Read-write circuit of magnetic random access memory
A random access memory, read-write circuit technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problems of miswriting reference unit configuration, long writing operation time, not clearly pointed out, etc., to avoid misjudgment , Improve the success rate, improve the effect of writing operation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
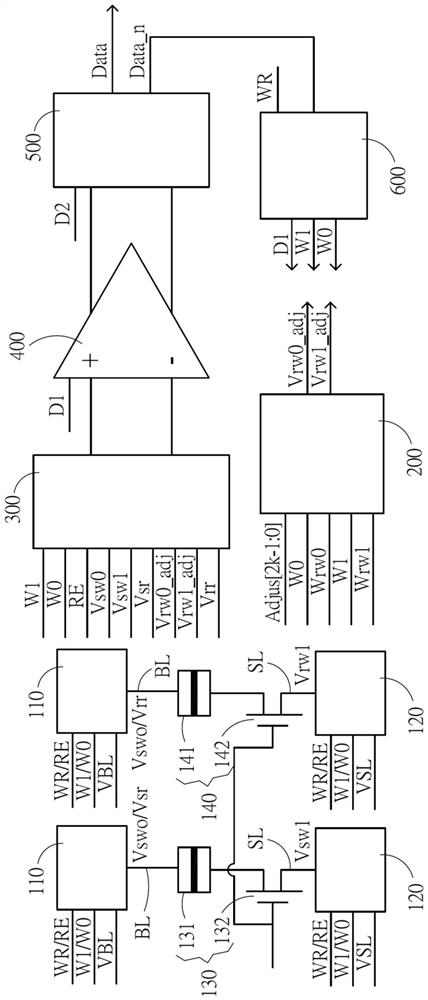
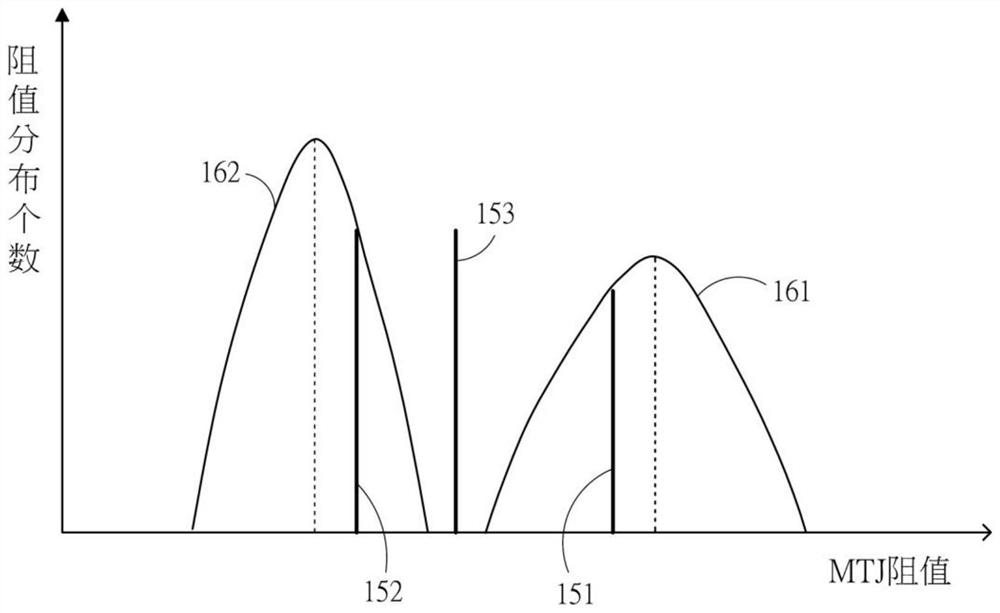
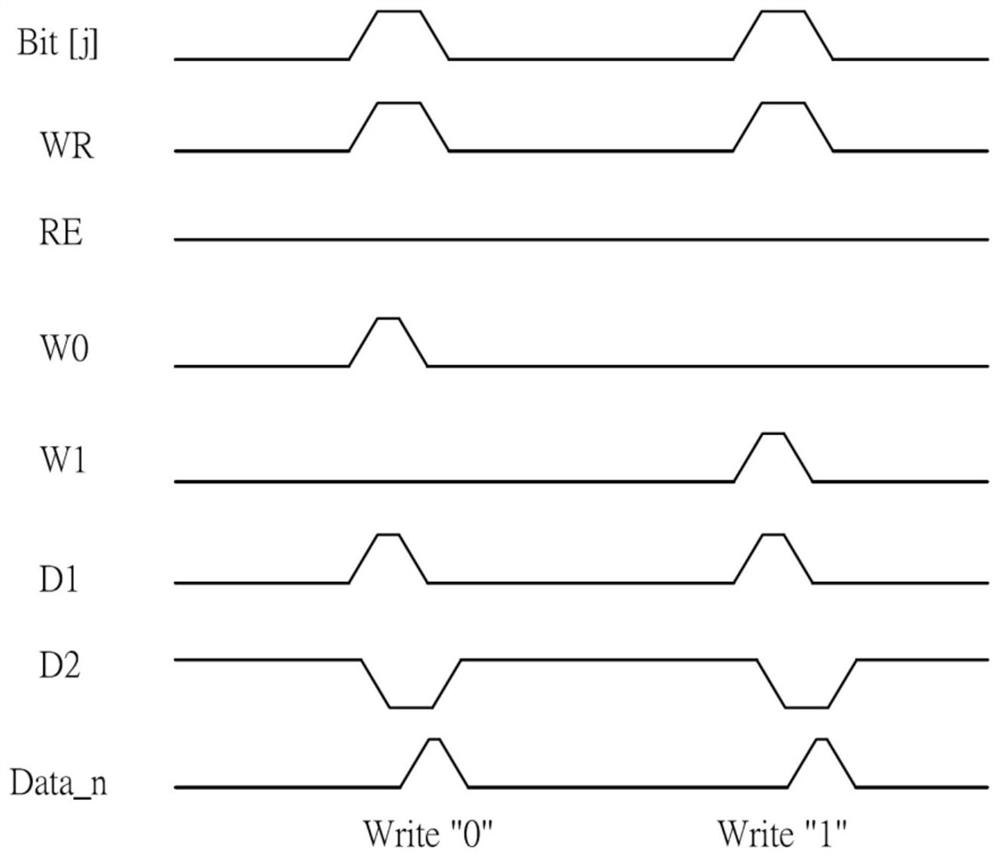
[0030]In order to better understand the present invention, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be described in connection with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention, and the embodiments described herein will be clearly understood. It is an embodiment of the invention, not all of the embodiments. Based on the embodiments in the present invention, those of ordinary skill in the art will belong to the scope of the invention in the present invention without making in the pre-creative labor premise.
[0031] It should be noted that the description and claims of the invention and the terms "including" and "have" and "have any modifications described above), intended to cover inclusion, for example, including a series of steps or units The processes, methods, devices, products, or devices are not necessarily limited to those steps or units that are clearly listed, but may include other steps or units that are not clearly listed or f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com