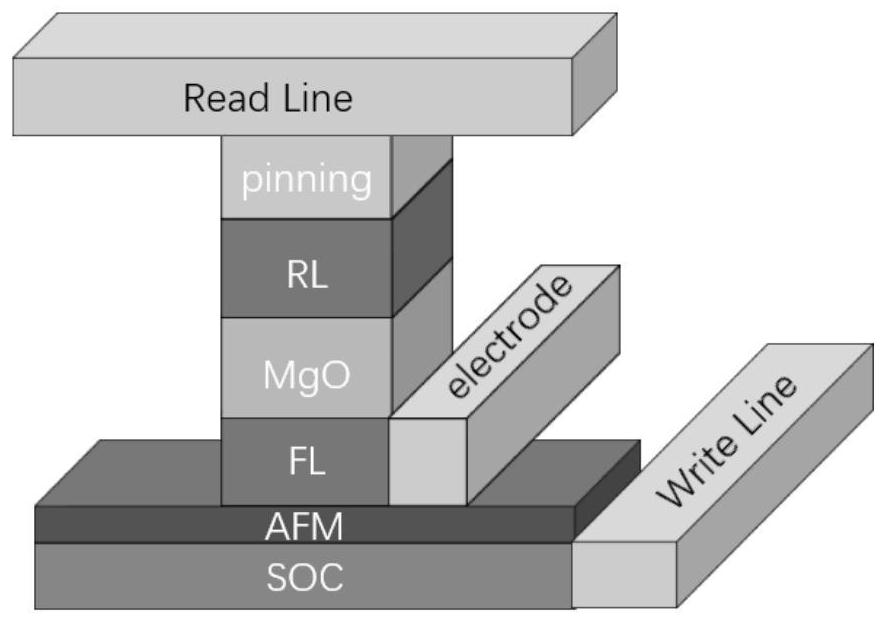
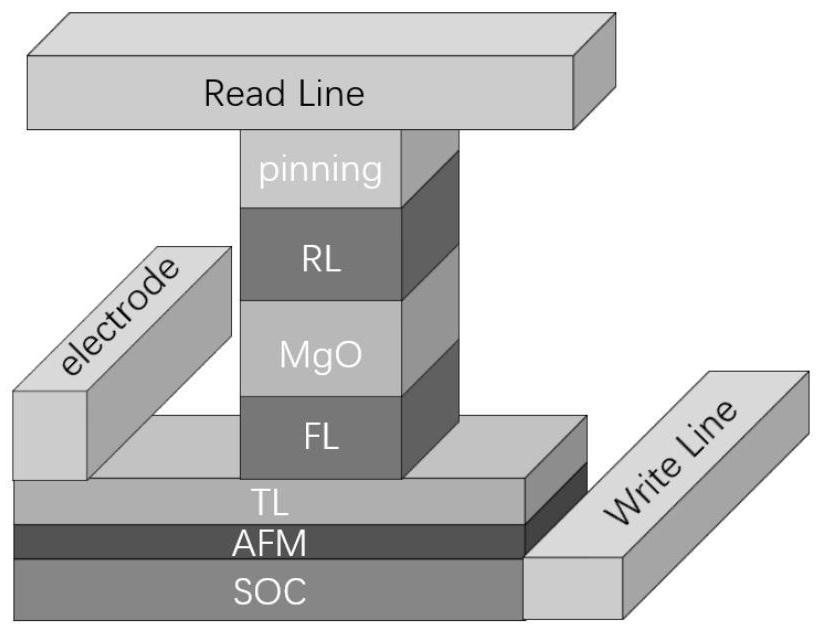
Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Reduce write power consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
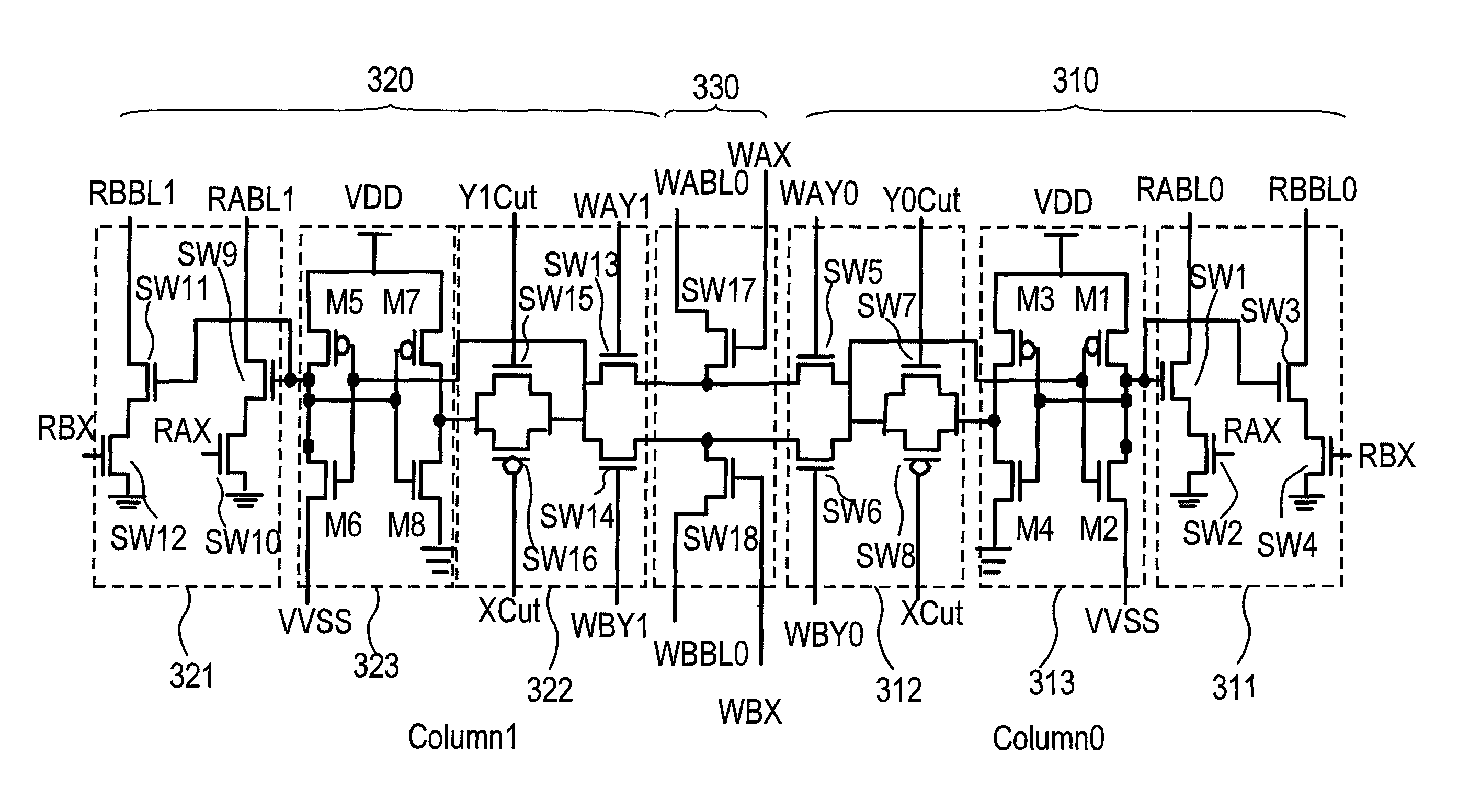
Multi-port SRAM with shared write bit-line architecture and selective read path for low power operation
InactiveUS9142285B2Low power operationImprove static noise marginDigital storageComputer architecturePre-charge
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
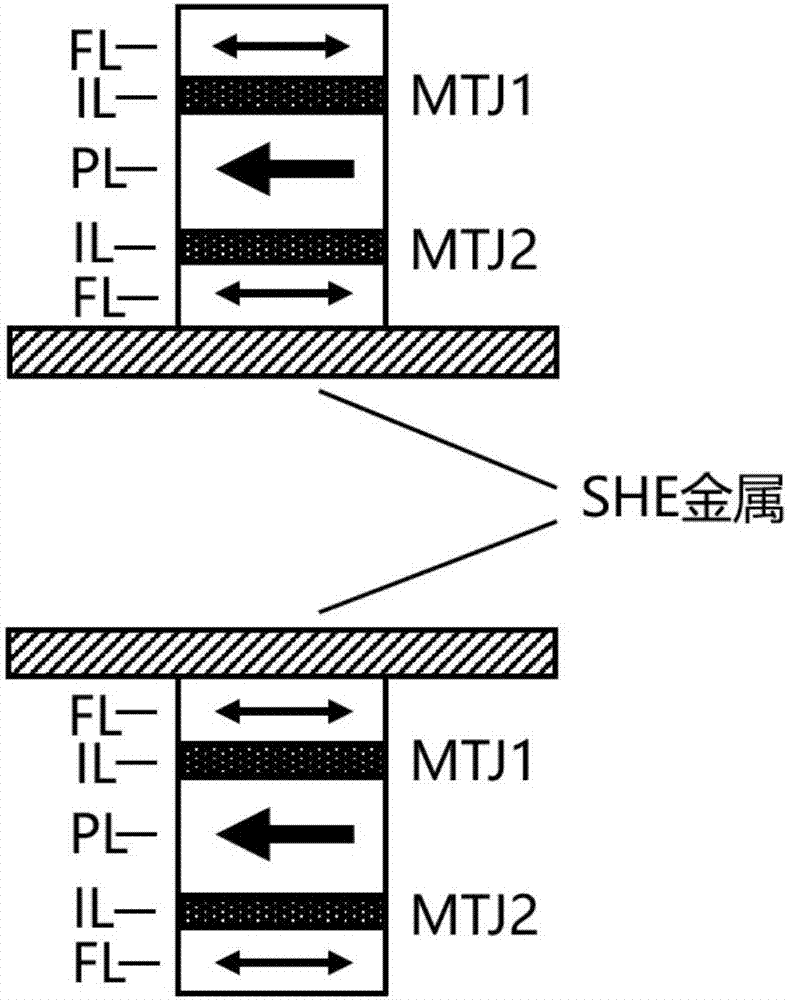
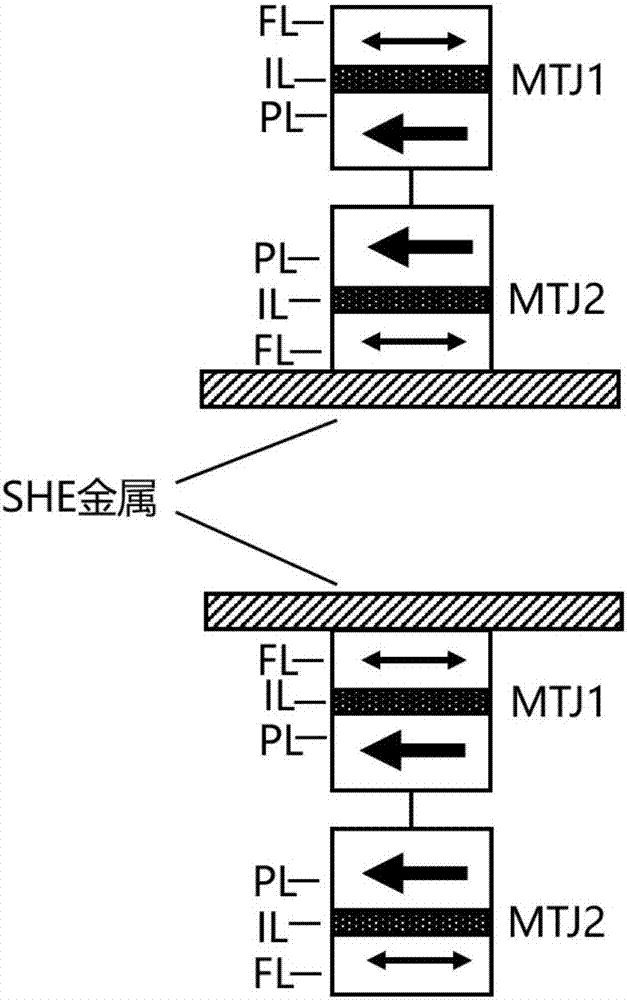
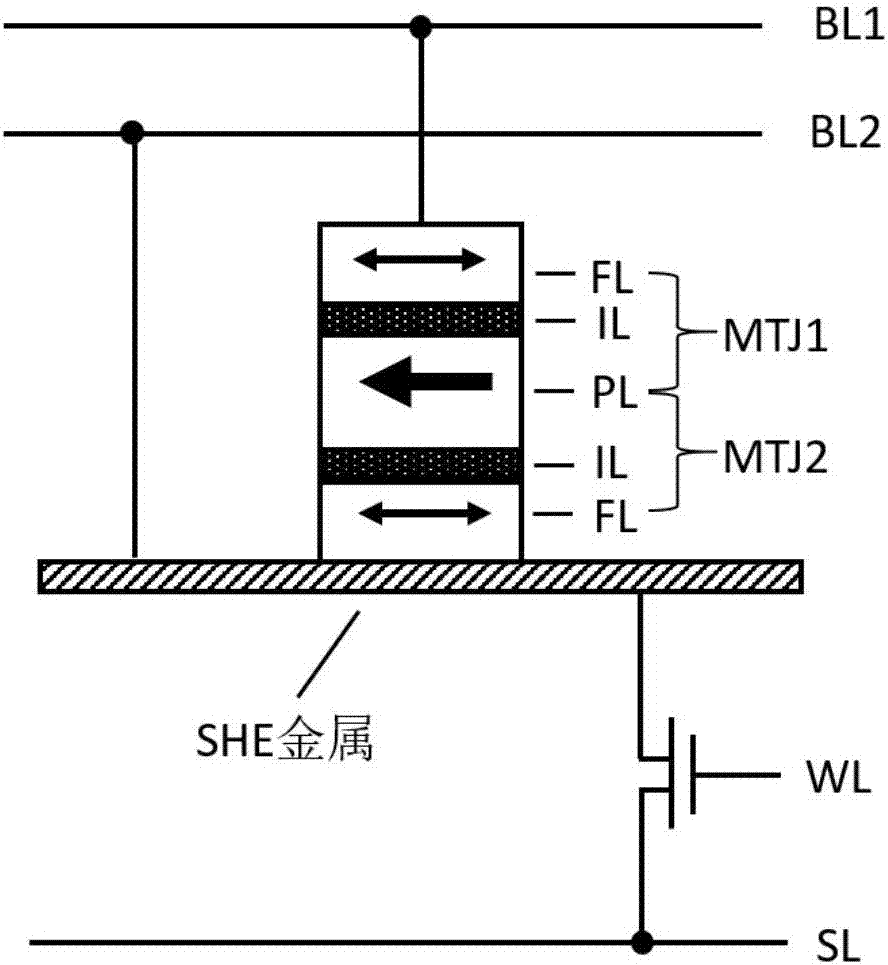
Spin Hall effect-assisted writing multi-state magnetic random access memory bit and spin Hall effect-assisted writing method
InactiveCN107481749AImprove reading speedReduce energy consumptionDigital storageStatic random-access memoryHemt circuits
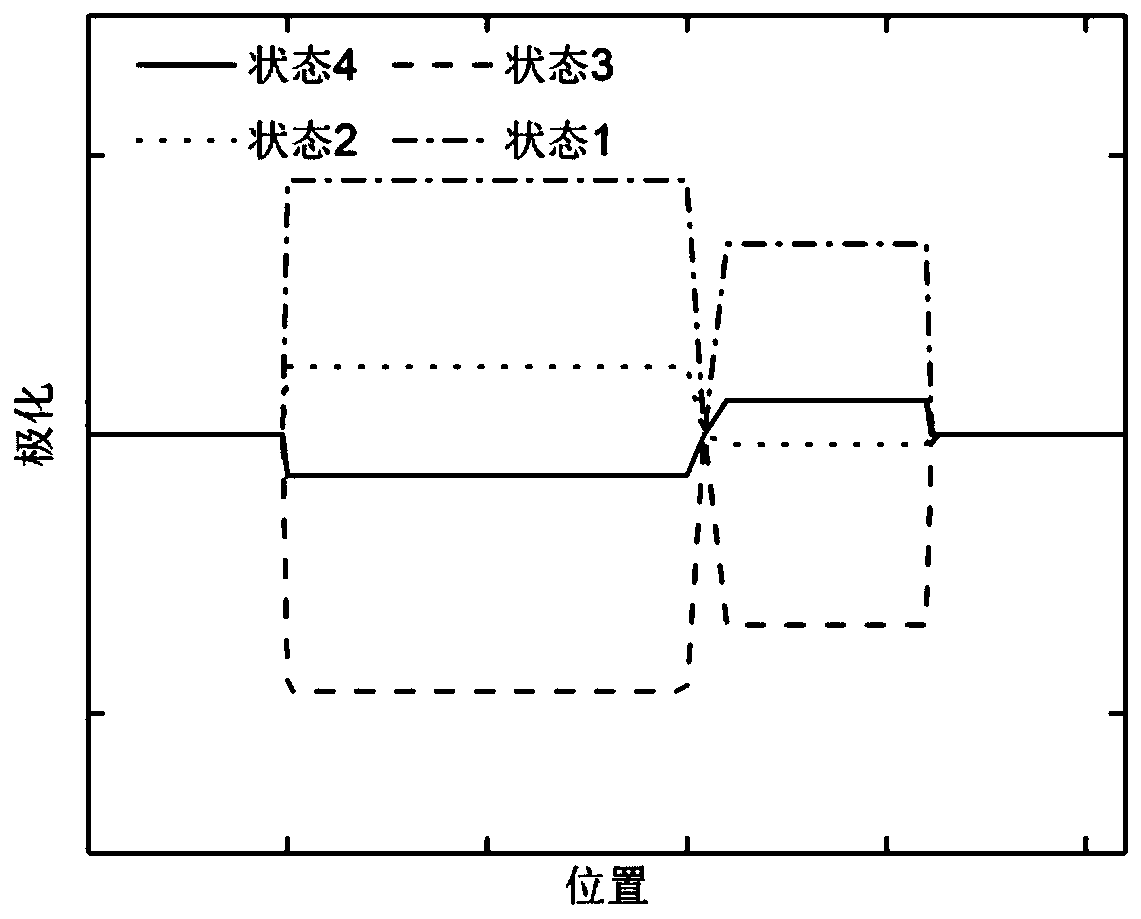
The invention relates to a spin Hall effect-assisted writing multi-state magnetic random access memory bit and a spin Hall effect-assisted writing method. The memory bit comprises a multi-state memory unit composed of two magnetic tunnel junctions, a spin Hall effect metal layer connected to a free layer of one of the magnetic tunnel junctions and a switch circuit composed of a word line, a bit line and a switching device. The multi-state magnetic random access memory composed of the spin Hall effect auxiliary bits has the magnetic random access memory (MRAM) advantages of fast reading speed, unlimited number of erasures, low energy consumption and radiation resistance, realizes polymorphic signal writing through spin Hall effect assistance, records 3 or 4 bits of information in the memory unit, effectively improves data storage density and reduces a chip area. The spin Hall effect can effectively reduce the writing current threshold and reduce the writing power consumption.
Owner:CETHIK GRP
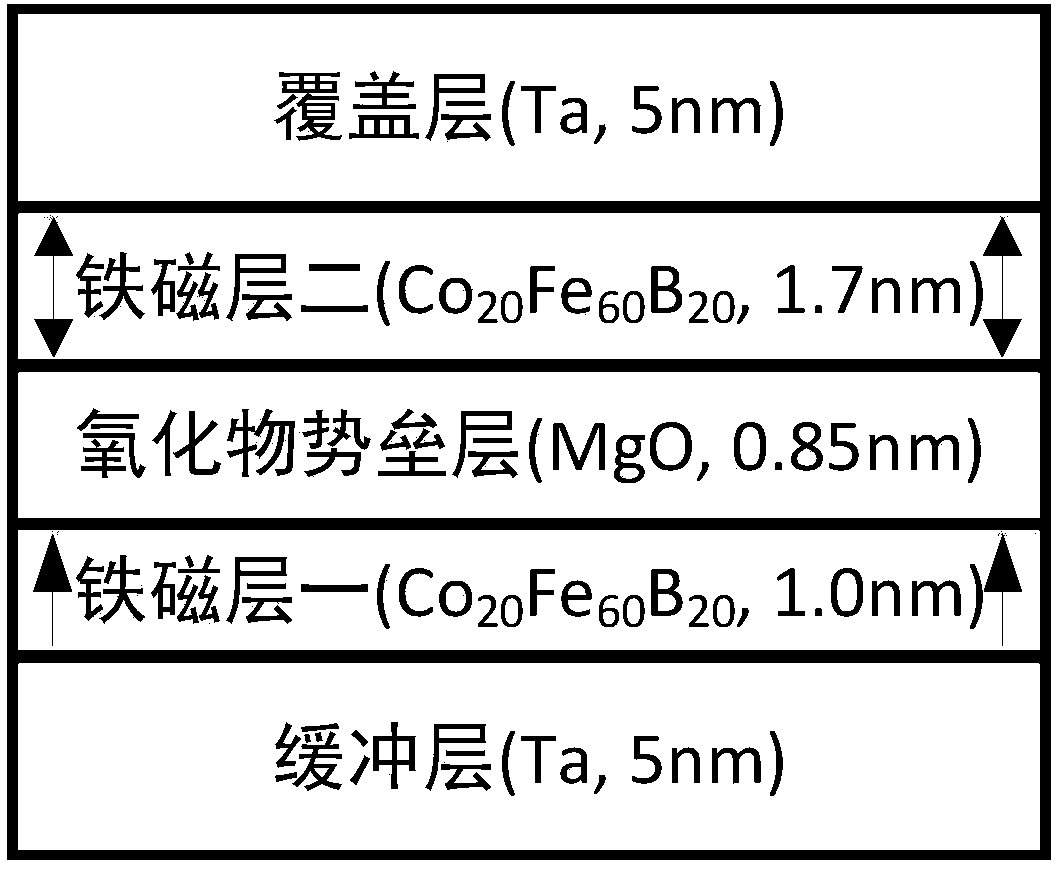
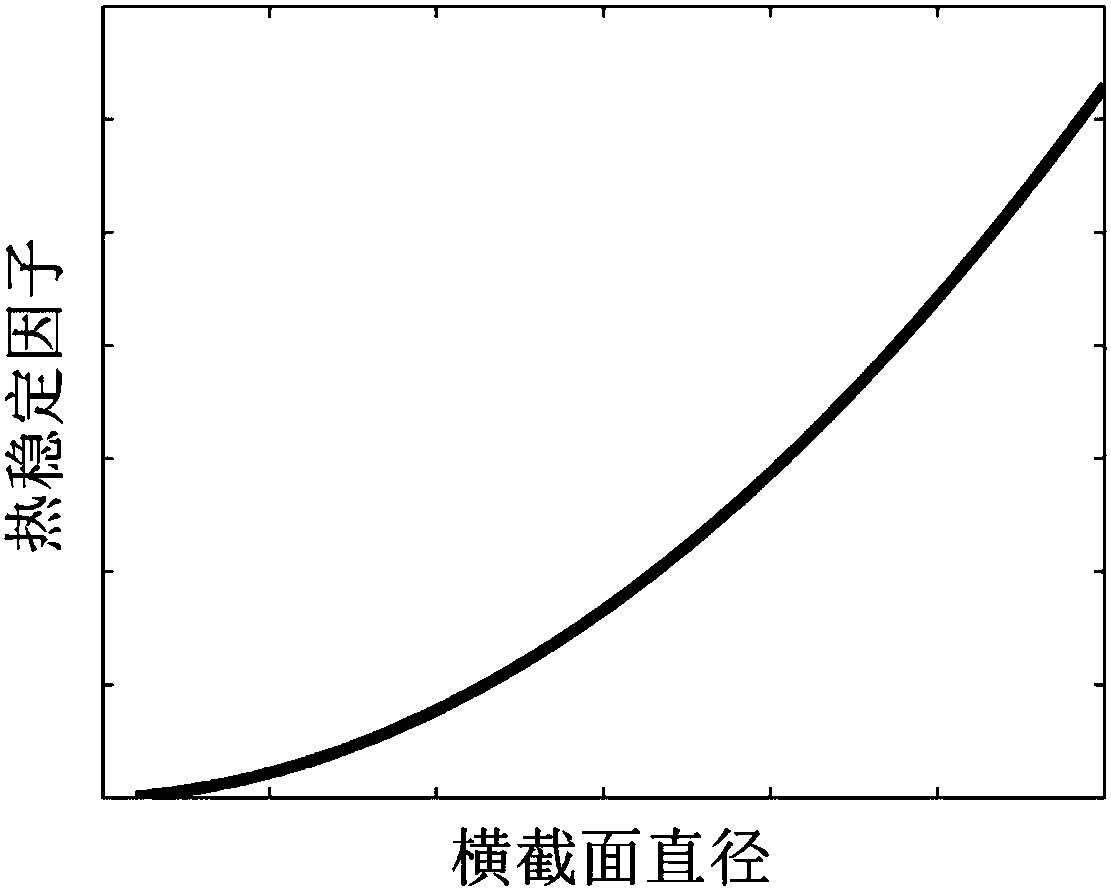
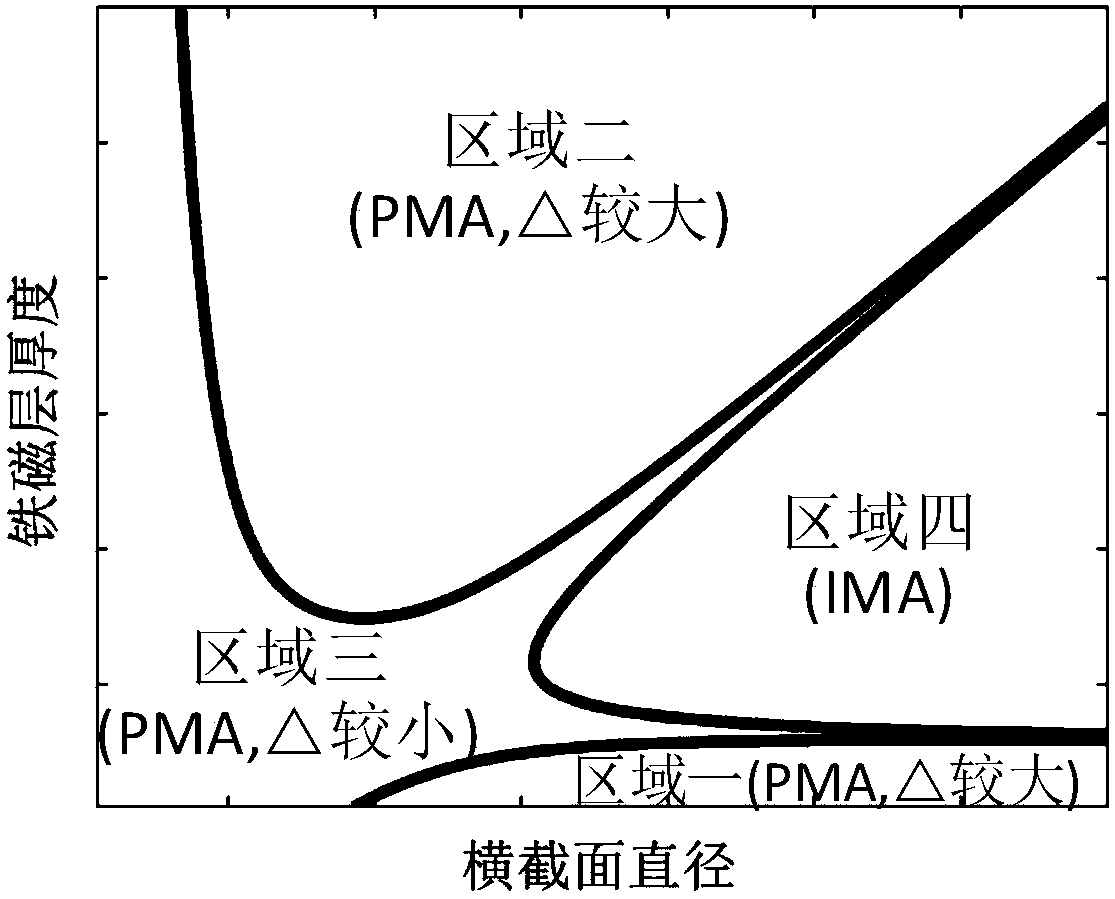
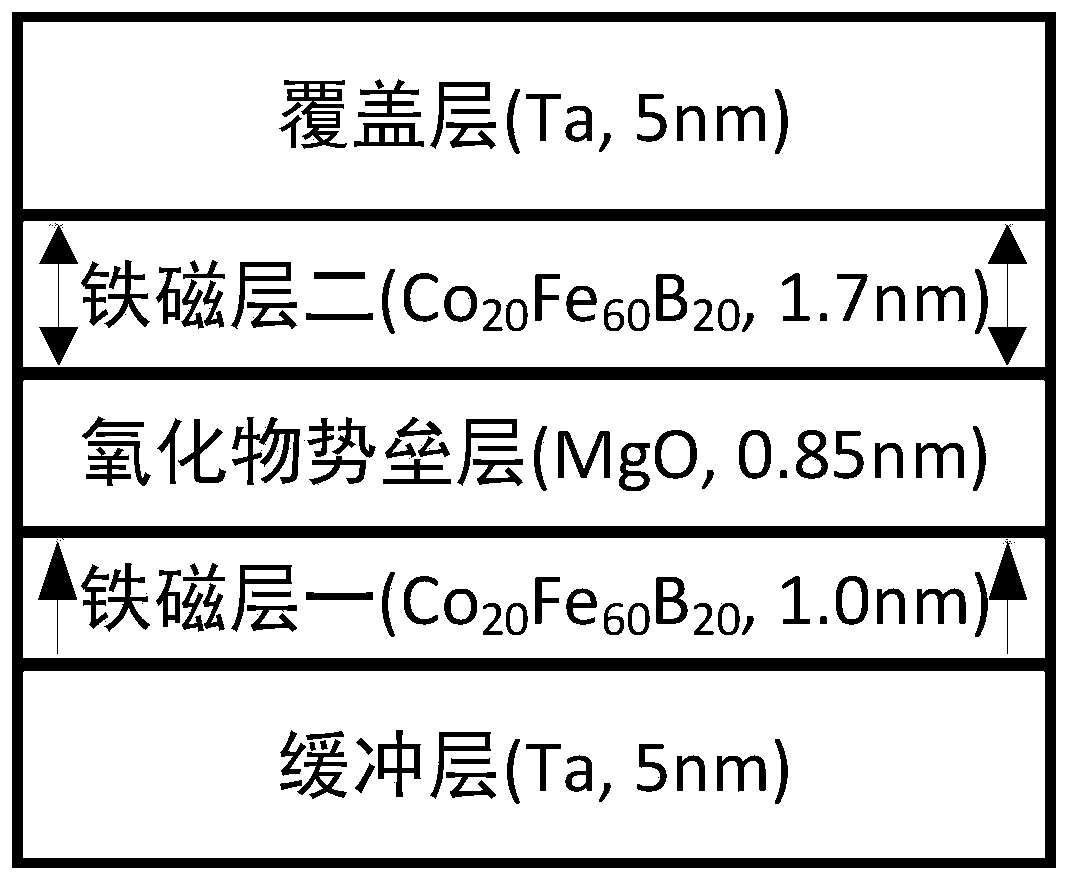
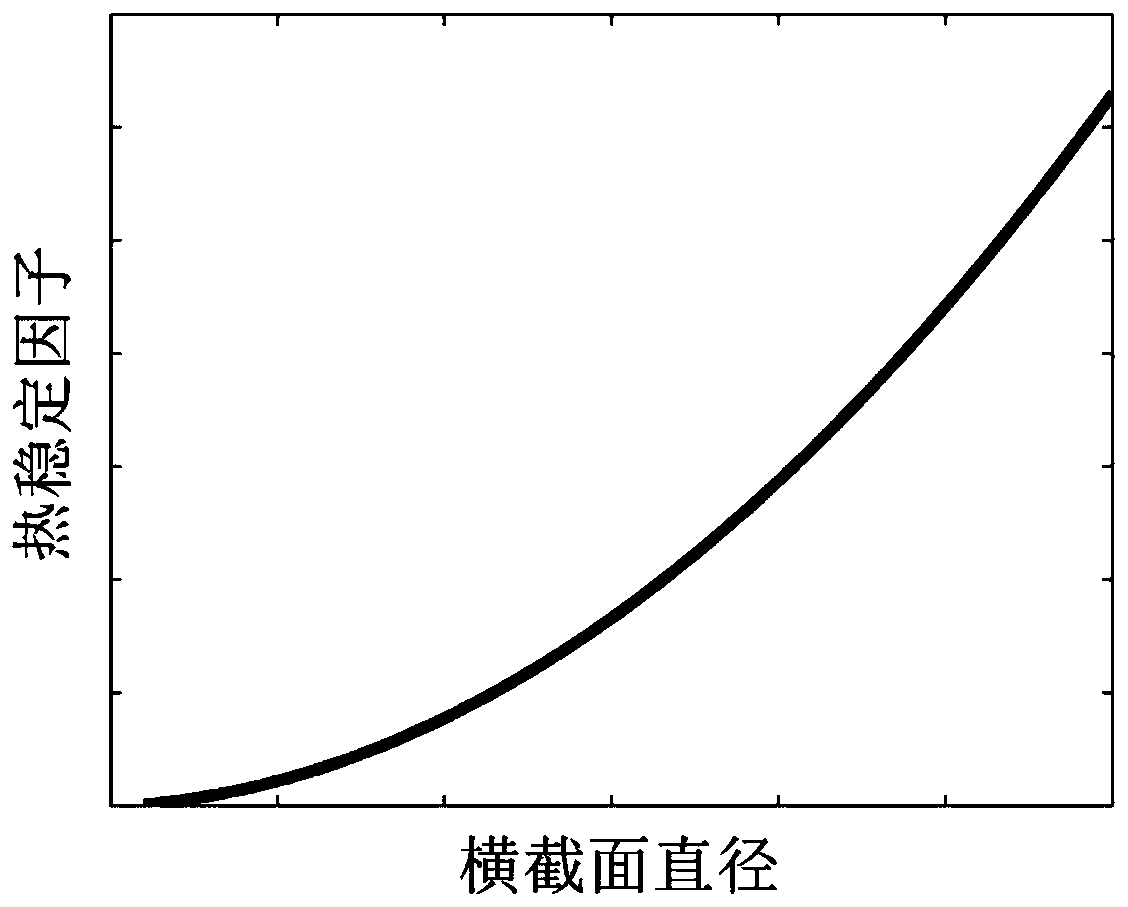
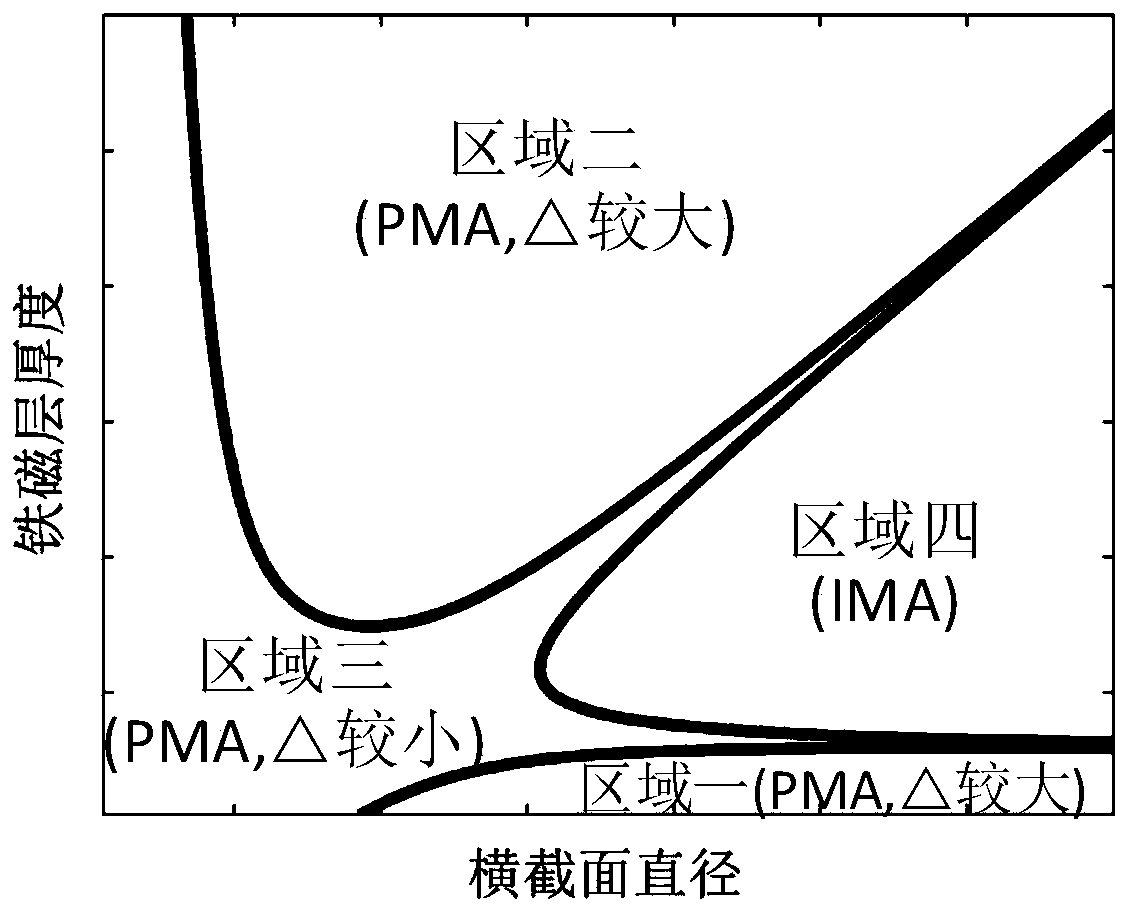
Magnetic tunnel junction with high perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
ActiveCN107946456AStrong perpendicular magnetic anisotropyImprove thermal stabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin-transfer torqueThermal stability
The invention relates to a magnetic tunnel junction with high perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, which structurally and sequentially comprises a first ferromagnetic layer, a barrier layer and a secondferromagnetic layer from bottom to top. The magnetic tunnel junction is characterized in that a size of a cross section of the magnetic tunnel junction is between 1nm to 150nm; thicknesses of both the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer are greater than 6nm, and the thicknesses of both the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer are greater than halfthe size of the cross section; and a thickness of the barrier layer is 0.2 to 10nm. Compared with the prior art, the magnetic tunnel junction has the advantages of high perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, high heat stability, small size of the cross section, high spin transfer torque turnover efficiency, small layer number of thin films and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
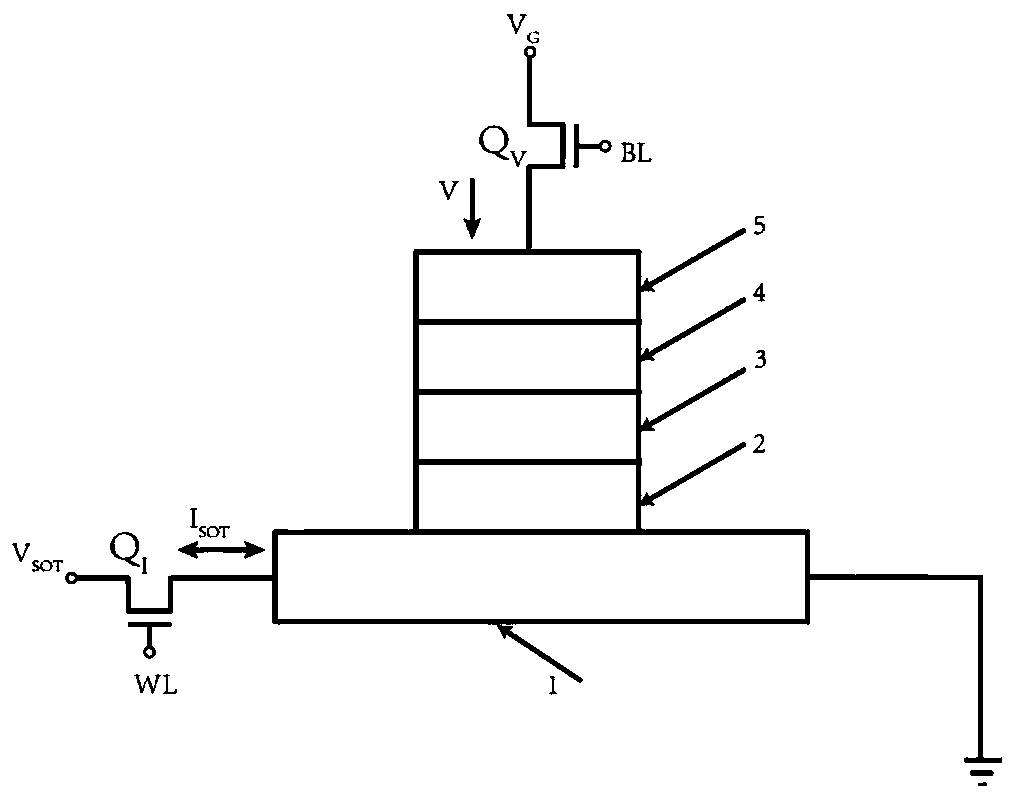
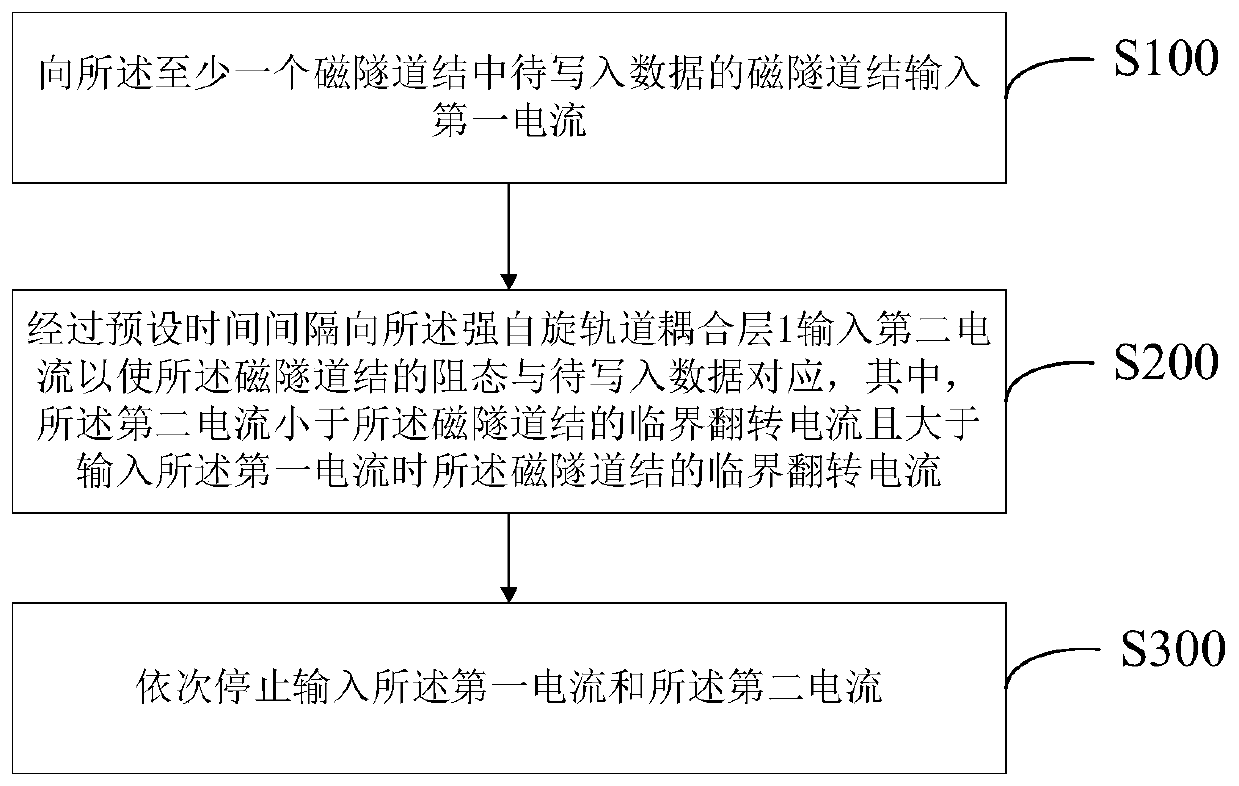
Magnetic random access memory unit and data writing method thereof
ActiveCN111540395AReduce critical flipping currentReduce the probability of writing errorsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageRandom access memoryTunnel junction
The invention provides a magnetic random access memory unit and a data writing method thereof. The magnetic random access memory unit comprises a spin orbital moment layer and at least one magnetic tunnel junction arranged on the spin orbital moment layer. The data writing method comprises: inputting a selection voltage to a magnetic tunnel junction of to-be-written data in the at least one magnetic tunnel junction; inputting writing current into the spin orbit moment layer at a preset time interval to enable the resistance state of the magnetic tunnel junction to correspond to-be-written data, wherein the writing current is smaller than the critical overturning current of the magnetic tunnel junction and larger than the critical overturning current of the magnetic tunnel junction when theselection voltage is input; and stopping inputting the selection voltage and the writing current in sequence. According to the method, deterministic overturning of the magnetic tunnel junction magnetic moment can be ensured, and the storage density is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
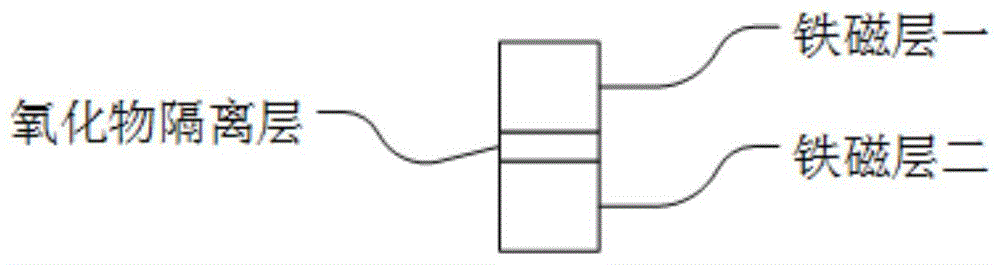
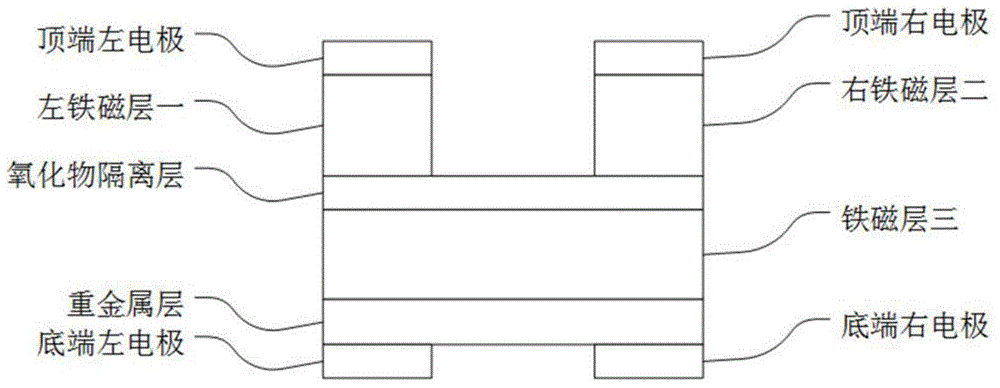
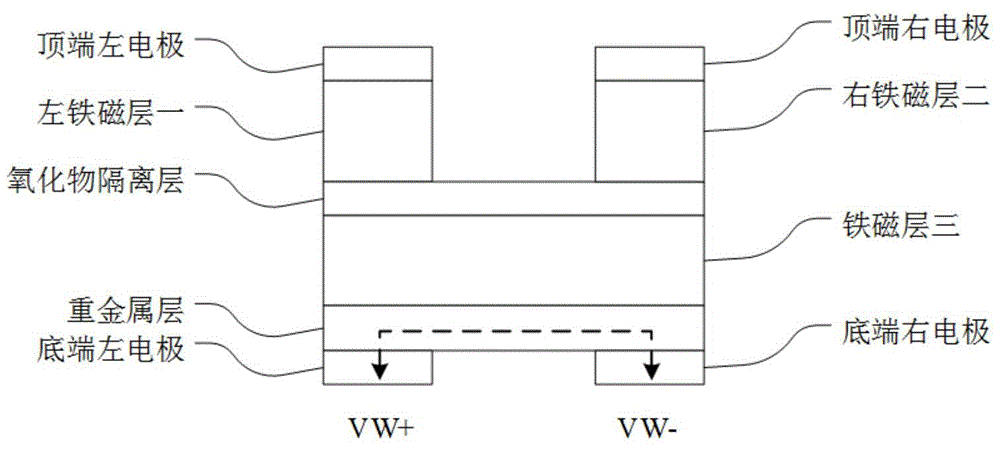
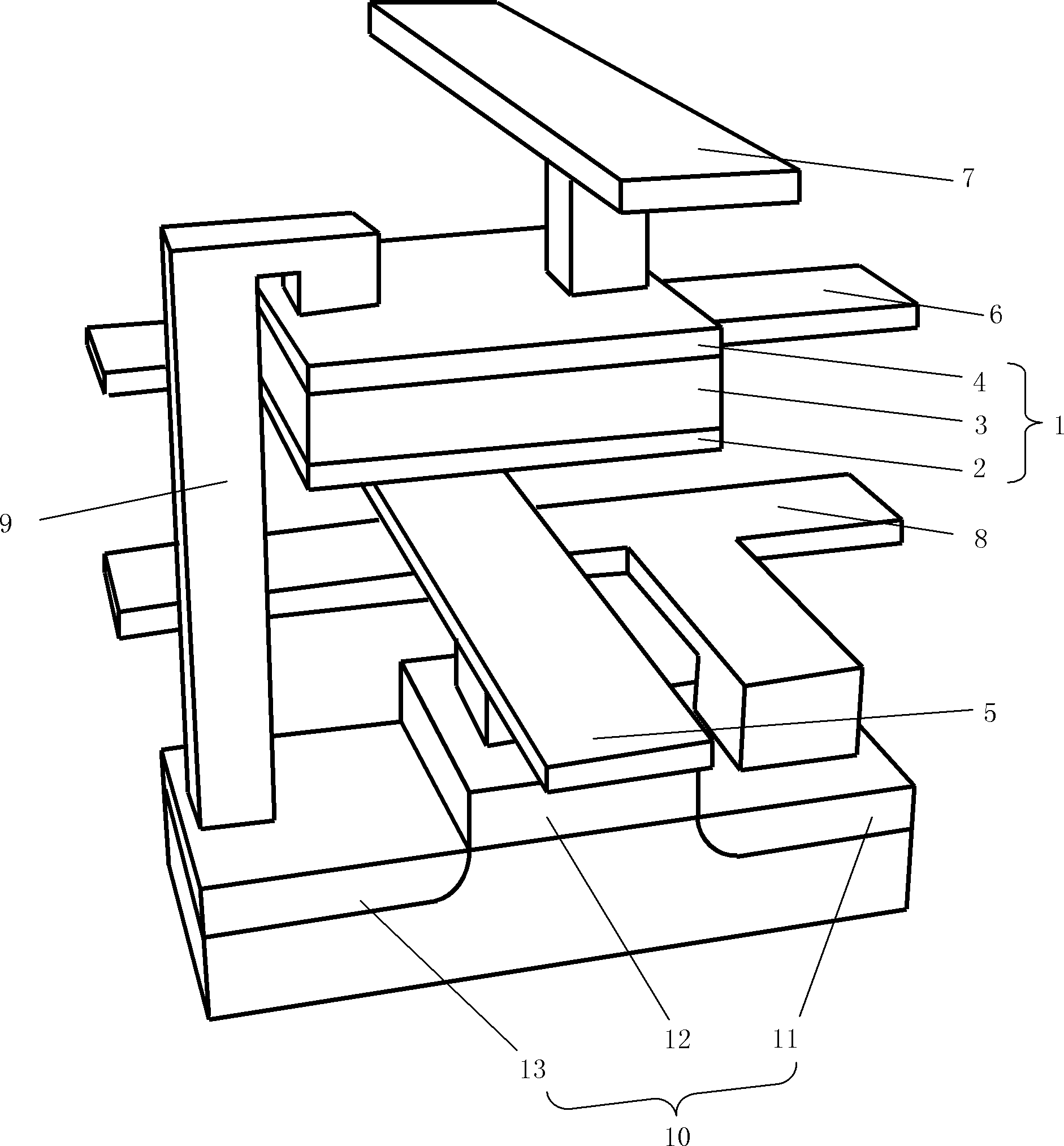
Novel four-port magnetic storage device
InactiveCN104795489AAlleviate Reliability IssuesReduce write power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionStorage cellMagnetic storage
Disclosed is a novel four-port magnetic storage device. A four-port magnetic storage device is composed of a top left electrode, a top right electrode, a first left ferromagnetic layer, a second right ferromagnetic layer, an oxide isolation layer, a third ferromagnetic layer, a heavy metal layer, a bottom left electrode and a bottom right electrode sequentially from top to bottom and left to right. A write-in branch and a read-in branch are separated, and reliability can be greatly improved. Furthermore, write-in current can flow through heavy metal with low resistivity instead of flowing through tunnel junction, so that write-in power consumption can be greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
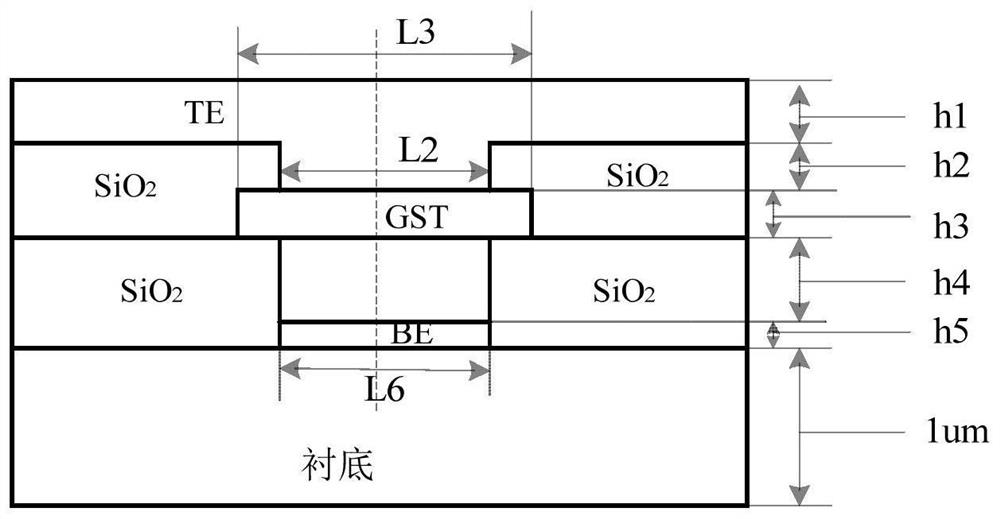
Asymmetric annular microelectrode phase change storage unit and device
ActiveCN107017341AReduce operating currentImprove thermal crosstalkSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesNon symmetricMicroelectrode
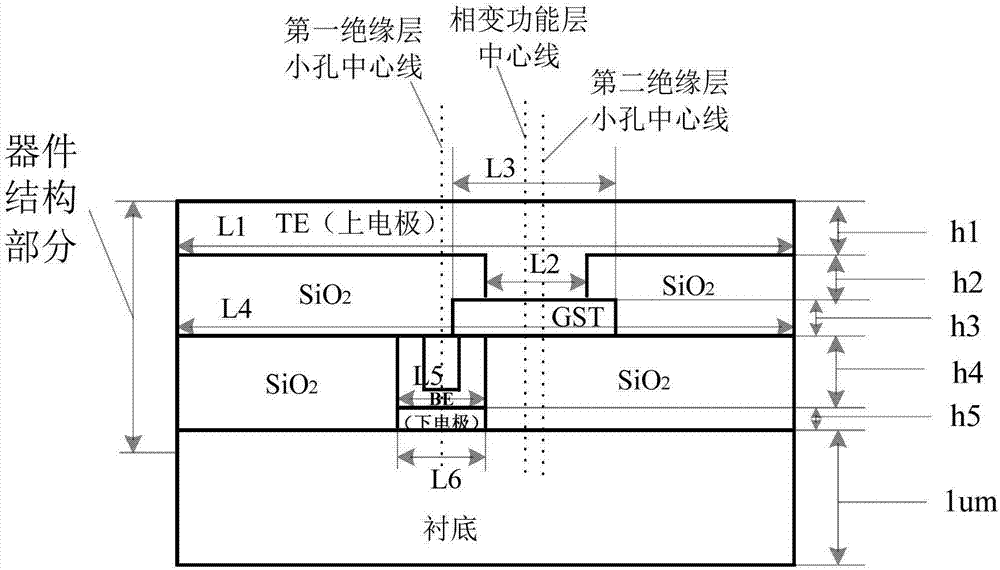
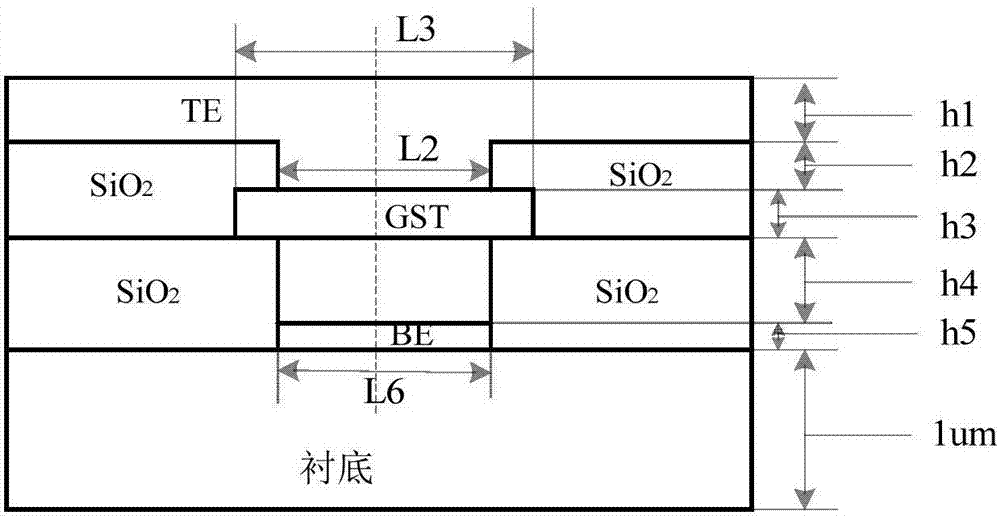
The invention discloses an asymmetric annular microelectrode phase change storage unit and device. The asymmetric annular microelectrode phase change storage unit comprises a lower electrode layer, a first insulating layer, a phase change function layer, a second insulating layer, and an upper electrode layer from bottom to top, the first insulating layer is provided with a small hole, a metal annular sidewall and an insulating core are arranged in the small hole, the phase change function layer is contacted with a lower electrode through the metal annular sidewall in the small hole of the first insulating layer, the second insulating layer is also provided with a small hole, and an upper electrode is contacted with the phase change function layer through the small hole of the second insulating layer. The asymmetric annular microelectrode phase change storage unit is characterized in that the lower electrode is an annular electrode, an electrode core is filled with an insulating material, and the center line of the small hole of the first insulating layer, the center line of the phase change function layer, and the center line of the small hole of the second insulating layer are all not in the same straight line. According to the asymmetric annular microelectrode phase change storage unit and device, the contact area of the lower electrode and the phase change material is greatly reduced, the operation current is reduced, the thermal property is good, the original property of the device can be maintained, the power consumption is reduced, and the thermal crosstalk is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
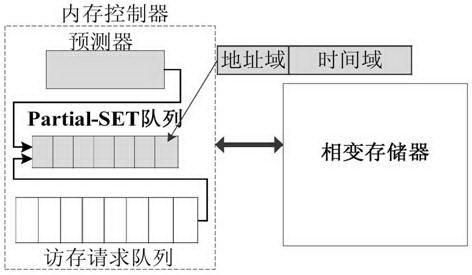
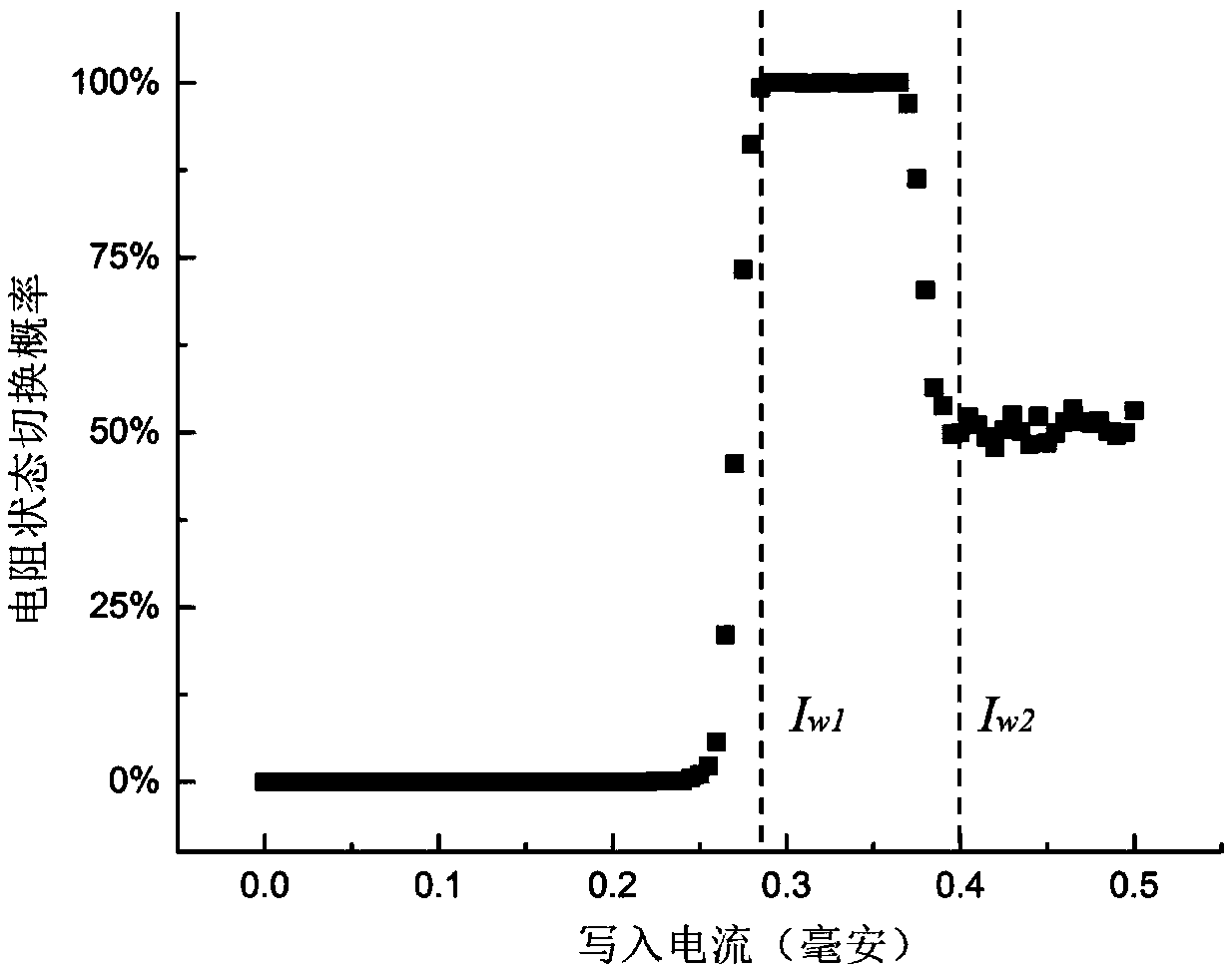
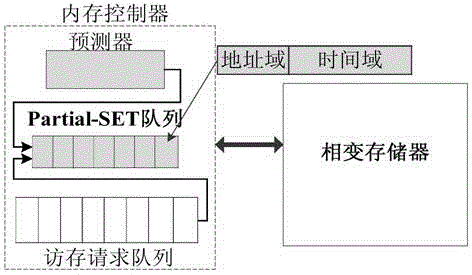
Writing acceleration method and system for phase change memory
ActiveCN103839580AAchieve technical effectImprove write performanceDigital storagePhase-change memoryComputer architecture
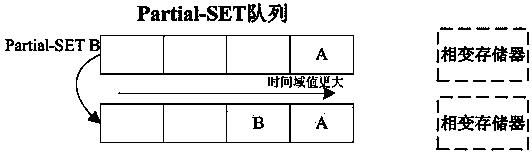
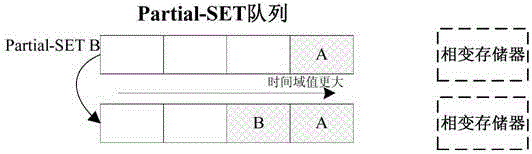
The invention discloses a writing acceleration method for a phase change memory. The method comprises the steps of Partial-SET writing operation judgment and writing request execution, wherein in the step of Partial-SET writing operation judgment, the adopted writing pulse type of a current writing request in the phase change memory is determined as SET or Partial-SET pulse; in the step of writing request execution, quick Partial-SET writing acceleration of the phase change memory is realized by using a SET or Partial-SET method at different writing speeds of SET operation and RESET operation according to the writing pulse type. The invention also discloses a writing acceleration system for the phase change memory.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A polymorphic non-volatile solid-state memory cell based on a vertical read/write operation
InactiveCN109003636AReduce horizontal sizeSmall sizeInput/output to record carriersDigital storageSolid-state storagePower flow
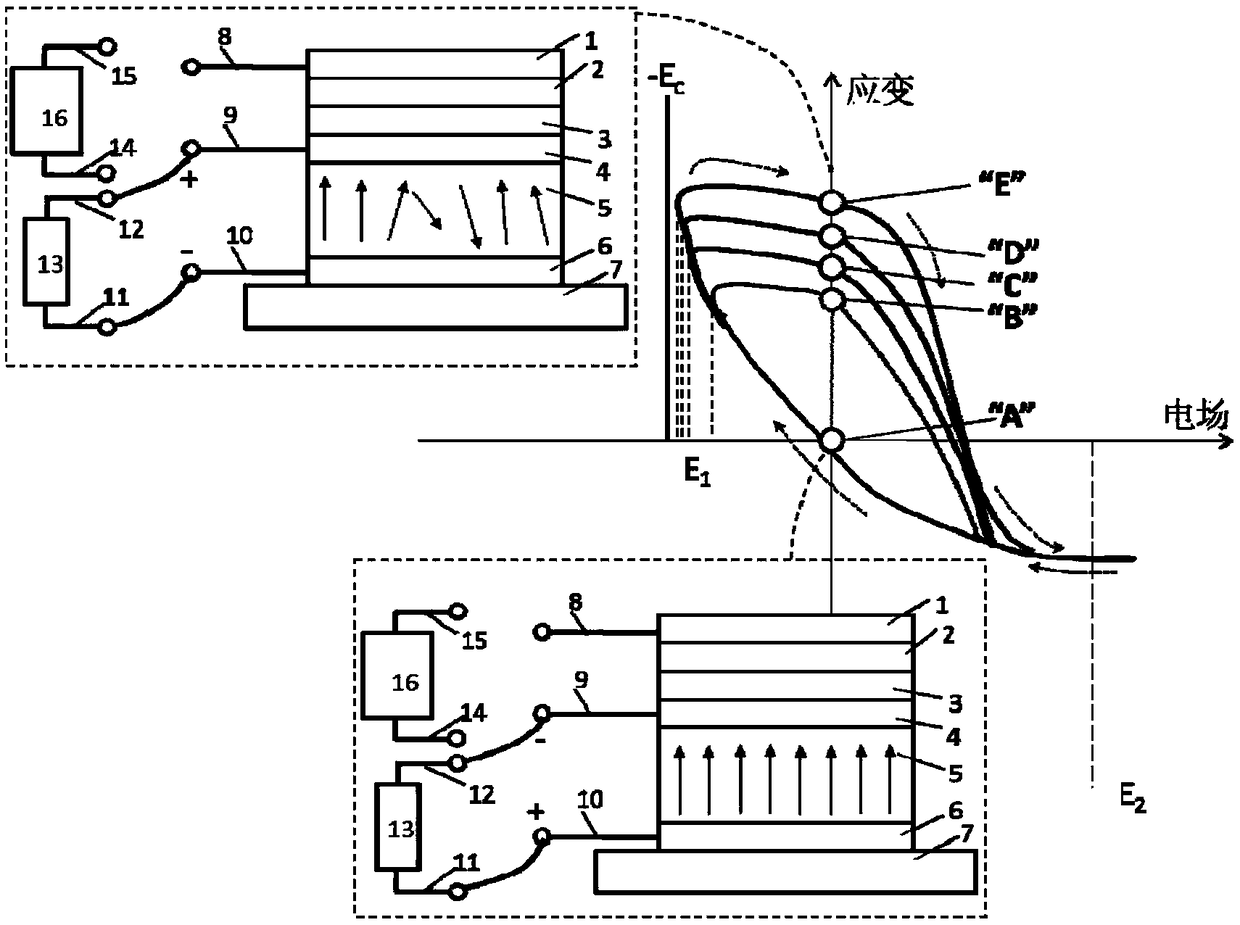
A polymorphic non-volatile solid-state memory cell based on a vertical read / write operation includes a bottom electrode layer, a ferroelectric piezoelectric layer formed on the bottom electrode layer,an intermediate electrode layer thereon, a pn junction layer adjacent to the intermediate electrode layer, and a top electrode layer thereon. The ferroelectric piezoelectric layer is used as the information writing layer and the pn junction layer is used as the information storage layer. The ferroelectric piezoelectric layer has a plurality of stress states under the vertical electric field, andthe pn junction layer has a plurality of non-volatile resistance states on the ferroelectric piezoelectric layer, so that the information can be written and erased. A read current or voltage is applied to the pn junction layer in a vertical direction so that information of the memory layer is read vertically. Vertical writing and reading of information and polymorphic features are conducive to greatly improve the storage density; the invention realizes information writing and erasing by utilizing an electric field, which is also conducive to reducing information access power consumption.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Voltage-adjustable reluctance-variable random memory cell and random memory
ActiveCN102683581AReduce distanceReduce the numberMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionElectrical resistance and conductanceInformation data
The invention provides a voltage-adjustable reluctance-variable random memory cell which comprises a bottom electrode layer, a ferroelectric oxide layer formed on the bottom electrode layer and a magnetic layer formed on the ferroelectric oxide layer, wherein the magnetic layer and the bottom electrode layer are respectively used as the upper and lower electrodes of the ferroelectric oxide layer to apply voltage on the ferroelectric oxide layer, the voltage direction is perpendicular to the ferroelectric oxide layer, and the ferroelectric oxide layer can adjust and control the arrangement of magnetic moment in the magnetic layer under the action of the voltage, so that the resistance of the magnetic layer in the set measuring direction changes. The invention also provides a memory with the reluctance-variable random memory cell. According to the invention, information data can be written by the voltage, and the voltage-adjustable reluctance-variable random memory cell has the advantages of nonvolatility, low writing power consumption, high storage density and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A magnetic tunnel junction
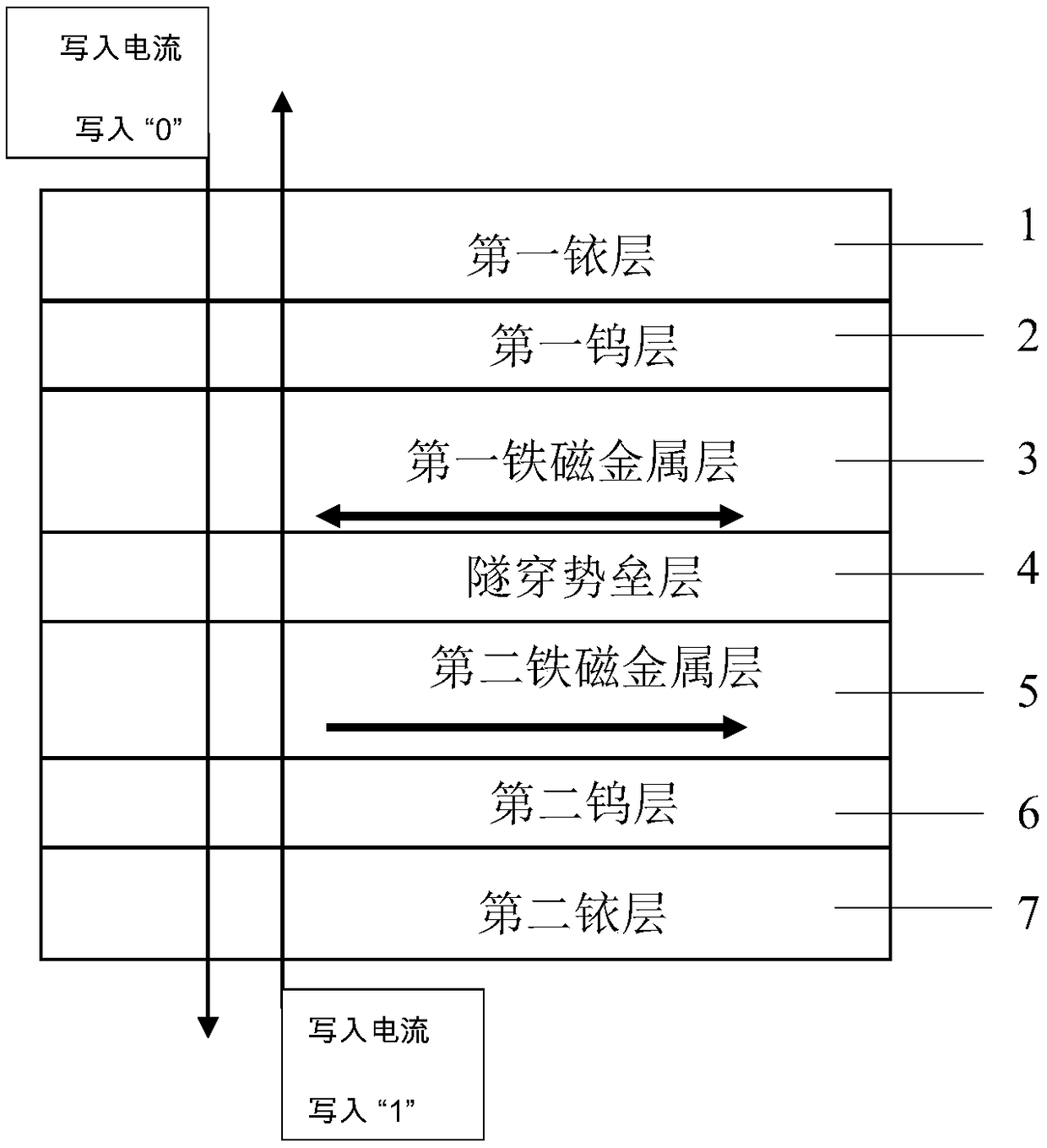
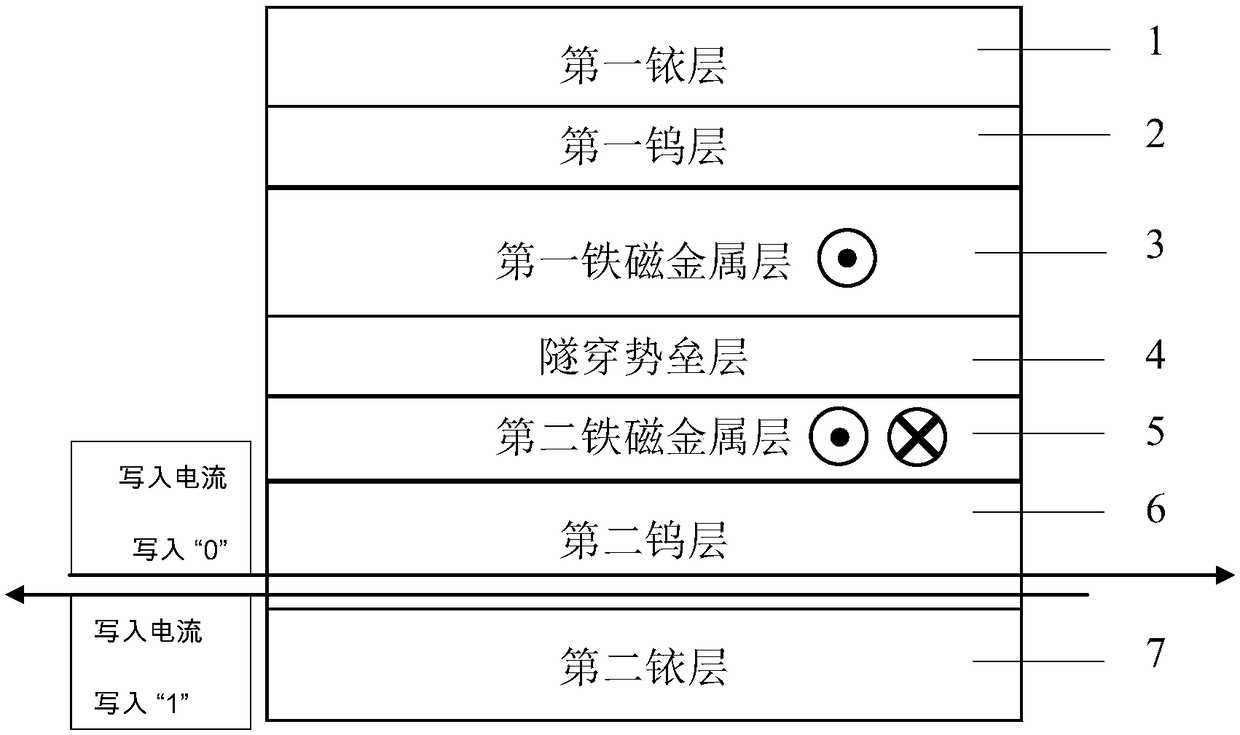
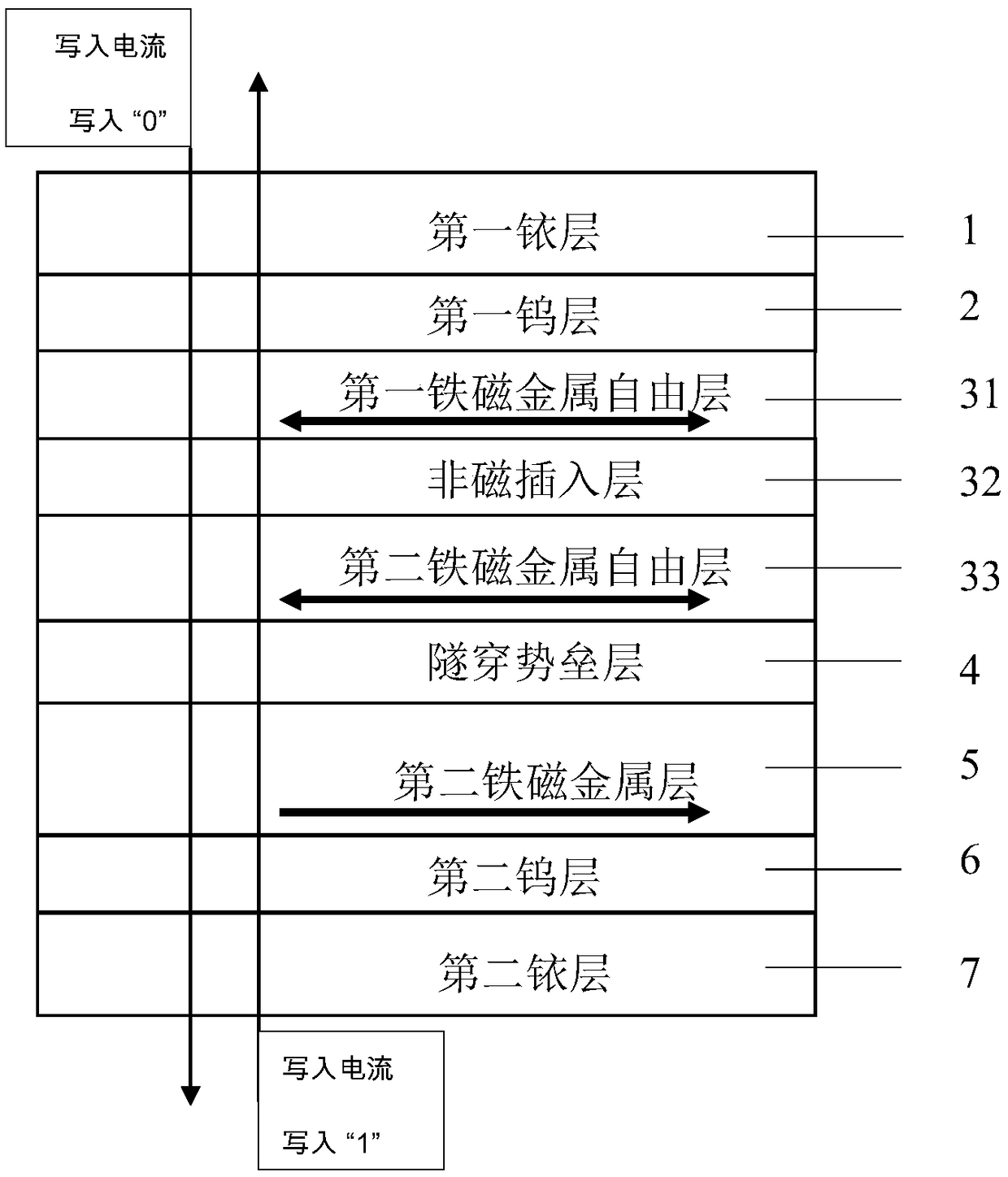
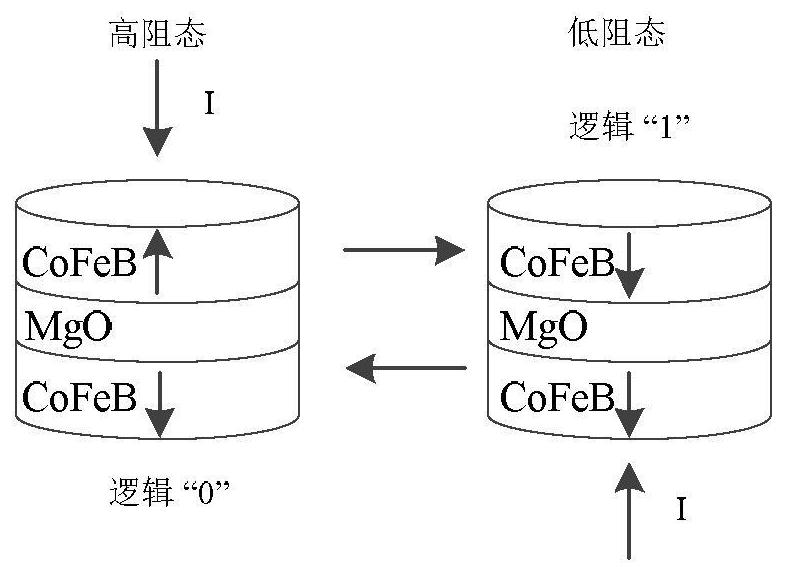
ActiveCN109065705AImprove read reliabilityReduce write power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
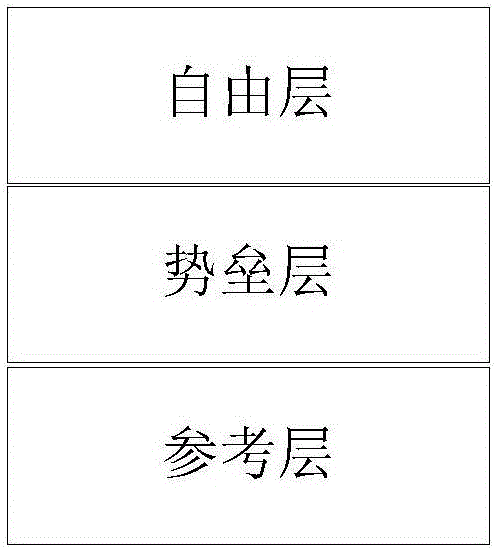
A magnetic tunnel junction is formed by forming a first iridium lay, a first tungsten layer, a first ferromagnetic metal layer, a tunneling barrier layer, a second ferromagnetic metal layer, a secondtungsten layer, and a second iridium layer. The two ferromagnetic metal layers are a reference layer and a free layer respectively. The magnetization direction of the reference layer is fixed and cannot be reversed; The magnetization direction of the free layer can be reversed. When the magnetization direction of the reference layer is parallel to that of the free layer, the magnetoresistive device exhibits a low resistance state and stores '0' in the binary system; When the magnetization direction of the reference layer is antiparallel to that of the free layer, the magnetoresistive device exhibits a high resistance state, storing a '1' in binary. The invention can generate high tunneling magnetoresistive rate, improve read reliability of magnetic tunnel junction, and reduce device writepower consumption at the same time.
Owner:致真存储(北京)科技有限公司
Modulation method of asymmetric ferroelectric tunneling junction multi-value storage unit
ActiveCN111211135AAccelerateReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesDigital storageStorage cellEngineering
The invention provides a modulation method of an asymmetric ferroelectric tunnel junction multi-value storage unit, a corresponding storage unit and a memory. The multi-value storage unit comprises Nferroelectric functional layers; the N ferroelectric functional layers have different coercive field values so that the N ferroelectric functional layers still show different residual polarization differences after first excitation is applied, and the multi-value storage unit shows 2N tunneling resistance states under action of second excitation; and the N is an integer greater than or equal to 2,and the first excitation comprises effects of changing a size of driving excitation anda direction of the driving excitation. The asymmetric ferroelectric tunnel junction multi-value storage unit hascharacteristics of non-volatility and low reading power consumption; and meanwhile, multiple different storage states can be realized in one storage unit so that astorage density and a unit storage capacity are greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
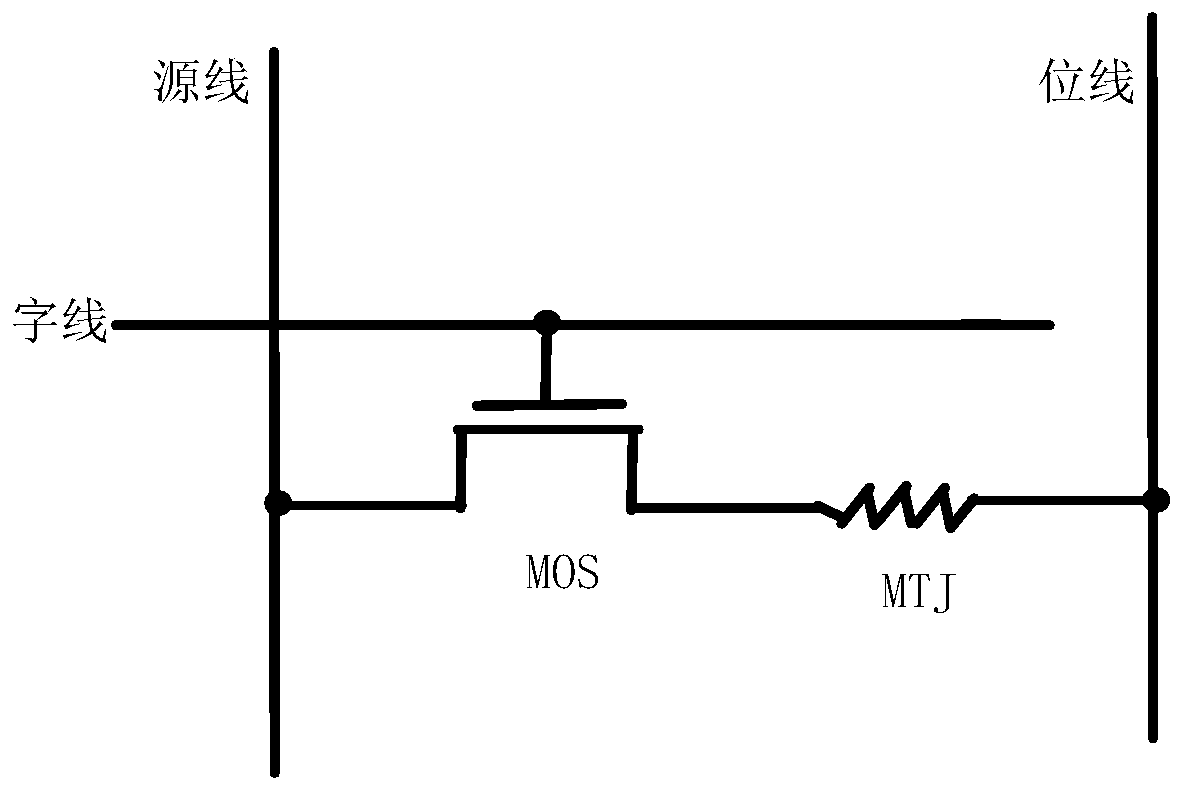
Write circuit structure for self-transfer torque magnetic random access memory
ActiveCN106297871AReduce dynamic power consumptionAvoid repeated write actionsDigital storageBit lineBistable circuits
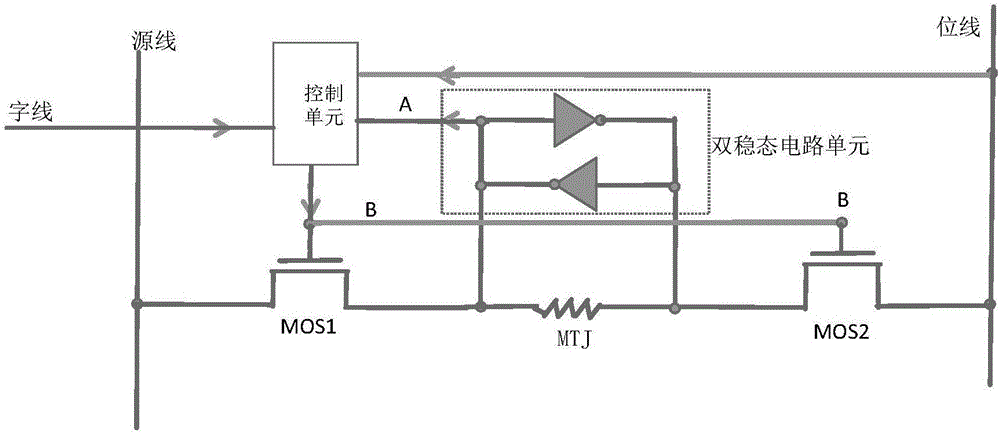
The invention discloses a write circuit structure for a self-transfer torque magnetic random access memory. The write circuit structure for the self-transfer torque magnetic random access memory comprises a magnetic tunnel junction, a source line, a bit line, a word line, a first switching tube, a second switching tube, a control unit and a bistable circuit unit, wherein a free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction is connected with a drain of the first switching tube; a reference layer of the magnetic tunnel junction is connected with a source of the second switching tube; the source of the first switching tube is connected with the source line; the drain of the second switching tube is connected with the bit line; a first end of the bistable circuit unit is connected with the free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction and the input of the control unit; a second end of the bistable circuit unit is connected with the reference layer of the magnetic tunnel junction; an input end of the control unit is connected with each of the word line, the source line and the bit line; a first end of the bistable circuit unit and an output end of the control unit are connected with the grid of the first switching tube and that of the second switching tube. According to the write circuit structure, repeated writing action can be avoided, and the purposes of reducing the writing power consumption of an MRAM and the dynamic power consumption of a chip are achieved.
Owner:CETHIK GRP +1
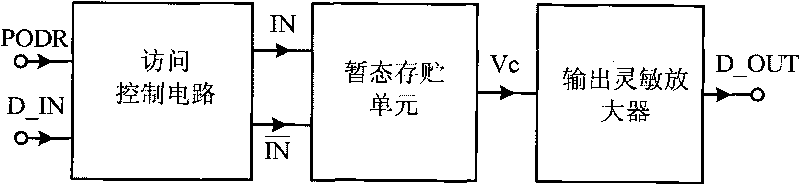
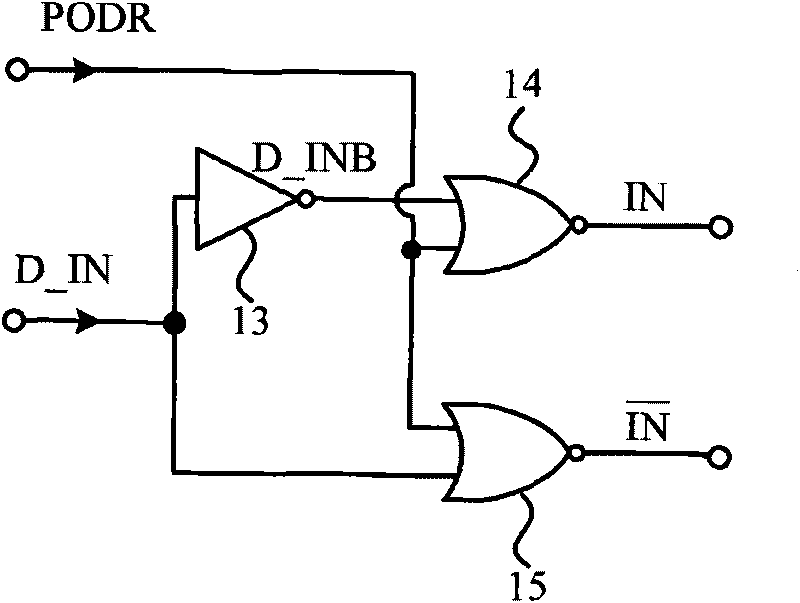
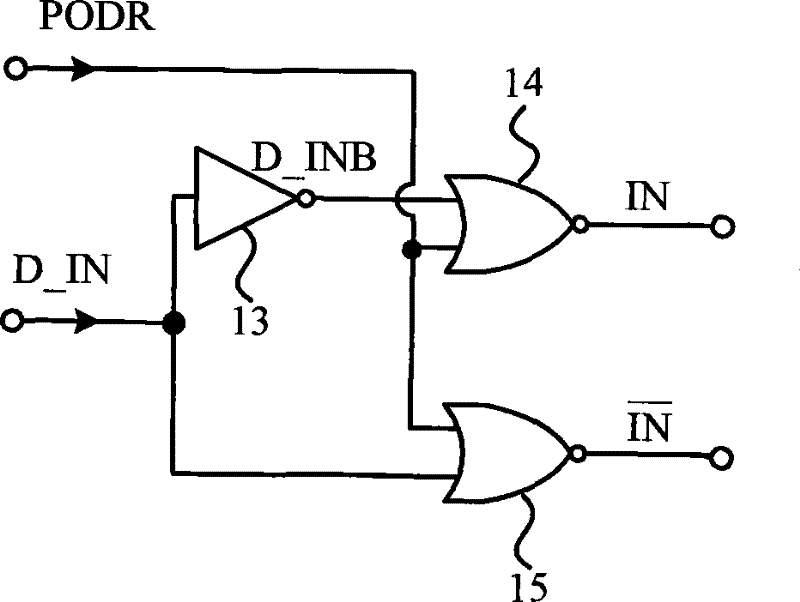
Transient storage circuit suitable for CMOS integration and using method thereof
ActiveCN101727974AAvoid repetitionSave time and costDigital storageRecord carriers used with machinesElectricityCMOS
The invention discloses a transient storage circuit suitable for CMOS integration and a using method thereof, which relate to the technical field of radio frequency identification (RFID). The transient storage circuit consists of an access control circuit, a transient storage unit and an output sensitive amplifier which are connected with one another in turn. A reset signal PODR and an input data signal D IN of a digital circuit of a tag chip are written into the transient storage unit by the access control circuit, and the temporary data output Vc of the transient storage unit is amplified by the output sensitive amplifier and then is output by a data wire D_OUT. The transient storage circuit can solve the problem of lowered identification efficiency caused by short time power down of the tag chip in application of passive radio-frequency identification, reduces the time cost for tag identification, improves the identification efficiency of a passive radio-frequency tag, and has the characteristics of economical efficiency, simplicity and convenience.
Owner:BEIJING TONGFANG MICROELECTRONICS
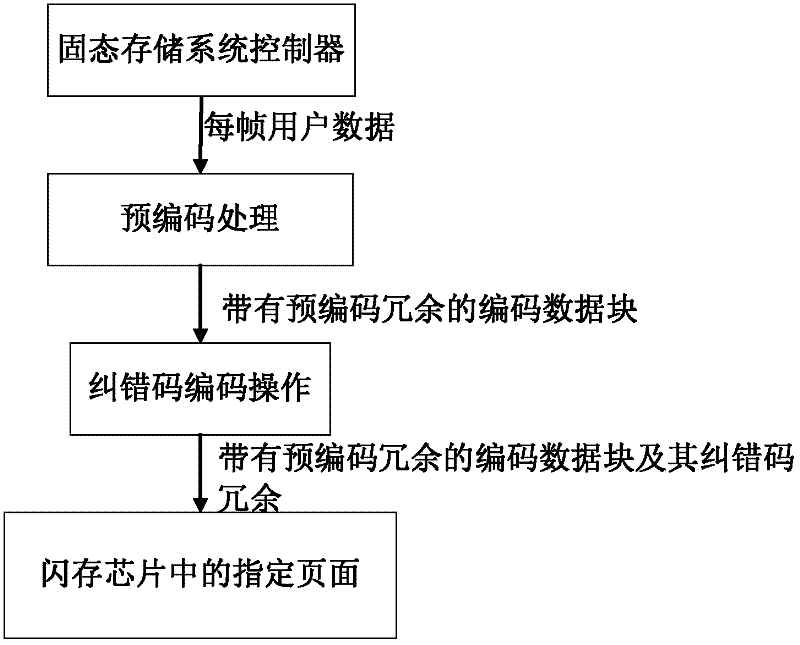
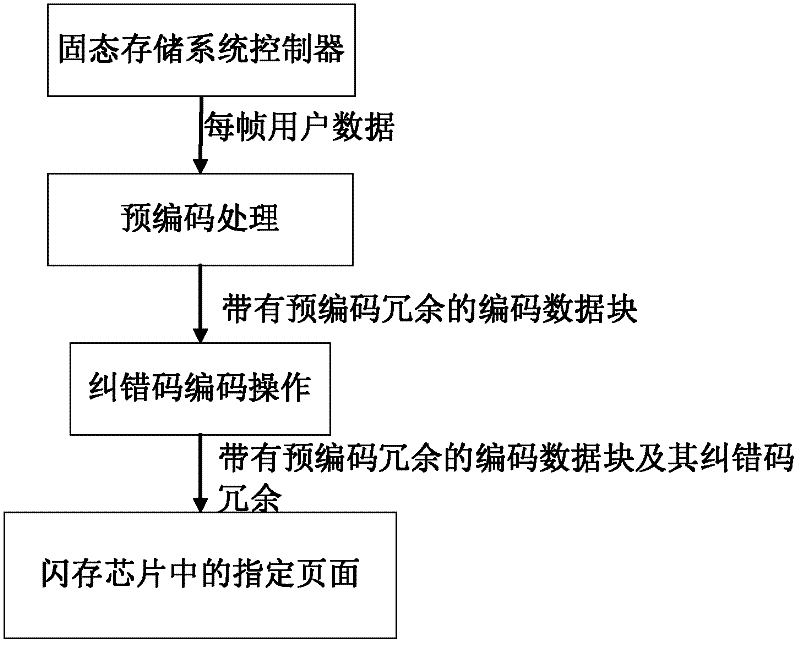
Method for reducing power consumption of flash memory chip data writing operation
InactiveCN102231284AReduce write power consumptionDynamic adjustment of error correction code encoding operationRead-only memoriesPrecodingCode redundancy
A method for reducing power consumption of flash memory chip data writing operation. Through a precoding processing, user data is changed, and corresponding precoding data redundancy is introduced; then the precoding is output to carry out an error correction code coding operation to generate corresponding error correcting code redundancy, so as to reduce power consumption of corresponding flash memory data writing; at last, the precoding is output and written into the flash memory chip together with the error correcting code redundancy. A flash memory chip reliability scope and a corresponding required error correcting code redundancy amount are given; when an estimated or detected flash memory chip reliability falls into the given flash memory chip reliability scope, a error correcting code redundancy amount can be obtained, so as to adjust error correcting code coding operation dynamically. Meanwhile, the required error correcting code redundancy amount is subtracted from a fixed redundancy storage space contained in a page itself, so as to obtain a precoding redundancy amount to adjust precoding operation dynamically. The power consumption of flash memory chip data writing operation is reduced effectively by utilizing a characteristic that the power consumption of flash memory chip data writing operation is directly related to the content of the written data.
Owner:孙飞
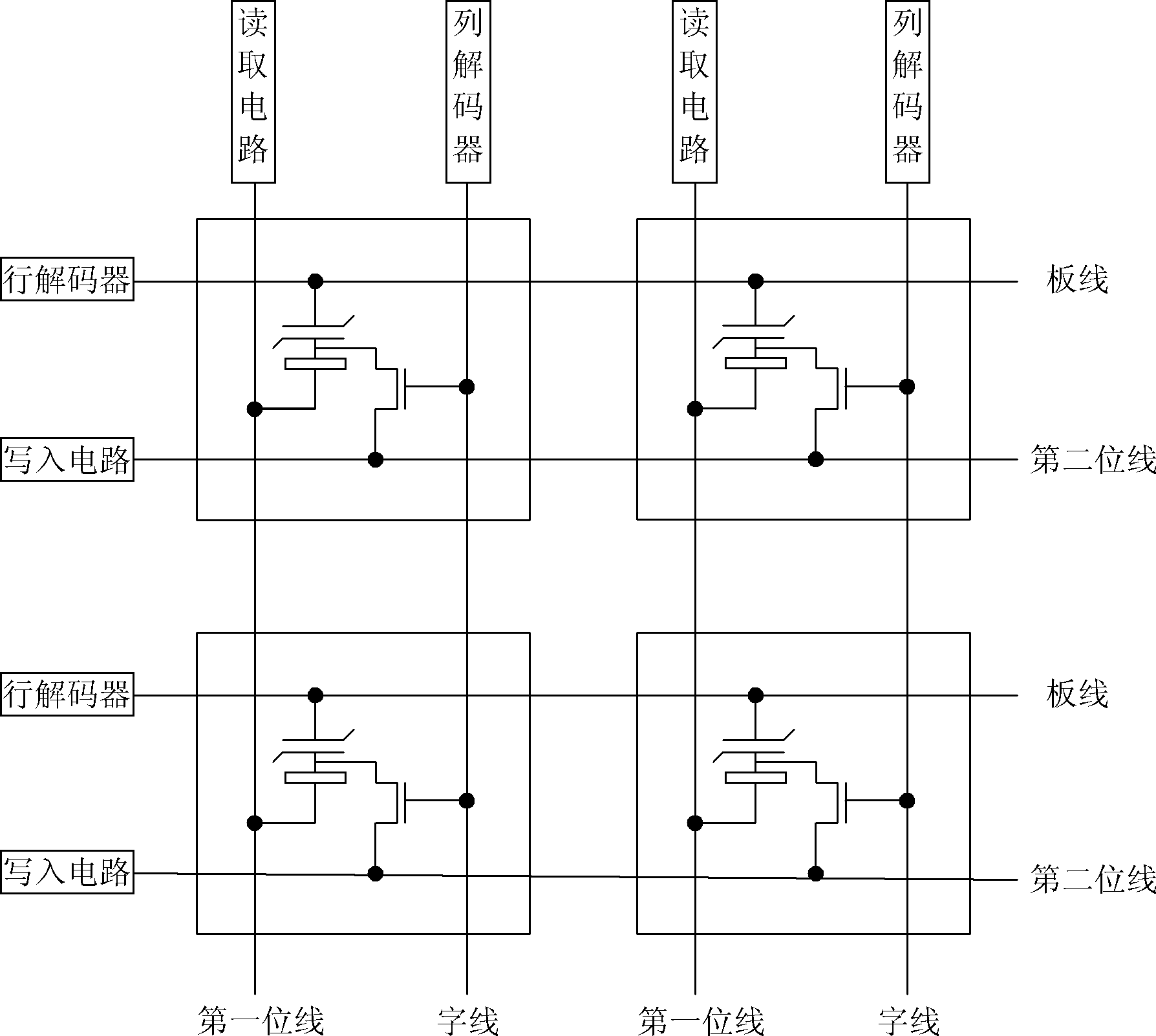
Read-write circuit of magnetic random access memory
PendingCN112927736AAffect magnificationReduce power consumptionDigital storageBit lineData translation
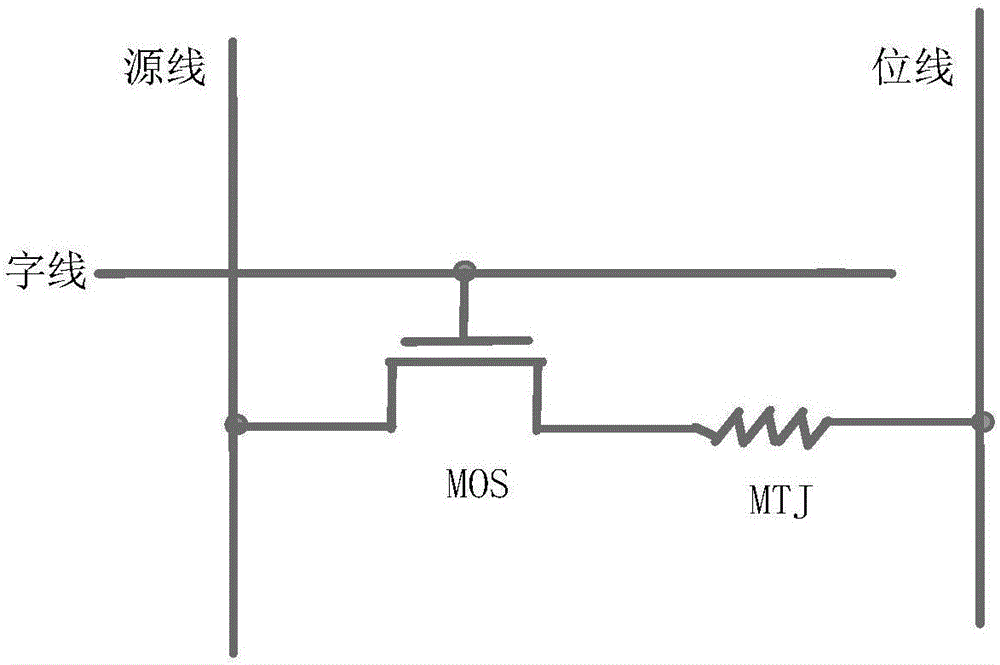
A read-write circuit of a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is characterized in that each data unit comprises a switch transistor, a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), a word line connection, a source line connection and a bit line connection, and the read-write circuit comprises a plurality of data units, a plurality of reference units, a bit line driving circuit and a source line driving circuit, a write-in voltage offset adjusting circuit is used for sensing voltage during write-in operation, a data selection circuit switches output of the voltage, a sensitive amplifier is in charge of effectively amplifying signals in combination with sequential control, data is converted into digital signals through the SR latch. A write termination circuit is used for controlling whether the write operation is completed or not according to the data signal output by the SR latch. According to the invention, a reading function, a writing function and a writing state monitoring function are respectively realized under different direct-current working points by adopting the same set of circuit, so that the power consumption can be reduced, and the reliability can also be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIYU INFORMATION TECH
Low-power-consumption magnetic random access memory and writing and reading method thereof
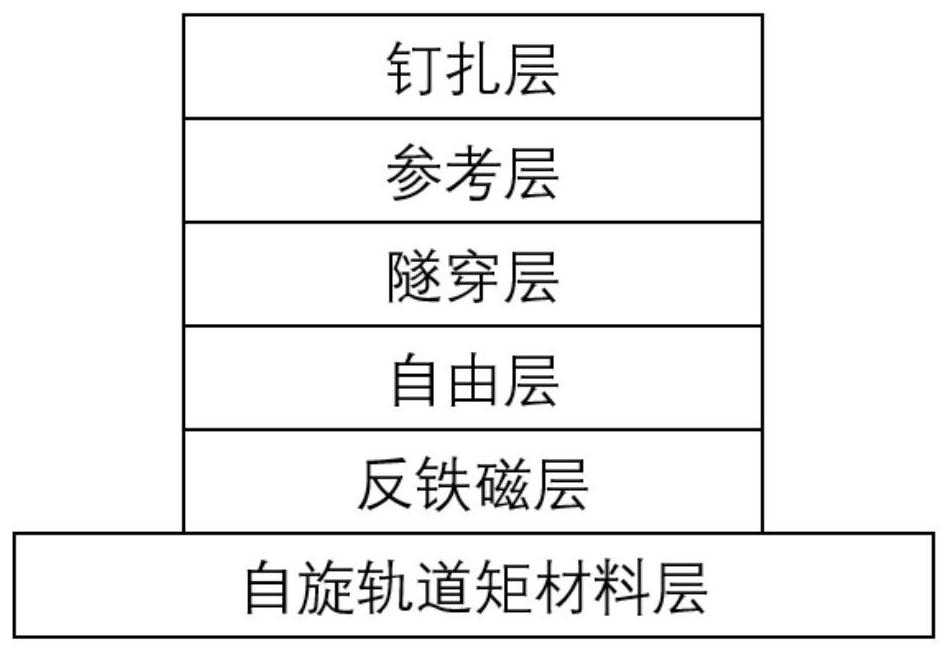
ActiveCN112201745ALow densityImprove current conversion efficiencyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsRandom access memoryEngineering
The invention discloses a low-power-consumption magnetic random access memory and a writing and reading method thereof, the memory is mainly composed of a spin orbit moment material layer, a free layer, a tunneling layer, a reference layer, a pinning layer, an electrode and the like, and an antiferromagnetic insulator layer is added between the spin orbit moment material layer and the free layer and used for conducting and amplifying spin current. The writing method comprises the following steps of: writing a parallel state and an anti-parallel state, wherein numbers 0 and 1 are respectively and correspondingly written; and the reading method comprises the following steps of: enabling a current to flow through the tunnel junction from the reading electrode, and then forming a closed loop by the other electrode, so that data reading operation is realized. According to the invention, the current conversion efficiency can be improved, and the critical flip current density is reduced, thereby reducing the write-in power consumption; and according to the method, a writing path and a reading path are completely separated, so that the thickness of a tunneling layer can be increased, and the TMR resistance is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
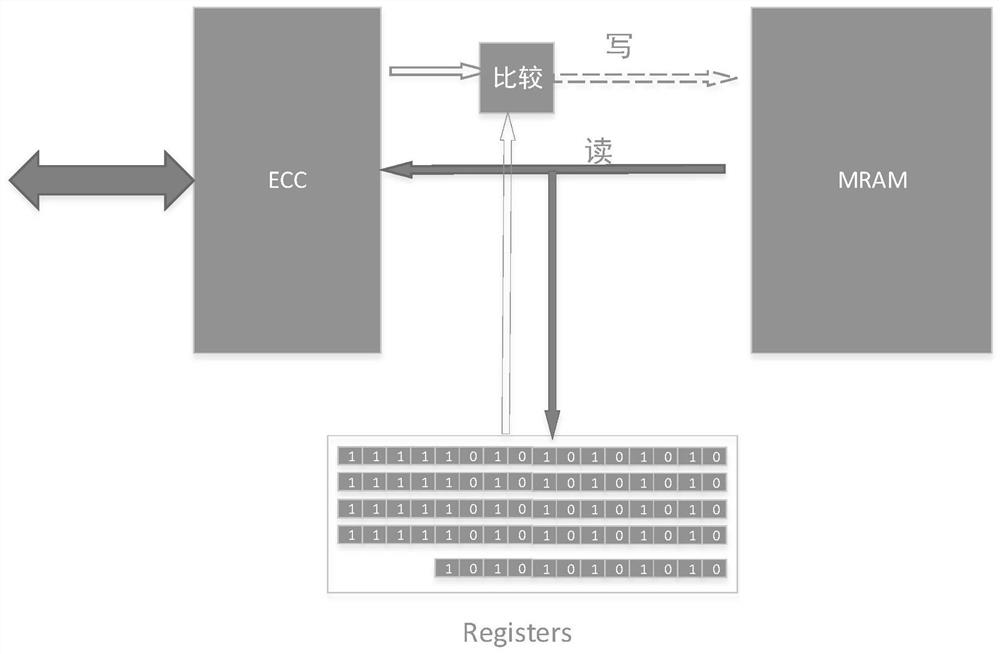
An MRAM system with ECC function and method of operating same
ActiveCN112289352AImprove reliabilityReduce write power consumptionDigital storageWrite bitComputer architecture
The MRAM system with the ECC function comprises an MRAM, an ECC circuit and a register set; the register set is arranged between the MRAM and the ECC circuit and electrically connected with the MRAM and the ECC circuit; and the register set is used for reading data from the MRAM and storing the read data into the register set; the ECC circuit is used for reading data from the MRAM together with the register set; and when the MRAM writes back the data, the MRAM is used for comparing the written-back data with the data stored in the register set and checking and correcting data errors. Accordingto the invention, the state of the written bit can be detected while the writing operation is carried out, the reliability of the MRAM is high, the writing power consumption is reduced, and the chipspeed and the design complexity are not influenced.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIYU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
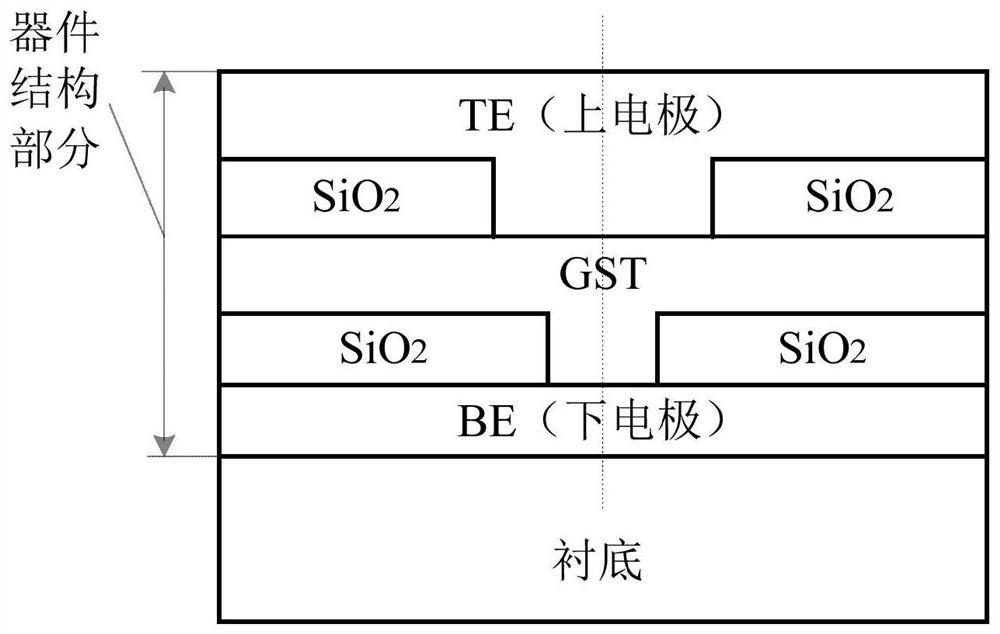
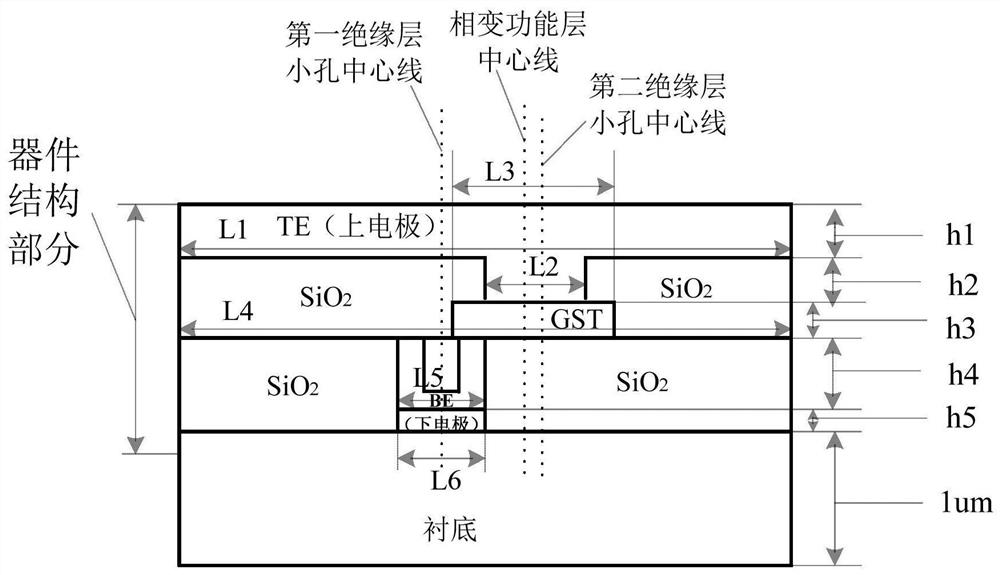
An asymmetric annular microelectrode phase-change memory unit and device
ActiveCN107017341BImprove cooling conditionsReduce thermal crosstalkSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringMicroelectrode
The invention discloses an asymmetric annular micro-electrode phase-change memory unit and a device, comprising a lower electrode layer, a first insulating layer, a phase-change functional layer, a second insulating layer, and an upper electrode layer from bottom to top; the first insulating layer There is a small hole in the layer, and the metal annular side wall and the insulating core are in the small hole; the phase change function layer is in contact with the lower electrode through the metal annular side wall in the small hole of the first insulating layer; the second insulating layer is also opened with a small hole; the upper electrode is in contact with the phase change functional layer through the small hole in the second insulating layer. Its core structure is characterized in that the lower electrode is a ring-shaped electrode, and the electrode core is filled with insulating material; the centerline of the first insulating layer, the centerline of the phase change functional layer, and the centerline of the second insulating layer are not on the same straight line. The asymmetric annular microelectrode phase-change memory unit and device provided by the present invention greatly reduce the contact area between the lower electrode and the phase-change material, reduce the operating current, have good thermal performance, and can maintain the original performance of the device. At the same time reduce power consumption and reduce thermal crosstalk.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magnetoelectric random storage unit and storage with same
ActiveCN101834271BReduce distractionsReduce distanceGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesBit lineComputer science
The invention discloses a memorizer having a magnetoelectric random storage unit, comprising a plurality of magnetoelectric random storage units; a plurality of access transistors connected to first electrodes in the magnetoelectric random storage units; a plurality of word lines for controlling the access transistors; a plurality of first printed lines connected to second electrodes in the magnetoelectric random storage units; a plurality of first bit lines connected to the access transistors; a plurality of second bit lines connected to ferroelectric fixed layers in the magnetoelectric random storage units; and a plurality of second printed lines connected to ferromagnetic free layers in the magnetoelectric random storage units. The embodiment of the invention can write in information data with the electric field, and has the advantages of nonvolatility, low write-in power consumption, high storage density and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
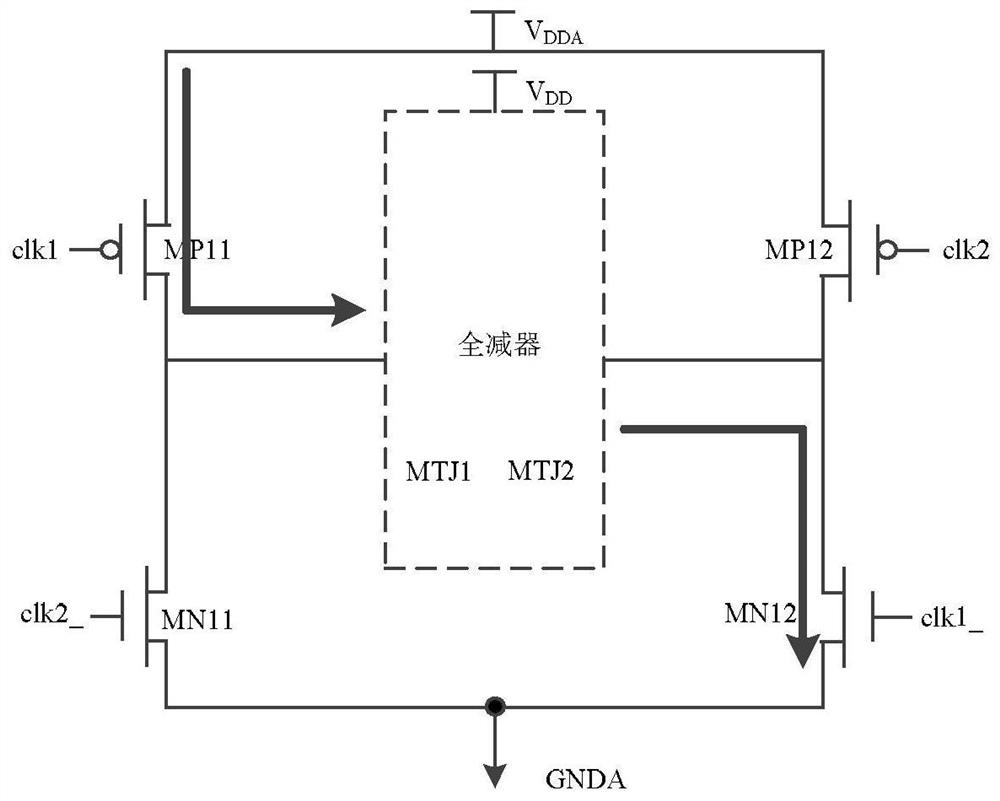
Full subtracter applying MTJ
ActiveCN113470715AReduce in quantityReduce write power consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesRead-only memoriesClock powerPower consumption
The invention relates to a full subtractor applying an MTJ, which solves the problem that the writing power consumption is increased due to a mode of adding an MOS tube in a power supply voltage direction when the MTJ of the full subtractor is written at any time in the prior art, and belongs to the technical field of electronic circuits. The invention discloses a full subtractor applying an MTJ. The full subtractor comprises a one-bit full subtractor, two write-in circuits and two clock logic control circuits, clock signals output by the two clock logic control circuits are simultaneously sent to the two write-in circuits; the clock logic control circuits are realized by NOR gate circuits; three inputs of the clock logic control circuit comprise a full subtractor work clock, a forward / reverse write-in enable control signal and a forward / reverse write-in input clock signal. The clock of the write-in circuit is controlled by adding the control gate, the number of MOS tubes in the clock power supply voltage direction of the write-in circuit is reduced, and the purpose of reducing write-in power consumption is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI +2
A Magnetic Nonvolatile Memory Cell Structure Based on Bidirectional Spin Hall Effect
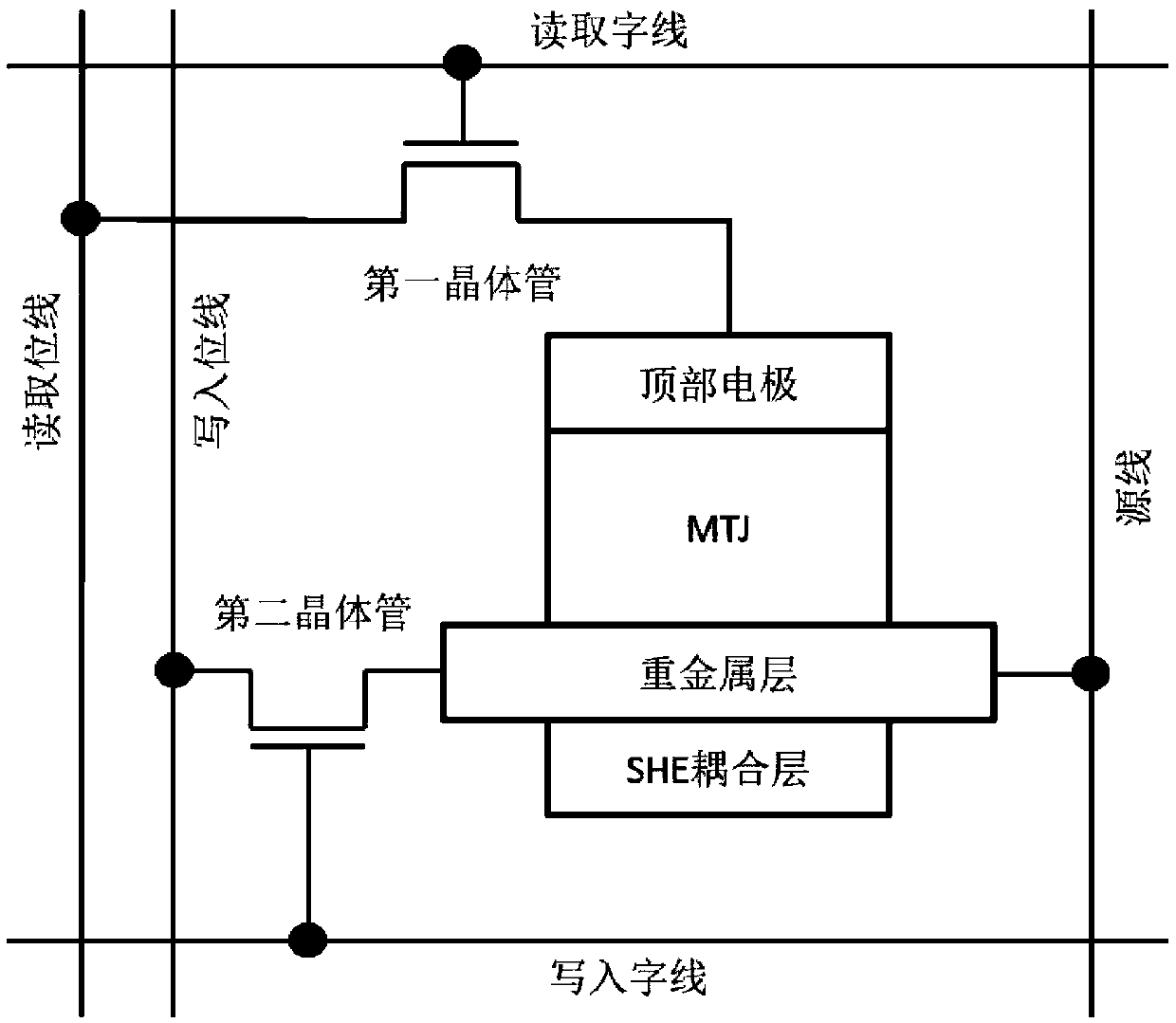
ActiveCN107316936BReduce write power consumptionReduce write operation timeGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesWrite bitMemory cell
The invention discloses a magnetic non-volatile memory unit structure based on the bidirectional spin Hall effect, comprising: a bidirectional spin Hall effect magnetic tunnel junction, a first transistor, a second transistor, a read word line, and a read bit lines, write word lines, write bit lines, and source lines; the new magnetic tunnel junction based on the bidirectional spin Hall effect includes a traditional vertical magnetic tunnel junction, a heavy metal layer, and a spin Hall effect coupling layer, wherein the The vertical magnetic tunnel junction includes a reference layer, a tunnel insulating layer and a first magnetic free layer from top to bottom, and the spin Hall effect coupling layer includes a second magnetic free layer and an insulating layer from top to bottom. The invention does not need auxiliary means, only by controlling the current flowing through the heavy metal layer to realize the switching of the vertical magnetic tunnel junction resistance between high resistance state, low resistance state and random resistance state, which can effectively reduce the writing power consumption of the magnetic storage unit, The write operation time of the magnetic memory cell is shortened.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
A phase-change memory write acceleration method and system thereof
ActiveCN103839580BAchieve technical effectImprove write performanceDigital storagePhase-change memoryComputer architecture
The invention discloses a writing acceleration method for a phase change memory. The method comprises the steps of Partial-SET writing operation judgment and writing request execution, wherein in the step of Partial-SET writing operation judgment, the adopted writing pulse type of a current writing request in the phase change memory is determined as SET or Partial-SET pulse; in the step of writing request execution, quick Partial-SET writing acceleration of the phase change memory is realized by using a SET or Partial-SET method at different writing speeds of SET operation and RESET operation according to the writing pulse type. The invention also discloses a writing acceleration system for the phase change memory.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic random access memory
The invention provides a magnetic random access memory, which is characterized in that when a write circuit provides a gradually increased line voltage and sets the line voltage to a bit line / source line of a selected unit, a write detection circuit detects the voltage change of the bit line / source line to form detection data, and the detection data is compared with data to be written; and determining whether to turn off the write driver corresponding to the selected unit line.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIYU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
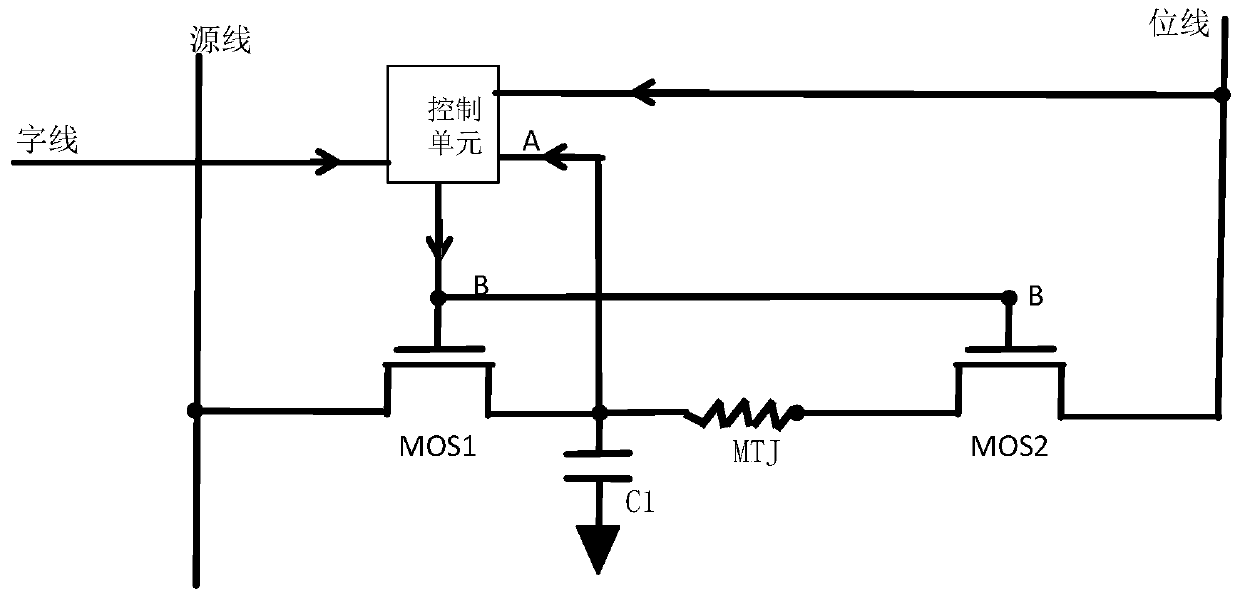
A Write Circuit Structure of Spin Torque Transfer Magnetic Random Access Memory
ActiveCN106205668BReduce M write power consumptionReduce write power consumptionDigital storageCapacitanceBit line
The invention discloses a write circuit structure of a spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory. The write circuit structure comprises a magnetic tunnel junction, and a source line, a bit line and a word line, a first switch tube, a second switch tube, a control unit and a capacitor, wherein a free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction is connected with a drain electrode of the first switch tube, a reference layer of the magnetic tunnel junction is connected with a source electrode of the second switch tube; the source electrode of the first switch tube is connected with the source line, and the drain electrode of the second electrode is connected with the bit line; one end of the capacitor is grounded, and the other end is connected to the input end of the control unit and is connected with the drain electrode of the first switch tube or the free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction; the input end of the control unit is respectively connected with the wore line, the source line or the bit line, and the drain electrode of the first switch tube or the free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction; the output end of the control unit is connected with the grid electrodes of the first switch tube and the second switch tube. Through the adoption of the write circuit structure disclosed by the invention, the repeated write action can be avoided, the aim of lowering the MRAM write power consumption and the chip dynamic power consumption is achieved.
Owner:CETHIK GRP +1
Read-write control circuit used in STT-MRAM
PendingCN112767981AAvoid duplicate writingShorten write timeDigital storageControl signalControl cell
The invention relates to the technical field of integrated circuits, and particularly discloses a read-write control circuit used in an STT-MRAM, which comprises a plurality of rows of read-write control units, and each row of read-write control unit comprises a write circuit connected with a storage array and used for controlling whether input data is written into the storage array or not according to a control signal; a reading circuit connected with the storage array and used for reading the storage data in the storage array; a storage array used for controlling gating of the storage units and storing the input data written by the writing circuit into the gated storage units to form storage data; a comparator respectively connected with the writing circuit and the latch and used for comparing the storage data temporarily stored in the latch with the input data and generating a control signal; and the latch used for acquiring the storage data read by the reading circuit and temporarily storing the storage data. According to the read-write control circuit used in the STT-MRAM, the write power consumption is reduced, and the write error rate is reduced.
Owner:中电海康无锡科技有限公司
Transient storage circuit suitable for CMOS integration and using method thereof
ActiveCN101727974BAvoid repetitionSave time and costDigital storageRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringRadio frequency
The invention discloses a transient storage circuit suitable for CMOS integration and a using method thereof, which relate to the technical field of radio frequency identification (RFID). The transient storage circuit consists of an access control circuit, a transient storage unit and an output sensitive amplifier which are connected with one another in turn. A reset signal PODR and an input datasignal D IN of a digital circuit of a tag chip are written into the transient storage unit by the access control circuit, and the temporary data output Vc of the transient storage unit is amplified by the output sensitive amplifier and then is output by a data wire D_OUT. The transient storage circuit can solve the problem of lowered identification efficiency caused by short time power down of the tag chip in application of passive radio-frequency identification, reduces the time cost for tag identification, improves the identification efficiency of a passive radio-frequency tag, and has the characteristics of economical efficiency, simplicity and convenience.
Owner:BEIJING TONGFANG MICROELECTRONICS
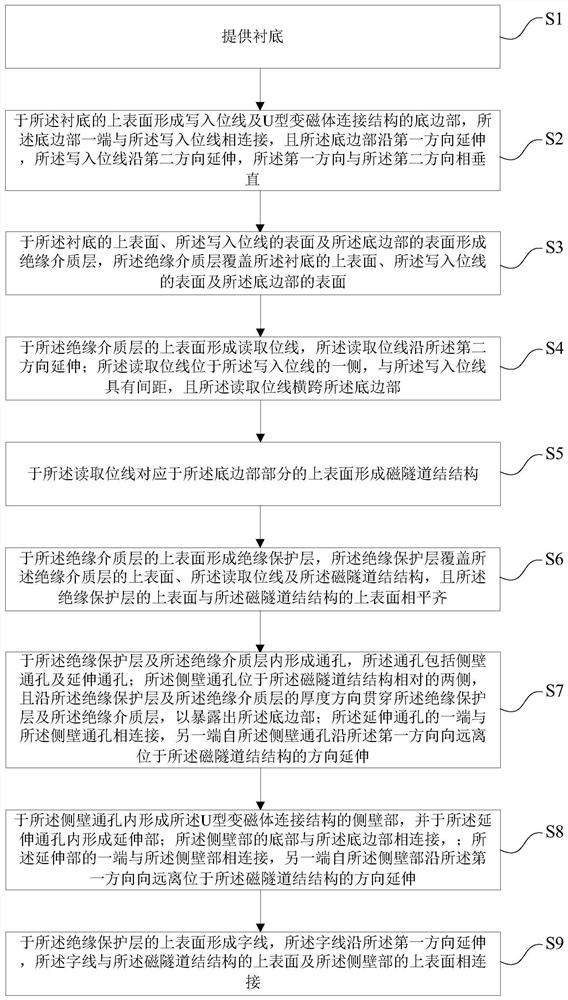
Magnetic random access memory and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111833930BSmall sizeSmall currentDigital storageGalvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatmentWrite bitRandom access memory
The invention provides a magnetic random access memory and a preparation method thereof, comprising: a magnetic tunnel junction structure; a word line, which is connected to the top of the magnetic tunnel junction structure; a read bit line, which is in contact with the bottom of the magnetic tunnel junction structure; The write bit line is located on one side of the read bit line; the U-shaped variable magnet connection structure includes a bottom edge, a side wall and an extension; the bottom edge is located below the read bit line, and one end is opposite to the write bit line connected, and the other end straddles the read bit line along the first direction; the sidewall portions are respectively located on opposite sides of the magnetic tunnel junction structure, and the top of the sidewall portion on the side of the magnetic tunnel junction structure away from the extension portion is connected to the word line The bottom of the sidewall portion is connected with the bottom edge portion; one end of the extension portion is connected with the sidewall portion, and the other end extends from the sidewall portion along the first direction to the direction away from the magnetic tunnel junction structure. The magnetic random access memory of the present invention reduces the current required for inversion of the magnetic tunnel junction structure, thereby reducing the required writing current and writing power consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI IND U TECH RES INST
A Modulation Method of Asymmetric Ferroelectric Tunneling Junction Multi-valued Memory Cell
ActiveCN111211135BReduce read power consumptionHigh speedSolid-state devicesDigital storageMemory cellCondensed matter physics
The present invention provides a modulation method of an asymmetric ferroelectric tunnel junction multi-value storage unit and a corresponding storage unit and memory. The multi-value memory cell includes N ferroelectric functional layers; the N ferroelectric functional layers have different coercive field values respectively, so that the N ferroelectric functional layers still exhibit different remanent polarizations after the first excitation is applied difference, and then under the action of the second excitation, the multi-valued storage unit presents 2 N A tunneling resistance state; wherein, N is an integer greater than or equal to 2, and the first excitation includes changing the magnitude and direction of the driving excitation. The asymmetric ferroelectric tunneling junction multi-value storage unit of the present invention has the characteristics of non-volatility and low reading power consumption; at the same time, a variety of different storage states can be realized in one storage unit, which greatly improves the storage density and unit storage.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Voltage-adjustable reluctance-variable random memory cell and random memory
ActiveCN102683581BReduce distanceReduce the numberMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionElectrical resistance and conductanceInformation data
The invention proposes a voltage-adjustable magnetoresistance random access memory unit, which includes: a bottom electrode layer; a ferroelectric oxide layer formed on the bottom electrode layer; and a magnetic layer formed on the ferroelectric oxide layer, wherein , the magnetic layer and the bottom electrode layer serve as the upper and lower electrodes of the ferroelectric oxide layer respectively to apply voltage to the ferroelectric oxide layer, where the direction of the voltage is perpendicular to the ferroelectric oxide layer, and the ferroelectric oxide layer can The arrangement of the magnetic moments in the magnetic layer is controlled so that the resistance of the magnetic layer changes in the set measurement direction. The present invention also proposes a memory having the magnetoresistive random access memory unit. The invention can write information data using voltage, and has advantages such as non-volatility, low writing power consumption, and high storage density.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A magnetic tunnel junction with strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
ActiveCN107946456BStrong anisotropyImprove thermal stabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin-transfer torqueThin membrane
The present invention is a magnetic tunnel junction with strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, its structure is ferromagnetic layer 1, potential barrier layer, and ferromagnetic layer 2 from bottom to top; it is characterized in that: the cross-sectional size of the magnetic tunnel junction is in Between 1nm and 150nm, the thickness of ferromagnetic layer 1 and ferromagnetic layer 2 is greater than 6nm, and the thickness of ferromagnetic layer 1 and ferromagnetic layer 2 is greater than half of the cross-sectional size; the thickness of the barrier layer is 0.2‑10nm . Compared with the existing technology, the device has the advantages of strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, high thermal stability, small cross-sectional size, high spin-transfer torque reversal efficiency, and fewer film layers.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com