Magnetic RAM and its reading-out method
A technology of random access memory and memory unit, which is applied in the direction of static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
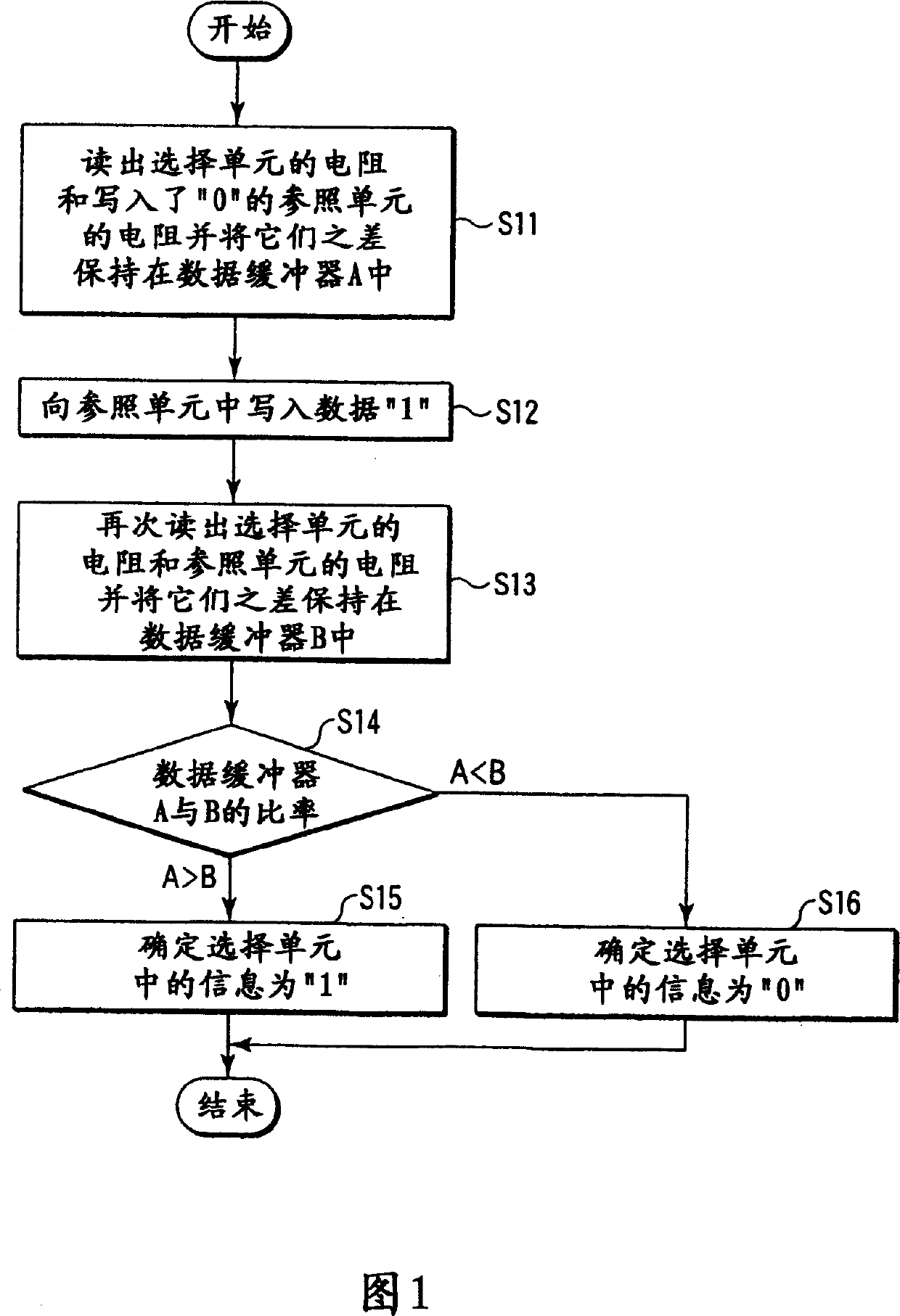
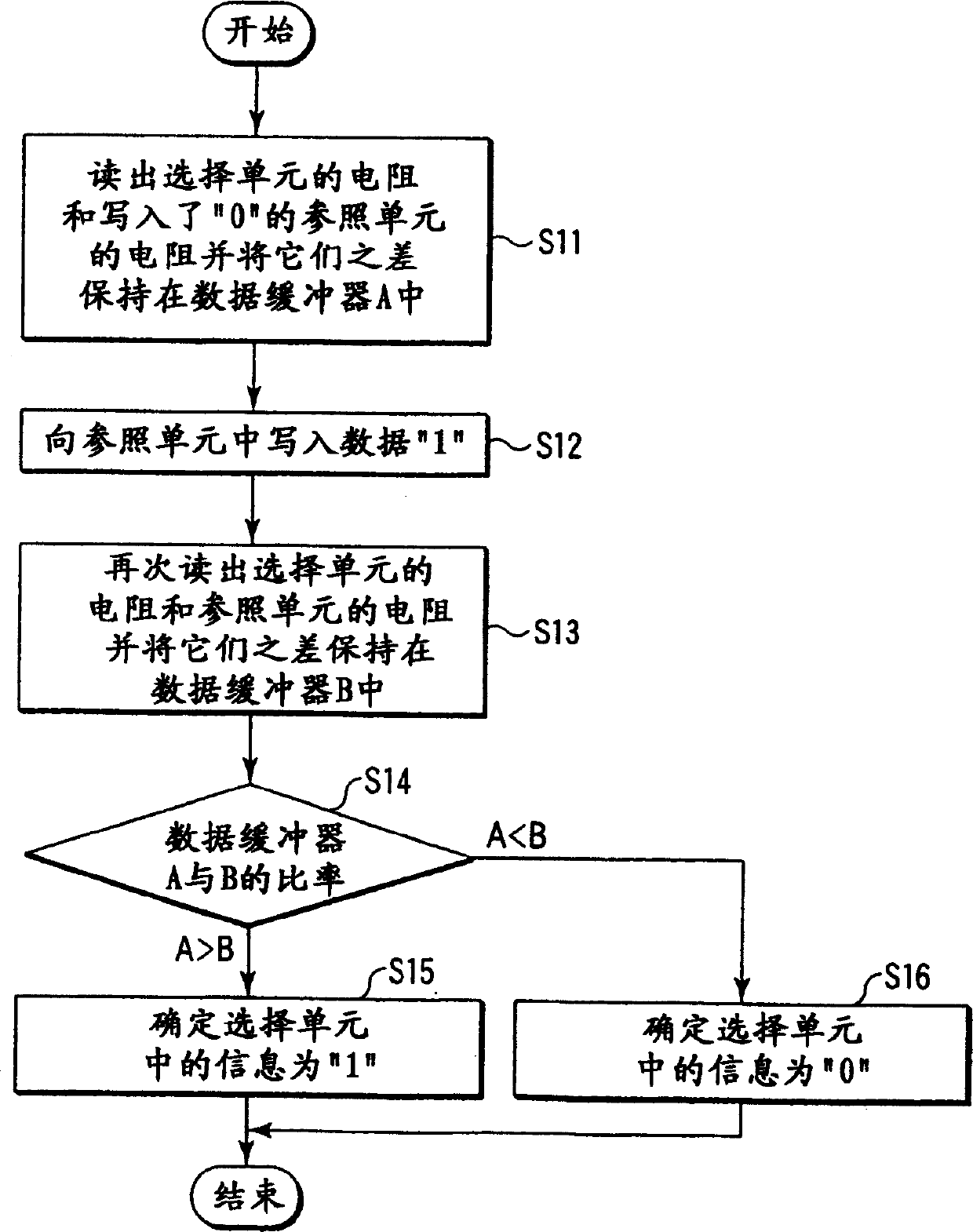
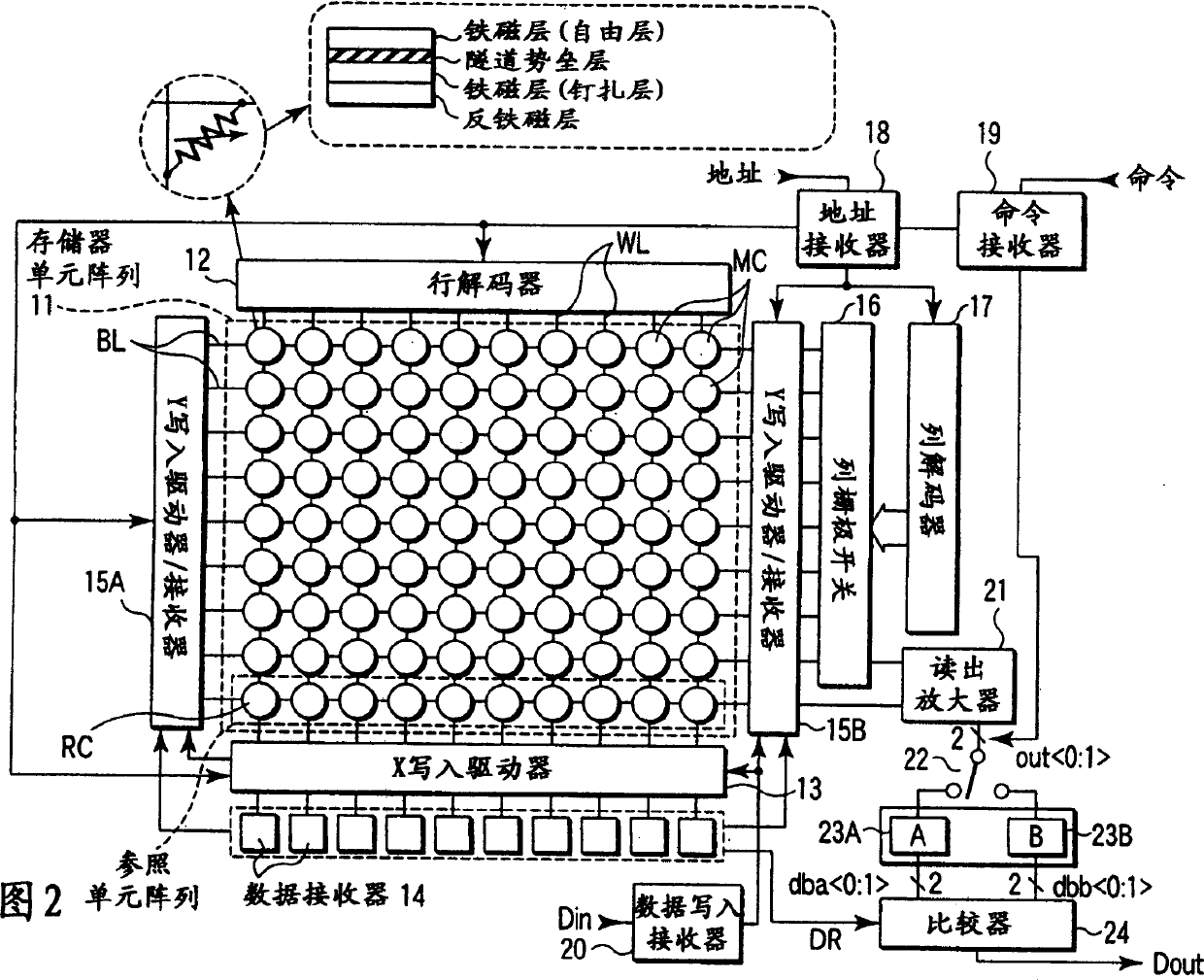
[0038] FIG. 2 shows an MRAM according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In the memory cell array 11, a plurality of memory cells MC having, for example, TMR as a basic element are arranged in a matrix. These memory cells MC are connected to word line WL and bit line BL, respectively. One end of each word line WL is connected to the row decoder 12 , and the other end of each word line WL is connected to the X write driver 13 . The X write driver 13 generates a current magnetic field in the X-axis direction by the current flowing in the word line WL.
[0039] For example, a column closest to the X write driver 13 in the memory cell array 11 is used as a reference cell RC that plays an important role in realizing non-destructive reading. These reference cells RC are connected to dedicated bit lines.
[0040] The same number of reference cell data registers 14 as the number of reference cells RC are arranged in the X write driver 13 . These data registers 14 hold...
no. 2 example
[0073] Fig. 13 shows a block diagram of the MRAM of the second embodiment. In FIG. 13, the same parts as those in FIG. 2 have the same symbols. The second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the structure of a memory cell array using TMR. That is, in the memory cell array 11 of the first embodiment, the memory cells MC and the reference cells RC are arranged at all intersections of the word lines WL and the bit lines BL, and bit lines dedicated to the reference cells RC are arranged in the memory cell array 11. It is located adjacent to the X write driver 13.
[0074] In contrast, in the second embodiment, as shown in FIG. 13 , memory cells MC and reference cells RC are arranged only in half of the intersections of word lines WL and bit lines BL. Reference cells RCA, RCB are arranged in the row direction, and word lines WL dedicated to reference cells RC are arranged at both ends of memory cell array 11 adjacent to Y write driver / receiver 15A, 15B.
[0075] Memo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com