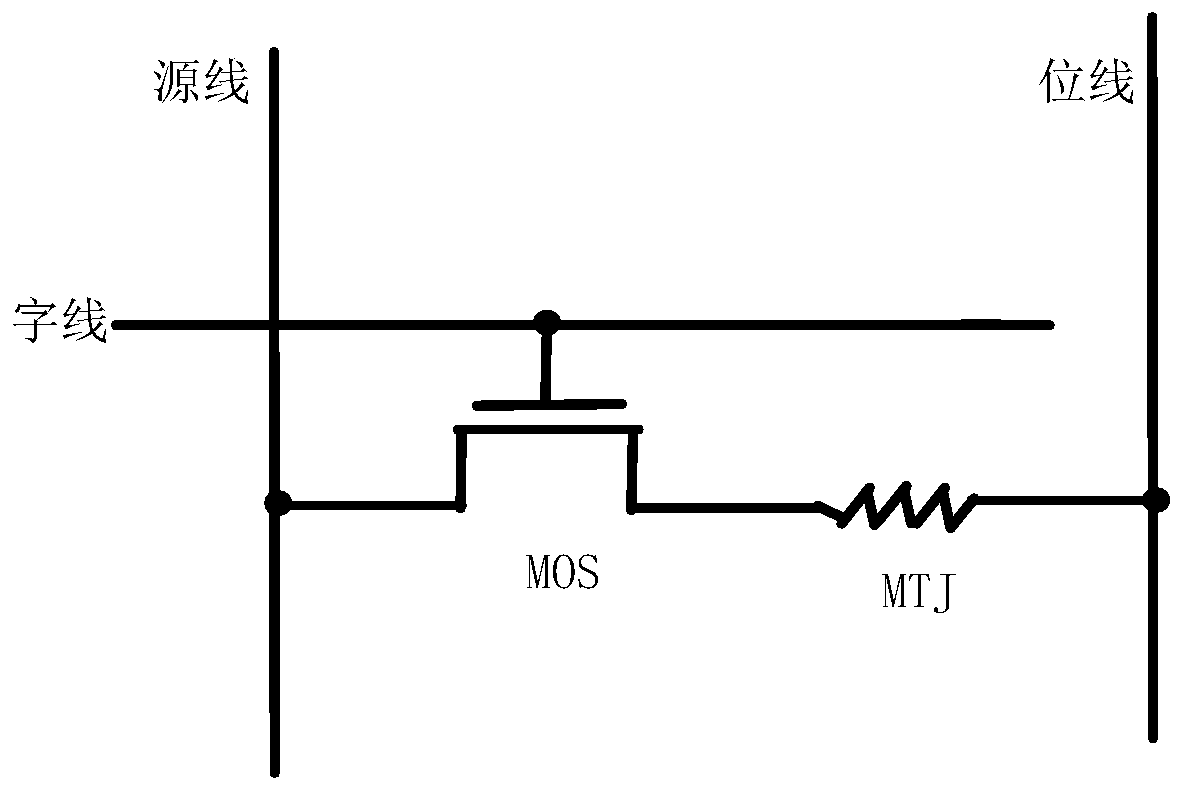
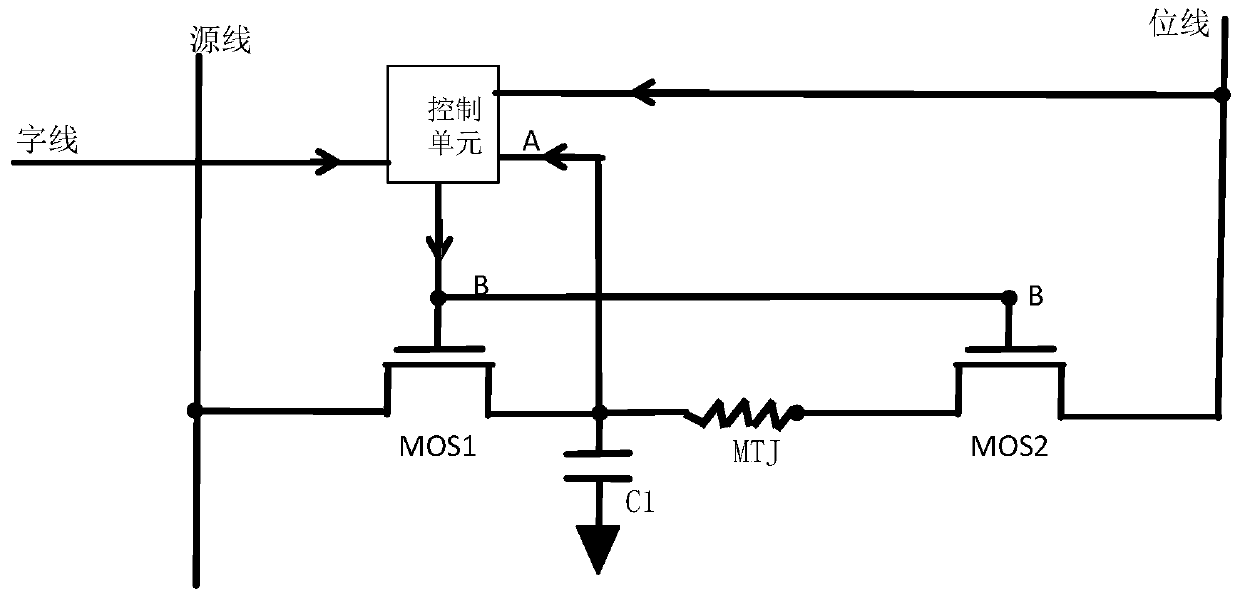
A Write Circuit Structure of Spin Torque Transfer Magnetic Random Access Memory
A technology of spin torque transfer and random access memory, which is applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., and can solve the problem of repeated writing of data bits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, such as Figure 5 As shown, the control unit includes a NOR gate and an AND gate.
[0031] Such as image 3 , Figure 5 As shown, the control unit of this embodiment includes a NOR gate and an AND gate, the two inputs of the NOR gate are respectively connected to the bit line and point A, one input terminal of the AND gate is connected to the output of the NOR gate, and the other The input end is connected to the word line, and the output of the AND gate is connected to point B, which is the output of the control unit.
[0032] Under the control of the word line, when the control signal of the write operation is input on the word line, the control unit first judges whether the content stored in the memory unit (that is, the potential of the capacitor C1) is equal to the bit line, and if they are equal, the potential of point B is "" 1", turn on MOS1 and MOS2, allowing data to be written and updated; if the stored content is different from the data writt...
Embodiment approach 2
[0039] Embodiment 2, such as Image 6 As shown, the control unit includes an XOR gate and an AND gate.
[0040] Such as Figure 4 , Image 6 As shown, the control unit of this embodiment includes an XOR gate and an AND gate, the two inputs of the XOR gate are respectively connected to the source line and point A, one input terminal of the AND gate is connected to the output of the XOR gate, and the other The input end is connected to the word line, and the output of the AND gate is connected to point B, which is the output of the control unit.
[0041] Under the control of the word line, when the control signal of the write operation is input on the word line, the control unit first judges whether the content stored in the memory cell is equal to the data to be written (source line), if they are equal, the potential of point B is " 0", MOS1 and MOS2 are not turned on, and this write operation is shielded; if the stored content is different from the data to be written, the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com