Patents
Literature
55 results about "Magnetic ram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
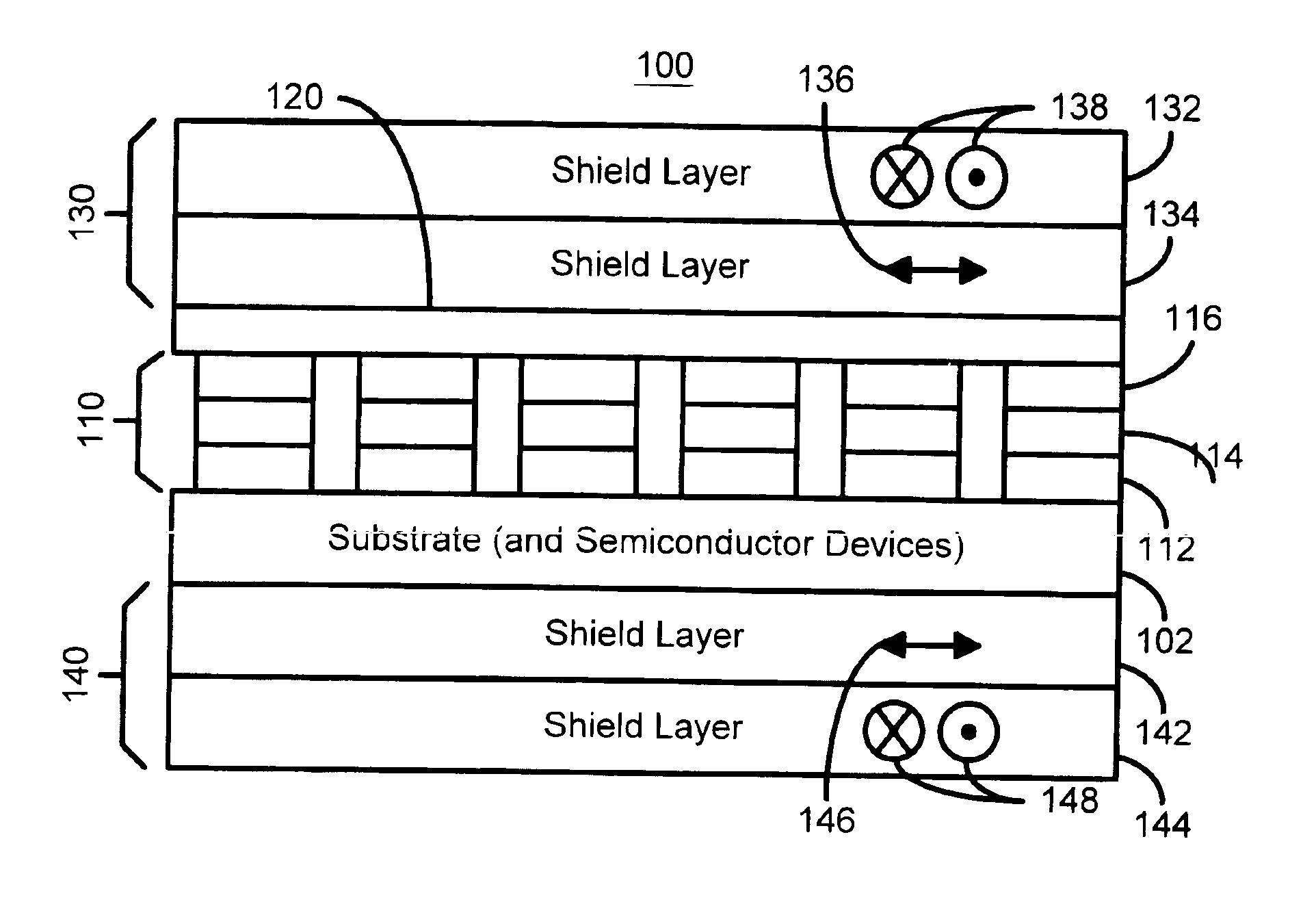
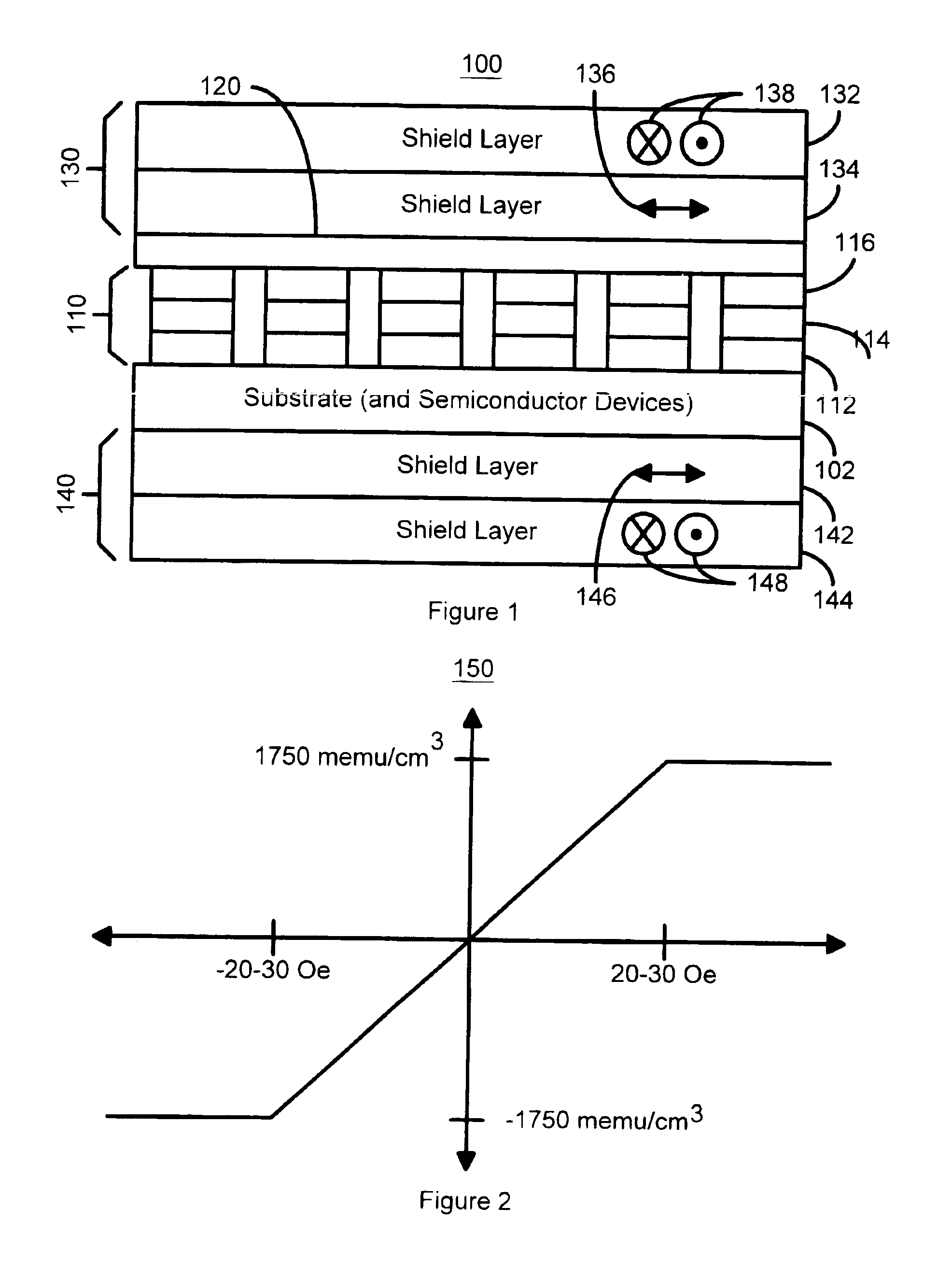
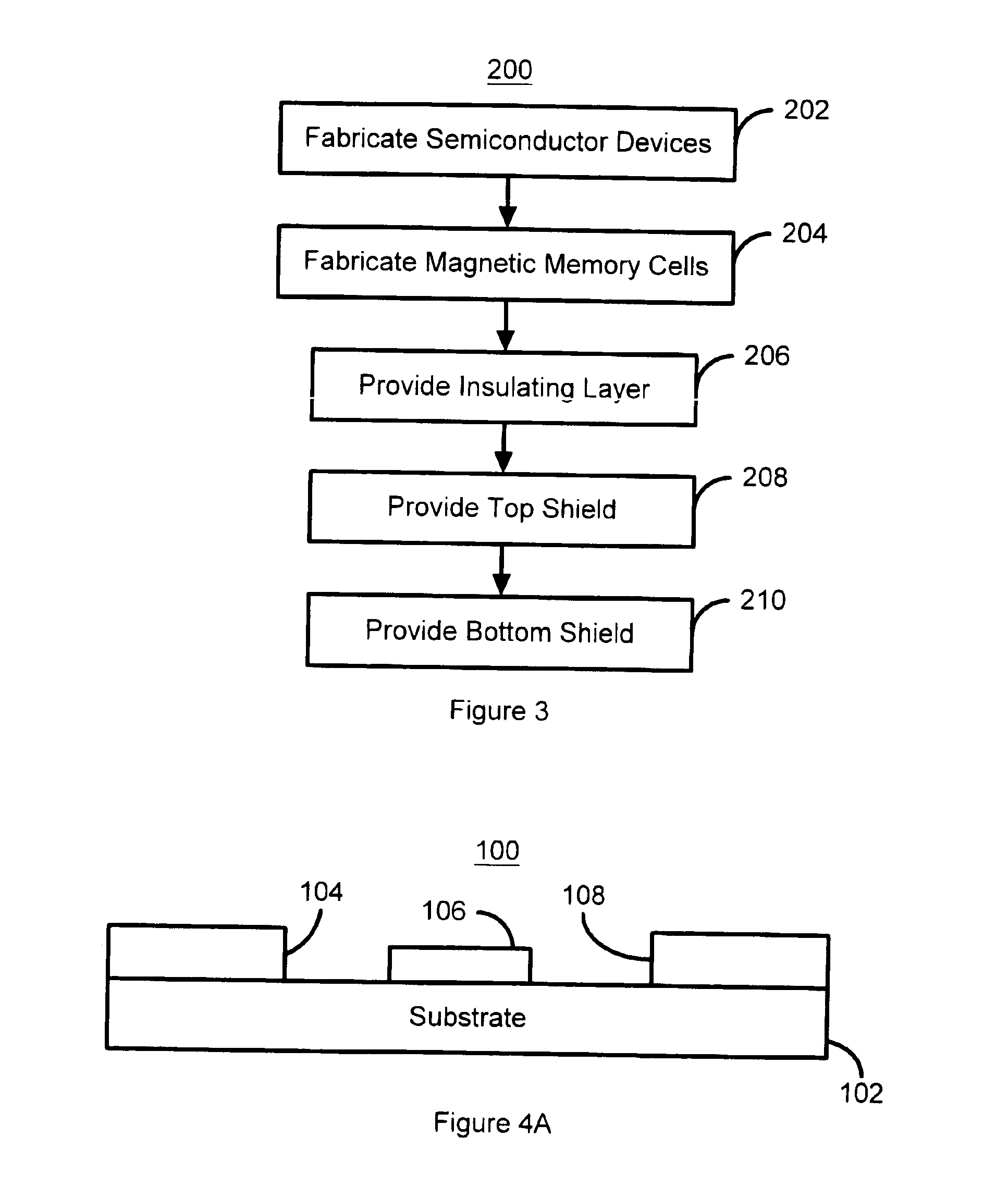
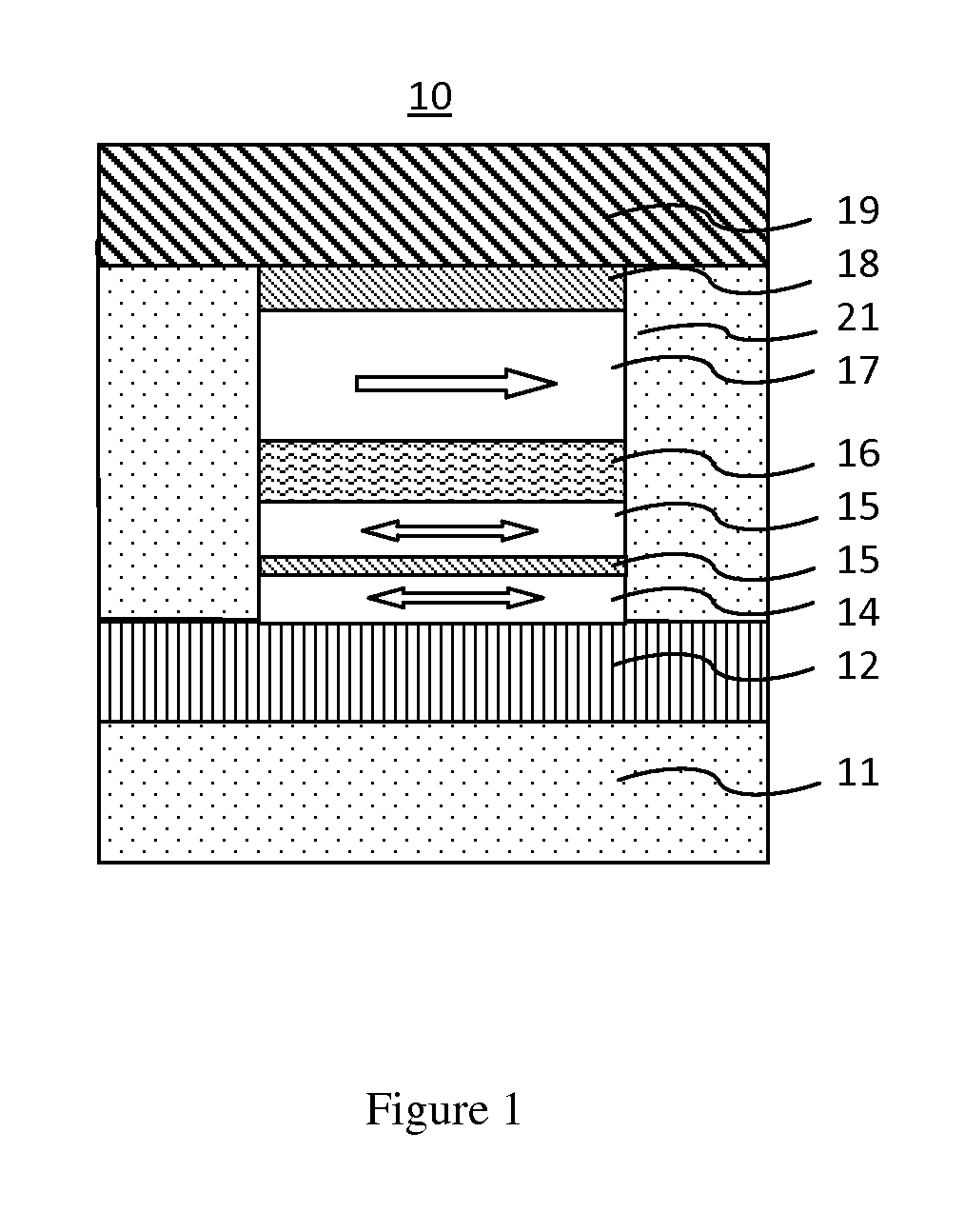
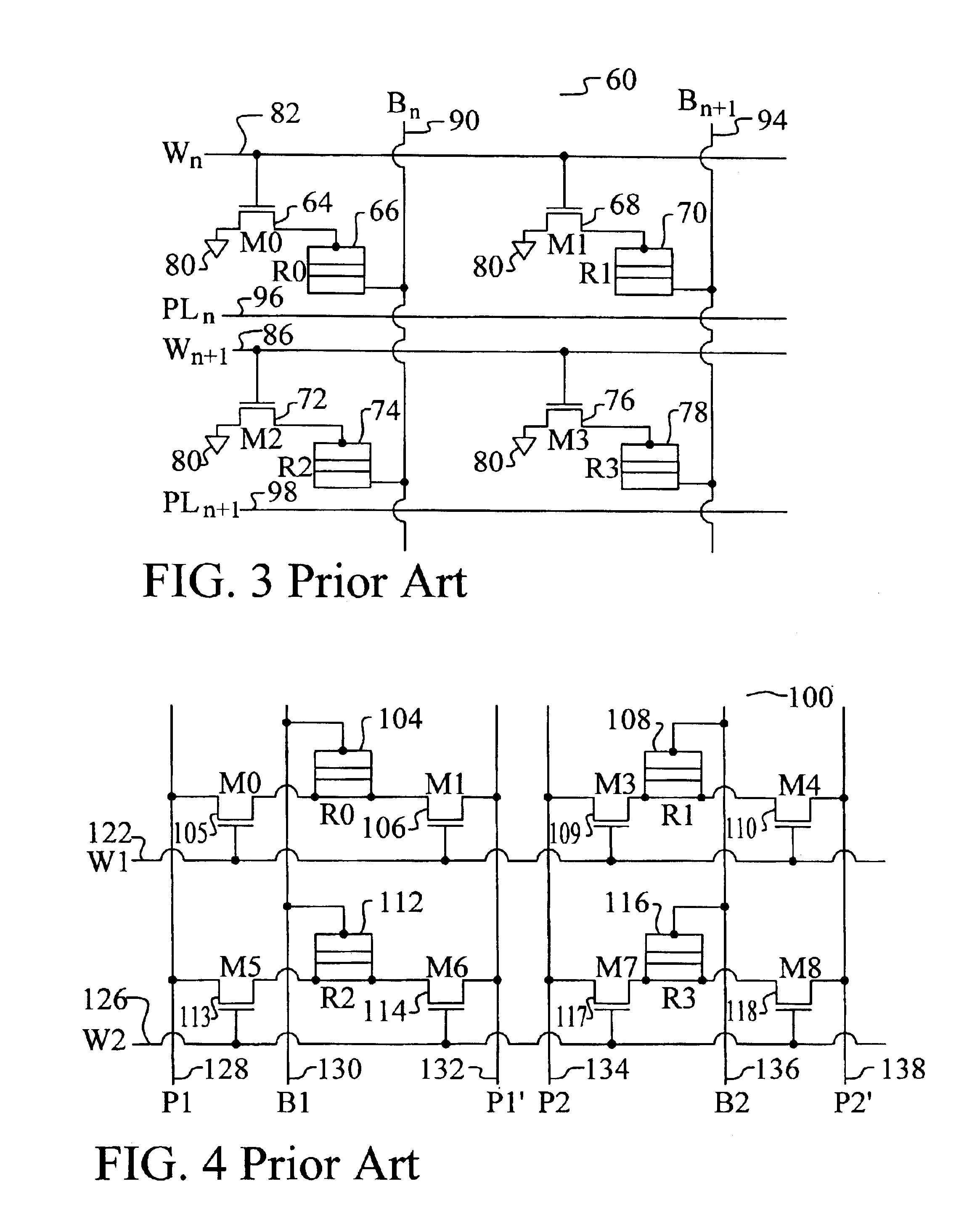
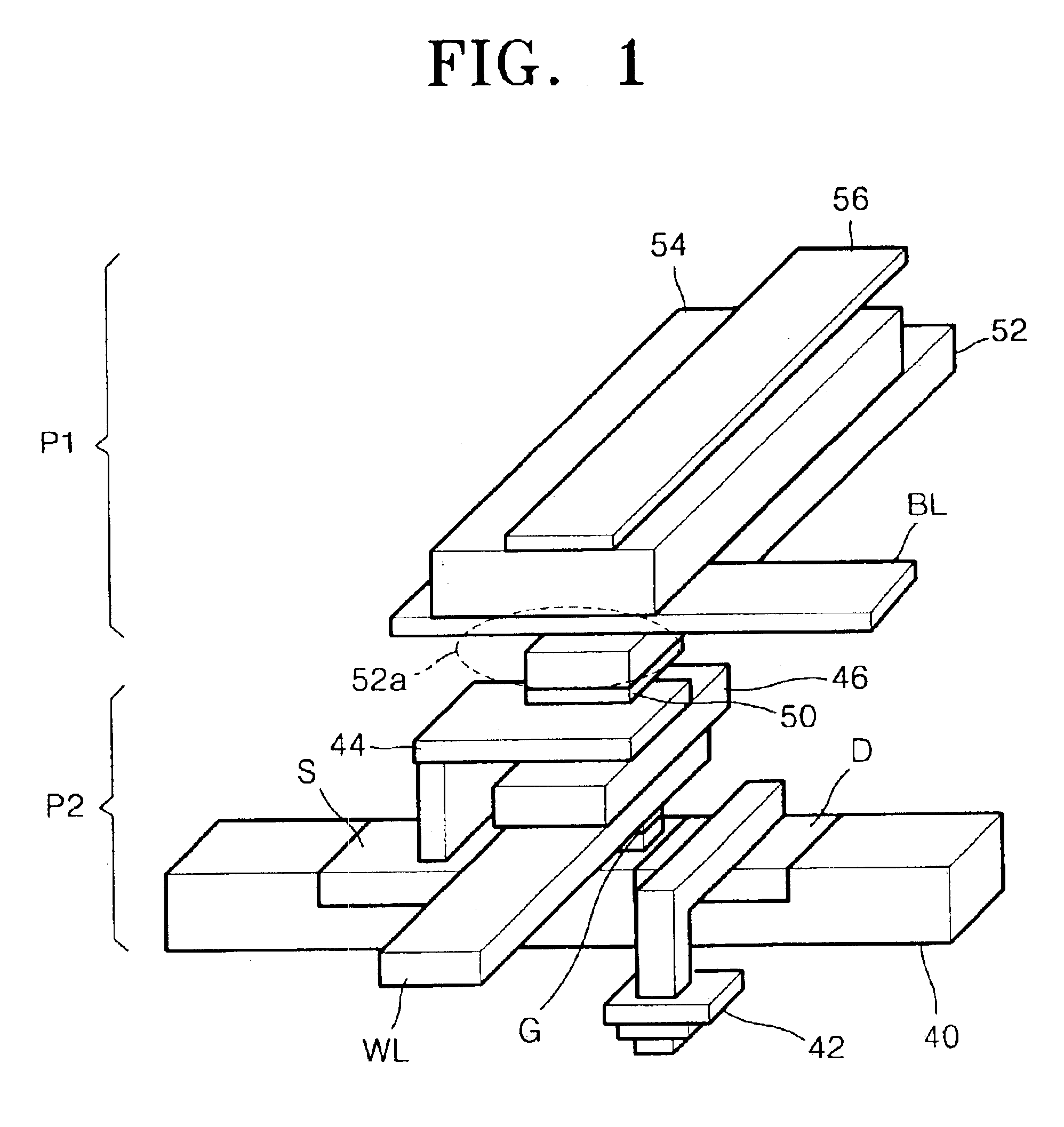
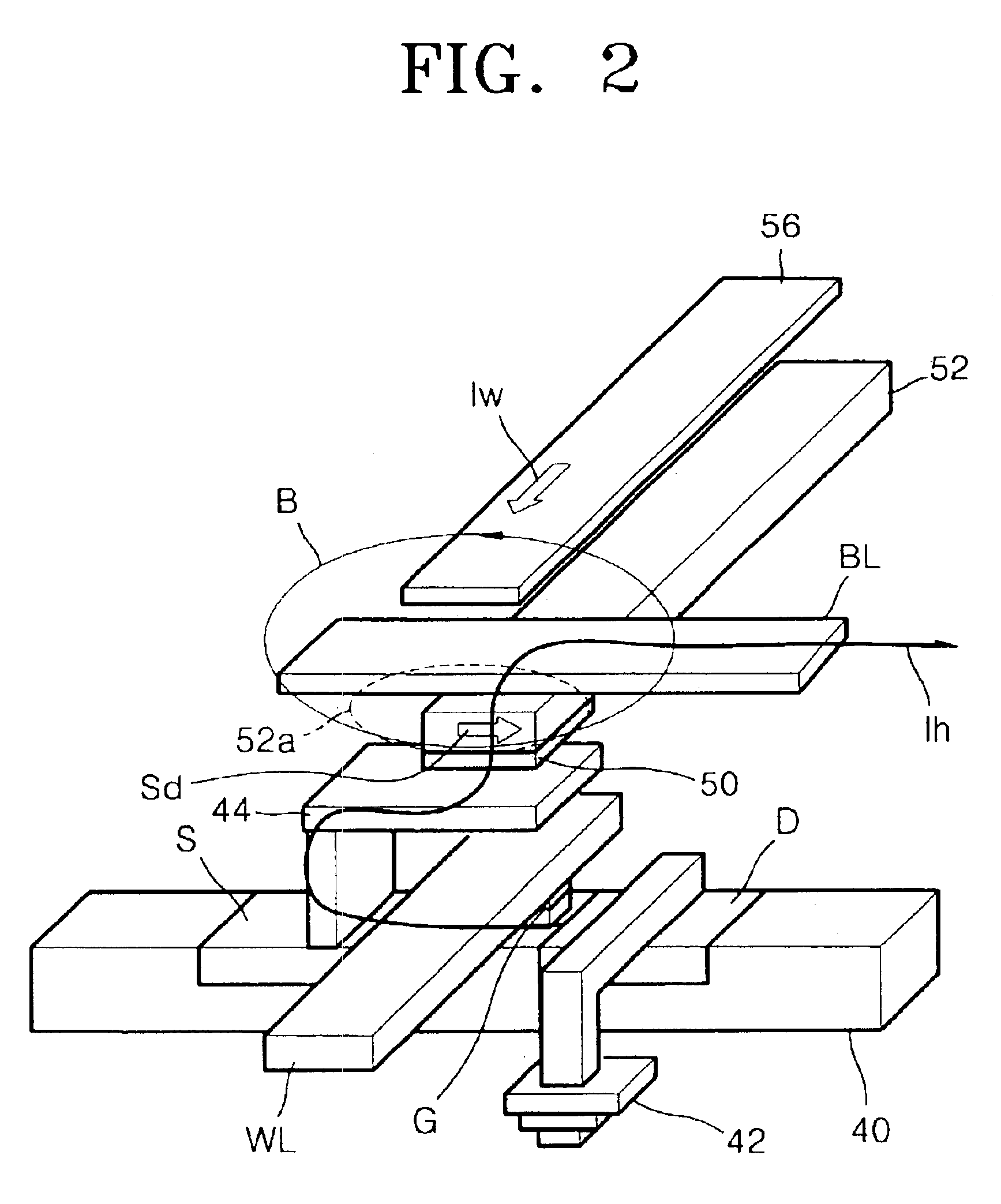
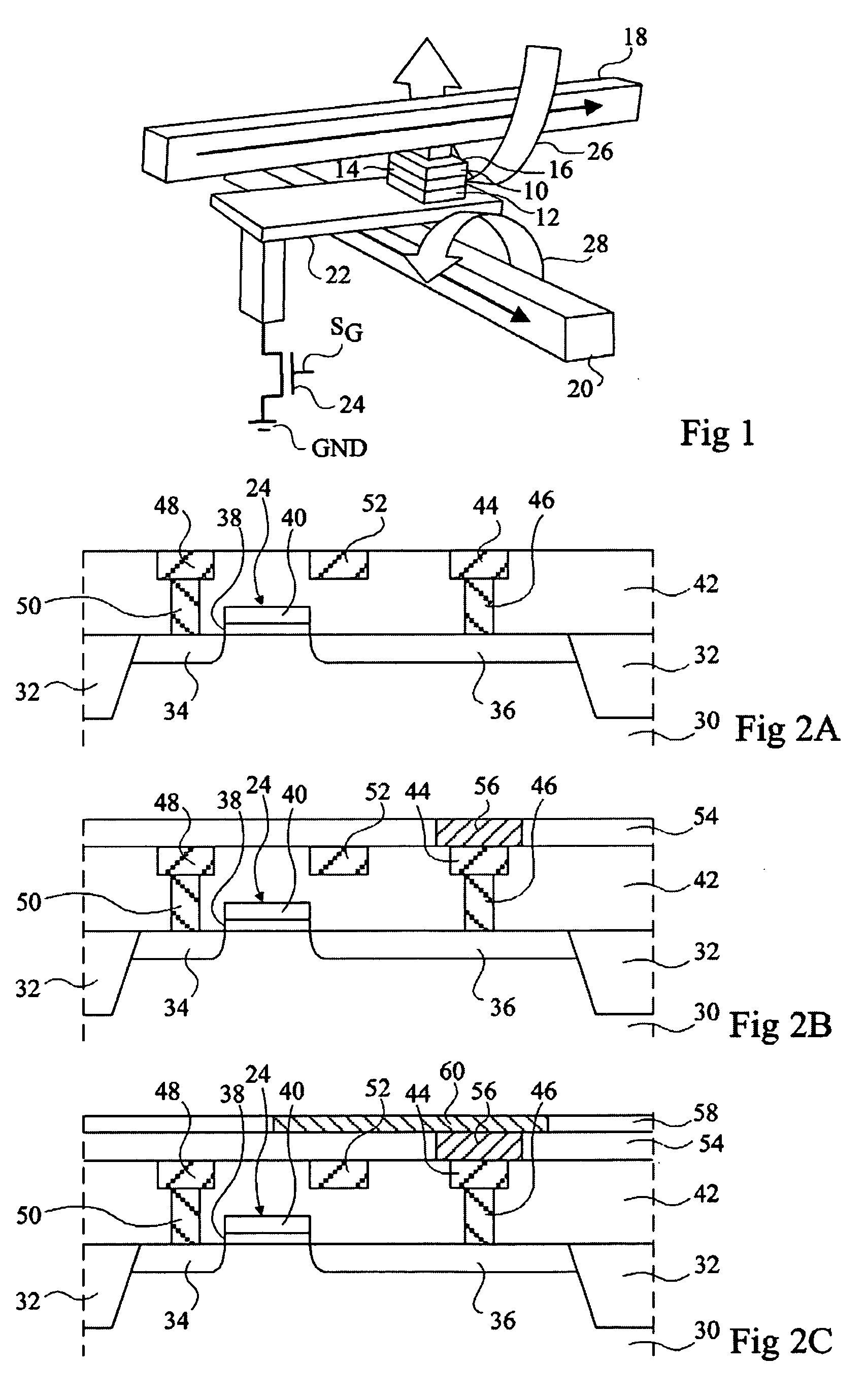
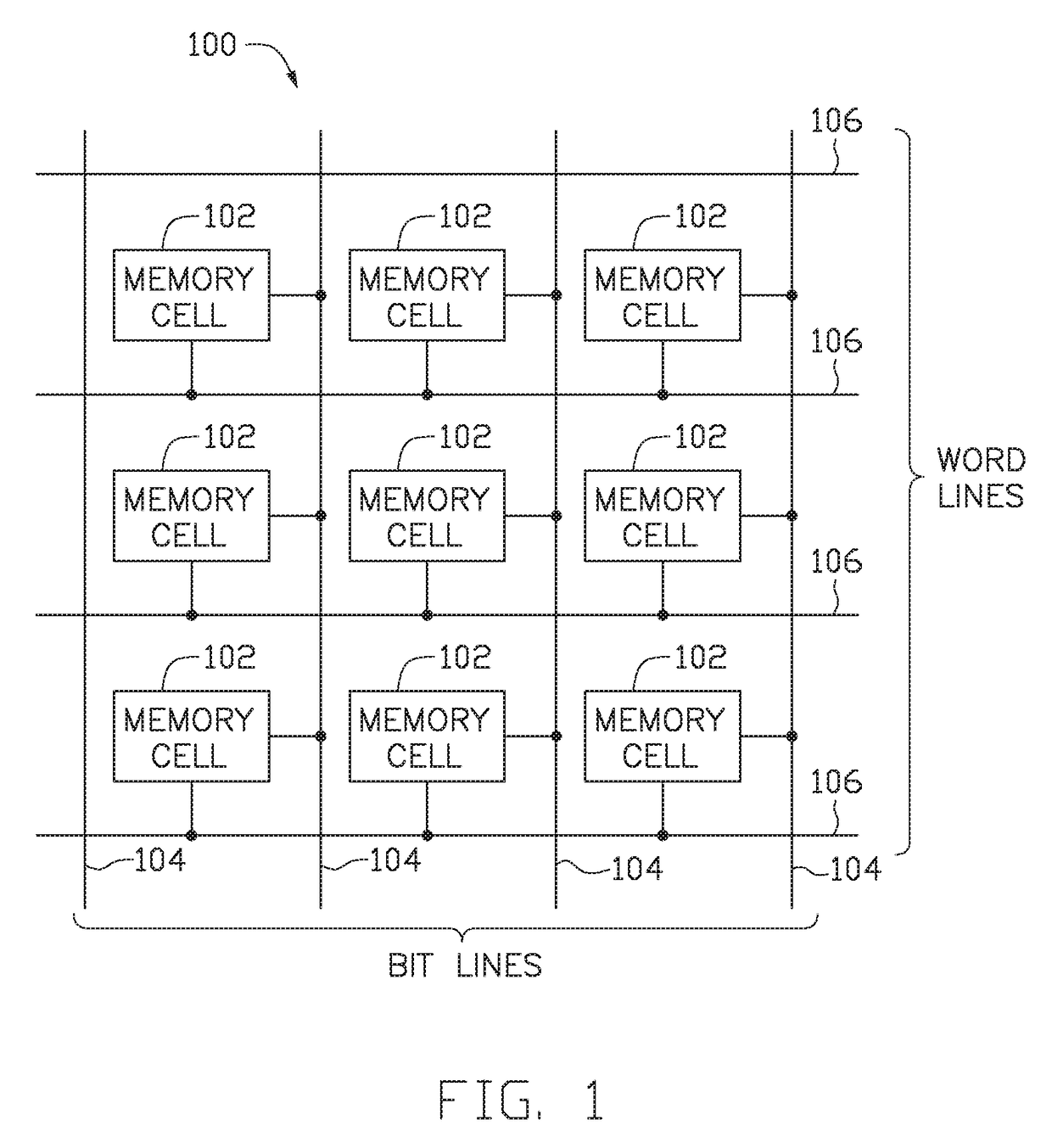
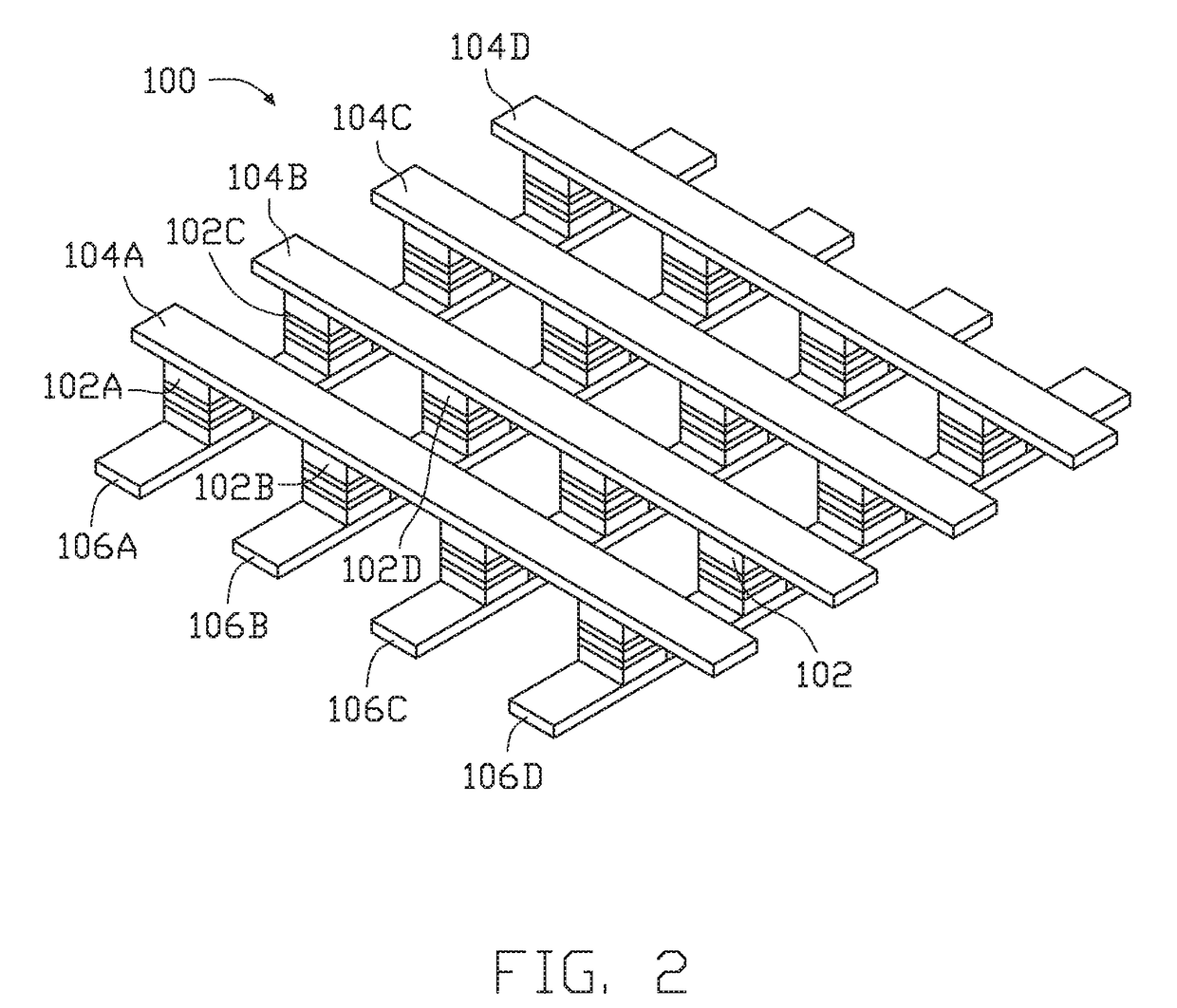
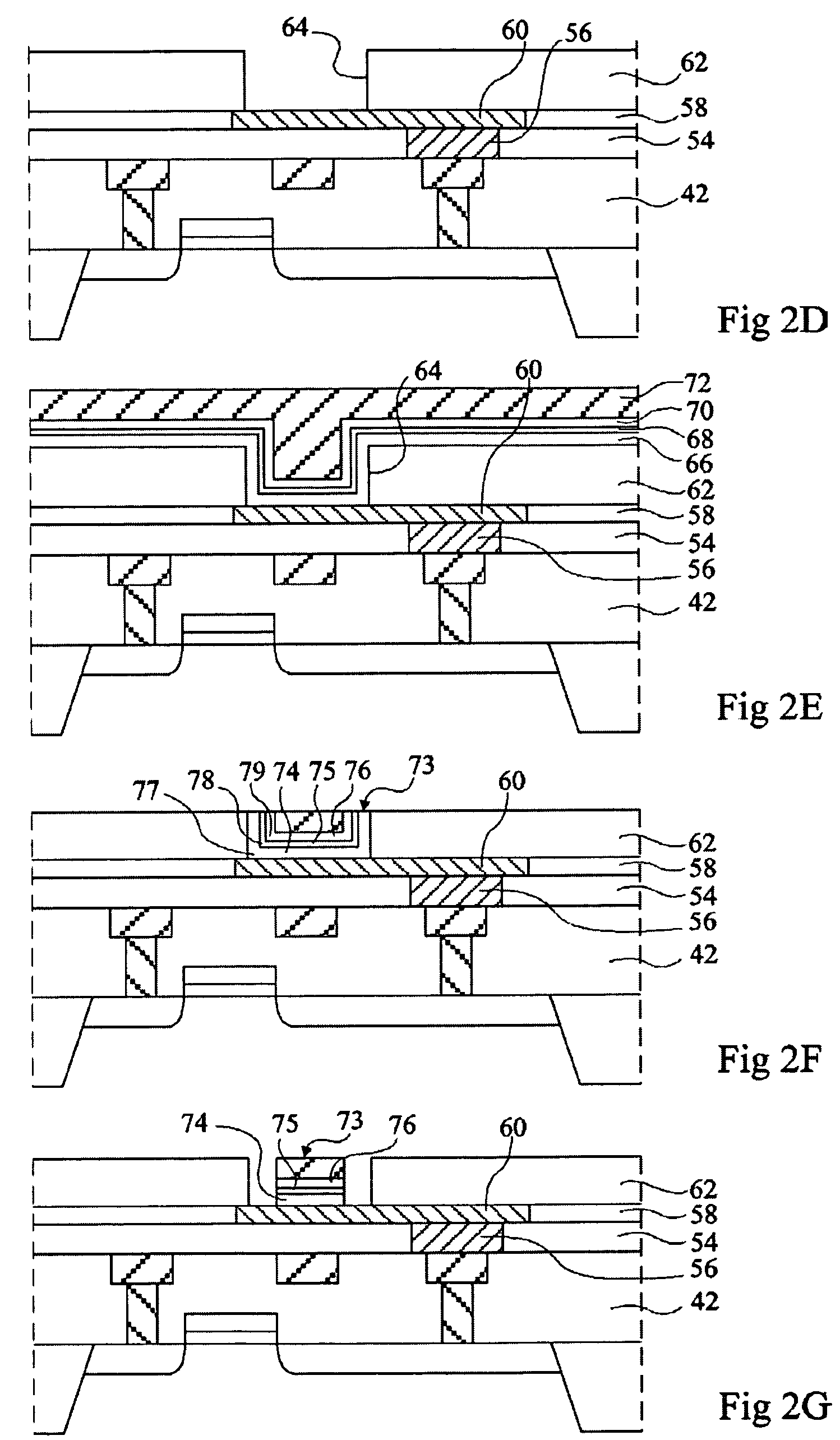
Shielded magnetic ram cells
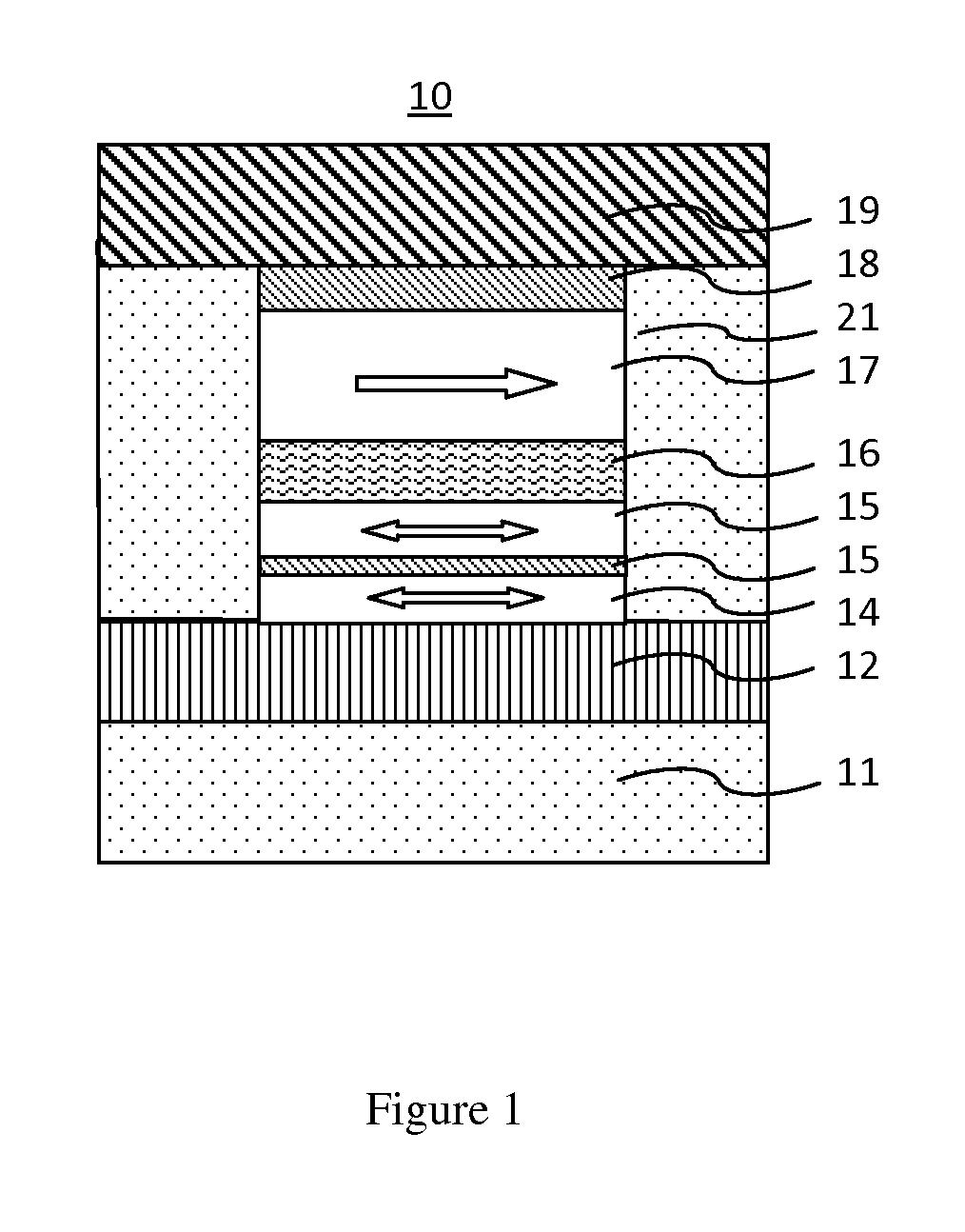
InactiveUS6888184B1High momentImprove permeabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic ramMagnetic memory
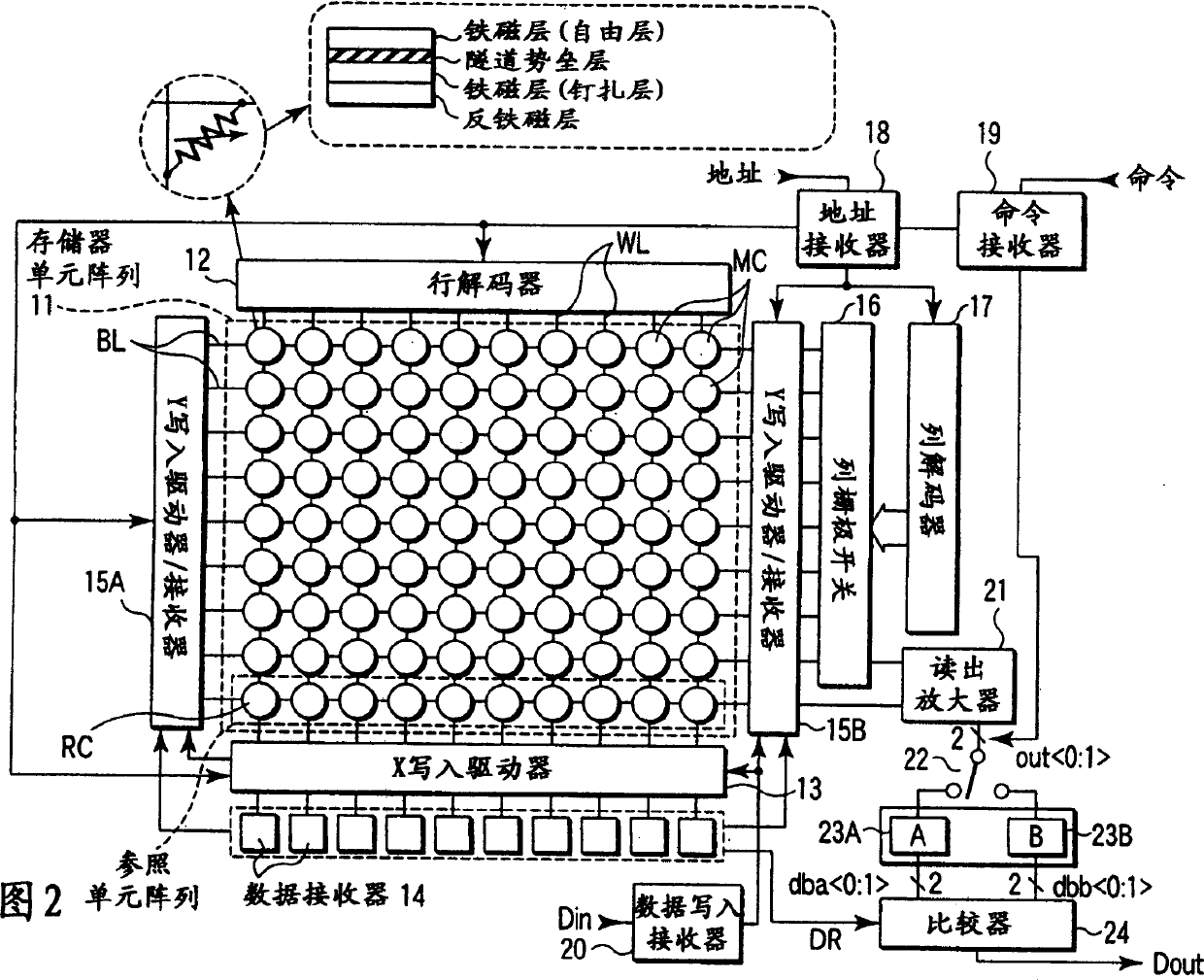
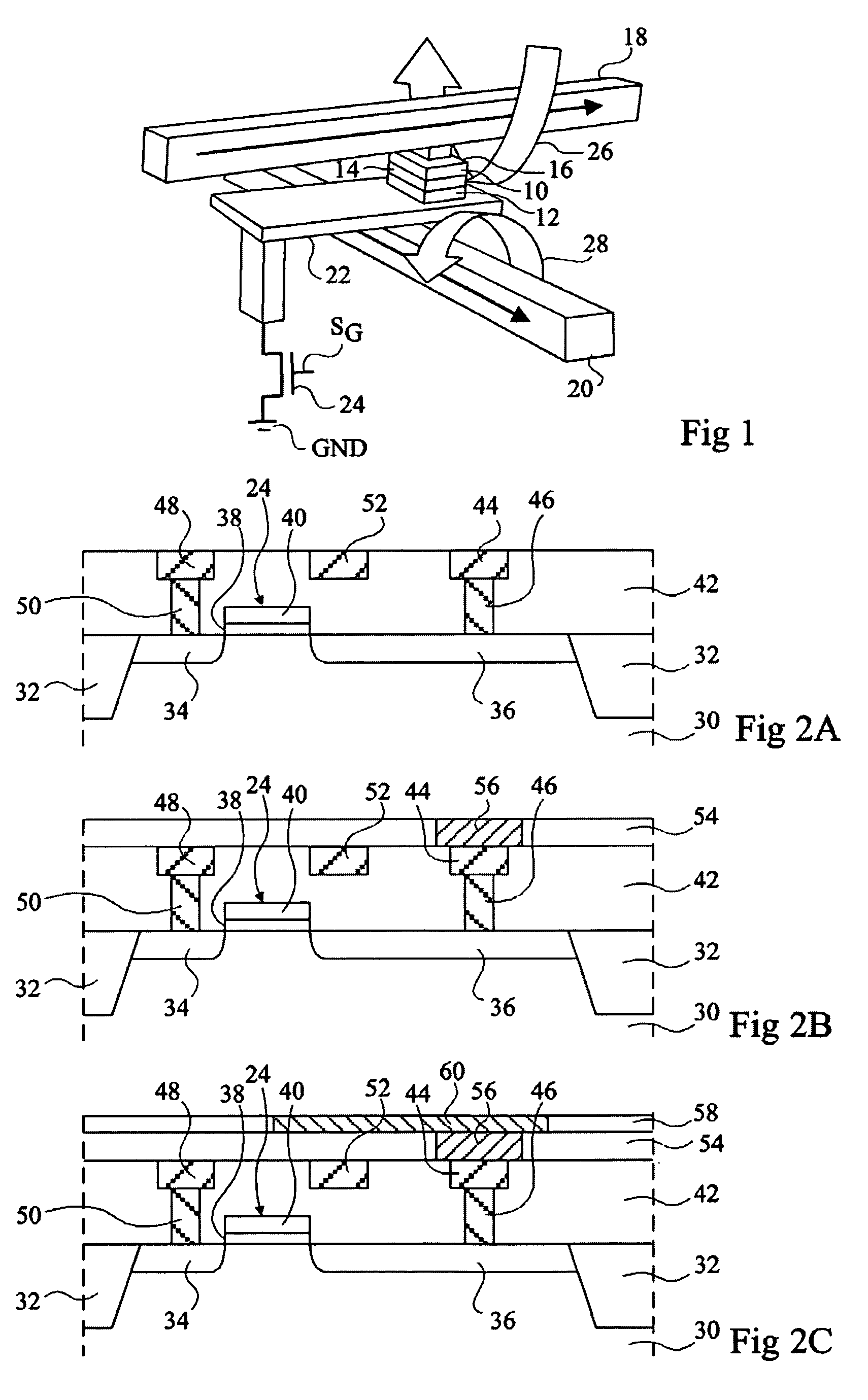
A magnetic memory fabricated on a semiconductor substrate is disclosed. The method and system include a plurality of magnetic tunneling junctions and a plurality of shields for magnetically shielding the plurality of magnetic tunneling junctions. Each of the plurality of magnetic tunneling junctions includes a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer and an insulating layer between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer. At least a portion of the plurality of shields have a high moment and a high permeability and are conductive. The plurality of shields are electrically isolated from the plurality of magnetic tunneling junctions. The plurality of magnetic tunneling junctions are between the plurality of shields.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
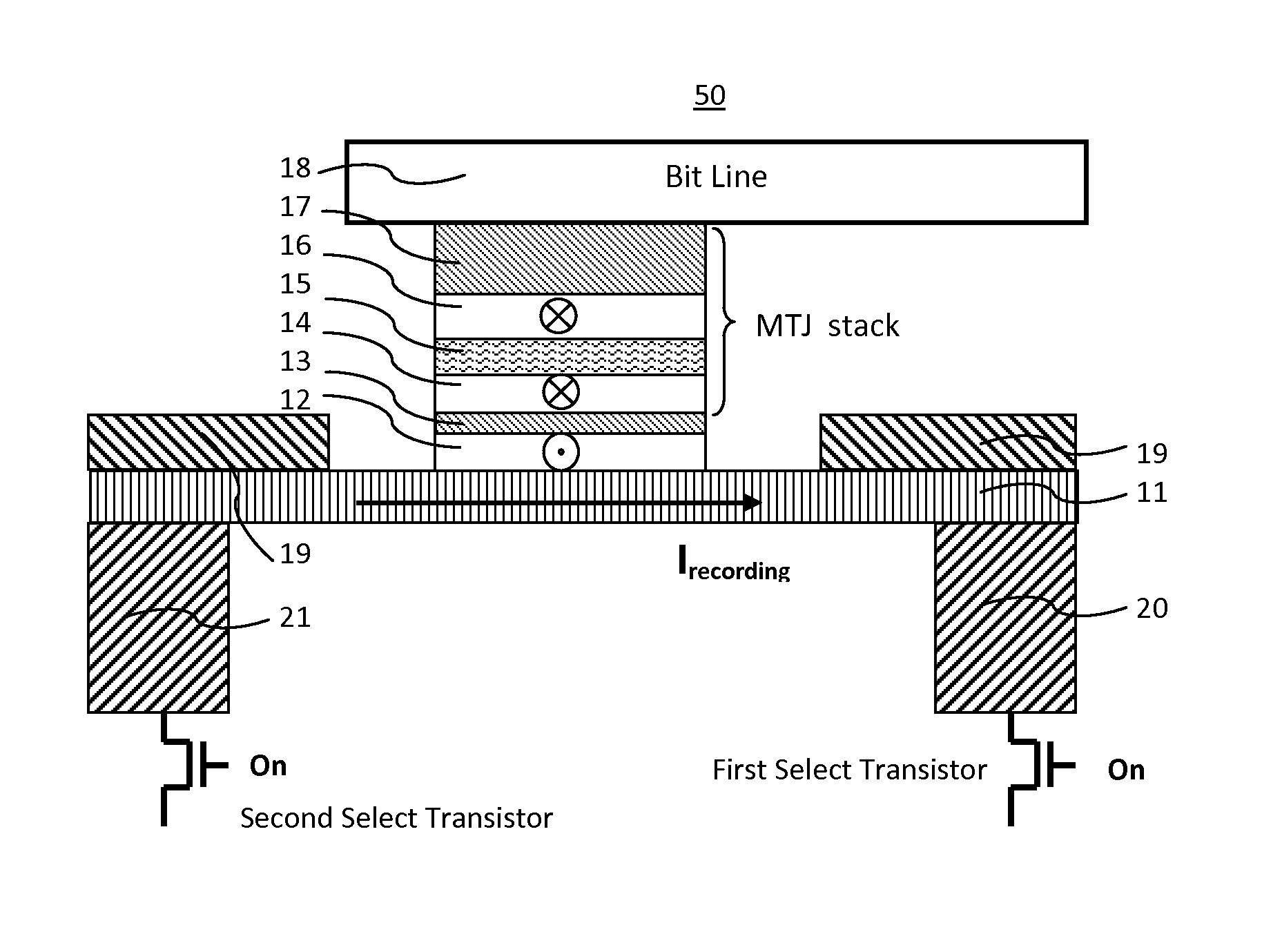
Novel spin hall effect magnetic-ram
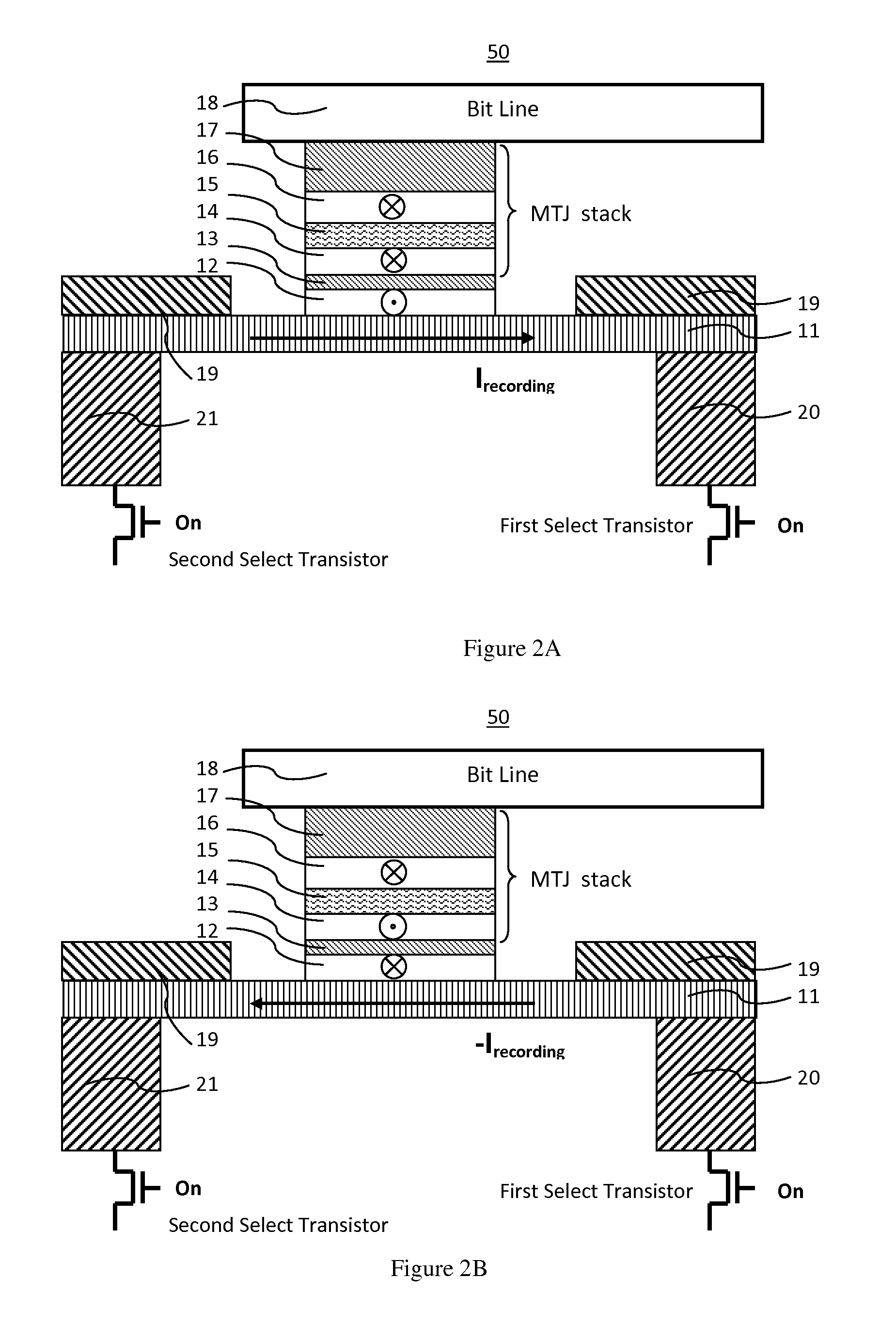
ActiveUS20140312441A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic ramMagnetization
A spin Hall effect magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus of a three terminal magnetoresistive memory cell having an MTJ stack, a functional magnetic layer having a magnetization anti-parallel or parallel coupled with a recording layer magnetization in the MTJ stack, and a SHE-metal base layer. The control circuitry coupled through the bit line and the two select transistors to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two bottom electrodes and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to directly switch the magnetization of the functional magnetic coupling layer and indirectly switching the magnetization of the recording layer through the coupling between the functional magnetic coupling layer and the recording layer.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
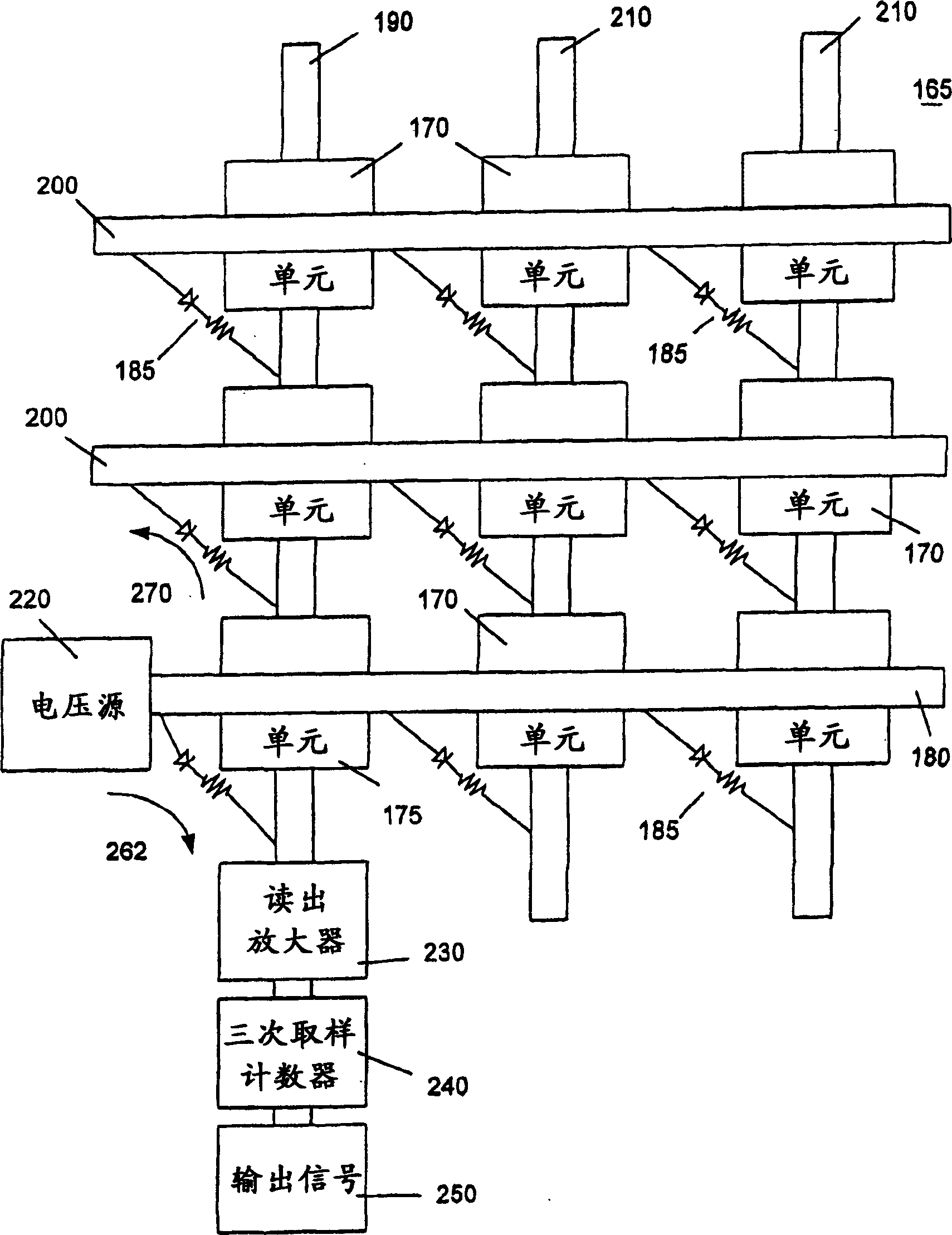
Triple sampling readout of magnetic RAM having series diode
InactiveCN1459792AMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
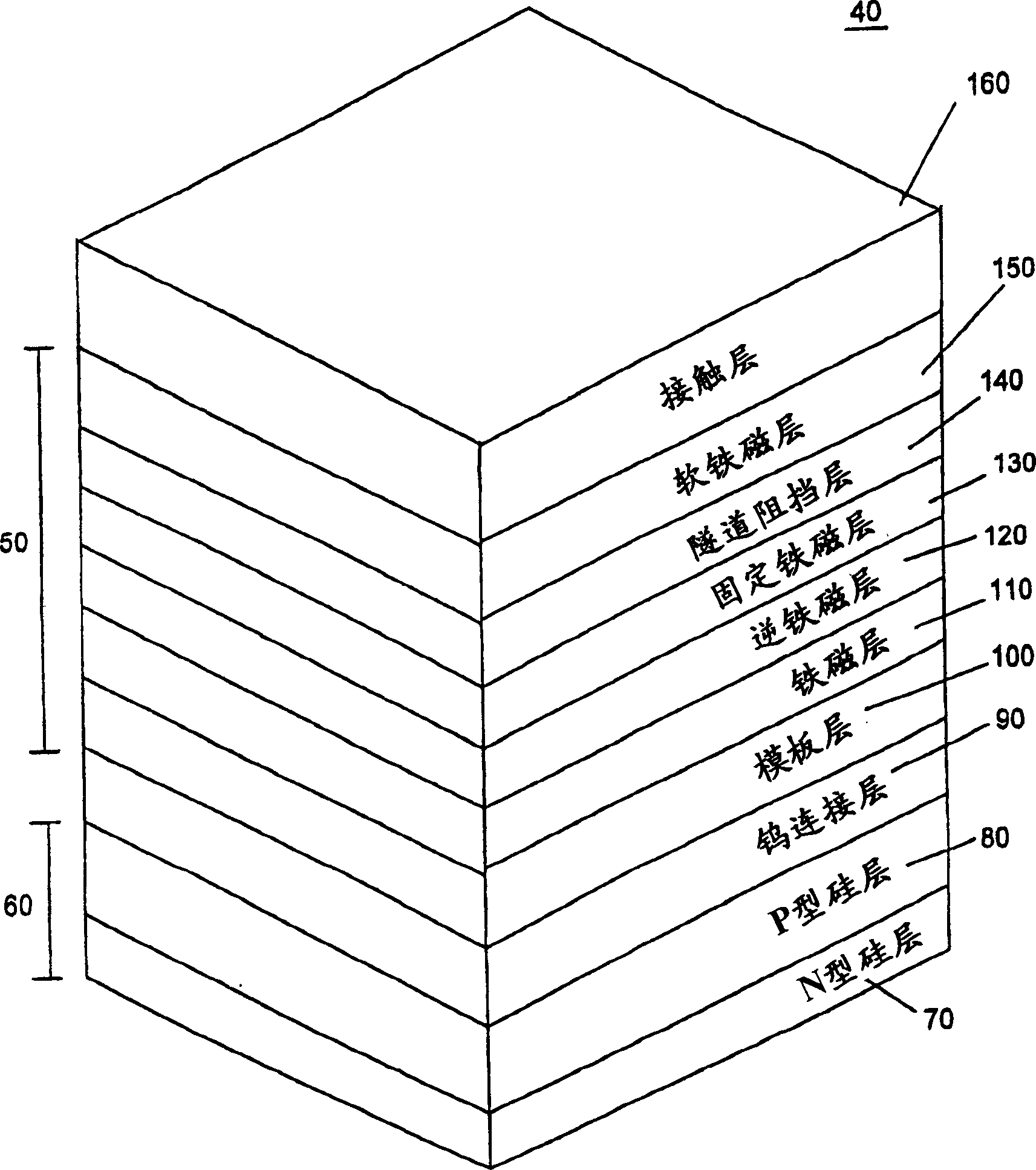
Magnetic RAM of transistor with vertical structure and making method thereof
InactiveCN1385905ANanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceBit line
The invention discloses a magnetic random access memory with a vertical structure transistor, which has faster access time than SRAM, high density similar to DRAM and non-volatile characteristics similar to flash memory. The magnetic random access memory comprises a vertical structure transistor, a first word line including the transistor, a contact line connected to the transistor, a magnetic tunnel junction unit deposited on the contact line, and a magnetic tunnel junction unit formed on the magnetic tunnel junction unit bit line, and a second word line formed on the bit line at the position of the magnetic tunnel junction cell. Through the disclosed structure, while using a simplified manufacturing process, the integration density of semiconductor devices can be increased, the short channel effect can be improved, and the control rate of resistance can be improved.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
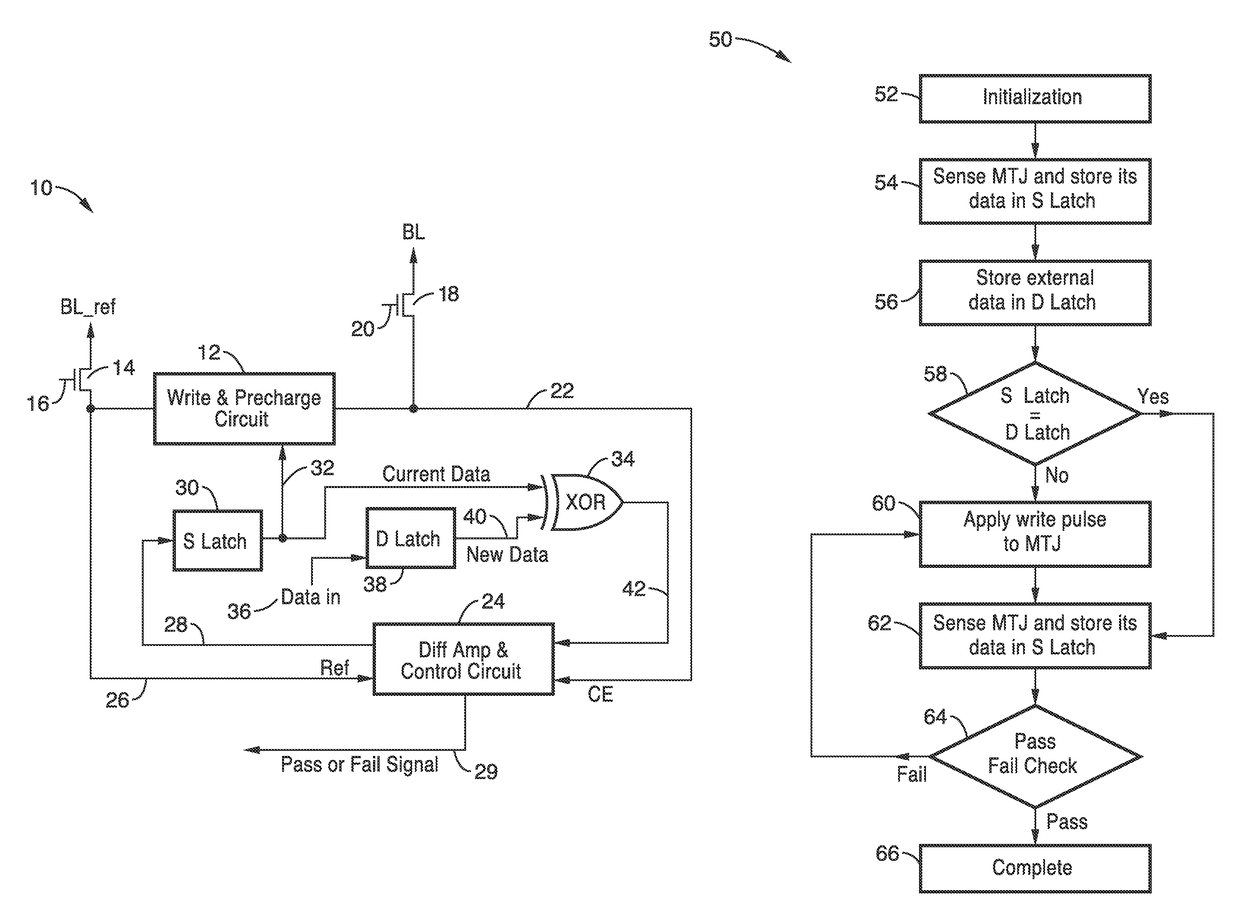
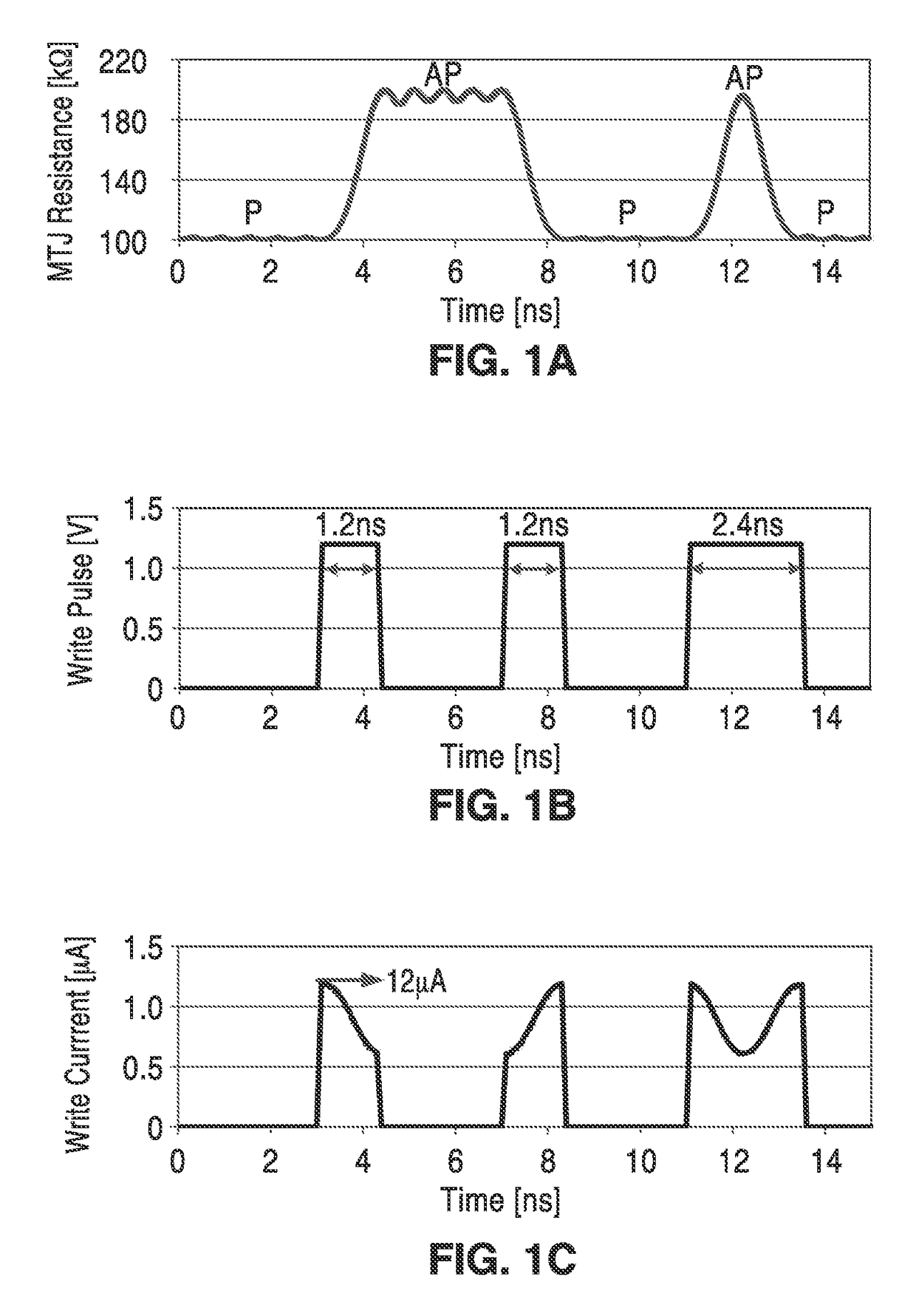
Fast and low-power sense amplifier and writing circuit for high-speed MRAM
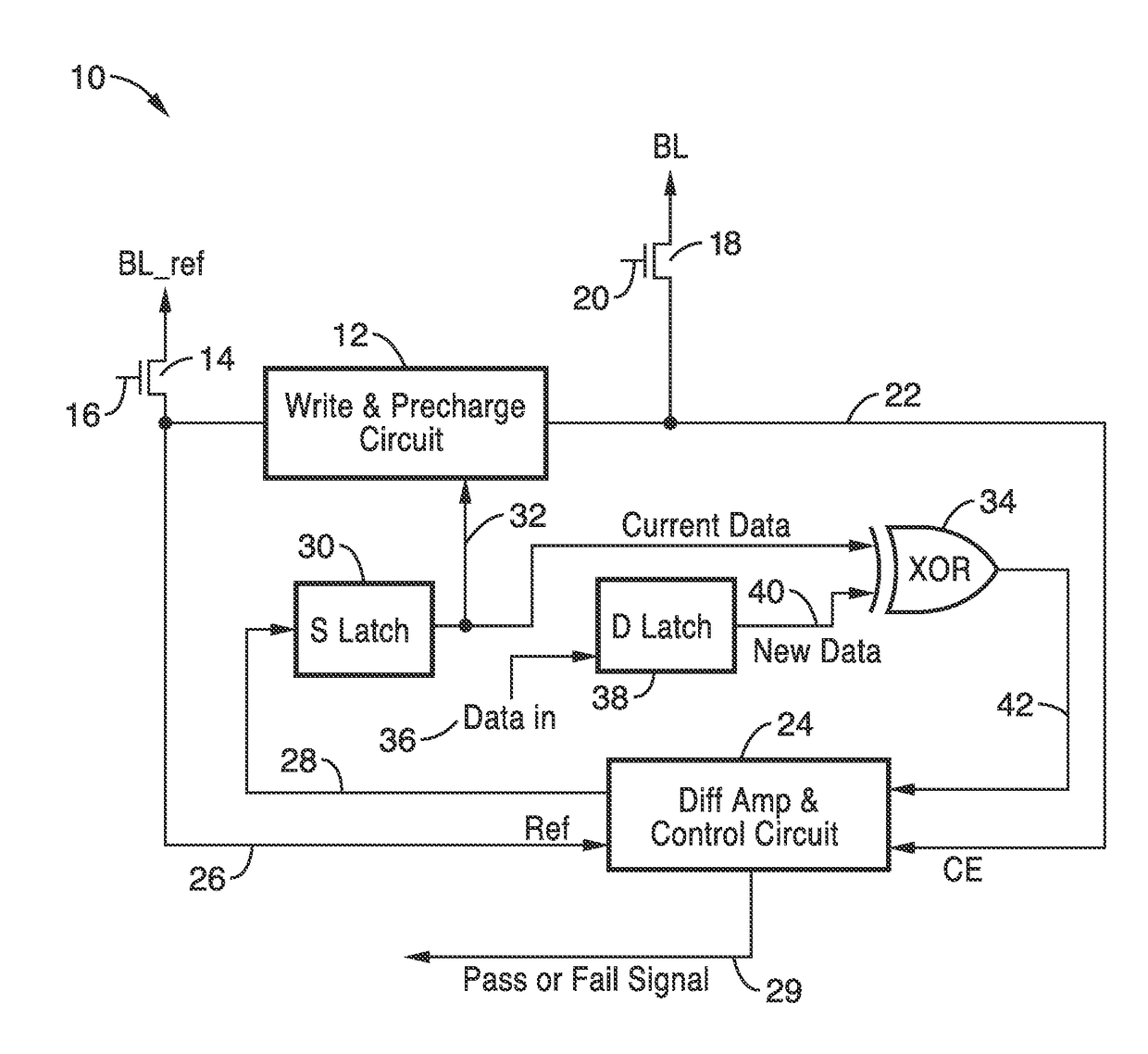
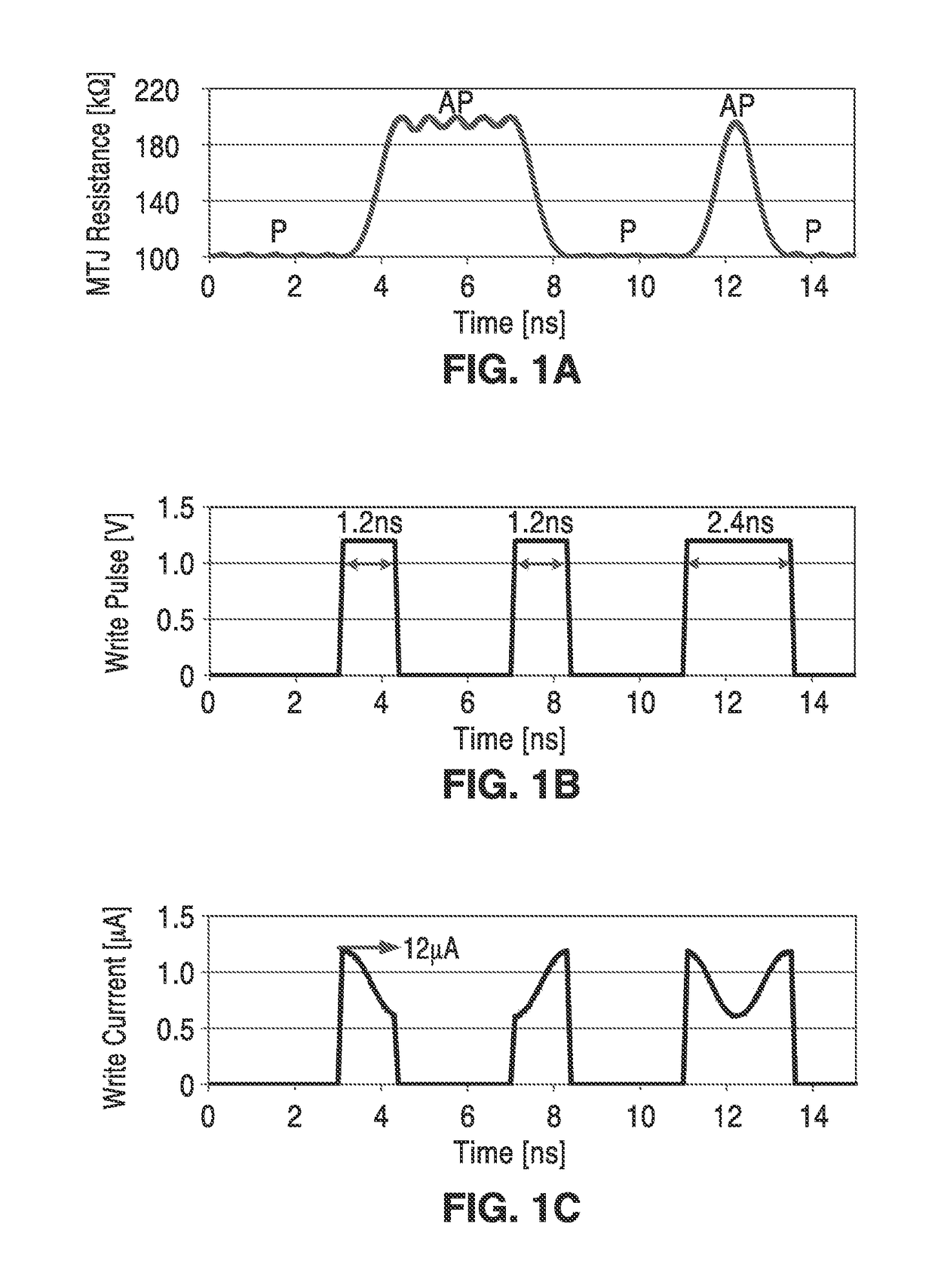
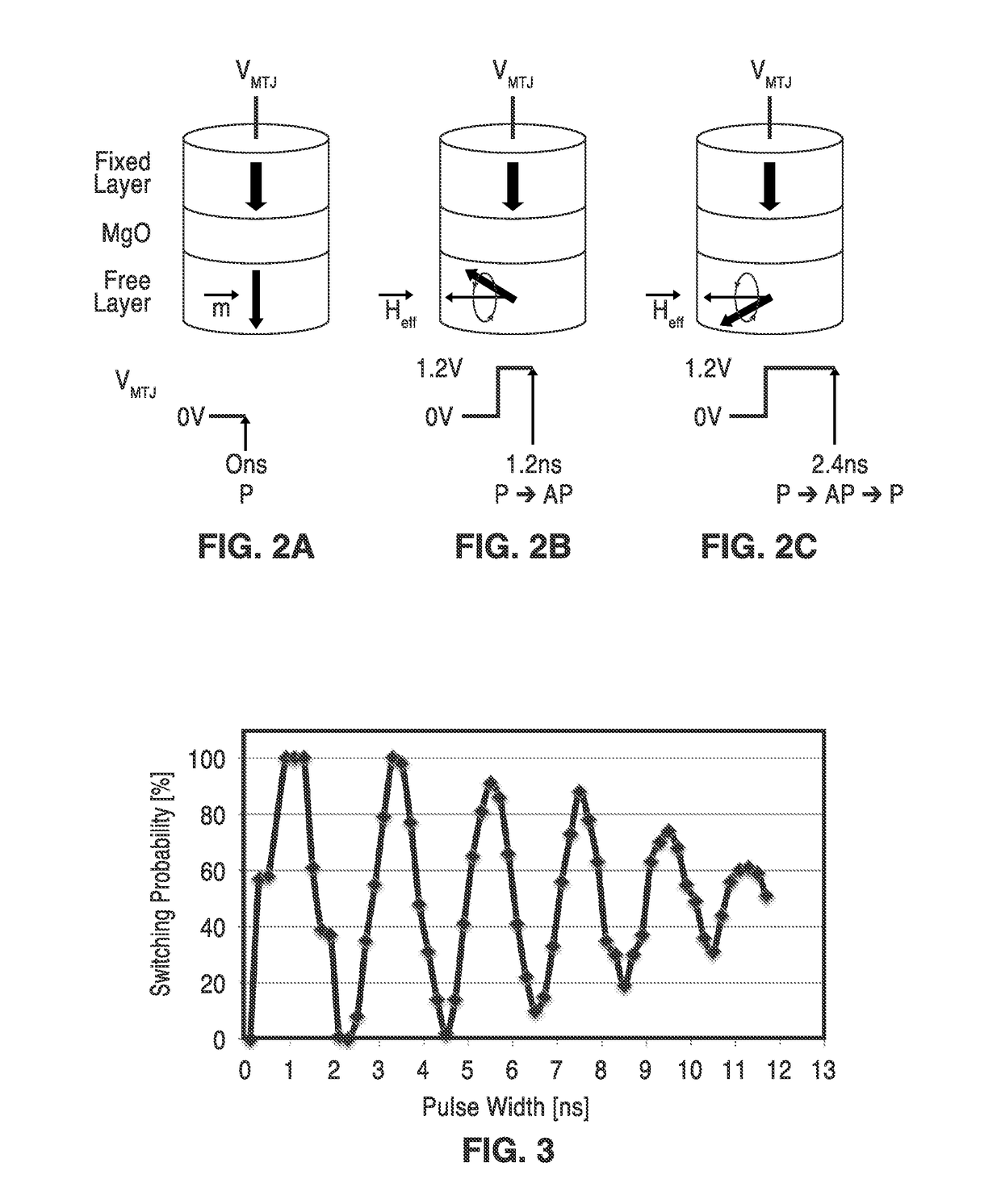
ActiveUS20170084322A1Increased sensing marginReduce error rateDigital storageMagnetic ramAudio power amplifier
A fast and low-power sense amplifier and writing circuit for high-speed Magnetic RAM (MRAM) which provides the long retention times and endurance of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cells, while providing faster access speeds, verified writes, and an increased sensing margin. A high-speed and low-power pre-read and write sense amplifier (PWSA) provide VCMA effect precessional switching of MTJ cells which include pre-read and comparison steps which reduce power consumption. An embodiment of the PWSA circuit is described with write and pre-charge circuit, S and D latches, comparison circuit, and a differential amplifier and control circuit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
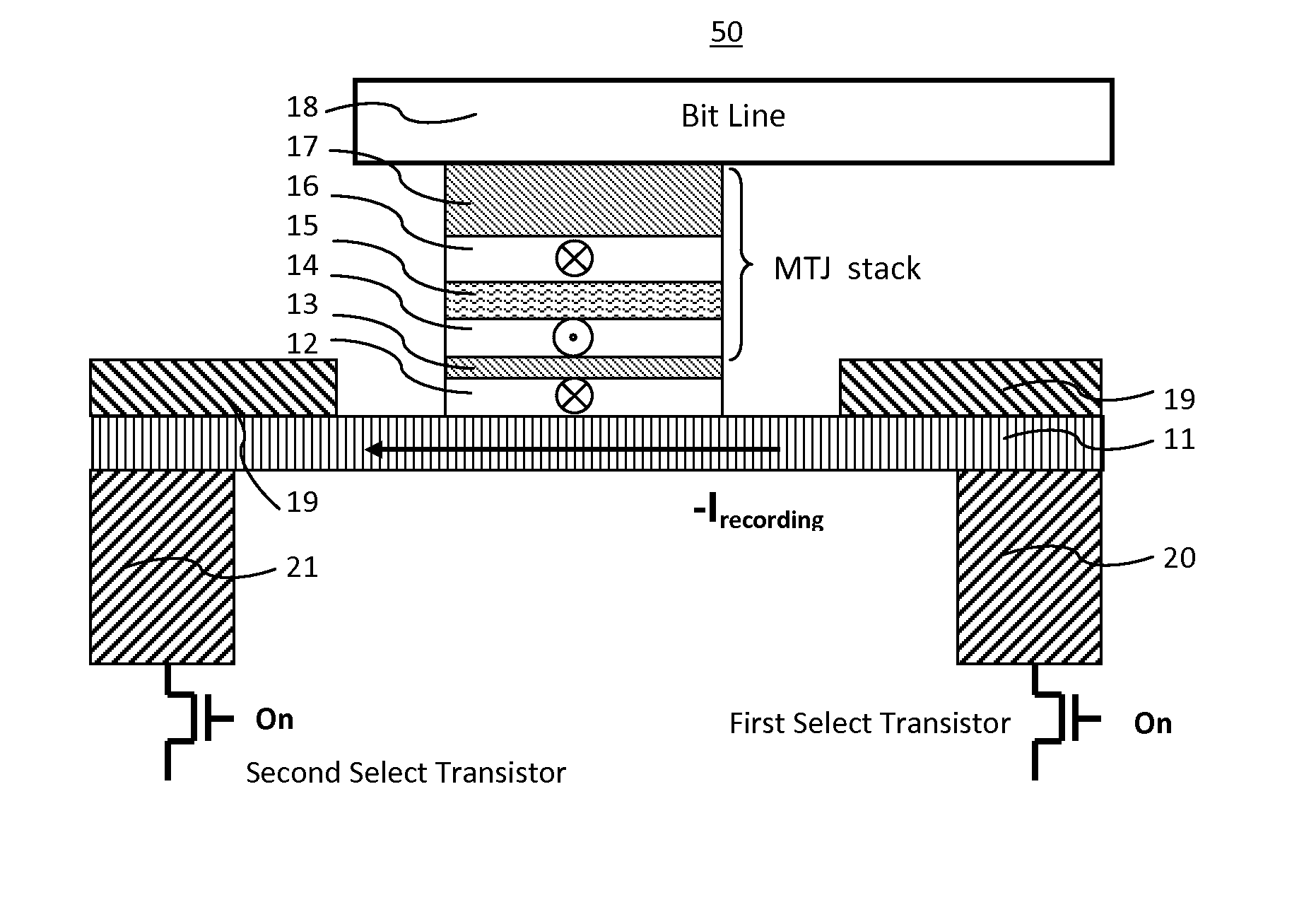
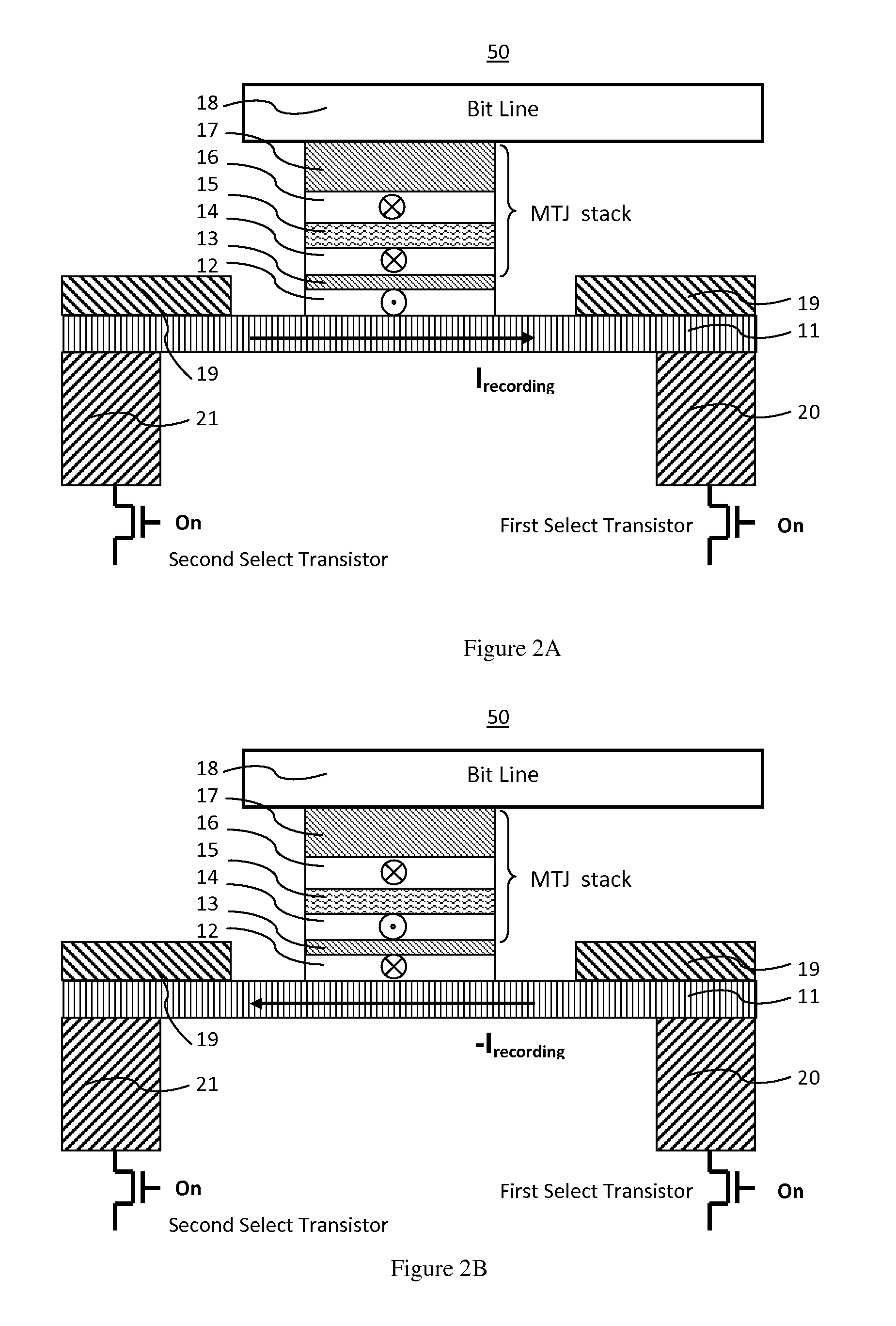
Spin hall effect magnetic-RAM
ActiveUS8963222B2Readily switched and reversedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic ramMagnetic reluctance
A spin Hall effect magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus of a three terminal magnetoresistive memory cell having an MTJ stack, a functional magnetic layer having a magnetization anti-parallel or parallel coupled with a recording layer magnetization in the MTJ stack, and a SHE-metal base layer. The control circuitry coupled through the bit line and the two select transistors to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two bottom electrodes and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to directly switch the magnetization of the functional magnetic coupling layer and indirectly switching the magnetization of the recording layer through the coupling between the functional magnetic coupling layer and the recording layer.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
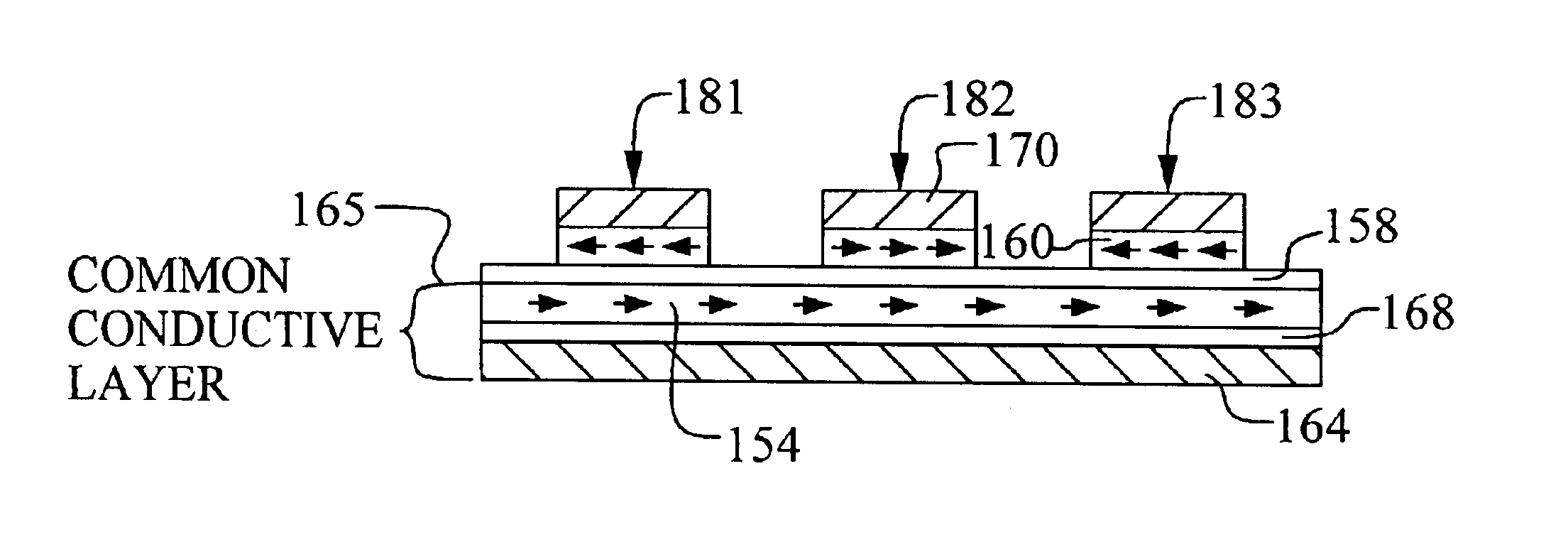
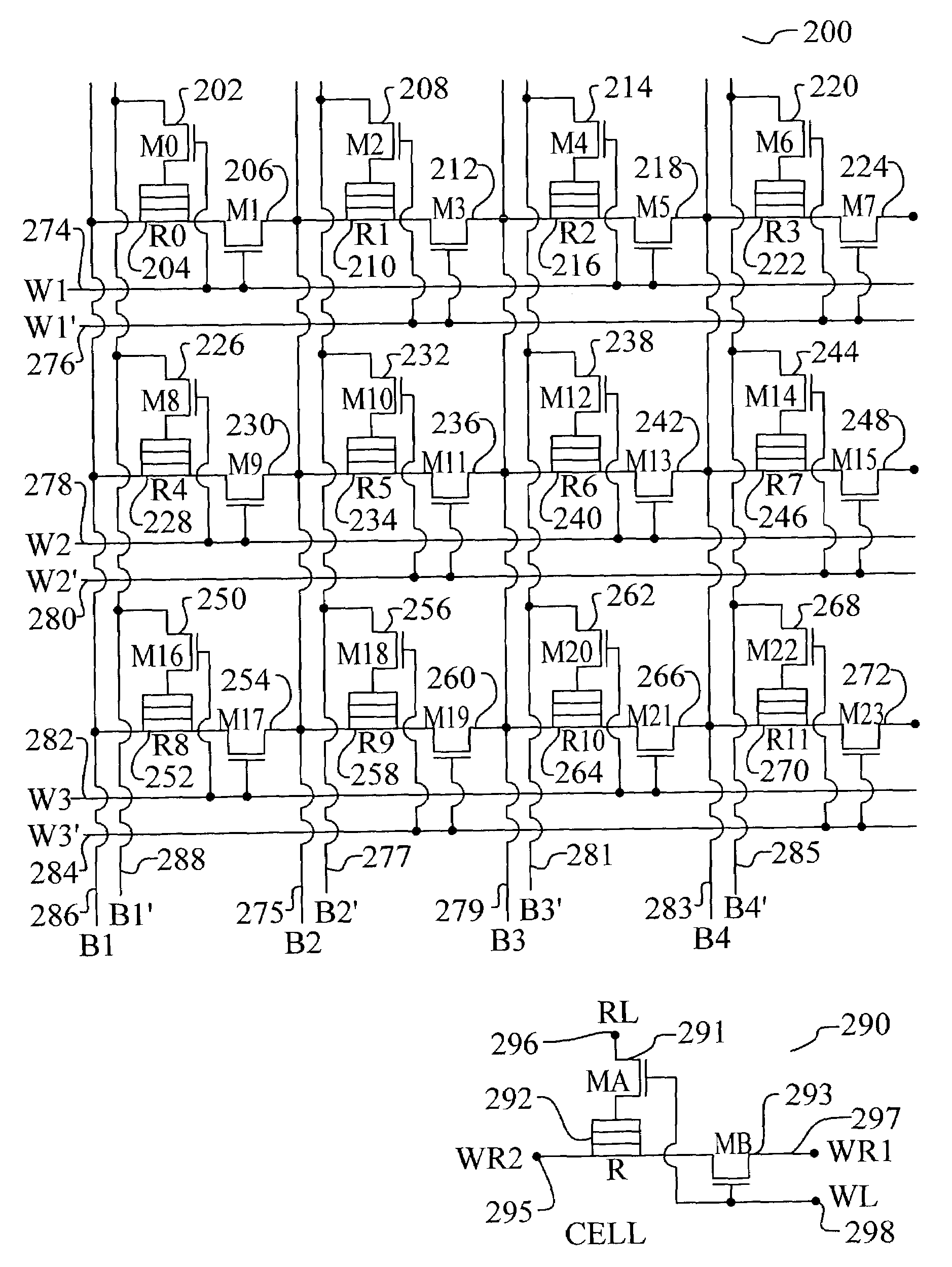
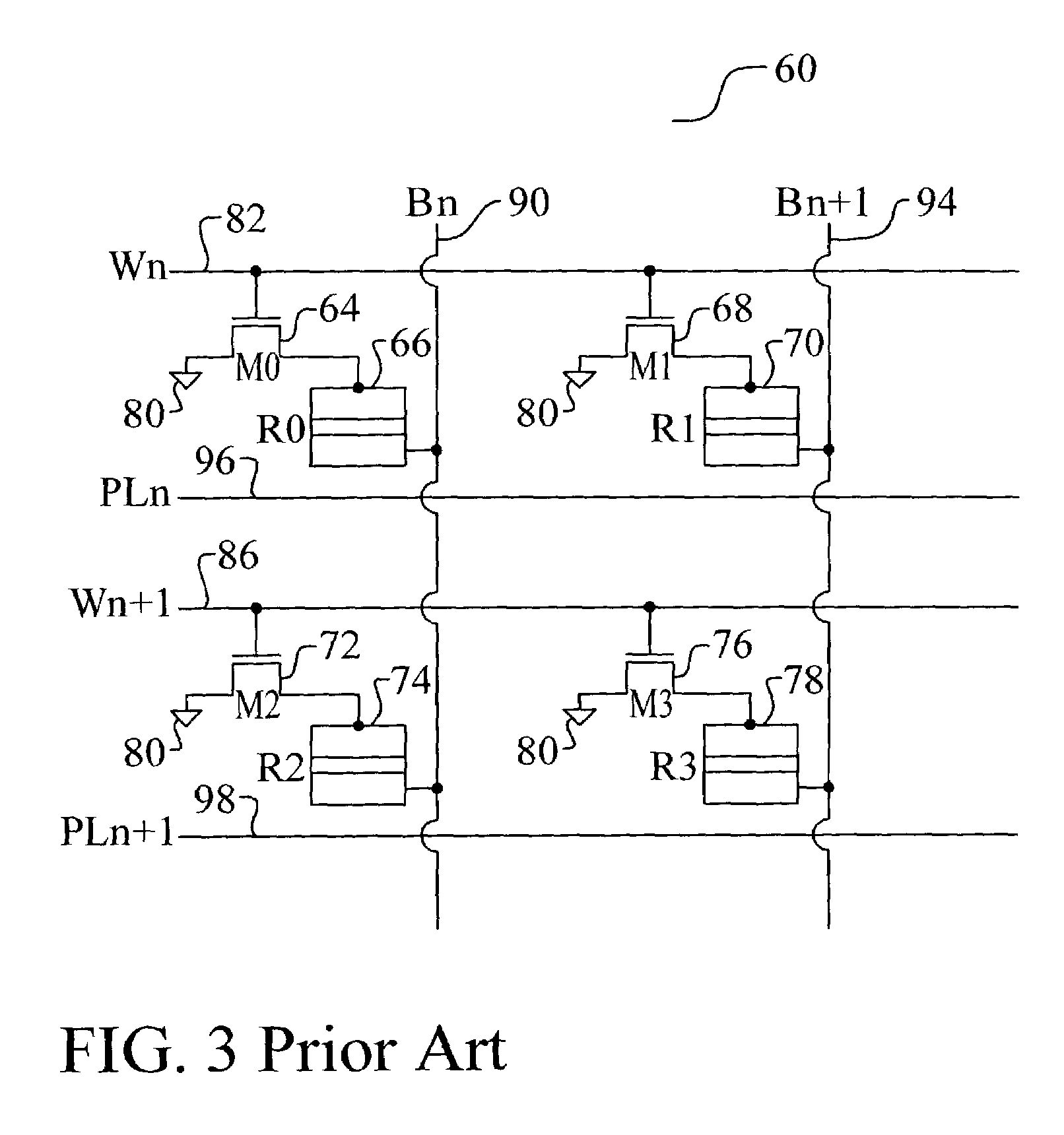
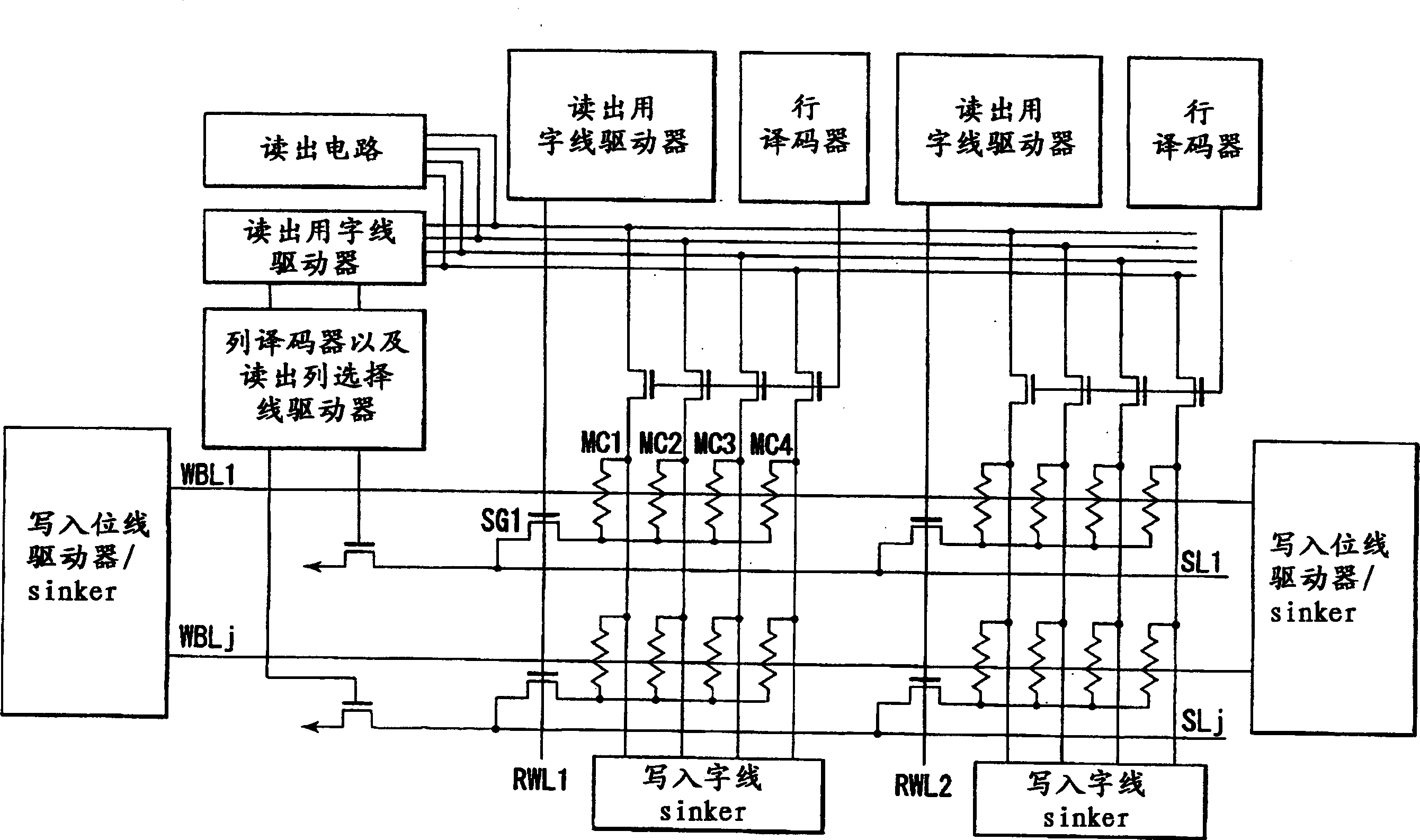
Magnetic RAM cell device and array architecture
A new magnetic RAM cell device is achieved. The device comprises a plurality MTJ cells each comprising a free layer and a pinned layer separated by a dielectric layer. A common conductive layer couples together all of the pinned layers of the MJT cell. A first end of the common conductive layer is switchably coupled to a programming line. A second end of the common conductive layer is switchably coupled to a ground. A pluraity of diodes is used. Each diode is coupled between one of the MJT cells and one of a plurality of bit lines.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
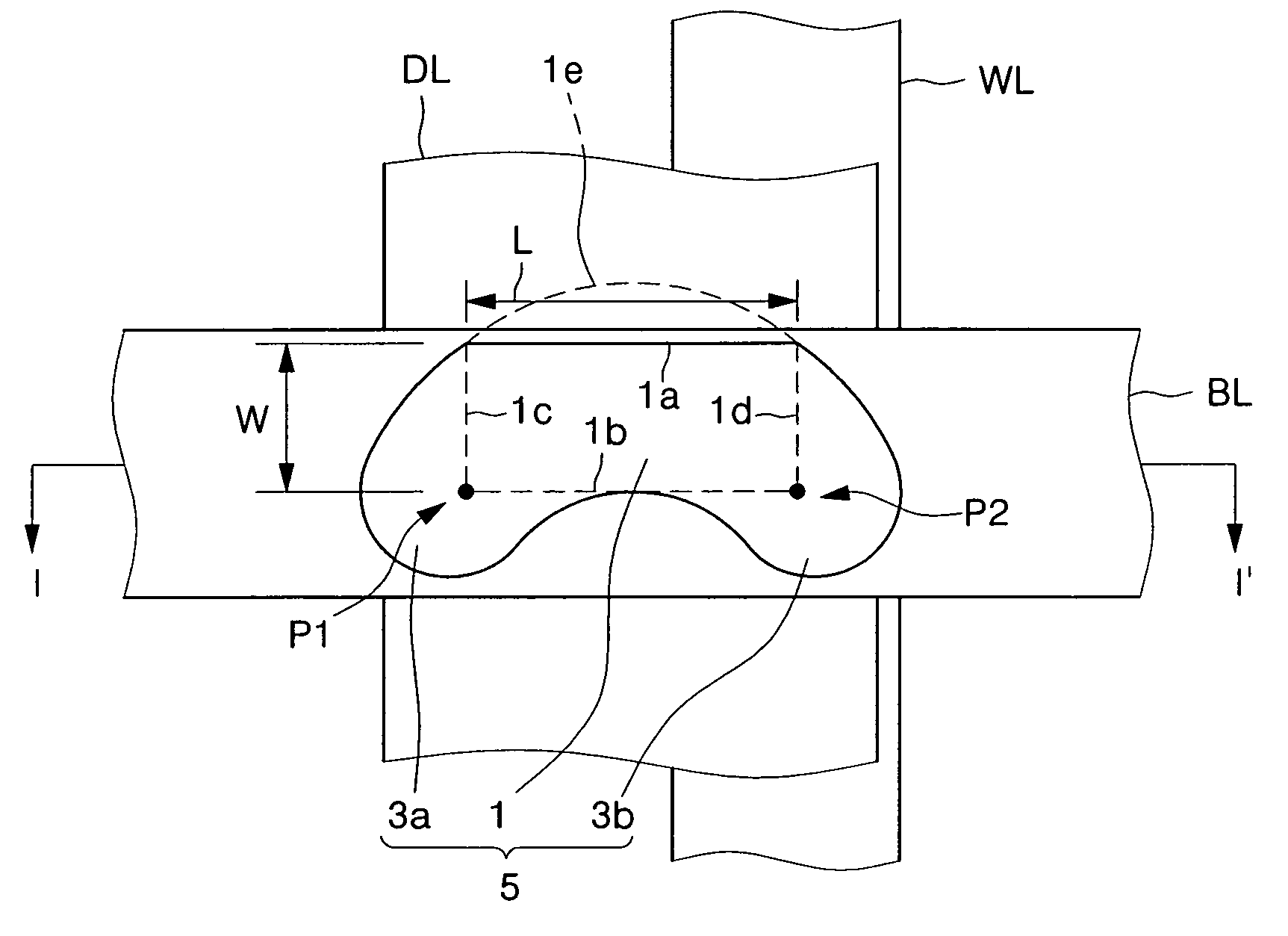
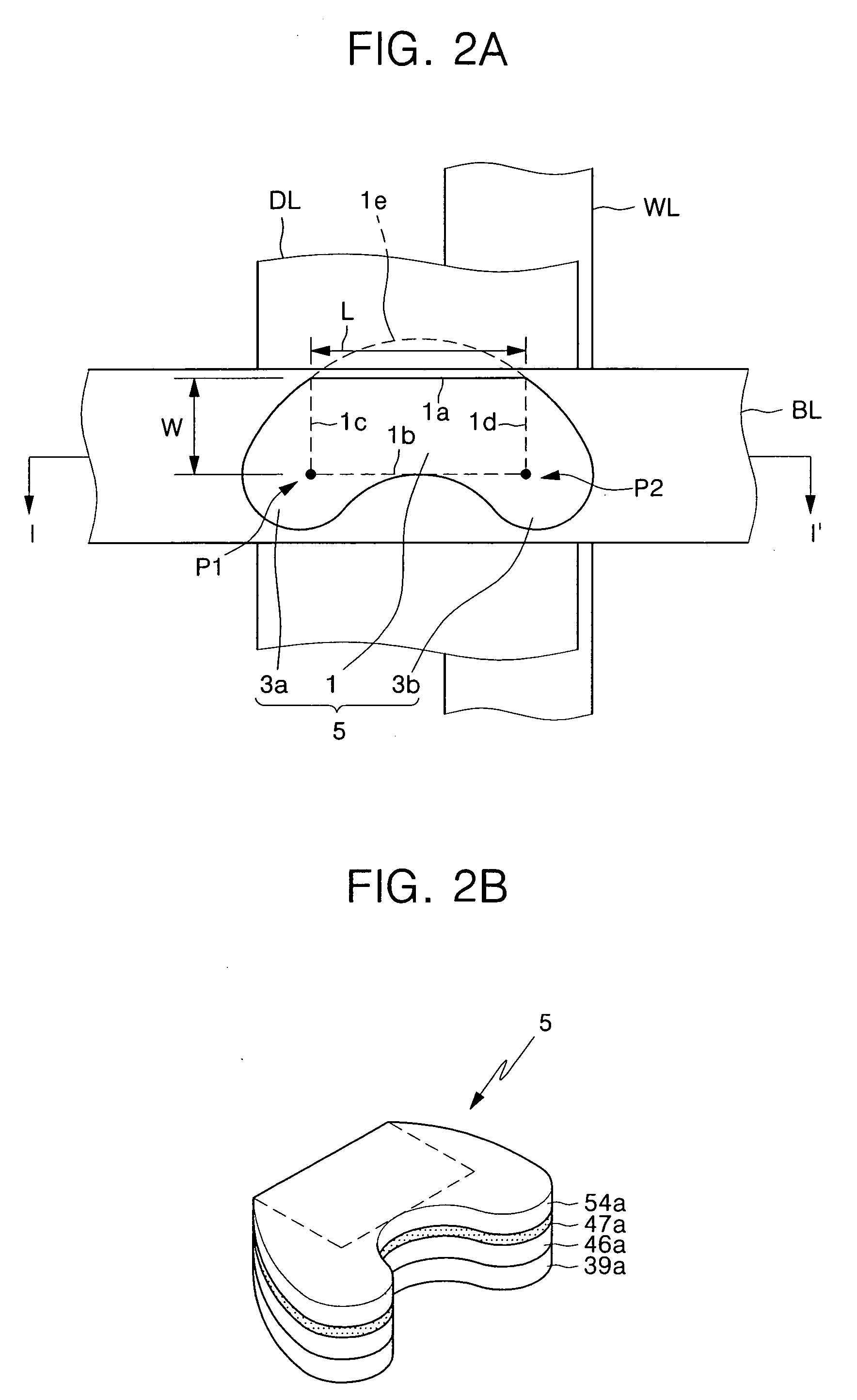
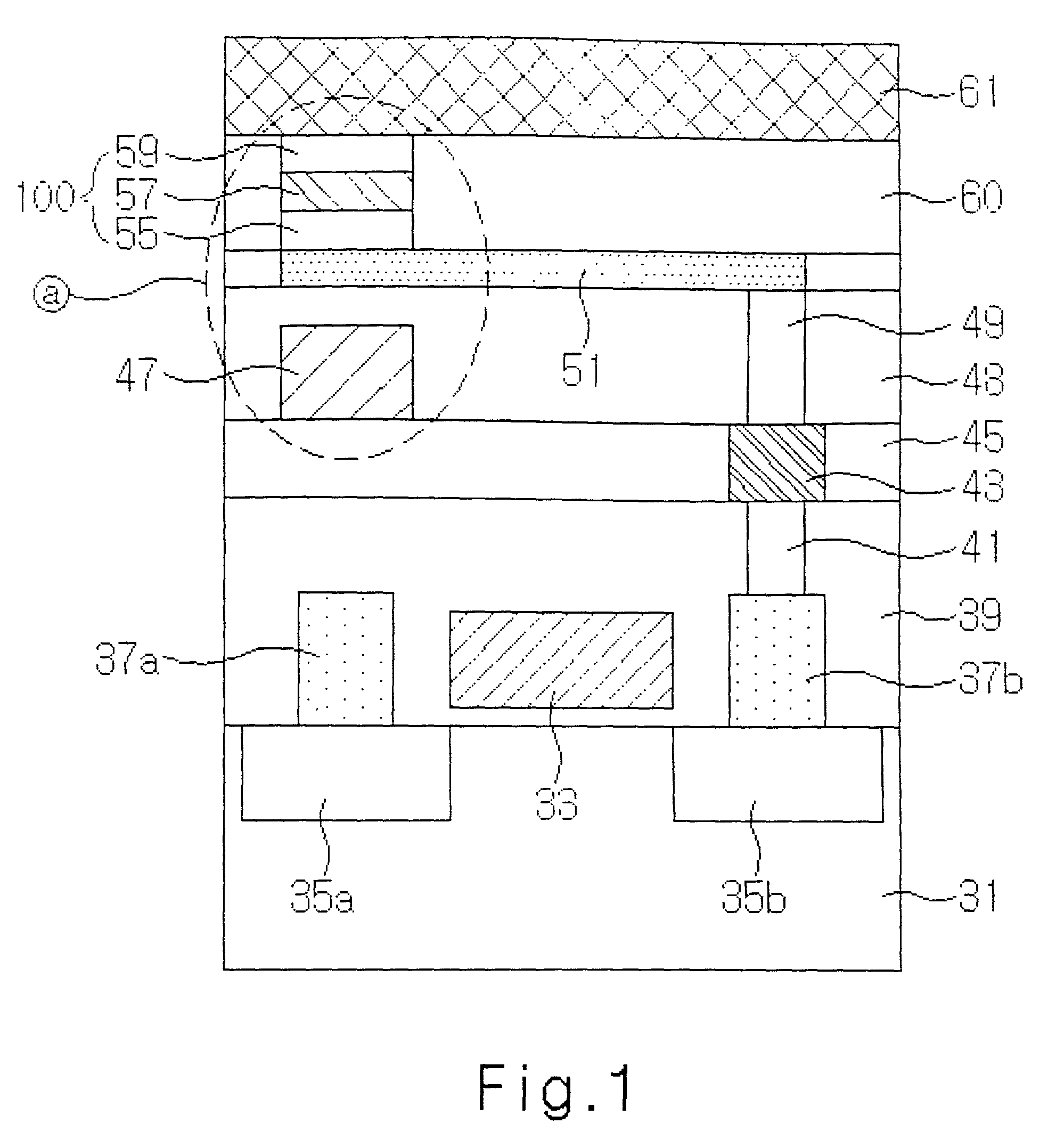
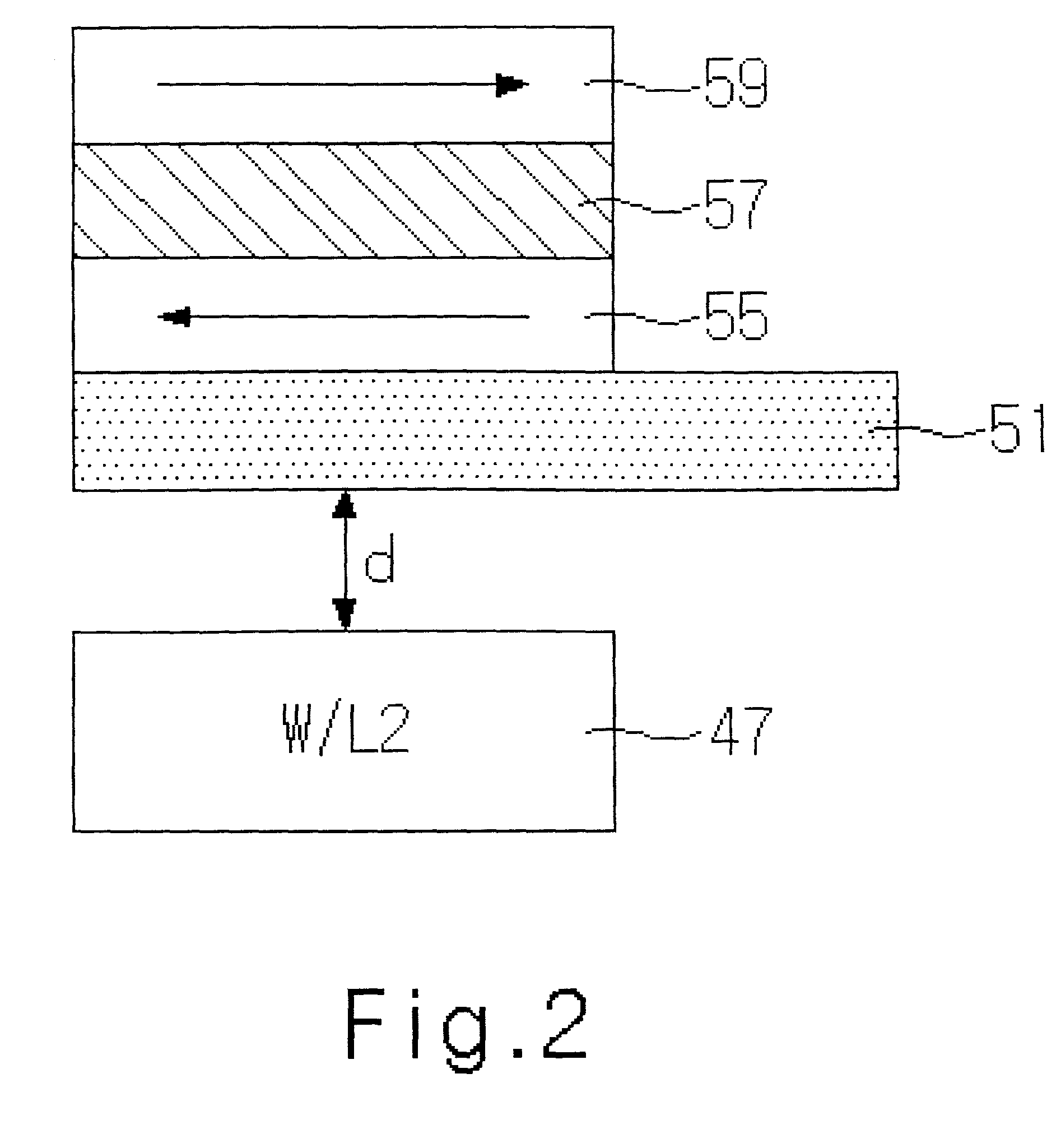
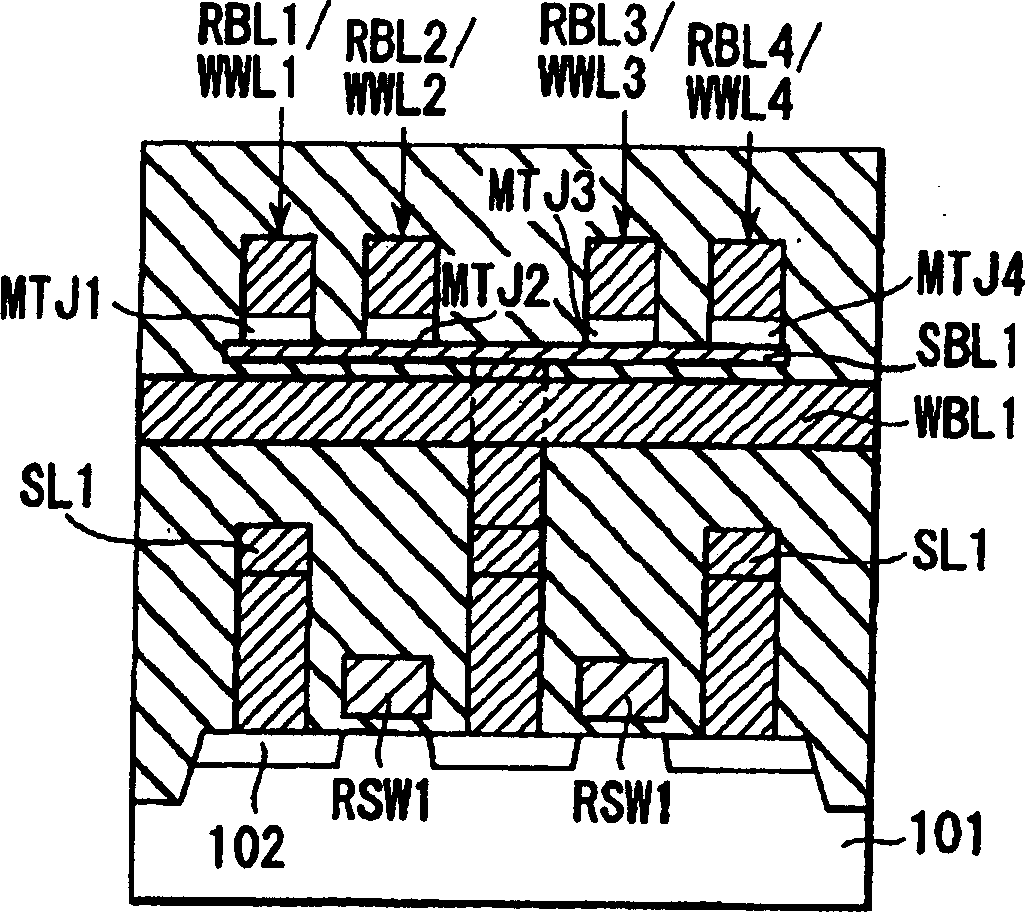
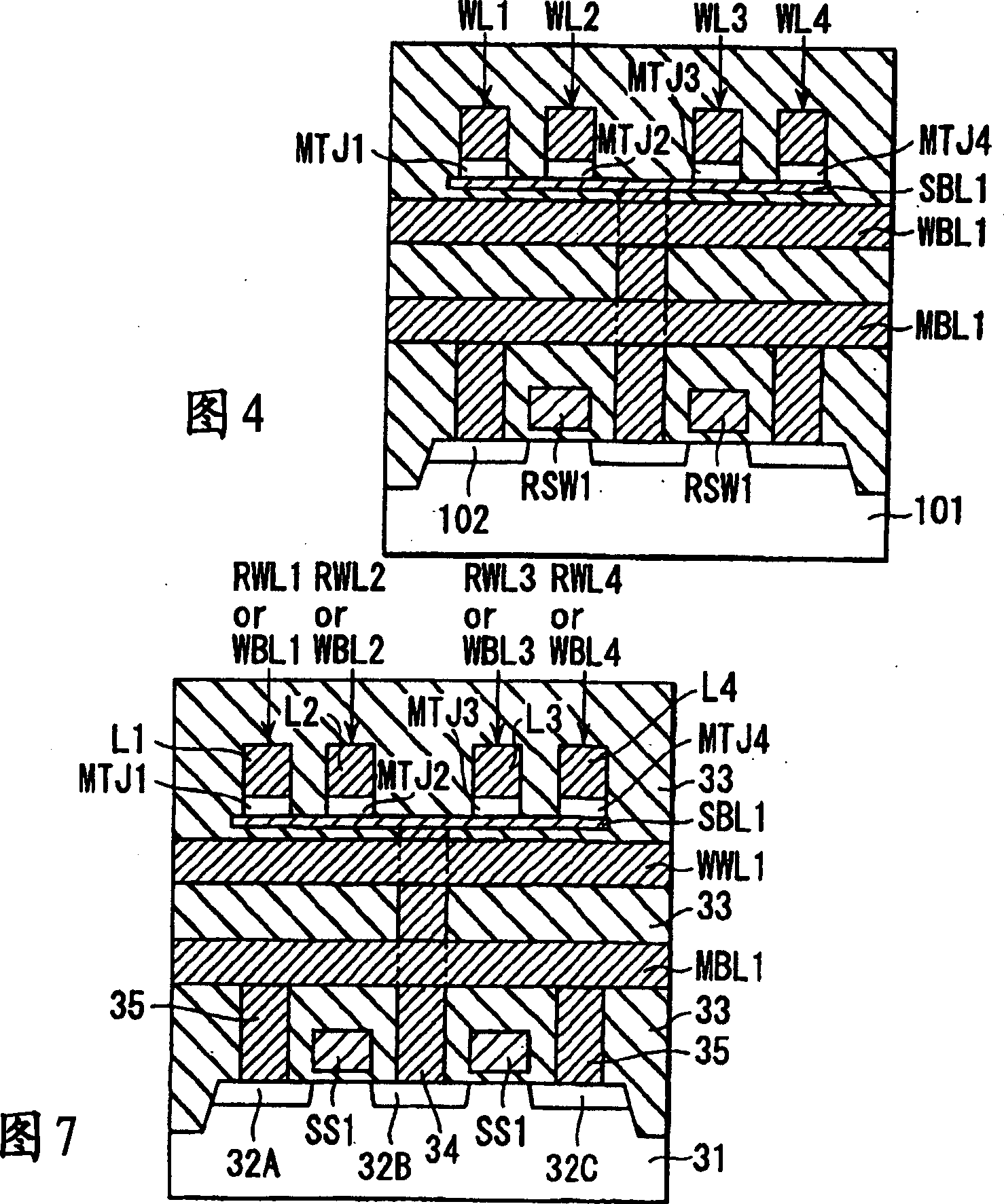
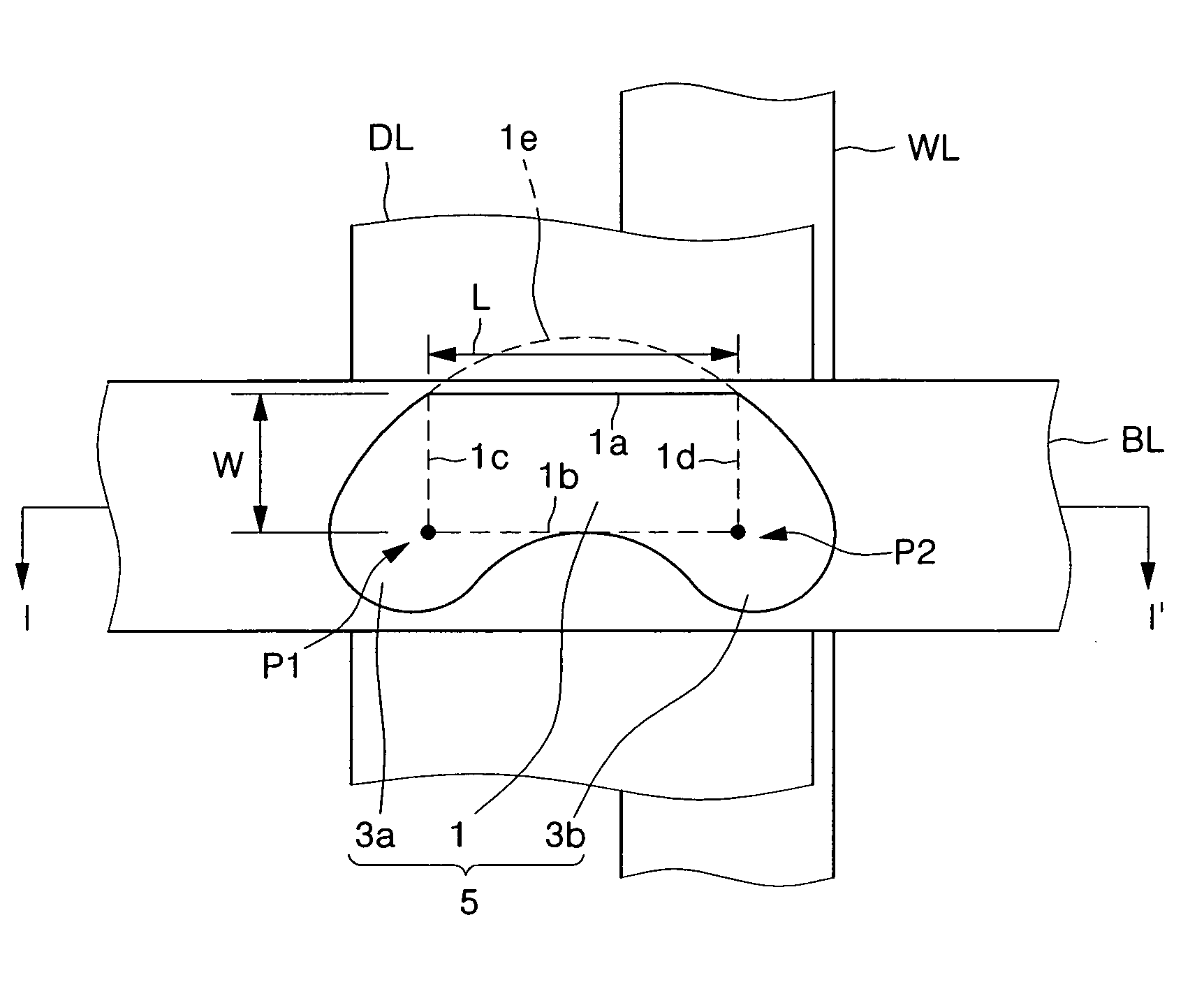
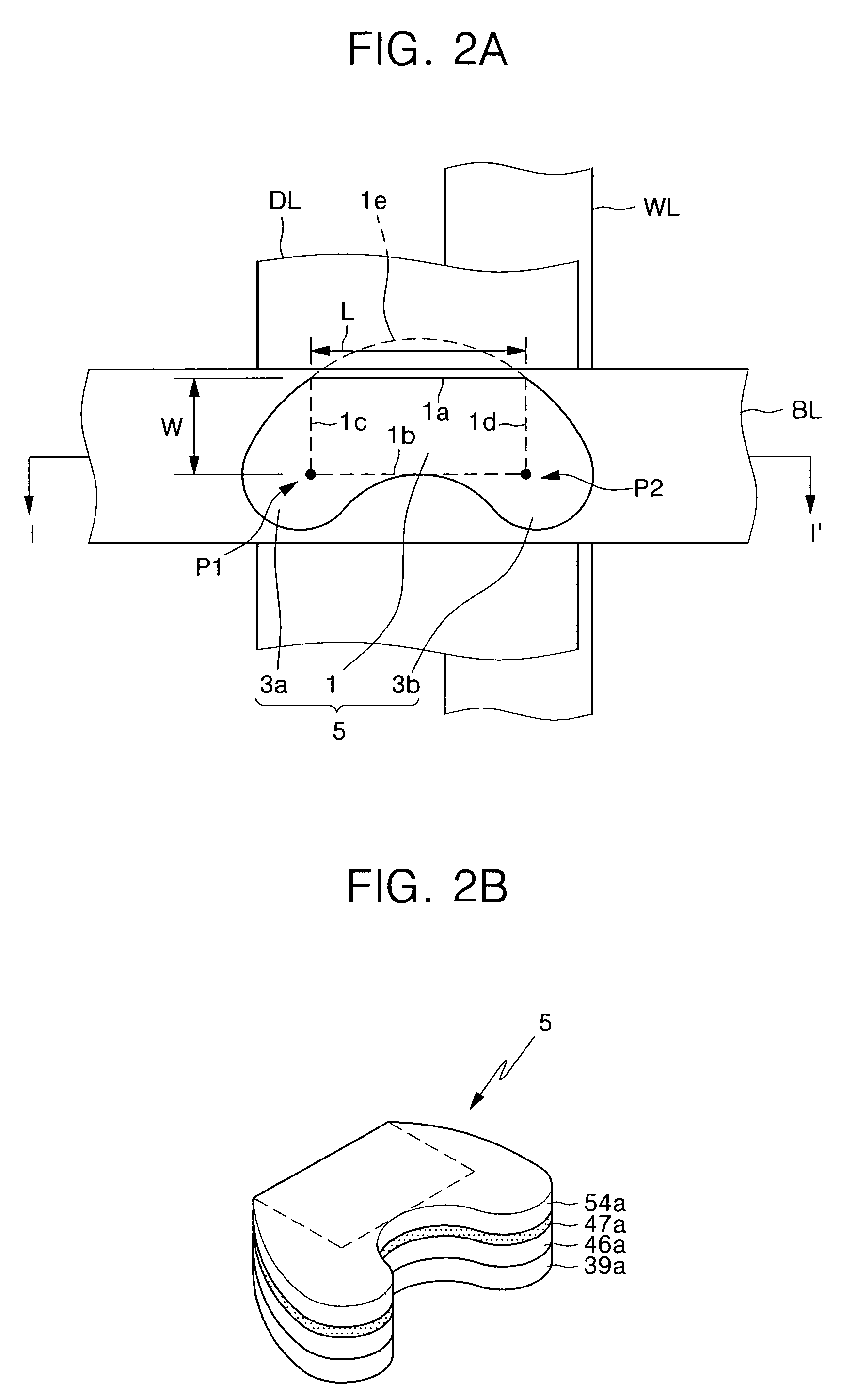
Magnetic tunnel junction structures having bended tips at both ends thereof, magnetic random access memory cells employing the same and photomasks used in formation thereof
InactiveUS20050230771A1NanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic ramInsulation layer
Provided are magnetic tunnel junction structures having bended tips at both ends thereof, magnetic RAM cells employing the same and photo masks used in formation thereof. The magnetic tunnel junction structures have a pinned layer pattern, a tunneling insulation layer pattern and a free layer pattern, which are stacked on an integrated circuit substrate. At least the free layer pattern has a main body as well as first and second bended tips each protruded from both ends of the main body when viewed from a plan view.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic ram array architecture
A magnetic random access memory (MRAM) array including: a plurality of MRAM cells arranged in an array configuration, each comprising a first type nTron and a magnetic memory element; a wordline select circuit comprising of a second type nTron to drive a plurality of parallel wordlines; and a plurality of bitline select circuits, each comprising of said second type nTron for writing to and reading from a column of memory cells in the array and each capable of selecting a single MRAM cell for a memory read or write operation, wherein the second nTron has a higher current drive than the first nTron.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP +1
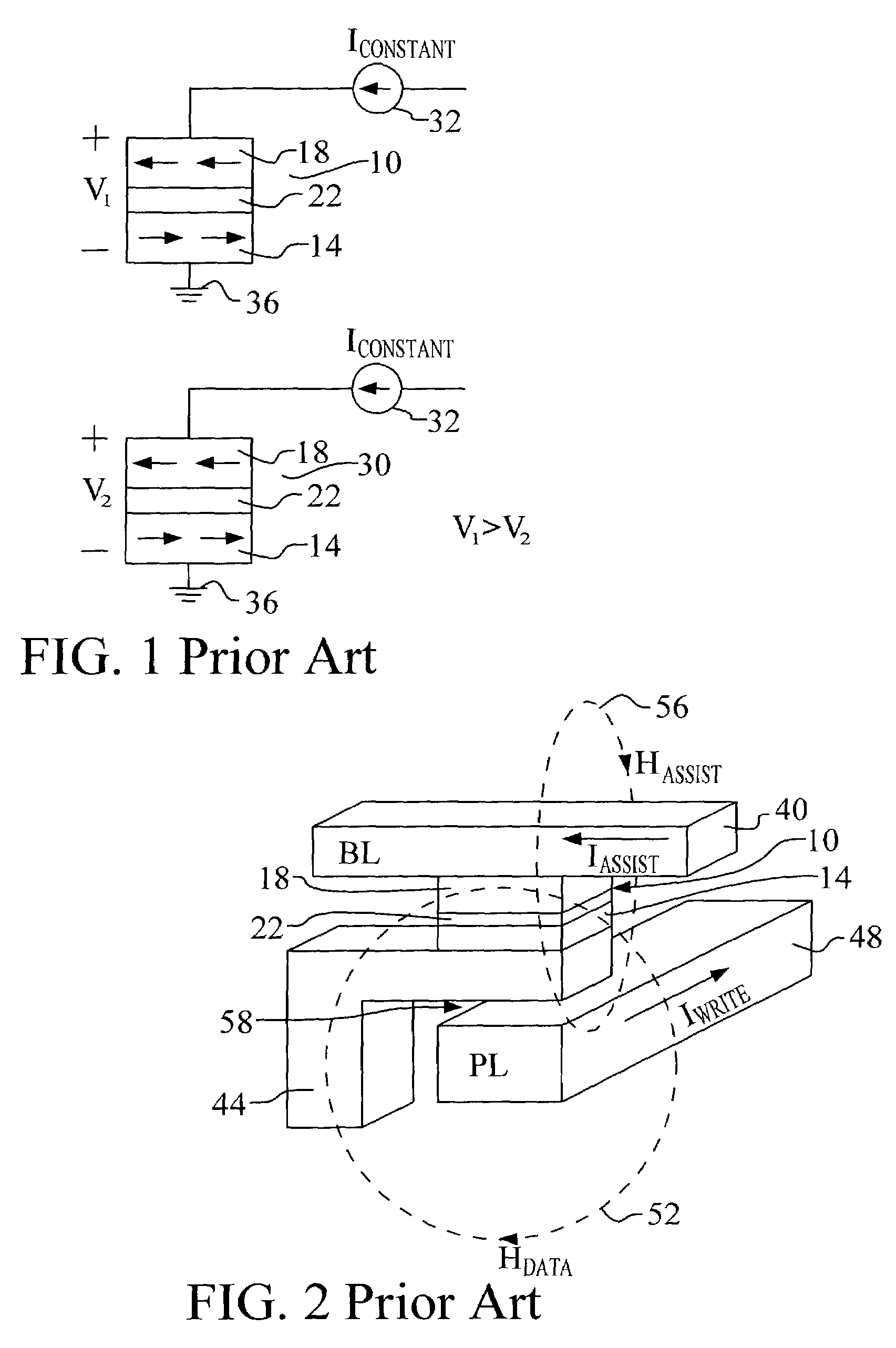
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) for spontaneous hall effect and method of writing and reading data using the MRAM
InactiveUS6894920B2Increase in coercivityImprove securitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineStatic random-access memory
A magnetic RAM (MRAM) using a thermo-magnetic spontaneous Hall effect includes a MOS transistor formed on a substrate; a heating layer formed above the MOS transistor and connected to a source region of the MOS transistor; a memory layer having a data write area to which data is written, the data write area being formed on the heating means; a bit line formed on the data write area; an upper insulating film formed on the bit line and the memory layer; and a write line formed on the upper insulating film so that a magnetic field necessary for writing data is generated in at least the data write area of the memory layer. The MRAM writes or reads data using the fact that a spontaneous Hall voltage greatly differs according to the magnetization state of a memory layer, thereby providing the device a high data sensing margin.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for forming MTJ of magnetic RAM
InactiveCN1538539AAvoid heat damageAvoid instabilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesMagnetic ramInsulation layer
A method of forming a magnetic tunneling junction (MTJ) layer for an MRAM includes sequentially forming a lower material layer, an insulation layer, and an upper material layer on a substrate, forming a mask pattern on a predetermined region of the upper material layer, sequentially removing the upper material layer, the insulation layer, and the lower material layer from around the mask pattern using plasma generated from an etching gas, wherein the etching gas is a mixture of a main gas and an additive gas having a predetermined mixture ratio and including no chlorine (Cl2) gas, and removing the mask pattern. Accordingly, an MTJ layer formed by the method may incur no thermal damage due to high temperature etching, no material deposits due to by-products of etching, and no step difference or corrosion due to chlorine gas, and may have an excellent profile.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic RAM and array architecture using a two transistor, one MTJ cell
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
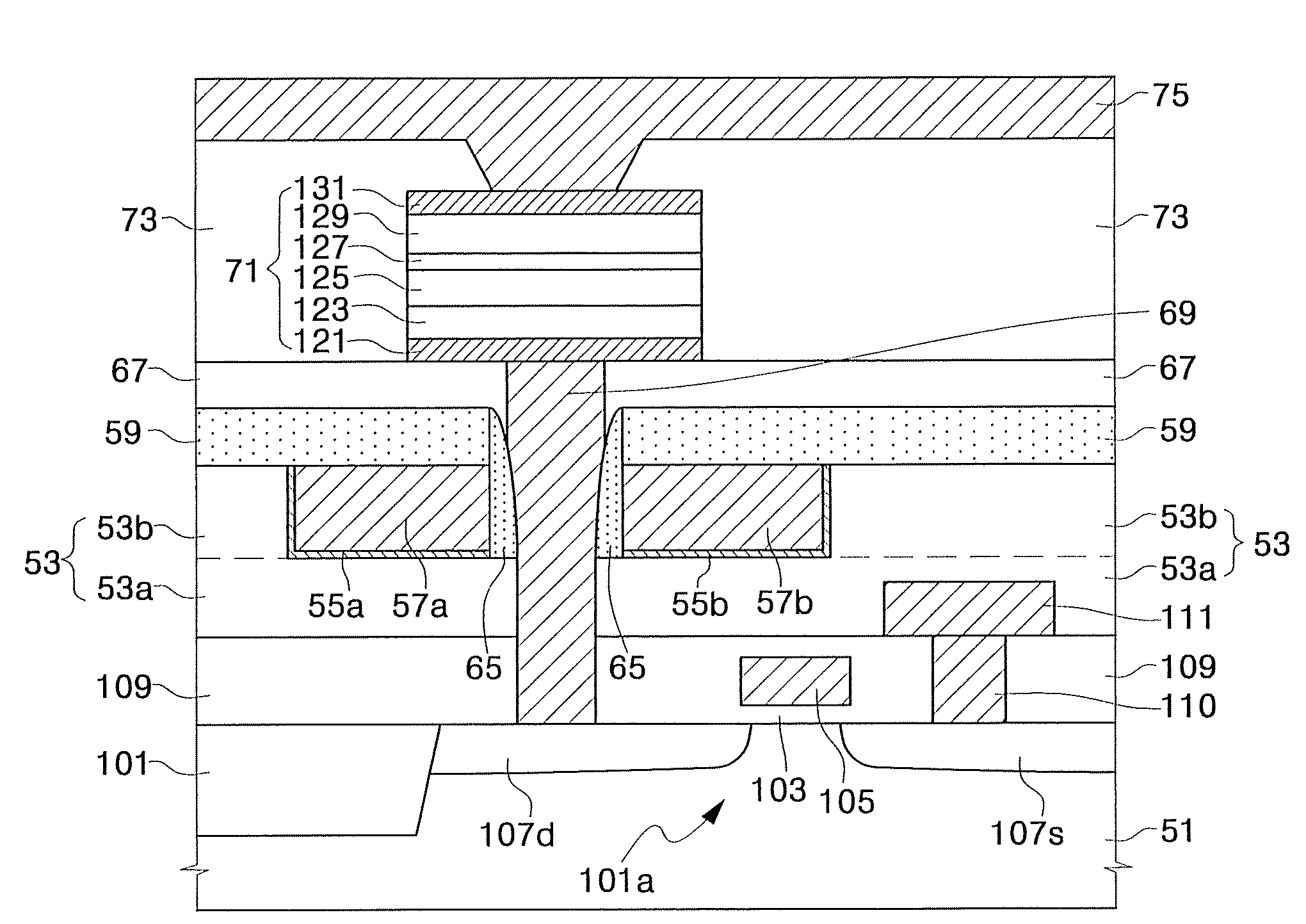
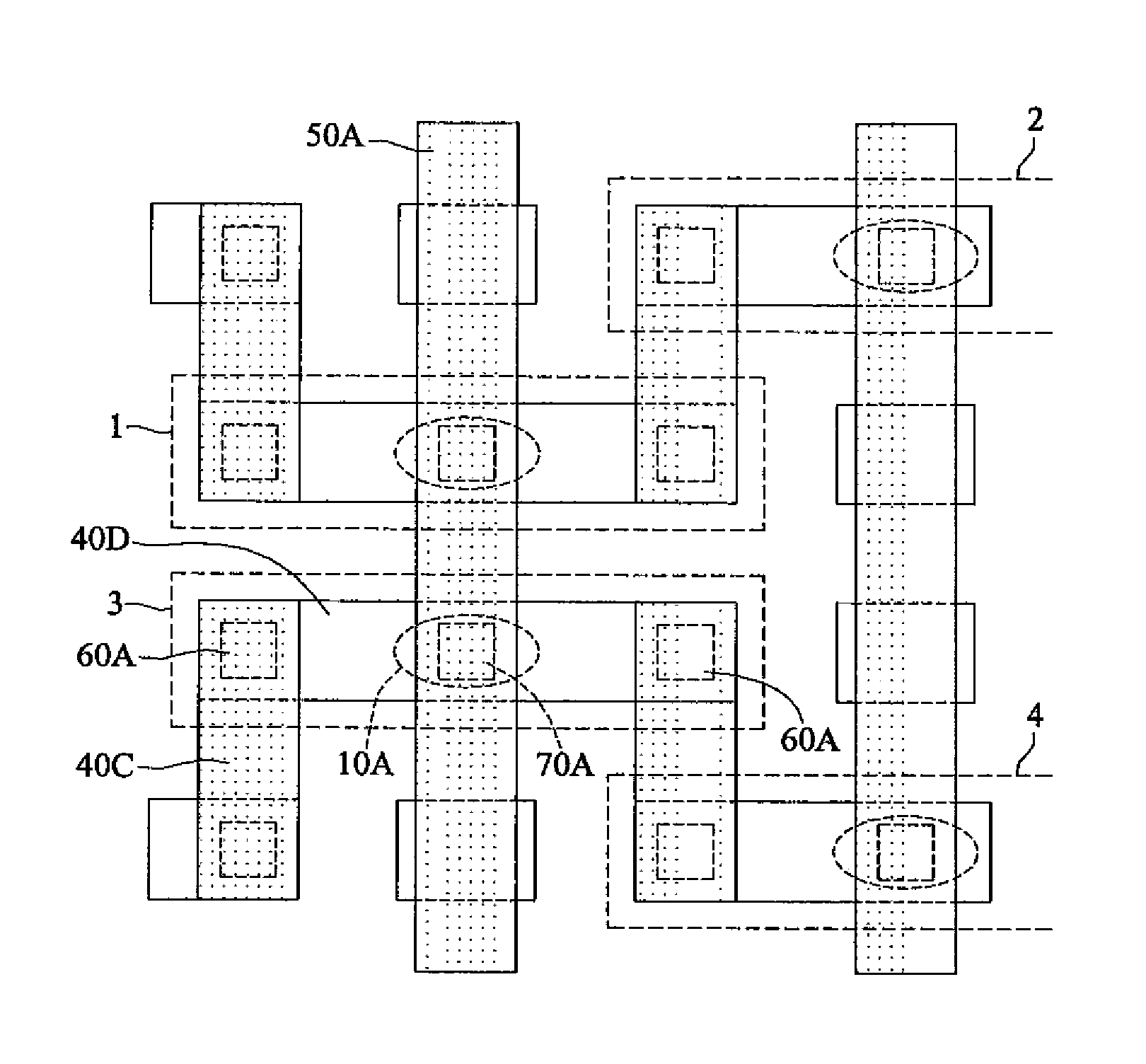
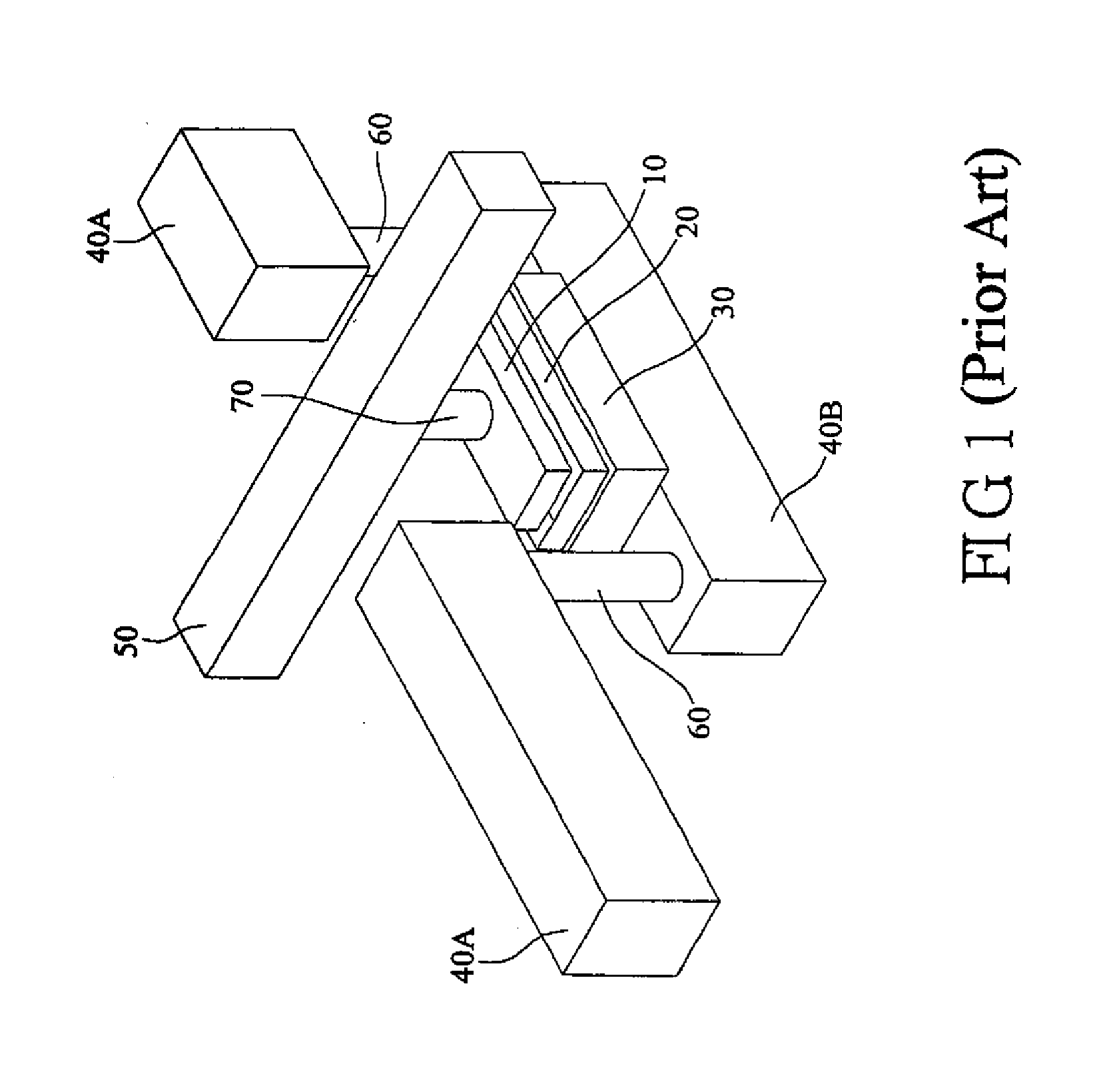
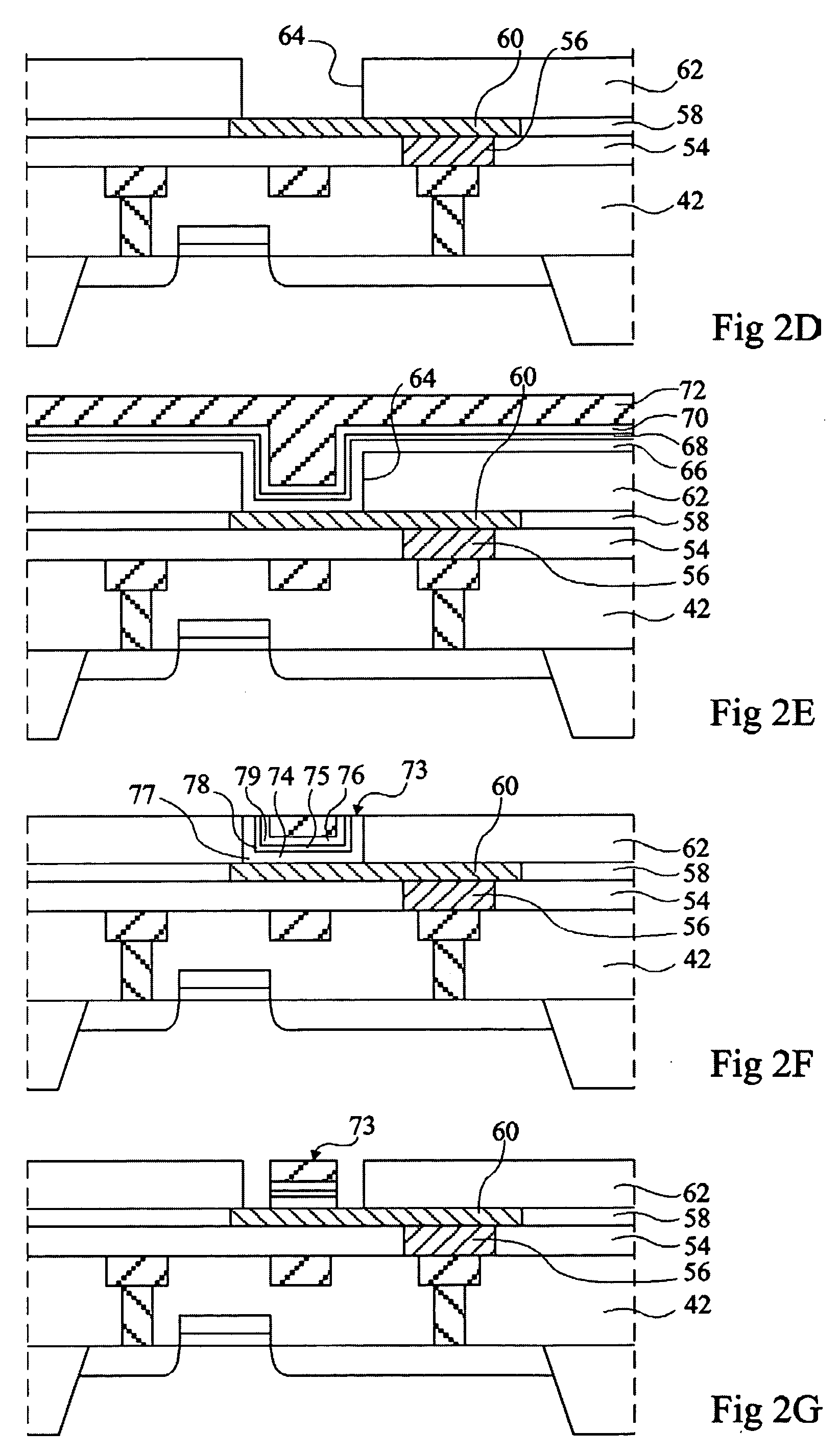
Magnetic Random Access Memory Cells Having Split Subdigit Lines Having Cladding Layers Thereon and Methods of Fabricating the Same
InactiveUS20080160643A1NanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic ramRandom access memory
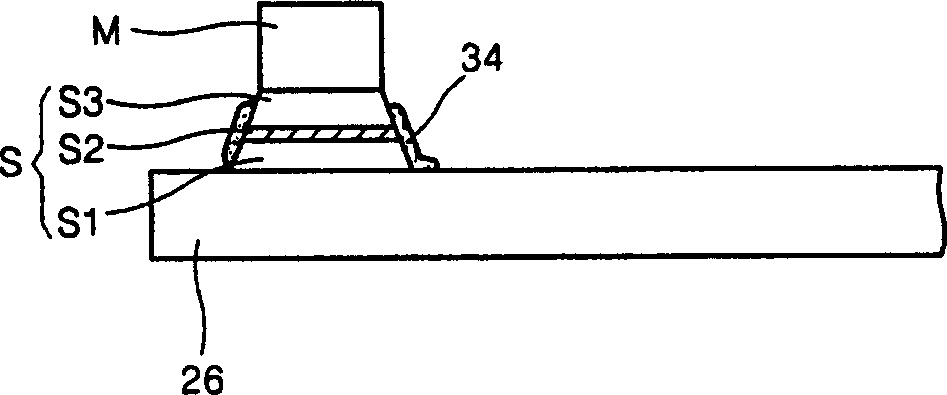
Magnetic RAM cells have split sub-digit lines surrounded by cladding layers and methods of fabricating the same are provided. The magnetic RAM cells include first and second sub-digit lines formed over a semiconductor substrate. Only a bottom surface and an outer sidewall of the first sub-digit line are covered with a first cladding layer pattern. In addition, only a bottom surface and an outer sidewall of the second sub-digit line are covered with a second cladding layer pattern. The outer sidewall of the first sub-digit line is located distal from the second sub-digit line and the outer sidewall of the second sub-digit line is located distal the first sub-digit line. Methods of fabricating the magnetic RAM cells are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
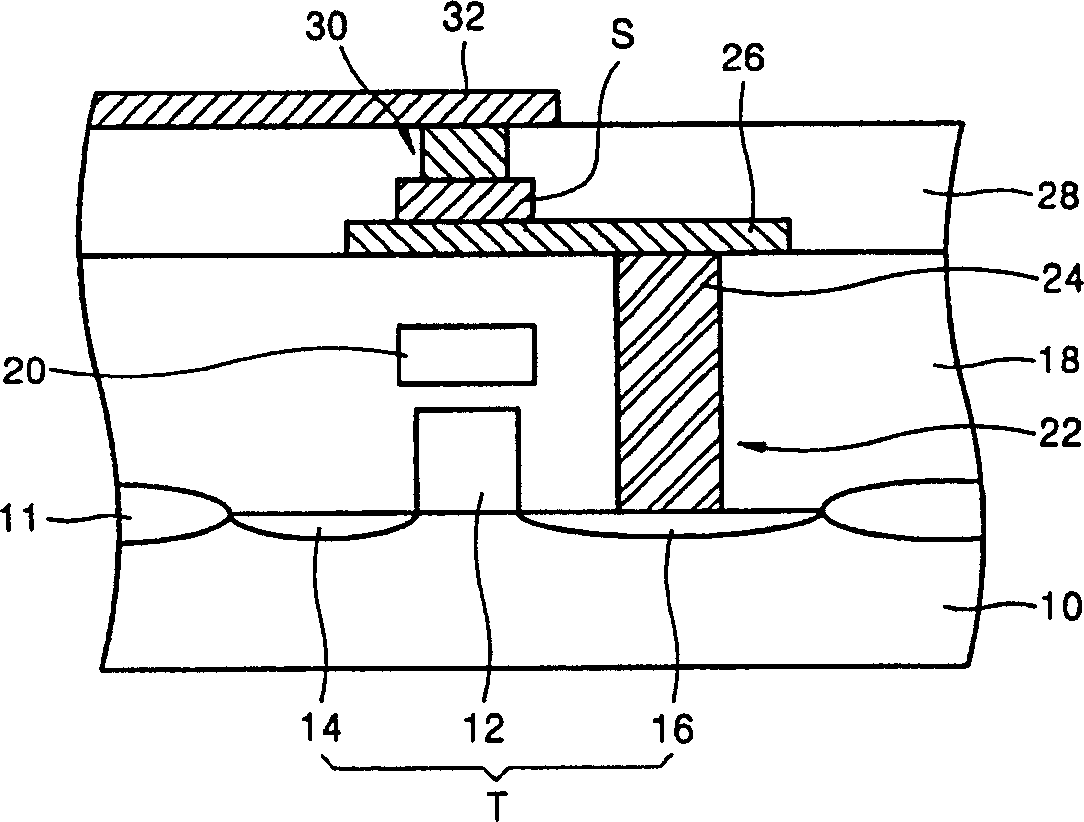
Memory device and method of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20020109167A1Small currentNanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic ramComputer science
A memory device and a fabrication method therefor. In order to improve an operation property of a magnetic RAM (abbreviated as "MRAM') having a higher speed than an SRAM, integration as high as a DRAM, and a property of a nonvolatile memory such as a flash memory, an oxide film is thinly formed on a second word line which is a write line, and an MTJ cell is formed according to a succeeding process. The MRAM is formed by reducing a distance between the write line and the MTJ cell. It is thus possible to perform a write operation with a small current.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
High write selectivity and low power magnetic random access memory and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070223270A1High selectivityReduce power consumptionDigital storageMagnetic ramMagnetic disturbance
A low-power magnetic random access memory (MRAM) with high write selectivity is provided. Write word lines and pillar write word lines covered with a magnetic material are disposed in an zigzag relation, solving the magnetic interference problem generated by cells adjacent to the pillar write word line in the magnetic RAM with the pillar write word line form. According to the disclosed structure, each of the cells has a smaller bit size and a lower write current. This effectively reduces the power consumption of the MRAM.
Owner:HUNG CHIEN CHUNG +3
Spin orbit torque magnetic ram
ActiveUS20190165254A1Low densityMaximize transparencySolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetic ramSpin orbit torque
A spin torque magnetic RAM according to the present invention includes at least one row selection line positioned on a silicon substrate to induce a spin orbit interaction therein; at least one first magnetic pattern positioned on the row selection line; a second magnetic pattern positioned on the first magnetic pattern; a tunnel barrier positioned on the second magnetic pattern; and a third magnetic pattern positioned on the tunnel barrier, wherein the first magnetic pattern is made of a cobalt film, the first magnetic pattern and the second magnetic pattern have a total thickness of 5 nm to form a free layer, and the third magnetic pattern is formed with a pinned layer in which a magnetization direction is fixed.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
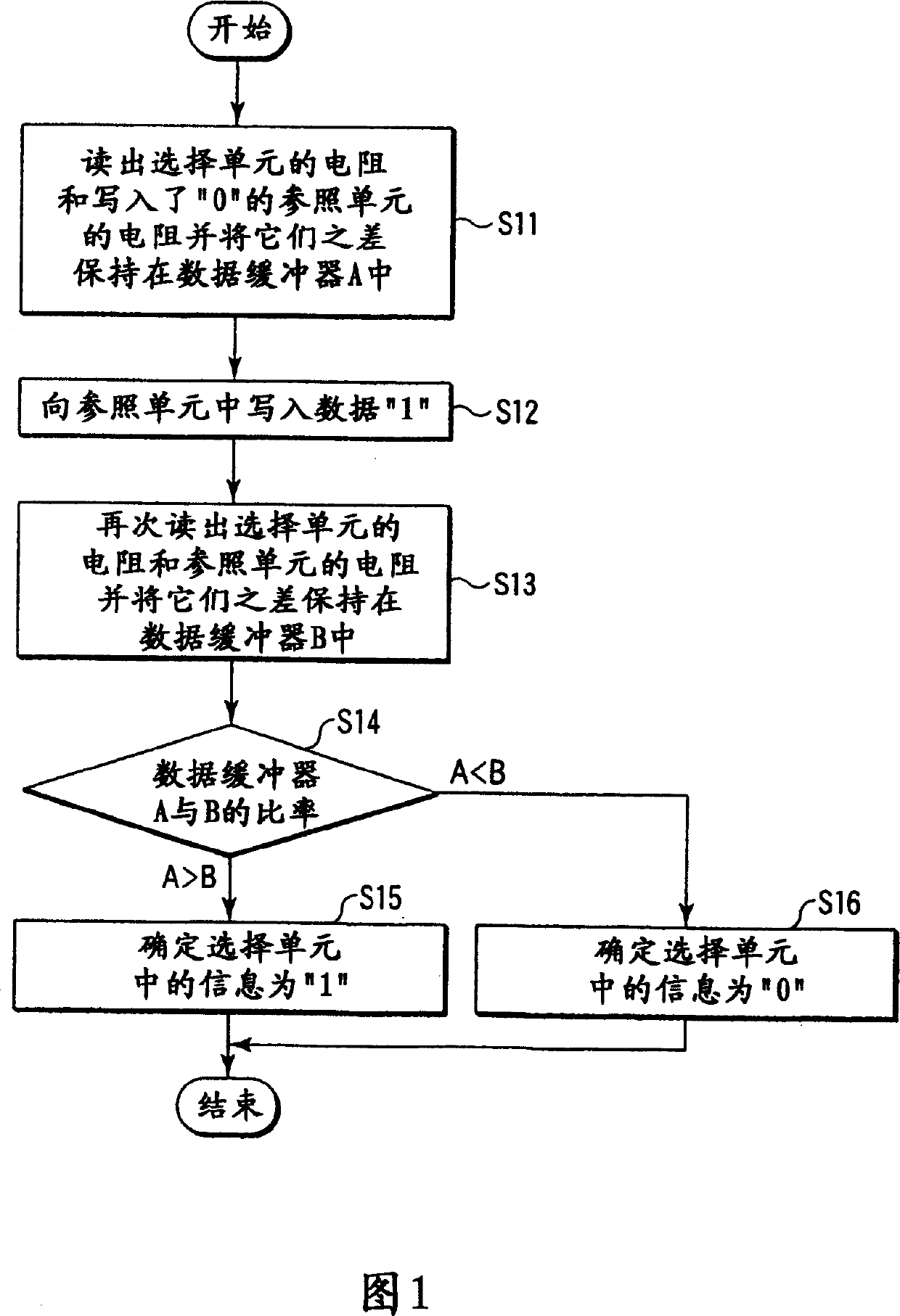
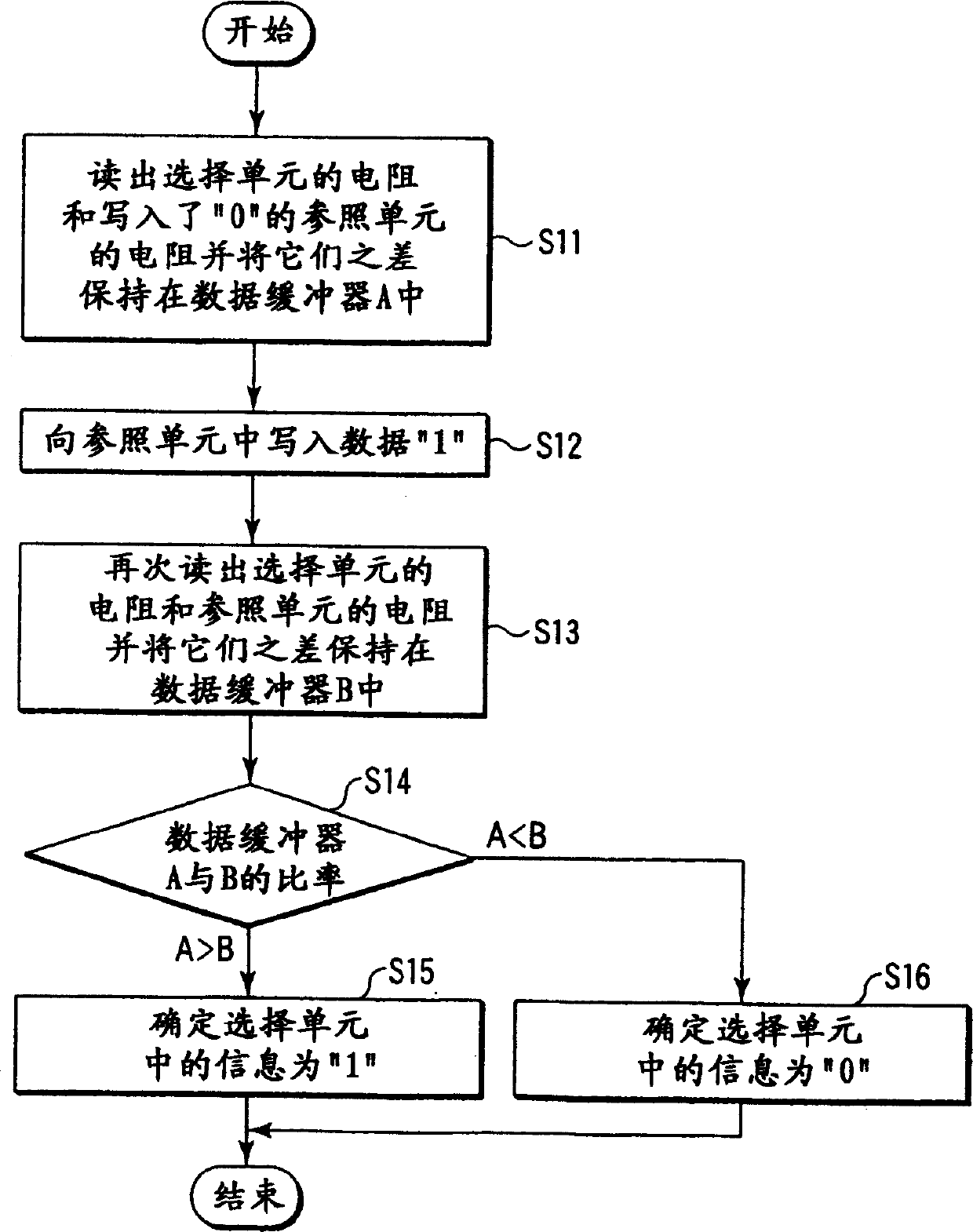
Magnetic RAM and its reading-out method
Reference cells are provided in a memory cell array. When the data is read, the data in the reference cells are inverted, thereby preventing the data in the selected cell from changing. This makes it possible to decrease the number of write operations and realize a high-speed read operation and lower power consumption.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
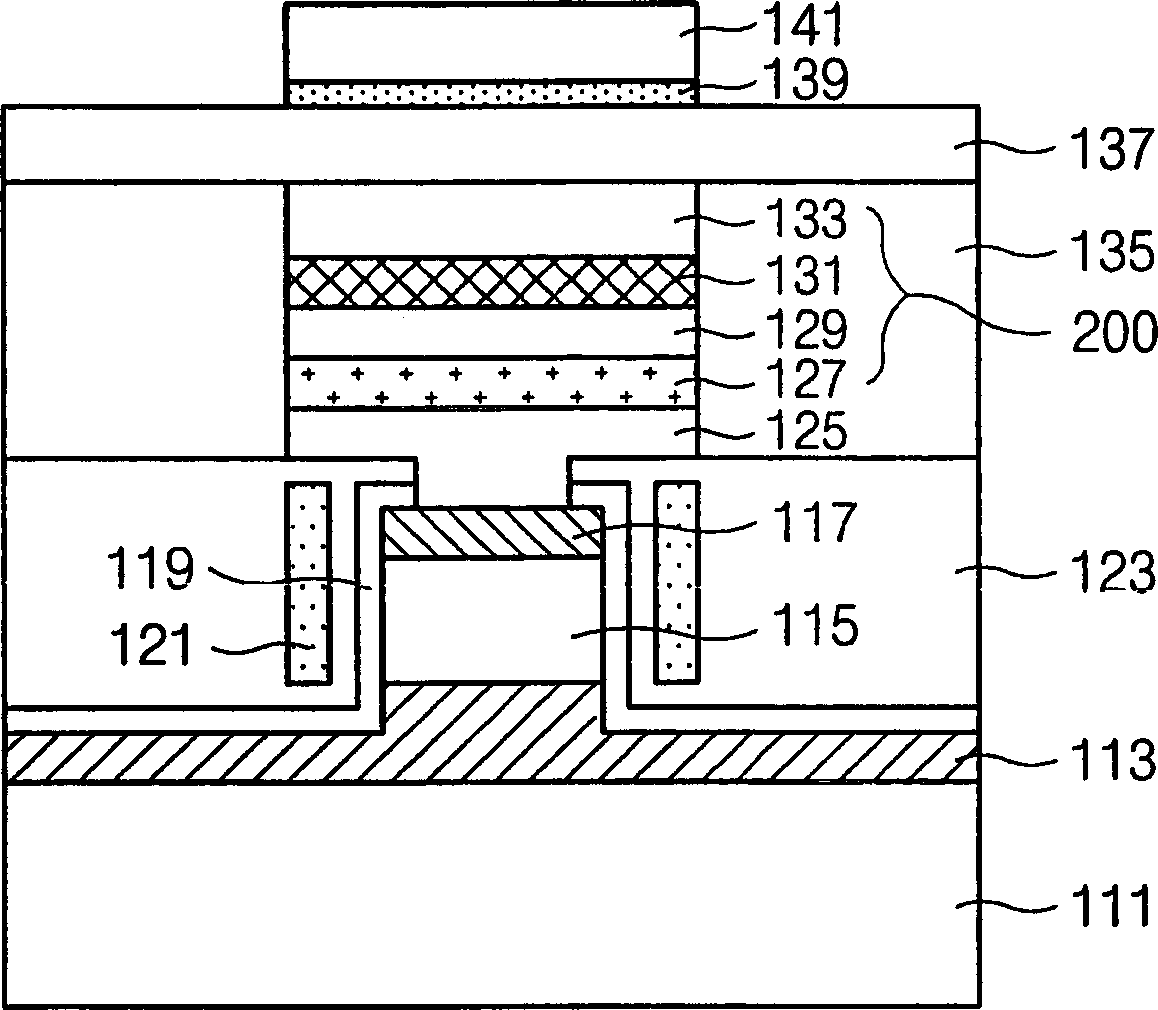
Magnetic random access memory and writing method, reading method and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107946454AAchieve writeReduce write energy consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageMagnetic ramAntiferromagnetic coupling
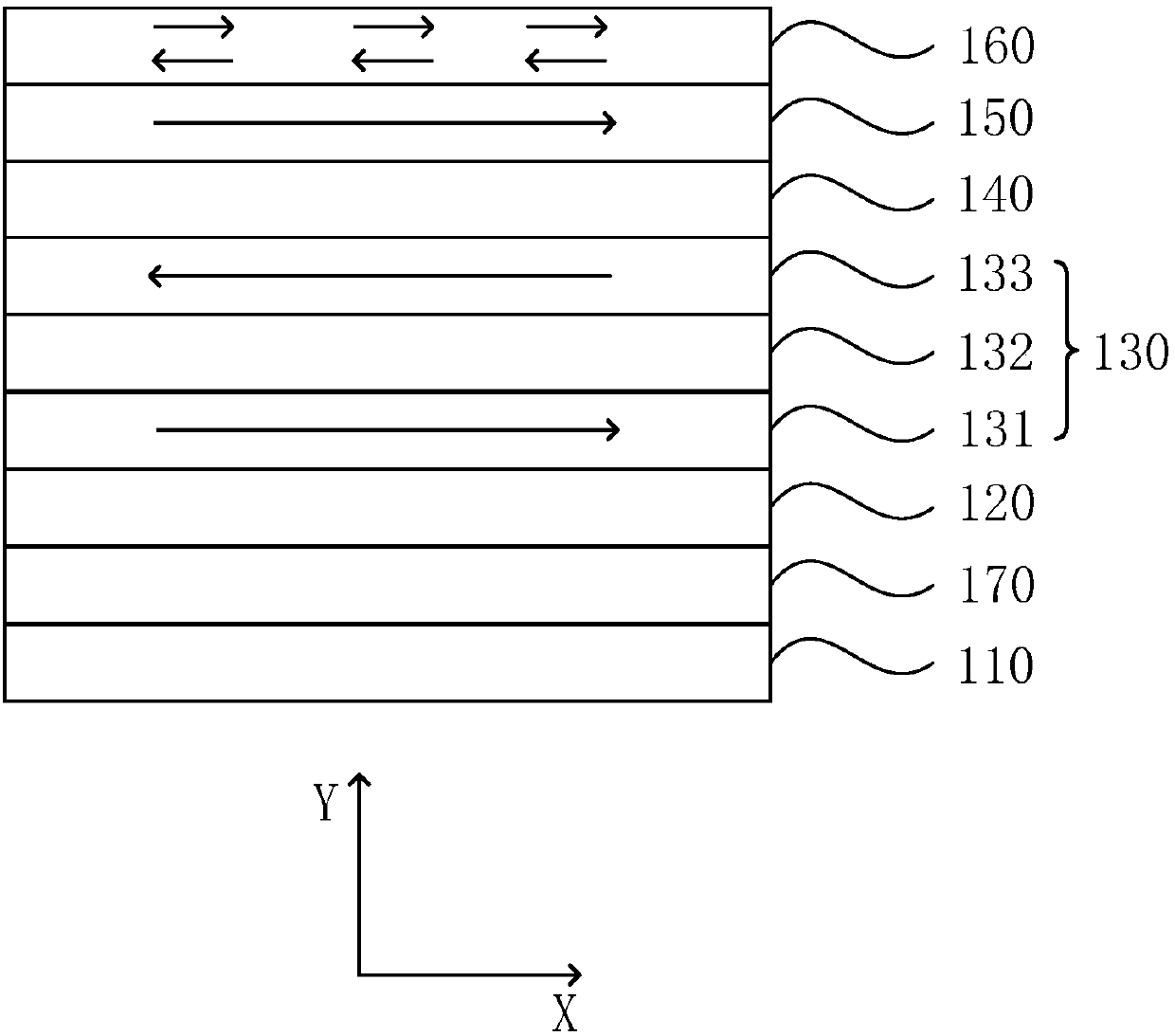
The invention discloses a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) and a writing method, a reading method and a preparation method thereof. The magnetic RAM includes a substrate layer, a ferroelectric layer, a composite anti-ferromagnetic structure, a first isolation layer and a first ferromagnetic layer that are successively stacked. The composite anti-ferromagnetic structure is the free layer of theMRAM. The first ferromagnetic layer is the fixed layer of the MRAM. The ferroelectric layer is subjected to polarization or lattice distortion under the effect of applied voltage in order to change the coupling state of the composite anti-ferromagnetic structure. The first ferromagnetic layer has a constant first magnetic moment direction. The first isolation layer is configured to control the first magnetic moment direction not to be affected by the coupling state of the composite anti-ferromagnetic structure. The MRAM achieves writing by using the transformation of ferromagnetic coupling and anti-ferromagnetic coupling of the composite anti-ferromagnetic structure under the effect of an electric field, and solves a problem that the MRAM has a large size and a low storage density becauseof a large line width during the writing achieved by the induction magnetic field or polarization current of a wire.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
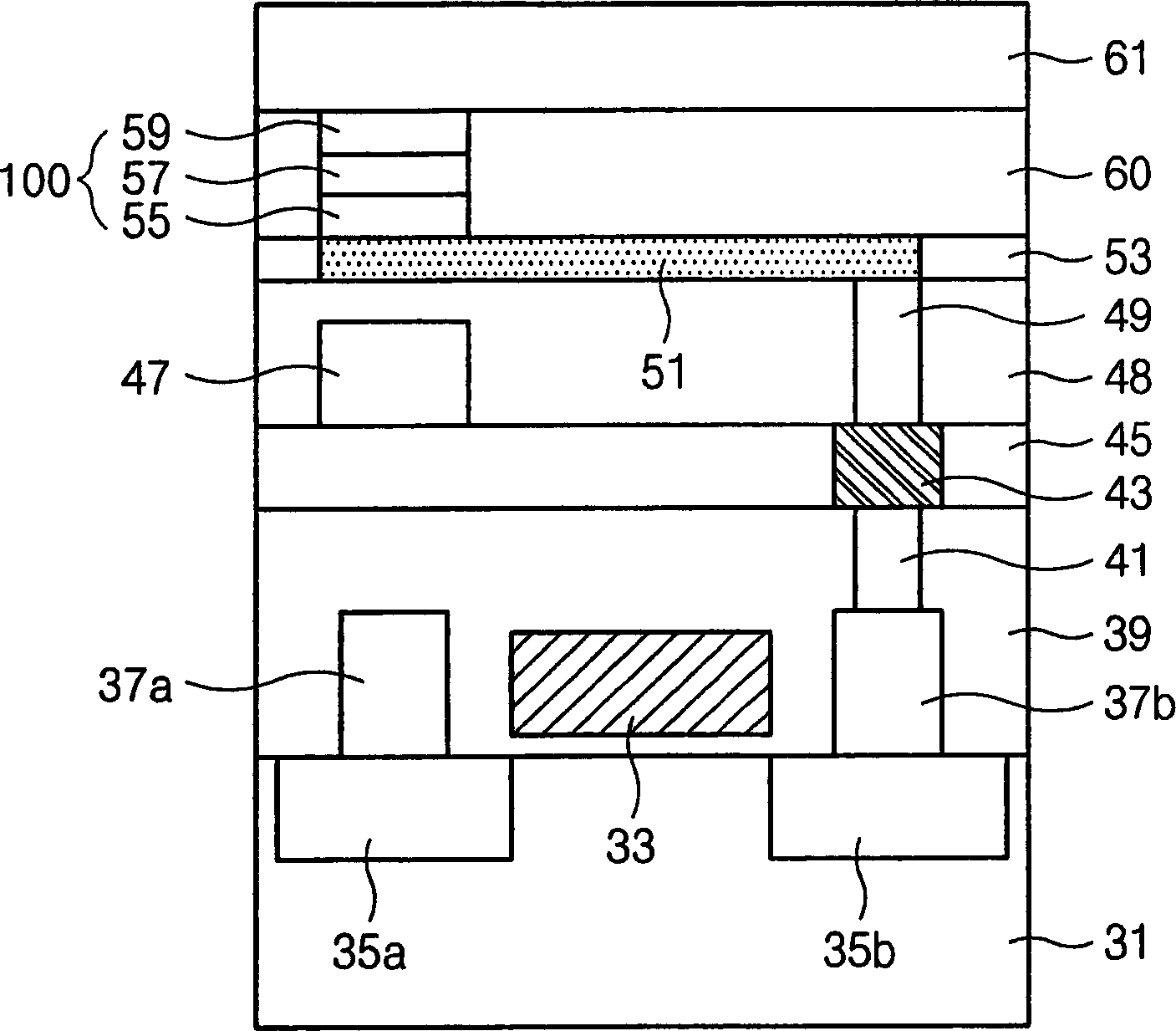
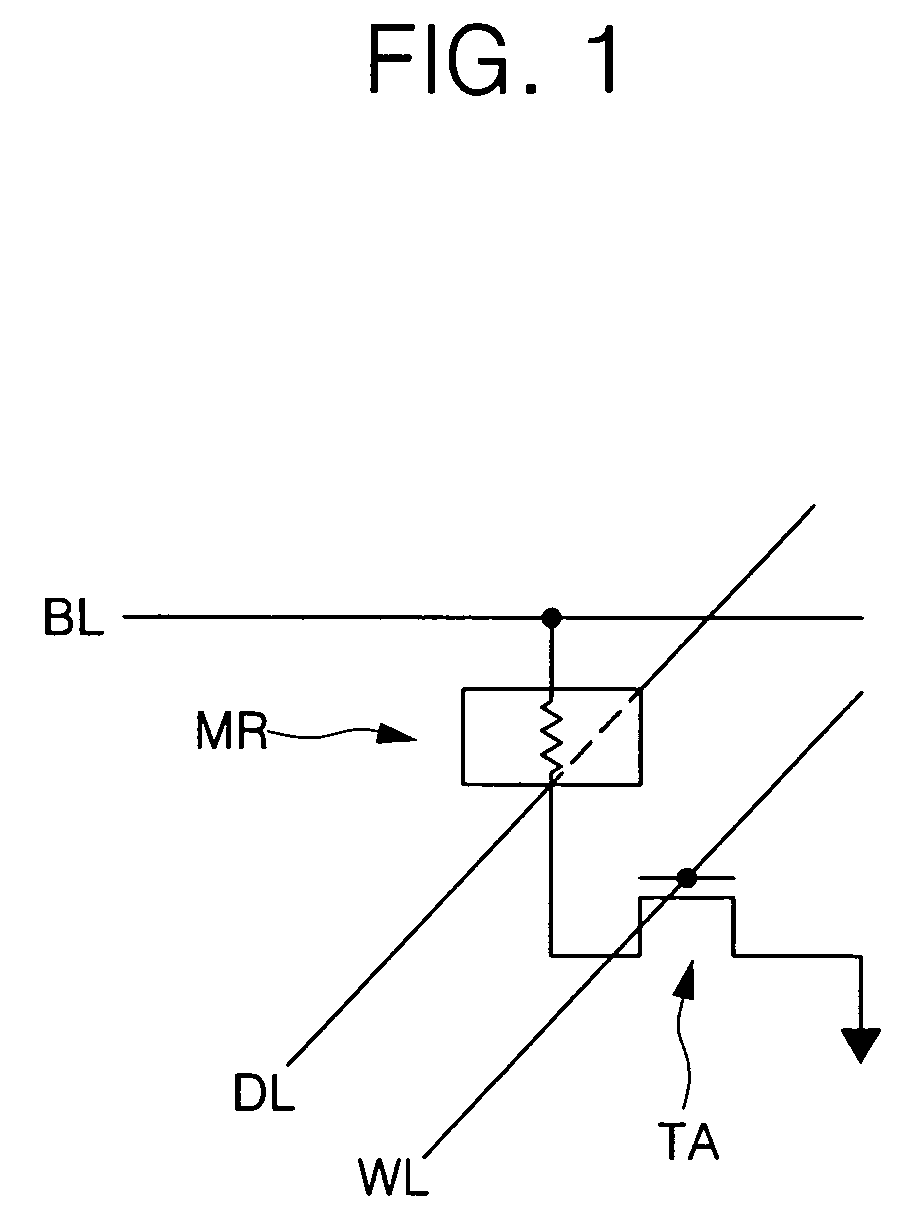
Magnetic RAM
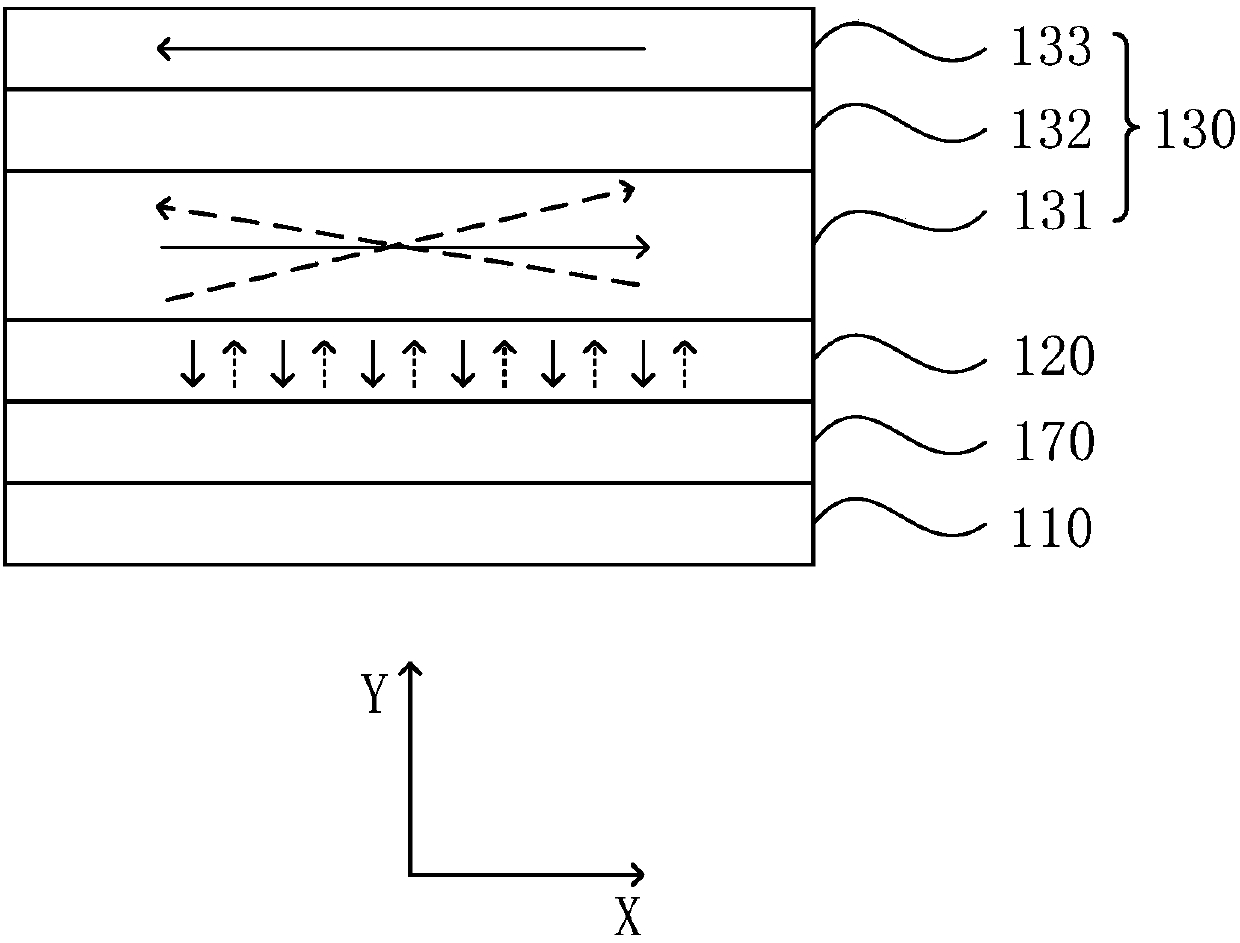
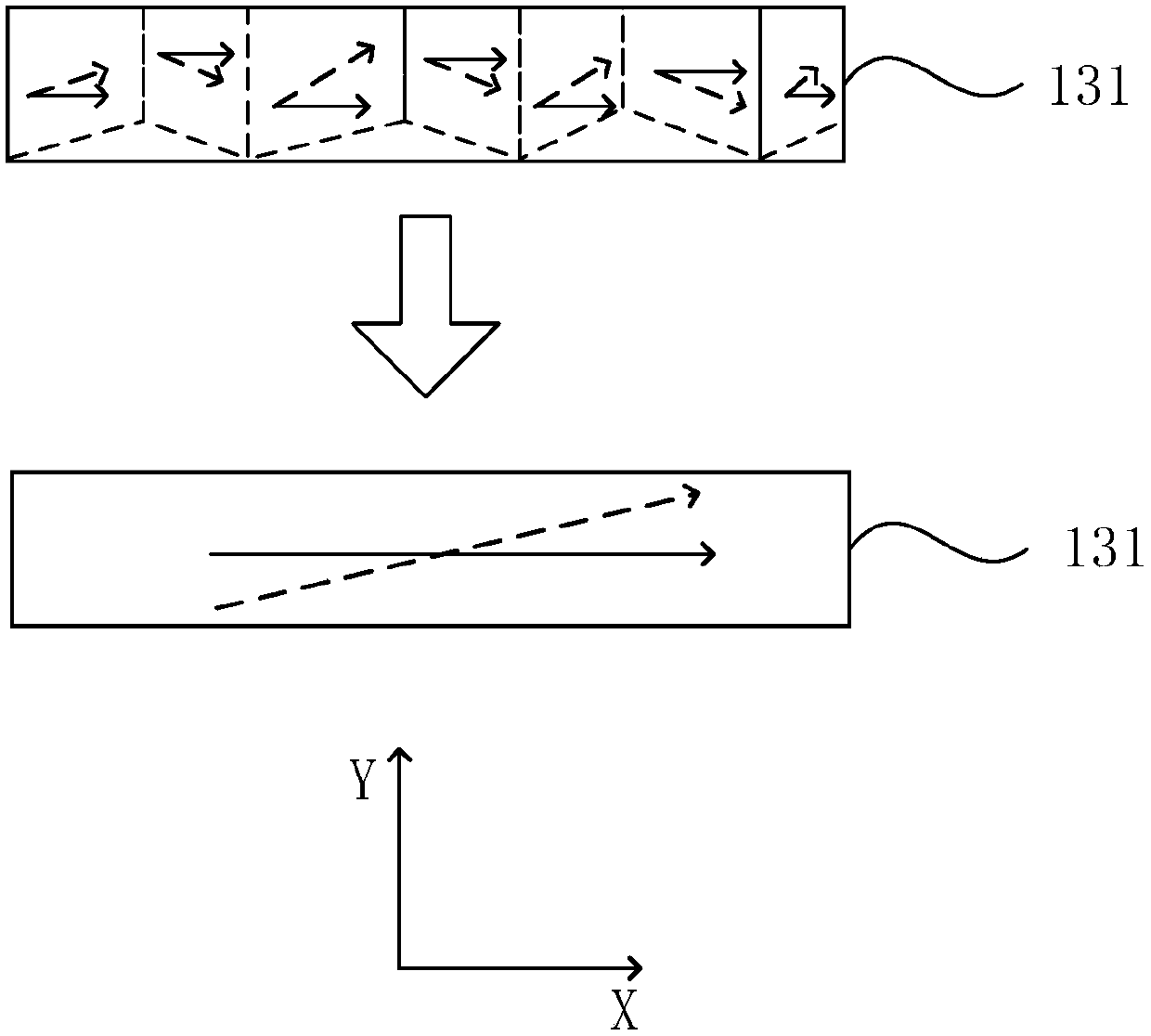
A memory element for a magnetic RAM, contained in a recess of an insulating layer, the recess including a portion with slanted sides extending down to the bottom of the recess, the memory element including a first magnetic layer portion substantially conformally covering the bottom of the recess and the recess portion with slanted sides and in contact, at the level of the bottom of the recess, with a conductive portion, a non-magnetic layer portion substantially conformally covering the first magnetic layer portion and a second magnetic layer portion covering the non-magnetic layer portion.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
Magnetic RAM, its mfg. and driving method
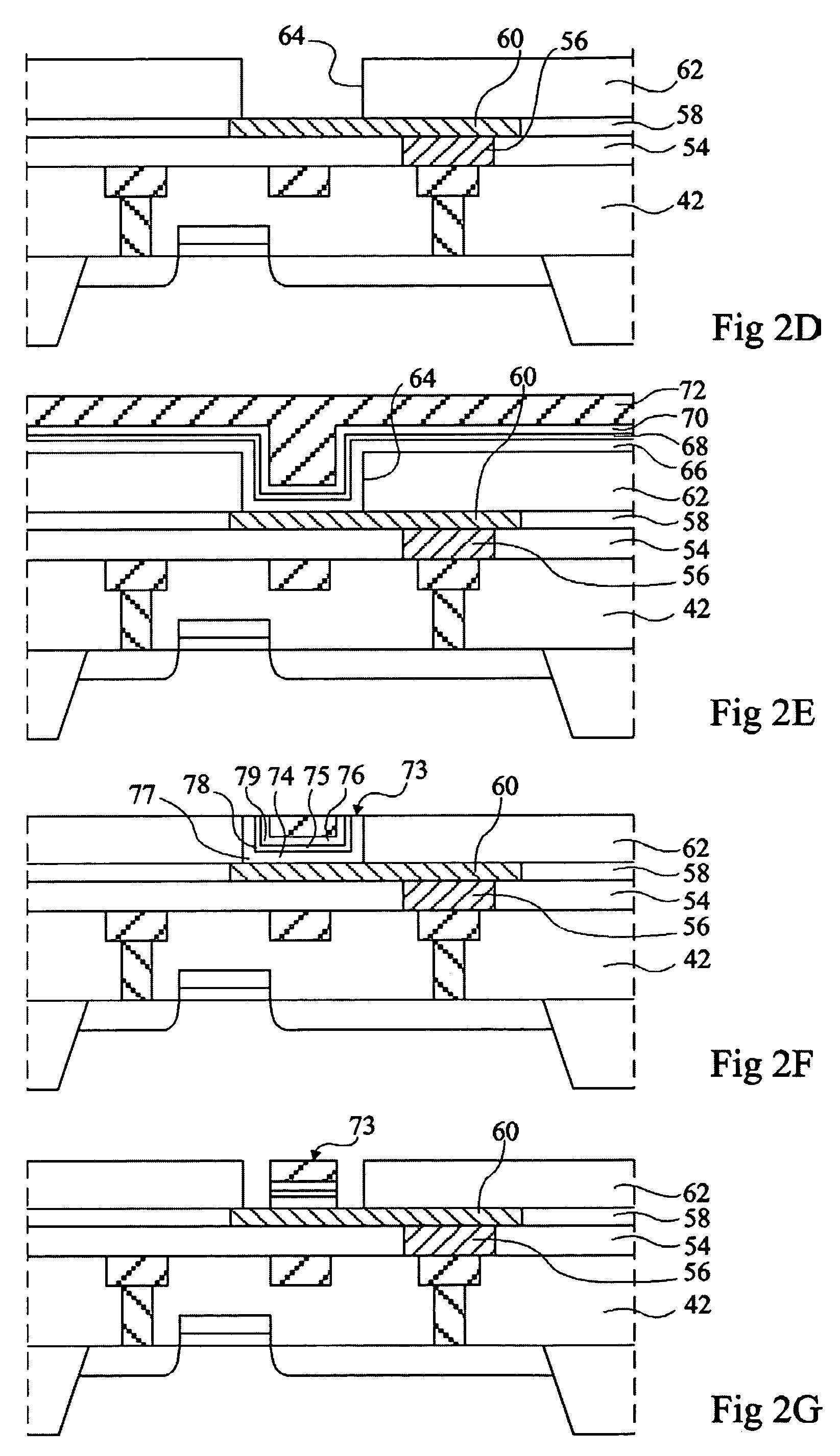
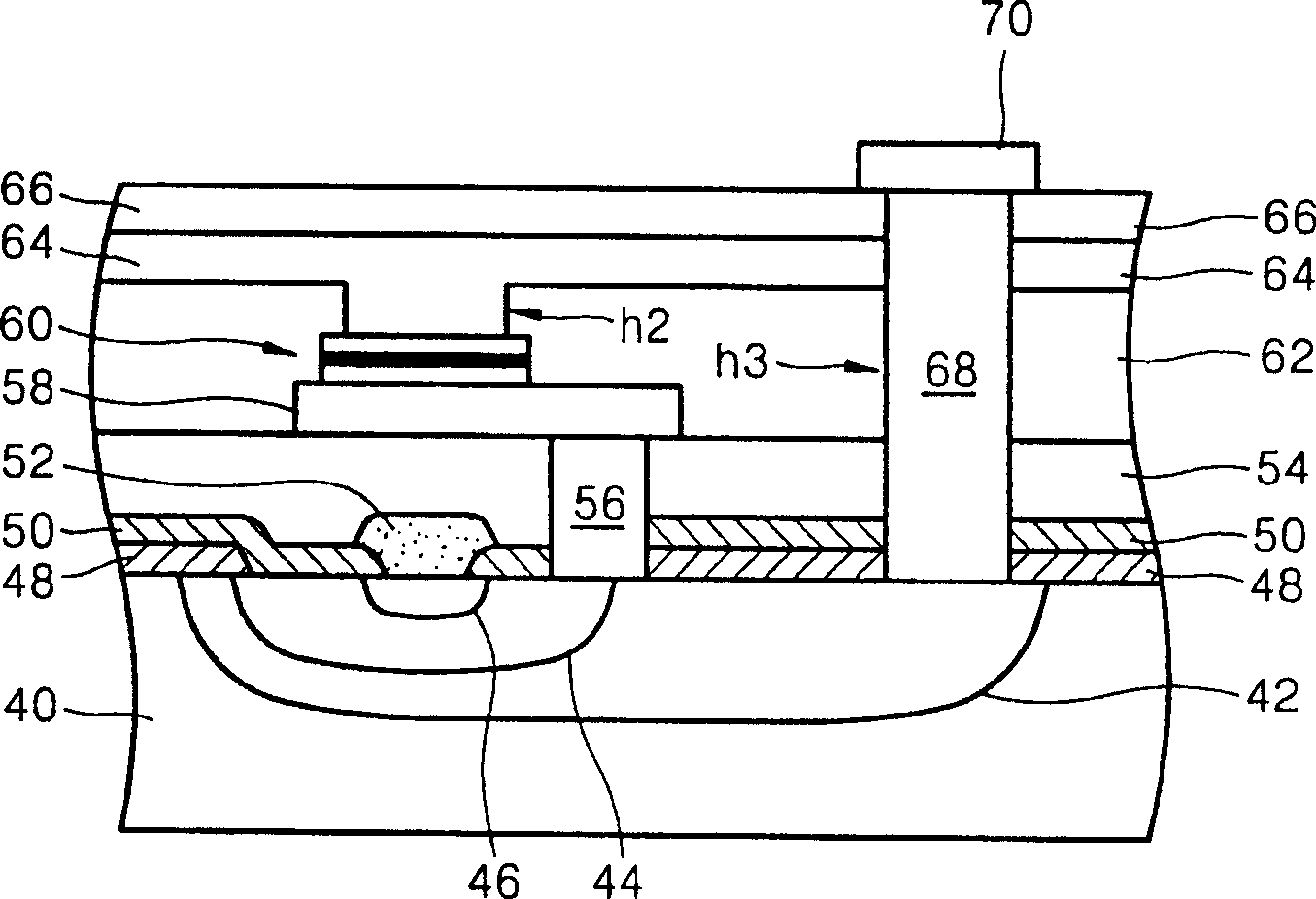
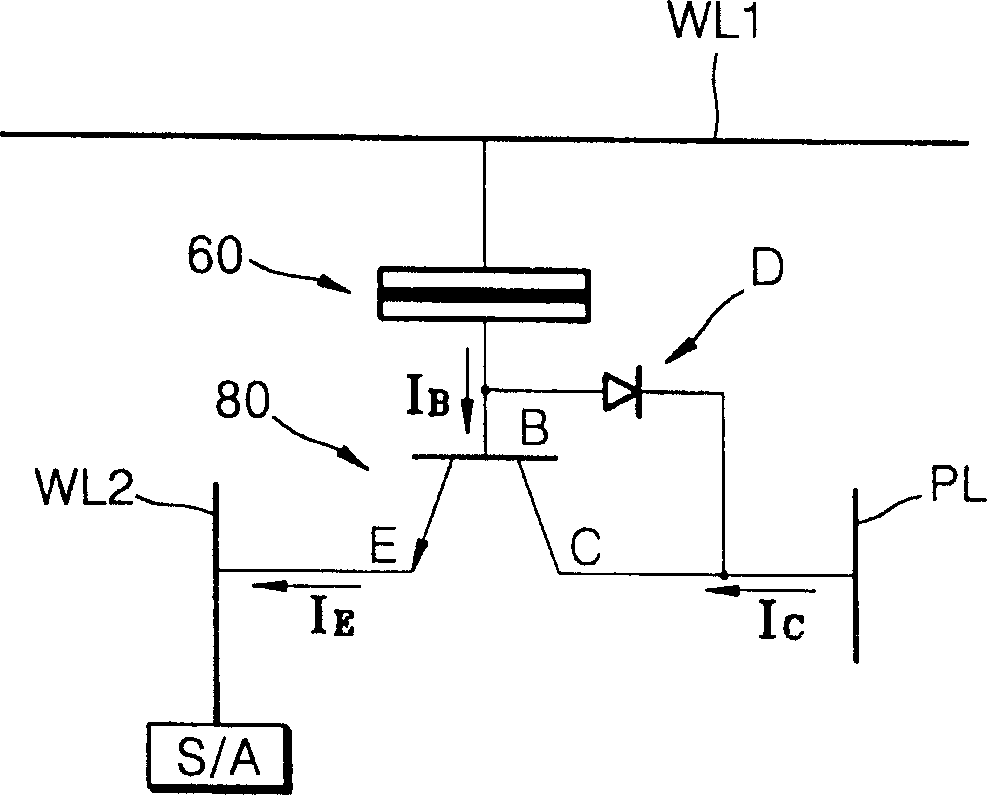
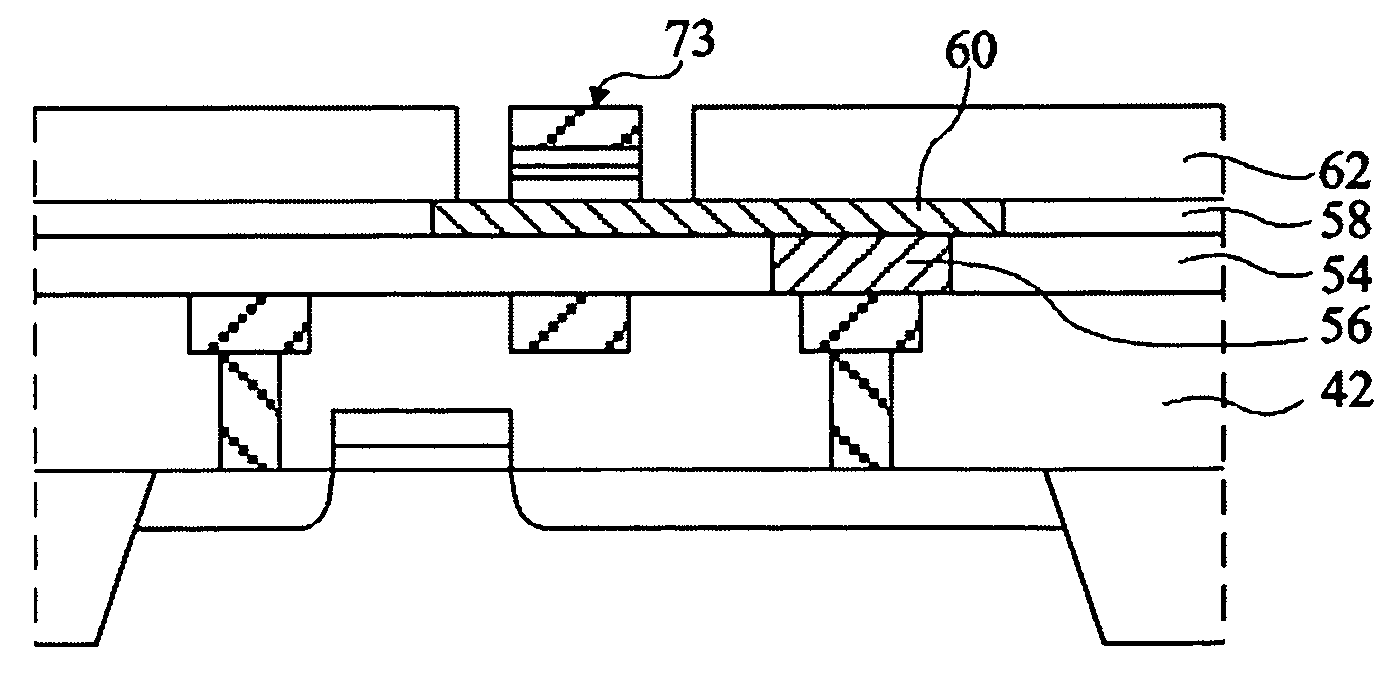
InactiveCN1499519AHighly integratedTransistorNanoinformaticsDielectricElectrical resistance and conductance
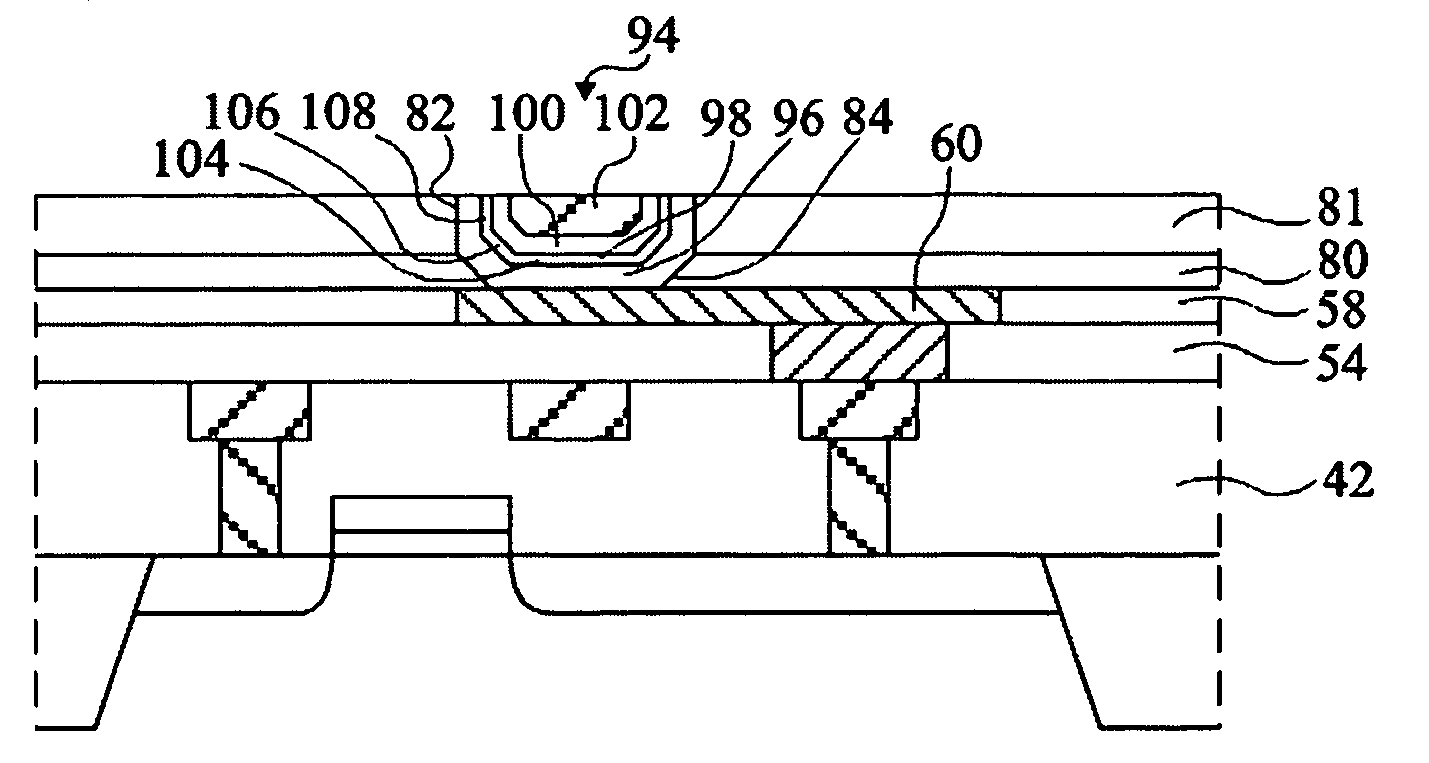
Provided are an MRAM and methods for manufacturing and driving the same. The MRAM includes a bit line coupled to an emitter of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), a magnetic tunneling junction (MTJ) layer coupled to the BJT, a word line coupled to the MTJ layer, a plate line coupled to the BJT so as to be spaced apart from the MTJ layer, and an interlayer dielectric formed between the components. The MTJ layer is coupled to a base and a collector of the BJT, the plate line is coupled to the collector, and an amplifying unit for amplifying a data signal during a read operation of data stored in the MTJ layer is coupled to the bit line. Because the bit line is formed of a metal and the BJT is used, a series resistance effect caused by the resistance of a MOS transistor and the parasitic resistances of other elements can be minimized, thus allowing data to be precisely read out from the MTJ layer. Also, compared to an MRAM with a MOS transistor, the MRAM with the BJT leads to improved integration density and can use an MTJ layer having a low MR ratio.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic RAM
A memory element for a magnetic RAM, contained in a recess of an insulating layer, the recess including a portion with slanted sides extending down to the bottom of the recess, the memory element including a first magnetic layer portion substantially conformally covering the bottom of the recess and the recess portion with slanted sides and in contact, at the level of the bottom of the recess, with a conductive portion, a non-magnetic layer portion substantially conformally covering the first magnetic layer portion and a second magnetic layer portion covering the non-magnetic layer portion.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
Fast and low-power sense amplifier and writing circuit for high-speed MRAM
ActiveUS9672886B2Fast operationMinimizes bit error rateDigital storageMagnetic ramAudio power amplifier
A fast and low-power sense amplifier and writing circuit for high-speed Magnetic RAM (MRAM) which provides the long retention times and endurance of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cells, while providing faster access speeds, verified writes, and an increased sensing margin. A high-speed and low-power pre-read and write sense amplifier (PWSA) provide VCMA effect precessional switching of MTJ cells which include pre-read and comparison steps which reduce power consumption. An embodiment of the PWSA circuit is described with write and pre-charge circuit, S and D latches, comparison circuit, and a differential amplifier and control circuit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Magnetic ram and method of writing and reading data using the magnetic ram
InactiveCN1467744AImprove thermal stabilityImprove coercive forceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic ram
A magnetic RAM (MRAM) using a thermo-magnetic spontaneous Hall effect includes a MOS transistor formed on a substrate; a heating means formed above the MOS transistor and connected to a source region of the MOS transistor; a memory layer having a data write area to which data is written, the data write area being formed on the heating means; a bit line formed on the data write area; an upper insulating film formed on the bit line and the memory layer; and a write line formed on the upper insulating film so that a magnetic field necessary for writing data is generated in at least the data write area of the memory layer. The MRAM writes or reads data using the fact that a spontaneous Hall voltage greatly differs according to the magnetization state of a memory layer, thereby providing the device a high data sensing margin.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
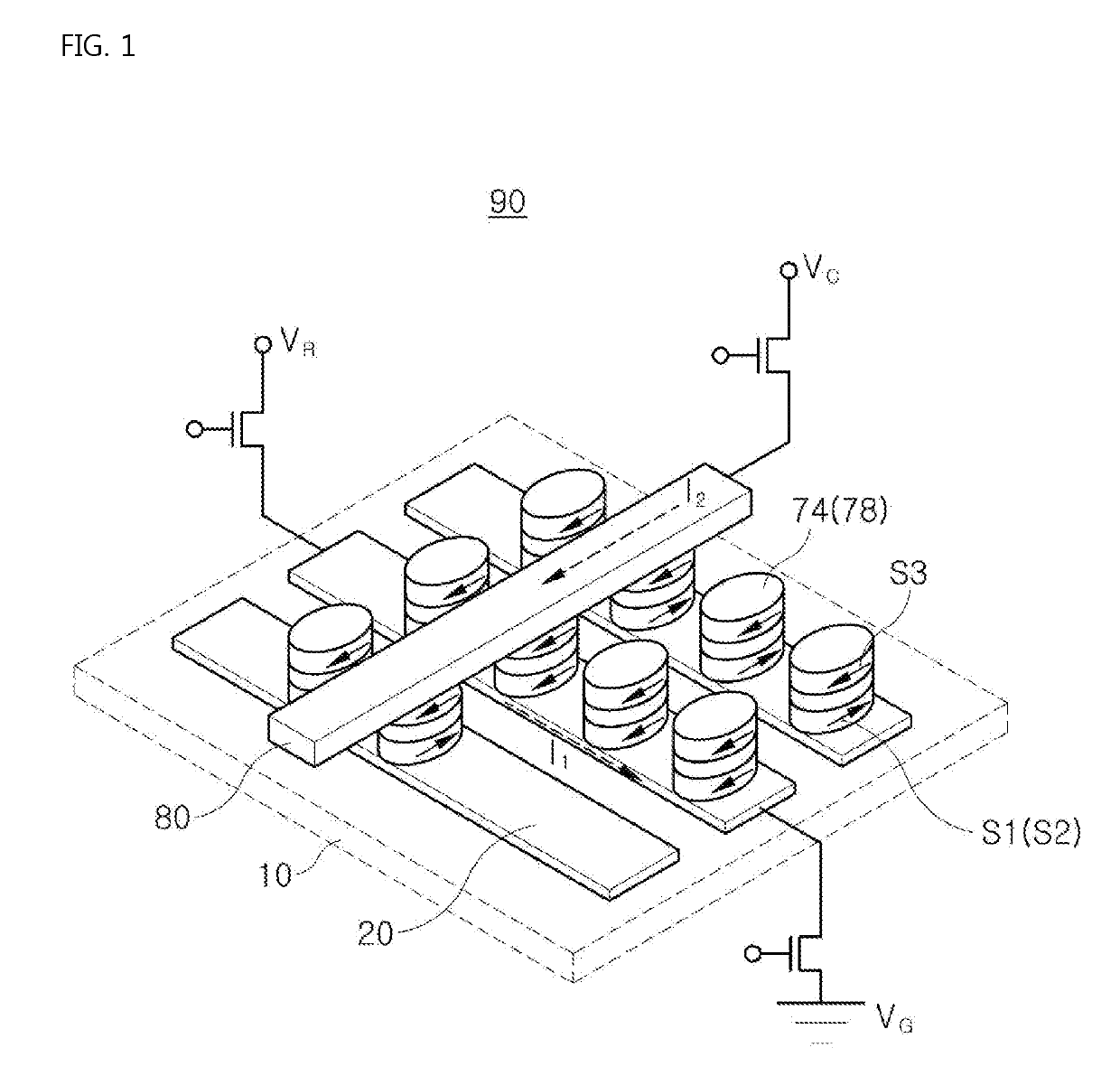
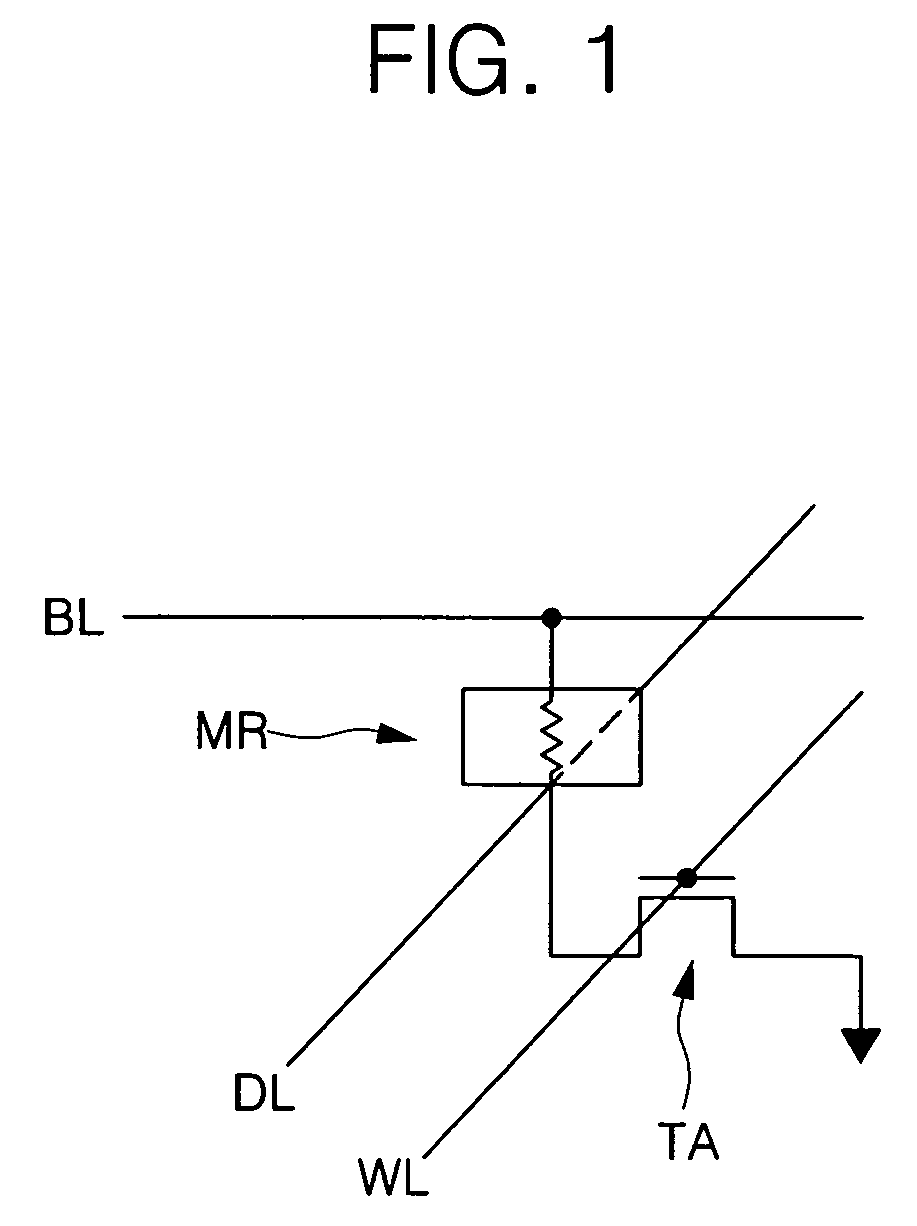
Magnetic RAM using magnetic resistance effect to store information
InactiveCN1534679ALower bit line currentMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesBit lineElectrical resistance and conductance
A memory cell comprises a magneto-resistive element of which electrical resistance value varies with magnetism. A sub-bit line is connected to one end of the memory cell. A main-bit line is connected to the sub-bit line via a first selection circuit. A sense-amplifier is connected to the main-bit line via a second selection circuit. A wiring line is connected to the other end of the memory cell and arranged in a first direction. A first operation circuit is connected to one end of the wiring line via a third selection circuit. A second operation circuit is connected to the other end of the wiring line. A word line passes over an intersection between the memory cell and the wiring line and is arranged in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
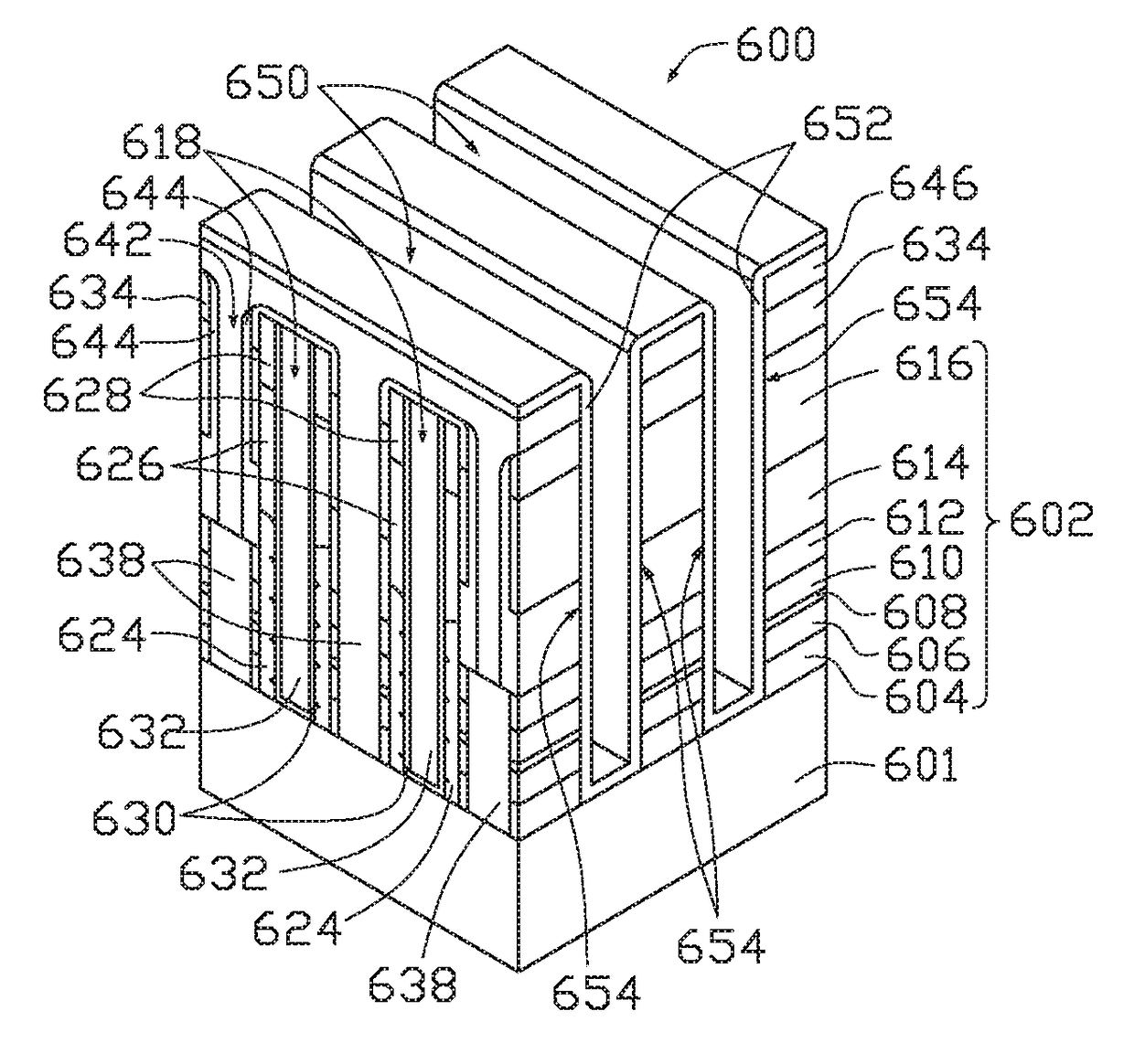
Method to fabricate discreet vertical transistors
ActiveUS20170279043A1Solid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic ram
The present disclosure generally relates to the fabrication of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) select transistors in a vertical orientation such that the transistor pair fits within the footprint of a 4F2 memory cell. The present disclosure further relates to the simultaneous fabrication of a vertical stack of transistors in which each transistor is distinct, as opposed to being serially connected in a NAND-like string. An initial stack of materials is built to include silicon layers to act as source and drain regions as well as to serve as epitaxial growth seed points. As such, the transistor disclosed may be utilized in conjunction with memory elements such as Phase Change, Resistive, or Magnetic RAM memory within array designs, among others.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic tunnel junction structures having bended tips at both ends thereof, magnetic random access memory cells employing the same and photomasks used in formation thereof
Provided are magnetic tunnel junction structures having bended tips at both ends thereof, magnetic RAM cells employing the same and photo masks used in formation thereof. The magnetic tunnel junction structures have a pinned layer pattern, a tunneling insulation layer pattern and a free layer pattern, which are stacked on an integrated circuit substrate. At least the free layer pattern has a main body as well as first and second bended tips each protruded from both ends of the main body when viewed from a plan view.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic RAM and its data reading method
A magnetic random access memory having a memory cell array in which one block is formed from a plurality of magnetoresistive elements using a magnetoresistive effect, and a plurality of blocks are arranged in row and column directions, includes a plurality of first magnetoresistive elements arranged in a first block, a plurality of first word lines each of which is independently connected to one terminal of a corresponding one of the first magnetoresistive elements and runs in the row direction, a first read sub bit line commonly connected to the other terminal of each of the first magnetoresistive elements, a first block select switch whose first current path has one end connected to one end of the first read sub bit line, and a first read main bit line which is connected to the other end of the first current path and runs in the column direction.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic random access storage
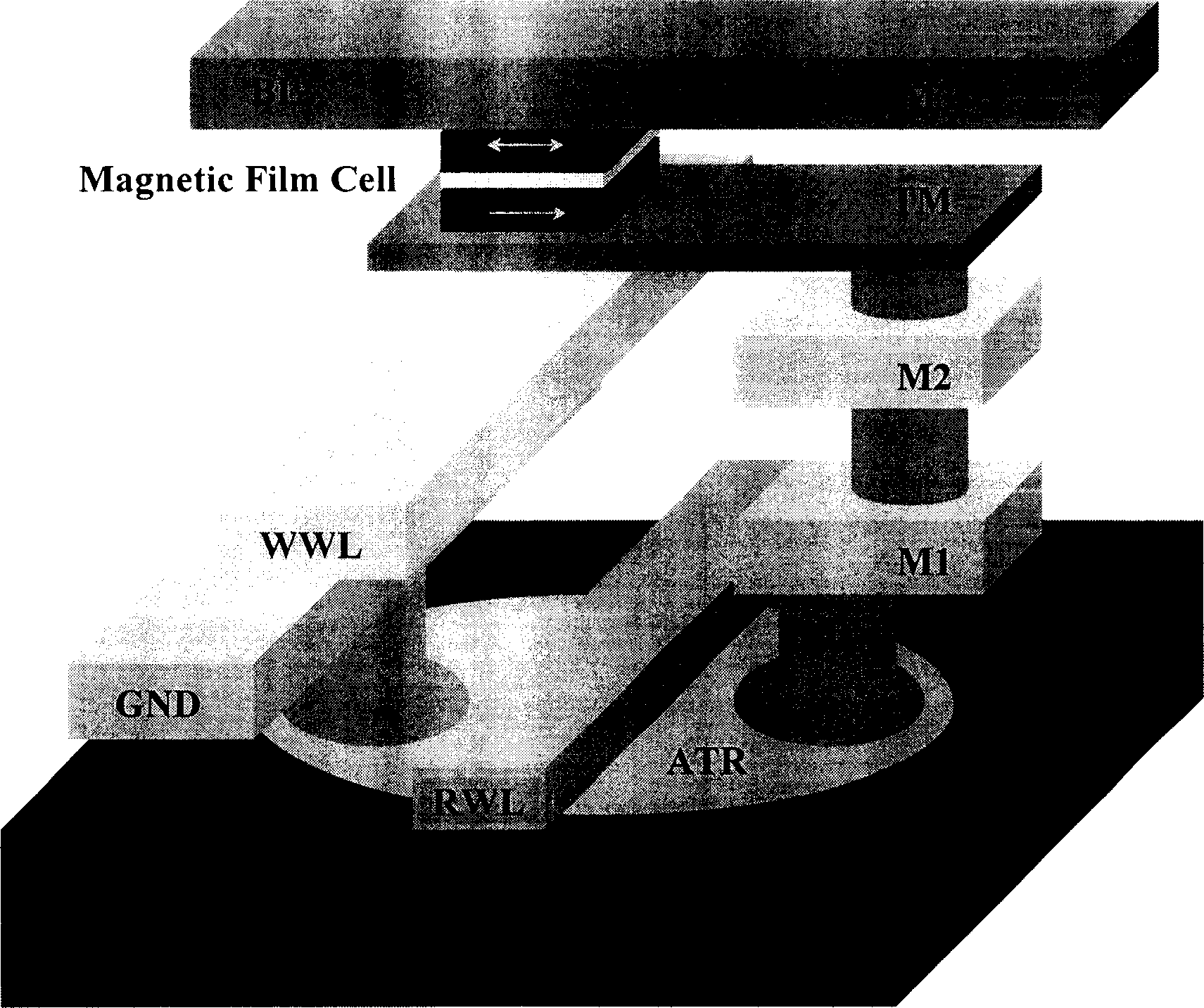
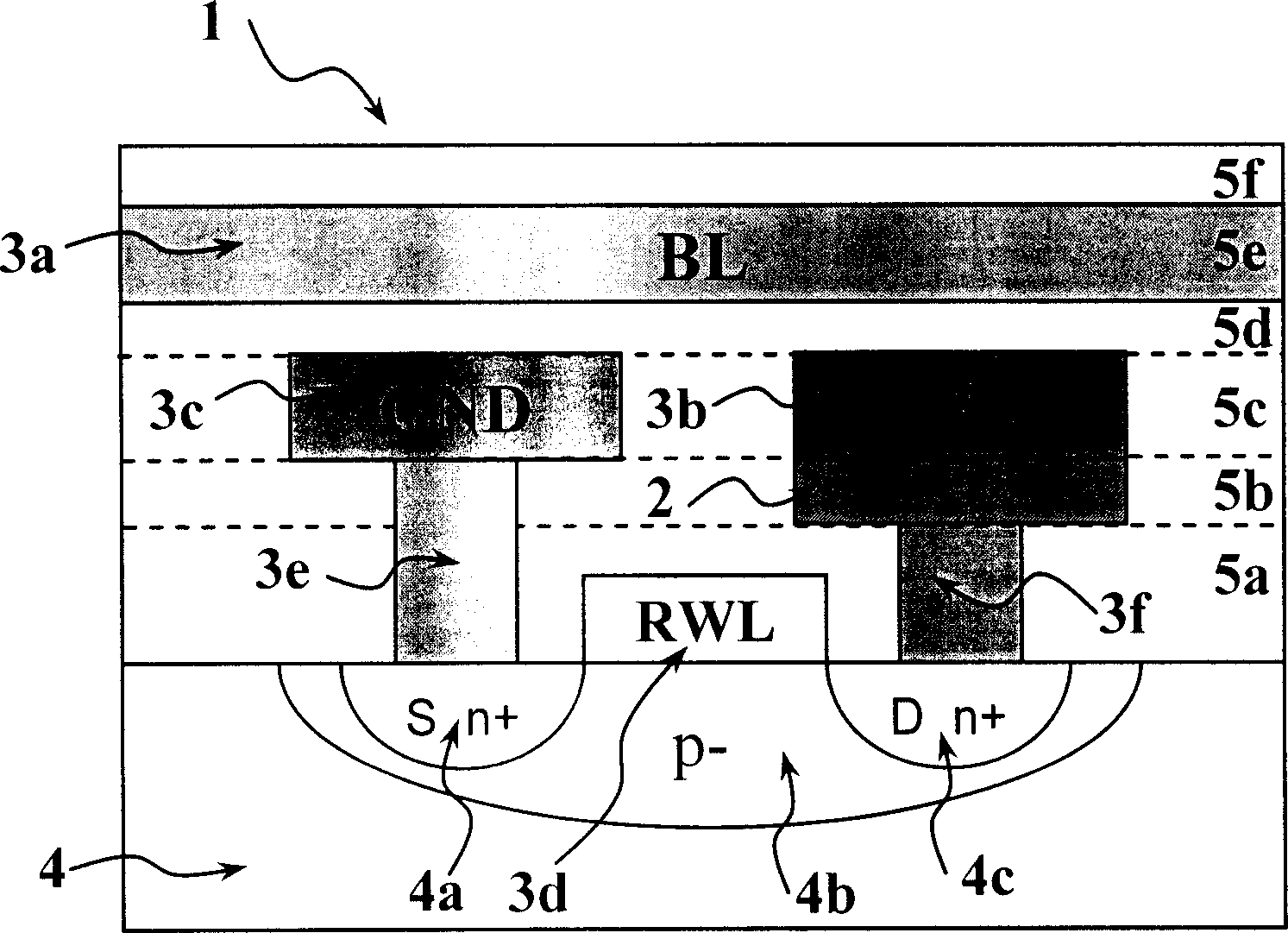
InactiveCN1617257ASimple unit structureReduce the numberGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesBit lineMagnetic ram
The present invention discloses a kind of magnetic RAM (MRAM). The MRAM unit has bit line BL and word write line WWL in the same side of magnetic film memory unit, and the magnetic film memory unit is connected to the drain of the transistor ART via the contact hole. MRAM unit has ground line GND and the word write line WWL configured in the identical metal wiring layer. This structure has the advantages of reduced metal wire layers and contact holes, simplified technological process, lowered manufacture cost and raised MRAM integration level.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic RAM
A memory element for a magnetic RAM, having a first magnetic portion in a first recess of a first insulating layer; and a non-magnetic portion and a second magnetic portion in a second recess of a second insulating layer covering the first insulating layer, the second recess exposing the first magnetic portion and a portion of the first insulating layer around the first magnetic portion, the non-magnetic portion being interposed between the first and second magnetic portions.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
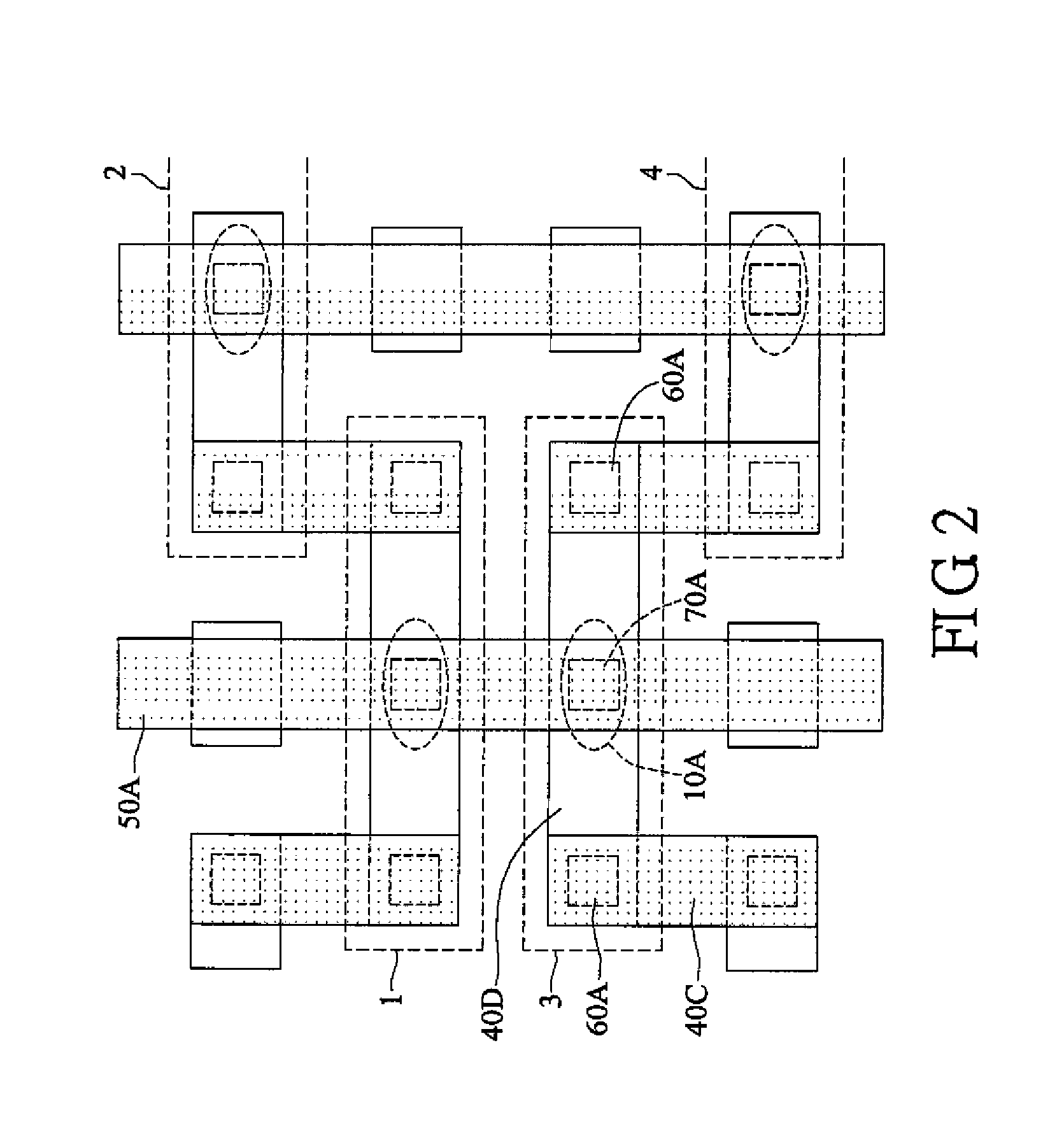
Semiconductor memory device and magnetic ram device
ActiveCN1988159AExclusion of migrationImproved High Current Interconnect StructuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh current densityMagnetic ram
The invention relates to a semiconductor memory device which is programmed by dualism of carrying characteristic of current passed through an adjacent memory cell. The semiconductor memory device includes a programmable memory cell and at least two current carrying structures. Wherein, at least one of the current carrying structures has a segmented current carrying structure comprising a plurality of first segments positioned on a first plane, the plurality of first segments is coupled with a plurality of second segments positioned on a second plane, and widths of the second segments are larger than the widths of the first segments. The semiconductor memory device of the invention improve a high current interconnection structure, eliminates an electron shift effect due to a high current density so as to enhance reliability.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com