Magnetic random access memory and writing method, reading method and preparation method thereof
A magnetic random access memory, magnetic moment direction technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage and other directions, can solve the problems of large size of MRAM and low storage density of MRAM, and achieve the effect of reducing write energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
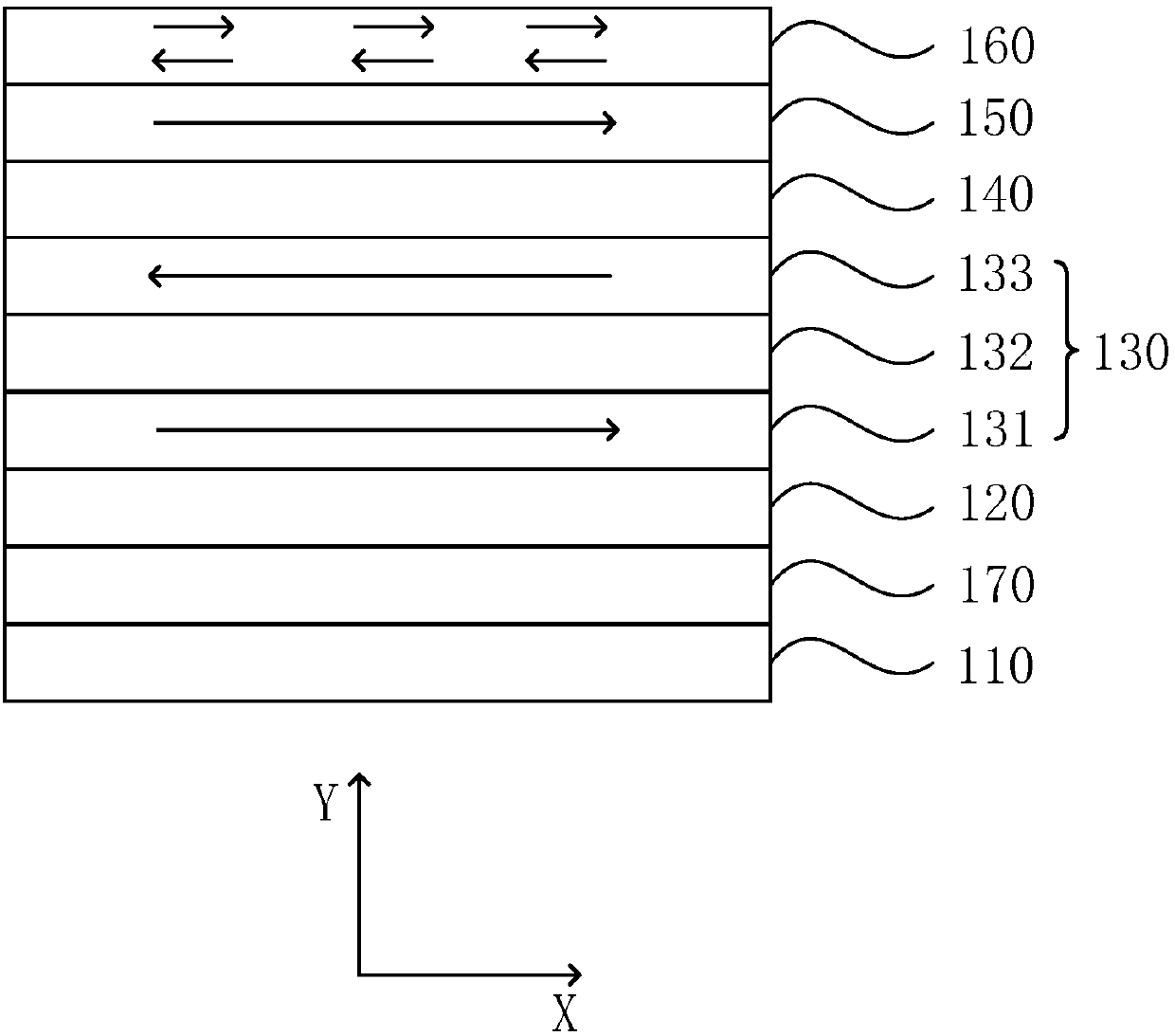
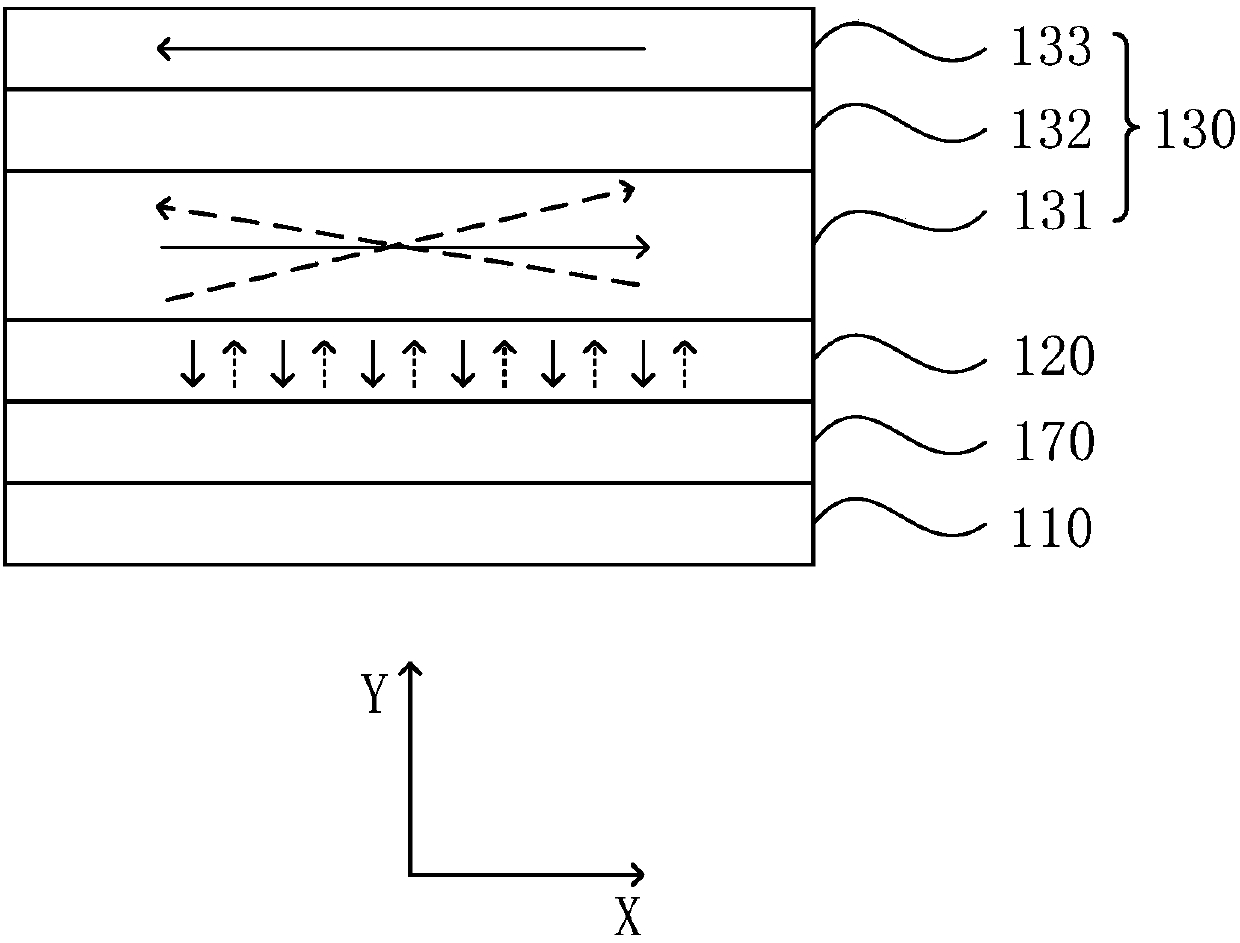
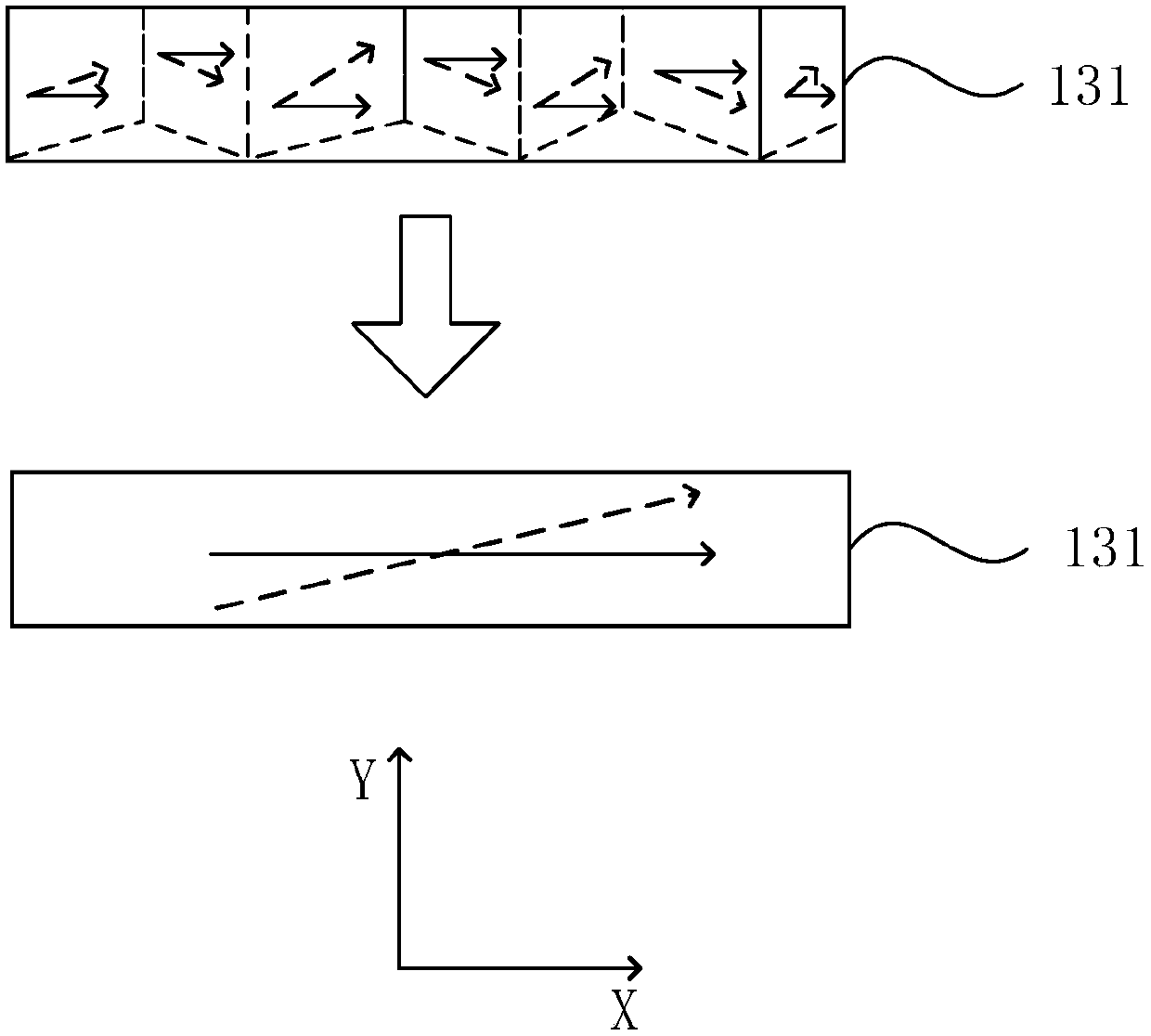
[0039] figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of a magnetic random access memory provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. see figure 1 , the MRAM includes a substrate layer 110, a ferroelectric layer 120, a composite antiferromagnetic structure 130, a first isolation layer 140, and a first ferromagnetic layer 150 stacked in sequence, and the composite antiferromagnetic structure 130 is an MRAM Free layer, the first ferromagnetic layer 150 is the fixed layer of MRAM; the ferroelectric layer 120 undergoes polarization or phase change under the action of an applied voltage, which is used to change the coupling state of the composite antiferromagnetic structure 130; the first ferromagnetic The layer 150 has a constant first magnetic moment direction; the first isolation layer is used to control the first magnetic moment direction from being affected by the coupling state of the composite antiferromagnetic structure 130 .
[0040] Exemplary, figure 1 The structu...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Figure 4 It is a schematic flowchart of a writing method of a magnetic random access memory provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, see Figure 4 , on the basis of Embodiment 1, the MRAM provided in this embodiment includes a substrate layer, a ferroelectric layer, a composite antiferromagnetic structure, a first isolation layer, and a first ferromagnetic layer stacked in sequence. The embodiment of the present invention The writing methods of the provided magnetic random access memory include:
[0053] S210. Obtain a write instruction of the MRAM.
[0054] Wherein, the write instruction refers to a machine instruction obtained by a control circuit connected to the magnetic random access memory, which exemplarily includes corresponding instructions such as typing characters or pasting pictures, and the acquisition path exemplarily includes using a keyboard to write, a mouse click, etc. The instruction generated corresponding to the click and the like is no...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Figure 5 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for reading a magnetic random access memory provided in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, see Figure 5 , on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, the MRAM provided by this embodiment includes a substrate layer, a ferroelectric layer, a composite antiferromagnetic structure, a first isolation layer and a first ferromagnetic layer that are stacked in sequence. The embodiment of the present invention The read method of the provided MRAM includes:
[0064] S310. Obtain a read instruction of the MRAM.
[0065] Wherein, the reading instruction refers to a machine instruction obtained by a control circuit connected to the magnetic random access memory, which exemplarily includes instructions corresponding to displaying characters, displaying pictures, playing audio and video, etc., and the acquisition path includes corresponding actions such as clicking the mouse Generated instructions.
[0066] S320. Apply a c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com