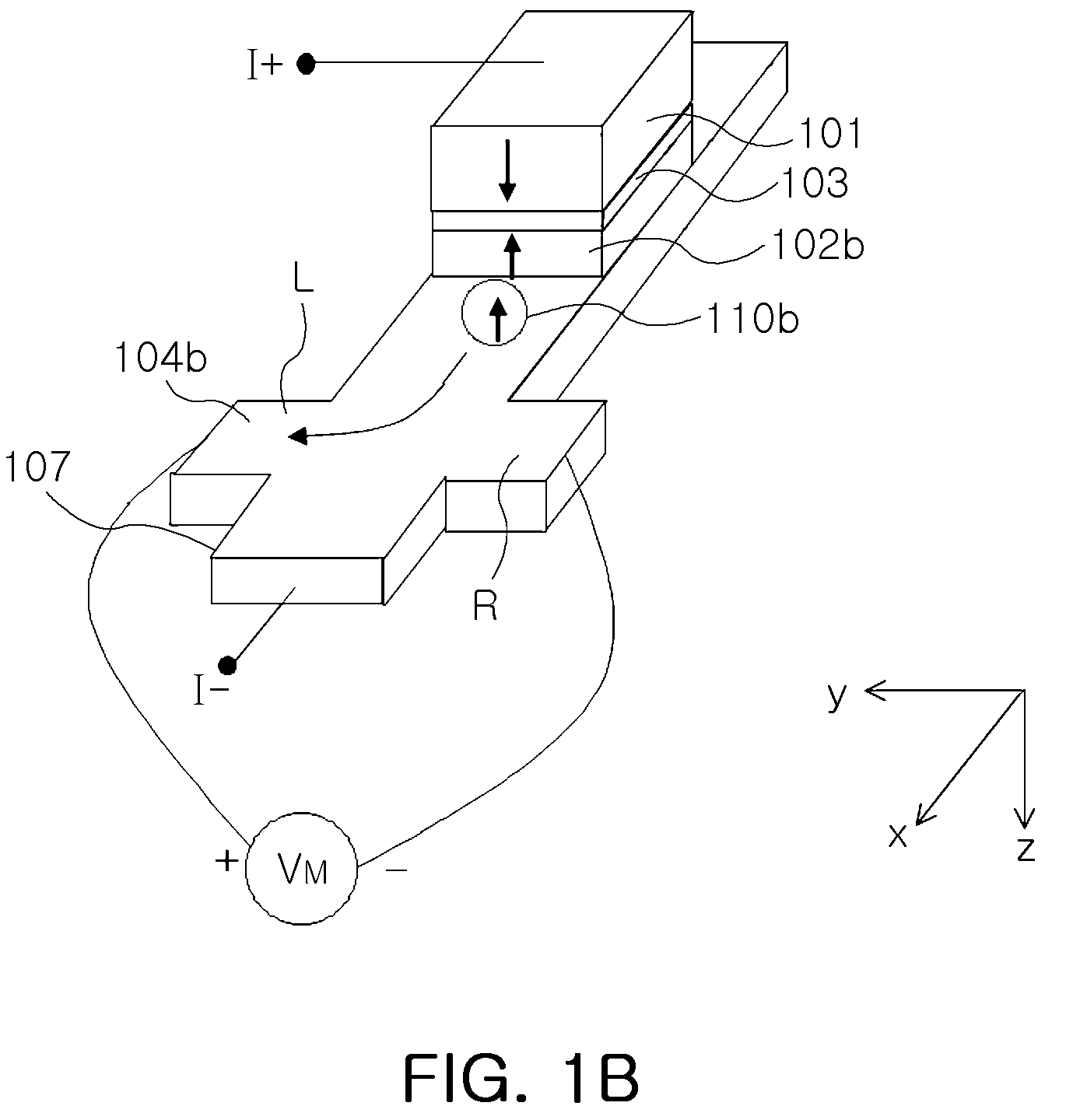
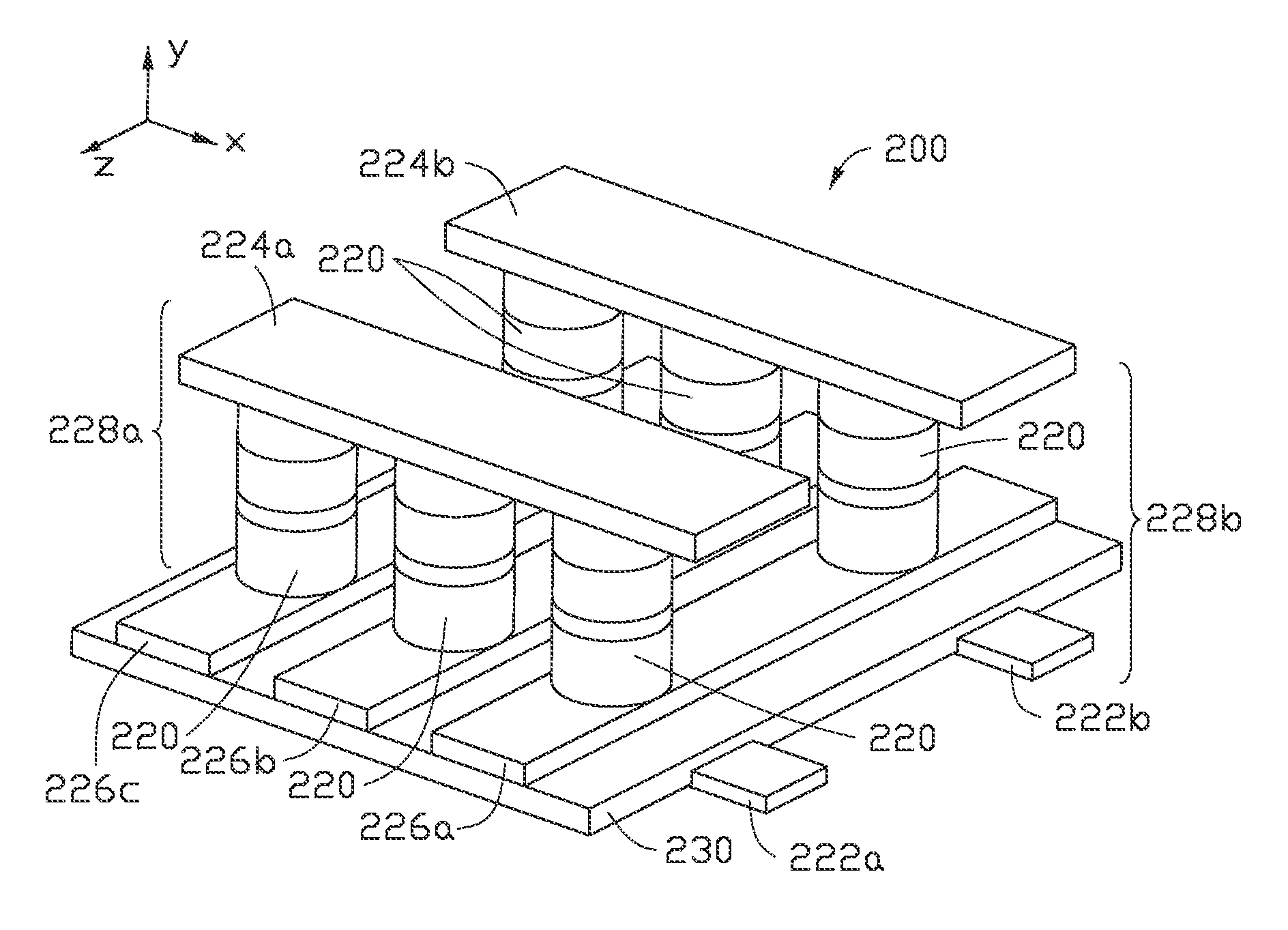
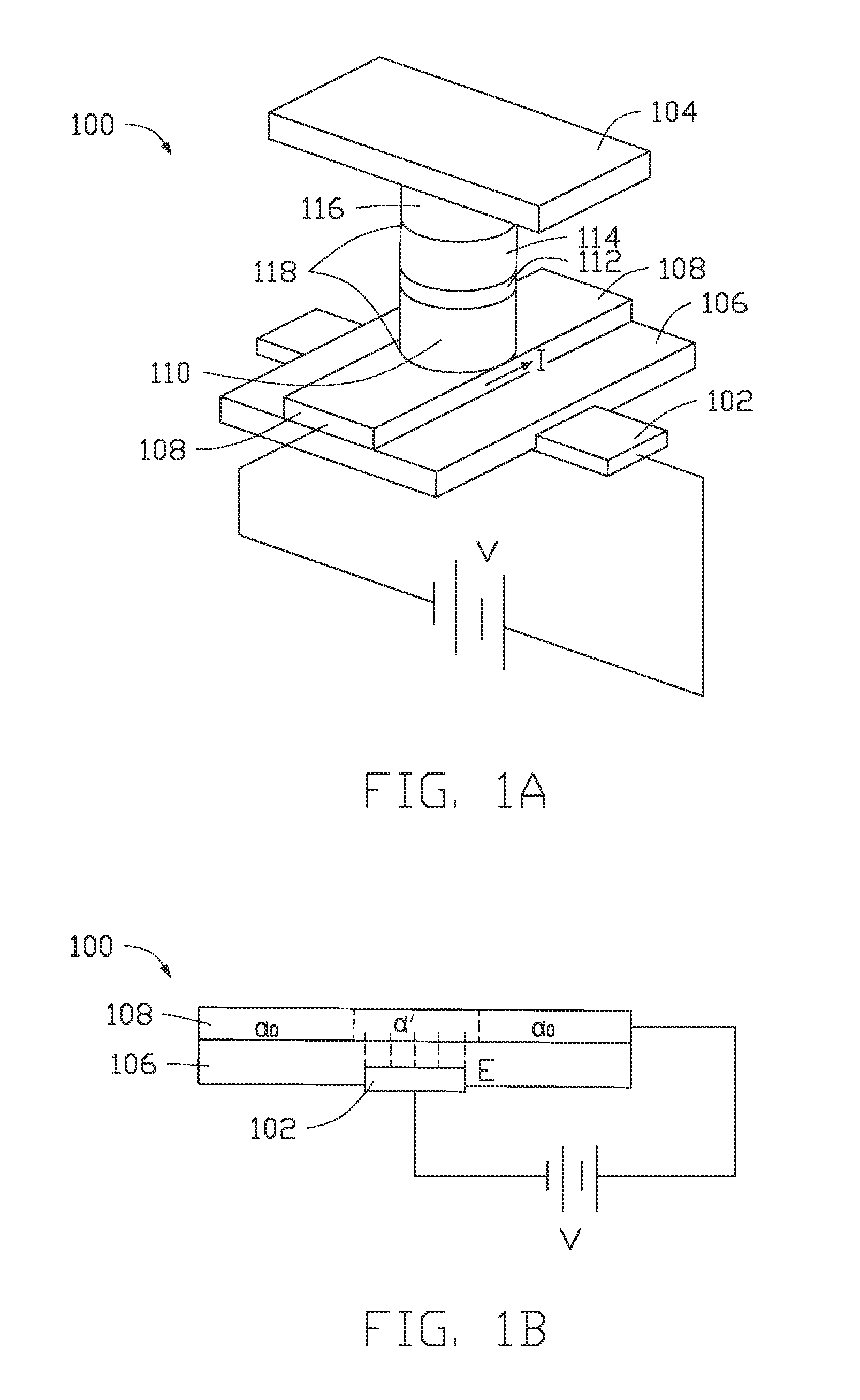
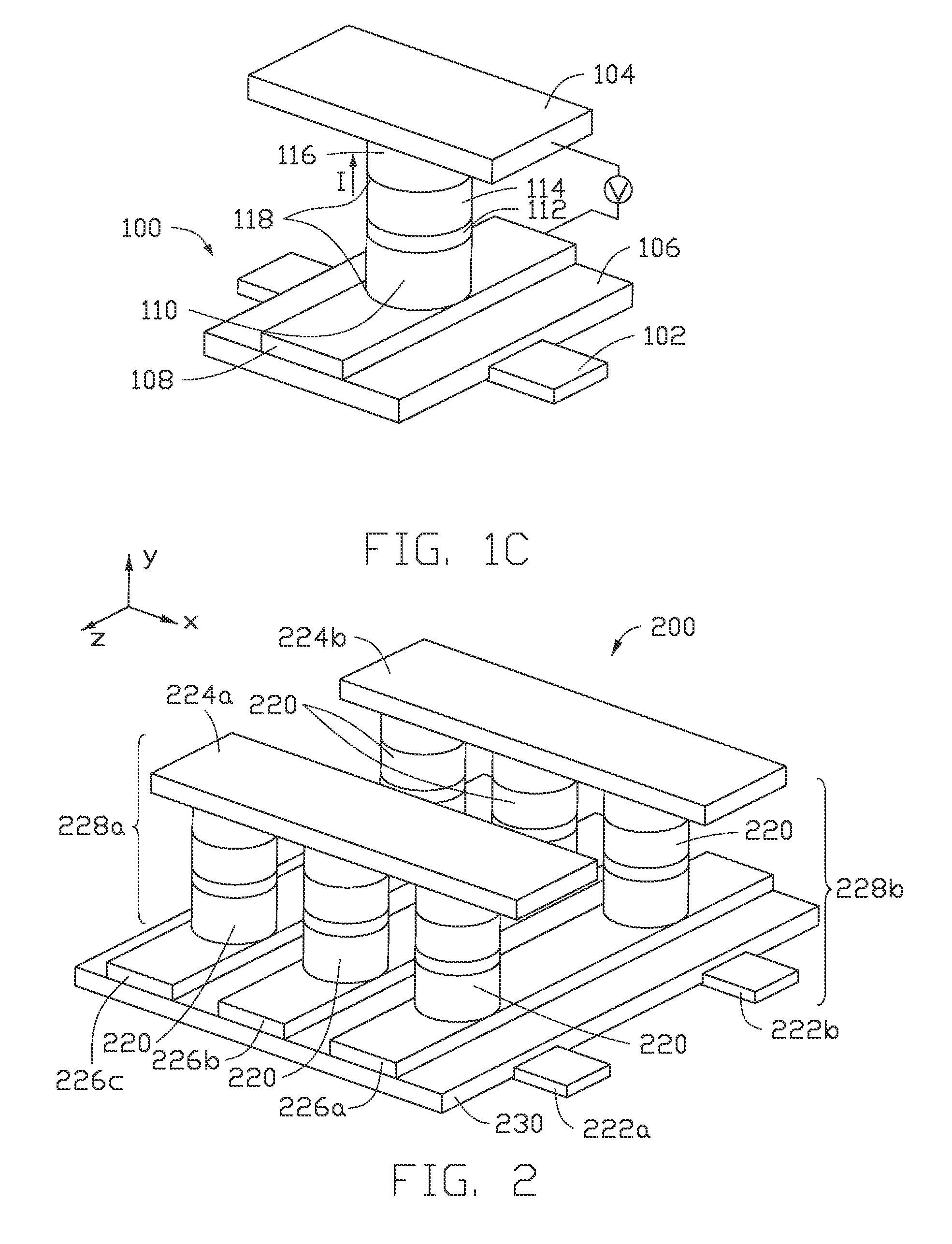
Patents
Literature
154 results about "Spin Hall effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
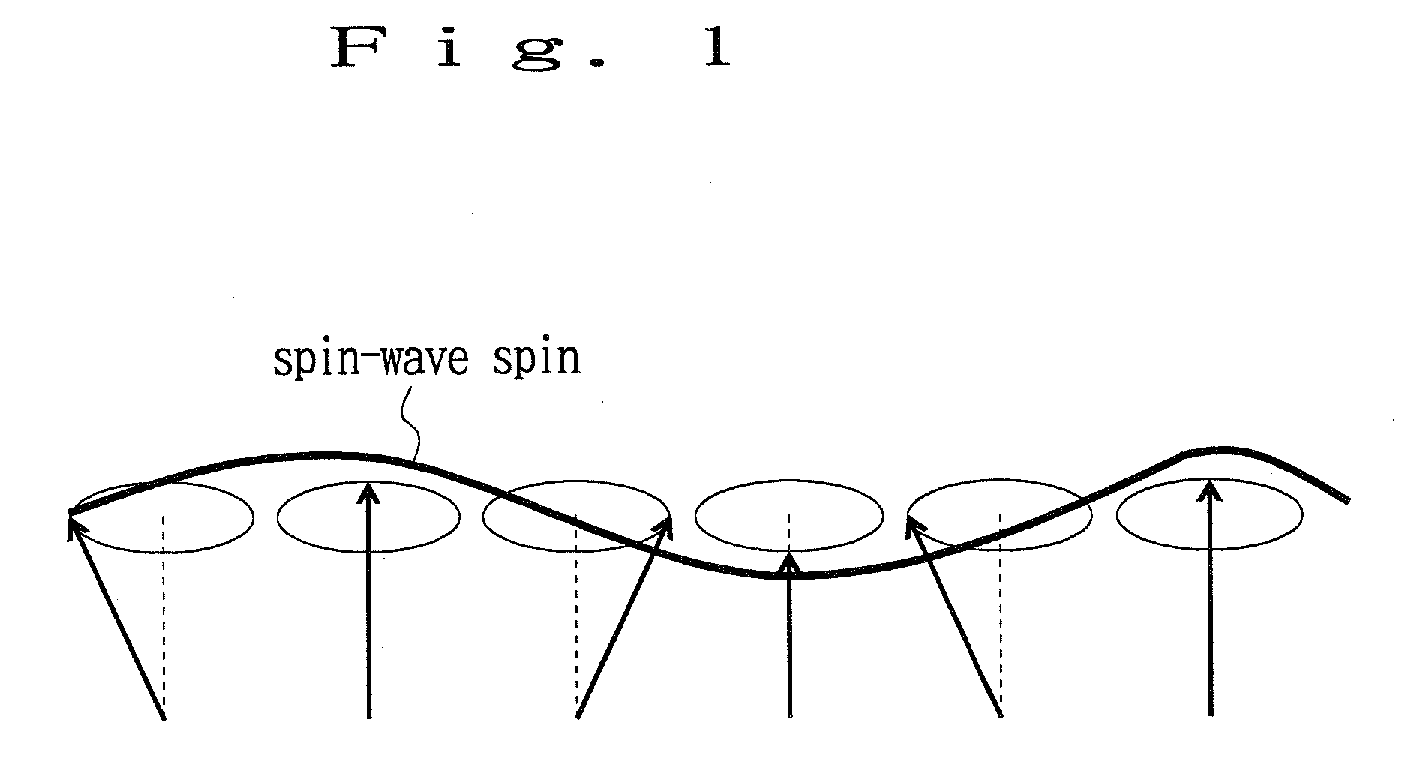
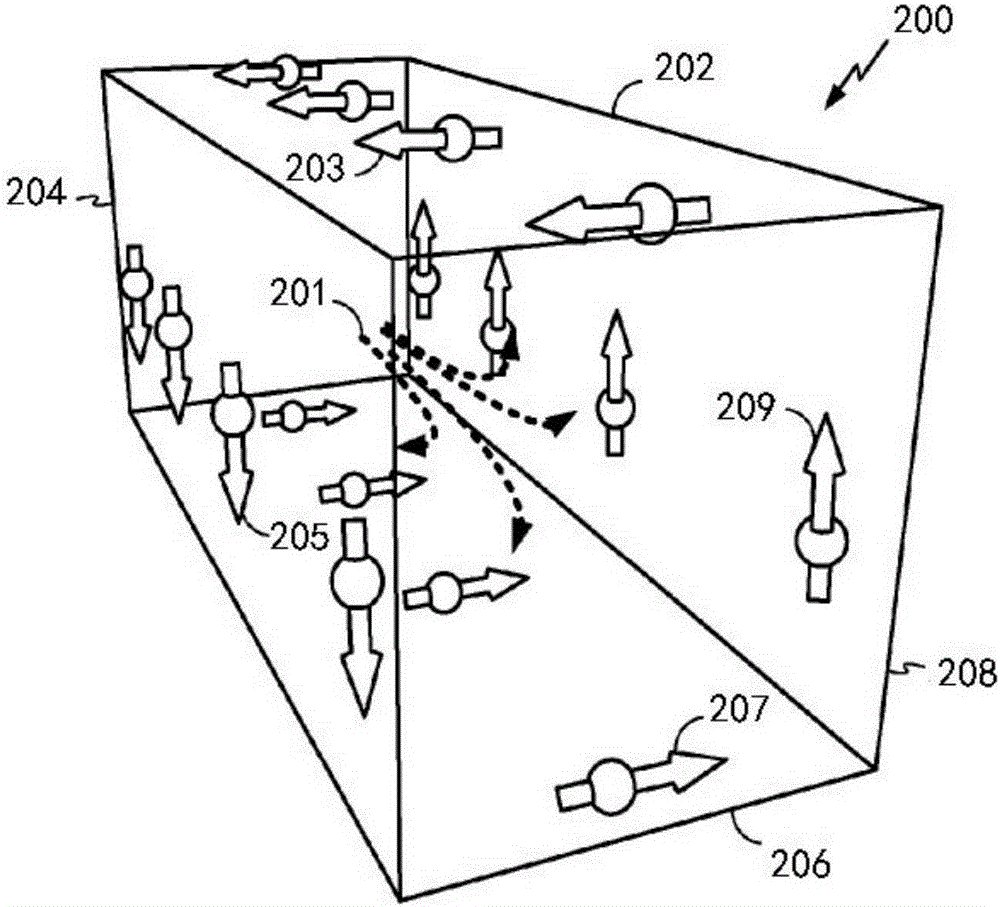
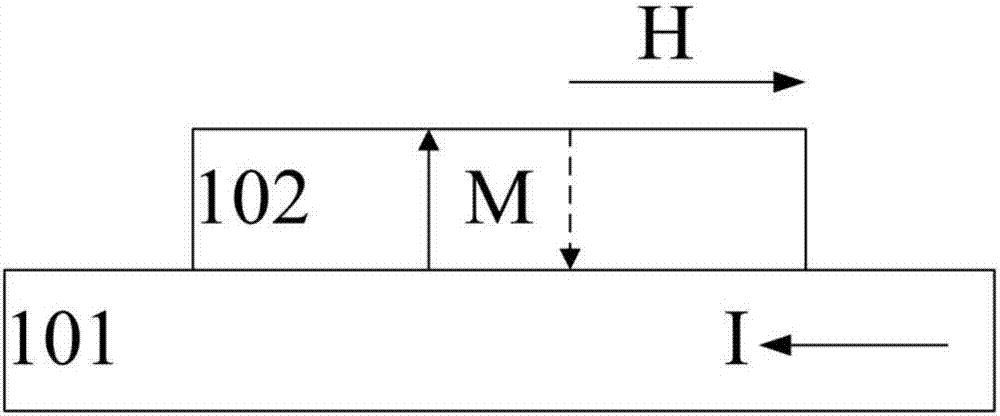
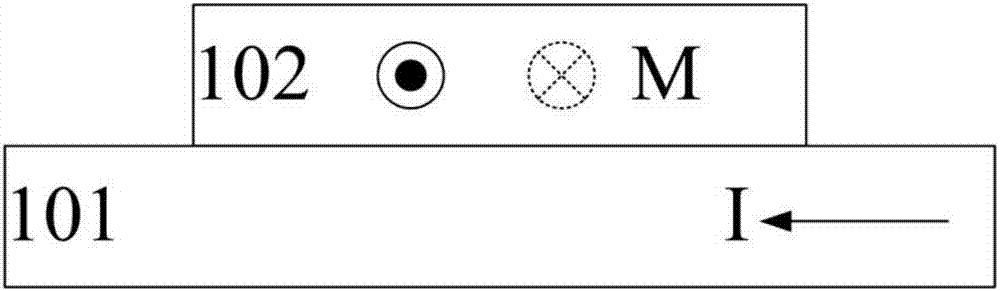
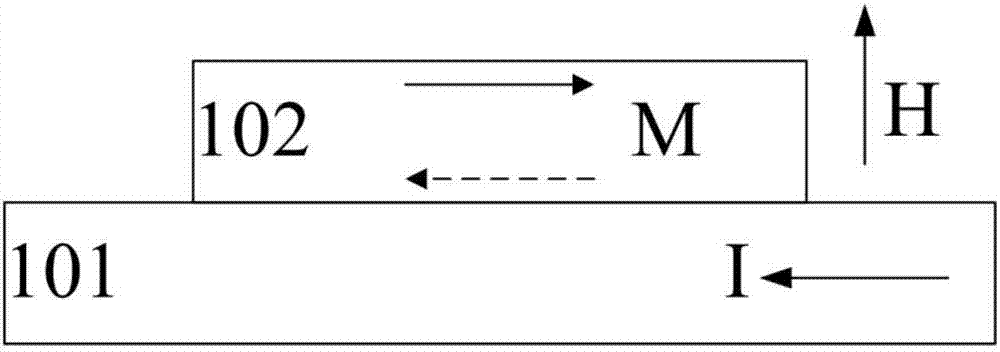
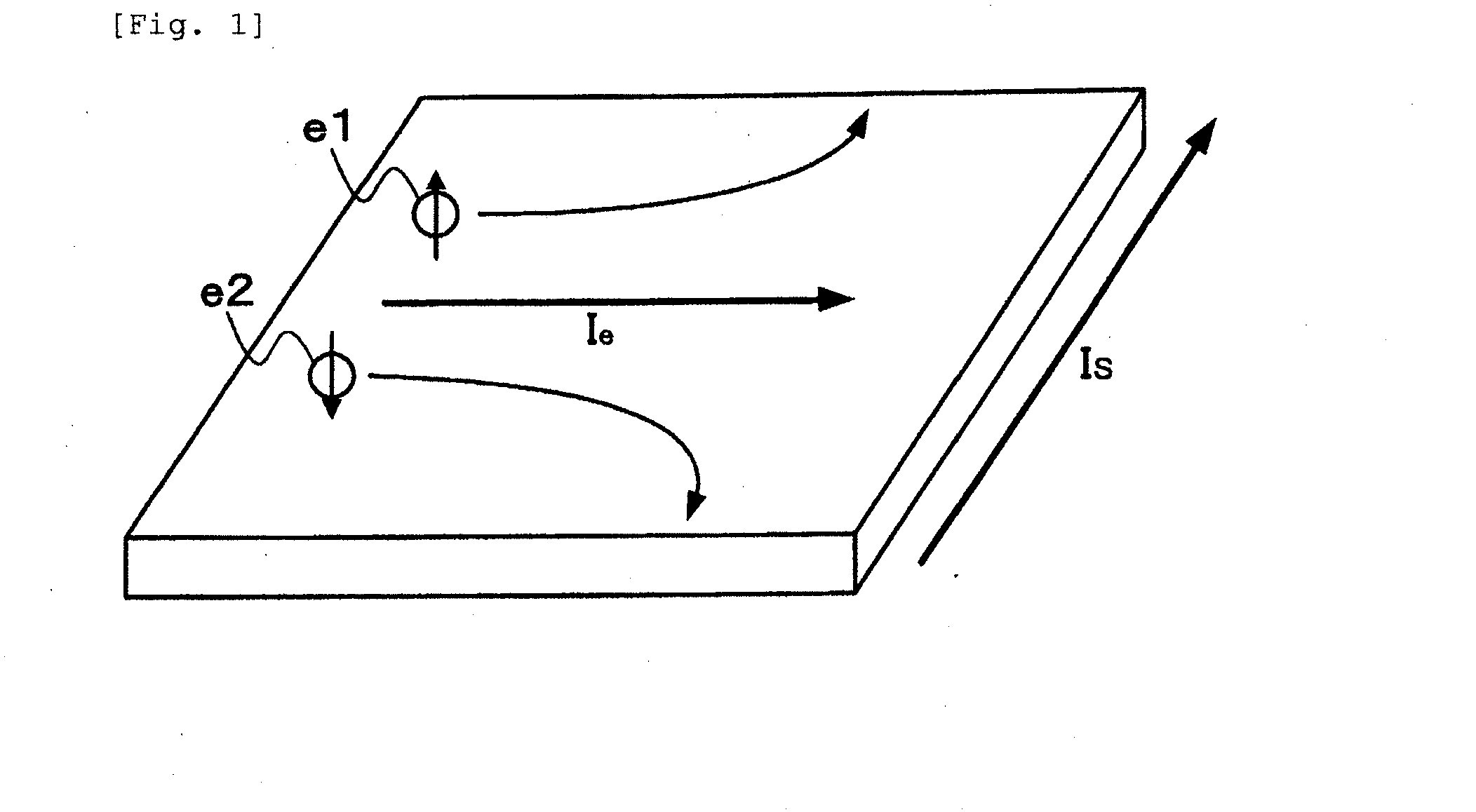
The spin Hall effect (SHE) is a transport phenomenon predicted by Russian physicists Mikhail I. Dyakonov and Vladimir I. Perel in 1971. It consists of the appearance of spin accumulation on the lateral surfaces of an electric current-carrying sample, the signs of the spin directions being opposite on the opposing boundaries. In a cylindrical wire, the current-induced surface spins will wind around the wire. When the current direction is reversed, the directions of spin orientation is also reversed.
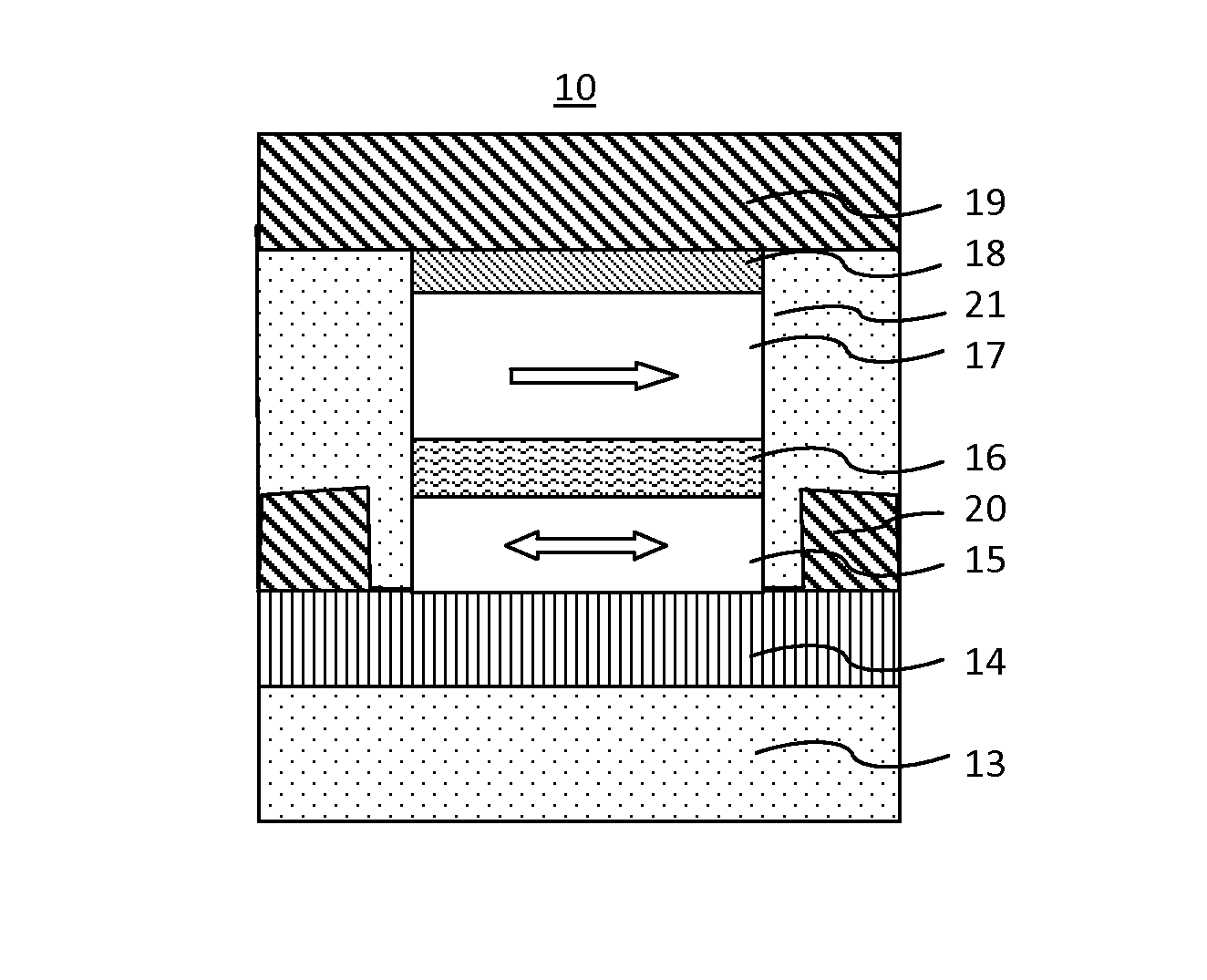
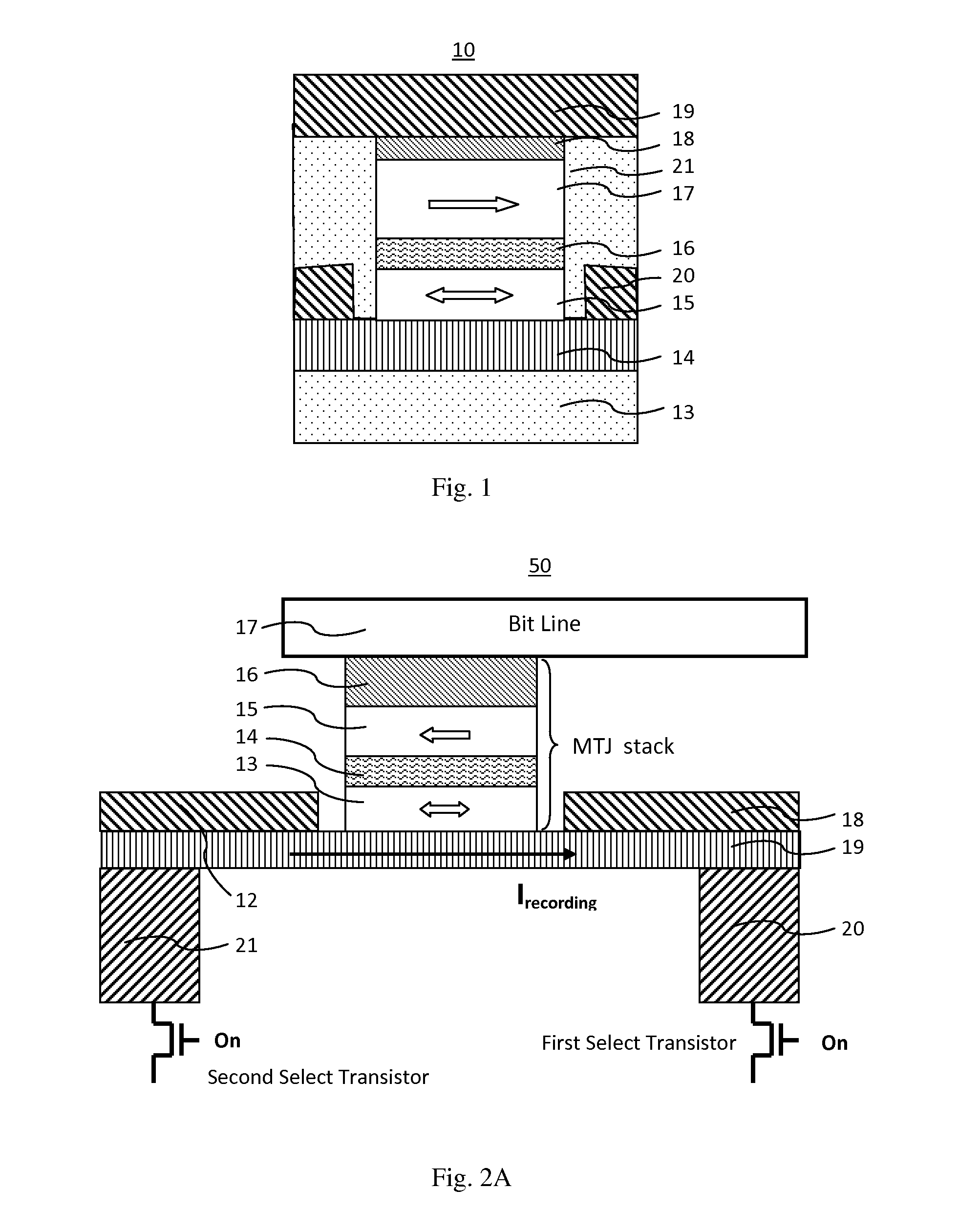
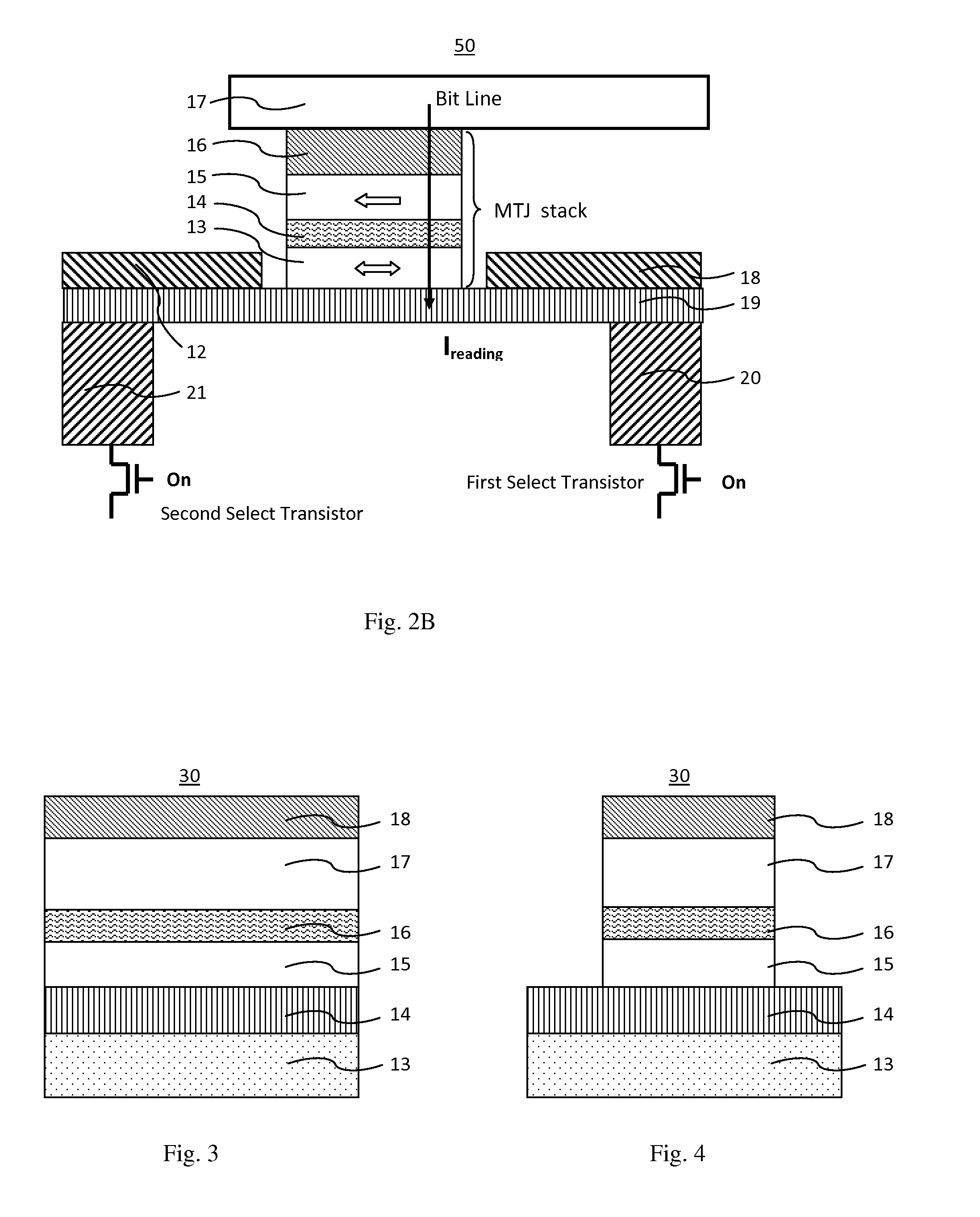
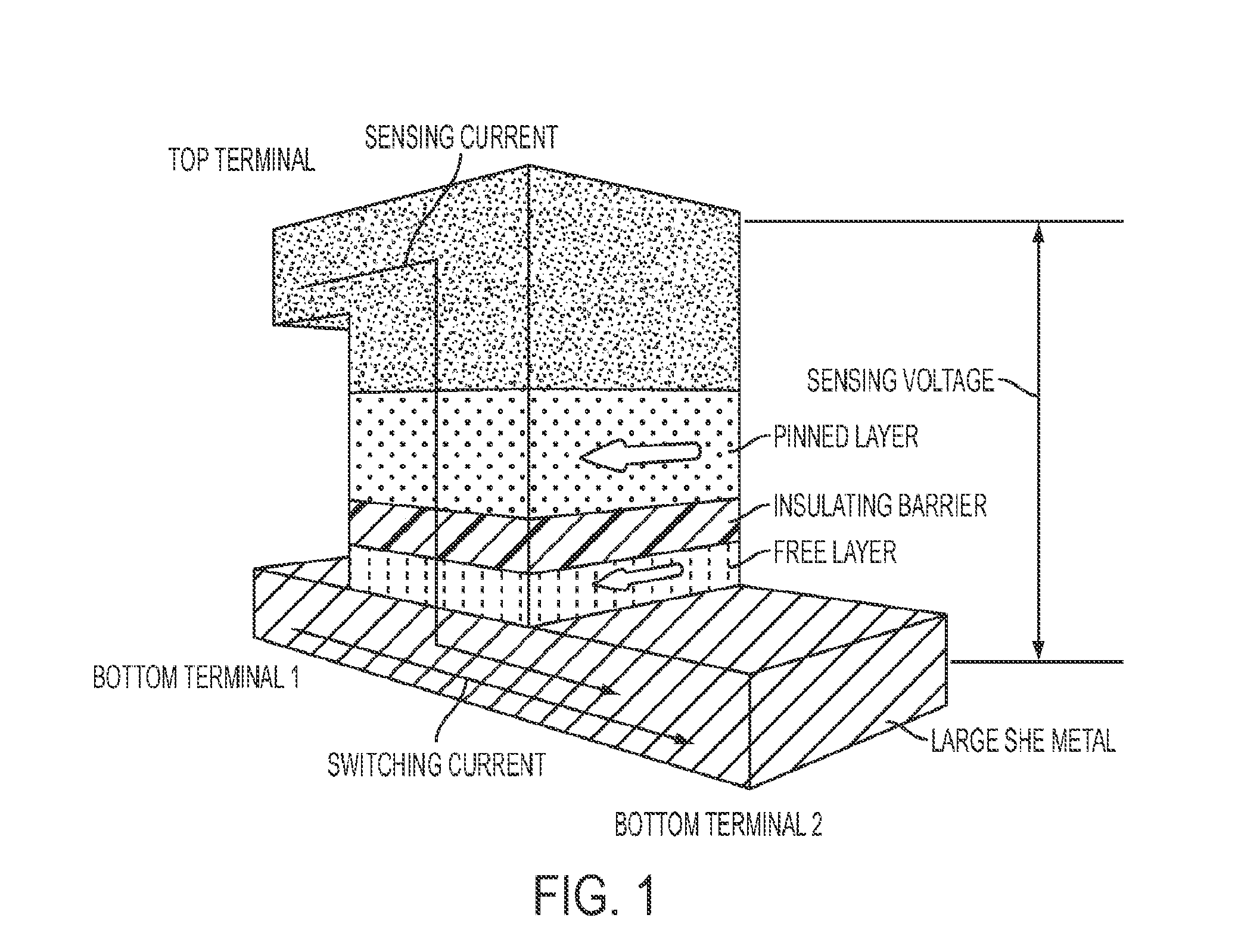
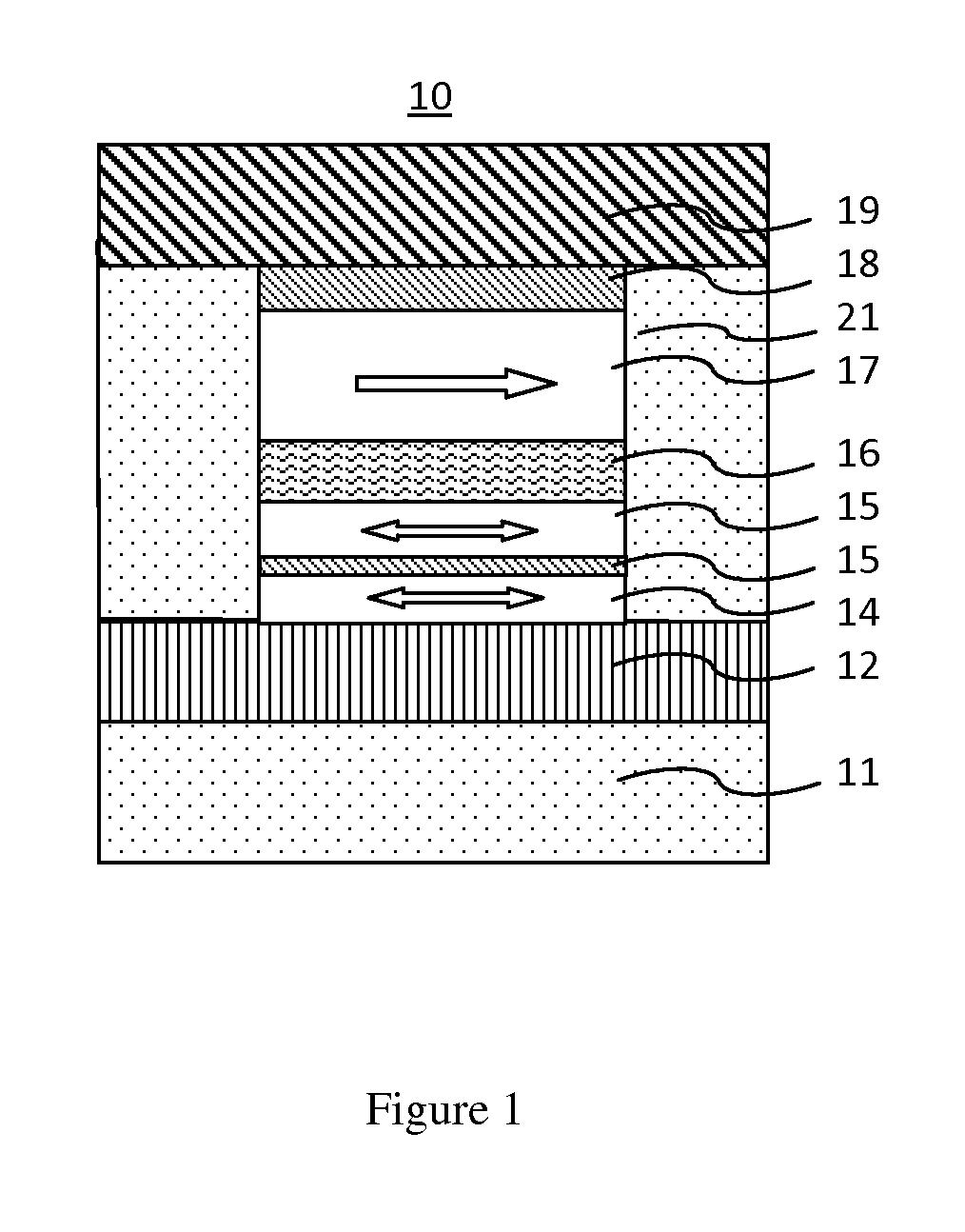
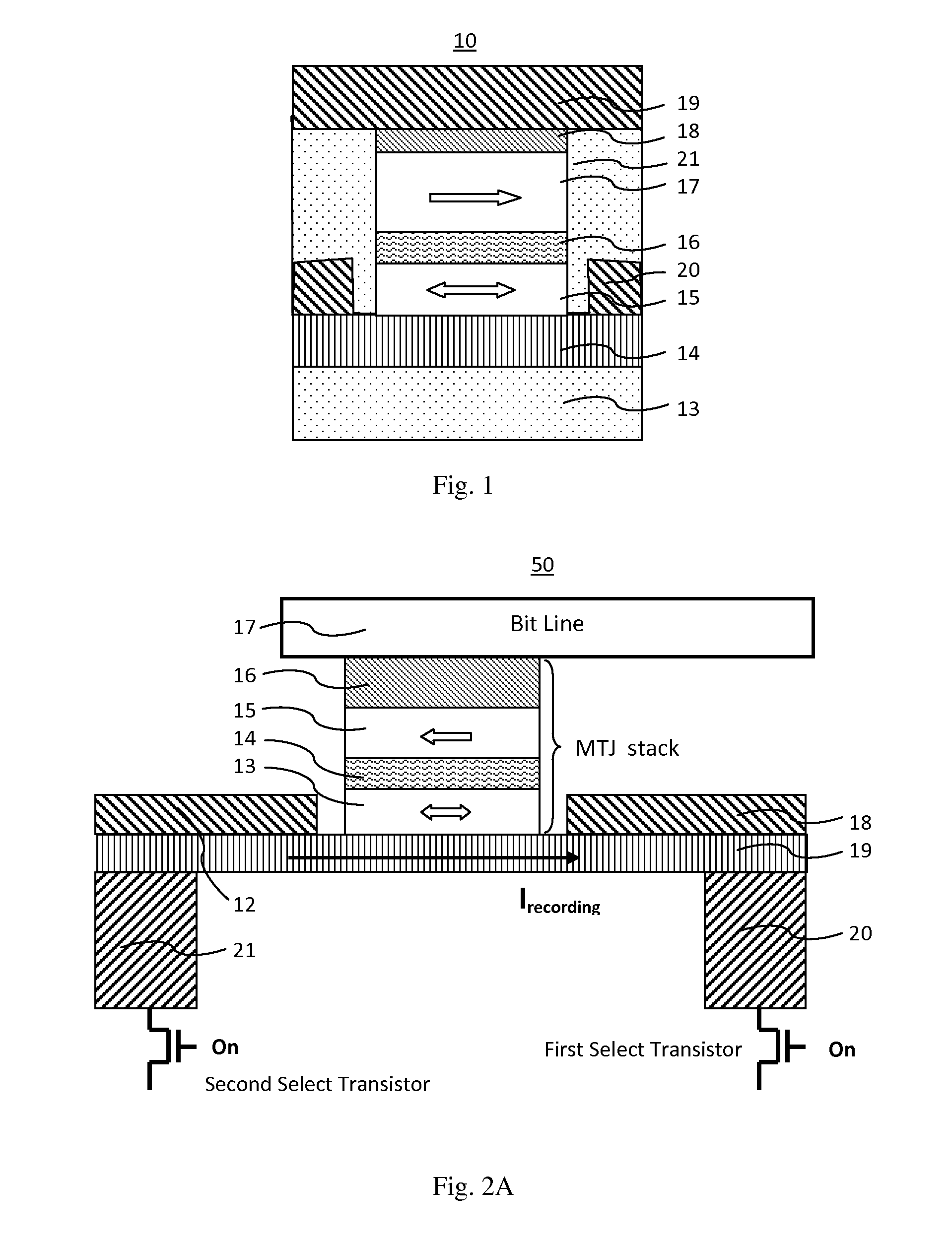
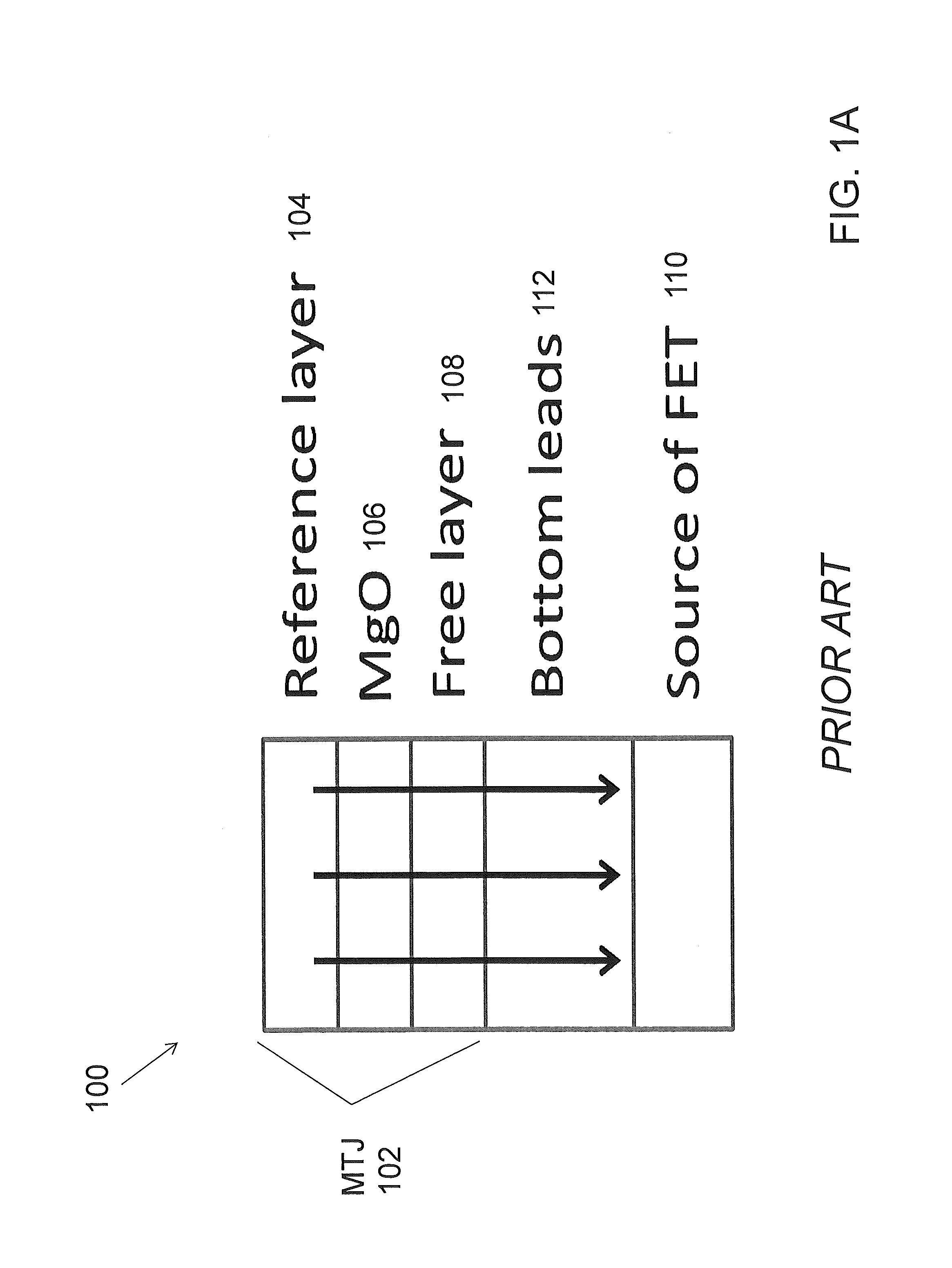
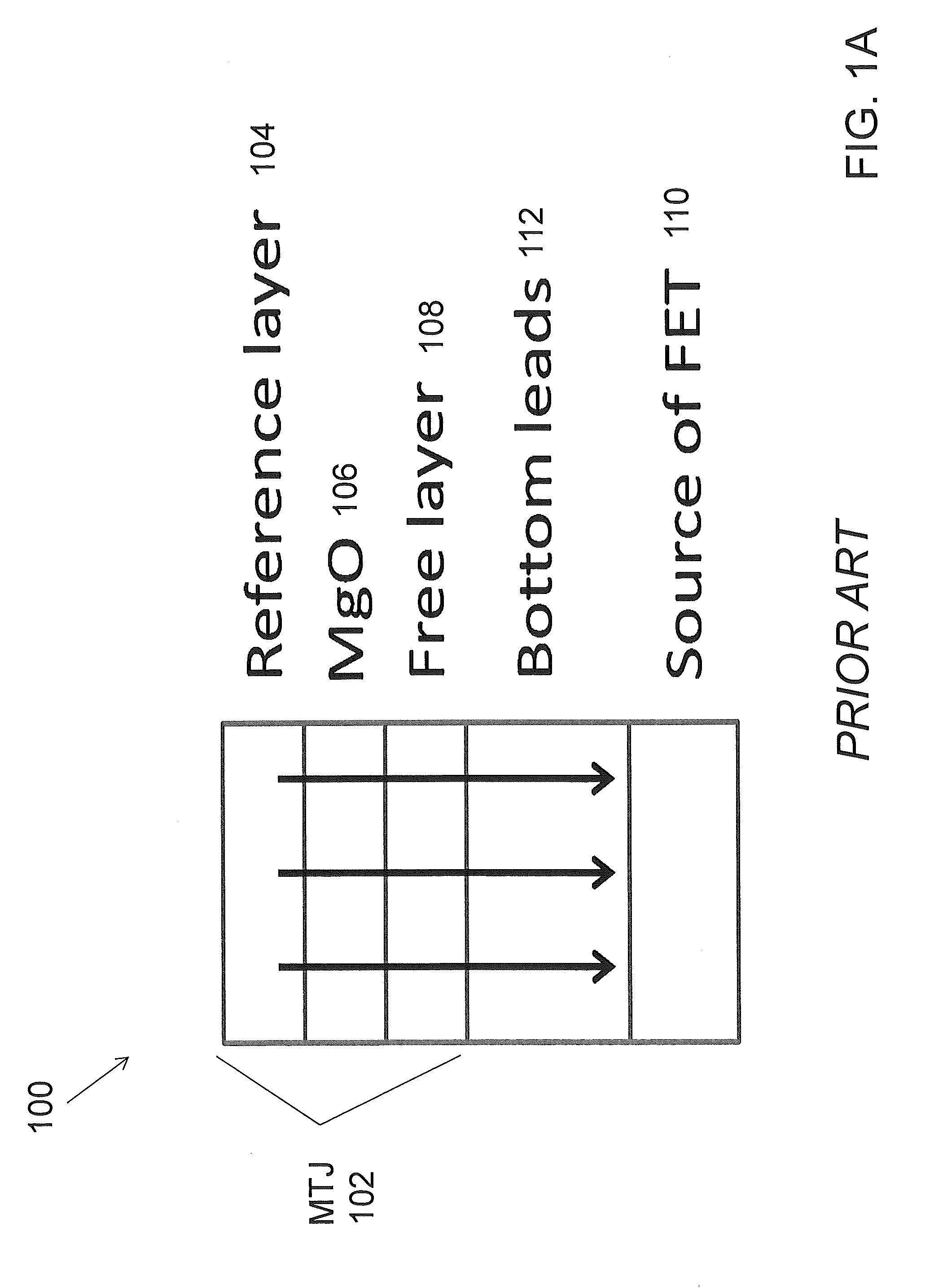
MRAM having spin hall effect writing and method of making the same
InactiveUS20140252439A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic reluctanceRecording layer
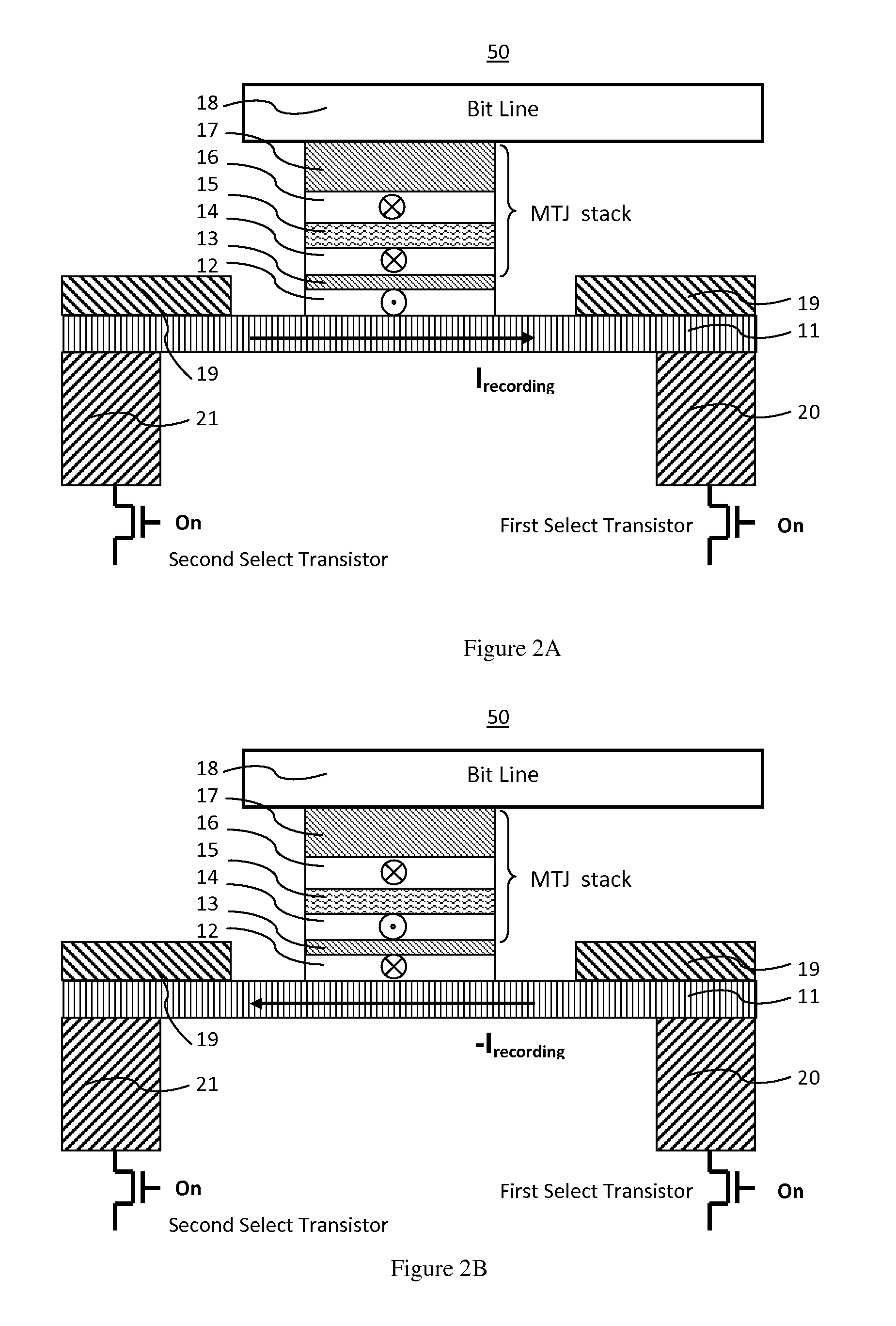
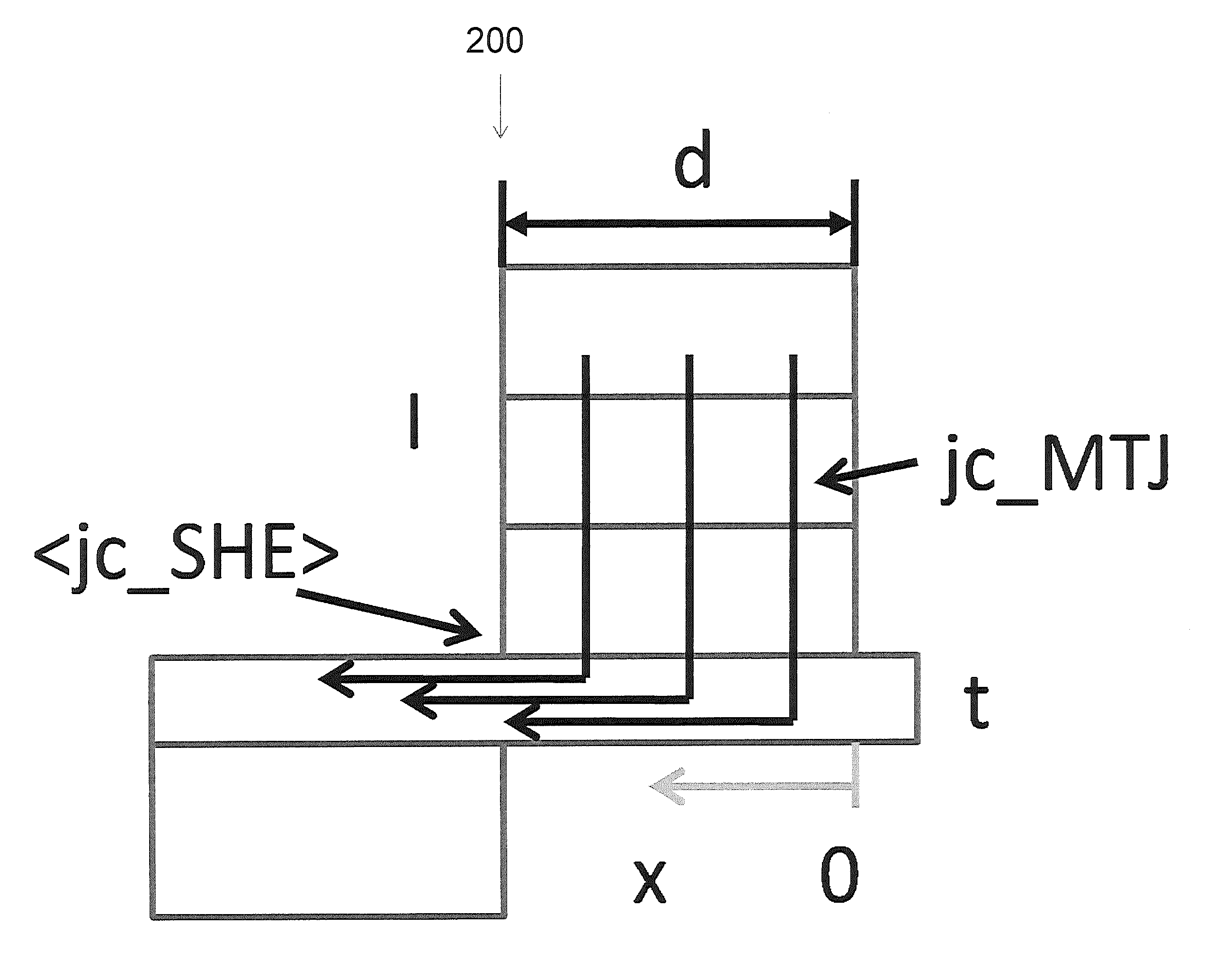
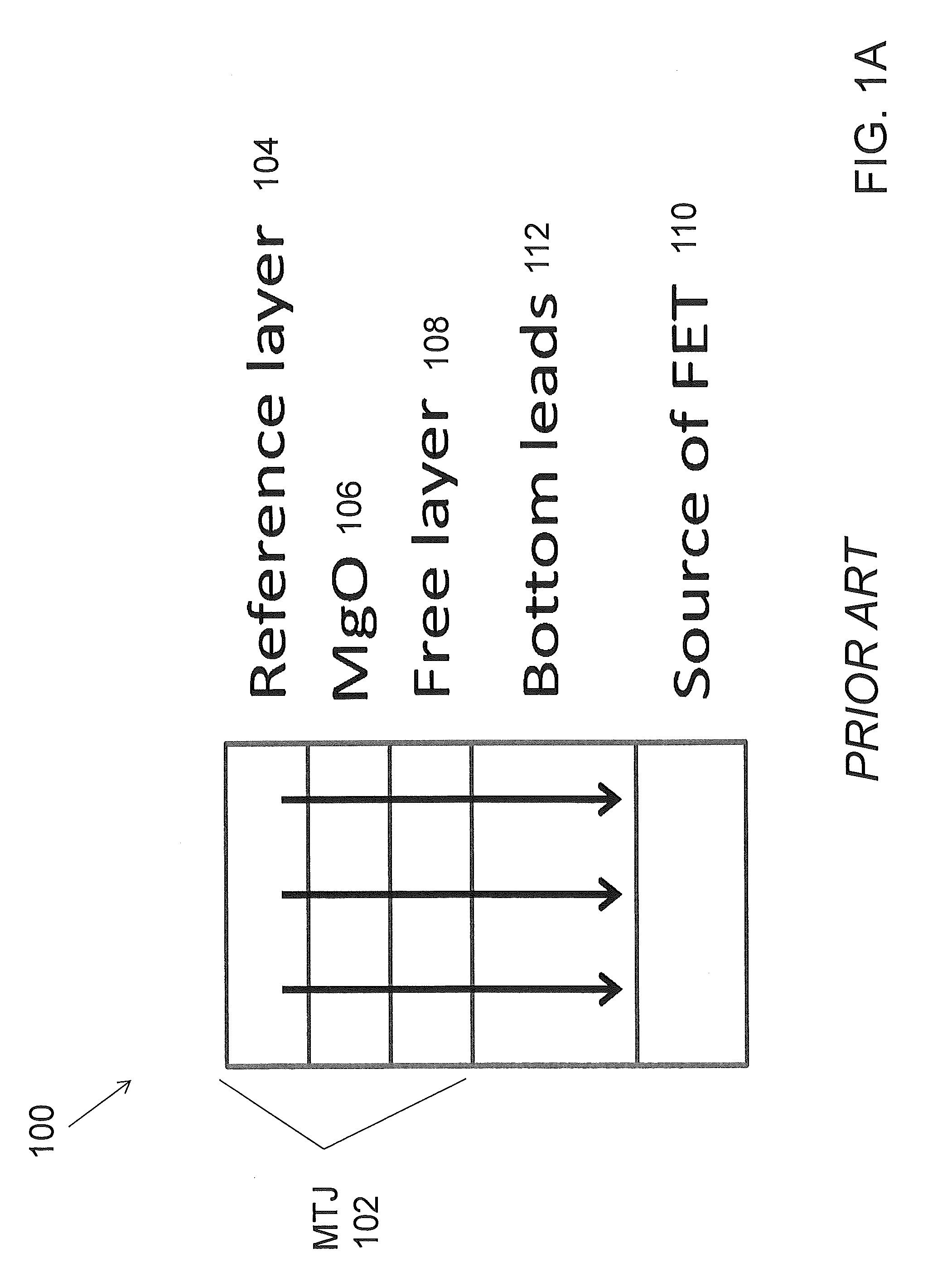
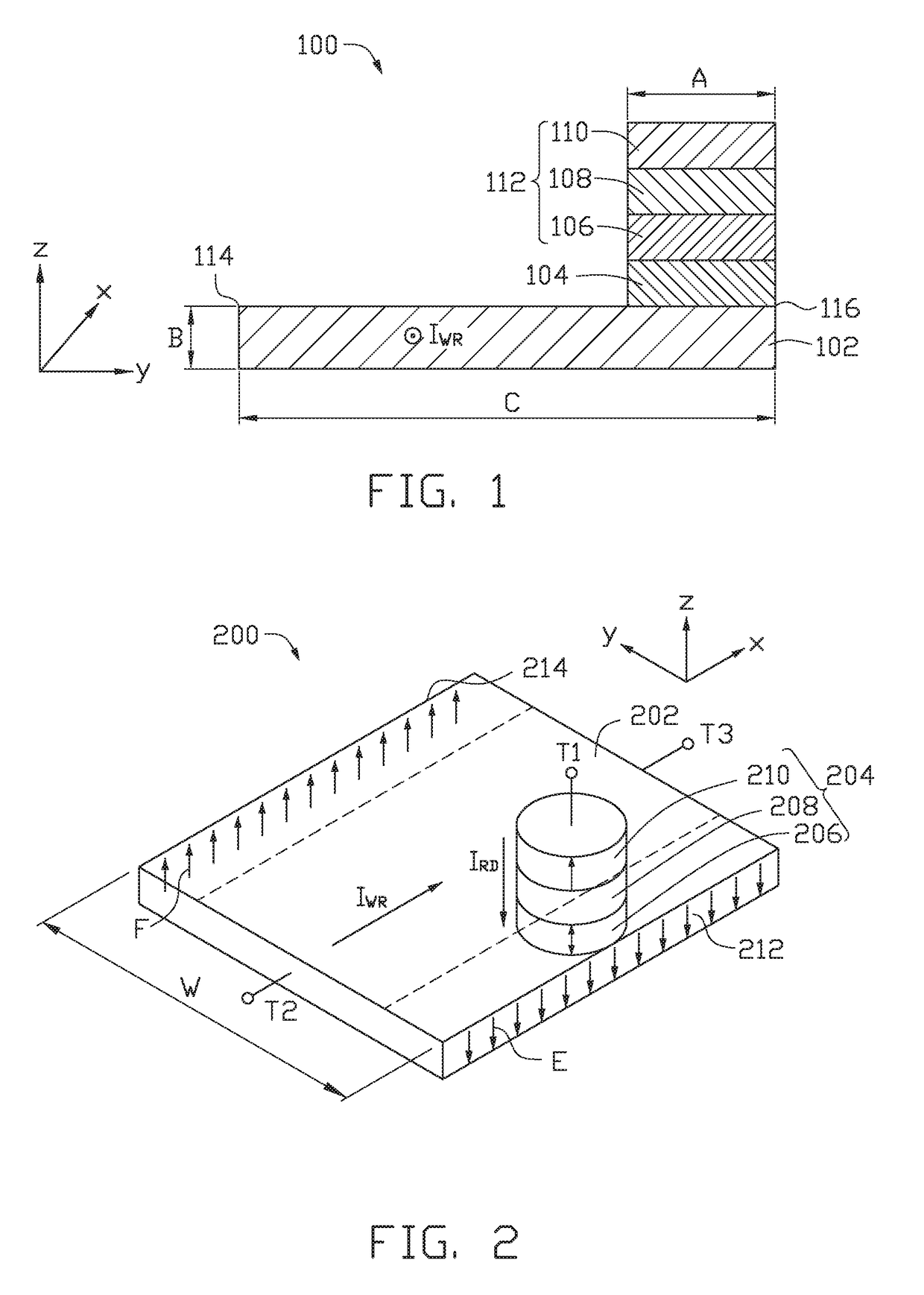
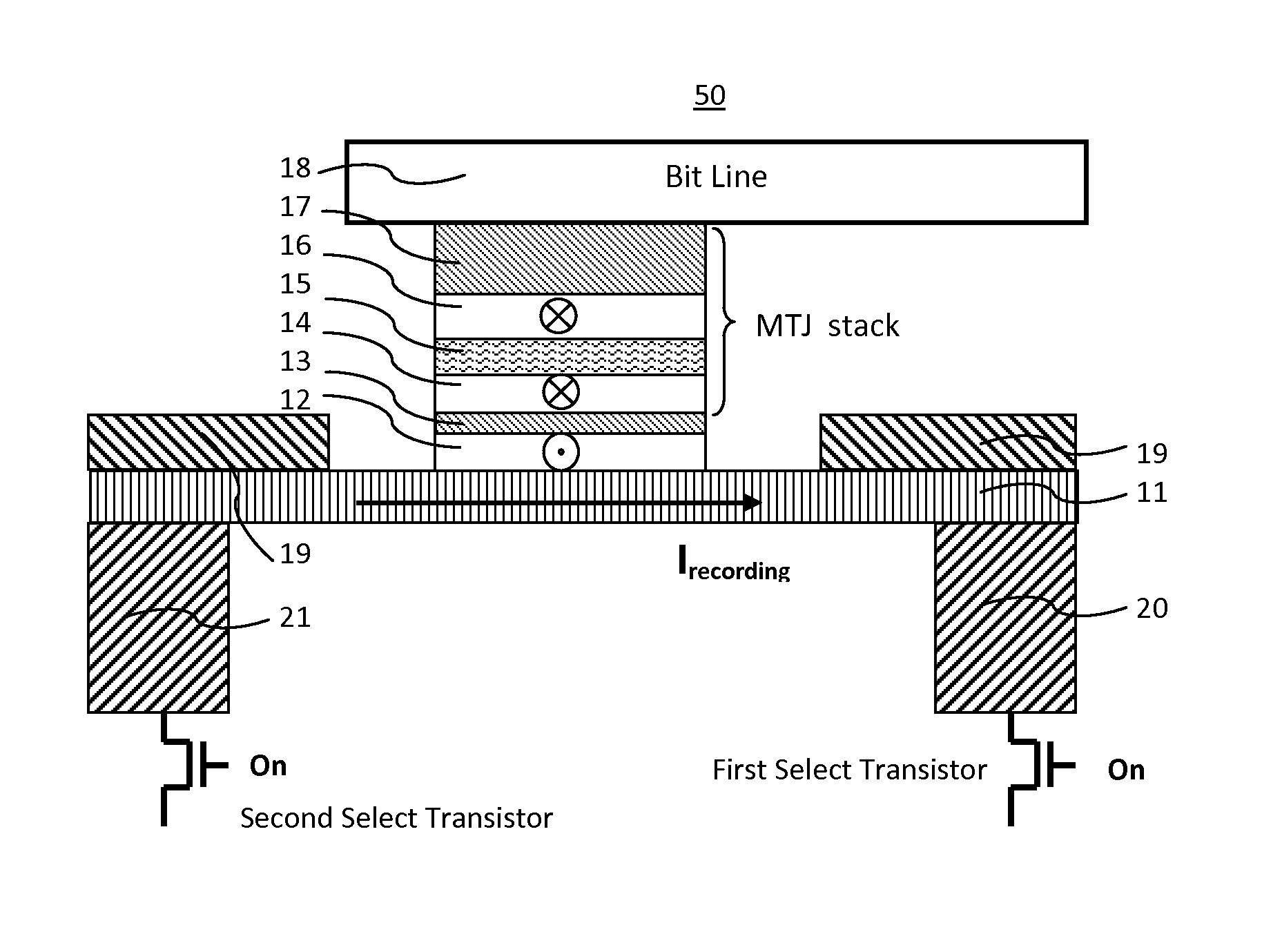
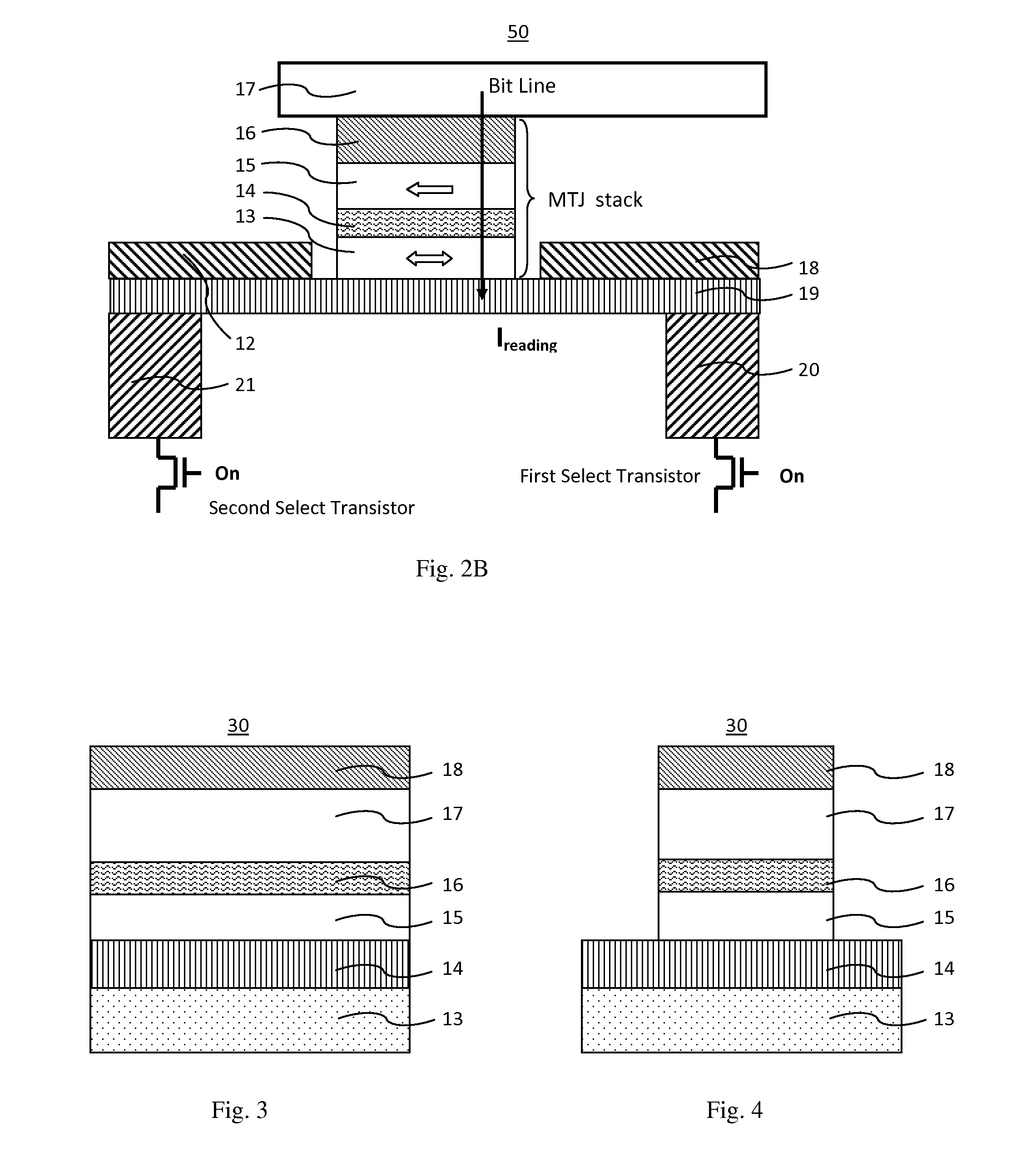
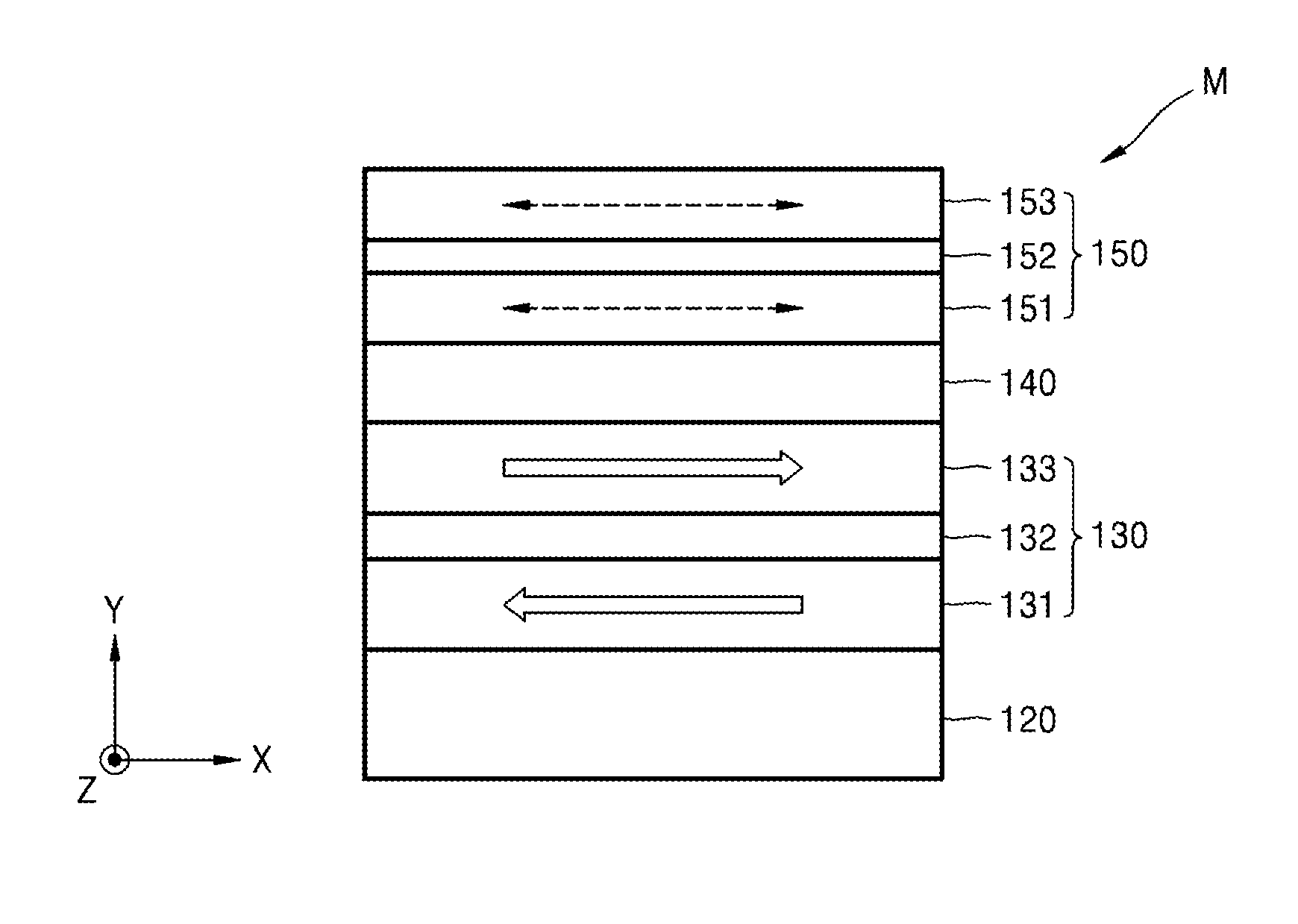
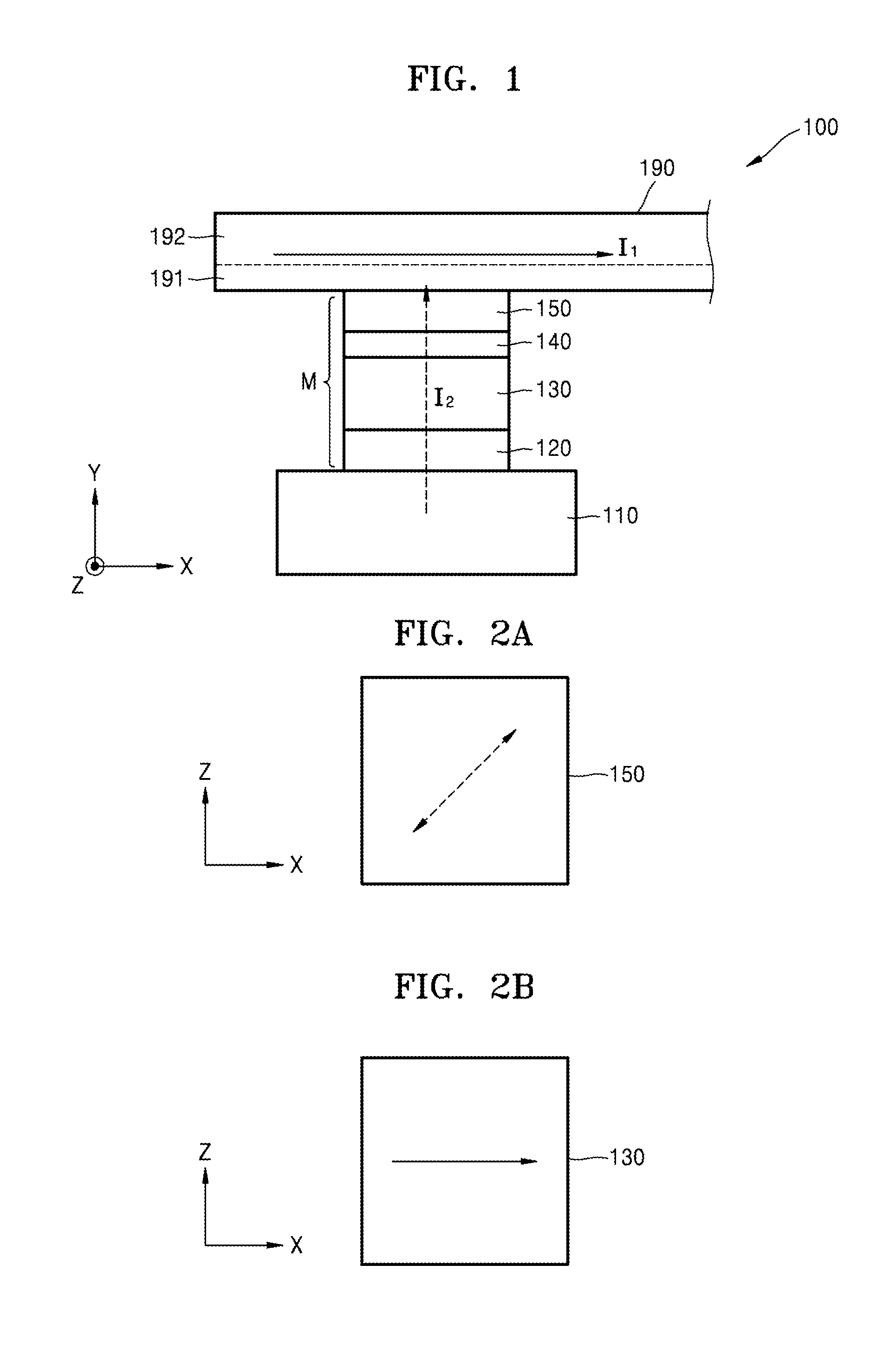
A spin-transfer-torque magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus and method of manufacturing a three terminal magnetoresistive memory element having highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid on top of a SHE-metal layer in the regions outside of an MTJ stack. The memory cell comprises a bit line positioned adjacent to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid and electrically contacting on top of a SHE-metal layer in the outside of an MTJ region and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to switch the magnetization of the recording layer. Thus magnetization of a recording layer can be readily switched or reversed to the direction in accordance with a direction of a current along the SHE-metal layer by applying a low write current.
Owner:T3MEMORY
Spin hall effect magnetic apparatus, method and applications
ActiveUS20150348606A1Improve efficiencySmall costRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectrical conductorSpin Hall effect
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
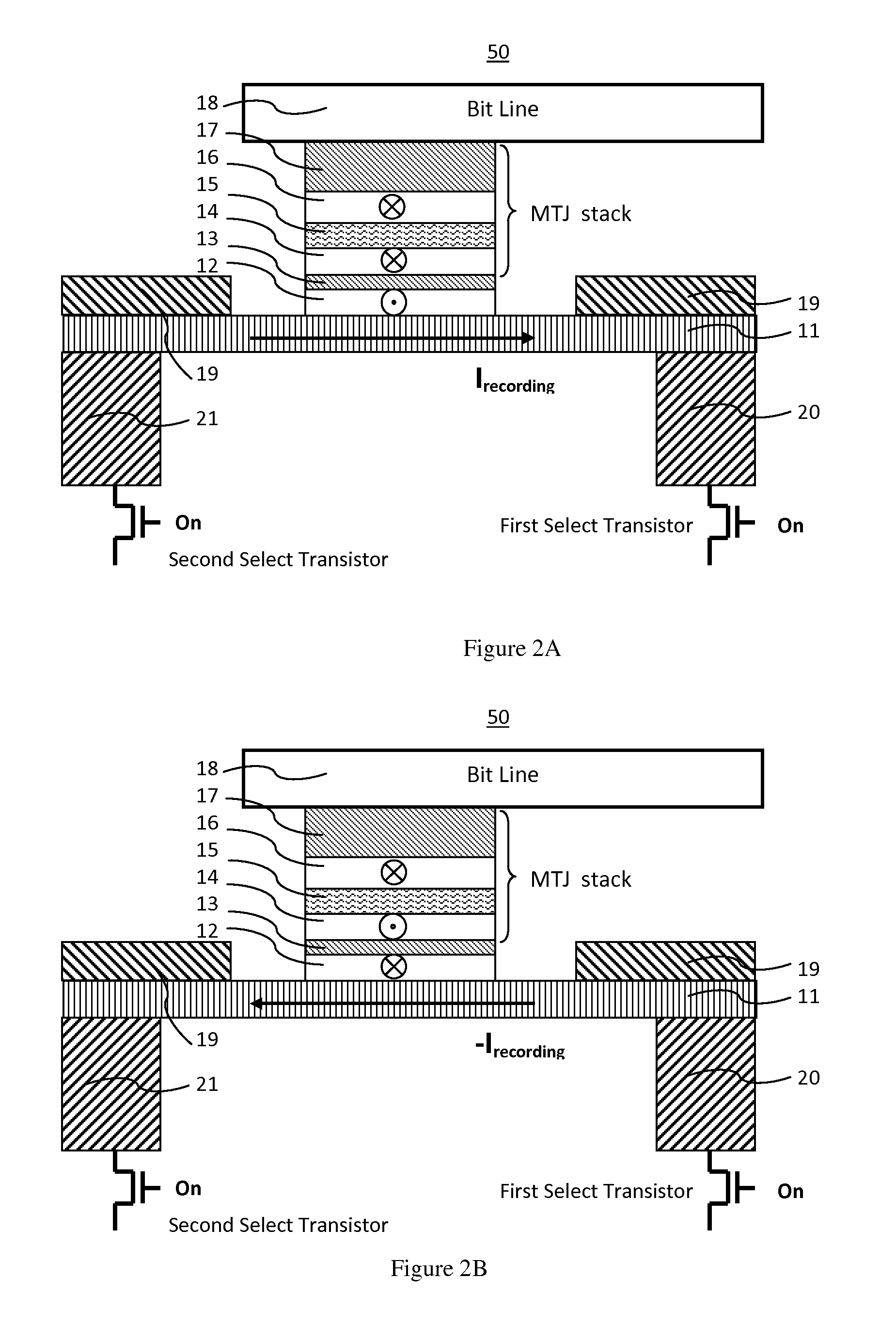
Novel spin hall effect magnetic-ram
ActiveUS20140312441A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic ramMagnetization
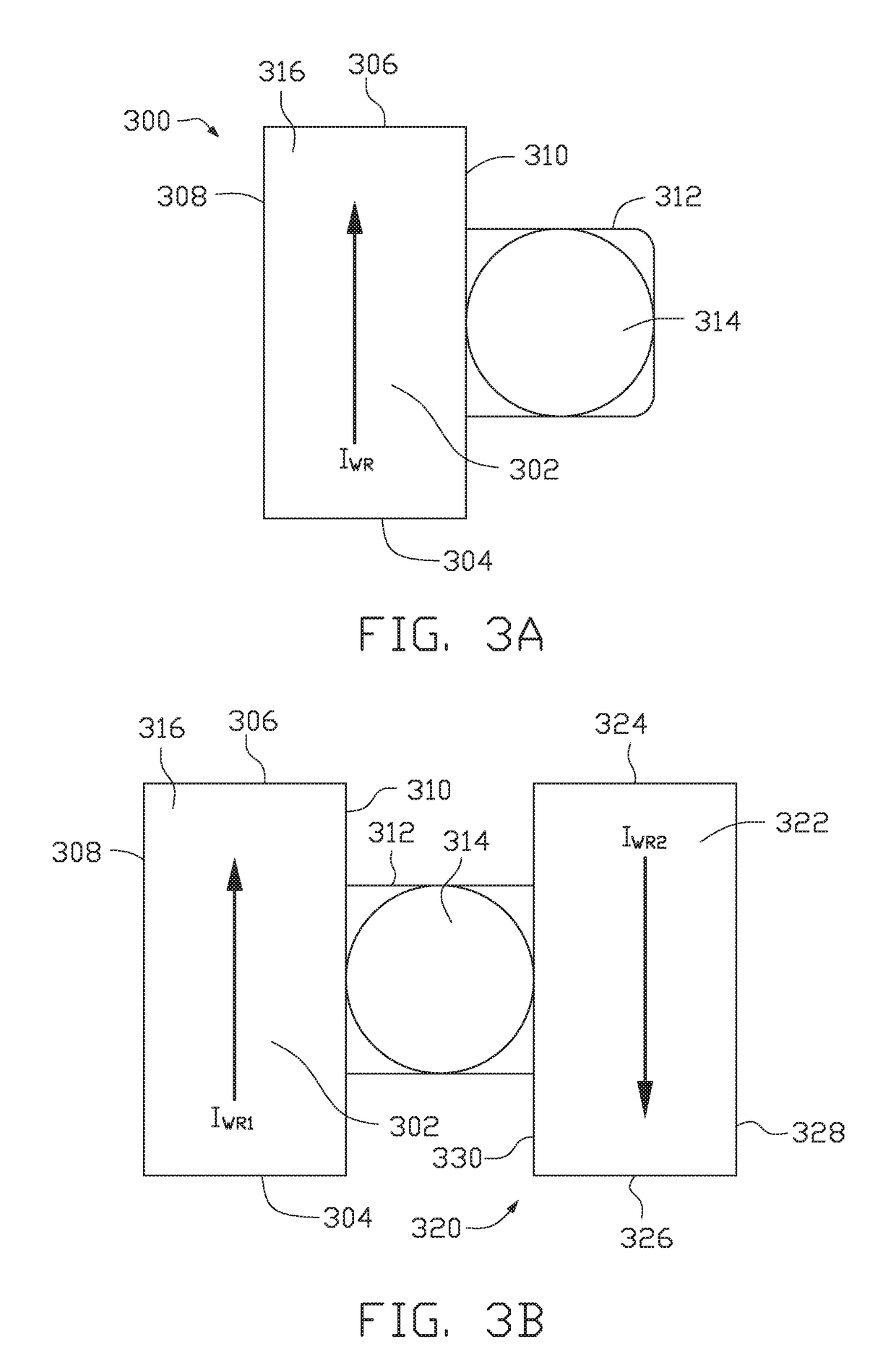
A spin Hall effect magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus of a three terminal magnetoresistive memory cell having an MTJ stack, a functional magnetic layer having a magnetization anti-parallel or parallel coupled with a recording layer magnetization in the MTJ stack, and a SHE-metal base layer. The control circuitry coupled through the bit line and the two select transistors to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two bottom electrodes and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to directly switch the magnetization of the functional magnetic coupling layer and indirectly switching the magnetization of the recording layer through the coupling between the functional magnetic coupling layer and the recording layer.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
Thermoelectric conversion device
ActiveUS20110084349A1Improve efficiencyLow thermal conductivityGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesIron compoundsSpin Hall effectSpins
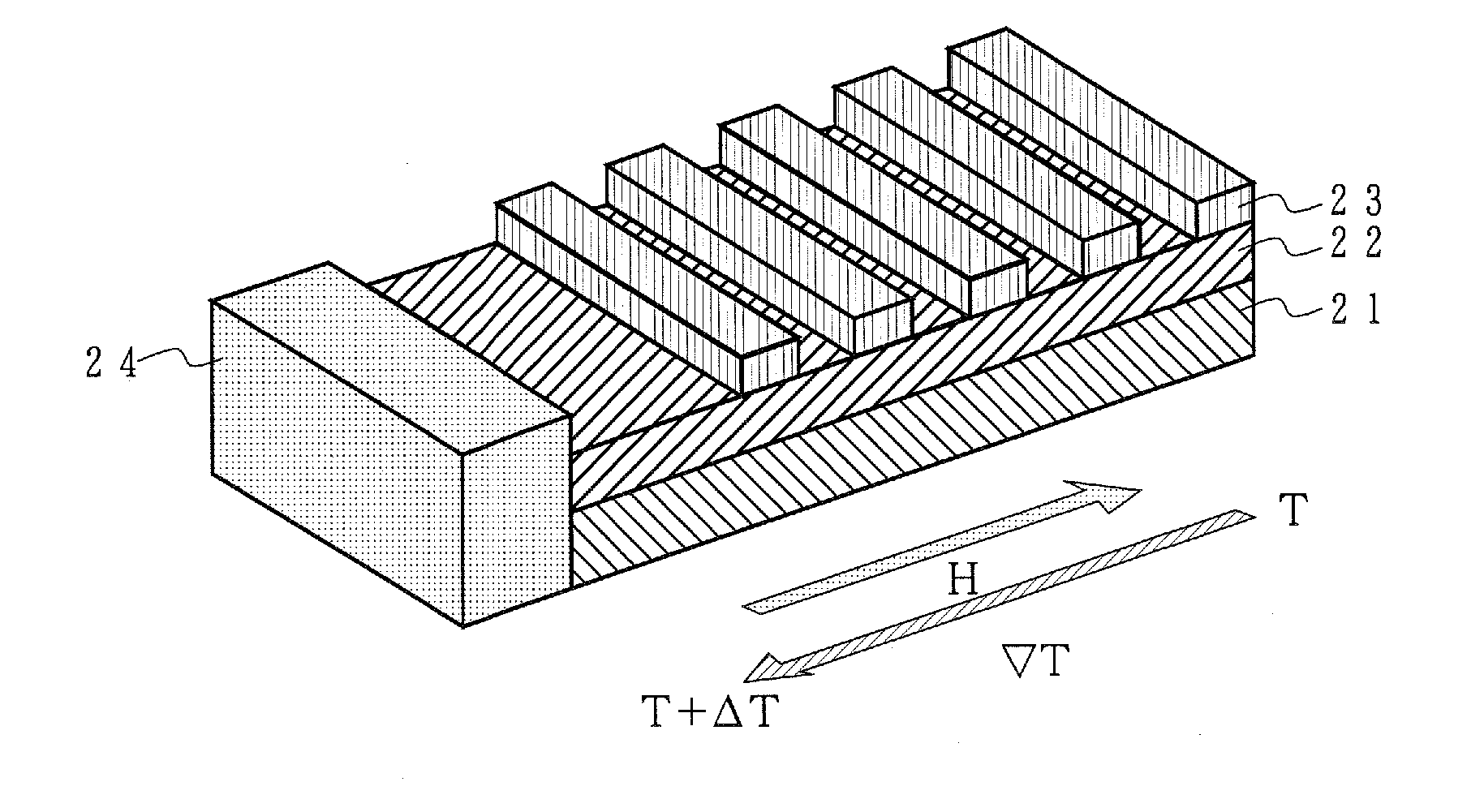
The thermoelectric conversion efficiency of a thermoelectric conversion device is increased by increasing the figure of merit of a spin-Seebeck effect element.An inverse spin-Hall effect material is provided to at least one end of a thermal spin-wave spin current generating material made of a magnetic dielectric material so that a thermal spin-wave spin current is converted to generate a voltage in the above described inverse spin-Hall effect material when there is a temperature gradient in the above described thermal spin-wave spin current generating material and a magnetic field is applied using a magnetic field applying means.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
System and method for cryogenic hybrid technology computing and memory
ActiveUS9520180B1Easy to combineTransmission lineCosmetic preparationsQuantum computersLow inductanceDatapath
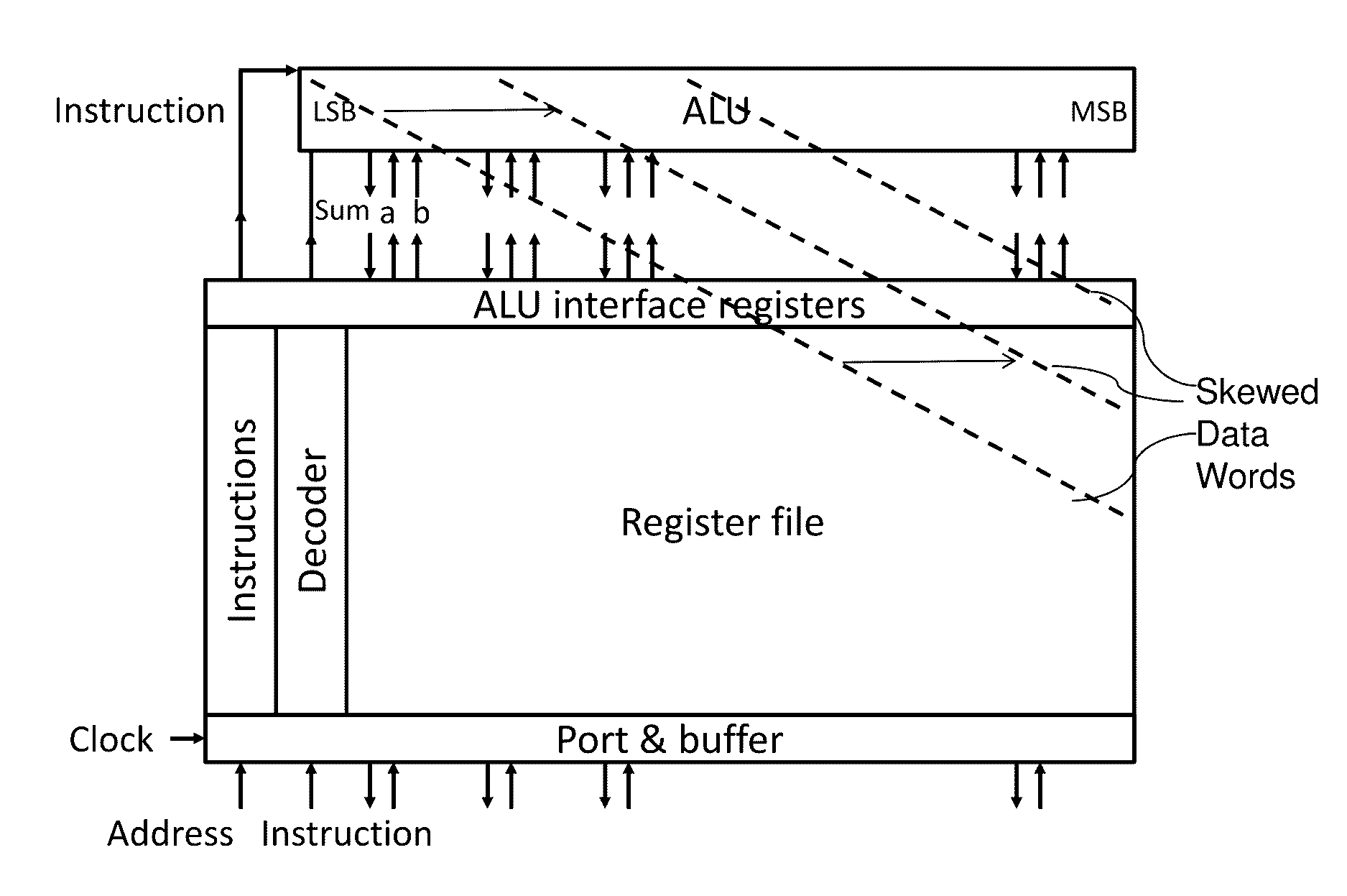
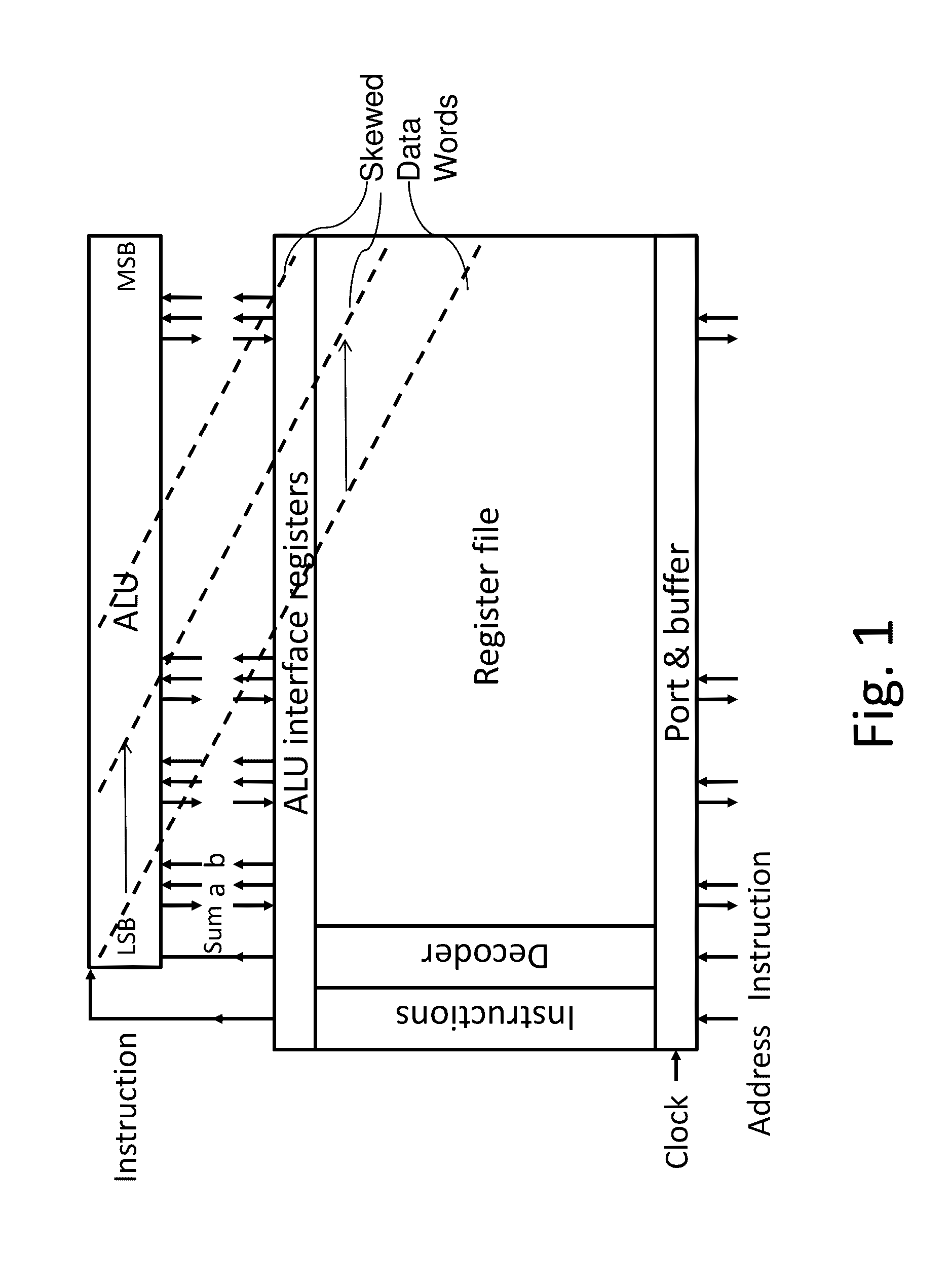
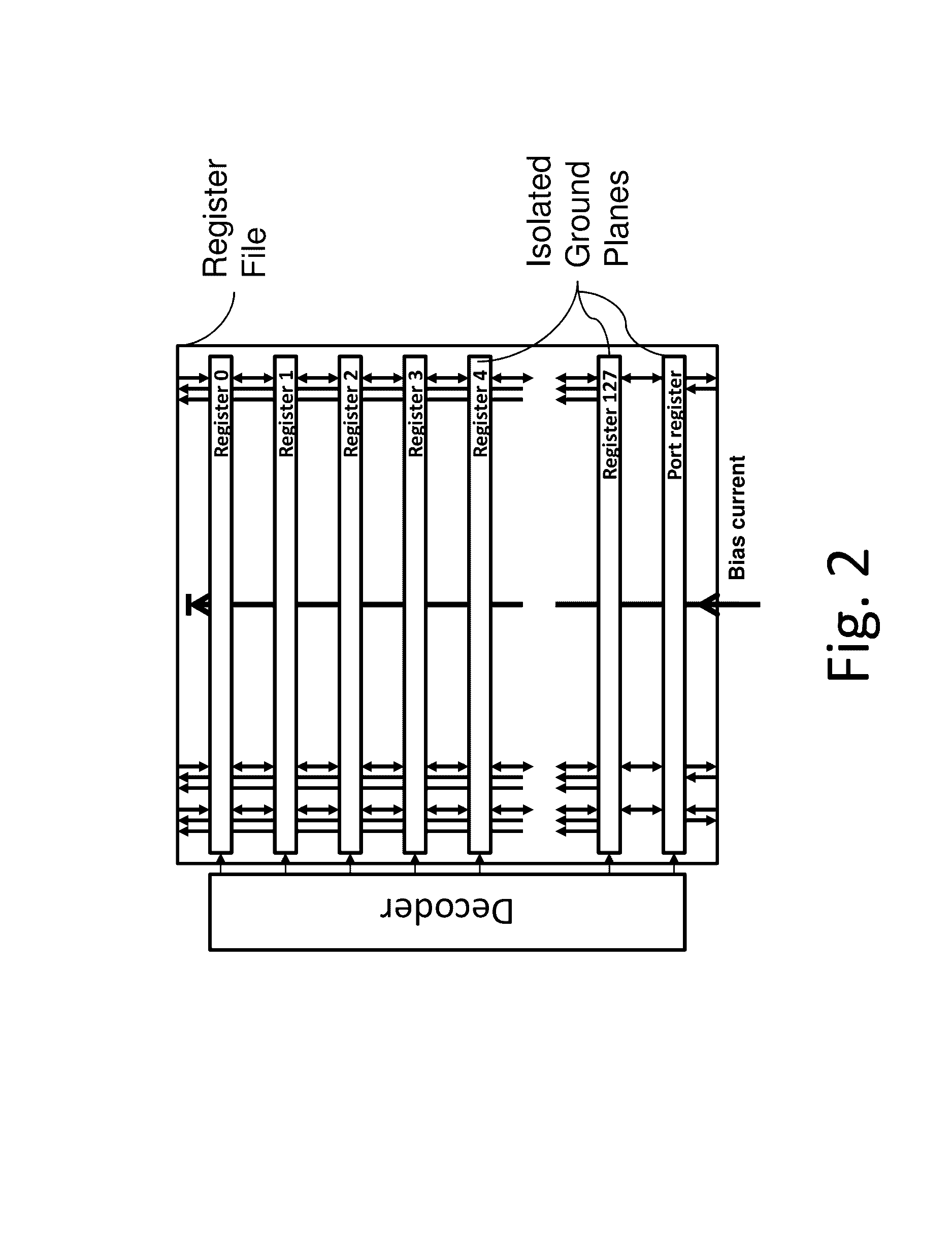
A system and method for high-speed, low-power cryogenic computing are presented, comprising ultrafast energy-efficient RSFQ superconducting computing circuits, and hybrid magnetic / superconducting memory arrays and interface circuits, operating together in the same cryogenic environment. An arithmetic logic unit and register file with an ultrafast asynchronous wave-pipelined datapath is also provided. The superconducting circuits may comprise inductive elements fabricated using both a high-inductance layer and a low-inductance layer. The memory cells may comprise superconducting tunnel junctions that incorporate magnetic layers. Alternatively, the memory cells may comprise superconducting spin transfer magnetic devices (such as orthogonal spin transfer and spin-Hall effect devices). Together, these technologies may enable the production of an advanced superconducting computer that operates at clock speeds up to 100 GHz.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Current-driven magnetic random access memory and spin logic device
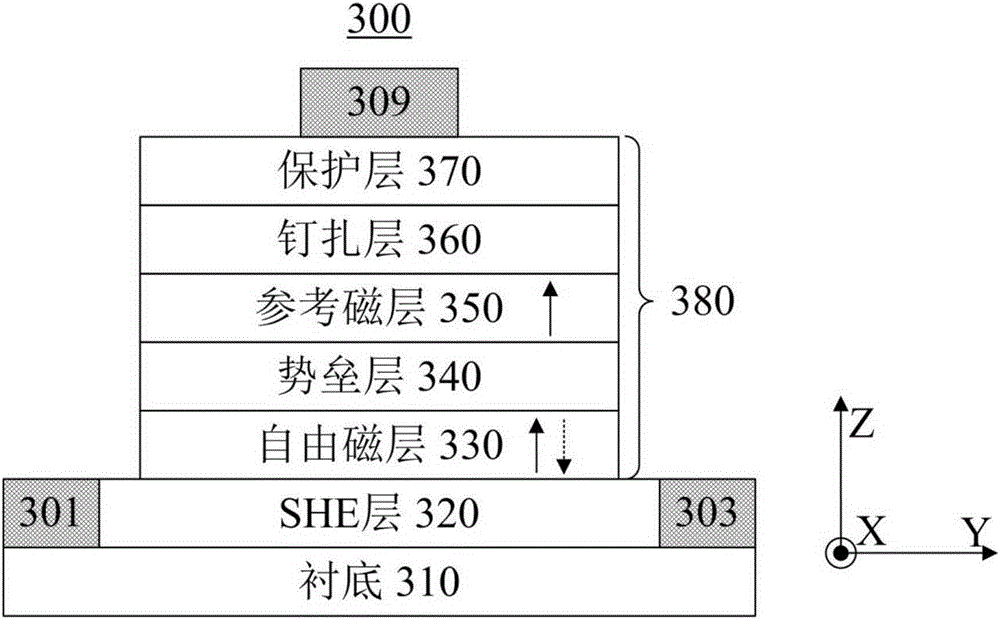
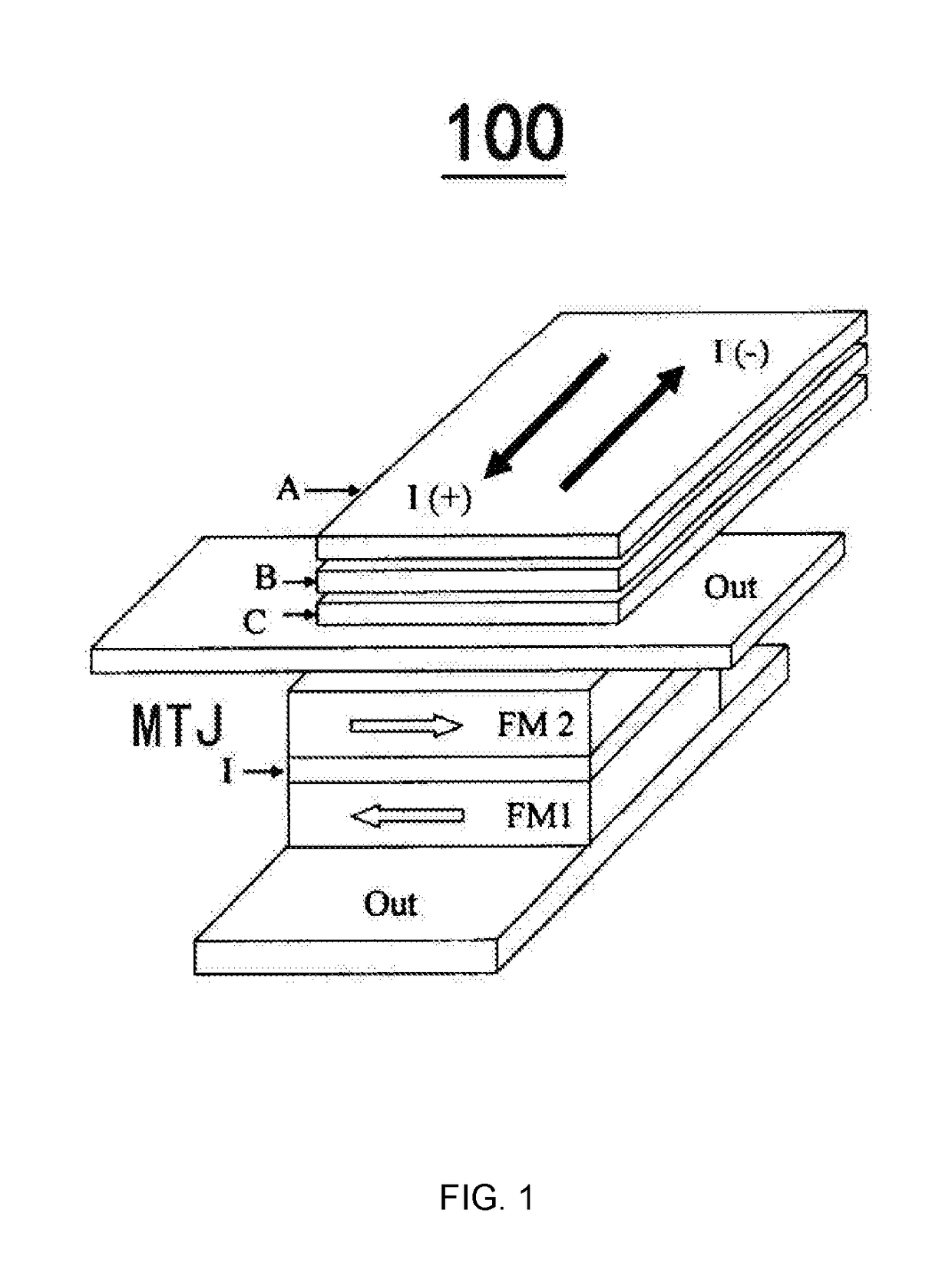
The invention relates to a current-driven magnetic random access memory and a spin logic device. The current-driven magnetic random access memory comprises a plurality of memory cells, and each memory cell comprises a magnetic tunnel junction, wherein the magnetic tunnel junction includes a free magnetic layer, a reference magnetic layer and a barrier layer located between the free magnetic layer and the reference magnetic layer, and the reference magnetic layer is coupled to a first terminal; and a spin Hall effect SHE layer adjacent to the free magnetic layer and contacted with the free magnetic layer, wherein the SHE layer is coupled to a second terminal, a third terminal, a fourth terminal and a fifth terminal at the periphery, and a phantom line connected with the second terminal and the fourth terminal is crossed with a phantom line connected with the third terminal and the fifth terminal. The invention further provides electronic equipment including at least one of the current-driven magnetic random access memory and the spin logic device.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
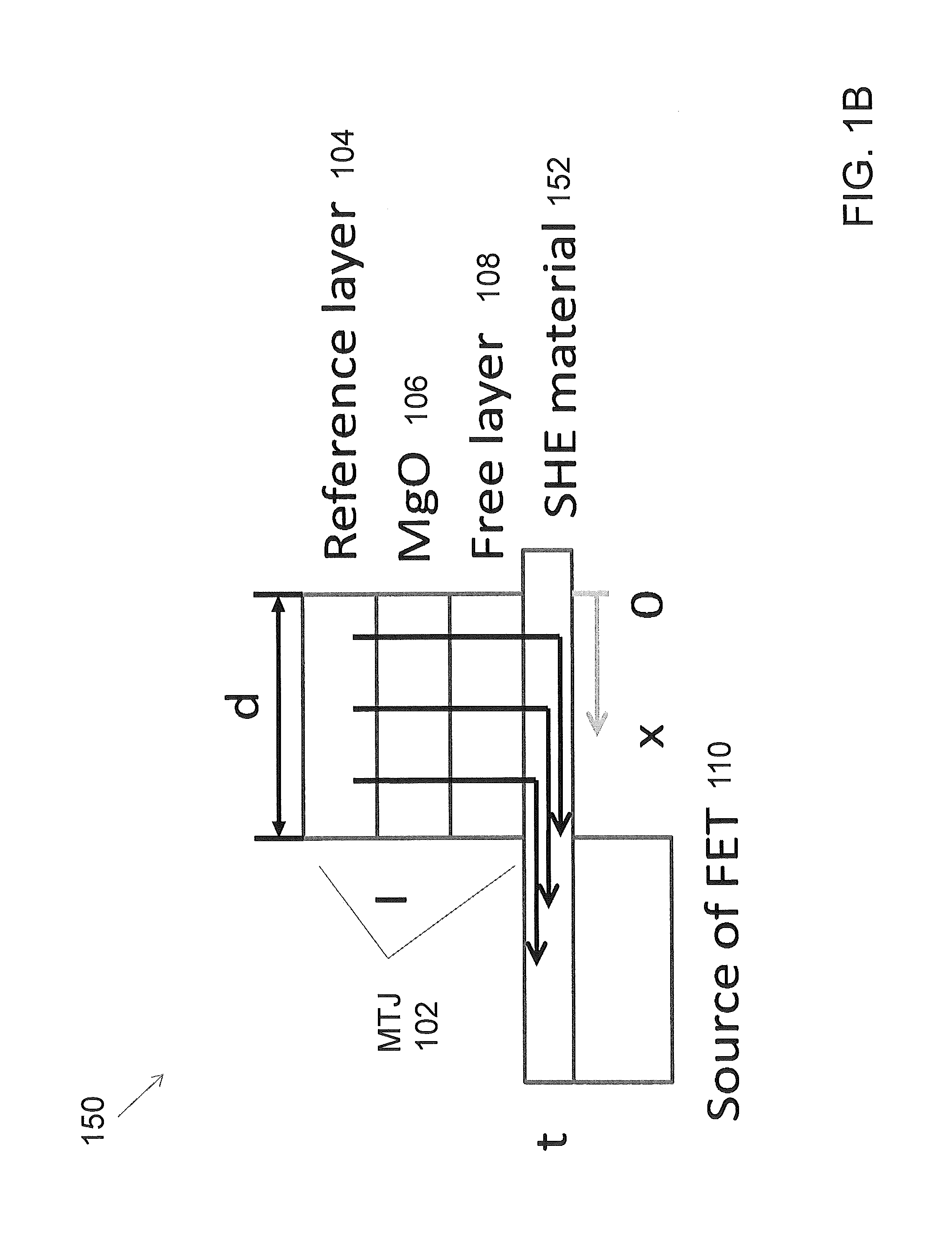
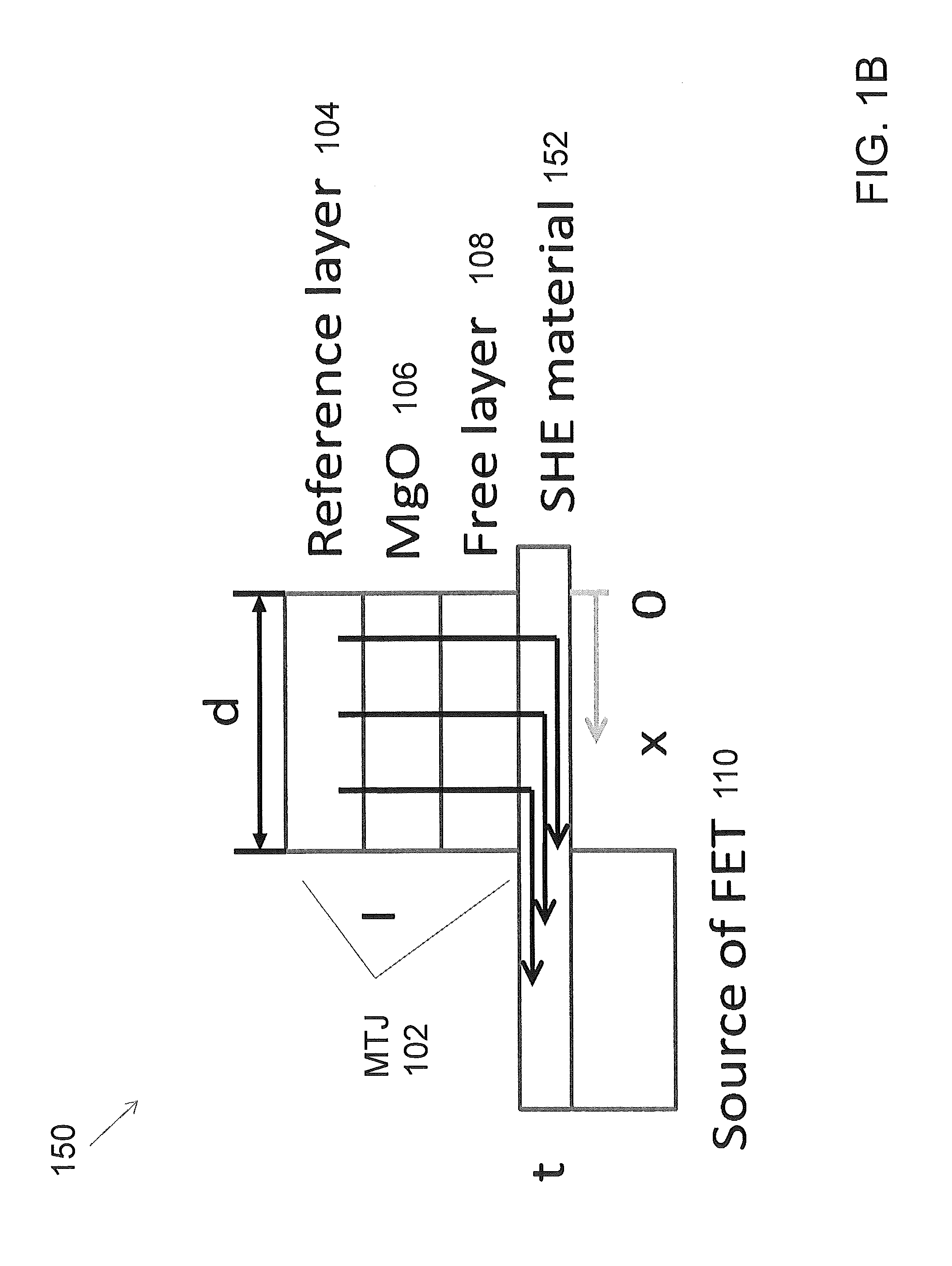
Spin hall effect assisted spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS20140264513A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpin Hall effectSpin-transfer torque
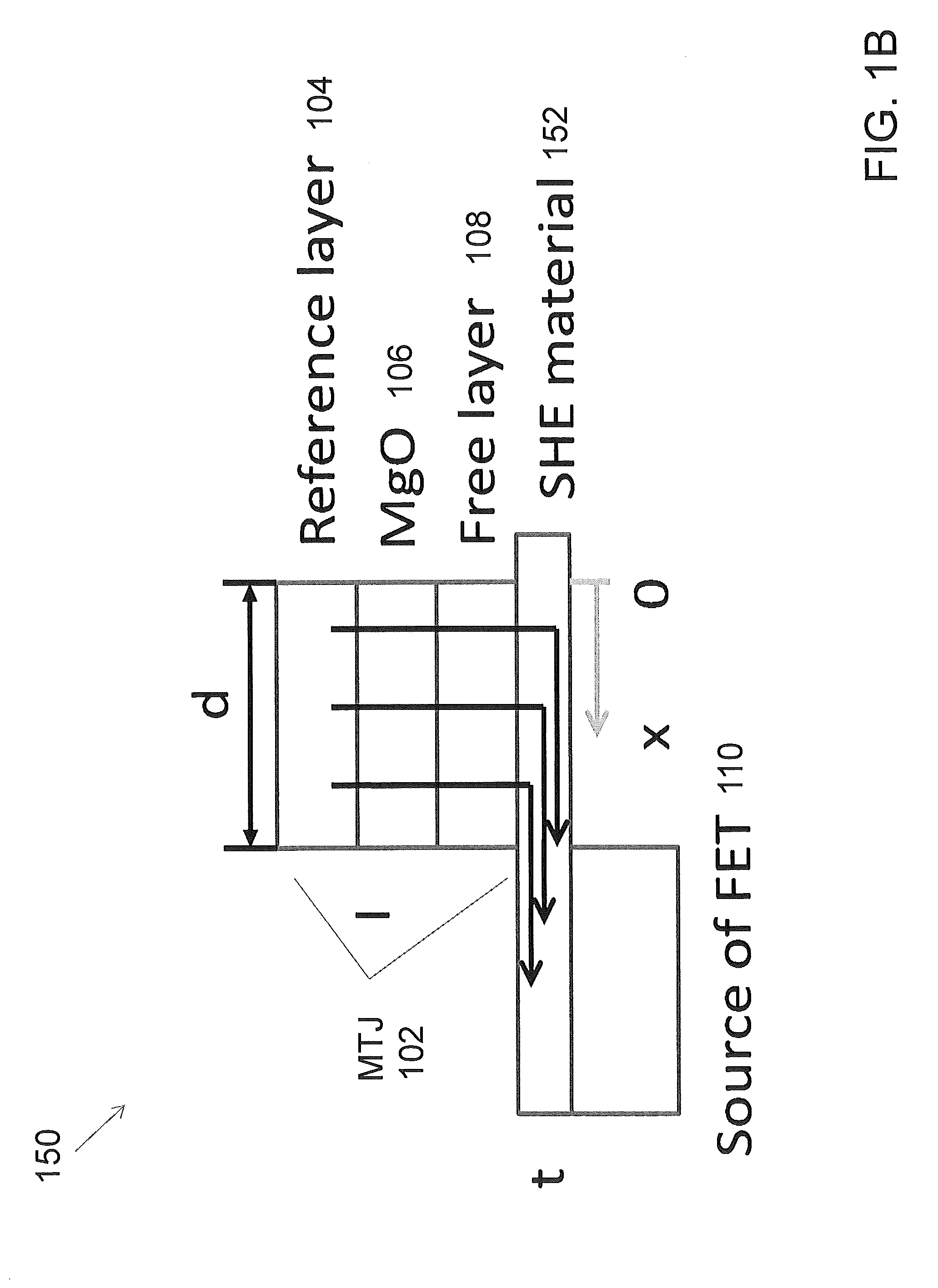
Embodiments are directed to providing a spin hall effect (SHE) assisted spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM) device by coupling a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) to a SHE material, and coupling the SHE material to a transistor. Embodiments are directed to a spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM) device comprising: a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) coupled to a spin hall effect (SHE) material, and a transistor coupled to the SHE material.
Owner:IBM CORP
Spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory containing composite spin hall effect layer including beta phase tungsten
ActiveUS20190080738A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin orbit torqueSpin Hall effect
A spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory (SOT MRAM) cell includes a magnetic tunnel junction that contains a free layer having two bi-stable magnetization directions, a reference magnetic layer having a fixed magnetization direction, and a tunnel barrier layer located between the free layer and the reference layer, and a nonmagnetic spin Hall effect layer. The spin Hall effect layer may include an alternating stack of beta phase tungsten layers and noble metal nonmagnetic dusting layers. Alternatively or in addition, a hafnium layer may be located between the nonmagnetic spin Hall effect layer and the free layer.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
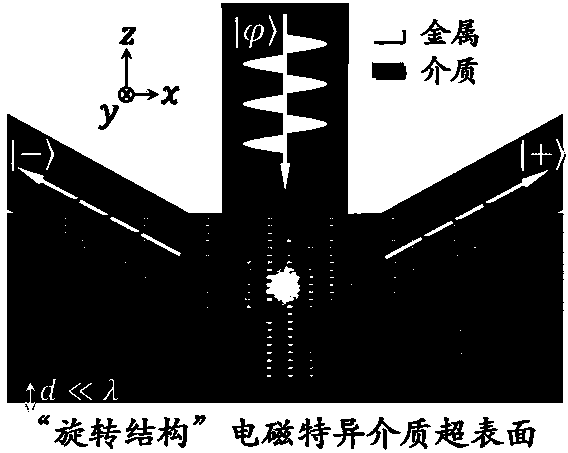
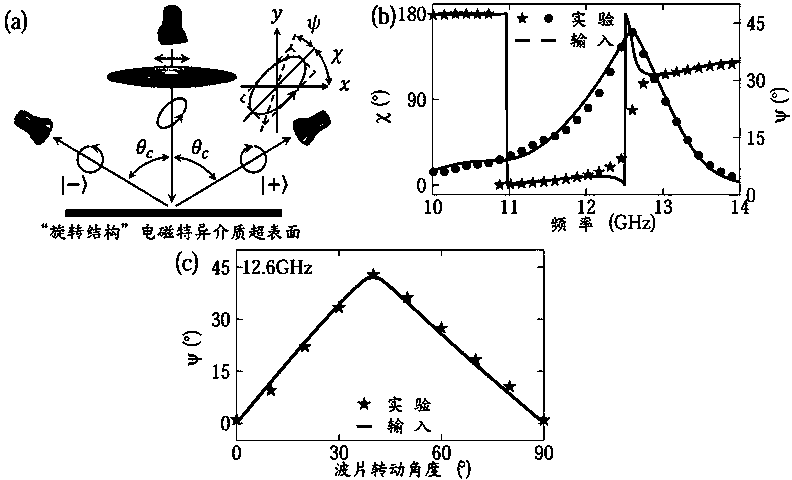
Efficient microwave polarization detection device based on photonic spin Hall effect
ActiveCN104569622AQuality improvementHigh precisionElectromagentic field characteristicsBacksteppingPhotonics
The invention belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic wave polarization detection, and particularly discloses an efficient microwave polarization detection device based on a photonic spin Hall effect. For the detection device, electromagnetic wave to be detected is decomposed into left-hand circularly polarized beam and right-hand circularly polarized beam through the efficient photonic spin Hall effect, the module values and phases of the left-hand circularly polarized beam and right-hand circularly polarized beam are respectively measured, and backstepping is carried out to obtain the polarization of the electromagnetic wave to be detected. The photonic spin Hall effect is realized through linear geometry Berry phase gradient of total-reflection type meta-surface with a spin structure. Compared with the traditional polarization detection manner (linear polarization loudspeakers opposite to each other are used for directly measuring x component and y component of electromagnetic wave), the efficient microwave polarization detection device has the advantages that higher convenience and quickness are achieved, the errors are few, and the stability is better. The operating frequency of the device is 10-14GHz, and the structure constants of meta-atoms are scaled in equal proportion or redesigned, so that the operating frequency can be applied to other operating frequency ranges.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Sot MRAM cell with perpendicular free layer and its cross-point array realization
The present disclosure generally relates to a SOT-MRAM cell that has a spin Hall effect layer and a magnetic tunnel junction. The magnetic tunnel junction is disposed at an edge of the spin Hall effect layer. In order to write the cell, current is applied through the spin Hall effect layer to create spin accumulation of z-polarized spins under the free layer due to the spin Hall effect. The spins exert a spin torque on the free layer via spin diffusion. Based upon the design, the SOT-MRAM cell has deterministic switching of the perpendicular free layer with the spin Hall effect layer without application of an external magnetic field.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spin logic device and electronic equipment including same
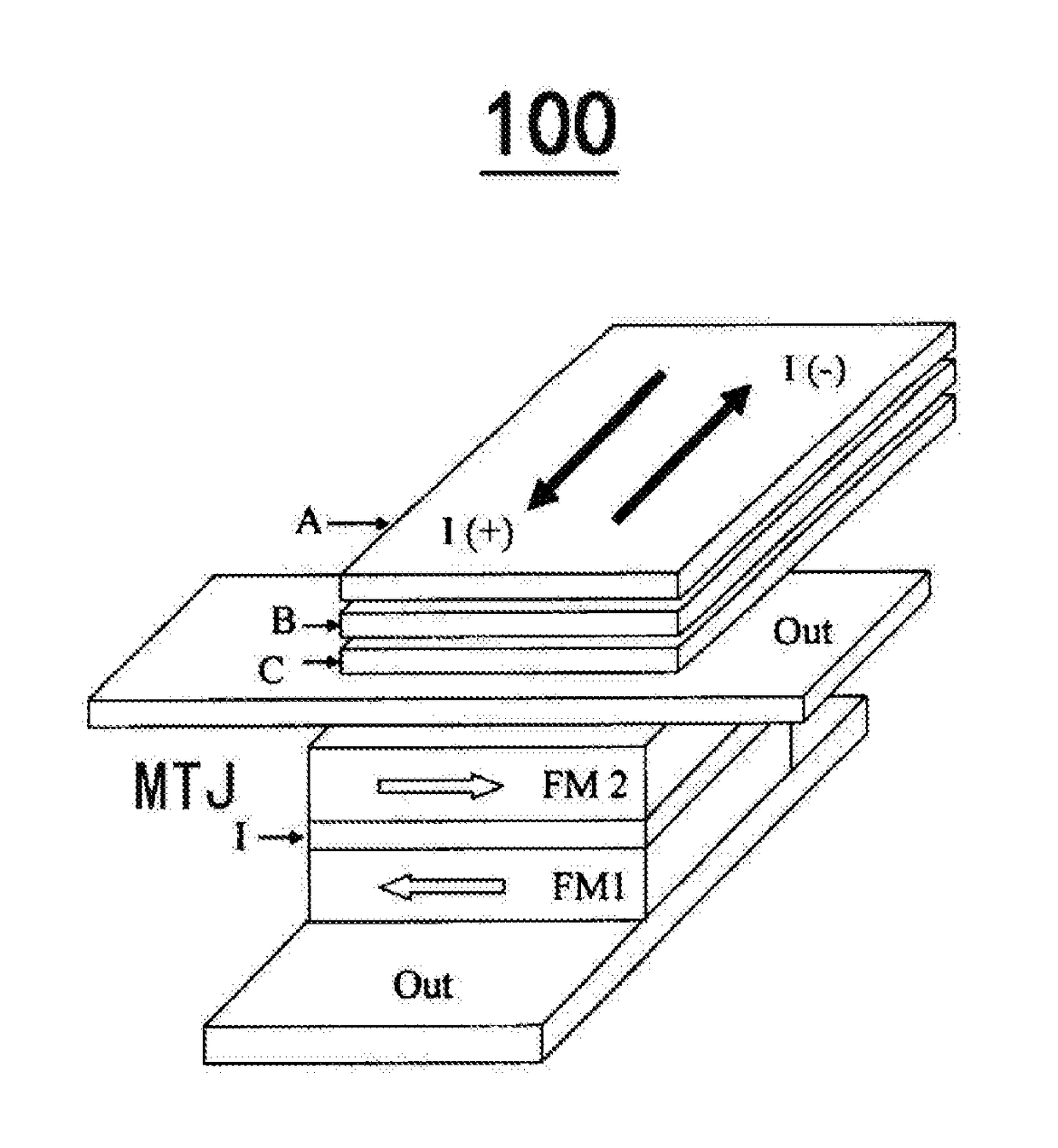
The present invention relates to a spin logic device and an electronic equipment comprising the same. A spin logic device may include a Spin Hall effect (SHE) layer formed of a conductive material having Spin Hall effect and configured to receive a first logic input current and a second logic input current, the first logic input current and the second logic input current both being an in-plane current, a magnetic tunnel junction provided on the SHE layer comprising a free magnetic layer in contact with the SHE layer, a barrier layer disposed on the free magnetic layer, and a reference magnetic layer disposed on the barrier layer, and a current wiring in connection to the reference magnetic layer side of the magnetic tunnel junction, the current wiring being in cooperation with the SHE layer to apply a read current passing through the magnetic tunnel junction therebetween.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
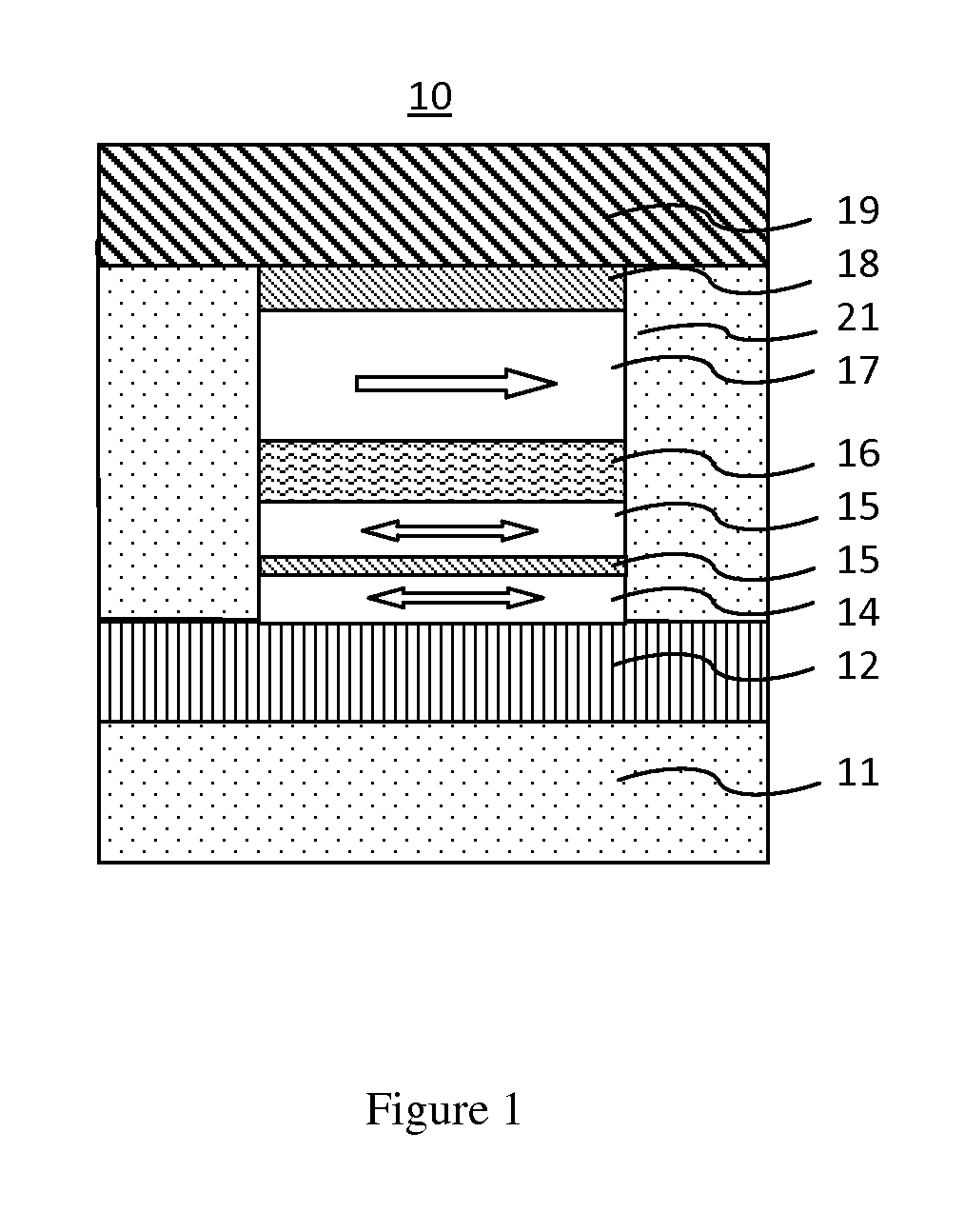
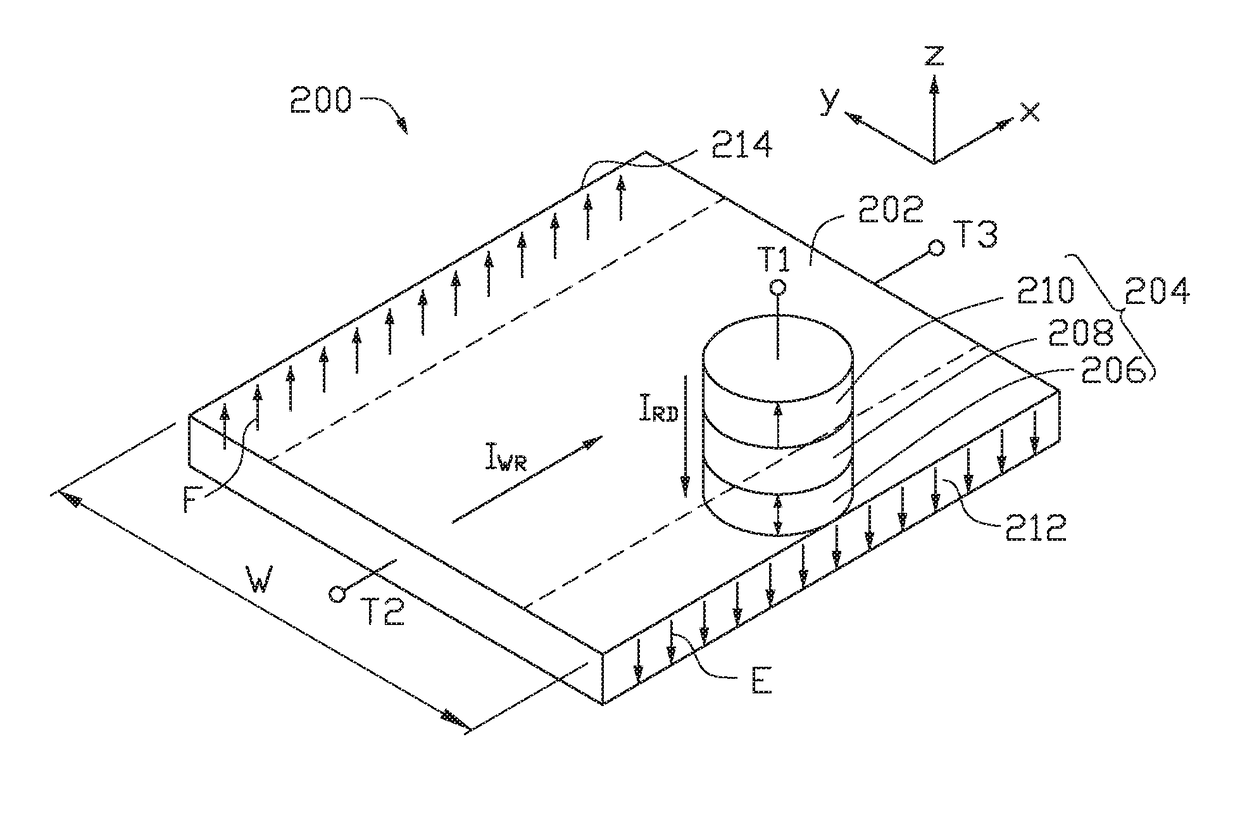
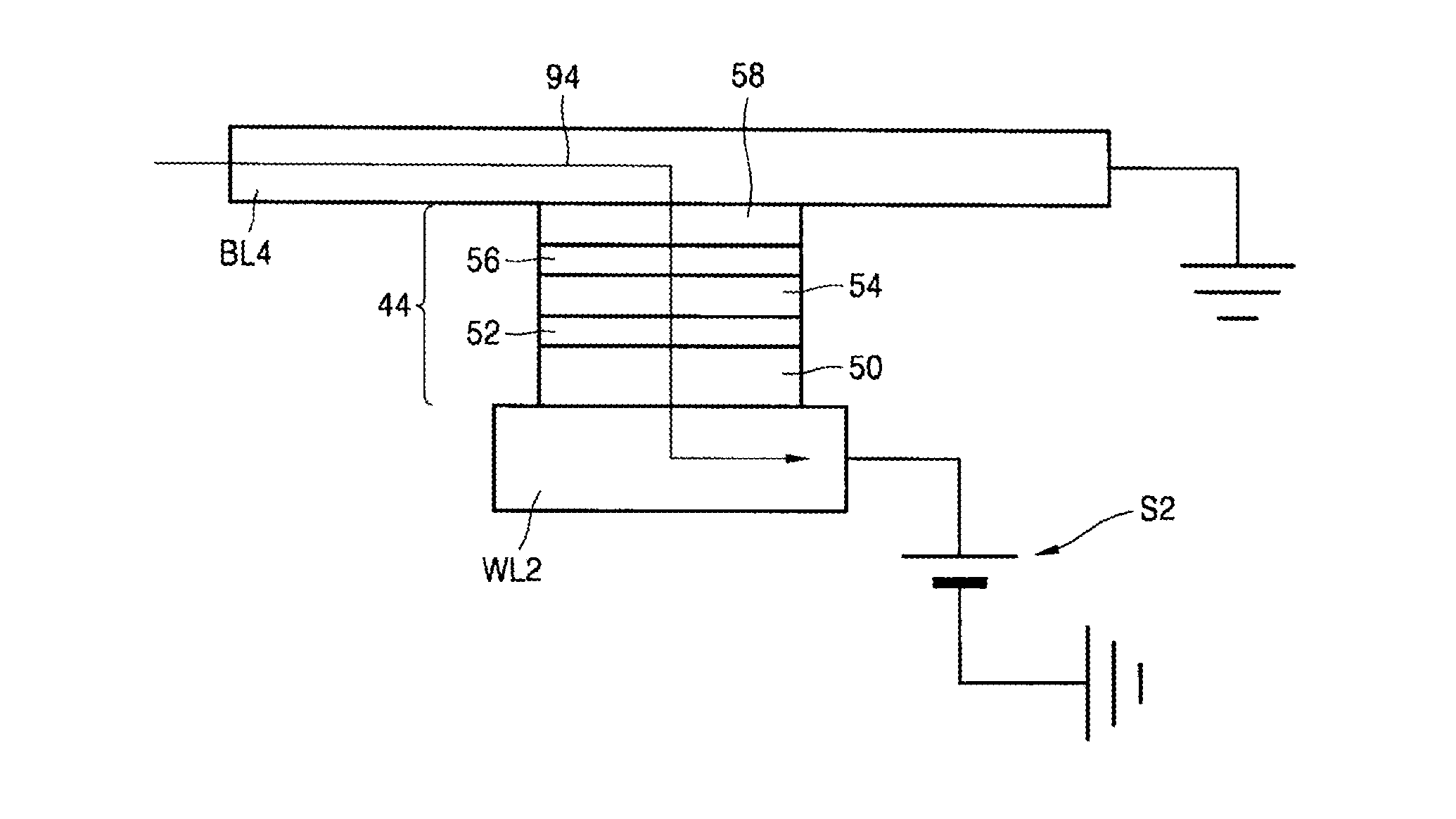
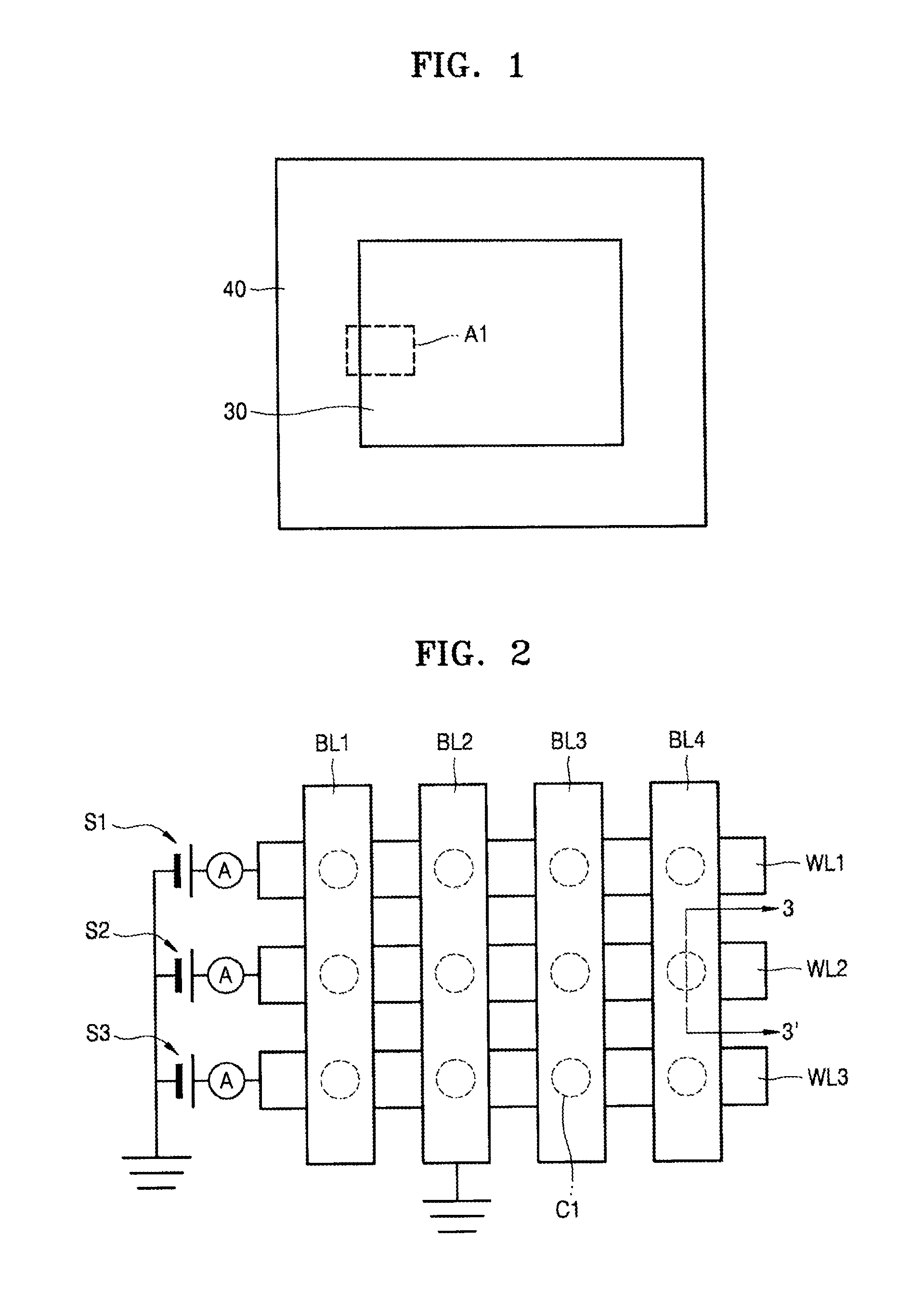
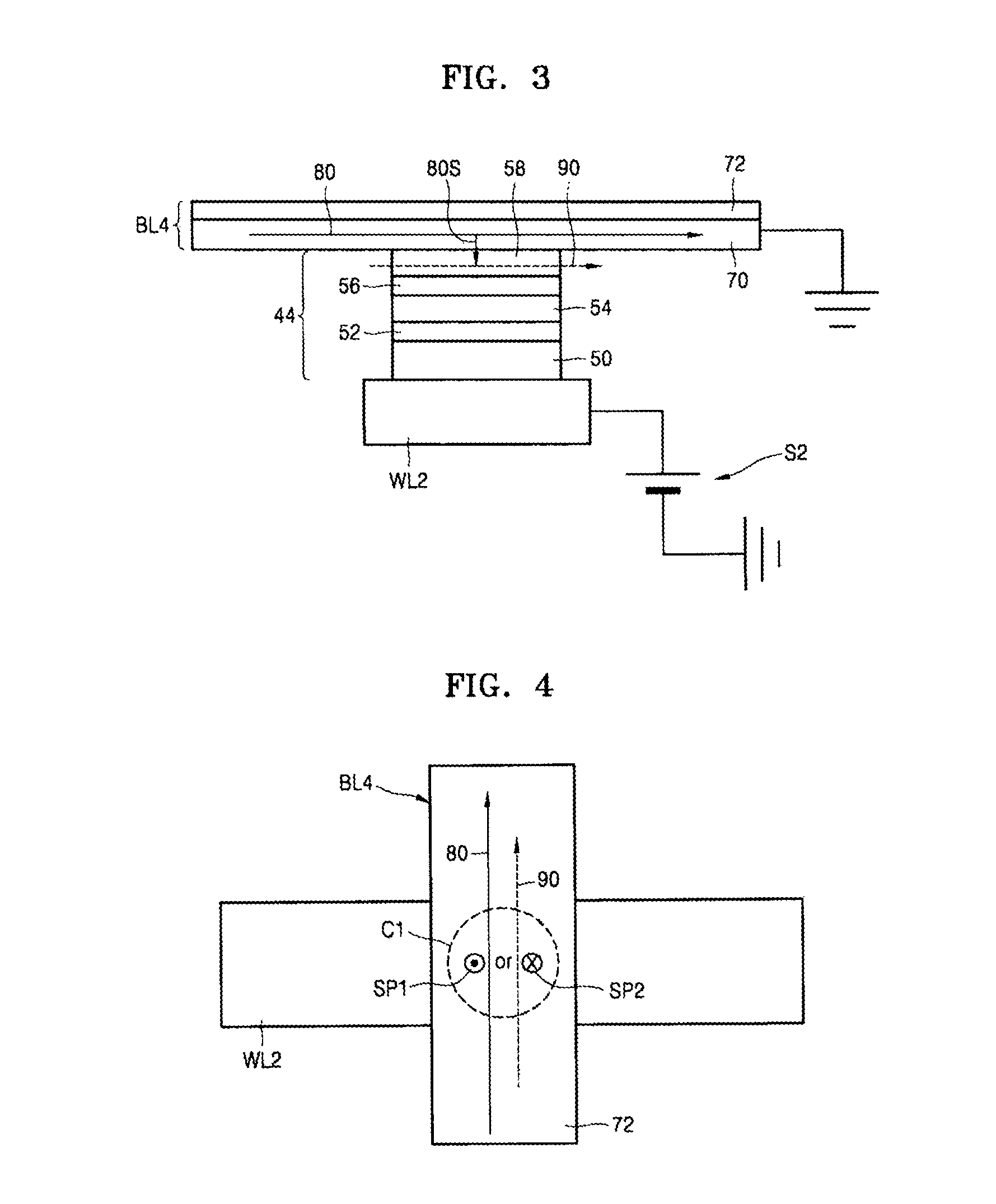
Memory device using spin hall effect and methods of manufacturing and operating the memory device
ActiveUS20140211552A1Small sizeGuaranteed uptimeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesBit lineElectricity
A memory device using a spin hall effect, and methods of manufacturing and operating the memory device, include applying a first operational current to a bit line of the memory device such that a spin current is applied to a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cell coupled to the bit line due to a material in the bit line, wherein the bit line is electrically connected to a word line via the MTJ cell, and the word line intersects the bit line.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic element based on spin hall effect, microwave oscillator and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103779495AReduce noiseLarge adjustment rangeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionManufacturing technologyMagnetization
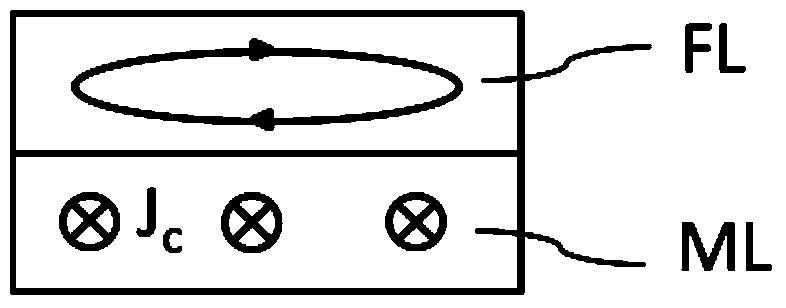
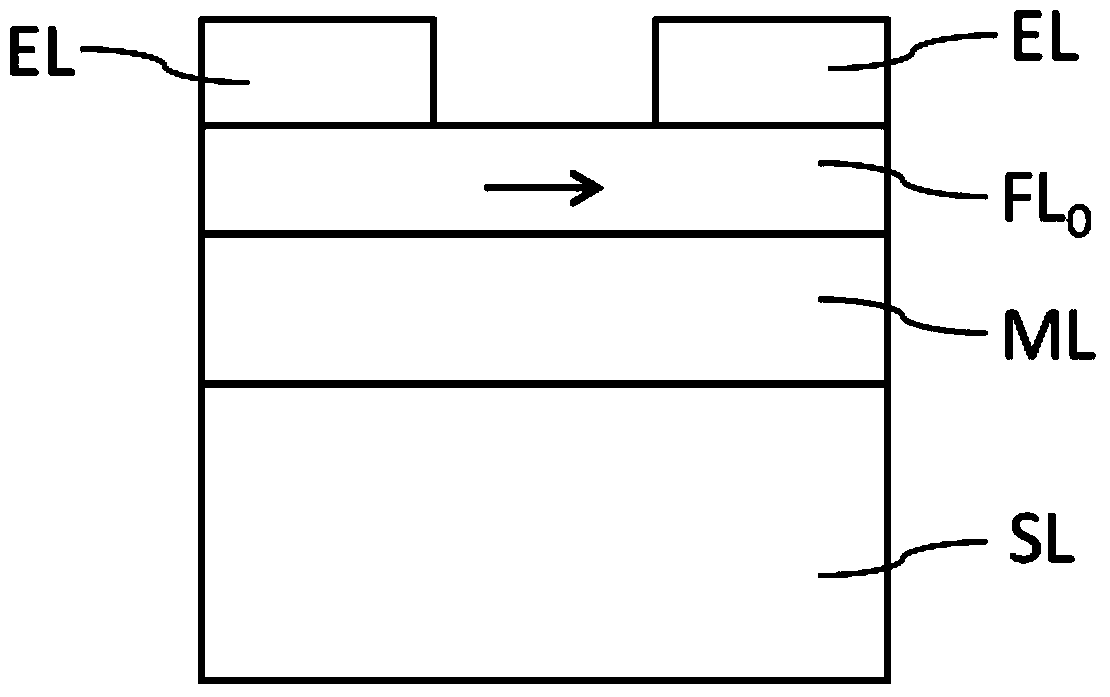
The invention discloses a magnetic element based on a spin hall effect, a microwave oscillator and a manufacturing method thereof. The magnetic element comprises a non-magnetic metal film layer (ML) and a magnetic film layer (FL), wherein the non-magnetic metal film layer (ML) can induce electrons to generate spin currents, and the magnetic film layer (FL) is formed on the non-magnetic metal film layer (ML) and can balance magnetization. The microwave oscillator comprises the magnetic element, the magnetic element is formed on a substrate layer (SL), and metal electrodes (EL) are formed on the magnetic element. The microwave oscillator can be formed by using a thin film deposit technology, a photoetching and / or etching technology and the like. The structure of the magnetic element is beneficial to reducing the noise of the microwave oscillator, device microwave frequency is wide in adjustable range under the effect of impressed currents, and output microwave signals are excellent in performance. The microwave oscillator has the advantages of being small in size, simple in structure and the like, and is simple in manufacturing technology, compatible with traditional nano-meter processing technologies, easy to manufacture in a mass mode and capable of serving as a microwave source to be widely applied in the fields of electronics, communication and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
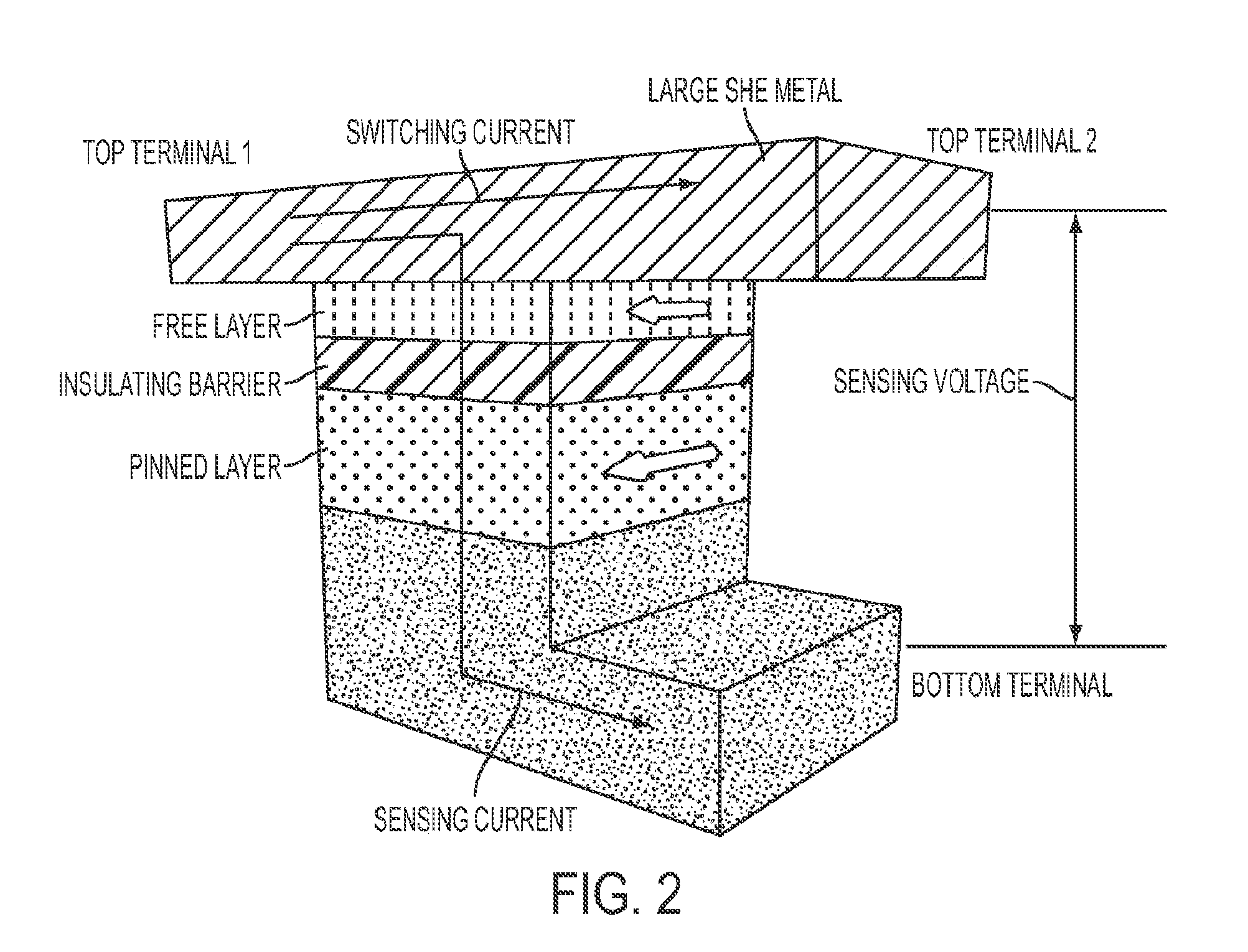
Spin hall effect magnetic-RAM
ActiveUS8963222B2Readily switched and reversedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic ramMagnetic reluctance
A spin Hall effect magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus of a three terminal magnetoresistive memory cell having an MTJ stack, a functional magnetic layer having a magnetization anti-parallel or parallel coupled with a recording layer magnetization in the MTJ stack, and a SHE-metal base layer. The control circuitry coupled through the bit line and the two select transistors to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two bottom electrodes and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to directly switch the magnetization of the functional magnetic coupling layer and indirectly switching the magnetization of the recording layer through the coupling between the functional magnetic coupling layer and the recording layer.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
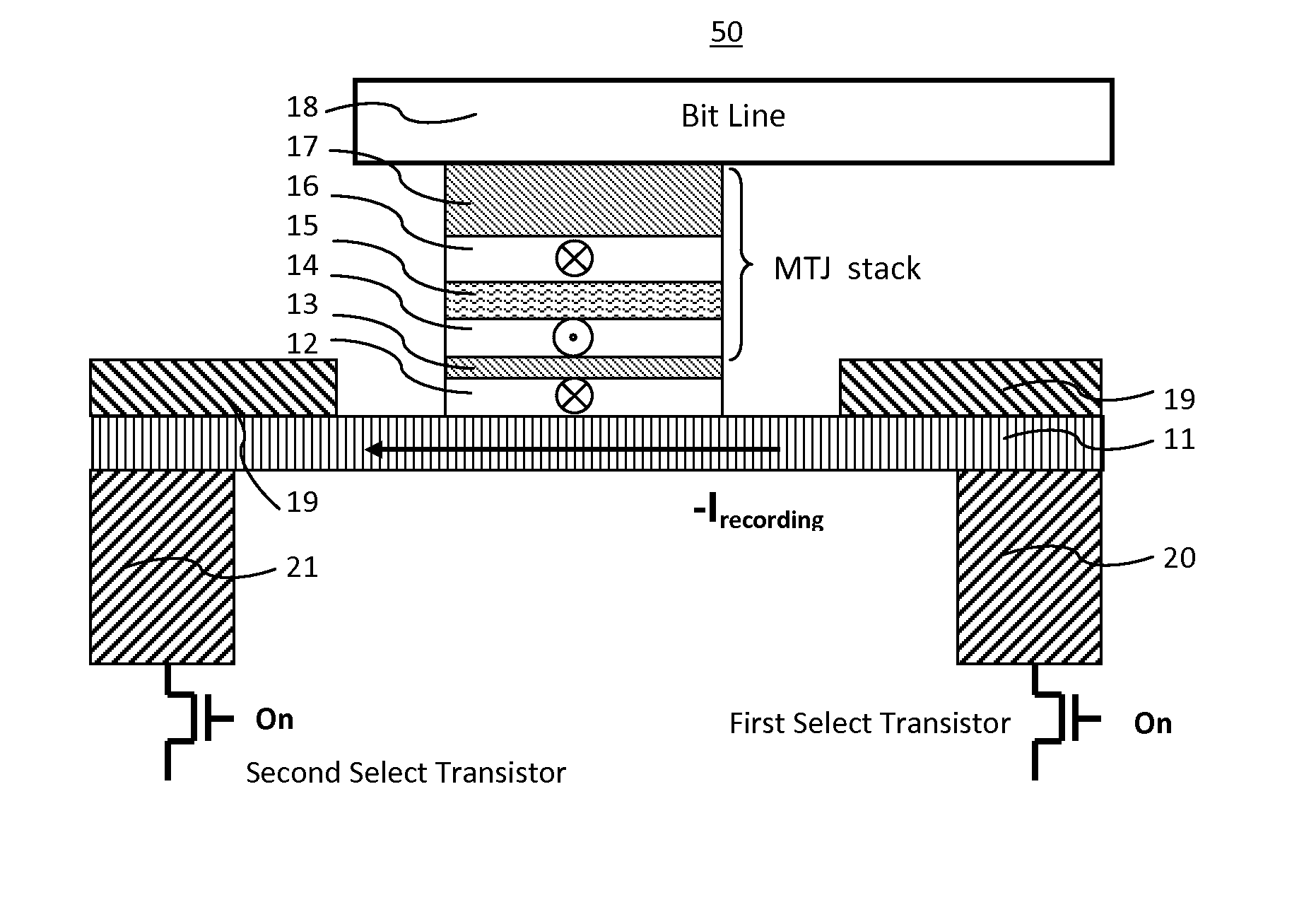
MRAM having spin hall effect writing and method of making the same
ActiveUS20160225982A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesBit lineSpin Hall effect
A spin-transfer-torque magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus and method of manufacturing a three terminal magnetoresistive memory element having highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid on top of a SHE-metal layer in the regions outside of an MTJ stack. The memory cell comprises a bit line positioned adjacent to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid and electrically contacting on top of a SHE-metal layer in the outside of an MTJ region and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to switch the magnetization of the recording layer. Thus magnetization of a recording layer can be readily switched or reversed to the direction in accordance with a direction of a current along the SHE-metal layer by applying a low write current.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
Magnetic memory device and method for reading magnetic memory cell using spin hall effect
InactiveUS20100027330A1Easily read stored dataGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesSpin Hall effectMagnetic memory
A magnetic memory device includes a substrate for reading and a magnetic memory cell. The substrate has a channel layer. The magnetic memory cell is formed on the substrate and has a magnetized magnetic material that transfers spin data to electrons passing the channel layer. Data stored in the magnetic memory cell are read by a voltage across both side ends of the channel layer that is generated when the electrons passing the channel layer deviate in the widthwise direction of the channel layer by a spin Hall effect.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic memory devices and methods of writing data to the same
Magnetic memory devices include a magnetoresistive cell including a free layer having a variable magnetization direction and a pinned layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a bit line on the magnetoresistive cell and including a spin Hall effect material layer exhibiting a spin Hall effect and contacting the free layer; and a lower electrode under the magnetoresistive cell. A voltage is applied between the bit line and the lower electrode so that current passes through the magnetoresistive cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic tunnel junction and magnetic device and electronic equipment comprising same
ActiveCN106876582AMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageIn planeAntiferromagnetic coupling
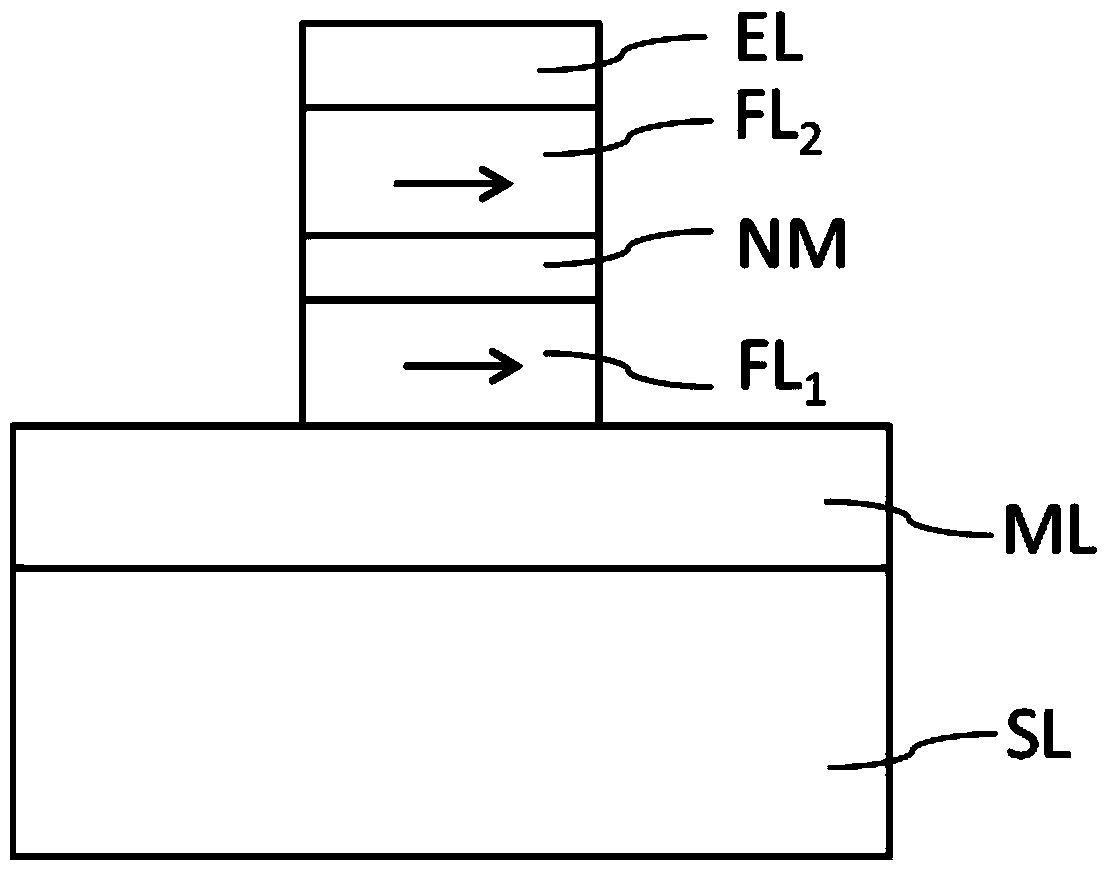
The invention relates to a magnetic tunnel junction and a magnetic device comparing the same. According to one embodiment, the magnetic tunnel junction can comprises a reference magnetic layer, a spacing layer and a composite free magnetic layer, wherein the spacing layer is arranged on the reference magnetic layer, the composite free magnetic layer is arranged on the spacing layer and comprises a first free magnetic layer, a spinning Hall effect (SHE) layer and a second bias magnetic layer, the first free magnetic layer is arranged at one side of the spacing layer, the SHE layer is arranged on the first free magnetic layer, the second bias magnetic layer is arranged on the SHE layer, ferromagnetic coupling or anti-ferromagnetic coupling between the first free magnetic layer and the second bias magnetic layer is induced by the SHE layer, one of the first free magnetic layer and the second bias magnetic layer has in-plane magnetic anisotropy, the other one of the first free magnetic layer and the second bias magnetic layer has vertical magnetic anisotropy, and the magnetic anisotropy of the second bias magnetic layer is larger than the magnetic anisotropy of the first free magnetic layer.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
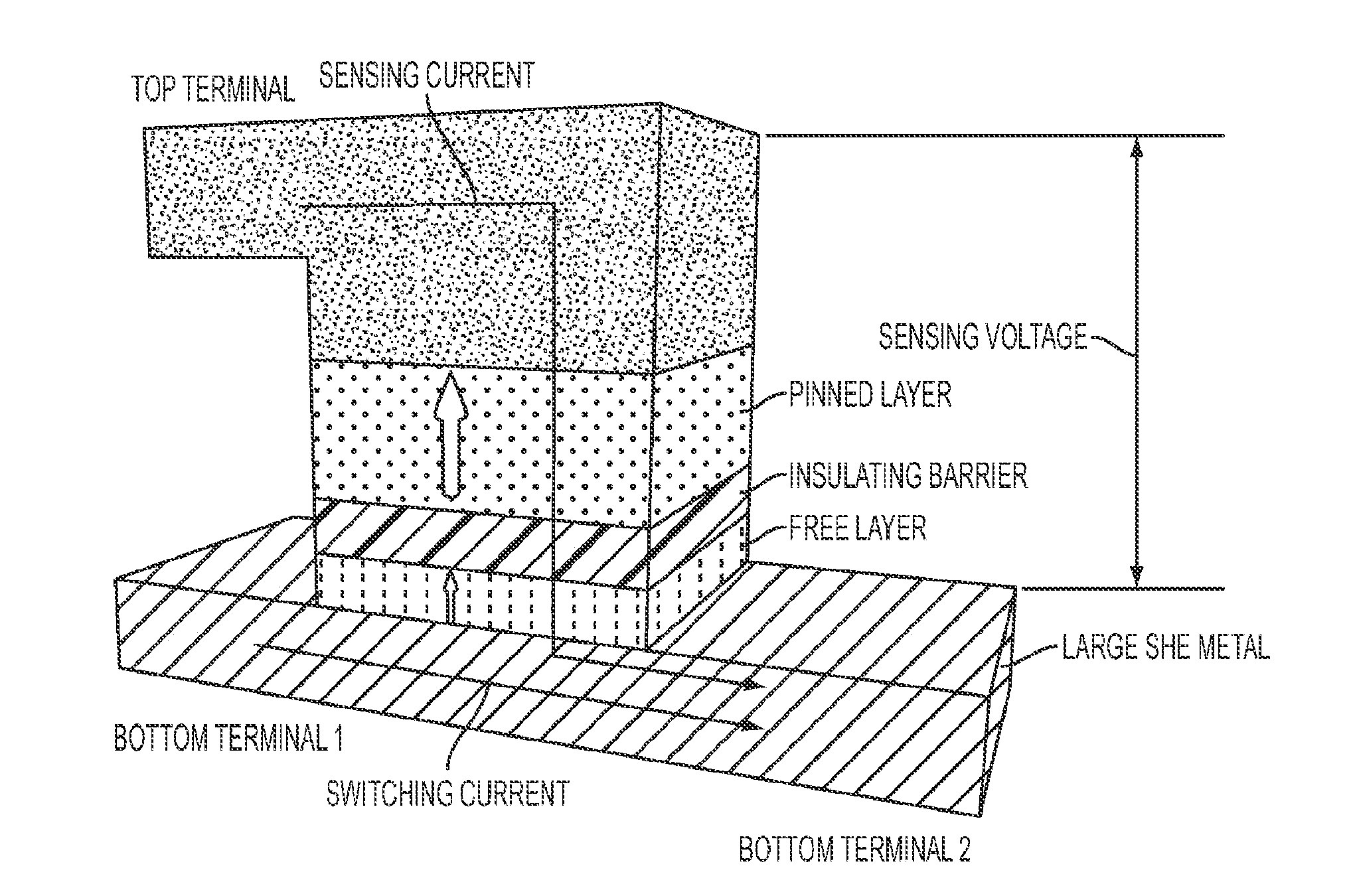
Magnetic read sensor using spin hall effect
ActiveUS20140226239A1Increase potential differenceOutput signalMagnetic measurementsRecord information storageSpin Hall effectMagnetization
A magnetic sensor utilizing the spin Hall effect to polarize electrons for use in measuring a magnetic field. The sensor eliminates the need for a pinned layer structure or antiferromagnetic layer (AFM layer), thereby reducing gap thickness for increased data density. The sensor includes a non-magnetic, electrically conductive layer that is configured to accumulate electrons predominantly of one spin at a side thereof when a current flows there-through. A magnetic free layer is located adjacent to the side of the non-magnetic, electrically conductive layer. A change in the direction of magnetization in the free layer relative to the orientation of the spin polarized electrons causes a change in voltage output of the sensor.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spinning logic device and electronic device comprising same
ActiveCN105514260AMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesSpin Hall effectConductive materials
The invention relates to a spinning logic device and an electronic device comprising the same. The spinning logic device comprises a spinning Hall effect (SHE) layer, a magnetic tunnel junction and current wiring, wherein the SHE layer is made of conductive materials with the SHE and used for receiving first input current and second input current in the first direction, the magnetic tunnel junction is located on the SHE layer, the magnetic tunnel junction is provided with a free magnetic layer, a reference magnetic layer and a barrier layer located between the free magnetic layer and the reference magnetic layer, the free magnetic layer makes direct contact with the SHE layer, the current wiring extends in the second direction above the magnetic tunnel junction and is electrically connected to the magnetic tunnel junction, the second direction and the first direction intersect with each other, and the current wiring is used for receiving third input current so as to generate a magnetic field at the magnetic tunnel junction.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spin-hall-effect-assisted spin-transfer torque nonvolatile trigger
ActiveCN104778967ANon-volatile satisfactionHigh speedDigital storageSpin Hall effectSpin-transfer torque
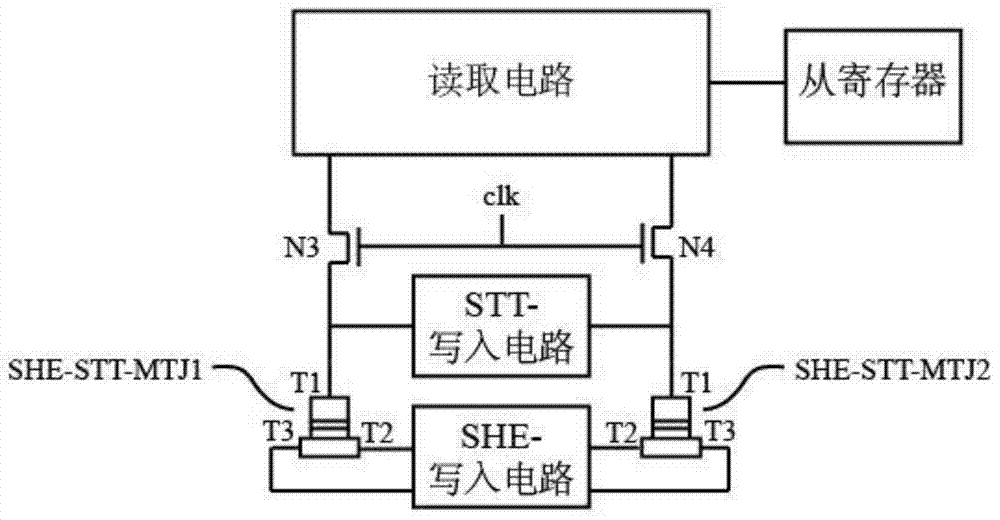
The invention relates to a spin-hall-effect-assisted spin-transfer torque nonvolatile trigger which is composed of a pair of spin-hall-effect-assisted spin-transfer torque magnetic tunnel junctions, namely SHE-STT-MTJ1 and SHE-STT-MTJ2, a pair of NMOS transistors, namely N3 and N4, an STT-writing circuit, an SHE-writing circuit, a reading circuit and a slave register, wherein the T1 ends of the SHE-STT-MTJ1 and the SHE-STT-MTJ2 are connected with the STT-writing circuit, the T2 and T3 ends of the SHE-STT-MTJ1 and the T2 and T3 ends of the SHE-STT-MTJ2 are connected with the SHE-writing circuit, the T1 ends of the SHE-STT-MTJ1 and the SHE-STT-MTJ2 are respectively connected with the source electrodes of the N3 and N4 transistors, and the gate electrodes of the two NMOS transistors are directly interconnected and are controlled by a clk clock signal. The spin-hall-effect-assisted spin-transfer torque nonvolatile trigger provided by the invention has the characteristics of being low in consumption and high in speed and being reliable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Spin hall effect assisted spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS8889433B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin Hall effectSpin-transfer torque
Owner:IBM CORP
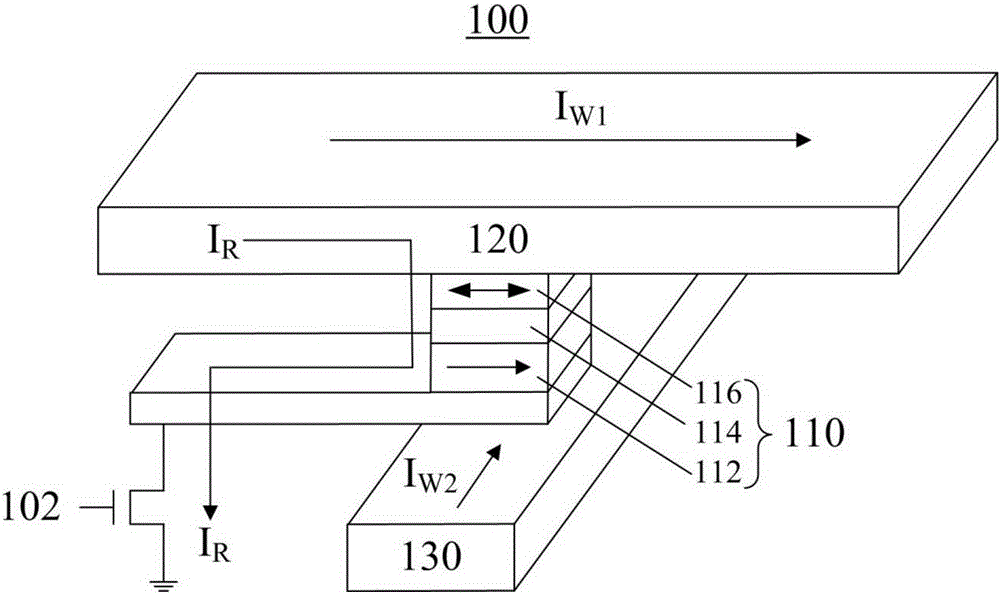
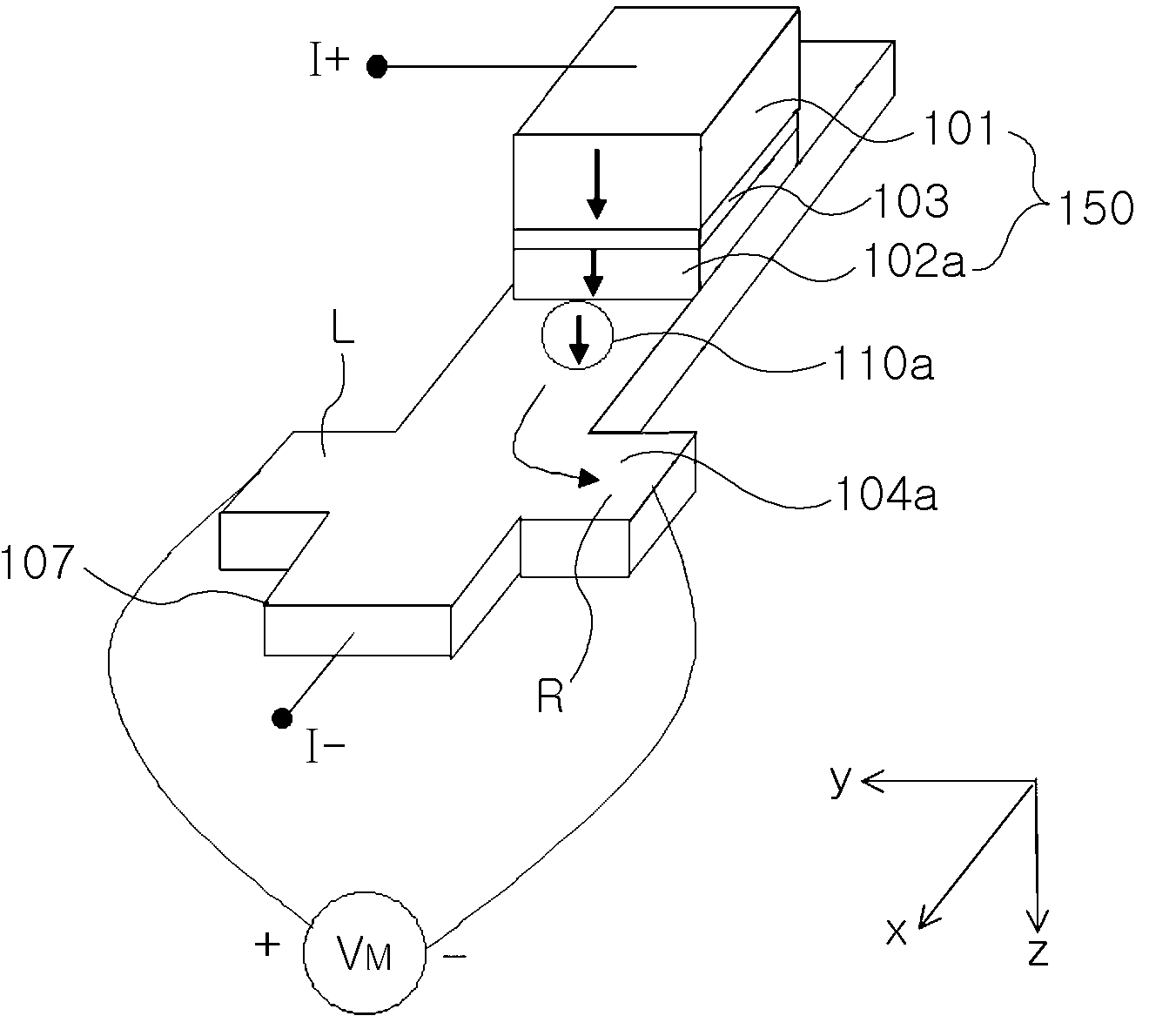
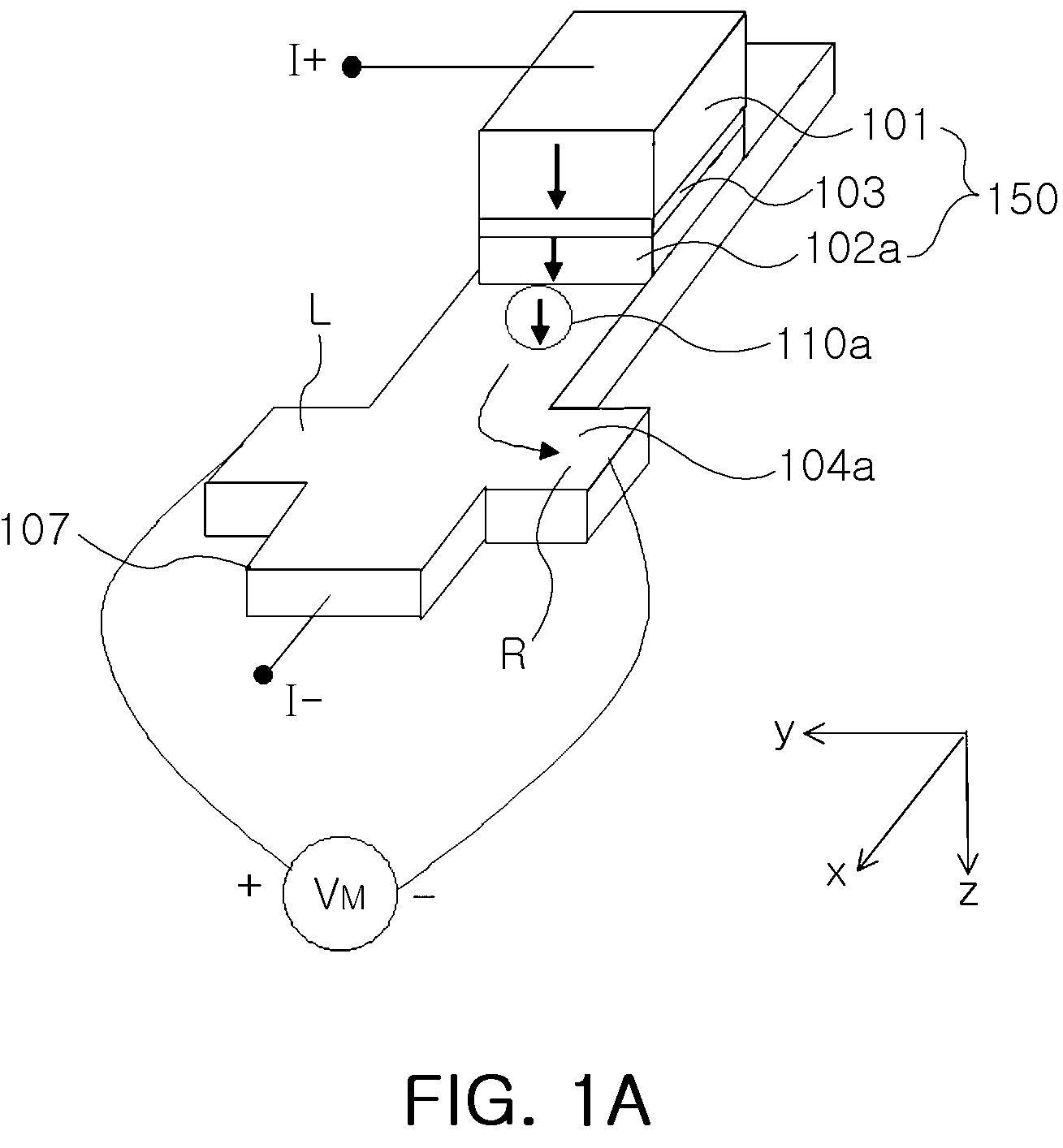
Electric current-spin current conversion device
InactiveUS20130154633A1Improve conversion efficiencyAc-dc conversionMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSpin Hall effectSpins
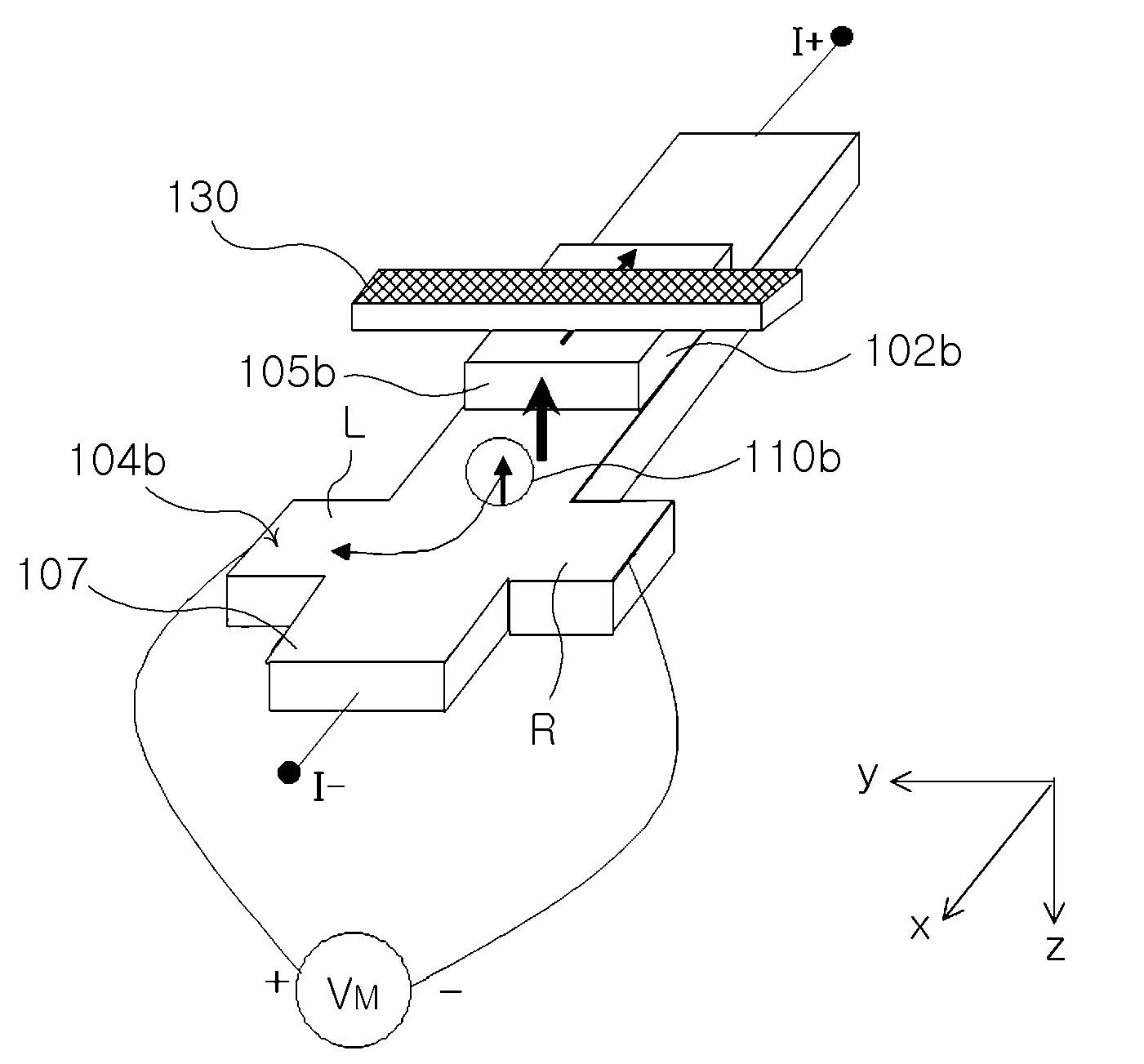
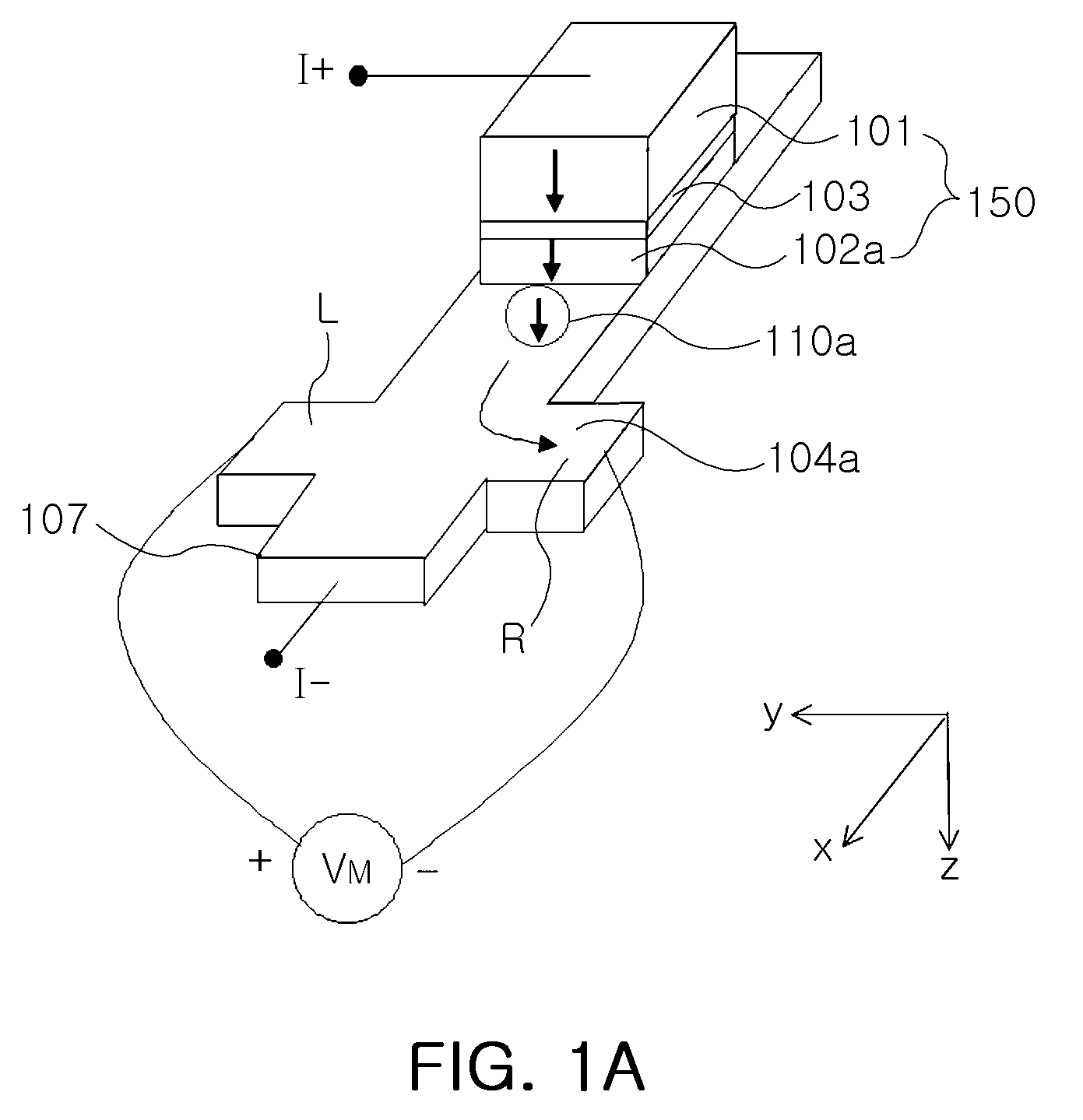
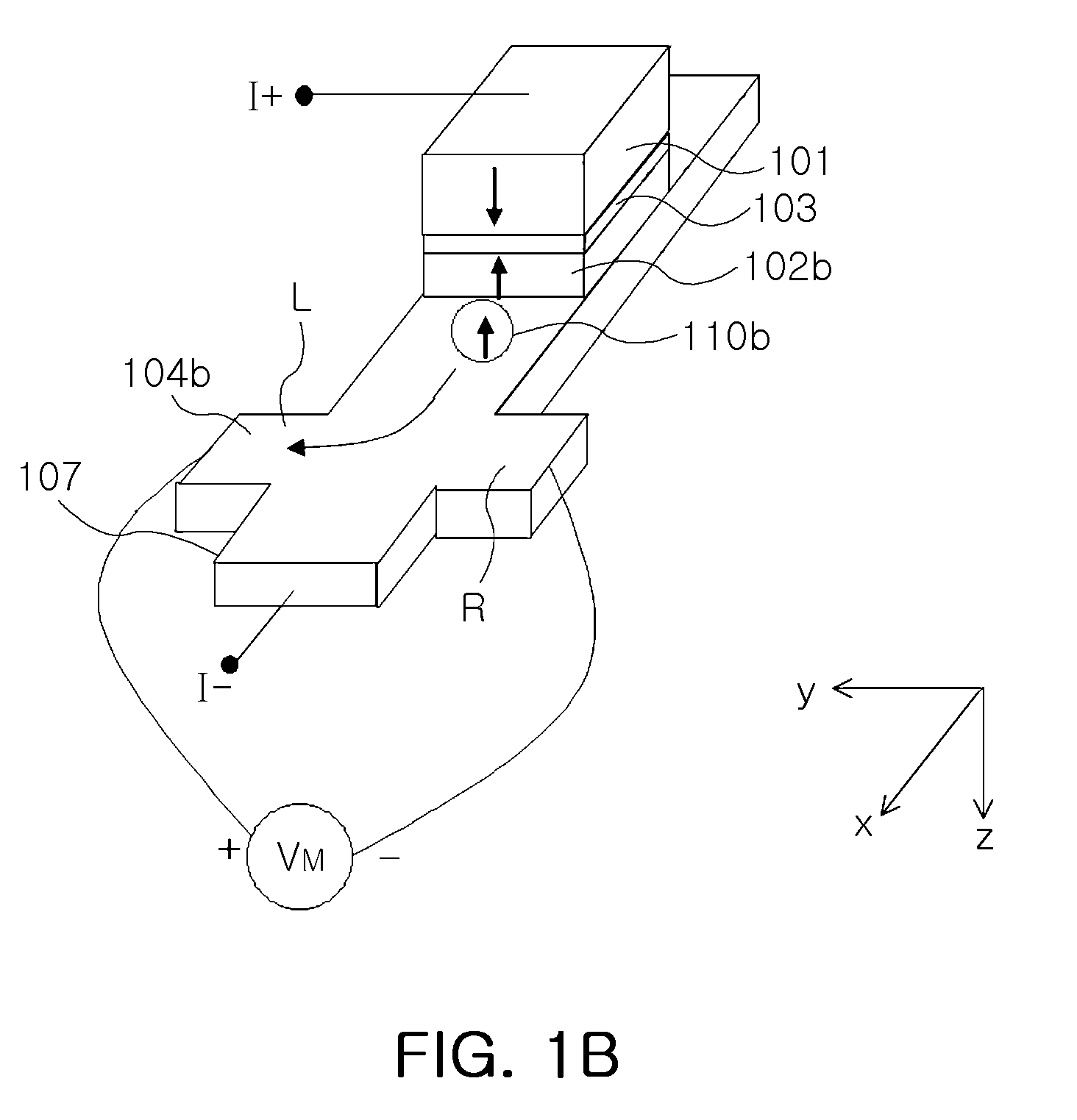
An electric current-spin current conversion device according to the invention performs conversion between electric current and spin current utilizing the spin Hall effect or the inverse spin Hall effect of a 5d transition metal. A spin accumulation apparatus according to the invention includes a non-magnetic body in which injected spins are accumulated and an injection unit that injects spins into the non-magnetic body, wherein said injection unit comprises said electric current-spin current conversion device provided on said non-magnetic body, and an electric power source that supplies an electric current to said electric current-spin current conversion device in such a way that a spin current flowing toward said non-magnetic body is generated by the spin Hall effect.
Owner:RIKEN
Spin hall effect assisted spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS20140264511A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin Hall effectSpin-transfer torque
Embodiments are directed to providing a spin hall effect (SHE) assisted spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM) device by coupling a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) to a SHE material, and coupling the SHE material to a transistor. Embodiments are directed to a spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM) device comprising: a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) coupled to a spin hall effect (SHE) material, and a transistor coupled to the SHE material.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic sensor using spin hall effect
Magnetic sensors using spin Hall effect and methods for fabricating same are provided. One such magnetic sensor includes a spin Hall layer including an electrically conductive, non-magnetic material, a magnetic free layer adjacent to the spin Hall layer, a pair of push terminals configured to enable an electrical current to pass through the magnetic free layer and the spin Hall layer in a direction that is perpendicular to a plane of the free and spin Hall layers, and a pair of sensing terminals configured to sense a voltage when the electrical current passes through the magnetic free layer and the spin Hall layer, where each of the push and sensing terminals is electrically isolated from the other terminals.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
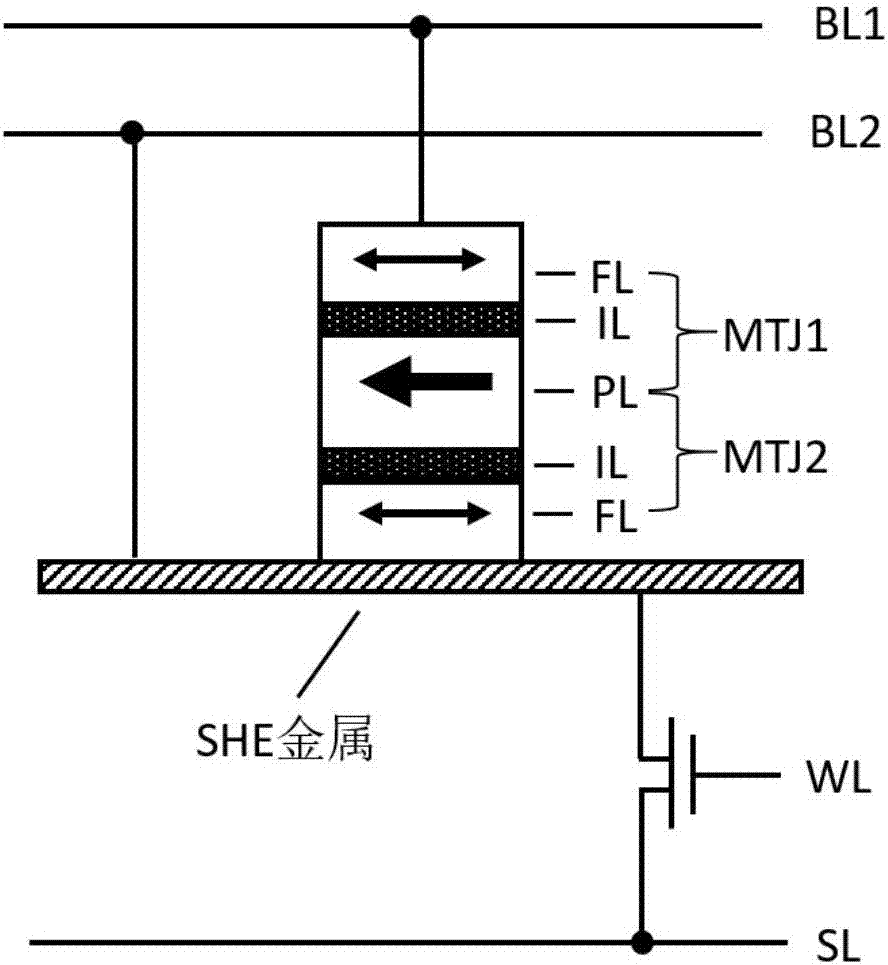
Spin Hall effect-assisted writing multi-state magnetic random access memory bit and spin Hall effect-assisted writing method
InactiveCN107481749AImprove reading speedReduce energy consumptionDigital storageStatic random-access memoryHemt circuits
The invention relates to a spin Hall effect-assisted writing multi-state magnetic random access memory bit and a spin Hall effect-assisted writing method. The memory bit comprises a multi-state memory unit composed of two magnetic tunnel junctions, a spin Hall effect metal layer connected to a free layer of one of the magnetic tunnel junctions and a switch circuit composed of a word line, a bit line and a switching device. The multi-state magnetic random access memory composed of the spin Hall effect auxiliary bits has the magnetic random access memory (MRAM) advantages of fast reading speed, unlimited number of erasures, low energy consumption and radiation resistance, realizes polymorphic signal writing through spin Hall effect assistance, records 3 or 4 bits of information in the memory unit, effectively improves data storage density and reduces a chip area. The spin Hall effect can effectively reduce the writing current threshold and reduce the writing power consumption.
Owner:CETHIK GRP
Magnetic memory device and method for reading magnetic memory cell using spin hall effect
InactiveUS7839675B2Easily read stored dataGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesSpin Hall effectMagnetic memory
A magnetic memory device includes a substrate for reading and a magnetic memory cell. The substrate has a channel layer. The magnetic memory cell is formed on the substrate and has a magnetized magnetic material that transfers spin data to electrons passing the channel layer. Data stored in the magnetic memory cell are read by a voltage across both side ends of the channel layer that is generated when the electrons passing the channel layer deviate in the widthwise direction of the channel layer by a spin Hall effect.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Half select method and structure for gating rashba or spin hall MRAM
ActiveUS9490297B1Improved writabilityEliminate the effects ofMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin Hall effectSpins
The present disclosure generally relates to SHE-MRAM memory cells. A memory cell array comprises one or more memory cells, wherein each of the one or more memory cells comprises a gate electrode, an insulating layer, a spin orbit material electrode, a MTJ, and a top electrode parallel to the gate electrode. The gate electrode and the top electrode are perpendicular to the spin orbit material electrode. By applying a voltage to the gate electrode, passing a current along the spin orbit material electrode, and utilizing Rashba and / or spin hall effects, writability of select memory cells is enhanced, allowing for individual memory cells to be written upon without disturbing neighboring memory cells. Additionally, Rashba and / or spin hall effects in neighboring memory cells may be suppressed to ensure only the selected memory cell is written.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
MRAM (Magnetic Random Access Memory) assisted by spin Hall effect
InactiveCN105390609AReduce power consumptionReduce distanceDigital storageGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesInsulation layerSpin Hall effect
The invention relates to an MRAM assisted by the spin Hall effect. The spin Hall effect is utilized to reduce the power consumption of the MRAM, a magnetic layer is placed on or under a heavy metal layer that can generate the spin Hall effect, and the magnetic layer is separated from a metal electrode by an insulation layer. According to the invention, the distance between a horizontal magnetized layer and a recording layer can be effectively reduced, and interference in adjacent recording bits is reduced.
Owner:CETHIK GRP
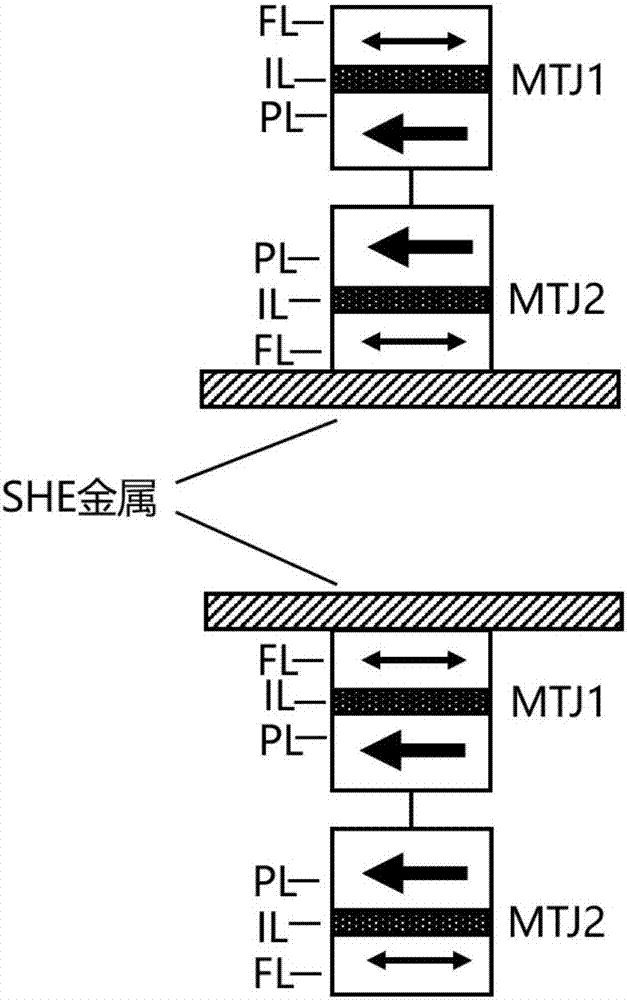
Bidirectional spin Hall effect-based magnetic non-volatile memory unit structure
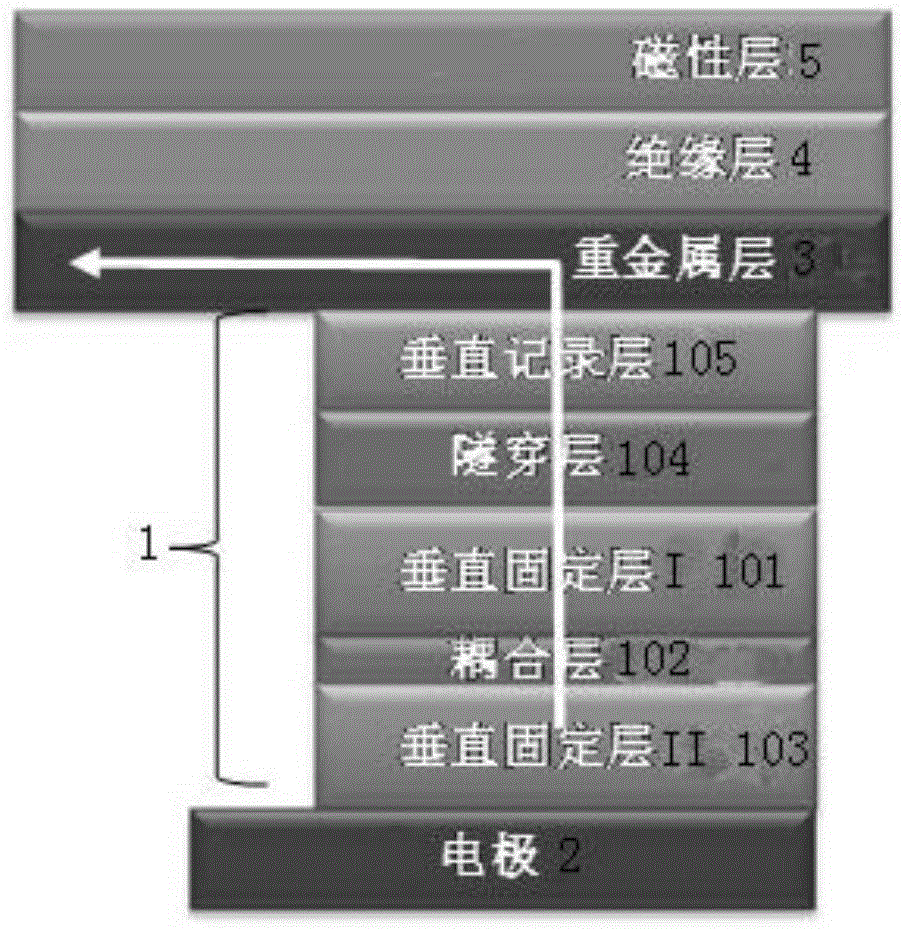
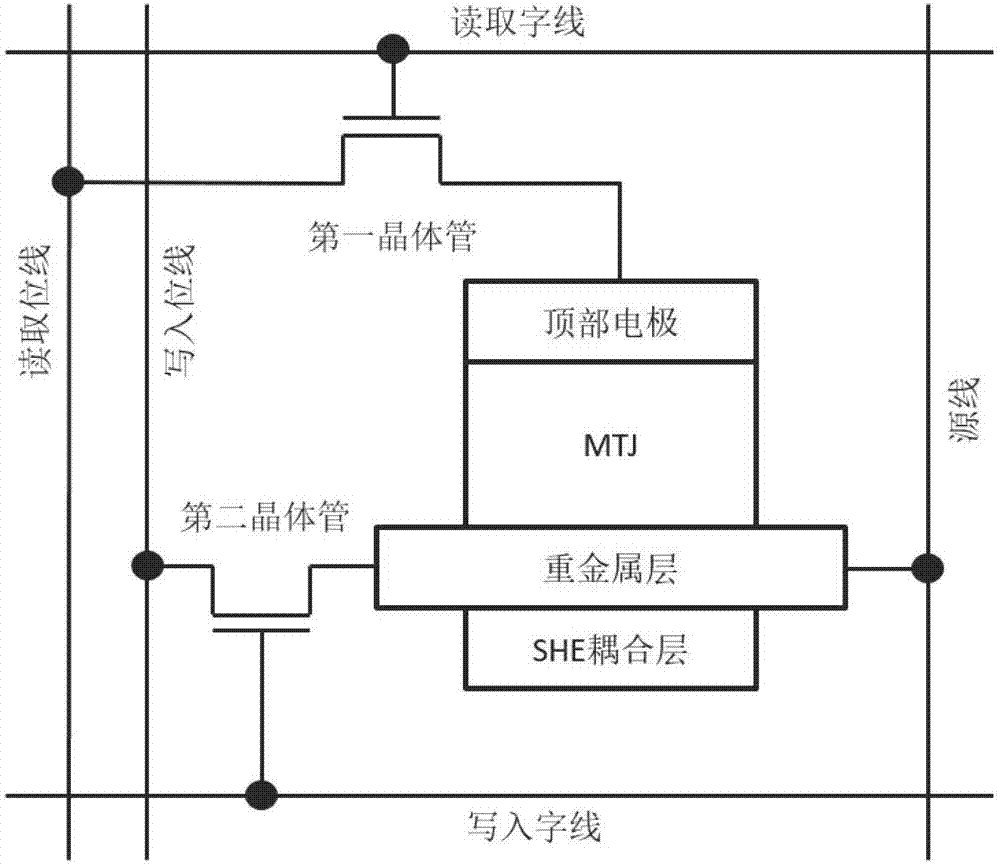
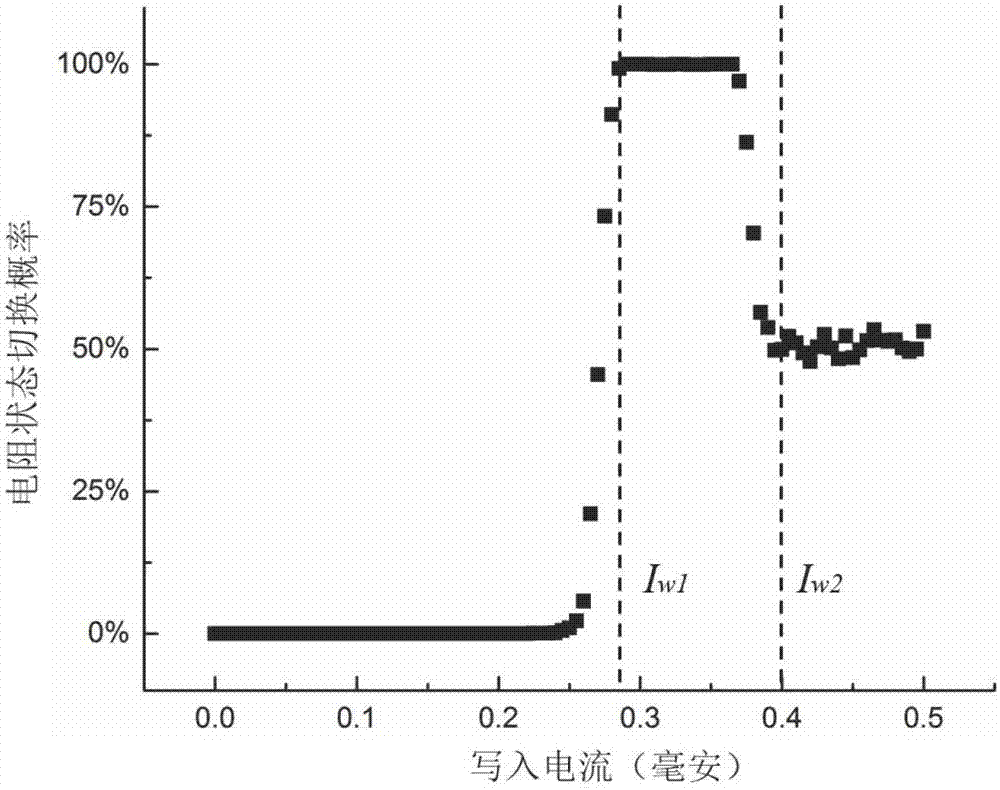
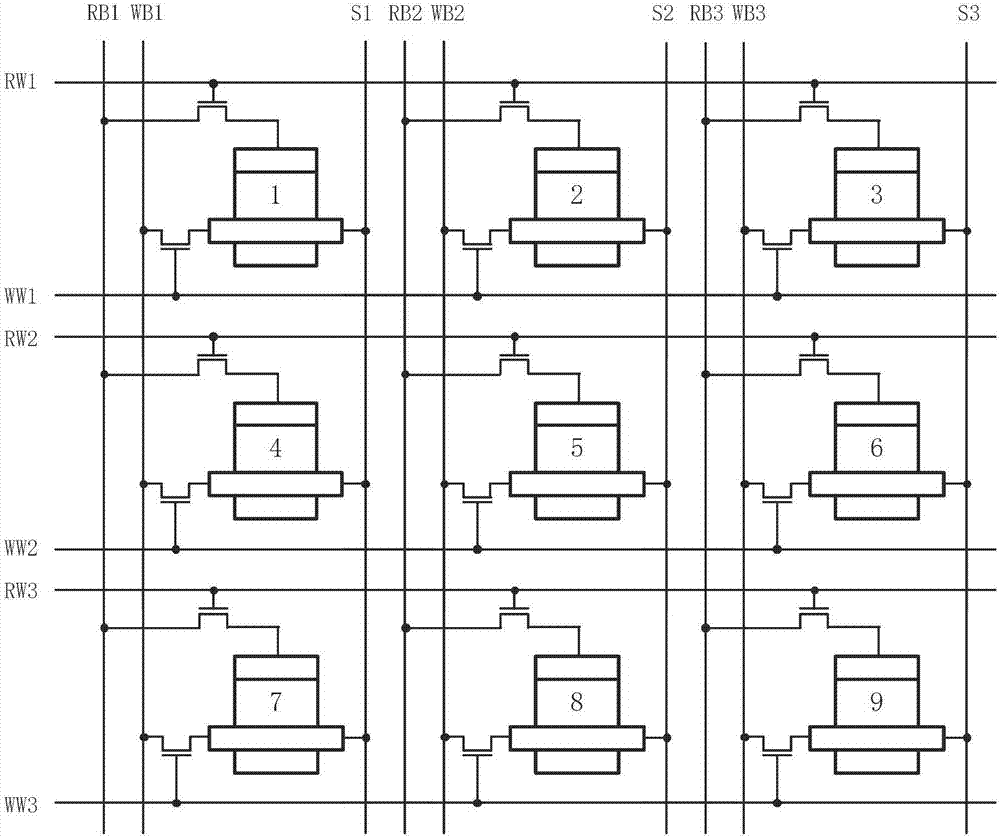
ActiveCN107316936AReduce write power consumptionReduce write operation timeGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesHigh resistanceWrite bit
The invention discloses a bidirectional spin Hall effect-based magnetic non-volatile memory unit structure. The bidirectional spin Hall effect-based magnetic non-volatile memory unit structure comprises a bidirectional spin Hall effect magnetic tunneling junction, a first transistor, a second transistor, a reading word line, a reading bit line, a writing word line, a writing bit line and a source line, wherein the bidirectional spin Hall effect-based novel magnetic tunneling junction comprises a traditional vertical magnetic tunneling junction, a heavy metal layer and a spin Hall effect coupling layer, the vertical magnetic tunneling junction comprises a reference layer, a tunneling insulation layer and a first magnetic free layer from top to bottom, and the spin Hall effect coupling layer comprises a second magnetic free layer and an insulation layer from top to bottom. By the bidirectional spin Hall effect-based magnetic non-volatile memory unit structure, an auxiliary means is not needed, the switching of the resistance of the vertical magnetic tunneling junction among a high-resistance state, a low-resistance state and a random-resistance state is achieved only by controlling a current passing through the heavy metal layer, the writing power consumption of the magnetic memory unit can be effectively reduced, and the writing operation time of the magnetic memory unit is shortened.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com