Nonlinear optical device
a technology of optical devices and optical waveguides, applied in the direction of optics, optical waveguide light guides, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the energy damage threshold, high attendant risk of surface or bulk damage to the sample, and generating other wavelengths using nonlinear optical processes, etc., to achieve efficient nonlinear interaction, enhance bandwidth access, and high intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
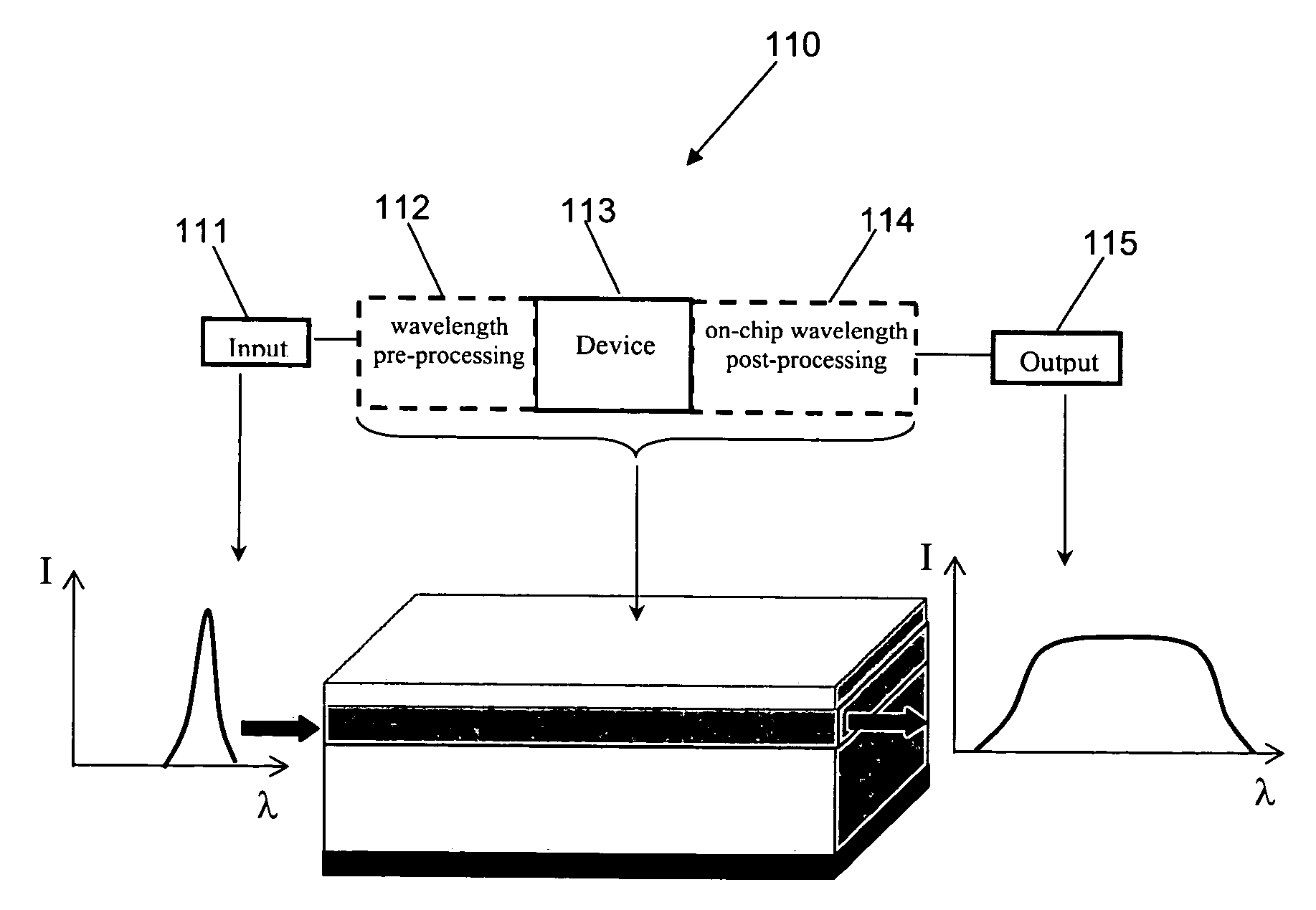
embodiment 130
FIG. 13 shows an embodiment 130 with two adjacent horizontally (laterally) tapering input regions 131 prior to the main interaction region 132. This embodiment allows for the independent coupling of two separate beams into the waveguide or, alternatively, a more complex coupling of a single large beam into the waveguide. Again, the input beam 133 reduces in size 134 as it propagates. With a slow smooth taper, input light is adiabatically coupled into a mode supported by the waveguide and able to propagate therein. Provision of an on-chip spot-size converter increases the range of light delivery systems that can be used with the waveguide device, including optical fiber.
Adding on-chip functionality is one of the great advantages of planar waveguide devices. On-chip structures for spatial profiling and beam shaping have already been described in the context of waveguide tapers. However, other types of functionality can be included that modify the phase or amplitude of a beam propagat...
embodiment 210
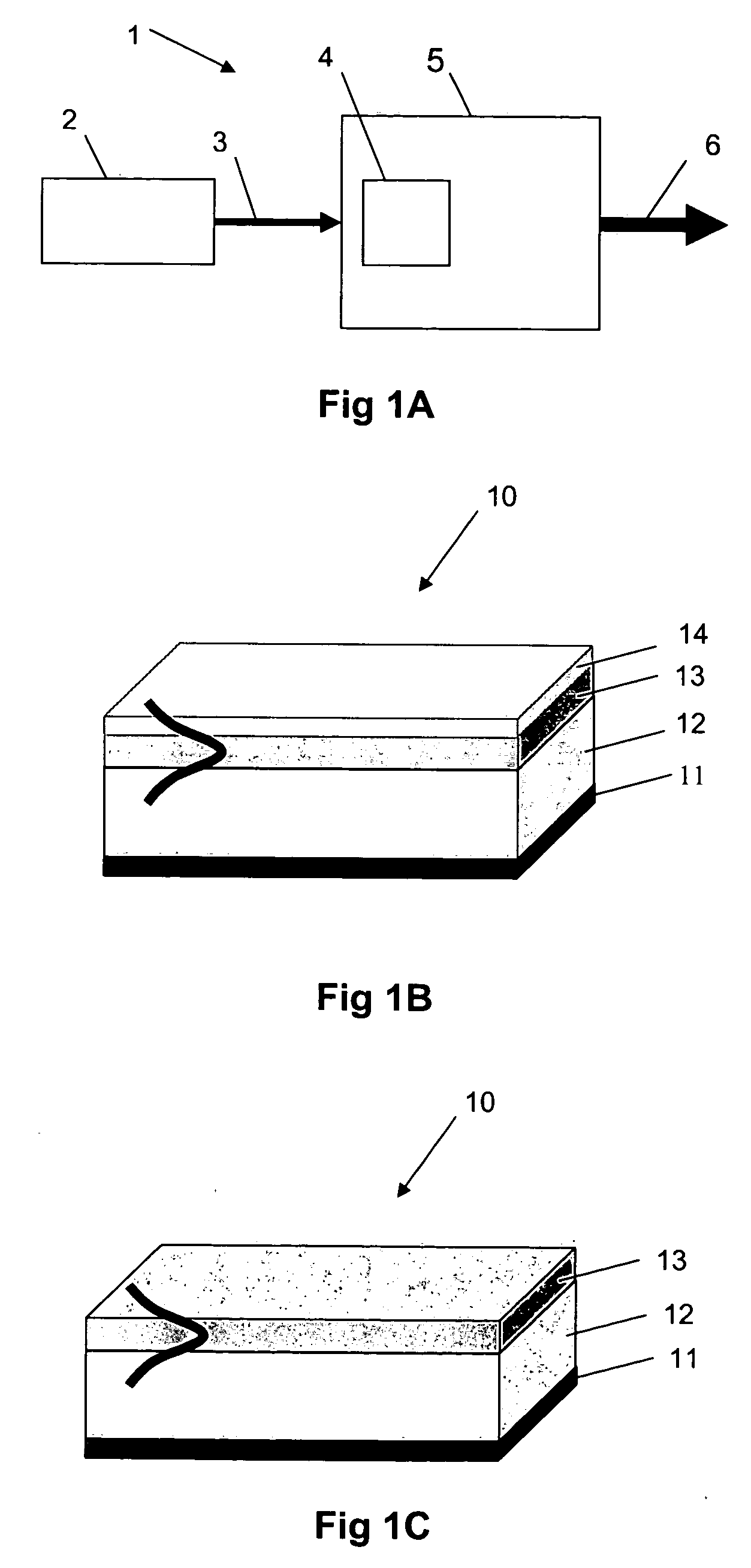
FIG. 21 illustrates a ridge embodiment 210 having a horizontally tapered input region 214 for spot size conversion and improved optical coupling efficiency. A vertical taper may also be employed. The structure 210 includes a buffer layer 212 and a core layer 213. On the core layer 213 is a core ridge layer 215 and it is the ridge layer that is tapered at the input region 214. FIG. 22 illustrates the same design applied to a rib structure 220. The structure includes a buffer layer 222 and a core rib layer 224. An input region 223 of the rib layer 224 is horizontally tapered for spot size conversion and improved optical coupling efficiency. A vertical taper may also be employed.
FIG. 23 illustrates other types of taper structure that may be implemented in a ridge (or rib) waveguide. Again the basic structure 230 comprises a buffer layer 231, a core layer 232 and a core ridge layer 233. Both of the two core ridges shown provide lateral confinement and have input waveguide regions 234 wi...
embodiment 280
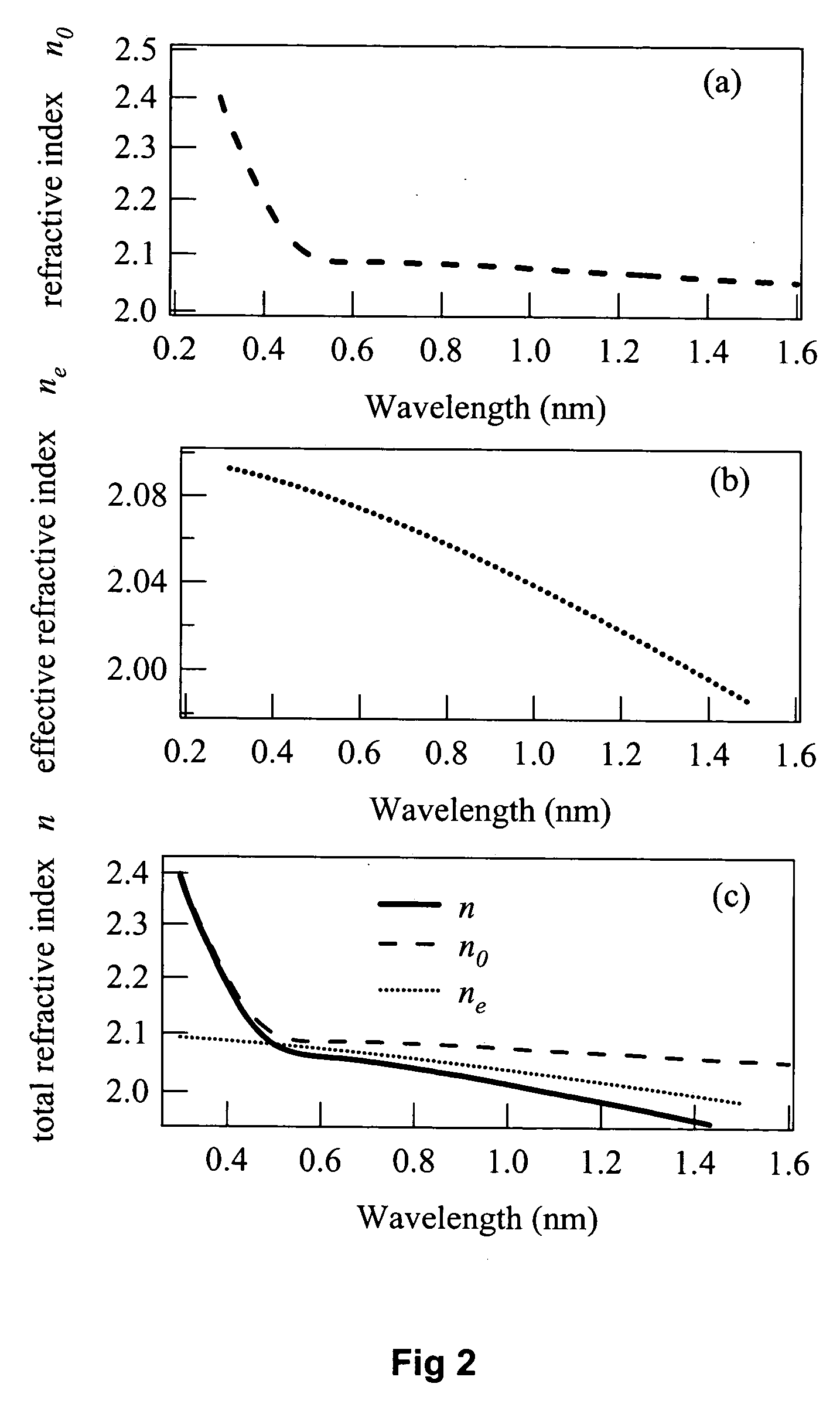
Furthermore, operating near the zero dispersion point can lead to broader continuum generation. FIG. 28 illustrates an example of this embodiment 280 having a 2-D photonic crystal structure 284 that extends from the cladding layer 285, through the core layer 283 and into the buffer layer 282. The 2-D structure permits additional functionality such as beam shaping within the generating region.
An alternative device structure for modifying the dispersion characteristics of the waveguide is a multilayered structure 290, as illustrated in FIG. 29. Here, the “core”296 comprises alternating layers 293, 294, 295 of high and low refractive index (n1, n2 . . . nn) on a buffer layer 292. The dimensions and materials used for each layer are calculated according to the desired dispersion characteristics. In this manner, as shown, three different spectral outputs can be obtained from a single input.
As has been described previously, in relation to tapers, the planar waveguide device may compris...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com