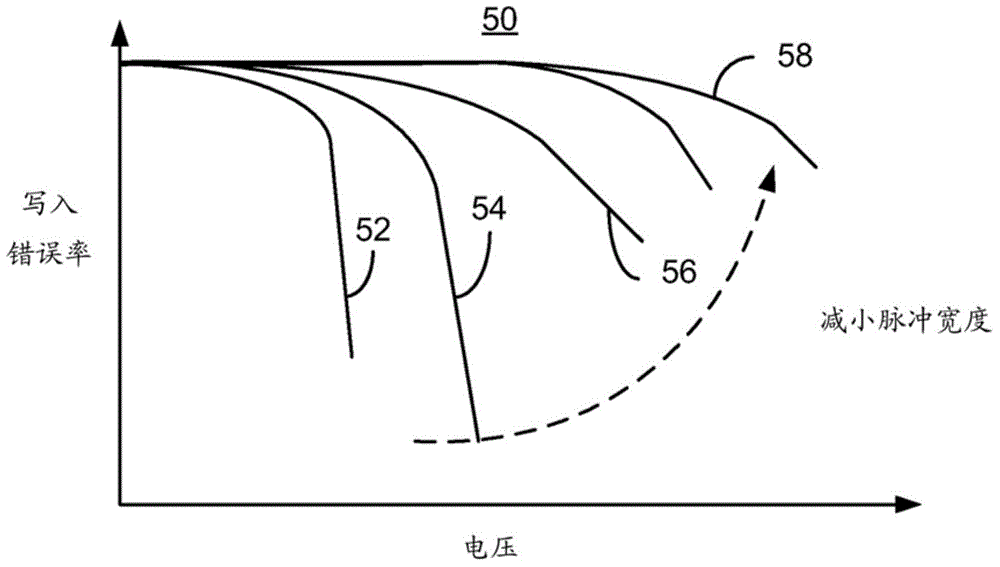
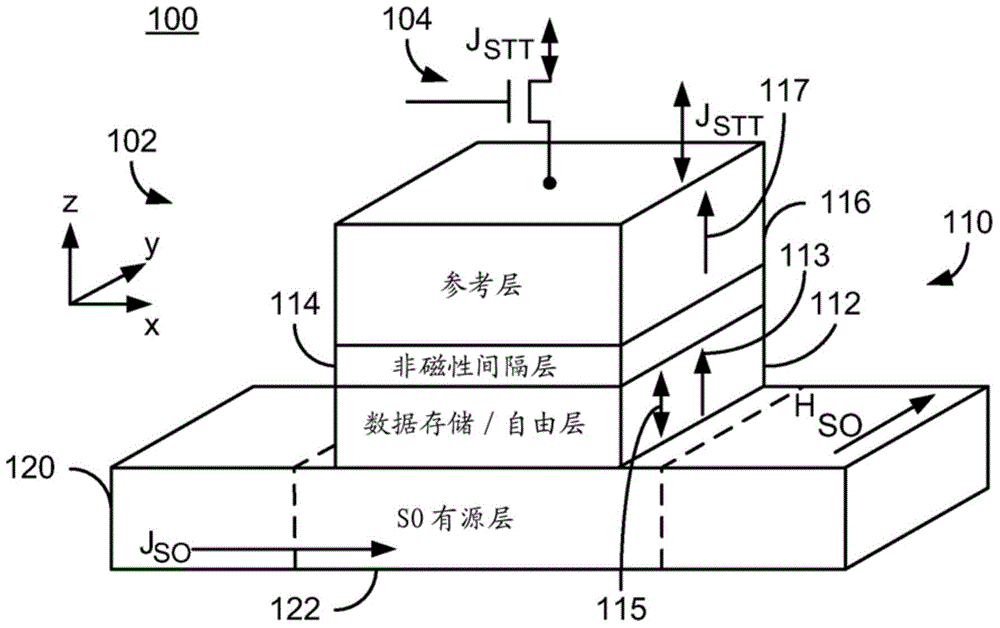
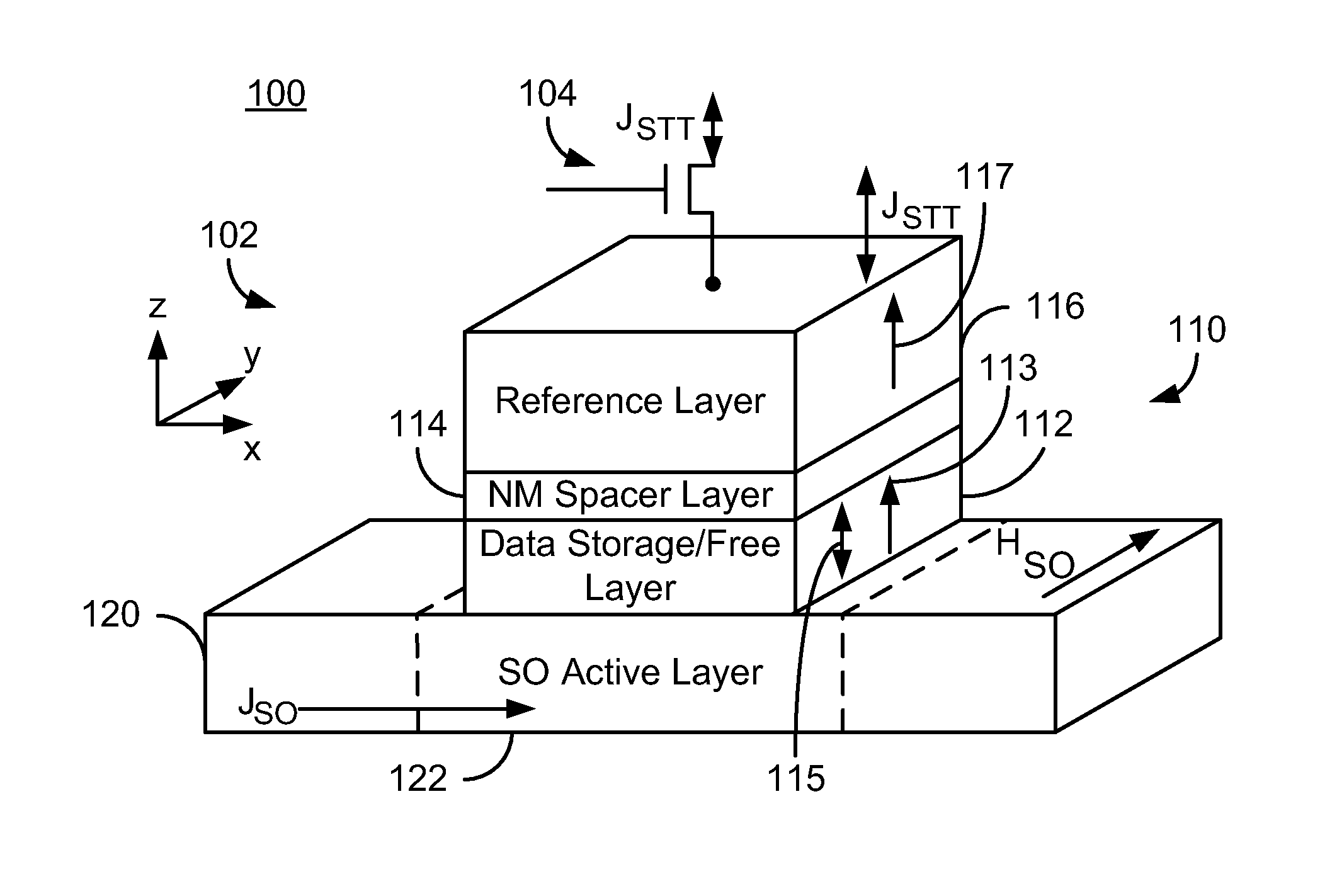
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Spin–orbit interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In quantum physics, the spin–orbit interaction (also called spin–orbit effect or spin–orbit coupling) is a relativistic interaction of a particle's spin with its motion inside a potential. A key example of this phenomenon is the spin–orbit interaction leading to shifts in an electron's atomic energy levels, due to electromagnetic interaction between the electron's magnetic dipole, its orbital motion, and the electrostatic field of the positively charged nucleus. This phenomenon is detectable as a splitting of spectral lines, which can be thought of as a Zeeman effect product of two relativistic effects: the apparent magnetic field seen from the electron perspective and the magnetic moment of the electron associated with its intrinsic spin. A similar effect, due to the relationship between angular momentum and the strong nuclear force, occurs for protons and neutrons moving inside the nucleus, leading to a shift in their energy levels in the nucleus shell model. In the field of spintronics, spin–orbit effects for electrons in semiconductors and other materials are explored for technological applications. The spin–orbit interaction is one cause of magnetocrystalline anisotropy and the spin Hall effect.
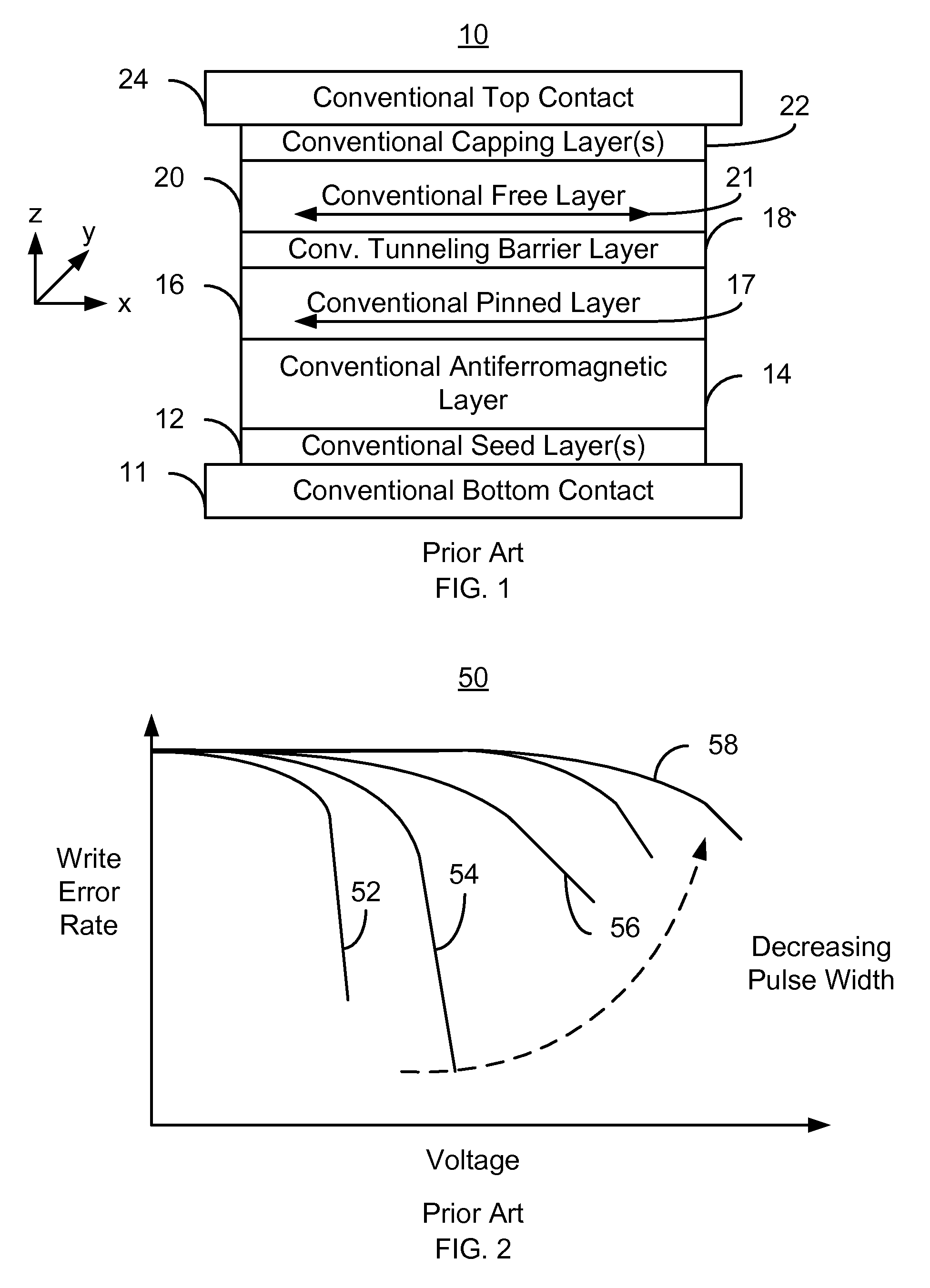
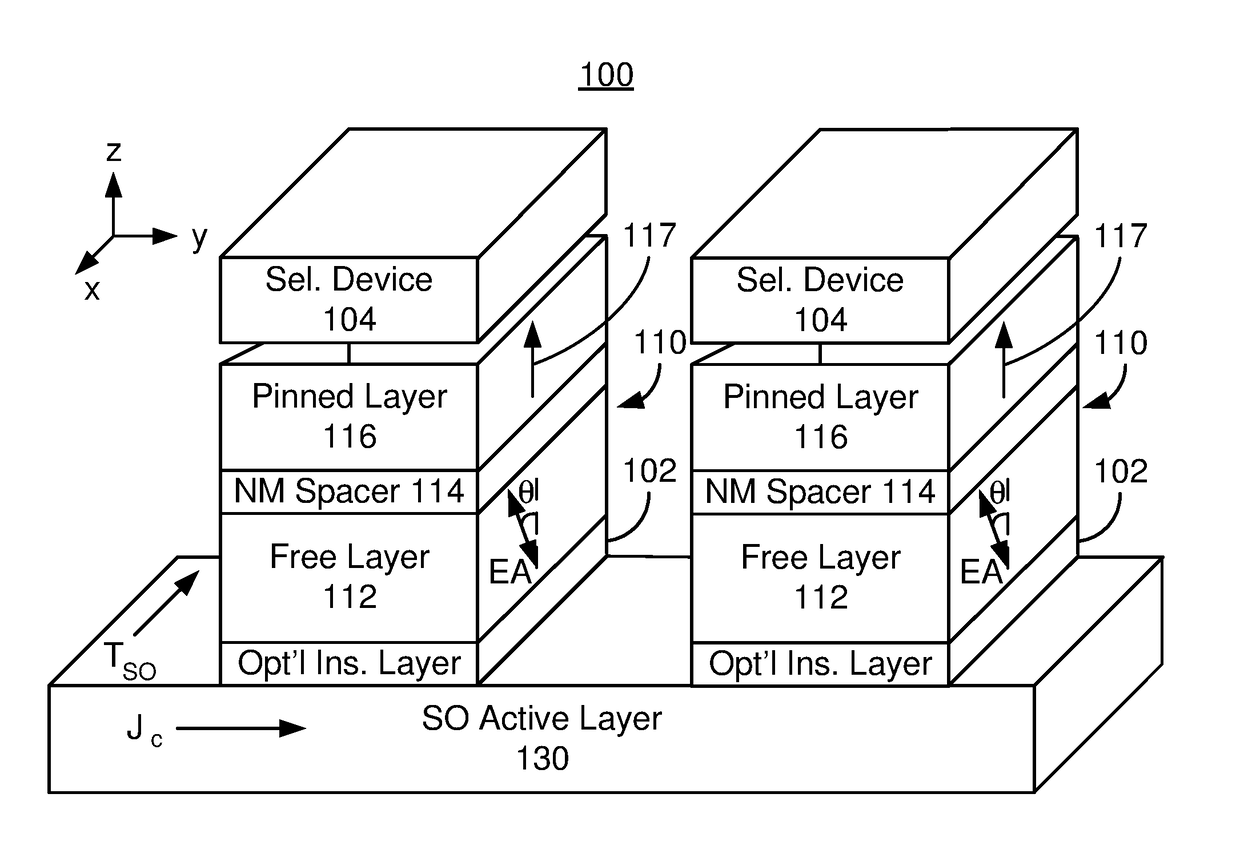
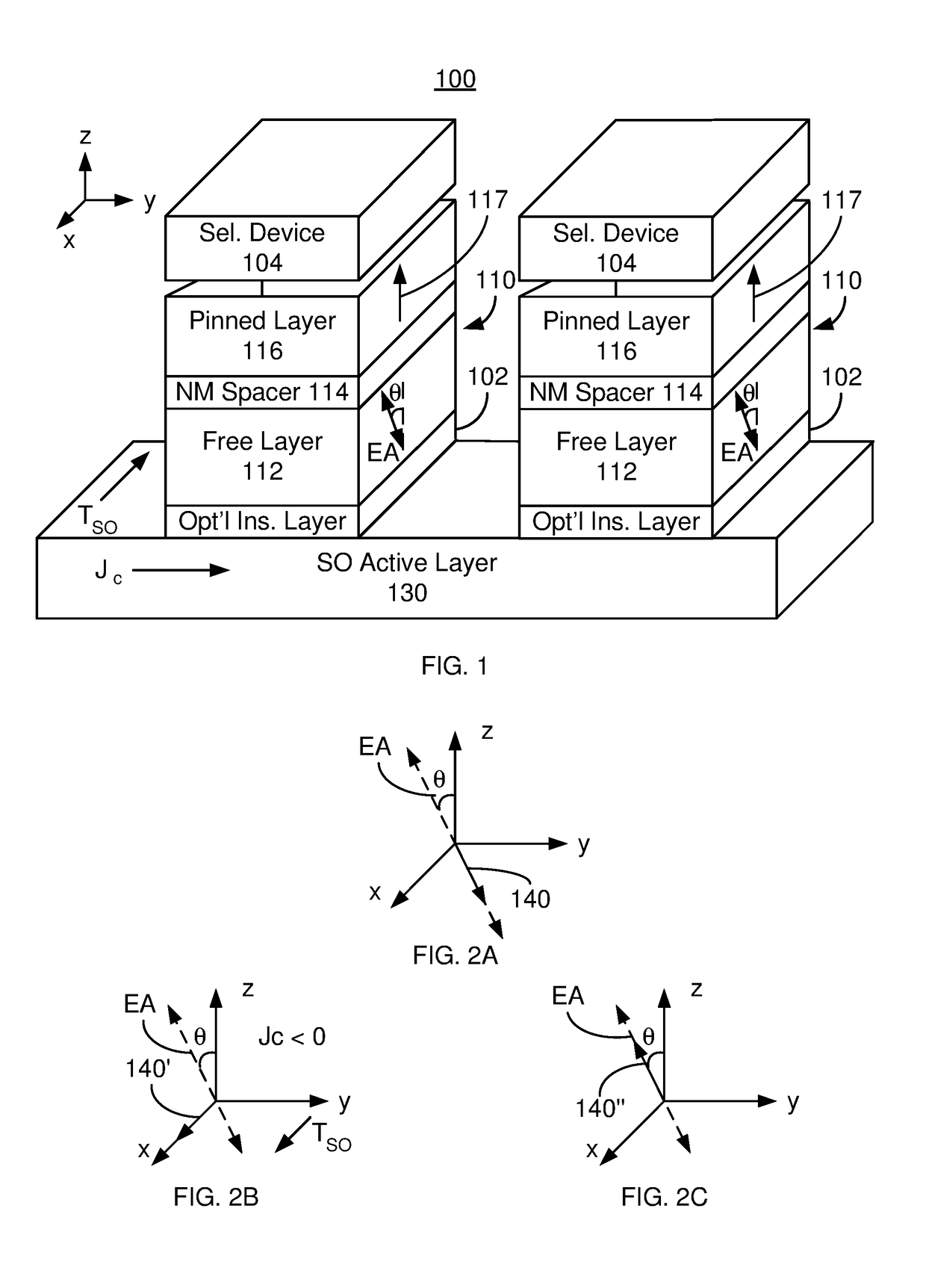
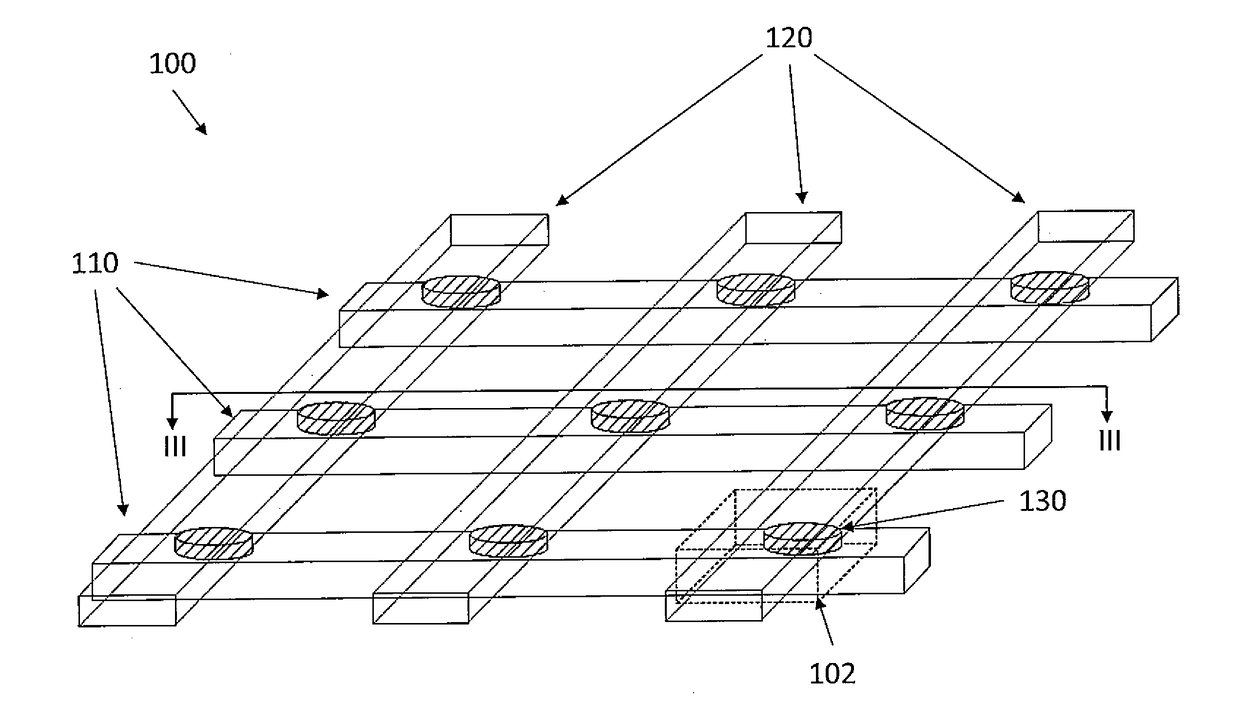
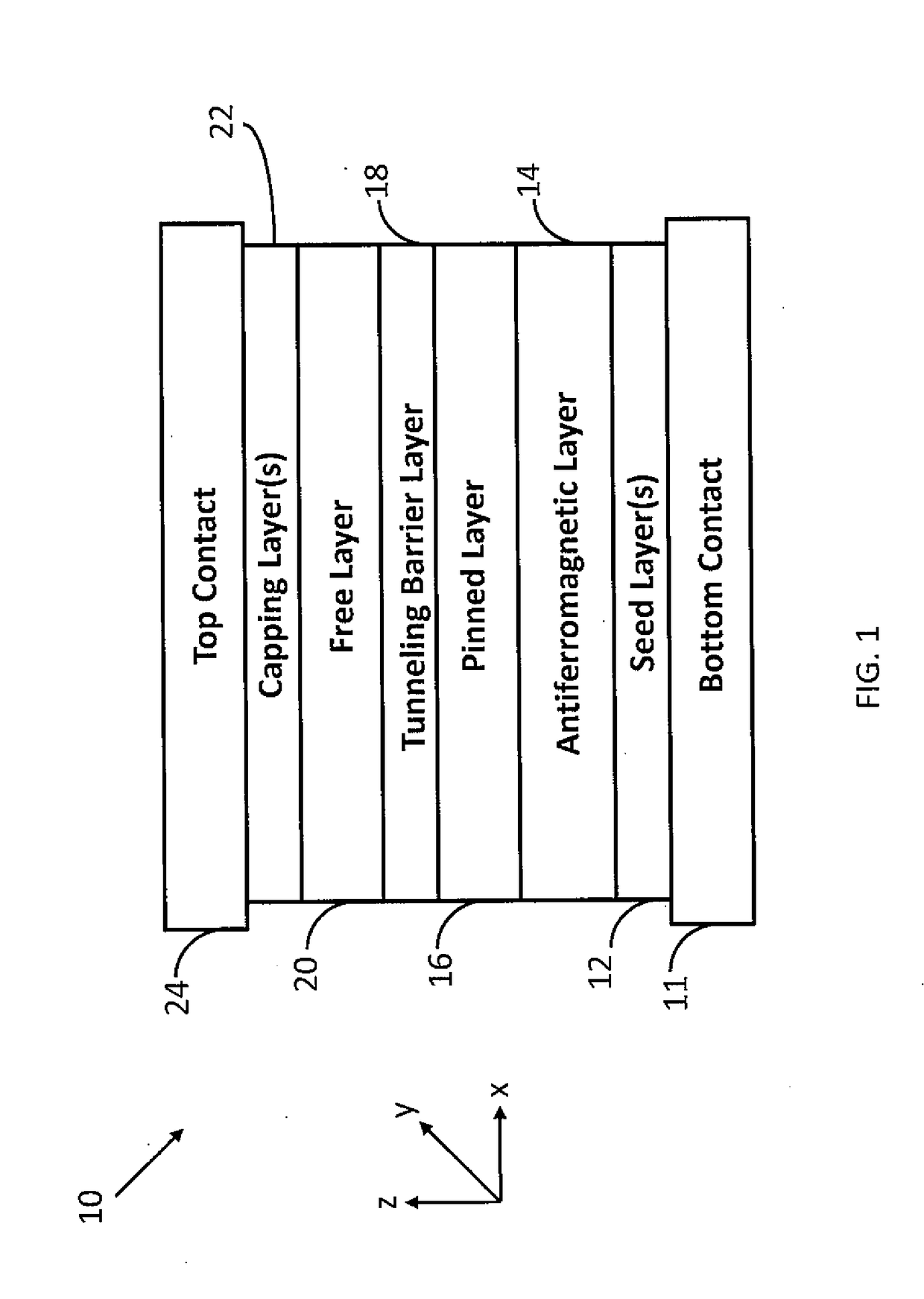
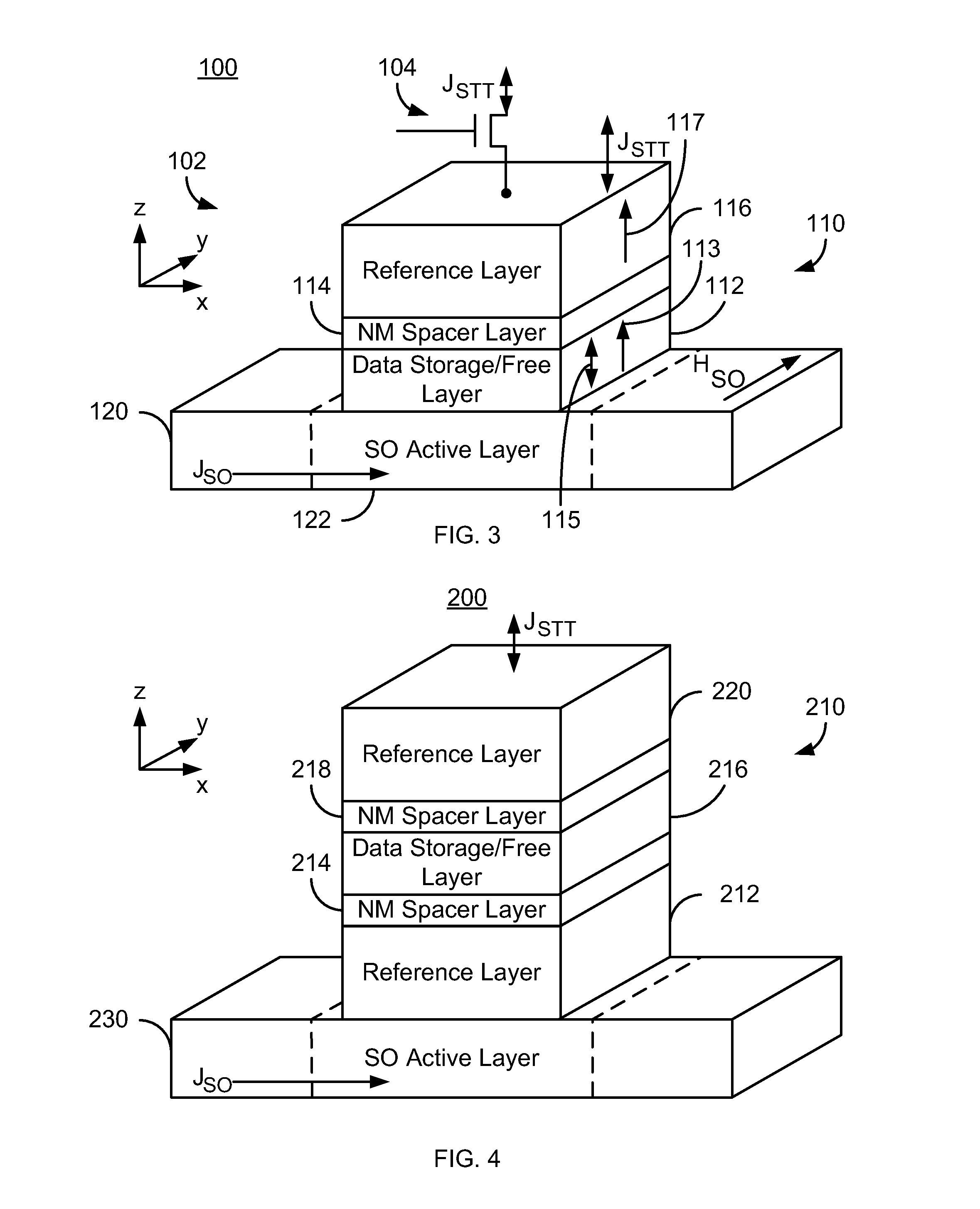
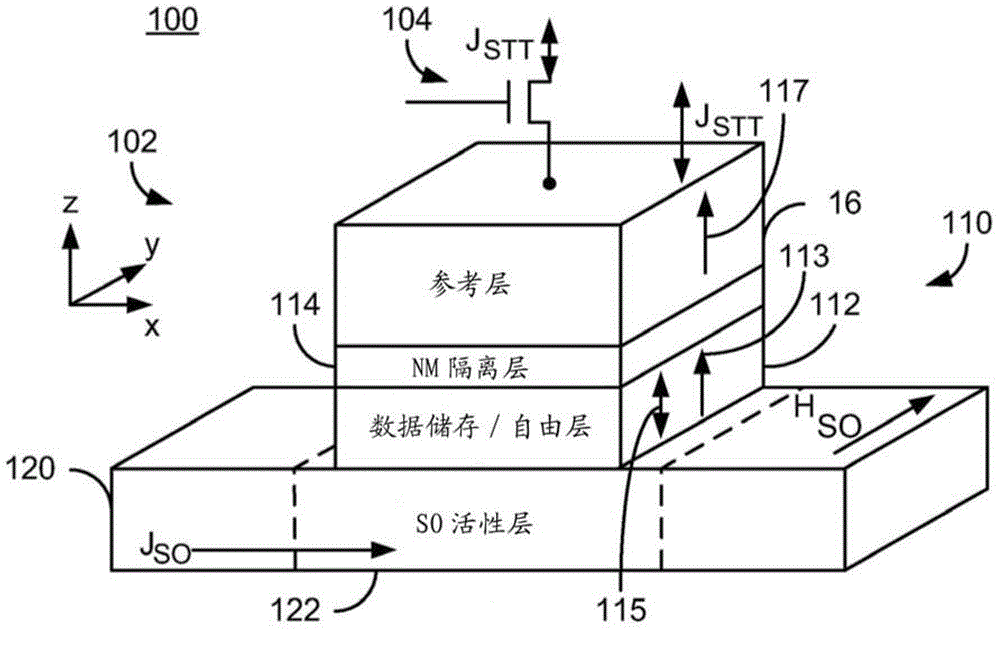
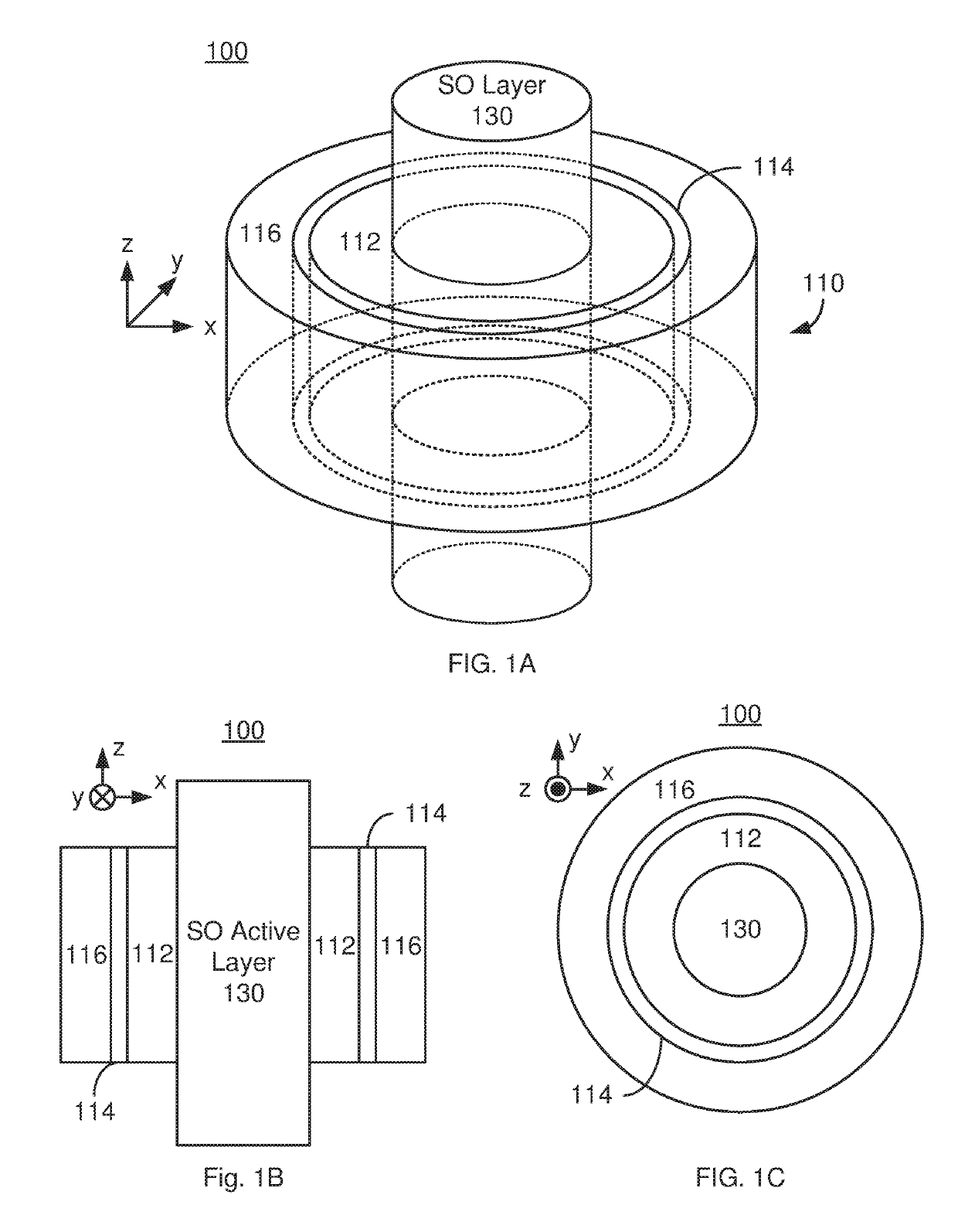
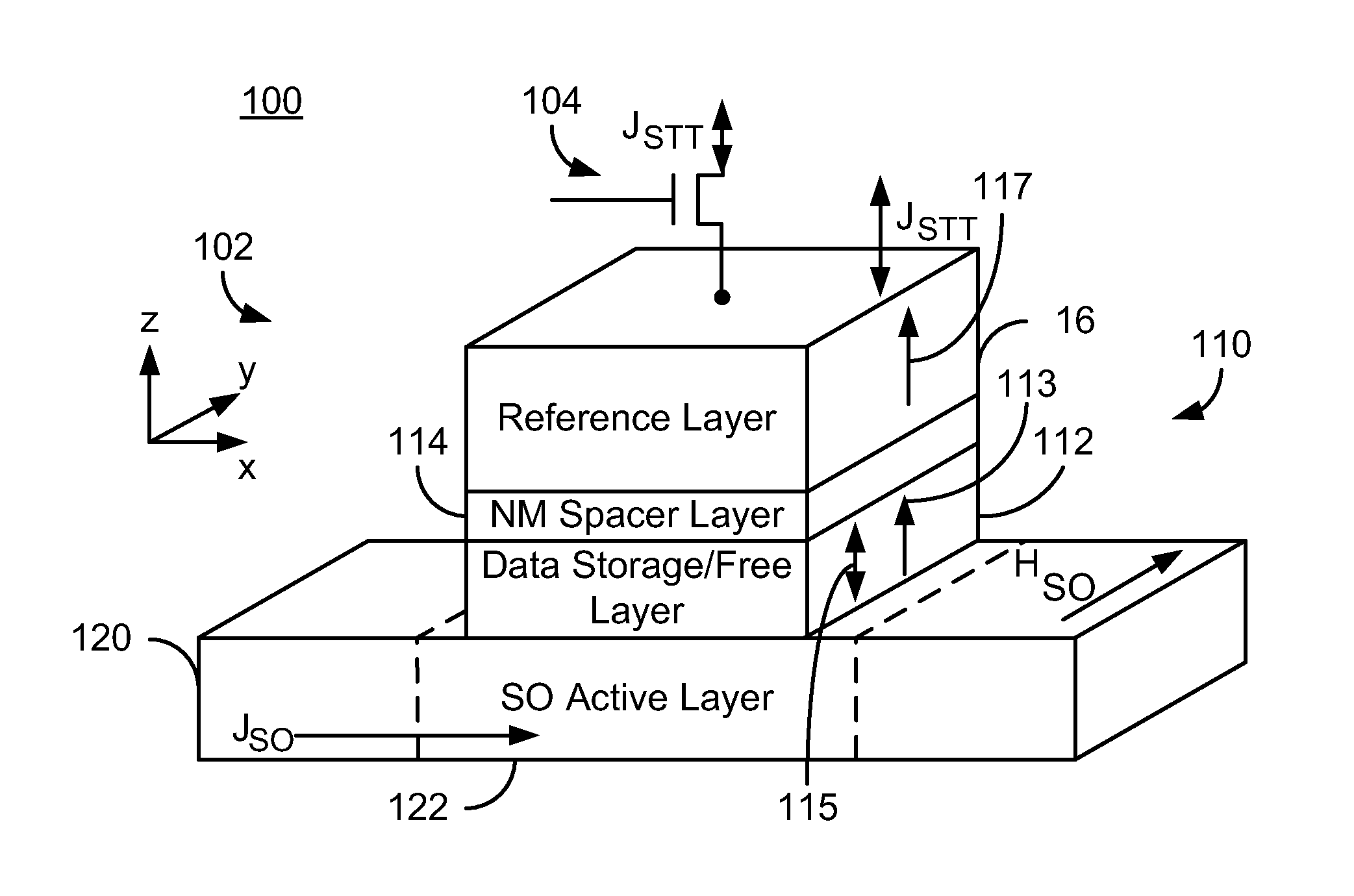
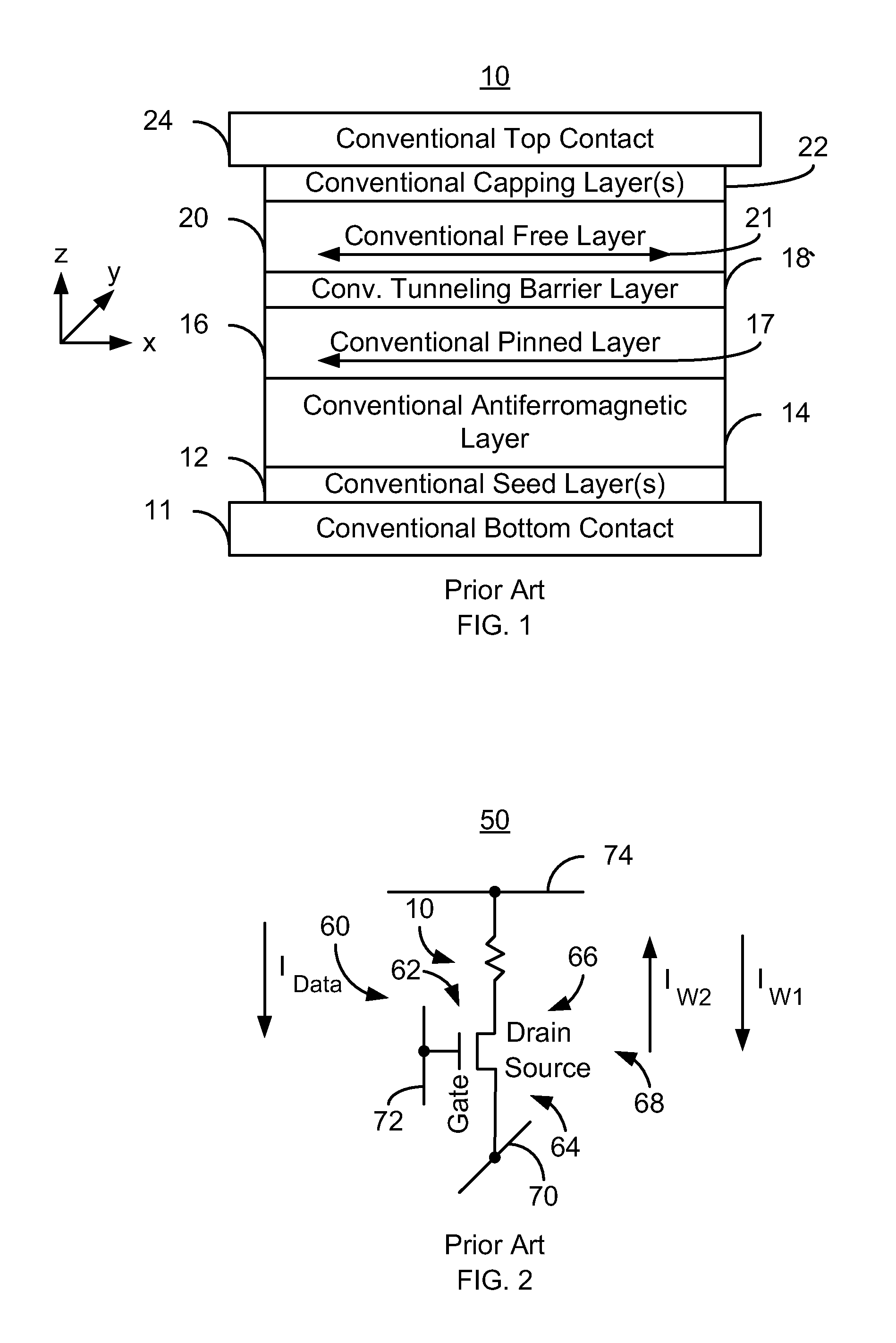
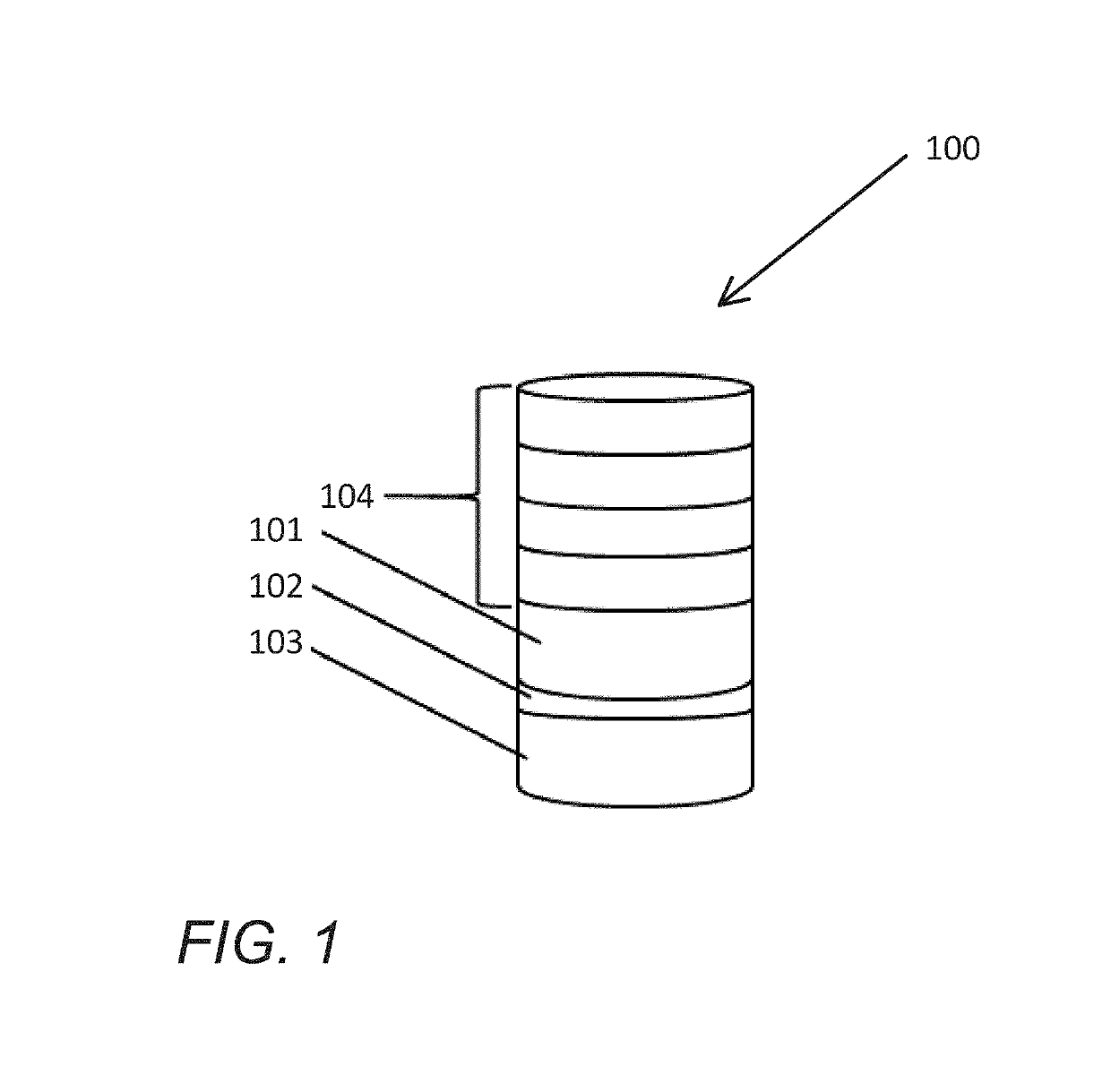
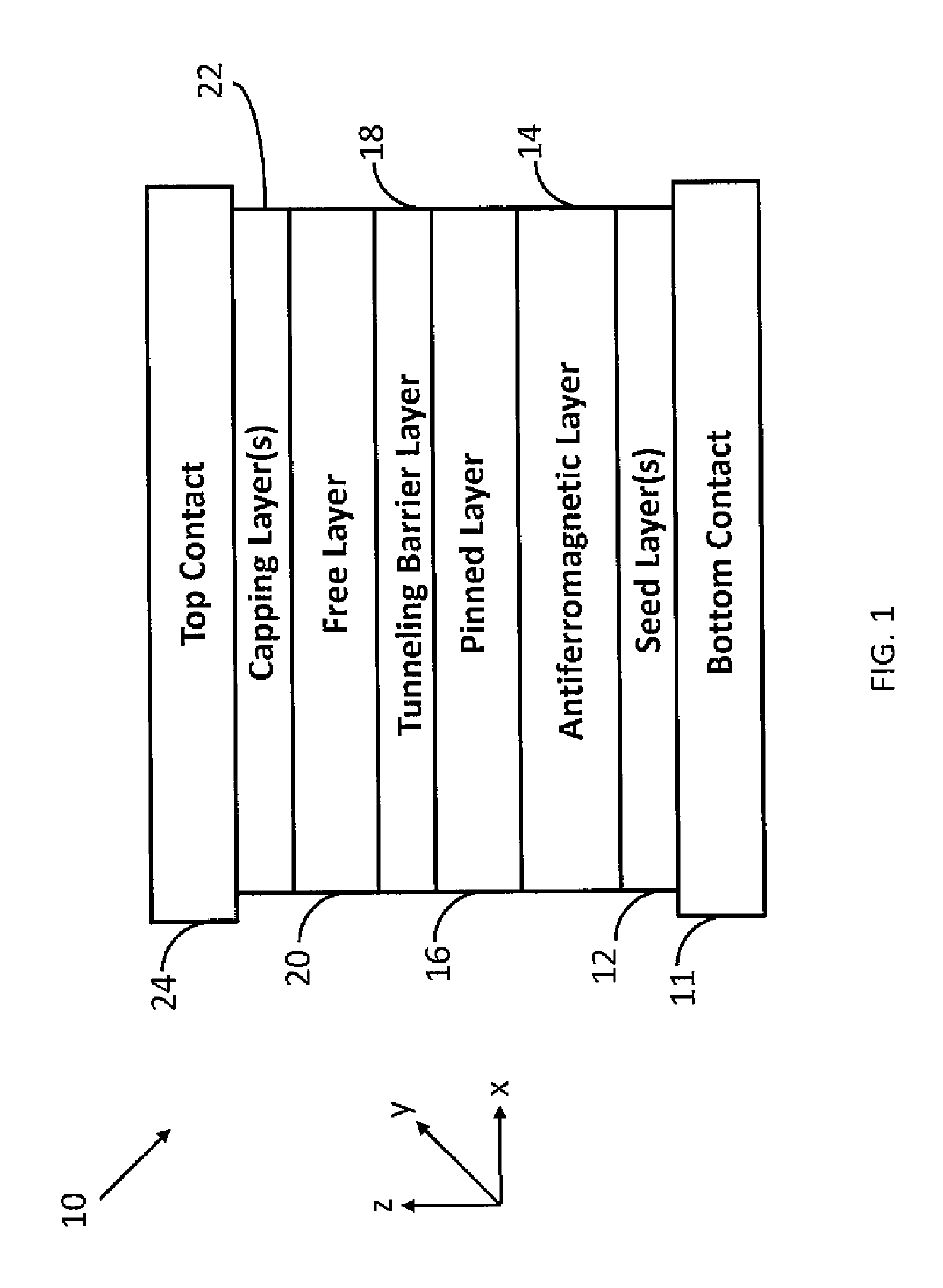
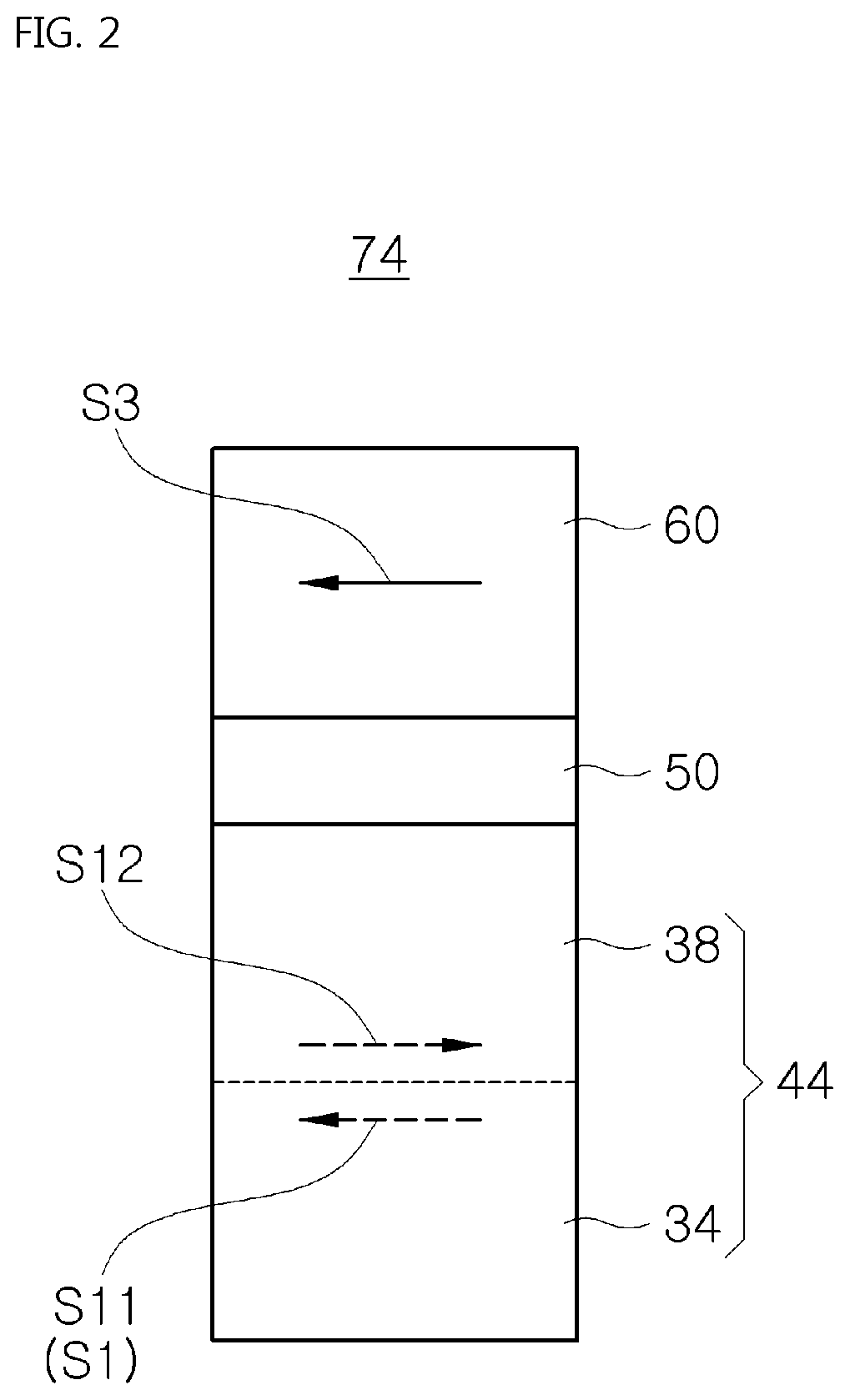
Method and system for providing a magnetic tunneling junction using spin-orbit interaction based switching and memories utilizing the magnetic tunneling junction
ActiveUS20140056060A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageMagnetic memoryActive layer
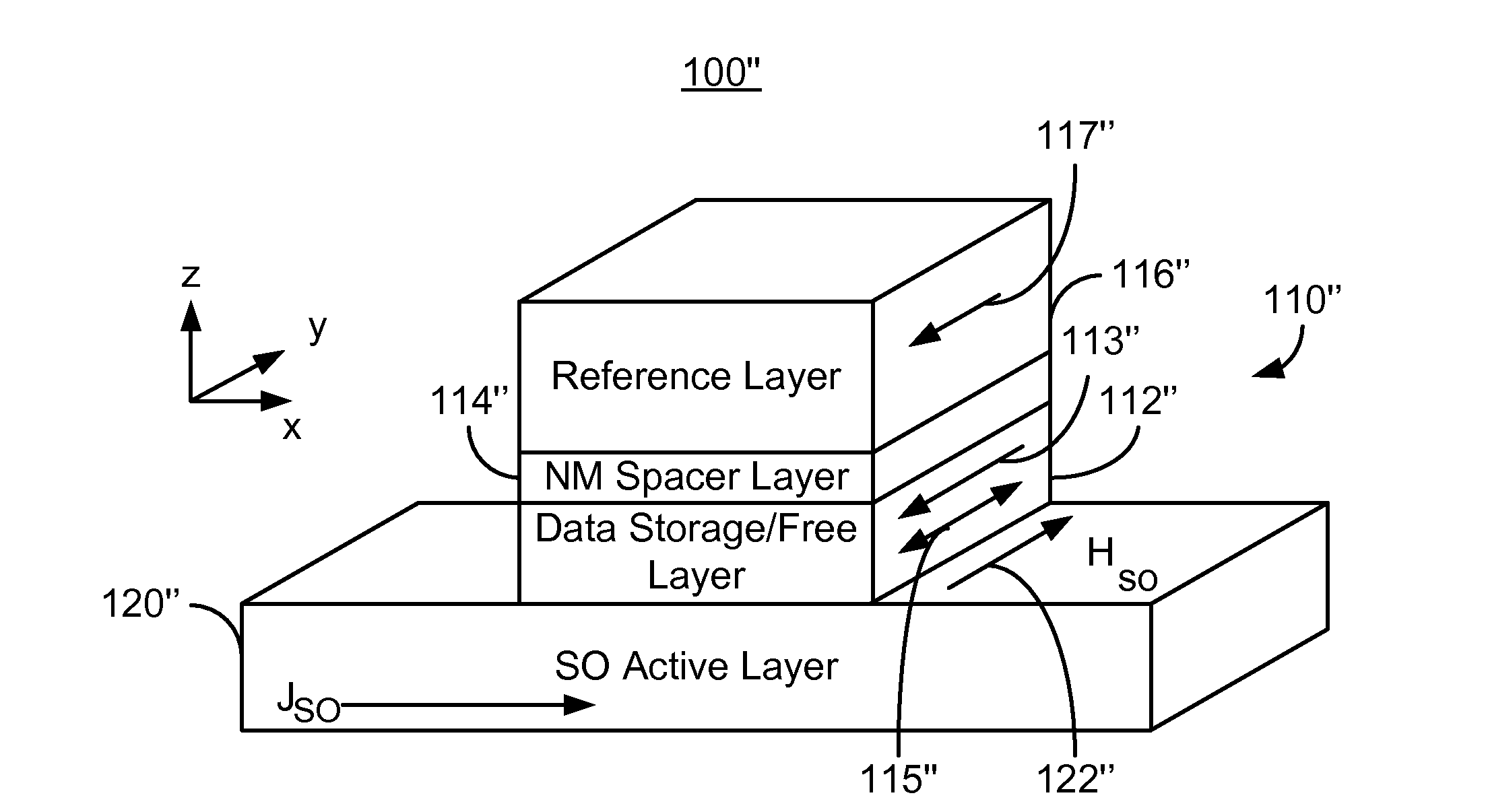
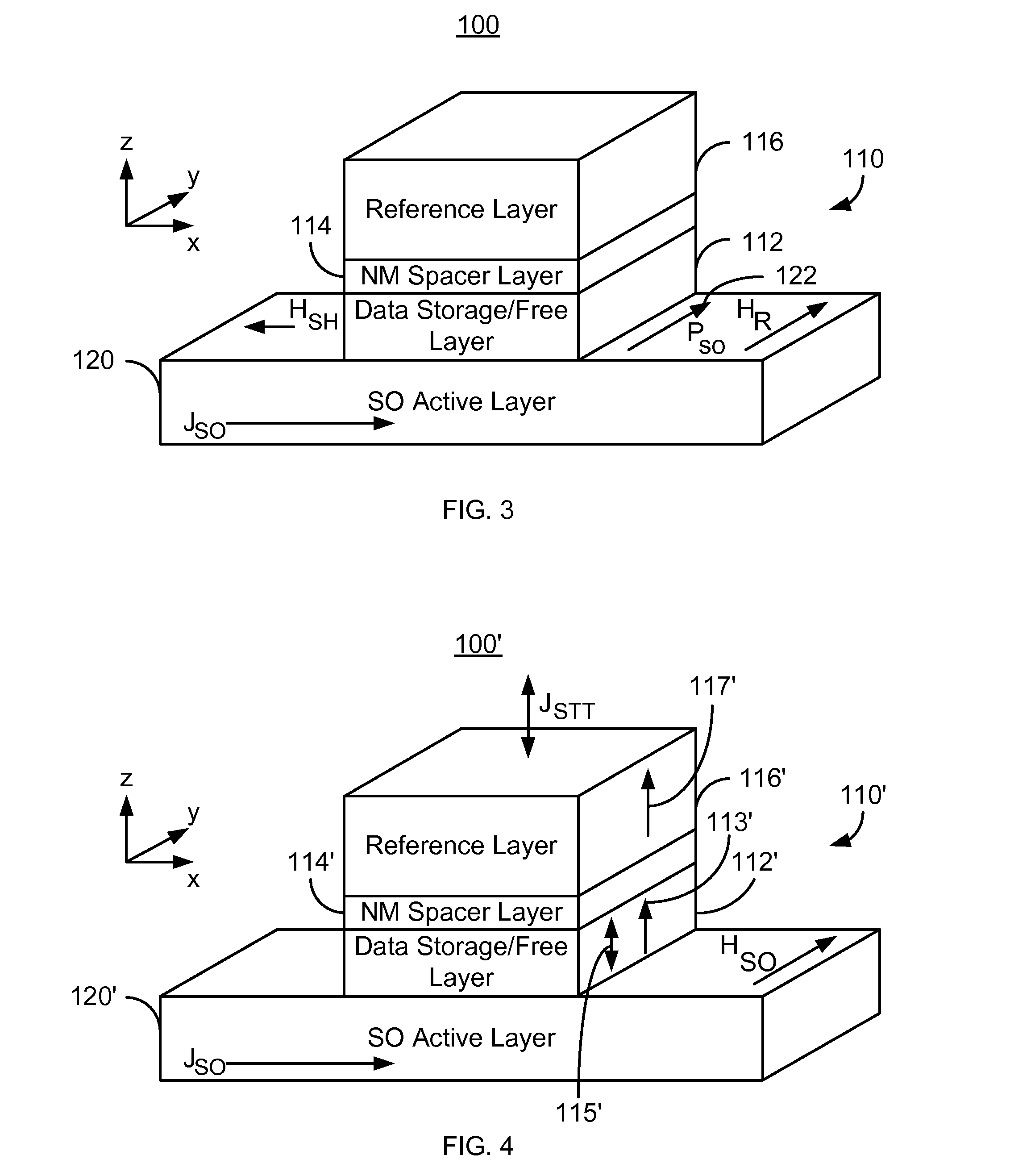
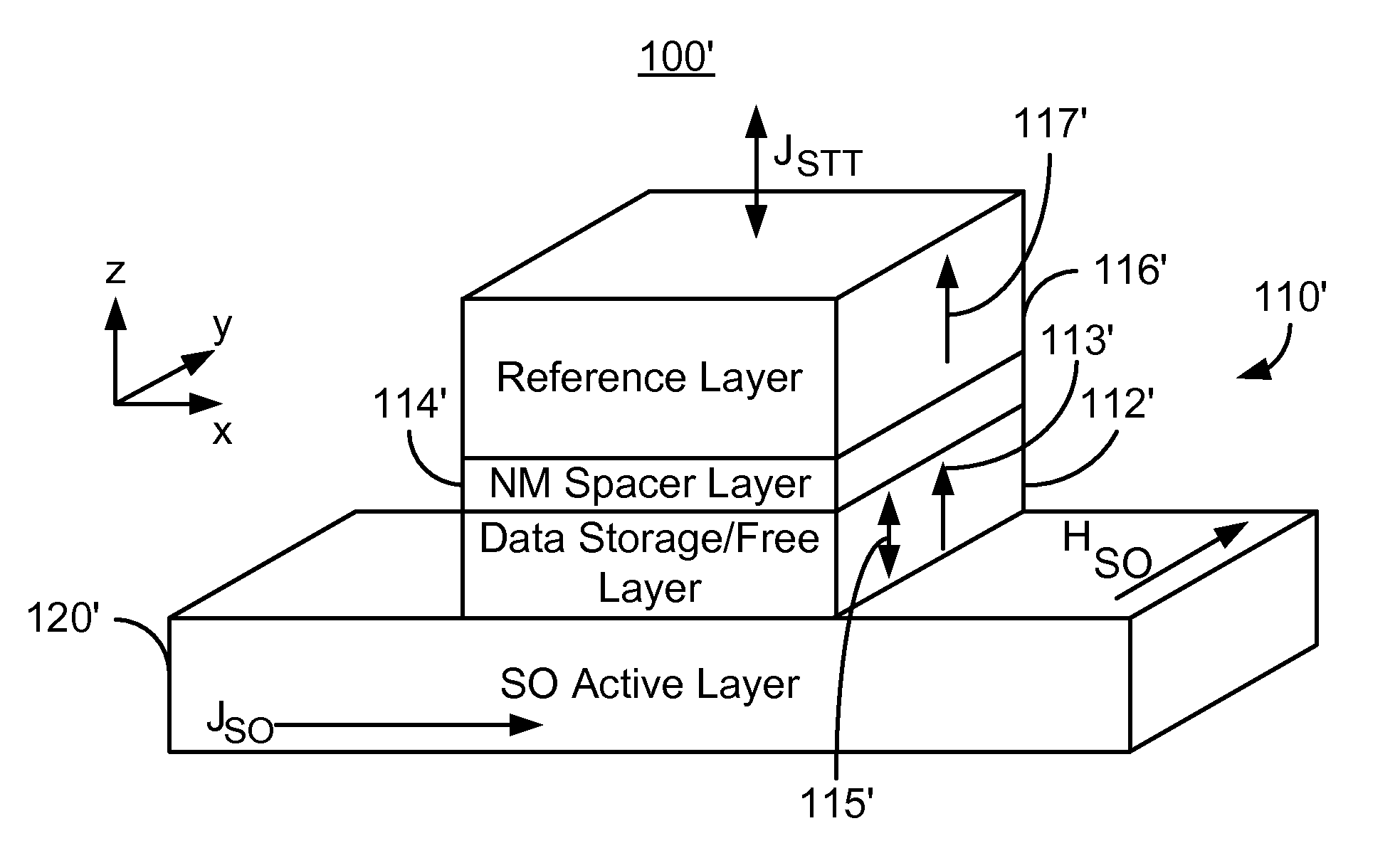
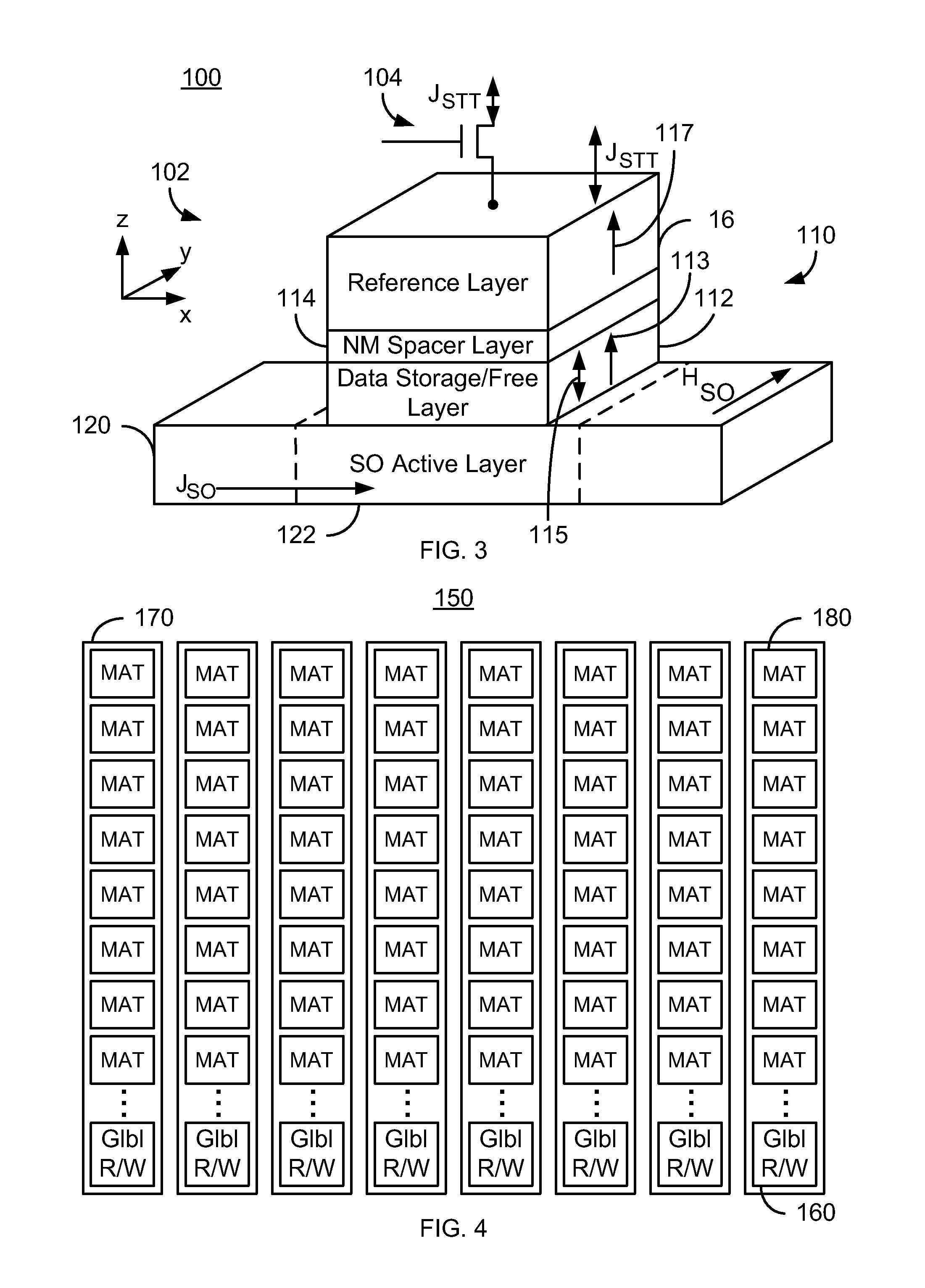
A magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer. Each of the magnetic junctions includes a data storage layer that is magnetic. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the data storage layer of the magnetic junction. The at SO active layer(s) are configured to exert a SO torque on the data storage layer due to a current passing through the at least one SO active layer in a direction substantially perpendicular to a direction between the at least one SO active layer and the data storage layer of a magnetic junction of the plurality of magnetic junctions closest to the at least one SO active layer. The data storage layer is configured to be switchable using at least the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing a magnetic tunneling junction using spin-orbit interaction based switching and memories utilizing the magnetic tunneling junction
A magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer. Each of the magnetic junctions includes a data storage layer that is magnetic. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the data storage layer of the magnetic junction. The at SO active layer(s) are configured to exert a SO torque on the data storage layer due to a current passing through the at least one SO active layer in a direction substantially perpendicular to a direction between the at least one SO active layer and the data storage layer of a magnetic junction of the plurality of magnetic junctions closest to the at least one SO active layer. The data storage layer is configured to be switchable using at least the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
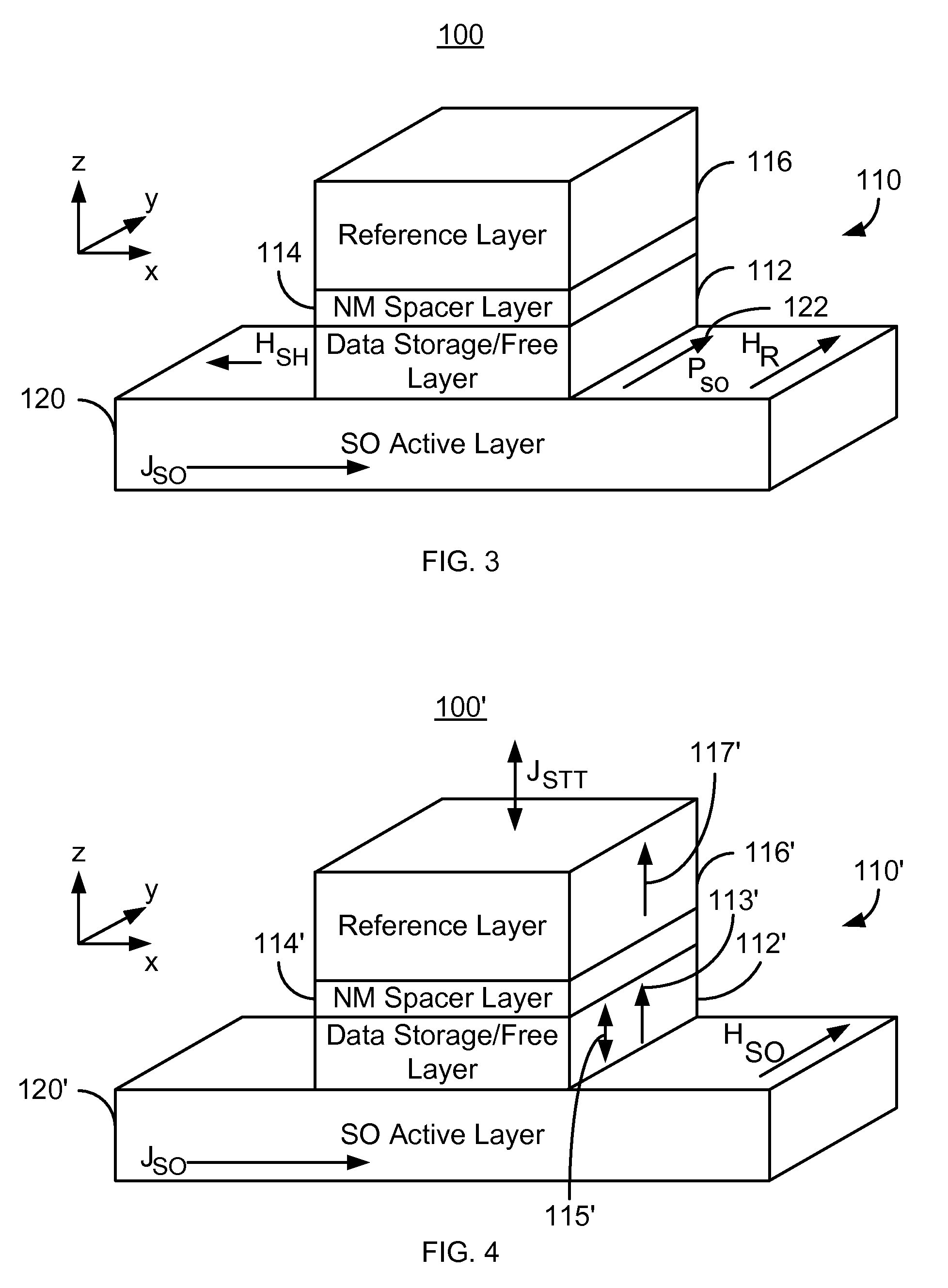
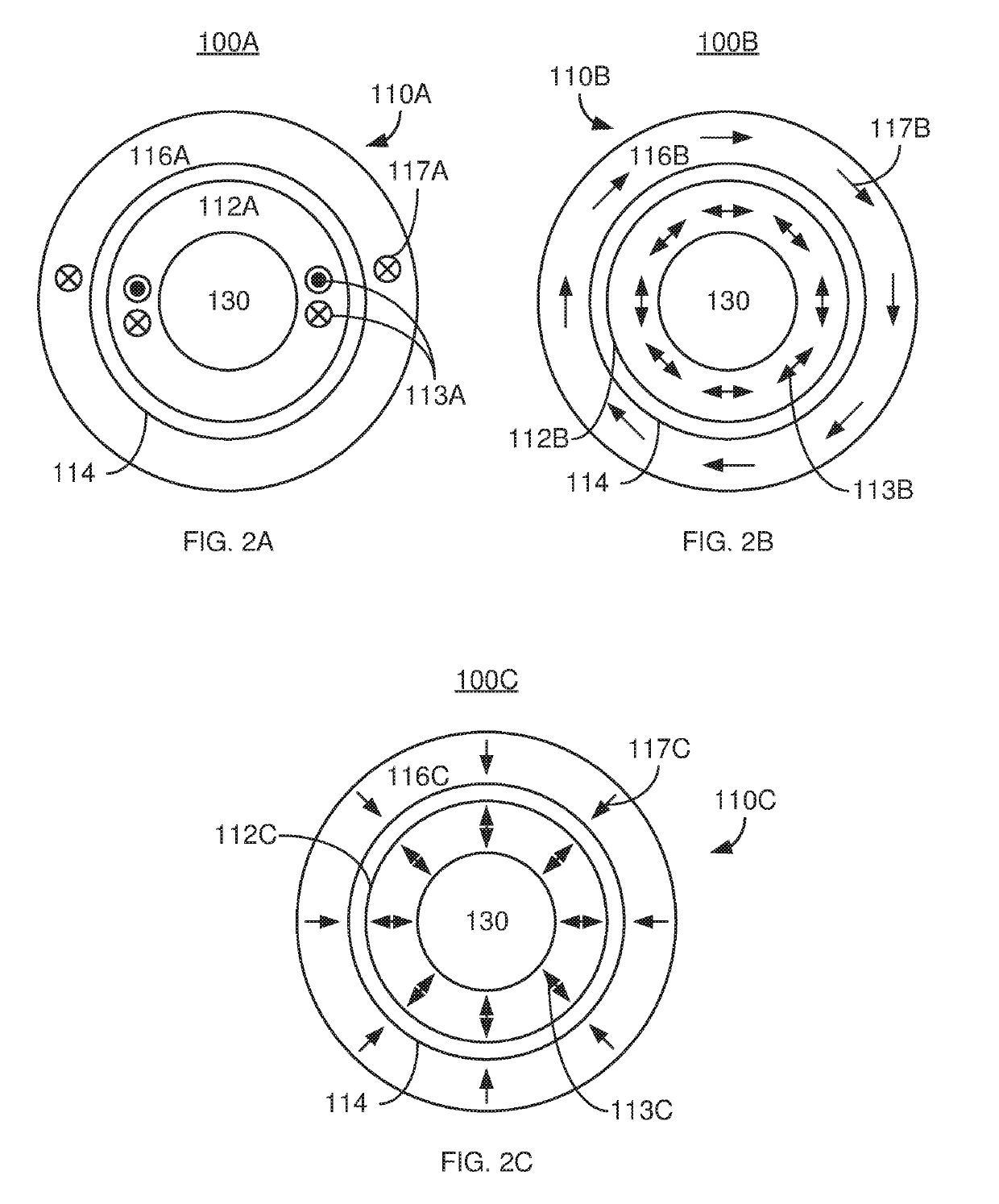
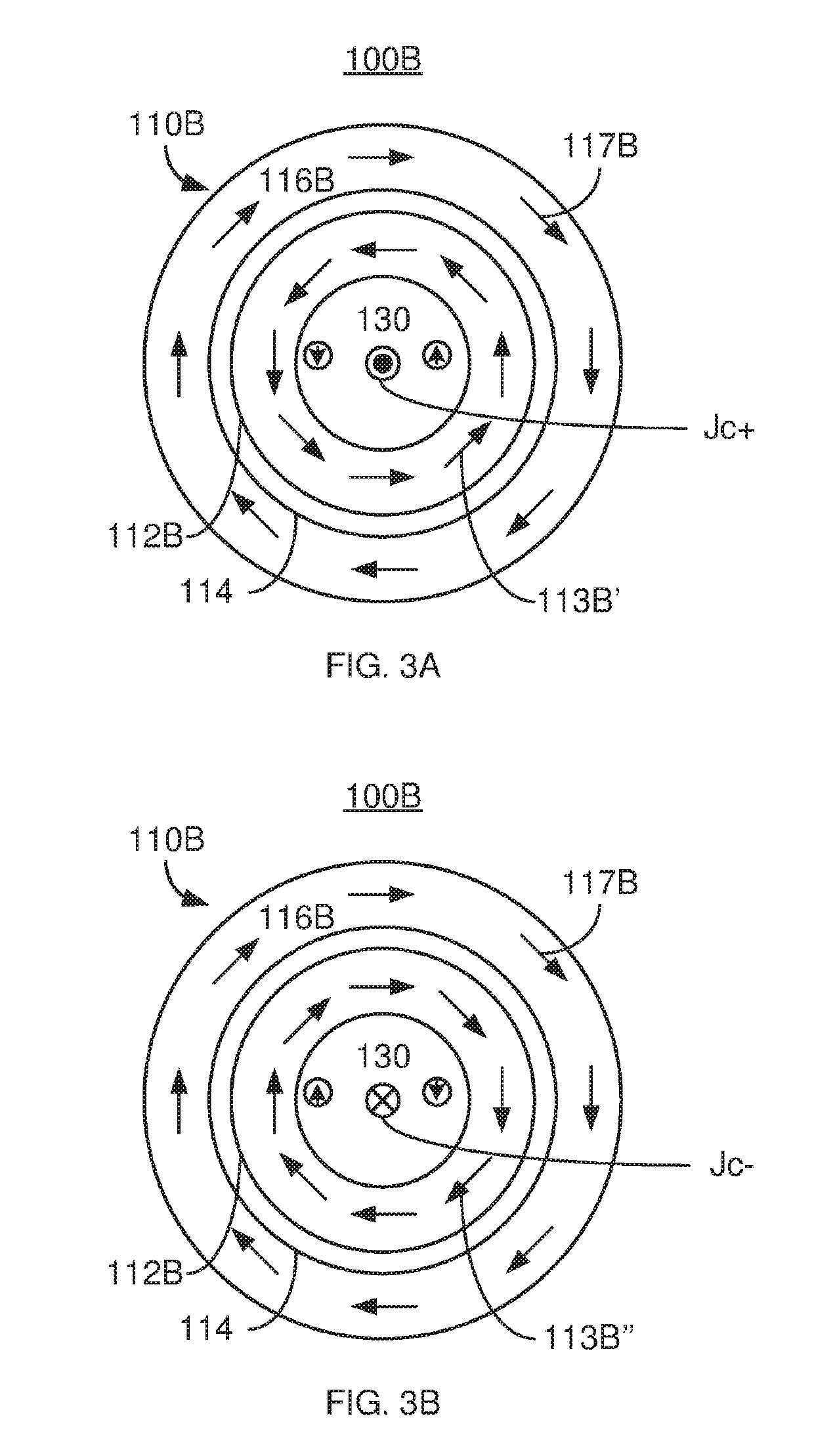
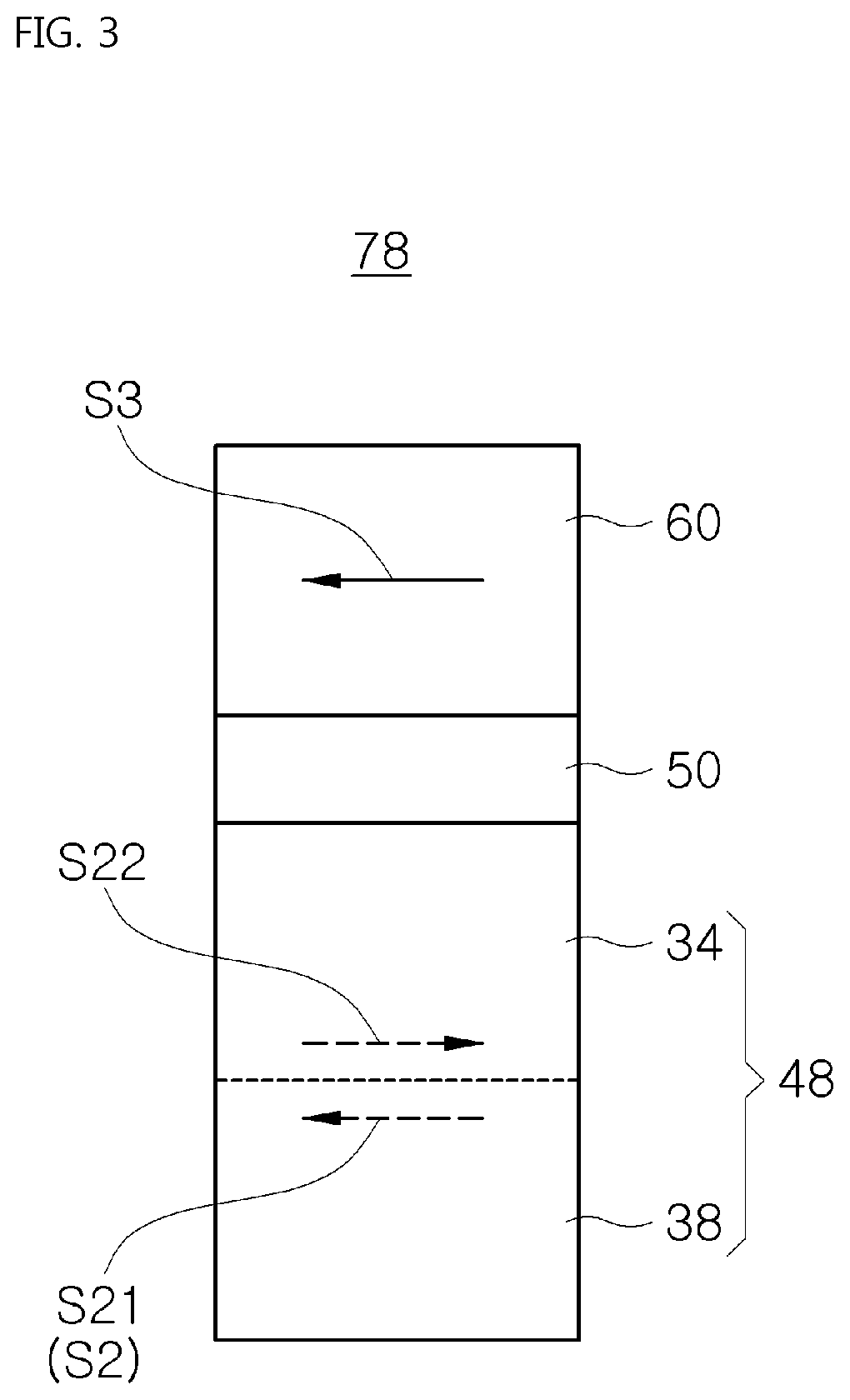
Magnetic junctions programmable using spin-orbit interaction torque in the absence of an external magnetic field
A magnetic memory including a plurality of magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer is described. Each of the magnetic junctions includes a reference layer, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between reference and free layers. The magnetic junction includes a biasing structure for providing a magnetic bias in a first direction and / or the free layer has a length in the first direction and a width in a second direction. The width is less than the length. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the free layer and carry a current in a third direction. The third direction is at a nonzero acute angle from the first direction. The SO active layer(s) exerts a SO torque on the free layer due to the current passing through the at least one SO active layer. The free layer is switchable using the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
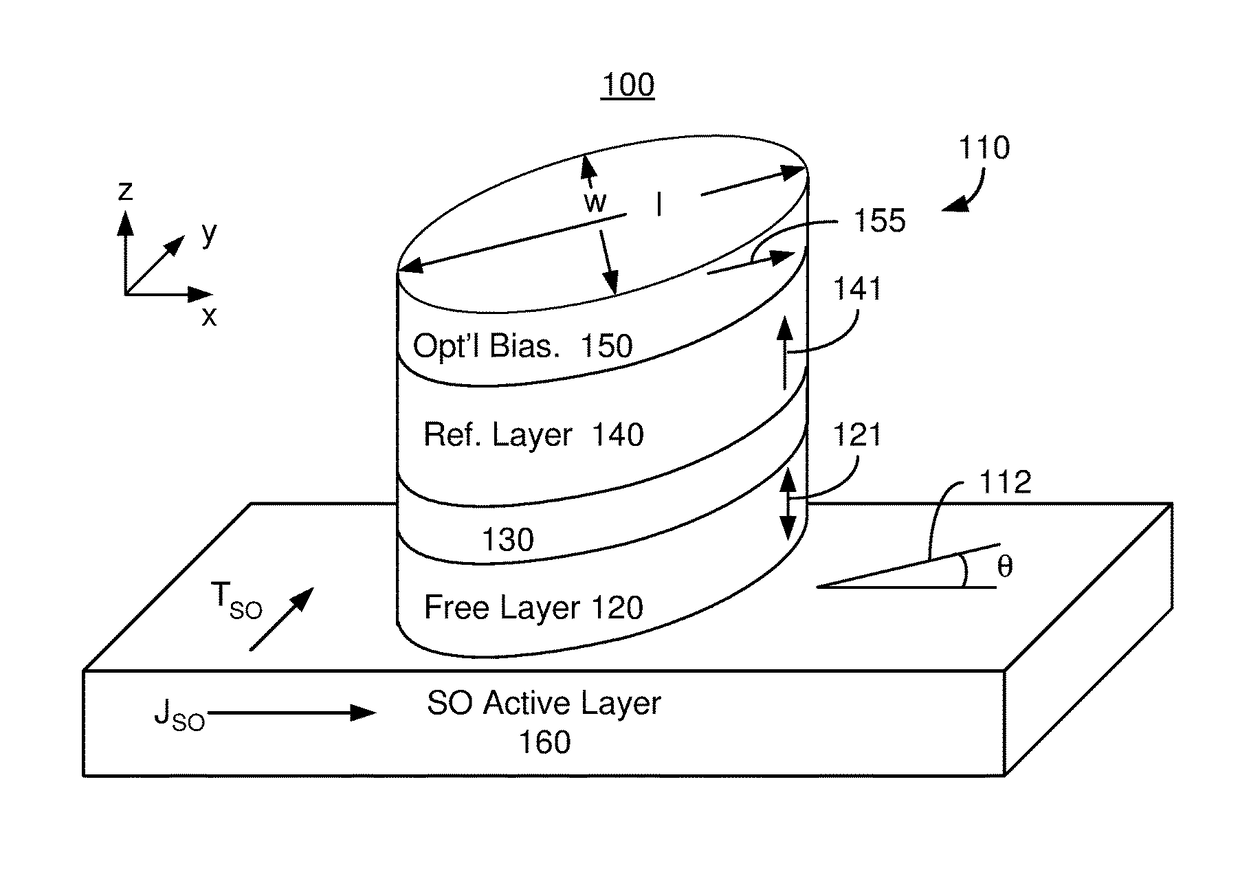
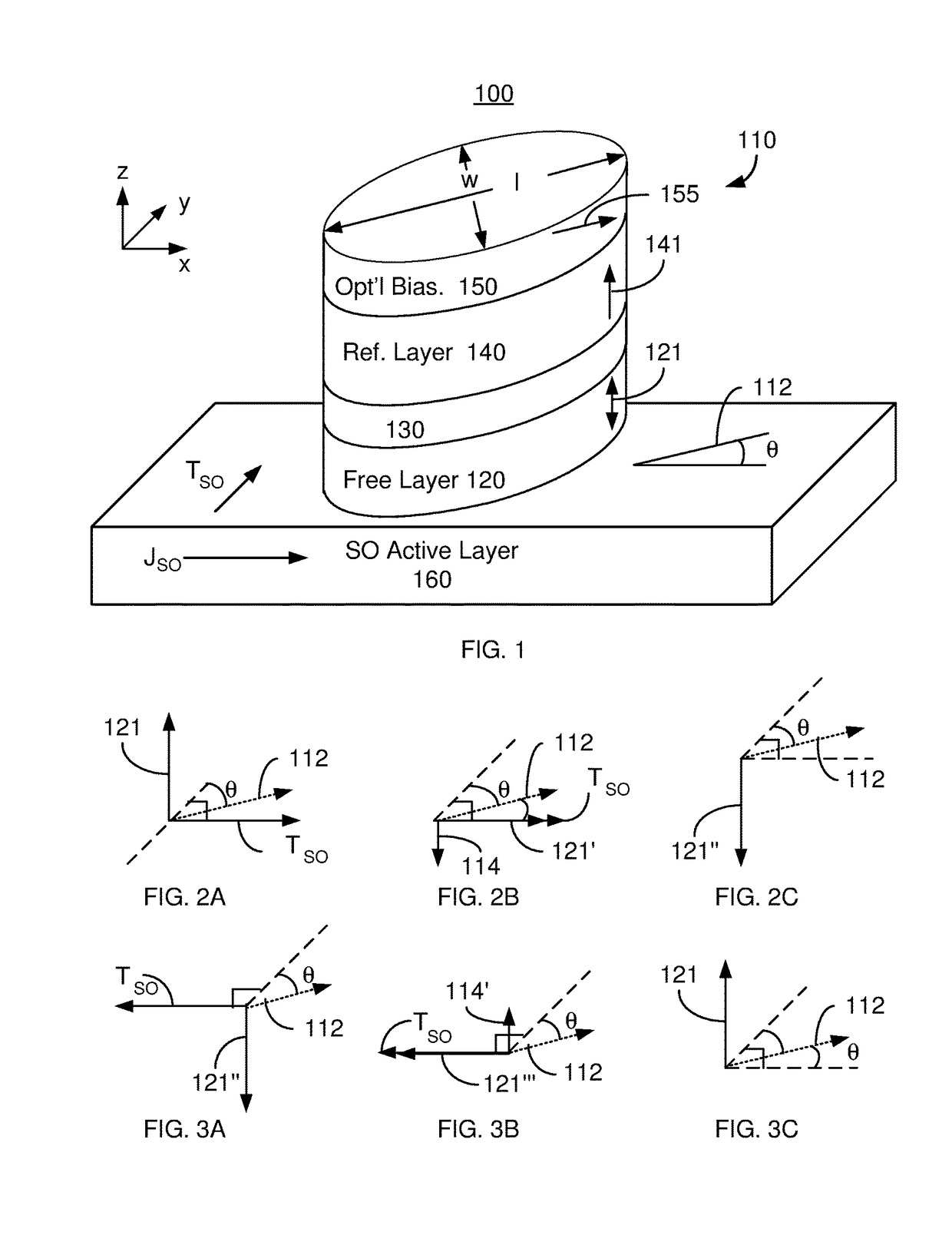
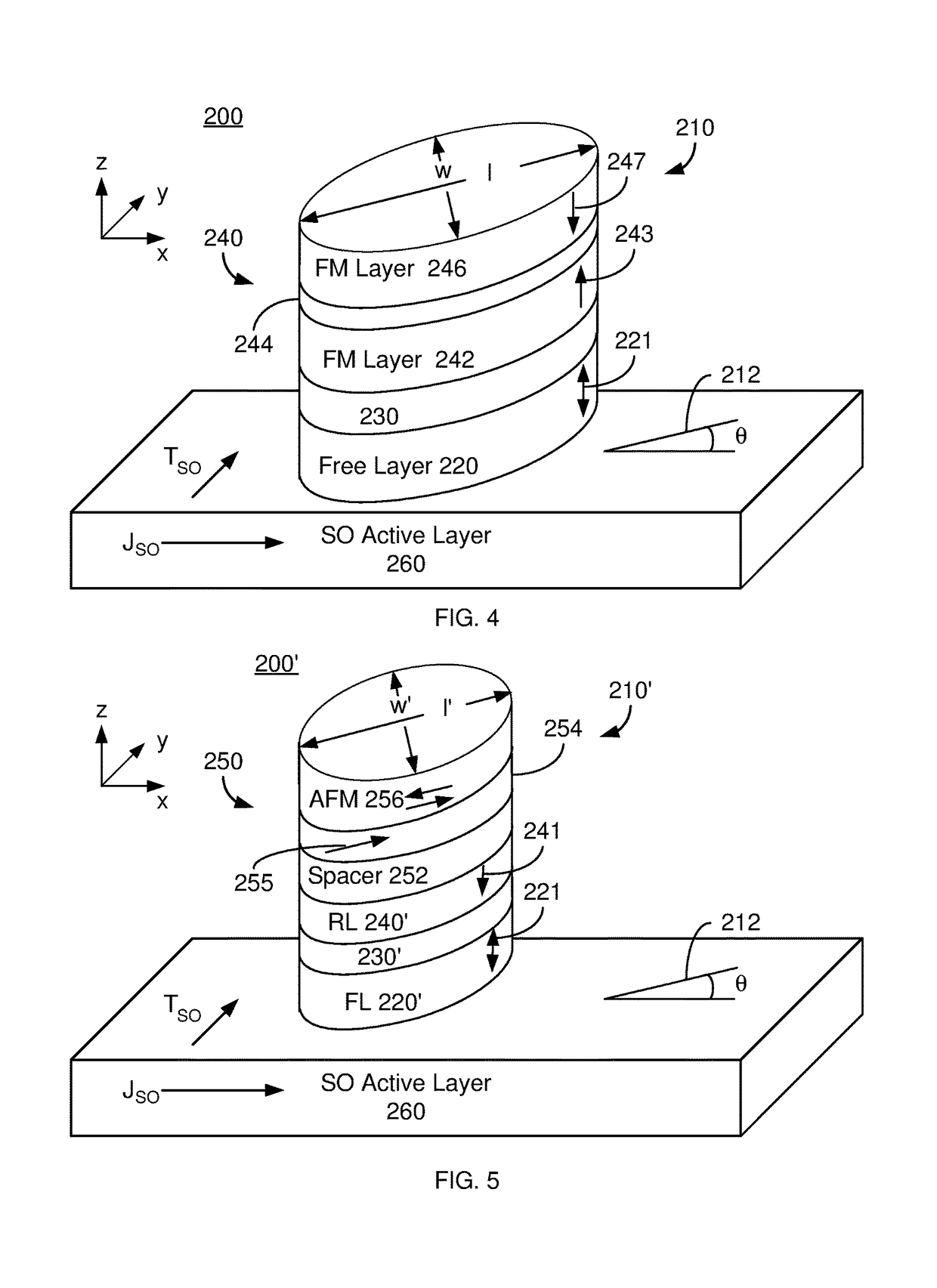
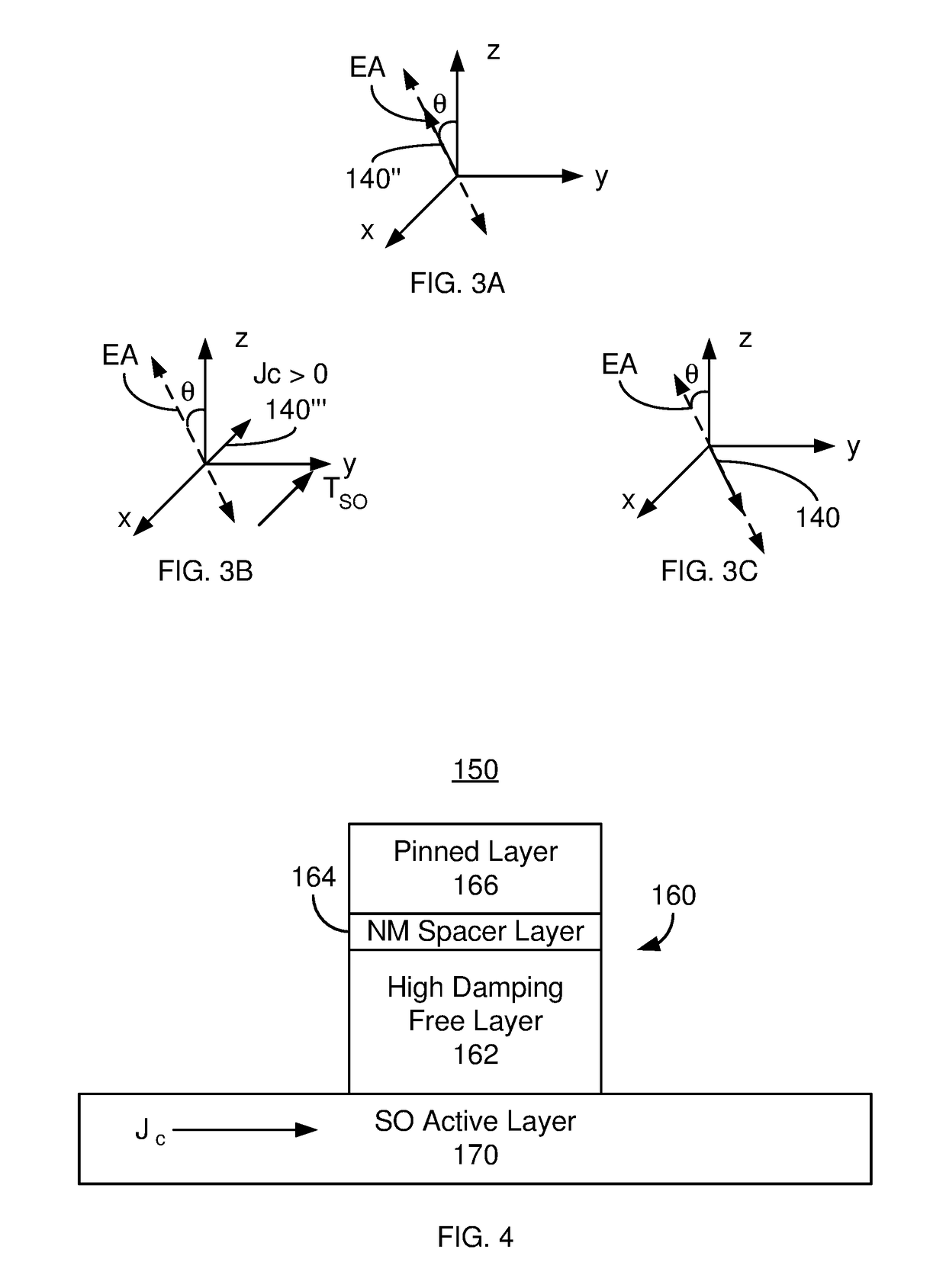
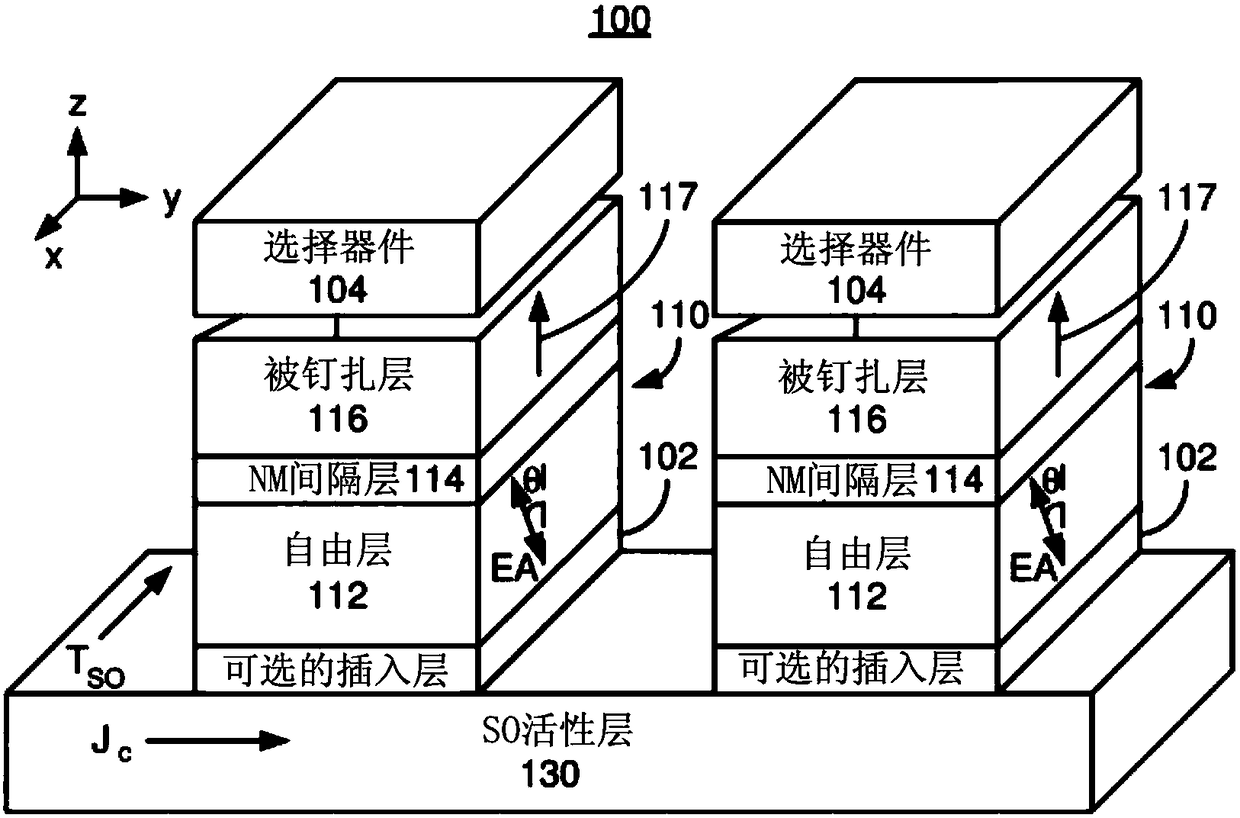
Magnetic devices including magnetic junctions having tilted easy axes and enhanced damping programmable using spin orbit torque
ActiveUS20180219152A1High damping constantHigh constantMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionIn planeDamping constant
A magnetic memory including a plurality of magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer is described. Each of the magnetic junctions includes a pinned layer, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between reference and free layers. The free layer has at least one of a tilted easy axis and a high damping constant. The tilted easy axis is at a nonzero acute angle from a direction perpendicular-to-plane. The high damping constant is at least 0.02. The at least one SO active layer is adjacent to the free layer and carries a current in-plane. The at least one SO active layer exerts a SO torque on the free layer due to the current. The free layer is switchable using the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
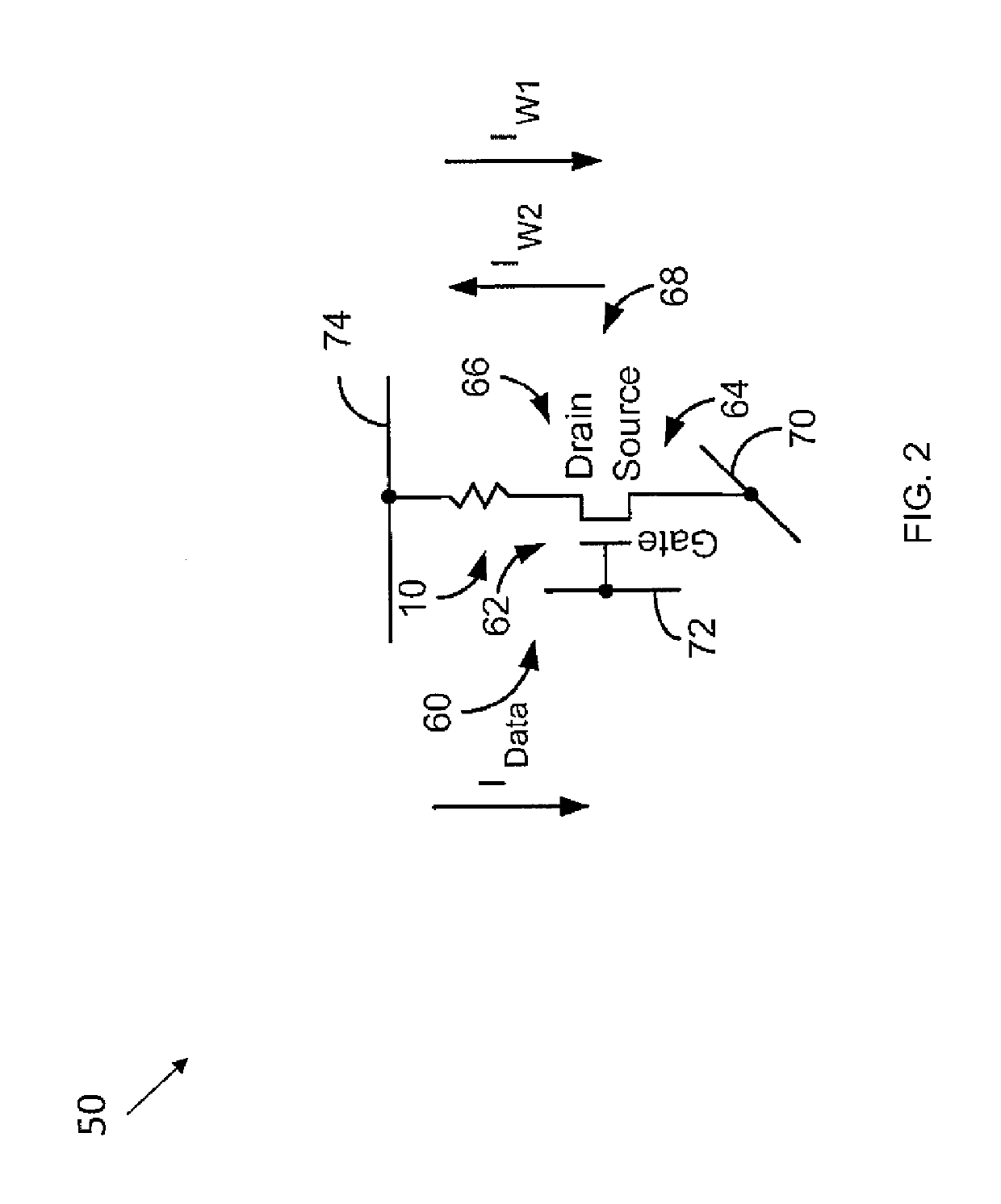
Cross-point architecture for spin-transfer torque magnetoresistive random access memory with spin orbit writing
ActiveUS20170148978A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin-transfer torqueMagnetic memory
A magnetic memory cell includes: a first spin-orbit interaction active layer; a first magnetic free layer on the first spin-orbit interaction active layer, the first magnetic free layer having a changeable magnetization; a first nonmagnetic spacer layer on the first magnetic free layer; a reference layer having a fixed magnetization on the first nonmagnetic spacer layer; a second nonmagnetic spacer layer on the reference layer; a second magnetic free layer on the second nonmagnetic spacer layer, the second magnetic free layer having a changeable magnetization; and a second spin-orbit interaction active layer on the second magnetic free layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic memory, providing method and programming method thereof
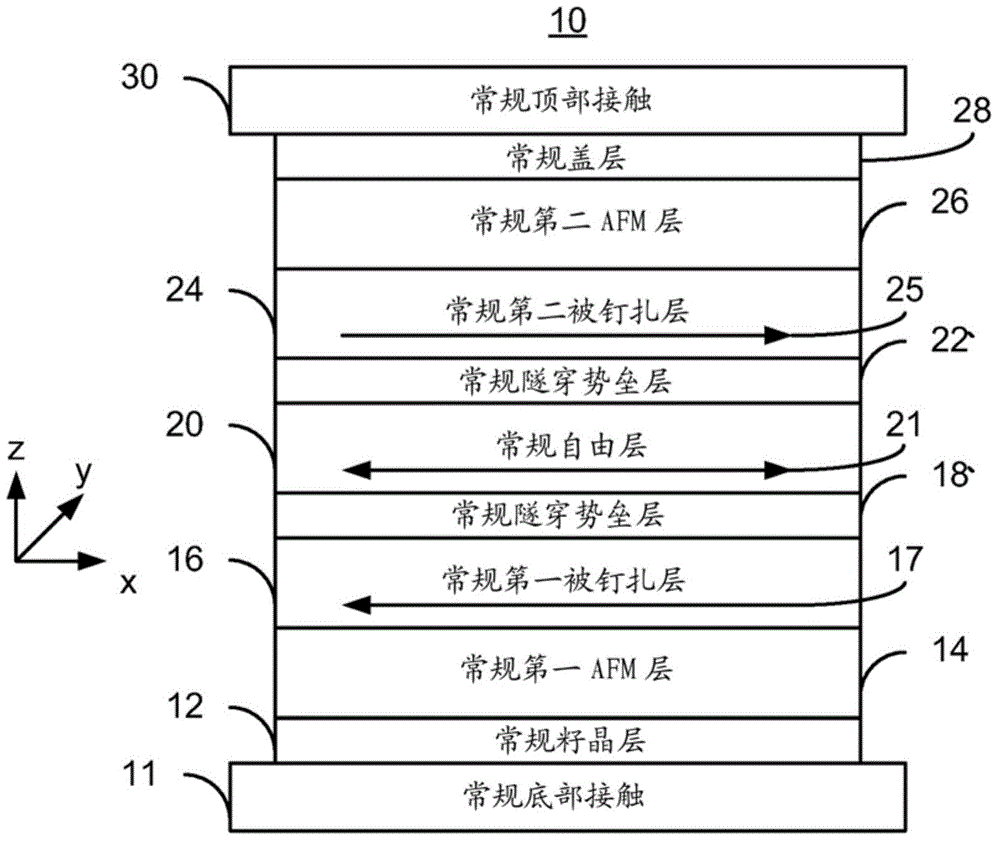
A magnetic memory, a providing method, and a programming method are described. The magnetic memory includes dual magnetic junctions and spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer(s). Each dual magnetic junction includes first and second reference layers, first and second nonmagnetic spacer layers and a free layer. The free layer is magnetic and between the nonmagnetic spacer layers. The nonmagnetic spacer layers are between the corresponding reference layers and the free layer. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the first reference layer of each dual magnetic junction. The SO active layer(s) exert a SO torque on the first reference layer due to a current passing through the SO active layer(s) substantially perpendicular to a direction between the SO active layer(s) and the first reference layer. The first reference layer has a magnetic moment changeable by at least the SO torque. The free layer is switchable using a spin transfer write current driven through the dual magnetic junction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing dual magnetic tunneling junctions using spin-orbit interaction-based switching and memories utilizing the dual magnetic tunneling junctions
A magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes dual magnetic junctions and spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer(s). Each dual magnetic junction includes first and second reference layers, first and second nonmagnetic spacer layers and a free layer. The free layer is magnetic and between the nonmagnetic spacer layers. The nonmagnetic spacer layers are between the corresponding reference layers and the free layer. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the first reference layer of each dual magnetic junction. The SO active layer(s) exert a SO torque on the first reference layer due to a current passing through the SO active layer(s) substantially perpendicular to a direction between the SO active layer(s) and the first reference layer. The first reference layer has a magnetic moment changeable by at least the SO torque. The free layer is switchable using a spin transfer write current driven through the dual magnetic junction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic memory and method for providing and programming the magnetic memory
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vertical spin orbit torque devices
ActiveUS20190273202A1PerformanceTorque may be improvedMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin orbit torqueEngineering
A magnetic device and method for programming the magnetic device are described. The magnetic device includes a plurality of magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer having a plurality of sides. The SO active layer(s) carry a current in direction(s) substantially perpendicular to the plurality of sides. Each of the magnetic junction(s) is adjacent to the sides and substantially surrounds a portion of the SO active layer. Each magnetic junction includes a free layer, a reference layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the pinned and free layers. The SO active layer(s) exert a SO torque on the free layer due to the current passing through the SO active layer(s). The free layer is switchable between stable magnetic states. The free layer may be written using the current and, in some aspects, another current driven through the magnetic junction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
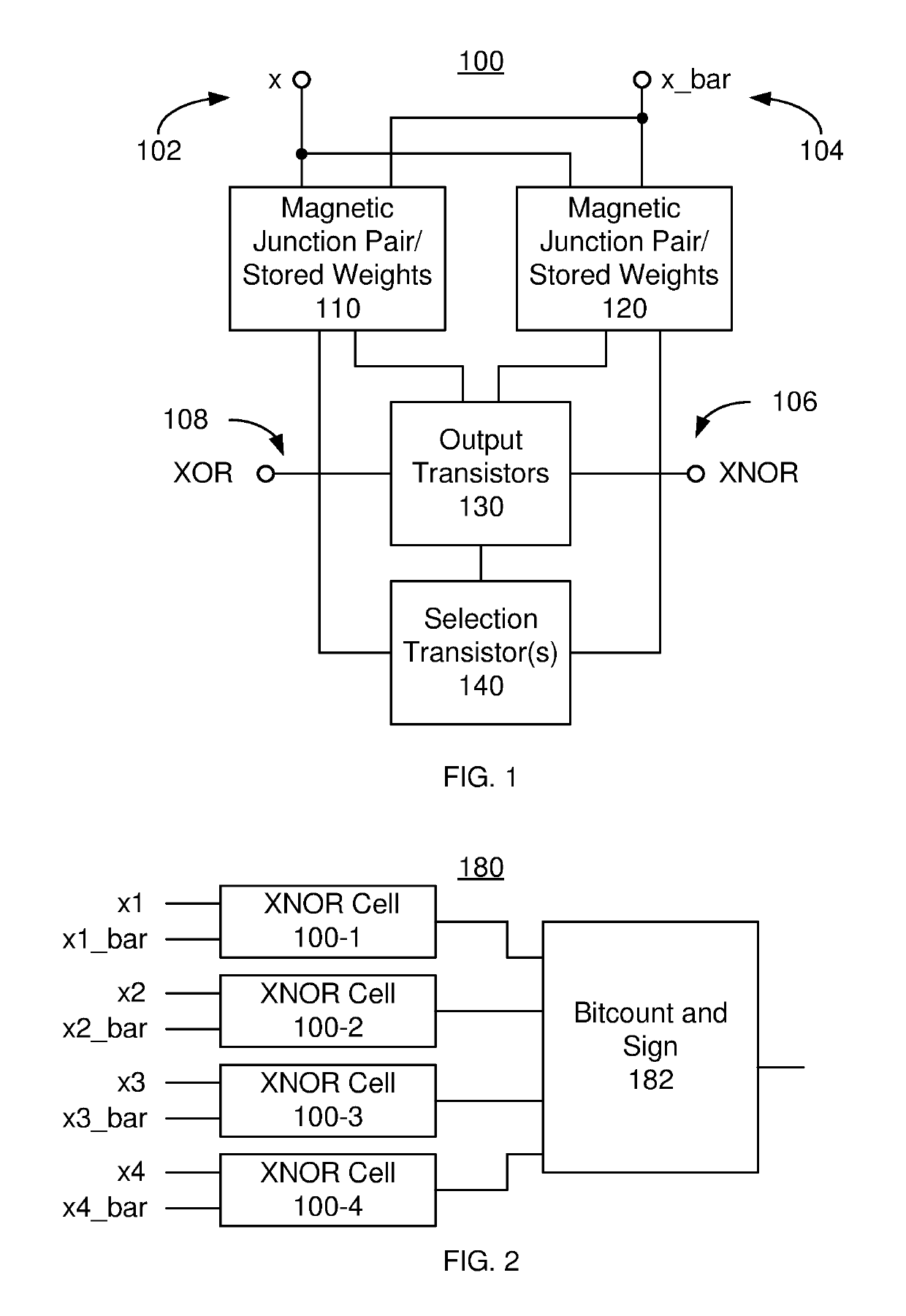
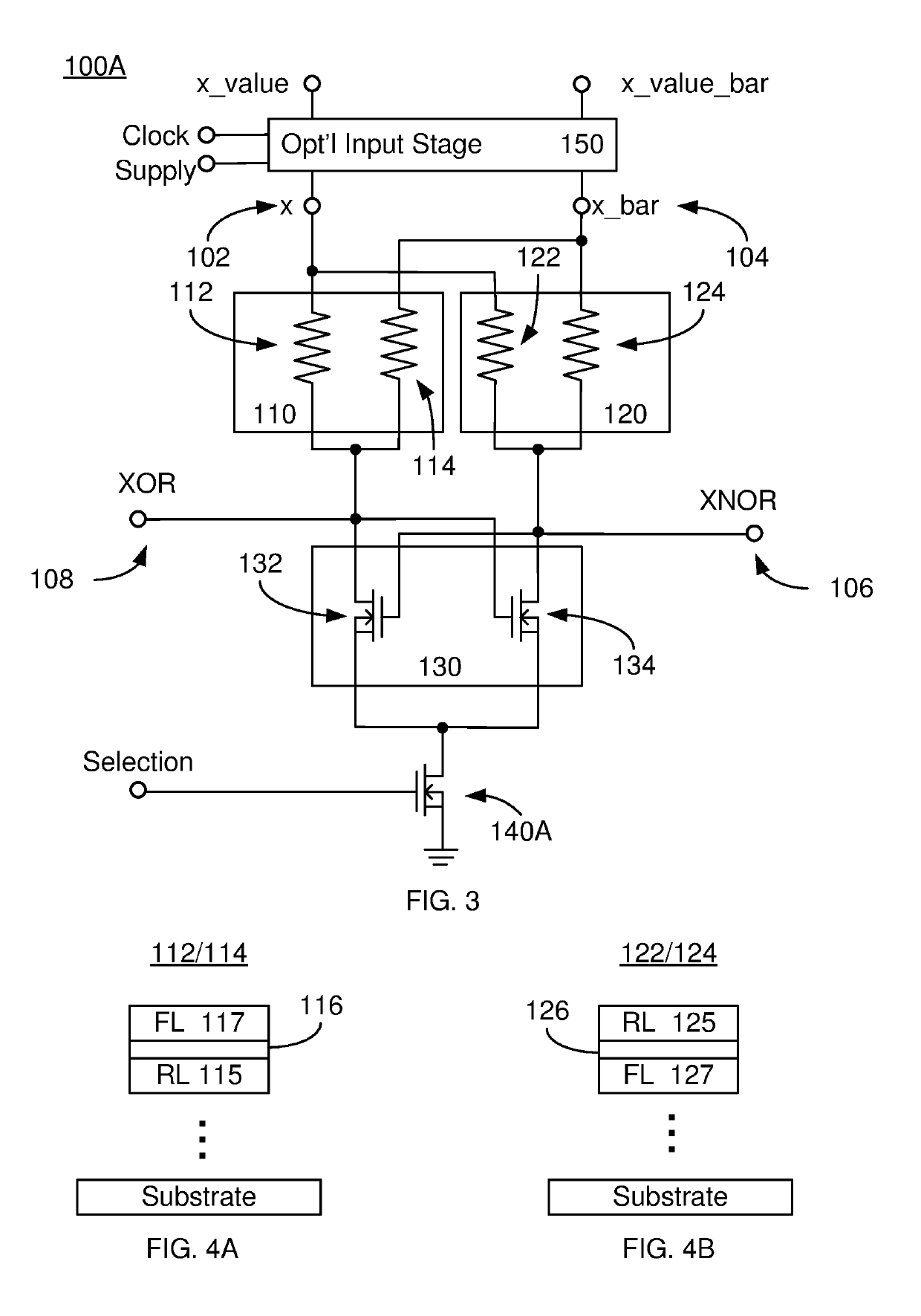
Method and system for providing a variation resistant magnetic junction-based xnor cell usable in neuromorphic computing
ActiveUS20190131977A1Perform XNORExclusive-OR circuitsDigital storageAudio power amplifierSpin-transfer torque
A hardware cell and method for performing a digital XNOR of an input signal and weights are described. The hardware cell includes input lines, a plurality of pairs of magnetic junctions, output transistors and at least one selection transistor coupled with the output transistors. The input lines receive the input signal and its complement. The magnetic junctions store the weight. Each magnetic junction includes a reference layer, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the reference layer and the free layer. The free layer has stable magnetic states and is programmable using spin-transfer torque and / or spin-orbit interaction torque. The first magnetic junction of a pair receives the input signal. The second magnetic junction of the pair receives the input signal complement. The output transistors are coupled with the magnetic junctions such that each pair of magnetic junctions forms a voltage divider. The output transistors form a sense amplifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
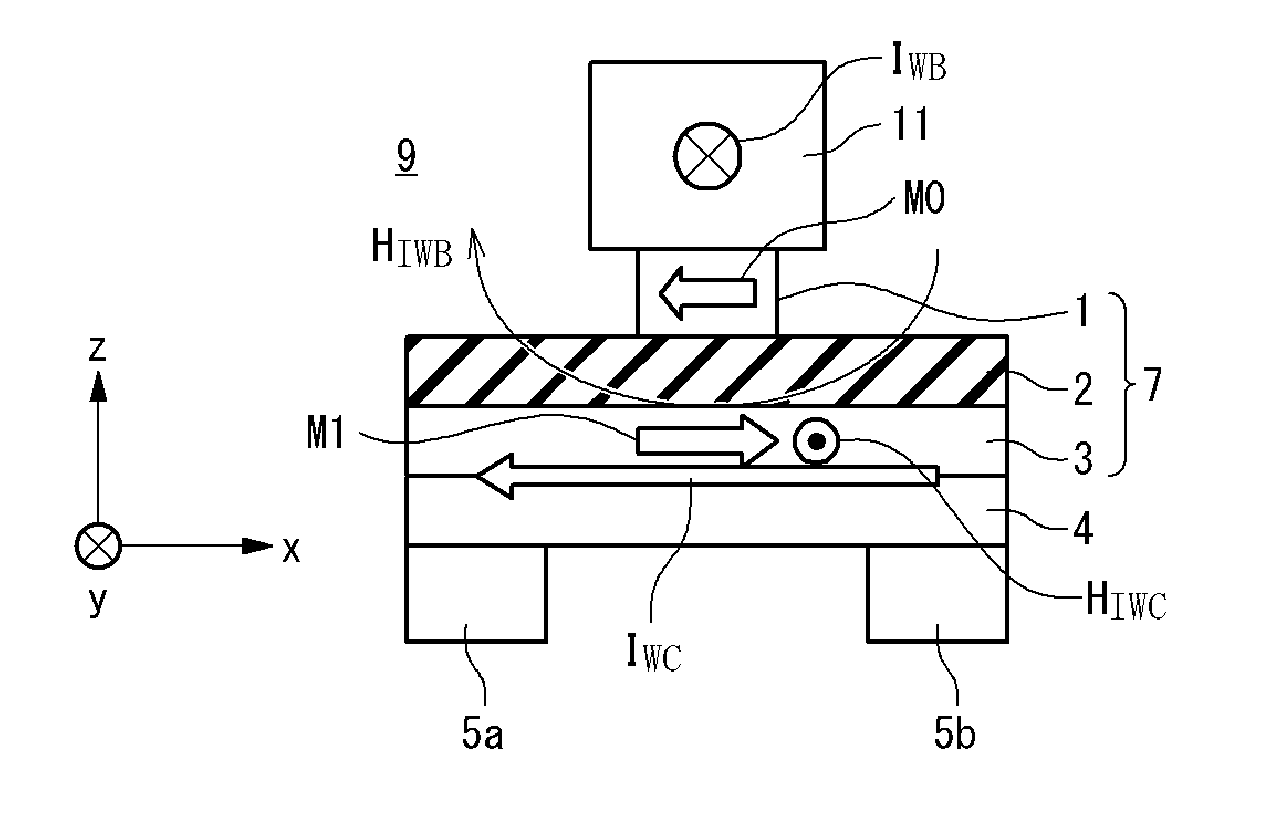
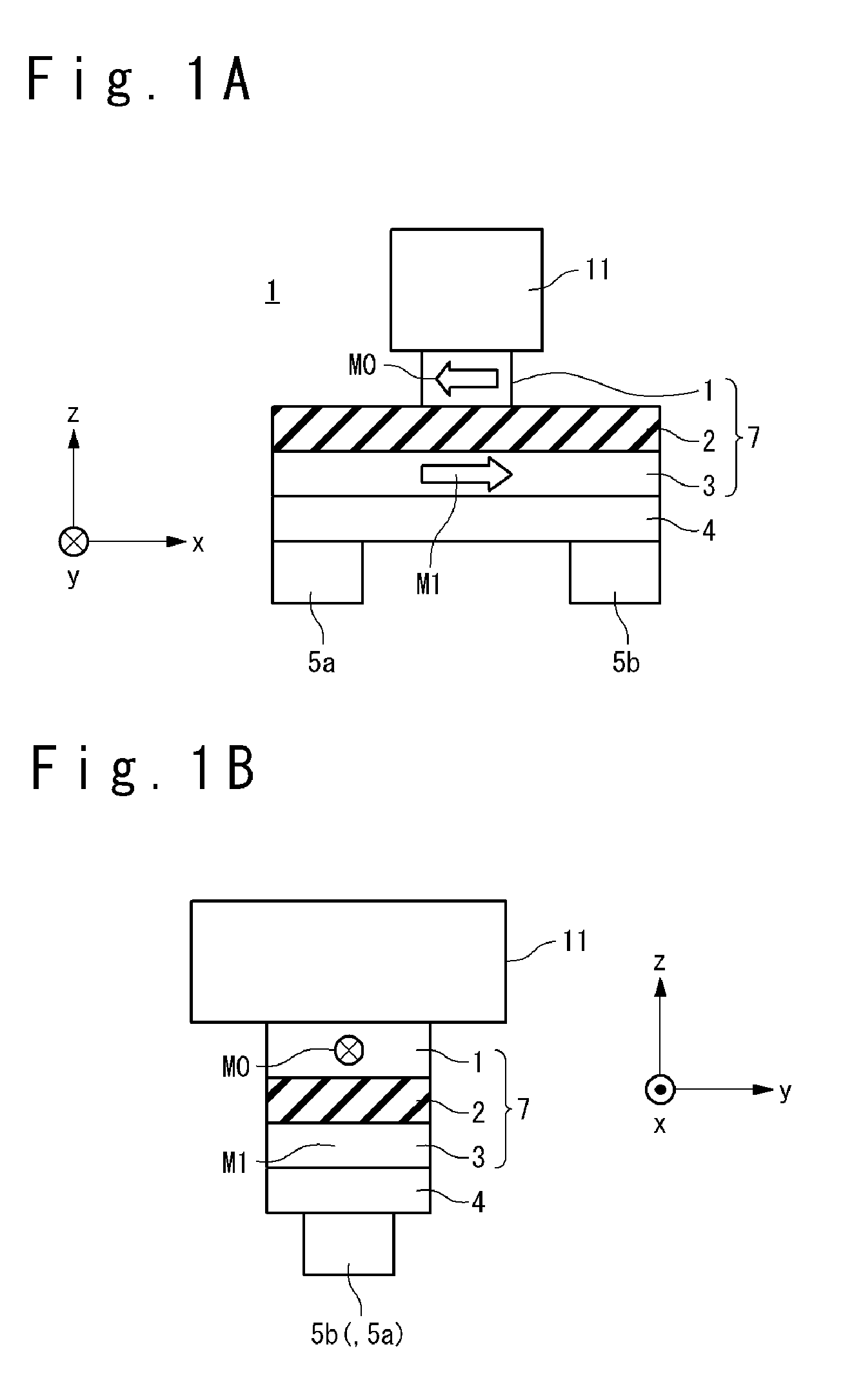
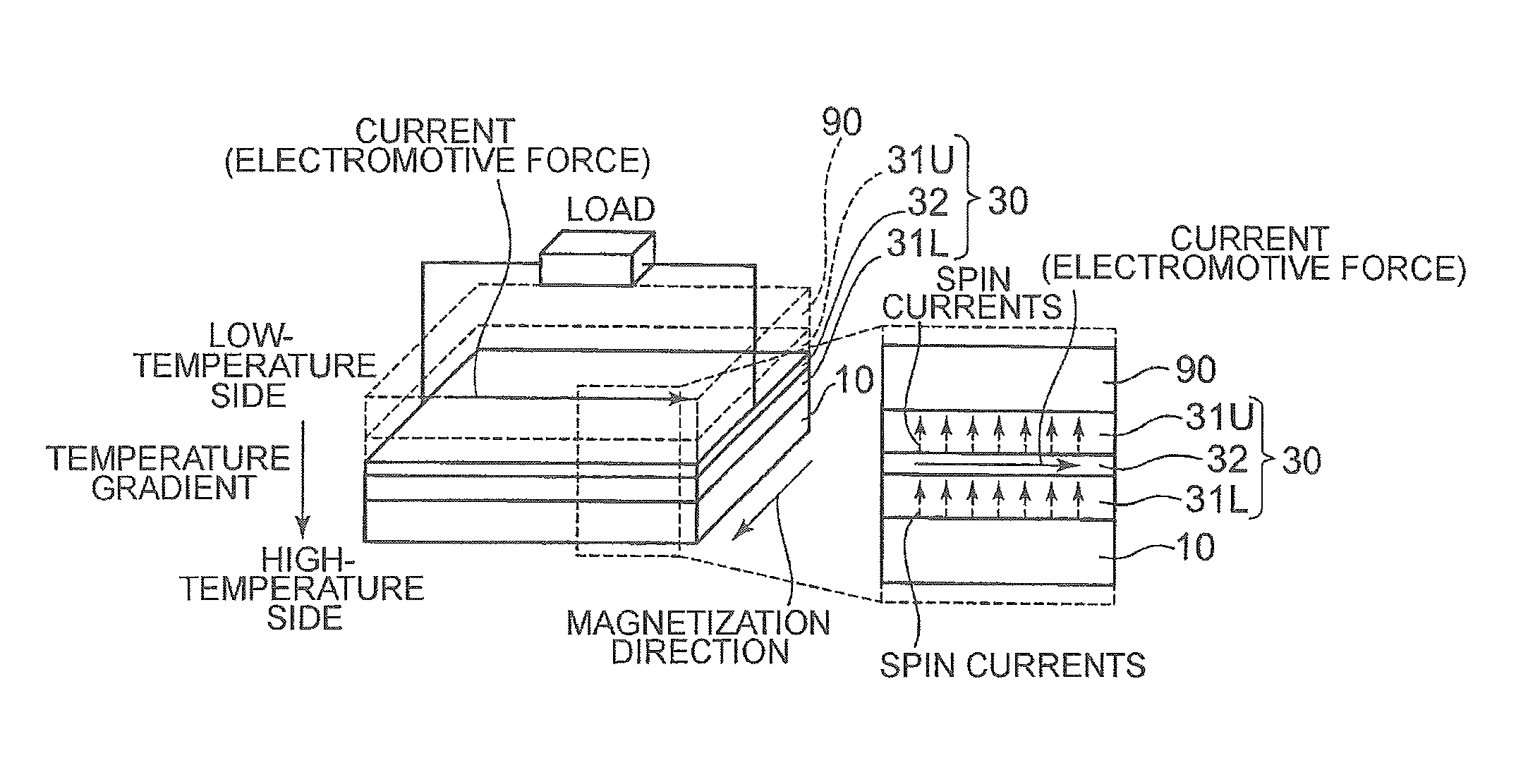
Magnetic memory using spin orbit interaction
A magnetic memory includes: a base layer; a magnetization free layer; a barrier layer; and a magnetization reference layer. The magnetization free layer, with which the base layer is covered, has invertible magnetization and is magnetized approximately uniformly. The barrier layer, with which the magnetization free layer is covered, is composed of material different from material of the base layer. The magnetization reference layer is arranged on the barrier layer and has a fixed magnetization. When the magnetization of the magnetization free layer is inverted, a first writing current is made to flow from one end to the other end of the magnetization free layer in an in-plane direction without through the magnetization reference layer.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Spin orbit torque magnetic ram
ActiveUS20190165254A1Low densityMaximize transparencySolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetic ramSpin orbit torque
A spin torque magnetic RAM according to the present invention includes at least one row selection line positioned on a silicon substrate to induce a spin orbit interaction therein; at least one first magnetic pattern positioned on the row selection line; a second magnetic pattern positioned on the first magnetic pattern; a tunnel barrier positioned on the second magnetic pattern; and a third magnetic pattern positioned on the tunnel barrier, wherein the first magnetic pattern is made of a cobalt film, the first magnetic pattern and the second magnetic pattern have a total thickness of 5 nm to form a free layer, and the third magnetic pattern is formed with a pinned layer in which a magnetization direction is fixed.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
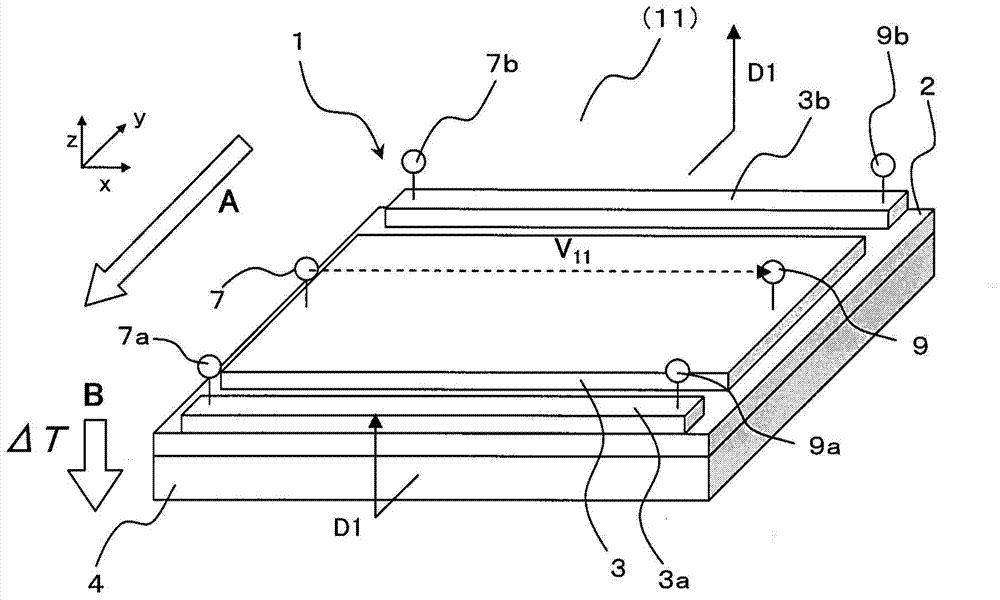
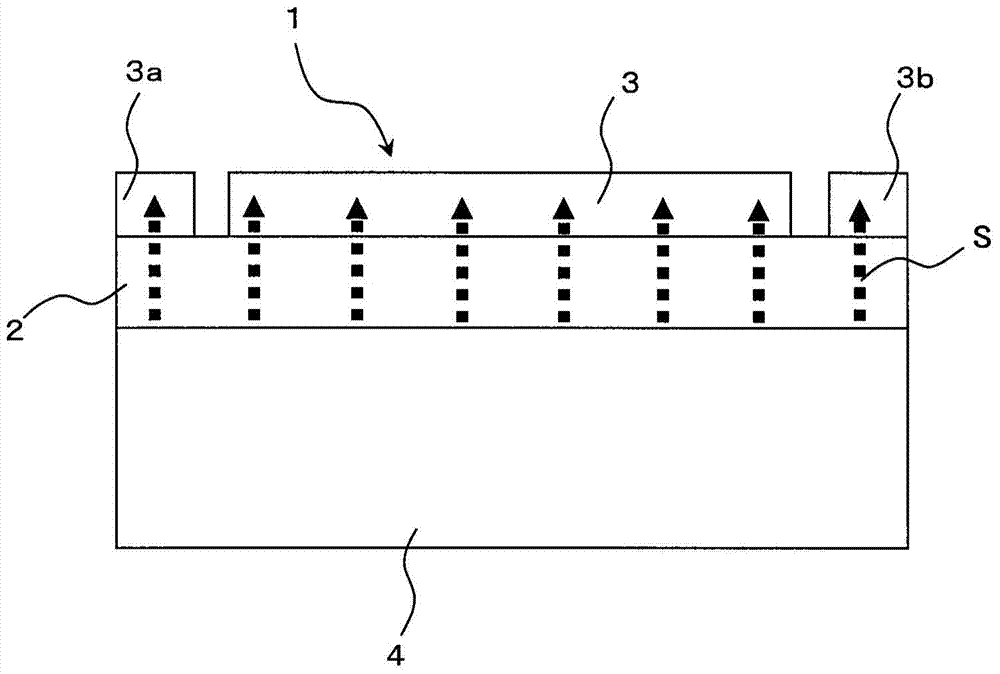
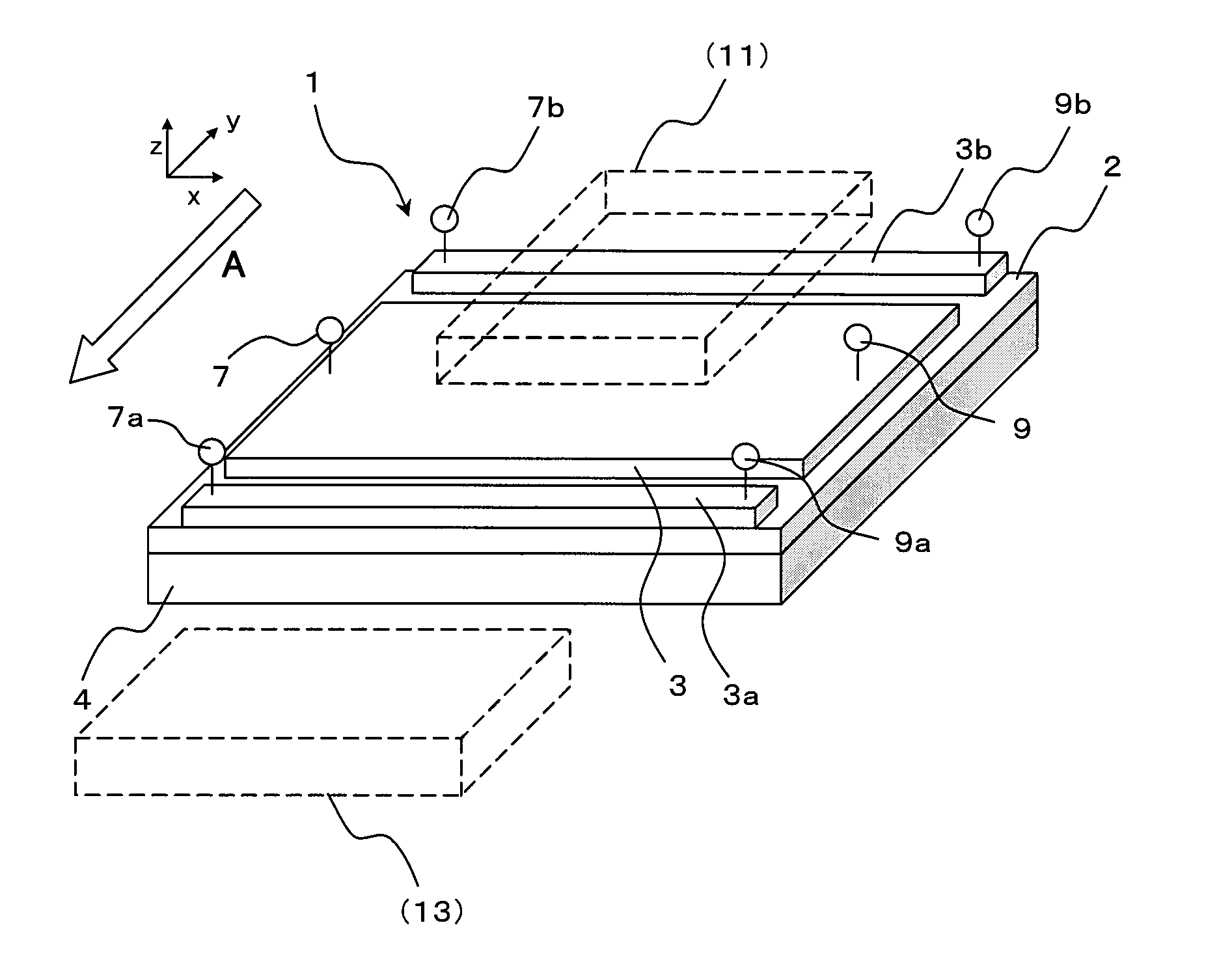
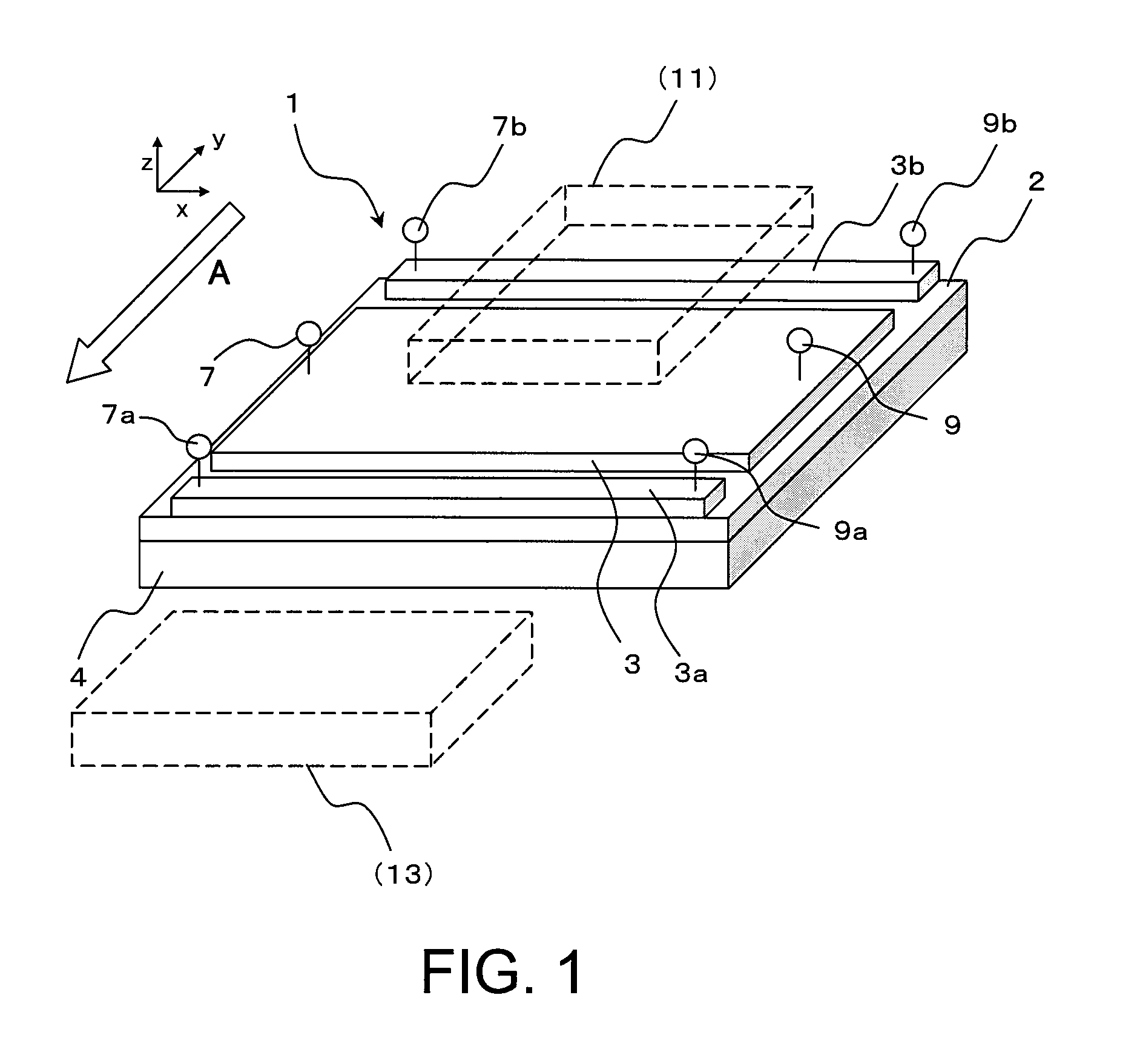
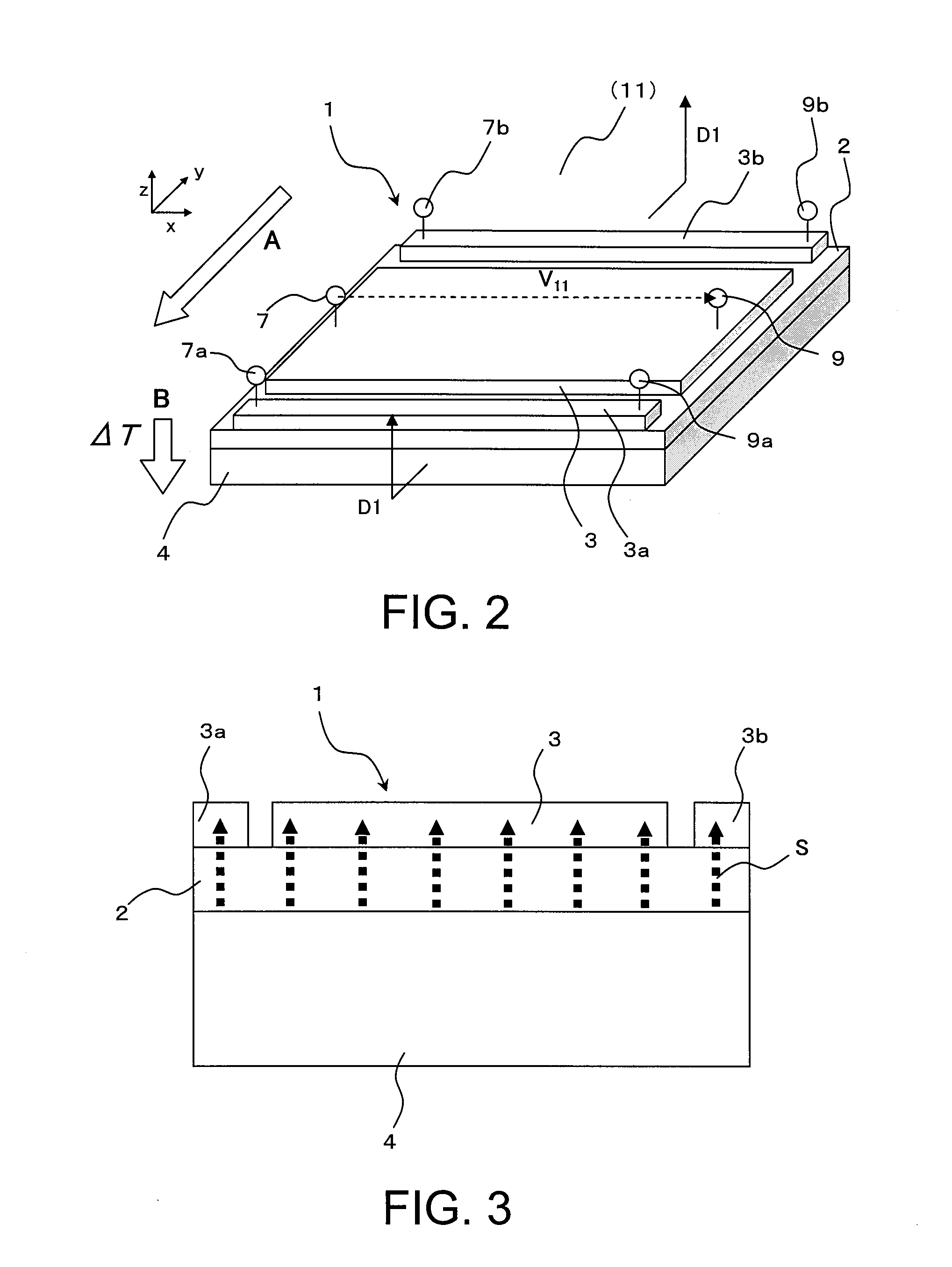
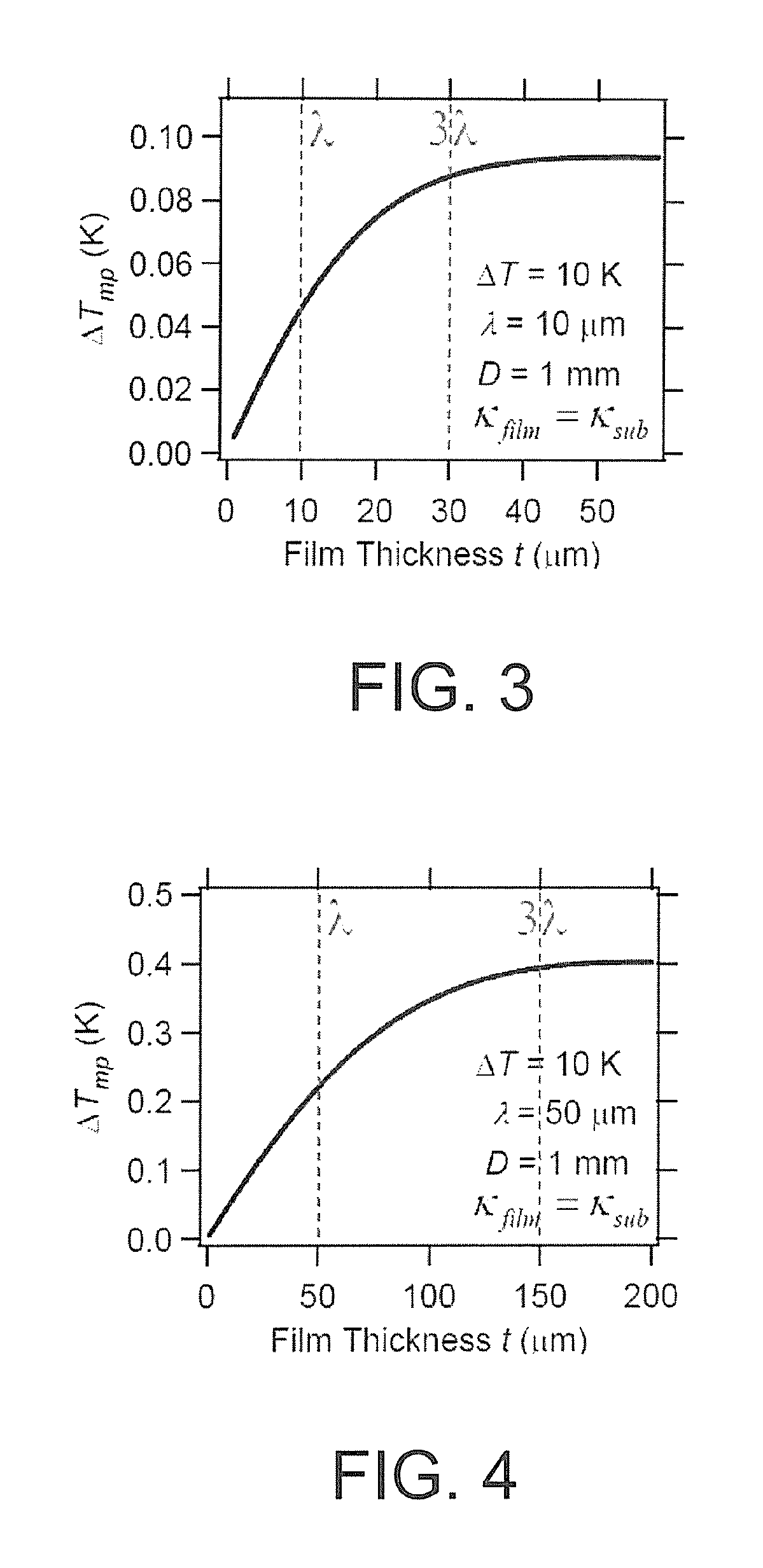
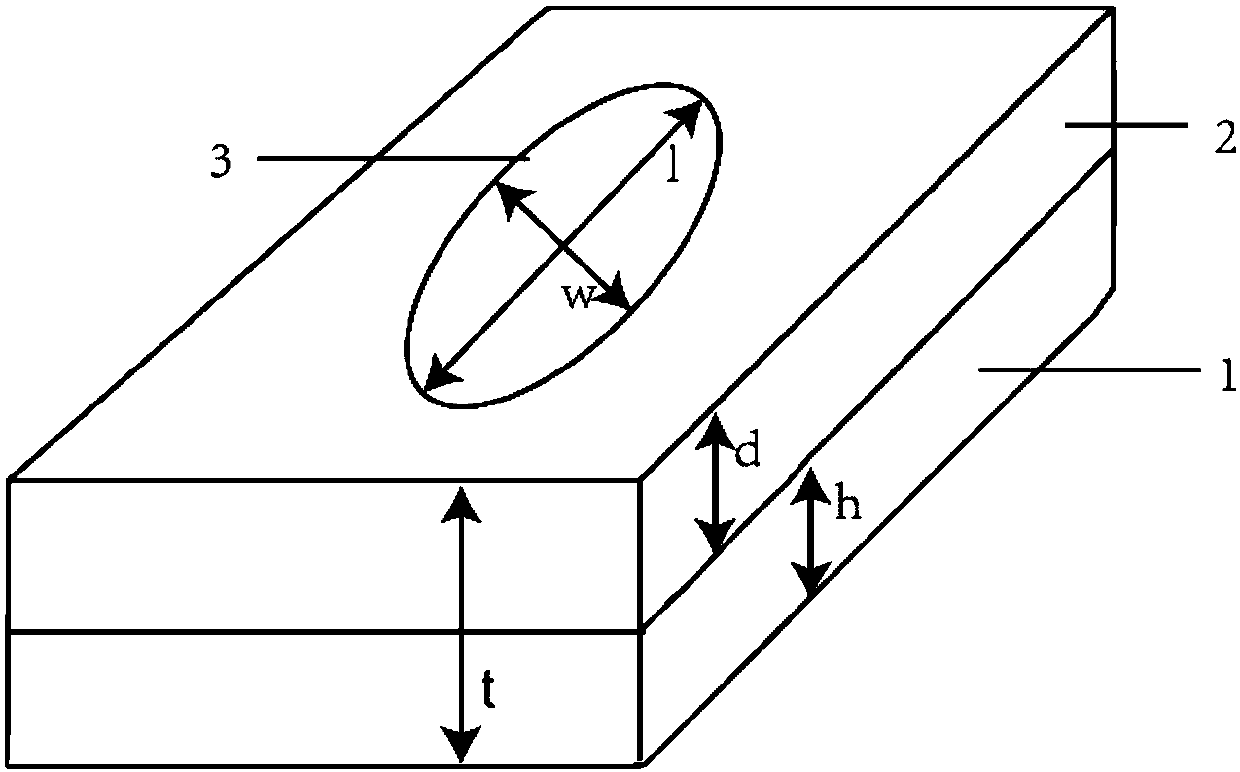
Thermoelectric converter element, method of manufacturing thermoelectric converter element, and thermoelectric conversion method
InactiveUS20130312802A1Improve productivityImprove conversion efficiencyThermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentMagnetizationMaterials science
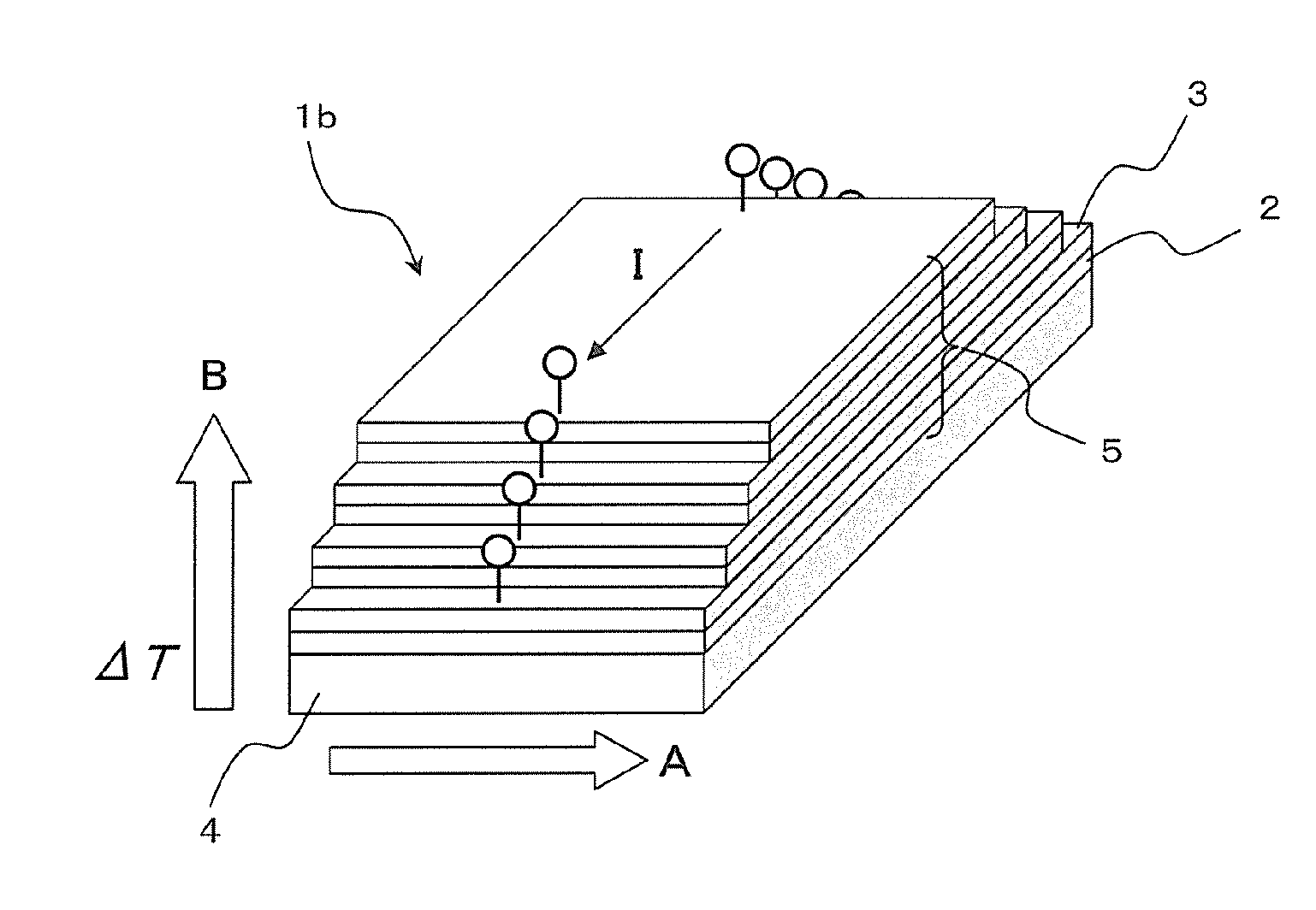
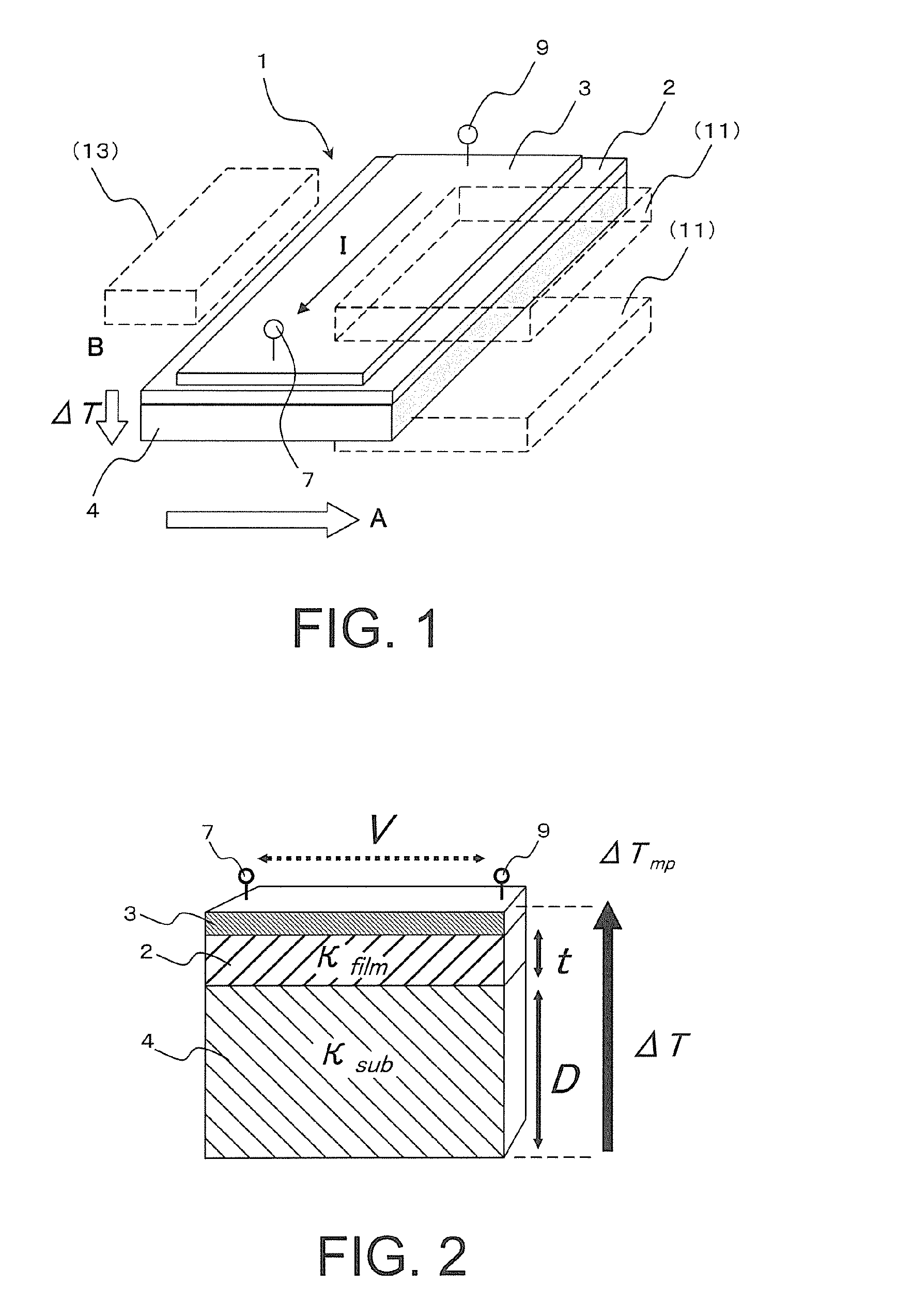
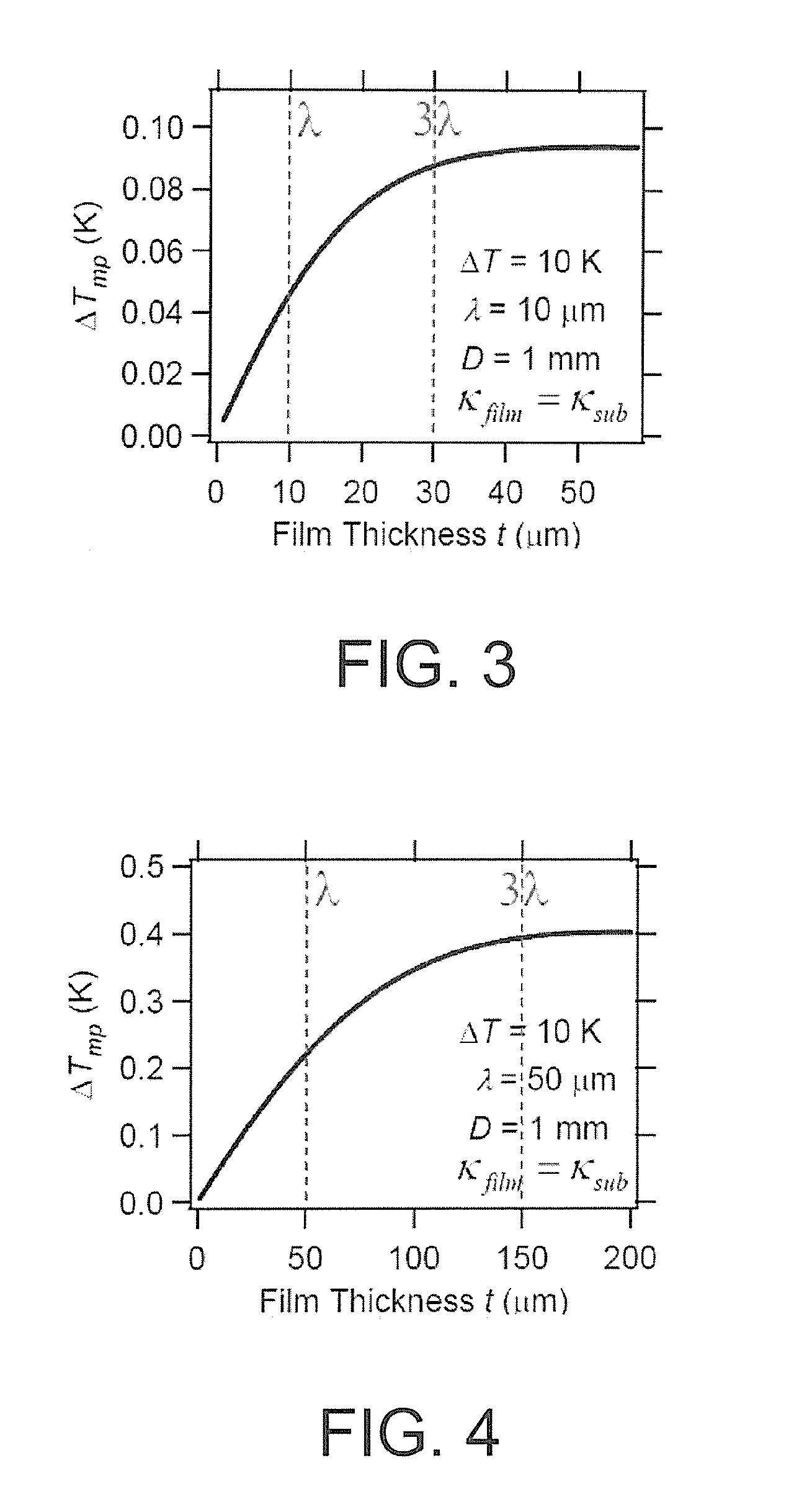
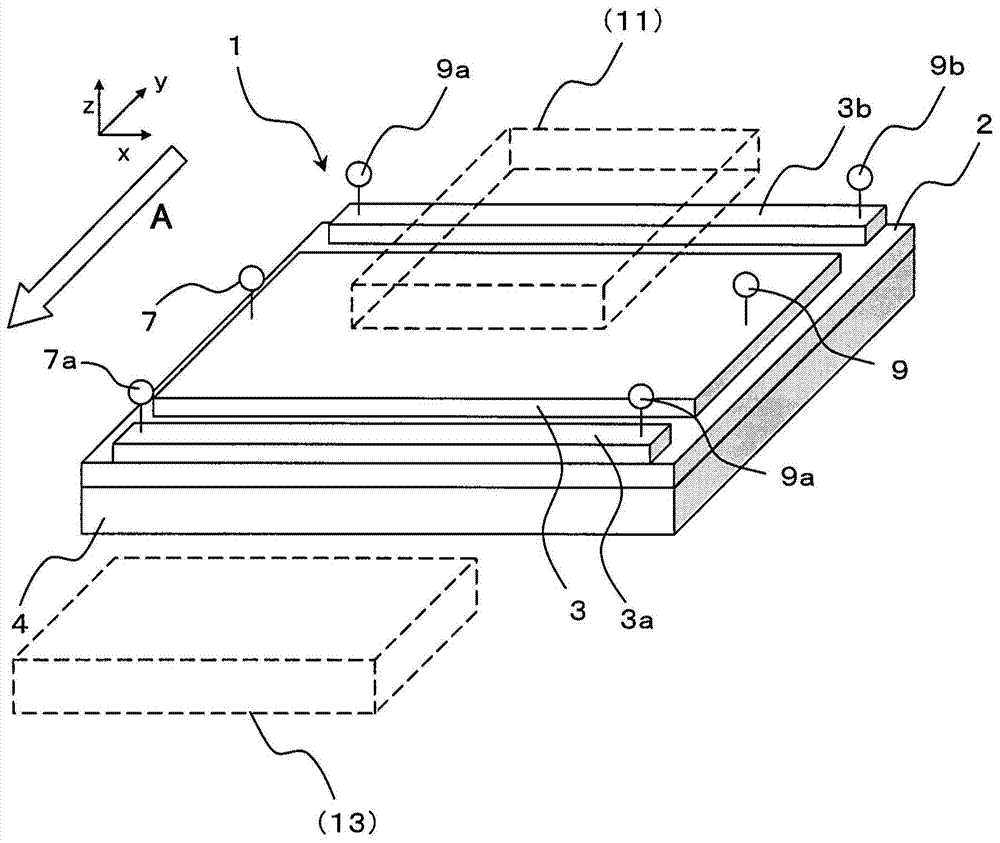
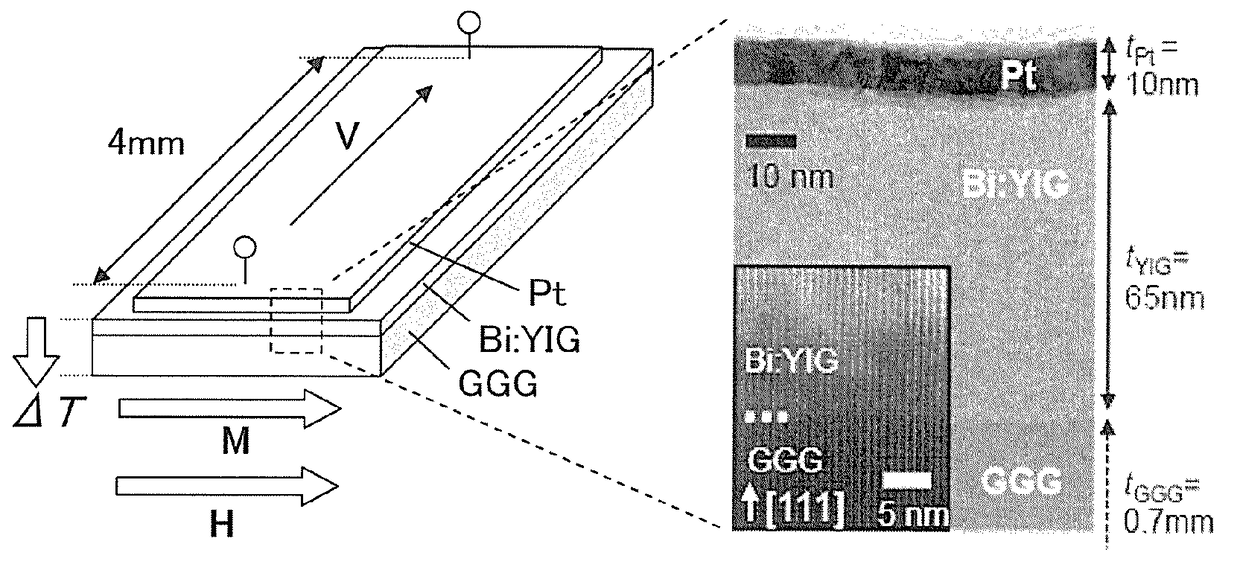
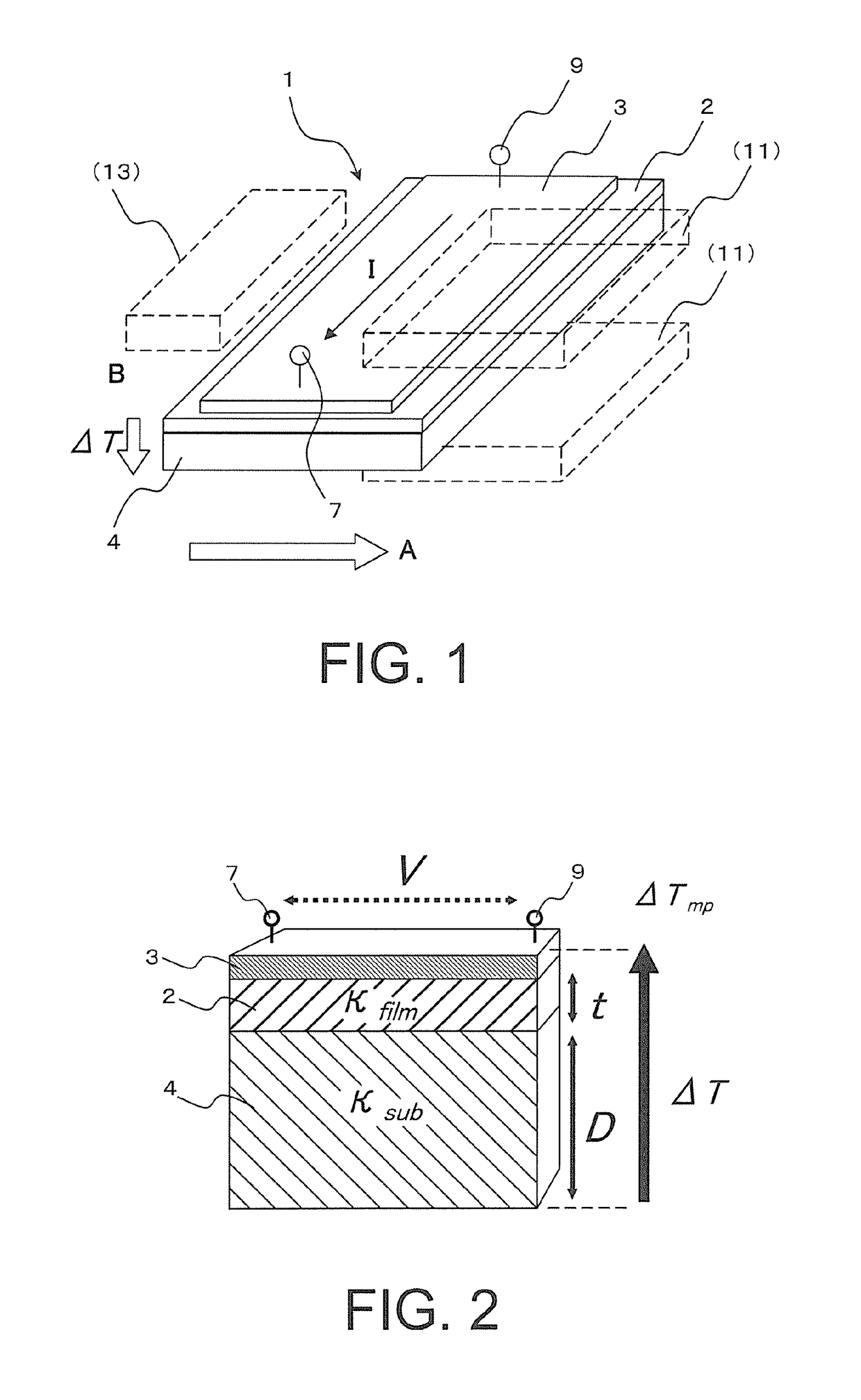
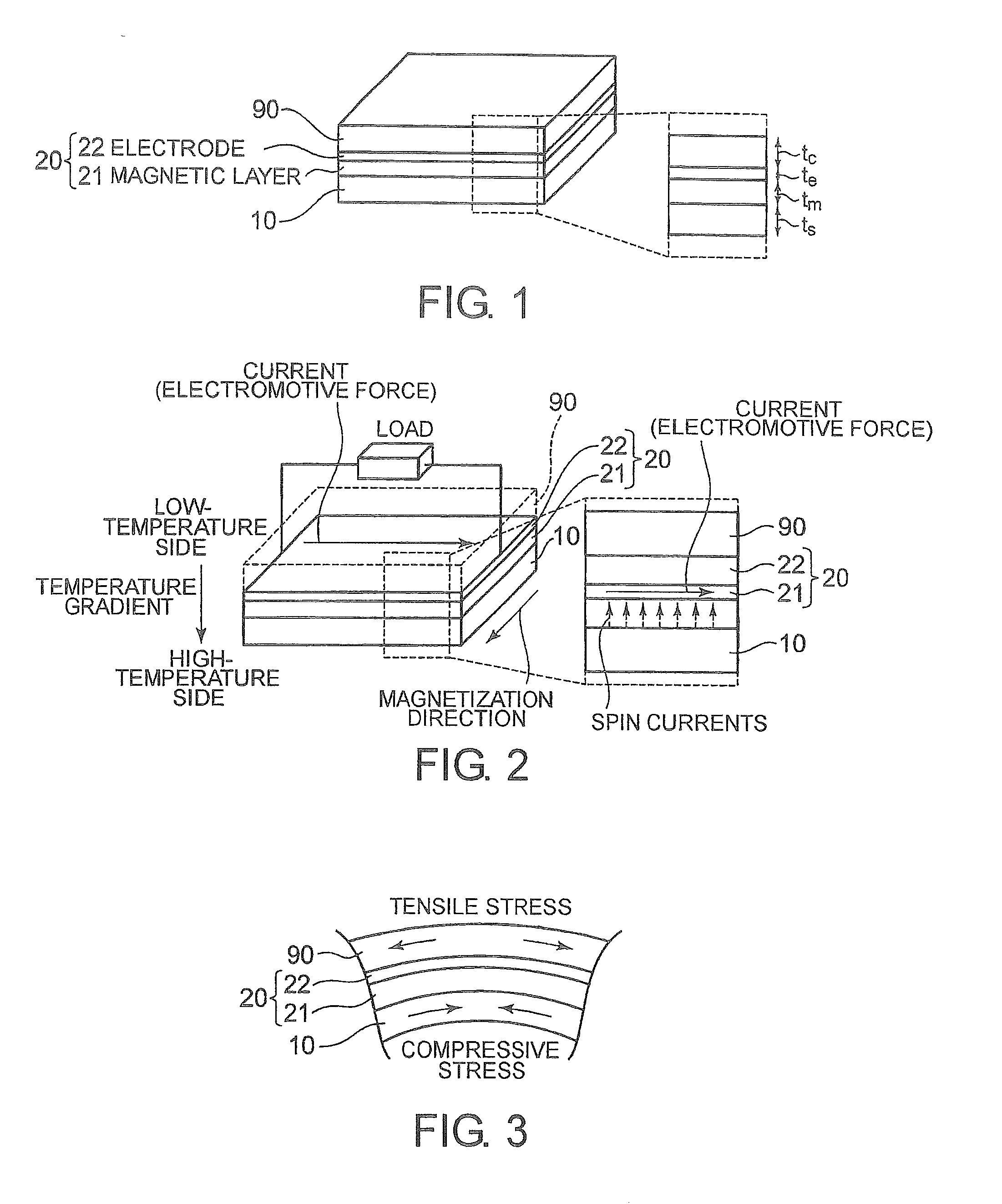
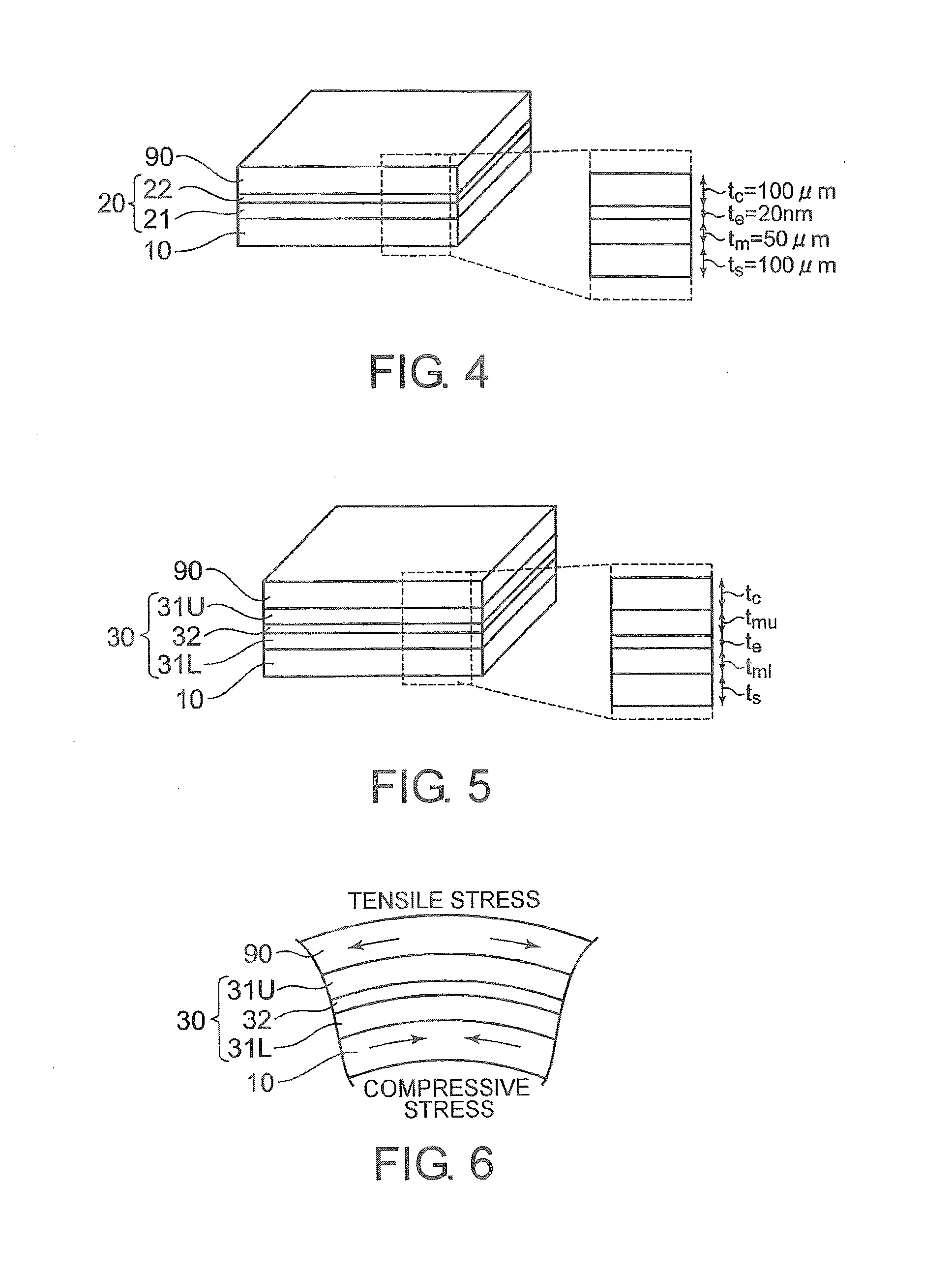
An object of the present invention is to provide a low-cost thermoelectric converter element having high productivity and excellent conversion efficiency. A thermoelectric converter element according to the present invention includes a substrate 4, a magnetic film 2 provided on the substrate 4 with a certain magnetization direction A and formed of a polycrystalline magnetically insulating material, and an electrode 3 provided on the magnetic film 2 with a material exhibiting a spin-orbit interaction. When a temperature gradient is applied to the magnetic film 2, a spin current is generated so as to flow from the magnetic film 2 toward the electrode 3. A current I is generated in a direction perpendicular to the magnetization direction A of the magnetic film 2 by the inverse spin Hall effect in the electrode 3.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
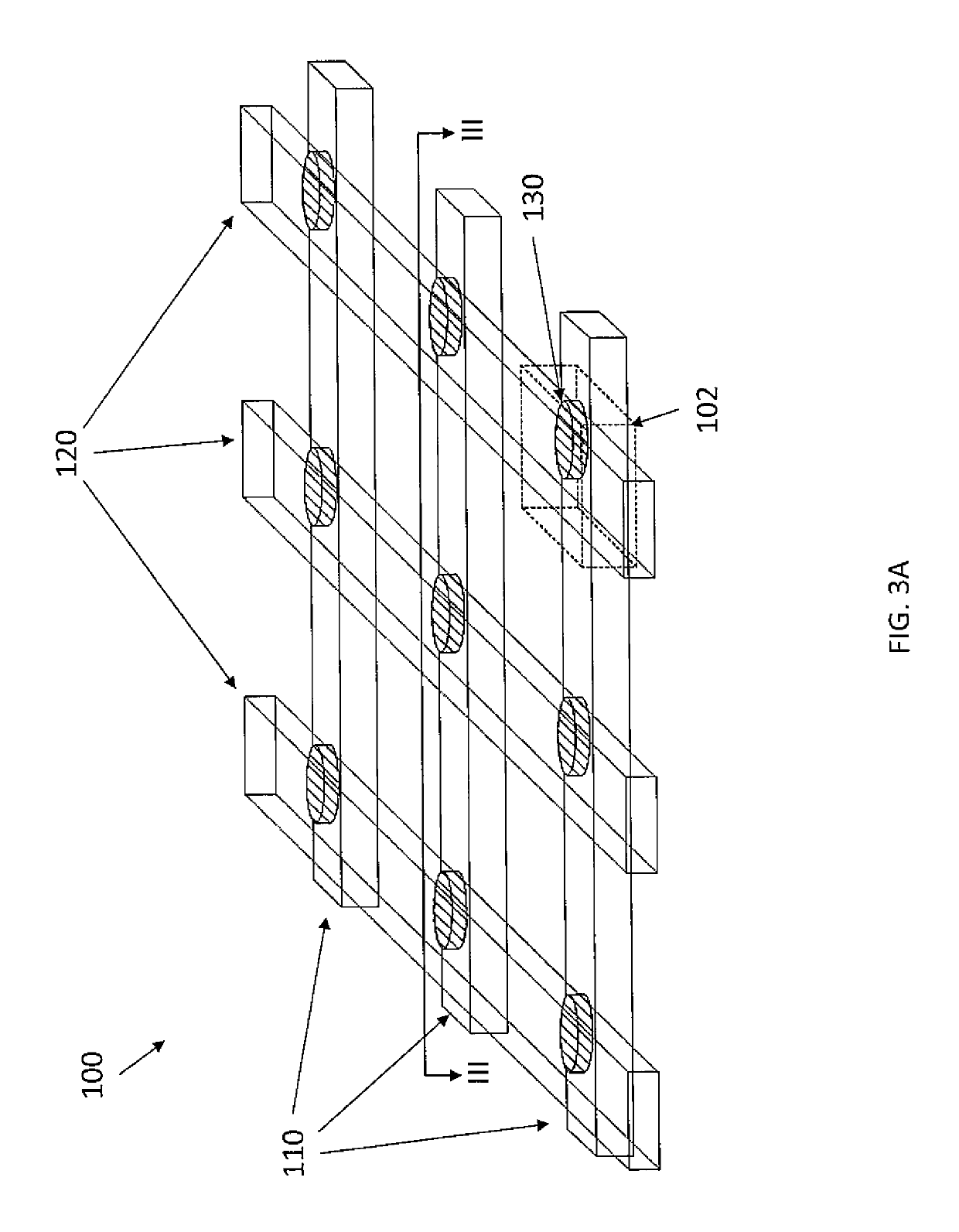
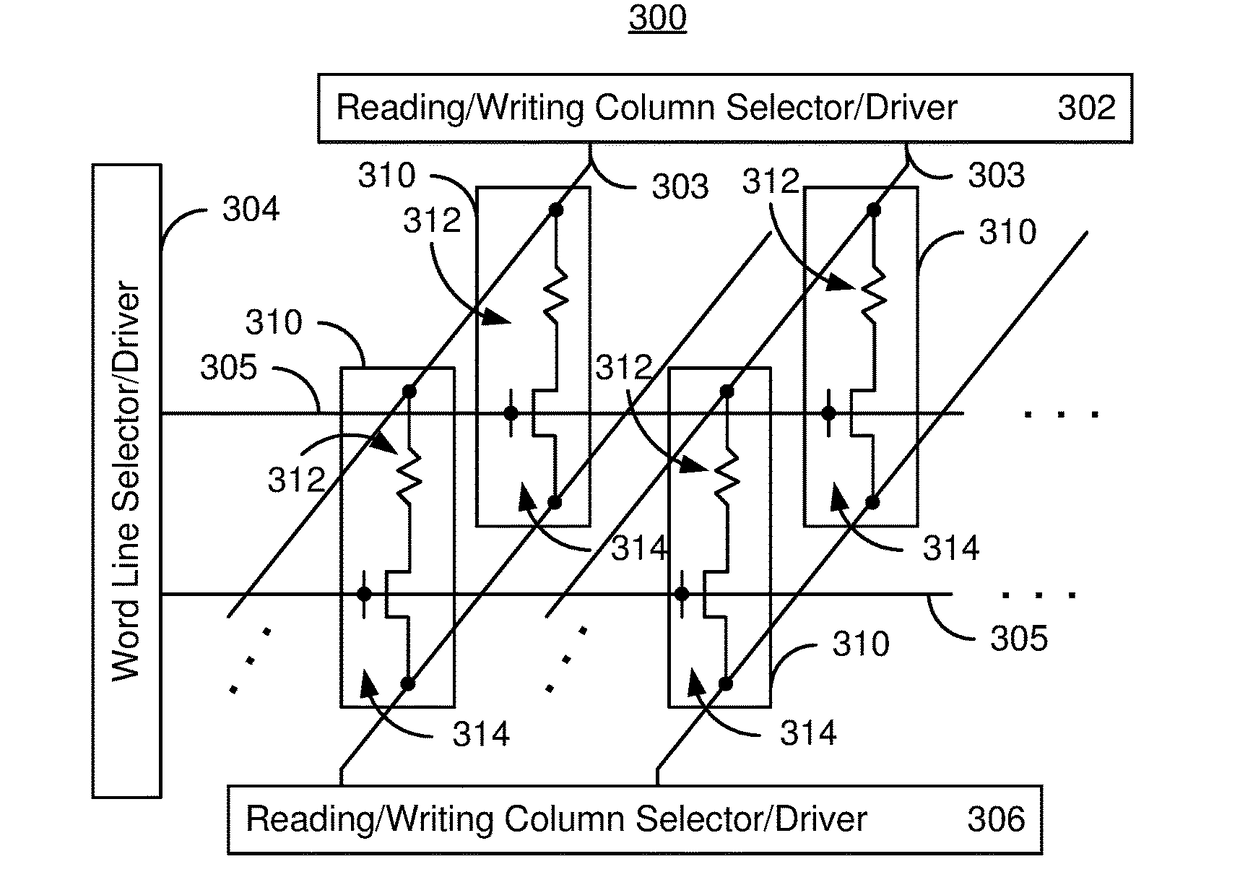
Architecture for magnetic memories including magnetic tunneling junctions using spin-orbit interaction based switching
A magnetic memory includes memory array tiles (MATs), intermediate circuitry, global bit lines and global circuitry. Each MAT includes bit lines, word lines, and magnetic storage cells having magnetic junction(s), selection device(s) and at least part of a spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer adjacent to the magnetic junction(s). The SO active layer exerts a SO torque on the magnetic junction(s) due to a preconditioning current passing through the SO active layer. The magnetic junction(s) are programmable using write current(s) driven through the magnetic junction(s) and the preconditioning current. The bit and word lines correspond to the magnetic storage cells. The intermediate circuitry controls read and write operations within the MATs. Each global bit line corresponds to a portion of the MATs. The global circuitry selects and drivesportions of the global bit lines for read operations and write operations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nano-light field spin-orbit interaction measurement system and method
ActiveCN109596576AAchieving handedness resolutionAchieving spin-orbit interactionsAnalysis by material excitationBeam splittingOptoelectronics
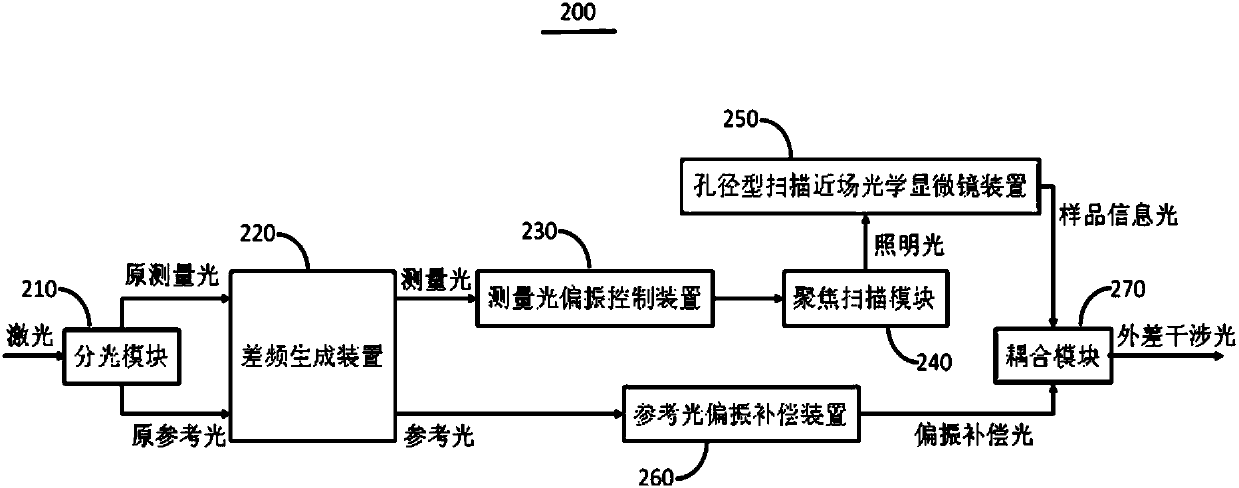
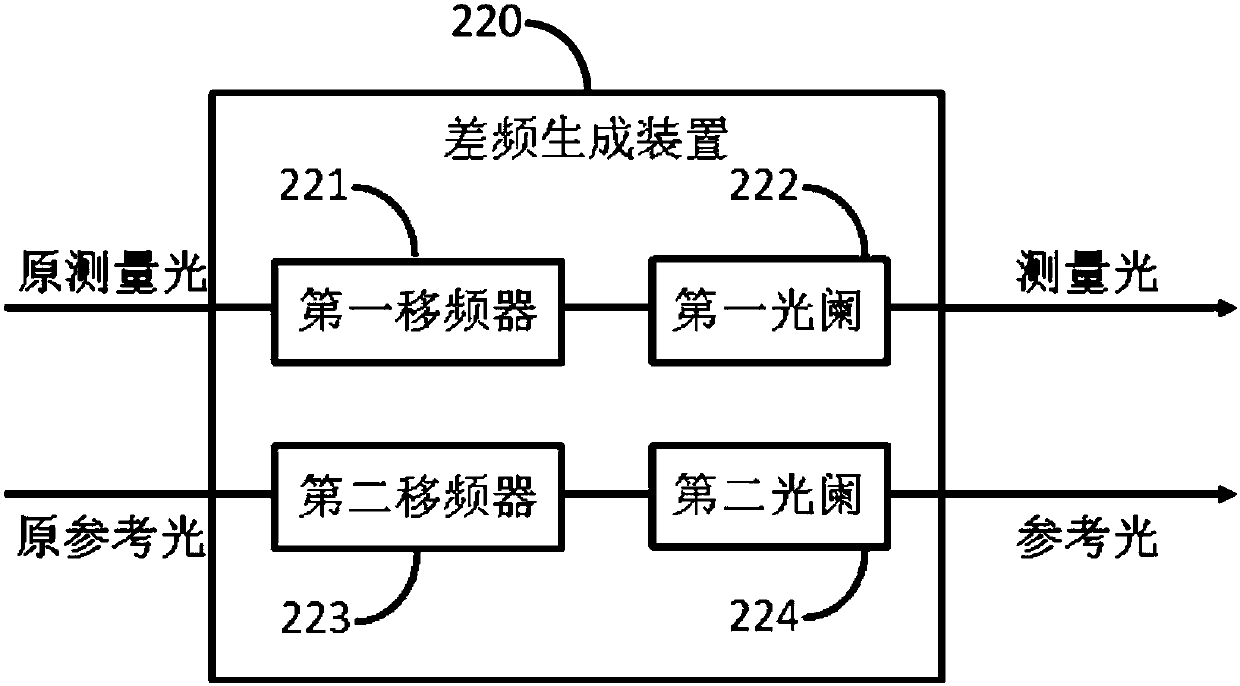
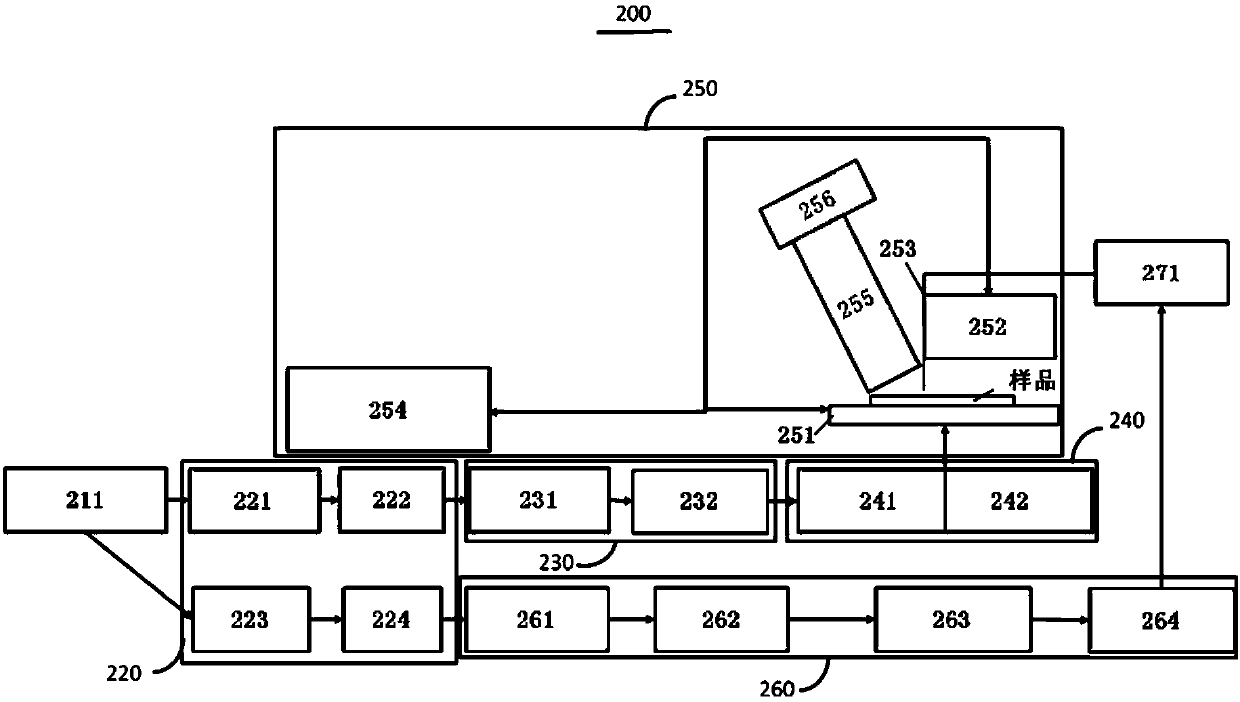
The invention discloses a spin-resolved probe heterodyne interference device, a nano-light field spin-orbit interaction measurement system and method. The probe heterodyne interference device comprises the following parts: a beam splitting module, through which the single beam laser is divided into an original measuring light and an original reference light; a difference frequency generating device, configured to perform frequency modulation on the original measuring light and the original reference light, and output a measuring light and a reference light with predetermined frequency difference; a measuring light polarization control device, disposed in the transmission direction of the measuring light; a focusing scanning device, arranged to output the illumination light in the output direction of the reference light of the measuring light polarization control device; an aperture type scanning near-field optical microscope device, wherein the illumination light excites samples to generate nano light fields, and the aperture type scanning near-field optical microscope device collects the nano-light fields in near-field detection and outputs sample information light; a reference light polarization compensation device, disposed in the transmission direction of reference light, wherein the reference light is incident on the reference light polarization compensation device to output polarization compensation light; and a coupling device, to which the sample information light and the polarization compensation light are transmitted to interfere to generate heterodyne interference light.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
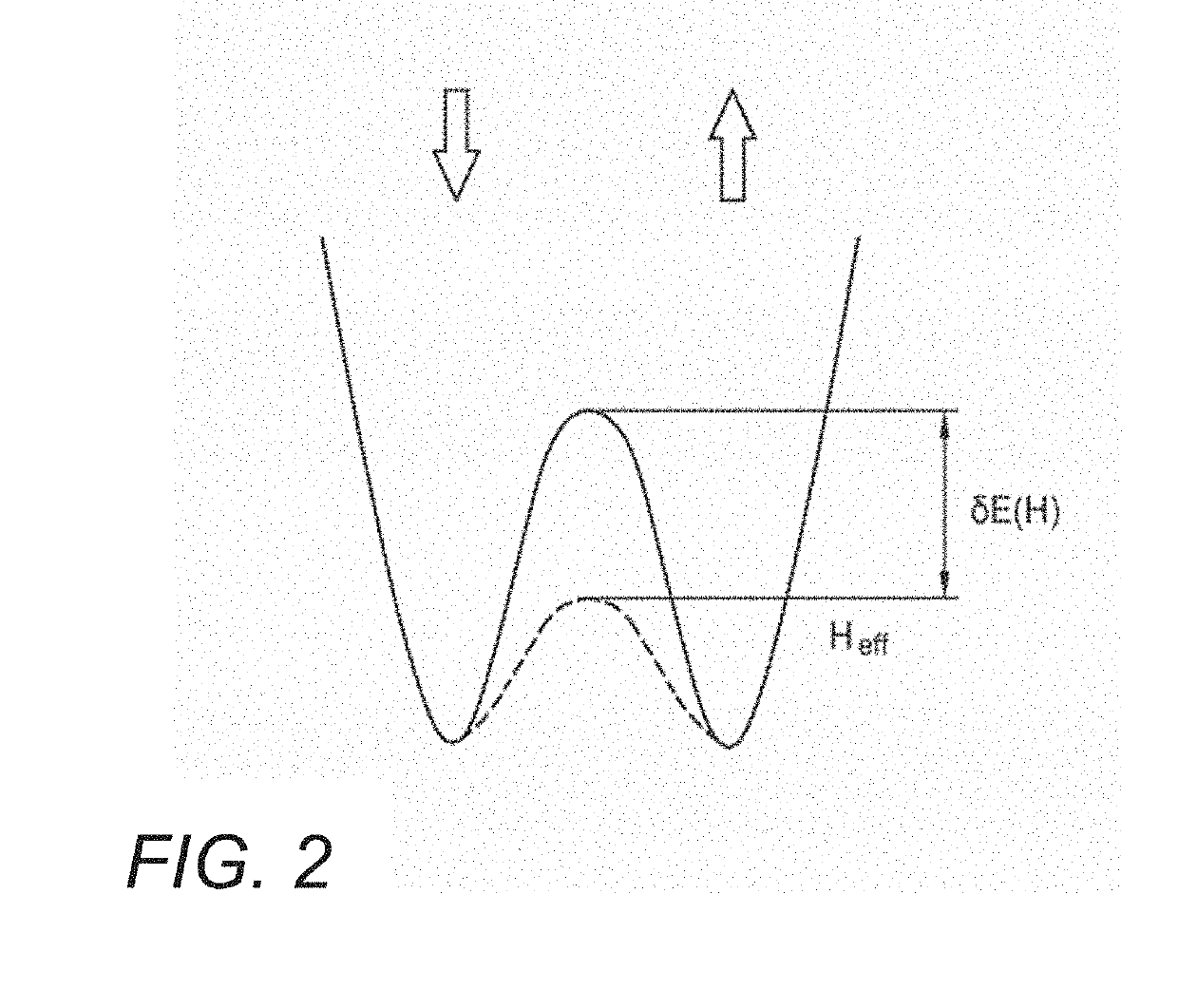
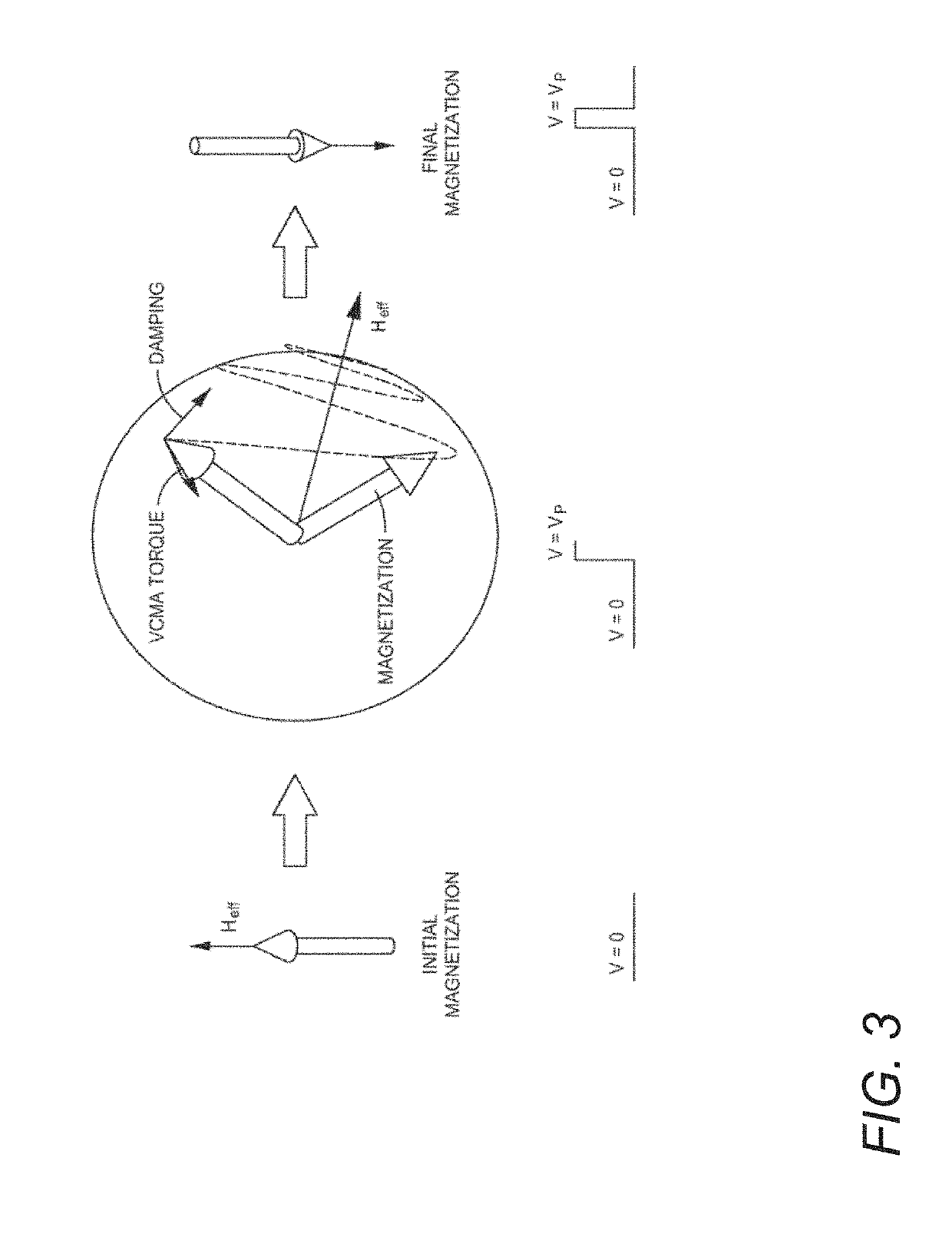
Heterostructures for Electric Field Controlled Magnetic Tunnel Junctions
InactiveUS20190189908A1Solid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionAtomic orbitalMagnetic anisotropy
In various embodiments, magnetic heterostructures and magnetic layers can be implemented and configured to provide electric field controlled magnetic tunnel junctions. Such magnetic heterostructures and magnetic layers can incorporate a variety of different materials and layers for various effects. In many embodiments, the magnetic heterostructures incorporate hybrid seed layers. Such layers can be incorporated for various reasons including but not limited to producing an enhanced voltage controlled magnetic anisotropy (“VCMA”) effect. The VCMA effect can be explained in terms of the electric-field-induced change of occupancy of atomic orbitals at the interface, which, in conjunction with spin-orbit interaction, results in a change of anisotropy. In some embodiments, the magnetic heterostructures and layers incorporate free layer insertions. In a number of embodiments, the magnetic heterostructures incorporate a material insertion at the interface of the tunneling barrier and the free layer.
Owner:INSTON
Thermoelectric conversion element and thermoelectric conversion method
InactiveUS20140182645A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentPotential differenceThermoelectric conversion
Provided is a thermoelectric conversion element capable of converting both a temperature gradient in an in-plane direction and a temperature gradient in a direction perpendicular to plane into electric power at the same time. The thermoelectric conversion element includes: a substrate; a magnetic film provided on the substrate and formed of a polycrystalline magnetic insulator material that is magnetizable in a predetermined direction having a component parallel to a film surface; and electrodes provided to the magnetic film and made of a material having a spin orbit interaction. The thermoelectric conversion element is configured to be capable of outputting a temperature gradient perpendicular to a surface of the magnetic film as a potential difference in a surface of one of the electrodes and outputting a temperature gradient parallel to the surface of the magnetic film as a potential difference between the electrodes.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Magnetic device and method for setting same
A magnetic device and a method for setting the same are provided. A magnetic memory including a plurality of magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer is described.Each of the magnetic junctions includes a pinned layer, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between reference and free layers. The free layer has at least one of a tilted easy axis and a highdamping constant. The tilted easy axis is at a nonzero acute angle from a direction perpendicular-to-plane. The high damping constant is at least 0.02. The at least one SO active layer is adjacent tothe free layer and carries a current in-plane. The at least one SO active layer exerts a SO torque on the free layer due to the current. The free layer is switchable using the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Non-linear spin-orbit interaction devices and methods for current-to-spin conversion and amplification of spin-polarizations
The present invention is notably directed to a spin-orbit coupled device. This device comprises a confinement part. It further includes a circuitry, having an input device, energizable to inject spin-polarizations to charge carriers in an input region of the confinement part. The circuitry further comprises an output device, usable to detect spin-polarizations of charge carriers in an output region of the confinement part. The confinement part may be configured to subject charge carriers drifting therein to a non linear spin-orbit interaction, which causes to rotate a spin polarization of thedrifting charge carriers by an angle that depends non-linearly on momenta of such charge carriers. The circuitry may be configured to allow momenta of charge carriers drifting in the confinement partto be varied, while injecting spin-polarizations in the input region. Varying momenta allows spin-polarizations of drifting charge carriers to be rotated, owing to said non-linear spin-orbit interaction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cross-point architecture for spin-transfer torque magnetoresistive random access memory with spin orbit writing
ActiveUS10305026B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin-transfer torqueMagnetic memory
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing a magnetic junction usable in spin transfer or spin-orbit torque applications and including a magnetic barrier layer
ActiveUS20180197589A1Inhibited DiffusionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic barrierIn plane
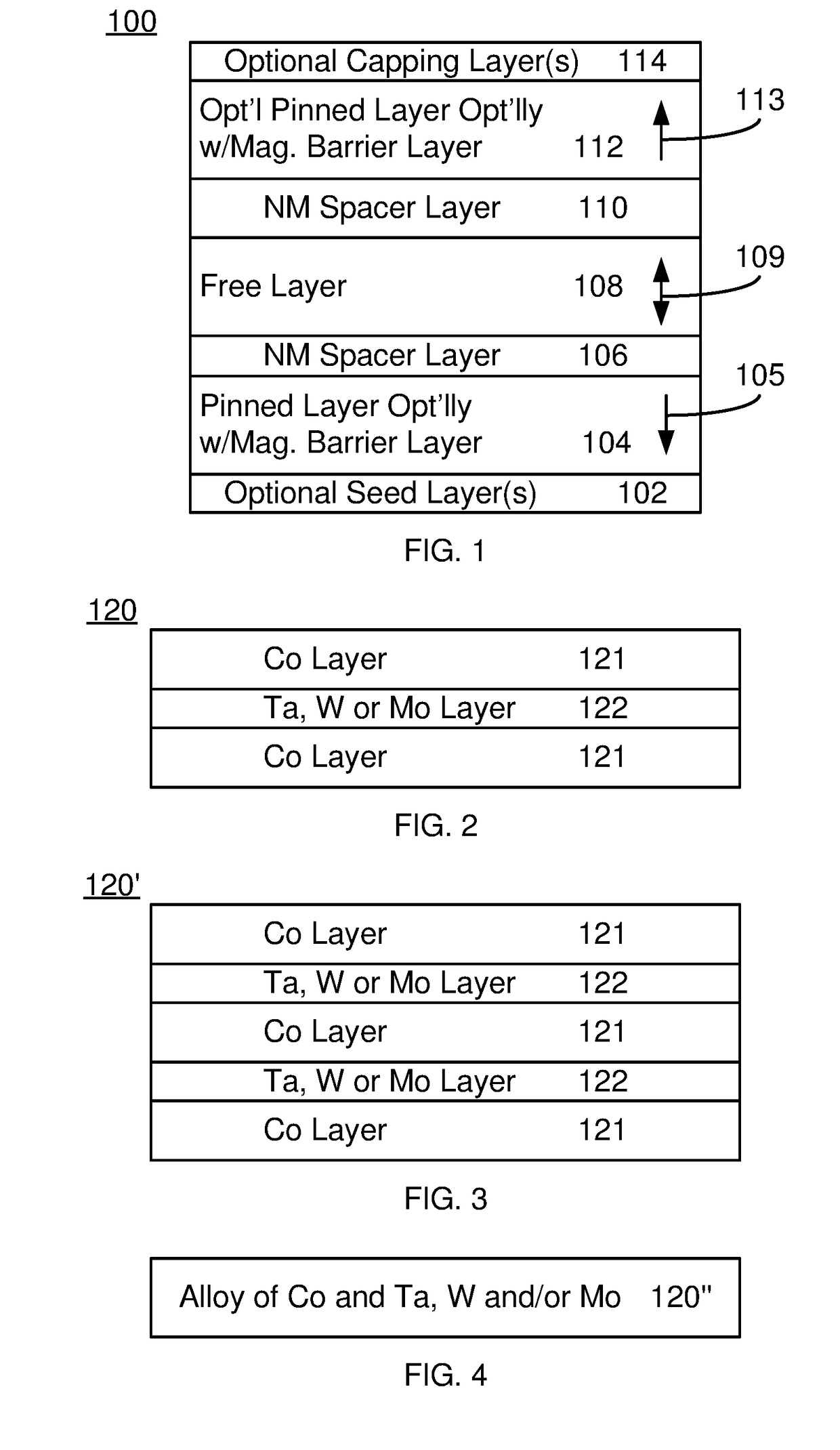
A magnetic device and method for providing the magnetic device are described. The magnetic device includes magnetic junctions and spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer(s). Each magnetic junction includes free and pinned layers separated by a nonmagnetic spacer layer. The pinned layer has a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) energy greater than an out-of-plane demagnetization energy. The pinned layer includes a magnetic barrier layer between a magnetic layer and a high PMA layer including at least one nonmagnetic component. The magnetic barrier layer includes Co and at least one of Ta, W and Mo. The magnetic barrier layer is for blocking diffusion of the nonmagnetic component. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the free layer. The SO active layer(s) carry a current in-plane and exert a SO torque on the free layer due to the current. The free layer is switchable between stable magnetic states using the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Thermoelectric converter element, method of manufacturing thermoelectric converter element, and thermoelectric conversion method
InactiveUS9991436B2Improve productivityImprove conversion efficiencyThermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetizationMaterials science
An object of the present invention is to provide a low-cost thermoelectric converter element having high productivity and excellent conversion efficiency. A thermoelectric converter element according to the present invention includes a substrate 4, a magnetic film 2 provided on the substrate 4 with a certain magnetization direction A and formed of a polycrystalline magnetically insulating material, and an electrode 3 provided on the magnetic film 2 with a material exhibiting a spin-orbit interaction. When a temperature gradient is applied to the magnetic film 2, a spin current is generated so as to flow from the magnetic film 2 toward the electrode 3. A current I is generated in a direction perpendicular to the magnetization direction A of the magnetic film 2 by the inverse spin Hall effect in the electrode 3.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Thermoelectric conversion apparatus
ActiveUS9496474B2Improve reliabilityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentMagnetizationEngineering
A thermoelectric conversion apparatus has a substrate and a power generation part. The power generation part has a magnetic layer with magnetization and an electrode layer made of a material exhibiting a spin-orbit interaction and formed on the magnetic layer. The substrate and the power generation part have flexibility. This thermoelectric conversion apparatus further has a cover layer having flexibility and formed on the substrate so as to cover at least the power generation part.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
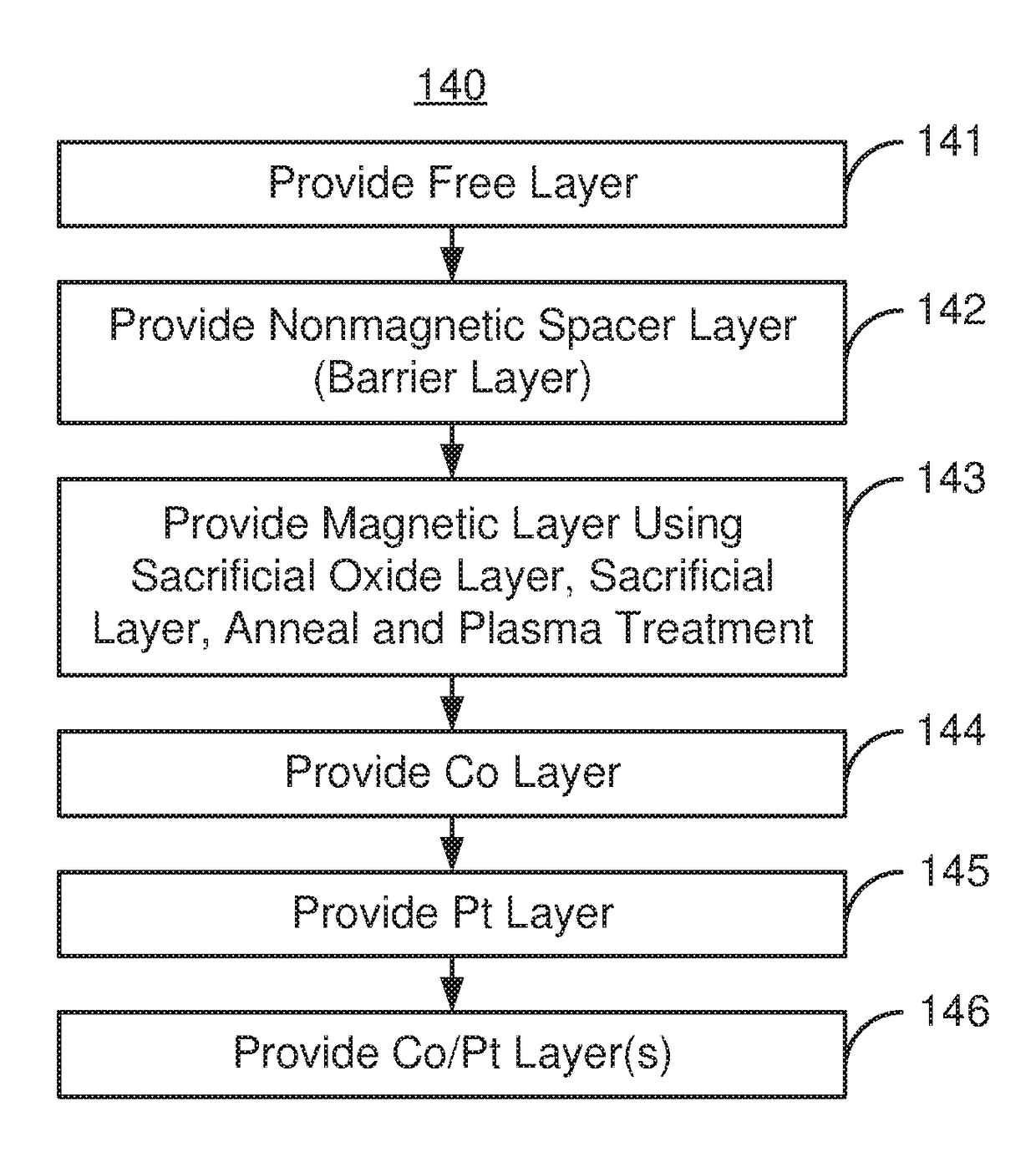
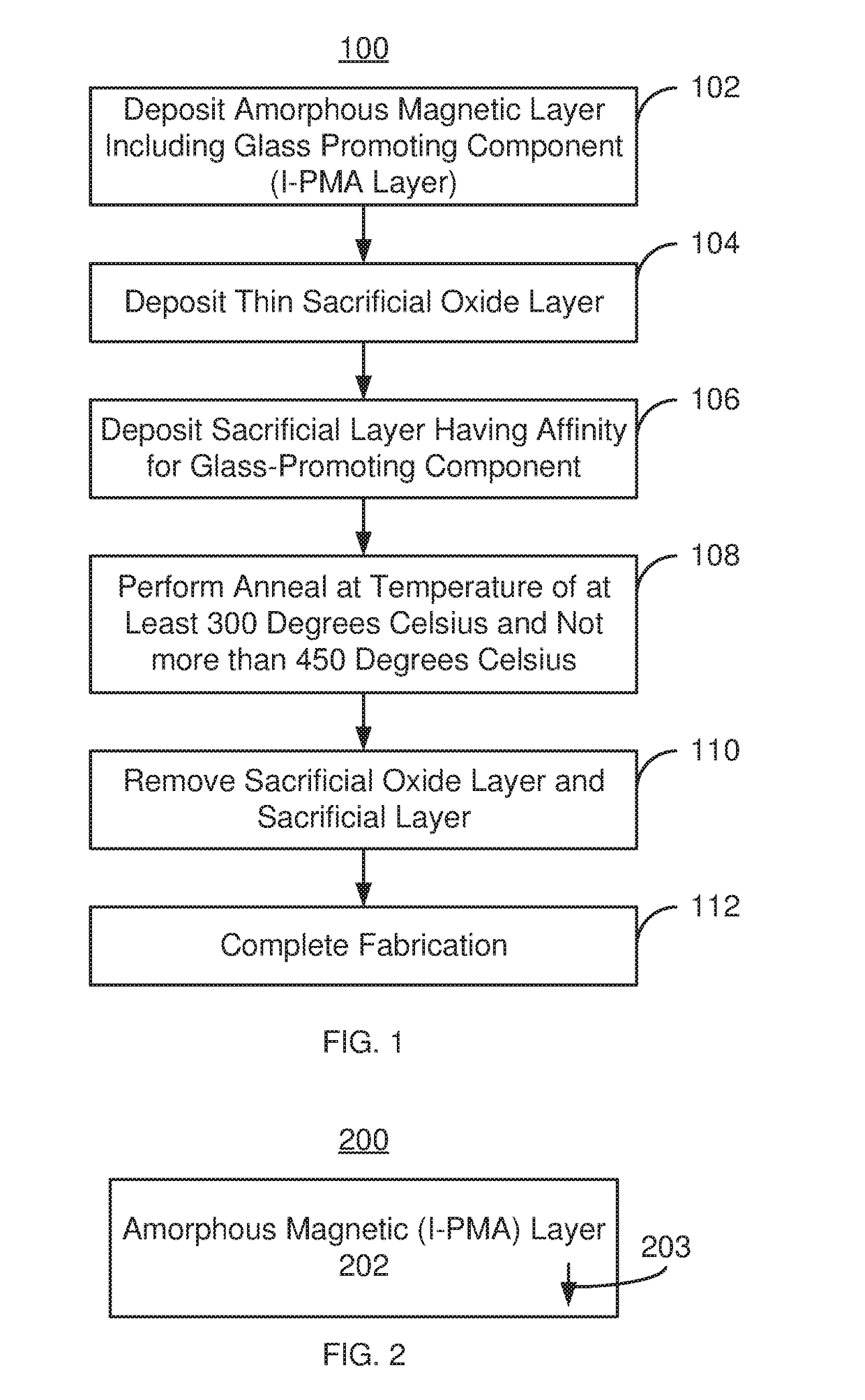
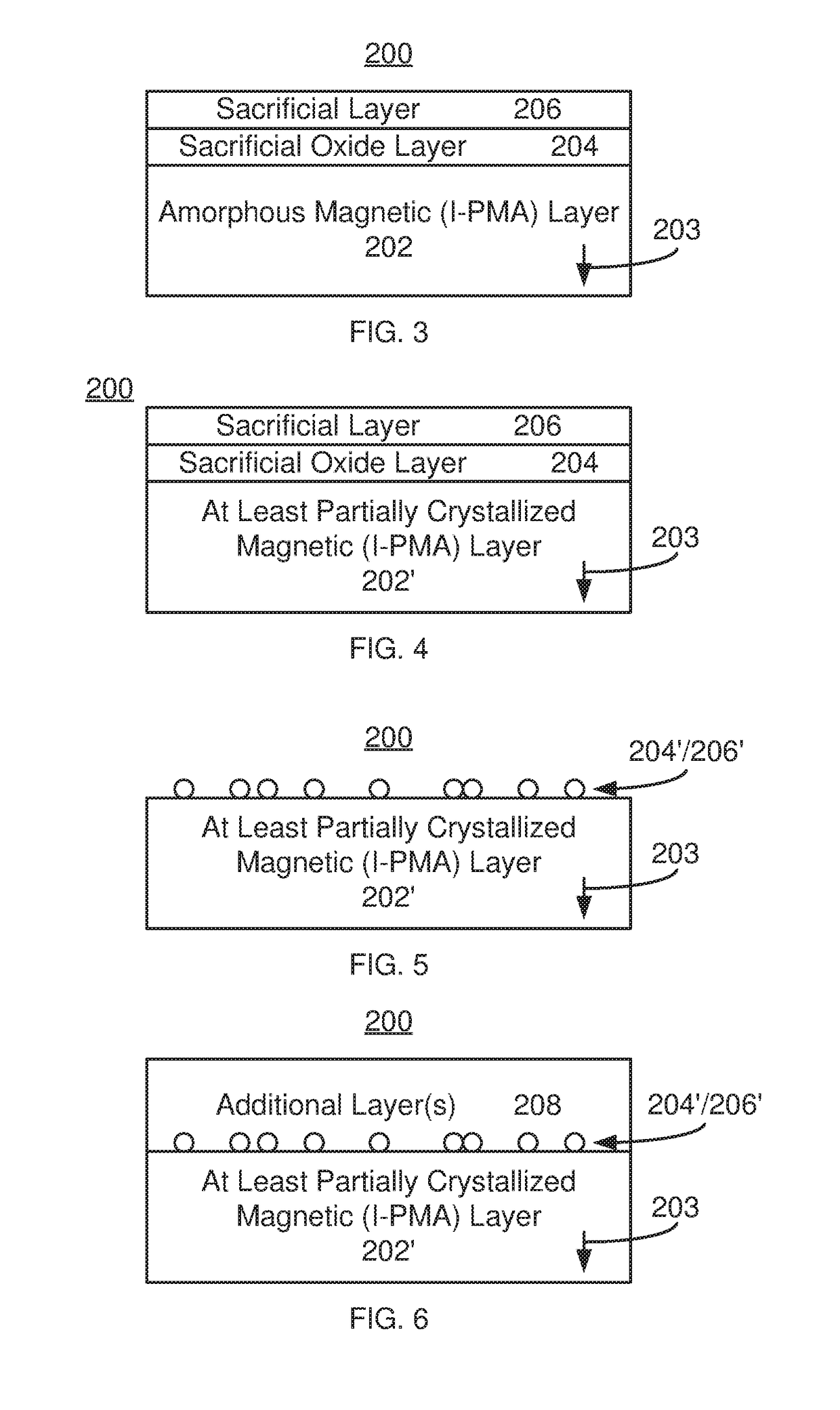
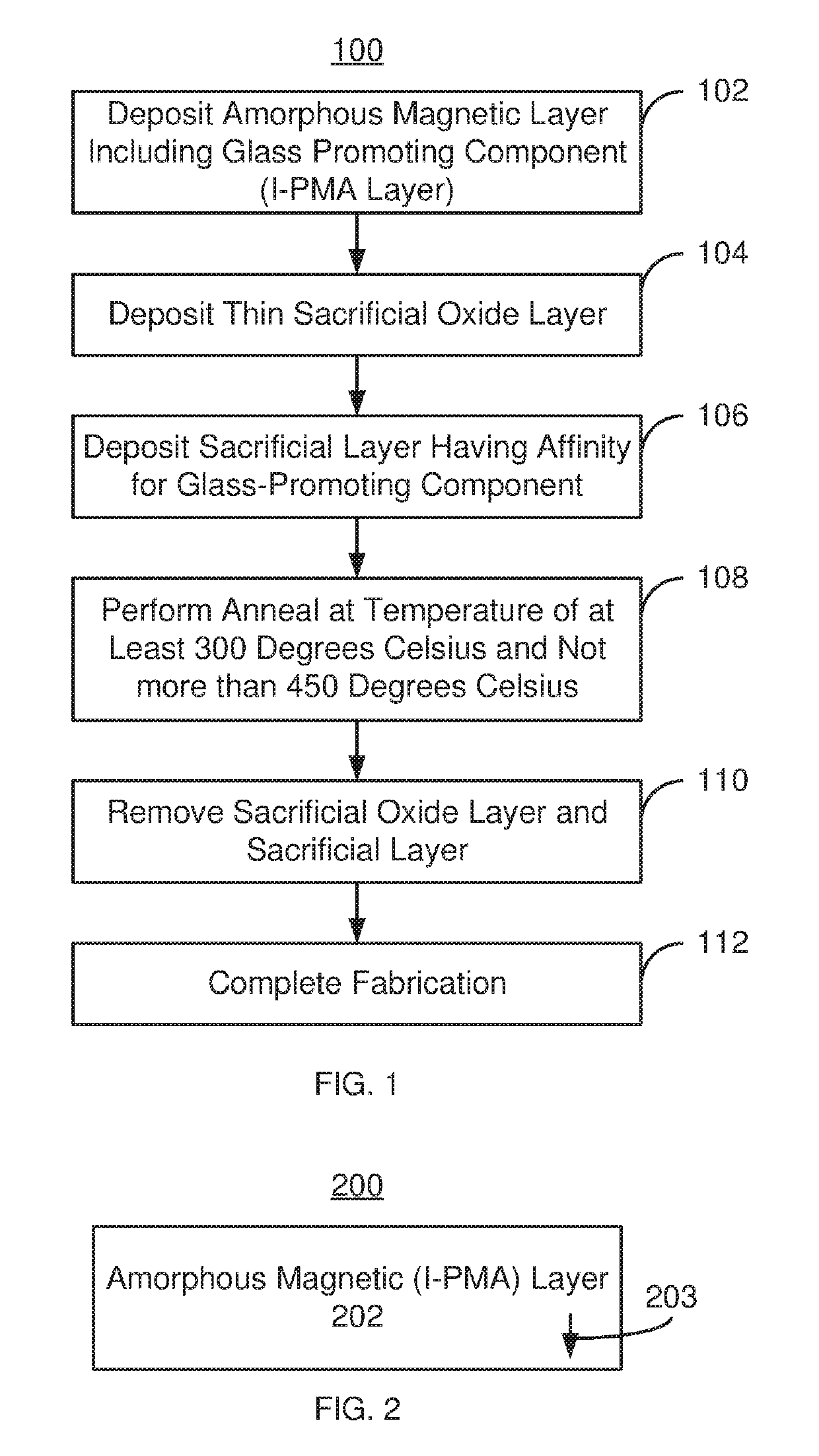
Method and system for providing a magnetic layer in a magnetic junction usable in spin transfer or spin orbit torque applications using a sacrificial oxide layer
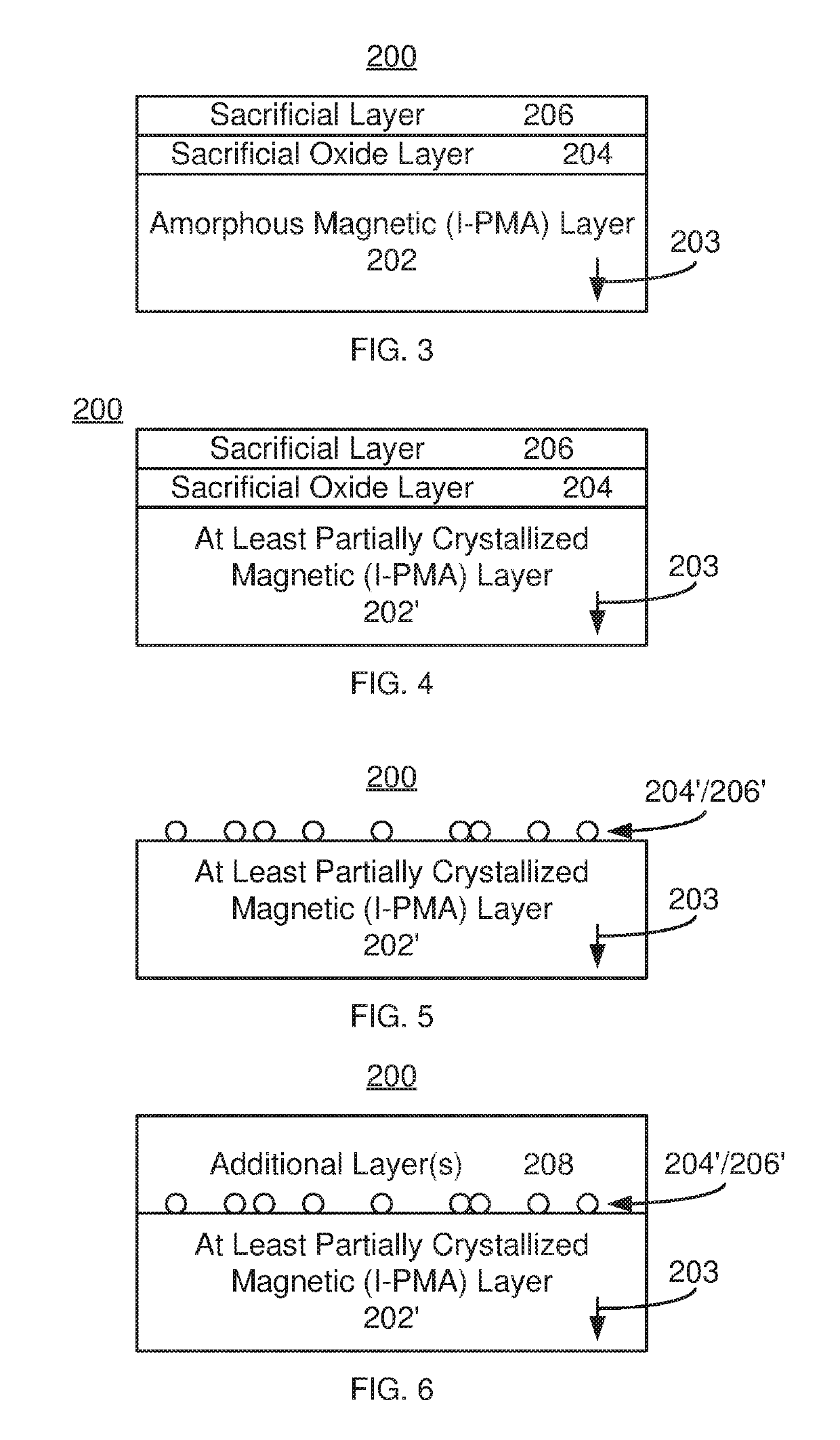
ActiveUS20180247684A1Galvano-magnetic material selectionDigital storageCelsius DegreeSpin orbit torque
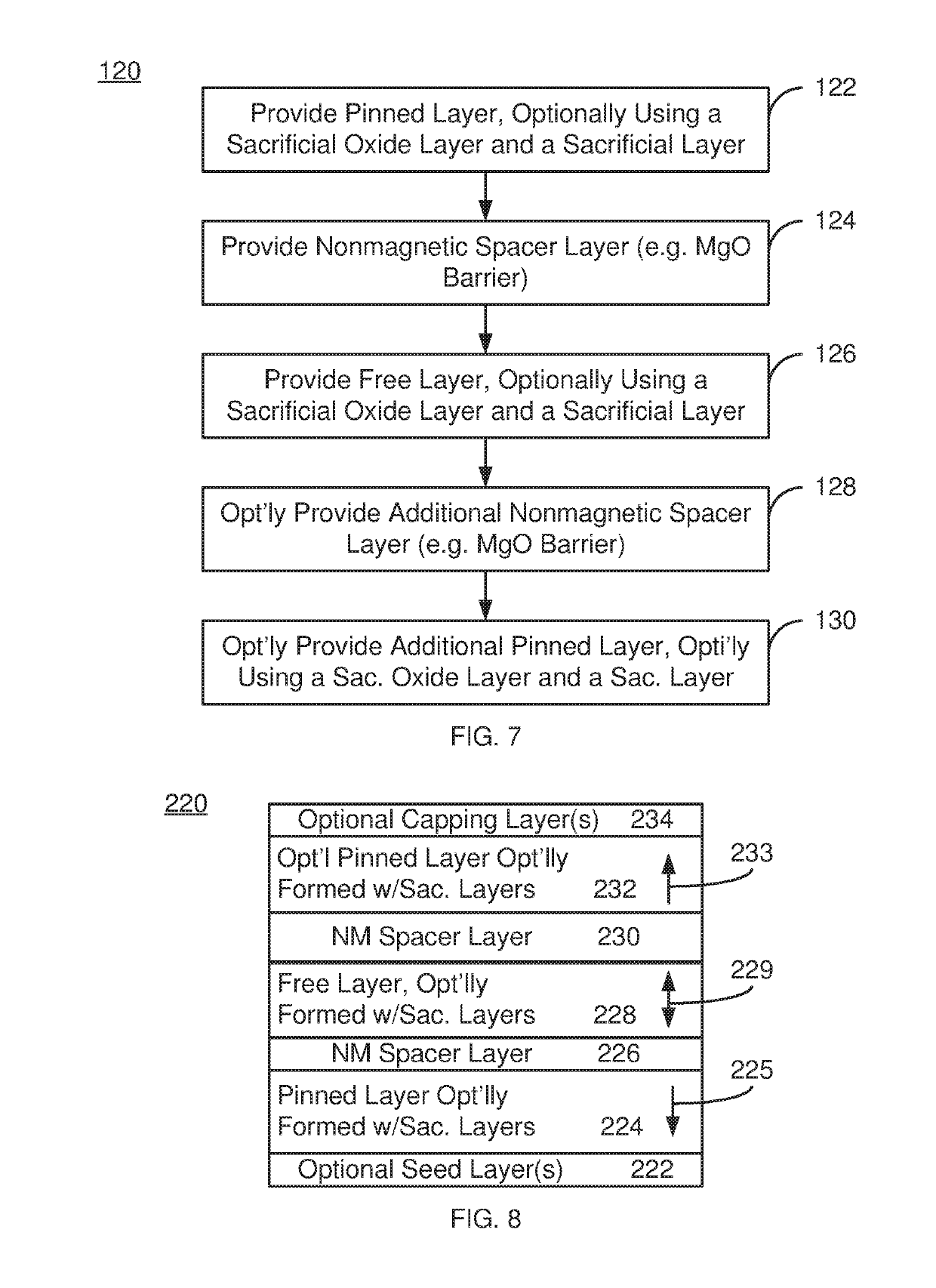
A magnetic device and method for providing the device are described. The magnetic device includes magnetic junction(s) and spin-orbit interaction active layer(s) adjacent to the magnetic junction free layer(s). The magnetic junction includes free and pinned layers separated by a nonmagnetic spacer layer. The free layer is switchable between stable magnetic states. Providing the pinned and / or free layer(s) includes providing a magnetic layer including a glass-promoting component, providing a sacrificial oxide on the magnetic layer, providing a sacrificial layer on the sacrificial oxide and performing anneal(s) of the magnetic layer, the sacrificial oxide layer and the sacrificial layer at anneal temperature(s) greater than 300 degrees Celsius and not exceeding 475 degrees Celsius. The magnetic layer is amorphous as-deposited but is at least partially crystallized after the anneal(s). The sacrificial layer includes a sink for the glass-promoting component. The sacrificial layer and the sacrificial oxide are removed after the anneal(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spin orbit torque magnetic RAM
ActiveUS10886457B2Low densityMaximize transparencySolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetic ramSpin orbit torque
A spin torque magnetic RAM according to the present invention includes at least one row selection line positioned on a silicon substrate to induce a spin orbit interaction therein; at least one first magnetic pattern positioned on the row selection line; a second magnetic pattern positioned on the first magnetic pattern; a tunnel barrier positioned on the second magnetic pattern; and a third magnetic pattern positioned on the tunnel barrier, wherein the first magnetic pattern is made of a cobalt film, the first magnetic pattern and the second magnetic pattern have a total thickness of 5 nm to form a free layer, and the third magnetic pattern is formed with a pinned layer in which a magnetization direction is fixed.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
A multispectral phase metasurface device
ActiveCN105676314BWith broadband characteristicsCompact structureOptical elementsThin metalUnit structure
The invention discloses a multi-spectral phase-type metasurface device and belongs to the metamaterial technical field. The multi-spectral phase-type metasurface device of the invention is composed of a nano unit structure array which is formed on ultra-thin metal or a medium through etching. According to the multi-spectral phase-type metasurface device of the invention, multi-frequency information is coded onto a metasurface; and phase regulation can be performed on electromagnetic waves of a plurality of wavelengths by using wide-band spin-orbit interaction of nanostructures on the metasurface, so that the electromagnetic waves with different wavelengths and different incident angles can be focused to a specific shape. Therefore, the multi-spectral phase-type metasurface device of the invention can be applied to the design of a multi-wavelength ultra-small optical device and an integrated optical system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Complementary logic device using spin-orbit interaction difference and method for manufacturing the same
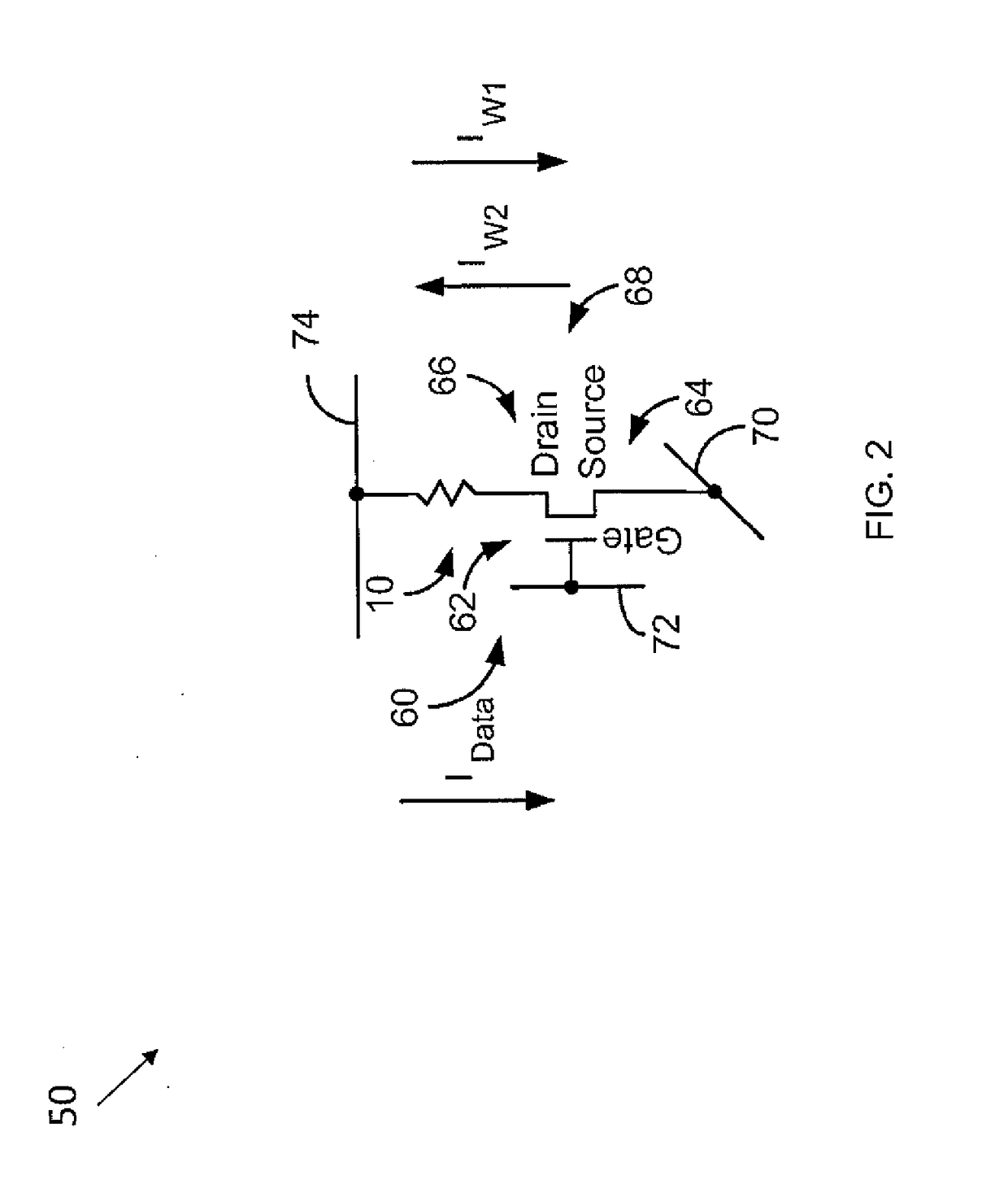
A complementary logic device includes i) a substrate, ii) a first semiconductor device located on the substrate and including a first channel layer, a carrier supply layer for supplying a carrier to the channel layer, and an upper cladding layer and a lower cladding layer respectively located at upper and lower portions of the channel layer, iii) a second semiconductor device located on the substrate and including a structure the same or similar to that of the first semiconductor device, iv) a source electrode located on the two semiconductors and made of a ferromagnetic body, v) a drain electrode located on the two semiconductors and made of a ferromagnetic body, and vi) a gate electrode located on the two semiconductors and located between the two electrodes so that a gate voltage is applied thereto to control a spin of electrons passing through the two channel layers.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
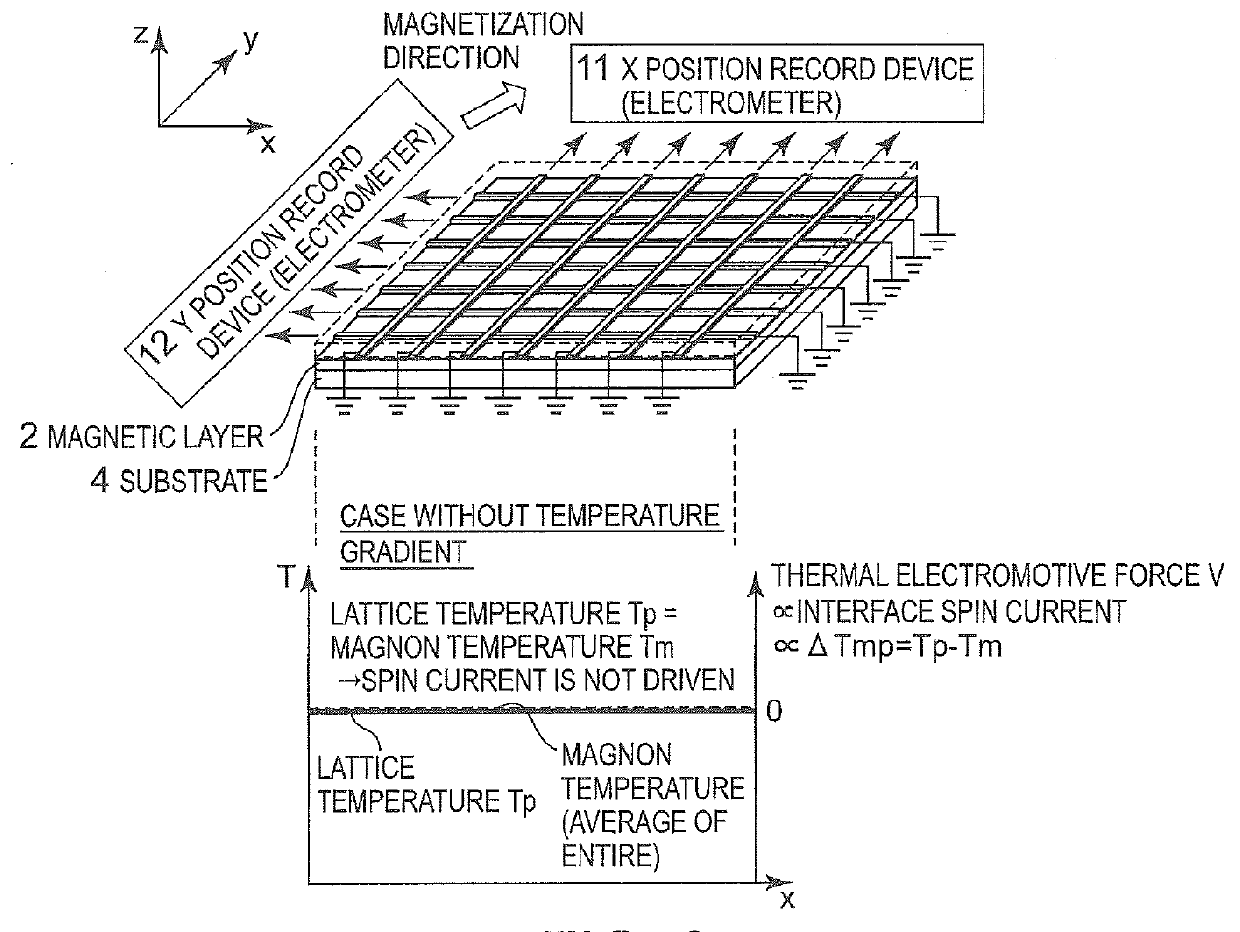
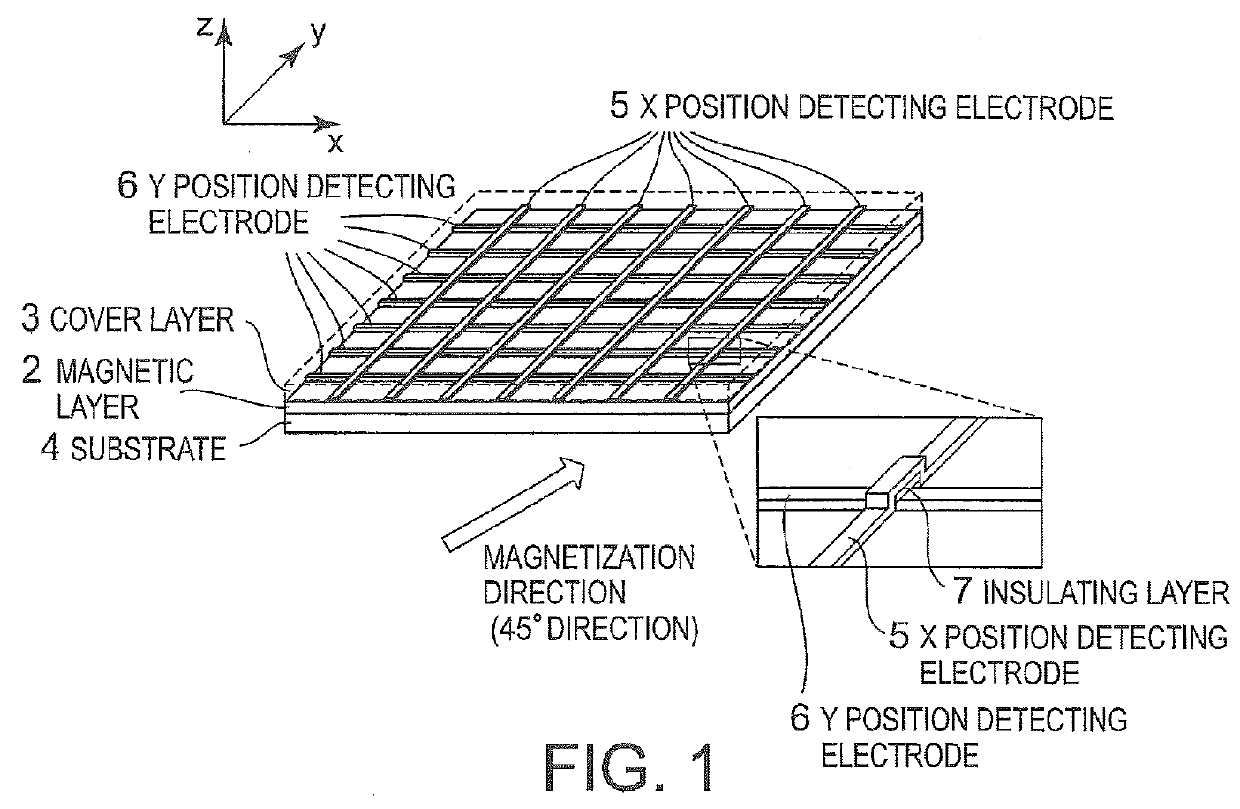
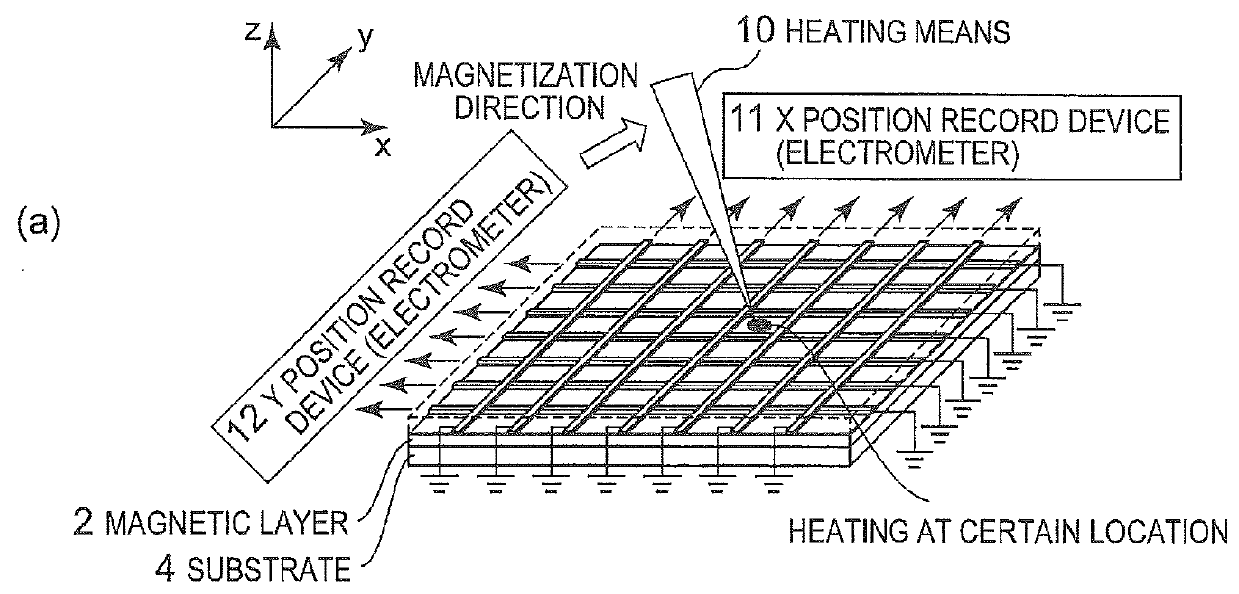
Position detection device
ActiveUS9343647B2Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectSolid-state devicesSpinsMagnetization
A position detection device includes a thermoelectric conversion portion which includes a magnetic layer and a plurality of electrodes. The magnetic layer has magnetization. The plurality of electrodes are formed of a material having spin-orbit interaction, and are formed on the magnetic layer so as to extend in a direction which intersects with the magnetization direction of the magnetic layer. When an arbitrary location on the layer-surface of the magnetic layer is heated, the thermoelectric conversion portion modulates the effective temperature in the magnetic layer and induces a spin Seebeck effect. As a result, the thermoelectric conversion portion generates, from the plurality of electrodes, a voltage corresponding to the heated position as position information.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and system for providing a magnetic layer in a magnetic junction usable in spin transfer or spin orbit torque applications using a sacrificial oxide layer
ActiveUS10438638B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesCelsius DegreeSpin orbit torque
A magnetic device and method for providing the device are described. The magnetic device includes magnetic junction(s) and spin-orbit interaction active layer(s) adjacent to the magnetic junction free layer(s). The magnetic junction includes free and pinned layers separated by a nonmagnetic spacer layer. The free layer is switchable between stable magnetic states. Providing the pinned and / or free layer(s) includes providing a magnetic layer including a glass-promoting component, providing a sacrificial oxide on the magnetic layer, providing a sacrificial layer on the sacrificial oxide and performing anneal(s) of the magnetic layer, the sacrificial oxide layer and the sacrificial layer at anneal temperature(s) greater than 300 degrees Celsius and not exceeding 475 degrees Celsius. The magnetic layer is amorphous as-deposited but is at least partially crystallized after the anneal(s). The sacrificial layer includes a sink for the glass-promoting component. The sacrificial layer and the sacrificial oxide are removed after the anneal(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com