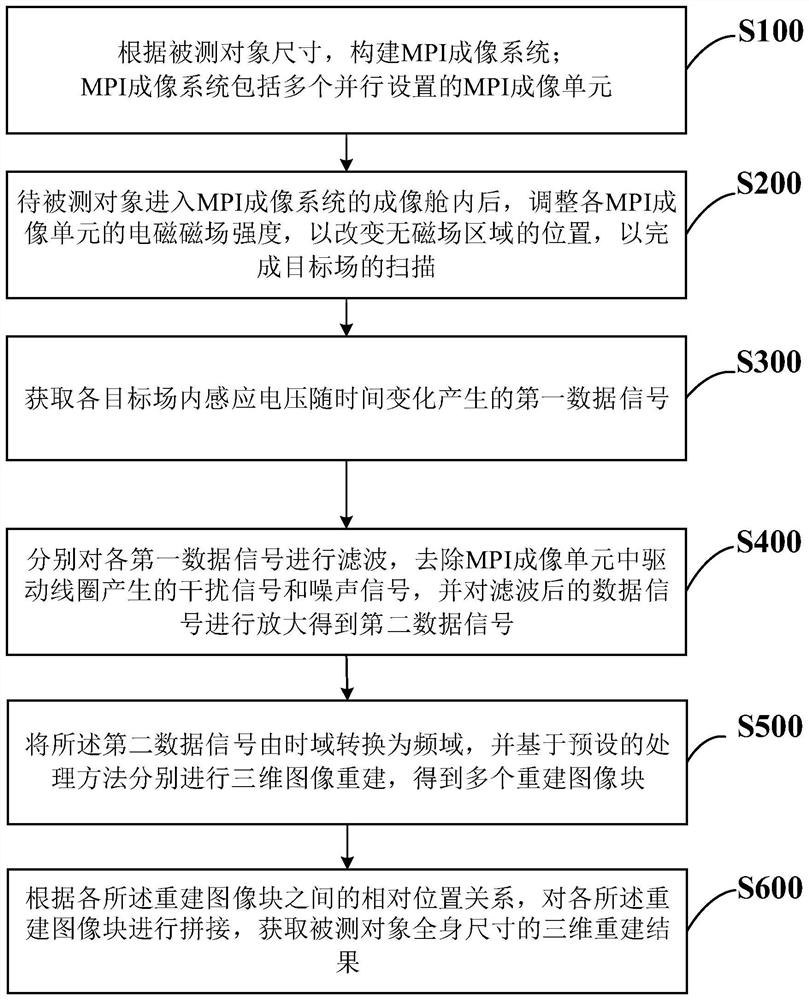
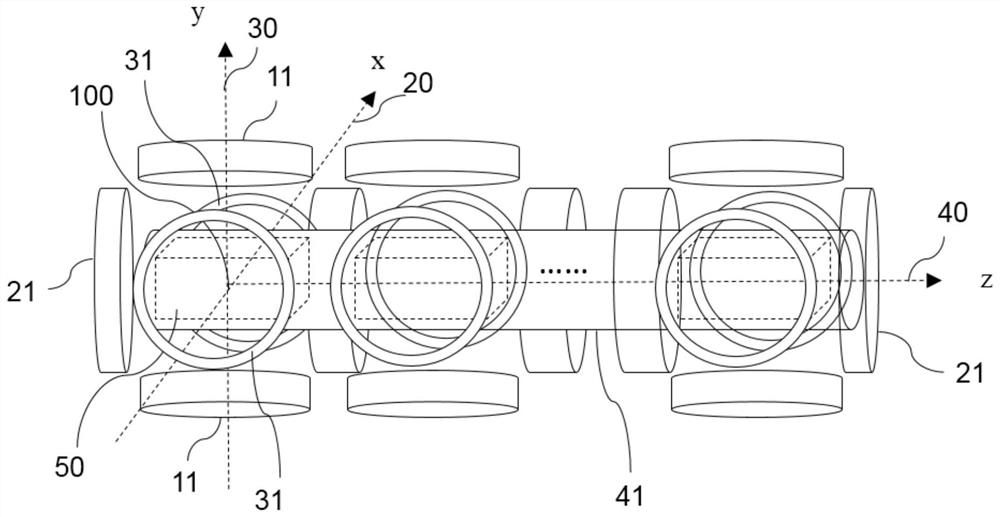
InactiveCN113331812AEnabling Whole Body ImagingImprove inspection accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNuclear physicsMagnetic particle imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic particle imaging, particularly relates to a whole-body-oriented three-dimensional magnetic particle imaging method, a system and an equipment, and aims to solve the problem that whole-body imaging cannot be performed simultaneously during magnetic particle imaging. According to the invention, a single group of magnetic particle imaging systems are coupled to form an array type magnetic particle imaging system, and the imaging view is enlarged from a local part to a whole body size. In the signal acquisition process, excitation and receiving coils of each group of magnets in the whole body magnetic particle imaging system are synchronized, denoising and filtering amplification are carried out on obtained electromagnetic induction signals, image reconstruction is carried out by utilizing a deconvolution or regularization method, reconstructed images in all imaging view fields are spliced, finally, a three-dimensional distribution image of the magnetic particles in the whole body is obtained, whole-body imaging of an observed object is achieved, and high examination and diagnosis accuracy is achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for non-invasive intracardiac electrocardiography using mpi
InactiveUS20120172738A1Easy and fast applicationPatient comfortElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalElectricity
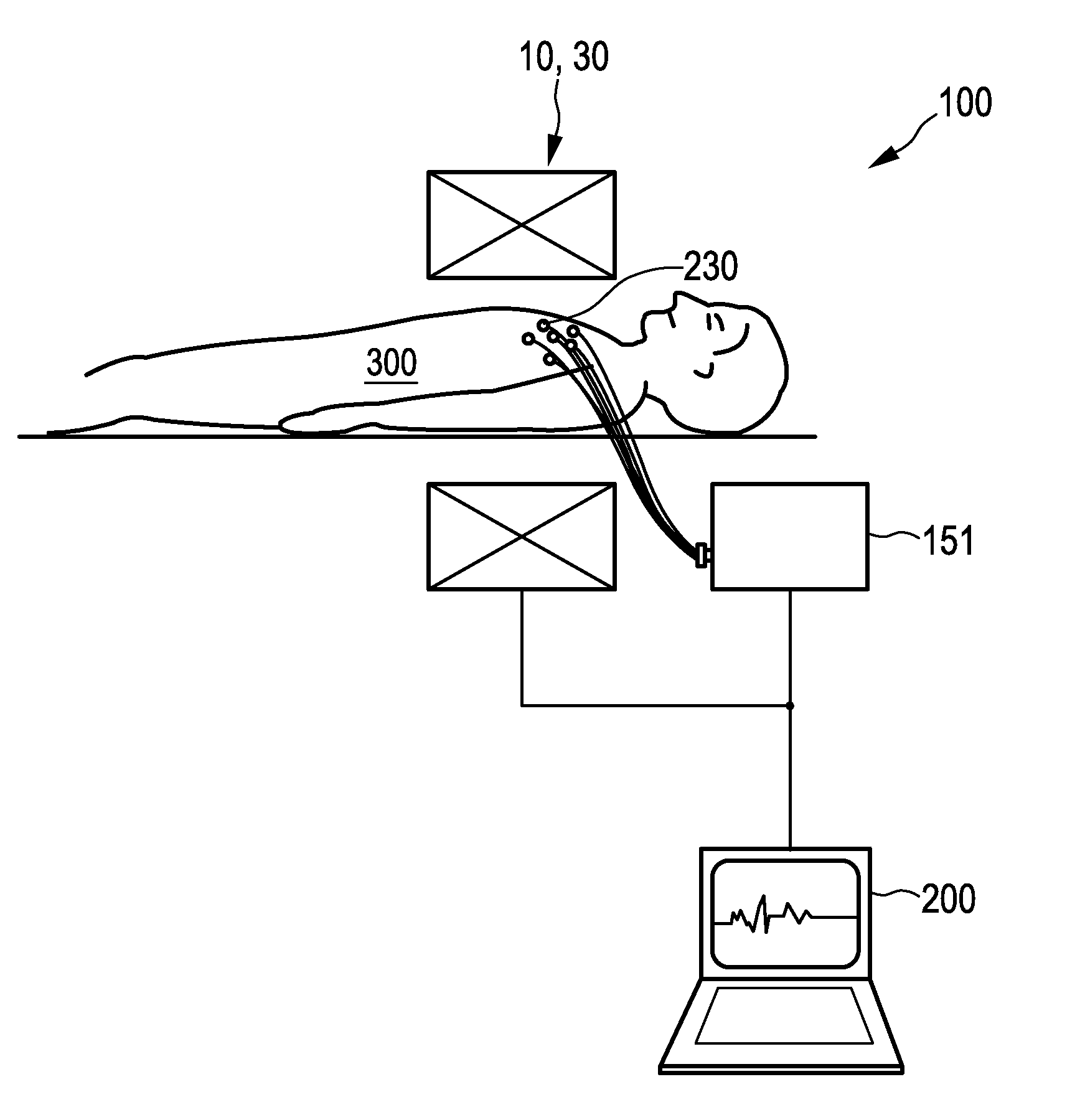
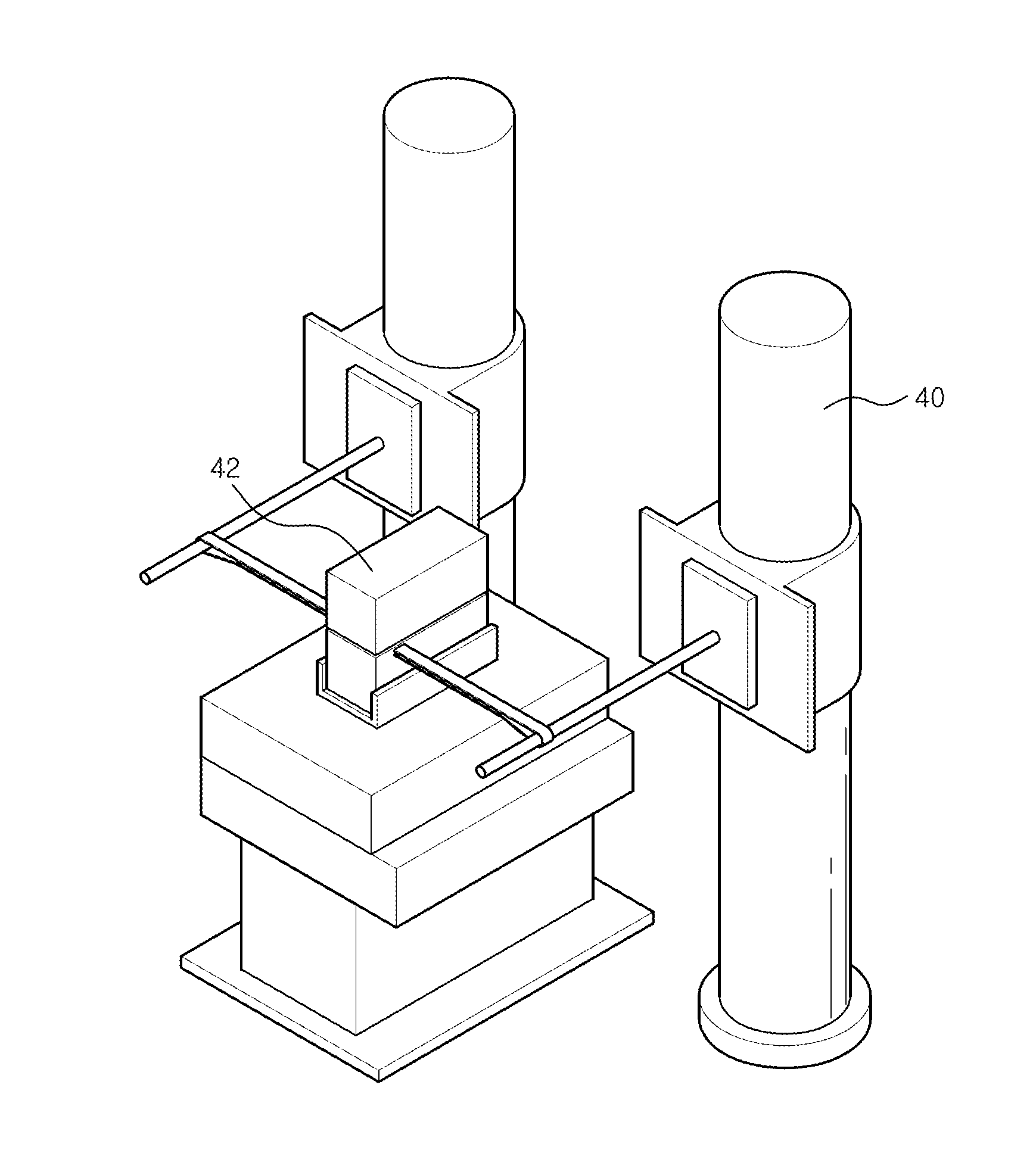
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a corresponding method for non-invasive intracardiac electrocardiography (ECG) by use of a magnetic and electrically conducting interference device (210). An MPI-based ECG mapping technique is proposed, wherein an interference device (210), e.g. an electrically conducting rod containing soft magnetic material, is steered through the vessel system and the heart using magnetic fields generated by a magnetic particle imaging (MPI) system so that the ECG signals measured in parallel are influenced. Using appropriately adapted evaluation means (153) this influence of the interference device (210) on the ECG signals can be evaluated to gain spatially resolved information about the electrical heart activity.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus for magnetic particle imaging
InactiveUS20140266172A1Easy to getMagnetic property measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic particle imagingElectromagnetic field
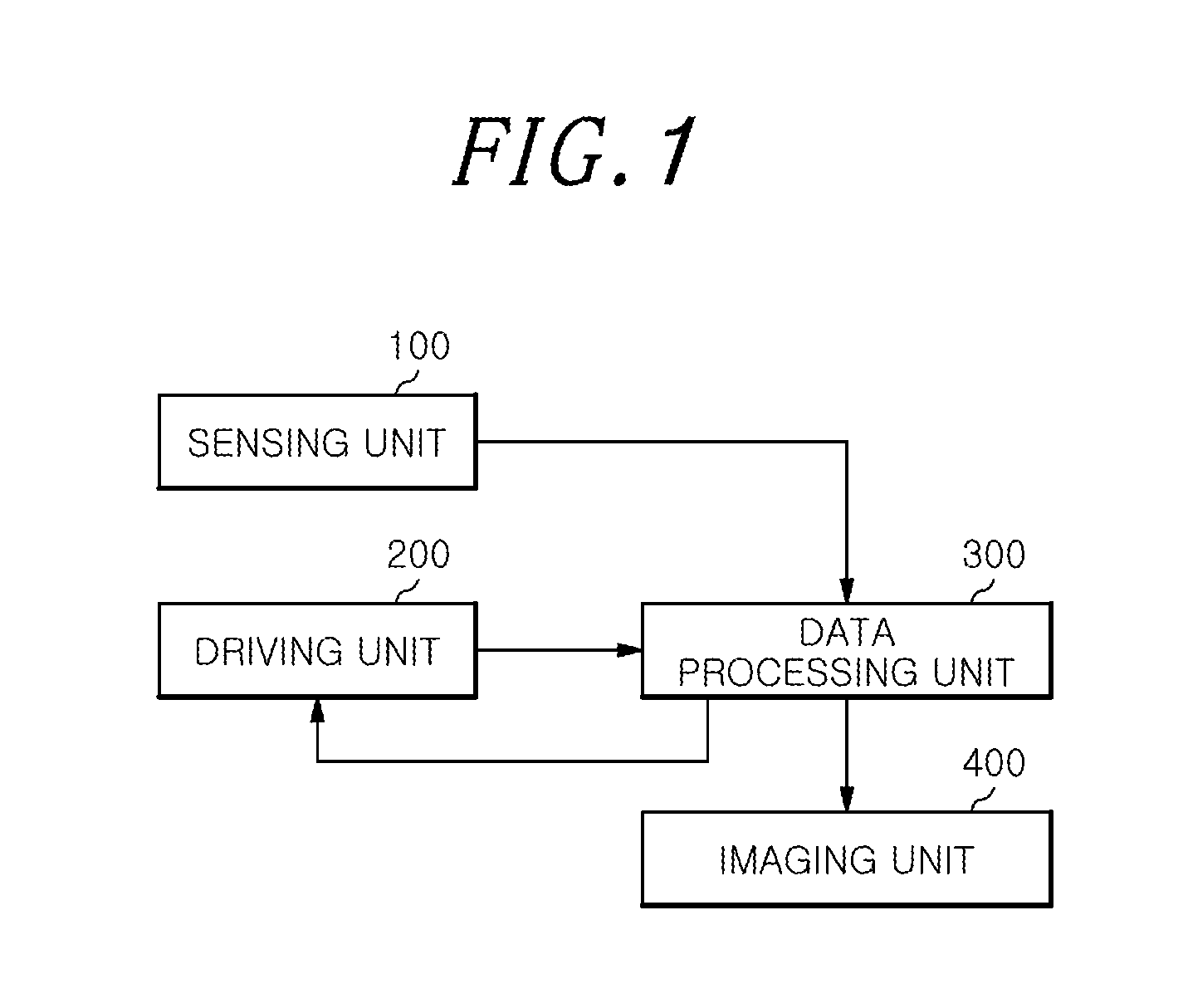
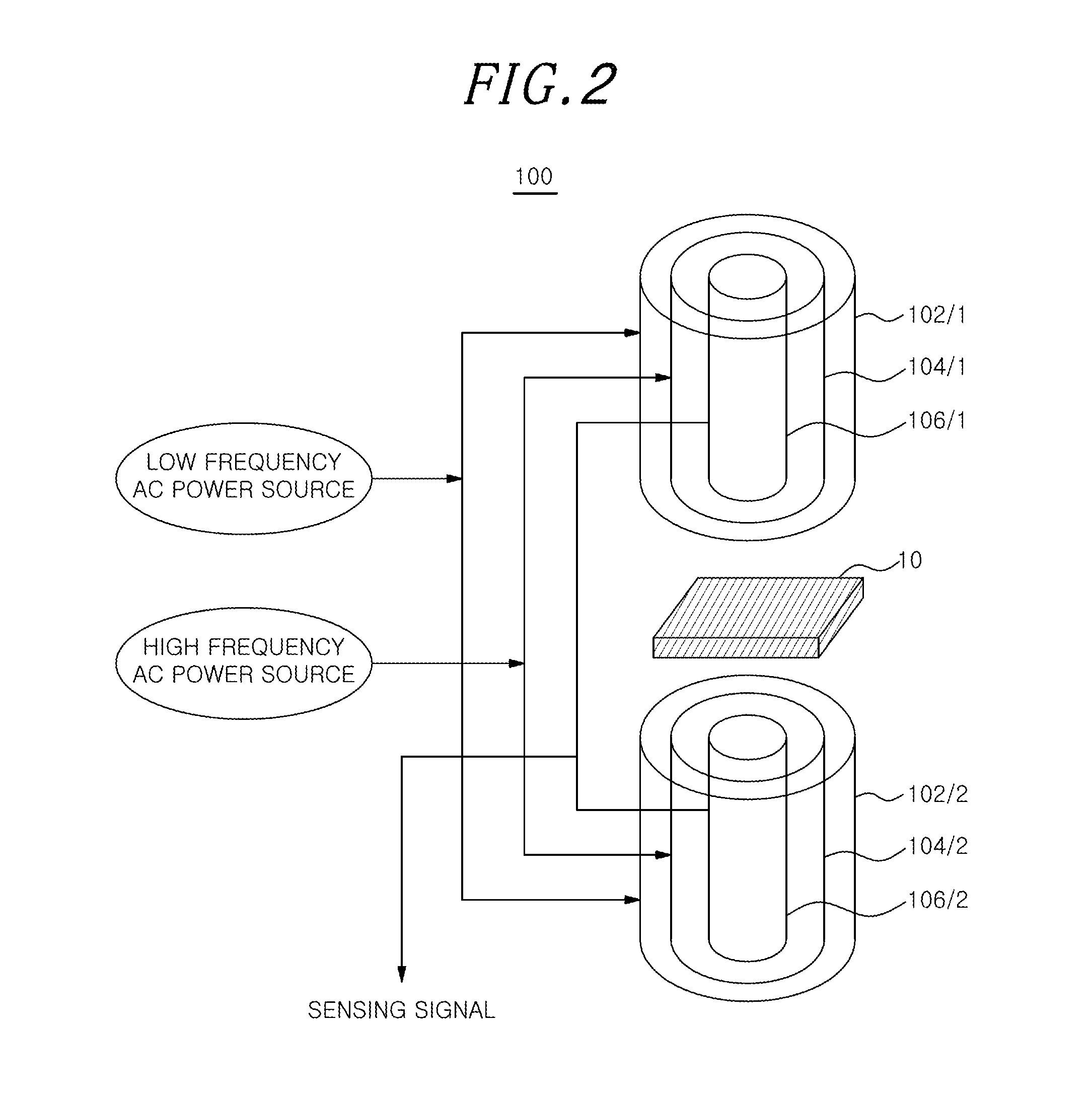
An apparatus for magnetic particle imaging, the apparatus comprising: a sensing unit configured to detect linear sample signals, which represent the mixed electromagnetic fields, generated from magnetic particles in a sample; a driving unit configured to move the sensing unit in a direction of X-axis, Y-axis, or Z-axis; and a data processing unit configured to rearrange in a matrix linear sample signals detected by the sensing unit that is moved by the driving unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Fast magnetic particle imaging reconstruction method based on undersampling
PendingCN113808234AShorten the timeImprove noise immunityReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic particle imagingData set
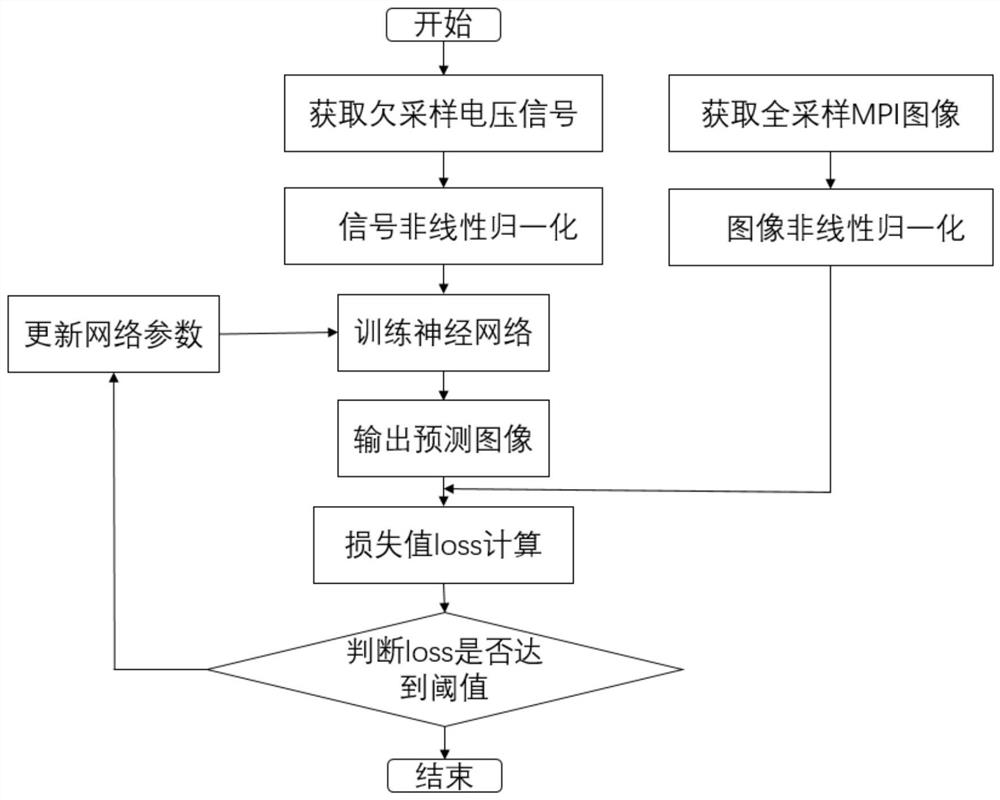
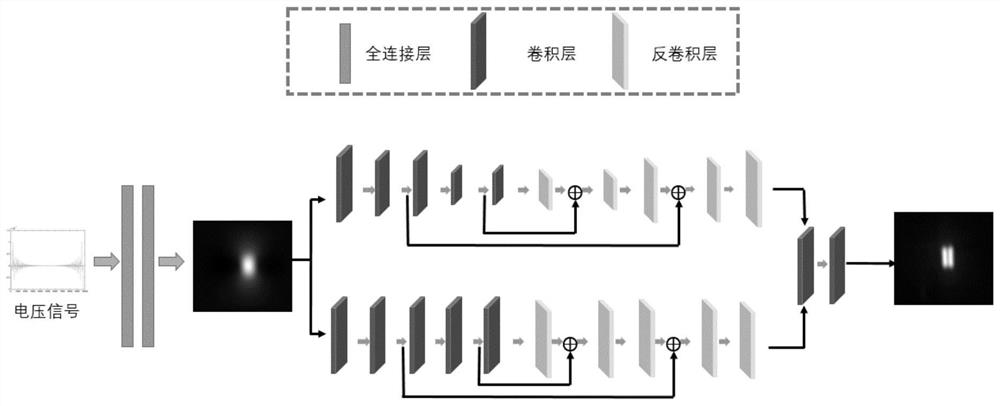
The invention discloses a fast magnetic particle imaging reconstruction method based on undersampling. The method comprises the steps of obtaining MPI undersampling voltage signals, obtaining full-sampling MPI images, conducting nonlinear normalization on the signals and the images, training a neural network and predicting magnetic particle concentration distribution. According to the method, the voltage signals are directly mapped to the image domain, reconstruction can be carried out within several milliseconds, wide evaluation on a large number of data sets shows that the method can reconstruct the full-sampling high-resolution MPI image from the under-sampling voltage signals, and the method has good anti-noise capacity and anti-artifact capacity; the method has good generalization ability, the reconstructed image quality is higher, the reconstruction speed is higher, the imaging potential of a magnetic particle imaging system is improved, and the problem that MPI equipment introduces a large amount of noise due to too long acquisition time is solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
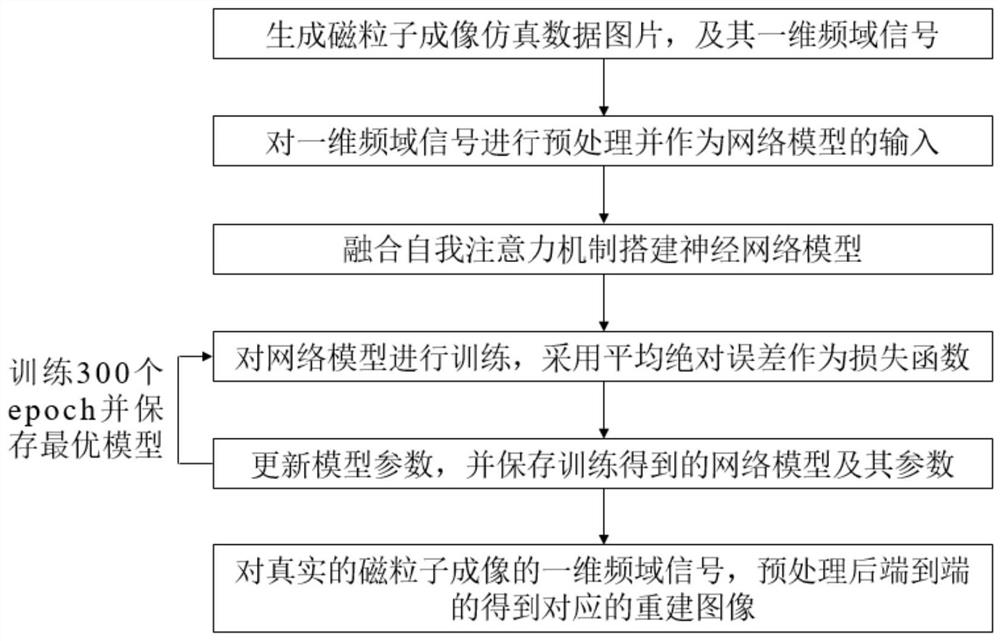
Magnetic particle imaging reconstruction method based on attention mechanism
PendingCN113850883AMatch Computing NeedsEasy extractionReconstruction from projectionNeural architecturesParticle imagingMagnetic particle imaging
The invention discloses a magnetic particle imaging reconstruction method based on an attention. According to the method, the strong computing power of a neural network model is utilized to match acquired large data volume, and effective information in signals is extracted by fusing self-attention mechanism learning, so that signal information loss caused by downsampling or truncation is reduced; and end-to-end reconstruction from a one-dimensional frequency domain signal to a two-dimensional image is realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com