Magnetoelectric random storage unit and storage with same
A random access storage and memory technology, applied in the field of semiconductor manufacturing and design, can solve the problems of excessive power consumption of magnetic random access memory and the influence of adjacent cells, and achieve the effects of reducing write power consumption, improving storage density, and reducing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
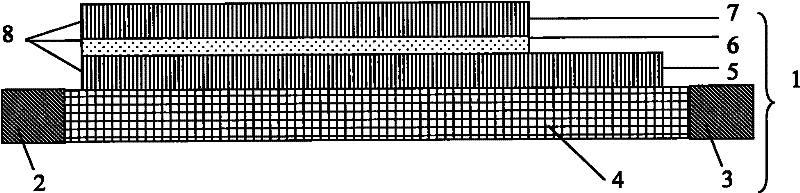
[0063] Prepare the ferroelectric oxide layer 4 as lead niobate zincate-lead titanate (PZN-PT) with a thickness of 250nm, and deposit 5nm thick Fe with (001) orientation 0.7 co 0.3 The ferromagnetic free layer 5 of the alloy, the magnesium oxide (MgO) tunnel barrier layer 6 with a thickness of 1.5nm, and the ferromagnetic fixed layer 7 of the CoFeB alloy with a thickness of 25nm, the ferromagnetic free layer 5 and the tunnel barrier layer obtained by etching technology 6. The multilayer composite film structure of the ferromagnetic fixed layer 7 has a length of 1 μm and a width of 0.5 μm. Apply a voltage parallel to the film length direction in the ferroelectric oxide layer 4, Figure 6 In this system, the resistance value of the interlayer structure 8 varies with the voltage applied to the ferroelectric oxide layer 4. In this system, the positive critical switching voltage U cr is 0.72V, the negative critical switching voltage U cr is 0.51V.
[0064] As shown in the above ...
no. 2 example
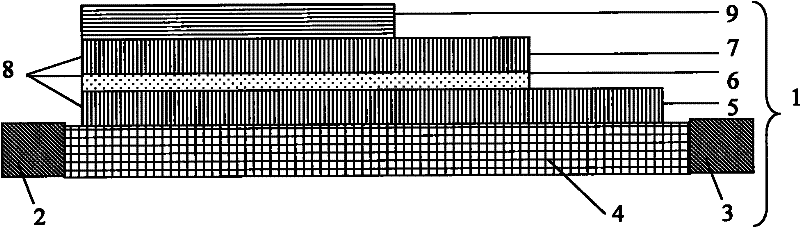
[0066] Prepare the ferroelectric oxide layer 4 as barium titanate (BTO) with a thickness of 250nm, deposit 5nm thick Fe with (001) orientation 0.7 co0.3 The ferromagnetic free layer 5 of the alloy, the magnesium oxide (MgO) tunnel barrier layer 6 with a thickness of 1.5nm, and the ferromagnetic fixed layer 7 of the CoFeB alloy with a thickness of 25nm, the ferromagnetic free layer 5 and the tunnel barrier layer obtained by etching technology 6. The ferromagnetic fixed layer 7 has a multilayer composite film structure with a length of 1 μm and a width of 0.5 μm. Apply a voltage parallel to the film length direction in the ferroelectric oxide layer 4, Figure 7 In this system, the resistance of the composite structure varies with the voltage applied to the ferroelectric oxide layer. In this system, the positive critical switching voltage U cr is 9.7V, the negative critical switching voltage U cr is 6.8V. As shown in the figure, due to the same principle as that of Embodiment ...
no. 3 example
[0068] Prepare a ferroelectric oxide layer of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) with a thickness of 250nm, deposit 5nm thick Fe with (001) orientation 0.7 co 0.3 Alloy ferromagnetic free layer, 1.5nm thick magnesium oxide (MgO) tunnel barrier layer, and 25nm thick CoFeB alloy ferromagnetic pinned layer, ferromagnetic free layer, tunnel barrier layer, ferromagnetic pinned layer obtained by etching technology The layer composite structure has a length of 1 μm and a width of 0.5 μm. Applying a voltage parallel to the lengthwise direction in the ferroelectric oxide layer, Figure 8 In this system, the resistance of the composite structure varies with the voltage applied to the ferroelectric oxide layer. In this system, the positive critical switching voltage U cr is 4.5V, the negative critical switching voltage U cr is 3.2V. As shown in the figure, due to the same principle as that of Embodiment 1, it shows that the random storage unit has non-volatile storage.
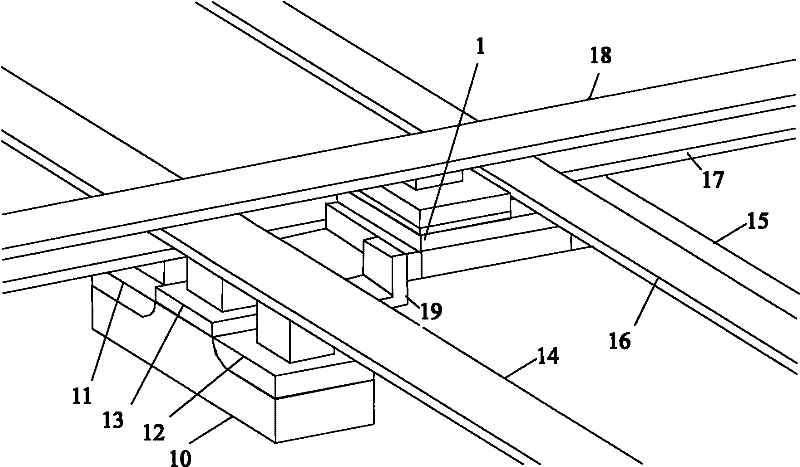
[0069] The embod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com