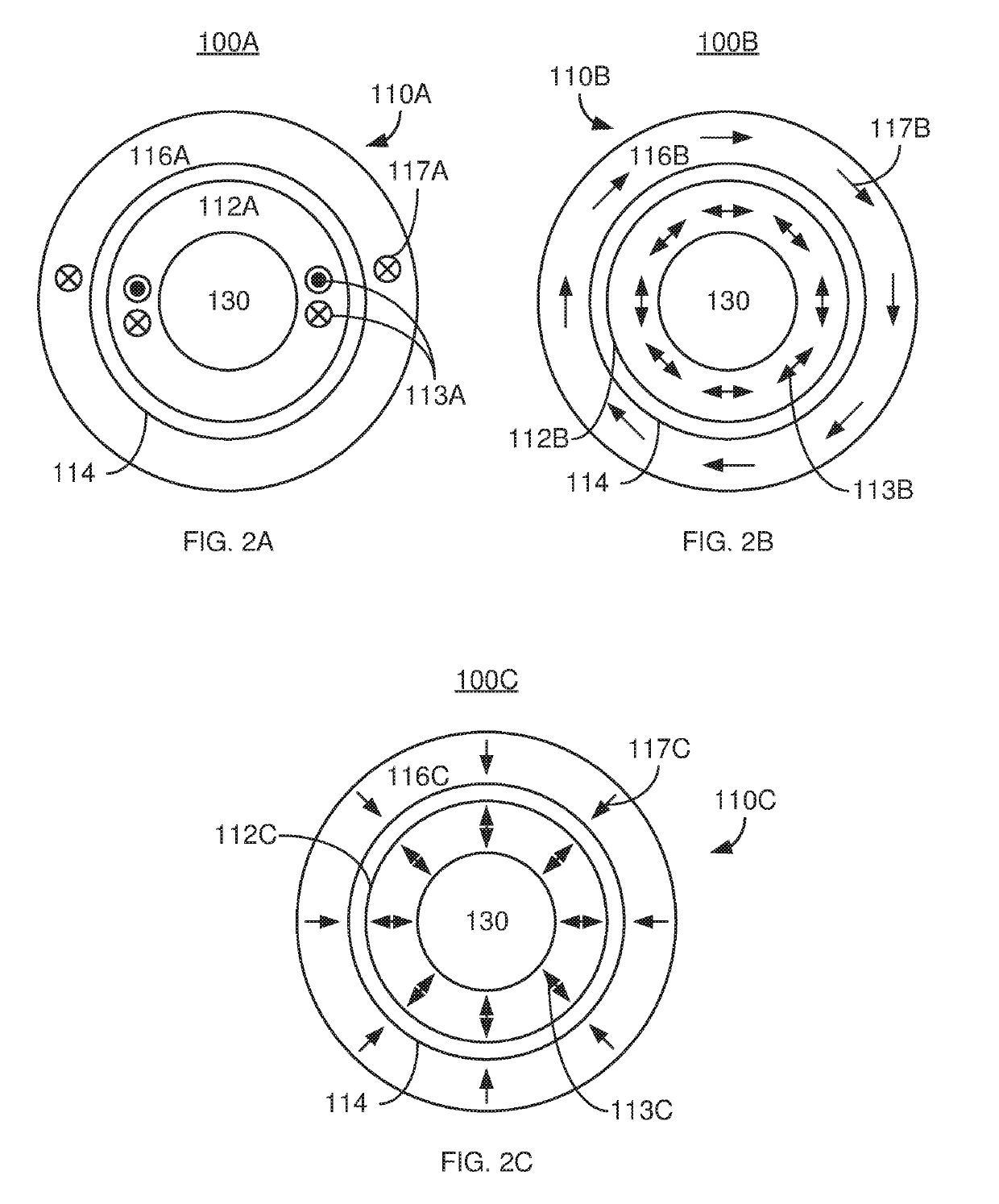
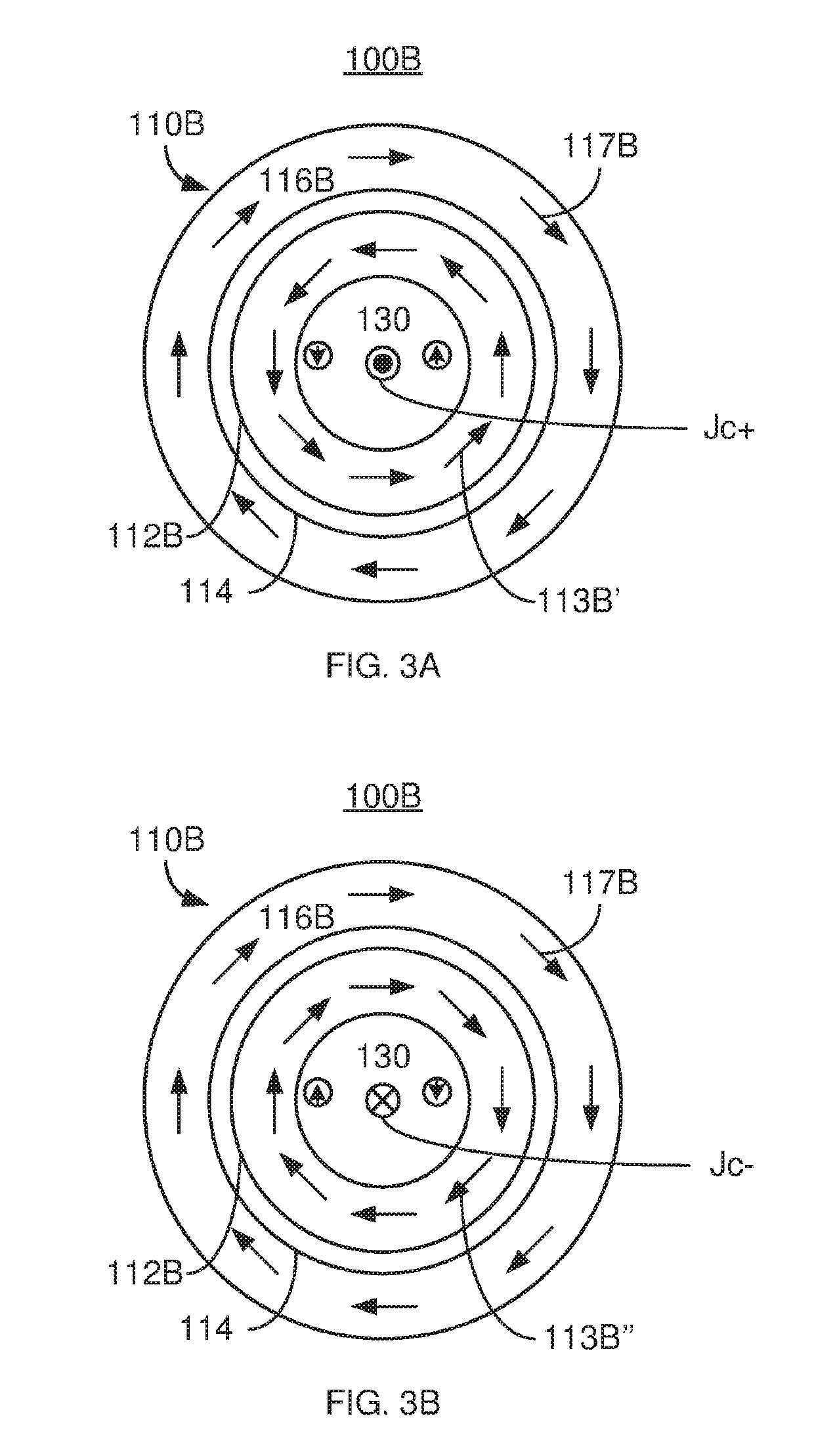
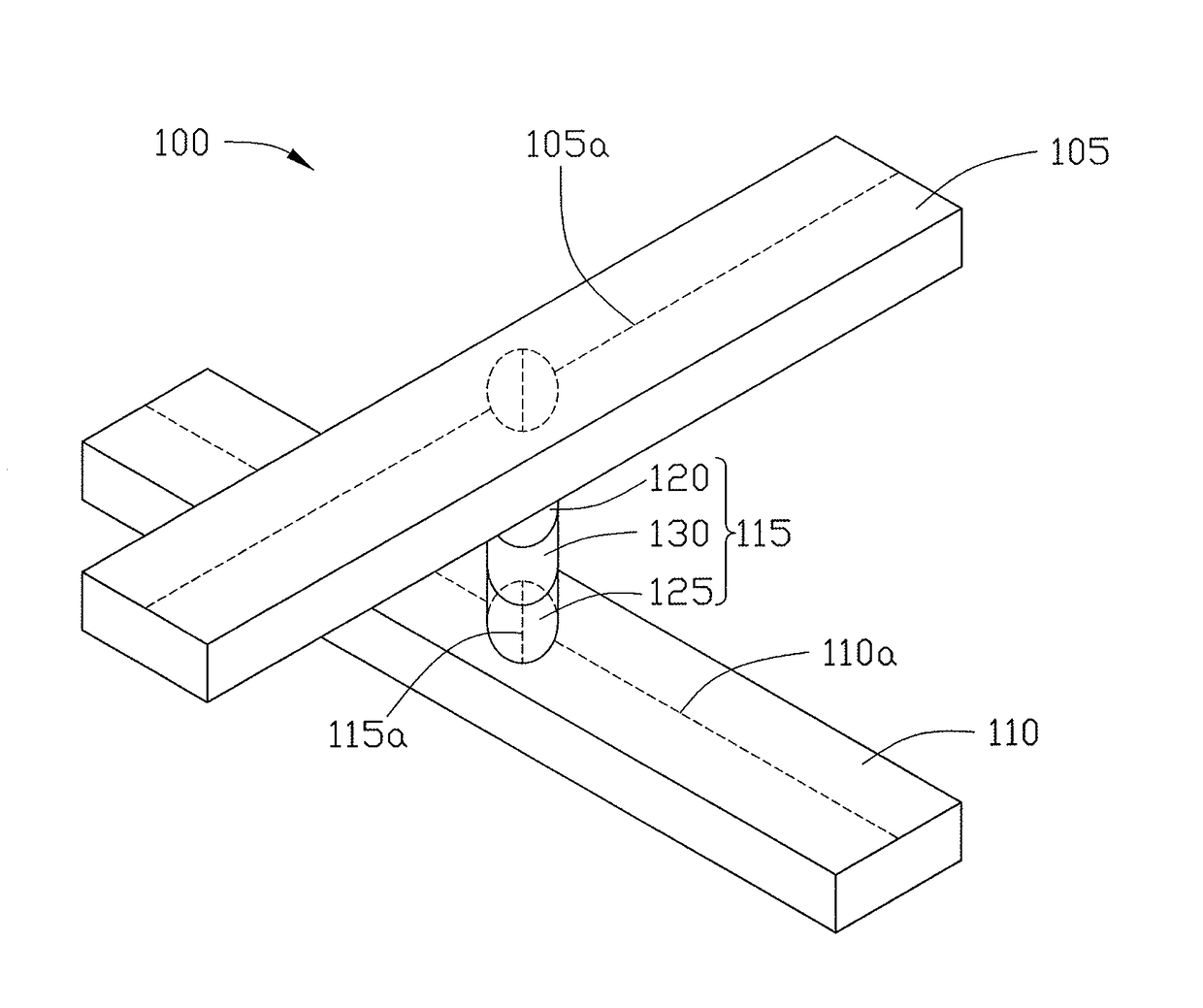
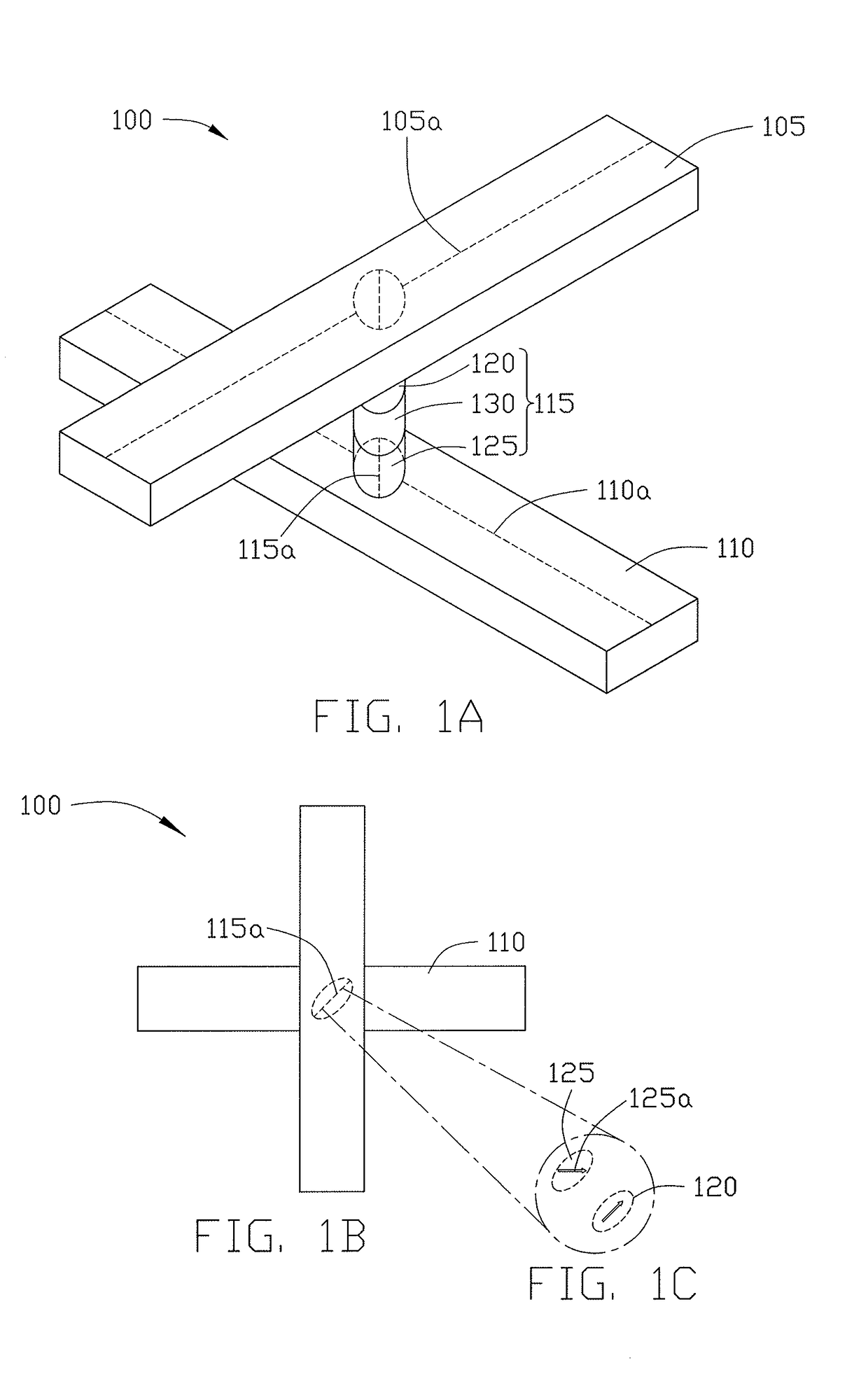
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Spin orbit torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
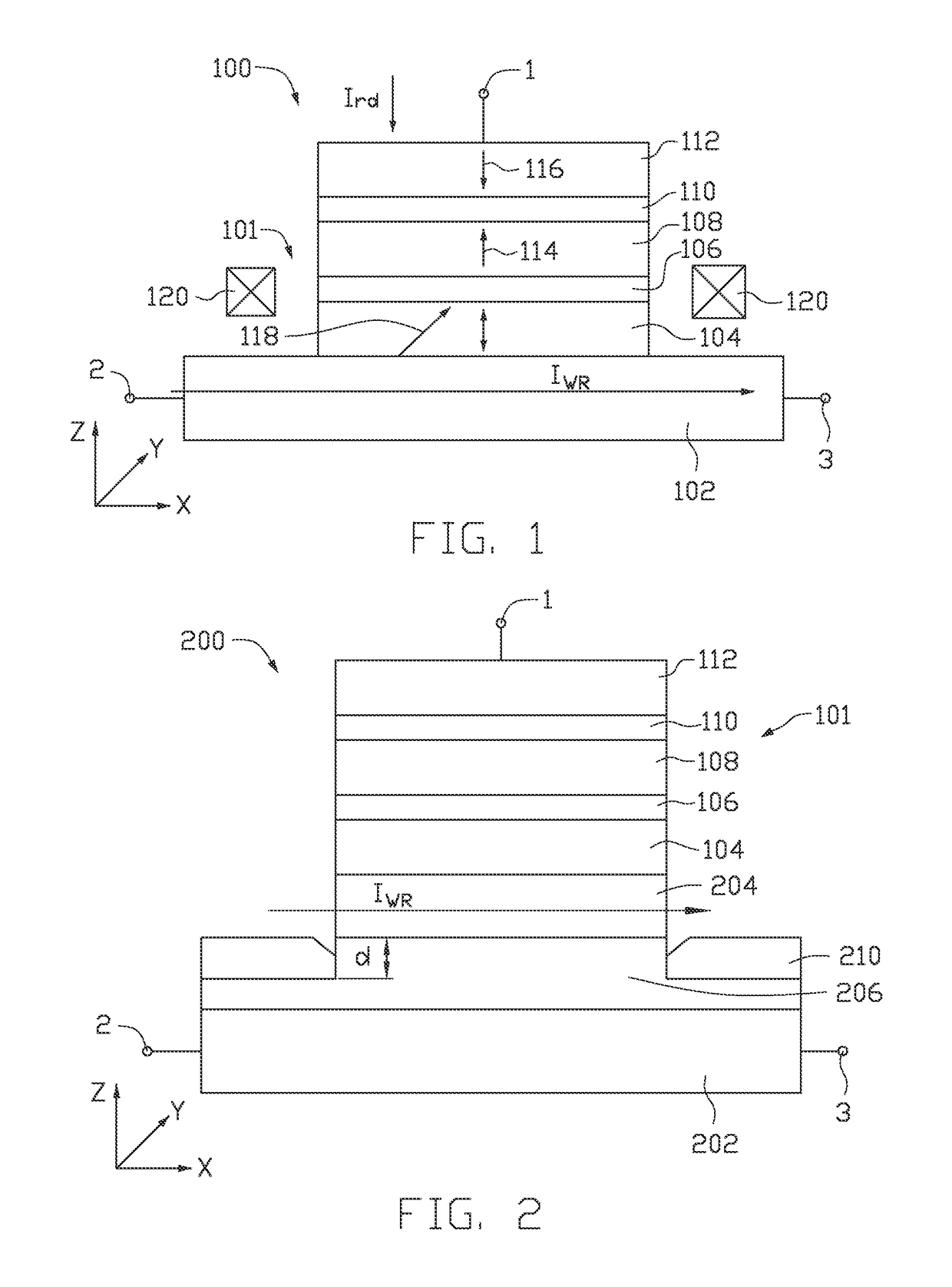
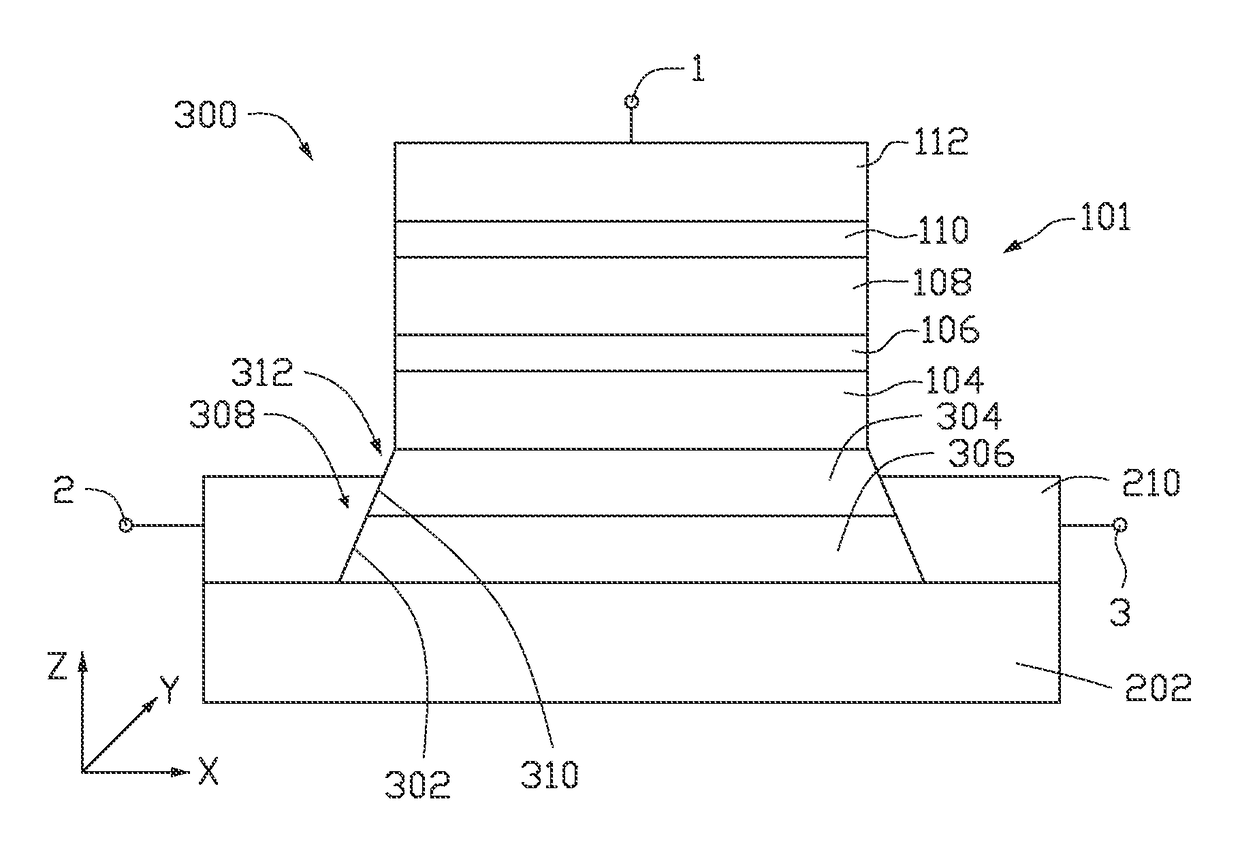
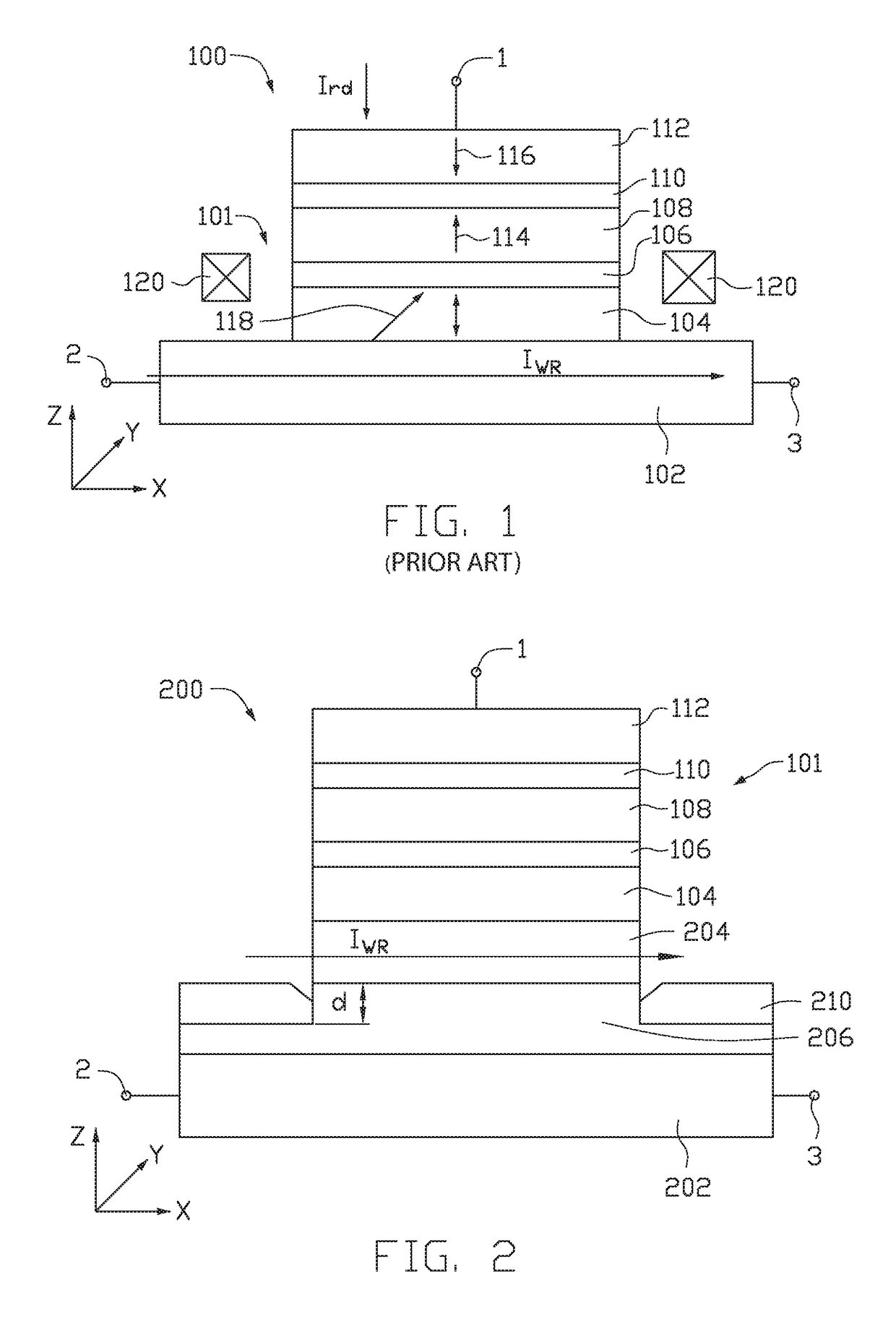
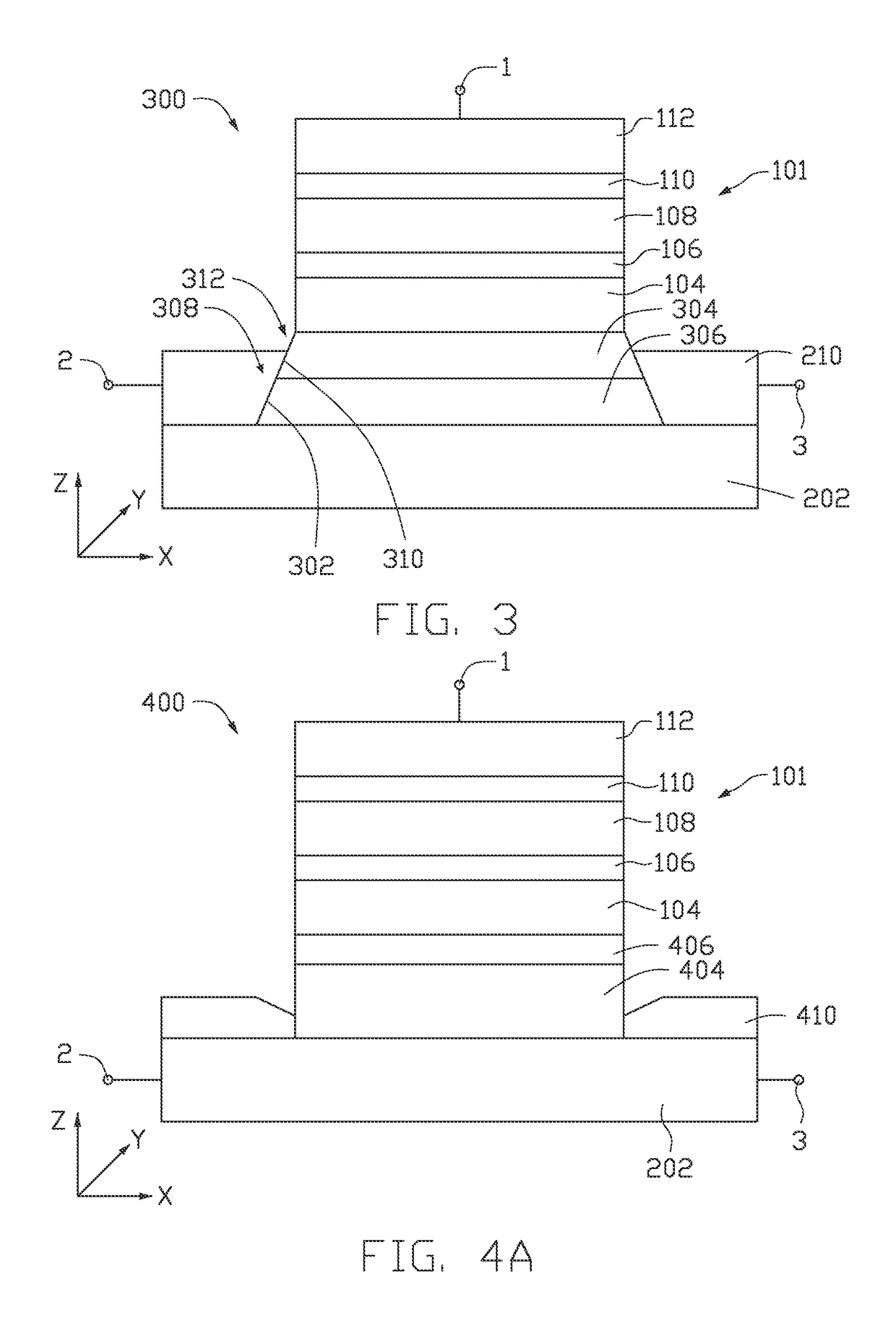
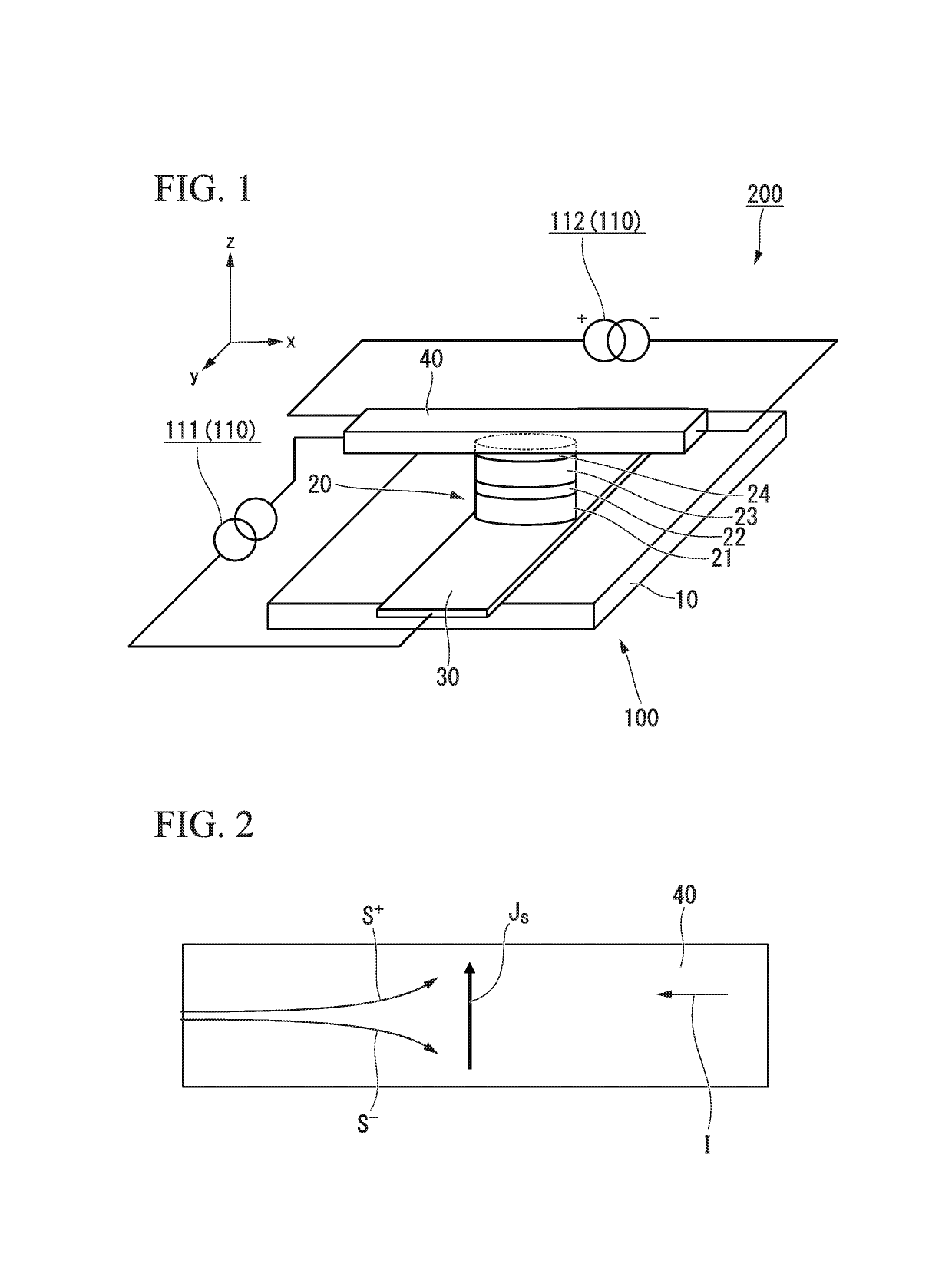
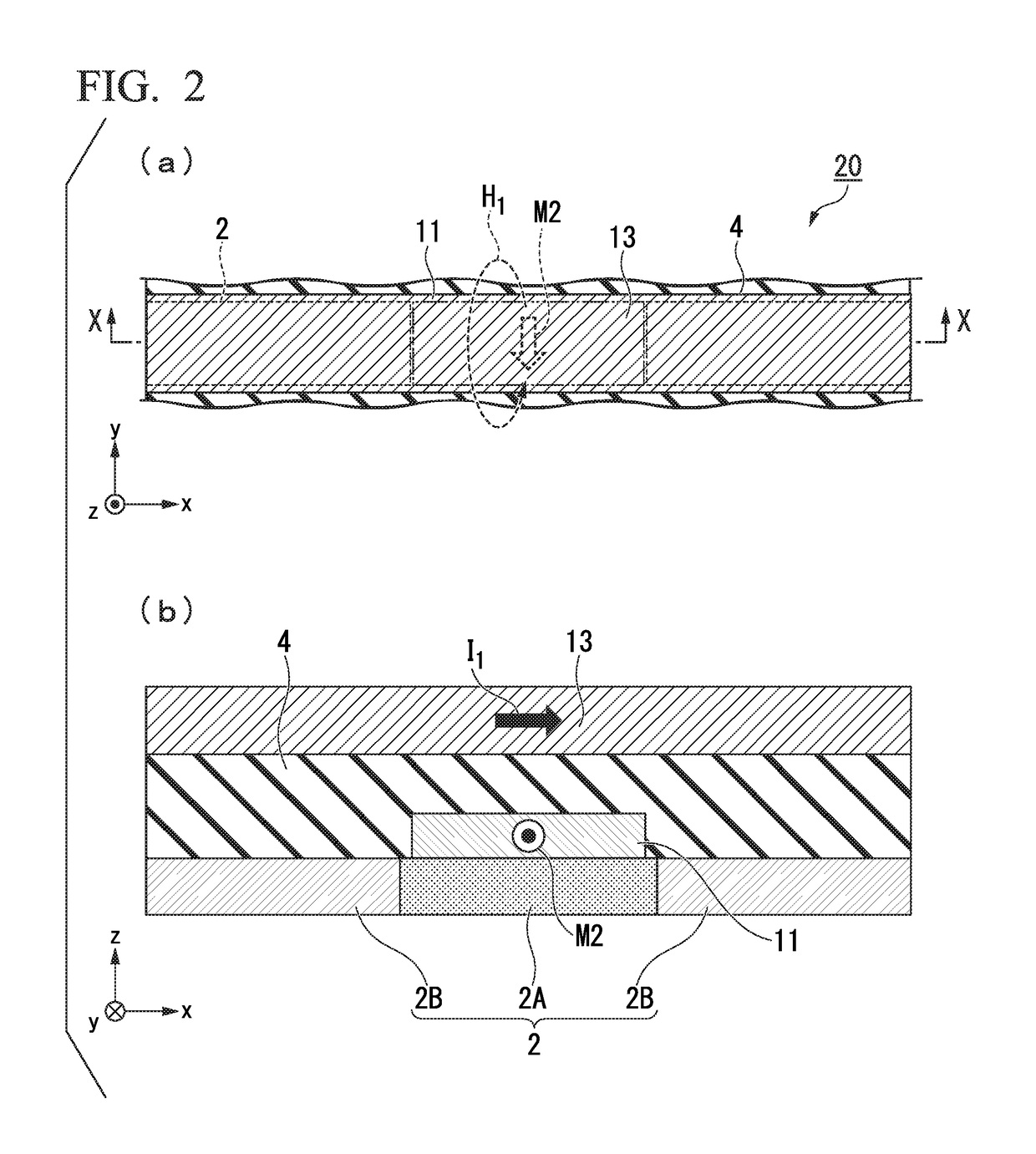
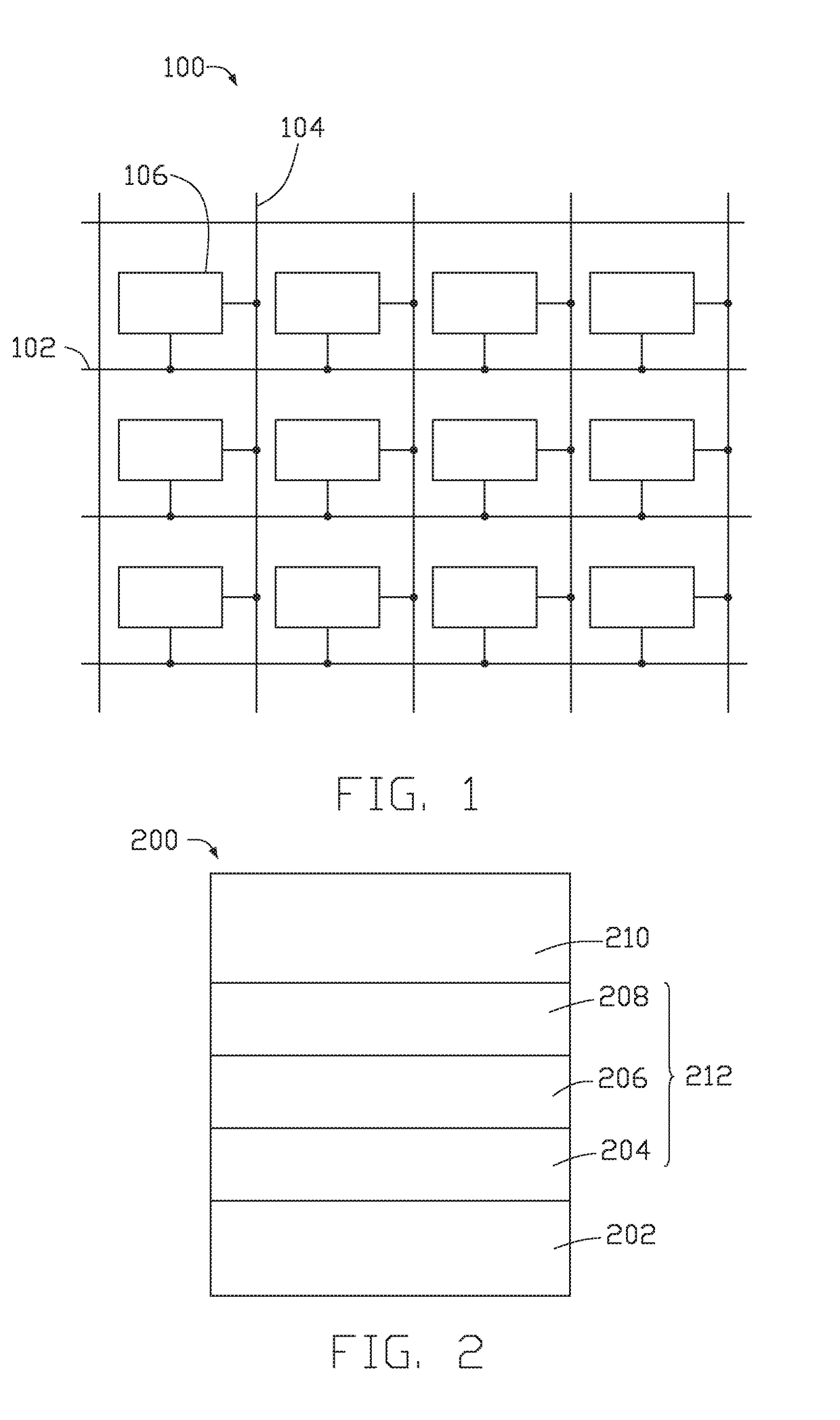
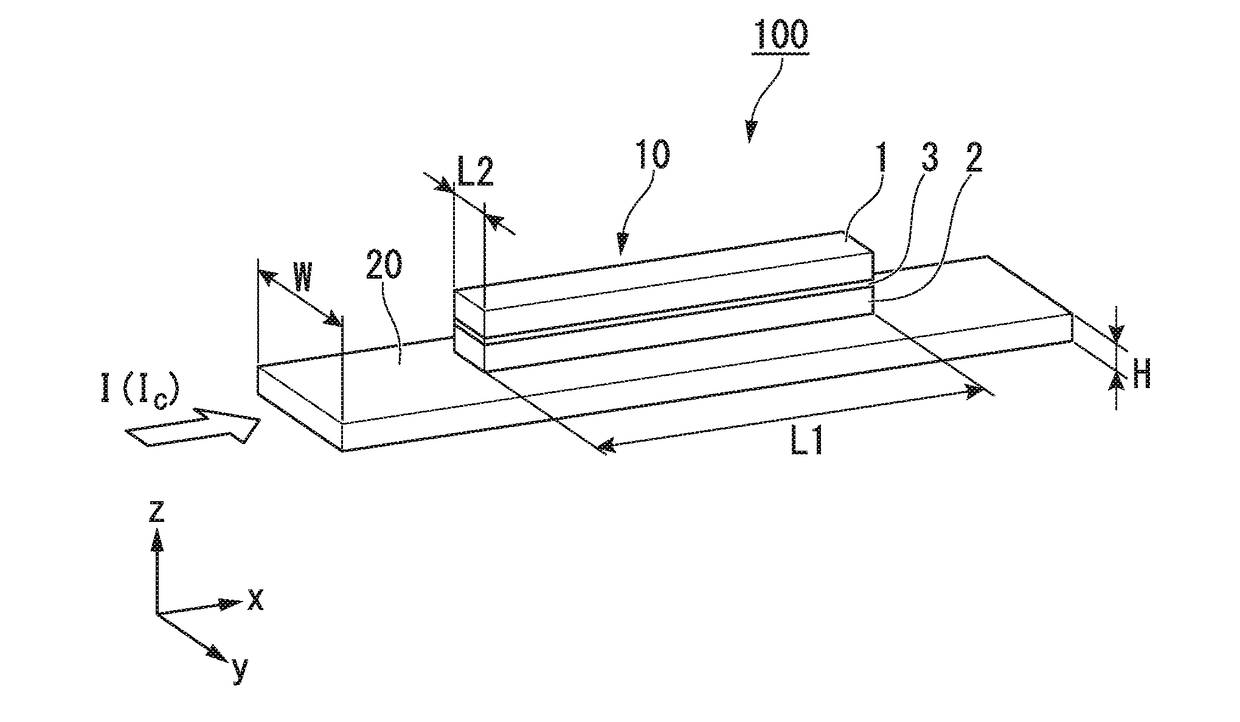
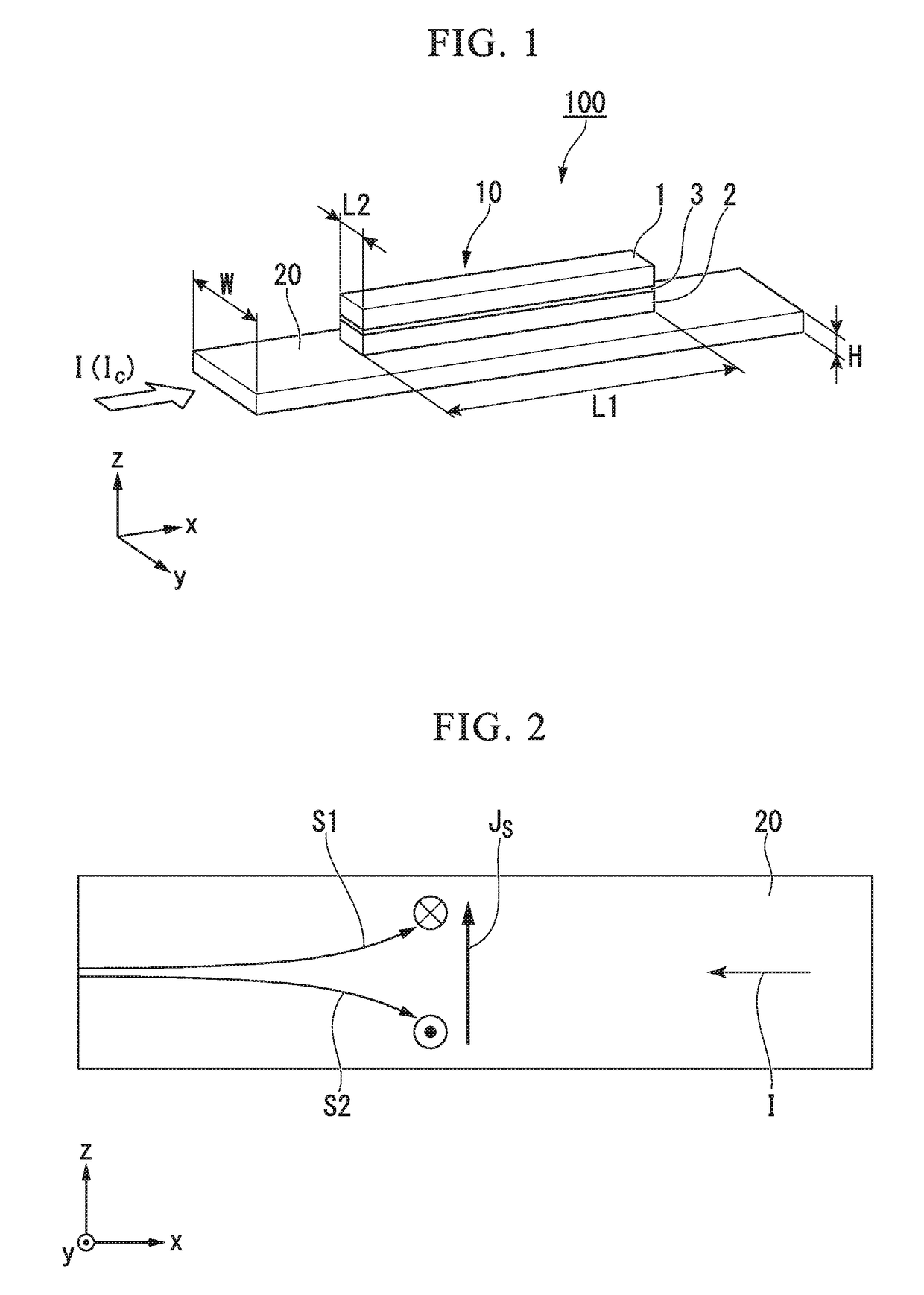
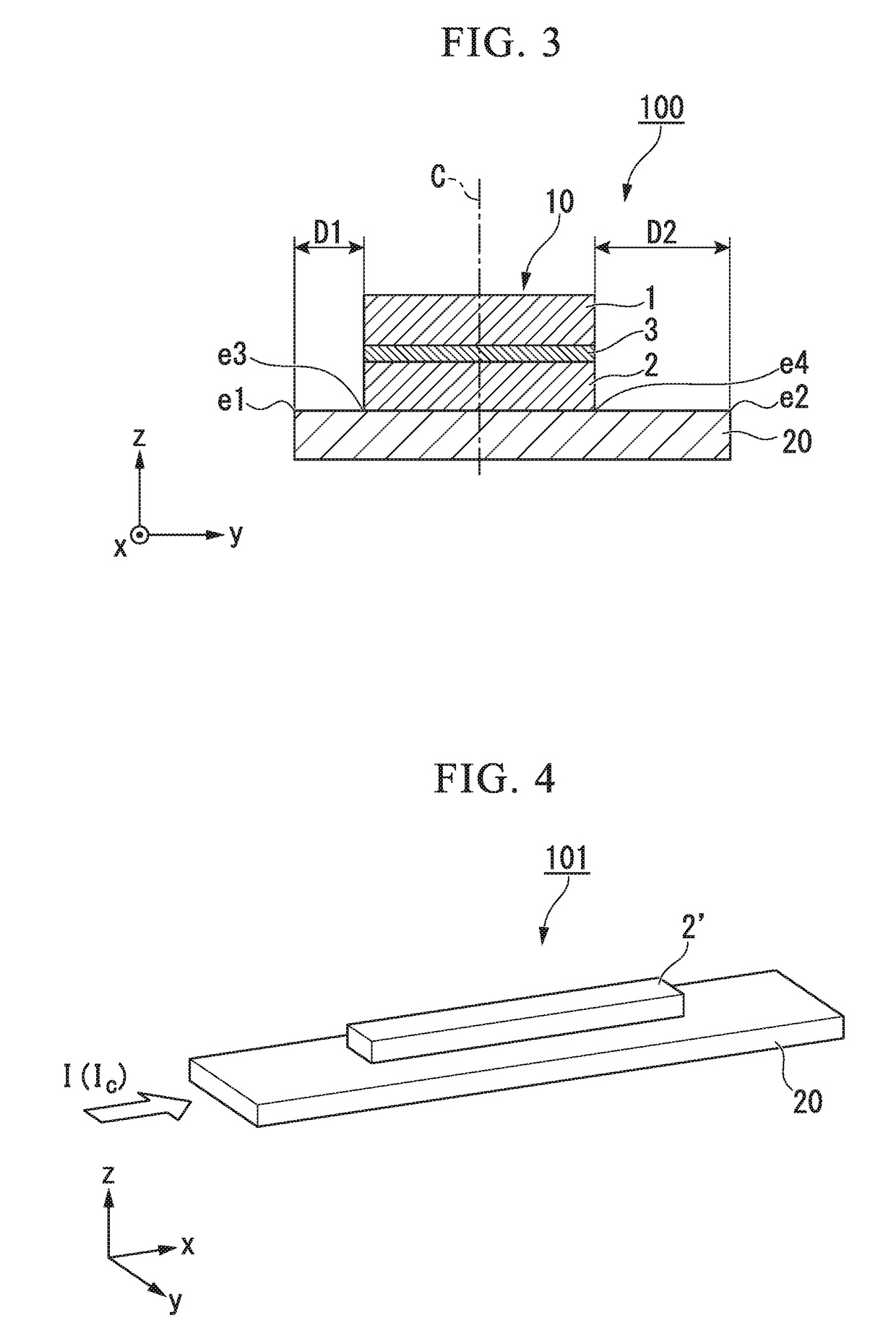
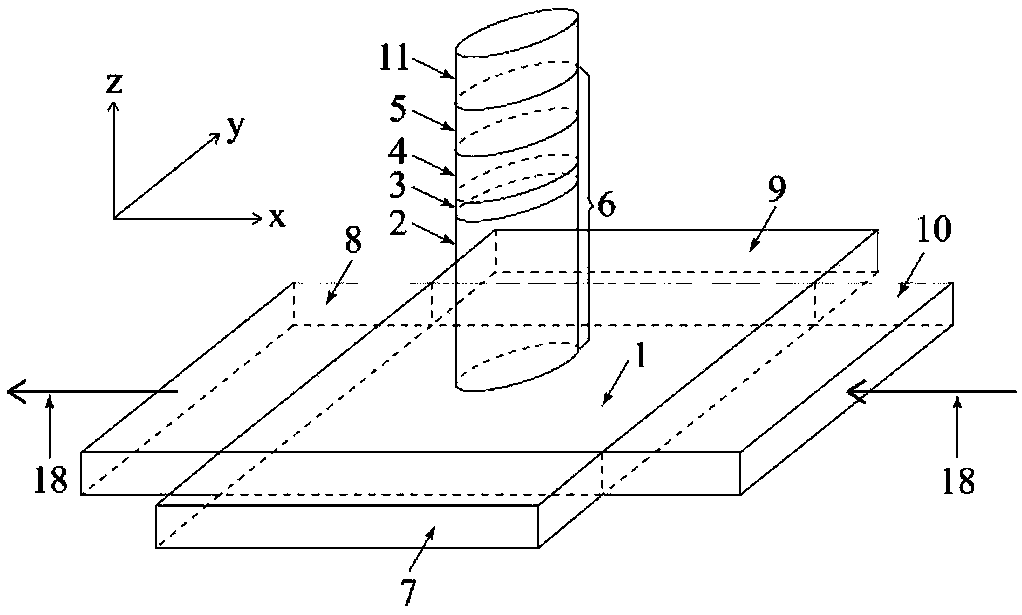
Spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) without external magnetic field
ActiveCN104393169AChange the state of magnetizationAddress reliabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin orbit torqueRandom access memory
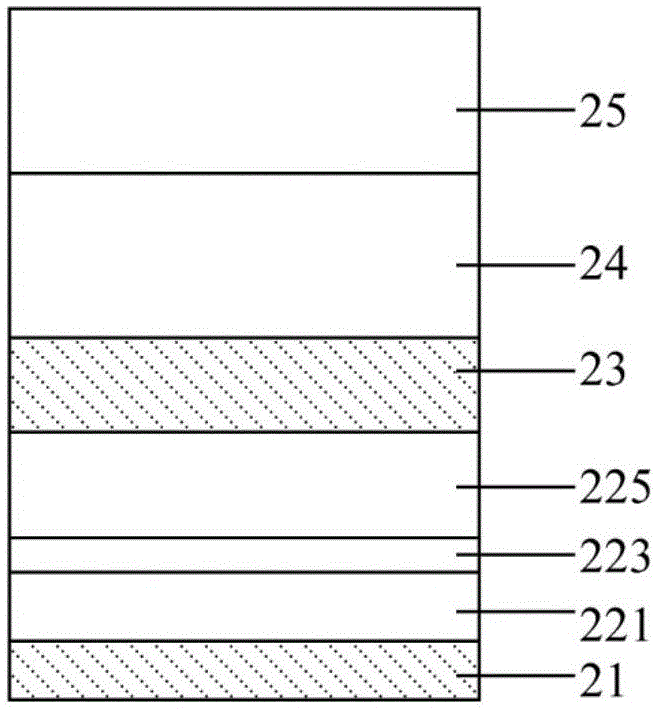
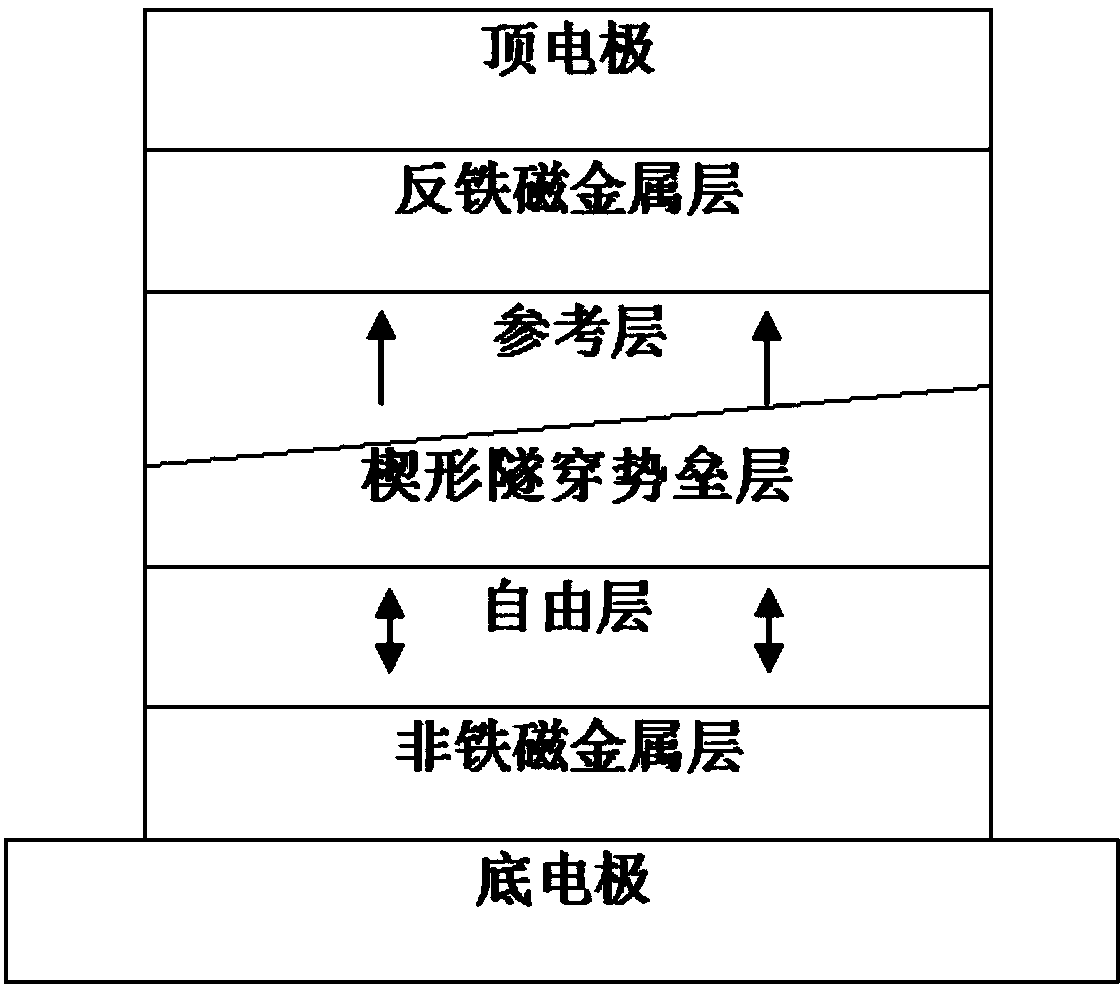
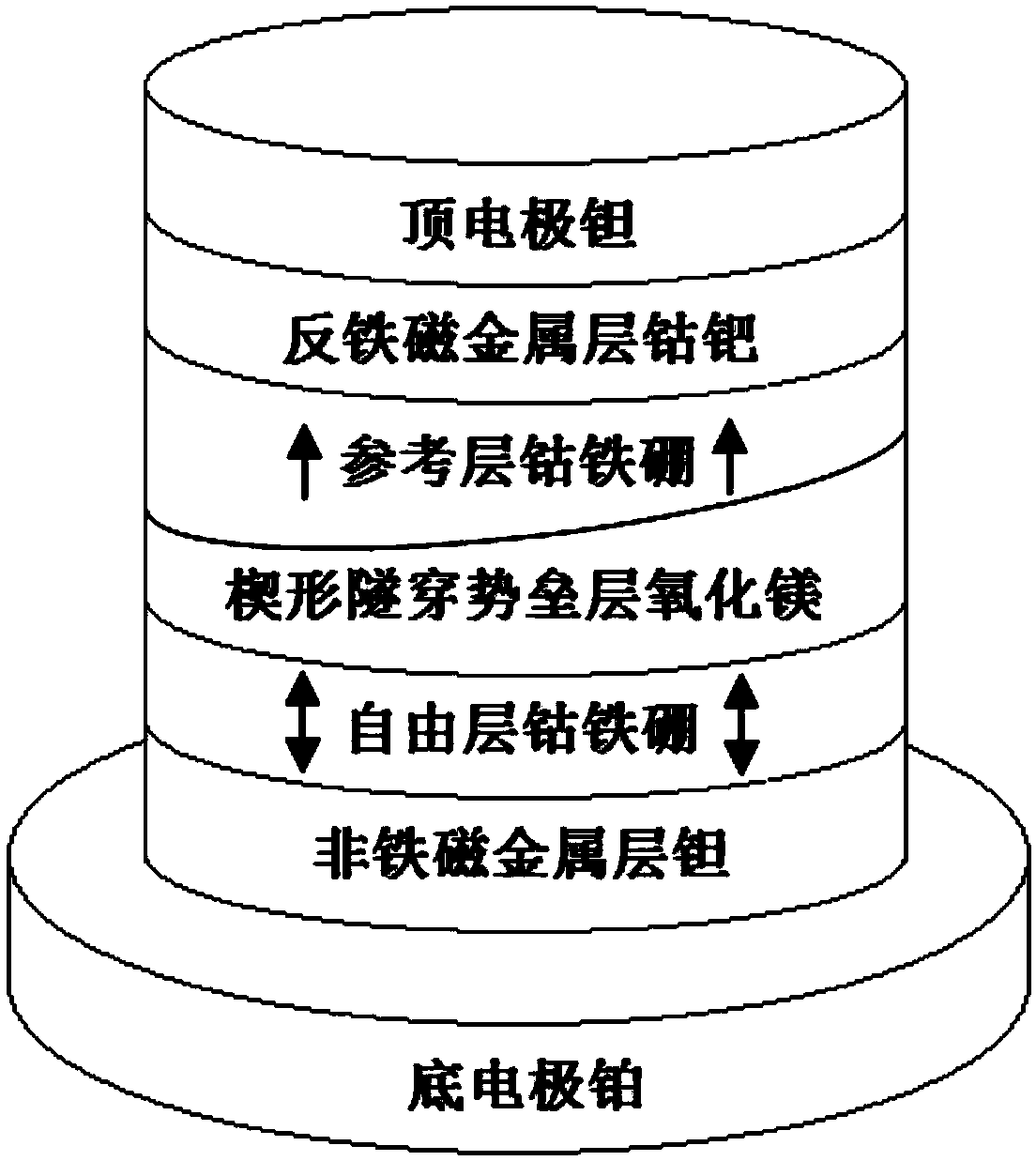
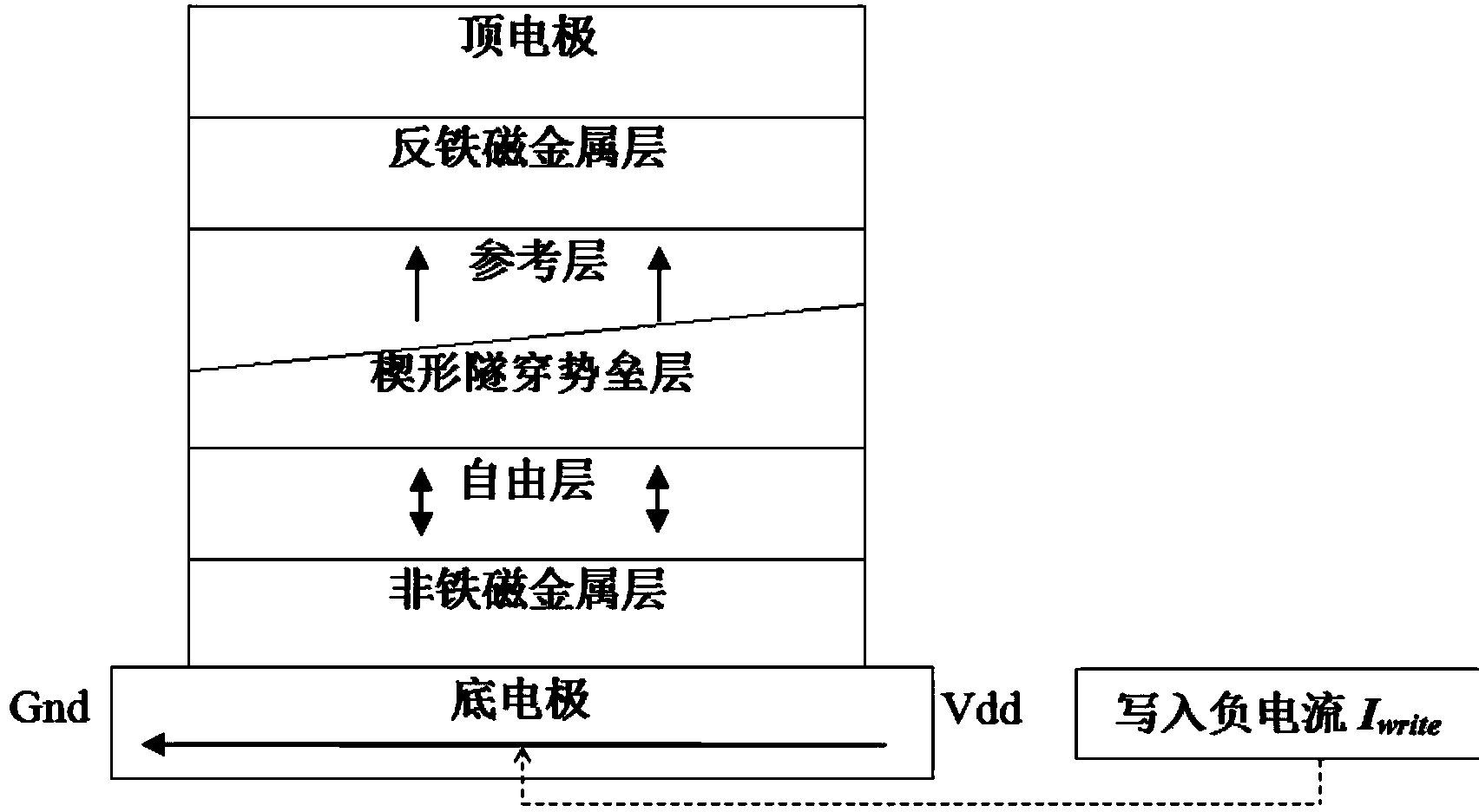
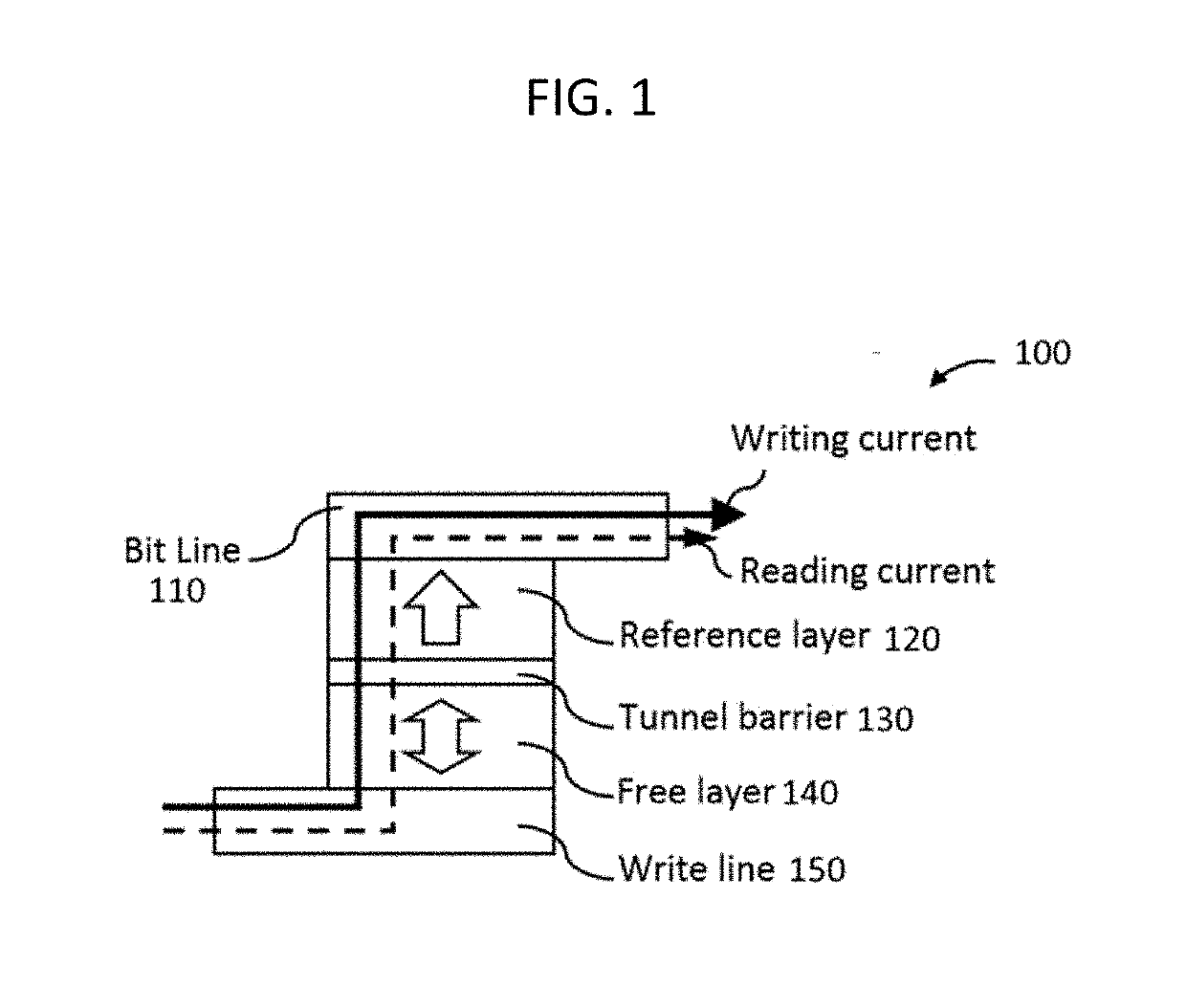
Disclosed is a spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) without an external magnetic field. The spin-orbit torque magnetic tunneling junction(SOT-MTJ) of the random access memory is based on perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, apart from comprising an anti-parallel layer, a tunneling barrier layer, a reference layer and an antiferromagnetc metal layer in a conventional MTJ structure, is also additionally provided with a nonferromagnetic metal layer, optimizes the material of the antiferromagnetc metal layer and improves the shape of the tunneling barrier layer; and the SOT-MTJ structure is successively provided with seven layers which are respectively a bottom electrode, the nonferromagnetic metal layer, a first ferromagnetic metal layer, i.e., the anti-parallel layer, a wedge tunneling barrier layer, a second ferromagnetic metal layer, i.e., the reference layer, the antiferromagnetc metal layer and a top electrode from the bottom to the top. According to the invention, writing operation can be carried out without the external magnetic field. Compared to a conventional SOT-MRAM, the energy consumption is smaller, and the geometric ratio micro-shrink performance reduced along with a technical node is more excellent.
Owner:致真存储(北京)科技有限公司
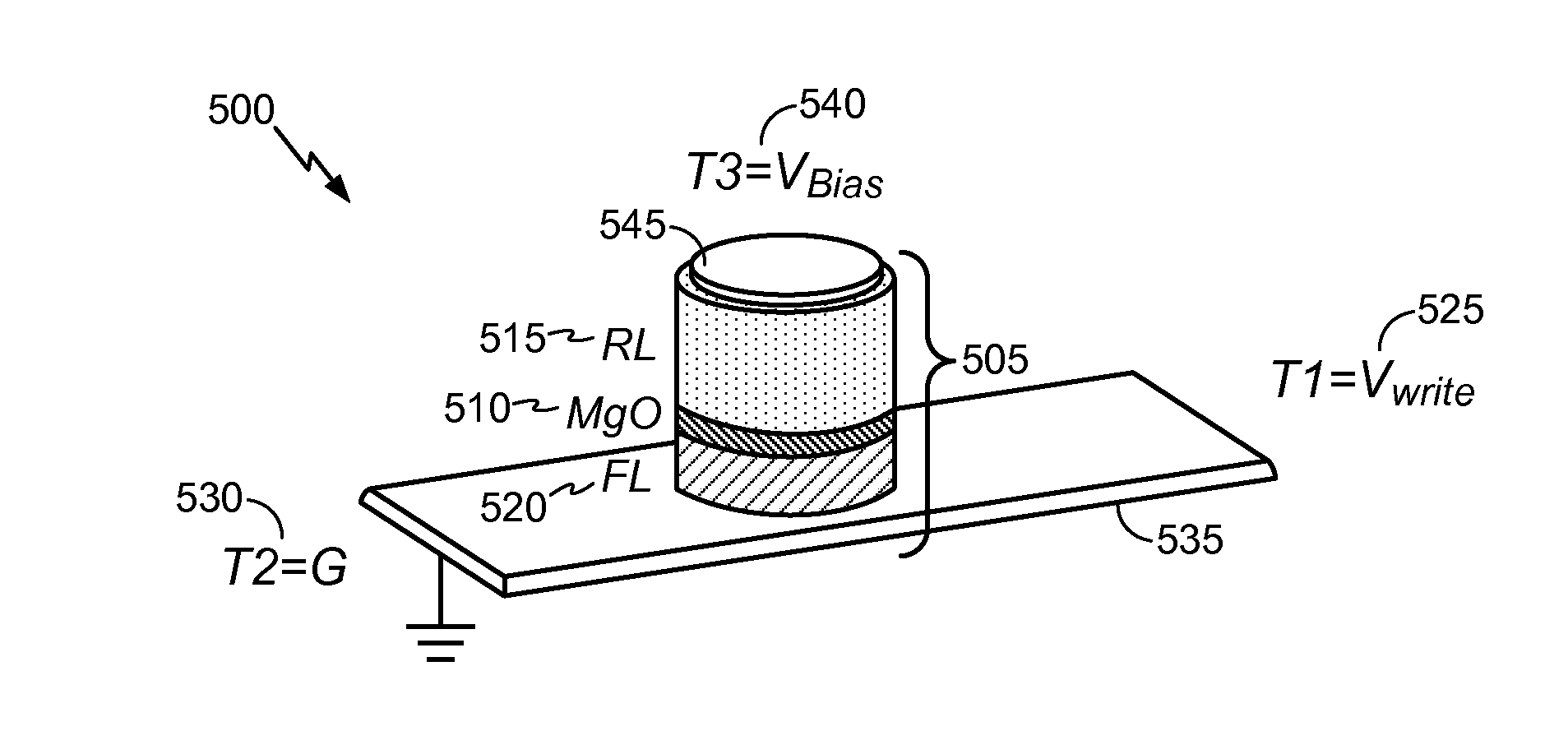
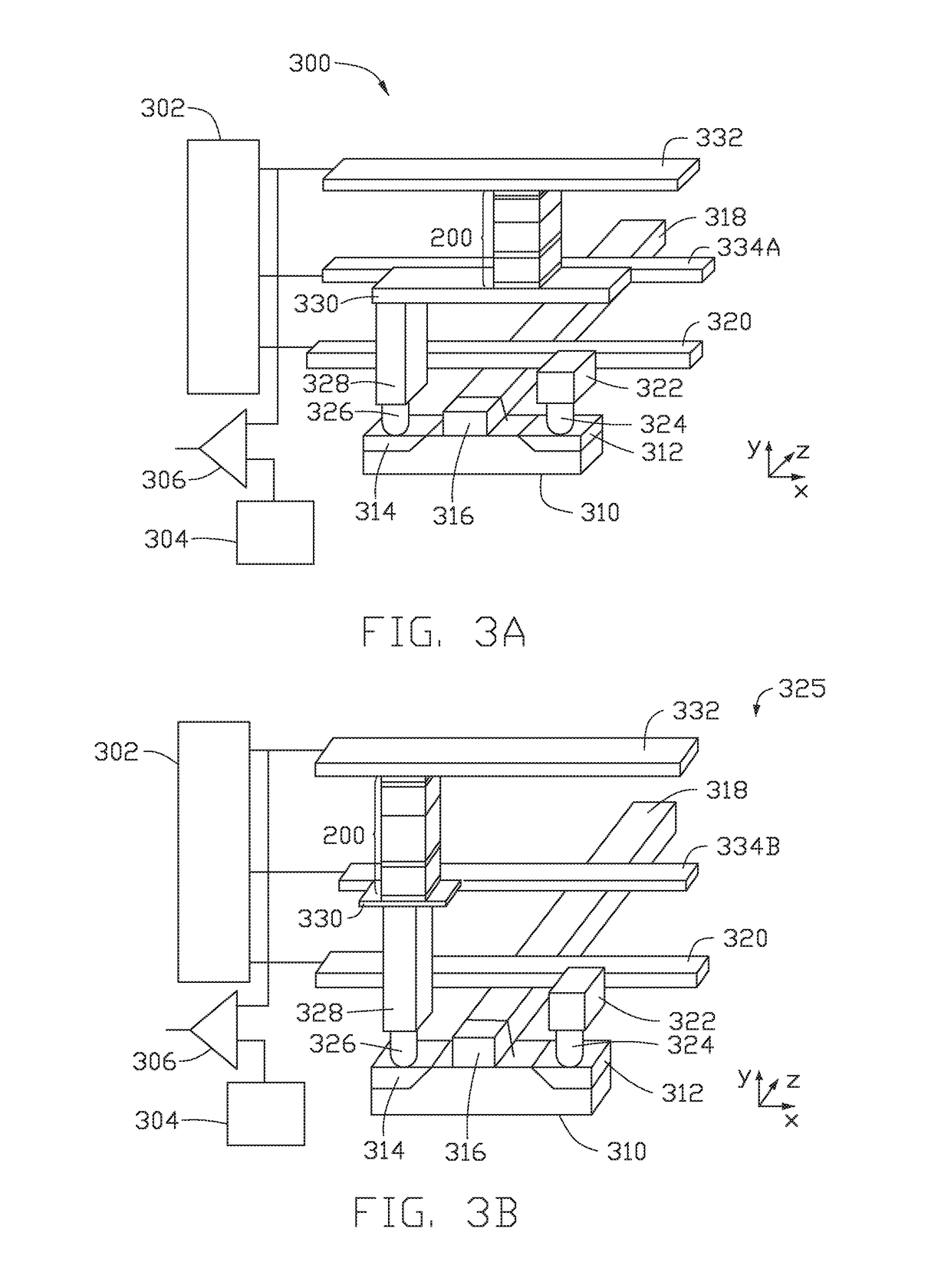
Three Terminal Spin Orbit Torque Memory Cell with In-Stack MAGNETIC LAYER THAT PROVIDES Magnetic Bias Field AND SPIN ORBIT TORQUE VIA Anomalous Hall Effect
ActiveUS20170125078A1Remarkable effectMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin orbit torqueBias field
A method and apparatus for deterministically switching a free layer in a spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory (SOT-MRAM) cell is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, an SOT-MRAM memory cell is provided. The SOT-MRAM memory cell includes a magnetic tunnel junction, a ferromagnetic bias layer, and an antiferromagnetic layer. The magnetic tunnel junction includes a free layer having primarily two bi-stable magnetization directions, a reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, and an insulating tunnel barrier layer positioned between the free layer and the reference layer. The ferromagnetic bias layer is configured to provide spin orbit torque via anomalous Hall effect and simultaneously configured to provide a magnetic bias field on the free layer to achieve deterministic switching. The antiferromagnetic layer is positioned below the ferromagnetic bias layer and is configured to pin a magnetization direction of the ferromagnetic bias layer in a predetermined direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
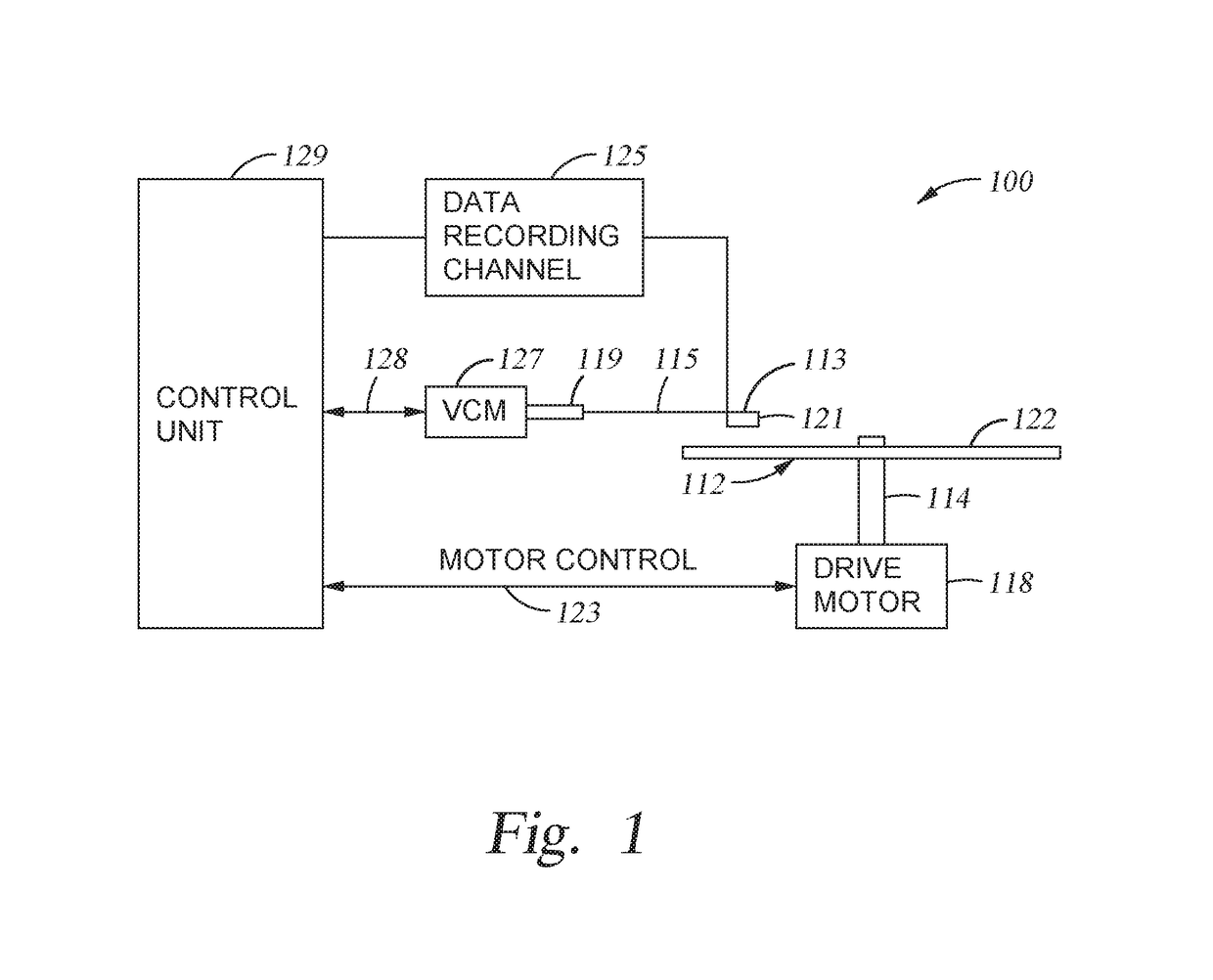
Dual spin-orbit torque oscillator in magnetic recording
ActiveUS10210888B1Reduce critical currentQuality improvementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsHeads using thin filmsIn planeMagnetic media
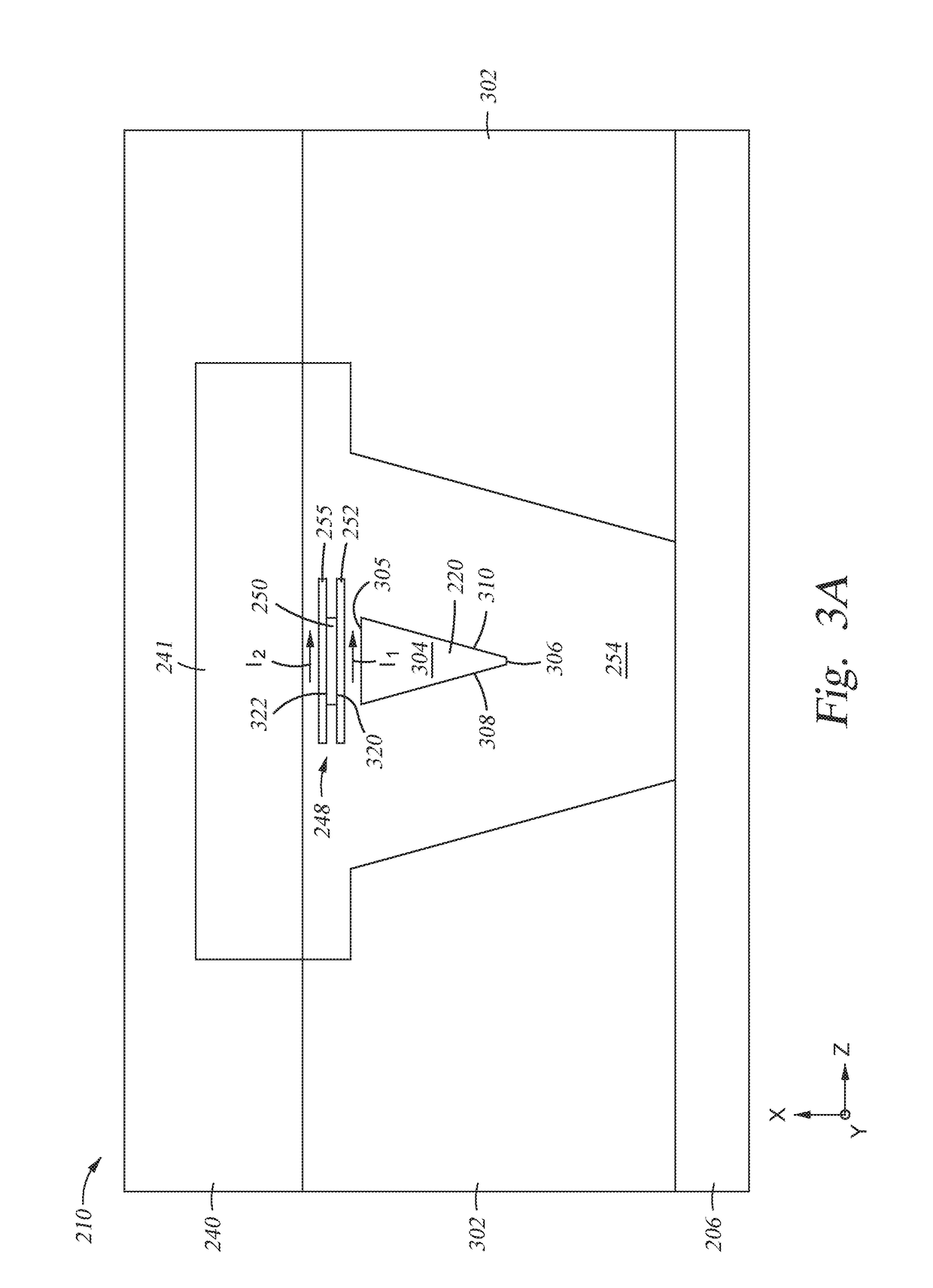
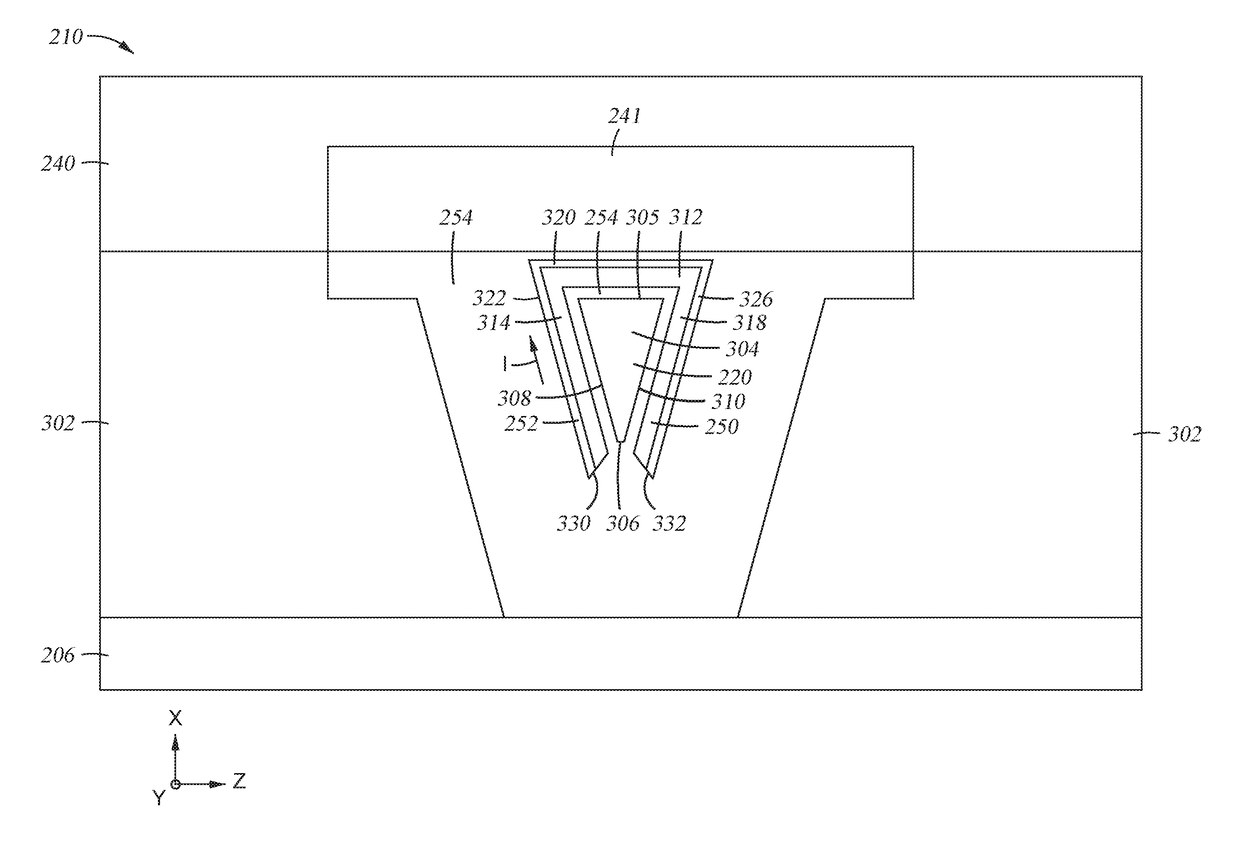
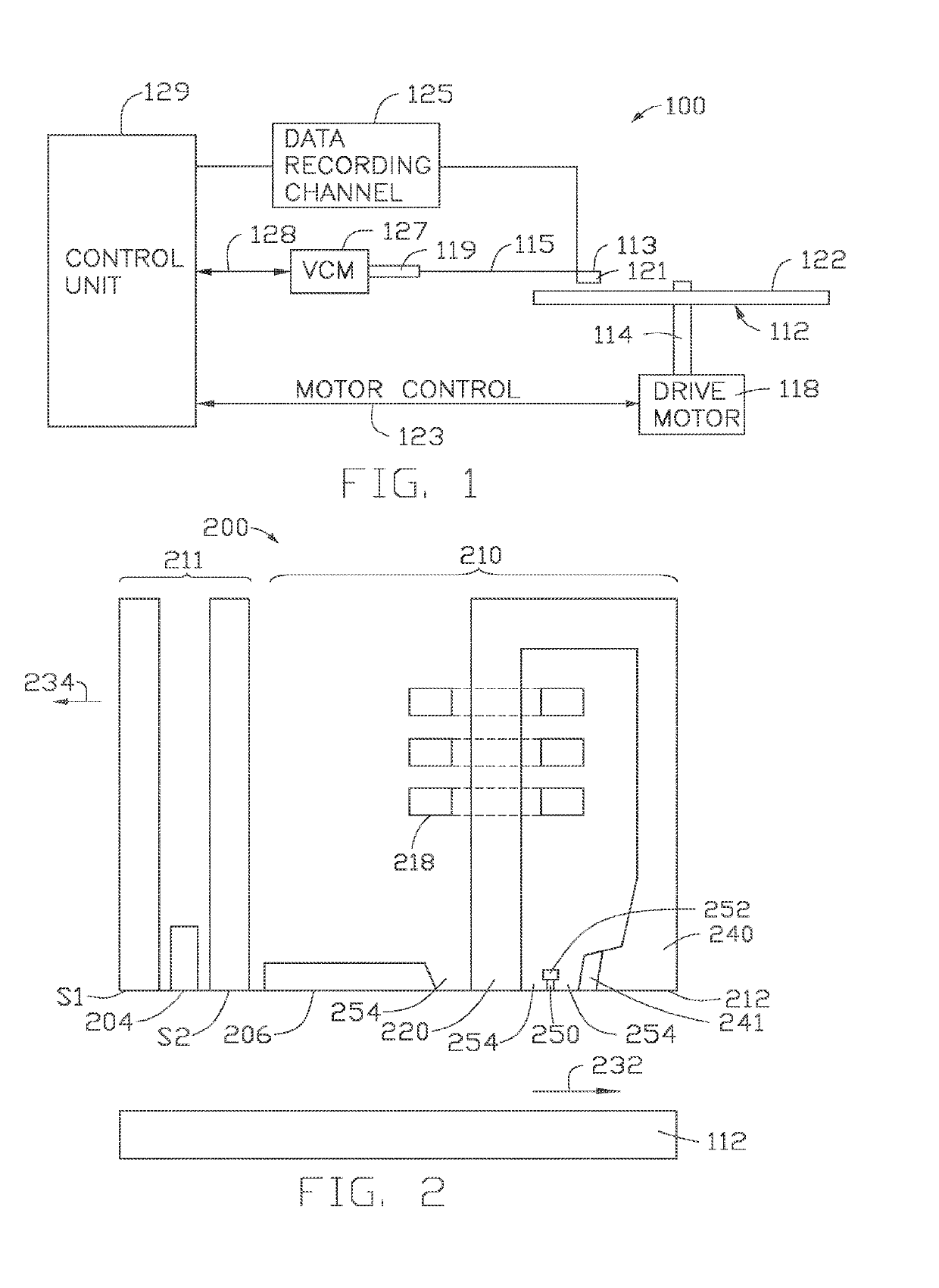
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a trailing shield, and an oscillator located between the main pole and the trailing shield. The oscillator is disposed at a media facing surface (MFS). The oscillator includes a spin-torque layer sandwiched between two distinct spin Hall layers. The two distinct spin Hall layers generate spin-orbit torque (SOT) that induces in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer, and both in-plane precessions are in the same direction. The same-direction in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer reduce the critical current of the oscillation of the oscillator, leading to high quality recording.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spin-orbit torque based magnetic recording
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a spin-torque structure surrounding at least a portion of the main pole at a media facing surface (MFS), and a spin Hall structure surrounding the spin-torque structure. Strong spin-orbit torque (SOT) is generated from the spin Hall structure, enforcing in-plane magnetization oscillation in the spin-torque structure. The SOT based head with the spin Hall structure surrounding the spin-torque structure utilizes less current flowed to the spin Hall structure due to the strong SOT generated by the spin Hall structure.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
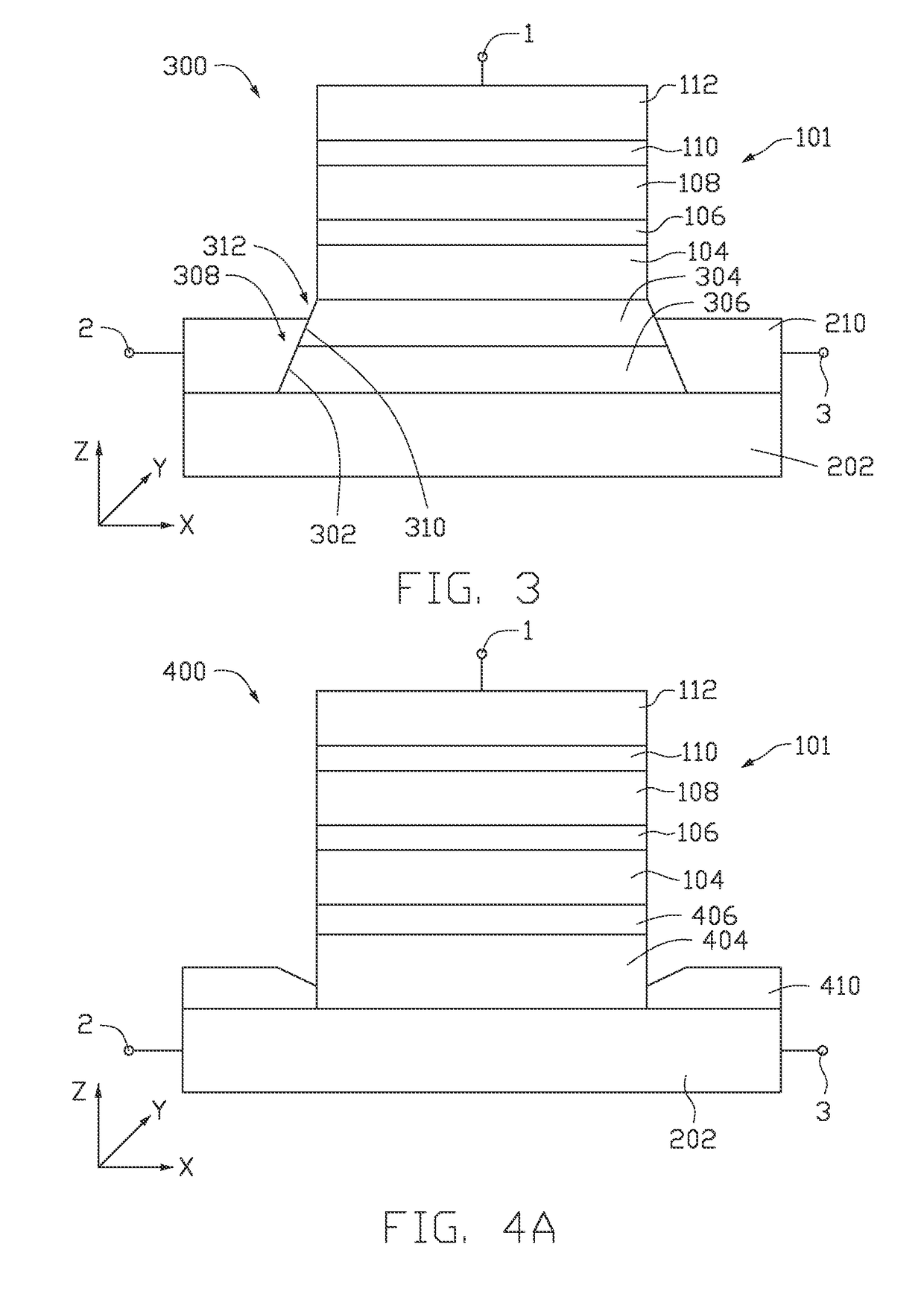
Double-barrier structure based magnetic memory device
InactiveCN105161613AImprove thermal stabilityPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy strengtheningMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceMetallic materials
A double-barrier structure based magnetic memory device is disclosed. The double-barrier structure is used to strengthen perpendicular magnetic anisotropy or tunnel magnetoresistance ratio of a magnetic tunnel junction; meanwhile, a three-port device based on a spin orbit torque is formed by combination of metal wire at the bottom; the double-barrier structure of the magnetic memory device comprises a metal oxide barrier layer, a free layer formed by ferromagnetic metal and the other metal oxide barrier layer; a reference layer formed by the ferromagnetic metal and a covering layer formed by non-magnetic metal are deposited on the top of the structure in sequence; the top of the structure is connected with a peripheral circuit through a metal electrode; and the wire at the bottom is formed by metal materials with a larger hall angle and used for data writing. By introducing the double-barrier structure into the magnetic memory device based on the spin orbit torque, the adverse effect on the data writing caused by too high resistance can be effectively avoided, and the thermal stability and the tunnel magnetoresistance ratio of the device are improved; and the good property of the STT-MRAM is maintained by the device, and the double-barrier structure based magnetic memory device is quite suitable for industrial production.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
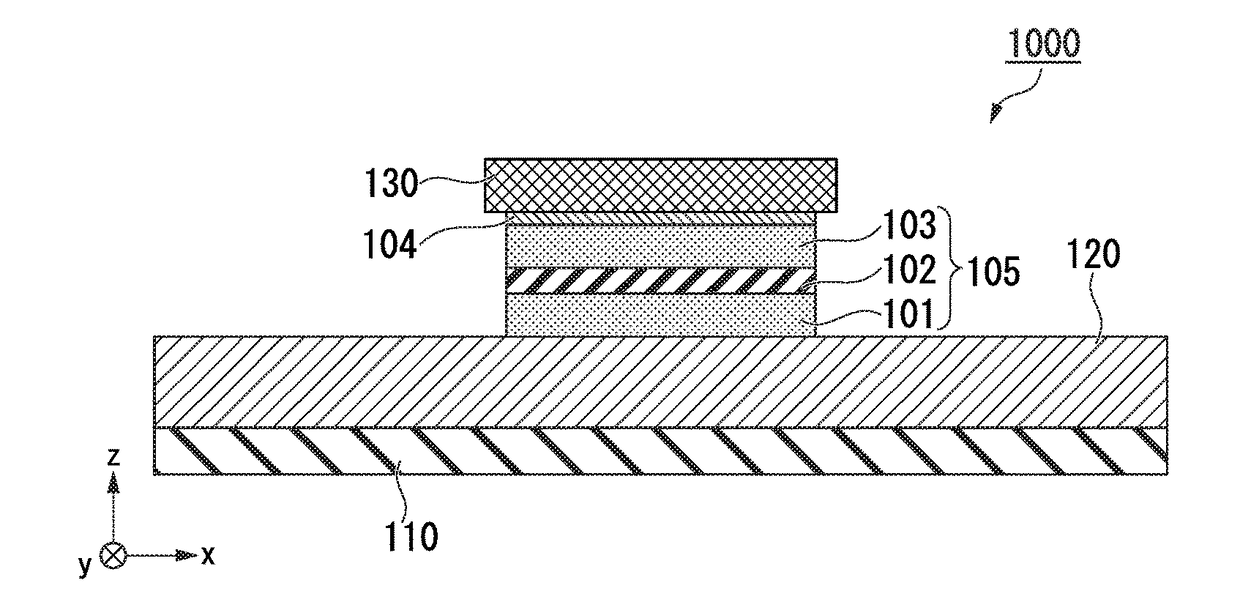
Spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory containing composite spin hall effect layer including beta phase tungsten
ActiveUS20190080738A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin orbit torqueSpin Hall effect
A spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory (SOT MRAM) cell includes a magnetic tunnel junction that contains a free layer having two bi-stable magnetization directions, a reference magnetic layer having a fixed magnetization direction, and a tunnel barrier layer located between the free layer and the reference layer, and a nonmagnetic spin Hall effect layer. The spin Hall effect layer may include an alternating stack of beta phase tungsten layers and noble metal nonmagnetic dusting layers. Alternatively or in addition, a hafnium layer may be located between the nonmagnetic spin Hall effect layer and the free layer.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
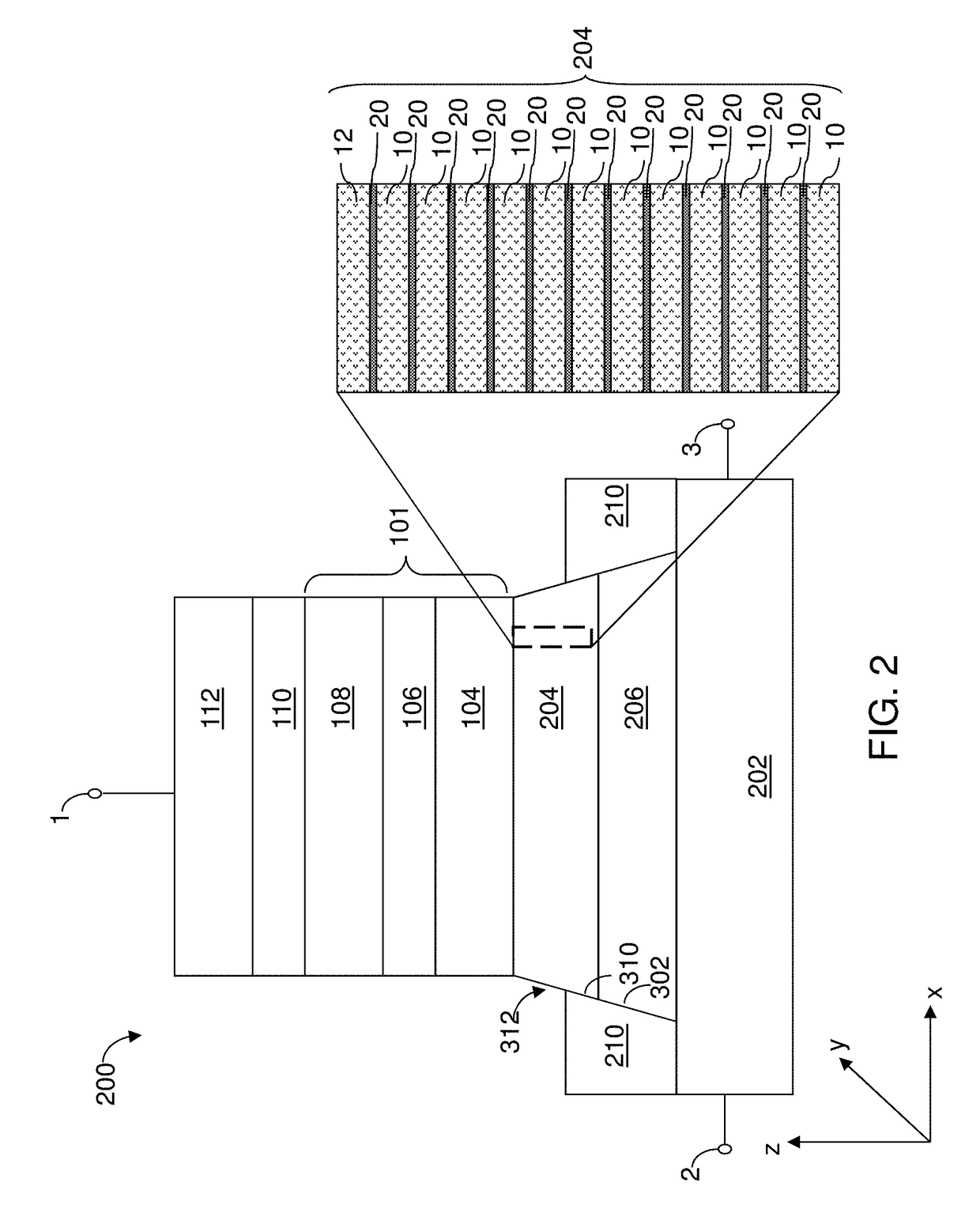
Magnetic devices including magnetic junctions having tilted easy axes and enhanced damping programmable using spin orbit torque
ActiveUS20180219152A1High damping constantHigh constantMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionIn planeDamping constant
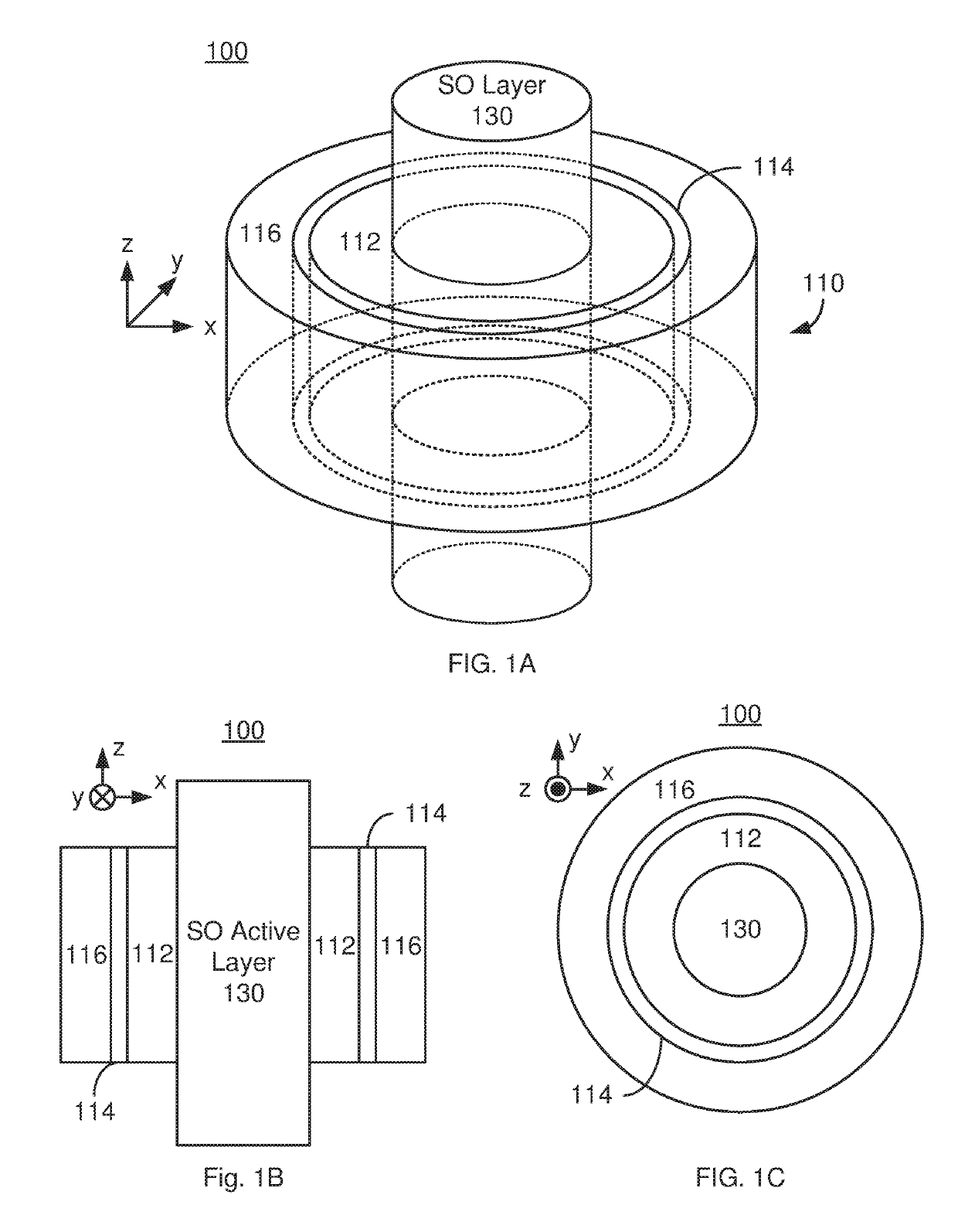
A magnetic memory including a plurality of magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer is described. Each of the magnetic junctions includes a pinned layer, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between reference and free layers. The free layer has at least one of a tilted easy axis and a high damping constant. The tilted easy axis is at a nonzero acute angle from a direction perpendicular-to-plane. The high damping constant is at least 0.02. The at least one SO active layer is adjacent to the free layer and carries a current in-plane. The at least one SO active layer exerts a SO torque on the free layer due to the current. The free layer is switchable using the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Areal density capability improvement with spin-orbit torque based structures surrounding main pole tip
ActiveUS10157632B1High track densityImproves write-abilityHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageTrack densityMagnetic media
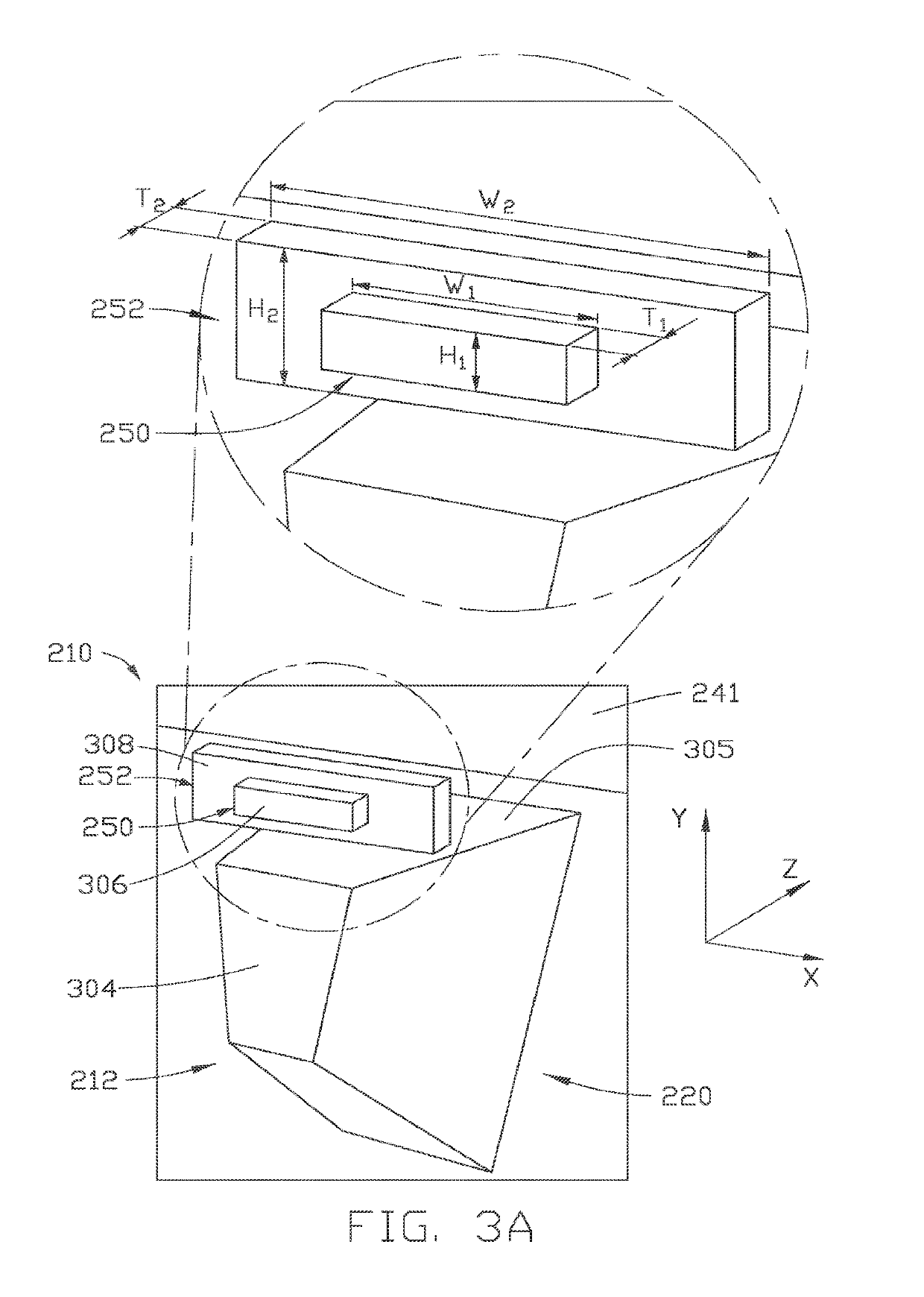
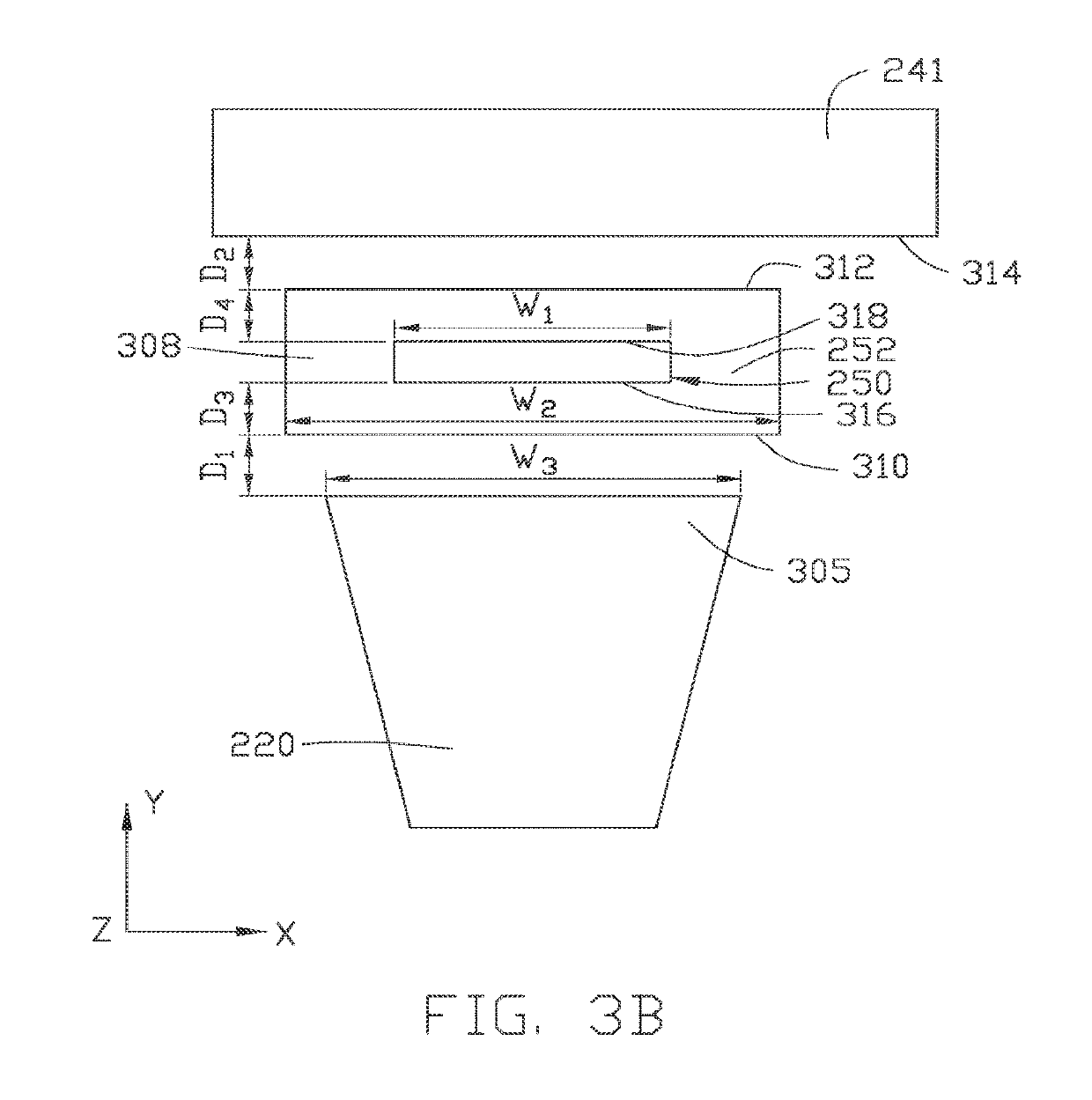
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a heavy metal structure surrounding at least a portion of the main pole at a media facing surface (MFS), and two magnetic structures sandwiching the heavy metal structure. Spin-orbit torque (SOT) is generated from the heavy metal structure, inducing magnetization switching (or precession) in the magnetic structures. The SOT reduces the magnetic flux shunting from the main pole to the trailing shield, and the magnetization switching sharpens the write field profile in the cross-track direction. The SOT based head with the magnetic structures sandwiching the heavy metal structure increases both track density (tracks per inch) and linear density (bit per inch), which in turn increases the areal density capability (ADC), which is the product of tracks per inch and bit per inch.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic structure based on antiferromagnet fixing layer, and SOT-MRAM
ActiveCN109560193AEnhanced antiferromagnetic coupling strengthReduce volumeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionHigh densitySpin orbit torque
The invention discloses a magnetic structure based on an artificial antiferromagnet fixing layer, and a spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory SOT-MRAM. The magnetic structure comprises a magnetic tunnel junction of a fixing layer that is regulated and controlled by an electric field and is based on an artificial antiferromagnet device and a spin-orbit torque material layer, wherein the fixing layer based on the artificial antiferromagnet device can achieve antiferromagnet coupling enhancement through the regulation and control of the electric field. The device can realize the stablewriting of data under the coaction of the electric field and current, has a simple structure, and has the advantages of high density, low power consumption, high speed, radiation resistance and non-volatility.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Spin orbit torque (SOT) memory devices with enhanced tunnel magnetoresistance ratio and their methods of fabrication
ActiveUS20190304653A1Nanostructure applicationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic exchangeIn plane
A perpendicular spin orbit torque (SOT) memory device includes an electrode having a spin orbit torque material, where the SOT material includes iridium and manganese and a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (pMTJ) device on a portion of the electrode. The pMTJ device includes a free magnet structure electrode, a fixed layer and a tunnel barrier between the free layer and the fixed layer and a SAF structure above the fixed layer. The Ir—Mn SOT material and the free magnet have an in-plane magnetic exchange bias.
Owner:INTE CORP
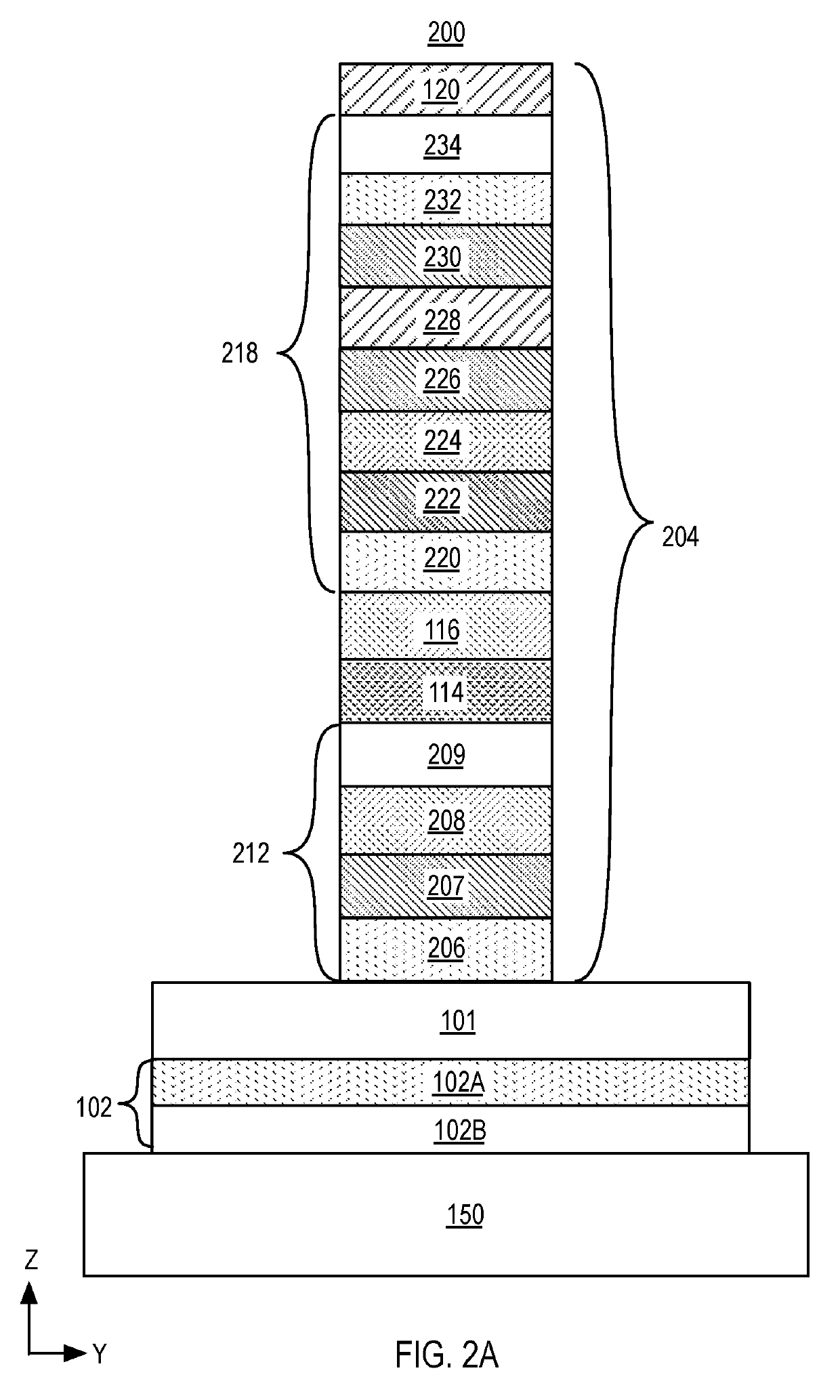
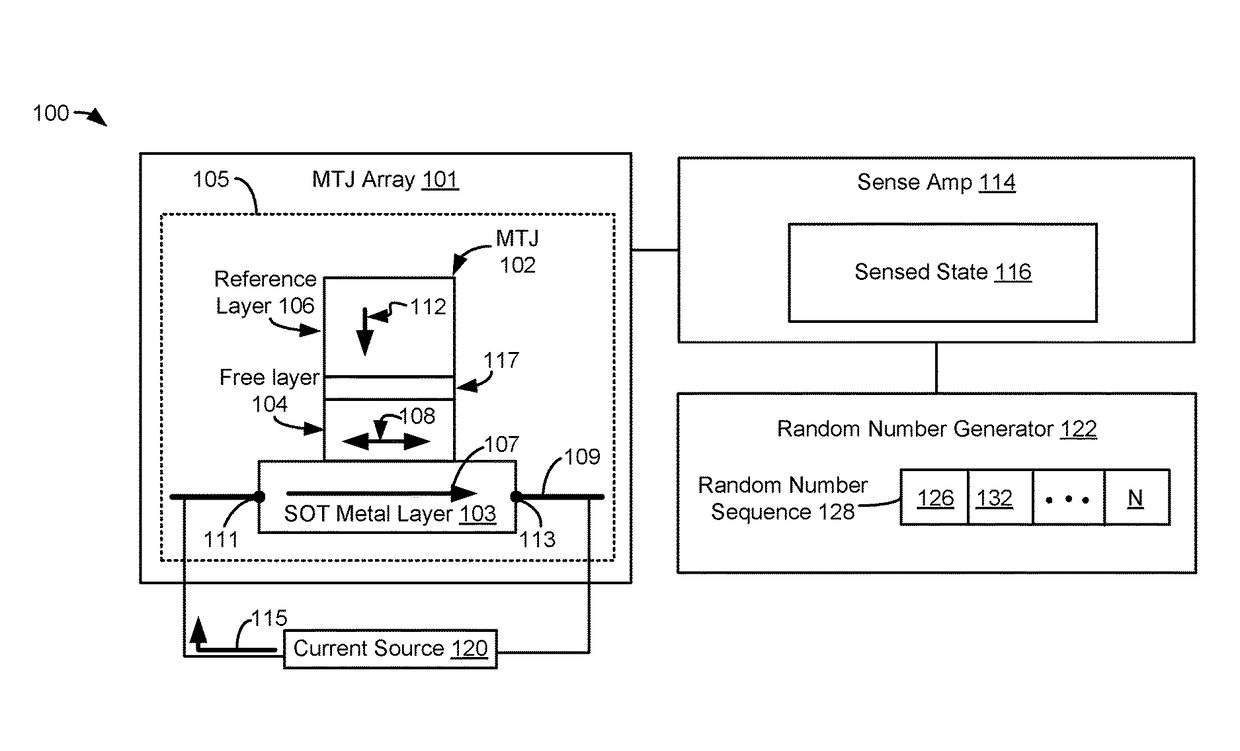
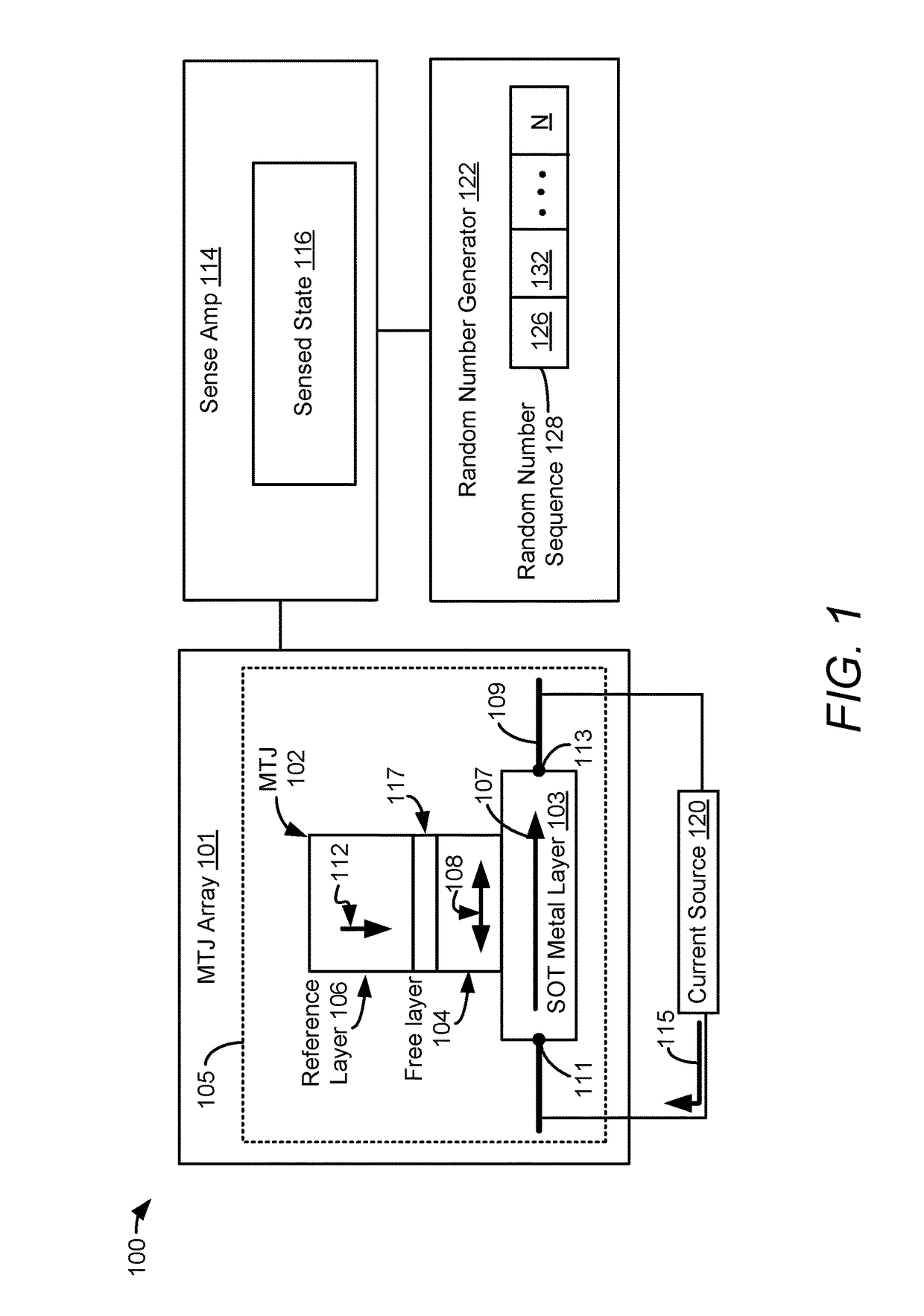
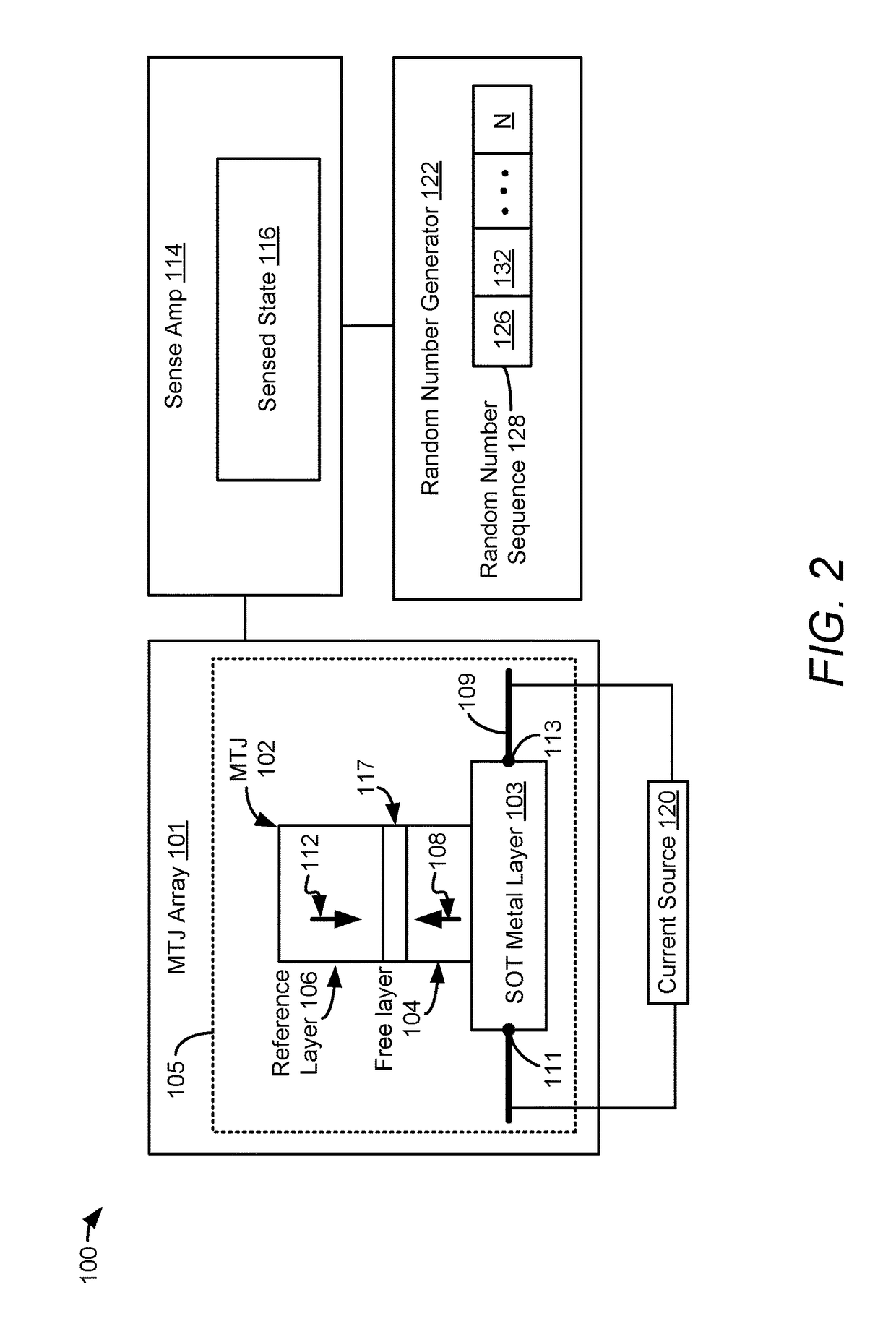
System and method to generate a random number
An apparatus includes a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) including a free layer. The apparatus includes a spin orbit torque metal layer coupled to the perpendicular MTJ and configured to change a magnetization state of the free layer responsive to flow of a current along the spin orbit torque metal layer. The apparatus includes a random number generator configured to generate a random number at least partially based on a state of the perpendicular MTJ.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
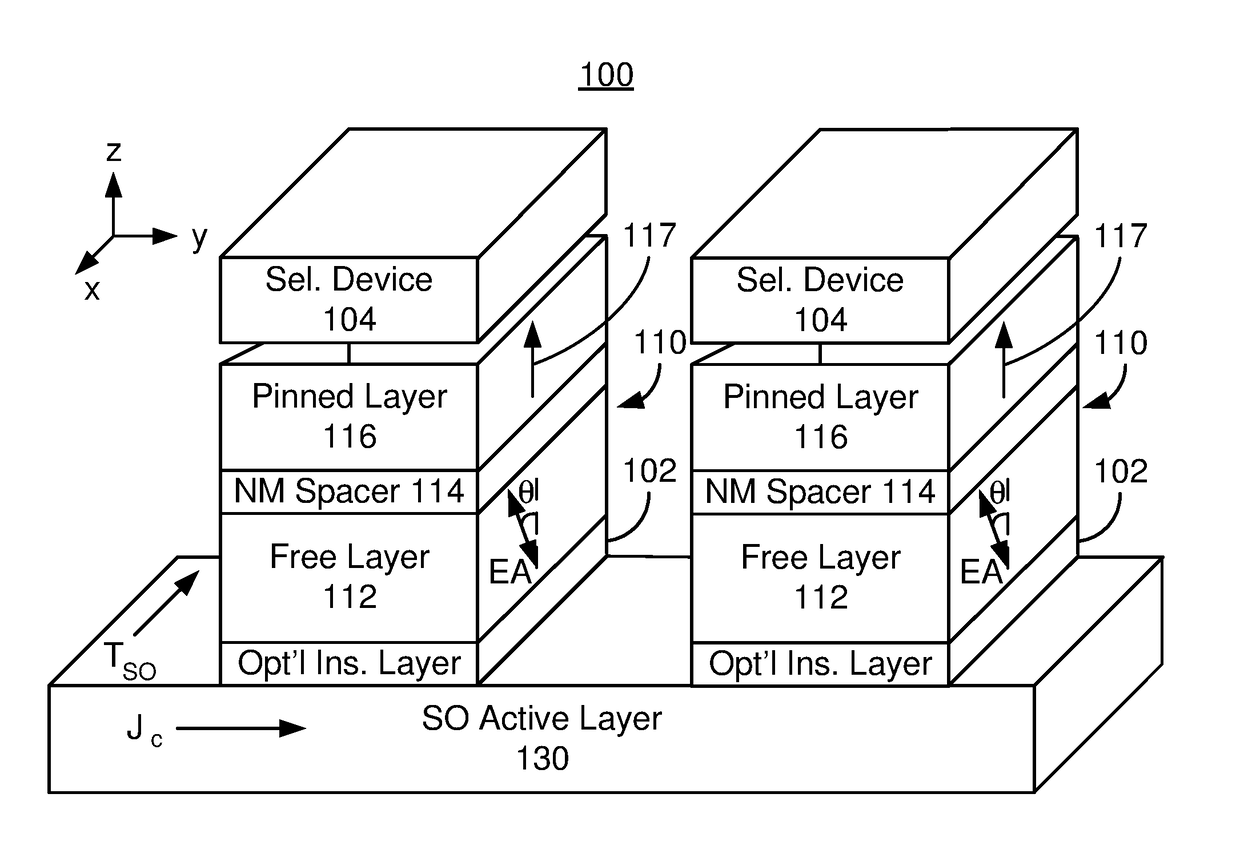
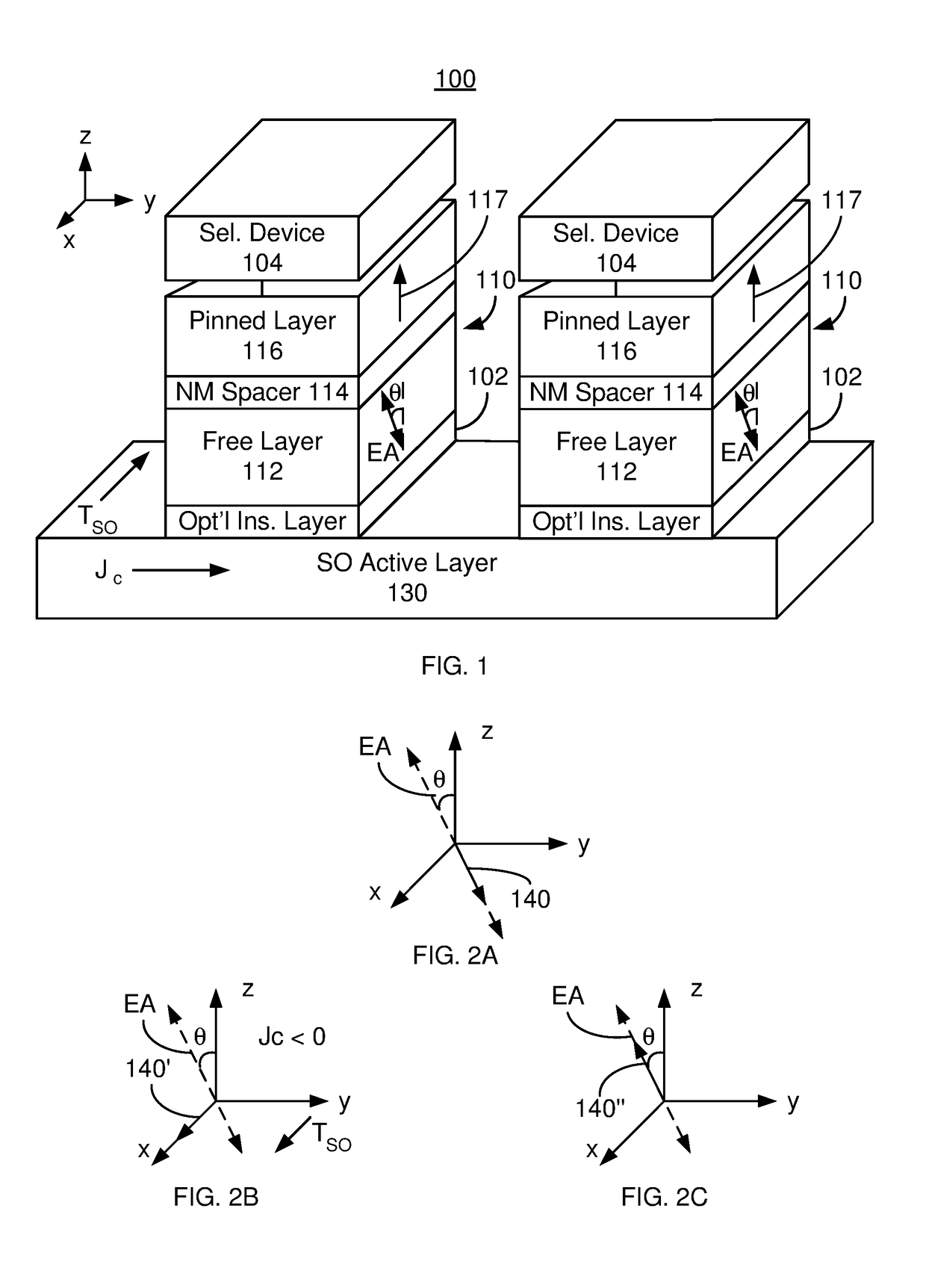
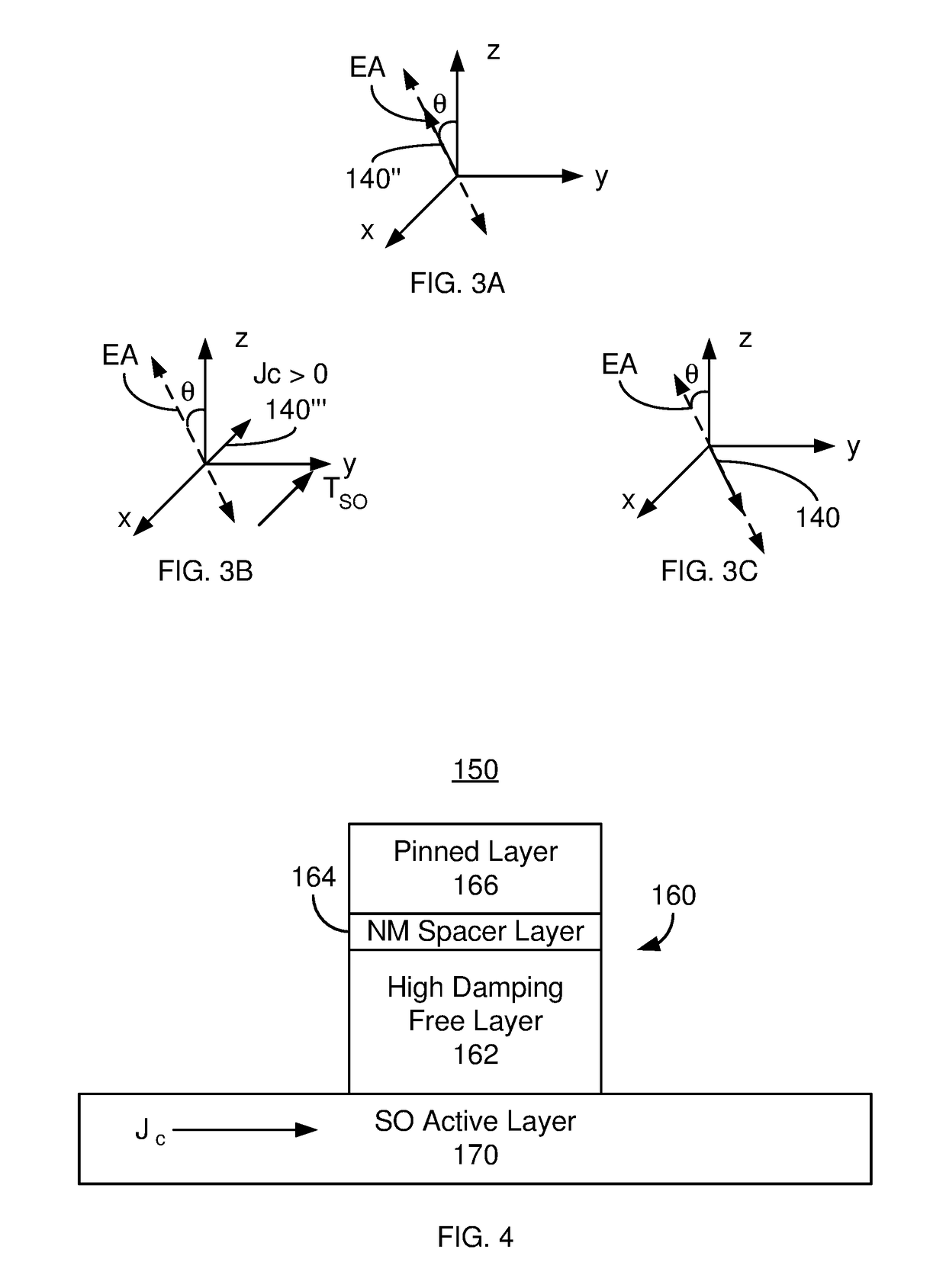
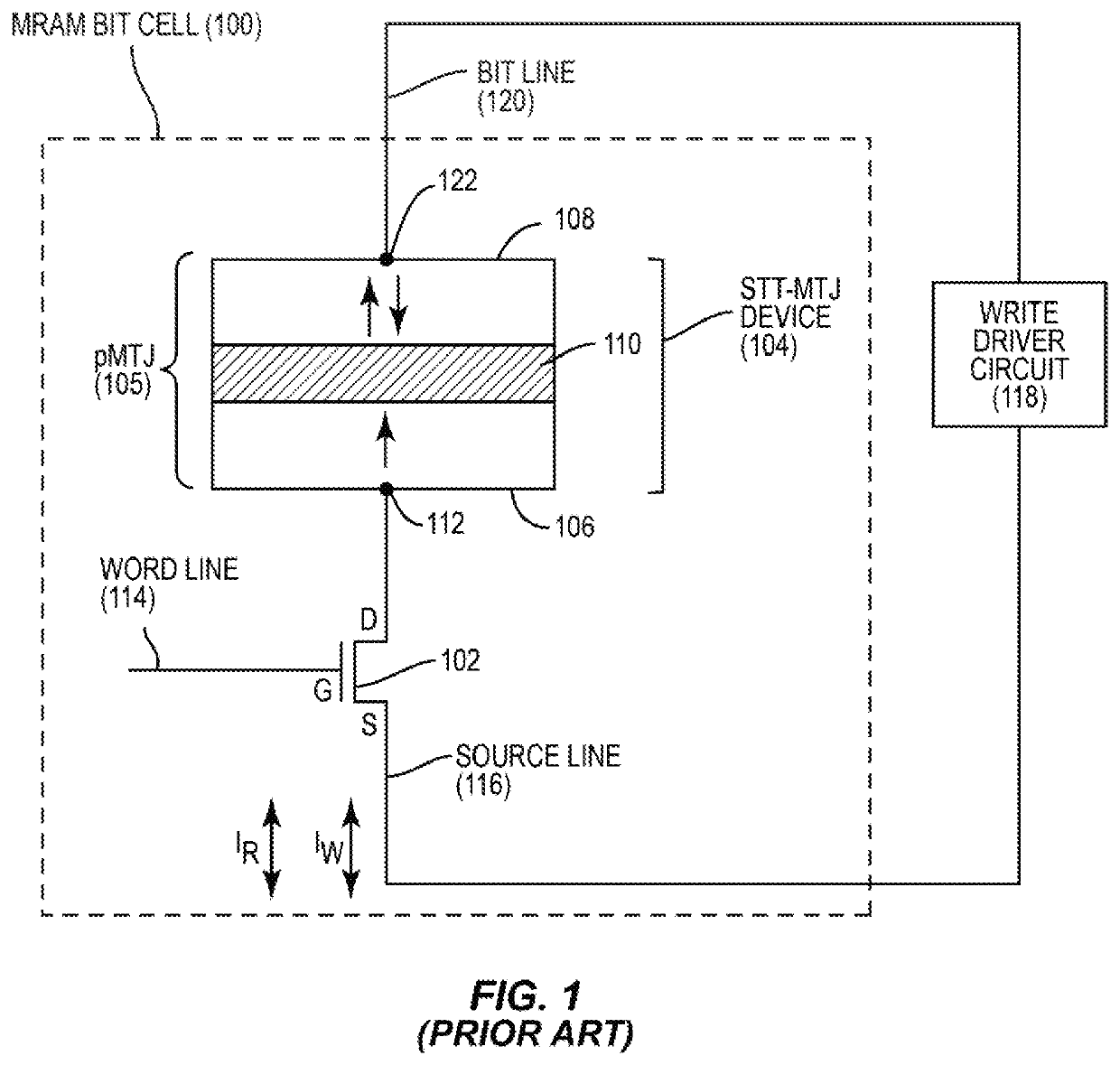
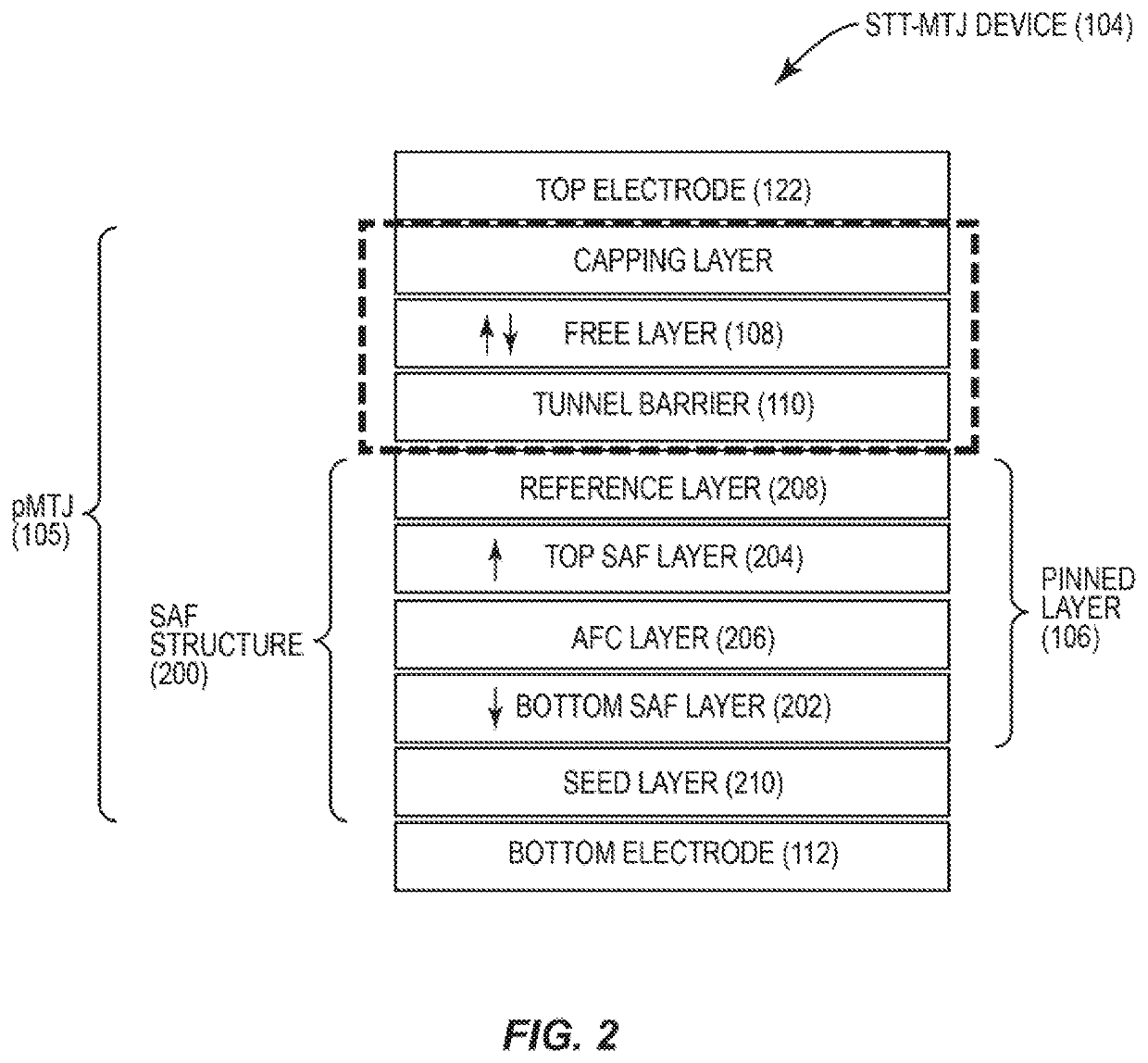
Magnetic memory bits with perpendicular magnetization switched by current-induced spin-orbit torques
ActiveUS9343658B2Easy to switchImprove efficiencyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsIn planeMagnetic memory
A basic Spin-Orbit-Torque (SOT) structure with lateral structural asymmetry is provided that produces a new spin-orbit torque, resulting in zero-field current-induced switching of perpendicular magnetization. More complex structures can also be produced incorporating the basic structure of a ferromagnetic layer with a heavy non-magnetic metal layer having strong spin-orbit coupling on one side, and an insulator layer on the other side with a structural mirror asymmetry along the in-plane direction. The lateral structural asymmetry and new spin-orbit torque, in effect, replaces the role of the external in-plane magnetic field. The direction of switching is determined by the combination of the direction of applied current and the direction of symmetry breaking in the device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Three terminal SOT memory cell with anomalous Hall effect
A method and apparatus for deterministically switching a free layer in a spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory (SOT-MRAM) cell is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, an SOT-MRAM memory cell is provided. The SOT-MRAM memory cell includes a magnetic tunnel junction, a ferromagnetic bias layer, and an antiferromagnetic layer. The magnetic tunnel junction includes a free layer having primarily two bi-stable magnetization directions, a reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, and an insulating tunnel barrier layer positioned between the free layer and the reference layer. The ferromagnetic bias layer is configured to provide spin orbit torque via anomalous Hall effect and simultaneously configured to provide a magnetic bias field on the free layer to achieve deterministic switching. The antiferromagnetic layer is positioned below the ferromagnetic bias layer and is configured to pin a magnetization direction of the ferromagnetic bias layer in a predetermined direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
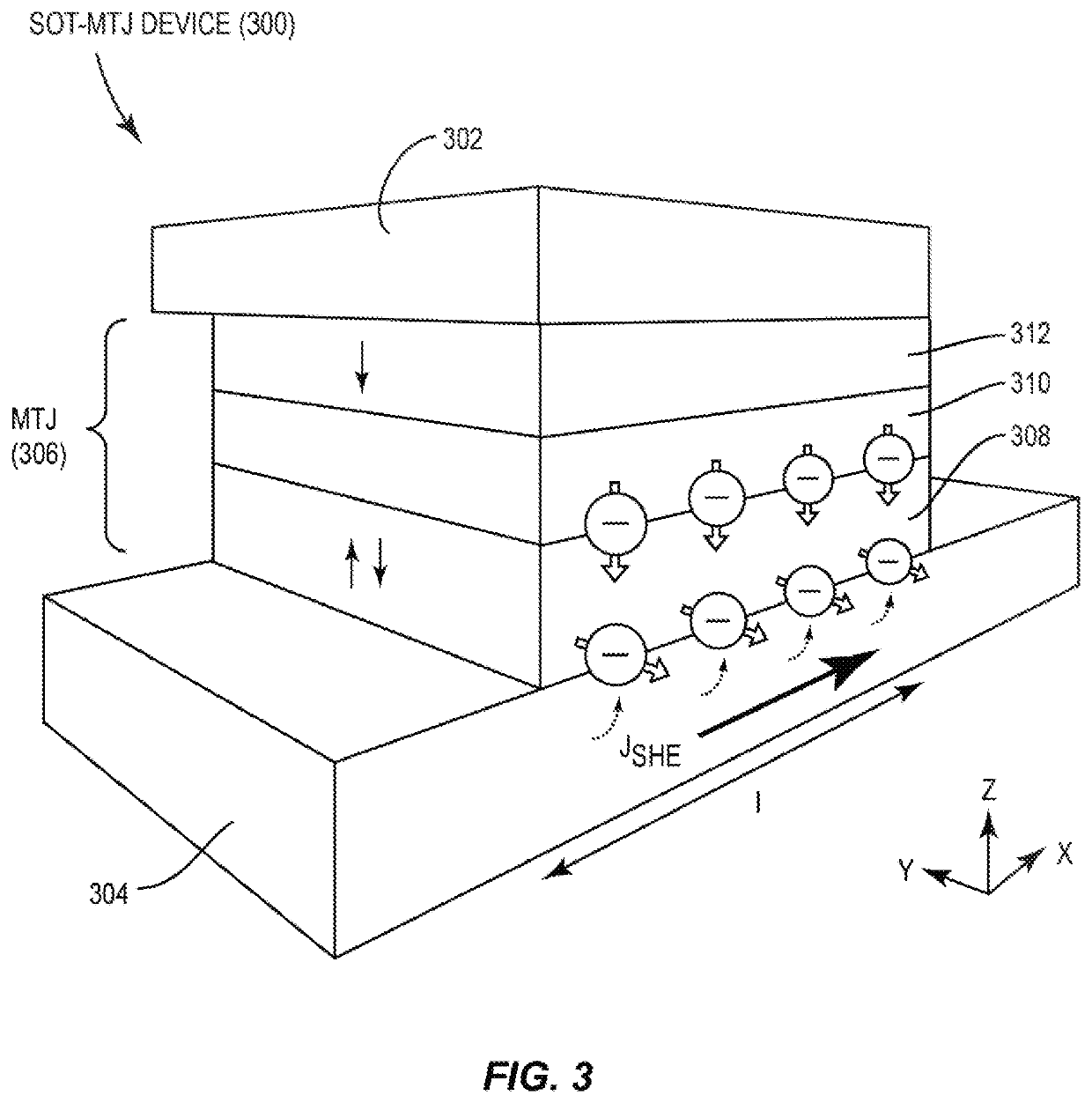
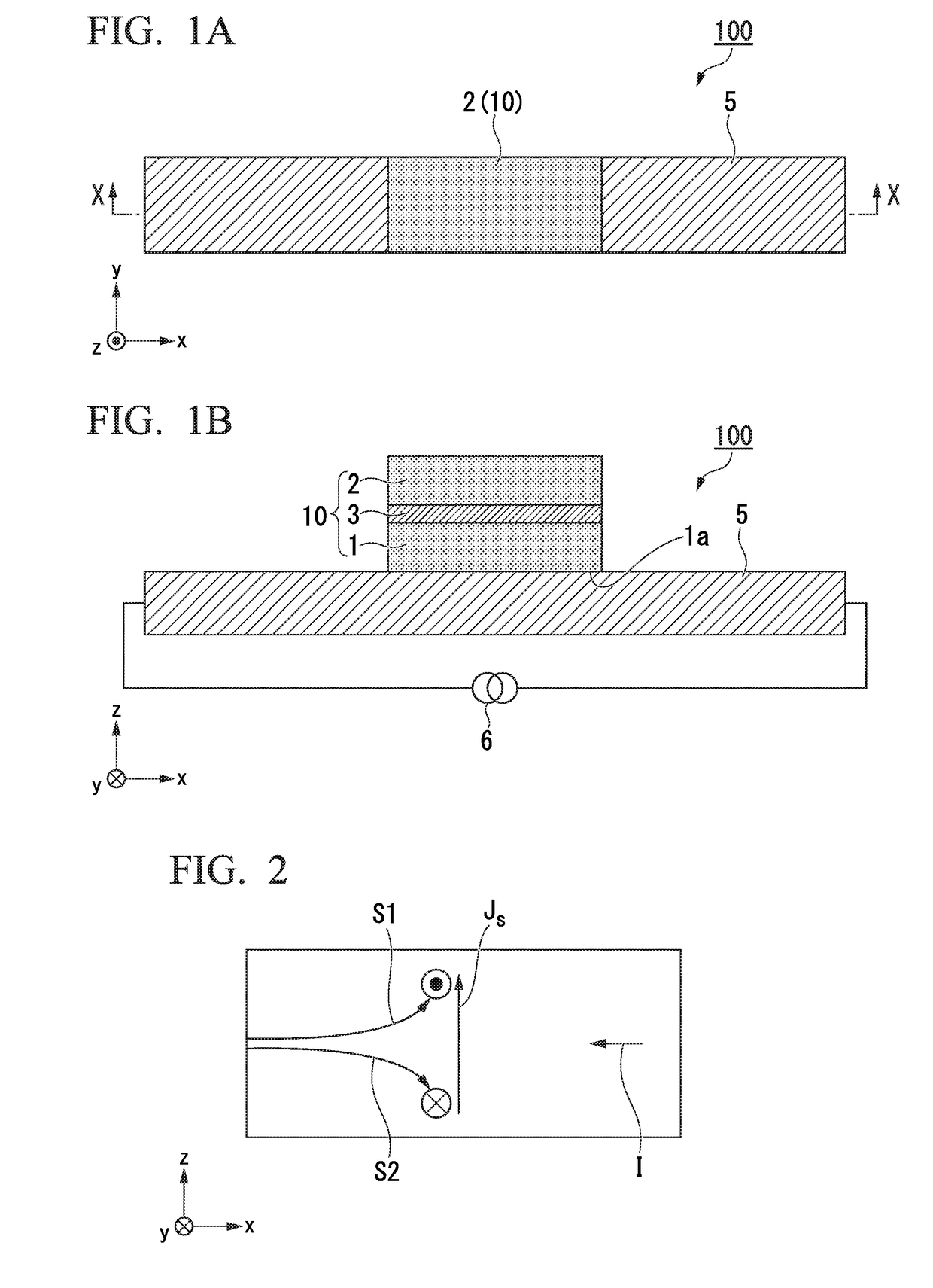
Spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect device
ActiveUS20190147929A1Increase write speedSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsSpin orbit torqueOrbit
A spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect device includes: a spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect element including a magnetoresistance effect element part and a spin-orbit torque wiring; and a controller electrically connected to the spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect element. In a portion in which the magnetoresistance effect element part and the spin-orbit torque wiring are bonded, an STT inversion current flowing through the magnetoresistance effect element part and an SOT inversion current flowing through the spin-orbit torque wiring merge or are divided, and the controller is configured to be capable of performing control for applying the STT inversion current to the spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect element at the same time as an application of the SOT inversion current or a time application of the SOT inversion current.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
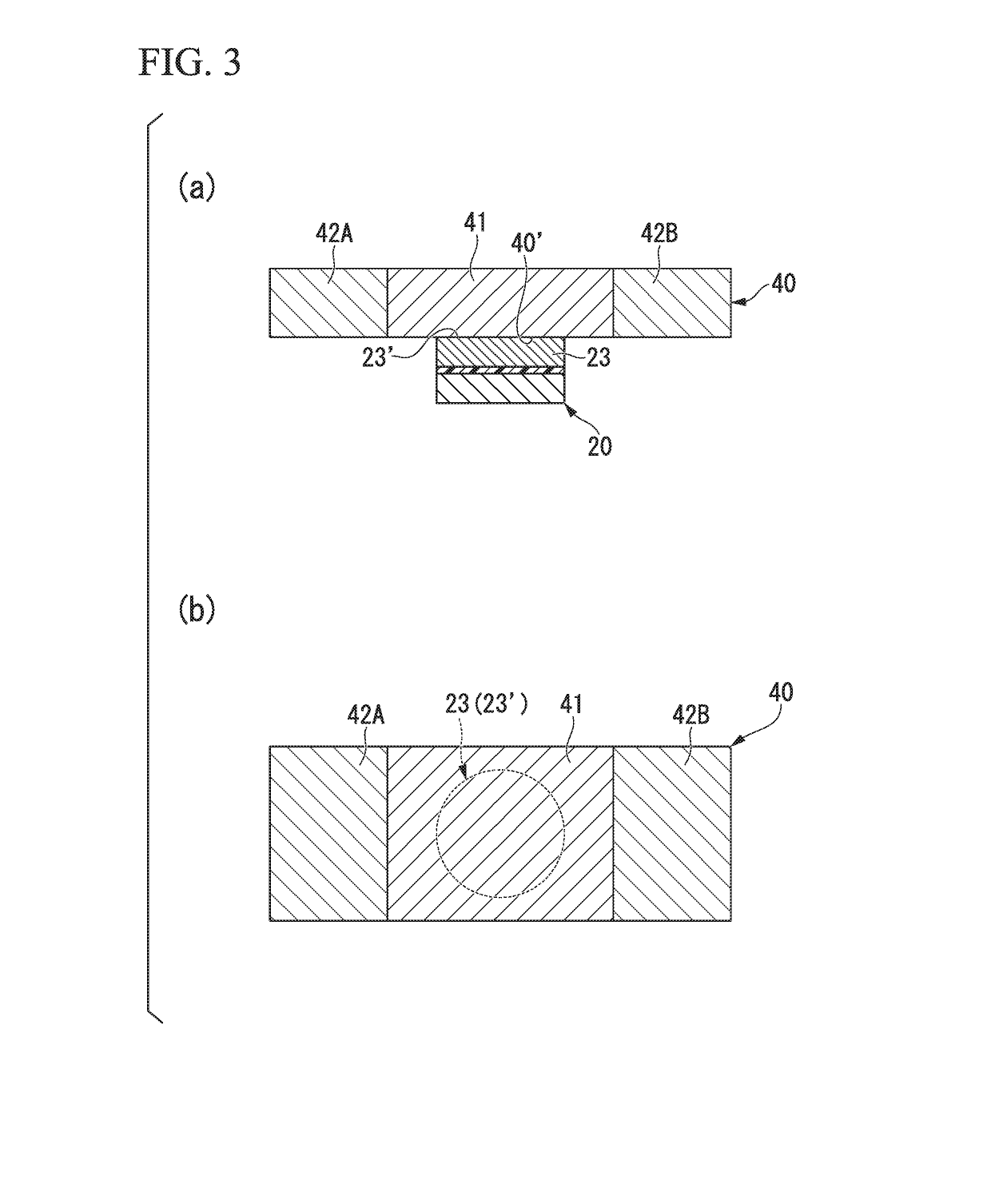
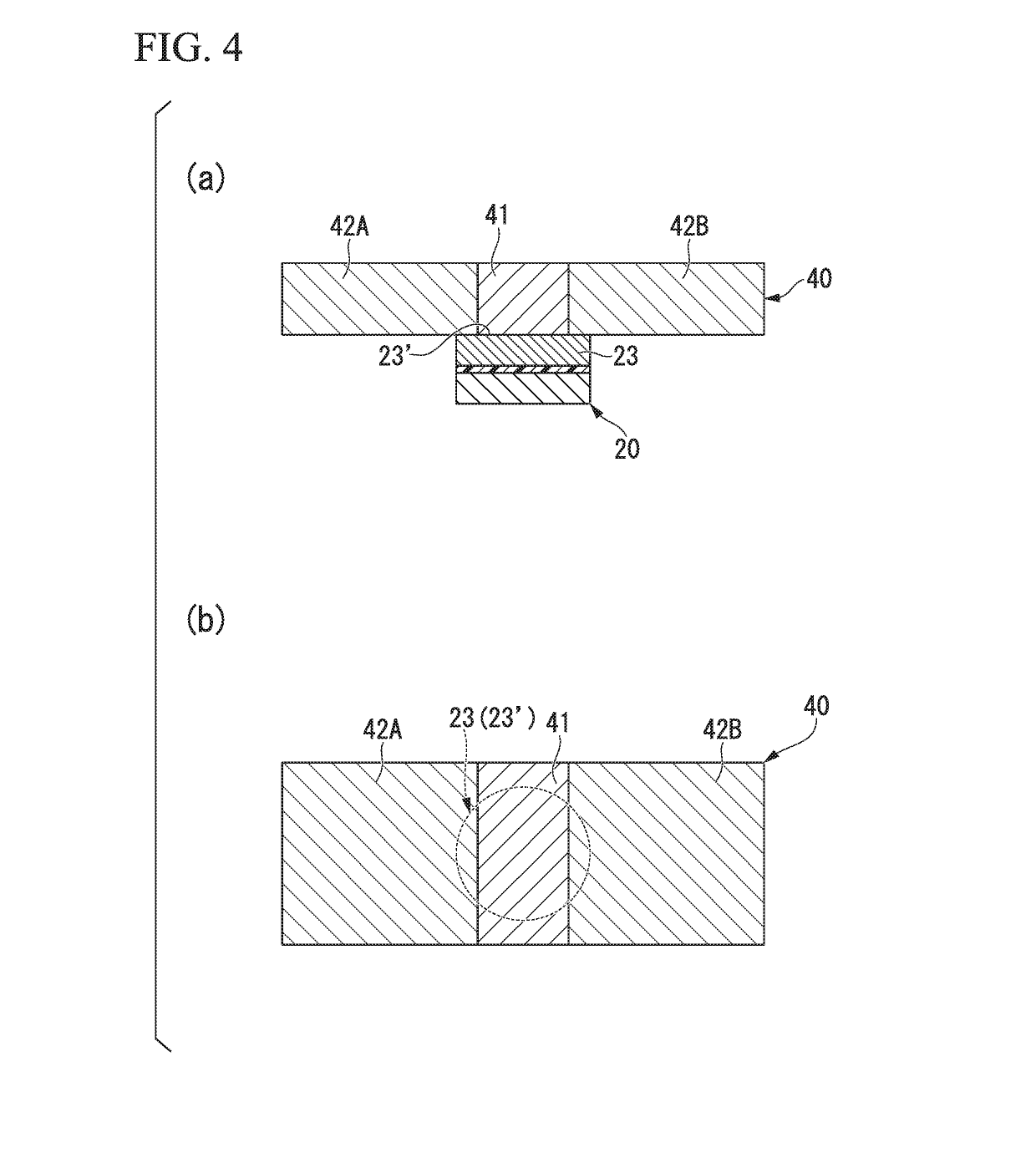
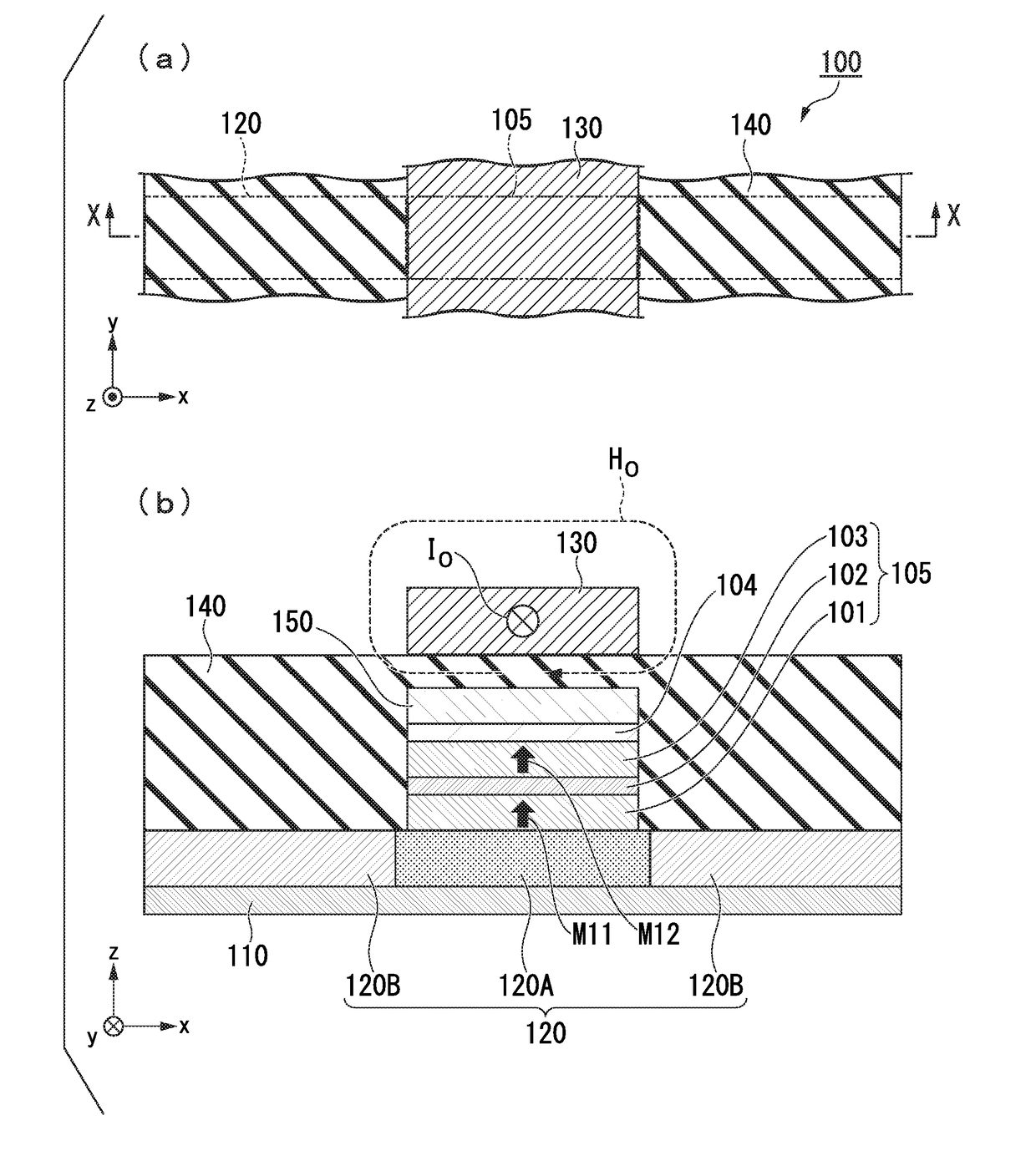
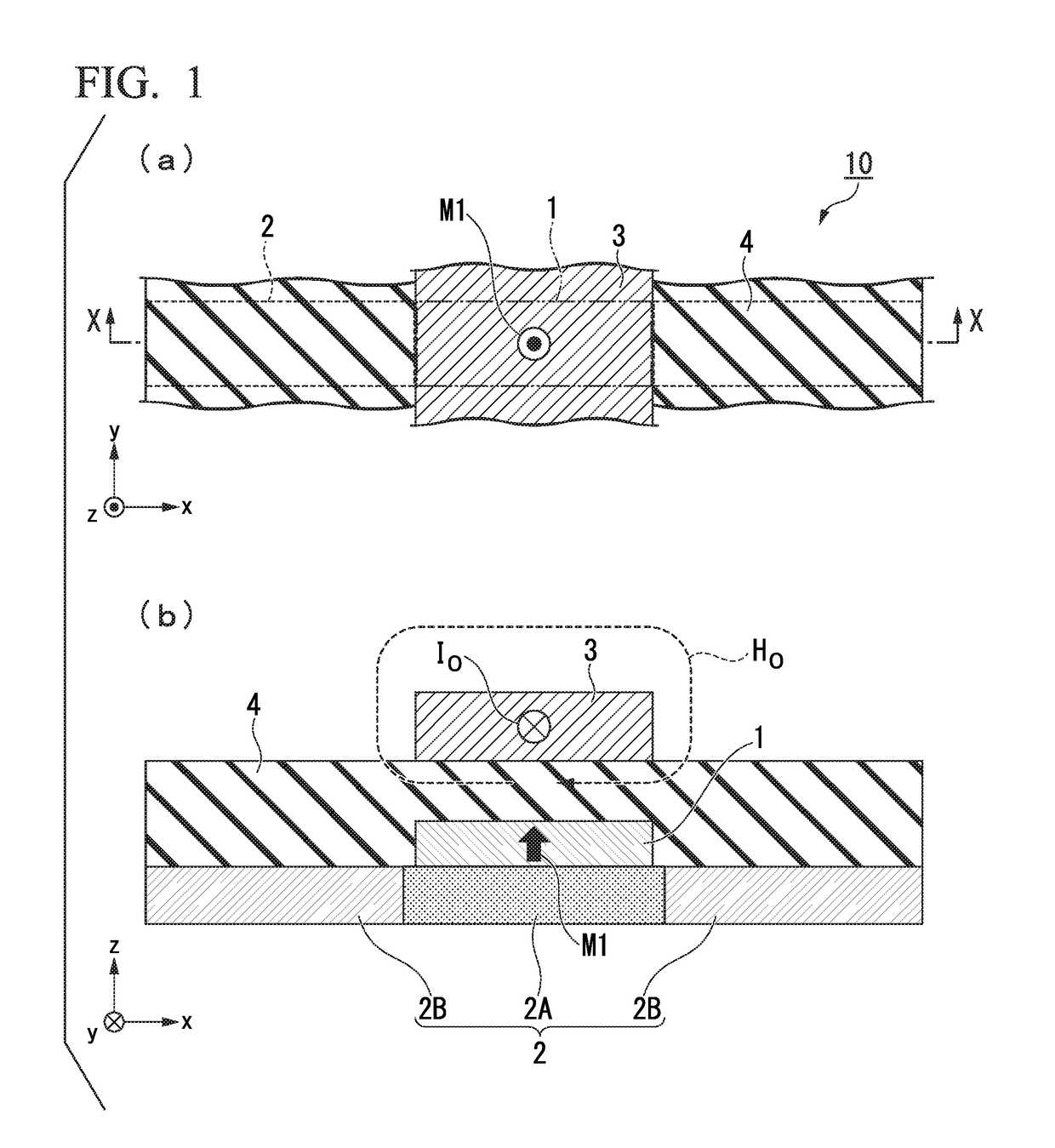
Electric-current-generated magnetic field assist type spin-current-induced magnetization reversal element, magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic memory and high-frequency filter
ActiveUS20180123026A1High currentProlong lifeMultiple-port networksMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention has the purpose of providing an electric-current-generated magnetic field assist type spin-current-induced magnetization reversal element that utilizes magnetization reversal based on pure spin current. The electric-current-generated magnetic field assist type spin-current-induced magnetization reversal element of the present invention includes a first ferromagnetic metal layer with a varying magnetization direction; spin-orbit torque wiring that adjoins the first ferromagnetic metal layer and that extends in a second direction in a plane orthogonal to a first direction normal to the first ferromagnetic metal layer; and electric-current-generated magnetic field assist wiring that is arranged so as to be electrically insulated from the first ferromagnetic metal layer by an insulating layer and in which flows an electric current I0 for forming a magnetic field H0 that assists magnetization reversal of the first ferromagnetic metal layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Spin-orbit torque (SOT) magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) (sot-mtj) devices employing perpendicular and in-plane free layer magnetic anisotropy to facilitate perpendicular magnetic orientation switching, suitable for use in memory systems for storing data
ActiveUS20200066968A1Fast switching speedEasy to switchSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionSwitched currentSpin orbit torque
Aspects disclosed include spin-orbit torque (SOT) magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) (SOT-MTJ) devices employing perpendicular and in-plane free layer magnetic anisotropy to facilitate perpendicular magnetic orientation switching. A free layer in a MTJ in the SOT-MTJ device includes both a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) region(s) and an in-plane magnetic anisotropy (IMA) region(s). A spin torque is generated in the free layer when a SOT switching current flows through an electrode adjacent to the free layer sufficient to switch the magnetic moment of the free layer to an in-plane magnetic orientation. To prevent a non-deterministic perpendicular magnetic orientation after the SOT switching current is removed, the free layer also includes the IMA region(s) to provide an in-plane magnetization to generate an effective magnetic field in the free layer to assist in switching the magnetic moment of the free layer past an in-plane magnetic orientation to a perpendicular magnetic orientation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
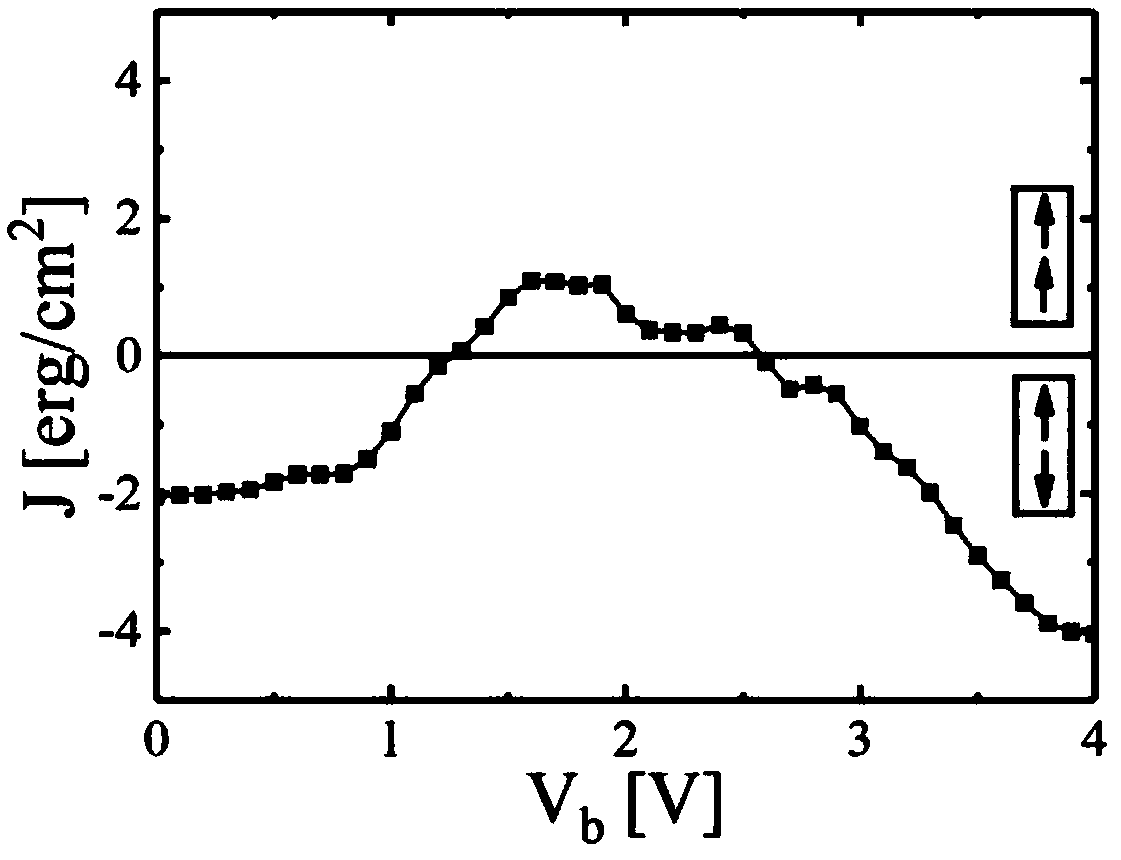
Spin-orbit-torque magnetoresistive random access memory with voltage-controlled anisotropy
InactiveUS9589619B2Increase speedImprove stateMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetic anisotropySpin orbit torque
Methods and apparatus relating to spin-orbit-torque magnetoresistive random access memory with voltage-controlled anisotropy are disclosed. In an example, disclosed is a three-terminal magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) storage element that is programmed via a combination of voltage-controlled magnetic anisotropy (VCMA) and spin-orbit torque (SOT) techniques. Also disclosed is a memory controller configured to program the three-terminal MTJ storage element via VCMA and SOT techniques. The disclosed devices improve efficiency over conventional devices by using less write energy, while having a design that is simpler and more scalable than conventional devices. The disclosed devices also have increased thermal stability without increasing required switching current, as critical switching current between states is essentially the same.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Shared source line architectures of perpendicular hybrid spin-torque transfer (STT) and spin-orbit torque (SOT) magnetic random access memory
The present disclosure relates to a hybrid spin-transfer torque (STT) and spin-bit torque (SOT) magnetic random access memory (MRAM). The cells of the hybrid STT-SOT MRAM has magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) with some ferromagnetic multilayers whose magnetization is oriented perpendicular to the plane of the substrate and some ferromagnetic multilayers whose magnetization is aligned within the plane of the substrate. The architecture results in high density memory. The hybrid STT-SOT MRAM lowers the programming current density while having a high switching speed higher thermal stability.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
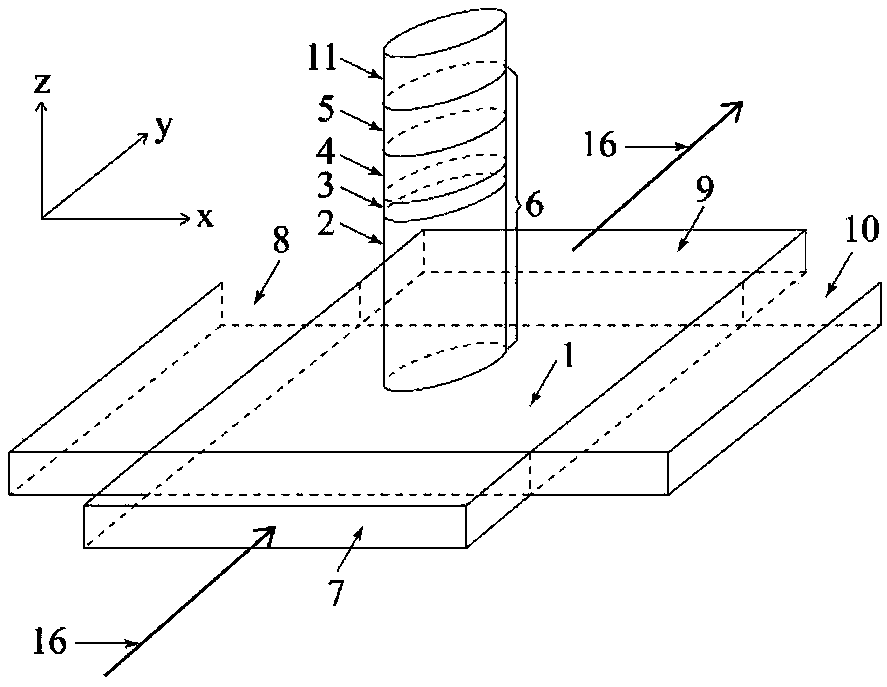
Spin current magnetization rotational element, magnetoresistance effect element, and magnetic memory
ActiveUS20180159026A1Improve thermal stabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin orbit torqueMagnetic memory
A spin current magnetization rotational element includes: a magnetization free layer including a synthetic structure consisting of a first ferromagnetic metal layer, a second ferromagnetic metal layer and a first non-magnetic layer sandwiched by the first ferromagnetic metal layer and the second ferromagnetic metal layer; and an antiferromagnetic spin-orbit torque wiring that extends in a second direction intersecting with a first direction that is a lamination direction of the synthetic structure and is joined to the first ferromagnetic metal layer, wherein the spin current magnetization rotational element is configured to change a magnetization direction of the magnetization free layer by applying current to the antiferromagnetic spin-orbit torque wiring.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method for providing a magnetic sensor with a biasing spin-orbit effective field
InactiveUS20180106873A1Avoid structureSimple designMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSpin orbit torqueBias field
The invention relates to magnetic sensor comprising a sensor element that is able to generate a spin-orbit torque (SOT). The SOT acts as a transverse bias field to set a proper working point for the sensor and so ensure that it responds linearly to an external field with maximized sensitivity. It also functions as a longitudinal bias field to suppress domain wall nucleation and propagation. The use of SOT effective field for biasing not only simplifies the sensor structure but also makes it possible to make an ultrathin and semi-transparent magnetic sensor.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Spin-orbit torque induced magnetization switching in a magnetic recording head
InactiveUS20190279665A1Heads using thin filmsRecord information storageSwitched currentMagnetic media
The present disclosure generally relates to magnetic media devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The recording head includes a main pole, a trailing shield hot seed layer, a spin Hall layer disposed between the main pole and the trailing shield hot seed layer, and a spin-torque layer disposed between the main pole and the trailing shield hot seed layer. Spin-orbit torque (SOT) is generated from the spin Hall layer. The spin-torque layer magnetization switching or precession is induced by the SOT. The SOT based head reduces the switching current and the Vjump due to higher spin polarization ratio, which improves energy efficiency. In addition, the spin Hall layer and the spin-torque layer are easier to form compared to the conventional pseudo spin-valve structure.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Vertical spin orbit torque devices
ActiveUS20190273202A1PerformanceTorque may be improvedMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin orbit torqueEngineering
A magnetic device and method for programming the magnetic device are described. The magnetic device includes a plurality of magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer having a plurality of sides. The SO active layer(s) carry a current in direction(s) substantially perpendicular to the plurality of sides. Each of the magnetic junction(s) is adjacent to the sides and substantially surrounds a portion of the SO active layer. Each magnetic junction includes a free layer, a reference layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the pinned and free layers. The SO active layer(s) exert a SO torque on the free layer due to the current passing through the SO active layer(s). The free layer is switchable between stable magnetic states. The free layer may be written using the current and, in some aspects, another current driven through the magnetic junction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
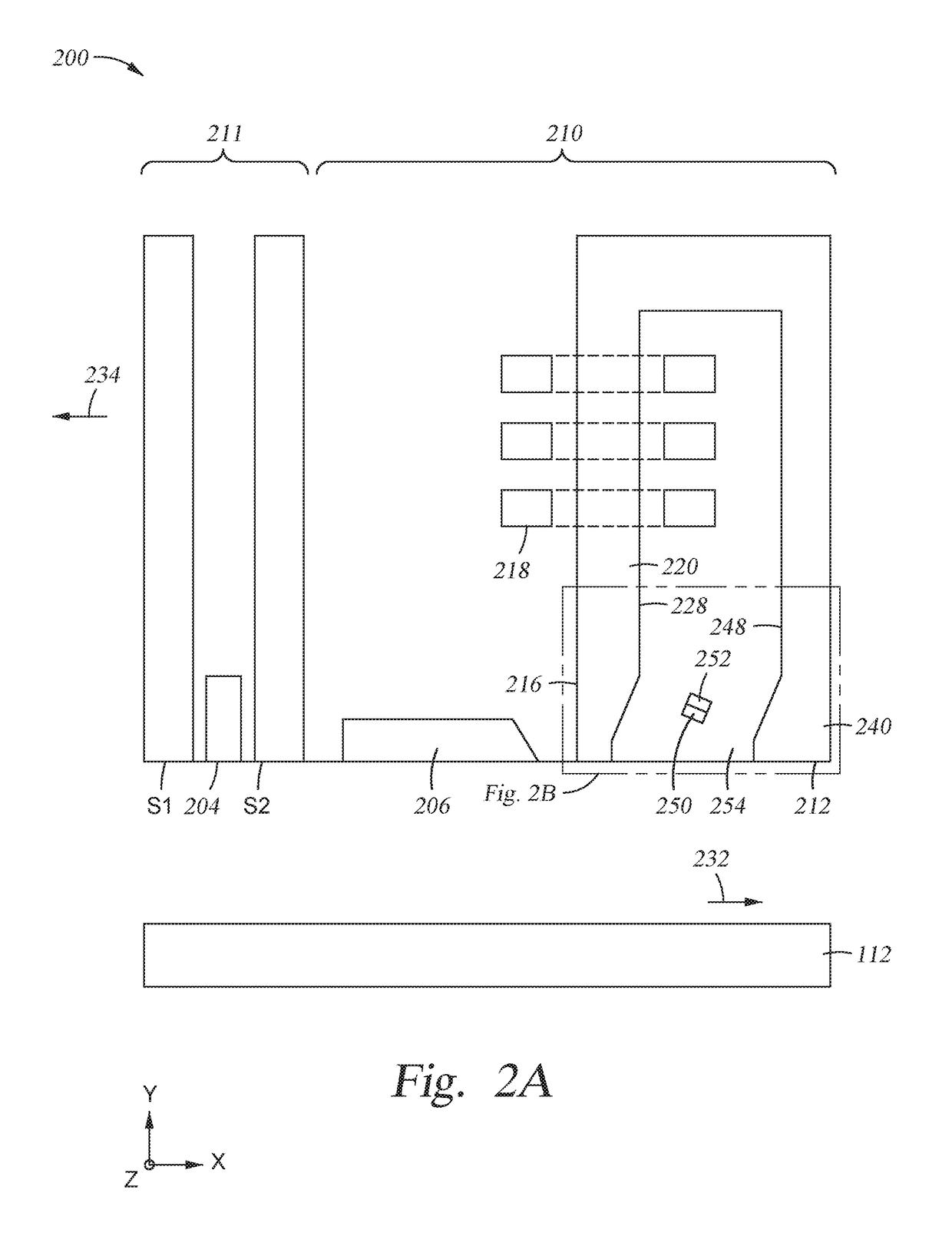
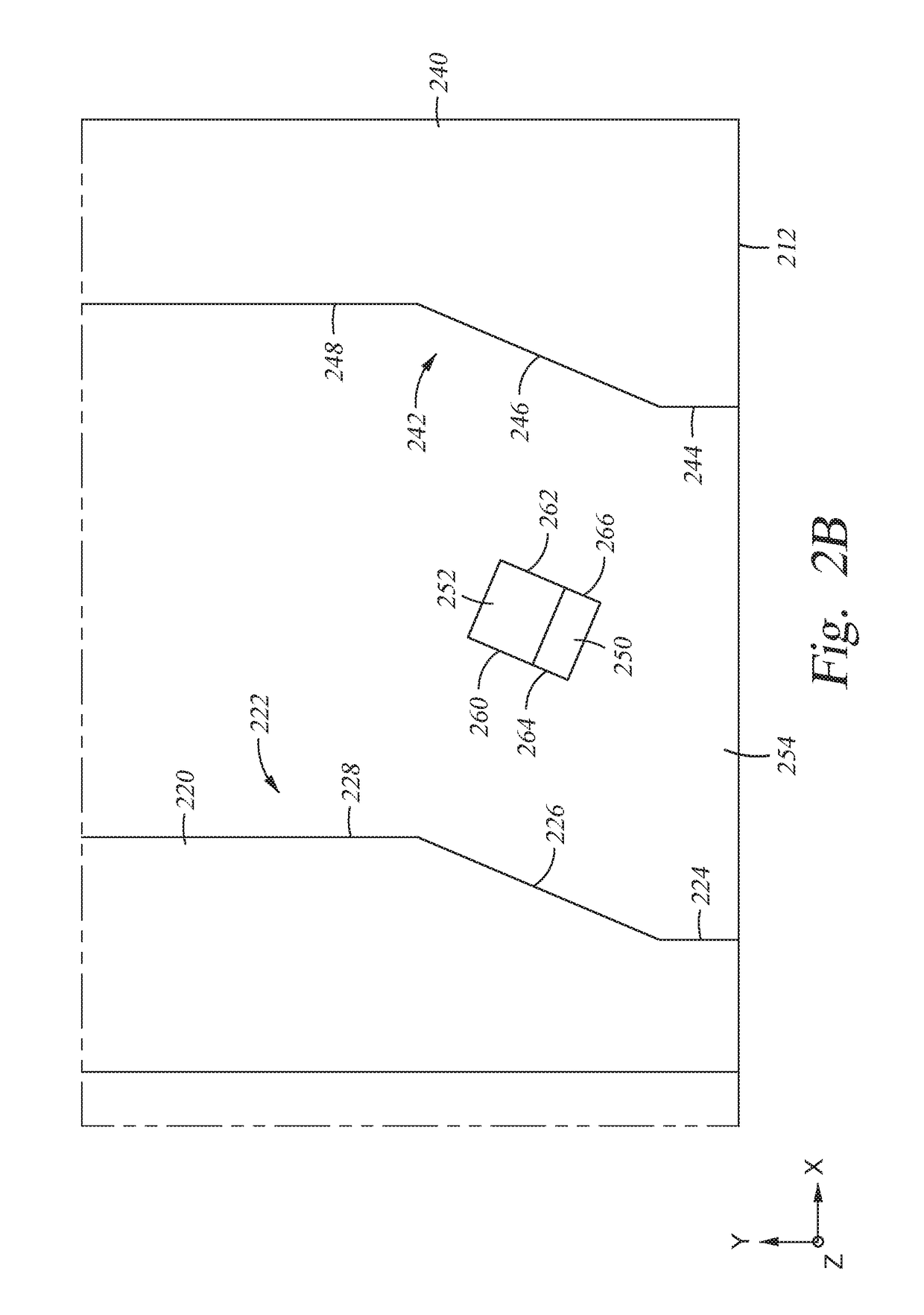
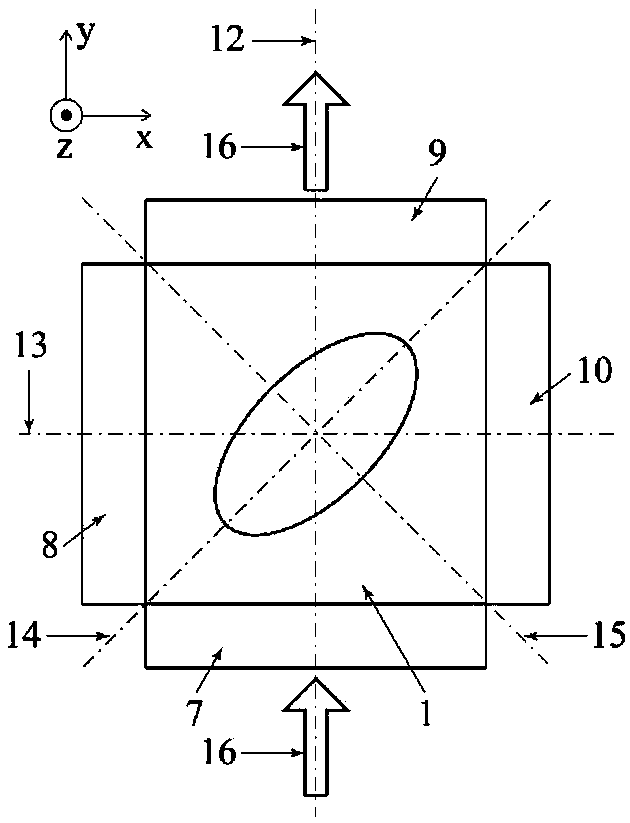
Spin-orbit torque bit design for improved switching efficiency
ActiveUS20170179372A1Reduce amountImprove switch reliabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin orbit torqueLong axis
A method for a non-volatile memory cell; specifically, a spin orbit torque MRAM (SOT-MRAM) memory cell which reduces the current required to switch individual bits. The memory cell includes a first interconnect line having a first longitudinal axis, an elliptically shaped MTJ bit (“bit”) having a long axis, and a second interconnect line having a second longitudinal axis perpendicular to the first interconnect line. The bit includes a polarized free layer, a barrier layer, and a polarized reference layer with a magnetic moment pinned at an angle different from the long axis. By disposing the long axis at an angle relative to the first longitudinal axis and second longitudinal axis and the reference layer as described, and applying a voltage to the interconnect line, a non-zero equilibrium angle can be induced between the free layer and the spin current or the Rashba field resulting in more coherent switching dynamics.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Dual spin-orbit torque oscillator in magnetic recording
ActiveUS20190147907A1Reduce critical currentQuality improvementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsHeads using thin filmsIn planeSpin orbit torque
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a trailing shield, and an oscillator located between the main pole and the trailing shield. The oscillator is disposed at a media facing surface (MFS). The oscillator includes a spin-torque layer sandwiched between two distinct spin Hall layers. The two distinct spin Hall layers generate spin-orbit torque (SOT) that induces in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer, and both in-plane precessions are in the same direction. The same-direction in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer reduce the critical current of the oscillation of the oscillator, leading to high quality recording.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spin-orbit torque type magnetization reversal element, magnetic memory, and high frequency magnetic device
ActiveUS20180123021A1Lower Level RequirementsEasy to implementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin orbit torqueMagnetic memory
A spin-orbit torque type magnetization reversal element including a ferromagnetic metal layer with a varying magnetization direction; and spin-orbit torque wiring that extends in a first direction intersecting with a stacking direction of the ferromagnetic metal layer and that is joined to the ferromagnetic metal layer; wherein when viewed from the first direction, the spin-orbit torque wiring is asymmetrical in a second direction that is orthogonal to the first direction and the stacking direction, with respect to an axis that passes through a center, in the second direction, of the ferromagnetic metal layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic storage unit and data writing method thereof
InactiveCN109637569AConducive to simplificationIncrease data processing bandwidthDigital storageTransverse axisMagnetic storage
The invention discloses a magnetic storage unit and a data writing method thereof, a magnetic tunnel junction with vertical magnetic anisotropy is manufactured above a strong spin orbit coupling layer, and four ports of the strong spin orbit coupling layer are respectively plated with an electrode. The surface of the magnetic tunnel junction is made into a shape with unequal long and short axes, the long axis of the shape of the surface of the magnetic tunnel junction and the longitudinal axis of the strong spin orbit coupling layer are not overlapped with each other, are not perpendicular toeach other, but are inclined with each other, and the inclined included angle is not equal to 0 degree and not equal to 90 degrees, but is between 0 degree and 90 degrees. In order to realize data writing operation by using spin orbit torque, current needs to be applied to the strong spin orbit coupling layer, and the path of the current can be divided into two choices along the longitudinal axisor the transverse axis of the strong spin orbit coupling layer. The final resistance state of the magnetic tunnel junction only depends on the path of the applied current and is independent of the positive and negative directions of the current. The data writing method does not need a magnetic field and has the advantages of high speed and low power consumption.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Magnetic memory
ActiveUS20180123022A1Low integrationReduce rateMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin orbit torqueMagnetic reluctance
A magnetic memory including a plurality of magnetoresistance effect elements that hold information, each including a first ferromagnetic metal layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a second ferromagnetic metal layer with a varying magnetization direction, and a non-magnetic layer sandwiched between the first and second ferromagnetic metal layers; a plurality of first control elements that control reading of the information, wherein each of the plurality of first ferromagnetic metal layers is connected to a first control element; a plurality of spin-orbit torque wiring lines that extend in a second direction intersecting with a first direction which is a stacking direction of the magnetoresistance effect elements, wherein each of the second ferromagnetic metal layers is joined to one spin-orbit torque wiring line; a plurality of second control elements that control electric current flowing through the spin-orbit torque wiring lines.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Spin current magnetization rotational element, spin-orbit-torque magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic memory, and high-frequency magnetic element
ActiveUS20190074124A1Without deterioration in integration propertyEasily causedSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsPower flowSpin orbit torque
A spin current magnetization rotational element is provided in which deterioration in the degree of integration is prevented from being caused and a magnetization rotation can be easily realized. A spin current magnetization rotational element includes a spin-orbit torque wiring which extends in a first direction, a first ferromagnetic layer which is laminated in a second direction intersecting the first direction; and a first magnetic field applying layer which is disposed to be separated from the first ferromagnetic layer in the first direction and configured to apply an assistant magnetic field assisting a magnetization rotation of the first ferromagnetic layer to the first ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Spin-orbit-torque magnetoresistive random access memory with voltage-controlled anisotropy
InactiveUS20160232959A1Reduce magnetic anisotropyReduces magnetic anisotropyDigital storageExtensibilityMagnetic reluctance
Methods and apparatus relating to spin-orbit-torque magnetoresistive random access memory with voltage-controlled anisotropy are disclosed. In an example, disclosed is a three-terminal magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) storage element that is programmed via a combination of voltage-controlled magnetic anisotropy (VCMA) and spin-orbit torque (SOT) techniques. Also disclosed is a memory controller configured to program the three-terminal MTJ storage element via VCMA and SOT techniques. The disclosed devices improve efficiency over conventional devices by using less write energy, while having a design that is simpler and more scalable than conventional devices. The disclosed devices also have increased thermal stability without increasing required switching current, as critical switching current between states is essentially the same.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Magnetic memory and a method of operating magnetic memory
ActiveUS20190244646A1High densityImprove scalabilitySolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsPower flowSpin orbit torque
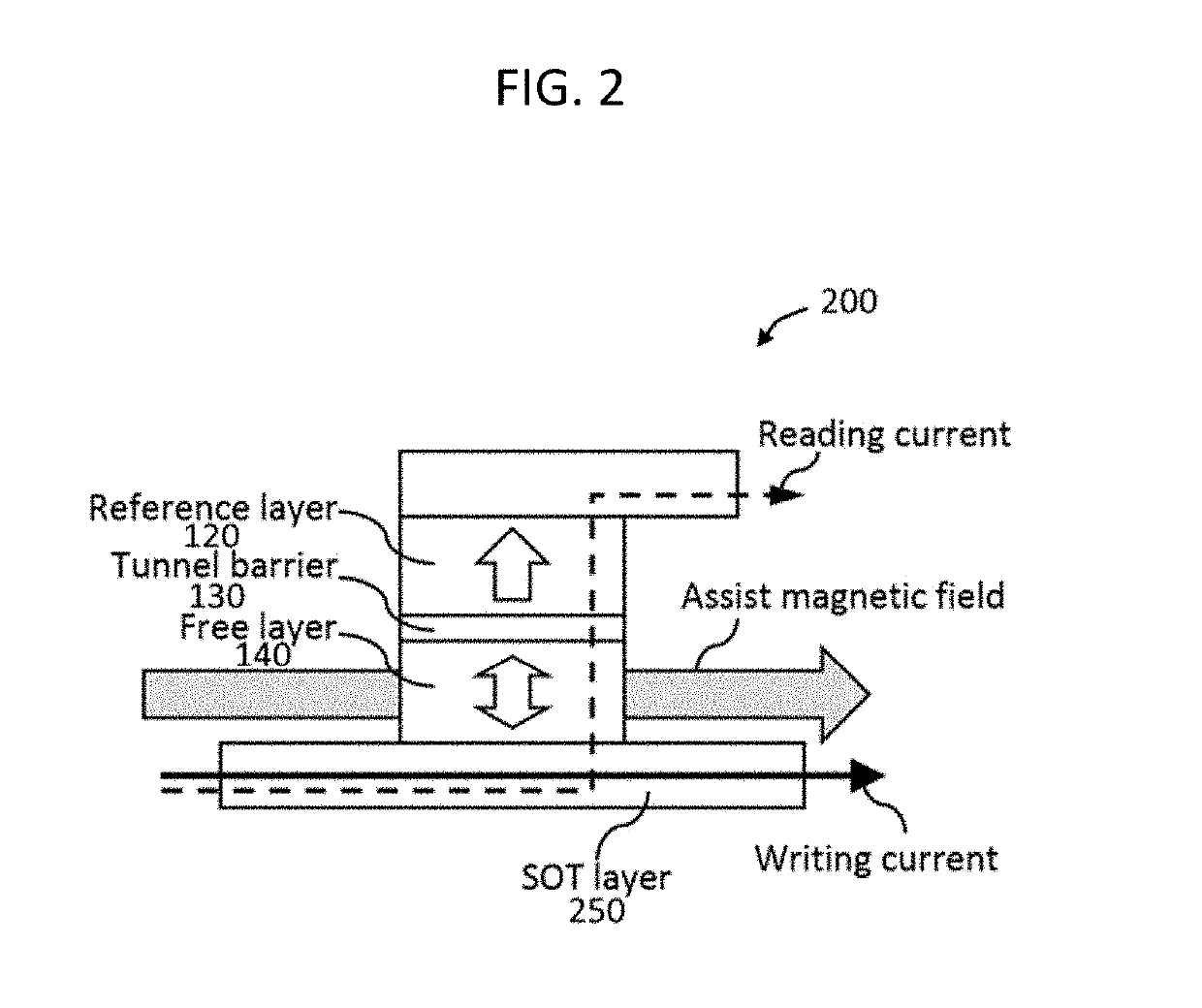
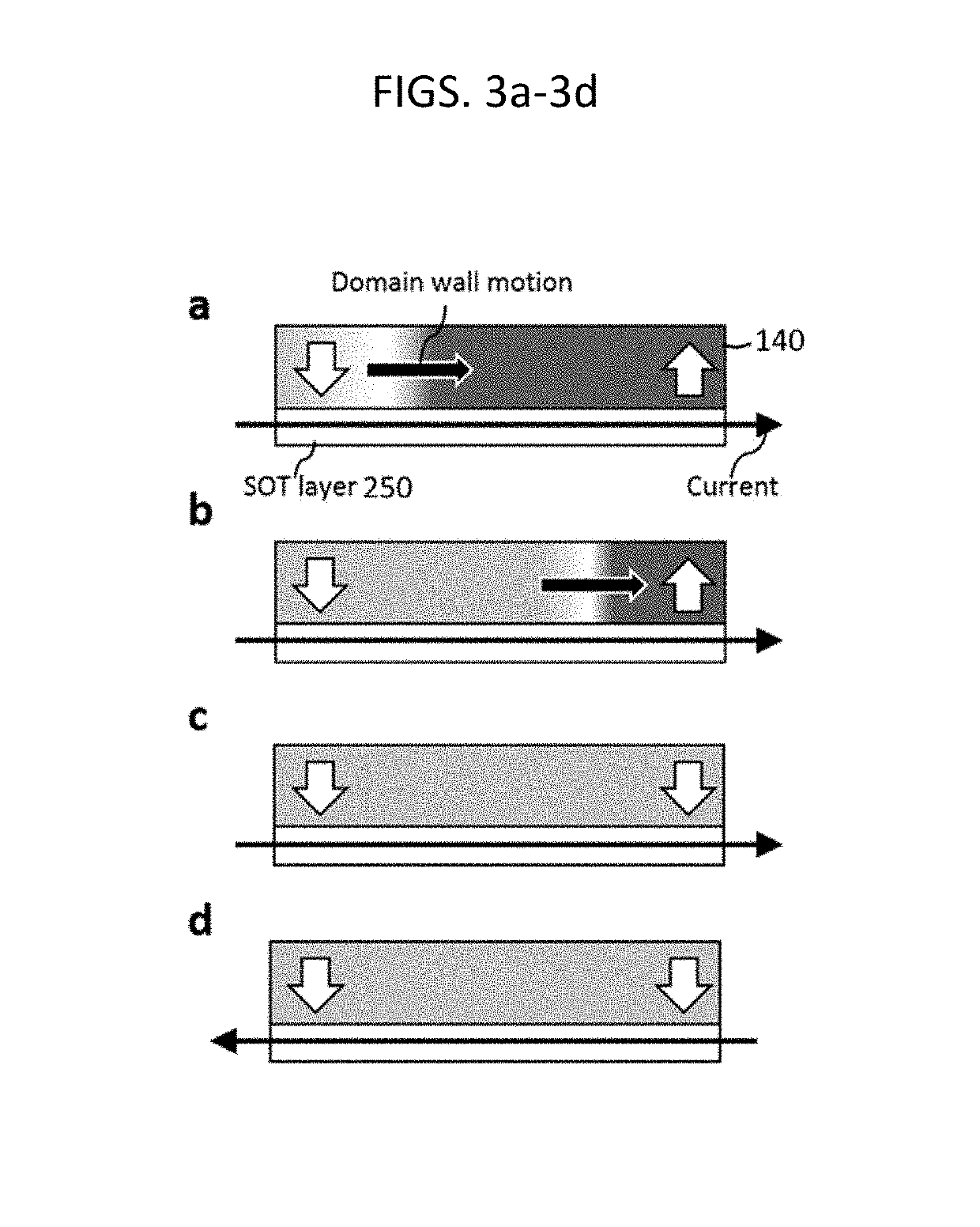
In example embodiments, a SOT magnetic memory and operation method are provided that utilize SOT driven domain wall motion to achieve subsequent switching without the need for an external assist magnetic field. The magnetic memory includes a magnetic tunnel junction having a reference layer, a tunnel barrier layer and a free layer, where the tunnel barrier layer is positioned between the reference layer and free layer. A spin-orbit torque layer is disposed adjacent to the free layer. A pair of pinning site are positioned at a longitudinal end of the free layer and each has an opposite magnetization direction from the other. The SOT layer is configured to exert SOT and switch a magnetization direction of the free layer via domain wall motion in a direction of current flow when an electric current is passed through a length of the SOT layer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com