Magnetic RAM and its data reading method
A memory, random access technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problem of impossible to fully improve the integration density of MTJ components, increase in chip size, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0121] 1. Outline of the present invention
[0122] An overview of a magnetic random access memory according to an embodiment of the present invention is provided below.
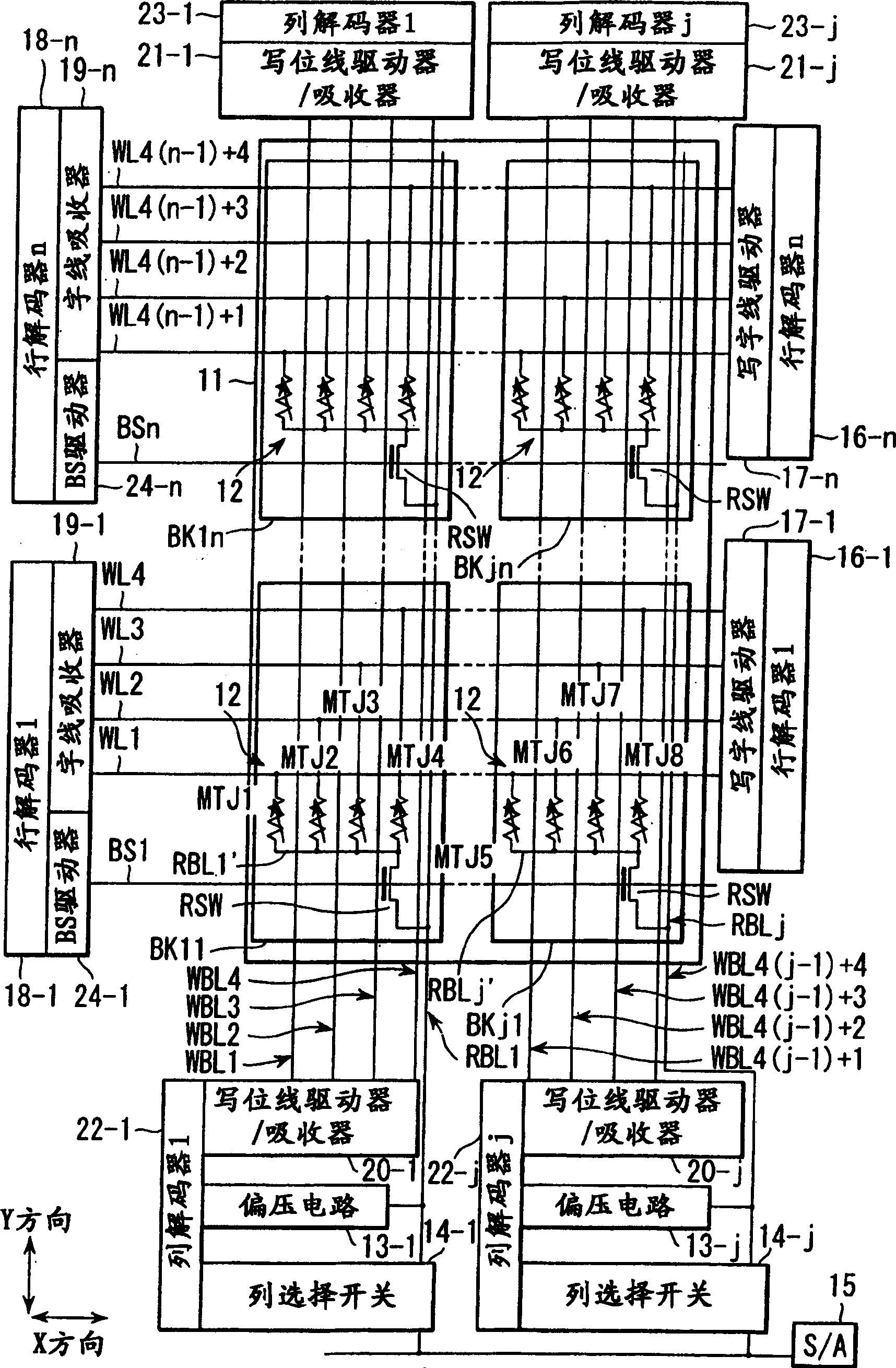
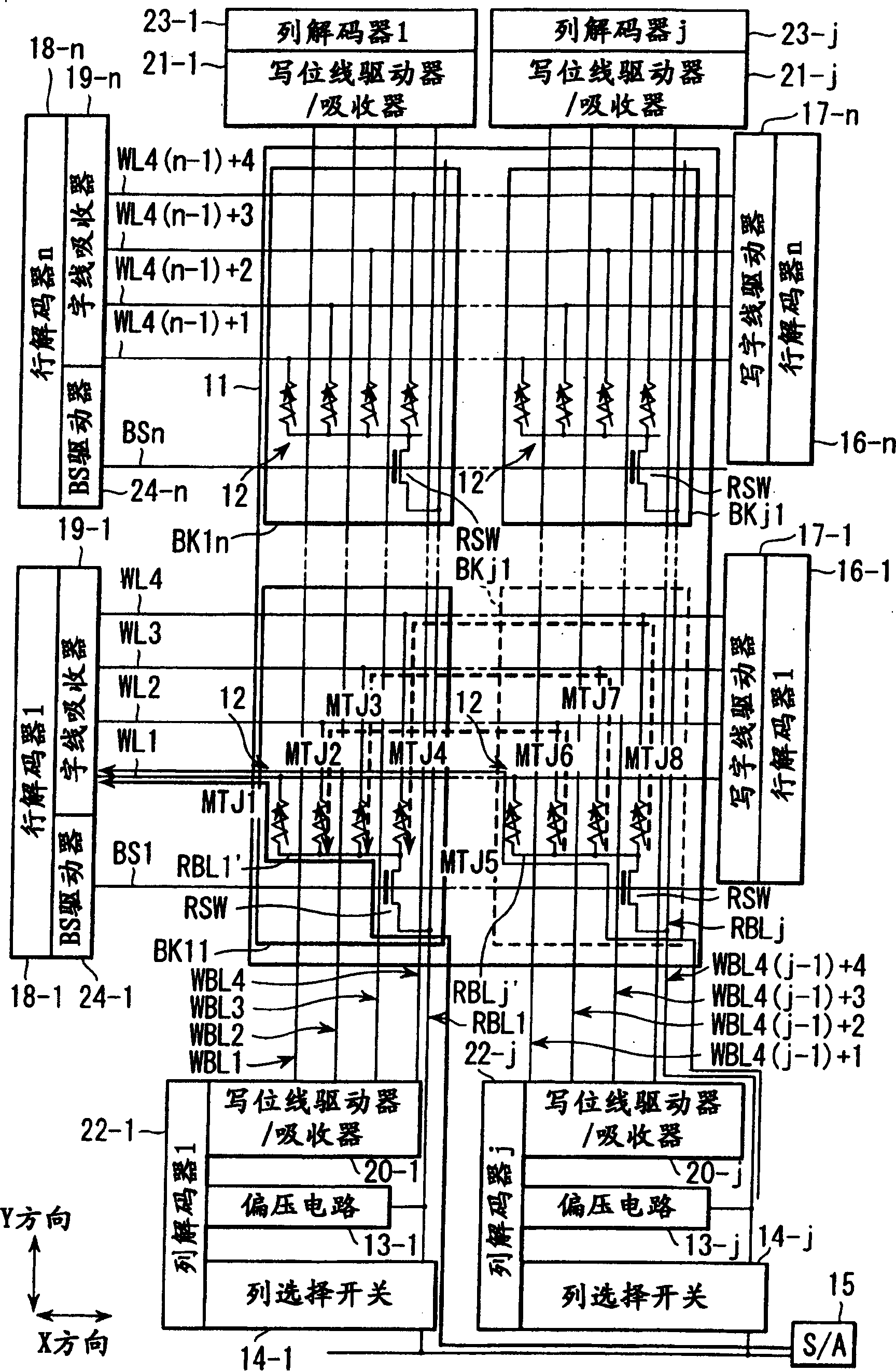
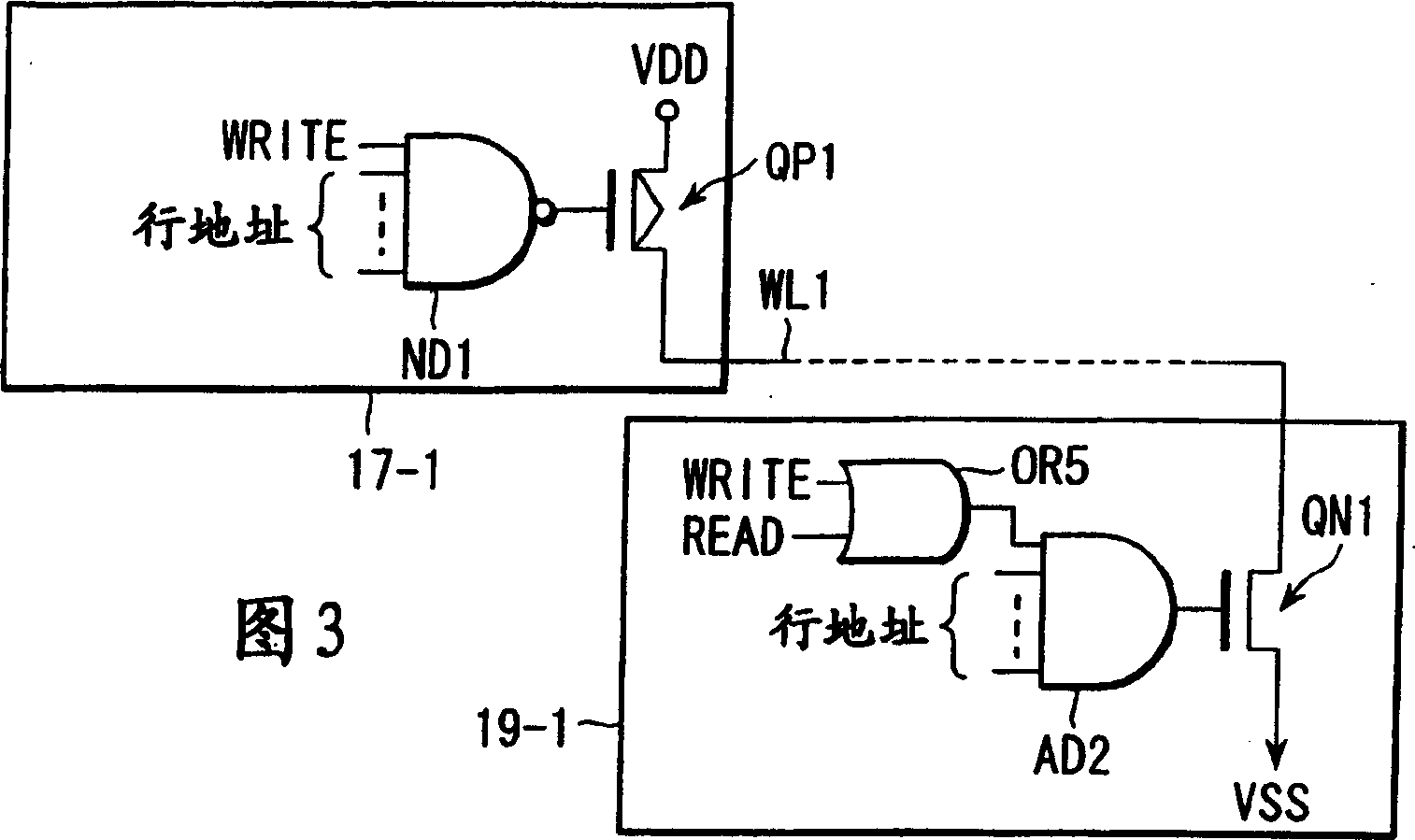
[0123] First, a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) according to an embodiment of the present invention uses [1] wherein one read switch element is shared by a plurality of MTJ (magnetic tunnel junction) elements, and the plurality of MTJ elements are aligned in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the semiconductor substrate (vertical direction) are stacked in multiple stages to form a module structure, [2] in which one read switch element is shared by multiple MTJ elements, and multiple MTJ elements are in a direction parallel to the surface of the semiconductor substrate (lateral direction) arranged to form a module structure, or [3] in which two read switch elements are shared by a plurality of MTJ elements arranged in a direction (lateral) parallel to the surface of the semiconductor substrate t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com